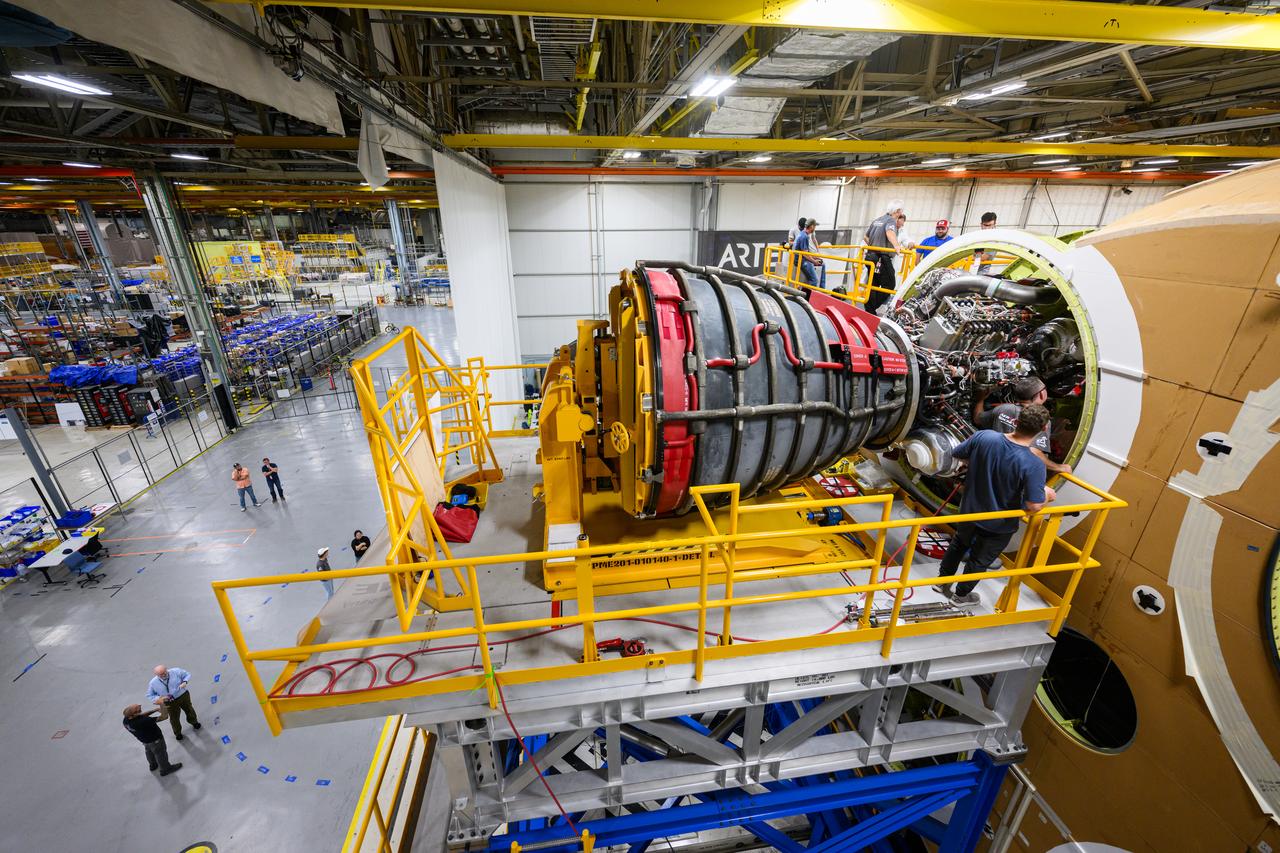
This photo shows the second RS-25 engine attached to the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for the agency’s Artemis I mission to the Moon. Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans structurally mated the second of four engines to the stage on Oct. 30 and are currently integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure to complete the installation. Integration of the RS-25 engines to the recently completed core stage structure is a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. The four RS-25 engines for Artemis I are modified heritage flight hardware from the Space Shuttle Program, ensuring high performance and reliability to power NASA’s next generation lunar missions. Each engine also has a special identification number, and NASA keeps a history of which engines are used on each mission. The second engine, Engine 2045, has flown on several shuttle missions, including the mission that returned NASA astronaut John Glenn to space in 1998 as well as the first and only shuttle launch to occur on Independence Day in 2006. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

This photo shows the second RS-25 engine attached to the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for the agency’s Artemis I mission to the Moon. Engineers and technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans structurally mated the second of four engines to the stage on Oct. 30 and are currently integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure to complete the installation. Integration of the RS-25 engines to the recently completed core stage structure is a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. The four RS-25 engines for Artemis I are modified heritage flight hardware from the Space Shuttle Program, ensuring high performance and reliability to power NASA’s next generation lunar missions. Each engine also has a special identification number, and NASA keeps a history of which engines are used on each mission. The second engine, Engine 2045, has flown on several shuttle missions, including the mission that returned NASA astronaut John Glenn to space in 1998 as well as the first and only shuttle launch to occur on Independence Day in 2006. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
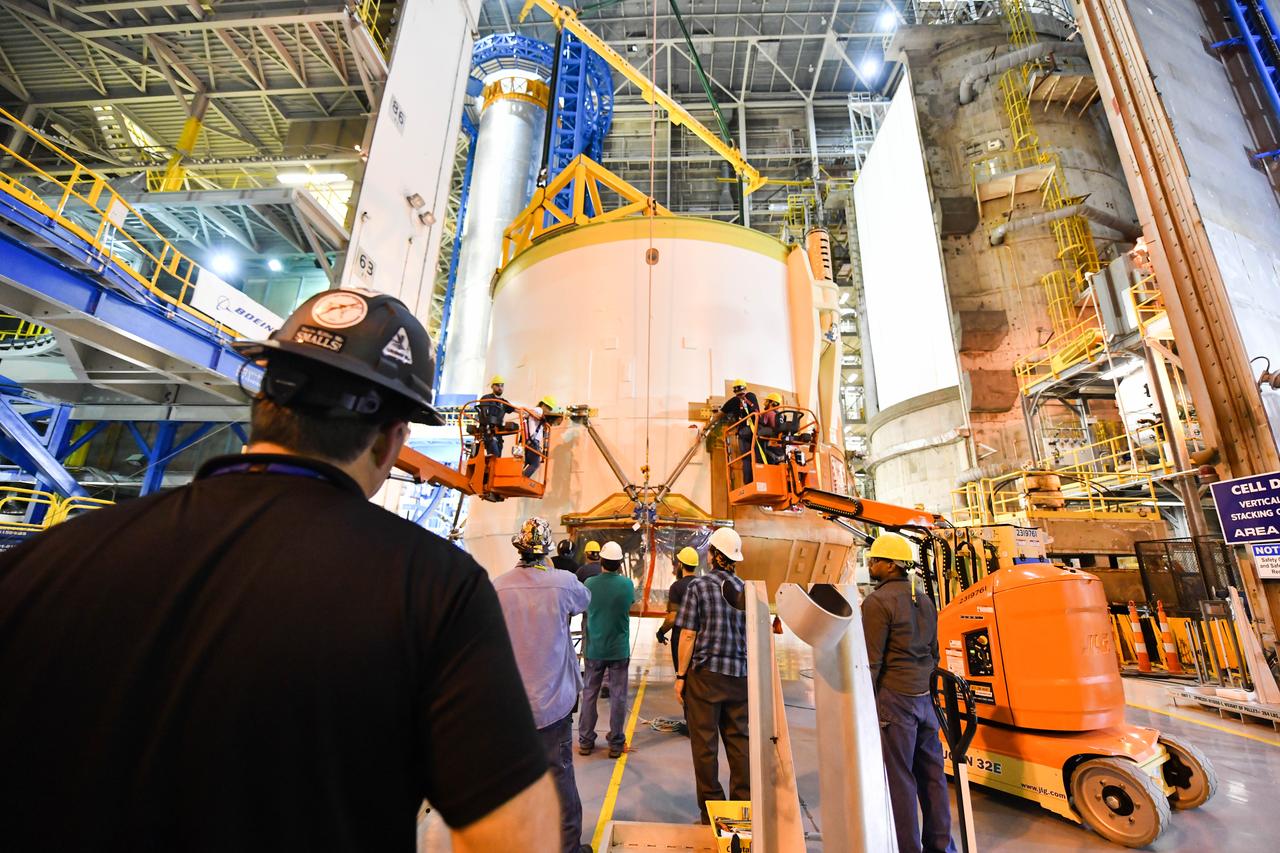

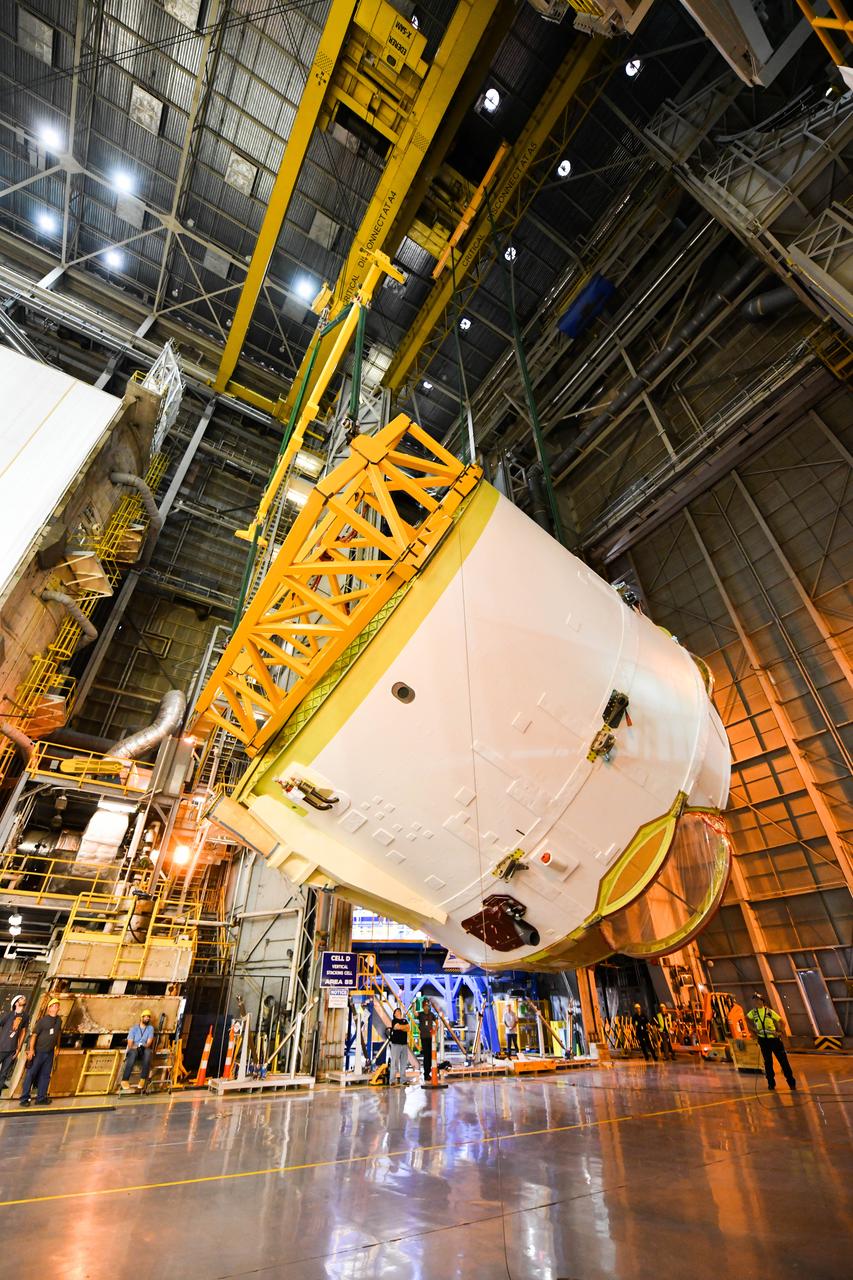
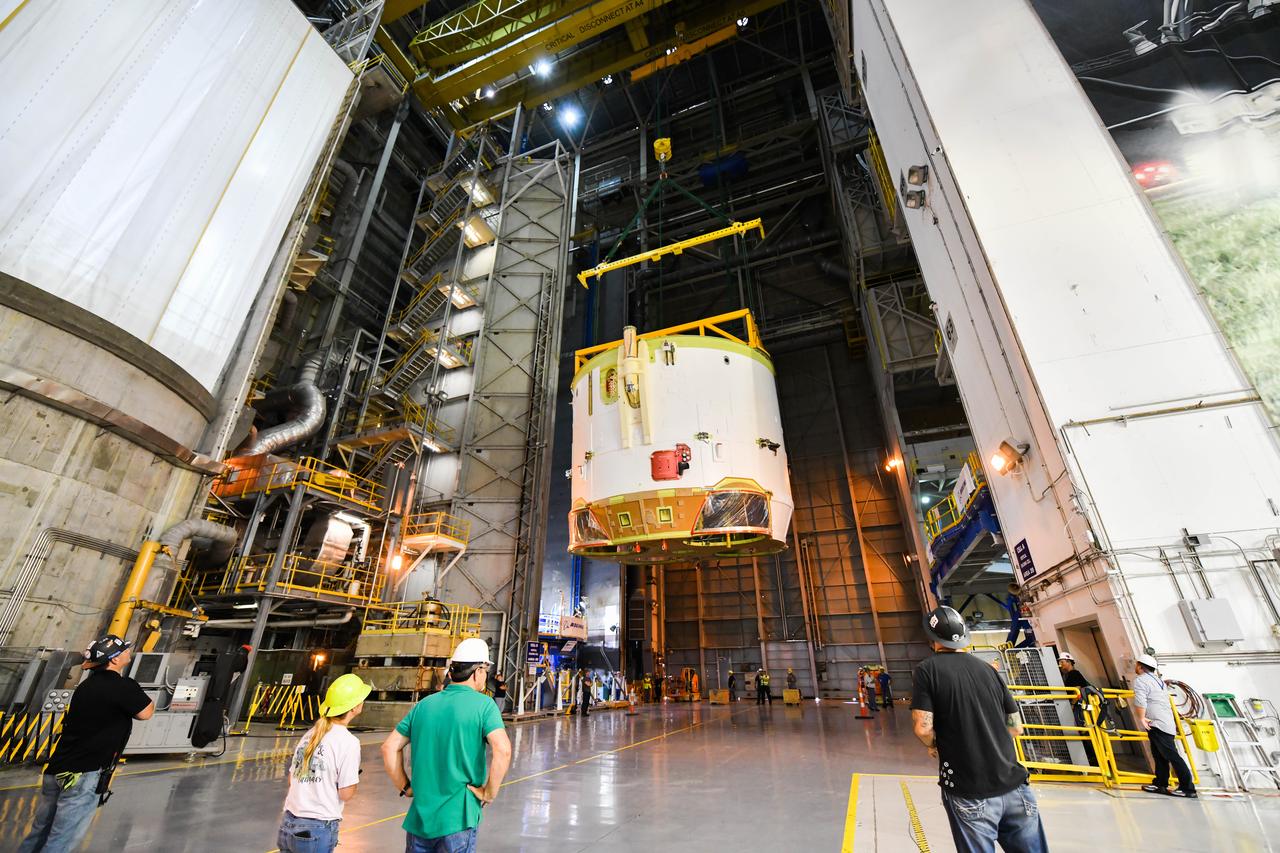
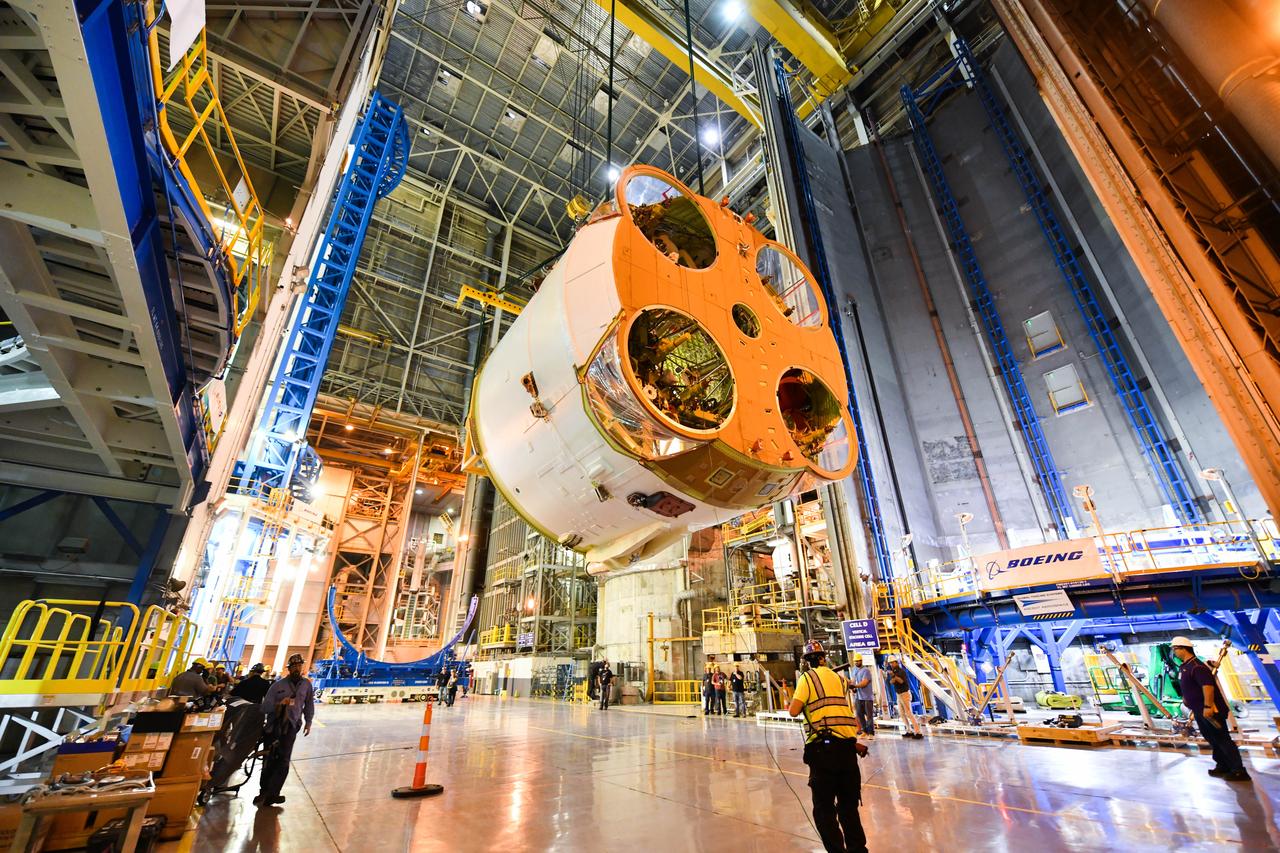
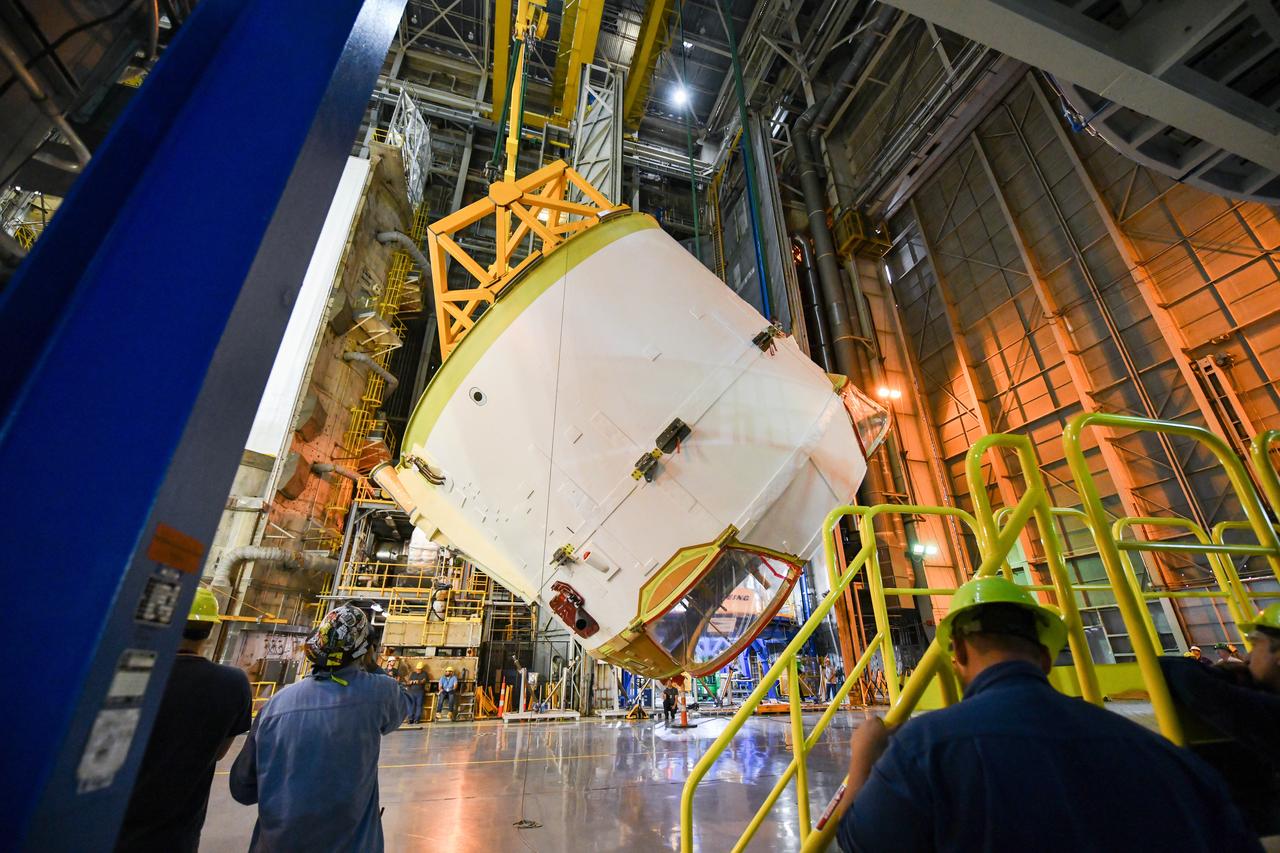
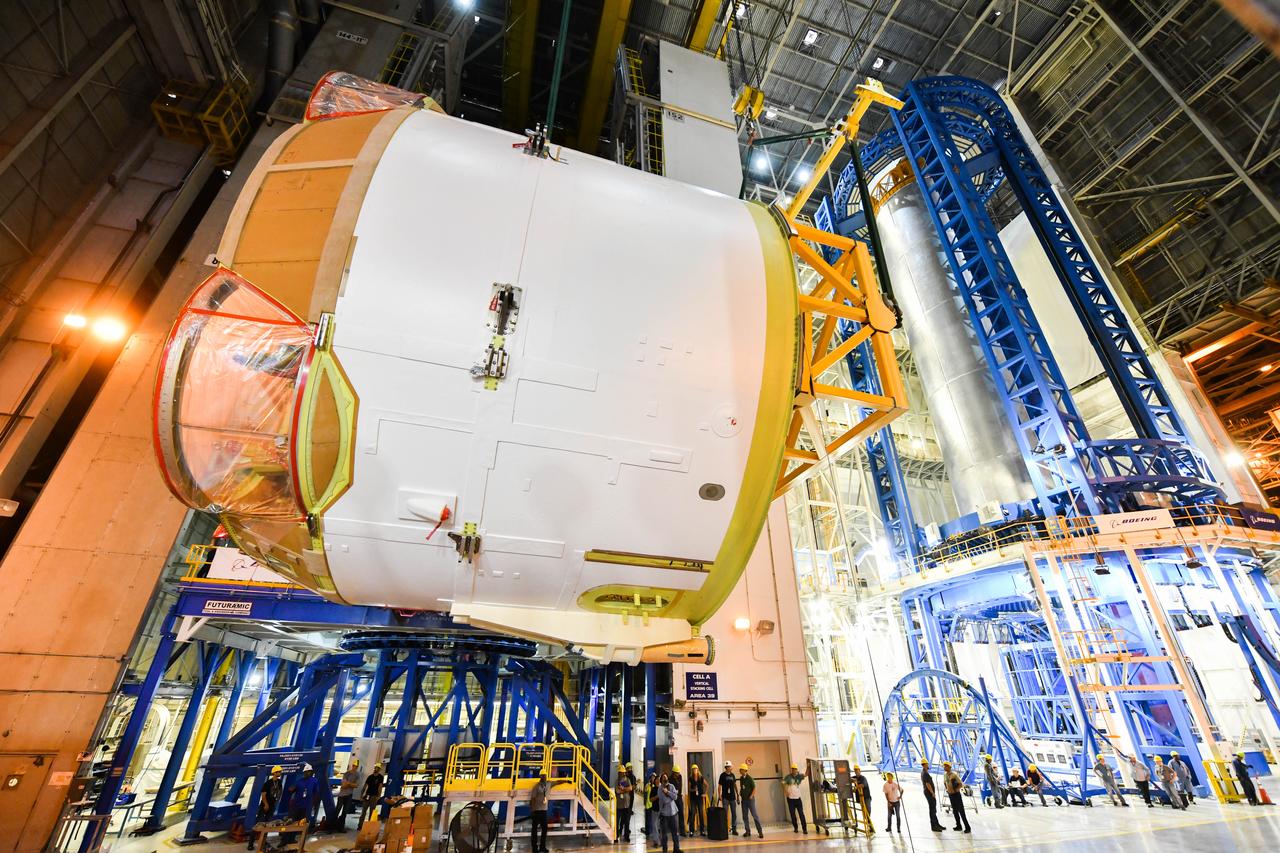
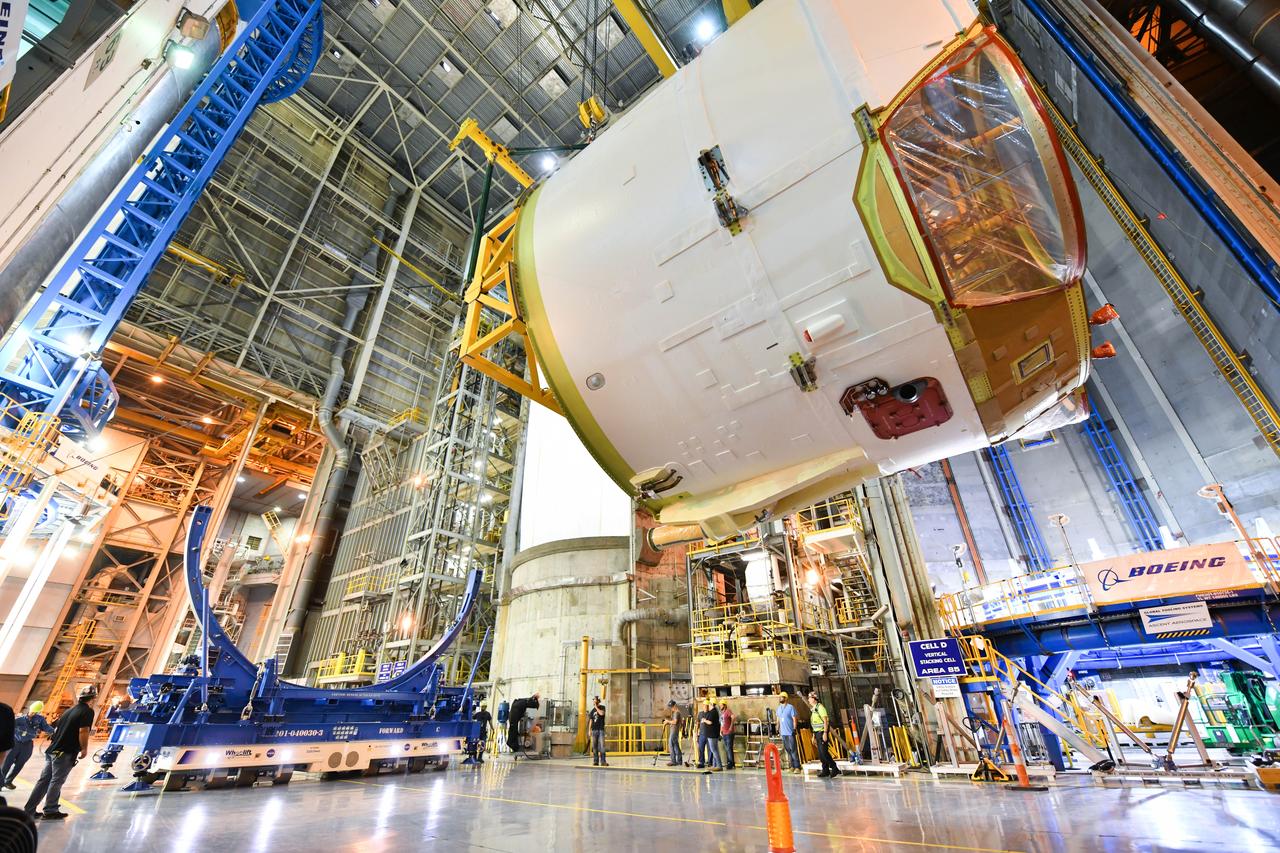
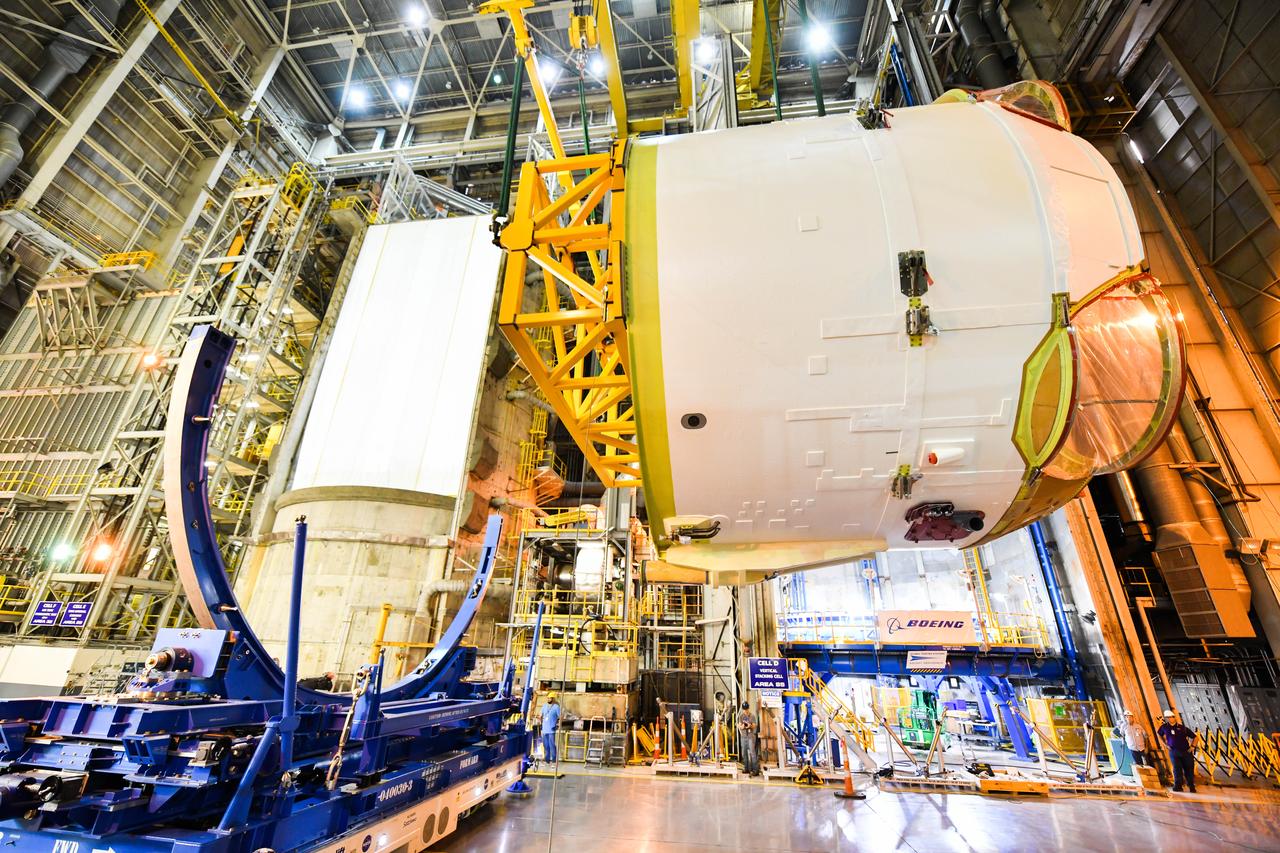
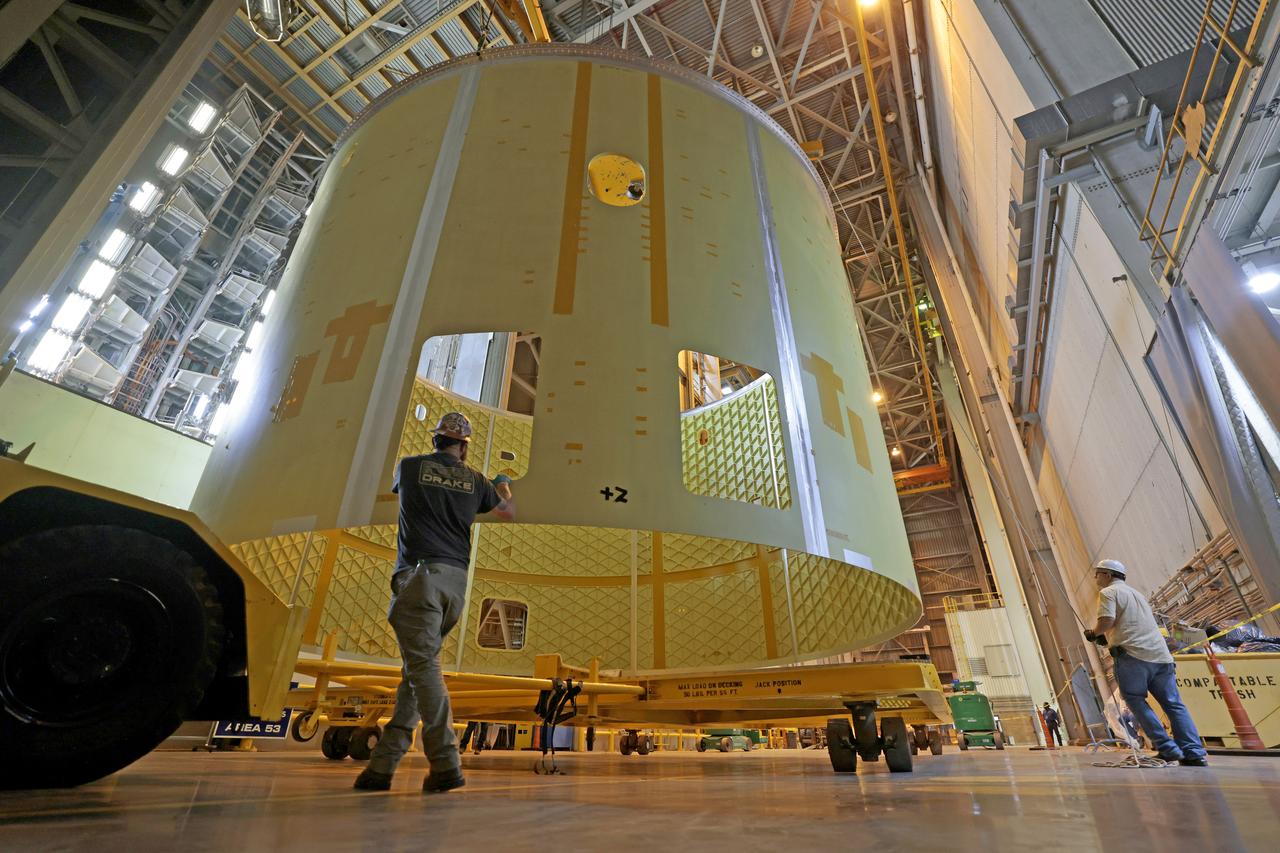
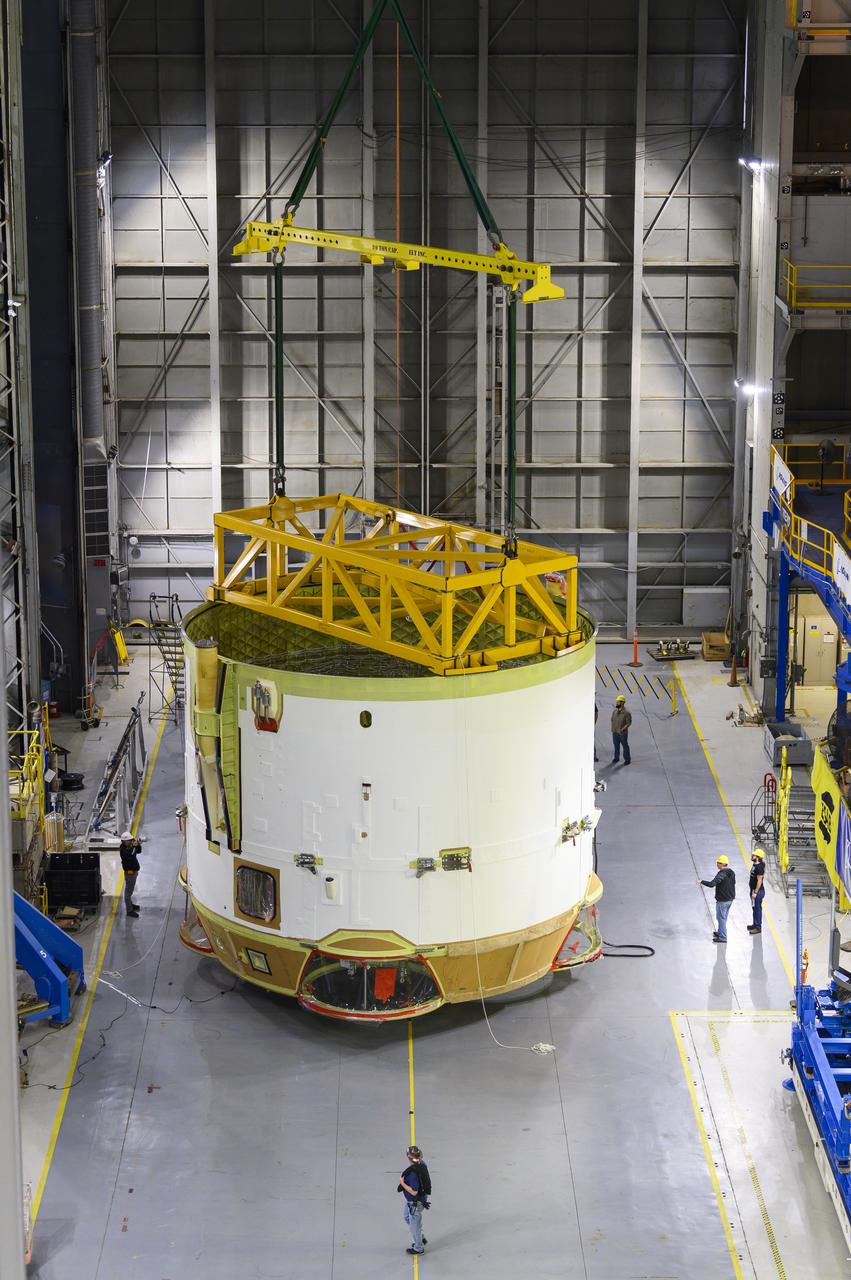
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines.
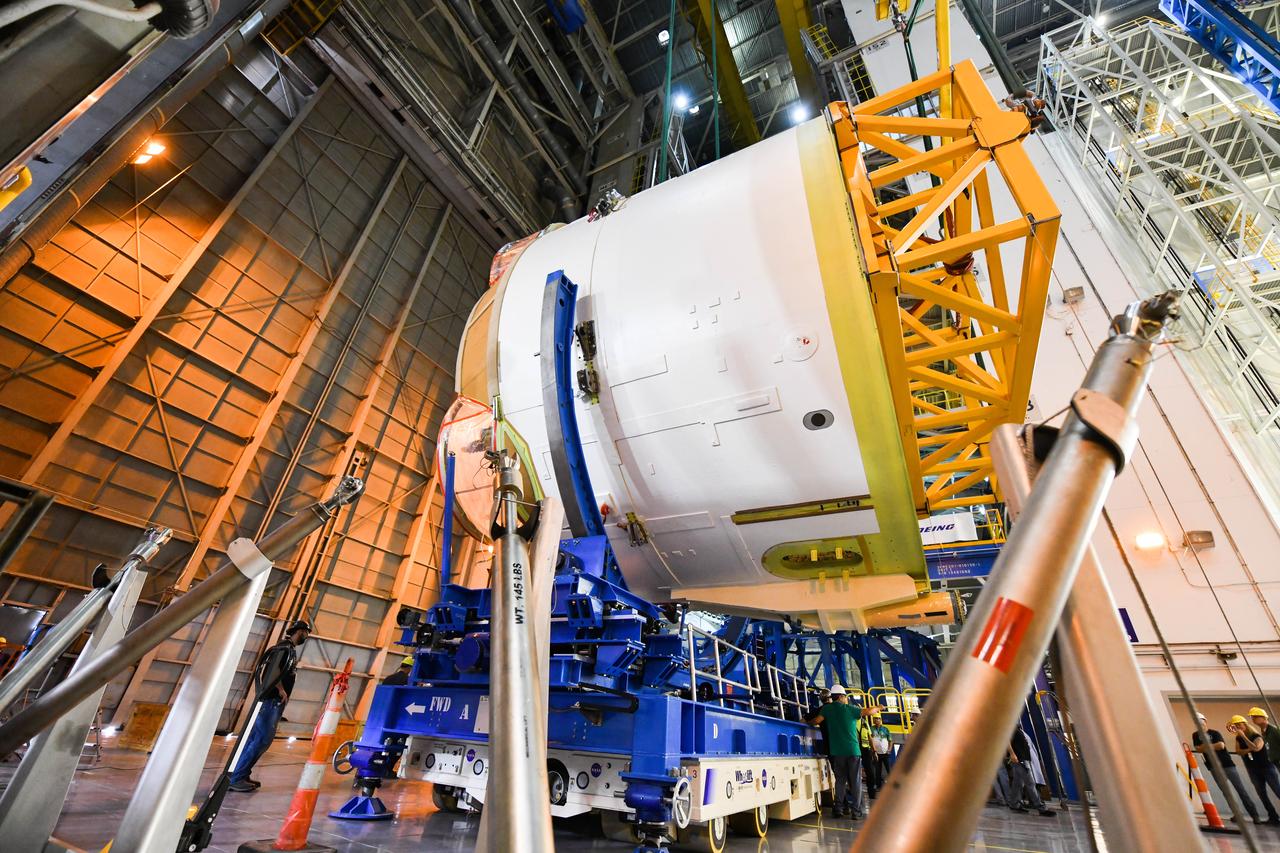

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
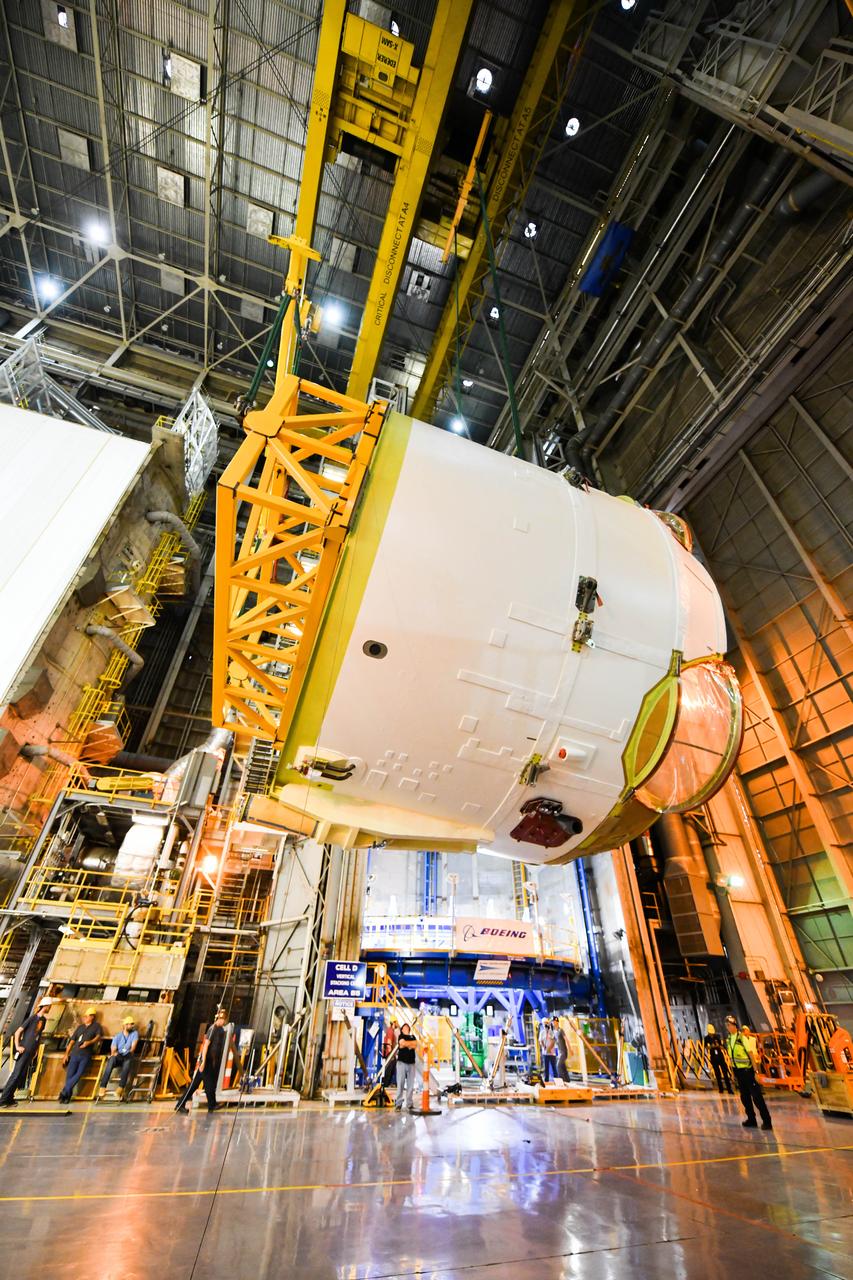

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
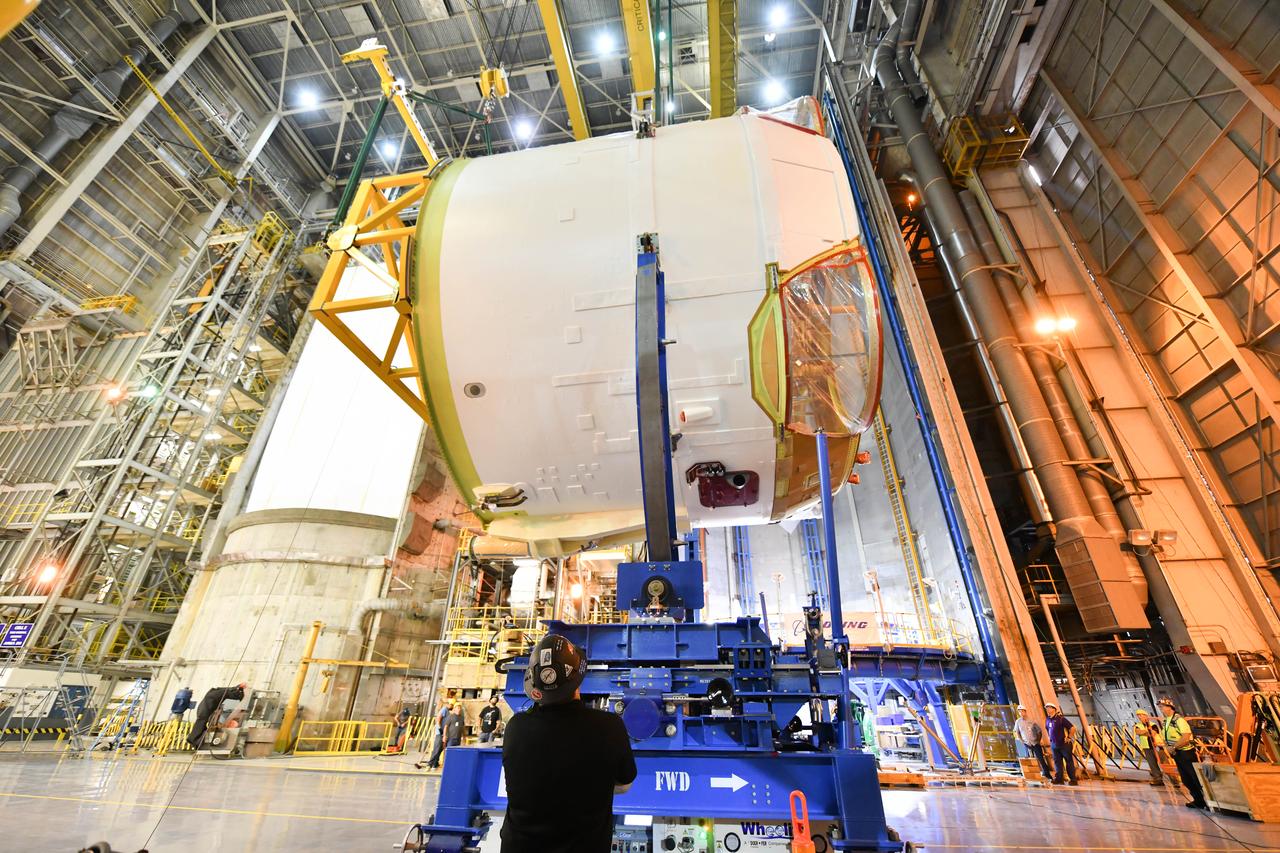

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
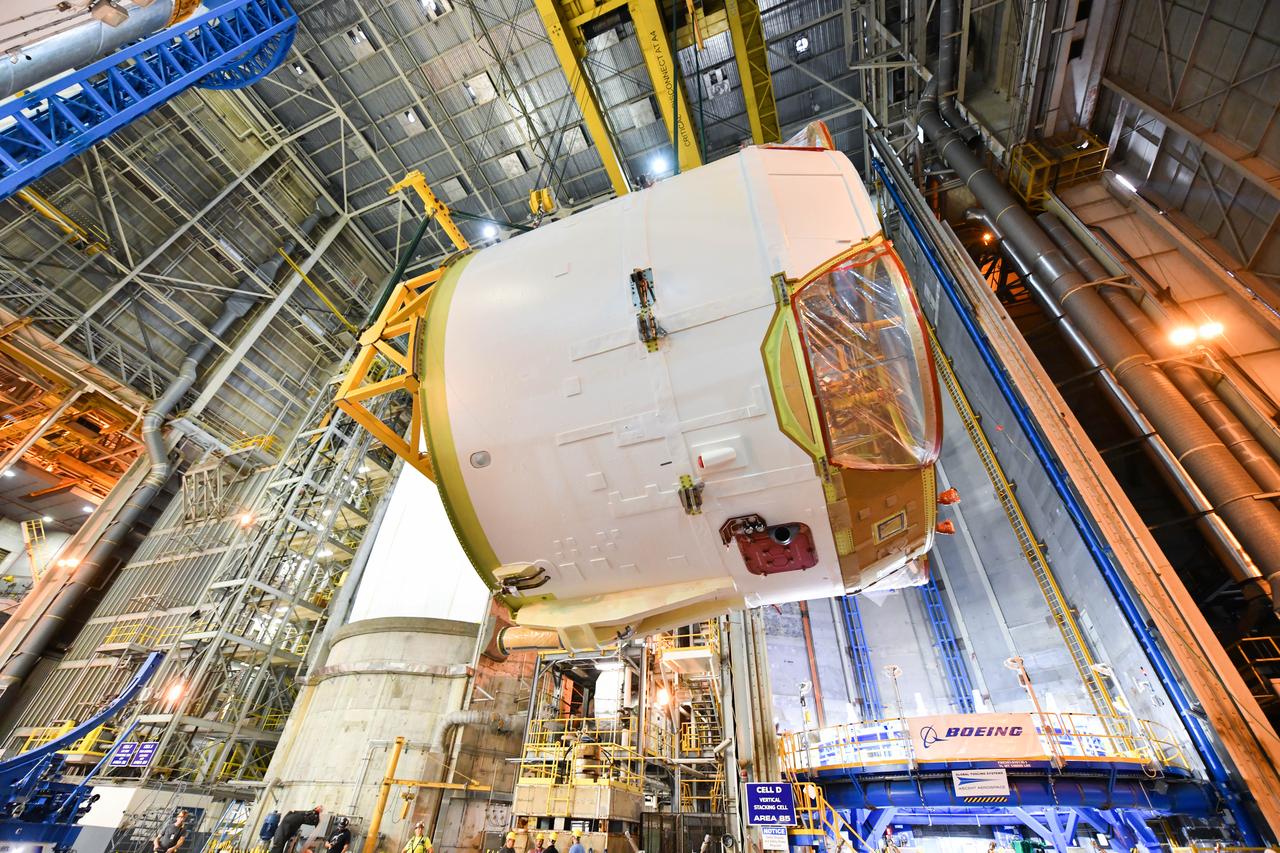

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
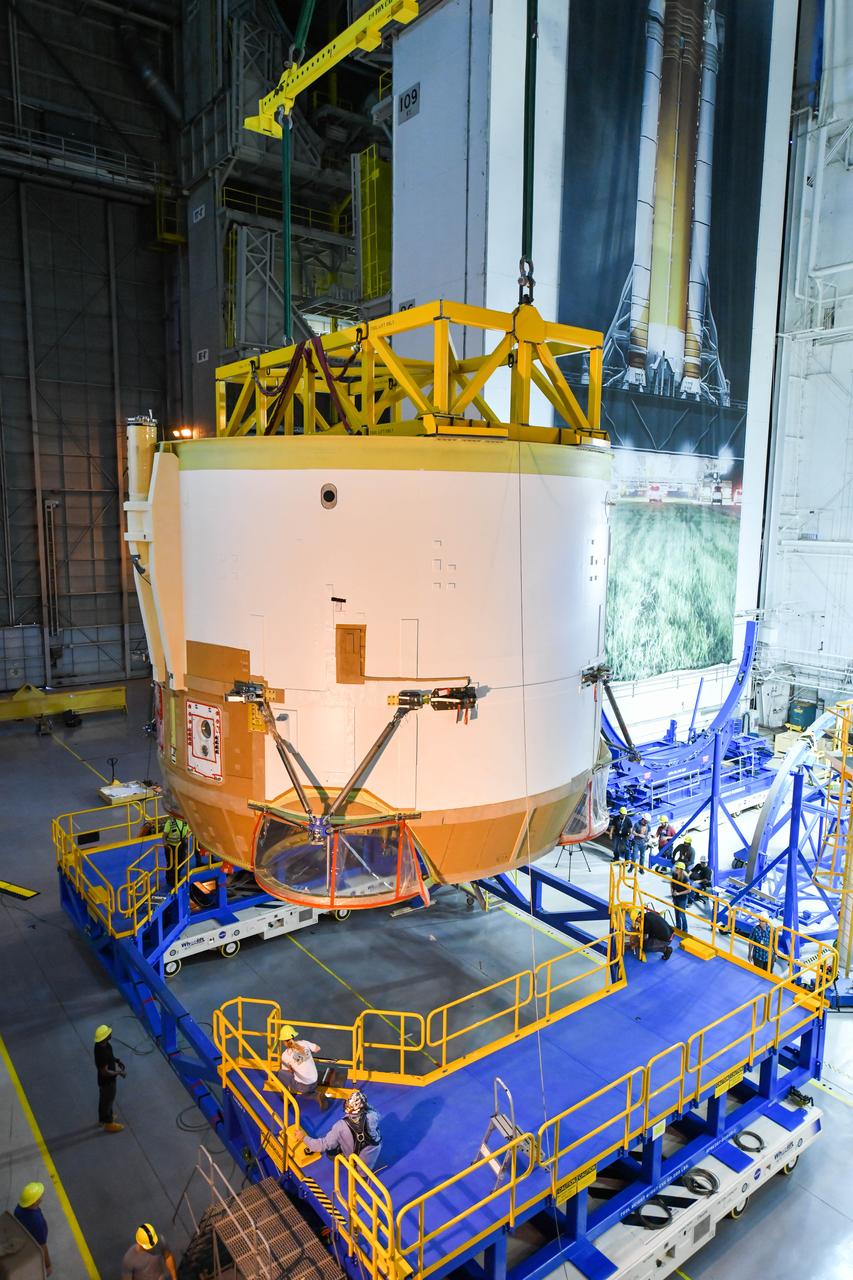

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans rotated the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from a vertical to horizontal position to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage on Sept. 13. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
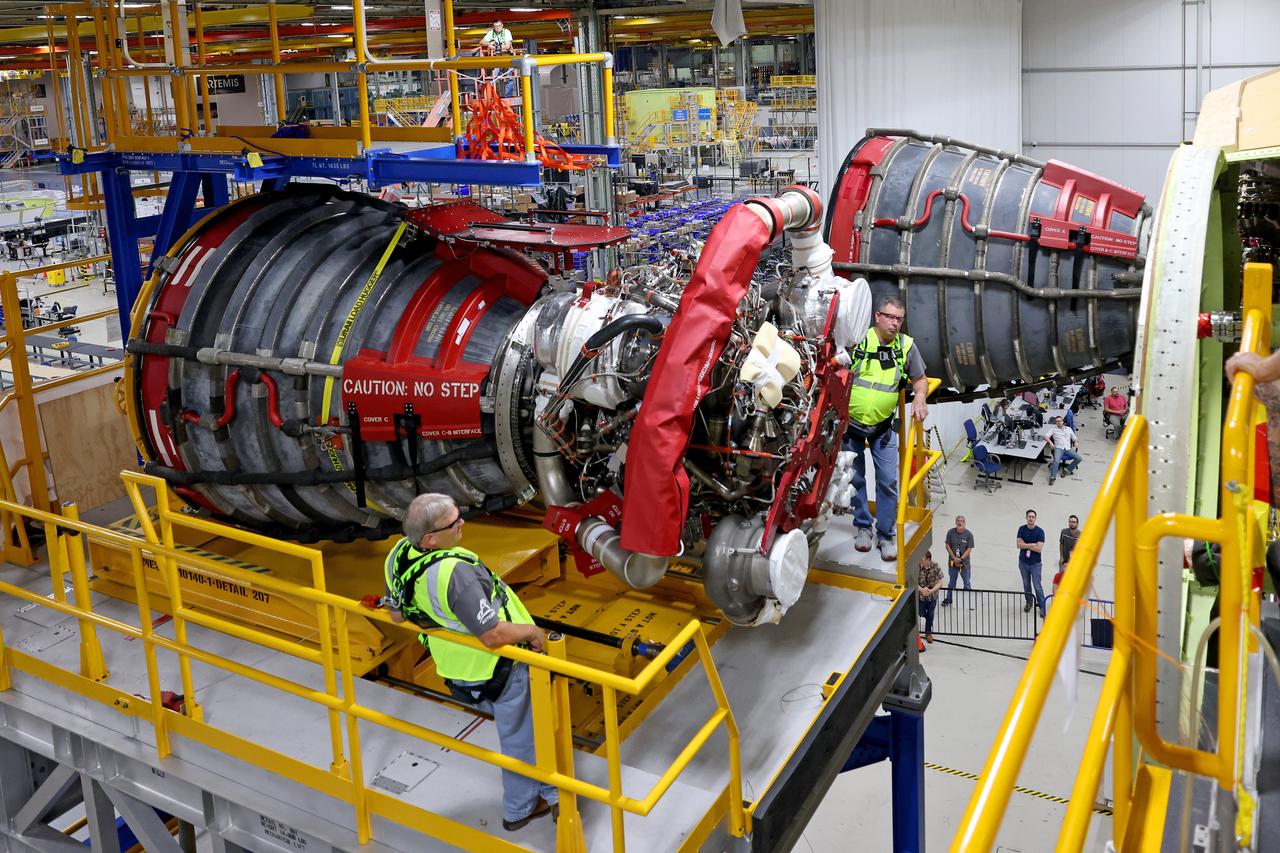

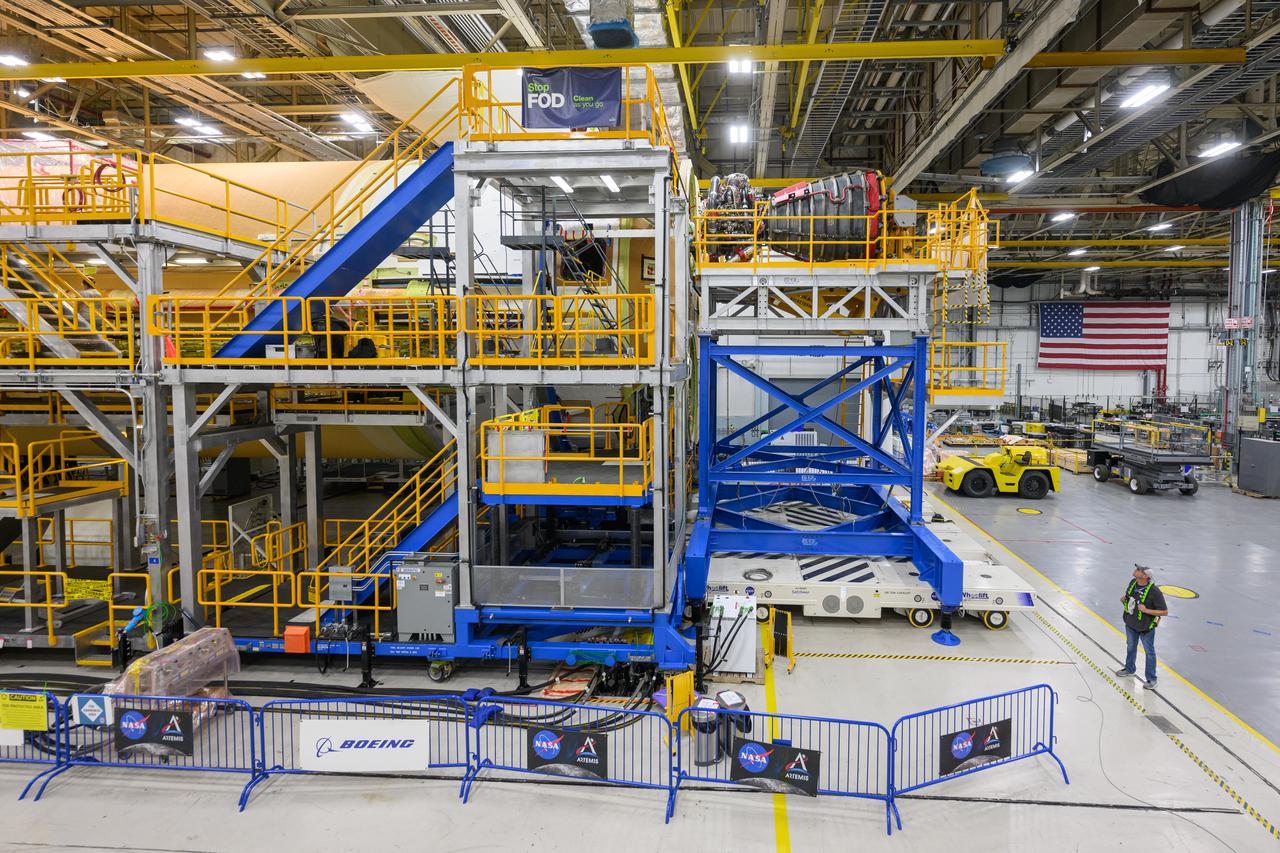
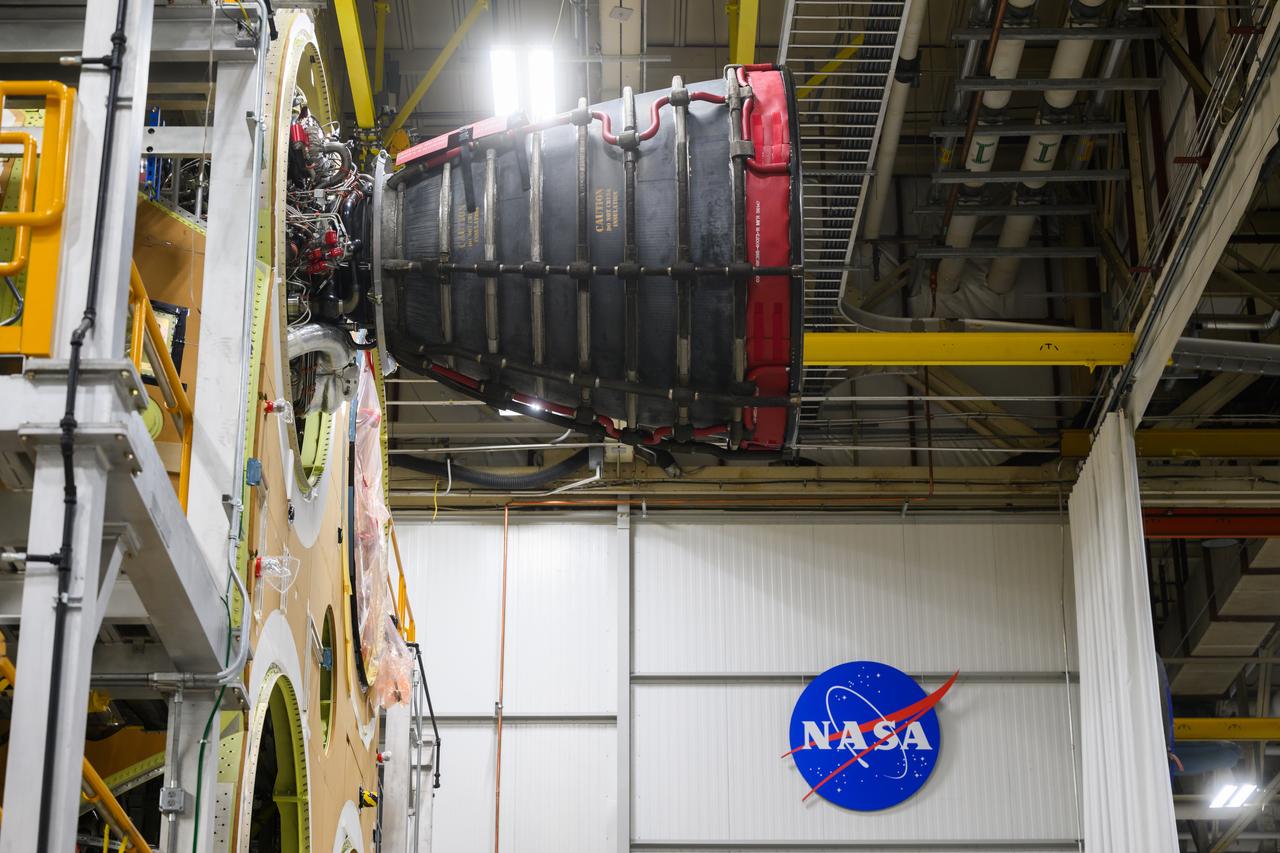
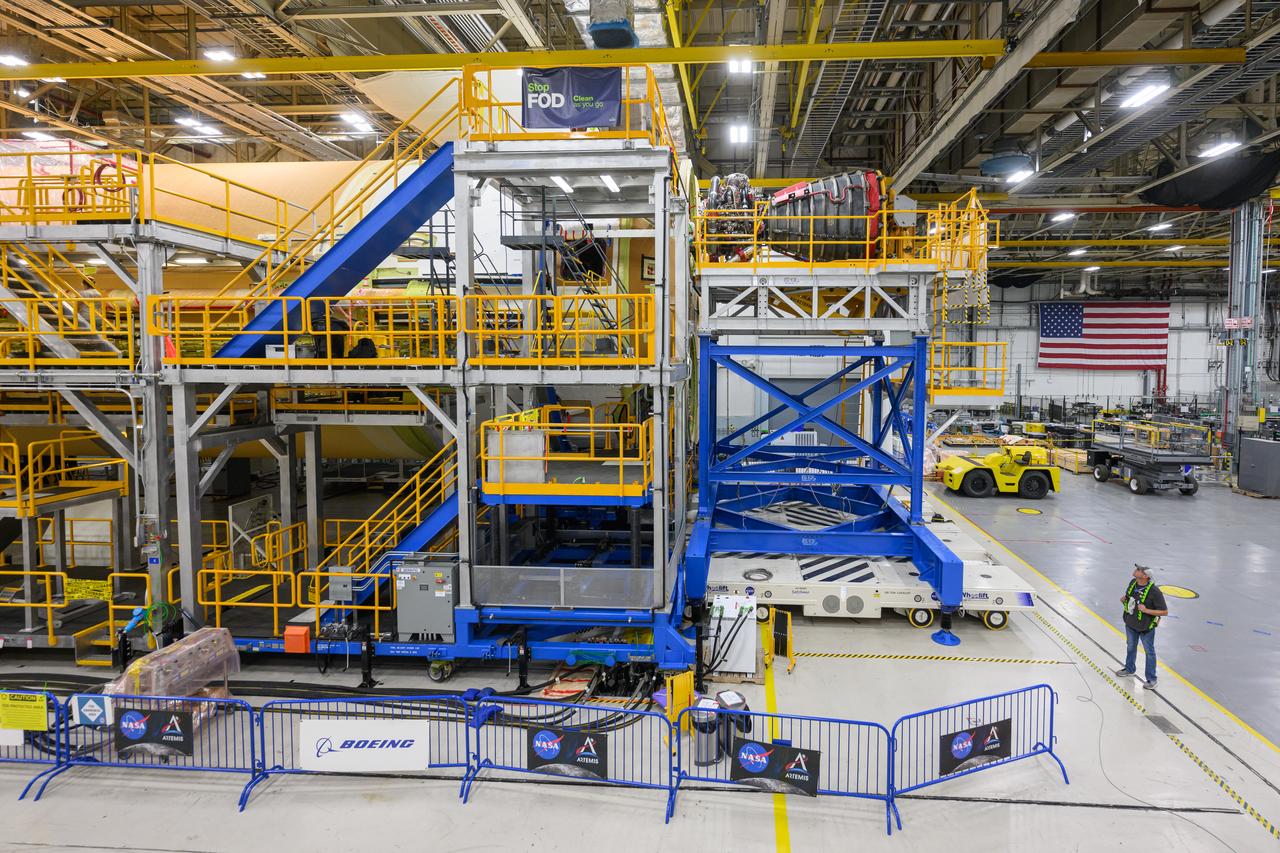
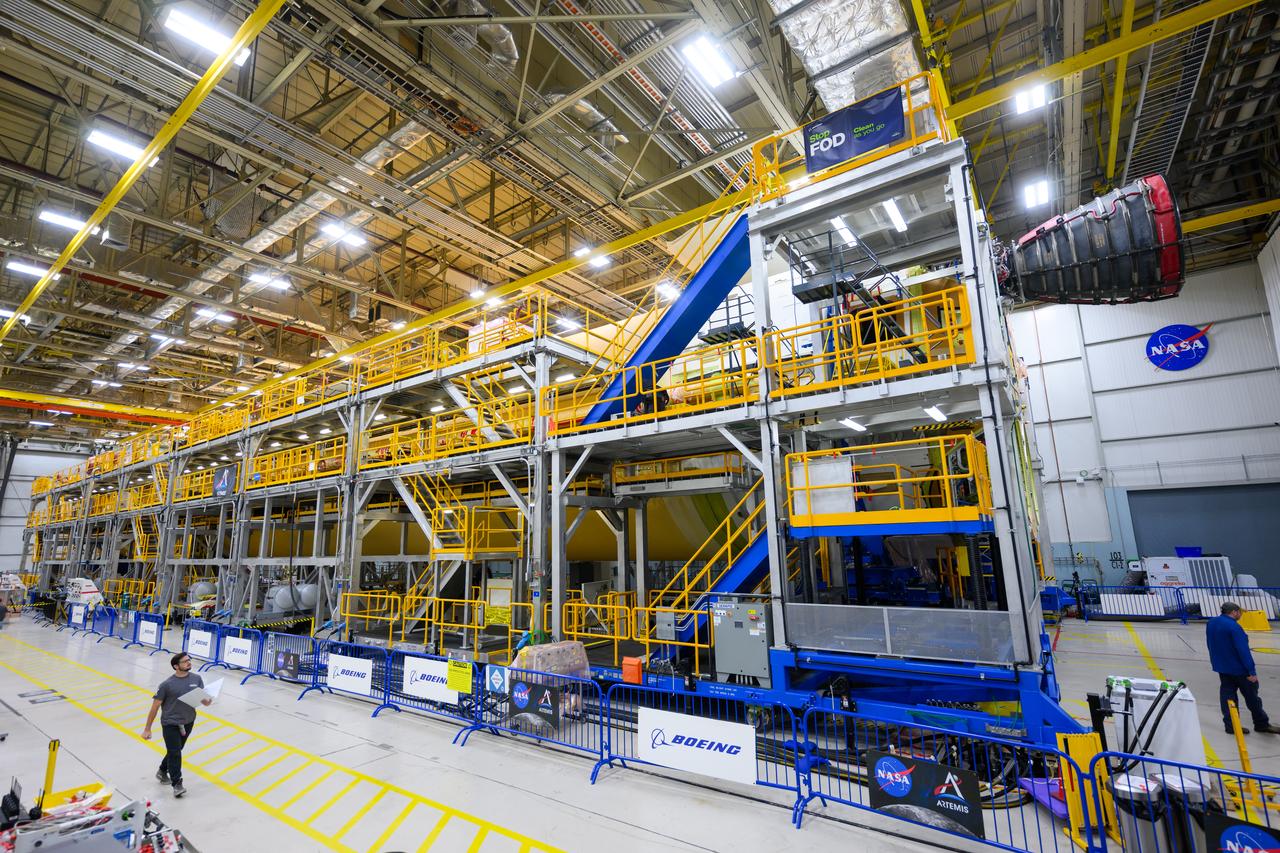
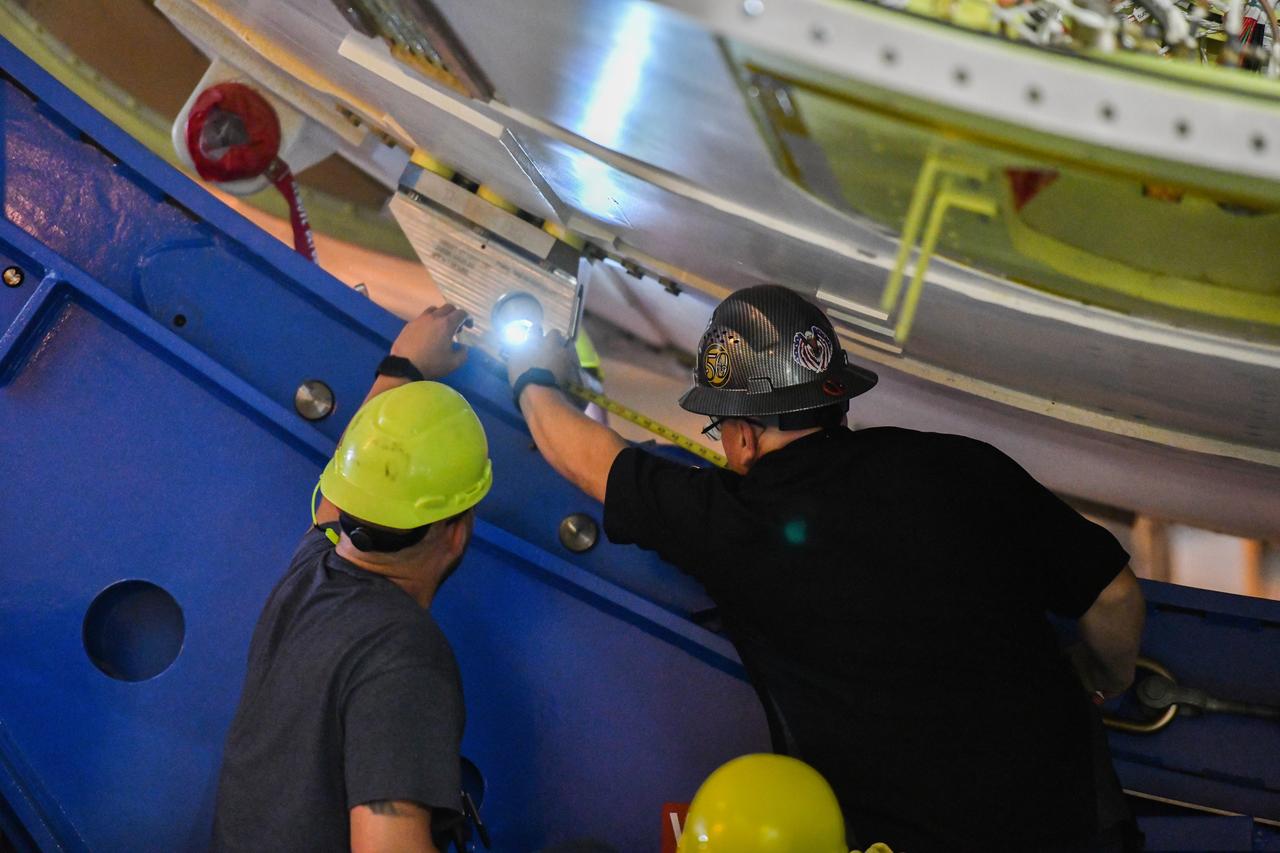
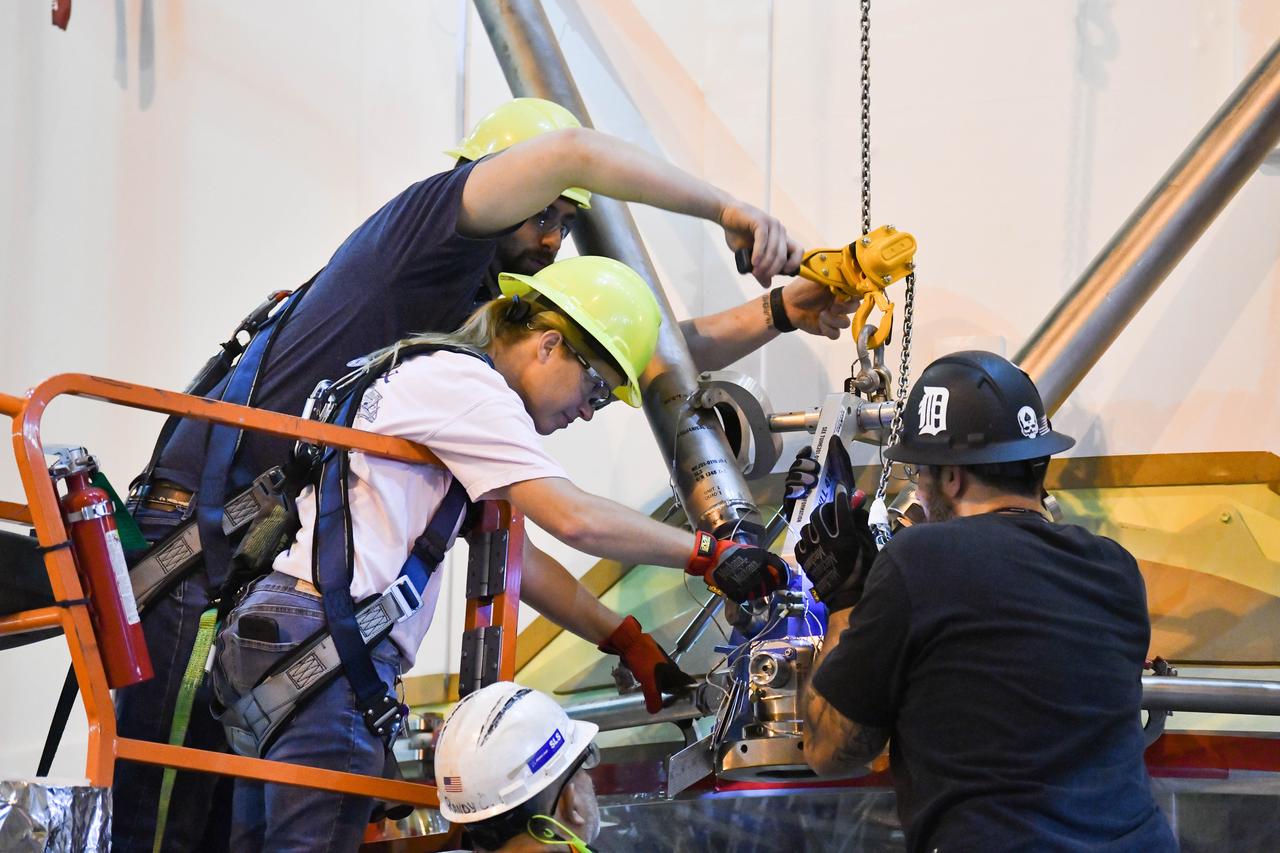
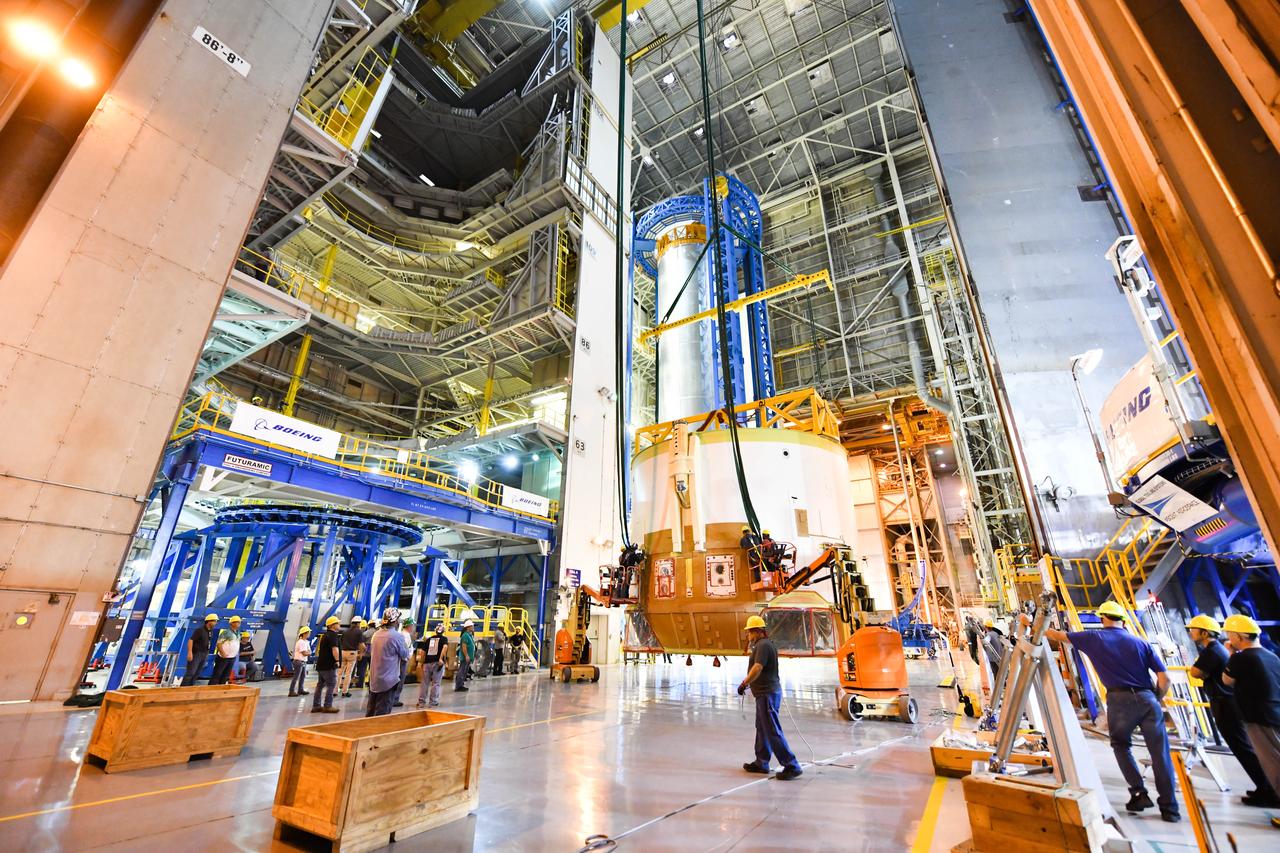
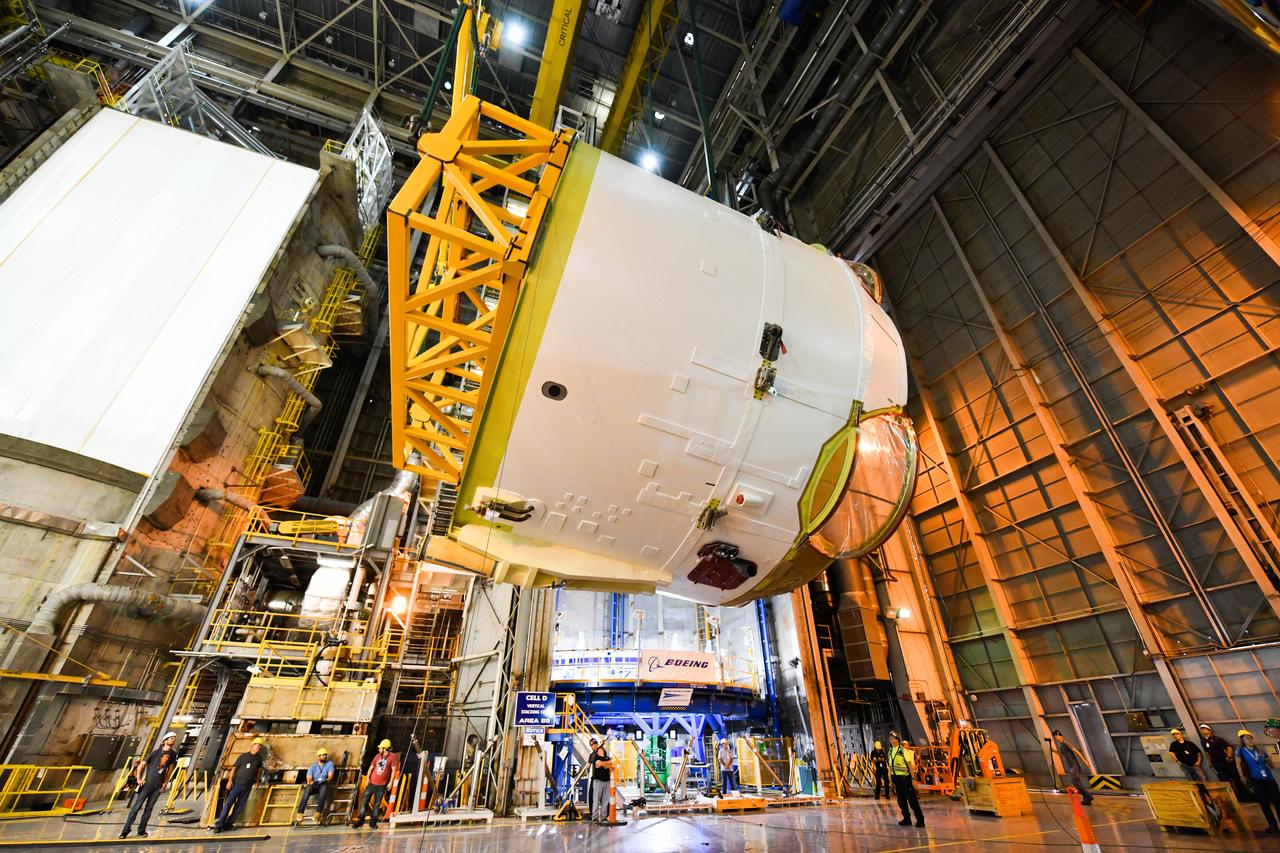
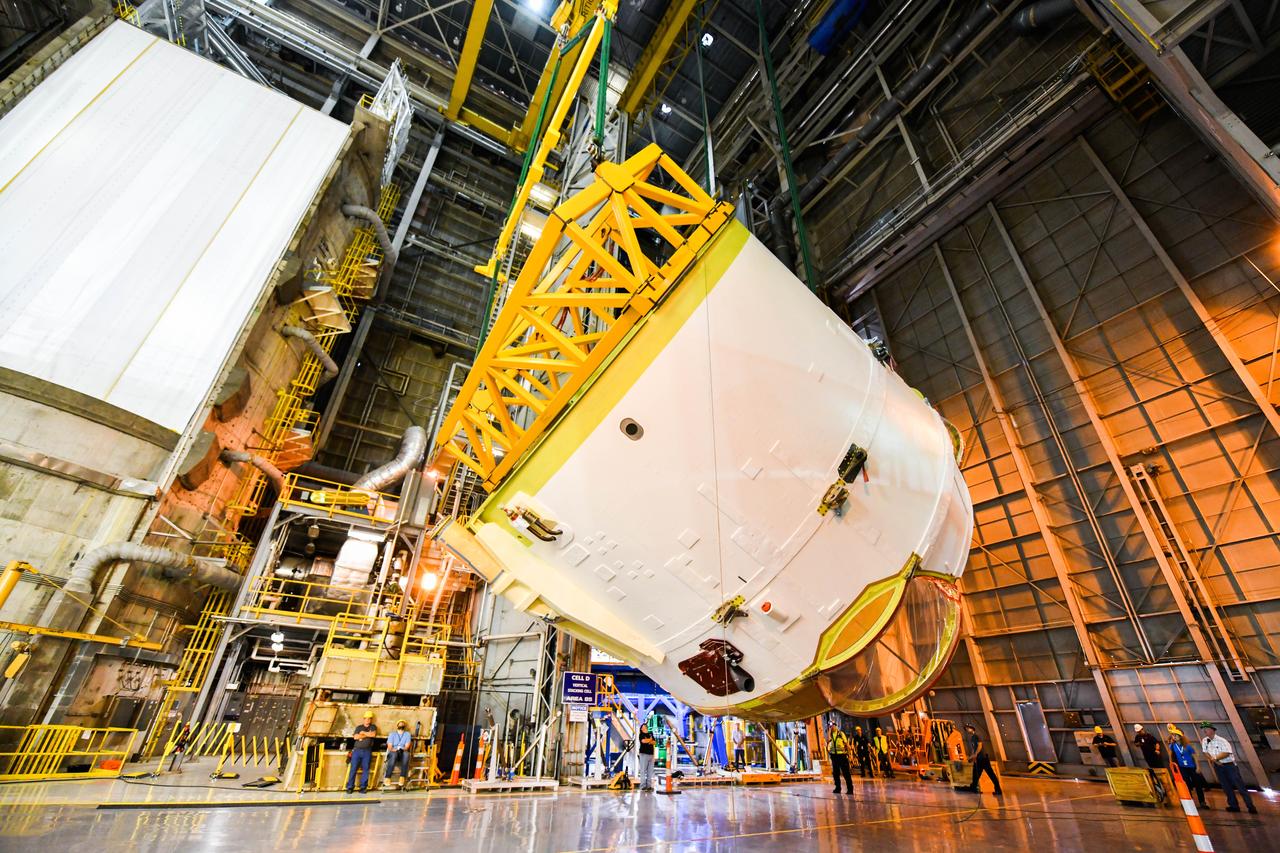
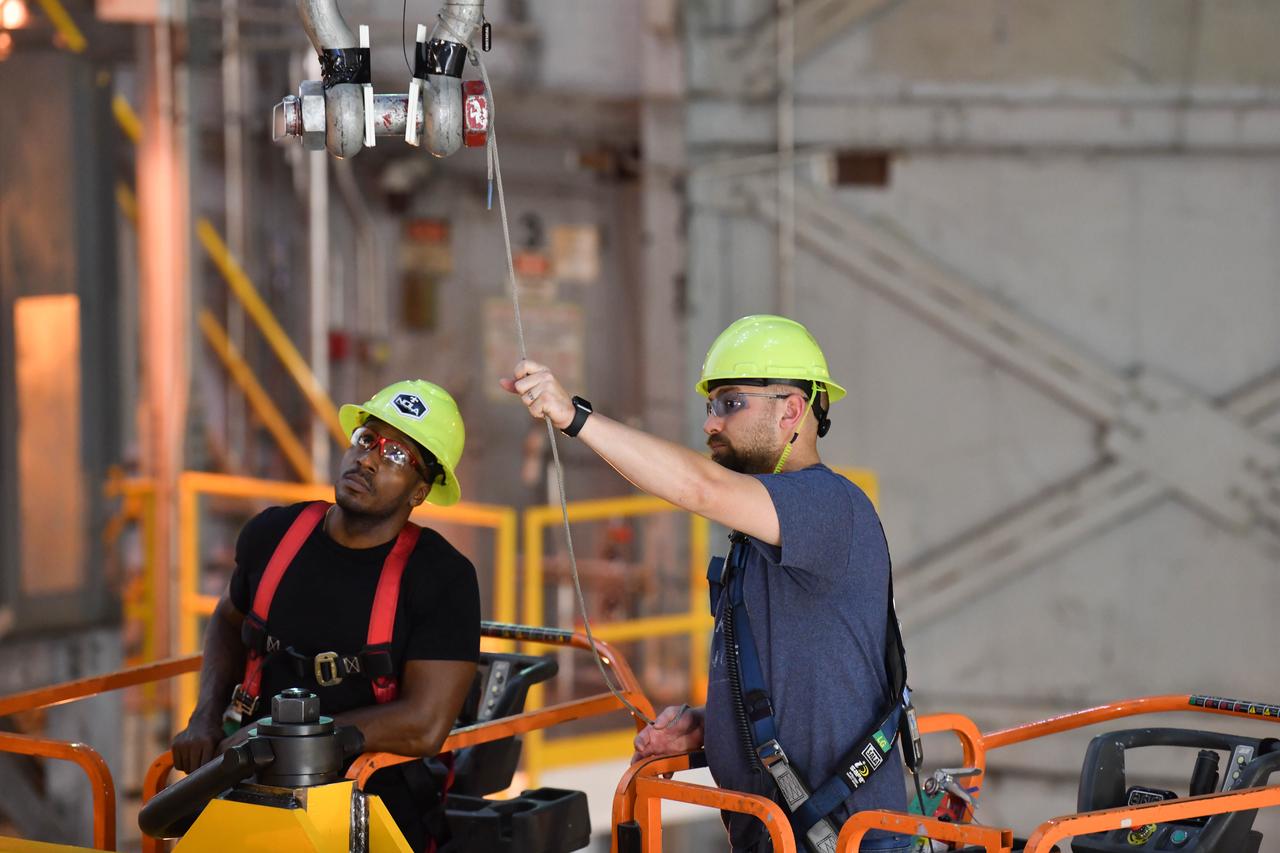
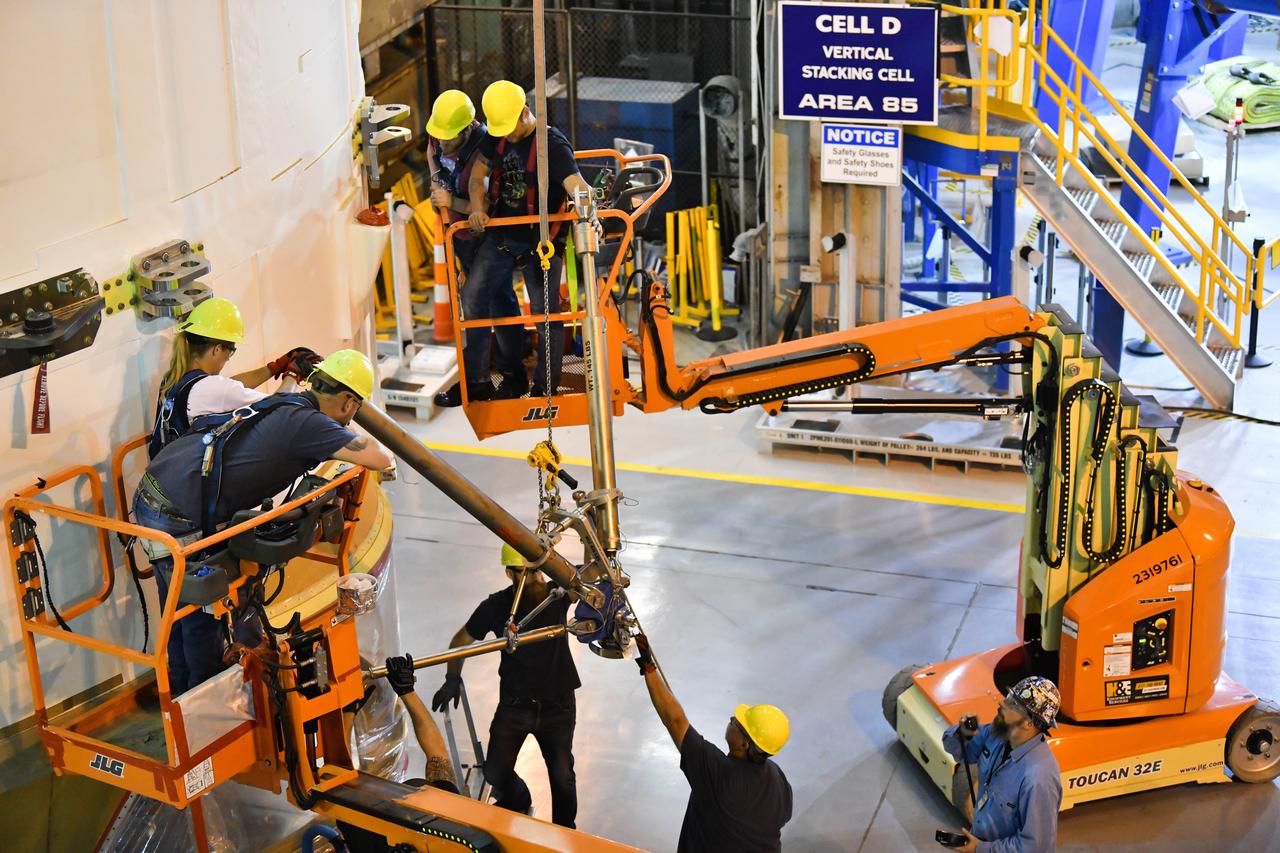
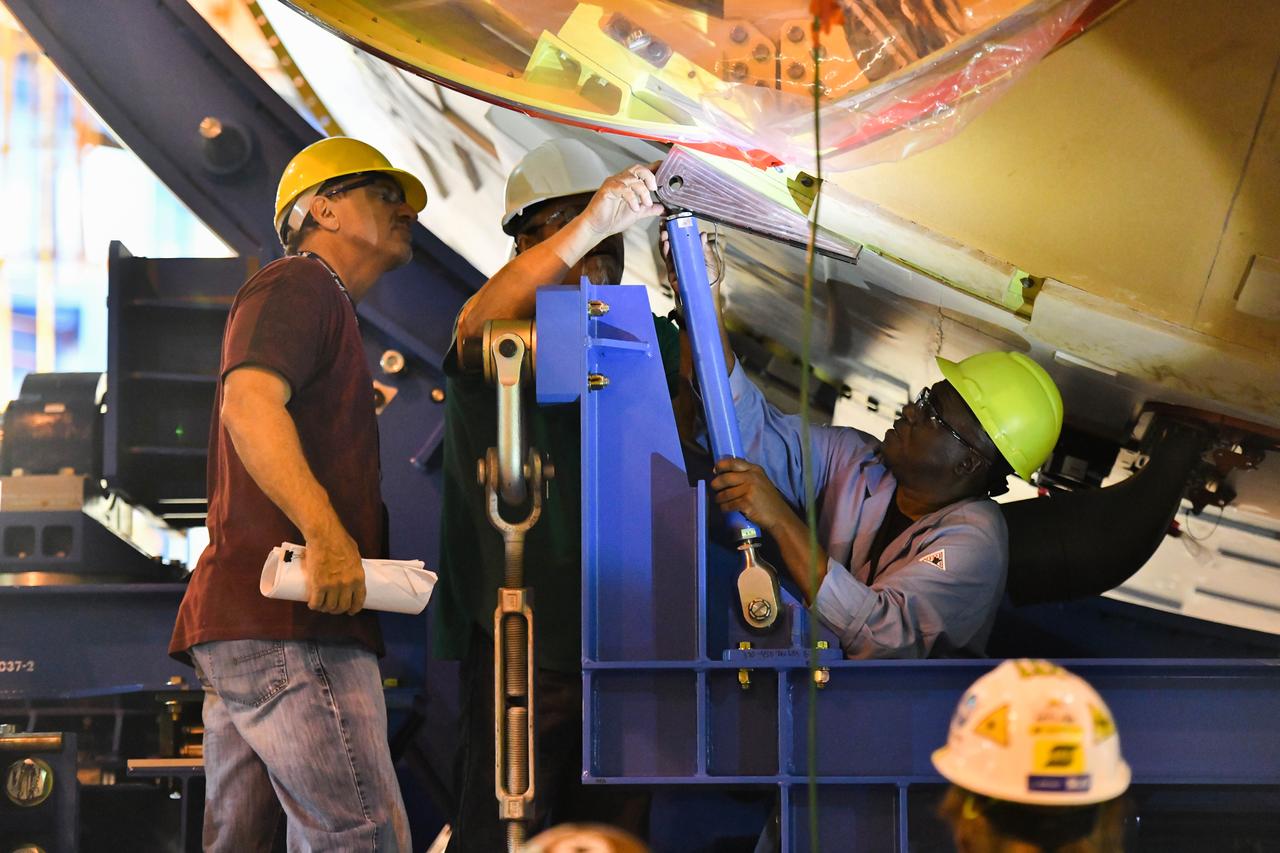
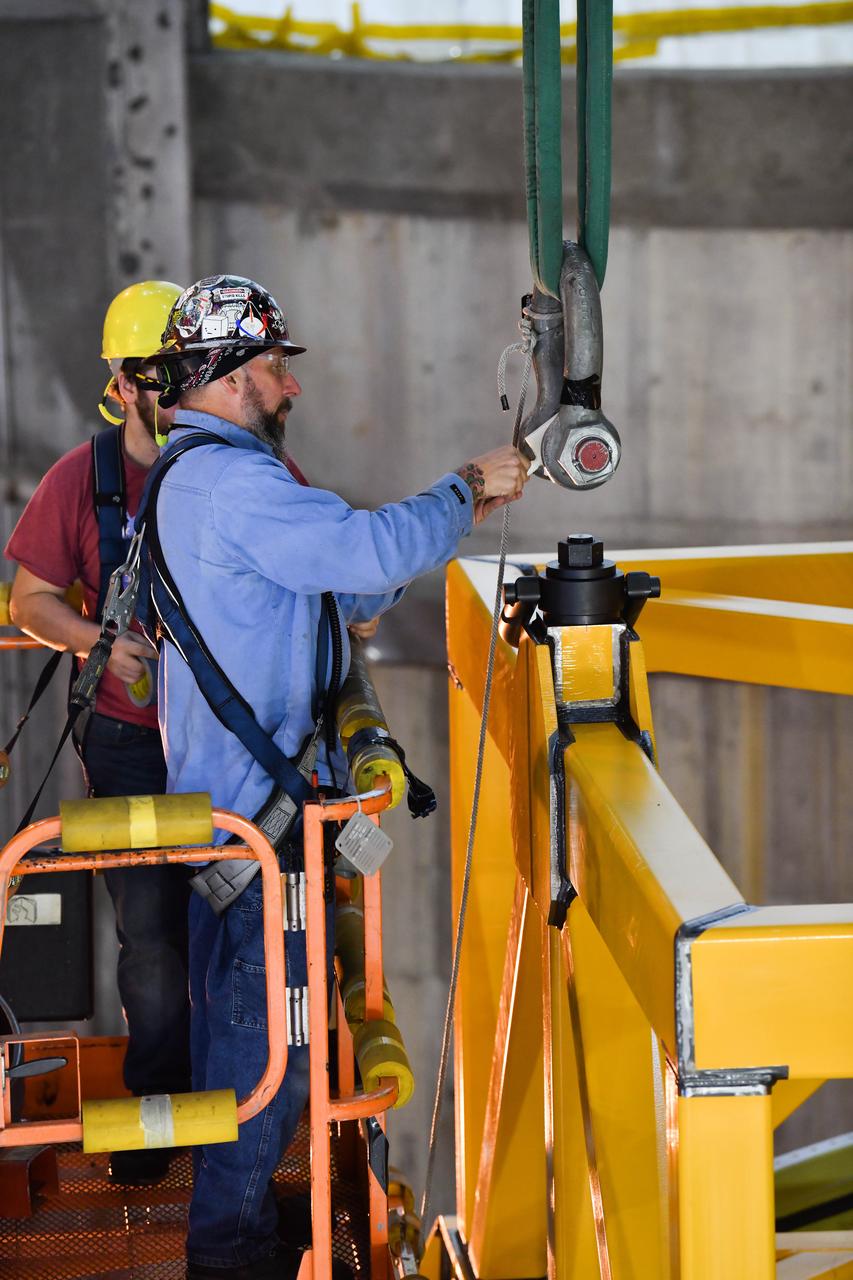
These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the second of four RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Crews added the second engine, with the serial number E2047 in position one, to the stage Sept. 15. The serial number for the engine installed Sept. 11 in position two on the core stage is E2059. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Following soft mate of all four engines, technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will fully secure the engines to the stage and integrate the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the second of four RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Crews added the second engine, with the serial number E2047 in position one, to the stage Sept. 15. The serial number for the engine installed Sept. 11 in position two on the core stage is E2059. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Following soft mate of all four engines, technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will fully secure the engines to the stage and integrate the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
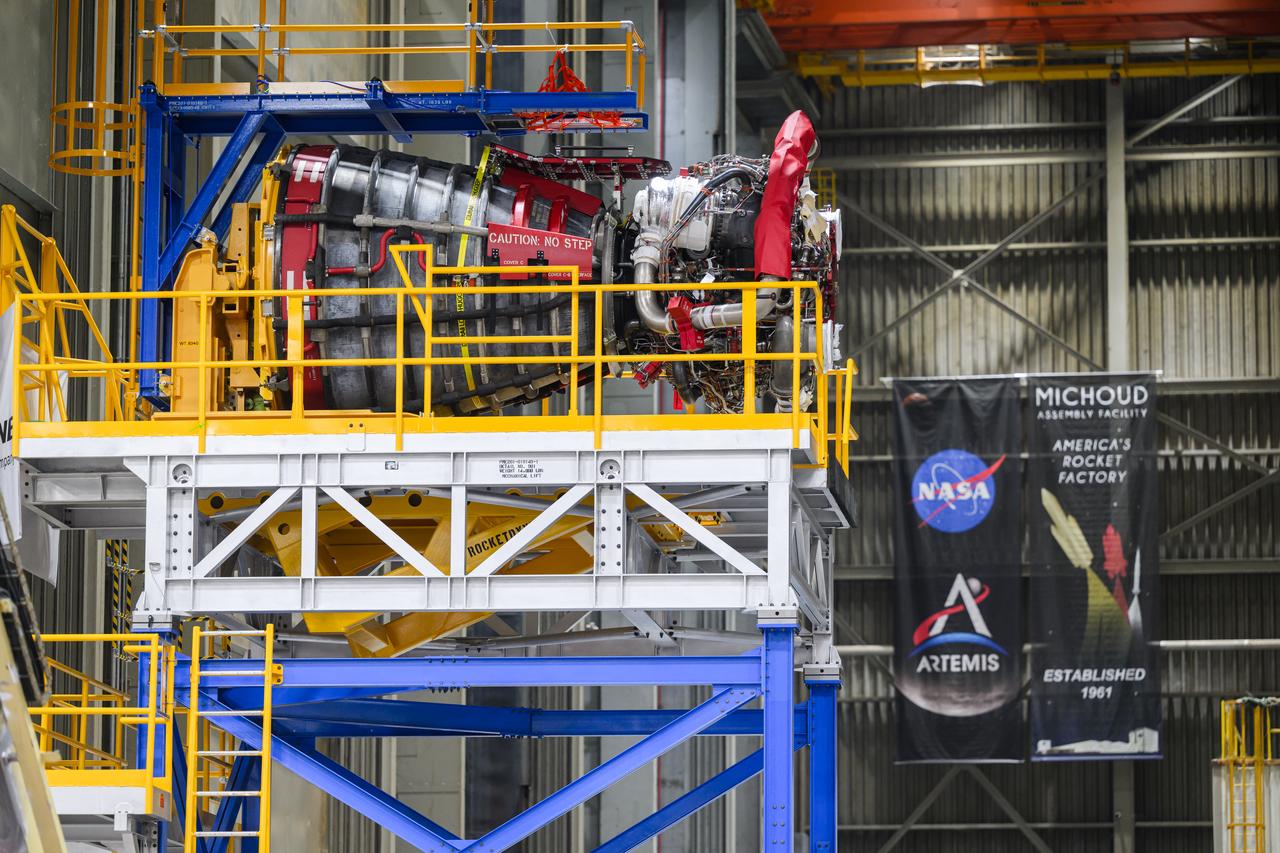

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the second of four RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Crews added the second engine, with the serial number E2047 in position one, to the stage Sept. 15. The serial number for the engine installed Sept. 11 in position two on the core stage is E2059. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Following soft mate of all four engines, technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will fully secure the engines to the stage and integrate the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the second of four RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Crews added the second engine, with the serial number E2047 in position one, to the stage Sept. 15. The serial number for the engine installed Sept. 11 in position two on the core stage is E2059. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Following soft mate of all four engines, technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will fully secure the engines to the stage and integrate the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
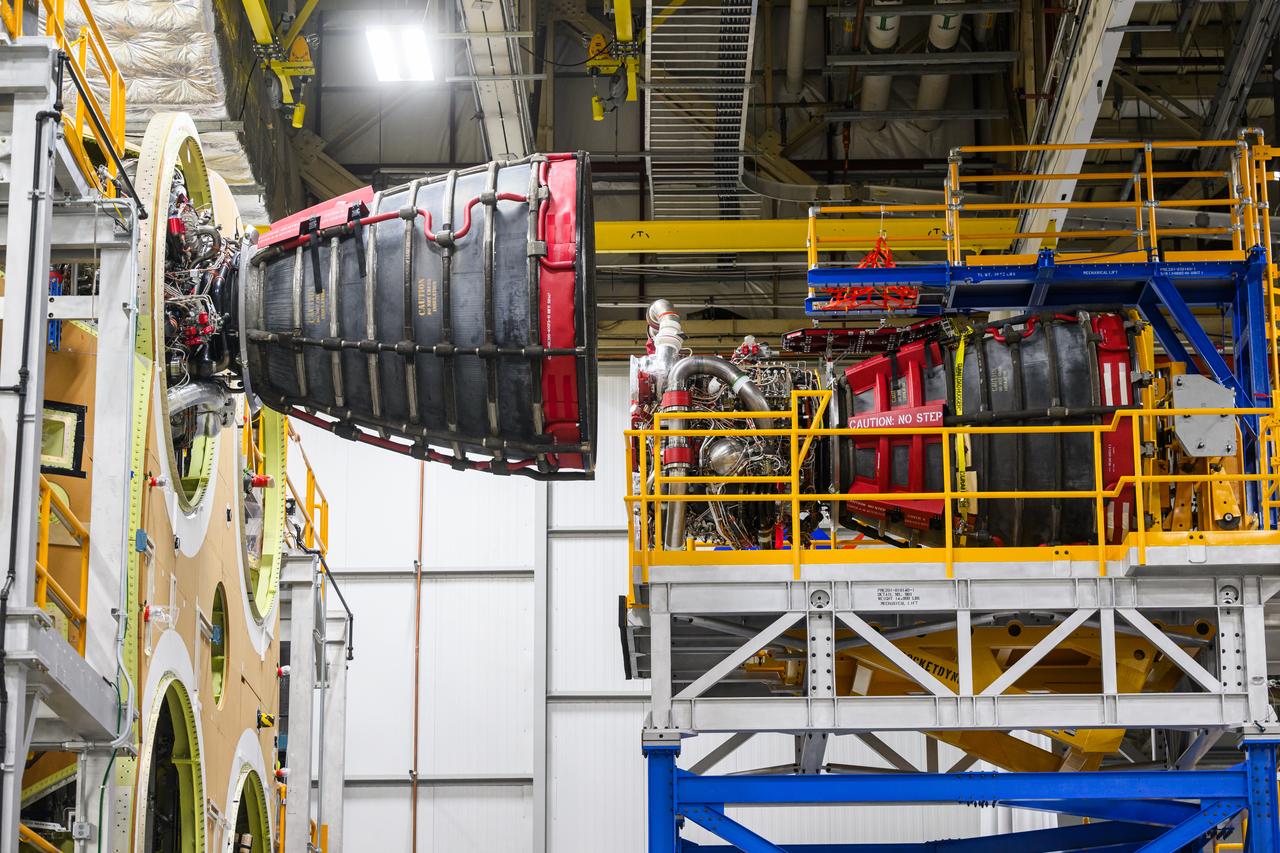

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the second of four RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Crews added the second engine, with the serial number E2047 in position one, to the stage Sept. 15. The serial number for the engine installed Sept. 11 in position two on the core stage is E2059. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Following soft mate of all four engines, technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will fully secure the engines to the stage and integrate the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
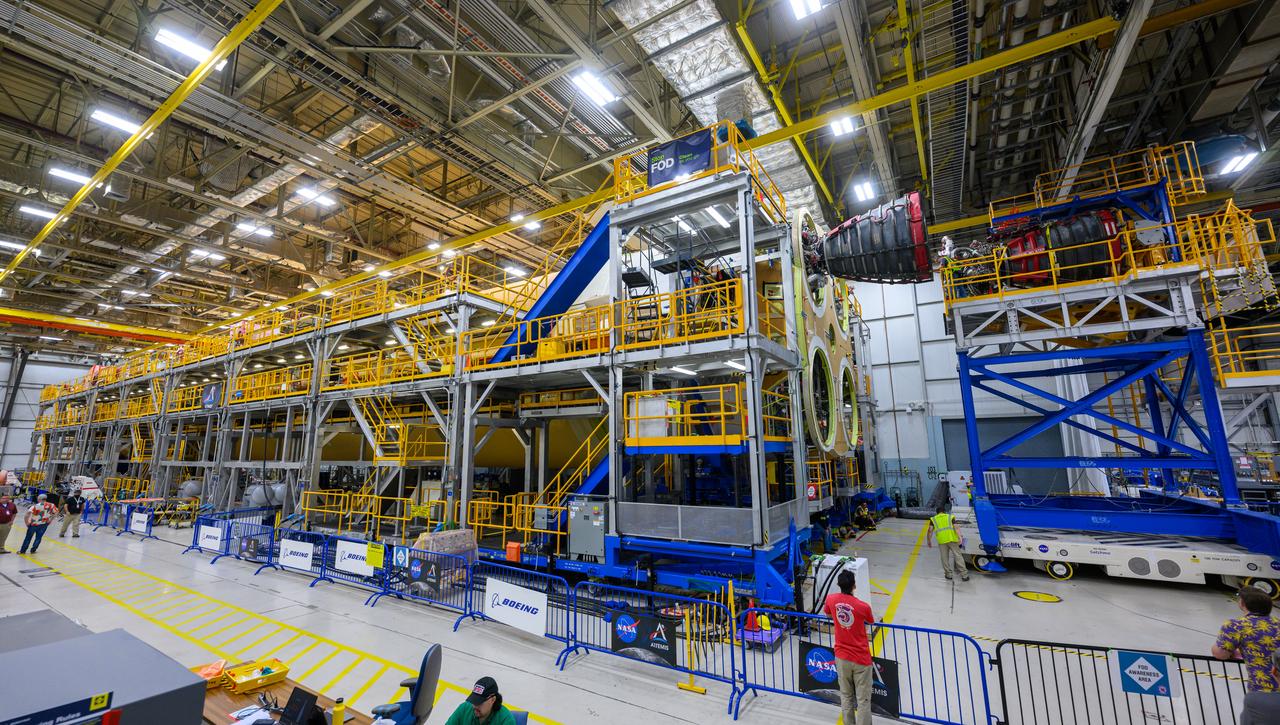

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the second of four RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Crews added the second engine, with the serial number E2047 in position one, to the stage Sept. 15. The serial number for the engine installed Sept. 11 in position two on the core stage is E2059. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Following soft mate of all four engines, technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will fully secure the engines to the stage and integrate the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
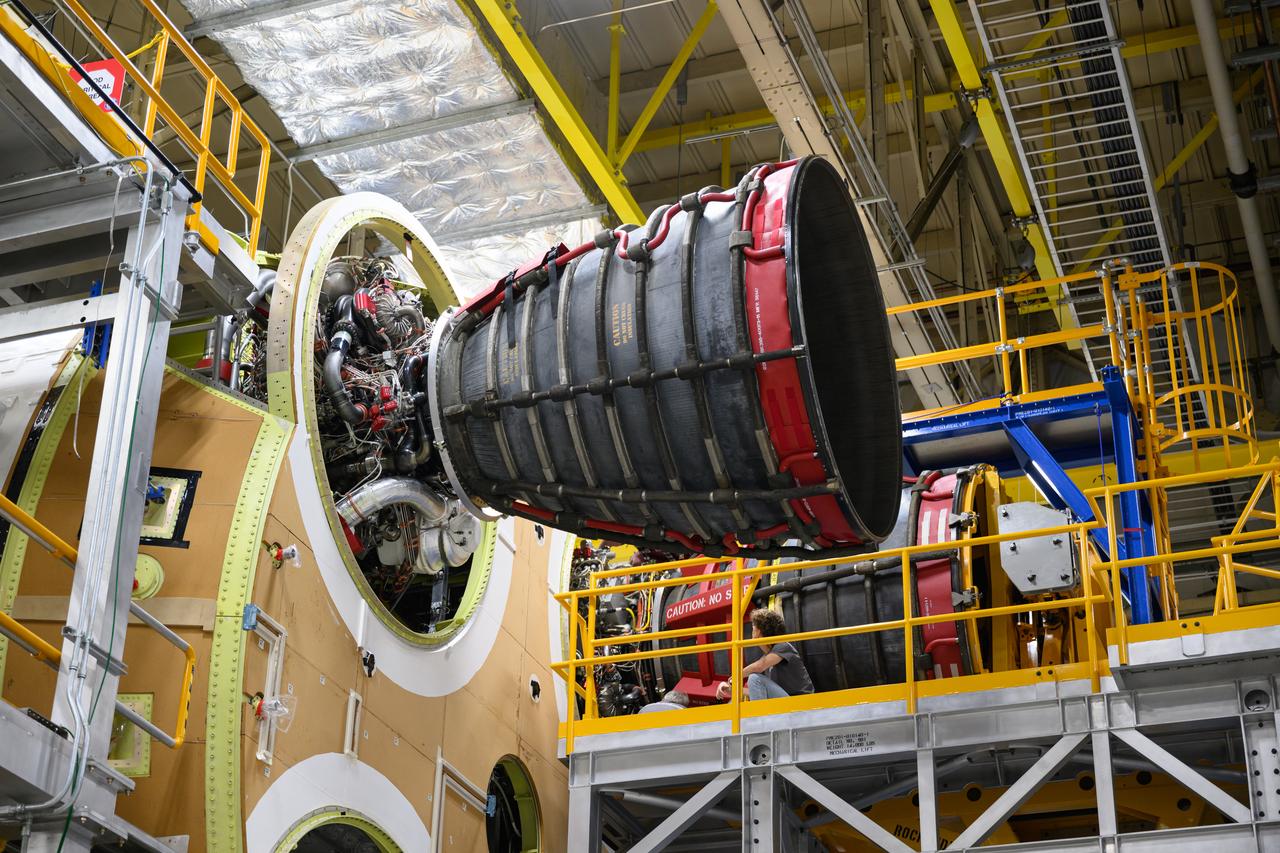

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the second of four RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Crews added the second engine, with the serial number E2047 in position one, to the stage Sept. 15. The serial number for the engine installed Sept. 11 in position two on the core stage is E2059. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Following soft mate of all four engines, technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will fully secure the engines to the stage and integrate the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
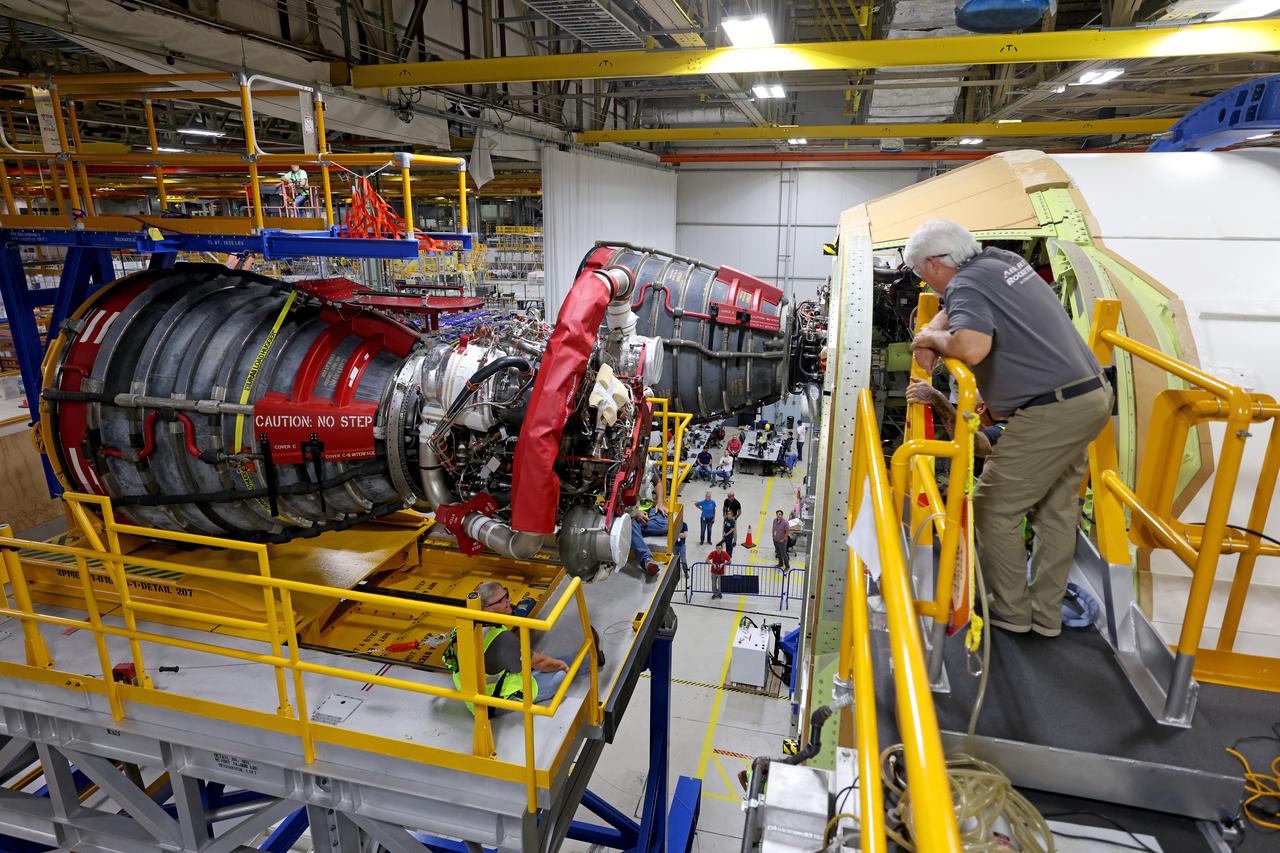

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the second of four RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Crews added the second engine, with the serial number E2047 in position one, to the stage Sept. 15. The serial number for the engine installed Sept. 11 in position two on the core stage is E2059. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Following soft mate of all four engines, technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will fully secure the engines to the stage and integrate the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
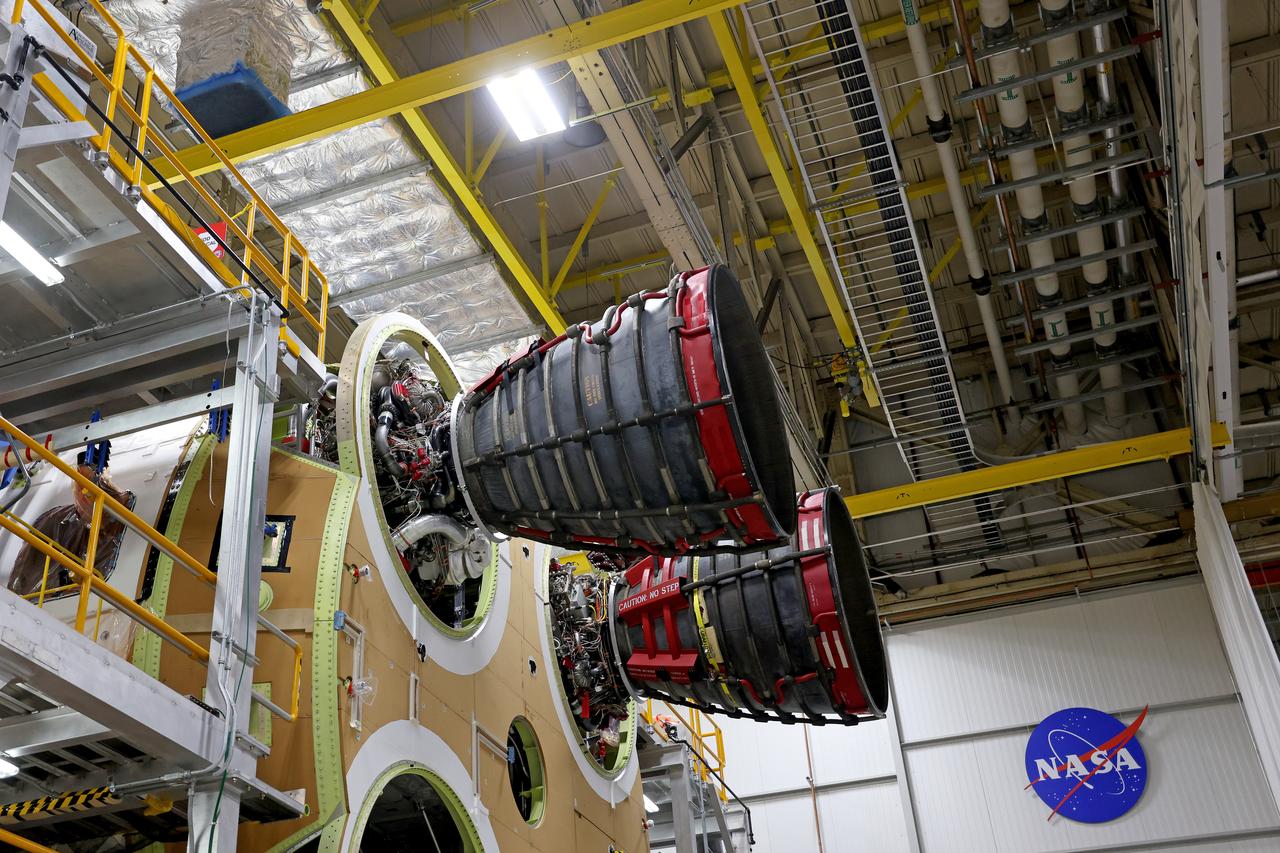

These photos and videos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the second of four RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Crews added the second engine, with the serial number E2047 in position one, to the stage Sept. 15. The serial number for the engine installed Sept. 11 in position two on the core stage is E2059. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Following soft mate of all four engines, technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will fully secure the engines to the stage and integrate the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
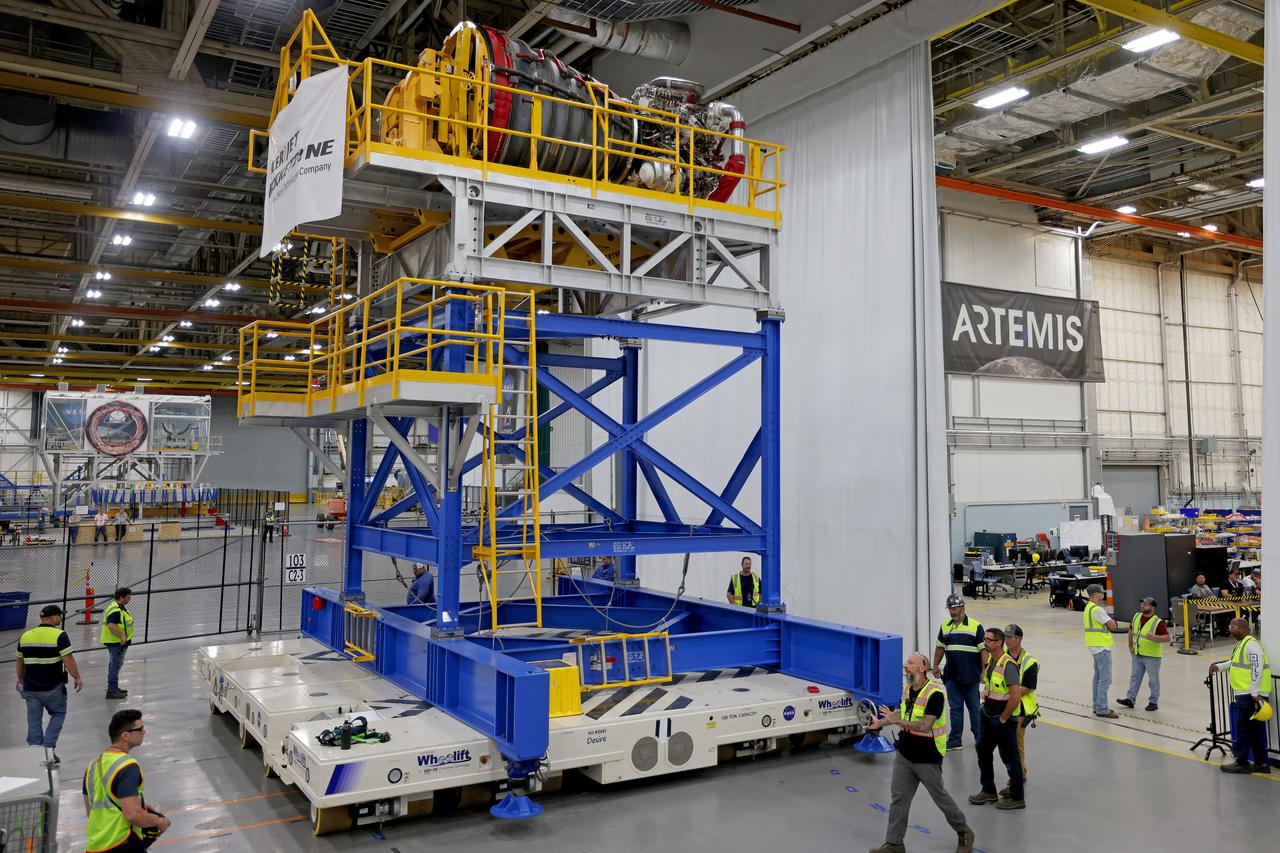

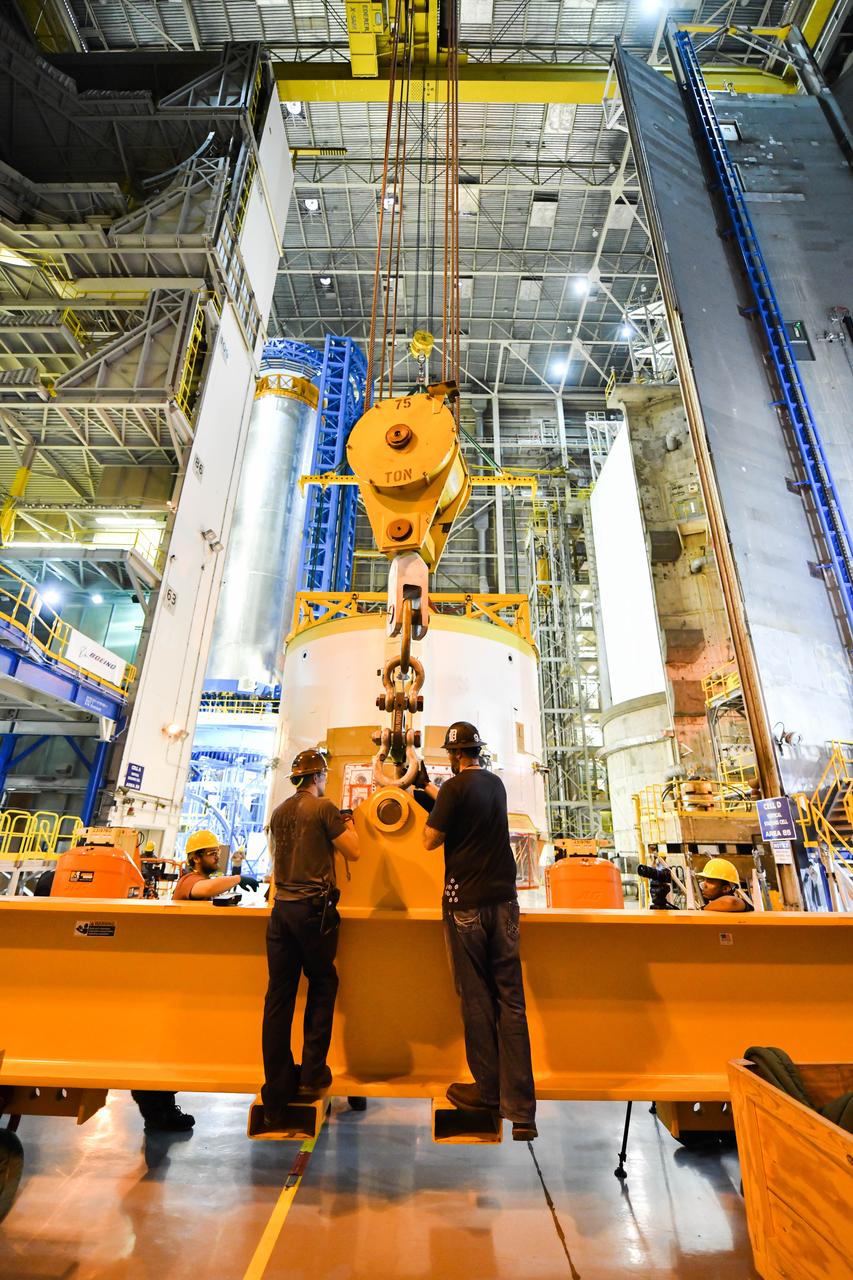
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans have installed the first of four RS-25 engines on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. The Sept. 11 engine installation follows the joining of all five major structures that make up the SLS core stage earlier this spring. NASA, lead RS-25 engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3 Harris Technologies company, and Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will continue integrating the remaining three engines into the stage and installing the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
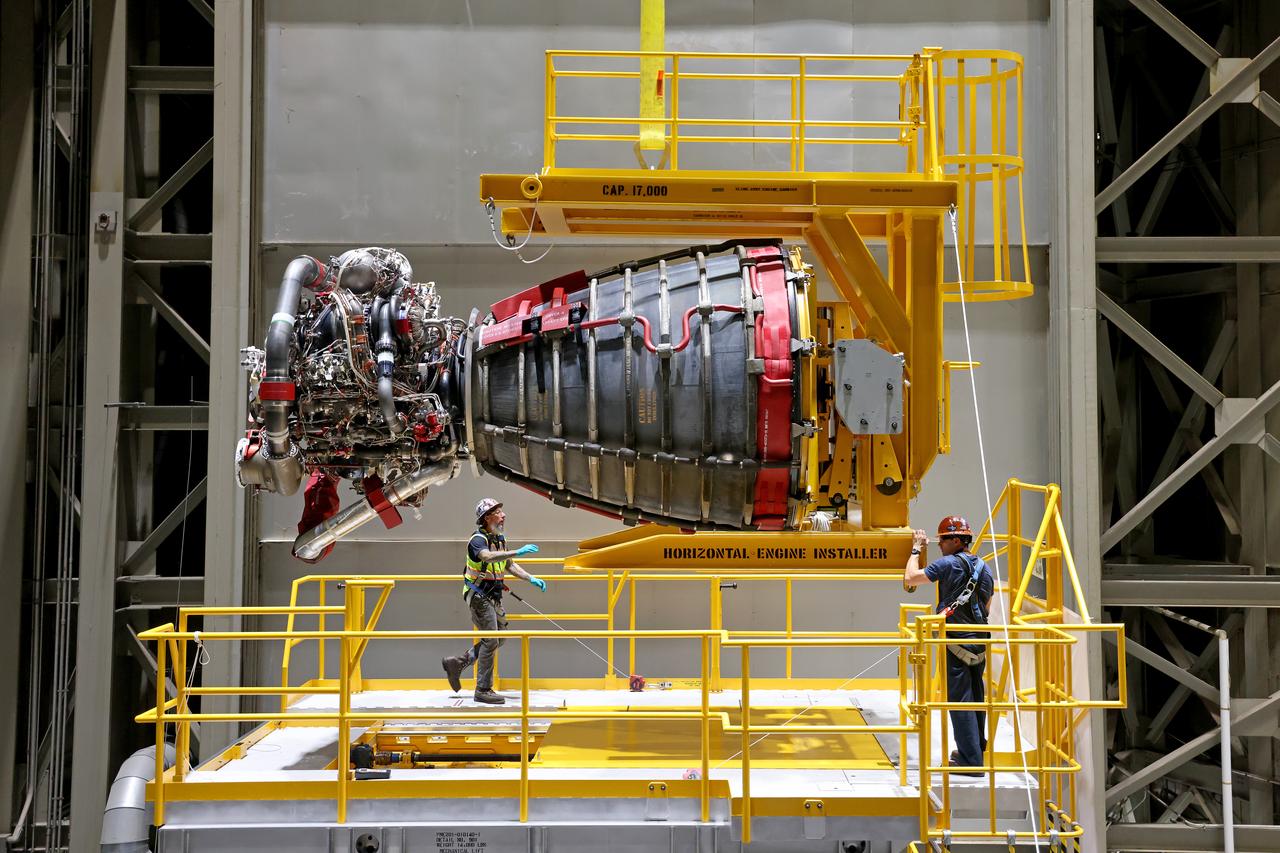
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans have installed the first of four RS-25 engines on the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. The Sept. 11 engine installation follows the joining of all five major structures that make up the SLS core stage earlier this spring. NASA, lead RS-25 engines contractor Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3 Harris Technologies company, and Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will continue integrating the remaining three engines into the stage and installing the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. All four RS-25 engines are located at the base of the core stage within the engine section. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

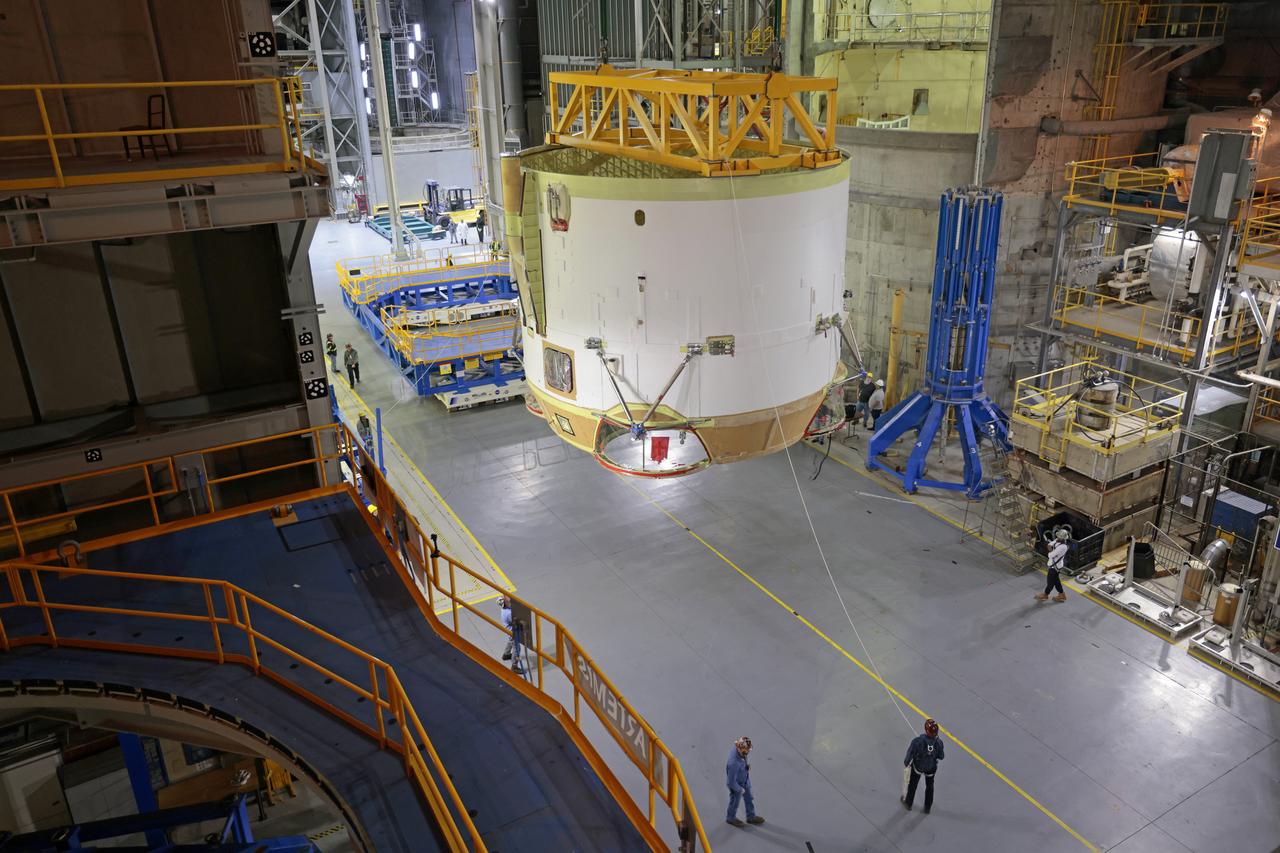
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis IV from the Vertical Assembly Building to Cell G for weld priming. This hardware is the first large piece manufactured for the Artemis IV mission and makes up the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis IV from the Vertical Assembly Building to Cell G for weld priming. This hardware is the first large piece manufactured for the Artemis IV mission and makes up the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
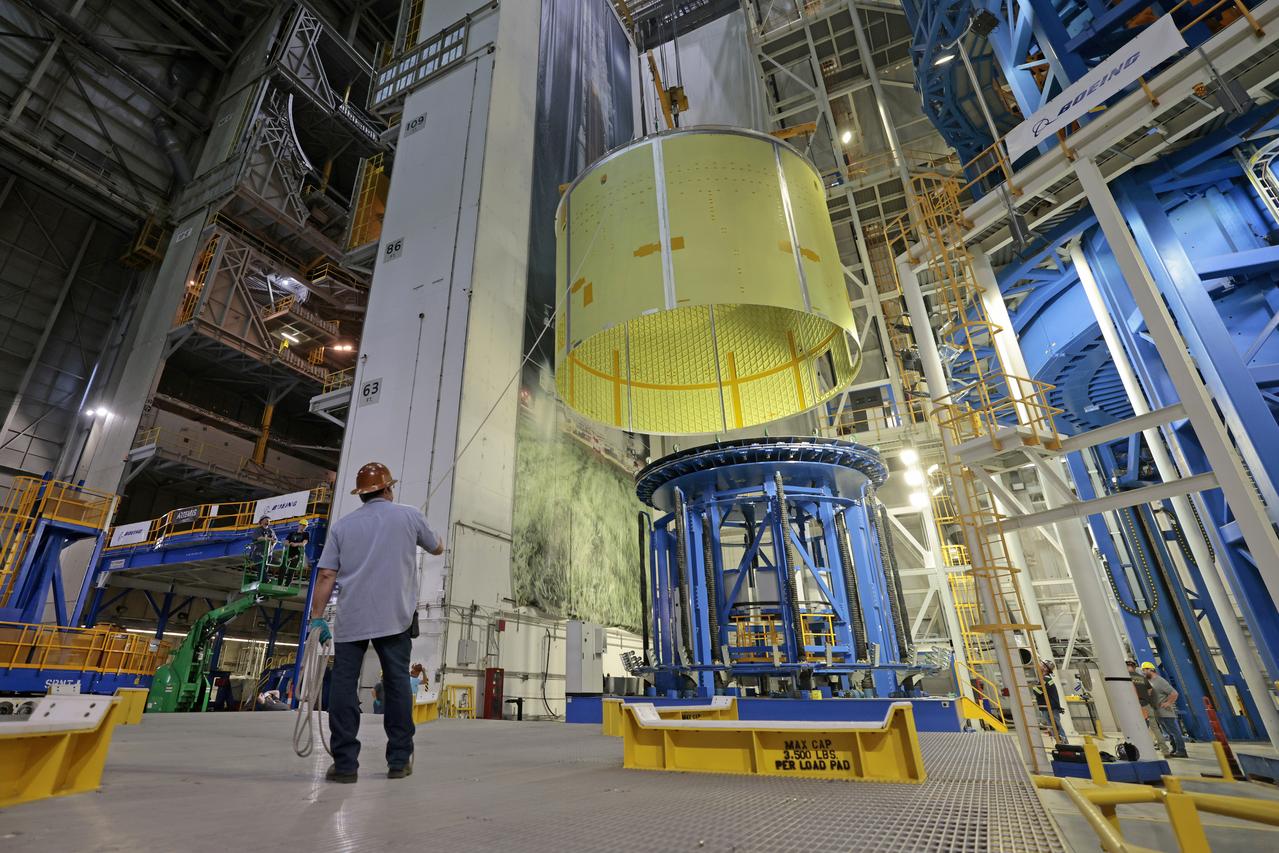

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis IV from the Vertical Assembly Building to Cell G for weld priming. This hardware is the first large piece manufactured for the Artemis IV mission and makes up the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
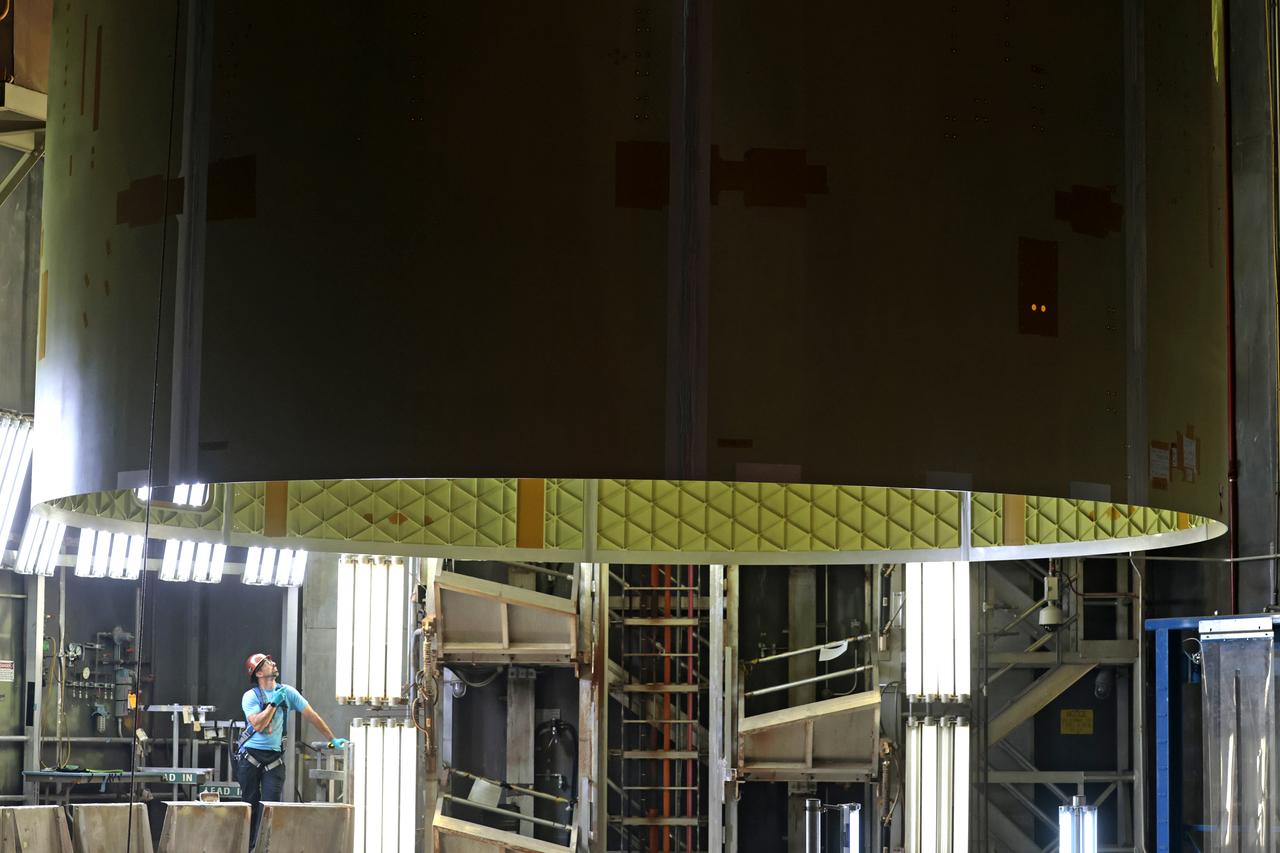

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis IV from the Vertical Assembly Building to Cell G for weld priming. This hardware is the first large piece manufactured for the Artemis IV mission and makes up the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
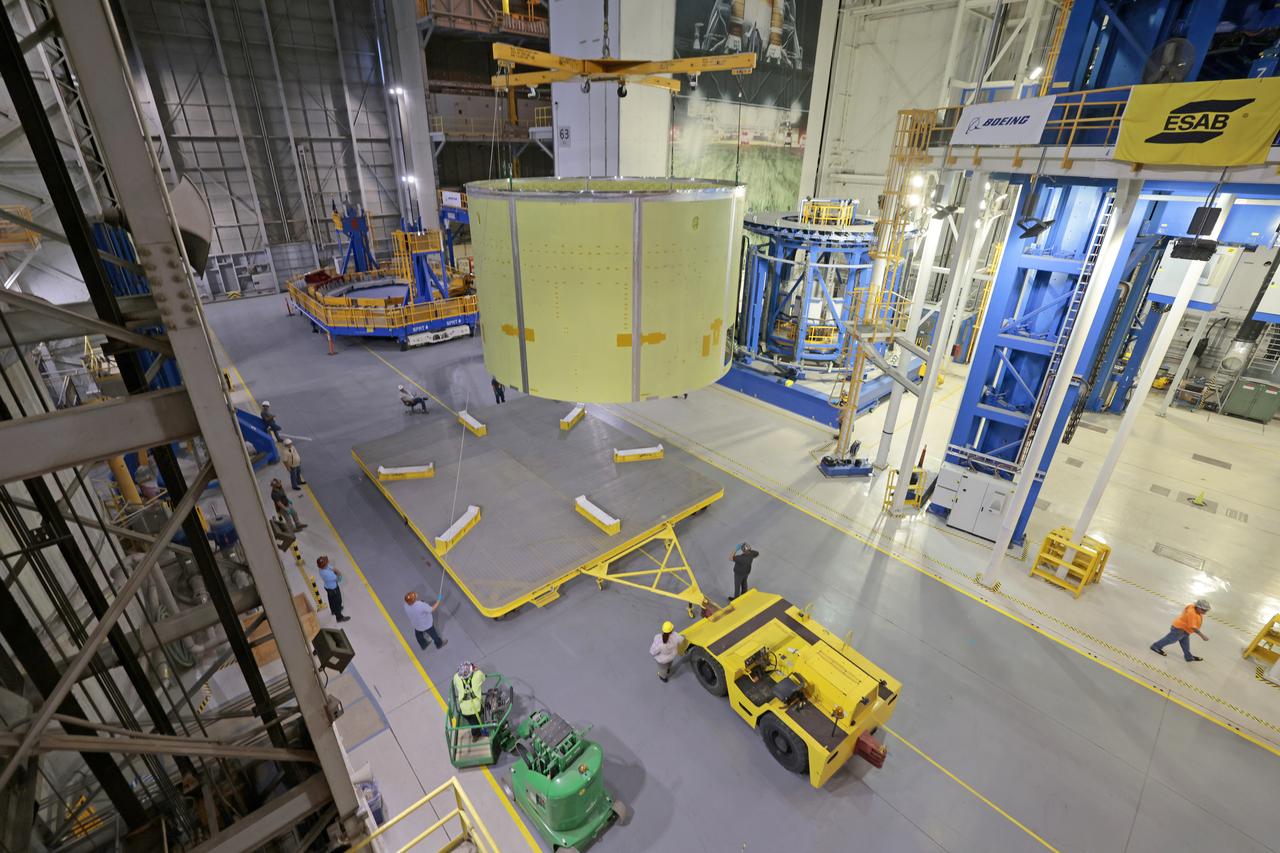

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis IV from the Vertical Assembly Building to Cell G for weld priming. This hardware is the first large piece manufactured for the Artemis IV mission and makes up the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis IV from the Vertical Assembly Building to Cell G for weld priming. This hardware is the first large piece manufactured for the Artemis IV mission and makes up the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis IV from the Vertical Assembly Building to Cell G for weld priming. This hardware is the first large piece manufactured for the Artemis IV mission and makes up the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis IV out of Cell G after weld priming. This hardware is the first large piece manufactured for the Artemis IV mission and makes up the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage. When complete, the engine section will house the four RS-25 engines and include vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel from the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Together with its four RS-25 engines and its twin solid rocket boosters, it will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability, and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the Human Landing System, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.

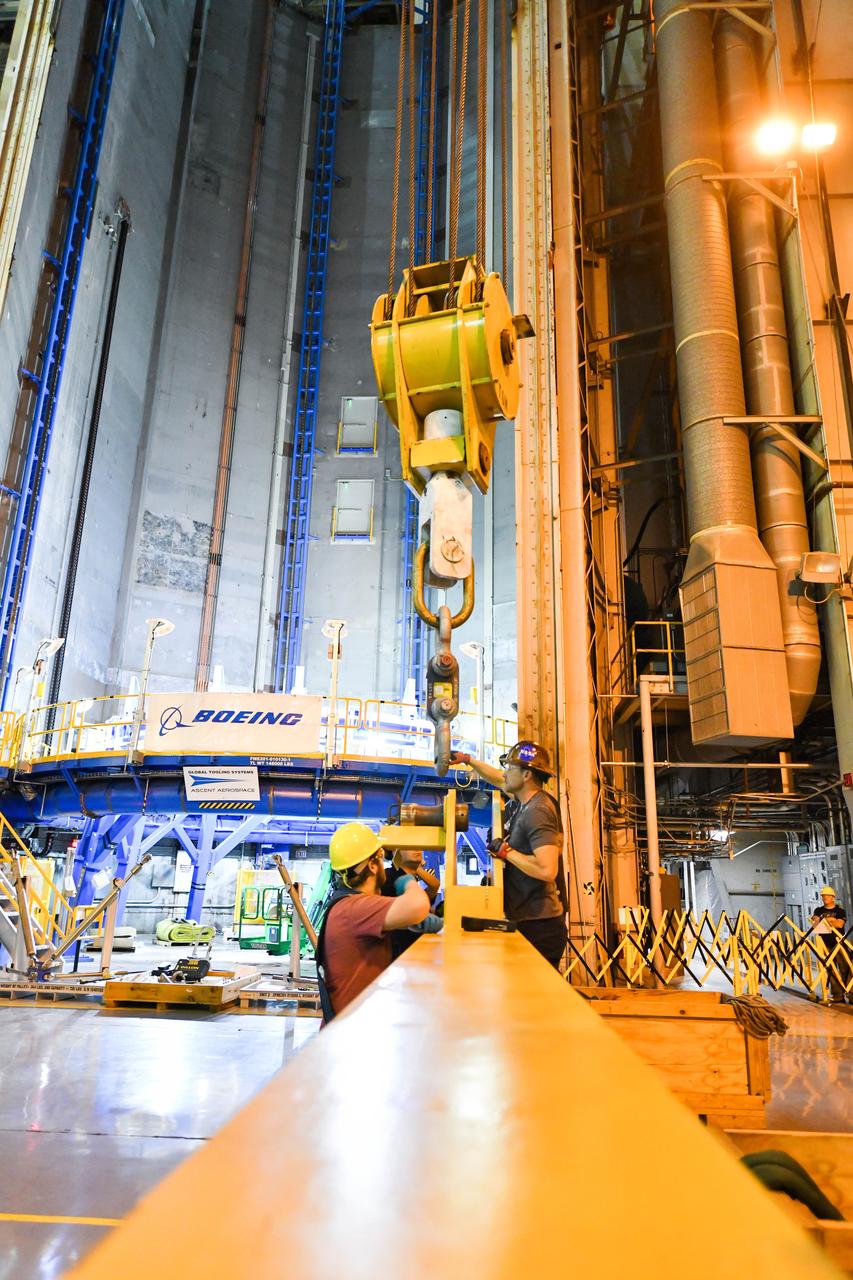
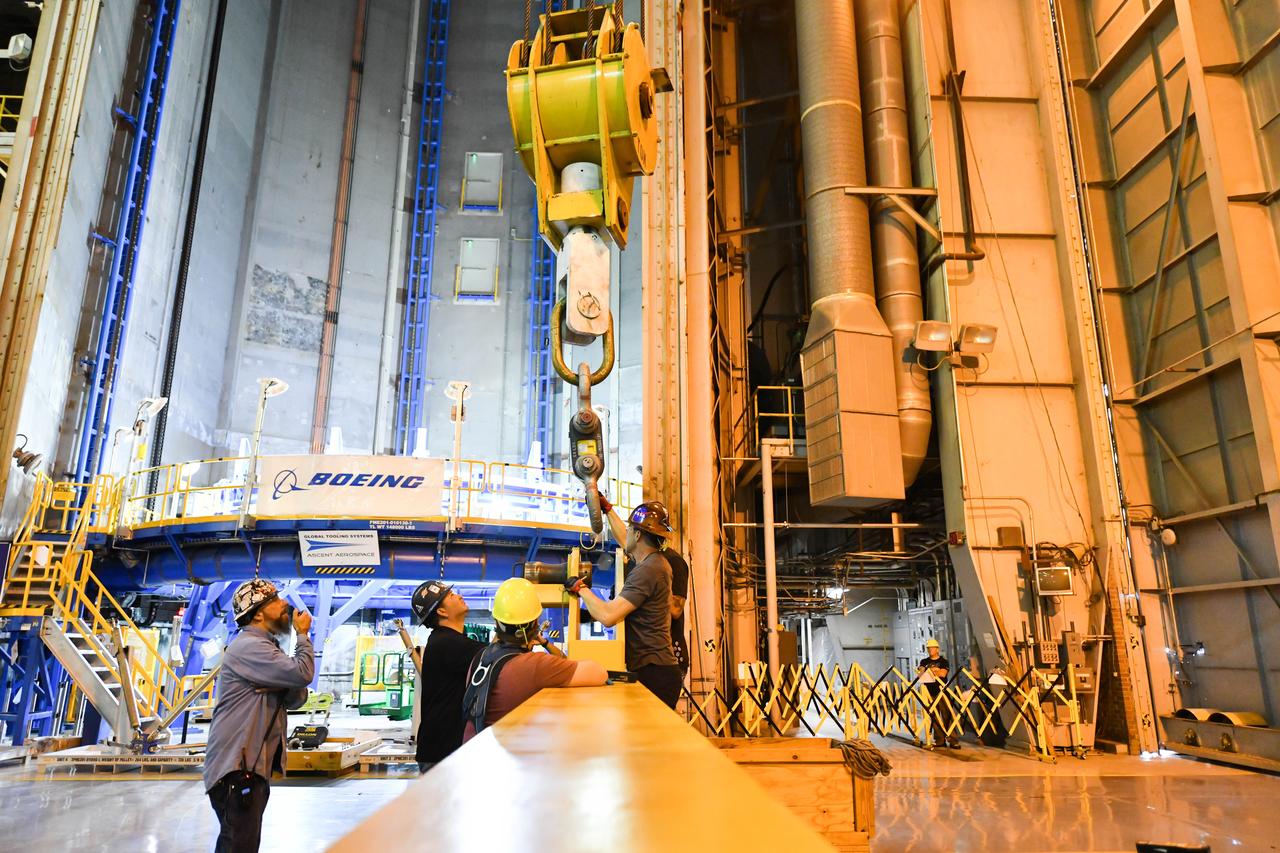
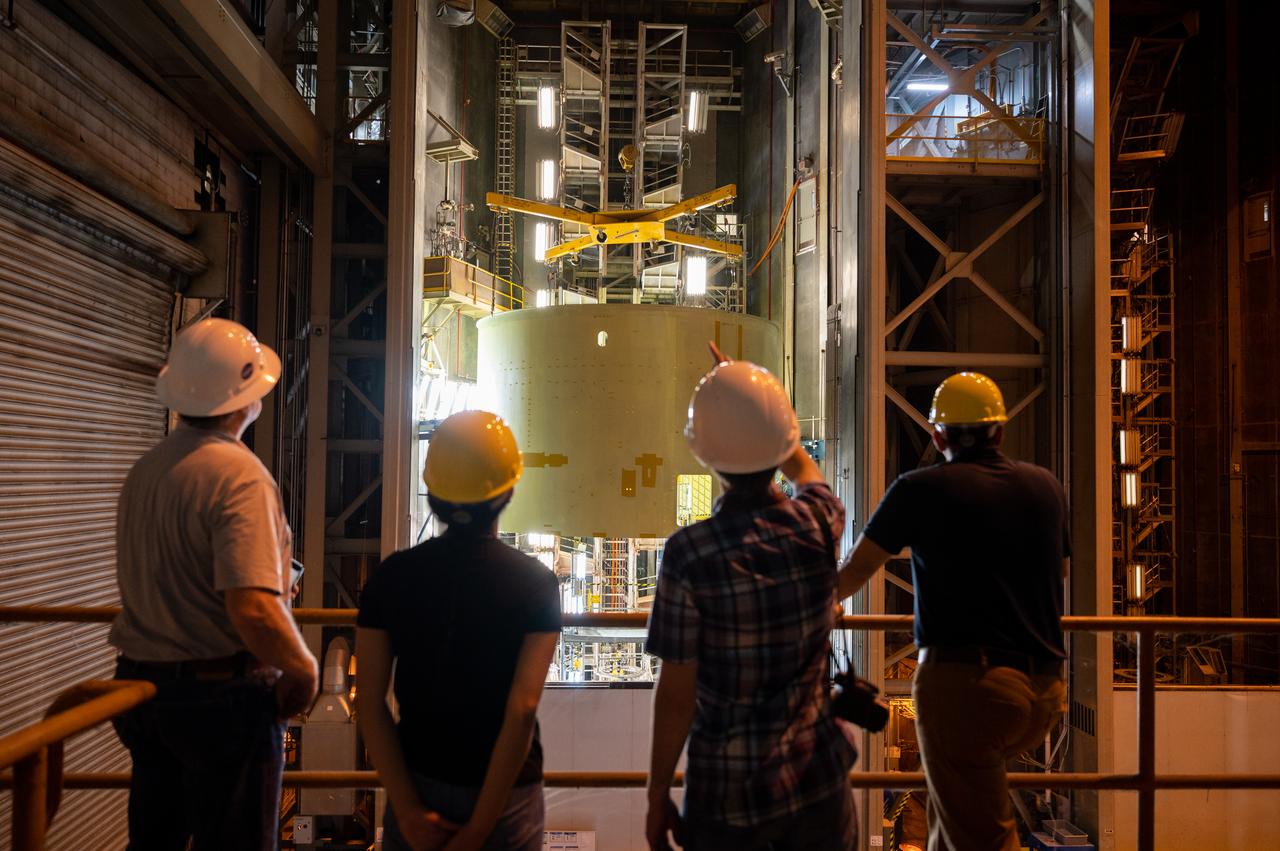
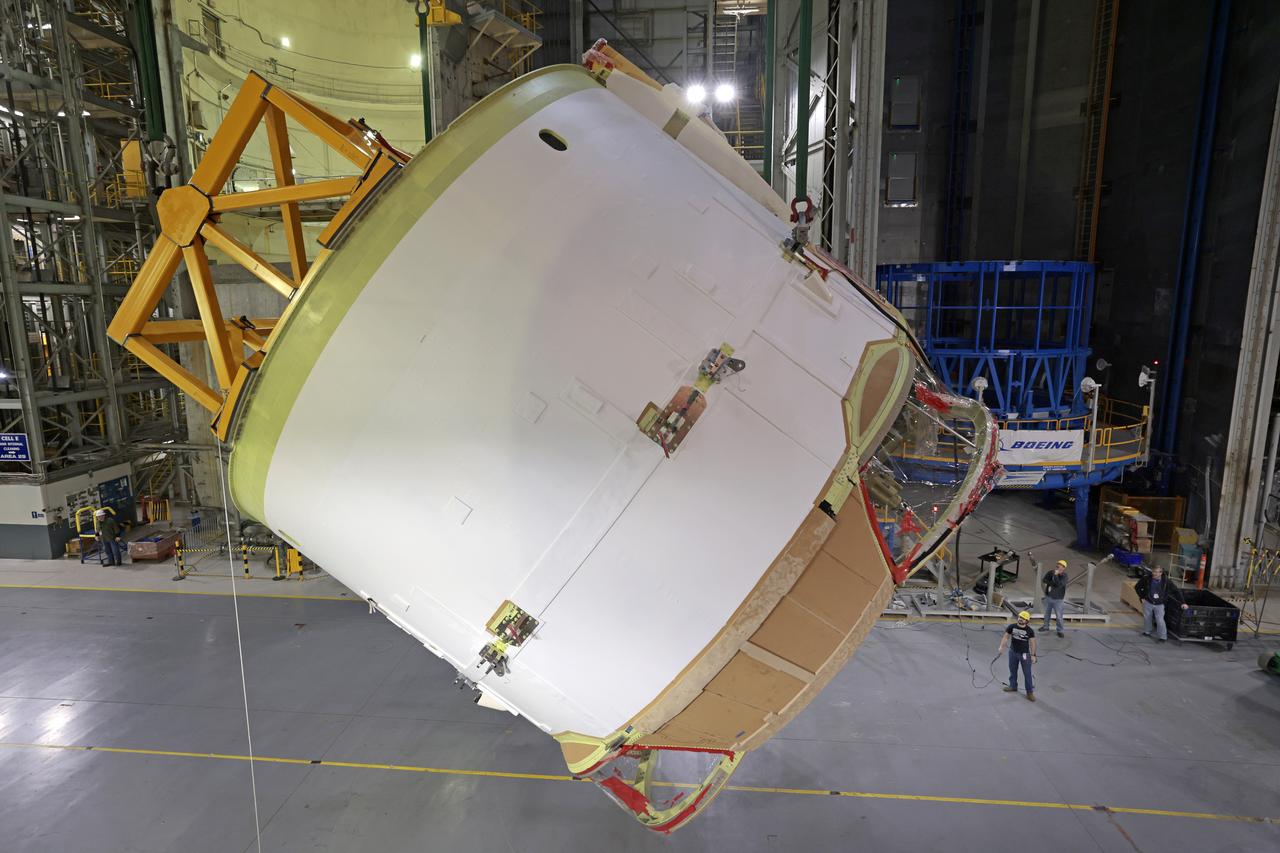
Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans flipped the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II from a vertical to a horizontal position Feb. 11. The flip, also known as a breakover, is in preparation for the final assembly and integration into the core stage for the second SLS rocket. The engine section is the bottom-most portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage and is one of the most complex and intricate portions of the rocket that will help power the first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. It is the last of five elements that is needed to join the stage as one structure. In addition to its miles of cabling and hundreds of sensors, the engine section is a crucial attachment point for the four RS-25 engines and two solid rocket boosters that produce a combined 8.8 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and flight. Next, teams will move the engine section into the final assembly area where they will complete the join. After the join is complete, teams will begin to add each of the four RS-25 engines. The completely assembled stage with its four RS-25 engines will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida later this year. The SLS rocket is the only rocket capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans flipped the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II from a vertical to a horizontal position Feb. 11. The flip, also known as a breakover, is in preparation for the final assembly and integration into the core stage for the second SLS rocket. The engine section is the bottom-most portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage and is one of the most complex and intricate portions of the rocket that will help power the first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. It is the last of five elements that is needed to join the stage as one structure. In addition to its miles of cabling and hundreds of sensors, the engine section is a crucial attachment point for the four RS-25 engines and two solid rocket boosters that produce a combined 8.8 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and flight. Next, teams will move the engine section into the final assembly area where they will complete the join. After the join is complete, teams will begin to add each of the four RS-25 engines. The completely assembled stage with its four RS-25 engines will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida later this year. The SLS rocket is the only rocket capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
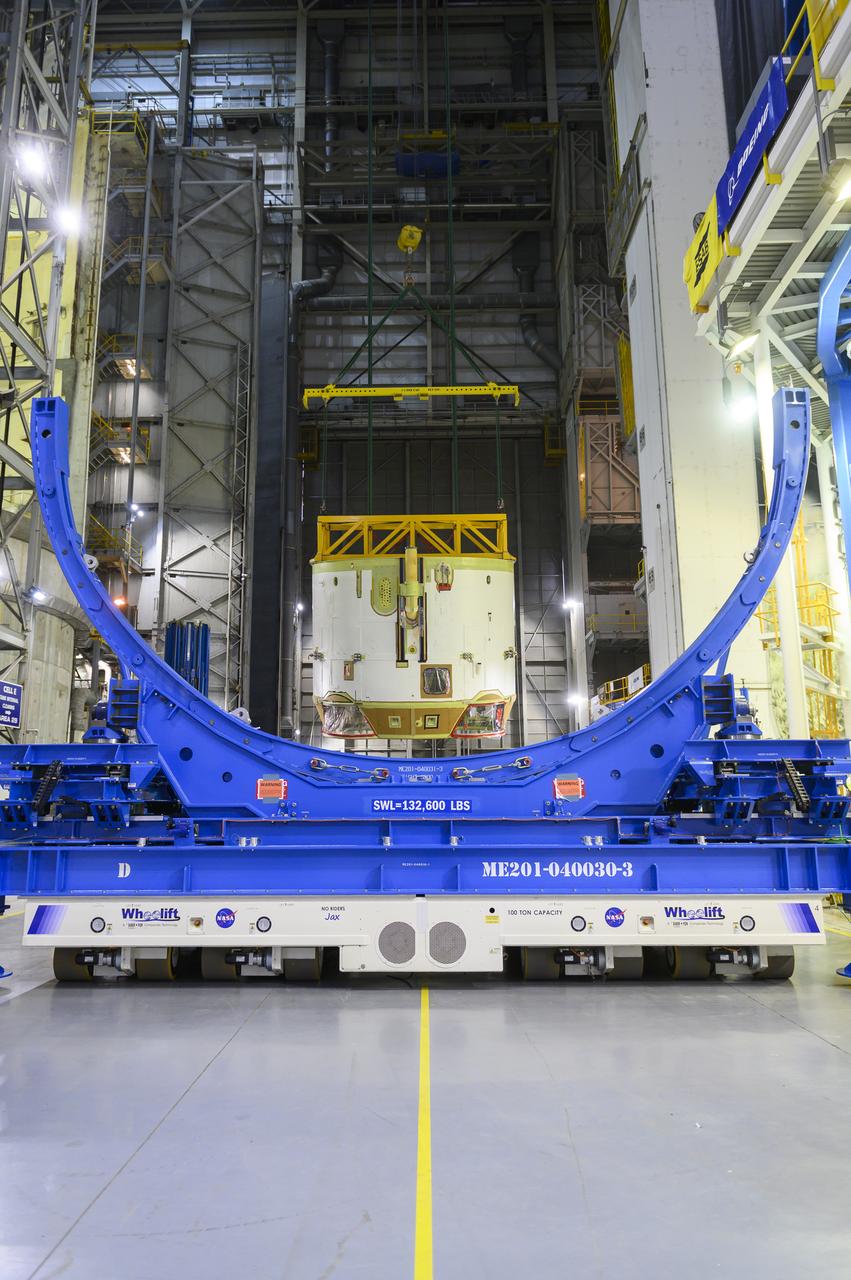

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans flipped the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II from a vertical to a horizontal position Feb. 11. The flip, also known as a breakover, is in preparation for the final assembly and integration into the core stage for the second SLS rocket. The engine section is the bottom-most portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage and is one of the most complex and intricate portions of the rocket that will help power the first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. It is the last of five elements that is needed to join the stage as one structure. In addition to its miles of cabling and hundreds of sensors, the engine section is a crucial attachment point for the four RS-25 engines and two solid rocket boosters that produce a combined 8.8 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and flight. Next, teams will move the engine section into the final assembly area where they will complete the join. After the join is complete, teams will begin to add each of the four RS-25 engines. The completely assembled stage with its four RS-25 engines will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida later this year. The SLS rocket is the only rocket capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Eric Bordelon

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans flipped the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II from a vertical to a horizontal position Feb. 11. The flip, also known as a breakover, is in preparation for the final assembly and integration into the core stage for the second SLS rocket. The engine section is the bottom-most portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage and is one of the most complex and intricate portions of the rocket that will help power the first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. It is the last of five elements that is needed to join the stage as one structure. In addition to its miles of cabling and hundreds of sensors, the engine section is a crucial attachment point for the four RS-25 engines and two solid rocket boosters that produce a combined 8.8 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and flight. Next, teams will move the engine section into the final assembly area where they will complete the join. After the join is complete, teams will begin to add each of the four RS-25 engines. The completely assembled stage with its four RS-25 engines will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida later this year. The SLS rocket is the only rocket capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Eric Bordelon

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans flipped the engine section of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II from a vertical to a horizontal position Feb. 11. The flip, also known as a breakover, is in preparation for the final assembly and integration into the core stage for the second SLS rocket. The engine section is the bottom-most portion of the 212-foot-tall core stage and is one of the most complex and intricate portions of the rocket that will help power the first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. It is the last of five elements that is needed to join the stage as one structure. In addition to its miles of cabling and hundreds of sensors, the engine section is a crucial attachment point for the four RS-25 engines and two solid rocket boosters that produce a combined 8.8 million pounds of thrust at liftoff and flight. Next, teams will move the engine section into the final assembly area where they will complete the join. After the join is complete, teams will begin to add each of the four RS-25 engines. The completely assembled stage with its four RS-25 engines will be shipped to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida later this year. The SLS rocket is the only rocket capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
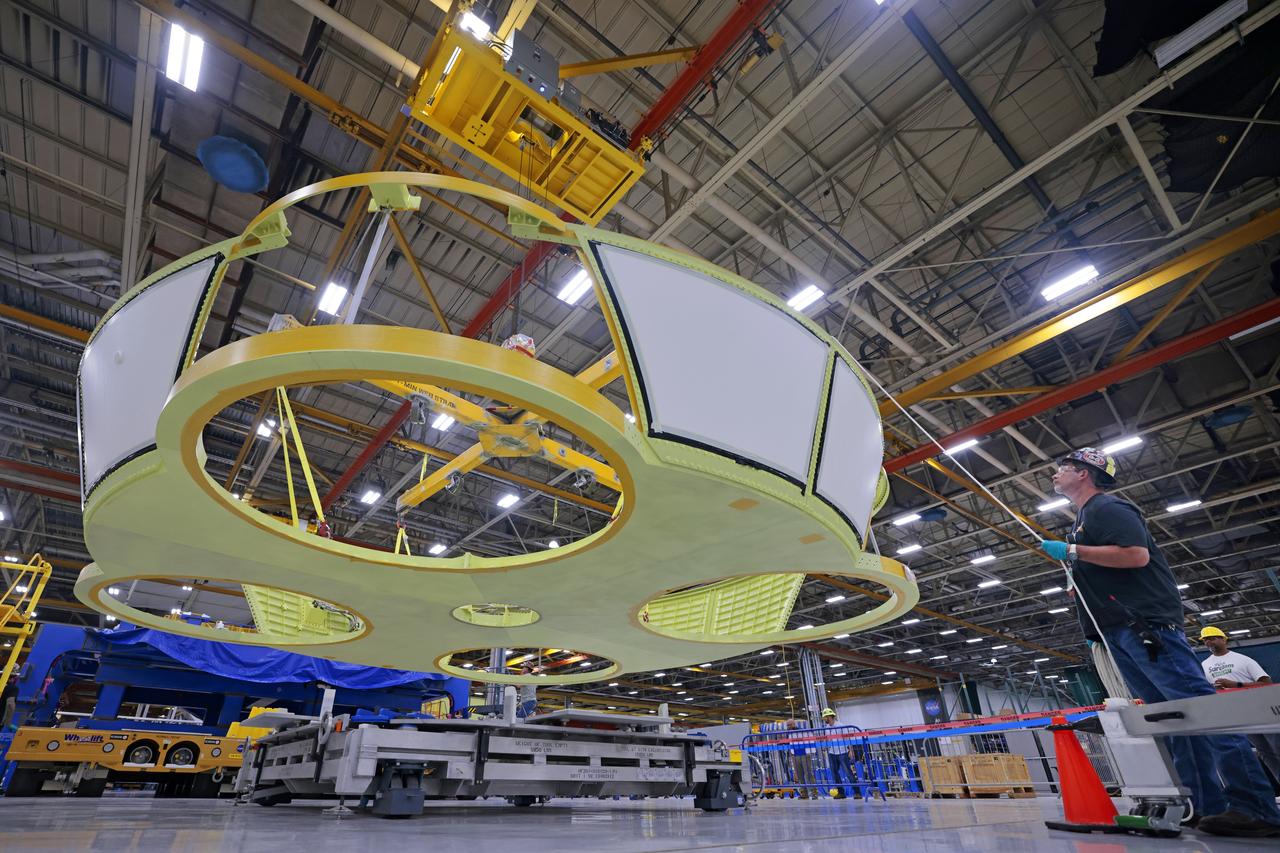

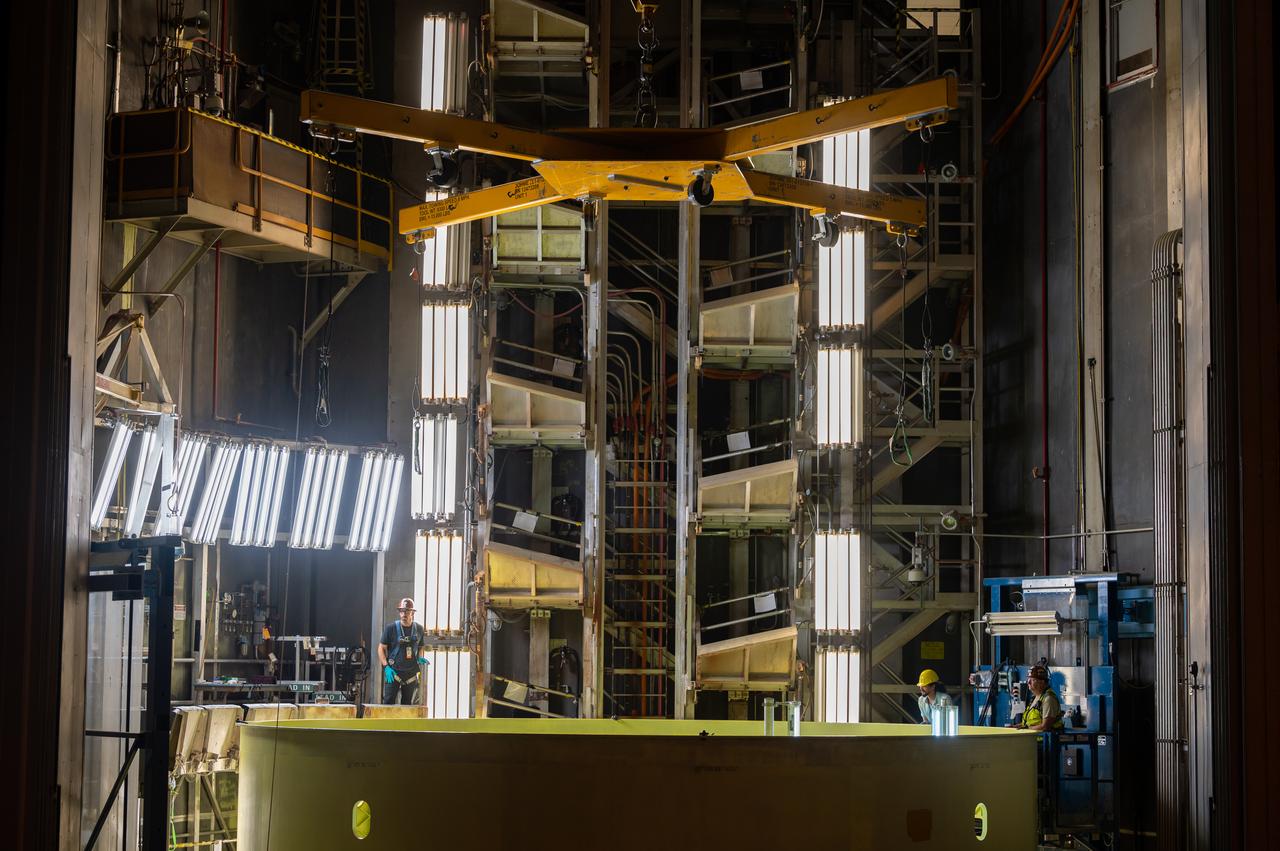
These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
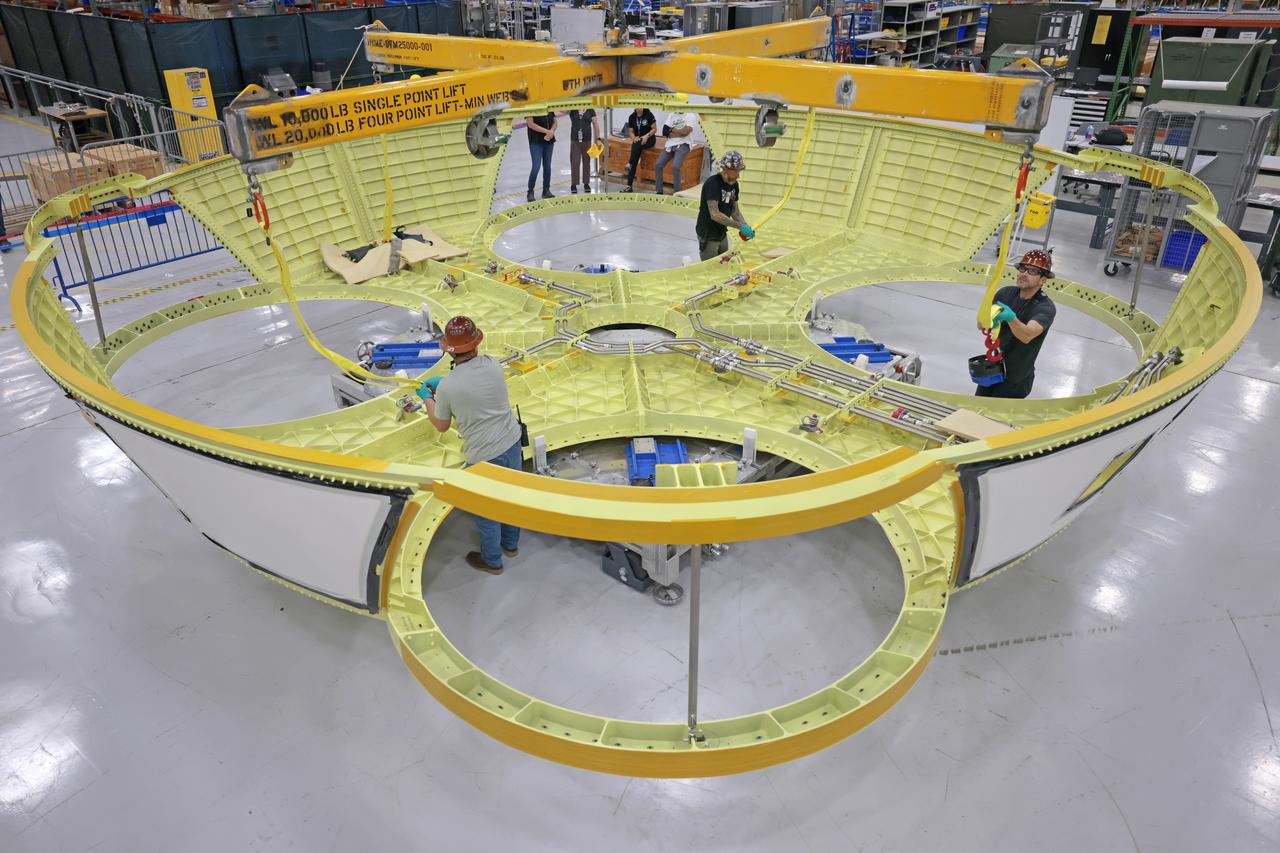

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
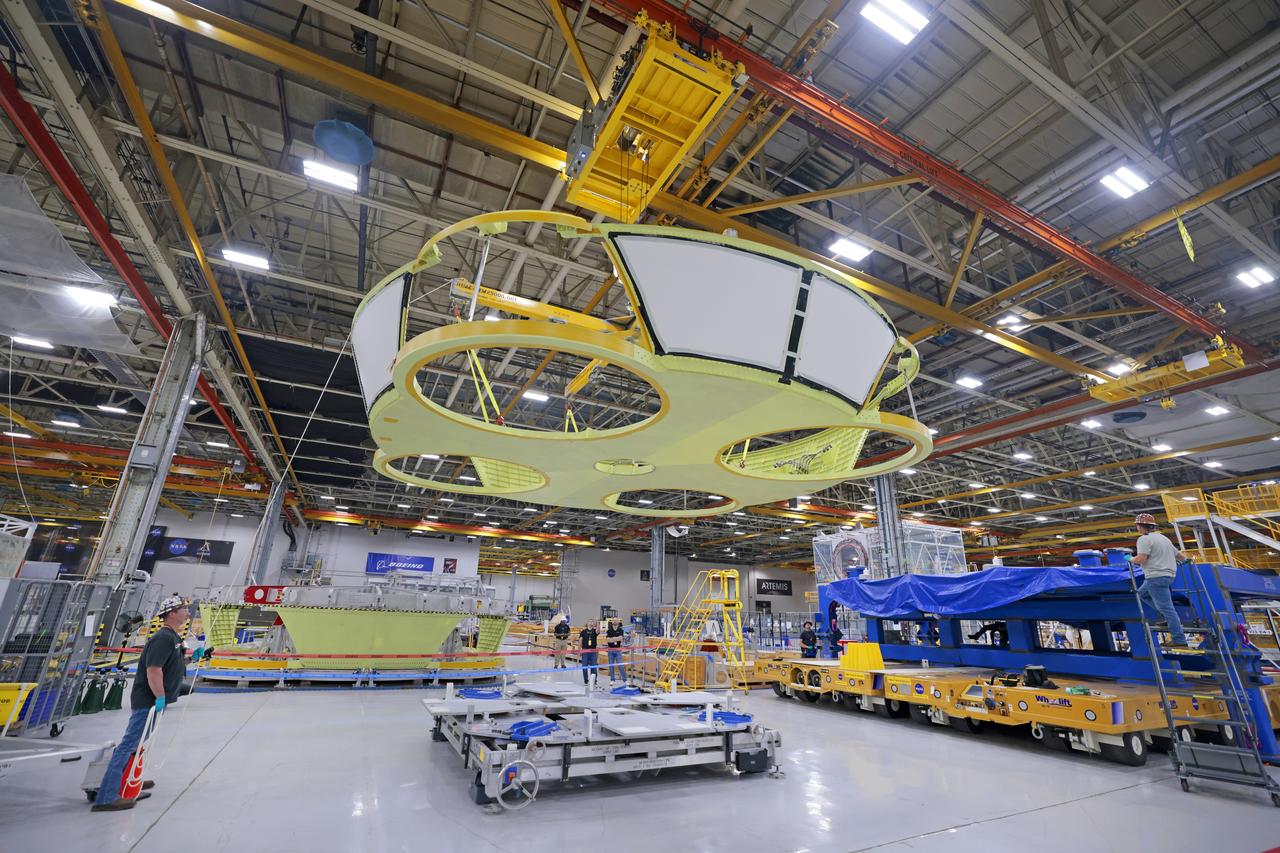

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
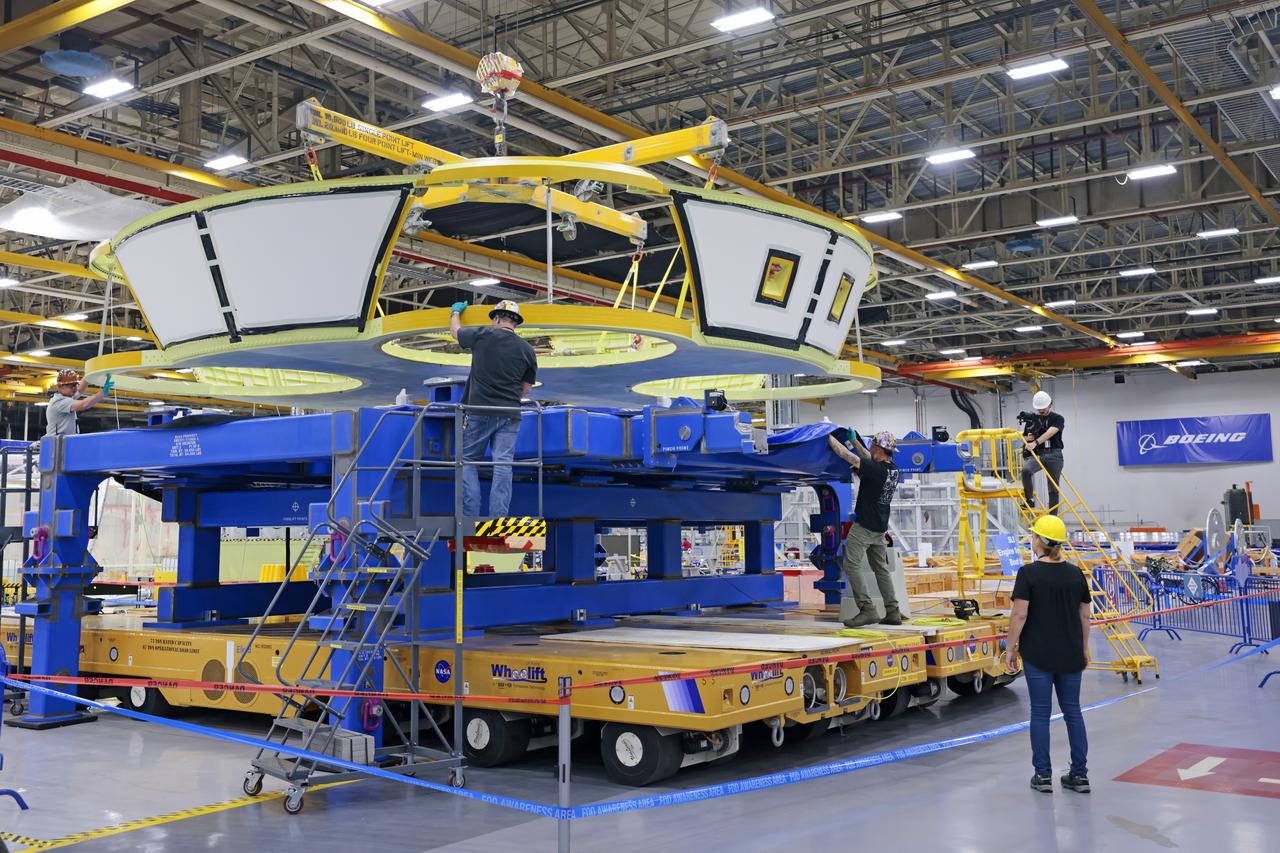

These photos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans installed the third and fourth RS-25 engines onto the core stage for the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power NASA’s first crewed Artemis mission to the Moon. Technicians added the first engine to the SLS core stage Sept. 11. The second engine was installed onto the stage Sept. 15 with the third and fourth engines following Sept. 19 and Sept. 20. Engineers consider the engines to be “soft” mated to the rocket stage. Technicians with NASA, Aerojet Rocketdyne, an L3Harris Technologies company and the RS-25 engines lead contractor, along with Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, will now focus efforts on the complex tax of fully securing the engines to the stage and integrating the propulsion and electrical systems within the structure. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with Orion and the Gateway in orbit around the Moon. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

Flight Engineer of Expedition 37/38 Visits Goddard, NASA Astronaut Mike Hopkins
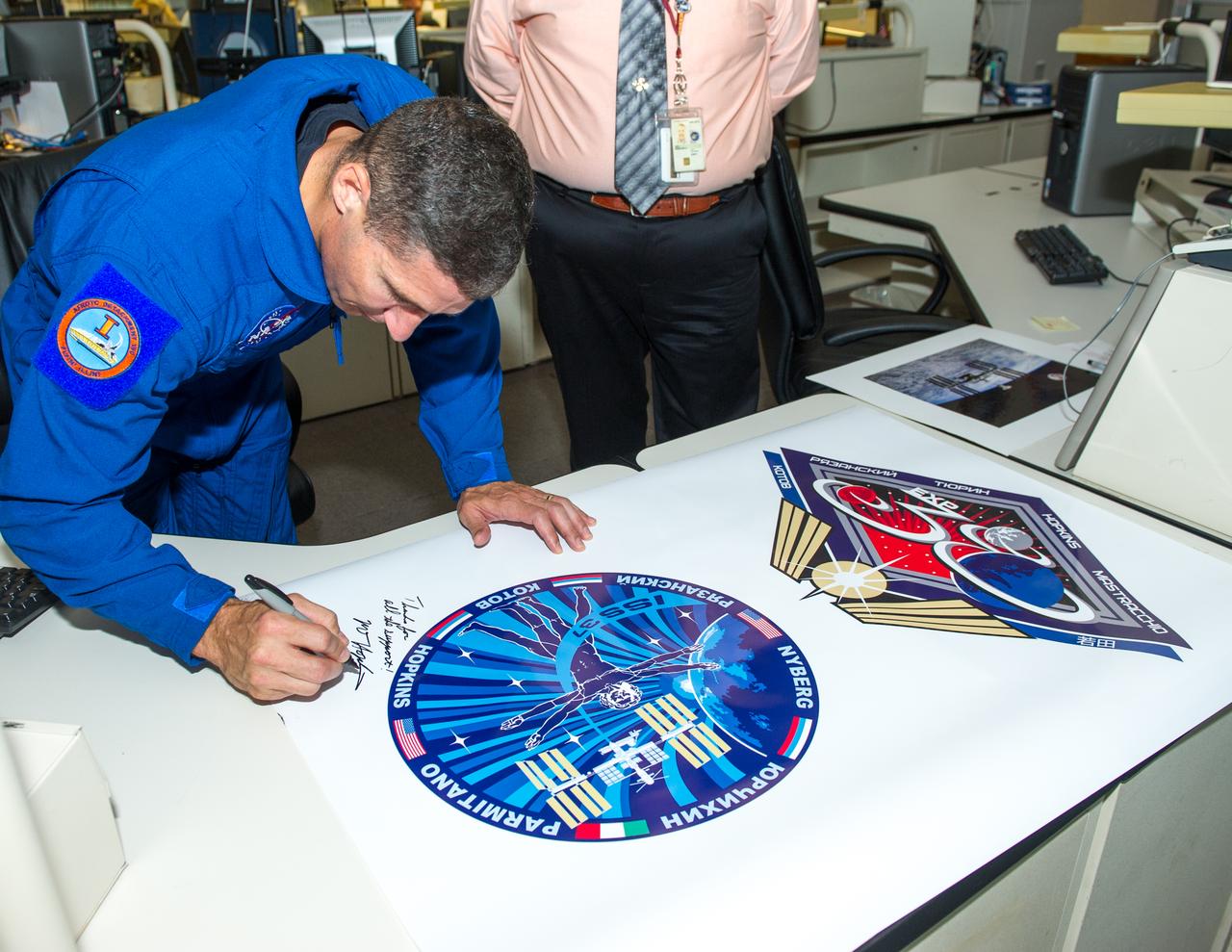

Flight Engineer of Expedition 37/38 Visits Goddard, NASA Astronaut Mike Hopkins
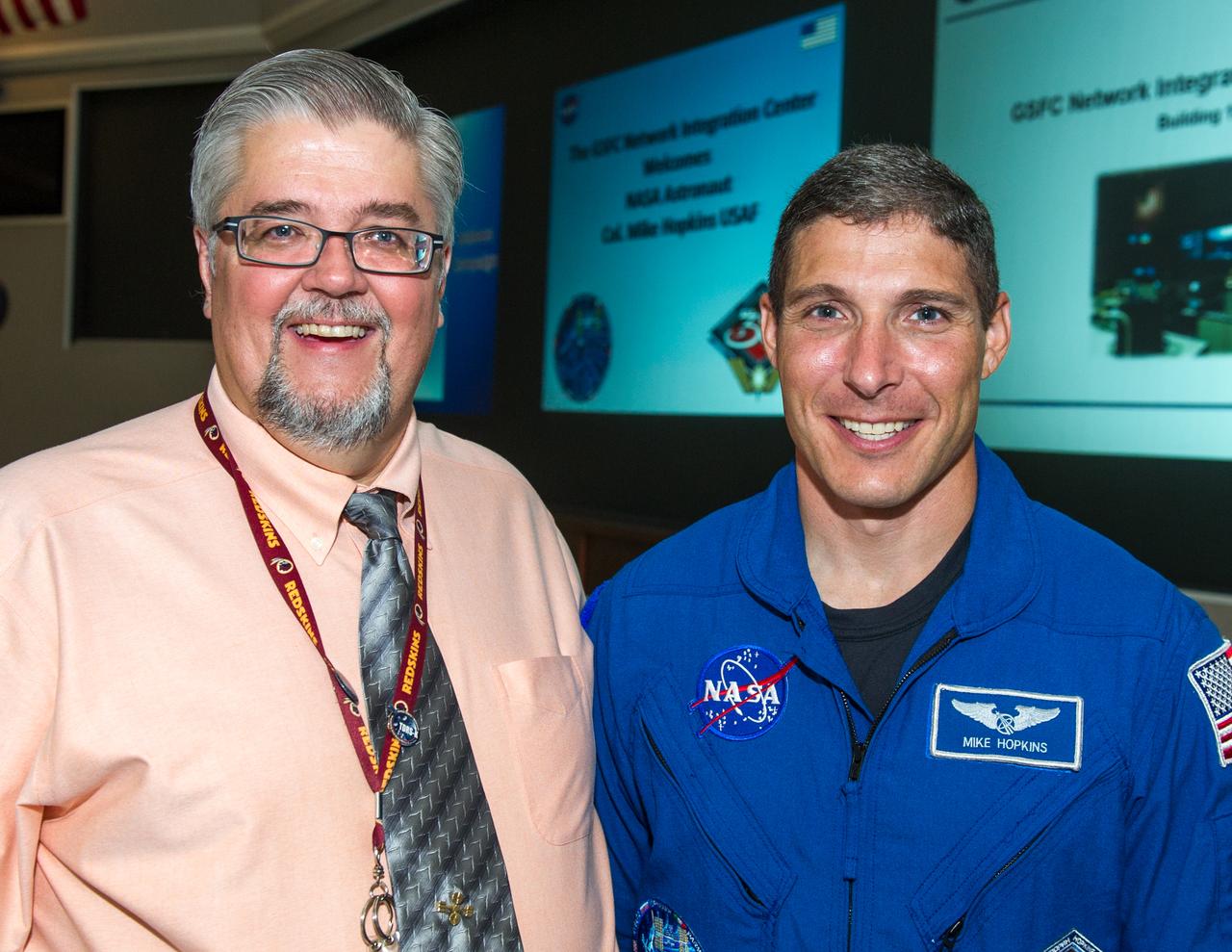

Flight Engineer of Expedition 37/38 Visits Goddard, NASA Astronaut Mike Hopkins
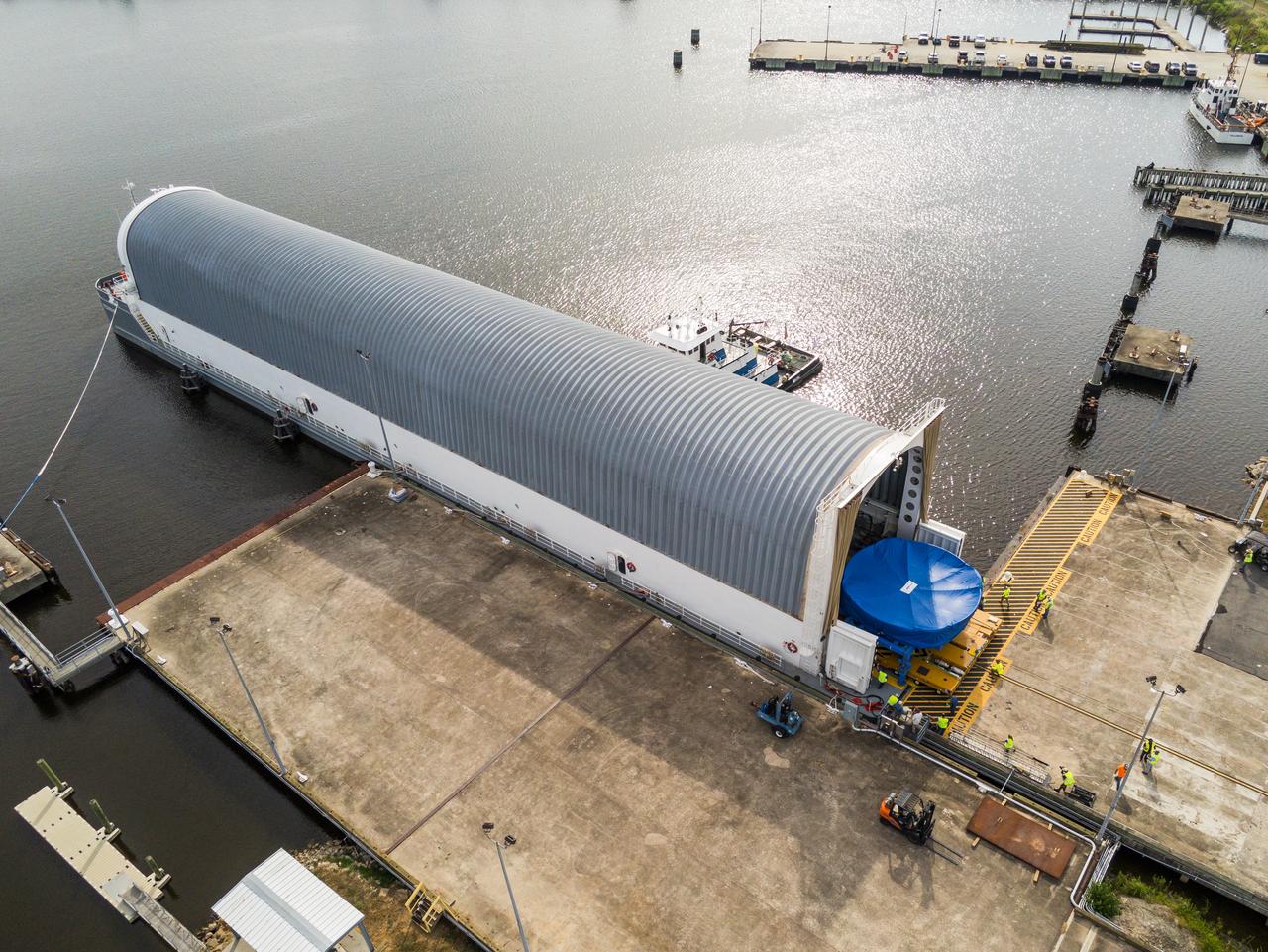

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.
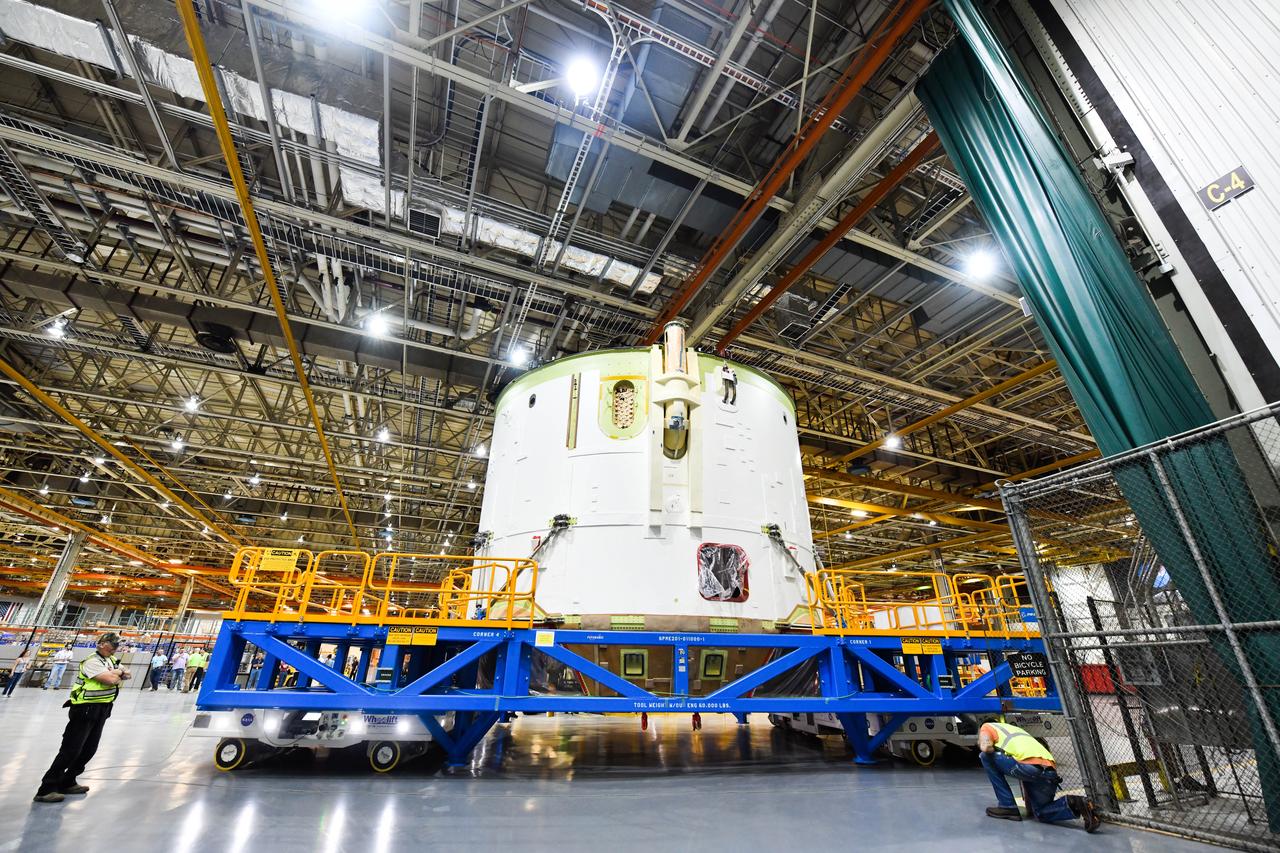

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
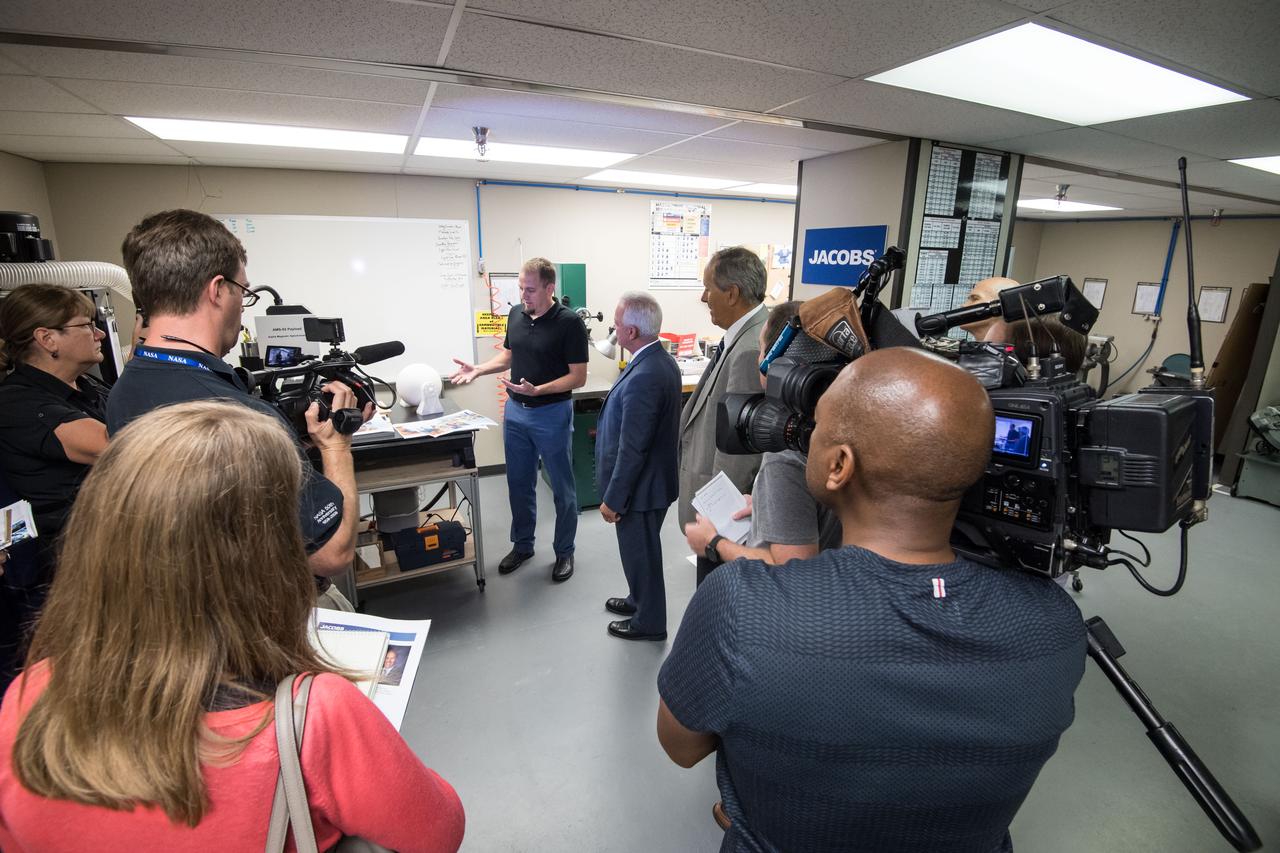

NASA Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier joined Jacobs General Manager Lon Miller during a tour of the company's Engineering Development Facility in Houston. Jacobs provides advanced technologies used aboard the International Space Station and for deep space exploration. Date: 08-10-2017 Location: B1 & Jacobs Engineering Subject: NASA Acting Chief Technology Officer Douglas Terrier Tours JSC and Jacobs Photographer: David DeHoyos

NASA Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier joins Jacobs General Manager Lon Miller during a tour of the company's Engineering Development Facility in Houston. Jacobs provides advanced technologies used aboard the International Space Station and for deep space exploration. From left: NASA’s Johnson Space Center Chief Technologist Chris Culbert, Chief Technologist Douglas Terrier, Jacobs Clear Lake Group Deputy General Manager Joy Kelly and Jacobs Clear Lake Group General Manager Lon Miller. Date: 08-10-2017 Location: B1 & Jacobs Engineering Subject: NASA Acting Chief Technology Officer Douglas Terrier Tours JSC and Jacobs Photographer: David DeHoyos
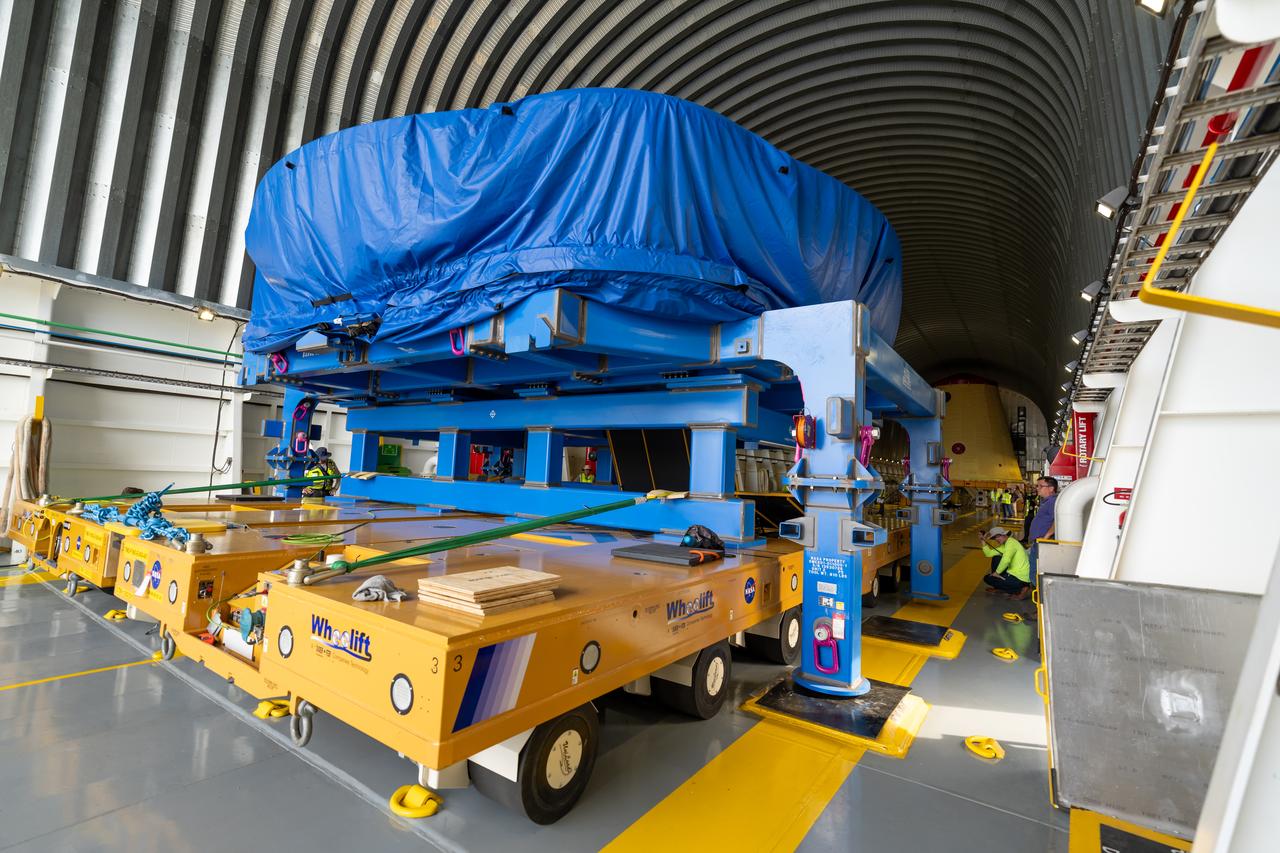

These photos and videos show teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans preparing, moving, and loading the engine section boat-tail of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the Artemis III mission for transportation to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida via the agency’s Pegasus barge. Inside the factory on Aug. 14 prior to the move, technicians covered the spaceflight hardware with a tarp to help protect it on its journey aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge. Crews then rolled out the hardware on Aug. 27 from the factory floor to the barge. Once in Florida, the boat-tail will be integrated with the engine section -- also manufactured at Michoud -- inside Kennedy’s Space Station Processing Facility. The engine section arrived at NASA Kennedy in Dec. 2022. Located at the bottom of the engine section, the aerodynamic boat-tail fairing channels airflow and protects the stage’s four RS-25 engines from extreme temperatures during launch. The engine section is one of five major elements that make up the 212-foot-tall rocket stage. The core stage, along with its four RS-25 engines, produce two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit and to the lunar surface for Artemis.

The F414-GE-100 engine, which will power NASA’s X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology X-plane (QueSST) in flight, is unboxed at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The engine, one of two delivered by GE, is approximately 13 feet long, and will power X-59 on missions to gather information about how the public perceives the sounds of quieter supersonic flight.

The F414-GE-100 engine, which will power NASA’s X-59 Quiet SuperSonic Technology X-plane (QueSST) in flight, is unboxed at NASA’s Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California. The engine, one of two delivered by GE, is approximately 13 feet long, and will power X-59 on missions to gather information about how the public perceives the sounds of quieter supersonic flight.
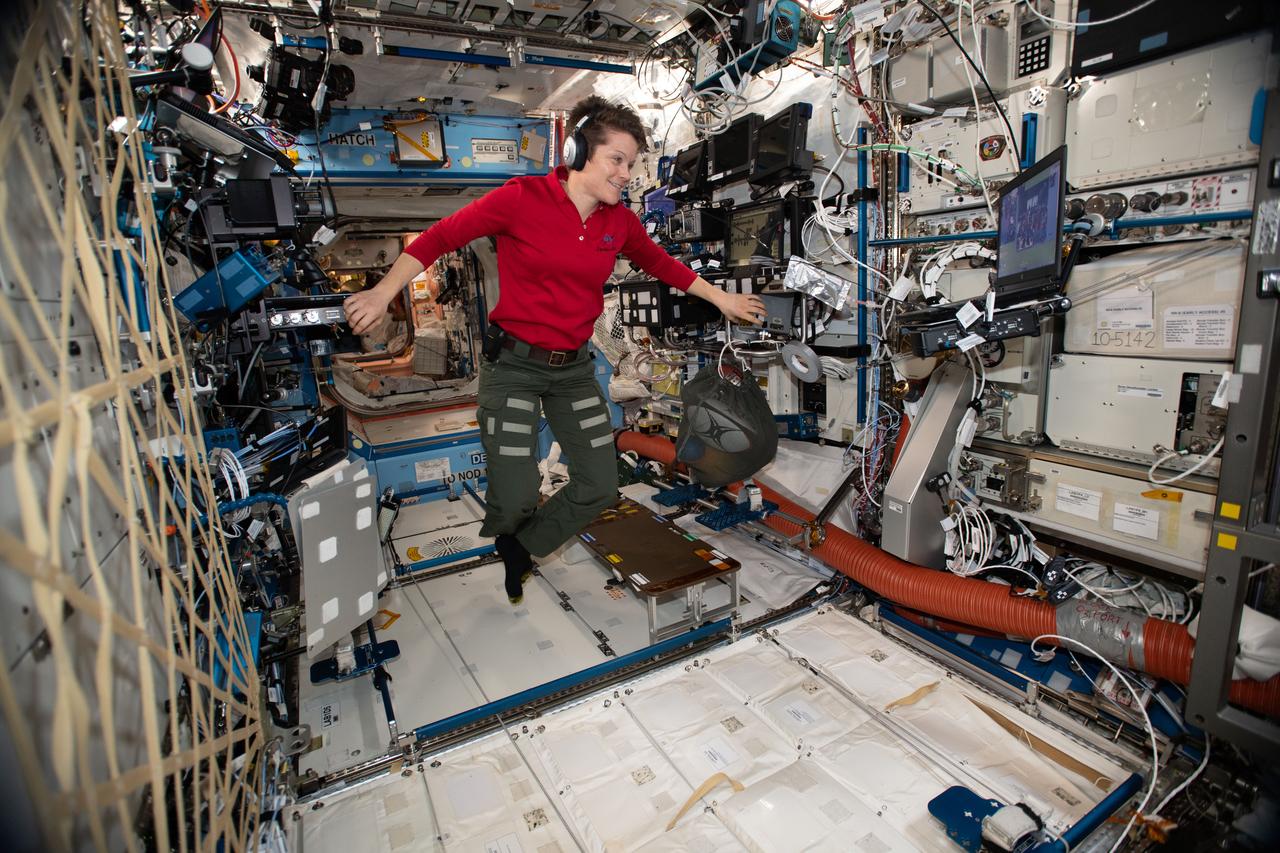

iss058e005069 (Jan. 18, 2019) --- Expedition 58 Flight Engineer Anne McClain of NASA looks at a laptop computer screen inside the U.S. Destiny laboratory module during ground conference operations.

NASA engineers inspect a new piece of technology developed for the James Webb Space Telescope, the micro shutter array, with a low light test at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Developed at Goddard to allow Webb's Near Infrared Spectrograph to obtain spectra of more than 100 objects in the universe simultaneously, the micro shutter array uses thousands of tiny shutters to capture spectra from selected objects of interest in space and block out light from all other sources. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Briou Bourgeois is a mechanical test operations engineer at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, where he enjoys working on a variety of projects to support NASA’s efforts of leading the way in space exploration for humanity.

NASA systems engineer, Daniel Eng, right, talks with student participants at the 2019 Aerospace Valley Robotics Competition at the Palmdale Aerospace Academy in Palmdale, California.
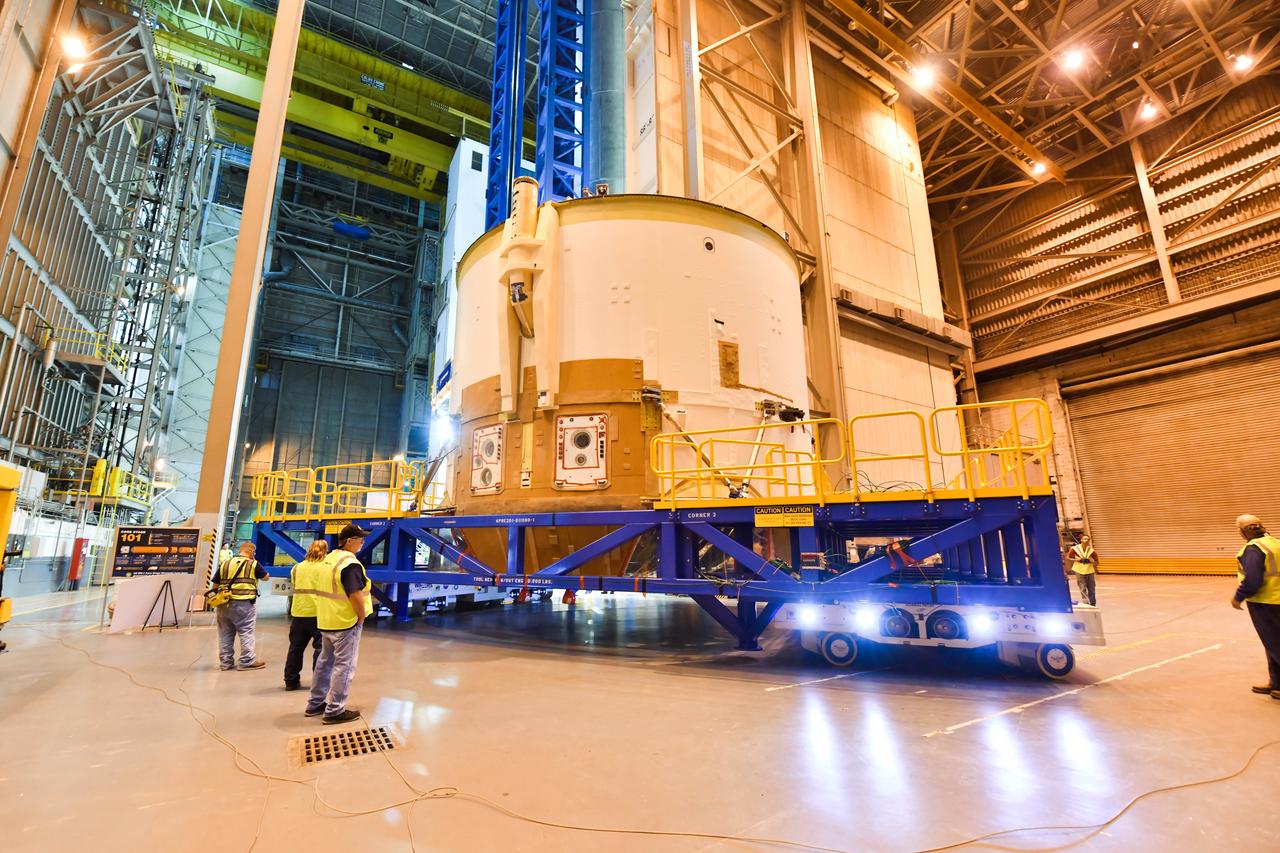

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
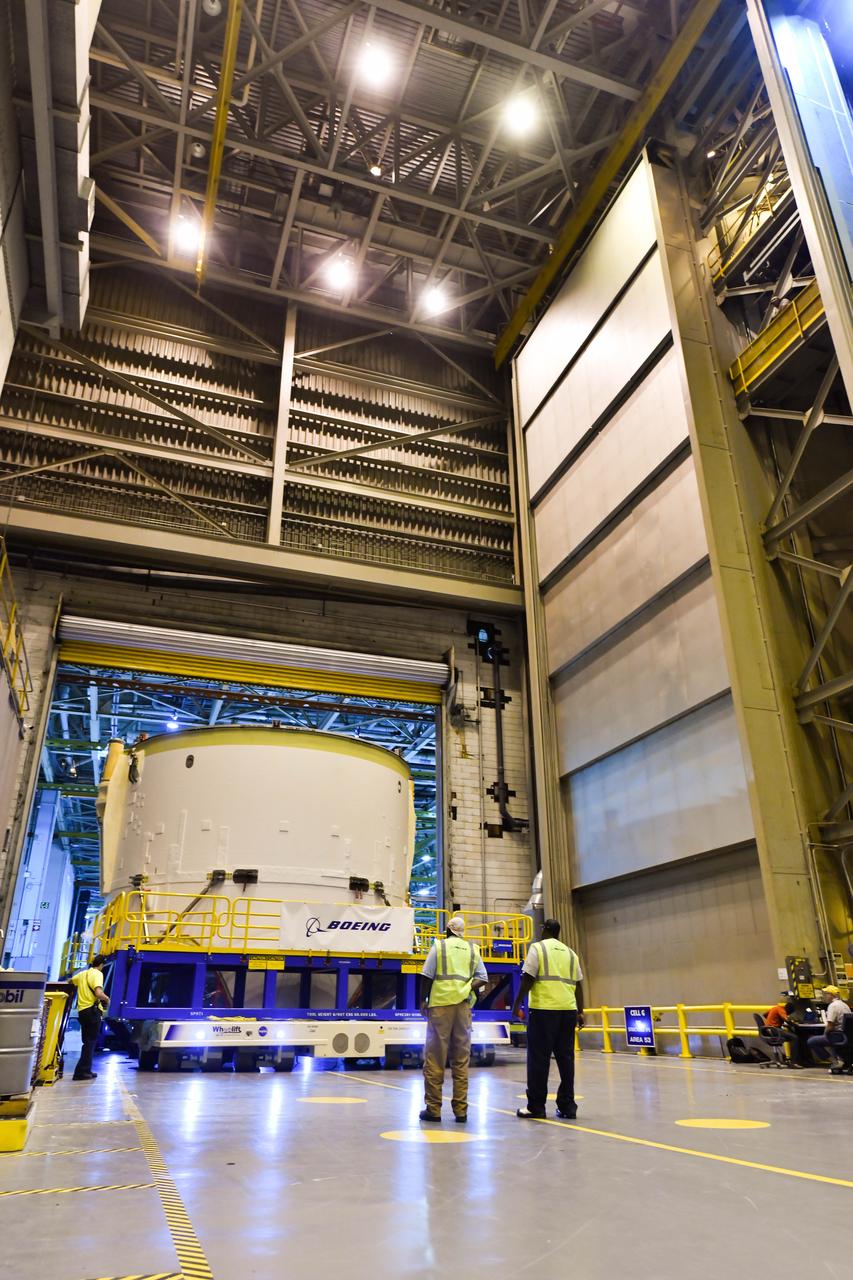

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
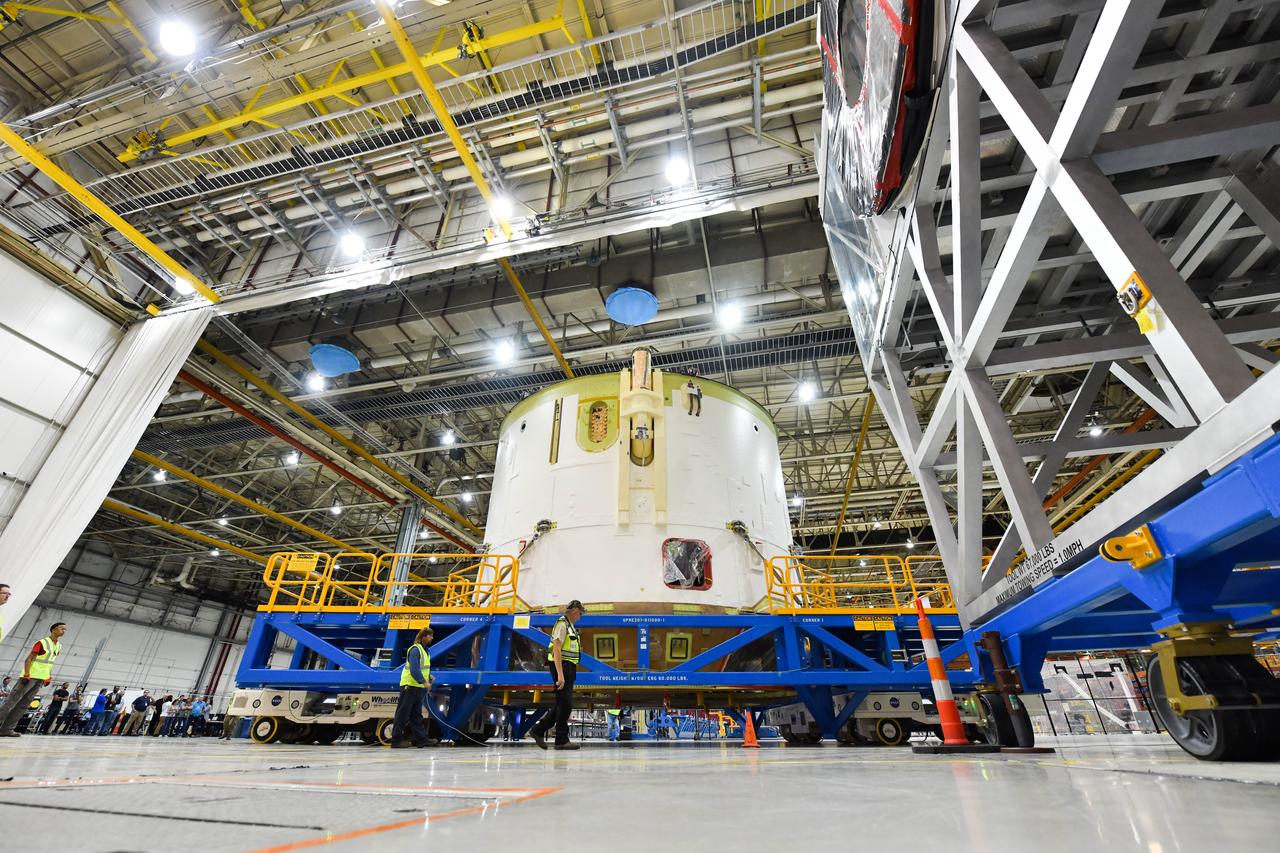

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
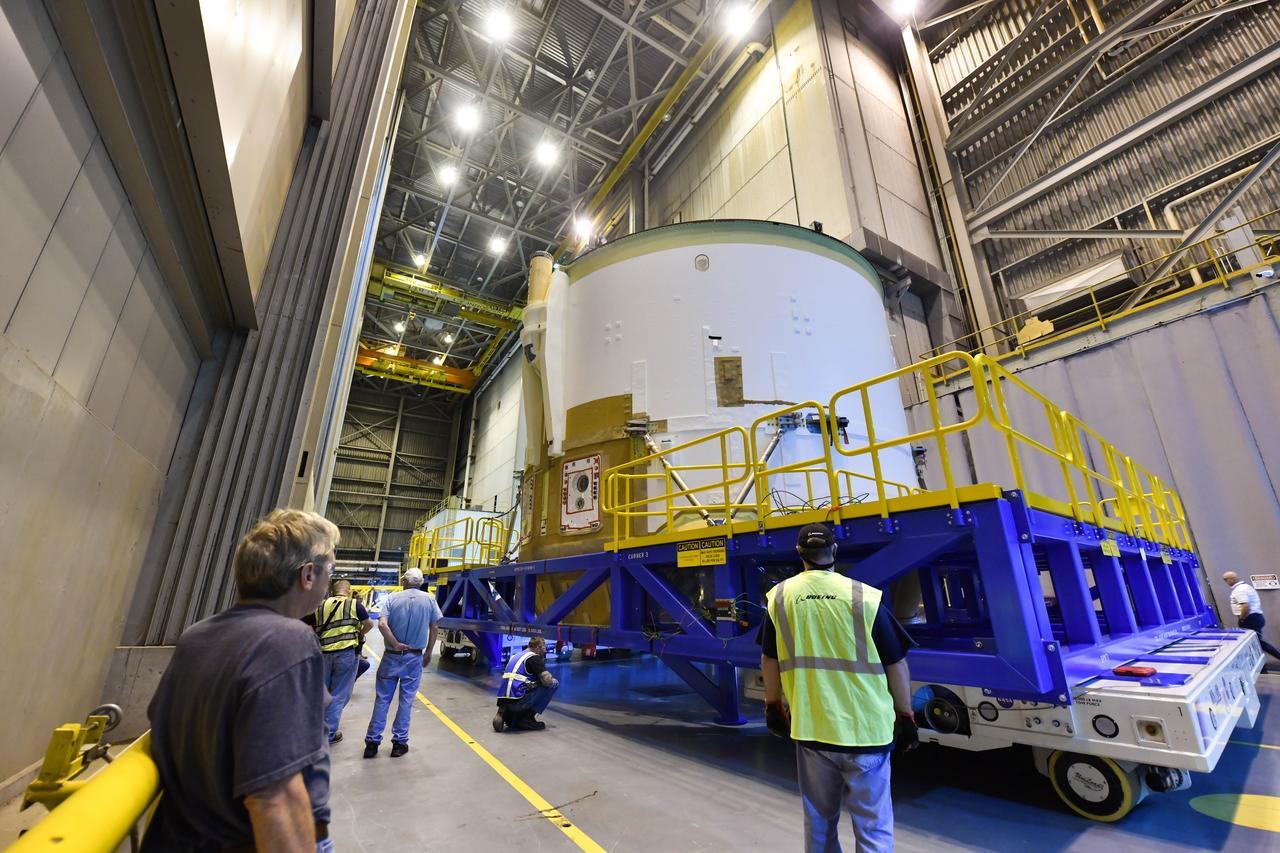

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
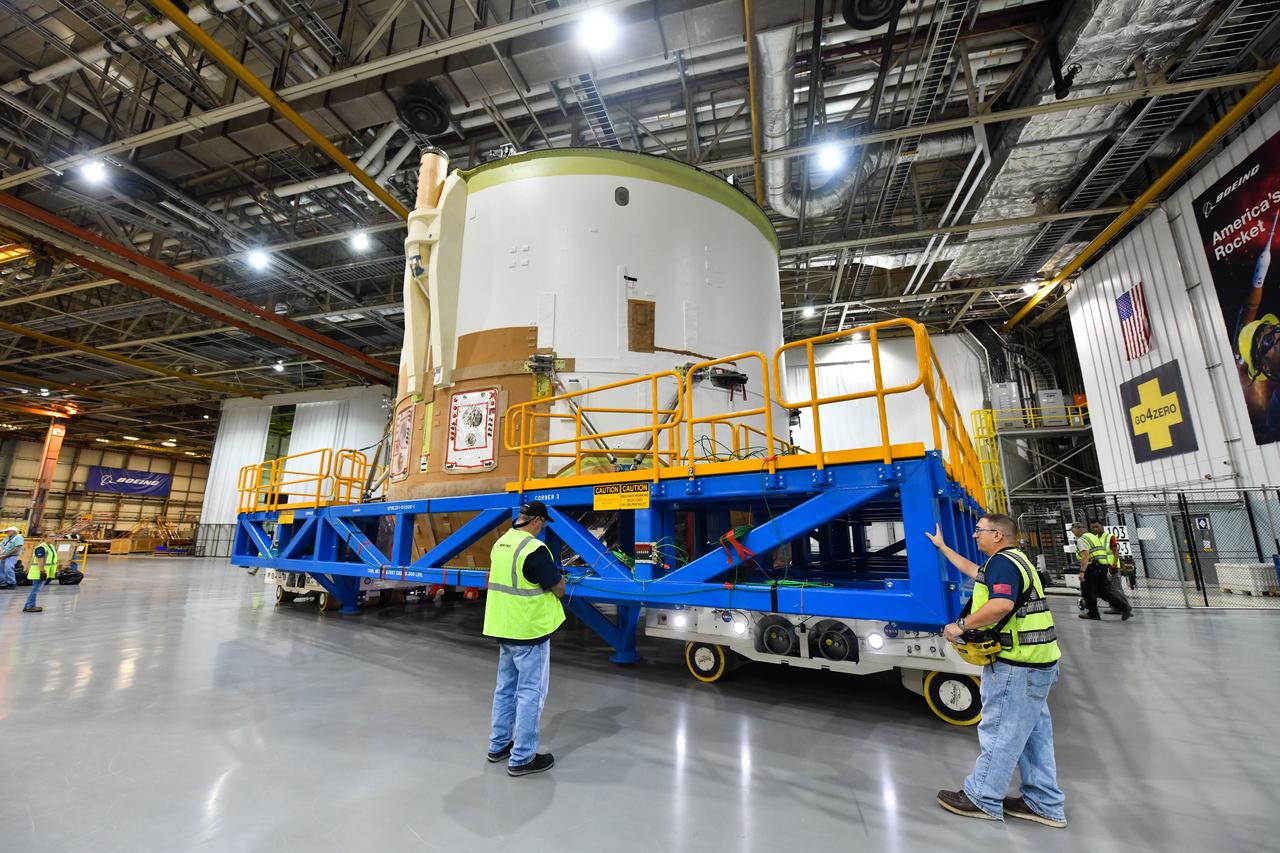

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
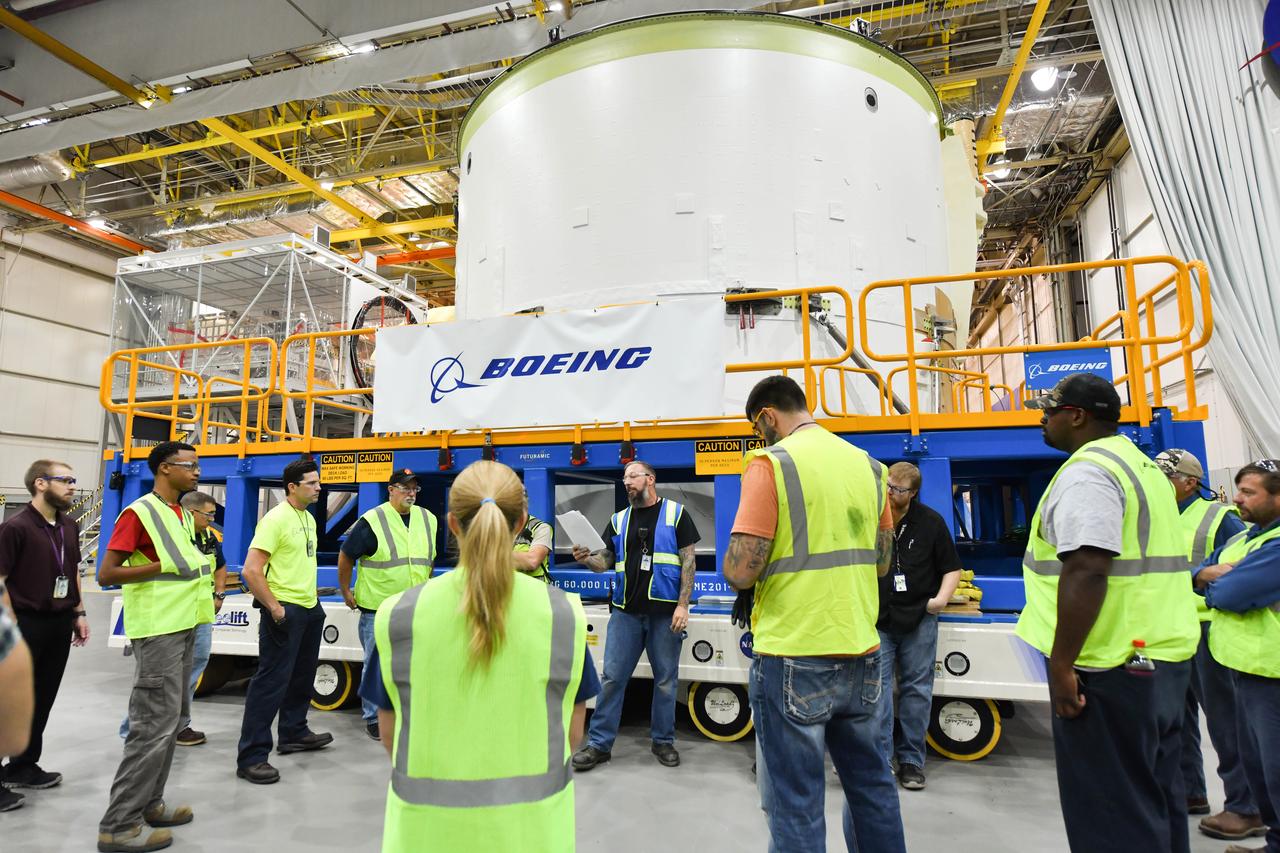

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
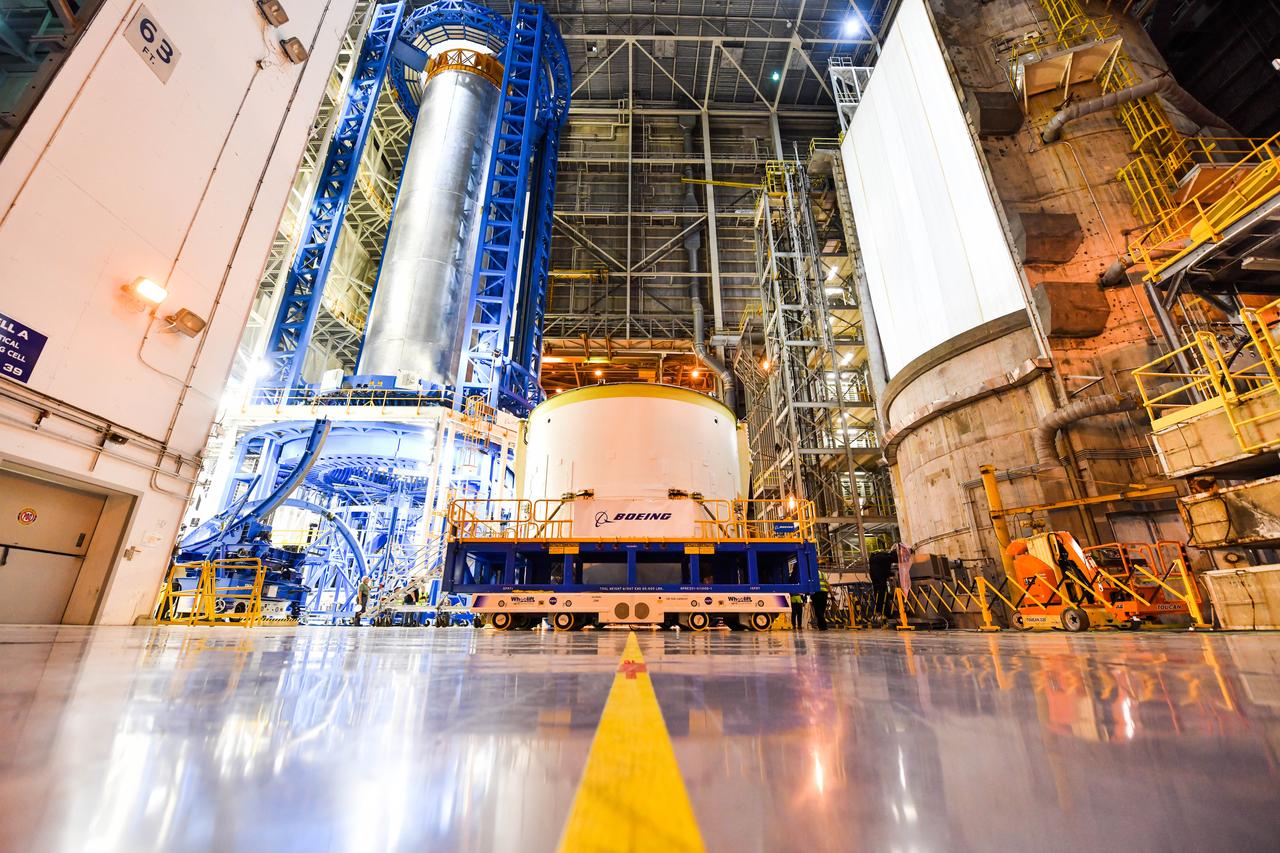

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
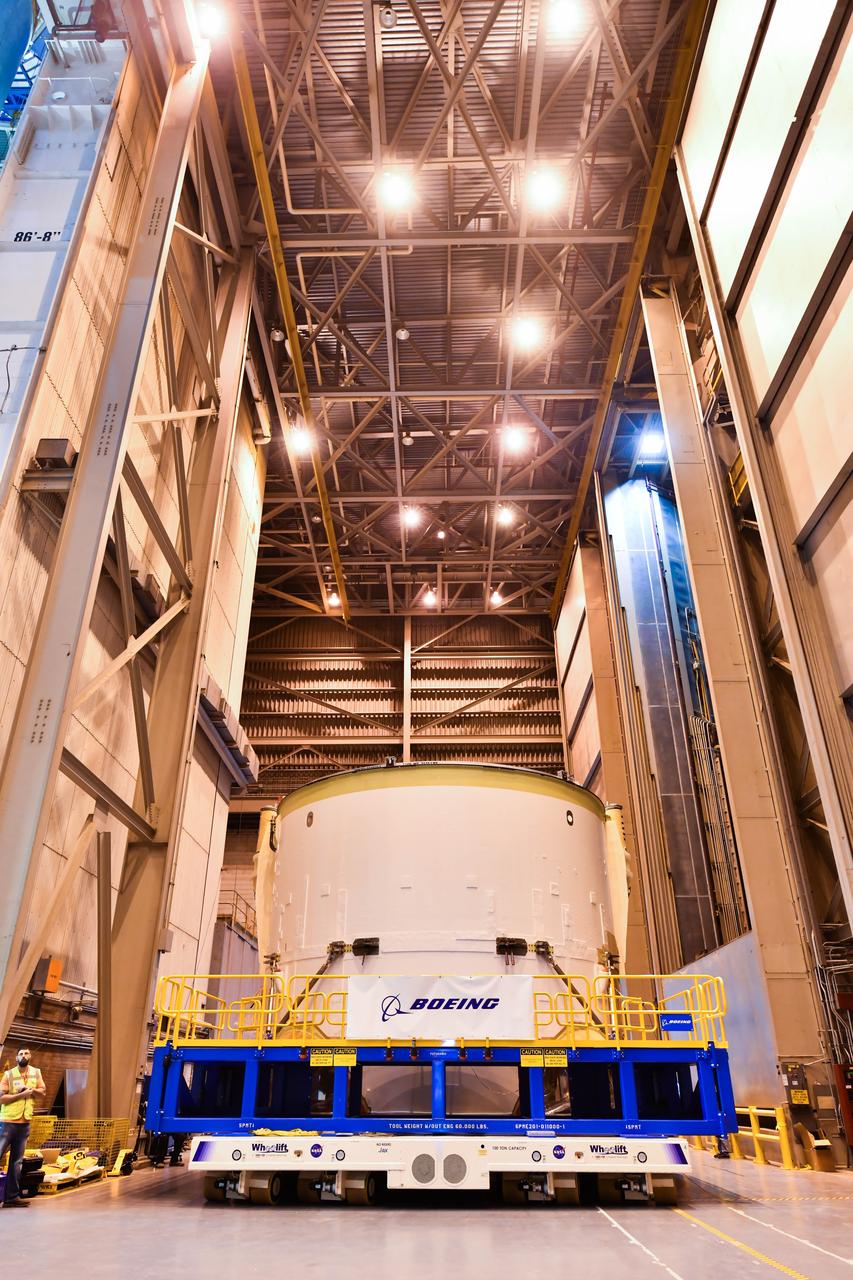

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
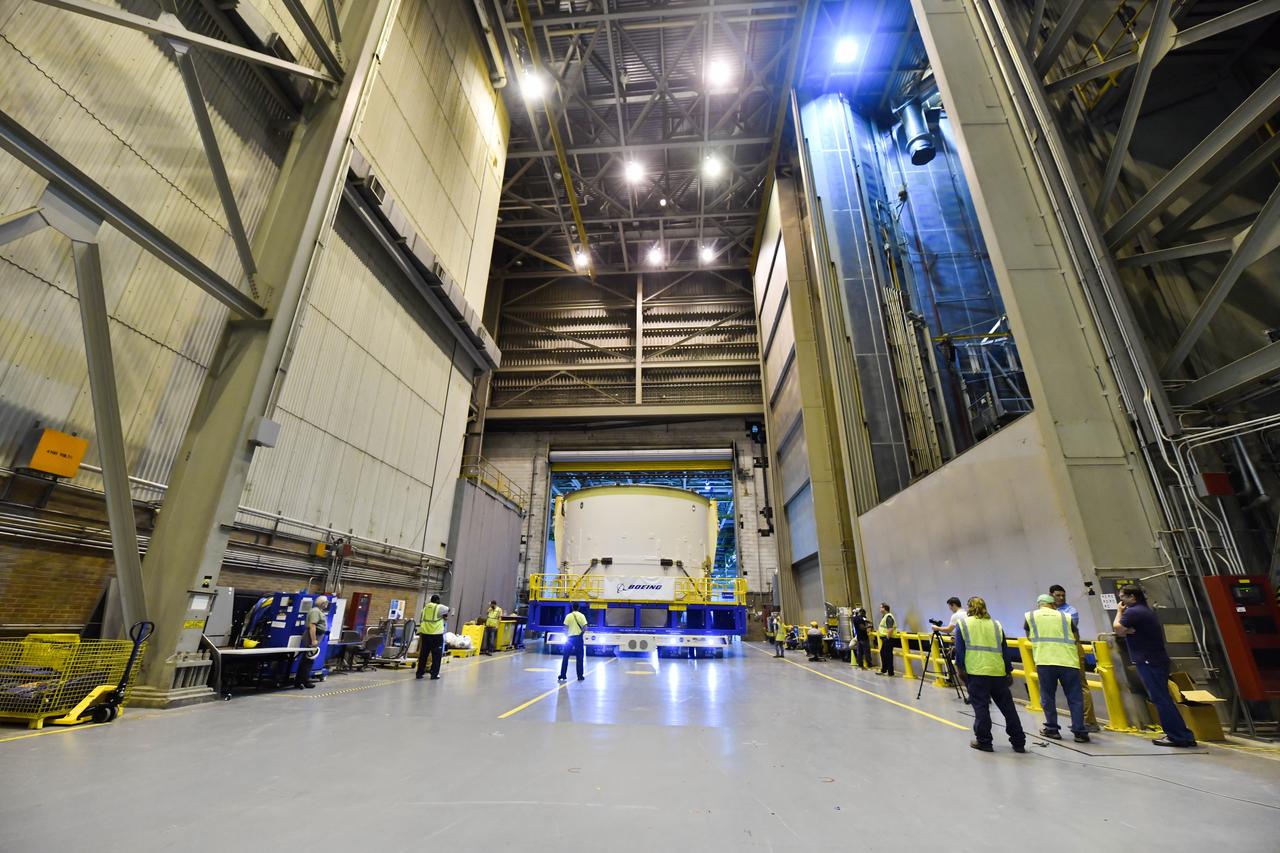

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
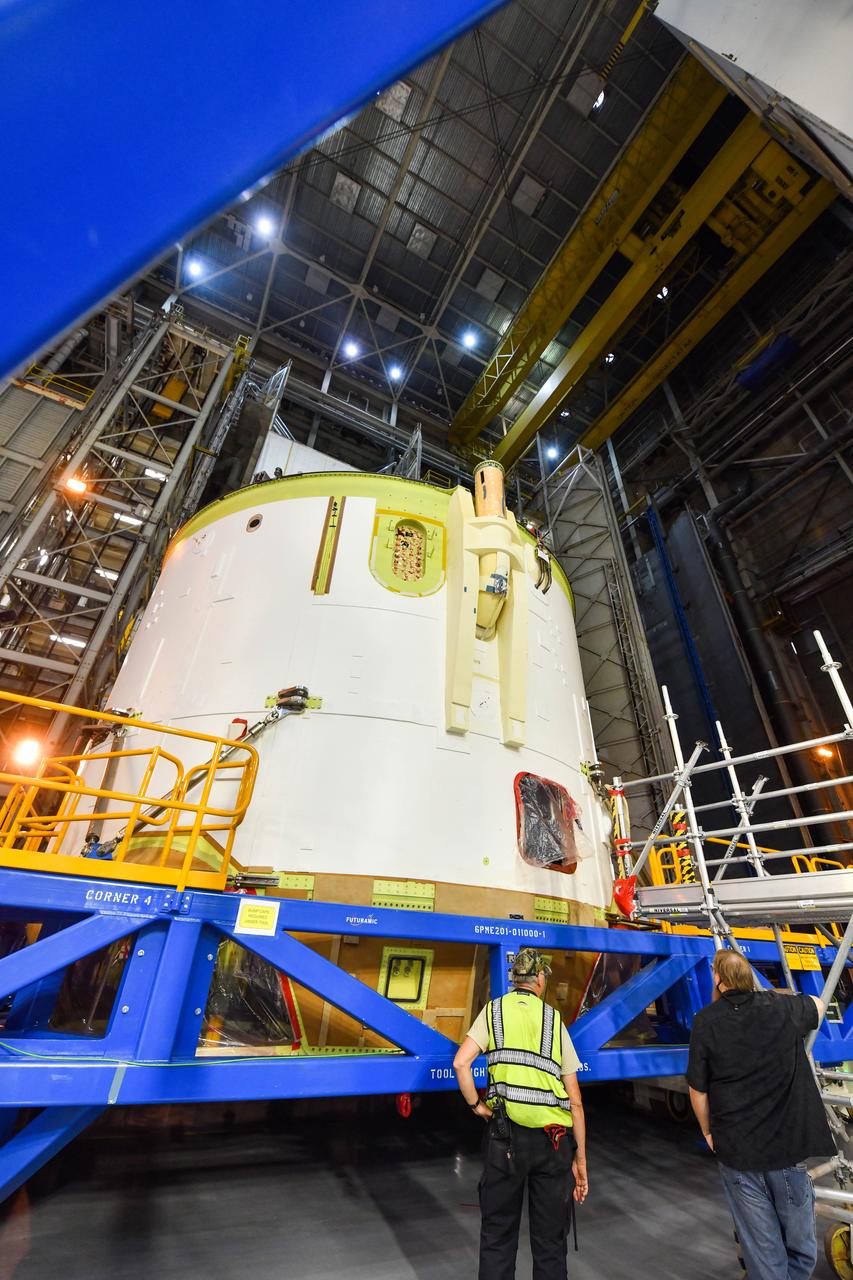

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
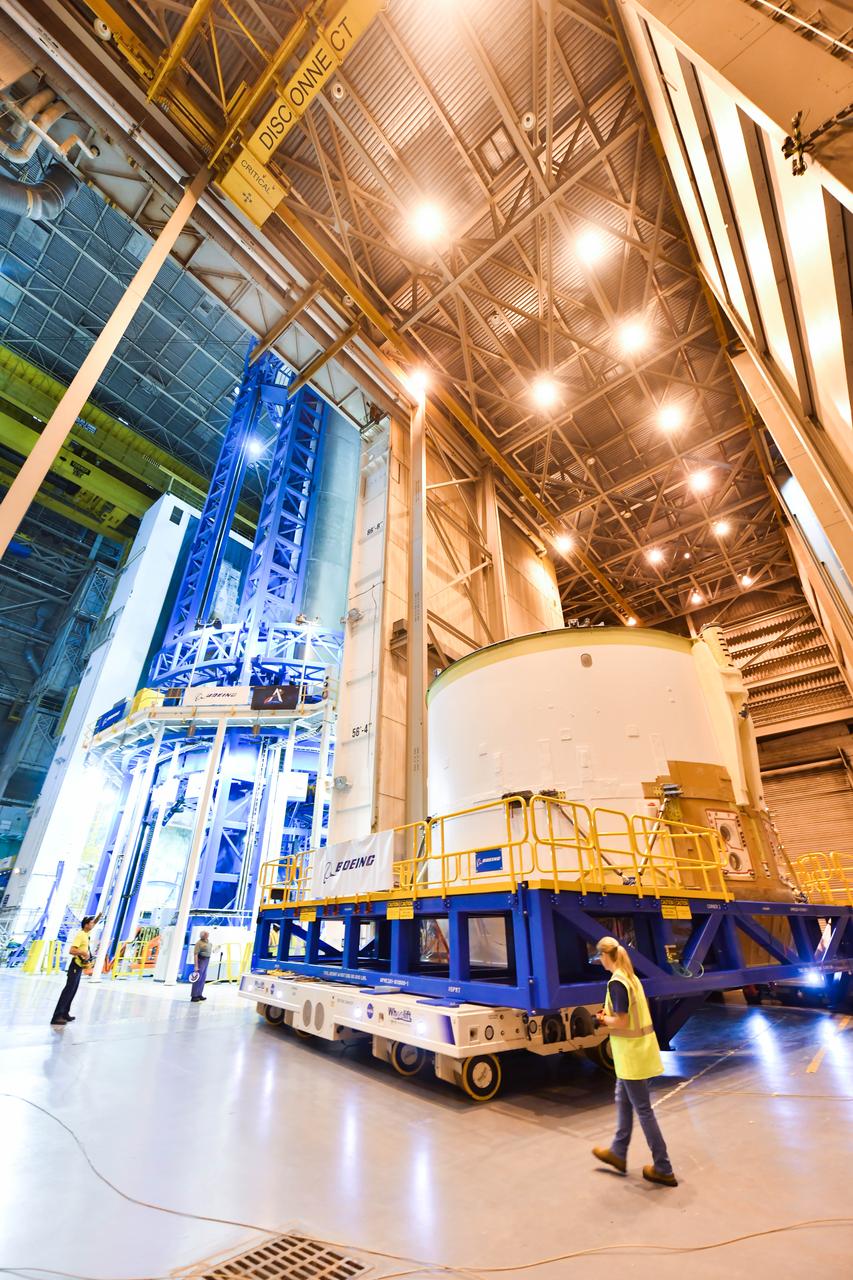

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
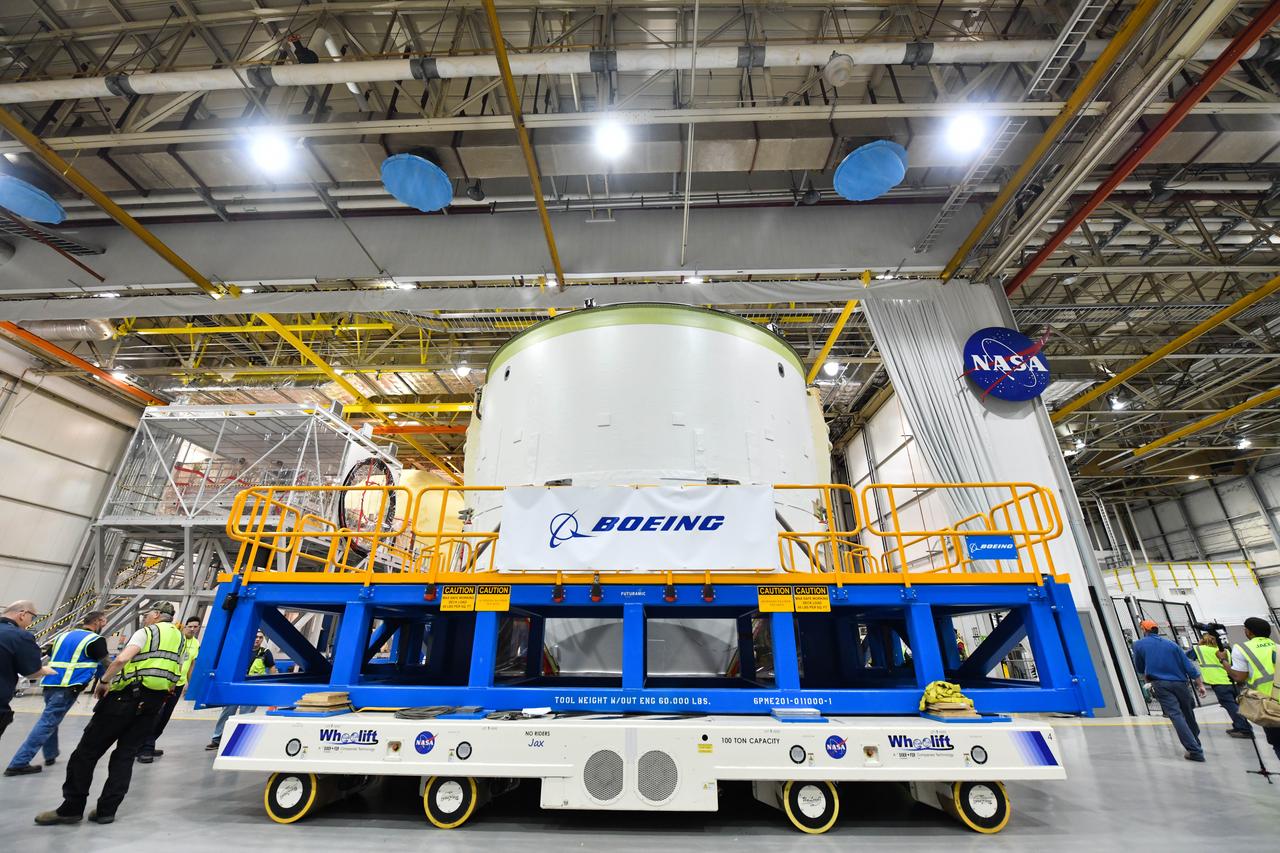

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
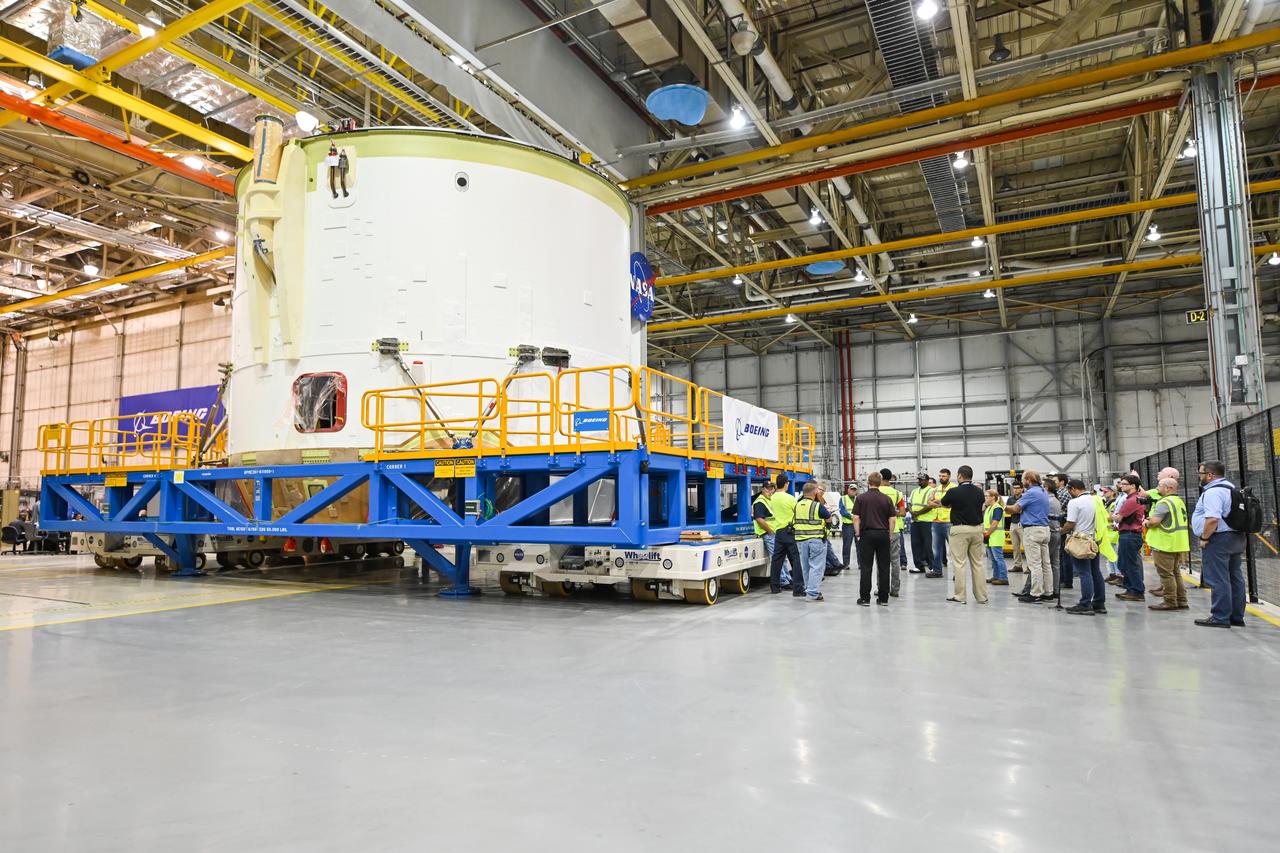

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
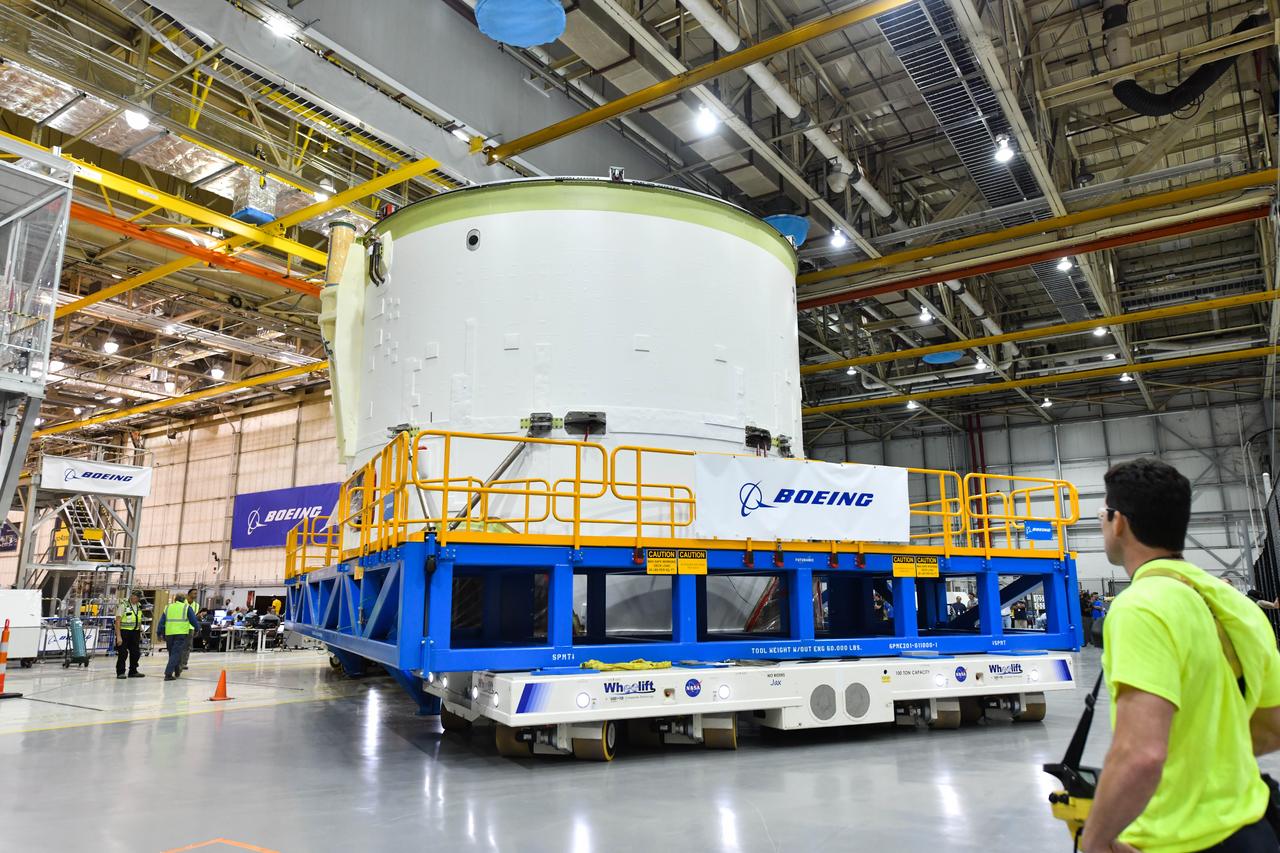

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
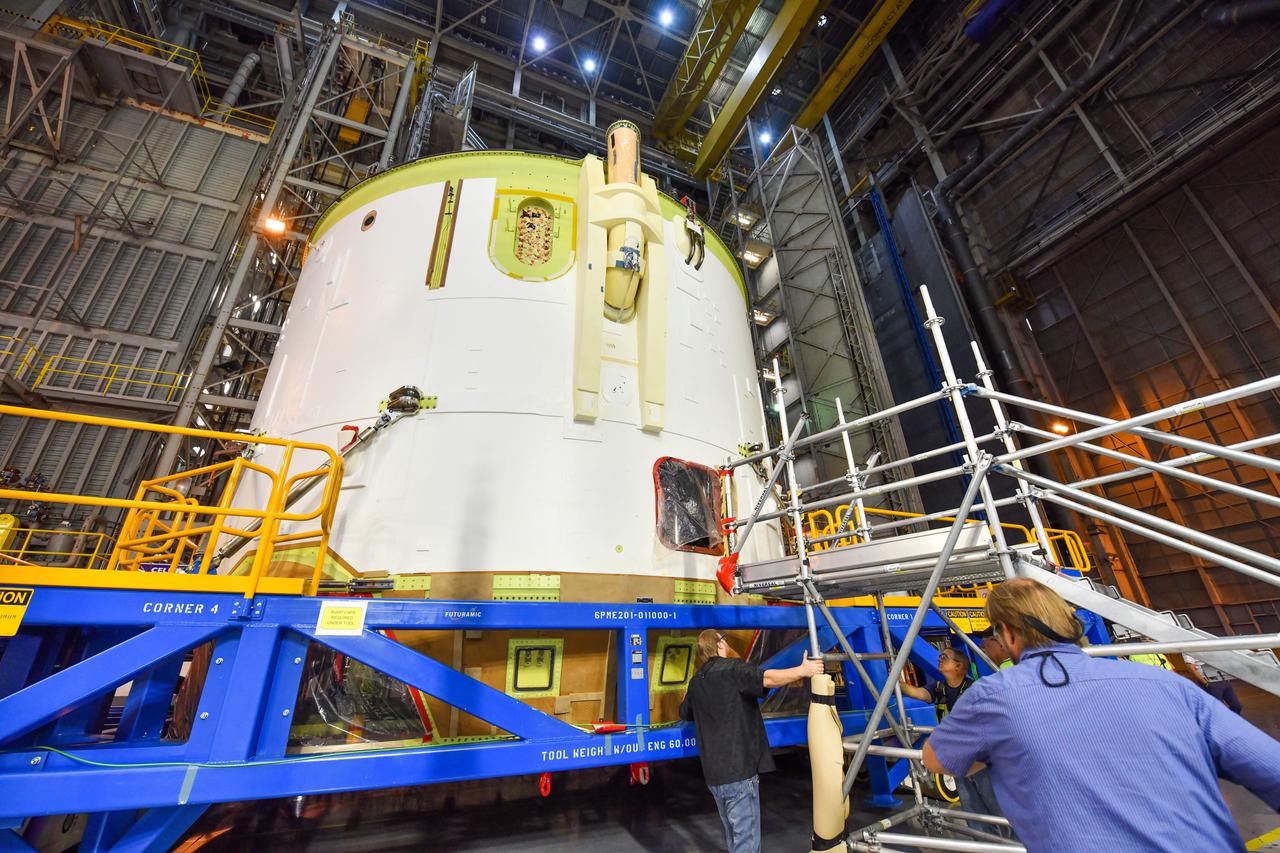

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
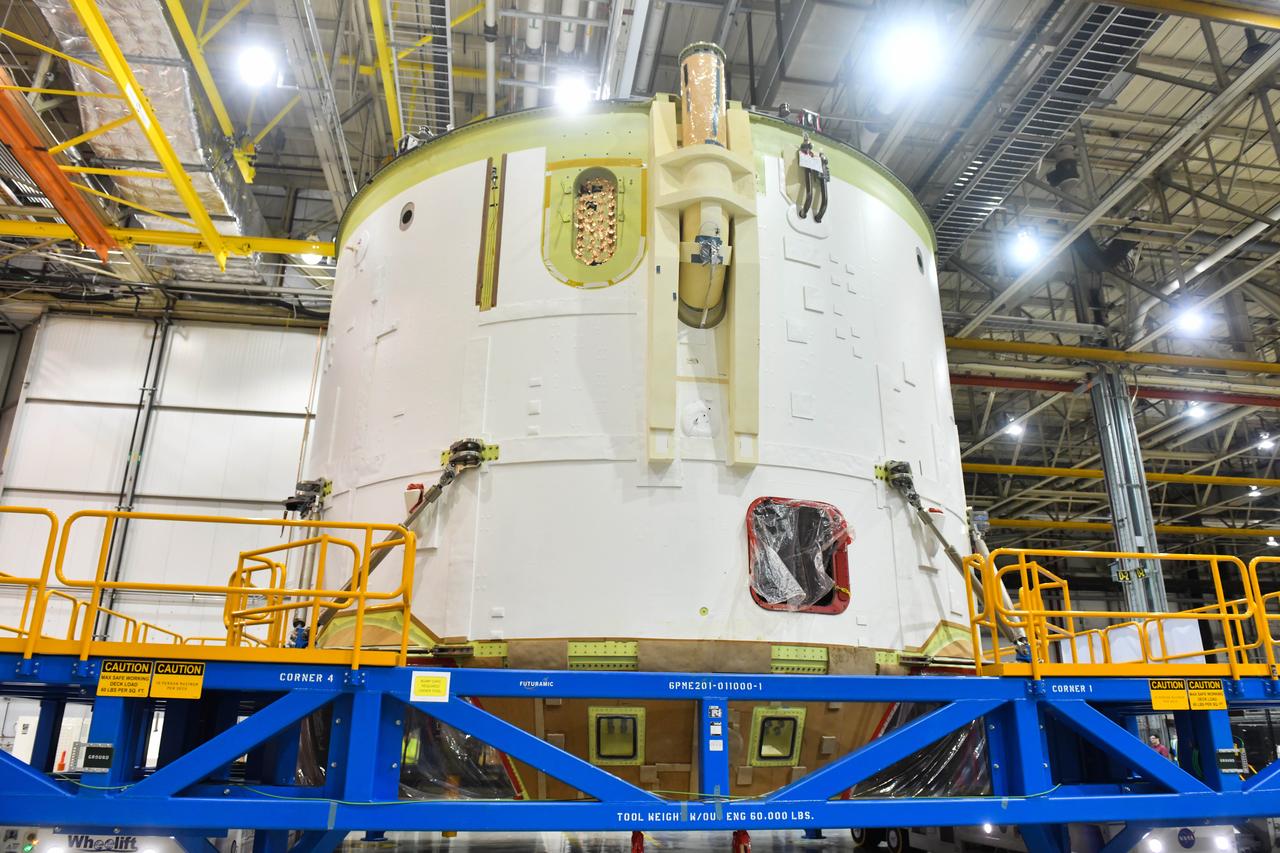

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
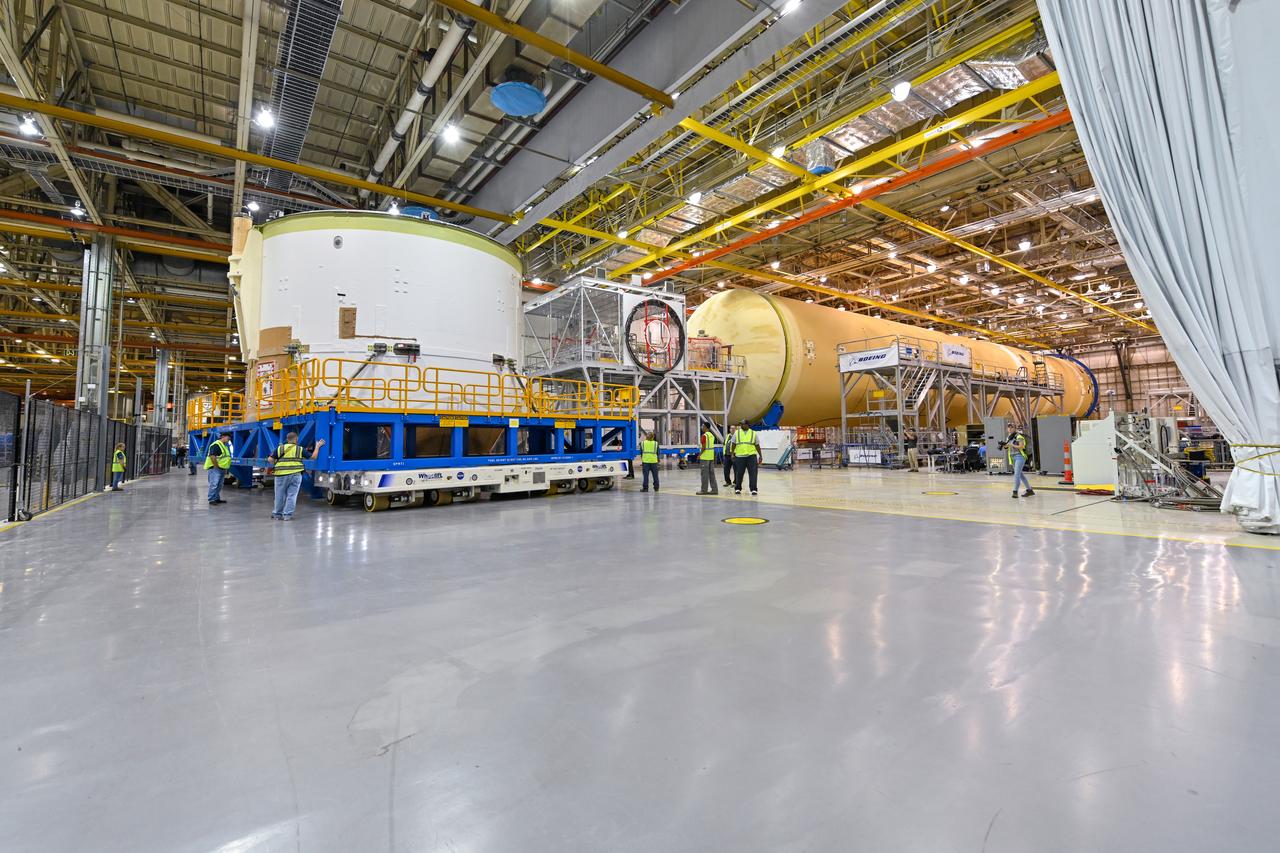

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
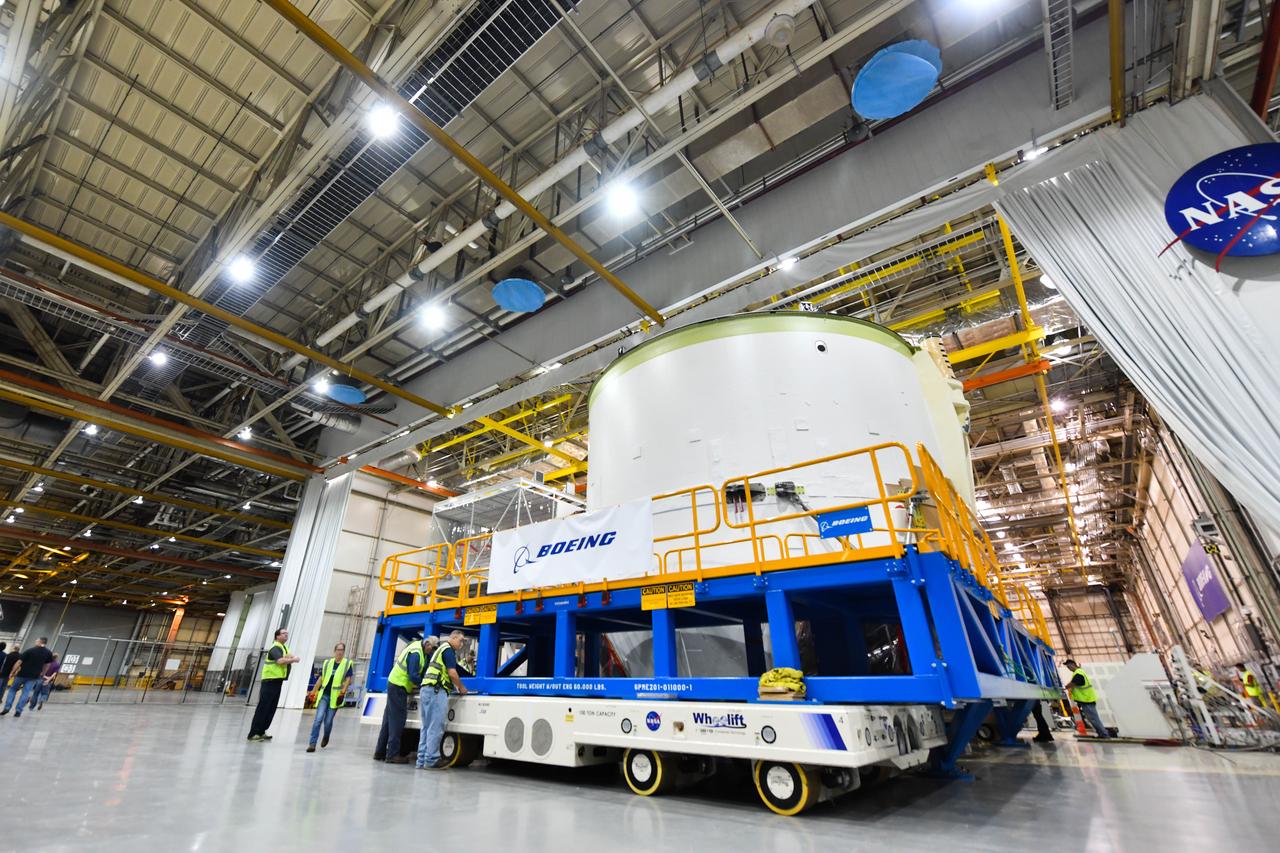

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
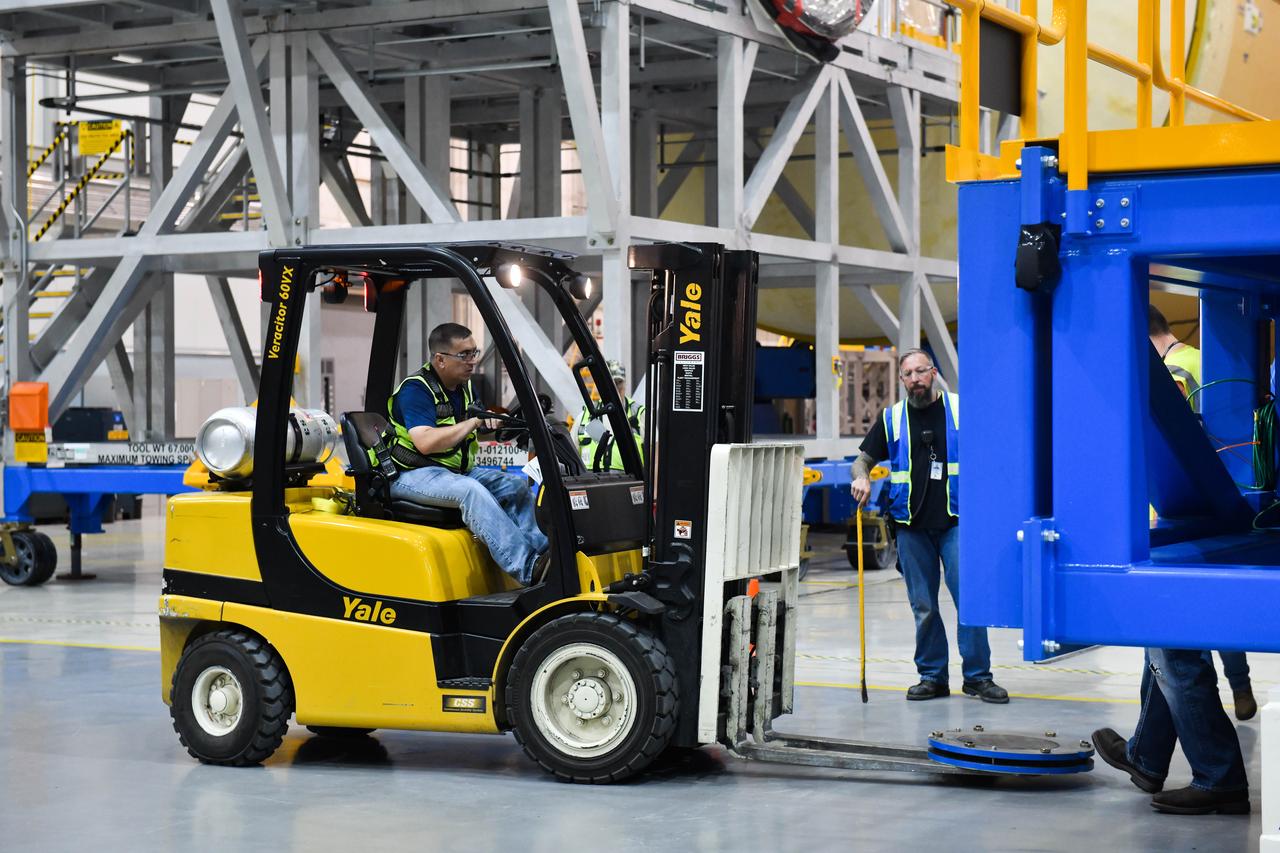

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
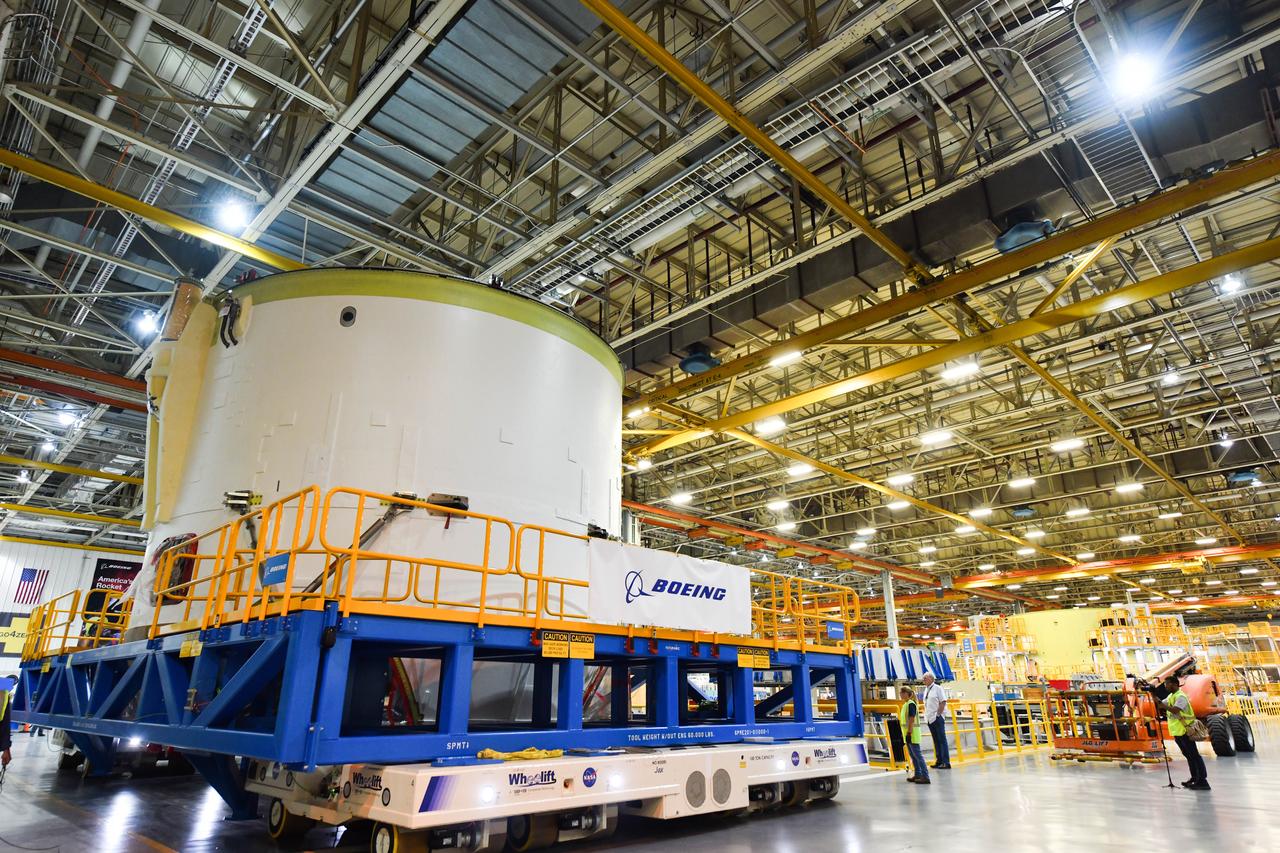

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.
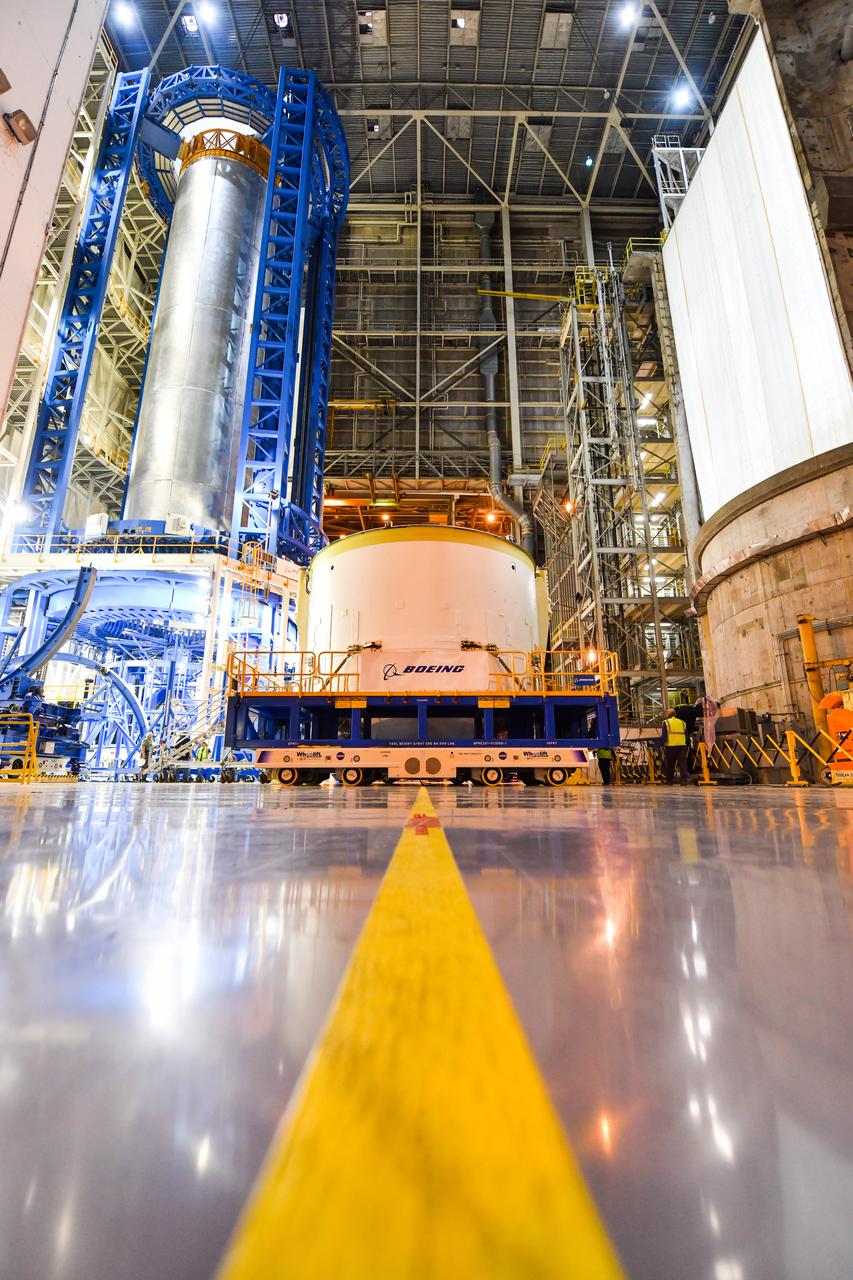

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans moved the engine section for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket to another part of the facility on Sept. 3 to prepare it for joining to the rest of the rocket’s core stage. The engine section, which comprises the lowest portion of the 212-foot-tall stage, is the last major component to be horizontally integrated to the core stage. Michoud crews completed assembly on the flight hardware that will be used for Artemis I, the first lunar mission of SLS and NASA’s Orion spacecraft, on Aug. 29. NASA and Boeing engineers removed the scaffolding surrounding the hardware to use a special tool to properly position the engine section for its attachment to the rest of the stage. The core stage’s two liquid propellant tanks and four RS-25 engines will produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to send the SLS rocket and Orion on the Artemis lunar missions. The engine section houses the four RS-25 engines and includes vital systems for mounting, controlling and delivering fuel form the propellant tanks to the rocket’s engines. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission.