
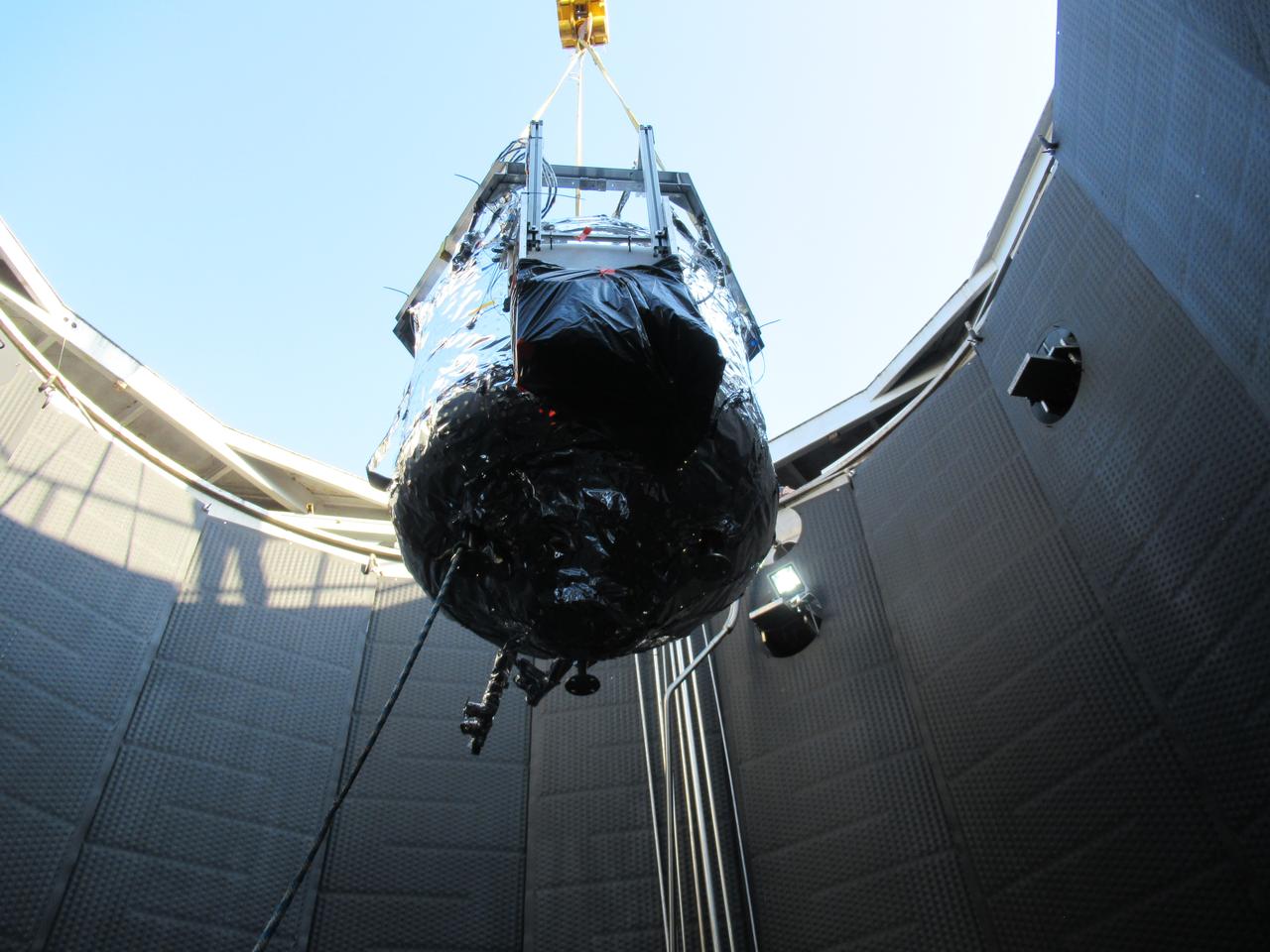
These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are testing an innovative approach to achieve zero boiloff storage of liquid hydrogen using two stages of active cooling, which could prevent the loss of valuable propellant during future long-duration spaceflight missions. Test teams installed the propellant tank in Test Stand 300 at NASA Marshall in early June, and the 90-day test campaign is scheduled to conclude in September. The tank is wrapped in a multi-layer insulation blanket that includes a thin aluminum heat shield fitted between layers. A second set of tubes, carrying helium at about minus 298 Fahrenheit, is integrated into the shield. This intermediate cooling layer intercepts and rejects incoming heat before it reaching the tank, easing the heat load on the tube-on-tank system. The Cryogenic Fluid Management Portfolio Project is a cross-agency team based at NASA Marshall and the agency’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland. The cryogenic portfolio’s work is under NASA’s Technology Demonstration Missions Program, part of NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate, and is comprised of more than 20 individual technology development activities. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
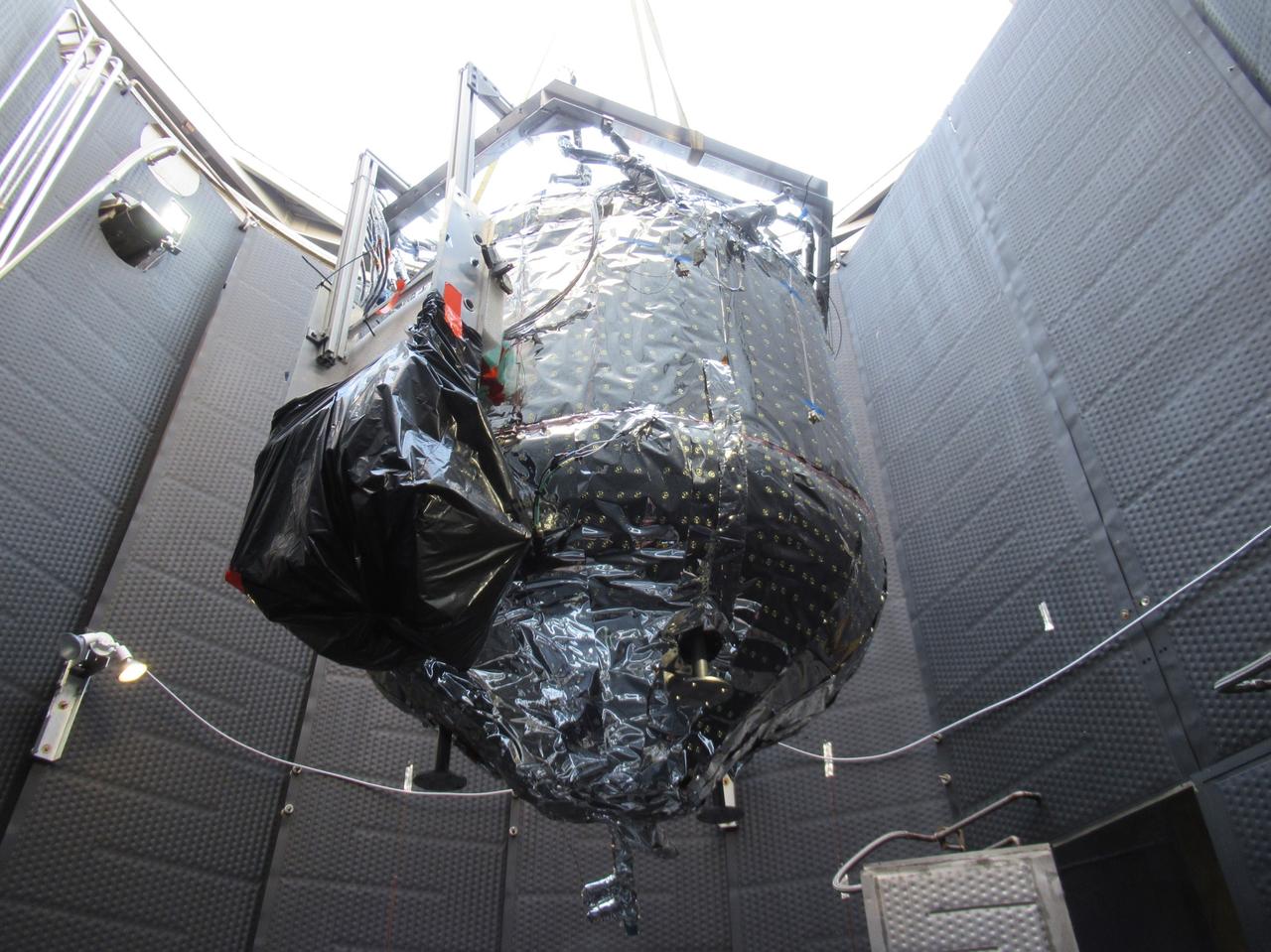

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are testing an innovative approach to achieve zero boiloff storage of liquid hydrogen using two stages of active cooling, which could prevent the loss of valuable propellant during future long-duration spaceflight missions. Test teams installed the propellant tank in Test Stand 300 at NASA Marshall in early June, and the 90-day test campaign is scheduled to conclude in September. The tank is wrapped in a multi-layer insulation blanket that includes a thin aluminum heat shield fitted between layers. A second set of tubes, carrying helium at about minus 298 Fahrenheit, is integrated into the shield. This intermediate cooling layer intercepts and rejects incoming heat before it reaching the tank, easing the heat load on the tube-on-tank system. The Cryogenic Fluid Management Portfolio Project is a cross-agency team based at NASA Marshall and the agency’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland. The cryogenic portfolio’s work is under NASA’s Technology Demonstration Missions Program, part of NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate, and is comprised of more than 20 individual technology development activities. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
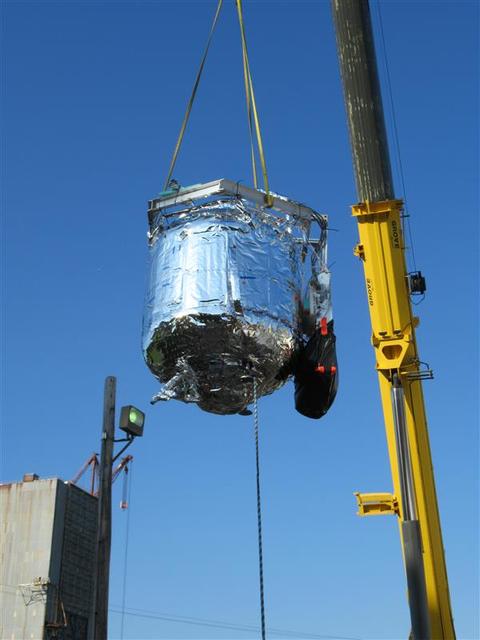

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are testing an innovative approach to achieve zero boiloff storage of liquid hydrogen using two stages of active cooling, which could prevent the loss of valuable propellant during future long-duration spaceflight missions. Test teams installed the propellant tank in Test Stand 300 at NASA Marshall in early June, and the 90-day test campaign is scheduled to conclude in September. The tank is wrapped in a multi-layer insulation blanket that includes a thin aluminum heat shield fitted between layers. A second set of tubes, carrying helium at about minus 298 Fahrenheit, is integrated into the shield. This intermediate cooling layer intercepts and rejects incoming heat before it reaching the tank, easing the heat load on the tube-on-tank system. The Cryogenic Fluid Management Portfolio Project is a cross-agency team based at NASA Marshall and the agency’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland. The cryogenic portfolio’s work is under NASA’s Technology Demonstration Missions Program, part of NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate, and is comprised of more than 20 individual technology development activities. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
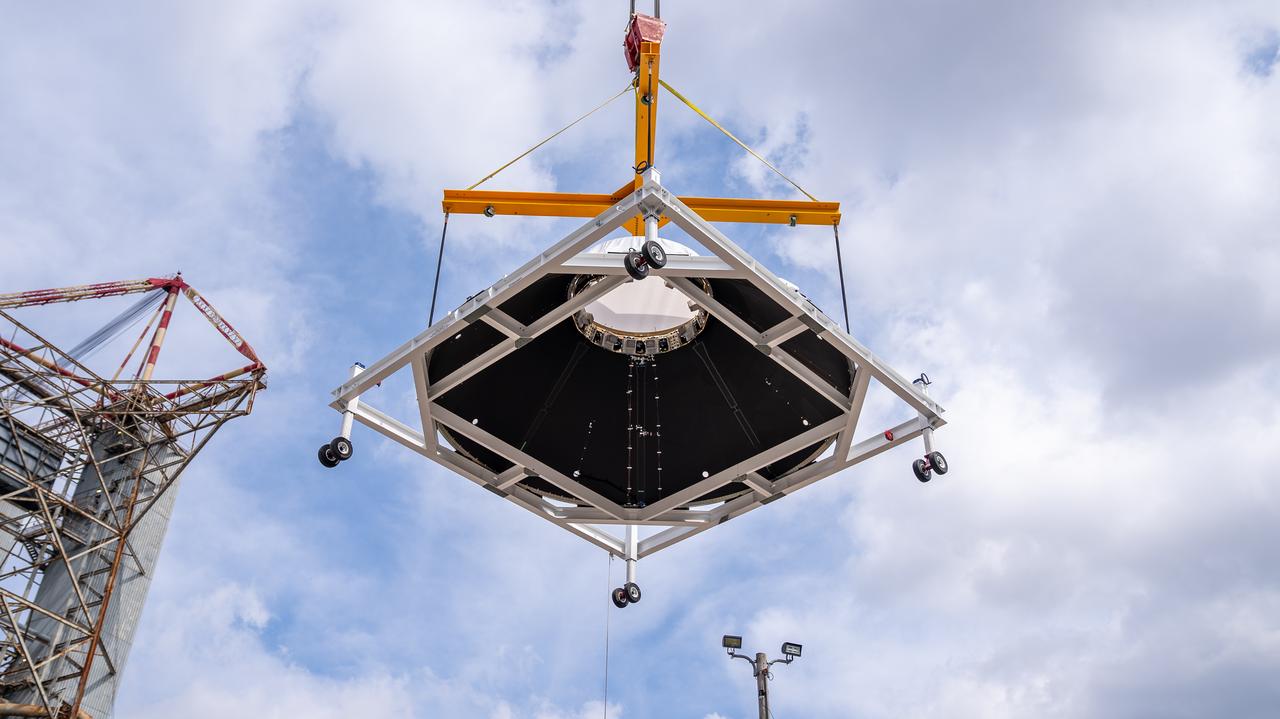

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
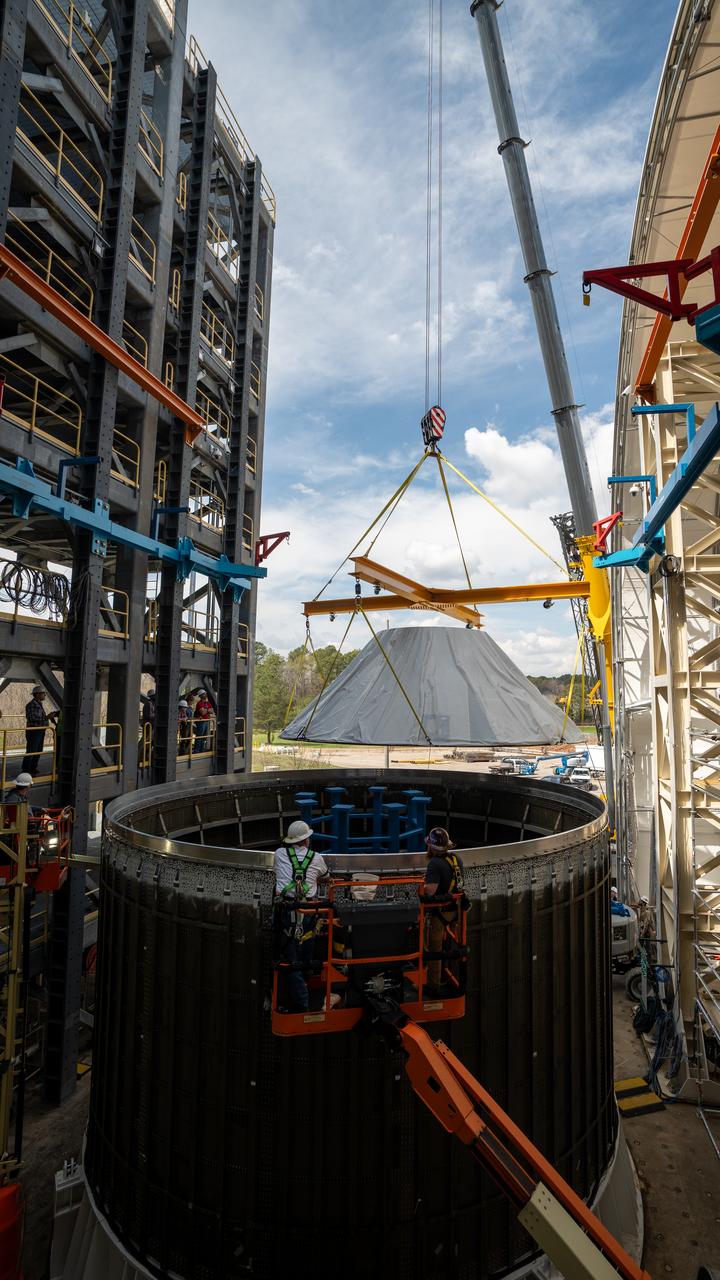

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
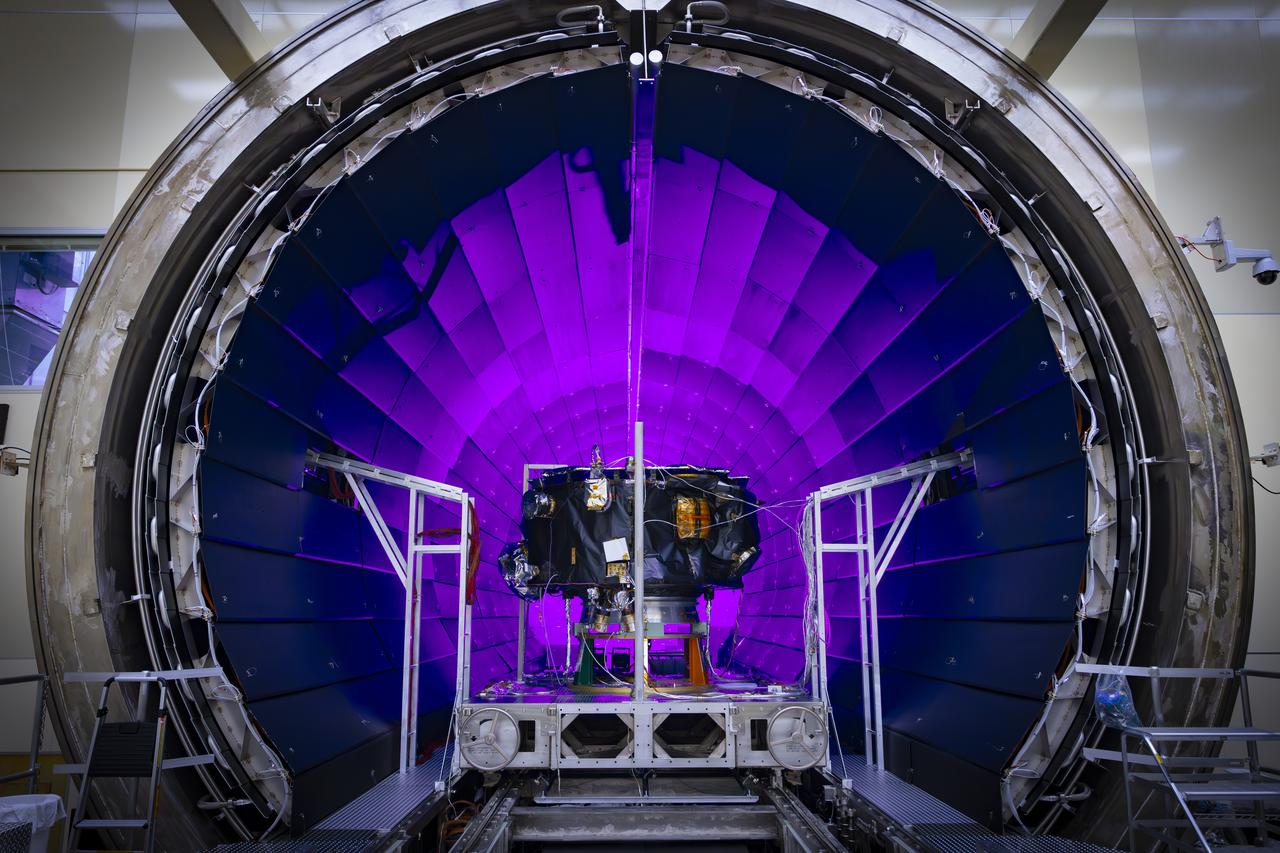

These photos and timelapse show NASA’s IMAP mission being loaded into the thermal vacuum chamber of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center’s X-Ray and Cryogenic Facility (XRCF) in Huntsville, Alabama. IMAP arrived at Marshall March 18 and was loaded into the chamber March 19. IMAP will undergo testing such as dramatic temperature changes to simulate the harsh environment of space. The XRCF’s vacuum chamber is is 20 feet in diameter and 60 feet long making it one of the largest across NASA. The IMAP mission is a modern-day celestial cartographer that will map the solar system by studying the heliosphere, a giant bubble created by the Sun’s solar wind that surrounds our solar system and protects it from harmful interstellar radiation. Photos and video courtesy of Ed Whitman from Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
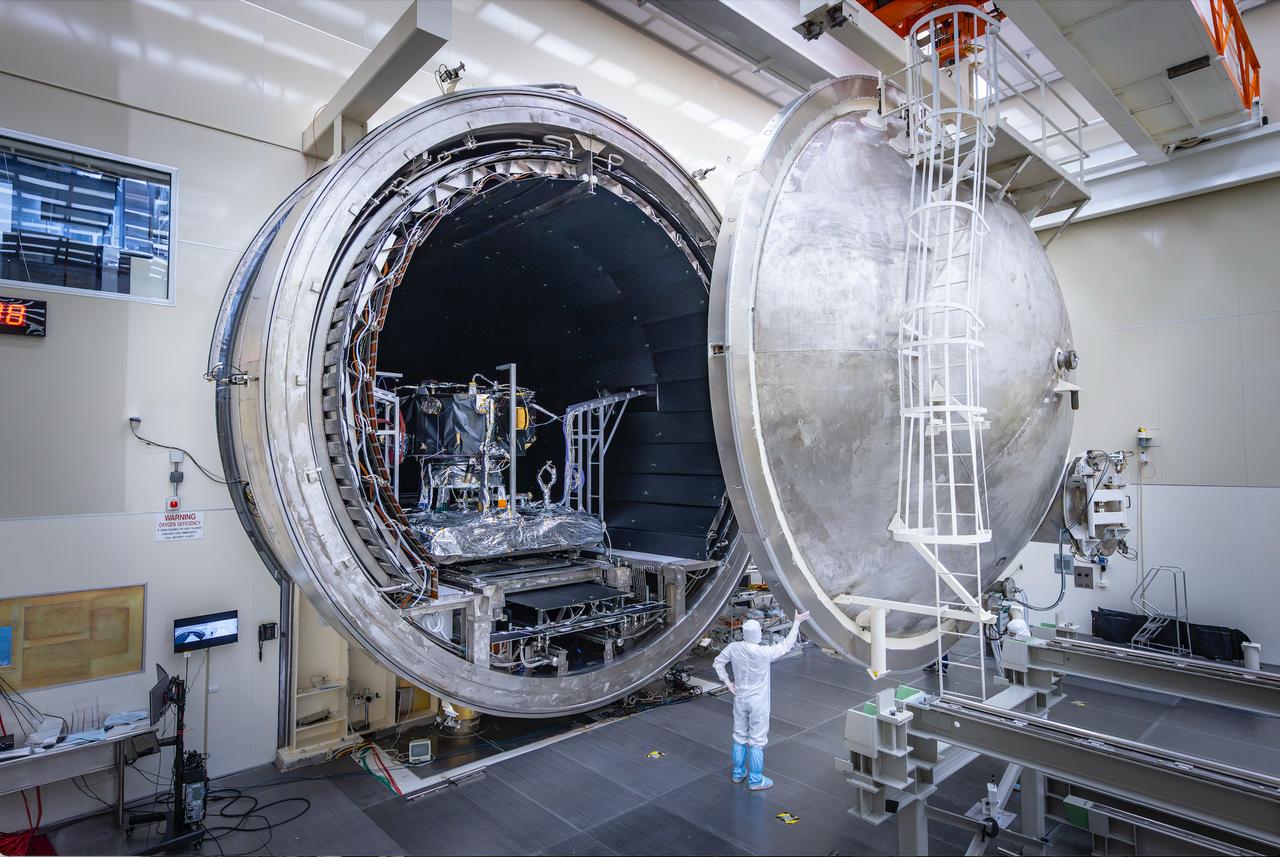
These photos and timelapse show NASA’s IMAP mission being loaded into the thermal vacuum chamber of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center’s X-Ray and Cryogenic Facility (XRCF) in Huntsville, Alabama. IMAP arrived at Marshall March 18 and was loaded into the chamber March 19. IMAP will undergo testing such as dramatic temperature changes to simulate the harsh environment of space. The XRCF’s vacuum chamber is is 20 feet in diameter and 60 feet long making it one of the largest across NASA. The IMAP mission is a modern-day celestial cartographer that will map the solar system by studying the heliosphere, a giant bubble created by the Sun’s solar wind that surrounds our solar system and protects it from harmful interstellar radiation. Photos and video courtesy of Ed Whitman from Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.
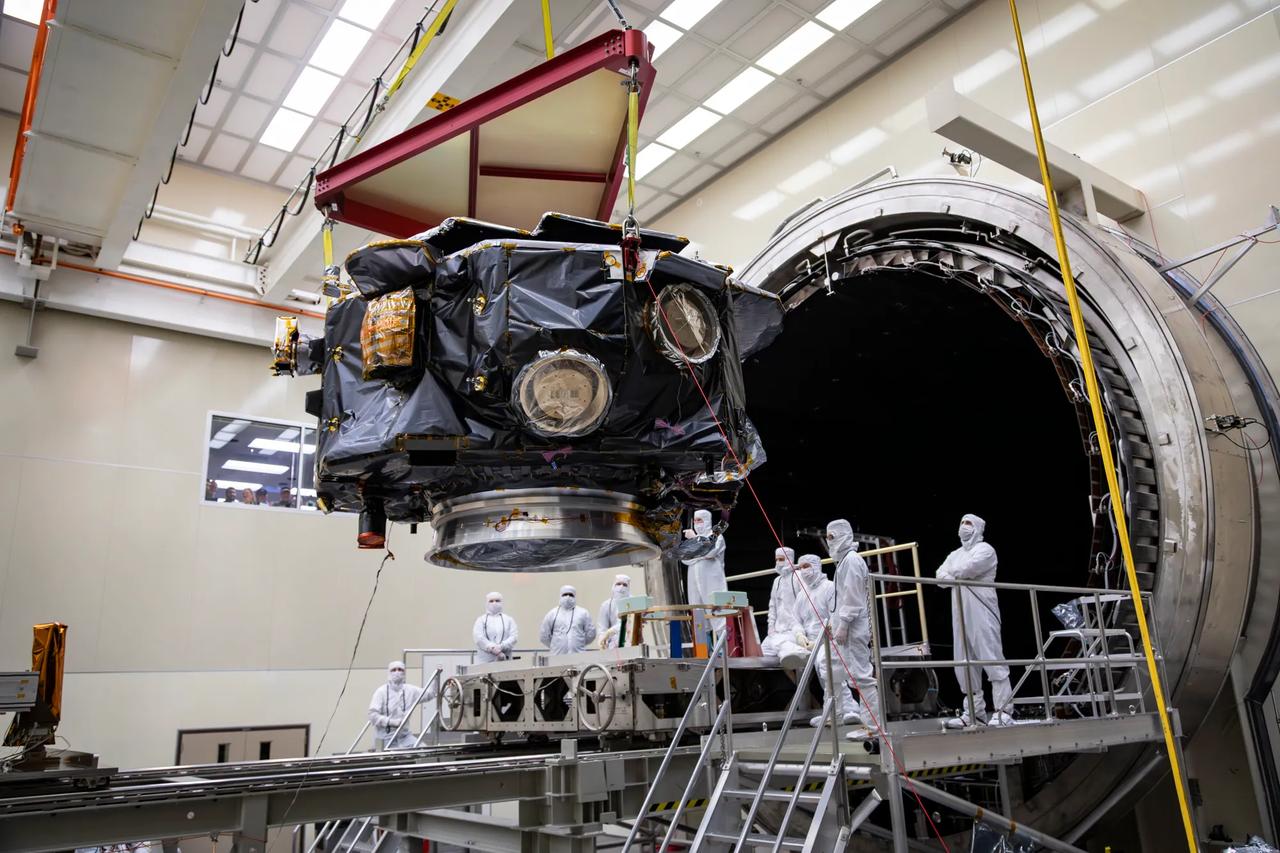

These photos and timelapse show NASA’s IMAP mission being loaded into the thermal vacuum chamber of NASA Marshall Space Flight Center’s X-Ray and Cryogenic Facility (XRCF) in Huntsville, Alabama. IMAP arrived at Marshall March 18 and was loaded into the chamber March 19. IMAP will undergo testing such as dramatic temperature changes to simulate the harsh environment of space. The XRCF’s vacuum chamber is is 20 feet in diameter and 60 feet long making it one of the largest across NASA. The IMAP mission is a modern-day celestial cartographer that will map the solar system by studying the heliosphere, a giant bubble created by the Sun’s solar wind that surrounds our solar system and protects it from harmful interstellar radiation. Photos and video courtesy of Ed Whitman from Johns Hopkins University’s Applied Physics Laboratory. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
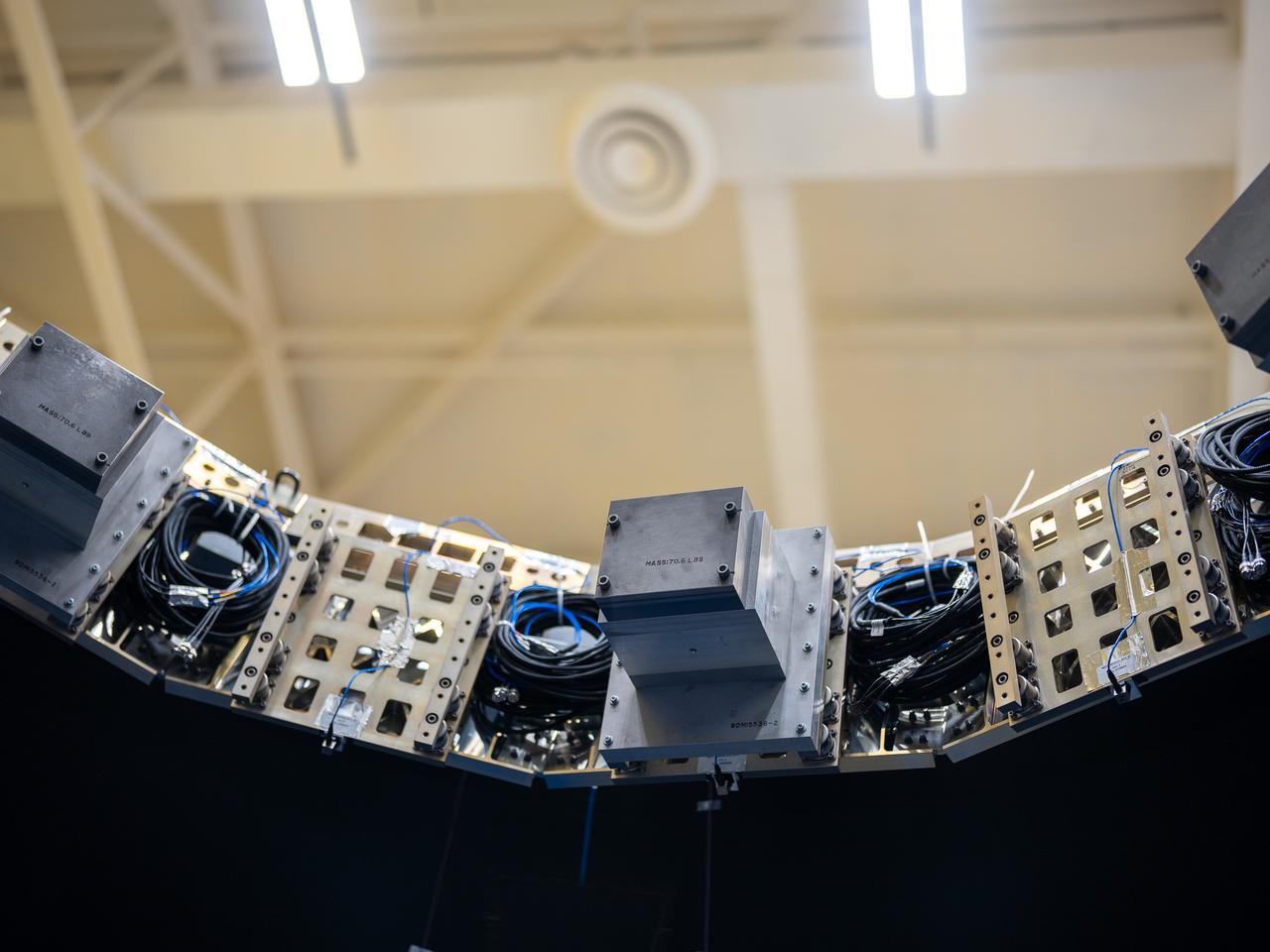
These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
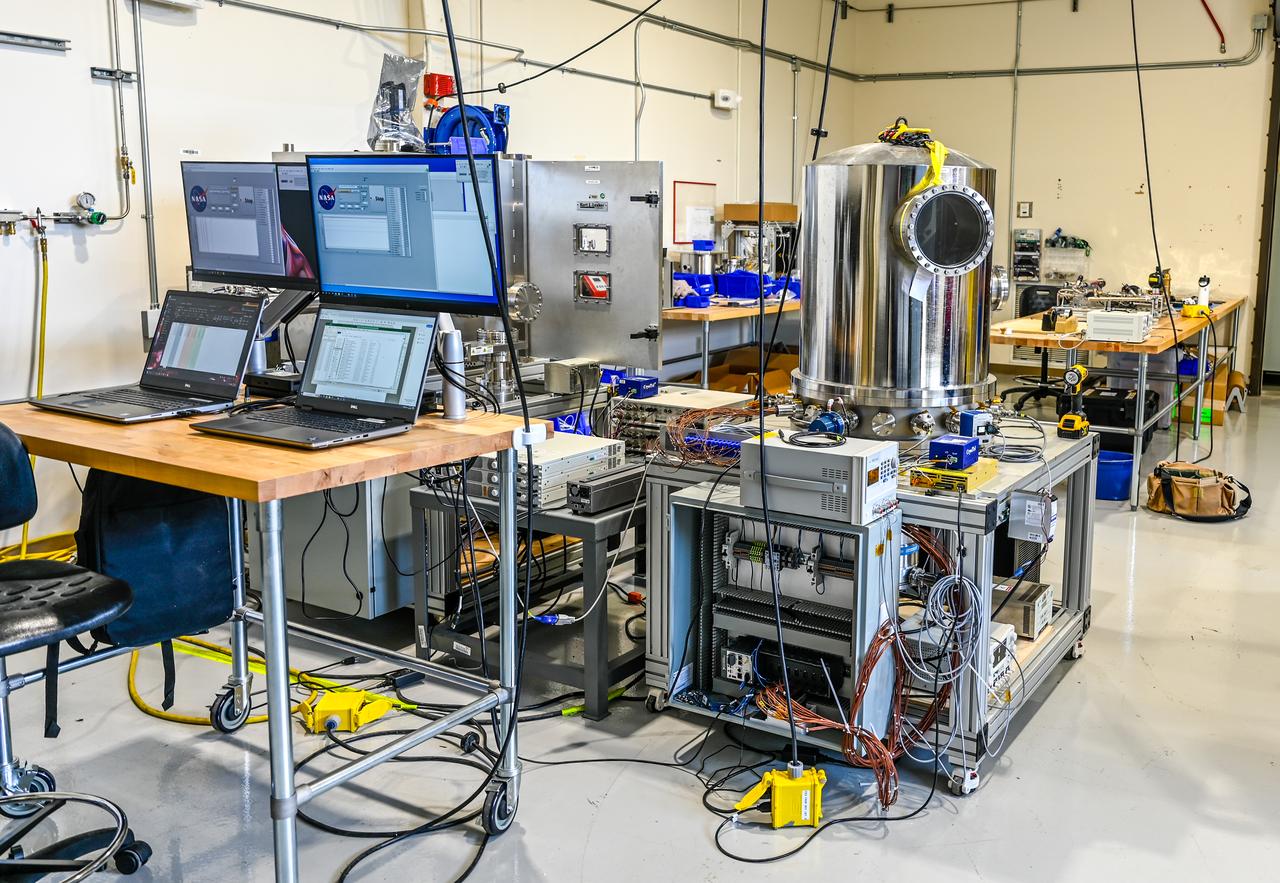

These photos, taken in fall 2024, show how NASA engineers use the Hub for Innovative Thermal Technology Maturation and Prototyping (Hi-TTeMP) laboratory at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. NASA engineers working in the HI-TTeMP lab not only design, set up, and run tests, they also provide insight and expertise in thermal engineering to assist NASA’s industry partners, such as SpaceX and other organizations, in validating concepts and models, or suggesting changes to designs. The lab is able to rapidly test and evaluate design updates or iterations. Engineering teams inside the lab are currently testing how well prototype insulation for SpaceX’s Starship HLS (Human Landing System) will insulate interior environments, including propellant storage tanks and the crew cabin. Starship HLS will land astronauts on the lunar surface during Artemis III and Artemis IV.
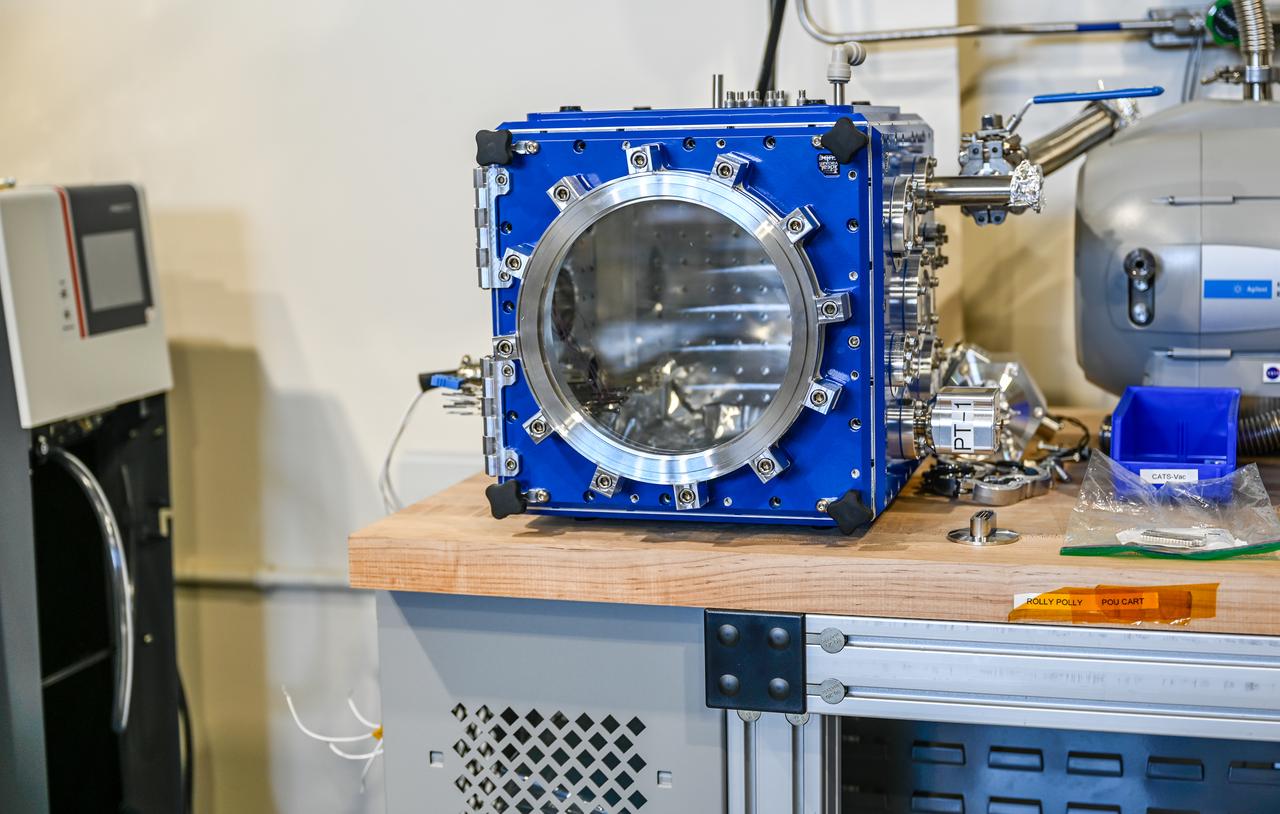
These photos, taken in fall 2024, show how NASA engineers use the Hub for Innovative Thermal Technology Maturation and Prototyping (Hi-TTeMP) laboratory at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. NASA engineers working in the HI-TTeMP lab not only design, set up, and run tests, they also provide insight and expertise in thermal engineering to assist NASA’s industry partners, such as SpaceX and other organizations, in validating concepts and models, or suggesting changes to designs. The lab is able to rapidly test and evaluate design updates or iterations. Engineering teams inside the lab are currently testing how well prototype insulation for SpaceX’s Starship HLS (Human Landing System) will insulate interior environments, including propellant storage tanks and the crew cabin. Starship HLS will land astronauts on the lunar surface during Artemis III and Artemis IV.
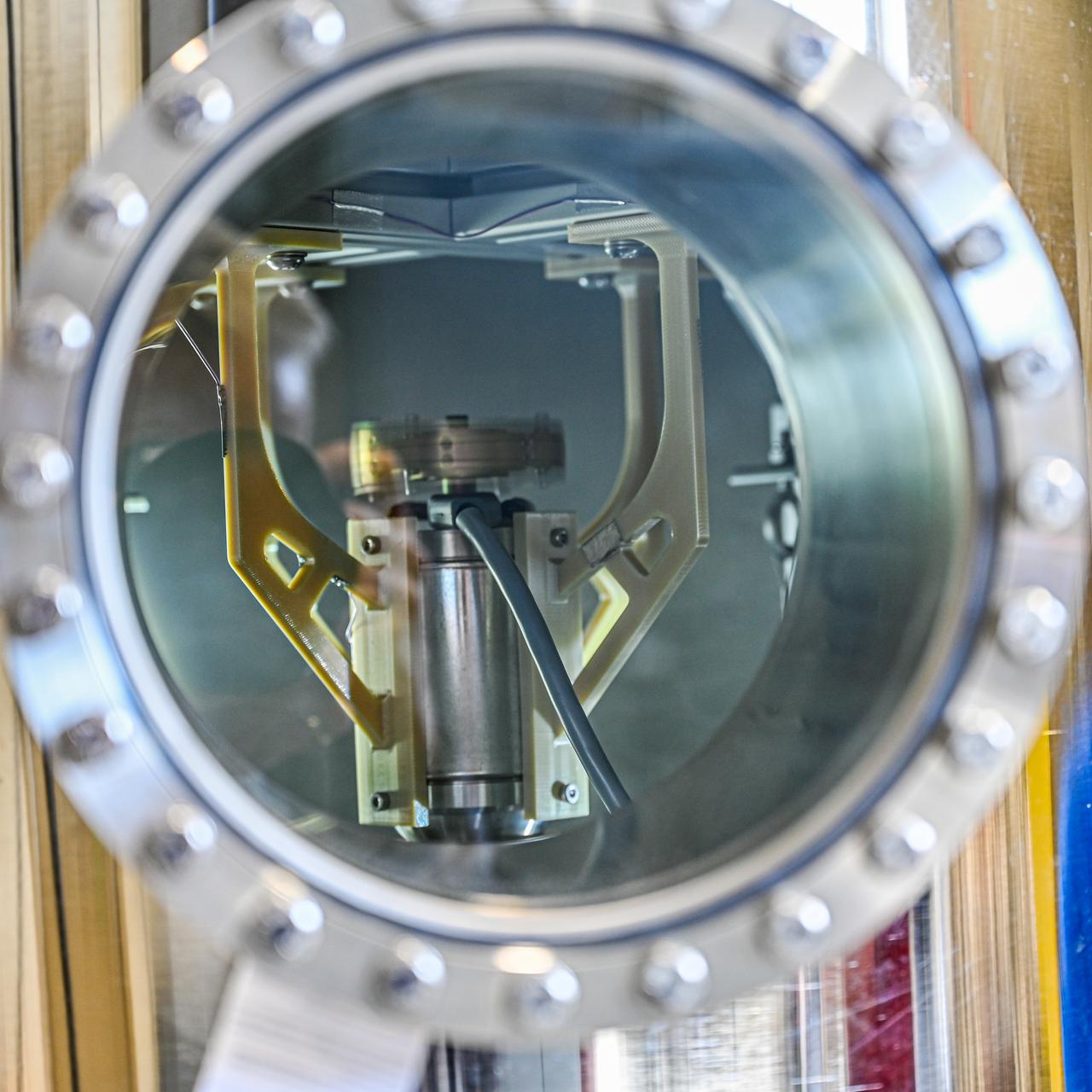
These photos, taken in fall 2024, show how NASA engineers use the Hub for Innovative Thermal Technology Maturation and Prototyping (Hi-TTeMP) laboratory at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. NASA engineers working in the HI-TTeMP lab not only design, set up, and run tests, they also provide insight and expertise in thermal engineering to assist NASA’s industry partners, such as SpaceX and other organizations, in validating concepts and models, or suggesting changes to designs. The lab is able to rapidly test and evaluate design updates or iterations. Engineering teams inside the lab are currently testing how well prototype insulation for SpaceX’s Starship HLS (Human Landing System) will insulate interior environments, including propellant storage tanks and the crew cabin. Starship HLS will land astronauts on the lunar surface during Artemis III and Artemis IV.
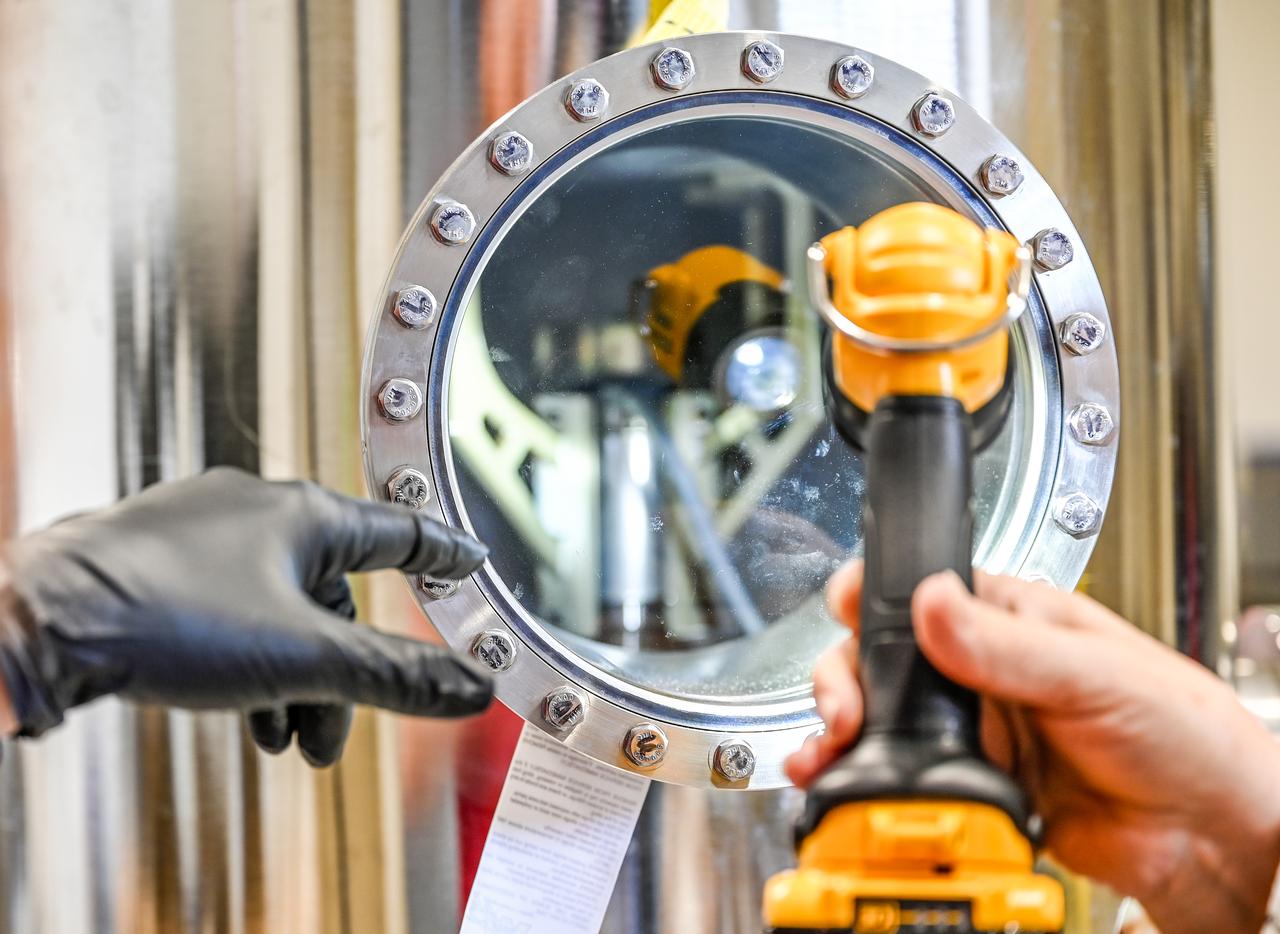

These photos, taken in fall 2024, show how NASA engineers use the Hub for Innovative Thermal Technology Maturation and Prototyping (Hi-TTeMP) laboratory at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. NASA engineers working in the HI-TTeMP lab not only design, set up, and run tests, they also provide insight and expertise in thermal engineering to assist NASA’s industry partners, such as SpaceX and other organizations, in validating concepts and models, or suggesting changes to designs. The lab is able to rapidly test and evaluate design updates or iterations. Engineering teams inside the lab are currently testing how well prototype insulation for SpaceX’s Starship HLS (Human Landing System) will insulate interior environments, including propellant storage tanks and the crew cabin. Starship HLS will land astronauts on the lunar surface during Artemis III and Artemis IV.
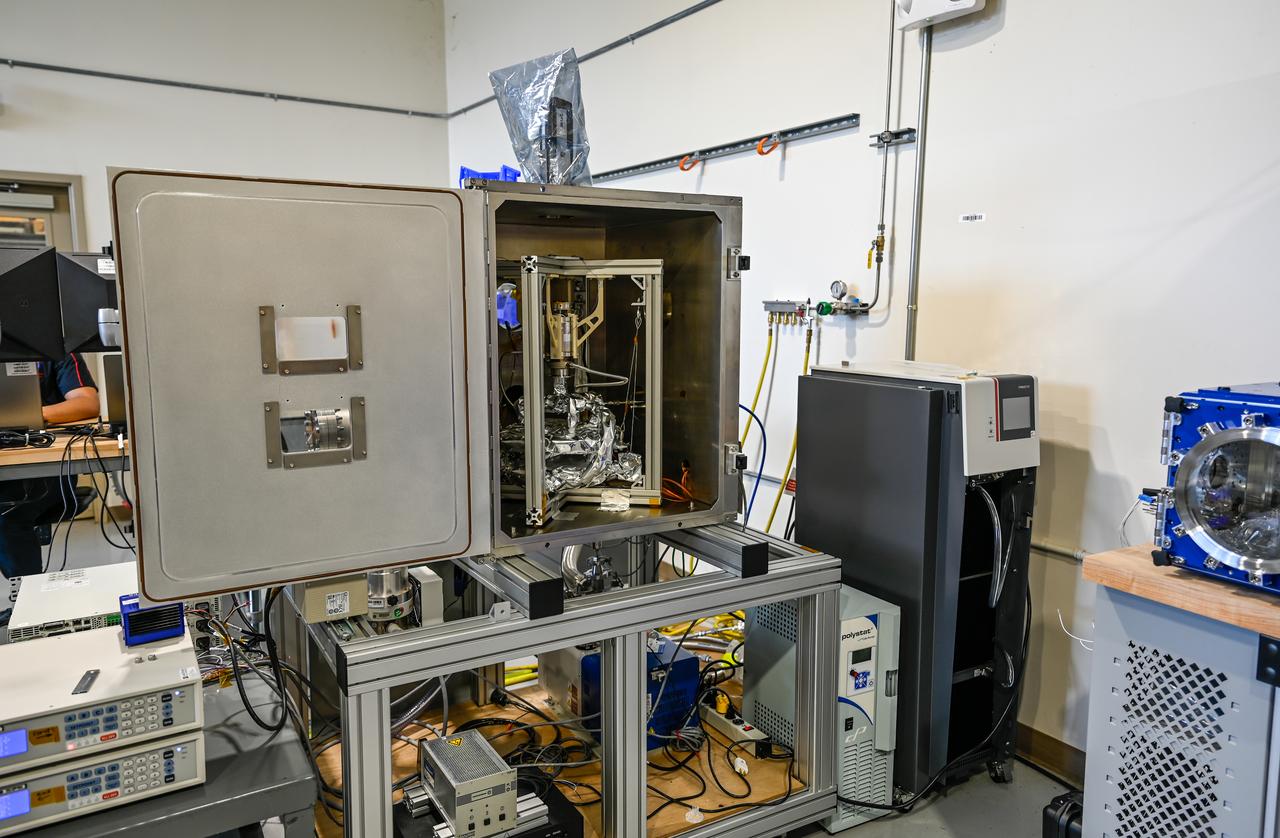

These photos, taken in fall 2024, show how NASA engineers use the Hub for Innovative Thermal Technology Maturation and Prototyping (Hi-TTeMP) laboratory at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. NASA engineers working in the HI-TTeMP lab not only design, set up, and run tests, they also provide insight and expertise in thermal engineering to assist NASA’s industry partners, such as SpaceX and other organizations, in validating concepts and models, or suggesting changes to designs. The lab is able to rapidly test and evaluate design updates or iterations. Engineering teams inside the lab are currently testing how well prototype insulation for SpaceX’s Starship HLS (Human Landing System) will insulate interior environments, including propellant storage tanks and the crew cabin. Starship HLS will land astronauts on the lunar surface during Artemis III and Artemis IV.
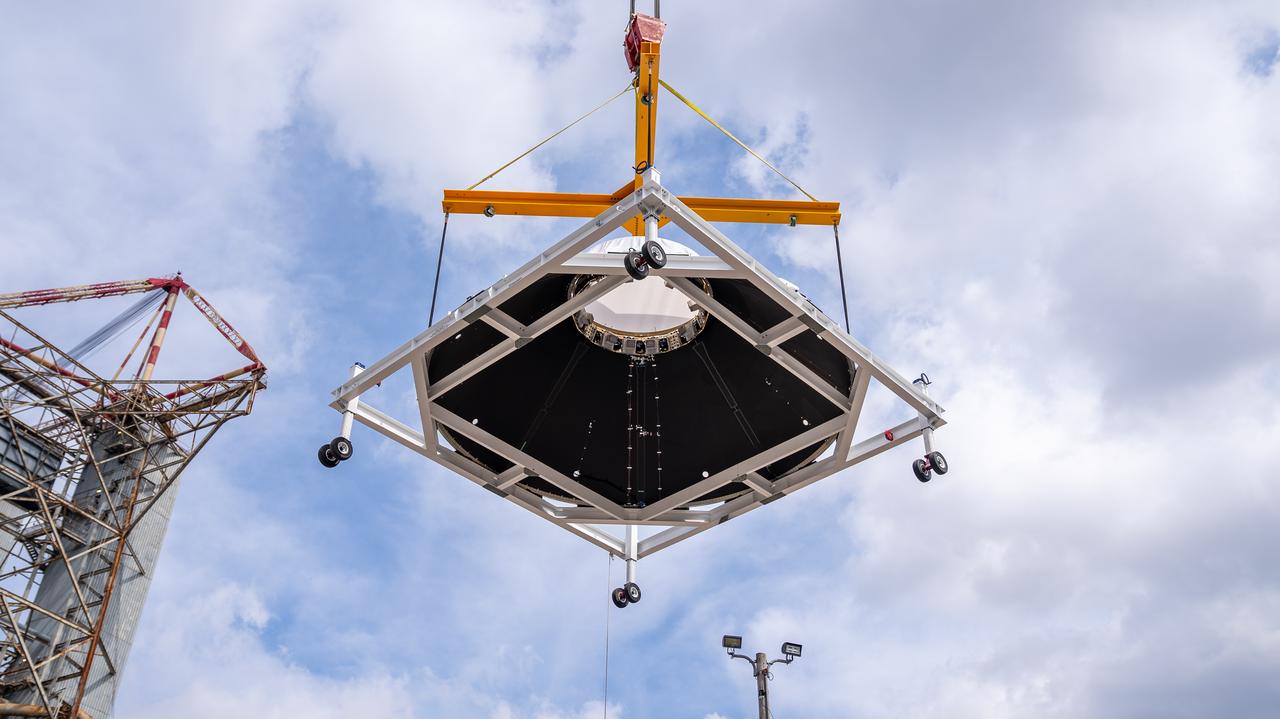

Crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13.
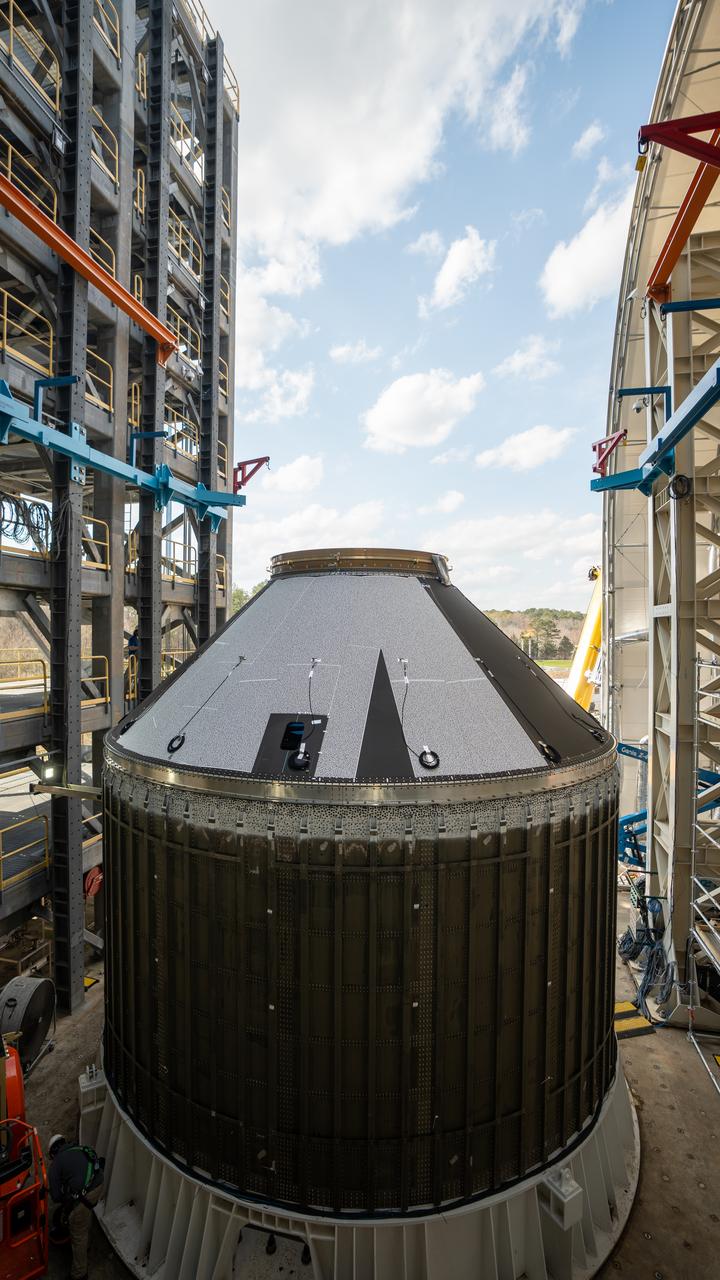

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
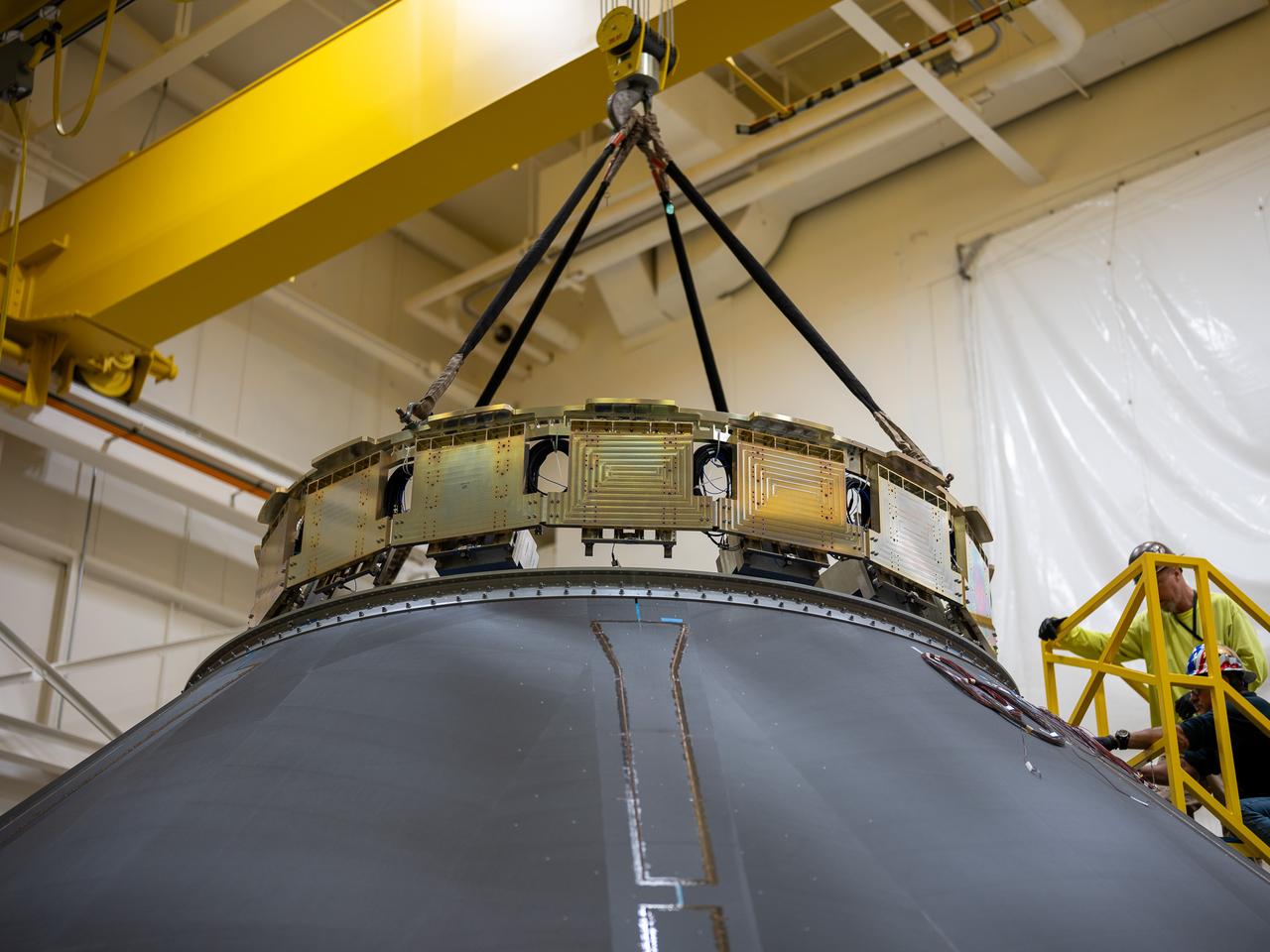

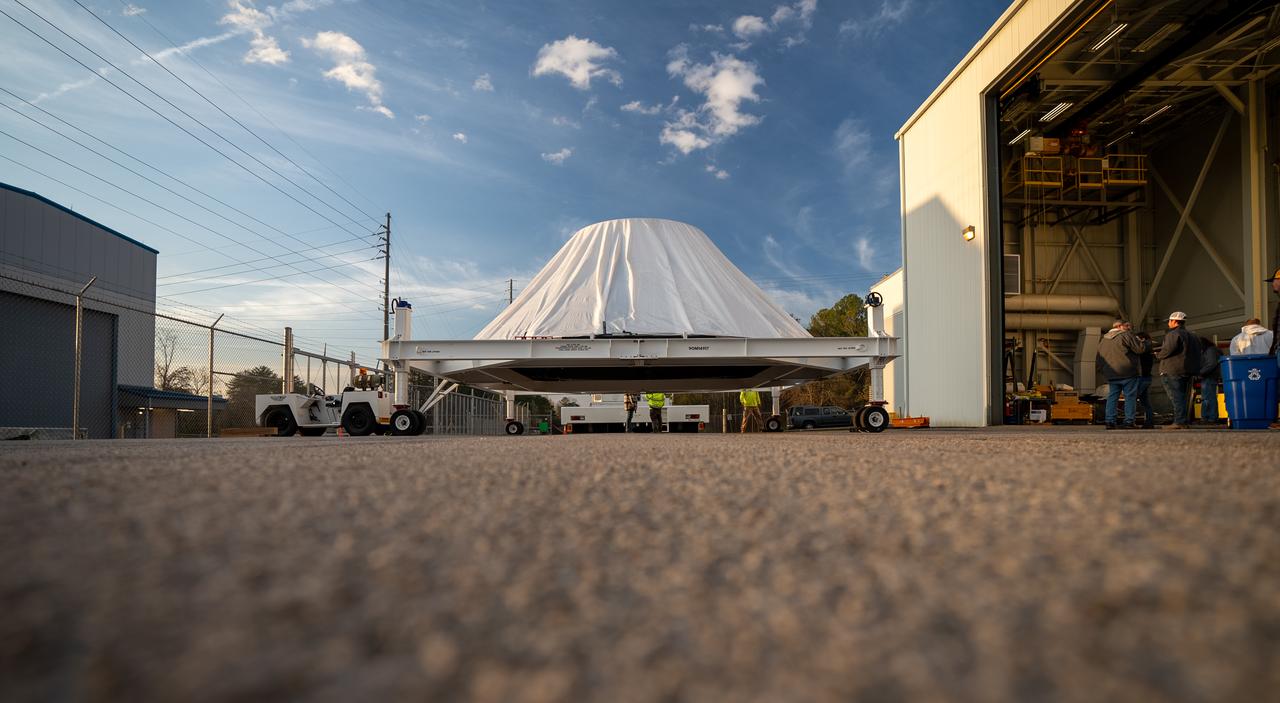
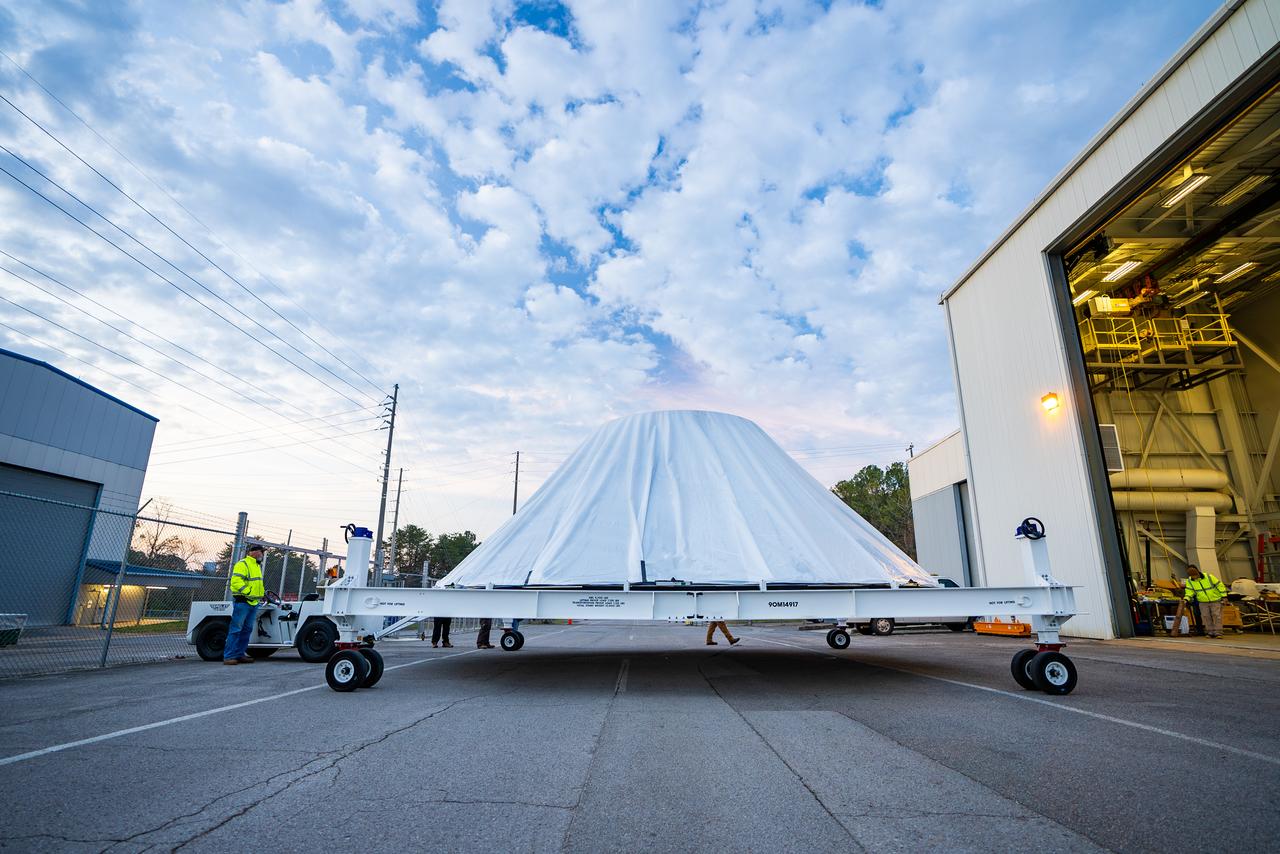
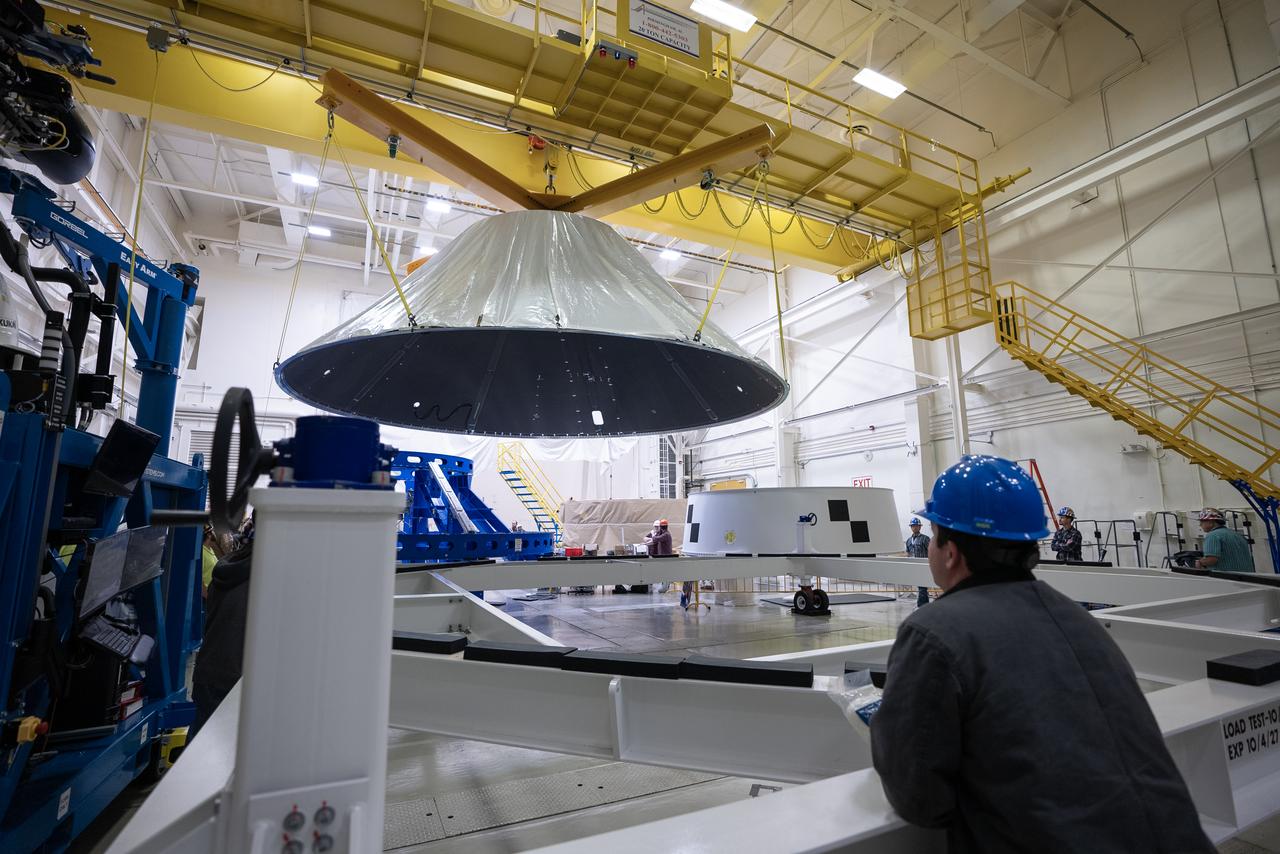
These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
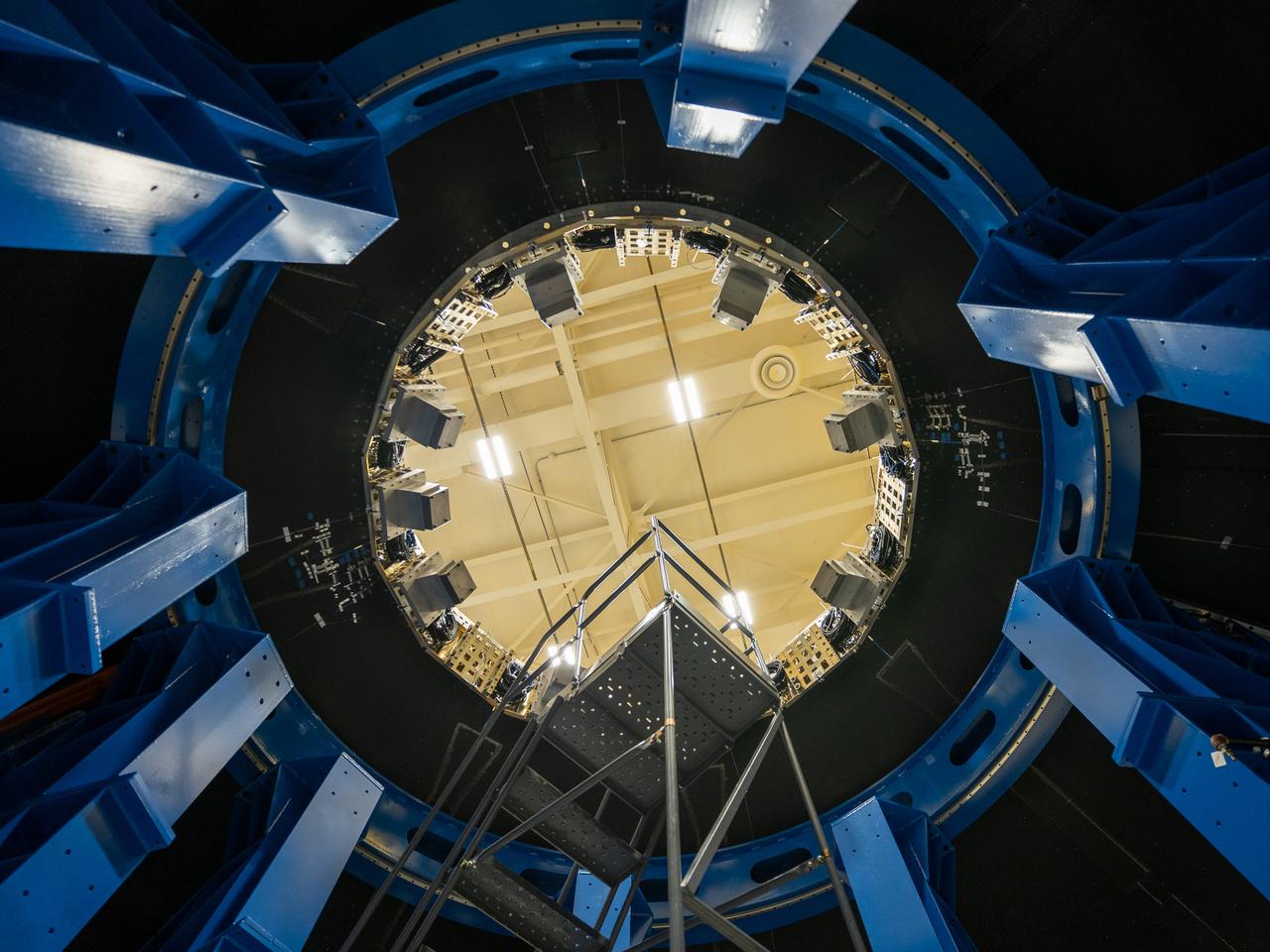

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
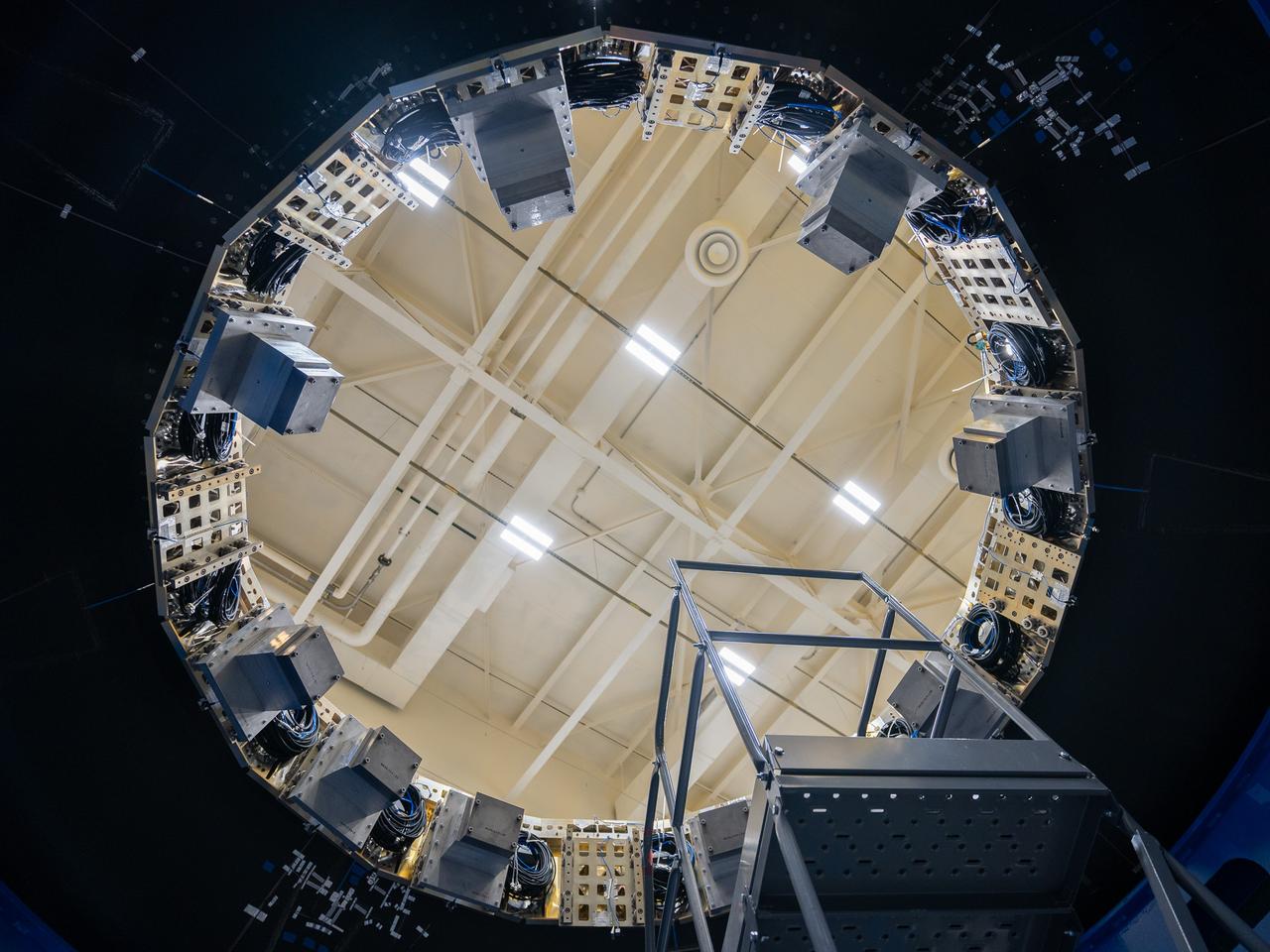

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
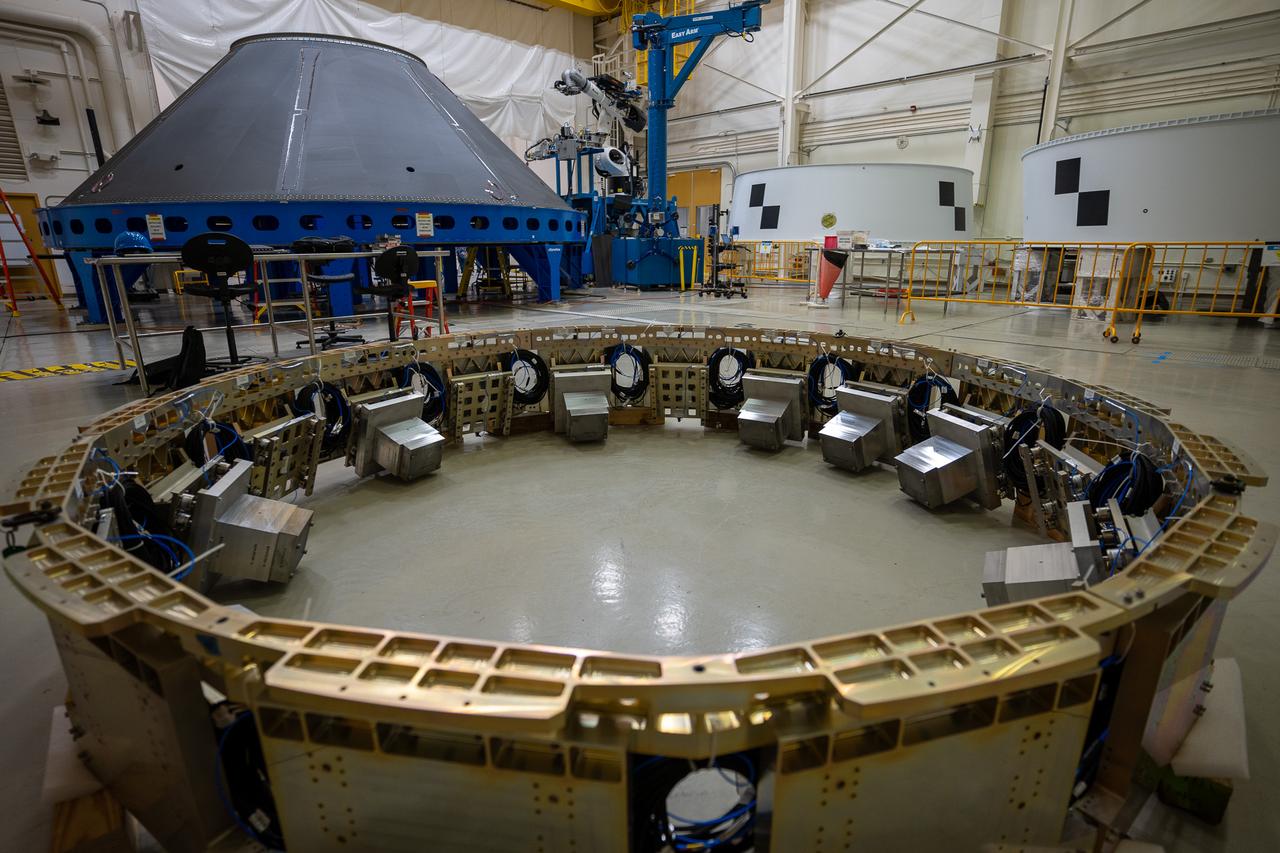

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
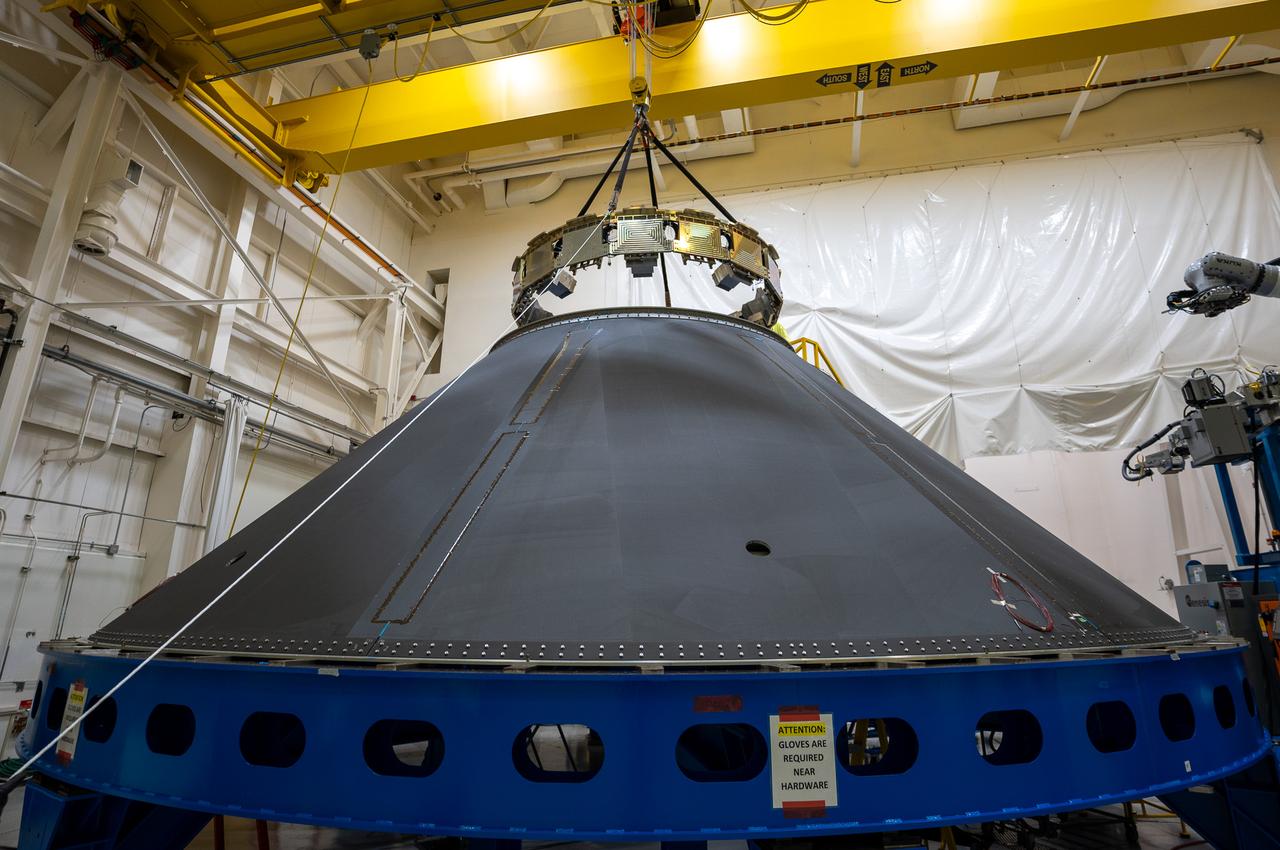

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
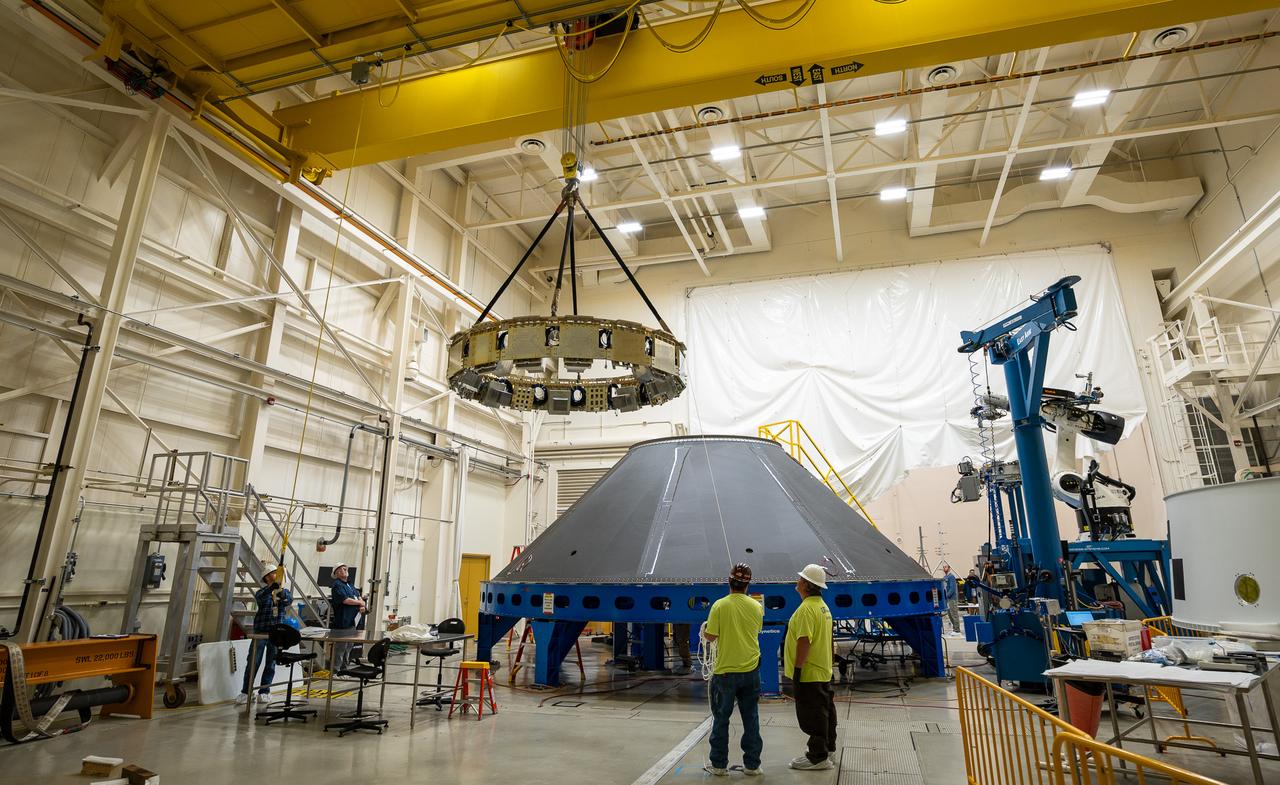

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
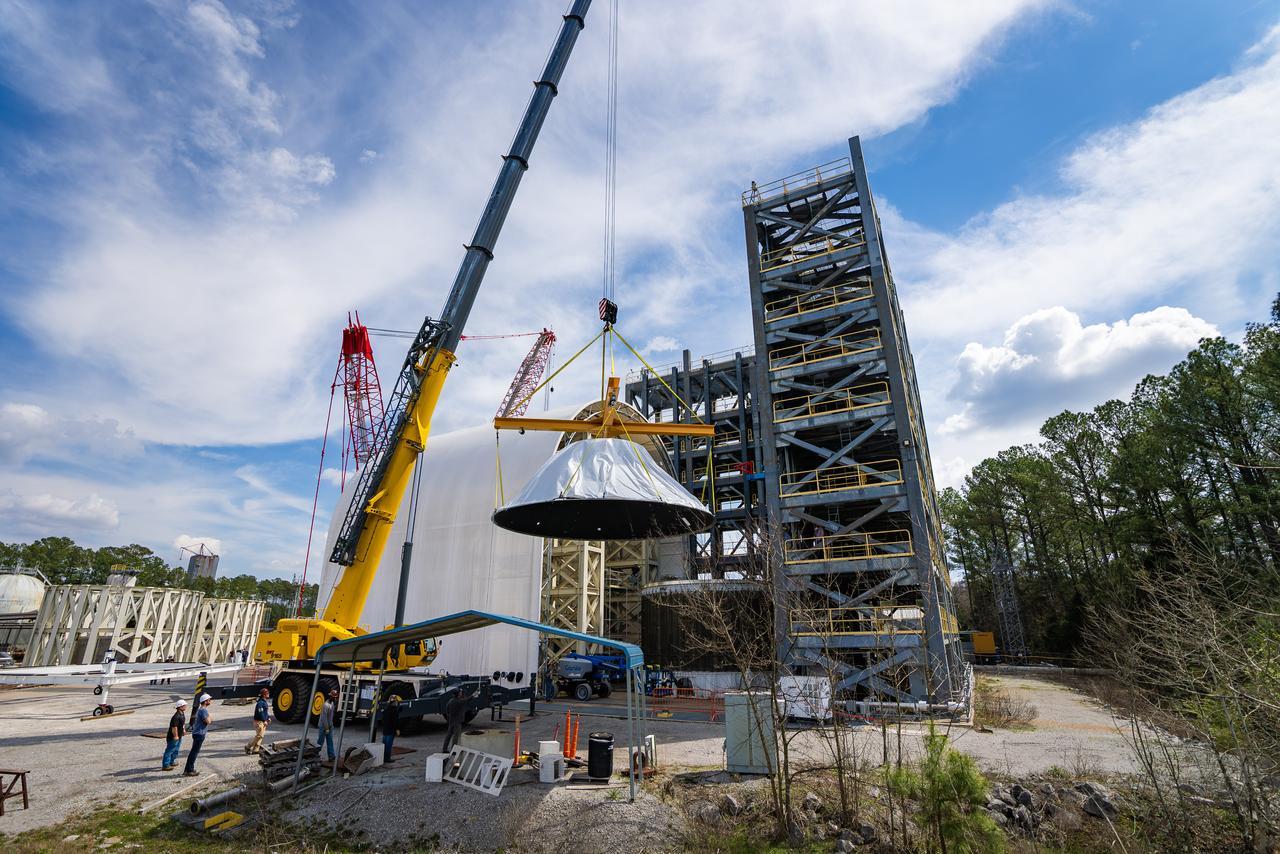

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
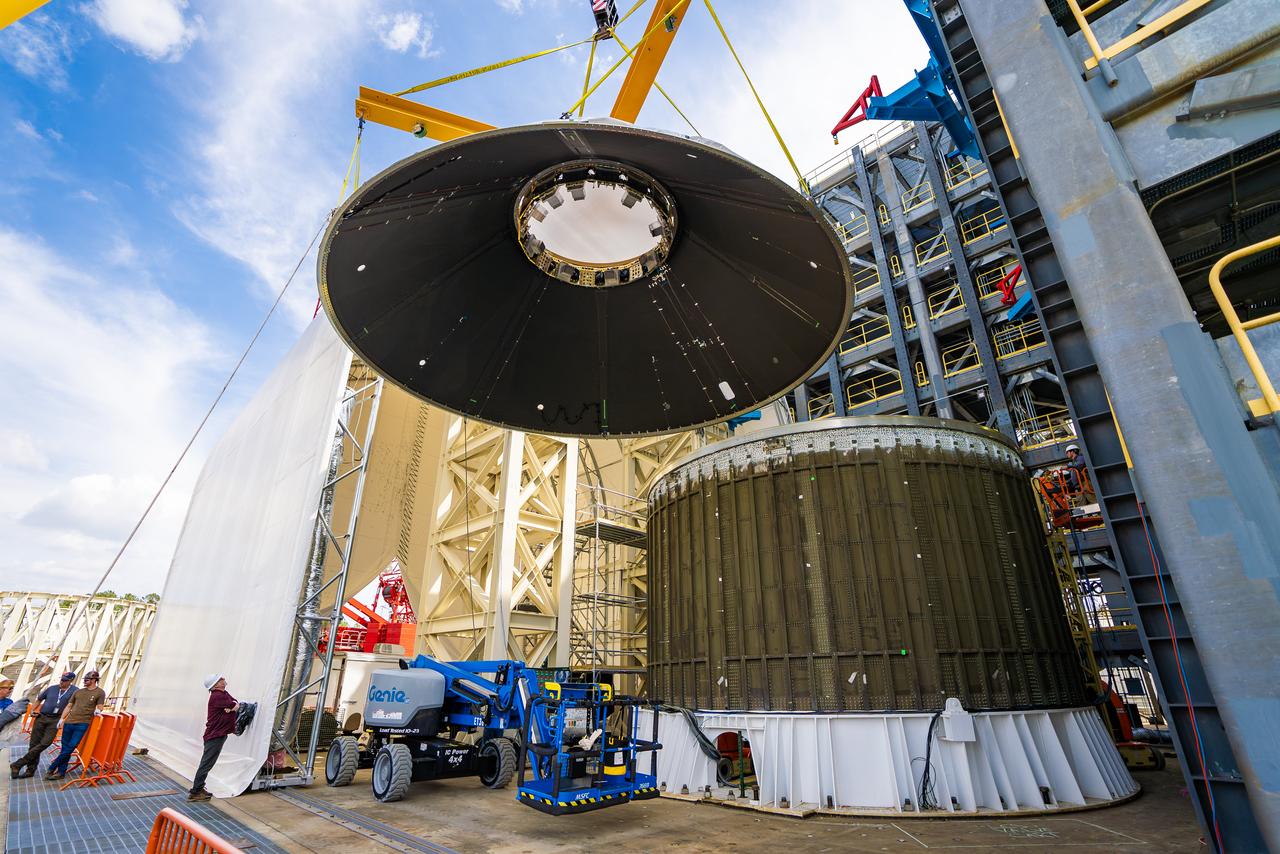

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
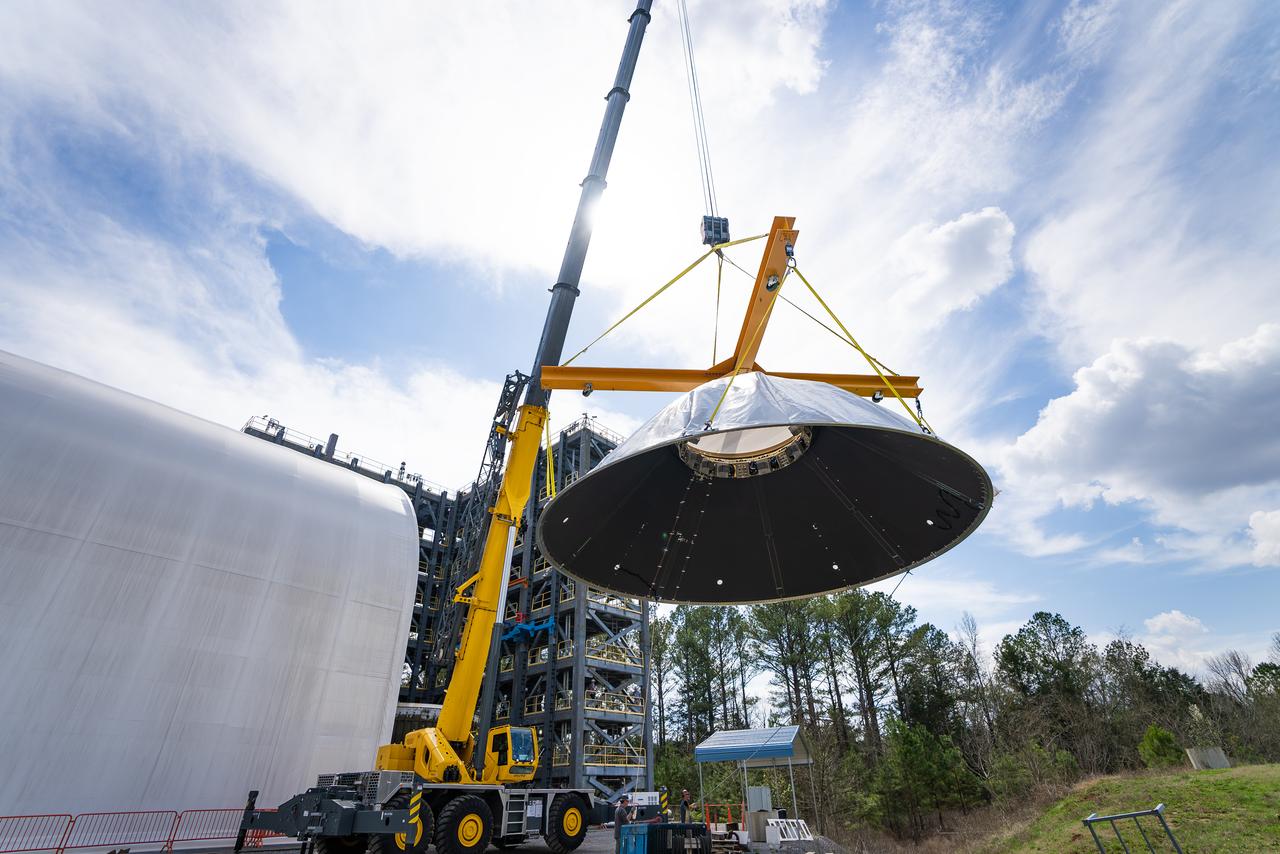

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
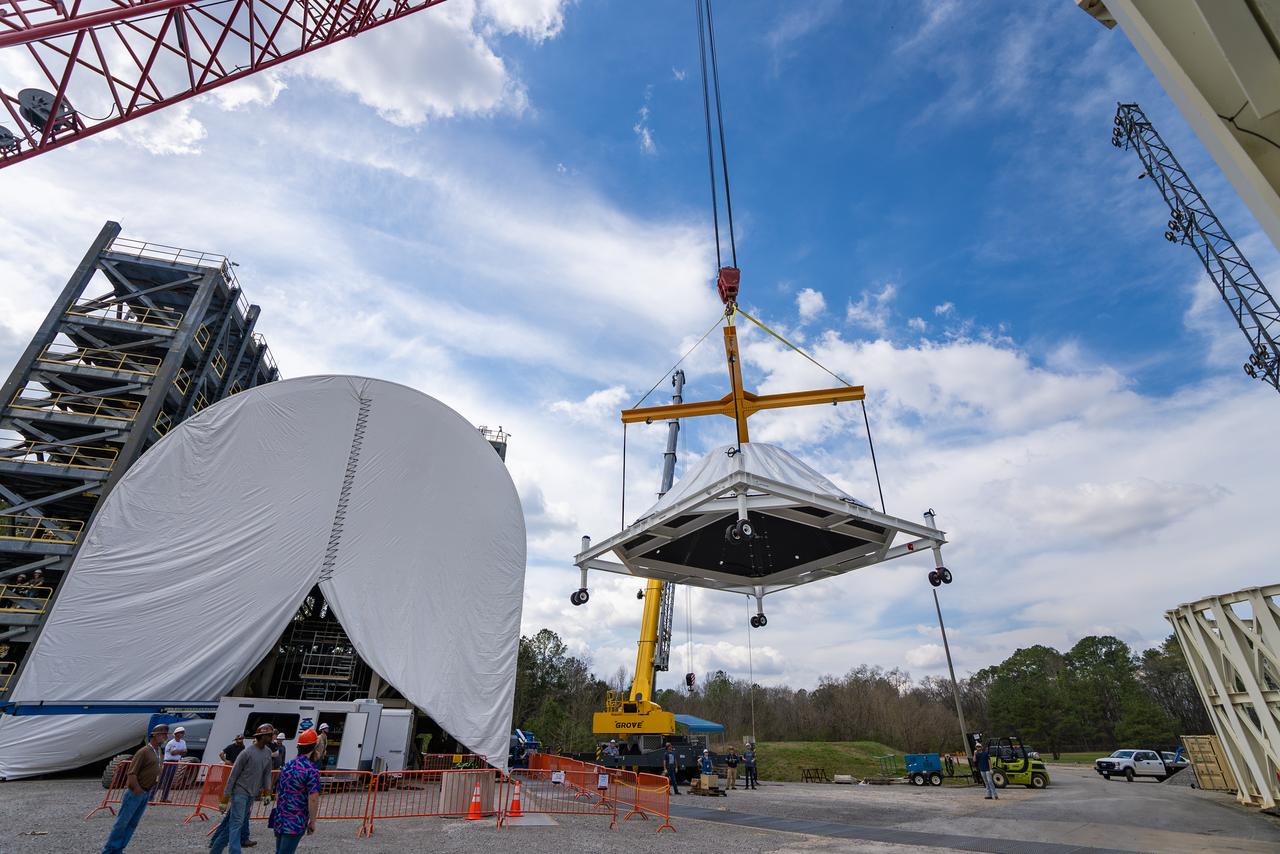

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
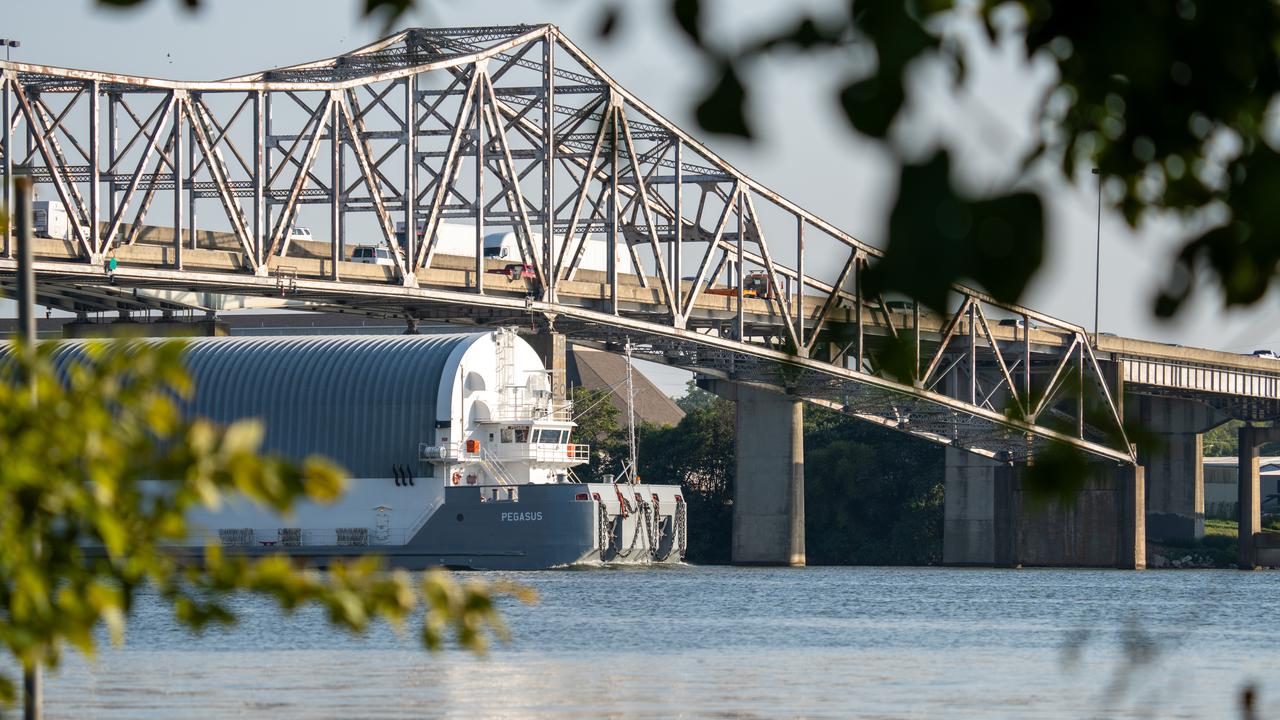

NASA’s Pegasus barge, ferrying the launch vehicle stage adapter for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, departed the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Aug. 21, passing through nearby Decatur. The cone-shaped adapter is part of the SLS rocket that will power Artemis II mission, the first crewed flight of the agency’s Artemis campaign. The barge will stop briefly at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to pick up additional hardware elements for Artemis III and Artemis IV before heading to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where the adapter will be readied for stacking and launch preparations.
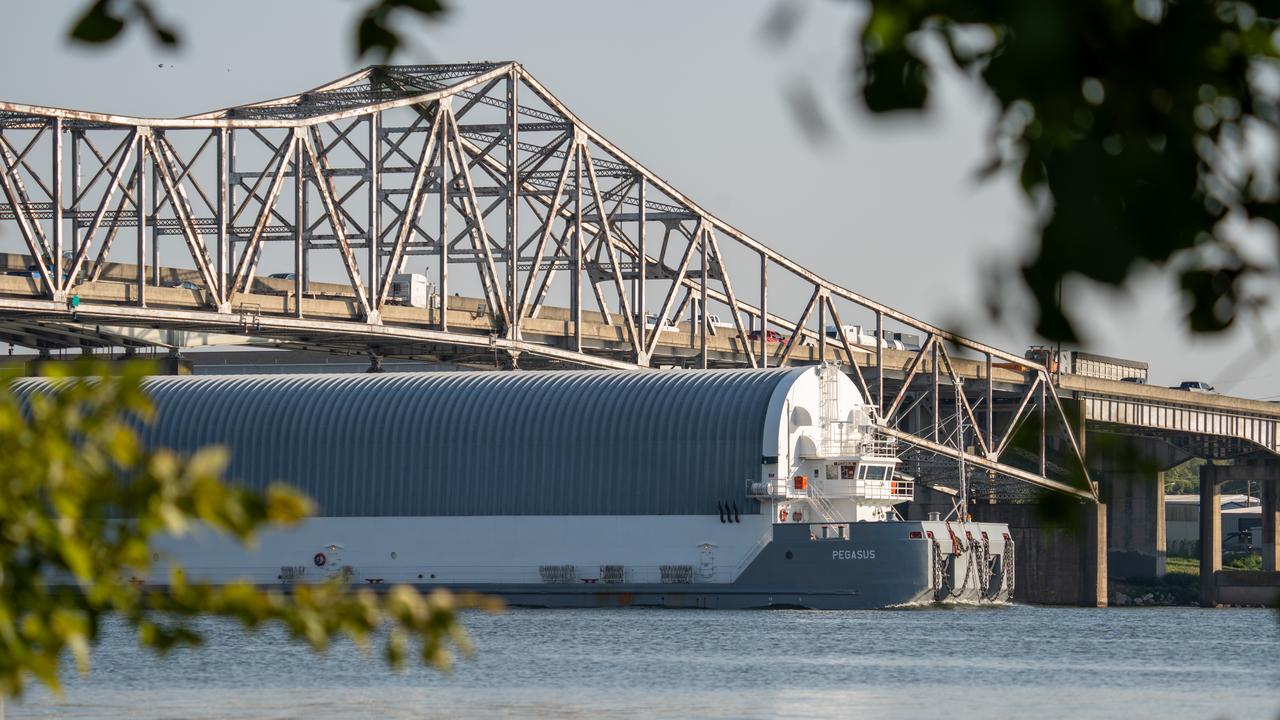

NASA’s Pegasus barge, ferrying the launch vehicle stage adapter for NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, departed the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Aug. 21, passing through nearby Decatur. The cone-shaped adapter is part of the SLS rocket that will power Artemis II mission, the first crewed flight of the agency’s Artemis campaign. The barge will stop briefly at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to pick up additional hardware elements for Artemis III and Artemis IV before heading to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where the adapter will be readied for stacking and launch preparations.
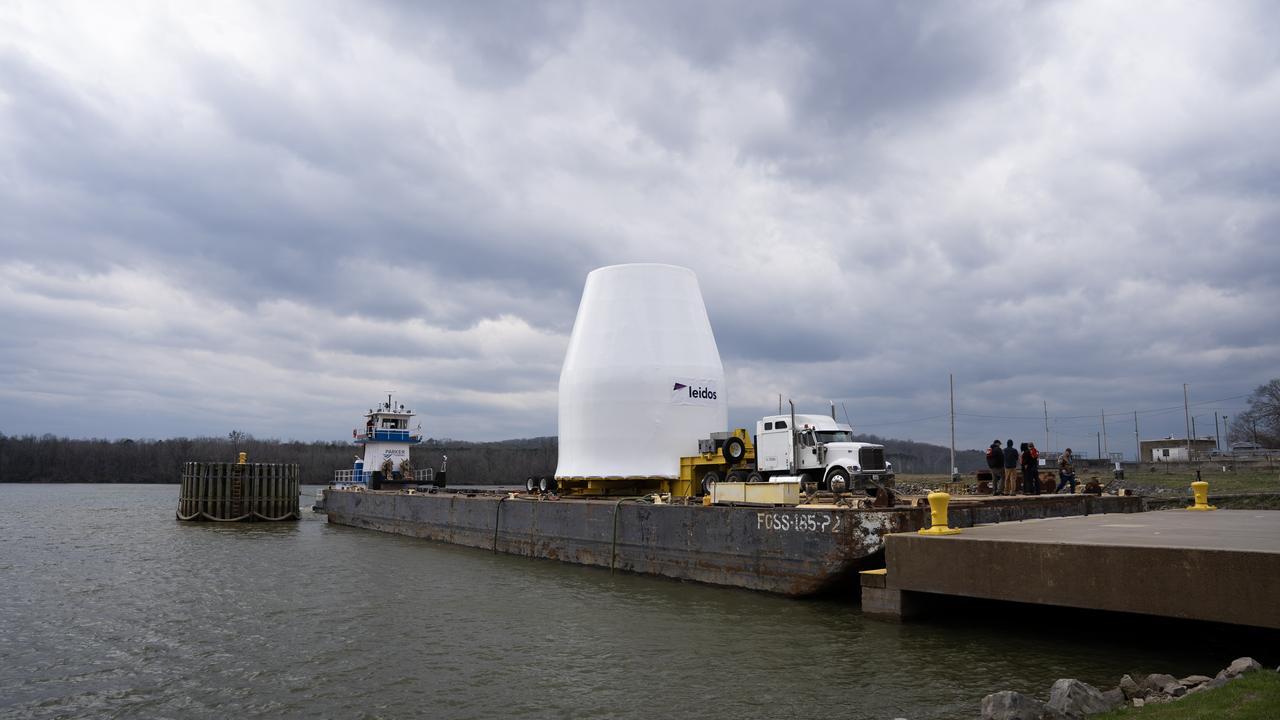

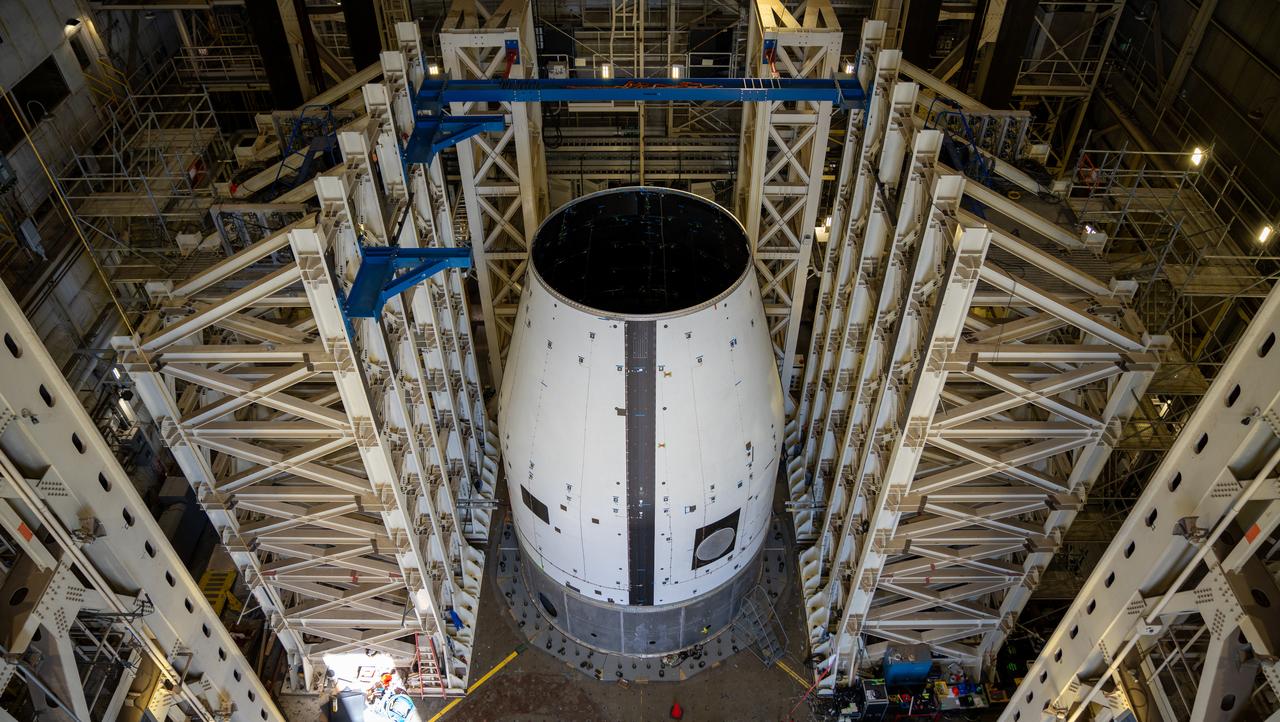
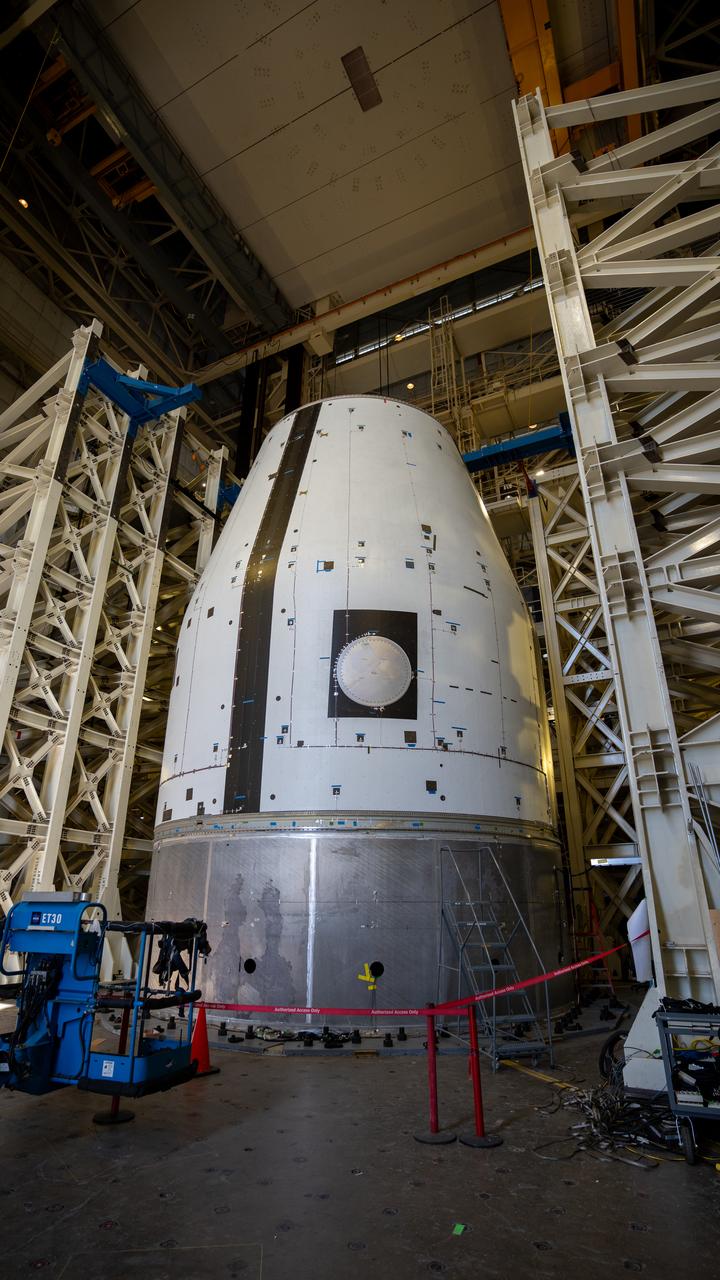
These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
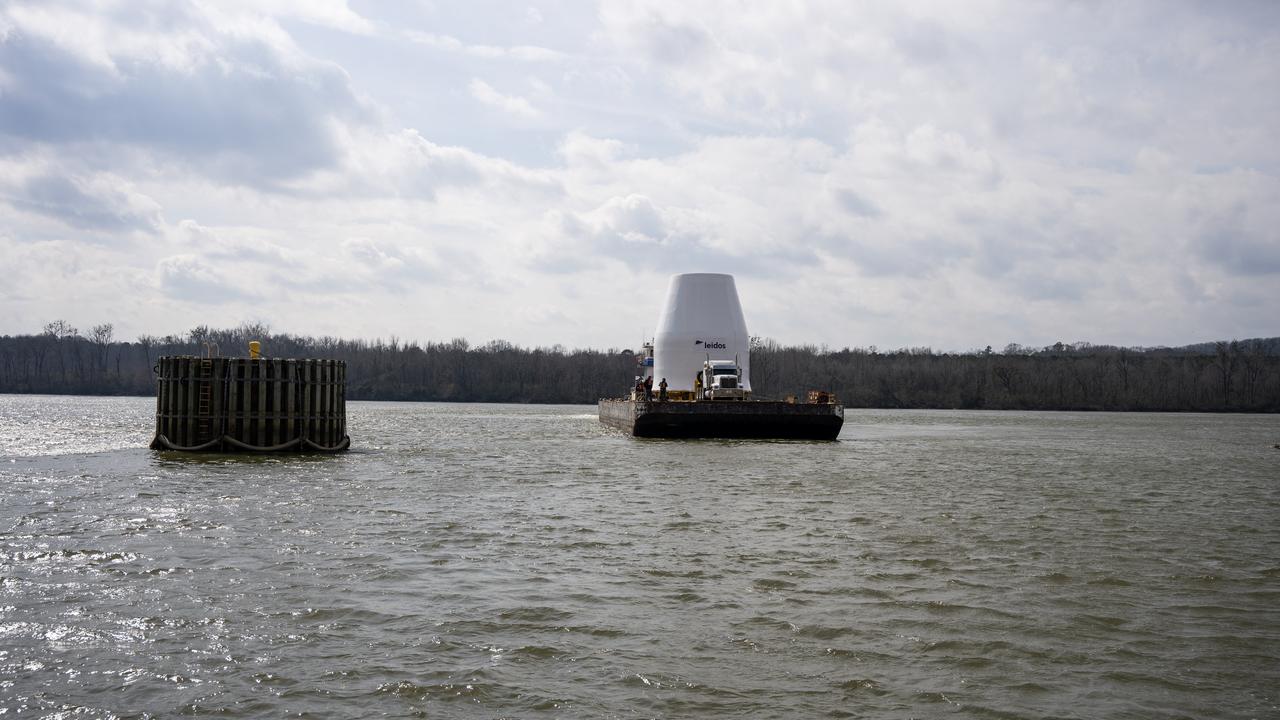

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
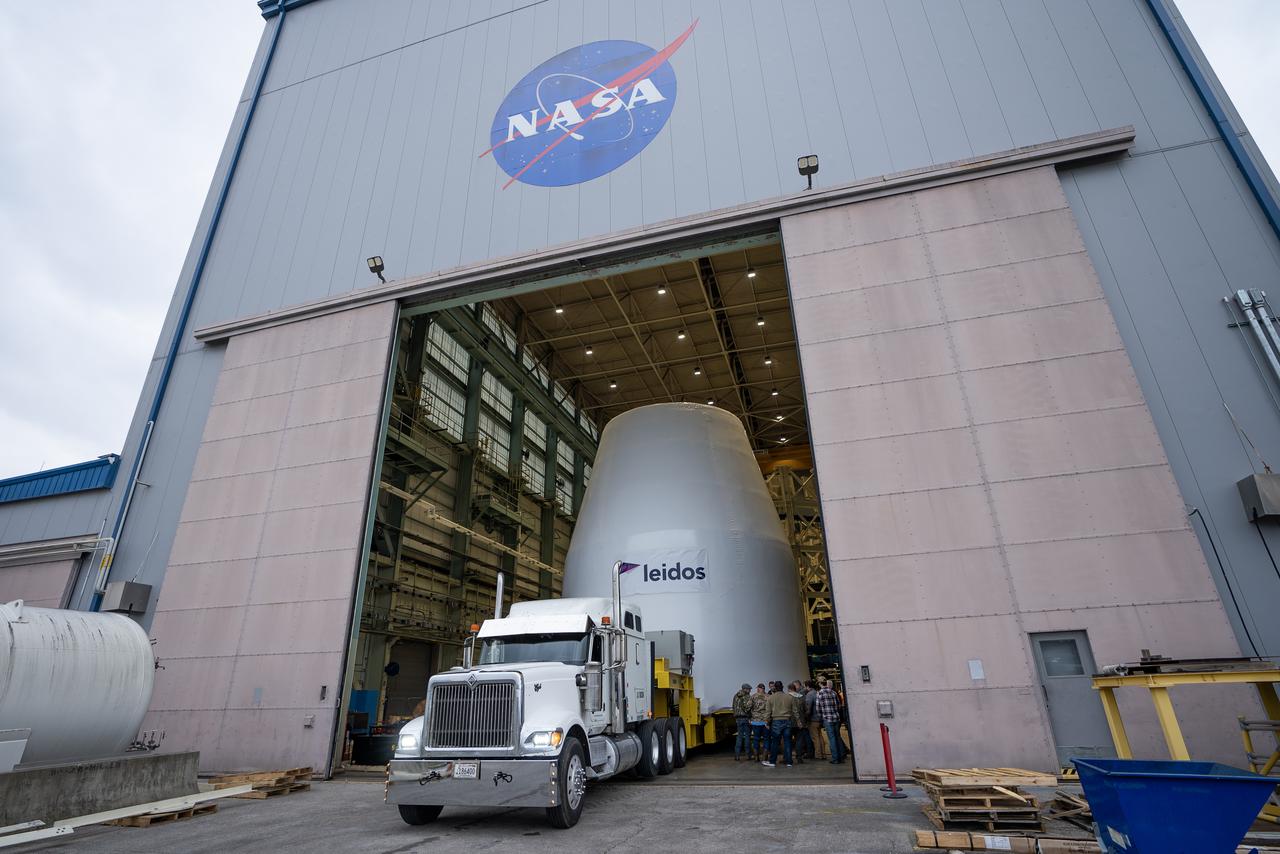

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
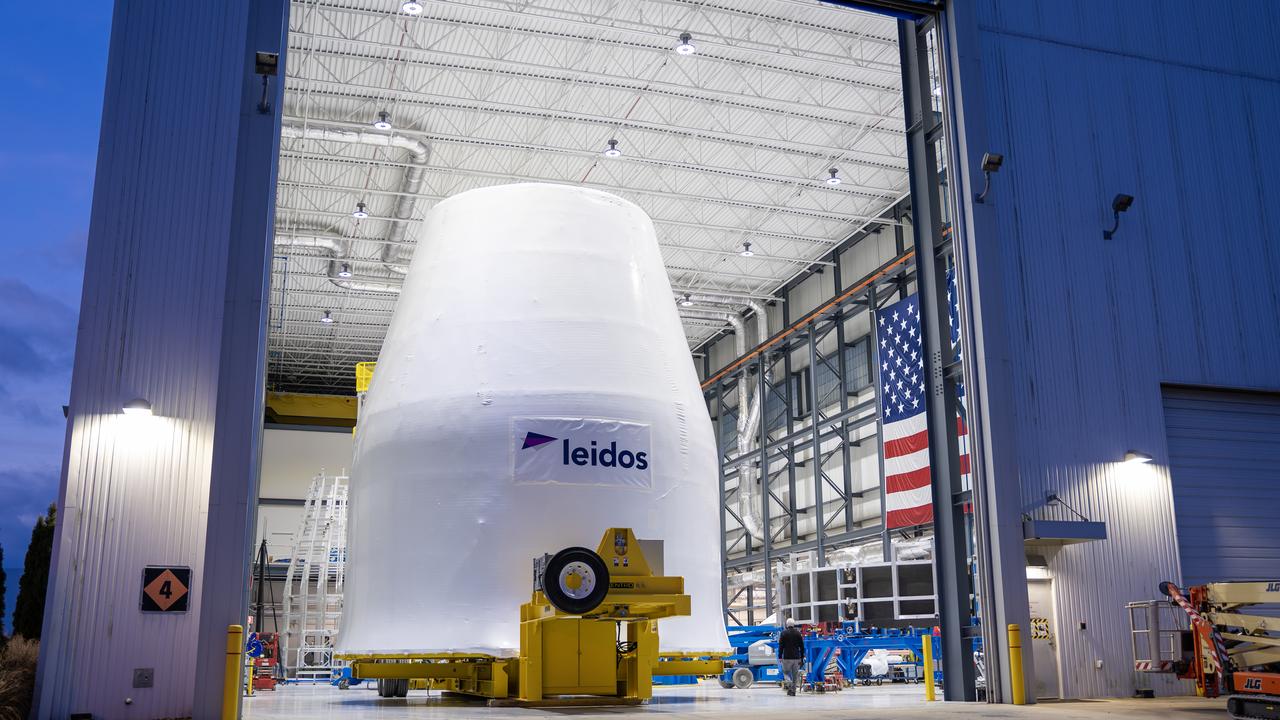

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
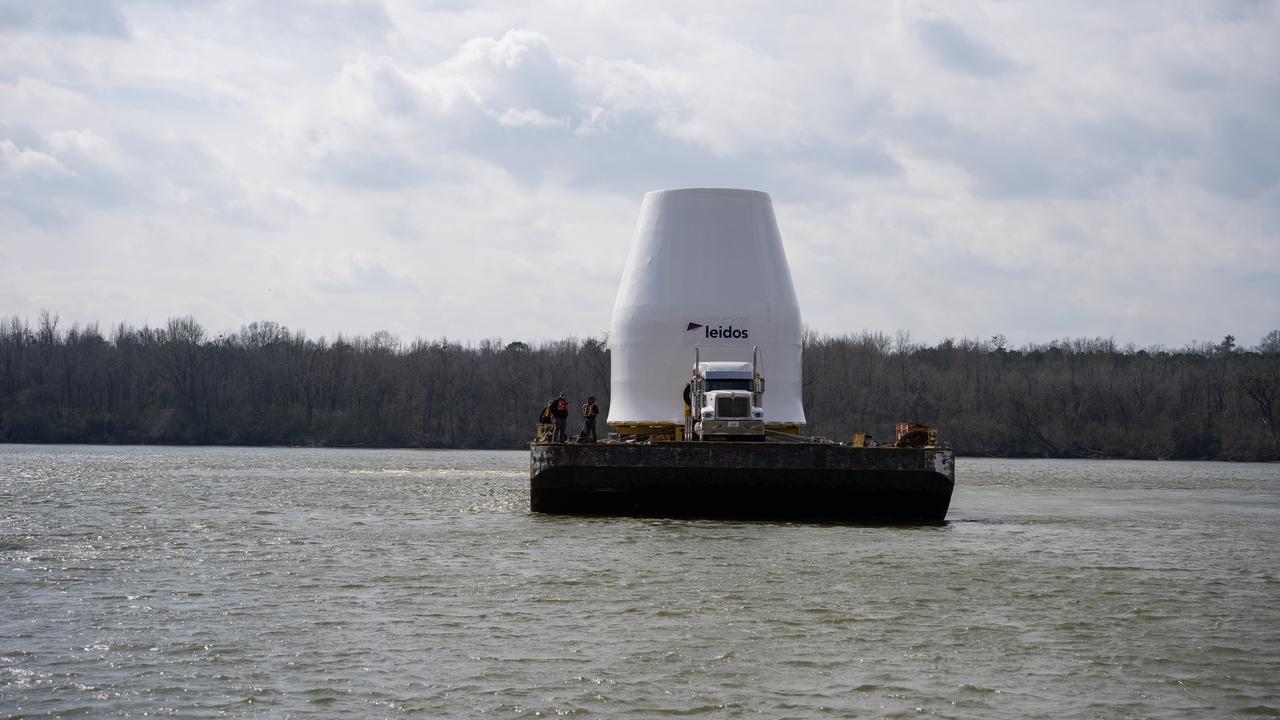

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
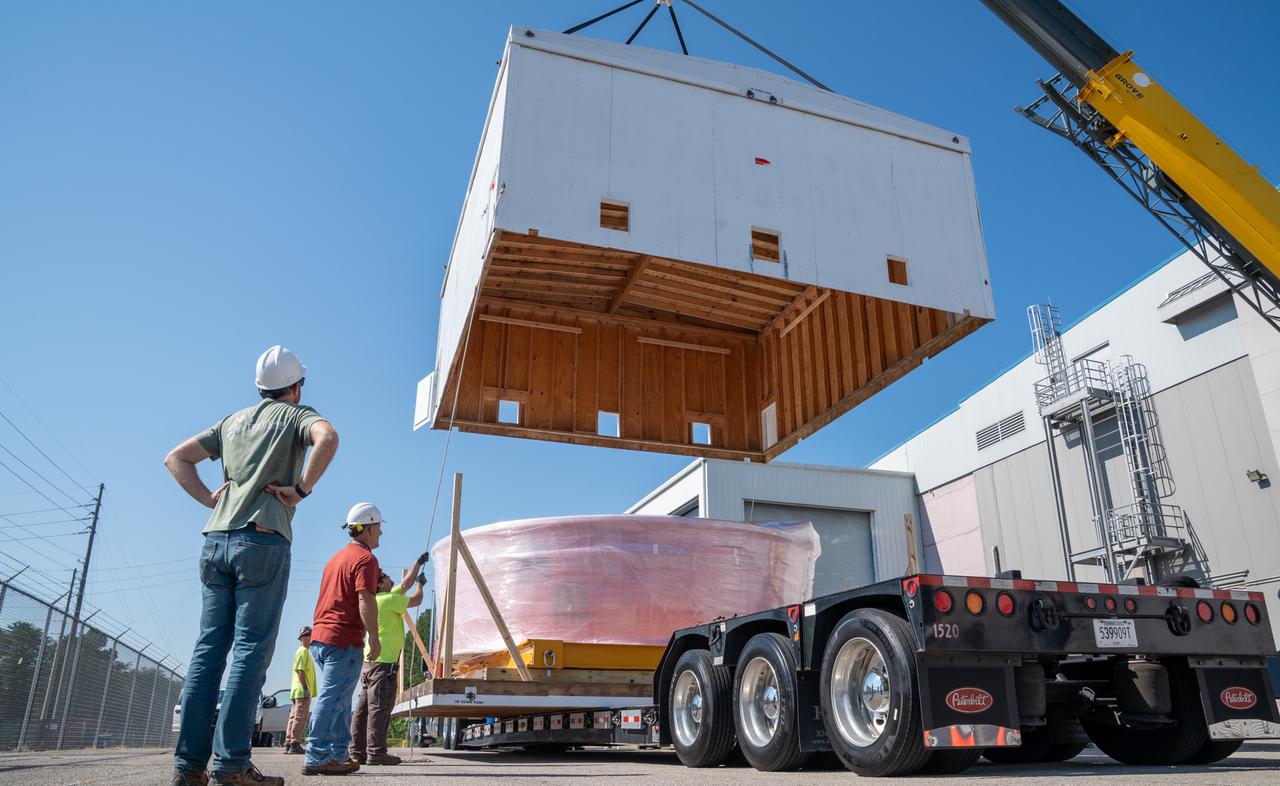

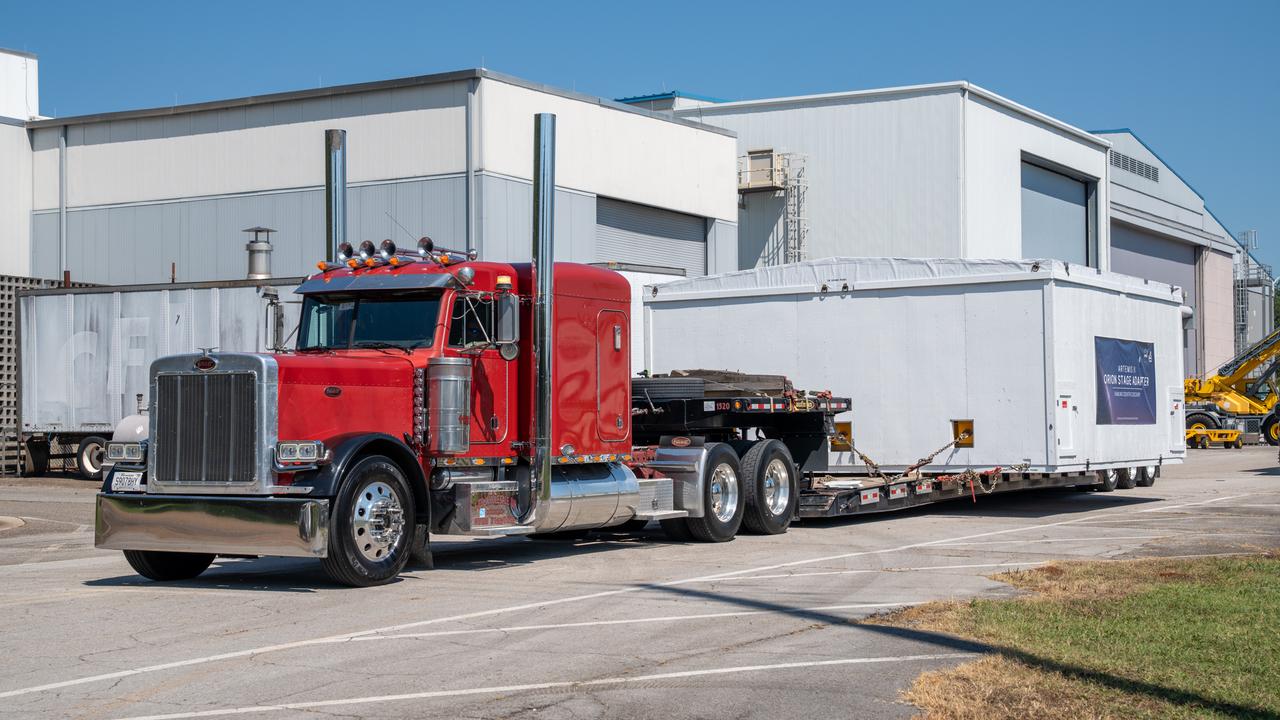
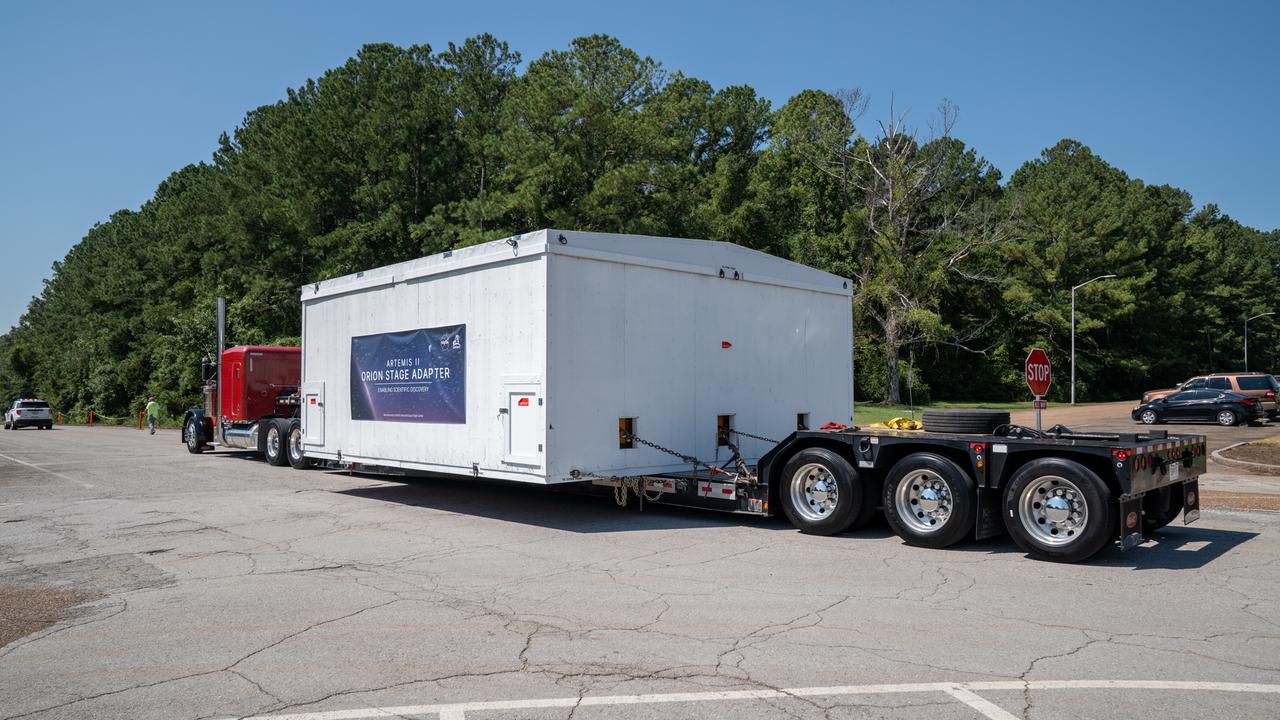
These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II being prepped for shipment and then packaged in a large box, loaded on a semi-truck. It is seen leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.

These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II being prepped for shipment and then packaged in a large box, loaded on a semi-truck. It is seen leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
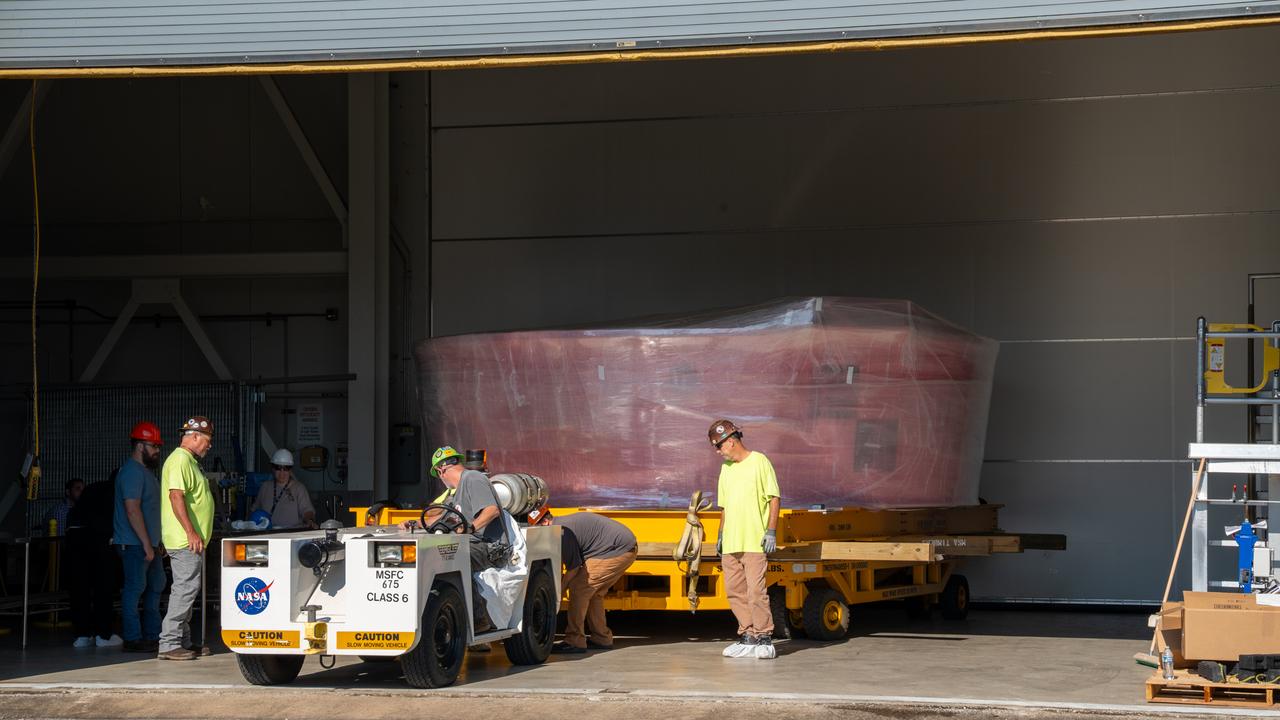

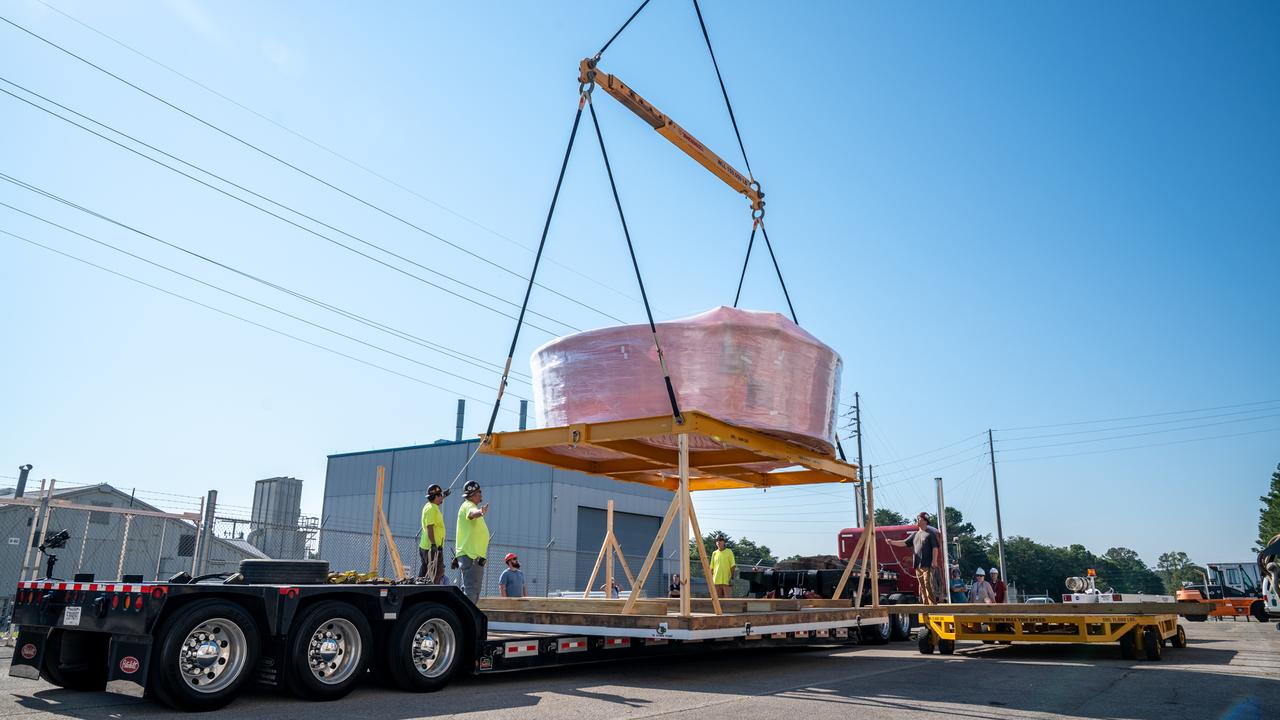
These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.
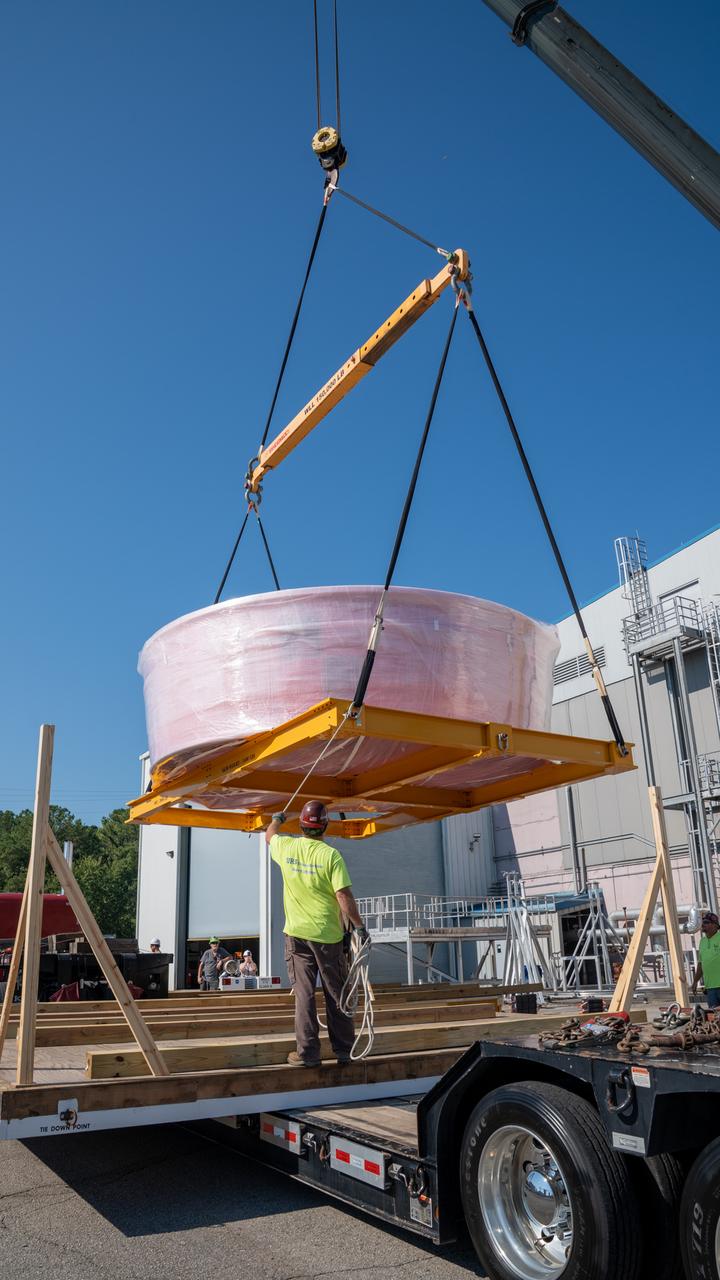

These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.

These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II being prepped for shipment and then packaged in a large box, loaded on a semi-truck. It is seen leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.

These images show the Orion stage adapter for Artemis II being prepped for shipment and then packaged in a large box, loaded on a semi-truck. It is seen leaving NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, as it begins its journey to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Manufactured at Marshall, this adapter for the SLS (Space Launch System) connects the rocket’s interim cryogenic propulsion stage to the Orion spacecraft and is the final piece of SLS hardware to be delivered to Kennedy Space Center in preparation for the Artemis II mission.

These photos show how teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are testing an innovative approach to achieve zero boiloff storage of liquid hydrogen using two stages of active cooling, which could prevent the loss of valuable propellant during future long-duration spaceflight missions. Test teams installed the propellant tank in Test Stand 300 at NASA Marshall in early June, and the 90-day test campaign is scheduled to conclude in September. The tank is wrapped in a multi-layer insulation blanket that includes a thin aluminum heat shield fitted between layers. A second set of tubes, carrying helium at about minus 298 Fahrenheit, is integrated into the shield. This intermediate cooling layer intercepts and rejects incoming heat before it reaching the tank, easing the heat load on the tube-on-tank system. The Cryogenic Fluid Management Portfolio Project is a cross-agency team based at NASA Marshall and the agency’s Glenn Research Center in Cleveland. The cryogenic portfolio’s work is under NASA’s Technology Demonstration Missions Program, part of NASA’s Space Technology Mission Directorate, and is comprised of more than 20 individual technology development activities. For more information, contact NASA Marshall’s Office of Communications at 256-544-0034.

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
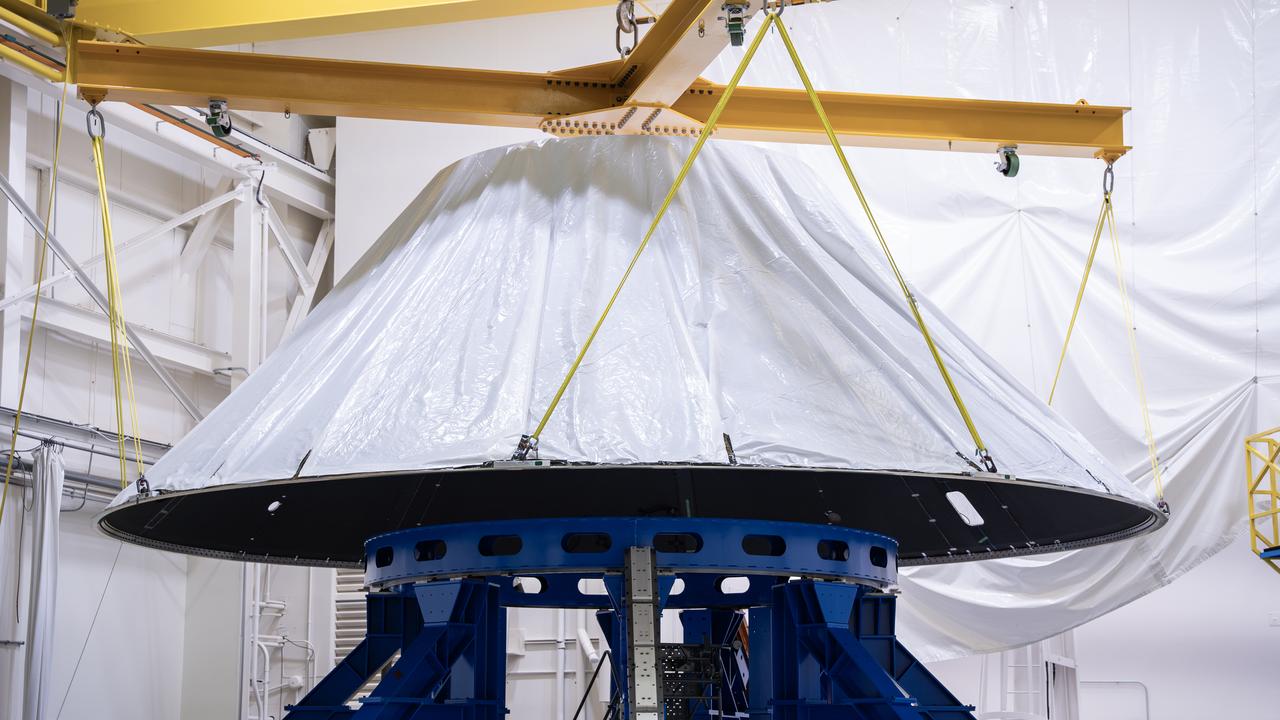

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
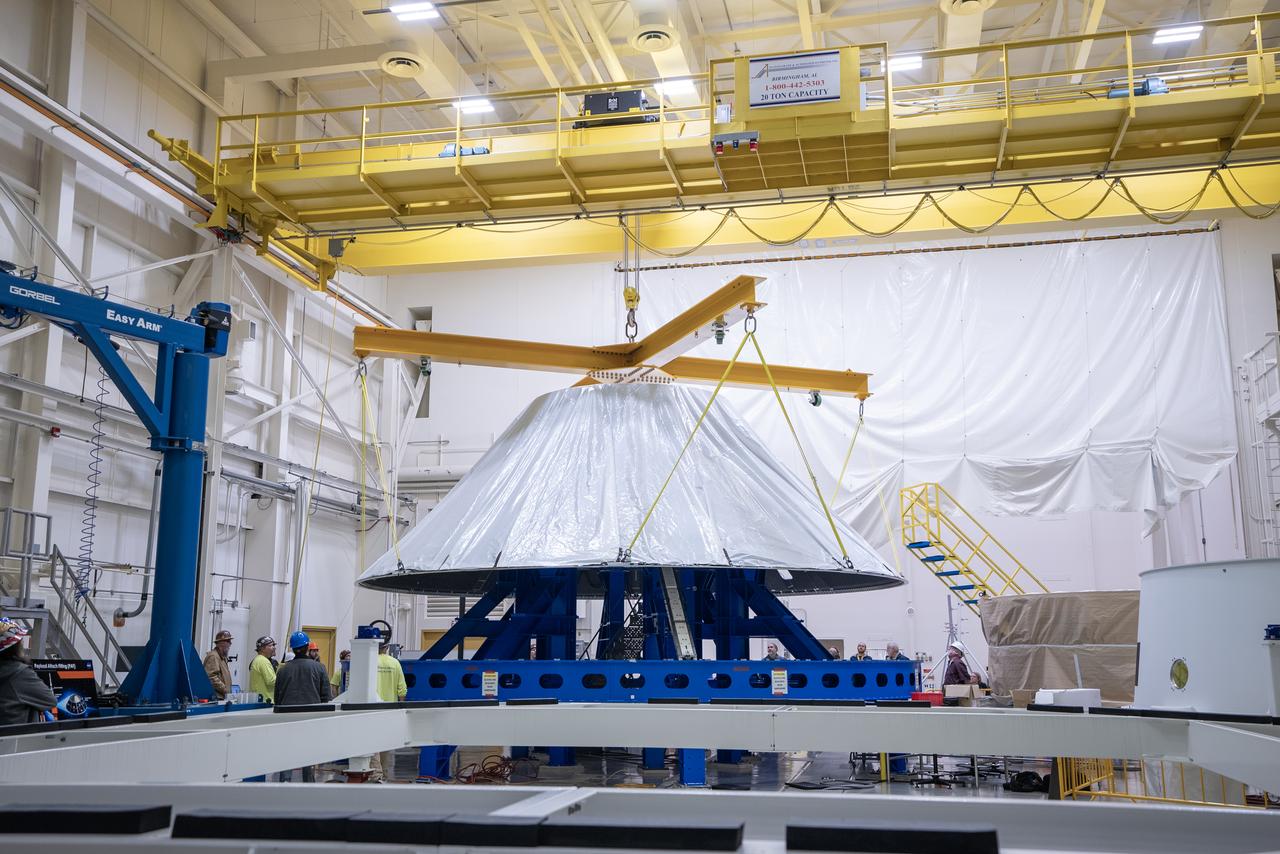

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

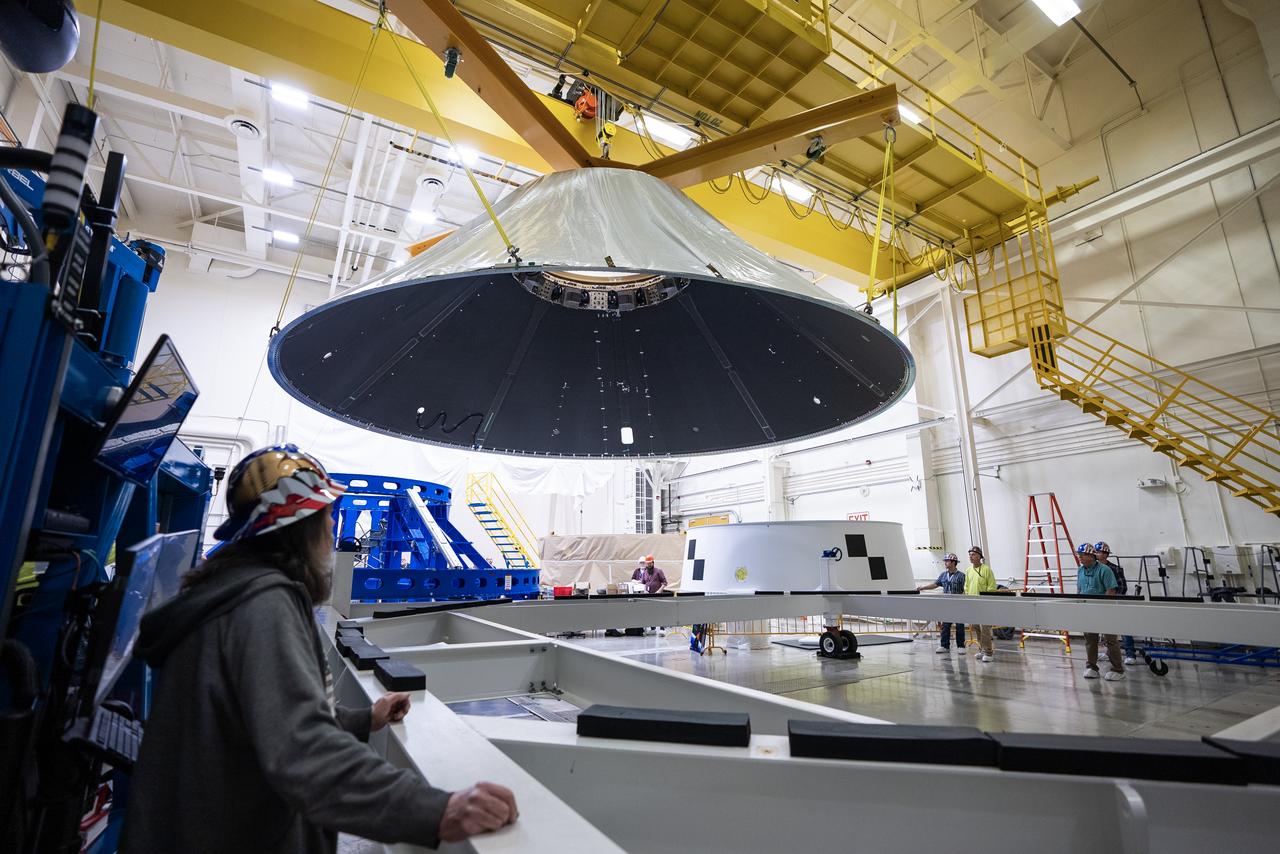
These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
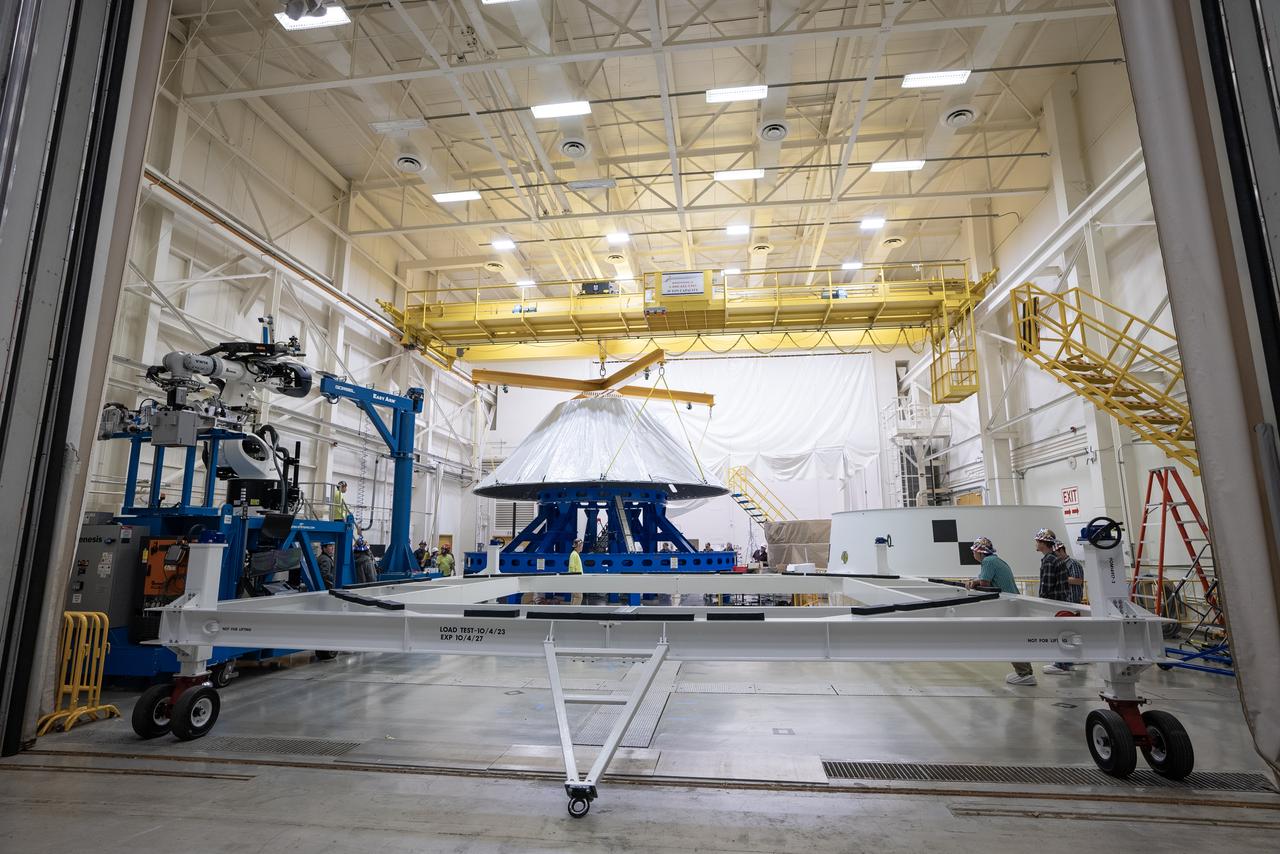

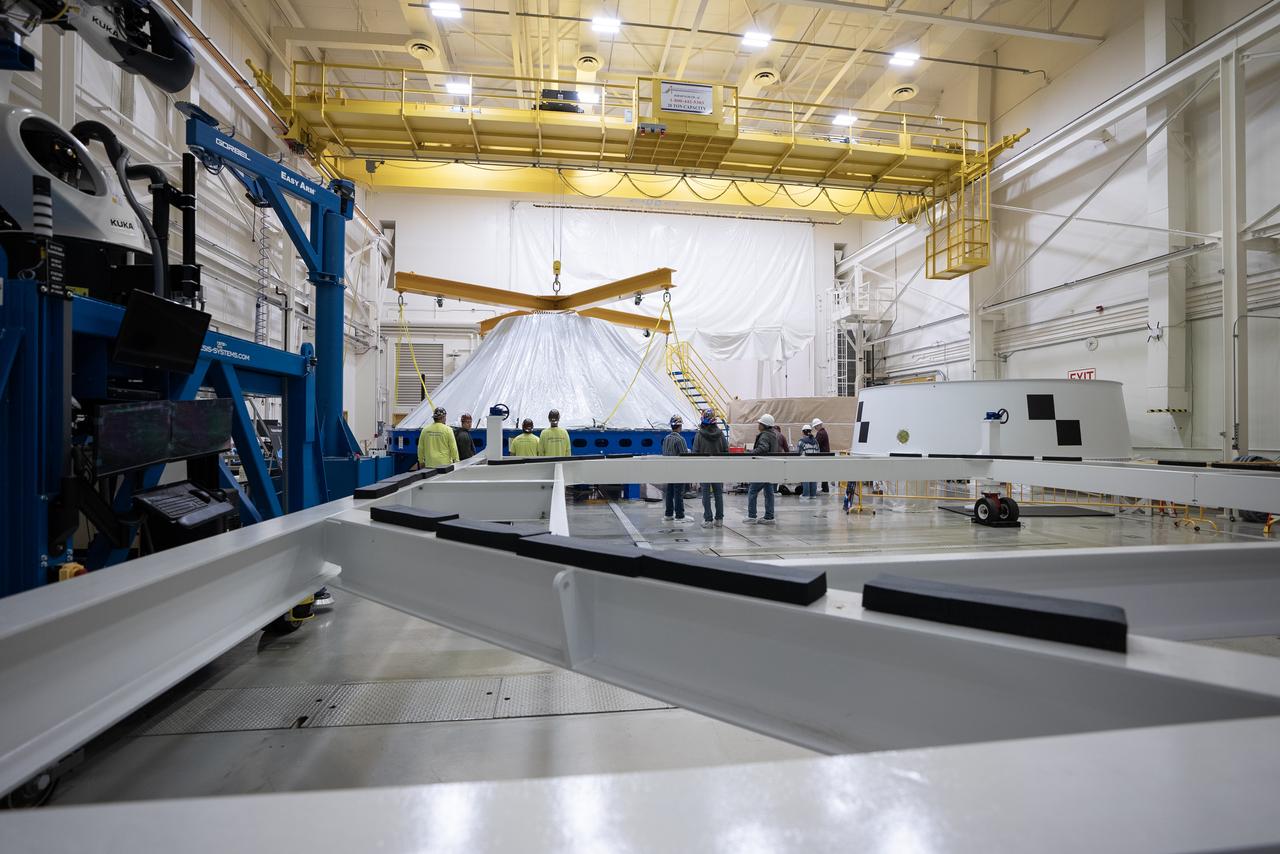
These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
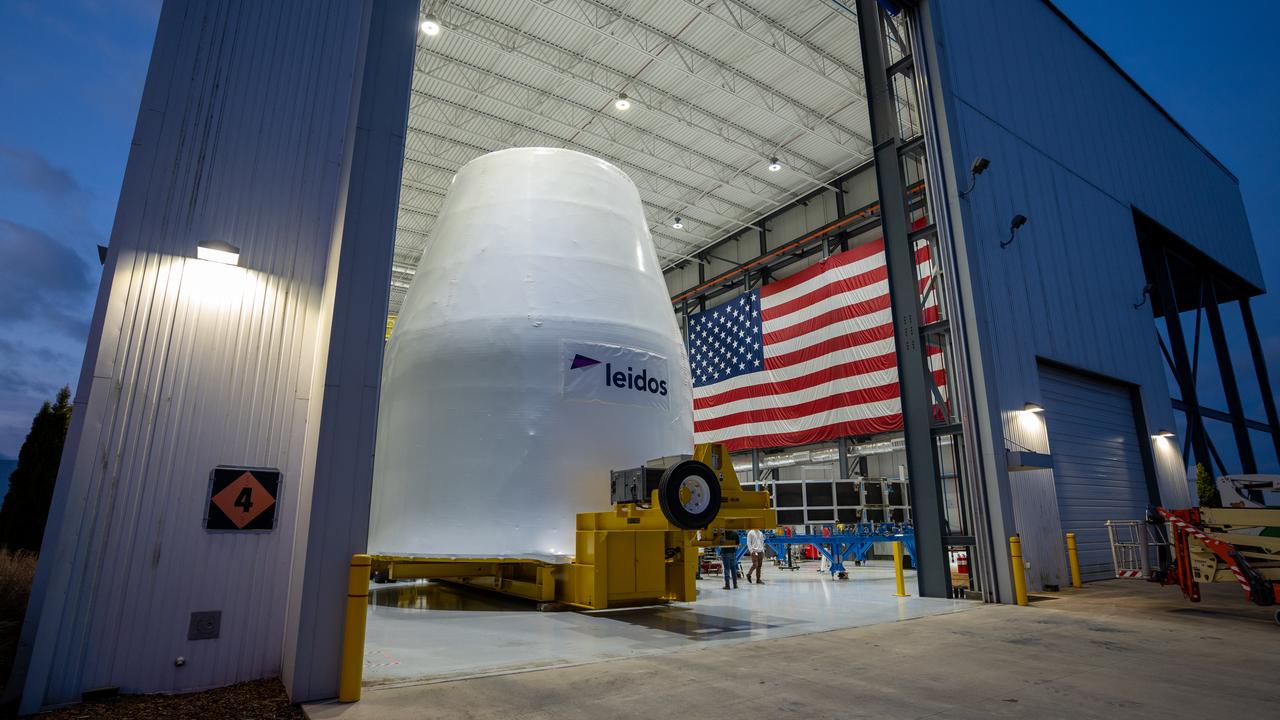

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
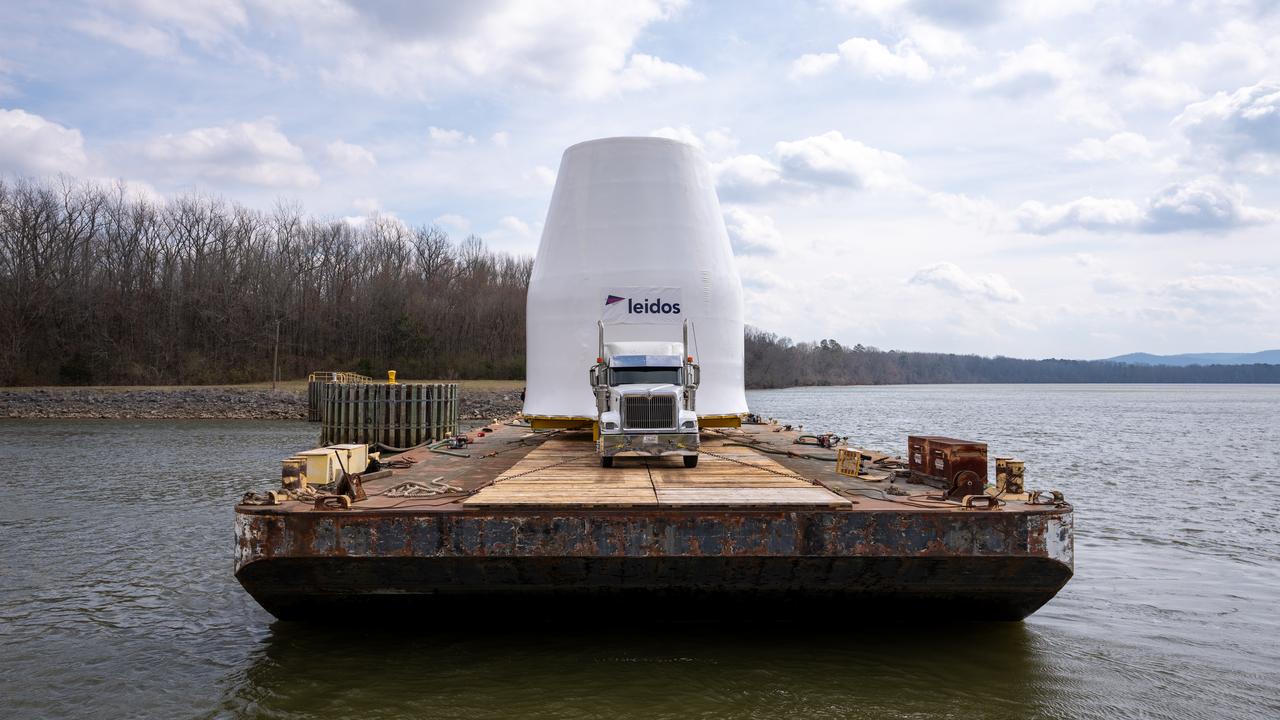

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
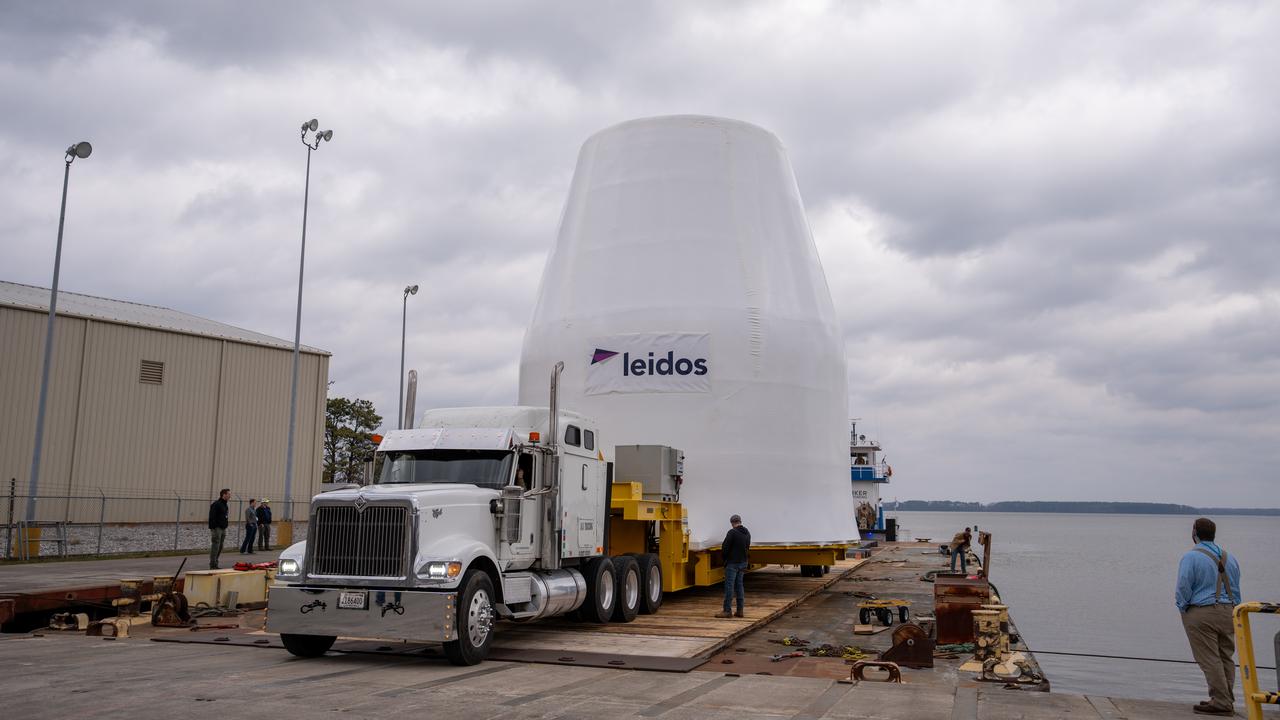

These photos and videos show how crews guided a test version of the universal stage adapter for NASA’s more powerful version of its SLS (Space Launch System) rocket to Building 4619 at the agency’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, Feb. 22. Built by Leidos, the lead contractor for the universal stage adapter, crews transported the hardware from a Leidos facility in Decatur, Alabama, the same day. The universal stage adapter will connect the SLS rocket’s upgraded in-space propulsion stage, called the exploration upper stage, to NASA’s Orion spacecraft as part of the evolved Block 1B configuration of the SLS rocket. It will also serve as a compartment capable of accommodating large payloads, such as modules or other exploration spacecraft. In Building 4619’s Load Test Annex High Bay at Marshall, the development test article will first undergo modal testing that will shake the hardware to validate dynamic models. Later, during ultimate load testing, force will be applied vertically and to the sides of the hardware. Unlike the flight hardware, the development test article has flaws intentionally included in its design, which will help engineers verity that the flight adapter can withstand the extreme forces it will face during launch and flight.
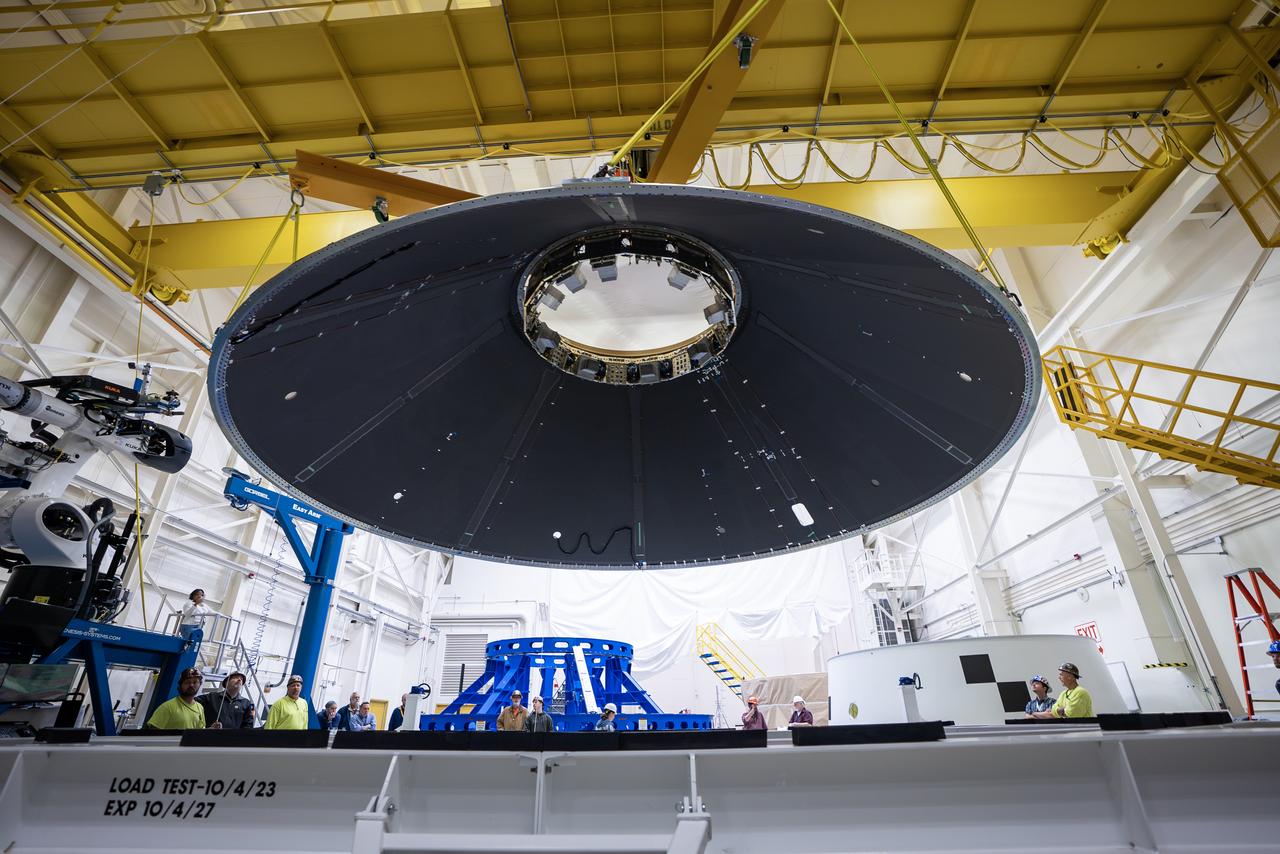

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

Red and white vapor clouds filled the skies over the Marshall Islands as part of NASA’s Equatorial Vortex Experiment (EVEX). The red cloud was formed by the release of lithium vapor and the white tracer clouds were formed by the release of trimethyl aluminum (TMA). These clouds allowed scientists on the ground from various locations in the Marshall Islands to observe the neutral winds in the ionosphere. Credit: NASA/Jon Grant --- The Equatorial Vortex Experiment (EVEX) was successfully conducted during the early morning hours (eastern time) May 7 from Roi Namur, Republic of the Marshall Islands. A NASA Terrier-Oriole sounding rocket was launched at 3:39 a.m. EDT and was followed by a launch of Terrier-Improved Malemute sounding rocket 90 seconds later. Preliminary indications are that both rockets released their vapor clouds of lithium or trimethyl aluminum, which were observed from various locations in the area, and all science instruments on the rockets worked as planned. More information on EVEX can be found at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sounding-rockets/news/evex.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/sounding-rockets/news/evex.html</a> These were the second and third rockets of four planned for launch during this year’s campaign in the Marshall Islands. The first and fourth rockets are supporting the Metal Oxide Space Cloud experiment (MOSC), which is studying radio frequency propagation. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
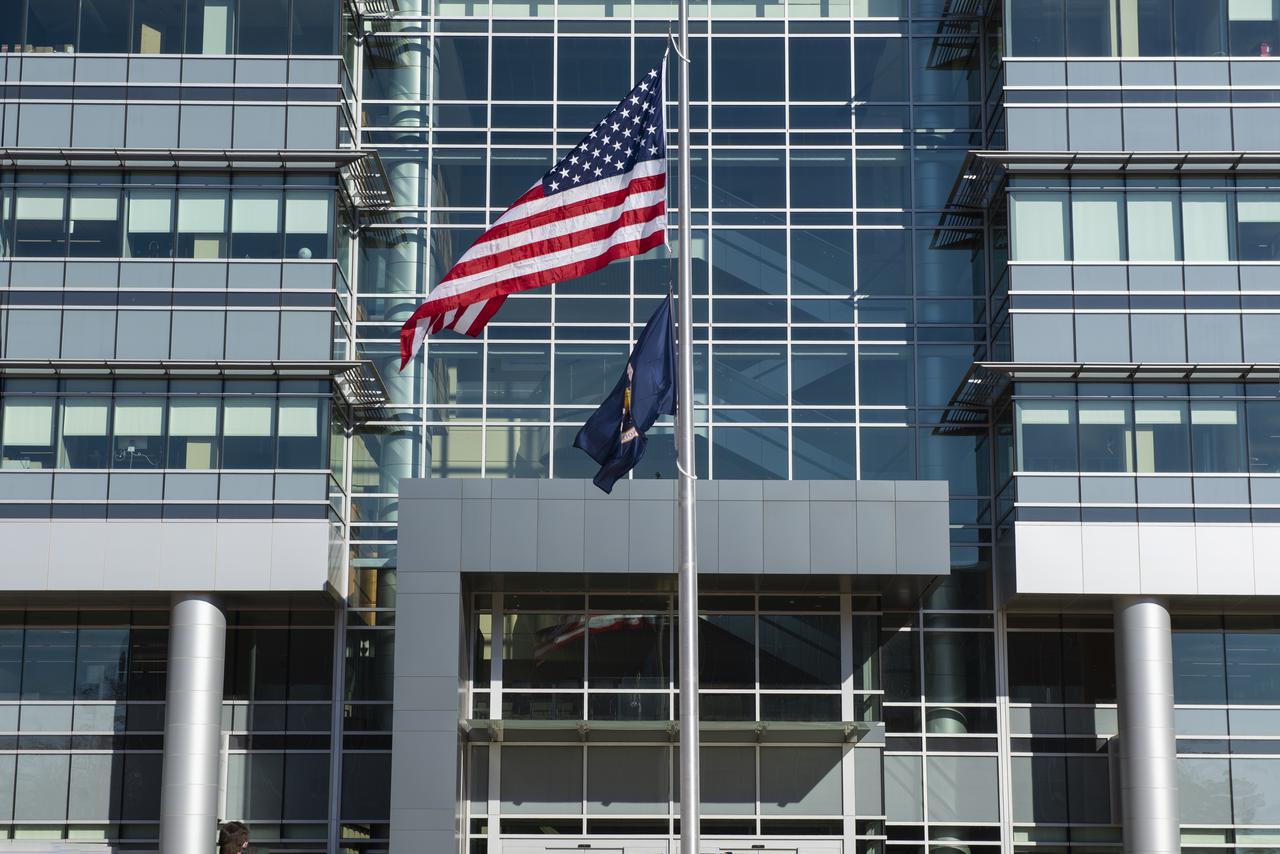

On Jan. 26, 2022, the U.S. and NASA flags were raised at Building 4221 to mark the transfer of headquarters to that building at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The doors to Building 4221, a new, environmentally friendly building, opened on Earth Day, April 22, 2019. Building 4200 served as Marshall’s original headquarters since 1963. Marshall center operations lowered flags at that building on Jan. 21, 2022.
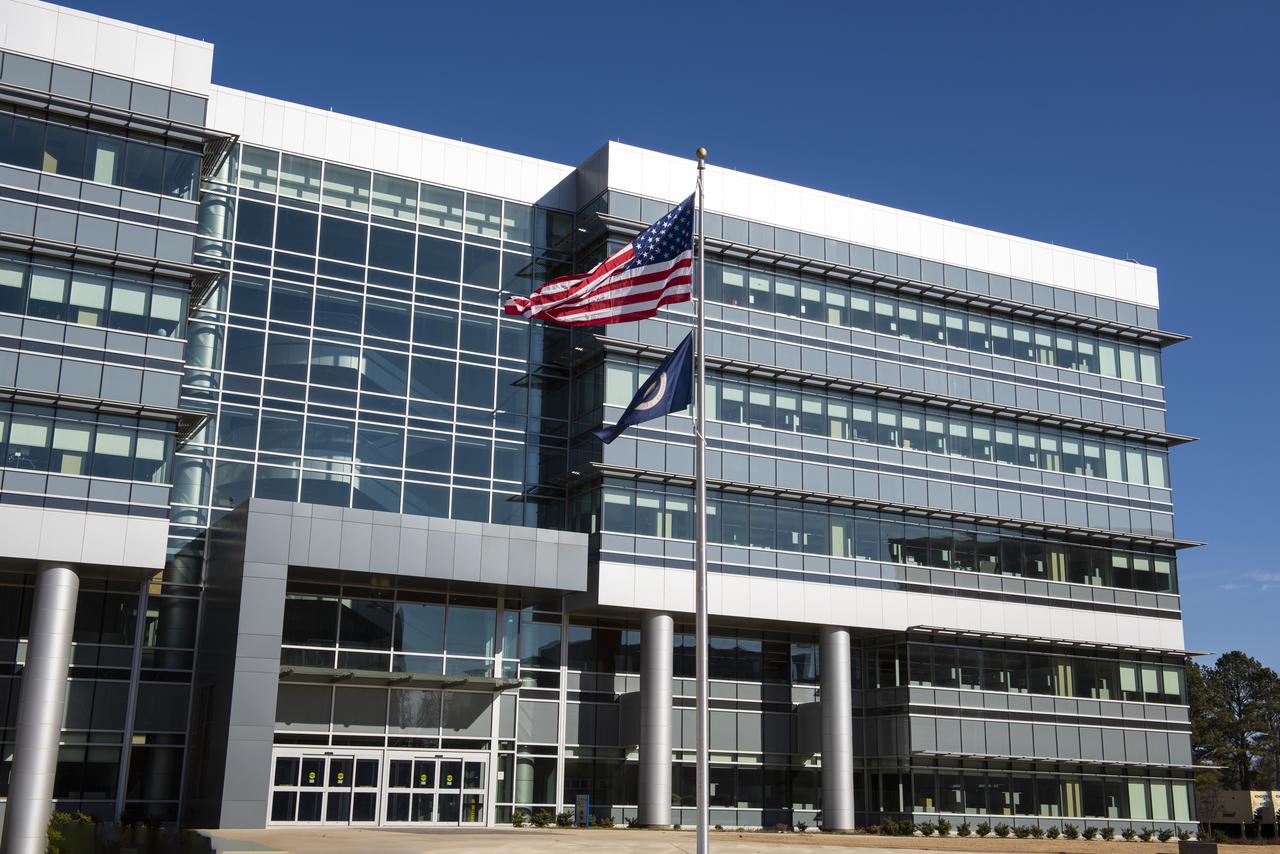

On Jan. 26, 2022, the U.S. and NASA flags were raised at Building 4221 to mark the transfer of headquarters to that building at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The doors to Building 4221, a new, environmentally friendly building, opened on Earth Day, April 22, 2019. Building 4200 served as Marshall’s original headquarters since 1963. Marshall center operations lowered flags at that building on Jan. 21, 2022.
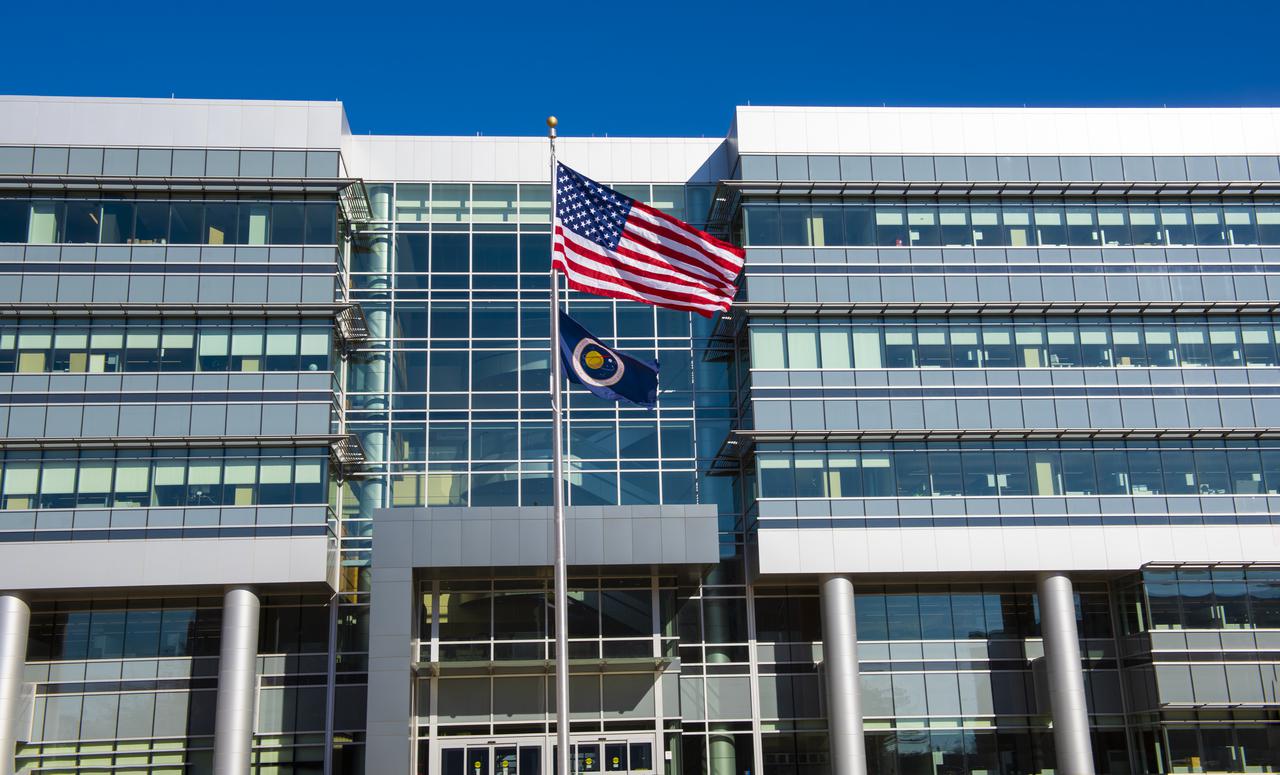

On Jan. 26, 2022, the U.S. and NASA flags were raised at Building 4221 to mark the transfer of headquarters to that building at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The doors to Building 4221, a new, environmentally friendly building, opened on Earth Day, April 22, 2019. Building 4200 served as Marshall’s original headquarters since 1963. Marshall center operations lowered flags at that building on Jan. 21, 2022.
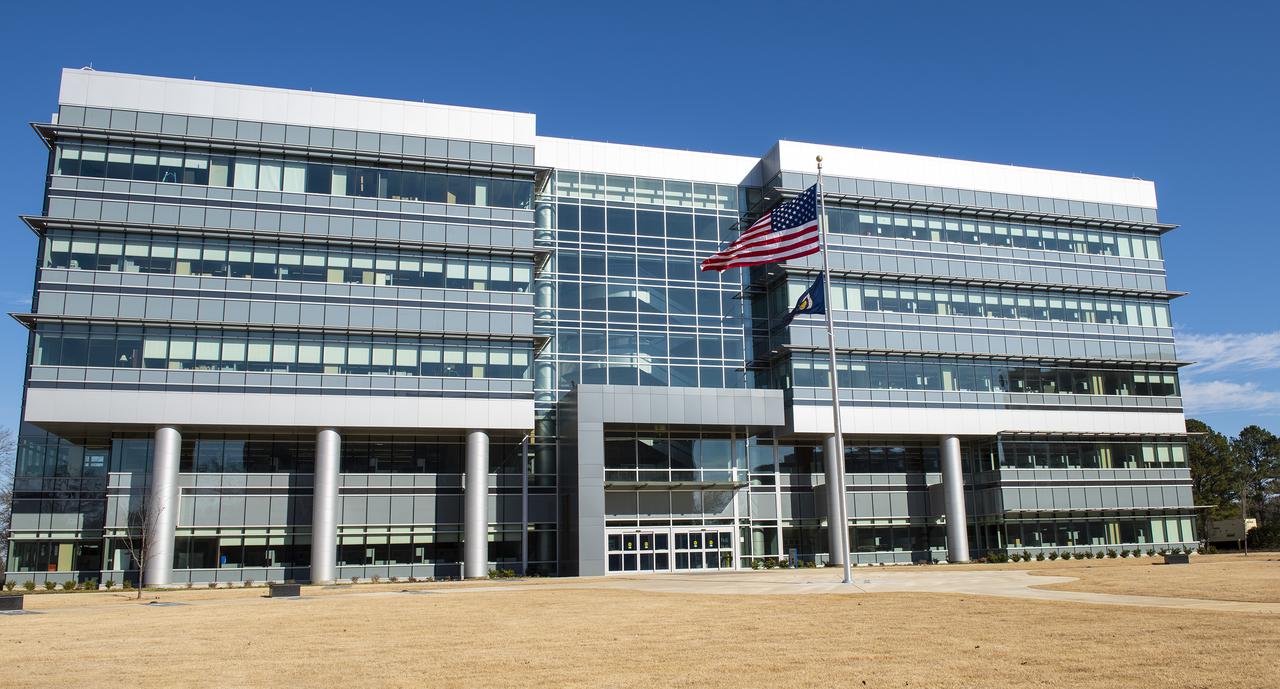

On Jan. 26, 2022, the U.S. and NASA flags were raised at Building 4221 to mark the transfer of headquarters to that building at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The doors to Building 4221, a new, environmentally friendly building, opened on Earth Day, April 22, 2019. Building 4200 served as Marshall’s original headquarters since 1963. Marshall center operations lowered flags at that building on Jan. 21, 2022.
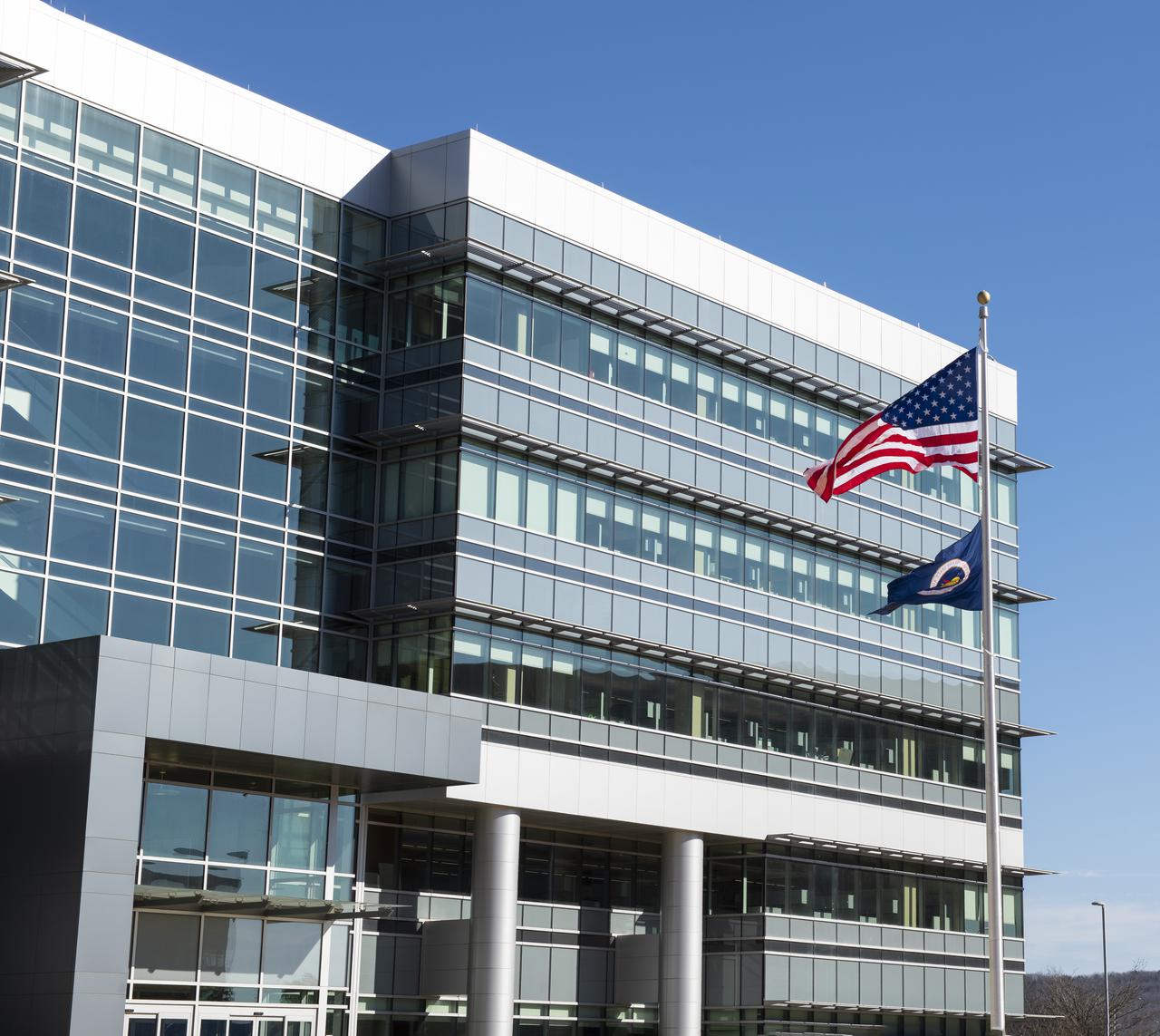

On Jan. 26, 2022, the U.S. and NASA flags were raised at Building 4221 to mark the transfer of headquarters to that building at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The doors to Building 4221, a new, environmentally friendly building, opened on Earth Day, April 22, 2019. Building 4200 served as Marshall’s original headquarters since 1963. Marshall center operations lowered flags at that building on Jan. 21, 2022.
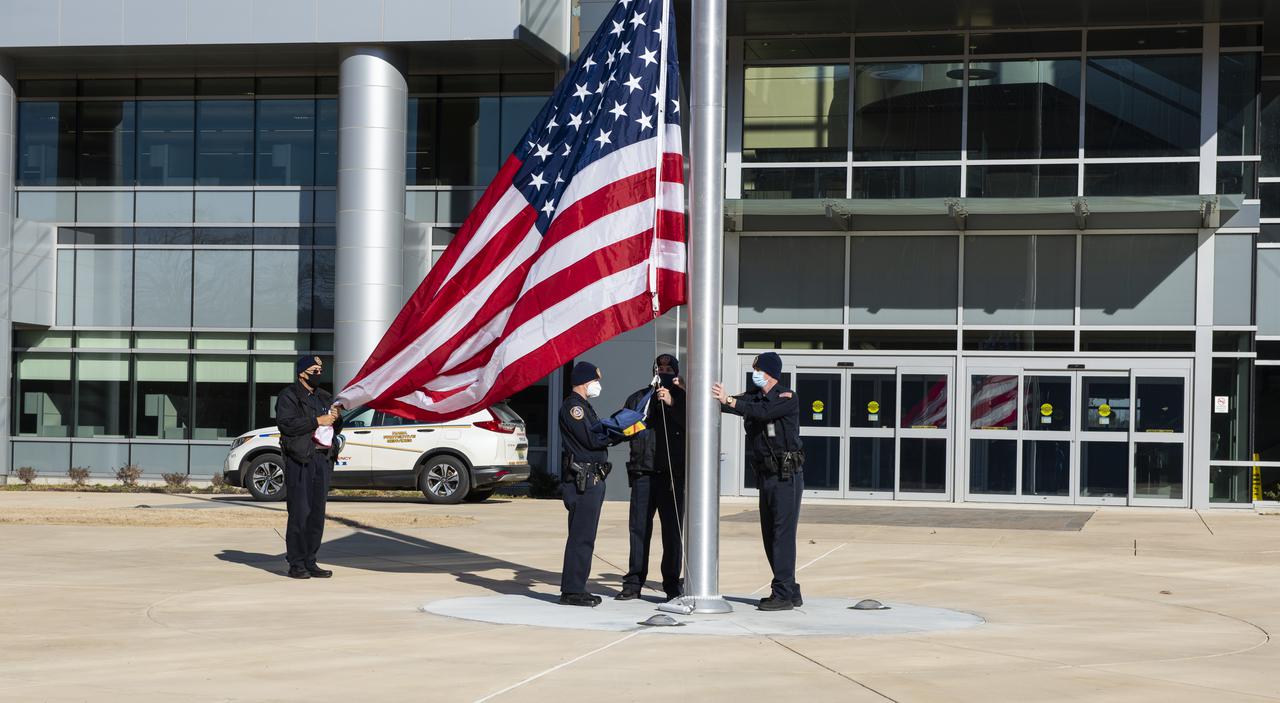

On Jan. 26, 2022, the U.S. and NASA flags were raised at Building 4221 to mark the transfer of headquarters to that building at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The doors to Building 4221, a new, environmentally friendly building, opened on Earth Day, April 22, 2019. Building 4200 served as Marshall’s original headquarters since 1963. Marshall center operations lowered flags at that building on Jan. 21, 2022.
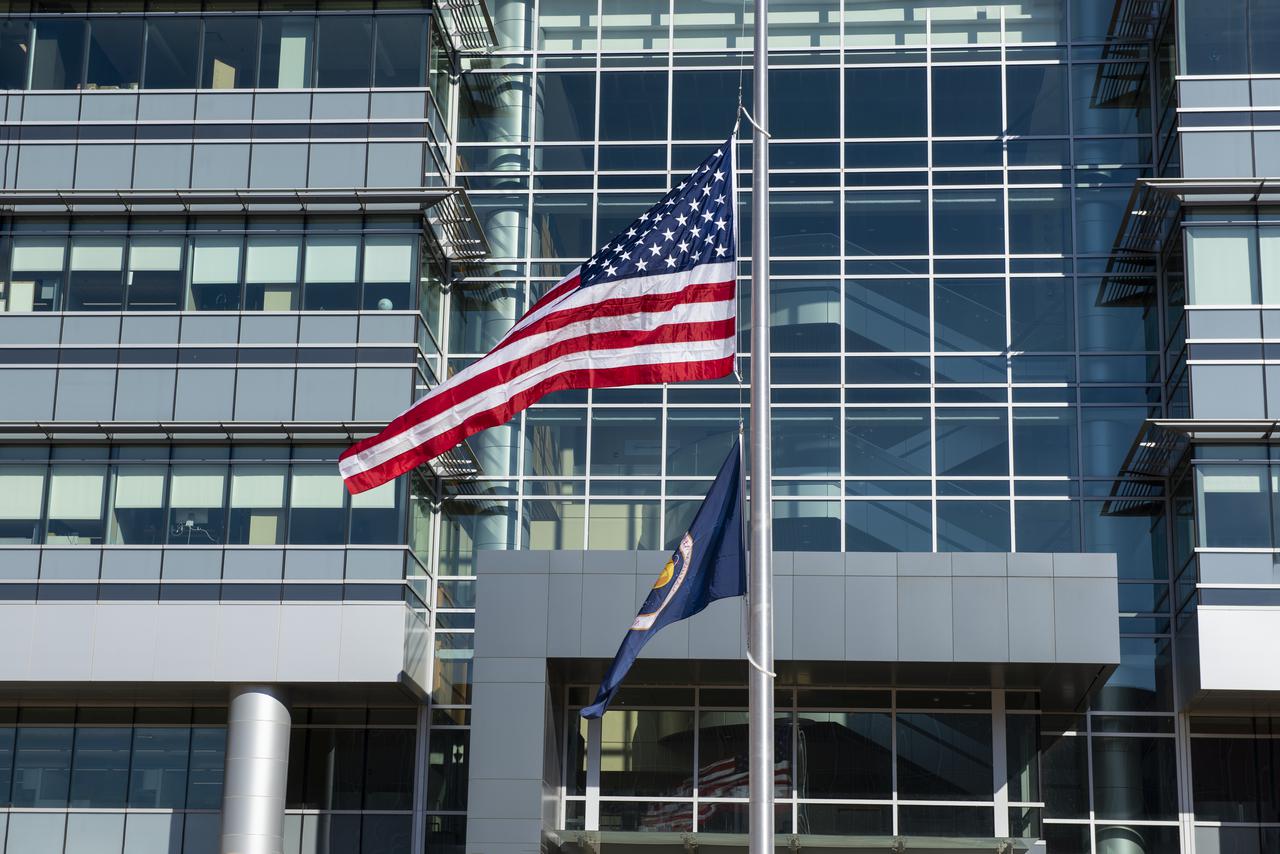

On Jan. 26, 2022, the U.S. and NASA flags were raised at Building 4221 to mark the transfer of headquarters to that building at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The doors to Building 4221, a new, environmentally friendly building, opened on Earth Day, April 22, 2019. Building 4200 served as Marshall’s original headquarters since 1963. Marshall center operations lowered flags at that building on Jan. 21, 2022.
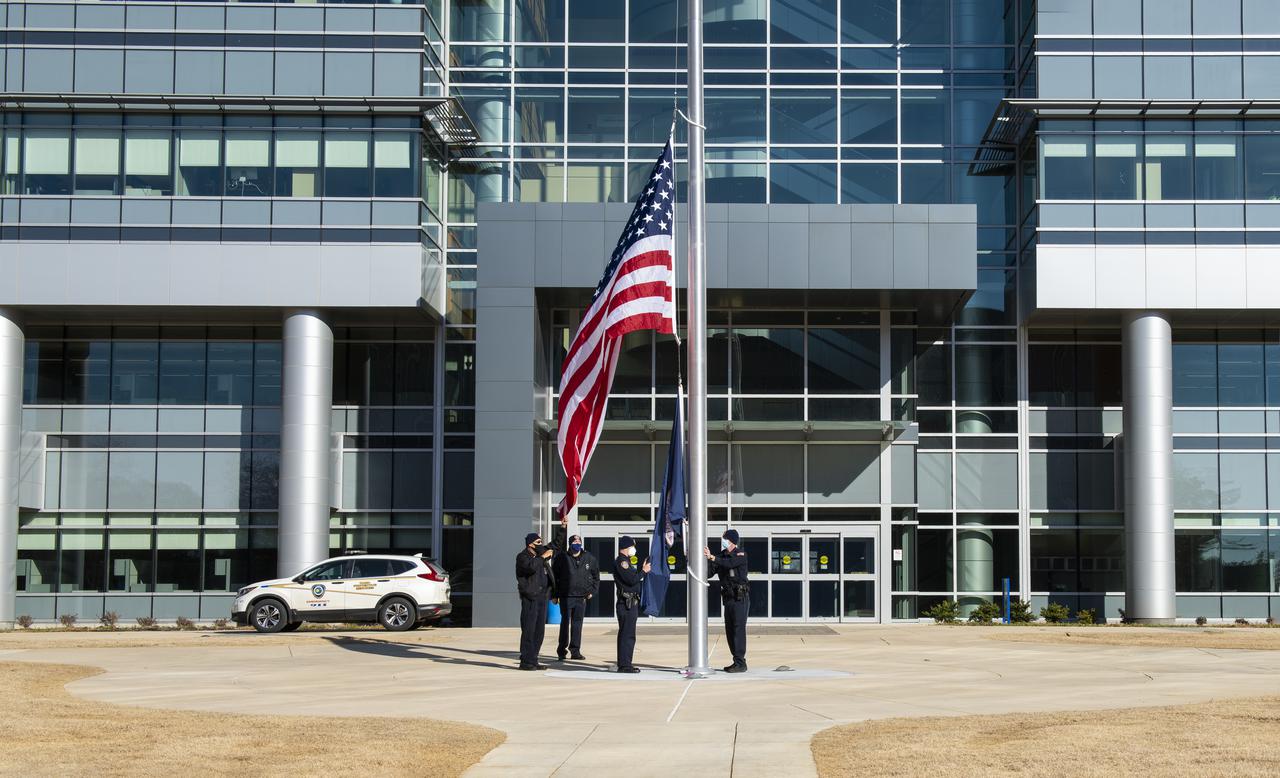

On Jan. 26, 2022, the U.S. and NASA flags were raised at Building 4221 to mark the transfer of headquarters to that building at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The doors to Building 4221, a new, environmentally friendly building, opened on Earth Day, April 22, 2019. Building 4200 served as Marshall’s original headquarters since 1963. Marshall center operations lowered flags at that building on Jan. 21, 2022.
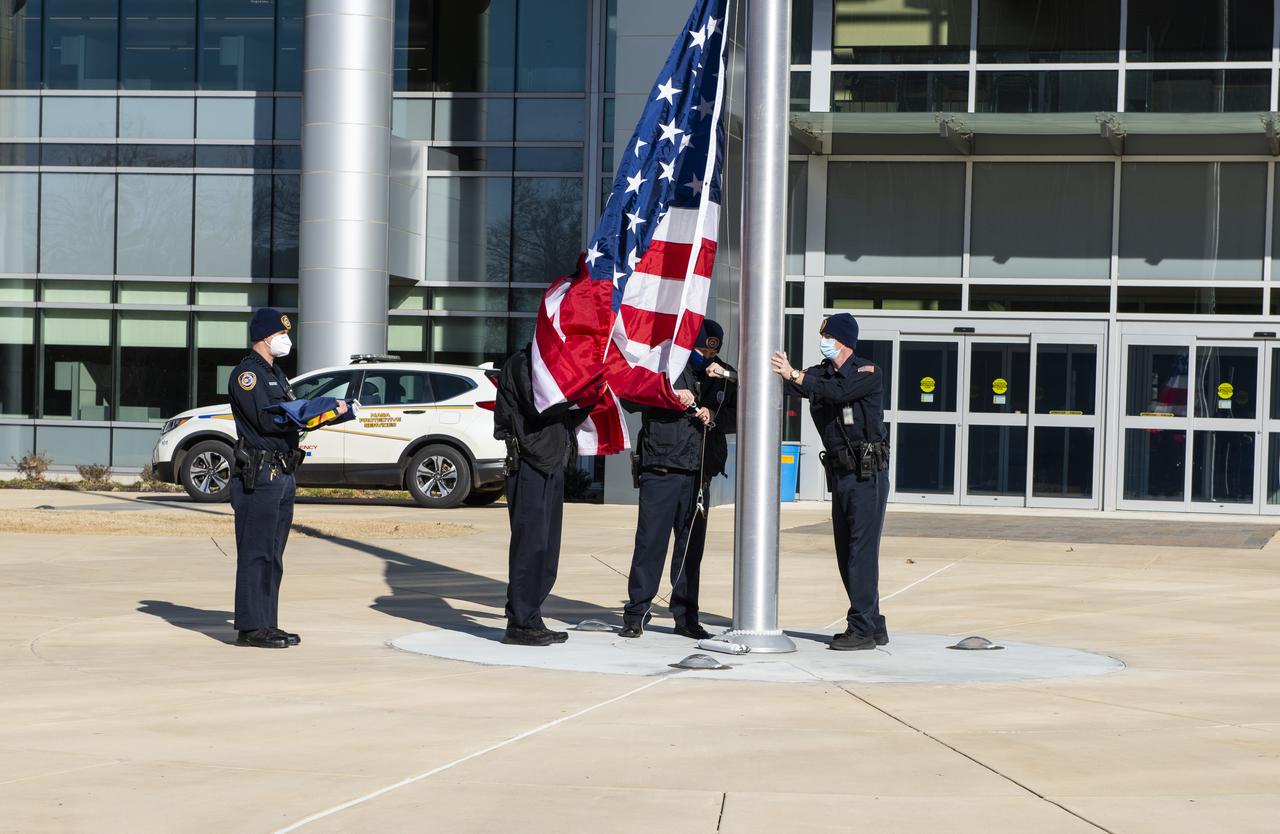

On Jan. 26, 2022, the U.S. and NASA flags were raised at Building 4221 to mark the transfer of headquarters to that building at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The doors to Building 4221, a new, environmentally friendly building, opened on Earth Day, April 22, 2019. Building 4200 served as Marshall’s original headquarters since 1963. Marshall center operations lowered flags at that building on Jan. 21, 2022.

On Jan. 26, 2022, the U.S. and NASA flags were raised at Building 4221 to mark the transfer of headquarters to that building at Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. The doors to Building 4221, a new, environmentally friendly building, opened on Earth Day, April 22, 2019. Building 4200 served as Marshall’s original headquarters since 1963. Marshall center operations lowered flags at that building on Jan. 21, 2022.
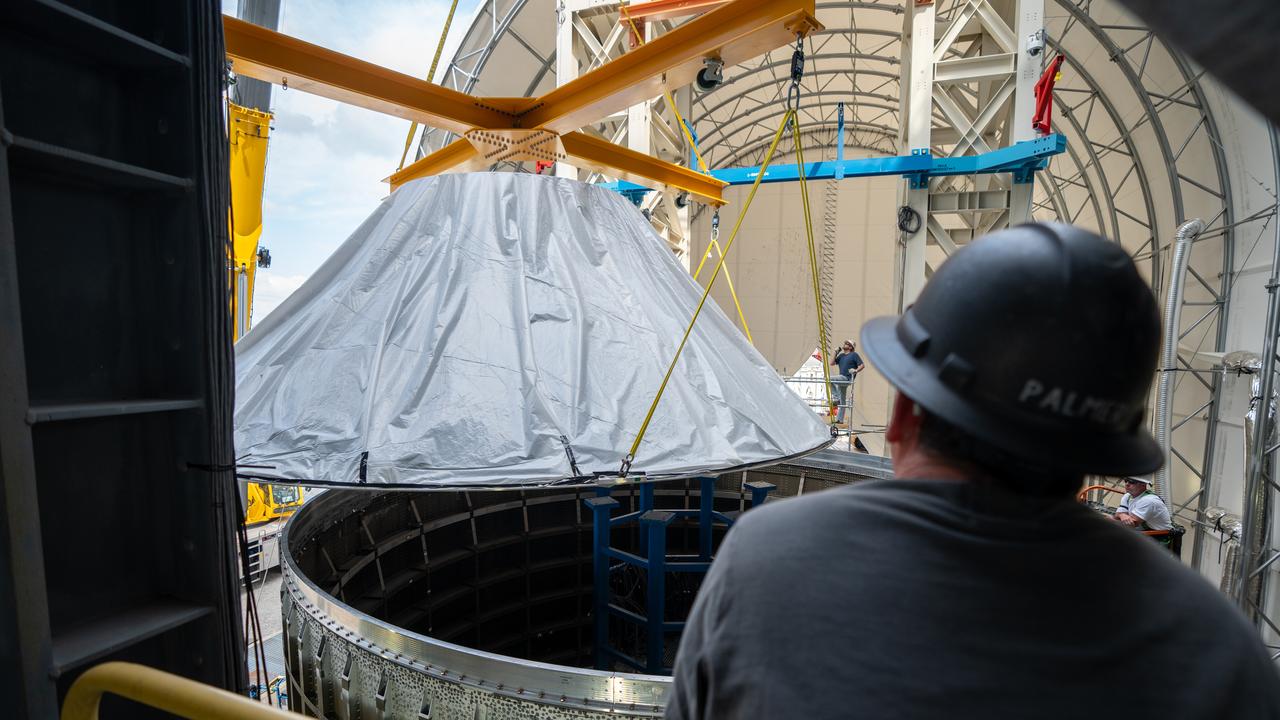

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
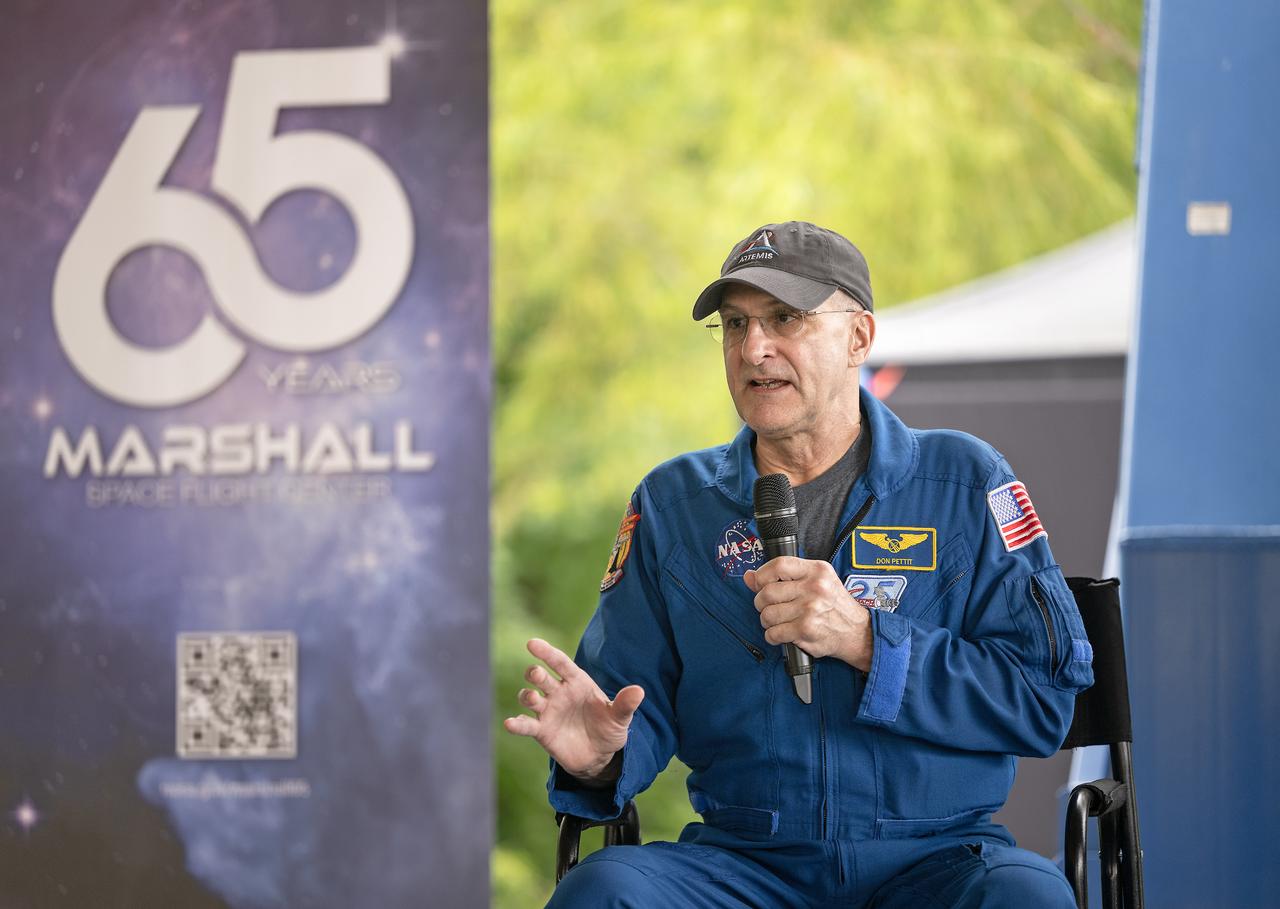

NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center celebrated the 65th anniversary of its founding on July 19, 2025, with a free, public celebration at The Orion Amphitheater in Huntsville, Alabama. Thousands of team members, families, and “Rocket City” residents took part, enjoying live music, games, food, and exhibits commemorating Marshall’s legacy of ingenuity and service to the U.S. space program. During a program for the celebration, guests heard remarks from Joseph Pelfrey, director of NASA Marshall, Huntsville Mayor Tommy Battle, and Kamerra Liles, assistant general manager of The Orion Amphitheater, followed by Pelfrey sharing a new video overview about Marshall. The program continued with a video presentation from NASA astronauts from the Expedition 72 crew – which contributed more than 1,000 total hours of scientific studies on plant growth, stem cell growth for treating diseases, the resilience of microorganisms to the harsh space environment, and more on the International Space Station. NASA astronauts Suni Williams and Don Pettit, who served as space station commander and flight engineer, respectively, shared their experiences in space with the community and told the audience how vital Marshall’s on the ground support was to their mission success. Marshall has shaped and expanded human space exploration every decade since the NASA center opened its doors on July 1, 1960. The center’s civil service and contract workers built the nation’s flagship rockets, from the Saturn V to the SLS (Space Launch System), managed the space shuttle propulsion program, delivered the Chandra X-ray Observatory and critical elements of the International Space Station to orbit, and continue to spearhead numerous advances in science and engineering.
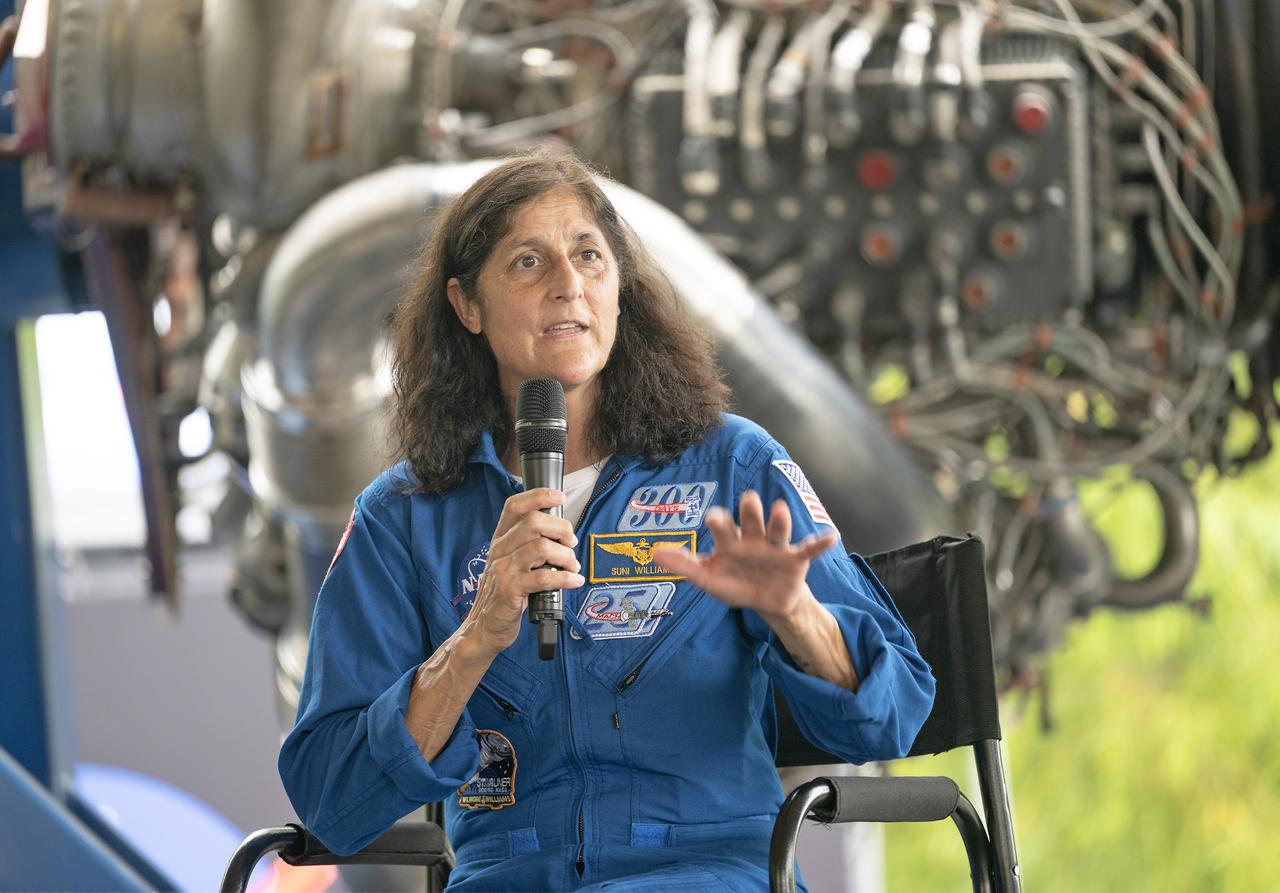

NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center celebrated the 65th anniversary of its founding on July 19, 2025, with a free, public celebration at The Orion Amphitheater in Huntsville, Alabama. Thousands of team members, families, and “Rocket City” residents took part, enjoying live music, games, food, and exhibits commemorating Marshall’s legacy of ingenuity and service to the U.S. space program. During a program for the celebration, guests heard remarks from Joseph Pelfrey, director of NASA Marshall, Huntsville Mayor Tommy Battle, and Kamerra Liles, assistant general manager of The Orion Amphitheater, followed by Pelfrey sharing a new video overview about Marshall. The program continued with a video presentation from NASA astronauts from the Expedition 72 crew – which contributed more than 1,000 total hours of scientific studies on plant growth, stem cell growth for treating diseases, the resilience of microorganisms to the harsh space environment, and more on the International Space Station. NASA astronauts Suni Williams and Don Pettit, who served as space station commander and flight engineer, respectively, shared their experiences in space with the community and told the audience how vital Marshall’s on the ground support was to their mission success. Marshall has shaped and expanded human space exploration every decade since the NASA center opened its doors on July 1, 1960. The center’s civil service and contract workers built the nation’s flagship rockets, from the Saturn V to the SLS (Space Launch System), managed the space shuttle propulsion program, delivered the Chandra X-ray Observatory and critical elements of the International Space Station to orbit, and continue to spearhead numerous advances in science and engineering.
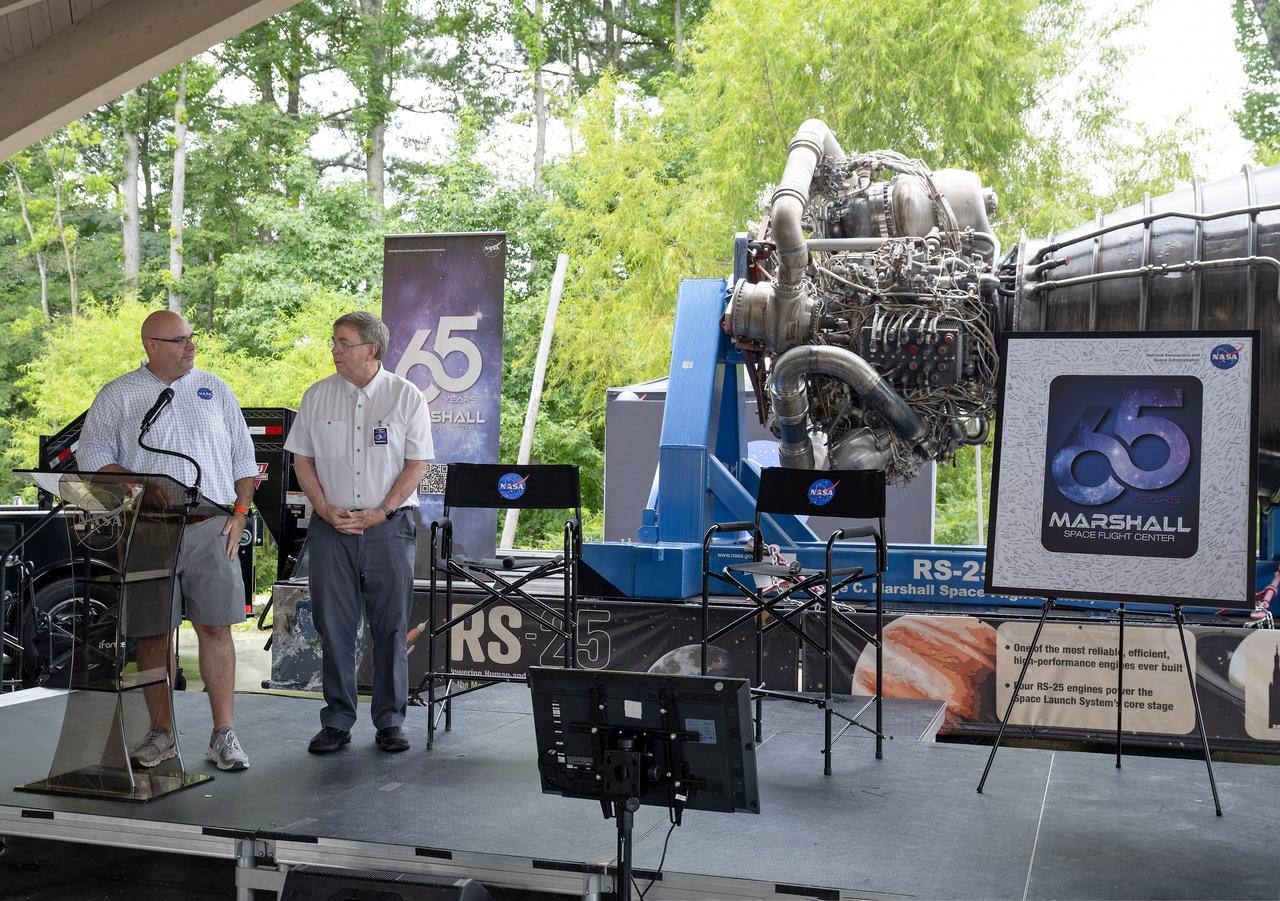
NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center celebrated the 65th anniversary of its founding on July 19, 2025, with a free, public celebration at The Orion Amphitheater in Huntsville, Alabama. Thousands of team members, families, and “Rocket City” residents took part, enjoying live music, games, food, and exhibits commemorating Marshall’s legacy of ingenuity and service to the U.S. space program. During a program for the celebration, guests heard remarks from Joseph Pelfrey, director of NASA Marshall, Huntsville Mayor Tommy Battle, and Kamerra Liles, assistant general manager of The Orion Amphitheater, followed by Pelfrey sharing a new video overview about Marshall. The program continued with a video presentation from NASA astronauts from the Expedition 72 crew – which contributed more than 1,000 total hours of scientific studies on plant growth, stem cell growth for treating diseases, the resilience of microorganisms to the harsh space environment, and more on the International Space Station. NASA astronauts Suni Williams and Don Pettit, who served as space station commander and flight engineer, respectively, shared their experiences in space with the community and told the audience how vital Marshall’s on the ground support was to their mission success. Marshall has shaped and expanded human space exploration every decade since the NASA center opened its doors on July 1, 1960. The center’s civil service and contract workers built the nation’s flagship rockets, from the Saturn V to the SLS (Space Launch System), managed the space shuttle propulsion program, delivered the Chandra X-ray Observatory and critical elements of the International Space Station to orbit, and continue to spearhead numerous advances in science and engineering.
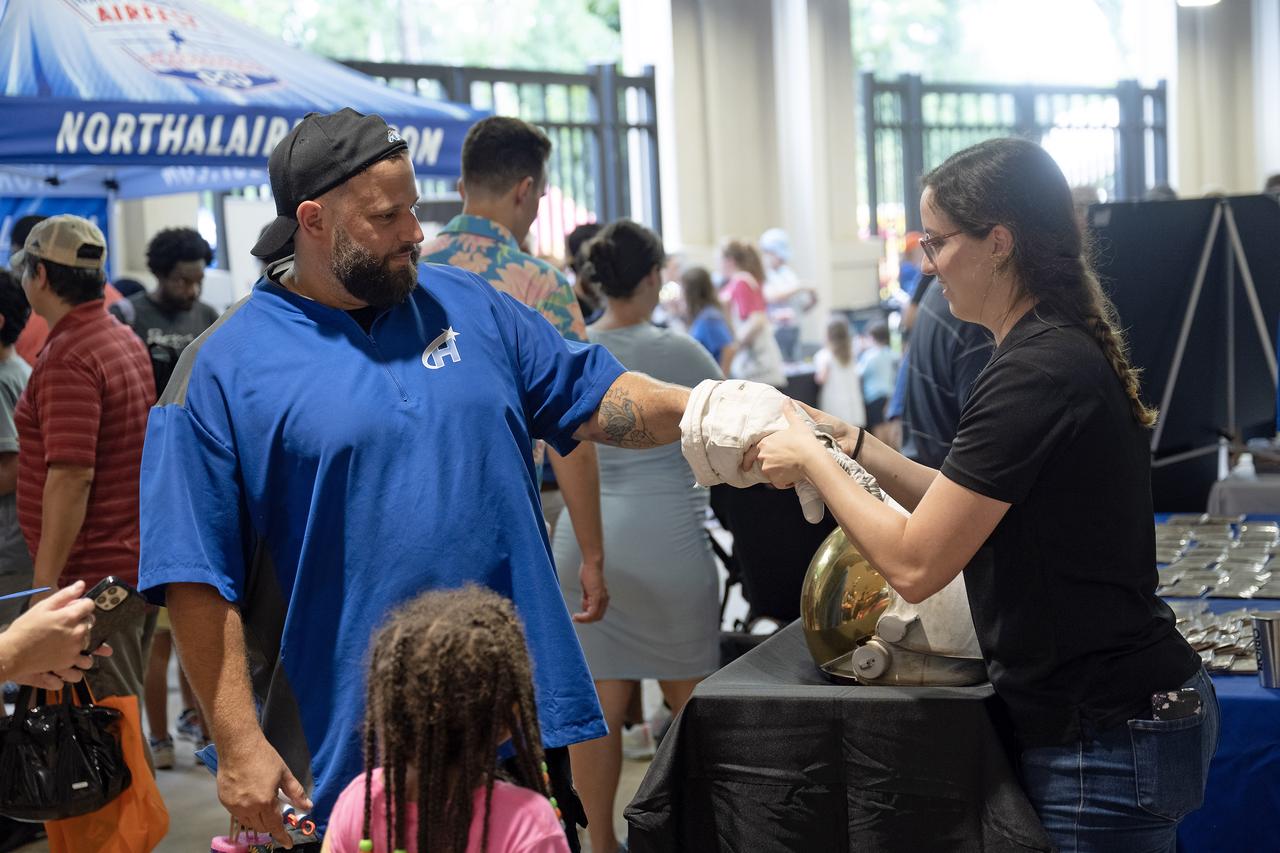

NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center celebrated the 65th anniversary of its founding on July 19, 2025, with a free, public celebration at The Orion Amphitheater in Huntsville, Alabama. Thousands of team members, families, and “Rocket City” residents took part, enjoying live music, games, food, and exhibits commemorating Marshall’s legacy of ingenuity and service to the U.S. space program. During a program for the celebration, guests heard remarks from Joseph Pelfrey, director of NASA Marshall, Huntsville Mayor Tommy Battle, and Kamerra Liles, assistant general manager of The Orion Amphitheater, followed by Pelfrey sharing a new video overview about Marshall. The program continued with a video presentation from NASA astronauts from the Expedition 72 crew – which contributed more than 1,000 total hours of scientific studies on plant growth, stem cell growth for treating diseases, the resilience of microorganisms to the harsh space environment, and more on the International Space Station. NASA astronauts Suni Williams and Don Pettit, who served as space station commander and flight engineer, respectively, shared their experiences in space with the community and told the audience how vital Marshall’s on the ground support was to their mission success. Marshall has shaped and expanded human space exploration every decade since the NASA center opened its doors on July 1, 1960. The center’s civil service and contract workers built the nation’s flagship rockets, from the Saturn V to the SLS (Space Launch System), managed the space shuttle propulsion program, delivered the Chandra X-ray Observatory and critical elements of the International Space Station to orbit, and continue to spearhead numerous advances in science and engineering.
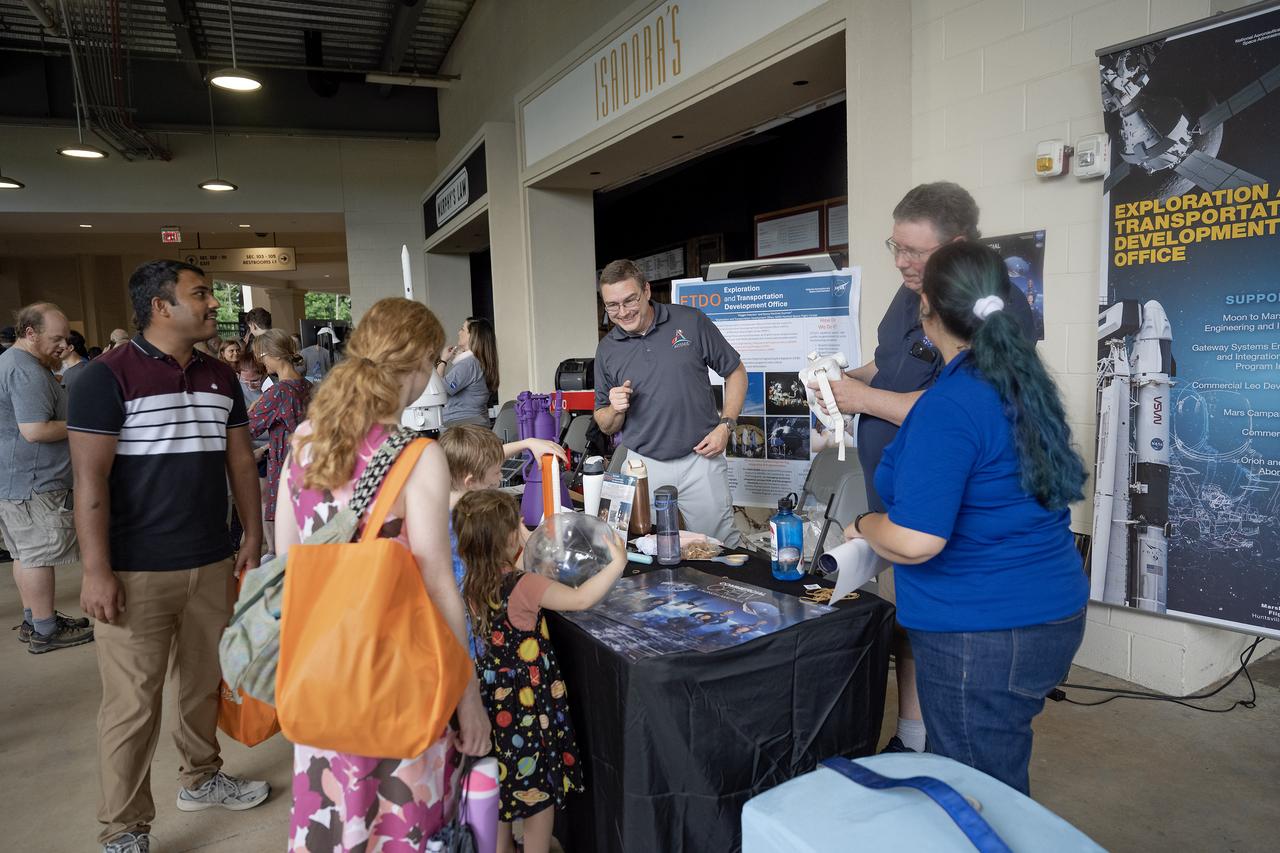

NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center celebrated the 65th anniversary of its founding on July 19, 2025, with a free, public celebration at The Orion Amphitheater in Huntsville, Alabama. Thousands of team members, families, and “Rocket City” residents took part, enjoying live music, games, food, and exhibits commemorating Marshall’s legacy of ingenuity and service to the U.S. space program. During a program for the celebration, guests heard remarks from Joseph Pelfrey, director of NASA Marshall, Huntsville Mayor Tommy Battle, and Kamerra Liles, assistant general manager of The Orion Amphitheater, followed by Pelfrey sharing a new video overview about Marshall. The program continued with a video presentation from NASA astronauts from the Expedition 72 crew – which contributed more than 1,000 total hours of scientific studies on plant growth, stem cell growth for treating diseases, the resilience of microorganisms to the harsh space environment, and more on the International Space Station. NASA astronauts Suni Williams and Don Pettit, who served as space station commander and flight engineer, respectively, shared their experiences in space with the community and told the audience how vital Marshall’s on the ground support was to their mission success. Marshall has shaped and expanded human space exploration every decade since the NASA center opened its doors on July 1, 1960. The center’s civil service and contract workers built the nation’s flagship rockets, from the Saturn V to the SLS (Space Launch System), managed the space shuttle propulsion program, delivered the Chandra X-ray Observatory and critical elements of the International Space Station to orbit, and continue to spearhead numerous advances in science and engineering.
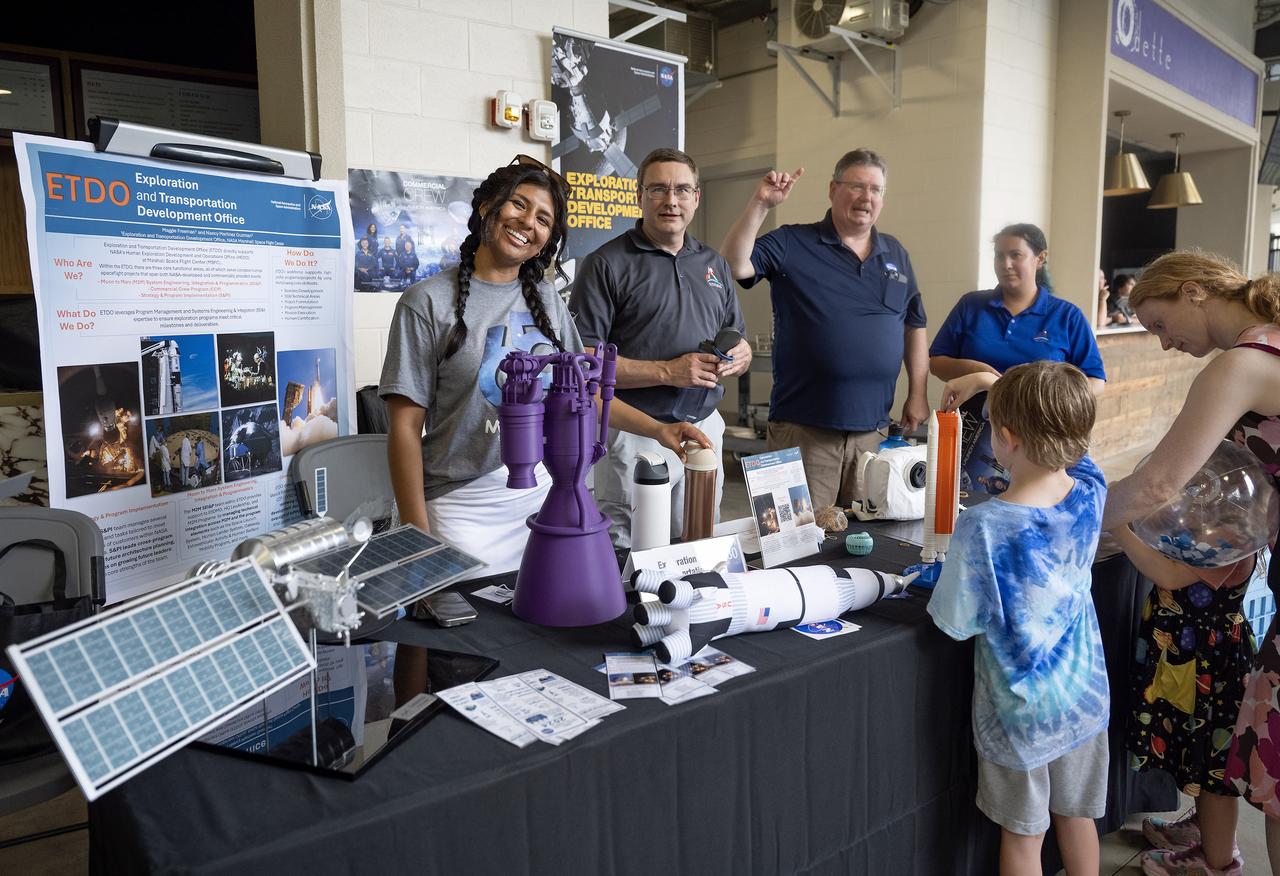

NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center celebrated the 65th anniversary of its founding on July 19, 2025, with a free, public celebration at The Orion Amphitheater in Huntsville, Alabama. Thousands of team members, families, and “Rocket City” residents took part, enjoying live music, games, food, and exhibits commemorating Marshall’s legacy of ingenuity and service to the U.S. space program. During a program for the celebration, guests heard remarks from Joseph Pelfrey, director of NASA Marshall, Huntsville Mayor Tommy Battle, and Kamerra Liles, assistant general manager of The Orion Amphitheater, followed by Pelfrey sharing a new video overview about Marshall. The program continued with a video presentation from NASA astronauts from the Expedition 72 crew – which contributed more than 1,000 total hours of scientific studies on plant growth, stem cell growth for treating diseases, the resilience of microorganisms to the harsh space environment, and more on the International Space Station. NASA astronauts Suni Williams and Don Pettit, who served as space station commander and flight engineer, respectively, shared their experiences in space with the community and told the audience how vital Marshall’s on the ground support was to their mission success. Marshall has shaped and expanded human space exploration every decade since the NASA center opened its doors on July 1, 1960. The center’s civil service and contract workers built the nation’s flagship rockets, from the Saturn V to the SLS (Space Launch System), managed the space shuttle propulsion program, delivered the Chandra X-ray Observatory and critical elements of the International Space Station to orbit, and continue to spearhead numerous advances in science and engineering.

Marshall’s Ruth Jones, a mishap investigation specialist, told her NASA story and spoke about minority statistics in science, technology, engineering and mathematics (STEM). Jones also led a panel discussing how to engage, encourage and draw more minority students in to STEM fields and careers.

More than 500 students with 75 teams from around the world participated in the 31st year of NASA’s Human Exploration Rover Challenge (HERC) on April 11 and April 12, 2025, near NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Participating teams represented 35 colleges and universities, 38 high schools, and two middle schools from 20 states, Puerto Rico, and 16 other nations. NASA expanded the 2025 challenge to include a remote-control division - named Remote-Operated Vehicular Research - and invited middle school students to participate. Teams were awarded points based on navigating a half-mile obstacle course, conducting mission-specific task challenges, and completing multiple safety and design reviews with NASA engineers.

More than 500 students with 75 teams from around the world participated in the 31st year of NASA’s Human Exploration Rover Challenge (HERC) on April 11 and April 12, 2025, near NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Participating teams represented 35 colleges and universities, 38 high schools, and two middle schools from 20 states, Puerto Rico, and 16 other nations. NASA expanded the 2025 challenge to include a remote-control division - named Remote-Operated Vehicular Research - and invited middle school students to participate. Teams were awarded points based on navigating a half-mile obstacle course, conducting mission-specific task challenges, and completing multiple safety and design reviews with NASA engineers.
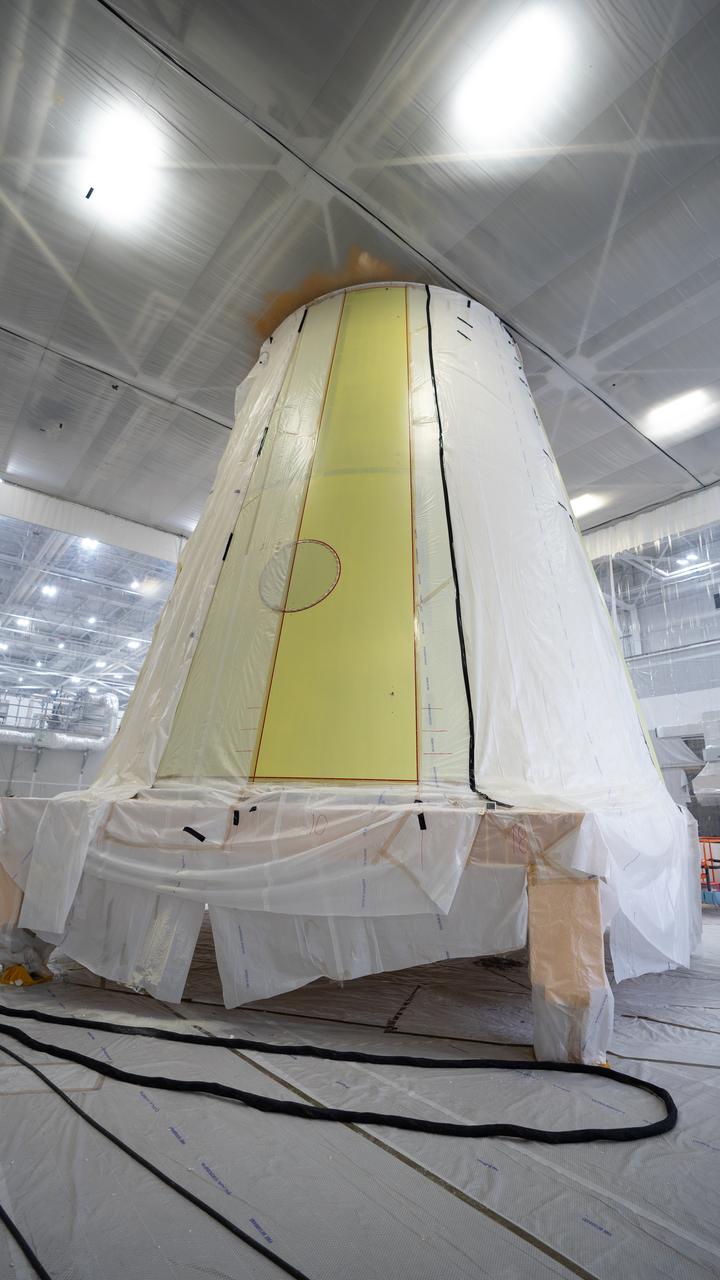

These photos show the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III before technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, applied the thermal protection system to it. Artemis III will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discover and inspire the Artemis Generation. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
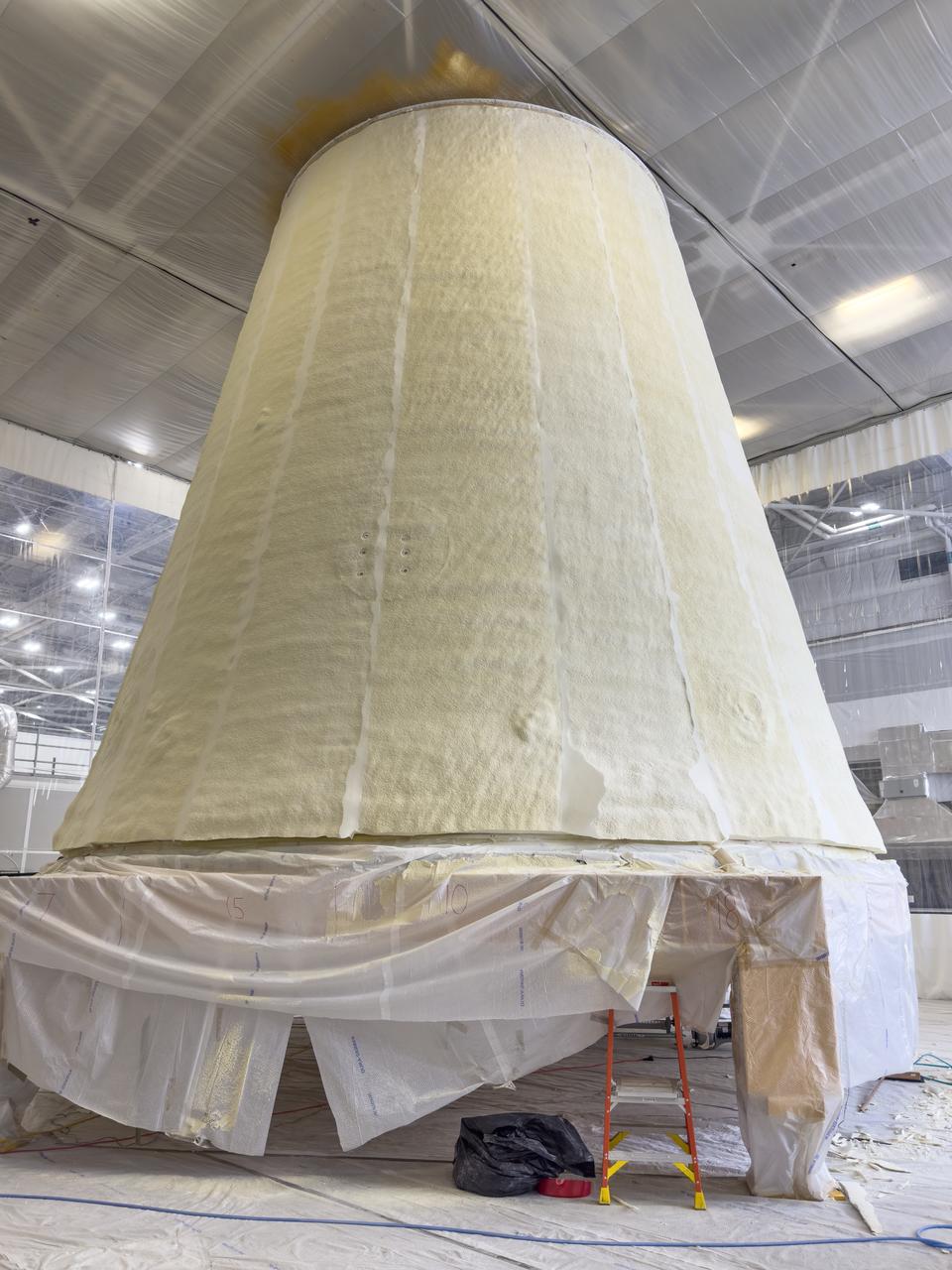

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, have applied the thermal protection system material to the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III, which will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discovery and inspire the Artemis Generation. The LVSA is a cone-shaped element that connects the mega rocket’s core stage to its interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS), partially enclosing it and protecting its avionics and electrical systems from the extreme pressures, sounds, and temperatures during launch and flight. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, have applied the thermal protection system material to the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III, which will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discovery and inspire the Artemis Generation. The LVSA is a cone-shaped element that connects the mega rocket’s core stage to its interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS), partially enclosing it and protecting its avionics and electrical systems from the extreme pressures, sounds, and temperatures during launch and flight. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
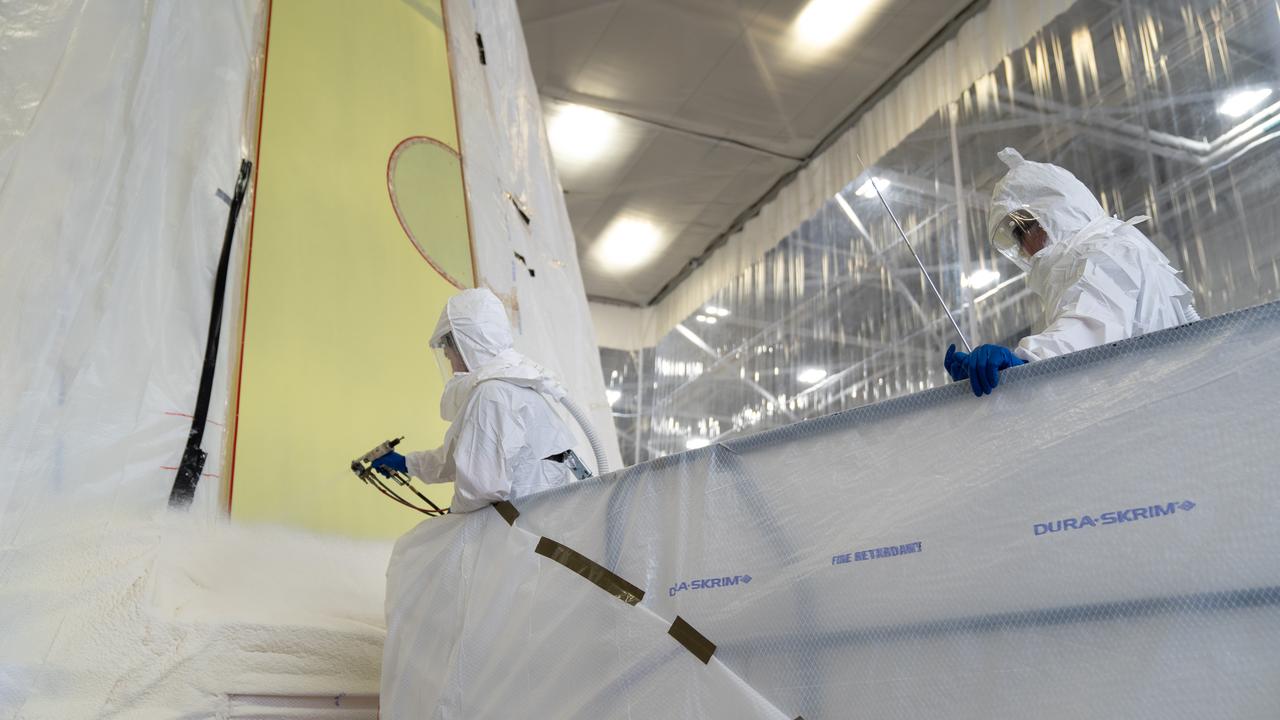

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, have applied the thermal protection system material to the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III, which will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discovery and inspire the Artemis Generation. The LVSA is a cone-shaped element that connects the mega rocket’s core stage to its interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS), partially enclosing it and protecting its avionics and electrical systems from the extreme pressures, sounds, and temperatures during launch and flight. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
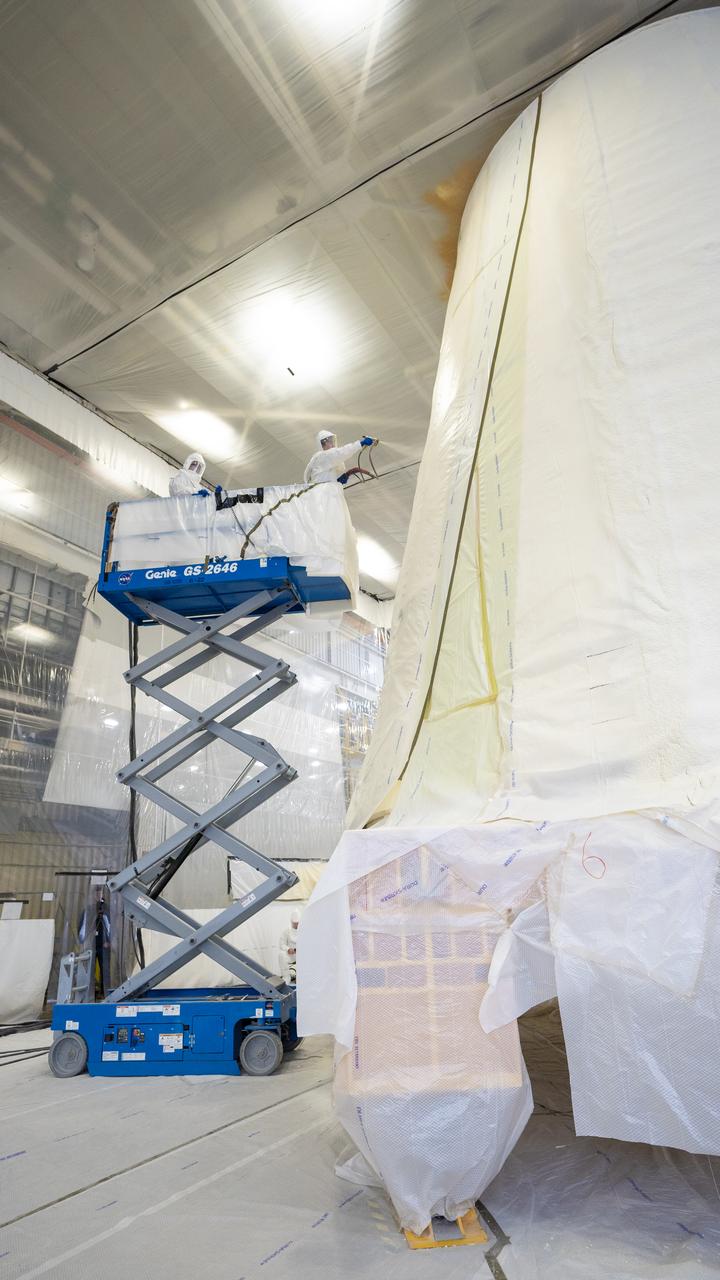

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, have applied the thermal protection system material to the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III, which will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discovery and inspire the Artemis Generation. The LVSA is a cone-shaped element that connects the mega rocket’s core stage to its interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS), partially enclosing it and protecting its avionics and electrical systems from the extreme pressures, sounds, and temperatures during launch and flight. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
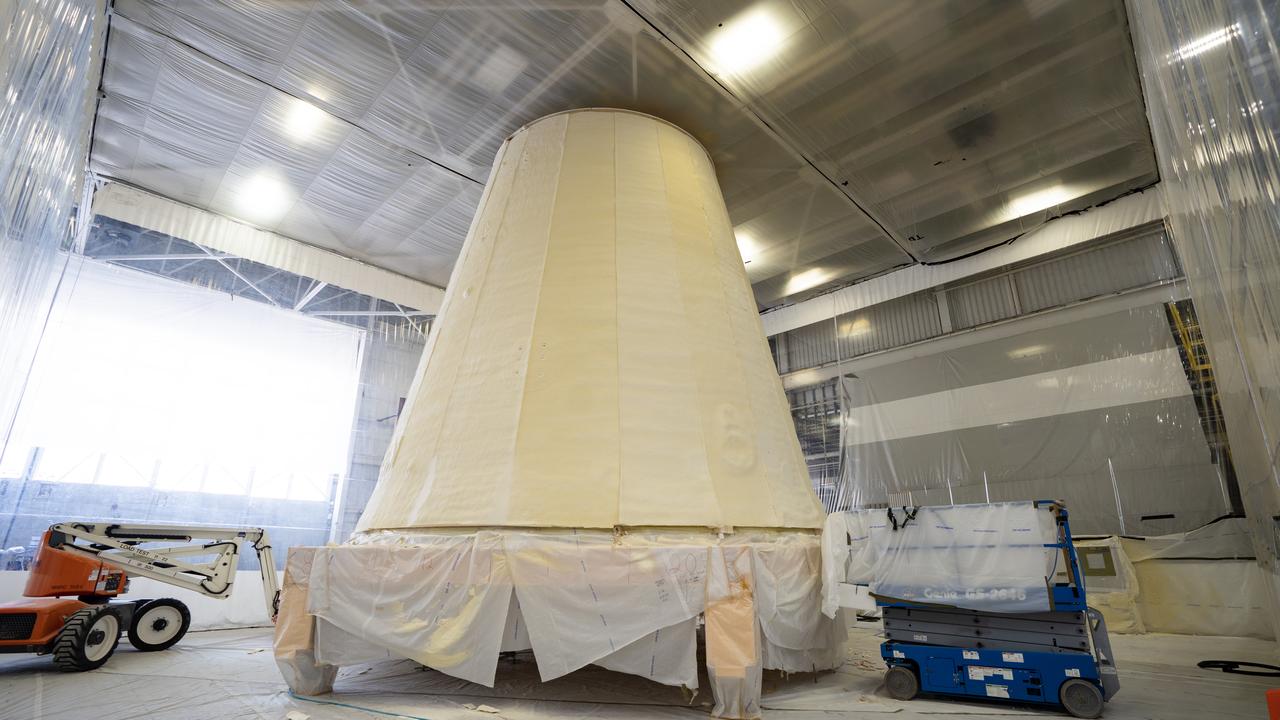

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, have applied the thermal protection system material to the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III, which will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discovery and inspire the Artemis Generation. The LVSA is a cone-shaped element that connects the mega rocket’s core stage to its interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS), partially enclosing it and protecting its avionics and electrical systems from the extreme pressures, sounds, and temperatures during launch and flight. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
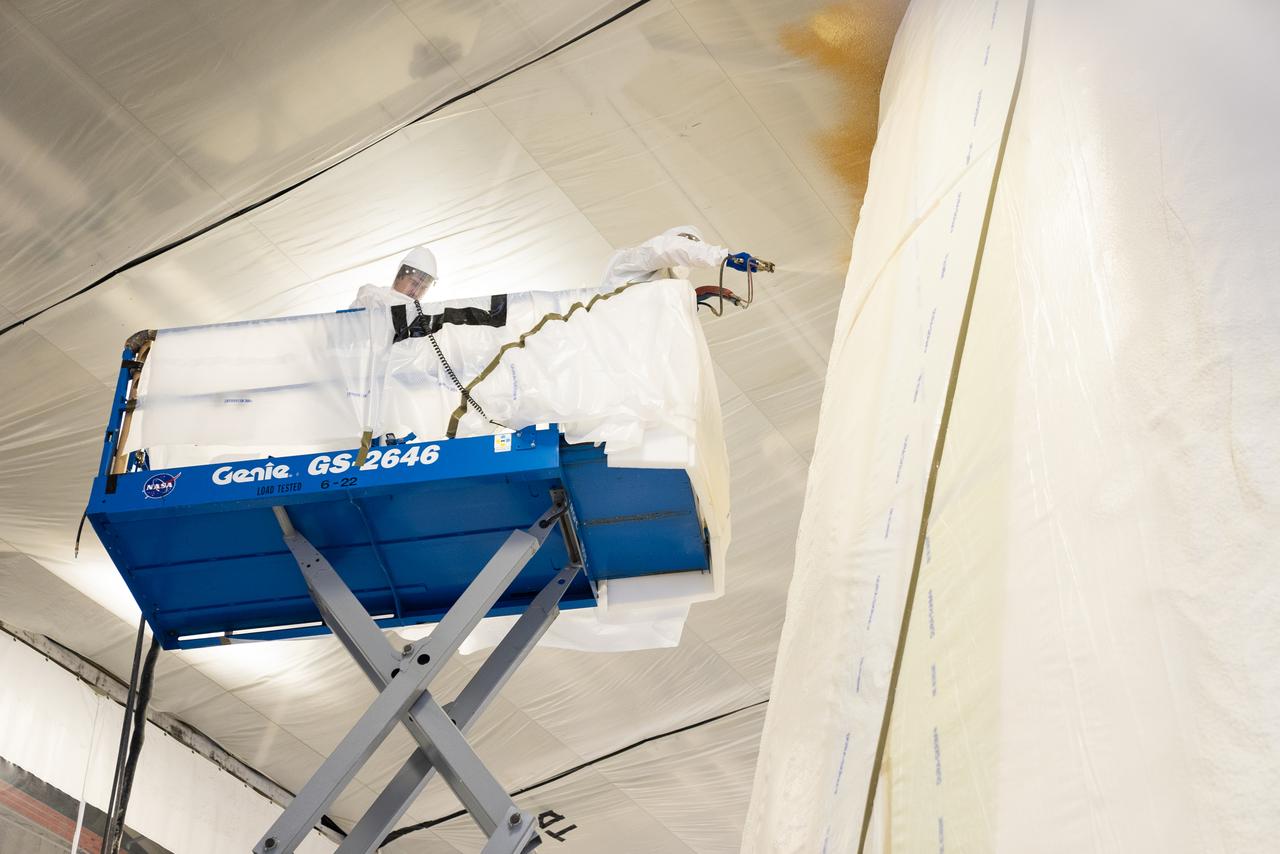

These photos show how technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, have applied the thermal protection system material to the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III, which will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discovery and inspire the Artemis Generation. The LVSA is a cone-shaped element that connects the mega rocket’s core stage to its interim cryogenic propulsion stage (ICPS), partially enclosing it and protecting its avionics and electrical systems from the extreme pressures, sounds, and temperatures during launch and flight. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
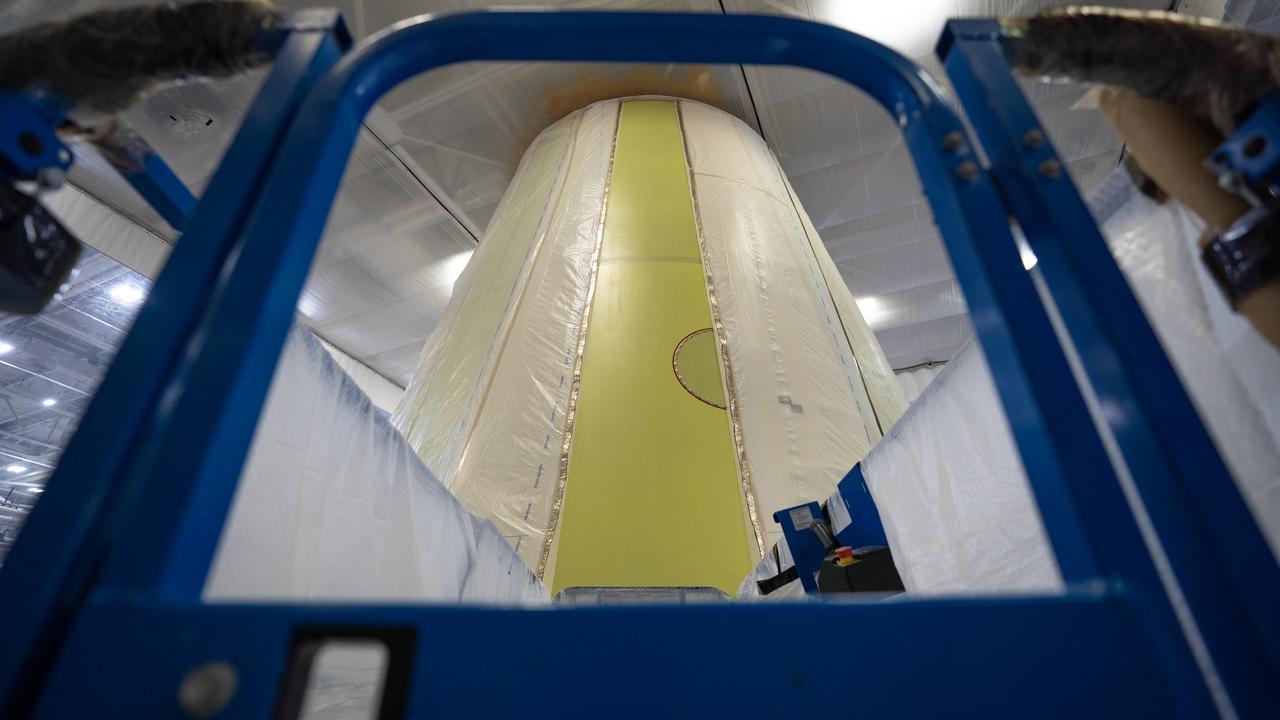
These photos show the launch vehicle stage adapter (LVSA) of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for Artemis III before technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, applied the thermal protection system to it. Artemis III will land astronauts on the Moon to advance long-term lunar exploration and scientific discover and inspire the Artemis Generation. Teams at Marshall began applying the thermal protection system material in the spring of 2023. Unlike other parts of the SLS rocket, the thermal protection system material for the LVSA is applied entirely by hand using a spray gun. During application, the technicians use a thin measuring rod to gauge the proper thickness. Once the thermal protection system has cured, certain areas are sanded down to meet parameters. The entire process takes several months. The LVSA is fully manufactured at Marshall by NASA, lead contractor Teledyne Brown Engineering, and the Jacobs Space Group’s ESSCA contract. The LVSA for Artemis III is the last of its kind as future SLS rockets will transition to its next, more powerful Block 1B configuration beginning with Artemis IV. NASA is working to land the first woman and first person of color on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission.
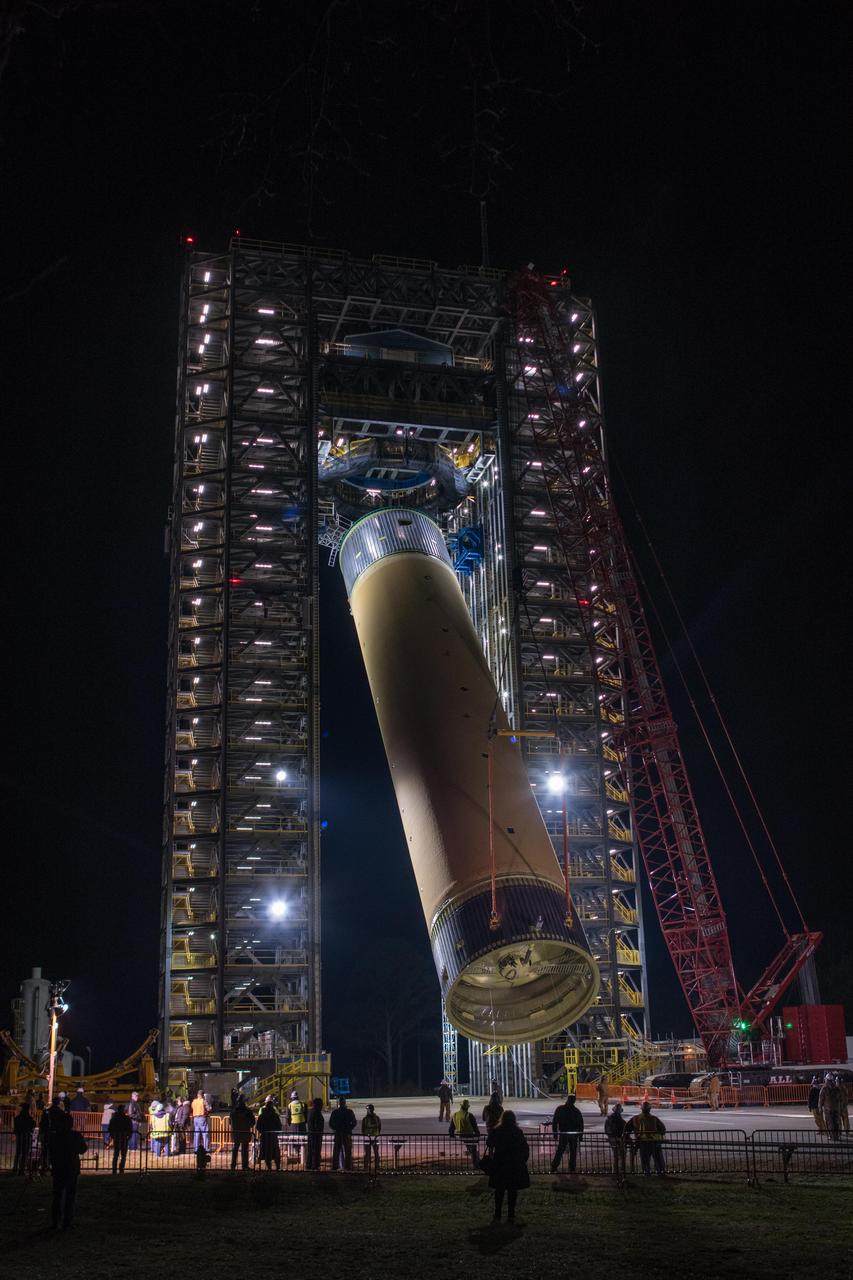

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.
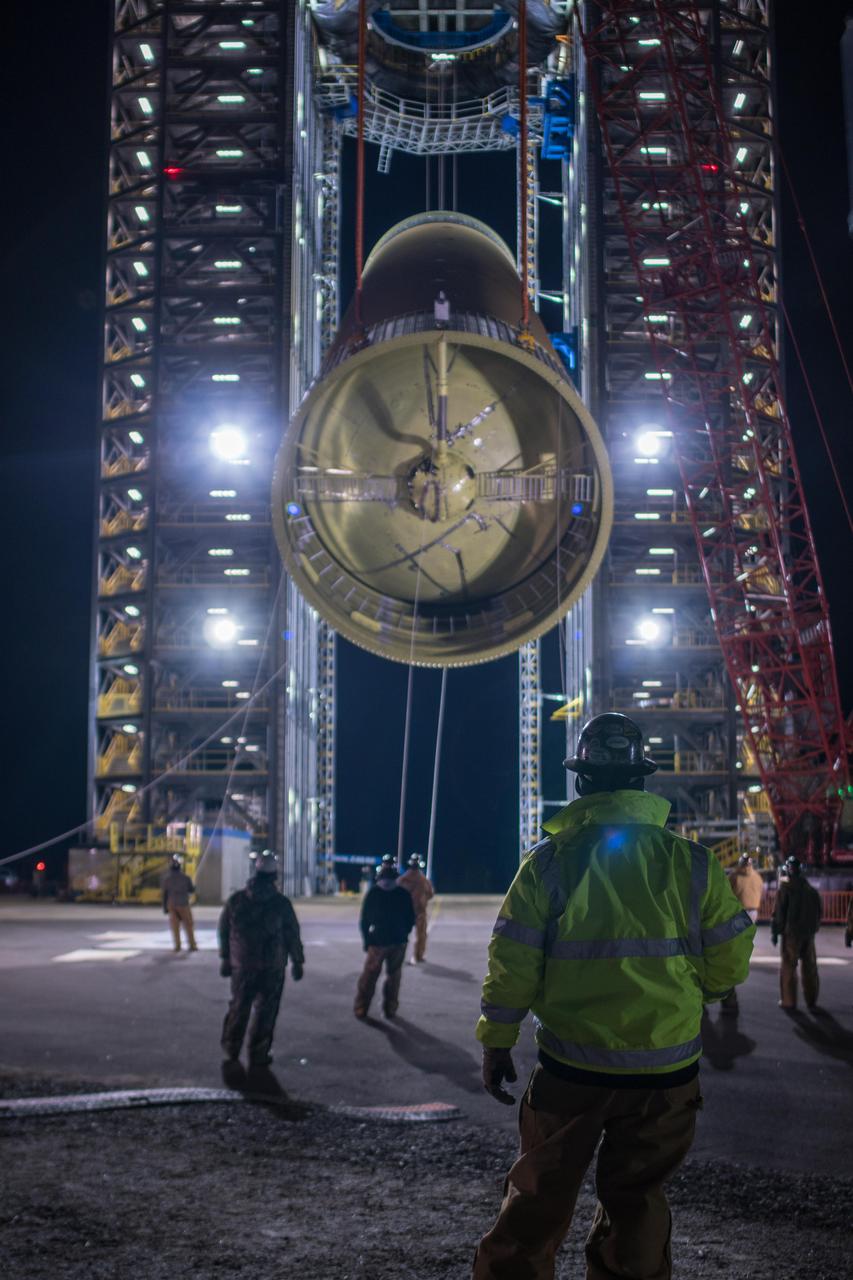

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.
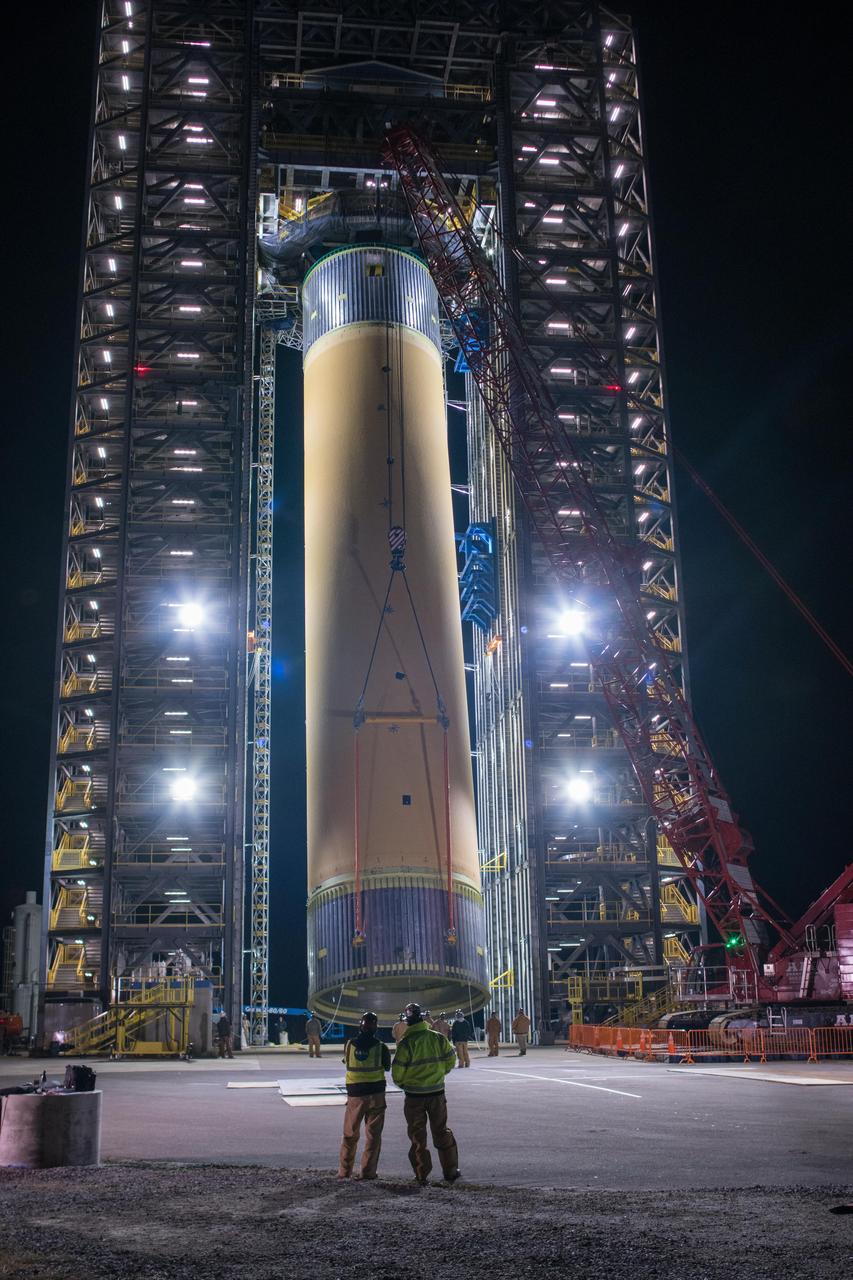

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.
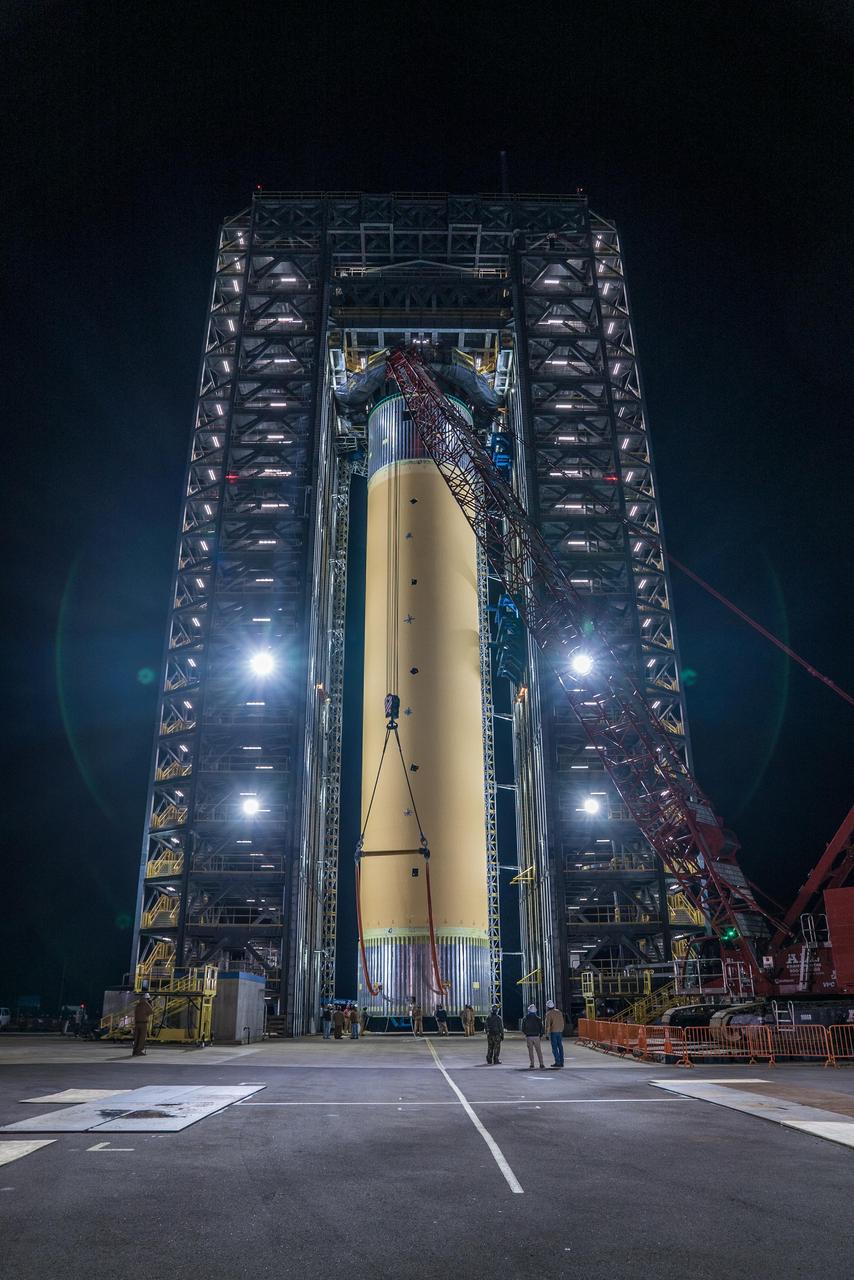

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.
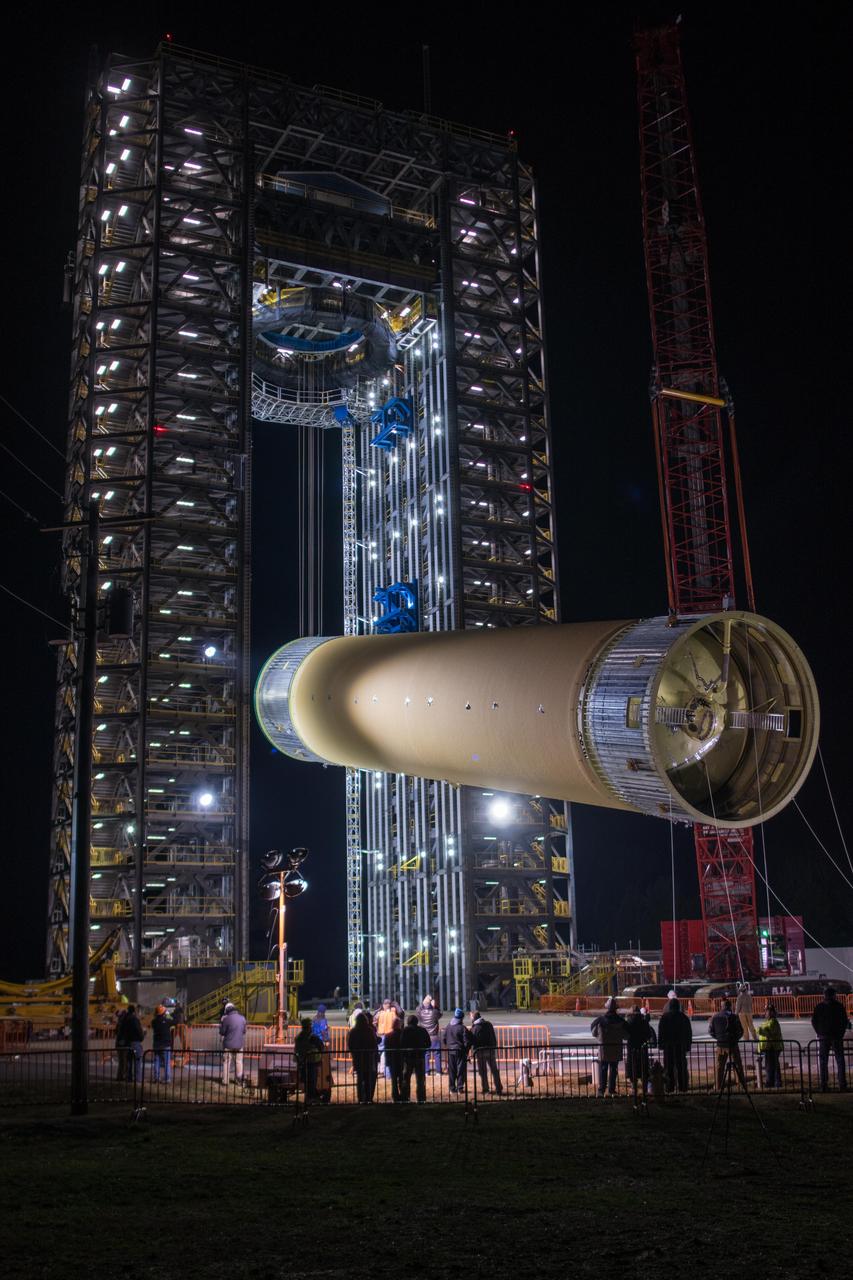

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.
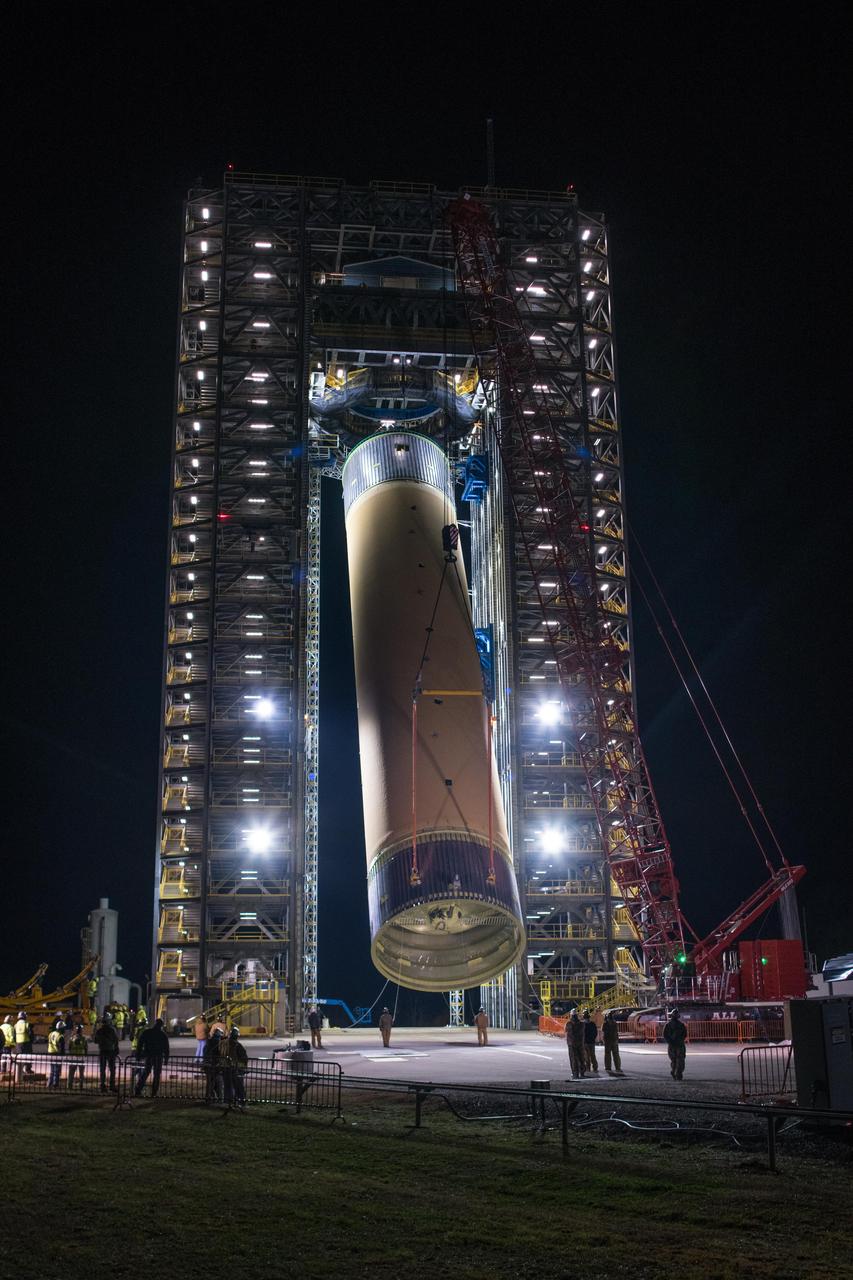

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.
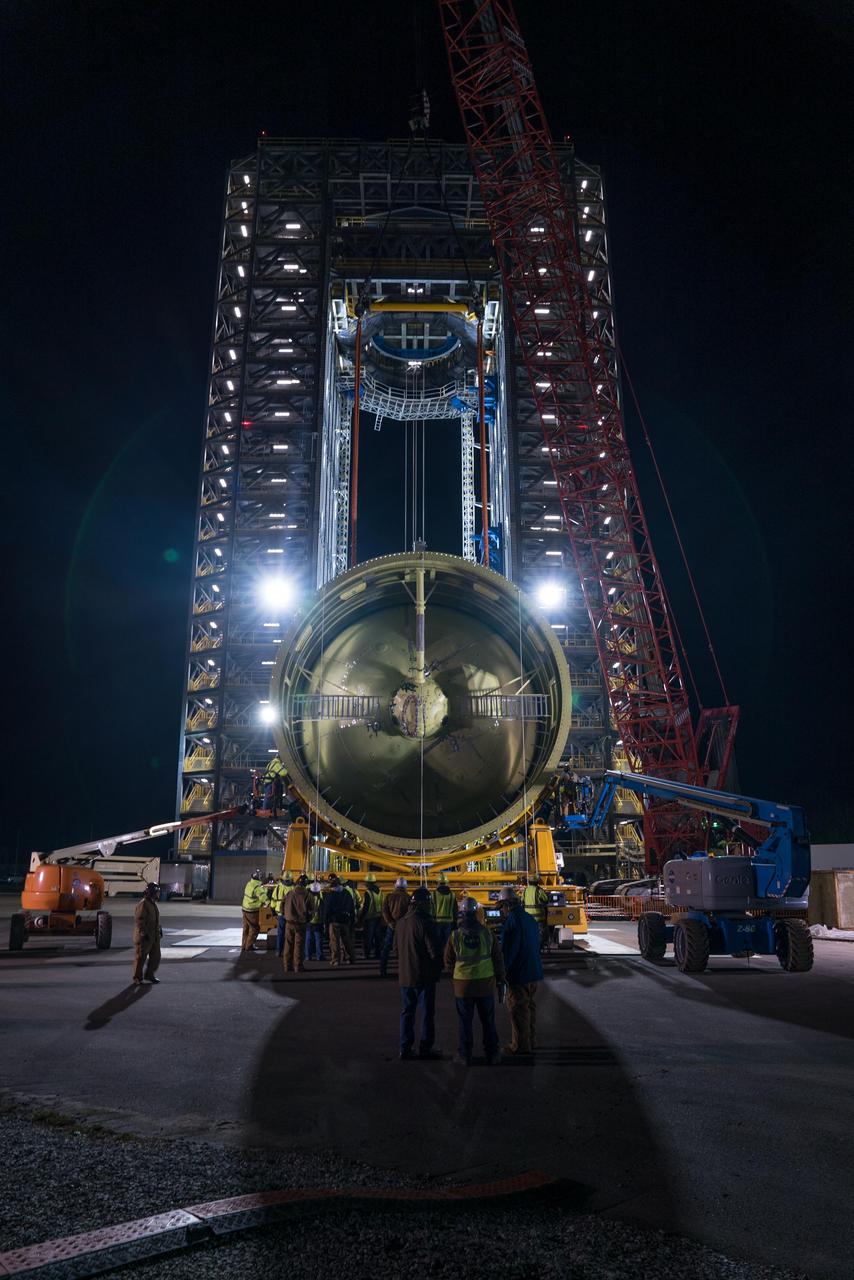

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.
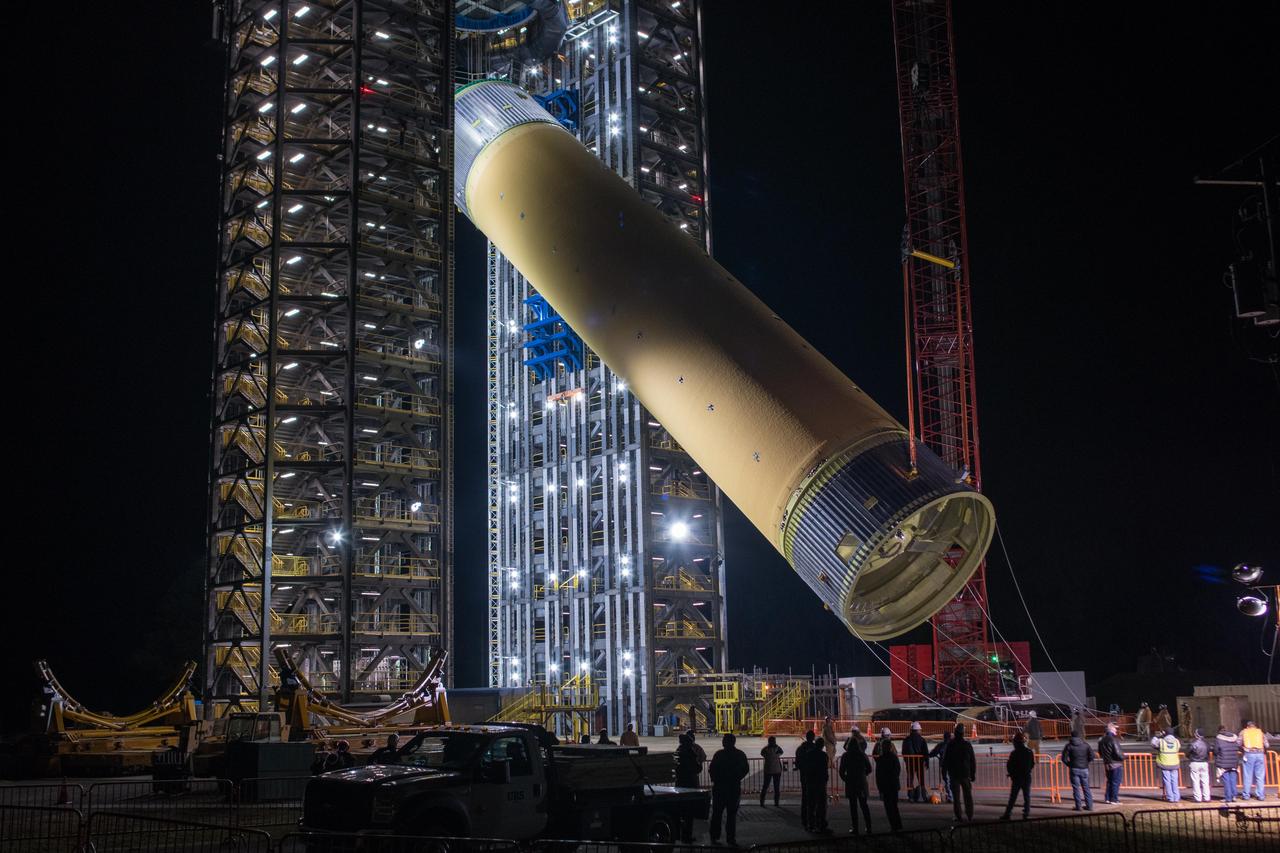

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.
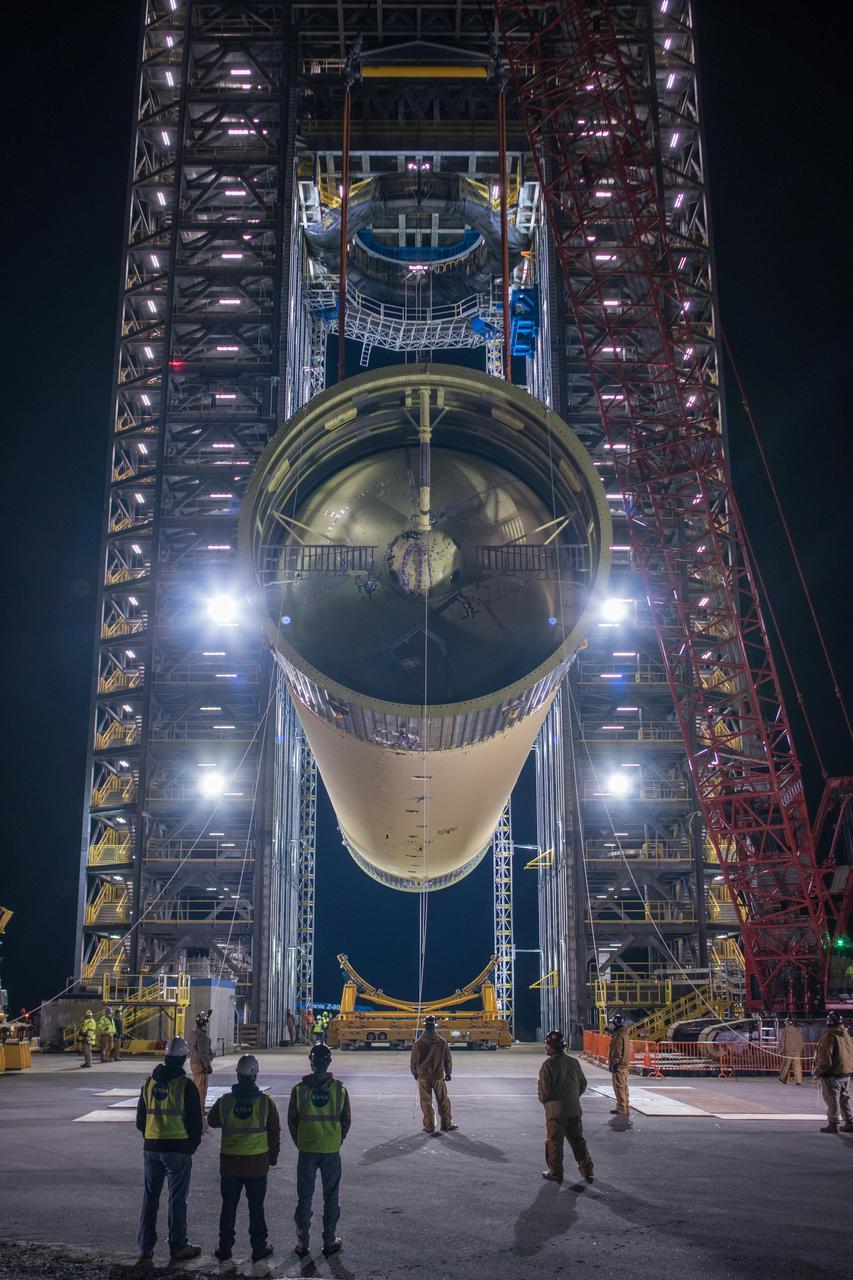

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.

The Space Launch System (SLS) liquid hydrogen tank structural test article is loaded into Test Stand 4693 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, on Jan. 14, 2019. The 149-foot piece of test hardware is the largest piece of structural hardware for the SLS core stage for America’s new deep space rocket Itis structurally identical to the flight version of the tank. It will undergo a series of tests in Test Stand 4693 to simulate the stresses and loads of liftoff and flight. These tests will help ensure designs are adequate for successful SLS missions to the Moon and beyond.

More than 500 students with 75 teams from around the world participated in the 31st year of NASA’s Human Exploration Rover Challenge (HERC) on April 11 and April 12, 2025, near NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Participating teams represented 35 colleges and universities, 38 high schools, and two middle schools from 20 states, Puerto Rico, and 16 other nations. NASA expanded the 2025 challenge to include a remote-control division - named Remote-Operated Vehicular Research - and invited middle school students to participate. Teams were awarded points based on navigating a half-mile obstacle course, conducting mission-specific task challenges, and completing multiple safety and design reviews with NASA engineers.

More than 500 students with 75 teams from around the world participated in the 31st year of NASA’s Human Exploration Rover Challenge (HERC) on April 11 and April 12, 2025, near NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Participating teams represented 35 colleges and universities, 38 high schools, and two middle schools from 20 states, Puerto Rico, and 16 other nations. NASA expanded the 2025 challenge to include a remote-control division - named Remote-Operated Vehicular Research - and invited middle school students to participate. Teams were awarded points based on navigating a half-mile obstacle course, conducting mission-specific task challenges, and completing multiple safety and design reviews with NASA engineers.

More than 500 students with 75 teams from around the world participated in the 31st year of NASA’s Human Exploration Rover Challenge (HERC) on April 11 and April 12, 2025, near NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Participating teams represented 35 colleges and universities, 38 high schools, and two middle schools from 20 states, Puerto Rico, and 16 other nations. NASA expanded the 2025 challenge to include a remote-control division - named Remote-Operated Vehicular Research - and invited middle school students to participate. Teams were awarded points based on navigating a half-mile obstacle course, conducting mission-specific task challenges, and completing multiple safety and design reviews with NASA engineers.

More than 500 students with 75 teams from around the world participated in the 31st year of NASA’s Human Exploration Rover Challenge (HERC) on April 11 and April 12, 2025, near NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Participating teams represented 35 colleges and universities, 38 high schools, and two middle schools from 20 states, Puerto Rico, and 16 other nations. NASA expanded the 2025 challenge to include a remote-control division - named Remote-Operated Vehicular Research - and invited middle school students to participate. Teams were awarded points based on navigating a half-mile obstacle course, conducting mission-specific task challenges, and completing multiple safety and design reviews with NASA engineers.

More than 500 students with 75 teams from around the world participated in the 31st year of NASA’s Human Exploration Rover Challenge (HERC) on April 11 and April 12, 2025, near NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Participating teams represented 35 colleges and universities, 38 high schools, and two middle schools from 20 states, Puerto Rico, and 16 other nations. NASA expanded the 2025 challenge to include a remote-control division - named Remote-Operated Vehicular Research - and invited middle school students to participate. Teams were awarded points based on navigating a half-mile obstacle course, conducting mission-specific task challenges, and completing multiple safety and design reviews with NASA engineers.