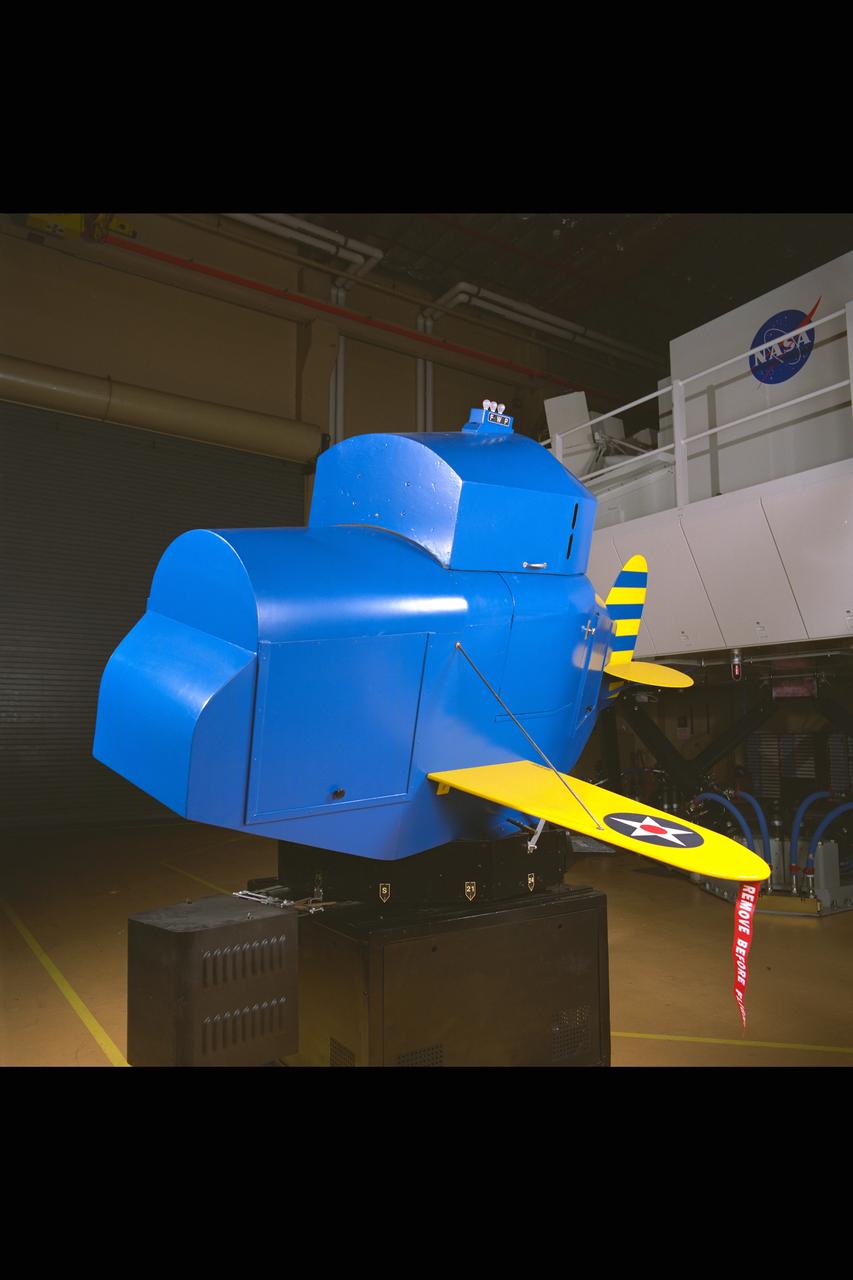
Link Trainer - Blue Box. Historical (1910's) at NASA Ames Research Center N-257 Crew Vehicle Systems Research Facility (CVSRF) Simulator.
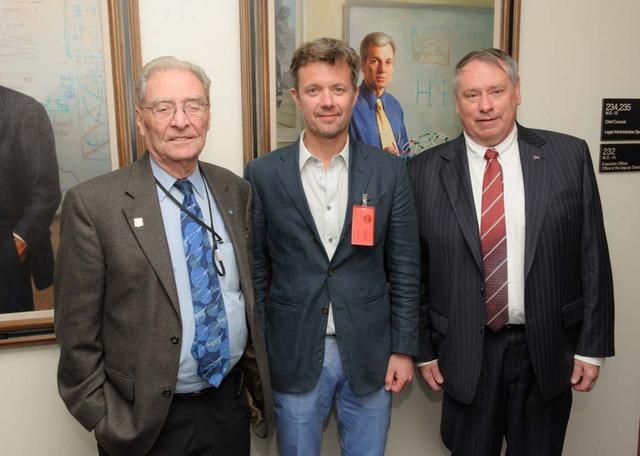

HRH Prince Frederik of Denmark visit and tour of NASA Ames Research Center. from Left to right Shown the with Ames Special Advisor to the Director John W. 'Jack' Boyd, HRH, and Ames Center Director S. Pete Worden.
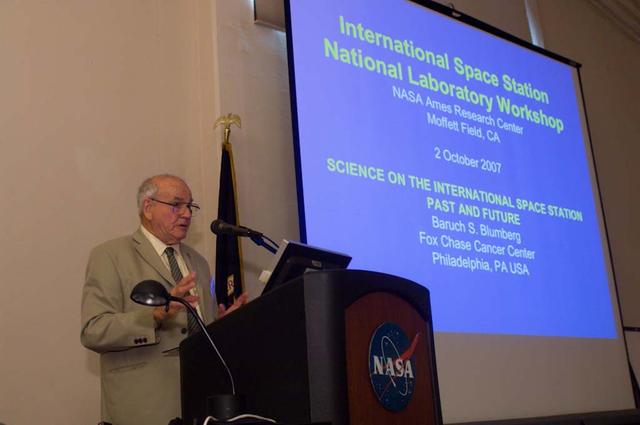

International Space Station (ISS) National Laboratory Workshop held at the NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, CA . Baruch S. Blumberg at podium.
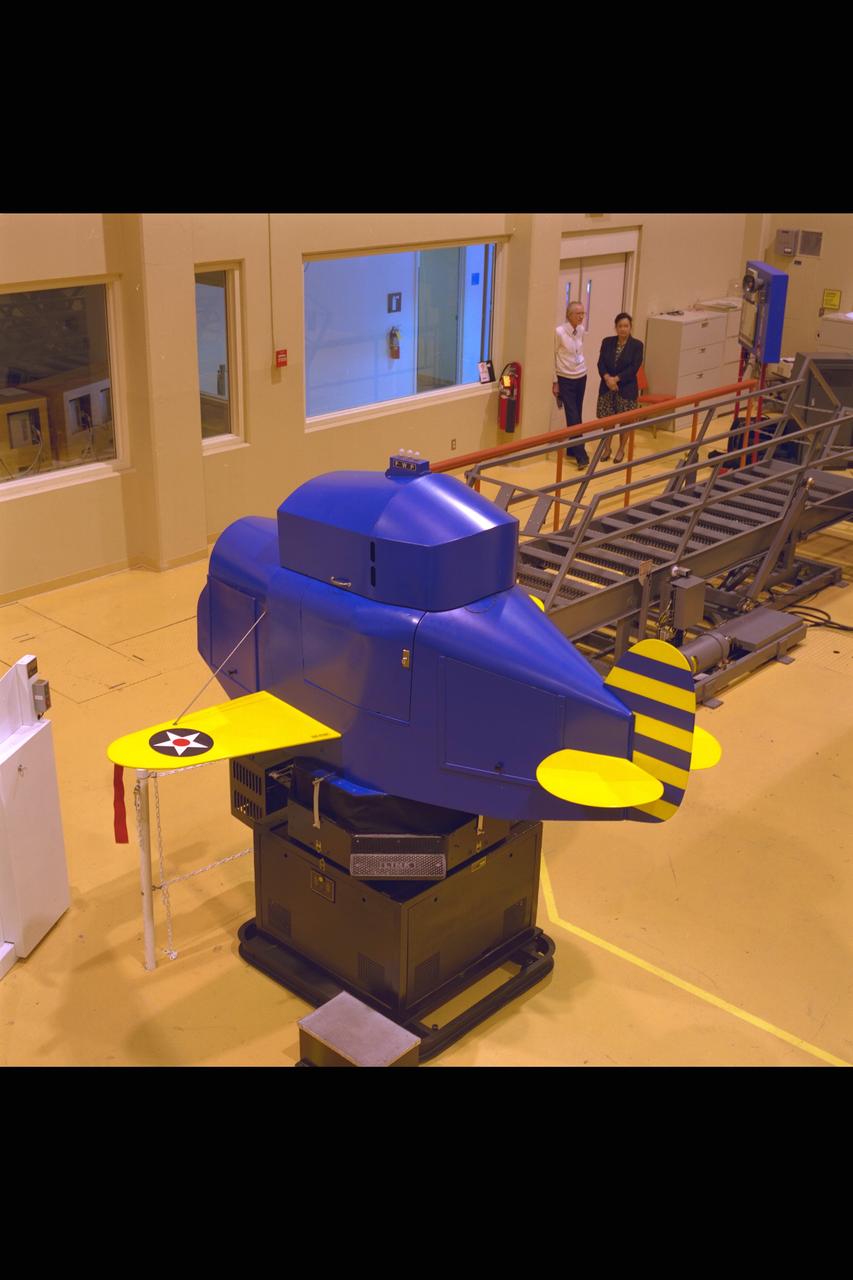

Link Trainer - Blue Box. Historical (1910's) Simulator installed in the NASA Ames Research Center N-257 Crew Vehicle Systems Research Facility (CVSRF)
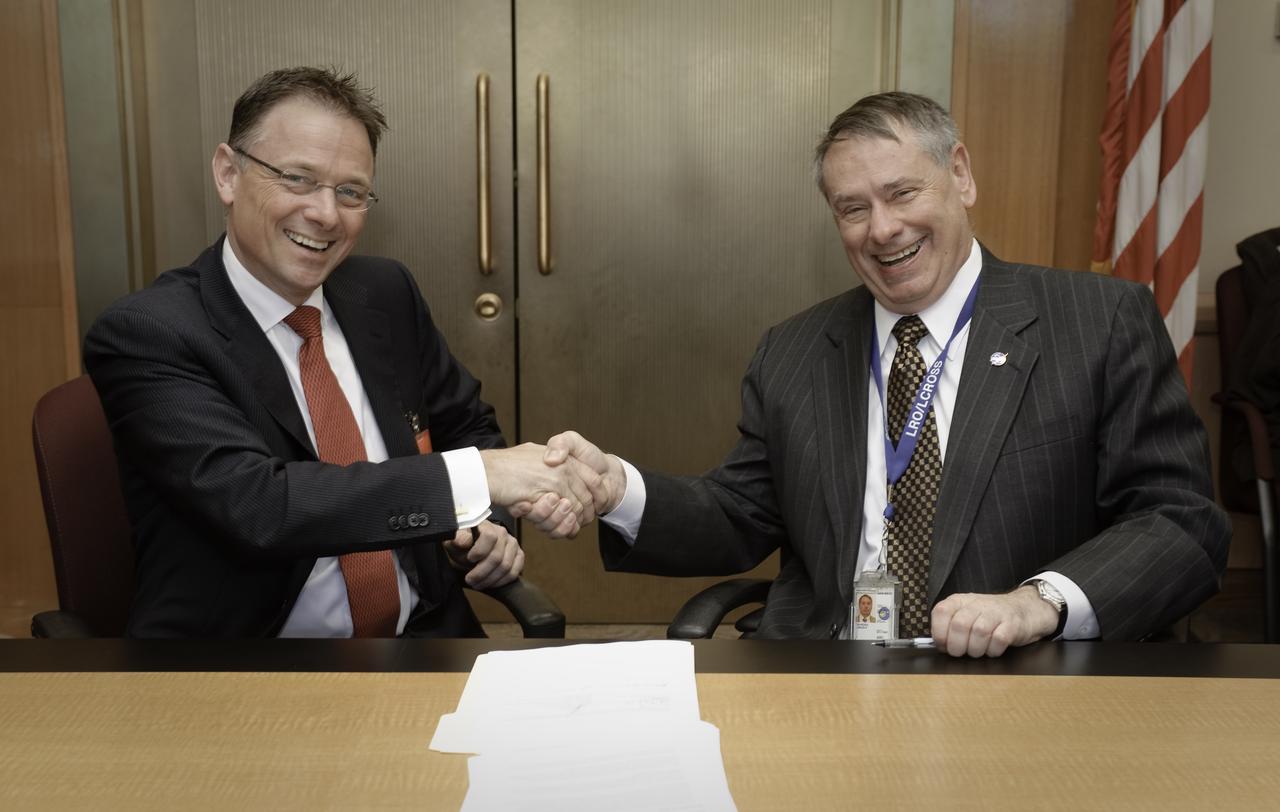

Netherlands Memorandum of Record (MOR) agreement signing the NASA Ames Research Center, Mofffett Field, California. Signing the MOR are on left Dr. Louis B.J.Vertegaal, Director of Physical Sciences, Chemistry, and Advanced Chemical Technologies for Sustainability, of the Netherlands Organisation for Scientific Research (NWO) and on right Dr. S. Pete Worden, Director NASA Ames Research Center
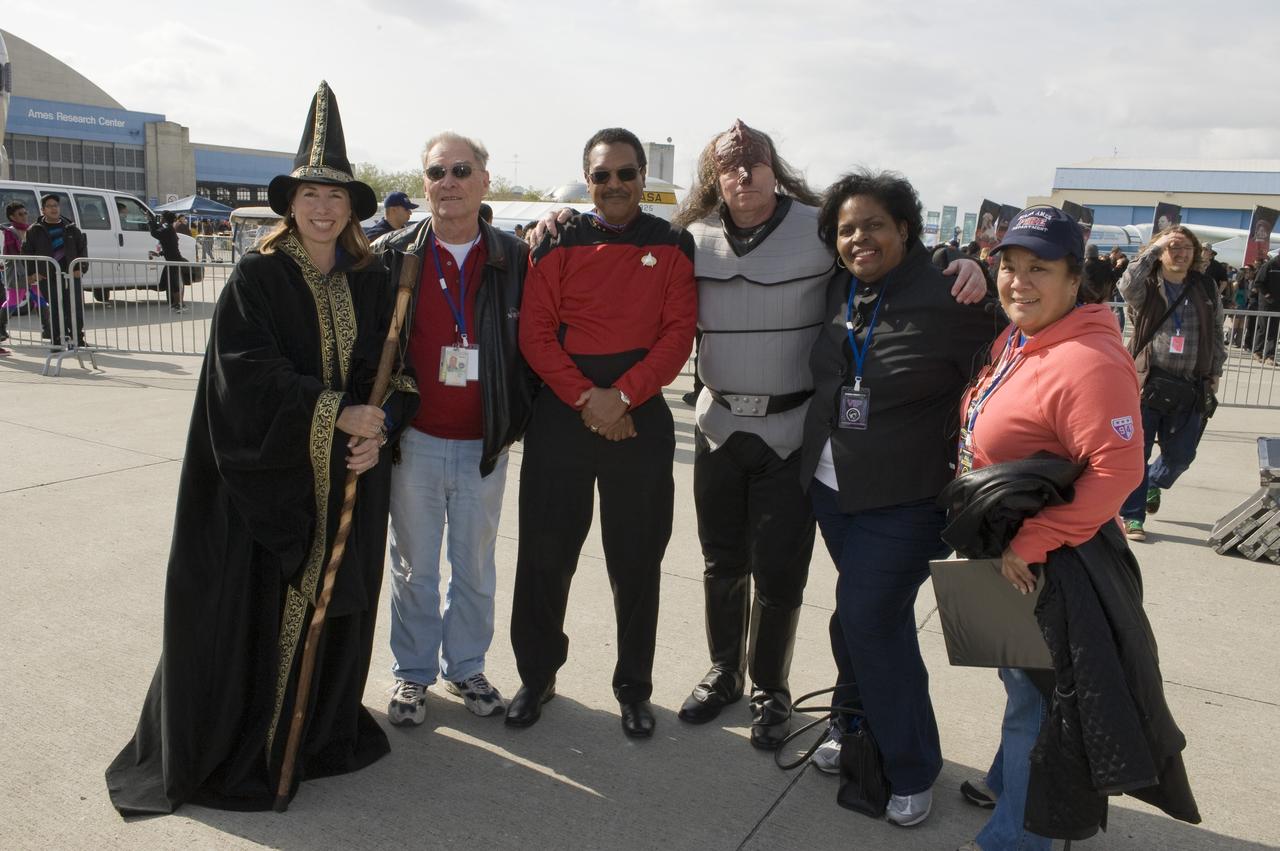

2010 Yuri's Night celebration held at the NASA Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif. as part of the world wide celebration of the first man in space and the Space Shuttle program that followed 20 years later. From left to Right, Wizard Lori Garver, Deputy Administrator of NASA, Jack Boyd, Senior Advisor to the Director, Lewis Braxton, III, Deputy Director of Ames Research Center, Klingon S. Pete Worden, Director, Ames Research Center, Karen Bradford, Chief of Staff, Deborah Feng, Director, Center Operations.
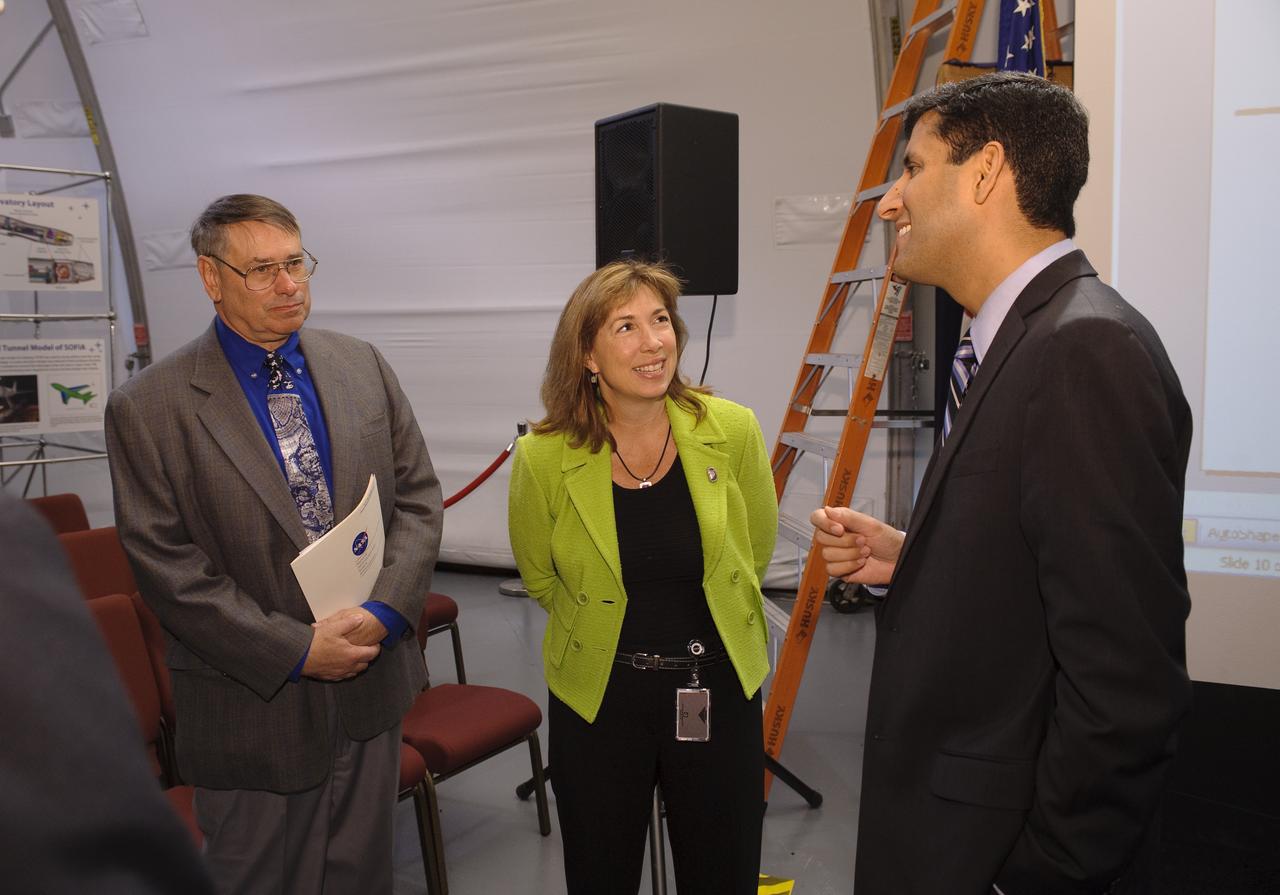

Obama Administration launches Cloud Computing Initiative at Ames Research Center with left to right; S. Pete Worden, Center Director, Lori Garver, NASA Deputy Administrator, Vivek Kundra, White House Chief Federal Information Officer
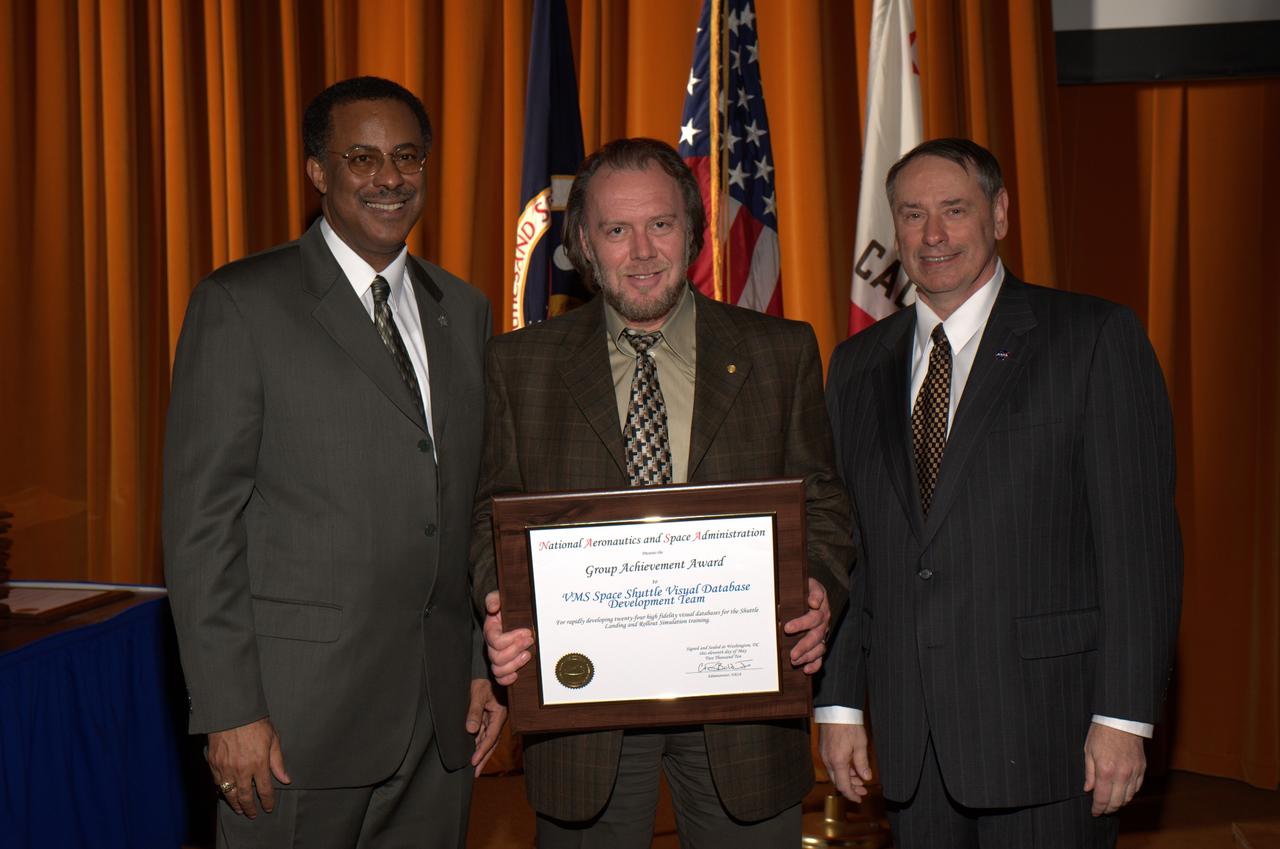

2010 NASA Honor Awards Awards Group Achievement Award to VMS Space Shuttle Visual Database Development Team. Boris M. Rabin accepting. Presenters are on left Mr. Charles H. Scales, NASA Associate Deputy Administrator, on right Dr. S. Pete Worden, Director, NASA Ames Research Center.
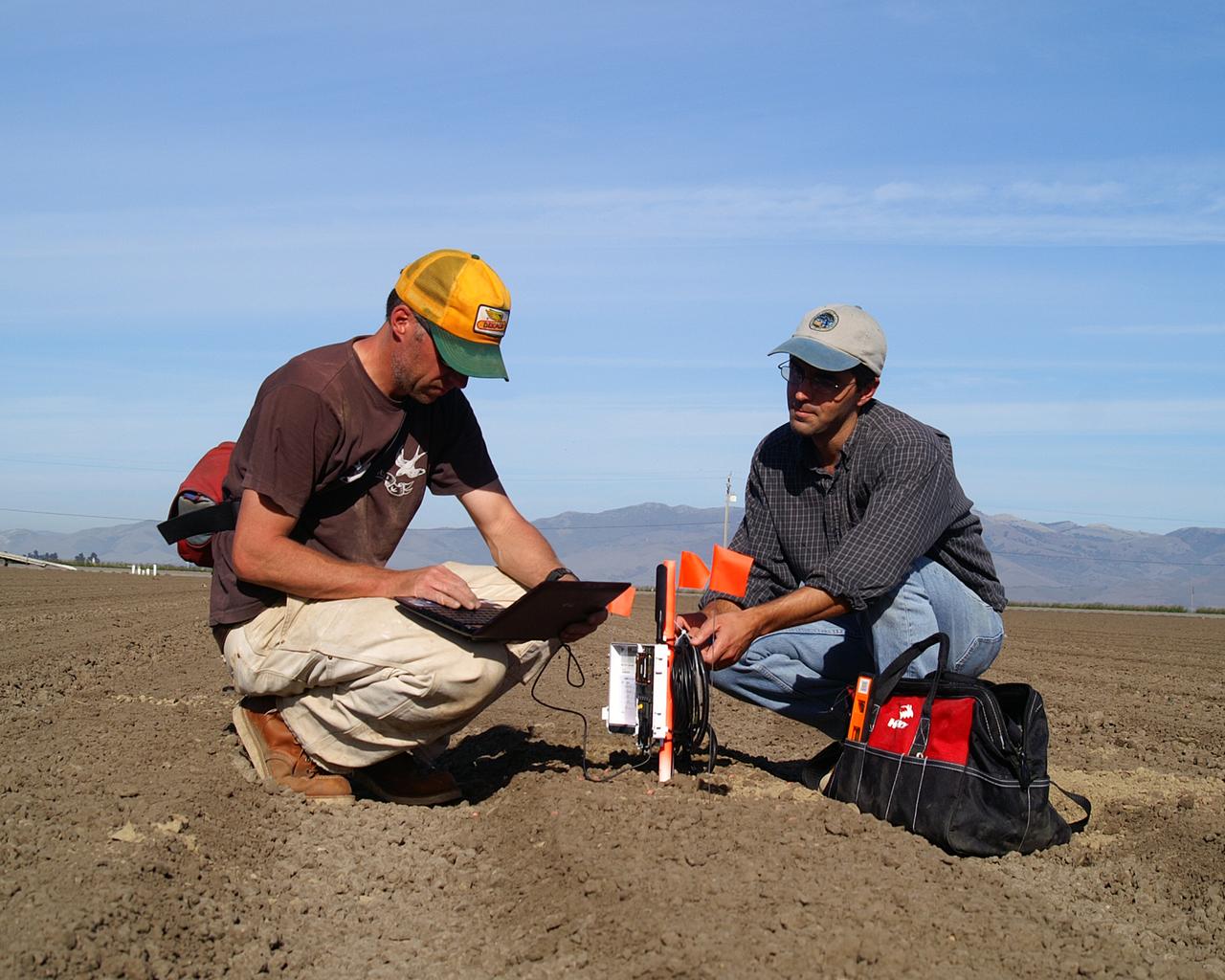

Wireless crop water monitoring project: Dr. Chris Lund and Forrest Melton, California State University Monterey Bay research scientists who work at NASA Ames Research Center, check data being returned from a wireless soil moisture monitoring network, installed in an agricultural field. Data from the soil moisture sensor network will be used to assist in interpretation of the satellite estimates of crop water demand. Image of courtesy of Forrest S. Melton
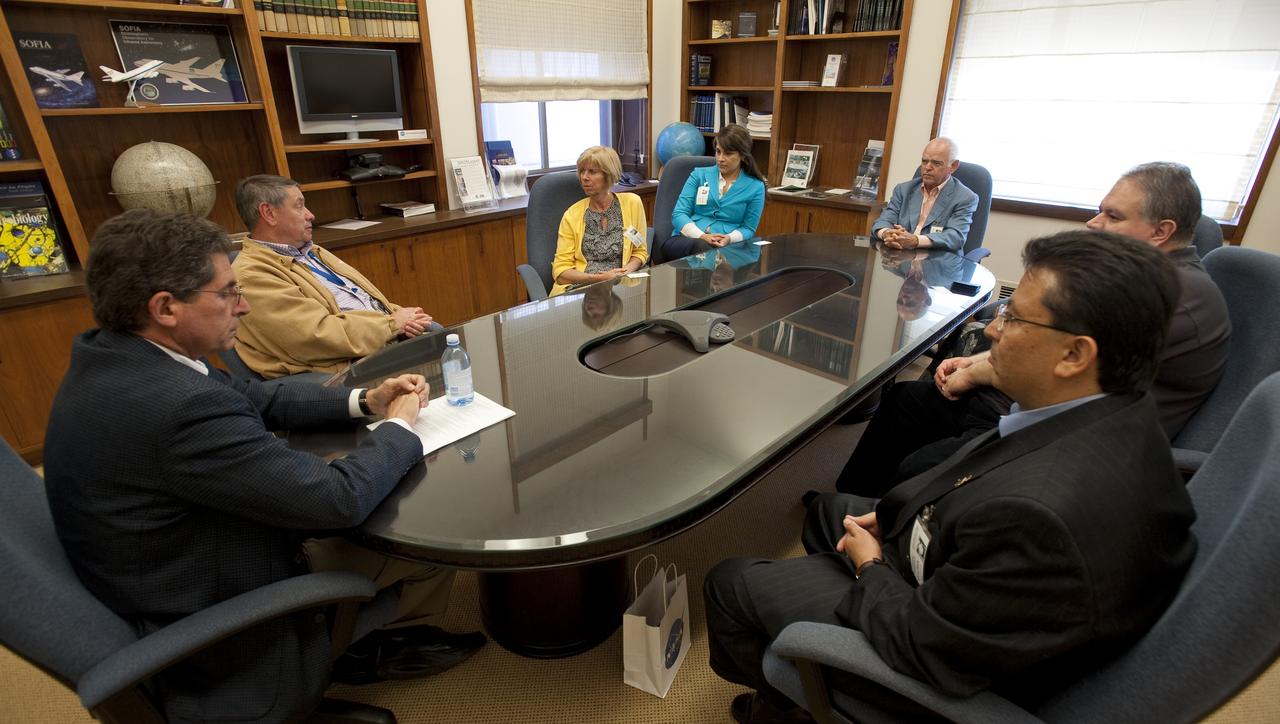

Janice Hahn, Councilwoman, District 15, City of Los Angeles visits NASA Ames Research Center. Associate Director Steve Zornetzer and Center Director S. Pete Worden meet with .Janice Hahn, Councilwoman, District 15, City of Los Angeles, Jenny Chavez, Staffer for Councilwoman Hahn, Walter Zifkin, Commissioner, Los Angles International Airport, Michael Molina, Chief of External Affairs, LAWA, Jaideep Vaswani. Chief of Airport Planning, LAWA
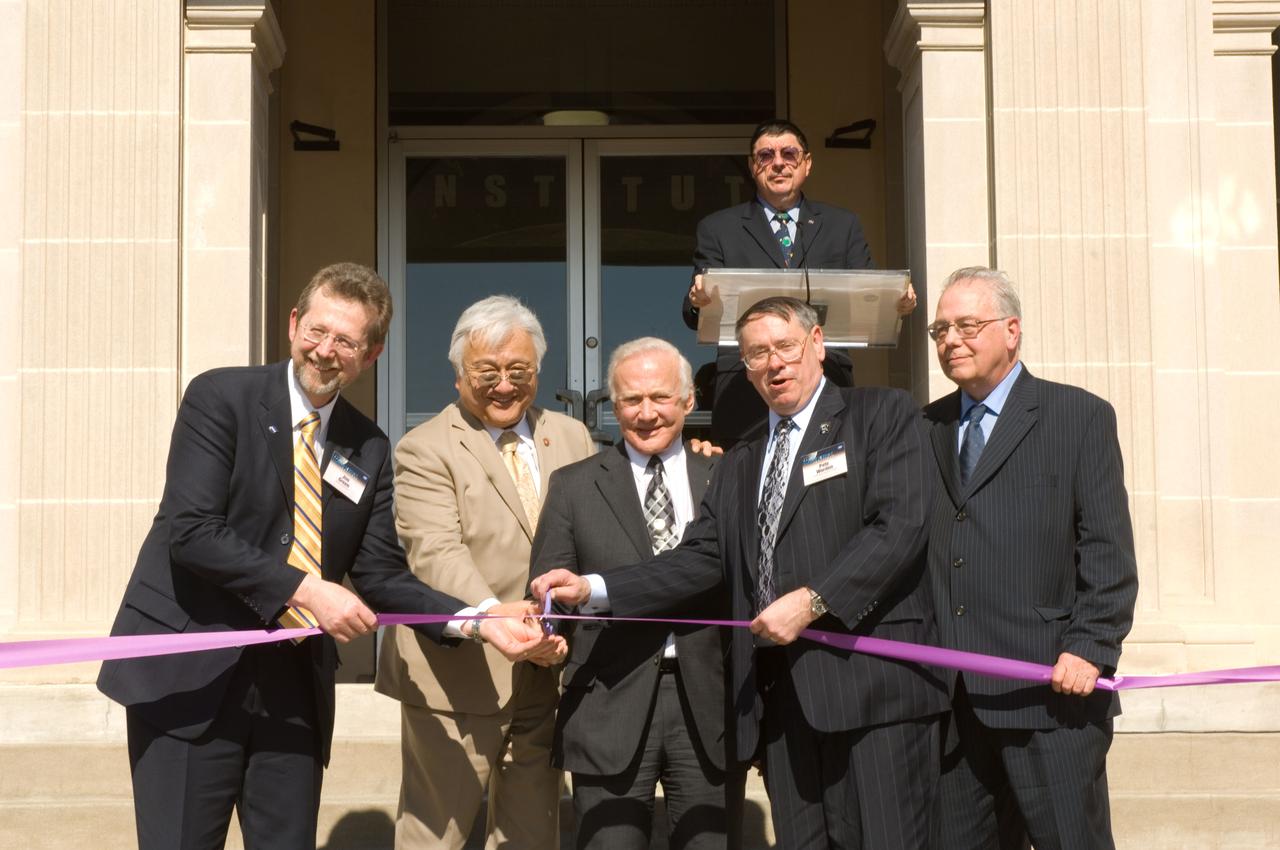

Lunar Science Institute (LSI) Grand Opening. Ribbon Cutting, L-R: James Green, Director, Planetary Programs, NASA Headquarters, Mike Honda, U.S. Congressman,15th District, Apollo Astronaut Buzz Aldrin, S. Pete Worden, Director, NASA Ames Research Center, David Morrison, Interiu Director, NASA Lunar Science Institute. David Morse at podium.
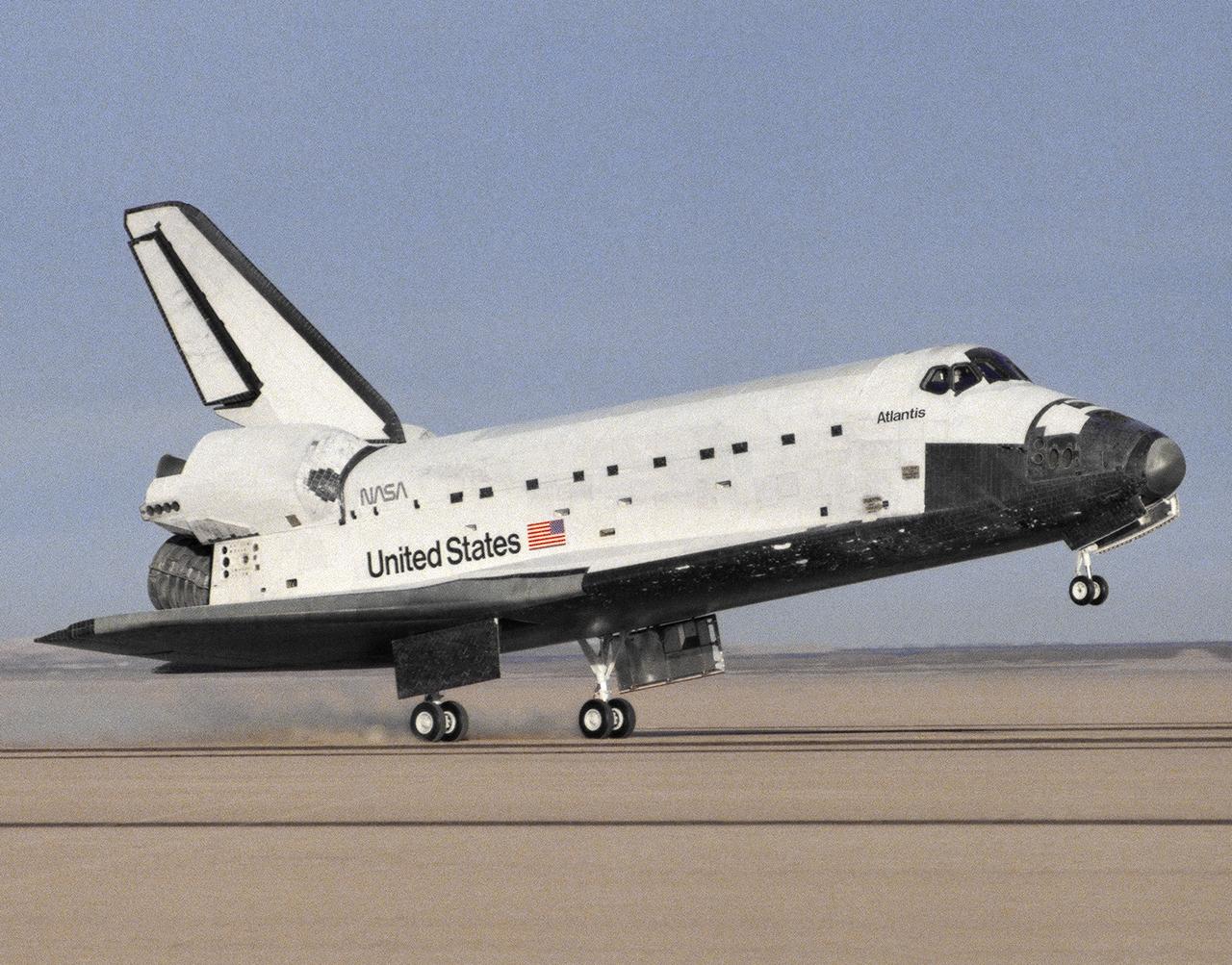

The Space Shuttle Atlantis touches down at 3:35 p.m. PST on 6 December 1988 at NASA's then Ames-Dryden Flight Research Facility at the conclusion of the STS-27 Department of Defense mission. Landing took place on runway 17 of the Rogers Dry Lake, concluding the 4-day, 9-hour, 6-minute mission. The five-man crew was led by Commander Robert L. Gibson and included Pilot Guy S. Gardner; Mission Specialists Jerry L. Ross, William M. Sheperd, and Richard M. Mullane. Atlantis was launched on December 2 from NASA's Kennedy Space Center.

Stephen Beitashour, a professional soccer player from the San Jose Earthquakes, was asked to demonstrate kicking the ball for his student audience. With the increased globalization of soccer, more young people are playing the sport and developing motor skills to compete effectively. To enhance their skills, students in the United States and Canada recently were given the opportunity to discuss with a NASA scientist the aerodynamics of the newly designed soccer ball. To help student soccer players better understand the movement of the ball, NASA scientists at the Fluid Mechanics Laboratory at NASA’s Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif., recently tested the performance of the Jabulani design, and compared it to the 2006 design. Included in this study was Rabi Mehta who had done previous tests on tennis and cricket balls in wind tunnels.
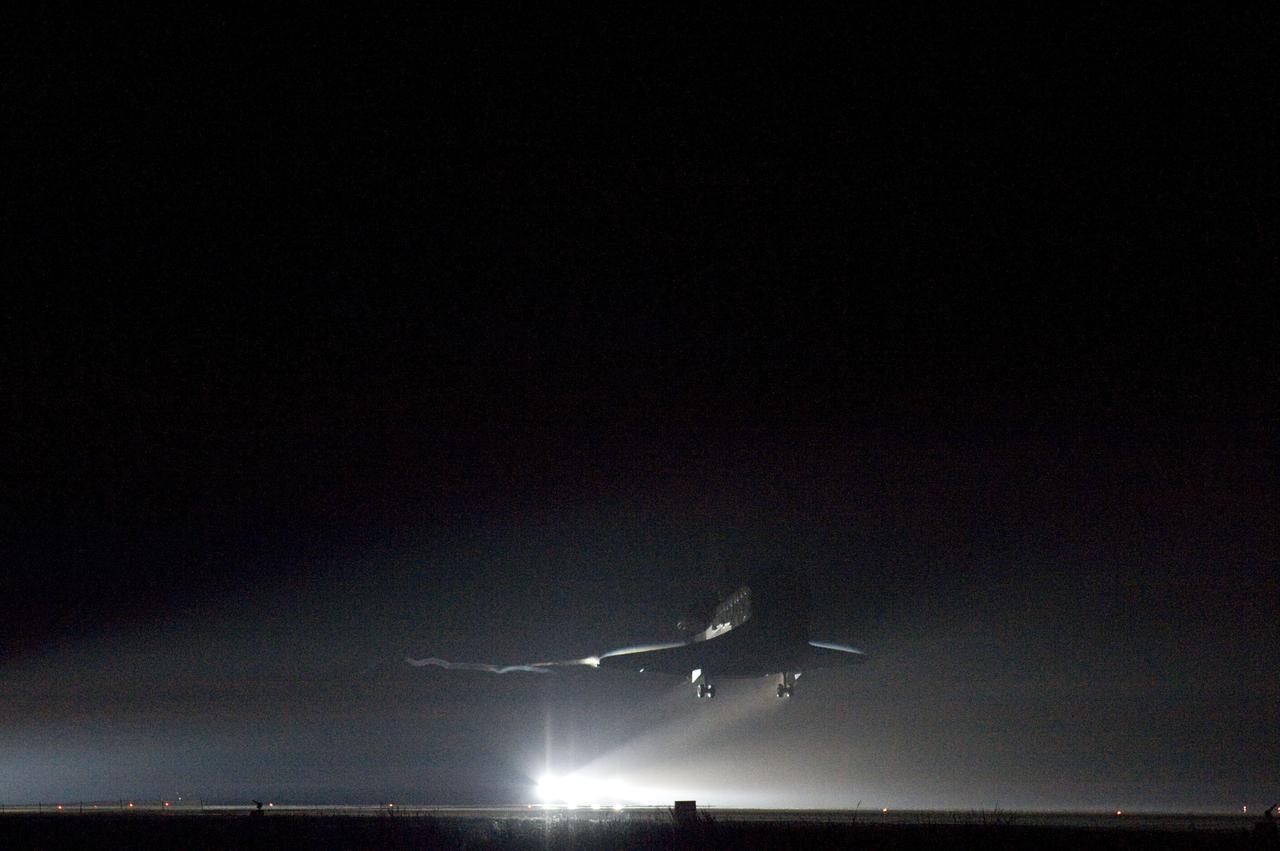

STS134-S-089 (1 June 2011) --- Xenon lights help lead space shuttle Endeavour home to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour landed for the final time on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15, marking the 24th night landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
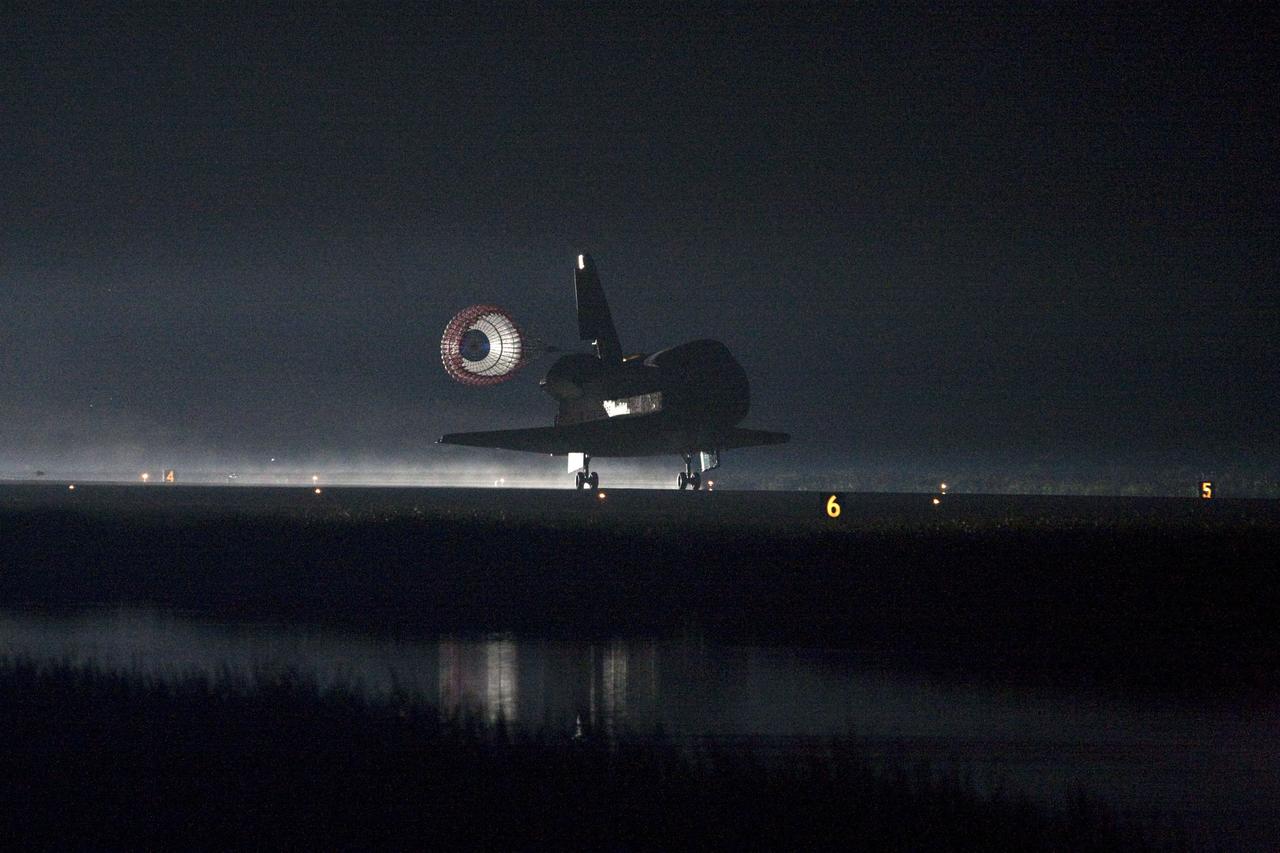

STS134-S-079 (1 June 2011) --- Xenon lights help lead space shuttle Endeavour home to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour landed for the final time on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15, marking the 24th night landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
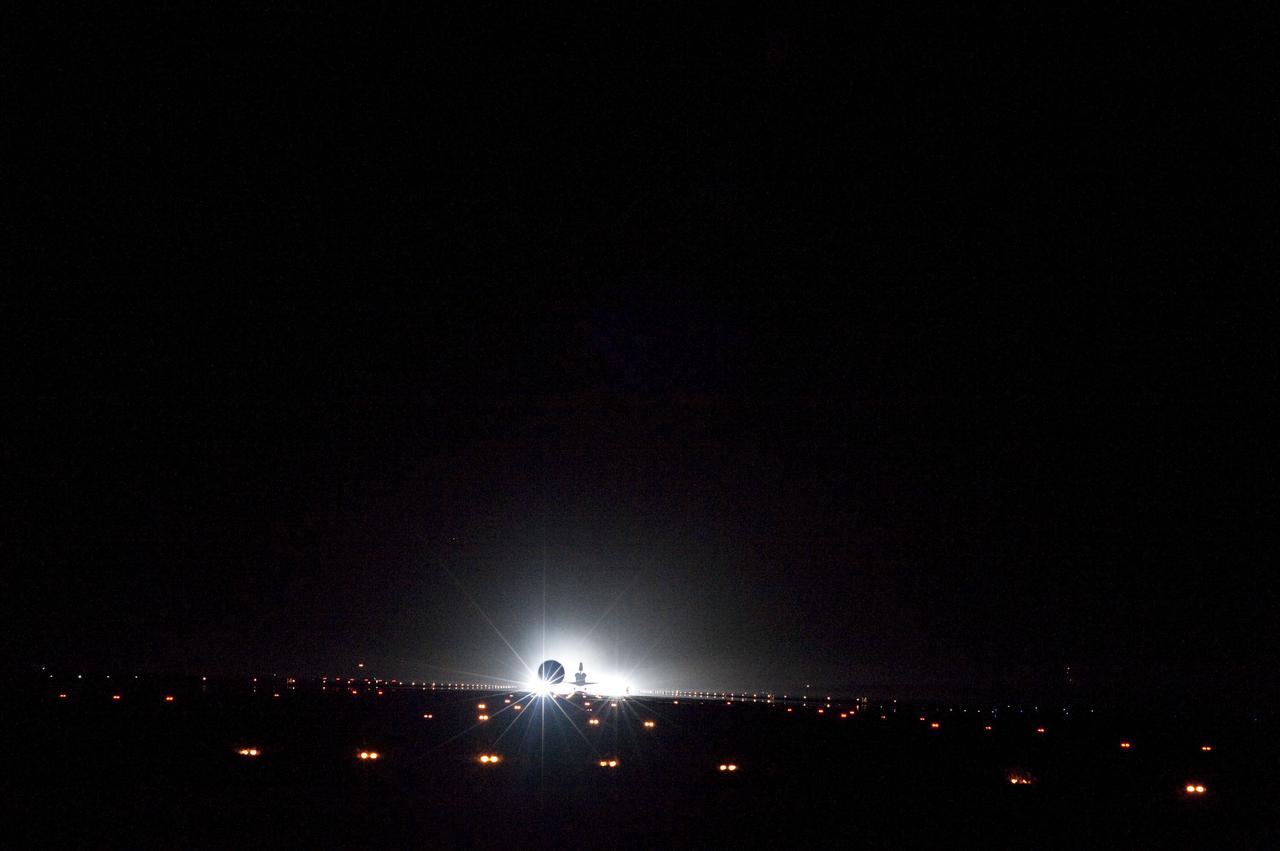

STS134-S-113 (1 June 2011) --- Xenon lights help lead space shuttle Endeavour home to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour landed for the final time on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15, marking the 24th night landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
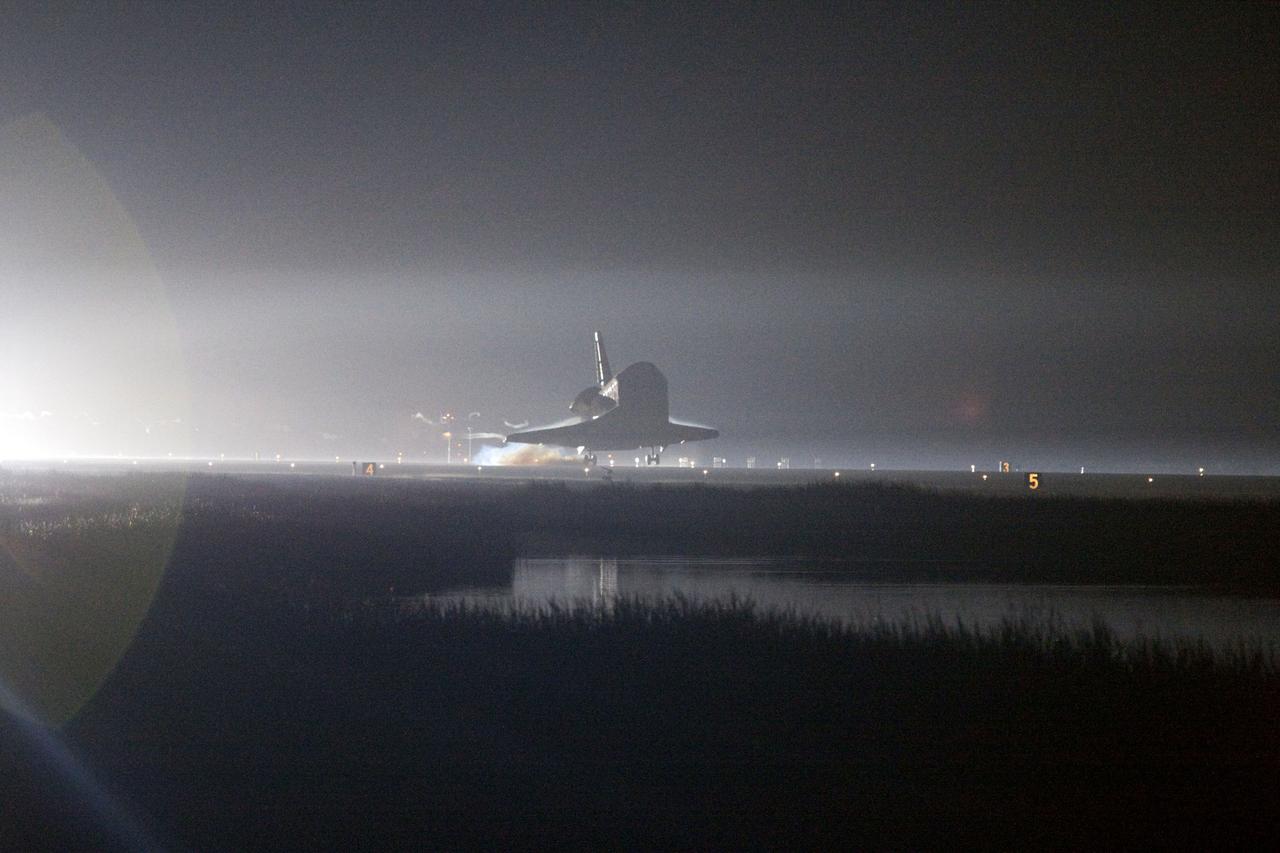

STS134-S-077 (1 June 2011) --- Xenon lights help lead space shuttle Endeavour home to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour landed for the final time on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15, marking the 24th night landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
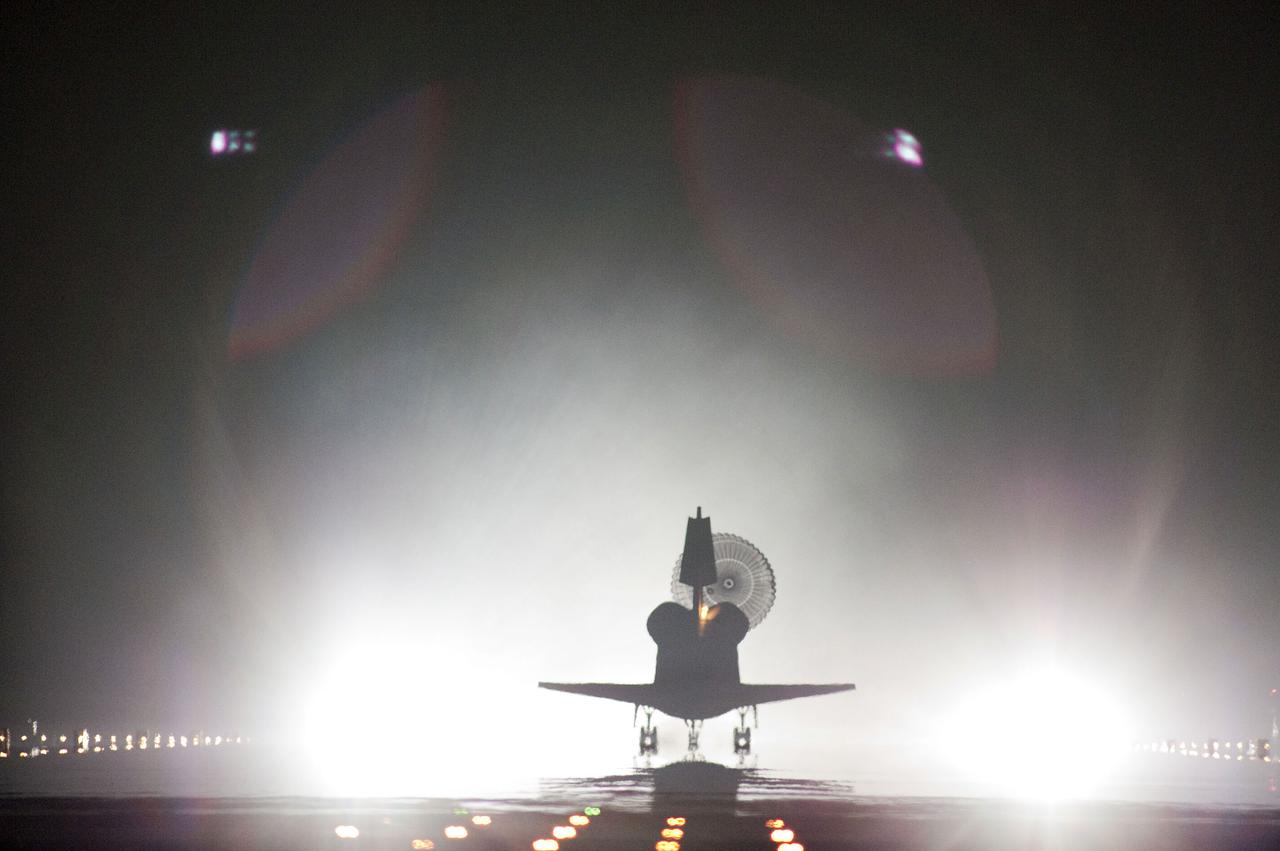

STS134-S-114 (1 June 2011) --- Xenon lights help lead space shuttle Endeavour home to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour landed for the final time on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15, marking the 24th night landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
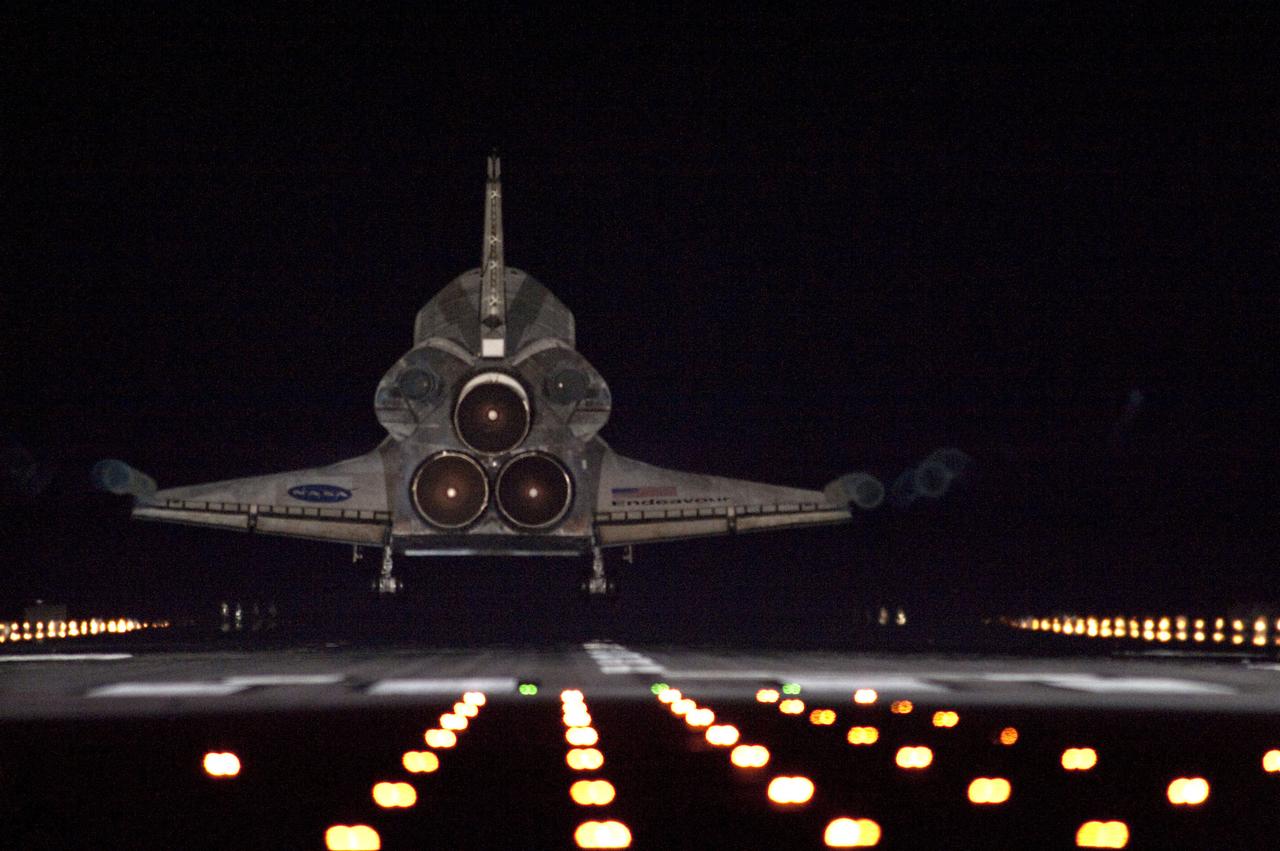

STS134-S-111 (1 June 2011) --- Space shuttle Endeavour approaches Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time marking the 24th night landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
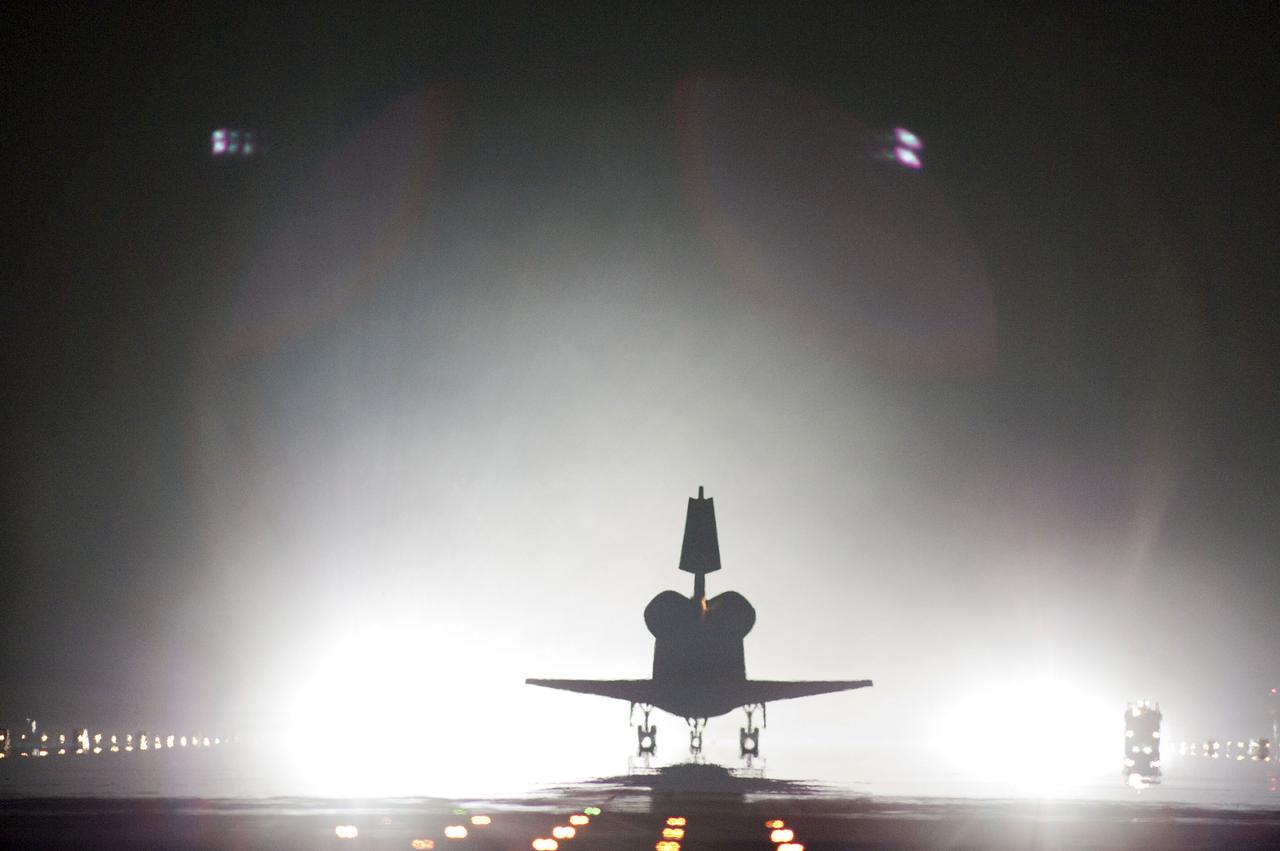

STS134-S-115 (1 June 2011) --- Xenon lights help lead space shuttle Endeavour home to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour landed for the final time on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15, marking the 24th night landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
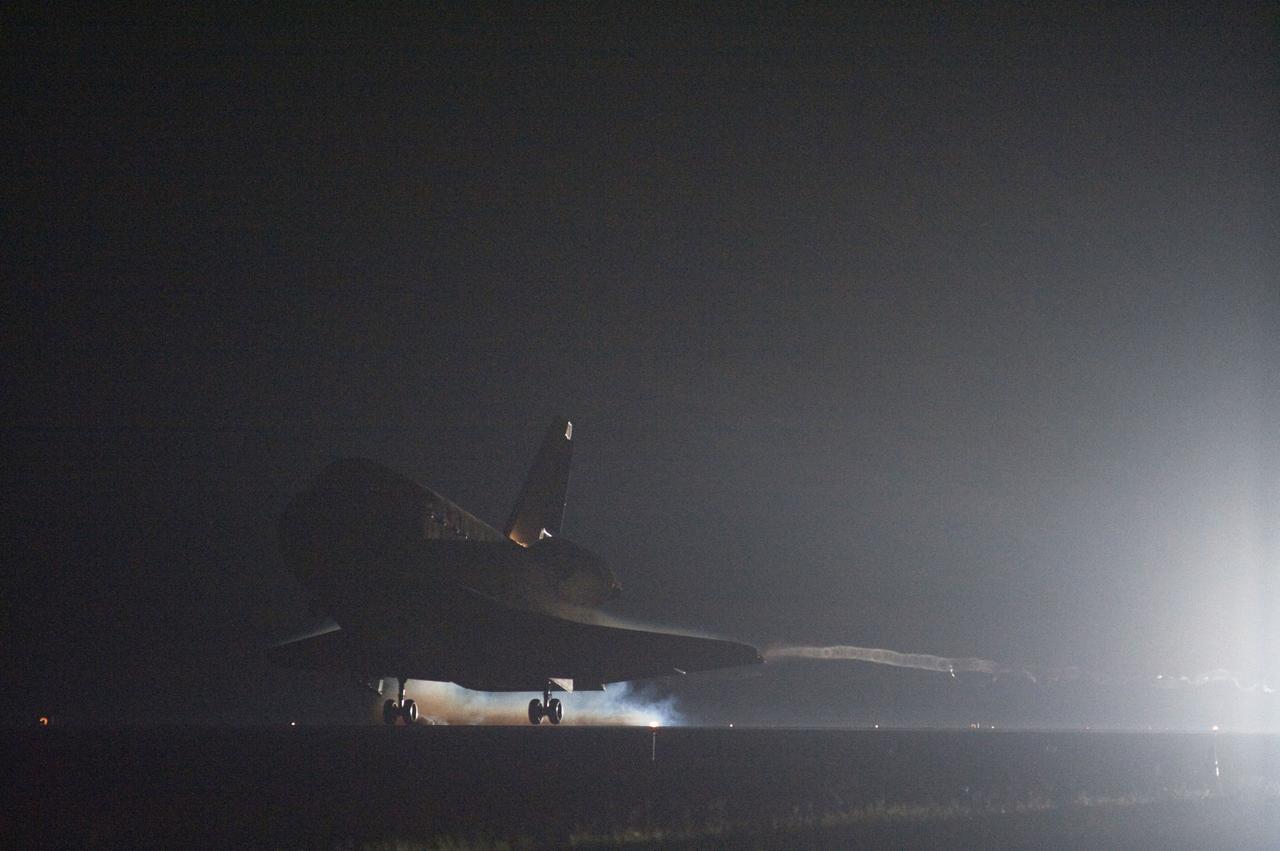

STS134-S-109 (1 June 2011) --- Streams of smoke trail from the main landing gear tires as space shuttle Endeavour touches down on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time marking the 24th night landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
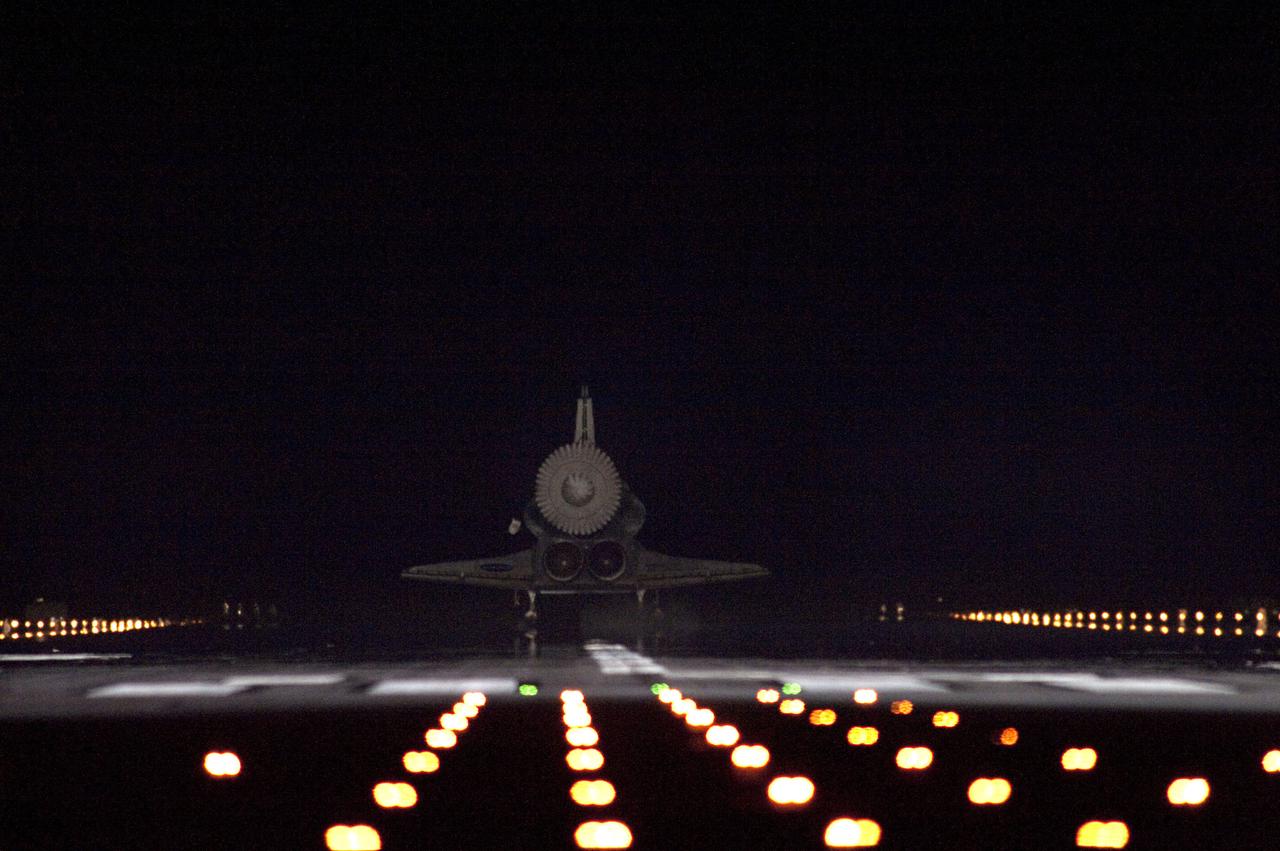

STS134-S-112 (1 June 2011) --- Space shuttle Endeavour touches down on Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time marking the 24th night landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
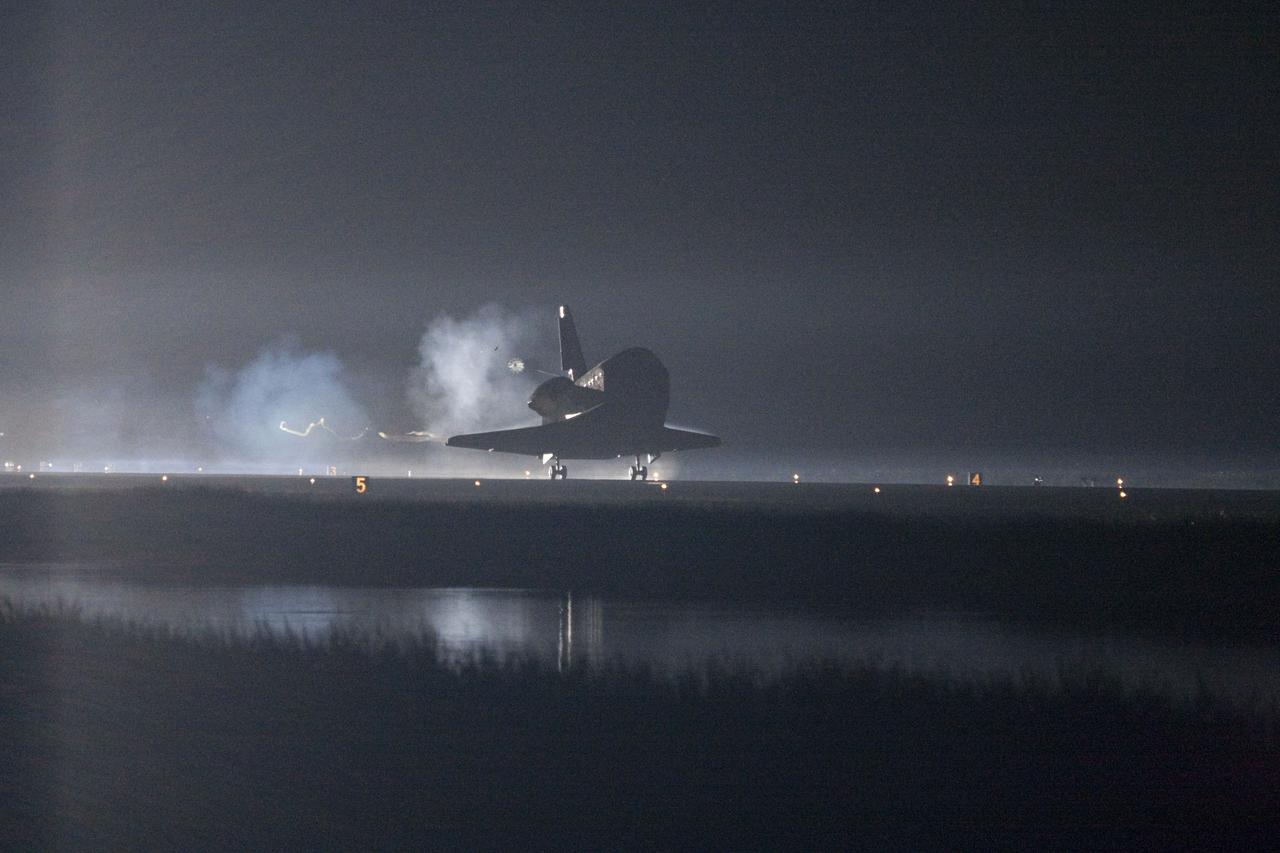

STS134-S-078 (1 June 2011) --- Xenon lights help lead space shuttle Endeavour home to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Endeavour landed for the final time on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15, marking the 24th night landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
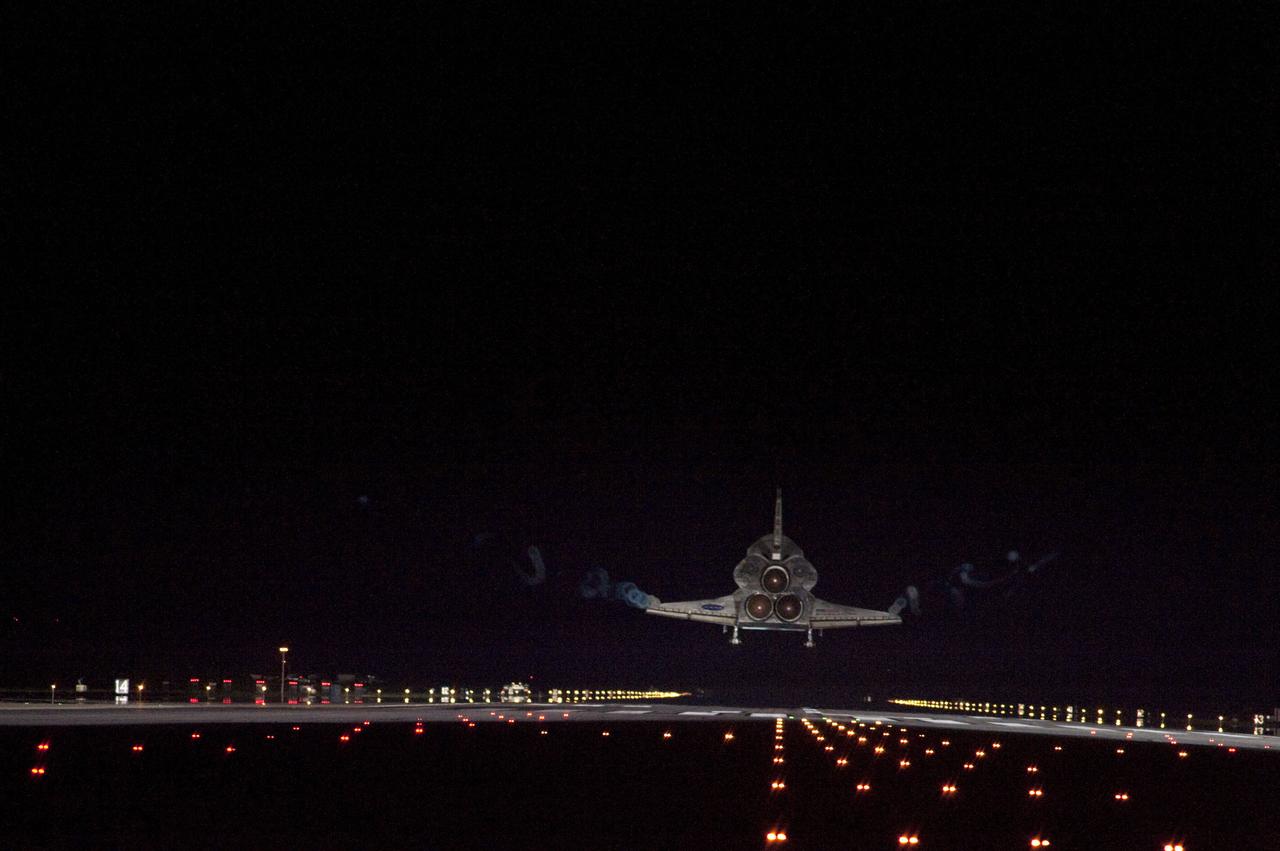

STS134-S-110 (1 June 2011) --- Space shuttle Endeavour approaches Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time marking the 24th night landing of NASA's Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
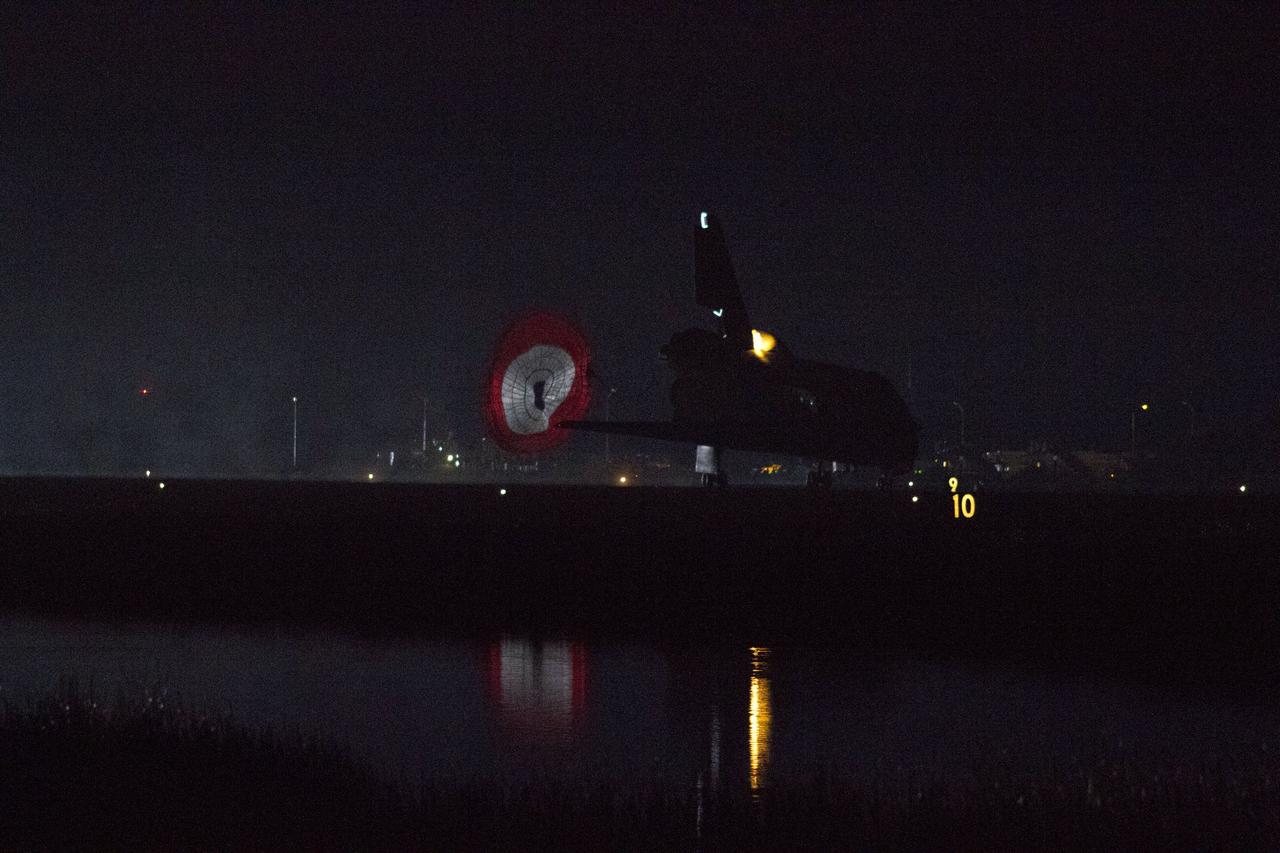

STS134-S-074 (1 June 2011) --- Space shuttle Endeavour rolls to a stop on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Heat from the shuttle's auxiliary power units, which provide hydraulic control, can be seen at the back of Endeavour, near the vertical tail. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
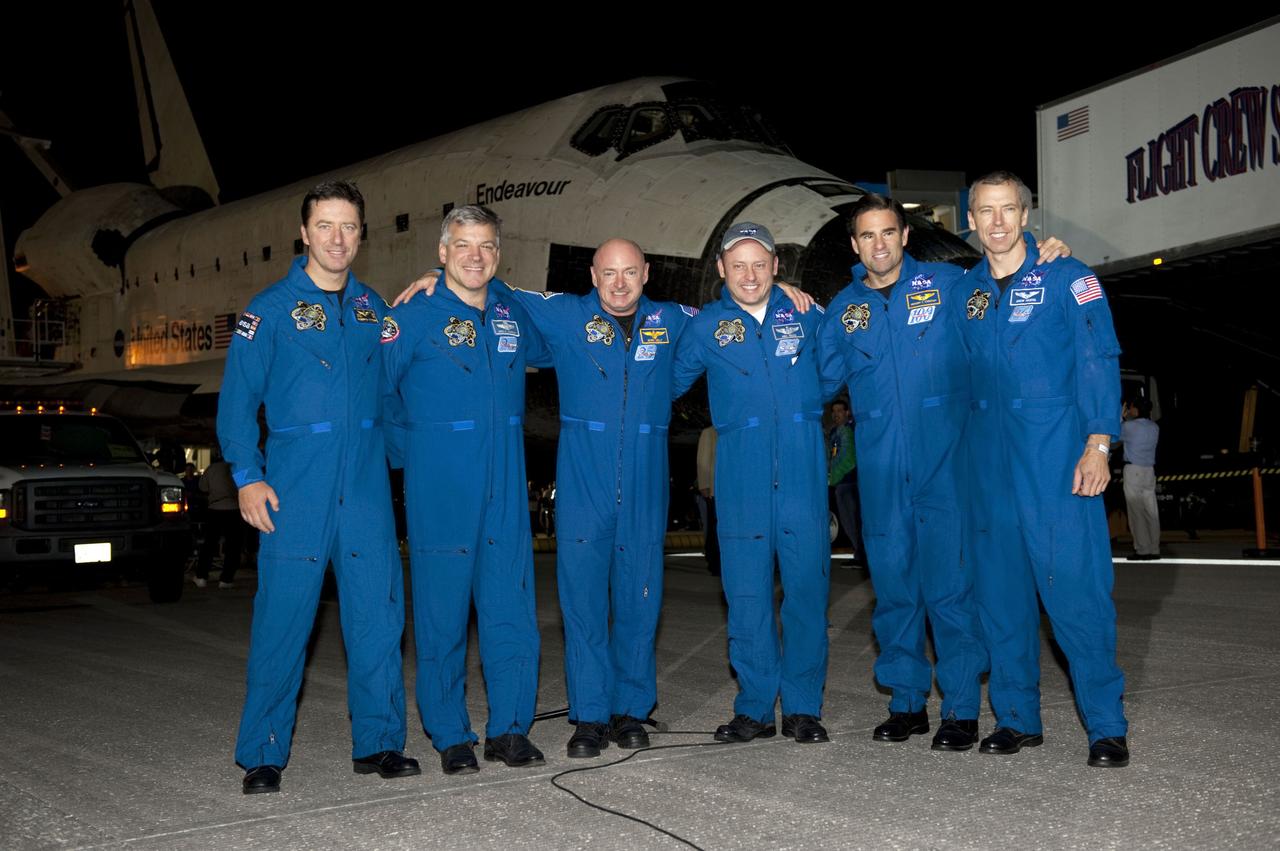

STS134-S-108 (1 June 2011) --- The crew of STS-134 pose for a photo on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida following the successful landing of space shuttle Endeavour. From left, are European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, mission specialist; NASA astronauts Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Mark Kelly, commander; Michael Fincke, Greg Chamitoff and Andrew Feustel, all mission specialists. The crew returned to Earth at 2:35 a.m. (EDT) June 1, 2011 on Runway 15, completing a 16-day, 6.5-million mile journey to the International Space Station. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the space station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
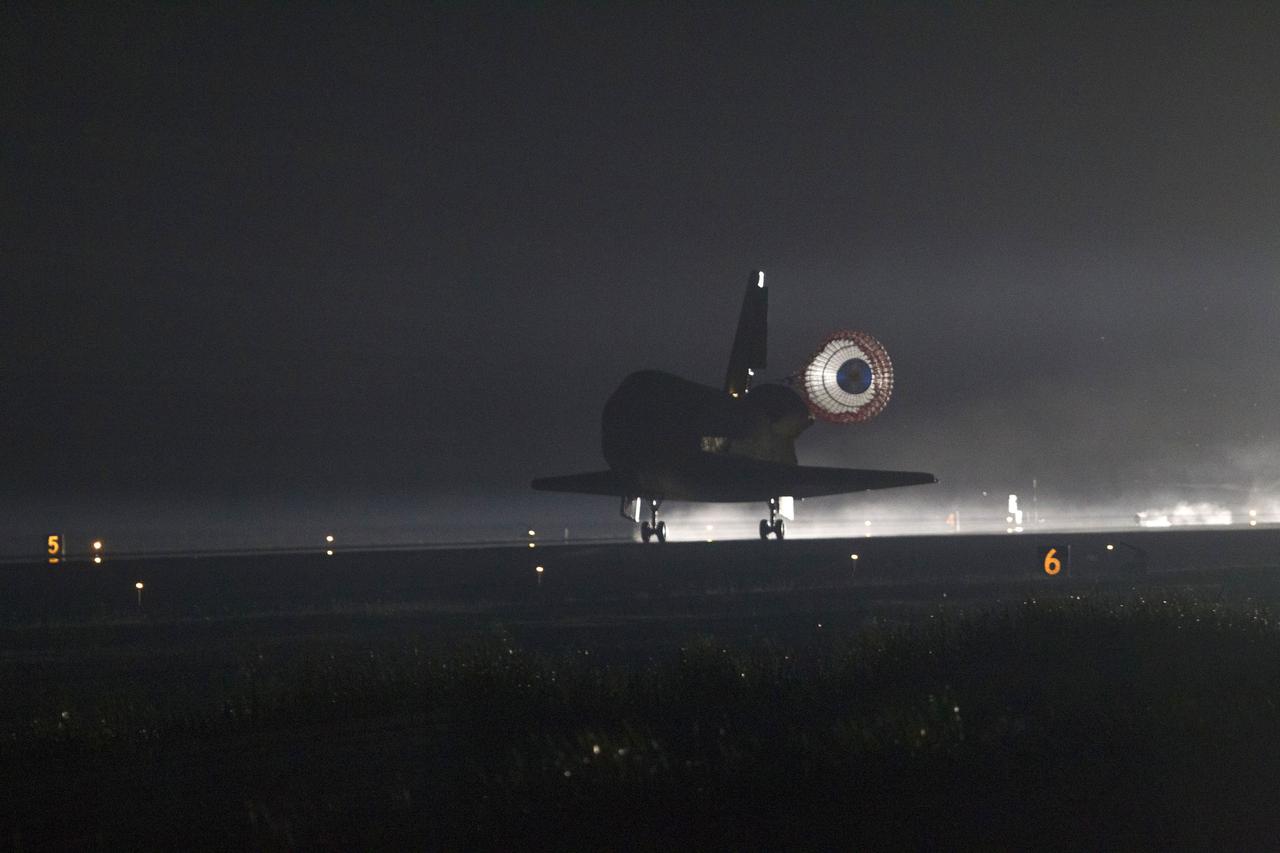

STS134-S-069 (1 June 2011) --- Xenon lights illuminate space shuttle Endeavour's unfurled drag chute as the vehicle rolls to a stop on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
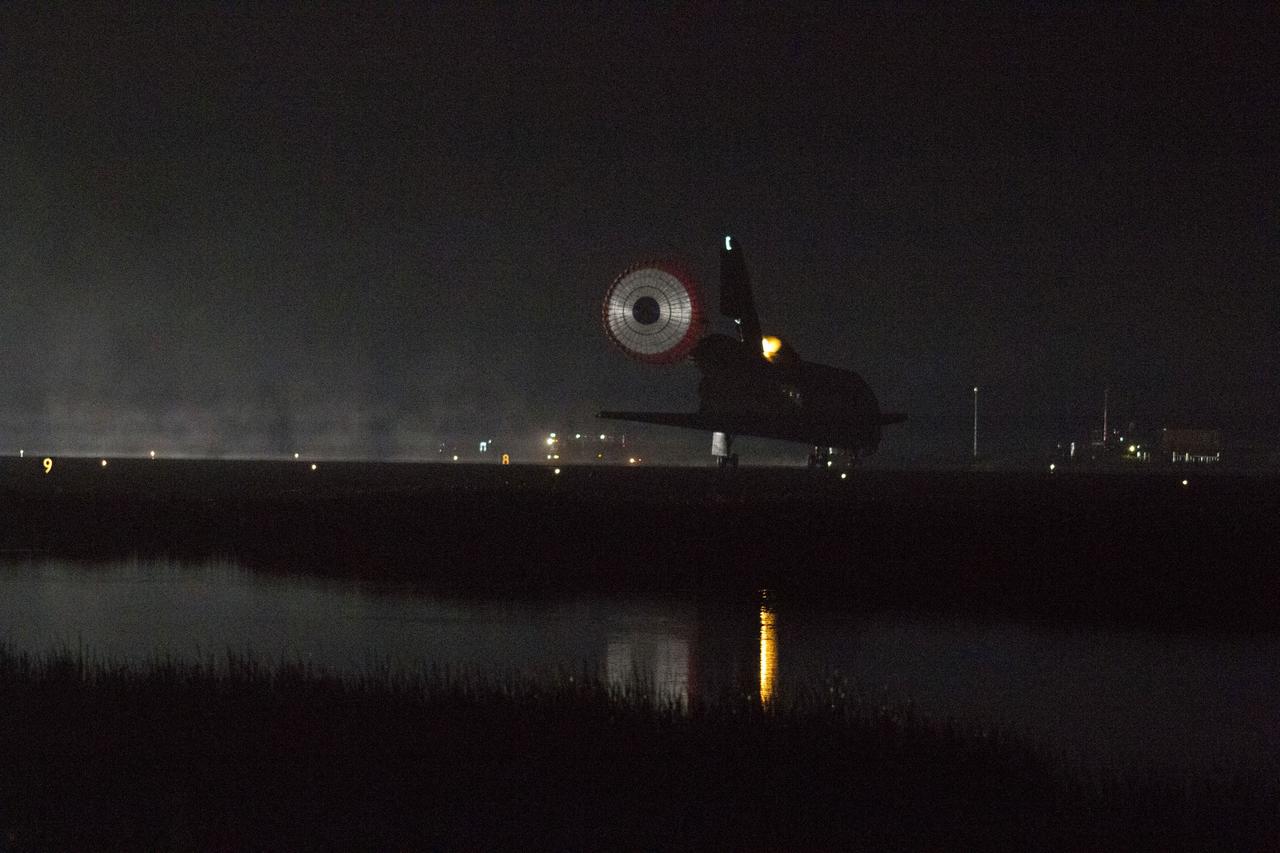

STS134-S-073 (1 June 2011) --- Xenon lights illuminate space shuttle Endeavour's unfurled drag chute as the vehicle rolls to a stop on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
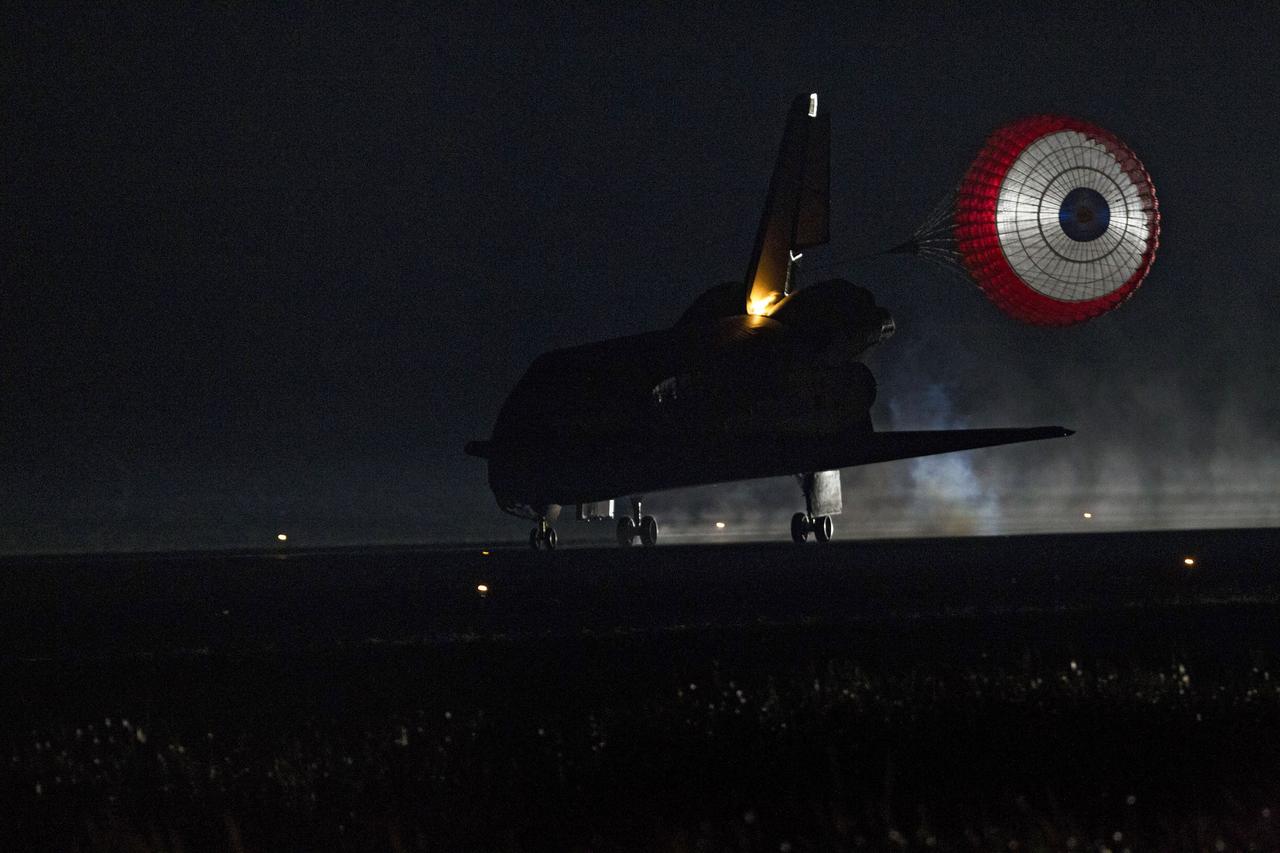

STS134-S-070 (1 June 2011) --- Xenon lights illuminate space shuttle Endeavour's unfurled drag chute as the vehicle rolls to a stop on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA

STS134-S-084 (1 June 2011) --- Space shuttle Endeavour approaches Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
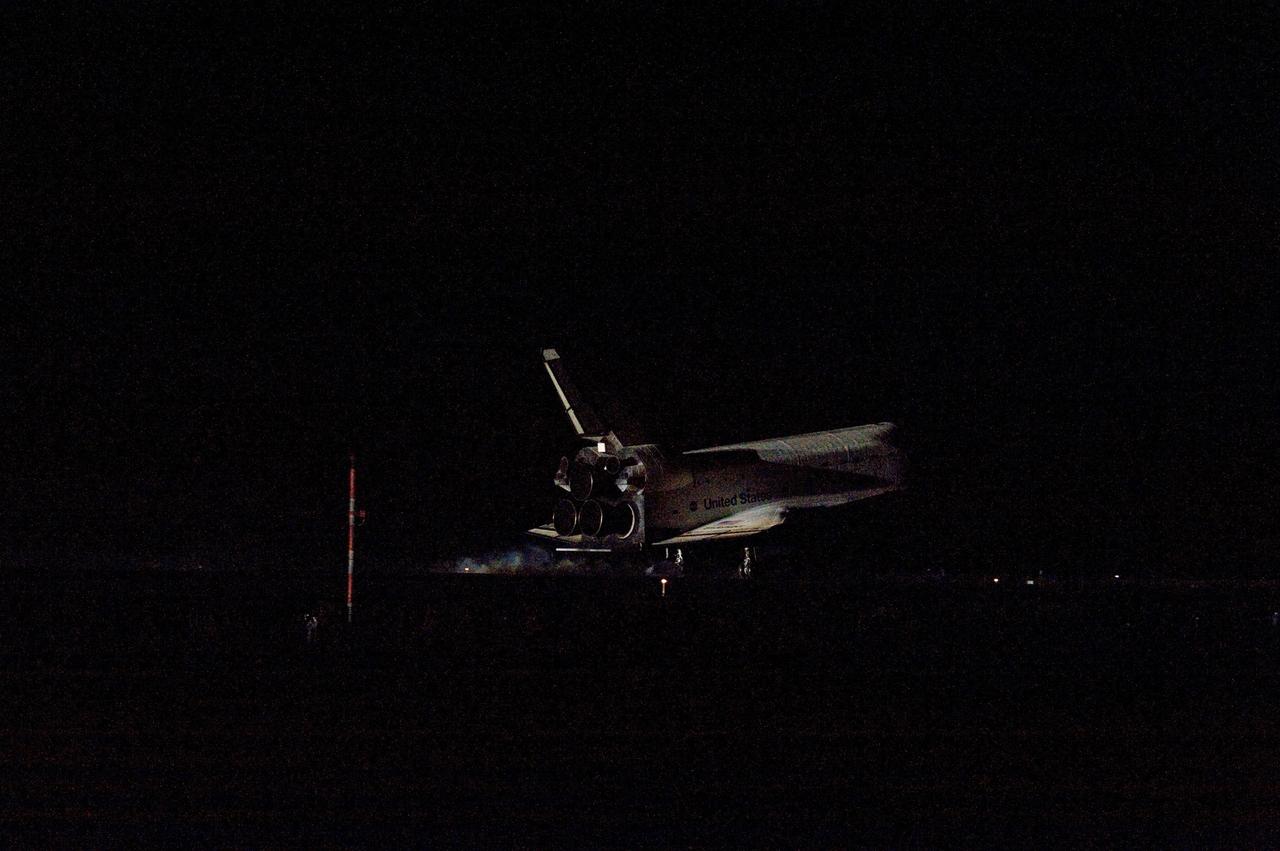

STS134-S-085 (1 June 2011) --- Space shuttle Endeavour rolls to a stop on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Heat from the shuttle's auxiliary power units, which provide hydraulic control, can be seen at the back of Endeavour, near the vertical tail. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
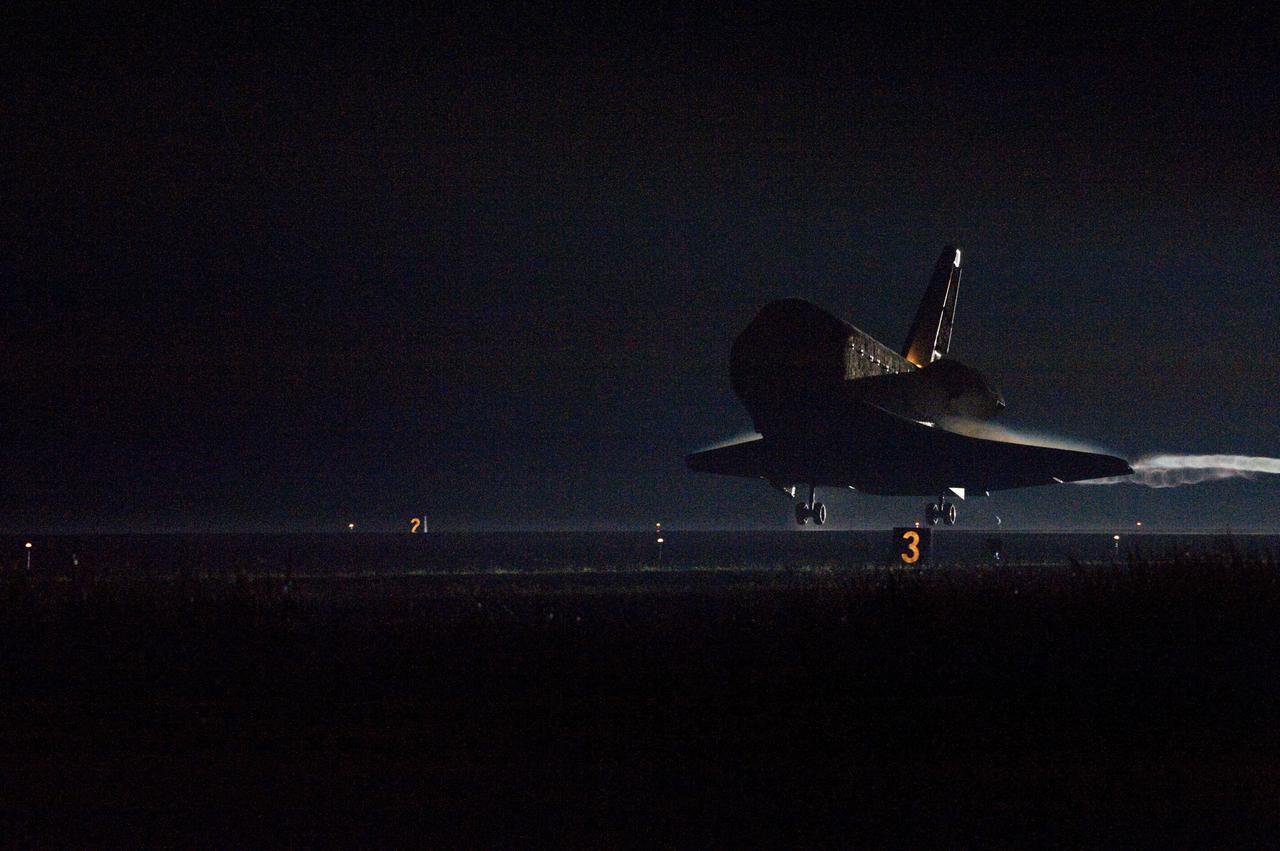

STS134-S-080 (1 June 2011) --- Space shuttle Endeavour lands on Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
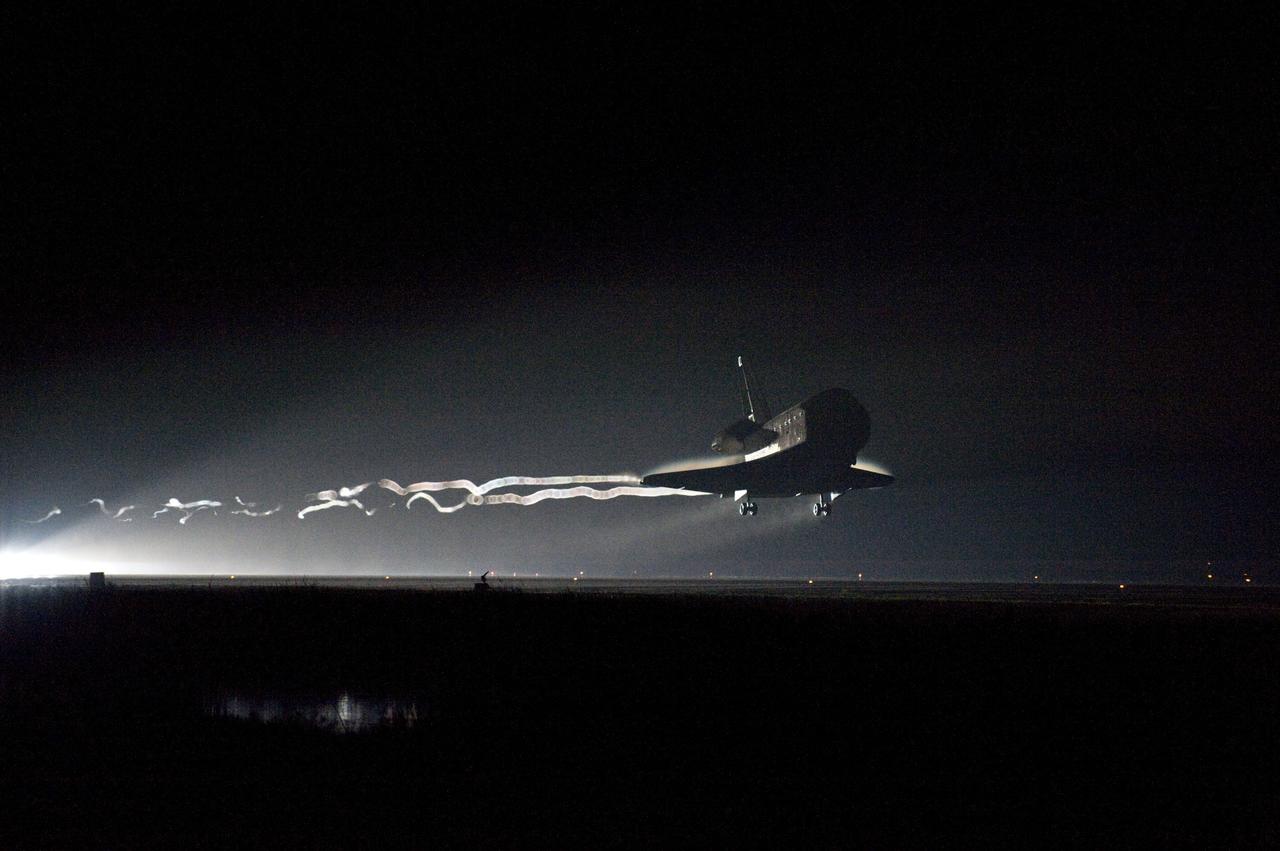

STS134-S-083 (1 June 2011) --- Space shuttle Endeavour approaches Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
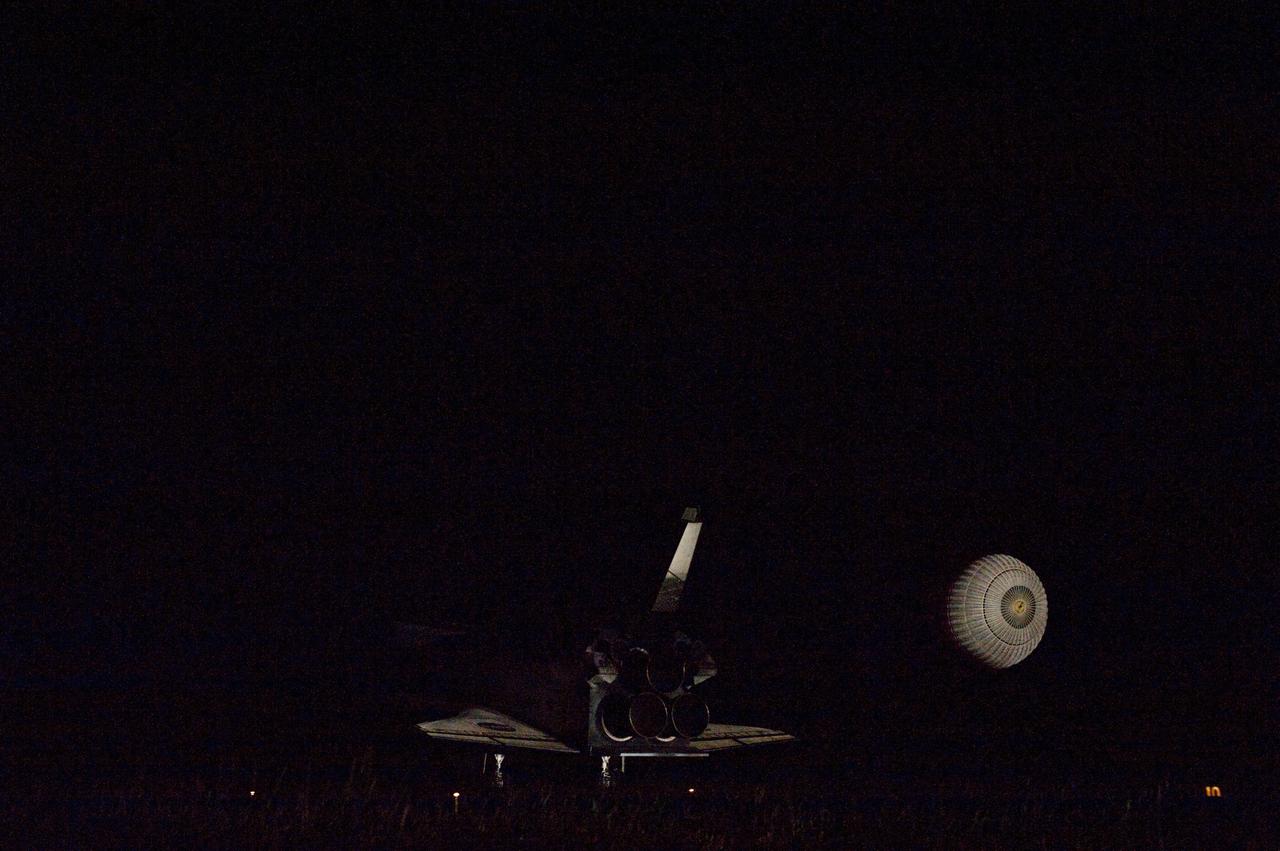

STS134-S-082 (1 June 2011) --- Xenon lights illuminate space shuttle Endeavour's unfurled drag chute as the vehicle rolls to a stop on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
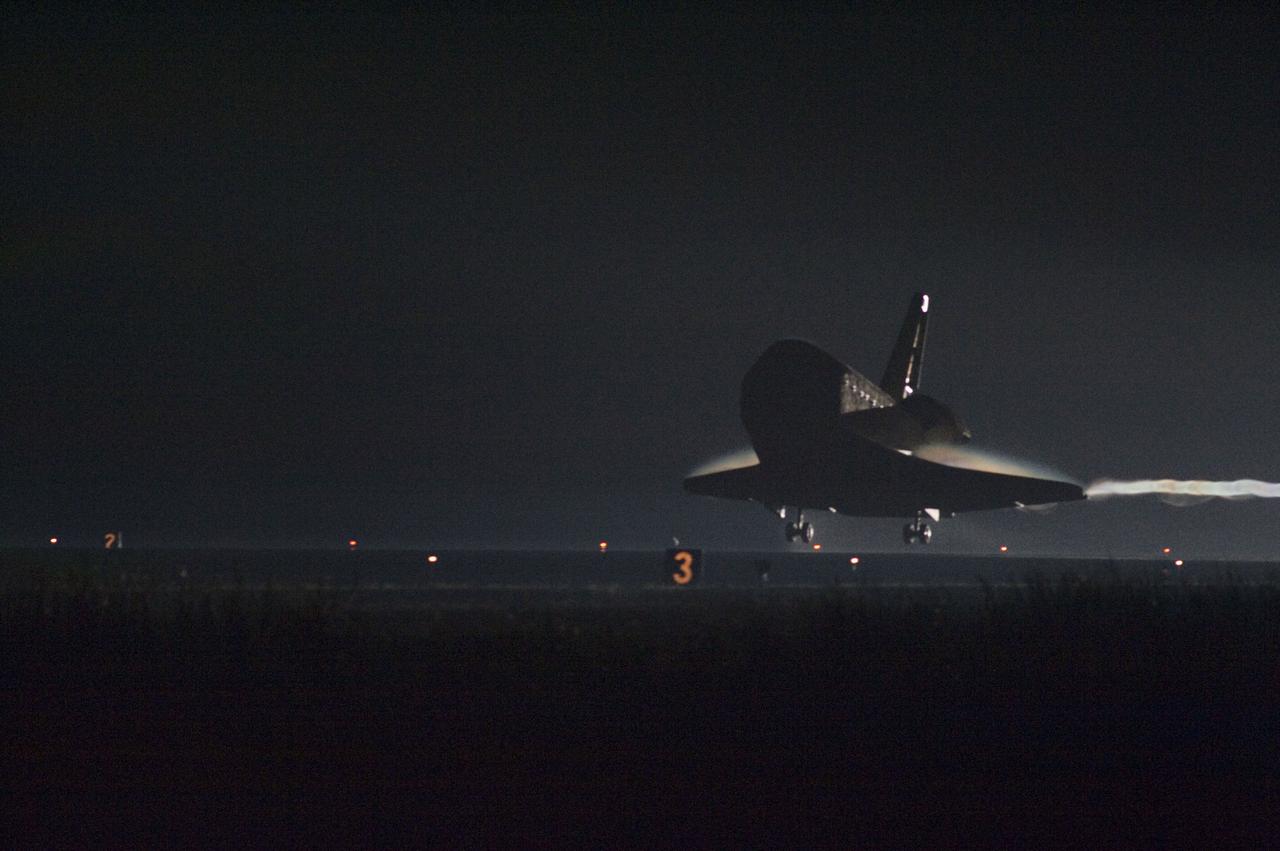

STS134-S-066 (1 June 2011) --- Space shuttle Endeavour approaches Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
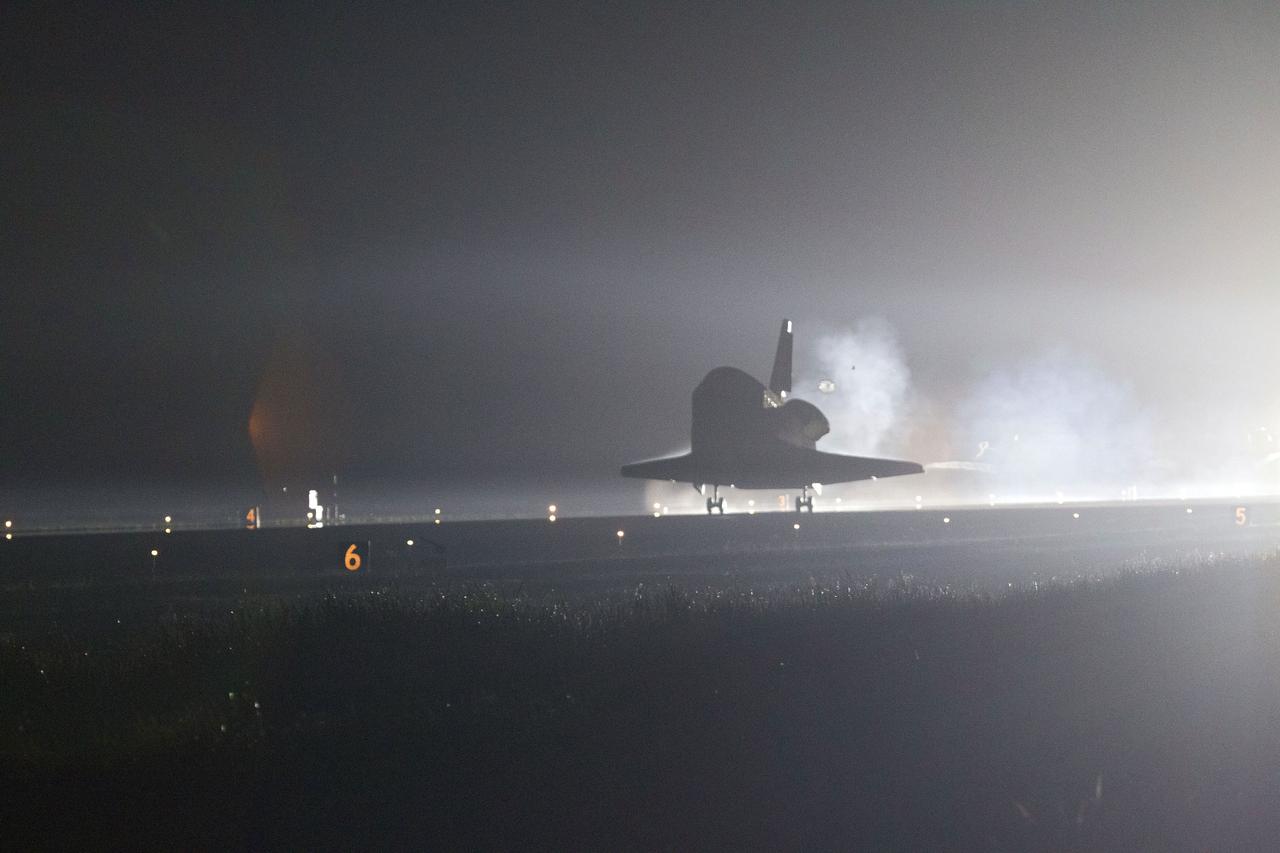

STS134-S-068 (1 June 2011) --- Space shuttle Endeavour lands on Runway 15 on the Shuttle Landing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
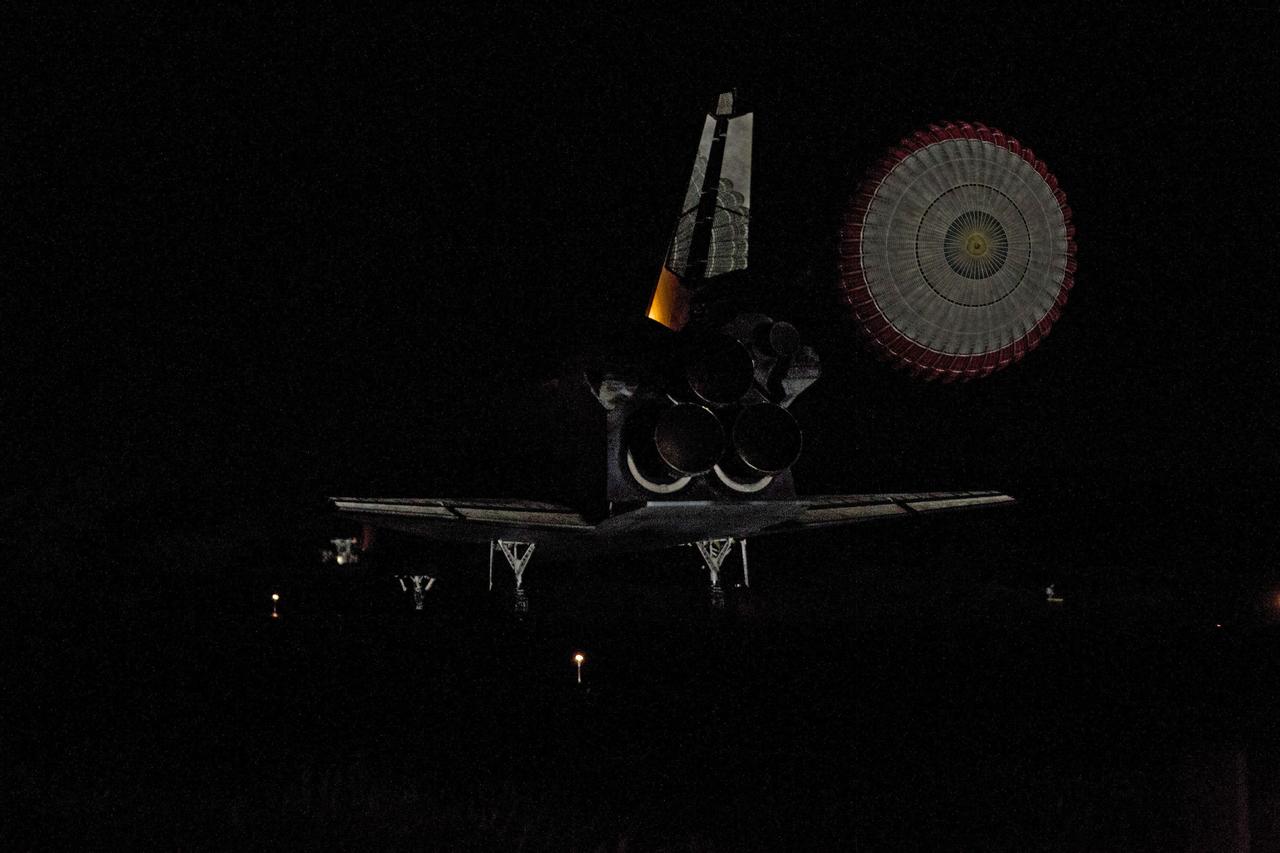

STS134-S-071 (1 June 2011) --- Space shuttle Endeavour's drag chute is reflected on the vehicle's tail end as it rolls to a stop on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
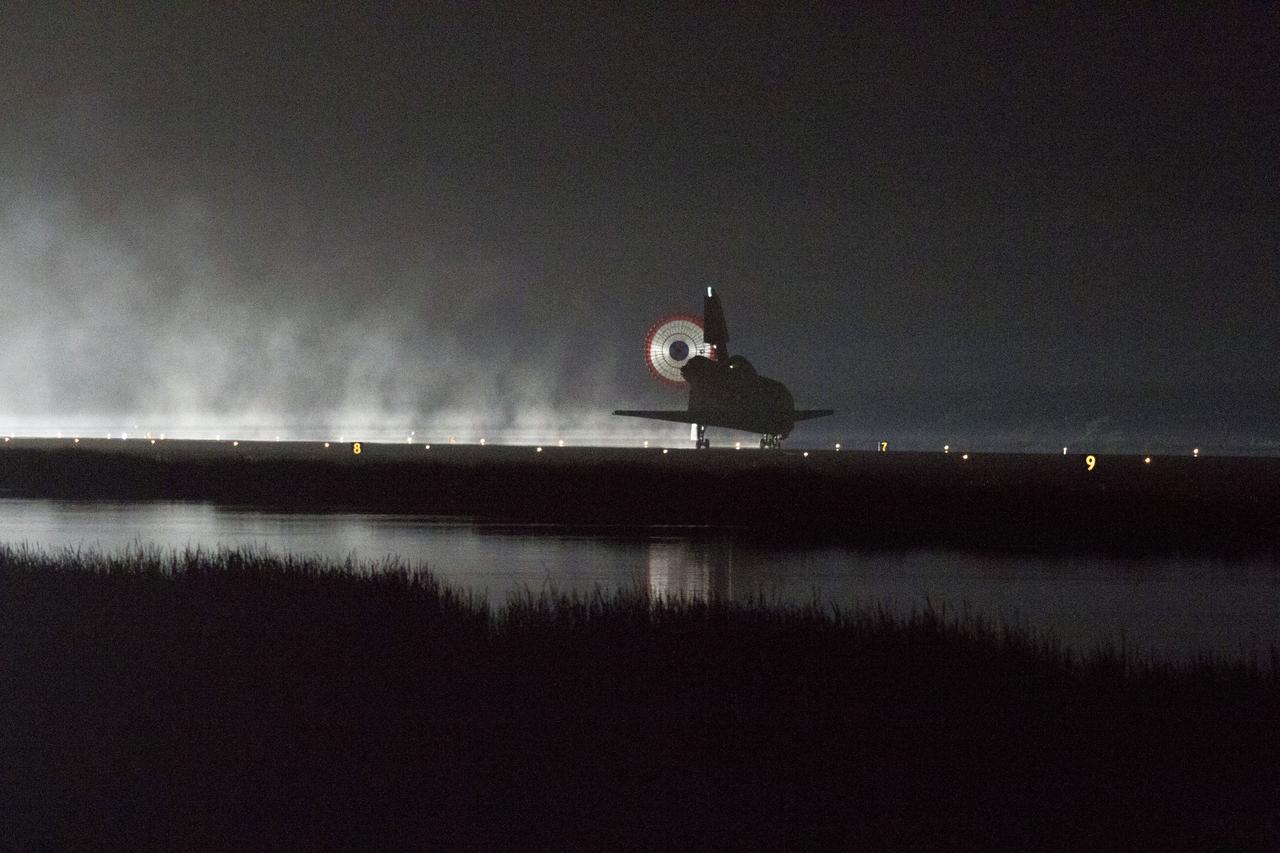

STS134-S-072 (1 June 2011) --- Xenon lights illuminate space shuttle Endeavour's unfurled drag chute as the vehicle rolls to a stop on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
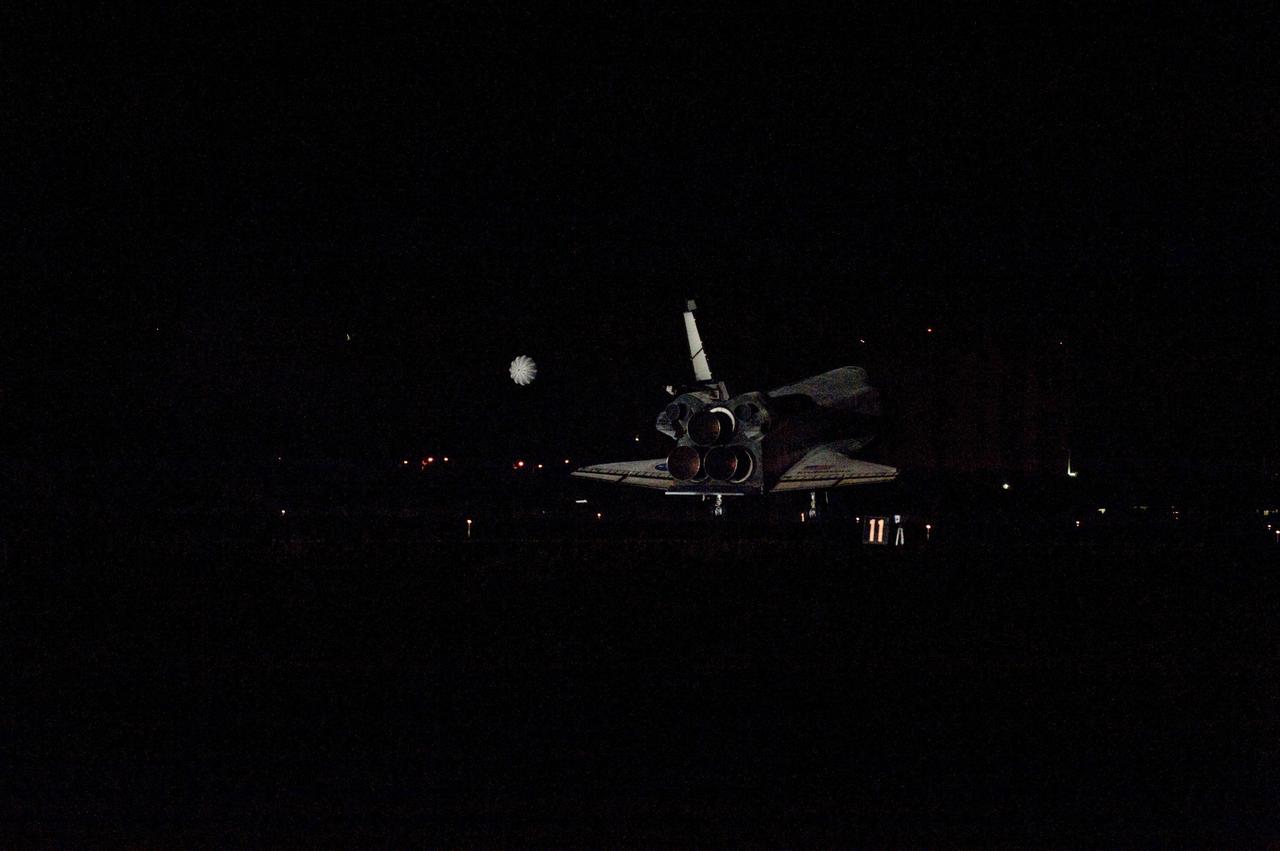

STS134-S-086 (1 June 2011) --- Space shuttle Endeavour rolls to a stop on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Heat from the shuttle's auxiliary power units, which provide hydraulic control, can be seen at the back of Endeavour, near the vertical tail. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
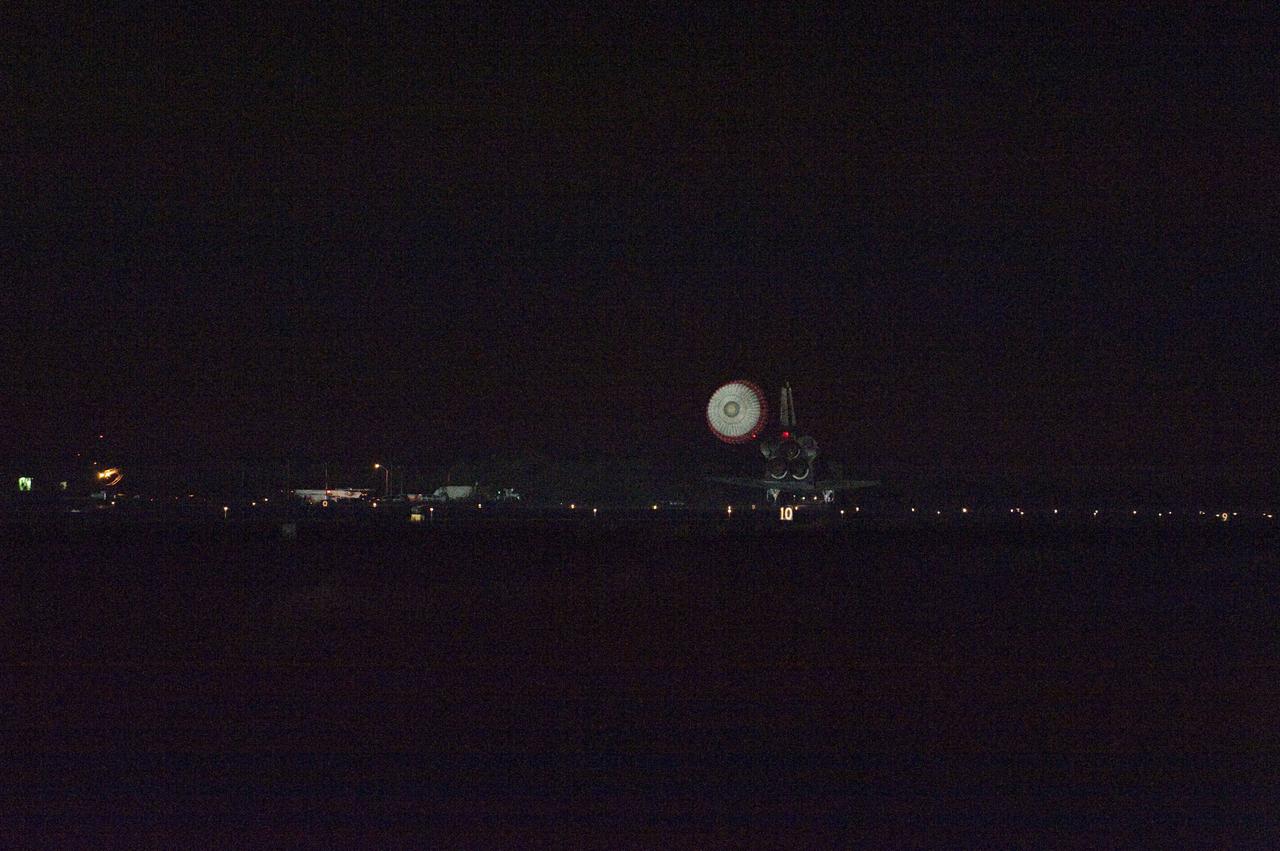

STS134-S-088 (1 June 2011) --- Space shuttle Endeavour rolls to a stop on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida for the final time. Heat from the shuttle's auxiliary power units, which provide hydraulic control, can be seen at the back of Endeavour, near the vertical tail. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
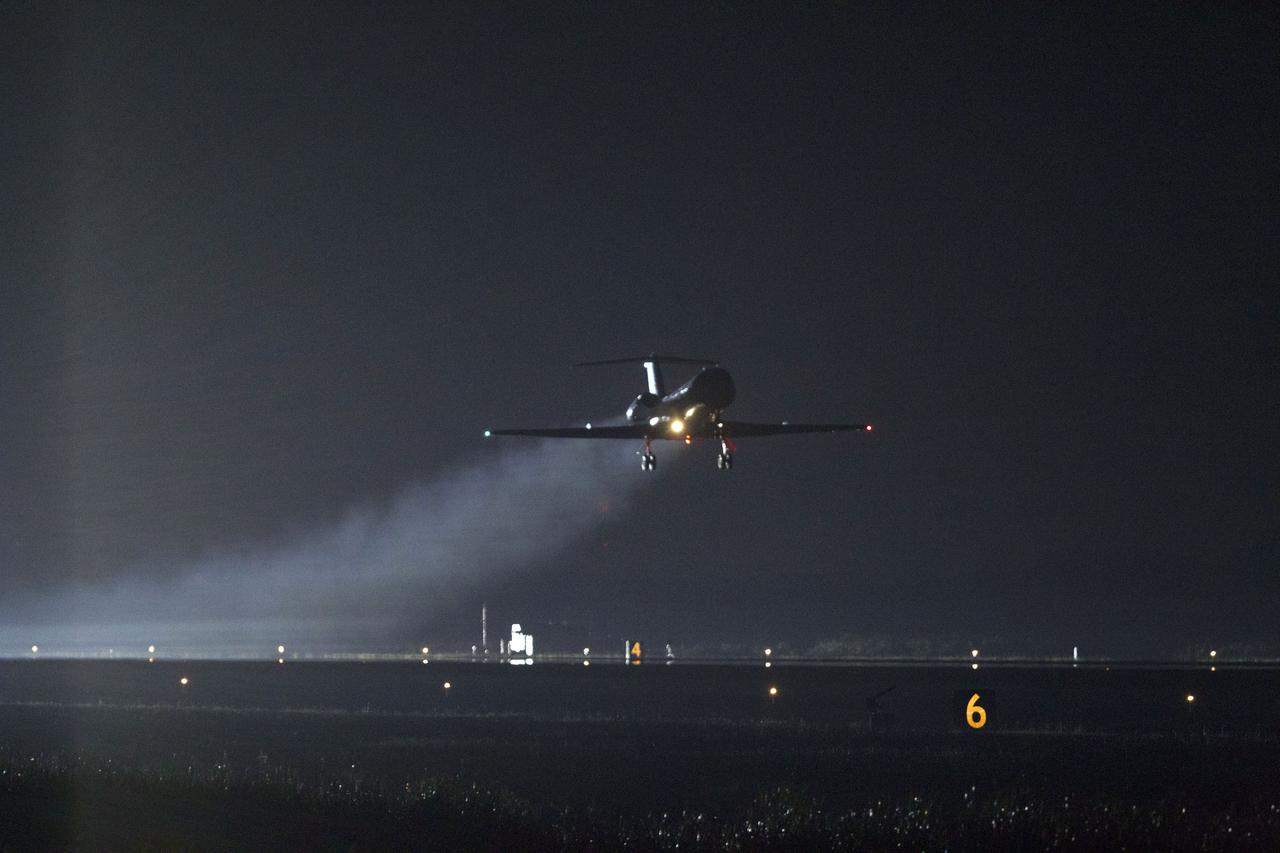

STS134-S-067 (1 June 2011) --- Astronaut Rick Sturckow flies weather reconnaissance in a Shuttle Training Aircraft over NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida to assess conditions before space shuttle Endeavour returns to Earth for the final time. Weather was observed "go" and Endeavour glided to a stop on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at 2:35 a.m. EDT, bringing an end to the STS-134 mission. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
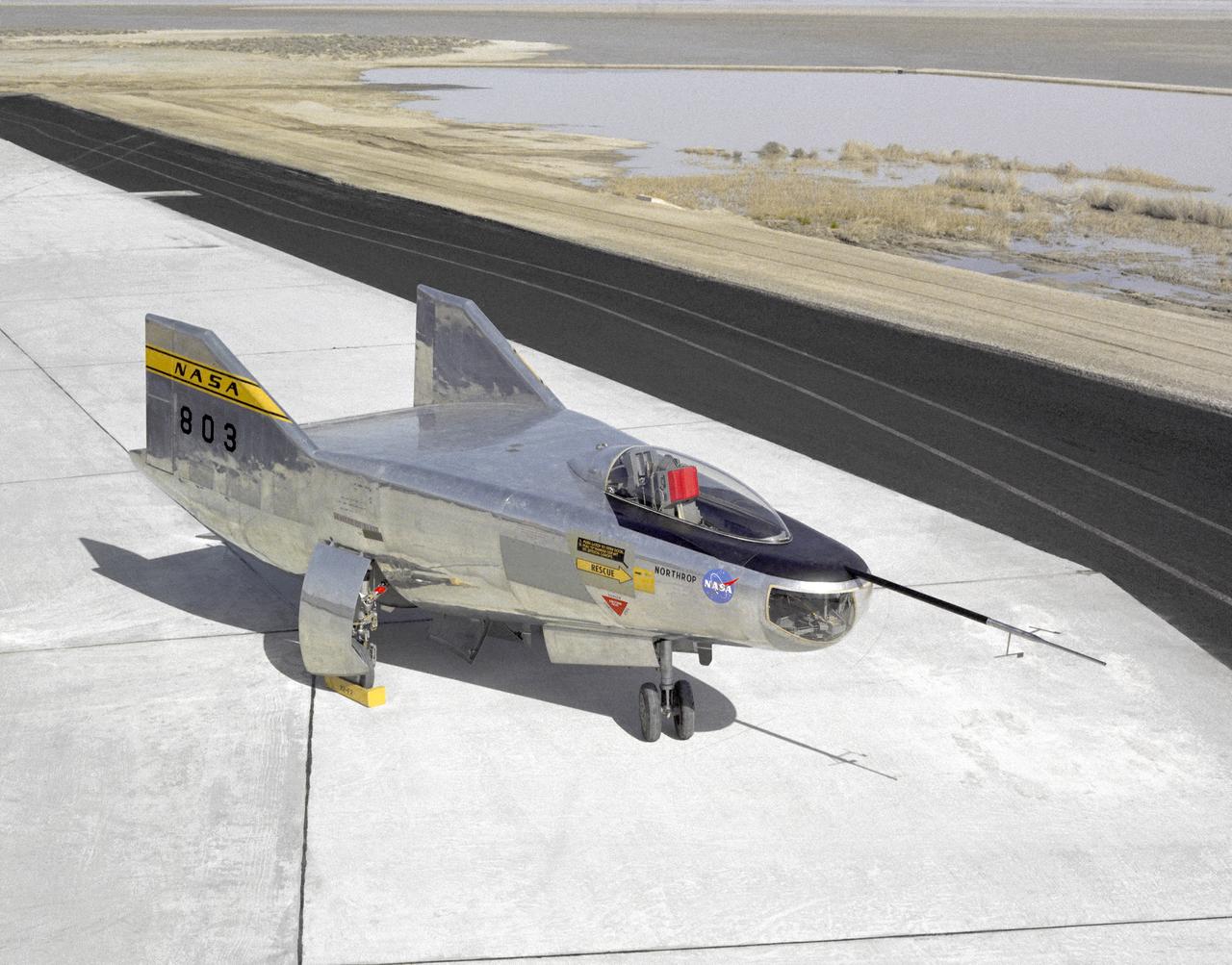

The M2-F2 Lifting Body is seen here on the ramp at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center. The success of Dryden's M2-F1 program led to NASA's development and construction of two heavyweight lifting bodies based on studies at NASA's Ames and Langley research centers -- the M2-F2 and the HL-10, both built by the Northrop Corporation. The "M" refers to "manned" and "F" refers to "flight" version. "HL" comes from "horizontal landing" and 10 is for the tenth lifting body model to be investigated by Langley. The first flight of the M2-F2 -- which looked much like the "F1" -- was on July 12, 1966. Milt Thompson was the pilot. By then, the same B-52 used to air launch the famed X-15 rocket research aircraft was modified to also carry the lifting bodies. Thompson was dropped from the B-52's wing pylon mount at an altitude of 45,000 feet on that maiden glide flight. The M2-F2 weighed 4,620 pounds, was 22 feet long, and had a width of about 10 feet. On May 10, 1967, during the sixteenth glide flight leading up to powered flight, a landing accident severely damaged the vehicle and seriously injured the NASA pilot, Bruce Peterson. NASA pilots and researchers realized the M2-F2 had lateral control problems, even though it had a stability augmentation control system. When the M2-F2 was rebuilt at Dryden and redesignated the M2-F3, it was modified with an additional third vertical fin -- centered between the tip fins -- to improve control characteristics. The M2-F2/F3 was the first of the heavy-weight, entry-configuration lifting bodies. Its successful development as a research test vehicle answered many of the generic questions about these vehicles. NASA donated the M2-F3 vehicle to the Smithsonian Institute in December 1973. It is currently hanging in the Air and Space Museum along with the X-15 aircraft number 1, which was its hangar partner at Dryden from 1965 to 1969.
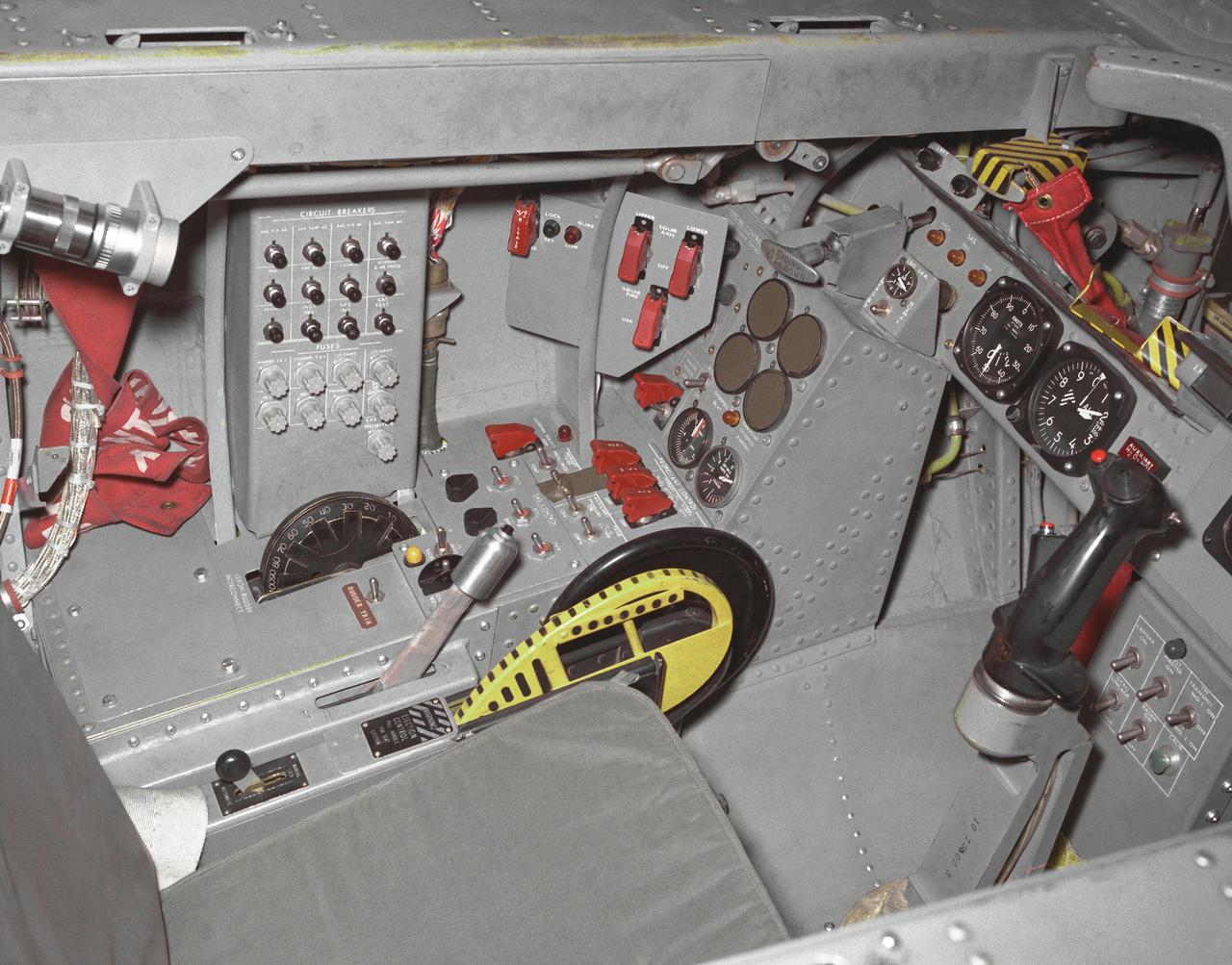

This photo shows the left side cockpit instrumentation panel of the M2-F2 Lifting Body. The success of Dryden's M2-F1 program led to NASA's development and construction of two heavyweight lifting bodies based on studies at NASA's Ames and Langley research centers -- the M2-F2 and the HL-10, both built by the Northrop Corporation. The "M" refers to "manned" and "F" refers to "flight" version. "HL" comes from "horizontal landing" and 10 is for the tenth lifting body model to be investigated by Langley. The first flight of the M2-F2 -- which looked much like the "F1" -- was on July 12, 1966. Milt Thompson was the pilot. By then, the same B-52 used to air launch the famed X-15 rocket research aircraft was modified to also carry the lifting bodies. Thompson was dropped from the B-52's wing pylon mount at an altitude of 45,000 feet on that maiden glide flight. The M2-F2 weighed 4,620 pounds, was 22 feet long, and had a width of about 10 feet. On May 10, 1967, during the sixteenth glide flight leading up to powered flight, a landing accident severely damaged the vehicle and seriously injured the NASA pilot, Bruce Peterson. NASA pilots and researchers realized the M2-F2 had lateral control problems, even though it had a stability augmentation control system. When the M2-F2 was rebuilt at Dryden and redesignated the M2-F3, it was modified with an additional third vertical fin -- centered between the tip fins -- to improve control characteristics. The M2-F2/F3 was the first of the heavy-weight, entry-configuration lifting bodies. Its successful development as a research test vehicle answered many of the generic questions about these vehicles. NASA donated the M2-F3 vehicle to the Smithsonian Institute in December 1973. It is currently hanging in the Air and Space Museum along with the X-15 aircraft number 1, which was its hangar partner at Dryden from 1965 to 1969.
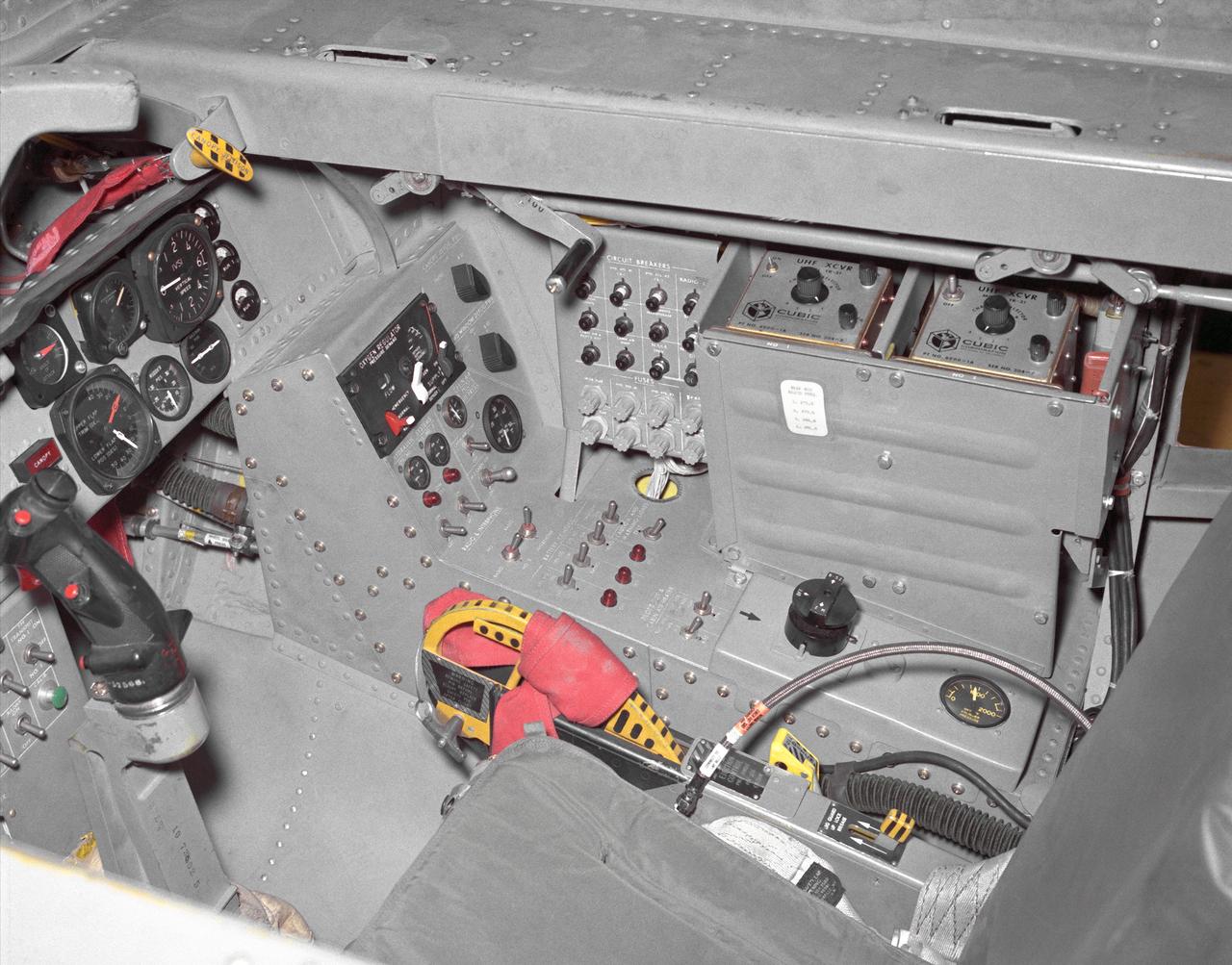

This photo shows the right side cockpit instrumentation panel of the M2-F2 Lifting Body. The success of Dryden's M2-F1 program led to NASA's development and construction of two heavyweight lifting bodies based on studies at NASA's Ames and Langley research centers -- the M2-F2 and the HL-10, both built by the Northrop Corporation. The "M" refers to "manned" and "F" refers to "flight" version. "HL" comes from "horizontal landing" and 10 is for the tenth lifting body model to be investigated by Langley. The first flight of the M2-F2 -- which looked much like the "F1" -- was on July 12, 1966. Milt Thompson was the pilot. By then, the same B-52 used to air launch the famed X-15 rocket research aircraft was modified to also carry the lifting bodies. Thompson was dropped from the B-52's wing pylon mount at an altitude of 45,000 feet on that maiden glide flight. The M2-F2 weighed 4,620 pounds, was 22 feet long, and had a width of about 10 feet. On May 10, 1967, during the sixteenth glide flight leading up to powered flight, a landing accident severely damaged the vehicle and seriously injured the NASA pilot, Bruce Peterson. NASA pilots and researchers realized the M2-F2 had lateral control problems, even though it had a stability augmentation control system. When the M2-F2 was rebuilt at Dryden and redesignated the M2-F3, it was modified with an additional third vertical fin -- centered between the tip fins -- to improve control characteristics. The M2-F2/F3 was the first of the heavy-weight, entry-configuration lifting bodies. Its successful development as a research test vehicle answered many of the generic questions about these vehicles. NASA donated the M2-F3 vehicle to the Smithsonian Institute in December 1973. It is currently hanging in the Air and Space Museum along with the X-15 aircraft number 1, which was its hangar partner at Dryden from 1965 to 1969.
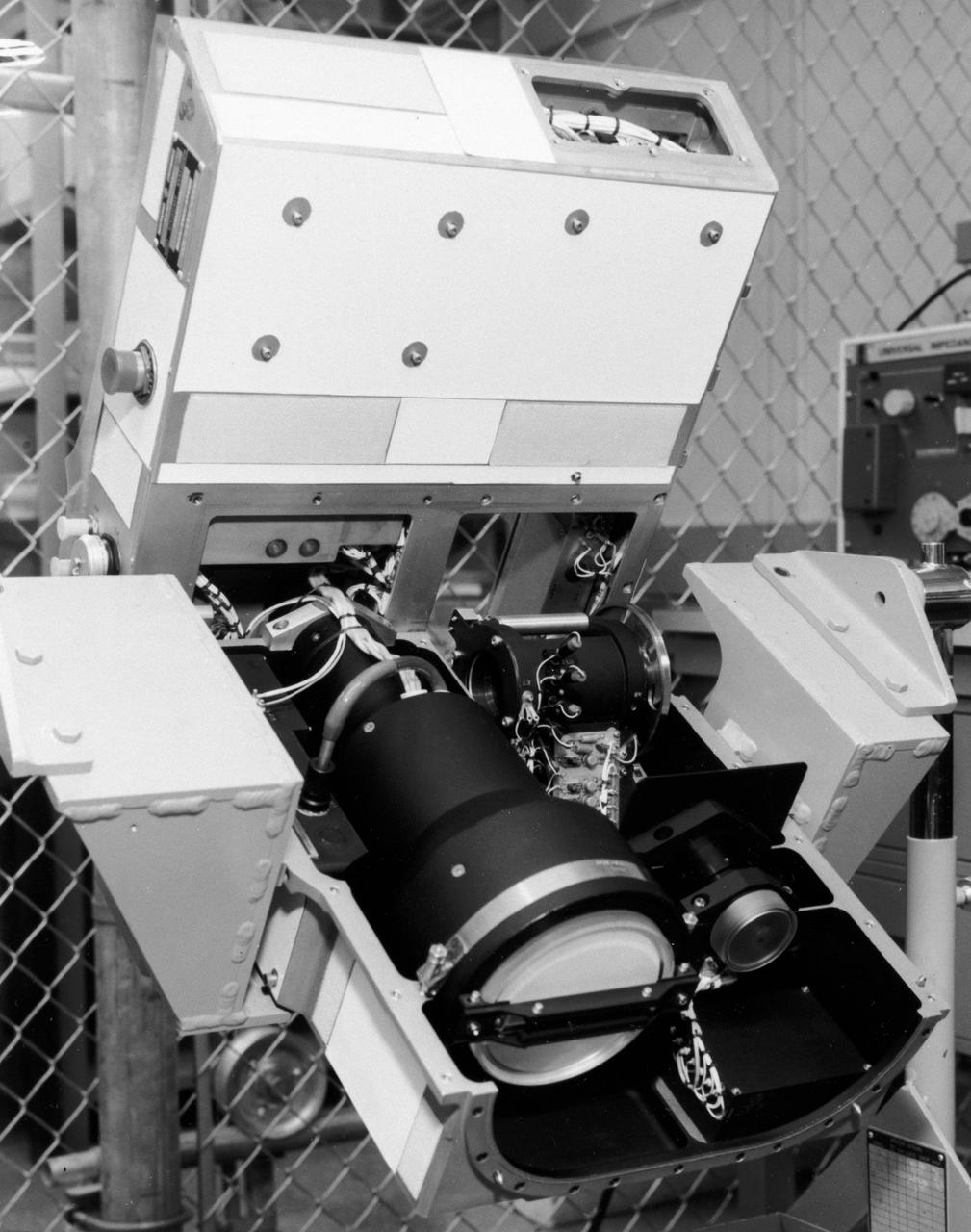

S72-49482 (November 1972) --- The Optical Recorder of the Lunar Sounder Experiment (S-209) which will be mounted in the SIM bay of the Apollo 17 Service Module. The three functional parts of the Lunar Sounder are the optical recorder, the coherent synthetic aperture radar, and the antennas, a retractable dipole for HF and a yagi for VHF. The Lunar Sounder will probe three-quarters of a mile below the moon's surface from the orbiting Apollo 17 spacecraft. Electronic data recorded on film will be retrieved by the crew during trans-Earth EVA. Geologic information on the lunar interior obtained by the sounder will permit scientific investigation of underground rock layers, lava flow patterns, rille (canyon) structures, mascon properties, and any areas containing water. A prototype lunar sounder has been flight tested in aircraft over selected Earth sites to confirm the equipment design and develop scientific analysis techniques. The Lunar Sounder Experiment was developed by North American Rockwell's (NR) Space Division for NASA's Manned Spacecraft Center to provide data for a scientific investigation team with representatives from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, University of Utah, University of Michigan, U.S. Geological Survey, and NASA Ames Research Center.
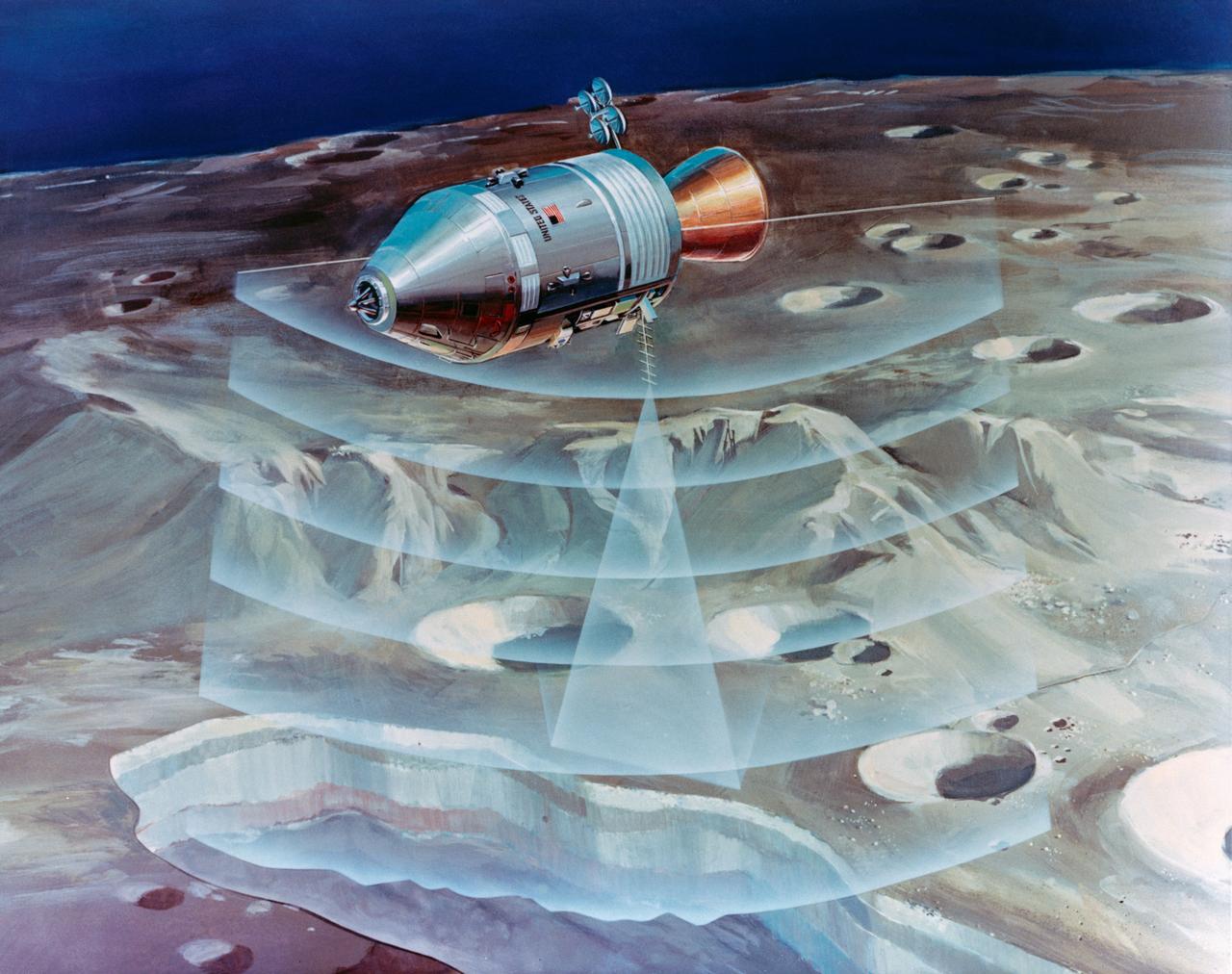

S72-53472 (November 1972) --- An artist's concept illustrating how radar beams of the Apollo 17 lunar sounder experiment will probe three-quarters of a mile below the moon's surface from the orbiting spacecraft. The Lunar Sounder will be mounted in the SIM bay of the Apollo 17 Service Module. Electronic data recorded on film will be retrieved by the crew during trans-Earth EVA. Geologic information on the lunar interior obtained by the sounder will permit scientific investigation of underground rock layers, lava flow patterns, rille (canyon) structures, mascon properties, and any areas containing water. A prototype lunar sounder has been flight tested in aircraft over selected Earth sites to confirm the equipment design and develop scientific analysis techniques. The Lunar Sounder Experiment (S-209) was developed by North American Rockwell's (NR) Space Division for NASA's Manned Spacecraft Center to provide data for a scientific investigation team with representatives from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory, University of Utah, University of Michigan, U.S. Geological Survey, and NASA Ames Research Center.
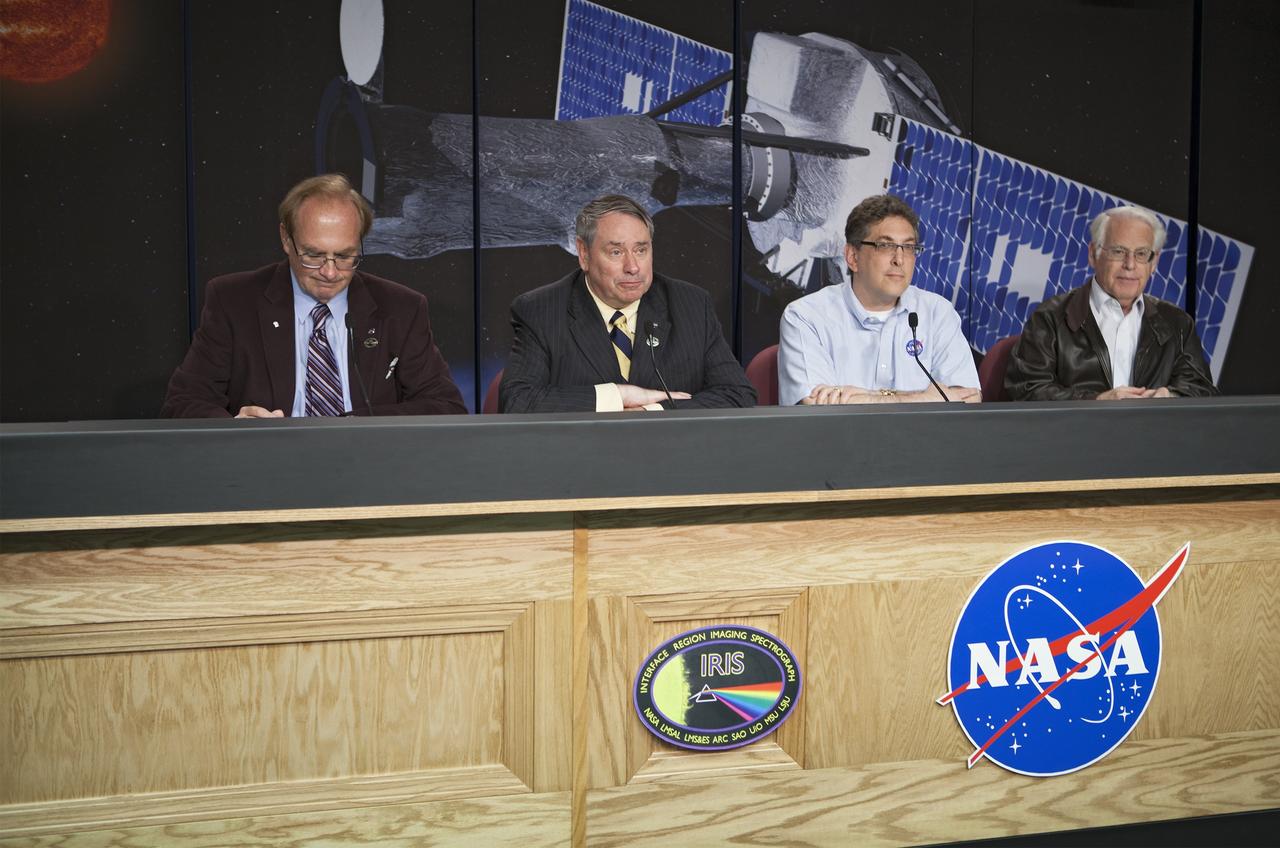

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA hosted a prelaunch mission briefing on the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory scheduled to launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Participating in the news conference are George Diller, NASA Public Affairs, Dr. S. Pete Worden, director of NASA's Ames Research Center in Calif., Jeffrey Newmark, IRIS Program scientist at NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C., and Alan Title, IRIS principal investigator with Lockheed Martin. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Casper

STS134-S-001 (March 2010) --- The design of the STS-134 crew patch highlights research on the International Space Station (ISS) focusing on the fundamental physics of the universe. On this mission, the crew of the space shuttle Endeavour will install the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) experiment - a cosmic particle detector. By studying subatomic particles in the background cosmic radiation and searching for antimatter, dark-matter, and dark energy, it will help scientists better understand the evolution and properties of our universe. The shape of the patch is inspired by the international atomic symbol, and represents the atom with orbiting electrons around the nucleus. The burst near the center refers to the origin of the universe. The space shuttle Endeavour and ISS fly together into the sunrise over the limb of the Earth, representing the dawn of a new age?understanding the nature of the universe. The NASA insignia design for space shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA Administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the forms of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which is not anticipated, the change will be publicly announced. Photo credit: NASA

STS134-S-001 (March 2010) --- The design of the STS-134 crew patch highlights research on the International Space Station (ISS) focusing on the fundamental physics of the universe. On this mission, the crew of space shuttle Endeavour will install the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) experiment -- a cosmic particle detector that utilizes the first-ever superconducting magnet to be flown in space. By studying sub-atomic particles in the background cosmic radiation, and searching for anti-matter and dark-matter, it will help scientists better understand the evolution and properties of our universe. The shape of the patch is inspired by the international atomic symbol, and represents the atom with orbiting electrons around the nucleus. The burst near the center refers to the big-bang theory and the origin of the universe. The shuttle Endeavour and ISS fly together into the sunrise over the limb of Earth, representing the dawn of a new age, understanding the nature of the universe. The NASA insignia design for shuttle flights is reserved for use by the astronauts and for other official use as the NASA administrator may authorize. Public availability has been approved only in the form of illustrations by the various news media. When and if there is any change in this policy, which we do not anticipate, it will be publicly announced.
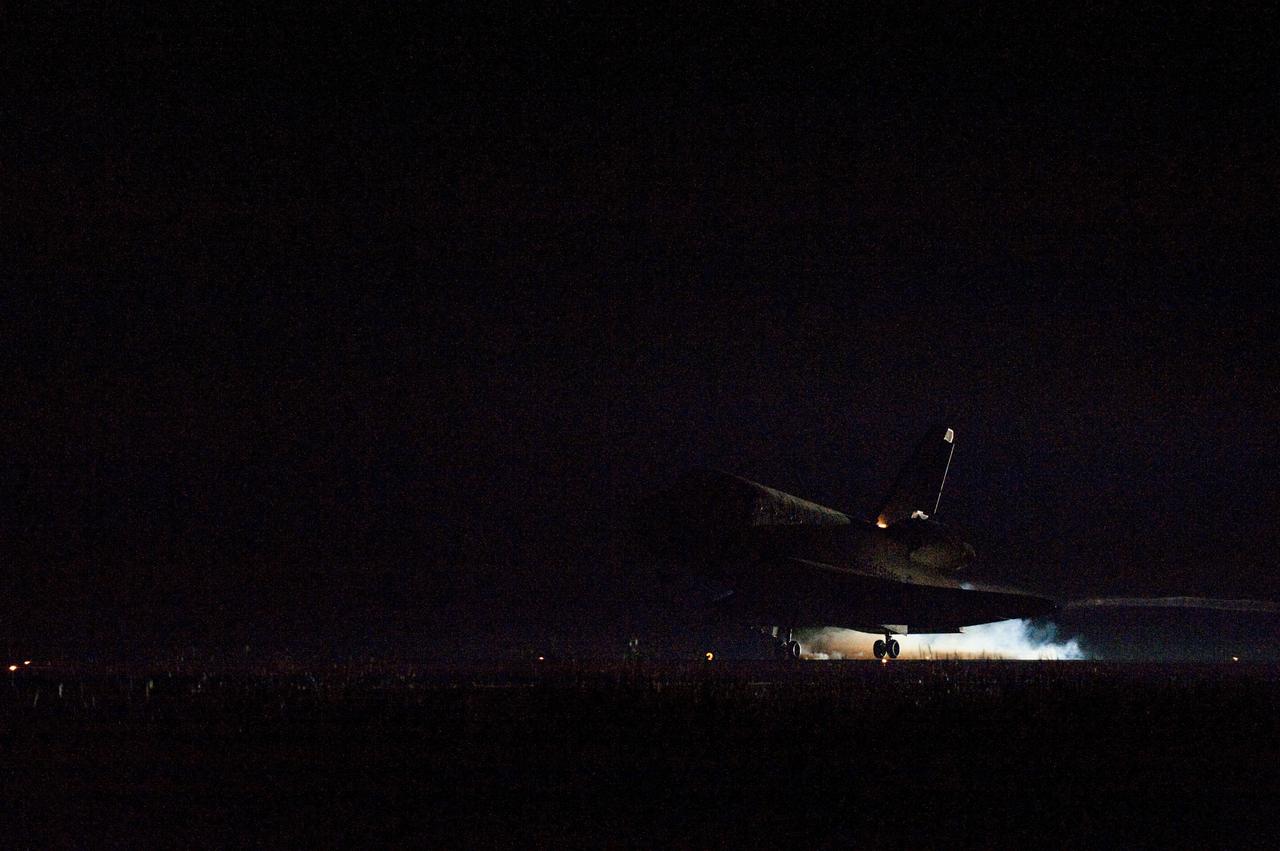

STS134-S-081 (1 June 2011) --- Heat from space shuttle Endeavour's auxiliary power units, which provide hydraulic control, can be seen at the back of the shuttle, near the vertical tail. Endeavour landed for the final time on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, marking the 24th night landing of the Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
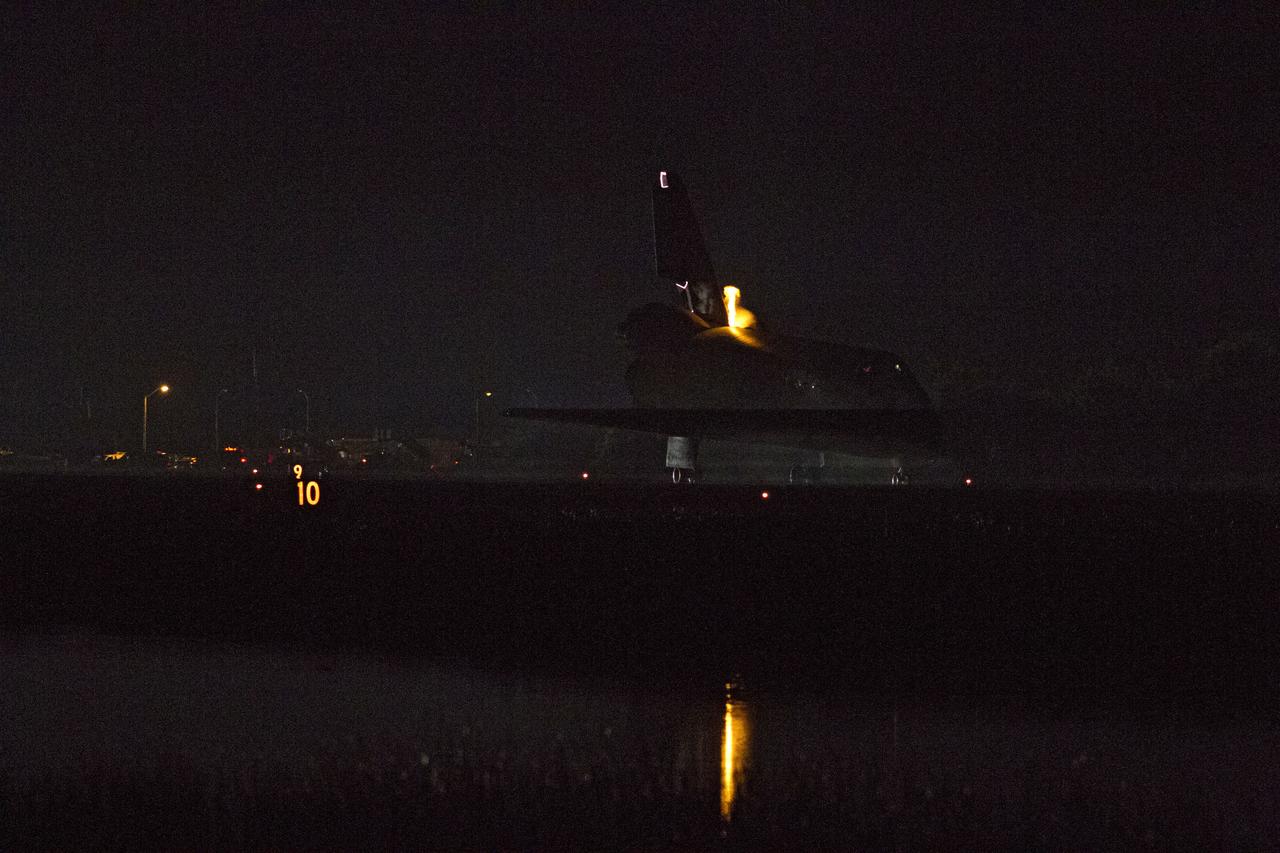

STS134-S-075 (1 June 2011) --- Heat from space shuttle Endeavour's auxiliary power units, which provide hydraulic control, can be seen at the back of the shuttle, near the vertical tail. Endeavour landed for the final time on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, marking the 24th night landing of the Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA
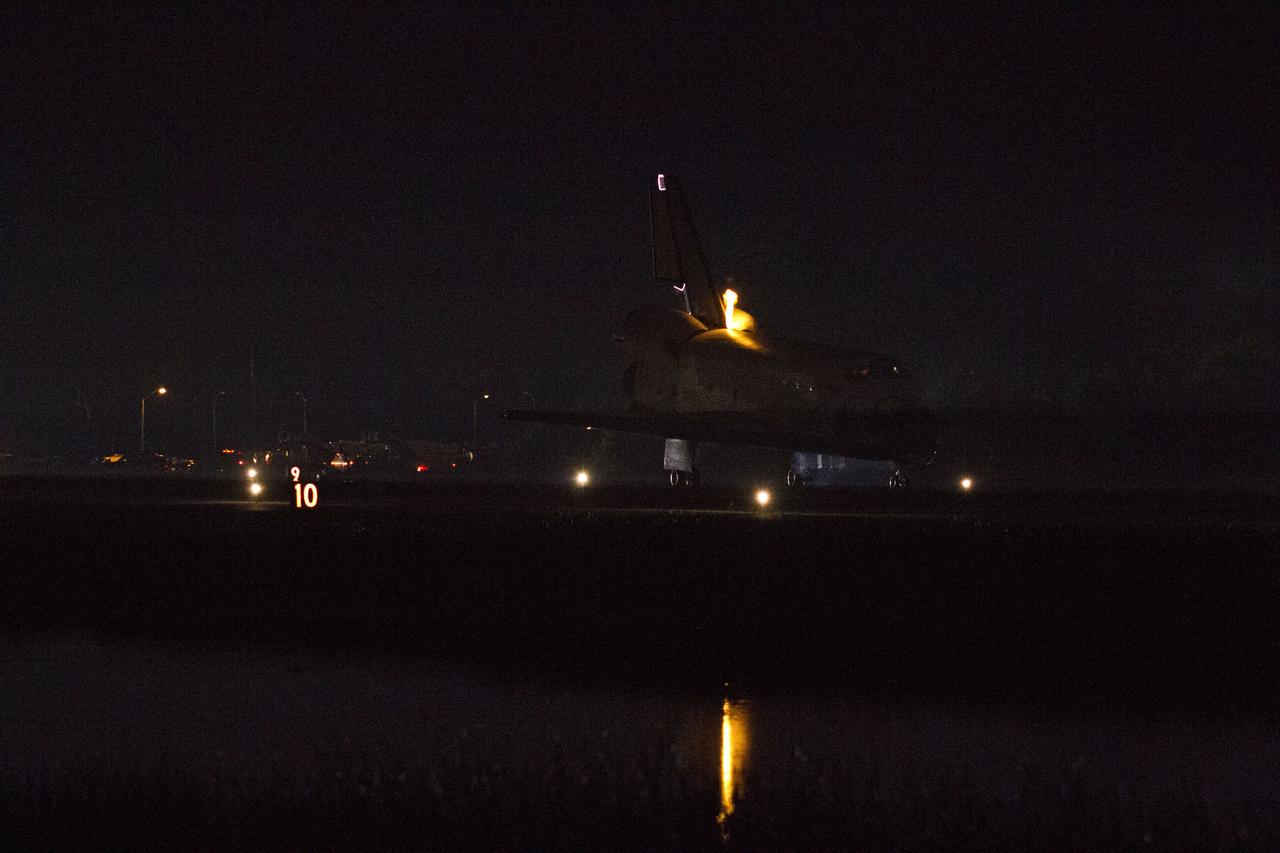

STS134-S-076 (1 June 2011) --- Heat from space shuttle Endeavour's auxiliary power units, which provide hydraulic control, can be seen at the back of the shuttle, near the vertical tail. Endeavour landed for the final time on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, marking the 24th night landing of the Space Shuttle Program. Main gear touchdown was at 2:34:51 a.m. (EDT) on June 1, 2011, followed by nose gear touchdown at 2:35:04 a.m., and wheelstop at 2:35:36 a.m. Onboard are NASA astronauts Mark Kelly, STS-134 commander; Greg H. Johnson, pilot; Michael Fincke, Andrew Feustel, Greg Chamitoff and European Space Agency astronaut Roberto Vittori, all mission specialists. STS-134 delivered the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) and the Express Logistics Carrier-3 (ELC-3) to the International Space Station. AMS will help researchers understand the origin of the universe and search for evidence of dark matter, strange matter and antimatter from the station. ELC-3 carried spare parts that will sustain station operations once the shuttles are retired from service. STS-134 was the 25th and final flight for Endeavour, which has spent 299 days in space, orbited Earth 4,671 times and traveled 122,883,151 miles. Photo credit: NASA