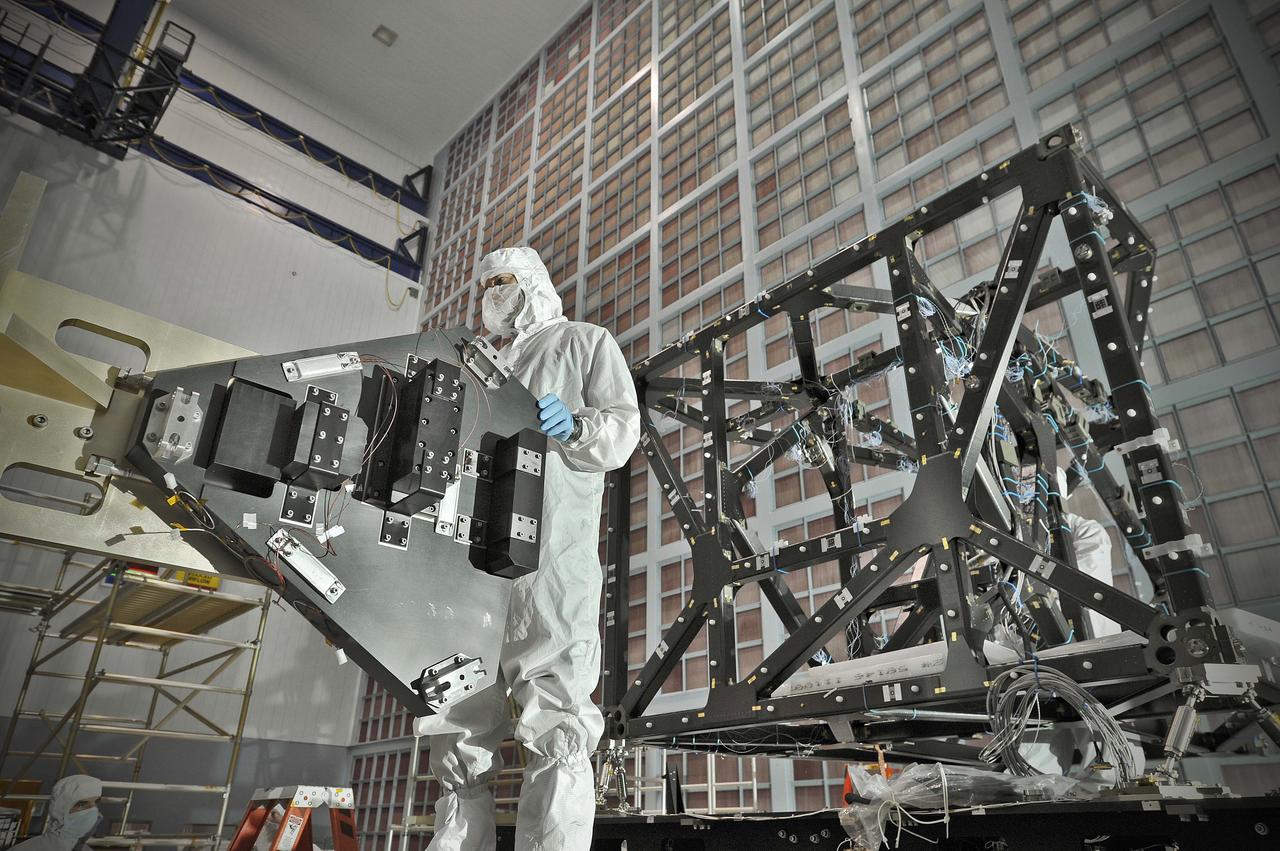

NASA image release September 17, 2010 In preparation for a cryogenic test NASA Goddard technicians install instrument mass simulators onto the James Webb Space Telescope ISIM structure. The ISIM Structure supports and holds the four Webb telescope science instruments : the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), the Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), the Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) and the Fine Guidance Sensor (FGS). Credit: NASA/GSFC/Chris Gunn To learn more about the James Webb Space Telescope go to: <a href="http://www.jwst.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">www.jwst.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> contributes to NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s endeavors by providing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
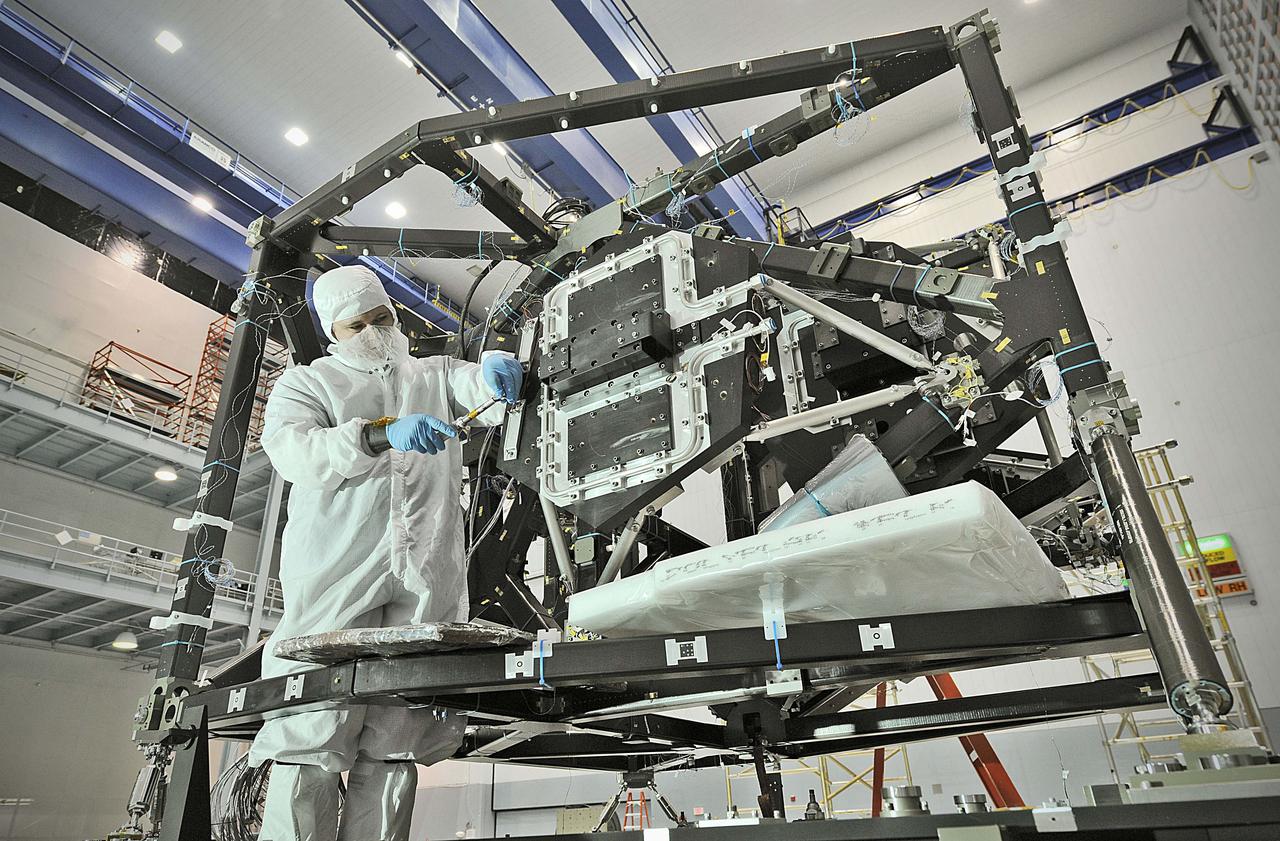

NASA image release September 17, 2010 In preparation for a cryogenic test NASA Goddard technicians install instrument mass simulators onto the James Webb Space Telescope ISIM structure. The ISIM Structure supports and holds the four Webb telescope science instruments : the Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), the Near-Infrared Camera (NIRCam), the Near-Infrared Spectrograph (NIRSpec) and the Fine Guidance Sensor (FGS). Credit: NASA/GSFC/Chris Gunn To learn more about the James Webb Space Telescope go to: <a href="http://www.jwst.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow">www.jwst.nasa.gov/</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> contributes to NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s endeavors by providing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope has successfully passed the center of curvature test, an important optical measurement of Webb’s fully assembled primary mirror prior to cryogenic testing, and the last test held at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, before the spacecraft is shipped to NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston for more testing. After undergoing rigorous environmental tests simulating the stresses of its rocket launch, the Webb telescope team at Goddard analyzed the results from this critical optical test and compared it to the pre-test measurements. The team concluded that the mirrors passed the test with the optical system unscathed. “The Webb telescope is about to embark on its next step in reaching the stars as it has successfully completed its integration and testing at Goddard. It has taken a tremendous team of talented individuals to get to this point from all across NASA, our industry and international partners, and academia,” said Bill Ochs, NASA’s Webb telescope project manager. “It is also a sad time as we say goodbye to the Webb Telescope at Goddard, but are excited to begin cryogenic testing at Johnson.” Rocket launches create high levels of vibration and noise that rattle spacecraft and telescopes. At Goddard, engineers tested the Webb telescope in vibration and acoustics test facilities that simulate the launch environment to ensure that functionality is not impaired by the rigorous ride on a rocket into space. Before and after these environmental tests took place, optical engineers set up an interferometer, the main device used to measure the shape of the Webb telescope’s mirror. An interferometer gets its name from the process of recording and measuring the ripple patterns that result when different beams of light mix and their waves combine or “interfere.” Waves of visible light are less than a thousandth of a millimeter long and optics on the Webb telescope need to be shaped and aligned even more accurately than that to work correctly. Making measurements of the mirror shape and position by lasers prevents physical contact and damage (scratches to the mirror). So, scientists use wavelengths of light to make tiny measurements. By measuring light reflected off the optics using an interferometer, they are able to measure extremely small changes in shape or position that may occur after exposing the mirror to a simulated launch or temperatures that simulate the subfreezing environment of space. During a test conducted by a team from Goddard, Ball Aerospace of Boulder, Colorado, and the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, temperature and humidity conditions in the clean room were kept incredibly stable to minimize fluctuations in the sensitive optical measurements over time. Even so, tiny vibrations are ever-present in the clean room that cause jitter during measurements, so the interferometer is a “high-speed” one, taking 5,000 “frames” every second, which is a faster rate than the background vibrations themselves. This allows engineers to subtract out jitter and get good, clean results on any changes to the mirror's shape. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn Read more: <a href="https://go.nasa.gov/2oPqHwR" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2oPqHwR</a> NASA’s Webb Telescope Completes Goddard Testing
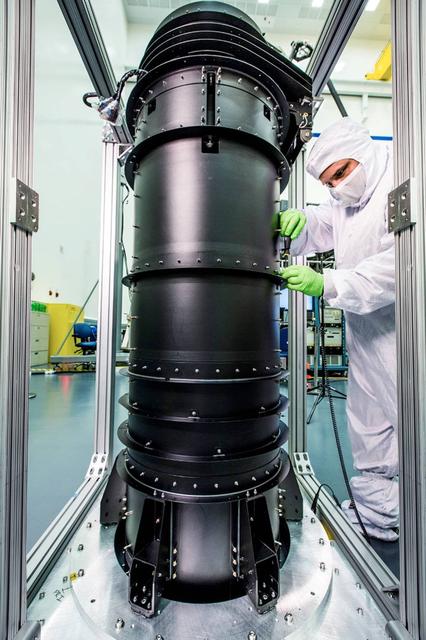

Building a space telescope to see the light from the earliest stars of our universe is a pretty complex task. Although much of the attention goes to instruments and the giant mirrors on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, there are other components that have big jobs to do and that required imagination, engineering, and innovation to become a reality. For example, engineers working on the Webb telescope have to think of everything from keeping instruments from overheating or freezing, to packing up the Webb, which is as big as a tennis court, to fit inside the rocket that will take it to space. Those are two areas where the "DTA" or Deployable Tower Assembly (DTA) plays a major role. The DTA looks like a big black pipe and is made out of graphite-epoxy composite material to ensure stability and strength with extreme changes in temperature like those encountered in space. When fully deployed, the DTA reaches ten feet in length. The DTA interfaces and supports the spacecraft and the telescope structures. It features two large nested telescoping tubes, connected by a mechanized lead screw. It is a deployable structure that is both very light and extremely strong and stable. The Webb telescope’s secondary mirror support structure and DTA contribute to how the telescope and instruments fit into the rocket fairing in preparation for launch. The DTA allows the Webb to be short enough when stowed to fit in the rocket fairing with an acceptably low center of gravity for launch. Several days after the Webb telescope is launched, the DTA will deploy, or separate, the telescope mirrors and instruments from the spacecraft bus and sunshield. This separation allows the sunshield to unfurl and shade the telescope and instruments from radiant heat and stray light from the sun and Earth. The DTA was designed, built and tested by Astro Aerospace - a Northrop Grumman Company, in Carpinteria, California. The James Webb Space Telescope is the scientific successor to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. It will be the most powerful space telescope ever built. The Webb telescope is an international project led by NASA with its partners, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. For more information about the Webb telescope, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/webb" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/webb</a> or jwst.nasa.gov <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
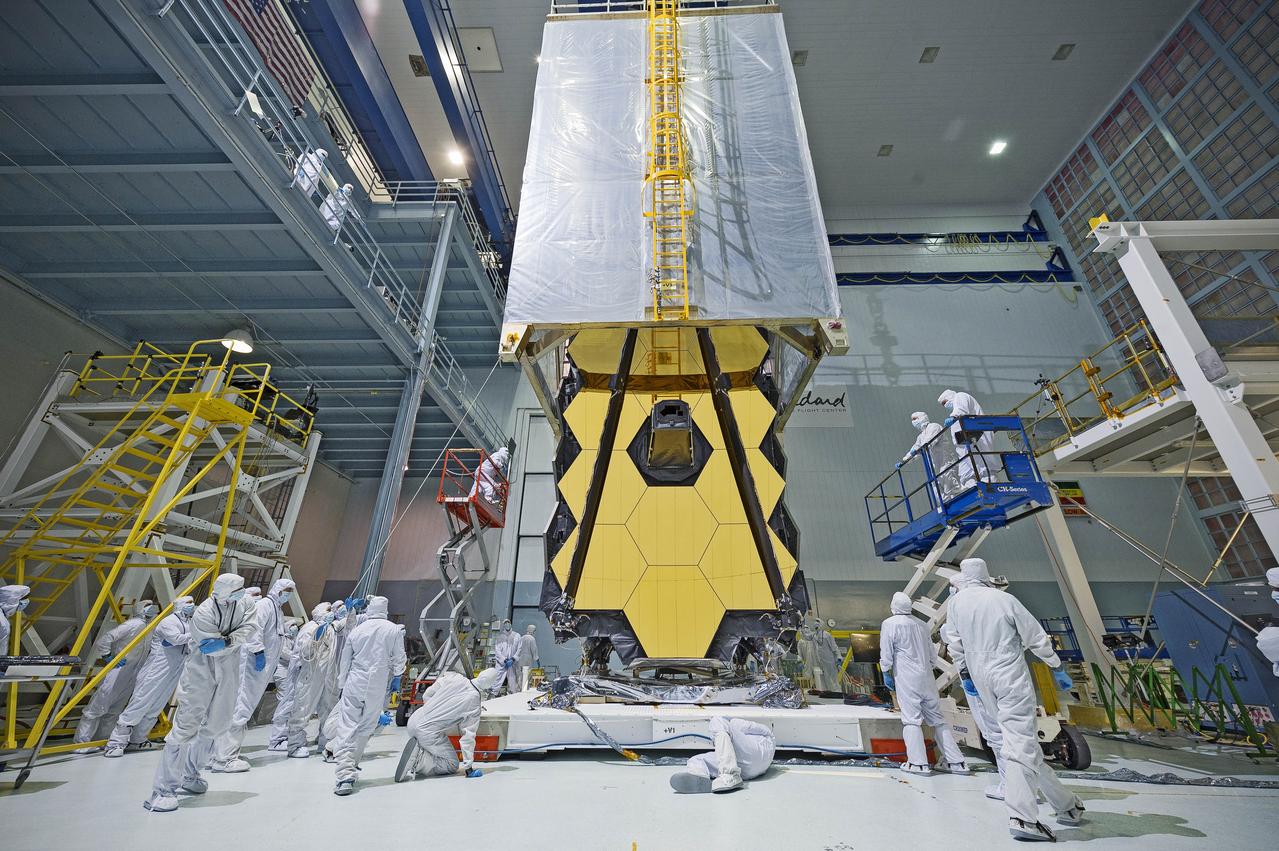

What looks like a teleporter from science fiction being draped over NASA's James Webb Space Telescope, is actually a "clean tent." The clean tent protects Webb from dust and dirt when engineers at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland transport the next generation space telescope out of the relatively dust-free cleanroom and into the shirtsleeve environment of the vibration and acoustics testing areas. In two years, a rocket will be the transporter that carries the Webb into space so it can orbit one million miles from Earth and peer back over 13.5 billion years to see the first stars and galaxies forming out of the darkness of the early universe. For more information about the Webb telescope, visit: <a href="http://www.jwst.nasa.gov" rel="nofollow">www.jwst.nasa.gov</a> or <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/webb" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/webb</a>. Photo Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
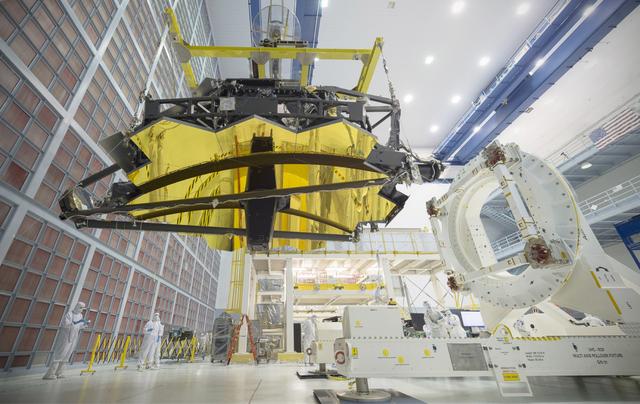

The James Webb Space Telescope was lifted out of its assembly stand for the last time at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. In this photo, the telescope was hanging upside down as the lift crew were about to install it in the rollover fixture where it will be situated before moving on to its upcoming center of curvature test. Image credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn
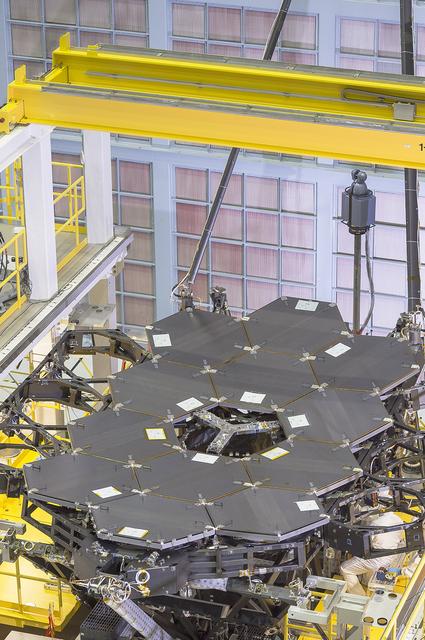

A view of the one dozen (out of 18) flight mirror segments that make up the primary mirror on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have been installed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn More: Since December 2015, the team of scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install all the primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure in the large clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The twelfth mirror was installed on January 2, 2016. "This milestone signifies that all of the hexagonal shaped mirrors on the fixed central section of the telescope structure are installed and only the 3 mirrors on each wing are left for installation," said Lee Feinberg, NASA's Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA Goddard. "The incredibly skilled and dedicated team assembling the telescope continues to find ways to do things faster and more efficiently." Each hexagonal-shaped segment measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). After being pieced together, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror. The primary mirror will unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. The mirrors are placed on the telescope's backplane using a robotic arm, guided by engineers. The full installation is expected to be completed in a few months. The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope. While the mirror assembly is a very significant milestone, there are many more steps involved in assembling the Webb telescope. The primary mirror and the tennis-court-sized sunshield are the largest and most visible components of the Webb telescope. However, there are four smaller components that are less visible, yet critical. The instruments that will fly aboard Webb - cameras and spectrographs with detectors able to record extremely faint signals — are part of the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), which is currently undergoing its final cryogenic vacuum test and will be integrated with the mirror later this year.

Caption: One dozen (out of 18) flight mirror segments that make up the primary mirror on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have been installed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn More: Since December 2015, the team of scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install all the primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure in the large clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The twelfth mirror was installed on January 2, 2016. "This milestone signifies that all of the hexagonal shaped mirrors on the fixed central section of the telescope structure are installed and only the 3 mirrors on each wing are left for installation," said Lee Feinberg, NASA's Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA Goddard. "The incredibly skilled and dedicated team assembling the telescope continues to find ways to do things faster and more efficiently." Each hexagonal-shaped segment measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). After being pieced together, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror. The primary mirror will unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. The mirrors are placed on the telescope's backplane using a robotic arm, guided by engineers. The full installation is expected to be completed in a few months. The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope. While the mirror assembly is a very significant milestone, there are many more steps involved in assembling the Webb telescope. The primary mirror and the tennis-court-sized sunshield are the largest and most visible components of the Webb telescope. However, there are four smaller components that are less visible, yet critical. The instruments that will fly aboard Webb - cameras and spectrographs with detectors able to record extremely faint signals — are part of the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), which is currently undergoing its final cryogenic vacuum test and will be integrated with the mirror later this year.
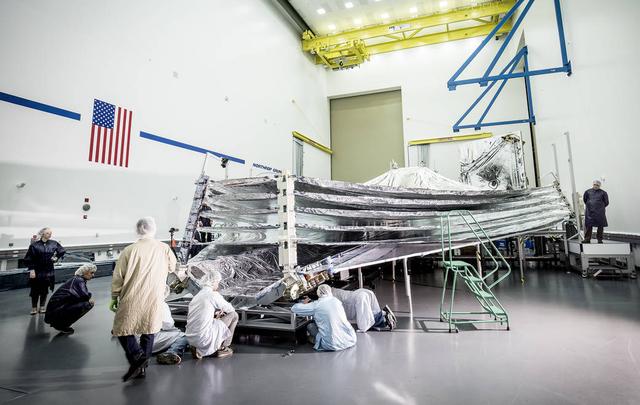

NASA's James Webb Space Telescope has a giant custom-built, kite-shaped sunshield driven by mechanics that will fold and unfold with a harmonious synchronicity 1 million miles from Earth. Like a car, many mechanical pieces in the Webb telescope's sunshield will work together to open it from its stored folded position in the rocket that will carry it into space. According to car manufacturers, a single car can have about 30,000 parts, counting every part down to the smallest screws. Like getting all of the parts in a car to operate together, the mechanical parts of the sunshield have to work in the same way. The sunshield support structure contains well over 7,000 flight parts, including springs, bearings, pulleys, magnets, etc. In addition, the sunshield has hundreds of custom fabricated pieces. Most mechanical pieces were developed exclusively for the sunshield, with a few from existing designs. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2cXcQMT" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2cXcQMT</a>
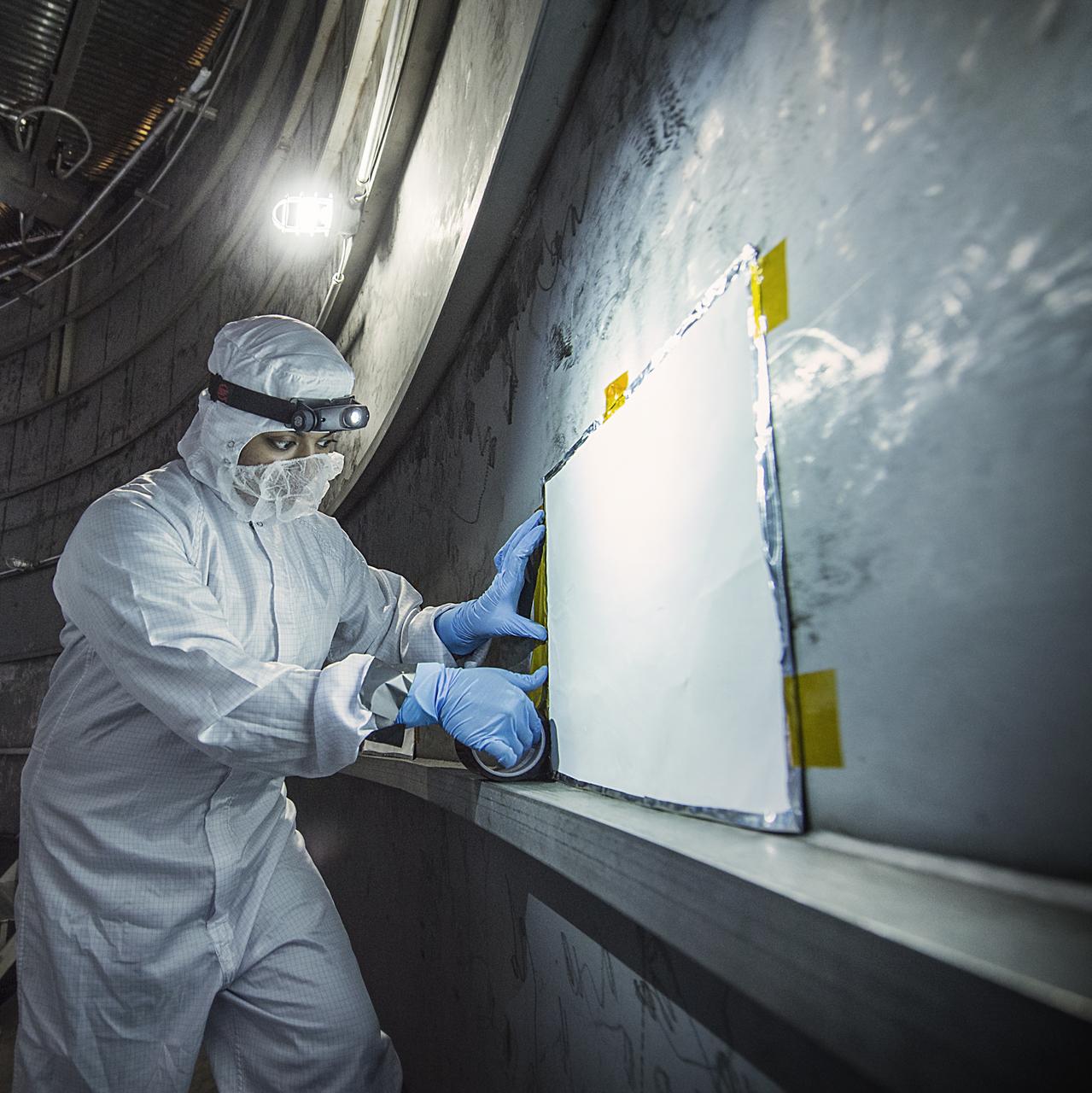

Contamination from organic molecules can harm delicate instruments and engineers are taking special care at NASA to prevent that from affecting the James Webb Space Telescope (and all satellites and instruments). Recently, Nithin Abraham, a Thermal Coatings Engineer placed Molecular Adsorber Coating or "MAC" panels in the giant chamber where the Webb telescope will be tested. This contamination can occur through a process when a vapor or odor is emitted by a substance. This is called "outgassing." The "new car smell" is an example of that, and is unhealthy for people and sensitive satellite instruments. So, NASA engineers have created a new way to protect those instruments from the damaging effects of contamination coming from outgassing. "The Molecular Adsorber Coating (MAC) is a NASA Goddard coatings technology that was developed to adsorb or entrap outgassed molecular contaminants for spaceflight applications," said Nithin Abraham, Thermal Coatings Engineer at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. MAC is currently serving as an innovative contamination mitigation tool for Chamber A operations at NASA Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. MAC can be used to keep outgassing from coming in from outside areas or to capture outgassing directly from hardware, components, and within instrument cavities. In this case, MAC is helping by capturing outgassed contaminants outside the test chamber from affecting the Webb components. MAC is expected to capture the outgassed contaminants that exist in the space of the vacuum chamber (not from the Webb components). Credit: NASA/GoddardChris Gunn Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/nasa-technology-protects-webb-telescope-from-contamination" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/nasa-technology-protects-web...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
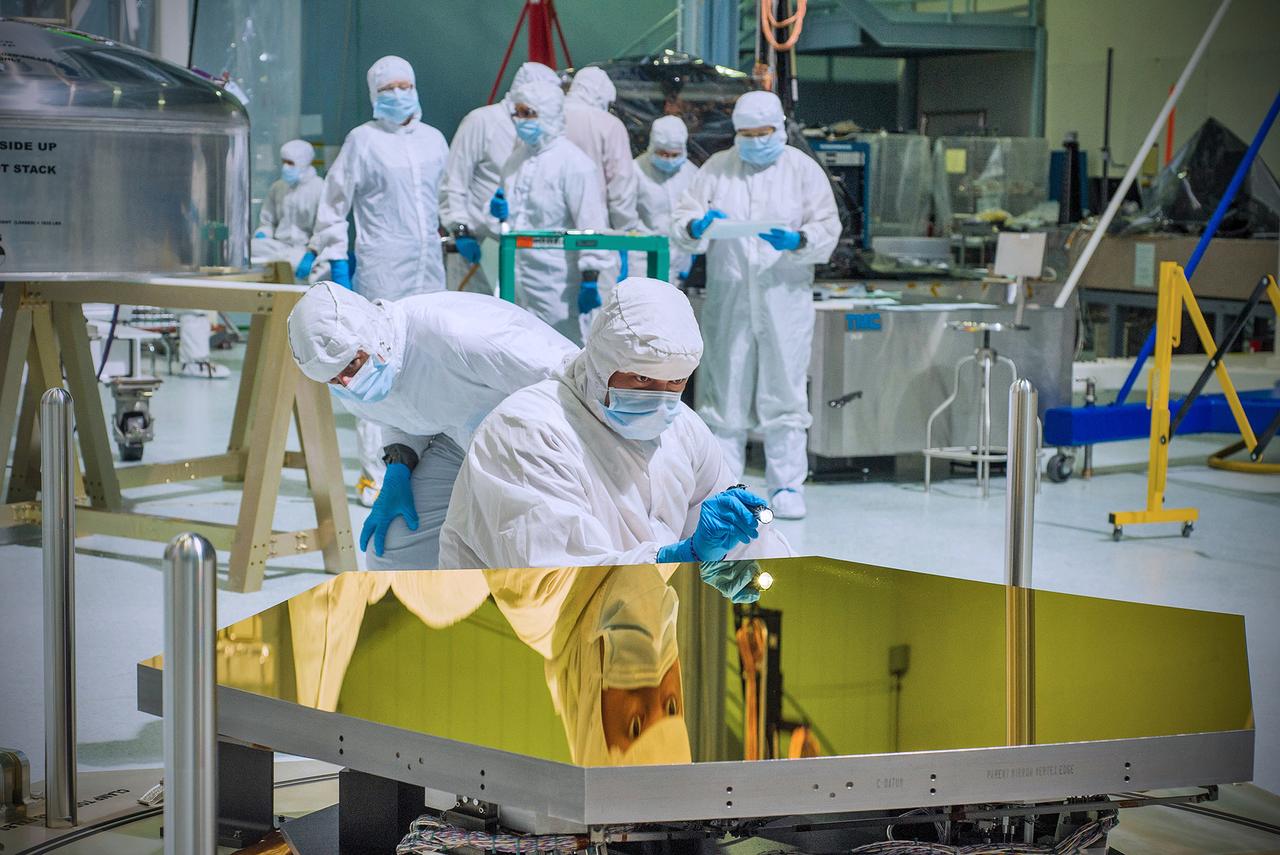

Technicians and scientists check out one of the Webb telescope's first two flight mirrors in the clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Credit: NASA/Chris Gunn ----- The first two of the 18 primary mirrors to fly aboard NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope arrived at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. The mirrors are going through receiving and inspection and will then be stored in the Goddard cleanroom until engineers are ready to assemble them onto the telescope's backplane structure that will support them. Ball Aerospace, Boulder, Colo., under contract to Northrop Grumman, is responsible for the Webb’s optical technology and lightweight mirror system. On September 17, 2012, Ball Aerospace shipped the first two mirrors in custom containers designed specifically for the multiple trips the mirrors made through eight U.S. states while completing their manufacturing. The remaining 16 mirrors will make their way from Ball Aerospace to Goddard over the next 12 months as they await telescope integration in 2015. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/features/webb-tech-mirrors-delivered.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/features/webb-tech-mirrors...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
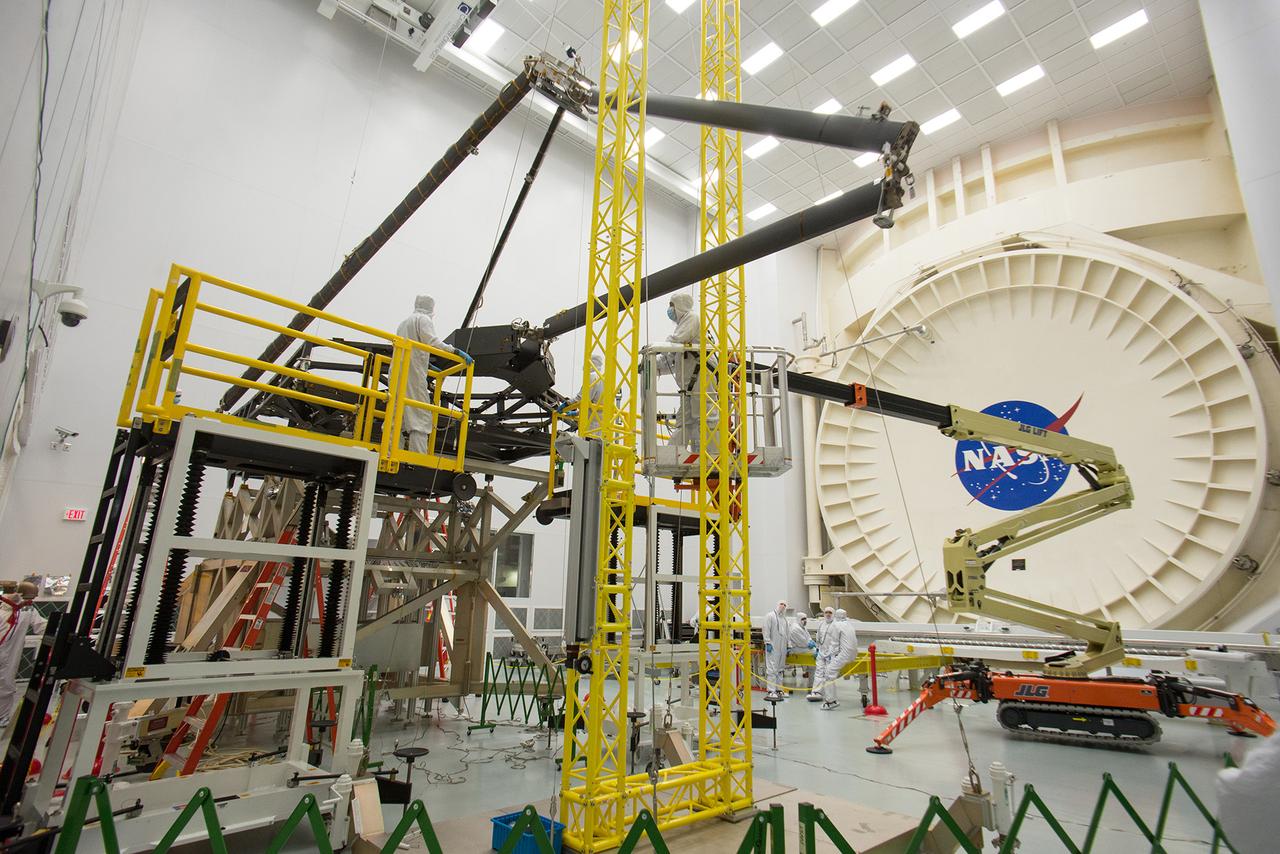

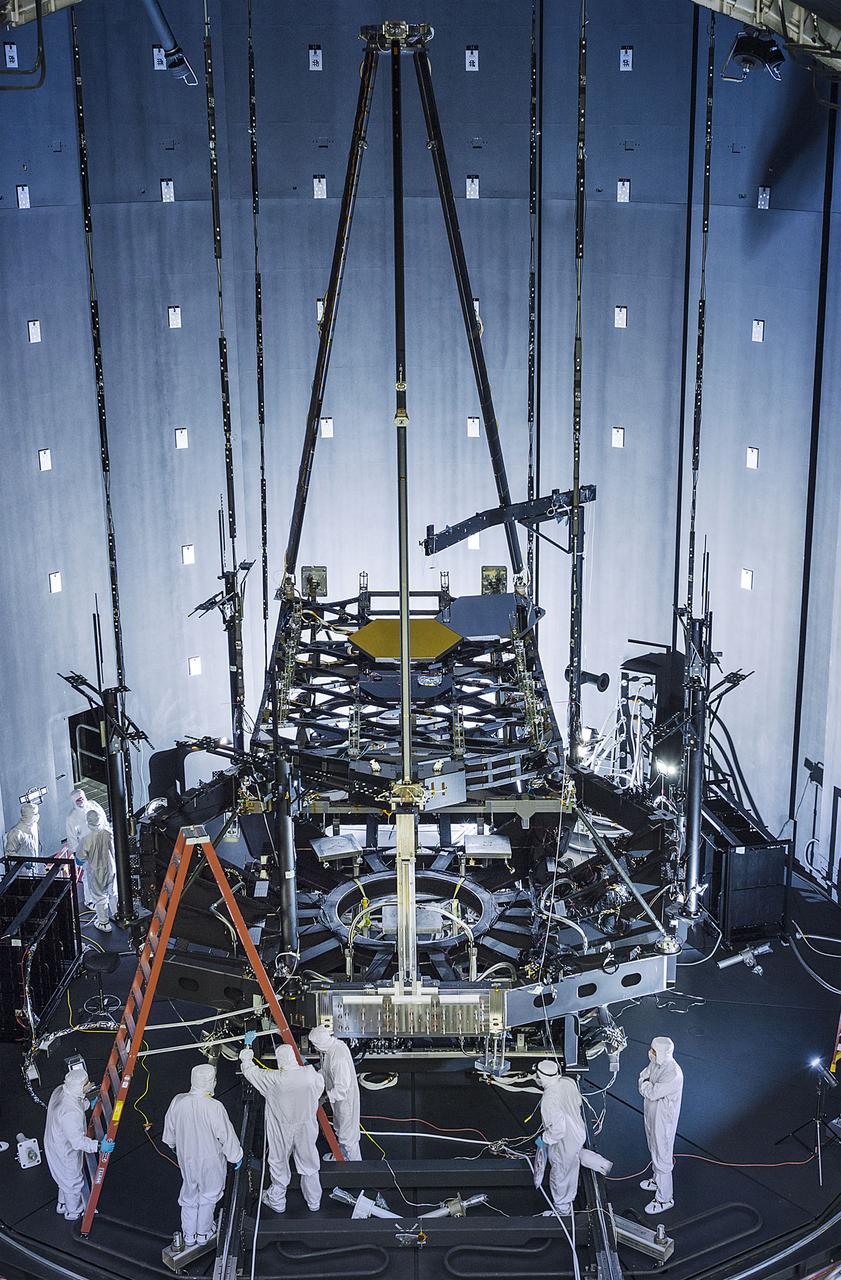
Engineers and technicians manually deployed the secondary mirror support structure (SMSS) of the James Webb Space Telescope's Pathfinder backplane test model, outside of a giant space simulation chamber called Chamber A, at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston. This historic test chamber was previously used in manned spaceflight missions and is being readied for a cryogenic test of a Webb telescope component. In the weightless environment of space, the SMSS is deployed by electric motors. On the ground, specially trained operators use a hand crank and a collection of mechanical ground support equipment to overcome the force of gravity. "This structure needs to be in the deployed configuration during the cryogenic test to see how the structure will operate in the frigid temperatures of space," said Will Rowland, senior mechanical test engineer for Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems, Redondo Beach, California. "The test also demonstrates that the system works and can be successfully deployed." After the deployment was completed, Chamber A's circular door was opened and the rails (seen in the background of the photo) were installed so that the Pathfinder unit could be lifted, installed and rolled into the chamber on a cart. The team completed a fit check for the Pathfinder. Afterwards they readied the chamber for the cryogenic test, which will simulate the frigid temperatures the Webb telescope will encounter in space. “The team has been doing a great job keeping everything on schedule to getting our first optical test results, " said Lee Feinberg, NASA Optical Telescope Element Manager. The James Webb Space Telescope is the scientific successor to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. It will be the most powerful space telescope ever built. Webb is an international project led by NASA with its partners, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. Image credit: NASA/Desiree Stover Text credit: Laura Betz, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
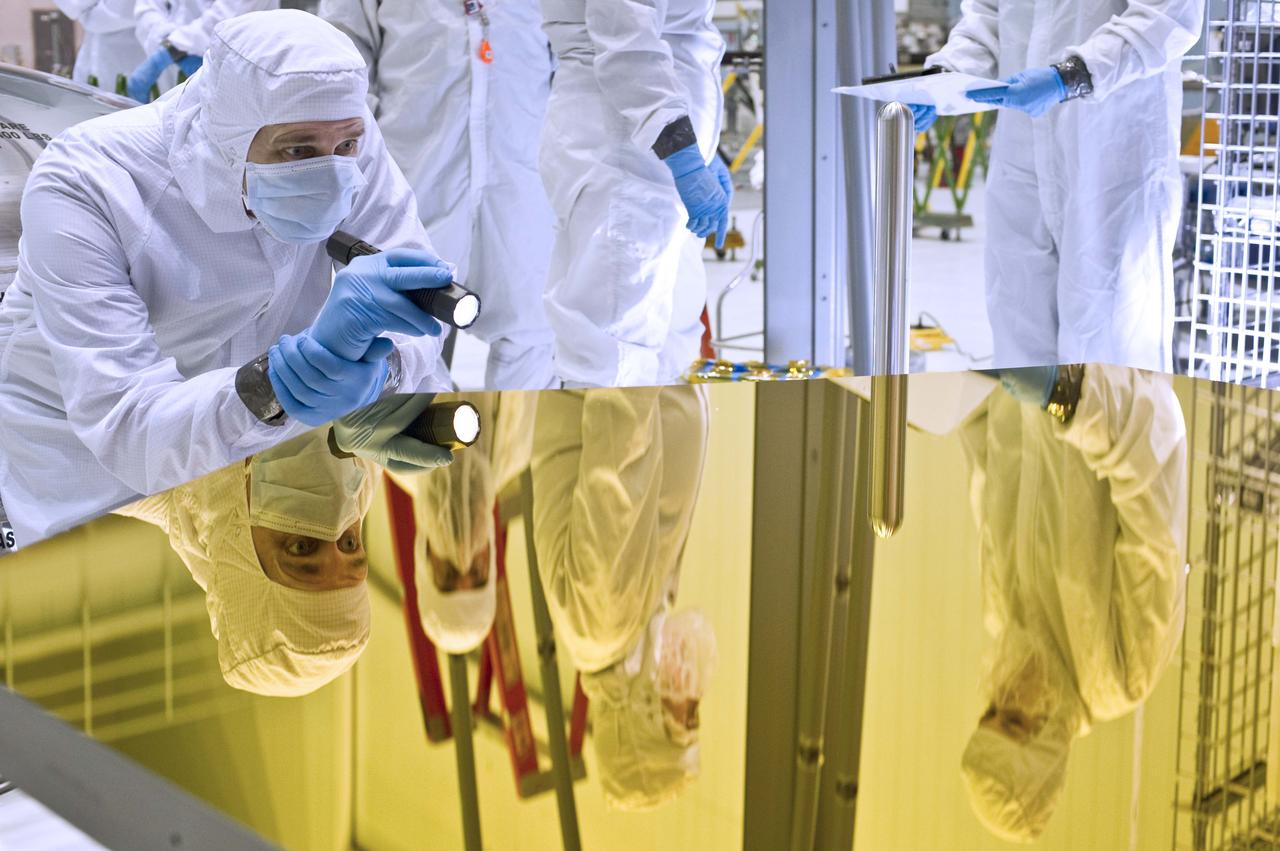

NASA image release April 13, 2011 An engineer examines the Webb telescope primary mirror Engineering Design Unit segment in the clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. It takes two unique types of mirrors working together to see farther back in time and space than ever before, and engineers at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center have just received one of each type. Primary and Secondary Mirror Engineering Design Units (EDUs) have recently arrived at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. from Northrop Grumman Aerospace Systems in Redondo Beach, Calif. and are undergoing examination and testing. When used on the James Webb Space Telescope those two types of mirrors will allow scientists to make those observations. "The Primary mirror EDU will be used next year to check out optical test equipment developed by Goddard and slated to be used to test the full Flight Primary mirror," said Lee Feinberg, the Optical Telescope Element Manager for the Webb telescope at NASA Goddard. "Following that, the primary and secondary EDU's will actually be assembled onto the Pathfinder telescope. The Pathfinder telescope includes two primary mirror segments (one being the Primary EDU) and the Secondary EDU and allows us to check out all of the assembly and test procedures (that occur both at Goddard and testing at Johnson Space Center, Houston, Texas) well in advance of the flight telescope assembly and test." To read more about this image go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/features/two-webb-mirrors.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/features/two-webb-mirrors....</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
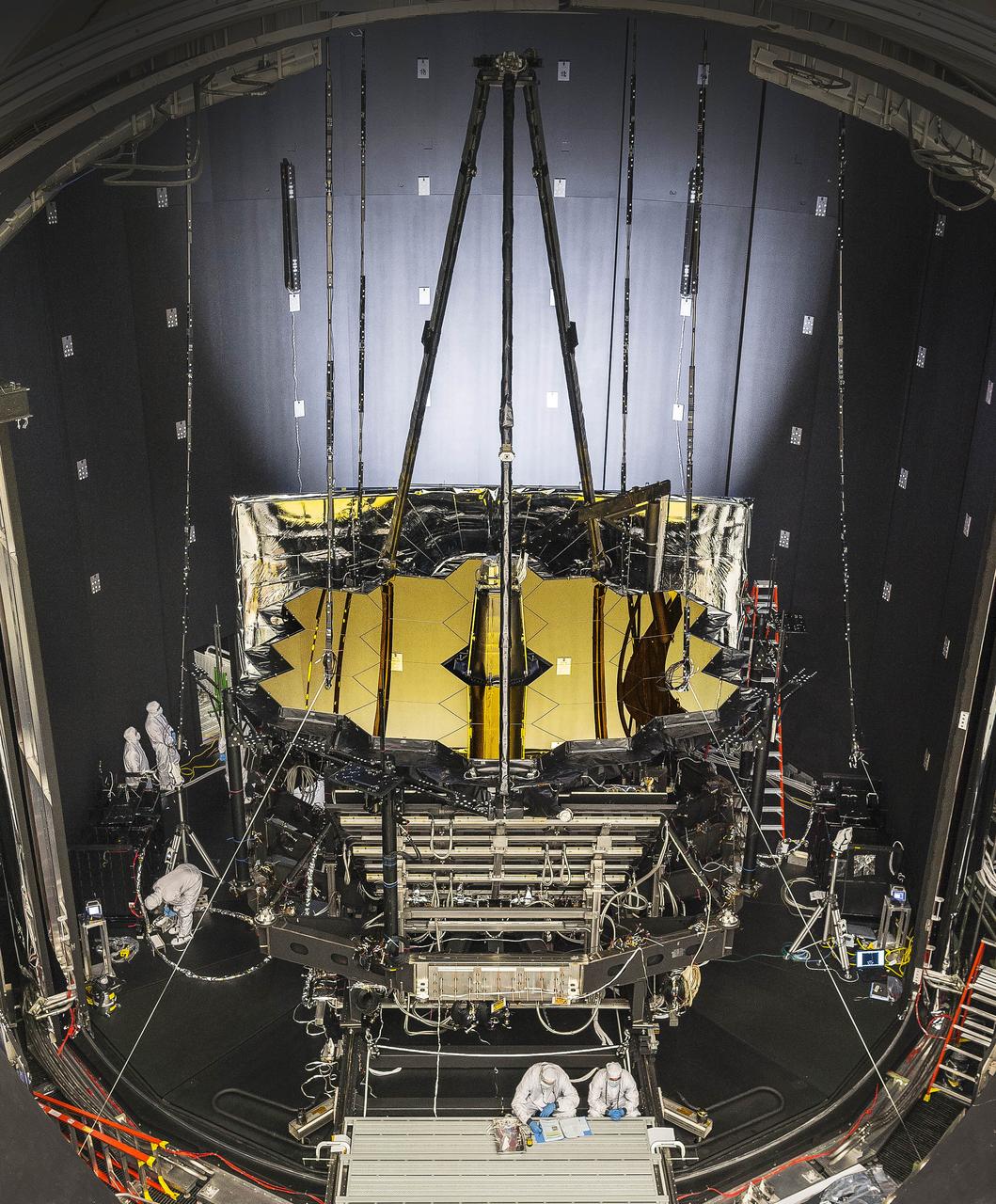

NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope was placed in Johnson Space Center’s historic Chamber A on June 20, 2017, to prepare for its final three months of testing in a cryogenic vacuum that mimics temperatures in space. Engineers will perform the test to prove that the telescope can operate in space at these temperatures. Chamber A will simulate an environment where the telescope will experience extreme cold -- around 37 Kelvin (minus 236 degrees Celsius or minus 393 degrees Fahrenheit). In space, the telescope must be kept extremely cold, in order to be able to detect the infrared light from very faint, distant objects. To protect the telescope from external sources of light and heat (like the sun, Earth, and moon), as well as from heat emitted by the observatory, a five-layer, tennis court-sized sunshield acts like a parasol that provides shade. The sunshield separates the observatory into a warm, sun-facing side (reaching temperatures close to 400 degrees Fahrenheit) and a cold side (185 degrees below zero). The sunshield blocks sunlight from interfering with the sensitive telescope instruments. Read more: <a href="https://go.nasa.gov/2sZAilS" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2sZAilS</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
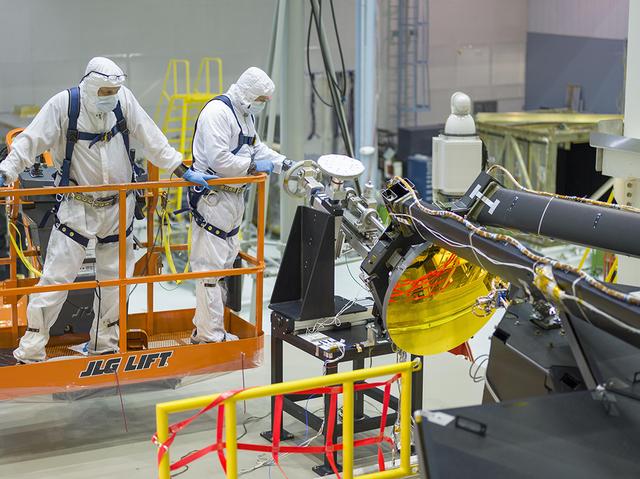

The sole secondary mirror that will fly aboard NASA's James Webb Space Telescope was installed onto the telescope at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland, on March 3, 2016. The Webb telescope uses many mirrors to direct incoming light into the telescope's instruments. The secondary mirror is called the secondary mirror because it is the second surface the light from the cosmos hits on its route into the telescope. In this photo, engineers are seen installing the secondary mirror onto the telescope. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/nasas-james-webb-space-telescope-secondary-mirror-installed" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/nasas-james-webb-space-...</a> Credits: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
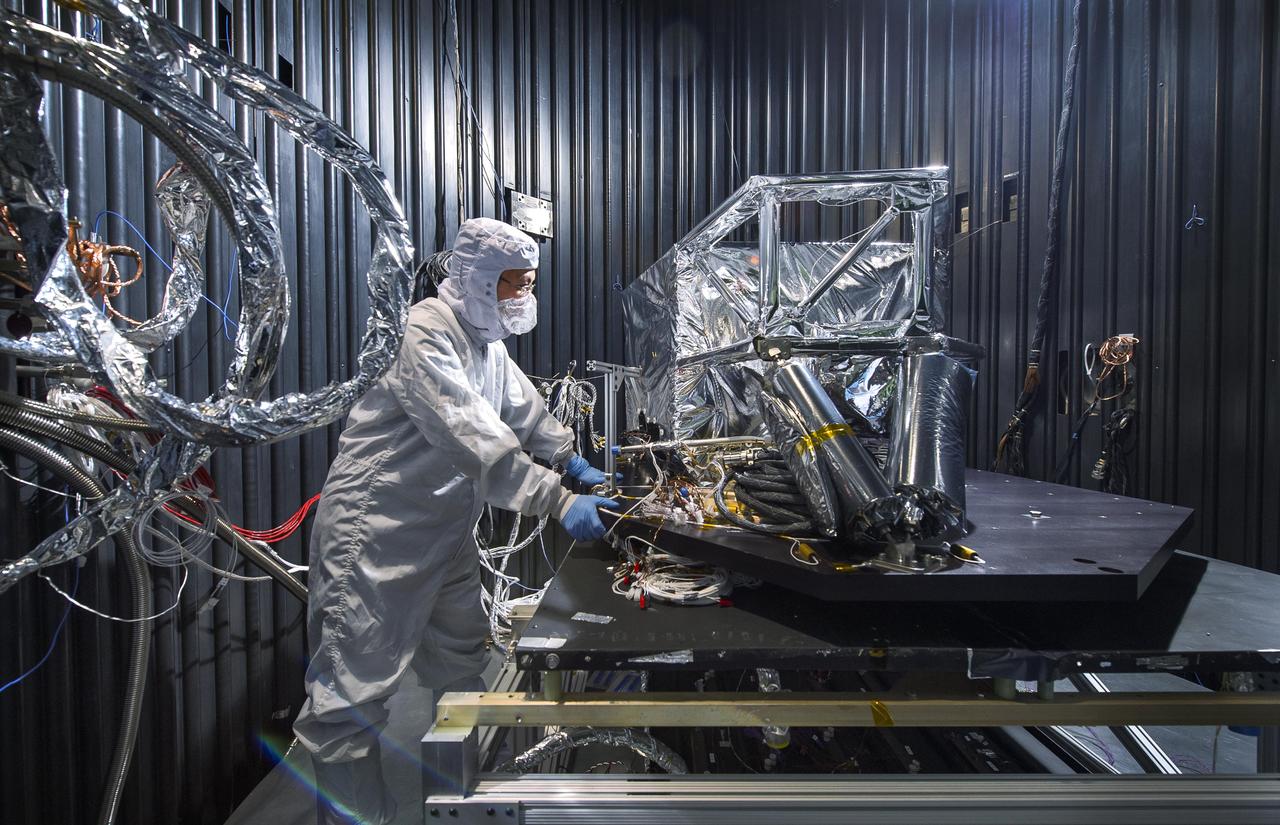

NASA engineer Acey Herrera recently checked out copper test wires inside the thermal shield of the Mid-Infrared Instrument, known as MIRI, that will fly aboard NASA's James Webb Space Telescope. The shield is designed to protect the vital MIRI instrument from excess heat. At the time of the photo, the thermal shield was about to go through rigorous environmental testing to ensure it can perform properly in the extreme cold temperatures that it will encounter in space. Herrera is working in a thermal vacuum chamber at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. As the MIRI shield lead, Herrera along with a thermal engineer and cryo-engineer verify that the shield is ready for testing. On the Webb telescope, the pioneering camera and spectrometer that comprise the MIRI instrument sit inside the Integrated Science Instrument Module flight structure, that holds Webb's four instruments and their electronic systems during launch and operations. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/15I0wrS" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/15I0wrS</a> Credit: NASA/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
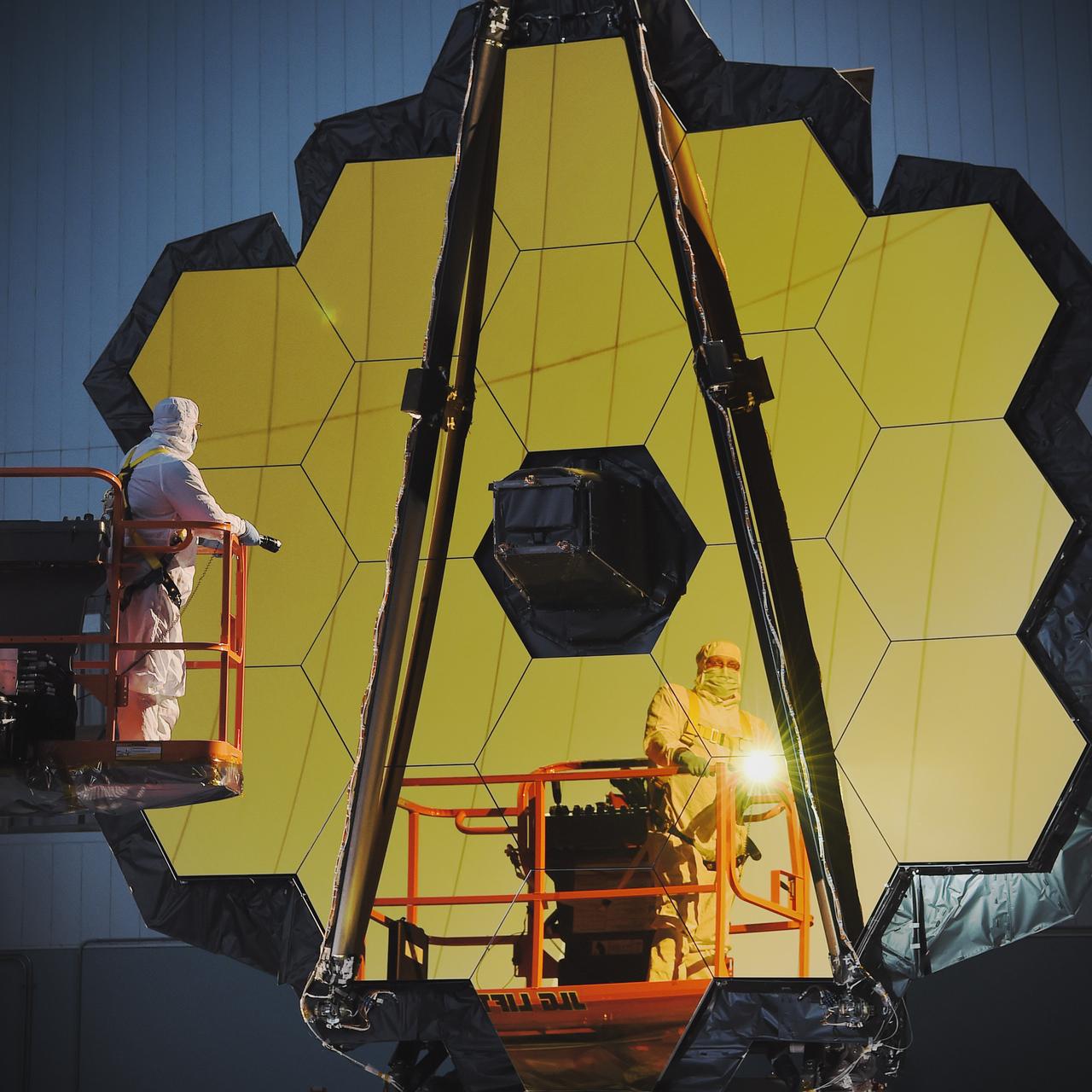

Engineers and technicians working on the James Webb Space Telescope successfully completed the first important optical measurement of Webb’s fully assembled primary mirror, called a Center of Curvature test. Taking a “before” optical measurement of the telescope’s deployed mirror is crucial before the telescope goes into several stages of rigorous mechanical testing. These tests will simulate the violent sound and vibration environments the telescope will experience inside its rocket on its way out into space. This environment is one of the most stressful structurally and could alter the shape and alignment of Webb’s primary mirror, which could degrade or, in the worst case, ruin its performance. Webb has been designed and constructed to withstand its launch environment, but it must be tested to verify that it will indeed survive and not change in any unexpected way. Making the same optical measurements both before and after simulated launch environment testing and comparing the results is fundamental to Webb’s development, assuring that it will work in space. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2enIgwP" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2enIgwP</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Media Invited to Rare View of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope Mirrors

Media Invited to Rare View of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope Mirrors

Media Invited to Rare View of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope Mirrors

Media Invited to Rare View of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope Mirrors

Media Invited to Rare View of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope Mirrors

Media Invited to Rare View of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope Mirrors

Media Invited to Rare View of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope Mirrors

Media Invited to Rare View of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope Mirrors

Media Invited to Rare View of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope Mirrors
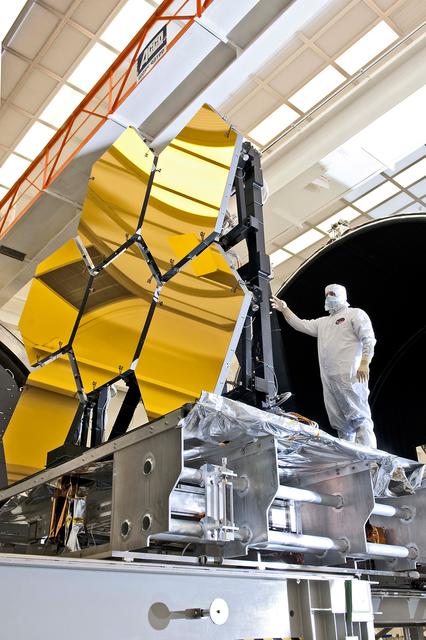

The first six flight ready James Webb Space Telescope's primary mirror segments are prepped to begin final cryogenic testing at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Ala. To read more go to: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/features/webb-mirror-coating.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/topics/technology/features/webb-mirror-coati...</a> Credit: NASA/GSFC/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
Inside NASA's giant thermal vacuum chamber, called Chamber A, at NASA's Johnson Space Center in Houston, the James Webb Space Telescope's Pathfinder backplane test model, is being prepared for its cryogenic test. Previously used for manned spaceflight missions, this historic chamber is now filled with engineers and technicians preparing for a crucial test. Exelis developed and installed the optical test equipment in the chamber. "The optical test equipment was developed and installed in the chamber by Exelis," said Thomas Scorse, Exelis JWST Program Manager. "The Pathfinder telescope gives us our first opportunity for an end-to-end checkout of our equipment." "This will be the first time on the program that we will be aligning two primary mirror segments together," said Lee Feinberg, NASA Optical Telescope Element Manager. "In the past, we have always tested one mirror at a time but this time we will use a single test system and align both mirrors to it as though they are a single monolithic mirror." The James Webb Space Telescope is the scientific successor to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. It will be the most powerful space telescope ever built. Webb is an international project led by NASA with its partners, the European Space Agency and the Canadian Space Agency. Image credit: NASA/Chris Gunn Text credit: Laura Betz, NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Maryland <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
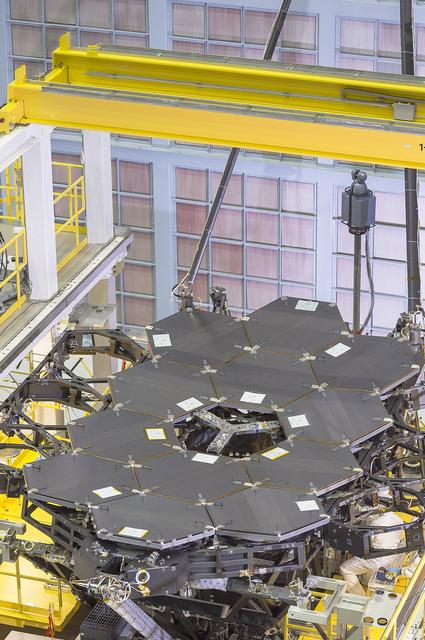

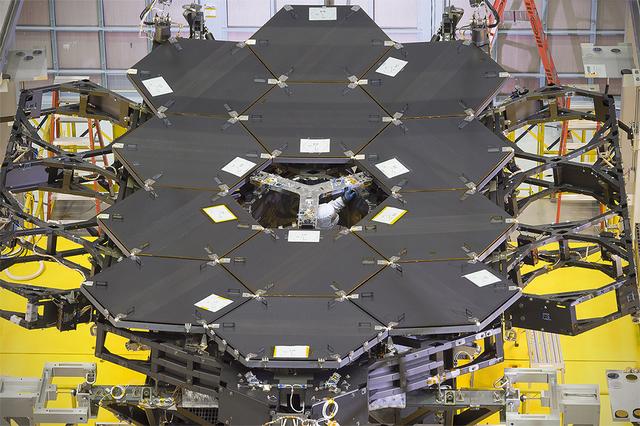
A view of the one dozen (out of 18) flight mirror segments that make up the primary mirror on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have been installed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn More: Since December 2015, the team of scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install all the primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure in the large clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The twelfth mirror was installed on January 2, 2016. "This milestone signifies that all of the hexagonal shaped mirrors on the fixed central section of the telescope structure are installed and only the 3 mirrors on each wing are left for installation," said Lee Feinberg, NASA's Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA Goddard. "The incredibly skilled and dedicated team assembling the telescope continues to find ways to do things faster and more efficiently." Each hexagonal-shaped segment measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). After being pieced together, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror. The primary mirror will unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. The mirrors are placed on the telescope's backplane using a robotic arm, guided by engineers. The full installation is expected to be completed in a few months. The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope. While the mirror assembly is a very significant milestone, there are many more steps involved in assembling the Webb telescope. The primary mirror and the tennis-court-sized sunshield are the largest and most visible components of the Webb telescope. However, there are four smaller components that are less visible, yet critical. The instruments that will fly aboard Webb - cameras and spectrographs with detectors able to record extremely faint signals — are part of the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), which is currently undergoing its final cryogenic vacuum test and will be integrated with the mirror later this year. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/by-the-dozen-nasas-james-webb-space-telescope-mirrors" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/by-the-dozen-nasas-jame...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
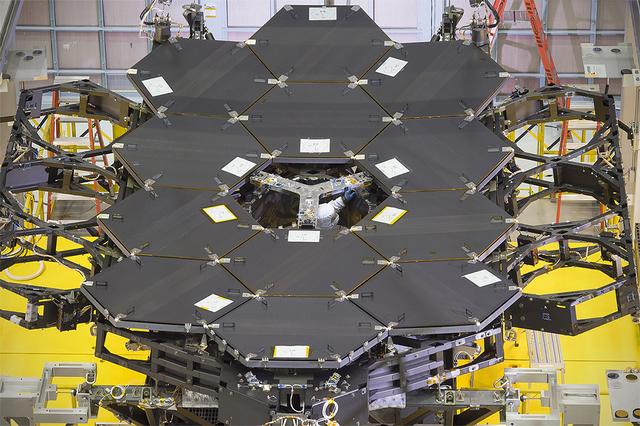

Caption: One dozen (out of 18) flight mirror segments that make up the primary mirror on NASA's James Webb Space Telescope have been installed at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn More: Since December 2015, the team of scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install all the primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure in the large clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The twelfth mirror was installed on January 2, 2016. "This milestone signifies that all of the hexagonal shaped mirrors on the fixed central section of the telescope structure are installed and only the 3 mirrors on each wing are left for installation," said Lee Feinberg, NASA's Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA Goddard. "The incredibly skilled and dedicated team assembling the telescope continues to find ways to do things faster and more efficiently." Each hexagonal-shaped segment measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). After being pieced together, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) mirror. The primary mirror will unfold and adjust to shape after launch. The mirrors are made of ultra-lightweight beryllium. The mirrors are placed on the telescope's backplane using a robotic arm, guided by engineers. The full installation is expected to be completed in a few months. The mirrors were built by Ball Aerospace & Technologies Corp., Boulder, Colorado. Ball is the principal subcontractor to Northrop Grumman for the optical technology and lightweight mirror system. The installation of the mirrors onto the telescope structure is performed by Harris Corporation of Rochester, New York. Harris Corporation leads integration and testing for the telescope. While the mirror assembly is a very significant milestone, there are many more steps involved in assembling the Webb telescope. The primary mirror and the tennis-court-sized sunshield are the largest and most visible components of the Webb telescope. However, there are four smaller components that are less visible, yet critical. The instruments that will fly aboard Webb - cameras and spectrographs with detectors able to record extremely faint signals — are part of the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), which is currently undergoing its final cryogenic vacuum test and will be integrated with the mirror later this year. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/by-the-dozen-nasas-james-webb-space-telescope-mirrors" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/2016/by-the-dozen-nasas-jame...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
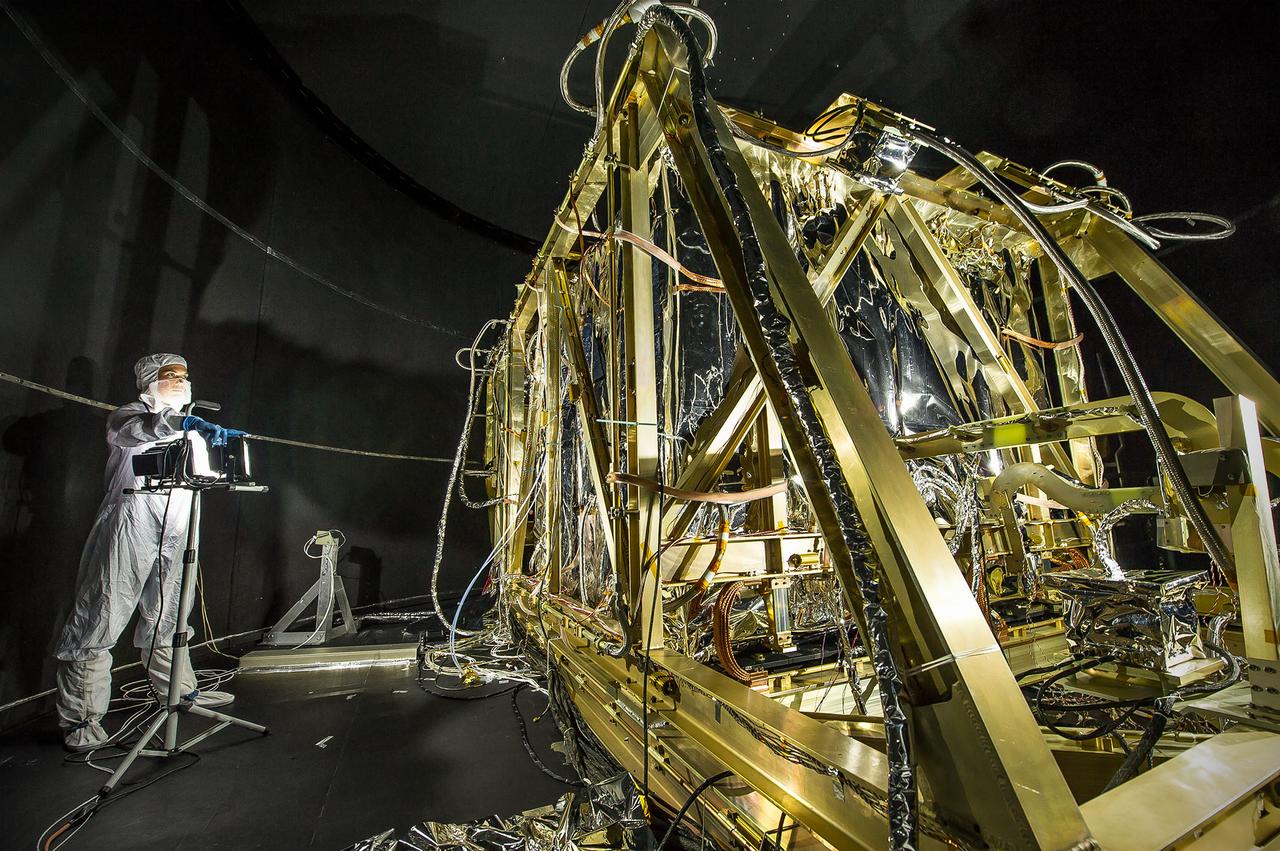

Dressed in a clean room suit, NASA photographer Desiree Stover shines a light on the Space Environment Simulator's Integration Frame inside the thermal vacuum chamber at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. Shortly after, the chamber was closed up and engineers used this frame to enclose and help cryogenic (cold) test the heart of the James Webb Space Telescope, the Integrated Science Instrument Module. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
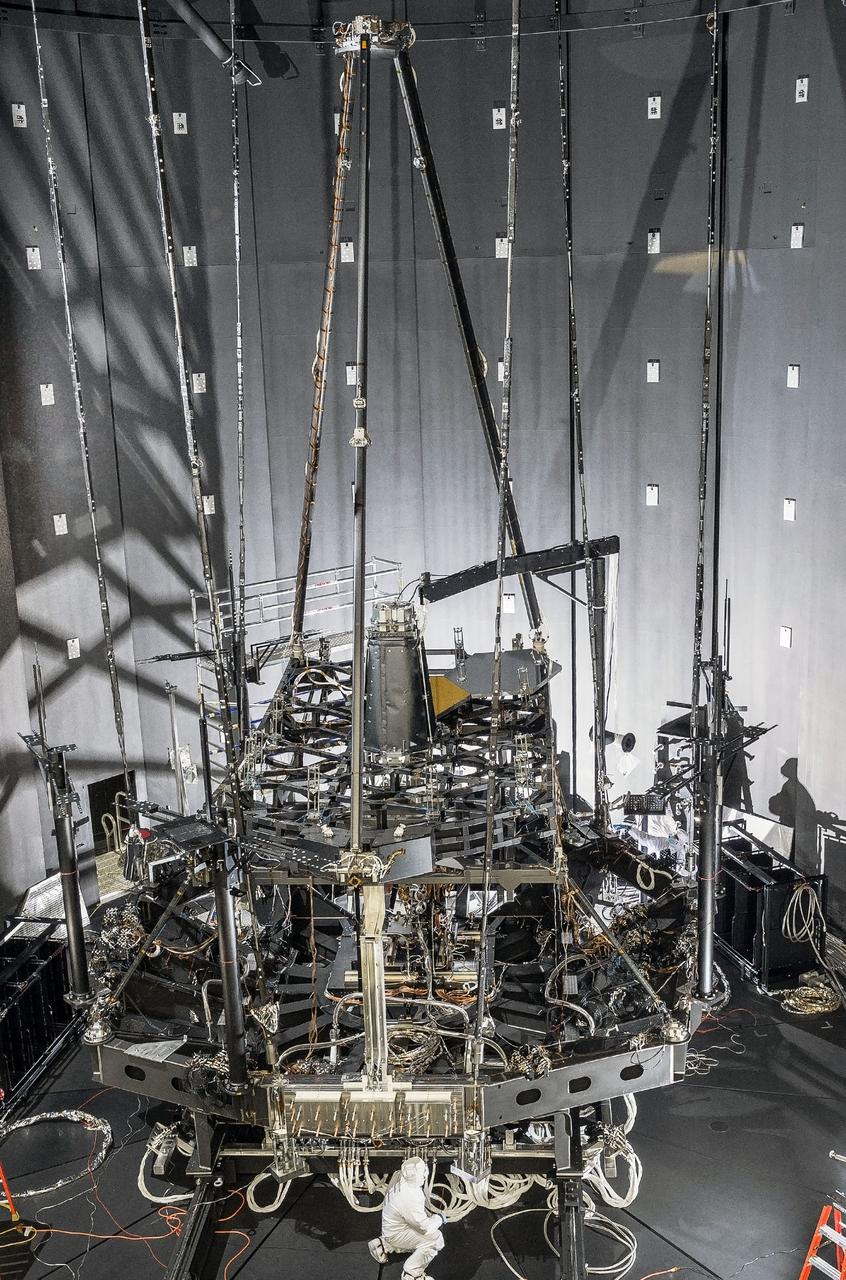

Testing is crucial part of NASA's success on Earth and in space. So, as the actual flight components of NASA's James Webb Space Telescope come together, engineers are testing the non-flight equipment to ensure that tests on the real Webb telescope later goes safely and according to plan. Recently, the "pathfinder telescope," or just “Pathfinder,” completed its first super-cold optical test that resulted in many first-of-a-kind demonstrations. "This test is the first dry-run of the equipment and procedures we will use to conduct an end-to-end optical test of the flight telescope and instruments," said Mark Clampin, Webb telescope Observatory Project Scientist at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. "It provides confidence that once the flight telescope is ready, we are fully prepared for a successful test of the flight hardware." The Pathfinder is a non-flight replica of the Webb telescope’s center section backplane, or “backbone,” that includes mirrors. The flight backplane comes in three segments, a center section and two wing-like parts, all of which will support large hexagonal mirrors on the Webb telescope. The pathfinder only consists of the center part of the backplane. However, during the test, it held two full size spare primary mirror segments and a full size spare secondary mirror to demonstrate the ability to optically test and align the telescope at the planned operating temperatures of -400 degrees Fahrenheit (-240 Celsius). Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/nasas-webb-pathfinder-telescope-successfully-completes-first-super-cold-optical-test" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/feature/goddard/nasas-webb-pathfinder-telesc...</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
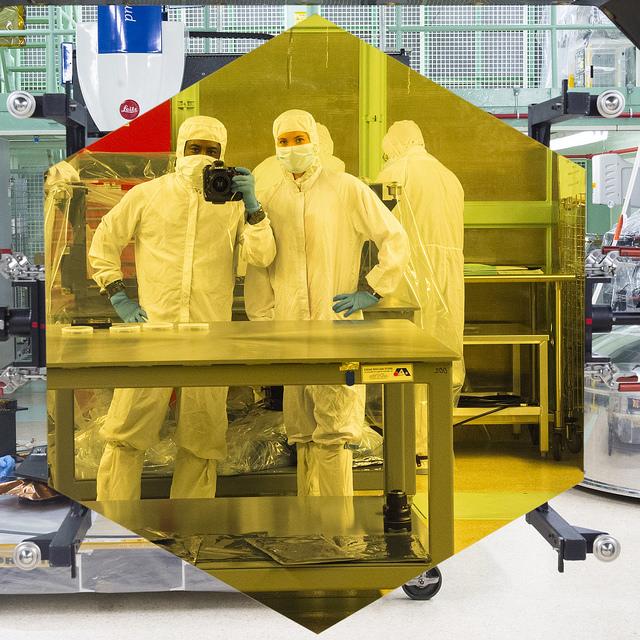

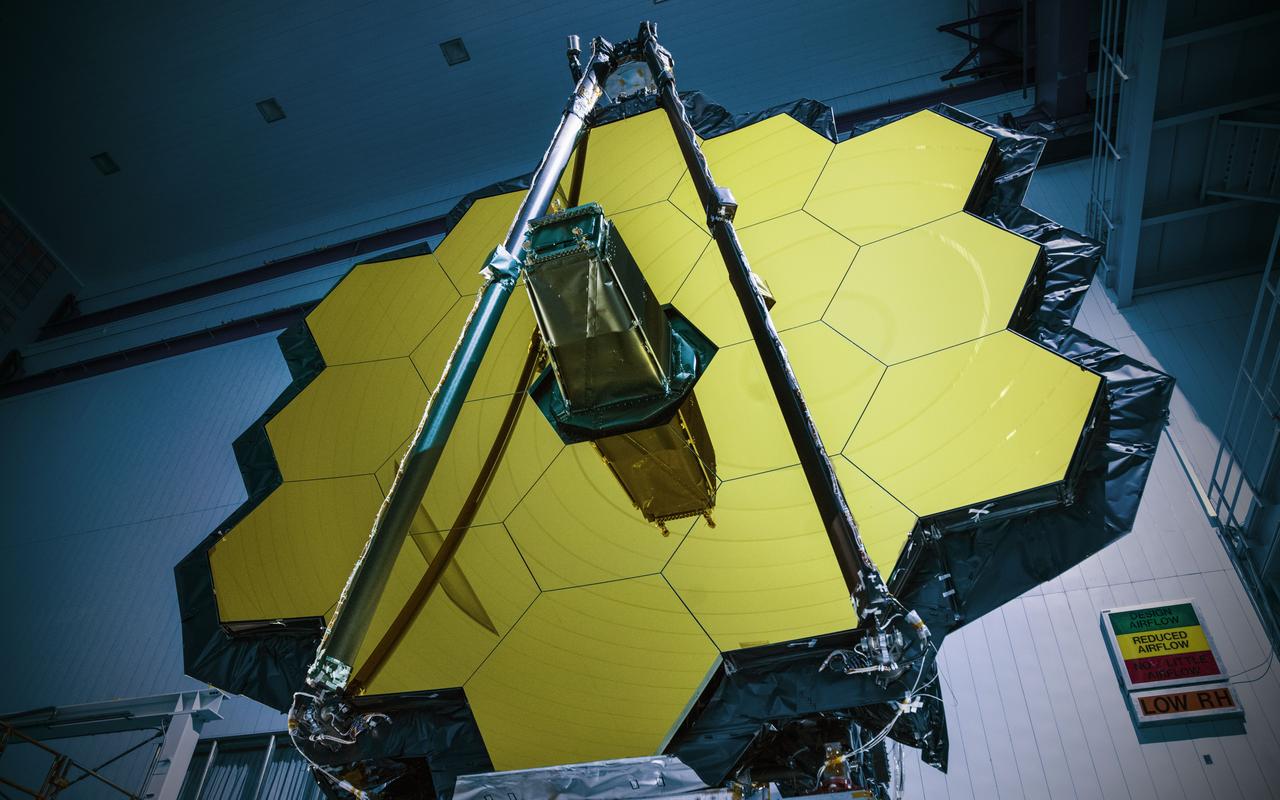
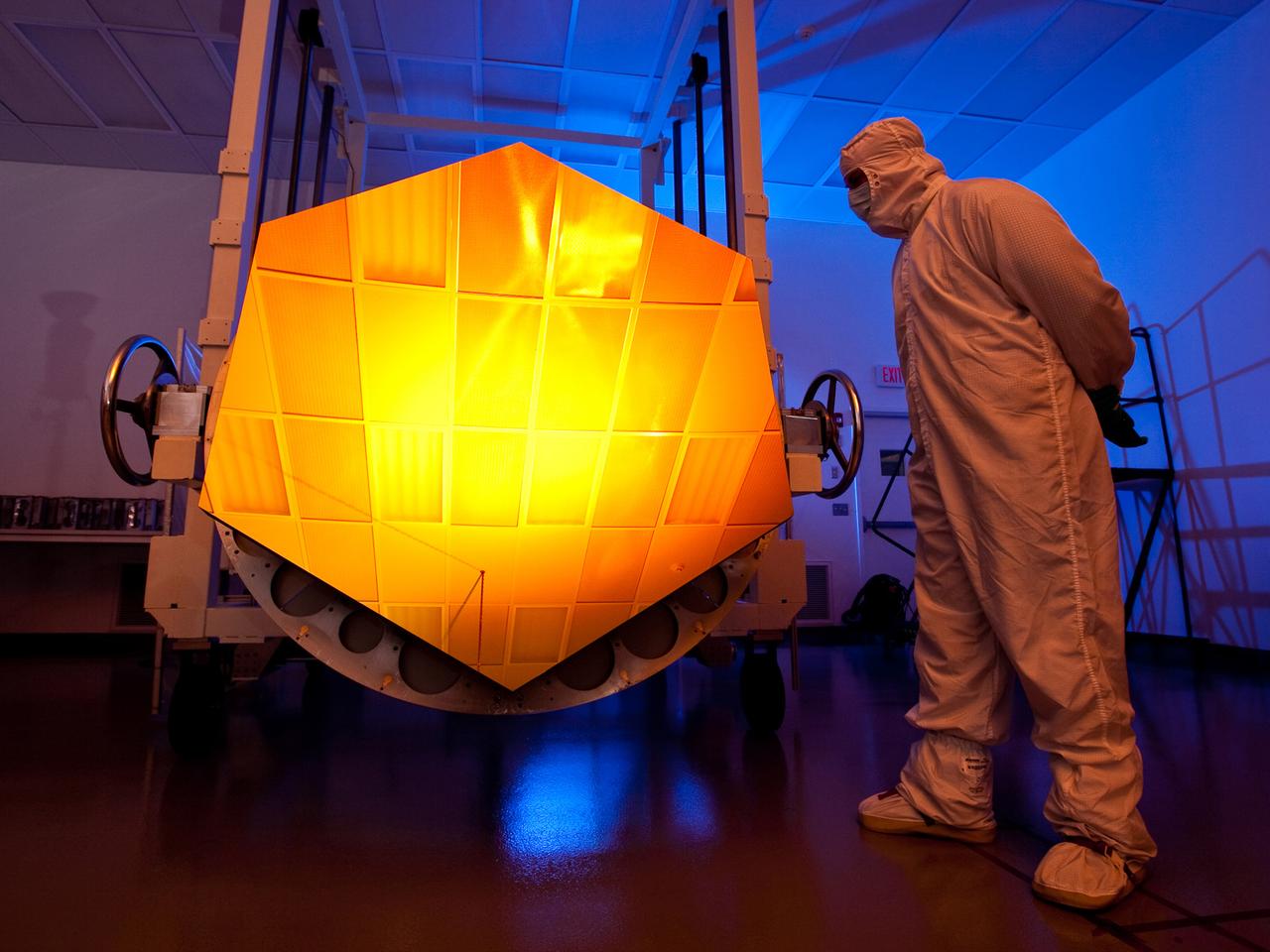
Witness History: Be inspired by giant, golden, fully-assembled James Webb Space Telescope mirror on display at NASA Goddard. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2dUOmSX" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2dUOmSX</a> Are you an artist? If so, we have a unique opportunity to view the amazing and aesthetic scientific marvel that is the James Webb Space Telescope. Because of Webb’s visually striking appearance, we are hosting a special viewing event on Wednesday, Nov. 2, 2016, at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Artists are invited to apply to attend. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
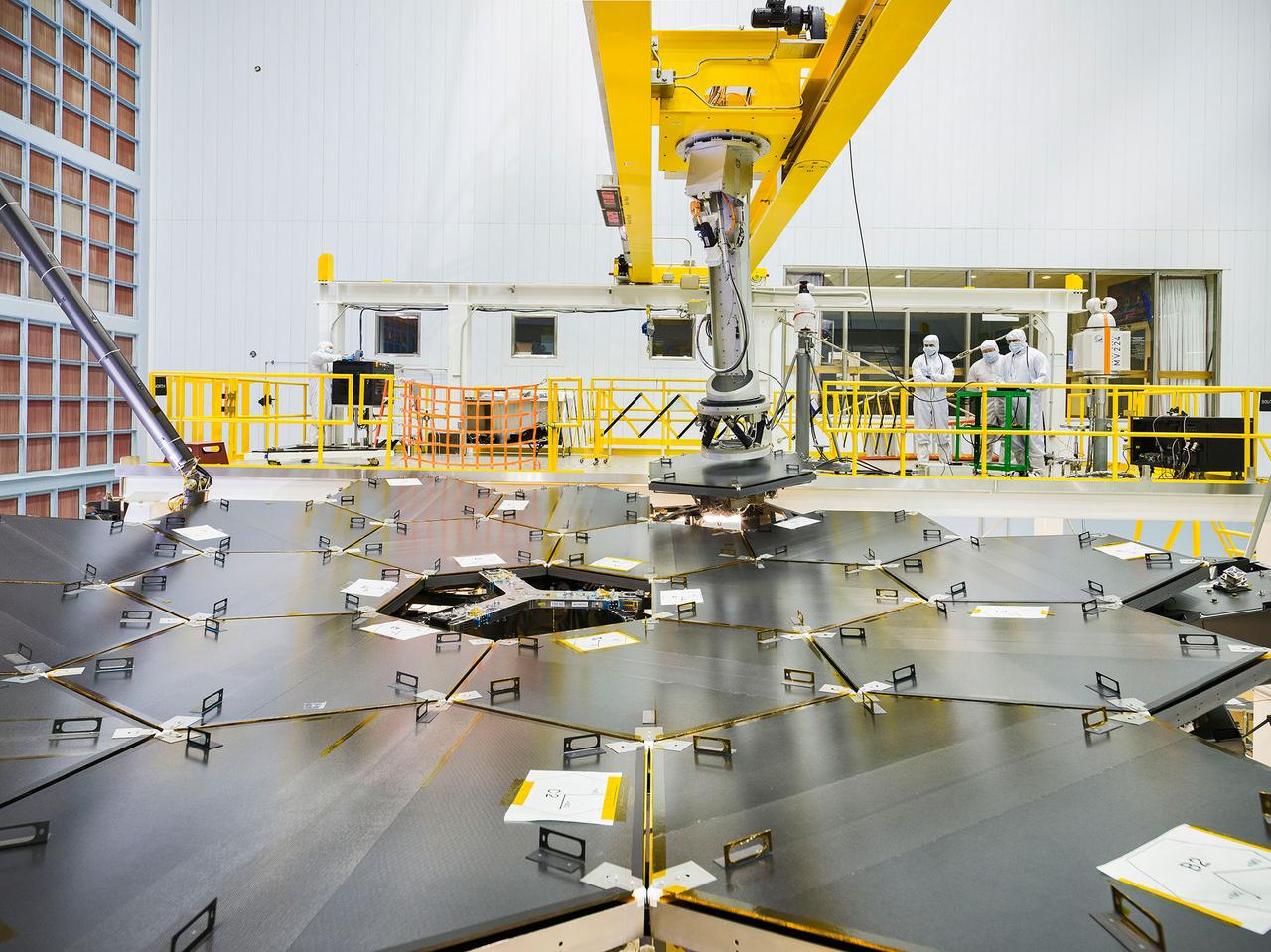

The 18th and final primary mirror segment is installed on what will be the biggest and most powerful space telescope ever launched. The final mirror installation Wednesday at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland marks an important milestone in the assembly of the agency’s James Webb Space Telescope. “Scientists and engineers have been working tirelessly to install these incredible, nearly perfect mirrors that will focus light from previously hidden realms of planetary atmospheres, star forming regions and the very beginnings of the Universe,” said John Grunsfeld, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate in Washington. “With the mirrors finally complete, we are one step closer to the audacious observations that will unravel the mysteries of the Universe.” Using a robotic arm reminiscent of a claw machine, the team meticulously installed all of Webb's primary mirror segments onto the telescope structure. Each of the hexagonal-shaped mirror segments measures just over 4.2 feet (1.3 meters) across -- about the size of a coffee table -- and weighs approximately 88 pounds (40 kilograms). Once in space and fully deployed, the 18 primary mirror segments will work together as one large 21.3-foot diameter (6.5-meter) mirror. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn Credits: NASA/Chris Gunn
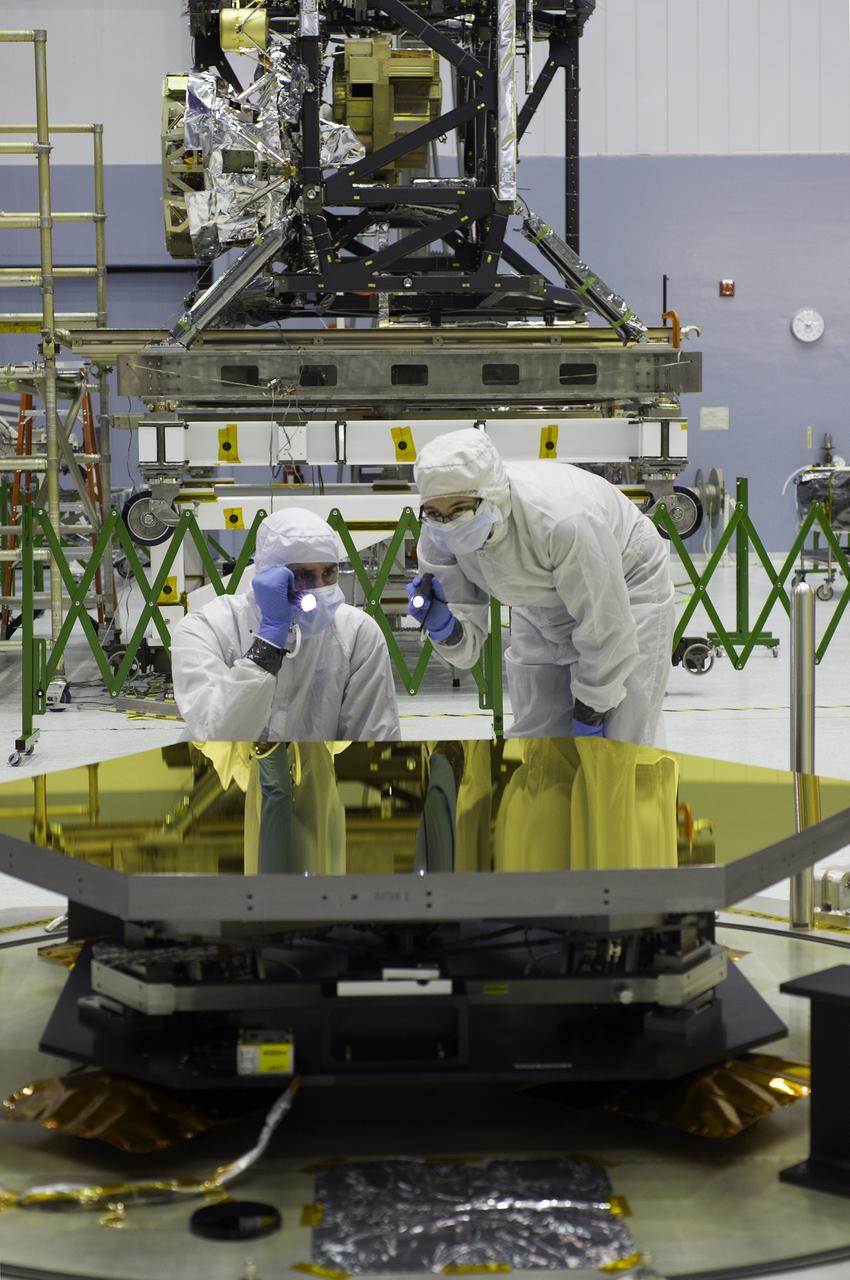

Webb telescope Quality Engineer Matt Magsamen and Product Assurance Engineer Jessica Lieberman inspect one of the primary mirror segments. The Webb telescope's third batch of flight mirrors now reside in the clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. The latest arrivals included the seventh, eighth and ninth primary mirror segments. Credit: NASA/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
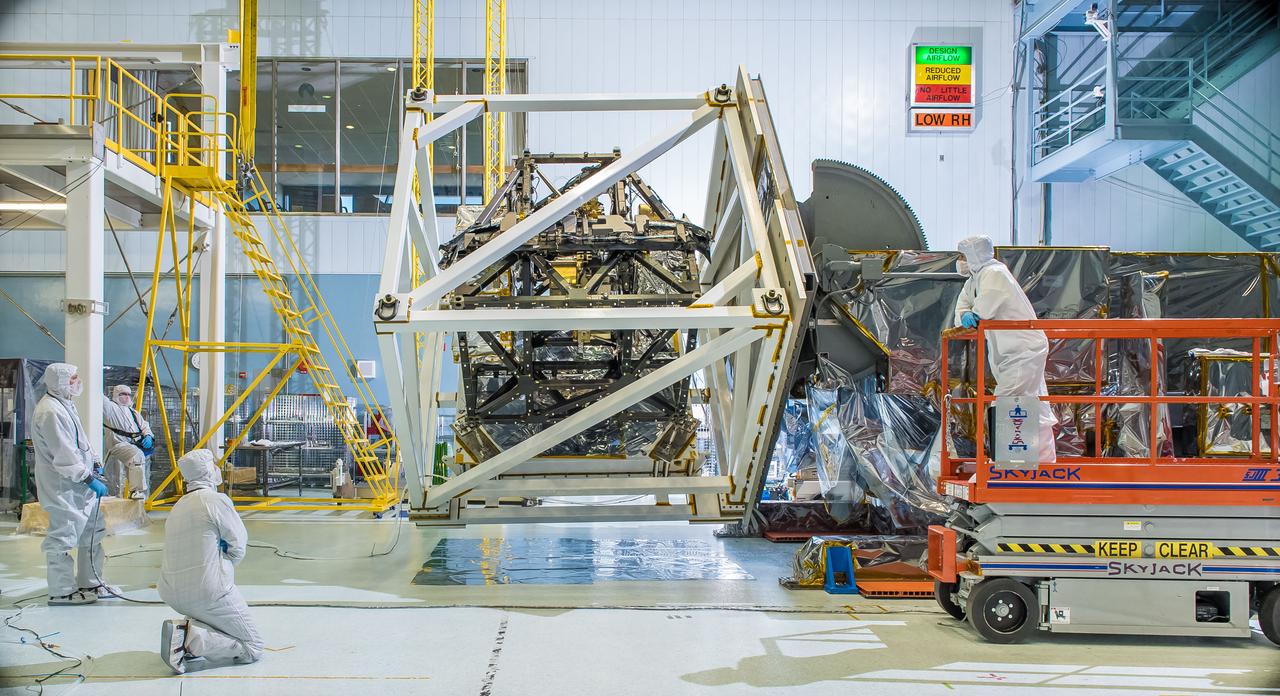

The James Webb Space Telescope's ISIM structure recently endured a "gravity sag test" as it was rotated in what looked like giant cube in a NASA clean room. The Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM) that will fly on the Webb telescope was rotated upside down inside a cube-like structure in the cleanroom at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. The purpose of "cubing" the ISIM was to test it for "gravity sag," which is to see how much the structure changes under its own weight due to gravity. The Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM) is one of three major elements that comprise the Webb Observatory flight system. The others are the Optical Telescope Element (OTE) and the Spacecraft Element (Spacecraft Bus and Sunshield). Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/1ze7u2l" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/1ze7u2l</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Inside a massive clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland the James Webb Space Telescope team is steadily installing the largest space telescope mirror ever. Unlike other space telescope mirrors, this one must be pieced together from segments using a high-precision robotic arm. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1ROaT4G" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1ROaT4G</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
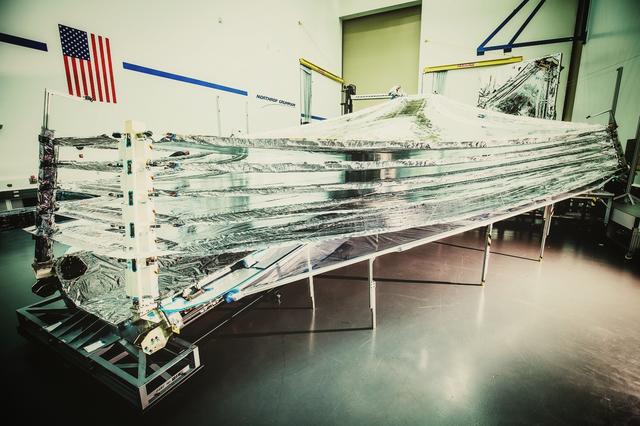

The last of the five sunshield layers responsible for protecting the optics and instruments of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope is now complete. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2erZV41" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2erZV41</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
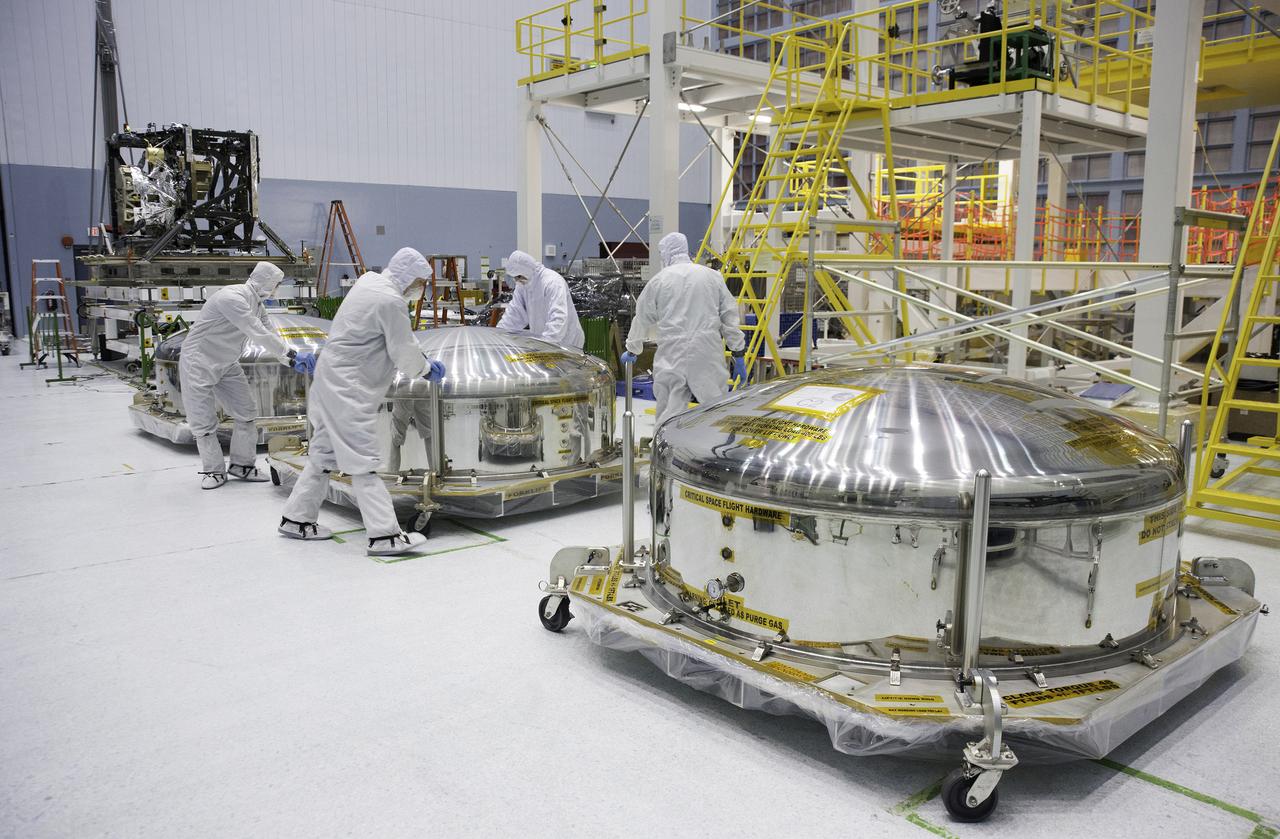

Three primary Webb telescope mirror segments sit in shipping cannisters and await opening. A mechanical integration engineer and technicians vent and prepare the mirror canisters for inspection. The mirrors have arrived at their new home at NASA, where they will be residing at the giant cleanroom at Goddard for a while as technicians check them out. Previously on Sept. 17, 2012, two other primary mirror segments arrived at Goddard and are currently being stored in the center's giant clean room. Credit: NASA/Desiree Stover <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
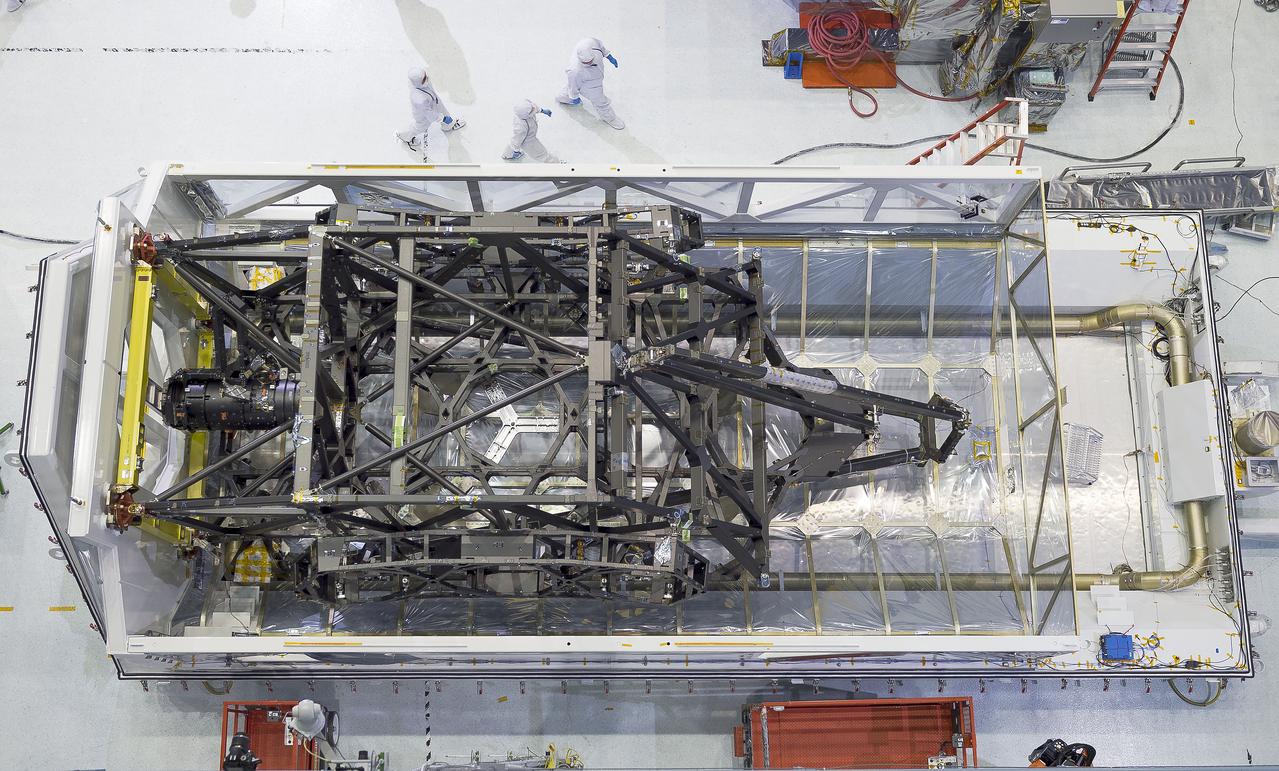

The James Webb Space Telescope's "spine" or backplane arrived on Aug. 25 at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland from Northrop Grumman. Credits: NASA Goddard/Chris Gunn Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1K2v8J2" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1K2v8J2</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
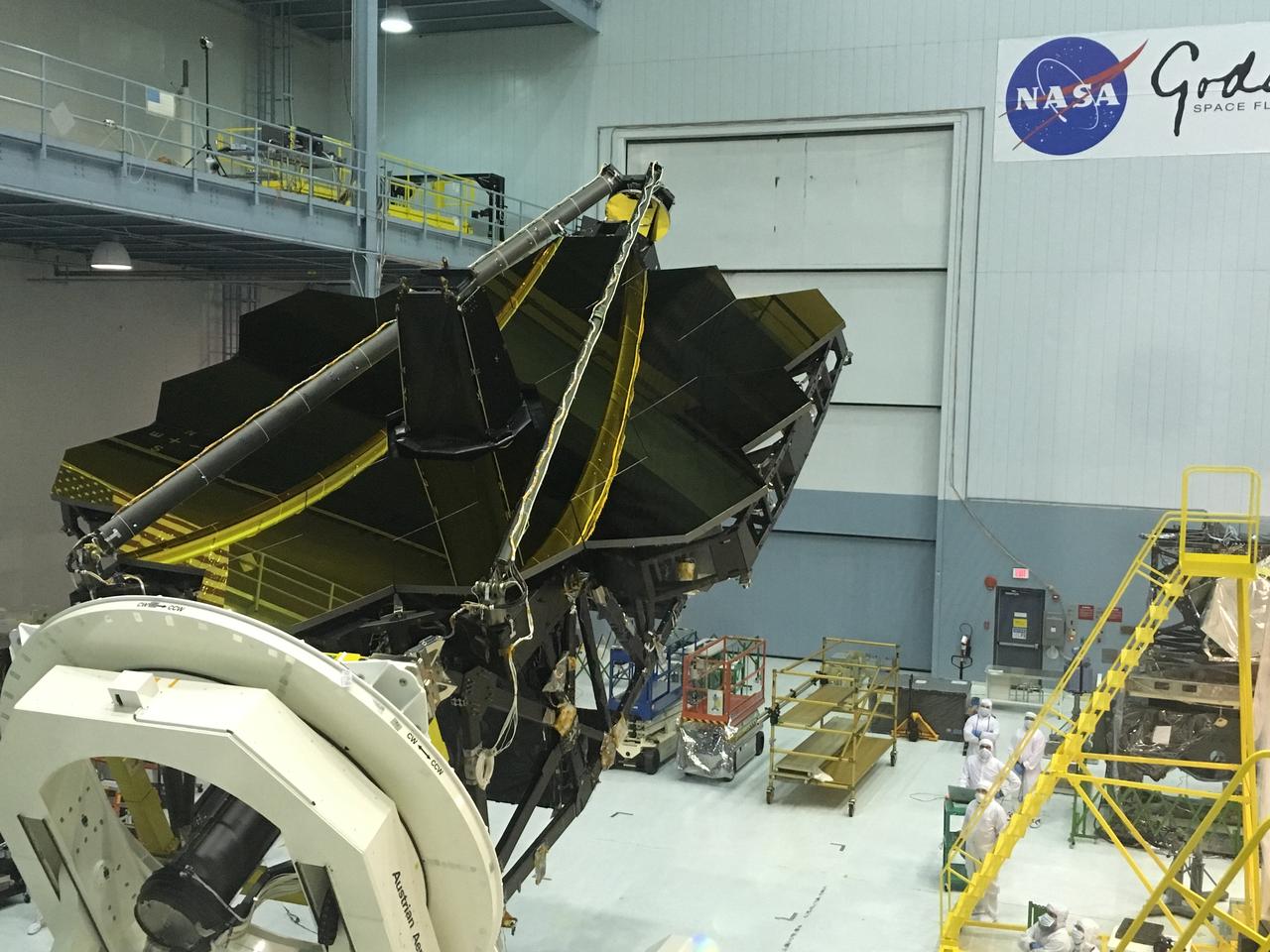

A rare view of the James Webb Space Telescope face-on, from the NASA Goddard cleanroom observation window.
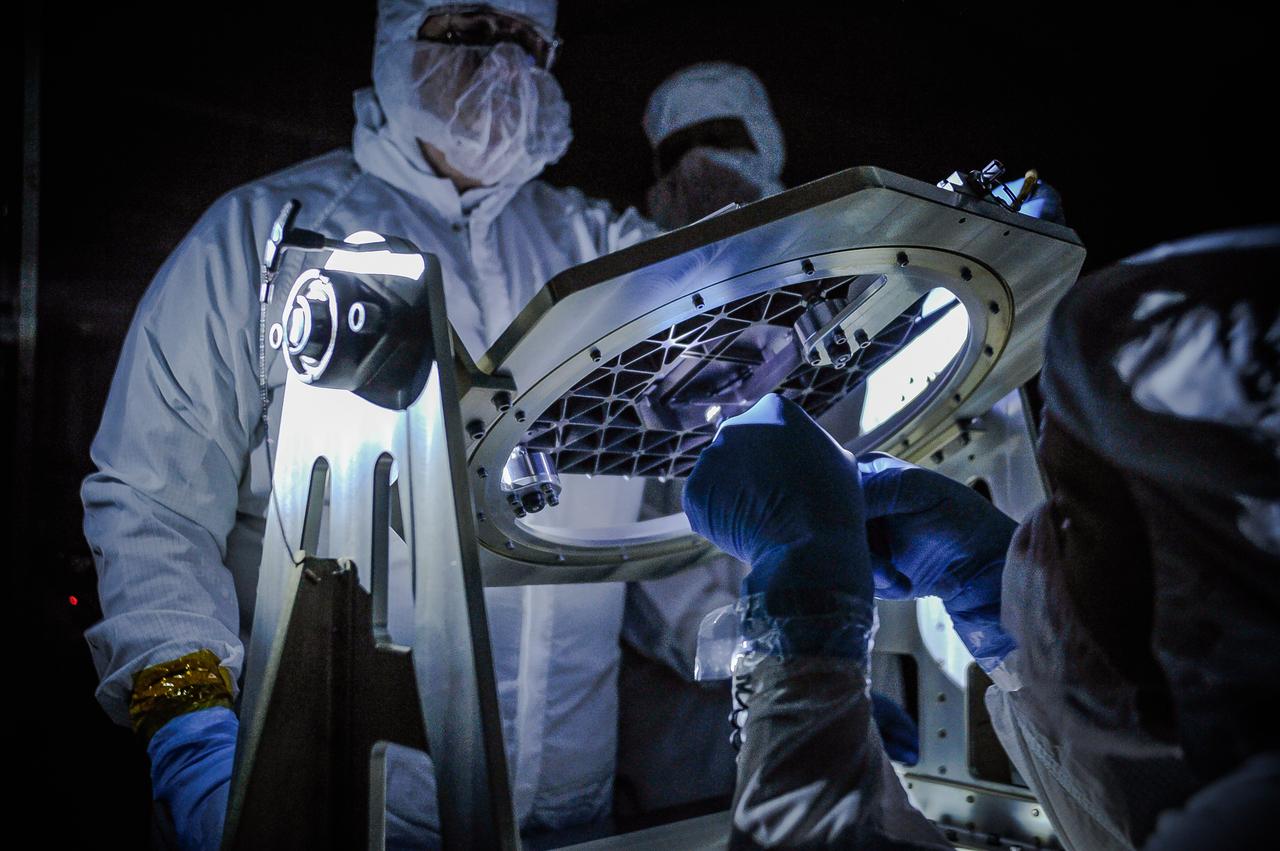

NASA engineers inspect a new piece of technology developed for the James Webb Space Telescope, the micro shutter array, with a low light test at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Developed at Goddard to allow Webb's Near Infrared Spectrograph to obtain spectra of more than 100 objects in the universe simultaneously, the micro shutter array uses thousands of tiny shutters to capture spectra from selected objects of interest in space and block out light from all other sources. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Dr. Amber Straughn, Lead Scientist for James Webb Space Telescope Education & Public Outreach at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks to students from Mapletown Jr/Sr High School and Margaret Bell Middle School during the NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Research Project Capstone Event in the James E. Webb Auditorium at NASA Headquarters on Monday, May 5, 2014 Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
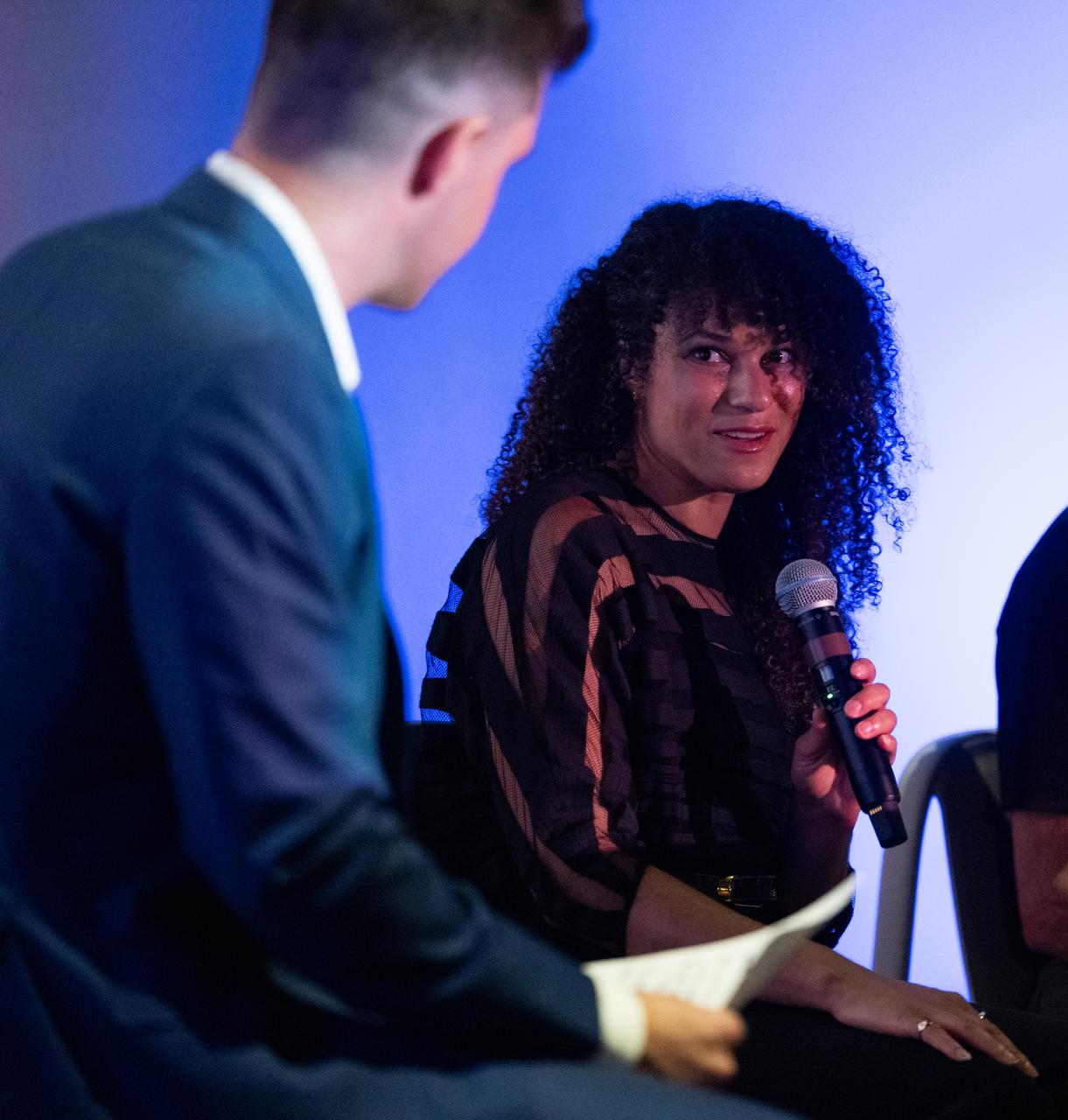

Sophia Roberts, a NASA video producer who documented the James Webb Space Telescope project, speaks during a panel discussion alongside Paul Geithner, former deputy project manager for NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope and Jacob Pinter, host of NASA’s Curious Universe Podcast following a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA image release December 9, 2010 Caption: The James Webb Space Telescope's Engineering Design Unit (EDU) primary mirror segment, coated with gold by Quantum Coating Incorporated. The actuator is located behind the mirror. Credit: Photo by Drew Noel NASA's James Webb Space Telescope is a wonder of modern engineering. As the planned successor to the Hubble Space telescope, even the smallest of parts on this giant observatory will play a critical role in its performance. A new video takes viewers behind the Webb's mirrors to investigate "actuators," one component that will help Webb focus on some of the earliest objects in the universe. The video called "Got Your Back" is part of an on-going video series about the Webb telescope called "Behind the Webb." It was produced at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, Md. and takes viewers behind the scenes with scientists and engineers who are creating the Webb telescope's components. During the 3 minute and 12 second video, STScI host Mary Estacion interviewed people involved in the project at Ball Aerospace in Boulder, Colo. and showed the actuators in action. The Webb telescope will study every phase in the history of our universe, ranging from the first luminous glows after the big bang, to the formation of solar systems capable of supporting life on planets like Earth, to the evolution of our own solar system. Measuring the light this distant light requires a primary mirror 6.5 meters (21 feet 4 inches) across – six times larger than the Hubble Space telescope’s mirror! Launching a mirror this large into space isn’t feasible. Instead, Webb engineers and scientists innovated a unique solution – building 18 mirrors that will act in unison as one large mirror. These mirrors are packaged together into three sections that fold up - much easier to fit inside a rocket. Each mirror is made from beryllium and weighs approximately 20 kilograms (46 pounds). Once in space, getting these mirrors to focus correctly on faraway galaxies is another challenge entirely. Actuators, or tiny mechanical motors, provide the answer to achieving a single perfect focus. The primary and secondary mirror segments are both moved by six actuators that are attached to the back of the mirrors. The primary segment has an additional actuator at the center of the mirror that adjusts its curvature. The third mirror segment remains stationary. Lee Feinberg, Webb Optical Telescope Element Manager at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. explained "Aligning the primary mirror segments as though they are a single large mirror means each mirror is aligned to 1/10,000th the thickness of a human hair. This alignment has to be done at 50 degrees above absolute zero! What's even more amazing is that the engineers and scientists working on the Webb telescope literally had to invent how to do this." With the actuators in place, Brad Shogrin, Webb Telescope Manager at Ball Aerospace, Boulder, Colo, details the next step: attaching the hexapod (meaning six-footed) assembly and radius of curvature subsystem (ROC). "Radius of curvature" refers to the distance to the center point of the curvature of the mirror. Feinberg added "To understand the concept in a more basic sense, if you change that radius of curvature, you change the mirror's focus." The "Behind the Webb" video series is available in HQ, large and small Quicktime formats, HD, Large and Small WMV formats, and HD, Large and Small Xvid formats. To see the actuators being attached to the back of a telescope mirror in this new "Behind the Webb" video, visit: <a href="http://webbtelescope.org/webb_telescope/behind_the_webb/7" rel="nofollow">webbtelescope.org/webb_telescope/behind_the_webb/7</a> For more information about Webb's mirrors, visit: <a href="http://www.jwst.nasa.gov/mirrors.html" rel="nofollow">www.jwst.nasa.gov/mirrors.html</a> For more information on the James Webb Space Telescope, visit: <a href="http://jwst.nasa.gov" rel="nofollow">jwst.nasa.gov</a> Rob Gutro NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, Md. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
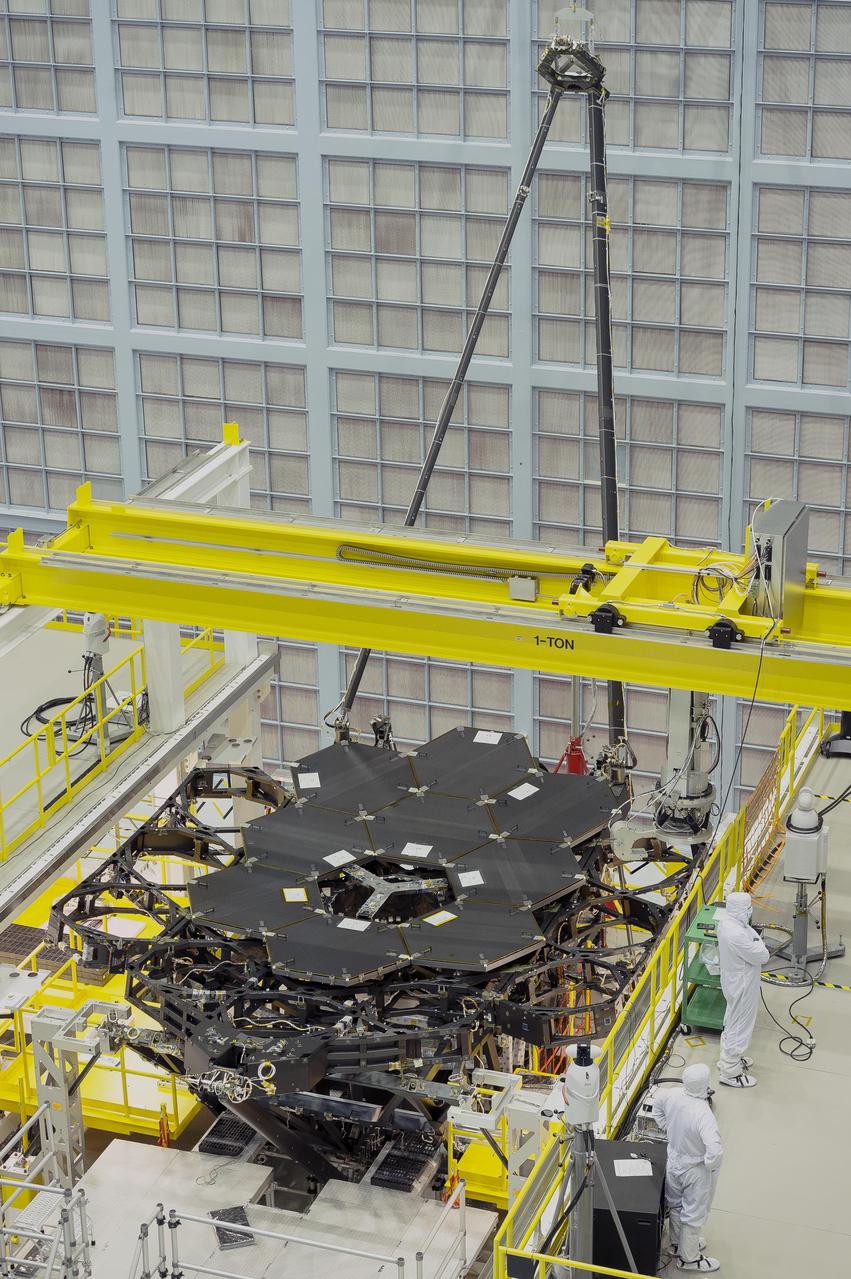
Inside NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center's massive clean room in Greenbelt, Maryland, the ninth flight mirror was installed onto the telescope structure with a robotic arm. This marks the halfway completion point for the James Webb Space Telescope's segmented primary mirror. Nine of the James Webb Space Telescope's 18 primary flight mirrors have been installed on the telescope structure. This marks the halfway point in the James Webb Space Telescope's primary mirror installation. Credit: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Chris Gunn Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1kqK6fW" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1kqK6fW</a>
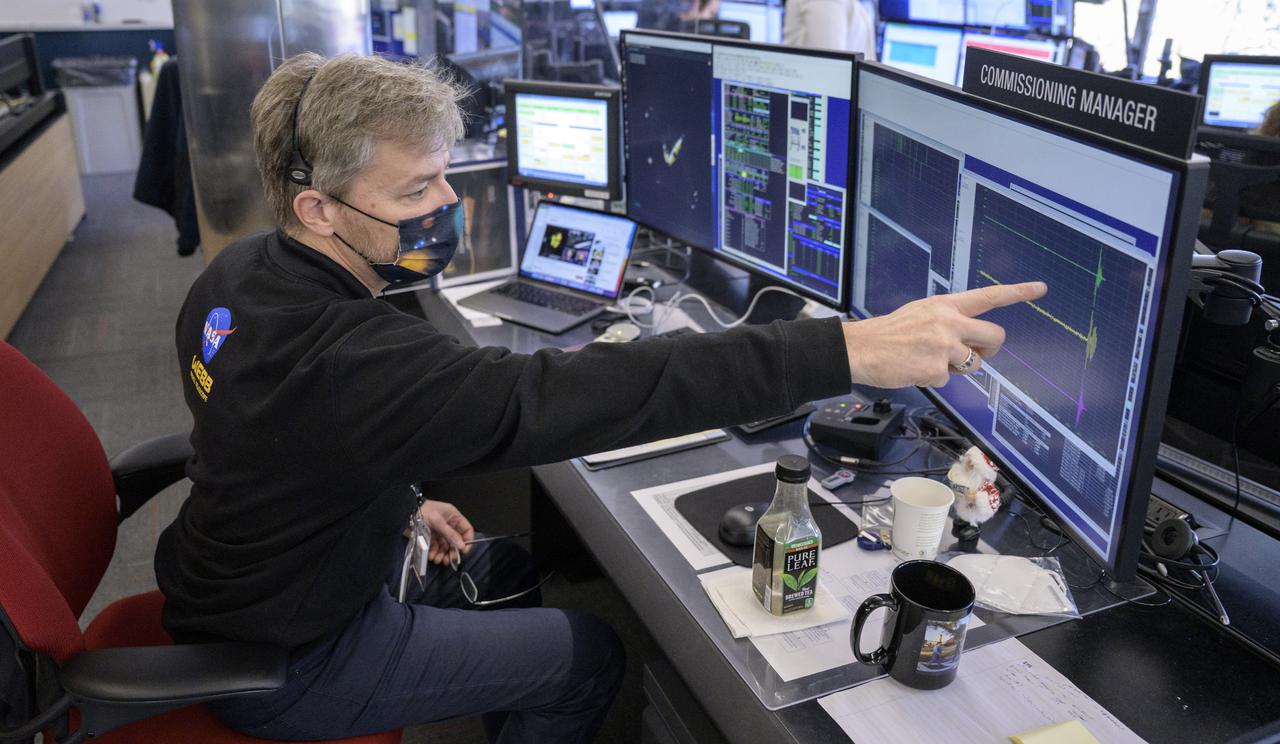

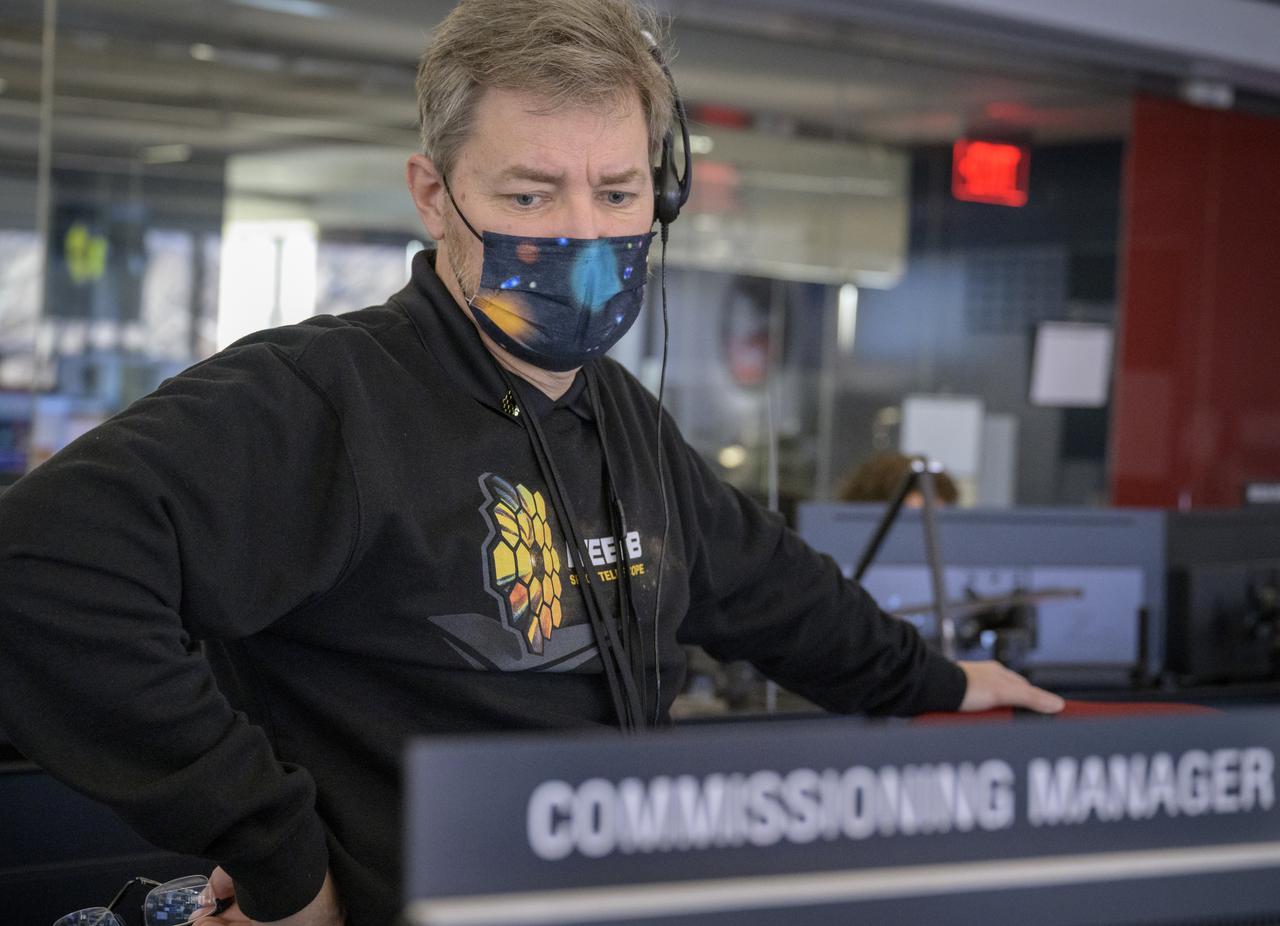
NASA James Webb Space Telescope Commissioning Manager John Durning monitors the progress of the Webb observatory as it’s second primary mirror wing is prepared to rotate into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
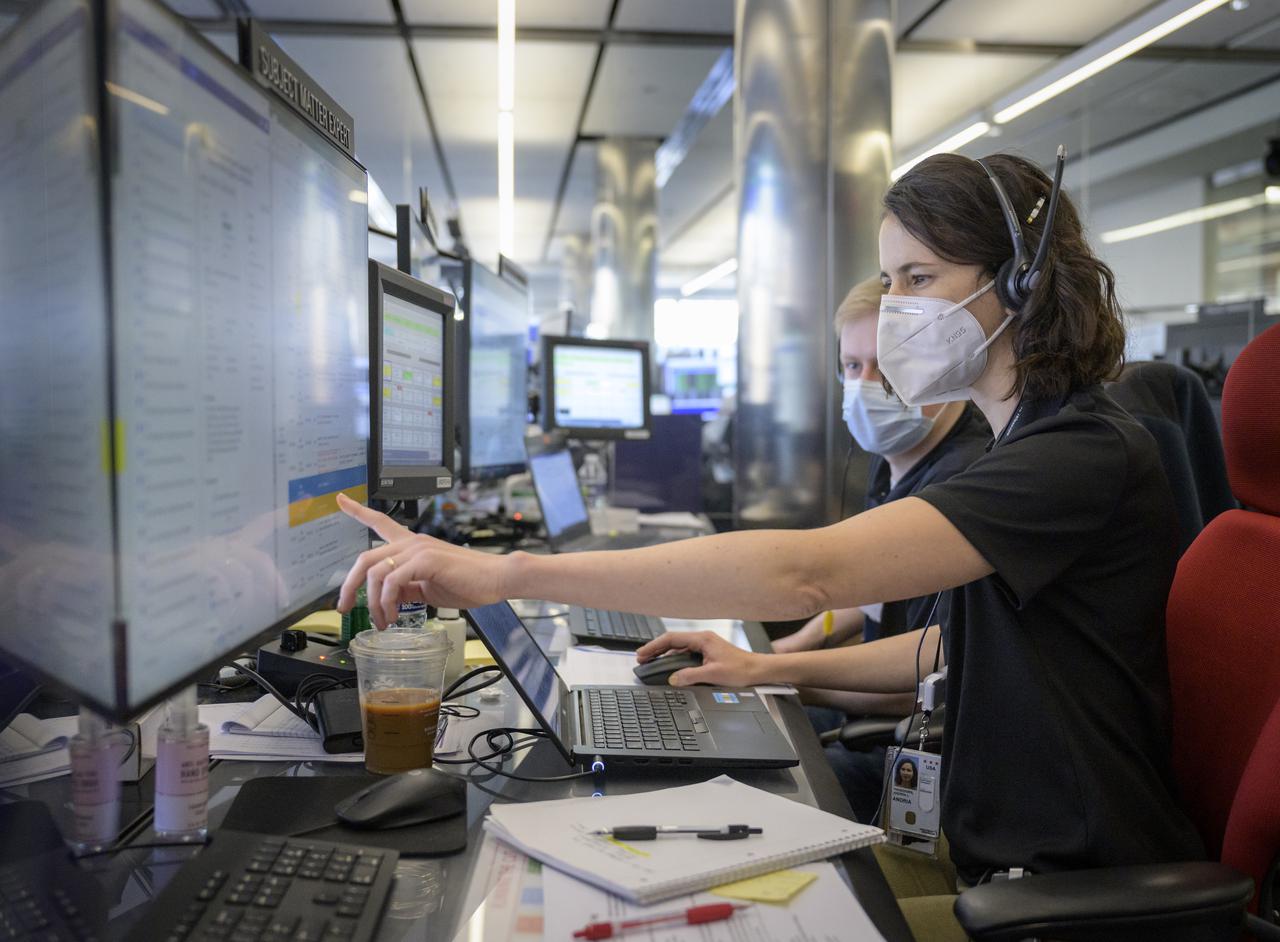

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Timeline Coordinator Andria Hagedorn monitors the progress of the Webb observatory’s second primary mirror wing as it rotates into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
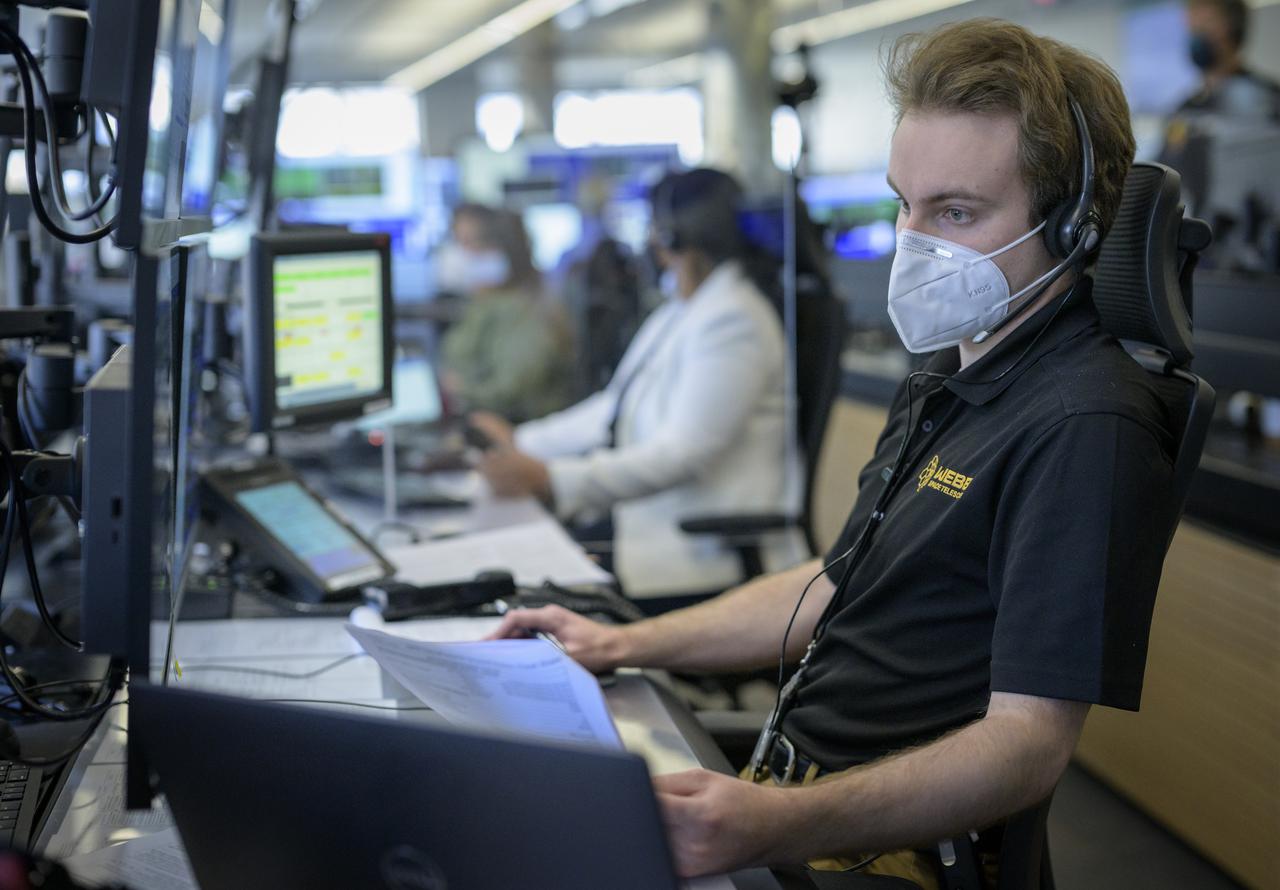

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Ground Engineer Evan Adams monitors the progress of the Webb observatory as it’s second primary mirror wing is prepared to rotate into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Commissioning Manager John Durning monitors the progress of the Webb observatory as it’s second primary mirror wing is rotated into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
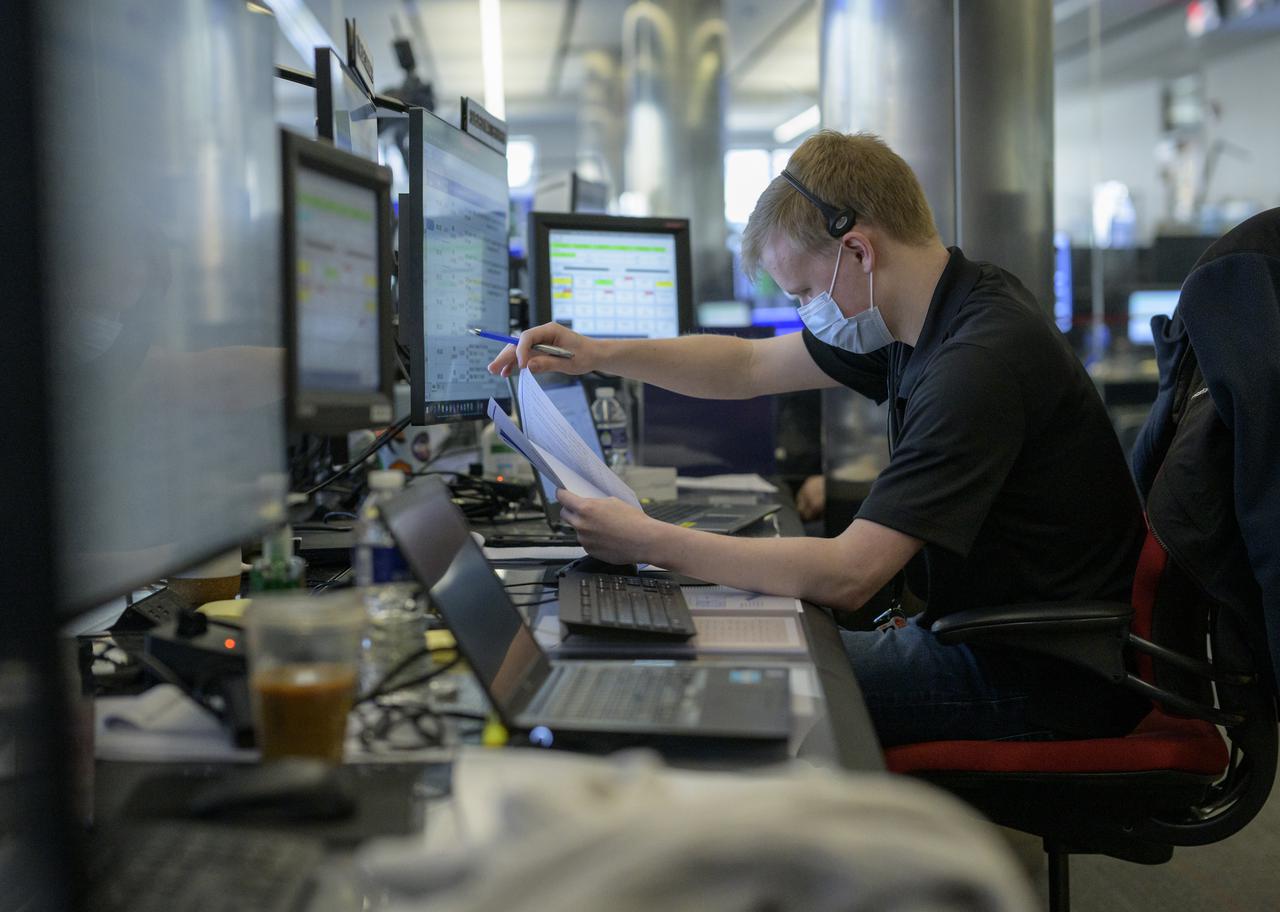

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Timeline Coordinator Matt Wasiak monitors the progress of the Webb observatory as it’s second primary mirror wing is prepared to rotate into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Project Manager Bill Ochs, left, and NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Manager Carl Starr, monitor the progress of the Webb observatory as it’s second primary mirror wing is prepared to rotate into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Manager Carl Starr, left, shows his Webb shirt to NASA James Webb Space Telescope Commissioning Manager John Durning, right, as they prepare to monitor the progress of the observatory’s second primary mirror wing rotating into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, at NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
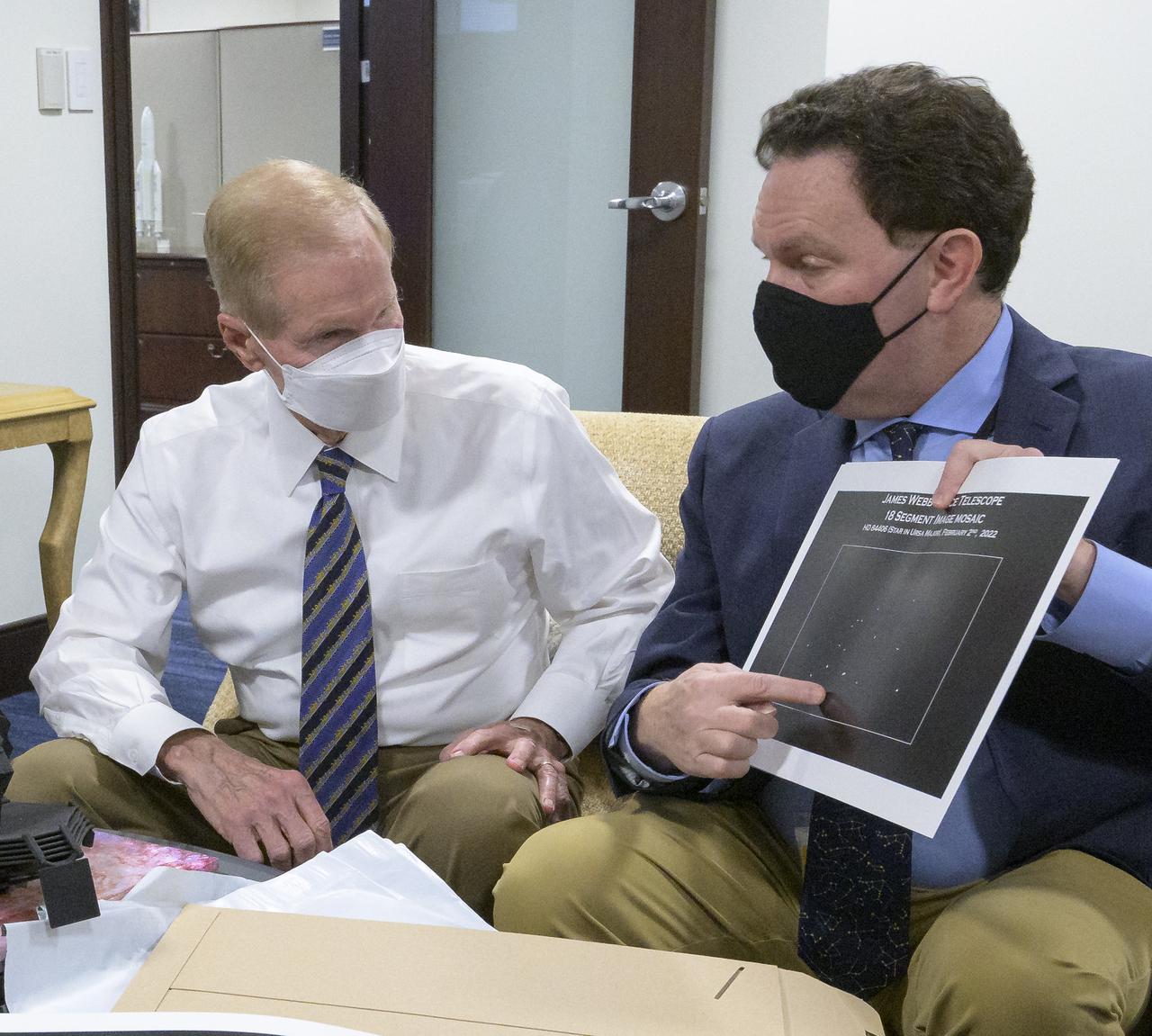

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, left, is shown an early mirror alignment image from the James Webb Space Telescope, by NASA Webb Optical Telescope Element Manager Lee Feinberg, Monday, Feb., 7, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. This engineering visual, which features 18 unfocused dots of light, demonstrates that the Webb team has successfully identified starlight through each of Webb’s 18 hexagonal mirror segments – the starting point in a months-long process to progressively align the segments into a single, precise mirror to prepare the telescope for science. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Project Manager Bill Ochs monitors the progress of the observatory’s second primary mirror wing as it rotates into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
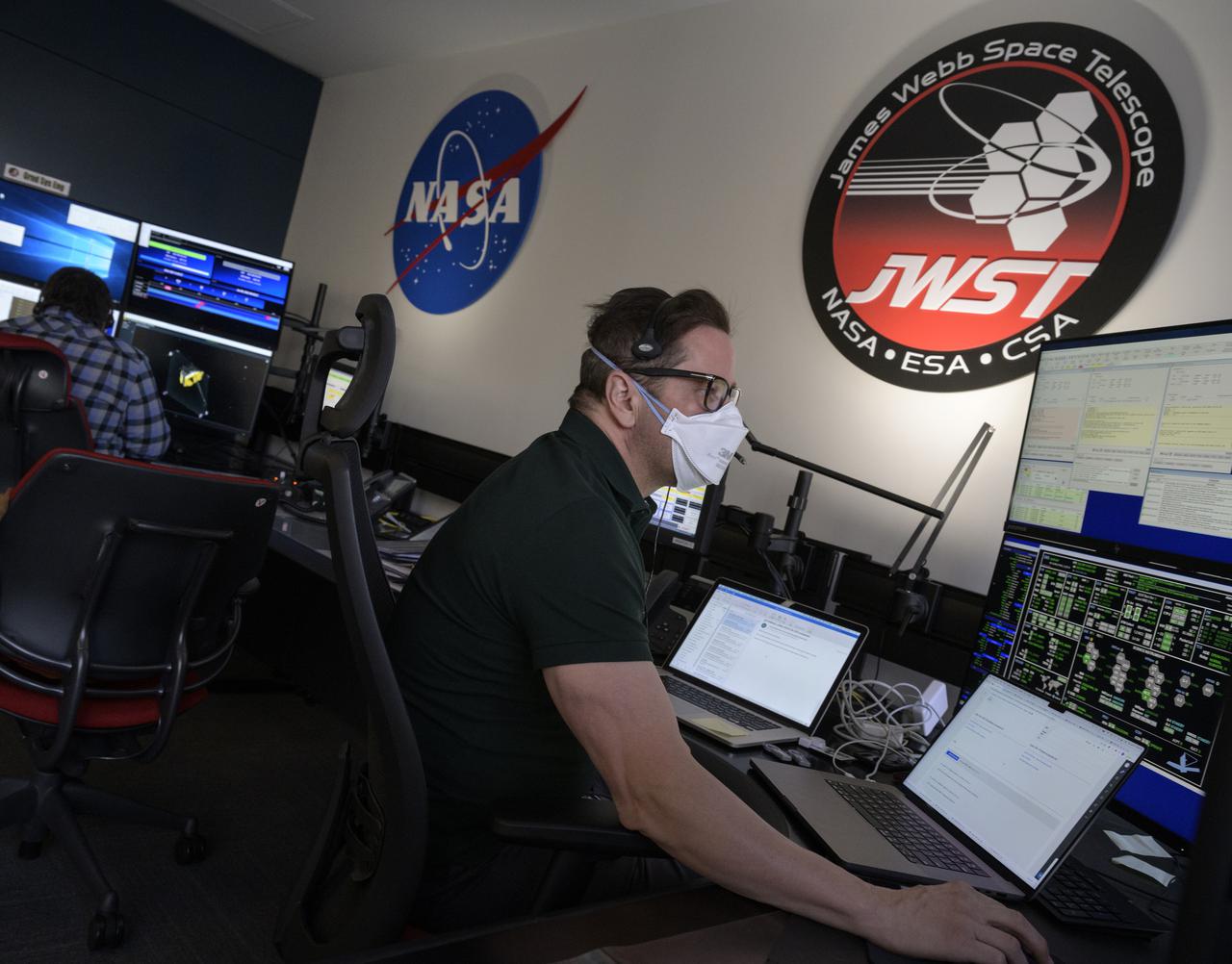

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Ground Systems Engineer Carl Reis at NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore monitors the progress as the observatory’s second primary mirror wing rotates into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, center, meets with NASA James Webb Space Telescope Timeline Controller Matt Wasiak, left, and NASA James Webb Space Telescope Deputy Mission Operations Manager Ron Jones, right, during a tour of the NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center, Wednesday, June 29, 2022, at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore. Prior to the tour the deputy spoke at a briefing that focused on the status of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope in its final weeks of preparing for its science mission, as well as overviews of planned science for Webb’s first year of operations. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Jacob Pinter, host of NASA’s Curious Universe Podcast, left, leads a discussion with Sophia Roberts, a NASA video producer who documented the Webb project, center, and Paul Geithner, former deputy project manager for NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, right, following a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
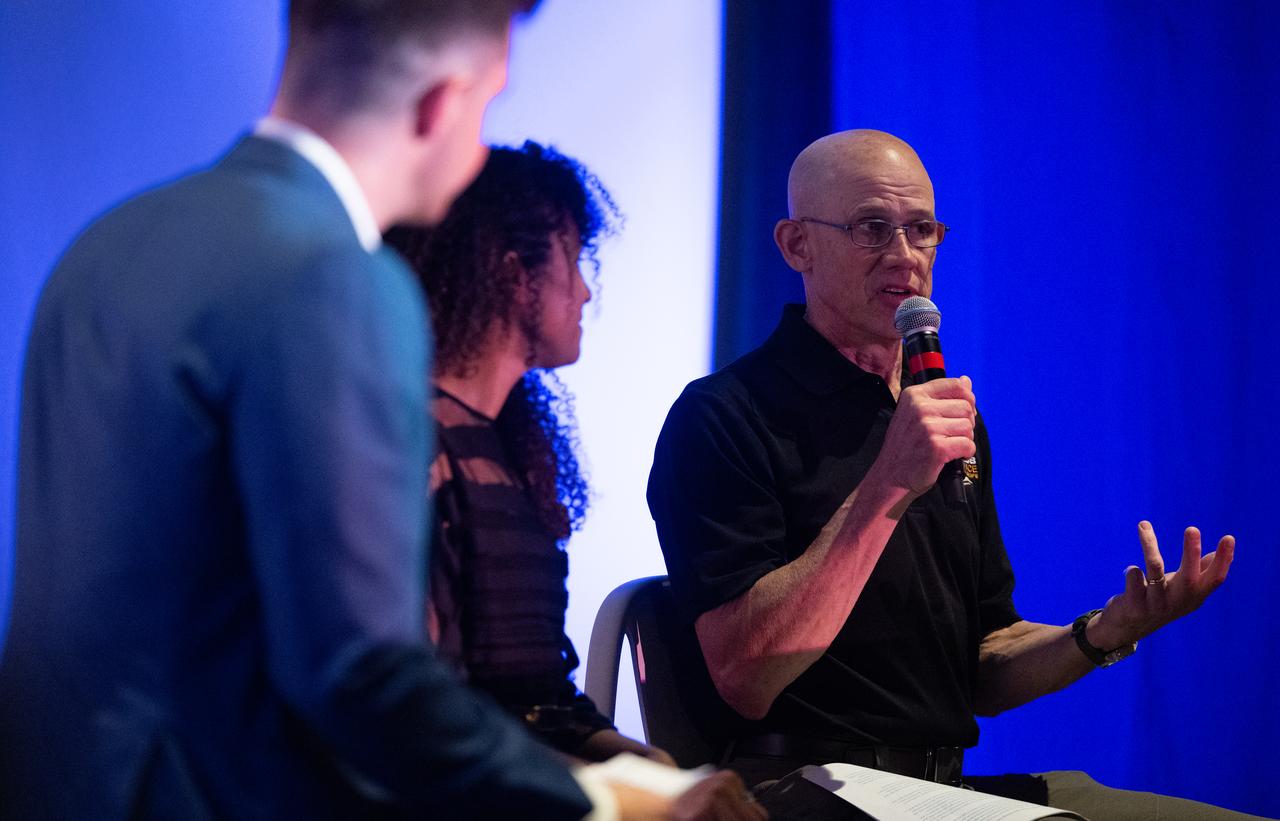

Paul Geithner, former deputy project manager for NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, right, speaks during a discussion alongside Sophia Roberts, a NASA video producer who documented the Webb project, and Jacob Pinter, host of NASA’s Curious Universe Podcast, following a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
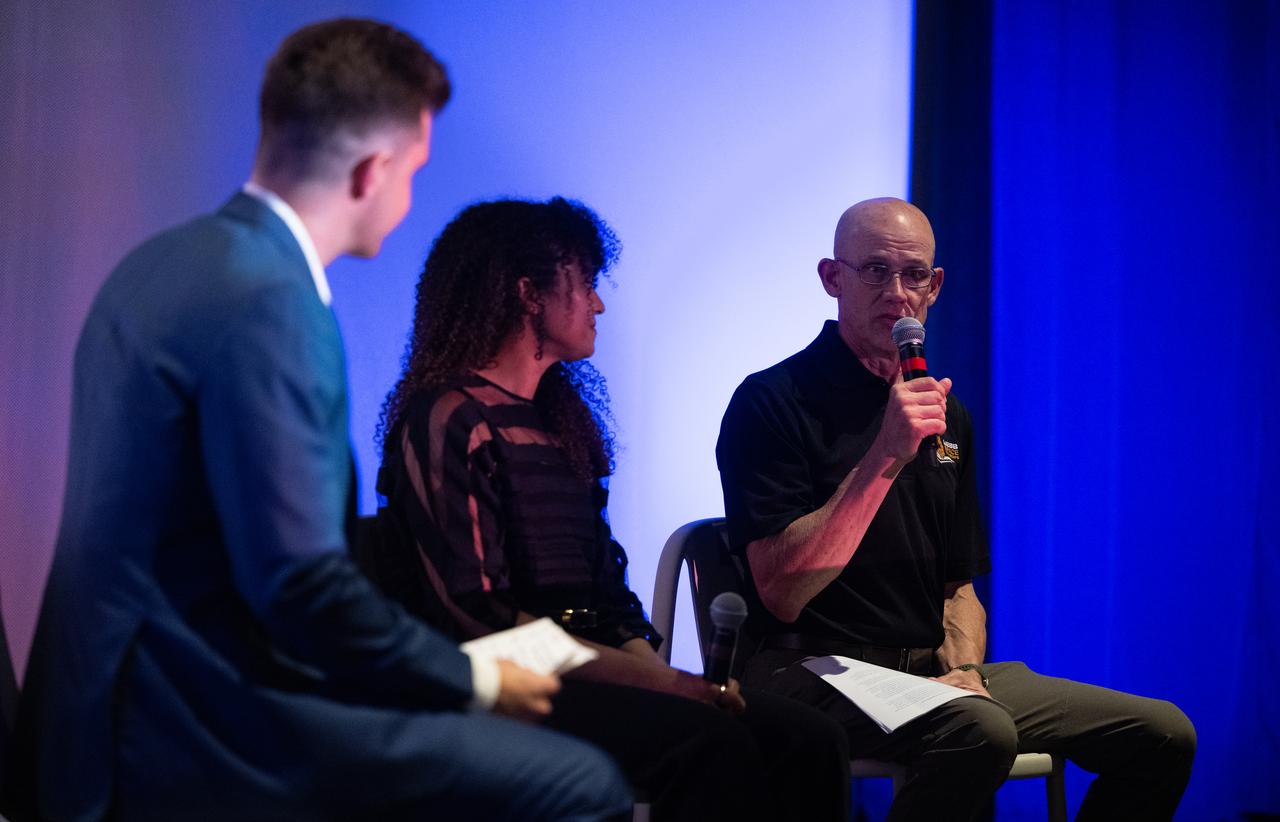

Paul Geithner, former deputy project manager for NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, right, participates in a discussion alongside Sophia Roberts, a NASA video producer who documented the Webb project, and Jacob Pinter, host of NASA’s Curious Universe Podcast, following a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Jacob Pinter, host of NASA’s Curious Universe Podcast, left, leads a discussion with Sophia Roberts, a NASA video producer who documented the Webb project, center, and Paul Geithner, former deputy project manager for NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope, right, following a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden speaks to students from Mapletown Jr/Sr High School and Margaret Bell Middle School during the NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Research Project Capstone Event in the James E. Webb Auditorium at NASA Headquarters on Monday, May 5, 2014. Administrator Bolden spoke about his involvement with the Hubble Space Telescope and took questions from the students. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
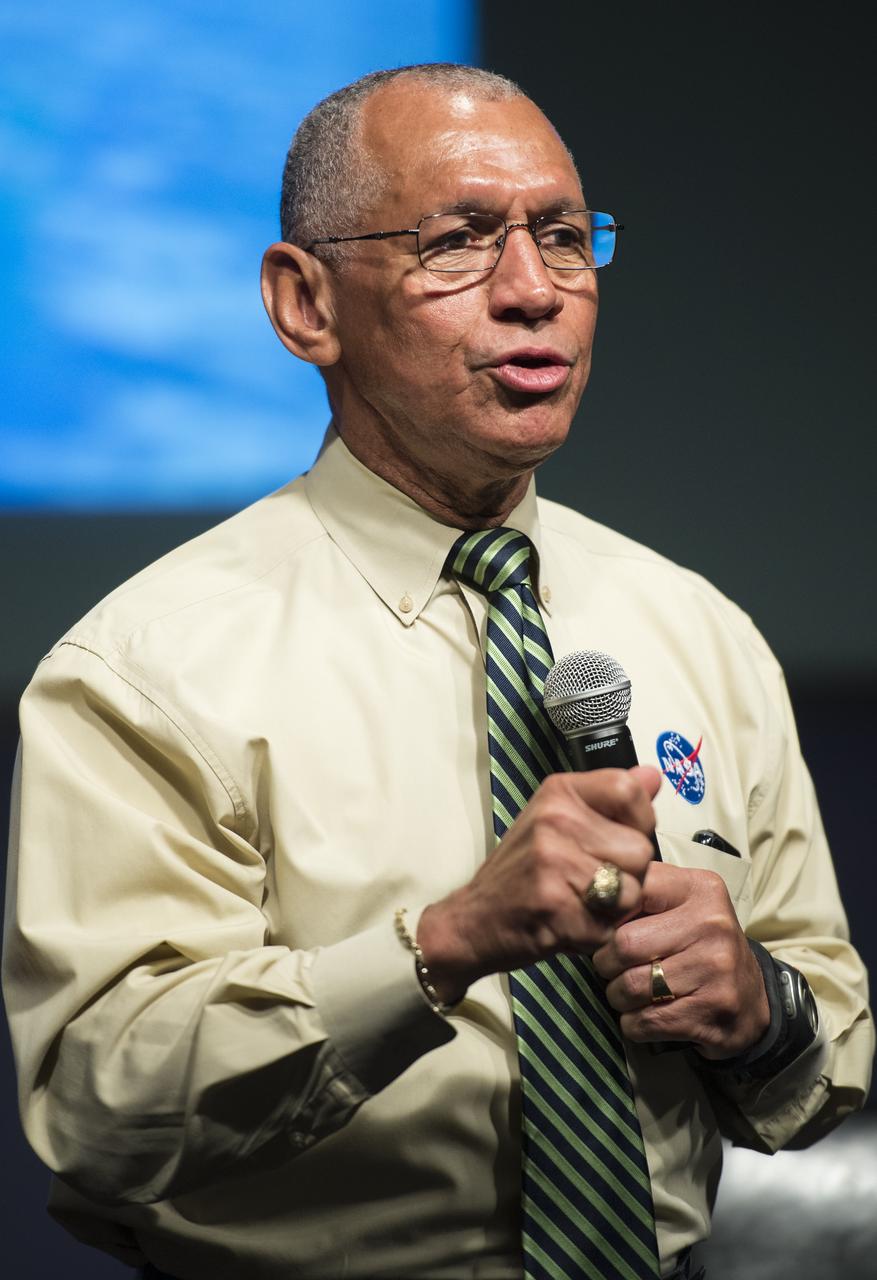

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden speaks to students from Mapletown Jr/Sr High School and Margaret Bell Middle School during the NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Research Project Capstone Event in the James E. Webb Auditorium at NASA Headquarters on Monday, May 5, 2014. Administrator Bolden spoke about his involvement with the Hubble Space Telescope and took questions from the students. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden speaks to students from Mapletown Jr/Sr High School and Margaret Bell Middle School during the NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Research Project Capstone Event in the James E. Webb Auditorium at NASA Headquarters on Monday, May 5, 2014. Administrator Bolden spoke about his involvement with the Hubble Space Telescope and took questions from the students. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
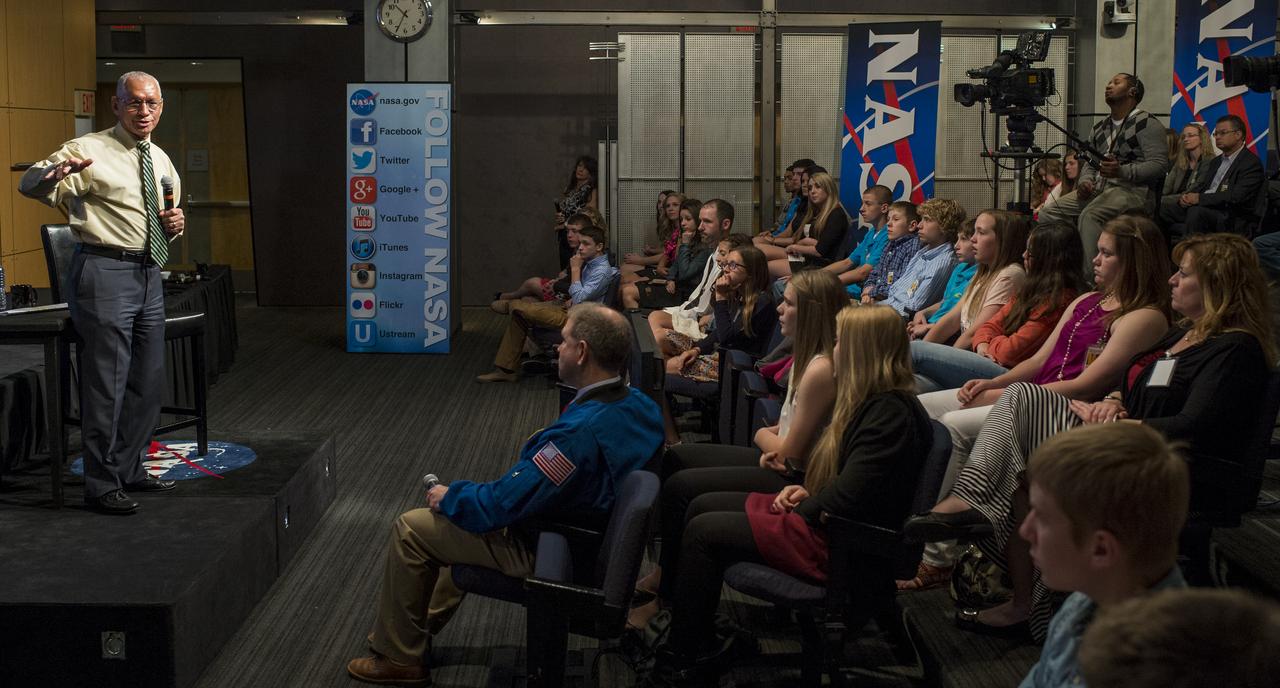

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden speaks to students from Mapletown Jr/Sr High School and Margaret Bell Middle School during the NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Research Project Capstone Event in the James E. Webb Auditorium at NASA Headquarters on Monday, May 5, 2014. Administrator Bolden spoke about his involvement with the Hubble Space Telescope and took questions from the students. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
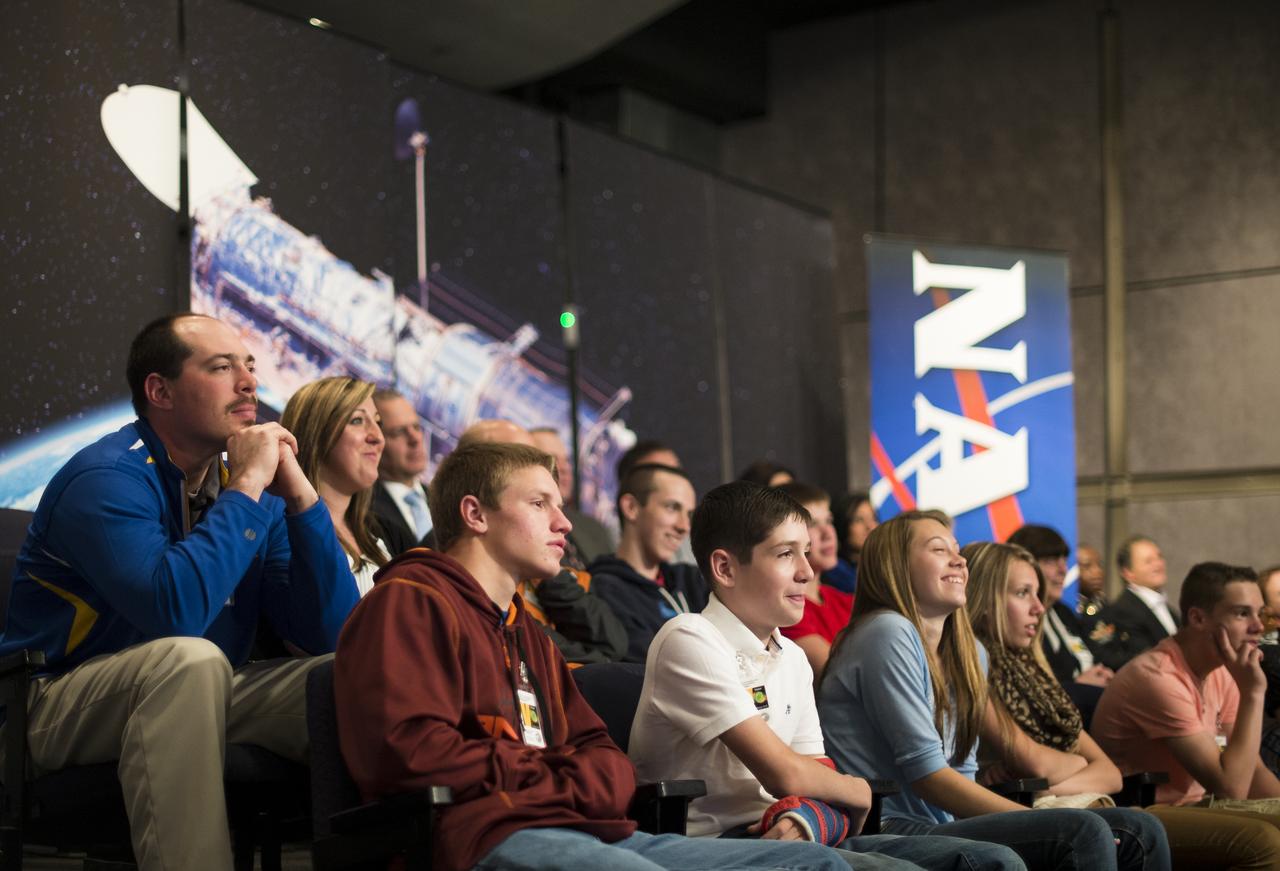

Students and faculty from Mapletown Jr/Sr High School and Margaret Bell Middle School listen as John Grunsfeld, NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, speaks about his experiences on the final space shuttle servicing mission to the Hubble Space Telescope during the NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Research Project Capstone Event in the James E. Webb Auditorium at NASA Headquarters on Monday, May 5, 2014. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Manager Carl Starr monitors the progress of the Webb observatory as it’s second primary mirror wing is prepared to rotate into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Manager Carl Starr monitors the progress of the Webb observatory as it’s second primary mirror wing is prepared to rotate into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
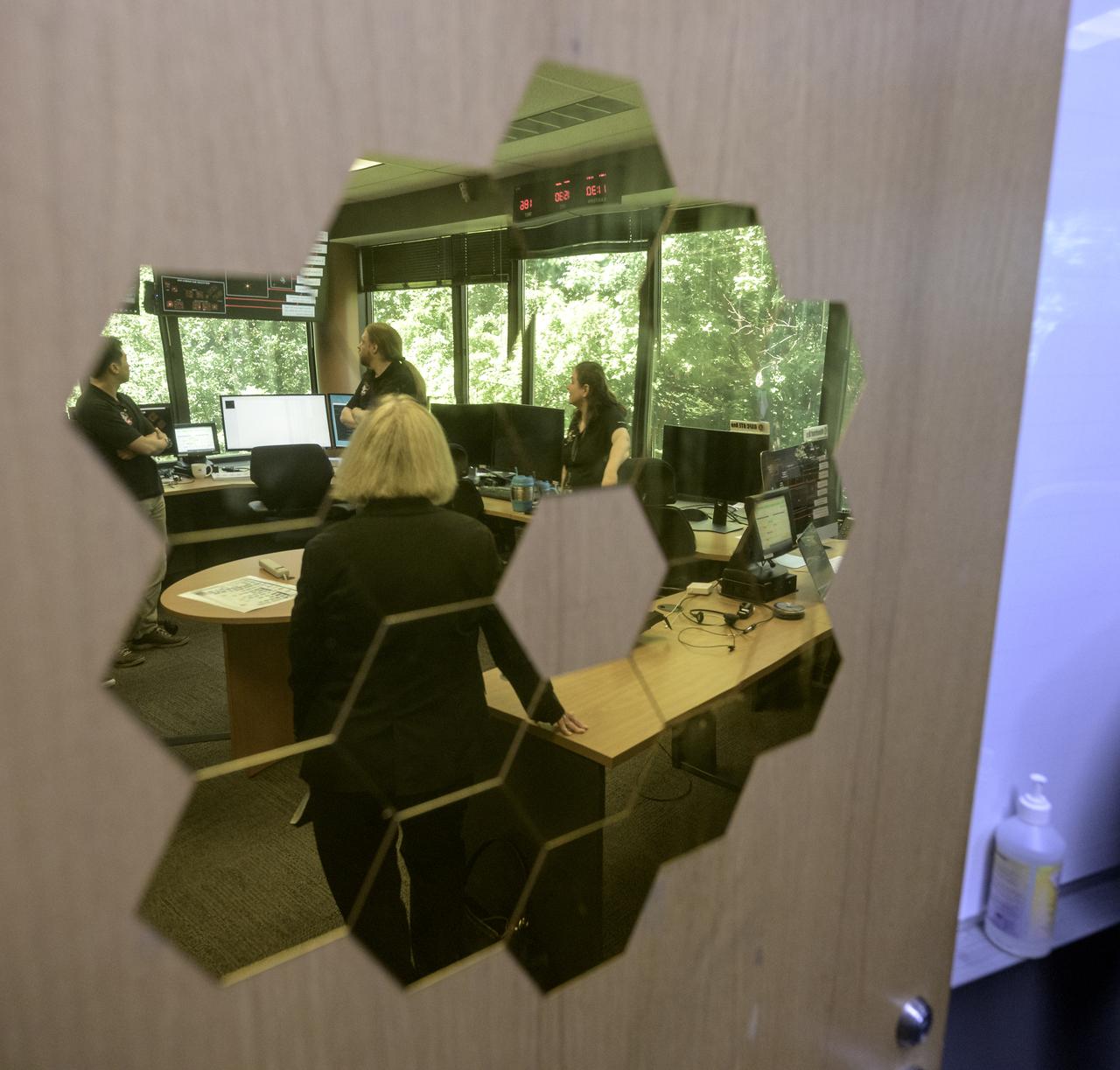

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, back to camera, is seen reflected in a door mirror decoration as she meets with members of the NASA James Webb Space Telescope wavefront sensing and control analysis office, Wednesday, June 29, 2022, at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore. Prior to the tour the deputy spoke at a briefing that focused on the status of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope in its final weeks of preparing for its science mission, as well as overviews of planned science for Webb’s first year of operations. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Senior Systems Engineer, Webb, Northrop Grumman, Nanci Shawger answers questions from the media during a briefing following the successful deployment of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope primary mirror, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from the Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. With Webb’s 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror fully deployed, the infrared observatory has completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
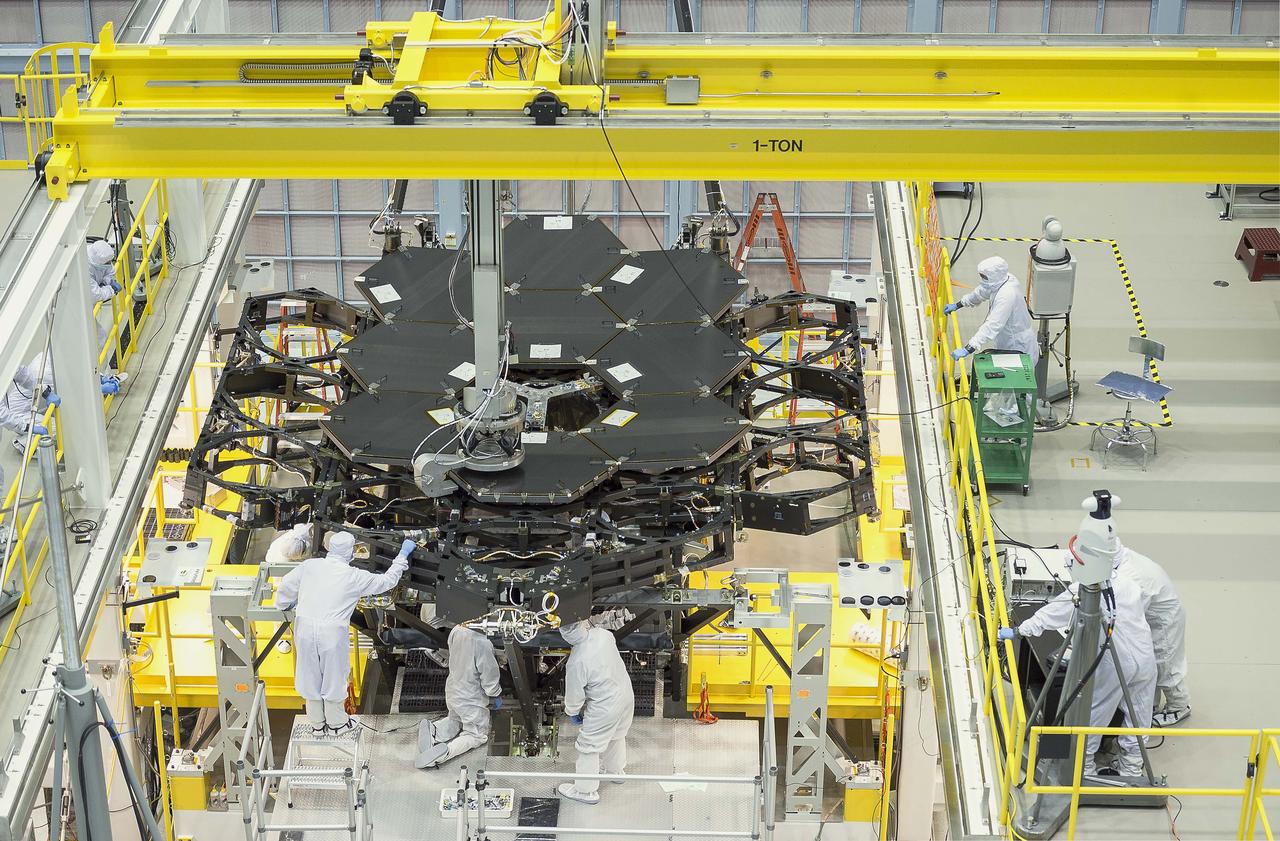
Inside NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center's massive clean room in Greenbelt, Maryland, the ninth flight mirror was installed onto the telescope structure with a robotic arm. This marks the halfway completion point for the James Webb Space Telescope's segmented primary mirror. This rare overhead shot of the James Webb Space Telescope shows the nine primary flight mirrors installed on the telescope structure in a clean room at NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Credits: NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center/Chris Gunn Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1kqK6fW" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1kqK6fW</a>

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, left, NASA Associate Administrator Bob Cabana, and NASA Administrator Bill Nelson are shown an early mirror alignment image from the James Webb Space Telescope, by NASA Webb Optical Telescope Element Manager Lee Feinberg, as NASA Program Director for the James Webb Space Telescope Program Greg Robinson, right, looks on, Monday, Feb., 7, 2022, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. This engineering visual, which features 18 unfocused dots of light, demonstrates that the Webb team has successfully identified starlight through each of Webb’s 18 hexagonal mirror segments – the starting point in a months-long process to progressively align the segments into a single, precise mirror to prepare the telescope for science. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Engineer Kenny McKenzie, background, NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Manager Carl Starr, middle, and NASA James Webb Space Telescope Project Manager Bill Ochs, monitor the progress of the Webb observatory as it’s second primary mirror wing is prepared to rotate into position, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. Webb, an infrared telescope with a 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror, was folded up for launch and underwent an unprecedented deployment process to unfold in space. As NASA's next flagship observatory, Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Cynthia Simmons, deputy director of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks before a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Cynthia Simmons, deputy director of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks before a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Patrick Lynch, director of the Office of Communications at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks before a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Patrick Lynch, director of the Office of Communications at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, speaks before a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Attendees pick up movie posters for the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope” following a screening at at the Greenbelt Cinema, Wednesday, June 11, 2025, in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Attendees take their seats before a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Attendees gather outside of the Greenbelt Cinema before a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The marquee of the Greenbelt Cinema before a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Attendees watch a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
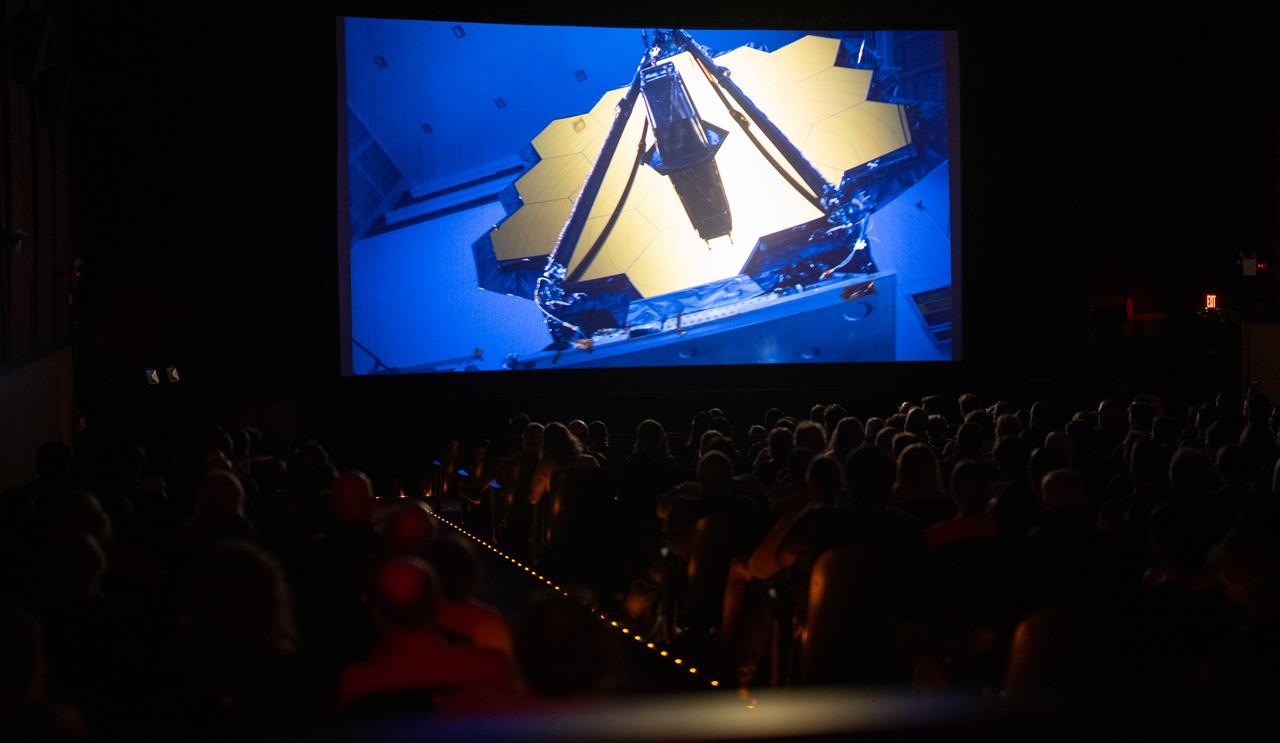

Attendees watch a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Attendees watch a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
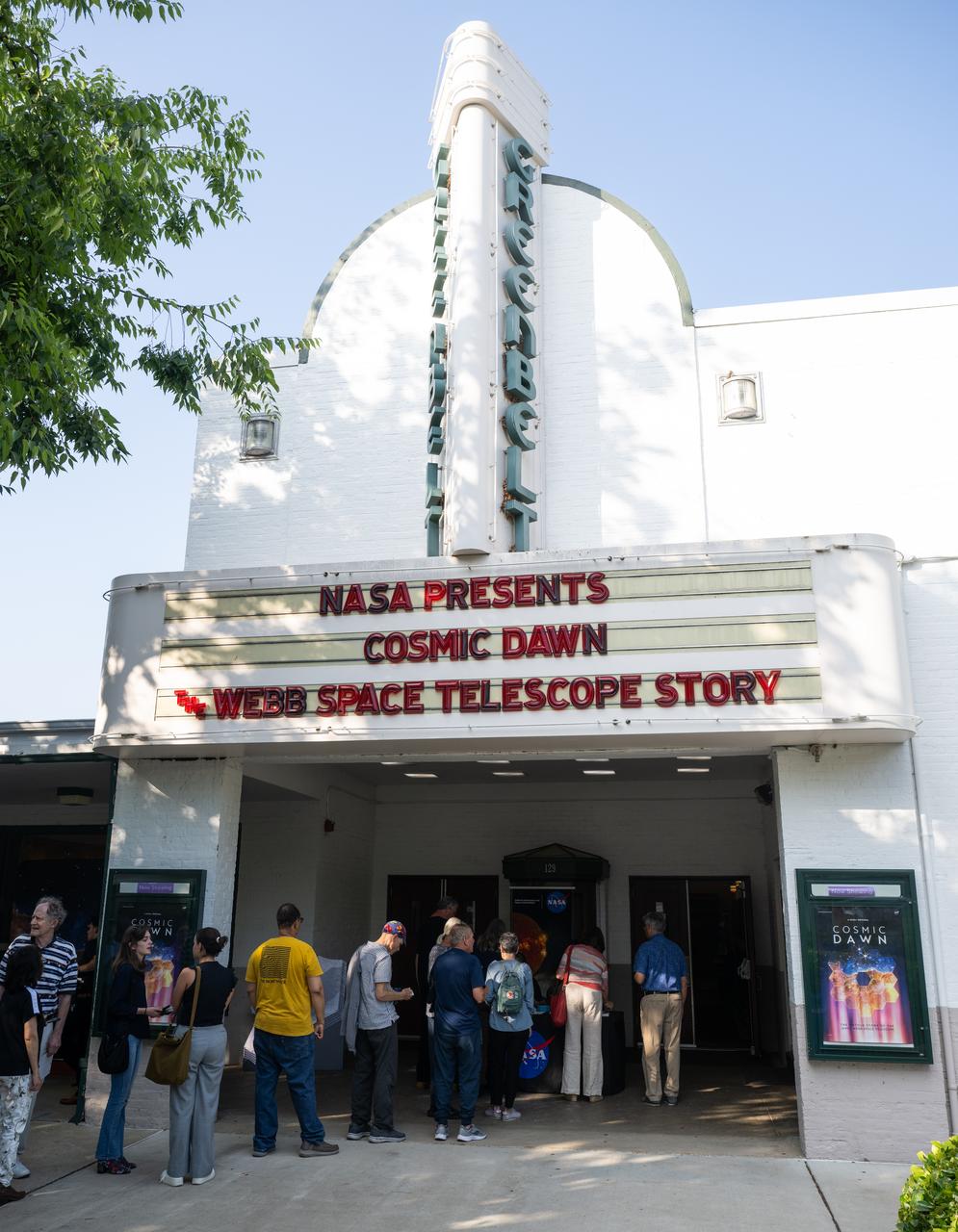

Attendees line up to enter the theater for a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Caitlin McGrath, executive director of the Greenbelt Cinema, welcomes attendees before a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

A movie poster for the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” is seen outside the Greenbelt Cinema, Wednesday, June 11, 2025, in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

John Grunsfeld, NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, speaks to students from Mapletown Jr/Sr High School and Margaret Bell Middle School about his experiences on the final space shuttle servicing mission to the Hubble Space Telescope during the NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Research Project Capstone Event in the James E. Webb Auditorium at NASA Headquarters on Monday, May 5, 2014. Grunsfeld flew on three of the five servicing missions to the Hubble Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

John Grunsfeld, NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, speaks to students from Mapletown Jr/Sr High School and Margaret Bell Middle School about his experiences on the final space shuttle servicing mission to the Hubble Space Telescope during the NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Research Project Capstone Event in the James E. Webb Auditorium at NASA Headquarters on Monday, May 5, 2014. Grunsfeld flew on three of the five servicing missions to the Hubble Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
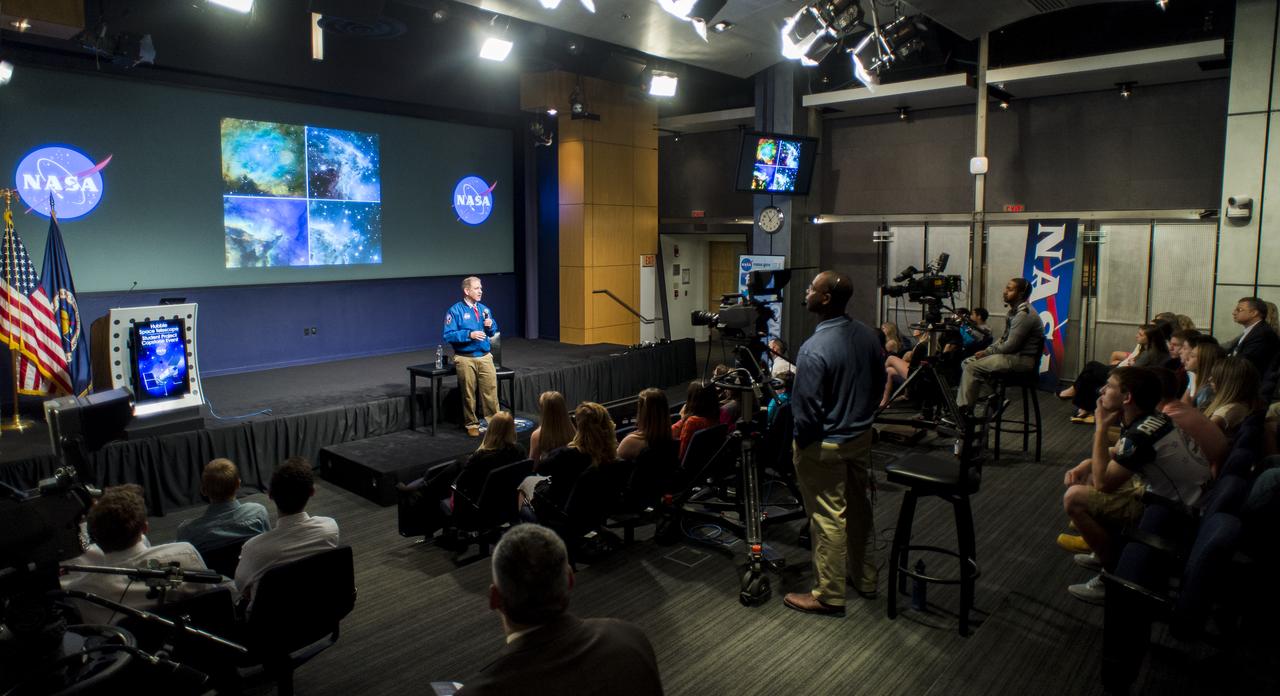

John Grunsfeld, NASA Associate Administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, speaks to students from Mapletown Jr/Sr High School and Margaret Bell Middle School about his experiences on the final space shuttle servicing mission to the Hubble Space Telescope during the NASA Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Research Project Capstone Event in the James E. Webb Auditorium at NASA Headquarters on Monday, May 5, 2014. Grunsfeld flew on three of the five servicing missions to the Hubble Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Program Scientist Eric Smith, wearing Webb themed socks, waits for Arianespace's Ariane 5 rocket with NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope onboard, to rollout to the launch pad, Thursday, Dec. 23, 2021, at Europe’s Spaceport, the Guiana Space Center in Kourou, French Guiana. The James Webb Space Telescope (sometimes called JWST or Webb) is a large infrared telescope with a 21.3 foot (6.5 meter) primary mirror. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
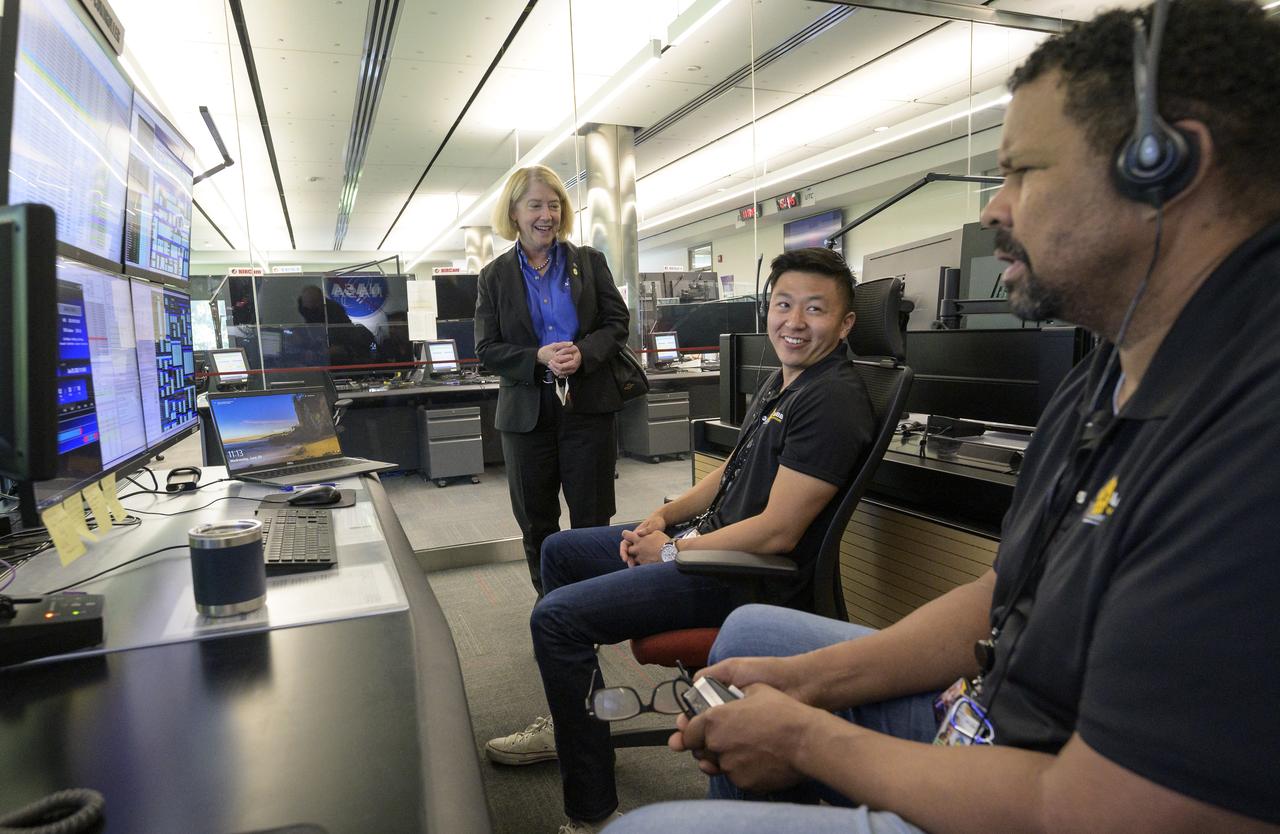

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, left, meets with NASA James Webb Space Telescope Command Controllers Justin Truing, and Phil Johnson, right, during a tour of the NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center, Wednesday, June 29, 2022, at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore. Prior to the tour the deputy spoke at a briefing that focused on the status of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope in its final weeks of preparing for its science mission, as well as overviews of planned science for Webb’s first year of operations. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
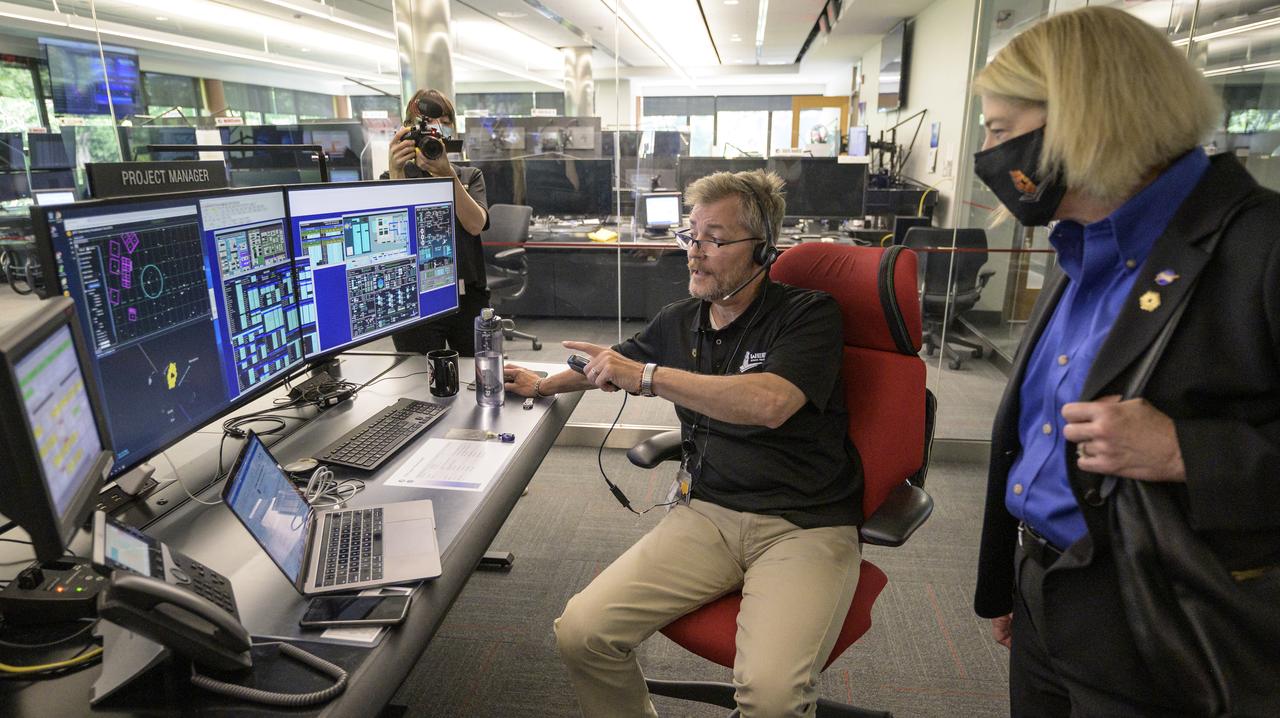

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, right, talks with NASA James Webb Space Telescope deputy senior project scientist Jon Gardner, as she is given a tour of the NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center, Wednesday, June 29, 2022, at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore. Prior to the tour the deputy spoke at a briefing that focused on the status of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope in its final weeks of preparing for its science mission, as well as overviews of planned science for Webb’s first year of operations. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
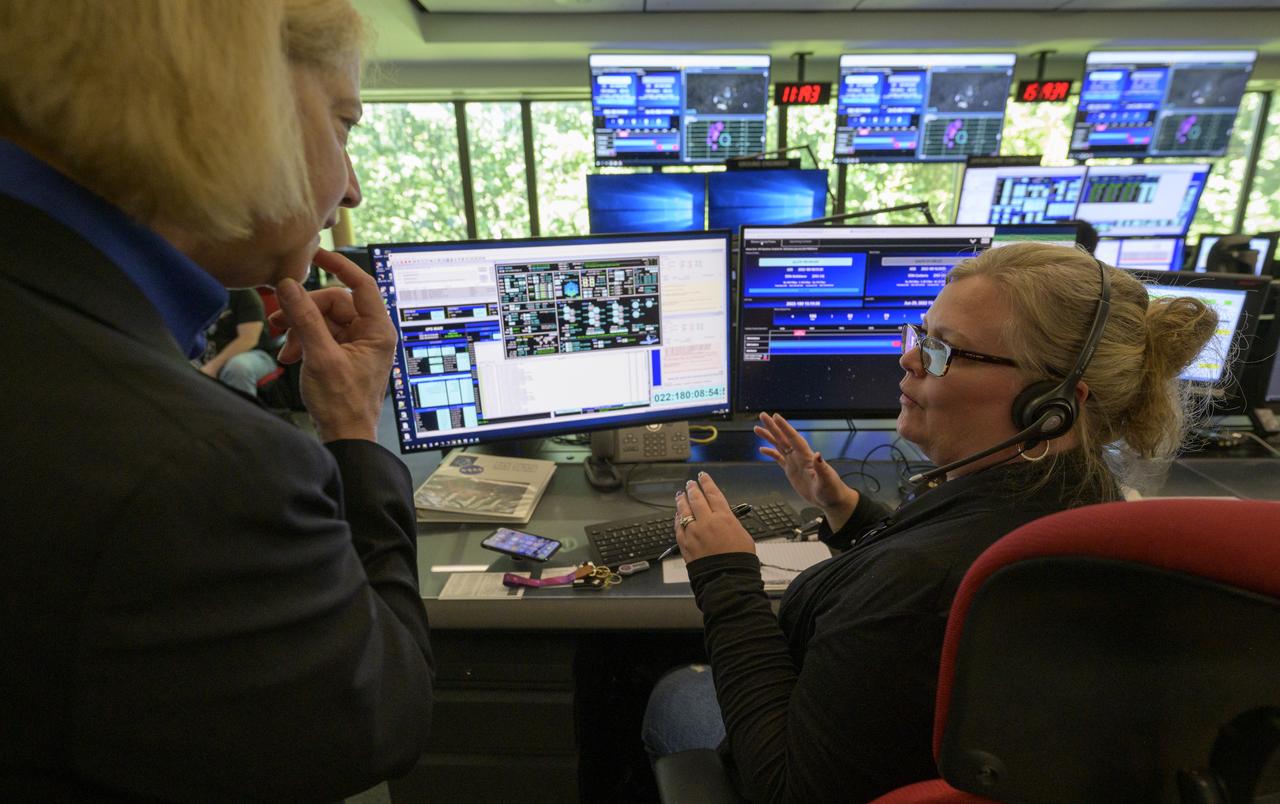

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, left, meets with NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission Planner Kari Bosley during a tour of the NASA James Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center, Wednesday, June 29, 2022, at the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore. Prior to the tour the deputy spoke at a briefing that focused on the status of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope in its final weeks of preparing for its science mission, as well as overviews of planned science for Webb’s first year of operations. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
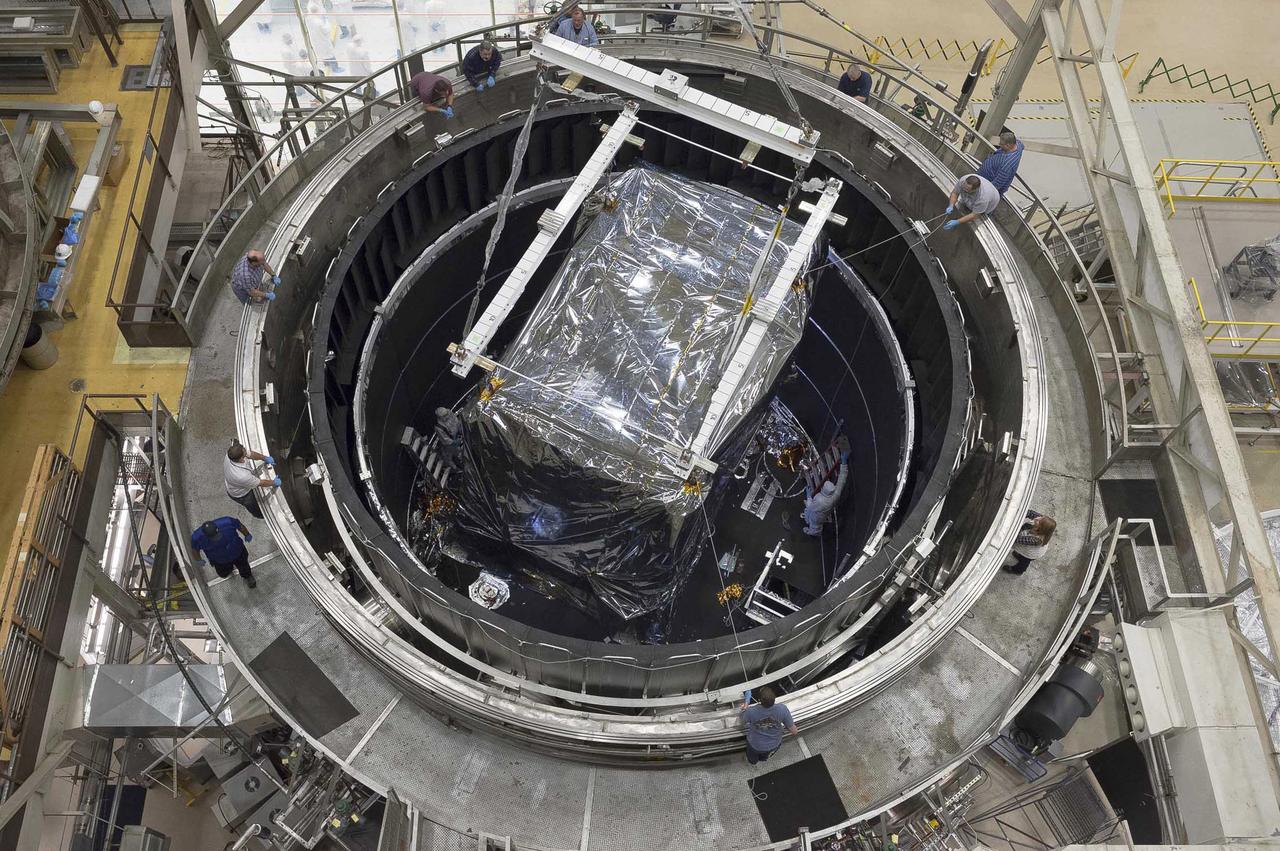

At NASA's James Webb Space Telescope's final destination in space, one million miles away from Earth, it will operate at incredibly cold temperatures of -387 degrees Fahrenheit, or 40 degrees Kelvin. This is 260 degrees Fahrenheit colder than any place on the Earth’s surface has ever been. So first, this final super cold test at Goddard will prepare the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), or the “heart” of the telescope, for space. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1KFPwJG" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1KFPwJG</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
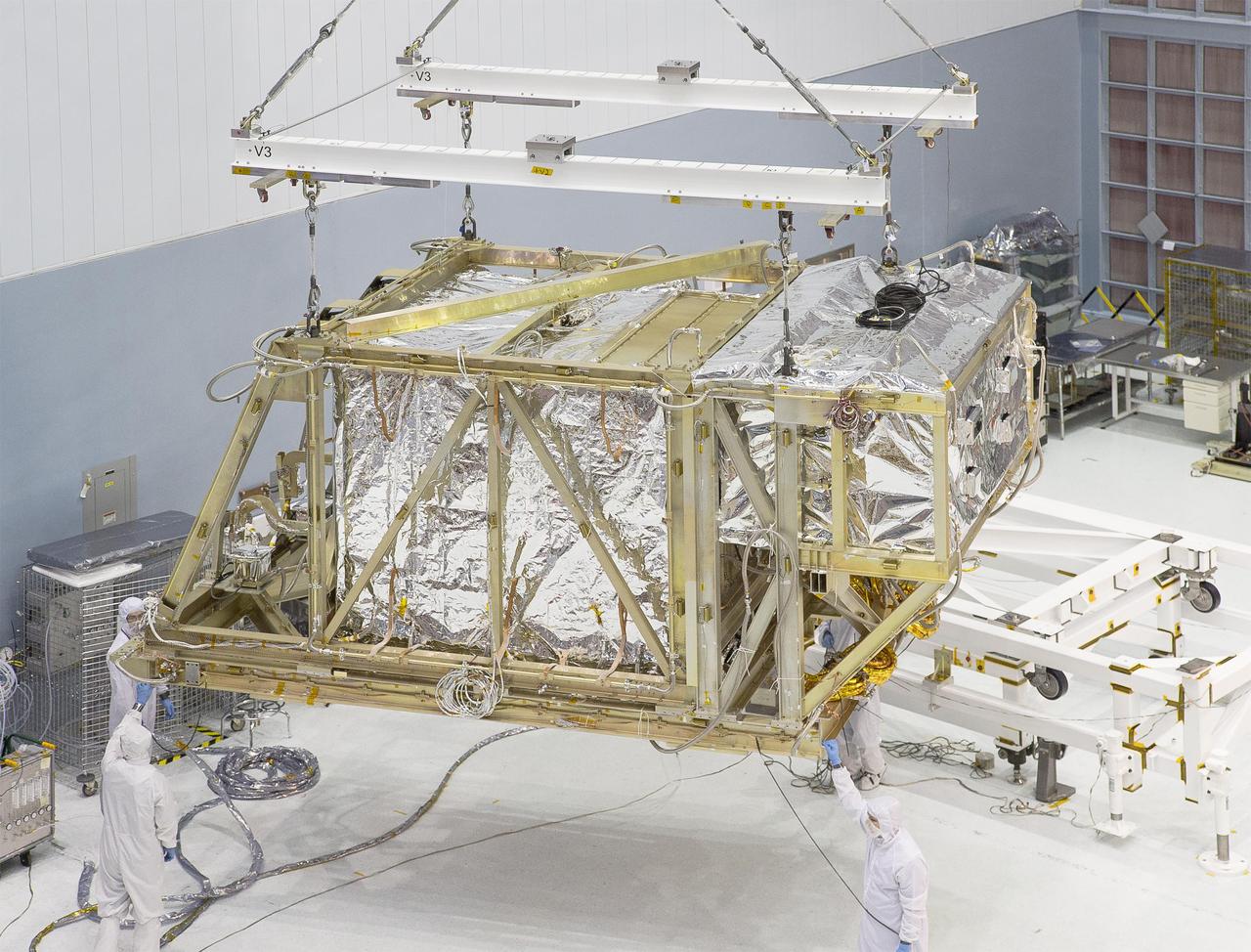

At NASA's James Webb Space Telescope's final destination in space, one million miles away from Earth, it will operate at incredibly cold temperatures of -387 degrees Fahrenheit, or 40 degrees Kelvin. This is 260 degrees Fahrenheit colder than any place on the Earth’s surface has ever been. So first, this final super cold test at Goddard will prepare the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), or the “heart” of the telescope, for space. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1KFPwJG" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1KFPwJG</a> Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

At NASA's James Webb Space Telescope's final destination in space, one million miles away from Earth, it will operate at incredibly cold temperatures of -387 degrees Fahrenheit, or 40 degrees Kelvin. This is 260 degrees Fahrenheit colder than any place on the Earth’s surface has ever been. So first, this final super cold test at Goddard will prepare the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM), or the “heart” of the telescope, for space. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1KFPwJG" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1KFPwJG</a> Contamination Control Engineer Alan Abeel conducts final inspections and places contamination foils before the start of the test. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Chris Gunn <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
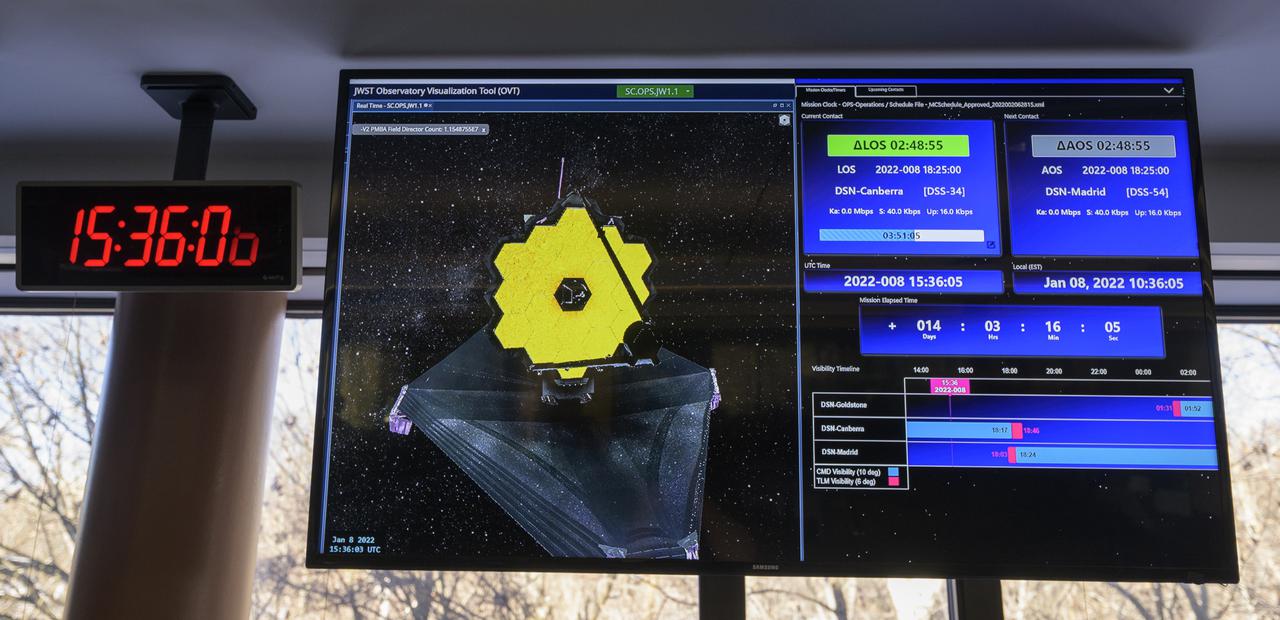
A monitor in the NASA James Webb Space Telescope flight control room of the Space Telescope Science Institute shows the progress of the second primary mirror wing latching on the Webb observatory, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, in Baltimore. When fully latched, the infrared observatory will have completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. Webb will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Cynthia Simmons, deputy director of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center, left, speaks with Paul Geithner, former deputy project manager for NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope before a screening of the new NASA+ documentary “Cosmic Dawn: The Untold Story of the James Webb Space Telescope,” Wednesday, June 11, 2025, at the Greenbelt Cinema in Greenbelt, Maryland. Featuring never-before-seen footage, Cosmic Dawn offers an unprecedented glimpse into the assembly, testing, and launch of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

NASA James Webb Space Telescope Element Manager Lee Feinberg answers questions from the media during a briefing following the successful deployment of NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope primary mirror, Saturday, Jan. 8, 2022, from the Webb Space Telescope Mission Operations Center at the Space Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore. With Webb’s 21.3-foot (6.5-meter) primary mirror fully deployed, the infrared observatory has completed its unprecedented process of unfolding in space to prepare for science operations. The observatory will study every phase of cosmic history—from within our solar system to the most distant observable galaxies in the early universe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)