2009 American Geophysical Union (AGU) conference in San Francisco, California. Dr David Morrison, Director Lunar Science Institute and Senior Scientist, NASA Astrobiology.
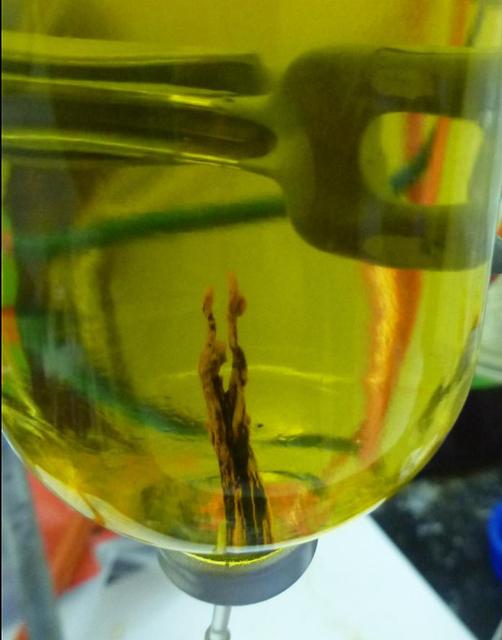

A laboratory-created "chemical garden" made of a combination of black iron sulfide and orange iron hydroxide/oxide is shown in this photo. Chemical gardens are a nickname for chimney-like structures that form at bubbling vents on the seafloor. Some researchers think that life may have originated at structures like these billions of years ago. JPL's research team is part of the Icy Worlds team of the NASA Astrobiology Institute, based at NASA's Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, California. JPL is managed by the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena for NASA. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19835
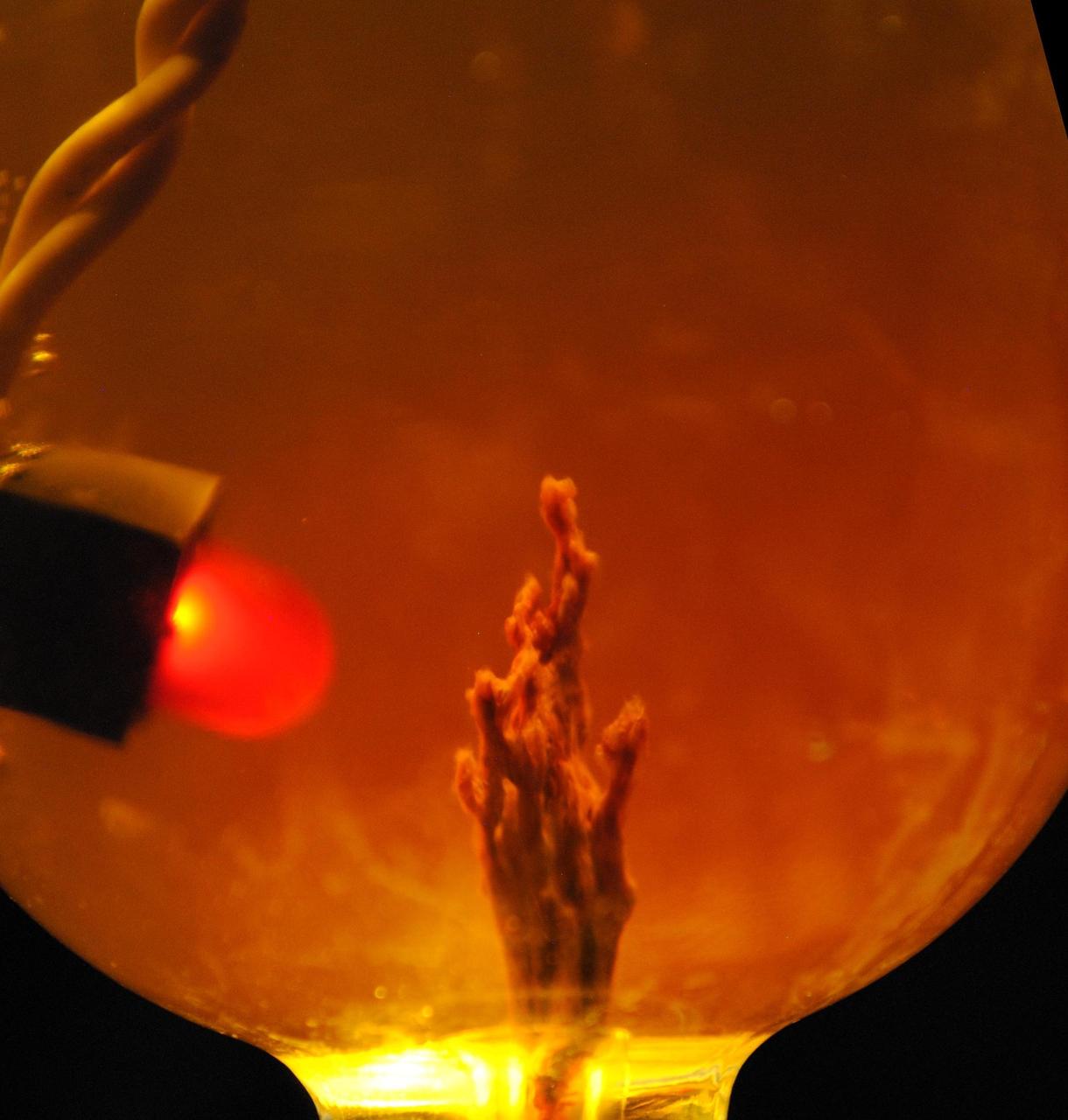

This photo simulation shows a laboratory-created "chemical garden," which is a chimney-like structure found at bubbling vents on the seafloor. Some researchers think life on Earth might have got its start at structures like these billions of years ago, partly due to their ability to transfer electrical currents -- an essential trait of life as we know it. The battery-like property of these chemical gardens was demonstrated by linking several together in series to light an LED (light-emitting diode) bulb. In this photo simulation, the bulb is not really attached to the chimney. The chimney membranes are made of iron sulfides and iron hydroxides, geologic materials that conduct electrons. JPL's research team is part of the Icy Worlds team of the NASA Astrobiology Institute, based at NASA's Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, California. JPL is managed by the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena for NASA. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19834

Deputy principal investigator, SuperCam instrument, Institut de Recherche Astrophysique et Planétologie, Toulouse, France, Sylvestre Maurice, gives remarks via remote during a NASA Perseverance rover mission science overview, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The Perseverance Mars rover is due to land on Mars Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
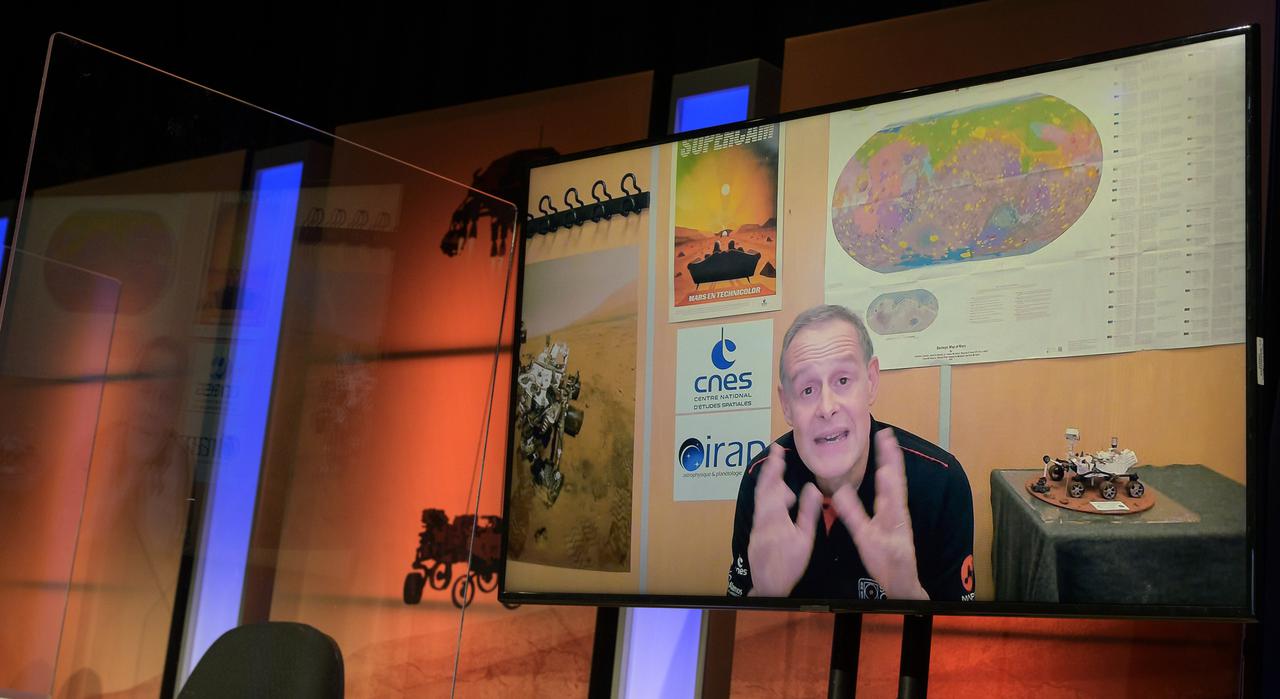

Deputy principal investigator, SuperCam instrument, Institut de Recherche Astrophysique et Planétologie, Toulouse, France, Sylvestre Maurice, gives remarks via remote during a NASA Perseverance rover mission science overview, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021, at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. The Perseverance Mars rover is due to land on Mars Thursday, Feb. 18, 2021. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet’s geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
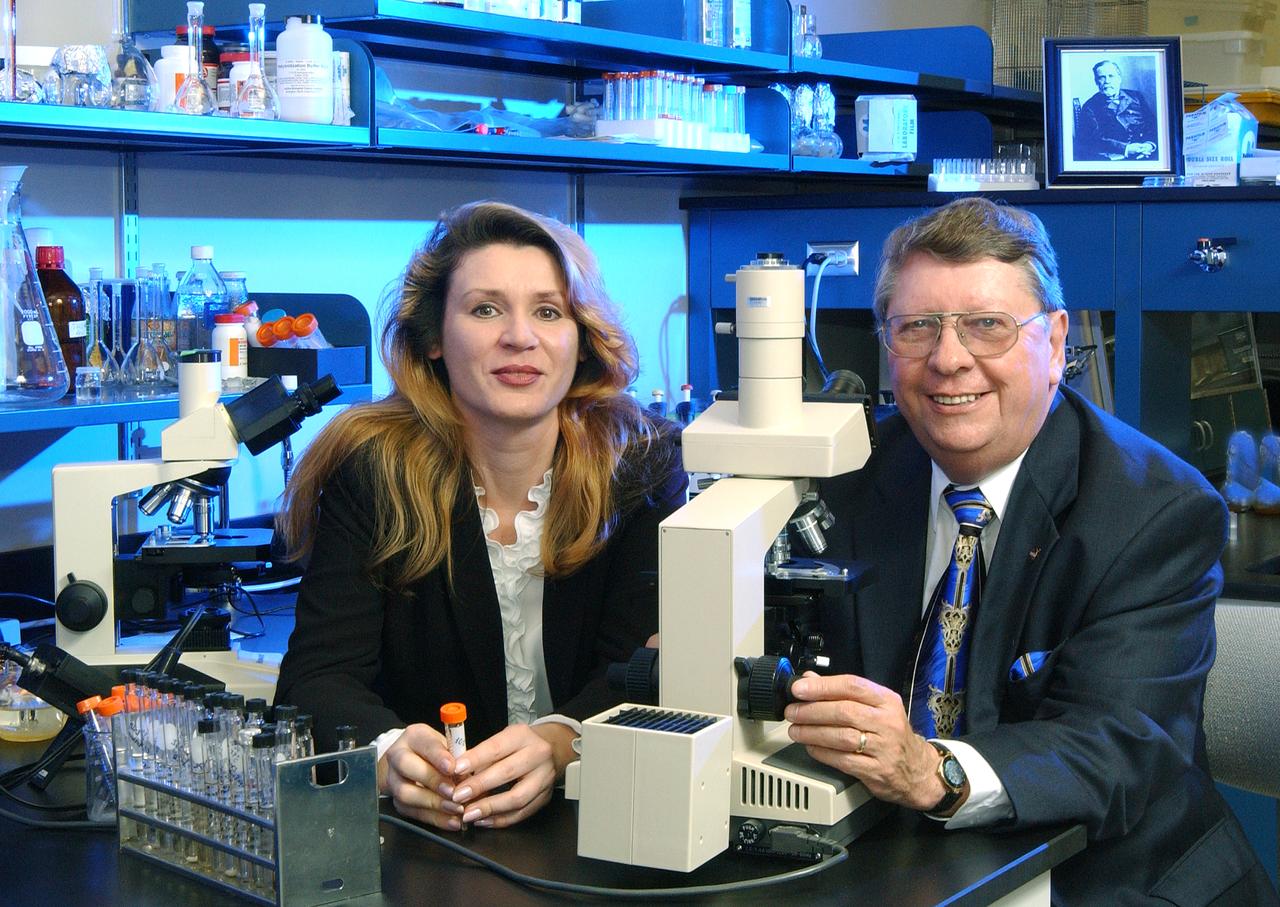

Microbiologist Dr. Elena V. Pikuta, and Astrobiologist Richard Hoover culture extremophiles, microorganisms that can live in extreme environments, in the astrobiology laboratory at the National Space Science and Technology Center (NSSTC) in Huntsville, Alabama. The scientists recently discovered a new species of extremophiles, Spirochaeta Americana. The species was found in Northern California's Mono Lake, an alkaline, briny oxygen-limited lake in a closed volcanic crater that Hoover believes may offer new clues to help identify sites to research for potential life on Mars. Hoover is an astrobiologist at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), and Pikuta is a microbiologist with the Center for Space Plasma and Aeronomy Research Laboratory at the University of Alabama in Huntsville. The NSSTC is a partnership with MSFC, Alabama universities, industry, research institutes, and federal agencies.
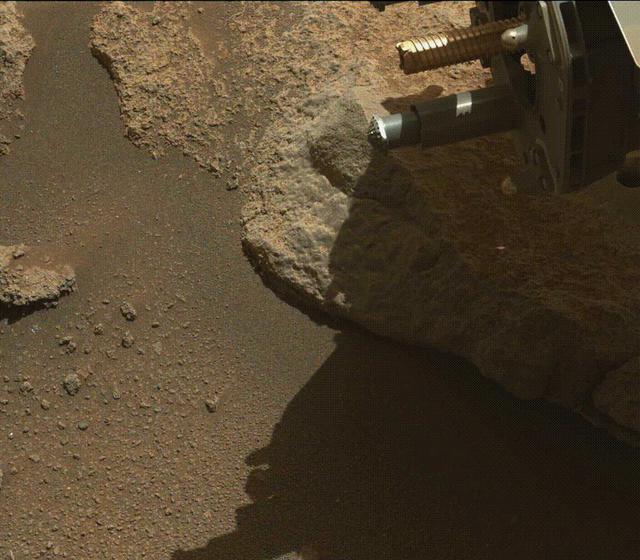

A portion of a cored-rock sample is ejected from the rotary percussive drill on NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. The imagery was collected by the rover's Mastcam-Z instrument on Jan. 15, 2022, the 322nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission, during an experiment that oriented the drill and sample tube (unseen here) around 9 degrees below horizontal and then rotated and extended the drill's spindle. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25072
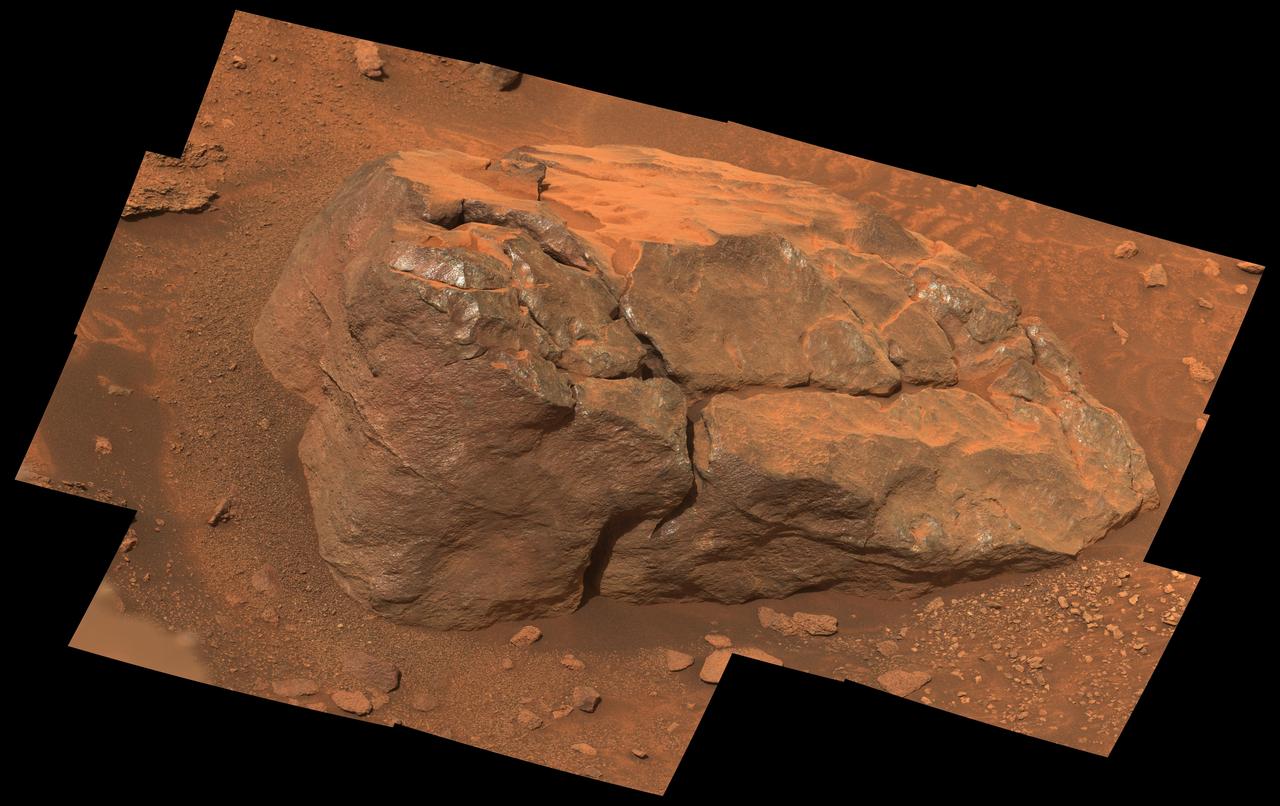

This natural-color, high-resolution mosaic showing "Observation Rock" was taken by the Mastcam-Z instrument on NASA's Perseverance as the rover climbed the western wall of Jezero Crater. The location is near an area the Perseverance science team is calling "Curtis Ridge." The 14 frames used to generate the mosaic were acquired on Oct. 18, 2024, the 1,302nd Martian day, or sol, of Perseverance's mission. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26481

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera to capture this 360-degree panorama of an area nicknamed "Rio Chiquito" on Nov. 23, 2024, the 1,337th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The rover's tracks can be seen in the center of the image. This enhanced-color version of the image is designed to bring out subtle details. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26474
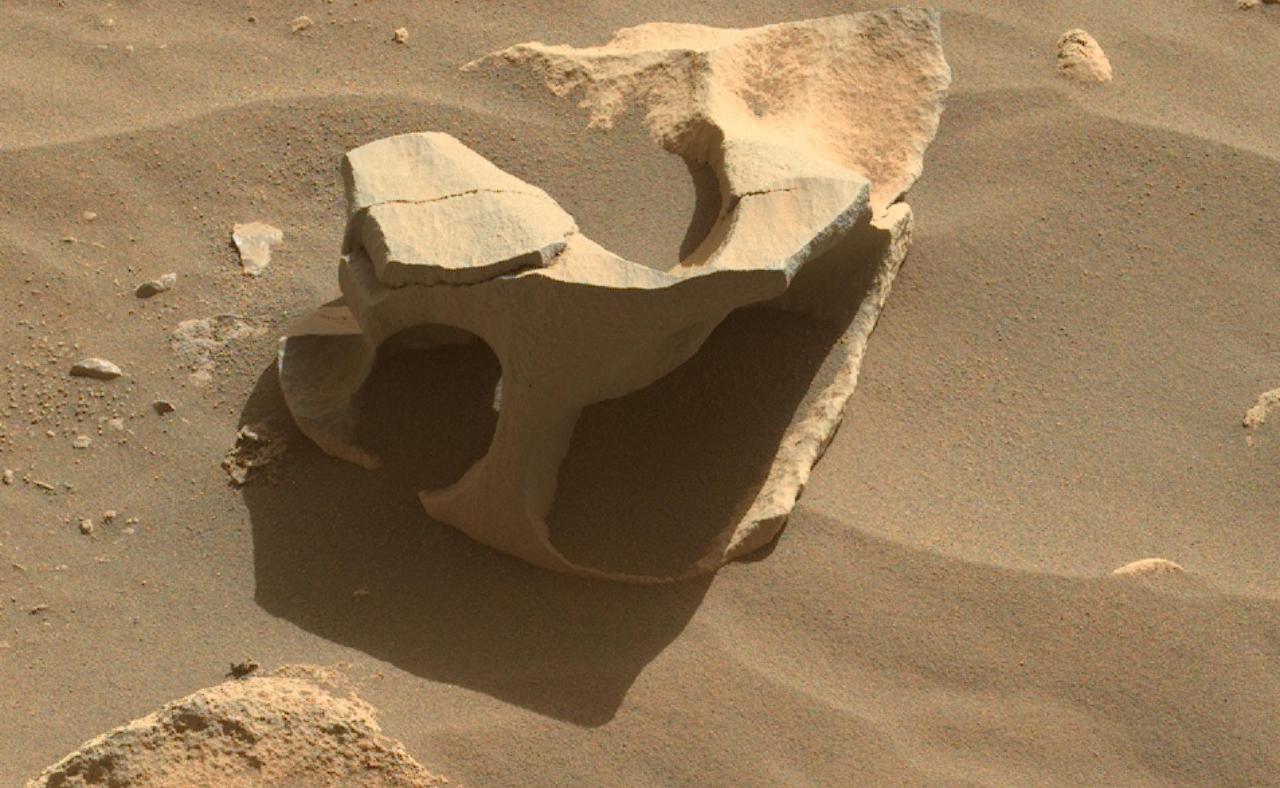

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover spotted this hollowed-out rock in Jezero Crater using its Mastcam-Z instrument on June 26, 2023, the 836th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Wind can erode all sorts of strange shapes by sandblasting rock surfaces over the course of eons. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25917

Composed of 53 images, this mosaic looks west toward the rim of Mars' Jezero Crater on July 8, 2023, the 847th Martian day, or sol, of NASA's Perseverance rover mission. The rover's Mastcam-Z instrument captured the images when Perseverance was about halfway through a boulder field that was 0.6 miles (1 kilometer) wide. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25965

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera system to capture this view as it was ascending to the rim of Jezero Crater on Dec. 5, 2024, the 1,349th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The scene shows just how steep some of the slopes leading to the crater rim can be. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26475

This view of NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was generated using data collected by the Mastcam-Z instrument aboard the agency's Perseverance Mars rover on Aug. 2, 2023, the 871st Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The image was taken a day before the rotorcraft's 54th flight, and about a week and a half after Flight 53, which was cut short by an unexpected landing. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25968
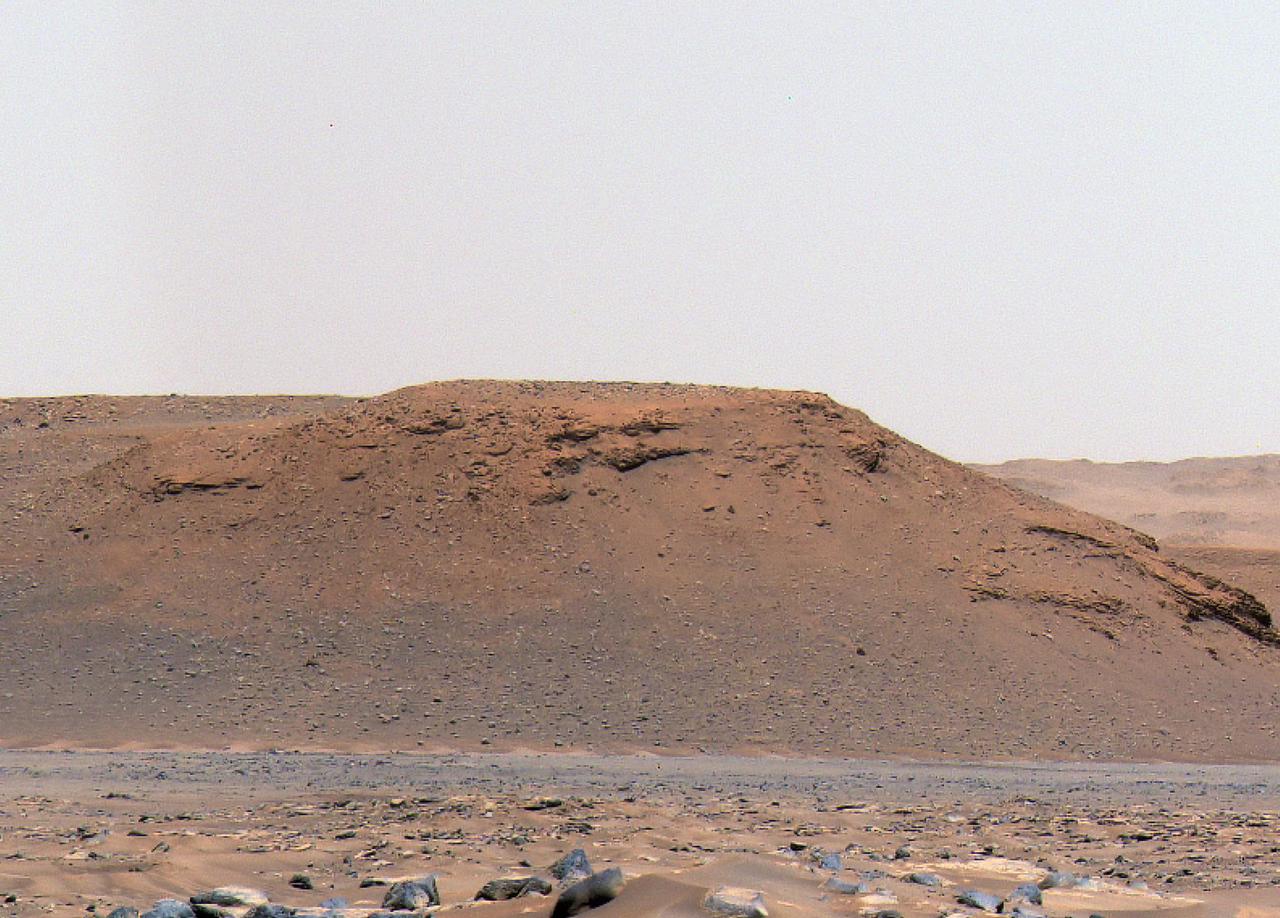

The long, steep slope known as an escarpment, or scarp, along the delta in Mars' Jezero Crater that the science team of NASA's Perseverance rover mission refers to as "Scarp a" is seen in this image captured by the rover's Mastcam-Z instrument on Apr. 17, 2021. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24813
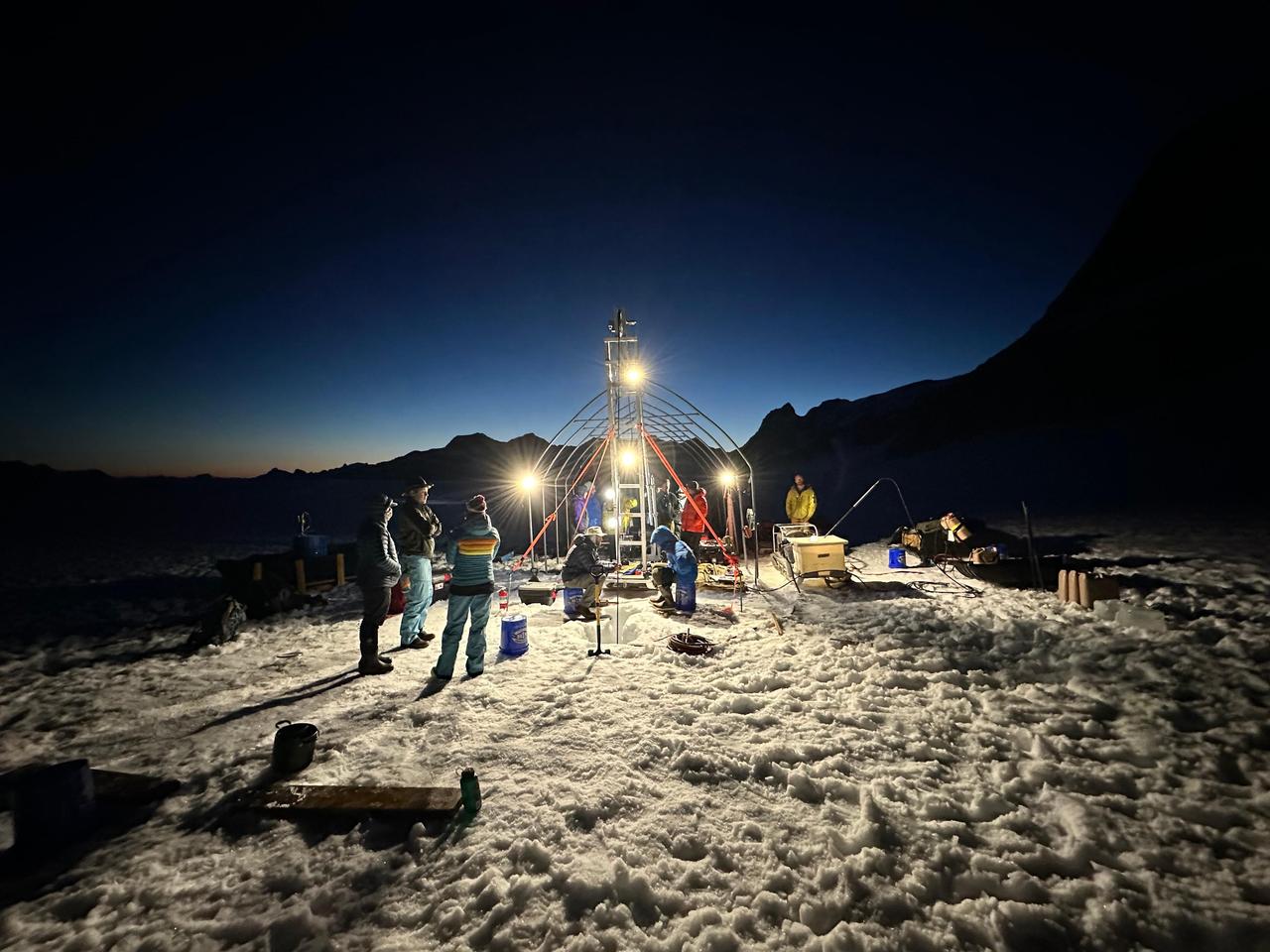

A group of researchers from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and other institutions spent two weeks on a glacier in Alaska in July 2023 for a project called ORCAA (Ocean Worlds Reconnaissance and Characterization of Astrobiological Analogs). Known as an analog mission, the project is working to answer science questions and test technology in preparation for a potential future mission to explore the surface or subsurface of icy moons like Jupiter's Europa and Saturn's Enceladus. Working at the Juneau Icefield, in coordination with the Juneau Icefield Research Project, the team used a hot-water drill to make a narrow hole in the glacier, melting its way progressively deeper. After three days, the drill reached bedrock, 890 feet (272 meters) below the surface. Science instruments were then sent down the borehole to take a variety of measurements and characterize the water environment. In 2025, the ORCAA team will return to the icefield and target a subglacial lake (a body of water inside the glacier) that has similarities to a reservoir scientists believe exists a few kilometers beneath the icy surface of Europa. ORCAA is funded by NASA's Planetary Science and Technology from Analog Research (PSTAR) program. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26345

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera to capture Mercury – seen as a tiny speck – passing in front of the Sun on Oct. 28, 2023, the 953th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The top portion of the GIF zooms in on the upper part of the Sun seen in Mastcam-Z's view; the reticle highlights the planet's transit. The GIF has been sped up 400 times; the portion of Mercury's transit captured by Mastcam-Z took place in just under an hour. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Video available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26250
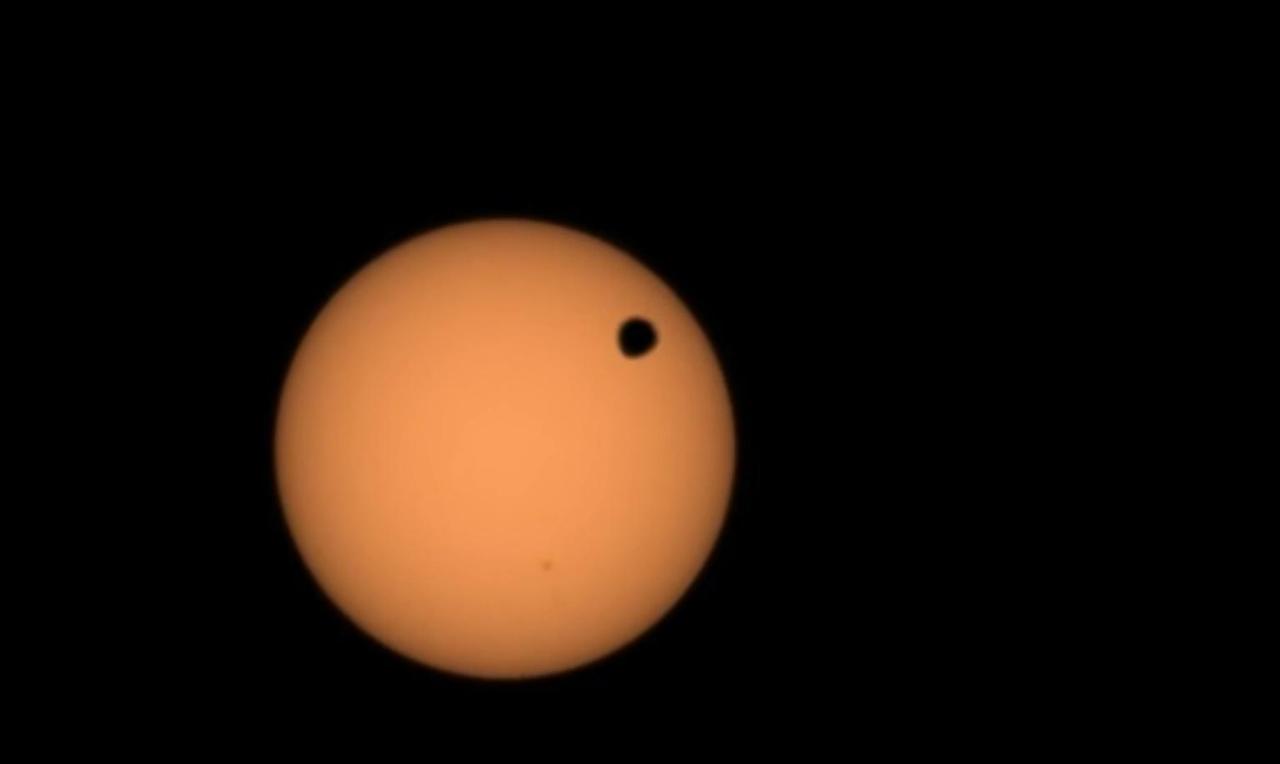

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera to capture the silhouette of Deimos, one of the two Martian moons, as it passed in front of the Sun on Jan. 19, 2024, the 1,037th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This is one of several transits of Deimos that NASA's Mars rovers have captured. By comparing the various recordings over time, scientists can refine their understanding of the tiny moon's orbit, learning how it's changing. The video has been sped up by four times; the full transit took over two minutes. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Video available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26249
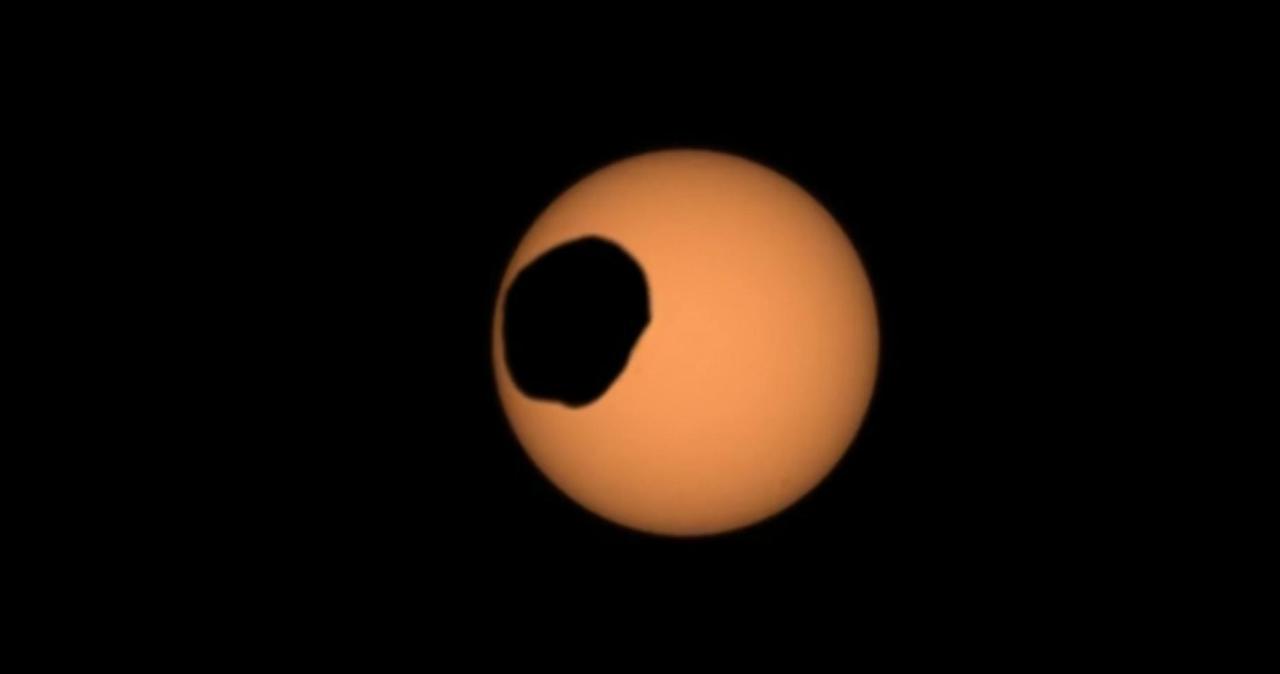
NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera to capture the silhouette of Phobos, one of the two Martian moons, as it passed in front of the Sun on Feb. 8, 2024, the 1,056th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This is one of several transits of Phobos that NASA's Mars rovers have captured. By comparing the various recordings, scientists can refine their understanding of the potato-shaped moon's orbit, learning how it's changing. Eons from now, Phobos' orbit is expected to eventually send the moon toward the Red Planet's surface. The video shows the transit as it happened in real time. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Video available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26248

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this series of images of sunspots – regions where solar flares erupt on the Sun's surface – using its Mastcam-Z cameras between May 8 and 20, 2024 (the 1,144th and 1156th Martian days, or sols, of the mission). These flares sent charged particles toward Mars, where several NASA spacecraft were able to study them. The Perseverance mission frequently uses Mastcam-Z to capture images of the Sun to help scientists assess how much dust is in the atmosphere, because airborne dust affects the brightness of the Sun. Inadvertently, the camera can also capture sunspots, which are relatively cool areas of the Sun with intense magnetic fields. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26301
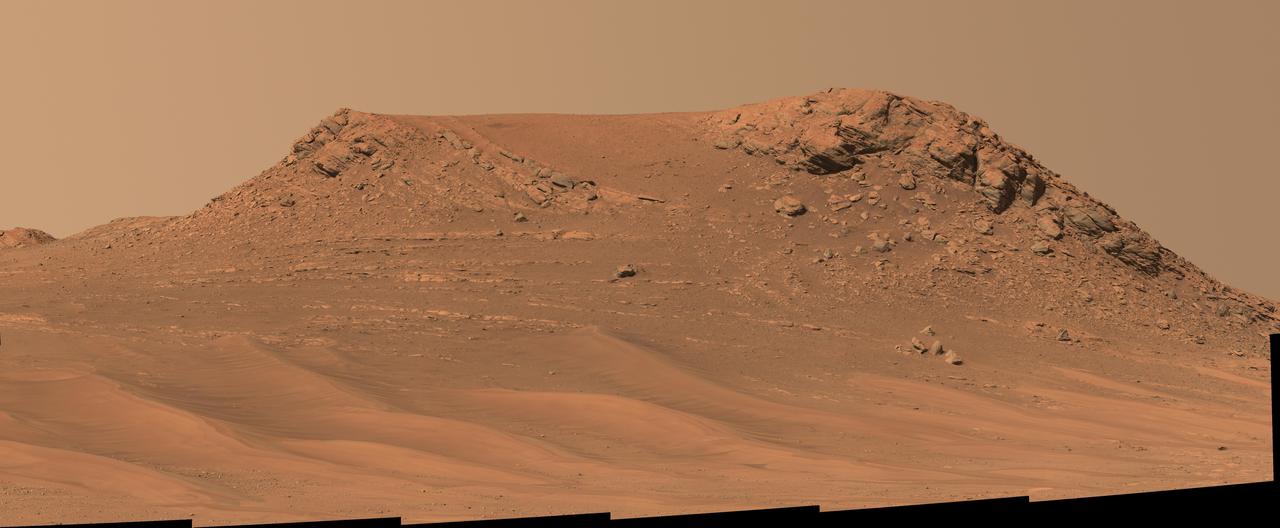

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this mosaic of an isolated hill nicknamed "Pinestand." Scientists think sedimentary layers stacked on top of one another here could have been formed by a deep, fast-moving river. But uncertainty about their formation remains because the layers are exceptionally tall by Earth geology standards to have been created by a river – some standing 66 feet (20 meters) high. The mosaic was captured by Perseverance's Mastcam-Z camera on Feb. 26, 2023, the 718th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The mosaic was stitched together from 18 individual Mastcam-Z images after they were sent back to Earth. This natural color view is approximately how the scene would appear to an average person if they were on Mars. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25830

This natural-color mosaic showing NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter at "Valinor Hills" was acquired by the agency's Perseverance Mars rover on Feb. 21, 2024, the 1,068th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The helicopter – the first aircraft to achieve powered, controlled flight on another world – sits just left of center, a speck-like figure amid a field of sand ripples. Ingenuity damaged its rotor blades during landing on its 72nd and final flight on Jan. 18, 2024. The helicopter team nicknamed the spot where the last flight concluded Valinor Hills after the fictional location in J.R.R. Tolkien's fantasy novels, which include "The Lord of the Rings" trilogy. The 67 images that were stitched together to make this mosaic were captured from about 1,365 feet (415 meters) away by the rover's Mastcam-Z camera. This is a wider and more detailed view of Valinor Hills than was shown in a previously released six-image Mastcam-Z mosaic that was taken from farther away. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26237

This mosaic featuring several of the escarpments, or scarps – long, steep slopes – of Jezero Crater's river delta was taken by the Mastcam-Z instrument aboard NASA's Perseverance rover on Apr. 17, 2021. The delta formed billions of years ago from sediment that an ancient river carried to the mouth of the lake that once existed in the crater. The images that stitched together to create the mosaic were taken from a distance of about 1.2 miles (2.2 kilometers). An annotated version of this image (Figure 1) indicates the location of four prominent scarps in the delta. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24815

NASA's Perseverance Mars Rover used its Mastcam-Z camera system to capture this panorama of a location nicknamed "Pico Turquino Hills" on Oct. 22, 2024, the 1,306th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This area is located on the rim of Jezero Crater. Perseverance landed on the crater's floor on Feb. 18, 2021, and has been steadily working its way up and out of the crater since August 2024. The rocks in Pico Turquino Hills are among the oldest yet found by Perseverance, forming in a different geologic era than almost everything the rover has seen before. They're likely part of the original surface that existed before Jezero Crater's formation by a massive asteroid about 3.9 billion years ago. The rocks here are mostly made up of volcanic minerals like olivine, plagioclase, and pyroxene. In the far-right corner of the panorama is a field of white cobbles. This represents the first time Perseverance has encountered pure quartz rock, which may have been created by a hydrothermal system like hot springs – an environment life could have survived in, if any existed on the Red Planet billions of years ago. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26473
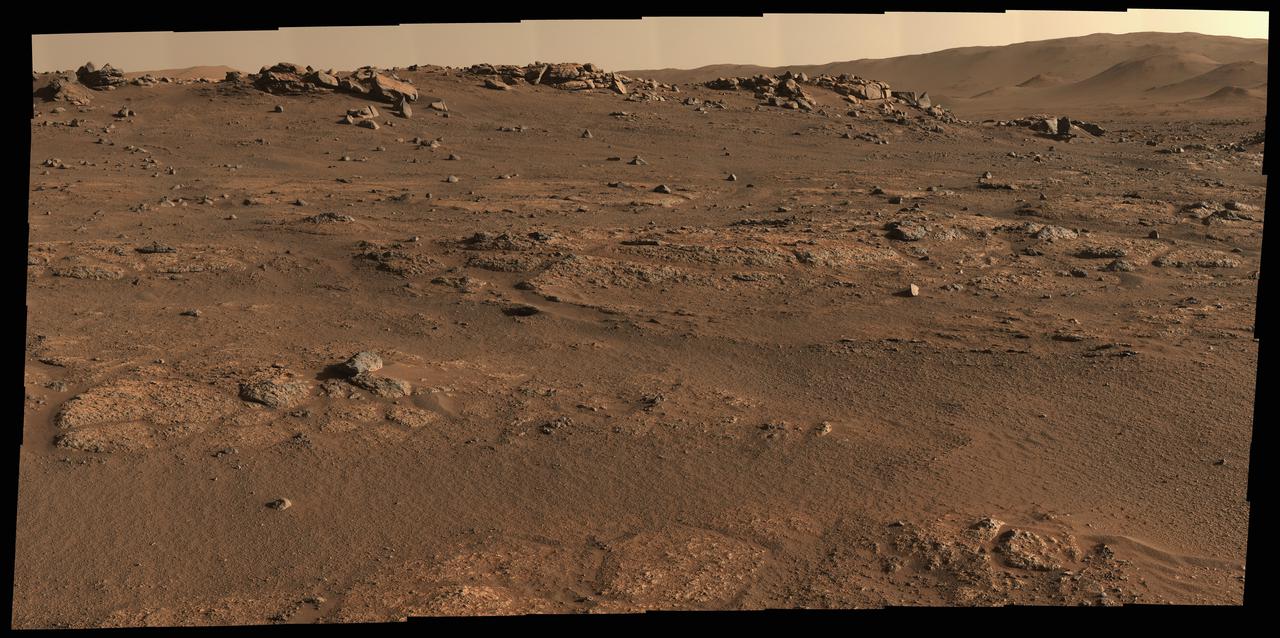

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera system to create this panorama of its first drill site. Scientists will be looking for a rock to drill somewhere in this. Perseverance's team has nicknamed this region the "Crater Floor Fractured Rough" unit. The flat, light-colored stones are informally referred to as "paver rocks" and will be the first type from which Perseverance will collect a sample for planned return to Earth by subsequent missions. Small hills to the south of the rover and the sloping inner walls of the Jezero Crater rim fill the distant background of this view. The panorama is stitched together from 70 individual images taken on July 28, 2021, the 155th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This panorama is seen here in natural color. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24765

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this video of the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter's 54th flight on Aug. 3, 2023. After performing a preflight "wiggle check" with its rotors, the helicopter takes off, hovers at an altitude of 16 feet (5 meters), and rotates to the left, before touching back down. The mission conducted the short pop-up flight to check Ingenuity's navigation system. The video was captured by the rover's Mastcam-Z imager from a distance of about 180 feet (55 meters). Arizona State University in Tempe leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25970
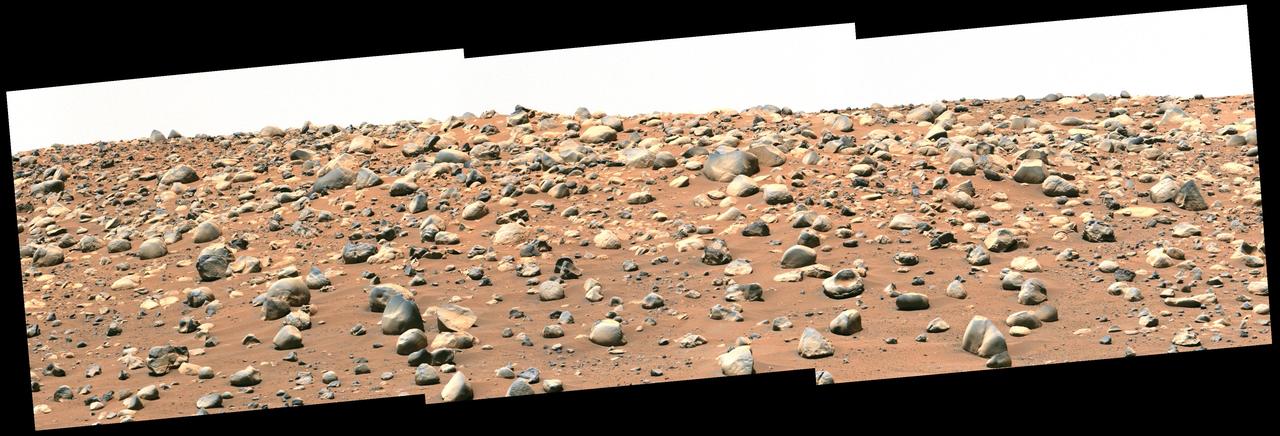

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this mosaic of a location nicknamed "Castell Henllys" using its Mastcam-Z camera on April 13, 2023, the 763rd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The rounded boulders seen here are believed to have been washed into Jezero Crater, which Perseverance is exploring, by strong flood waters billions of years ago. This occurred during one of three major periods that scientists have identified in the development of the lake and river system that occupied Jezero in the ancient past. This view looks toward the southwest, with the Castell Henllys area approximately 328 feet (100 meters) away. The mosaic is made up of three images that were stitched together after being sent back to Mars. The image has been processed to improve contrast on the terrain. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26208

Composed of 993 individual images and 2.38 billion pixels, this 360-degree mosaic taken by NASA's Perseverance looks in all directions from a location the rover science team calls "Airey Hill." The rover remained parked at Airey Hill during the entirety of solar conjunction. Captured by the rover's Mastcam-Z, the images used to create the mosaic were acquired on Nov. 3, Nov. 4, and Nov. 6, 2023, the 962nd, 963rd, and 965th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's mission. The main image is a natural color version at half-resolution. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26080

This sunset on Mars was captured by NASA's Perseverance Mars rover using its Mastcam-Z camera system on Nov. 9, 2021, the 257th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Martian sunsets typically stand out for their distinctive blue color. Fine dust in the atmosphere permits blue light to penetrate the atmosphere more efficiently than colors with longer wavelengths. But this sunset looks different: less dust in the atmosphere resulted in a more muted color than average. The color has been calibrated and white-balanced to remove camera artifacts. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24935
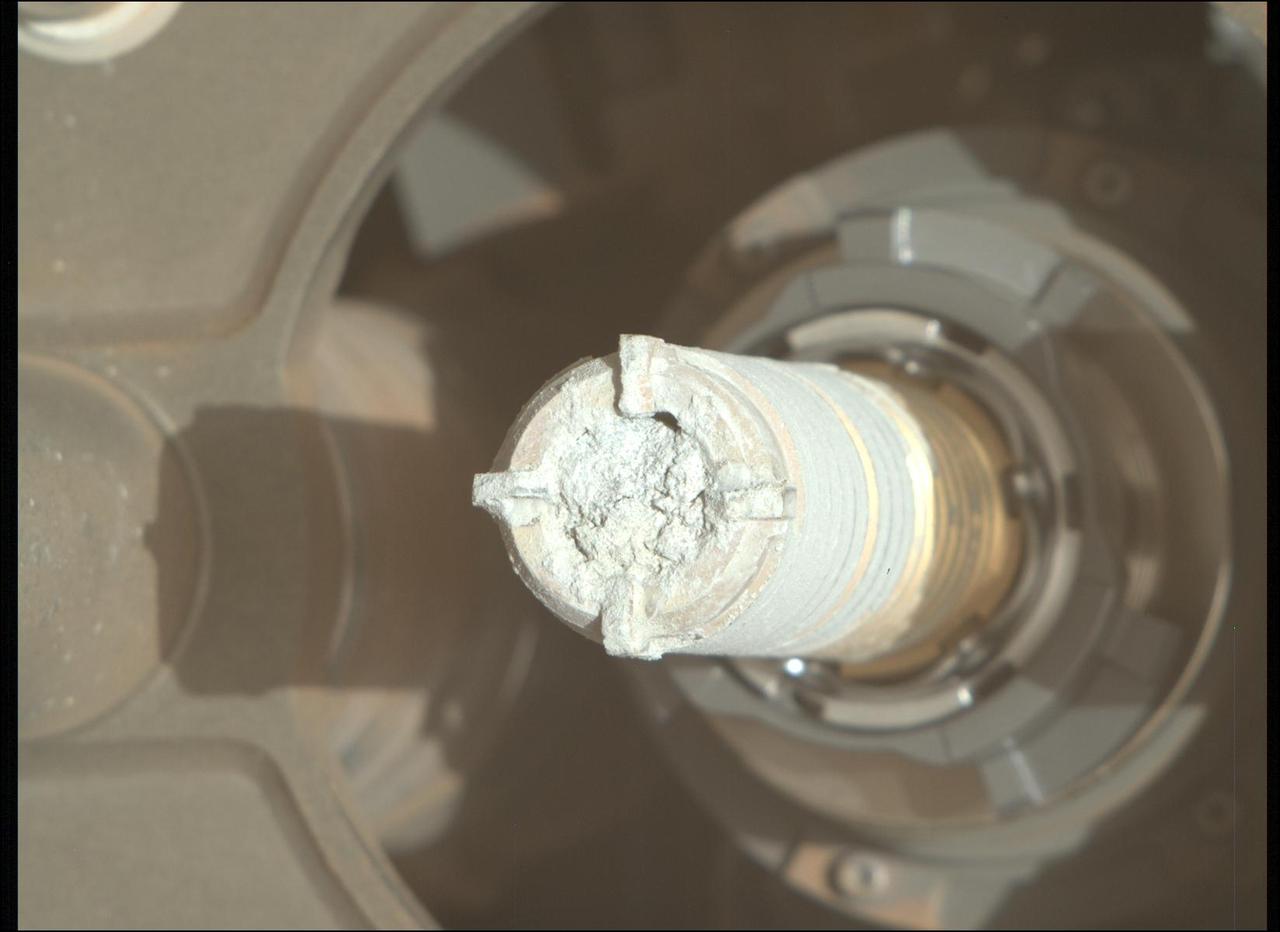
This image shows a cylinder of rock the size of a piece of classroom chalk inside the drill of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover. The sample, dubbed "Green Gardens," was taken from a rock called "Tablelands" on the rim of Mars' Jezero Crater. The image was captured by the Mastcam-Z instrument on Feb. 16, 2025, the 1,420th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Each core the rover takes is about 0.5 inches (13 millimeters) in diameter and 2.4 inches (60 millimeters) long. Data from the rover's instruments indicates that Tablelands is made almost entirely of serpentine minerals, which form when large amounts of water react with iron- and magnesium-bearing minerals in igneous rocks. During this process, called serpentinization, the rock's original structure and mineralogy change, often causing it to expand and fracture. Byproducts of the process sometimes include hydrogen gas, which can lead to the generation of methane in the presence of carbon dioxide. On Earth, such rocks can support microbial communities. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program (MEP) portfolio and the agency's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26529
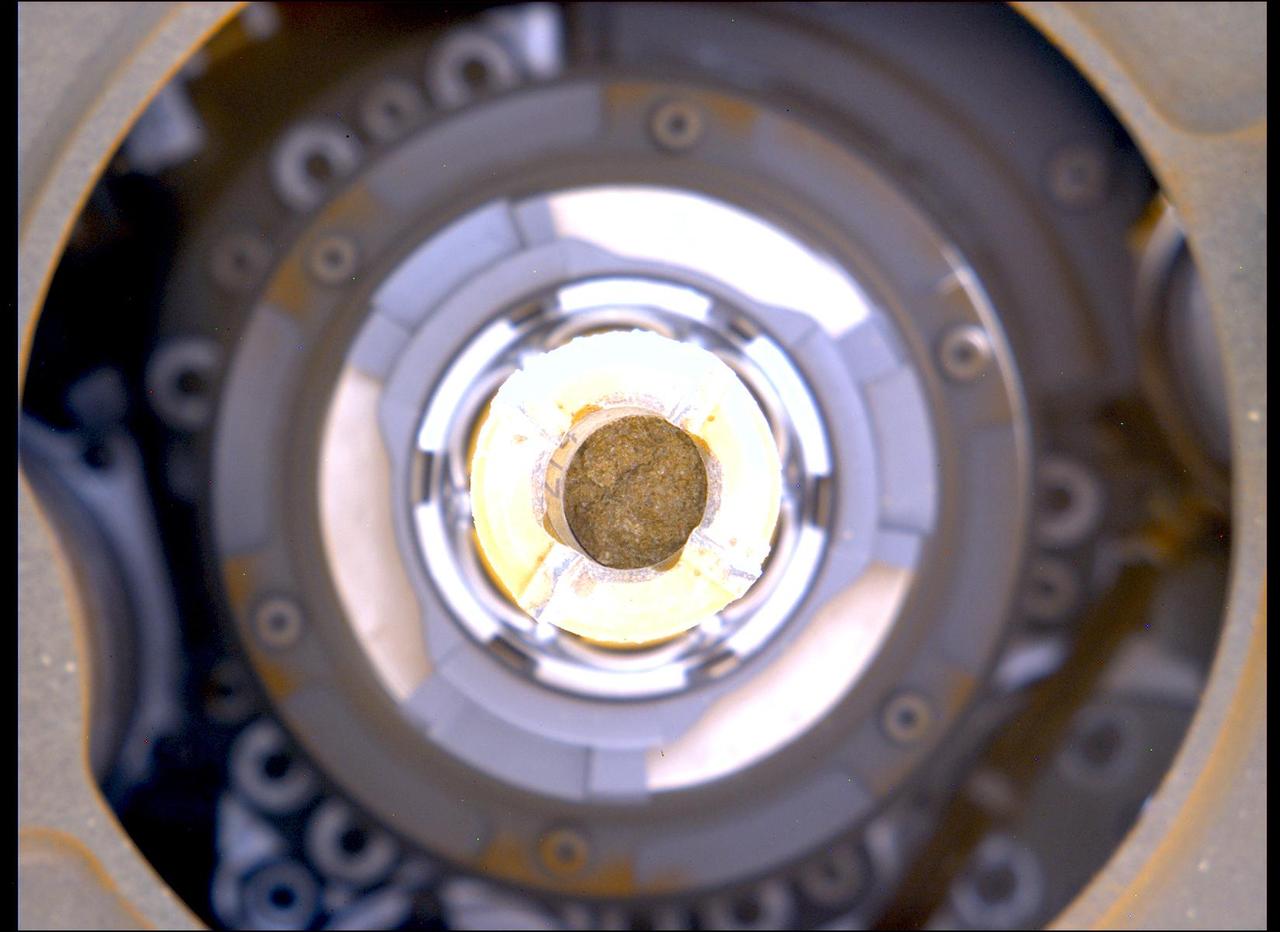
This image shows a cylinder of rock the size of a piece of classroom chalk inside the drill of NASA's Perseverance rover. The sample was taken from an outcrop called "Berea" in Mars' Jezero Crater. The image was captured by Perseverance's Mastcam-Z instrument on March 30, 2023, the 749th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Each core the rover takes is about 0.5 inches (13 millimeters) in diameter and 2.4 inches (60 millimeters) long. The samples Perseverance has taken are from an ancient river delta in Jezero Crater, a fan-shaped area where, billions of years ago, a river once flowed into a lake and deposited rocks and sediment. These rock cores have been sealed in ultra-clean sample tubes and stored in Perseverance's Sampling and Caching System as part of the mission's search for ancient signs of microbial life. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25690

This enhanced-color mosaic showing the Martian surface outside of Jezero Crater was taken by NASA's Perseverance from the crater rim at a location where the rover collected a sample dubbed "Silver Mountain." The 83 frames used to generate the mosaic were acquired by the rover's Mastcam-Z instrument on Dec. 25, 2024, the 1,368th Martian day, or sol, of Perseverance's mission. Enhanced-color images have their color bands processed to improve visual contrast and accentuate color differences. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program (MEP) portfolio and the agency's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26530

This enhanced-color, high-resolution mosaic showing Mars' Jezero Crater was taken by the Mastcam-Z instrument on NASA's Perseverance as the rover climbed the crater's western wall. Many of the landmarks visited by the rover during its 3½-year exploration of Jezero can be seen, and the vehicle's tracks are also visible. The 44 frames used to generate the mosaic were acquired on Sept. 27, 2024, the 1,282nd Martian day, or sol, of Perseverance's mission. The rover was near a location the Perseverance science team calls "Faraway Rock," about halfway up the climb. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26378
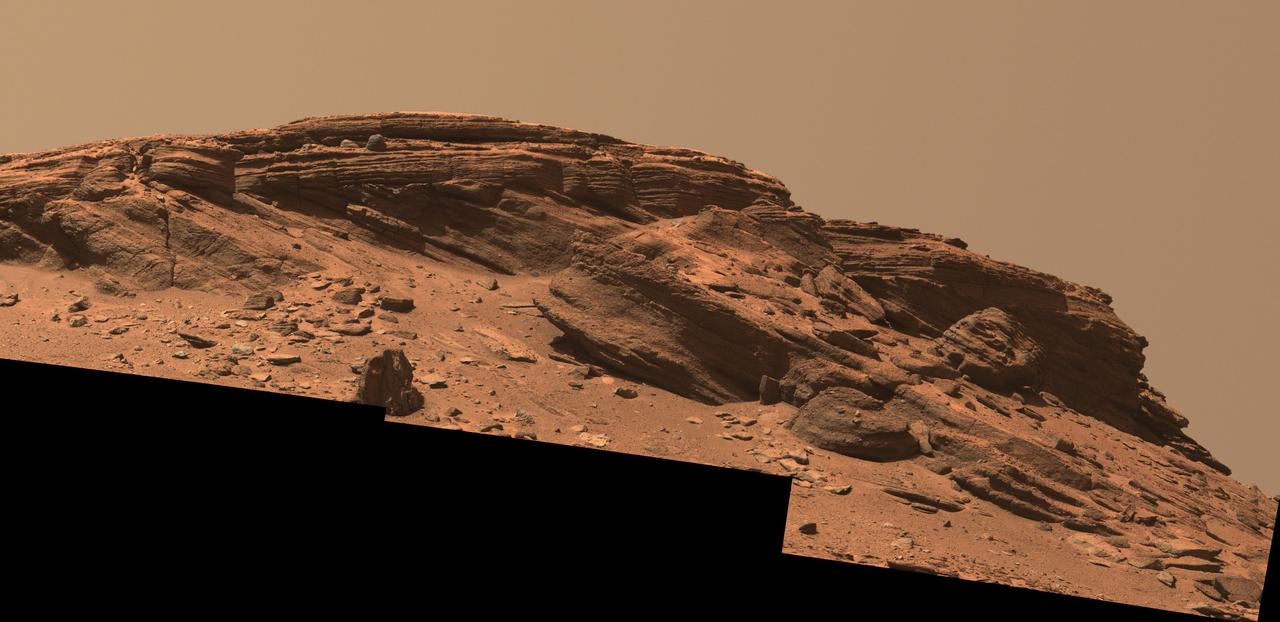

Sedimentary layers at "Franklin Cliffs" are displayed in a mosaic captured by NASA's Perseverance Mars rover using its Mastcam-Z camera on Feb. 12, 2023, the 704th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The mosaic is made up of three individual images that were stitched together after being sent back from Mars. This natural color view is approximately how the scene would appear to an average person if they were on Mars. Franklin Cliffs, along with other locations like "Skrinkle Haven" and "Pinestand" may have been created as sediment built up here in an ancient river or delta. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25911
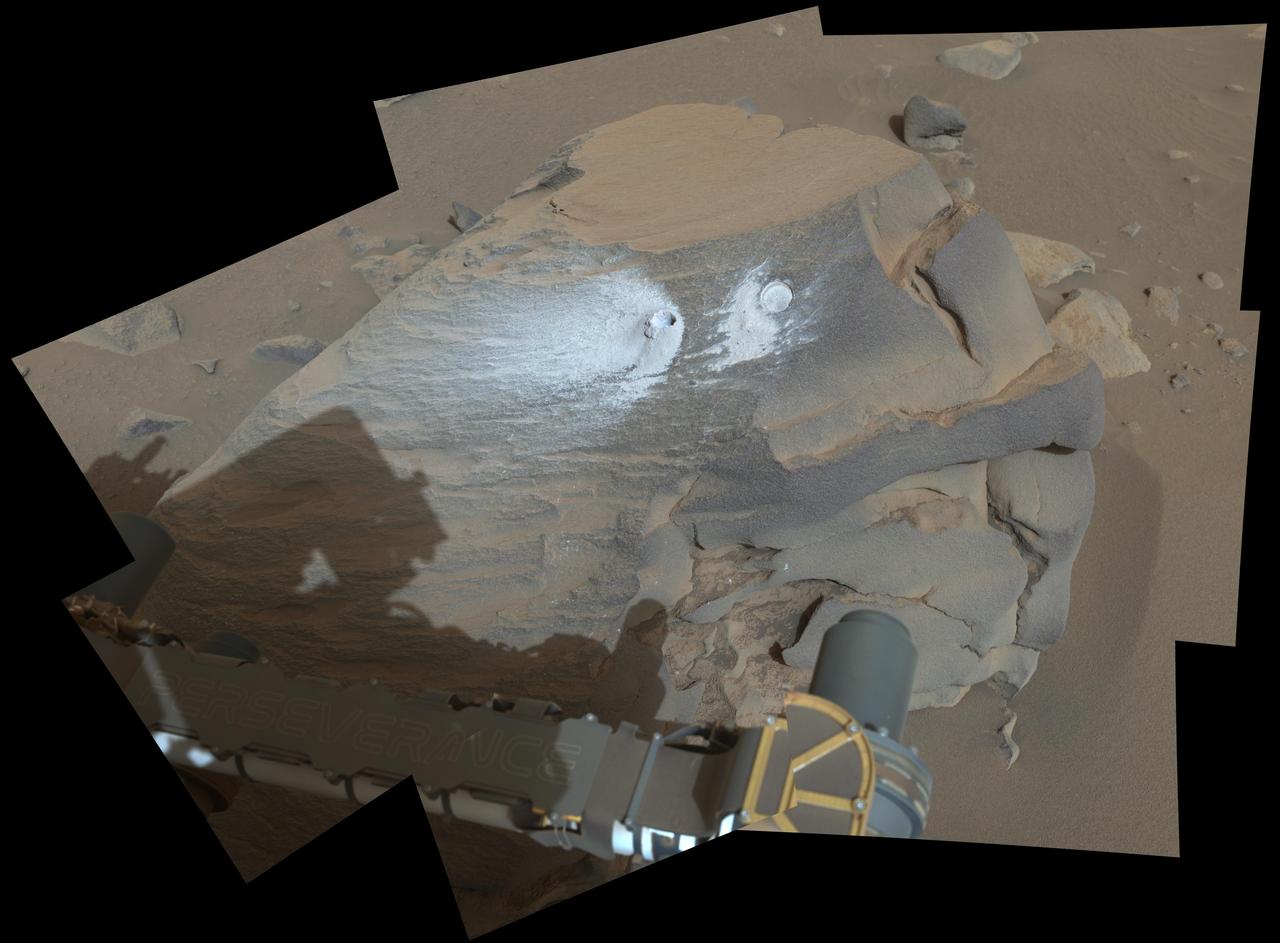

This view shows a rock nicknamed "Bunsen Peak" where NASA's Perseverance Mars rover extracted its 21st rock core (left) and abraded a circular patch (right) to investigate the rock's composition. Perseverance's Mastcam-Z camera system took the eight images that make up this mosaic on March 12, 2024, the 1,088th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's mission to Mars. For scale, the abrasion patch is approximately 2 inches (5 centimeters) in diameter. In this enhanced-color view, the color bands of the image have been processed to improve visual contrast and accentuate color differences. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26312

This wide view of Mars' Jezero Crater was taken by NASA's Perseverance rover on July 15, 2021 (the 143rd sol, or Martian day, of its mission). The rover has driven nearly a mile (1.5 kilometers) south of its landing site, "Octavia E. Butler Landing," into a region the team has nicknamed the "Crater Floor Fractured Rough" unit. The stones that appear light-colored and flat in this image are informally referred to as the "paver rocks" and will be the first type from which Perseverance will collect a sample for planned return to Earth by subsequent missions. Small hills to the south of the rover and the sloping inner walls of the Jezero Crater rim fill the distant background of this view. Five images from the rover's Mastcam-Z instrument were calibrated and combined to make this mosaic. Perseverance has been exploring the floor of Jezero since landing on Feb. 18, 2021. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24745
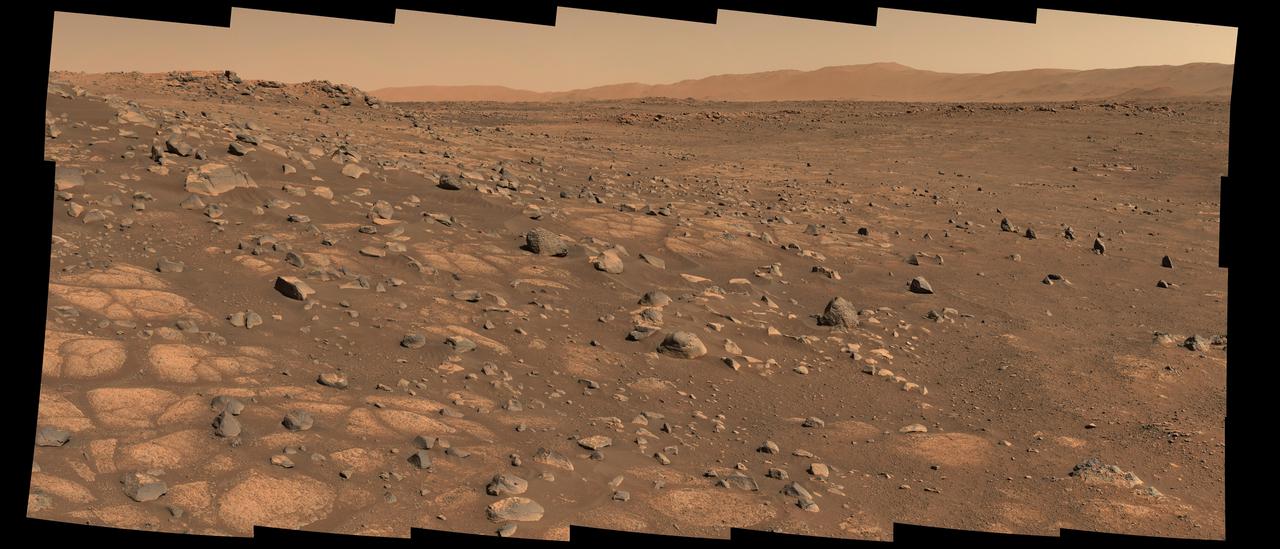

This image shows the area on Mars from which NASA's Perseverance rover will collect its first rock sample. Scientists are particularly interested in the flat stones that appear light-colored (informally called "paver rocks"). The Perseverance team has nicknamed this area in Mars' Jezero Crater the "Crater Floor Fractured Rough" area. The 28 individual images that were combined to make the larger main image were taken by the rover's Mastcam-Z right-eye camera on July 8, 2021 (the 136th sol, or Martian day, of the mission). The images have been calibrated and are presented in natural color, simulating the approximate view that we would see with our own eyes if we were there. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24746

Stitched together from 56 images from NASA's Perseverance Mars rover, this natural-color mosaic looks downstream of the Neretva Vallis river channel, which fed Jezero Crater with fresh water billions of years ago. The rover captured the images with its Mastcam-Z camera on May 17, 2024, the 1152nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. "Mount Washburn" is to the far left (north is to the left; southeast is to the right), about 660 feet (200 meters) away. Approximately quarter-mile (400 meters) wide with sand dunes and ripples, Neretva Vallis is at the center of the image. Prior to entering the channel, Perseverance had driven for several months along a boulder-filled route just beyond the camera view on the right of this mosaic. Perseverance's ultra-high-frequency antenna is visible right of center in the foreground. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26335
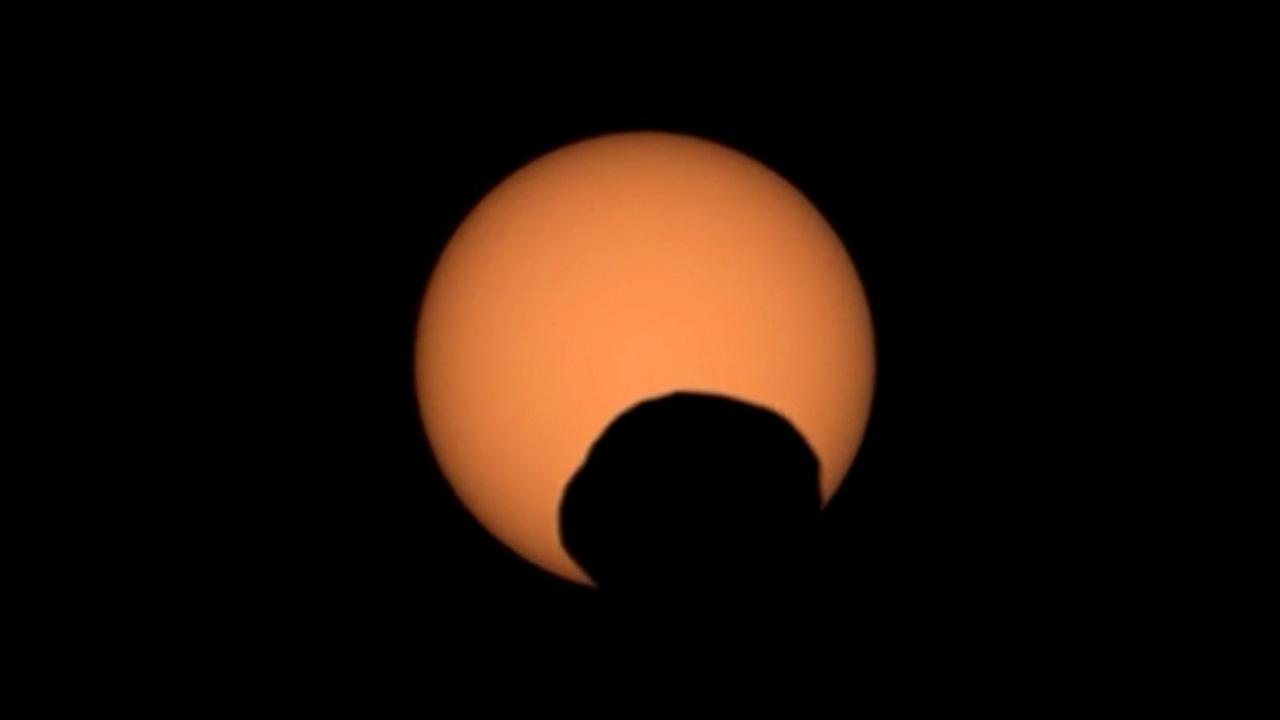

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera to capture the silhouette of Phobos, one of the two Martian moons, as it passed in front of the Sun on Sept. 30, 2024, the 1,285th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Perseverance has captured several Phobos transits since its landing at Mars' Jezero Crater in February 2021. By comparing the various recordings, scientists can refine their understanding of the potato-shaped moon's orbit, learning how it is changing. Eons from now, Phobos' orbit is expected to eventually send the moon toward the Red Planet's surface. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Video available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26380
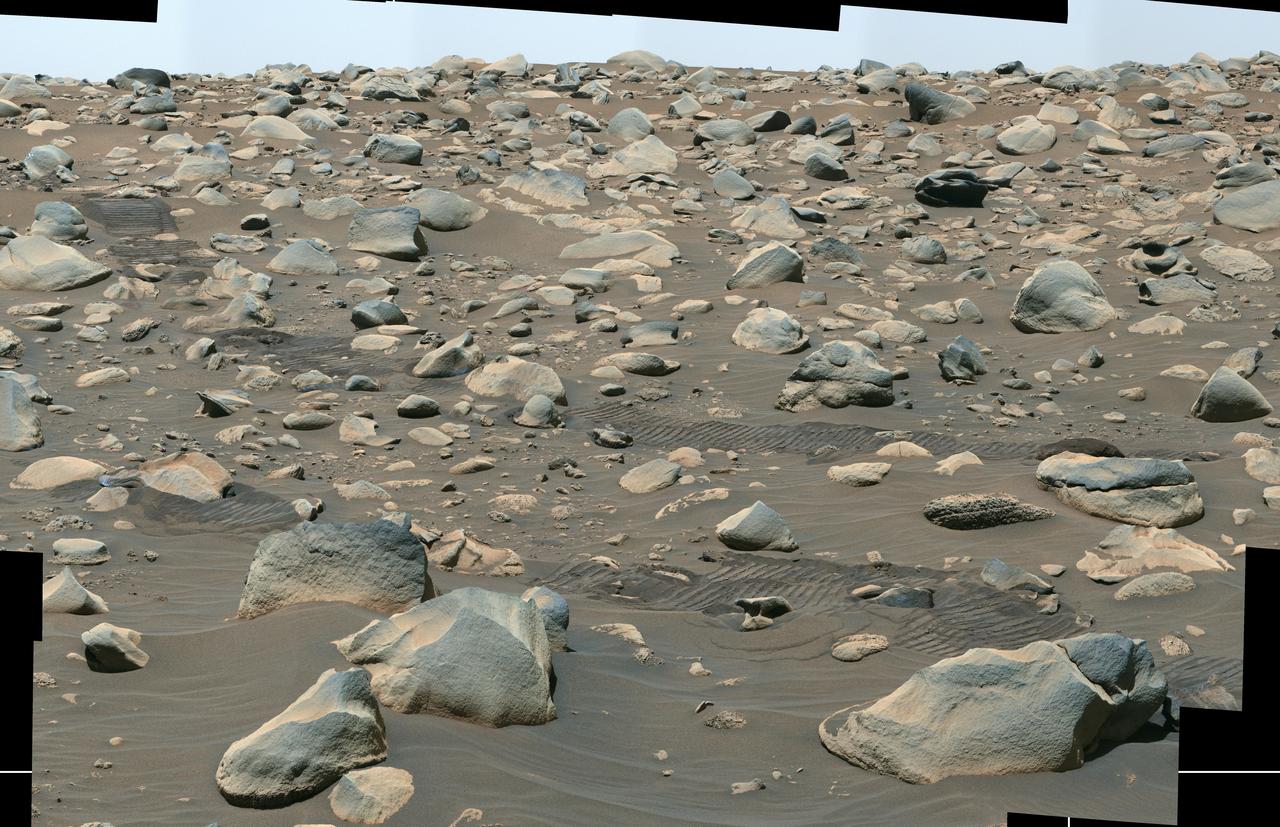

This composite image captured by NASA's Perseverance Mars rover shows boulders that decorate the top of the Jezero Crater fan deposit. Rover tracks across the middle of the image give a sense of scale. These boulders were transported by water that was either deeper or flowed faster than the ancient waterway that deposited the smaller pebbles that also populate the area. Because these boulders are sitting on top of the pebbles, scientists believe they arrived later, possibly much later. Perseverance's Mastcam-Z camera system took the series of images that make up this composite on July 6, 2023, the 845th day, or sol, of the rover's mission to Mars. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25963

The image on the left is an enhanced-color image taken by the Mastcam-Z imager aboard NASA's Perseverance rover of a rocky outcrop in the "Séítah" geologic unit of Jezero Crater. In the background, a portion of Jezero's ancient river delta can be made out. The image on the right is a mineral map created using Mastcam-Z's multispectral-imaging capability. Olivine is shown in red. Calcium-poor pyroxene is in green. Calcium-rich pyroxene in blue. Séítah rocks contain abundant olivine, and the regolith, or broken rock and soil, is diverse. The data for these images was taken on Oct. 19, 2021 (the 237th sol, or Martian day, of Perseverance's mission to Mars). The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25023
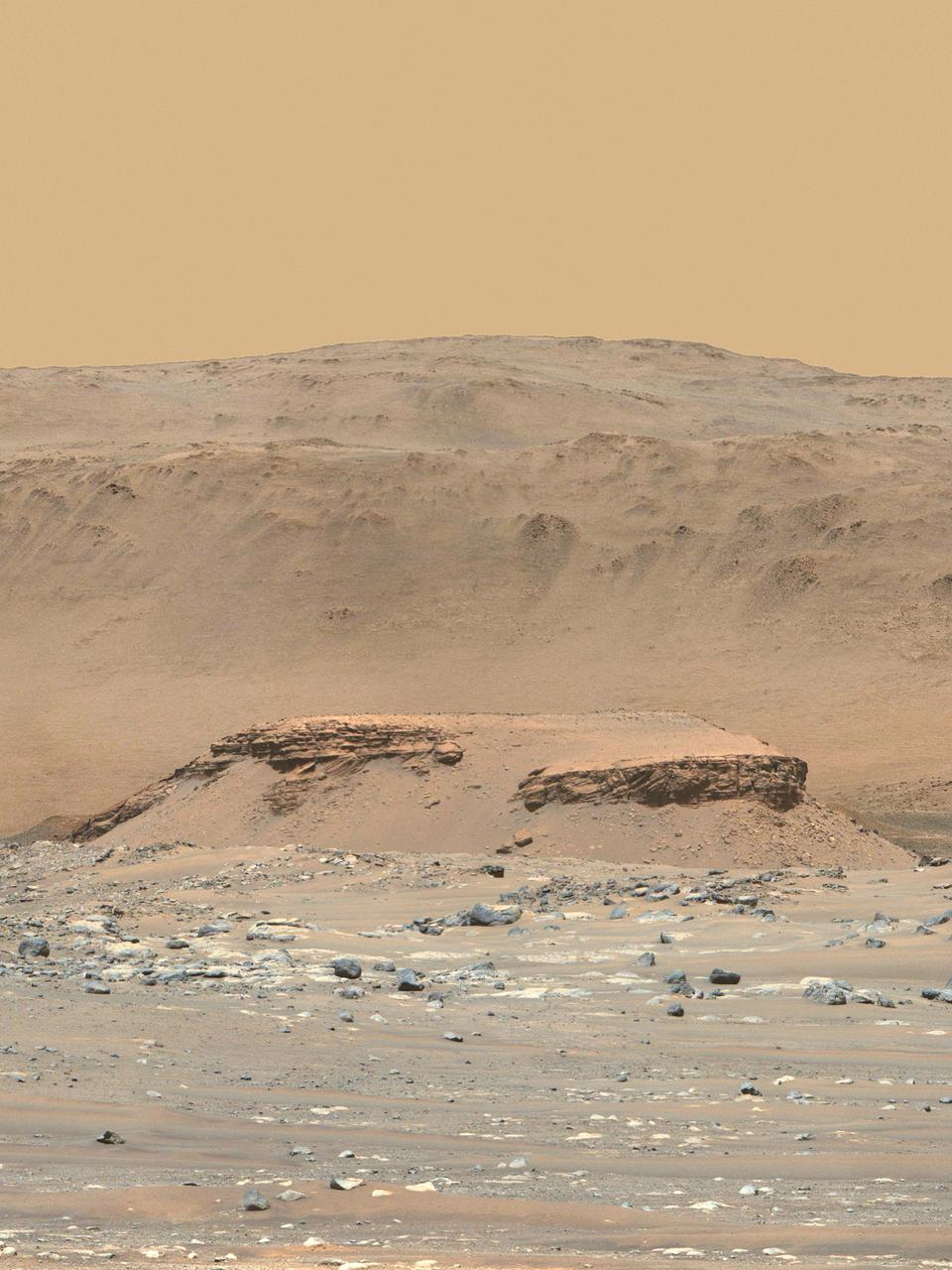

This enhanced-color image of Mars' Jezero Crater was taken by the Mastcam-Z instrument aboard NASA's Perseverance rover on April 18, 2021. The foreground flat-topped hill, informally named "Kodiak," is 1.4 miles (2.2 kilometers) from the rover and 820 feet (250 meters) wide. It exposes ancient layered rocks that indicate gradual deposition of sediments in a river delta, followed by floods. The color bands of the image have been processed to improve visual contrast and accentuate color differences. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24802

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z instrument to capture this 360-degree view of a region on Mars called "Bright Angel," where an ancient river flowed billions of years ago. The panorama was captured on June 12, 2024, the 1,178th Martian day, or sol, of the mission, and is made up of 346 individual images that were stitched together after being sent back to Earth. The color has been enhanced to bring out subtle details. It was not far from here that the rover took a sample at a rock dubbed "Cheyava Falls," finding one of the most exciting discoveries of the mission thus far. Cheyava Falls is slightly right of center, about 361 feet (110 meters) from the rover. Also visible is Perseverance itself, though not all of the rover was imaged in this panorama. The rover's mast, or "head," is visible in silhouette at bottom center. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance’s mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover is also characterizing the planet’s geology and past climate, which paves the way for human exploration of the Red Planet. NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which is managed for the agency by Caltech in Pasadena, California, built and manages operations of the Perseverance rover. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26369

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z instrument to capture this view looking south toward the rim of Jezero Crater. The panorama, which encompasses 80 degrees, is made up of 59 individual images. They were captured on Aug. 4, 2024, the 1,229th Martian day, or sol, of the mission, and stitched together after being sent back to Earth. The color has been enhanced to bring out subtle details. "Dox Castle," a region the Perseverance science team wants to visit during the rover's climb up the crater rim, is about a half-mile (740 meters) away, on the left side of the hill at right. After the exploration of Dox Castle is complete, the rover will continue its climb up the crater rim, taking a route somewhere in between the two hills. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26373
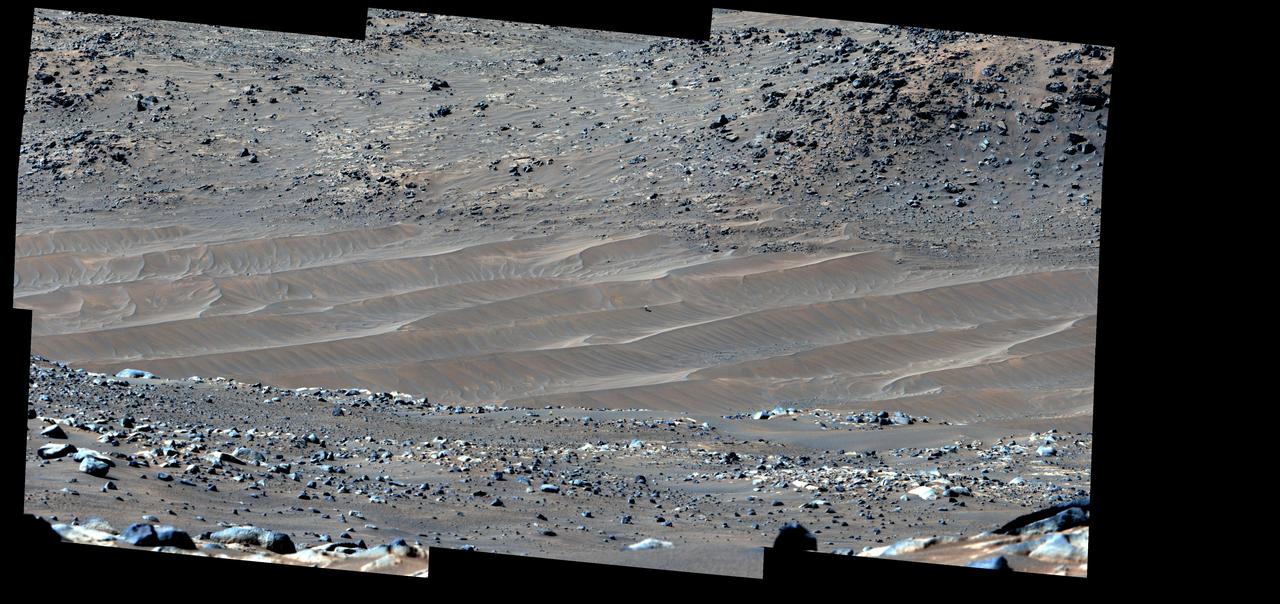

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this mosaic showing the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter at its final airfield on Feb. 4, 2024. The helicopter damaged its rotor blades during landing on its 72nd flight on Jan. 18, 2024. The Ingenuity team has nicknamed the spot where the helicopter completed its final flight "Valinor Hills" after the fictional location in J.R.R. Tolkien's fantasy novels, which include "The Lord of the Rings" trilogy. The six images that were stitched together to make up this mosaic were captured from about 1,475 feet (450 meters) away by the rover's Mastcam-Z imager. Shown here is an enhanced-color view that exaggerates subtle color differences in the scene to show more detail. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter was built by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which manages the project for NASA Headquarters. It is supported by NASA's Science Mission Directorate. NASA's Ames Research Center in California's Silicon Valley and NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia, provided significant flight performance analysis and technical assistance during Ingenuity's development. AeroVironment Inc., Qualcomm, and SolAero also provided design assistance and major vehicle components. Lockheed Martin Space designed and manufactured the Mars Helicopter Delivery System. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26236

Video footage from NASA's Perseverance Mars rover provides a big-picture perspective of the 13th flight of NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter. The 160.5-second reconnaissance sortie involved flying into challenging terrain and taking images of a specific rocky outcrop from multiple angles. Captured from a distance of about 980 feet (300 meters) by the rover's two-camera Mastcam-Z, Ingenuity is barely discernable near the lower left of frame at the beginning of the video. An annotated version of this video highlighting the location of Ingenuity can be found here. At 0:04 seconds into the video Ingenuity takes off and climbs to an altitude of to 26 feet (8 meters) before beginning its sideways translation to the right. At the video's 0:59 second point, Ingenuity leaves the camera's field of view on the right. Soon after (1:02), the helicopter returns into the field of view (the majority of frames that did not capture helicopter after it exited the camera's field of view were purposely not downlinked from Mars by the team) and lands at a location near its takeoff point. To obtain the footage, the "left eye" of the Mastcam-Z instrument is set for a wide-angle shot (26 mm focal length). The video is shot at 6 frames per second. Another view (PIA24979) is taken at the same time by Mastcam-Z's other ("right eye") imager and provides a closer perspective of the helicopter as it took off and landed. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24978

This 60-second video pans across an enhanced-color composite image, or mosaic, of the delta at Jezero Crater on Mars. The delta formed billions of years ago from sediment that an ancient river carried to the mouth of the lake that once existed in the crater. Taken by the Mastcam-Z instrument aboard NASA's Perseverance rover, the video begins looking almost due west of the rover, and sweeps to the right until it faces almost due north. Fourteen images compose the mosaic that provides the base image for this video (included as an additional figure); they were acquired on Nov. 28, 2021 (the 275th sol, or Martian day, of Perseverance's mission) as the rover sat at the highest vantage point in the "South Séítah" geological unit, allowing a perspective that included boulders and other features atop the delta as well as farther west and northwest across its surface. The mountains in the background are the rim of Jezero Crater. The view also shows brown hills in the middle distance that are part of an ancient delta, where a river hit a lake in the crater. The rover has spent the last several months exploring the sandy and rocky terrain in the foreground. The color bands of the image have been processed to improve visual contrast and accentuate color differences. The sky would not actually look blue to a human explorer on the Red Planet. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25022

This view of the interior of Belva Crater was generated using data collected by the Mastcam-Z instrument aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover on April 22, 2023, the 772nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. When the 152 individual images that make up this mosaic were taken, the rover was parked at the west side of the crater's rim, on a light-toned rocky outcrop the science team is calling "Echo Creek." Belva Crater is about 0.6 miles (0.9 kilometers) in diameter. The view here is looking across the crater towards the distant east-northeast wall of the much-larger Jezero Crater (center of the image), some 25 miles (40 kilometers) away. Impact craters like Belva can offer grand views and contain vertical cuts that provide important clues to the geologic history of the area. The mosaic shows multiple locations of bedrock exposed in vertical cross-section. One of these exposed sections of bedrock (located on the hill seen between the 60 and 75 hashmarks) is angled steeply downward and is nearly 65 feet (20 meters) tall. Called "dipping beds," such a steeply angled bedrock section could indicate the presence of a large Martian sandbar made of sediment that billions of years ago was deposited by a river flowing into the lake that Jezero Crater once held. The most distant point on Belva Crater's rim (just to the left of center in the mosaic) is about 3,500 feet (1,060 meters) away from the rover. The large boulder seen in the far right of the mosaic is about 65 feet (20 meters) away and is about 5 feet (1.5 meters) in diameter. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25889
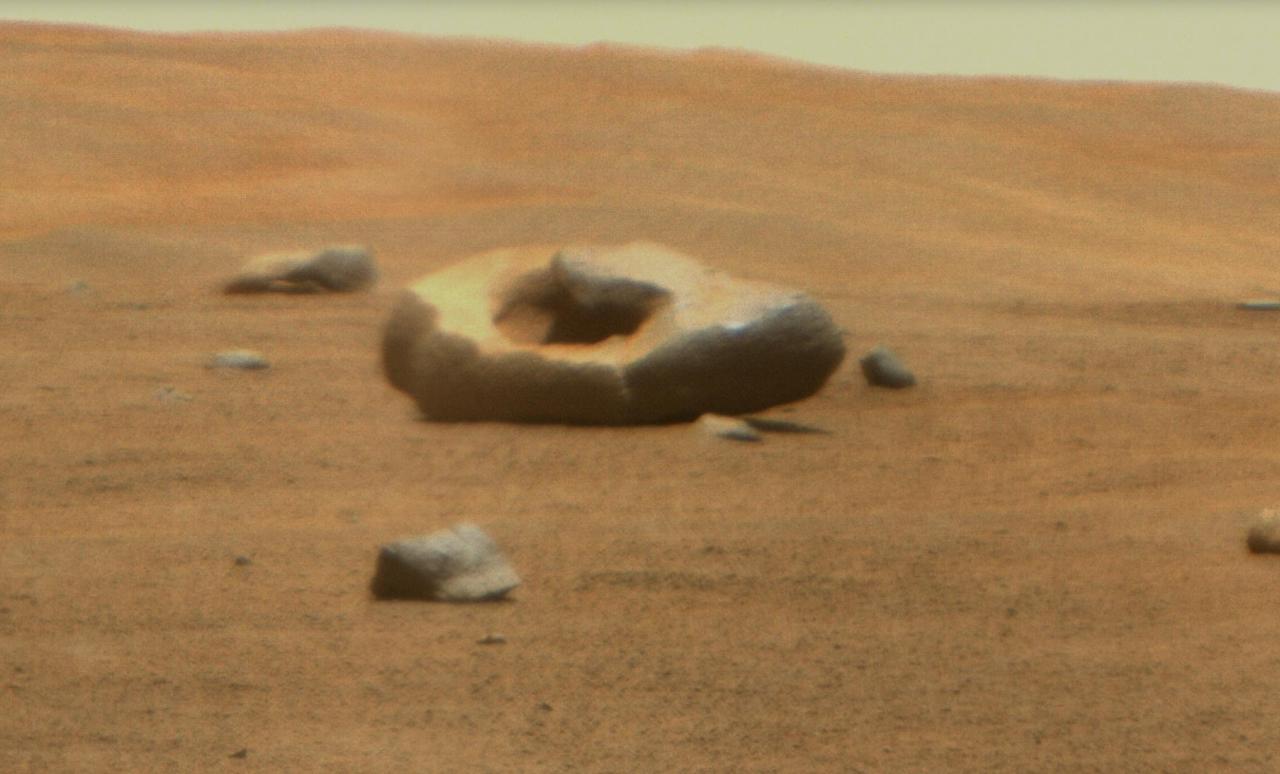

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this doughnut-shaped rock in Jezero Crater from about 328 feet (100 meters) away using its Remote Microscopic Imager (RMI), part of the SuperCam instrument, on June 22, 2023, the 832nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Oddly shaped rocks aren't uncommon, either on Earth or Mars; they're often formed over eons as winds sandblast rock faces. This particular rock may have formed after a smaller rock (or multiple rocks) eroded near its center. That left behind a cavity that was later enlarged by the wind. Figure A shows the same rock in its broader context, when it was first spotted by the rover's Mastcam-Z instrument from about 1,312 feet (400 meters away) on April 15, 2023, the 765th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. SuperCam is led by Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico, where the instrument's body unit was developed. That part of the instrument includes several spectrometers as well as control electronics and software. The mast unit, including RMI, was developed and built by several laboratories of the CNRS (the French research center) and French universities under the contracting authority of Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES), the French space agency. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25916

Composed of 18 images, this natural-color mosaic shows a boulder field on "Mount Washburn" (named after a mountain in Wyoming) in Mars' Jezero Crater. The Perseverance science team nicknamed the light-toned boulder with dark speckles near the center of the mosaic "Atoko Point" (after a feature in the eastern Grand Canyon). The images were acquired by NASA's Perseverance Mars rover on May 27, 2024, the 1,162nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Analysis by the rover's SuperCam and Mastcam-Z instruments indicate Atoko Point is composed of the mineral pyroxene, similar to some boulders the rover has encountered elsewhere in Jezero Crater. In terms of the size, shape, and arrangement of its mineral grains and crystals – and potentially its chemical composition – Atoko Point is different from any of the rocks the rover has encountered before. Some Perseverance scientists speculate the minerals that make up Atoko Point were produced in a subsurface body of magma that is possibly exposed now on the crater rim. Others on the team wonder if the boulder, which stands about 18 inches (45 centimeters) wide and 14 inches (35 centimeters) tall, had been created far beyond the walls of Jezero and transported there by swift Martian waters eons ago. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26333
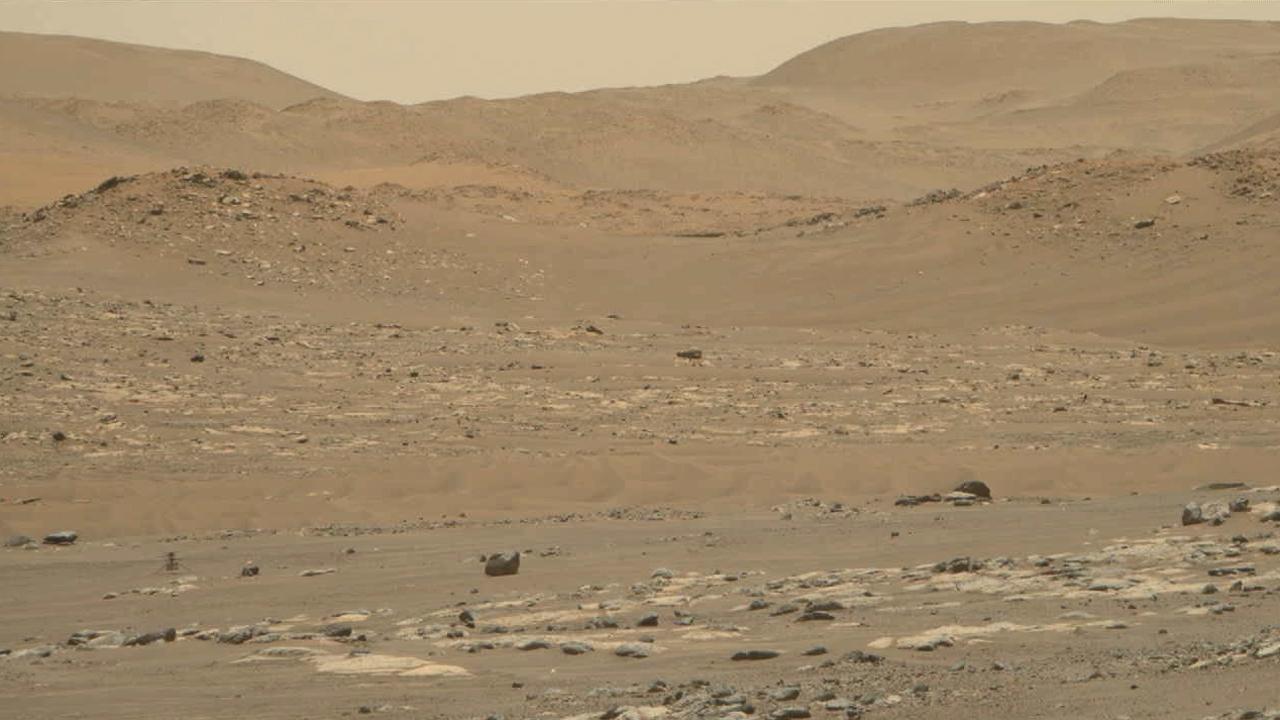

Video footage from the Mastcam-Z instrument aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this closeup view of the takeoff and landing of the 13th flight of the Ingenuity Mars Helicopter on Sept. 4, 2021. The 160.5-second reconnaissance sortie involved flying into challenging terrain and taking images of a specific outcrop from multiple angles. The closeup video of takeoff and landing was acquired as part of a science observation intended to measure the dust plumes generated by the helicopter. At the beginning of the video, Ingenuity is near the lower left of frame, at a distance of about 980 feet (300 meters) from the rover. It climbs to an altitude of to 26 feet (8 meters) before beginning its sideways translation. The helicopter leaves the camera's field of view on the right. Soon after, the helicopter returns into the field of view (the majority of frames that did not capture helicopter after it exited the camera's field of view were purposely not downlinked from Mars by the team) and lands at a location near its takeoff point. To obtain the footage, the two-camera Mastcam-Z's "right eye" was at its maximum zoom setting (110mm focal length). The video is shot at 6 frames per second. Another view (PIA24978) was taken at the same time by Mastcam-Z's "left eye" imager and provides a wider perspective of the same flight. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24979
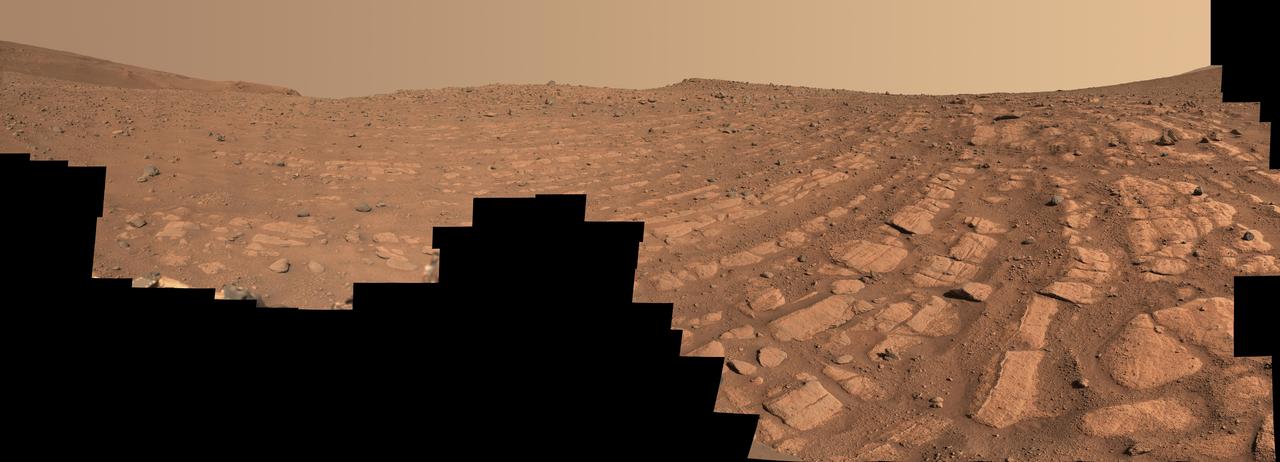

Scientists think that the bands of rocks seen in this image may have been formed by a very fast, deep river – the first of its kind evidence has been found for on Mars. NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this mosaic at a location nicknamed "Skrinkle Haven" using its Mastcam-Z camera between Feb. 28 and March 9, 2023 (between the 721st and 729th Martian days, or sols, of the mission). The mosaic is made up of 203 individual images that were stitched together after being sent back from Mars. This natural color view is approximately how the scene would appear to an average person if they were on Mars. "Skrinkle Haven" offers the clearest example of these curved rock layers – called "the curvilinear unit" – that had previously only been seen from space. Scientists are now debating what kind of powerfully flowing water formed those curves: a river like the Mississippi, which winds snakelike across the landscape, or a braided river like Nebraska's Platte, which forms small islands of sediment called sandbars. When viewed from the ground, the curved layers are arranged in rows, and appear to ripple out across the landscape. They could be the remnants of a river's banks that shifted over time – or the remnants of sandbars that formed in the river. The layers were likely much taller in the past; scientists suspect that after these piles of sediment turned to rock, they were sand-blasted by wind over the course of eons and carved down to their present size. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25829

This mosaic features a rover-eye view of the "South Séítah" geologic unit of Jezero Crater. Composed of 84 enhanced-color images that were later stitched together, the mosaic was taken on Sept. 12, 2021 (the 201st Martian day, or sol, of the mission), by the Mastcam-Z imager as the rover was parked on an elevated overlook just outside its entry point into South Séítah. An annotated version of this image (Figure 1) indicates the location of several prominent geologic features. At the top left and running about a third of the way to the center of the image is a portion of the delta front, a river delta that billions of years ago fed the lake at Jezero Crater. Below and to the right of that is a ridge nicknamed "Faillefeu" (after a medieval abbey in the French Alps). Farther to the right, at the top of the image is the distant peak called "Santa Cruz." While not a planned destination of the rover, Santa Cruz is geologically interesting since it has mineral signatures – seen both from orbit and by the rover (from its landing site) – consistent with alteration minerals, primarily clays. Near the top at the far right is a portion of the route Perseverance took to get to this location. At the time, Perseverance was traveling south, skirting the outside of the Séítah geologic unit. To the right (and out of frame), Perseverance would take a hard right and head northwest along a ridgeline just outside of Séítah. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24816
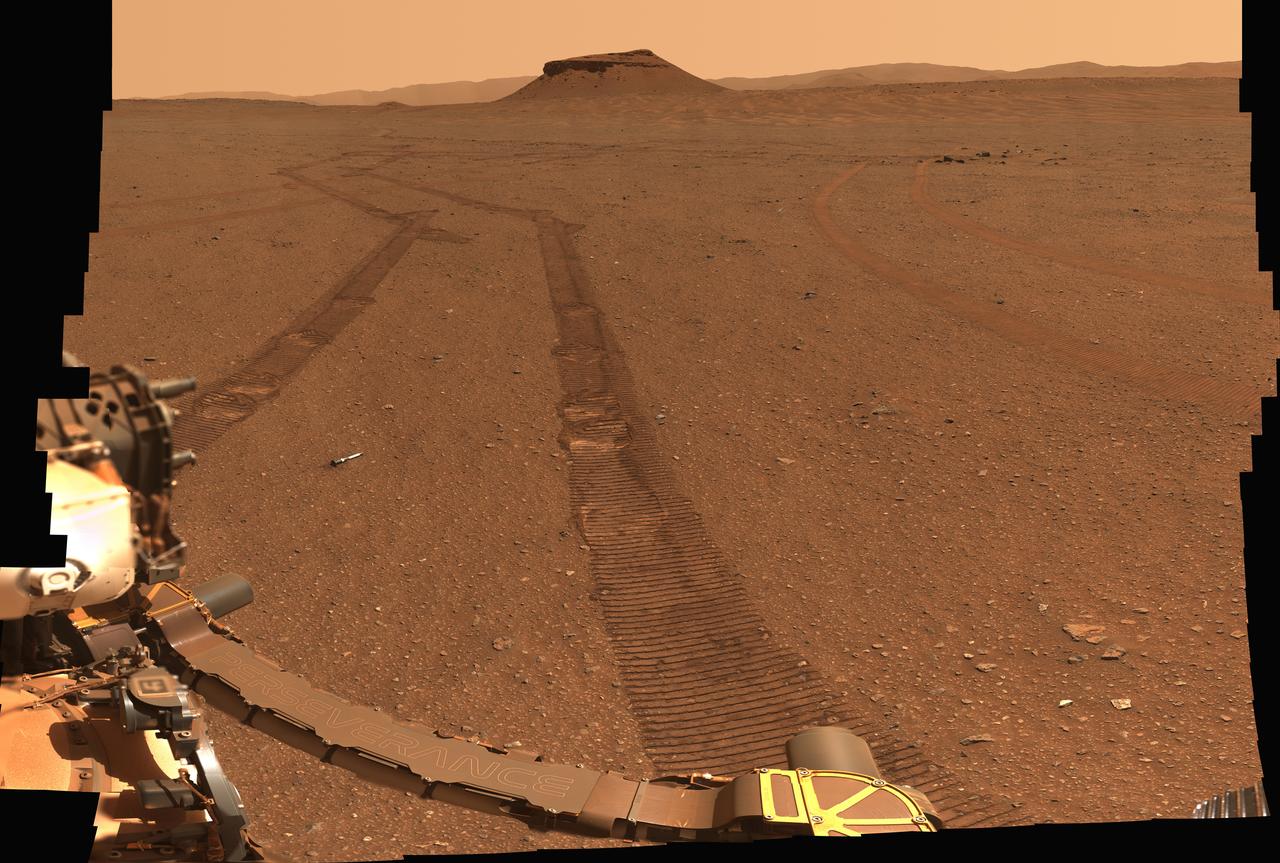

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this portrait of its recently completed sample depot using its Mastcam-Z camera on Jan. 31, 2023, the 693rd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This panorama is made up of 368 individual images that were stitched together after being sent back to Earth. The color in the scene has been adjusted to show the Martian surface as it would look to the human eye. Each sample tube is approximately 7 inches (18 centimeters) long and .8 inches (2 centimeters) in diameter. The "Amalik" sample closest to the rover was approximately 10 feet (3 meters) away from the camera at the time the image was taken. The "Atsah" and "Skyland" samples were approximately 66 feet (20 meters) away. "Bearwallow," "Coulettes," "Montdenier," "Crosswind Lake," and "Roubion" were approximately 115 to 164 feet (35 to 50 meters) away. "Mageik" and "Malay" were approximately 197 feet (60 meters) away. This is a natural-color view of the scene, showing the surface as it would appear to a human observer. Throughout its science campaigns, the rover has been taking a pair of samples from rocks the mission team deems scientifically significant. One sample from each pair taken so far now sits in the depot – along with one atmospheric sample and one "witness" tube – for a total of 10 tubes that were carefully arranged on the surface in a zigzag pattern. The depot is a crucial milestone in the NASA-ESA (European Space Agency) Mars Sample Return campaign, which aims to bring Mars samples to Earth for closer study. The Perseverance rover will be the primary means to hand off the collected samples to a future robotic lander as part of the campaign. The lander would, in turn, use a robotic arm to place the samples in a containment capsule aboard a small rocket that would blast off to Mars orbit, where another spacecraft would capture the sample container and return it safely to Earth. Hosting a duplicate set, the depot will serve as a backup if Perseverance can't deliver its samples. Perseverance built the depot at "Three Forks," a location within Mars' Jezero Crater. Billions of years ago, this crater was filled by a lake and delta. Sediment that built up in the delta formed a steep mound that Perseverance will be driving up in the months ahead to arrive at the top of the delta. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25736
