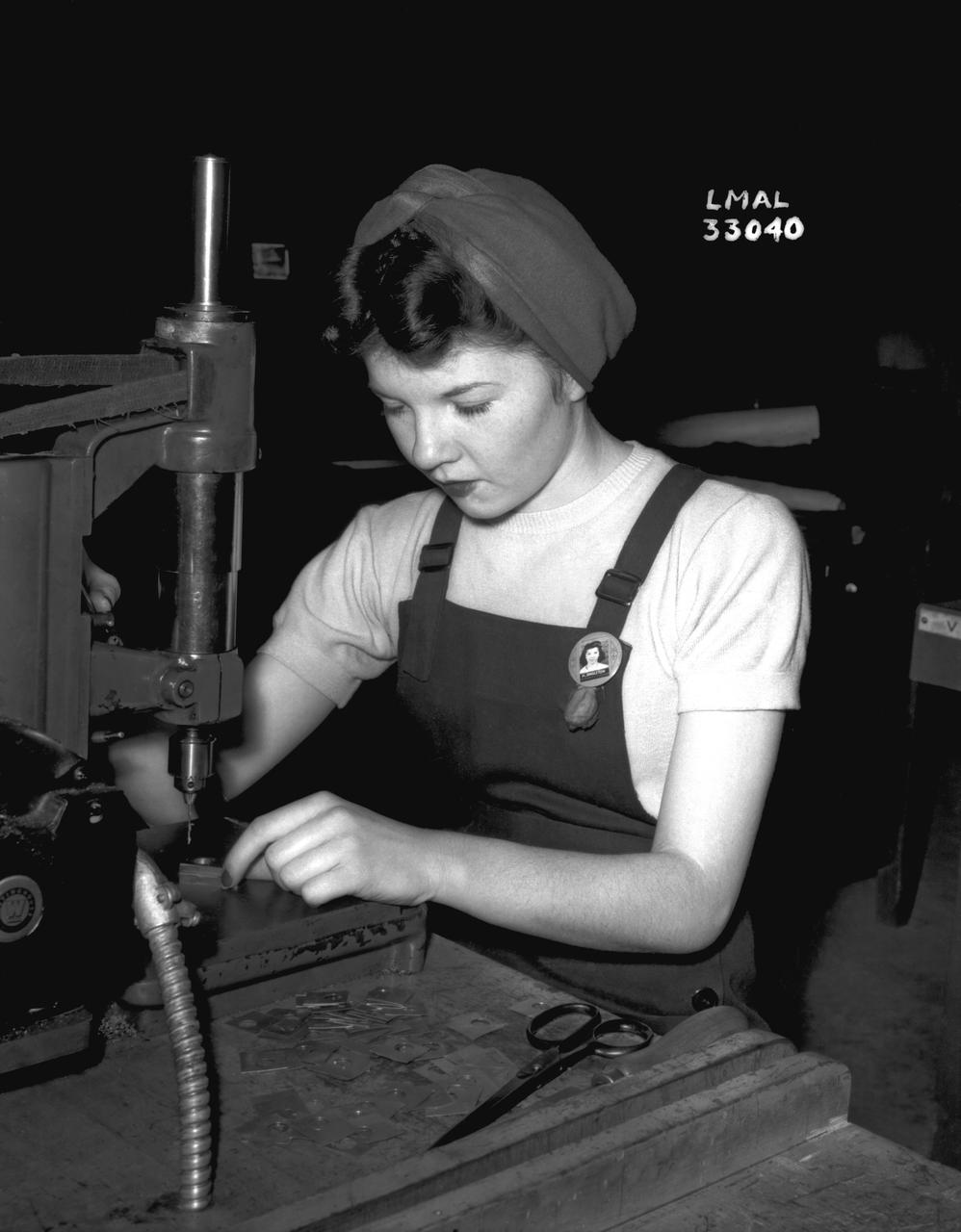

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
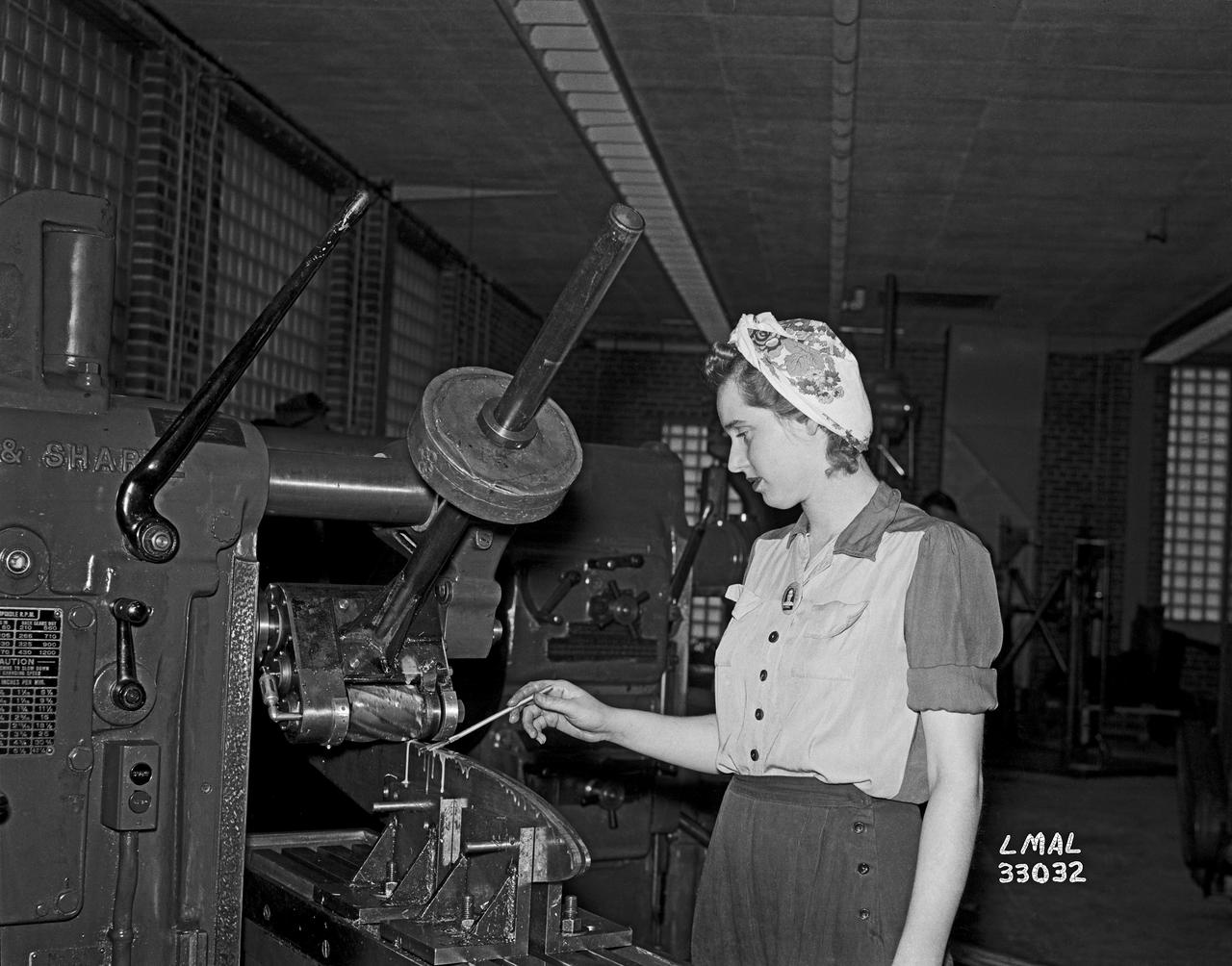

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
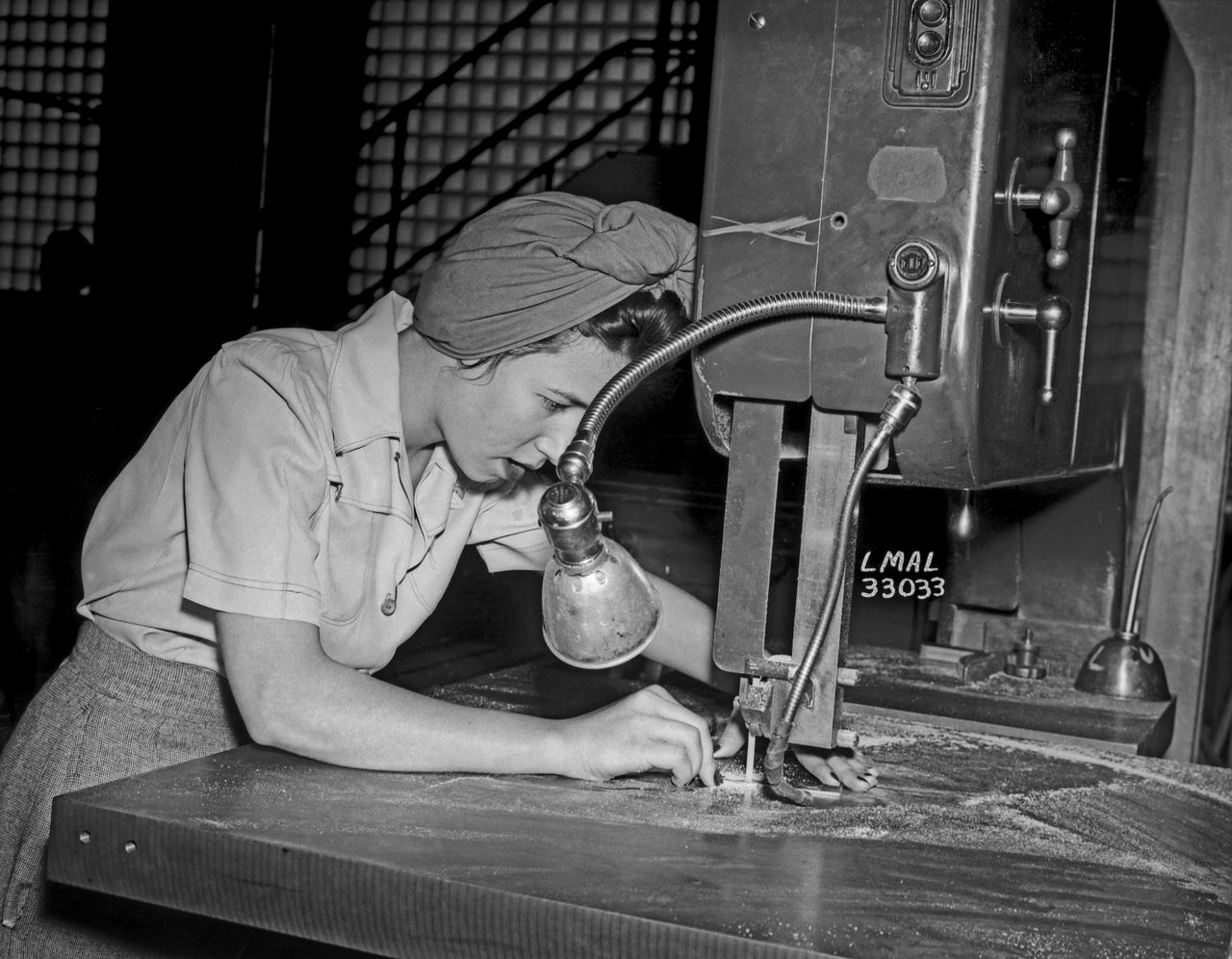

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
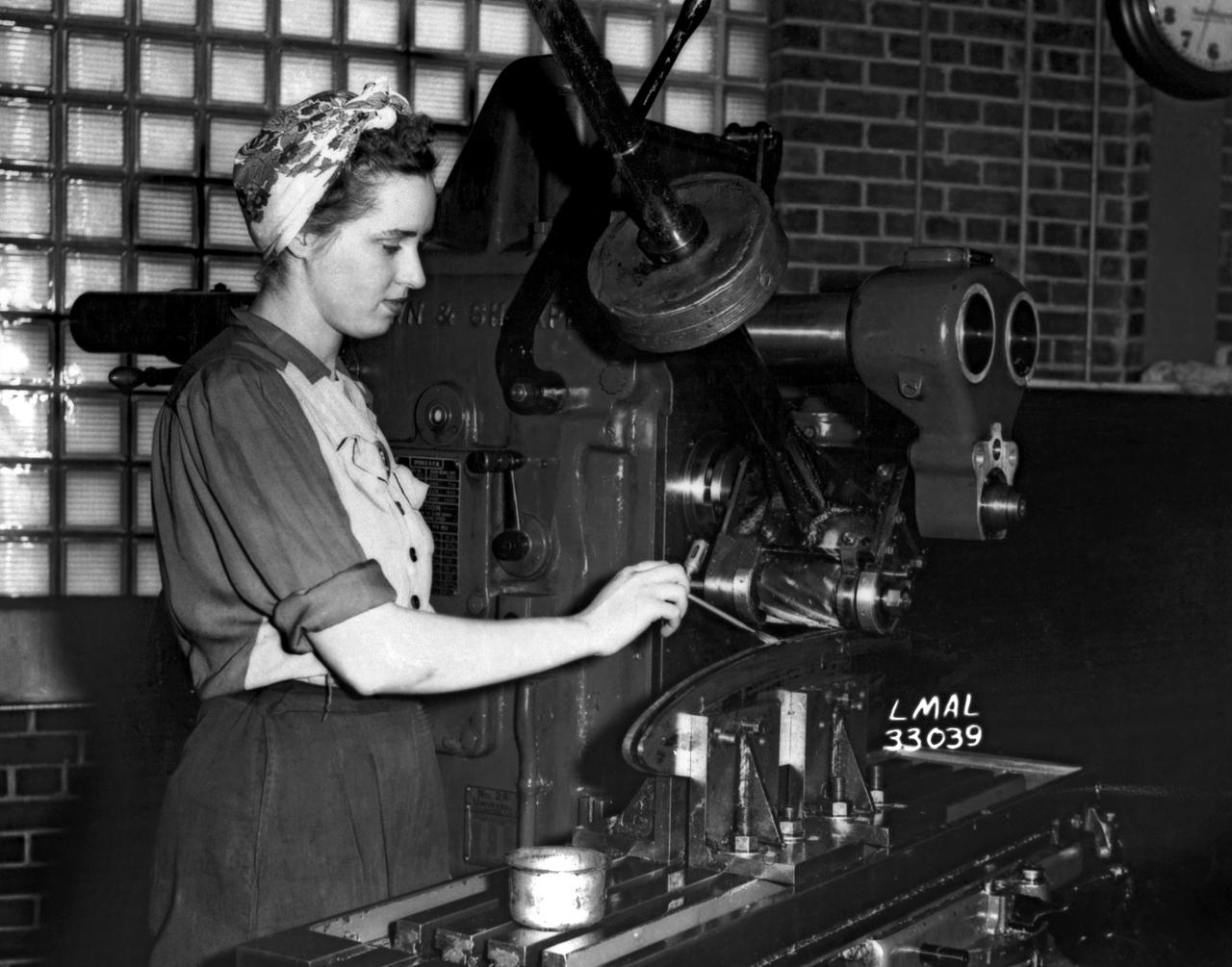

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
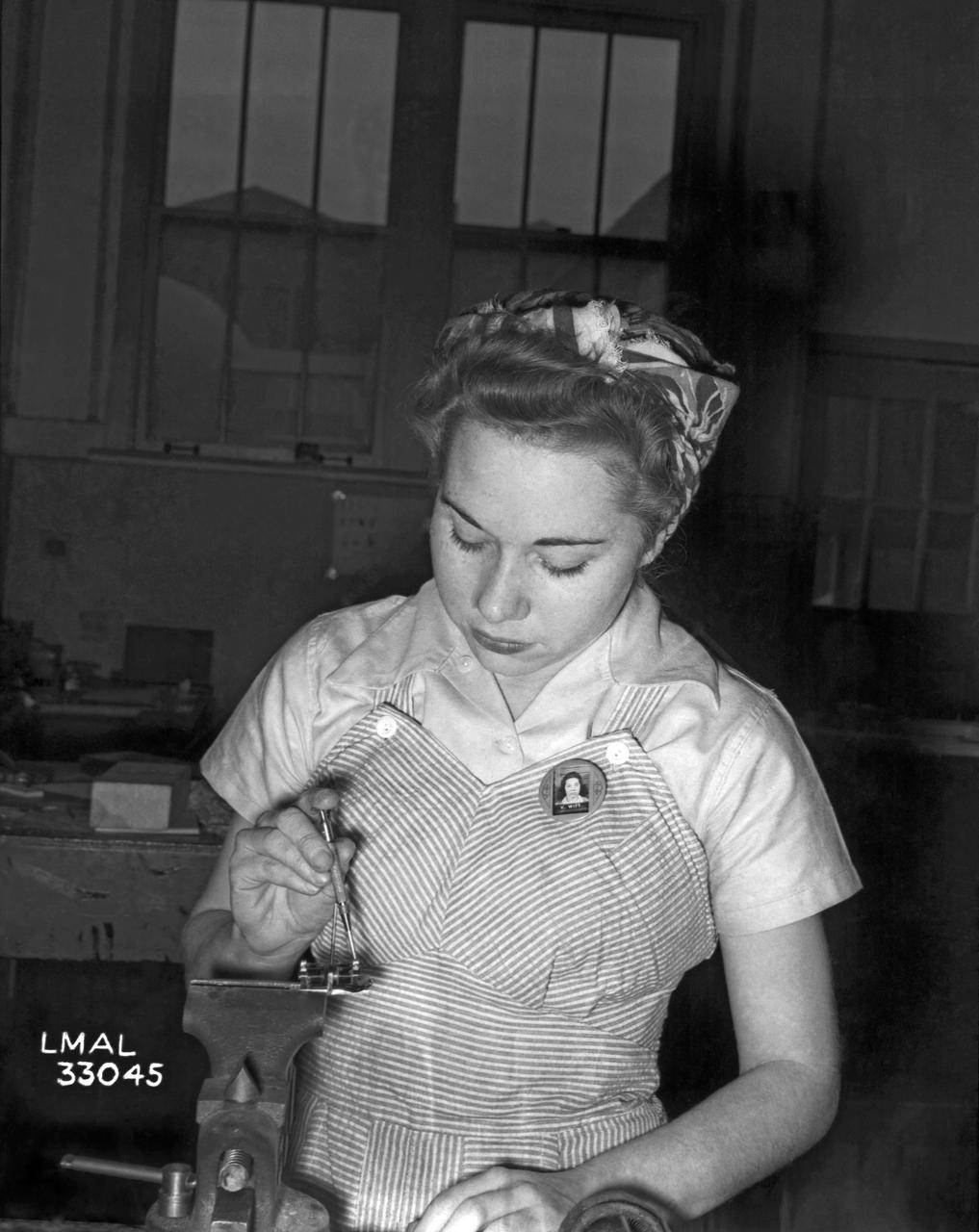

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
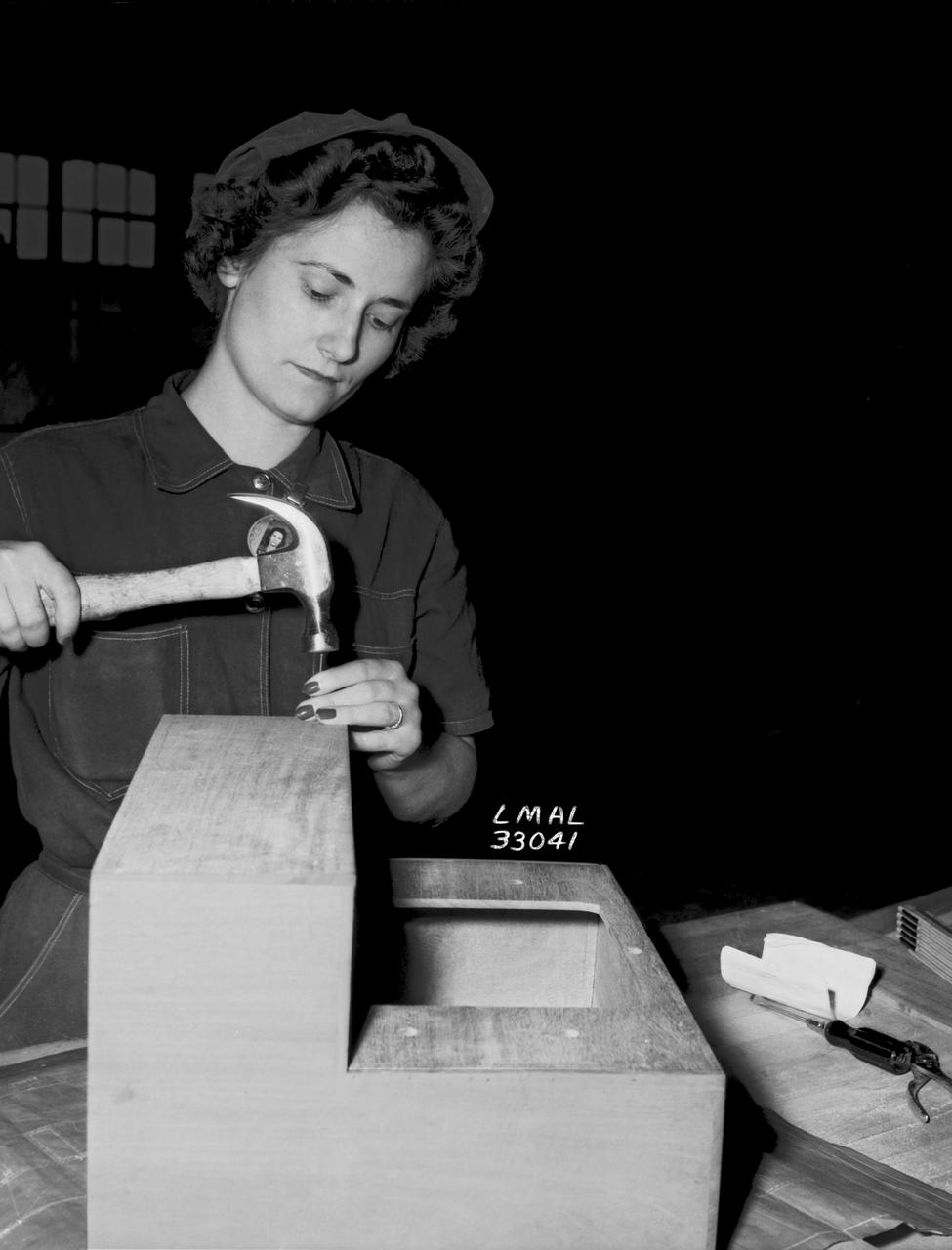

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
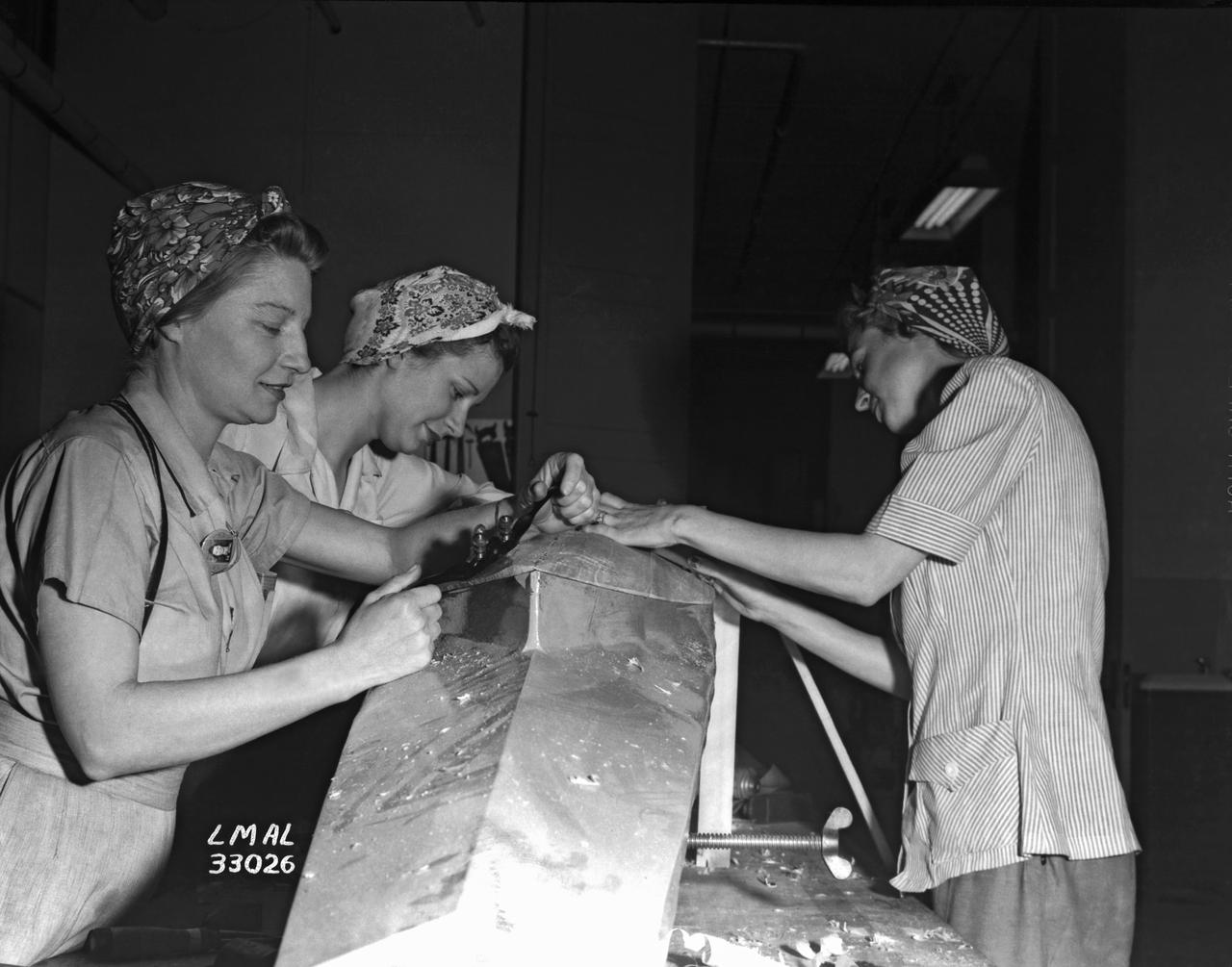

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
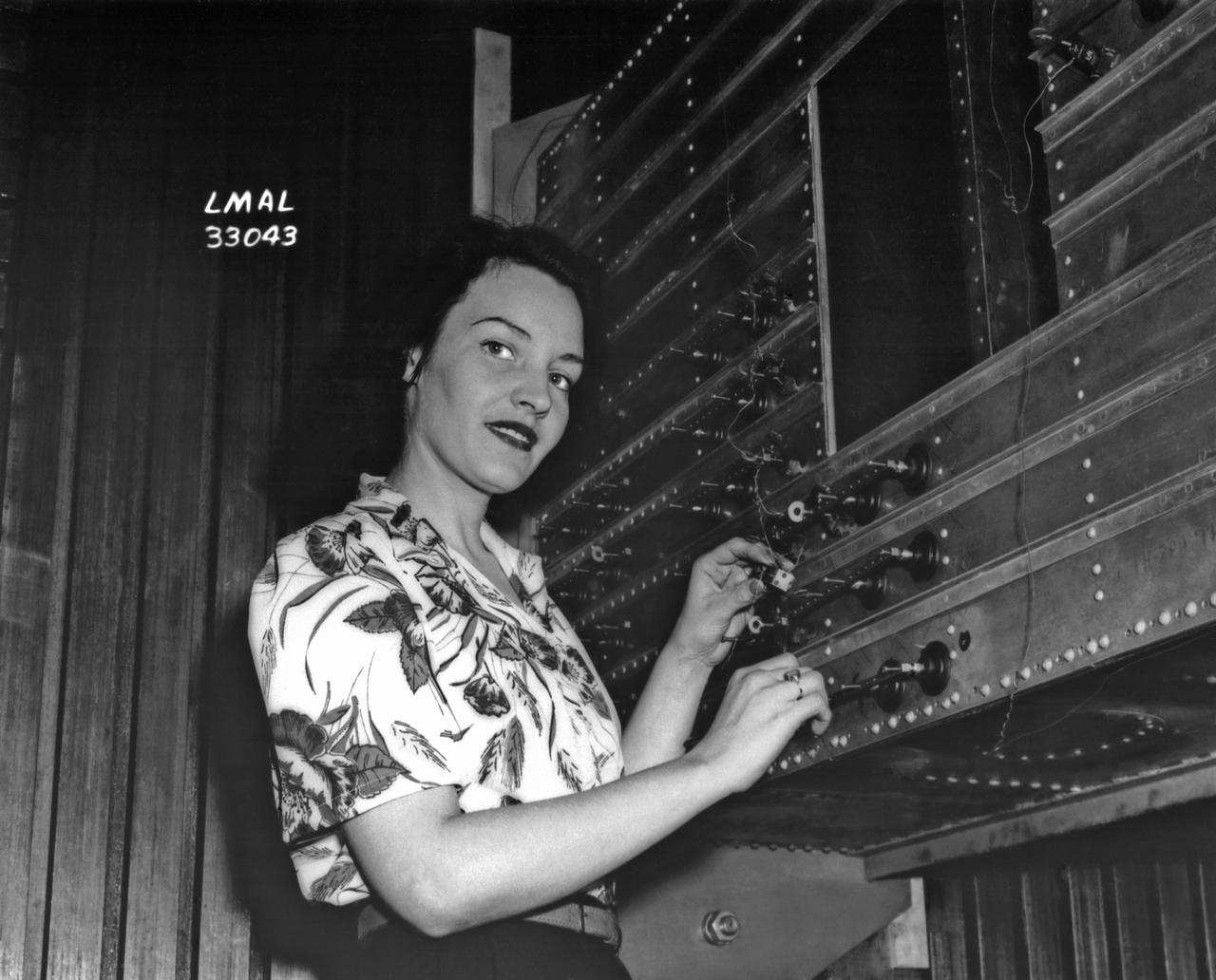

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
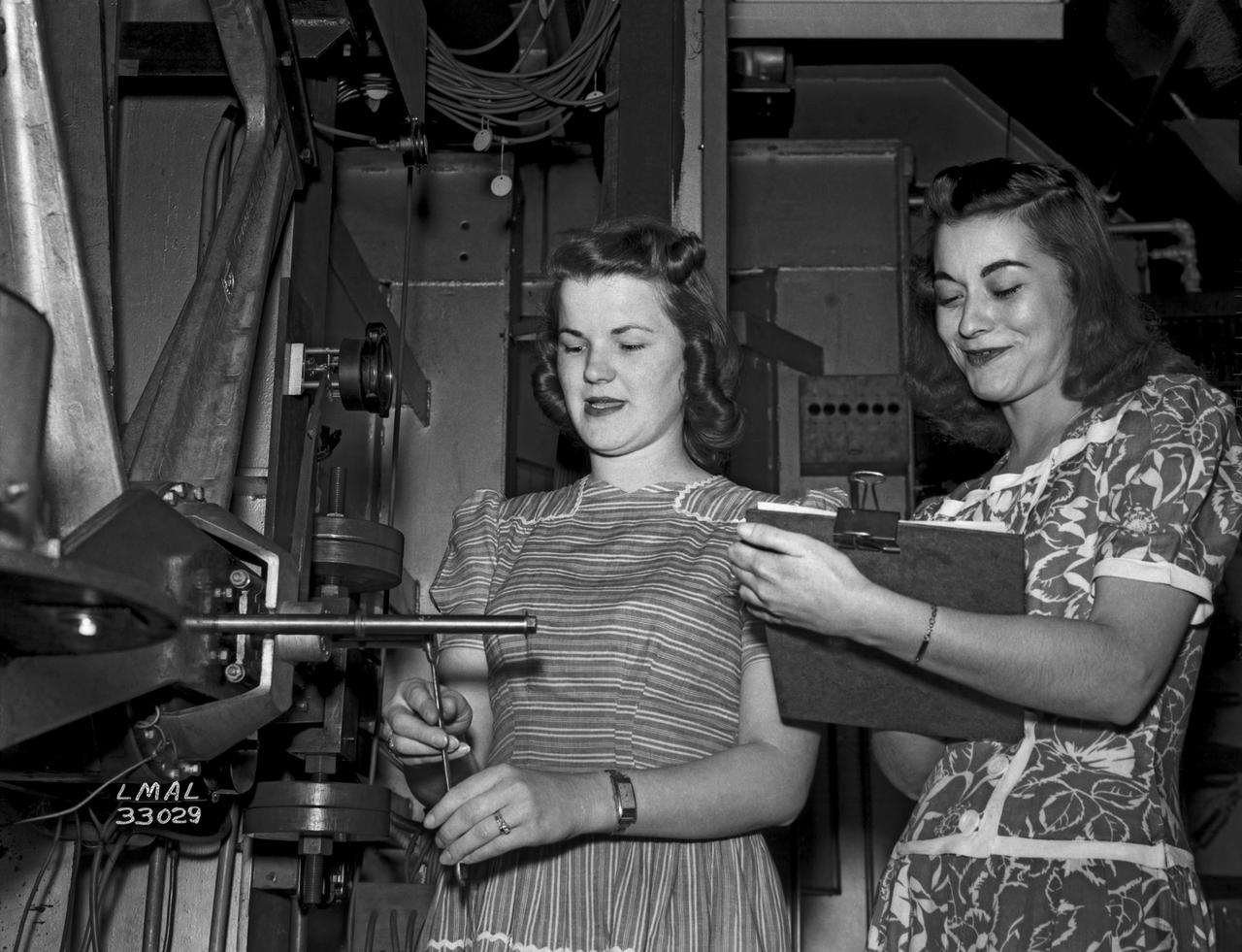

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
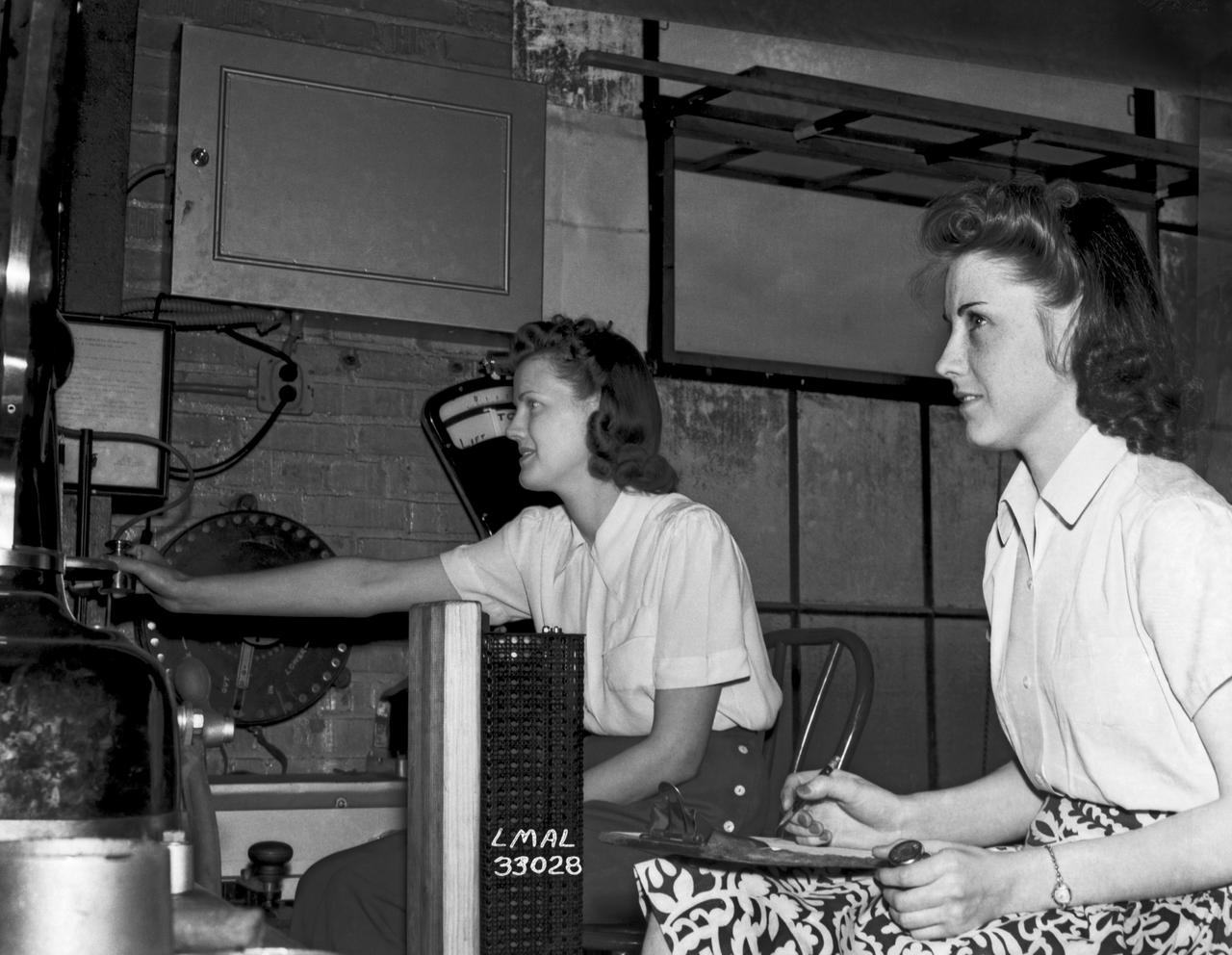

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
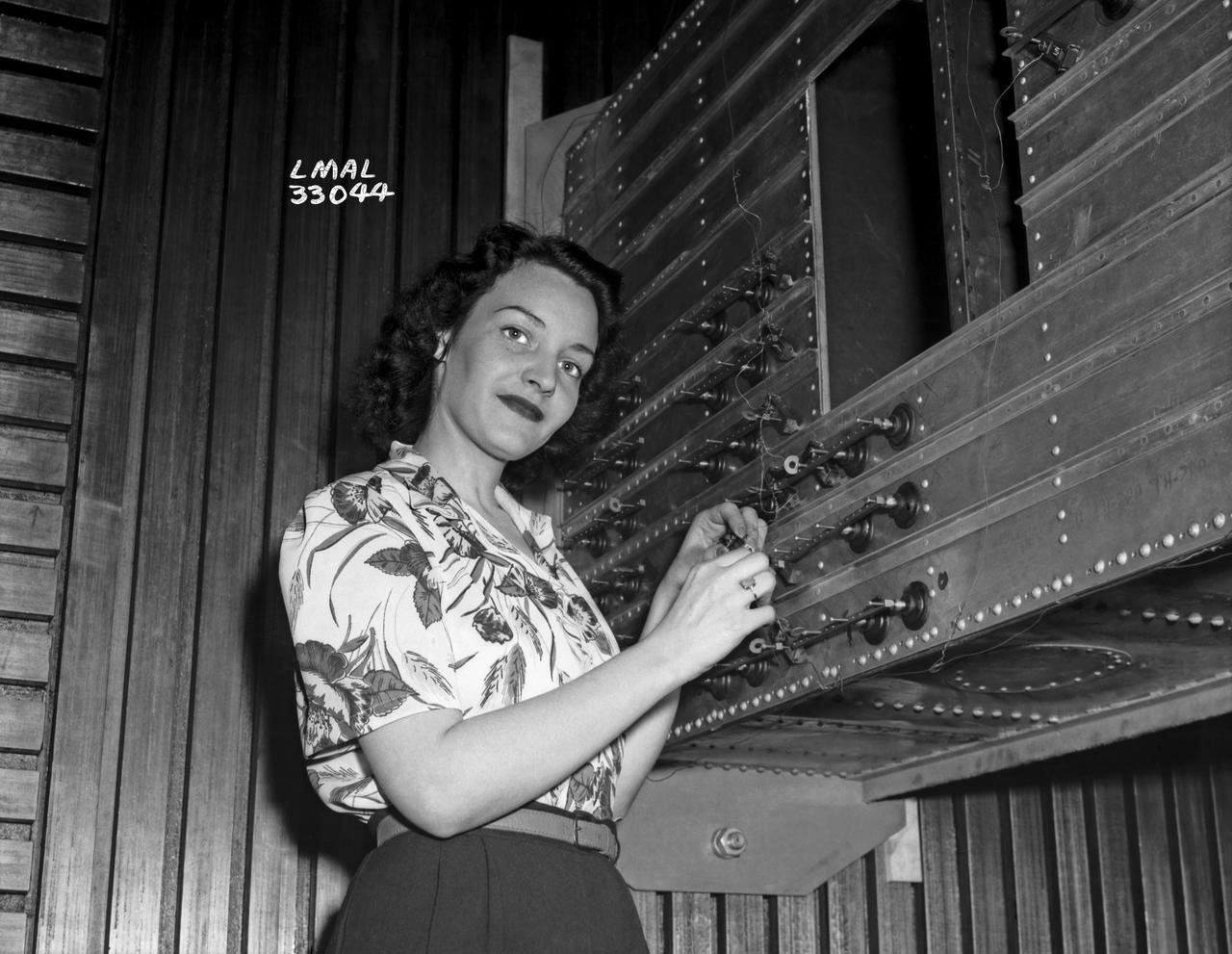

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
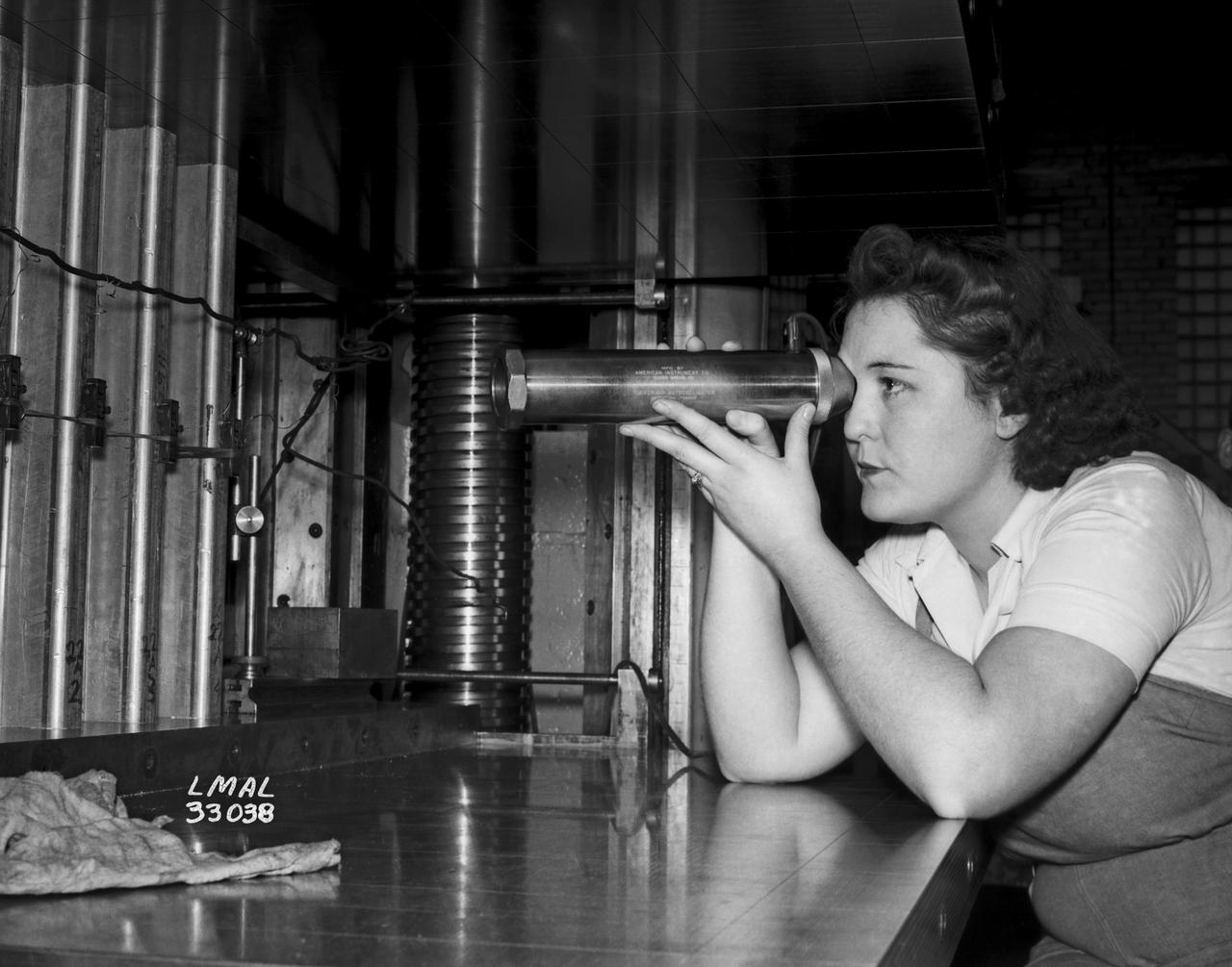

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
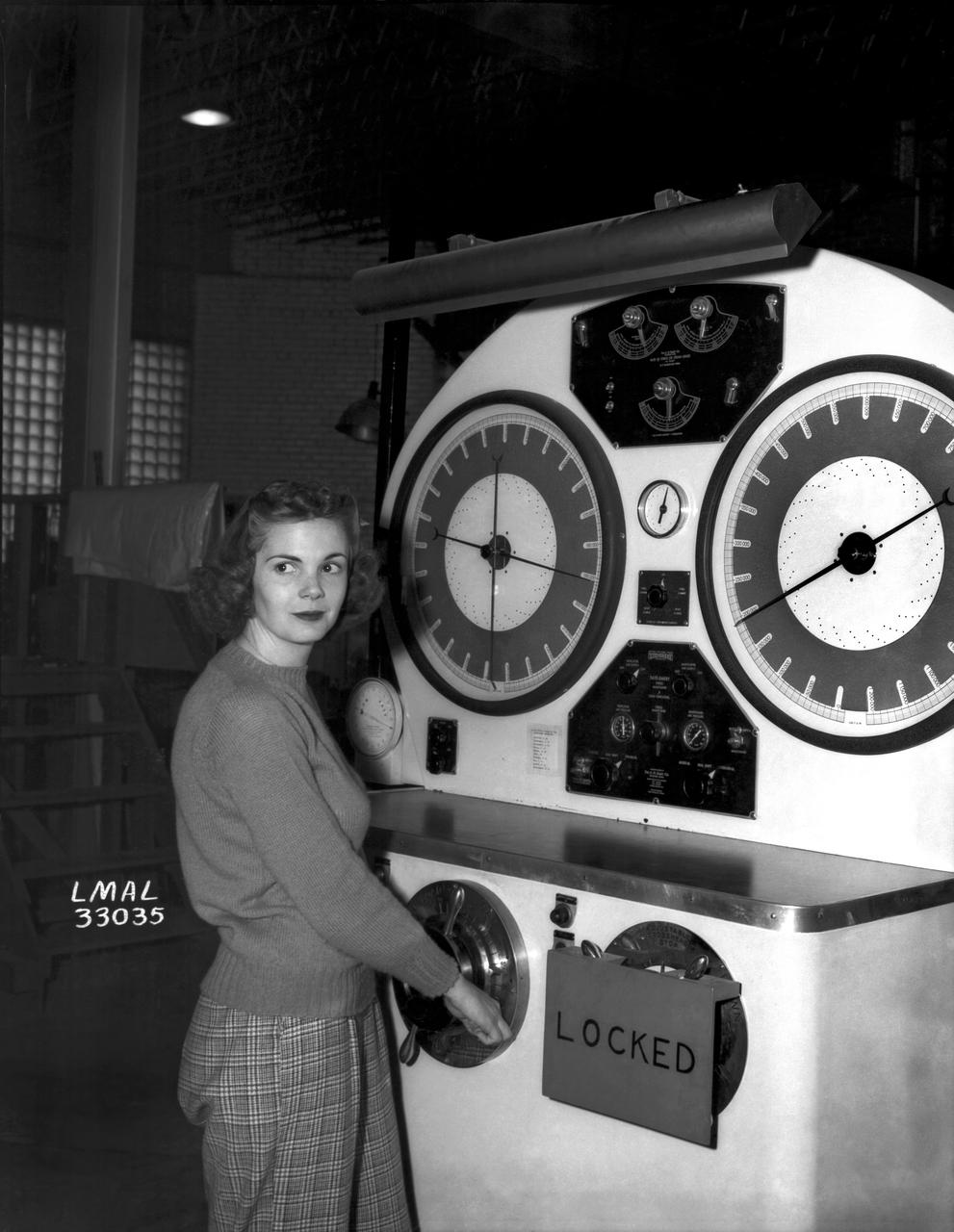

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
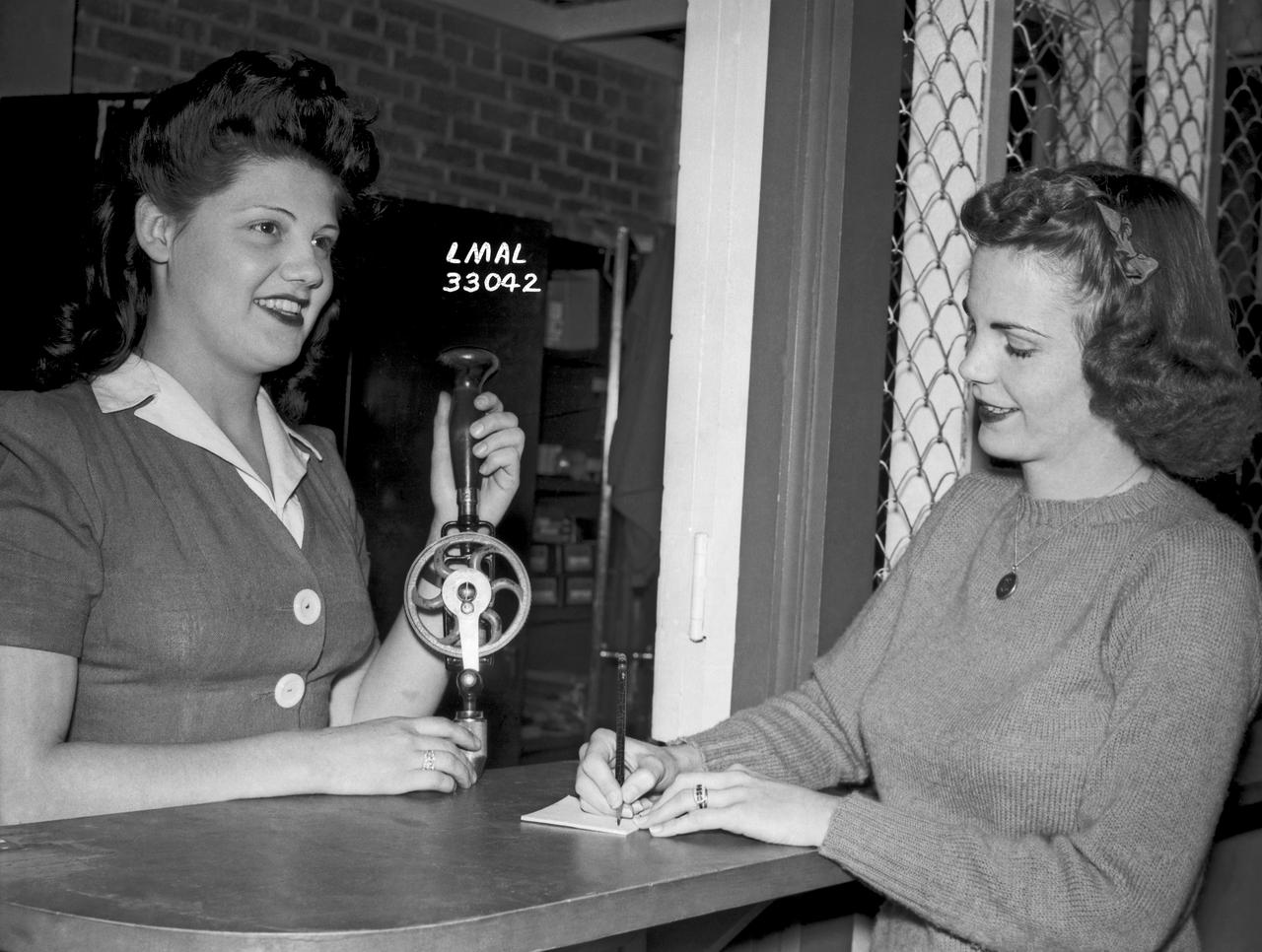

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
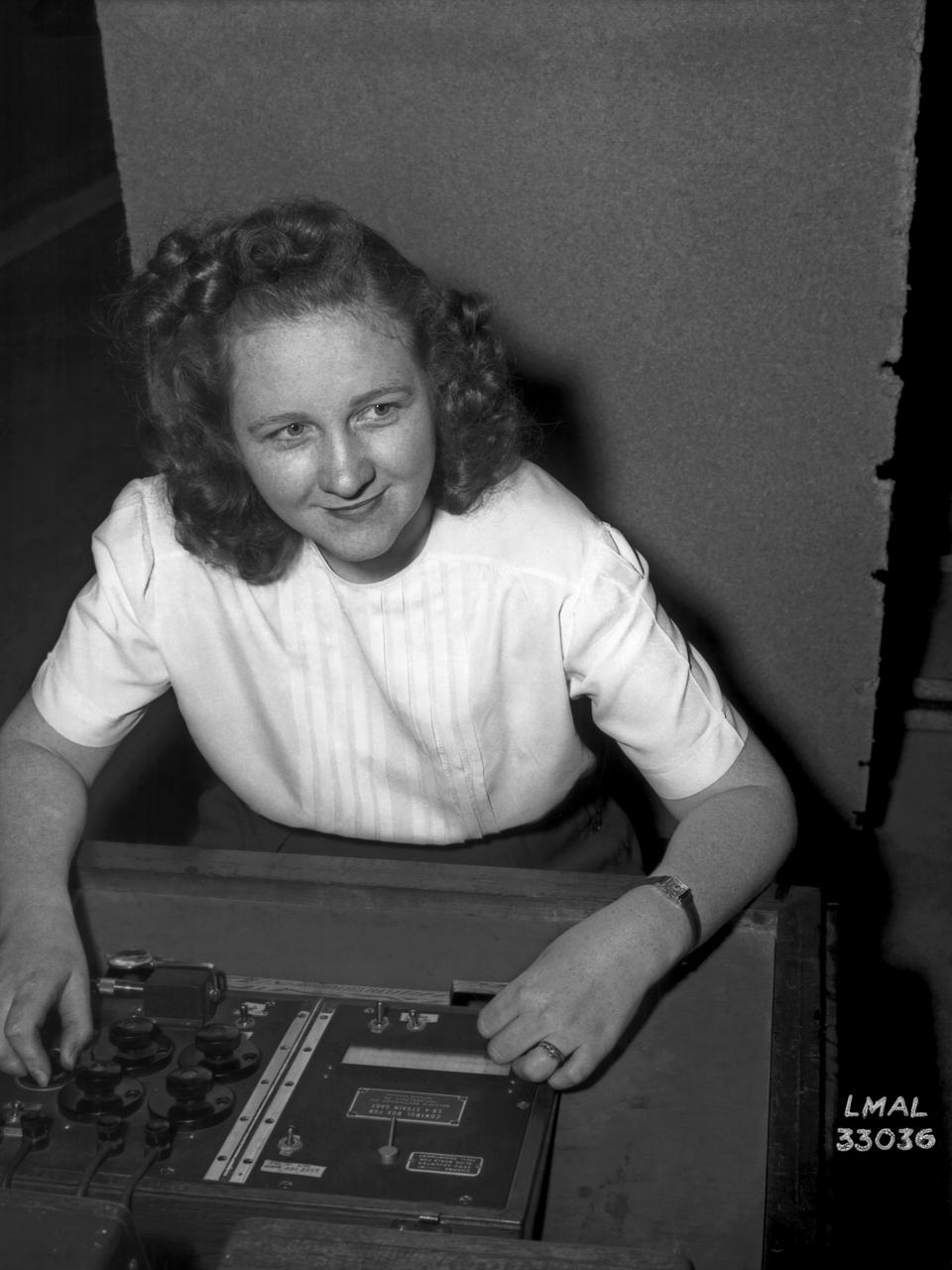

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
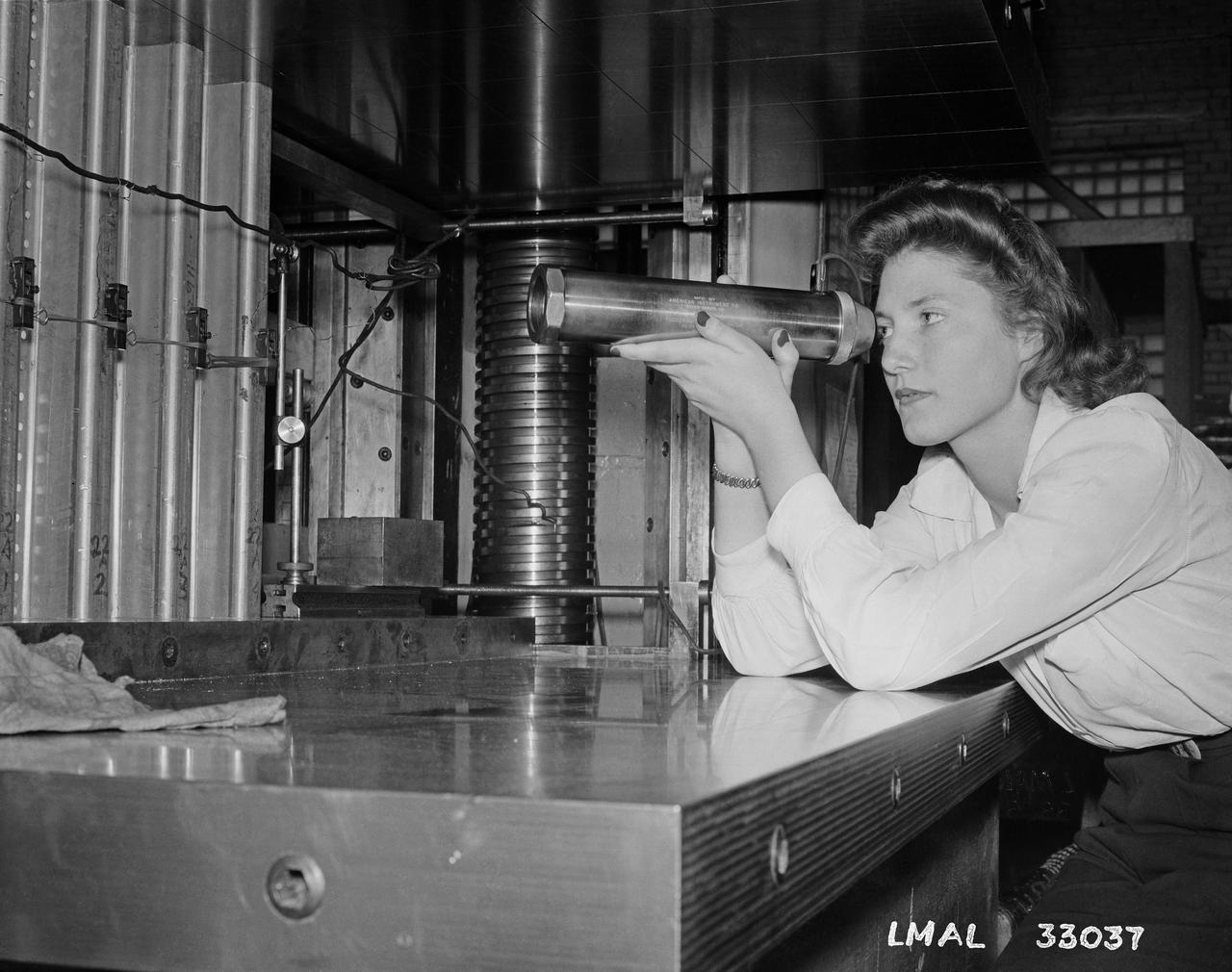

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
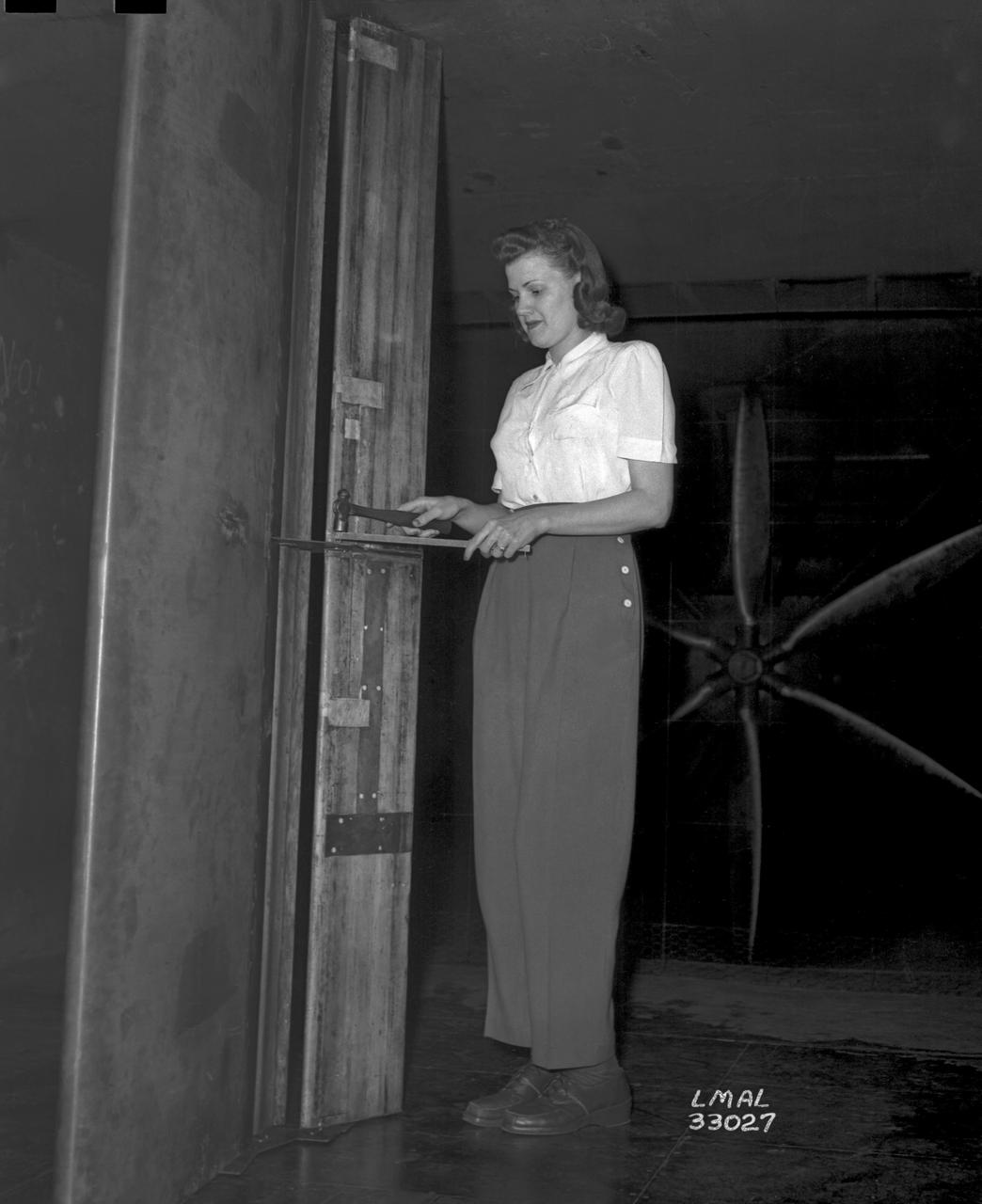

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
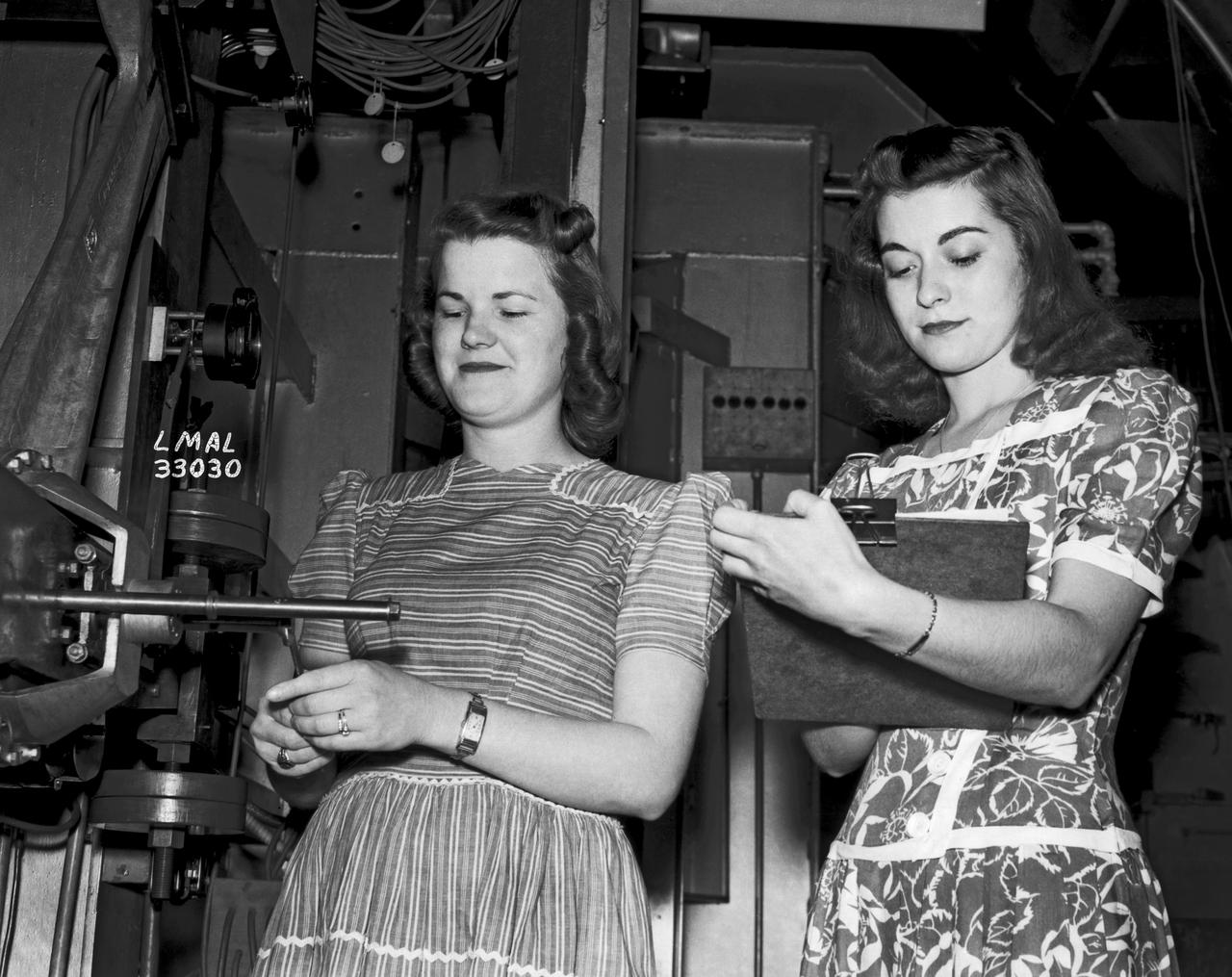

Women Adequately Filling Posts in NACA Laboratory: Nearly 200 women are employed at the Langley Laboratory of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics in a limited capacity as mechanics’ helpers and minor laboratory aids on the jobs formerly handled by men, according to E.H. Derring, of the Aerodynamics Division. Many phases of the operations of various wind tunnels at the laboratory are now handled by women with experienced male supervision. Mr. Derring said, pointing out that the reading of the data indicated on wind tunnel instruments during a test is done in a large measure by women. In addition to reading the instruments and computing and integrating engineering test data obtained from tunnel investigations, the minor laboratory aides assist in the preparation of aircraft models preliminary to testing. Women employees who will serve in the Aerodynamics Division of the Laboratory attend an orientation class for two weeks, during which they receive instruction on phases of the work they will do and their aptitudes for different types of work are evaluated in order that they may be properly placed. More than 100 women are employed in minor laboratory apprentices, performing mechanical work heretofore done by men. These women are employed in the various shops of the laboratory. Women in the woodworking shops are taught to operate 15 different machines in carrying out their assignments. Norfolk new paper article from 1943 by Lee Dickinson.
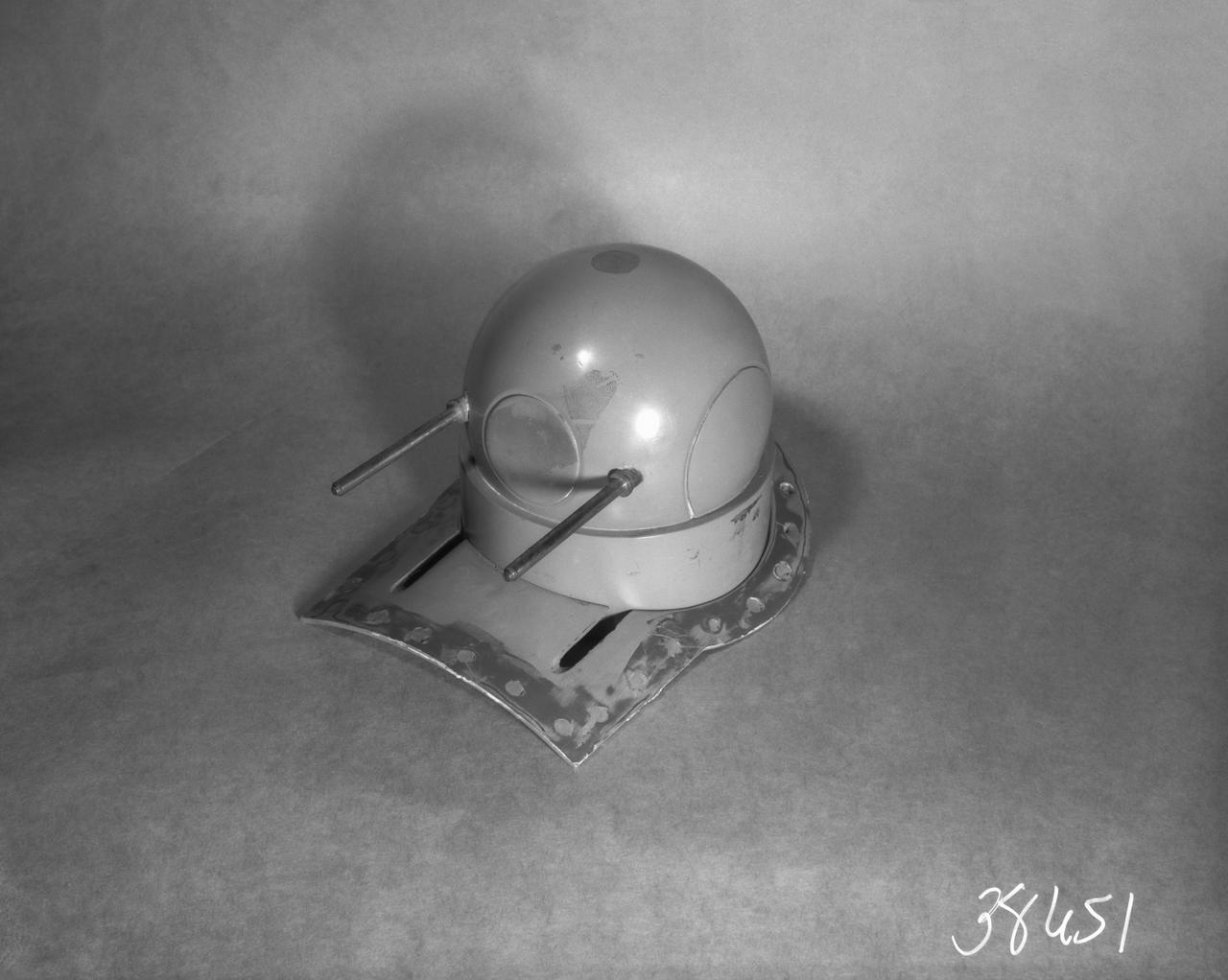

1/8 Scale B-32 Turrets. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.
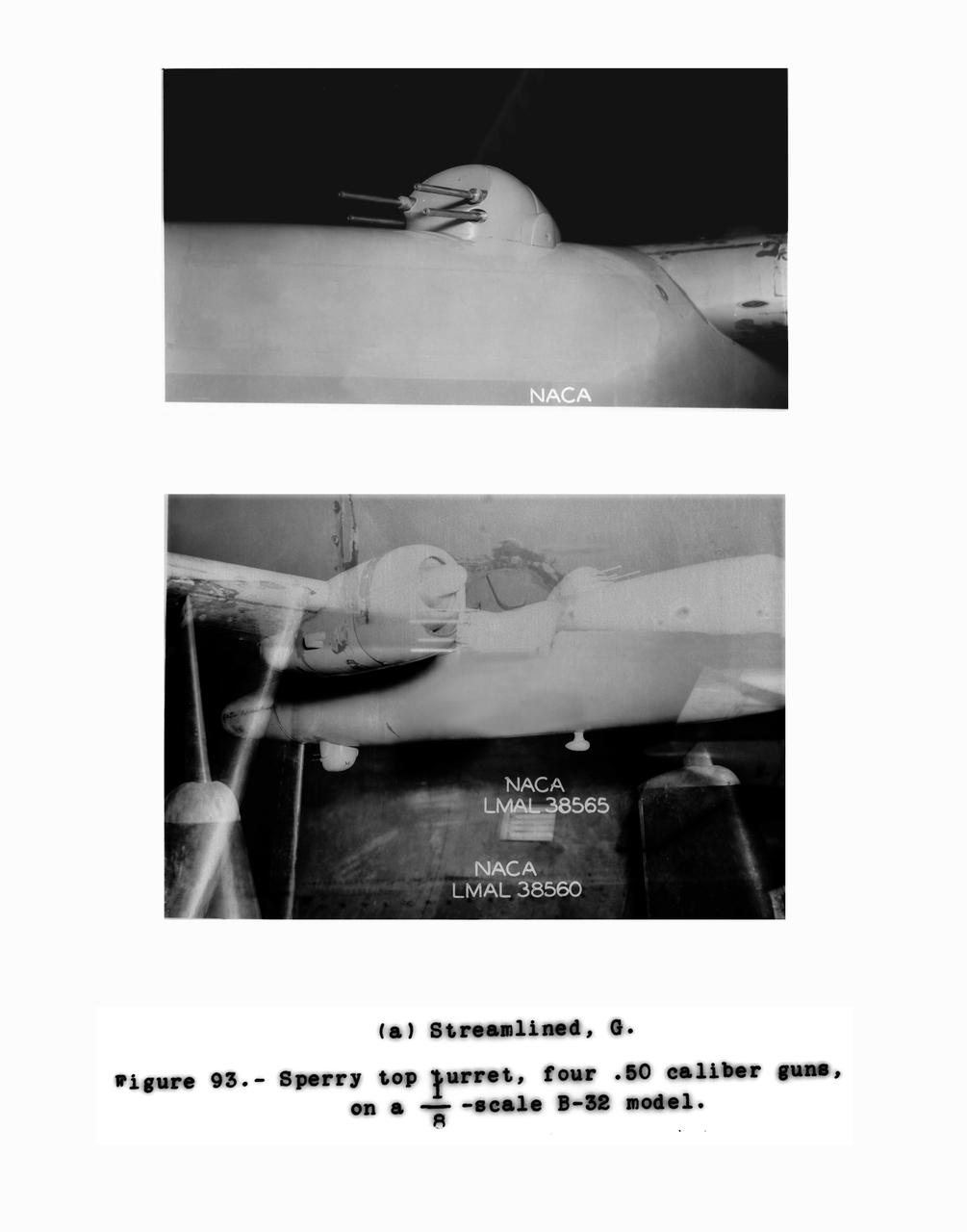
Detail Shots of B-32 Turret Figure 93. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.
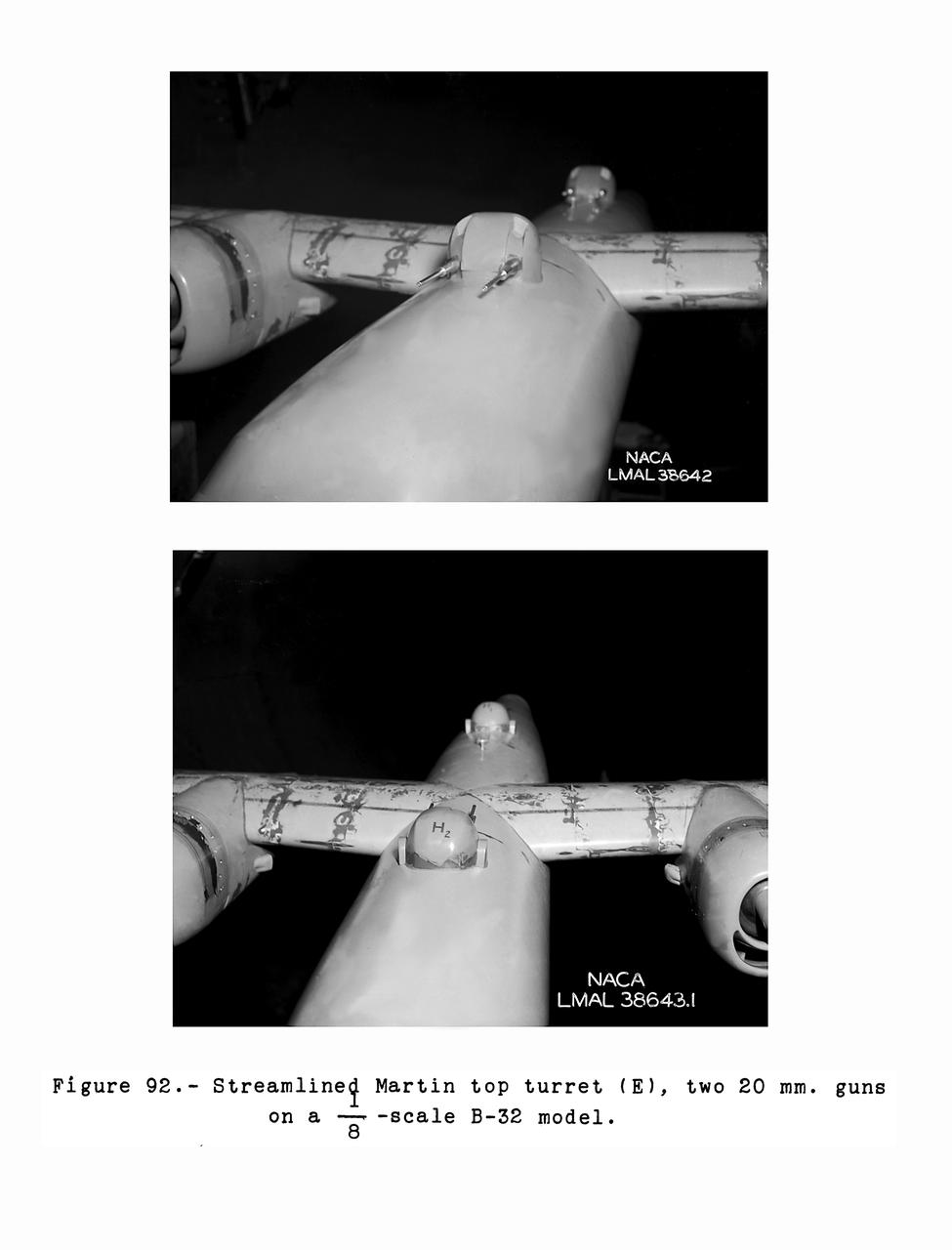
Gun Turrets of XP-35 Figure 92 Streamlined Martin Top Turret. B-33 Vega Turrets. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.
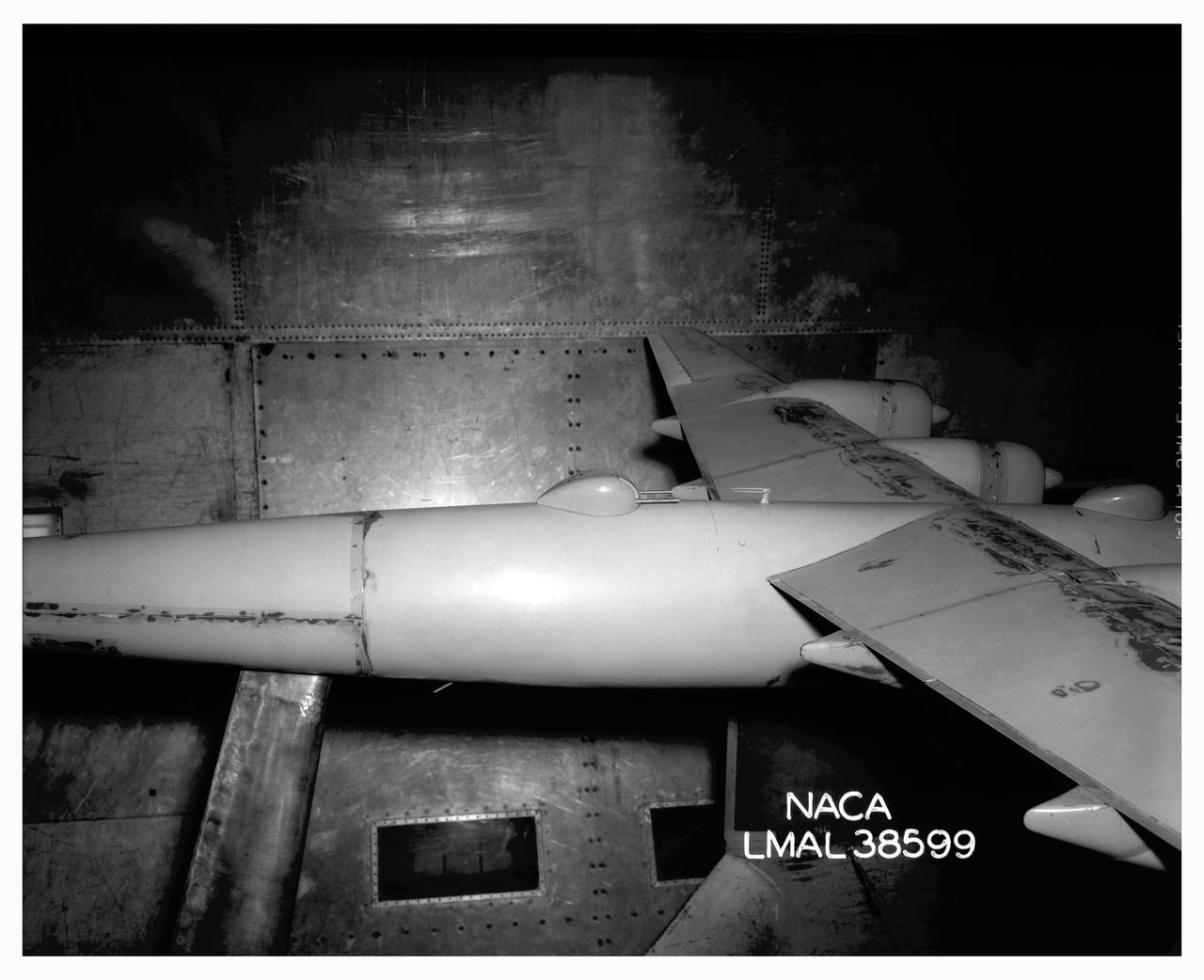

B-32 Model Close Up. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.
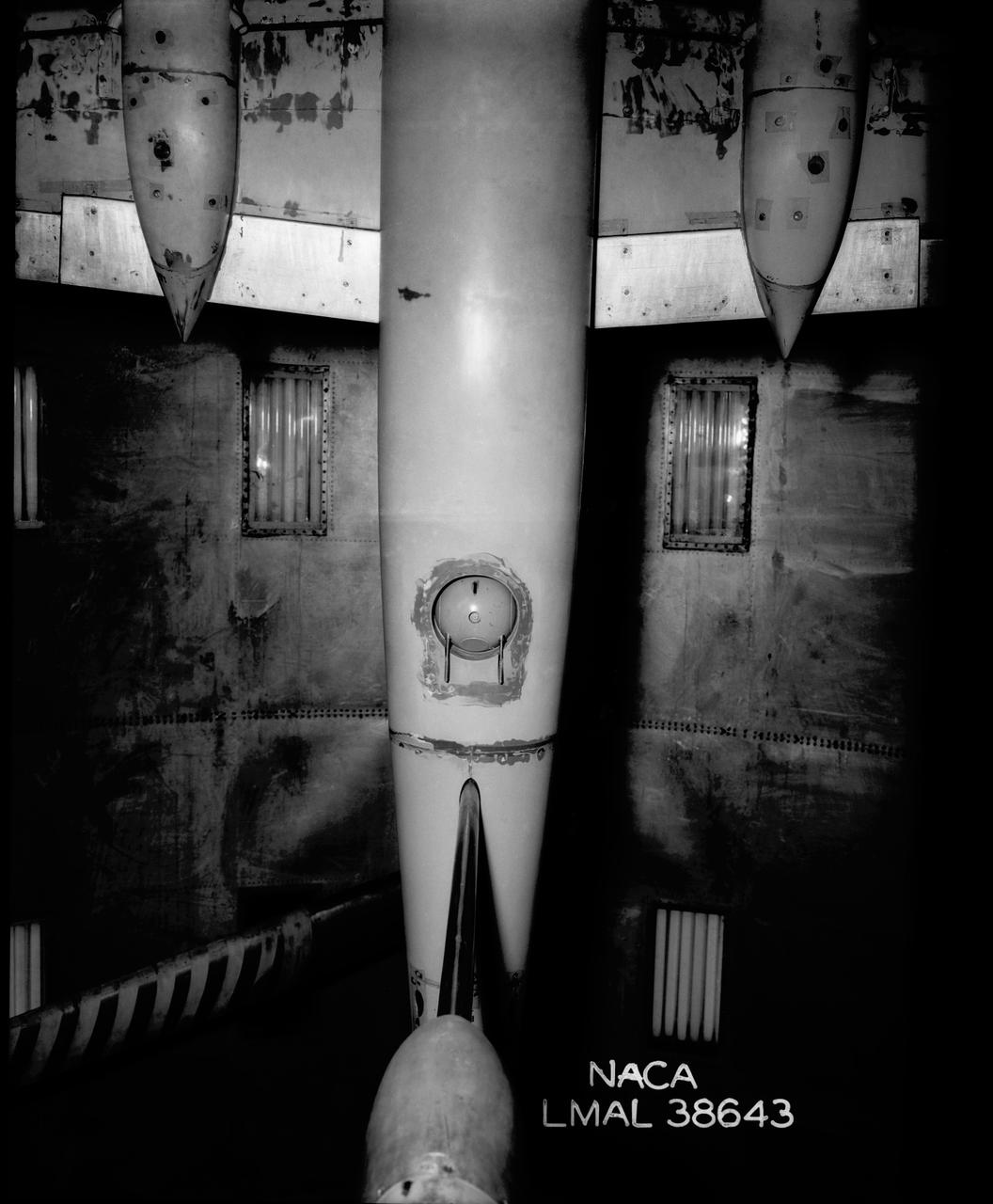

Gun Turrets of XP-35. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.
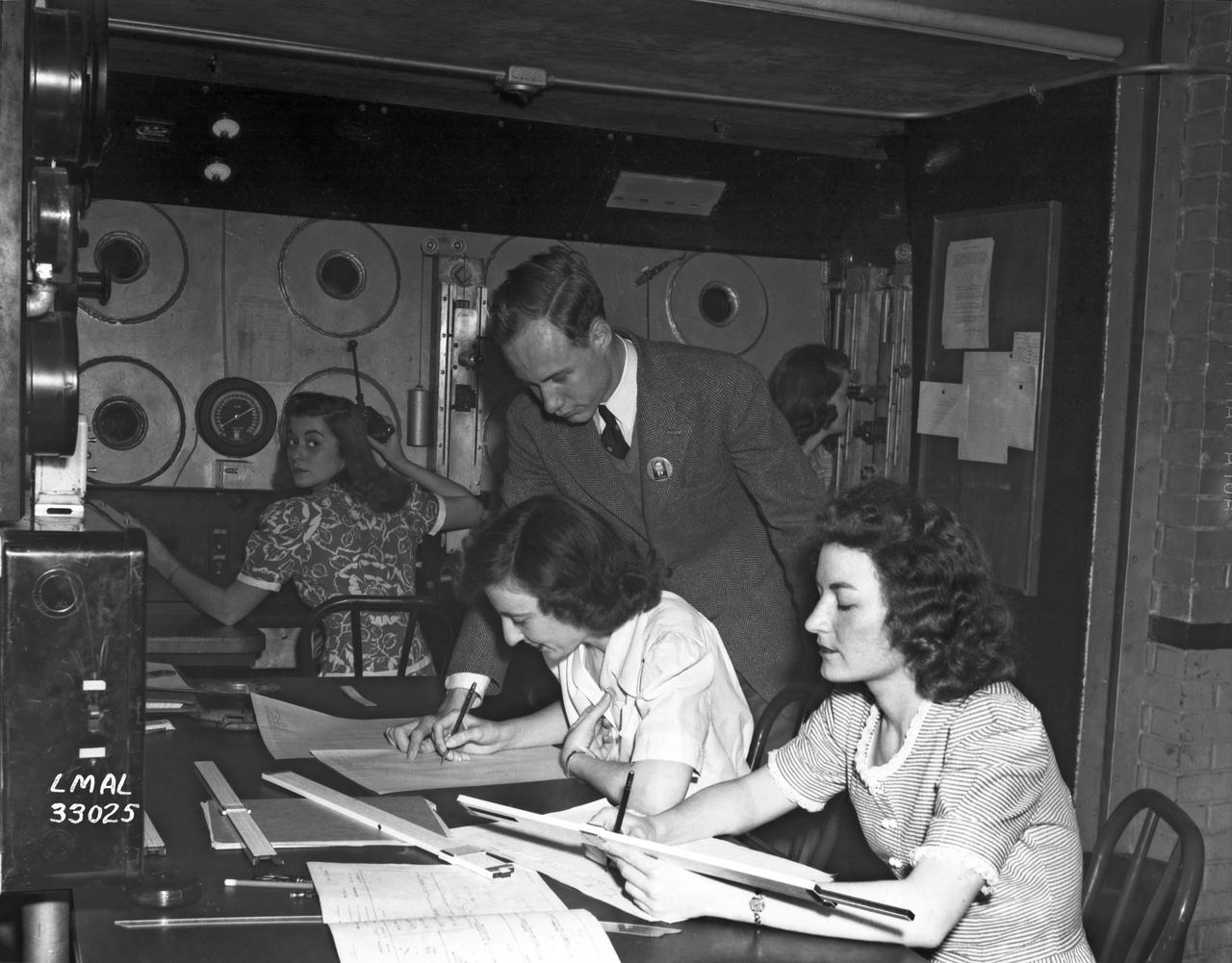

In the picture are F.F. Fullmer, aeronautical engineer, supervise a group of women who are helping operate the research equipment in the two-dimensional wind tunnel. Miss Elizabeth Patterson, left foreground, and Miss Katherine Thomason, right foreground obtains aerodynamic data, while Miss Lenore Woodland left background and Mrs. Blanche White help operate the tunnel. By Lee Dickinson 1943
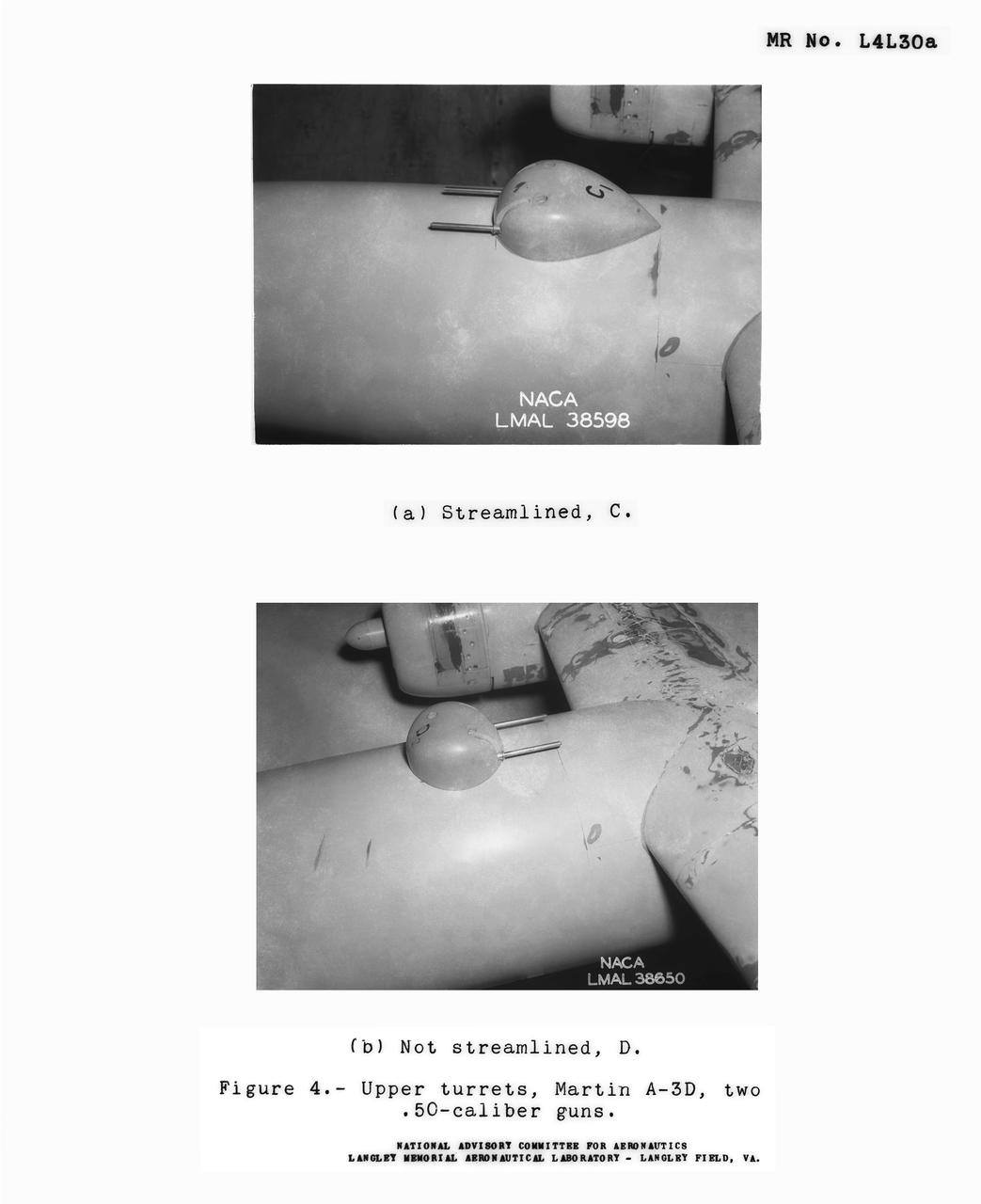
Detail Shots of B-32 Turret Figure 4. Upper turrets, Martin A-3D, Two .50 Caliber guns. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.
B-32 Model Close Up. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.
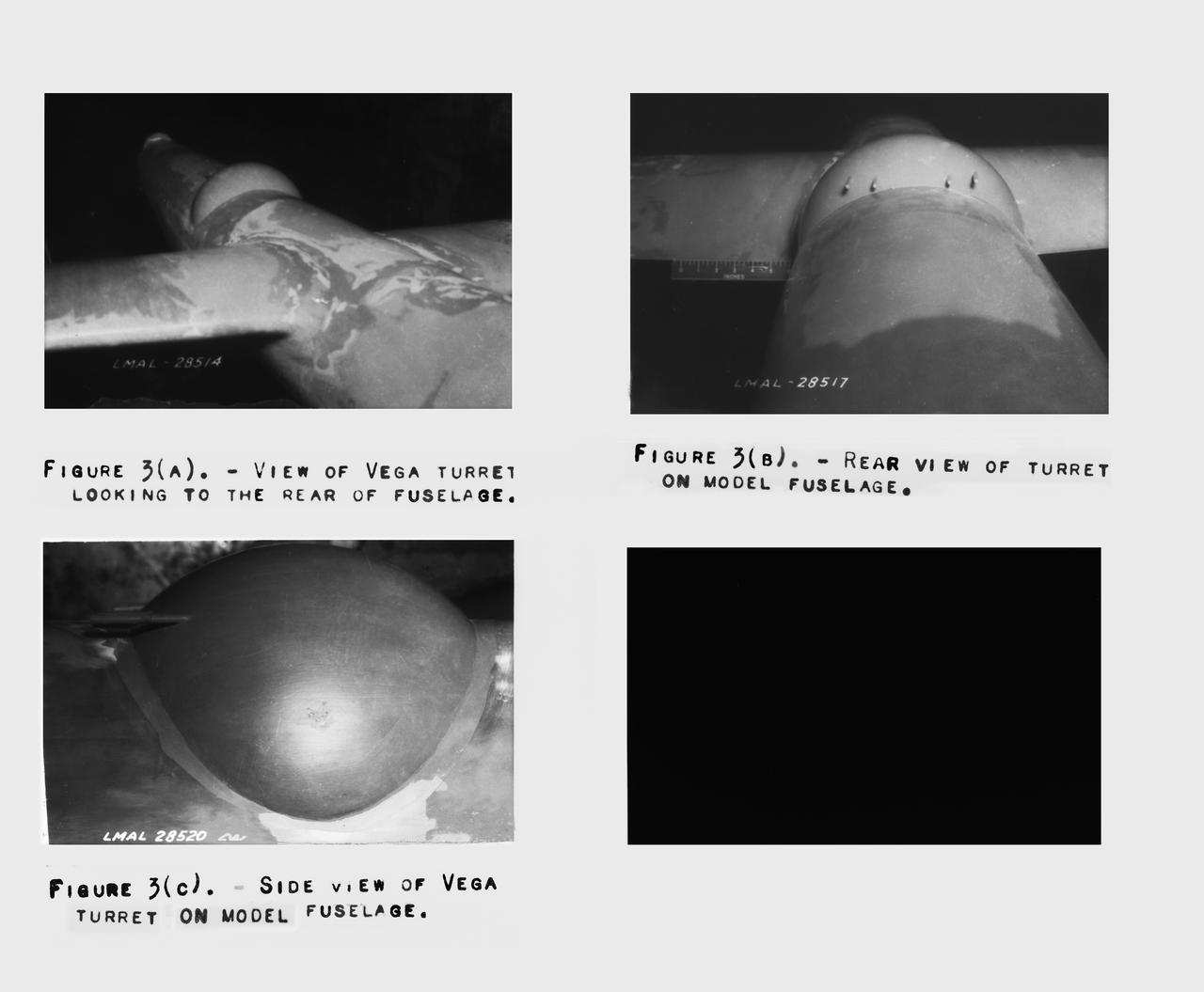
B-33 Vega Turrets. Photo are listed in the NACA Wartime report L-463, October 1942, Test of a Large Spherical Turret and a modified Turret on a Typical Bomber Fuselage by Axel T. Mattson.
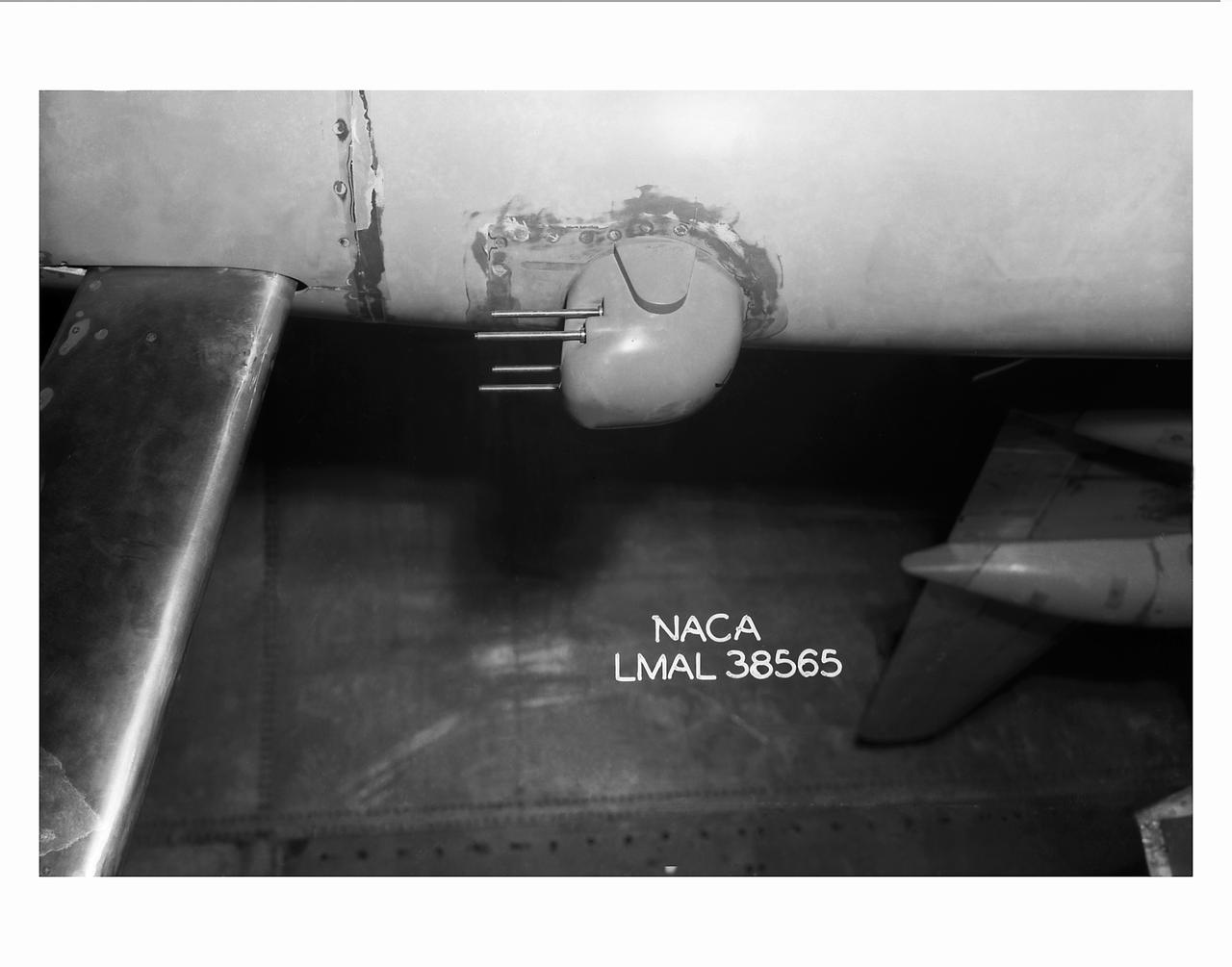

Detail Shots of B-32 Turret. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.
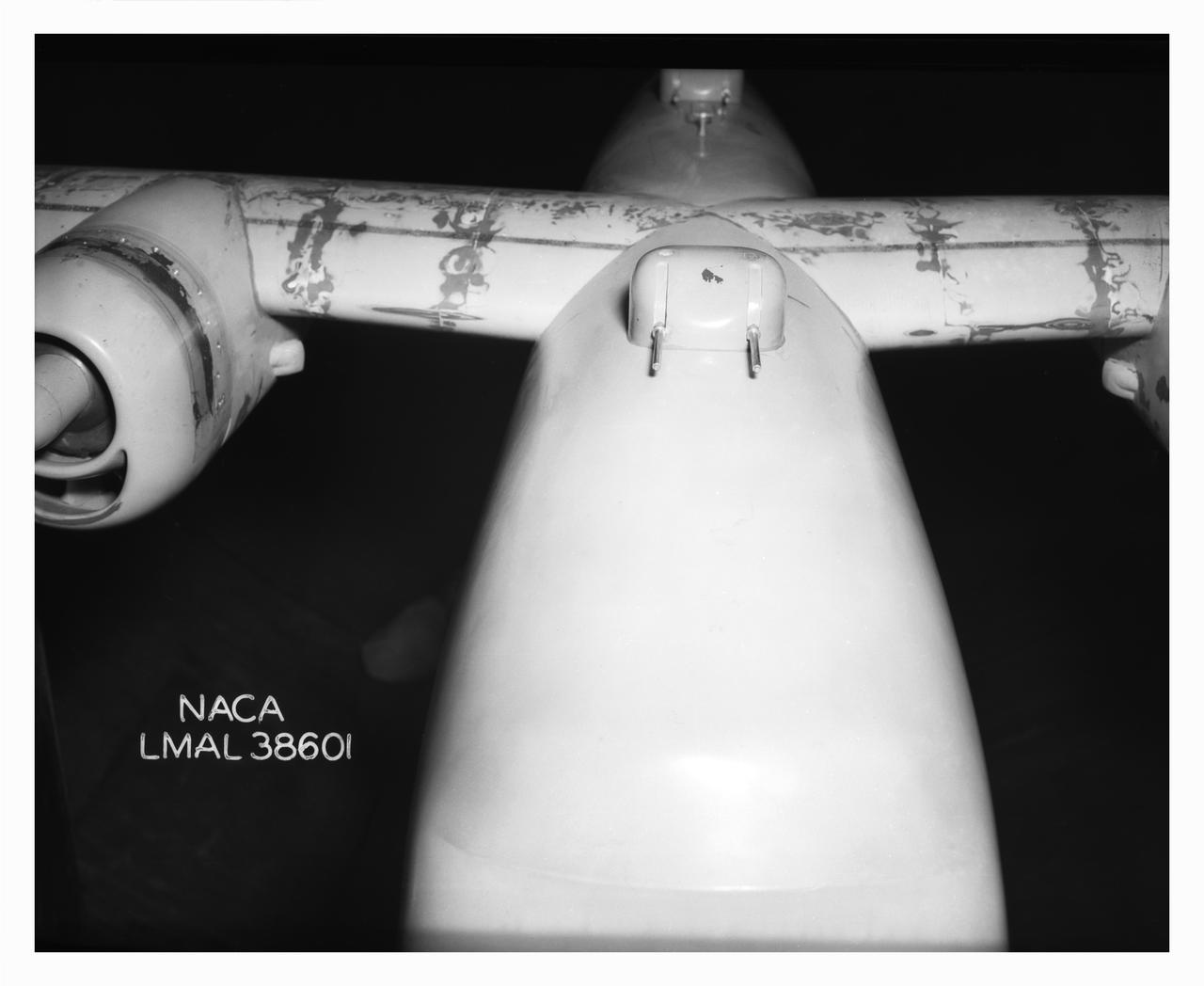
B-32 Model Close Up. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.
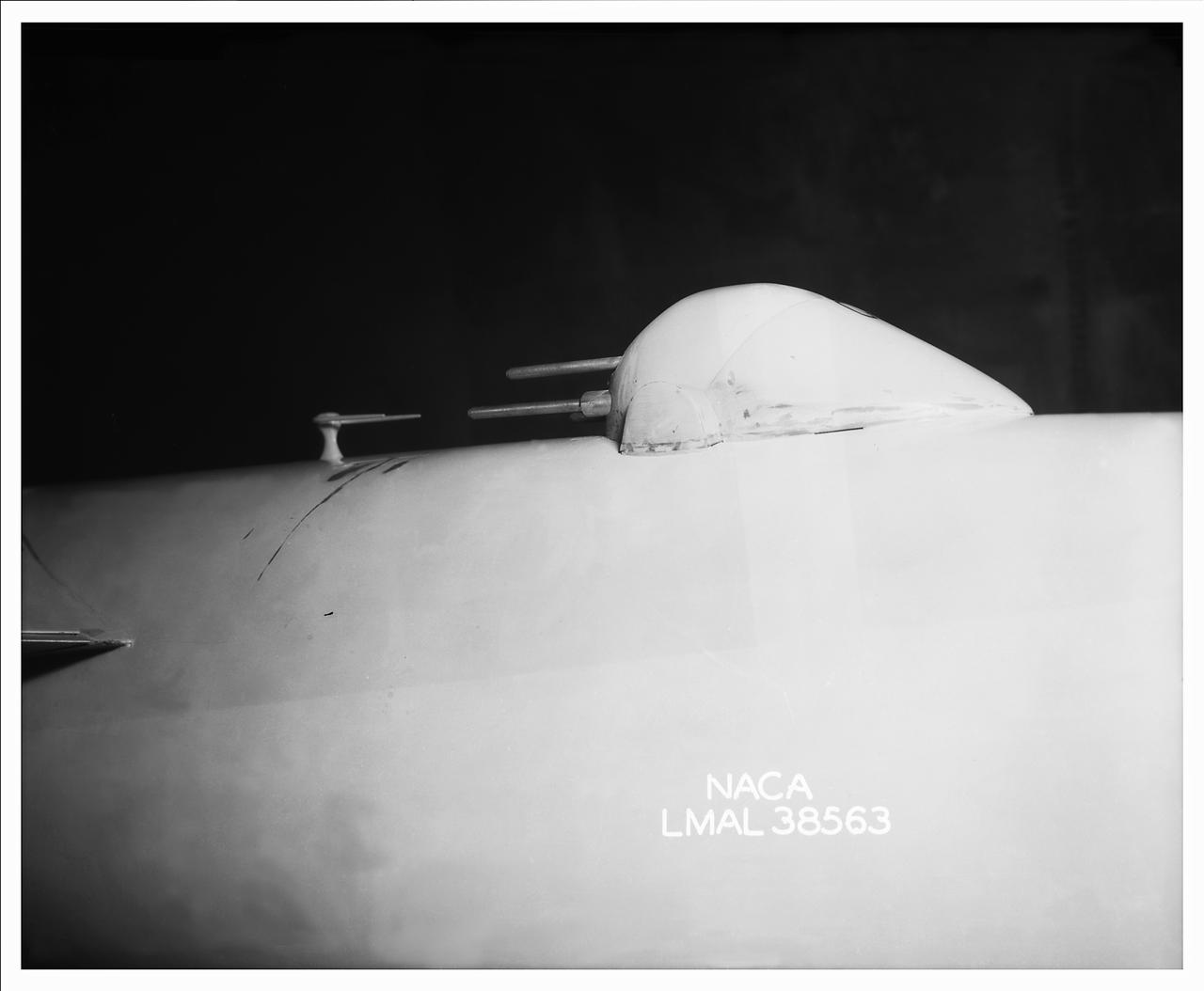

Detail Shots of B-32 Turret. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.

B-33 Vega Turrets. Photo are listed in the NACA Wartime report L-463, October 1942, Test of a Large Spherical Turret and a modified Turret on a Typical Bomber Fuselage by Axel T. Mattson.
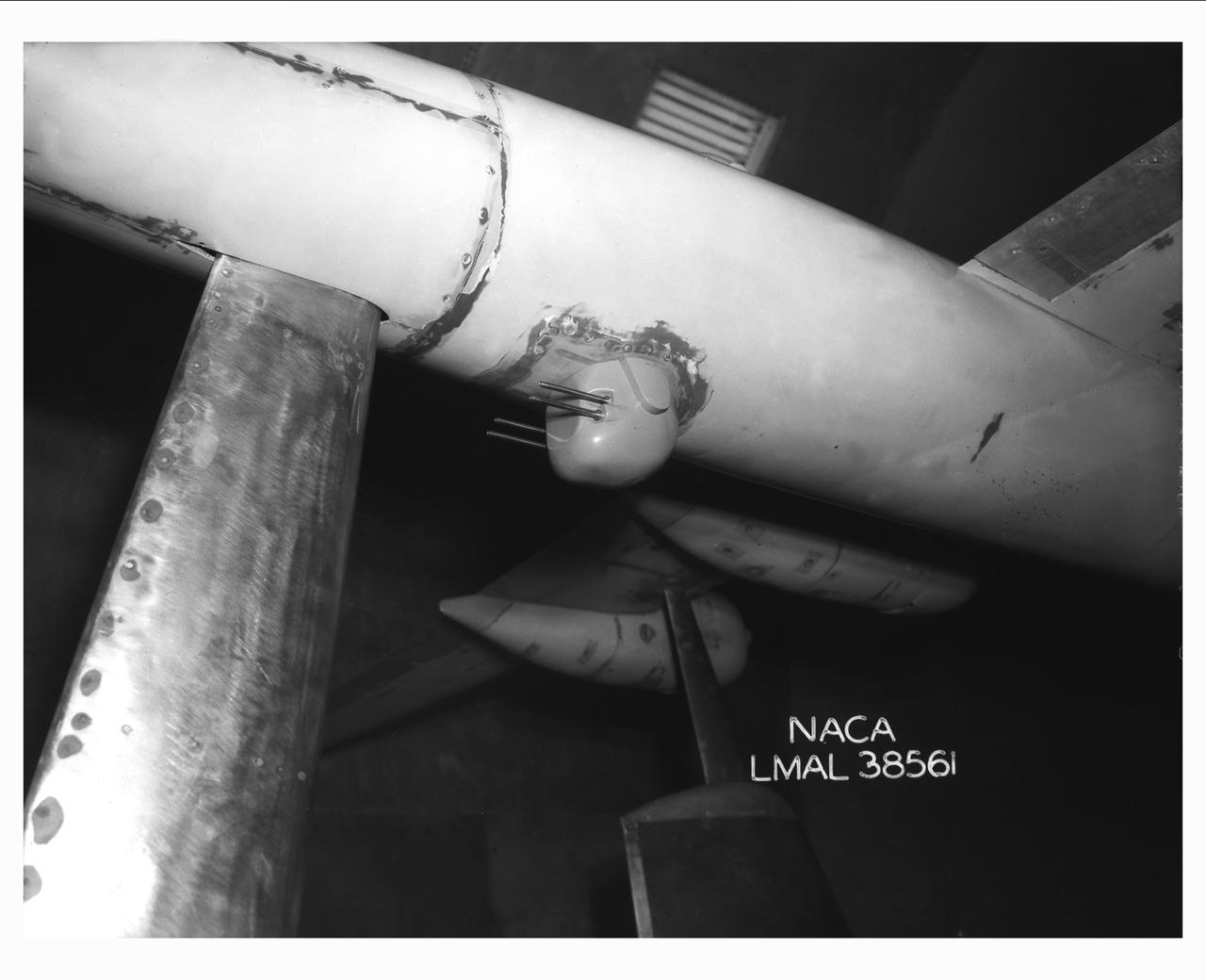

Detail Shots of B-32 Turret. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.
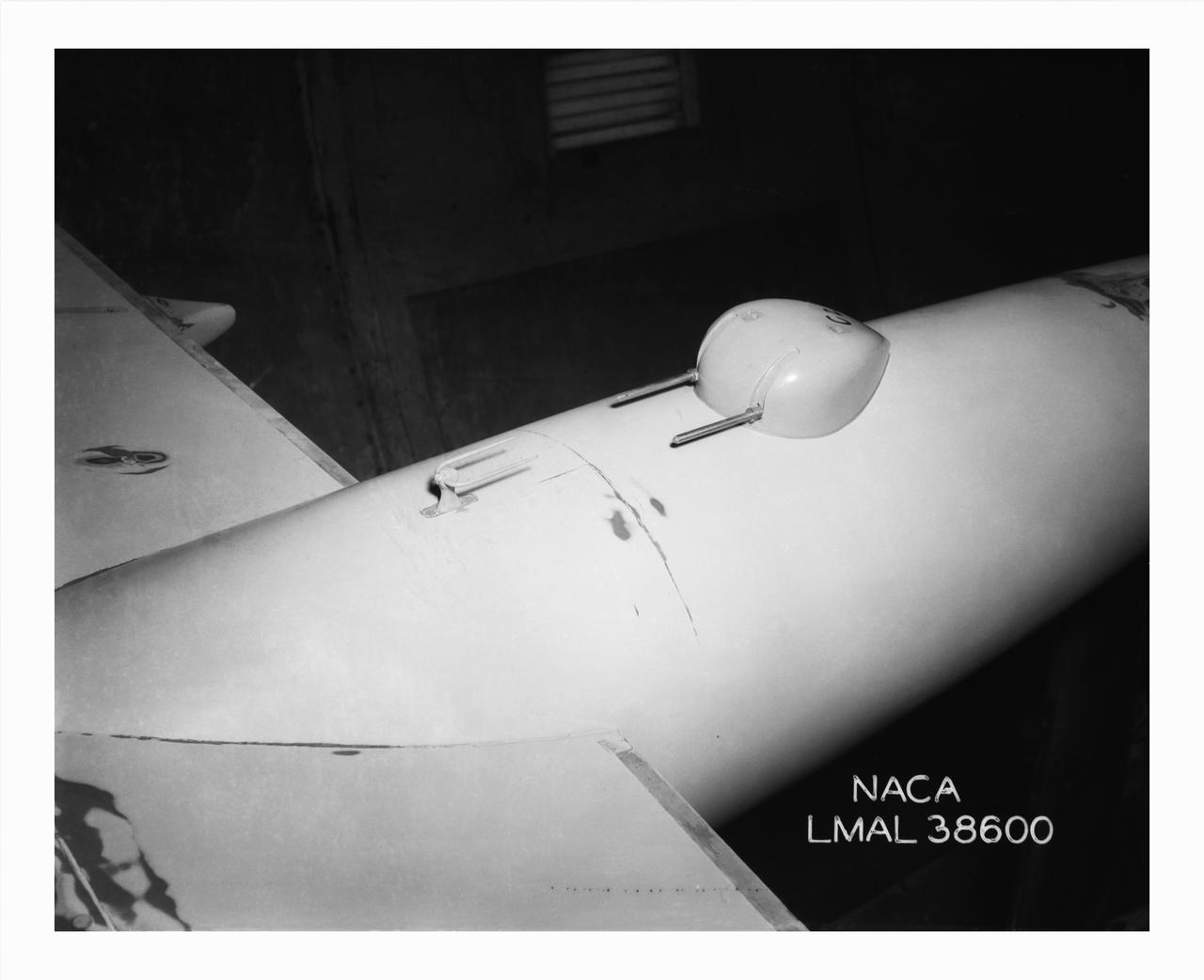
B-32 Model Close Up, Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.
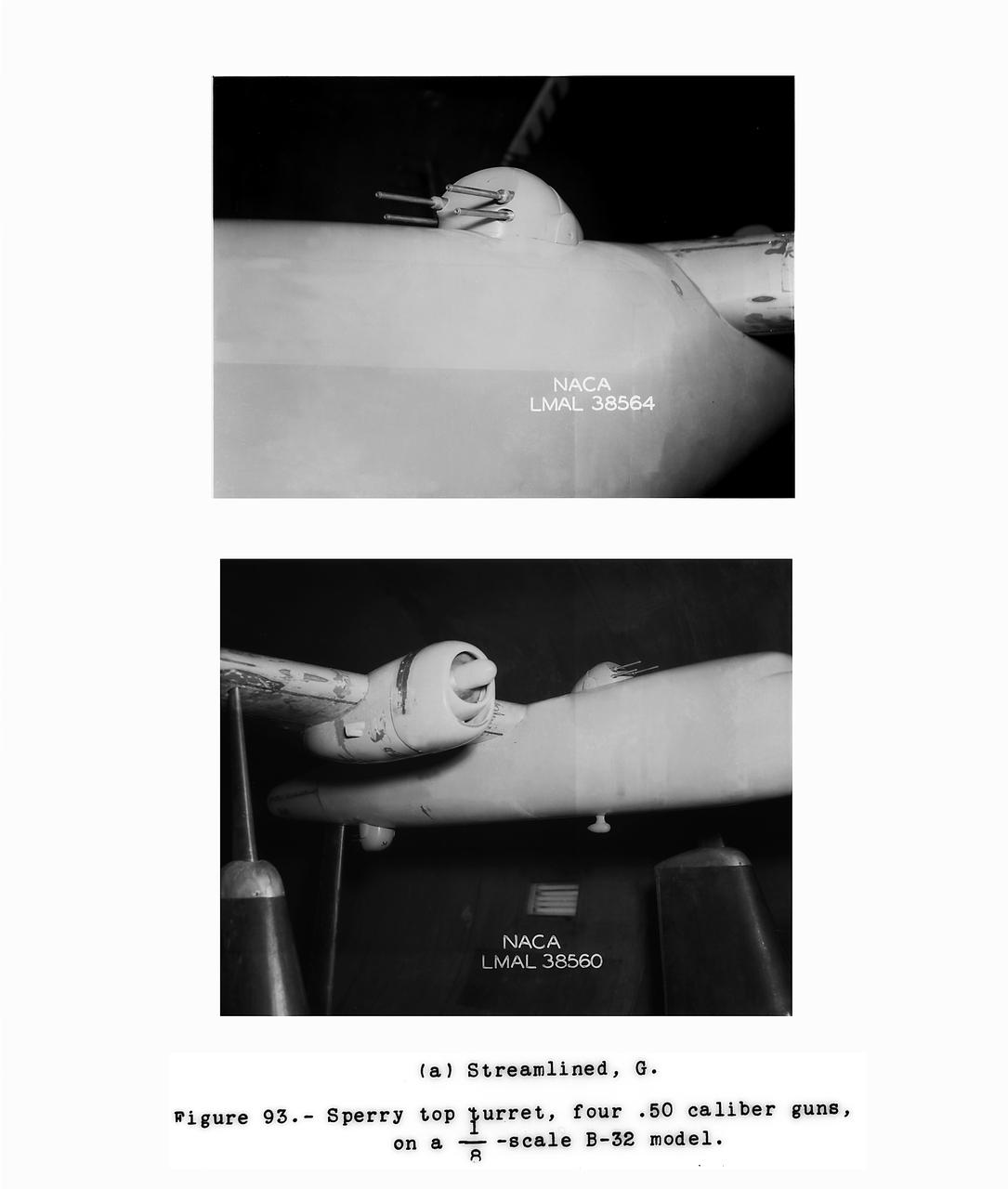
Detail Shots of B-32 Turret. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.

Detail Shots of B-32 Turret. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.
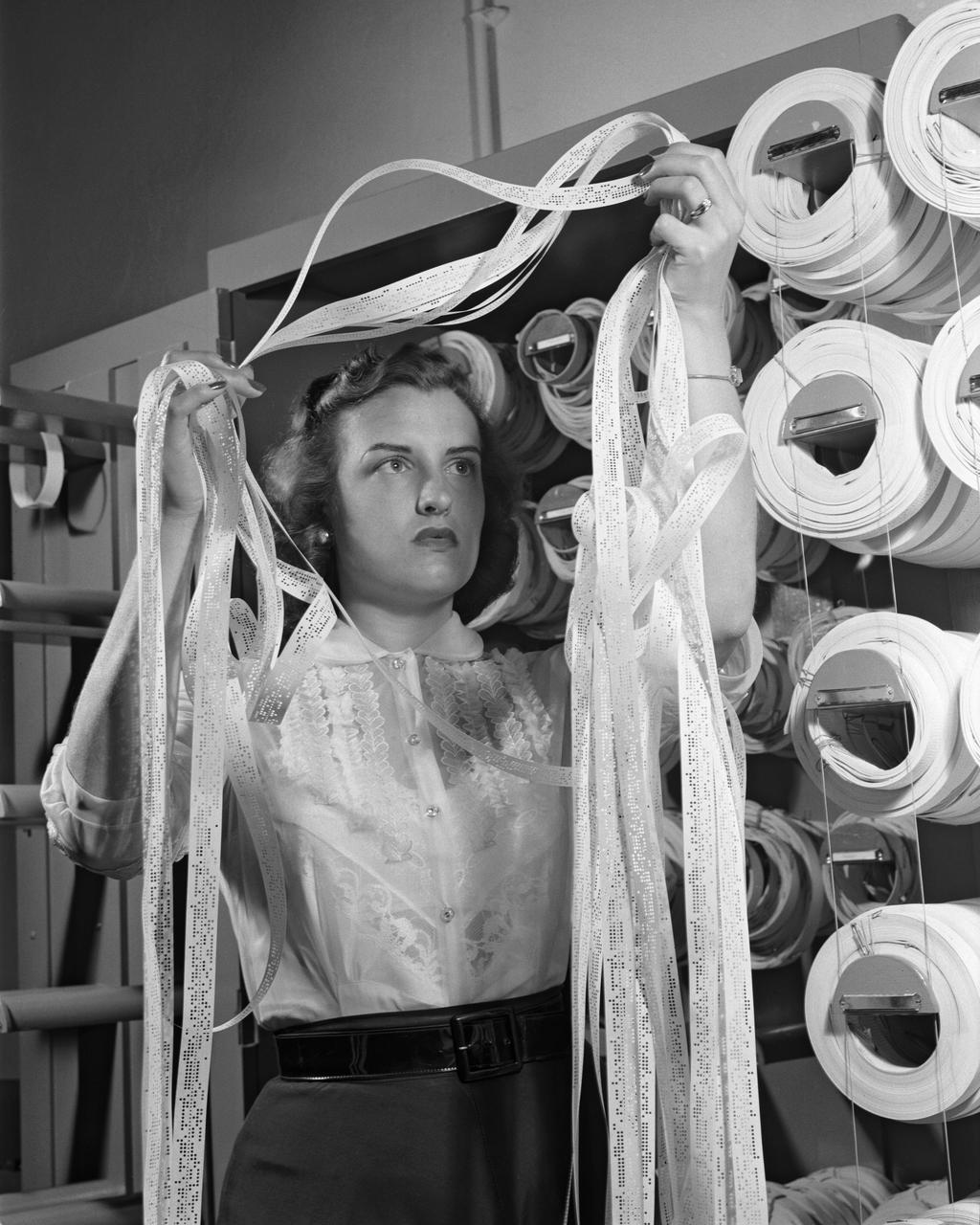

Women Adequately Filling Posts In NACA Laboratory: Mrs. Doris Rudd Porter Baron handling Manometertape, Bell computer.

B-32 Model Close Up. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.

Gun turrets of XP-35. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.

Detail Shots of B-32 Turret. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.

Detail Shots of B-32 Turret. B-33 Vega Turrets. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.

16 Foot Wind Tunnel personnel at work
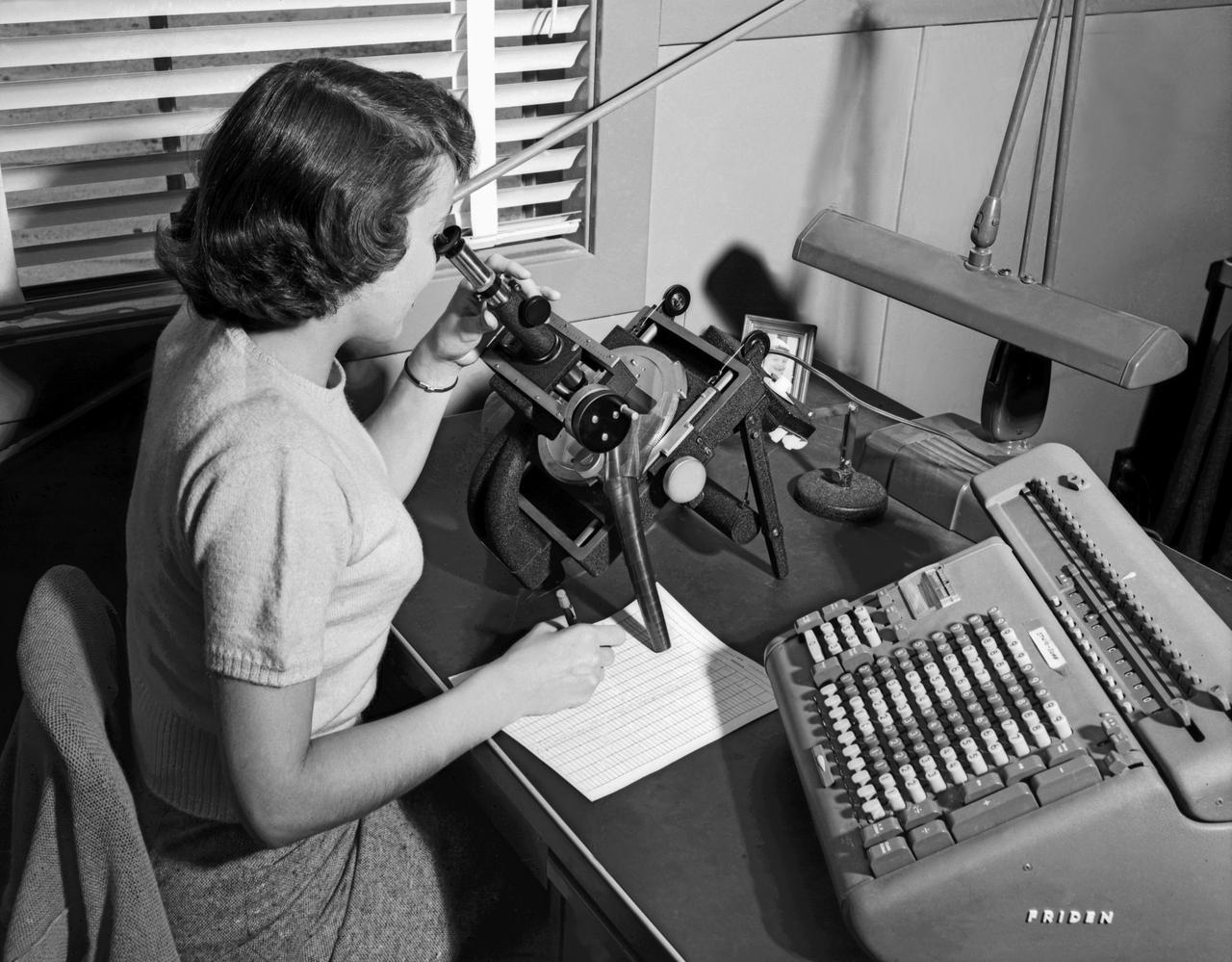

Langely Women Computer with X-4 with Friden machine. Publicity photo from Muroc California, showing female support personnel with equipment. Langley Computer with Friden machine.

Gun Turrets of XP-35. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.
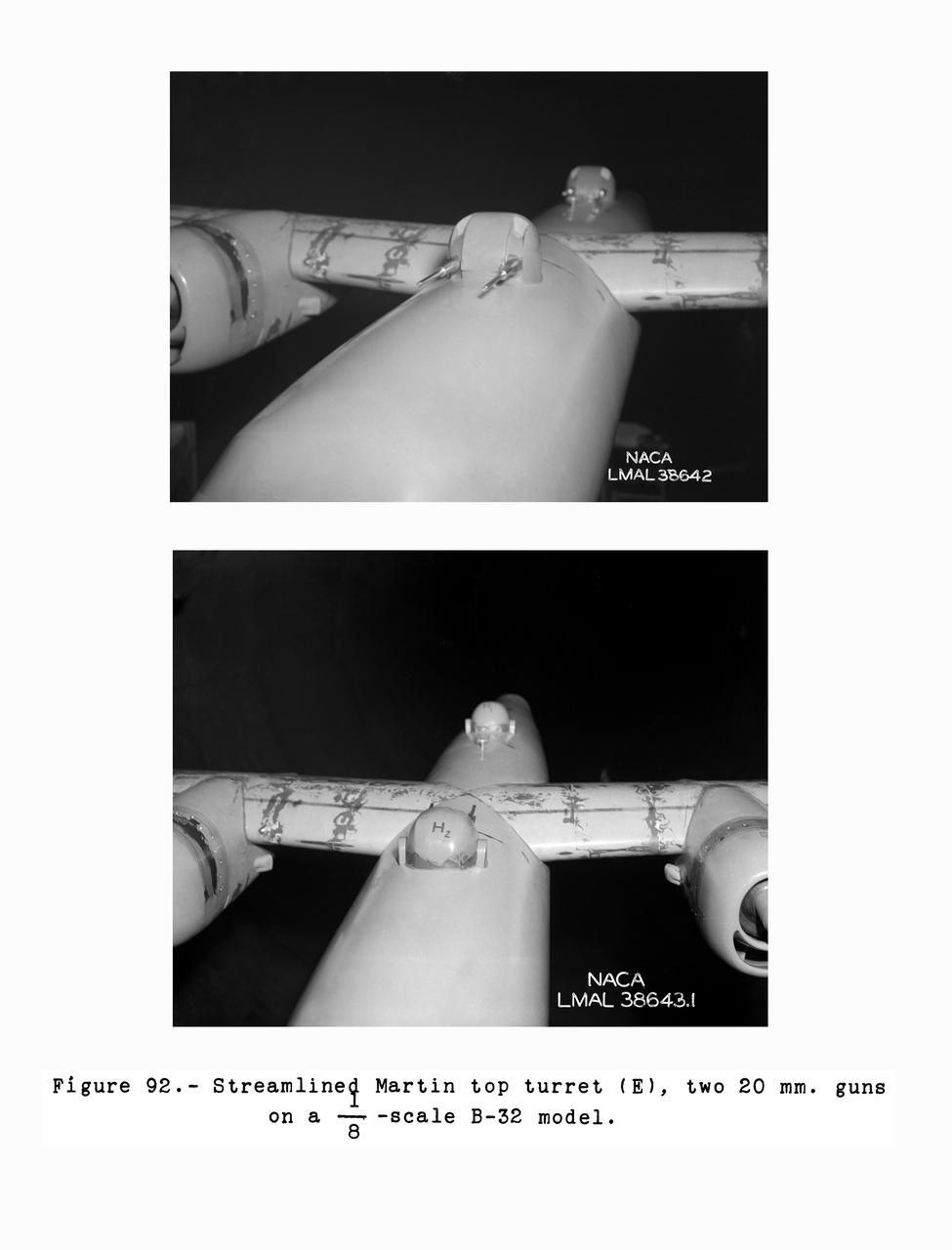
Gun Turrets of XP-35. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.

B-32 Model Close Up. Test conducted in the NACA 19 foot pressure tunnel LMAL-38560 NACA document.
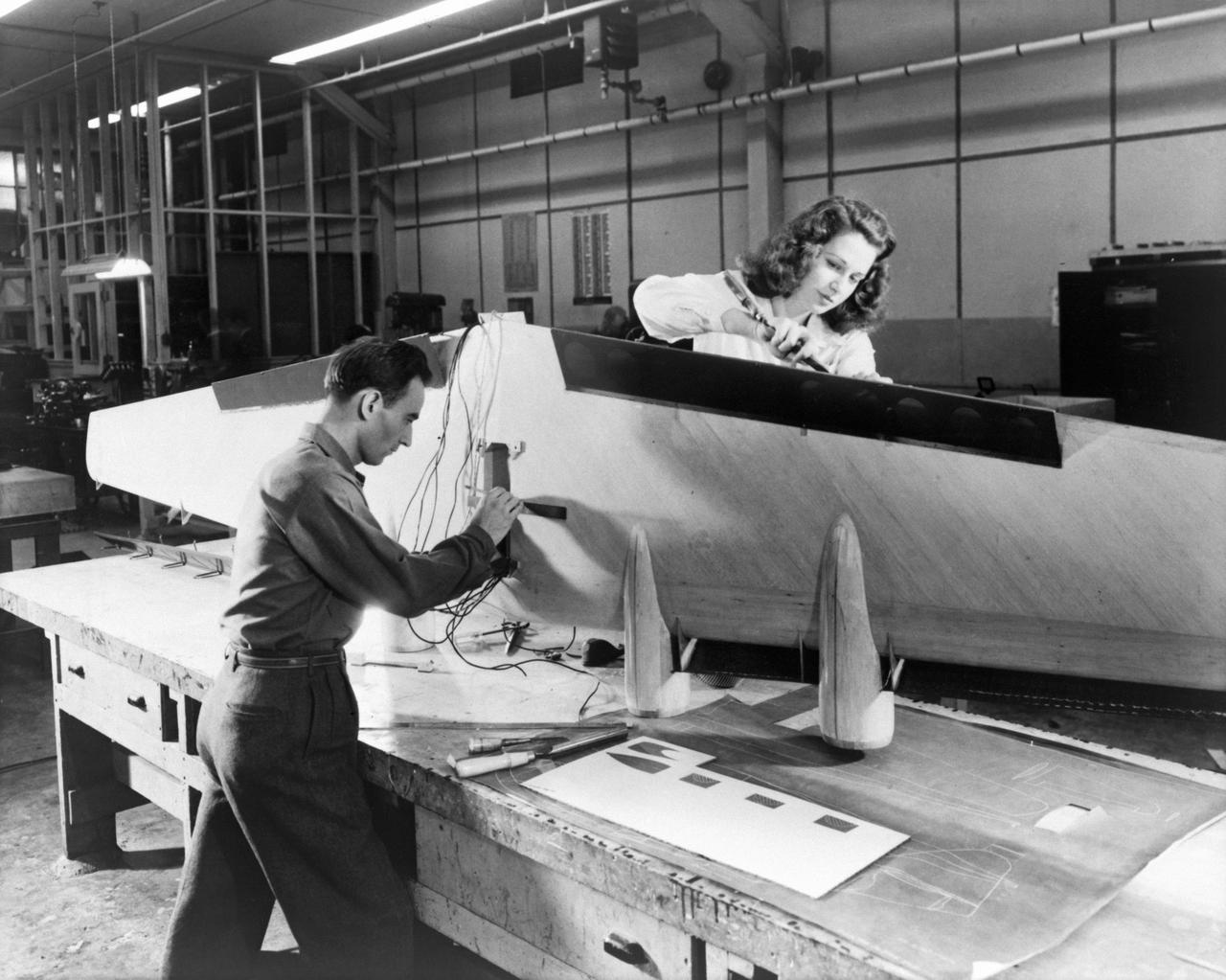

Technicians are pictured installing flaps and wiring on a flying-boat model, circa 1944 (page 47). Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication, by James Schultz. Photograph also published in Engineer in Charge: A History of the Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, 1917-1958 by James R. Hansen (page 209). -- Photographed on: 04/24/1946.
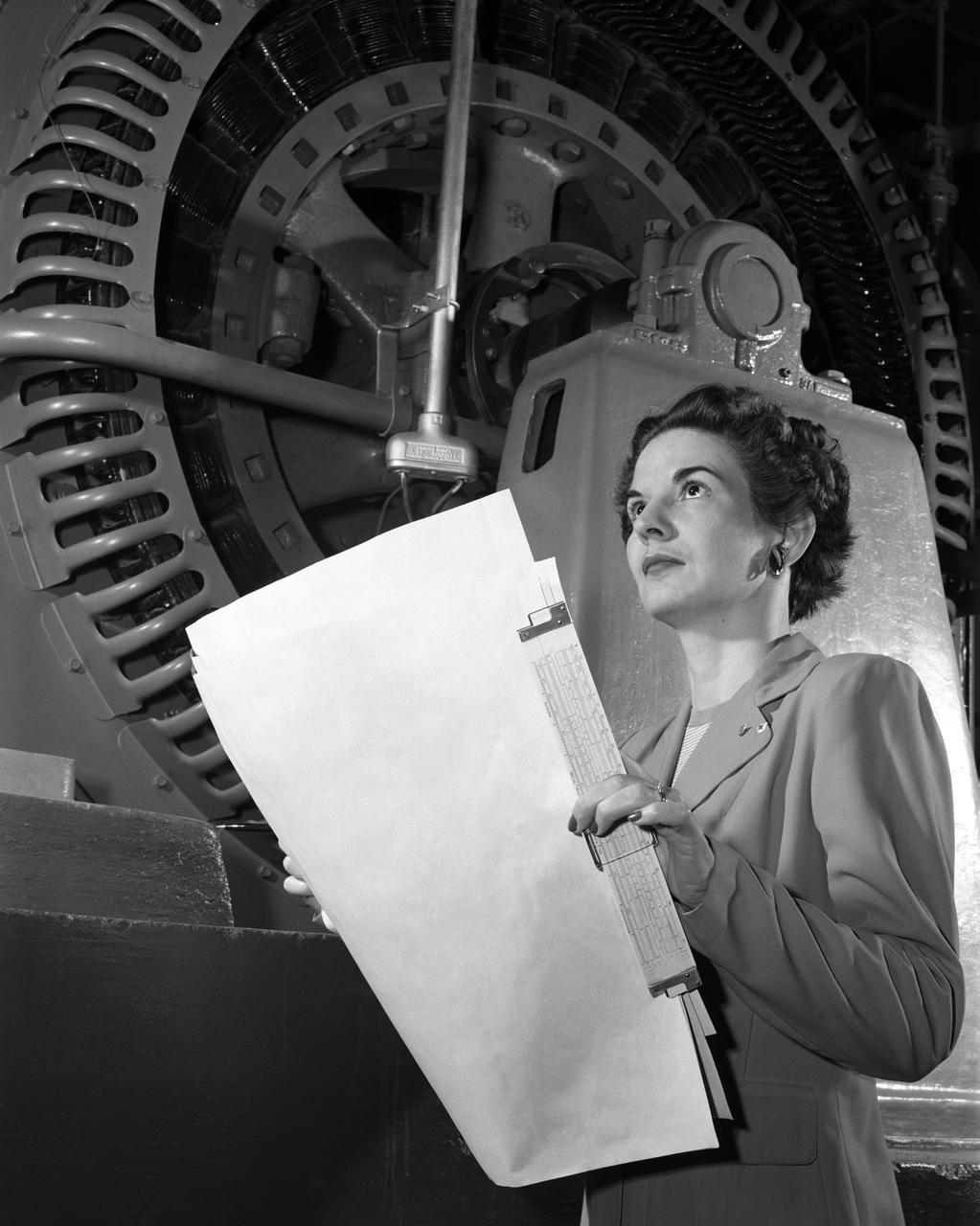

electrical engineer.NACA engineer Kitty Joyner, believed to be the first NACA female engineer, as well as the first women engineer to graduate from UVA.
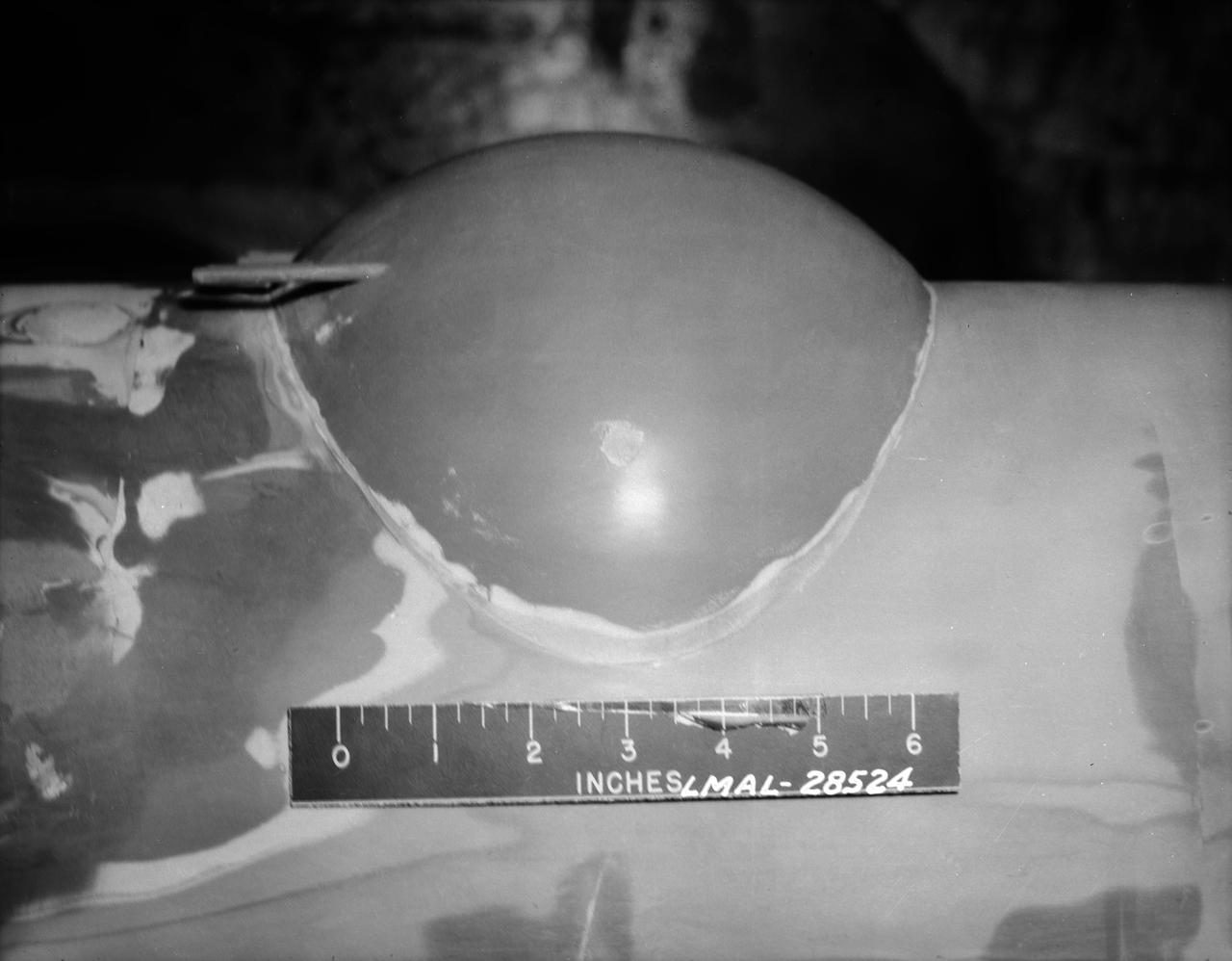
B-33 Vega Turrets. Photo are listed in the NACA Wartime report L-463, October 1942, Test of a Large Spherical Turret and a modified Turret on a Typical Bomber Fuselage by Axel T. Mattson.
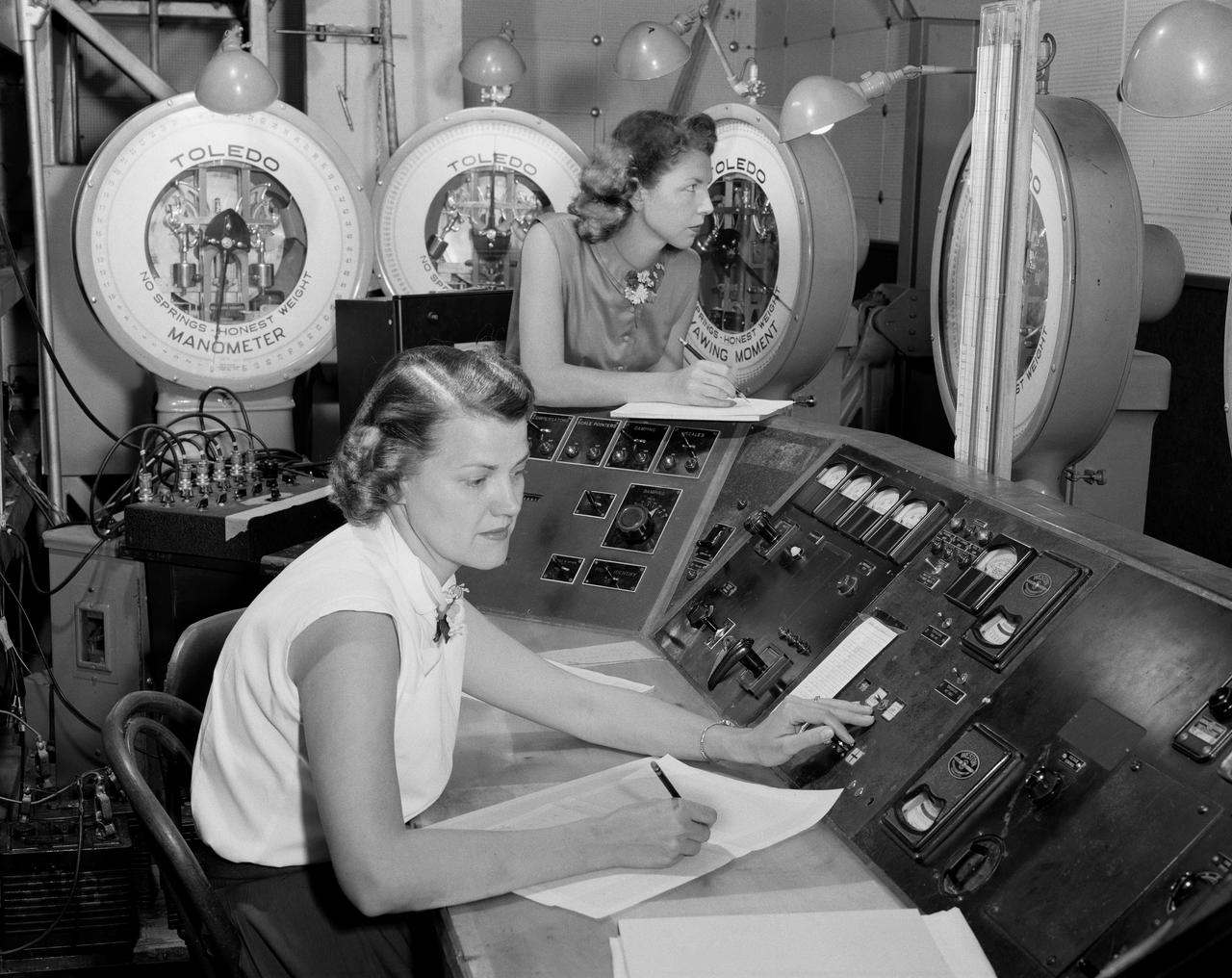

Women Workers at NACA
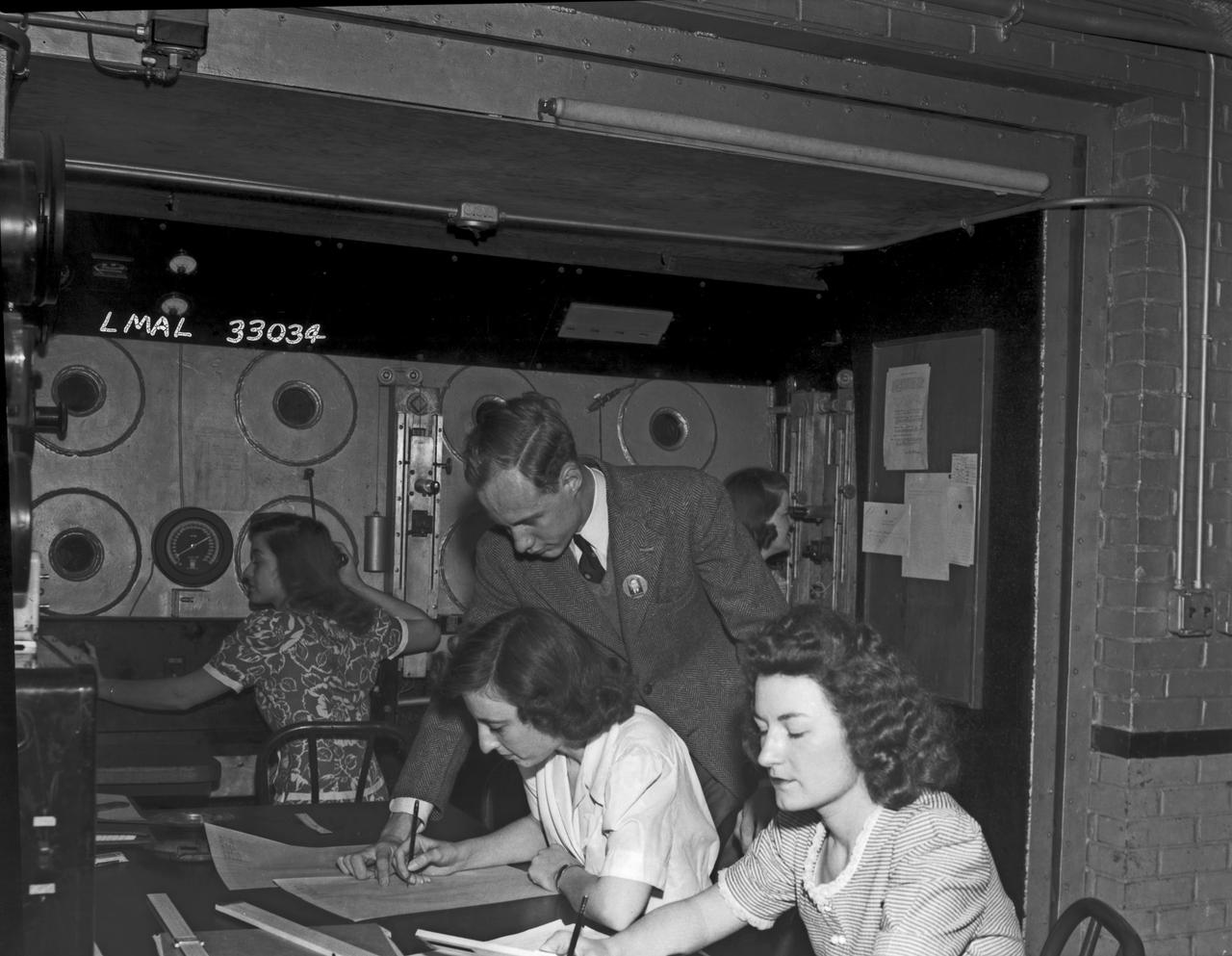

Women Adequately Filling Posts In NACA Laboratory: In the picture are F.F. Fullmer, aeronautical engineer, supervise a group of women who are helping operate the research equipment in the two-dimensional wind tunnel. Miss Elizabeth Patterson, left foreground, and Miss Katherine Thomason, right foreground obtains aerodynamic data, while Miss Lenore Woodland left background and Mrs. Blanche White help operate the tunnel. By Lee Dickinson 1943
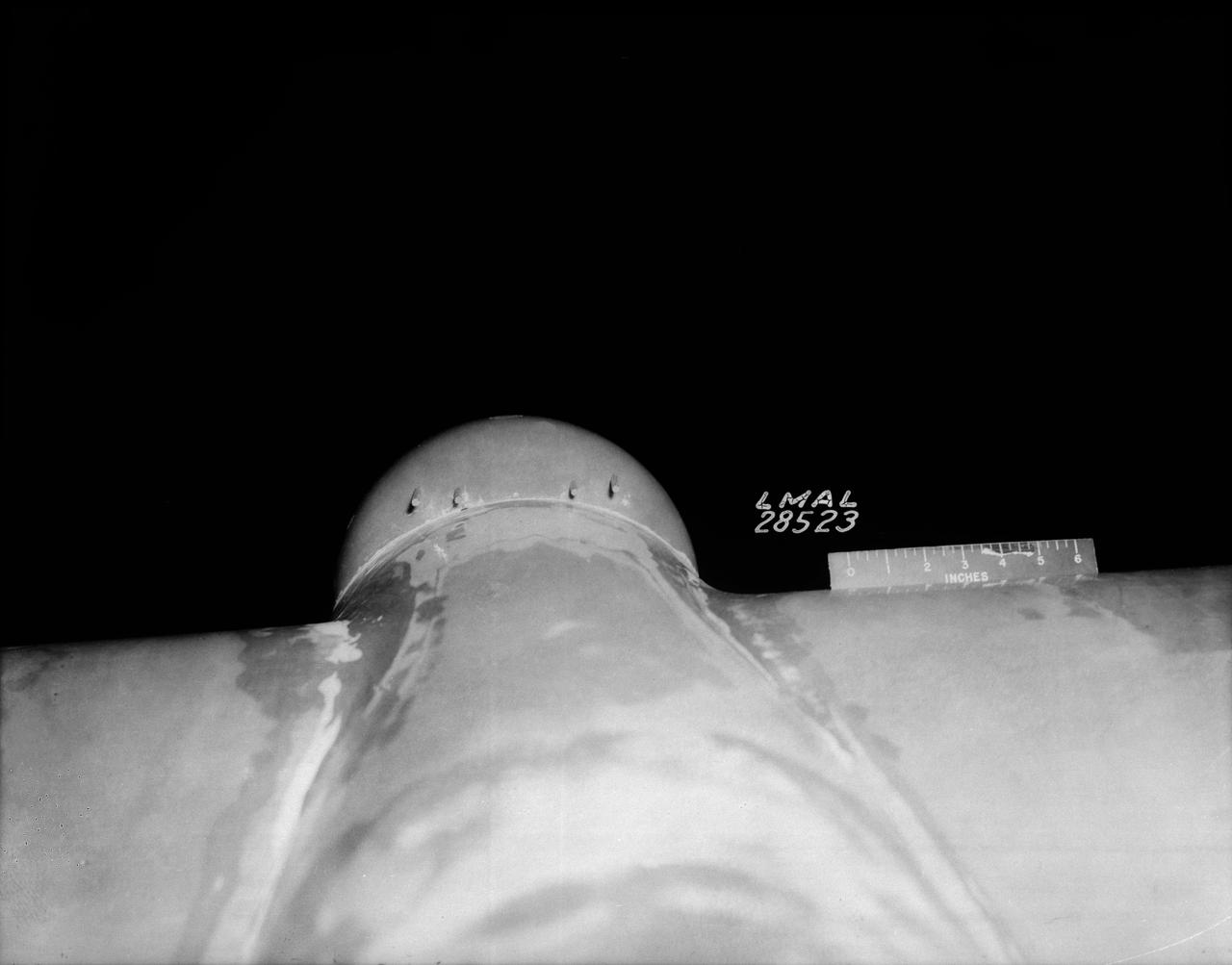

B-33 Vega Turrets. Photo are listed in the NACA Wartime report L-463, October 1942, Test of a Large Spherical Turret and a modified Turret on a Typical Bomber Fuselage by Axel T. Mattson.
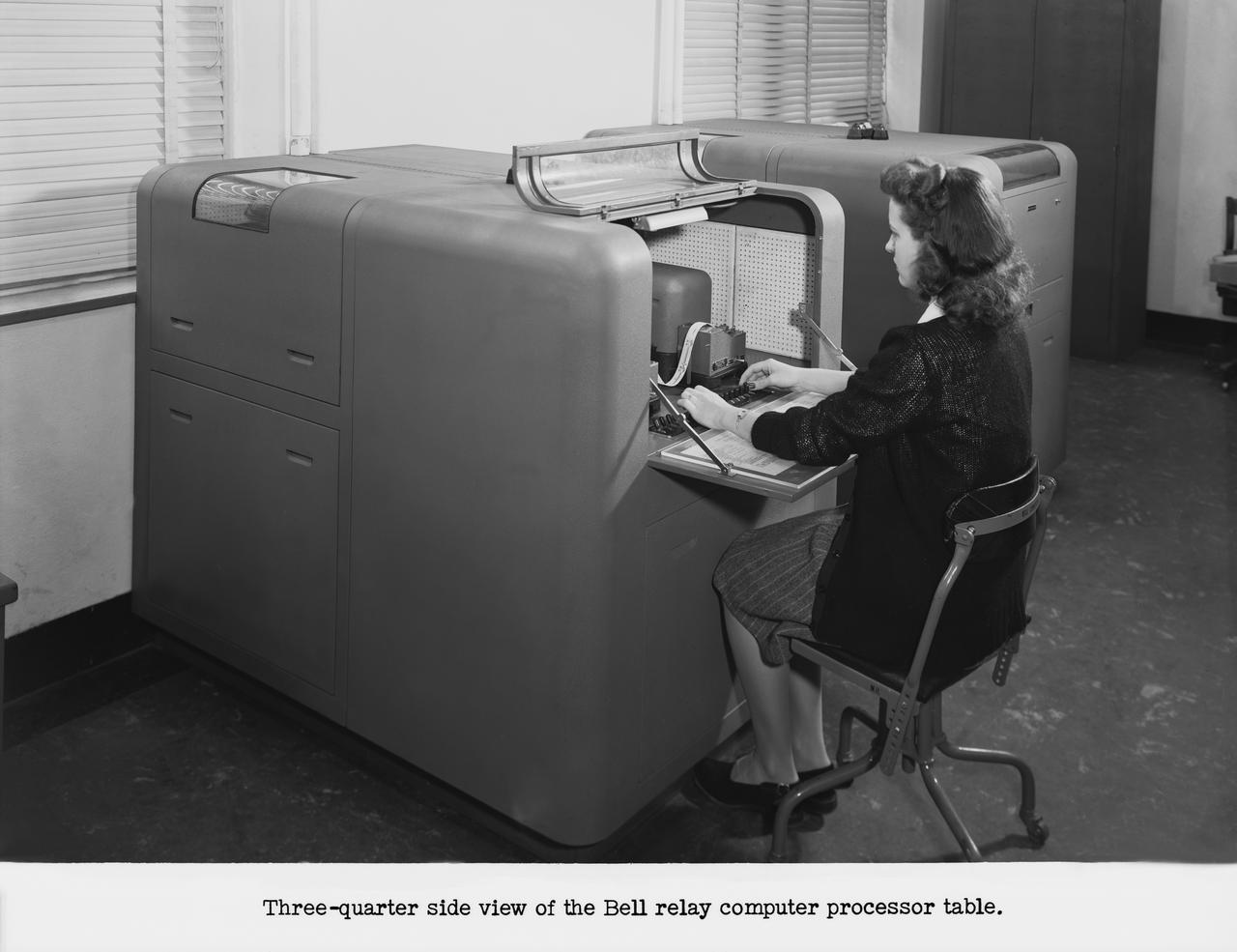

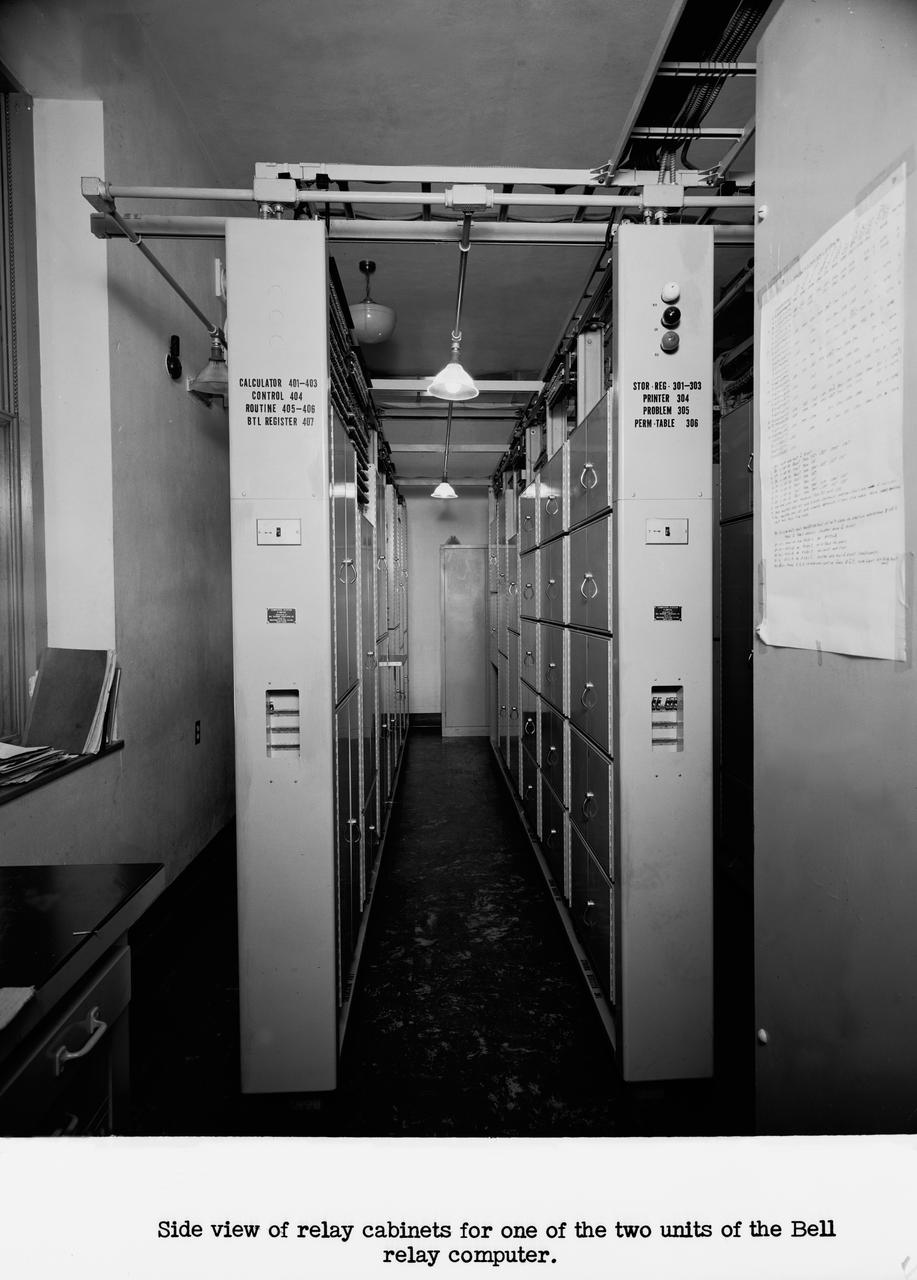
Langley's human computers at work in 1947. The female presence at Langley, who performed mathematical computations for male staff. Bell computers.
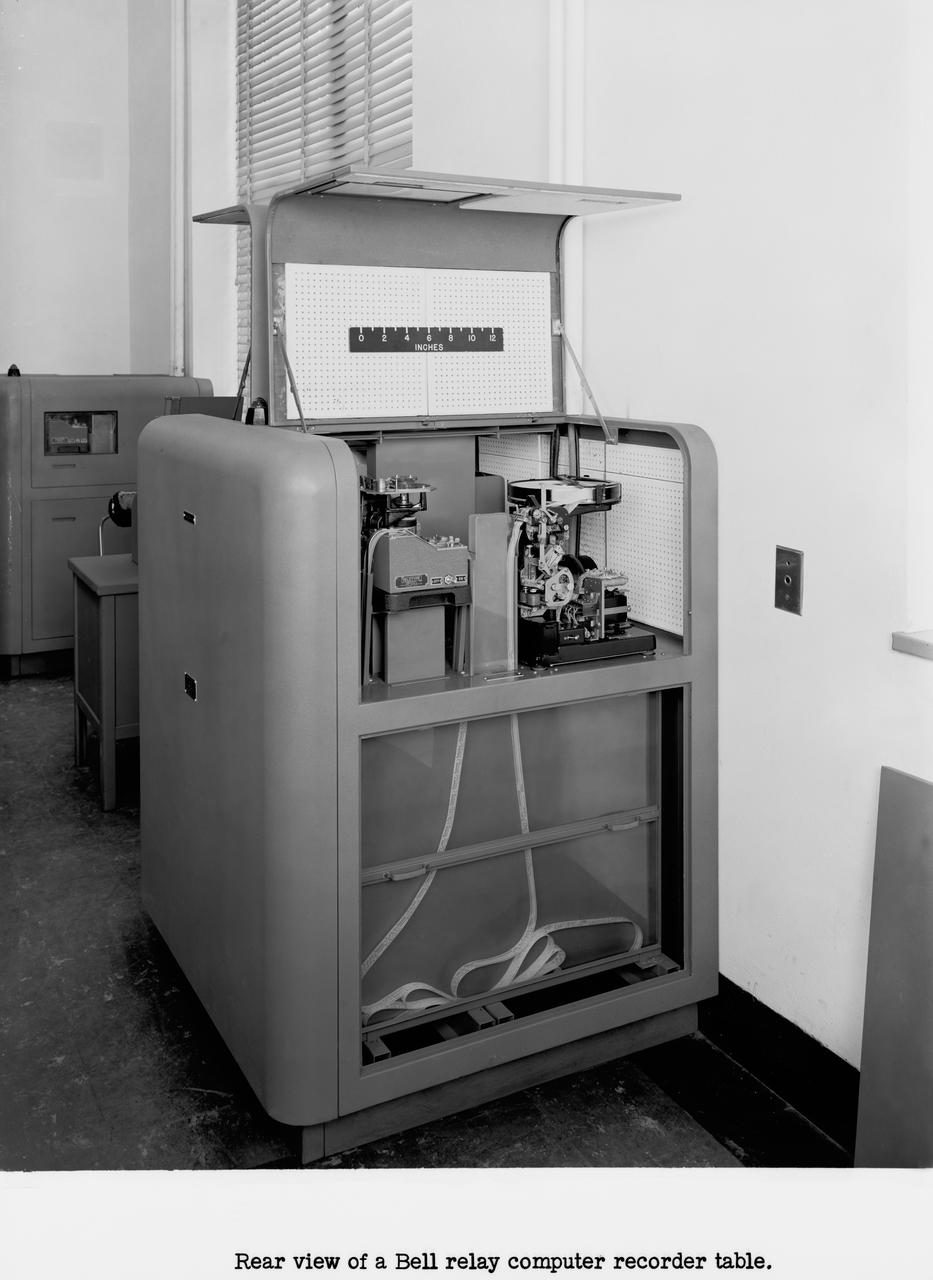

Langley's human computers at work in 1947. The female presence at Langley, who performed mathematical computations for male staff. Bell computers.
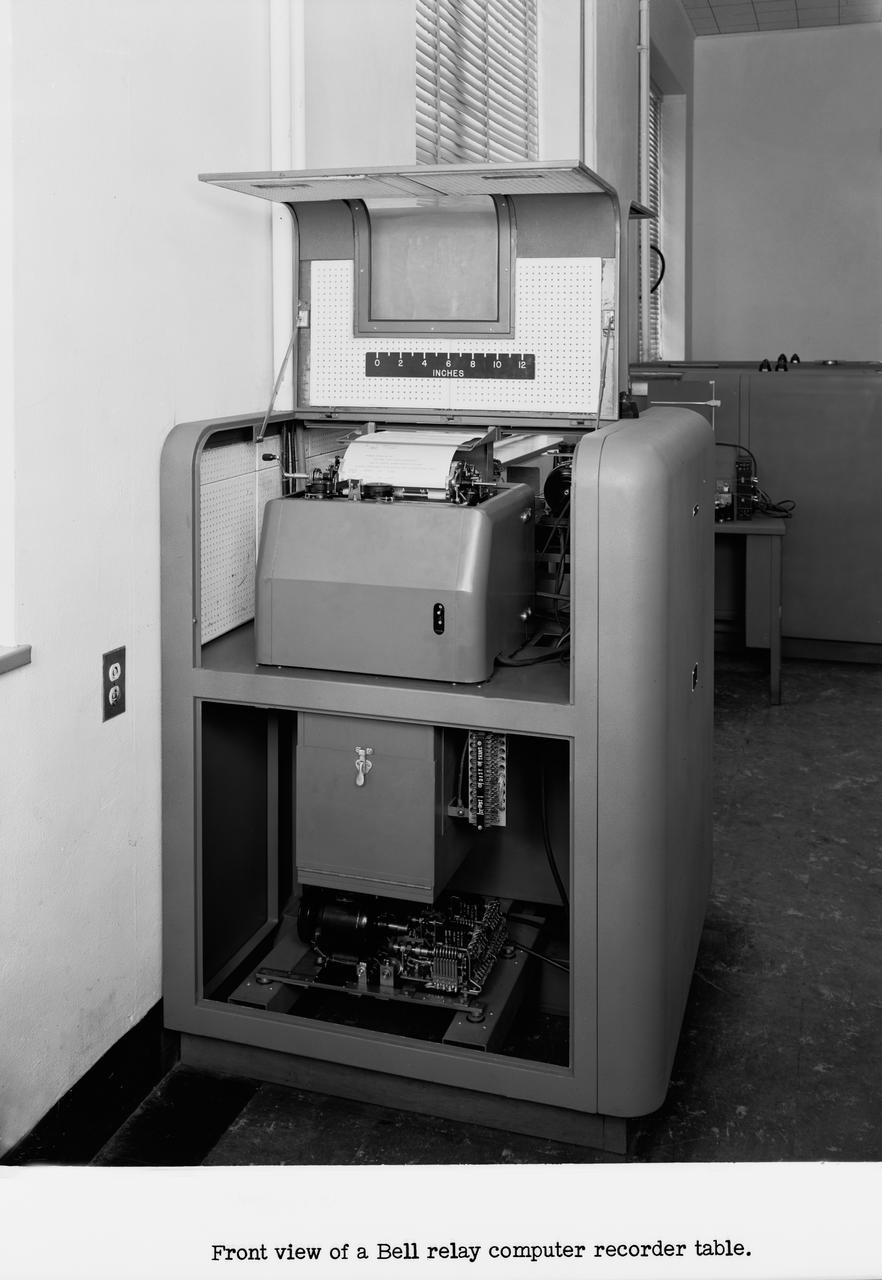

Langley's human computers at work in 1947. The female presence at Langley, who performed mathematical computations for male staff. Bell computers.
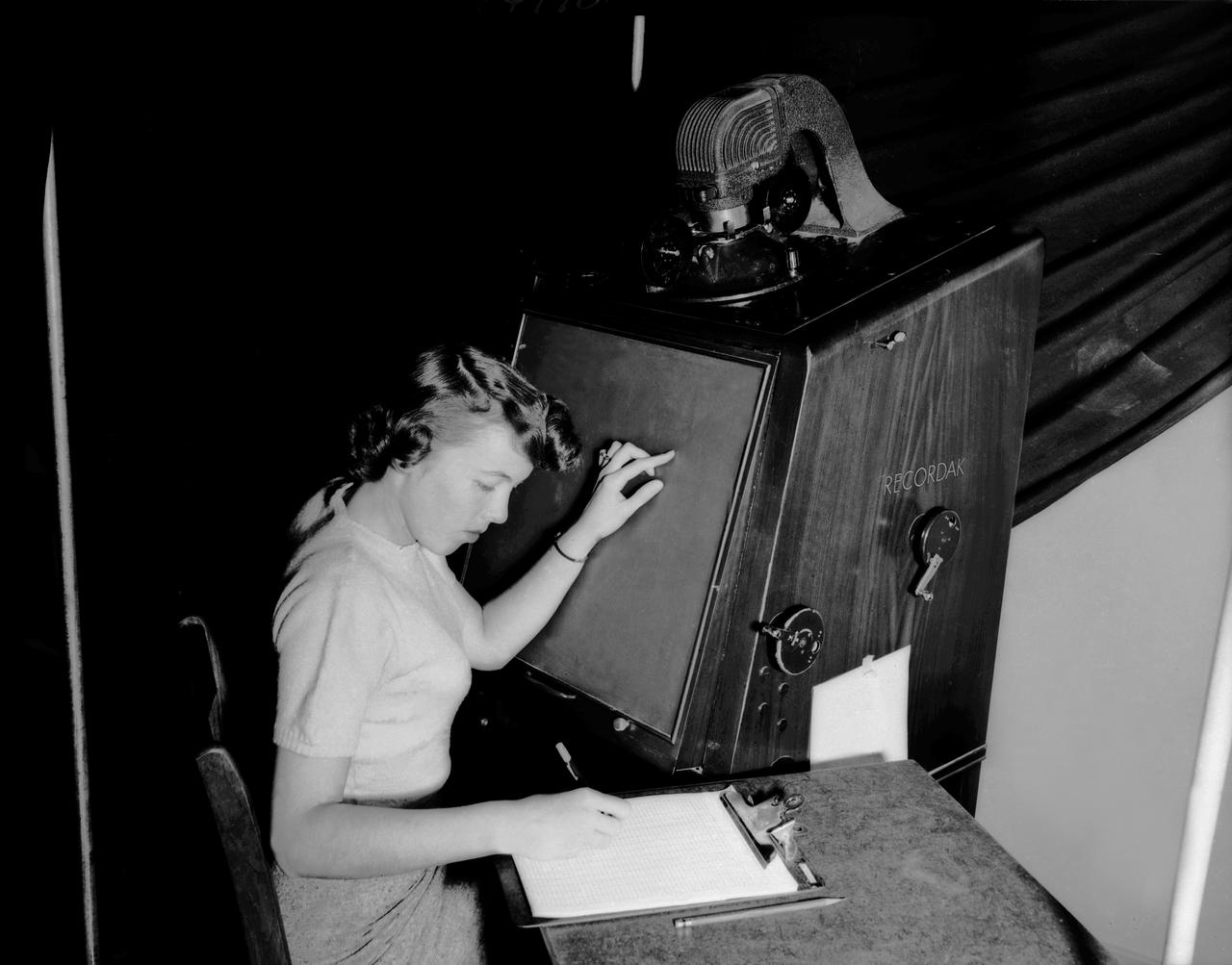

Publicity photo from Muroc California, showing female support personnel with equipment. A women working on a Kodak Recordak microfilm reader.
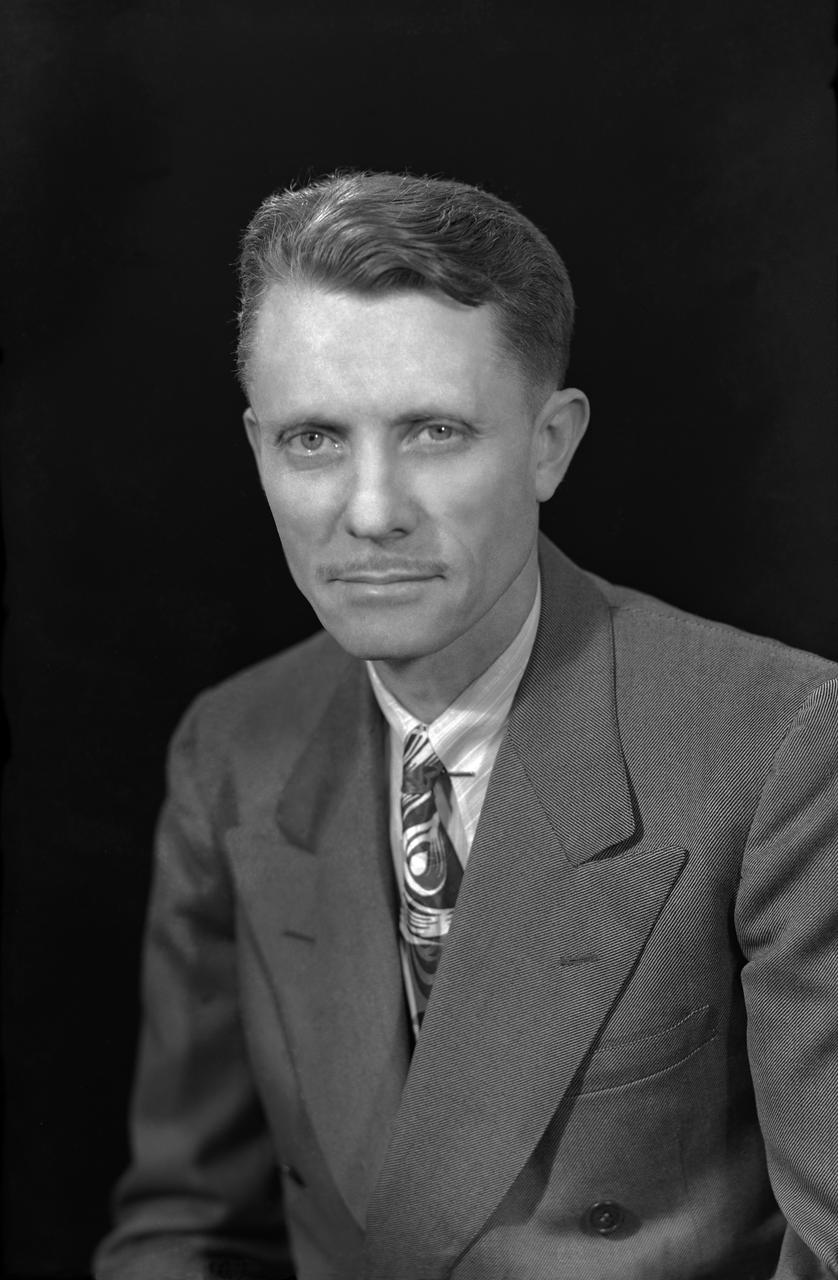

Portrait of Floyd L. Thompson NASA Langley Center Director from 1960 to 1968. Died in 1976
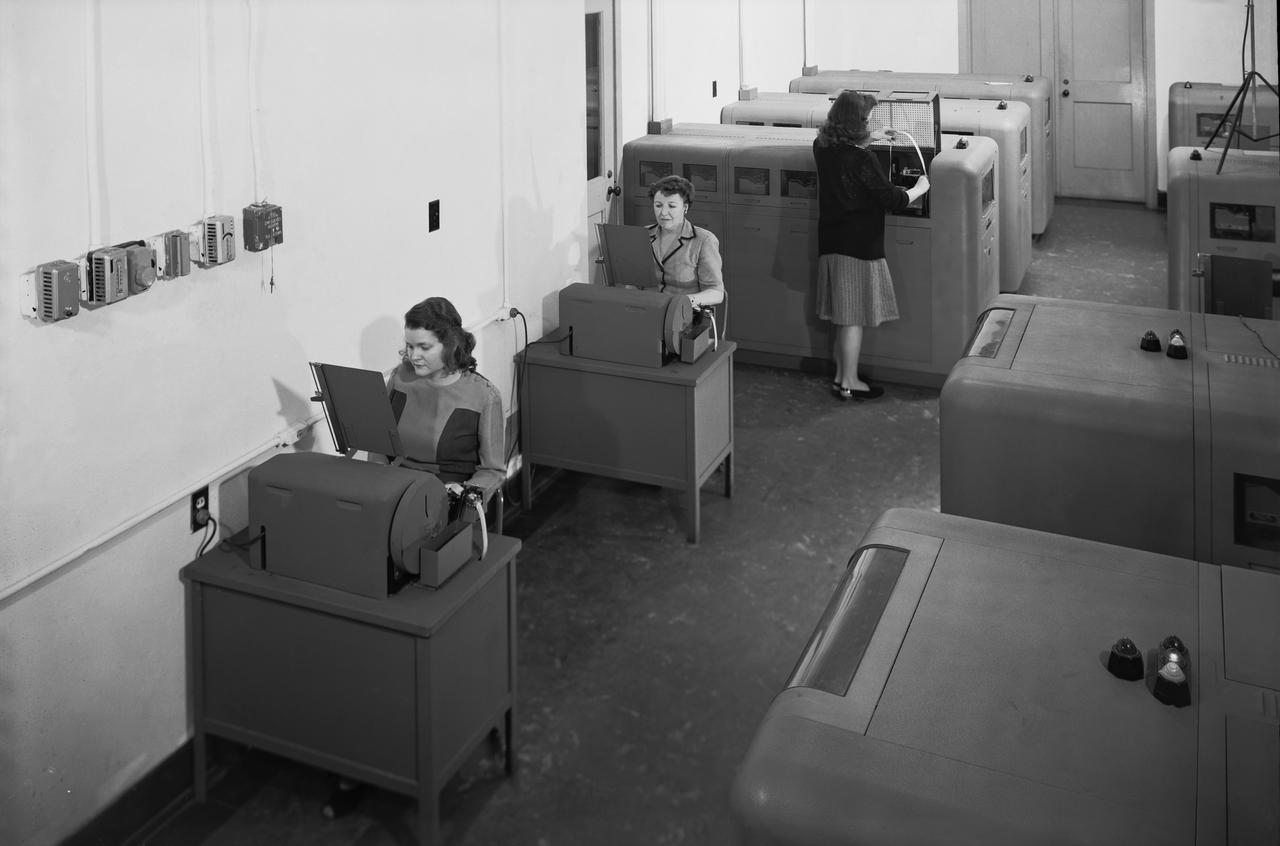

Langley's human computers at work in 1947. The female presence at Langley, who performed mathematical computations for male staff. -- Photograph published in Winds of Change, 75th Anniversary NASA publication (page 48), by James Schultz.
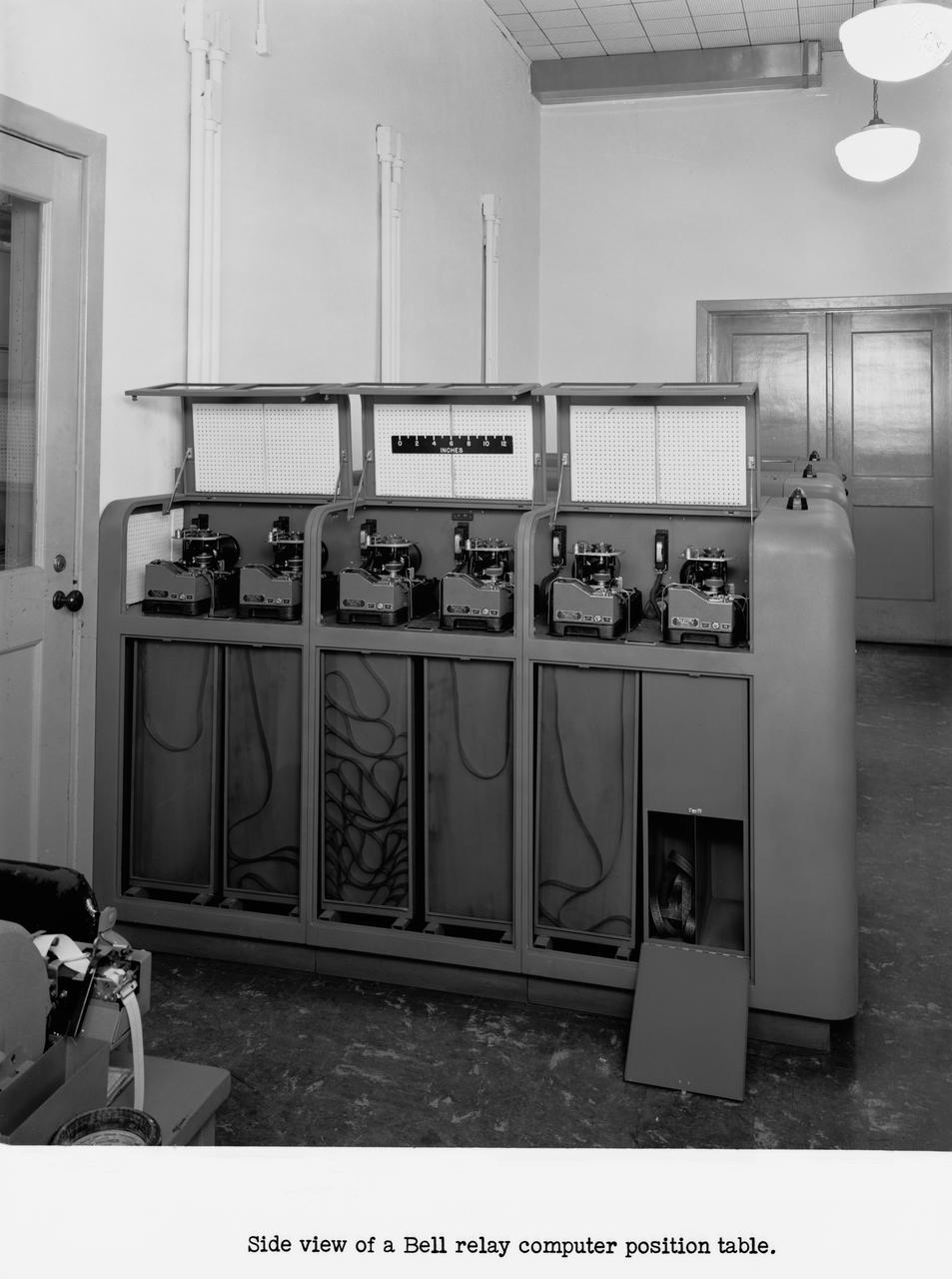

Langley's human computers at work in 1947. The female presence at Langley, who performed mathematical computations for male staff. Bell computers.
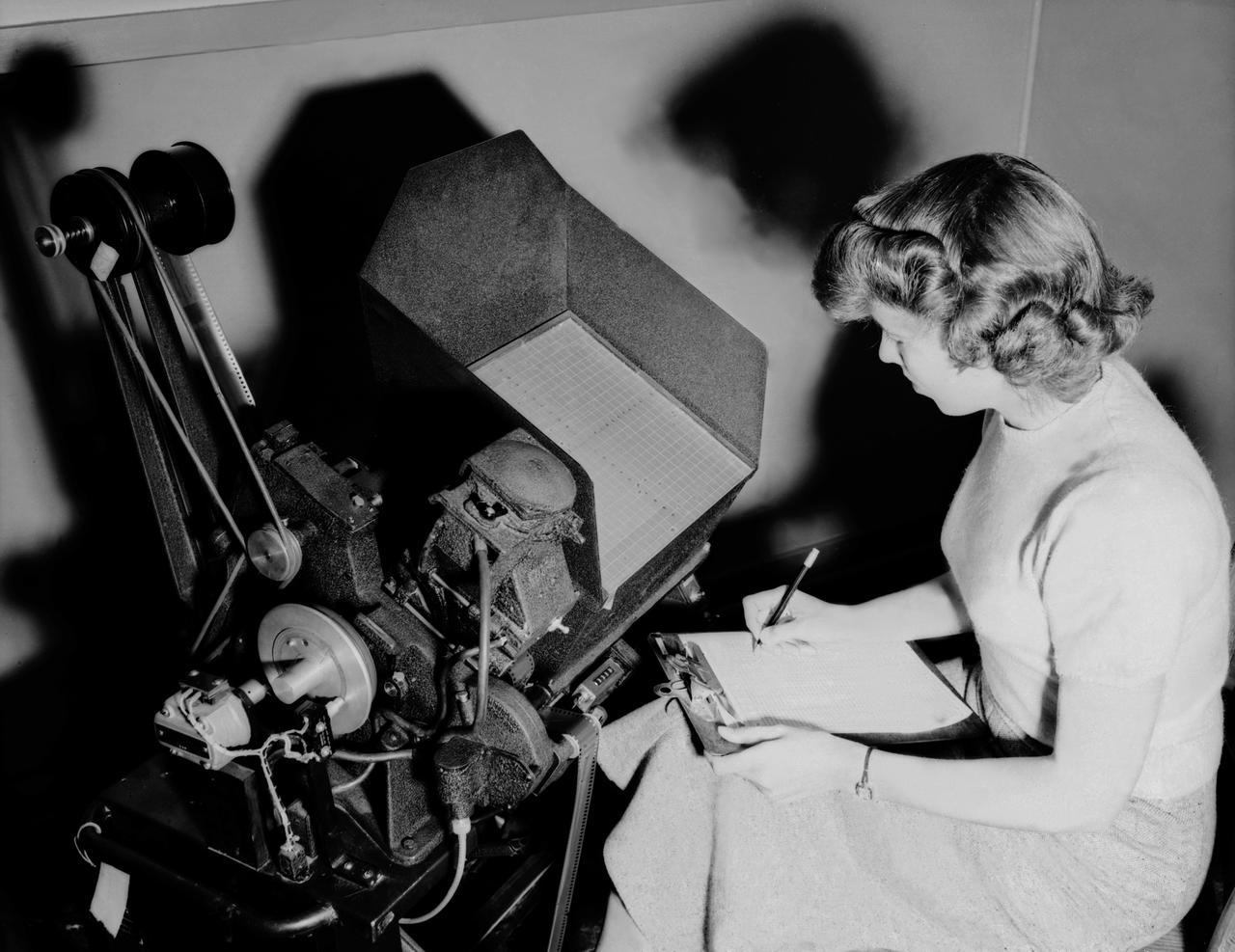

Publicity photo from Muroc California, showing female support personnel with equipment.

Langley's human computers at work in 1947. The female presence at Langley, who performed mathematical computations for male staff. Bell computers.

Langley's human computers at work in 1947. The female presence at Langley, who performed mathematical computations for male staff. Bell computers.

Langley's human computers at work in 1947. The female presence at Langley, who performed mathematical computations for male staff. Bell computers.
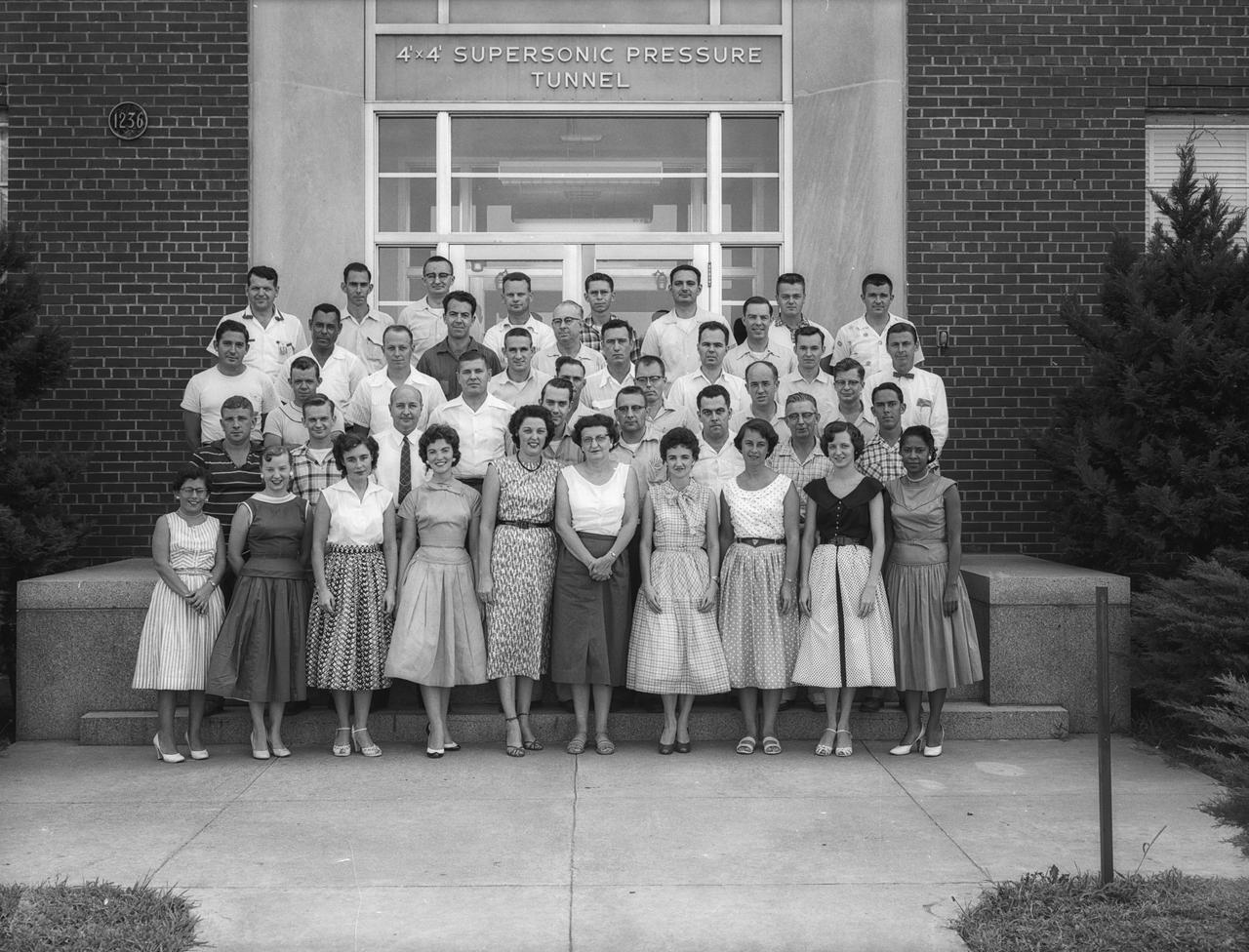

This photograph was taken August 15, 1956. Mary Jackson first person in the front row right side. Mary Jackson began at Langley in 1951 as a computer. She was later assigned to work at the 4-Foot by 4-Foot Supersonic Pressure Tunnel where she worked with Kazimierz "Kaz" Czarnecki, who encouraged her to become an engineer. To attend the university extension engineering classes held at the then all-white Hampton High School, Jackson was required to petition the courts, which she did successfully. The 4’ x 4’ Supersonic Pressure Tunnel was the NACA’s first supersonic wind tunnel. At the time of the photo, Mary Jackson was still a human computer, but was participating in the hands-on experimental work. Mrs. Jackson had begun her studies to be an engineer in the Spring of the same year the photo was taken. She obtained a degree in aerospace engineering in 1958. Photo published in "A Century at Langley" by Joseph R. Chambers page 74.
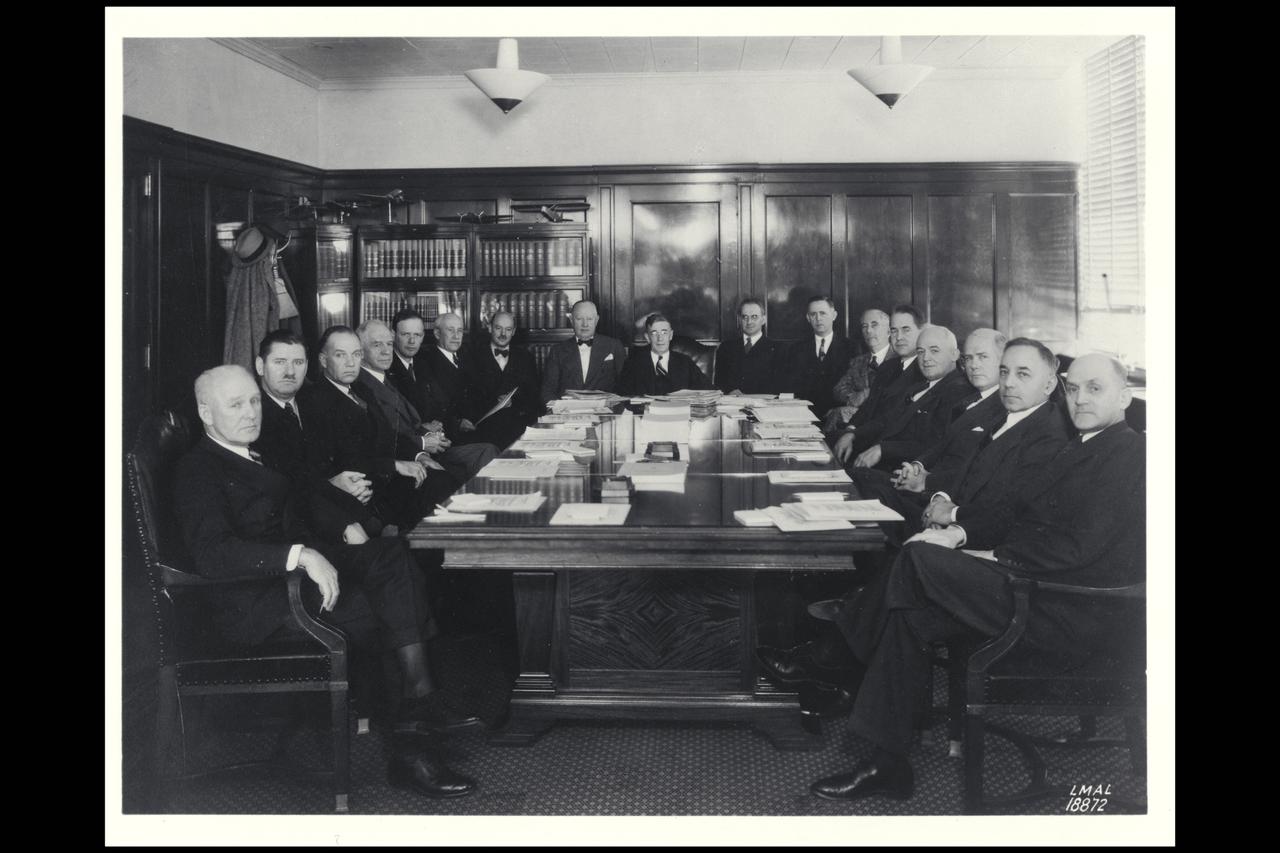

Langley Photographer NACA Annual Committee meeting: All Members present - including C Abbot, Arnold, Briggs, Bush, Hester and Lindbergh Ref: Langley No. LMAL-188872

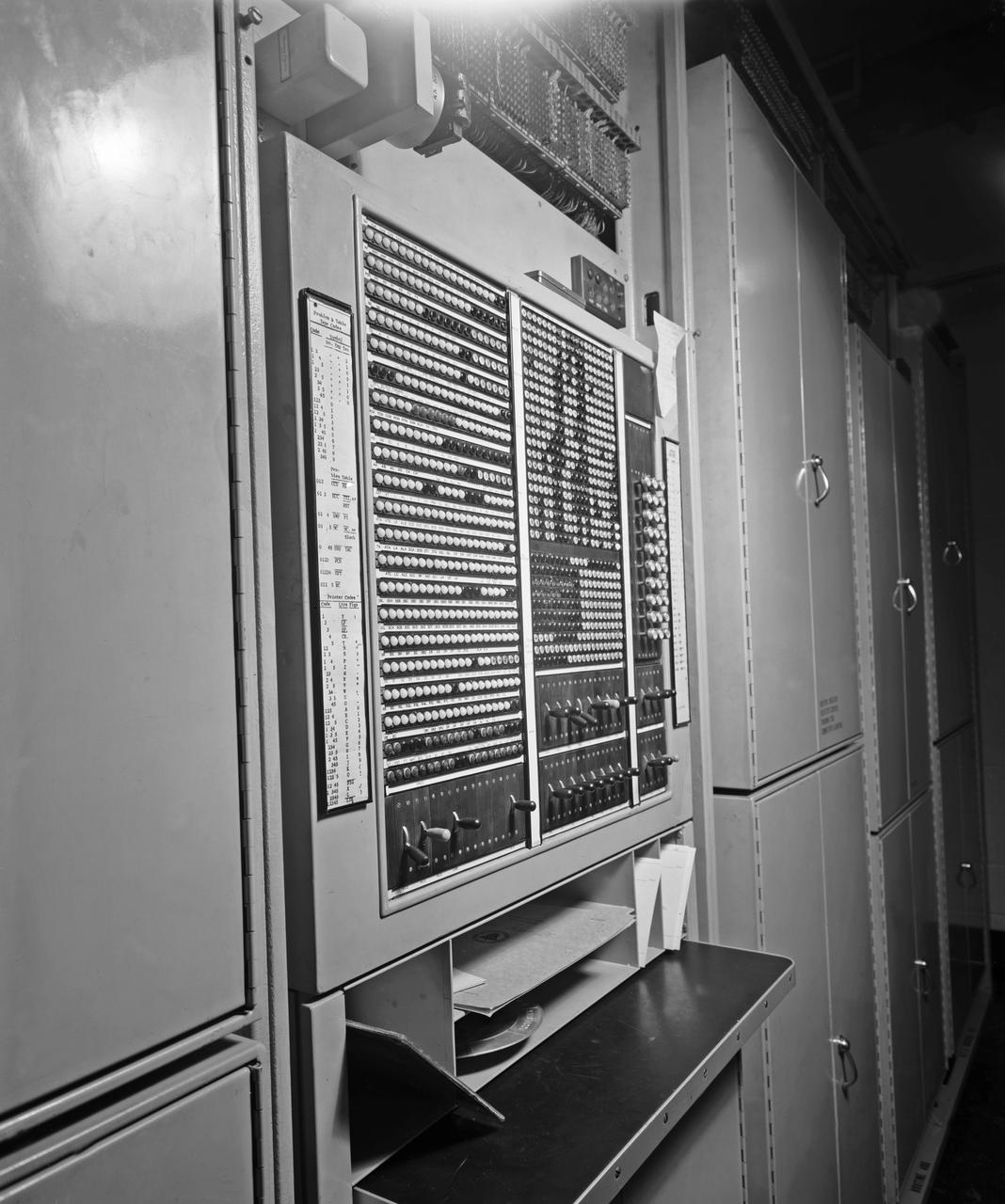
Publicity Photos of Bell Computing Machines at 19 Foot Pressure Tunnel Mrs. Doris Rudd Porter Baron photographed in the photos.
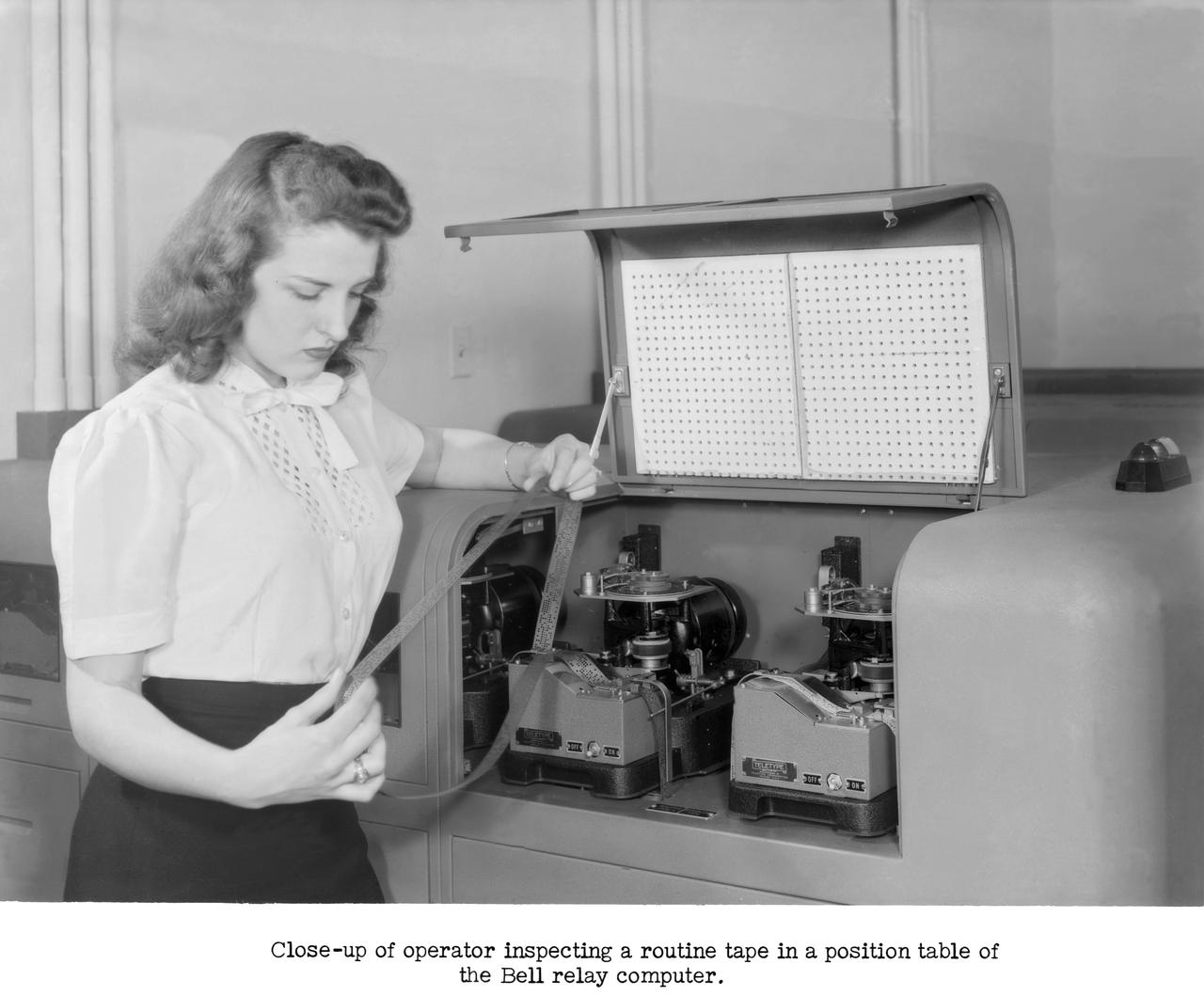

Publicity Photos of Bell Computing Machines at 19 Foot Pressure Tunnel Mrs. Doris Rudd Porter Baron photographed in the photos.
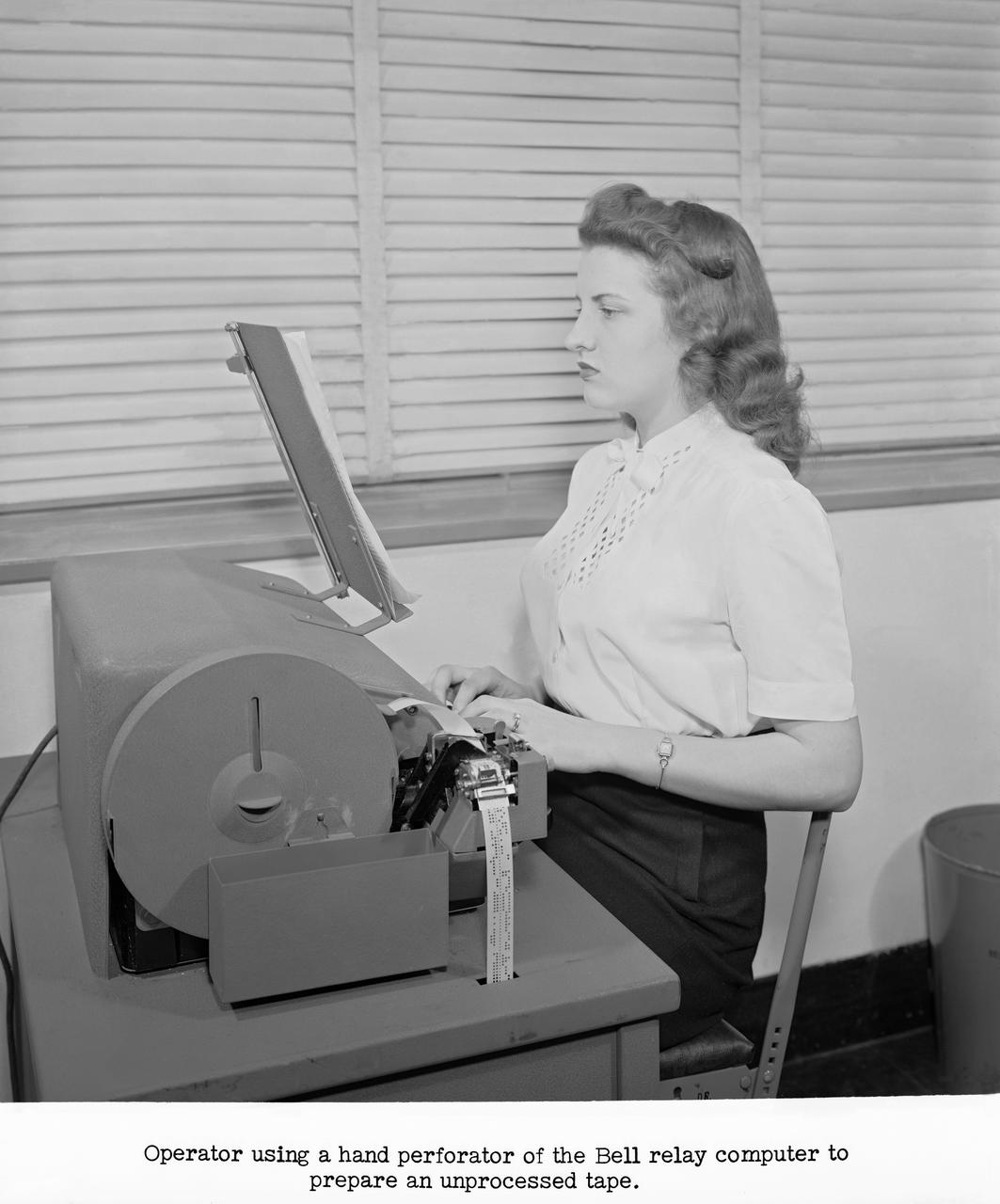

Publicity Photos of Bell Computing Machines at 19 Foot Pressure Tunnel Mrs. Doris Rudd Porter Baron photographed in the photos.
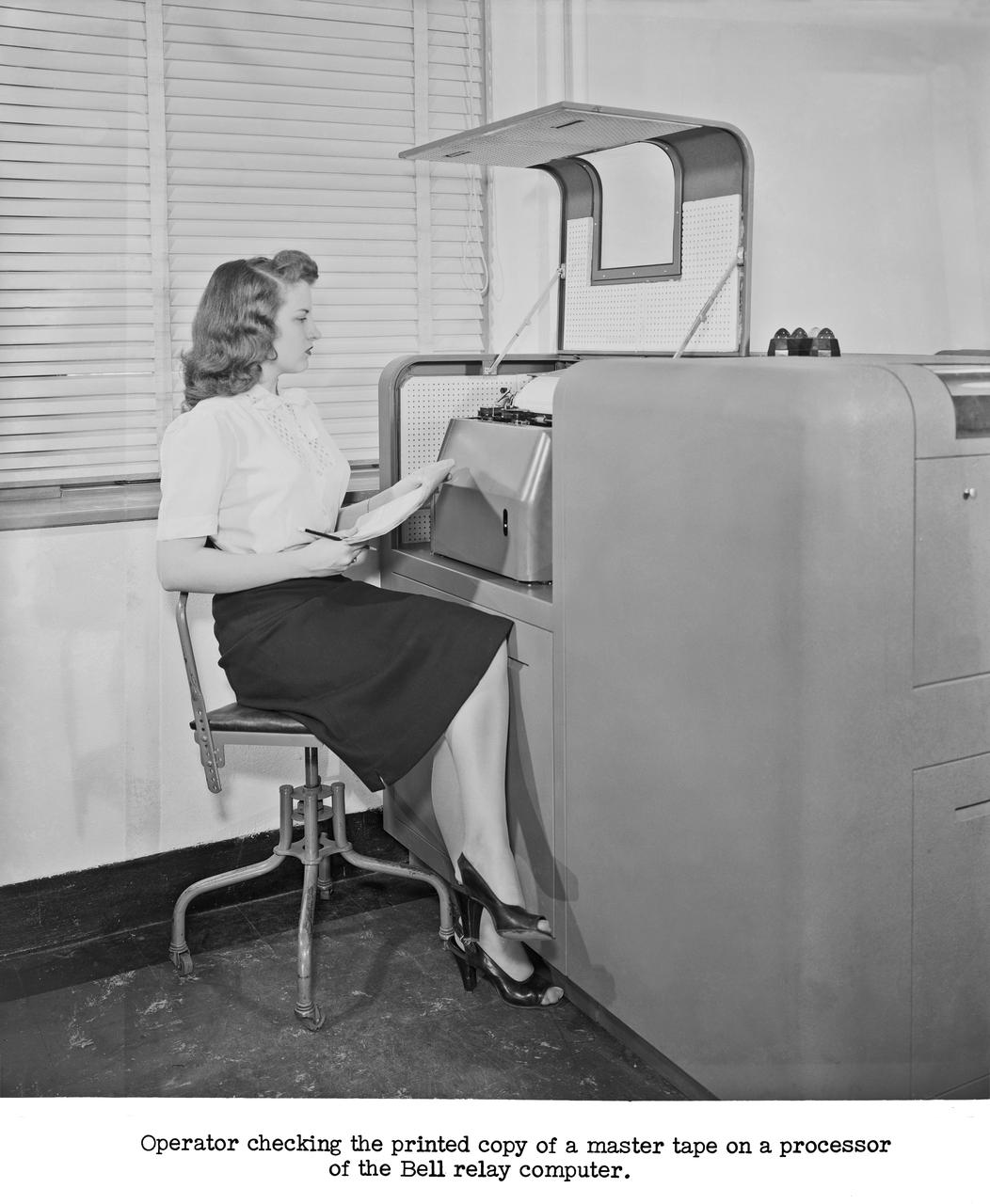

Publicity Photos of Bell Computing Machines at 19 Foot Pressure Tunnel Mrs. Doris Rudd Porter Baron photographed in the photos.
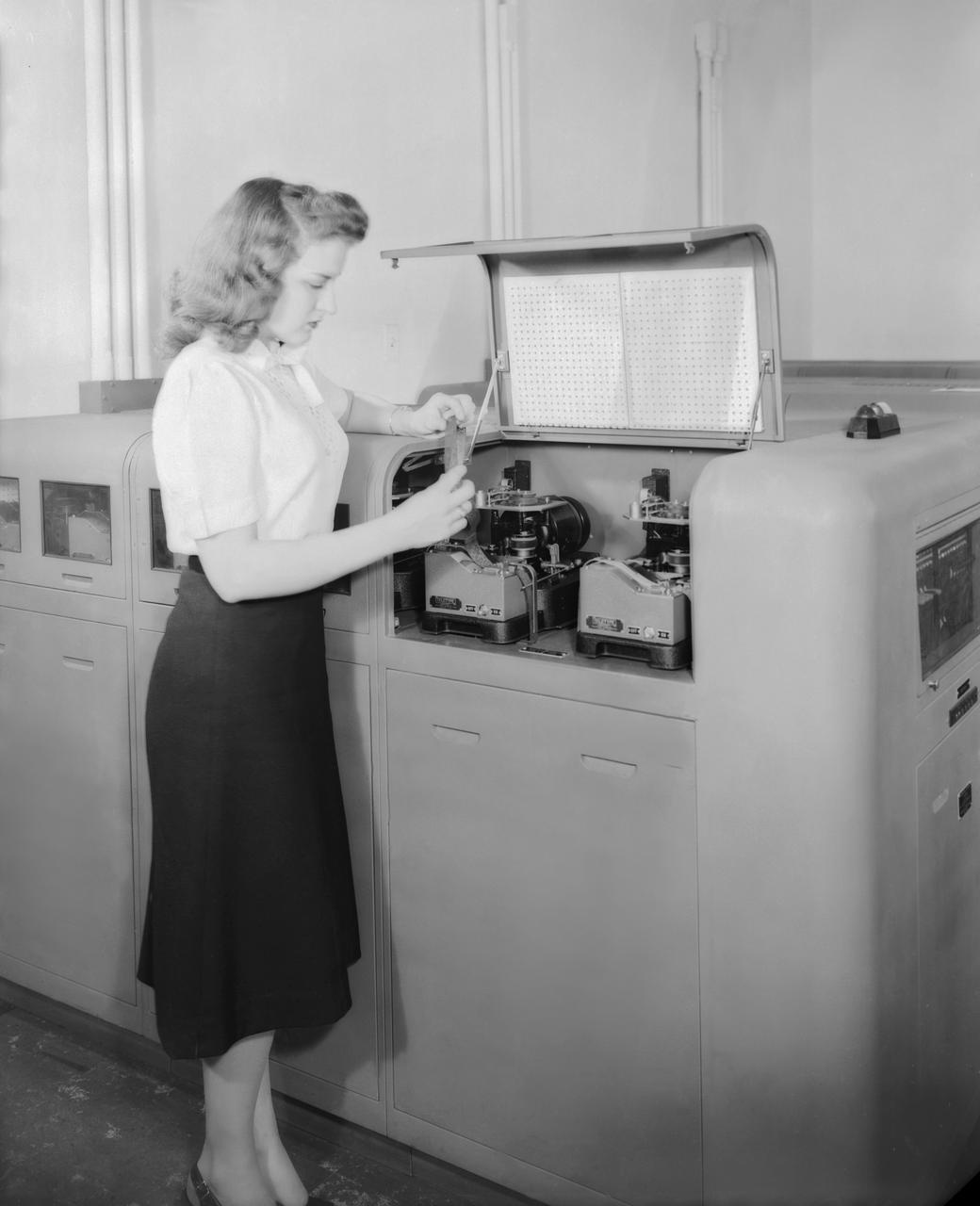

Publicity Photos of Bell Computing Machines at 19 Foot Pressure Tunnel Mrs. Doris Rudd Porter Baron photographed in the photos.

Publicity Photos of Bell Computing Machines at 19 Foot Pressure Tunnel Mrs. Doris Rudd Porter Baron photographed in the photos.
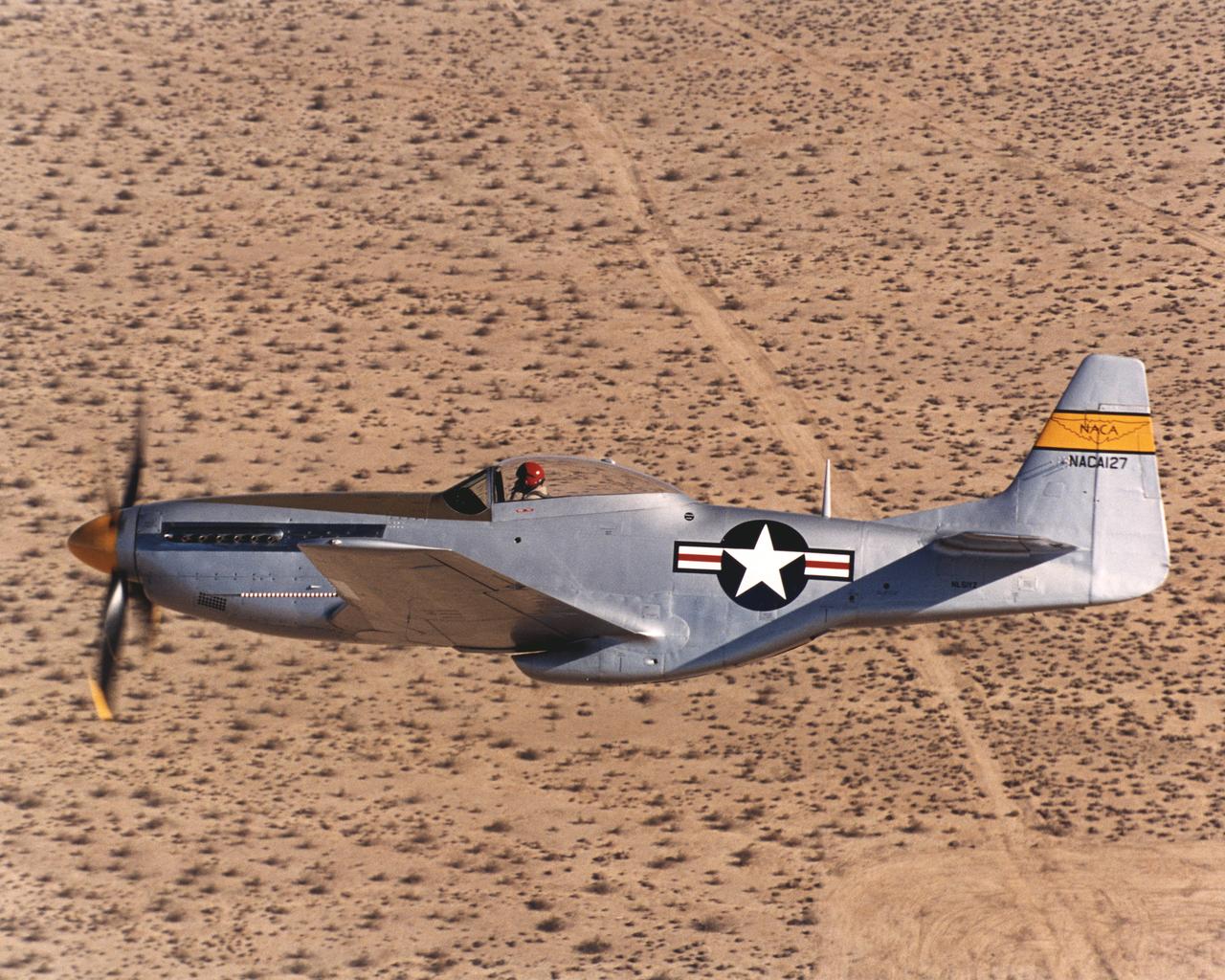

Bill Allmon of Las Vegas, Nevada, brought his restored NACA P-51D to a reunion of former NACA employees at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center located at Edwards Air Force Base, Calif., on Sept. 15, 2000. Allmon's award-winning restoration is a genuine former NACA testbed that saw service at the Langley Research Center in Virginia in the late 1940s. Later this Mustang was put on outdoor static display as an Air National Guard monument in Pittsburgh, Pa., where exposure to the elements ravaged its metal structure, necessitating an extensive four-year rebuild.
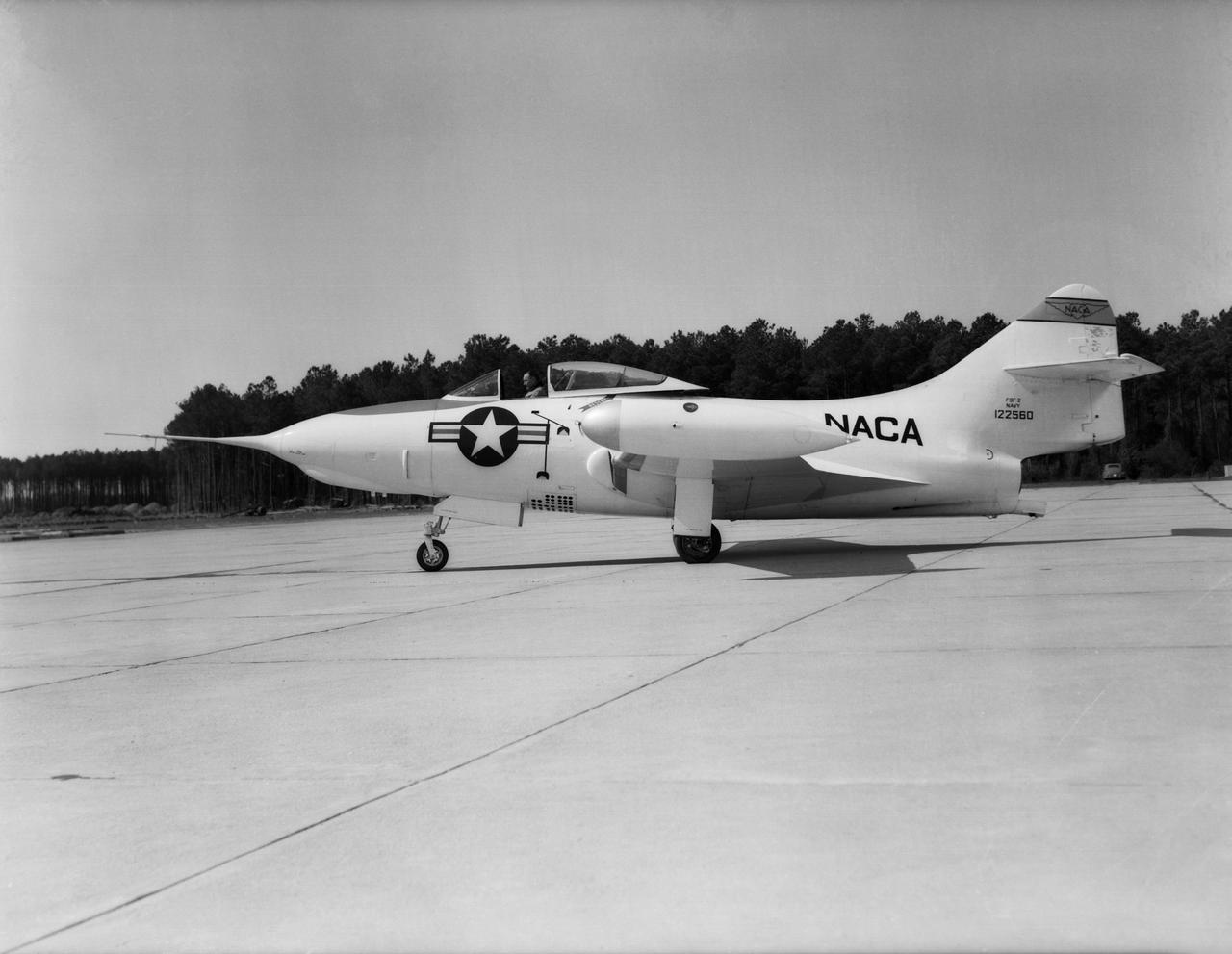

Grumman F9F-2 Panther: Originally built as a F9F-3, this Grumman F9F-2 Panther has a Pratt and Whitney J42 turbojet power plant, hence the designation change. This Panther underwent handling quality tests, serving long enough at Langley to witness the change from the NACA to NASA.
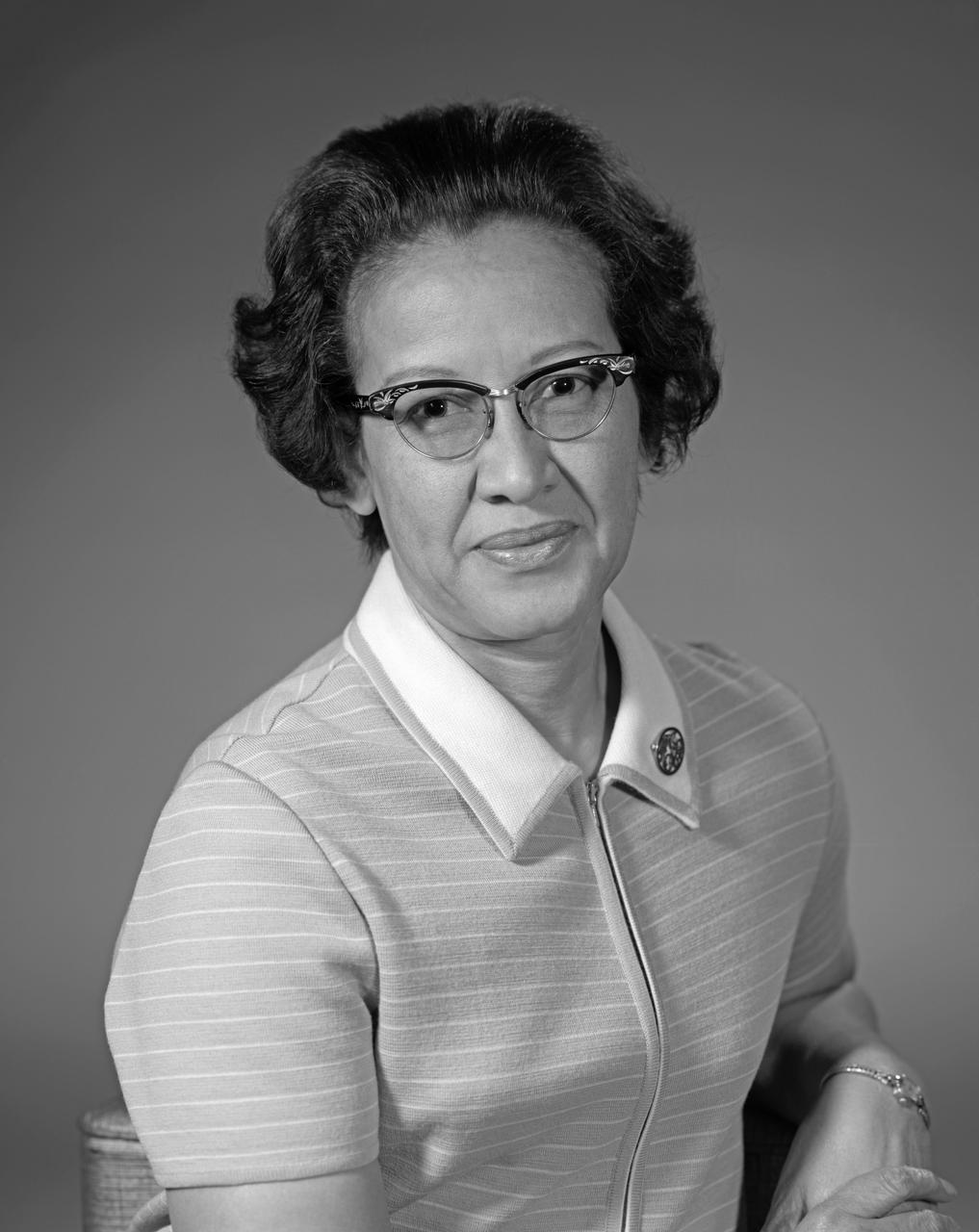

Portrait Katherine G. Johnson. Hall of Honor inductee 2017. Langley Research Center NACA and NASA Hall of Honor. In recognition of contributions to the development of methodologies for analysis of manned mission (from Mercury to Apollo) and satellite (Echo) trajectories, and dynamic control of large space structures.
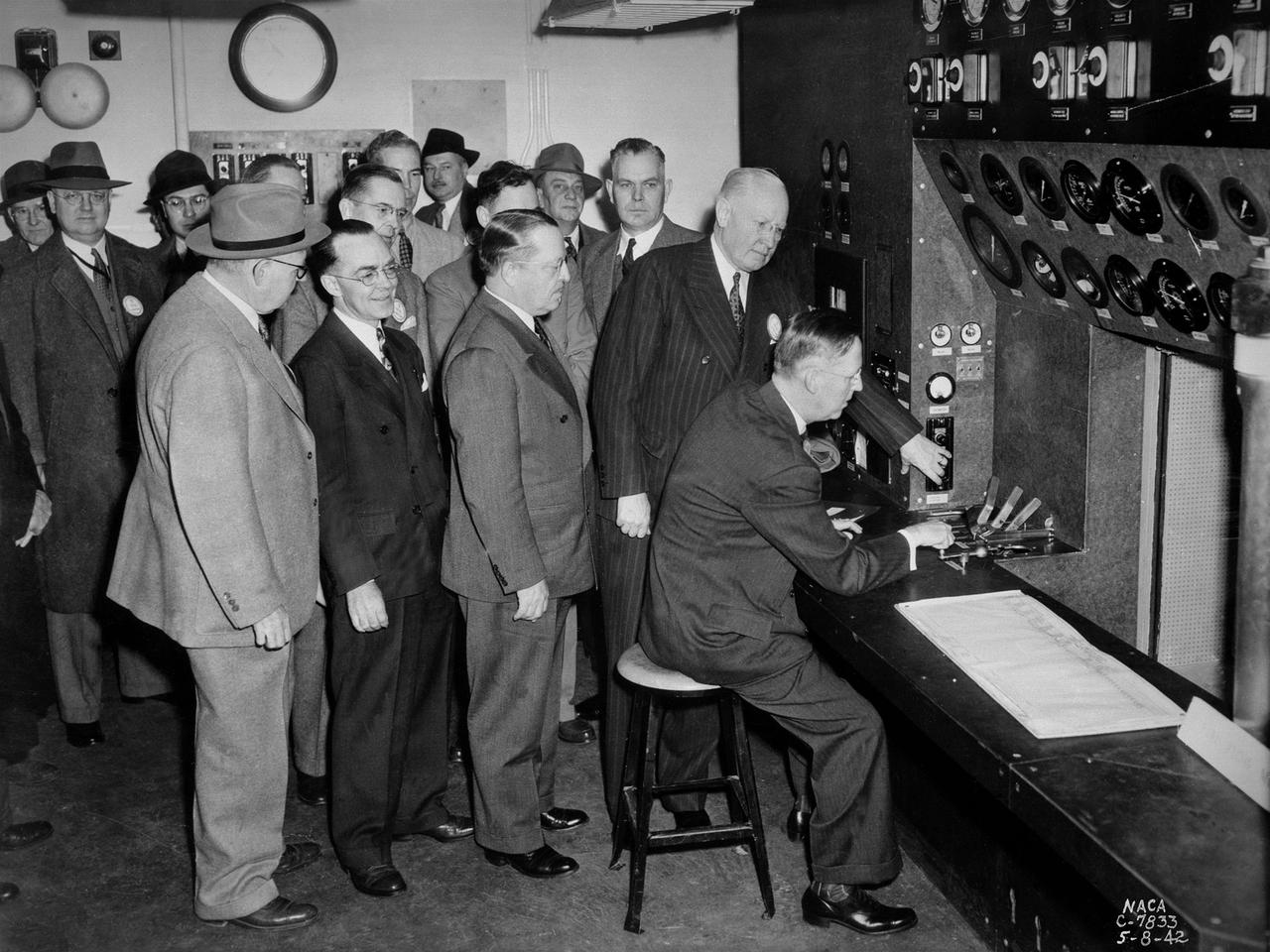

A group of National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) officials and local dignitaries were on hand on May 8, 1942, to witness the Initiation of Research at the NACA's new Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory in Cleveland, Ohio. The group in this photograph was in the control room of the laboratory's first test facility, the Engine Propeller Research Building. The NACA press release that day noted, "First actual research activities in what is to be the largest aircraft engine research laboratory in the world was begun today at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics laboratory at the Cleveland Municipal Airport.” The ceremony, however, was largely symbolic since most of the laboratory was still under construction. Dr. George W. Lewis, the NACA's Director of Aeronautical Research, and John F. Victory, NACA Secretary, are at the controls in this photograph. Airport Manager John Berry, former City Manager William Hopkins, NACA Assistant Secretary Ed Chamberlain, Langley Engineer-in-Charge Henry Reid, Executive Engineer Carlton Kemper, and Construction Manager Raymond Sharp are also present. The propeller building contained two torque stands to test complete engines at ambient conditions. The facility was primarily used at the time to study engine lubrication and cooling systems for World War II aircraft, which were required to perform at higher altitudes and longer ranges than previous generations.
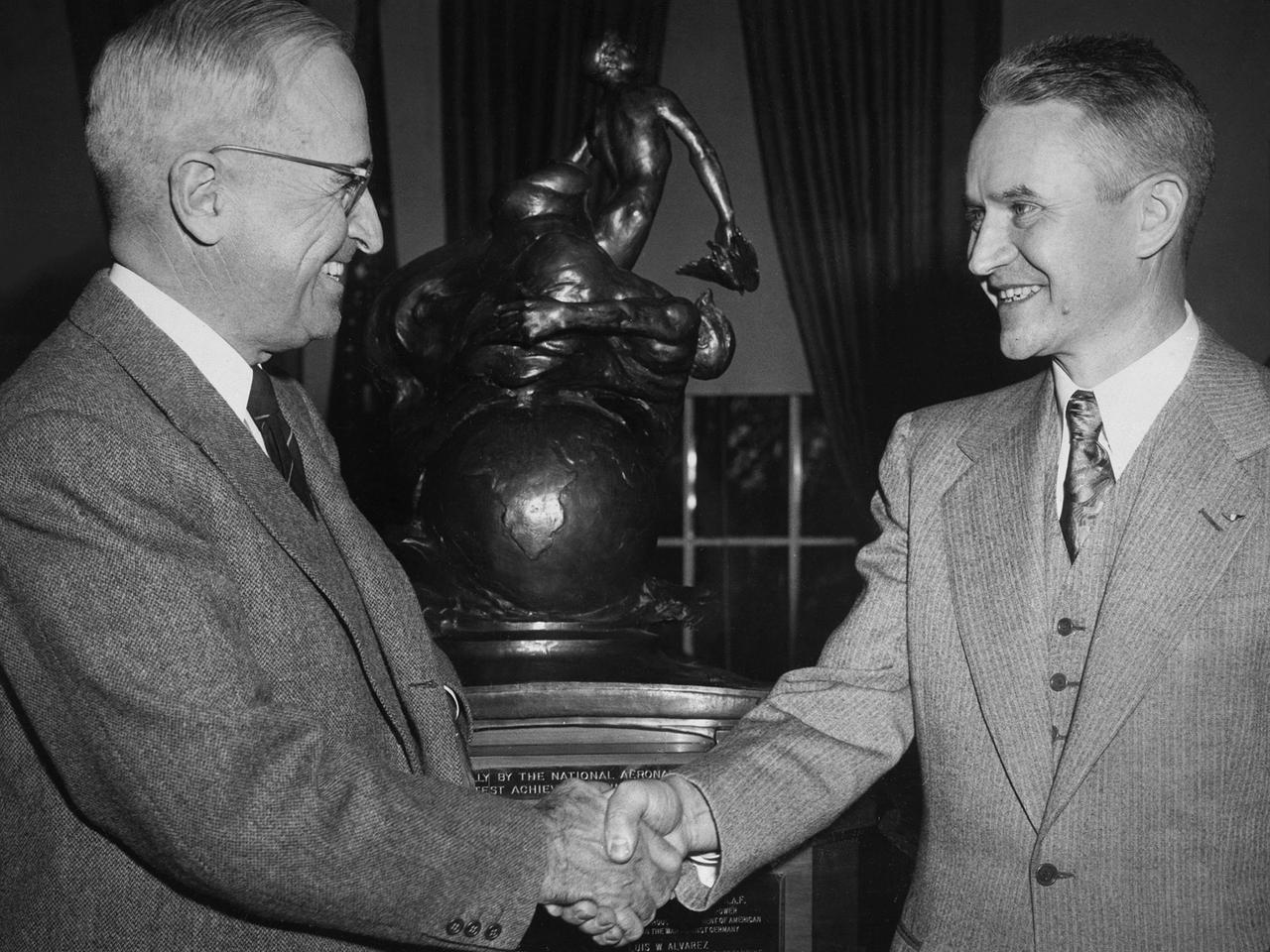

Lewis Rodert, then of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory, receives the Collier Trophy from President Harry Truman for his work in the design and development of an ice prevention system for aircraft. The accumulation of ice on an aircraft had been a critical issue for years. Rodert developed a method of transferring engine heat to the wings and other vulnerable components to prevent ice buildup. Rodert began his icing investigations at Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory in 1936. The NACA ordered a Lockheed 12A aircraft to be built using Rodert’s deicing system. The aircraft successfully flew through icing conditions during the following winter. Soon thereafter the military incorporated the system into a Consolidated B-24D Liberator and several other military aircraft, including a North American XB-25F. Rodert and the NACA icing program transferred to the Lewis lab in Cleveland in 1946. In Cleveland, the focus turned to the study of cloud composition and the causes of icing. Rodert’s role at Lewis diminished over the ensuing years. Rodert was honored in 1947 for his Collier Trophy at ceremonies at Langley, Ames, and then finally Lewis.
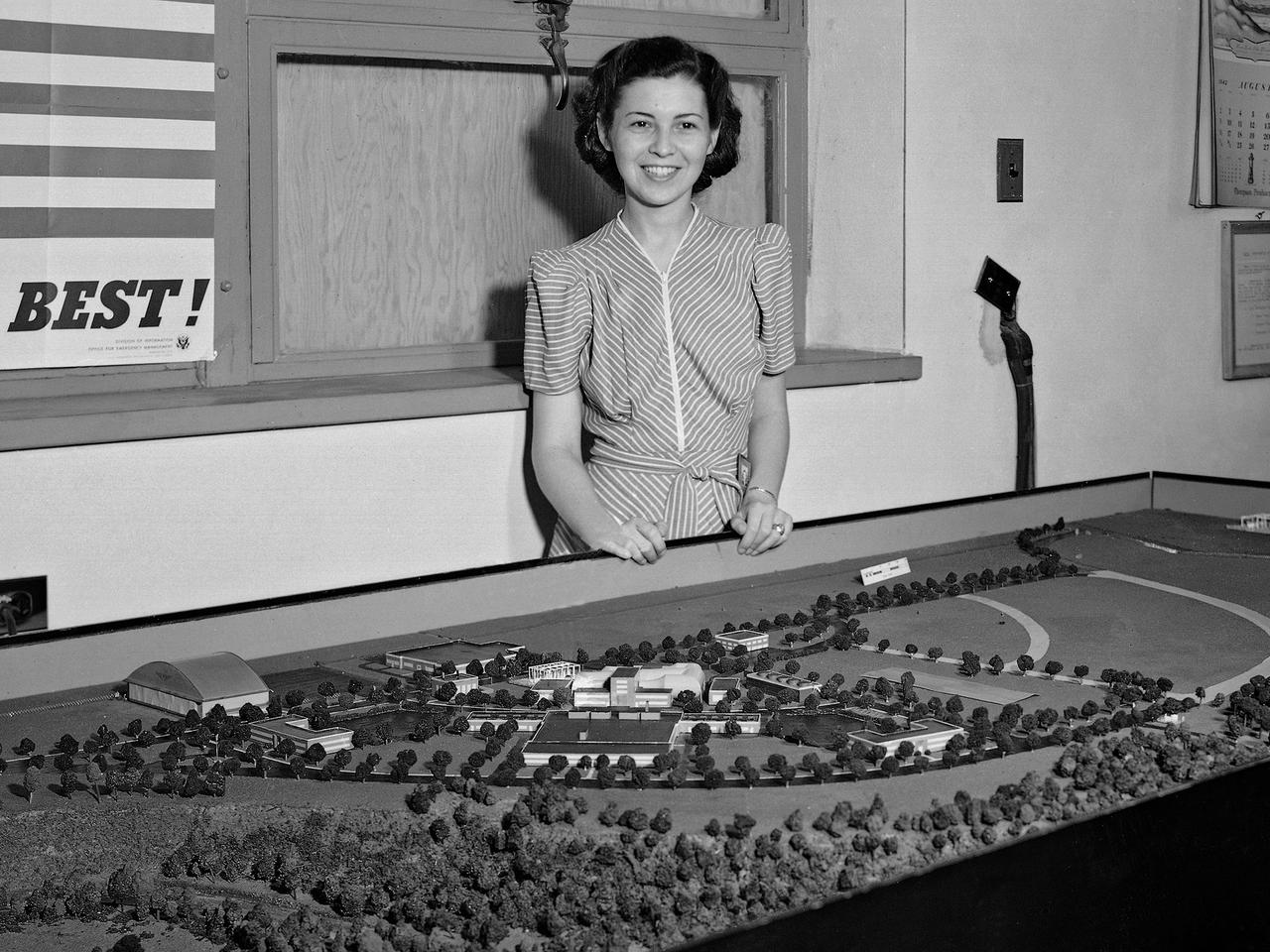

Zella Morewitz poses with a model of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory, currently the NASA Glenn Research Center. The model was displayed in the Administration Building during the construction of the laboratory in the early 1940s. Detailed models of the individual test facilities were also fabricated and displayed in the facilities. The laboratory was built on a wedge of land between the Cleveland Municipal Airport on the far side and the deep curving valley etched by the Rocky River on the near end. Roughly only a third of the laboratory's semicircle footprint was initially utilized. Additional facilities were added to the remaining areas in the years after World War II. In the late 1950s the site was supplemented by the acquisition of additional adjacent land. Morewitz joined the NACA in 1935 as a secretary in the main office at the Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory. In September 1940 she took on the task of setting up and guiding an office dedicated to the design of the NACA’s new engine research laboratory. Morewitz and the others in the design office transferred to Cleveland in December 1941 to expedite the construction. Morewitz served as Manager Ray Sharp’s secretary for six years and was a popular figure at the new laboratory. In December 1947 Morewitz announced her engagement to Langley researcher Sidney Batterson and moved back to Virginia.
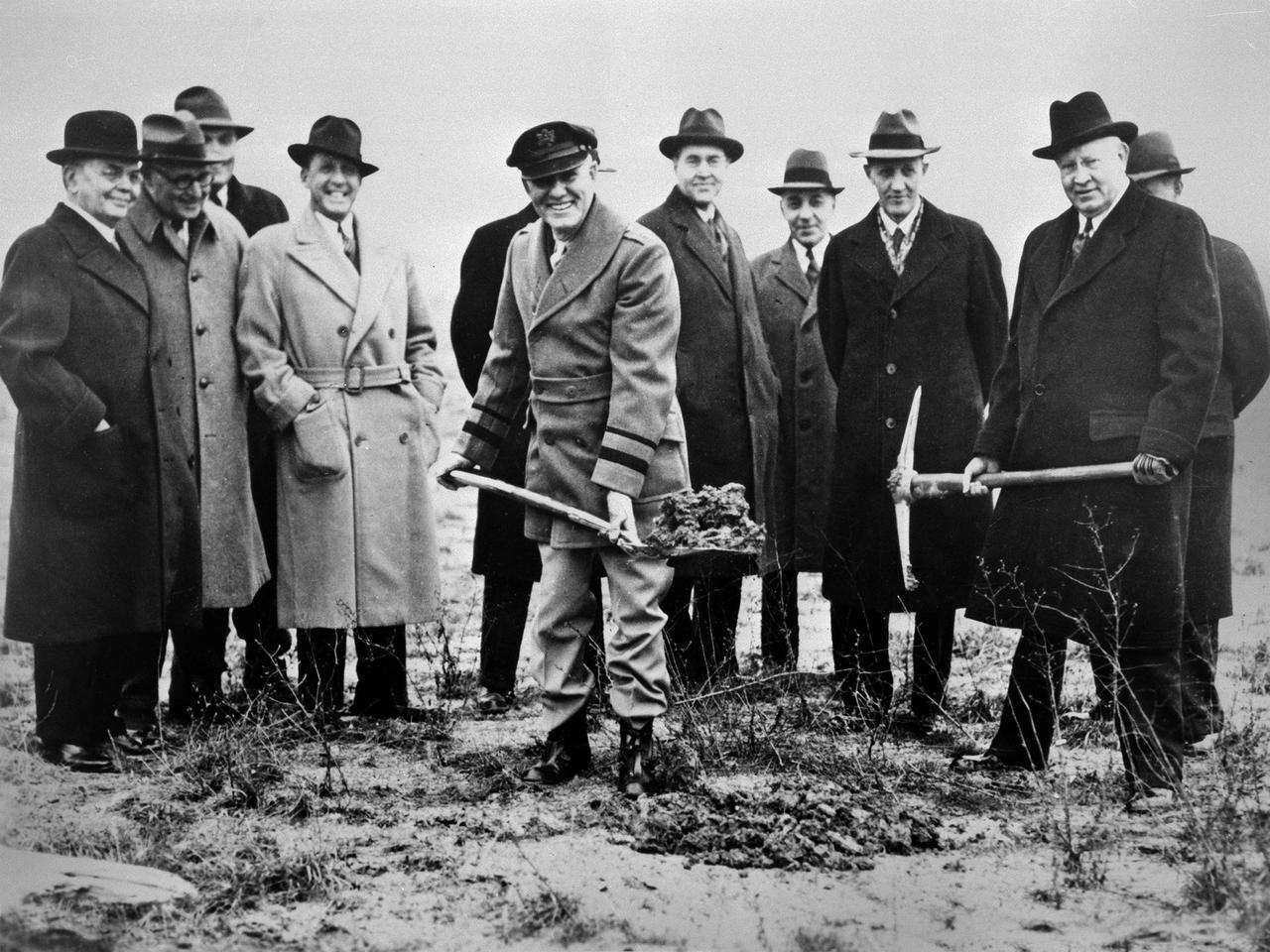

Local politicians and National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) officials were on hand for the January 23, 1941 groundbreaking for the NACA’s Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory (AERL). The NACA was established in 1915 to coordinate the nation’s aeronautical research. The committee opened a research laboratory at Langley Field in 1920. By the late 1930s, however, European nations, Germany in particular, were building faster and higher flying aircraft. The NACA decided to expand with a new Ames Aeronautical Laboratory dedicated to high-speed flight and the AERL to handle engine-related research. The NACA examined a number of Midwest locations for its new engine lab before deciding on Cleveland. At the time, Cleveland possessed the nation’s most advanced airport, several key aircraft manufacturing companies, and was home to the National Air Races. Local officials were also able to broker a deal with the power company to discount its electricity rates if the large wind tunnels were operated overnight. The decision was made in October 1940, and the groundbreaking alongside the airport took place on January 23, 1941. From left to right: William Hopkins, John Berry, Ray Sharp, Frederick Crawford, George Brett, Edward Warner, Sydney Kraus, Edward Blythin, and George Lewis
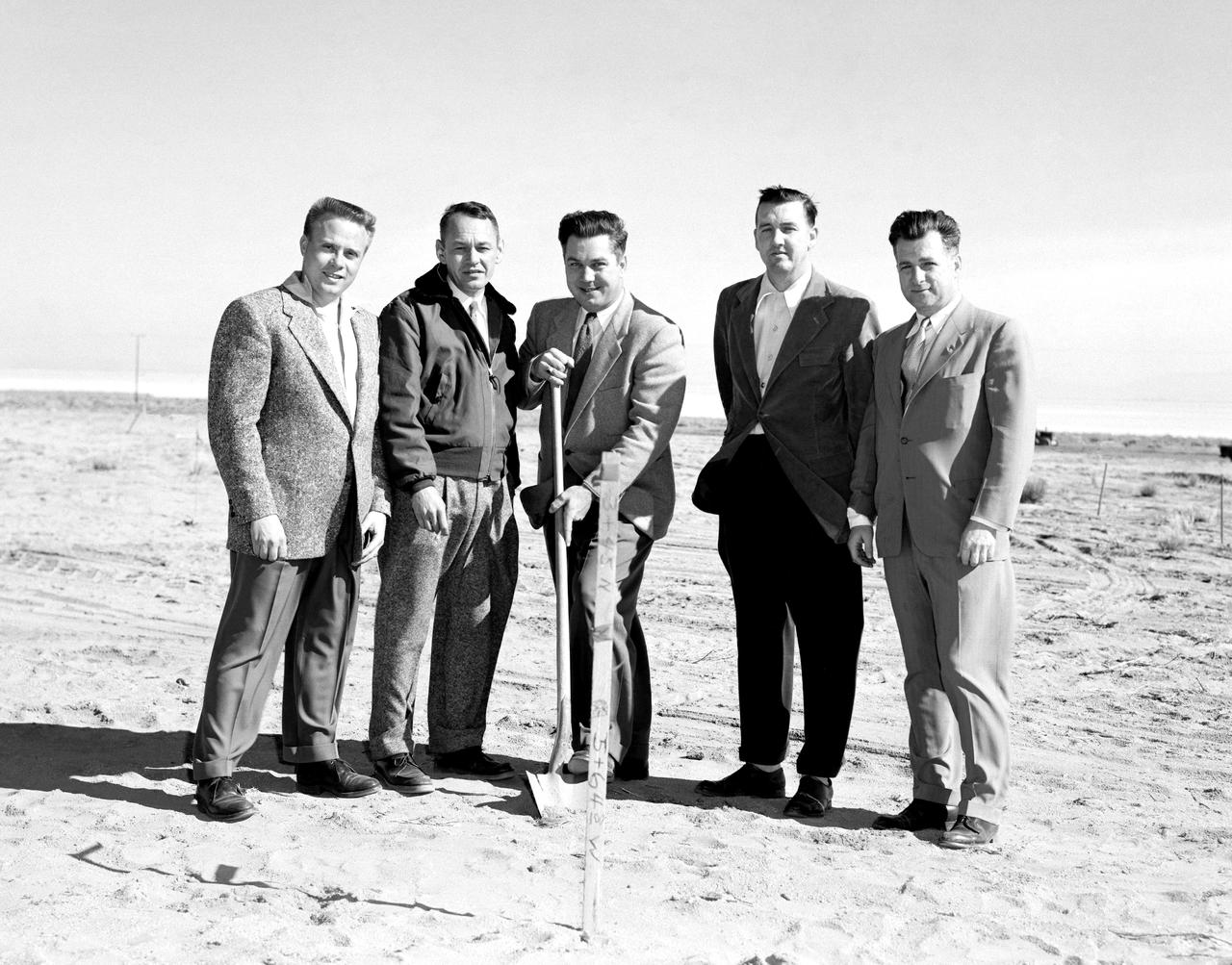

The NACA High-Speed Flight Research Station, had initially been subordinate to the Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory near Hampton, Virginia, but as the flight research in the Mojave Desert increasingly proved its worth after 1946, it made sense to make the Flight Research Station a separate entity reporting directly to the headquarters of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics. But an autonomous center required all the trappings of a major research facility, including good quarters. With the adoption of the Edwards “Master Plan,” the Air Force had committed itself to moving from its old South Base to a new location midway between the South and North Bases. The NACA would have to move also--so why not take advantage of the situation and move into a full-blown research facility. The Air Force issued a lease to NACA for a location on the northwestern shore of the Roger Dry Lake. Construction started on the NACA station in early February 1953. On a windy day, January 27, 1953, at a groundbreaking ceremony stood left to right: Gerald Truszynski, Head of Instrumentation Division; Joseph Vensel, Head of the Operations Branch; Walter Williams, Head of the Station, scooping the first shovel full of dirt; Marion Kent, Head of Personnel; and California state official Arthur Samet.

Portrait of Mary Jackson. 2017 Hall of Honor inductee. Langley Research Center NACA and NASA Hall of Honor. In honor and recognition of the ambition and motivation that enabled her career progression from human computer to NASA' s first African-American female engineer, and subsequent career supporting the hiring and promotion of other deserving female and minority employees.

Portrait of Mary Jackson. 2017 Hall of Honor inductee. Langley Research Center NACA and NASA Hall of Honor. In honor and recognition of the ambition and motivation that enabled her career progression from human computer to NASA' s first African-American female engineer, and subsequent career supporting the hiring and promotion of other deserving female and minority employees.
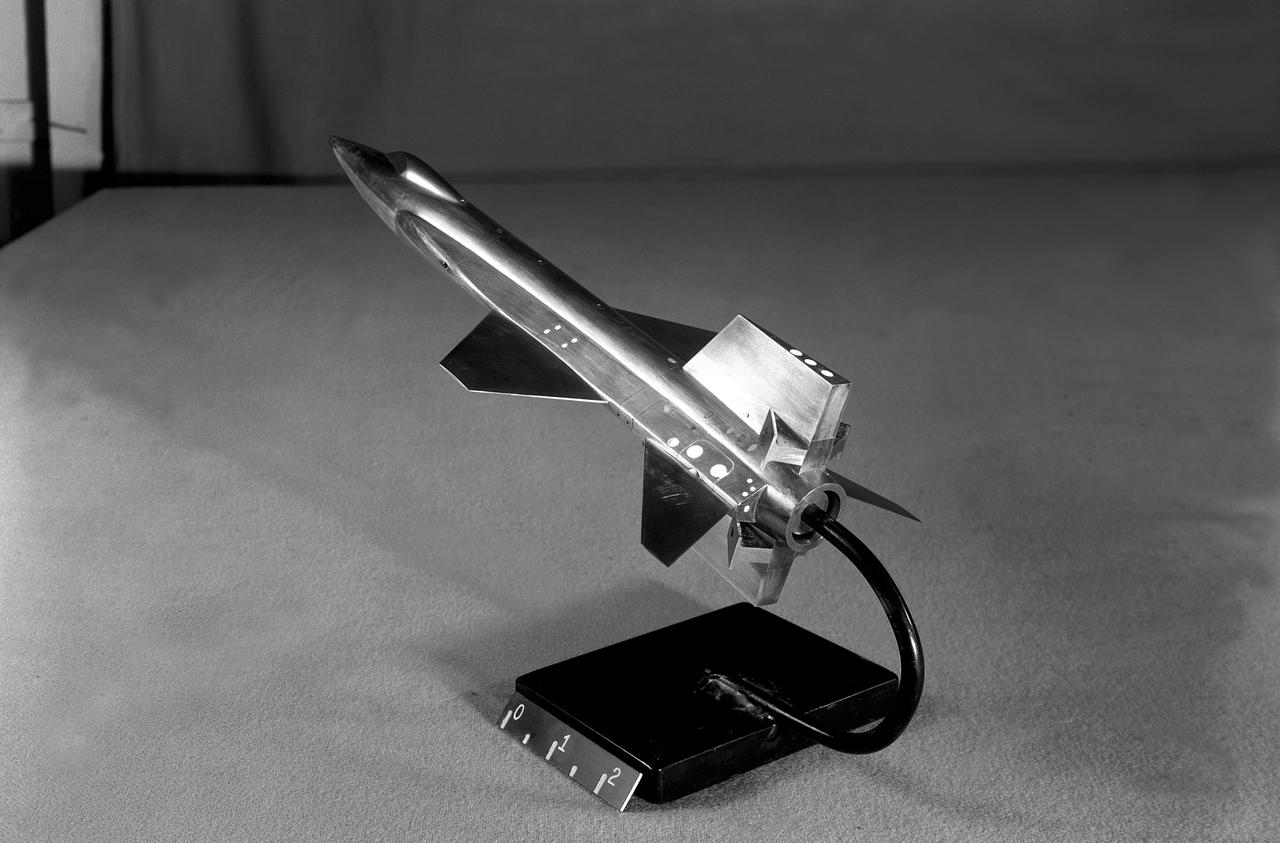

This scale-model of North American's initial X-15 design was tested in North American and NACA wind tunnels note the conventional tail and fuselage side-tunnels that extend far toward the aircraft nose. North American engineers would determine that the variable wedge-angle stabilizer created a weight issue, and aeronautical testing by Langley engineers confirmed that the side-tunnels made the design less stable.

Portrait of Mary Jackson. 2017 Hall of Honor inductee. Langley Research Center NACA and NASA Hall of Honor. In honor and recognition of the ambition and motivation that enabled her career progression from human computer to NASA' s first African-American female engineer, and subsequent career supporting the hiring and promotion of other deserving female and minority employees.
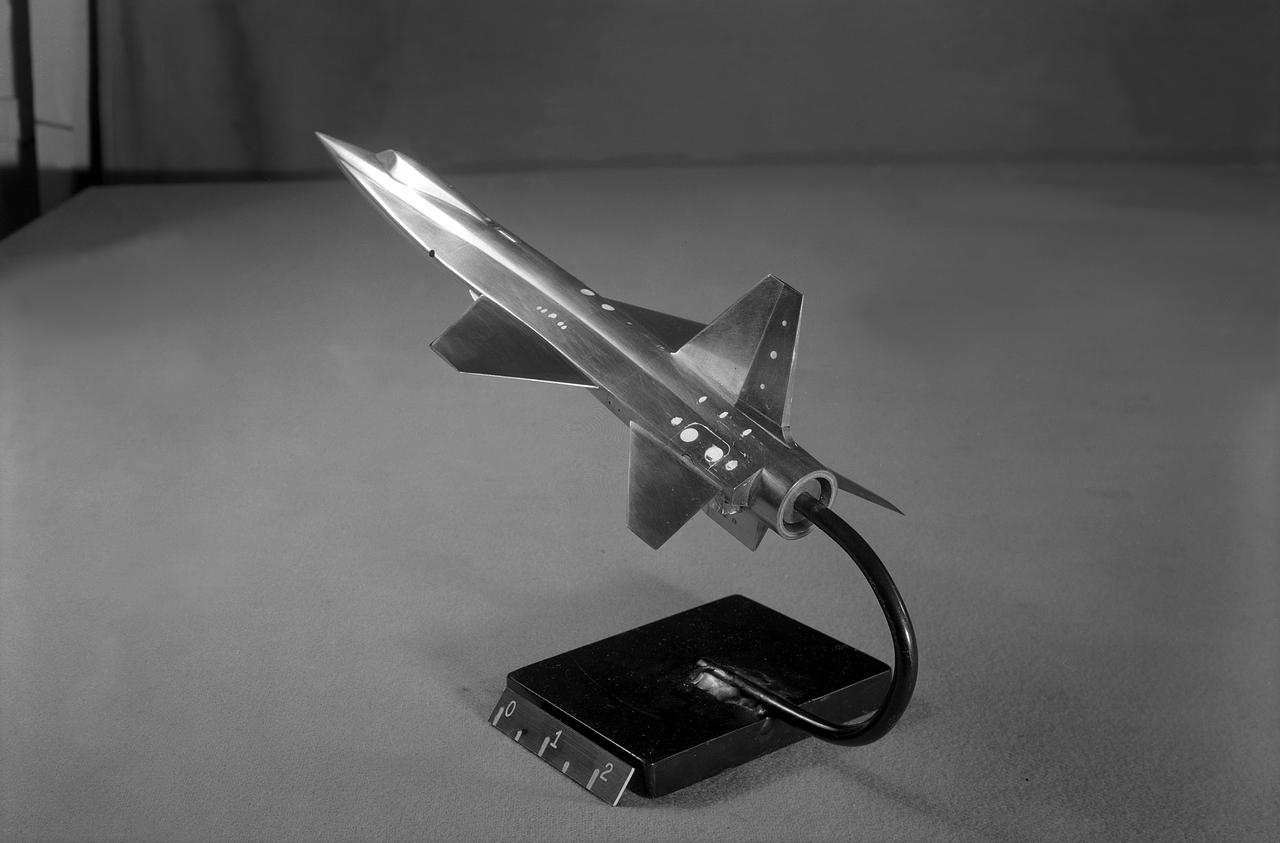

This scale-model of North American's initial X-15 design was tested in North American and NACA wind tunnels note the conventional tail and fuselage side-tunnels that extend far toward the aircraft nose. North American engineers would determine that the variable wedge-angle stabilizer created a weight issue, and aeronautical testing by Langley engineers confirmed that the side-tunnels made the design less stable.

Portrait of Mary Jackson. 2017 Hall of Honor inductee. Langley Research Center NACA and NASA Hall of Honor. In honor and recognition of the ambition and motivation that enabled her career progression from human computer to NASA's s first African-American female engineer, and subsequent career supporting the hiring and promotion of other deserving female and minority employees.
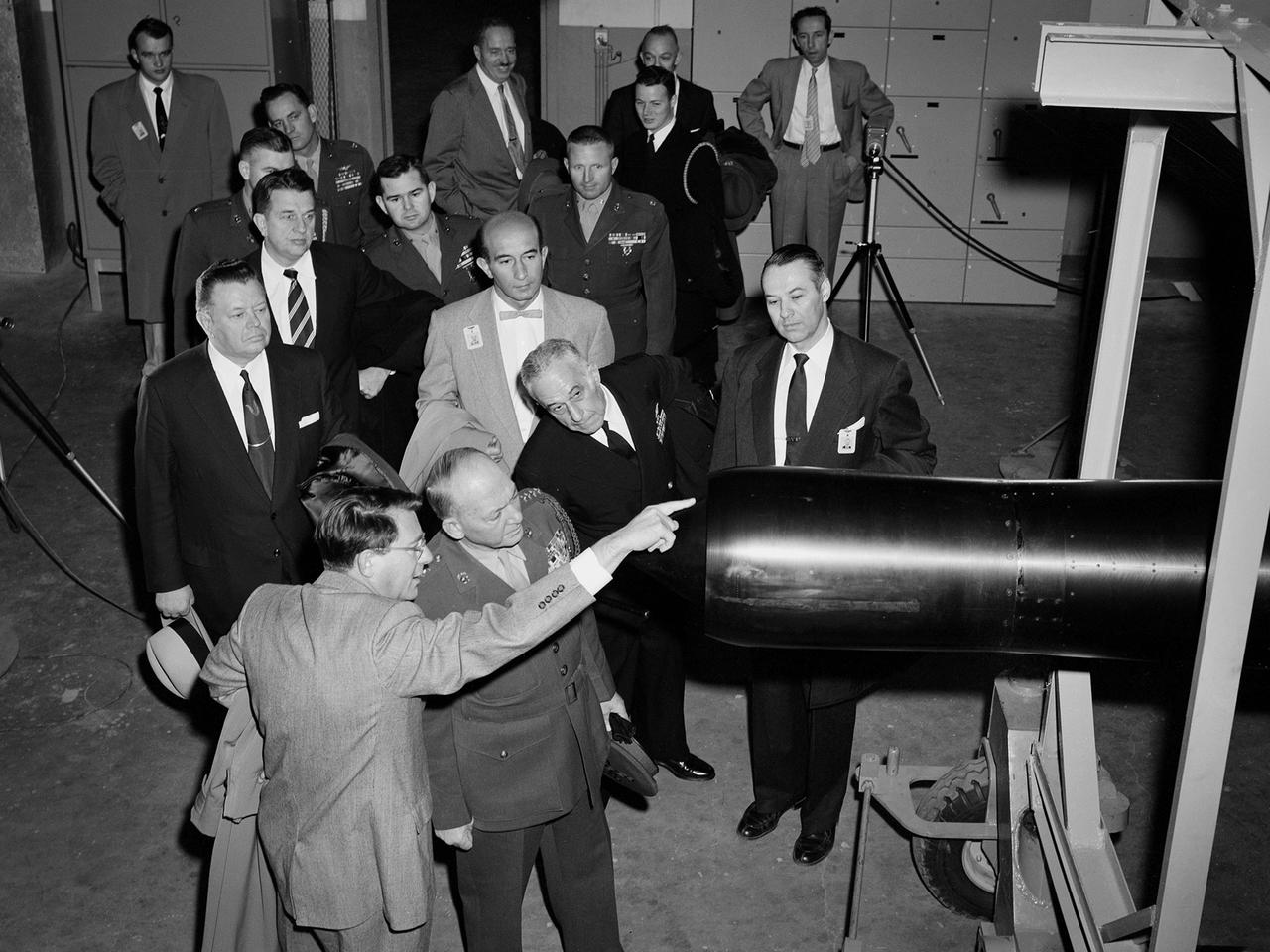

Abe Silverstein, Associate Director of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory, provides a personal tour of the new 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel for US Senator George Bender (hat in hand) and General Lemuel Shepherd. Shepherd was Commandant of the Marine Corps and had served in World War I, World War II, and the Korean War. The general was accompanied by Admiral Herbert Leary, in dark uniform. Bender was a Republican Senator from Ohio. Behind Bender is President of the Cleveland Chamber of Commerce Curtis Smith. NACA Lewis managers Eugene Manganiello and Wilson Hunter assist with the tour. Abe Silverstein oversaw all research at the laboratory. Upon taking his post in 1952 he reorganized the research staff and began shifting the focus away from airbreathing aircraft engines to new fields such as high energy fuels, electric propulsion, and nuclear power and propulsion. He was an early advocate of the NACA’s involvement in the space program and crucial to the founding of National Aeronautics and Space Administration in 1958. Silverstein began his career helping design and conduct research in the Full Scale Tunnel in 1929 at the Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory. Silverstein advocated a series of increasingly large supersonic wind tunnels after the war, culminating in the 10- by 10.
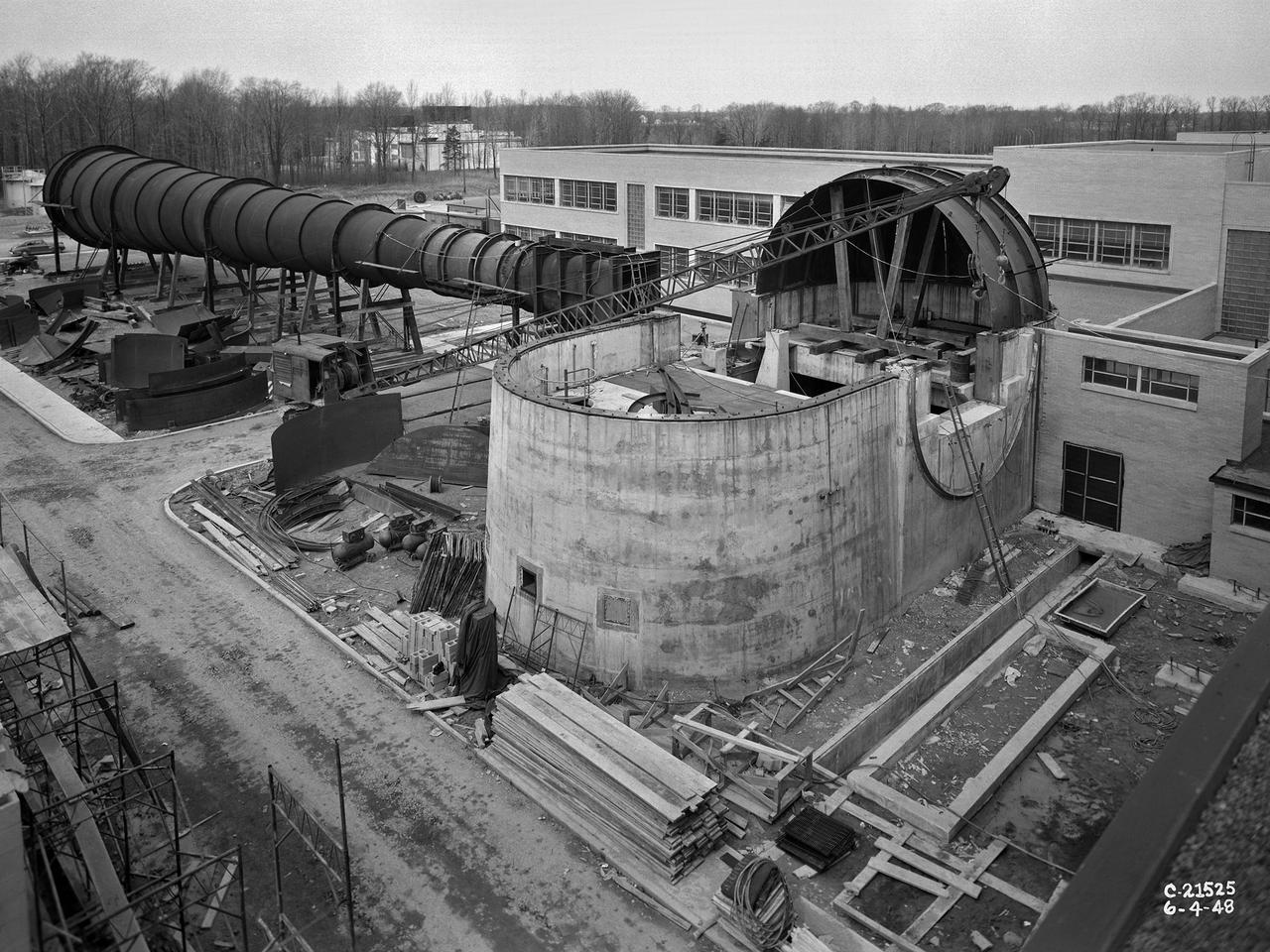

The 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory was the nation’s largest supersonic facility when it began operation in April 1949. The emergence of new propulsion technologies such as turbojets, ramjets, and rockets during World War II forced the NACA and the aircraft industry to develop new research tools. In late 1945 the NACA began design work for new large supersonic wind tunnels at its three laboratories. The result was the 4- by 4-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory, 6- by 6-foot supersonic wind tunnel at Ames Aeronautical Laboratory, and the largest facility, the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel in Cleveland. The two former tunnels were to study aerodynamics, while the 8- by 6 facility was designed for supersonic propulsion. The 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel was used to study propulsion systems, including inlets and exit nozzles, combustion fuel injectors, flame holders, exit nozzles, and controls on ramjet and turbojet engines. Flexible sidewalls alter the tunnel’s nozzle shape to vary the Mach number during operation. A seven-stage axial compressor, driven by three electric motors that yield a total of 87,000 horsepower, generates air speeds from Mach 0.36 to 2.0. A section of the tunnel is seen being erected in this photograph.
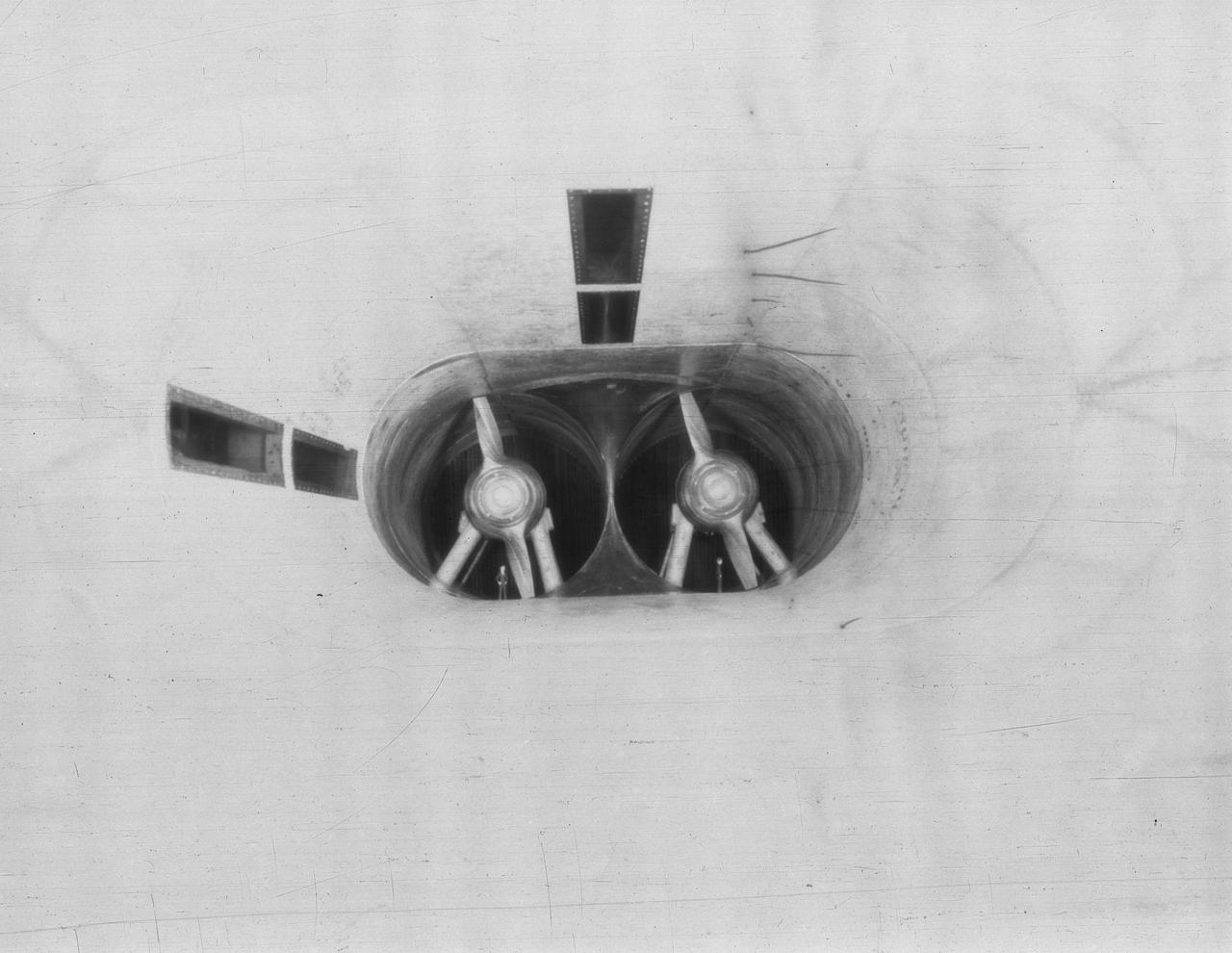
Smoke Flow Investigation XF7C-1 (Cowling Exhaust J.1 Type)
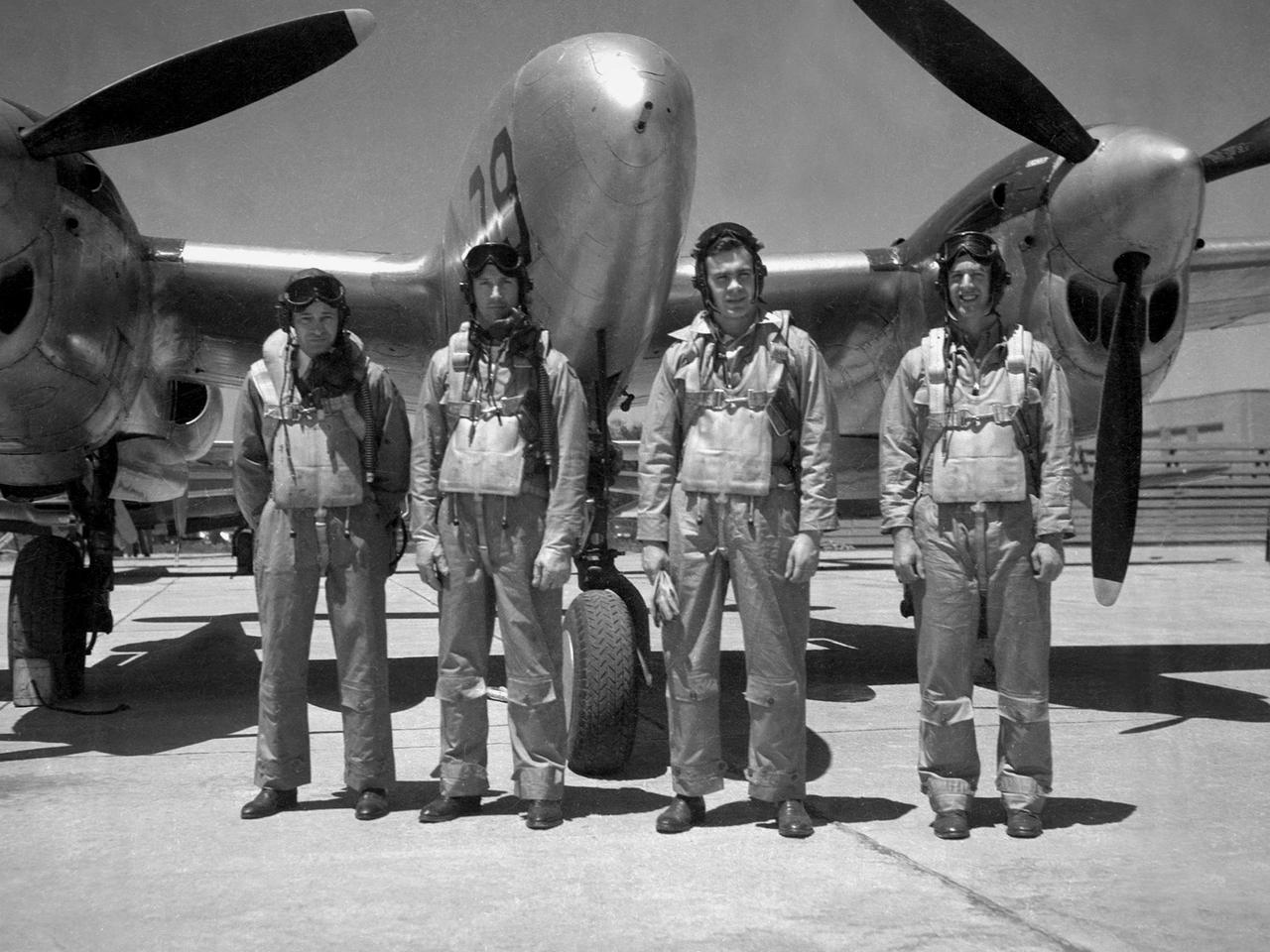

The Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory’s pilot corps during the final days of World War II: from left to right, Joseph Vensel, Howard Lilly, William Swann, and Joseph Walker. William “Eb” Gough joined the group months after this photograph. These men were responsible for flying the various National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) aircraft to test new engine modifications, study ice buildup, and determine fuel performance. Vensel, a veteran pilot from Langley, was the Chief of Flight Operations and a voice of reason at the laboratory. In April 1947 Vensel was transferred to lead the new Muroc Flight Tests Unit in California until 1966. Lilly was a young pilot with recent Navy experience. Lilly also flew in the 1946 National Air Races. He followed Vensel to Muroc in July 1947 where he became the first NACA pilot to penetrate the sound barrier. On May 3, 1948, Lilly became the first NACA pilot to die in the line of duty. Swann was a young civilian pilot when he joined the NACA. He spent his entire career at the Cleveland laboratory, and led the flight operations group from the early 1960s until 1979. Two World War II veterans joined the crew after the war. Walker was a 24-year-old P–38 reconnaissance pilot. He joined the NACA as a physicist in early 1945 but soon worked his way into the cadre of pilots. Walker later gained fame as an X-plane pilot at Muroc and was killed in a June 1966 fatal crash. Gough survived being shot down twice during the war and was decorated for flying rescue missions in occupied areas.

Portrait of Author W. Vogeley
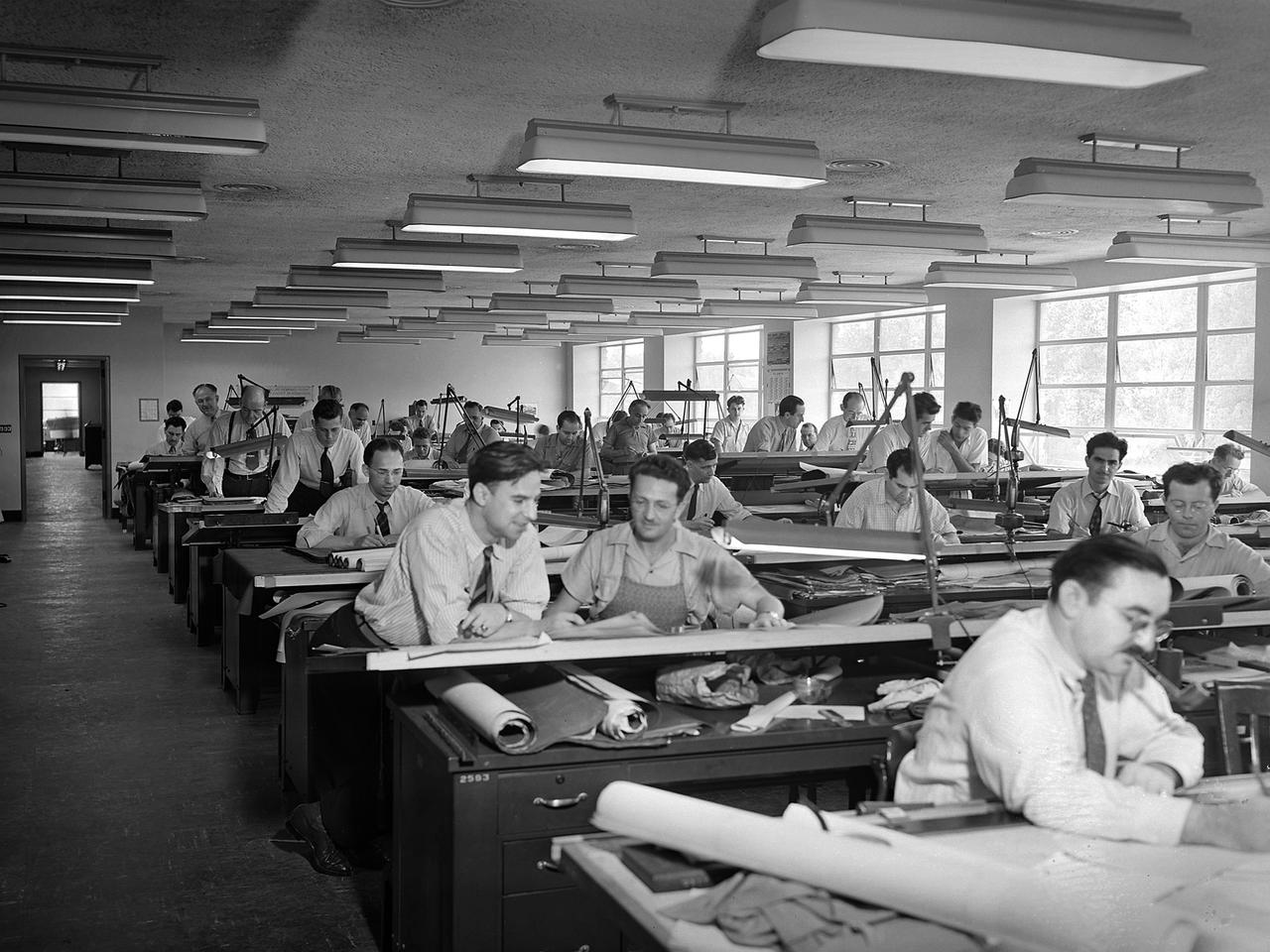

The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory was designed by a group of engineers at the Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory in late 1940 and 1941. Under the guidance of Ernest Whitney, the men worked on drawings and calculations in a room above Langley’s Structural Research Laboratory. The main Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory design group originally consisted of approximately 30 engineers and draftsmen, but there were smaller groups working separately on specific facilities. The new engine lab would have six principal buildings: the Engine Research Building, hangar, Fuels and Lubricants Building, Administration Building, Propeller Test Stand, and Altitude Wind Tunnel. In December 1941 most of those working on the project transferred to Cleveland from Langley. Harrison Underwood and Charles Egan led 18 architectural, 26 machine equipment, 3 structural and 10 mechanical draftsmen. Initially these staff members were housed in temporary offices in the hangar. As sections of the four-acre Engine Research Building were completed in the summer of 1942, the design team began relocating there. The Engine Research Building contained a variety of test cells and laboratories to address virtually every aspect of piston engine research. It also contained a two-story office wing, seen in this photograph that would later house many of the powerplant research engineers.
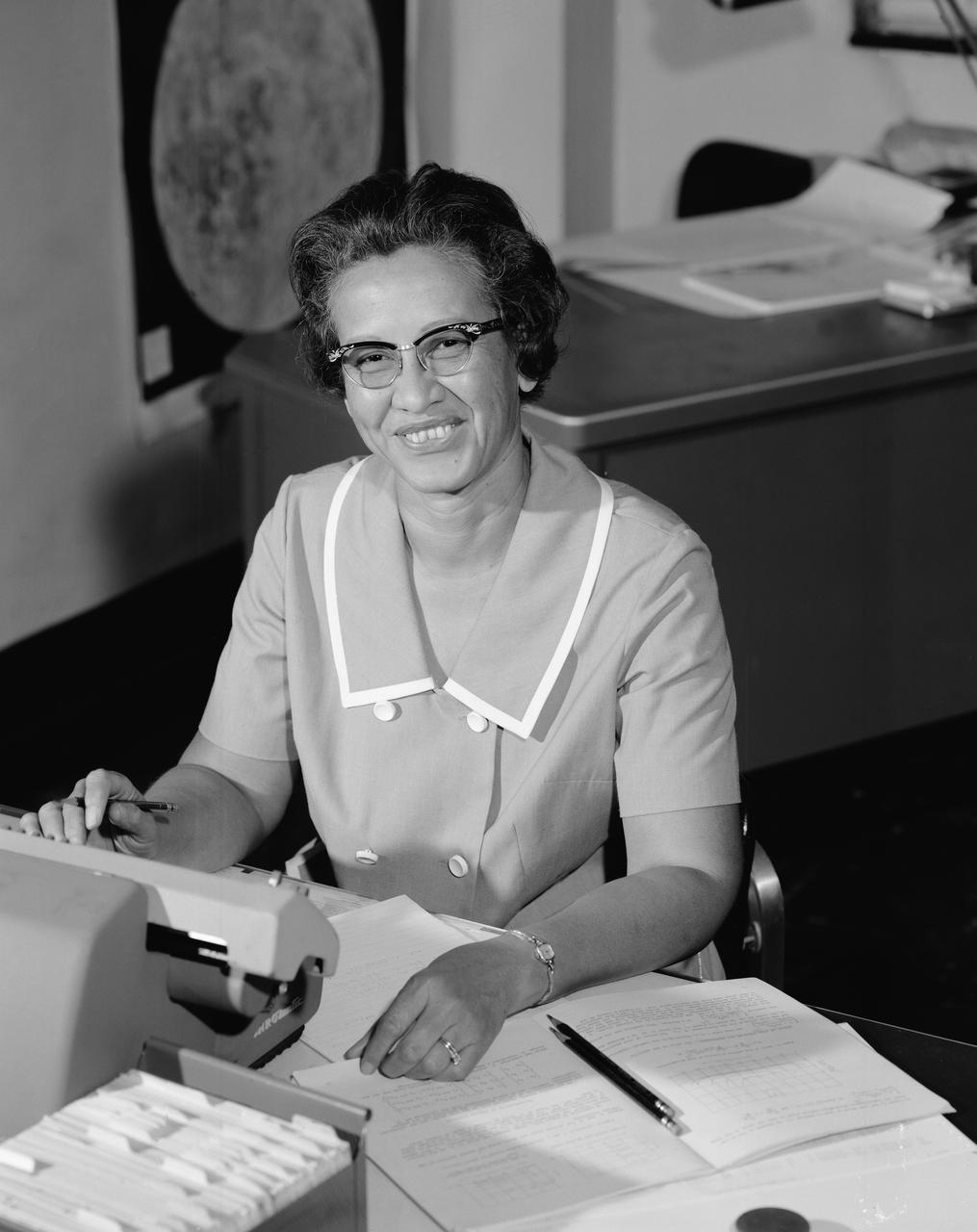

Katherine Johnson At Her Desk at NASA Langley Research Center
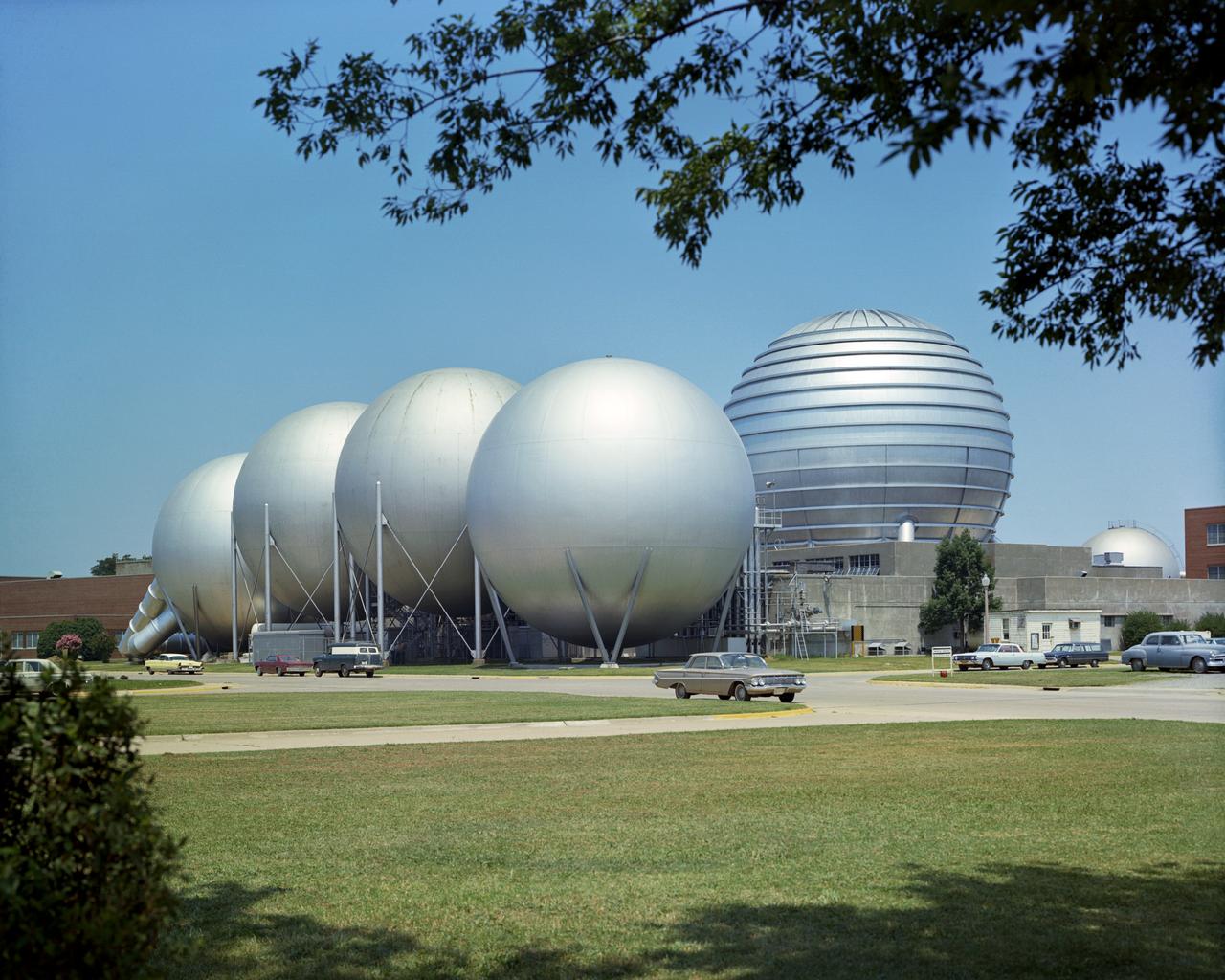

L65-5505 In the Gas Dynamics Laboratory, completed in 1951, researchers explored basic aerodynamic, heating and fluid-mechanical problems in the speed range from Mach 1.5 to Mach 8.0. Photograph published in Engineer in Charge: A History of the Langley Aeronautical Laboratory, 1917-1958 by James R. Hansen. Page 348.
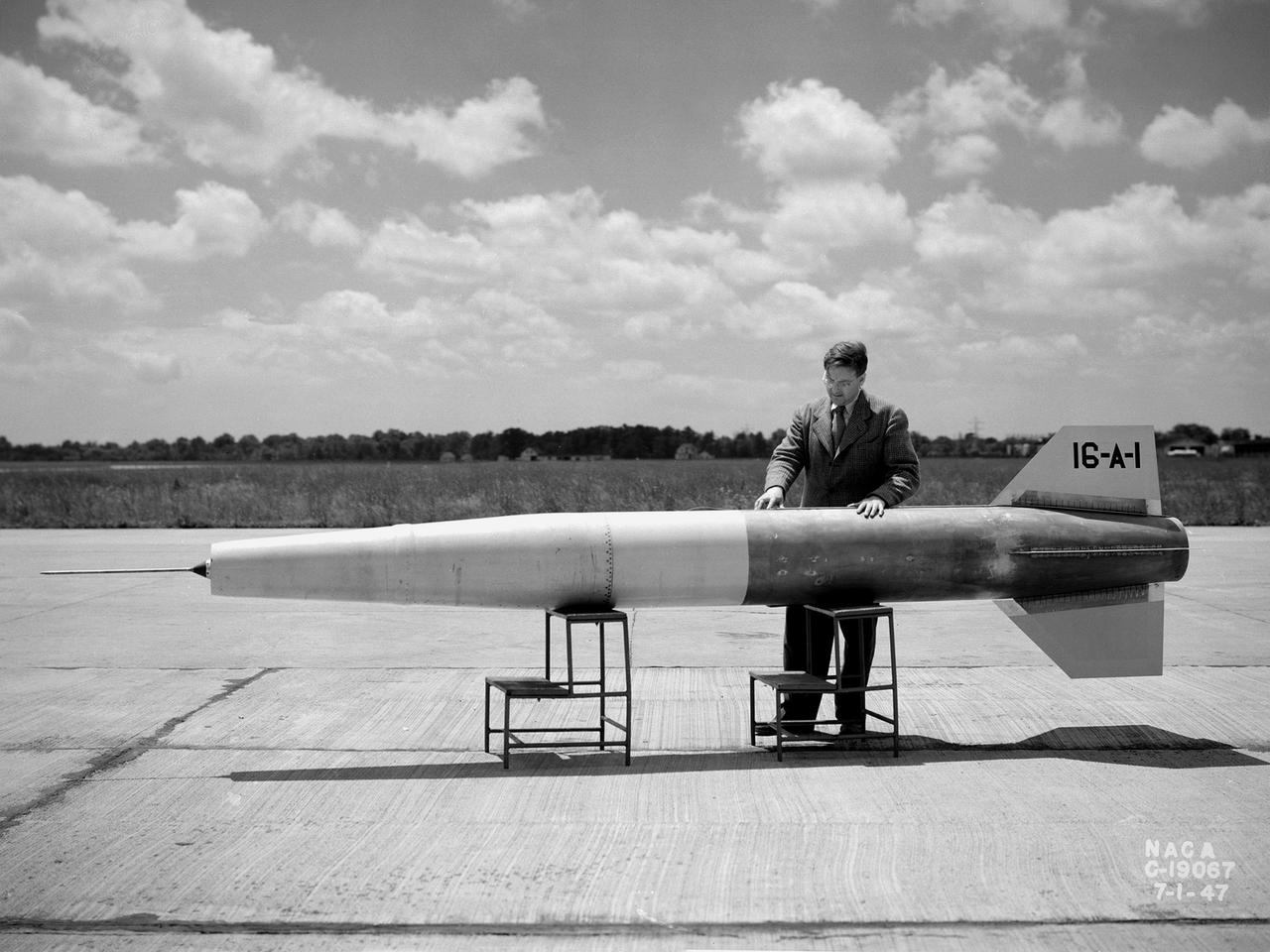

A NACA researcher prepares a 16-inch diameter and 16-foot long ramjet for a launch over Wallops Island in July 1947. The Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory conducted a wide variety of studies on ramjets in the 1940s and 1960s to determine the basic operational data necessary to design missiles. Although wind tunnel and test stand investigations were important first steps in determining these factors, actual flight tests were required. Lewis possessed several aircraft for the ramjet studies, including North American F-82 Mustangs, a Northrup P-61 Black Widow, and a Boeing B-29 Superfortress, which was used for this particular ramjet. This was Lewis’ first flight at over the experimental testing ground at Wallops Island. The NACA’s Langley laboratory established the station on the Virginia coast in 1945 to conduct early missile tests. This ramjet-powered missile was affixed underneath the B-29’s left wing and flown up to 29,000 feet. The ramjet was ignited as the aircraft reached Mach 0.5 and released. The flight went well, but a problem with the data recording prevented a successful mission. Nonetheless additional flights in November 1947 provided researchers with data on the engine’s combustion efficiency at different levels of fuel-air ratios, thrust coefficients, temperatures, and drag. Transonic flight data such as the rapid acceleration through varying flight conditions could not be easily captured in wind tunnels.
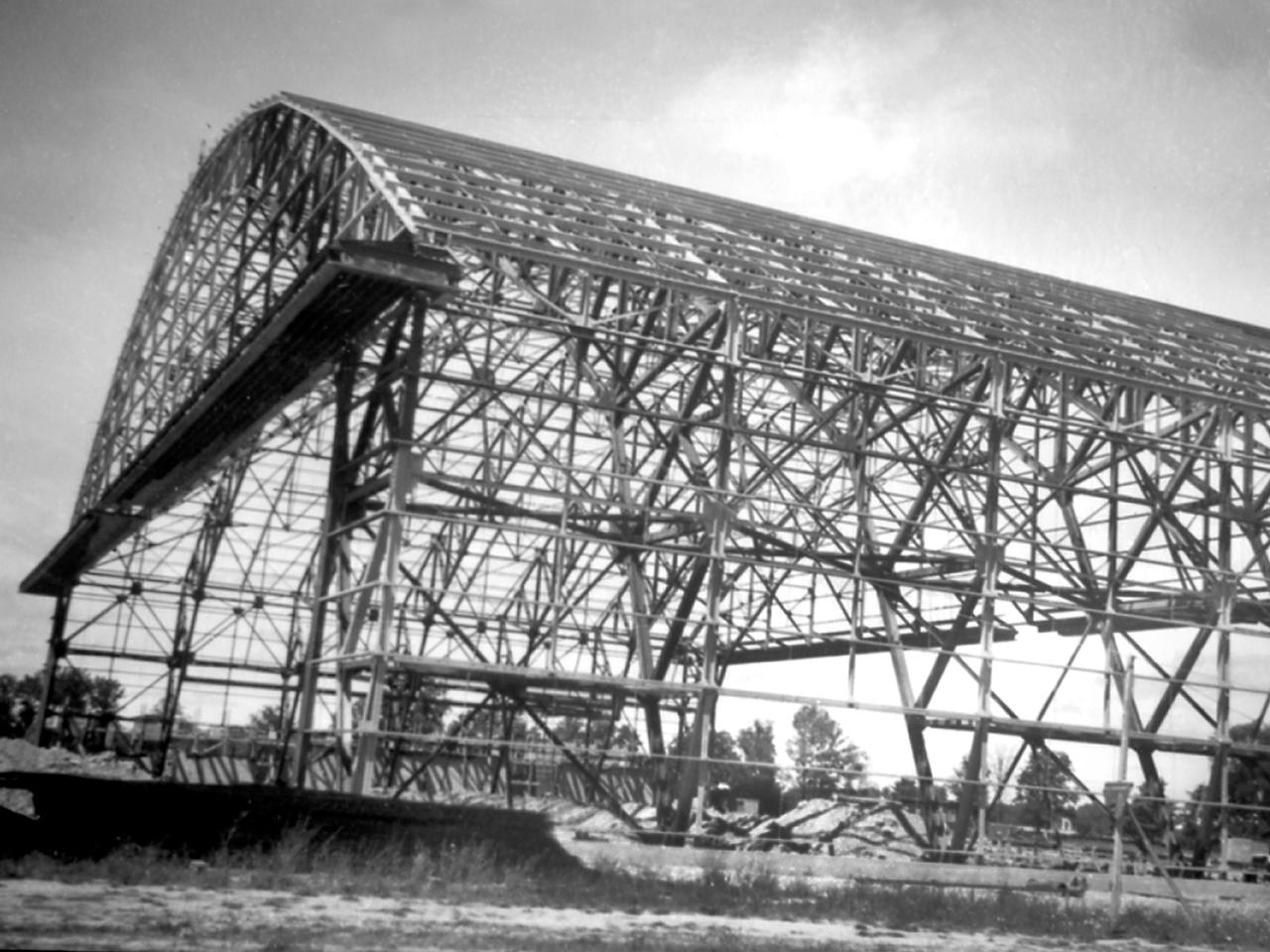

Northward view of the Flight Research Building's steel framework in August 1941 as it neared completion at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory. The 272- by 150-foot hangar had a 90-foot clearance at its highest point. The hangar was the first structure built and was needed as a shelter for the growing staff, who occupied a nearby Farm House at this point. In January 1941 the Cleveland-area R.P. Carbone Construction Company was selected to build the hangar. Over the ensuing months, however, the NACA management became frustrated by the slow progress on the project. Although Carbone was contracted to complete the entire hangar by August, it was September before even the structural steel frame, seen in this photograph, was in place. Officials estimated the roof and siding were four months behind schedule. This was a serious concern because the lab’s research, support and administrative staff members would soon begin arriving. By mid-September the transite walls began enclosing the skeleton. In October work began on the temporary offices inside. The building was completed in mid-December just in time for the staff arriving from Langley.
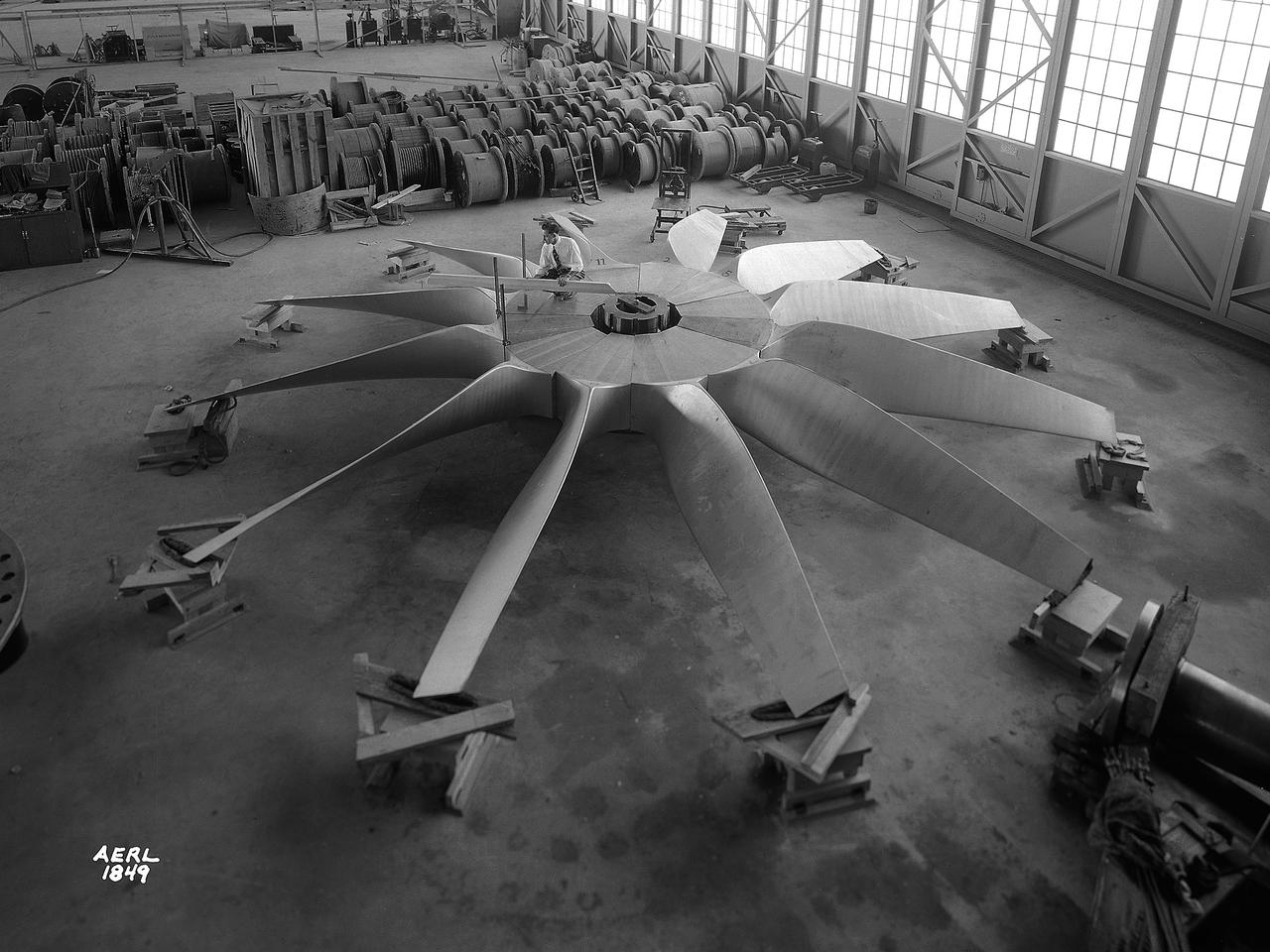

National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) engineers assembled the Altitude Wind Tunnel’s (AWT) large wooden drive fan inside the hangar at the Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory. When it was built at the in the early 1940s the AWT was among the most complex test facilities ever designed. It was the first wind tunnel capable of operating full-scale engines under realistic flight conditions. This simulation included the reduction of air temperature, a decrease in air pressure, and the creation of an airstream velocity of up to 500 miles per hour. The AWT was constructed in 1942 and 1943. This photograph shows NACA engineers Lou Hermann and Jack Aust assembling the tunnel’s drive fan inside the hangar. The 12-bladed, 31-foot-diameter spruce wood fan would soon be installed inside the wind tunnel to create the high-speed airflow. This massive propeller was designed and constructed by the engine lab's design team at Langley Field. John Breisch, a Langley technician with several years of wind tunnel installation experience, arrived in Cleveland at the time of this photograph to supervise the fan assembly inside the hangar. He would return several weeks later to oversee the actual installation in the tunnel. The fan was driven at 410 revolutions per minute by an 18,000-horsepower General Electric induction motor that was located in the rear corner of the Exhauster Building. An extension shaft connected the motor to the fan. A bronze screen protected the fan against damage from failed engine parts sailing through the tunnel. Despite this screen the blades did become worn or cracked over time and had to be replaced. An entire new fan was installed in 1951.
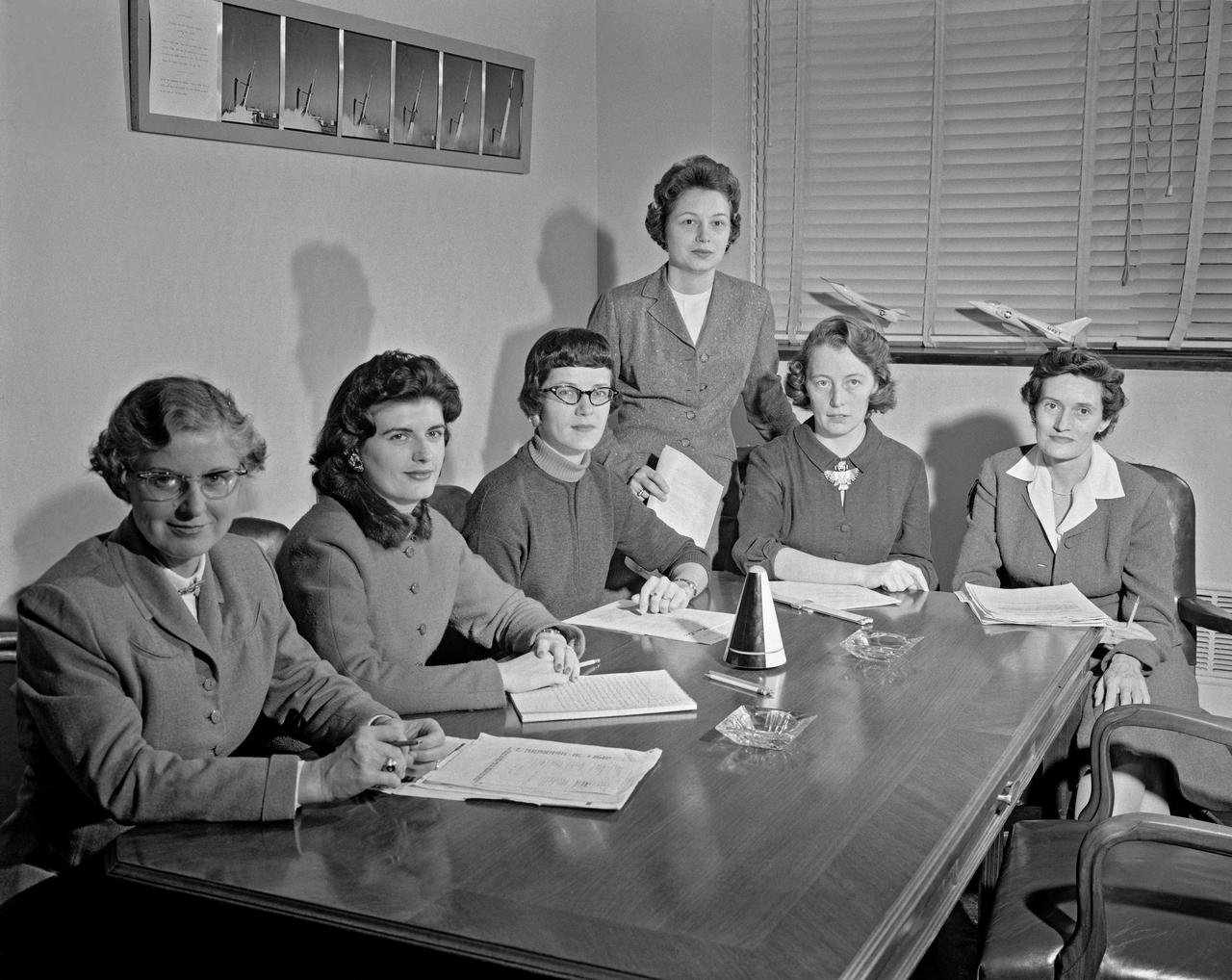

Women Scientists: Lucille Coltrane, Jean Clark Keating, Katherine Cullie Speegle, Doris 'Dot' Lee, Ruth Whitman, and Emily Stephens Mueller,Lucille Coltrane is at the far left. She was a computer and worked for Norm Crabill who provided positive identification. Lucille authored a NACA Research Memorandum, Investigation of Two Bluff Shapes in Axial Free Flight Over a Mach Number Range From 0.35 to 2.15 in 1958. Next to Lucille is Jean Clark Keating. Jean was identified by Mary Woerner who said that both Jean and her husband Jerry are now deceased. The third woman from the left is Katherine Cullie Speegle. Katherine co-authored two research papers: Preliminary Results From a Free-Flight Investigation of Boundary-Layer Transition and Heat Transfer on a Highly Polished 8-Inch-Diameter Hemisphere-Cylinder at Mach Numbers up to 3 and Reynolds Numbers Based on a Length of 1 Foot up to 17.7 x 10 to the 6th and Heat Transfer For Mach Numbers Up to 2.2 and Pressure Distributions for Mach Numbers Up to 4.7 From Flight Investigations of a Flat-Face Cone and a Hemisphere-Cone. Norm remembered the woman standing as Doris. Mary Alice identified her as Doris 'Dot' Lee, who worked with Katherine Speegle. Dot was married to a NASA engineer named John Lee. Next to Doris is Ruth Whitman. Norm remembered she and her husband owned a Howard DGA 15 at the airport in WEst Point. That prompted Mary Alice to remember her name and that her husband was Jim. The woman seated on the right is Emily Stephens Mueller. Norm remembers that Emily went to Houston as part of the Space Task Group, but retired back here on the peninsula. In 2008, Emily attended the NACA Reunion X11. She walked over to a table of books about the history of NACA, former NACA facilities and the organization's aviation pioneers and saw a book about women of flight from the Dryden Research Center and paused, then pointed somewhat in amazement. "That’s me," she said of a picture on the cover of her on the far left of a li
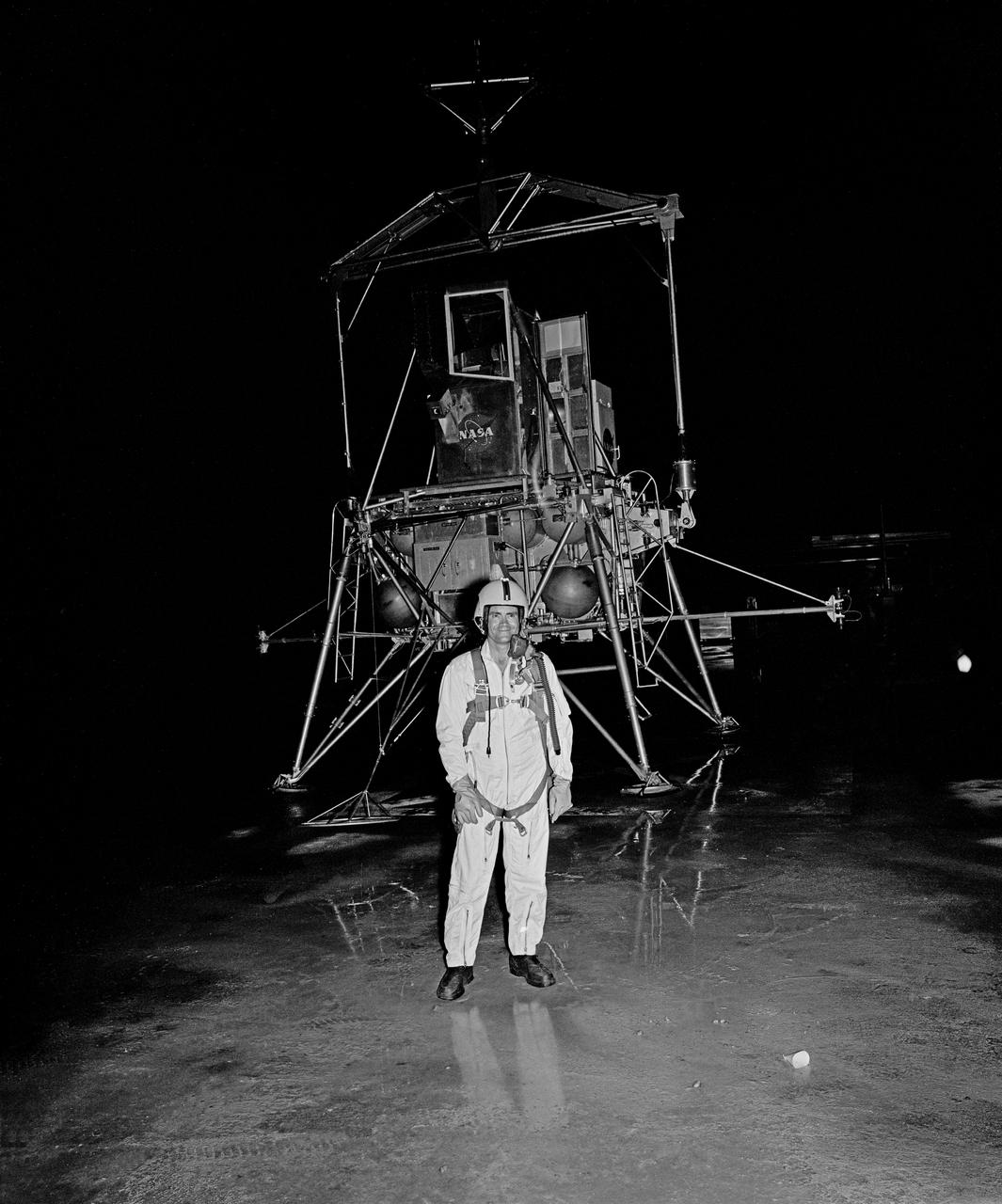

Astronaut Fred Wallace Haise, Jr. at NASA Langley Lunar Research Facility, Gantry test at night. Haise was the lunar module pilot on Apollo 13 (April 11-17, 1970) and has logged 142 hours and 54 minutes in space.
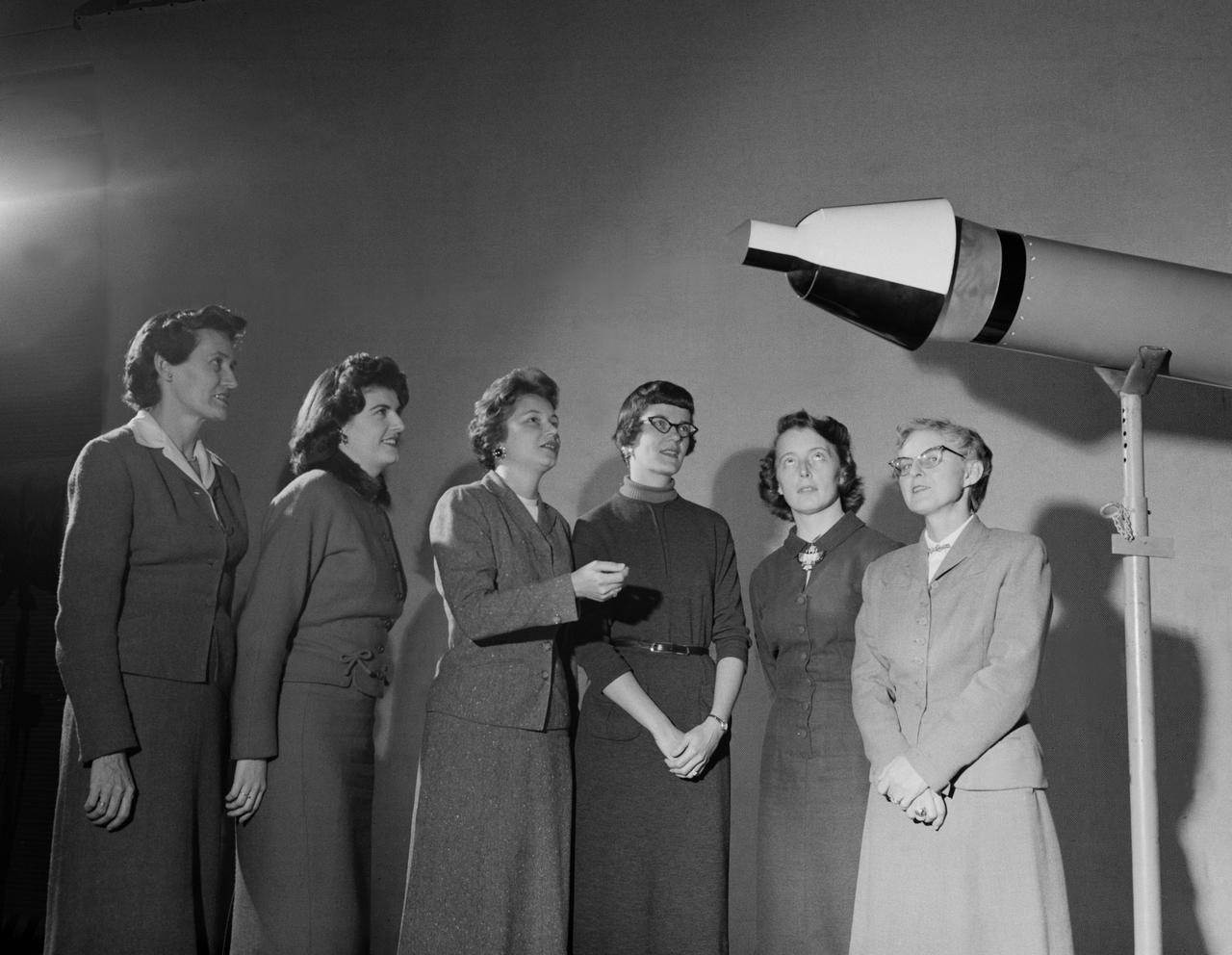

Women Scientists: Lucille Coltrane, Jean Clark Keating, Katherine Cullie Speegle, Doris 'Dot' Lee, Ruth Whitman, and Emily Stephens Mueller,Lucille Coltrane is at the far left. She was a computer and worked for Norm Crabill who provided positive identification. Lucille authored a NACA Research Memorandum, Investigation of Two Bluff Shapes in Axial Free Flight Over a Mach Number Range From 0.35 to 2.15 in 1958. Next to Lucille is Jean Clark Keating. Jean was identified by Mary Woerner who said that both Jean and her husband Jerry are now deceased. The third woman from the left is Katherine Cullie Speegle. Katherine co-authored two research papers: Preliminary Results From a Free-Flight Investigation of Boundary-Layer Transition and Heat Transfer on a Highly Polished 8-Inch-Diameter Hemisphere-Cylinder at Mach Numbers up to 3 and Reynolds Numbers Based on a Length of 1 Foot up to 17.7 x 10 to the 6th and Heat Transfer For Mach Numbers Up to 2.2 and Pressure Distributions for Mach Numbers Up to 4.7 From Flight Investigations of a Flat-Face Cone and a Hemisphere-Cone. Norm remembered the woman standing as Doris. Mary Alice identified her as Doris 'Dot' Lee, who worked with Katherine Speegle. Dot was married to a NASA engineer named John Lee. Next to Doris is Ruth Whitman. Norm remembered she and her husband owned a Howard DGA 15 at the airport in WEst Point. That prompted Mary Alice to remember her name and that her husband was Jim. The woman seated on the right is Emily Stephens Mueller. Norm remembers that Emily went to Houston as part of the Space Task Group, but retired back here on the peninsula. In 2008, Emily attended the NACA Reunion X11. She walked over to a table of books about the history of NACA, former NACA facilities and the organization's aviation pioneers and saw a book about women of flight from the Dryden Research Center and paused, then pointed somewhat in amazement. "That’s me," she said of a picture on the cover of her on the far left of a li
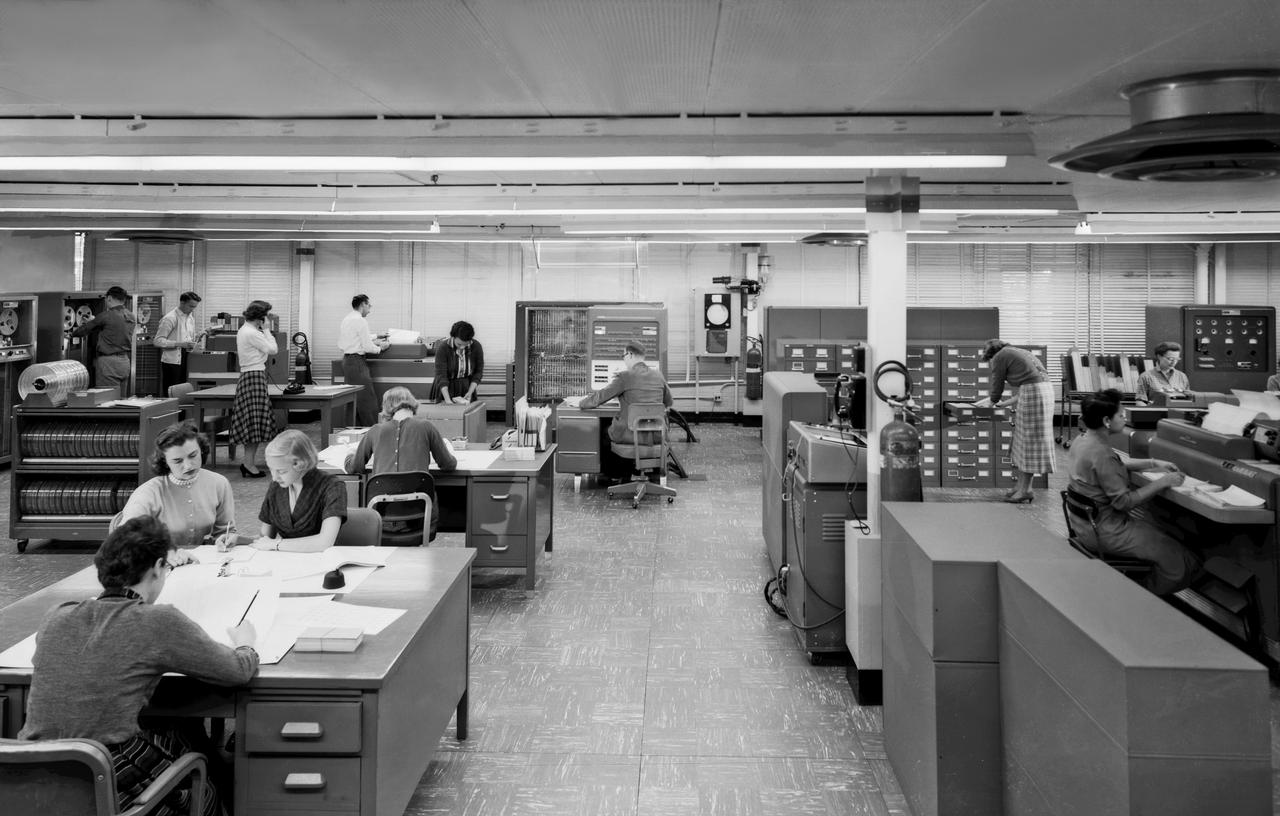

IBM 704 Computer Operations People on the photo are: Woman in the front with her back to the camera is Jean Ruddle Migneault. She provided the names for the rest of the staff in the photo. Kathy Christian Young, Mary Talmage Kaylor, Willie Terrell Ruffin (computer operator not mathematician), Joyce Alston Clemens, Lou Mayo Ladson, Rachel Richardson Mayo, Sadie Livingston Boyer , Joann Shipp Buschman worked in hangar in West Area, Shelva Blevins Stroud (programmer in data reduction), Jackie Kilby, Rita Englebert, Harriet Seals Winestein, Lillian Boney, Jane Thompson Kemper, Helen Thompson ( math aide) Jane and Helen were daughters of Floyd Thompson, center director.