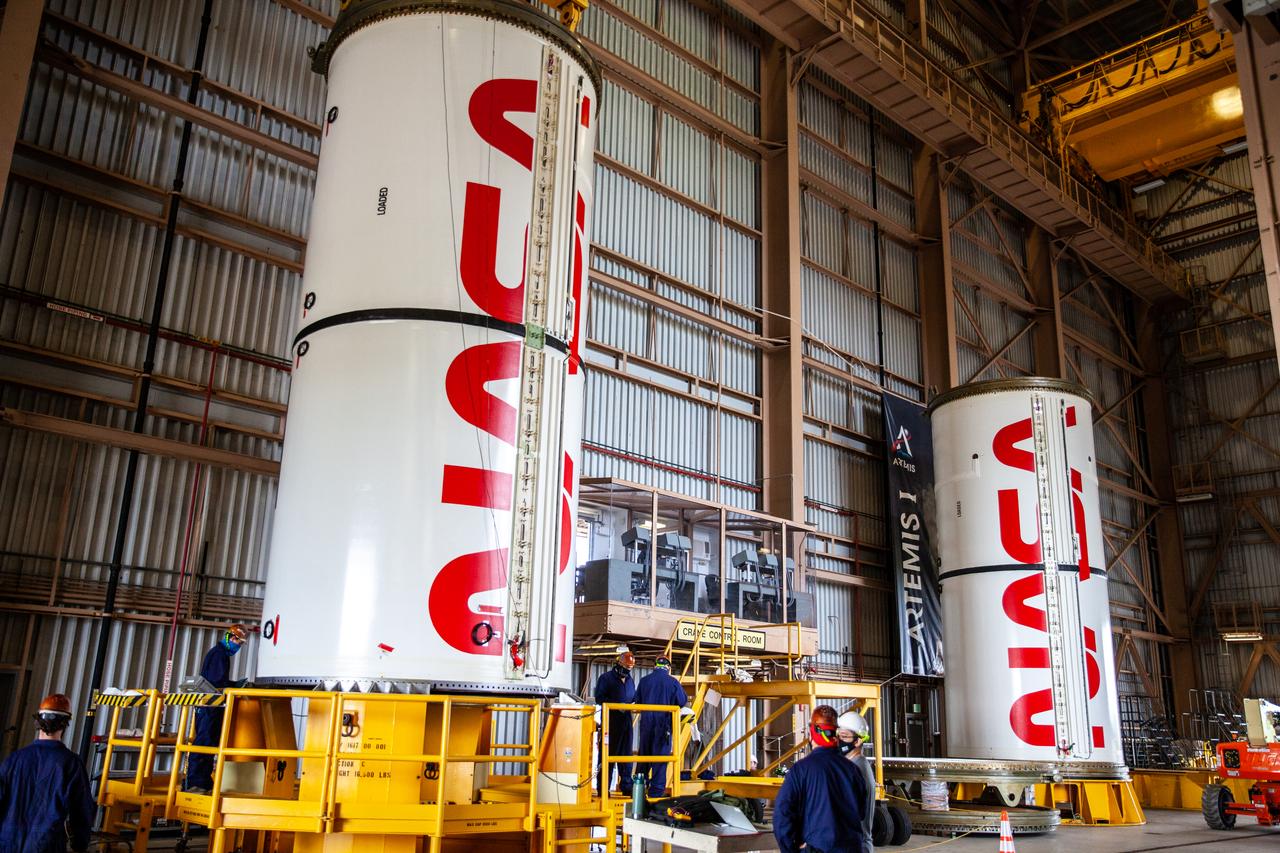

Inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs TOSC workers completed painting of NASA’s iconic “worm” logo on the Artemis I Space Launch System twin solid rocket boosters on Sept. 23, 2020. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the iconic “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
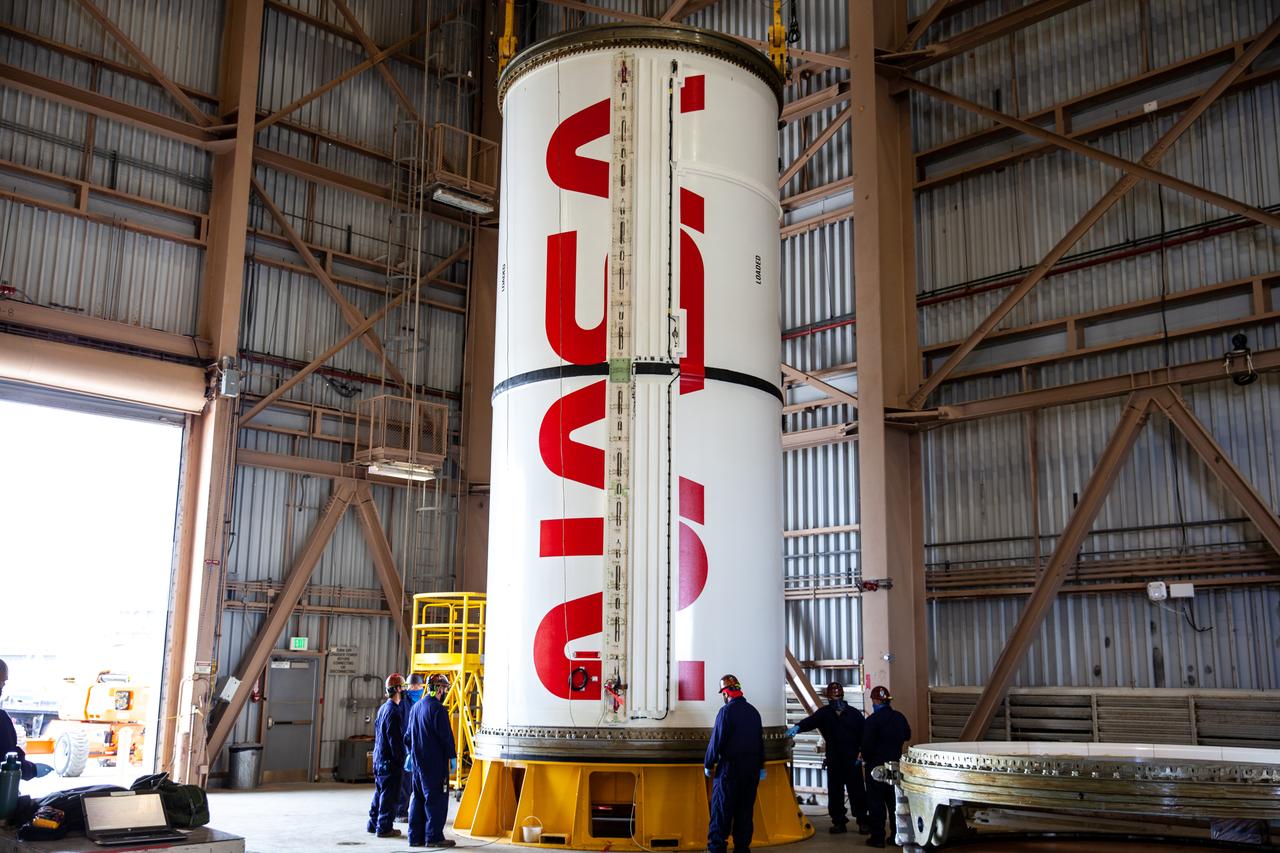

Inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs TOSC workers completed painting of NASA’s iconic “worm” logo on the Artemis I Space Launch System twin solid rocket boosters on Sept. 23, 2020. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the iconic “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
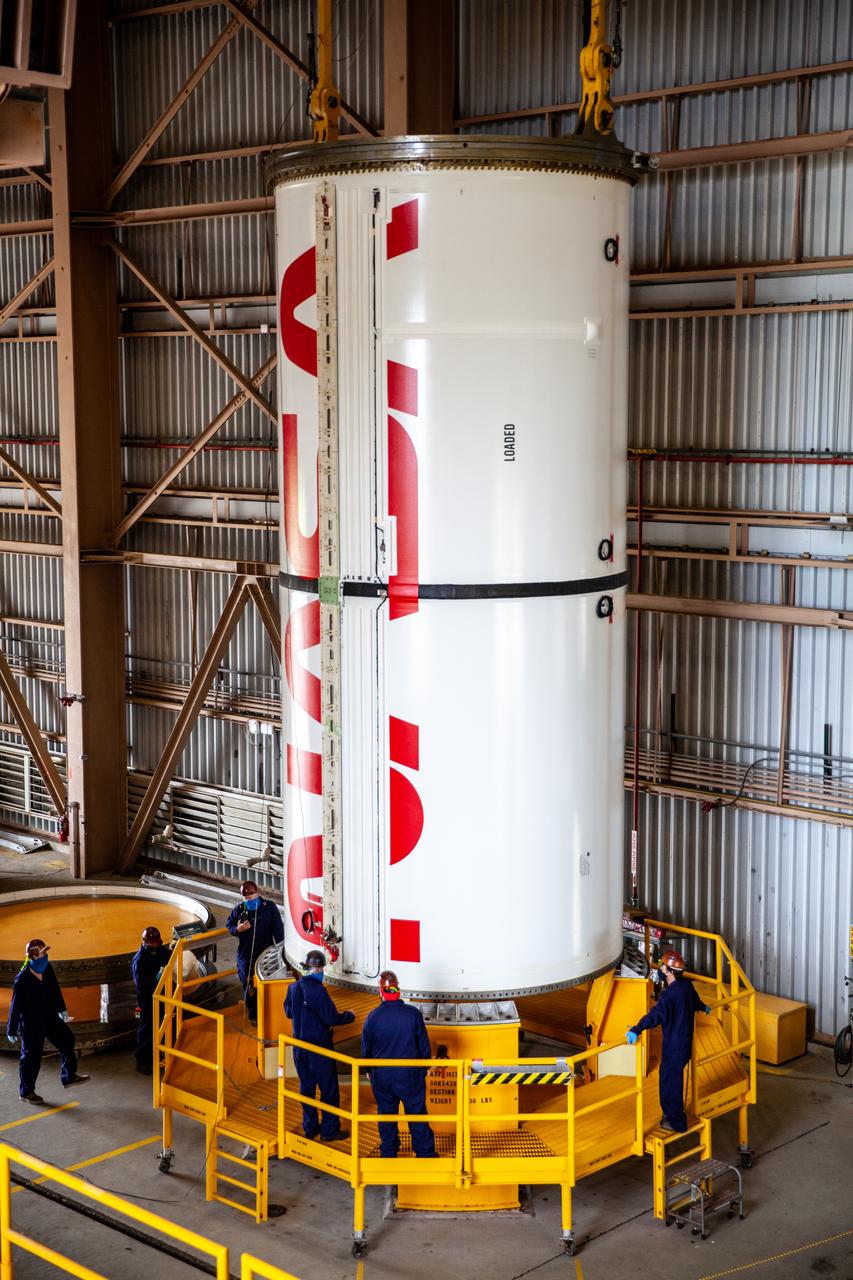

Inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs TOSC workers completed painting of NASA’s iconic “worm” logo on the Artemis I Space Launch System twin solid rocket boosters on Sept. 23, 2020. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the iconic “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
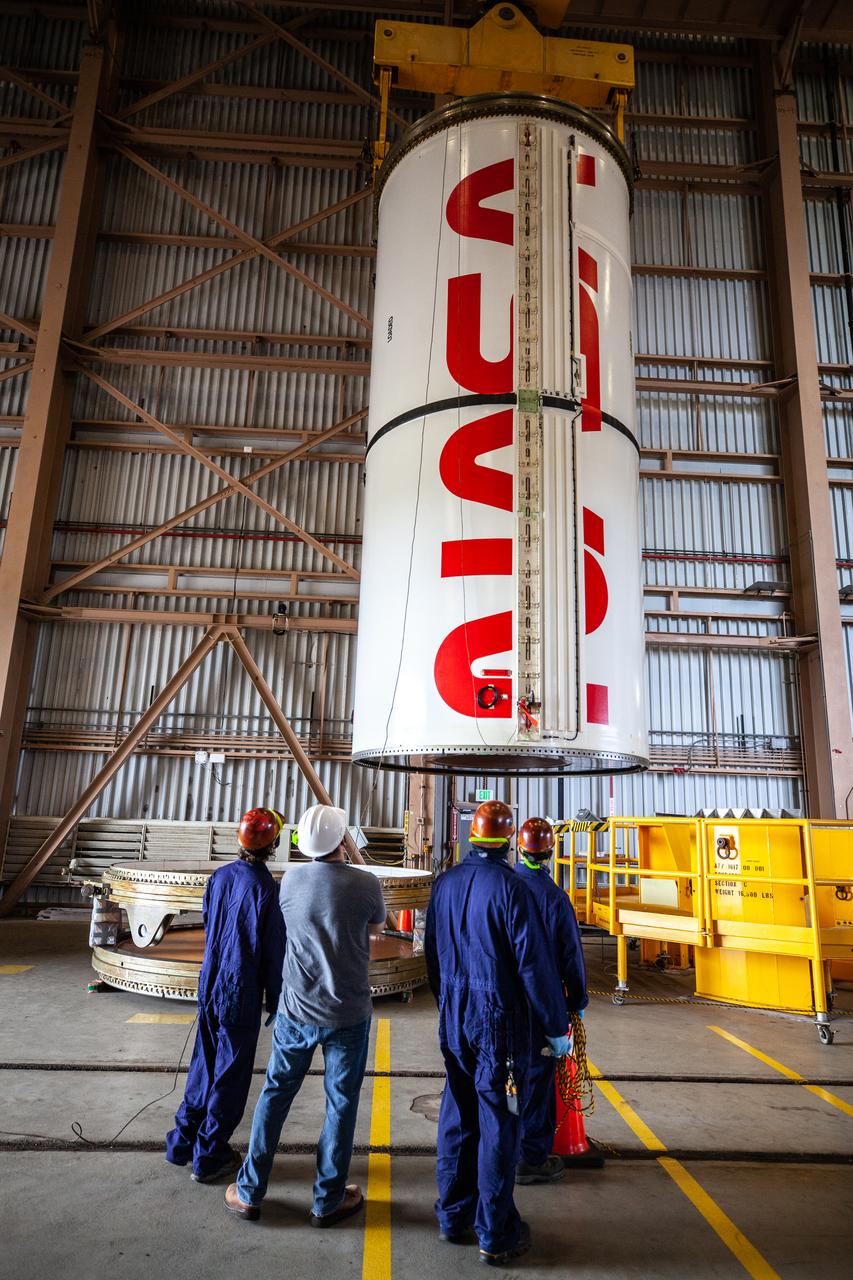

Inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs TOSC workers completed painting of NASA’s iconic “worm” logo on the Artemis I Space Launch System twin solid rocket boosters on Sept. 23, 2020. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the iconic “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
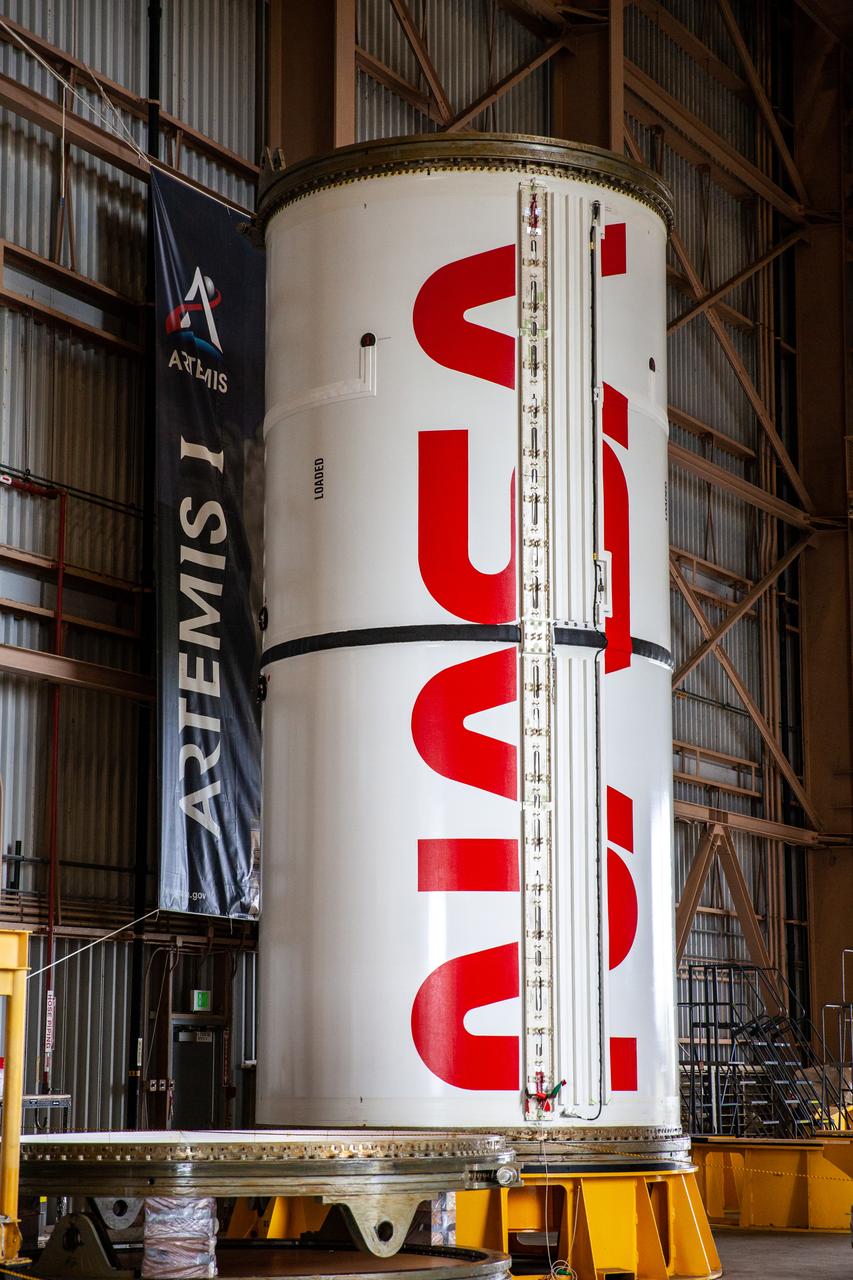

Inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs TOSC workers completed painting of NASA’s iconic “worm” logo on the Artemis I Space Launch System twin solid rocket boosters on Sept. 23, 2020. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the iconic “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
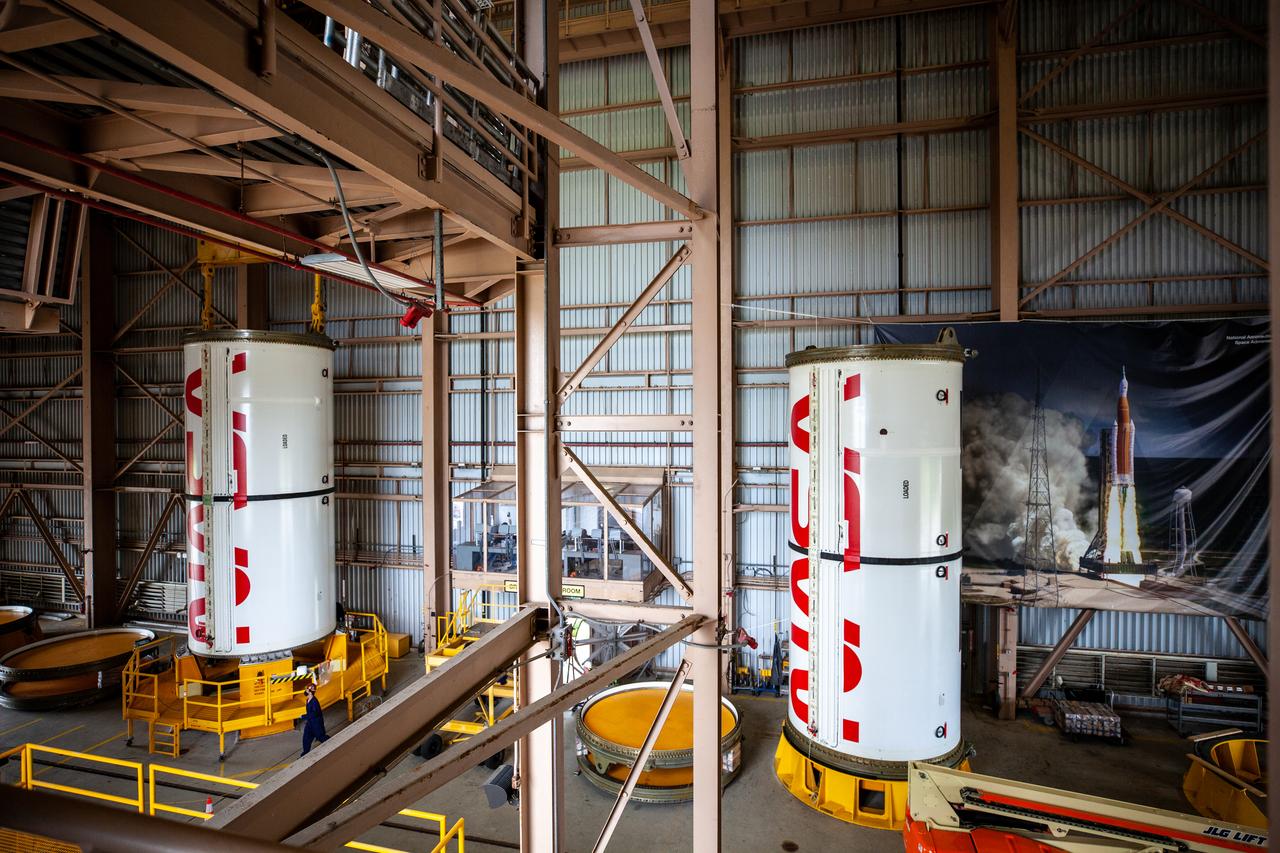

Inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs TOSC workers completed painting of NASA’s iconic “worm” logo on the Artemis I Space Launch System twin solid rocket boosters on Sept. 23, 2020. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the iconic “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
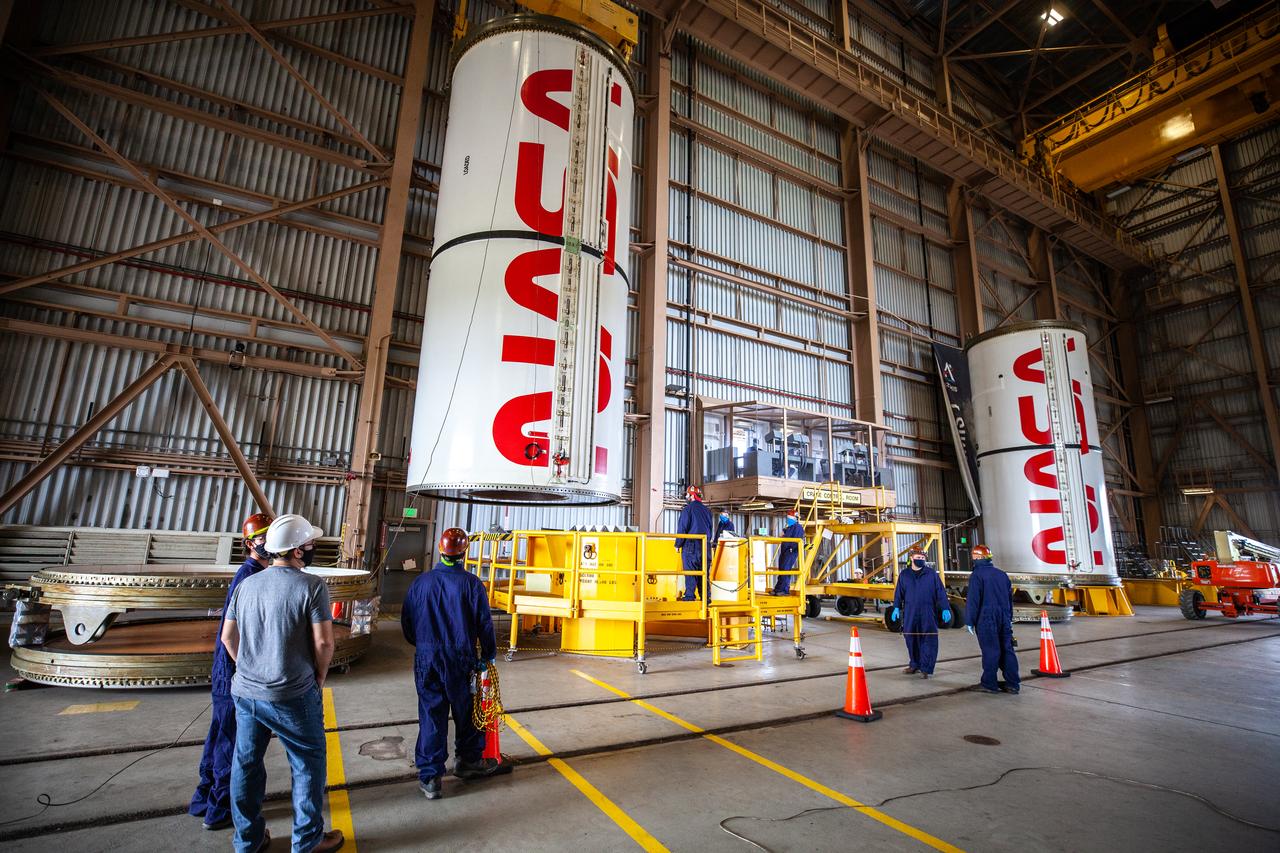

Inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs TOSC workers completed painting of NASA’s iconic “worm” logo on the Artemis I Space Launch System twin solid rocket boosters on Sept. 23, 2020. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the iconic “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
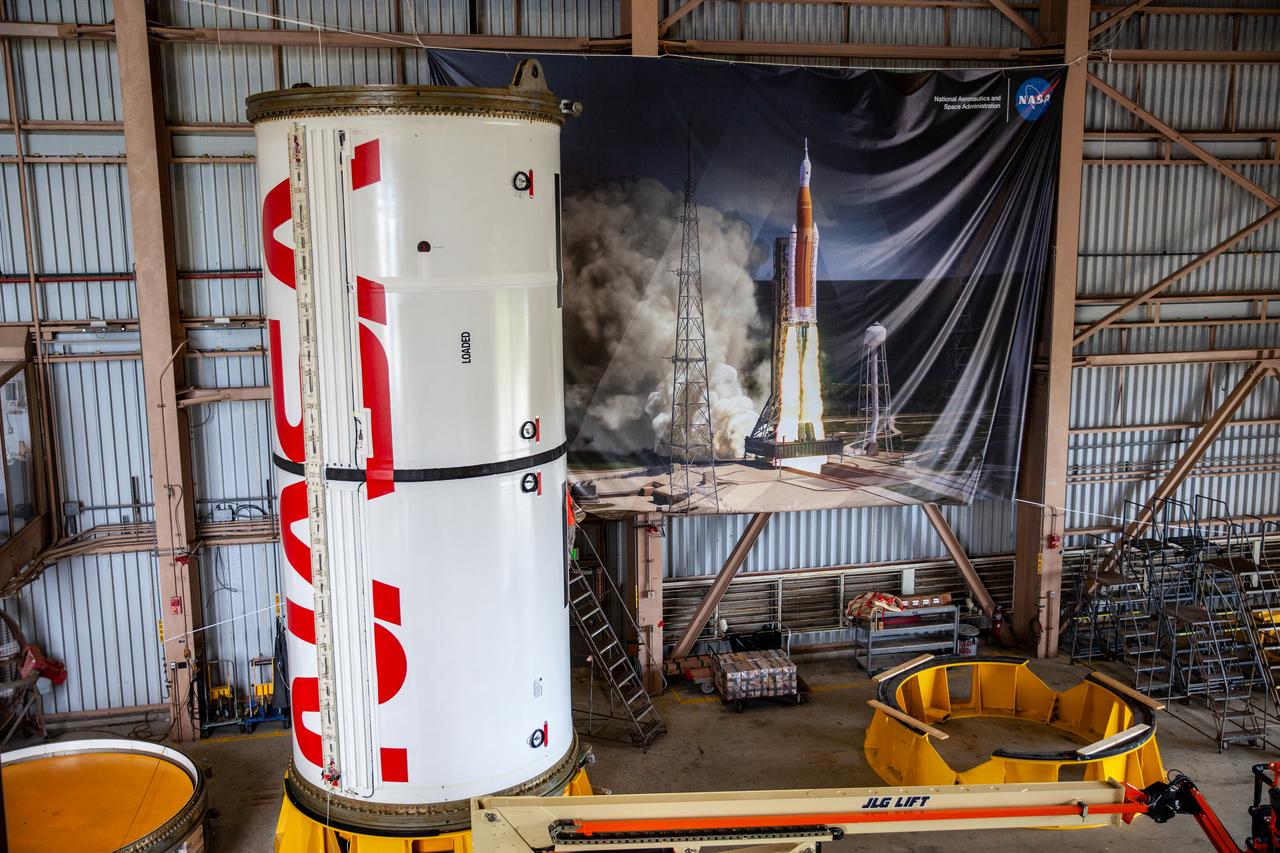

Inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Exploration Ground Systems and Jacobs TOSC workers completed painting of NASA’s iconic “worm” logo on the Artemis I Space Launch System twin solid rocket boosters on Sept. 23, 2020. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the iconic “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.

Frank Pelkey, ASRC technician, adheres NASA’s iconic “worm” logo decal on the aft wall of Orion’s crew module adapter ahead of NASA’s Artemis I mission. The work is complete inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at Kennedy Space Center on Sept. 20, 2020. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.

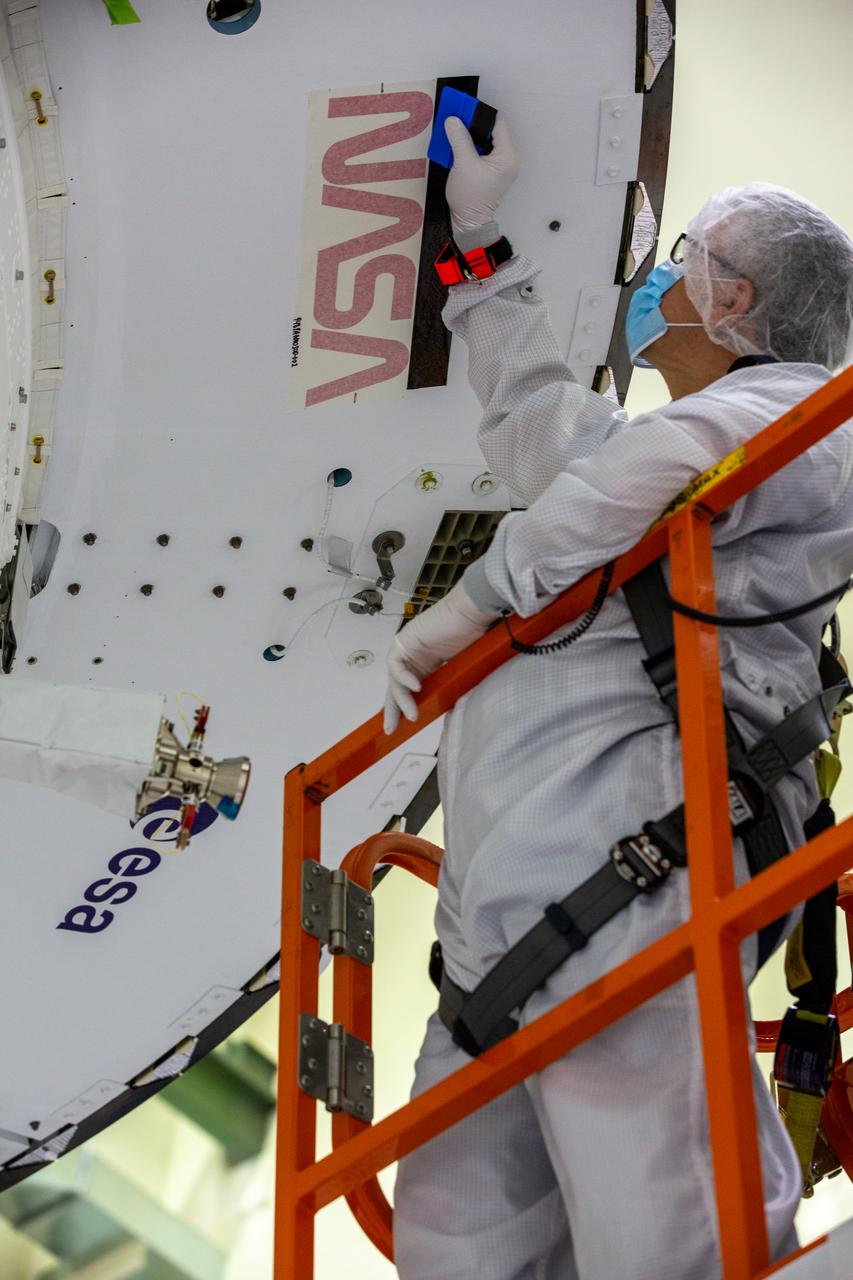
Frank Pelkey, ASRC technician, works to complete the application of NASA’s iconic “worm” logo decal on the aft wall of Orion’s crew module adapter ahead of NASA’s Artemis I mission. The work is complete inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at Kennedy Space Center on Sept. 20, 2020. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.

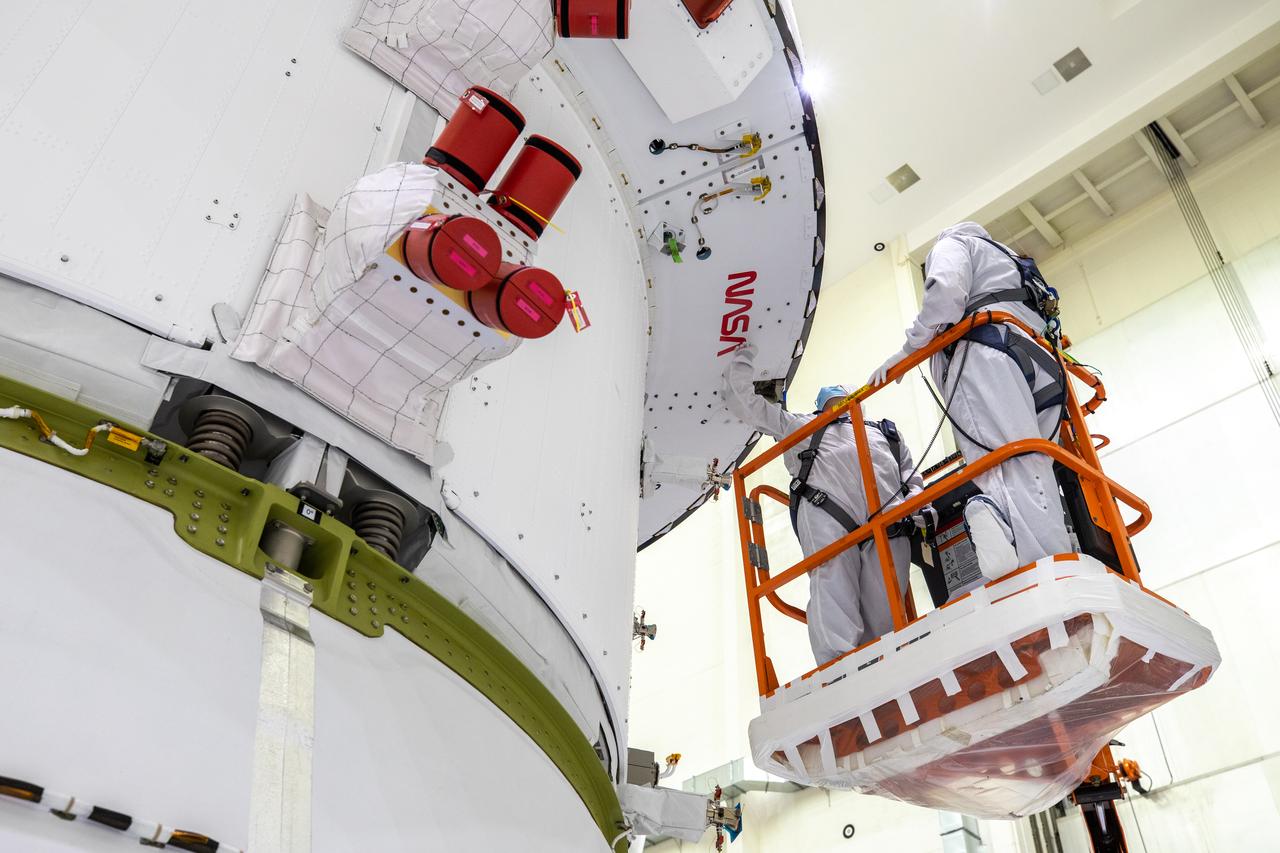
Frank Pelkey, ASRC technician, places tape around the outline of NASA’s iconic “worm” logo on the aft wall of Orion’s crew module adapter ahead of NASA’s Artemis I mission. The work is complete inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at Kennedy Space Center on Sept. 20, 2020. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.

Frank Pelkey, ASRC technician, adheres removable tape around NASA’s iconic “worm” logo decal on the aft wall of Orion’s crew module adapter ahead of NASA’s Artemis I mission. The work is complete inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at Kennedy Space Center on Sept. 20, 2020. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.

Frank Pelkey, ASRC technician, works to adhere NASA’s iconic “worm” logo decal on the aft wall of Orion’s crew module adapter ahead of NASA’s Artemis I mission. The work is complete inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at Kennedy Space Center on Sept. 20, 2020. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.

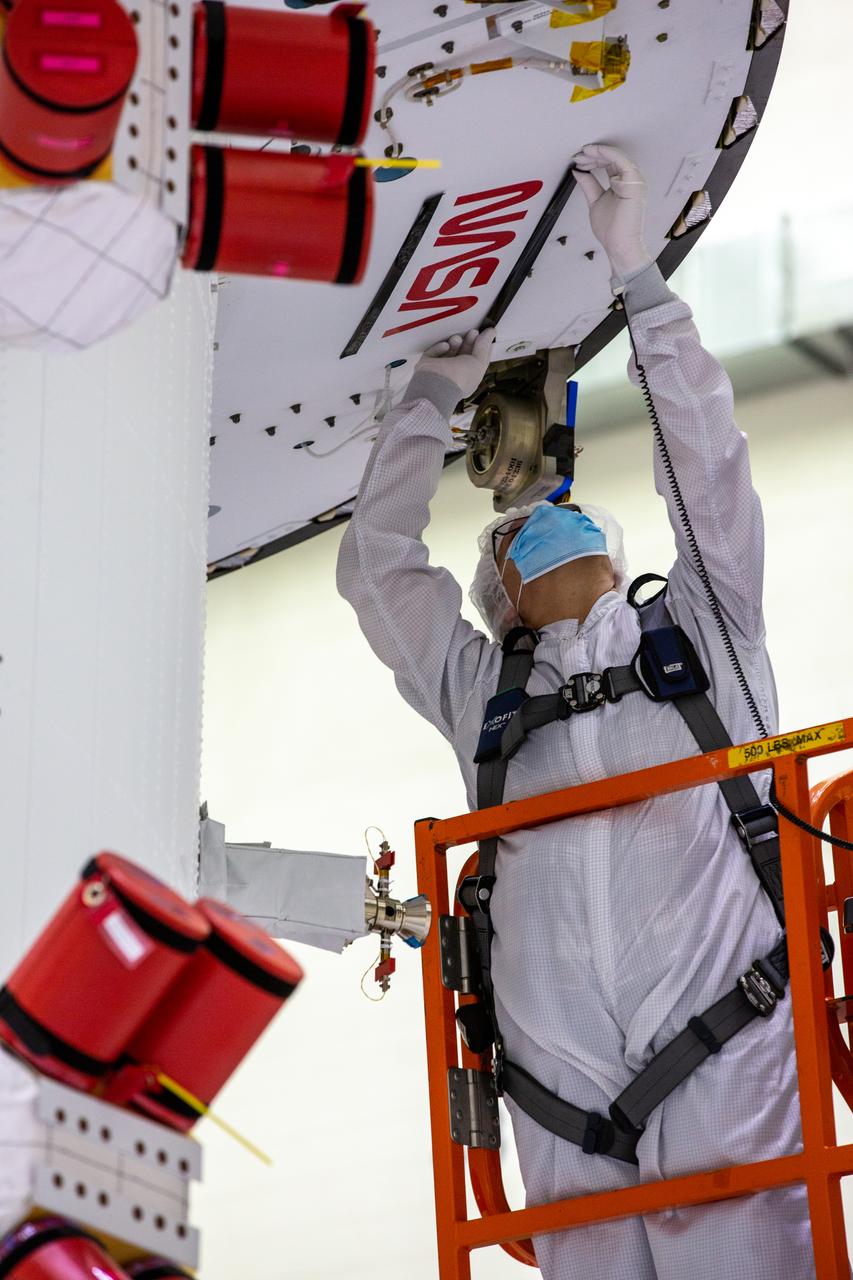
Frank Pelkey, ASRC technician, works to adhere NASA’s iconic “worm” logo decal on the aft wall of Orion’s crew module adapter ahead of NASA’s Artemis I mission. The work is complete inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at Kennedy Space Center on Sept. 20, 2020. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.

jsc2024e050146 (May 13, 2024) --- NASA's Crew-9 members stand in front of NASA’s worm logo on the launch tower at Launch Complex 39A at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left are, Mission Spedialist Alexsandr Gorbunov from Roscosmos; Pilot Nick Hague from NASA; Commander Zena Cardman from NASA; and Mission Specialist Stephanie Wilson from NASA. Credit: SpaceX
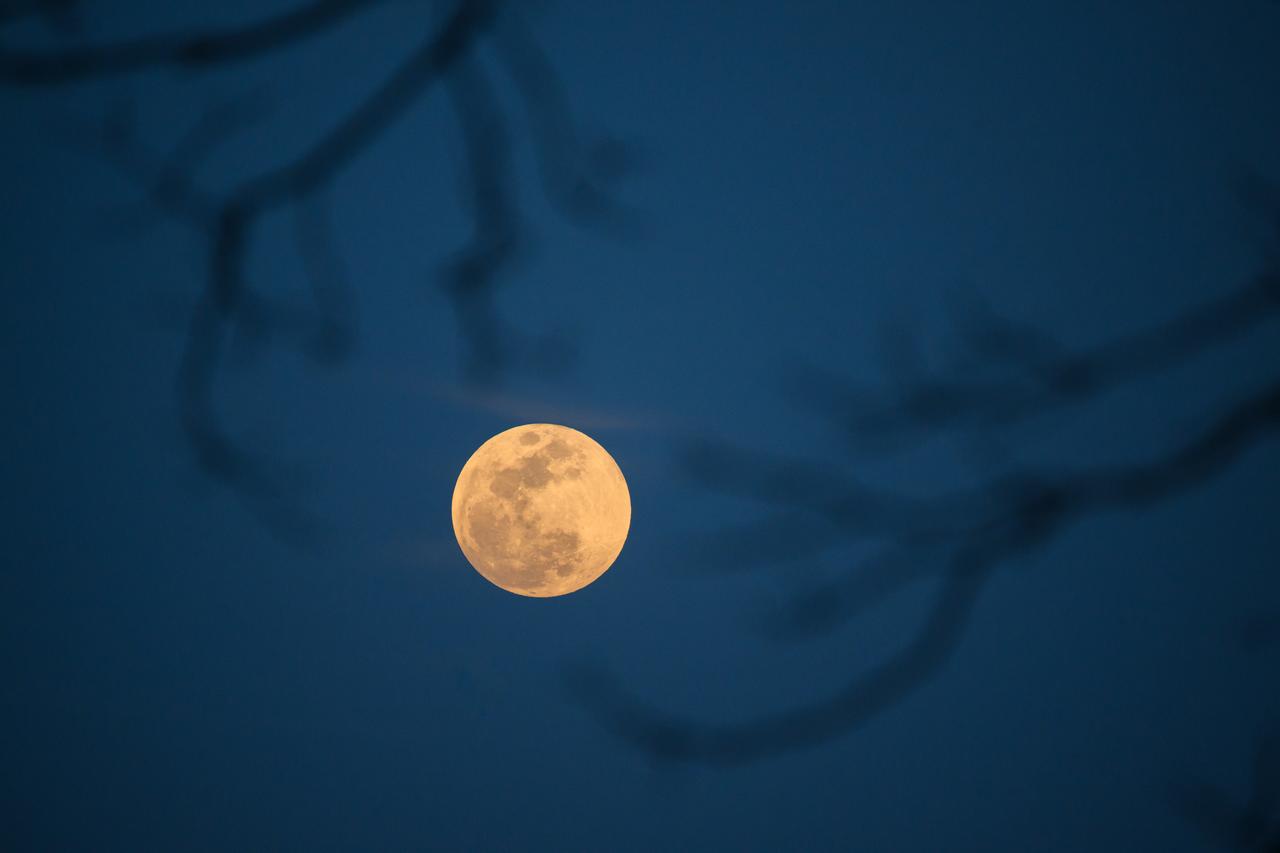

The Worm Moon rises over the city of New Orleans home of NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility on the evening of March 13th, 2025.

The Worm Moon rises over the city of New Orleans home of NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility on the evening of March 13th, 2025.
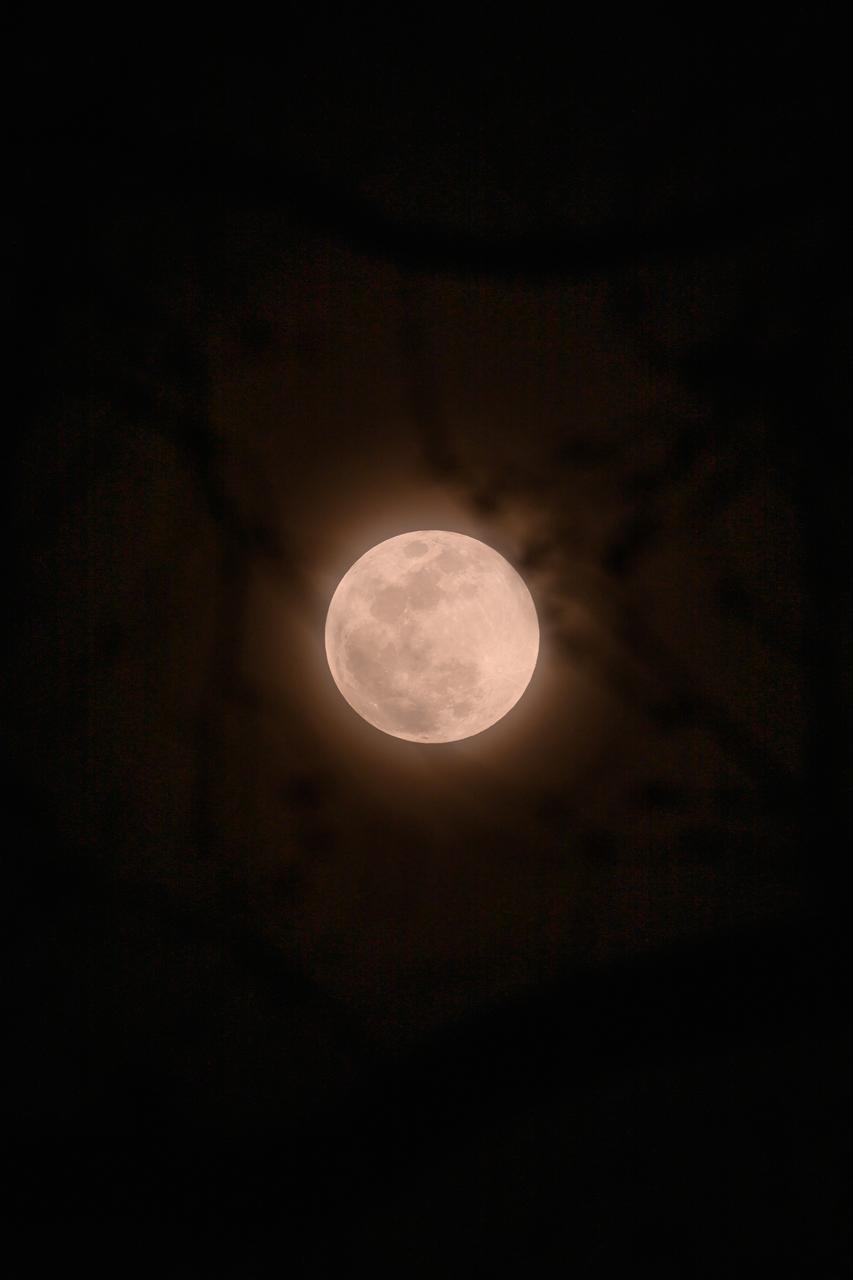

The Worm Moon rises over the city of New Orleans home of NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility on the evening of March 13th, 2025.
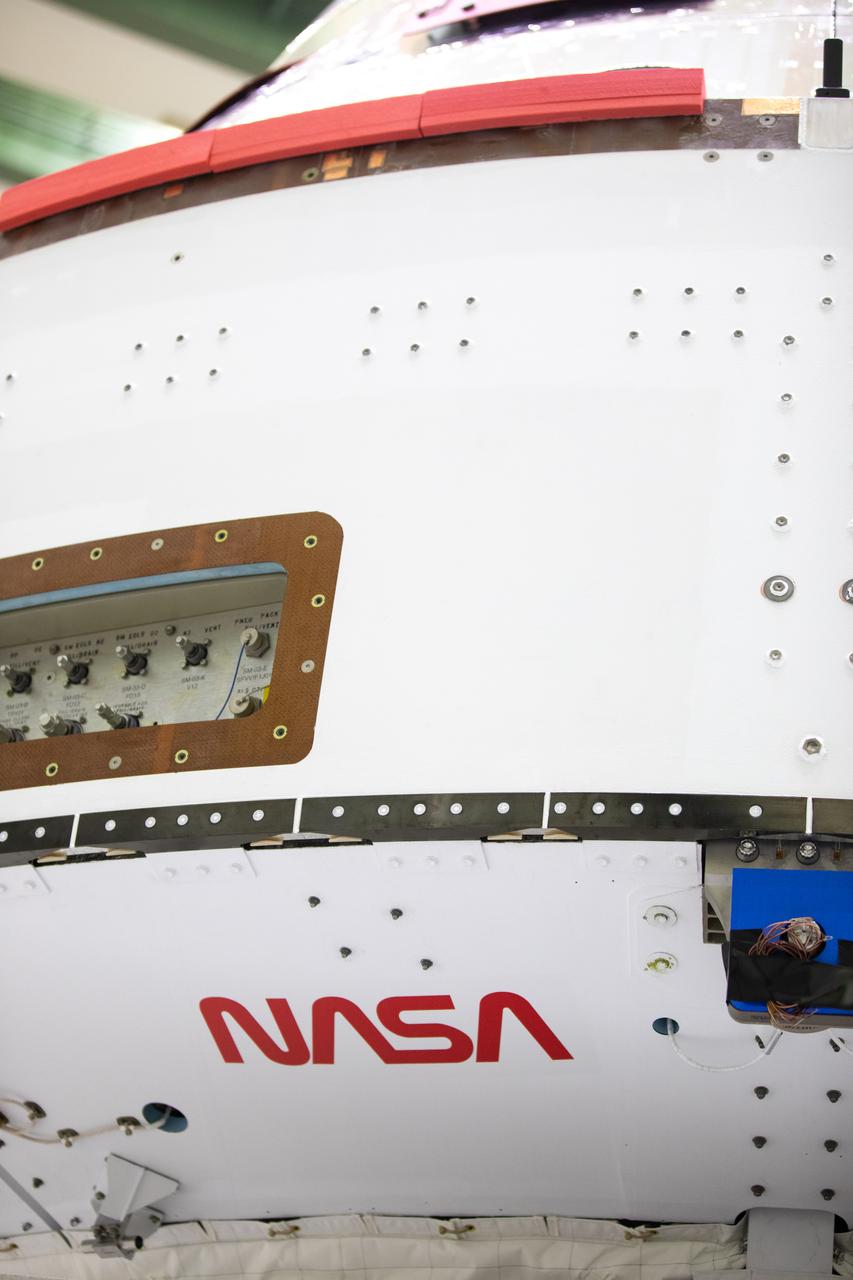
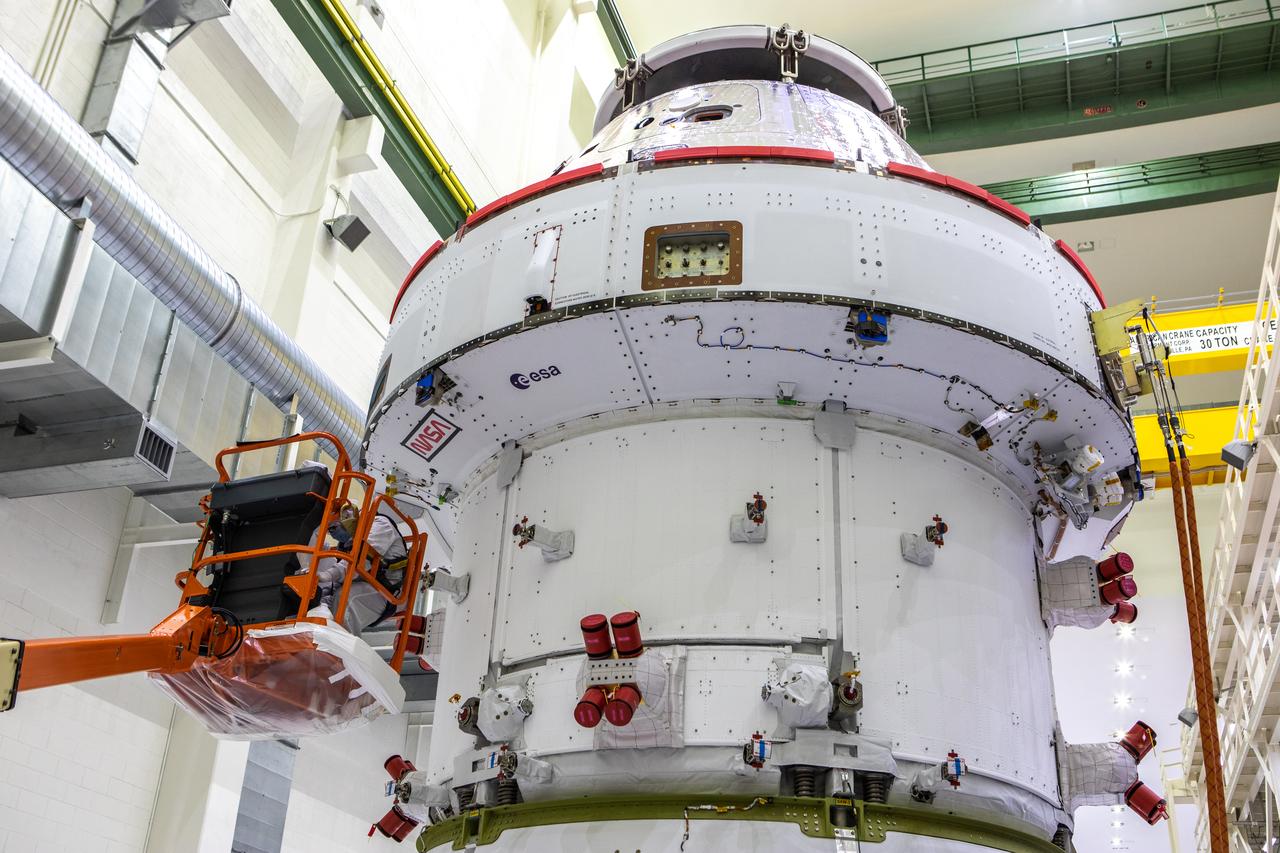
Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at Kennedy Space Center, NASA’s iconic “worm” logo has been added to the aft wall of Orion’s crew module adapter ahead of NASA’s Artemis I mission. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for installation of the solar array wings on Sept. 23, 2020. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
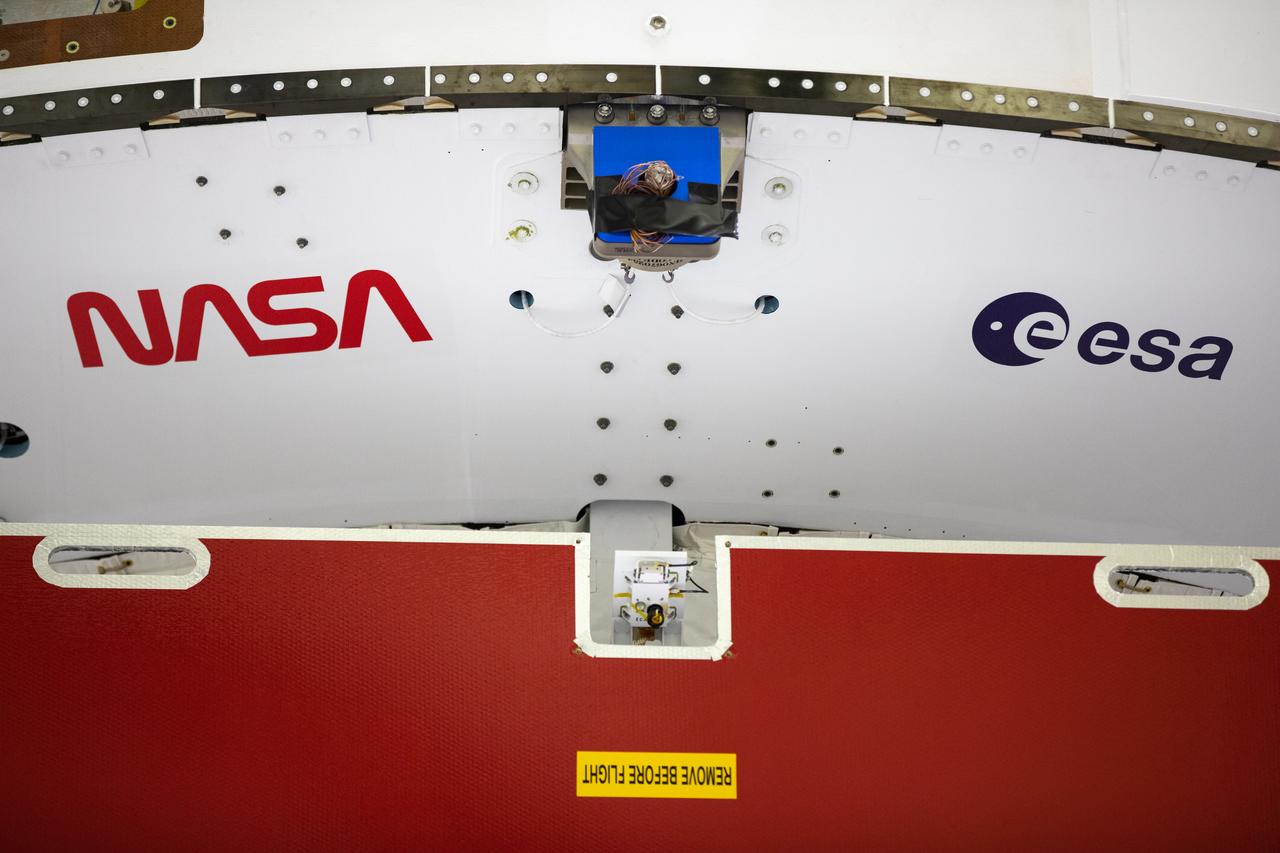

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at Kennedy Space Center, NASA’s iconic “worm” logo and European Space Agency (ESA) logo have been added to the aft wall of Orion’s crew module adapter ahead of NASA’s Artemis I mission. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for installation of the solar array wings on Sept. 23, 2020. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
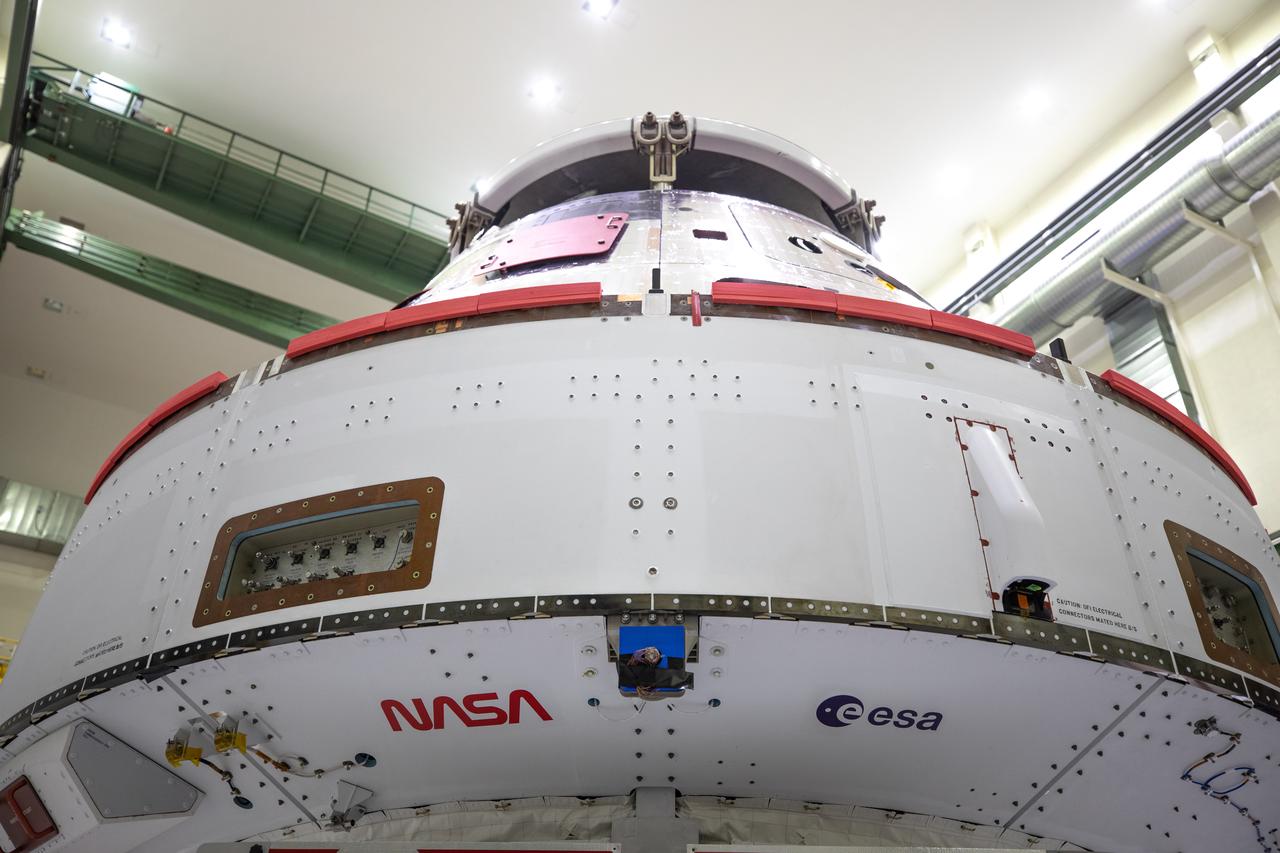

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at Kennedy Space Center, NASA’s iconic “worm” logo and European Space Agency (ESA) logo have been added to the aft wall of Orion’s crew module adapter ahead of NASA’s Artemis I mission. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for installation of the solar array wings on Sept. 23, 2020. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at Kennedy Space Center, NASA’s iconic “worm” logo and European Space Agency (ESA) logo have been added to the aft wall of Orion’s crew module adapter ahead of NASA’s Artemis I mission. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for installation of the solar array wings on Sept. 23, 2020. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
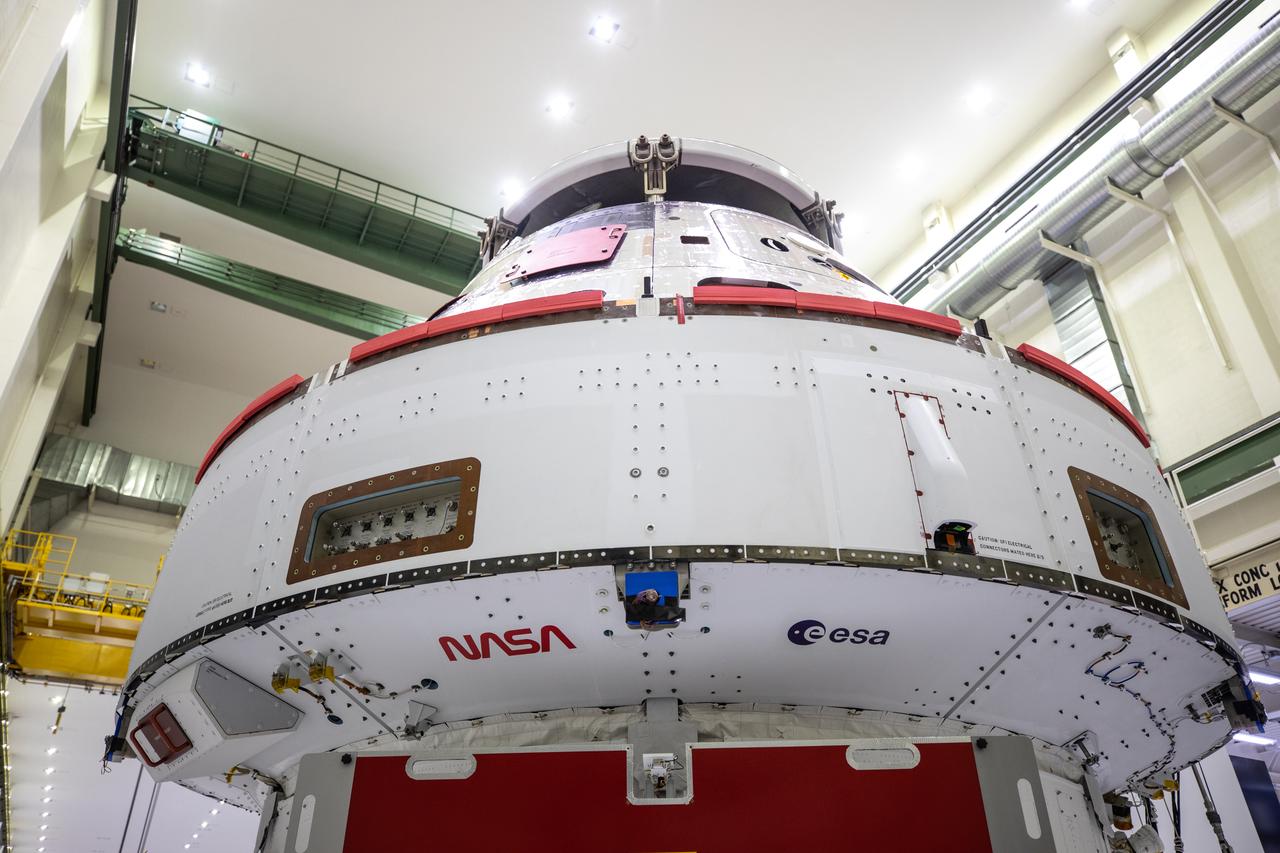

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at Kennedy Space Center, NASA’s iconic “worm” logo and European Space Agency (ESA) logo have been added to the aft wall of Orion’s crew module adapter ahead of NASA’s Artemis I mission. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for installation of the solar array wings on Sept. 23, 2020. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
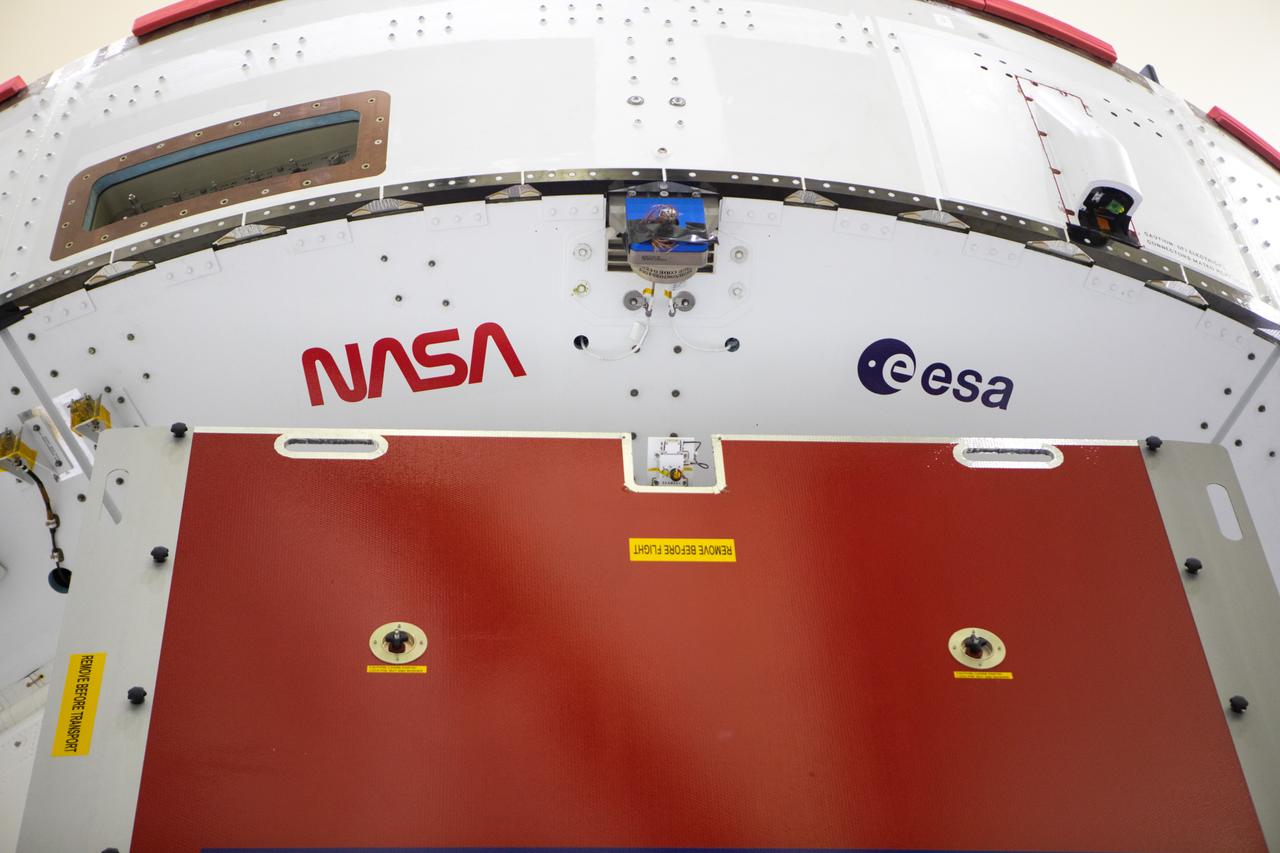

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at Kennedy Space Center, NASA’s iconic “worm” logo and European Space Agency (ESA) logo have been added to the aft wall of Orion’s crew module adapter ahead of NASA’s Artemis I mission. Originally created by the firm of Danne & Blackburn, the “worm” logo’s bold, sleek design was officially introduced in 1975 and was incorporated into many of the agency’s next-generation programs. It was retired in 1992, but has made a comeback in 2020 as the agency ushers in a new, modern era of human spaceflight. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for installation of the solar array wings on Sept. 23, 2020. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
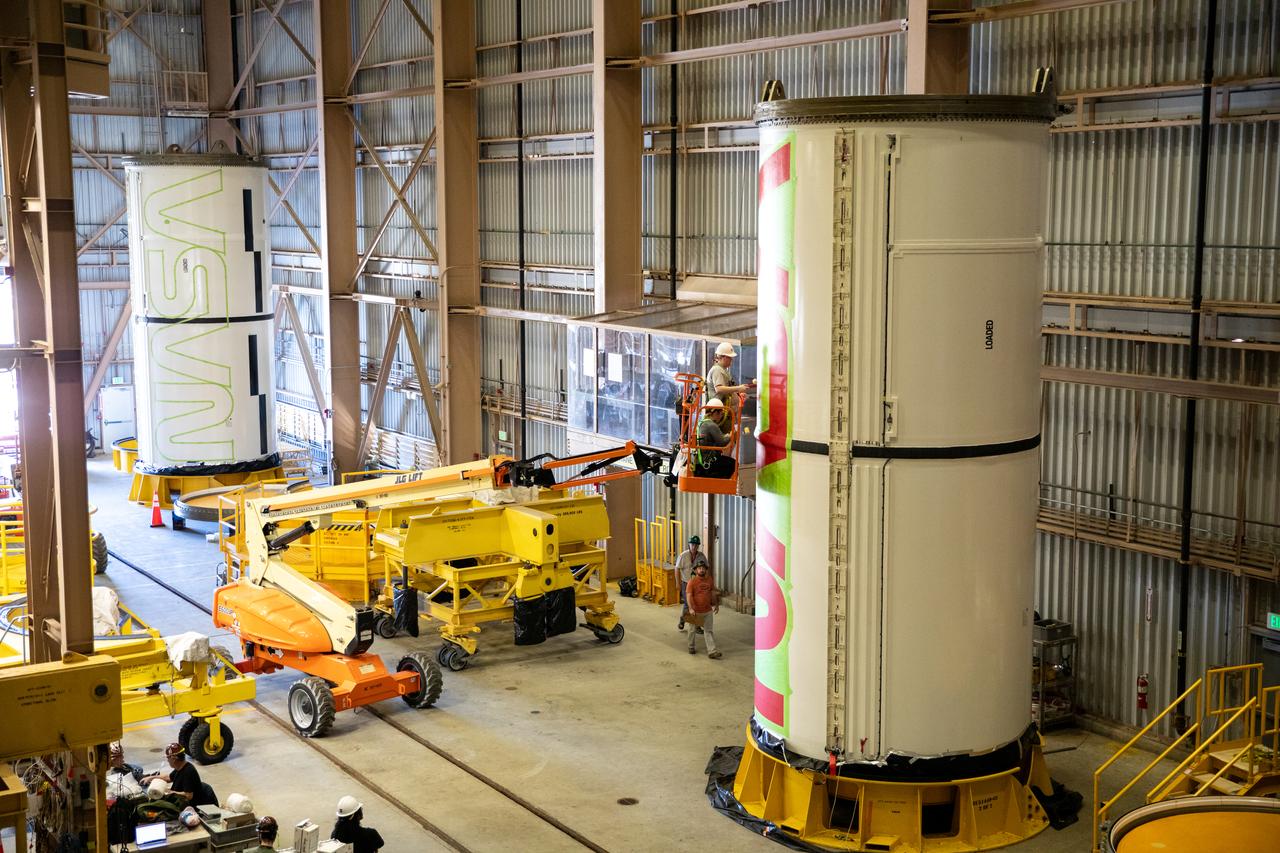

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) paint the bright red NASA “worm” logo on the side of an Artemis II solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
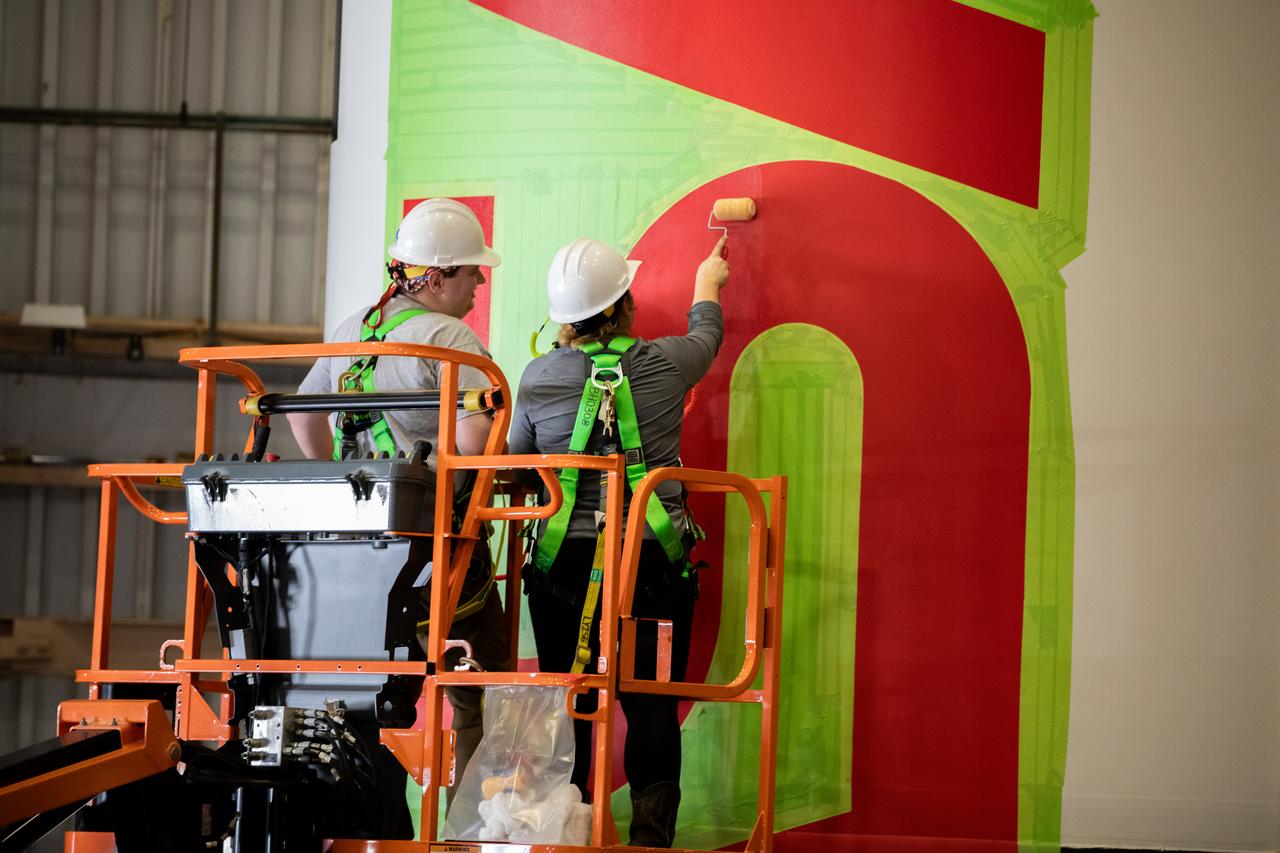

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) paint the bright red NASA “worm” logo on the side of an Artemis II solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
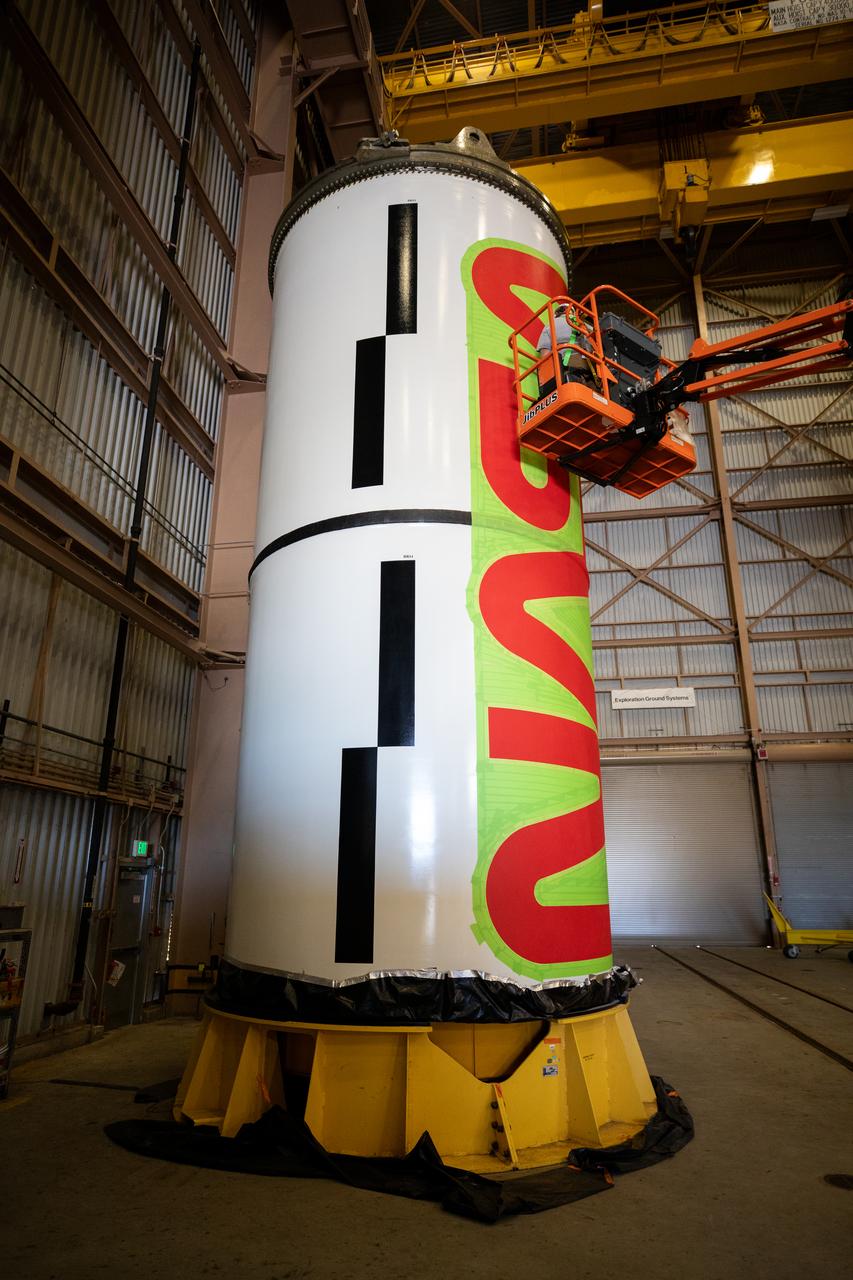

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) paint the bright red NASA “worm” logo on the side of an Artemis II solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
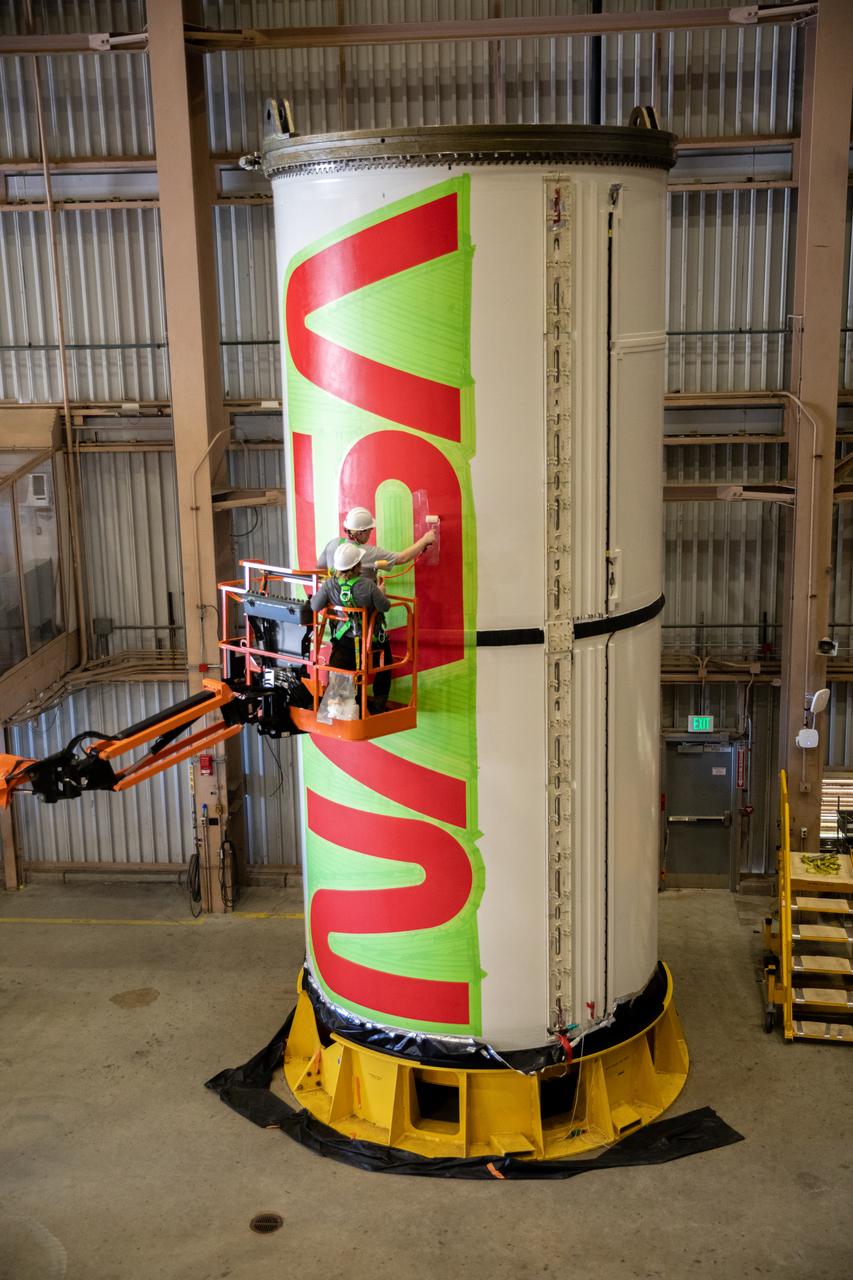

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) paint the bright red NASA “worm” logo on the side of an Artemis II solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
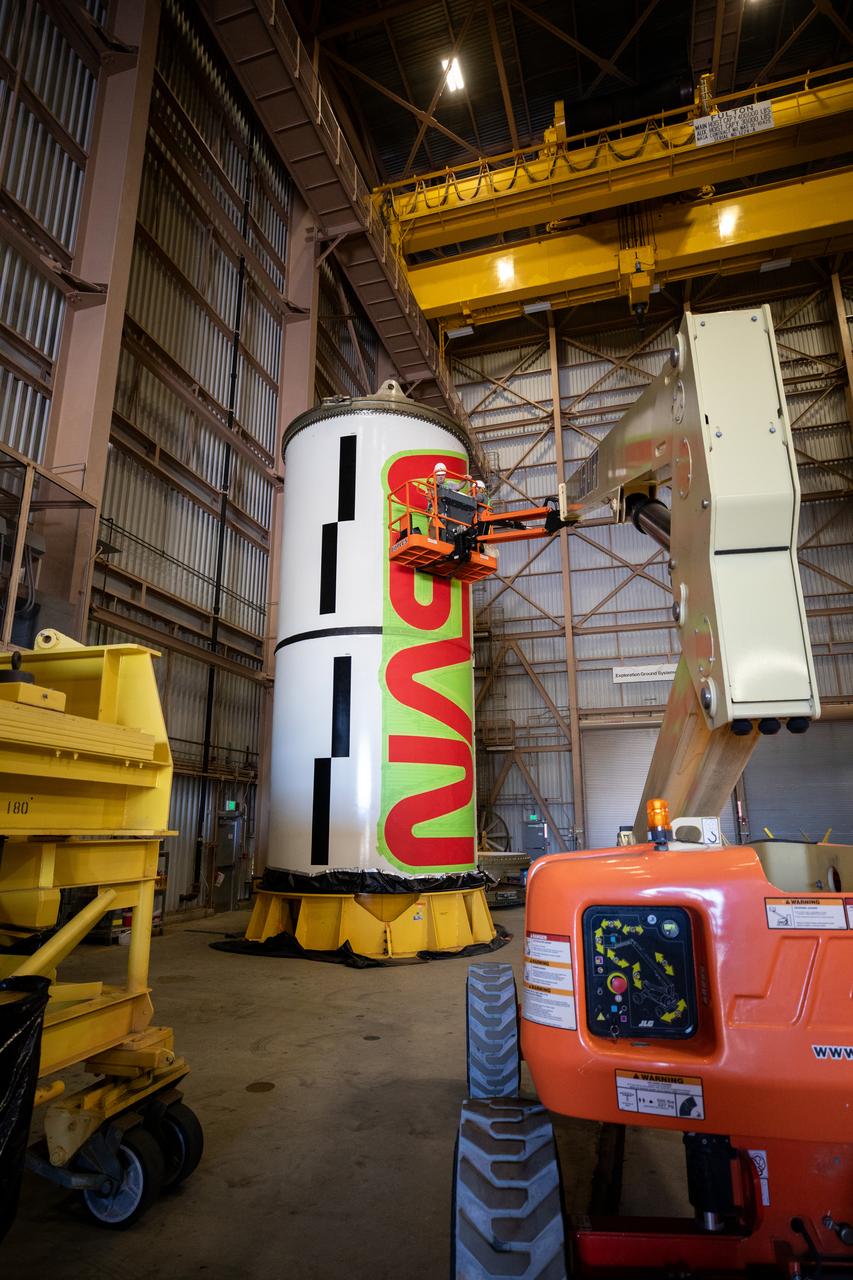

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) paint the bright red NASA “worm” logo on the side of an Artemis II solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
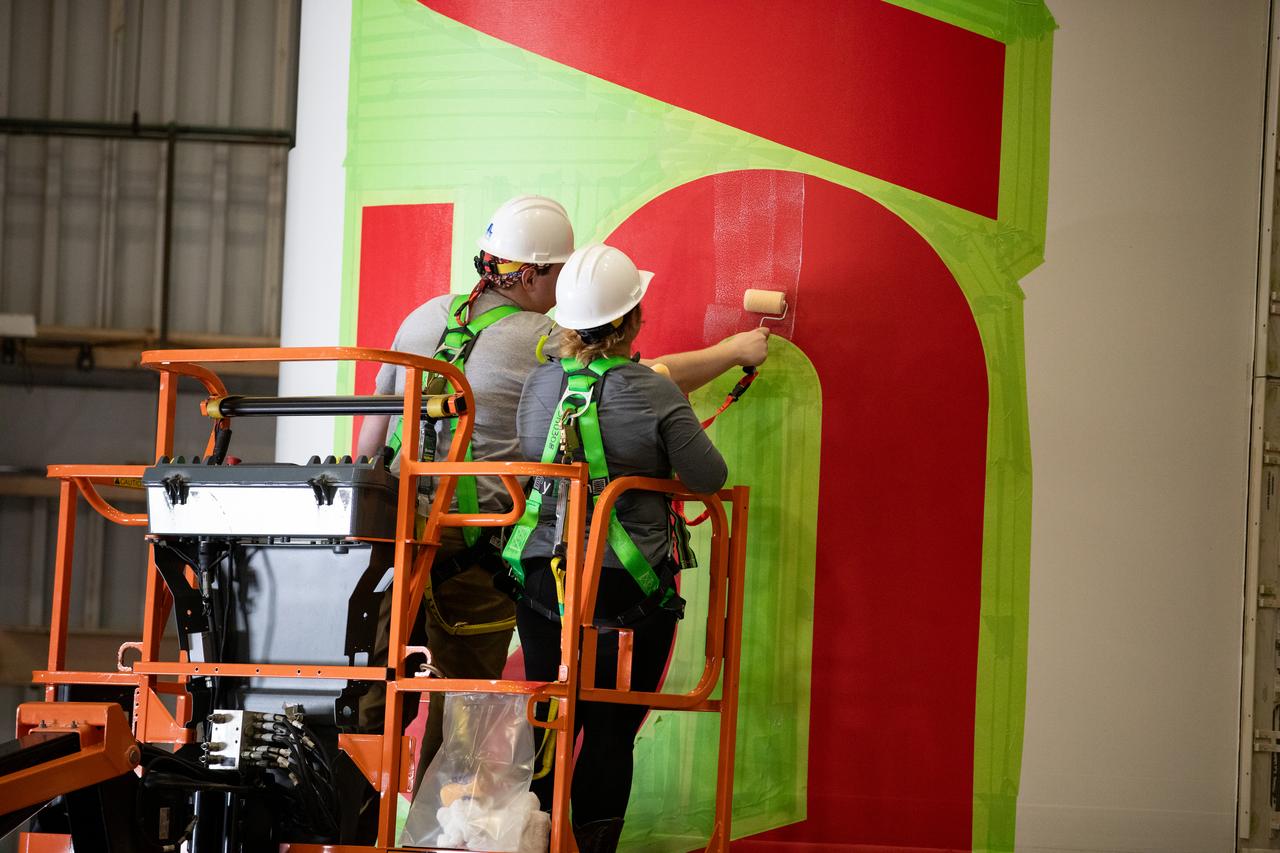

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) paint the bright red NASA “worm” logo on the side of an Artemis II solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
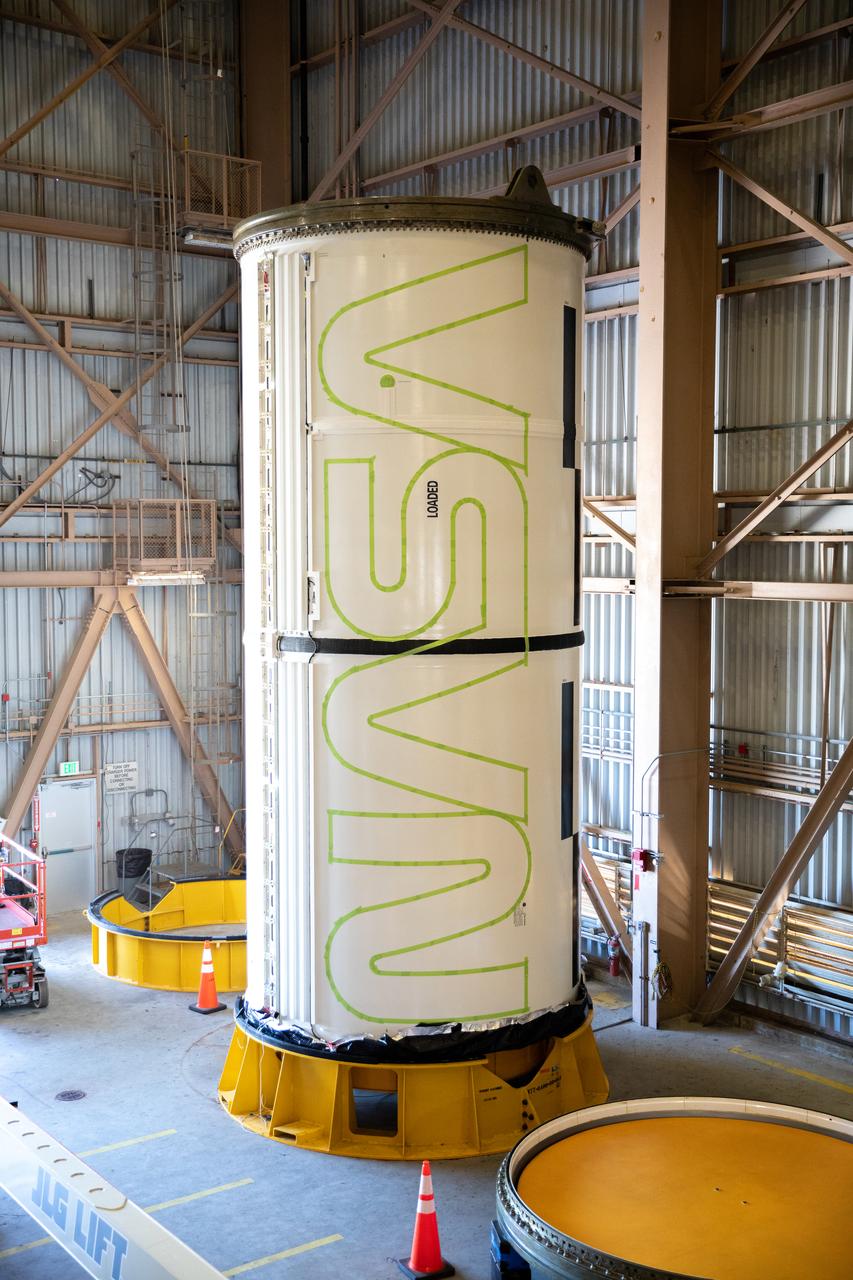

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) paint the bright red NASA “worm” logo on the side of an Artemis II solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
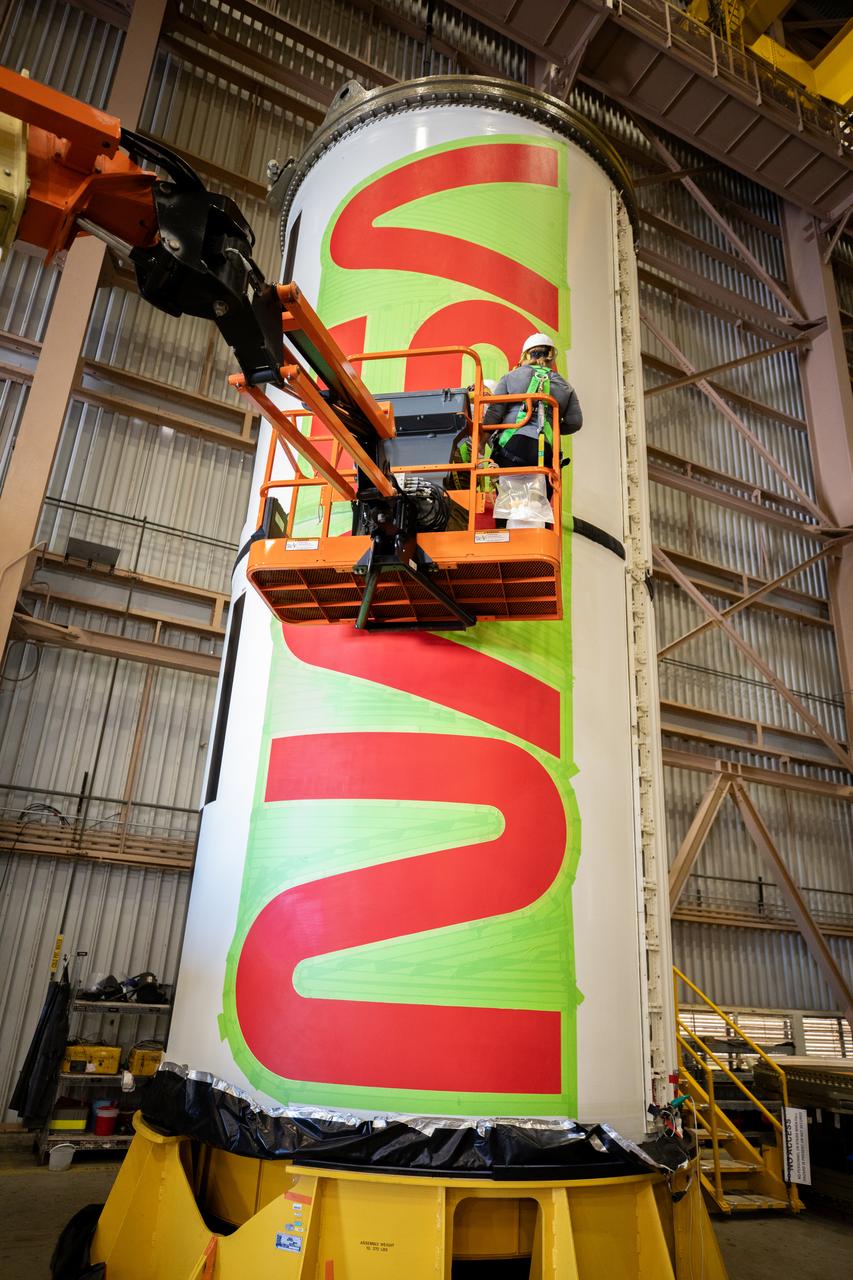

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) paint the bright red NASA “worm” logo on the side of an Artemis II solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
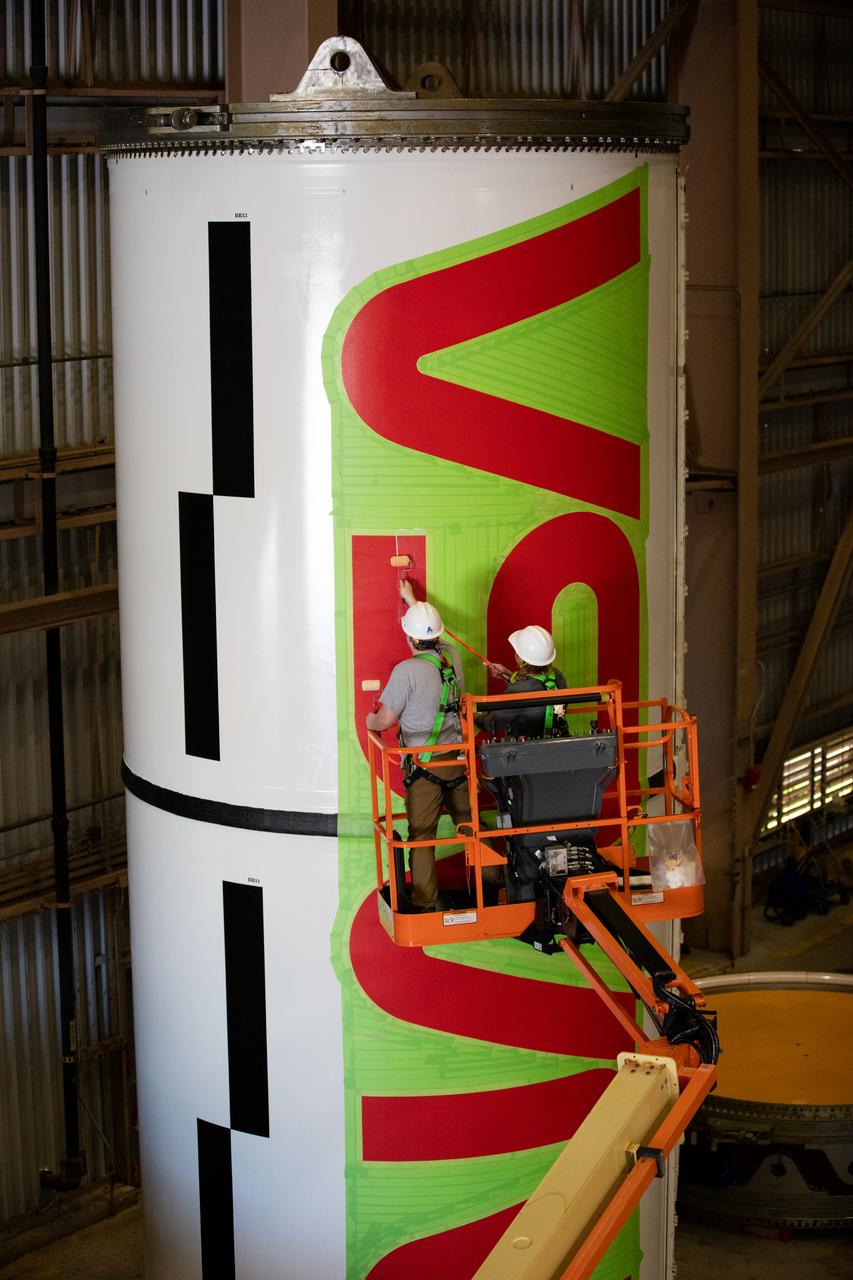

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) paint the bright red NASA “worm” logo on the side of an Artemis II solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
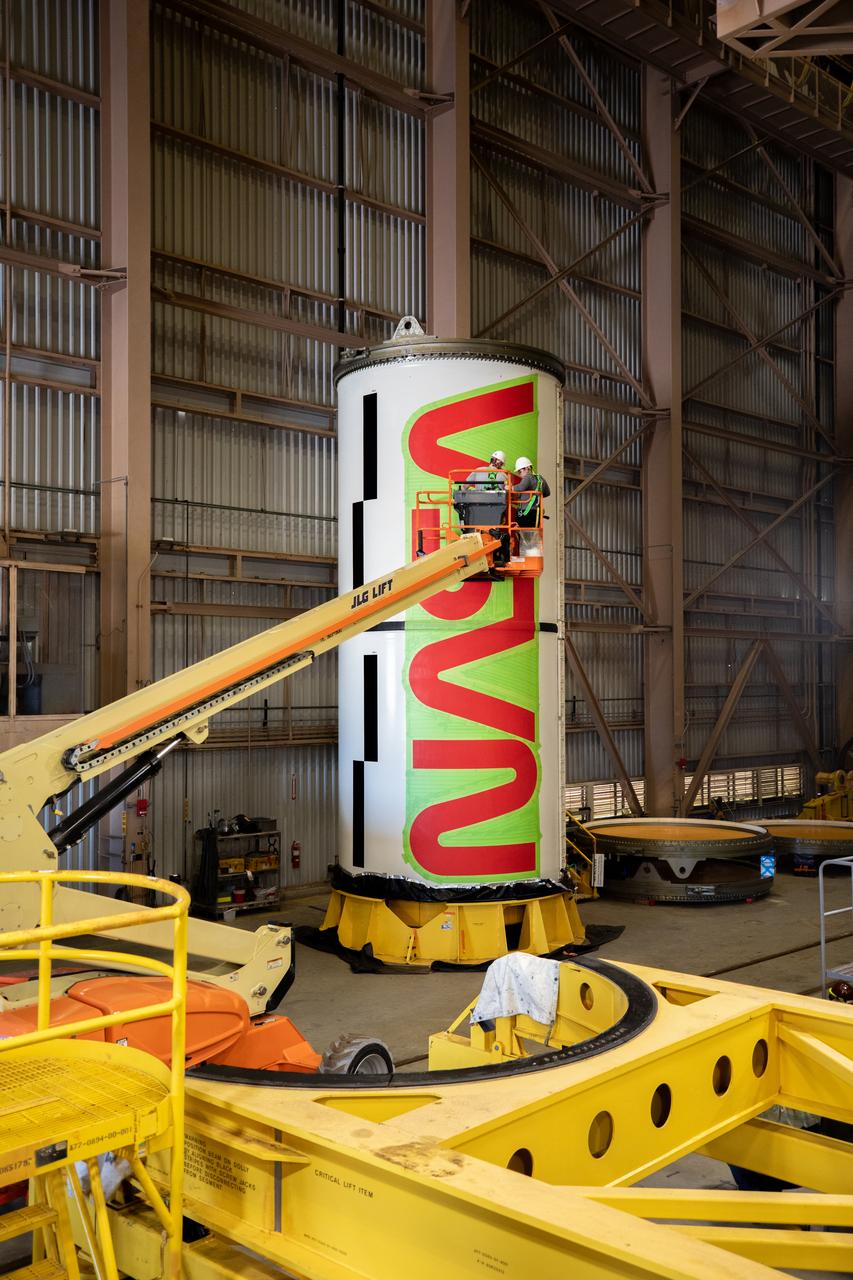

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) paint the bright red NASA “worm” logo on the side of an Artemis II solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
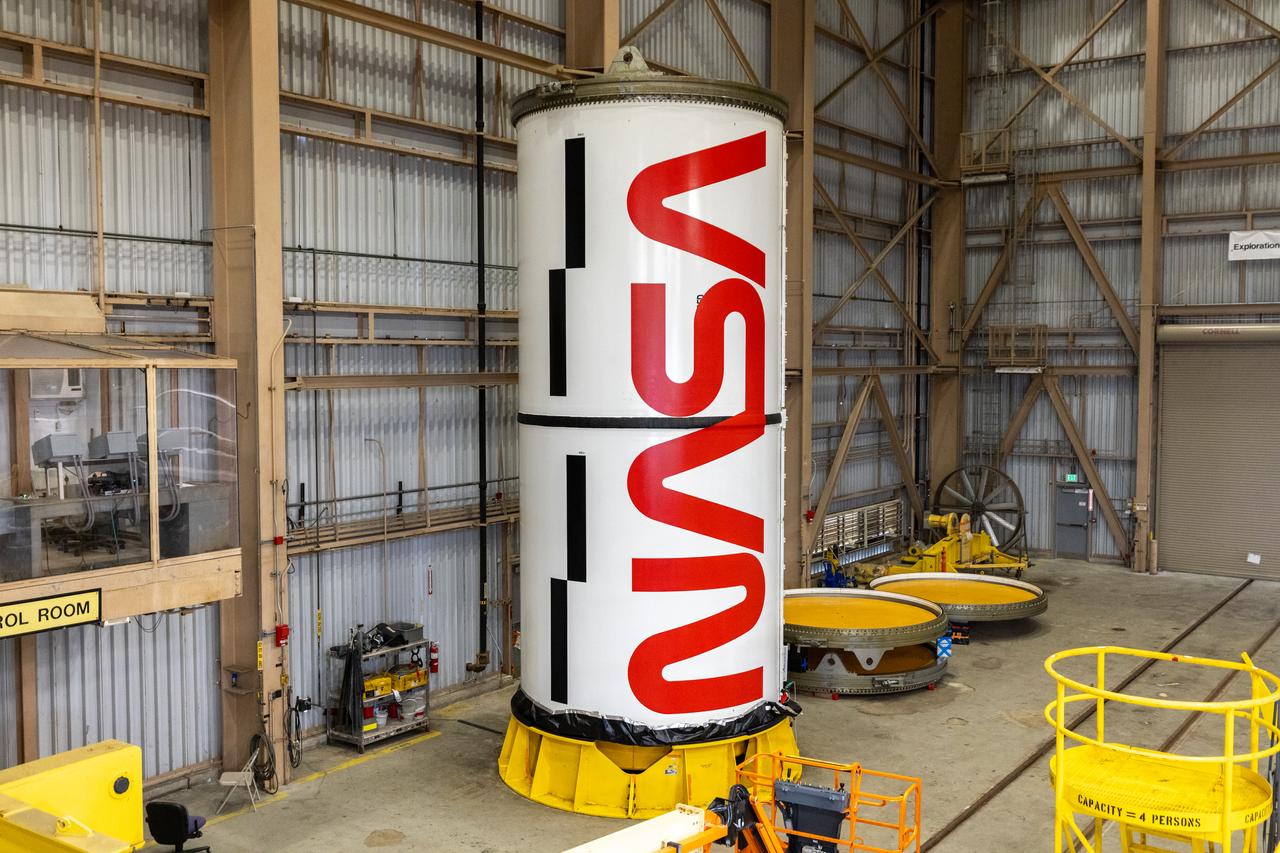

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor, Jacobs, complete the painting of the agency’s iconic “worm” logo along the side of the twin Artemis II solid rocket booster motor segments inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Feb. 16, 2024. Using a laser projector, the logo was mapped out with tape by workers with Jacobs, for the spaceport, before using two coats of red paint, plus several coats of clear primer to complete the logo that stretches 25 feet long. The booster segments will help propel the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
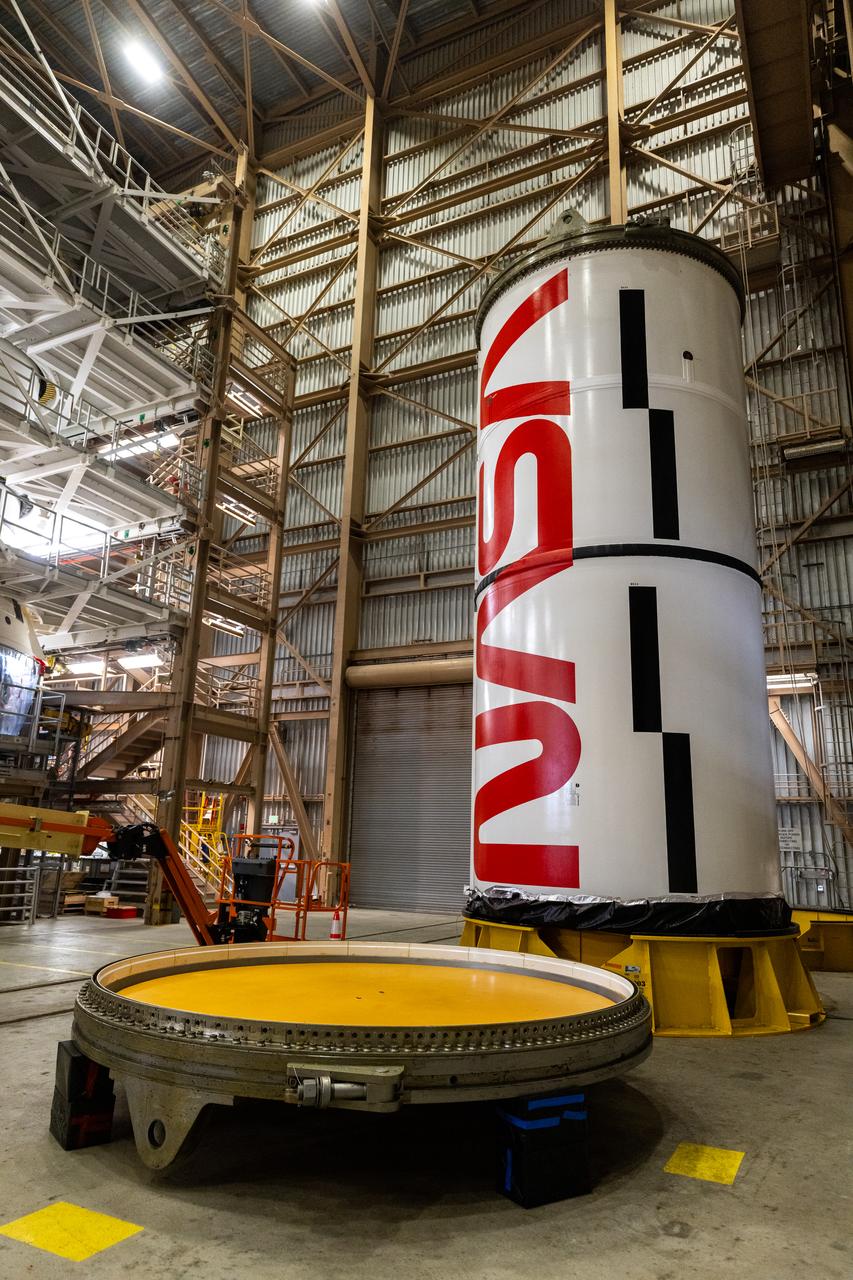

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor, Jacobs, complete the painting of the agency’s iconic “worm” logo along the side of the twin Artemis II solid rocket booster motor segments inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Feb. 16, 2024. Using a laser projector, the logo was mapped out with tape by workers with Jacobs, for the spaceport, before using two coats of red paint, plus several coats of clear primer to complete the logo that stretches 25 feet long. The booster segments will help propel the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor, Jacobs, complete the painting of the agency’s iconic “worm” logo along the side of the twin Artemis II solid rocket booster motor segments inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Feb. 16, 2024. Using a laser projector, the logo was mapped out with tape by workers with Jacobs, for the spaceport, before using two coats of red paint, plus several coats of clear primer to complete the logo that stretches 25 feet long. The booster segments will help propel the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
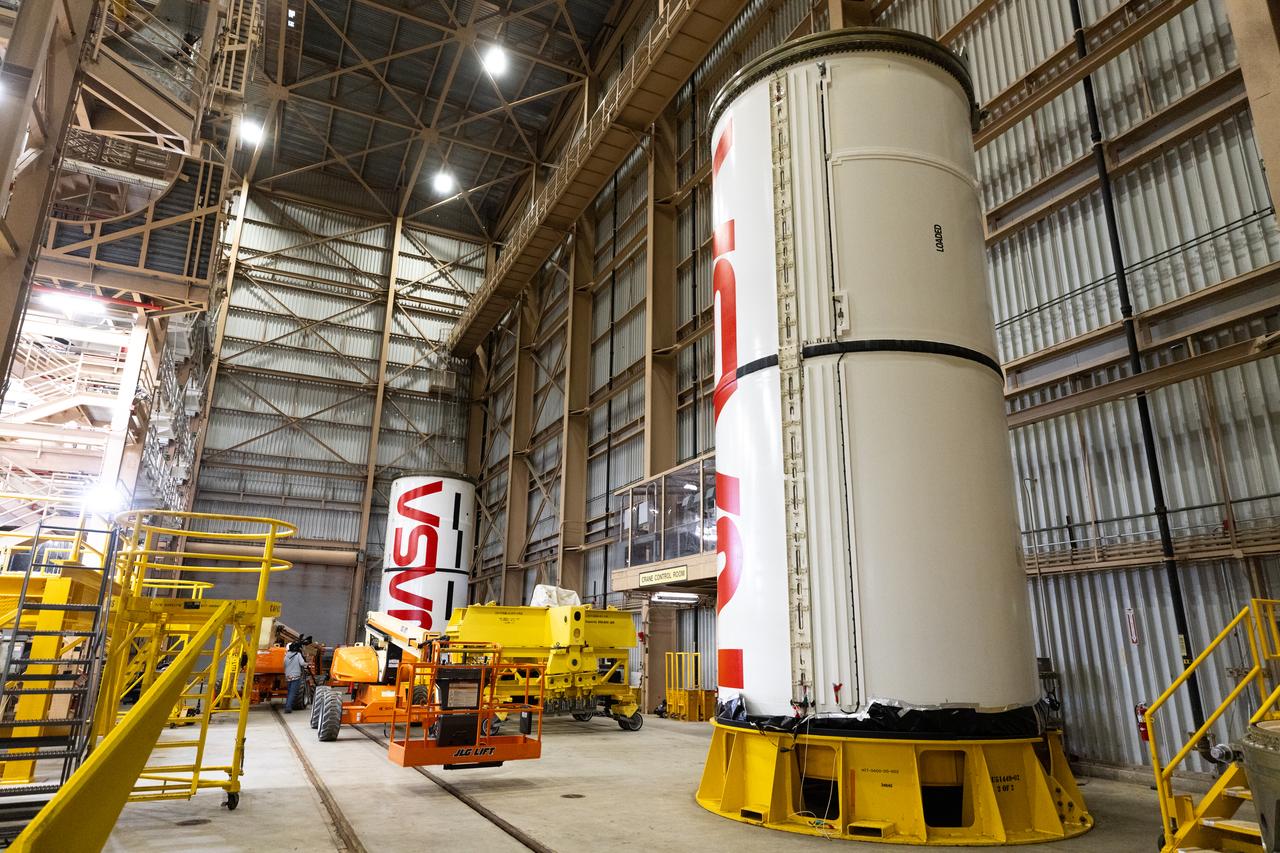

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor, Jacobs, complete the painting of the agency’s iconic “worm” logo along the side of the twin Artemis II solid rocket booster motor segments inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Feb. 16, 2024. Using a laser projector, the logo was mapped out with tape by workers with Jacobs, for the spaceport, before using two coats of red paint, plus several coats of clear primer to complete the logo that stretches 25 feet long. The booster segments will help propel the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
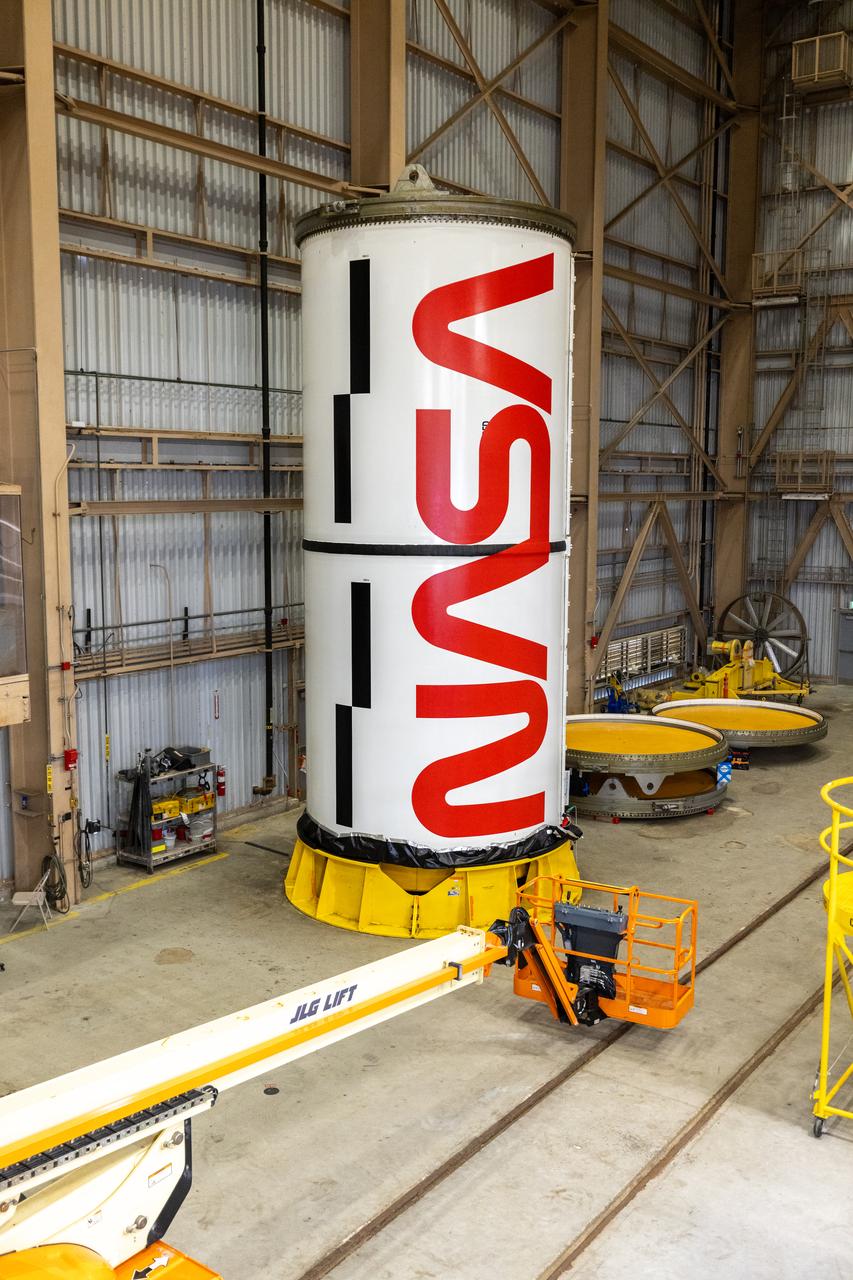

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor, Jacobs, complete the painting of the agency’s iconic “worm” logo along the side of the twin Artemis II solid rocket booster motor segments inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Feb. 16, 2024. Using a laser projector, the logo was mapped out with tape by workers with Jacobs, for the spaceport, before using two coats of red paint, plus several coats of clear primer to complete the logo that stretches 25 feet long. The booster segments will help propel the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
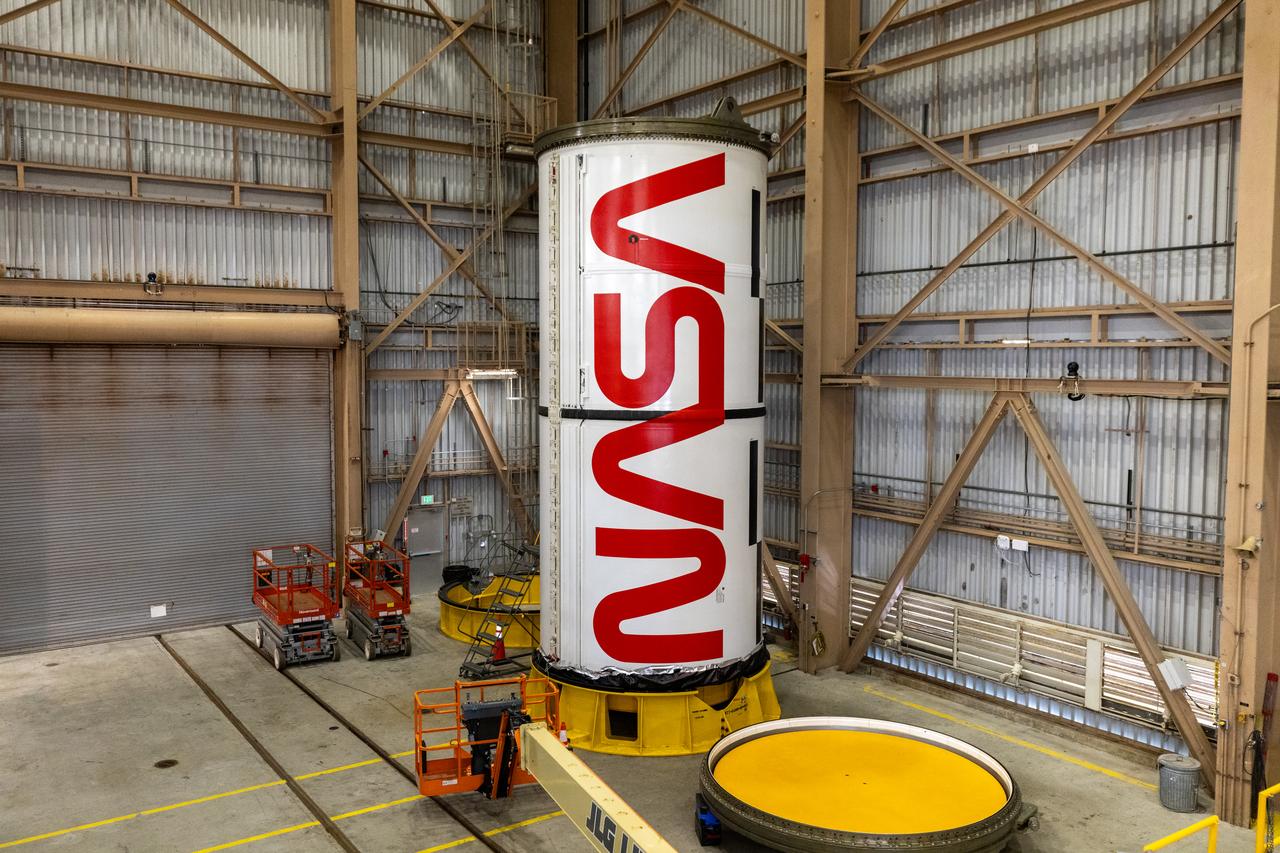

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems and primary contractor, Jacobs, complete the painting of the agency’s iconic “worm” logo along the side of the twin Artemis II solid rocket booster motor segments inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Feb. 16, 2024. Using a laser projector, the logo was mapped out with tape by workers with Jacobs, for the spaceport, before using two coats of red paint, plus several coats of clear primer to complete the logo that stretches 25 feet long. The booster segments will help propel the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.

Inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, application of the NASA worm logo is complete on the first of two solid rocket boosters for the Artemis I Space Launch System on March 14, 2022. The SLS and Orion spacecraft are stacked in the high bay and ready for rollout to Launch Complex 39B for a wet dress rehearsal. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In later missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.

Inside High Bay 3 of the Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, application of the NASA worm logo is complete on the second of two solid rocket boosters for the Artemis I Space Launch System on March 14, 2022. The SLS and Orion spacecraft are stacked in the high bay and ready for rollout to Launch Complex 39B for a wet dress rehearsal. Artemis I will be the first integrated test of the SLS and Orion spacecraft. In later missions, NASA will land the first woman and the first person of color on the surface of the Moon, paving the way for a long-term lunar presence and serving as a steppingstone on the way to Mars.
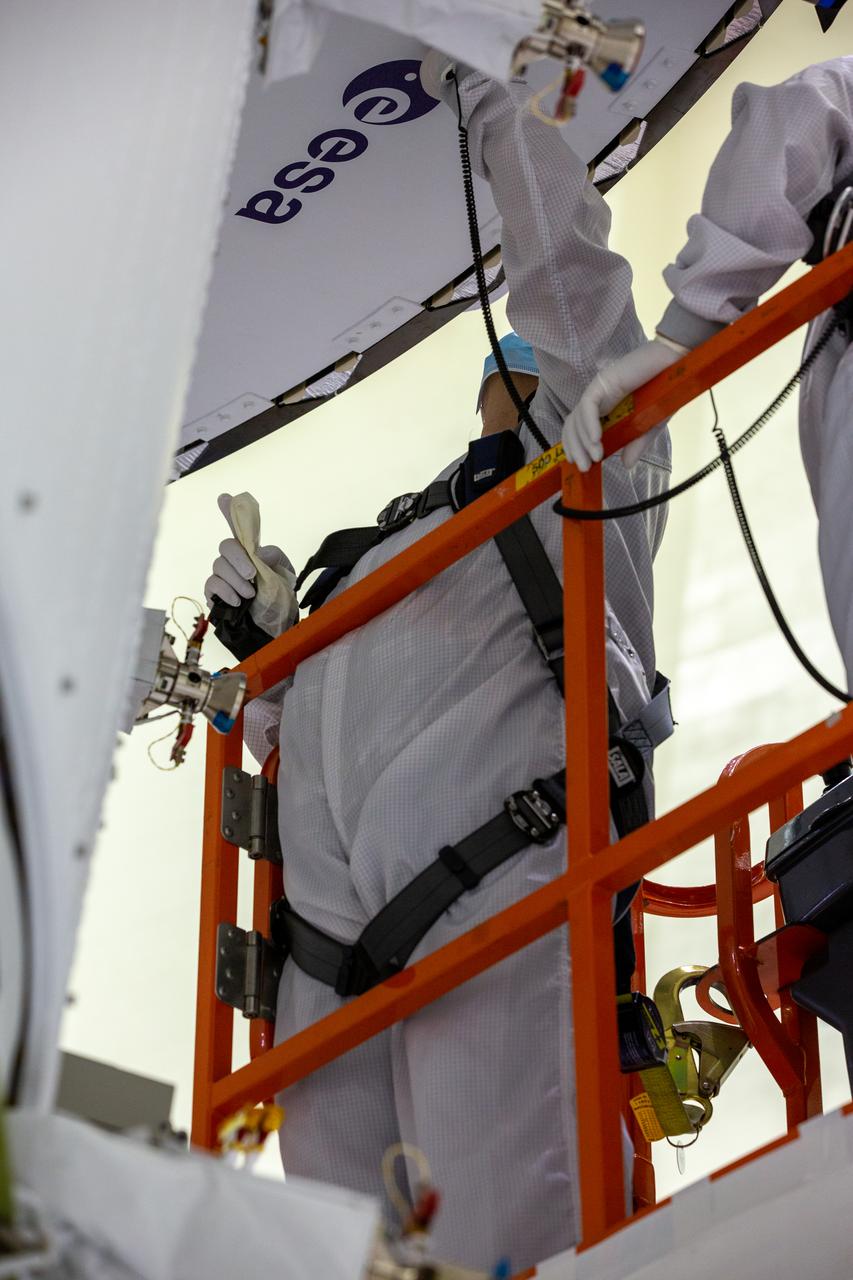

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at Kennedy Space Center, ASRC technician Frank Pelkey works to adhere the European Space Agency (ESA) logo to the aft wall of Orion’s crew module adapter on Sept. 20, 2020, ahead of NASA’s Artemis I mission. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
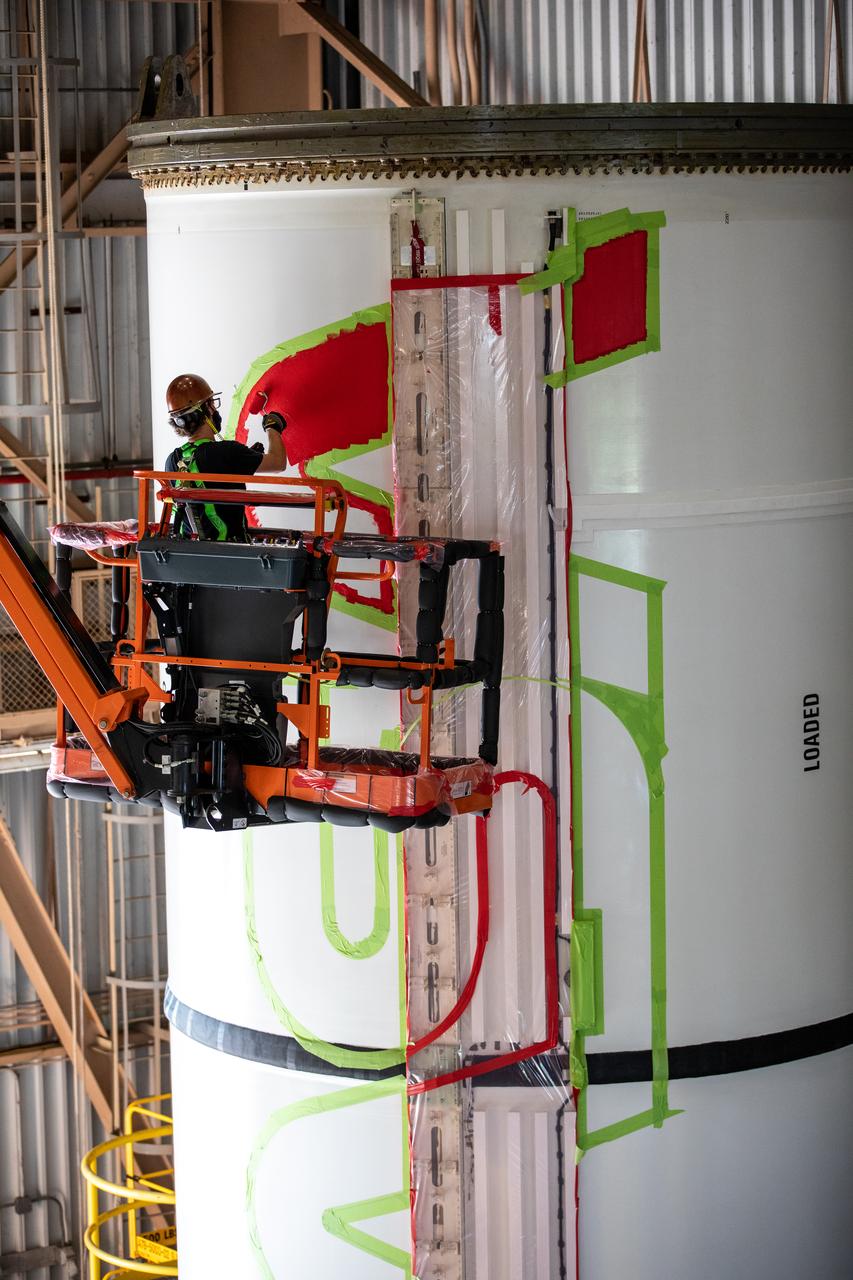

A worker with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) applies bright red paint to the agency’s “worm” logo taking shape on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
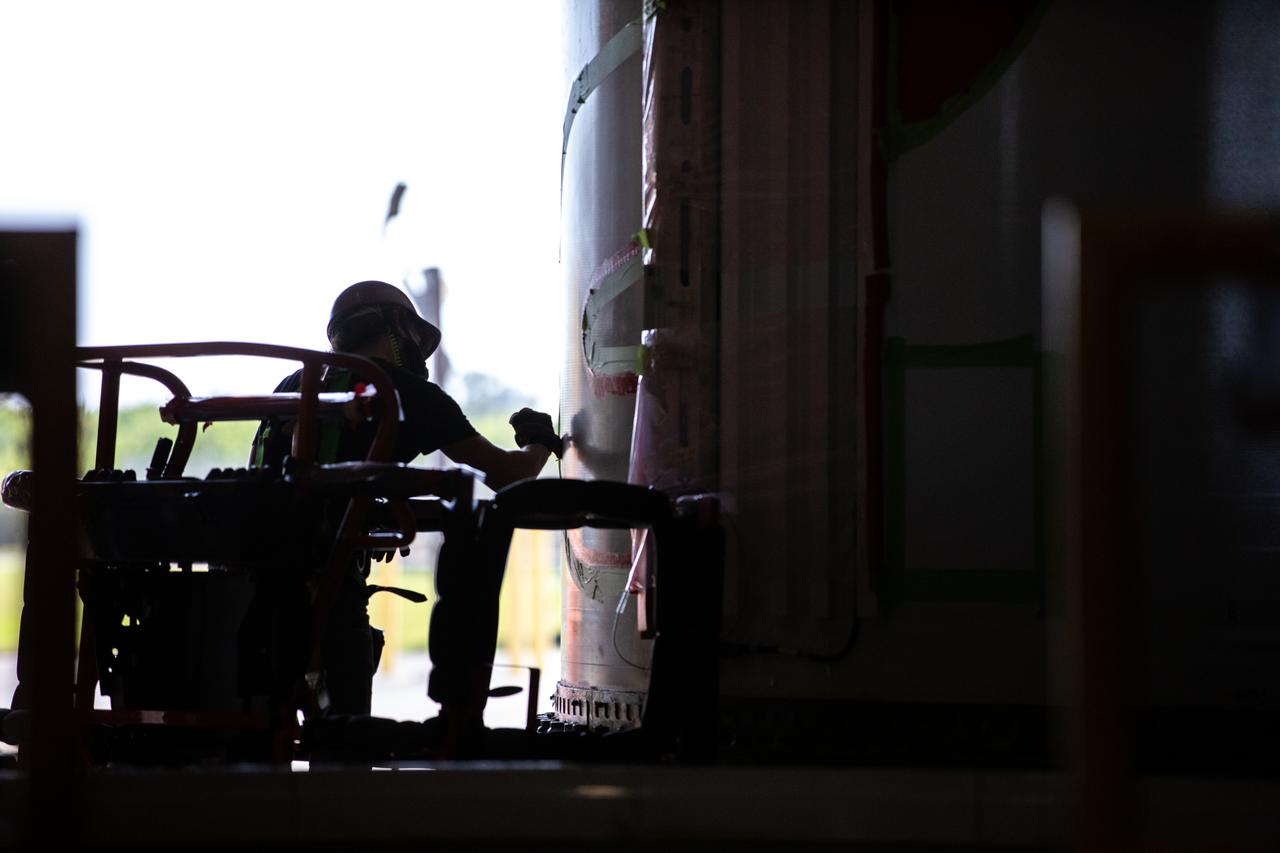

Silhouetted against the bright Florida sunlight outside, a worker with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) applies bright red paint to the agency’s “worm” logo taking shape on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
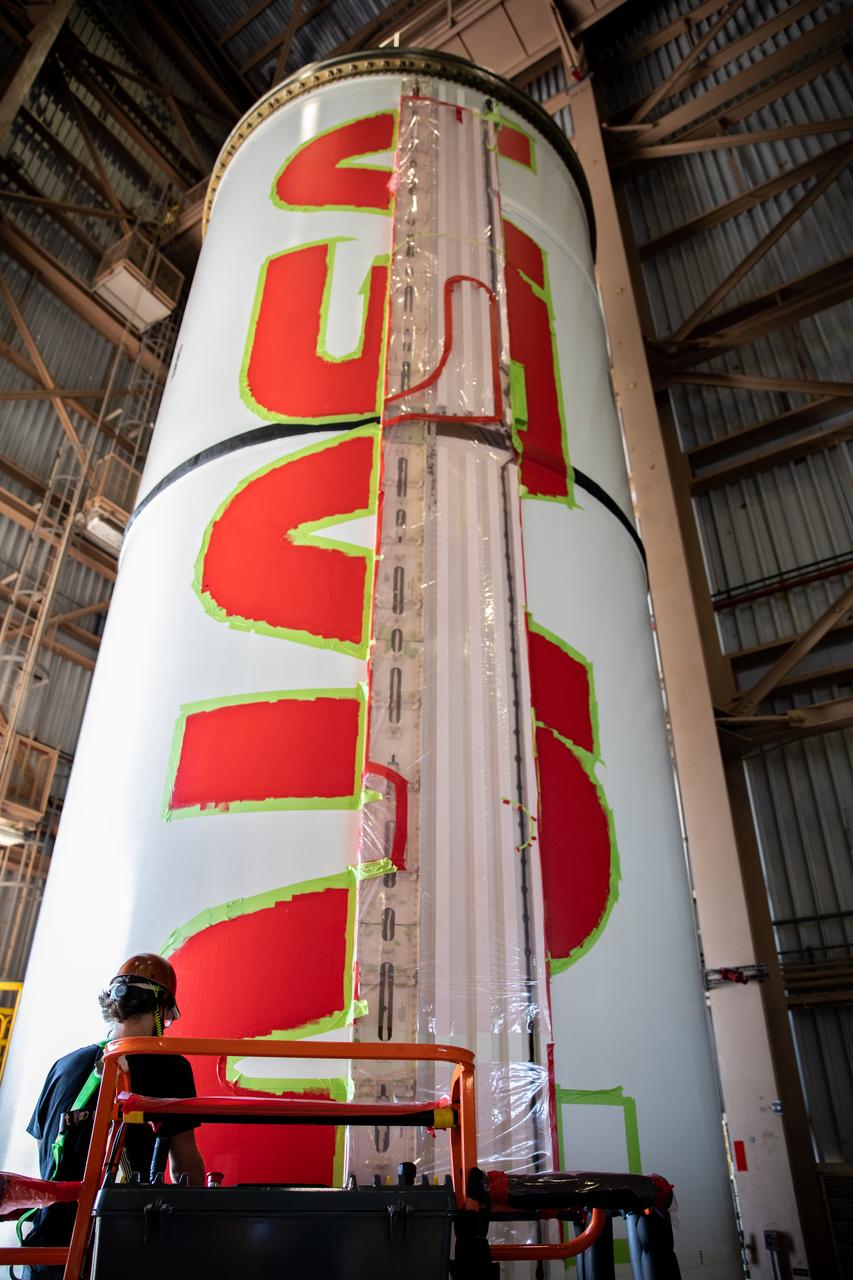

A worker with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) finishes the first coat of the bright red “worm” logo taking shape on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
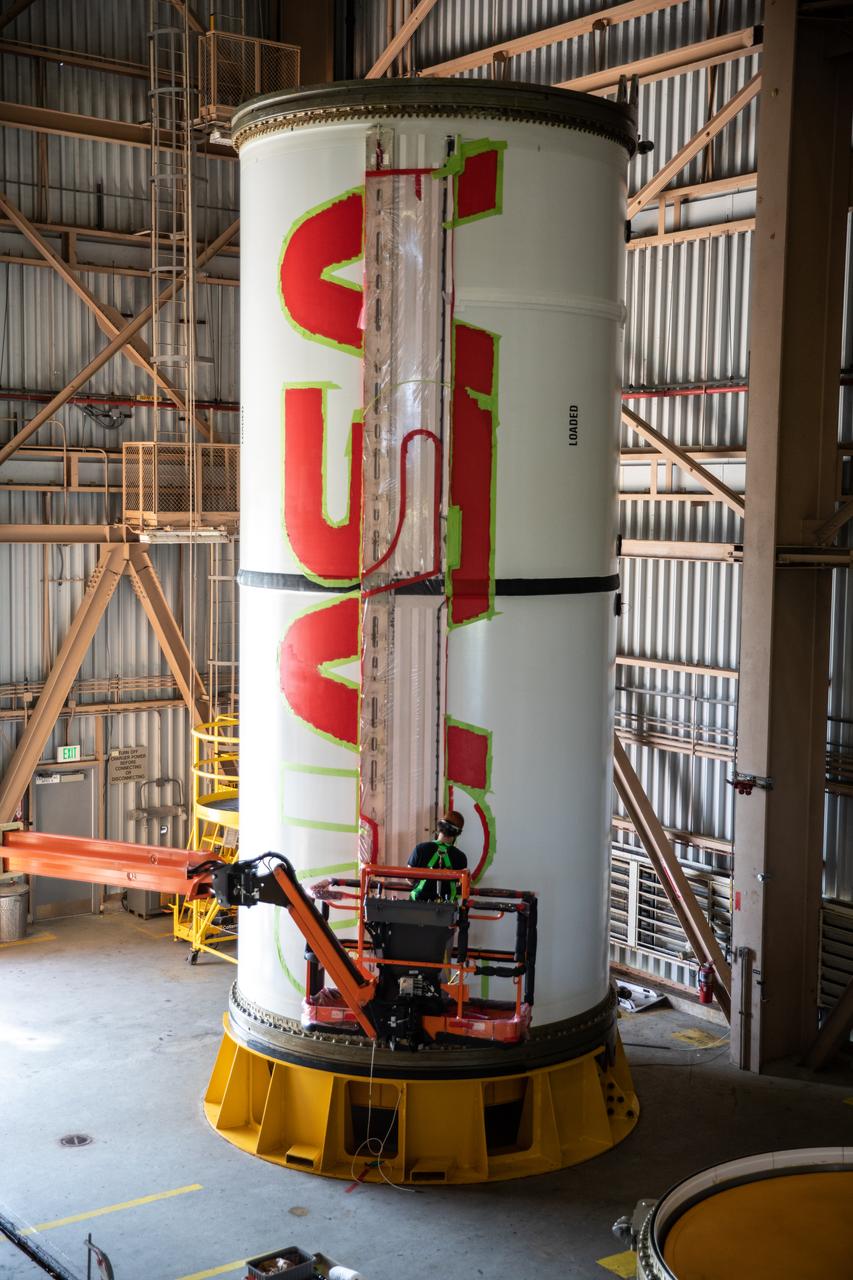

A worker with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) finishes the first coat of the bright red “worm” logo taking shape on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) use a laser projector and green tape to mask off the shape of the agency’s “worm” logo on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Sept. 3, 2020. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
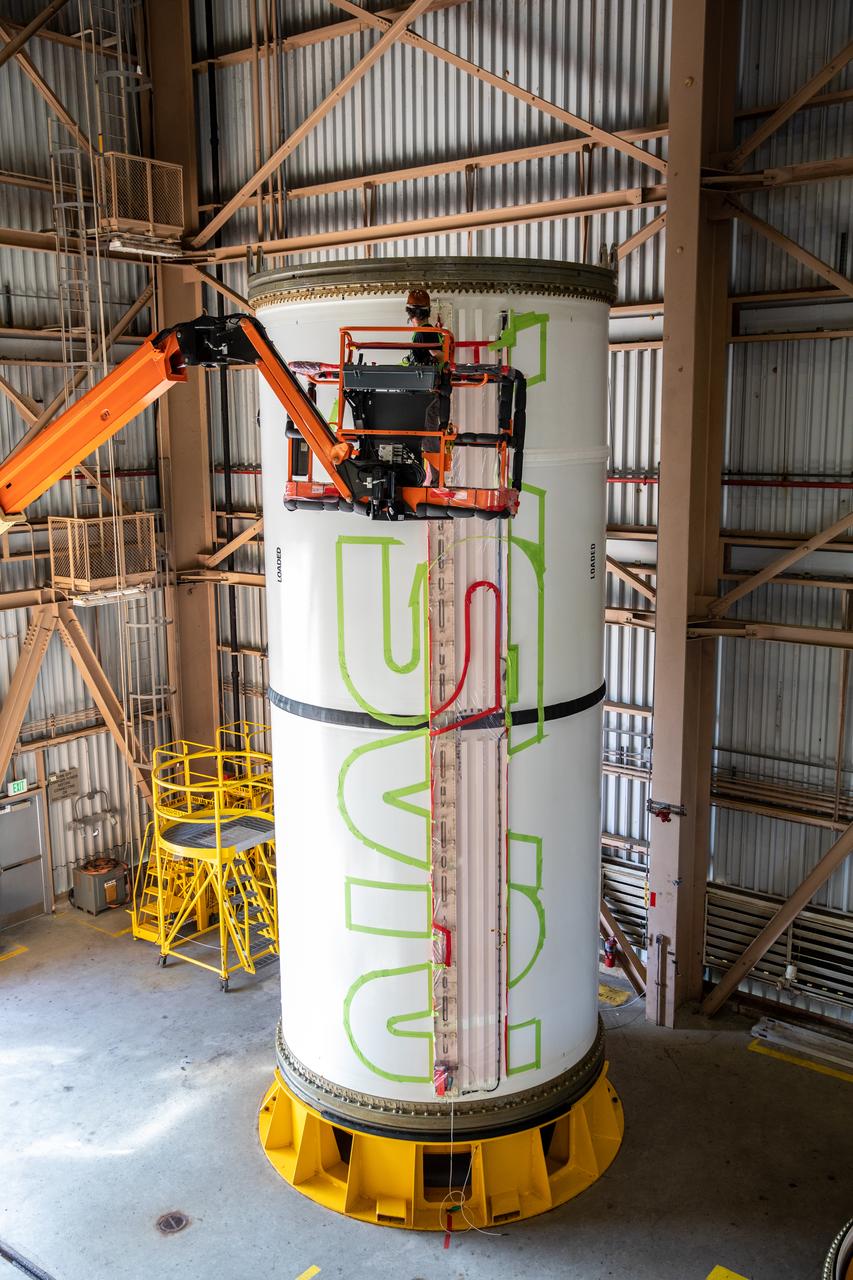

A worker with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) applies bright red paint to the agency’s “worm” logo taking shape on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
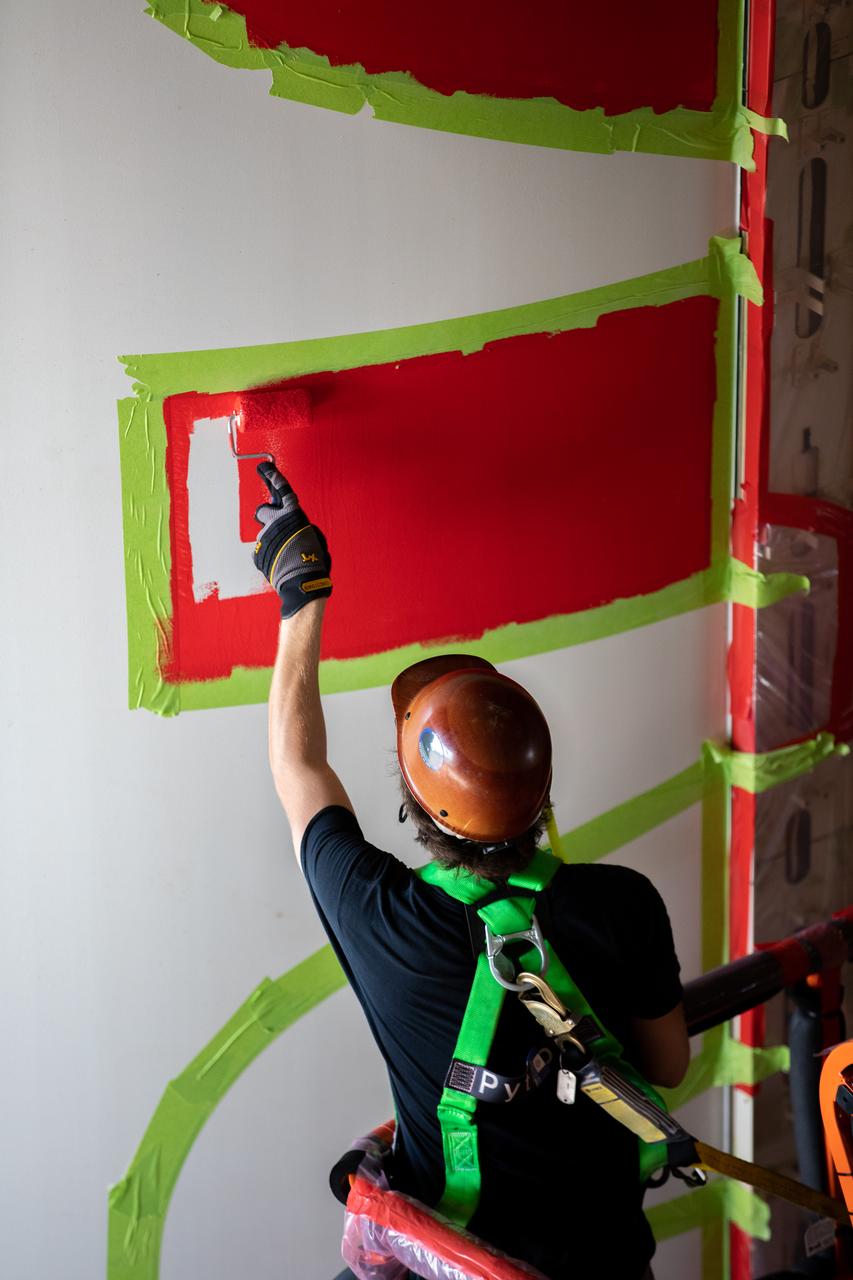

A worker with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) applies bright red paint to the agency’s “worm” logo taking shape on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
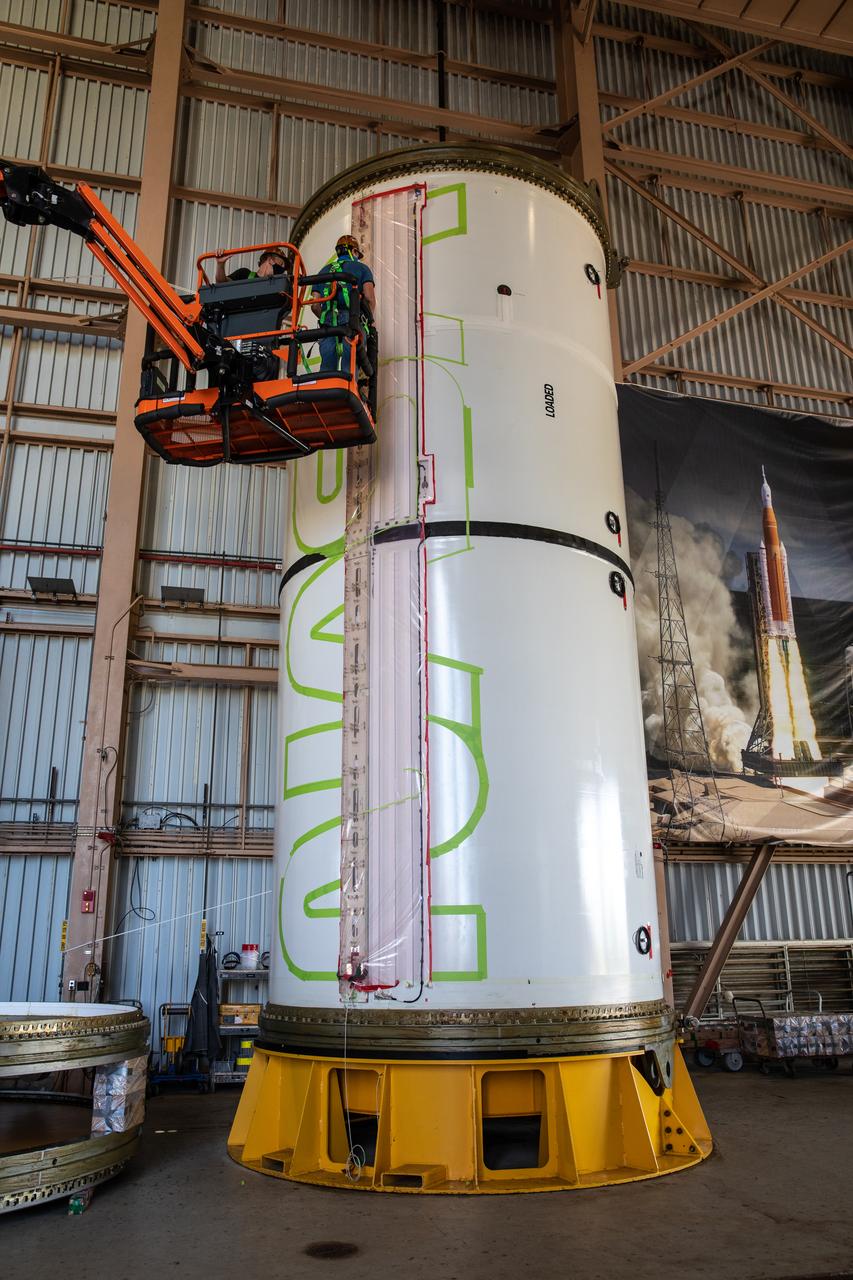

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) use a laser projector and green tape to mask off the shape of the agency’s “worm” logo on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Sept. 3, 2020. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
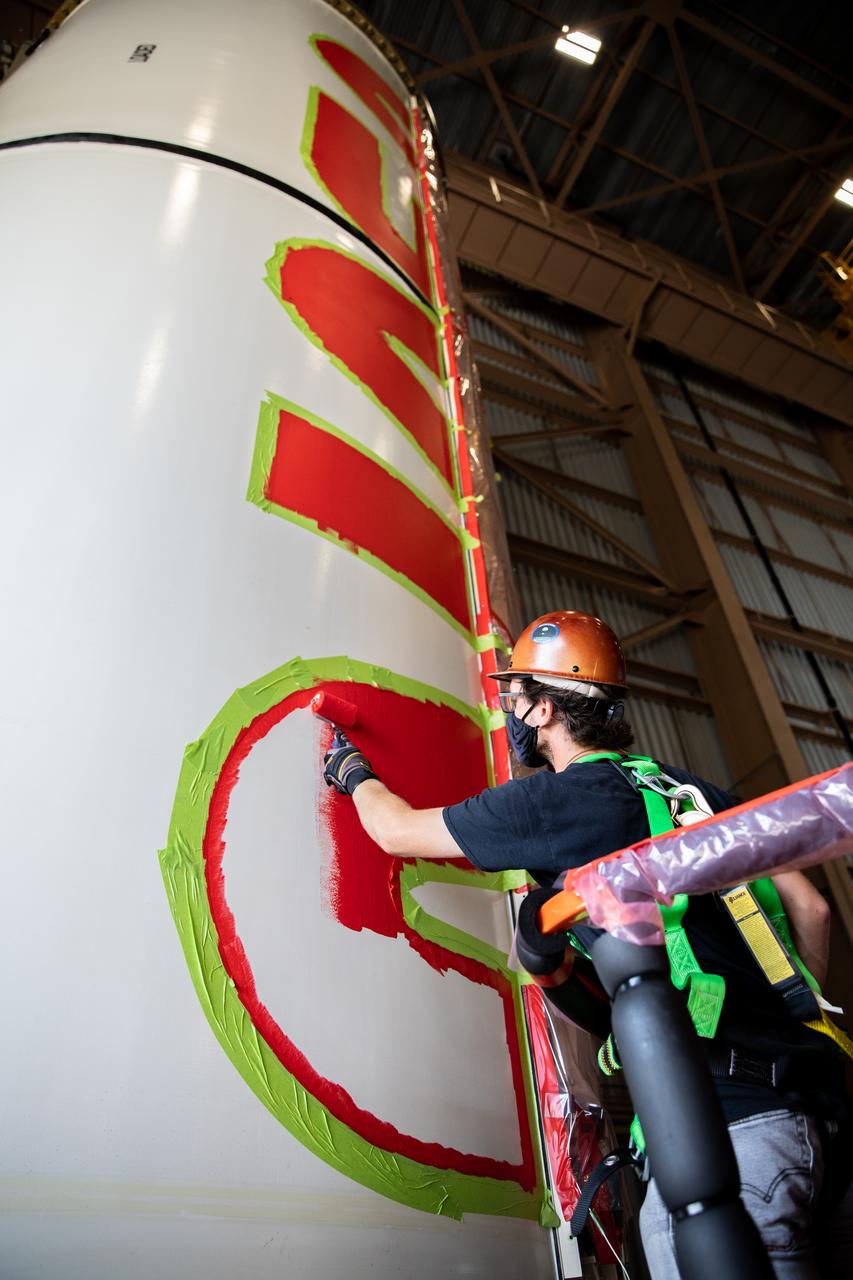

A worker with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) finishes the first coat of the bright red “worm” logo taking shape on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
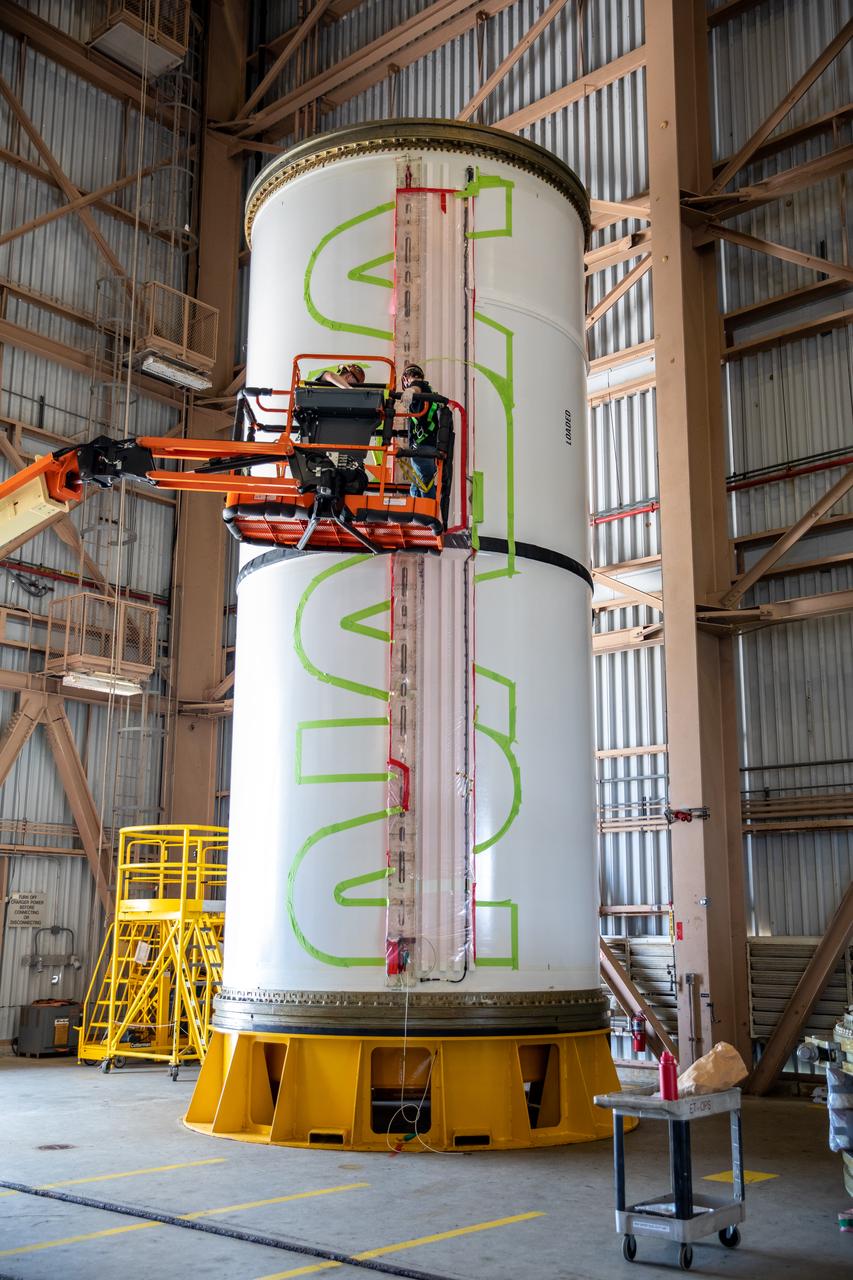

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) use a laser projector and green tape to mask off the shape of the agency’s “worm” logo on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Sept. 3, 2020. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
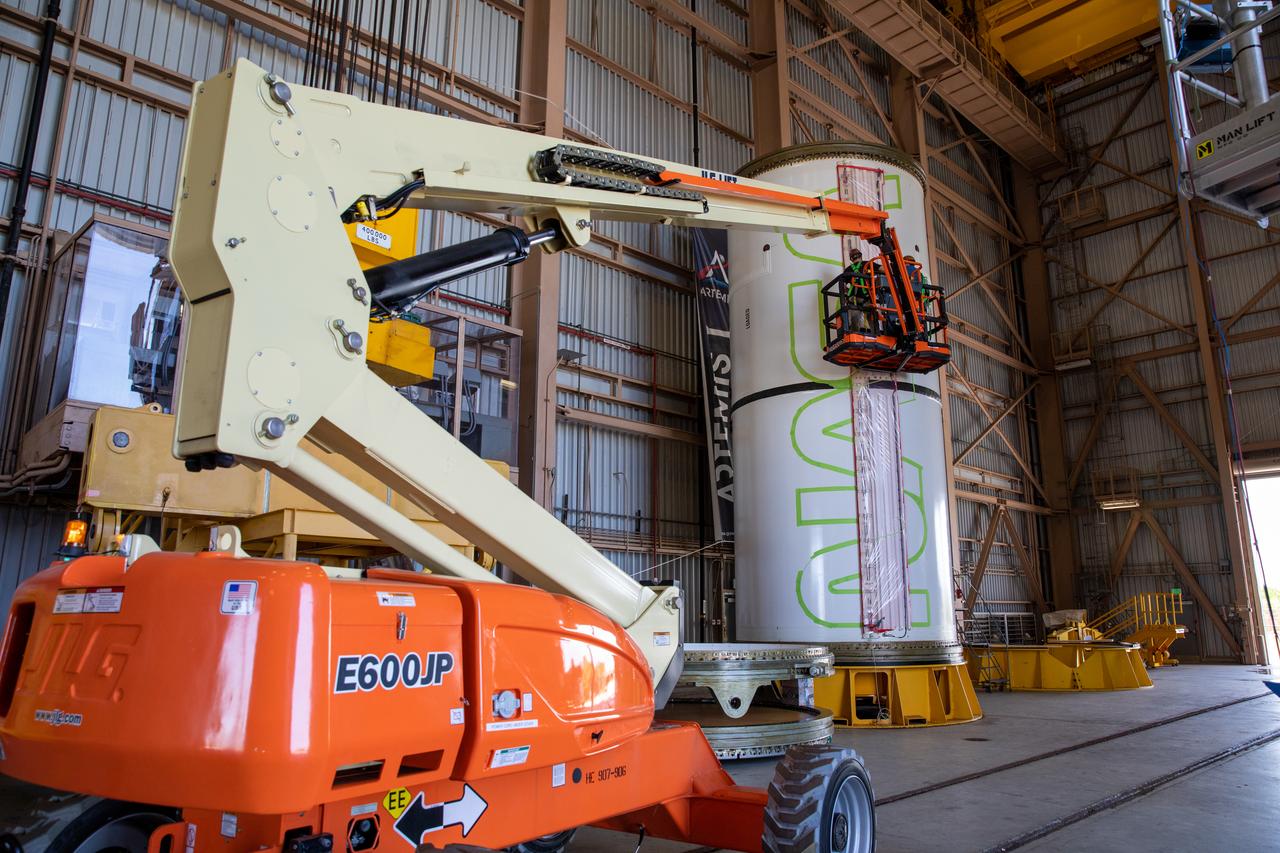

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) use a laser projector and green tape to mask off the shape of the agency’s “worm” logo on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Sept. 3, 2020. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
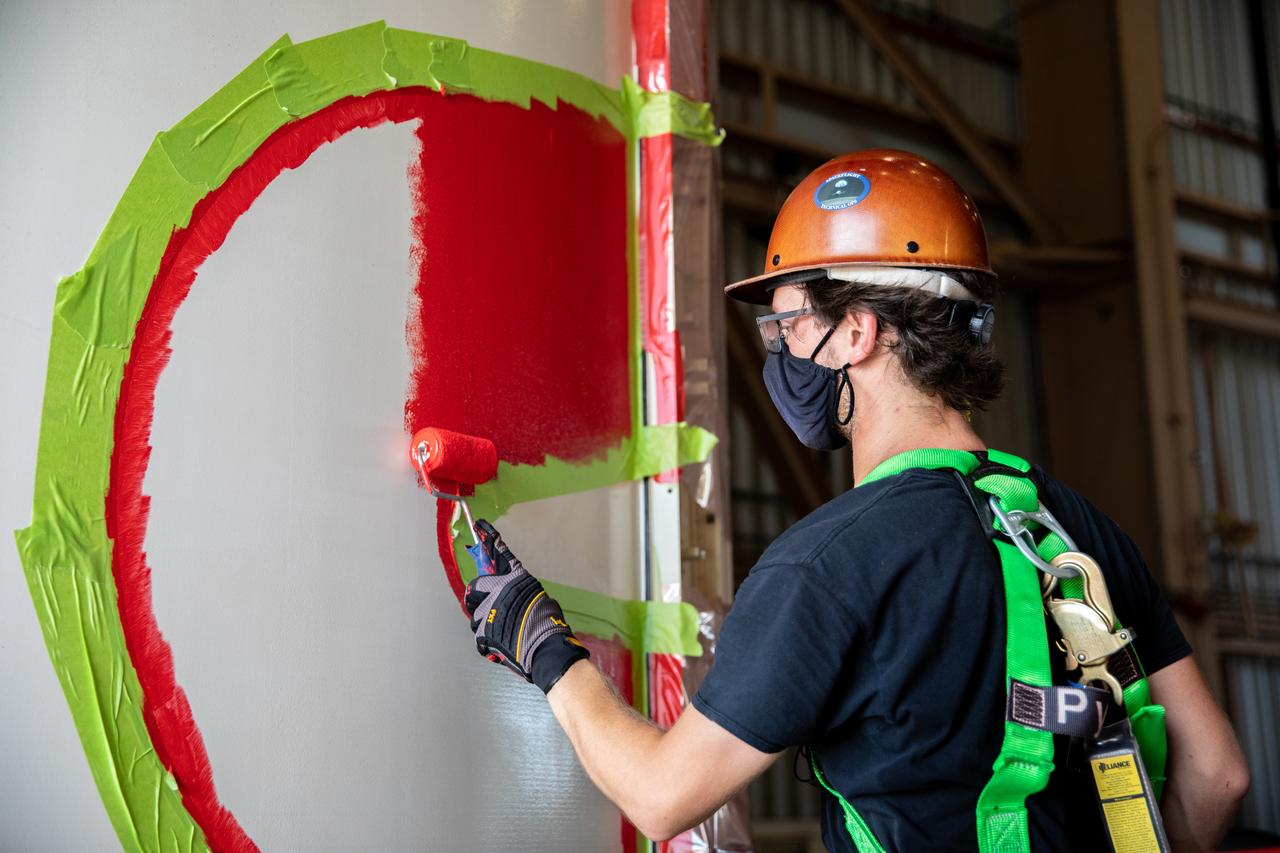

A worker with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) finishes the first coat of the bright red “worm” logo taking shape on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
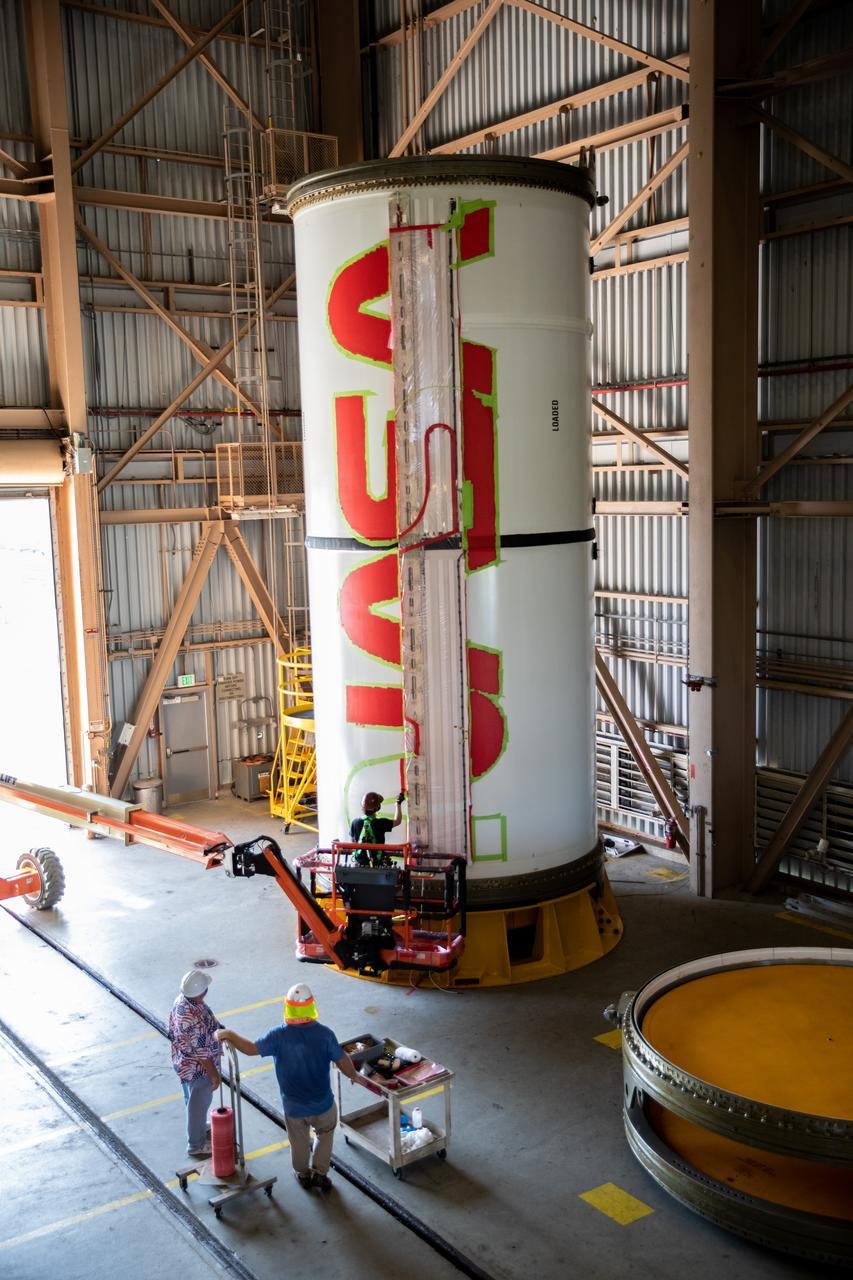

Workers with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) finishes the first coat of the bright red “worm” logo taking shape on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
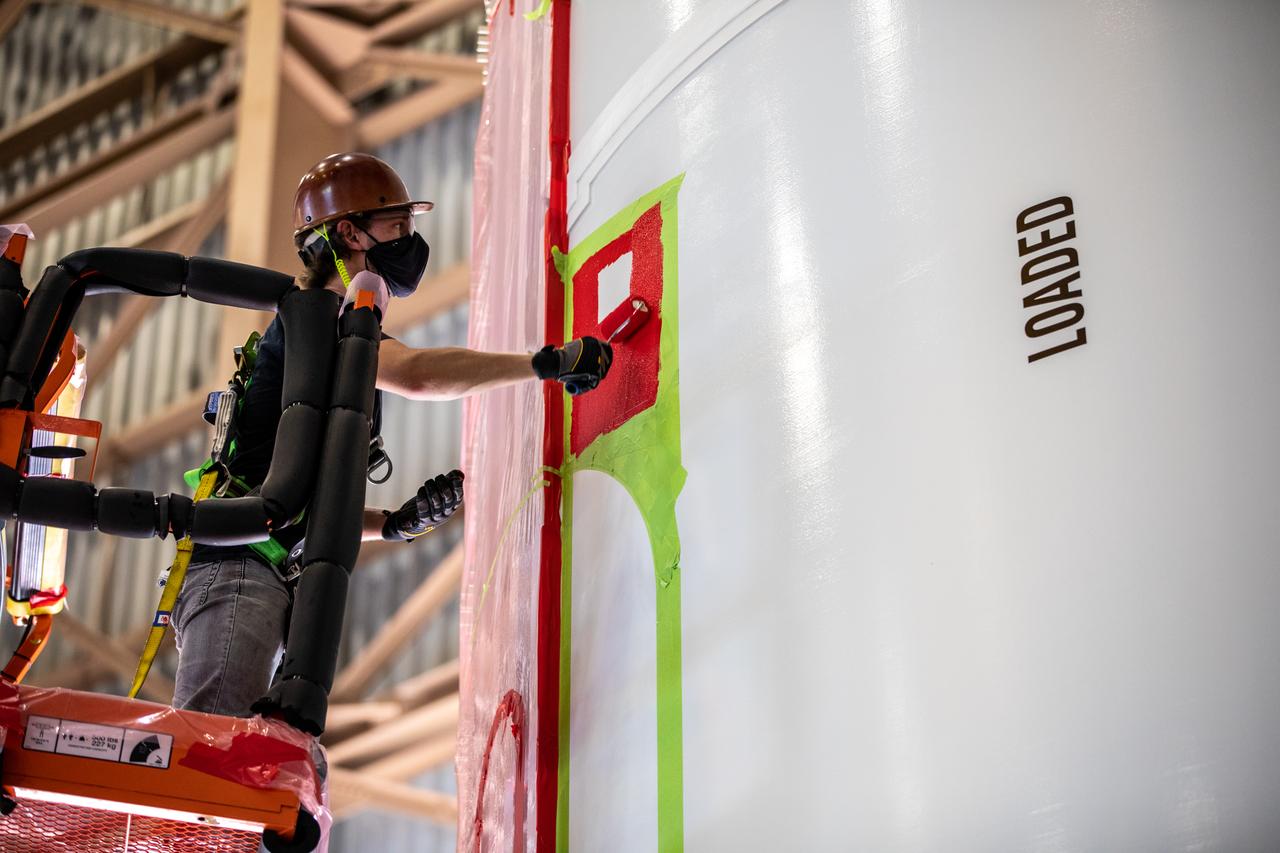

A worker with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) applies bright red paint to the agency’s “worm” logo taking shape on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
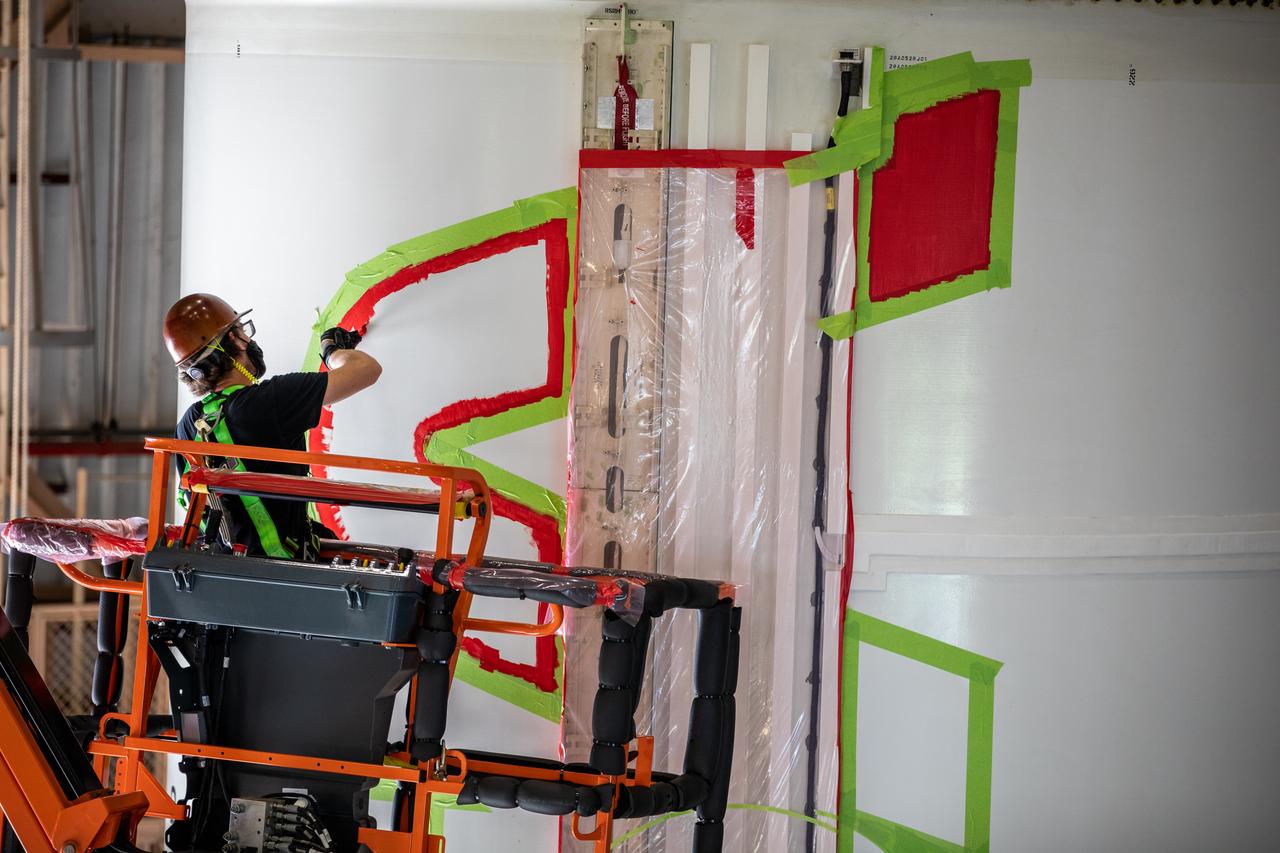

A worker with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) applies bright red paint to the agency’s “worm” logo taking shape on the side of an Artemis I solid rocket booster segment inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
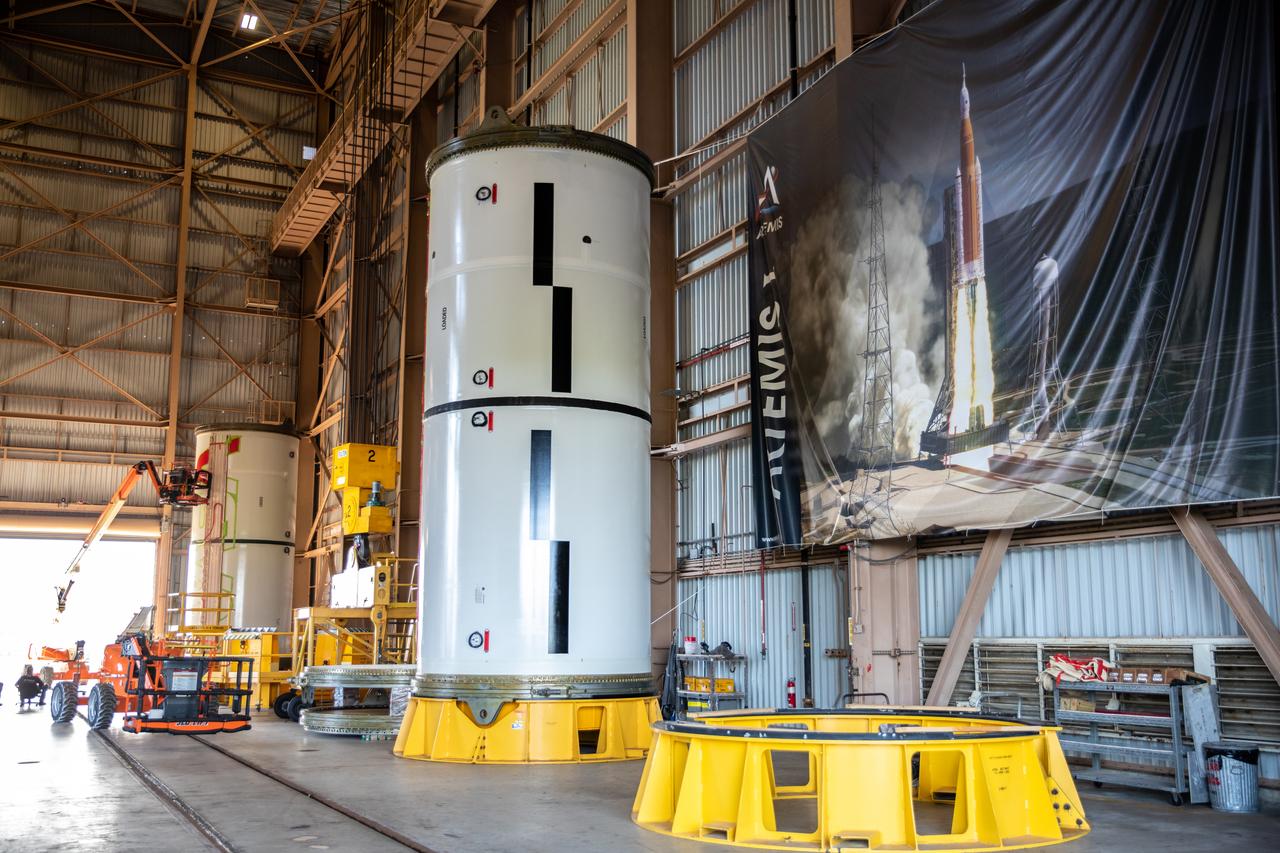

In this view inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, an Artemis I solid rocket booster center segment stands in the foreground; in the background, a worker with NASA’s Exploration Ground Systems (EGS) applies bright red paint to the agency’s “worm” logo taking shape on the side of the other center segment. The EGS team used a laser projector to mask off the logo with tape, then painted the first coat of the iconic design. The booster segments will help propel the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket on Artemis I, a test of the Orion spacecraft and SLS as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Northrop Grumman, which built the booster segments, is covering the cost of the painting.
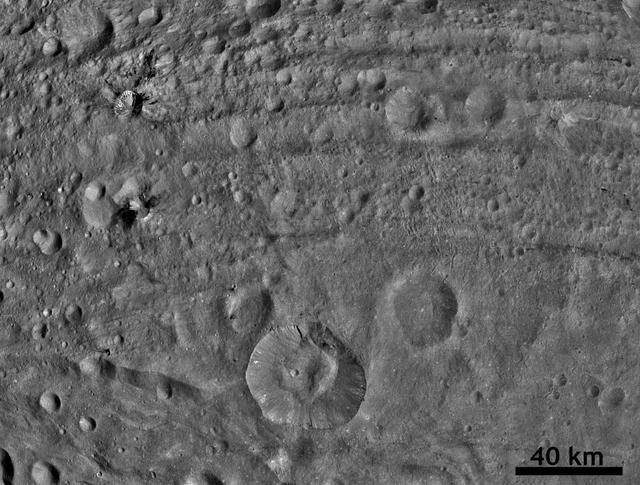
This image from NASA Dawn spacecraft shows dark material at impact craters, up to 12.5 miles-wide 20 kilometer-wide and sets of worm-like tracks in the north-south direction.
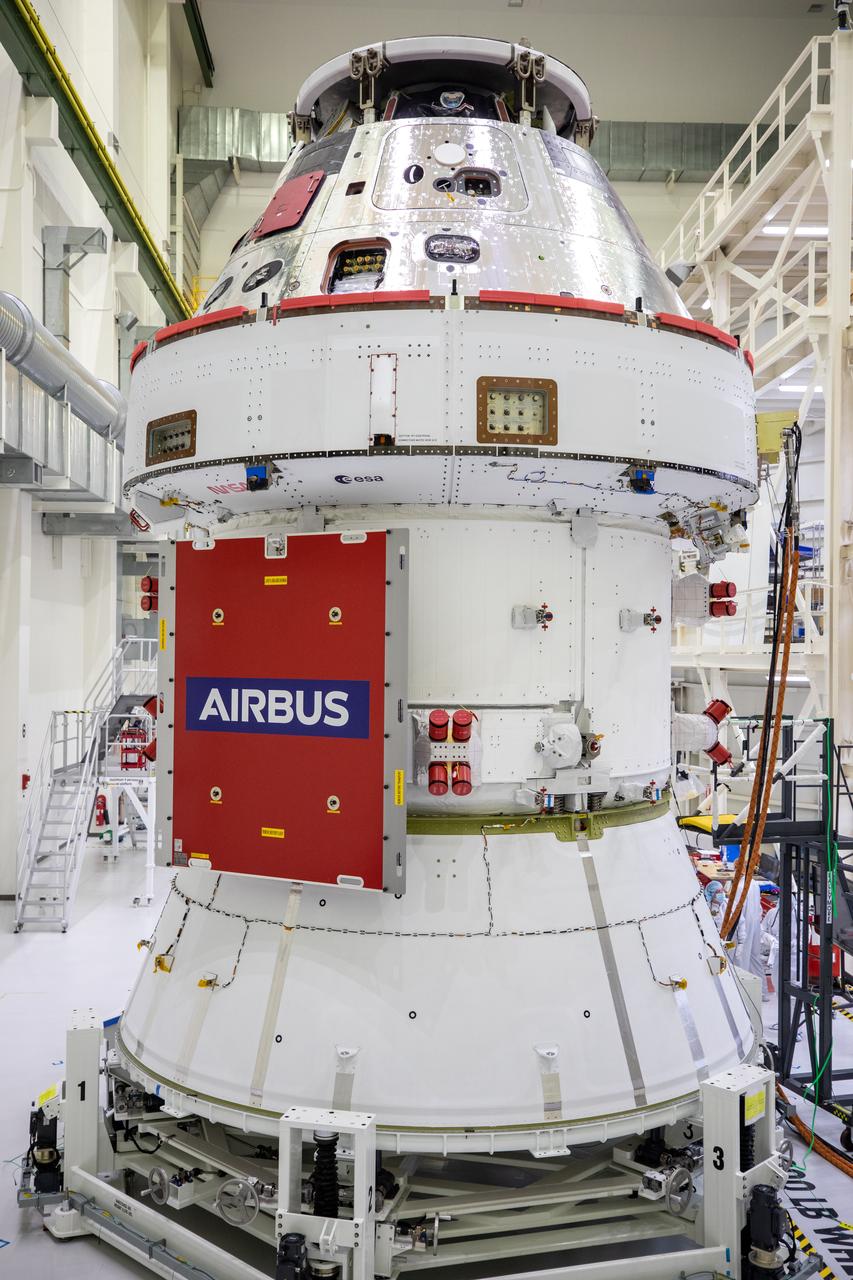

A protective cover panel has been installed over one of the solar arrays shown on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The iconic NASA worm and European Space Agency insignias on the Crew Module Adapter outer wall can be seen just above the panel. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each of the four solar array panels will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
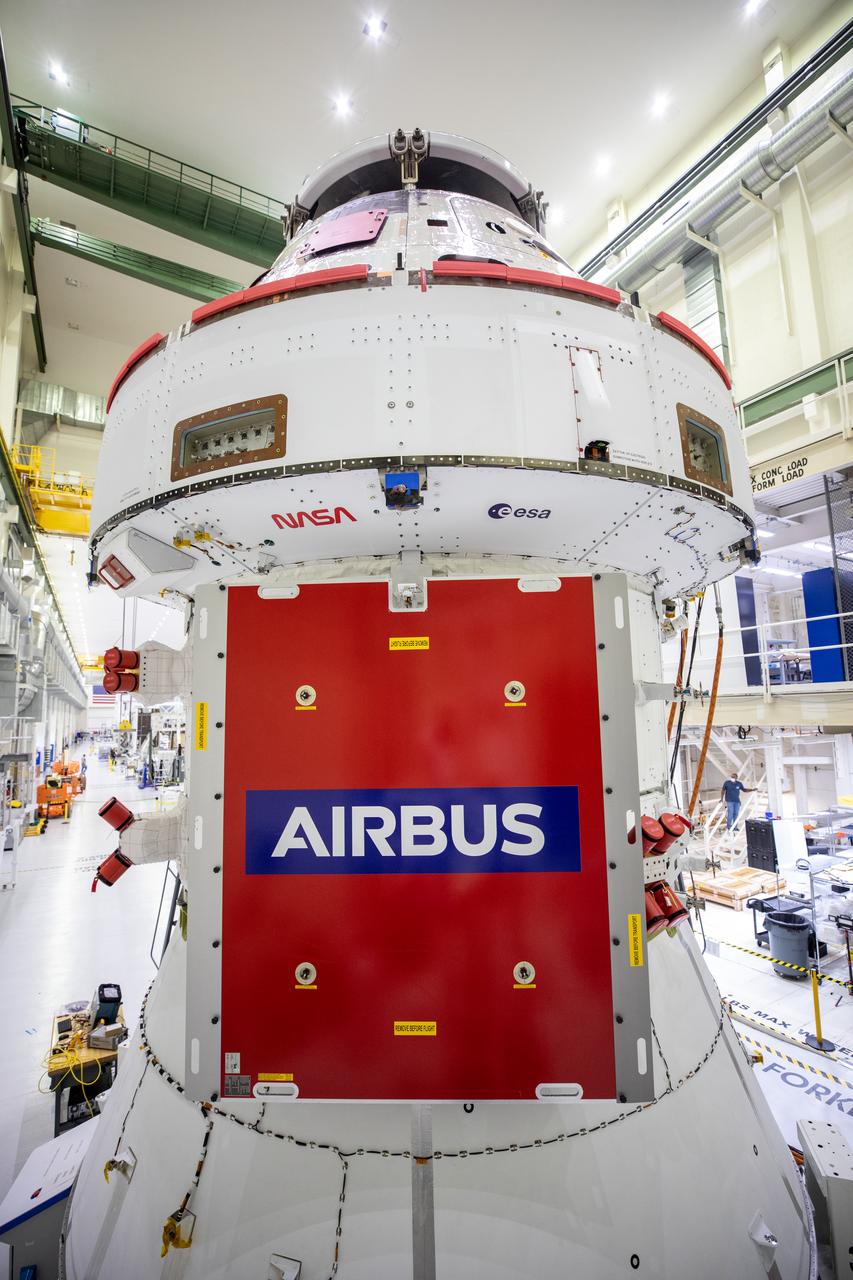

A protective cover panel has been installed over one of the solar arrays on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The iconic NASA worm and European Space Agency insignias on the Crew Module Adapter outer wall can be seen just above the panel. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each of the four solar array panels will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.

A protective cover panel has been installed over one of the solar arrays on the Orion spacecraft for Artemis I inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The iconic NASA worm and European Space Agency insignias on the Crew Module Adapter outer wall can be seen just above the panel. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each of the four solar array panels will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
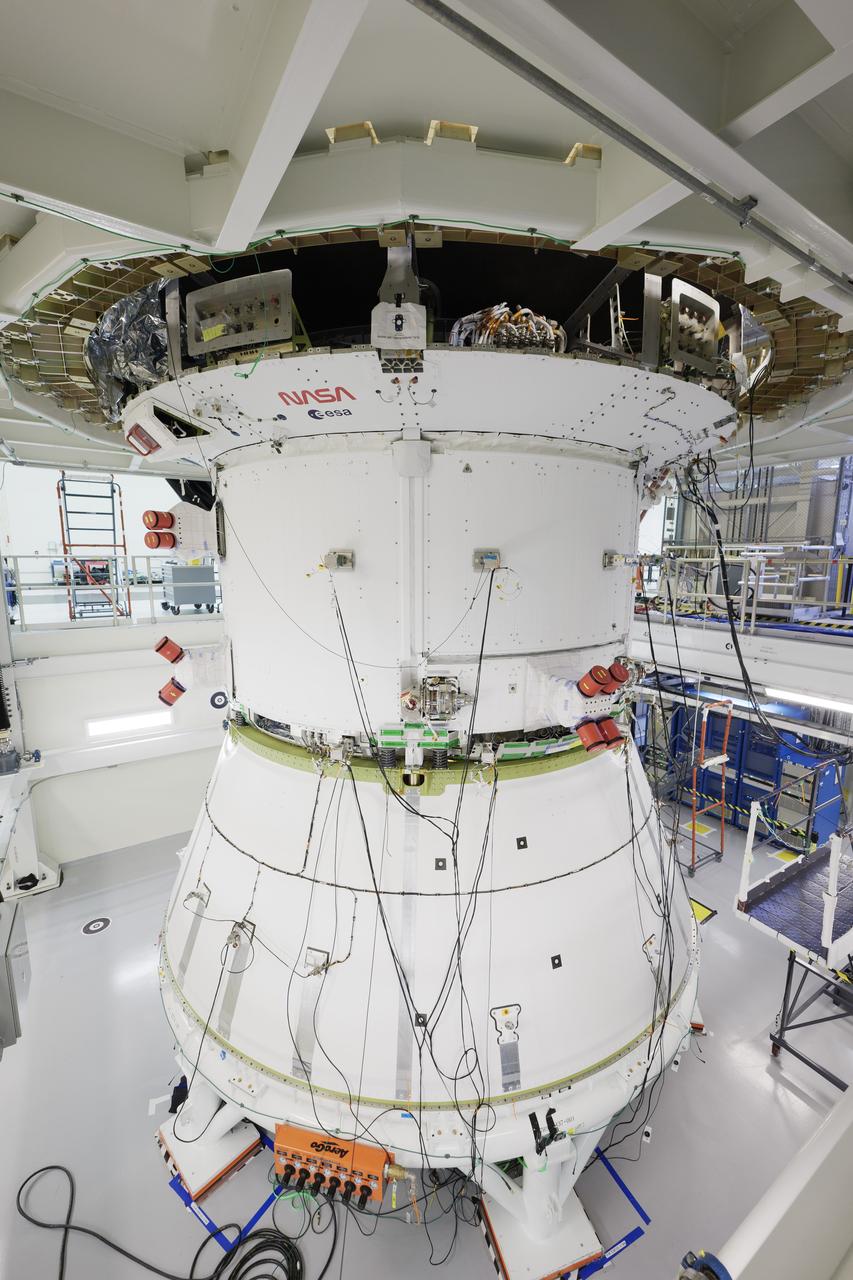

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis II mission received its latest makeover. Teams adhered the agency’s iconic “worm” logo and ESA (European Space Agency) insignia on the spacecraft’s crew module adapter on Sunday, Jan. 28, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.
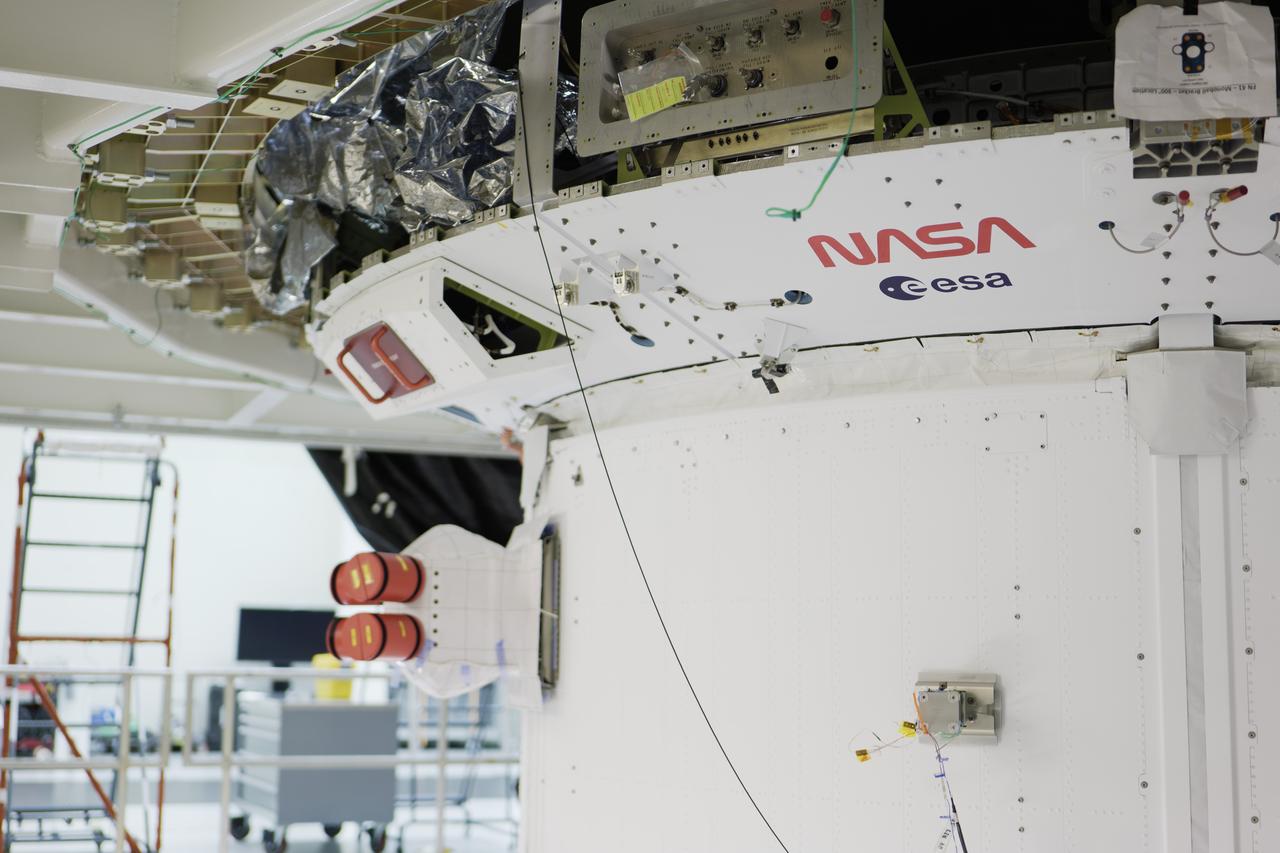

The Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis II mission received its latest makeover. Teams adhered the agency’s iconic “worm” logo and ESA (European Space Agency) insignia on the spacecraft’s crew module adapter on Sunday, Jan. 28, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida.

A plaque is seen at the base of the NASA Worm Logo sign during a Richard Danne dedication event, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
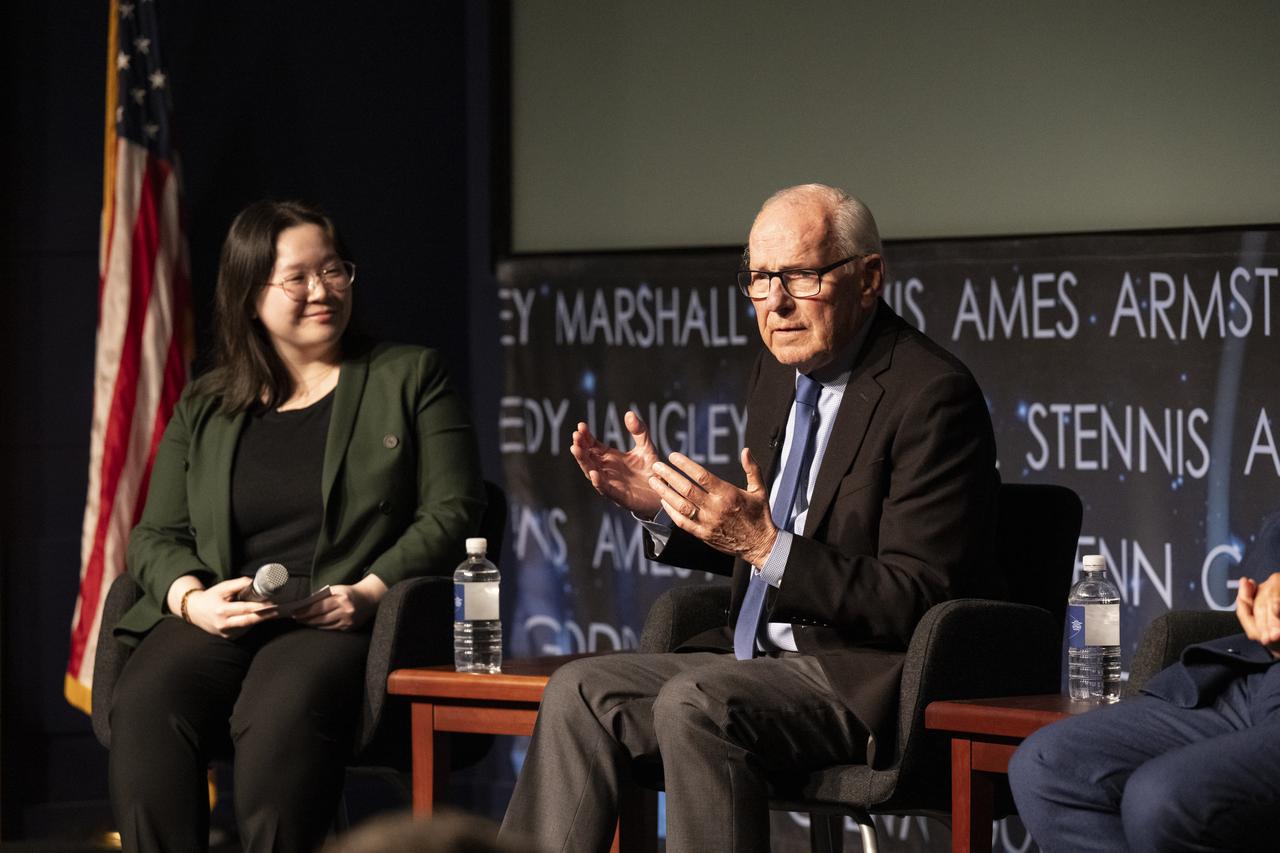

Richard Danne, creator of the NASA worm logotype, right, answers questions during a dedication event, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
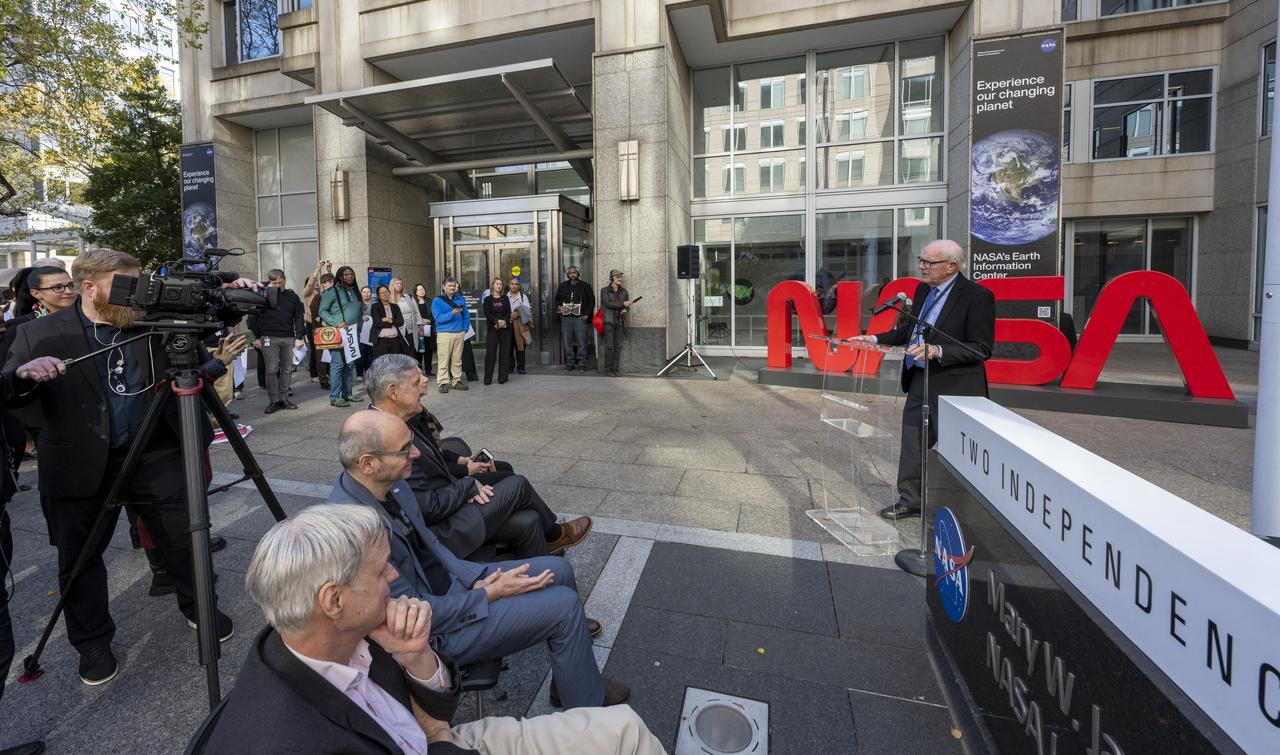

Richard Danne, creator of the NASA worm logotype, delivers remarks during a dedication event, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
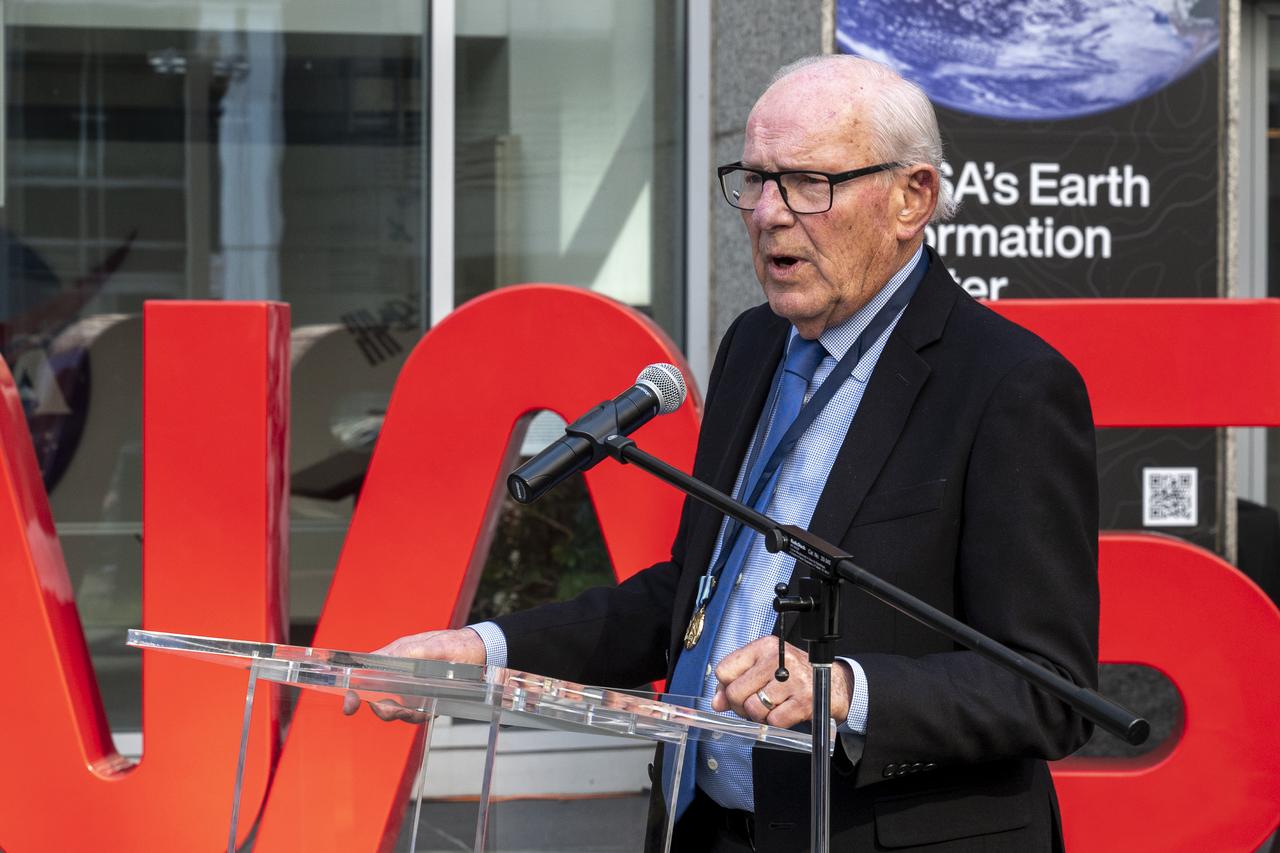

Richard Danne, creator of the NASA worm logotype, delivers remarks during a dedication event, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
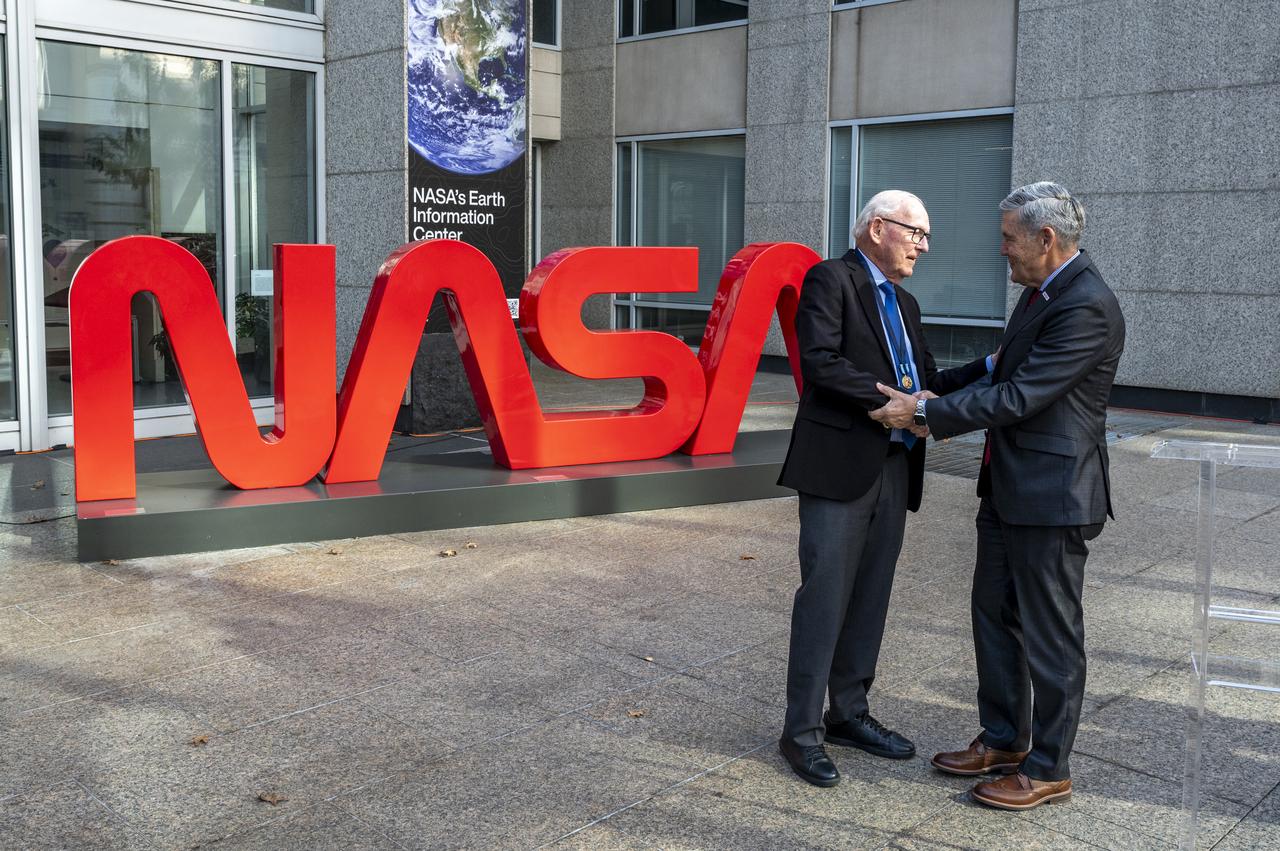

NASA Associate Administrator Bob Cabana, right, shakes hands with Richard Danne after awarding him the Exceptional Public Achievement Medal for his outstanding achievement in creating the NASA worm logotype, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

NASA Associate Administrator Bob Cabana, right, poses for a photo with Richard Danne after awarding him the Exceptional Public Achievement Medal for his outstanding achievement in creating the NASA worm logotype, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
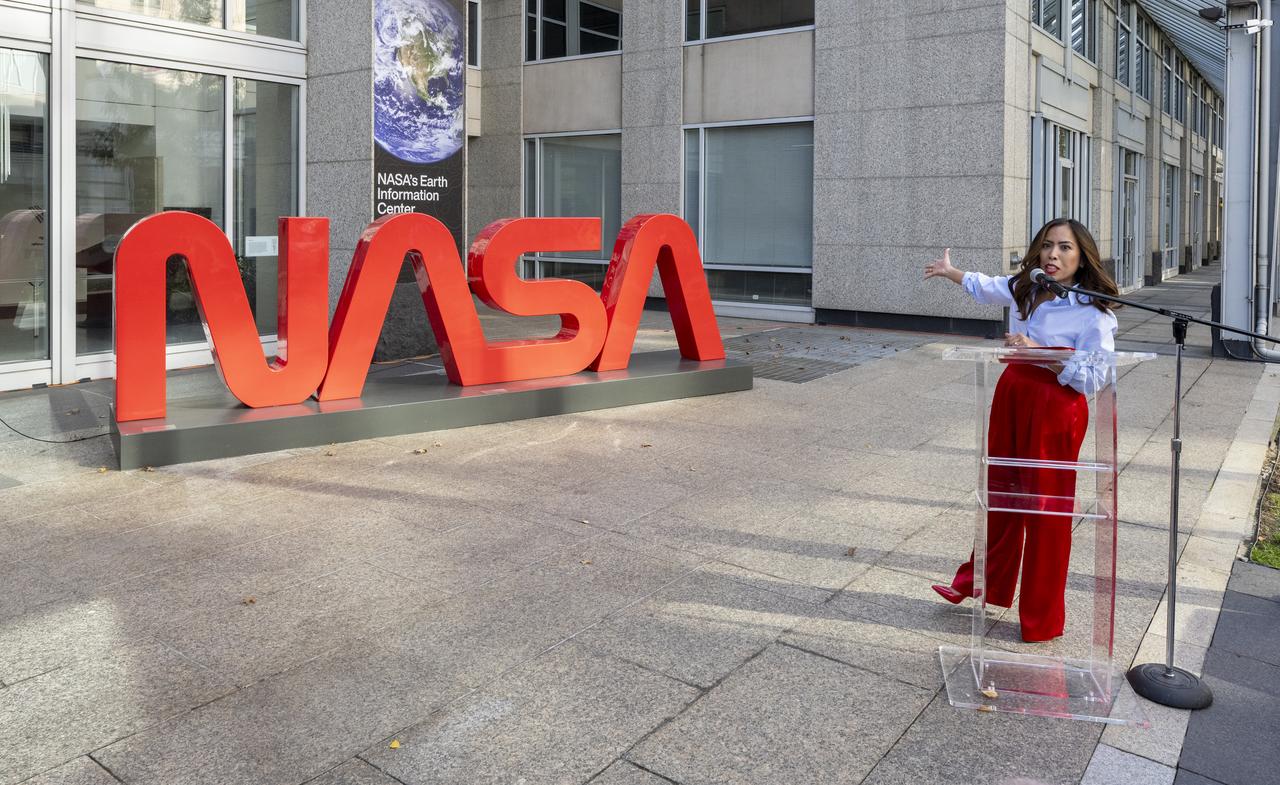

NASA Public Affairs Specialist Megan Cruz delivers remarks during a dedication event for Richard Danne, creator of the NASA worm logotype, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
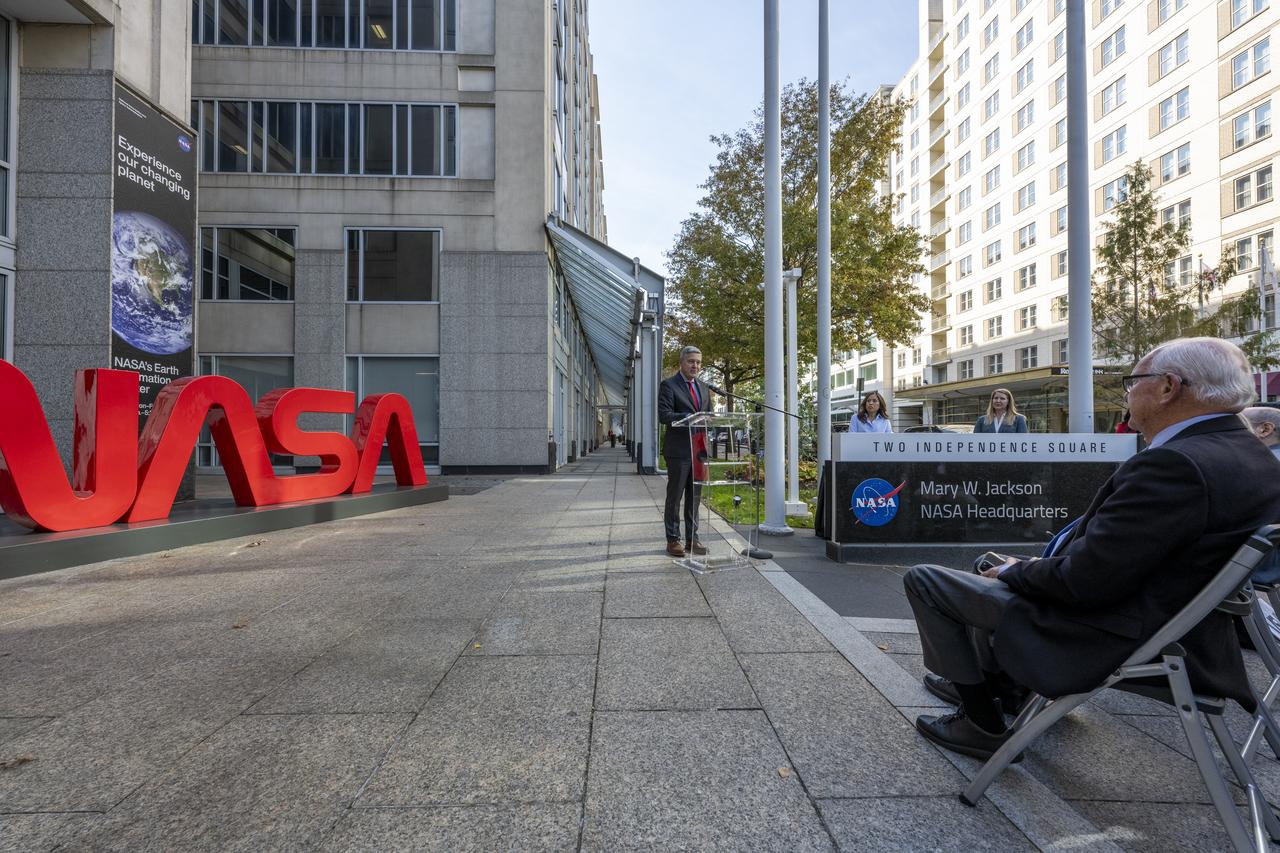

NASA Associate Administrator Bob Cabana delivers remarks during a dedication event for Richard Danne, creator of the NASA worm logotype, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
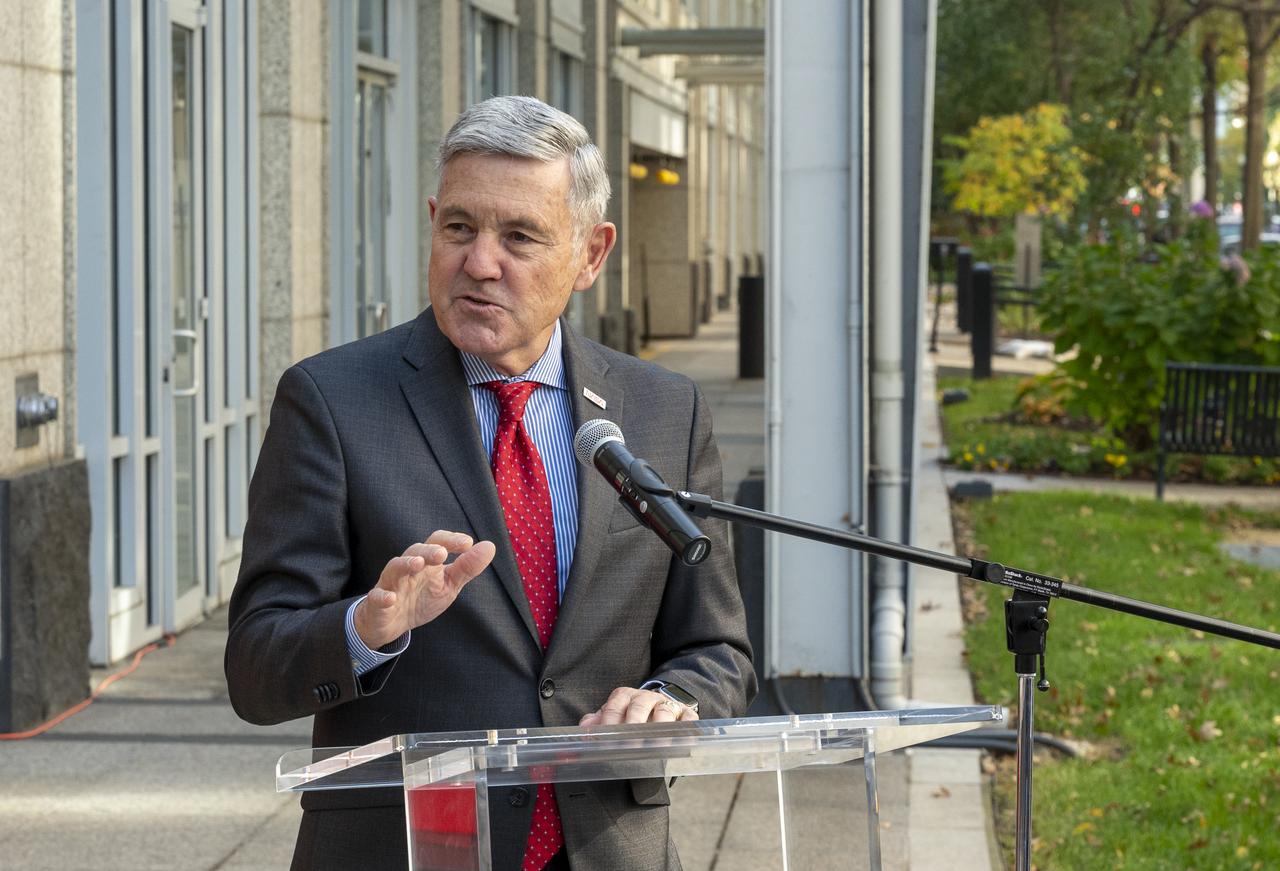

NASA Associate Administrator Bob Cabana delivers remarks during a dedication event for Richard Danne, creator of the NASA worm logotype, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
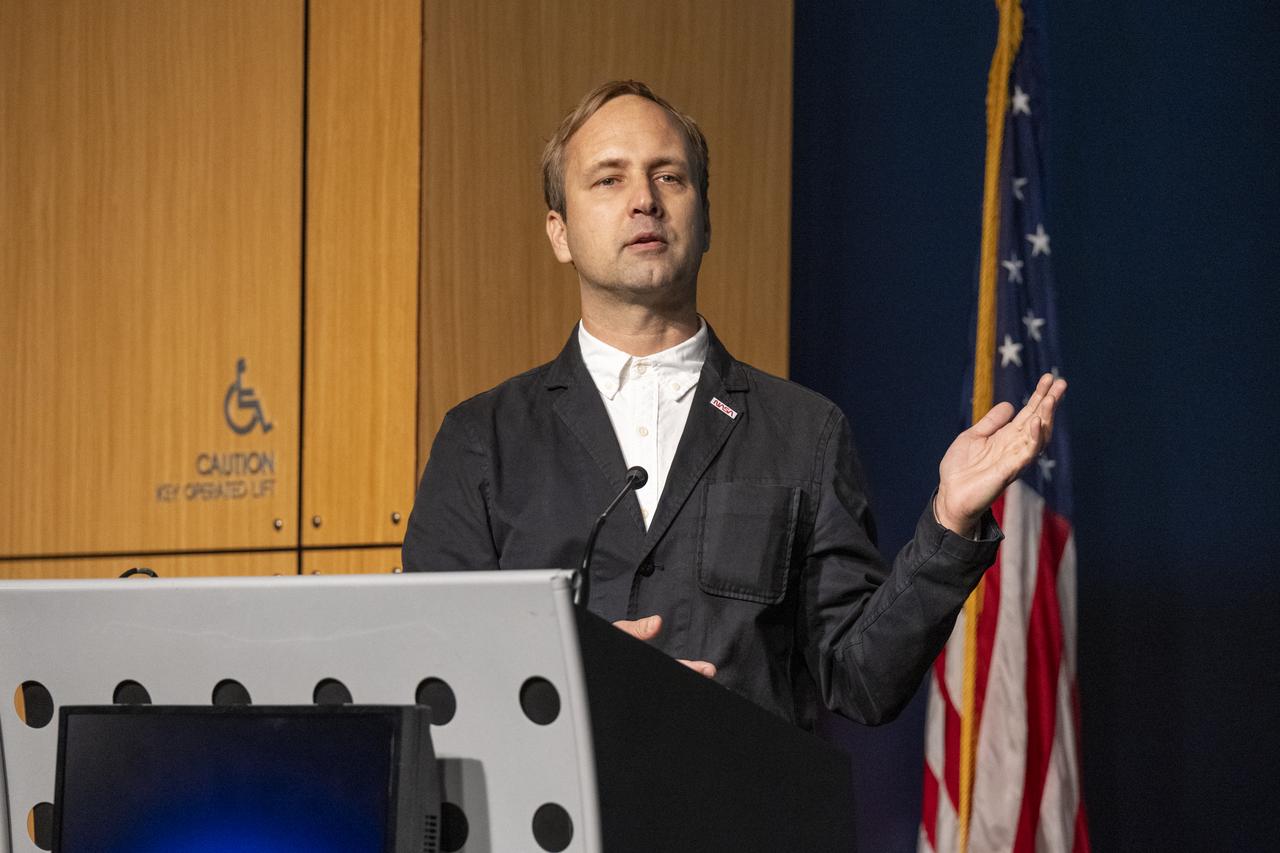

NASA Creative Art Director David Rager delivers remarks during a dedication event for Richard Danne, creator of the NASA worm logotype, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
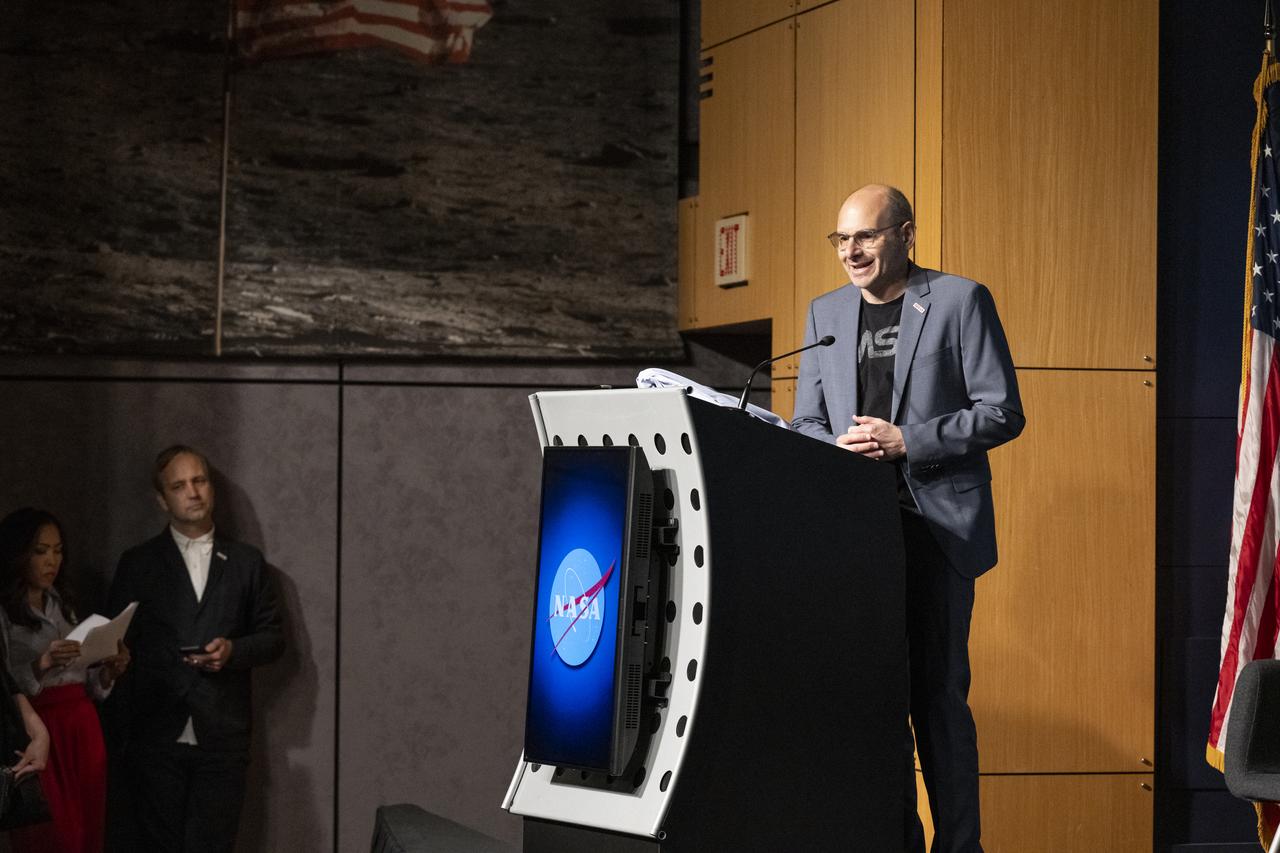

Associate Administrator for Communications Marc Etkind delivers remarks during a dedication event for Richard Danne, creator of the NASA worm logotype, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
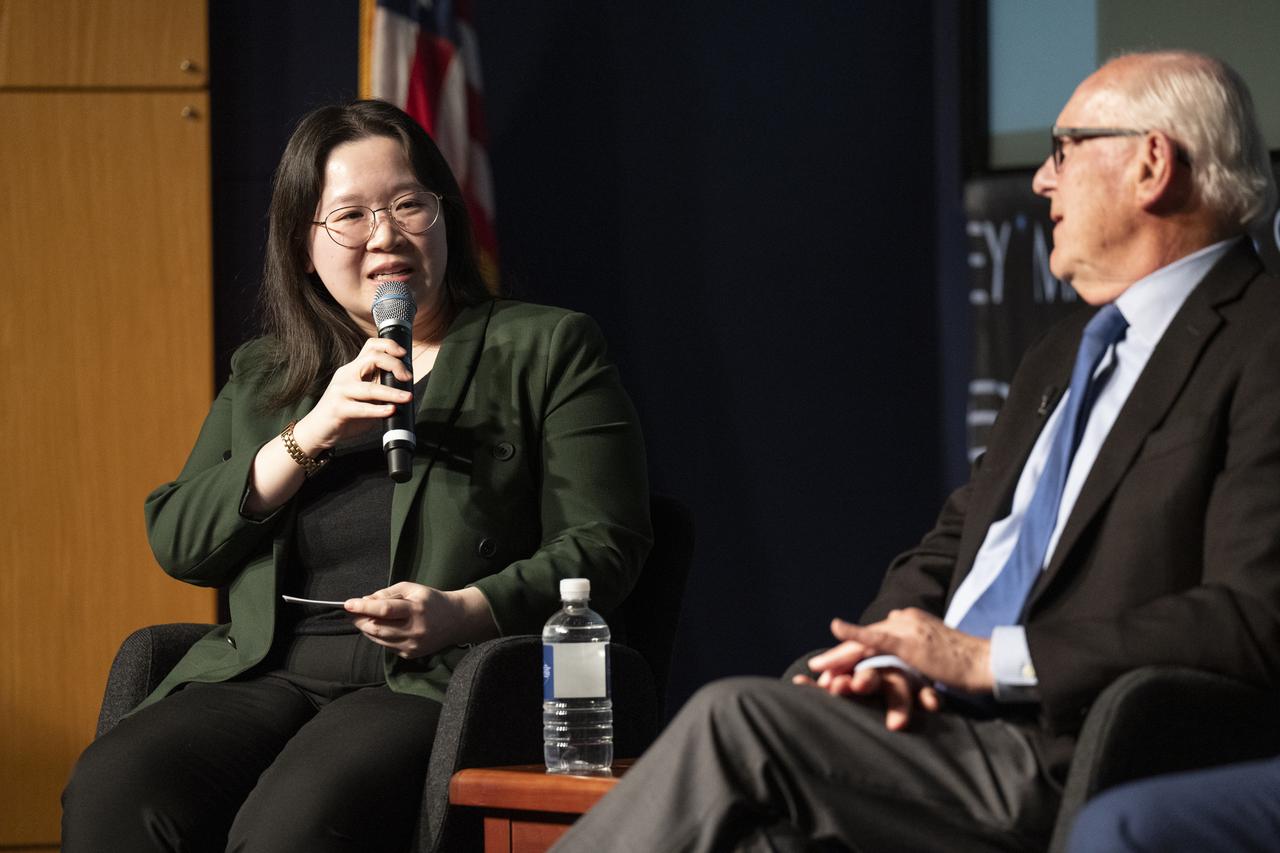

Moderator and Washington Post design reporter Shelly Tan, left, and creator of the NASA worm logotype Richard Danne, right, participate in a panel discussion during a Richard Danne dedication event, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
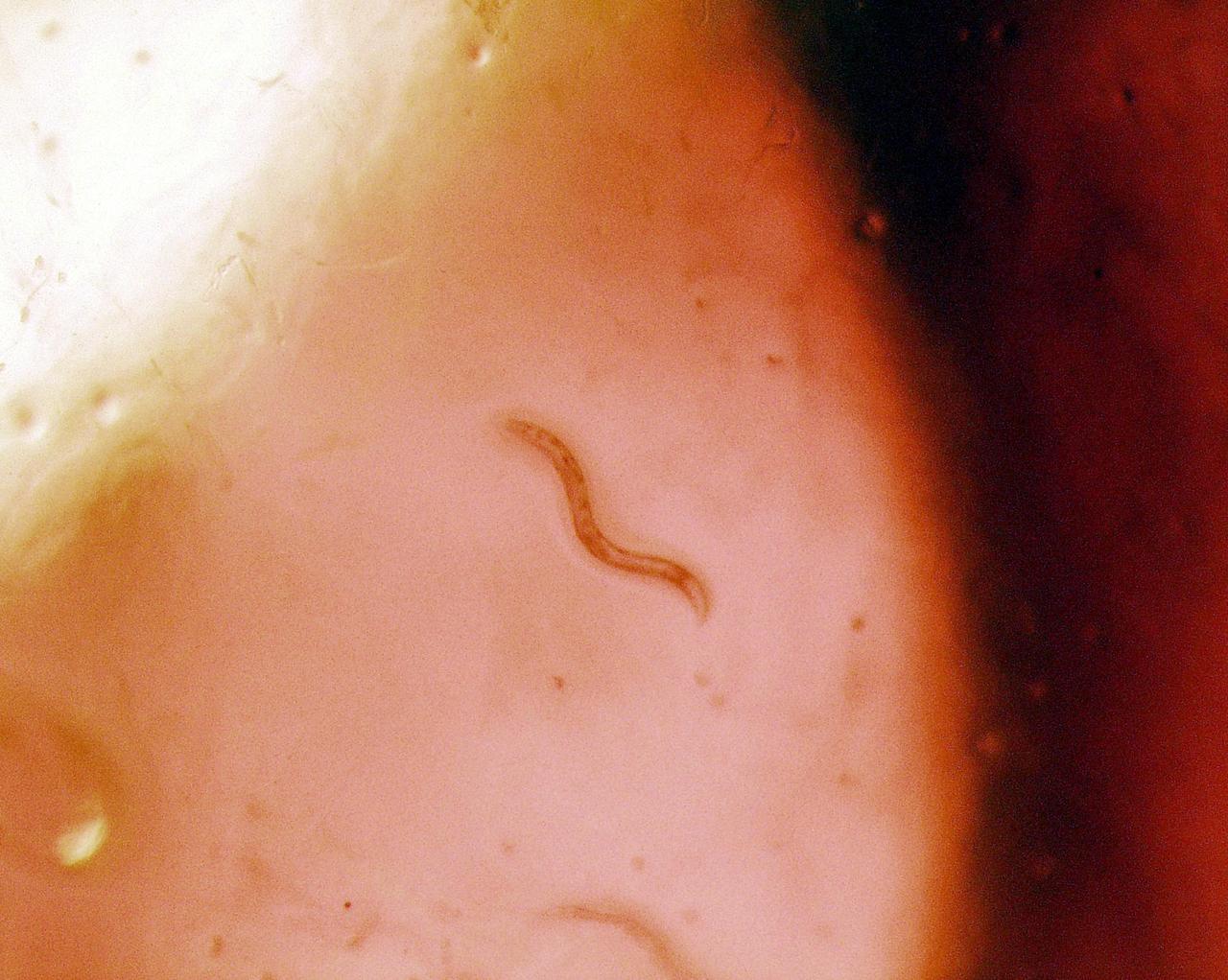
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - C. elegans nemotodes (round worms) undergo examination by project scientists. These specimens were found in a Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) container, a middeck experiment that was among the Columbia debris recovered in East Texas. The worms are descendants of those that were part of an experiment that flew on Columbia's last mission, STS-107. The experiment was designed to verify a new synthetic nutrient solution for an International Space Station (ISS) "model" specimen planned to be used extensively for ISS gene expression studies and was sponsored by the NASA Ames Research Center. Scientists are now looking over the experiment at KSC to determine if it will yield any scientific results. The investigation into the cause of the Columbia accident is ongoing. (Photo Credit: Volker Kern, NASA Ames Research Center)
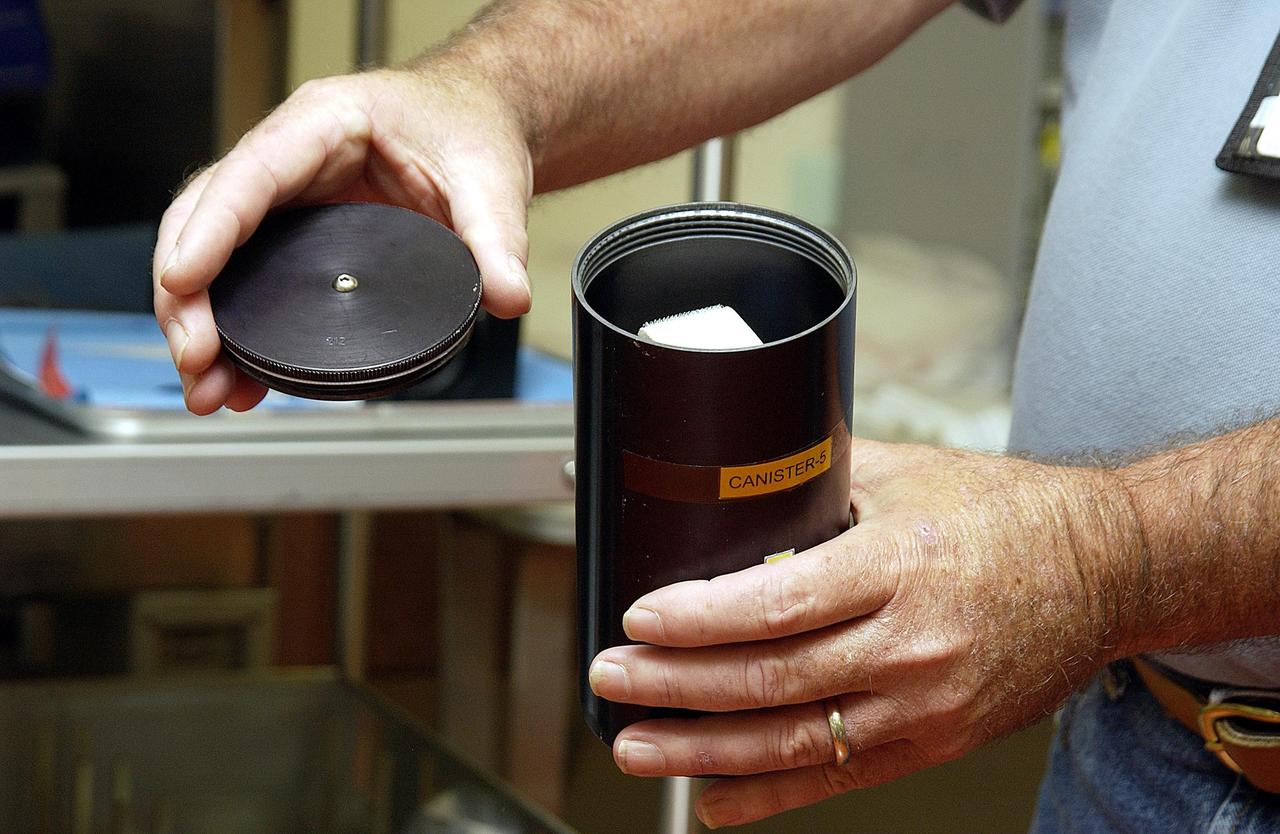

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Project Manager Fred Ahmay holds a Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) container in which C. elegans nemotodes (round worms) were found. The container was part of a middeck experiment that was among the Columbia debris recovered in East Texas. The worms are descendants of those that were part of an experiment that flew on Columbia's last mission, STS-107. The experiment was designed to verify a new synthetic nutrient solution for an International Space Station (ISS) "model" specimen planned to be used extensively for ISS gene expression studies and was sponsored by the NASA Ames Research Center. Scientists are now looking over the experiment at KSC to determine if it will yield any scientific results. The investigation into the cause of the Columbia accident is ongoing.
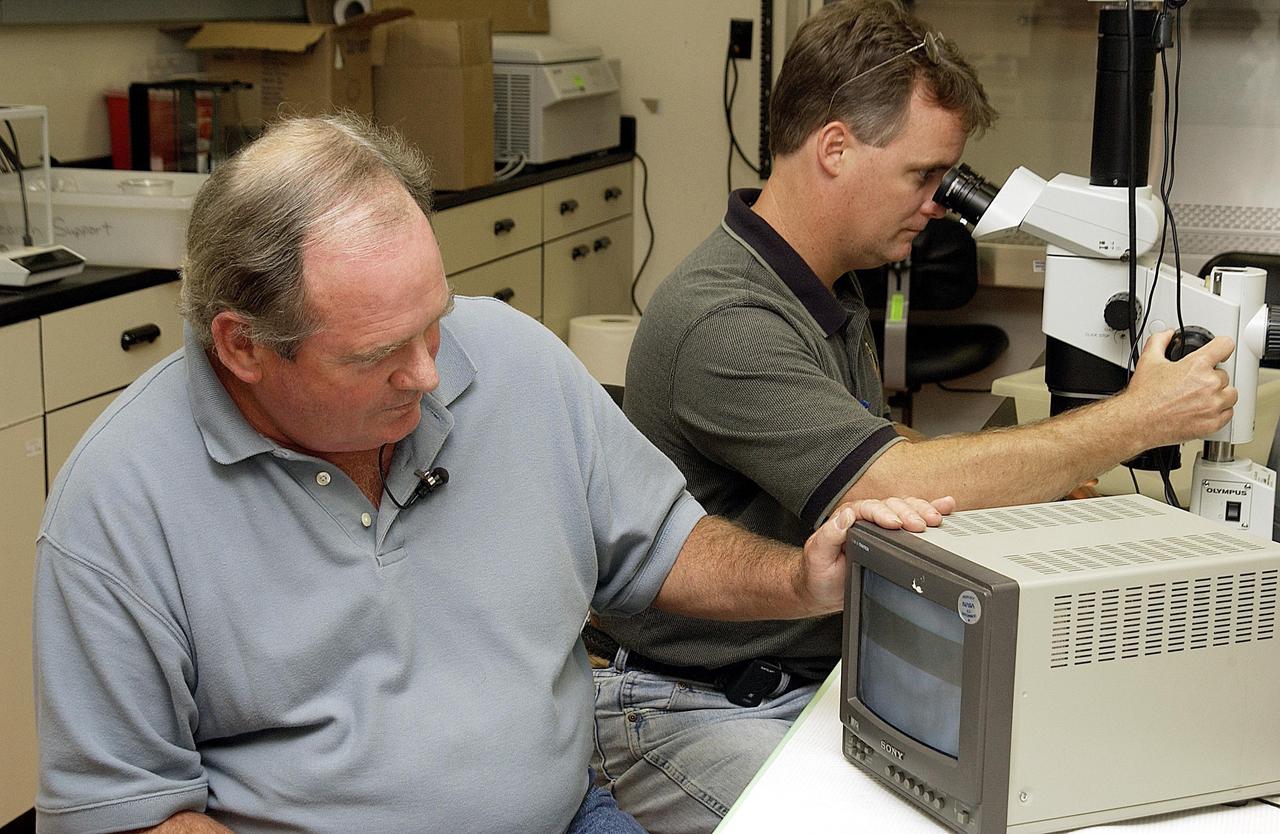

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Project Manager Fred Ahmay (left) and Bionetics Project Engineer William McLamb examine C. elegans nemotodes (round worms) using a microscope. These specimens were found in a Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) container, a middeck experiment that was among the Columbia debris recovered in East Texas. The worms are descendants of those that were part of an experiment that flew on Columbia's last mission, STS-107. The experiment was designed to verify a new synthetic nutrient solution for an International Space Station (ISS) "model" specimen planned to be used extensively for ISS gene expression studies and was sponsored by the NASA Ames Research Center. Scientists are now looking over the experiment at KSC to determine if it will yield any scientific results. The investigation into the cause of the Columbia accident is ongoing.
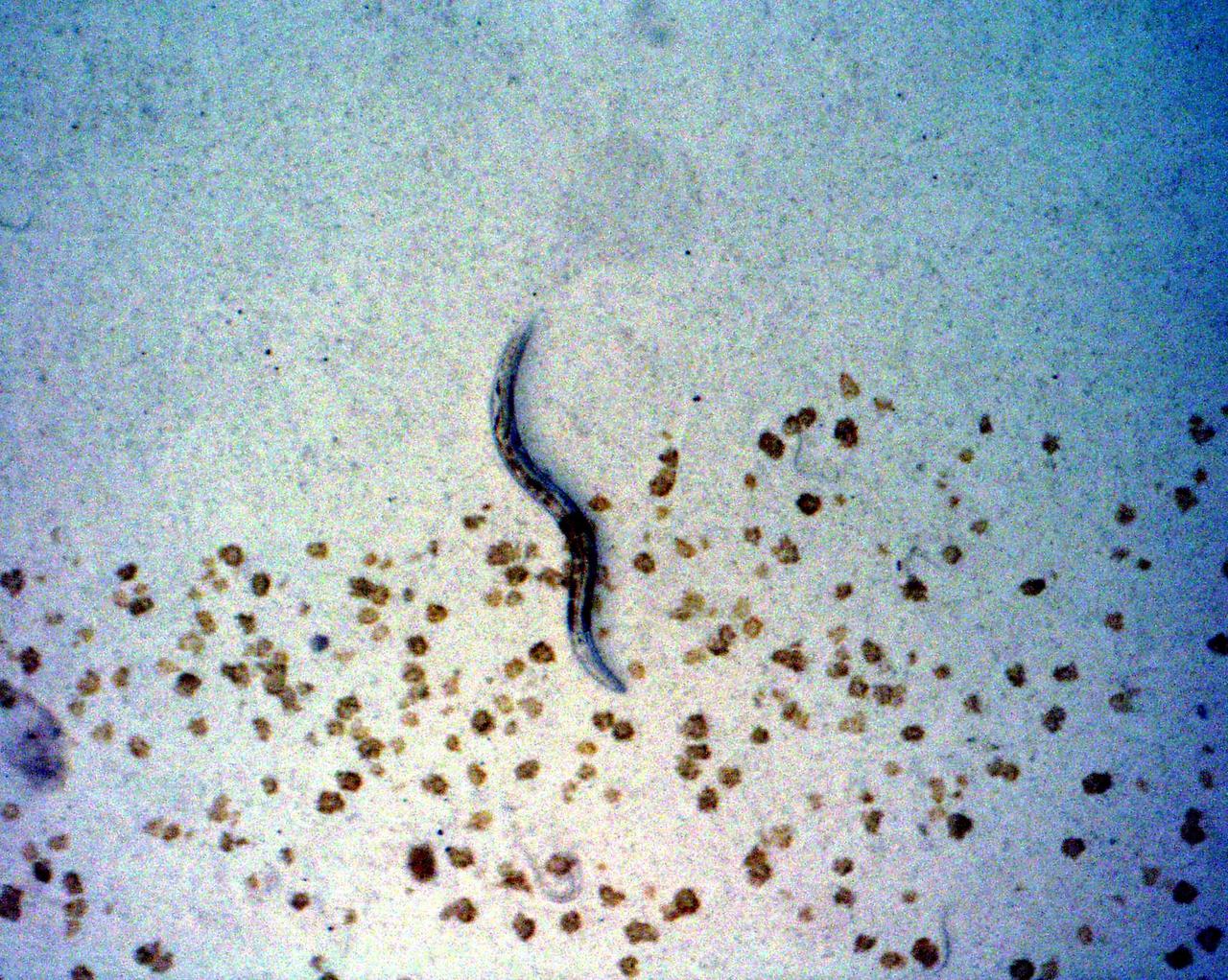
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - C. elegans nemotodes (round worms) undergo examination by project scientists. These specimens were found in a Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) container, a middeck experiment that was among the Columbia debris recovered in East Texas. The worms are descendants of those that were part of an experiment that flew on Columbia's last mission, STS-107. The experiment was designed to verify a new synthetic nutrient solution for an International Space Station (ISS) "model" specimen planned to be used extensively for ISS gene expression studies and was sponsored by the NASA Ames Research Center. Scientists are now looking over the experiment at KSC to determine if it will yield any scientific results. The investigation into the cause of the Columbia accident is ongoing. (Photo Credit: Volker Kern, NASA Ames Research Center)
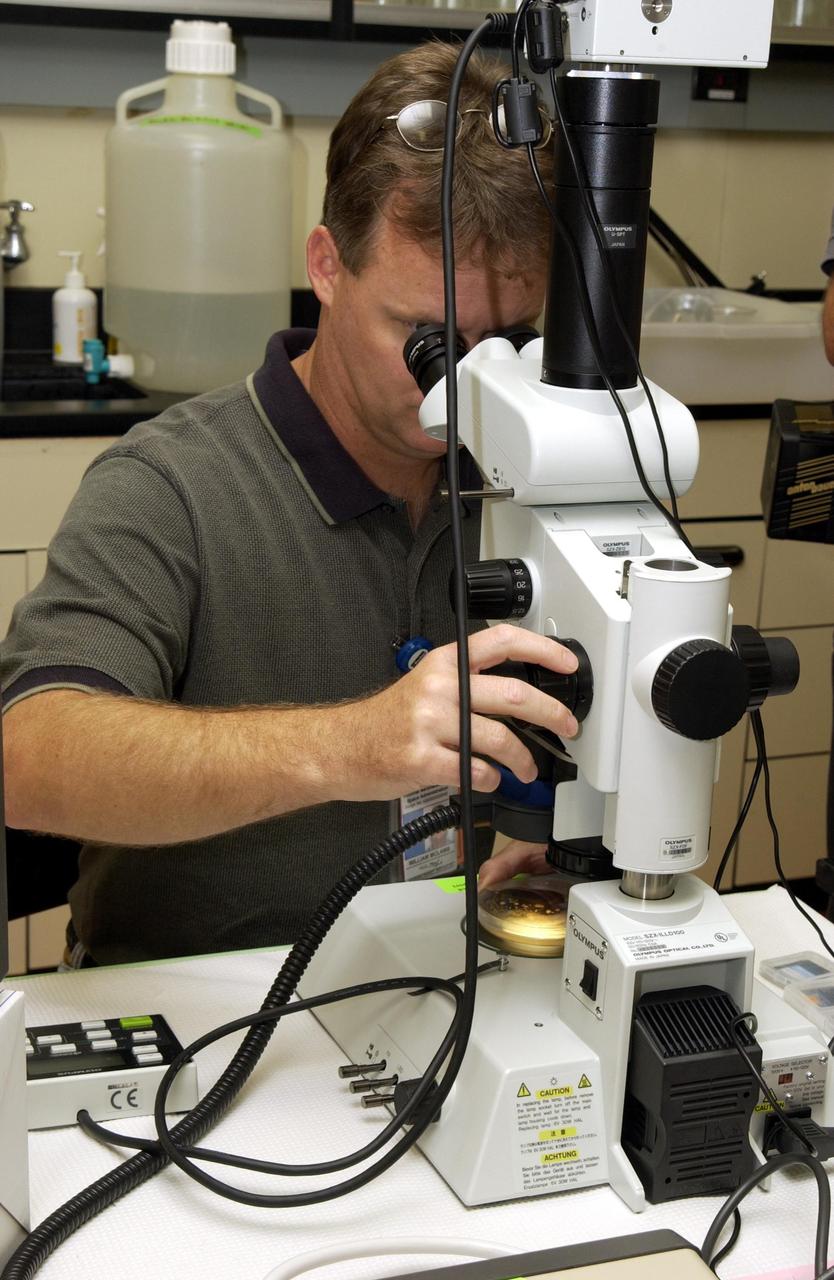

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Project Manager Guy Ethridge examines C. elegans nemotodes (round worms) under a microscope. These specimens were found in a Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) container, a middeck experiment that was among the Columbia debris recovered in East Texas. The worms are descendants of those that were part of an experiment that flew on Columbia's last mission, STS-107. The experiment was designed to verify a new synthetic nutrient solution for an International Space Station (ISS) "model" specimen planned to be used extensively for ISS gene expression studies and was sponsored by the NASA Ames Research Center. Scientists are now looking over the experiment at KSC to determine if it will yield any scientific results. The investigation into the cause of the Columbia accident is ongoing.
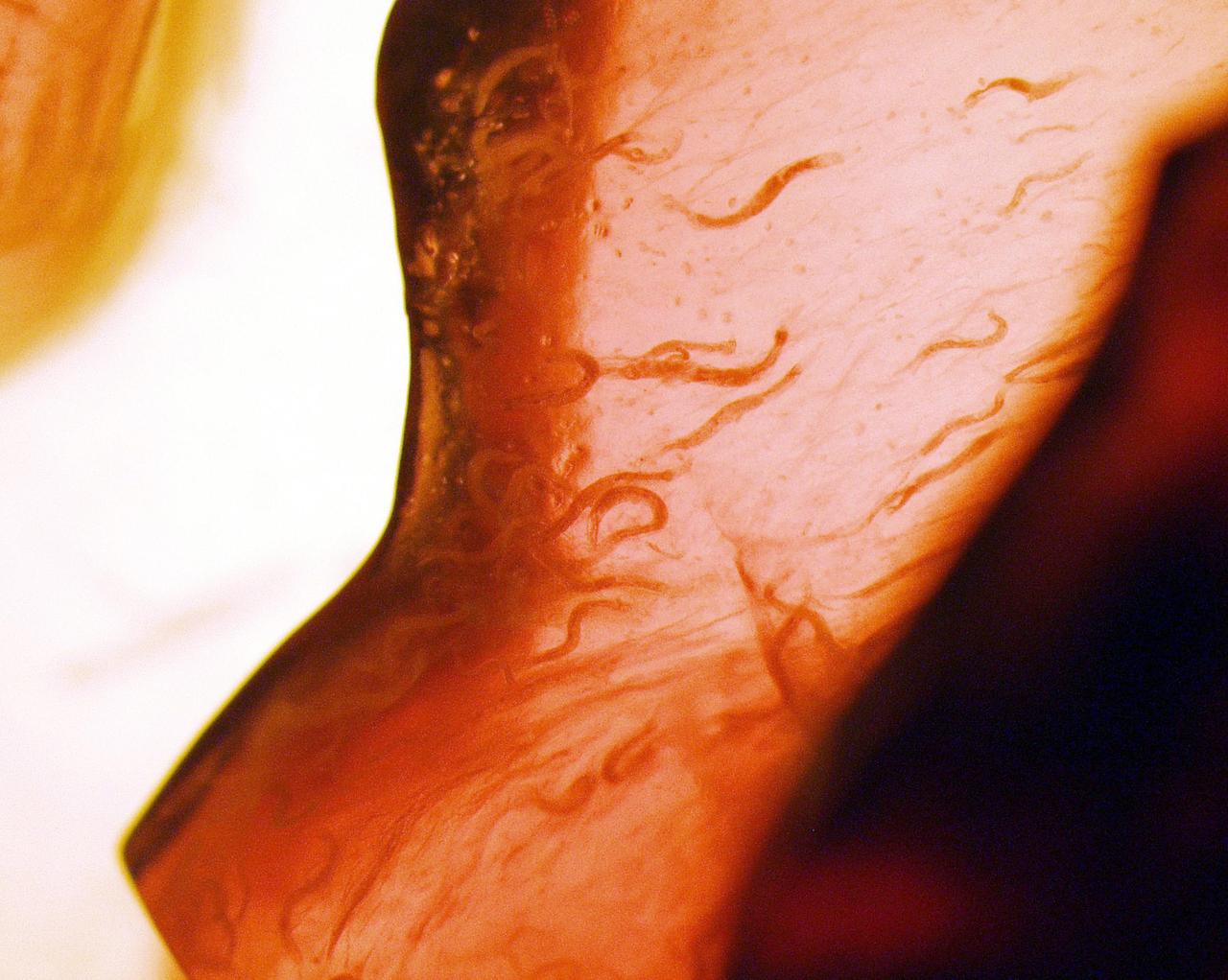
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - C. elegans nemotodes (round worms) undergo examination by project scientists. These specimens were found in a Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) container, a middeck experiment that was among the Columbia debris recovered in East Texas. The worms are descendants of those that were part of an experiment that flew on Columbia's last mission, STS-107. The experiment was designed to verify a new synthetic nutrient solution for an International Space Station (ISS) "model" specimen planned to be used extensively for ISS gene expression studies and was sponsored by the NASA Ames Research Center. Scientists are now looking over the experiment at KSC to determine if it will yield any scientific results. The investigation into the cause of the Columbia accident is ongoing. (Photo Credit: Volker Kern, NASA Ames Research Center)
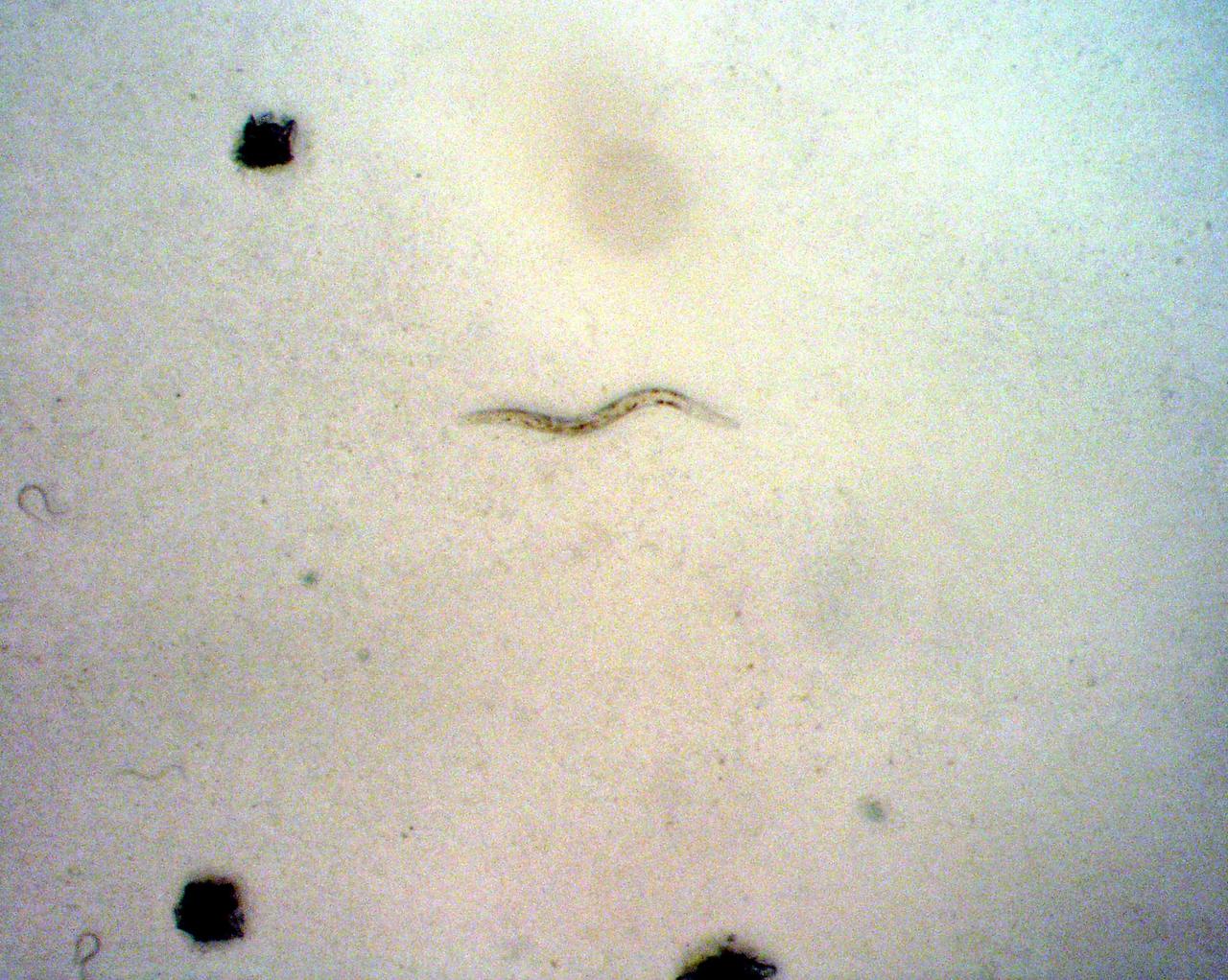
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - C. elegans nemotodes (round worms) undergo examination by project scientists. These specimens were found in a Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) container, a middeck experiment that was among the Columbia debris recovered in East Texas. The worms are descendants of those that were part of an experiment that flew on Columbia's last mission, STS-107. The experiment was designed to verify a new synthetic nutrient solution for an International Space Station (ISS) "model" specimen planned to be used extensively for ISS gene expression studies and was sponsored by the NASA Ames Research Center. Scientists are now looking over the experiment at KSC to determine if it will yield any scientific results. The investigation into the cause of the Columbia accident is ongoing. (Photo Credit: Volker Kern, NASA Ames Research Center)
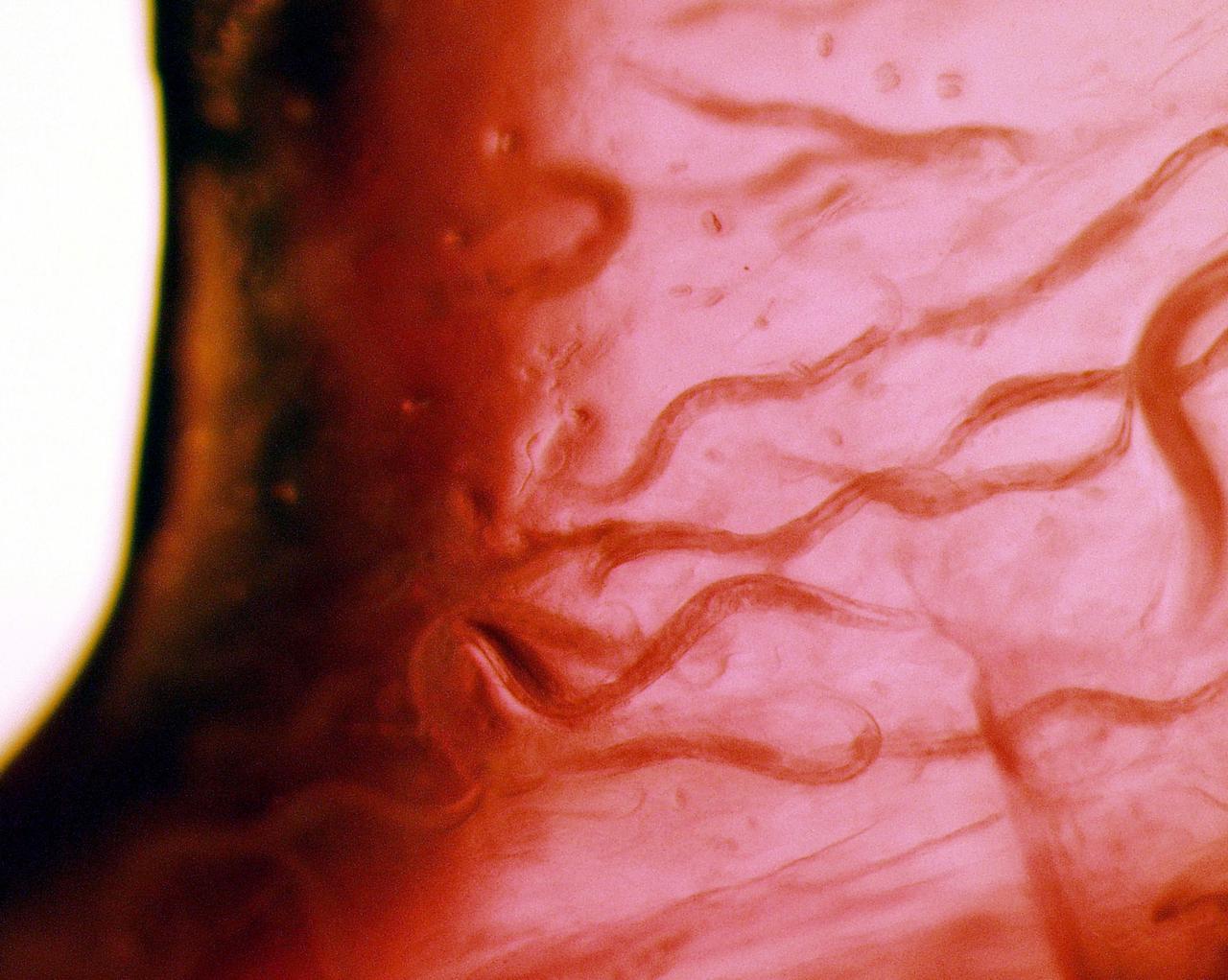
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - C. elegans nemotodes (round worms) undergo examination by project scientists. These specimens were found in a Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) container, a middeck experiment that was among the Columbia debris recovered in East Texas. The worms are descendants of those that were part of an experiment that flew on Columbia's last mission, STS-107. The experiment was designed to verify a new synthetic nutrient solution for an International Space Station (ISS) "model" specimen planned to be used extensively for ISS gene expression studies and was sponsored by the NASA Ames Research Center. Scientists are now looking over the experiment at KSC to determine if it will yield any scientific results. The investigation into the cause of the Columbia accident is ongoing. (Photo Credit: Volker Kern, NASA Ames Research Center)
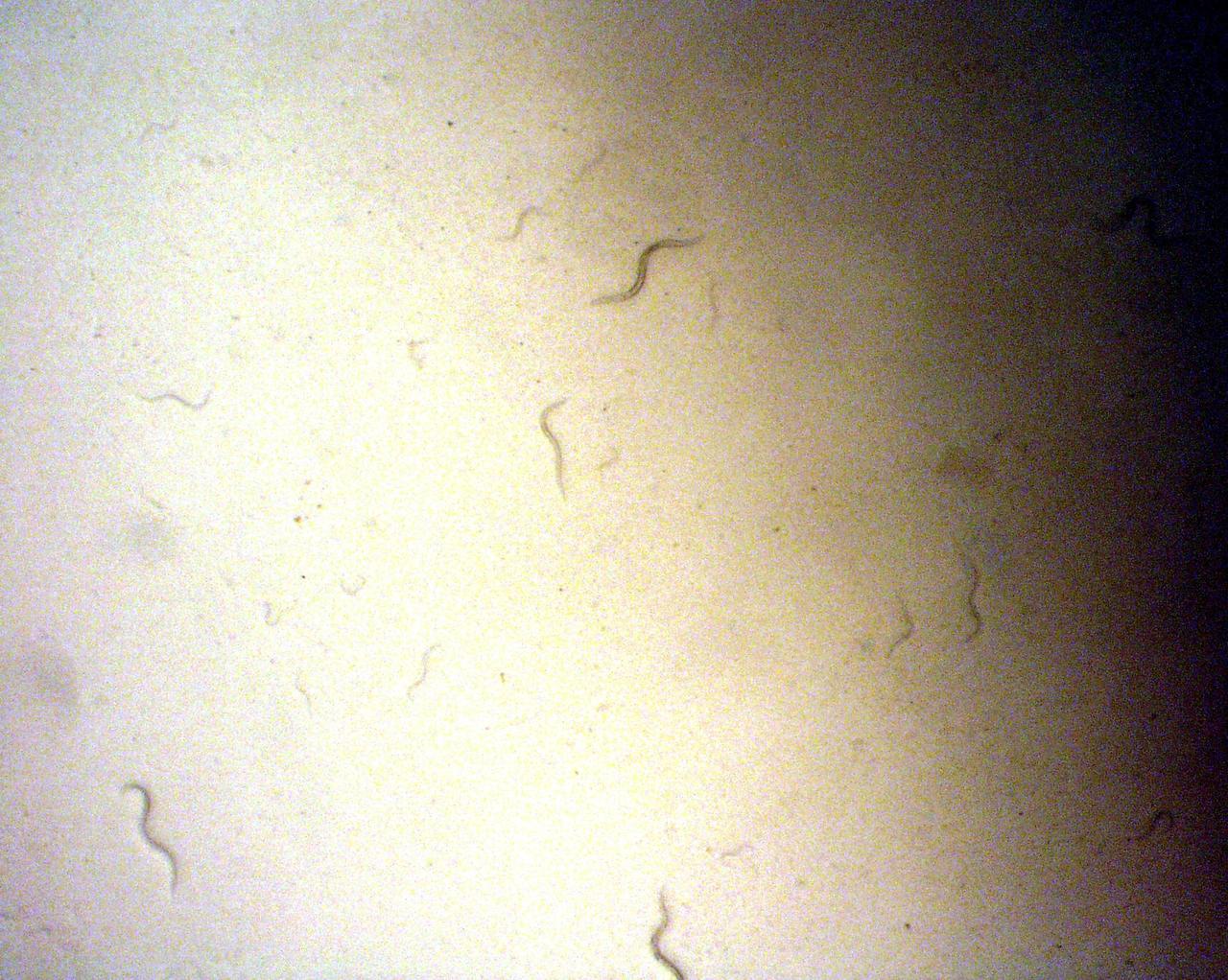
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - C. elegans nemotodes (round worms) undergo examination by project scientists. These specimens were found in a Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) container, a middeck experiment that was among the Columbia debris recovered in East Texas. The worms are descendants of those that were part of an experiment that flew on Columbia's last mission, STS-107. The experiment was designed to verify a new synthetic nutrient solution for an International Space Station (ISS) "model" specimen planned to be used extensively for ISS gene expression studies and was sponsored by the NASA Ames Research Center. Scientists are now looking over the experiment at KSC to determine if it will yield any scientific results. The investigation into the cause of the Columbia accident is ongoing. (Photo Credit: Volker Kern, NASA Ames Research Center)
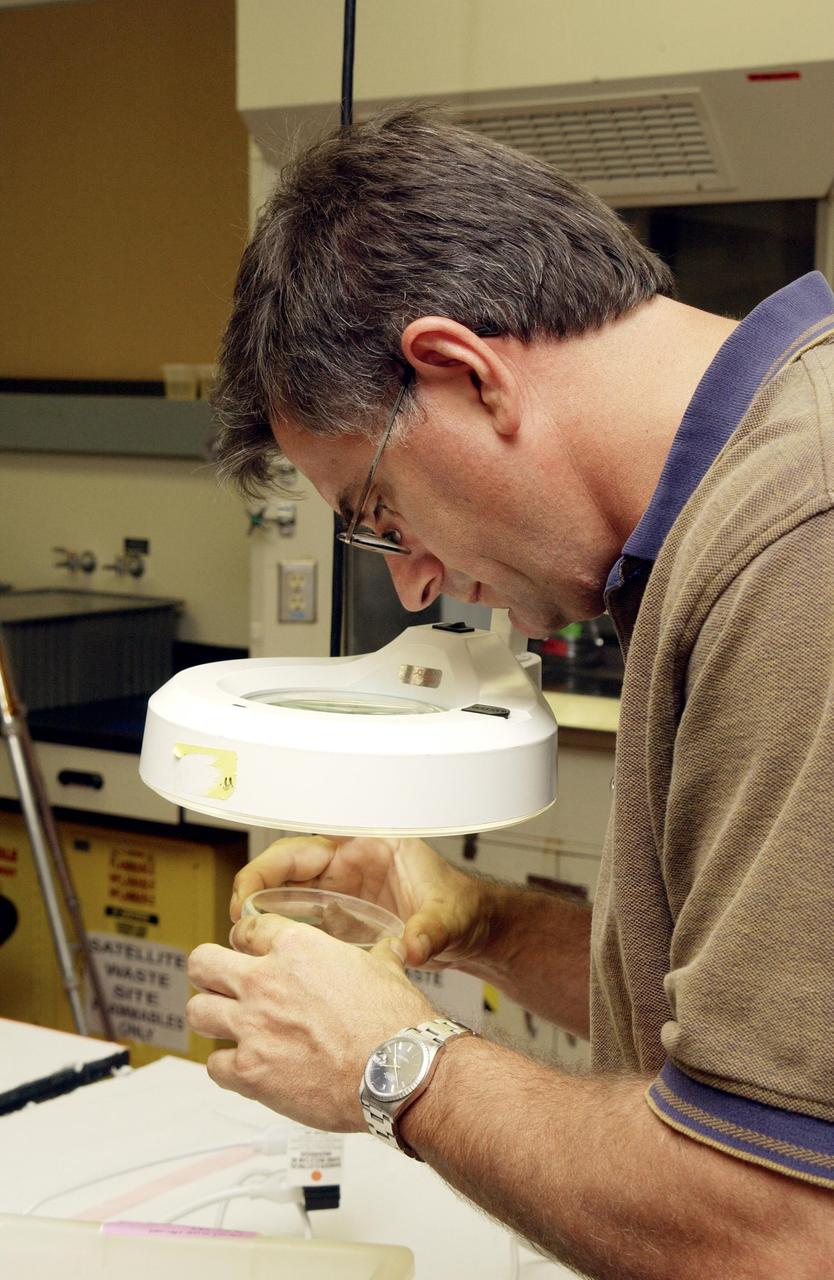

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Bionetics Project Engineer William McLamb examines a petri dish containing C. elegans nemotodes (round worms). These specimens were found in a Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) container, a middeck experiment that was among the Columbia debris recovered in East Texas. The worms are descendants of those that were part of an experiment that flew on Columbia's last mission, STS-107. The experiment was designed to verify a new synthetic nutrient solution for an International Space Station (ISS) "model" specimen planned to be used extensively for ISS gene expression studies and was sponsored by the NASA Ames Research Center. Scientists are now looking over the experiment at KSC to determine if it will yield any scientific results. The investigation into the cause of the Columbia accident is ongoing.
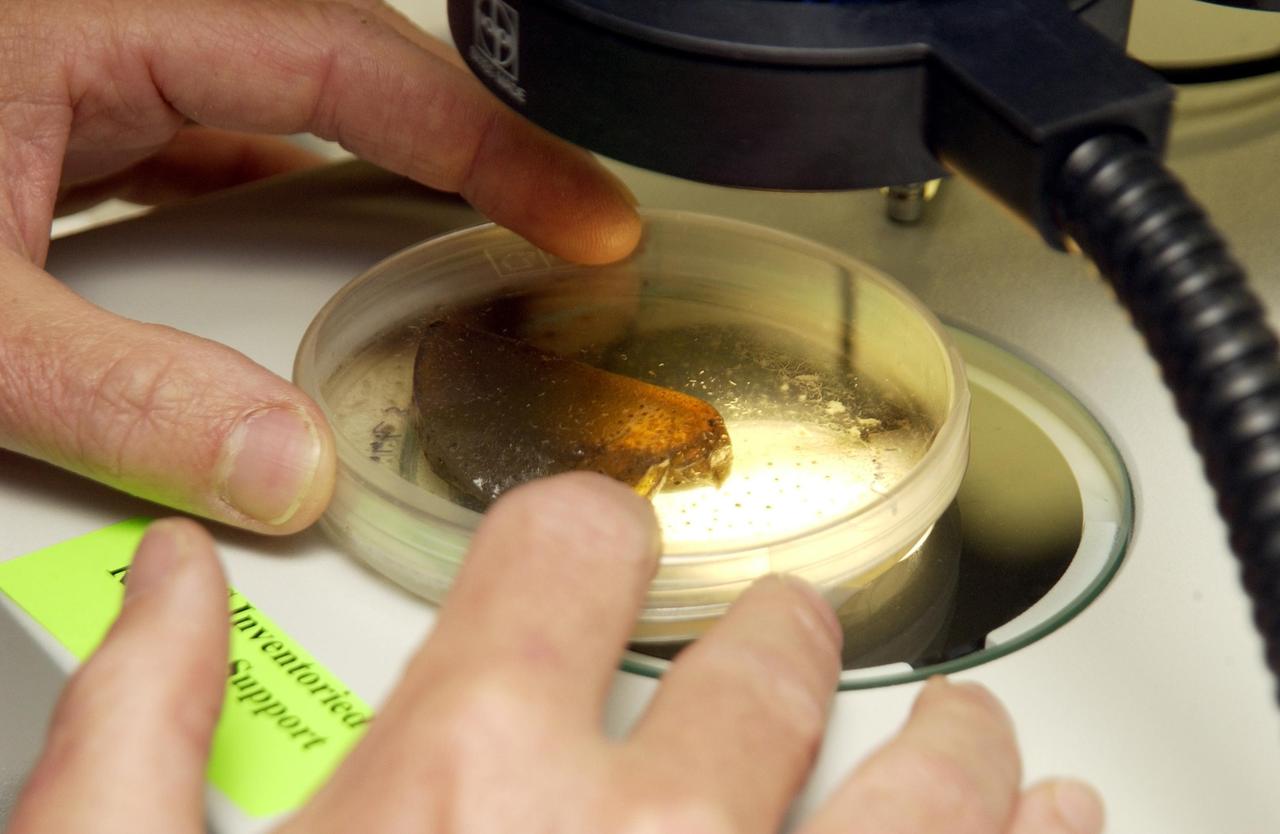
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A petri dish containing C. elegans nemotodes (round worms) is prepared for examination by project scientists. These specimens were found in a Biological Research in Canisters (BRIC) container, a middeck experiment that was among the Columbia debris recovered in East Texas. The worms are descendants of those that were part of an experiment that flew on Columbia's last mission, STS-107. The experiment was designed to verify a new synthetic nutrient solution for an International Space Station (ISS) "model" specimen planned to be used extensively for ISS gene expression studies and was sponsored by the NASA Ames Research Center. Scientists are now looking over the experiment at KSC to determine if it will yield any scientific results. The investigation into the cause of the Columbia accident is ongoing.
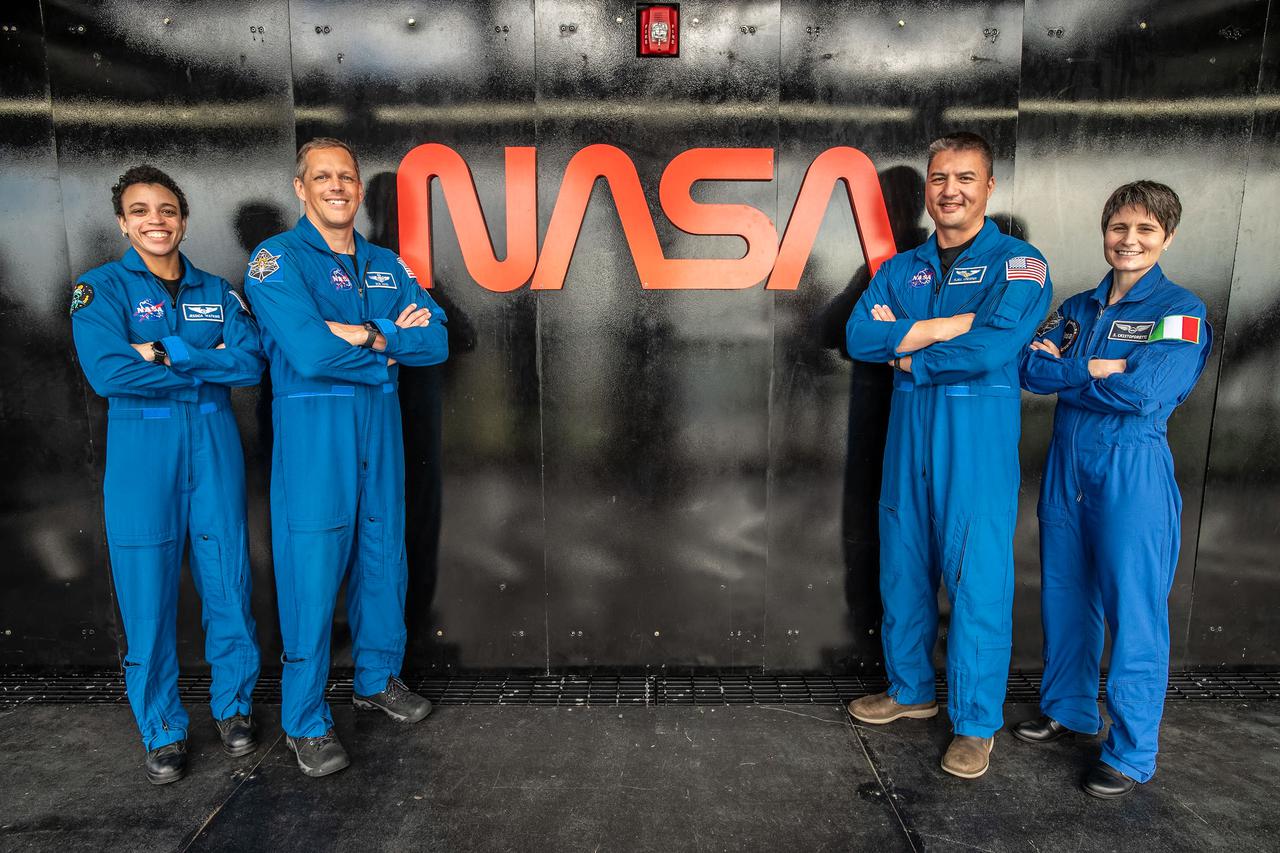

jsc2022e003354 (Dec. 1, 2021) --- NASA’s SpaceX Crew-4 astronauts pose in front of the NASA “worm” logo during a training session at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. From left to right: NASA astronaut and SpaceX Crew-4 mission specialist Jessica Watkins; NASA astronaut and SpaceX Crew-4 pilot Robert “Bob” Hines; NASA astronaut and SpaceX Crew-4 commander Kjell Lindgren; and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut and Crew-4 mission specialist Samantha Cristoforetti of Italy.

The NASA Worm Logo sign is unveiled before the ribbon cutting ceremony to open NASA’s Earth Information Center, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The Earth Information Center is new immersive experience that combines live data sets with cutting-edge data visualization and storytelling to allow visitors to see how our planet is changing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

The NASA Worm Logo sign is unveiled before the ribbon cutting ceremony to open NASA’s Earth Information Center, Wednesday, June 21, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The Earth Information Center is new immersive experience that combines live data sets with cutting-edge data visualization and storytelling to allow visitors to see how our planet is changing. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
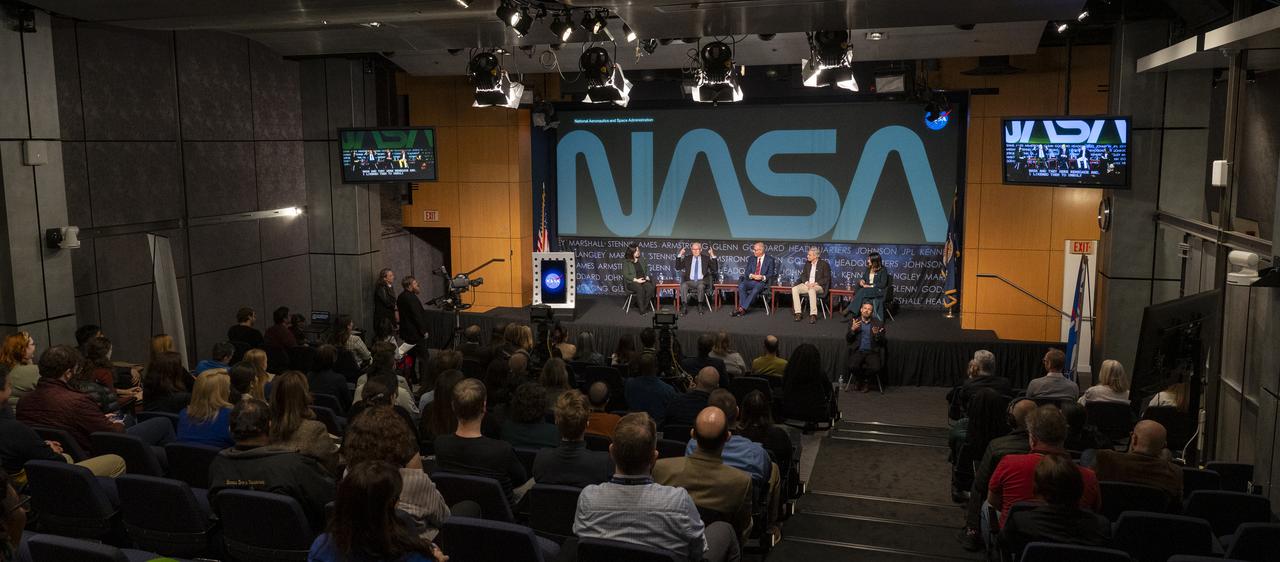

From left to right, moderator and Washington Post design reporter Shelly Tan, creator of the NASA worm logotype Richard Danne, Pentagram designer Michael Bierut, NASA entertainment and branding liaison Bert Ulrich, and Amazon Music head of live event merchandise Julia Heiser, participate in a panel discussion during a Richard Danne dedication event, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

From left to right, moderator and Washington Post design reporter Shelly Tan, creator of the NASA worm logotype Richard Danne, Pentagram designer Michael Bierut, NASA entertainment and branding liaison Bert Ulrich, and Amazon Music head of live event merchandise Julia Heiser, participate in a panel discussion during a Richard Danne dedication event, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)

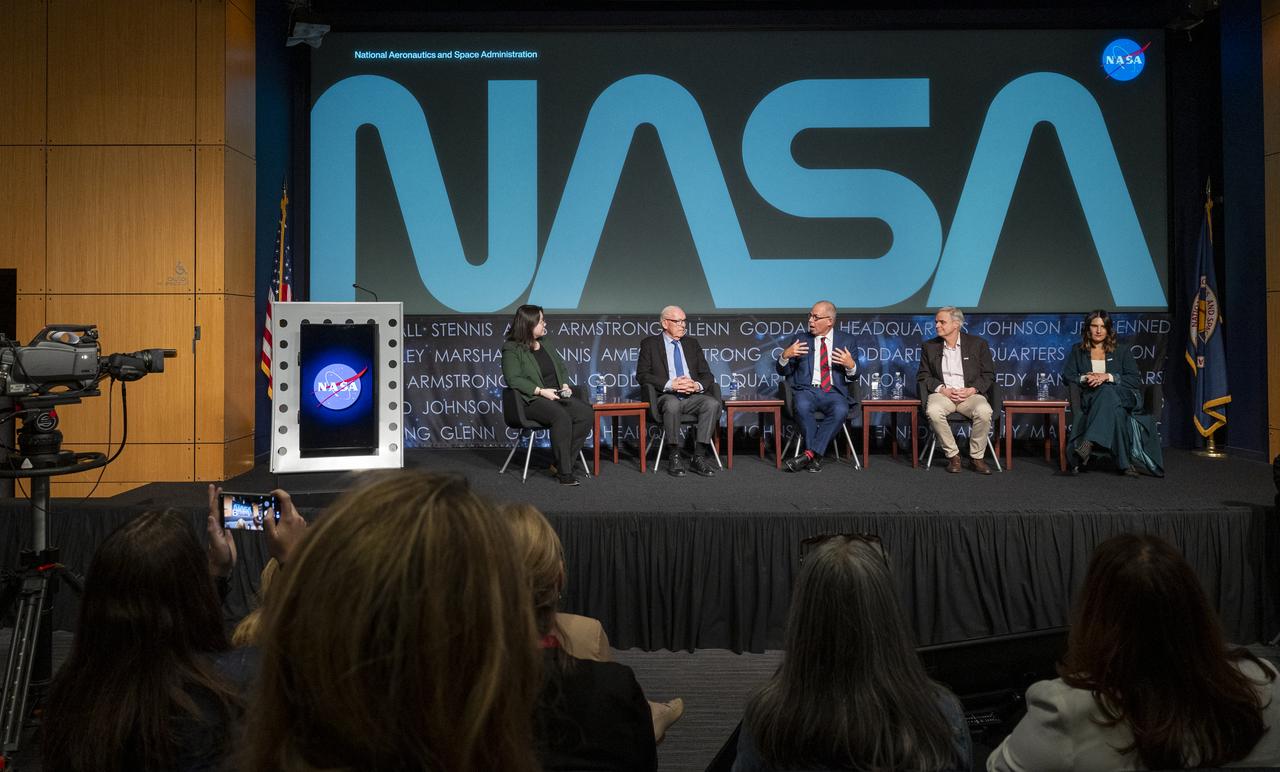
From left to right, moderator and Washington Post design reporter Shelly Tan, creator of the NASA worm logotype Richard Danne, and Pentagram designer Michael Bierut, participate in a panel discussion during a Richard Danne dedication event, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
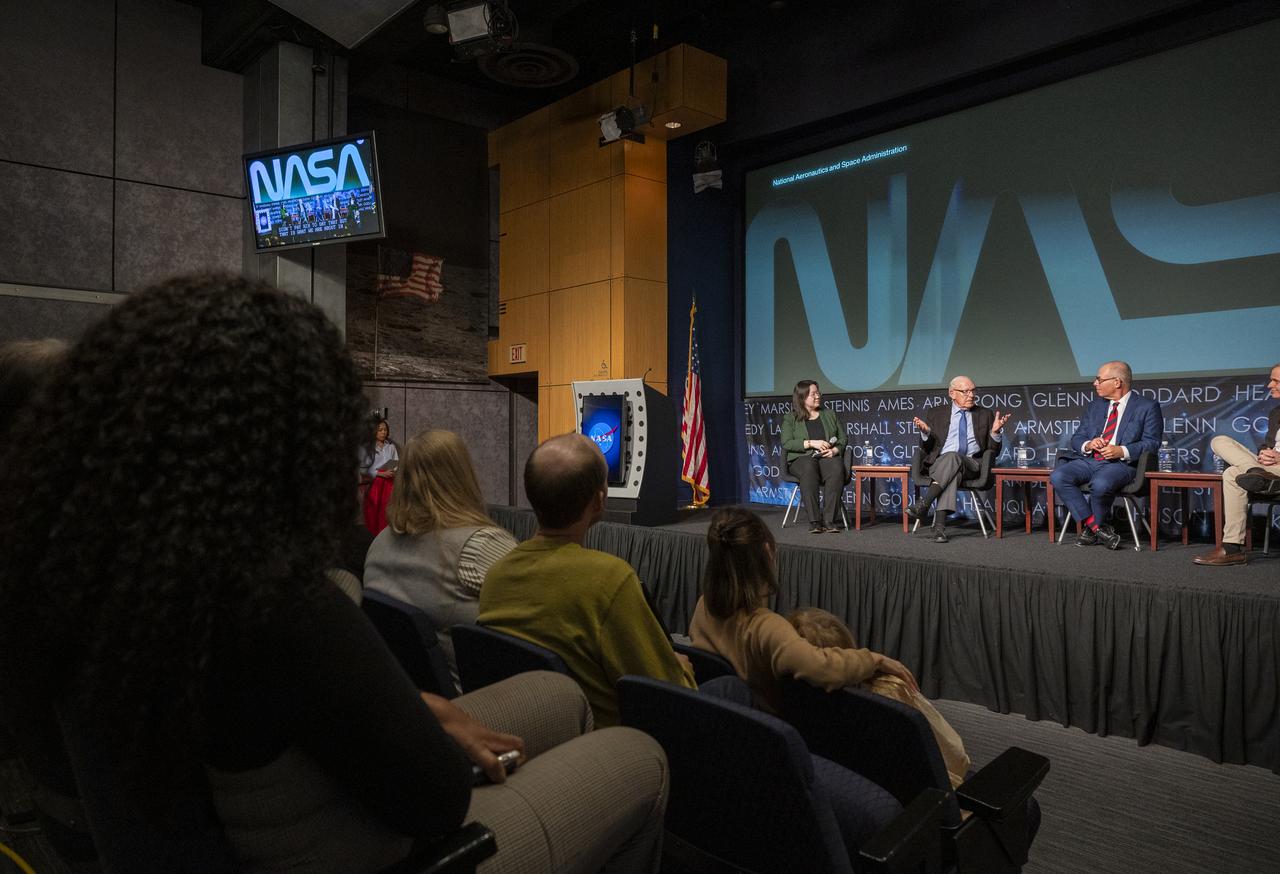

From left to right, moderator and Washington Post design reporter Shelly Tan, creator of the NASA worm logotype Richard Danne, and Pentagram designer Michael Bierut, participate in a panel discussion during a Richard Danne dedication event, Monday, Nov. 6, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
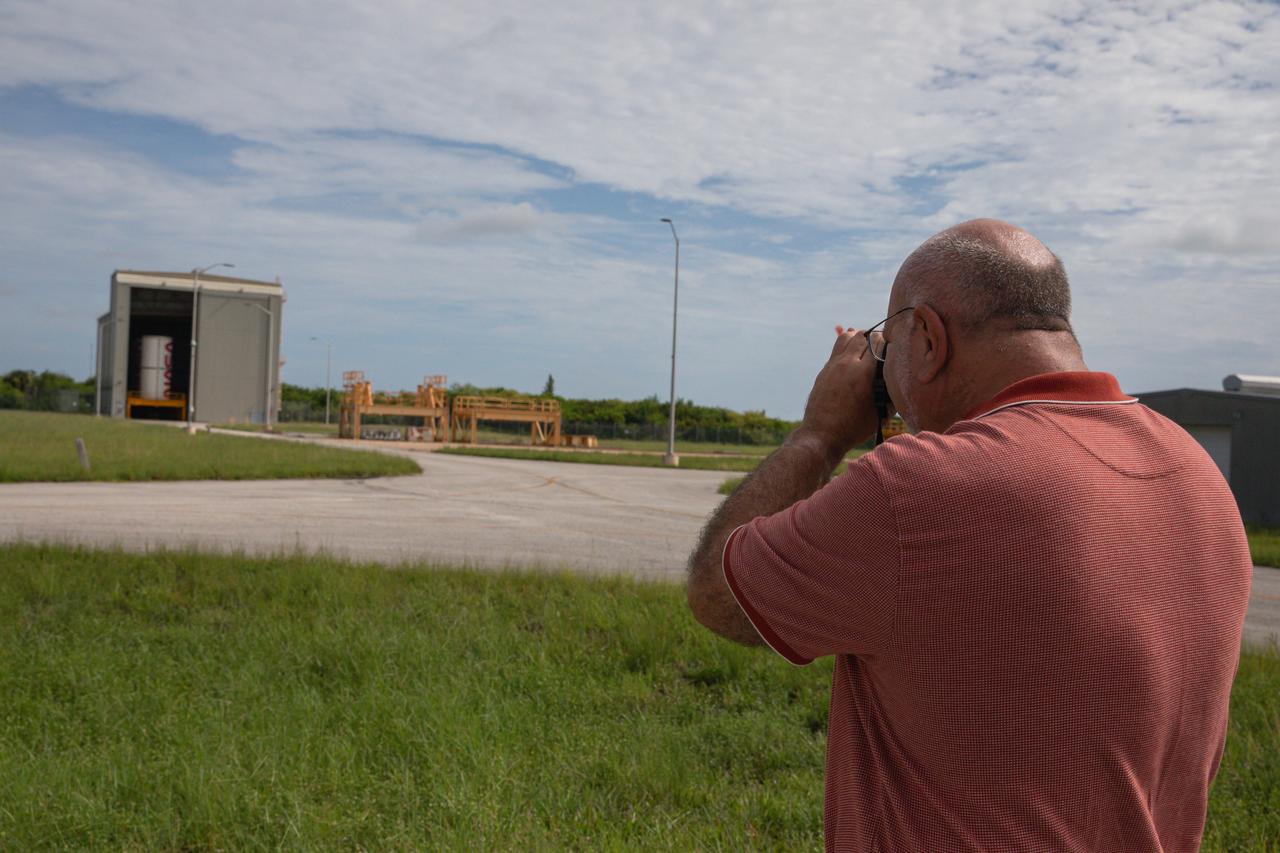

A member of the media takes a photo of the NASA worm on one of the solid rocket booster segments inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Tuesday, July 23, 2024. The booster segments will help propel the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket on the Artemis II mission to send four astronauts around the Moon as part of the agency’s effort to establish a long-term science and exploration presence at the Moon, and eventually Mars.
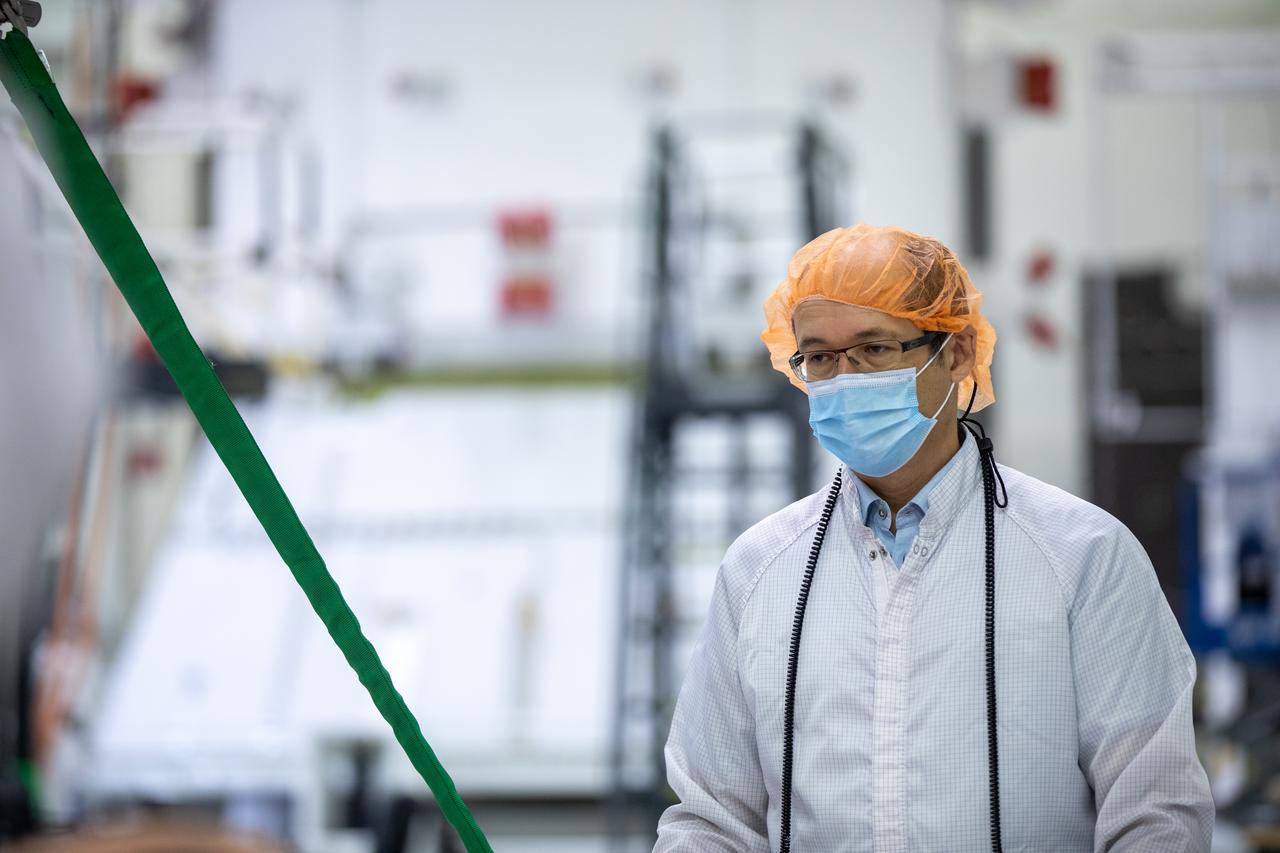

Rachid Amekrane, Airbus Defence and Space Integration test director, assists with securing a protective cover as a crane prepares to lift the panel during installation of one of four solar array wings inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The Orion spacecraft for Artemis I is shown in the background. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
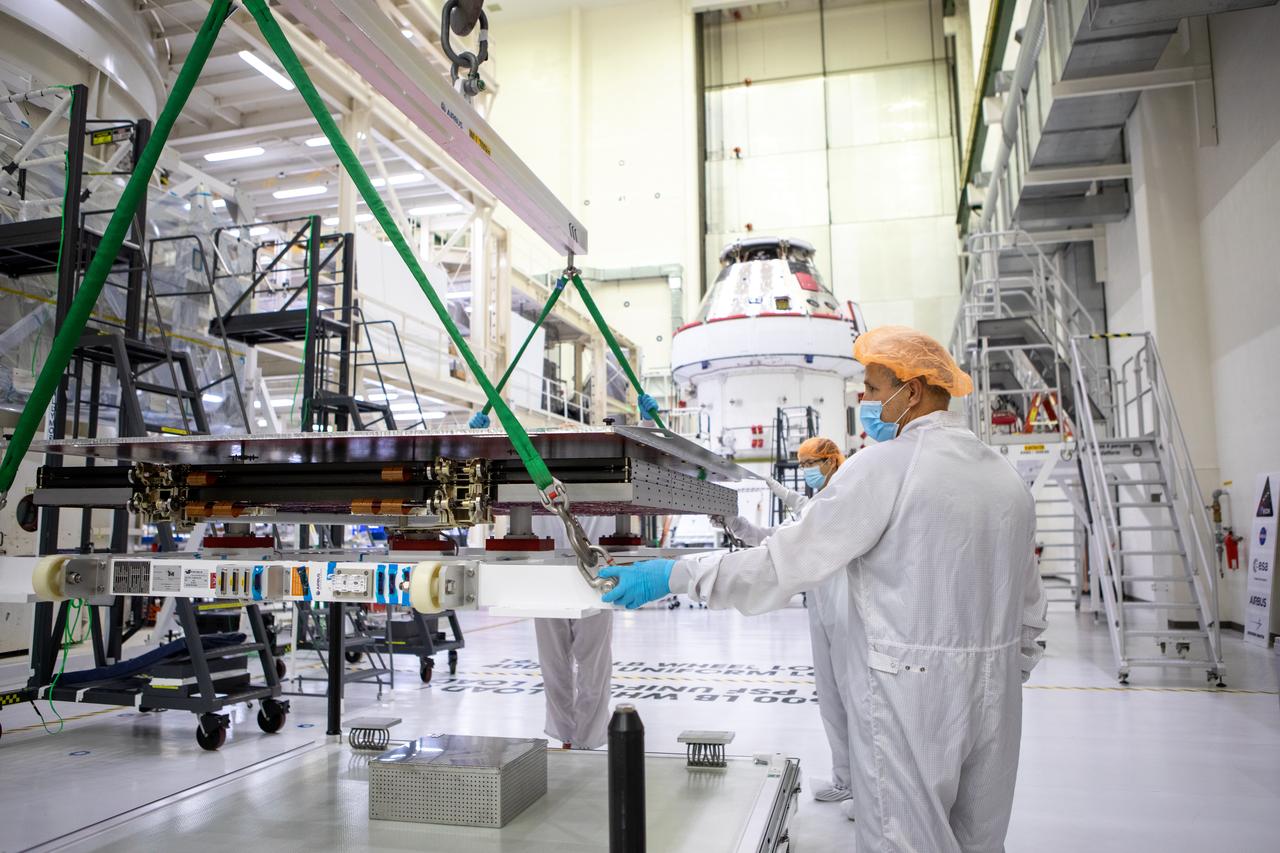

Technicians with European Service Module processing teams from the European Space Agency, Airbus, and Airbus Netherlands assist with securing a protective cover as a crane prepares to lift the panel during installation of one of four solar array wings inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The Orion spacecraft for Artemis I is shown in the background. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.
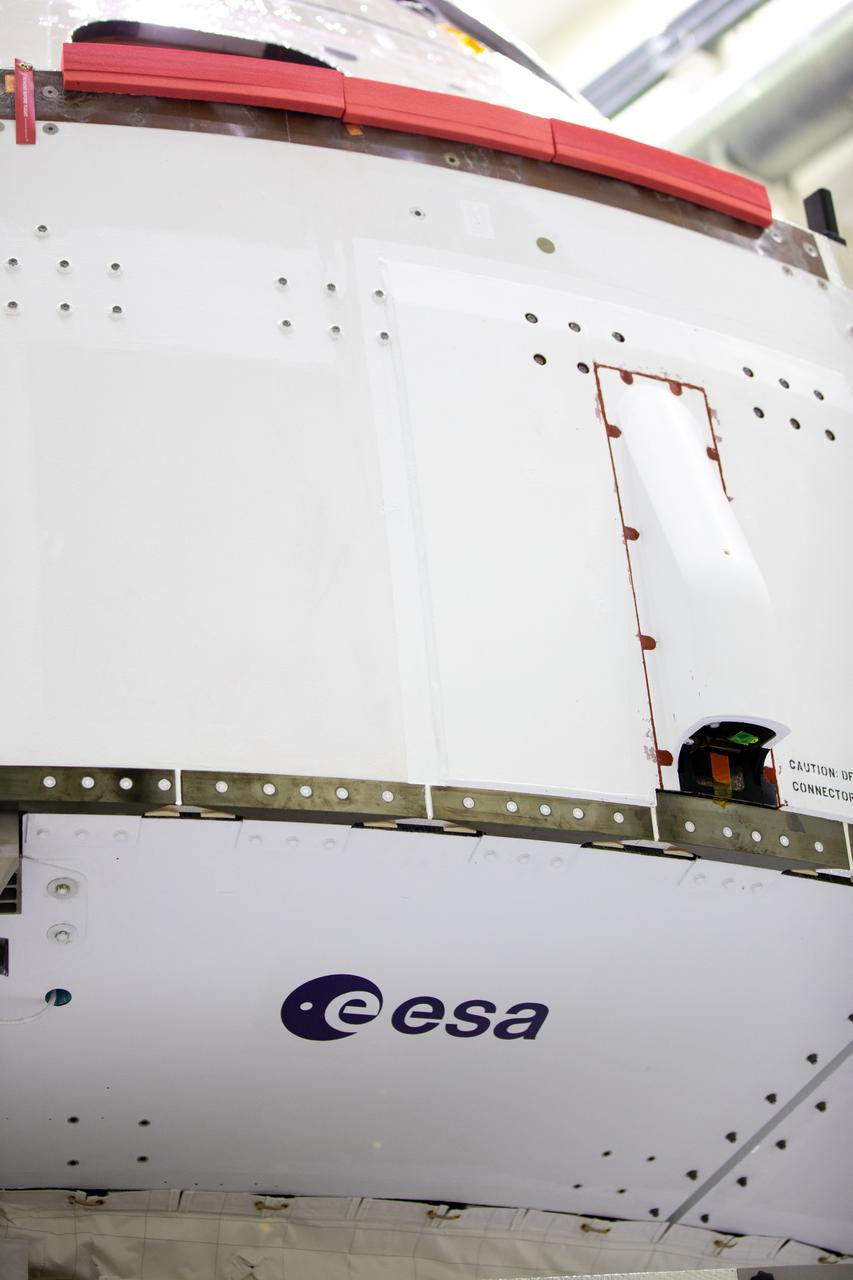

Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at Kennedy Space Center, the European Space Agency (ESA) logo has been added to the aft wall of Orion’s crew module adapter ahead of NASA’s Artemis I mission. The Orion spacecraft is being prepared for installation of the solar array wings on Sept. 23, 2020. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon by 2024.
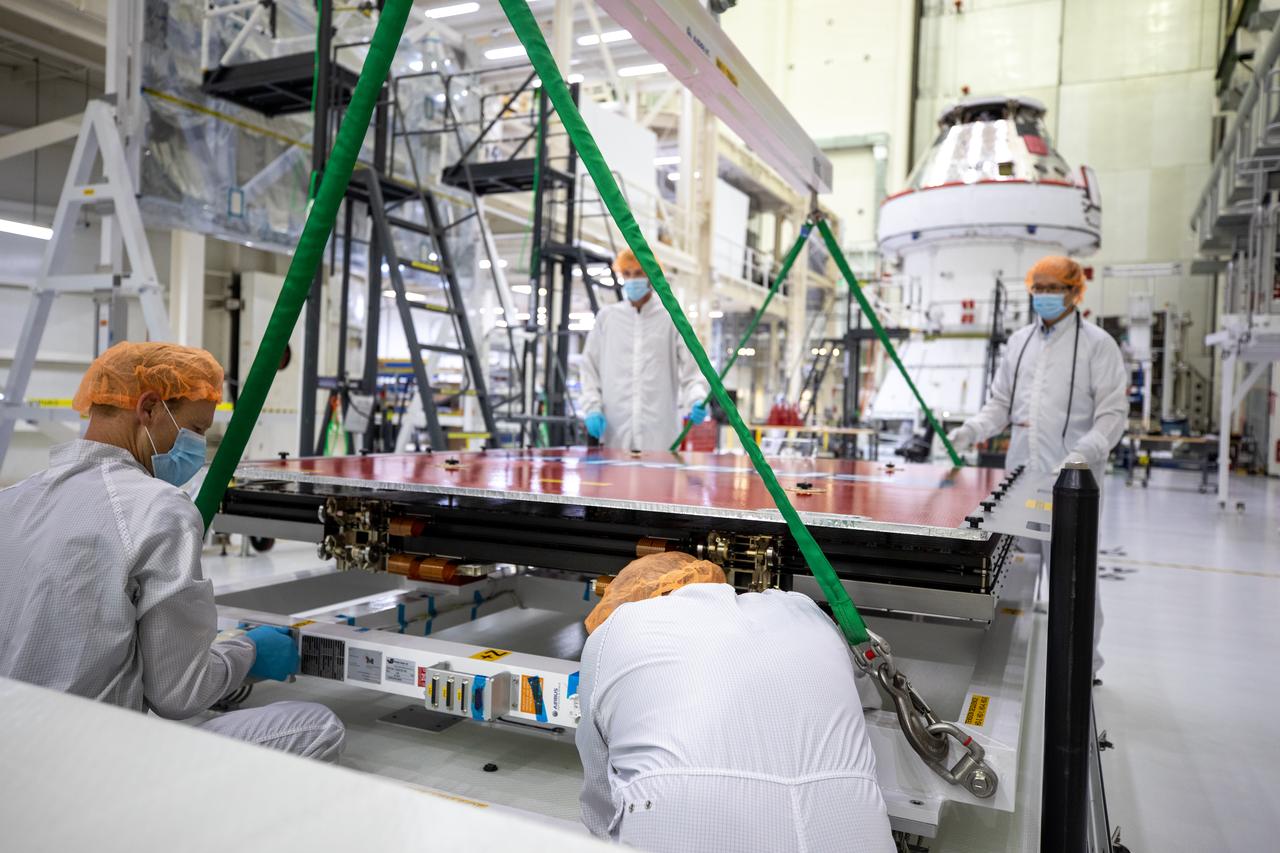

Technicians with European Service Module processing teams from the European Space Agency, Airbus, and Airbus Netherlands assist with securing a protective cover as a crane prepares to lift the panel during installation of one of four solar array wings inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sept. 23, 2020. The Orion spacecraft for Artemis I is shown in the background. The solar arrays were extended, inspected, and then retracted, before installation on the spacecraft. Each solar array panel will generate 11 kilowatts of power and span about 63 feet. The array is a component of Orion’s service module, which is provided by the European Space Agency and built by Airbus Defence and Space to supply Orion’s power, propulsion, air and water. The first in a series of increasingly complex missions, Artemis I will test the Orion spacecraft and Space Launch System as an integrated system ahead of crewed flights to the Moon. Under the Artemis program, NASA will land the first woman and the next man on the Moon in 2024.