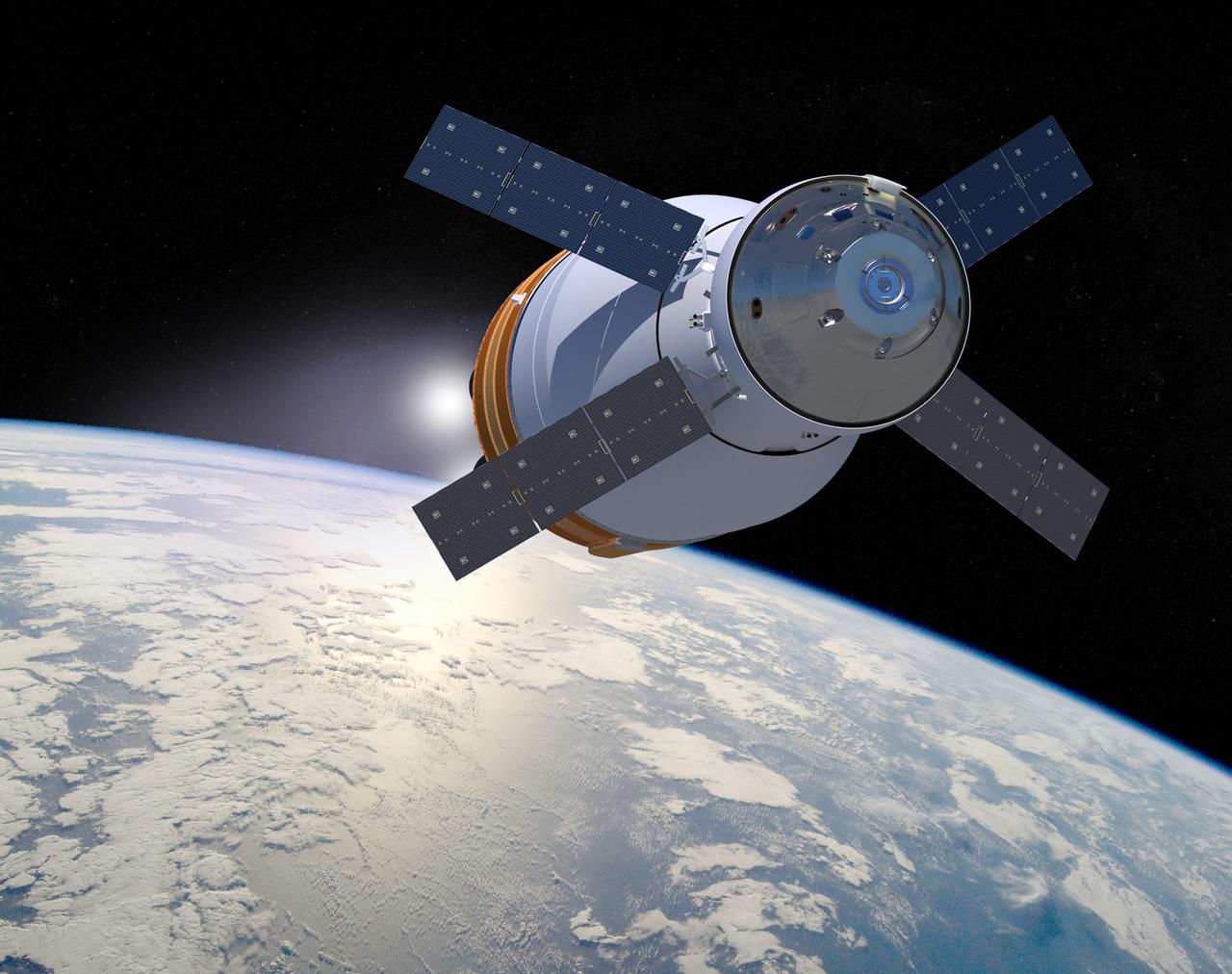

Seen here is an image of the SLS Exploration Upper Stage with the Orion Space craft on its way to a deep space mission. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
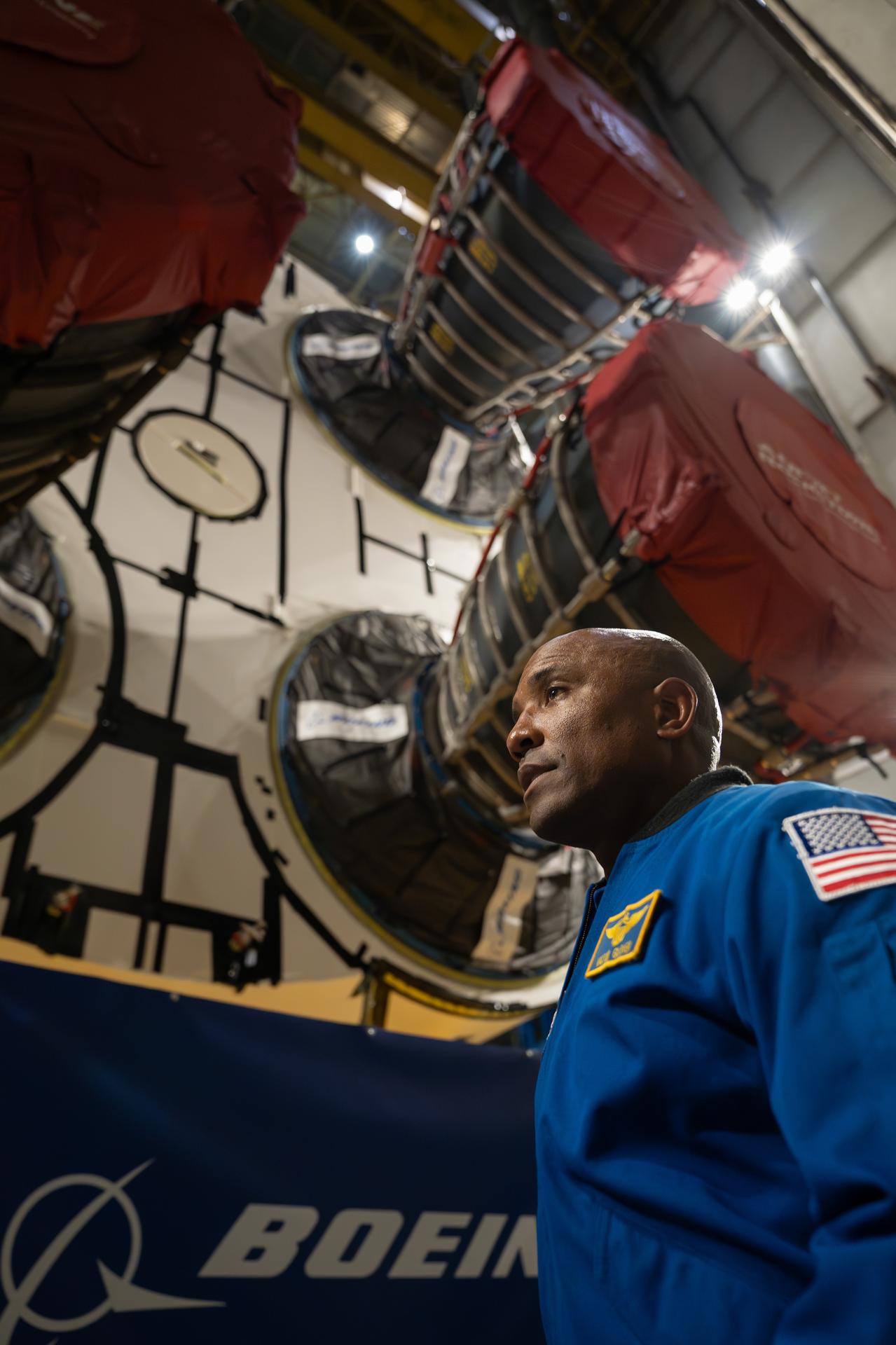

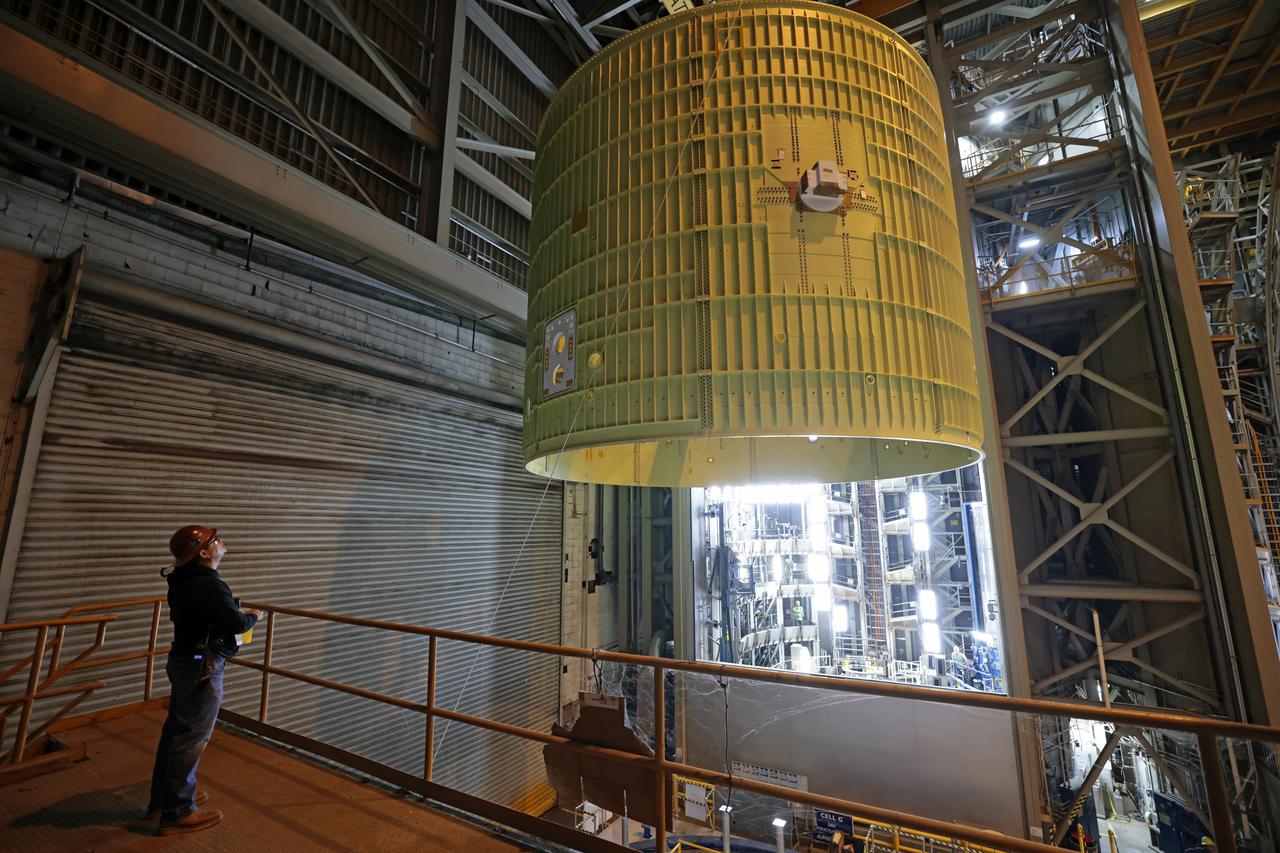
NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
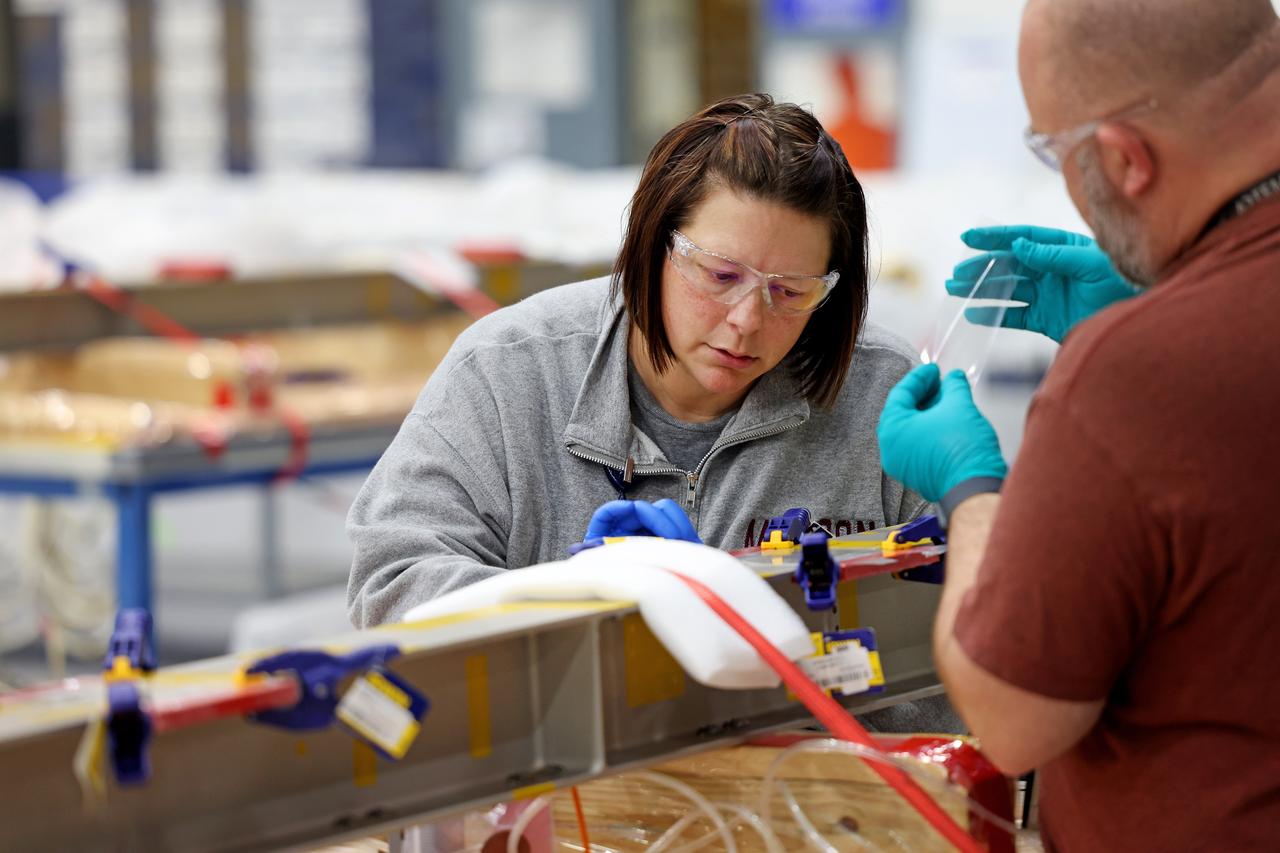

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Feb. 22 prepare elements that will form part of the midbody for the future exploration upper stage for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The midbody struts, or V-struts, will create the midbody’s cage-like outer structure to connect the upper stage’s larger liquid hydrogen tank to its smaller liquid oxygen tank. Manufacturing flight and test hardware for the future SLS upper stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. Beginning with Artemis IV, SLS will evolve to its more powerful Block 1B configuration with the advanced exploration upper stage that gives the rocket the capability to launch 40% more to the Moon along with Artemis astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft. The evolved in-space stage for SLS will use a combination of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen propellants to help power the engines to send large cargo and crew inside Orion to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Feb. 22 prepare elements that will form part of the midbody for the future exploration upper stage for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The midbody struts, or V-struts, will create the midbody’s cage-like outer structure to connect the upper stage’s larger liquid hydrogen tank to its smaller liquid oxygen tank. Manufacturing flight and test hardware for the future SLS upper stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. Beginning with Artemis IV, SLS will evolve to its more powerful Block 1B configuration with the advanced exploration upper stage that gives the rocket the capability to launch 40% more to the Moon along with Artemis astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft. The evolved in-space stage for SLS will use a combination of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen propellants to help power the engines to send large cargo and crew inside Orion to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans on Feb. 22 prepare elements that will form part of the midbody for the future exploration upper stage for the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket. The midbody struts, or V-struts, will create the midbody’s cage-like outer structure to connect the upper stage’s larger liquid hydrogen tank to its smaller liquid oxygen tank. Manufacturing flight and test hardware for the future SLS upper stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. Beginning with Artemis IV, SLS will evolve to its more powerful Block 1B configuration with the advanced exploration upper stage that gives the rocket the capability to launch 40% more to the Moon along with Artemis astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft. The evolved in-space stage for SLS will use a combination of liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen propellants to help power the engines to send large cargo and crew inside Orion to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
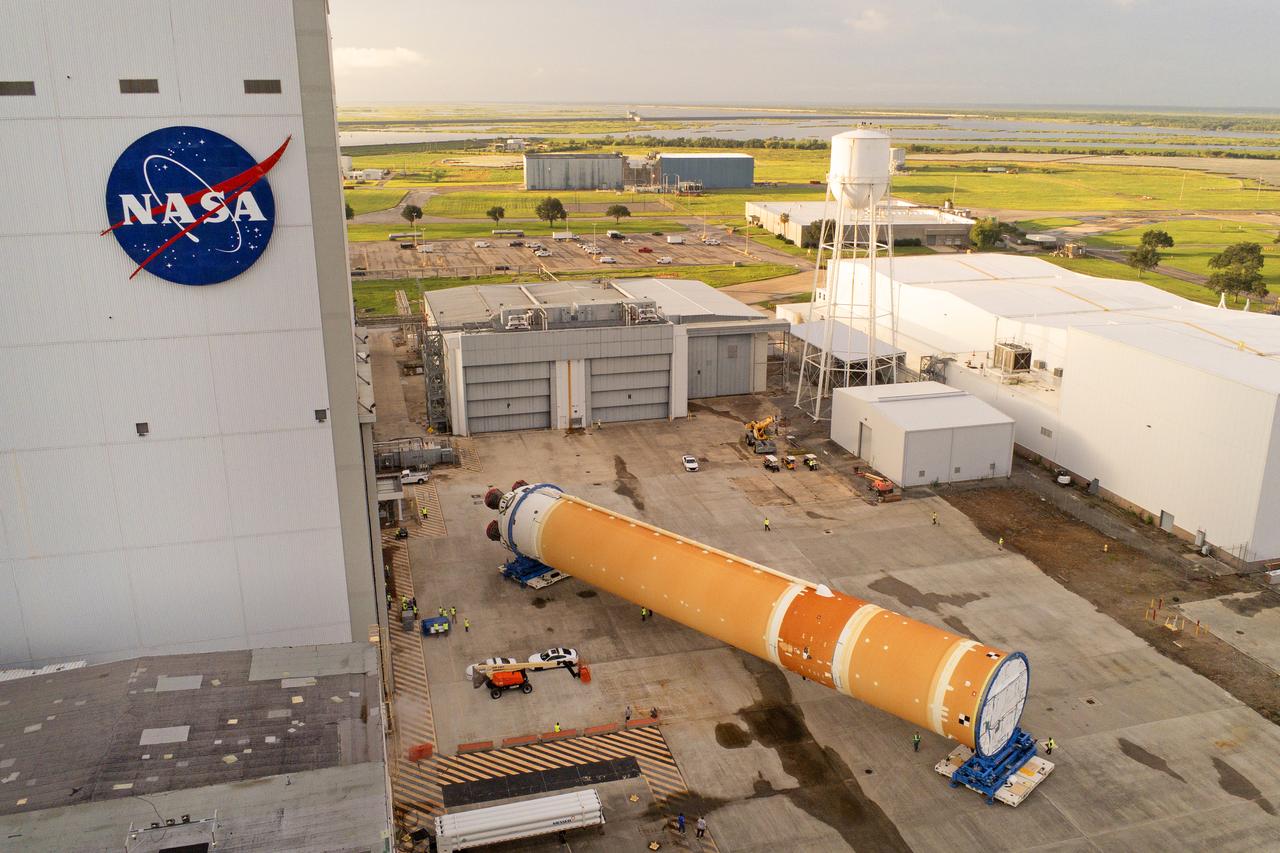

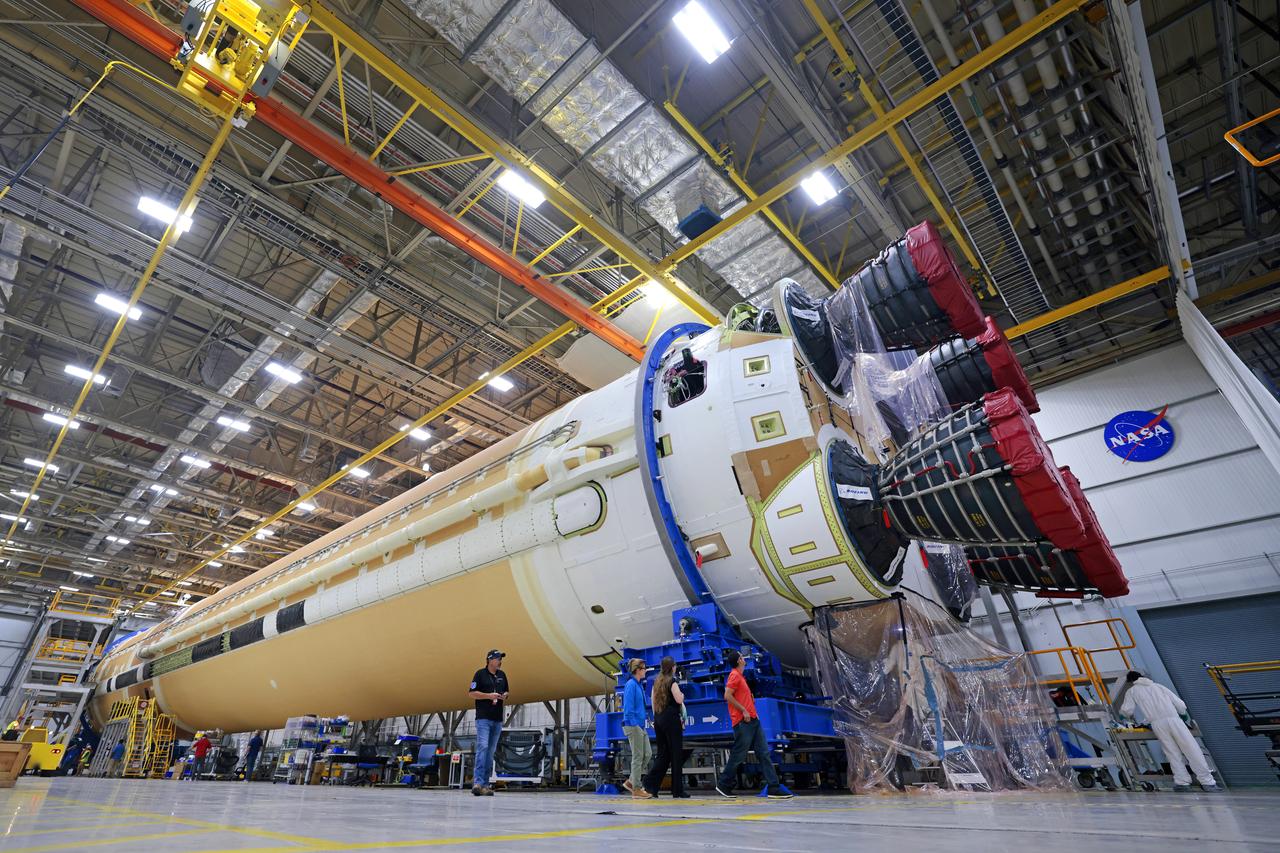
This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

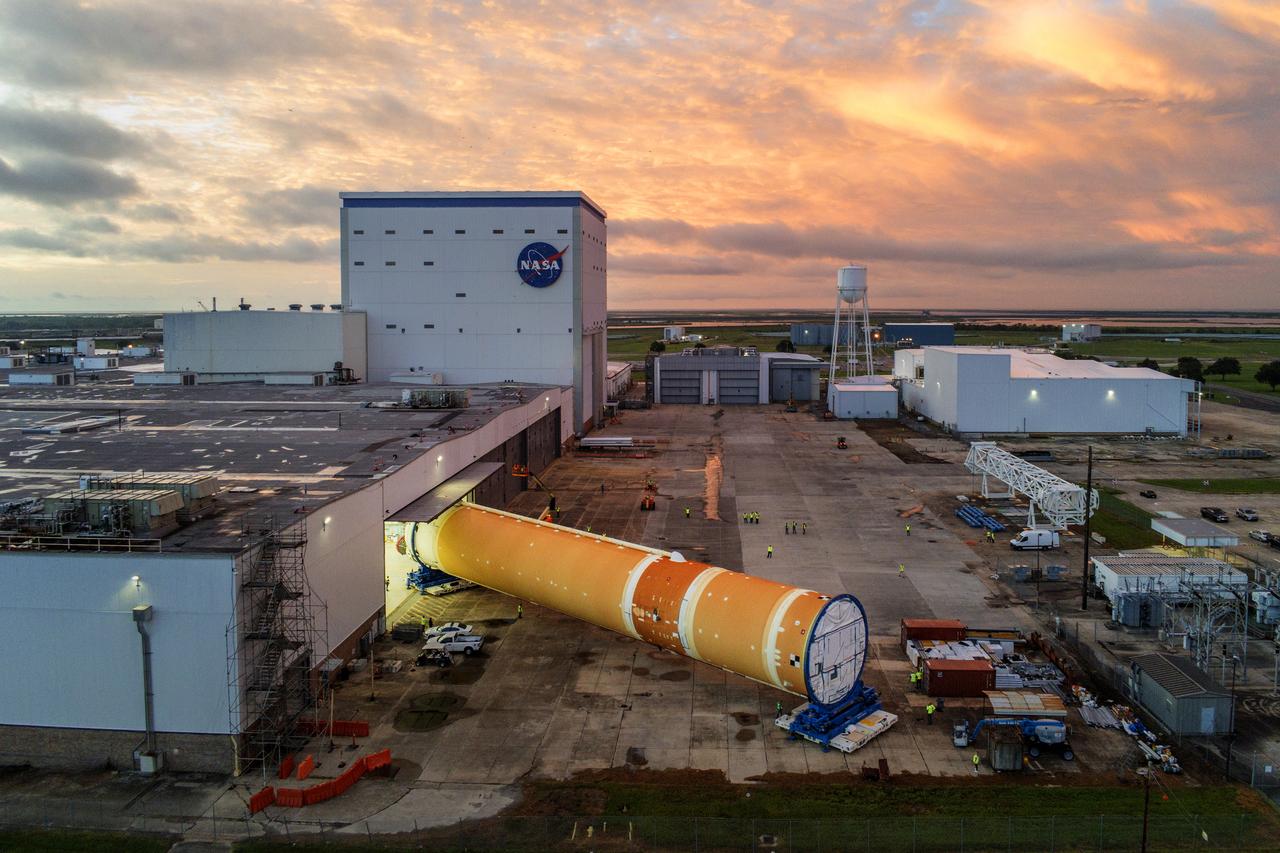
This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud.
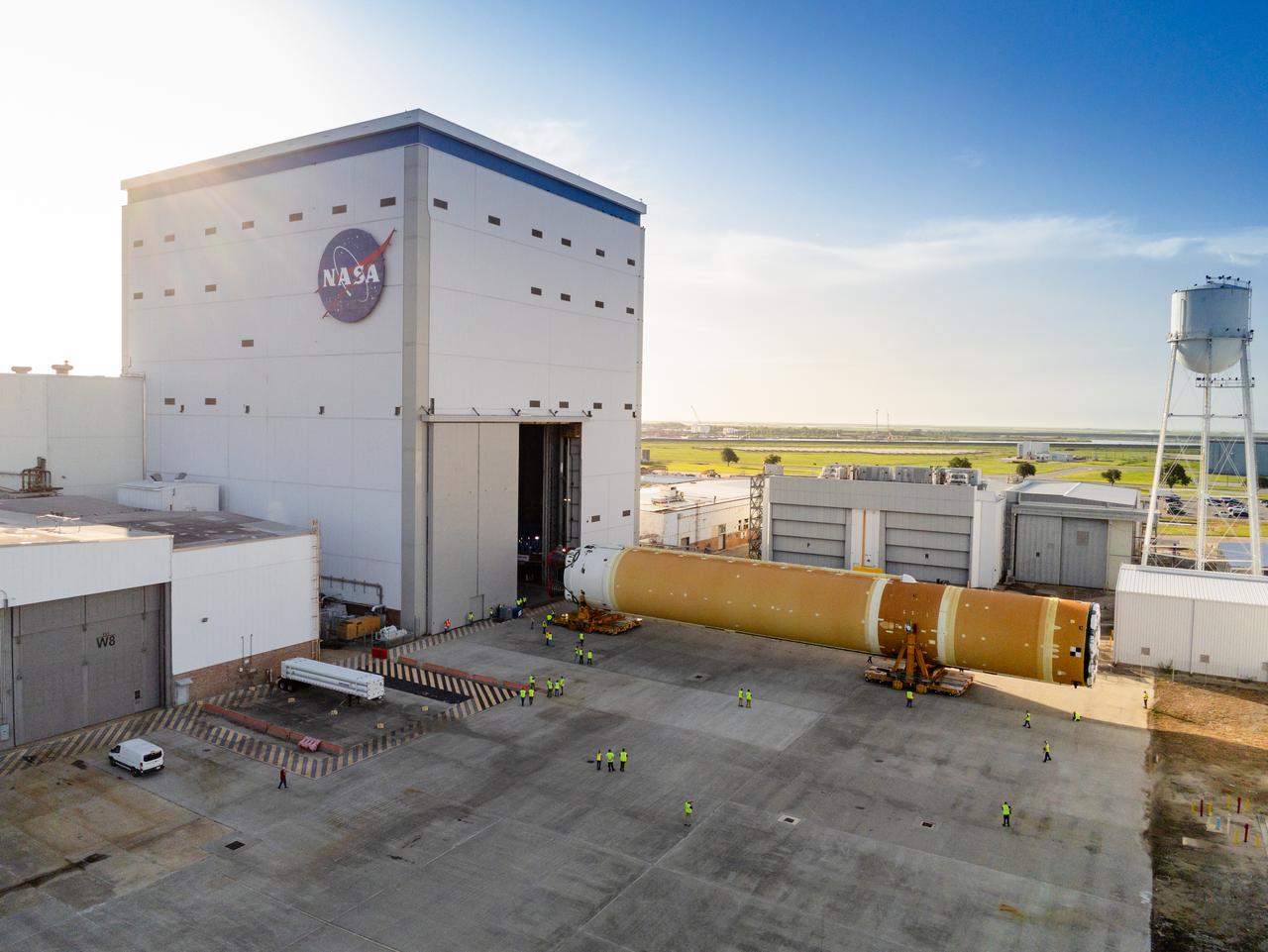

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud.
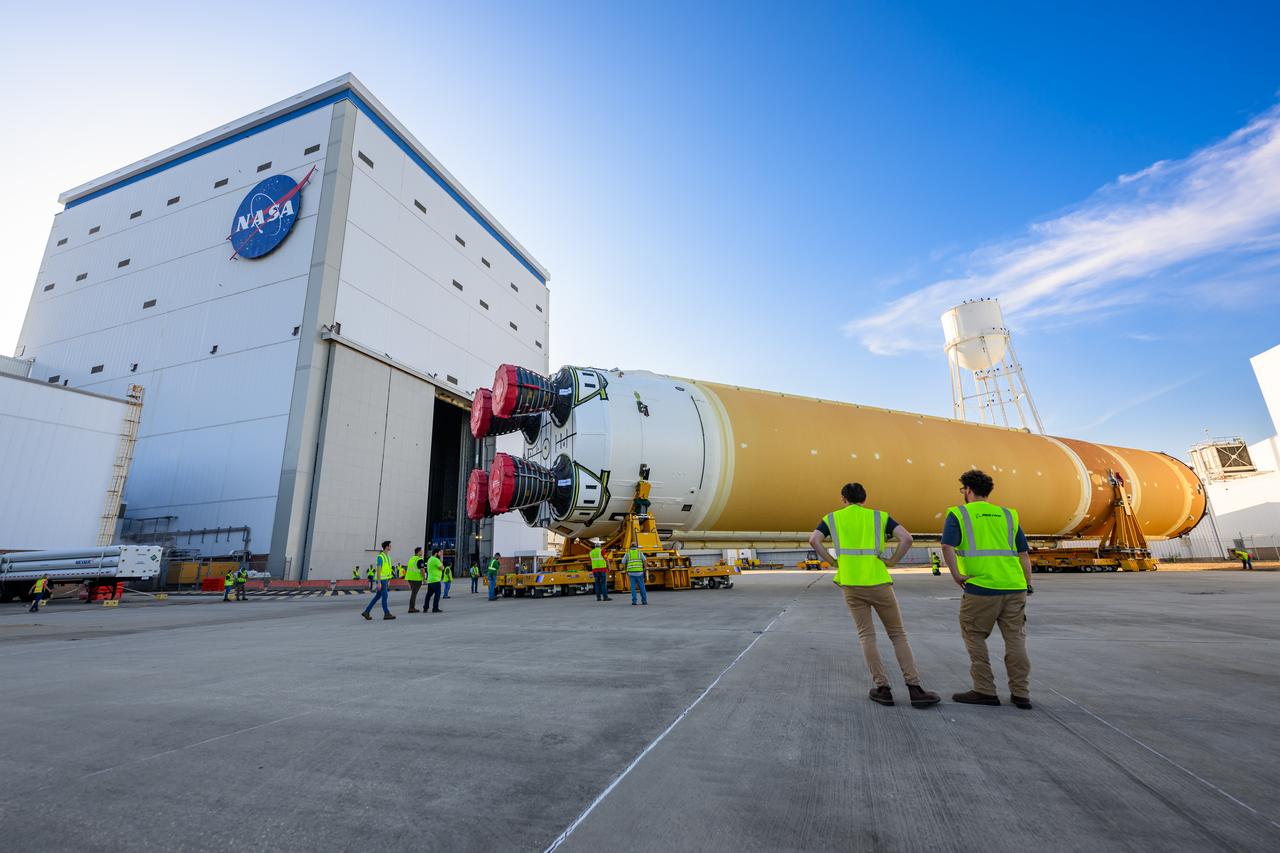

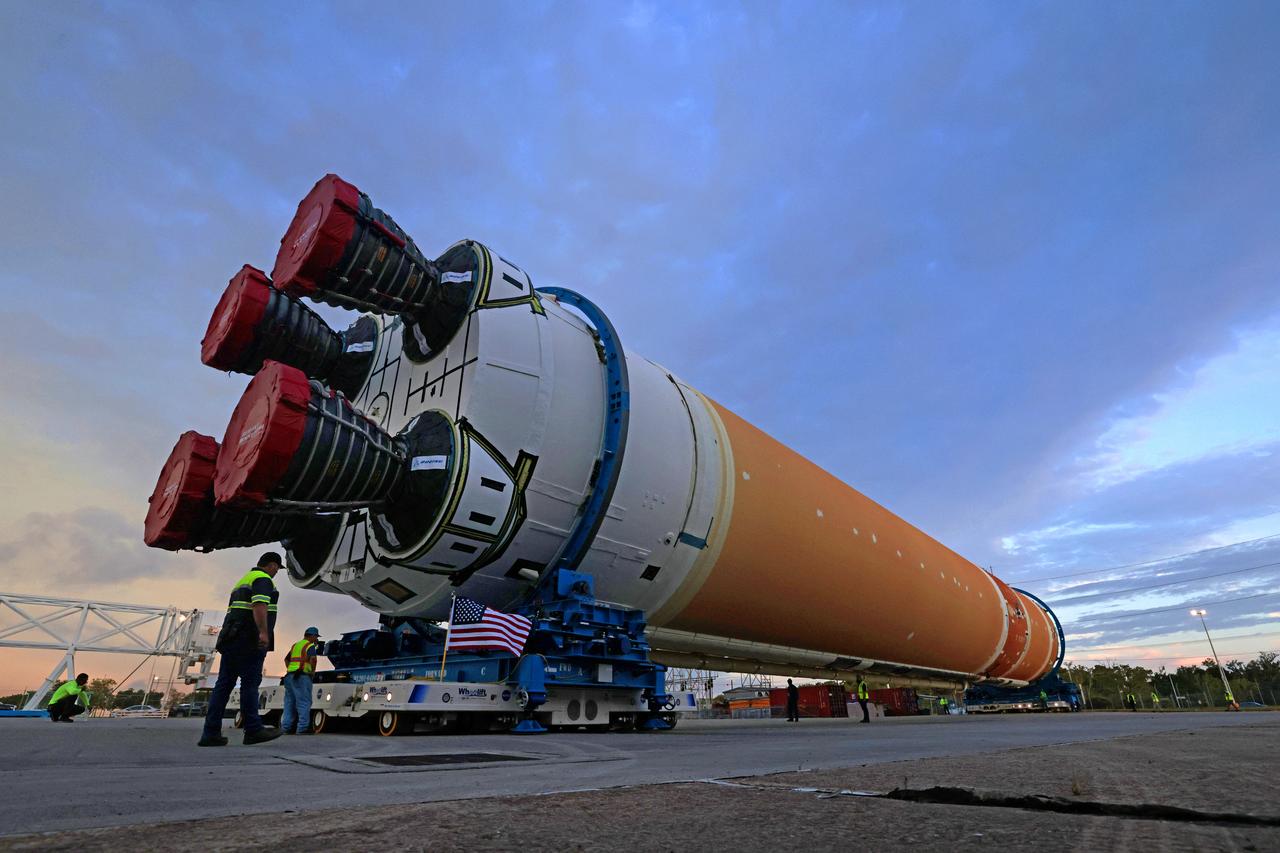
This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud.
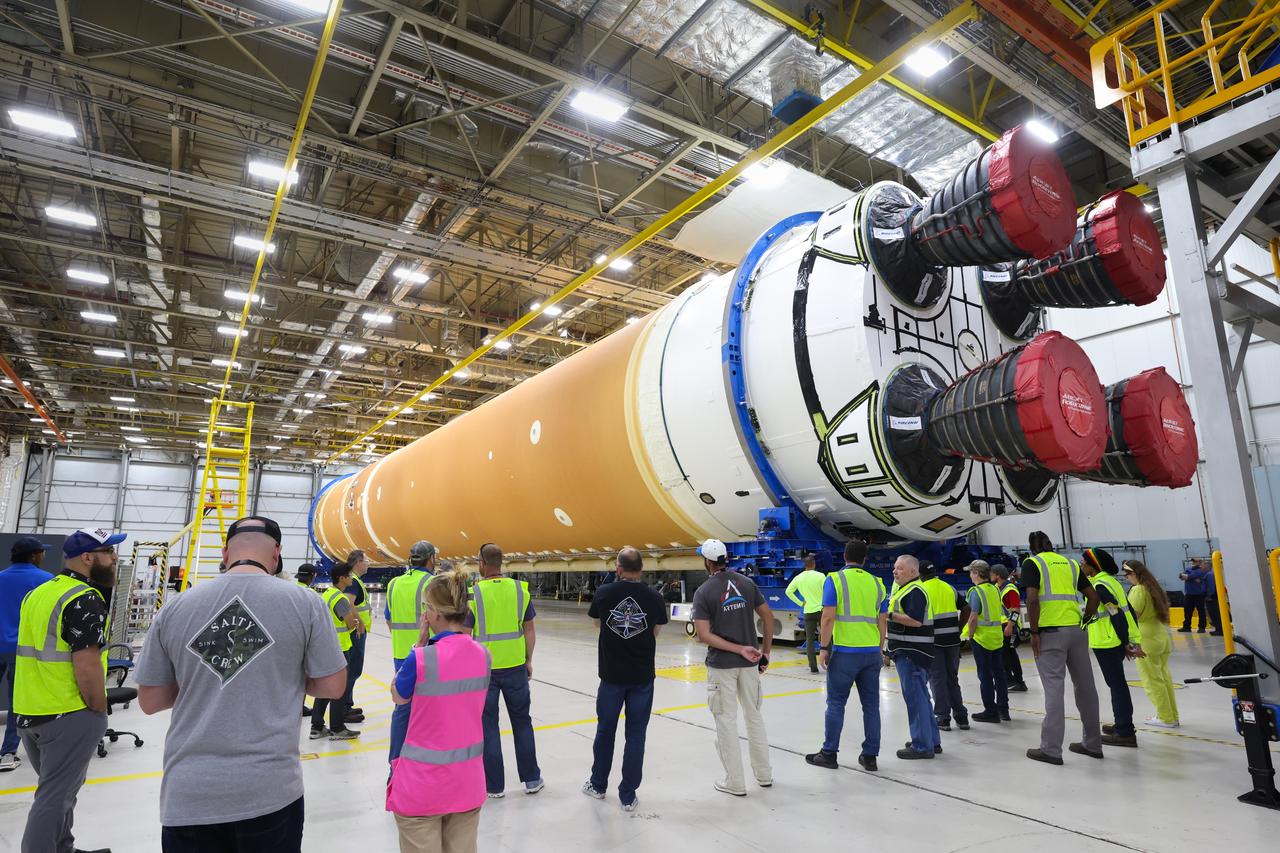

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
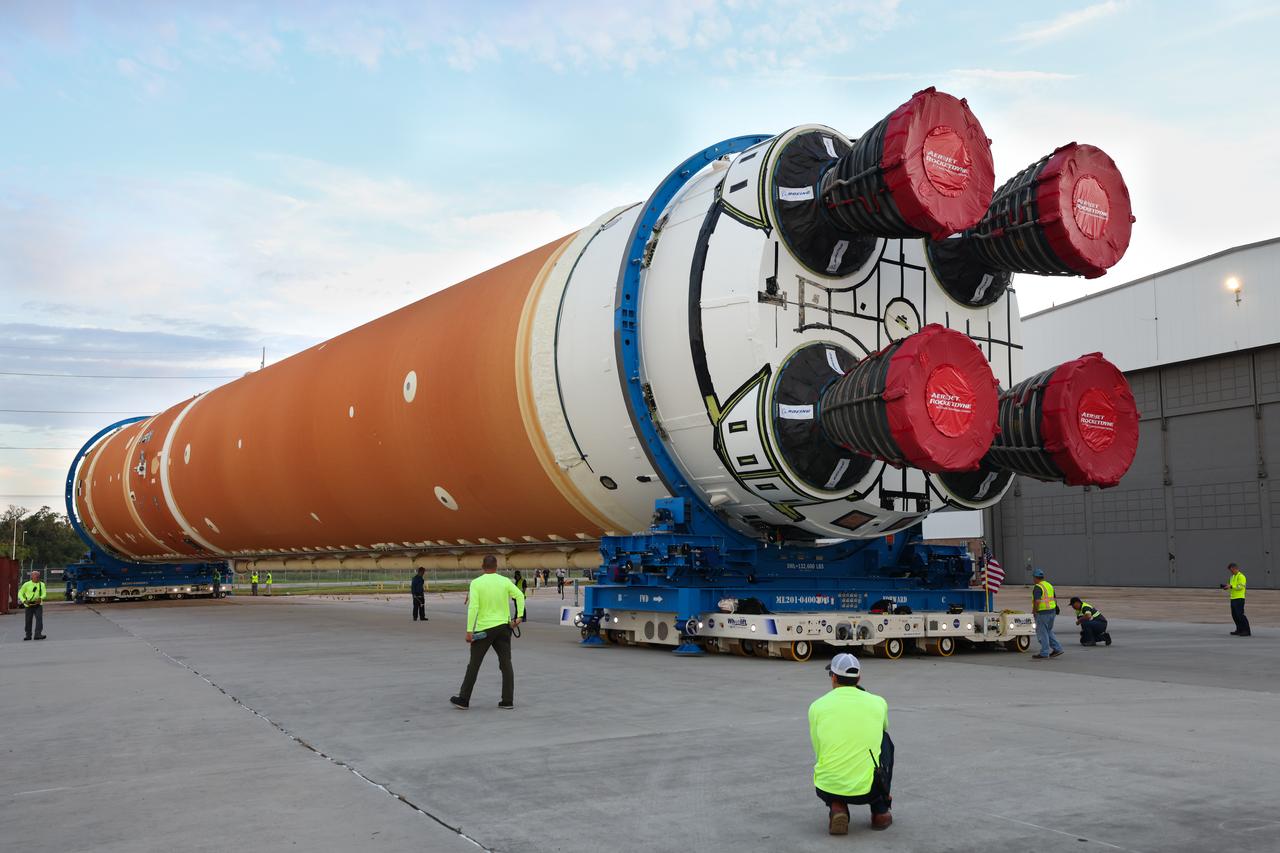

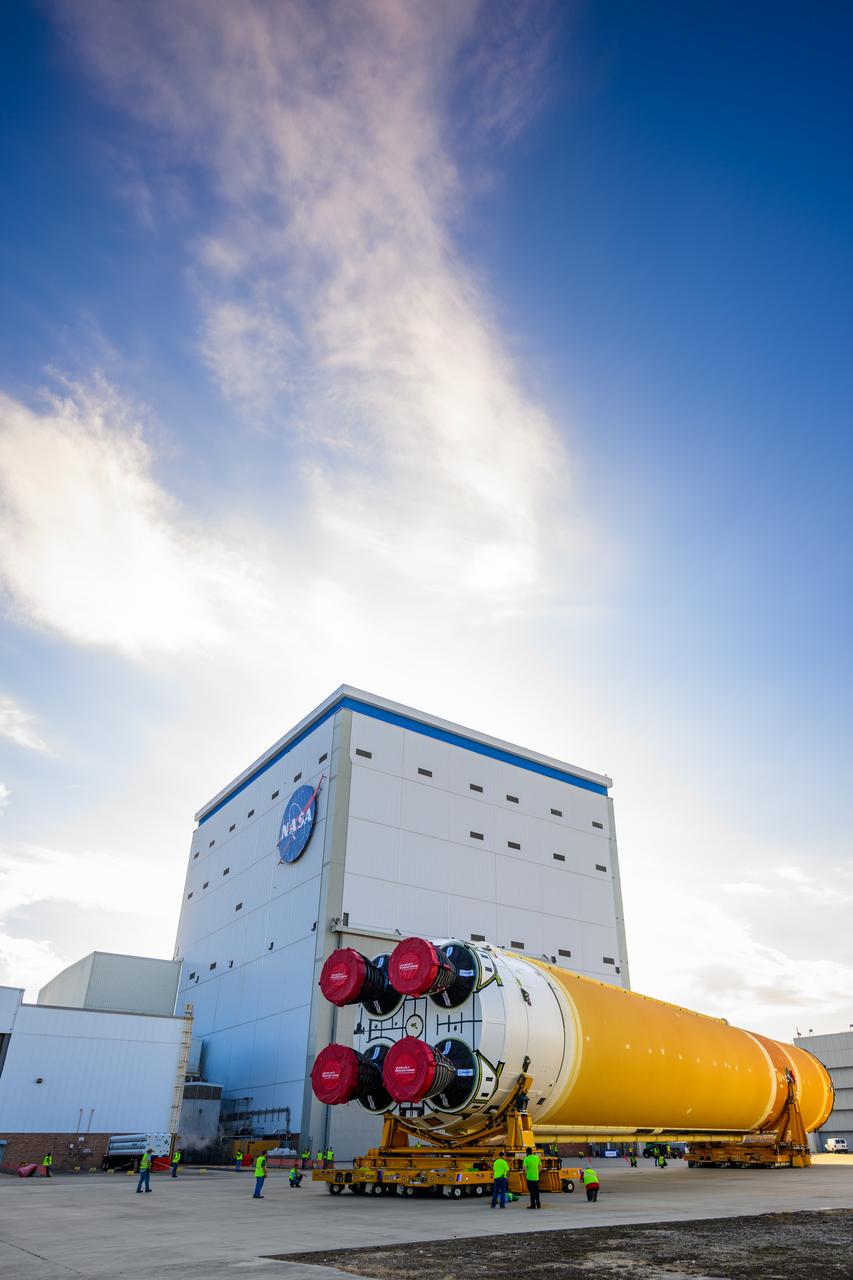
This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
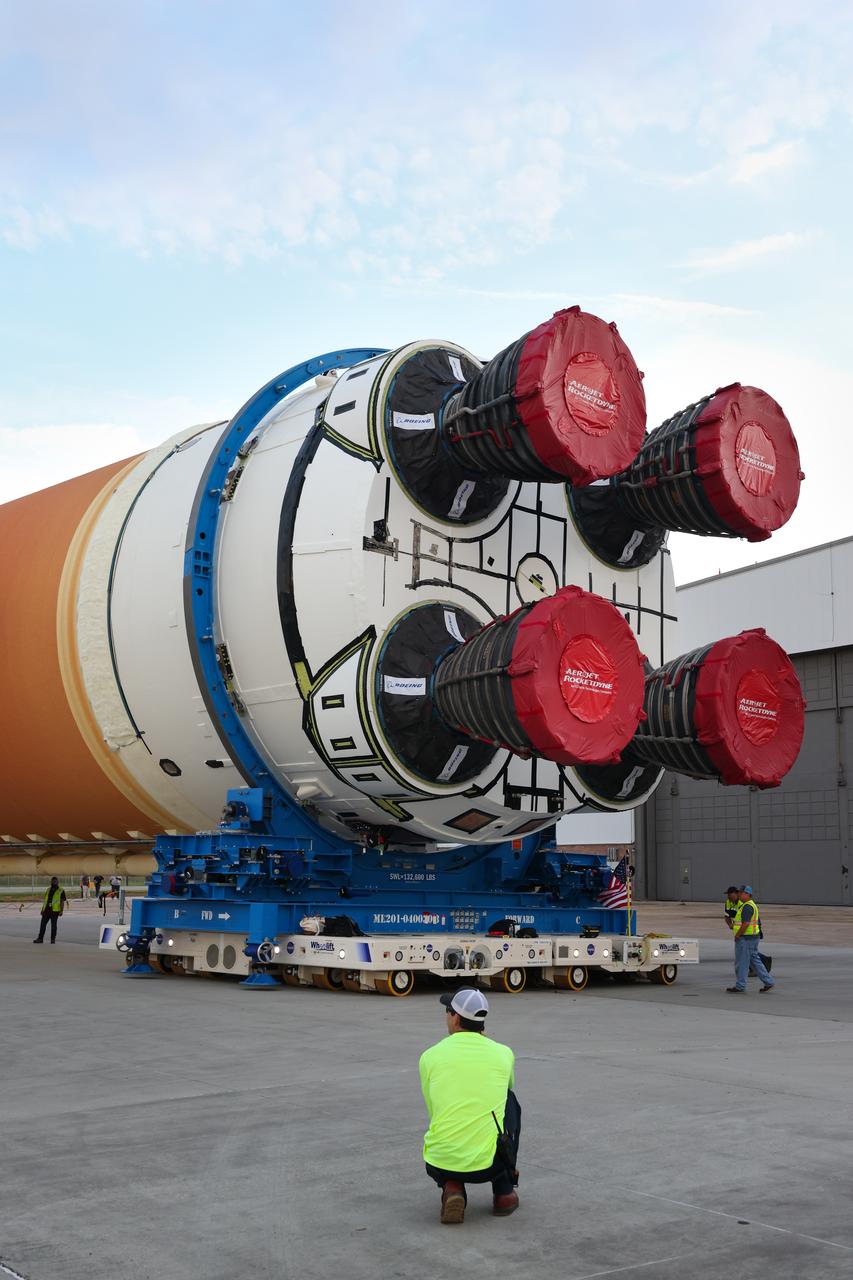

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
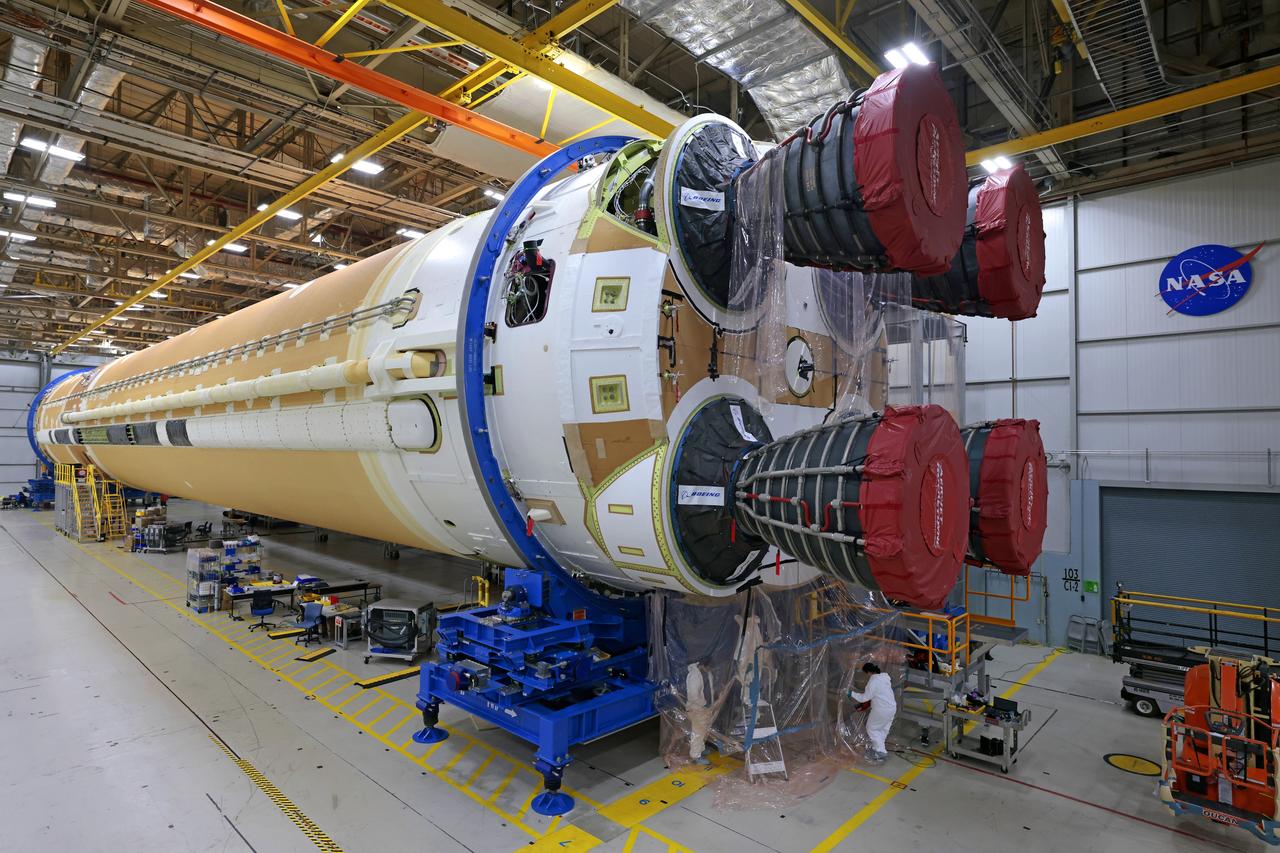

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans are preparing the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) for shipment to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 212-foot-tall core stage and its four RS-25 engines will help power Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews removed the external access stands, or scaffolding, in preparation for moving the rocket hardware to another area of the facility. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans are preparing the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) for shipment to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 212-foot-tall core stage and its four RS-25 engines will help power Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews removed the external access stands, or scaffolding, in preparation for moving the rocket hardware to another area of the facility. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
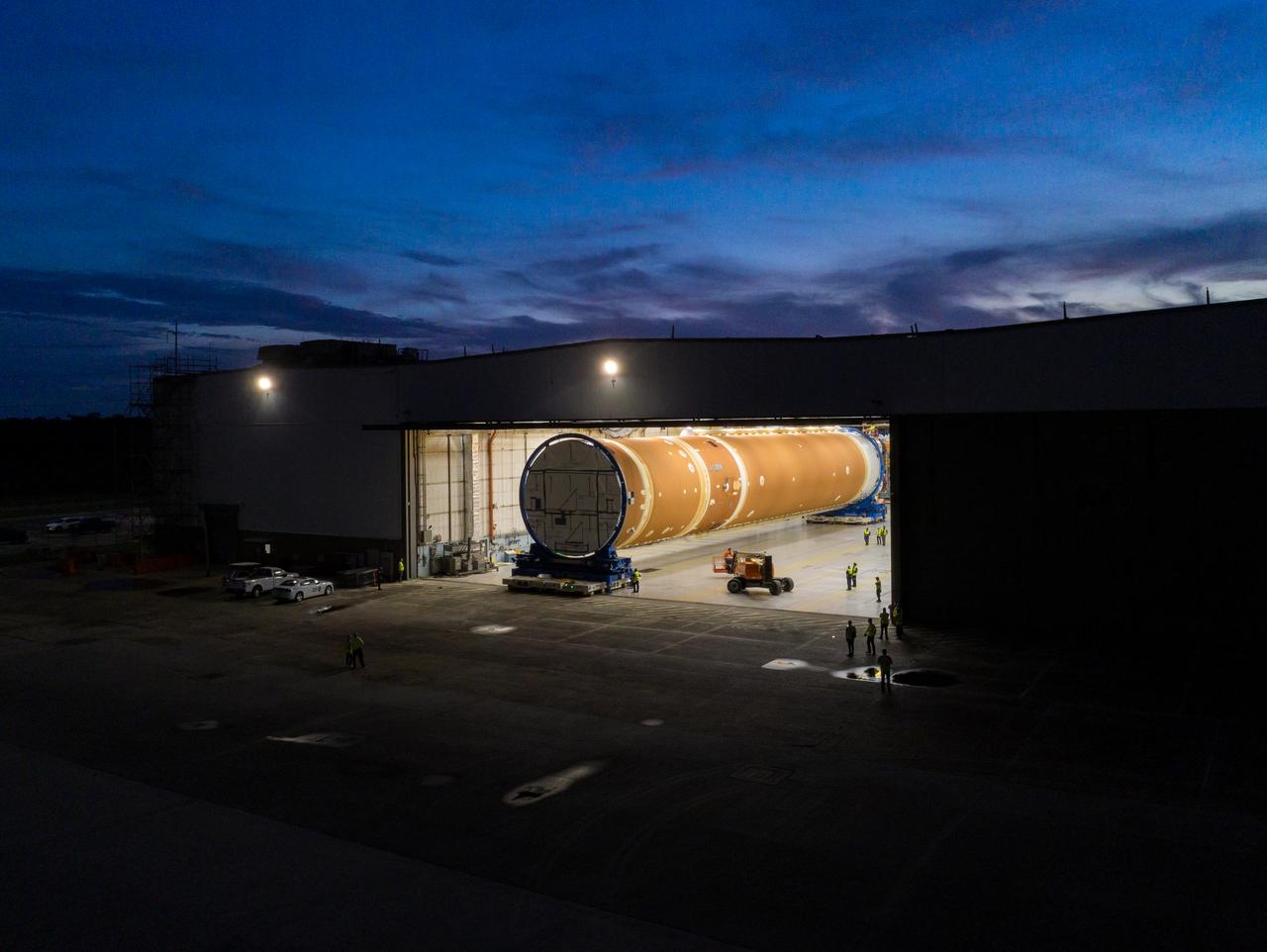

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
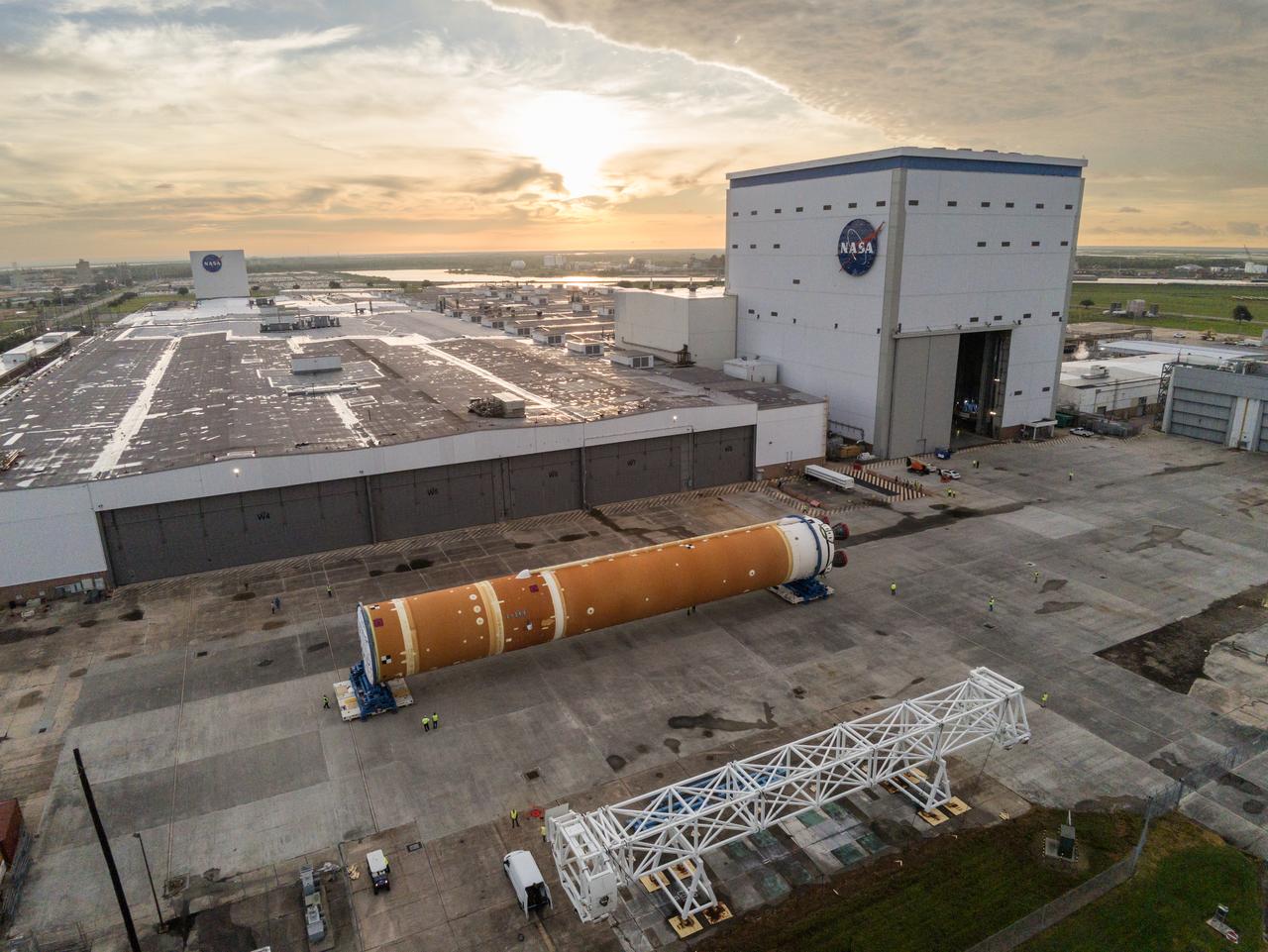

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
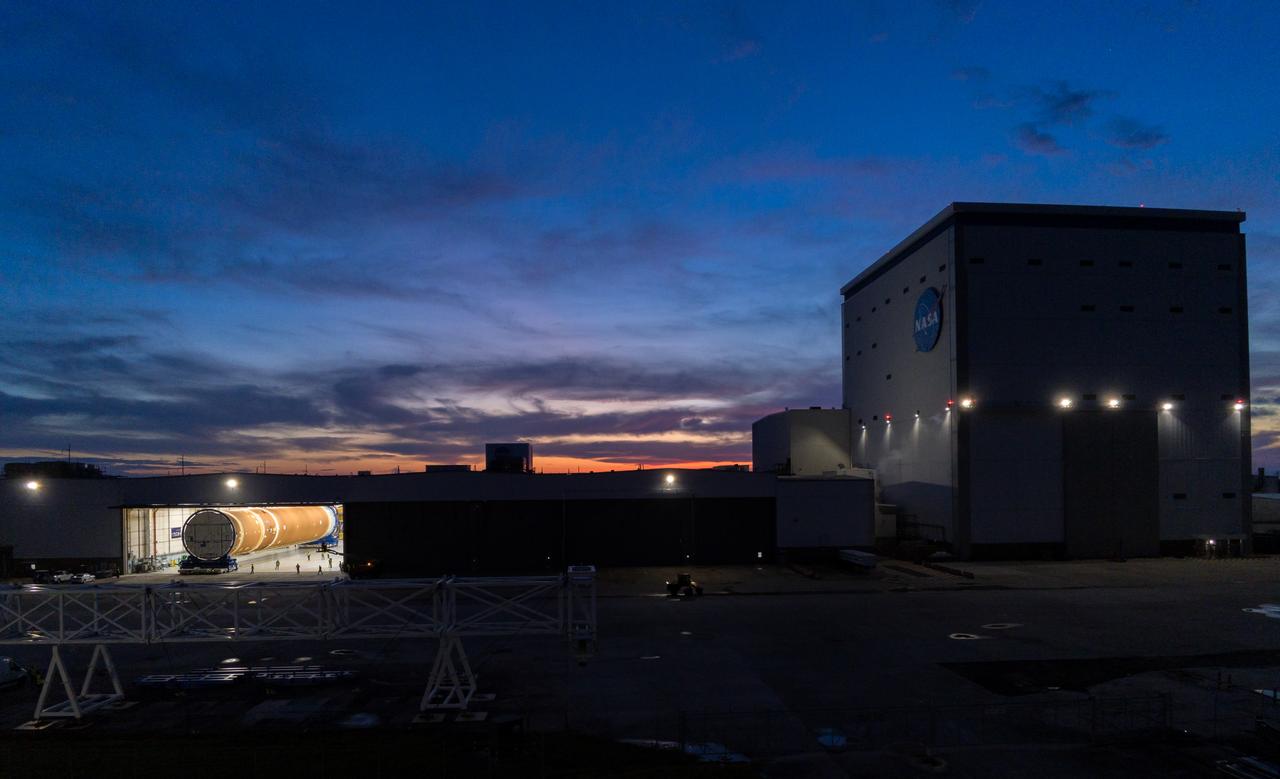

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
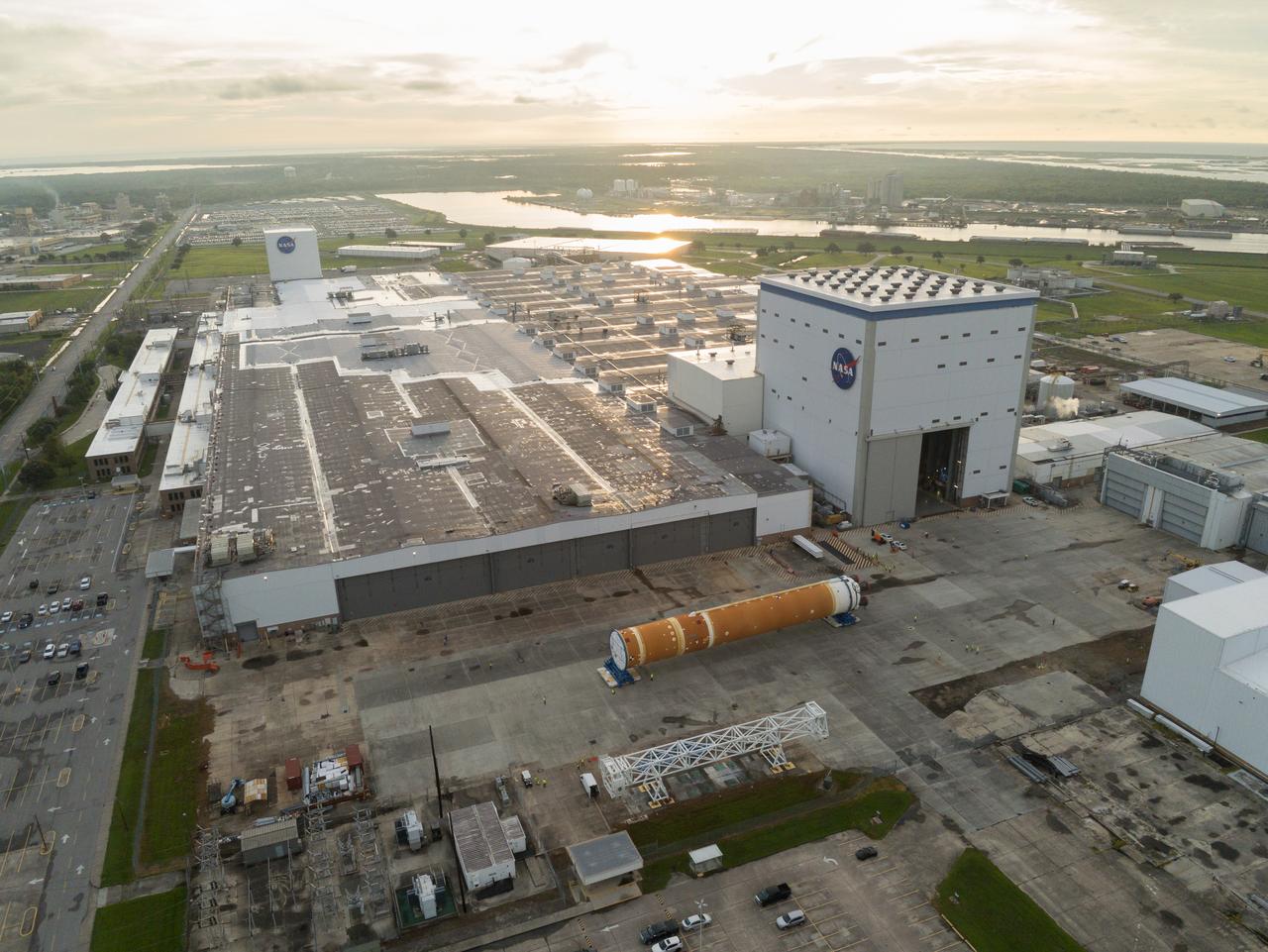

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
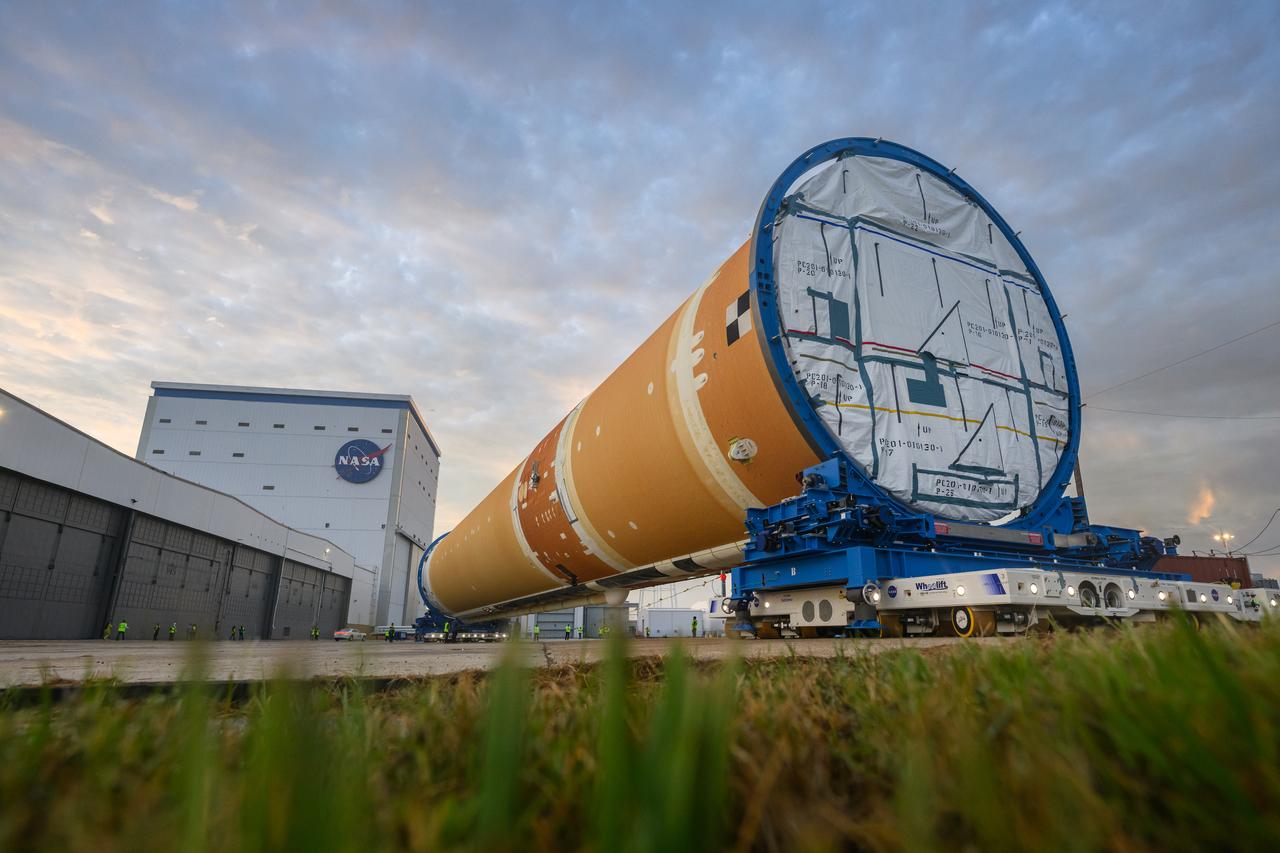

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

This photo shows NASA and Boeing, the SLS core stage lead contractor, preparing the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket core stage for shipment at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. On July 6, NASA and Boeing moved the Artemis II rocket stage to Building 110. The move comes as teams prepare to roll the massive rocket stage with its four RS-25 engines to the agency’s Pegasus barge for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in mid-July. Prior to the move, technicians began removing external access stands, or scaffolding, surrounding the core stage to assess the interior elements, including its complex avionics and flight propulsion systems. The stage is fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
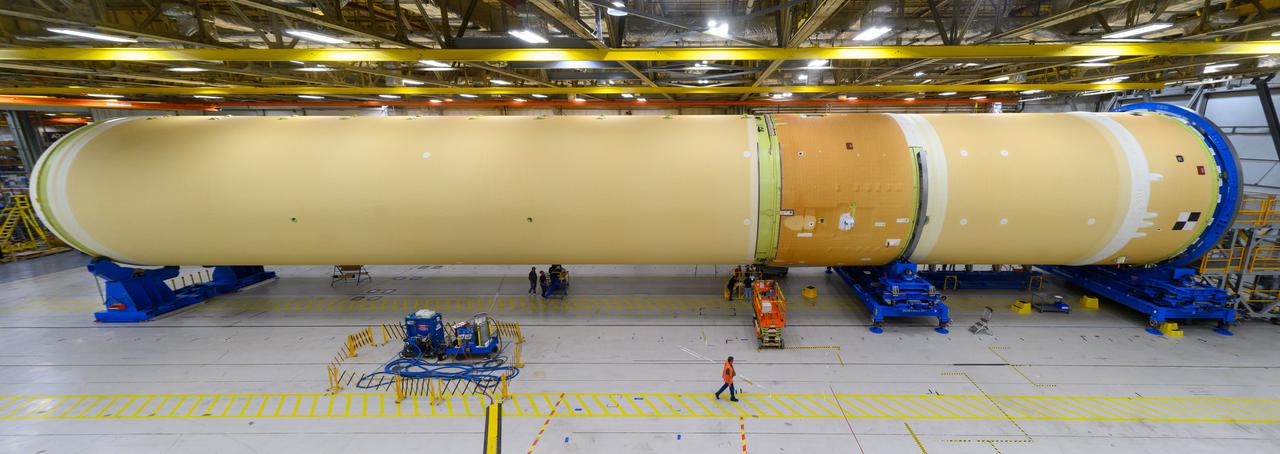

NASA joined the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis II mission on March 18. This completes assembly of four of the five large structures that make up the core stage that will help send the first astronauts to lunar orbit on Artemis II. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. Engineers inserted 360 bolts to connect the forward assembly to the liquid hydrogen tank to make up the bulk of the stage. Only the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, remains to be added to form the final core stage. All parts of the core stage are manufactured by NASA and Boeing, the core stage lead contractor at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Currently, the team is building core stages for three Artemis missions. The first core stage is stacked with the rest of the SLS rocket, which will launch the Artemis I mission to the Moon this year. Together with its twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for Artemis missions and future deep space exploration.

NASA joined the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis II mission on March 18. This completes assembly of four of the five large structures that make up the core stage that will help send the first astronauts to lunar orbit on Artemis II. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. Engineers inserted 360 bolts to connect the forward assembly to the liquid hydrogen tank to make up the bulk of the stage. Only the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, remains to be added to form the final core stage. All parts of the core stage are manufactured by NASA and Boeing, the core stage lead contractor at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Currently, the team is building core stages for three Artemis missions. The first core stage is stacked with the rest of the SLS rocket, which will launch the Artemis I mission to the Moon this year. Together with its twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for Artemis missions and future deep space exploration.
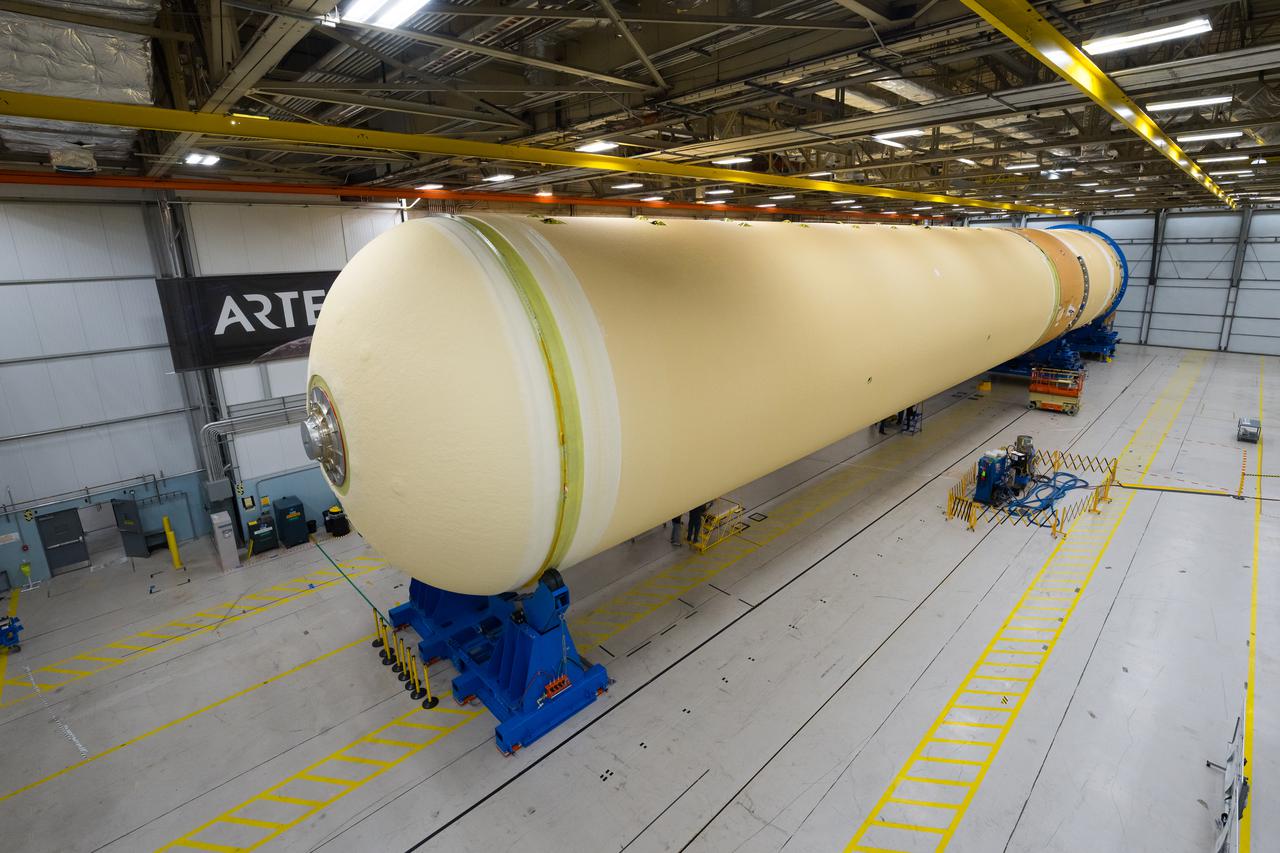

NASA joined the Space Launch System rocket’s core stage forward assembly with the 130-foot liquid hydrogen tank for the Artemis II mission on March 18. This completes assembly of four of the five large structures that make up the core stage that will help send the first astronauts to lunar orbit on Artemis II. The 66-foot forward assembly consists of the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank and the intertank, which were mated earlier. Engineers inserted 360 bolts to connect the forward assembly to the liquid hydrogen tank to make up the bulk of the stage. Only the engine section, which is currently being outfitted and includes the main propulsion systems that connect to the four RS-25 engines, remains to be added to form the final core stage. All parts of the core stage are manufactured by NASA and Boeing, the core stage lead contractor at the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Currently, the team is building core stages for three Artemis missions. The first core stage is stacked with the rest of the SLS rocket, which will launch the Artemis I mission to the Moon this year. Together with its twin solid rocket boosters, the core stage will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. The SLS rocket and the Orion spacecraft form the foundation for Artemis missions and future deep space exploration.
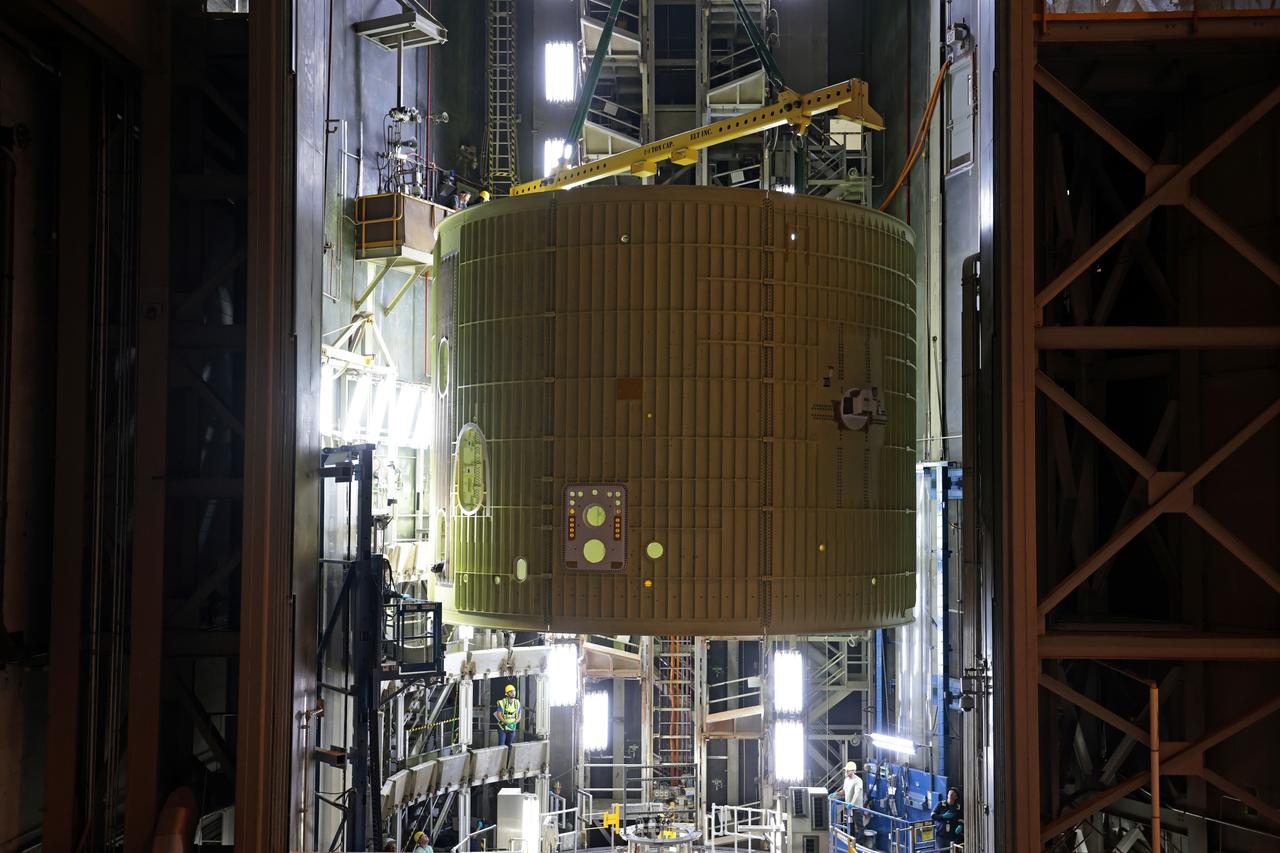

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
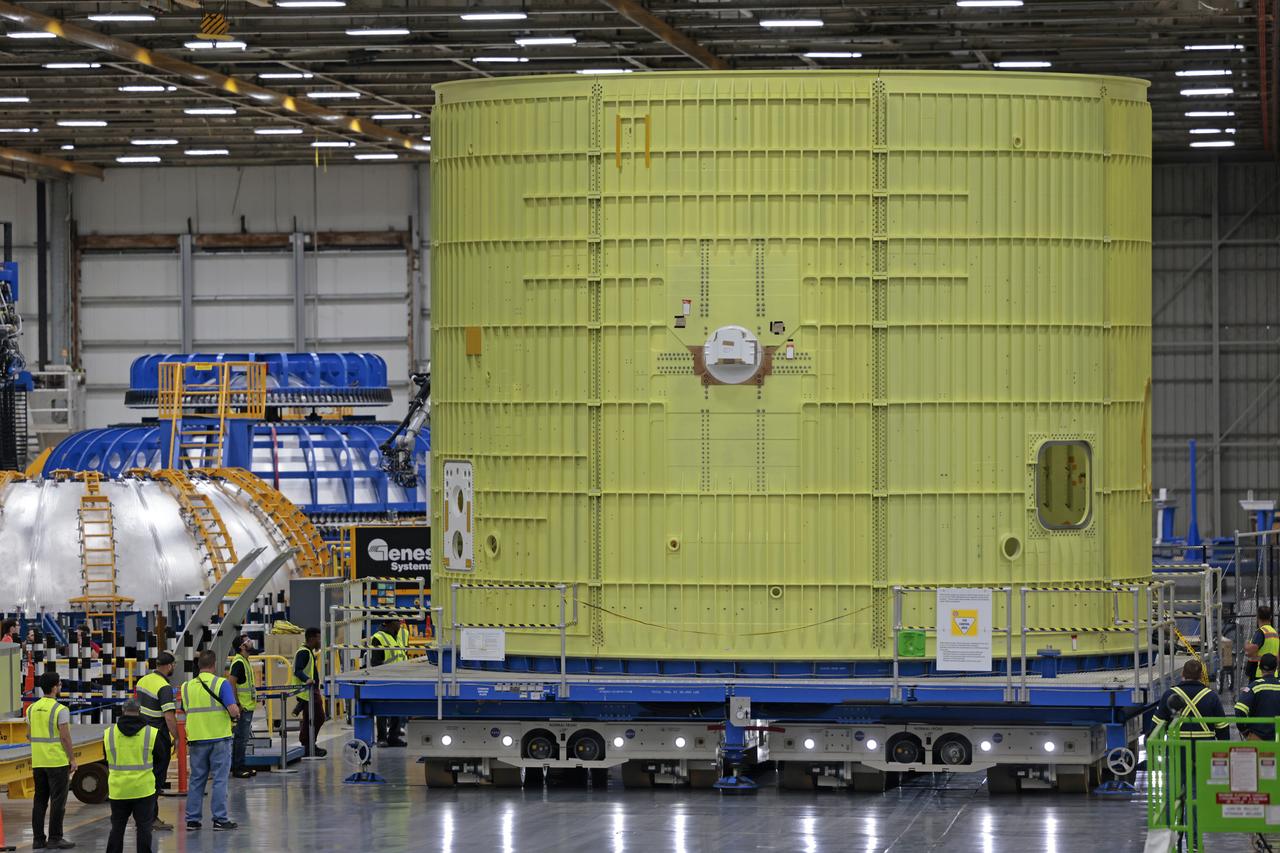

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
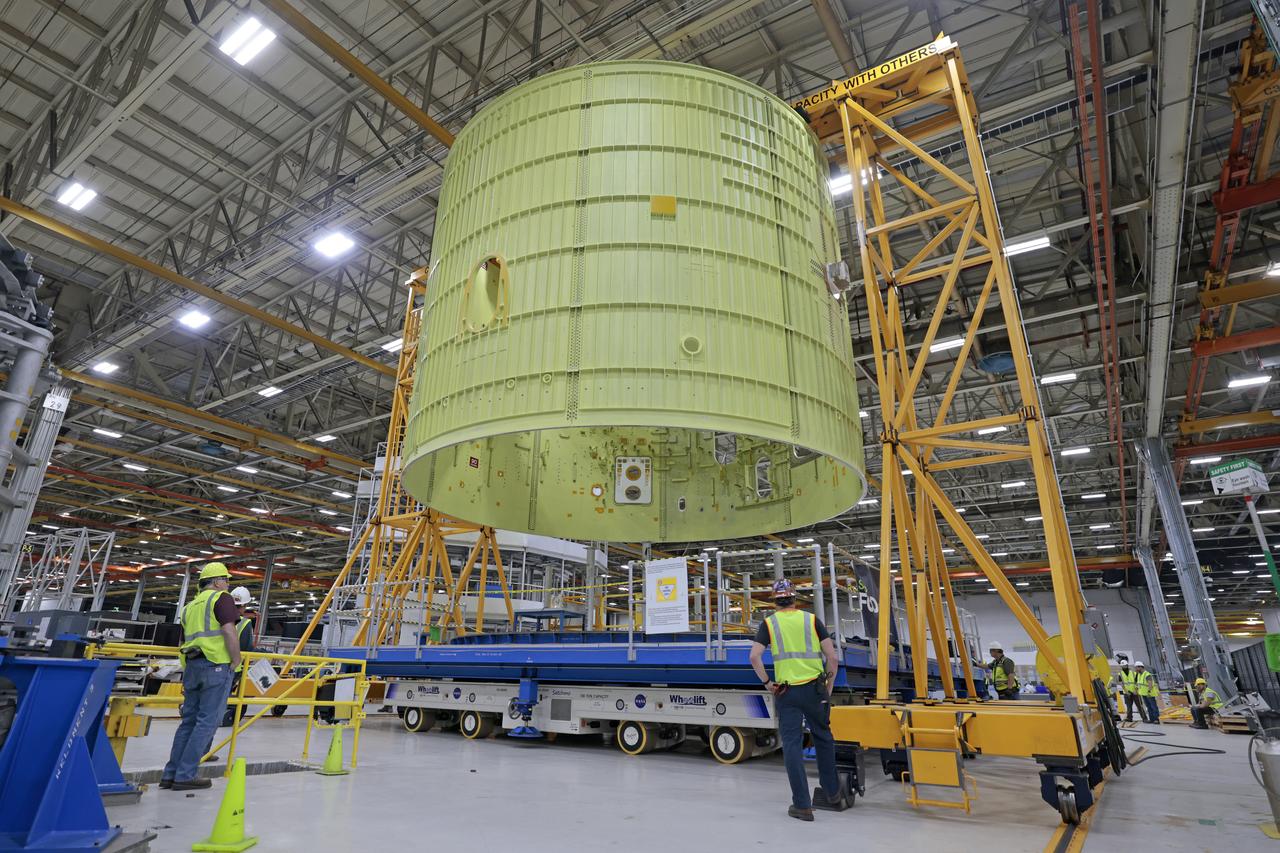

Technicians at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility move the intertank of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis III to Cell G on October 26, 2022 to await application of the thermal protection system. Thermal protection systems protect space vehicles from aerodynamic heating during entry to planet atmosphere and re-entry to earth atmosphere. The intertank lays between the liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank. Together with the engine section and the forward skirt, they comprise the SLS core stage. The liquid hydrogen tank and liquid oxygen tank hold 733,000 gallons of propellant to power the stage’s four RS-25 engines needed for liftoff and Artemis missions to the Moon and future missions to Mars. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
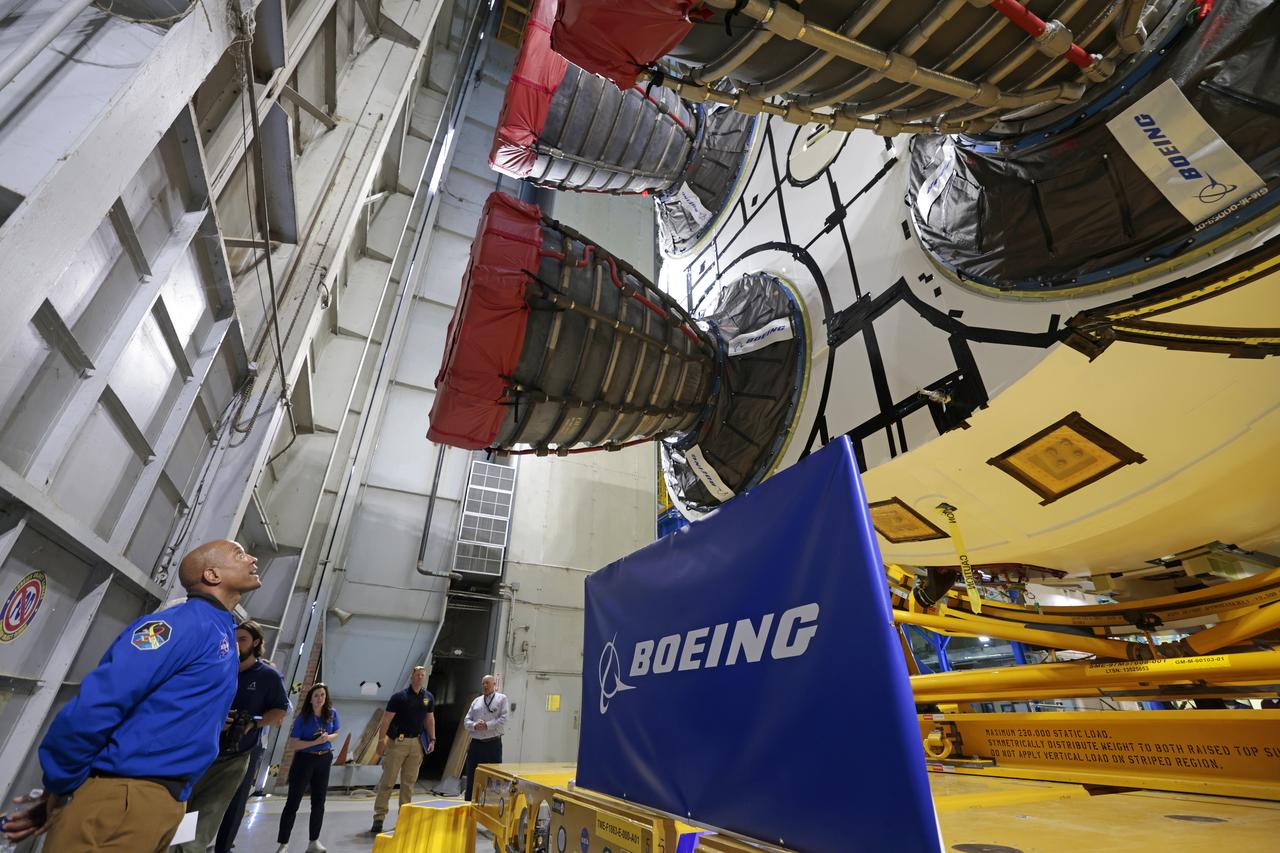

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
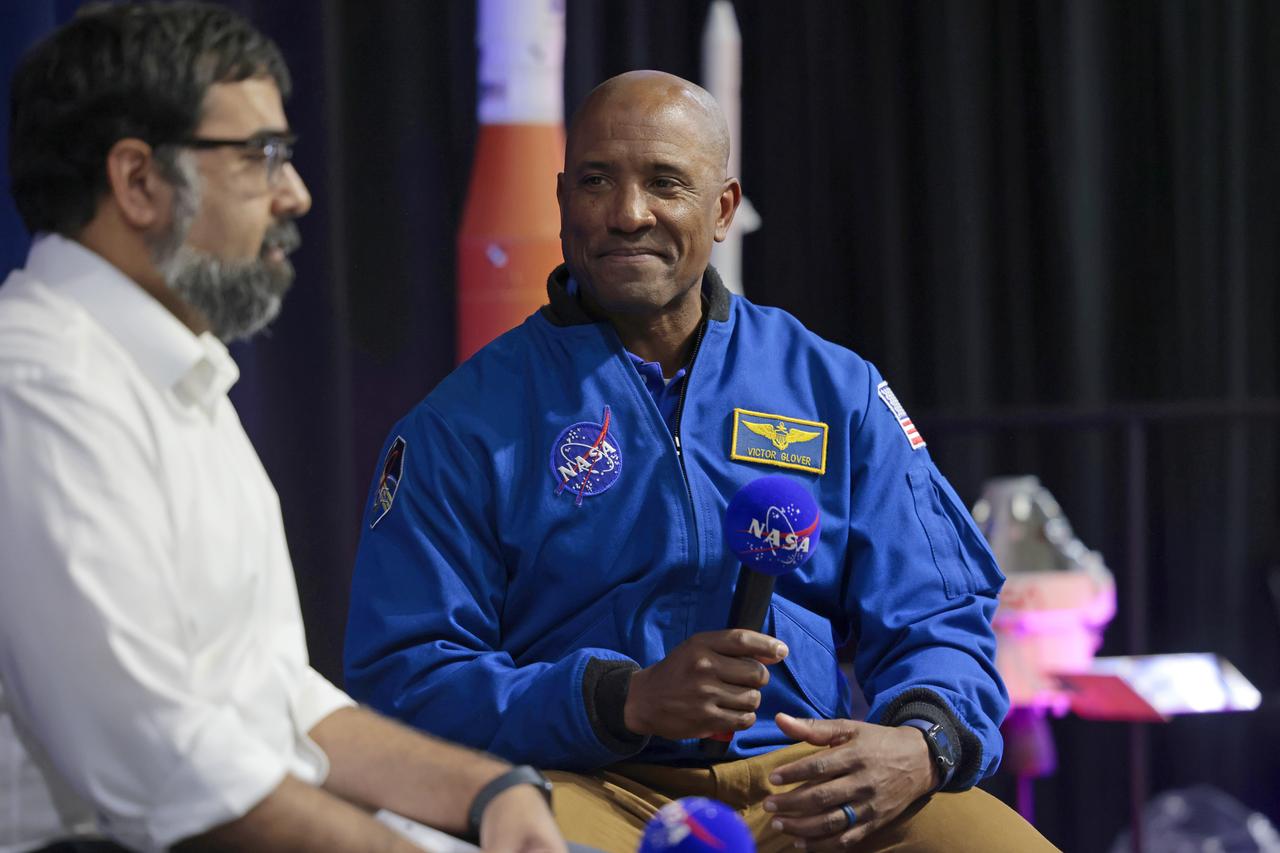

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
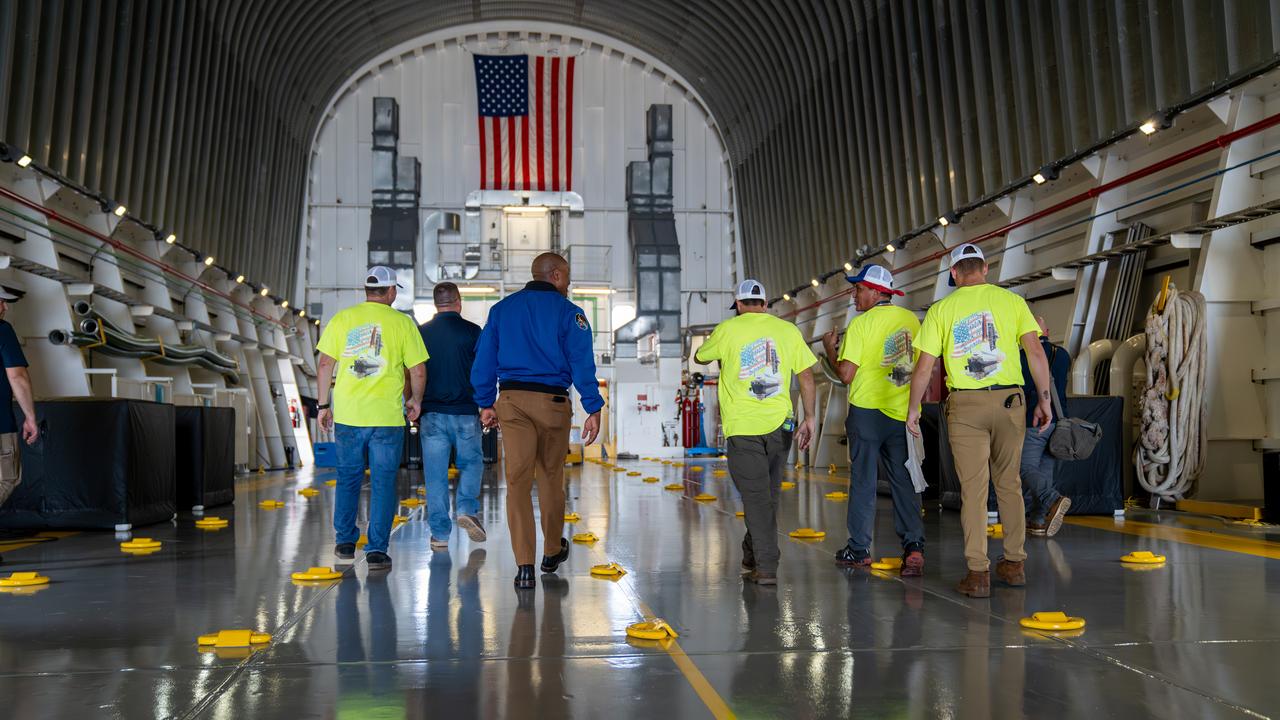

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
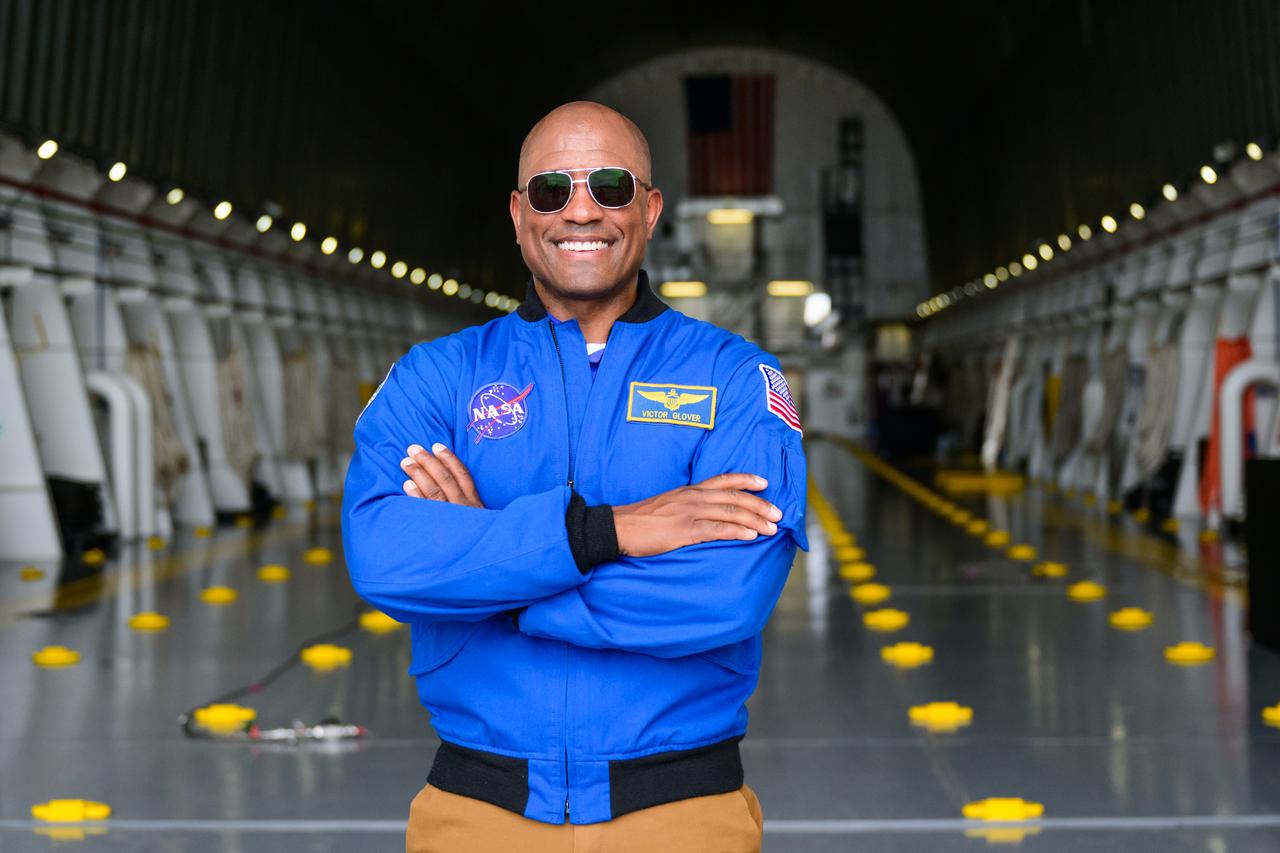

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
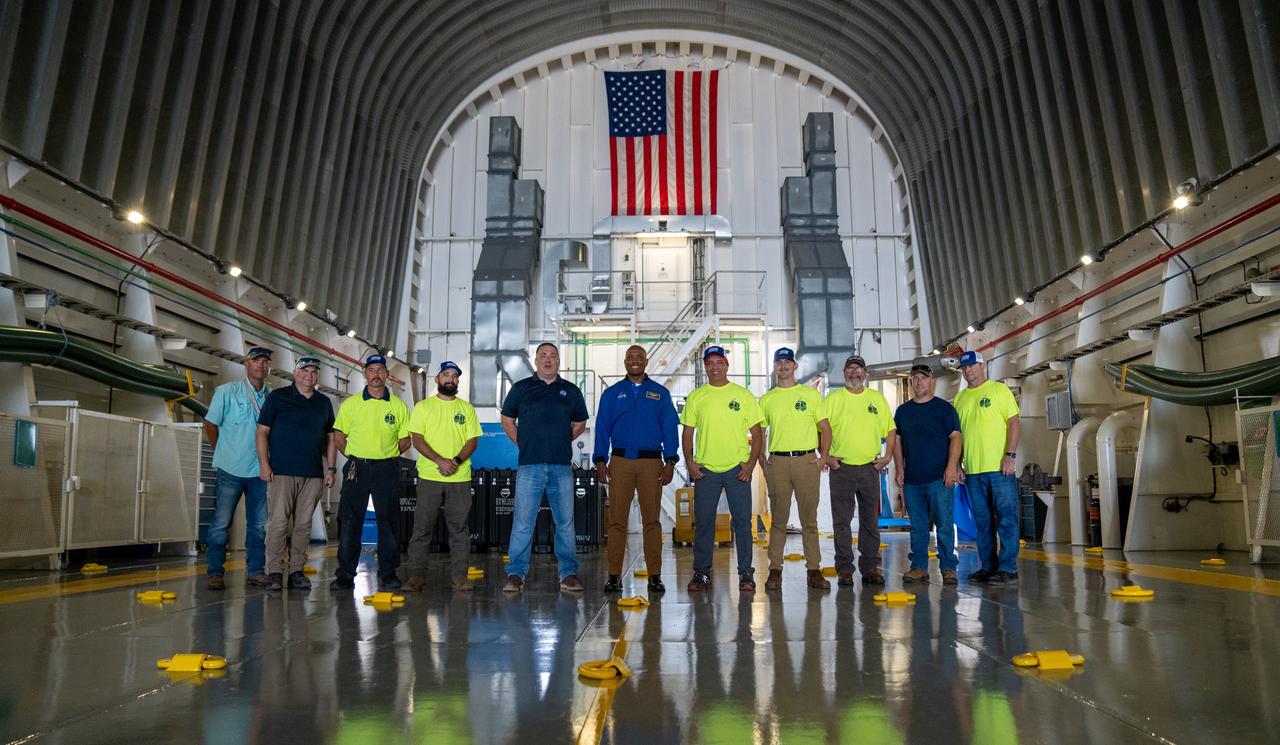

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
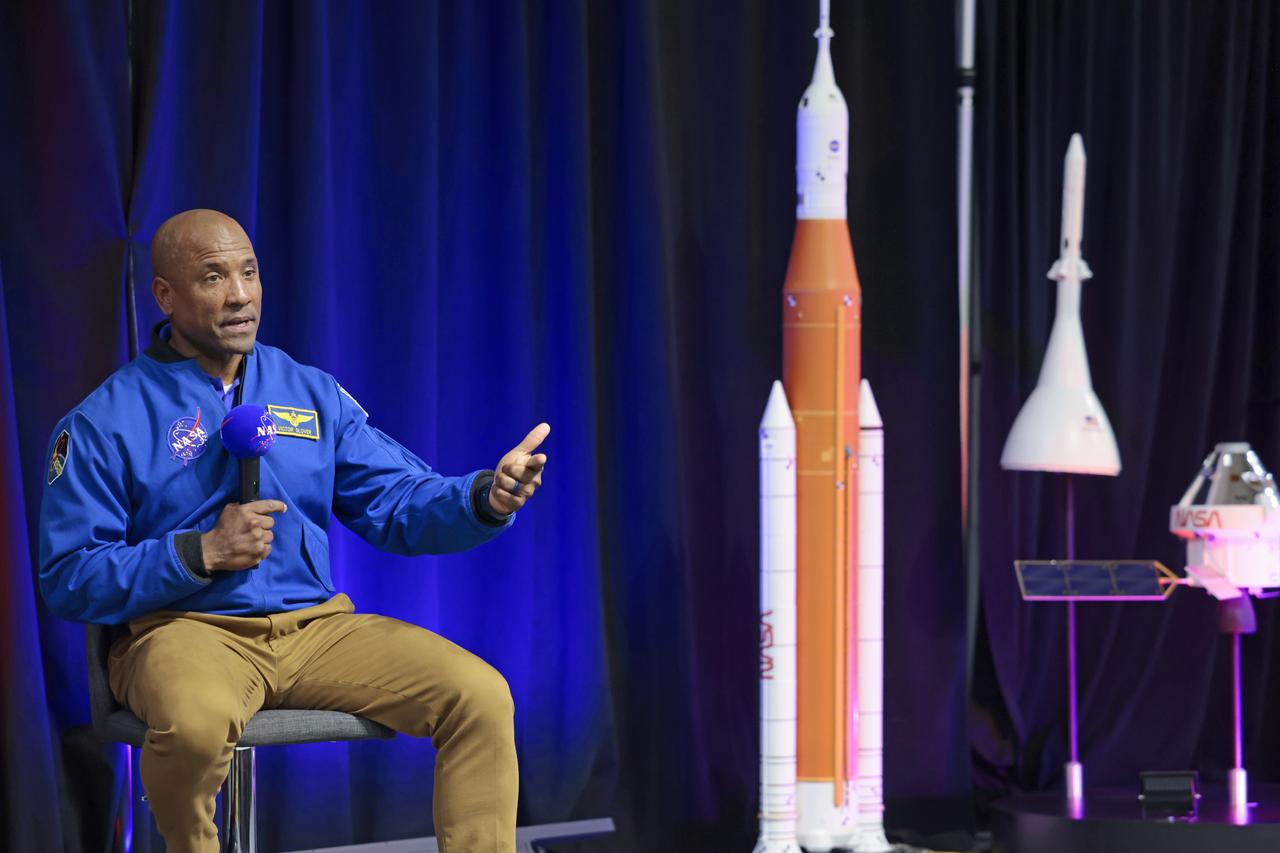

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
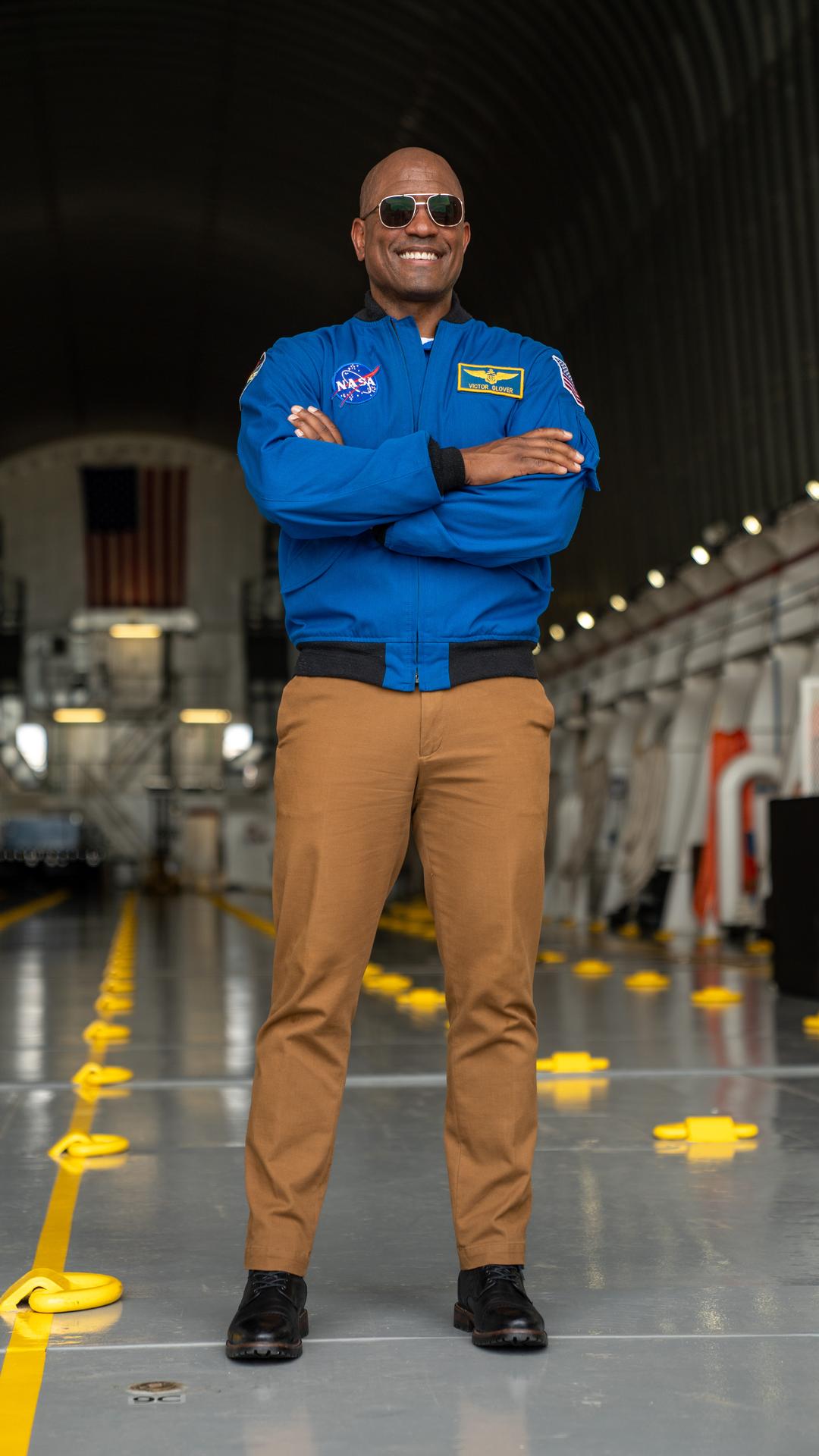

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

Illustration of the SLS Exploration Upper Stage, or EUS. The Exploration Upper Stage will be used on the second configuration of the SLS rocket, known as Block 1B, and will provide in-space propulsion to send astronauts in NASA’s Orion spacecraft and heavy cargo on a precise trajectory to the Moon. The evolution of the rocket to SLS Block 1B configuration with EUS enables SLS to launch 40% more cargo to the Moon along with the crew. Manufacturing both the core stage and Exploration Upper Stage is a collaborative effort between NASA and Boeing, the lead contractor for EUS and the SLS core stage. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single mission. The SLS rocket, NASA’s Orion spacecraft, Gateway, and human landing system are part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration. Under the Artemis program, NASA is working to land the first woman and the next man on the Moon to pave the way for sustainable exploration at the Moon and future missions to Mars. (NASA)
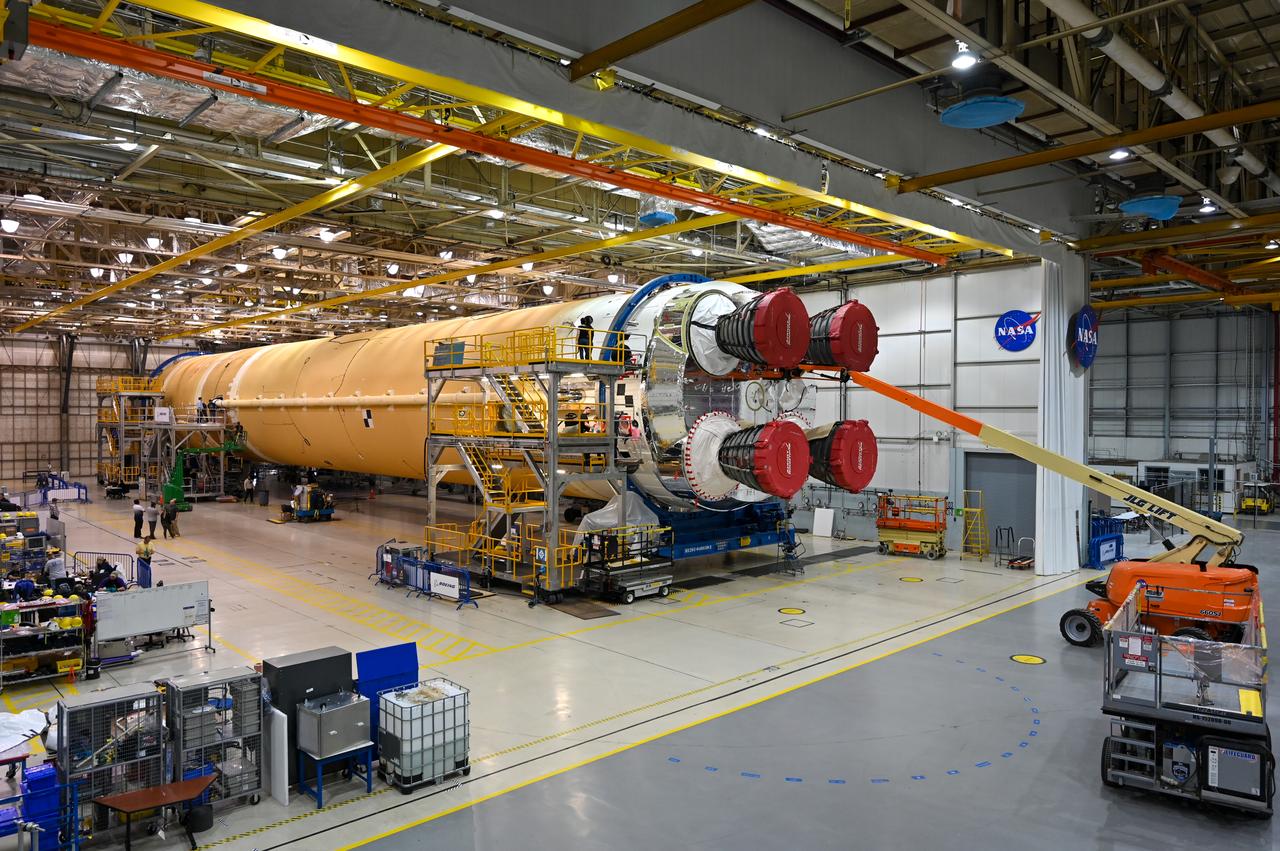

This image shows the core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket without scaffolding at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. NASA and the contractor team used the scaffolding previously positioned around the 212-foot core stage to assess the stage’s inside and check out the electronic systems distributed throughout the stage, including avionics and propulsion systems, that will enable the stage to operate during launch and flight. The team will continue to check out these systems at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi, where it will undergo the core stage Green Run testing.

Lockheed Martin spacecraft specialists check the cruise stage of NASA's InSight spacecraft in this photo taken June 22, 2017, in a Lockheed Martin clean room facility in Littleton, Colorado. The cruise stage will provide vital functions during the flight from Earth to Mars, and then will be jettisoned before the InSight lander, enclosed in its aeroshell, enters Mars' atmosphere. The InSight mission (for Interior Exploration using Seismic Investigations, Geodesy and Heat Transport) is scheduled to launch in May 2018 and land on Mars Nov. 26, 2018. It will investigate processes that formed and shaped Mars and will help scientists better understand the evolution of our inner solar system's rocky planets, including Earth. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21845
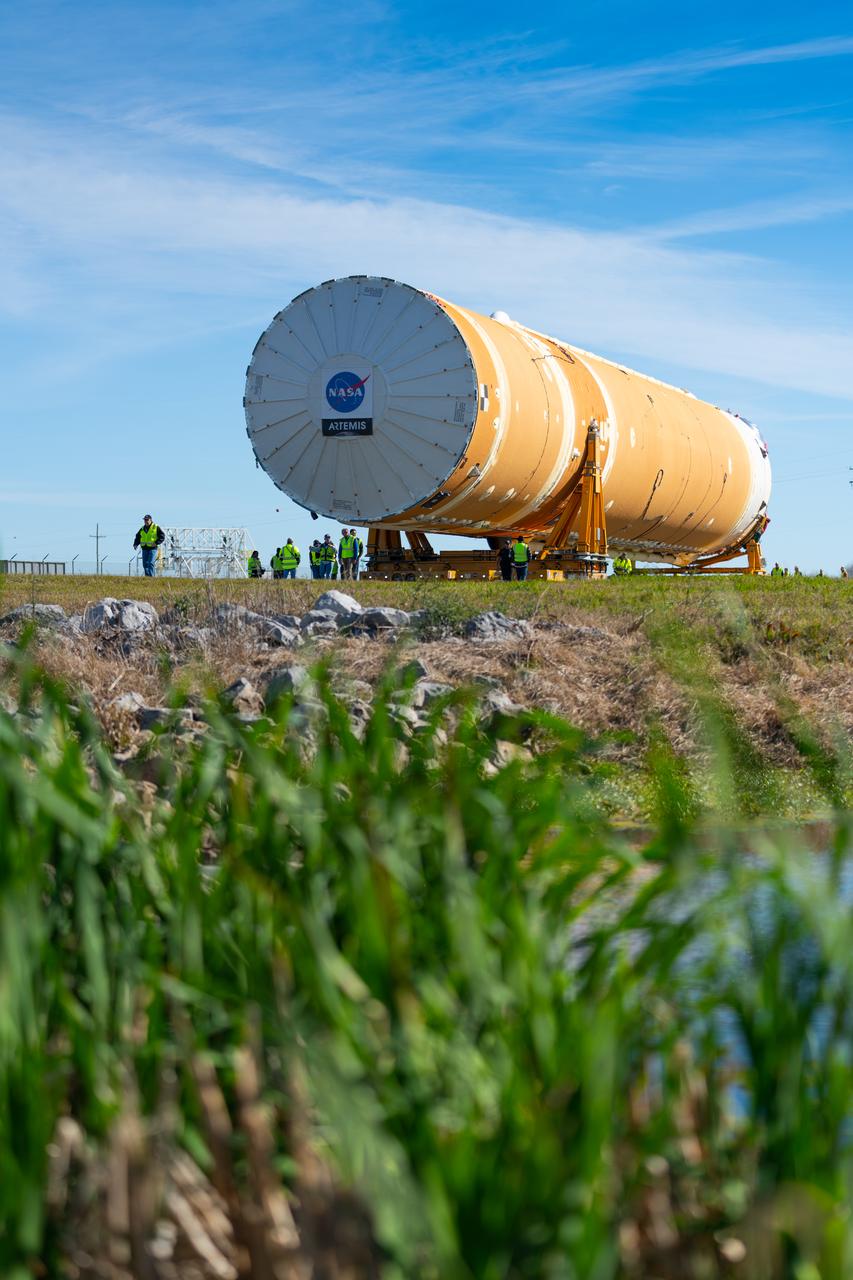

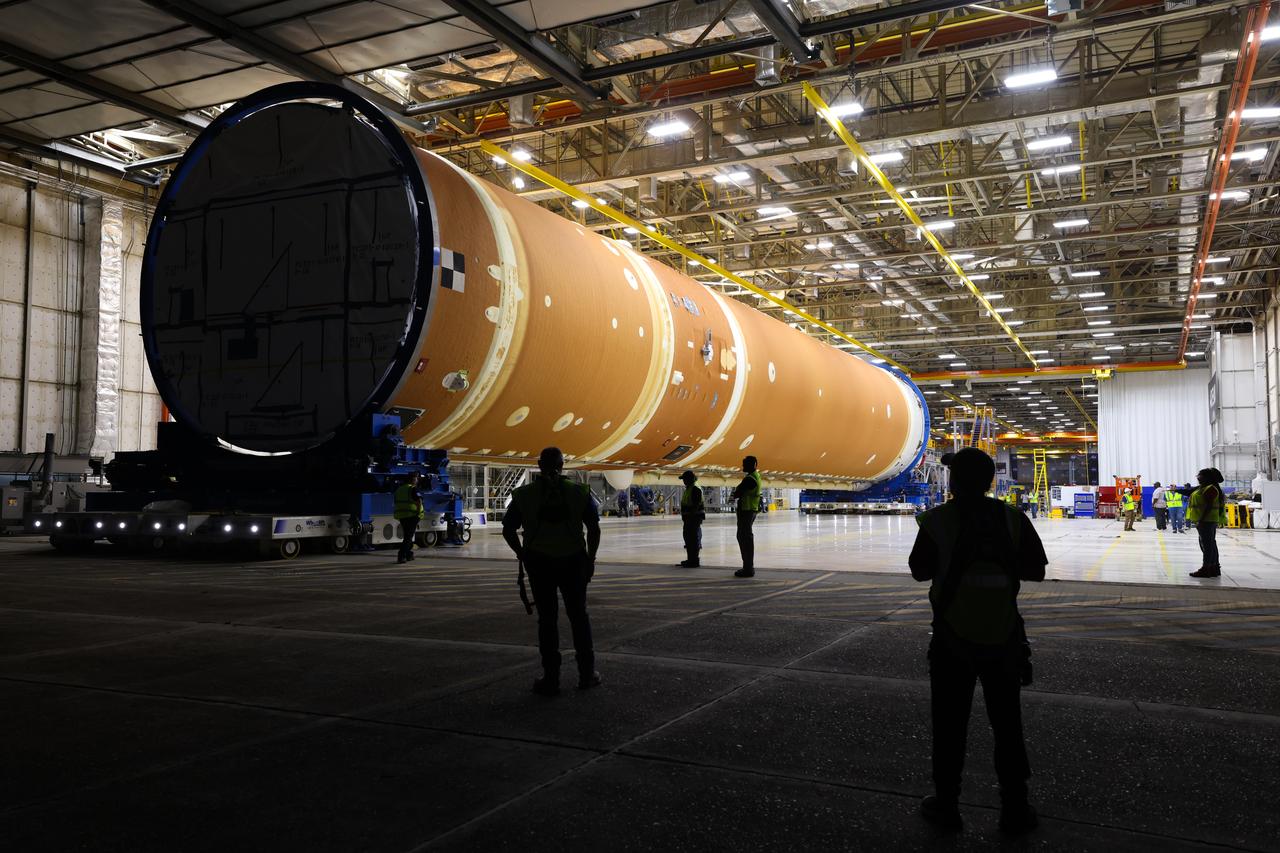
These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
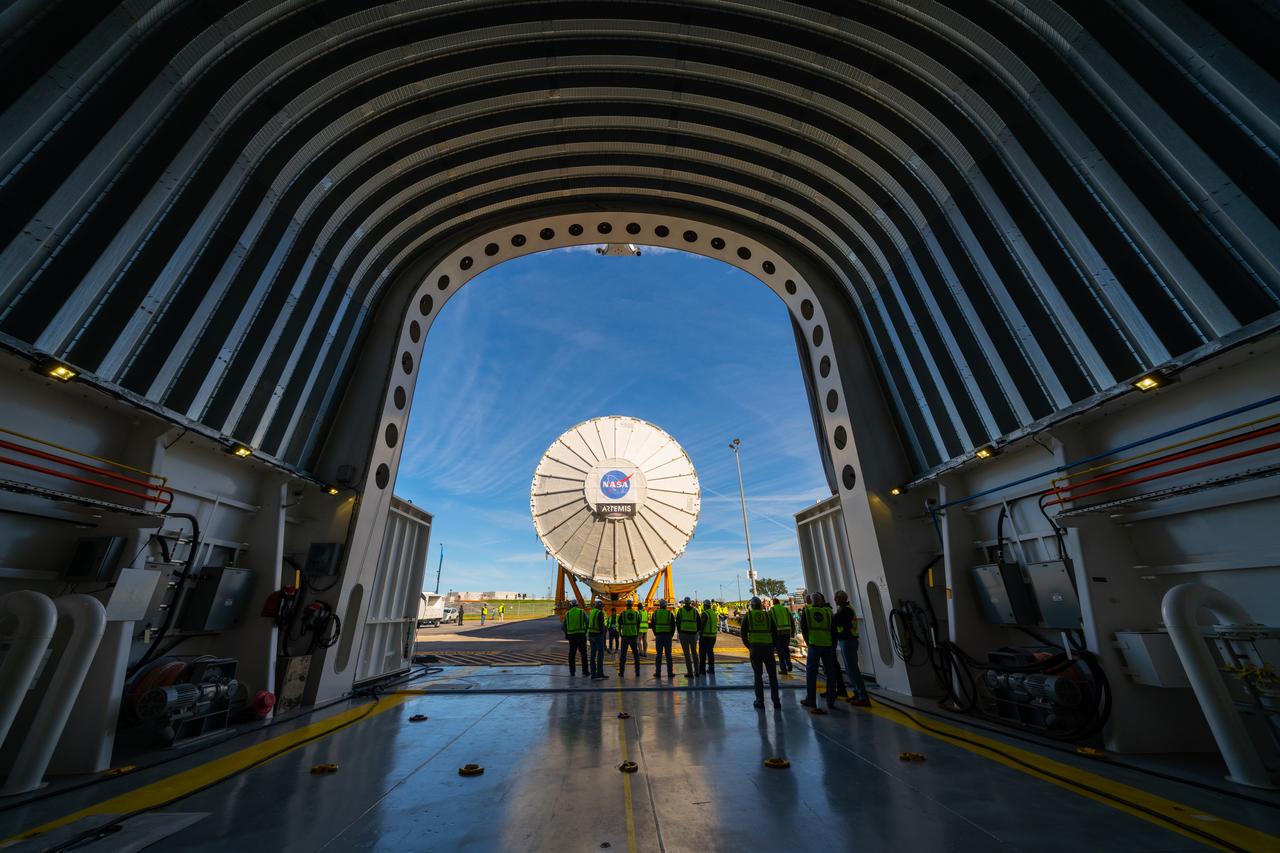

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
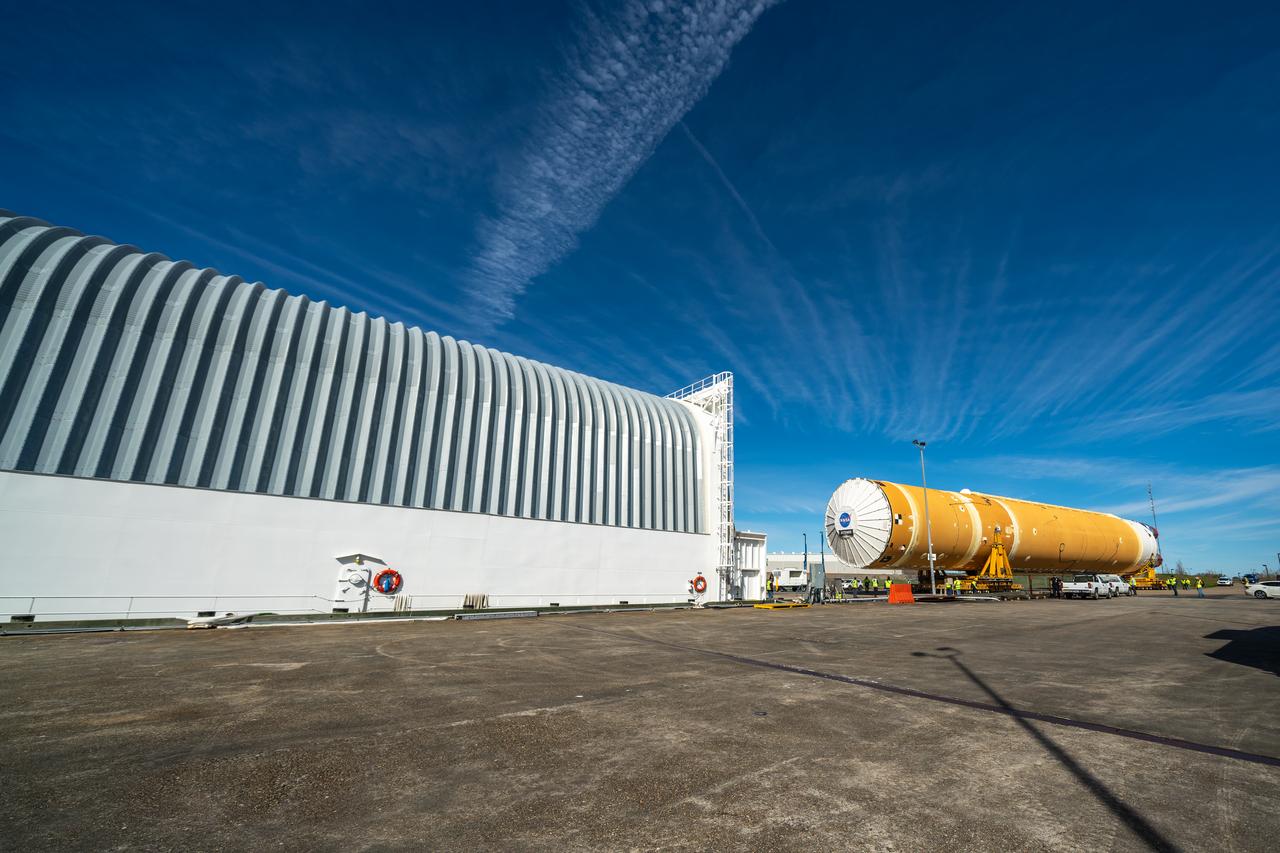

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
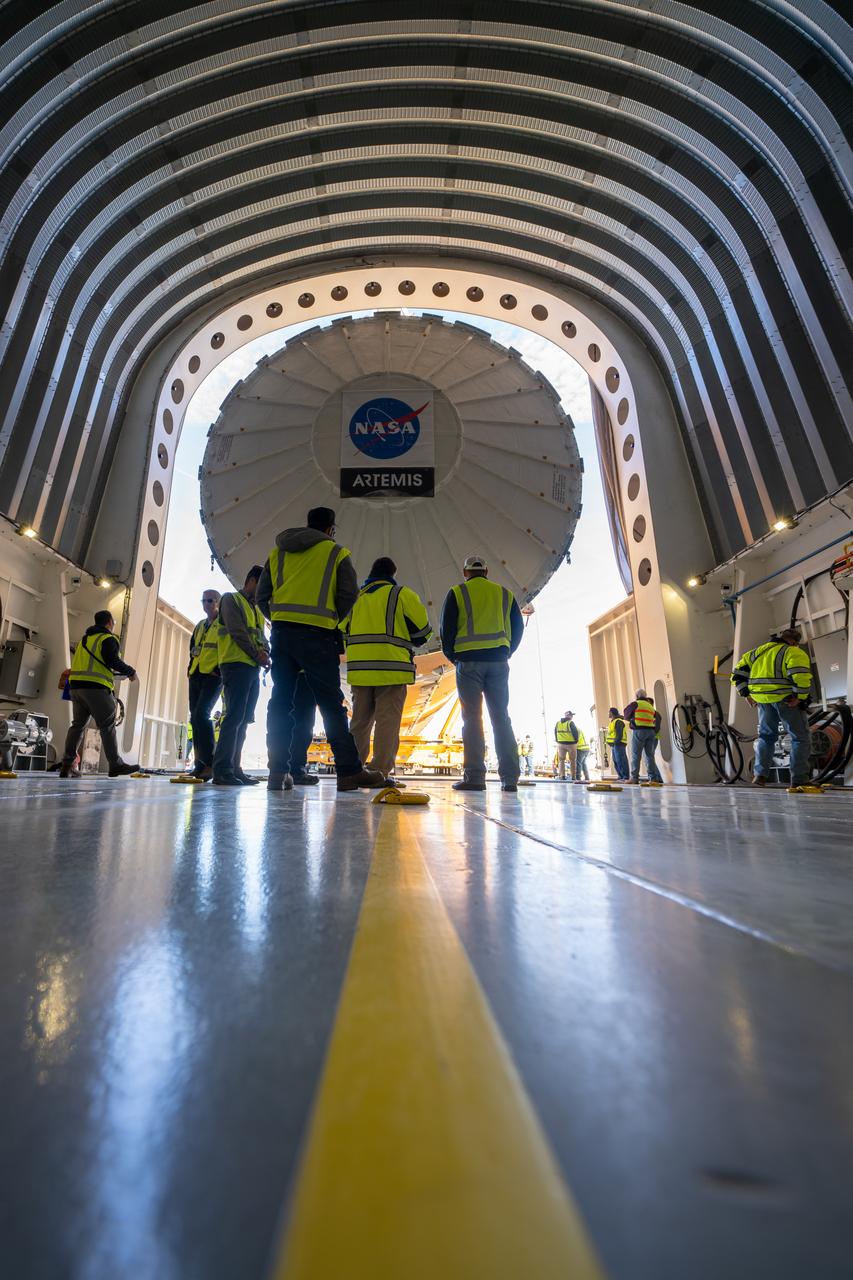

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
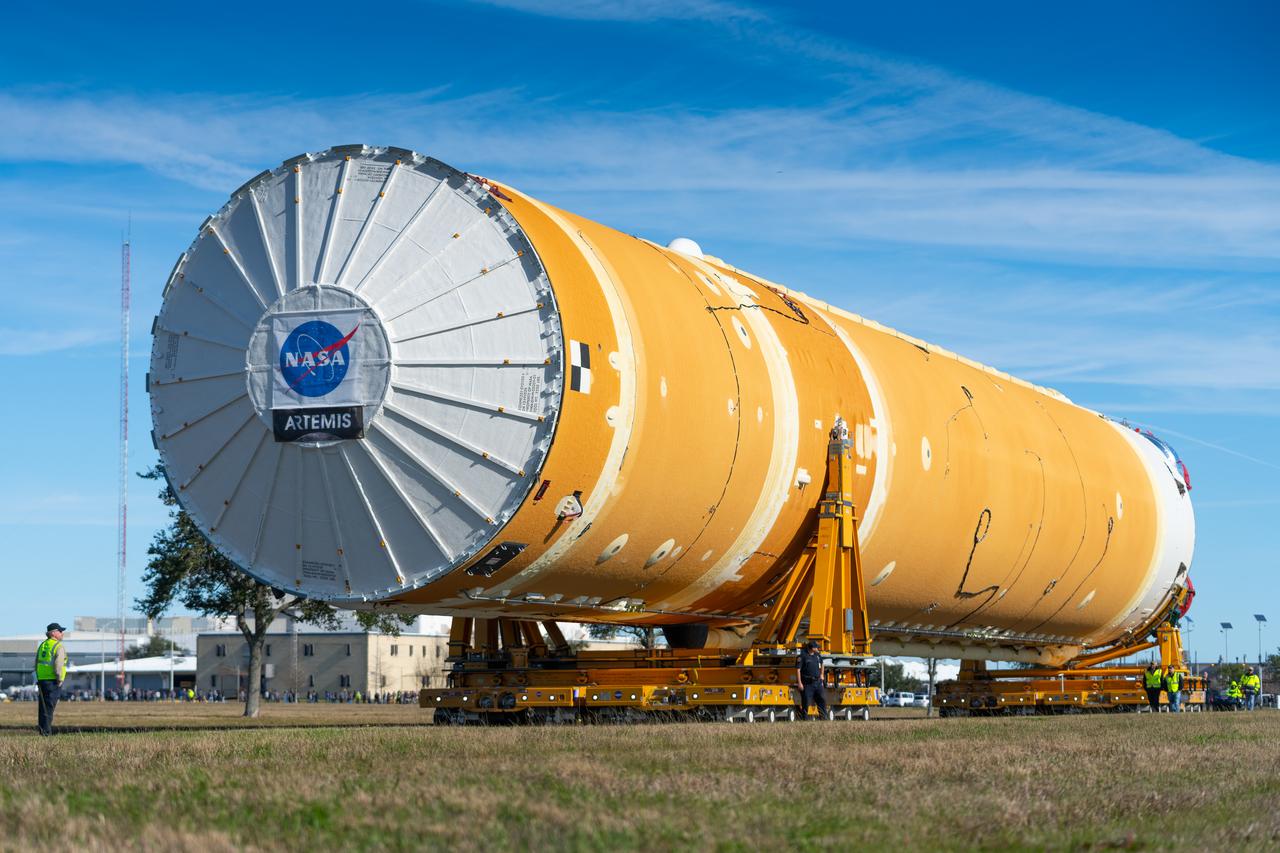

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
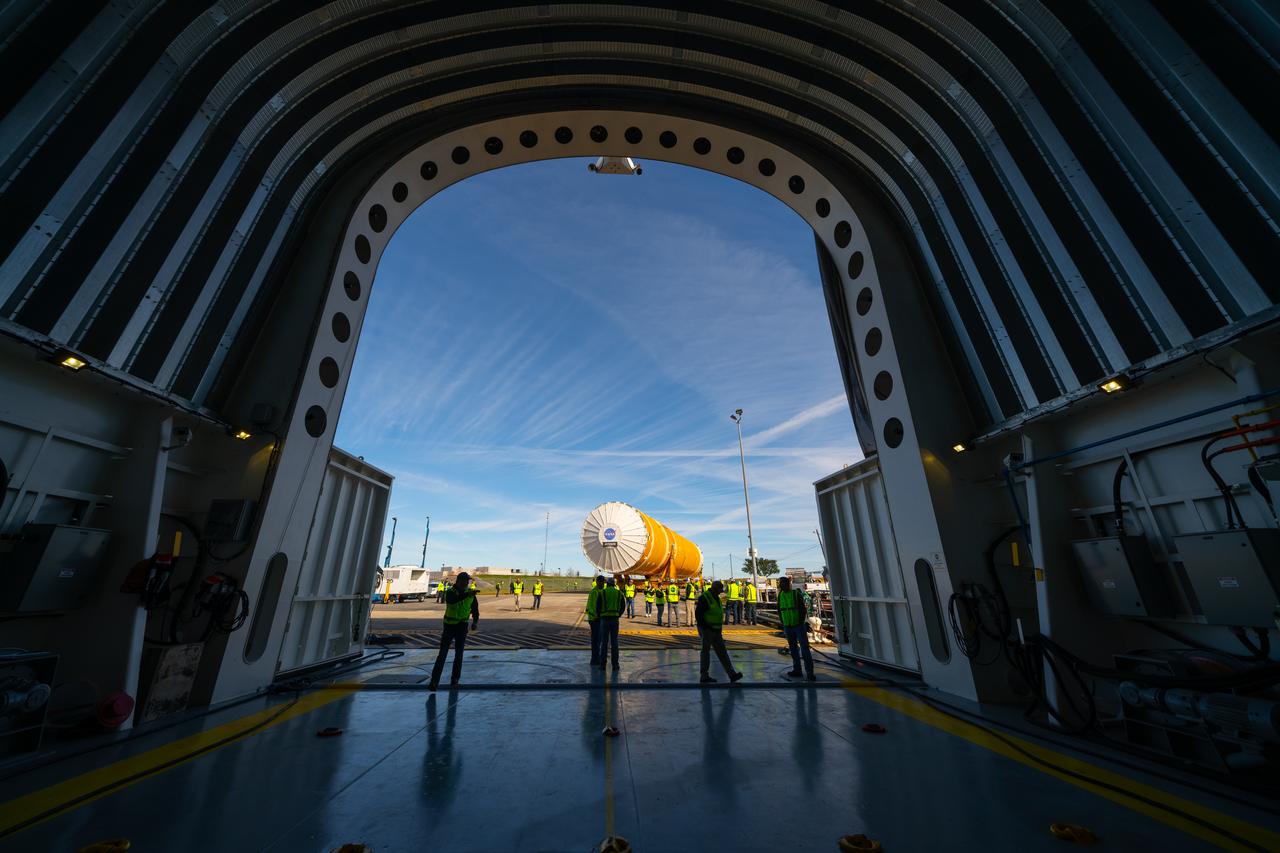

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
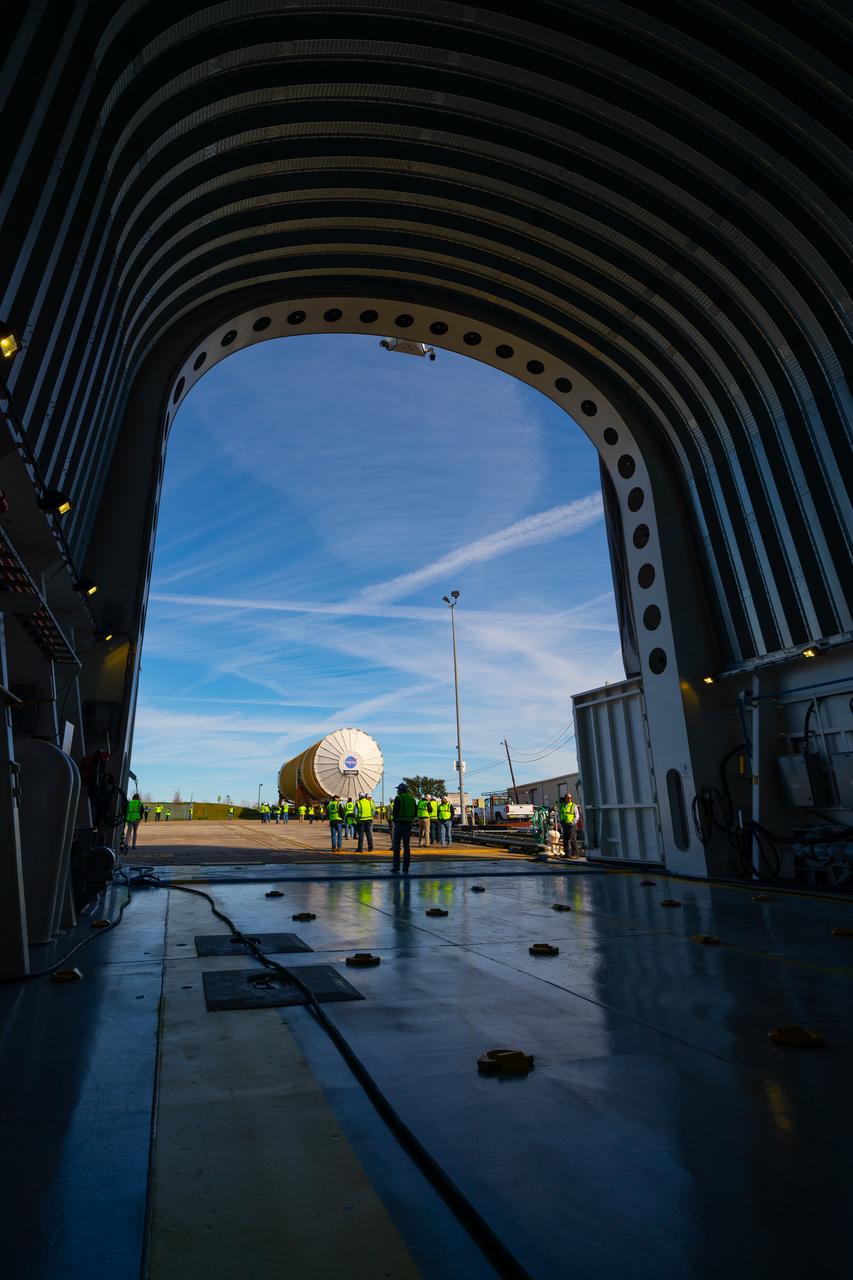

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
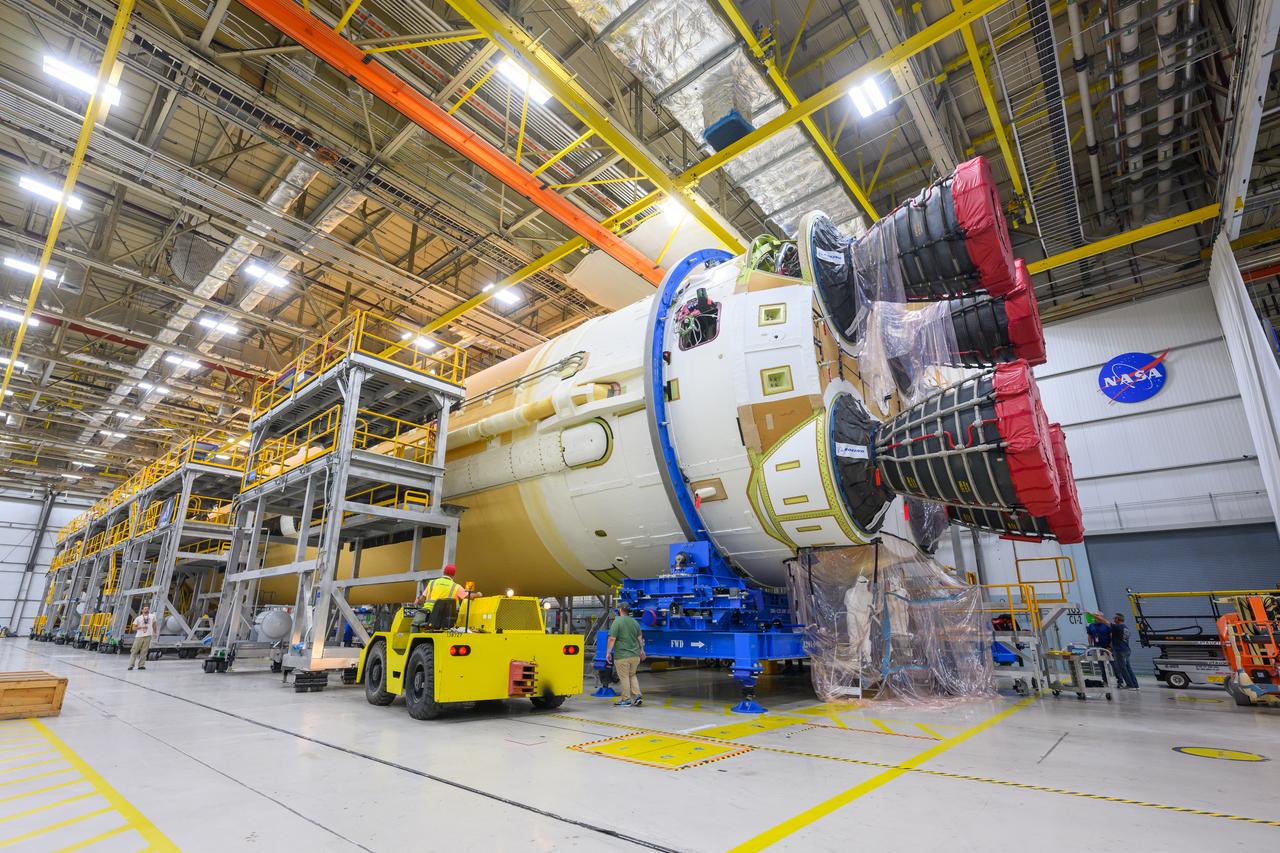

Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans are preparing the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) for shipment to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 212-foot-tall core stage and its four RS-25 engines will help power Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews removed the external access stands, or scaffolding, in preparation for moving the rocket hardware to another area of the facility.
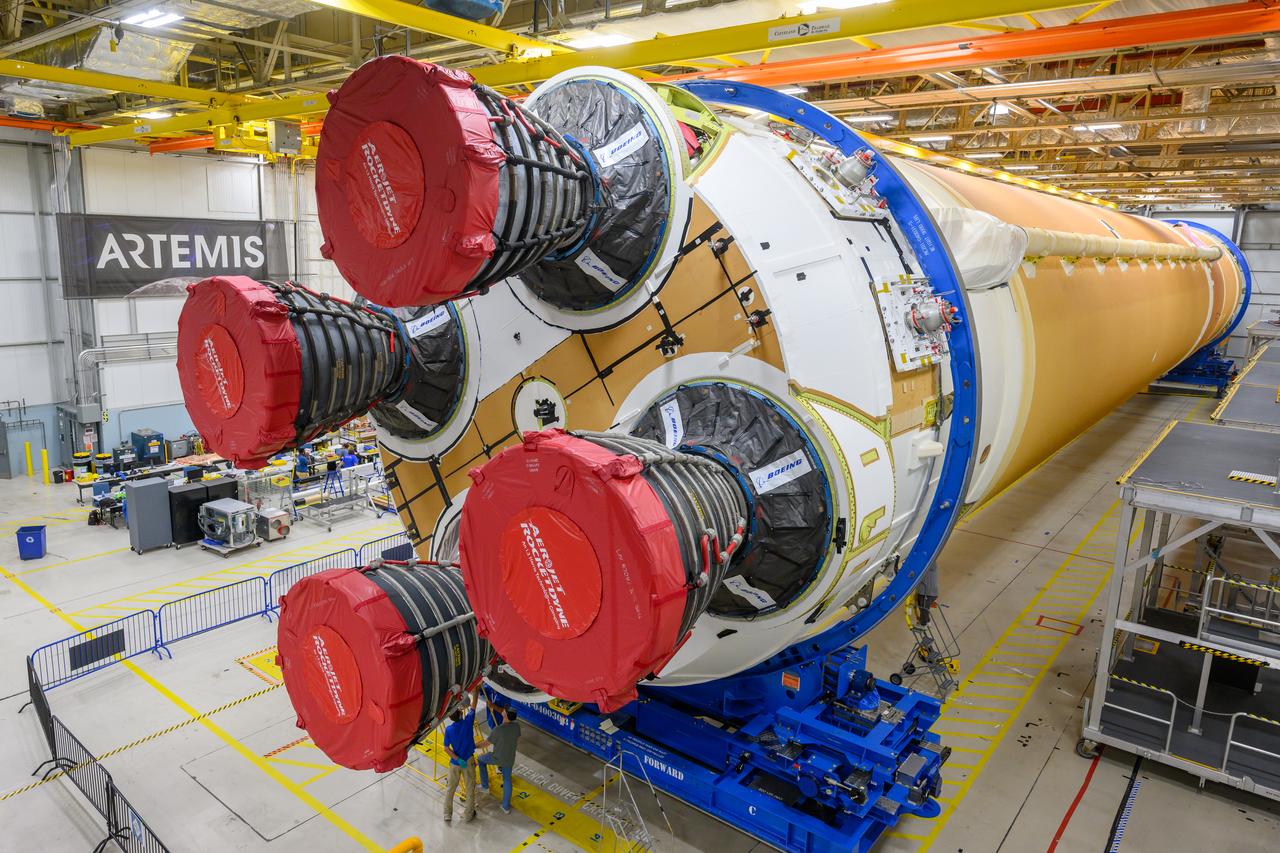
Teams at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans are preparing the core stage of the agency’s SLS (Space Launch System) for shipment to the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The 212-foot-tall core stage and its four RS-25 engines will help power Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews removed the external access stands, or scaffolding, in preparation for moving the rocket hardware to another area of the facility.

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
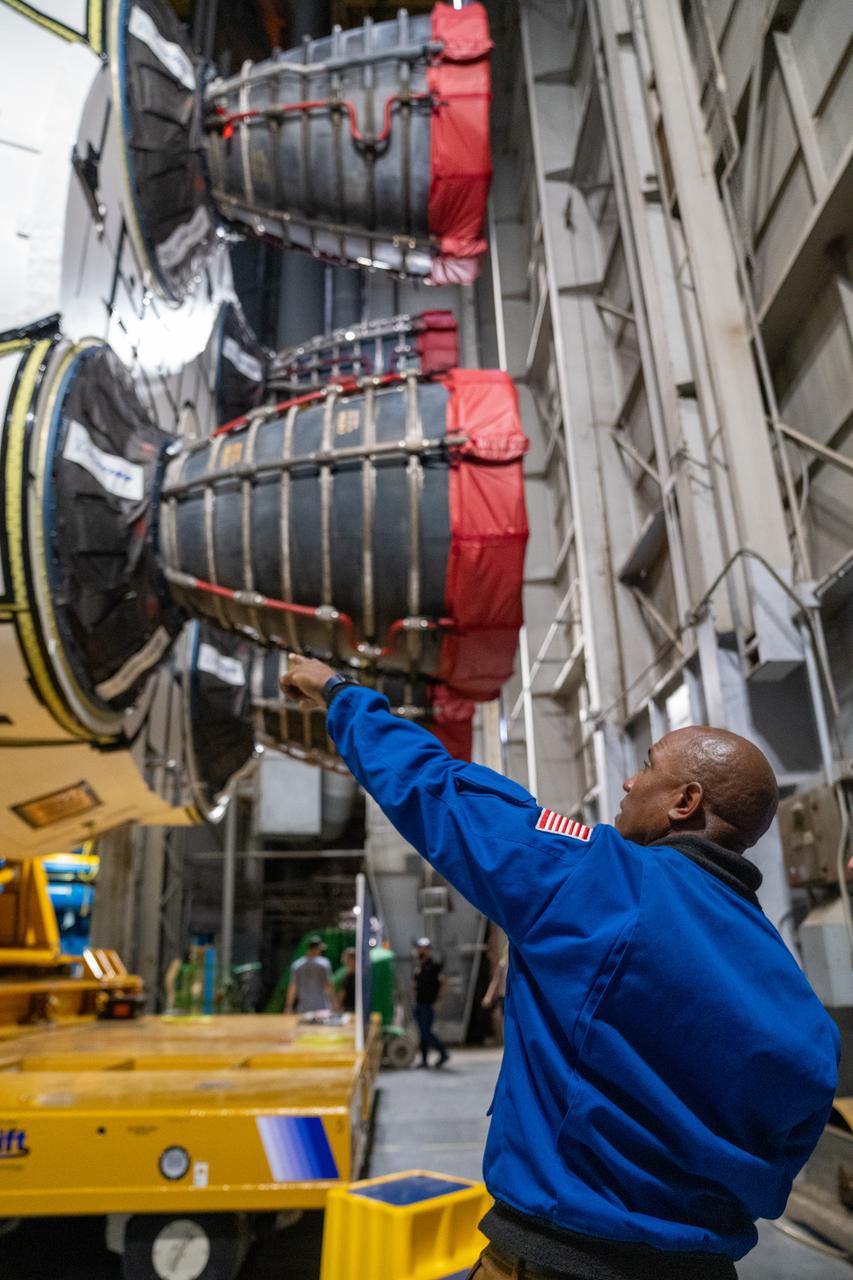

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
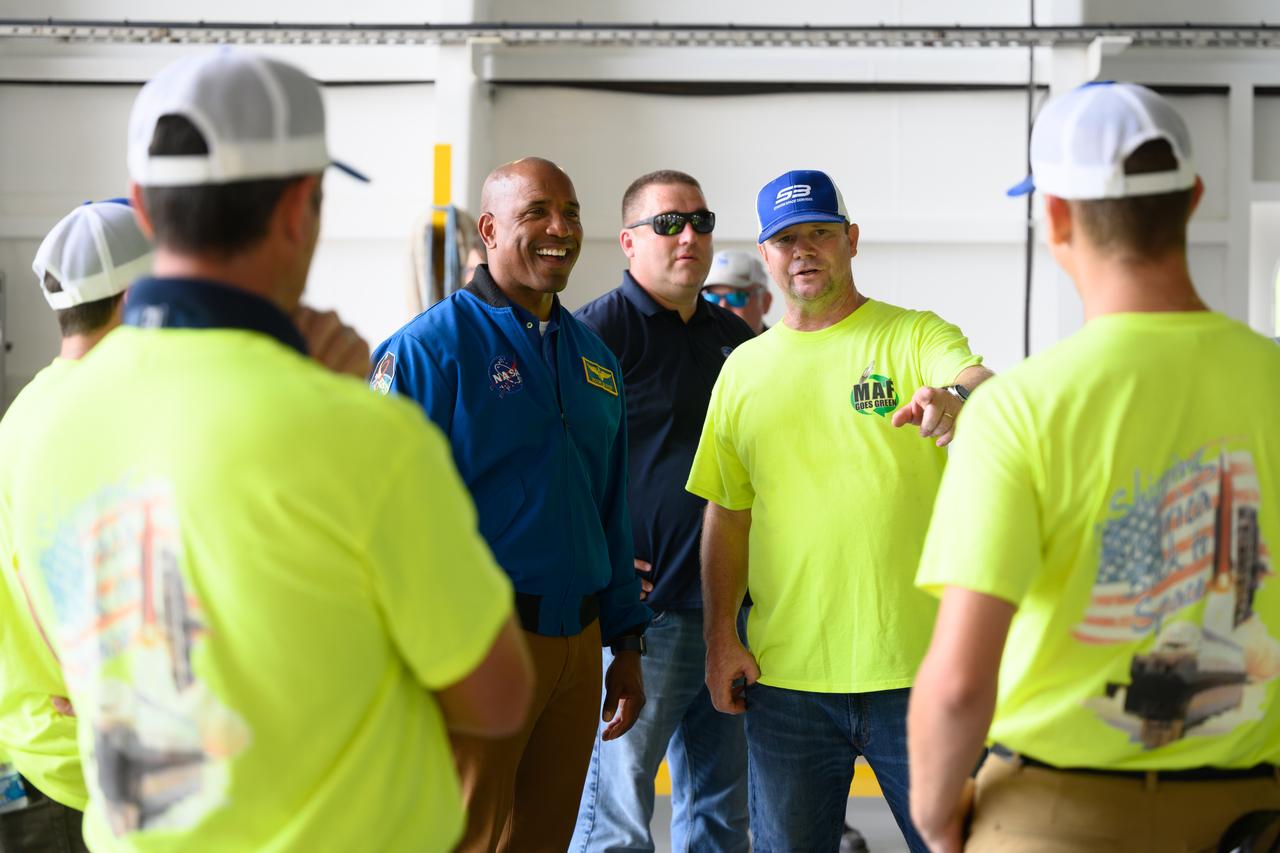

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
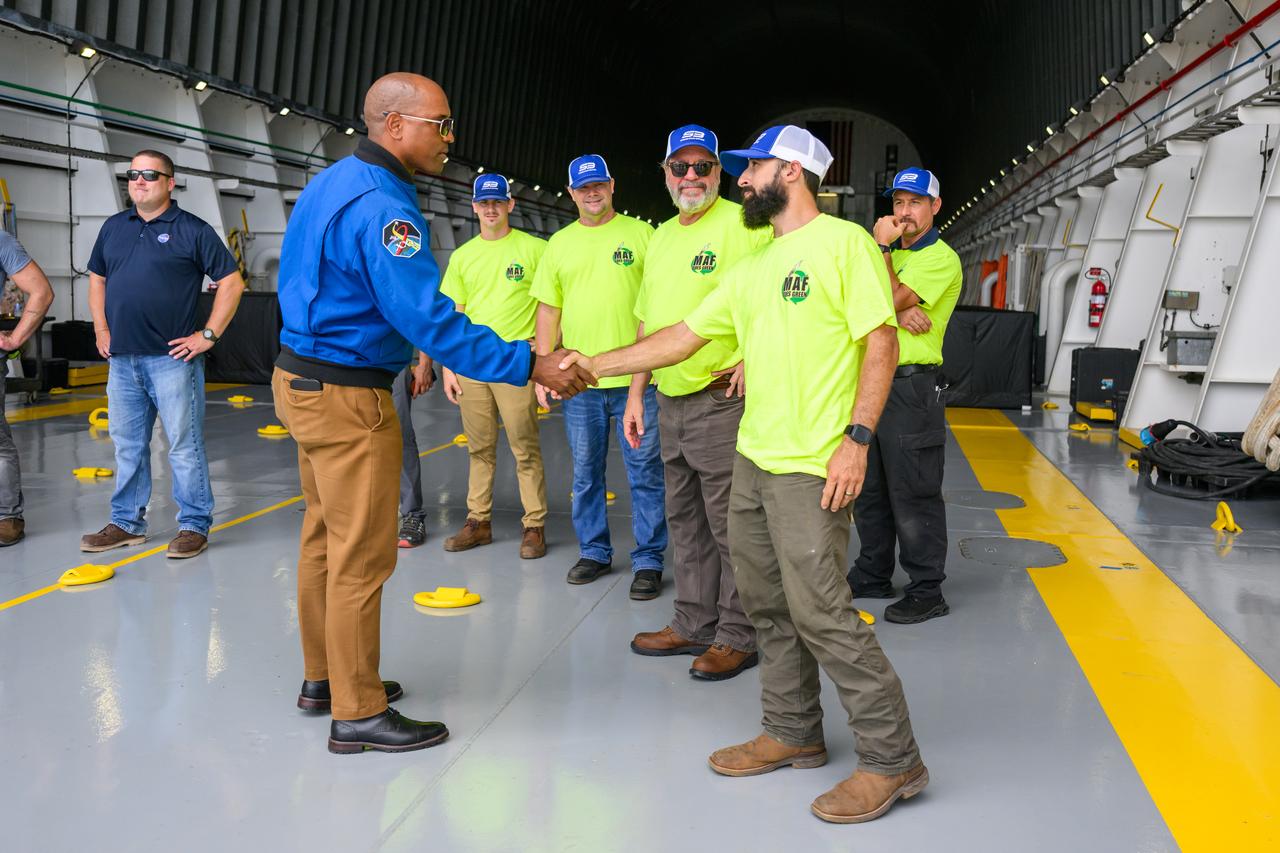

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
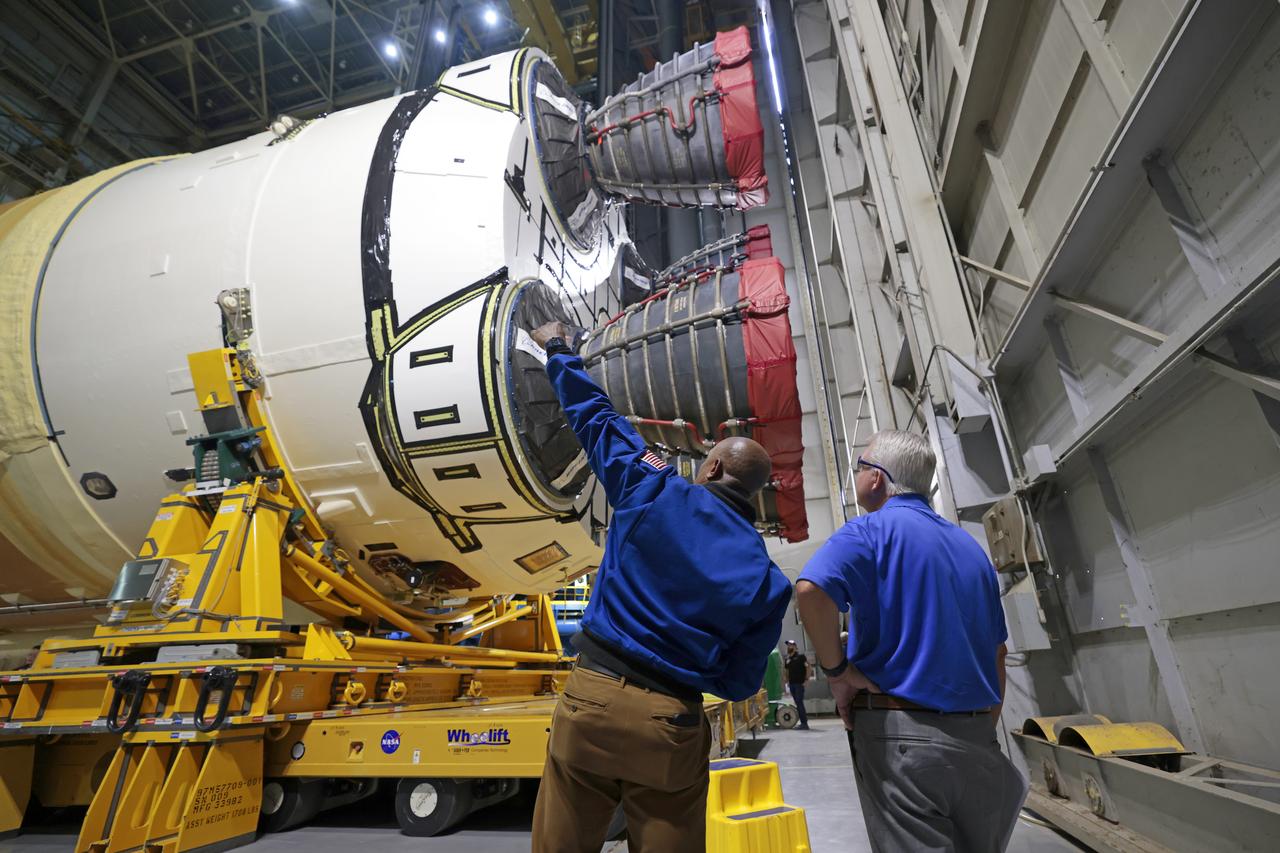

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
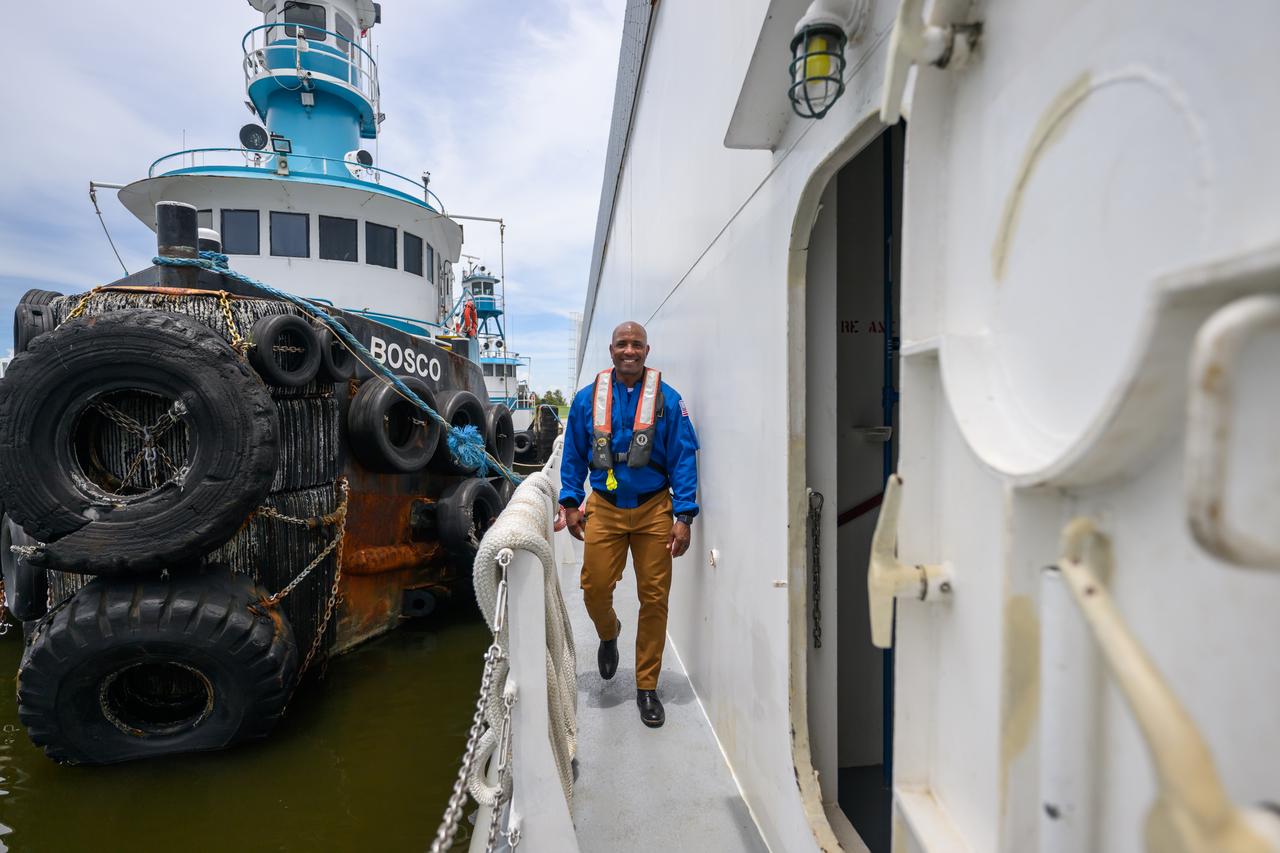

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
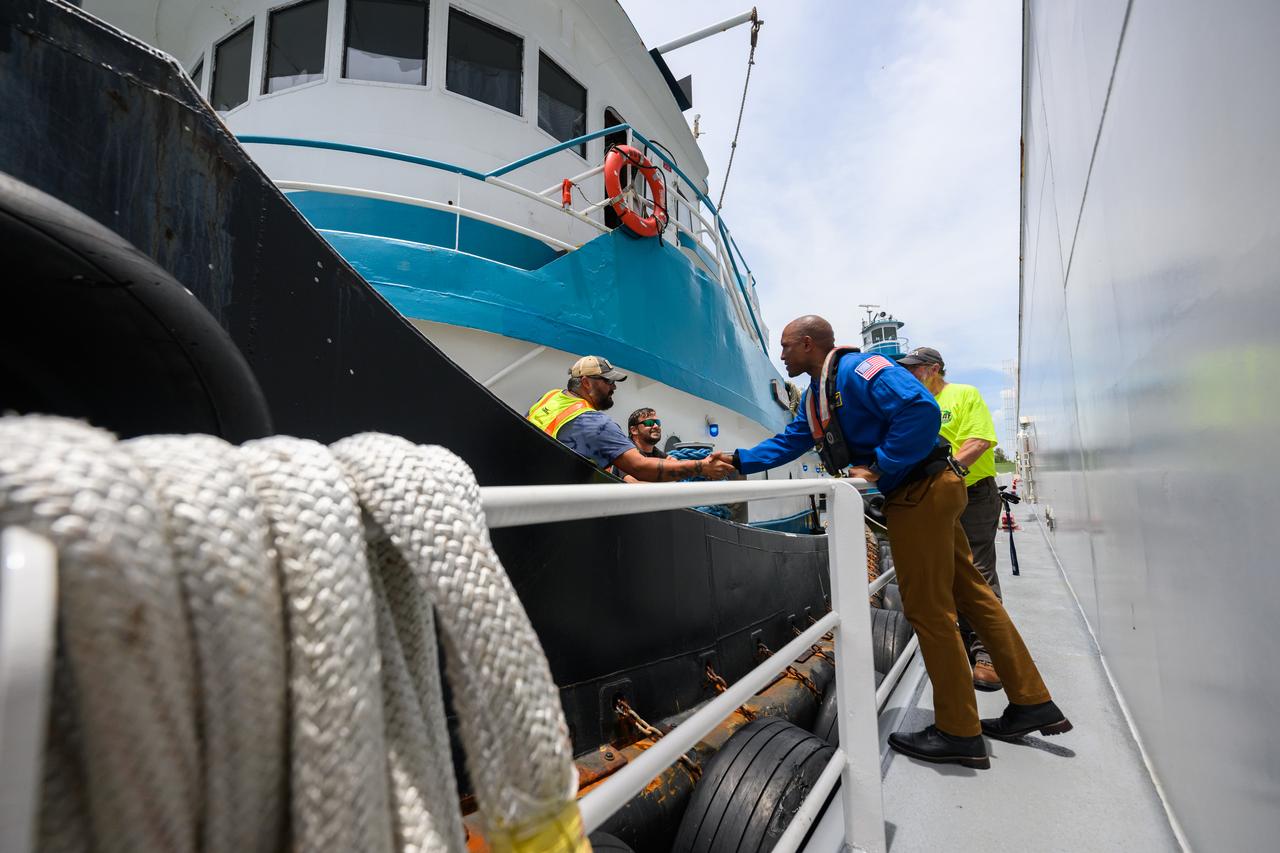

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
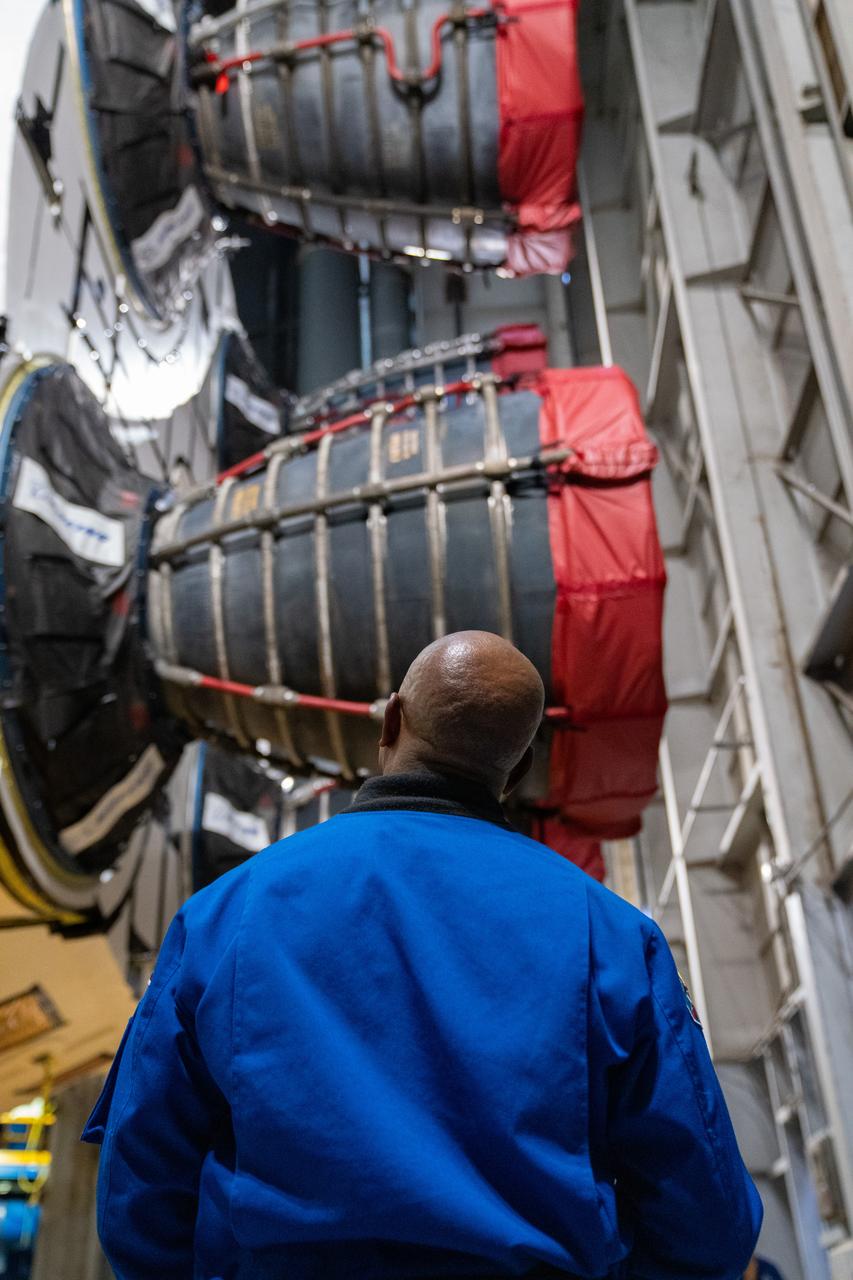

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
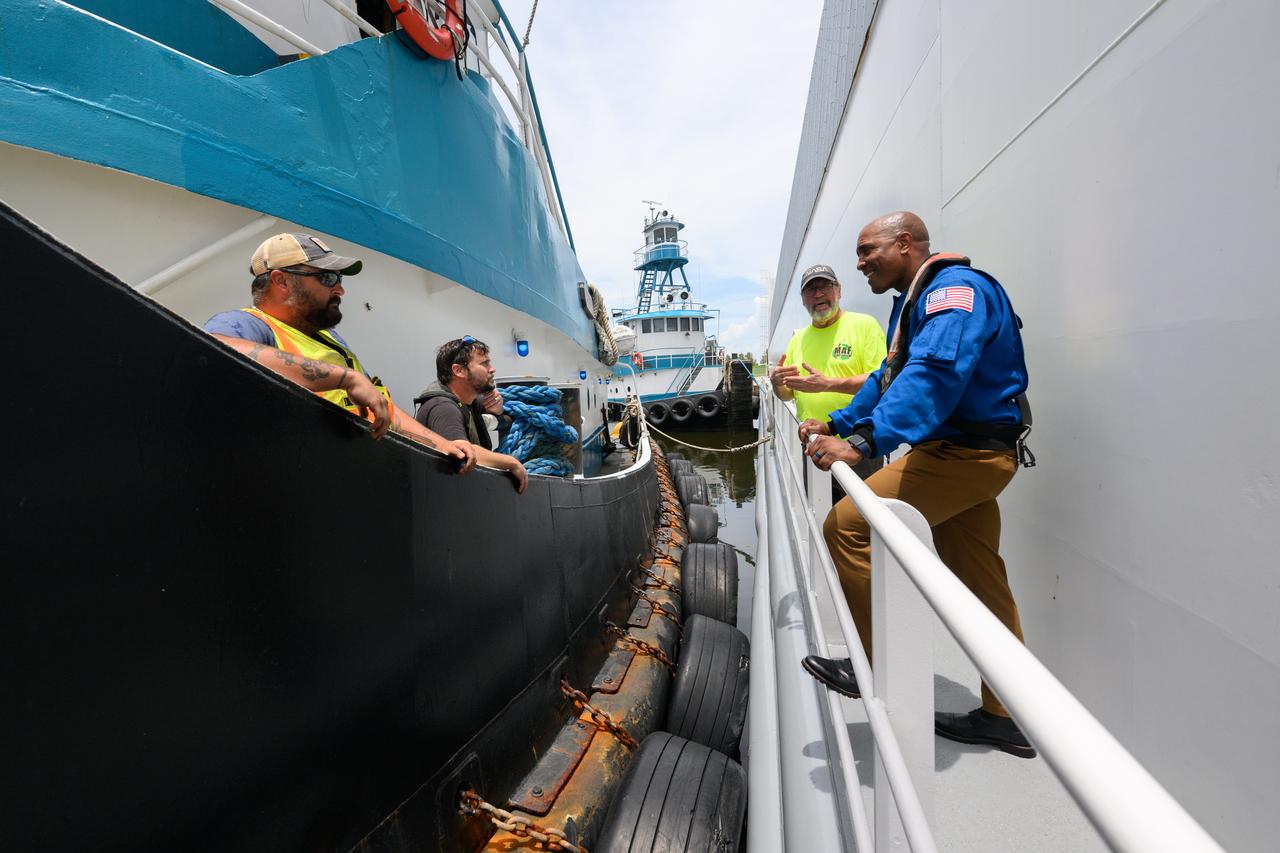

NASA astronaut Victor Glover views the core stage of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket that will help power Artemis II at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans July 15. Glover will pilot Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis campaign. Crews moved the 212-foot-tall core stage with its four RS-25 engines to Building 110 at NASA Michoud prior to rolling it out to NASA’s Pegasus barge July 16 for delivery to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The core stage has two giant propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super cold liquid propellant to feed the stage’s four RS-25 engines. Together, the engines produce more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft to venture around the Moon for Artemis II. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
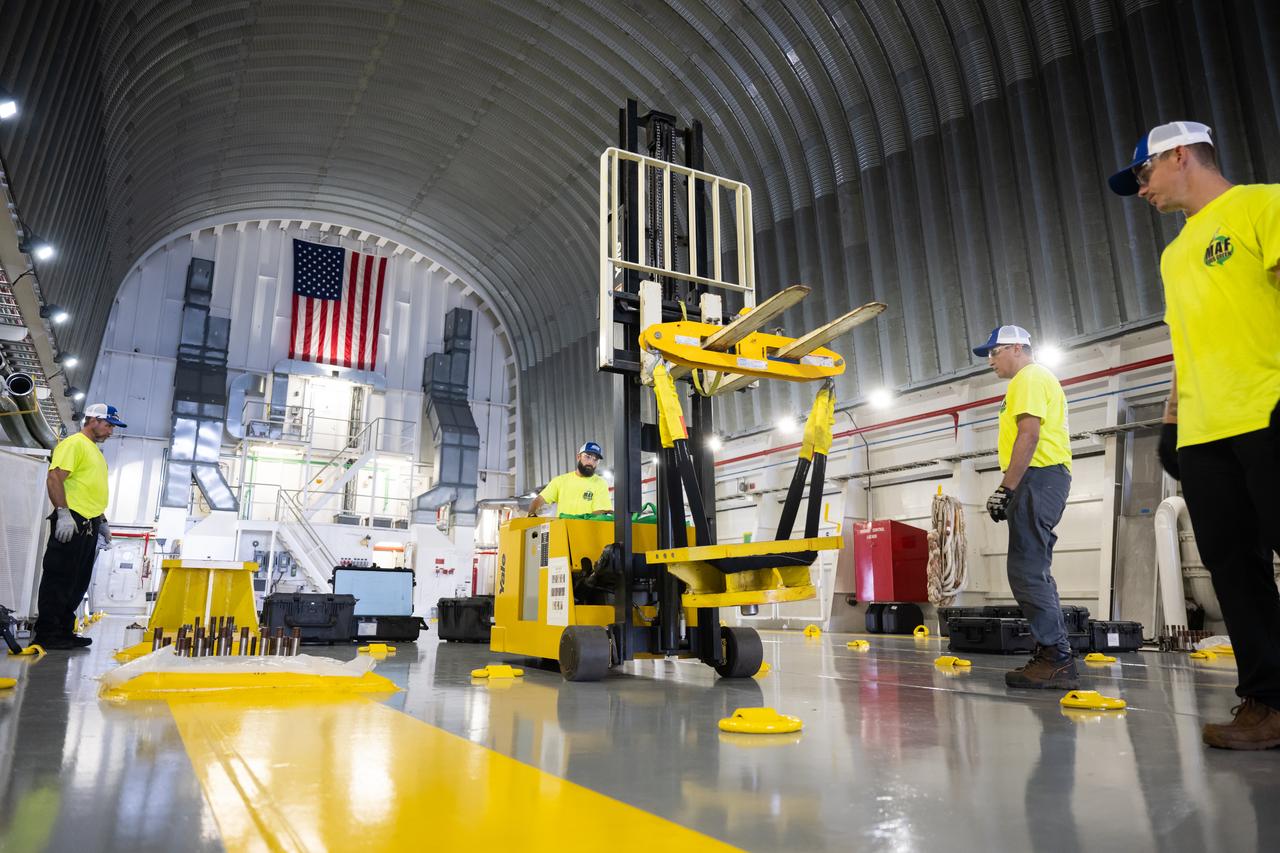

These photos show how team members installed pedestals aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge to hold and secure the massive core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, indicating the barge and its crew are nearly ready for the barge’s first delivery to support the Artemis II test flight around the Moon. The barge will ferry the fully assembled core stage on a 900-mile journey from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to its Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Pegasus crew began installing the pedestals July 10. Pegasus is maintained at NASA Michoud. The SLS core stage is fully manufactured at Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
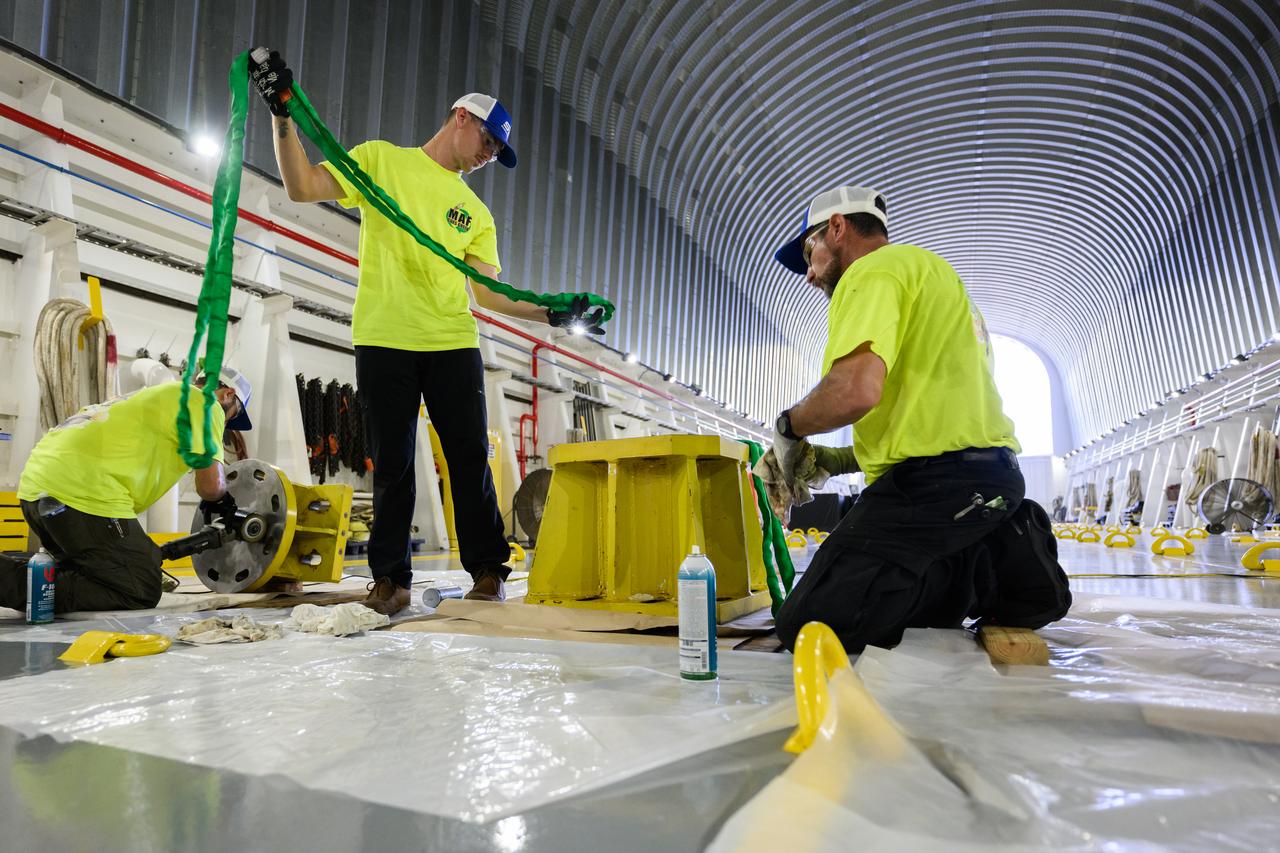

These photos show how team members installed pedestals aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge to hold and secure the massive core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, indicating the barge and its crew are nearly ready for the barge’s first delivery to support the Artemis II test flight around the Moon. The barge will ferry the fully assembled core stage on a 900-mile journey from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to its Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Pegasus crew began installing the pedestals July 10. Pegasus is maintained at NASA Michoud. The SLS core stage is fully manufactured at Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
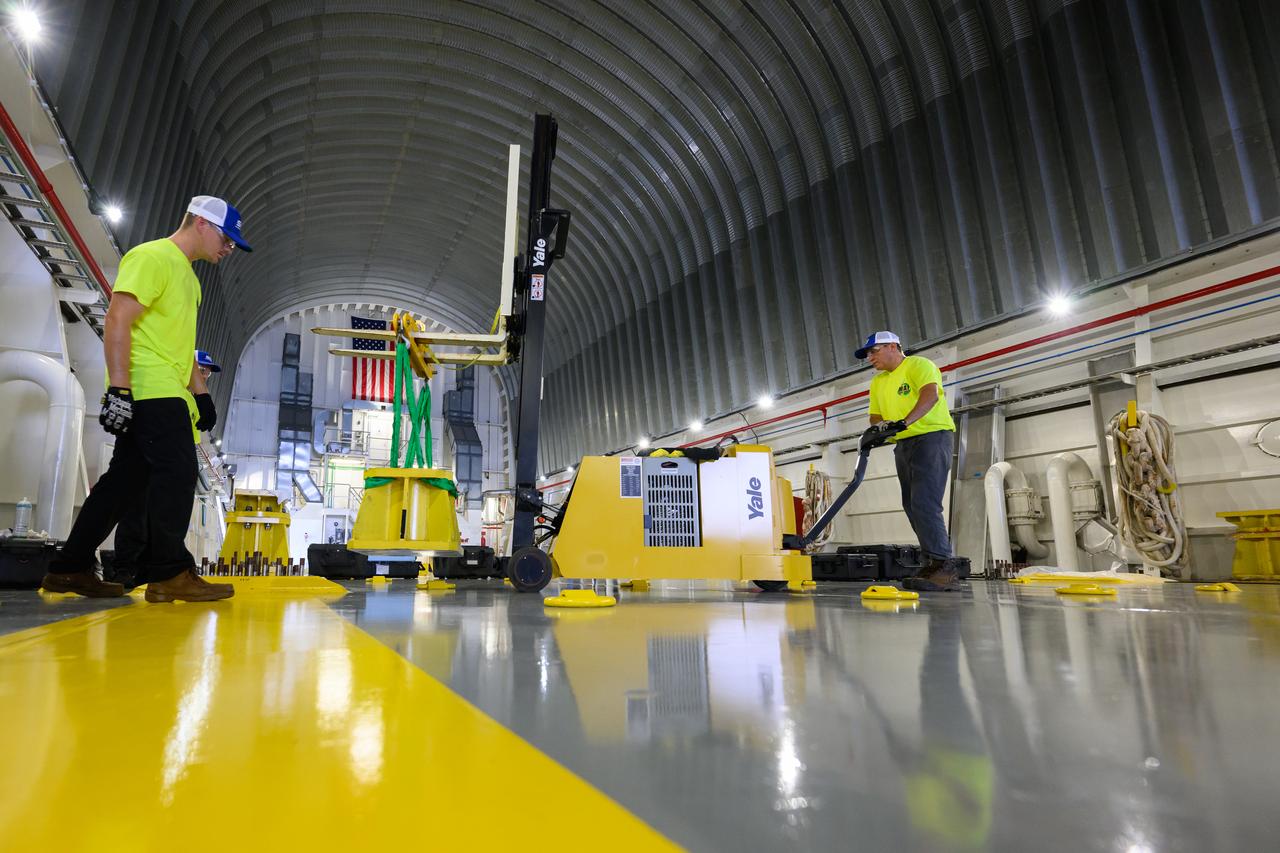

These photos show how team members installed pedestals aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge to hold and secure the massive core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, indicating the barge and its crew are nearly ready for the barge’s first delivery to support the Artemis II test flight around the Moon. The barge will ferry the fully assembled core stage on a 900-mile journey from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to its Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Pegasus crew began installing the pedestals July 10. Pegasus is maintained at NASA Michoud. The SLS core stage is fully manufactured at Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
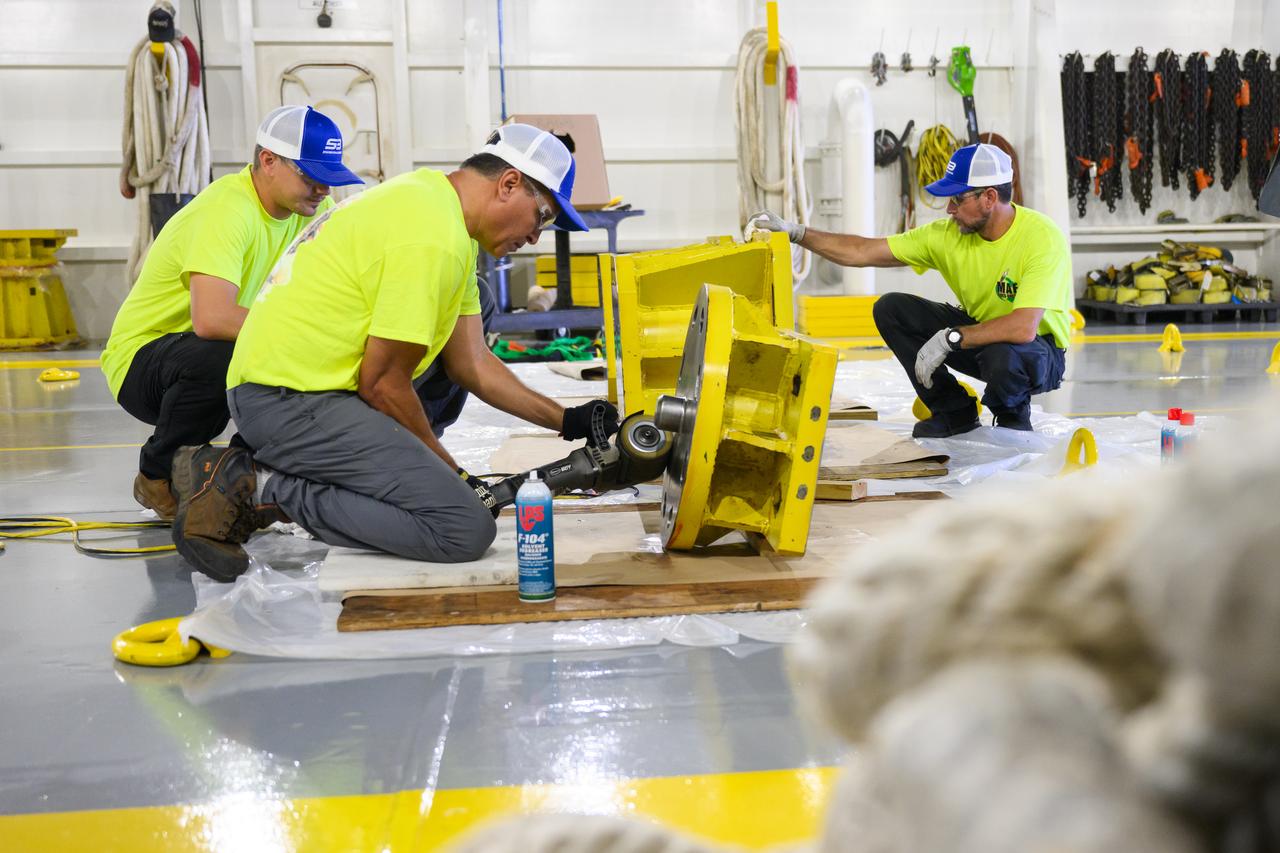

These photos show how team members installed pedestals aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge to hold and secure the massive core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, indicating the barge and its crew are nearly ready for the barge’s first delivery to support the Artemis II test flight around the Moon. The barge will ferry the fully assembled core stage on a 900-mile journey from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to its Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Pegasus crew began installing the pedestals July 10. Pegasus is maintained at NASA Michoud. The SLS core stage is fully manufactured at Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
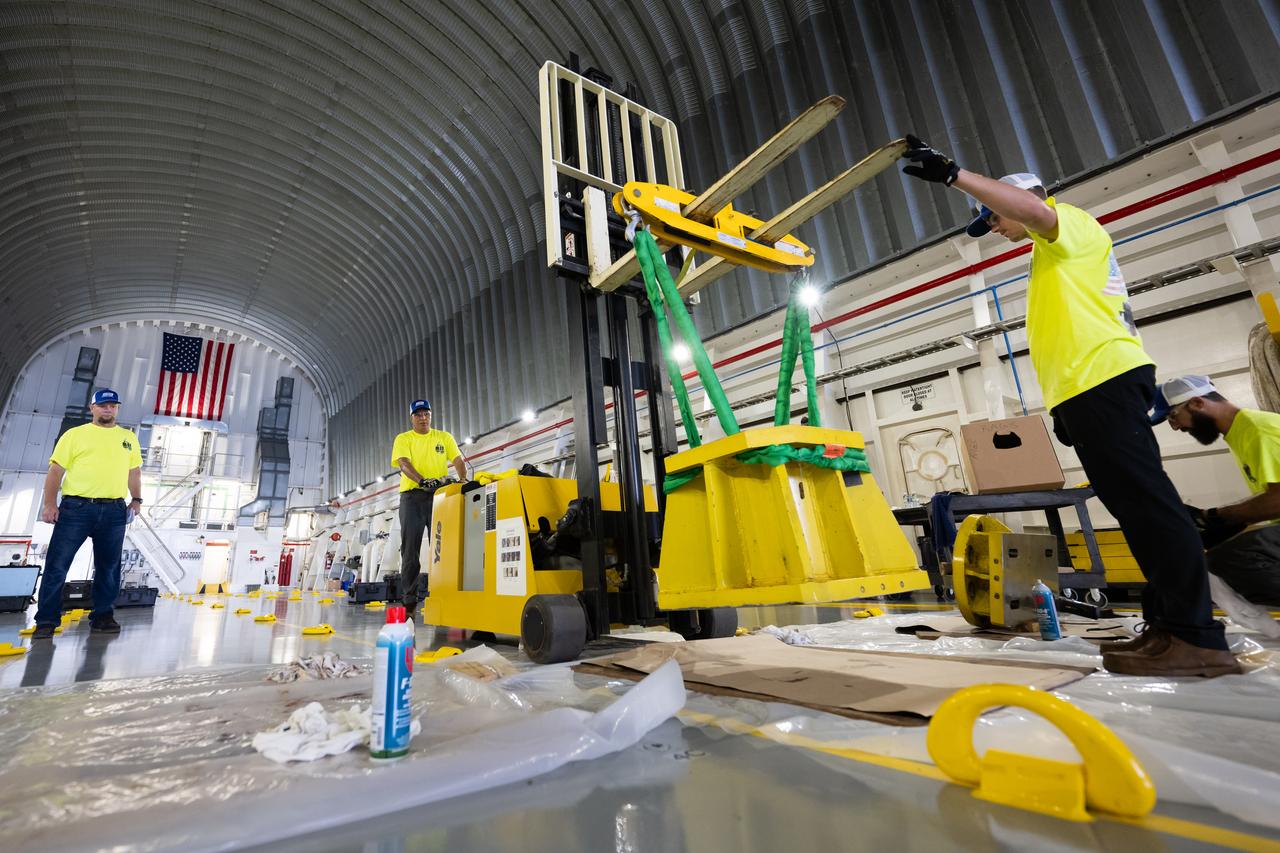

These photos show how team members installed pedestals aboard NASA’s Pegasus barge to hold and secure the massive core stage of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, indicating the barge and its crew are nearly ready for the barge’s first delivery to support the Artemis II test flight around the Moon. The barge will ferry the fully assembled core stage on a 900-mile journey from the agency’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans to its Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Pegasus crew began installing the pedestals July 10. Pegasus is maintained at NASA Michoud. The SLS core stage is fully manufactured at Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft, supporting ground systems, advanced spacesuits and rovers, the Gateway in orbit around the Moon, and commercial human landing systems. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
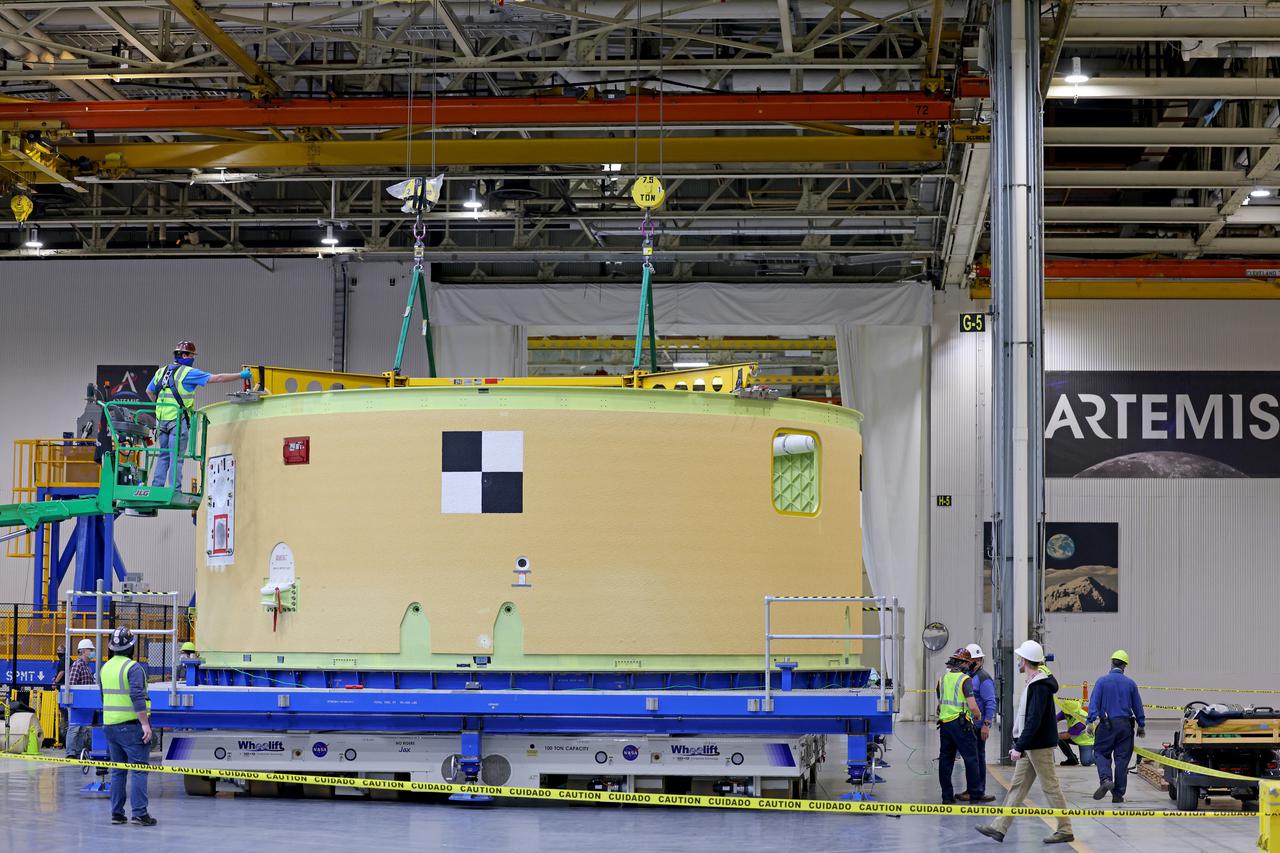

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the human landing system, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
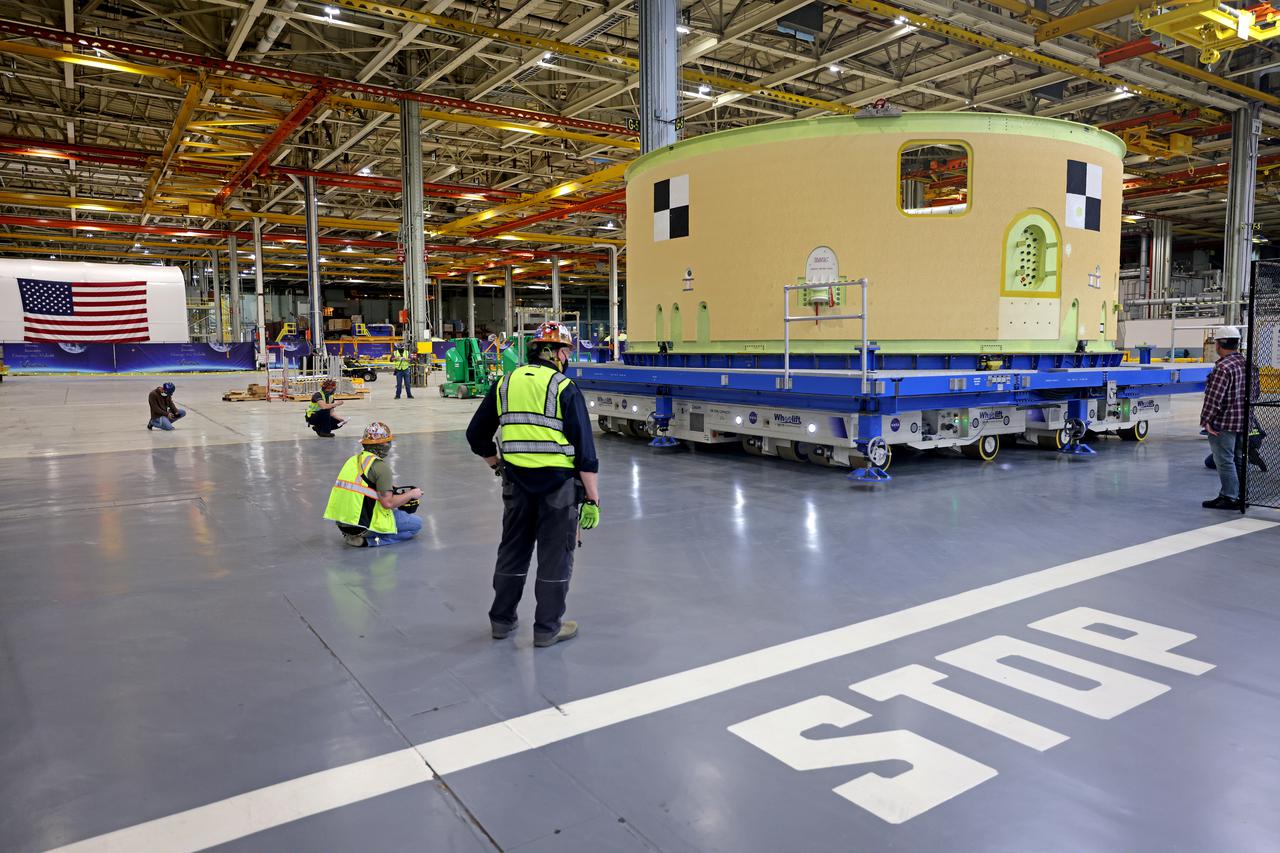

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the human landing system, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
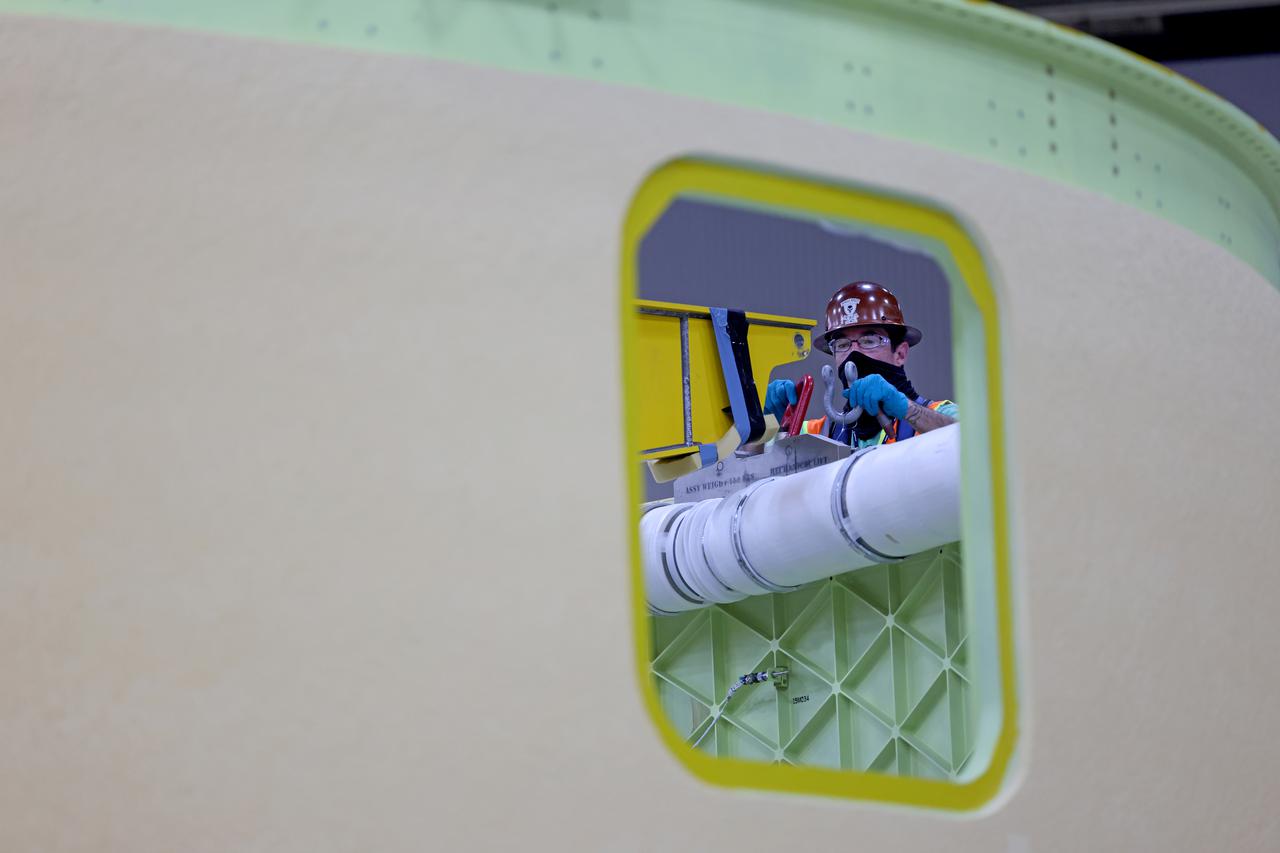

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the human landing system, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
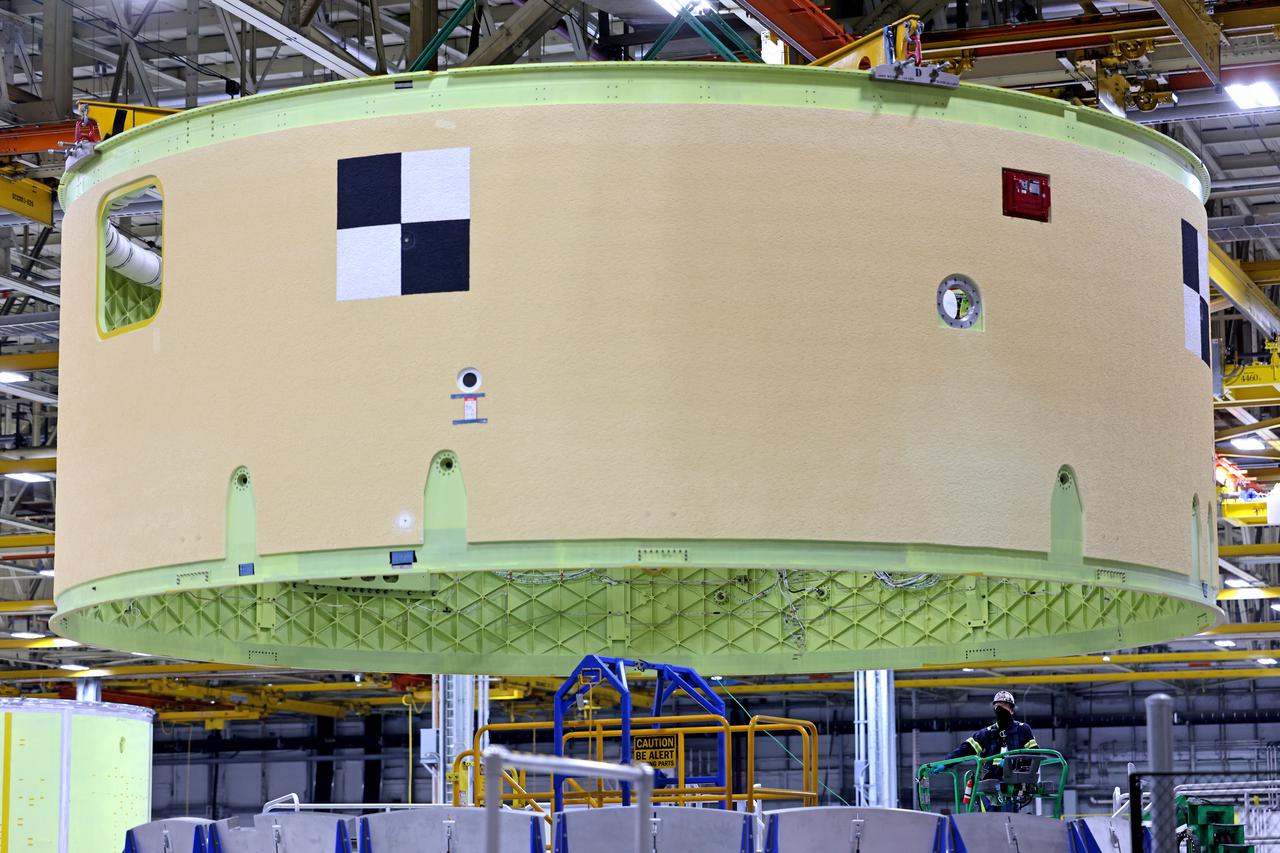

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the human landing system, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
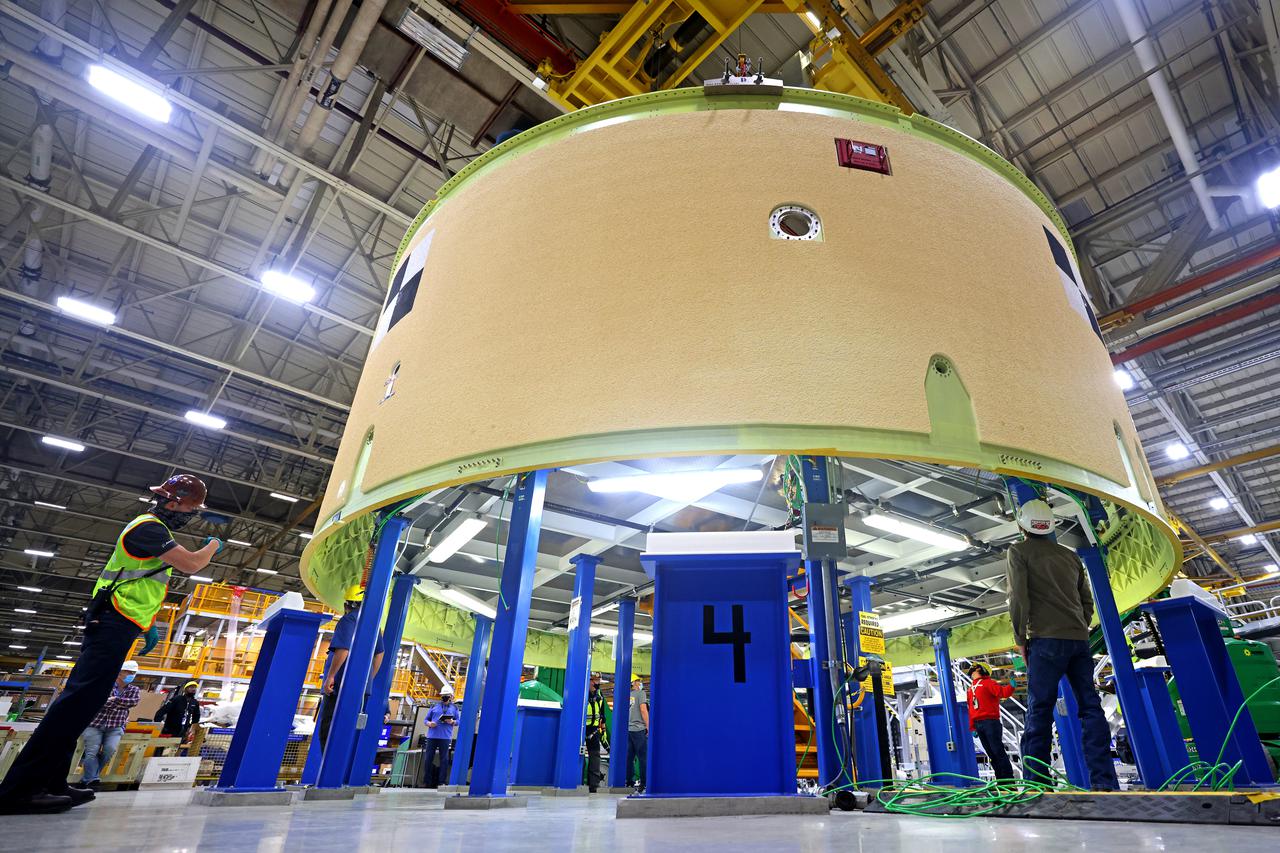

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the human landing system, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
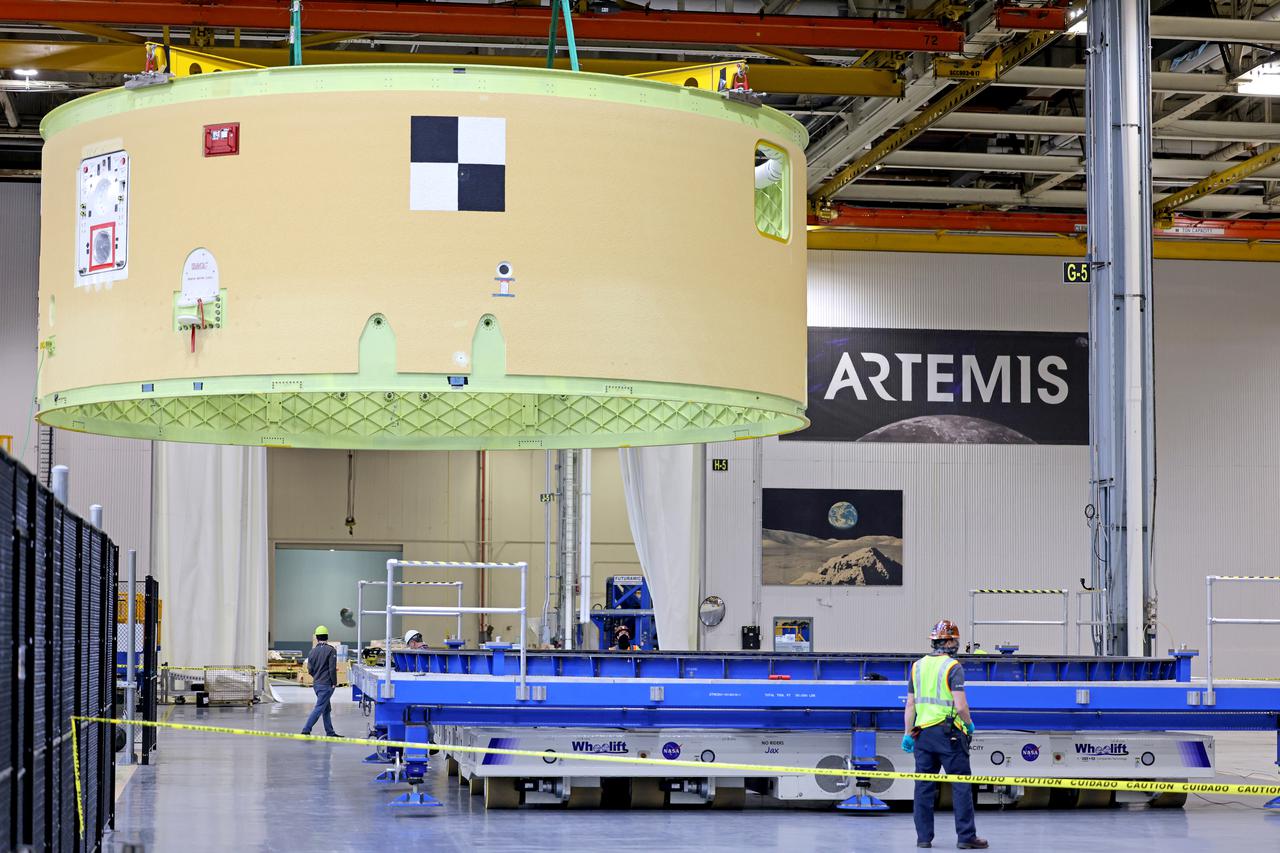

This image shows the forward skirt that will be used on the core stage of NASA’s Space Launch System rocket for Artemis II, the first crewed mission of NASA’s Artemis program, at NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The forward skirt houses flight computers, cameras, and avionics systems. The hardware is located at the top of the 212-foot-tall core stage and connects the upper part of the rocket to the core stage. Soon, technicians will ready the forward skirt for the first of three core stage assembly mates called the forward join. The forward join consists of three main parts -- the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, and intertank – to create the top, or forward part, of the core stage. Together with its four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit, the human landing system, and Orion spacecraft, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program. No other rocket is capable of carrying astronauts in Orion around the Moon in a single mission. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
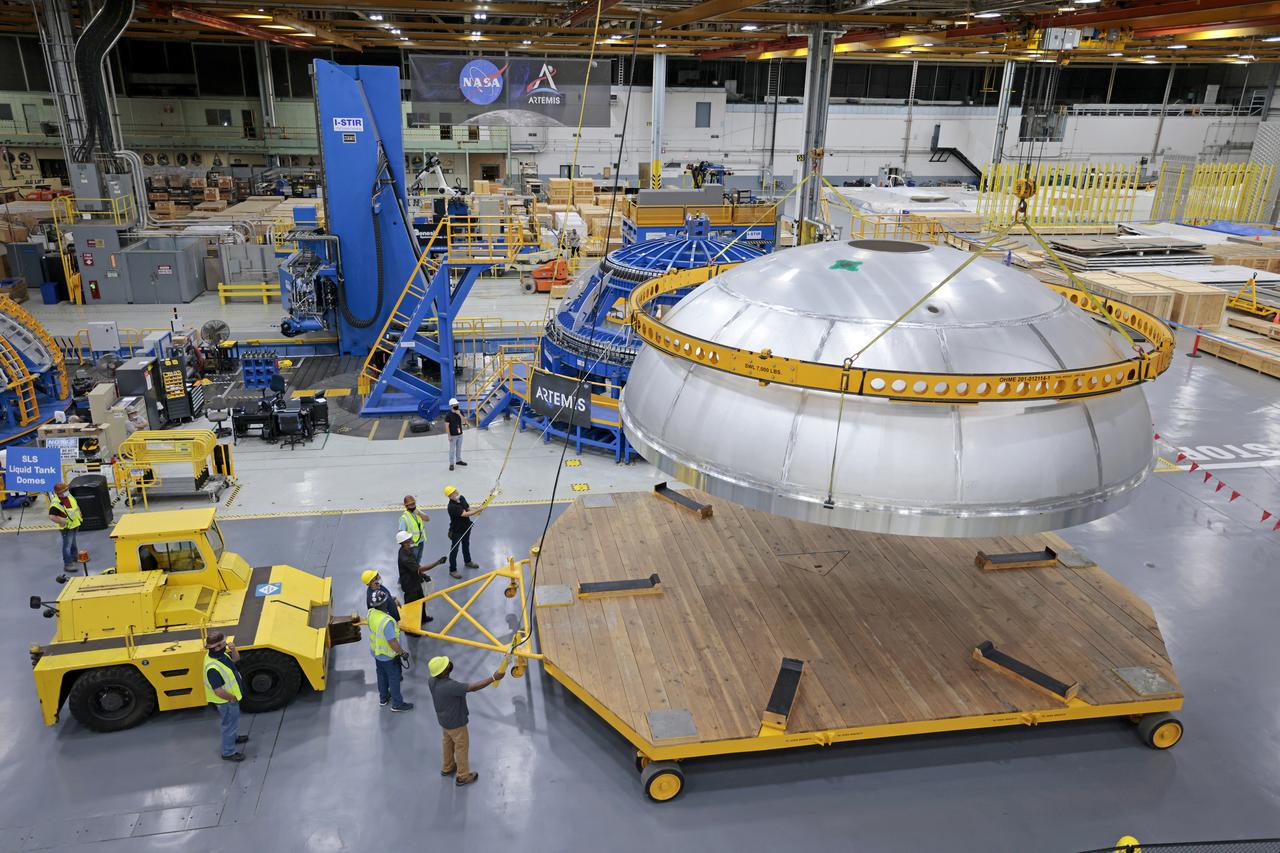

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
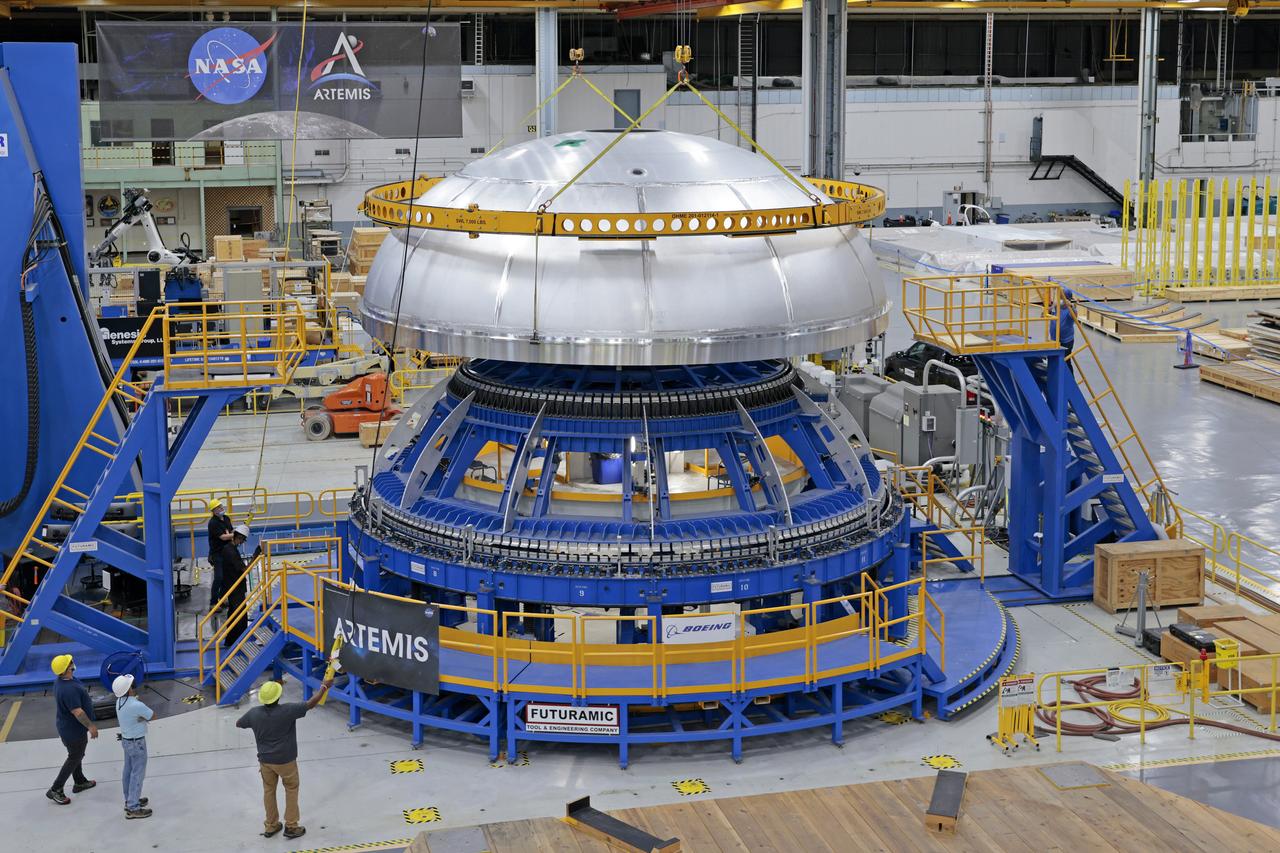
Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker

Teams completed the welding of the Artemis III core stage liquid oxygen tank dome at the NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the dome, which is the top of the tank. The dome was moved to an assembly area where it will be loaded into a robotic welder that will join it with the forward barrel to create half of the liquid oxygen tank. Later another barrel and dome will be added to complete the entire tank. The Space Launch System (SLS) core stage liquid oxygen tank holds 196,000 gallons of super-cooled liquid propellant that serves as one of the propellants for the four RS-25 engines. The SLS core stage is made up of five unique elements: the forward skirt, liquid oxygen tank, intertank, liquid hydrogen tank, and the engine section. The liquid oxygen and the liquid hydrogen tank will provide propellant to the four RS-25 engines to produce more than two million pounds of thrust to help launch NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts, and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
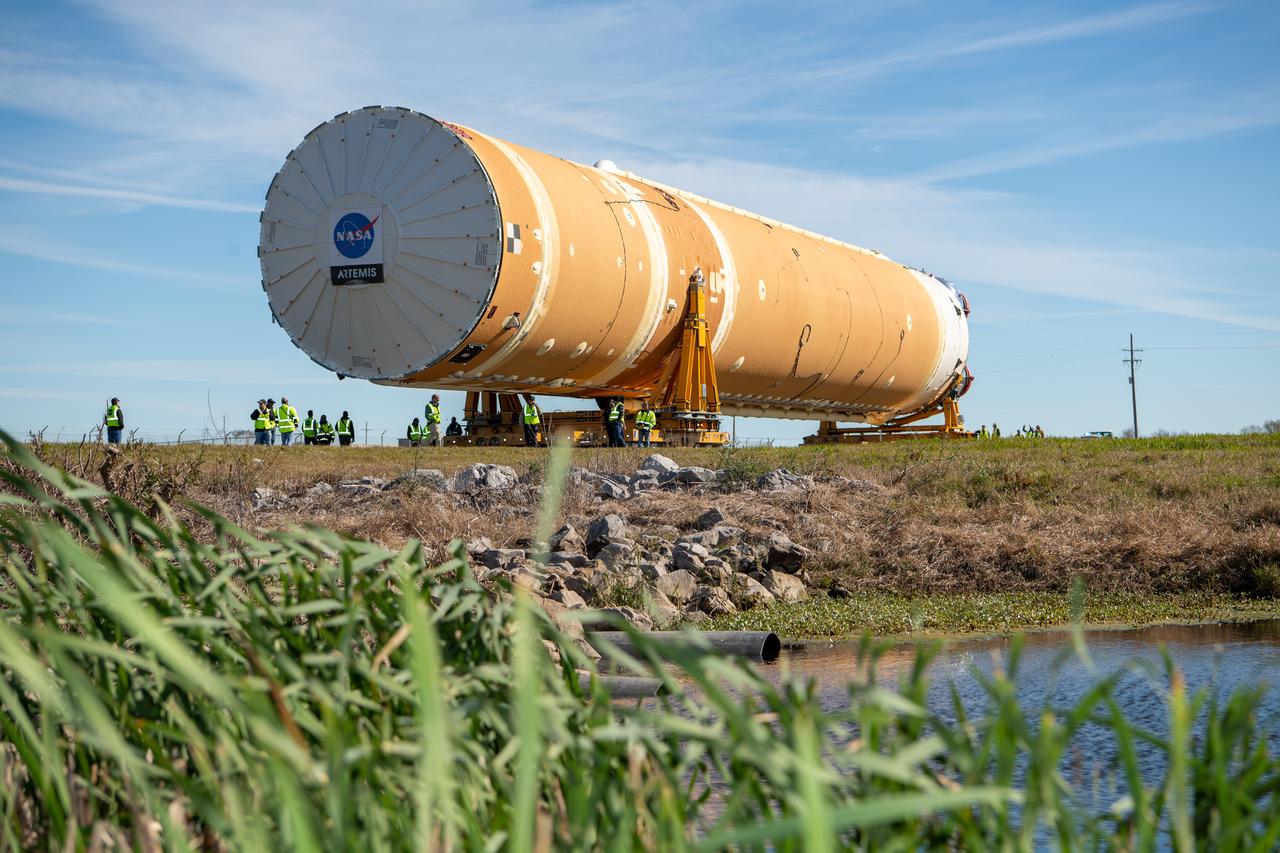

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
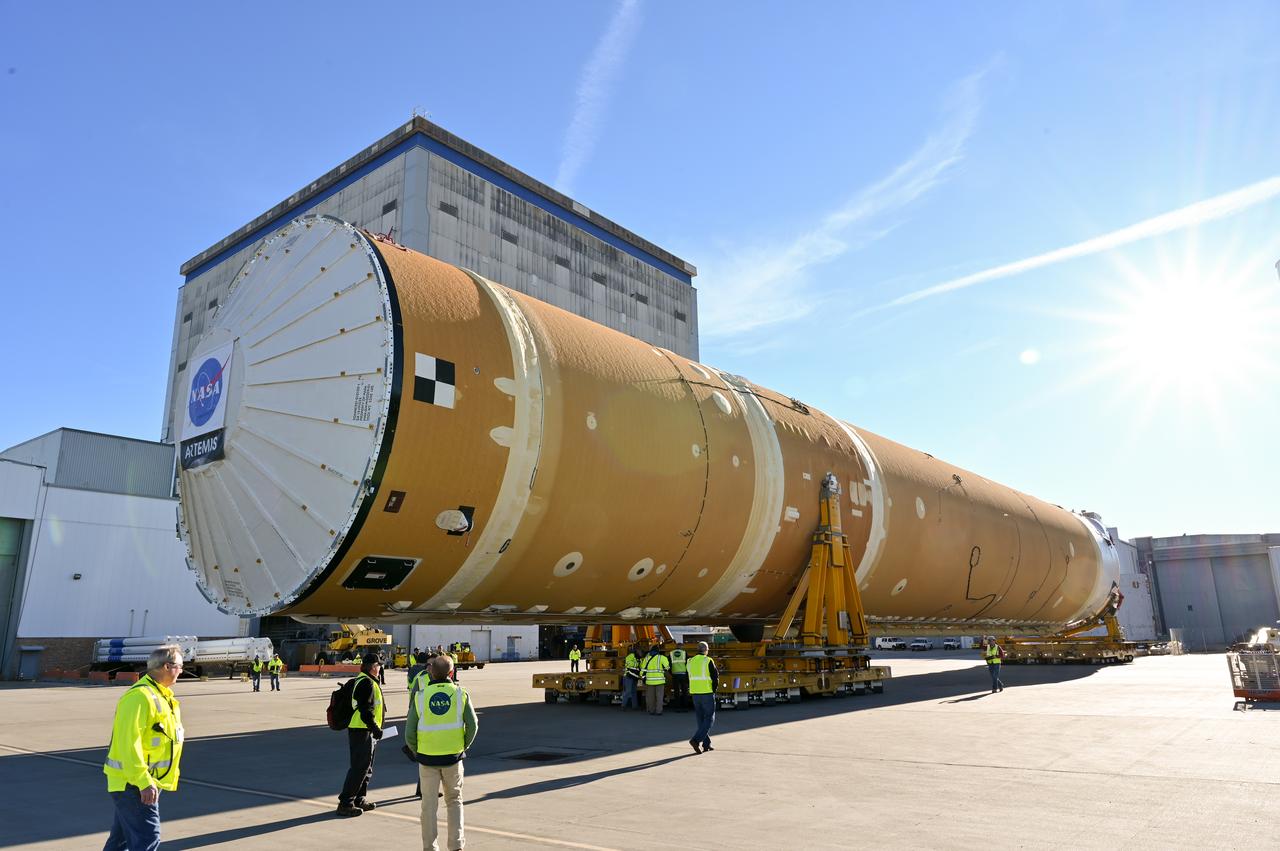

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
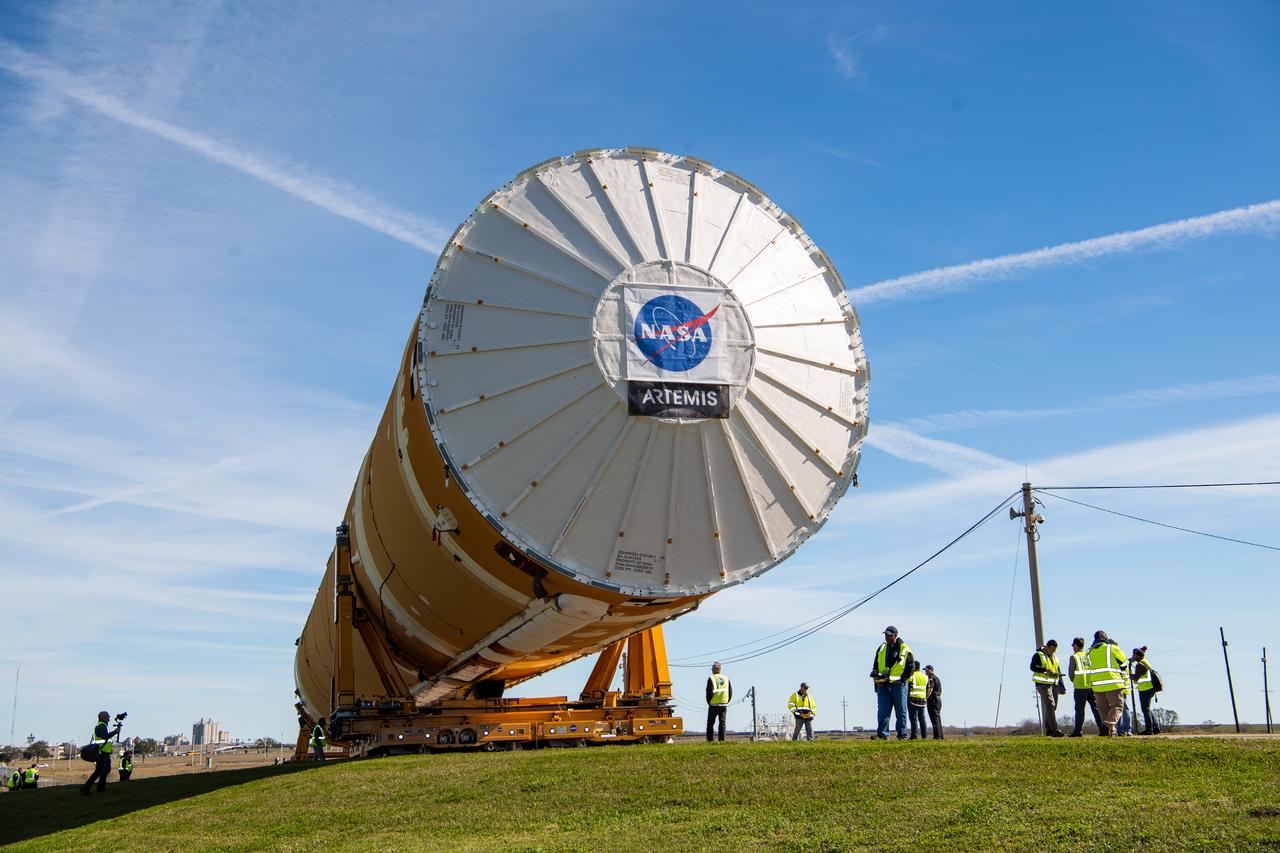

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
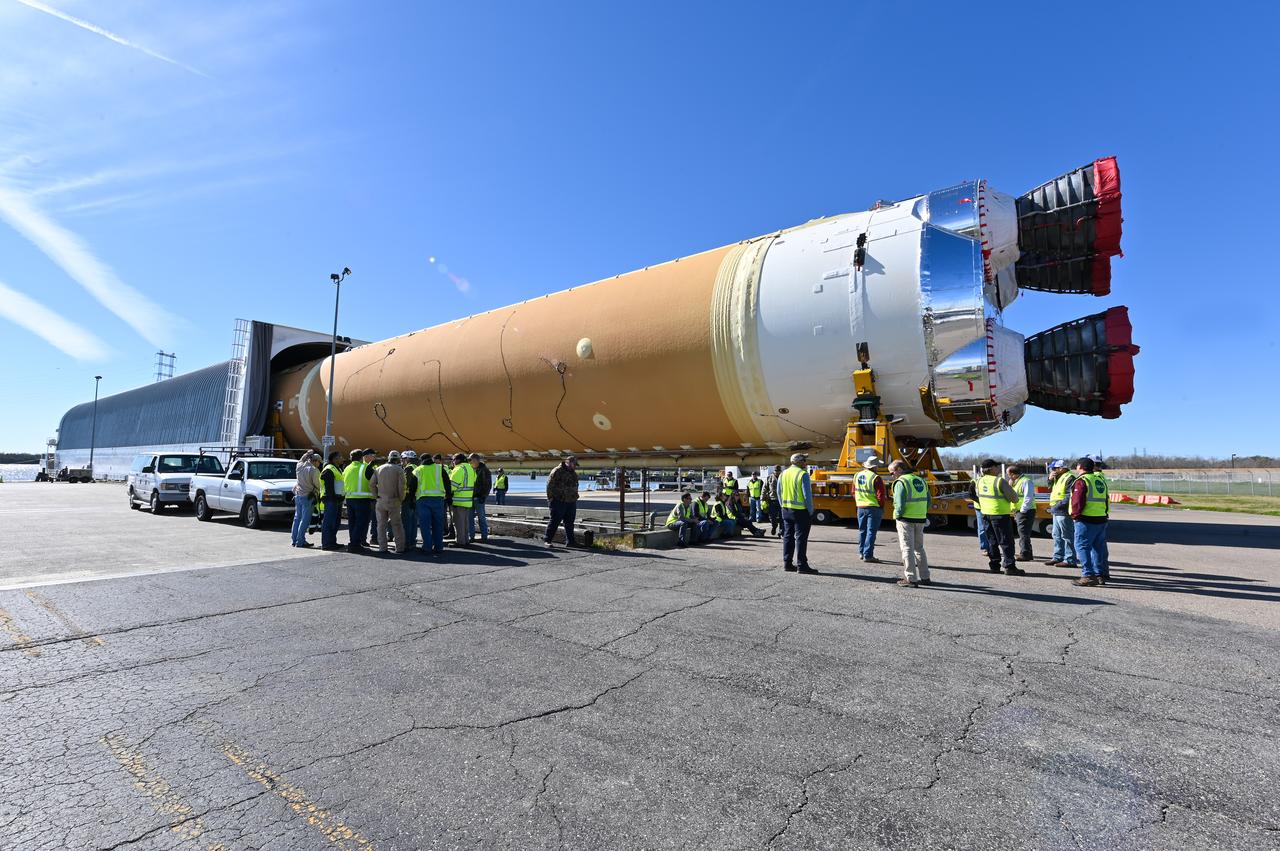

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
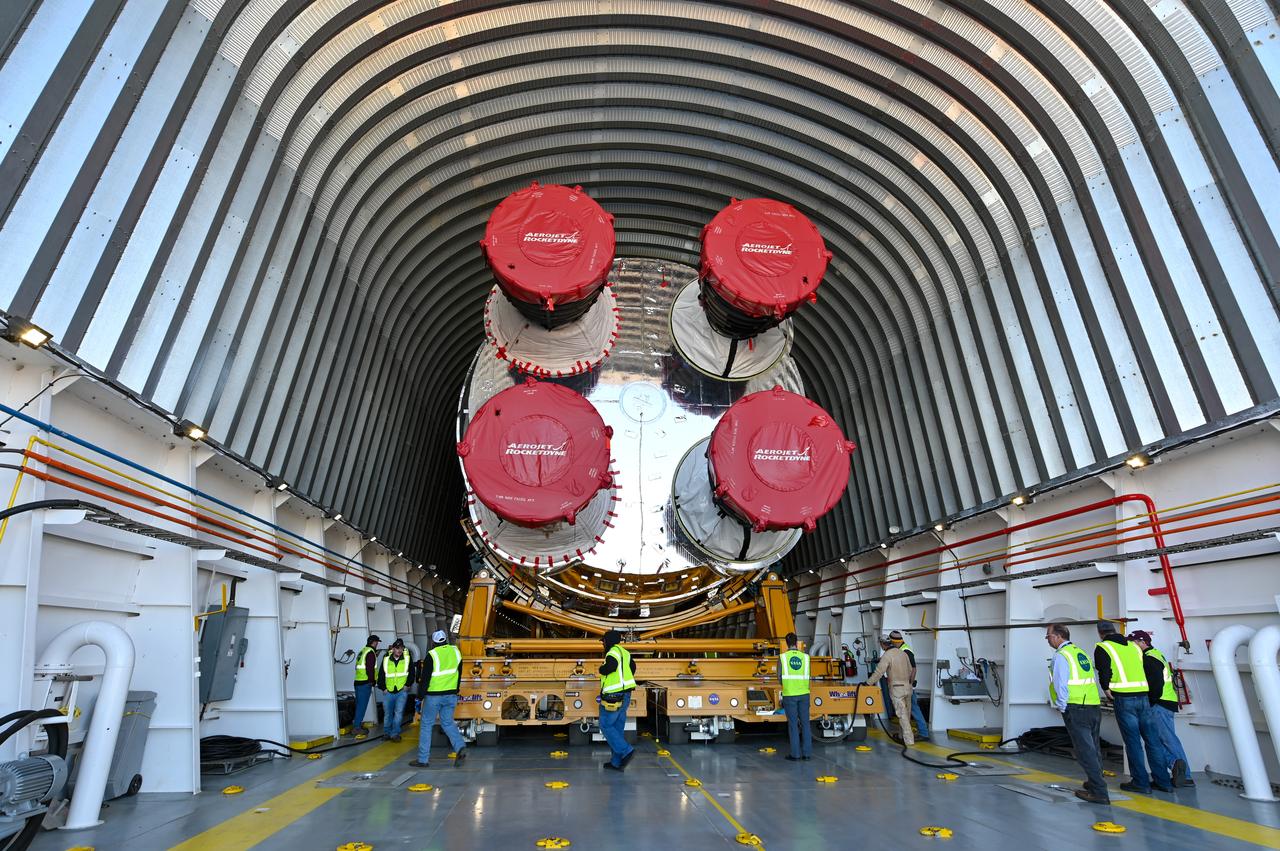

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
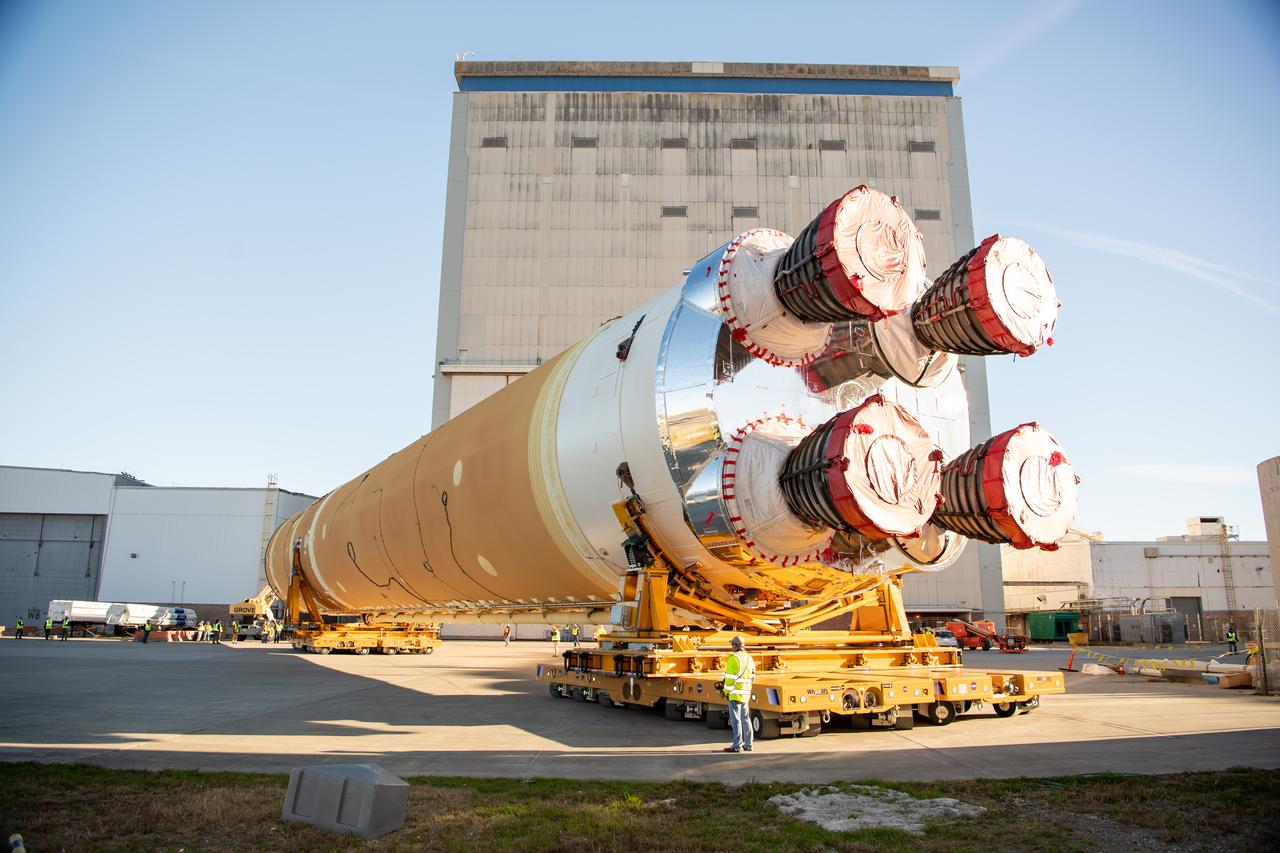

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
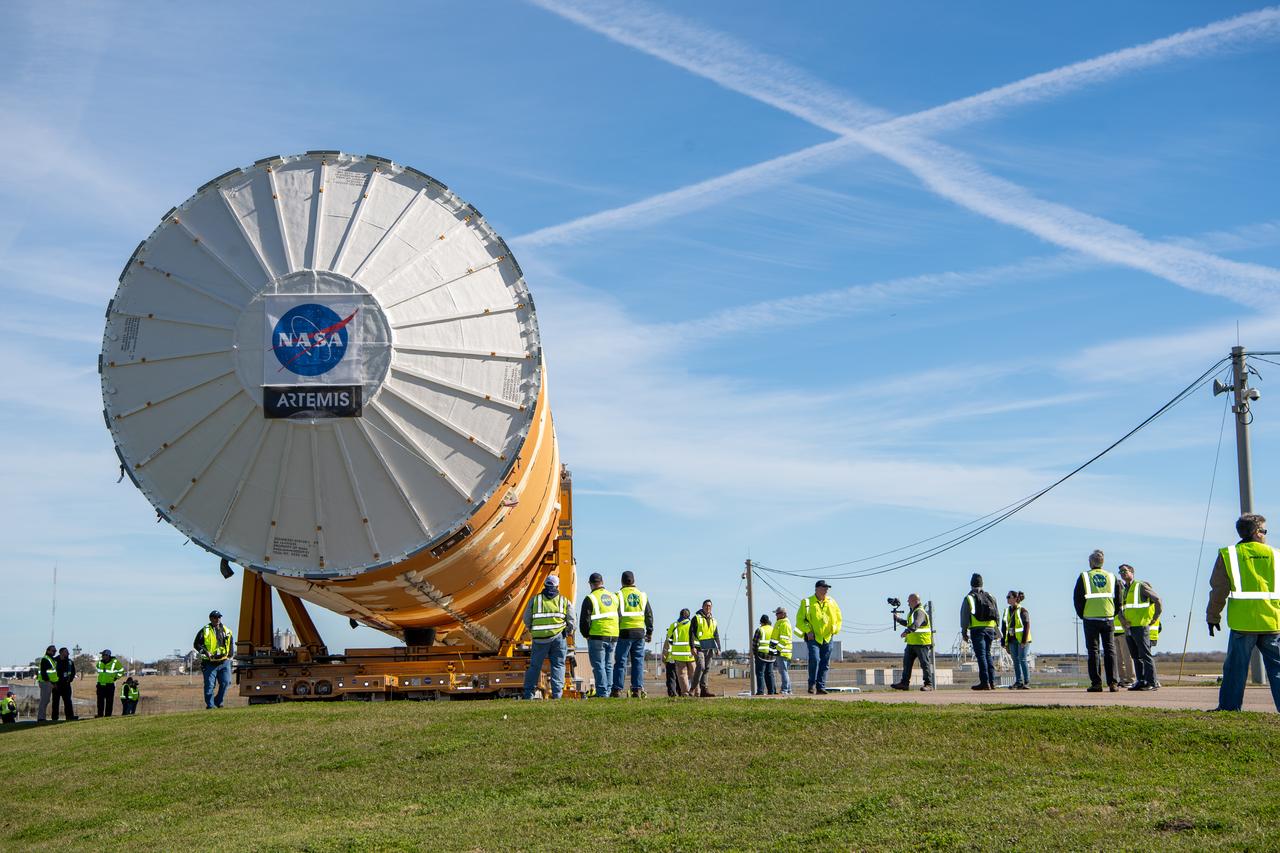

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
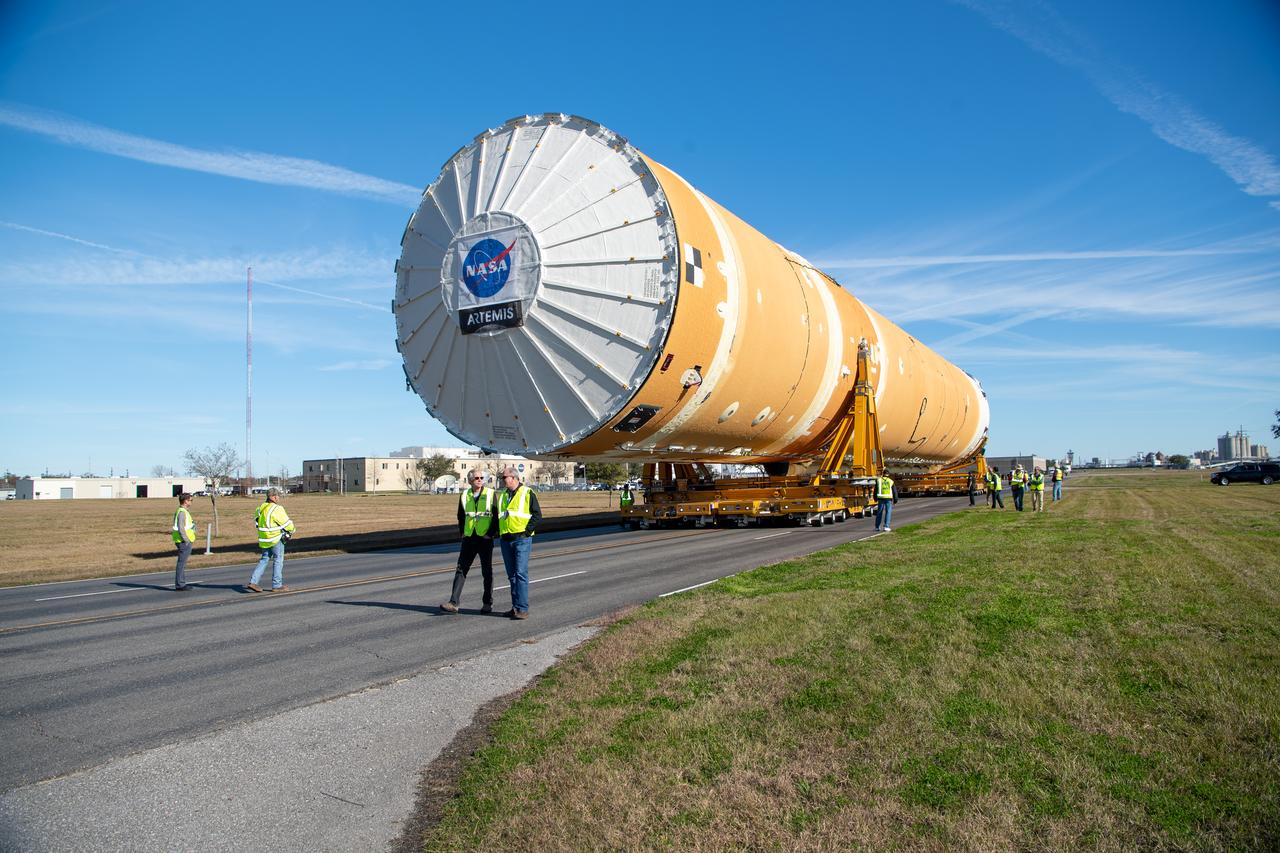

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
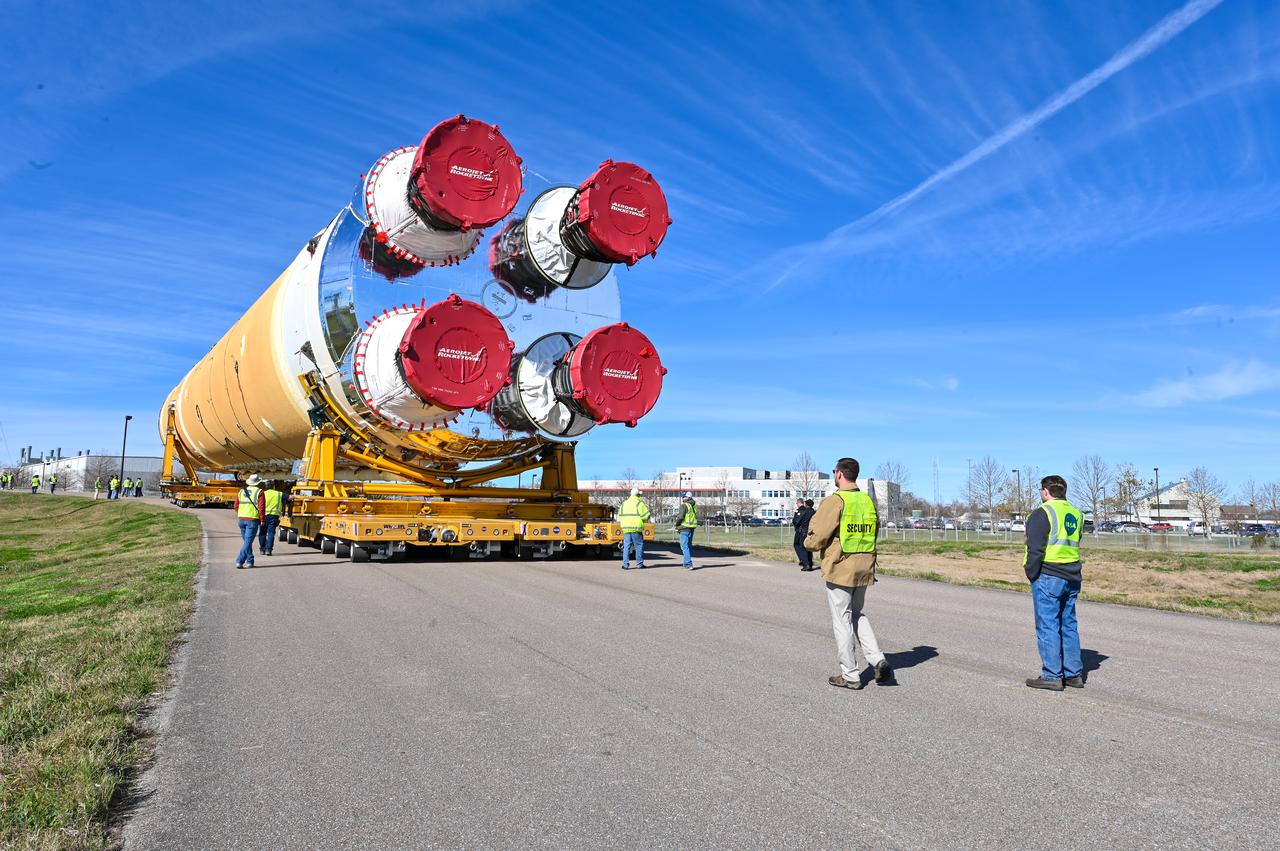

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
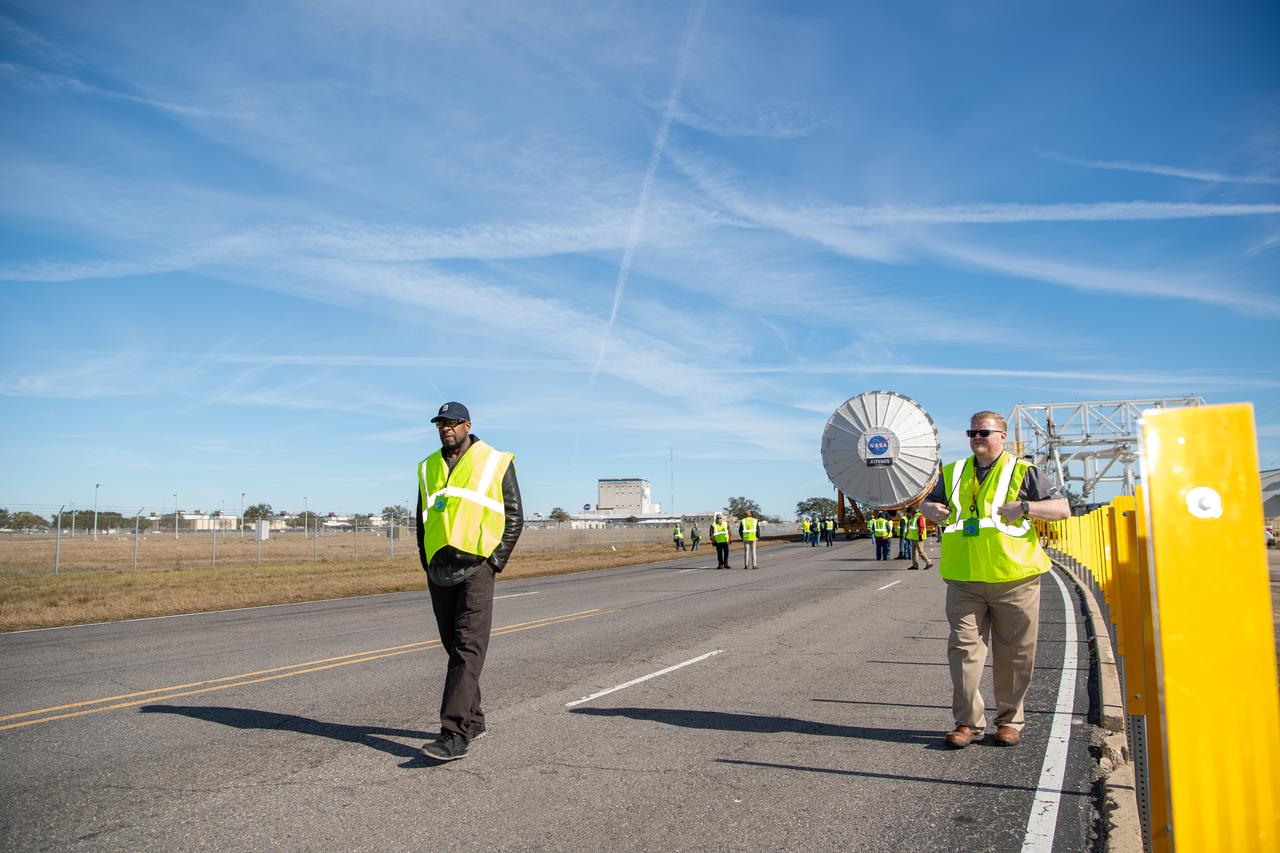

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
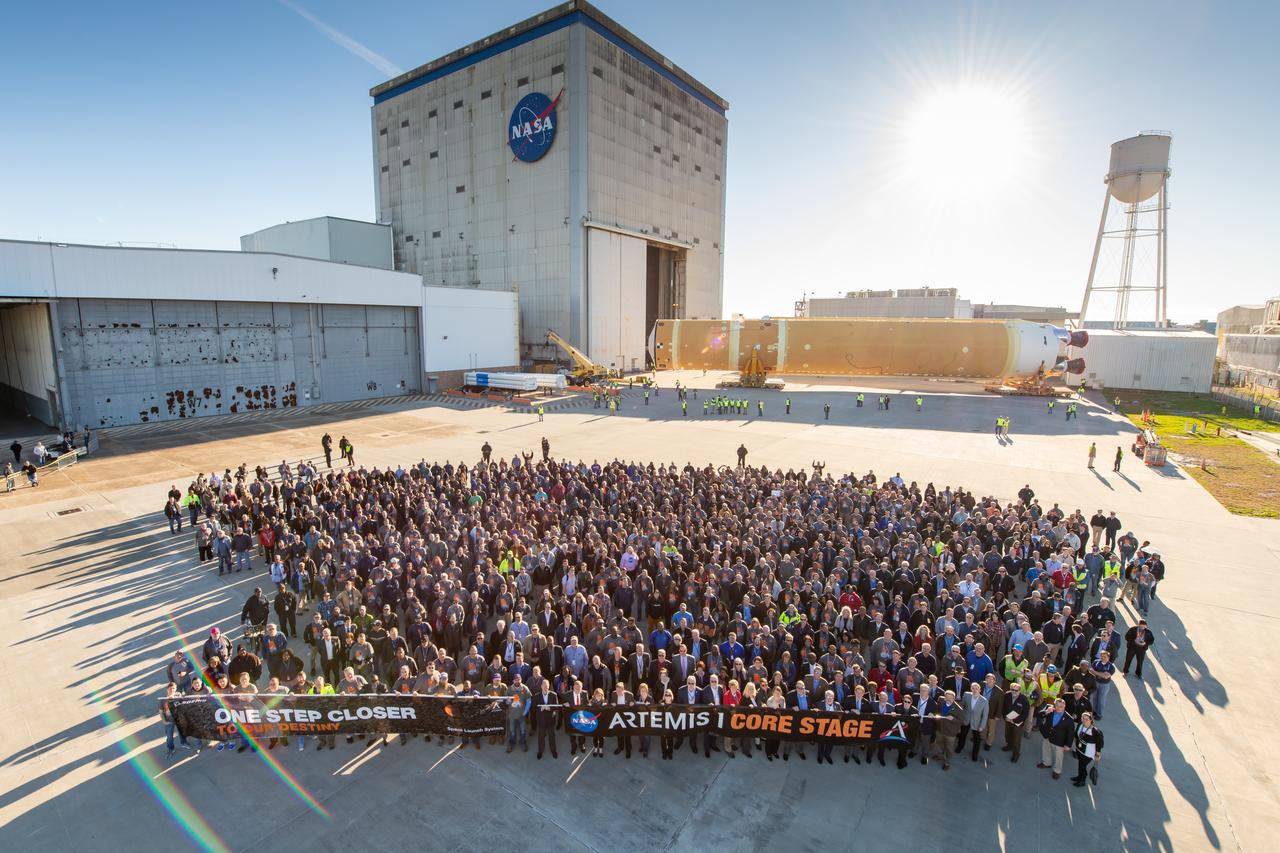

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
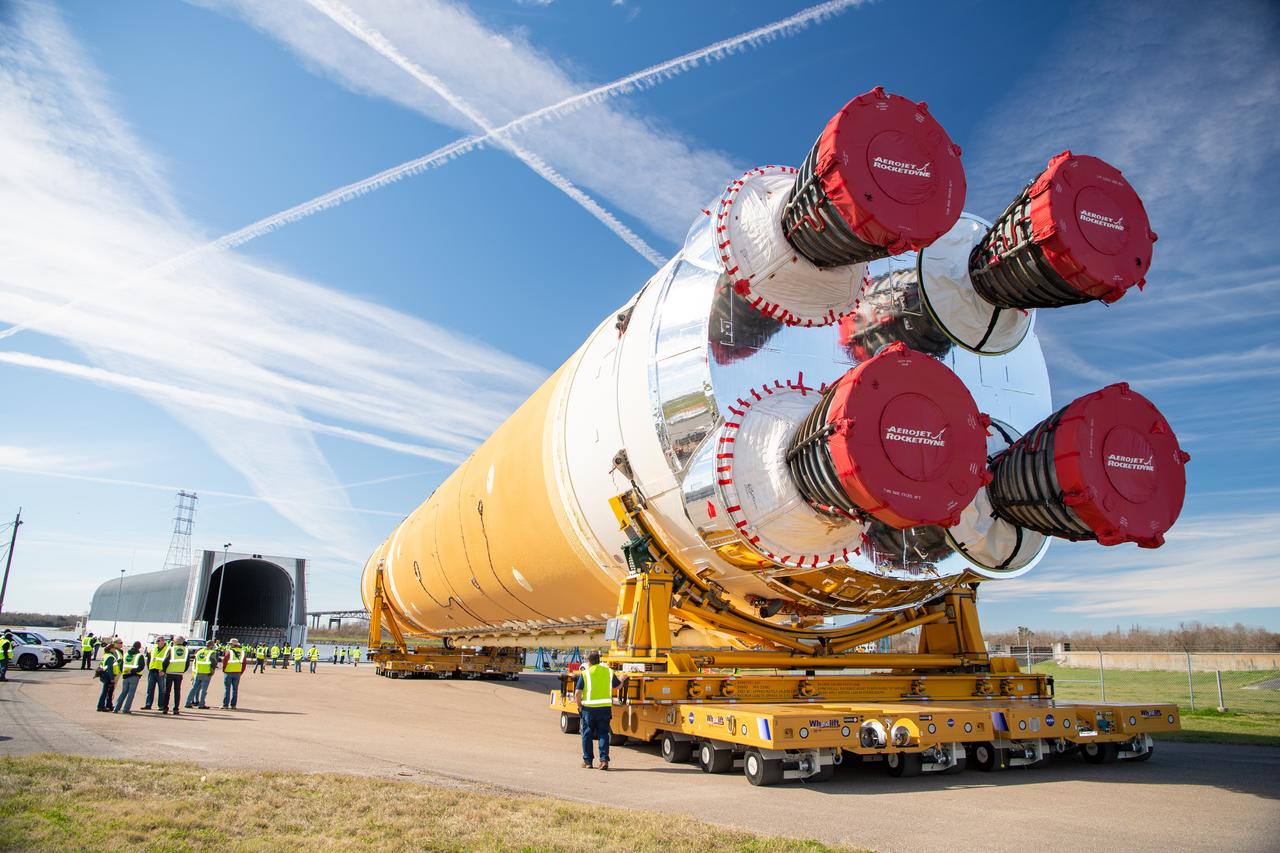

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
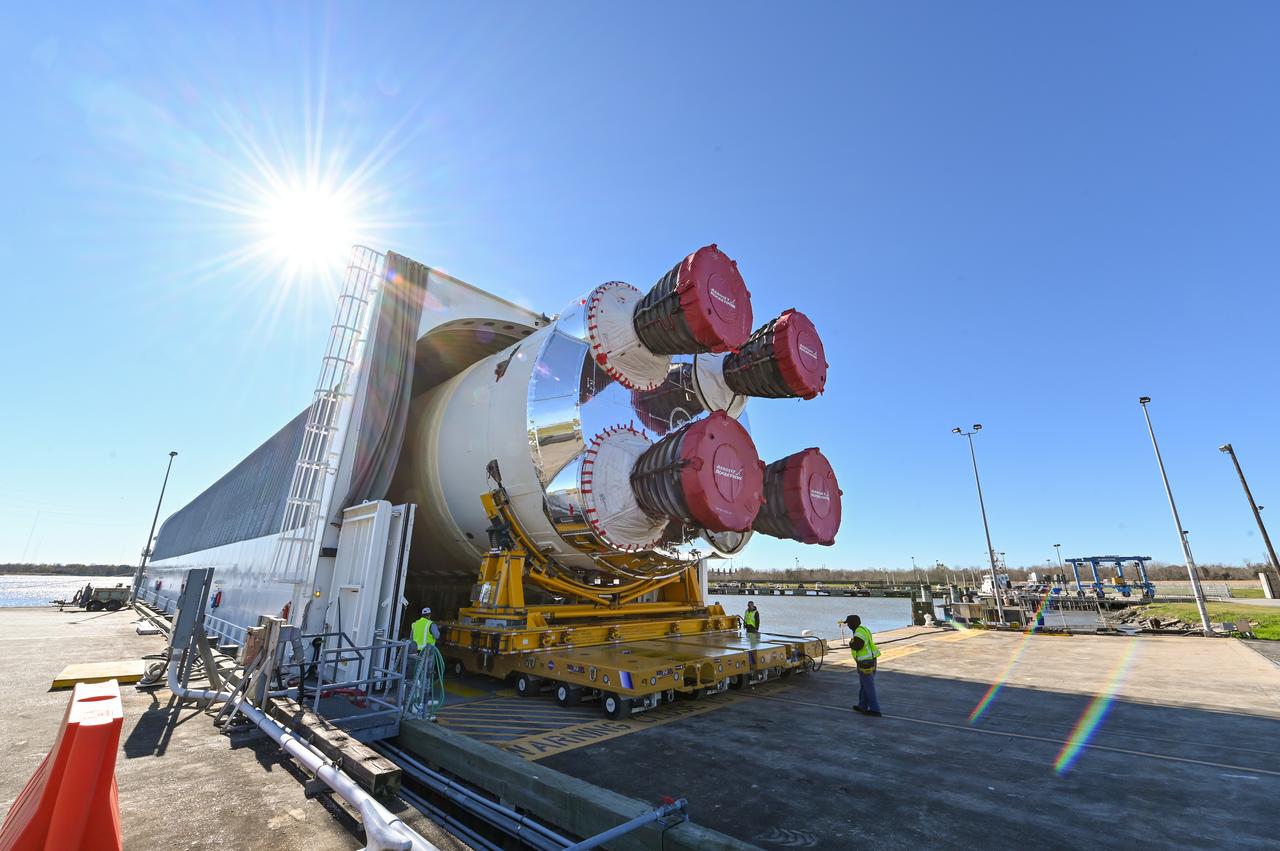

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
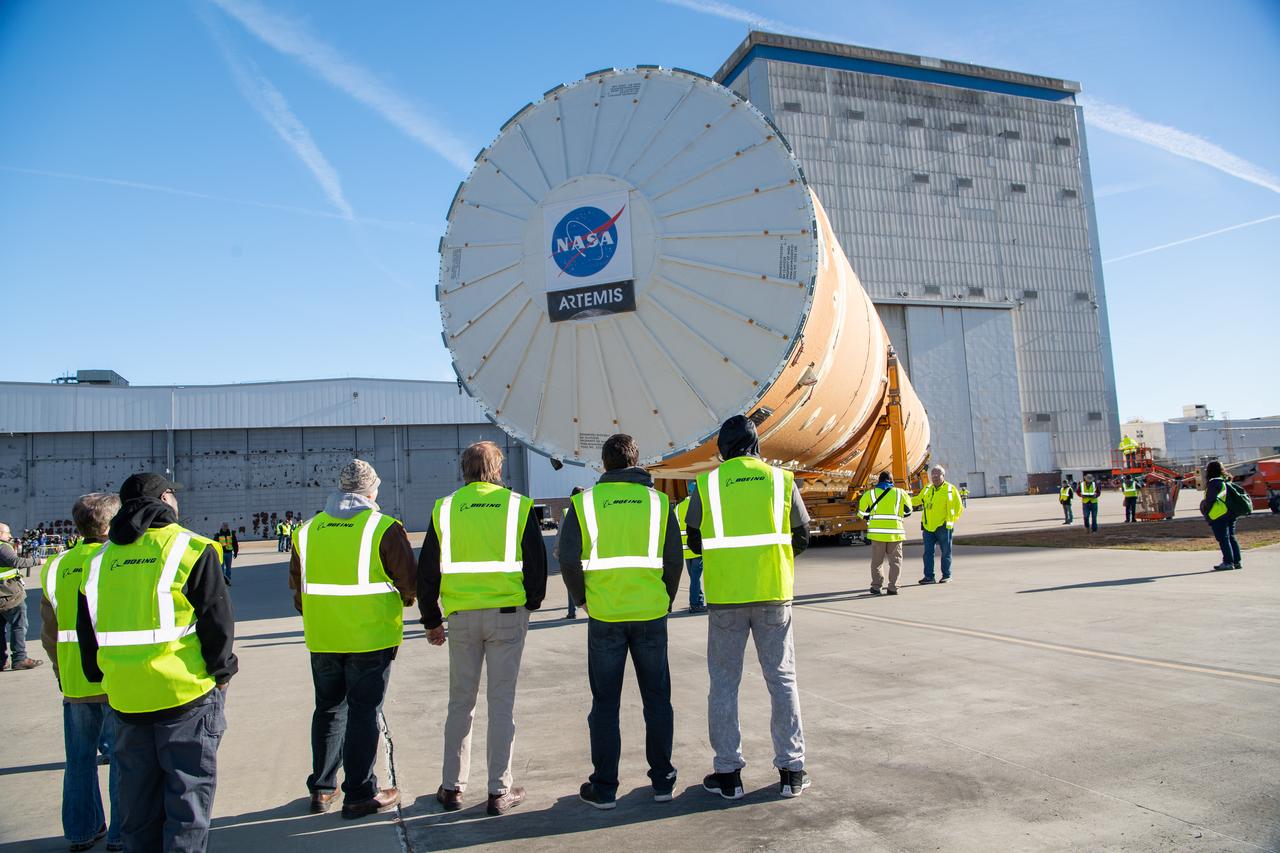

These images/video show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
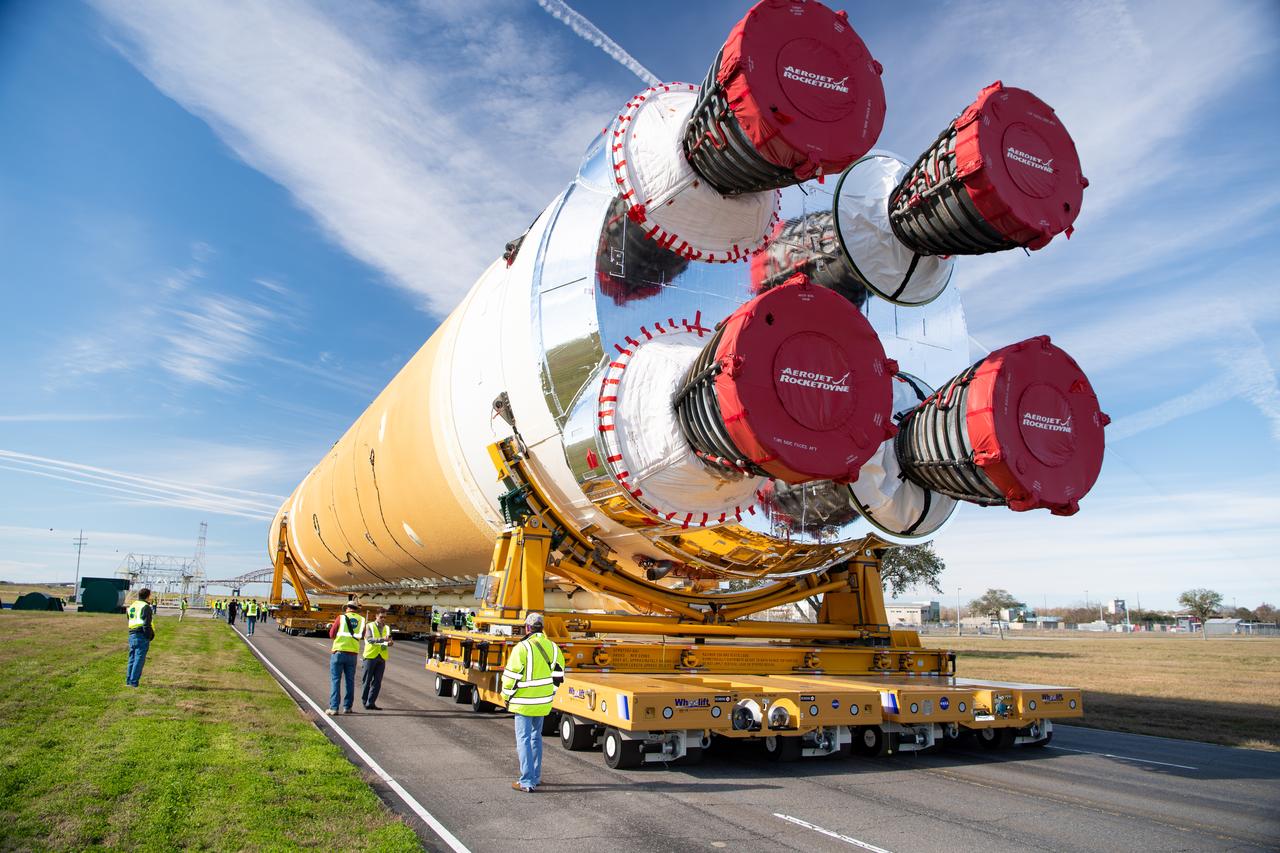

These images show how teams rolled out, or moved, the completed core stage for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket from NASA’s Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans. Crews moved the flight hardware for the first Artemis mission to NASA’s Pegasus barge on Jan. 8 in preparation for the core stage Green Run test series at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. Pegasus, which was modified to ferry SLS rocket hardware, will transport the core stage from Michoud to Stennis for the comprehensive core stage Green Run test series. Once at Stennis, the Artemis rocket stage will be loaded into the B-2 Test Stand for the core stage Green Run test series. The comprehensive test campaign will progressively bring the entire core stage, including its avionics and engines, to life for the first time to verify the stage is fit for flight ahead of the launch of Artemis I. Assembly and integration of the core stage and its four RS-25 engines has been a collaborative, multistep process for NASA and its partners Boeing, the core stage lead contractor, and Aerojet Rocketdyne, the RS-25 engines lead contractor. Together with four RS-25 engines, the rocket’s massive 212-foot-tall core stage — the largest stage NASA has ever built — and its twin solid rocket boosters will produce 8.8 million pounds of thrust to send NASA’s Orion spacecraft, astronauts and supplies beyond Earth’s orbit to the Moon and, ultimately, Mars. Offering more payload mass, volume capability and energy to speed missions through space, the SLS rocket, along with NASA’s Gateway in lunar orbit and Orion, is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration and the Artemis lunar program.
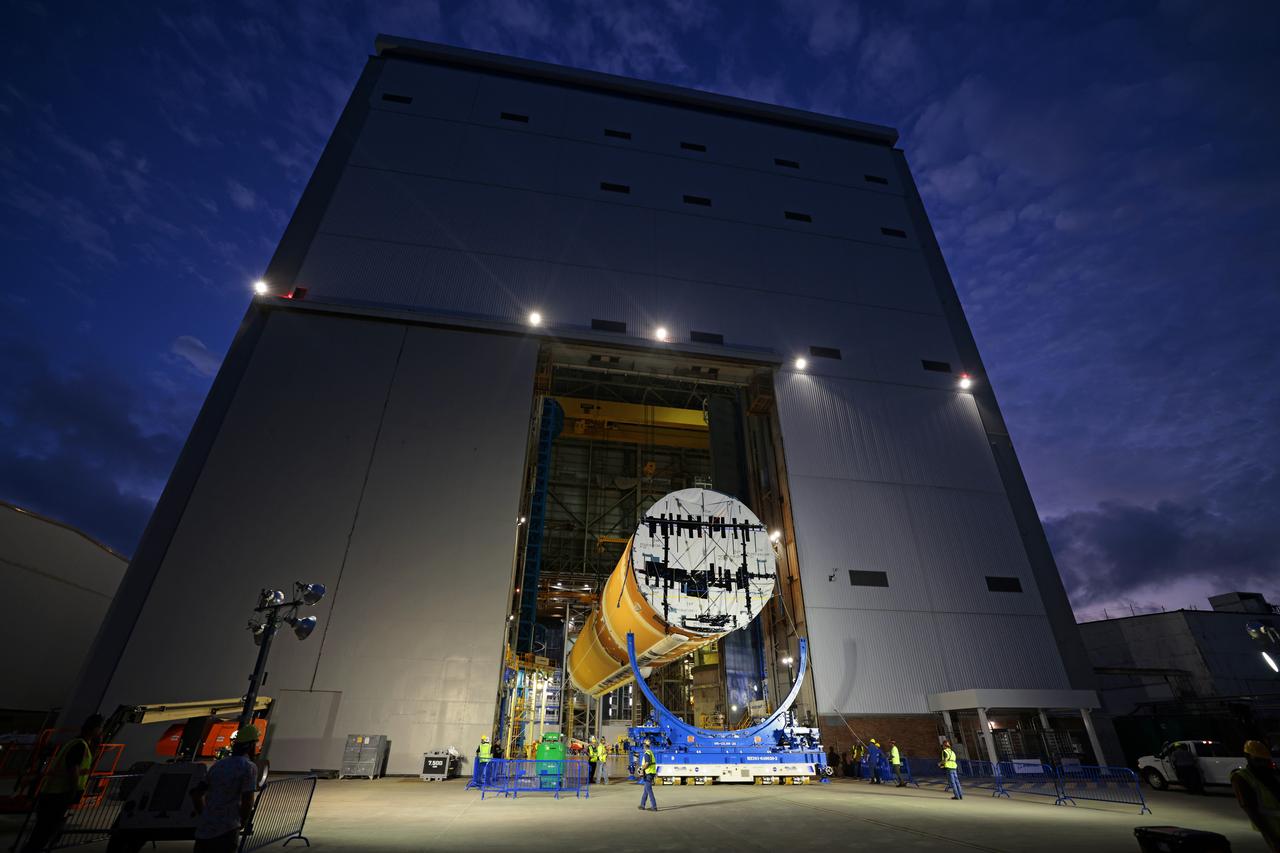

Technicians at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. Teams at Michoud lifted the core stage on Thursday, July 11, 2024, onto NASA’s Multi-Purpose Transportation System, designed to transport SLS vehicle segments by waterway and roadway. It is tasked with transporting the vehicle from where it is manufactured to its intermediate test location and final launch destination. The core stage was lifted in preparation for its move onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pegasus is maintained at Michoud. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. All the major structures for every SLS core stage are fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
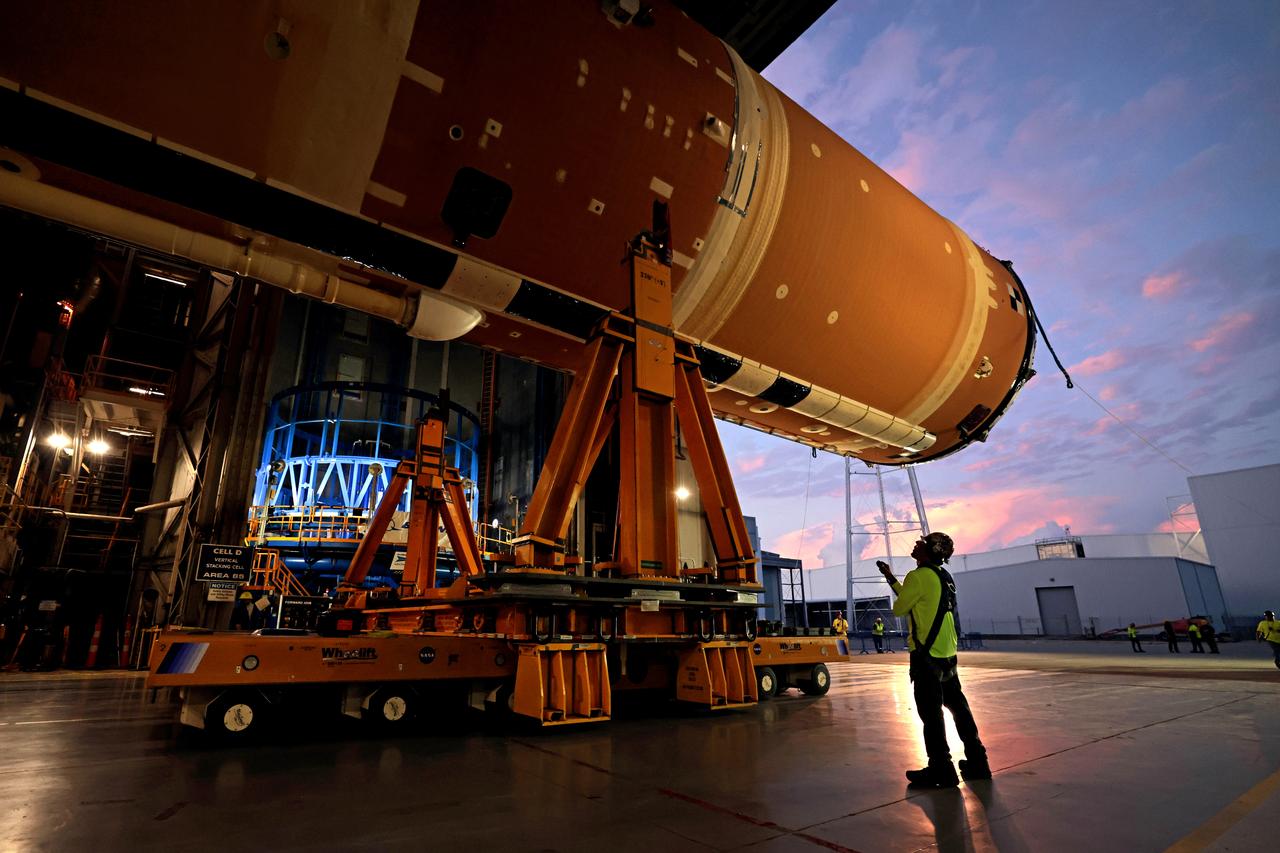

Technicians at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. Teams at Michoud lifted the core stage on Thursday, July 11, 2024, onto NASA’s Multi-Purpose Transportation System, designed to transport SLS vehicle segments by waterway and roadway. It is tasked with transporting the vehicle from where it is manufactured to its intermediate test location and final launch destination. The core stage was lifted in preparation for its move onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pegasus is maintained at Michoud. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. All the major structures for every SLS core stage are fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
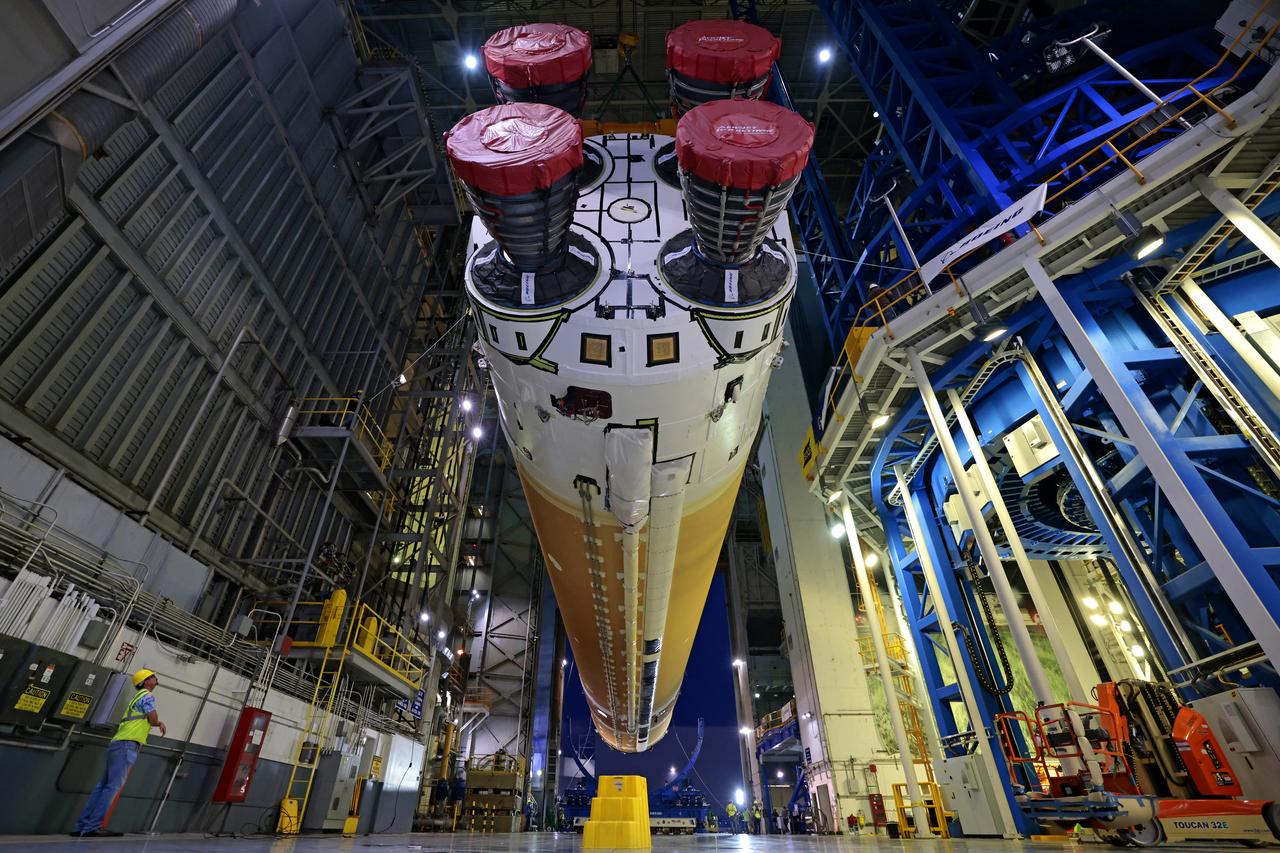

Technicians at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. Teams at Michoud lifted the core stage on Thursday, July 11, 2024, onto NASA’s Multi-Purpose Transportation System, designed to transport SLS vehicle segments by waterway and roadway. It is tasked with transporting the vehicle from where it is manufactured to its intermediate test location and final launch destination. The core stage was lifted in preparation for its move onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pegasus is maintained at Michoud. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. All the major structures for every SLS core stage are fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
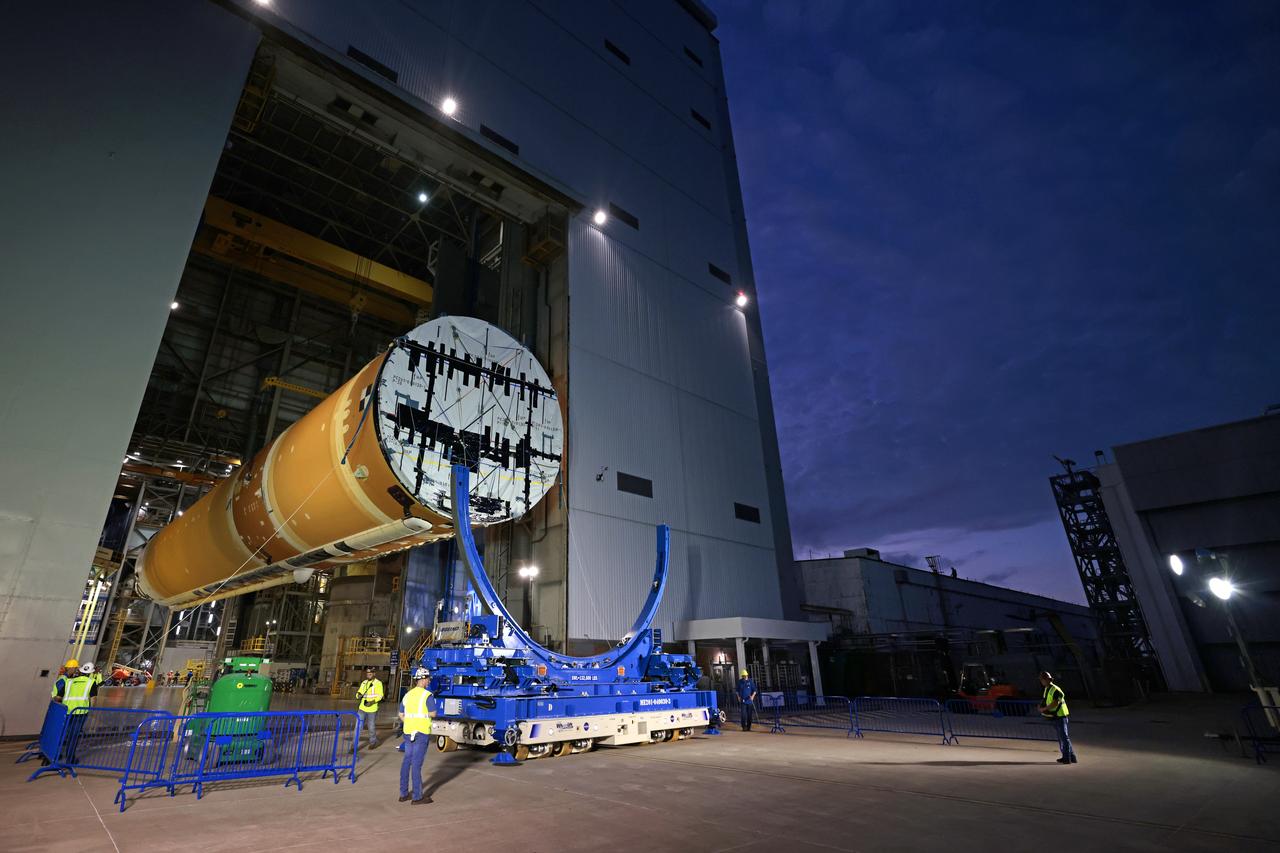

Technicians at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. Teams at Michoud lifted the core stage on Thursday, July 11, 2024, onto NASA’s Multi-Purpose Transportation System, designed to transport SLS vehicle segments by waterway and roadway. It is tasked with transporting the vehicle from where it is manufactured to its intermediate test location and final launch destination. The core stage was lifted in preparation for its move onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pegasus is maintained at Michoud. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. All the major structures for every SLS core stage are fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
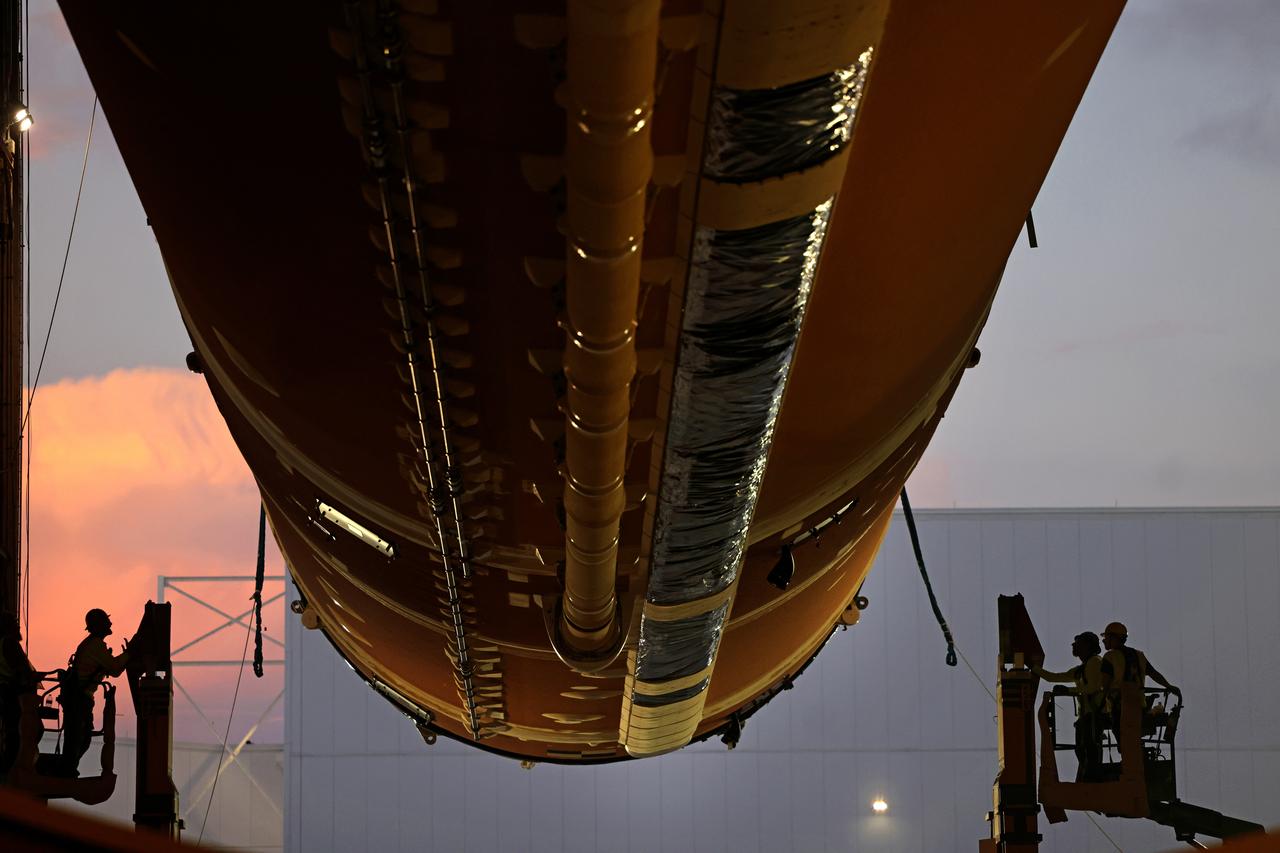

Technicians at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. Teams at Michoud lifted the core stage on Thursday, July 11, 2024, onto NASA’s Multi-Purpose Transportation System, designed to transport SLS vehicle segments by waterway and roadway. It is tasked with transporting the vehicle from where it is manufactured to its intermediate test location and final launch destination. The core stage was lifted in preparation for its move onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pegasus is maintained at Michoud. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. All the major structures for every SLS core stage are fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker
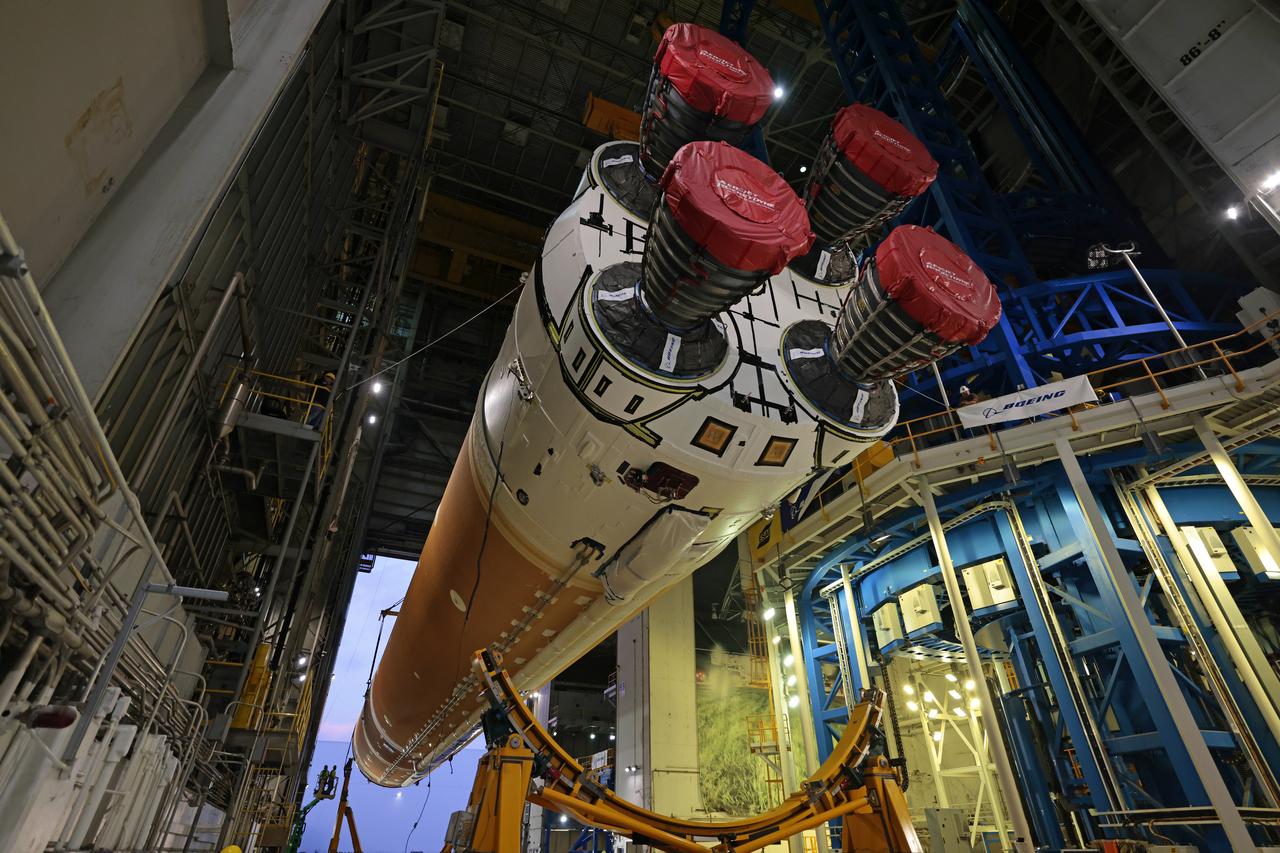

Technicians at Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans lift the core stage that will help launch the first crewed flight of NASA’s SLS (Space Launch System) rocket for the agency’s Artemis II mission. Teams at Michoud lifted the core stage on Thursday, July 11, 2024, onto NASA’s Multi-Purpose Transportation System, designed to transport SLS vehicle segments by waterway and roadway. It is tasked with transporting the vehicle from where it is manufactured to its intermediate test location and final launch destination. The core stage was lifted in preparation for its move onto the agency’s Pegasus barge, where it will be ferried to NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Pegasus is maintained at Michoud. The core stage for the SLS mega rocket is the largest stage NASA has ever produced. At 212 feet tall, the stage consists of five major elements, including two huge propellant tanks that collectively hold more than 733,000 gallons of super chilled liquid propellant to feed four RS-25 engines at its base. During launch and flight, the stage will operate for just over eight minutes, producing more than 2 million pounds of thrust to help send a crew of four astronauts inside NASA’s Orion spacecraft onward to the Moon. All the major structures for every SLS core stage are fully manufactured at NASA Michoud. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generation space, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch. Image credit: NASA/Michael DeMocker