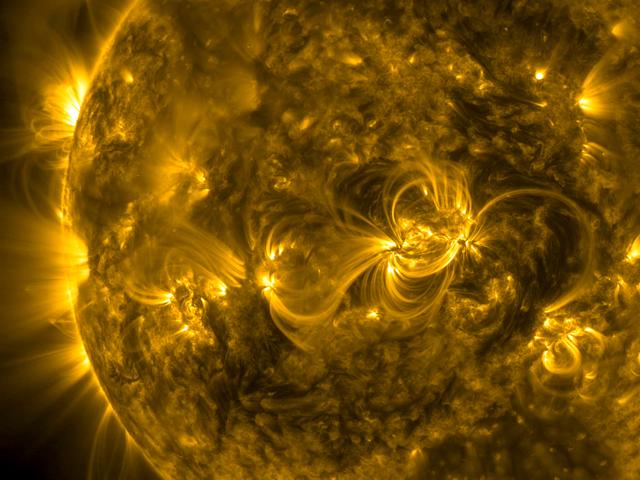

A series of linked loops across the face of the Sun highlighted the dynamic magnetic connections generated by several active regions (Jan. 3-6, 2015). Active regions have magnetic north and south polarity and the arcing loops find the opposite pole to make the connection. What is unusual here is that they all kind of line up and link nicely together. These movies are made in a wavelength of extreme ultraviolet light. Credit: NASA/Solar Dynamics Observatory <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Students at Williams Technology Middle School in Huntsville were featured in a new segment of NASA CONNECT, a video series aimed to enhance the teaching of math, science, and technology to middle school students. The segment premiered nationwide May 15, 2003, and helped viewers understand Sir Isaac Newton's first, second, and third laws of gravity and how they relate to NASA's efforts in developing the next generation of space transportation.
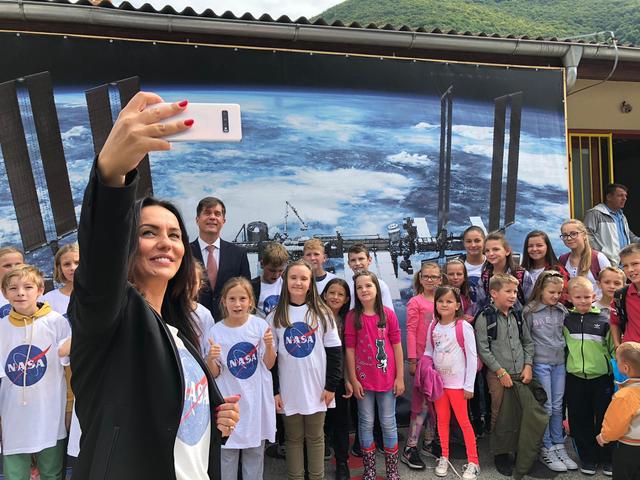

On Sept. 23, 2019, Eric Nelson, the U.S. Ambassador to Bosnia and Herzegovina, presented a framed letter to Snezana Ružičić, mayor of the Balkan municipality of Jezero. The letter, from NASA's director of Mars Exploration, James Watzin, honored the connection between the small Balkan town and Jezero Crater the landing site of NASA's upcoming Mars 2020 mission. In this picture, Ružičić snaps a selfie of the ambassador with local school children. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23463
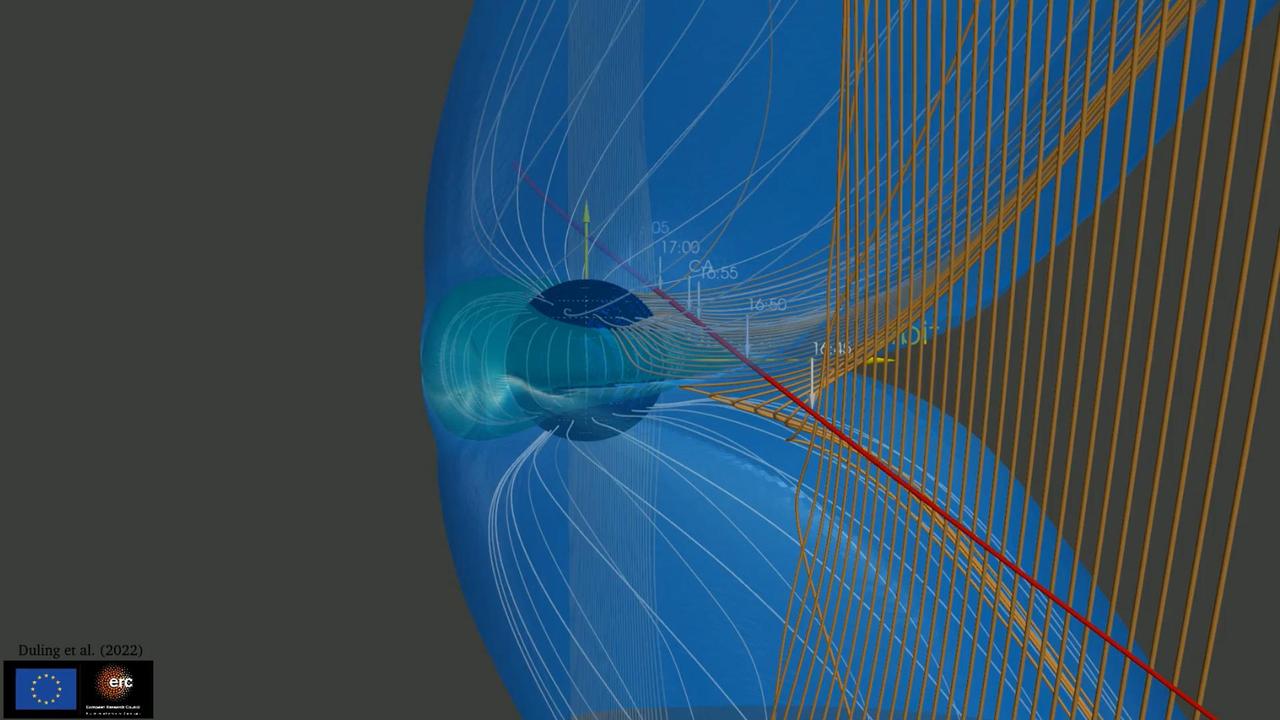
This animation illustrates how the magnetic field surrounding Jupiter's moon Ganymede (represented by the blue lines) interacts with and disrupts the magnetic field surrounding Jupiter (represented by the orange lines). During the June 2021 close approach to Ganymede by NASA's Juno spacecraft, the Magnetic Field (MAG) and Jovian Auroral Distributions Experiment (JADE) instruments aboard the spacecraft recorded data showing evidence of the breaking and reforming of magnetic field connections between Jupiter and Ganymede. Studying Ganymede's magnetic field can provide scientists with clues about the nature of the salty water reservoir suspected to exist deep under the moon's surface. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25724
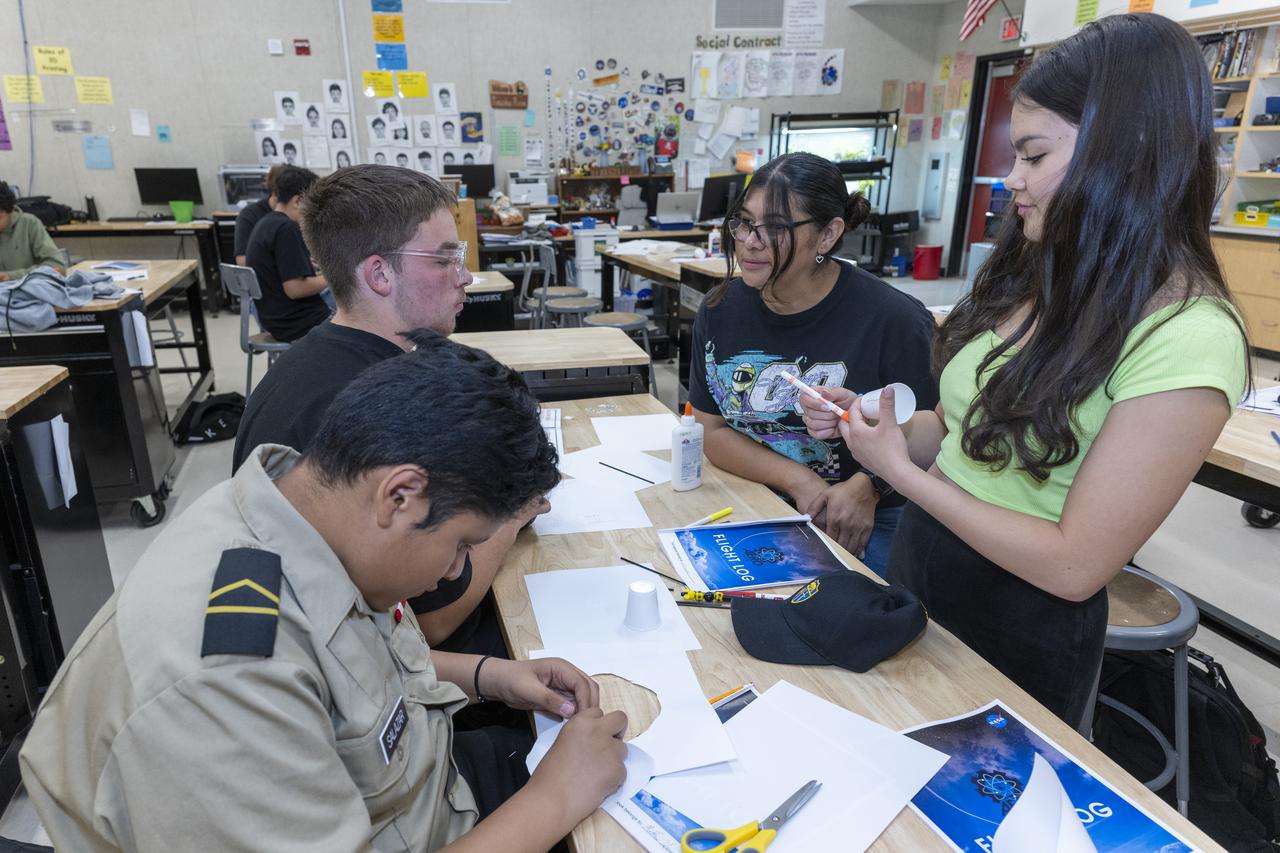

Students from Tropico Middle School in Rosamond, California, build their own paper planes as part of a project during NASA Aero Fair on April 9, 2025.
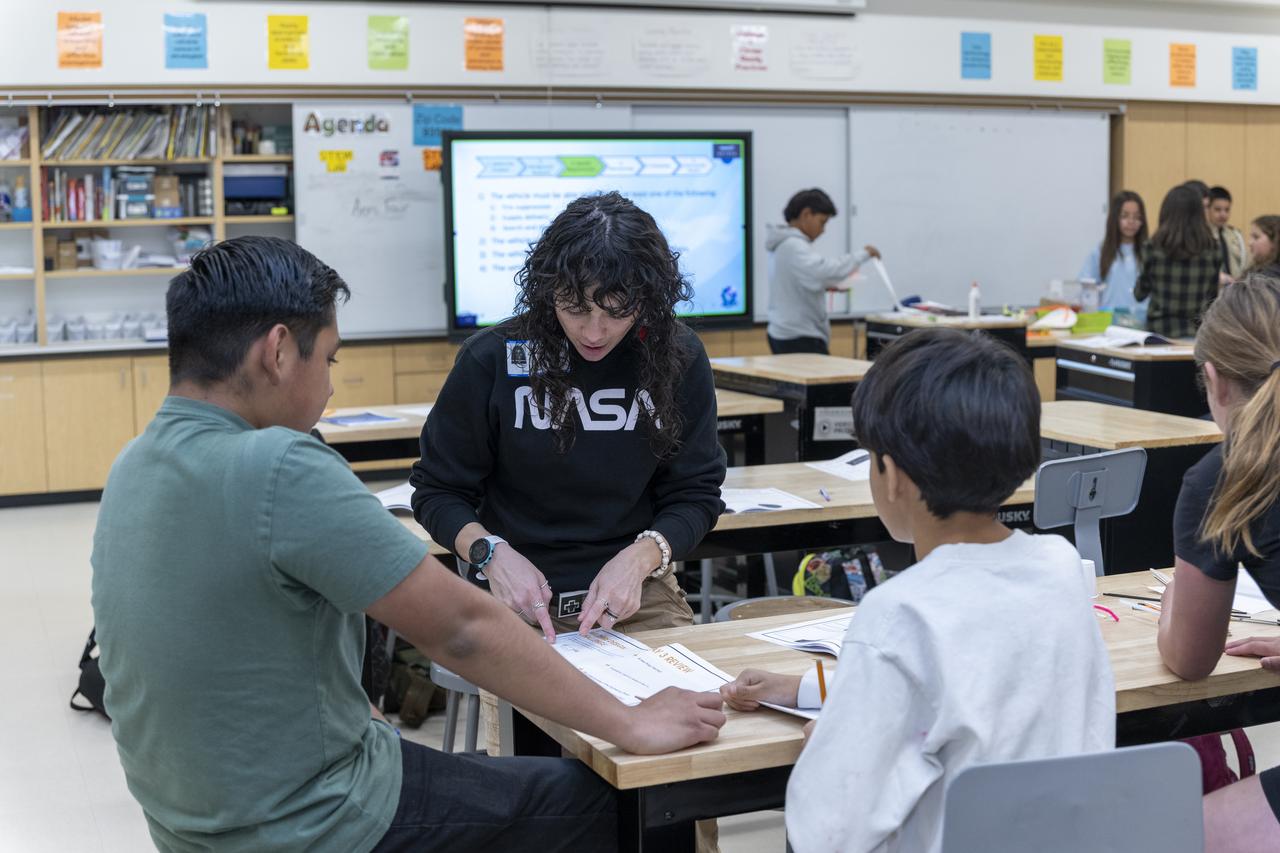

Giovanna Camacho, Pathways systems engineering intern from NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, teaches students about aeronautics during Aero Fair at Tropico Middle School in Rosamond, California, on April 9, 2025.
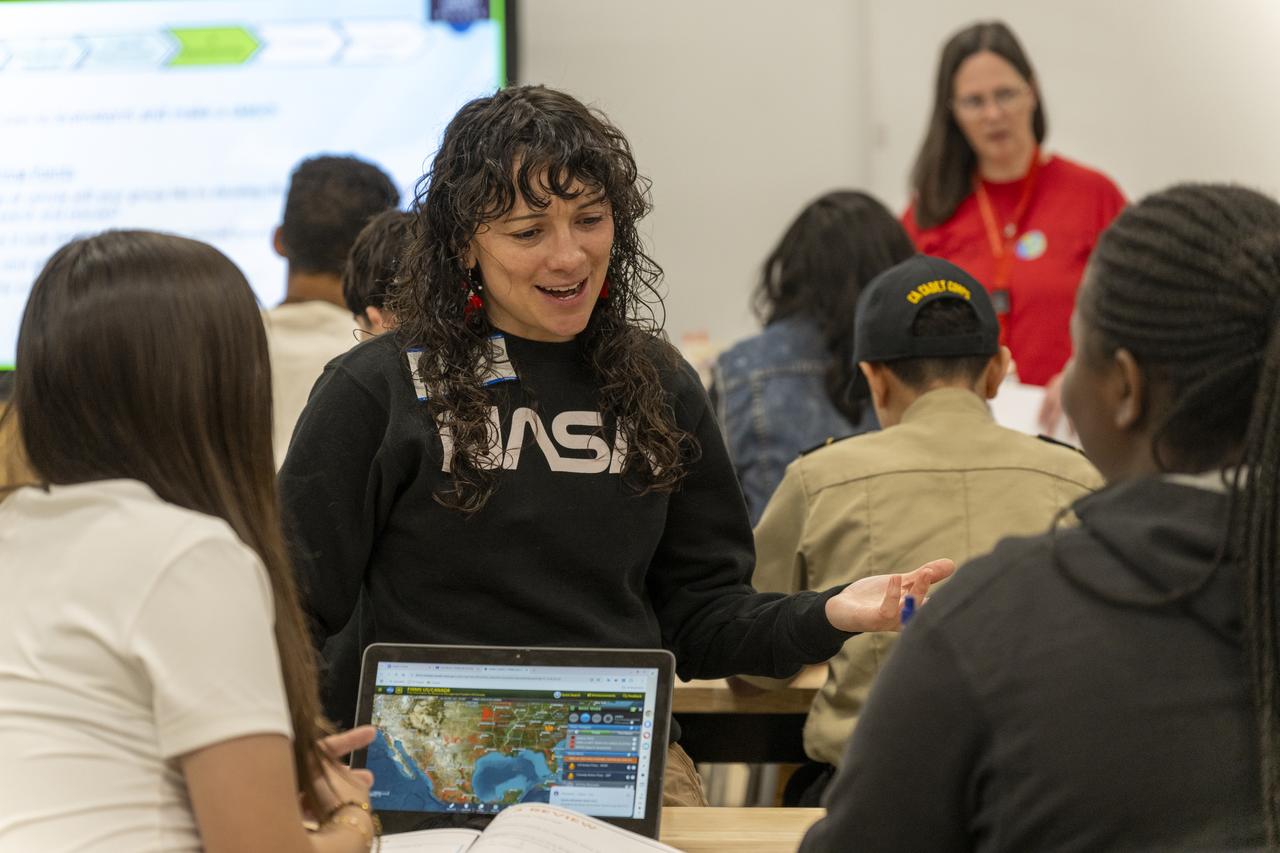

Giovanna Camacho, Pathways systems engineering intern at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, teaches students about aeronautics during Aero Fair at Tropico Middle School in Rosamond, California, on April 9, 2025.

Gary Laier, center liaison for the Small Business Innovation Research/Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR/STTR) program at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, teaches students about aeronautics during Aero Fair at Tropico Middle School in Rosamond, California, on April 9, 2025.
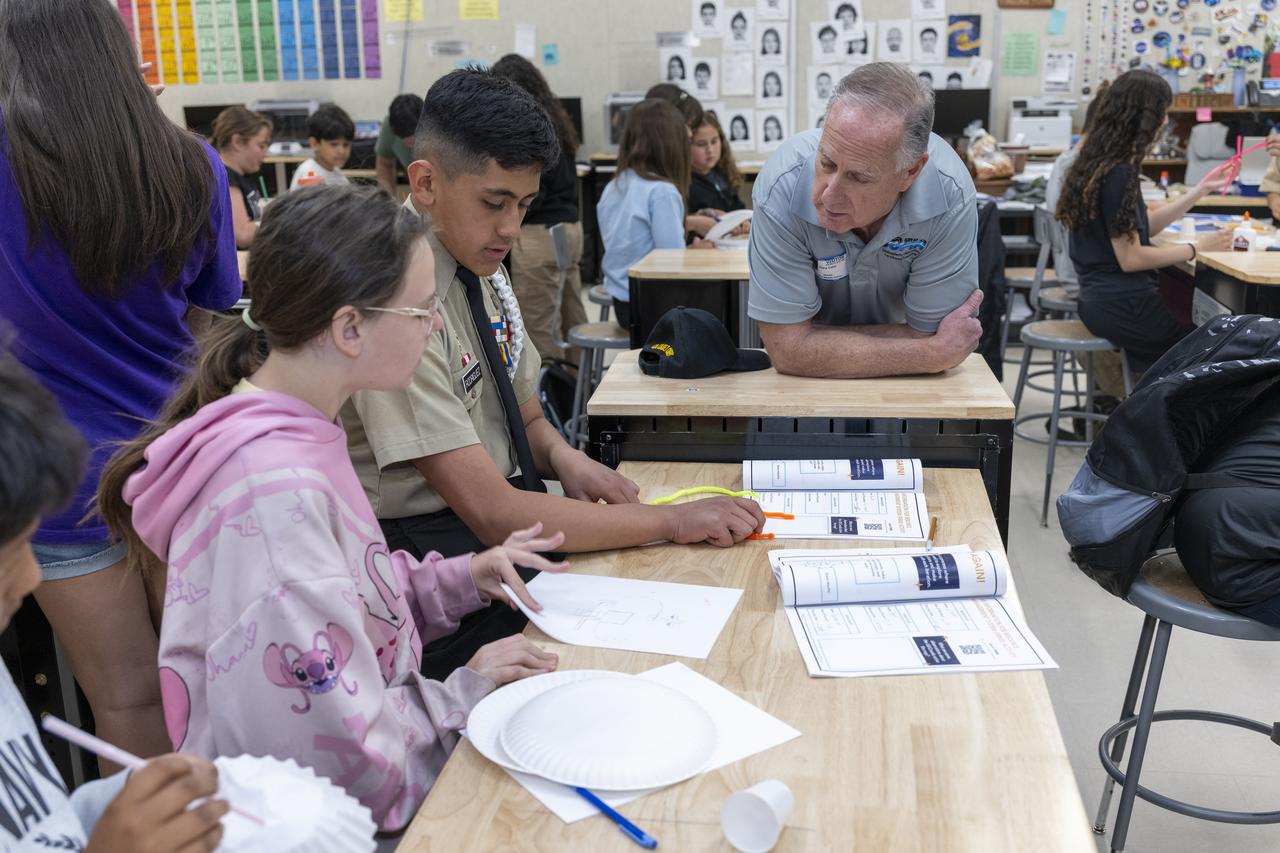

Gary Laier, center liaison for the Small Business Innovation Research/Small Business Technology Transfer (SBIR/STTR) program at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California, teaches students about aeronautics during Aero Fair at Tropico Middle School in Rosamond, California, on April 9, 2025.
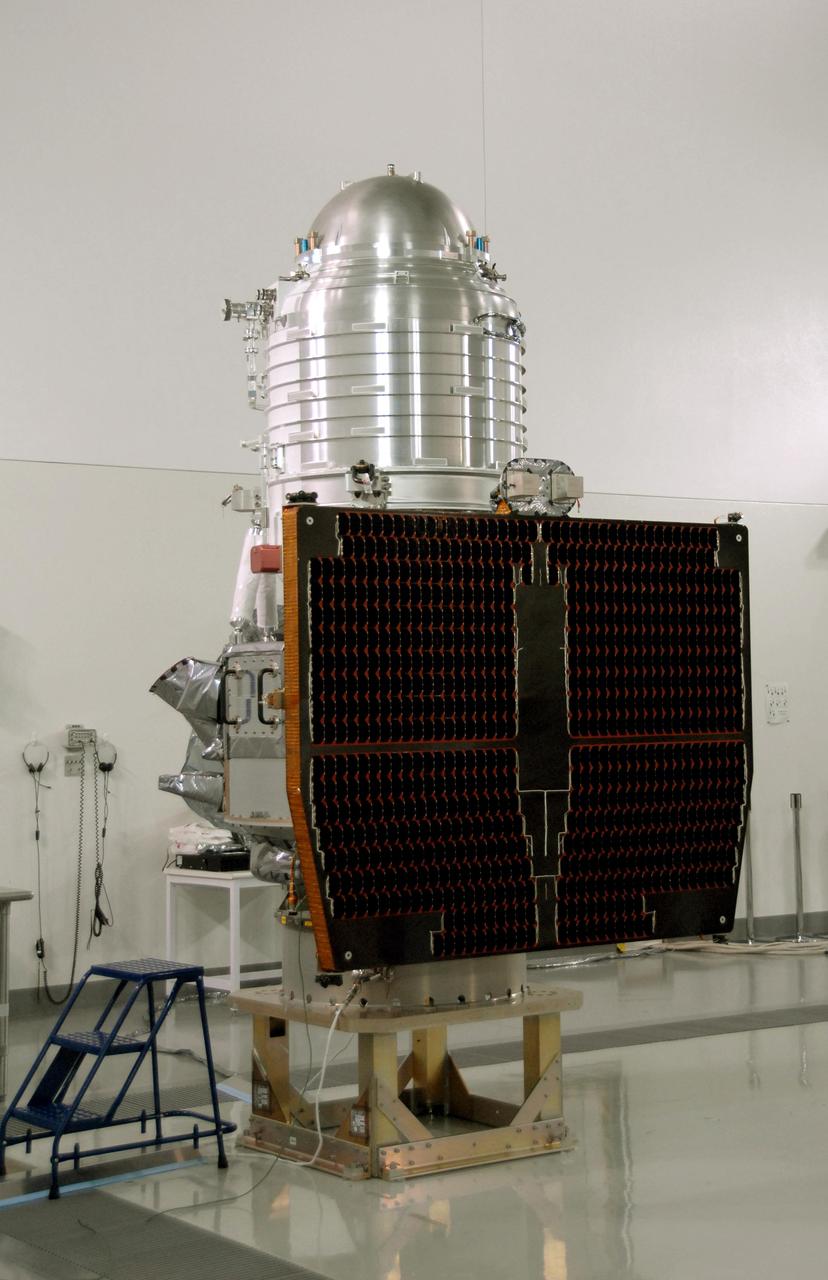

NASA Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer, or WISE, spacecraft sits on the test stand after connection to the conical adapter.
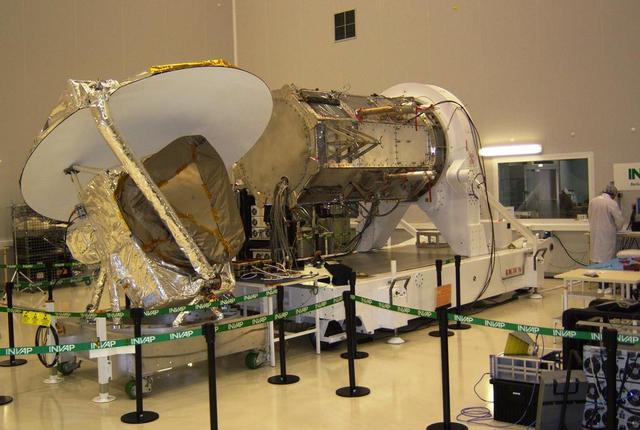

All NASA Aquarius electrical interfaces have successfully been connected to the SAC-D service platform S/P.
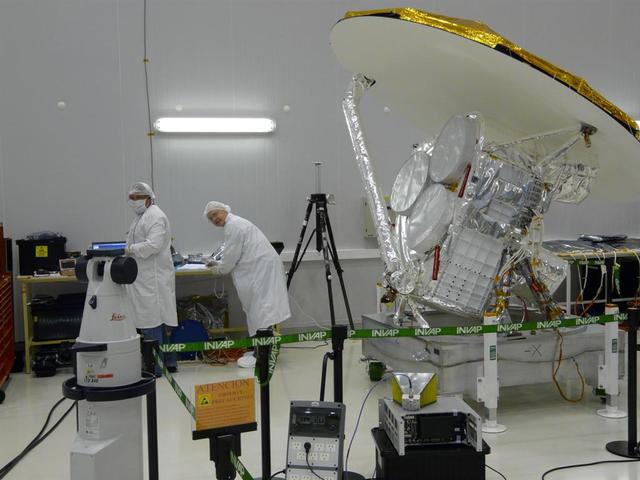

NASA Aquarius instrument power interfaces are tested prior to connection with the SAC-D service platform at the INVAP facility in Bariloche, Argentina.
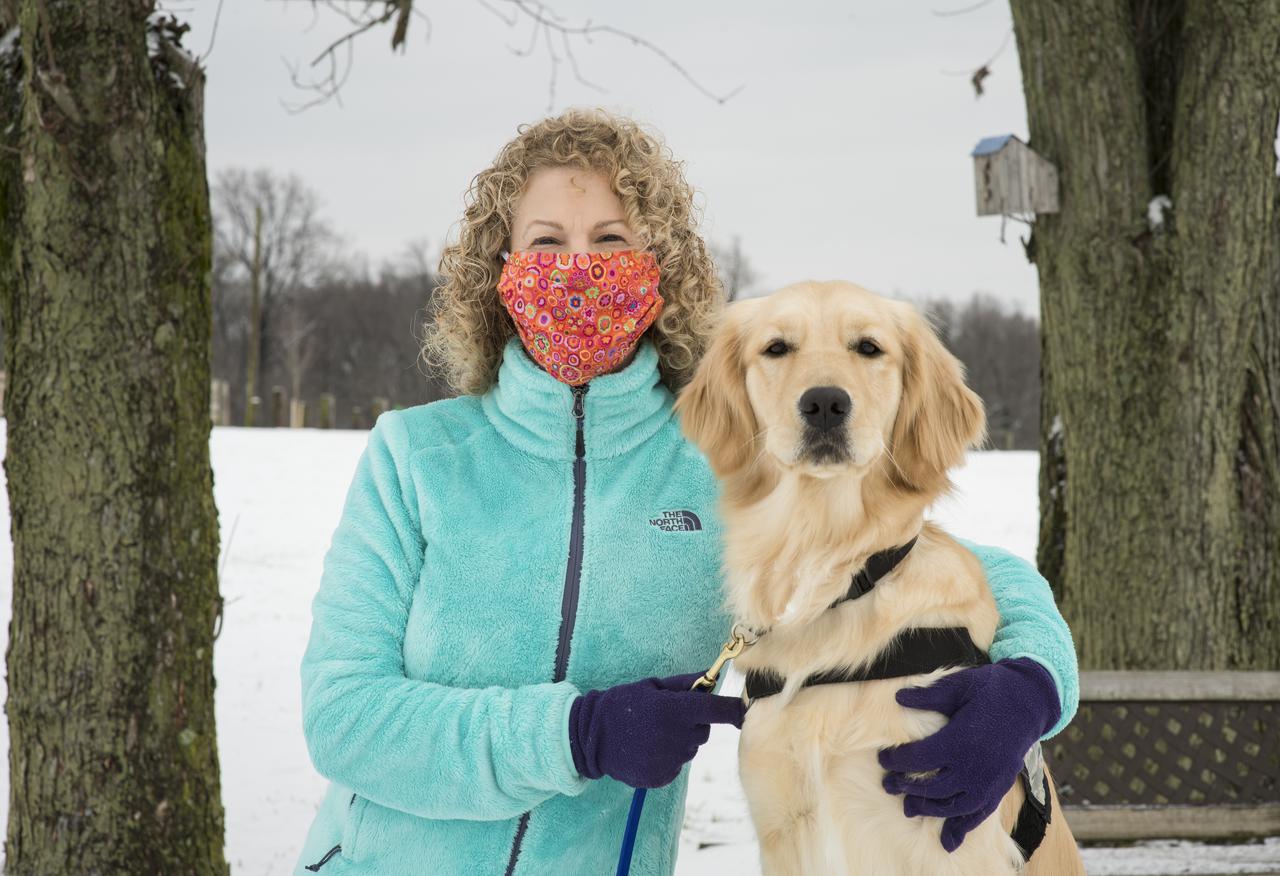

“It was part of my career, but then it was also personal. I was doing it on a volunteer basis, but it was part of my work because I was bringing my service dog in training everywhere with me, which meant to work every day and to meetings at NOAA (National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration). And I was taking the dog across the country to meetings over at Ball Aerospace; that was all part of the training of a service dog. That was an incredible time. I really enjoyed it. “The fact that I was able to do the two combined, that to me was just such an accomplishment. To some people, it could be they got permission to do it and then that’s all they focused on was the dog, but no. I had my job I had to do. I’ve always gotten a distinguished rating in my performances my entire career, and it didn't change when I was training this service dog. “It was a challenge for sure. “After I had to turn back over the service dog I trained, it was really very difficult because the dog was with me for two years, even though I knew it was for a wonderful cause. I ended up going out and getting my own dog who I’ve trained to be a therapy dog, so now we do therapy visits with veterans, elderly, and others. ” Jean Wolfe, Program Executive for the Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite (GOES)-R Series Program at NASA Headquarters, poses for a portrait with Bonnie, who was named for U.S. Air Force Reserve Major Bonnie Carroll, Ret., Friday, Dec. 18, 2020 at the Warrior Canine Connection in Boyds, MD. “Warrior Canine Connection enlists service members and veterans with combat stress in the critical mission of training service dogs for fellow Wounded Warriors.” Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
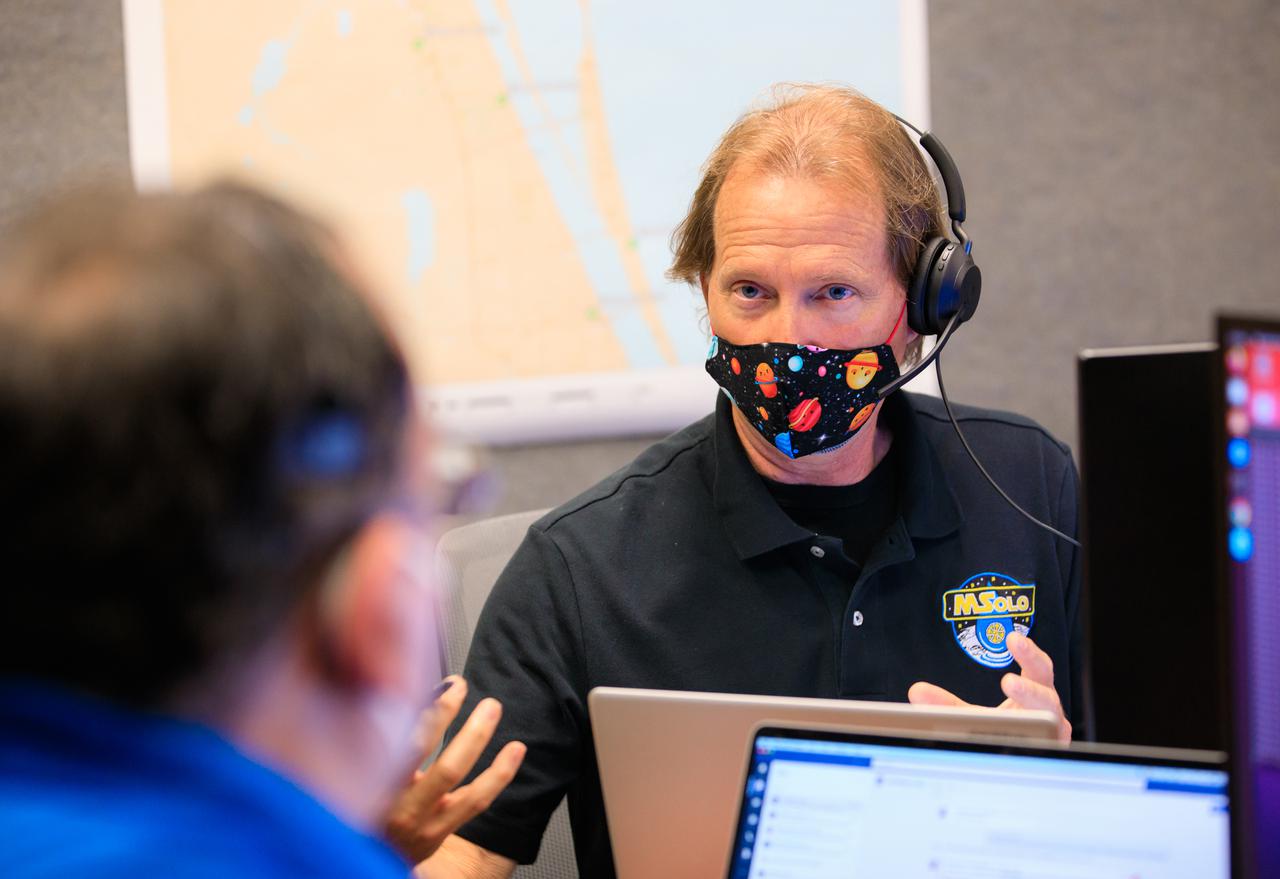

Kevin Smith, software team and science team liaison for NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo), takes part in a joint simulation of the Peregrine One Mission on March 26, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where MSolo connected from inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building to Astrobotic’s mission control facility in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This was the first mission round of simulations for Peregrine Mission One to develop and refine procedures between Astrobotic’s Peregrine Lander and MSolo. Later, there will be other simulations with multiple instruments. Peregrine Mission One will be one of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2021 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
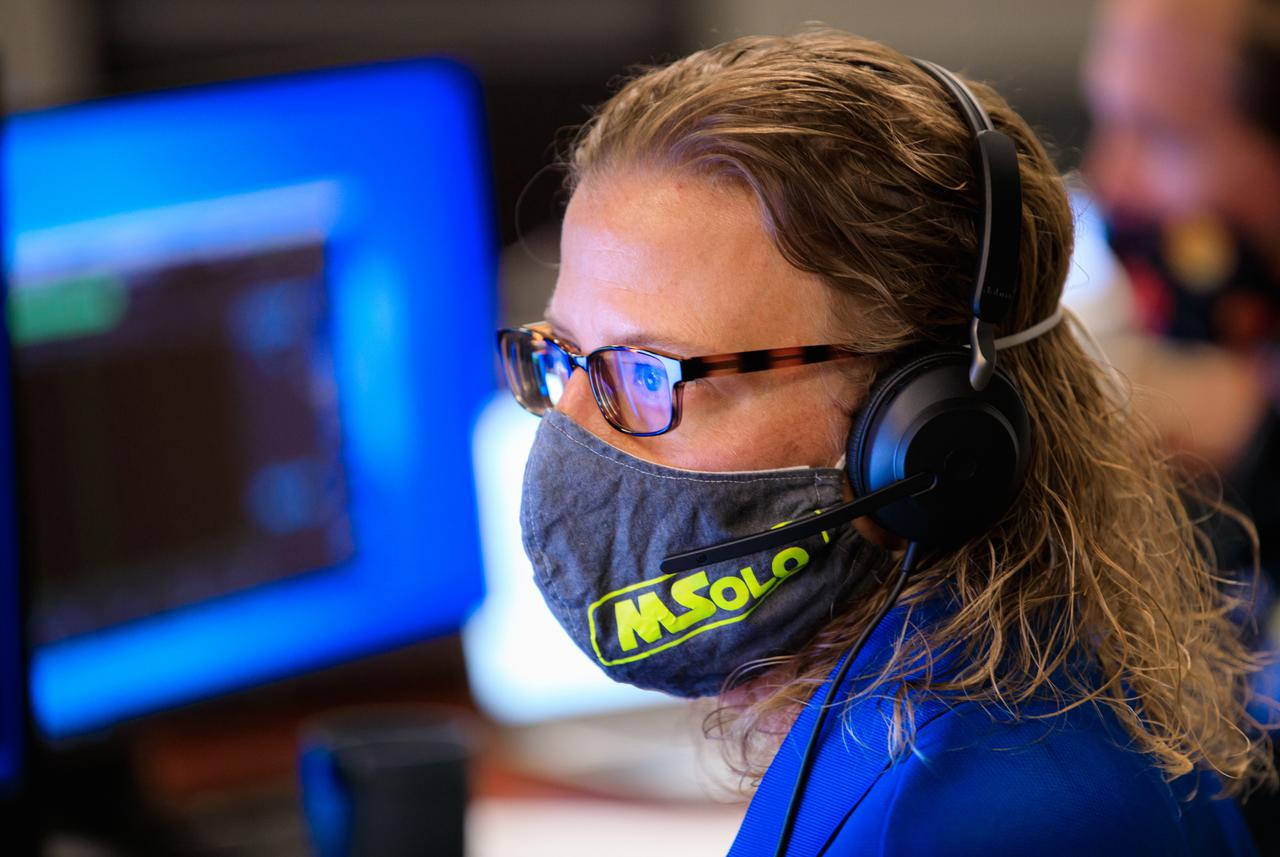

Janine Captain, principal investigator for NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) takes part in a joint simulation of the Peregrine One Mission on March 26, 2021, where MSolo connected from inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to Astrobotic’s mission control facility in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This was the first mission round of simulations for Peregrine Mission One to develop and refine procedures between Astrobotic’s Peregrine Lander and MSolo. Later, there will be other simulations with multiple instruments. Peregrine Mission One will be one of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2021 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
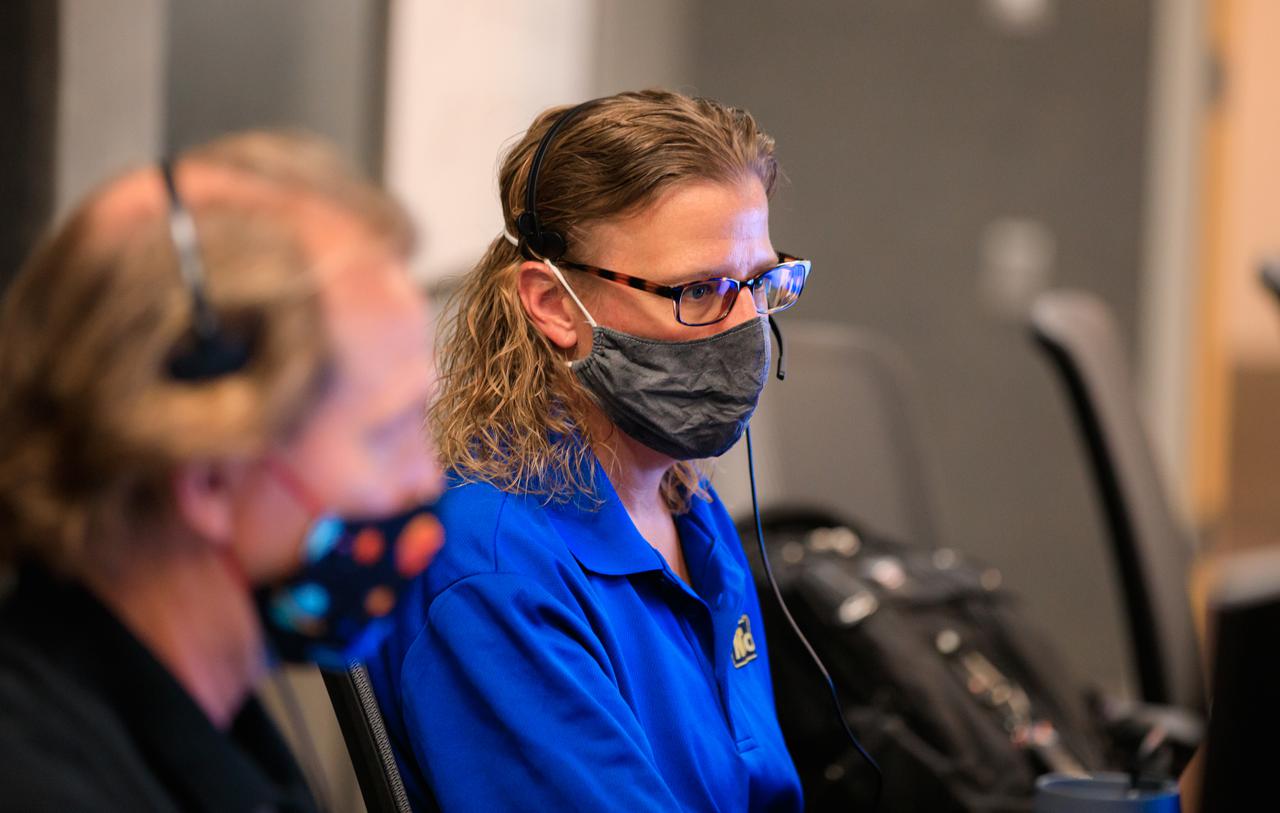

Janine Captain, at right, principal investigator for NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) takes part in a simulation of the Peregrine One Mission on March 26, 2021, where MSolo connected from inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to Astrobotic’s mission control facility in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This was the first mission round of simulations for Peregrine Mission One to develop and refine procedures between Astrobotic’s Peregrine Lander and MSolo. Later, there will be other simulations with multiple instruments. Peregrine Mission One will be one of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2021 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
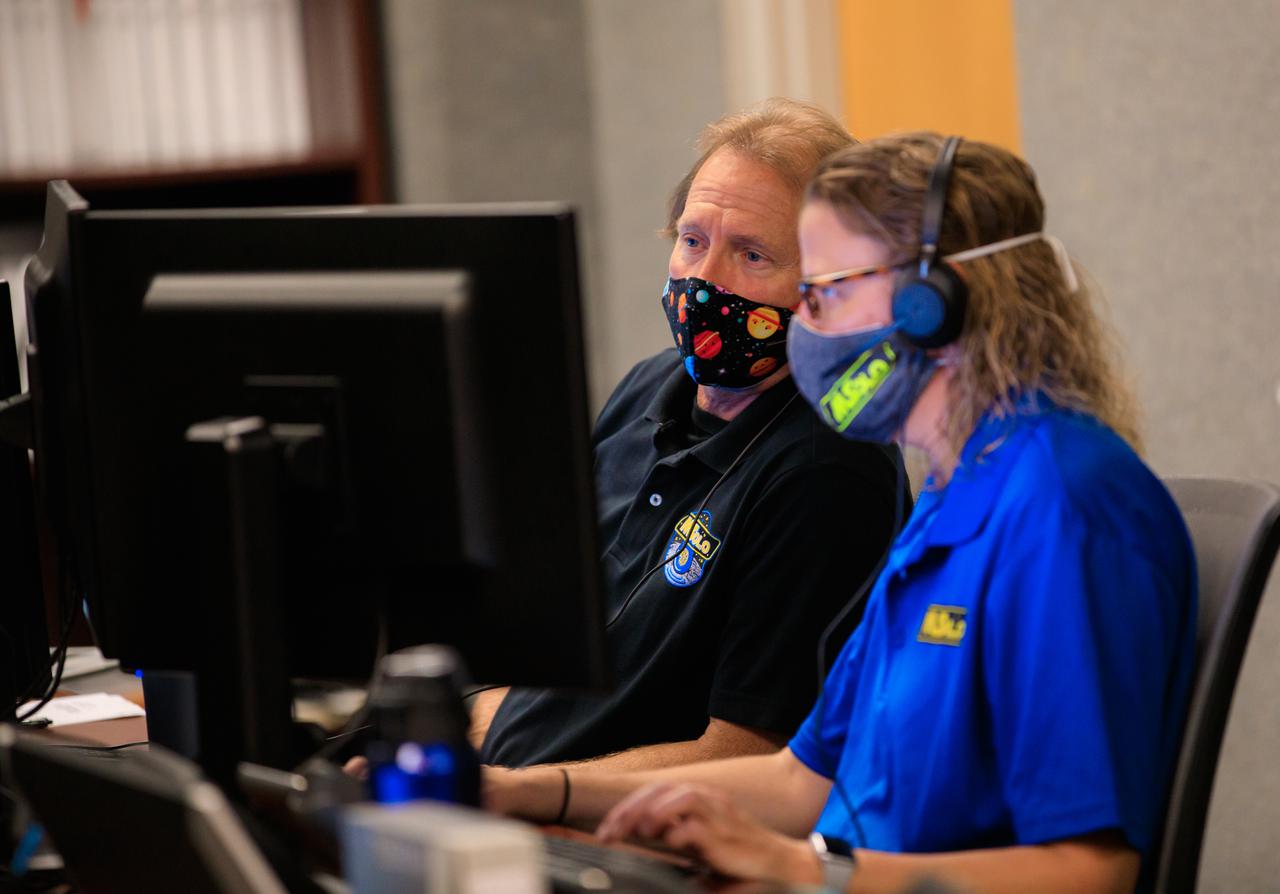

Janine Captain, at right, principal investigator for NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) and Kevin Smith, software team and science team liaison at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, confer during a joint simulation of the Peregrine One Mission on March 26, 2021, where MSolo is connected from inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building to Astrobotic’s mission control facility in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This was the first mission round of simulations for Peregrine Mission One to develop and refine procedures between Astrobotic’s Peregrine Lander and MSolo. Later, there will be other simulations with multiple instruments. Peregrine Mission One will be one of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2021 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
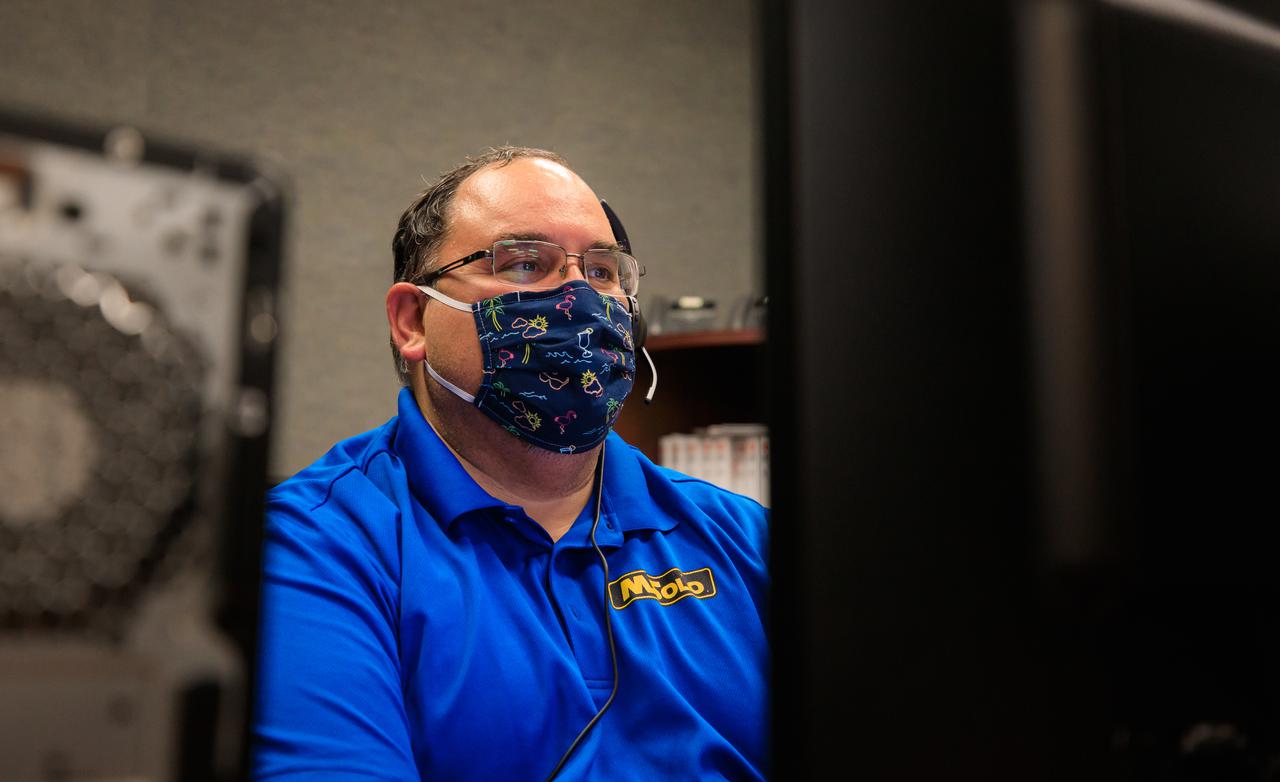

Rolando Nieves, software architect for NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo) takes part in a joint simulation of the Peregrine One Mission on March 26, 2021, where MSolo is connected from inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to Astrobotic’s mission control facility in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This was the first mission round of simulations for Peregrine Mission One to develop and refine procedures between Astrobotic’s Peregrine Lander and MSolo. Later, there will be other simulations with multiple instruments. Peregrine Mission One will be one of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2021 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
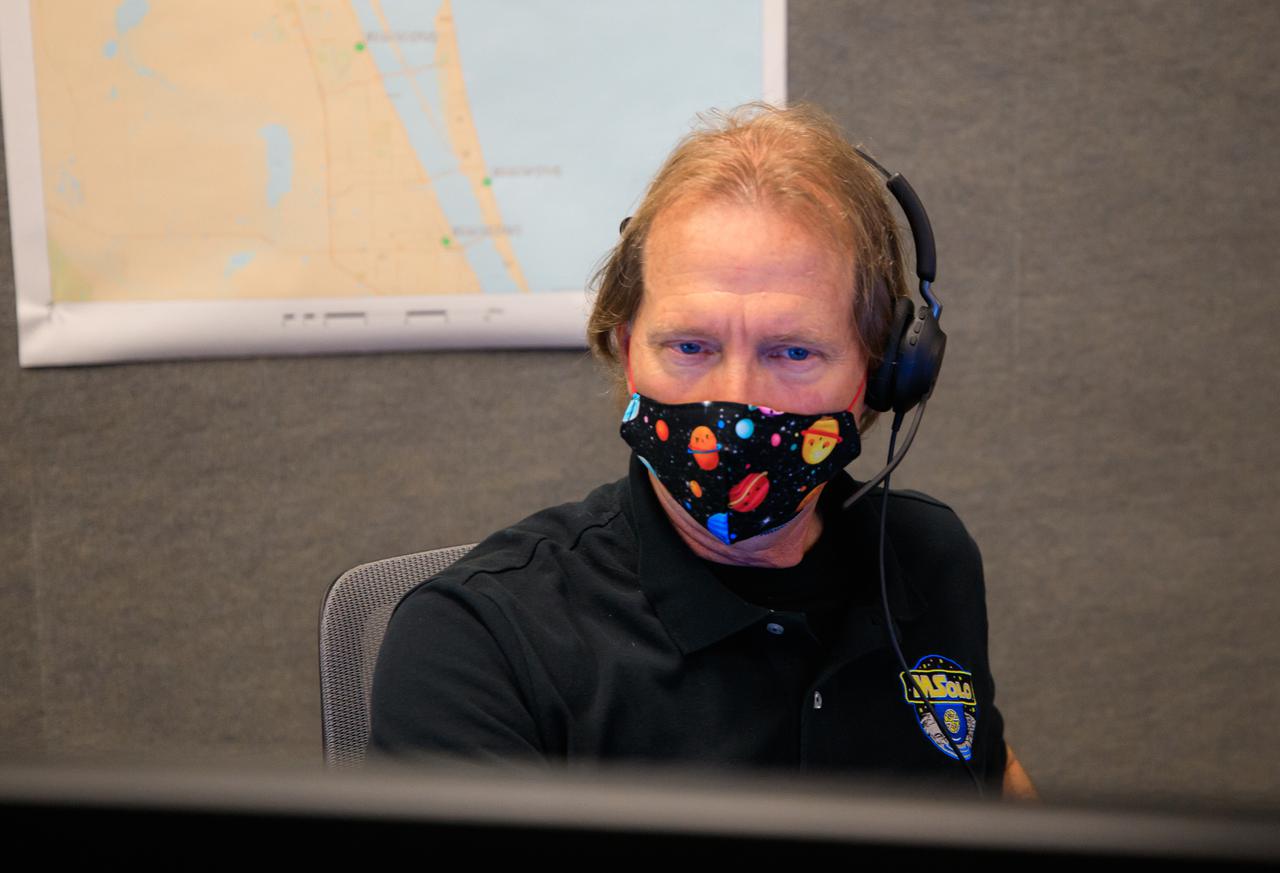

Kevin Smith, software team and science team liaison for NASA’s Mass Spectrometer observing lunar operations (MSolo), takes part in a joint simulation of the Peregrine One Mission on March 26, 2021, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where MSolo connected from inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building to Astrobotic’s mission control facility in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. MSolo is a commercial off-the-shelf mass spectrometer modified to work in space and it will help analyze the chemical makeup of landing sites on the Moon, as well as study water on the lunar surface. This was the first mission round of simulations for Peregrine Mission One to develop and refine procedures between Astrobotic’s Peregrine Lander and MSolo. Later, there will be other simulations with multiple instruments. Peregrine Mission One will be one of NASA’s first Commercial Lunar Payload Delivery Service (CLPS) missions where under the Artemis program, commercial deliveries beginning in 2021 will perform science experiments, test technologies and demonstrate capabilities to help NASA explore the Moon and prepare for human missions.
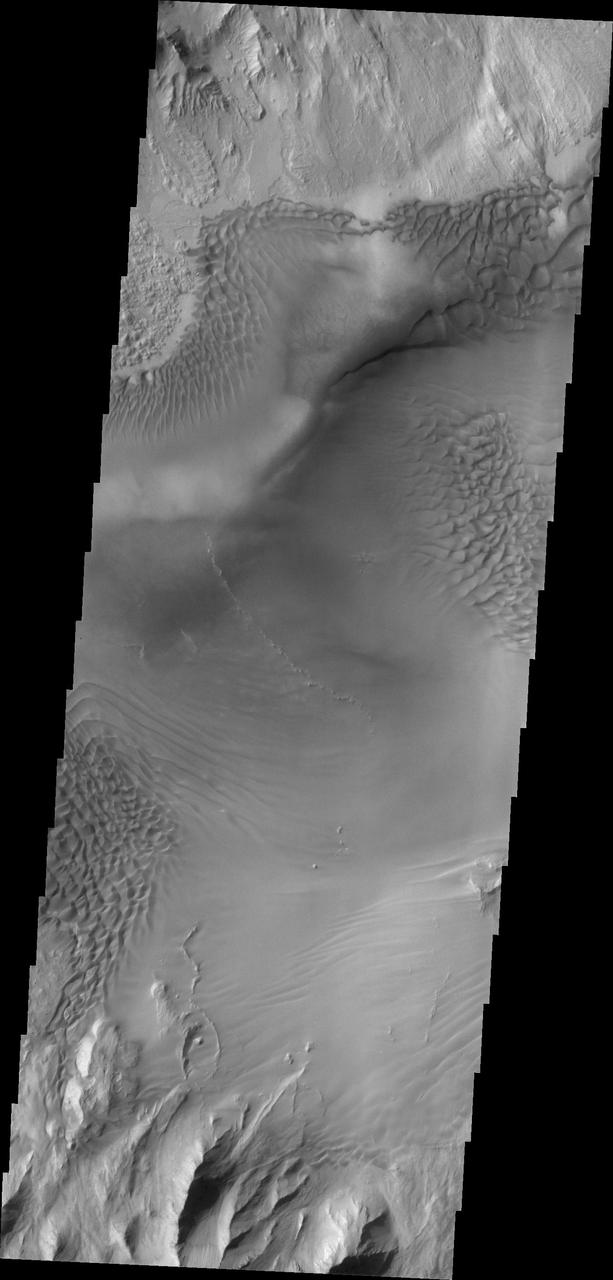

Baetis Chasma is a chasmata near but not directly connected to Valles Marineris. Dunes are prevalent on the floor of this portion of Juventae Chasma in this image taken by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey.
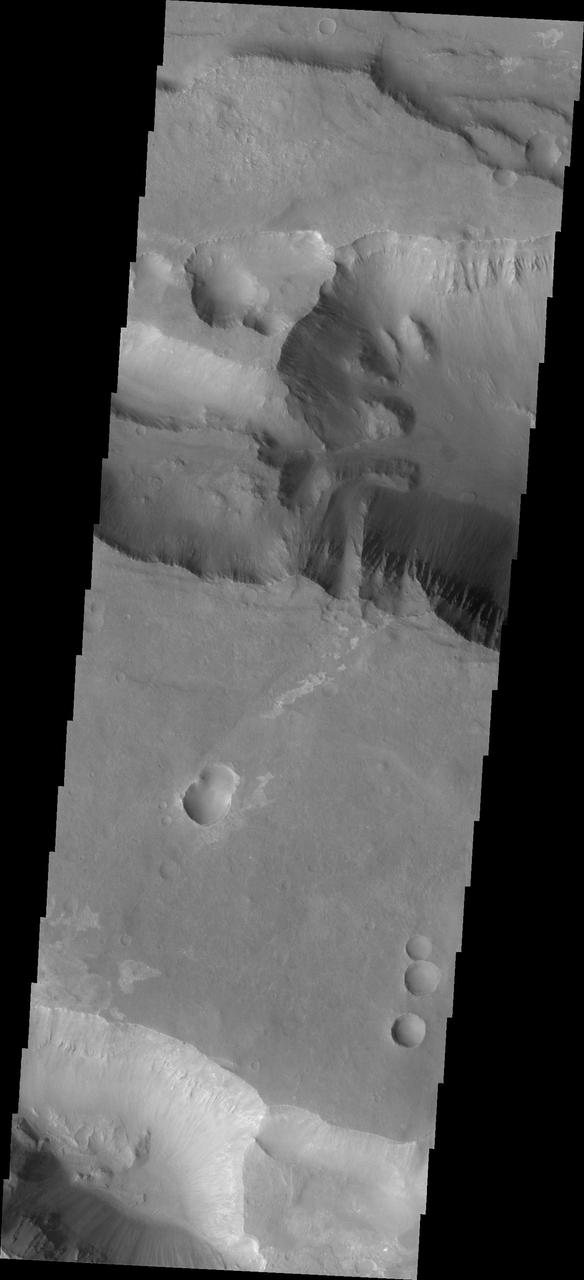

This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows a portion of Coprates Catena, a shallow system of connecting depressions south of Coprates Chasma.
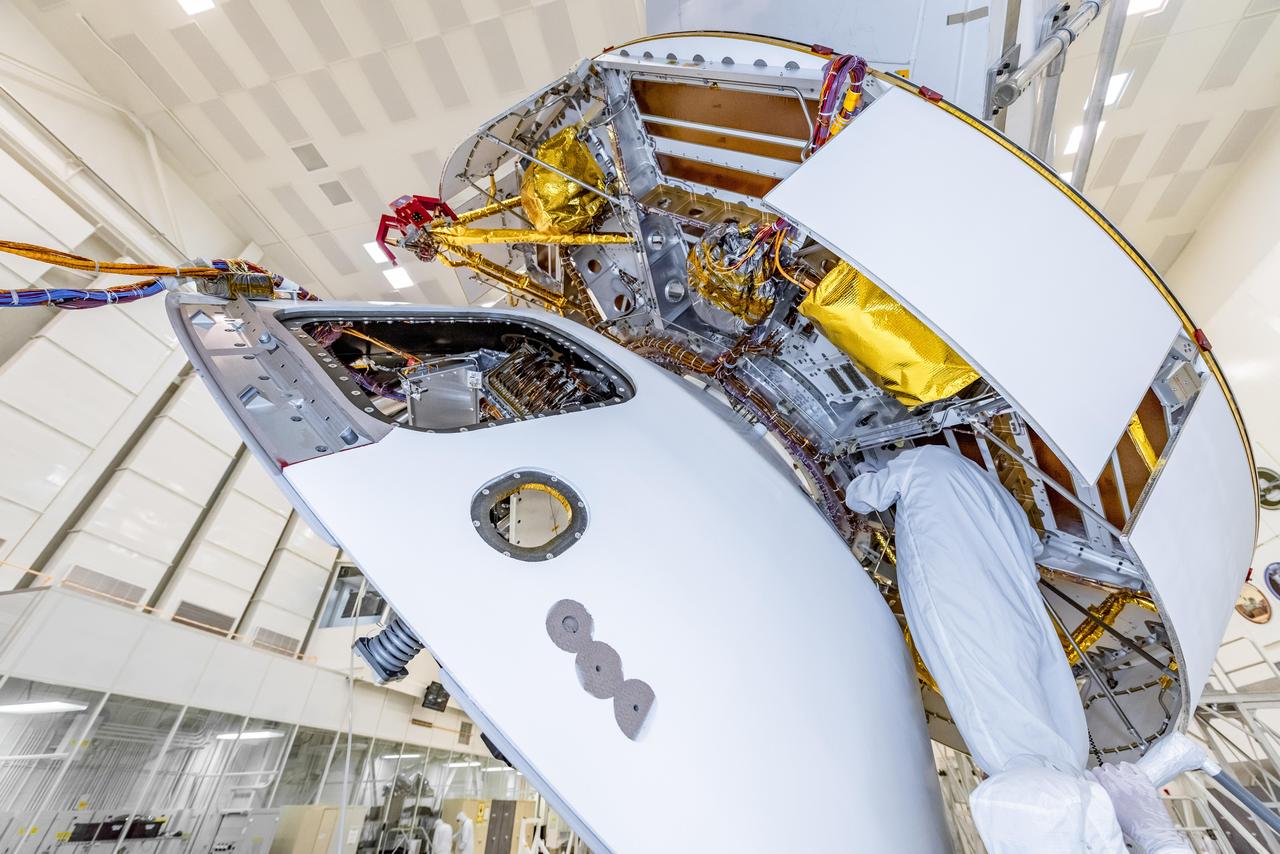

A member of NASA's Mars 2020 project checks connections between the spacecraft's back shell and cruise stage. The image was taken on March 26, 2019, in the Spacecraft Assembly Facility's High Bay 1 clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, in Pasadena, California. During the mission's voyage to Mars, the cruise stage houses the hardware that steers and provides power to the spacecraft. The back shell, along with the heatshield (not pictured), protects the 2020 rover and the sky crane landing system during Mars atmospheric entry. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23163
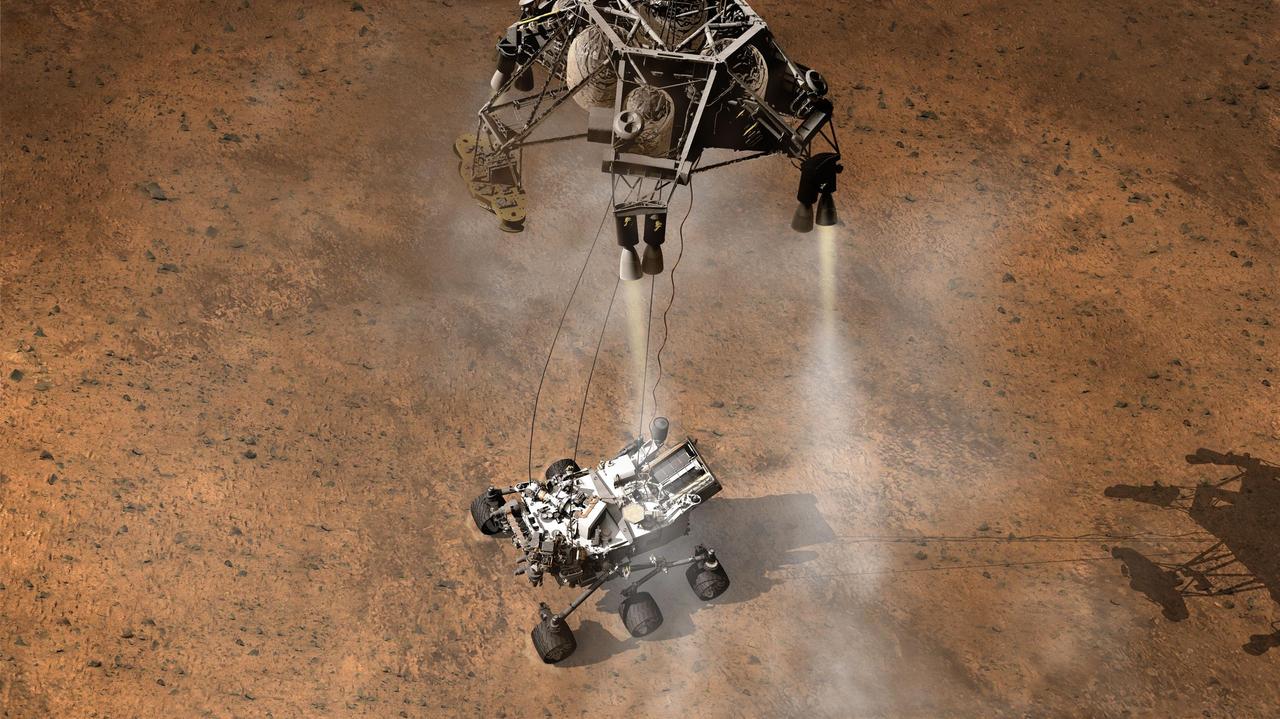
This artist concept depicts the moment immediately after NASA Curiosity rover touches down onto the Martian surface. The spacecraft has detected touchdown, and pyrotechnic cutters have severed connections between rover and spacecraft descent stage.
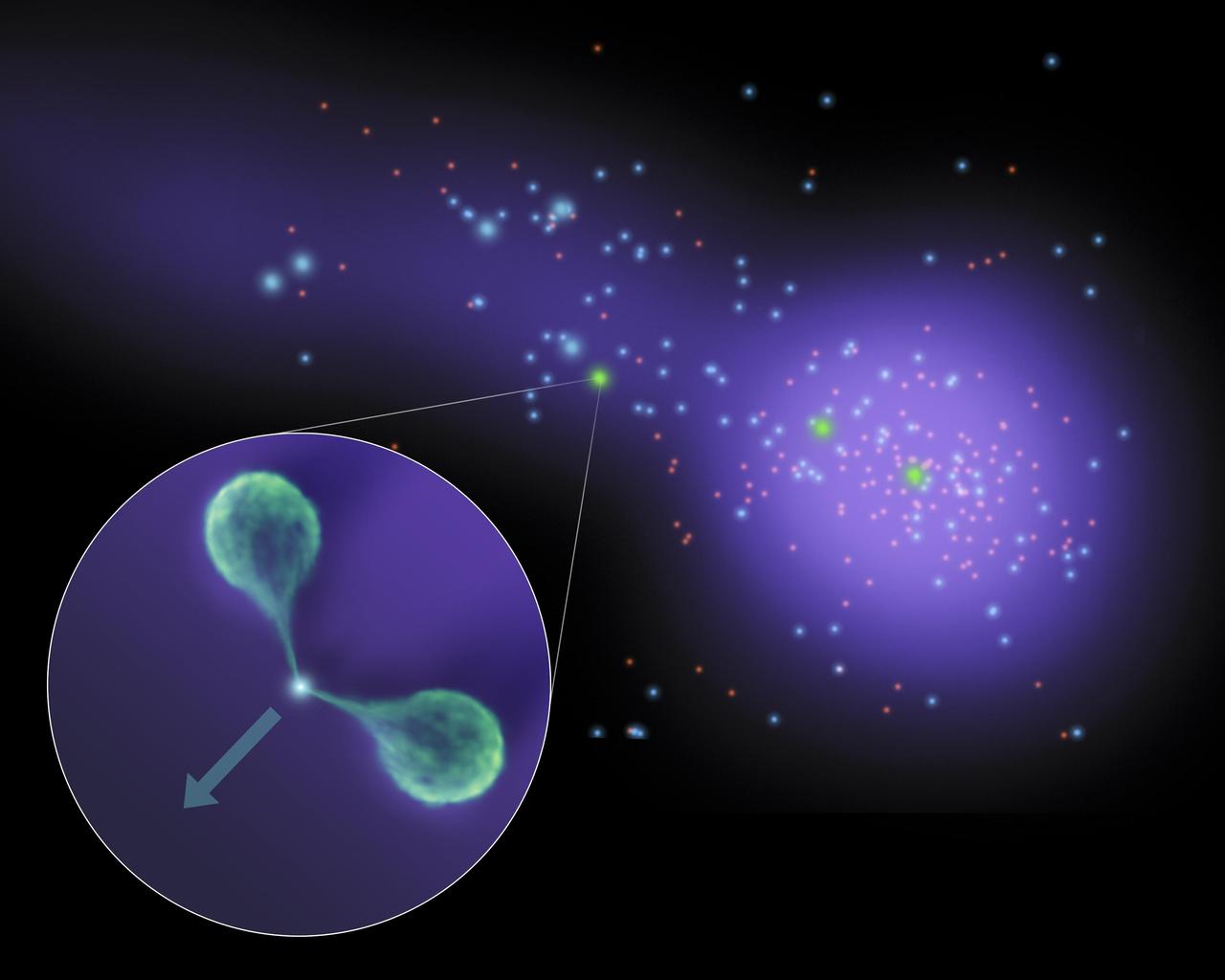
This diagram shows findings of results of observations made primarily by NASA Spitzer Telescopes and the Very Large Array radio telescope and illuminates new details about a celestial andbar connecting two massive islands of galaxies.
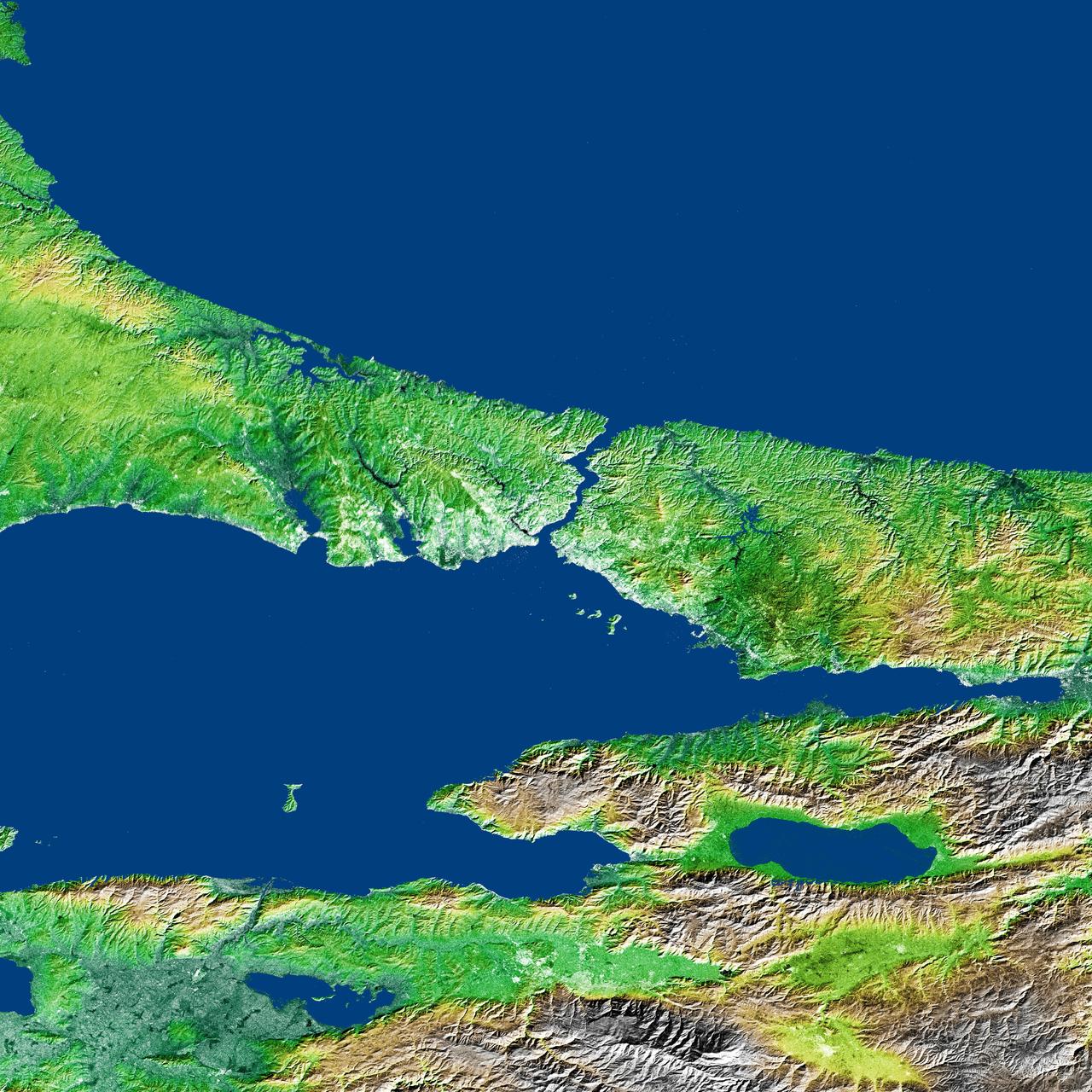
The Bosporus also spelled Bosphorus is a strait that connects the Black Sea with the Sea of Marmara in the center of this view of northwest Turkey, taken during NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission.
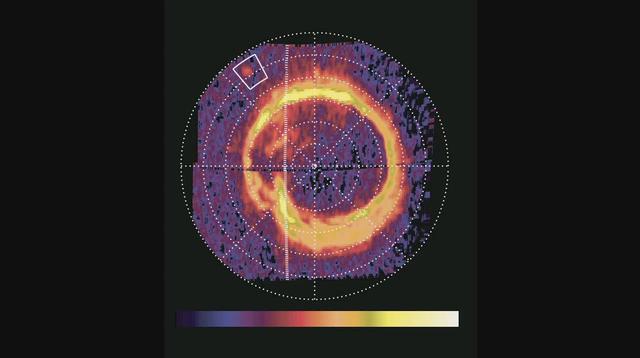
NASA Cassini spacecraft has spotted a glowing patch of ultraviolet light near Saturn north pole that marks the presence of an electrical circuit that connects Saturn with its moon Enceladus. Movie available at the Photojournal.
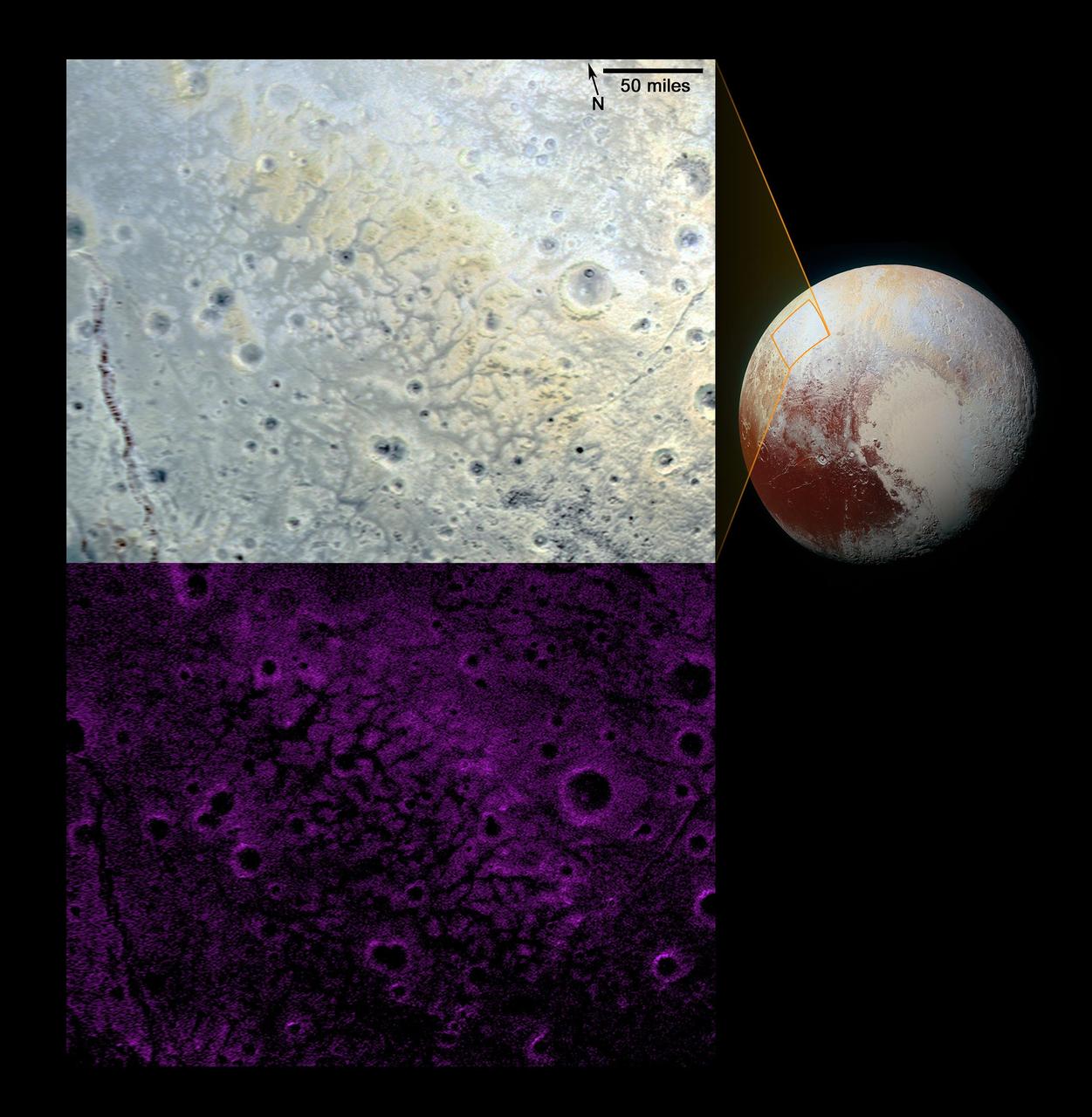
NASA New Horizons scientists have spotted an expanse of terrain they describe as fretted bright plains divided into polygon-shaped blocks by a network of dark, connected valleys in Pluto informally named Venera Terra region.

A dense network of small rivers or swampy areas appears to connect some of the seas on Saturn moon Titan, as seen in this comparison of data of the same area from two instruments on NASA Cassini spacecraft.
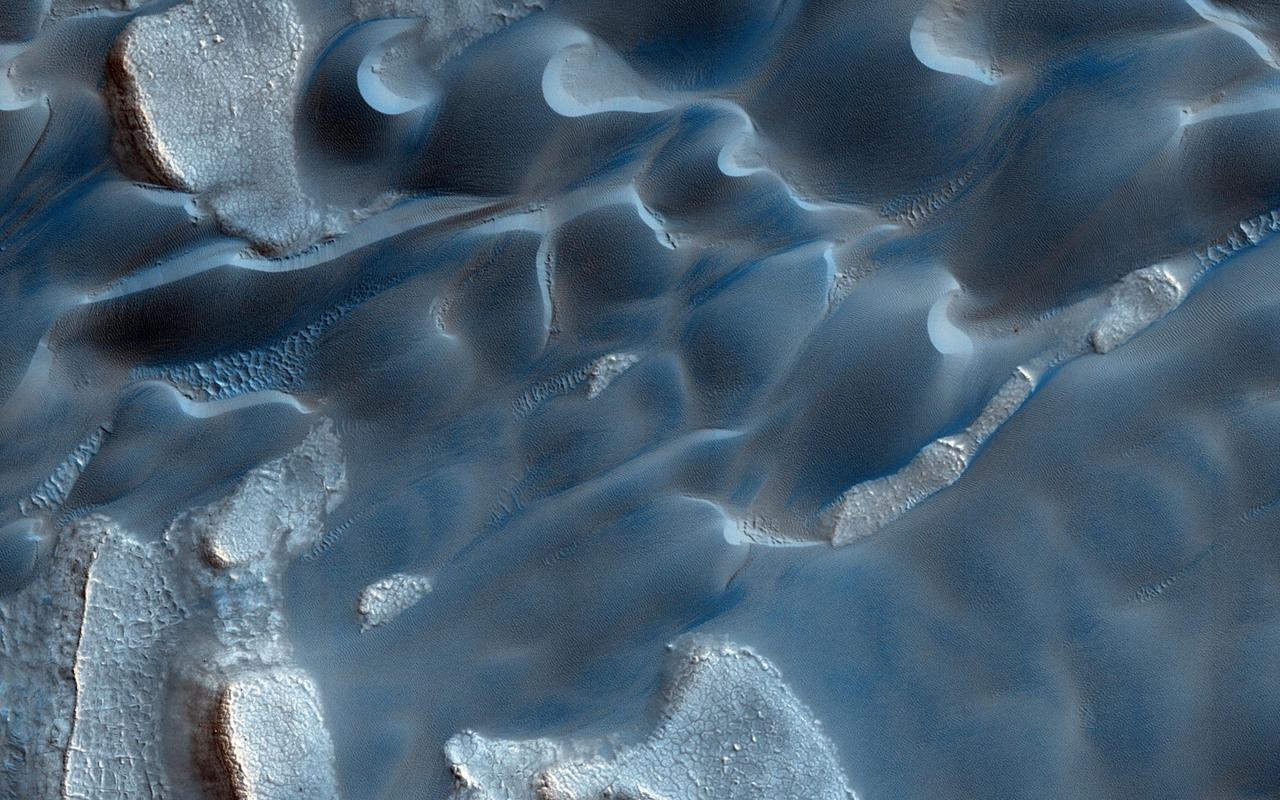

The deep chasm that formed on the polar cap edge is identified as an area of strong down-slope winds and has a clear connection to Mars largest dune field, Olympia Undae as observed by NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
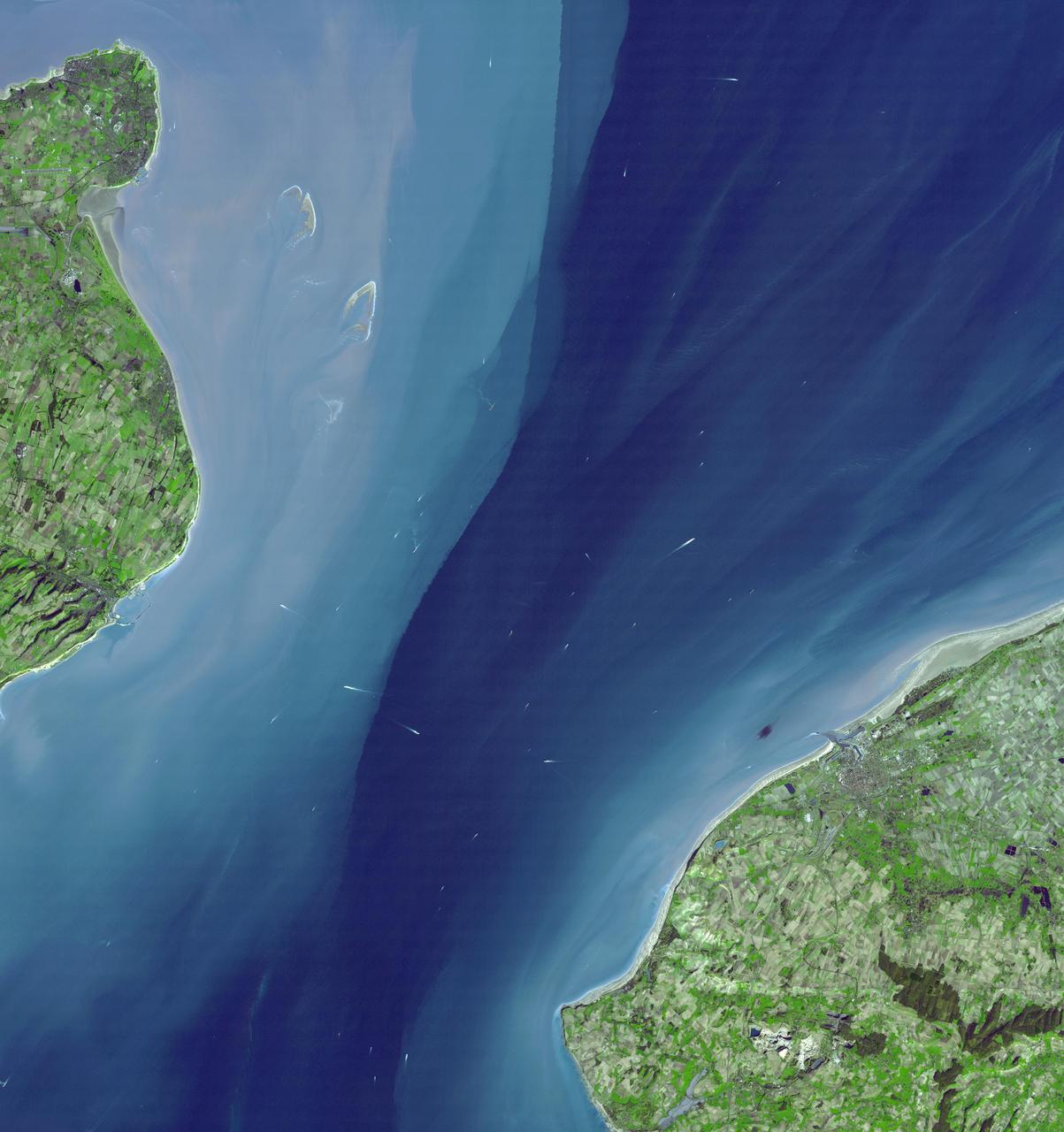

The Channel Tunnel is a 50.5 km-long rail tunnel beneath the English Channel at the Straits of Dover. It connects Dover, Kent in England with Calais, northern France. This image was acquired by NASA Terra spacecraft.
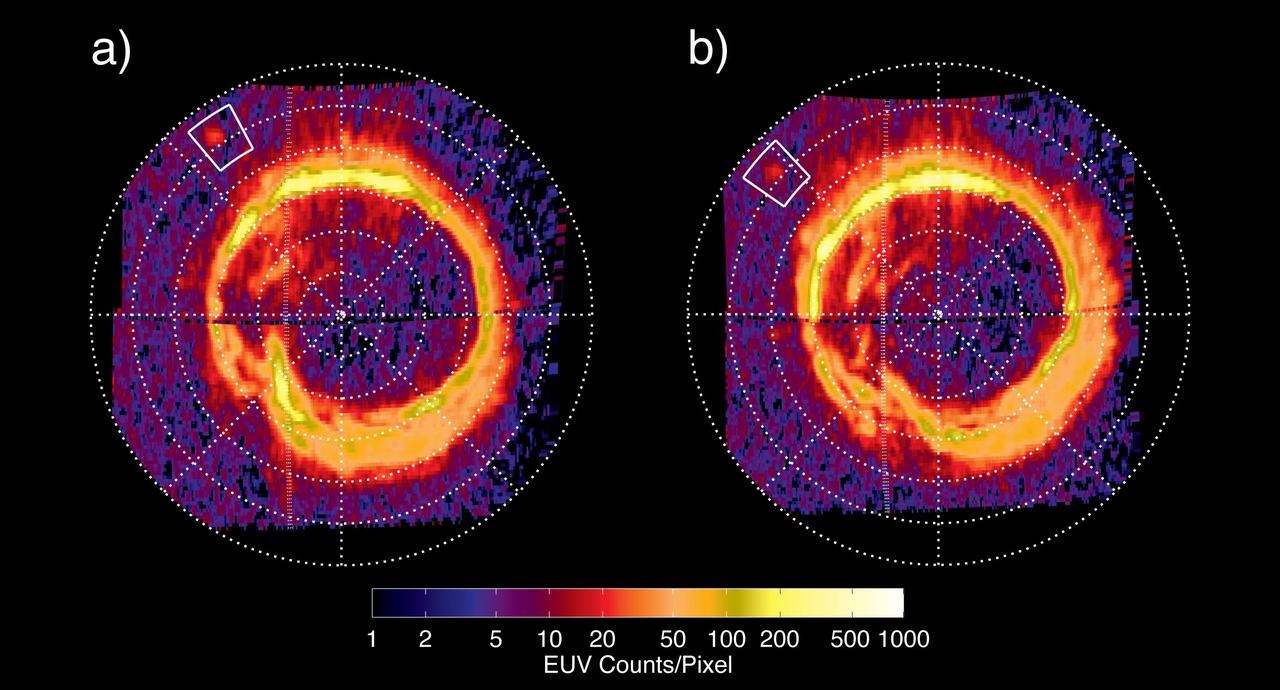
NASA Cassini spacecraft has spotted a glowing patch of ultraviolet light near Saturn north pole that marks the presence of an electrical circuit that connects Saturn with its moon Enceladus.
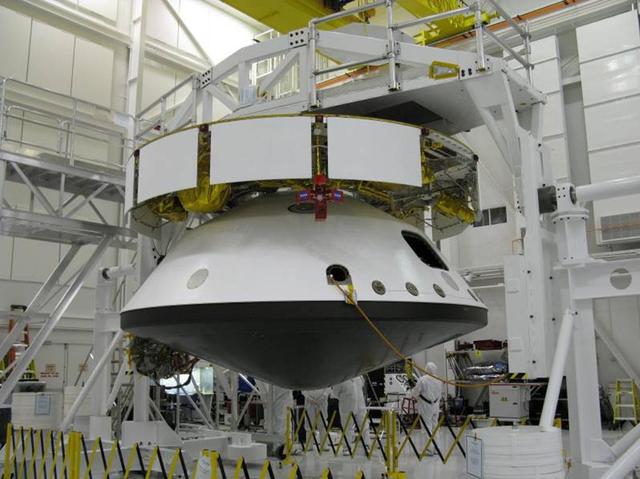

The major components of NASA Mars Science Laboratory spacecraft -- cruise stage atop the aeroshell, which has the descent stage and rover inside -- were connected together in October 2008 for several weeks of system testing.
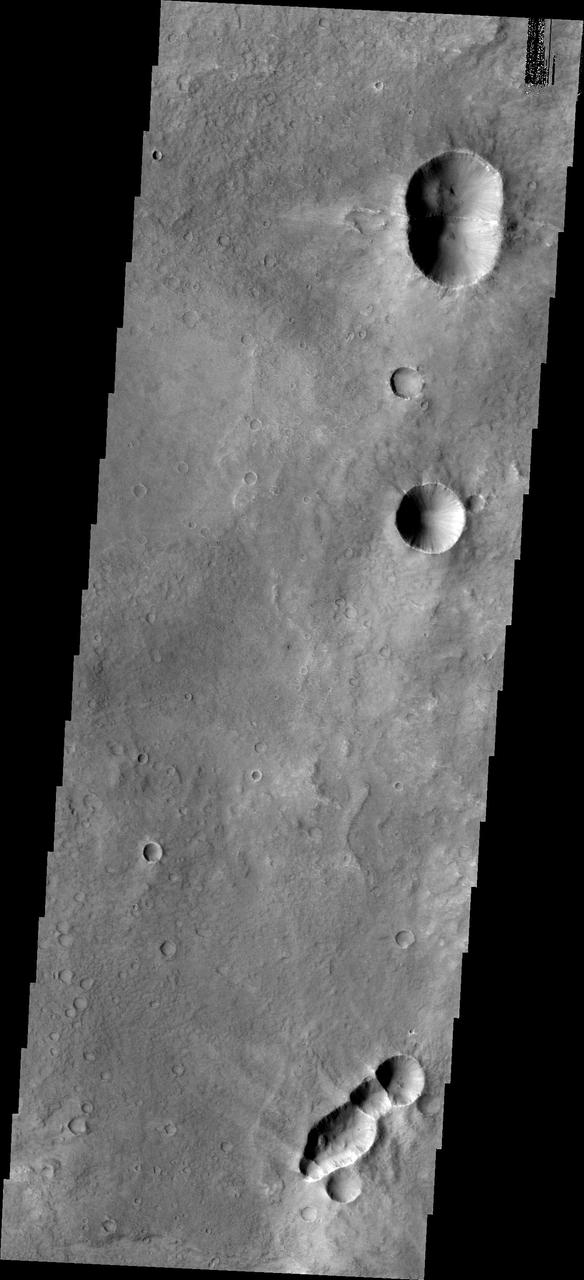

Do you see what I see in this image from NASA Mars Odyssey spacecraft? The connected craters at the top and bottom of this image look like bugs, perhaps a bumble bee at the top and a wasp at the bottom.

This artist concept based on data from NASA Cassini spacecraft, shows a glowing patch of ultraviolet light near Saturn north pole that occurs at the footprint of the magnetic connection between Saturn and its moon Enceladus.

NASA Stennis Director John Bailey hosted a Java with John session with Office of Procurement employees on Oct. 15. Java with John is an employee-led discussion in a casual environment aimed at fostering a culture in which employees are welcome to share what matters most to them at work.
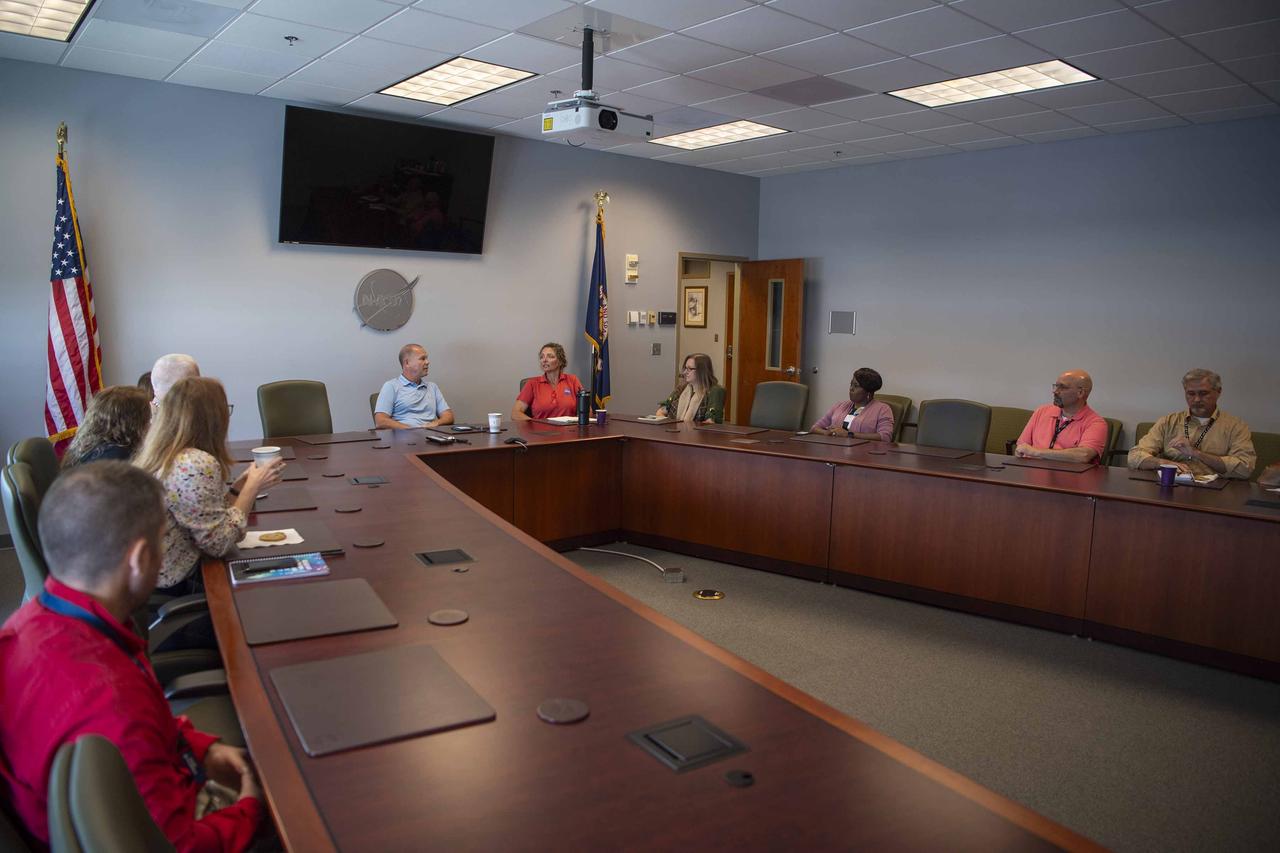

NASA Stennis Director John Bailey hosted a Java with John session with Office of Procurement employees on Oct. 15. Java with John is an employee-led discussion in a casual environment aimed at fostering a culture in which employees are welcome to share what matters most to them at work.
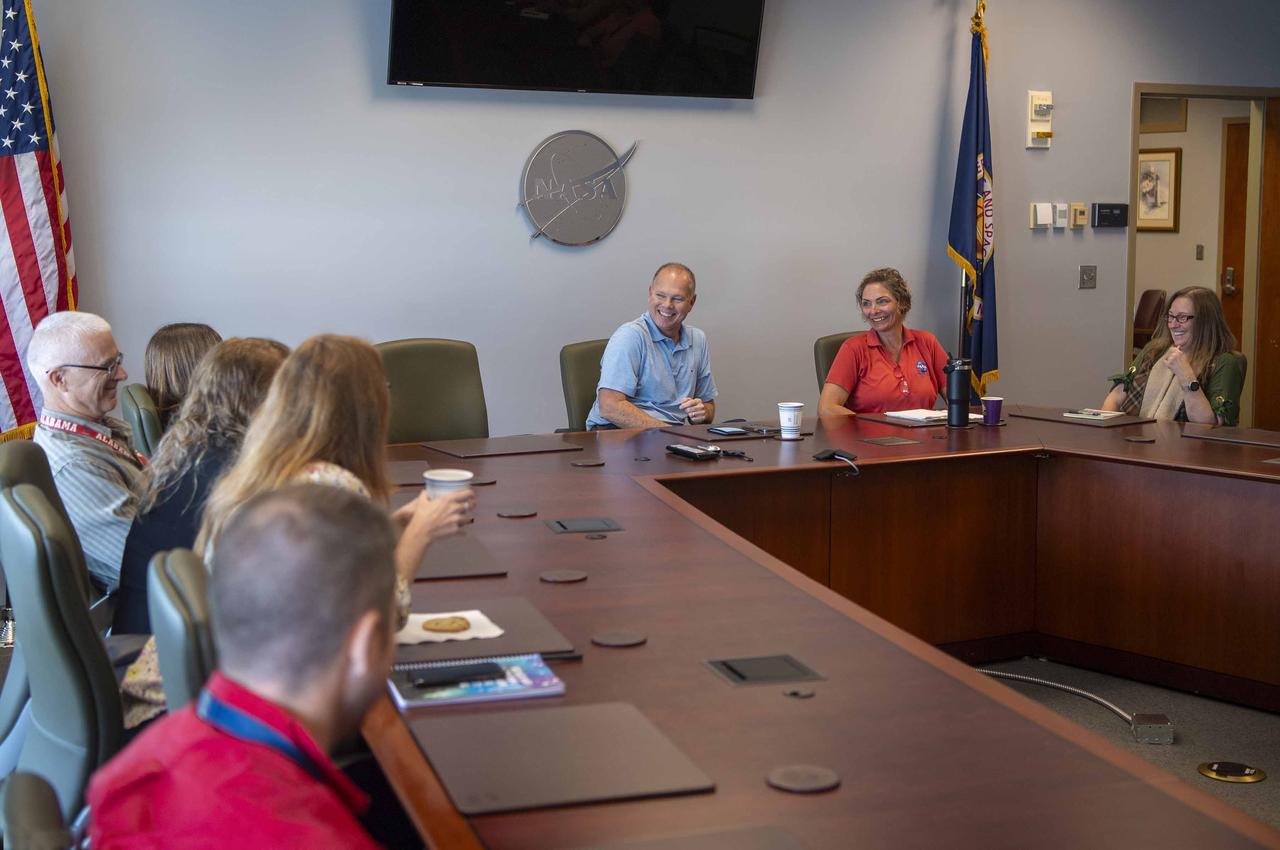

NASA Stennis Director John Bailey hosted a Java with John session with Office of Procurement employees on Oct. 15. Java with John is an employee-led discussion in a casual environment aimed at fostering a culture in which employees are welcome to share what matters most to them at work.
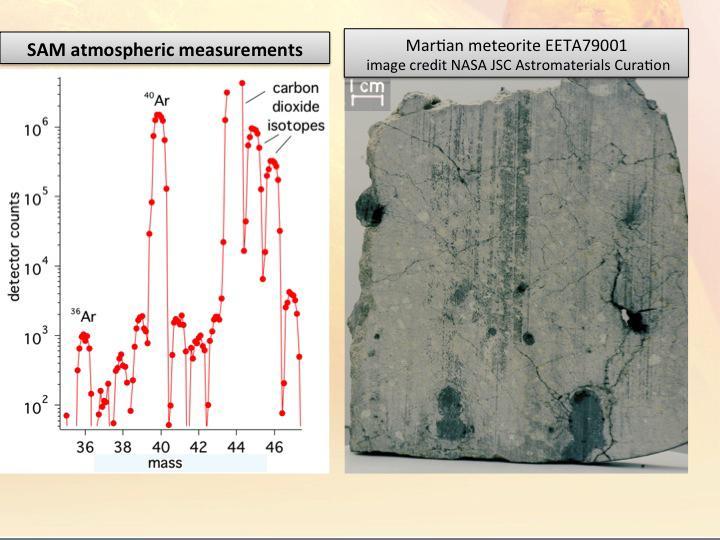
New results from the Sample Analysis at Mars, or SAM, instrument on NASA Curiosity rover detected about 2,000 times as much argon-40 as argon-36, which weighs less, confirming the connection between Mars and Martian meteorites found on Earth.
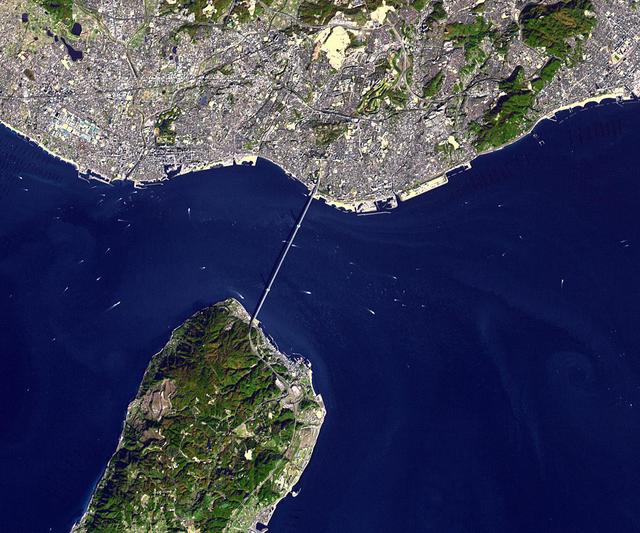

NASA Terra spacecraft shows the Akashi Kaikyo Bridge or Pearl Bridge, the longest central span of any suspension bridge in the world, at 1991 meters, connecting the city of Kobe, Japan with Iwaja on Awaji Island by crossing the busy Akashi Strait.
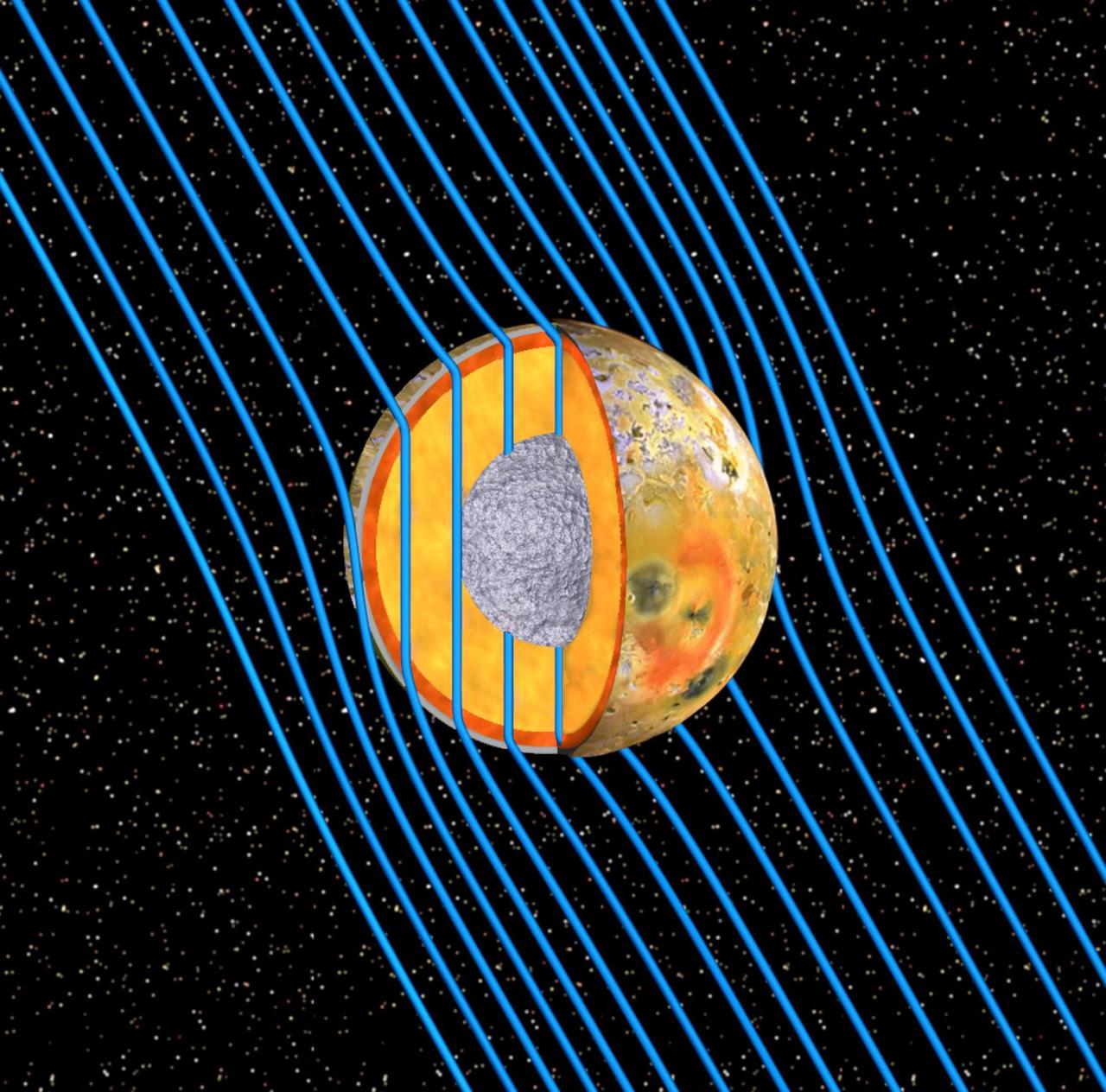
This graphic shows the internal structure of Jupiter moon Io as revealed by data from NASA Galileo spacecraft. Io is bathed in magnetic field lines shown in blue that connect the north polar region of Jupiter to the planet south polar region.

A technician assists with connections as NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is attached to the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket May 14, 2018, inside a clean room in Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on the Pegasus XL rocket, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
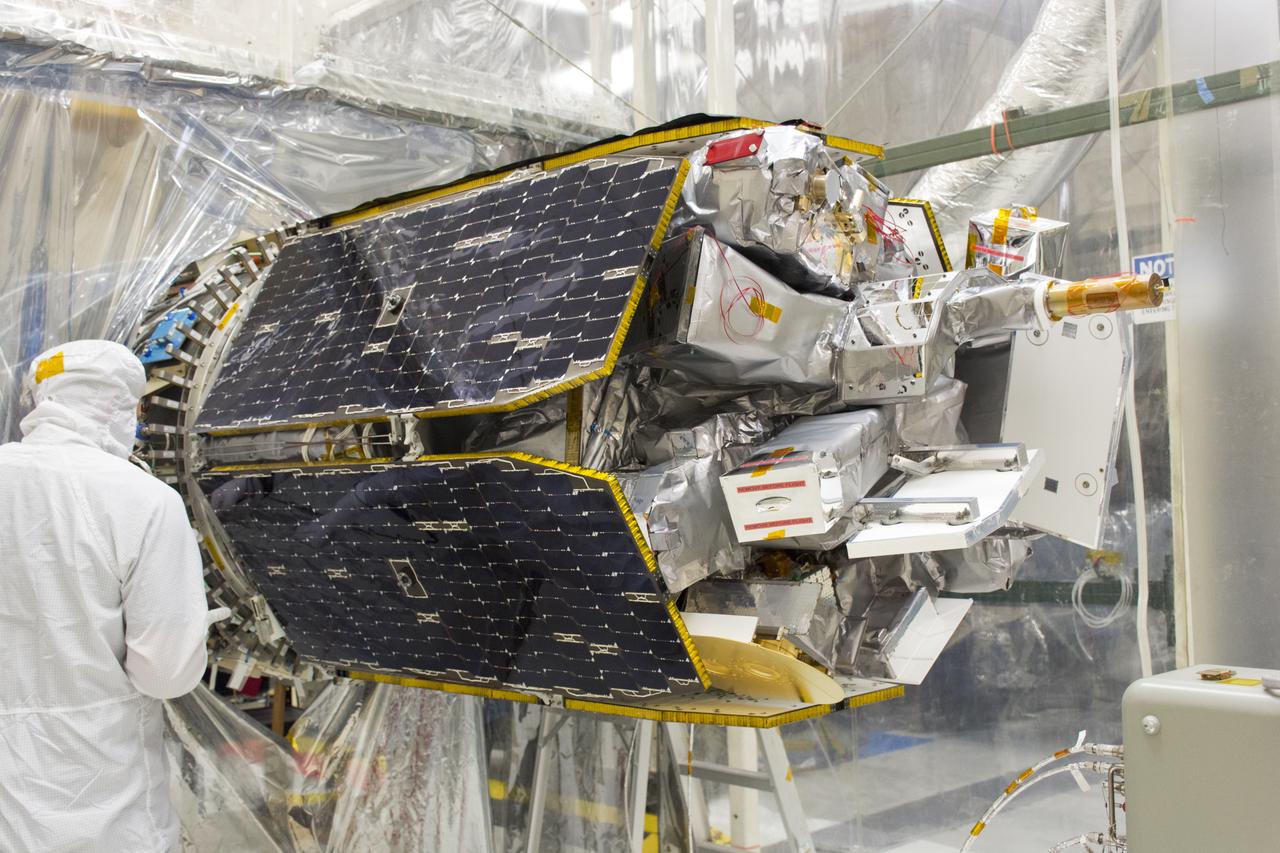
A technician assists with connections as NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is attached to the Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket May 14, 2018, inside a clean room in Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The explorer will launch on June 15, 2018, from Kwajalein Atoll in the Marshall Islands (June 14 in the continental United States) on the Pegasus XL rocket, which is attached to the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is attached to the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Sept. 10, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 9, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.
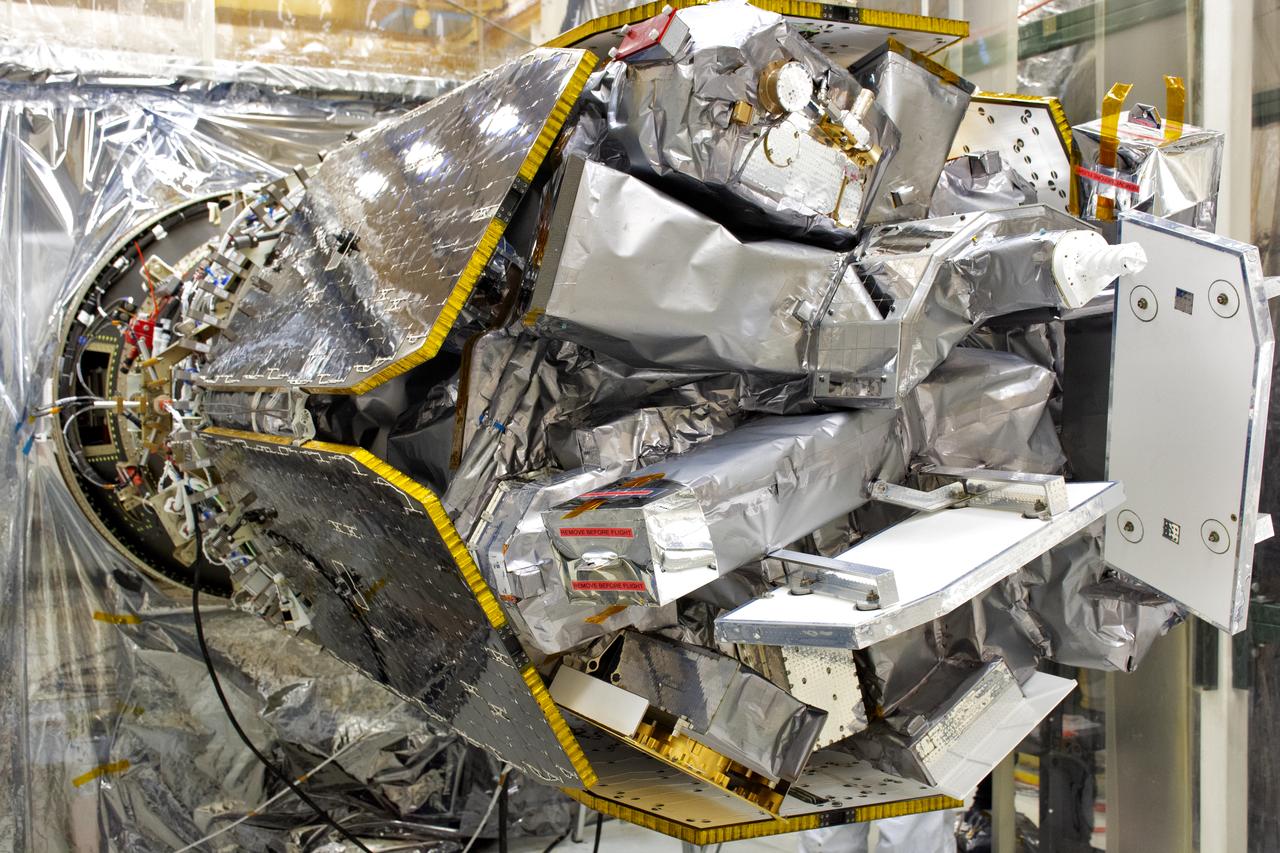

A stereographic view of NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) in a clean room at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Aug. 16, 2018. ICON will launch on a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL vehicle, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 26. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.

Technicians attach NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) to the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 10, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 9, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.

Technicians attach NASA’s Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) to the Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, on Sept. 10, 2019. The Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, will launch ICON from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Launch is scheduled for Oct. 9, 2019. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology and communications systems.

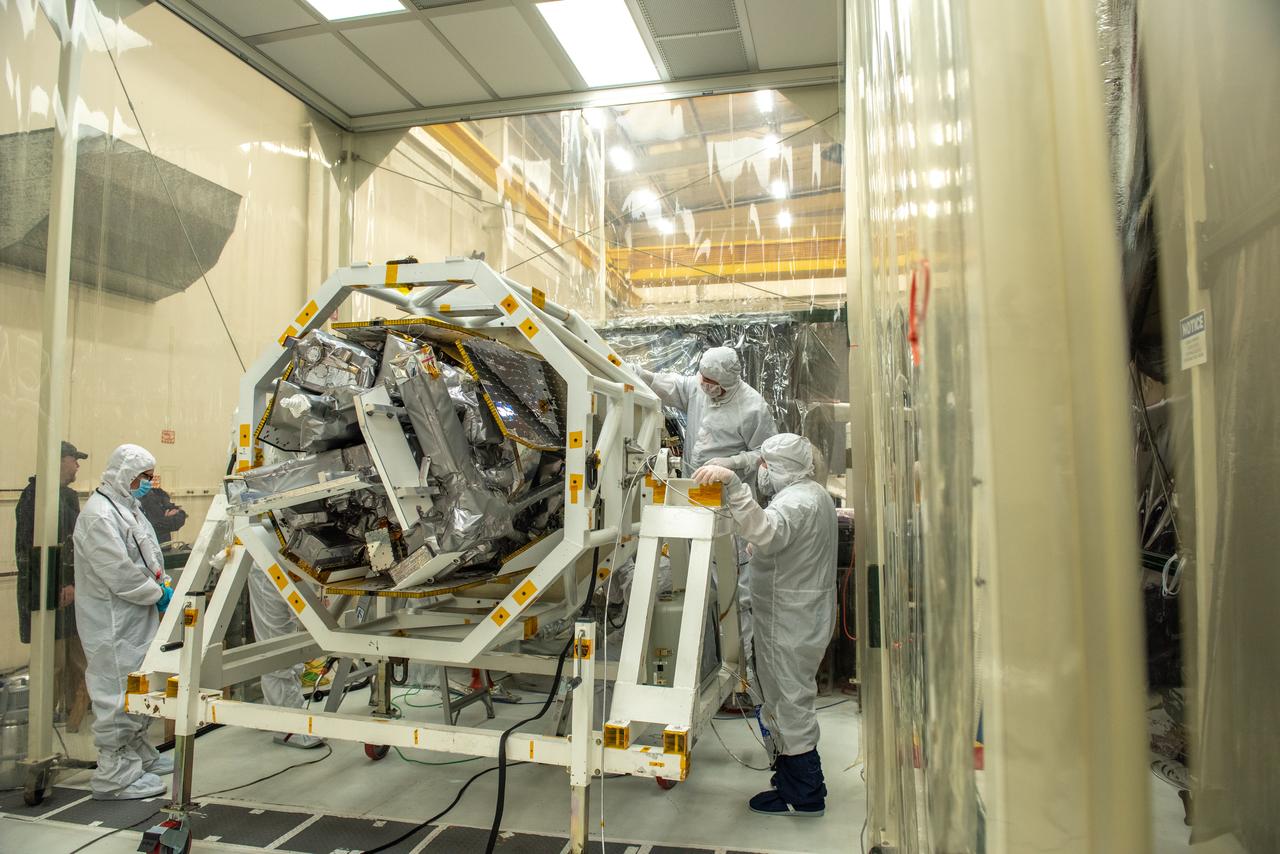
These images show NASA employees attending an event April 10, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.

These images show NASA employees attending an event April 10, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.

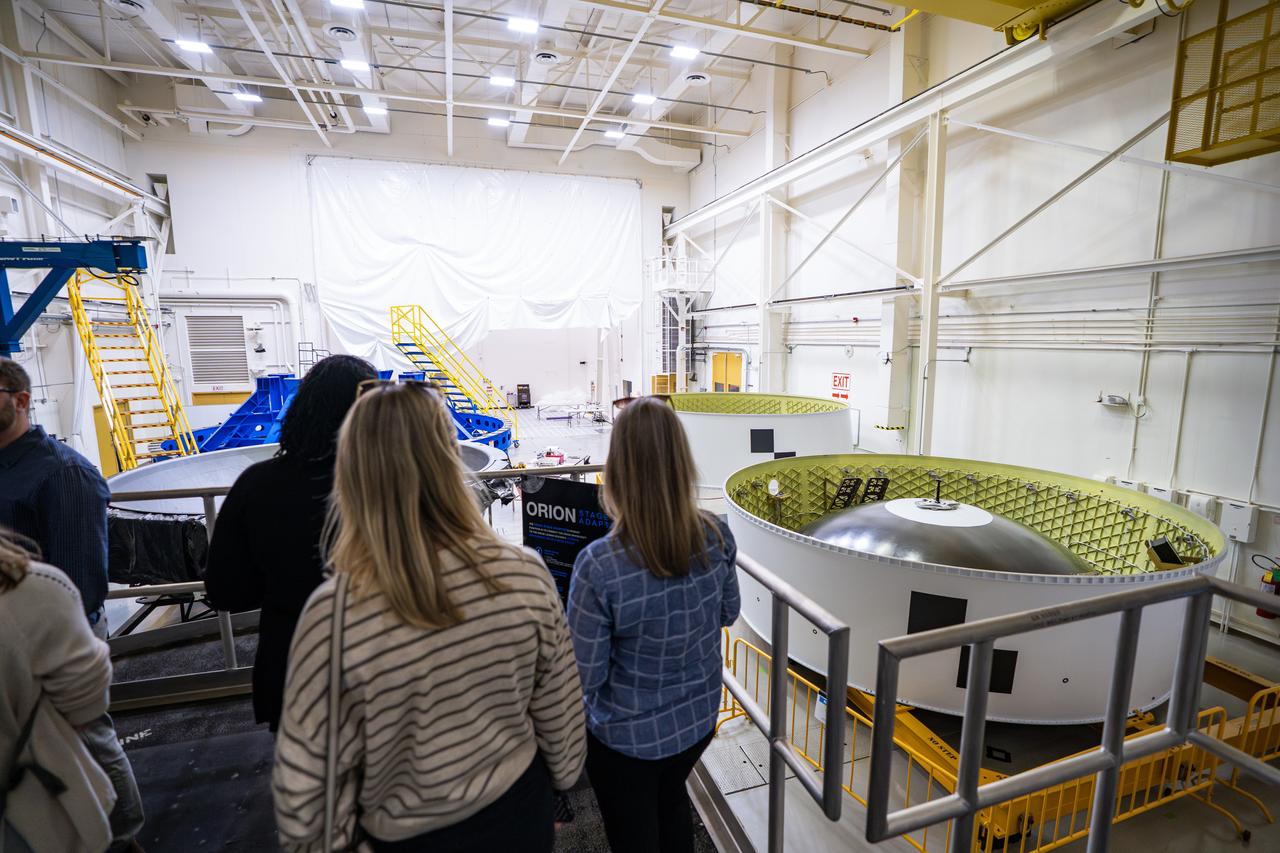
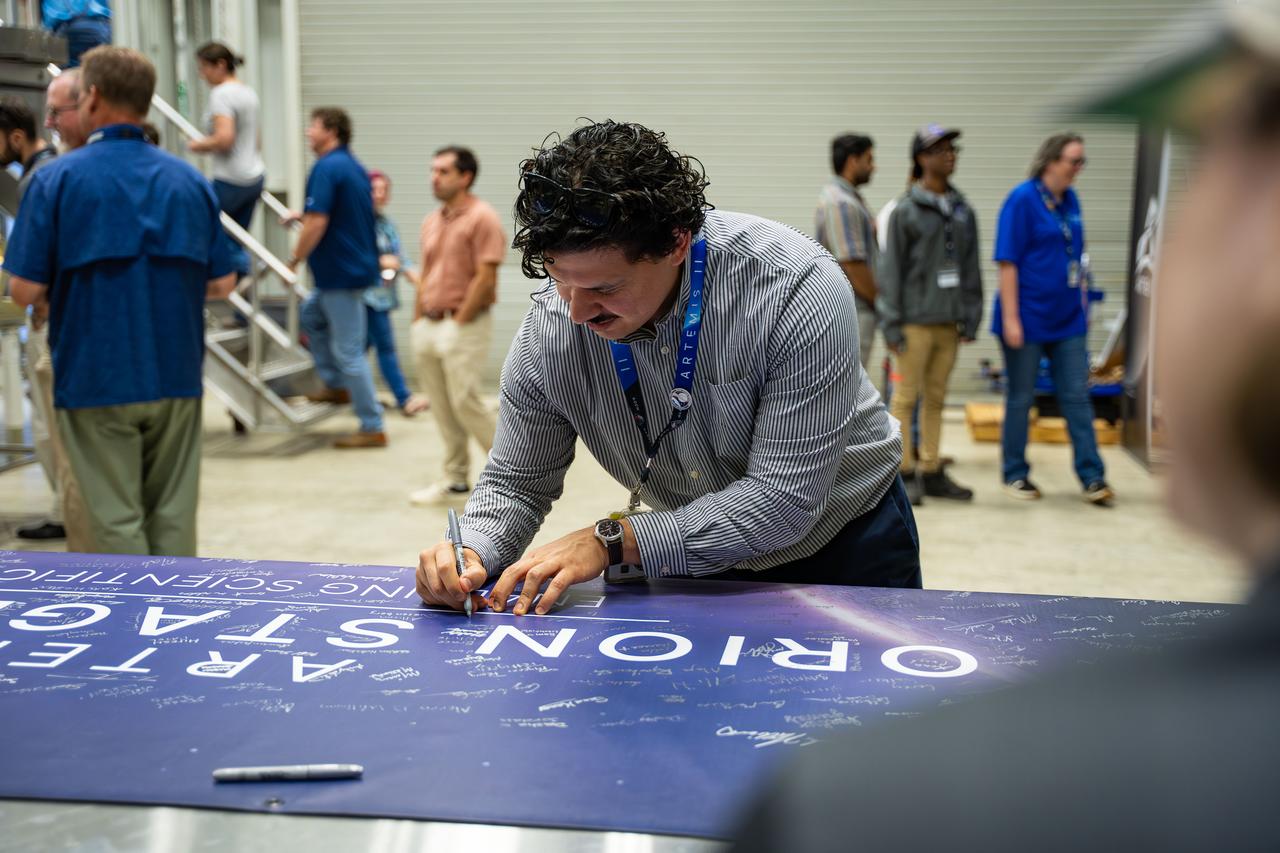
These images show NASA employees attending an event August 14, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
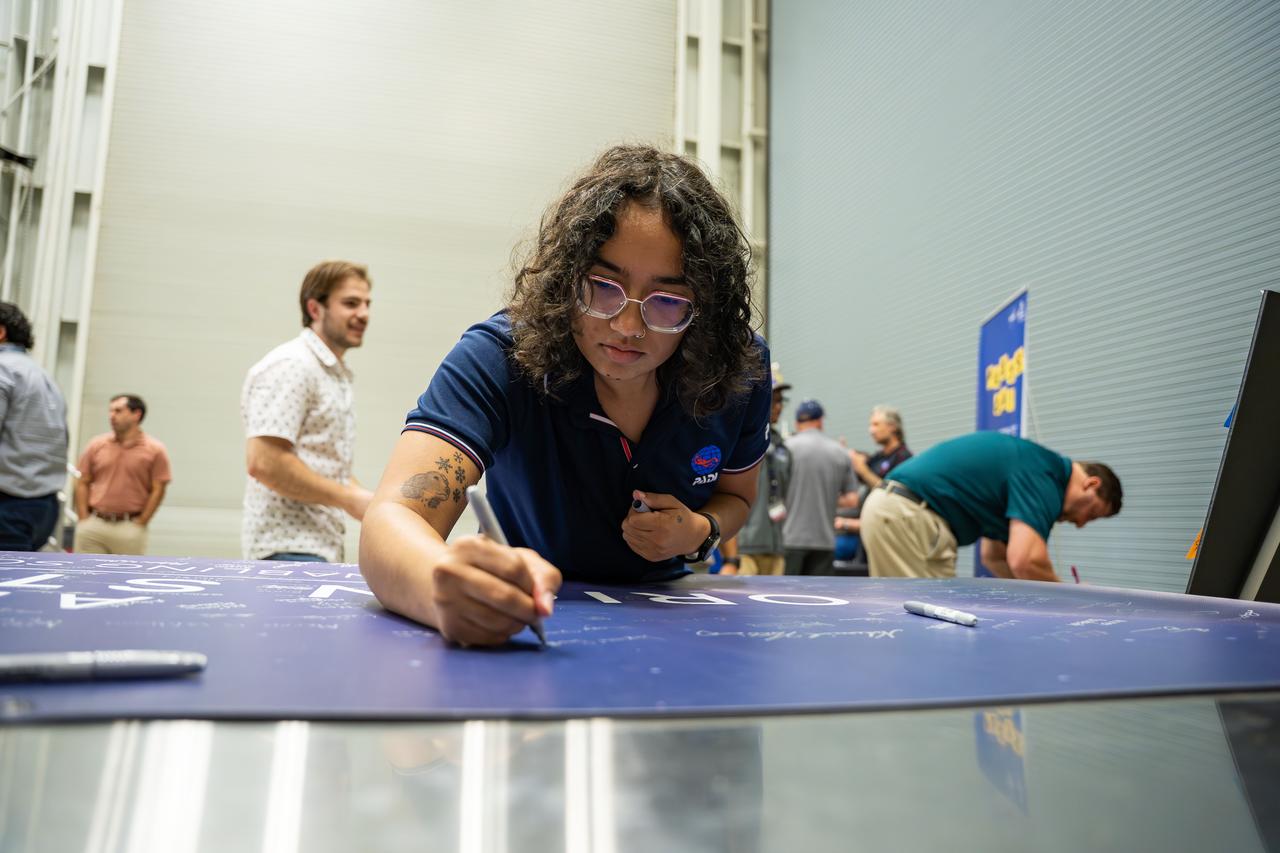

These images show NASA employees attending an event August 14, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.

These images show NASA employees attending an event August 14, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
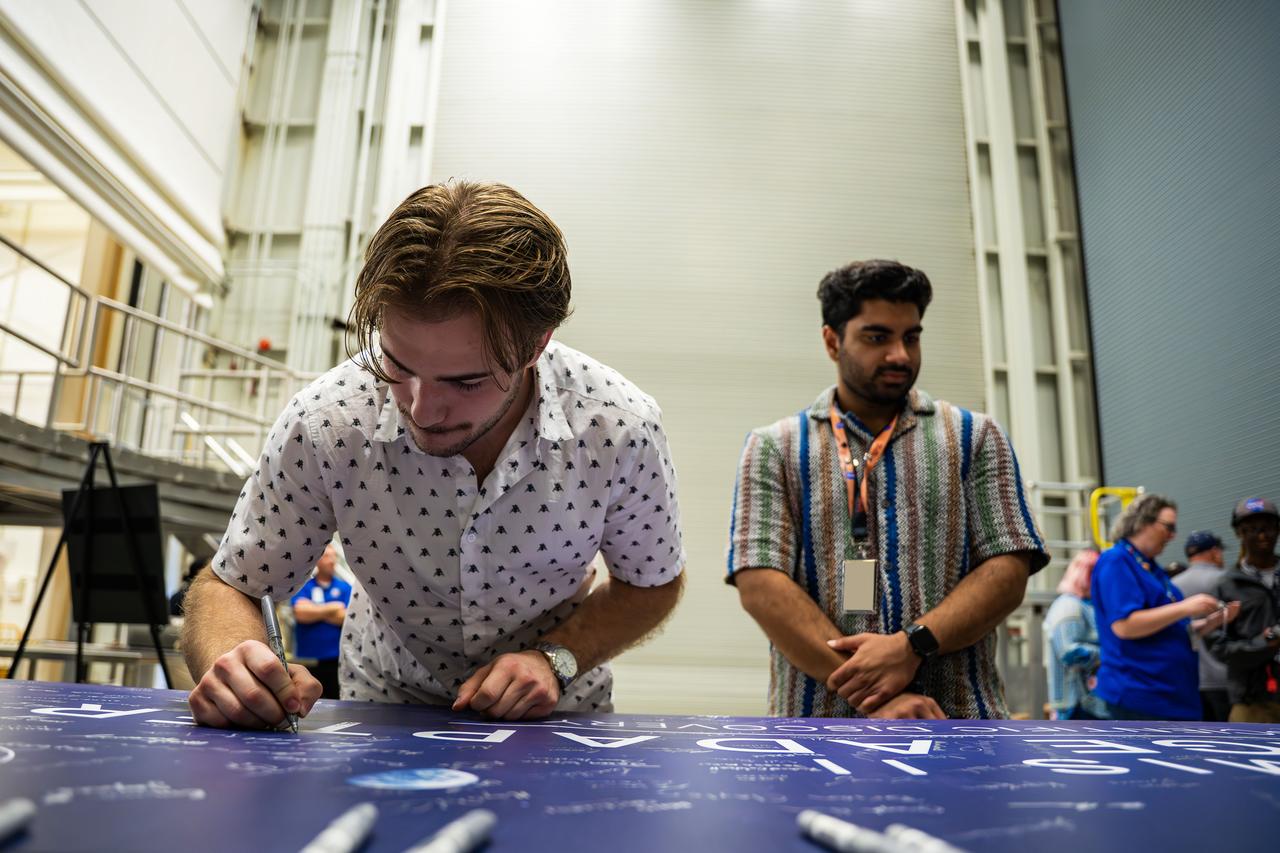

These images show NASA employees attending an event August 14, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
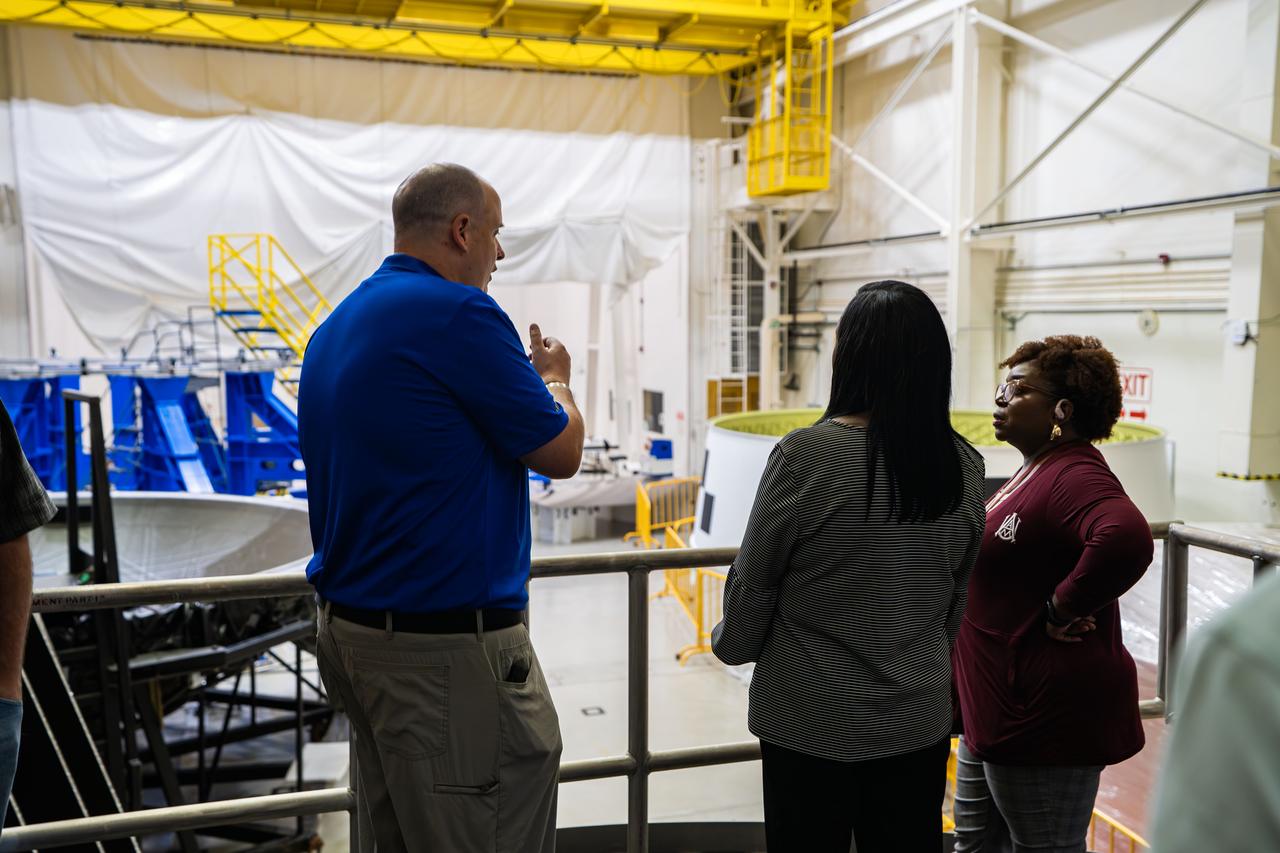

These images show NASA employees attending an event August 14, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
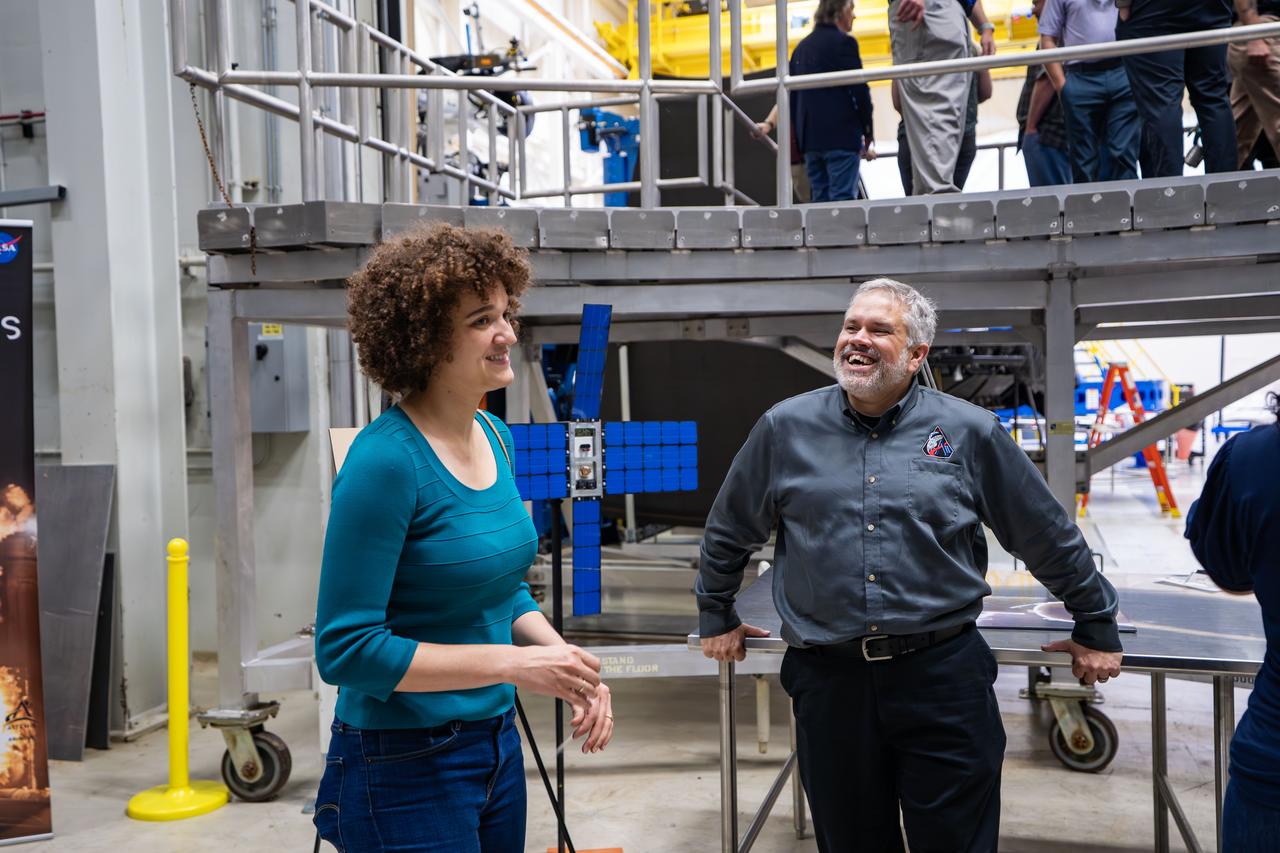

These images show NASA employees attending an event August 14, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
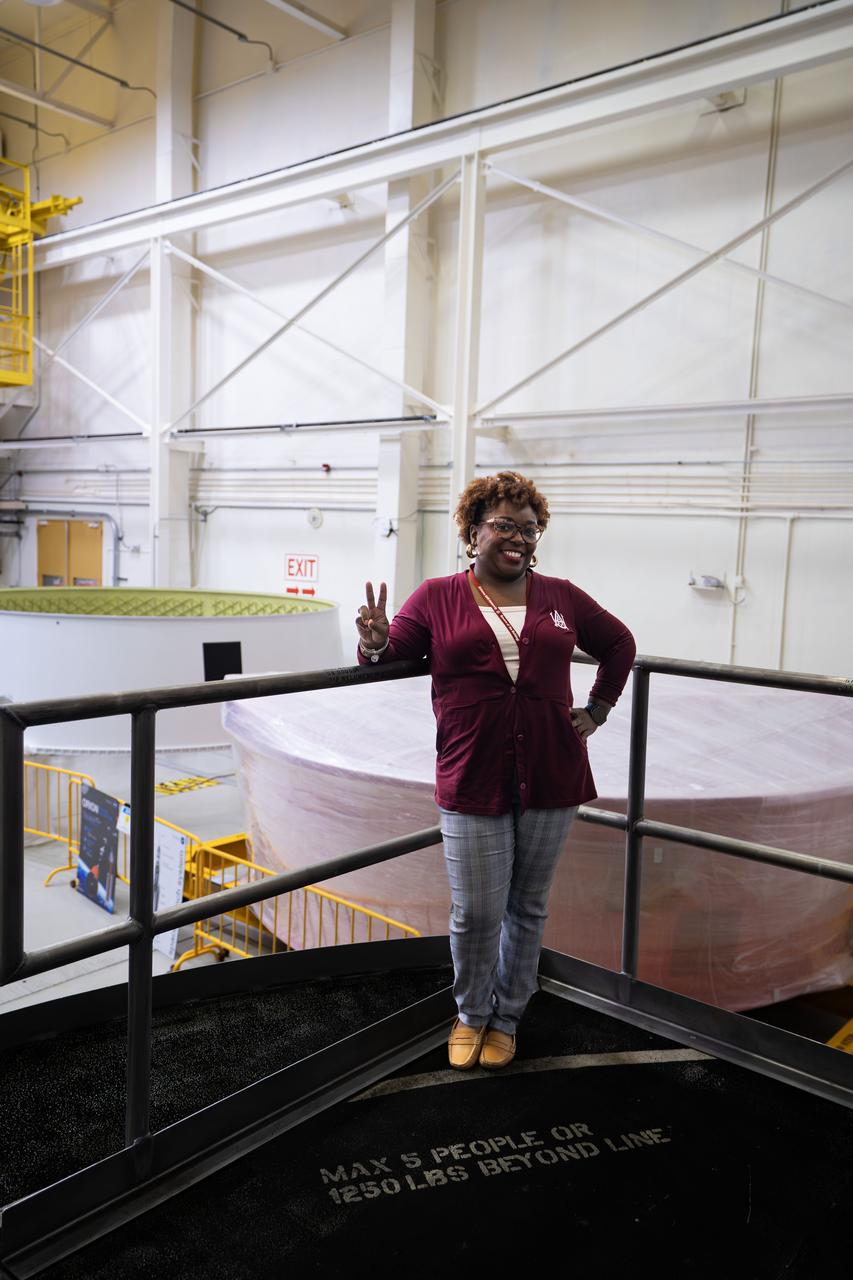

These images show NASA employees attending an event August 14, 2025, at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, to view the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II before it is transported to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured entirely at NASA Marshall, the adapter plays a crucial role in connecting the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft. This adapter is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
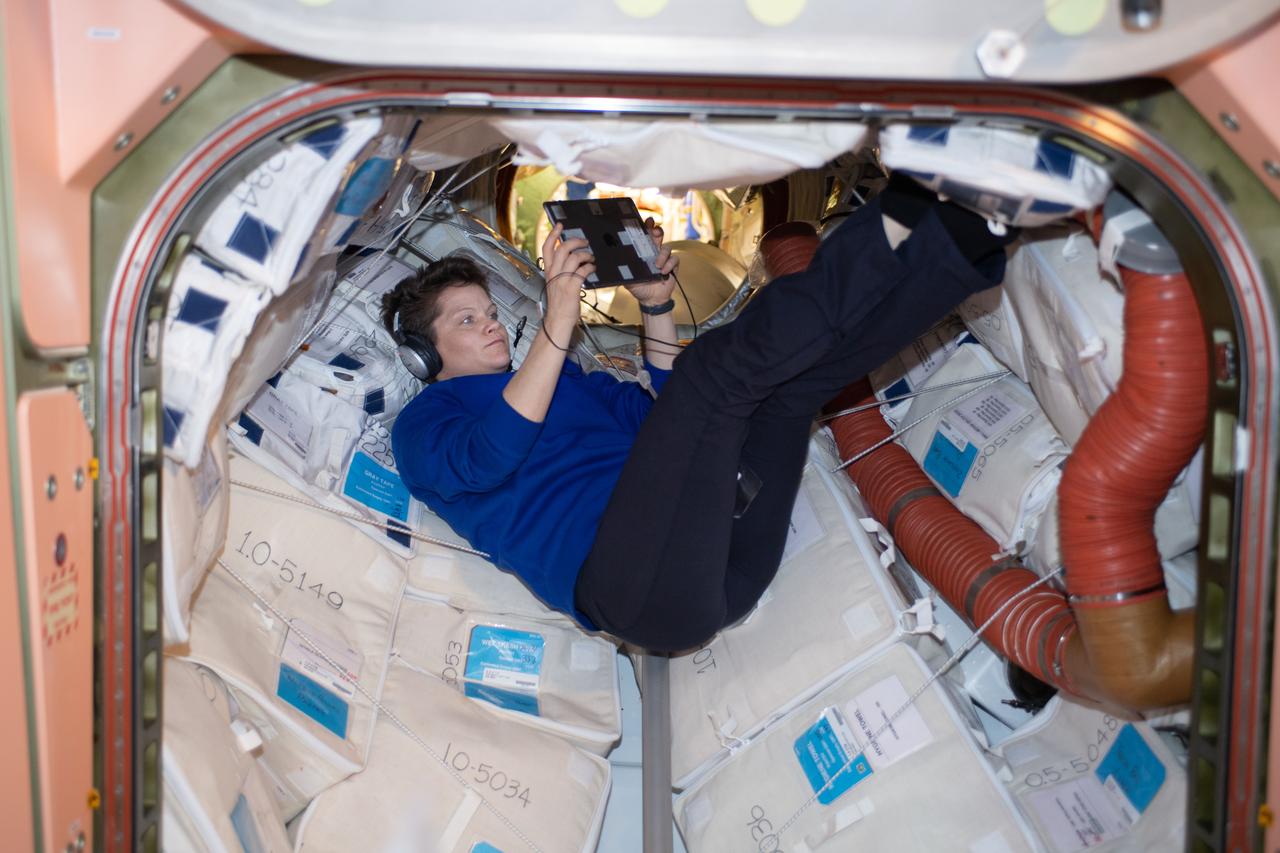

iss059e027379 (April 21, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Anne McClain relaxes with an electronic tablet on a Sunday morning inside the vestibule that connects the Unity module to the Zarya module.
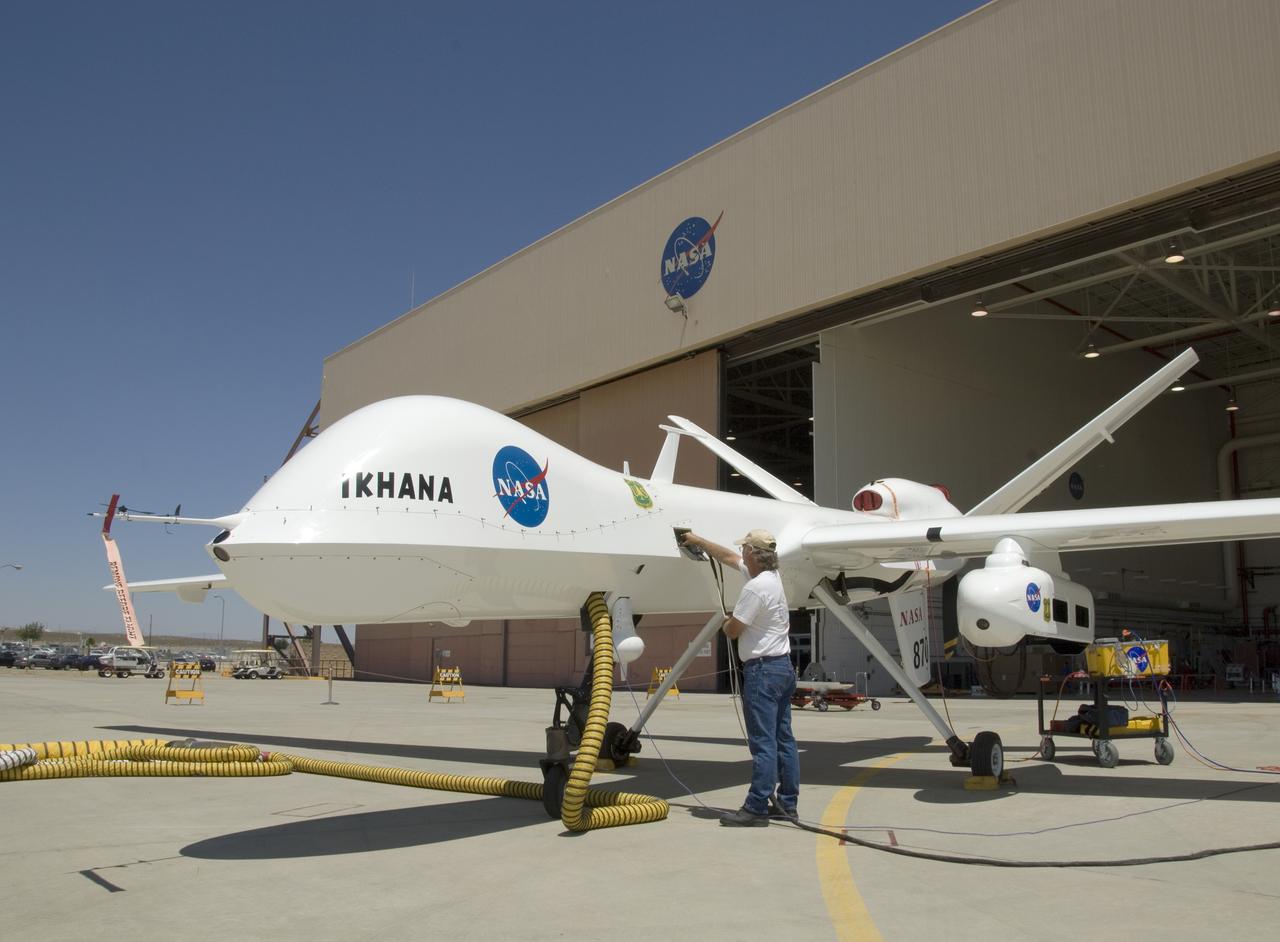

A ground crewman unplugs electrical connections during pre-flight checks of NASA's Ikhana research aircraft. Ikhana's payload pod is mounted on the left wing.
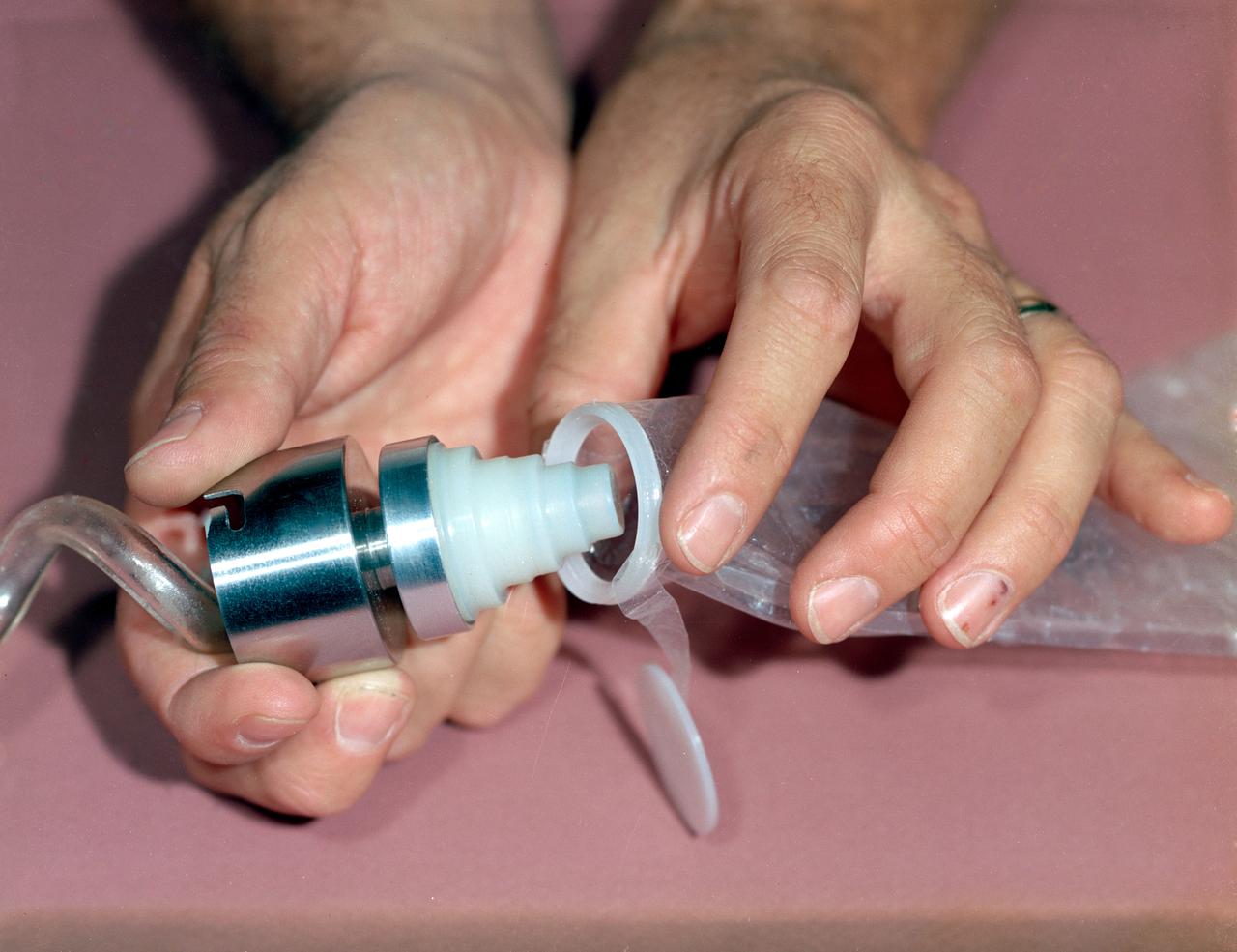
S62-08744 (1962) --- Mechanism for connecting water dispensor to dehydrated food containers to facilitate rehydration used by Mercury astronauts. Photo credit: NASA
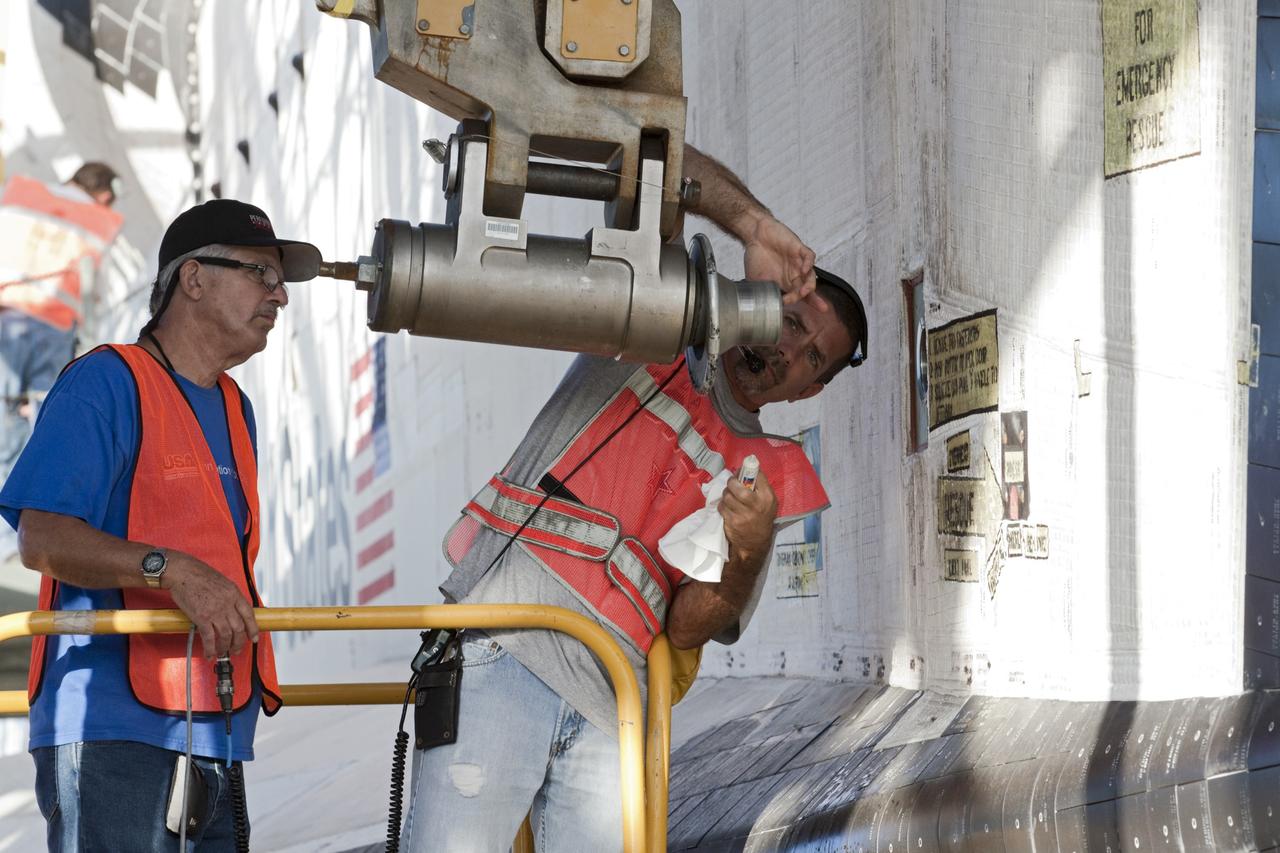

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Workers inspect an attachment point before it is connected to space shuttle Endeavour so the shuttle can be raised for connection to the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft, or SCA. The shuttle is inside the Mate-Demate Device, or MDD, at the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The SCA will carry Endeavour to Los Angeles where it will be placed on public display. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
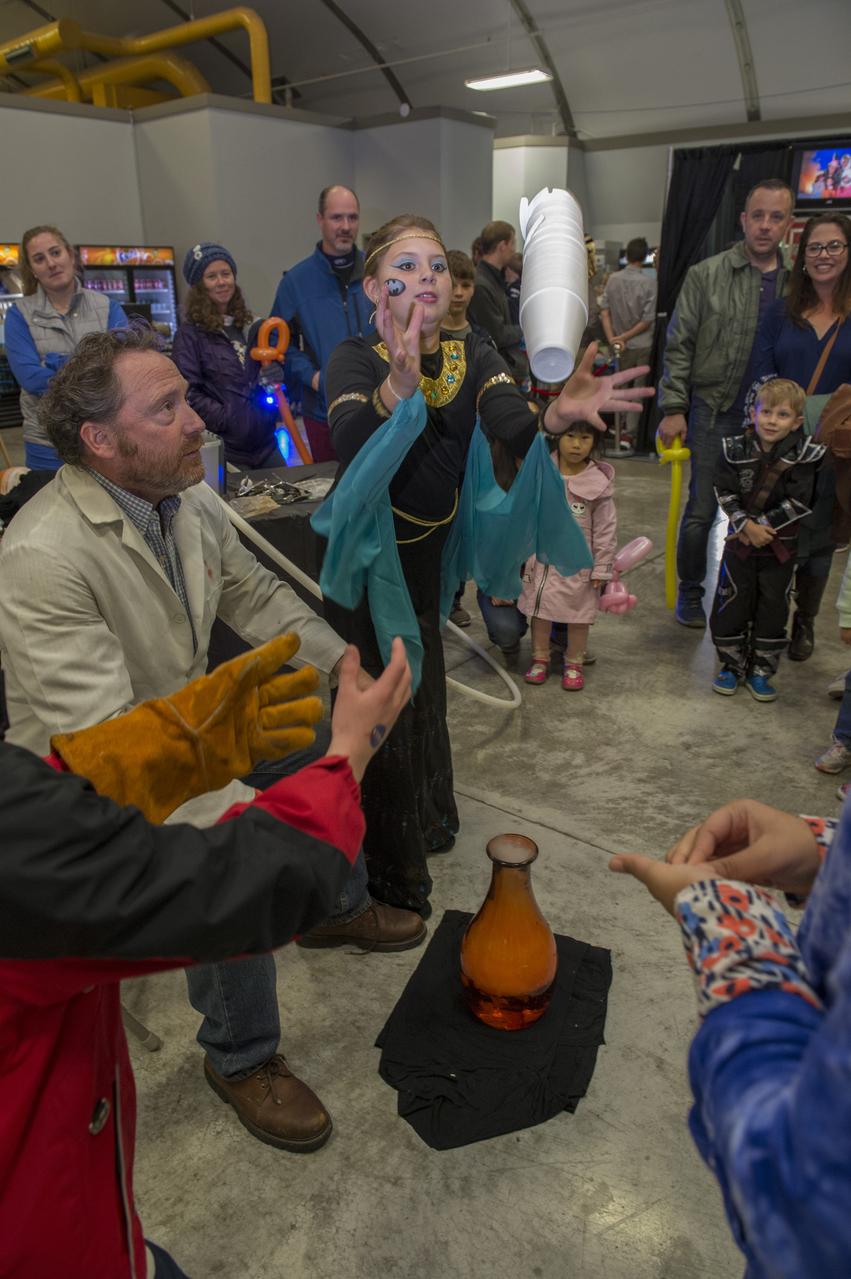

A volunteer assists an eager participant at International Observe the Moon Night Oct. 28 at the U.S. Space & Rocket Center. The event, hosted by the Planetary Missions Program at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, encourages observation and appreciation of the Moon and its connection to NASA planetary science and exploration, as well as our cultural and personal connections to it. Children attending the event had the opportunity to participate in planetary, science-based, hands-on activities
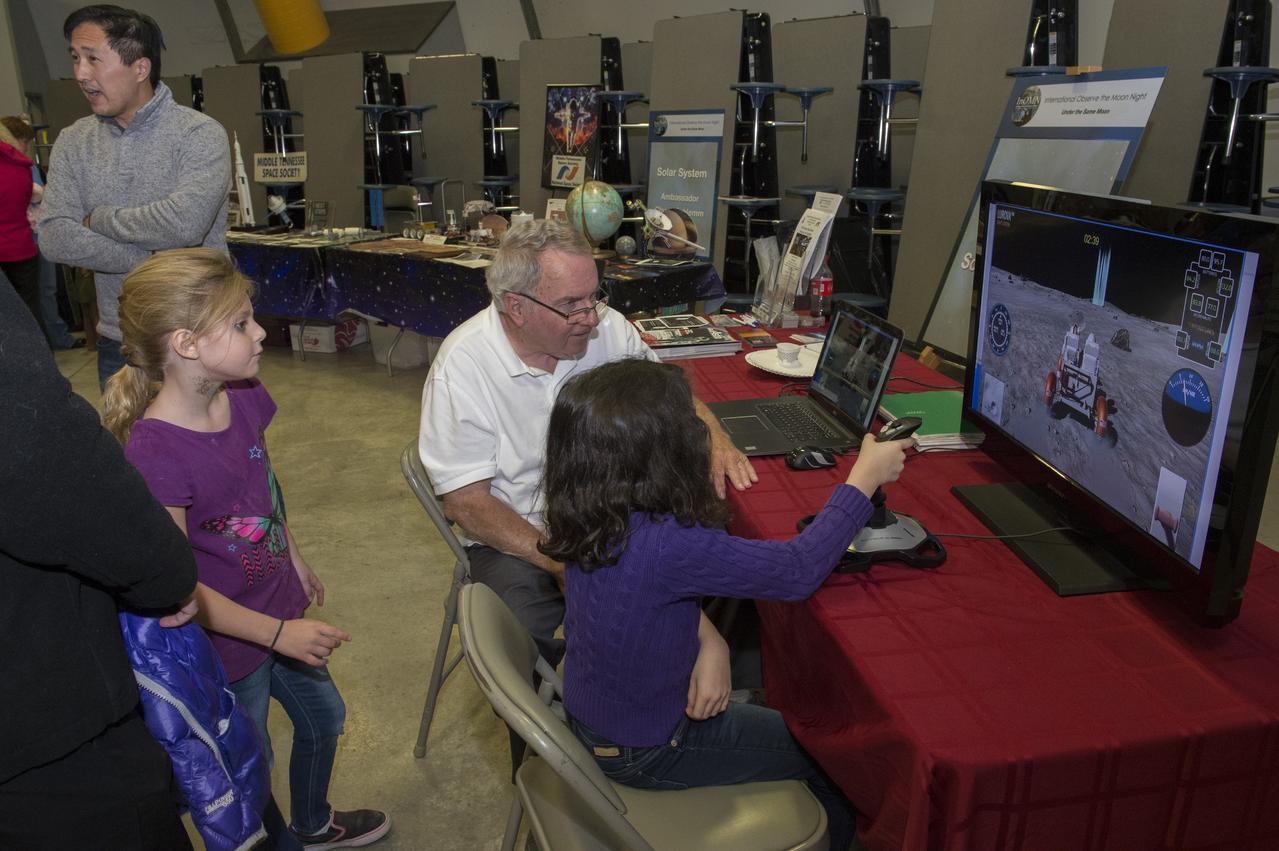

Marshall Space Flight Center retiree Ron Creel with young participant at LUROVA exhibit. The event, hosted by the Planetary Missions Program at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, encourages observation and appreciation of the Moon and its connection to NASA planetary science and exploration, as well as our cultural and personal connections to it. Children attending the event had the opportunity to participate in planetary, science-based, hands-on activities
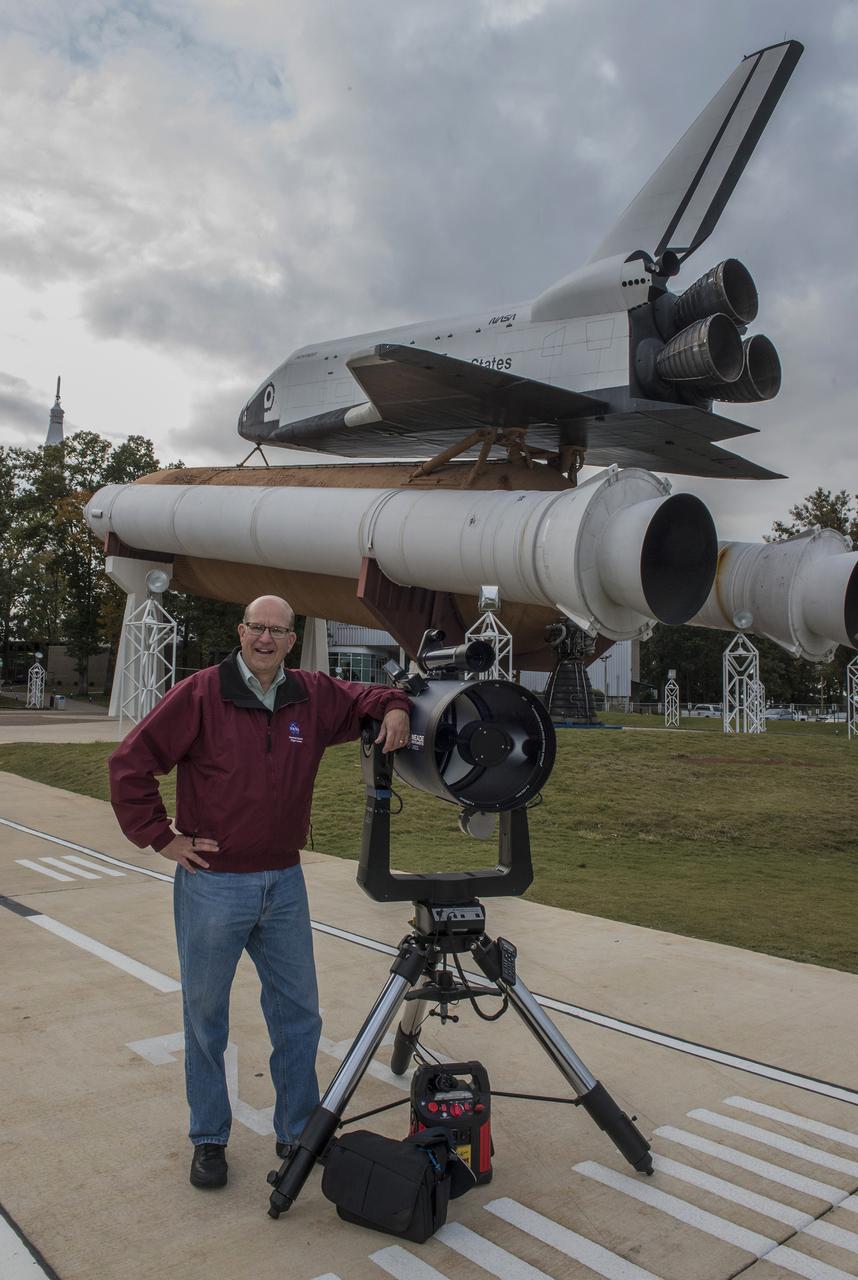

Volunteer Billy Hix with his telescope at International Observe the Moon Night. The event, hosted by the Planetary Missions Program at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, encourages observation and appreciation of the Moon and its connection to NASA planetary science and exploration, as well as our cultural and personal connections to it. Children attending the event had the opportunity to participate in planetary, science-based, hands-on activities
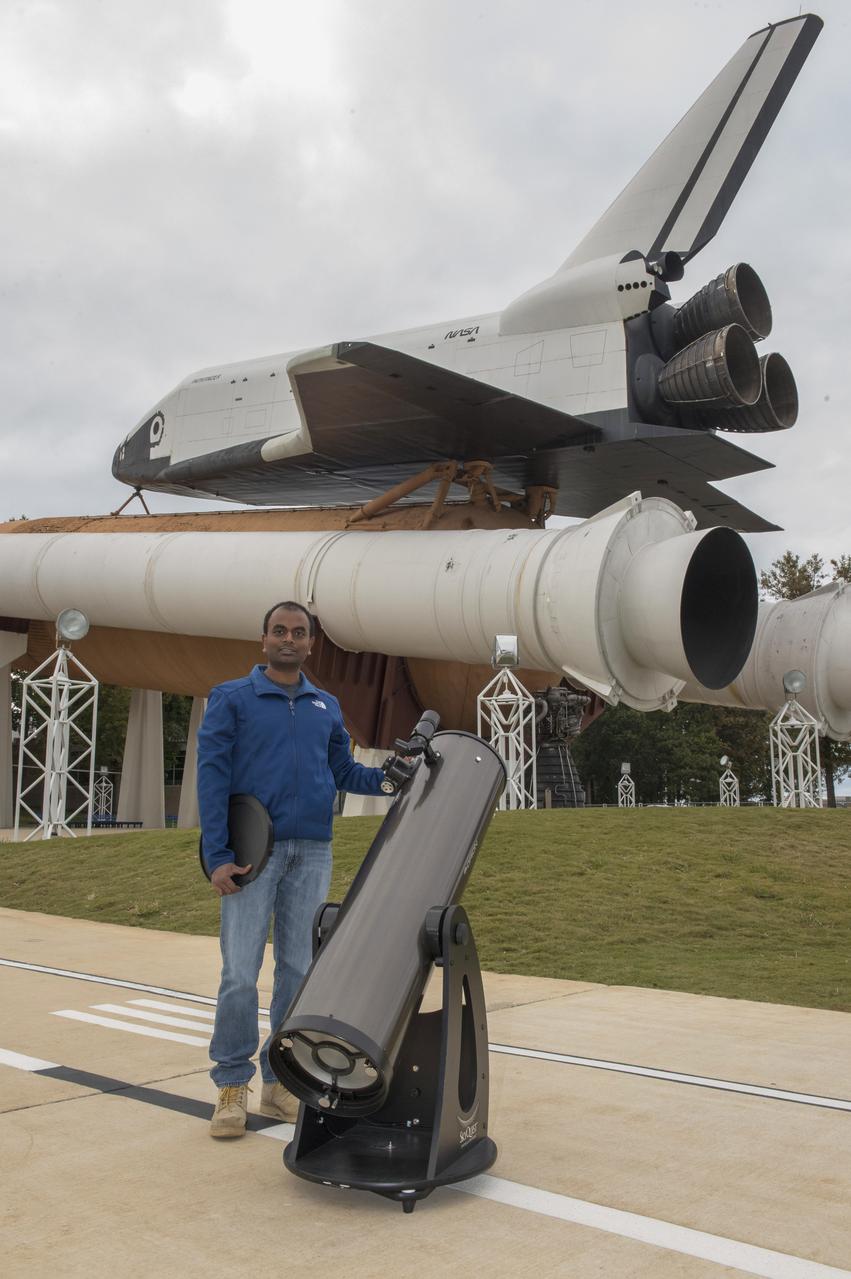

Marshall engineer Naveen Vetcha with his telescope. The event, hosted by the Planetary Missions Program at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, encourages observation and appreciation of the Moon and its connection to NASA planetary science and exploration, as well as our cultural and personal connections to it. Children attending the event had the opportunity to participate in planetary, science-based, hands-on activities
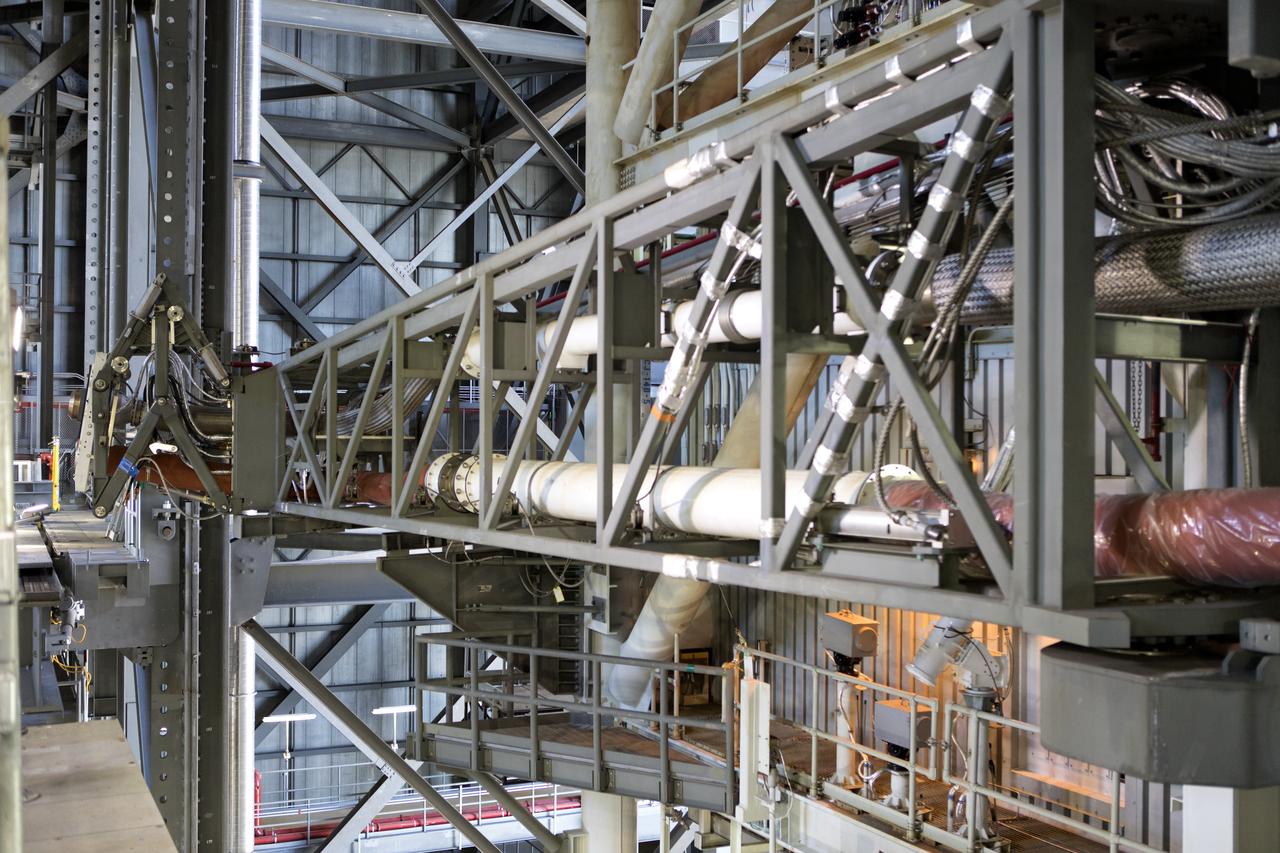

Preparations are underway to perform a preliminary swing test of the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Feb. 22, 2019, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. The Exploration Ground Systems Program is overseeing installation of the umbilicals.
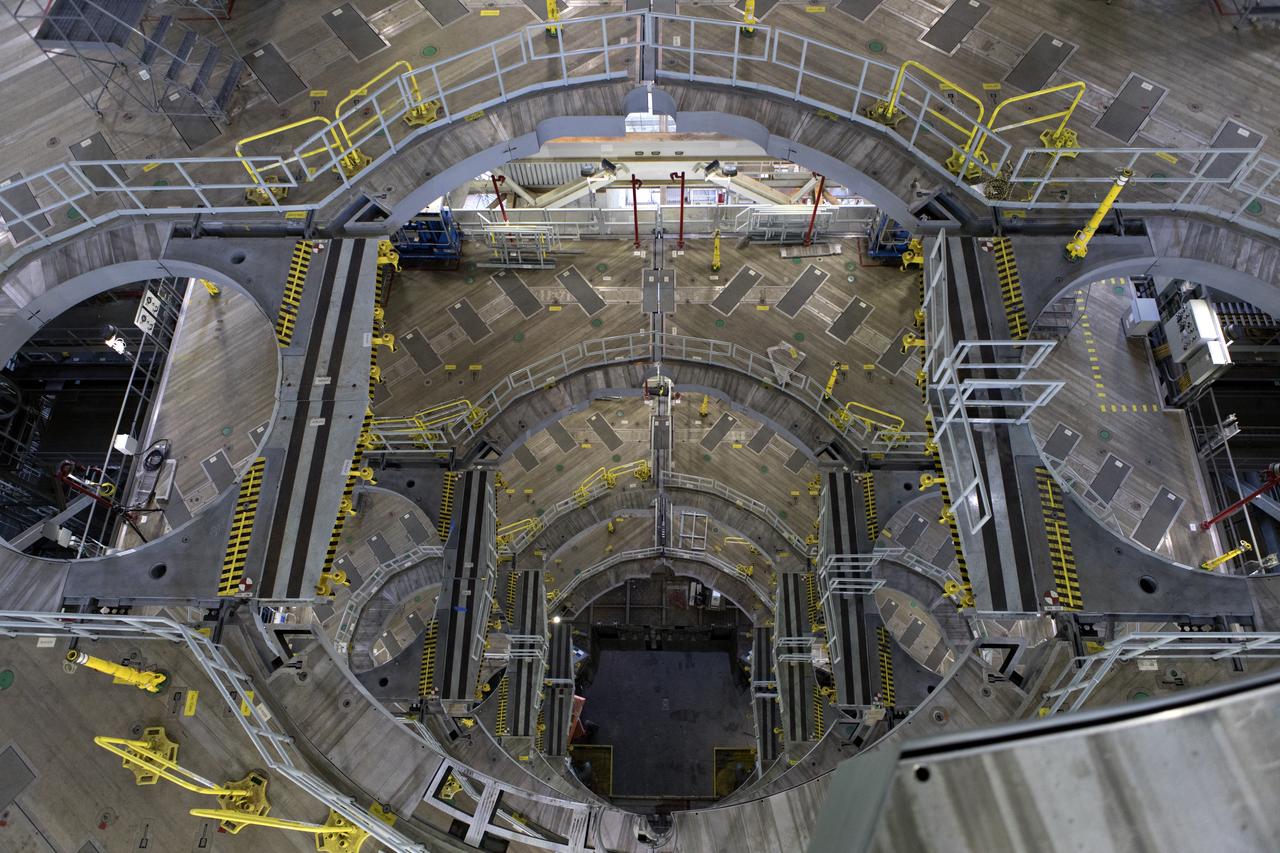

A view of the new work platforms in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Feb. 22, 2019, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Preparations are underway to perform an initial swing test of the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) on the mobile launcher. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy is conducting the swing test.
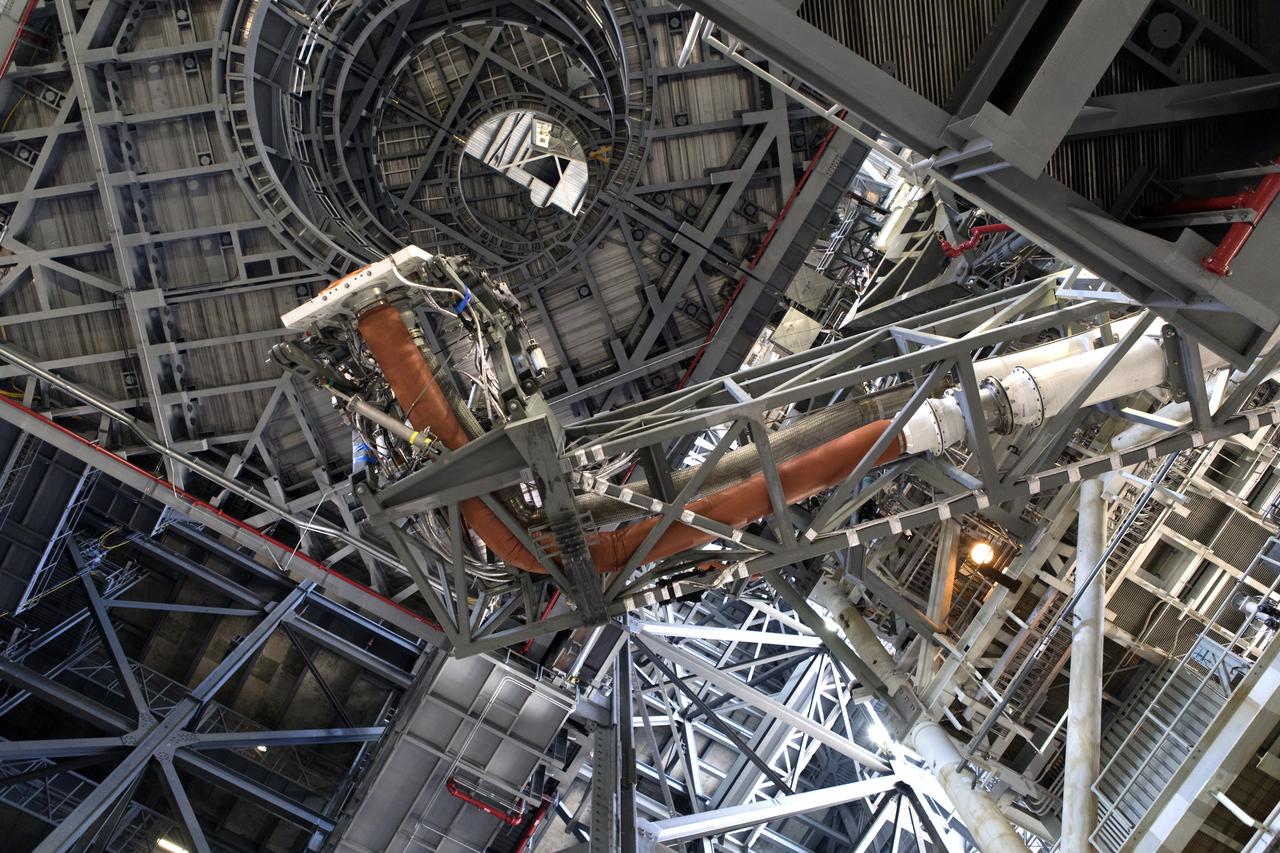

In this view looking up in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a preliminary swing test is being performed on the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) on Feb. 22, 2019. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy is conducting the swing test.
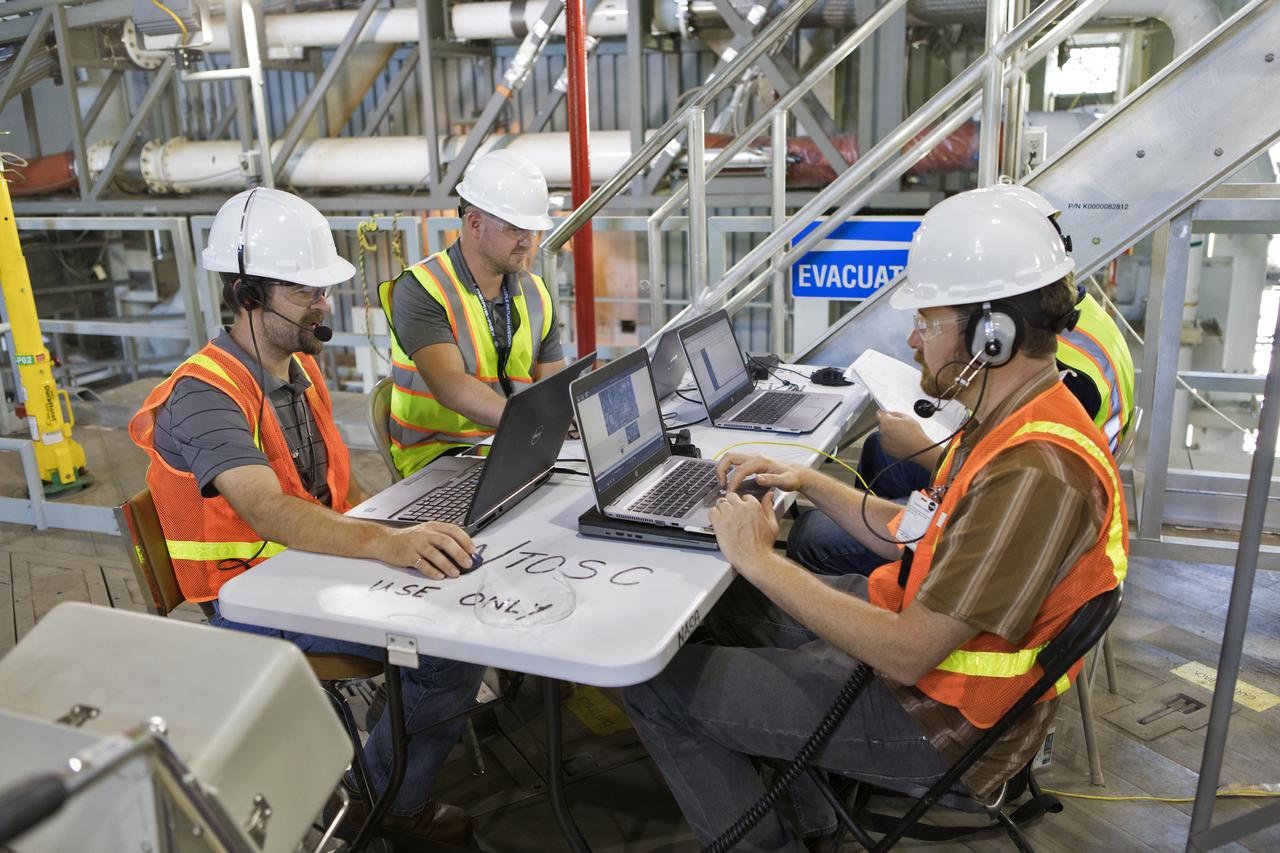

Technicians and engineers with Jacobs on the Test and Operations Support Contract, prepare for a swing test of the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) on the mobile launcher in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Feb. 22, 2019, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy is conducting the swing test.
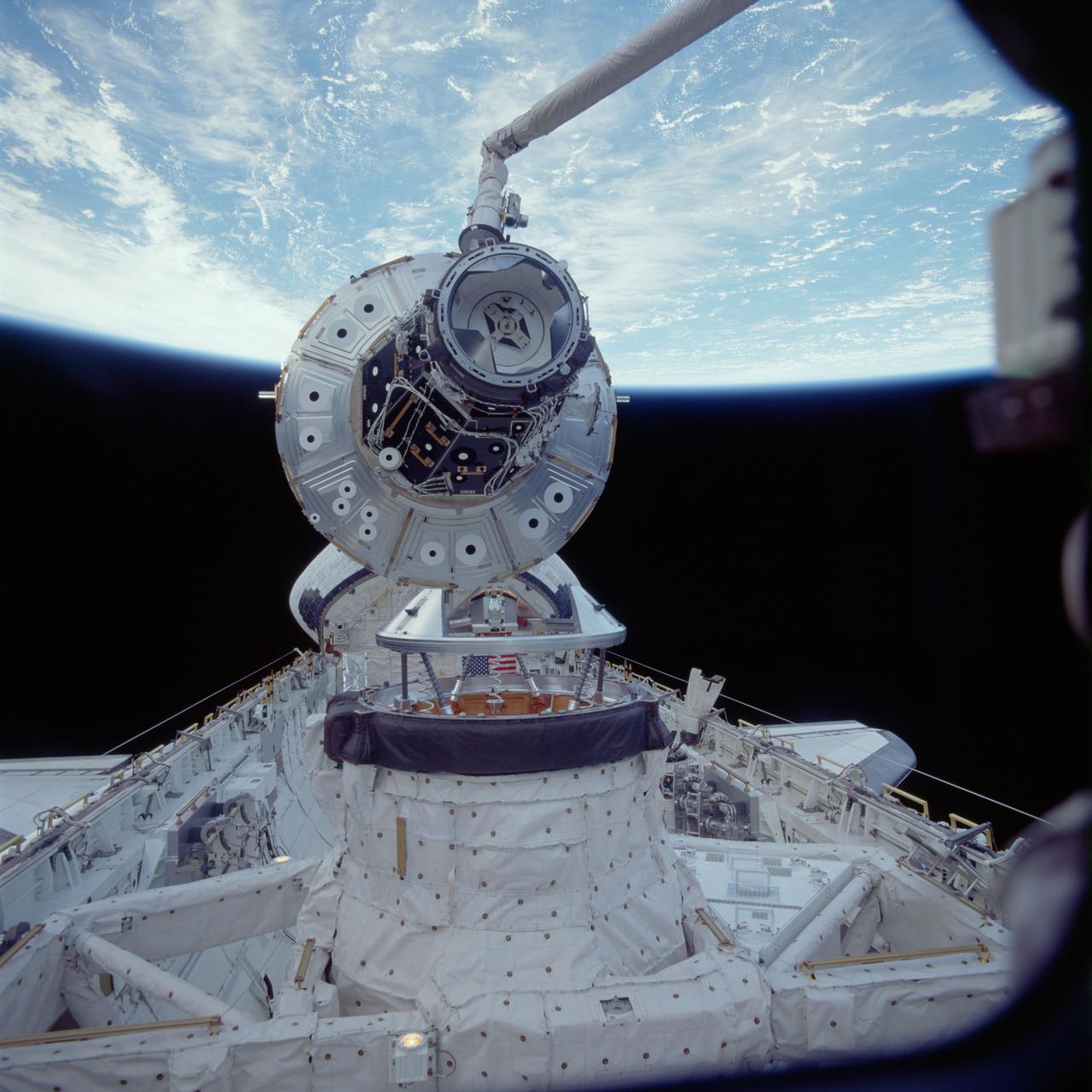

STS088-705-070 (5 Dec. 1998) --- One of the STS-88 astronauts aimed a 70mm camera through Endeavour's aft flight deck windows to record this Dec. 5 image of the Unity connecting module as it was being put into position to be mated to Endeavour's docking system in the cargo bay. The mating was the first link in a long chain of events that led up to the eventual deployment in Earth orbit of the connected Unity and Zarya modules later in the 11-day mission. Photo credit: NASA
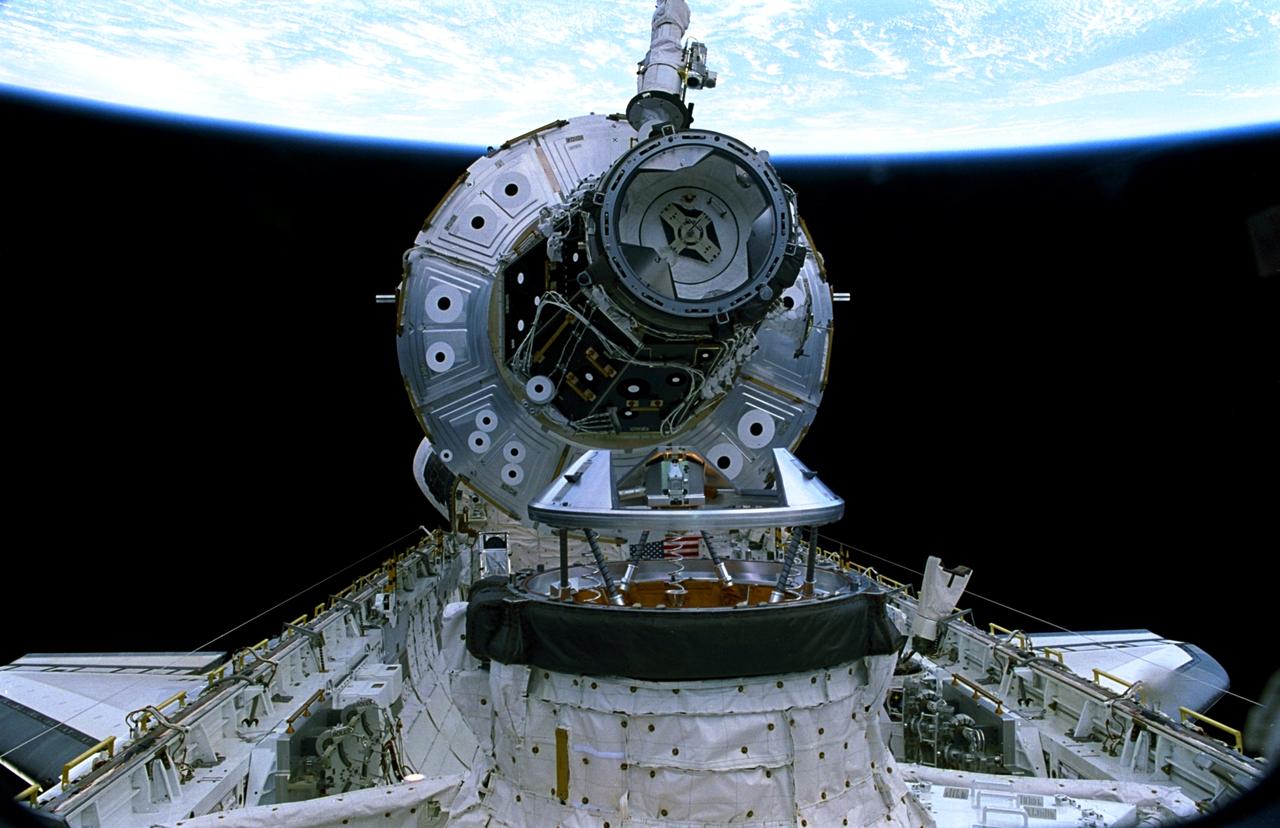
STS088-335-017 (5 Dec. 1998) --- One of the STS-88 astronauts aimed a 35mm camera through Endeavour's aft flight deck windows to record this Dec. 5 image of the Unity connecting module as it was being unberthed in the cargo bay. The berthing and mating process constituted the first link in a long chain of events that led up to the eventual deployment in Earth orbit of the connected Unity and Zarya modules later in the 11-day mission. Photo credit: NASA
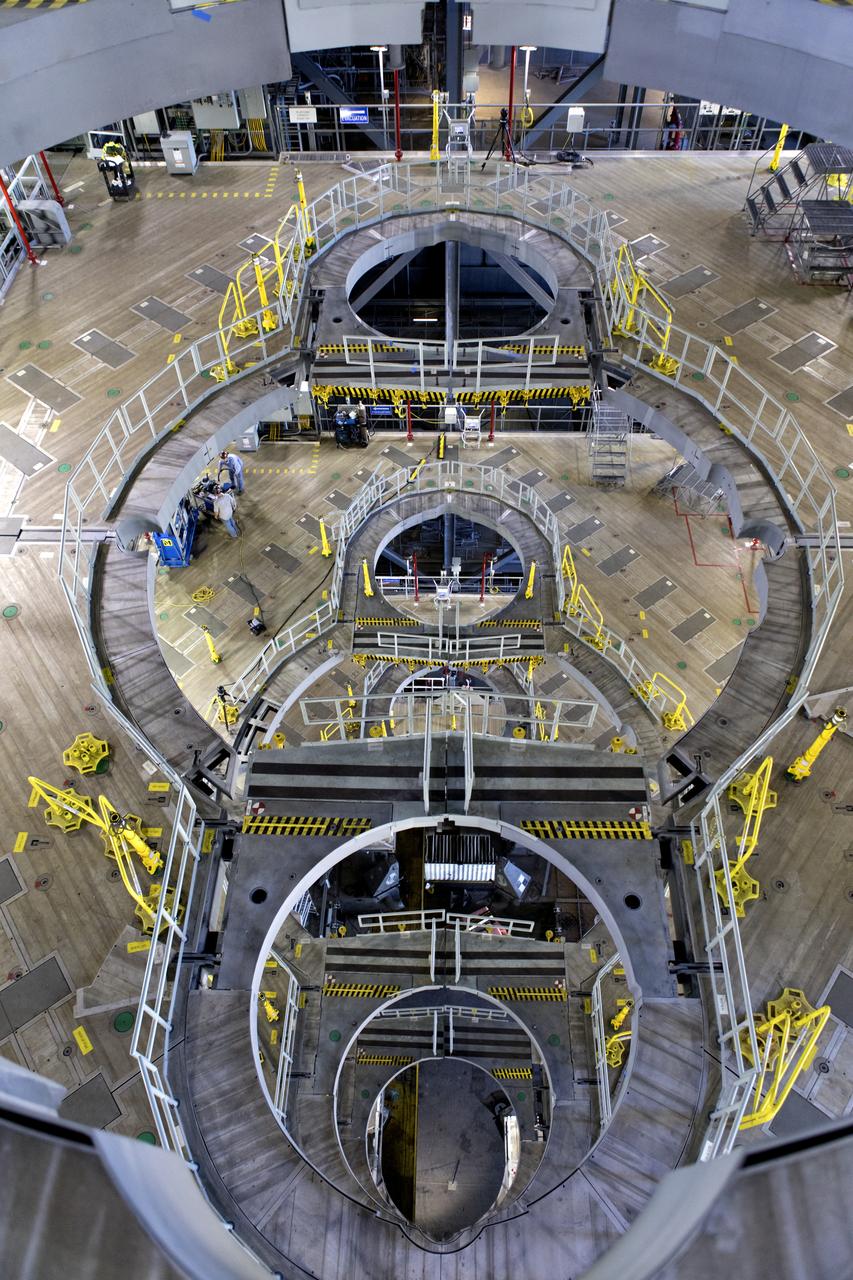

A view from above of new work platforms in High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building on Feb. 22, 2019, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Preparations are underway to perform an initial swing test of the Core Stage Inter-tank Umbilical (CSITU) on the mobile launcher. The CSITU is a swing-arm umbilical that will connect to the Space Launch System core stage inter-tank. It will provide conditioned air, pressurized gases and power and data connection to the core stage. Exploration Ground Systems at Kennedy is conducting the swing test.
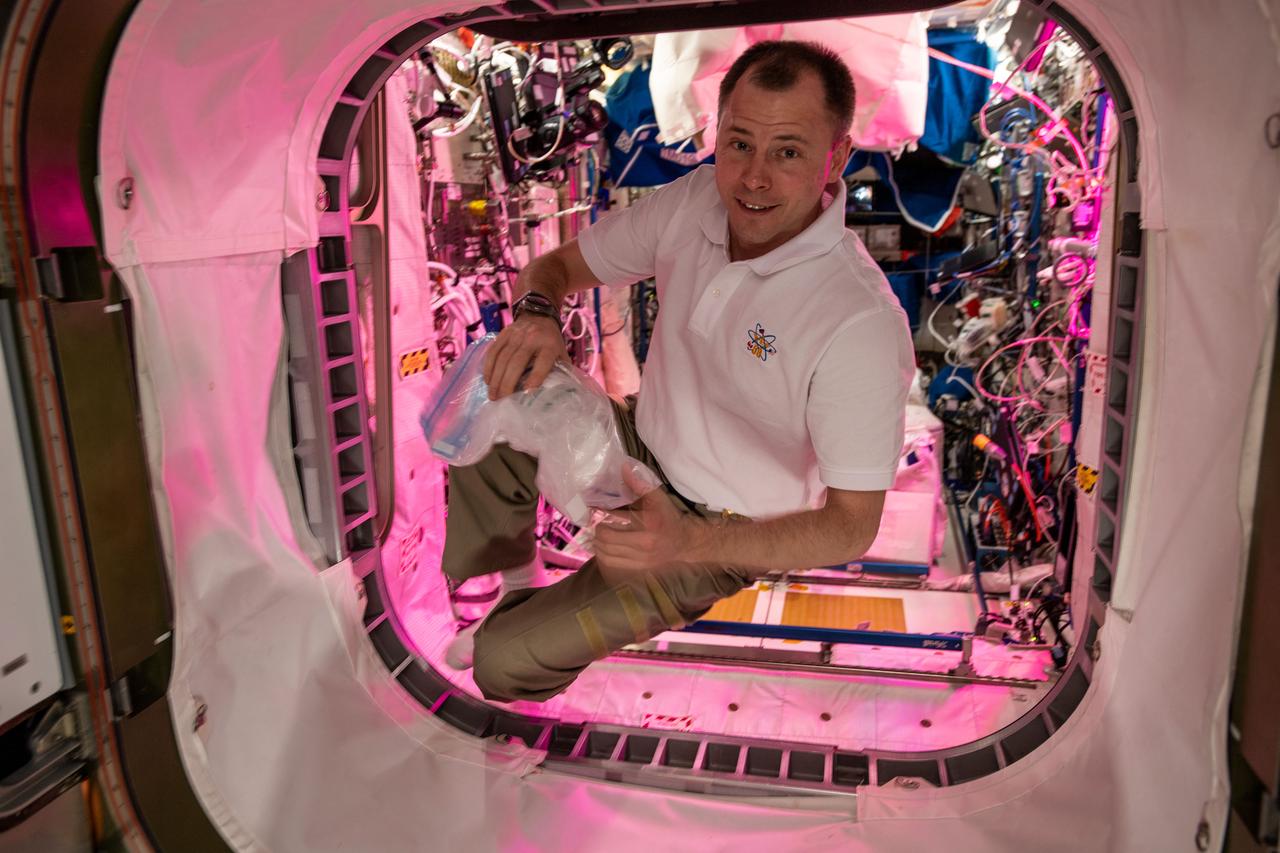

iss059e078446 (May 28, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Nick Hague floats inside the vestibule that connects the European Space Agency's Columbus laboratory module with NASA's Harmony module.
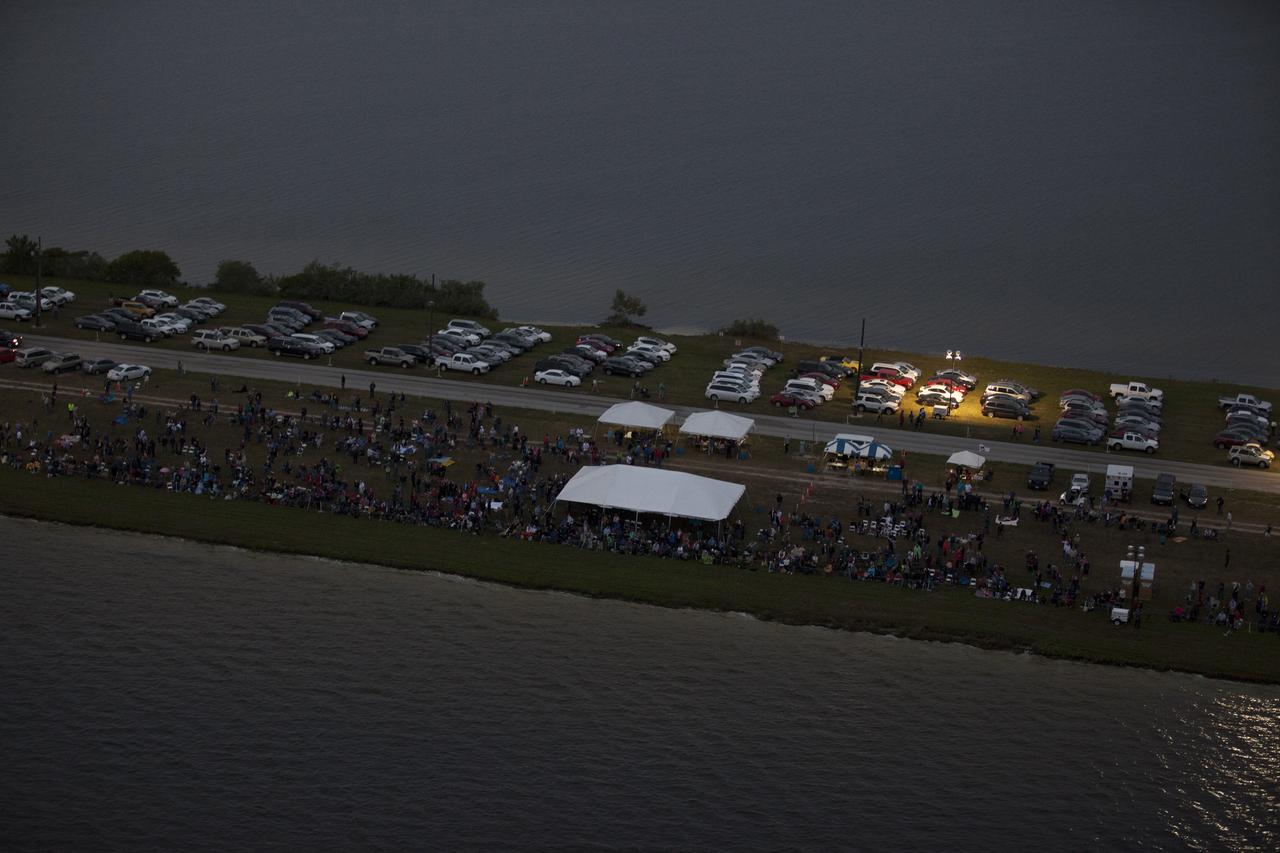

This helicopter view of the NASA Causeway connecting NASA's Kennedy Space Center with Cape Canaveral Air Force Staton shows the thousands of vehicles parked where guests gather to see the launch of the Orion Flight Test.

The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU), at left, is lowered for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. In view at right is the TSMU that will provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.

VANDENBERG AFB - Orbital Sciences engineers connect the payload fairing over NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin
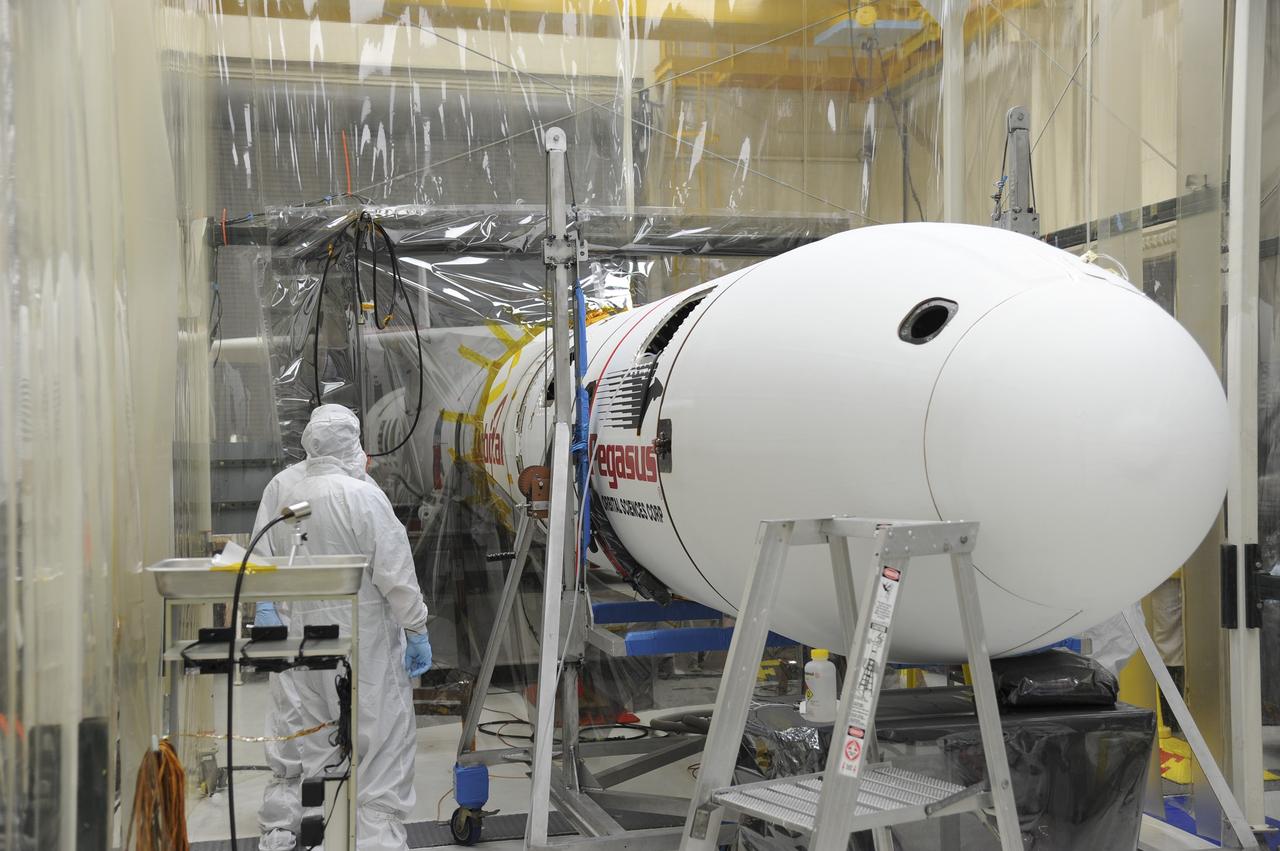

VANDENBERG AFB – Orbital Sciences engineers monitor the connection of the payload fairing over NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin
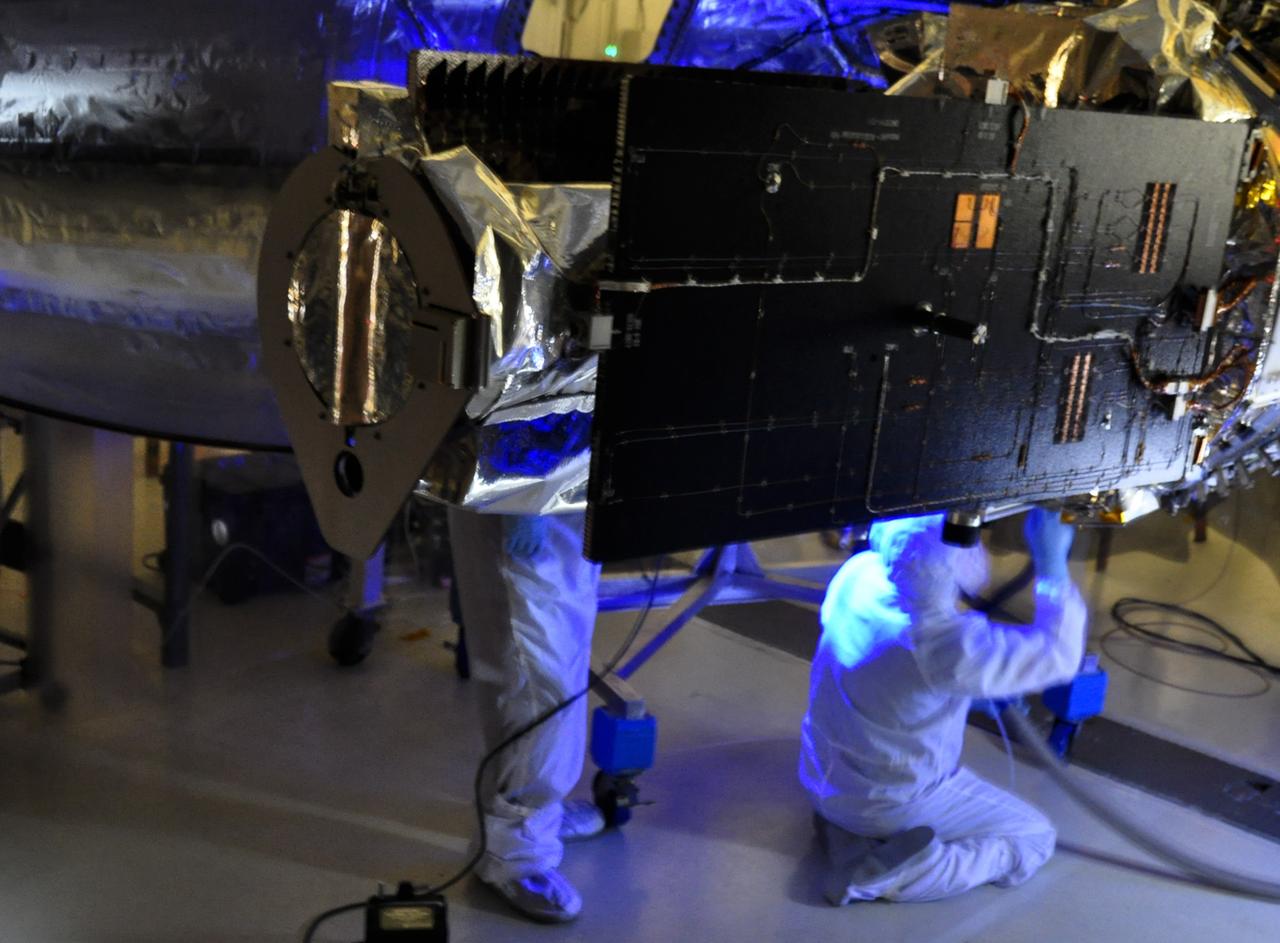

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers conduct inspections on NASA's IRIS spacecraft with blacklights before the payload fairing before it is connected. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
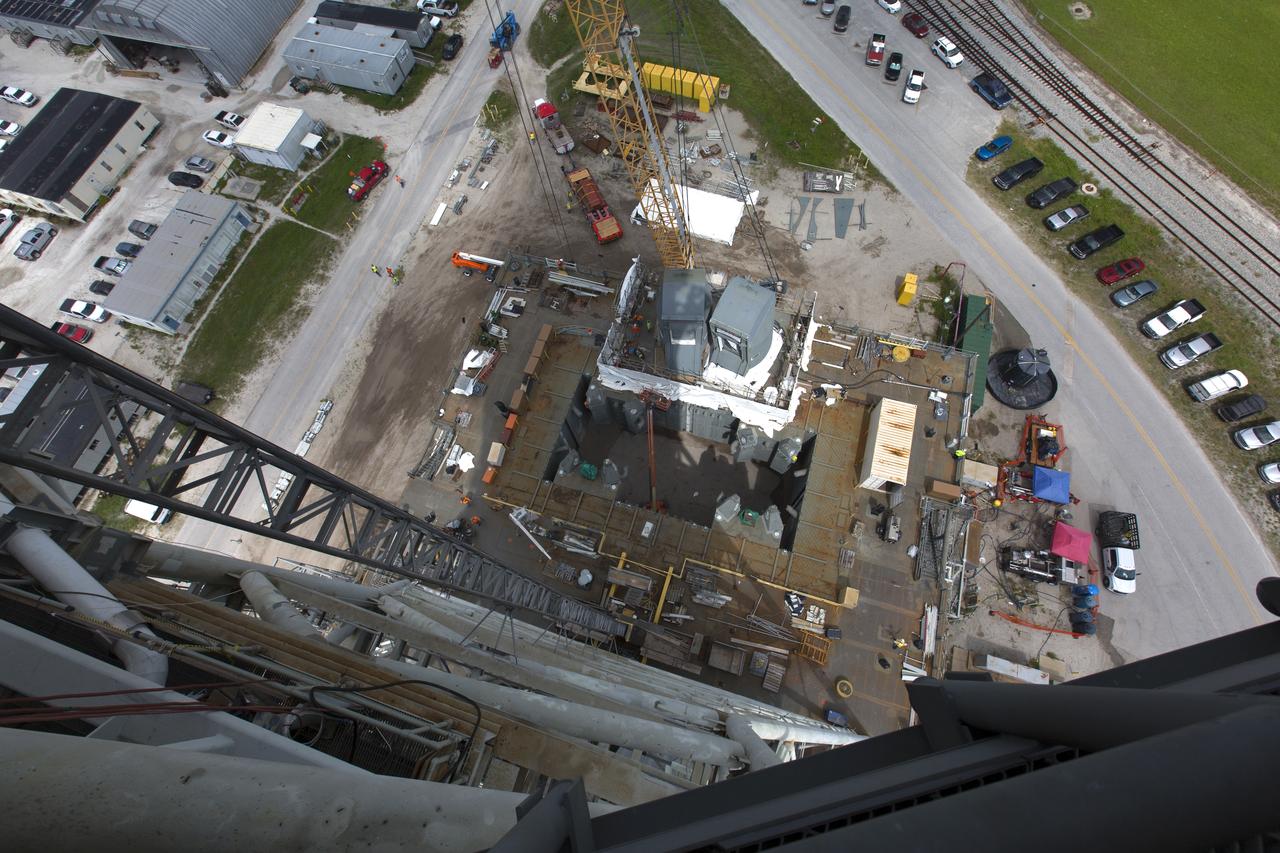

In this view from high above on the mobile launcher tower, a crane is used to lower the second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU) for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. In view at right is the TSMU that will provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
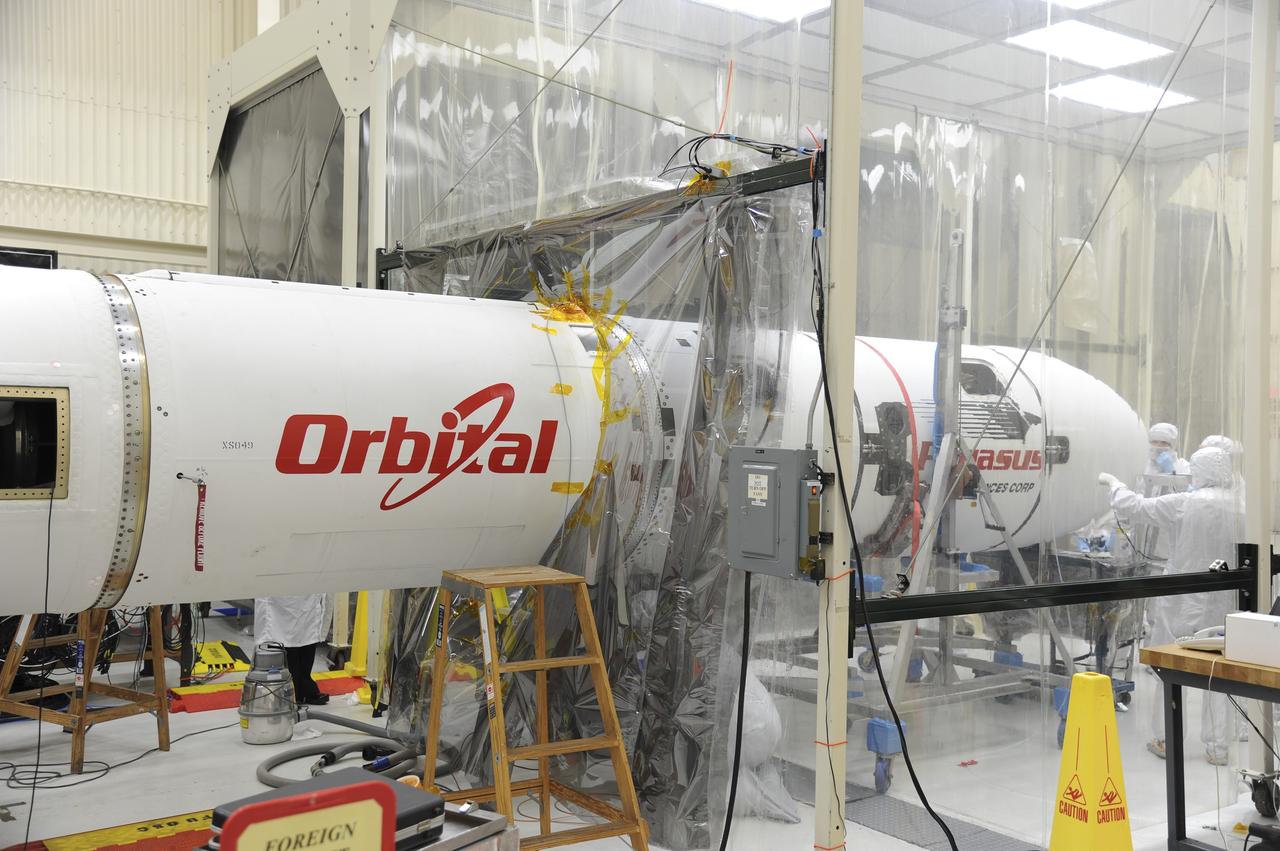

VANDENBERG AFB – Orbital Sciences team engineers monitor the connection of the payload fairing over NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin
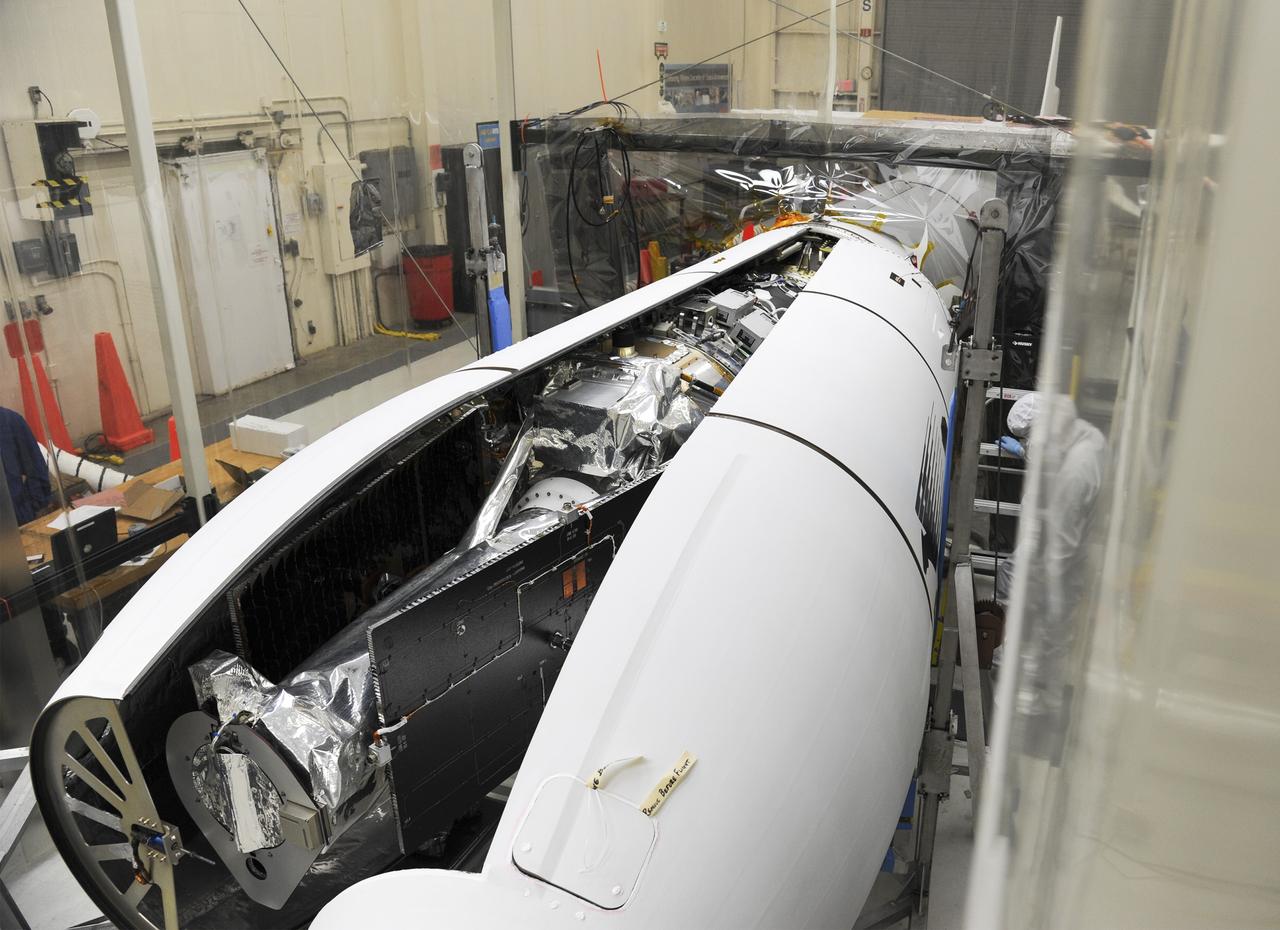

VANDENBERG AFB – Orbital Sciences engineers connect the payload fairing over NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin
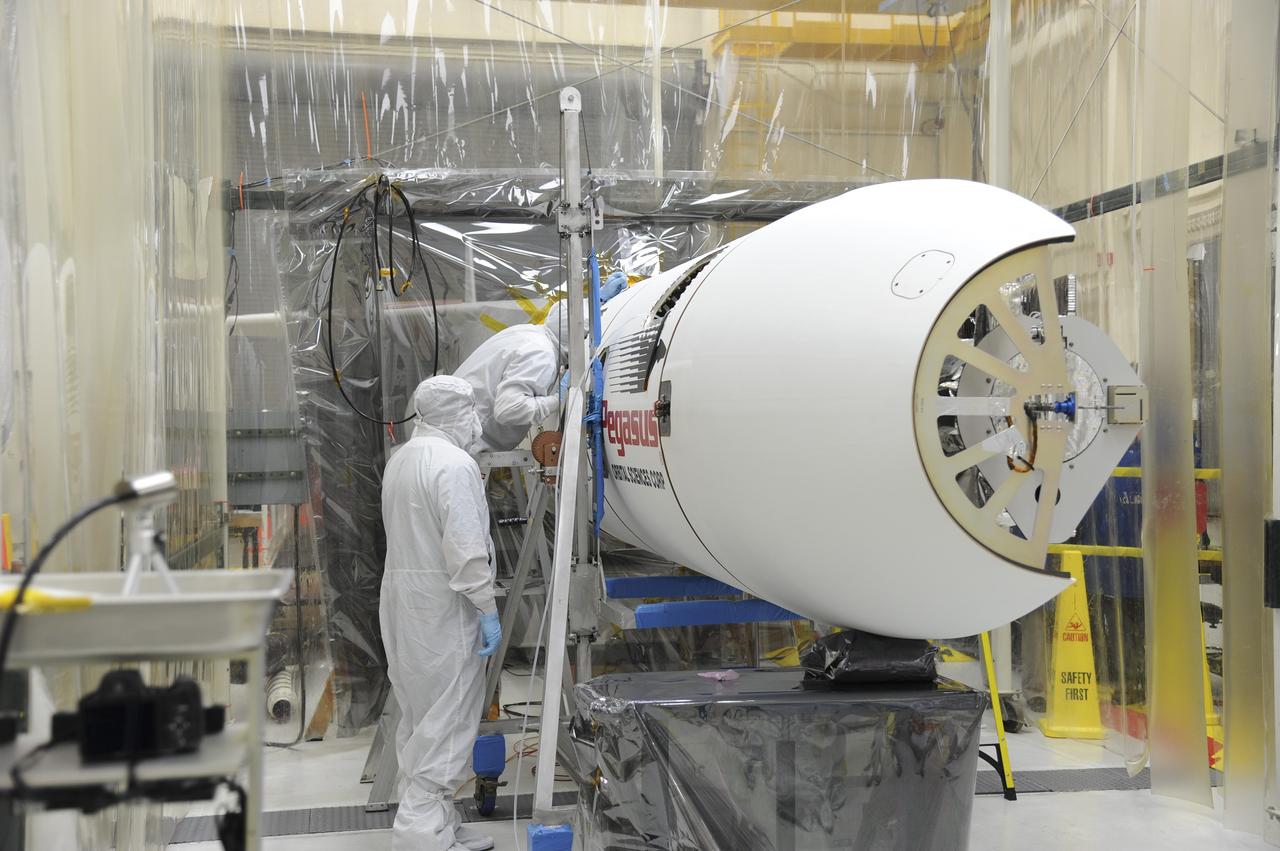

Orbital Sciences engineers connect the payload fairing over NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin
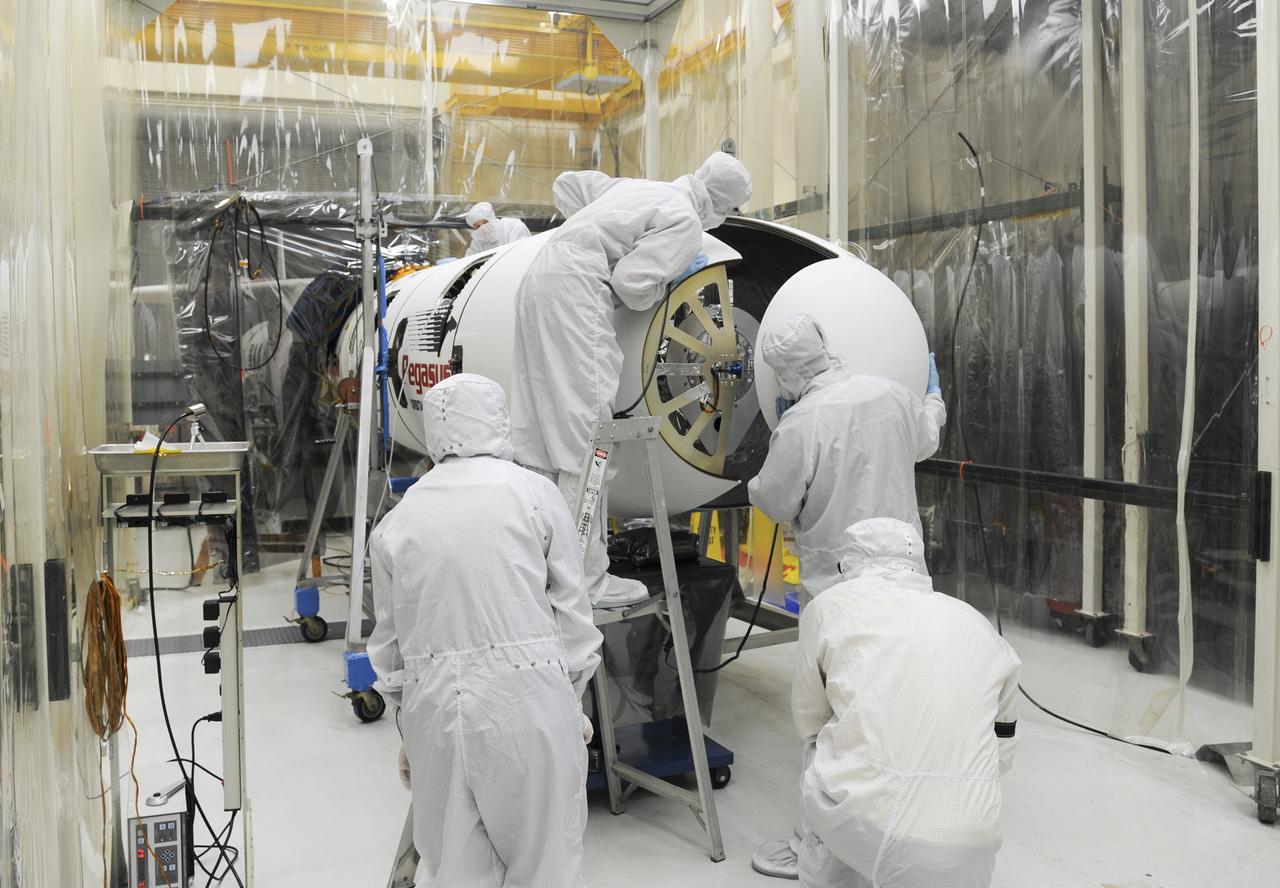

VANDENBERG AFB – Orbital Sciences engineers connect the payload fairing over NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin
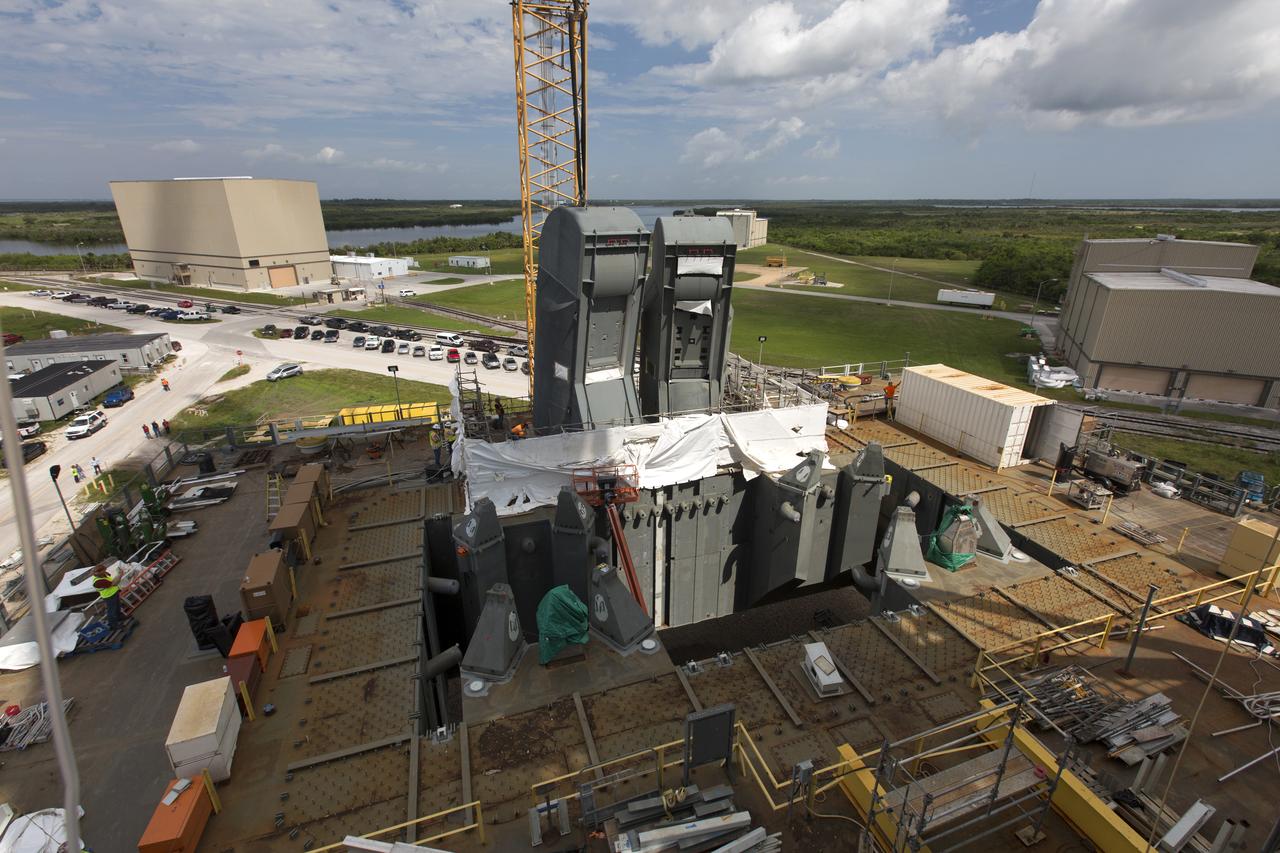

The second of two Tail Service Mast Umbilicals (TSMU), at left, is lowered for installation on the 0-level deck of the mobile launcher on July 27, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 35-foot-tall umbilical will connect to NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) rocket core stage aft section and provide liquid hydrogen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section to support propellant handling during prelaunch operations. In view at right is the TSMU that will provide liquid oxygen and electrical cable connections to the core stage engine section. The installation brings Exploration Ground Systems one step closer to supporting prelaunch operations for the agency's SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft on Exploration Mission-1 and deep space destinations.
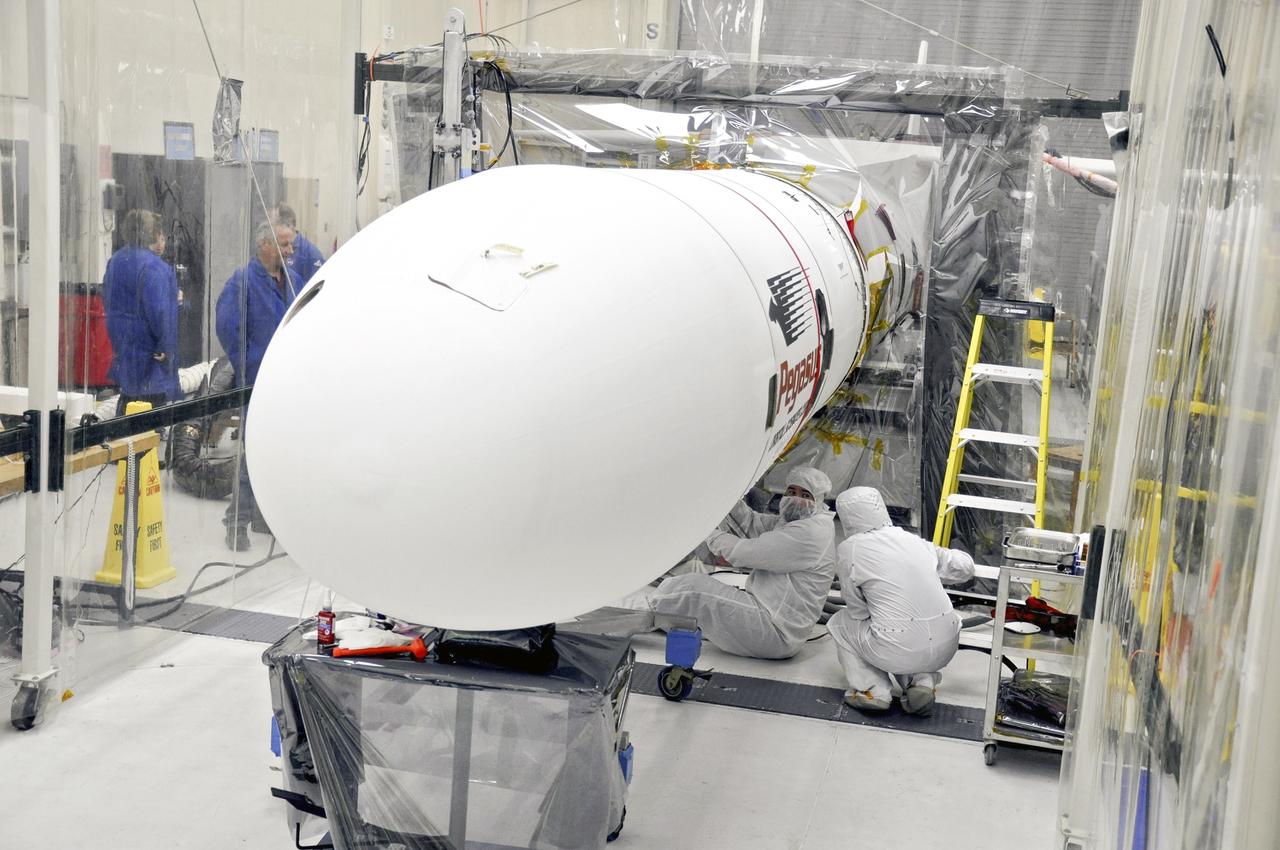

VANDENBERG AFB – Engineers connect the payload fairing over NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
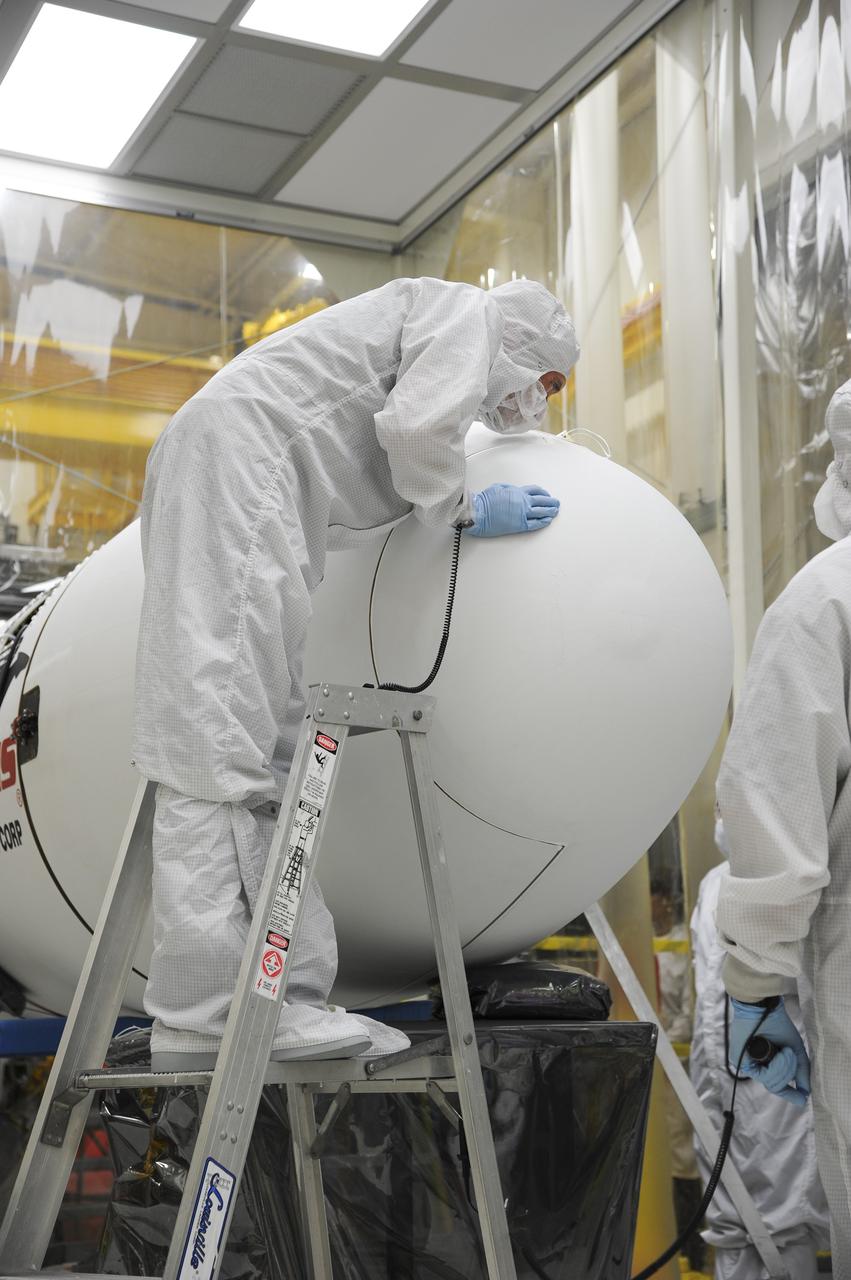

VANDENBERG AFB – Orbital Sciences engineers connect the payload fairing over NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin
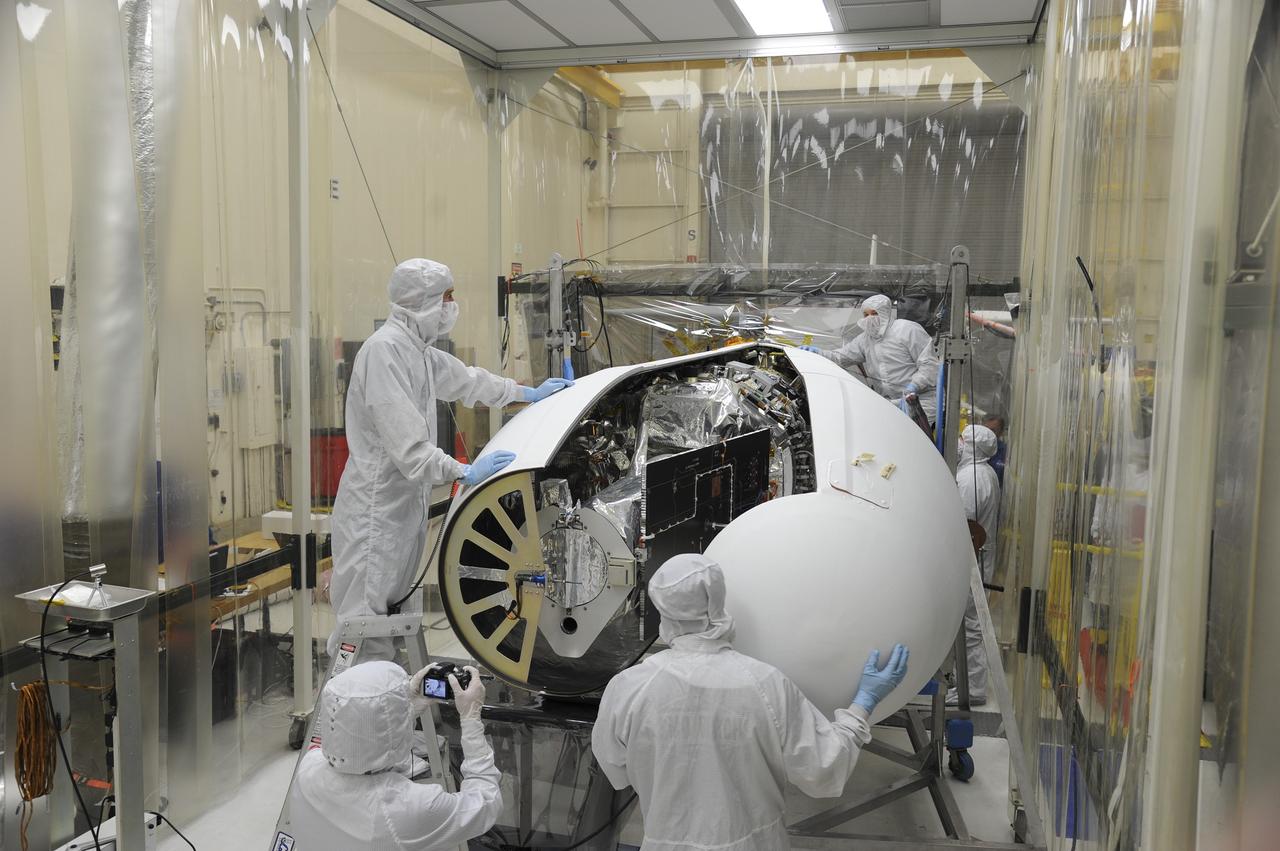

VANDENBERG AFB – Orbital Sciences engineers connect the payload fairing over NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin
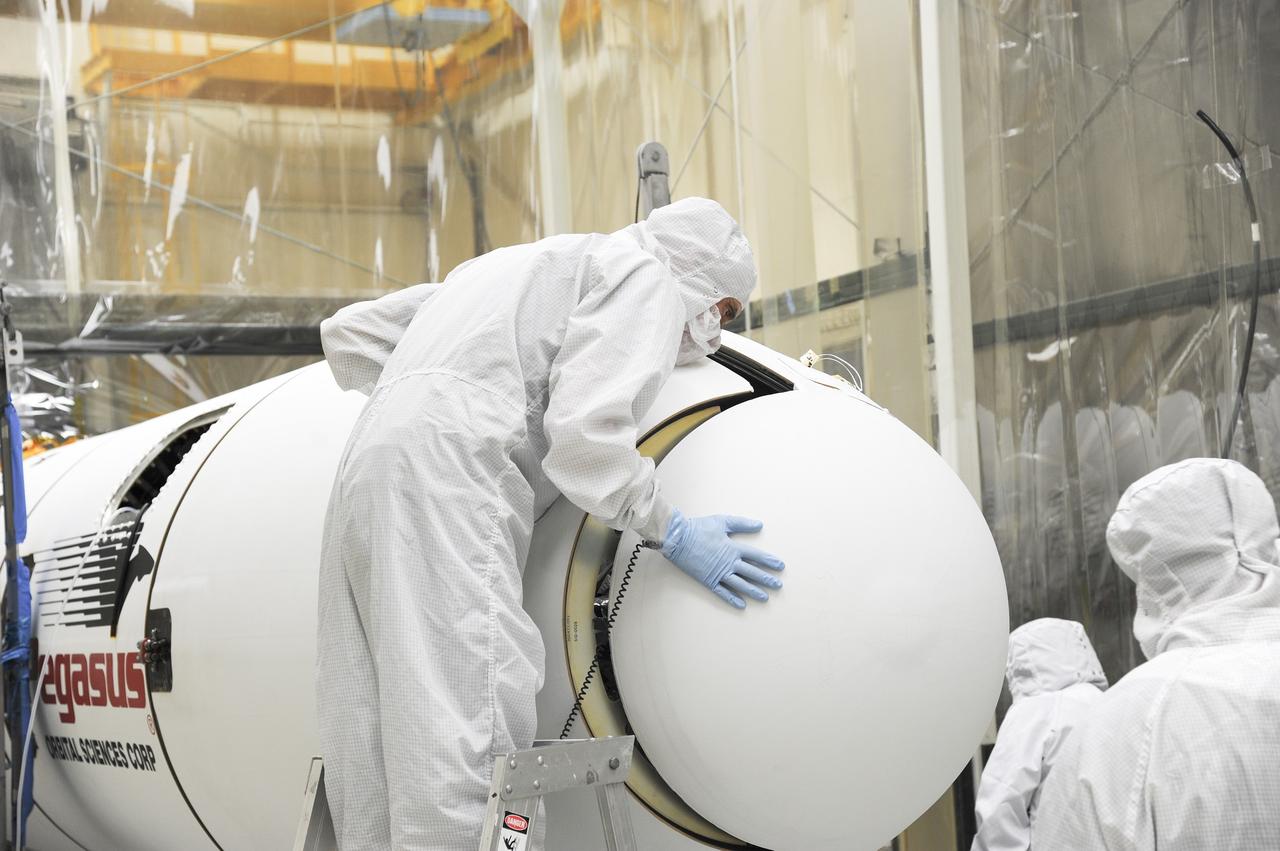

VANDENBERG AFB – Orbital Sciences engineers connect the payload fairing over NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin
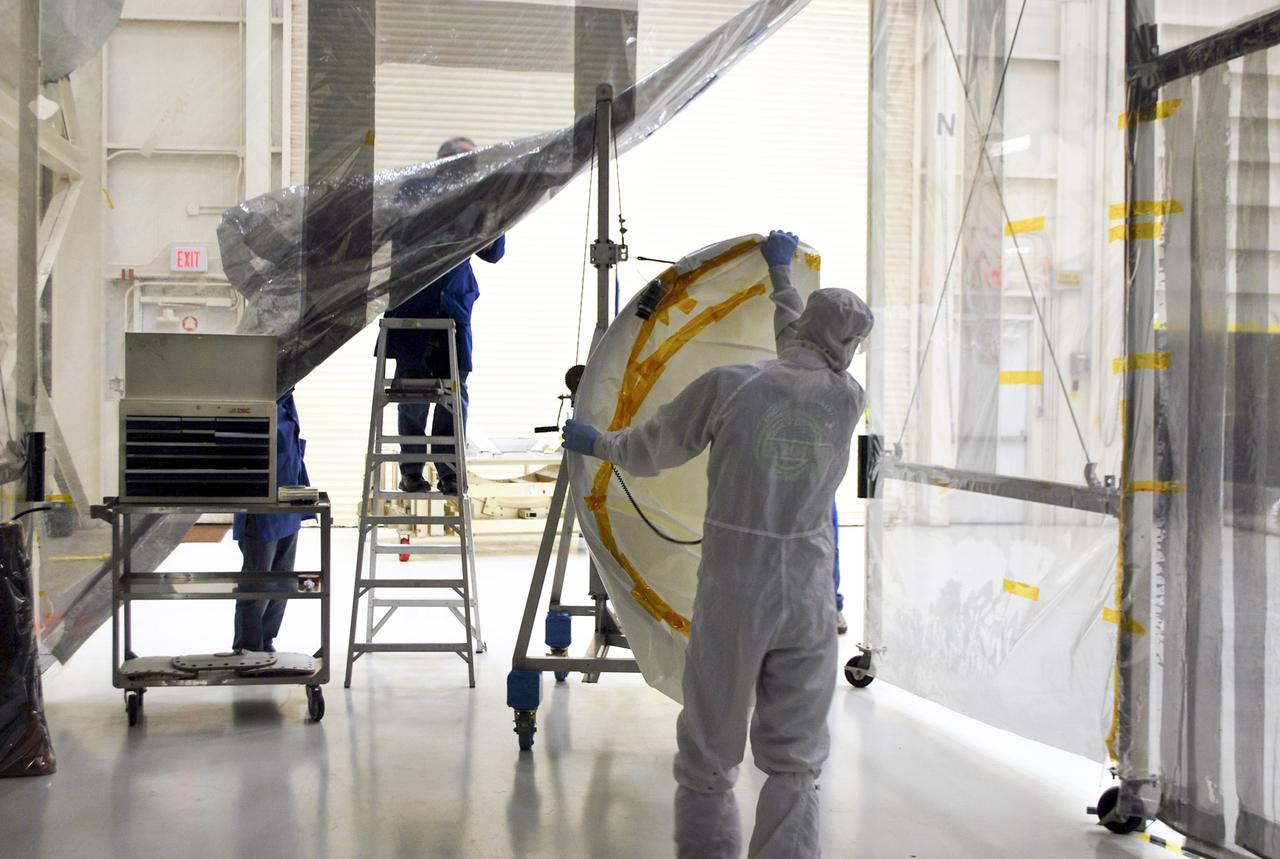

VANDENBERG AFB – Engineers move the port side of the payload fairing before it is connected into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
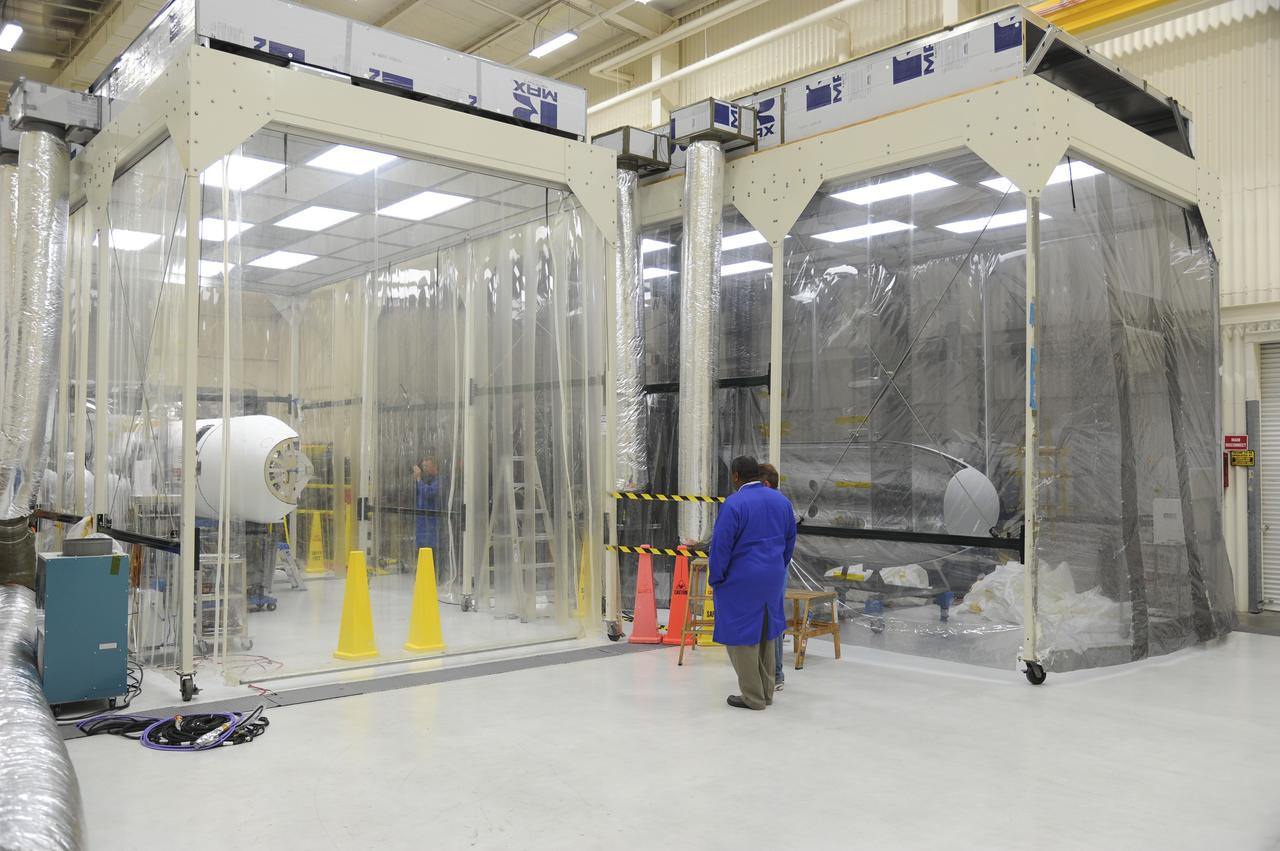

VANDENBERG AFB – Orbital Sciences team members watch as engineers connect the payload fairing over NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin

VANDENBERG AFB – Orbital Sciences engineers connect the payload fairing over NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin
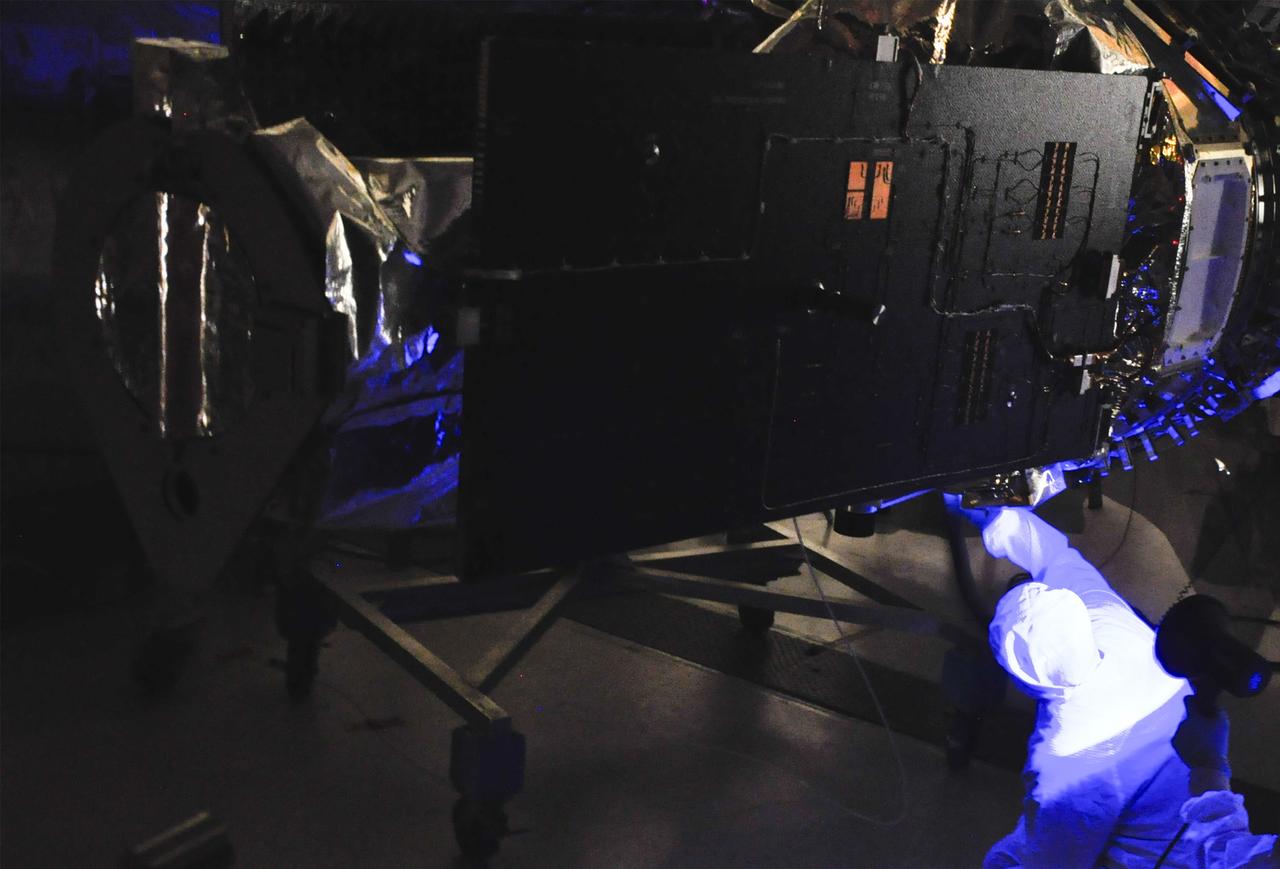

VANDENBERG AFB, Calif. – Engineers conduct inspections on NASA's IRIS spacecraft with blacklights before the payload fairing before it is connected. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
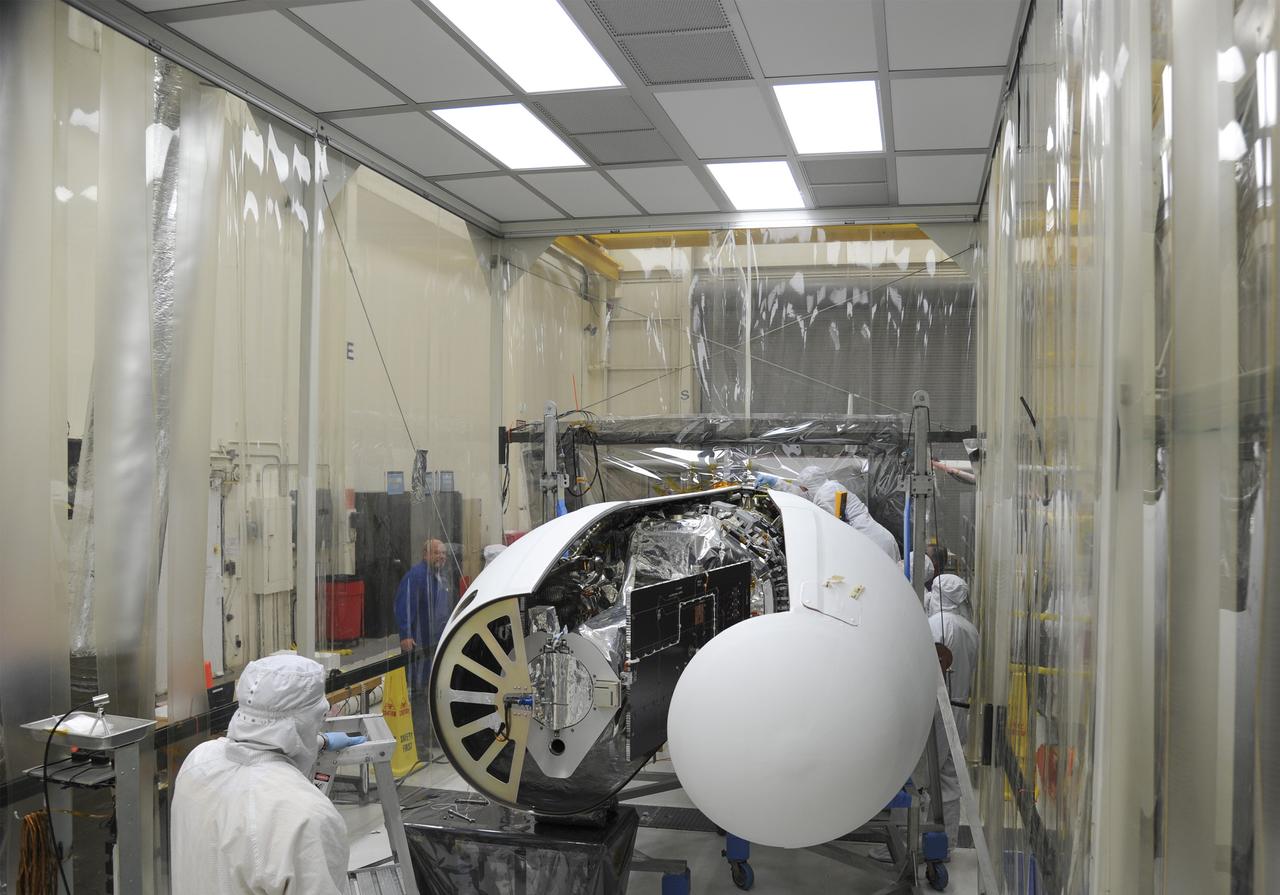

VANDENBERG AFB – Orbital Sciences engineers connect the payload fairing over NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin
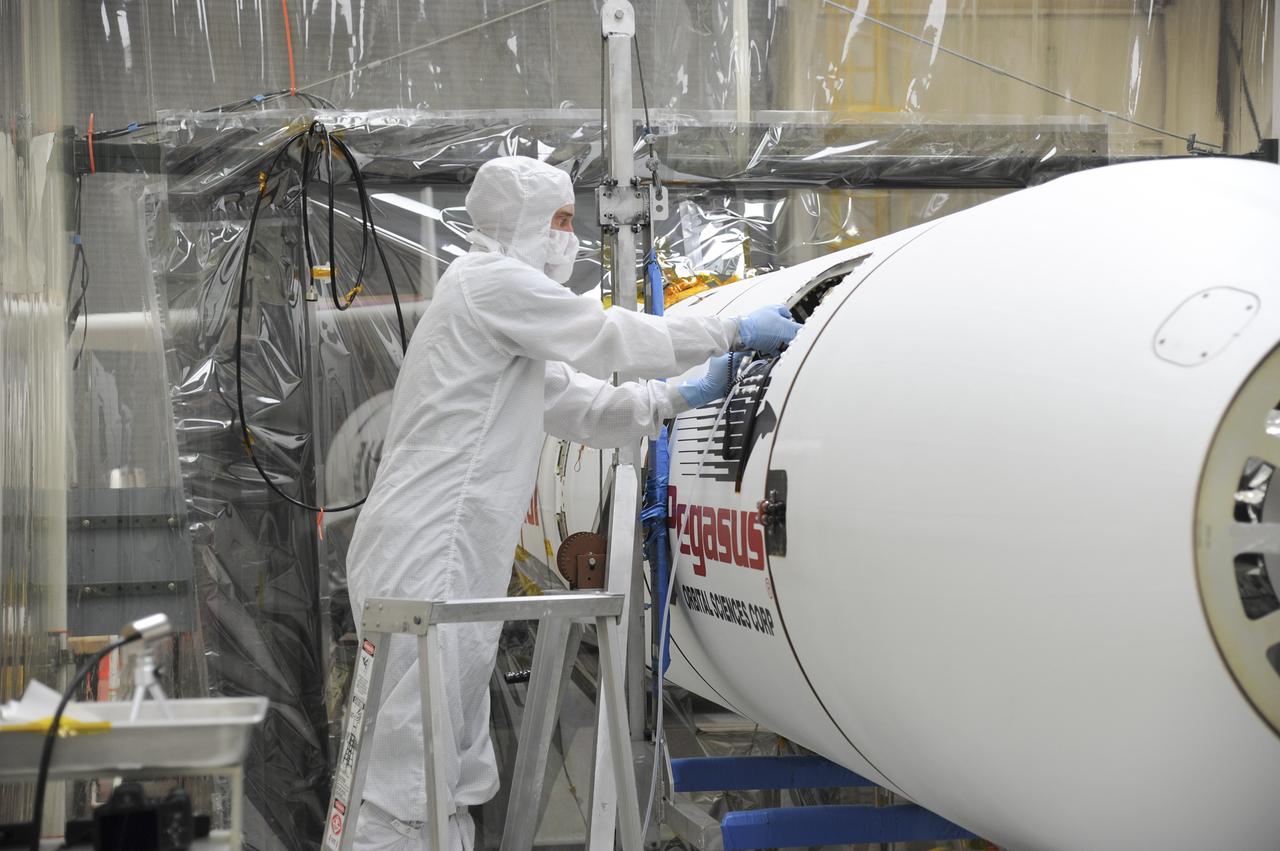

VANDENBERG AFB – Orbital Sciences engineers connect the payload fairing over NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Vauclin
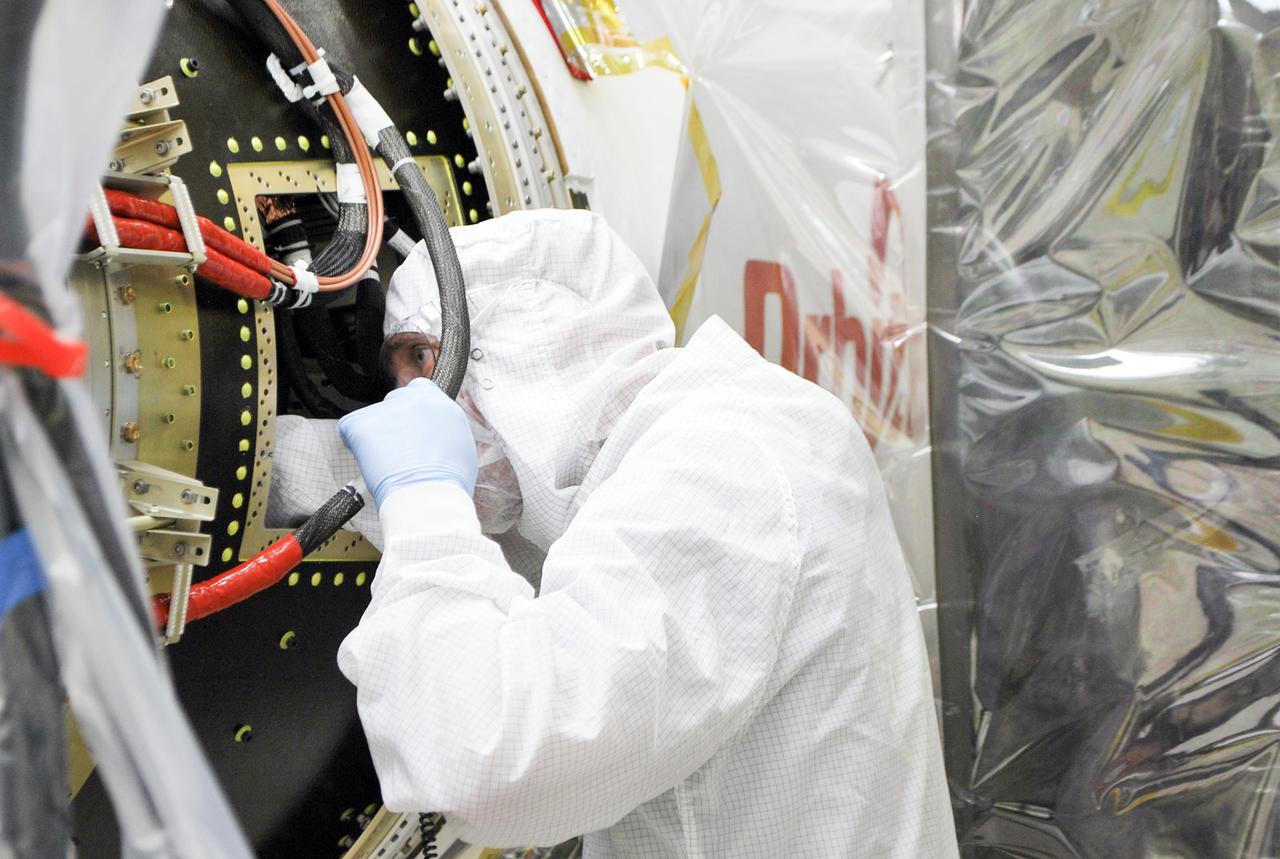

- VANDENBERG AFB – An engineer makes preparations on the starboard side of the payload fairing before it is connected into place for NASA's IRIS spacecraft. The fairing connects to the nose of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket that will lift the solar observatory into orbit in June. The work is taking place in a hangar at Vandenberg Air Force Base where IRIS, short for Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, is being prepared for launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg June 26, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. IRIS fills a crucial gap in our ability to advance studies of the sun-to-Earth connection by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the foundation of the corona and the region around the sun known as the heliosphere. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
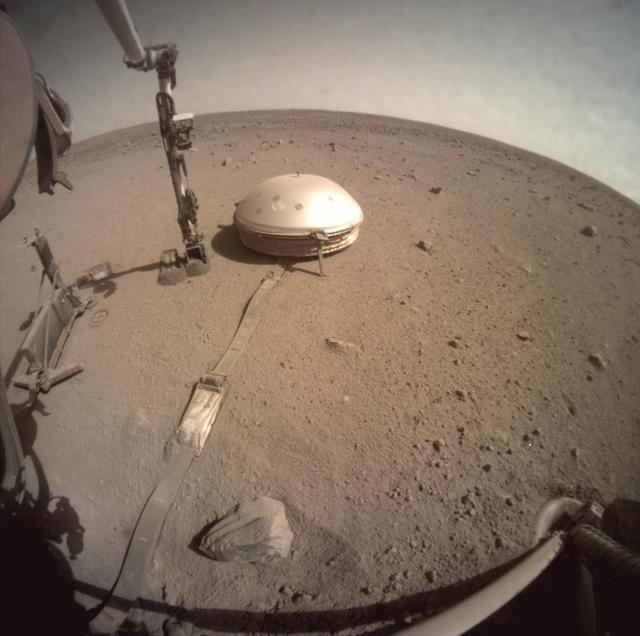

NASA's InSight lander used the scoop on its robotic arm to begin trickling soil over the cable connecting its seismometer to the spacecraft on March 14, 2021, the 816th Martian day, or sol of the mission. Scientists hope this make it easier to detect marsquakes by helping to insulate the cable from the wind and from the extreme temperature shifts that cause the cable to expand and contract. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24450
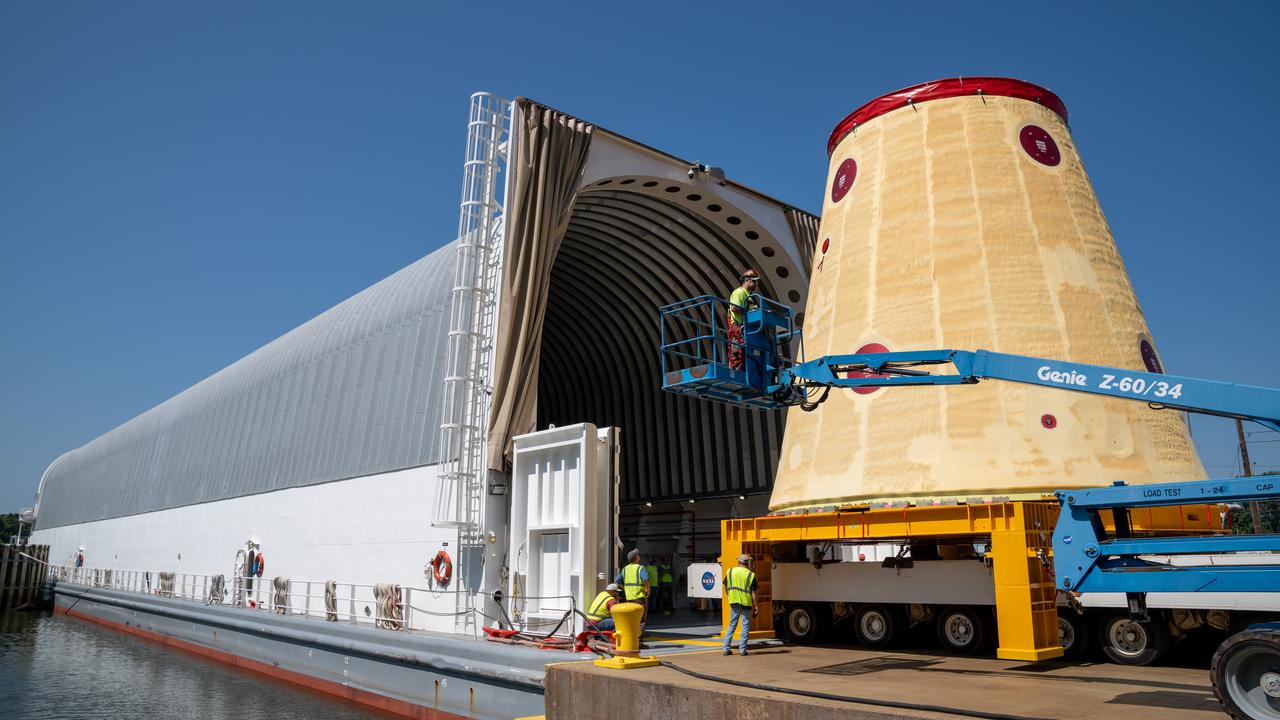

NASA rolled out a key piece of space flight hardware for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign from Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Wednesday, Aug. 21 to board the Pegasus barge for shipment to the agency’s spaceport in Florida. The cone-shaped launch vehicle stage adapter connects the rocket’s core stage to the upper stage and helps protect the upper stage’s engine that will help propel the Artemis II test flight around the Moon, slated for 2026.
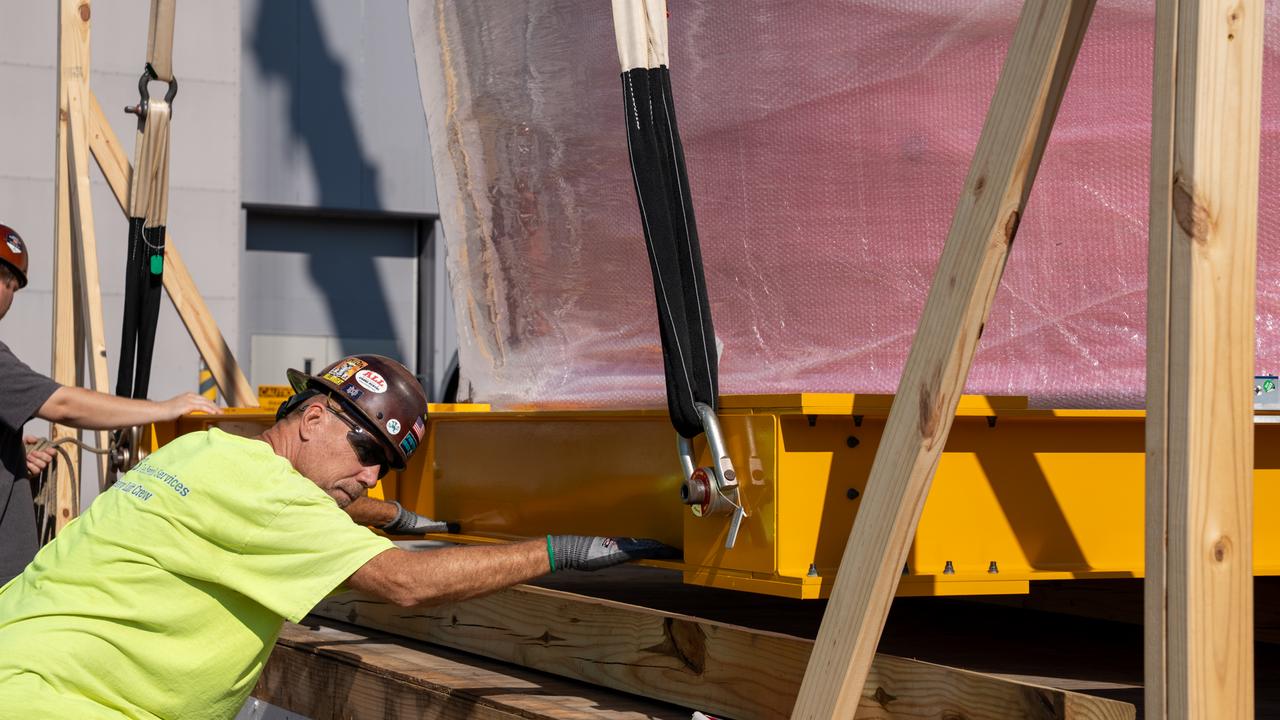

These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II being prepped for shipment and then packaged in a large box, loaded on a semi-truck. It is seen leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
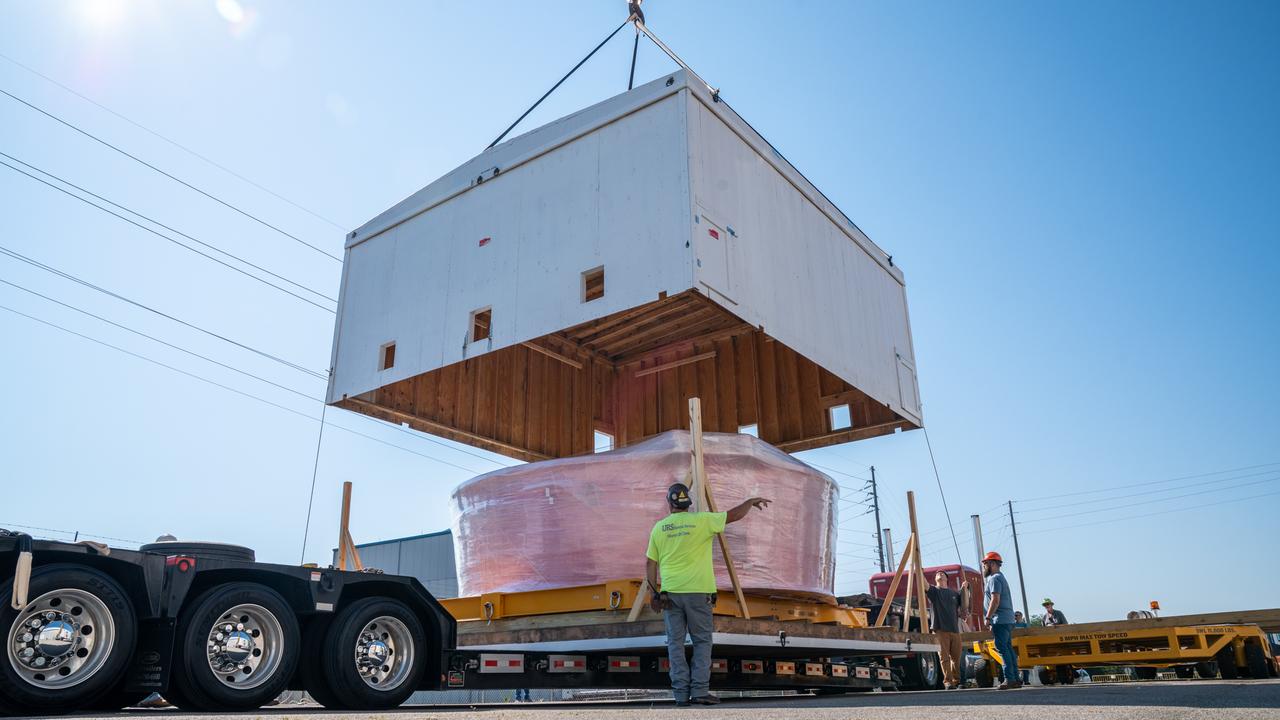

These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II being prepped for shipment and then packaged in a large box, loaded on a semi-truck. It is seen leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
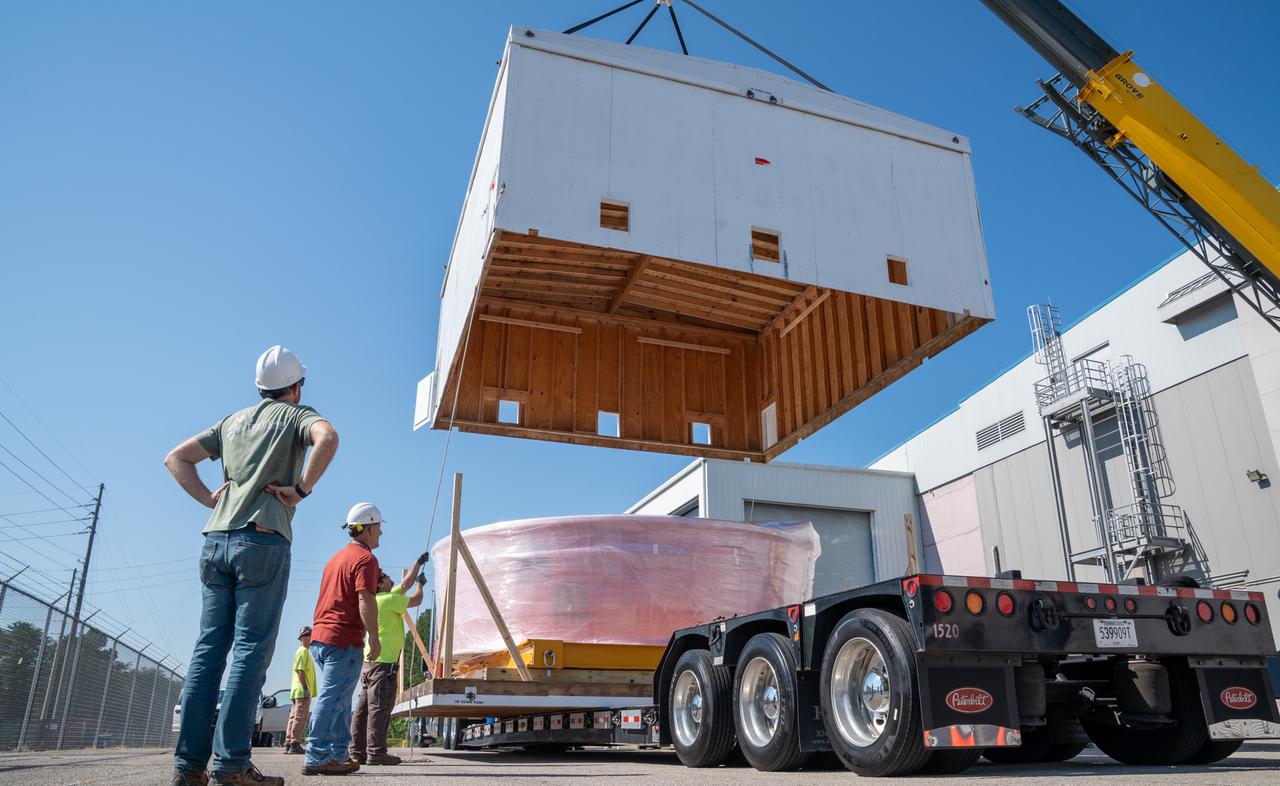

These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II being prepped for shipment and then packaged in a large box, loaded on a semi-truck. It is seen leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
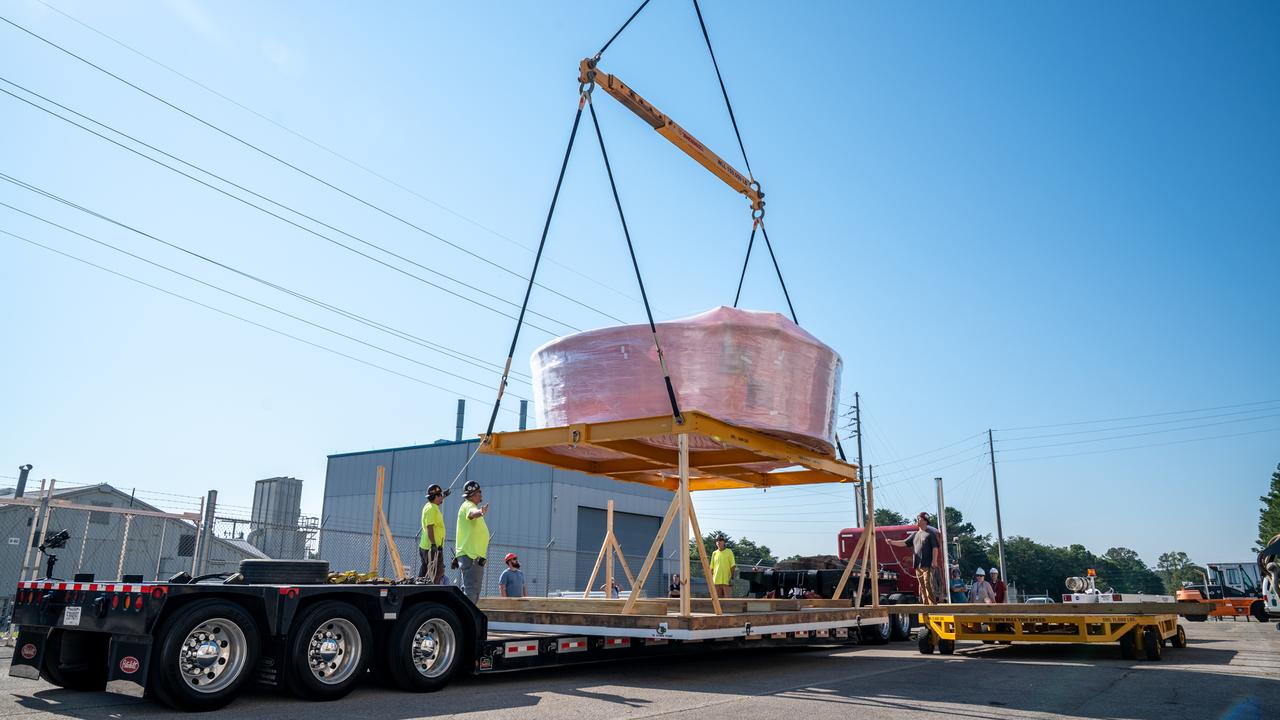

These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II being prepped for shipment and then packaged in a large box, loaded on a semi-truck. It is seen leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
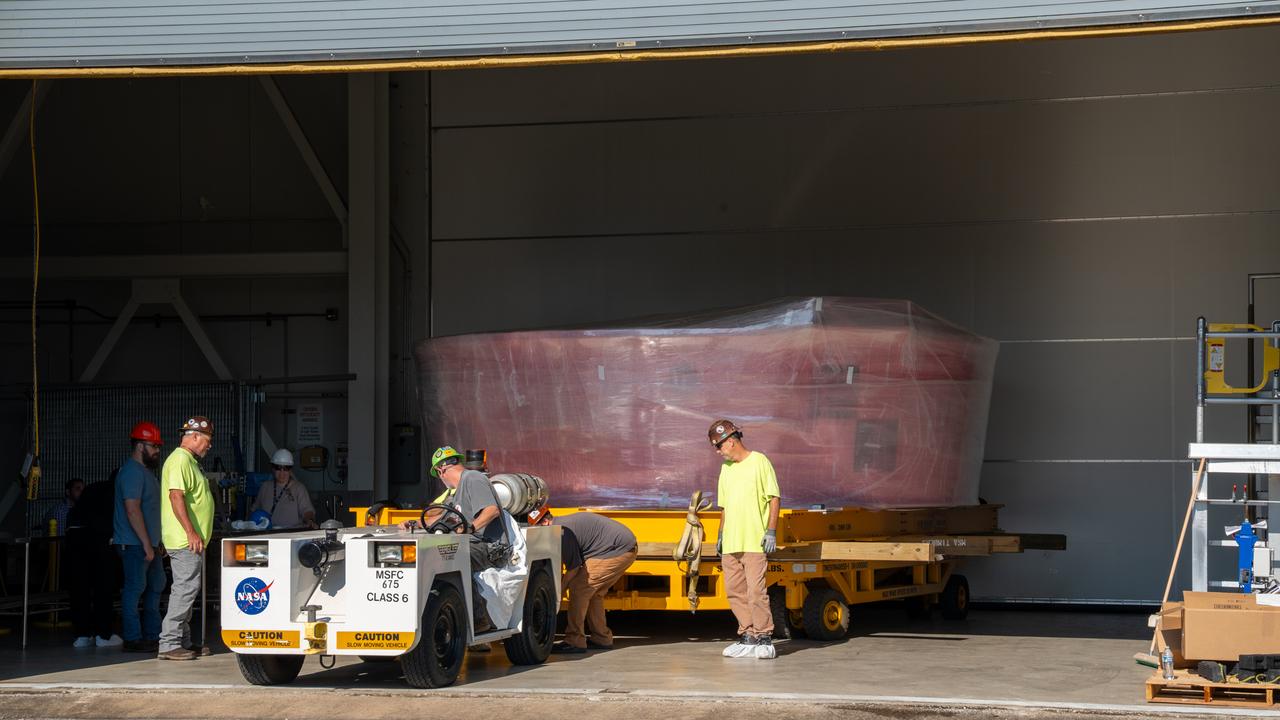

These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.