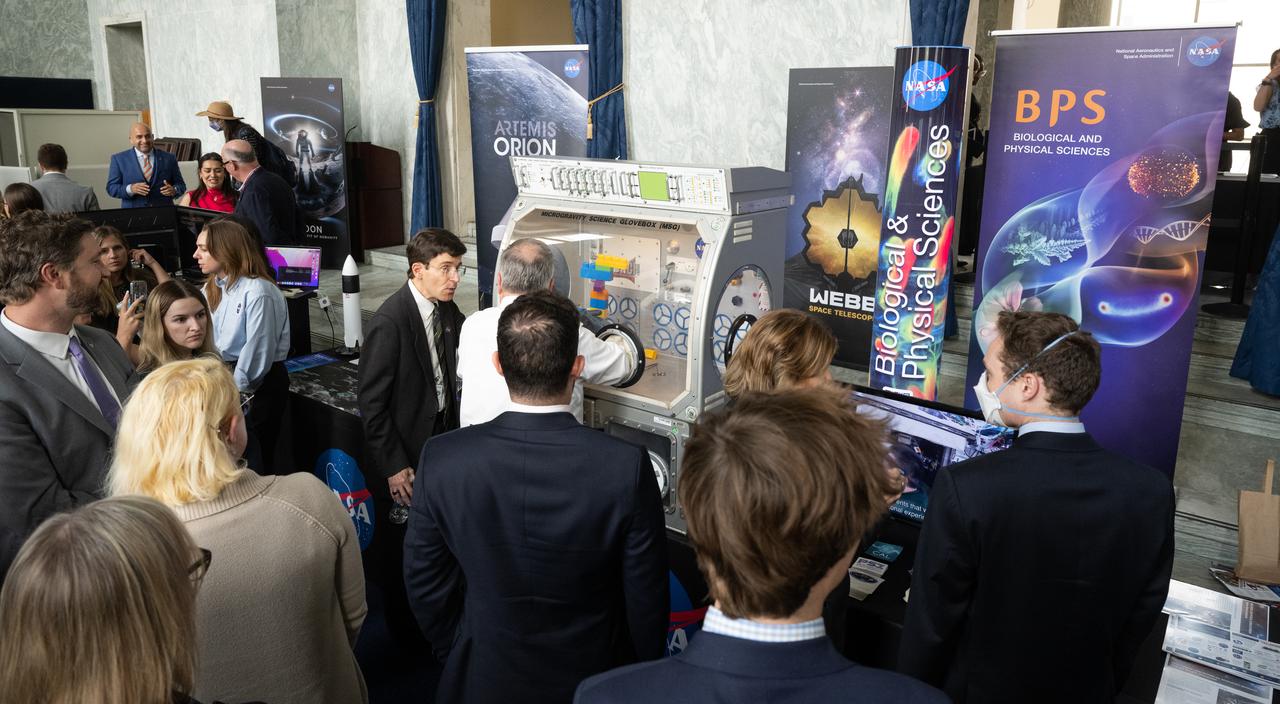

Attendees view exhibits during NASA’s Science Day on the Hill event, Wednesday, June 7, 2023, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
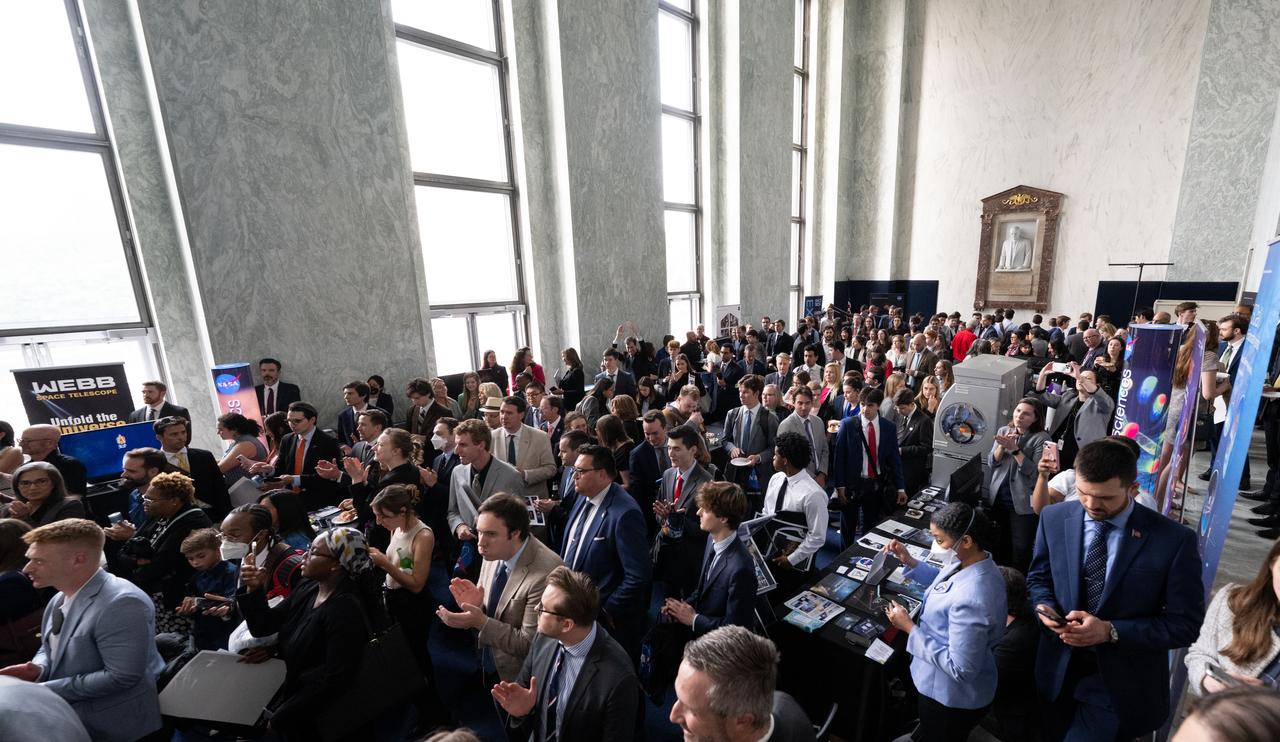

Attendees view exhibits and listen to speakers during NASA’s Science Day on the Hill event, Wednesday, June 7, 2023, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
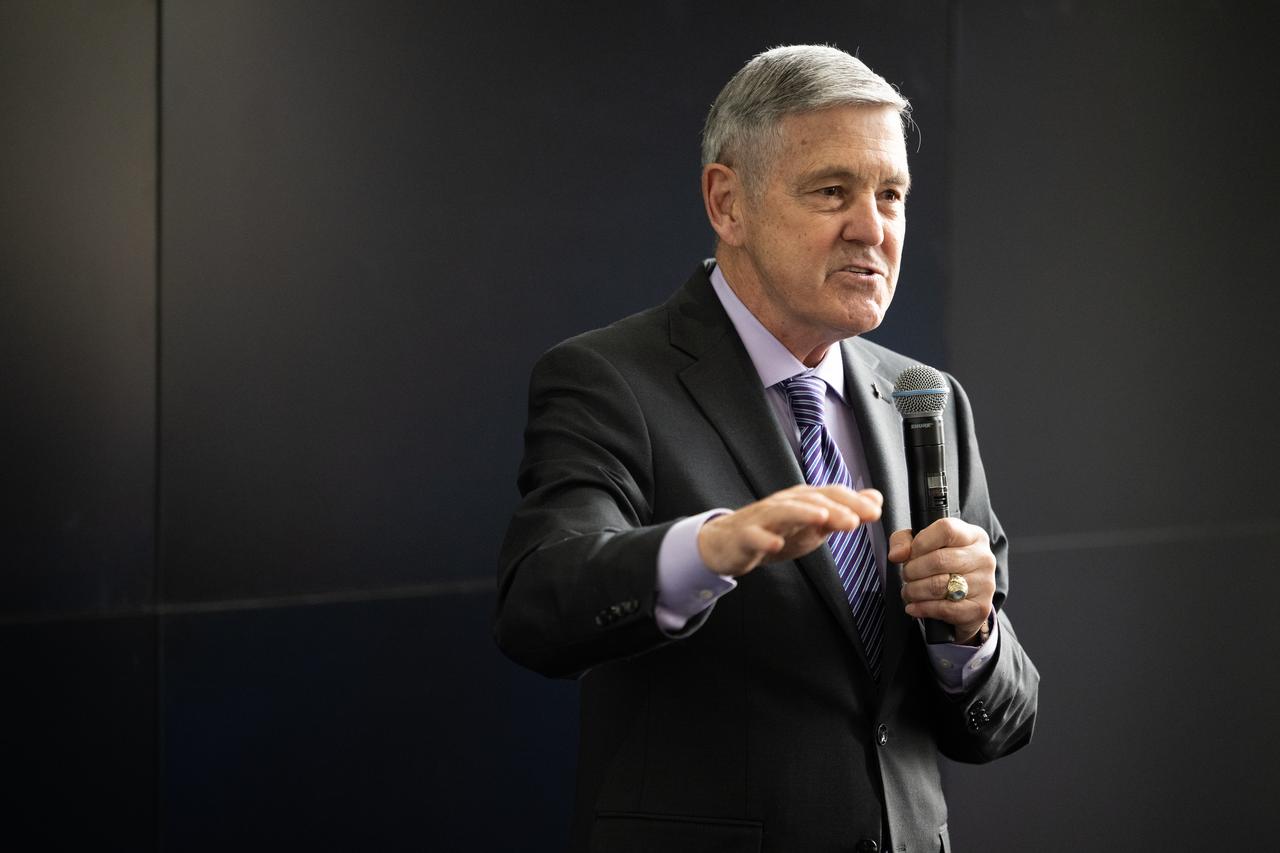

NASA Associate administrator Bob Cabana speaks during NASA’s Science Day on the Hill event, Wednesday, June 7, 2023, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
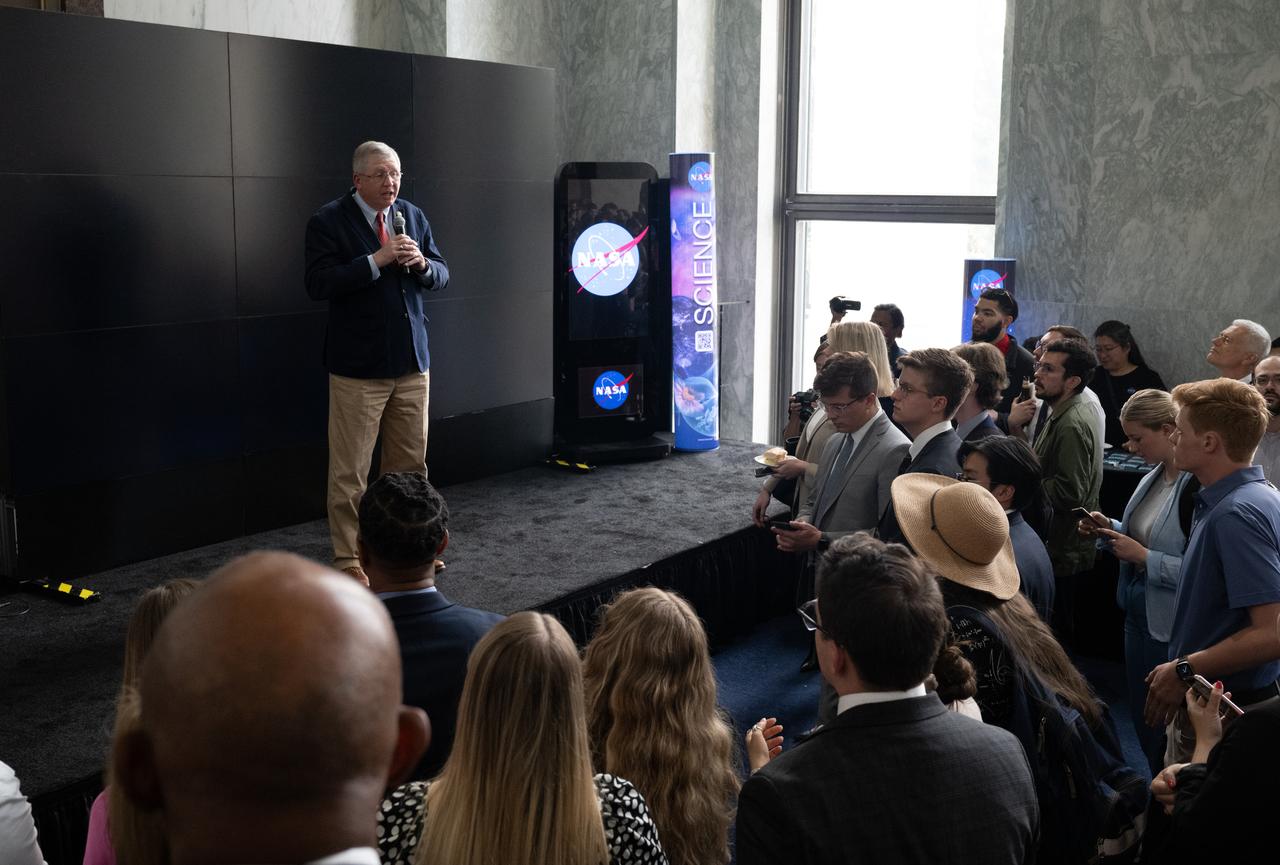

Rep. Frank Lucas, R-Okla., speaks during NASA’s Science Day on the Hill event, Wednesday, June 7, 2023, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
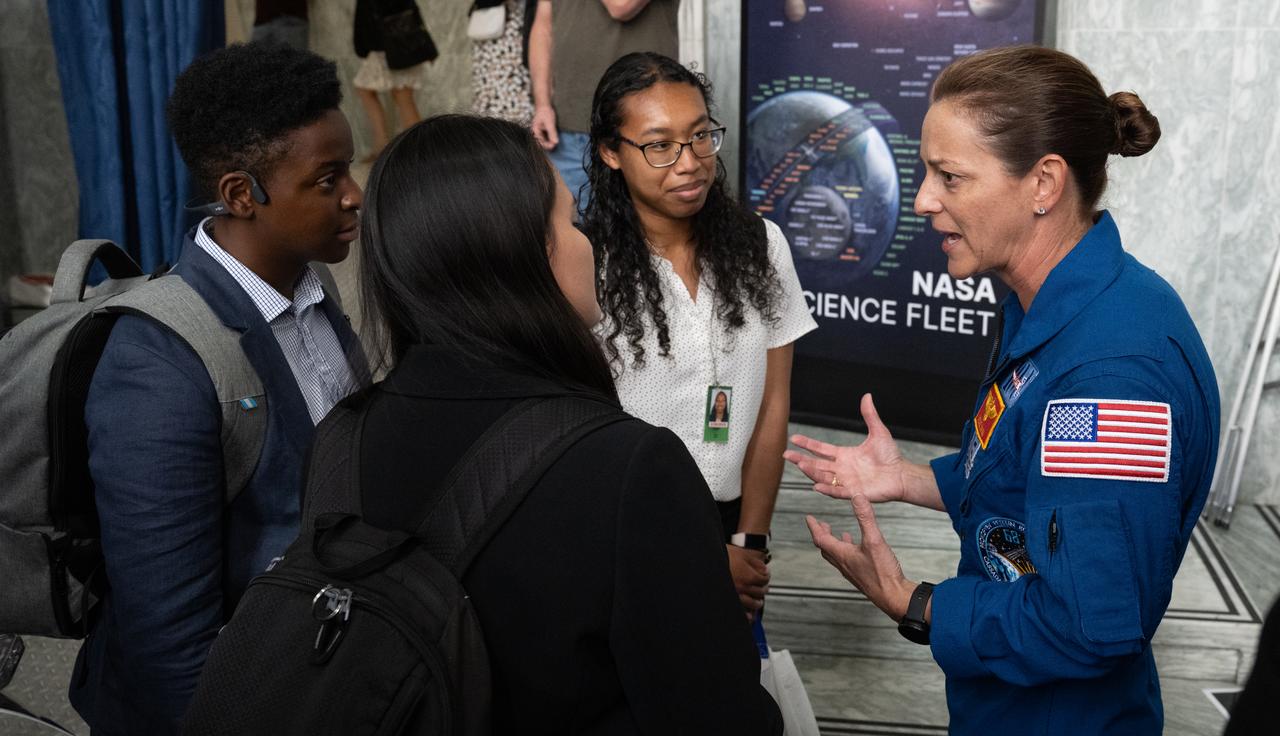

NASA’s SpaceX Crew-5 astronaut Nicole Mann of NASA speaks to attendees of NASA’s Science Day on the Hill event, Wednesday, June 7, 2023, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Mann and fellow crewmates Josh Cassada of NASA and Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) spent 157 days in space as part of Expedition 68 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
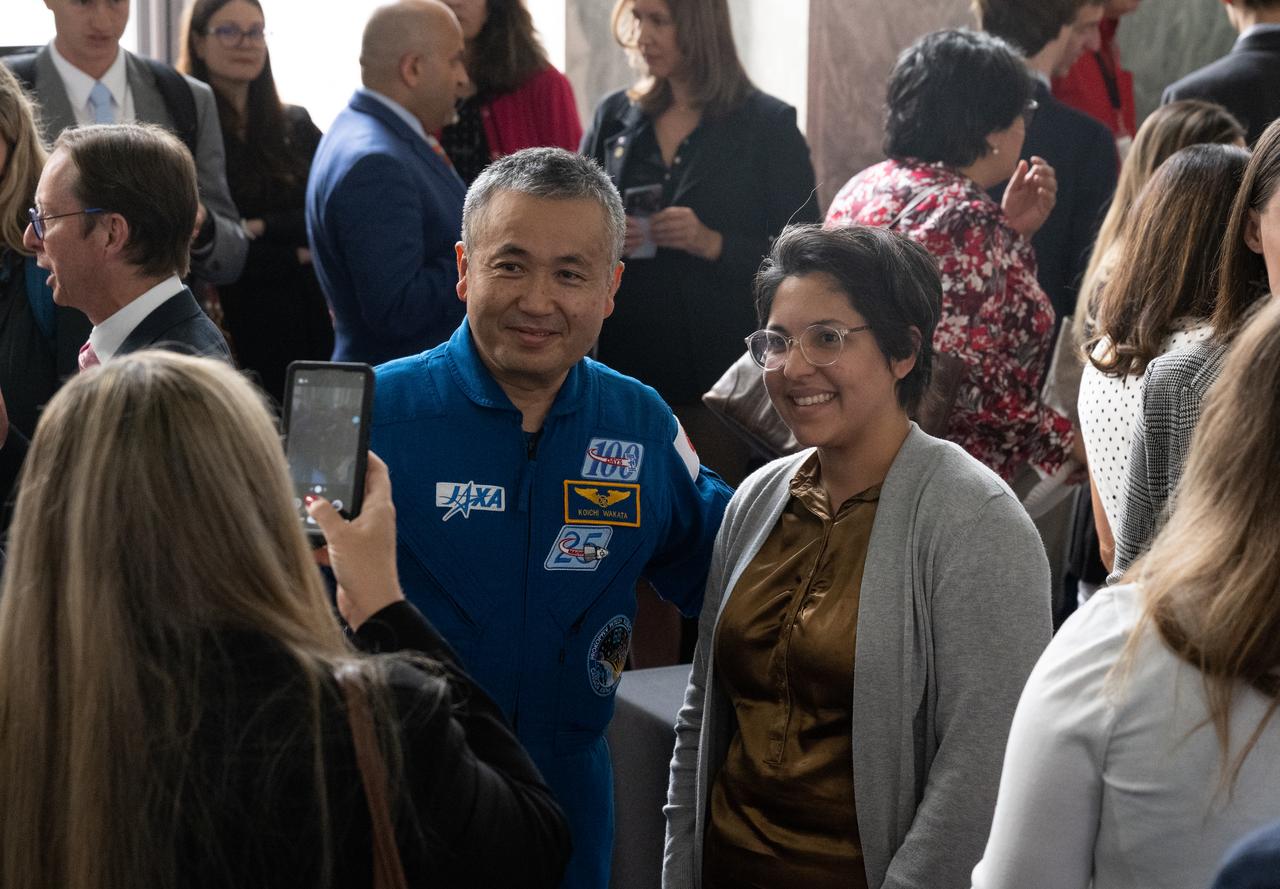

NASA’s SpaceX Crew-5 astronaut Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) takes a picture with an attendee during NASA’s Science Day on the Hill event, Wednesday, June 7, 2023, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
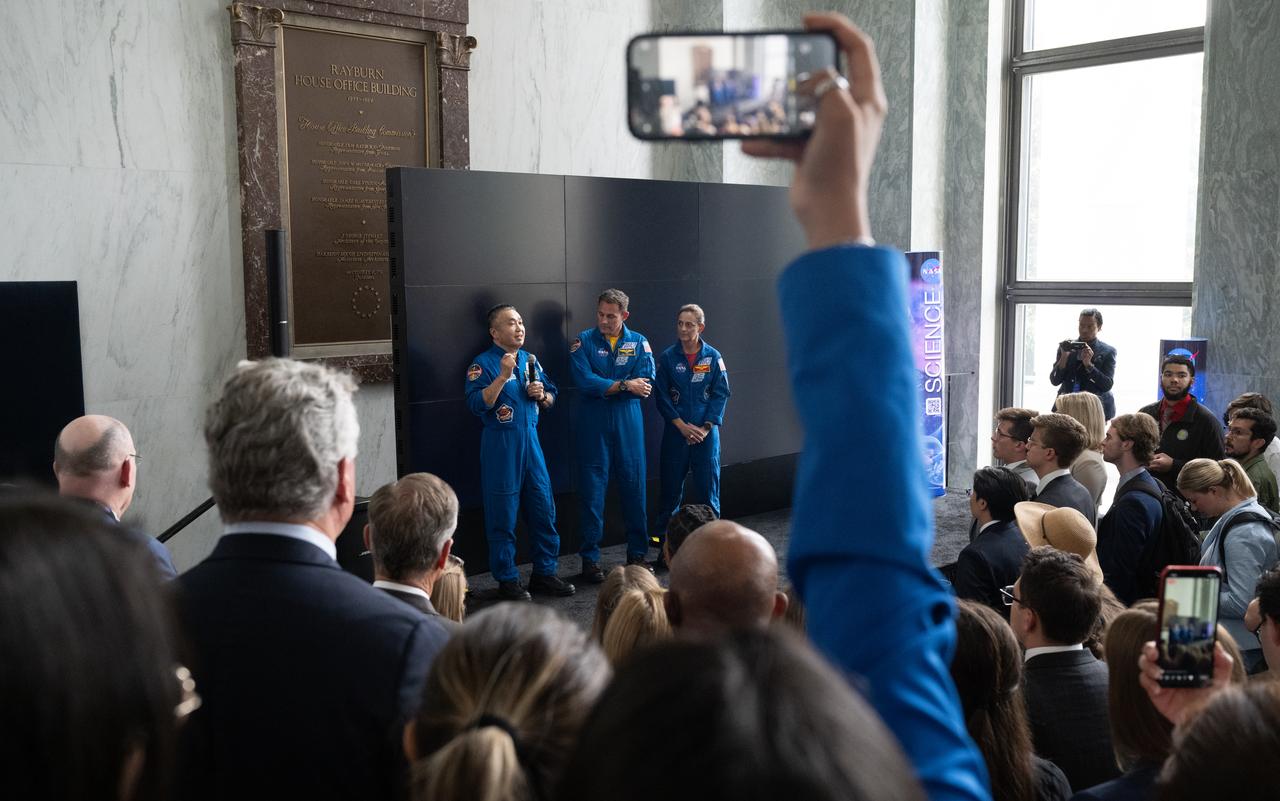

NASA’s SpaceX Crew-5 astronauts Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), left, and Josh Cassada and Nicole Mann of NASA, speak during NASA’s Science Day on the Hill event, Wednesday, June 7, 2023, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Mann, Cassada, and Wakata spent 157 days in space as part of Expedition 68 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
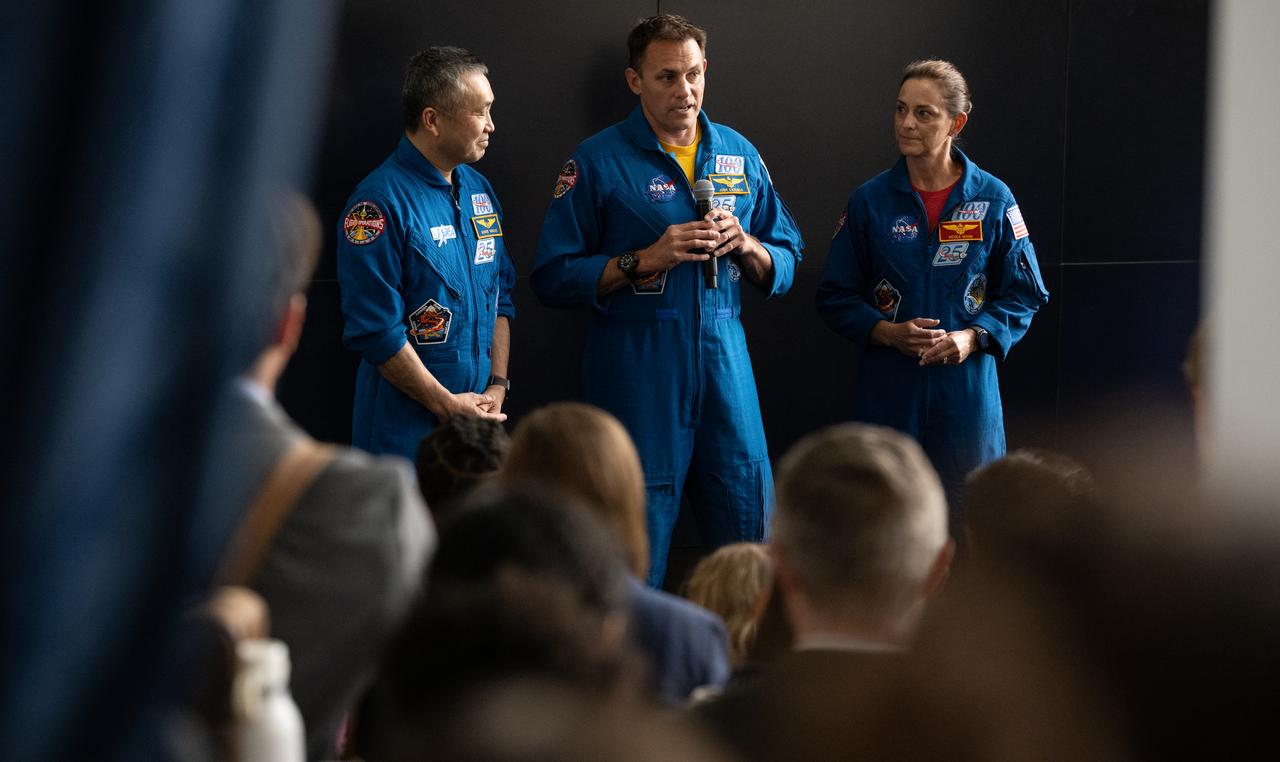

NASA’s SpaceX Crew-5 astronauts Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), left, and Josh Cassada and Nicole Mann of NASA, speak during NASA’s Science Day on the Hill event, Wednesday, June 7, 2023, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Mann, Cassada, and Wakata spent 157 days in space as part of Expedition 68 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA’s SpaceX Crew-5 astronauts Koichi Wakata of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), left, and Josh Cassada and Nicole Mann of NASA, speak during NASA’s Science Day on the Hill event, Wednesday, June 7, 2023, at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Mann, Cassada, and Wakata spent 157 days in space as part of Expedition 68 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
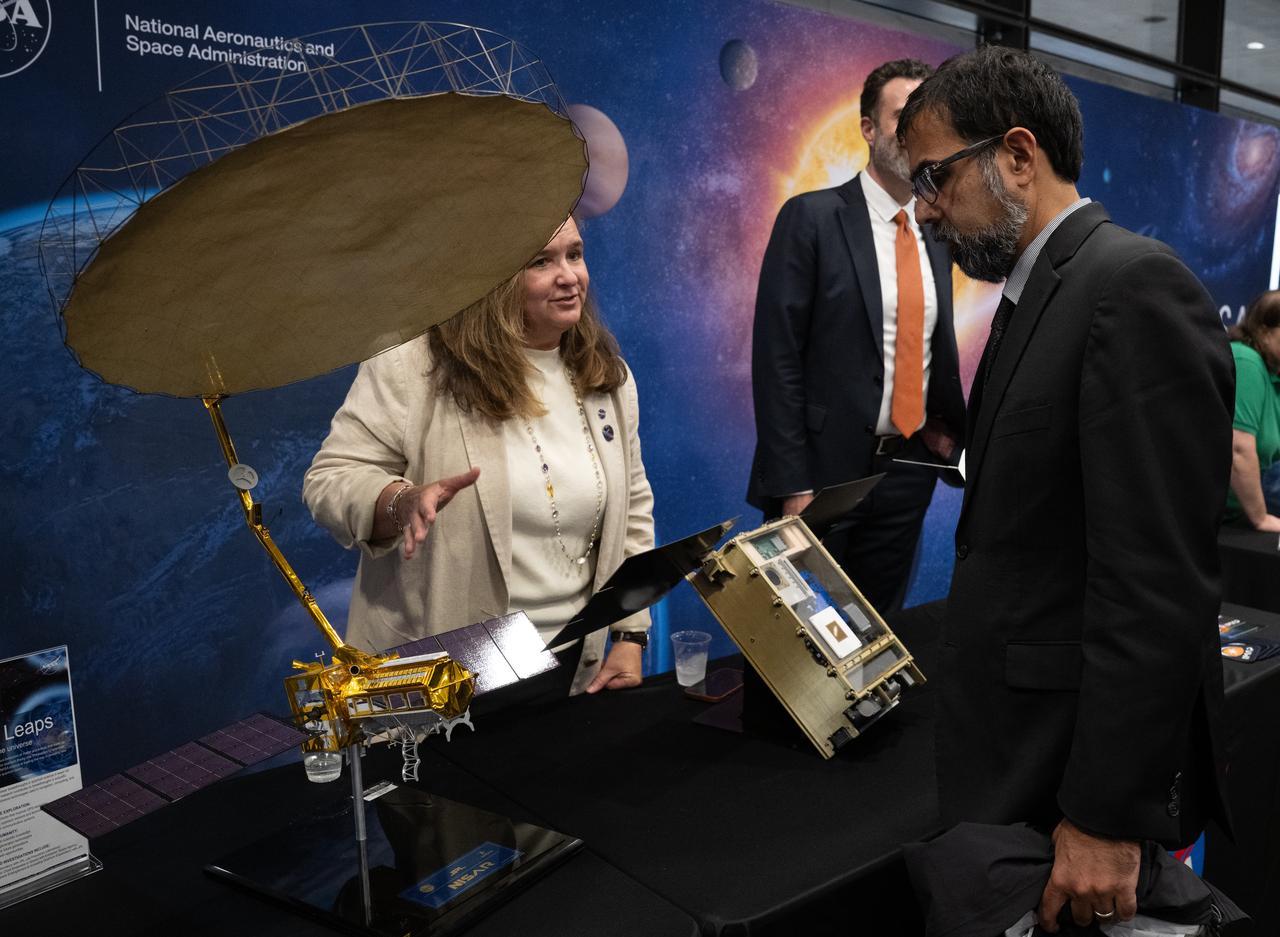

Karen St. Germain, director of the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, left, speaks with NASA Associate Administrator Amit Kshatriya during NASA’s Day on the Hill, Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, at the Hart Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
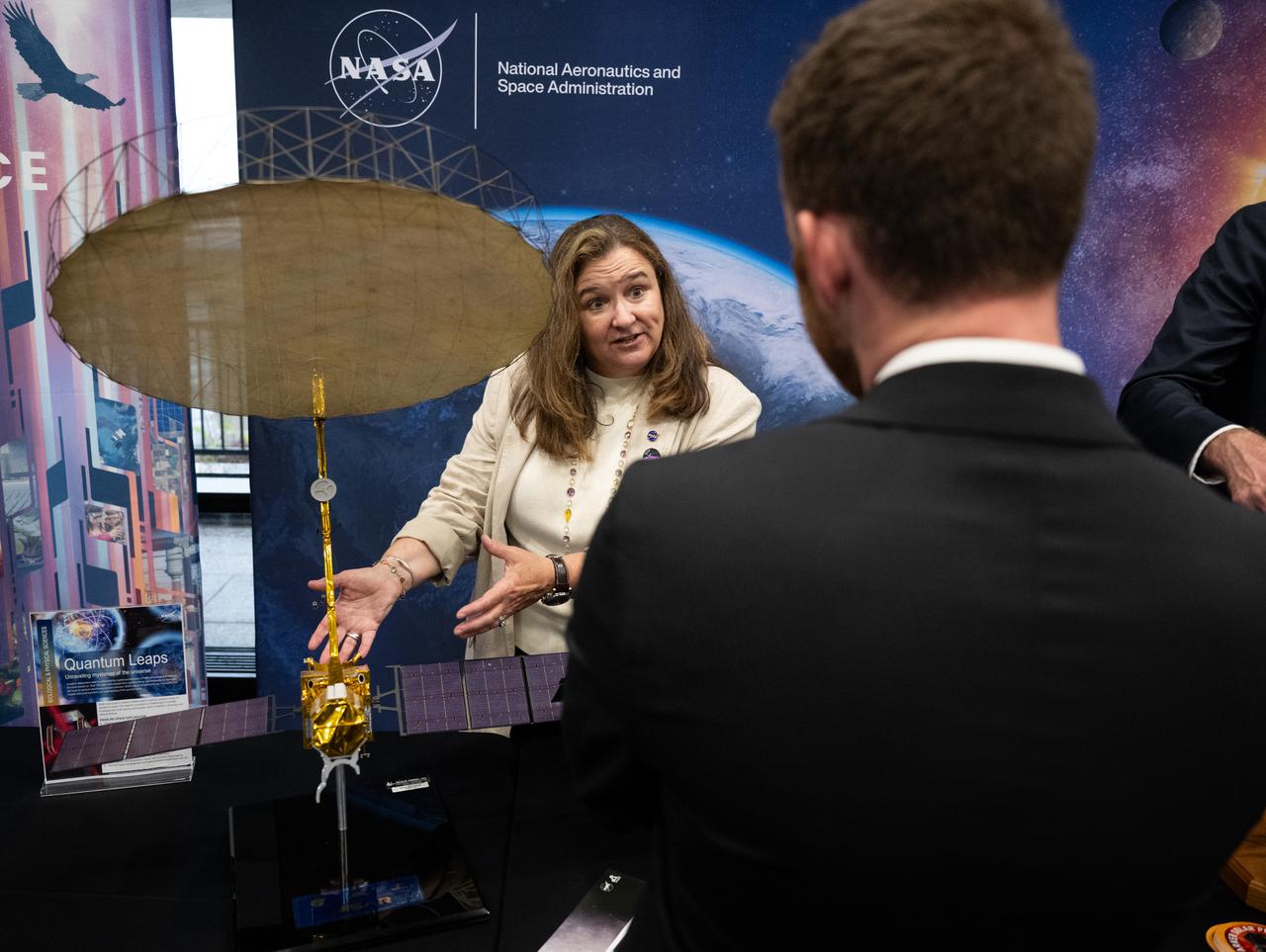

Karen St. Germain, director of the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate speaks with an attendee as he views exhibits during NASA’s Day on the Hill, Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, at the Hart Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
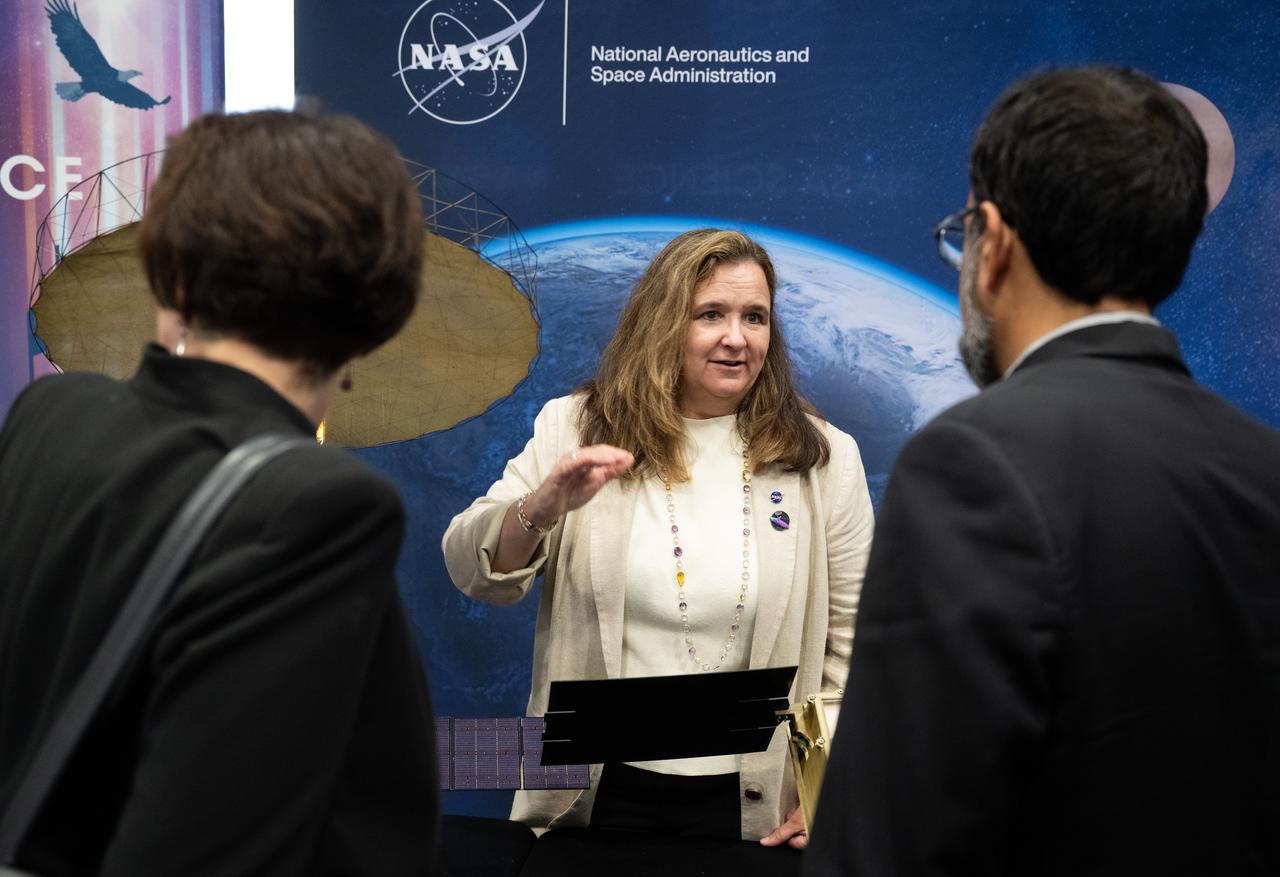

Karen St. Germain, director of the Earth Science Division of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, center, speaks with Nicola Fox, associate administrator of NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, left, and NASA Associate Administrator Amit Kshatriya during NASA’s Day on the Hill, Tuesday, Sept. 16, 2025, at the Hart Senate Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
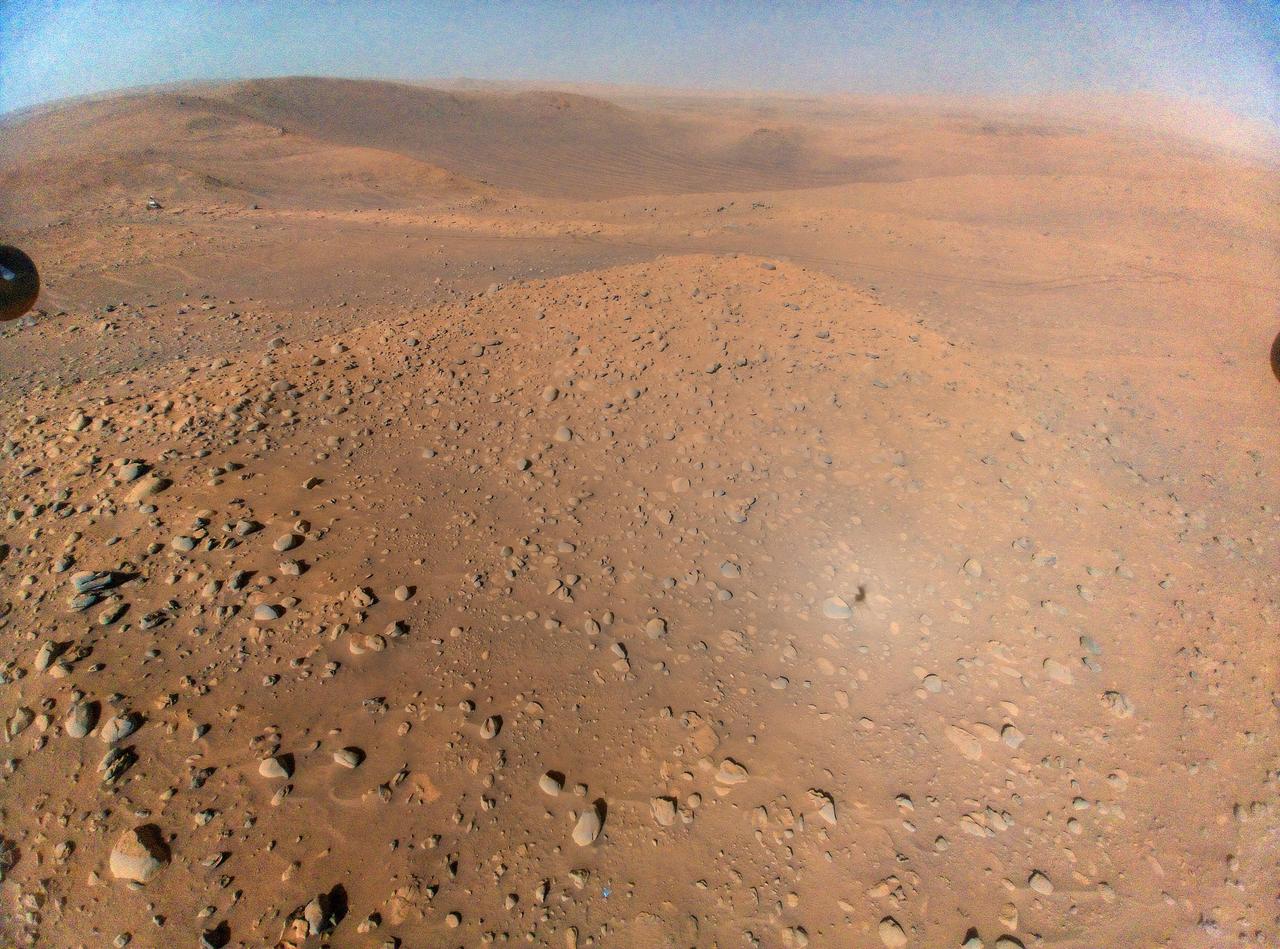

This image of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover at the rim of Belva Crater was taken by the agency's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter during the rotorcraft's 51st flight on April 22, 2023, the 772nd Martian day, or sol, of the rover's mission. At the time the image was taken, the helicopter was at an altitude of about 40 feet (12 meters). The rover is in the upper left of the image, parked at a light-toned rocky outcrop the science team is calling "Echo Creek." Perseverance's tracks can be seen extending from its location to the upper-right side of image. The helicopter's shadow can be seen on the rocky hill in the foreground, just to the right and below the image's center. The hill, designated "Mount Julian" by the science team, is a planned future stop for the rover. A small triangular piece of debris from the rover's entry, descent, and landing system can be seen at the lower center of image. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25884
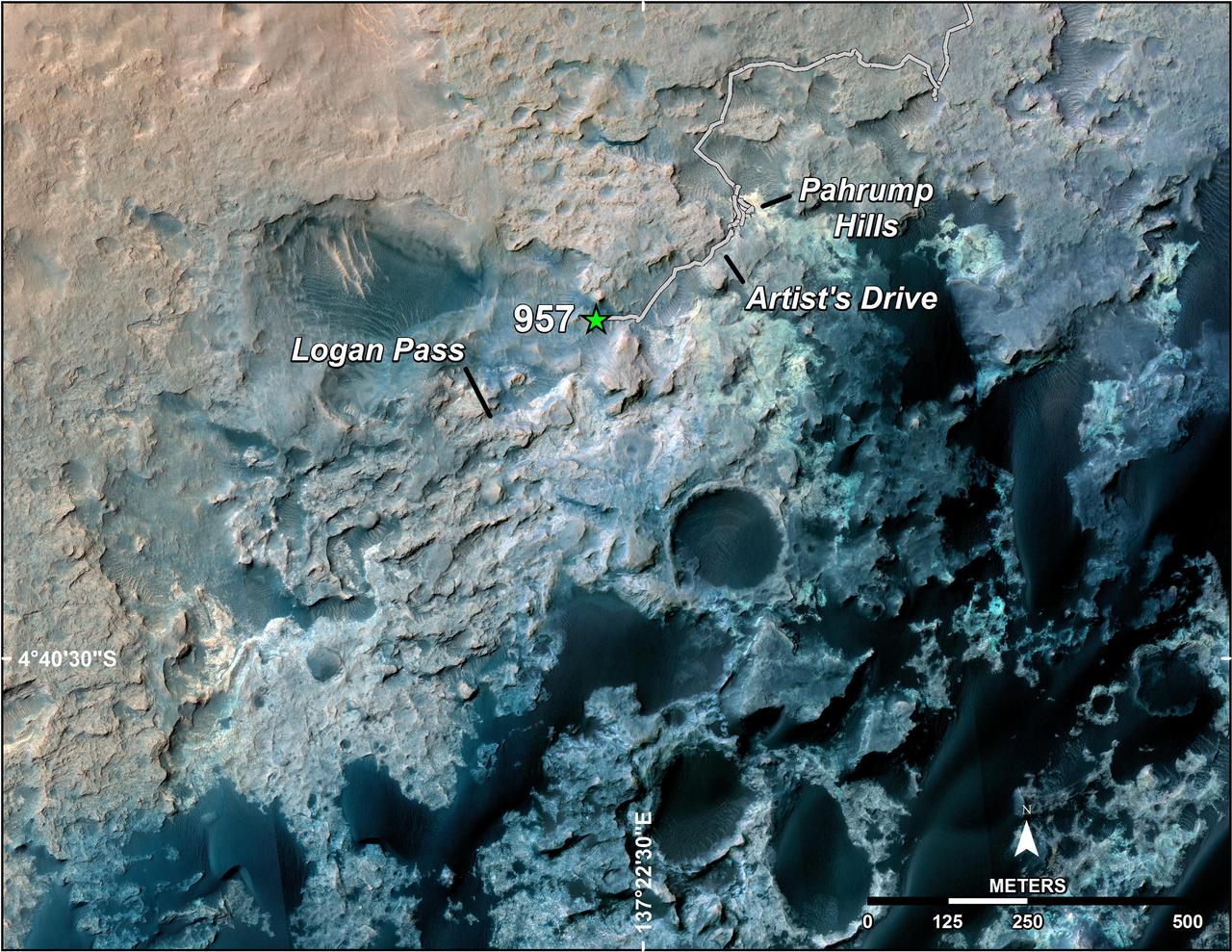
A green star marks the location of NASA's Curiosity Mars rover after a drive on the mission's 957th Martian day, or sol, (April 16, 2015). The map covers an area about 1.25 miles (2 kilometers) wide. Curiosity landed on Mars in August 2012. The drive on Sol 957 brought the mission's total driving distance past the 10-kilometer mark (6.214 miles). The rover is passing through a series of shallow valleys on a path from the "Pahrump Hills" outcrop, which it investigated for six months, toward its next science destination, called "Logan Pass." The rover's traverse line enters this map at the location Curiosity reached in mid-July 2014. The base map uses imagery from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19390

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its dual-camera Mastcam-Z imager to capture this image of "Santa Cruz," a hill about 1.5 miles (2.5 kilometers) away from the rover, on April 29, 2021, the 68th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The entire scene is inside of Mars' Jezero Crater; the crater's rim can be seen on the horizon line beyond the hill. This scene is not white balanced; instead, it is displayed in a preliminary calibrated version of a natural-color composite, approximately simulating the colors of the scene as it would appear to a person on Mars. Arizona State University in Tempe leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24546
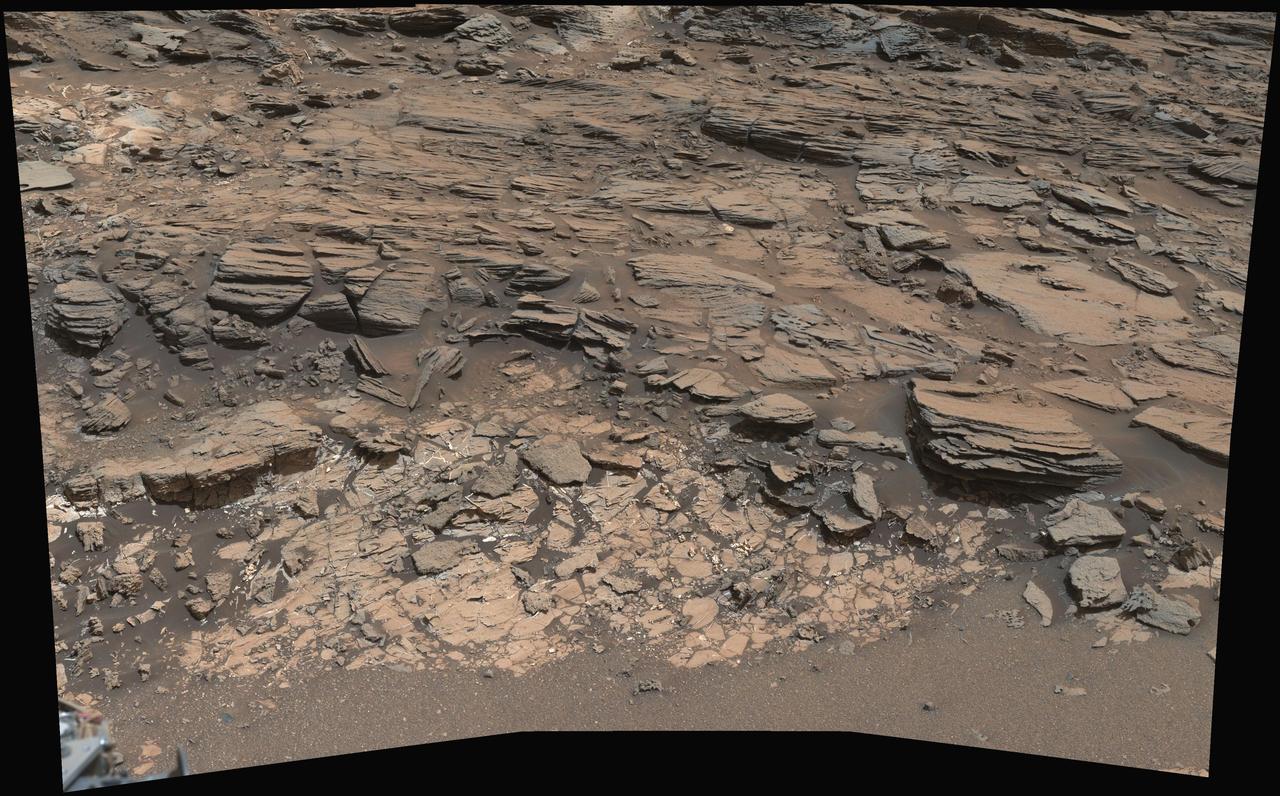

This view from the Mast Camera (Mastcam) on NASA's Curiosity Mars rover shows a site where two different types of bedrock meet on lower Mount Sharp. The scene combines multiple images taken by the left-eye camera of Mastcam on May 25, 2015, during the 995th Martian day, or sol, of Curiosity's work on Mars, in a valley just below "Marias Pass." The color has been approximately white-balanced to resemble how the scene would appear under daytime lighting conditions on Earth. The paler part of the outcrop, in the foreground, is mudstone similar to what Curiosity examined in 2014, and in early 2015, at "Pahrump Hills." The darker, finely bedded bedrock higher in the image and overlying the mudstone stratigraphically is sandstone that the rover team calls the "Stimson" unit. The scene covers an area about 10 feet (3 meters) wide in the foreground. Malin Space Science Systems, San Diego, built and operates the rover's Mastcam. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, manages the Mars Science Laboratory Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19676

This natural-color mosaic showing NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter at "Valinor Hills" was acquired by the agency's Perseverance Mars rover on Feb. 21, 2024, the 1,068th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The helicopter – the first aircraft to achieve powered, controlled flight on another world – sits just left of center, a speck-like figure amid a field of sand ripples. Ingenuity damaged its rotor blades during landing on its 72nd and final flight on Jan. 18, 2024. The helicopter team nicknamed the spot where the last flight concluded Valinor Hills after the fictional location in J.R.R. Tolkien's fantasy novels, which include "The Lord of the Rings" trilogy. The 67 images that were stitched together to make this mosaic were captured from about 1,365 feet (415 meters) away by the rover's Mastcam-Z camera. This is a wider and more detailed view of Valinor Hills than was shown in a previously released six-image Mastcam-Z mosaic that was taken from farther away. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26237
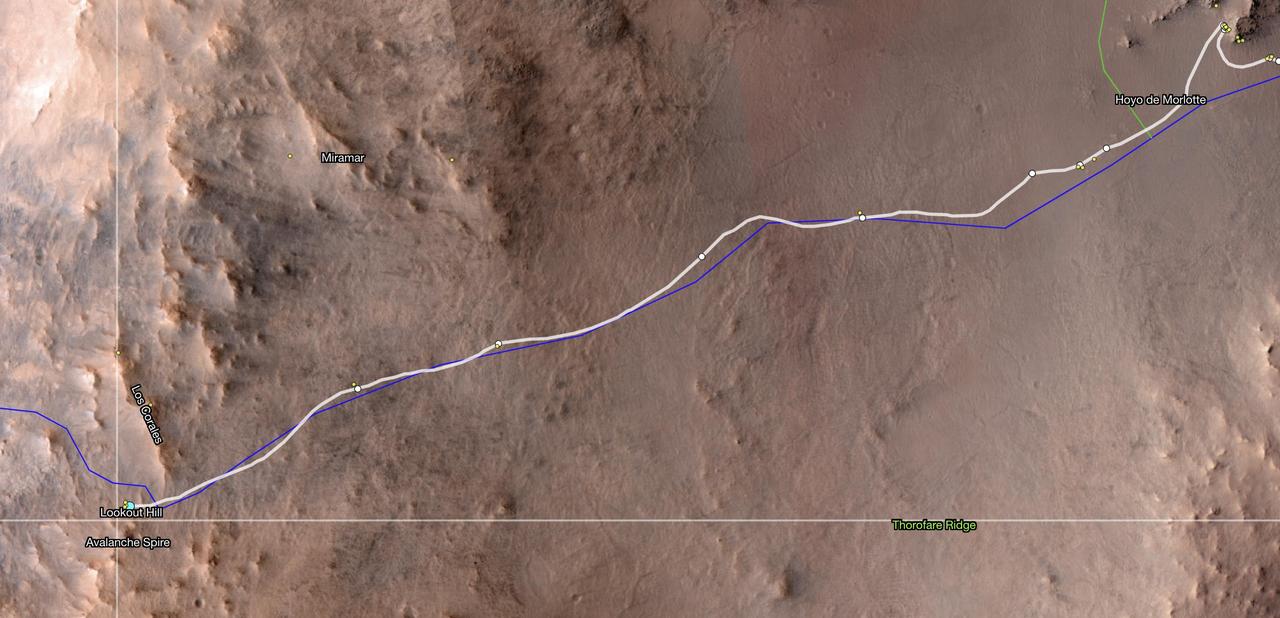

This map shows the location of NASA's Perseverance Mars rover as of Dec. 10, 2024, the 1,354th Martian day, or sol, of the mission, which it reached "Lookout Hill" at the top of Jezero Crater's rim after a monthslong climb. This map was made using data from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter's High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera as well as the European Space Agency's (ESA) High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC). The University of Arizona, in Tucson, operates HiRISE, which was built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., in Boulder, Colorado, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory manages the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter Project for NASA's Science Mission Directorate, Washington. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26512
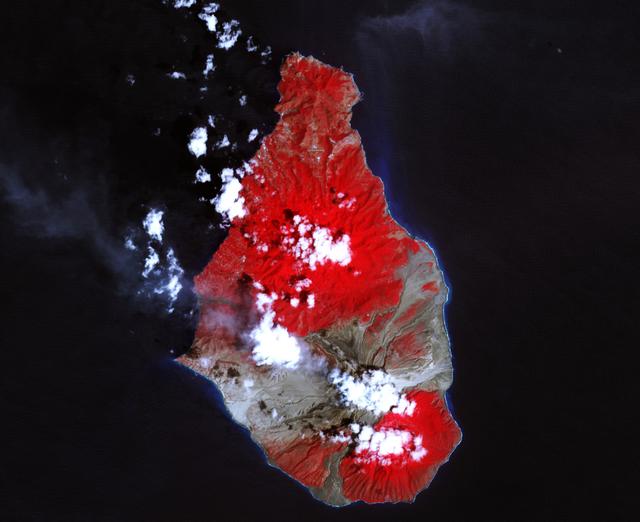

A massive eruption of Montserrat’s Soufrière Hills Volcano covered large portions of the island in debris. The eruption was triggered by a collapse of Soufrière Hills’ summit lava dome on February 11, 2010. Pyroclastic flows raced down the northern flank of the volcano, leveling trees and destroying buildings in the village of Harris, which was abandoned after Soufrière Hills became active in 1995. The Montserrat Volcano Observatory reported that some flows, about 15 meters (49 feet) thick, reached the sea at Trant’s Bay. These flows extended the island’s coastline up to 650 meters (2,100 feet). These false-color satellite images show the southern half of Montserrat before and after the dome collapse. The top image shows Montserrat on February 21, 2010, just 10 days after the event. For comparison, the bottom image shows the same area on March 17, 2007. Red areas are vegetated, clouds are white, blue/black areas are ocean water, and gray areas are covered by flow deposits. Fresh deposits tend to be lighter than older deposits. On February 21, the drainages leading down from Soufrière Hills, including the White River Valley, the Tar River Valley, and the Belham River Valley, were filled with fresh debris. According to the Montserrat Volcano Observatory, pyroclastic flows reached the sea through Aymers Ghaut on January 18, 2010, and flows entered the sea near Plymouth on February 5, 2010. NASA Earth Observatory image by Robert Simmon, using data from the NASA/GSFC/METI/ERSDAC/JAROS, and U.S./Japan ASTER Science Team. Caption by Robert Simmon. To read more go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=42792" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/IOTD/view.php?id=42792</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a><b> </b></b>

Composed of 993 individual images and 2.38 billion pixels, this 360-degree mosaic taken by NASA's Perseverance looks in all directions from a location the rover science team calls "Airey Hill." The rover remained parked at Airey Hill during the entirety of solar conjunction. Captured by the rover's Mastcam-Z, the images used to create the mosaic were acquired on Nov. 3, Nov. 4, and Nov. 6, 2023, the 962nd, 963rd, and 965th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's mission. The main image is a natural color version at half-resolution. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26080

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z instrument to capture this view looking south toward the rim of Jezero Crater. The panorama, which encompasses 80 degrees, is made up of 59 individual images. They were captured on Aug. 4, 2024, the 1,229th Martian day, or sol, of the mission, and stitched together after being sent back to Earth. The color has been enhanced to bring out subtle details. "Dox Castle," a region the Perseverance science team wants to visit during the rover's climb up the crater rim, is about a half-mile (740 meters) away, on the left side of the hill at right. After the exploration of Dox Castle is complete, the rover will continue its climb up the crater rim, taking a route somewhere in between the two hills. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26373
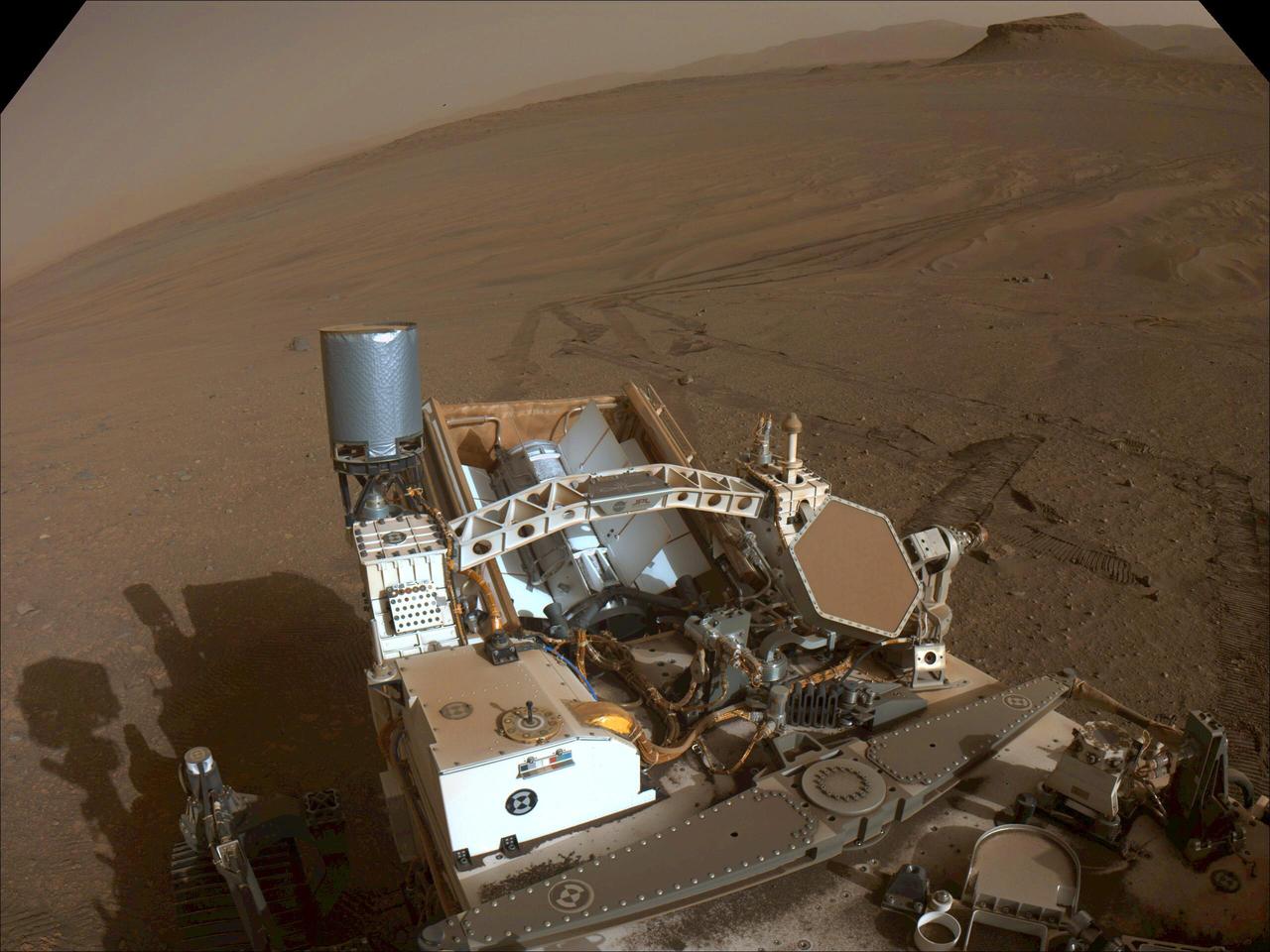

This image of the floor of Jezero Crater was taken by one of the Navcam imagers aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover on Feb. 5, 2023, the 698th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The rover's tracks can be seen disappearing into the distance. The flat-topped hill that the science team refers to as "Kodiak," a remnant of Jezero Crater's river delta, is in the upper right of image, about 0.6 miles (1 kilometer) away. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25684
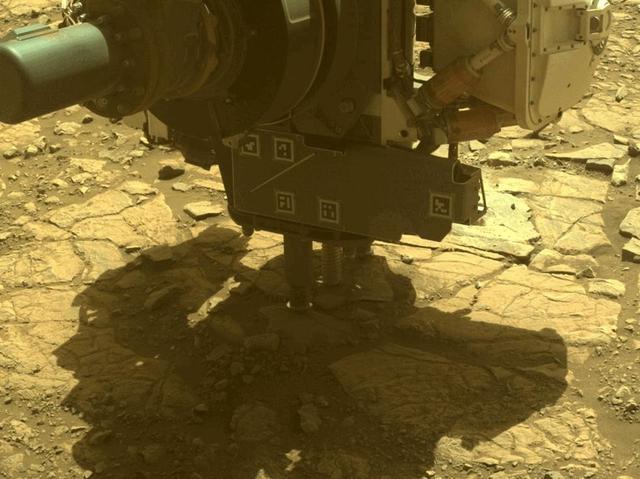

The robotic arm on NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its percussive drill to core and collect the "Main River" rock sample on March 10, 2025, the 1,441st Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The time-lapse movie, taken by one of the rover's hazard cameras, is made up of 35 images taken over the course of 34 minutes. The sample was taken from a rock the rover science team named "Broom Point" at a location near the rim of Jezero Crater called "Witch Hazel Hill." A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Mars Exploration Program (MEP) portfolio and the agency's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26571

NASA's Perseverance Mars Rover used its Mastcam-Z camera system to capture this panorama of a location nicknamed "Pico Turquino Hills" on Oct. 22, 2024, the 1,306th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This area is located on the rim of Jezero Crater. Perseverance landed on the crater's floor on Feb. 18, 2021, and has been steadily working its way up and out of the crater since August 2024. The rocks in Pico Turquino Hills are among the oldest yet found by Perseverance, forming in a different geologic era than almost everything the rover has seen before. They're likely part of the original surface that existed before Jezero Crater's formation by a massive asteroid about 3.9 billion years ago. The rocks here are mostly made up of volcanic minerals like olivine, plagioclase, and pyroxene. In the far-right corner of the panorama is a field of white cobbles. This represents the first time Perseverance has encountered pure quartz rock, which may have been created by a hydrothermal system like hot springs – an environment life could have survived in, if any existed on the Red Planet billions of years ago. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26473
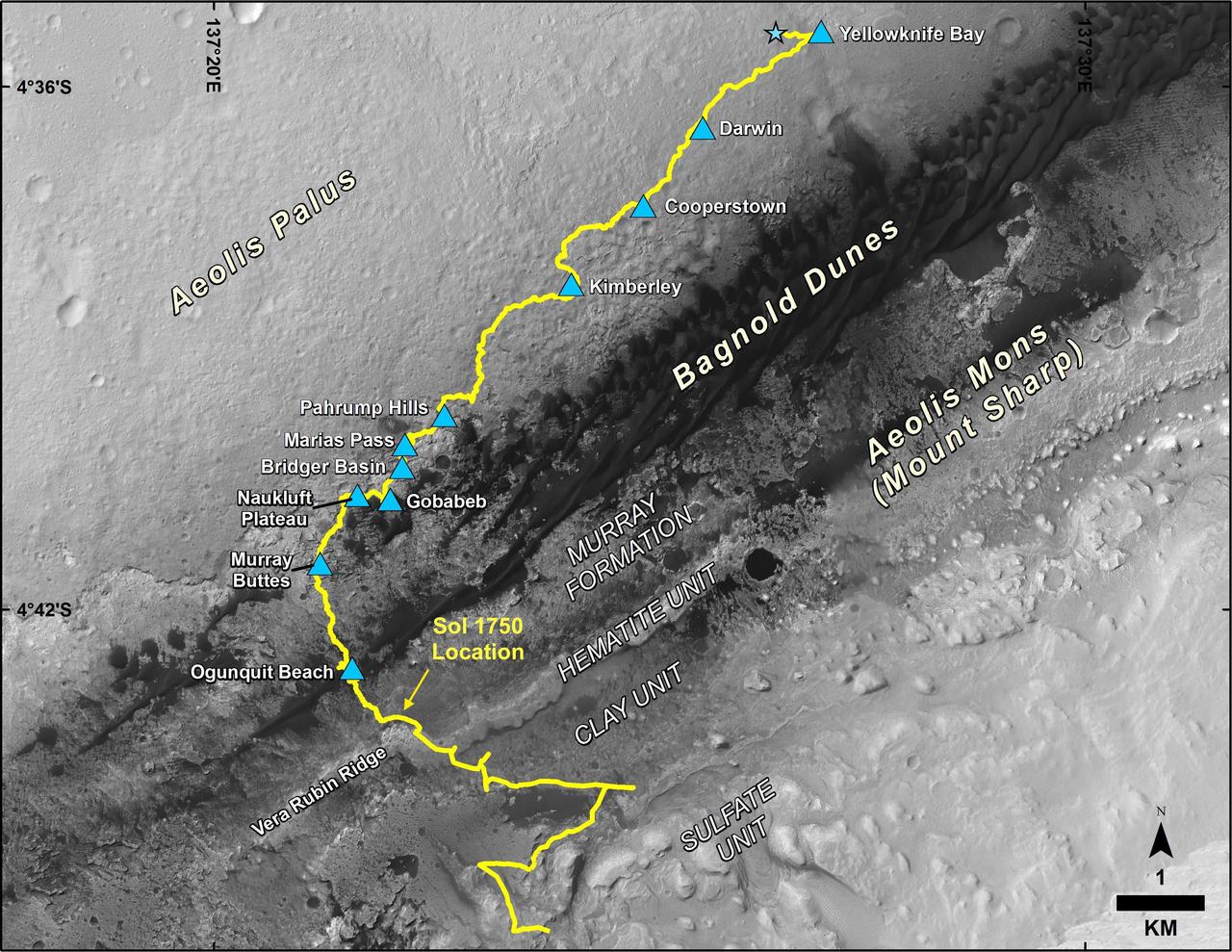
This map shows the route driven by NASA's Curiosity Mars rover, from the location where it landed in August 2012 to its location in July 2017, and its planned path to additional geological layers of lower Mount Sharp. The blue star near top center marks "Bradbury Landing," the site where Curiosity arrived on Mars on Aug. 5, 2012, PDT (Aug. 6, EDT and Universal Time). Blue triangles mark waypoints investigated by Curiosity on the floor of Gale Crater and, starting with "Pahrump Hills," on Mount Sharp. The Sol 1750 label identifies the rover's location on July 9, 2017, the 1,750th Martian day, or sol, since the landing. In July 2017, the mission is examining "Vera Rubin Ridge" from the downhill side of the ridge. Spectrometry observations from NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter have detected hematite, an iron-oxide mineral, in the ridge. Curiosity's planned route continues to the top of the ridge and then to geological units where clay minerals and sulfate minerals have been detected from orbit. The base image for the map is from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. North is up. "Bagnold Dunes" form a band of dark, wind-blown material at the foot of Mount Sharp. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21720
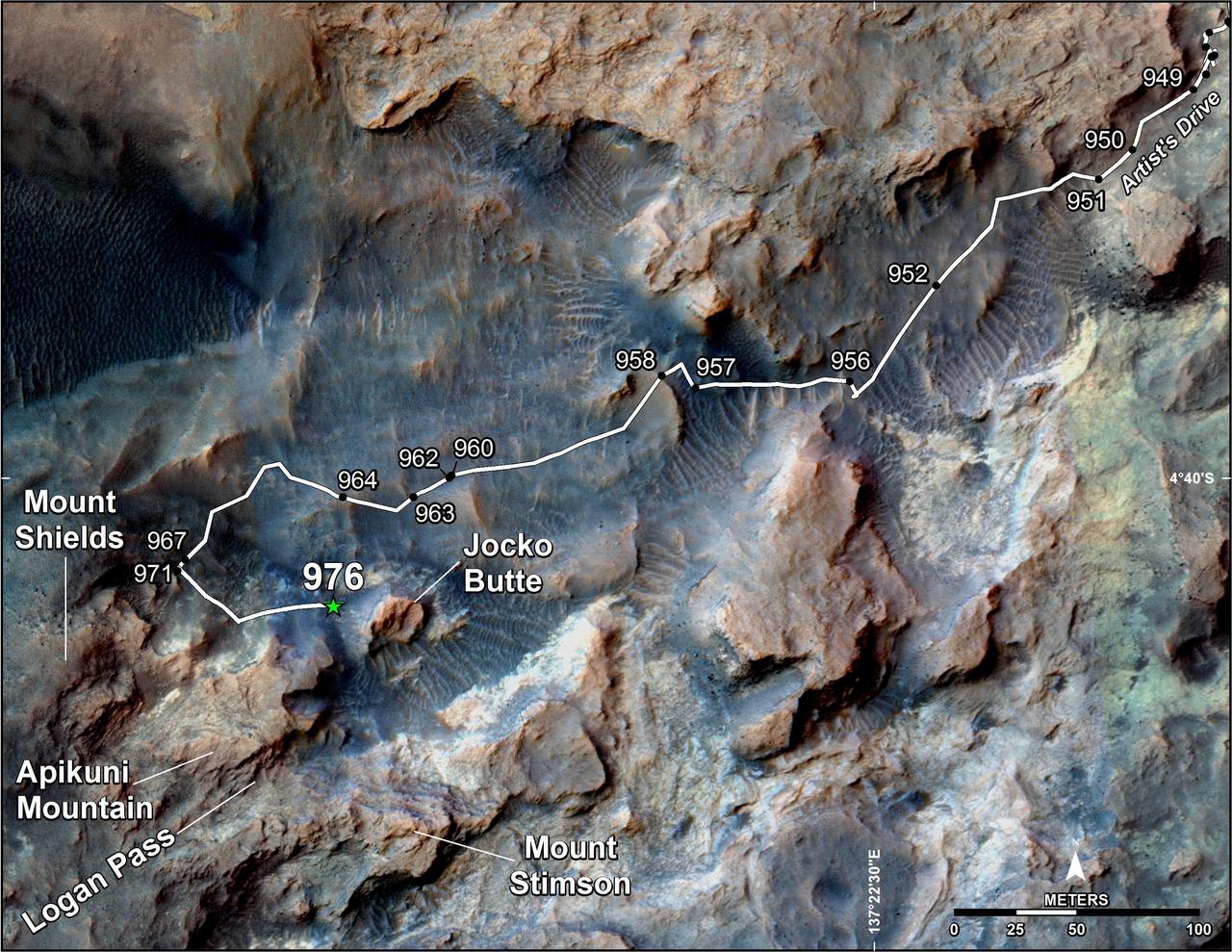
This map shows the route on lower Mount Sharp that NASA's Curiosity followed in April and early May 2015, in the context of the surrounding terrain. Numbers along the route identify the sol, or Martian day, on which it completed the drive reaching that point, as counted since its 2012 landing. The map covers an area about one-third of a mile (half a kilometer) across. North is up. The base image is from the High Resolution Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. Curiosity departed the "Pahrump Hills" outcrop -- mostly off the upper right corner of the map -- through "Artist's Drive" valley. The Sol 949 drive was completed on April 7, 2015. A HiRISE image actually showing Curiosity at that spot is at PIA19392. At that time, the rover's next planned science destination was "Logan Pass," an area where two geological units meet. At the Sol 951 location, Curiosity's Mast Camera (Mastcam) took component images for a sweeping panorama to the south and southwest, at PIA19397 and http://mars.nasa.gov/msl/multimedia/deepzoom/PIA19397. At the Sol 956 location, the Mastcam took component images for a westward panorama, at PIA19398 and http://mars.nasa.gov/msl/multimedia/deepzoom/PIA19398. From views such as these, Curiosity's science team selected an additional site for close inspection, at the base of a rise called "Mount Shields." The rover arrived there with the Sol 967 drive, completed on April 26, 2015. After the observations and measurements made by Curiosity's instruments at the base of Mount Shields, the rover resumed its approach to Logan Pass, on a route passing west of "Jocko Butte." The Sol 976 drive was completed on May 5, 2015. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19399
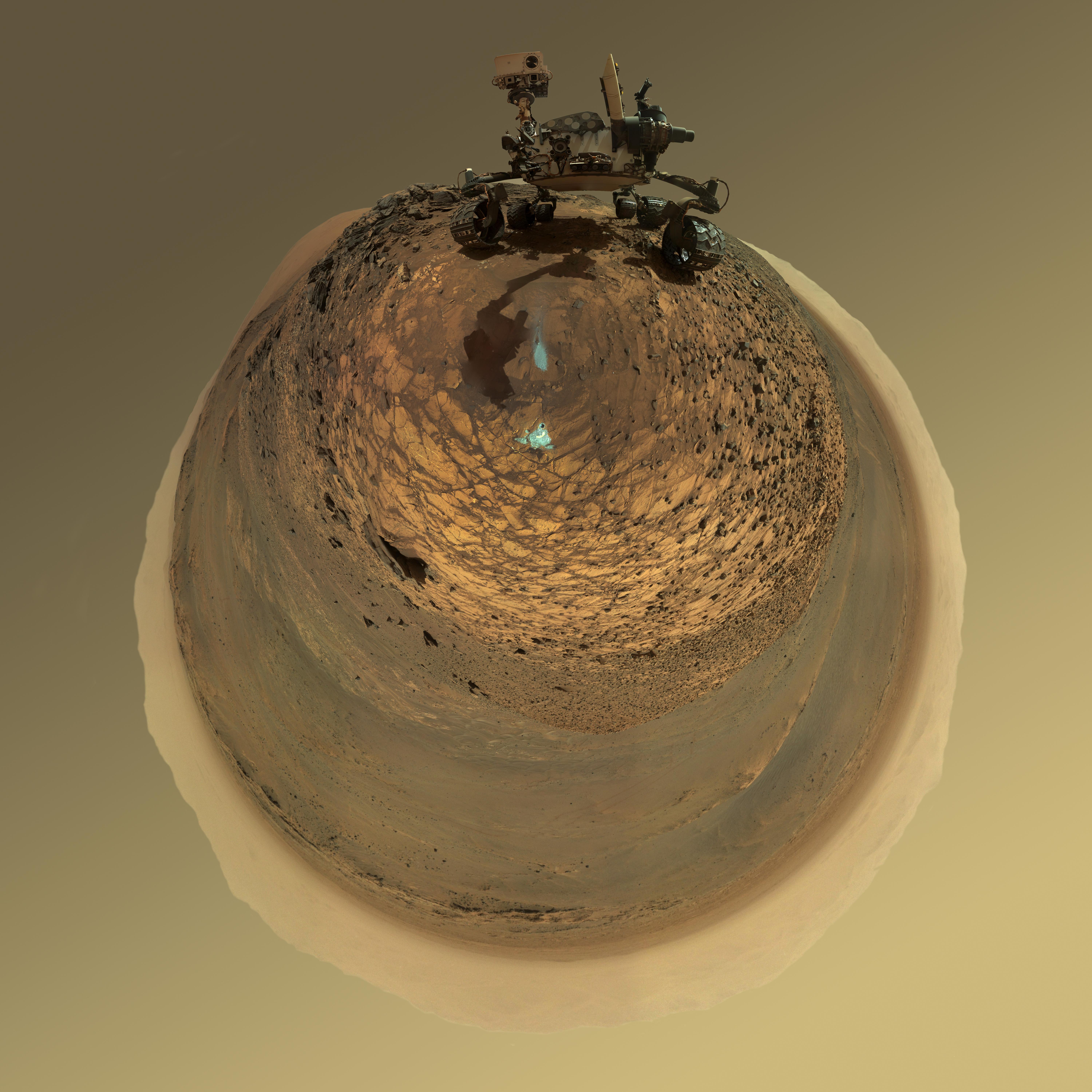
This version of a self-portrait of NASA's Curiosity Mars rover at a drilling site called "Buckskin" on lower Mount Sharp is presented as a stereographic projection, which shows the horizon as a circle. It is a mosaic assembled from the same set of 92 component raw images used for the flatter-horizon version at PIA19807. The component images were taken by Curiosity's Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) on Aug. 5, 2015, during the 1,065th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's work on Mars. Curiosity drilled the hole at Buckskin during Sol 1060 (July 30, 2015). Two patches of pale, powdered rock material pulled from inside Buckskin are visible in this scene, in front of the rover. The patch closer to the rover is where the sample-handling mechanism on Curiosity's robotic arm dumped collected material that did not pass through a sieve in the mechanism. Sieved sample material was delivered to laboratory instruments inside the rover. The patch farther in front of the rover, roughly triangular in shape, shows where fresh tailings spread downhill from the drilling process. The drilled hole, 0.63 inch (1.6 centimeters) in diameter, is at the upper point of the tailings. The rover is facing northeast, looking out over the plains from the crest of a 20-foot (6-meter) hill that it climbed to reach the "Marias Pass" area. The upper levels of Mount Sharp are visible behind the rover, while Gale Crater's northern rim dominates most of the rest of the horizon.the horizon on the left and right of the mosaic. MAHLI is mounted at the end of the rover's robotic arm. For this self-portrait, the rover team positioned the camera lower in relation to the rover body than for any previous full self-portrait of Curiosity. The assembled mosaic does not include the rover's arm beyond a portion of the upper arm held nearly vertical from the shoulder joint. Shadows from the rest of the arm and the turret of tools at the end of the arm are visible on the ground. With the wrist motions and turret rotations used in pointing the camera for the component images, the arm was positioned out of the shot in the frames or portions of frames used in this mosaic. MAHLI was built by Malin Space Science Systems, San Diego. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Science Laboratory Project for the NASA Science Mission Directorate, Washington. JPL designed and built the project's Curiosity rover. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19806
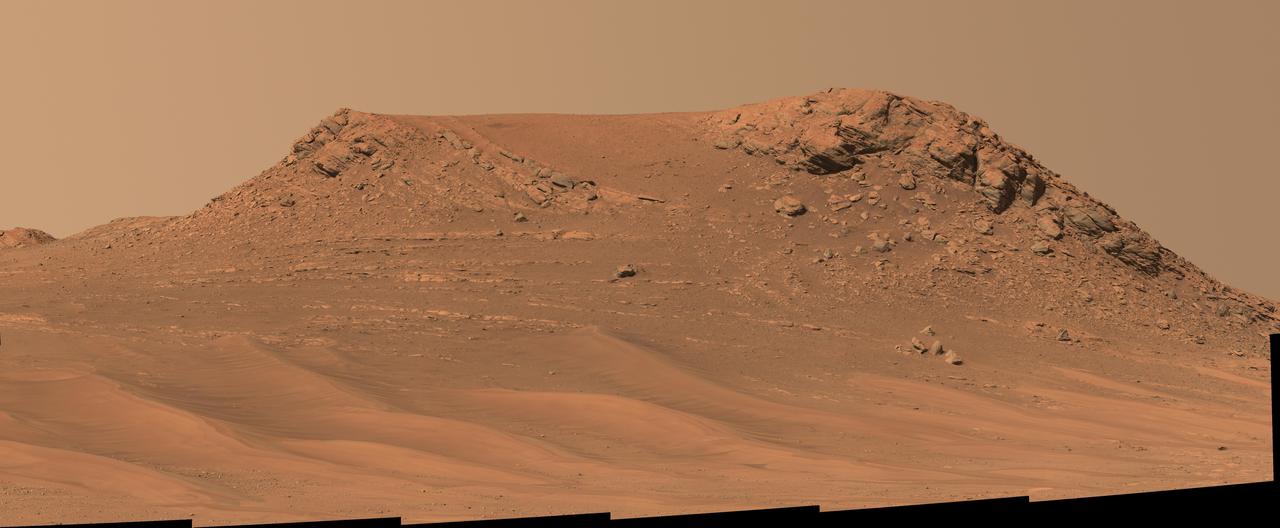

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this mosaic of an isolated hill nicknamed "Pinestand." Scientists think sedimentary layers stacked on top of one another here could have been formed by a deep, fast-moving river. But uncertainty about their formation remains because the layers are exceptionally tall by Earth geology standards to have been created by a river – some standing 66 feet (20 meters) high. The mosaic was captured by Perseverance's Mastcam-Z camera on Feb. 26, 2023, the 718th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. The mosaic was stitched together from 18 individual Mastcam-Z images after they were sent back to Earth. This natural color view is approximately how the scene would appear to an average person if they were on Mars. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25830
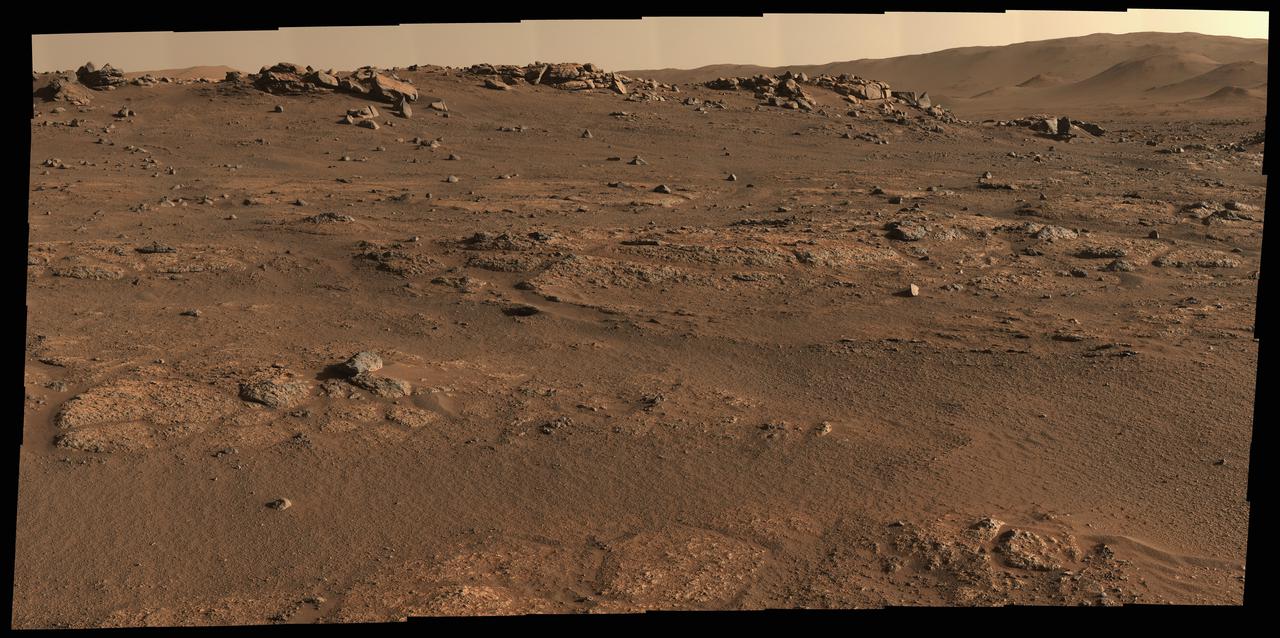

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover used its Mastcam-Z camera system to create this panorama of its first drill site. Scientists will be looking for a rock to drill somewhere in this. Perseverance's team has nicknamed this region the "Crater Floor Fractured Rough" unit. The flat, light-colored stones are informally referred to as "paver rocks" and will be the first type from which Perseverance will collect a sample for planned return to Earth by subsequent missions. Small hills to the south of the rover and the sloping inner walls of the Jezero Crater rim fill the distant background of this view. The panorama is stitched together from 70 individual images taken on July 28, 2021, the 155th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. This panorama is seen here in natural color. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24765

This wide view of Mars' Jezero Crater was taken by NASA's Perseverance rover on July 15, 2021 (the 143rd sol, or Martian day, of its mission). The rover has driven nearly a mile (1.5 kilometers) south of its landing site, "Octavia E. Butler Landing," into a region the team has nicknamed the "Crater Floor Fractured Rough" unit. The stones that appear light-colored and flat in this image are informally referred to as the "paver rocks" and will be the first type from which Perseverance will collect a sample for planned return to Earth by subsequent missions. Small hills to the south of the rover and the sloping inner walls of the Jezero Crater rim fill the distant background of this view. Five images from the rover's Mastcam-Z instrument were calibrated and combined to make this mosaic. Perseverance has been exploring the floor of Jezero since landing on Feb. 18, 2021. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24745
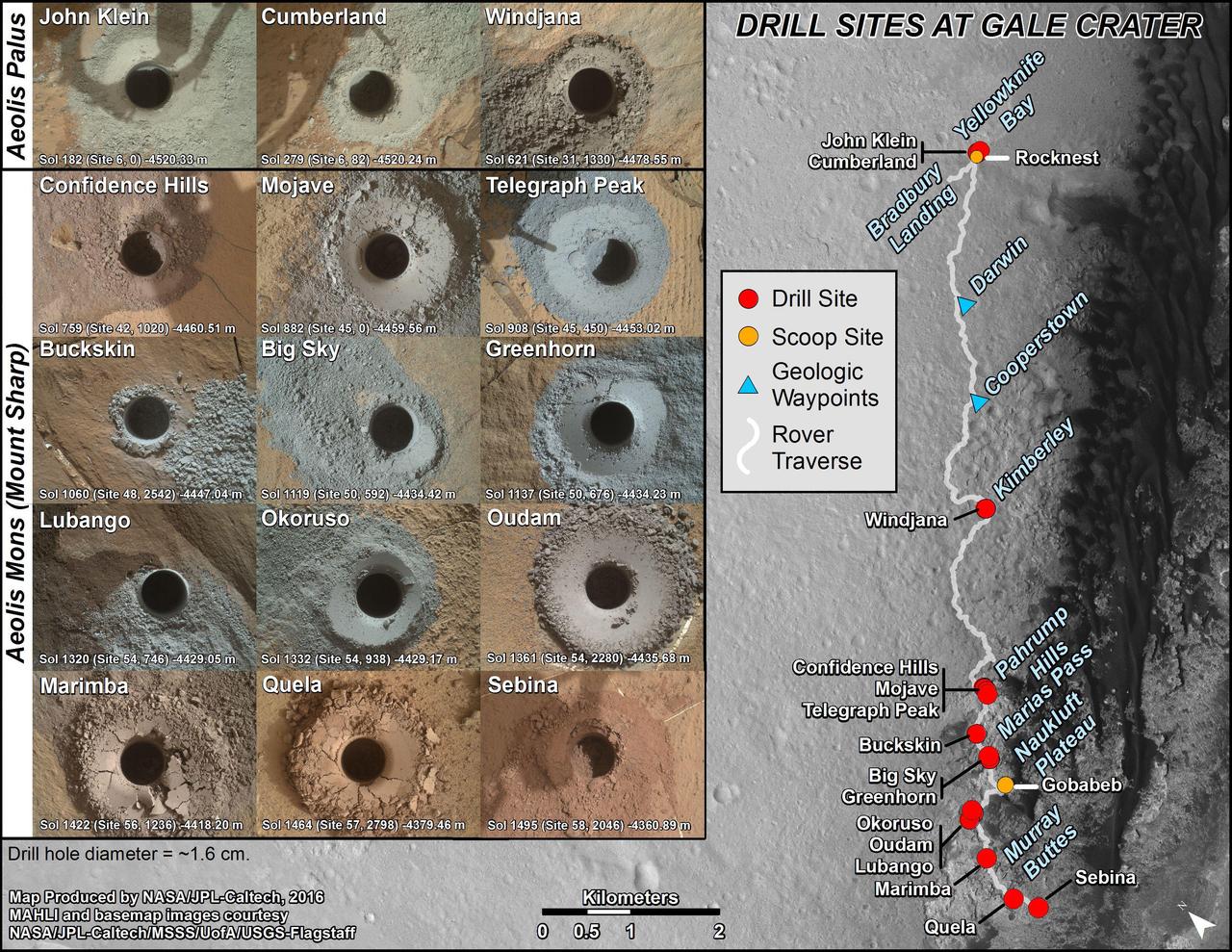
nal Caption Released with Image: This graphic maps locations of the sites where NASA's Curiosity Mars rover collected its first 19 rock or soil samples for analysis by laboratory instruments inside the vehicle. It also presents images of the drilled holes where 15 rock-powder samples were acquired. Curiosity scooped two soil samples at each of the other two sites: Rocknest and Gobabeb. The diameter of each drill hole is about 0.6 inch (1.6 centimeters), slightly smaller than a U.S. dime. The images used here are raw color, as recorded by the rover's Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera. Notice the differences in color of the material at different drilling sites. For the map, north is toward the upper left corner. The scale bar represents 2 kilometers (1.2 miles). The base map is from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The latest sample site included is "Sebina,"where Curiosity drilled into bedrock of the Murray formation on Oct. 20, 2016, during the 1,495th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Curiosity landed in August 2012 on the plain (named Aeolis Palus) near Mount Sharp (or Aeolis Mons). The drilling dates for the first 13 rock samples collected are, by location: "John Klein" on Feb. 8, 2013 (Sol 182); "Cumberland" on May 19, 2013 (Sol 279); "Windjana" on May 5, 2014 (Sol 621); "Confidence Hills" on Sept. 24, 2014 (Sol 759); "Mojave" on Jan. 29, 2015 (Sol 882); "Telegraph Peak" on Feb. 24, 2015 (Sol 908); "Buckskin" on July 30, 2015 (Sol 1060); "Big Sky" on Sept. 29, 2015 (Sol 1119); "Greenhorn" on Oct. 18, 2015 (Sol 1137); "Lubango" on April 23, 2016 (Sol 1320); "Okoruso" on May 5, 2016 (Sol 1332); "Oudam" on June 4, 2016 (Sol 1361); "Quela" on Sept. 18, 2016 (Sol 1464). http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21254

This view of the interior of Belva Crater was generated using data collected by the Mastcam-Z instrument aboard NASA's Perseverance Mars rover on April 22, 2023, the 772nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. When the 152 individual images that make up this mosaic were taken, the rover was parked at the west side of the crater's rim, on a light-toned rocky outcrop the science team is calling "Echo Creek." Belva Crater is about 0.6 miles (0.9 kilometers) in diameter. The view here is looking across the crater towards the distant east-northeast wall of the much-larger Jezero Crater (center of the image), some 25 miles (40 kilometers) away. Impact craters like Belva can offer grand views and contain vertical cuts that provide important clues to the geologic history of the area. The mosaic shows multiple locations of bedrock exposed in vertical cross-section. One of these exposed sections of bedrock (located on the hill seen between the 60 and 75 hashmarks) is angled steeply downward and is nearly 65 feet (20 meters) tall. Called "dipping beds," such a steeply angled bedrock section could indicate the presence of a large Martian sandbar made of sediment that billions of years ago was deposited by a river flowing into the lake that Jezero Crater once held. The most distant point on Belva Crater's rim (just to the left of center in the mosaic) is about 3,500 feet (1,060 meters) away from the rover. The large boulder seen in the far right of the mosaic is about 65 feet (20 meters) away and is about 5 feet (1.5 meters) in diameter. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25889
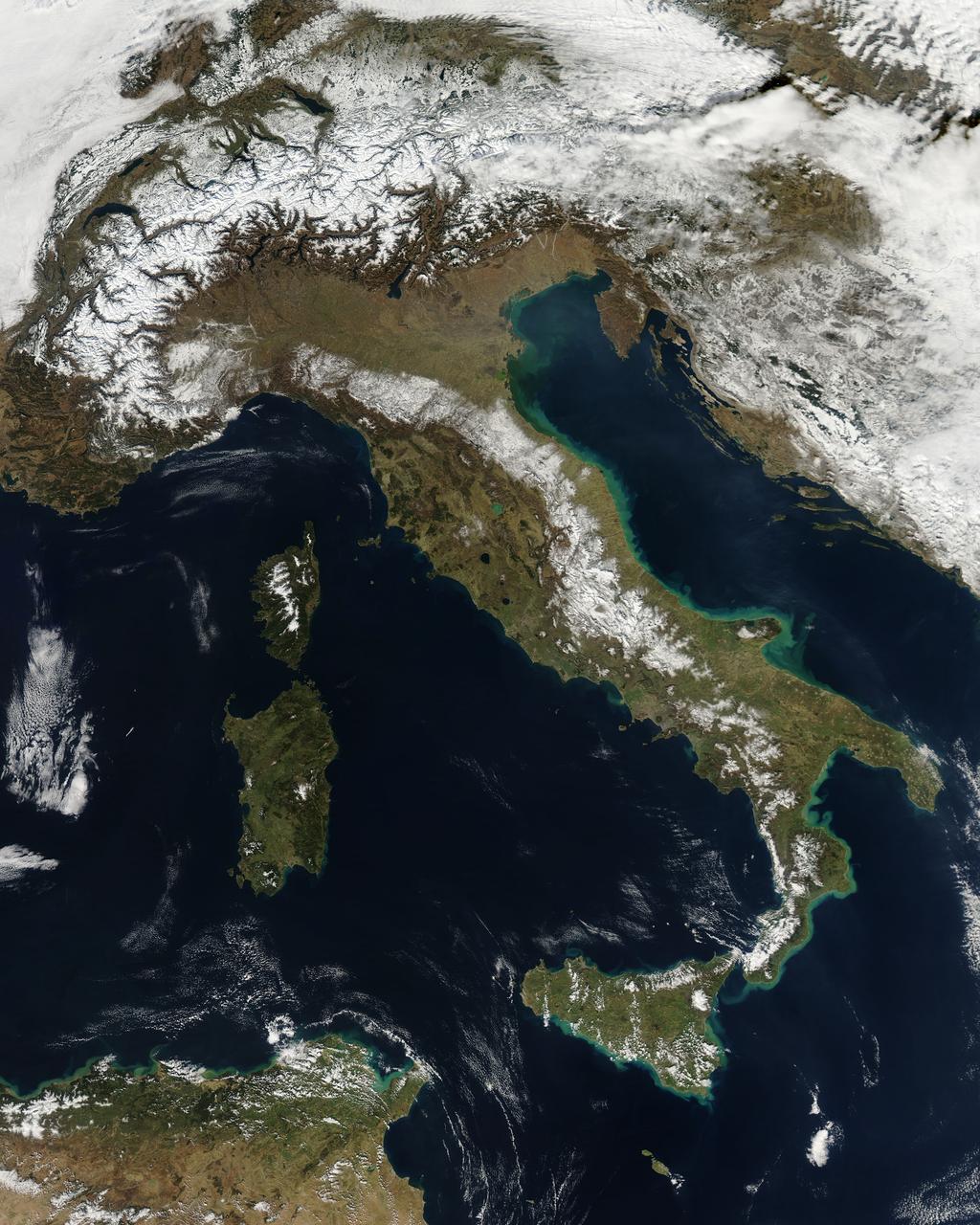

NASA image acquired February 24, 2012 By late February, 2012, the great European cold wave had begun to loosen its frigid grip, but significant snow still remained in the region. The Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) aboard the Aqua satellite captured this true-color image of snow in Italy on February 24 at 12:35 UTC (1:30 p.m. local time). In the north of the image, bright white clouds blanket the region in a broad arc. Snow, which tends to be generally less bright that clouds, covers the Alps in the north of Italy. The Apennine Mountains, which form the backbone of the Italian peninsula, also carry a blanket of snow. Although clouds and snow can, at times, be distinguished visually in a true-color image, sometimes they can appear very similar. When it is important to clearly define snow from cloud, false color images are often helpful. Rome, which can be seen as a gray smudge on the southwestern coast of the peninsula, recorded highs of a spring-like 50°F the day this image was captured, but earlier in the month the temperatures dove as low as 26°F on February 5. During that cold snap a rare intense snowfall blanketed Rome, causing the closure of the Colosseum, the Roman Forum and the Palatine Hill due to concerns of the risk of icy footing for tourists, and roads became impassible. Further north, temperatures plummeted to −21 °C (−6 °F) on 7 February. On February 11, news media reported over 2 meters (6.5 feet) of snow had fallen in Urbino, a walled town situated on a high sloping hillside on the eastern side of the Apennine Mountains. That same snowfall cut access to many remote towns in the Apennines, blocking roads and trapping some people in the homes. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS Land Rapid Response Team <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
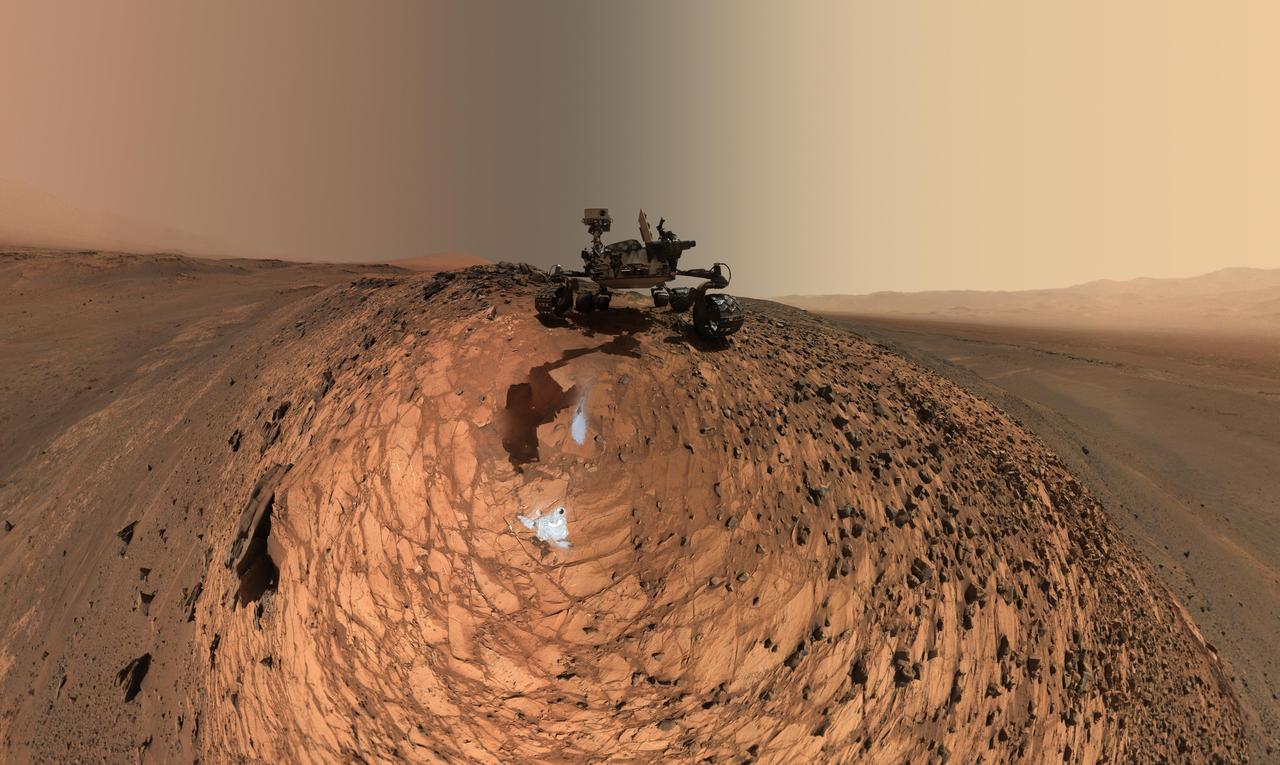

This low-angle self-portrait of NASA's Curiosity Mars rover shows the vehicle above the "Buckskin" rock target, where the mission collected its seventh drilled sample. The site is in the "Marias Pass" area of lower Mount Sharp. The scene combines dozens of images taken by Curiosity's Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) on Aug. 5, 2015, during the 1,065th Martian day, or sol, of the rover's work on Mars. The 92 component images are among MAHLI Sol 1065 raw images at http://mars.nasa.gov/msl/multimedia/raw/?s=1065&camera=MAHLI. For scale, the rover's wheels are 20 inches (50 centimeters) in diameter and about 16 inches (40 centimeters) wide. Curiosity drilled the hole at Buckskin during Sol 1060 (July 30, 2015). Two patches of pale, powdered rock material pulled from Buckskin are visible in this scene, in front of the rover. The patch closer to the rover is where the sample-handling mechanism on Curiosity's robotic arm dumped collected material that did not pass through a sieve in the mechanism. Sieved sample material was delivered to laboratory instruments inside the rover. The patch farther in front of the rover, roughly triangular in shape, shows where fresh tailings spread downhill from the drilling process. The drilled hole, 0.63 inch (1.6 centimeters) in diameter, is at the upper point of the tailings. The rover is facing northeast, looking out over the plains from the crest of a 20-foot (6-meter) hill that it climbed to reach the Marias Pass area. The upper levels of Mount Sharp are visible behind the rover, while Gale Crater's northern rim dominates the horizon on the left and right of the mosaic. A portion of this selfie cropped tighter around the rover is at PIA19808. Another version of the wide view, presented in a projection that shows the horizon as a circle, is at PIA19806. MAHLI is mounted at the end of the rover's robotic arm. For this self-portrait, the rover team positioned the camera lower in relation to the rover body than for any previous full self-portrait of Curiosity. This yielded a view that includes the rover's "belly," as in a partial self-portrait (PIA16137) taken about five weeks after Curiosity's August 2012 landing inside Mars' Gale Crater. Before sending Curiosity the arm-positioning commands for this Buckskin belly panorama, the team previewed the low-angle sequence of camera pointings on a test rover in California. A mosaic from that test is at PIA19810. This selfie at Buckskin does not include the rover's robotic arm beyond a portion of the upper arm held nearly vertical from the shoulder joint. Shadows from the rest of the arm and the turret of tools at the end of the arm are visible on the ground. With the wrist motions and turret rotations used in pointing the camera for the component images, the arm was positioned out of the shot in the frames or portions of frames used in this mosaic. This process was used previously in acquiring and assembling Curiosity self-portraits taken at sample-collection sites "Rocknest" (PIA16468), "John Klein" (PIA16937), "Windjana" (PIA18390) and "Mojave" (PIA19142). MAHLI was built by Malin Space Science Systems, San Diego. NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, a division of the California Institute of Technology in Pasadena, manages the Mars Science Laboratory Project for the NASA Science Mission Directorate, Washington. JPL designed and built the project's Curiosity rover. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19807

This 60-second video pans across an enhanced-color composite image, or mosaic, of the delta at Jezero Crater on Mars. The delta formed billions of years ago from sediment that an ancient river carried to the mouth of the lake that once existed in the crater. Taken by the Mastcam-Z instrument aboard NASA's Perseverance rover, the video begins looking almost due west of the rover, and sweeps to the right until it faces almost due north. Fourteen images compose the mosaic that provides the base image for this video (included as an additional figure); they were acquired on Nov. 28, 2021 (the 275th sol, or Martian day, of Perseverance's mission) as the rover sat at the highest vantage point in the "South Séítah" geological unit, allowing a perspective that included boulders and other features atop the delta as well as farther west and northwest across its surface. The mountains in the background are the rim of Jezero Crater. The view also shows brown hills in the middle distance that are part of an ancient delta, where a river hit a lake in the crater. The rover has spent the last several months exploring the sandy and rocky terrain in the foreground. The color bands of the image have been processed to improve visual contrast and accentuate color differences. The sky would not actually look blue to a human explorer on the Red Planet. The Mastcam-Z investigation is led and operated by Arizona State University in Tempe, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, California, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Neils Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25022