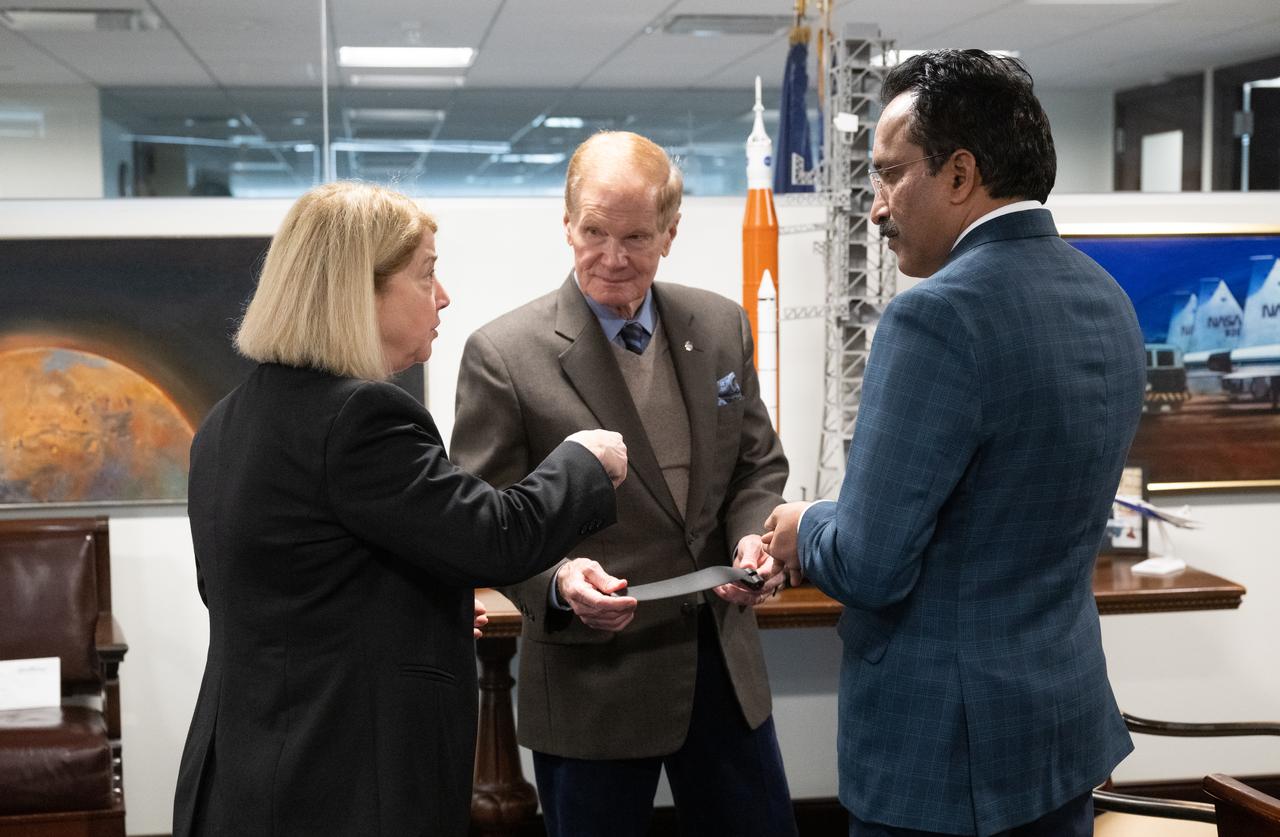

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, and S Somanath, Chairman of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), meet to discuss ways to enhance bilateral space cooperation on Wednesday, Feb. 1, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
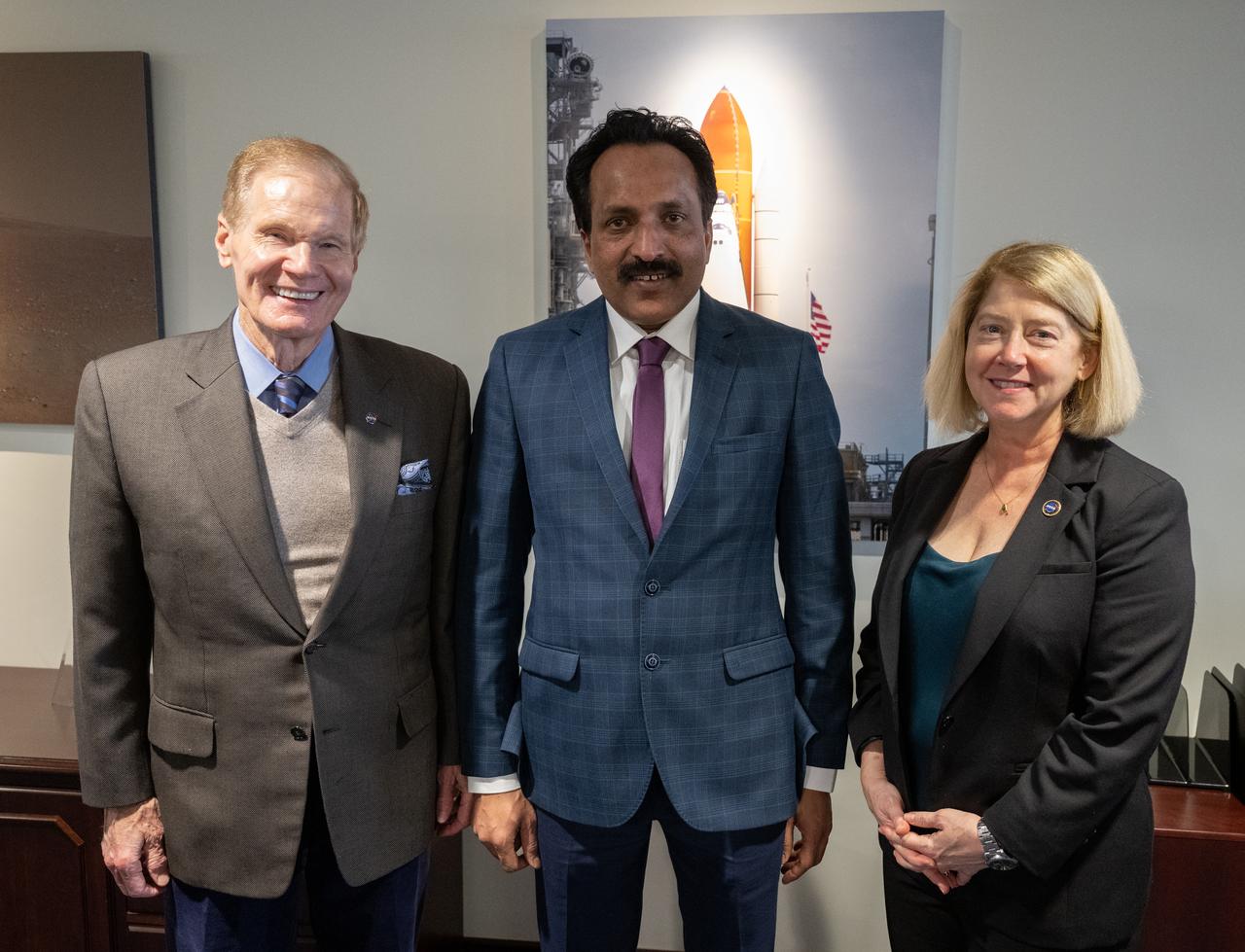
NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, left, NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, right, and S Somanath, Chairman of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), center, pose for a picture following a meeting to discuss ways to enhance bilateral space cooperation on Wednesday, Feb. 1, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
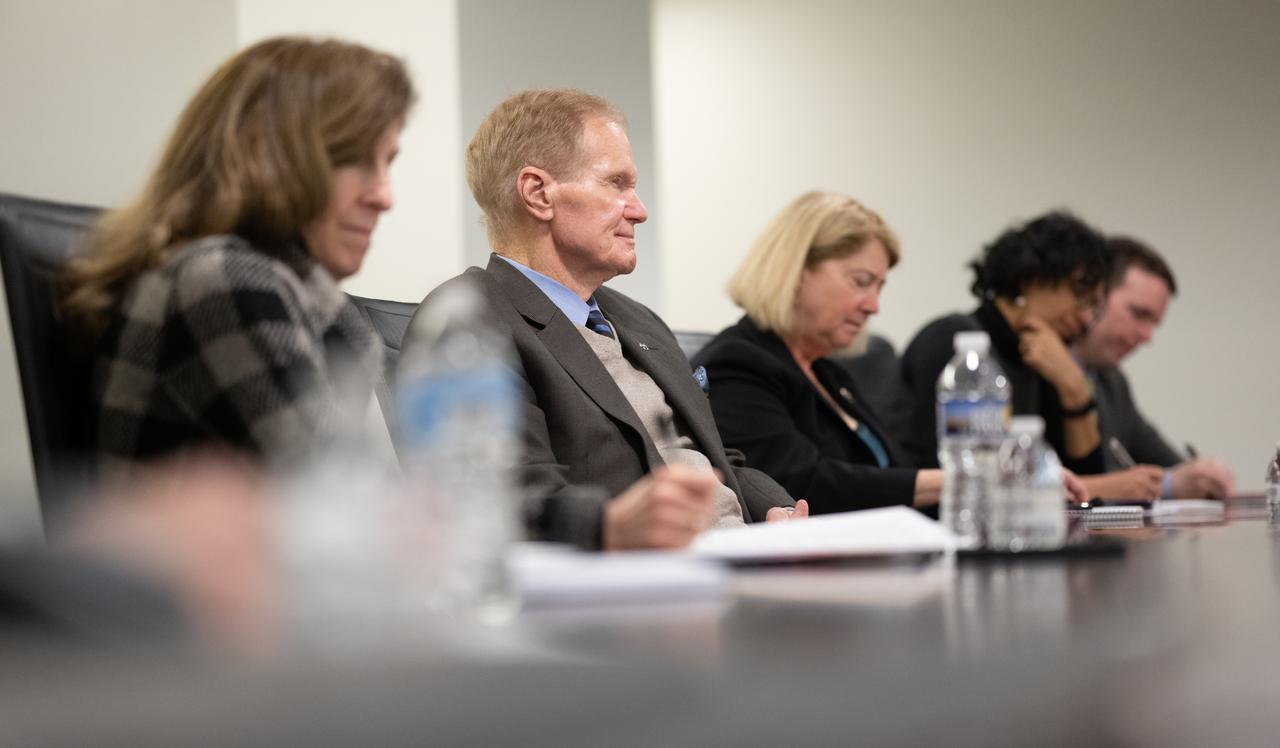

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson and NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy are seen during a meeting with S Somanath, Chairman of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), to discuss ways to enhance bilateral space cooperation on Wednesday, Feb. 1, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
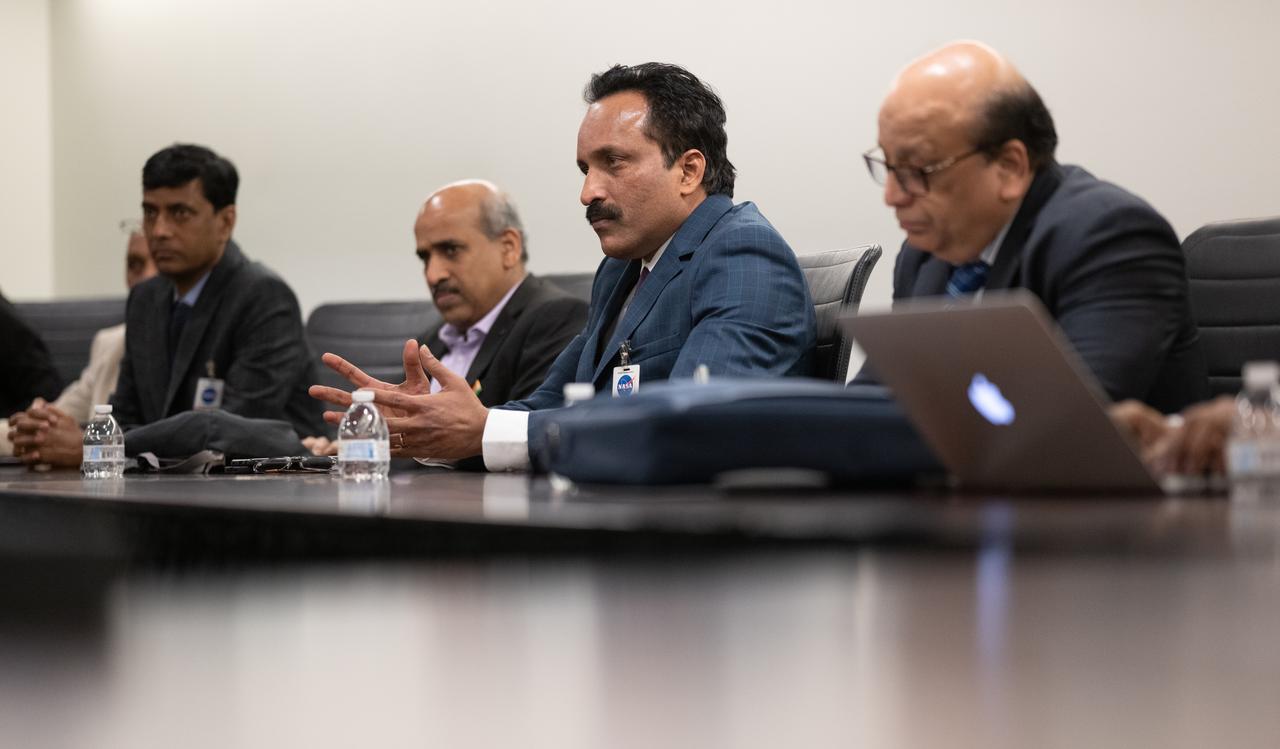

S Somanath, Chairman of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), center, is seen during a meeting with NASA Administrator Bill Nelson and NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy to discuss ways to enhance bilateral space cooperation on Wednesday, Feb. 1, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Crew 1 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center in Huntsville, Alabama. SpaceX will launch a Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA astronauts aboard the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station on Nov. 15, 2020. The Marshall team is supporting flight control teams working with NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, and SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, as they monitor the different phases of the upcoming mission. Engineers and technicians at Marshall will use headsets and loops to communicate with the multiple locations on console for the launch.
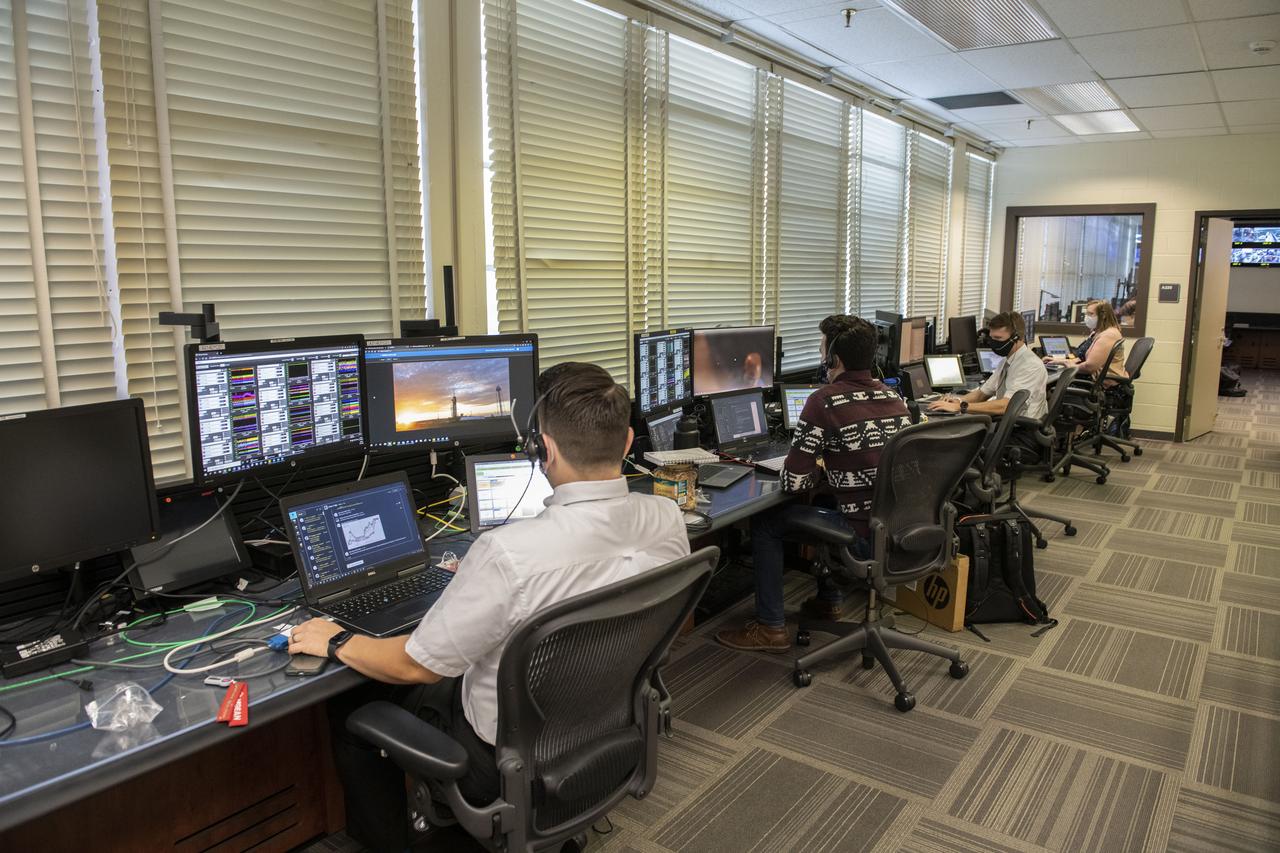

Teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Crew 1 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center in Huntsville, Alabama. SpaceX will launch a Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA astronauts aboard the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station on Nov. 15, 2020. The Marshall team is supporting flight control teams working with NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, and SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, as they monitor the different phases of the upcoming mission. Engineers and technicians at Marshall will use headsets and loops to communicate with the multiple locations on console for the launch.
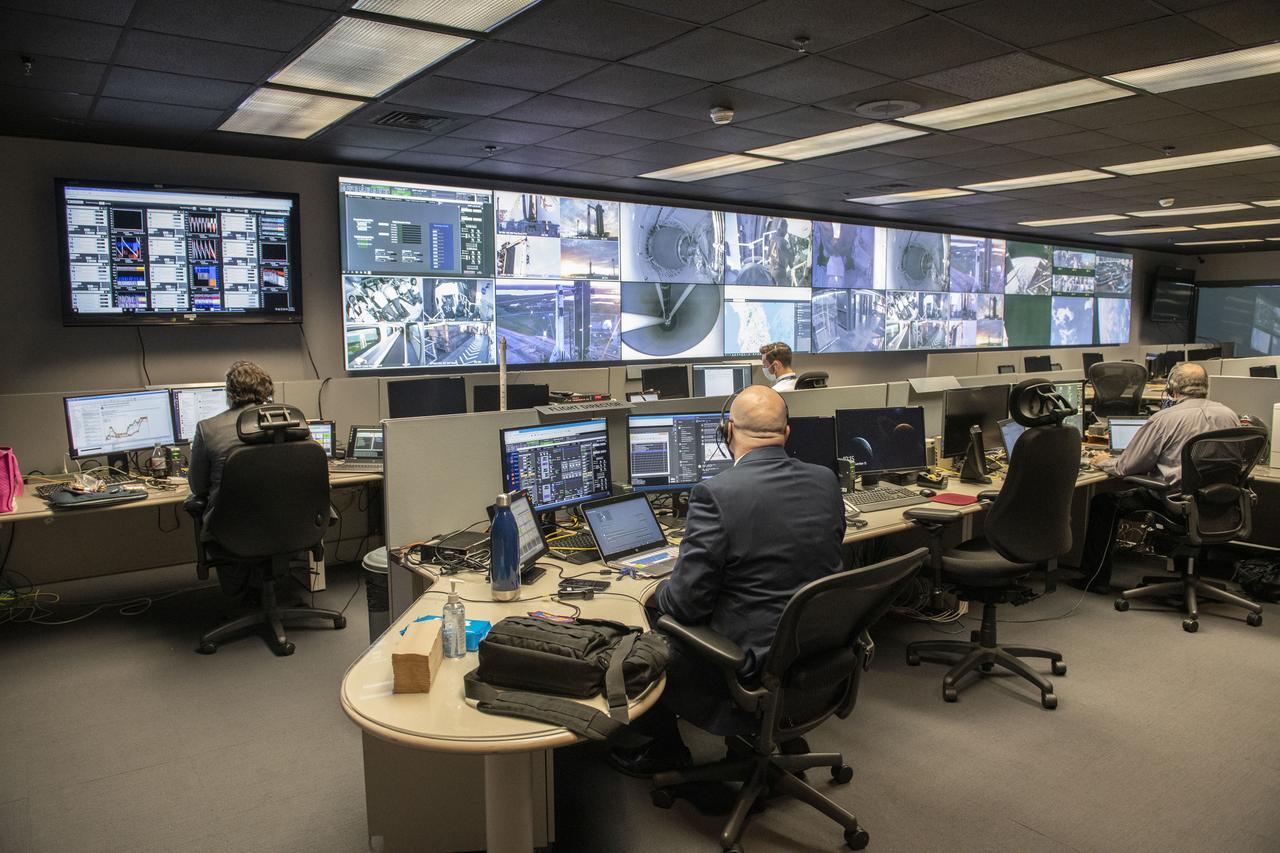

Teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Crew 1 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center in Huntsville, Alabama. SpaceX will launch a Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA astronauts aboard the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station on Nov. 15, 2020. The Marshall team is supporting flight control teams working with NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, and SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, as they monitor the different phases of the upcoming mission. Engineers and technicians at Marshall will use headsets and loops to communicate with the multiple locations on console for the launch.
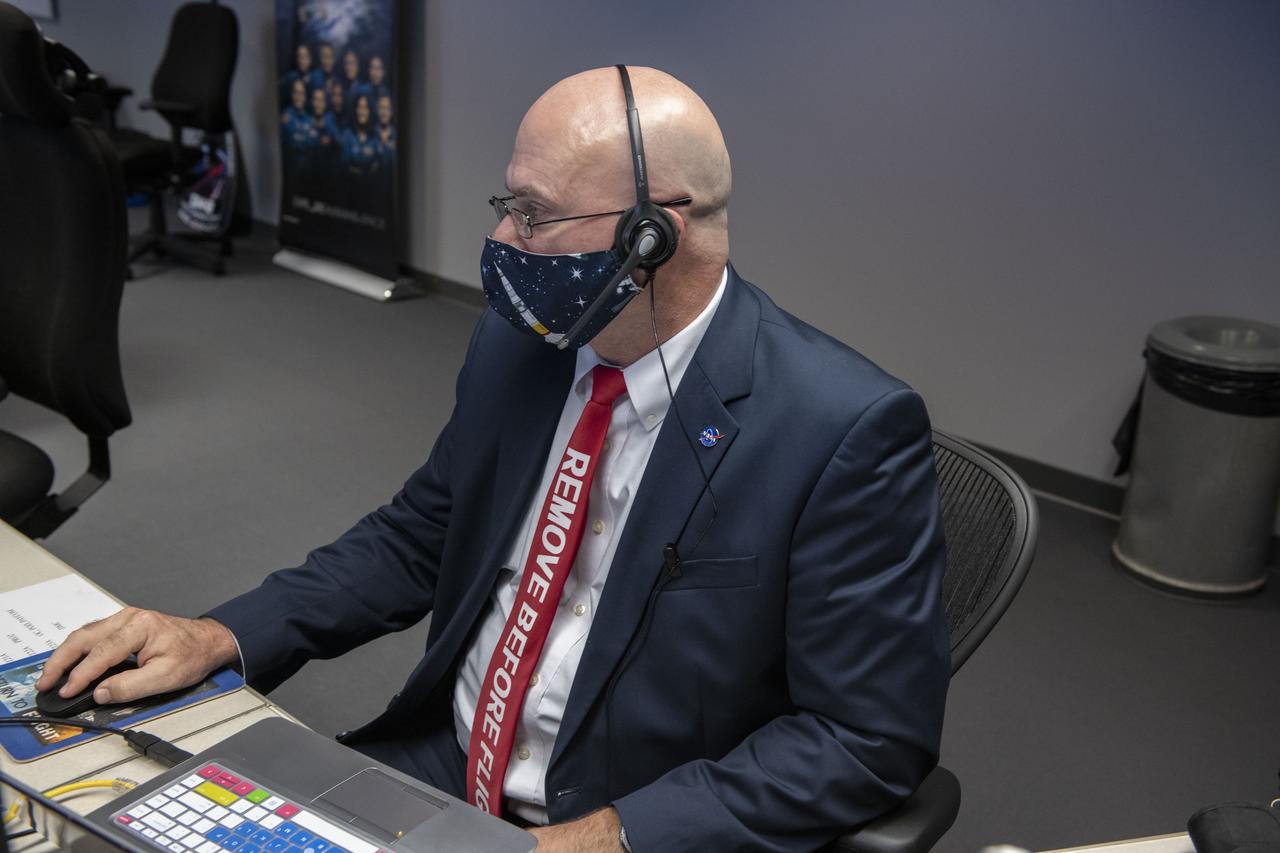

Teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Crew 1 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center in Huntsville, Alabama. SpaceX will launch a Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA astronauts aboard the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station on Nov. 15, 2020. The Marshall team is supporting flight control teams working with NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, and SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, as they monitor the different phases of the upcoming mission. Engineers and technicians at Marshall will use headsets and loops to communicate with the multiple locations on console for the launch.
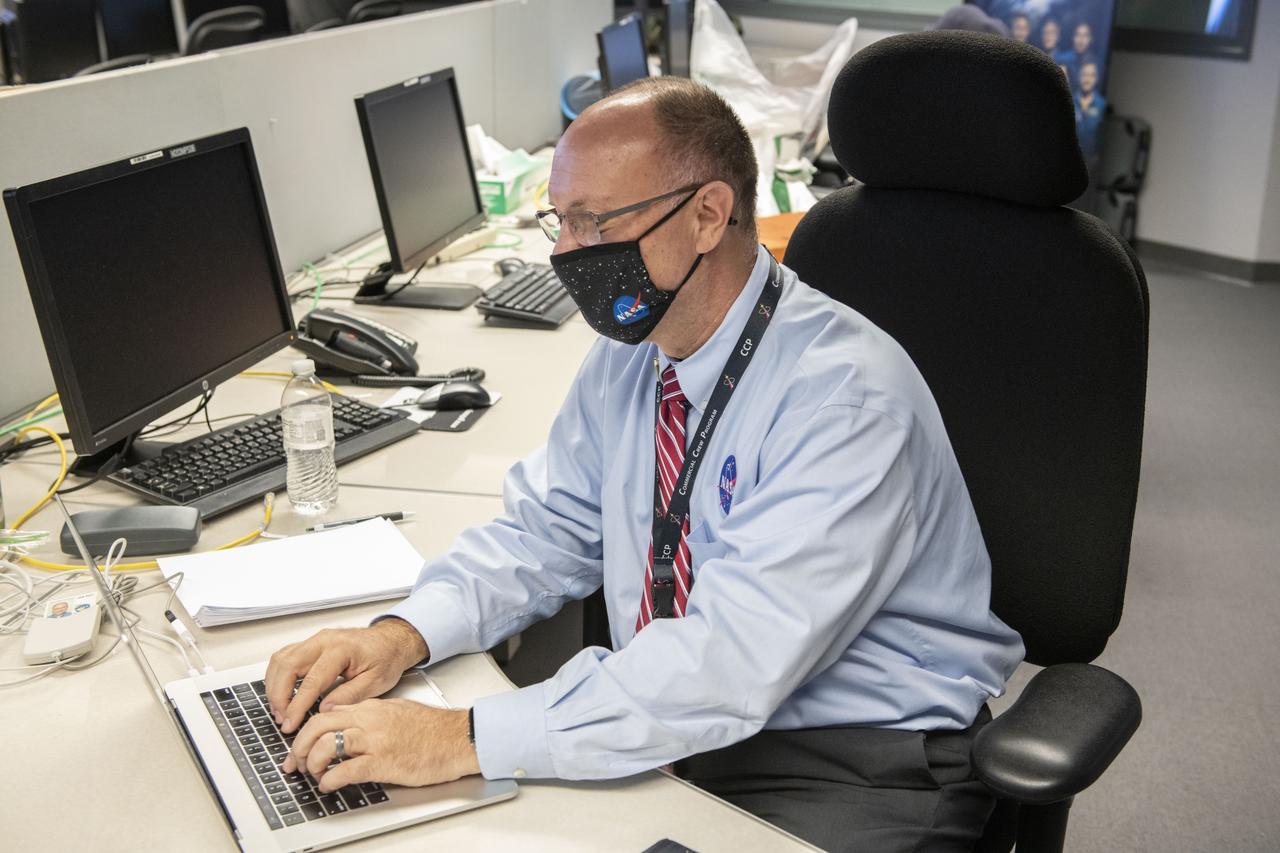

Teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Crew 1 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center in Huntsville, Alabama. SpaceX will launch a Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA astronauts aboard the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station on Nov. 15, 2020. The Marshall team is supporting flight control teams working with NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, and SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, as they monitor the different phases of the upcoming mission. Engineers and technicians at Marshall will use headsets and loops to communicate with the multiple locations on console for the launch.

Teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Crew 1 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center in Huntsville, Alabama. SpaceX will launch a Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA astronauts aboard the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station on Nov. 15, 2020. The Marshall team is supporting flight control teams working with NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, and SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, as they monitor the different phases of the upcoming mission. Engineers and technicians at Marshall will use headsets and loops to communicate with the multiple locations on console for the launch.
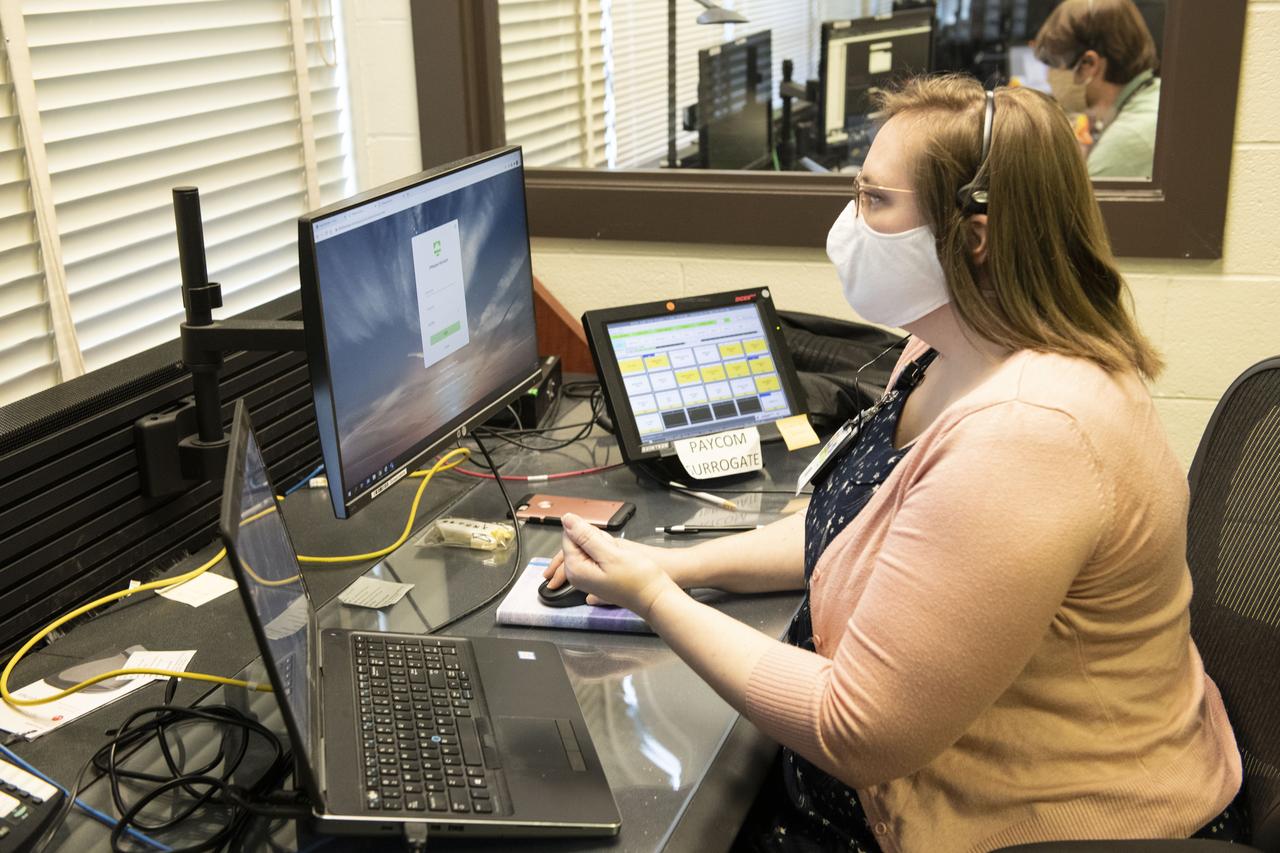

Teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Crew 1 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center in Huntsville, Alabama. SpaceX will launch a Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA astronauts aboard the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station on Nov. 15, 2020. The Marshall team is supporting flight control teams working with NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, and SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, as they monitor the different phases of the upcoming mission. Engineers and technicians at Marshall will use headsets and loops to communicate with the multiple locations on console for the launch.

Teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Crew 1 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center in Huntsville, Alabama. SpaceX will launch a Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA astronauts aboard the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station on Nov. 15, 2020. The Marshall team is supporting flight control teams working with NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, and SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, as they monitor the different phases of the upcoming mission. Engineers and technicians at Marshall will use headsets and loops to communicate with the multiple locations on console for the launch.
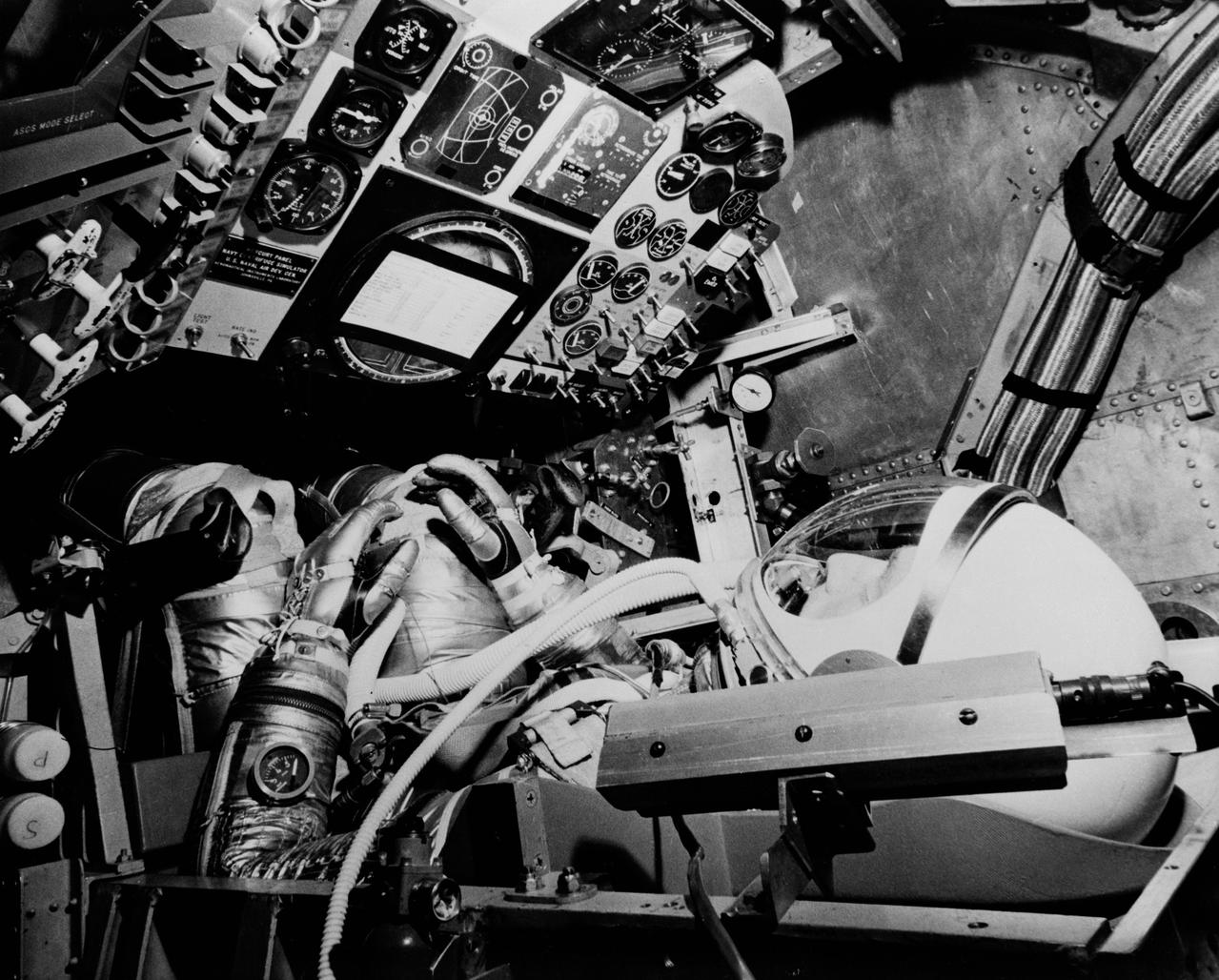
S61-03506 (1961) --- Project Mercury astronaut M. Scott Carpenter, prime pilot for the United States second manned orbital flight, undergoes a simulated mission in the procedures trainer at Langley Air Force Base, Virginia, headquarters for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration?s Manned Spacecraft Center. Photo credit: NASA
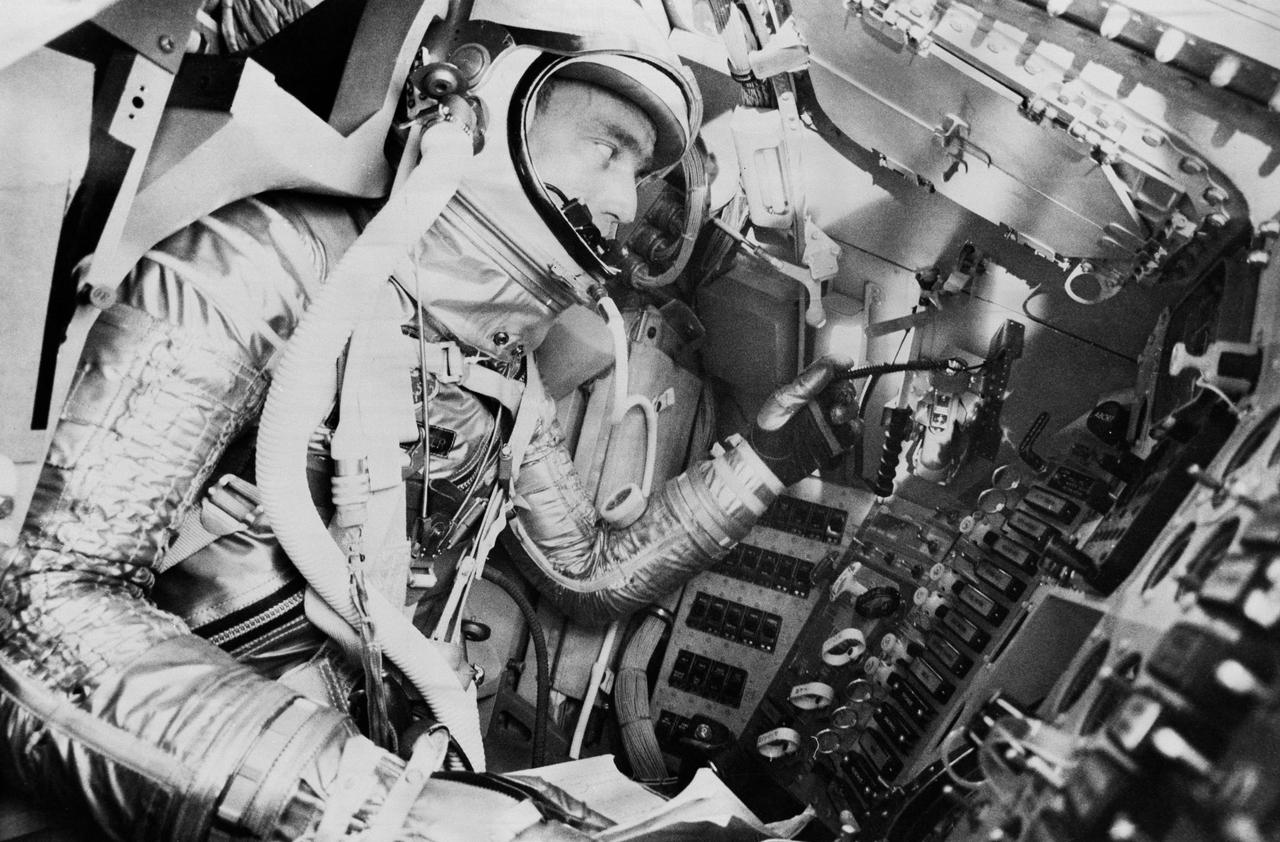

S62-01033 (1961) --- Project Mercury astronaut M. Scott Carpenter, prime pilot for the United States second manned orbital flight, undergoes a simulated mission in the procedures trainer at Langley Air Force Base, Virginia, headquarters for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration?s Manned Spacecraft Center. Photo credit: NASA

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, Sandra Smalley, director of the Joint Agency Satellite Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C., speaks to members of the media at a prelaunch news conference about National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's, or NOAA's, Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. The GOES series of satellites will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to lift off at 5:02 p.m. EST on March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
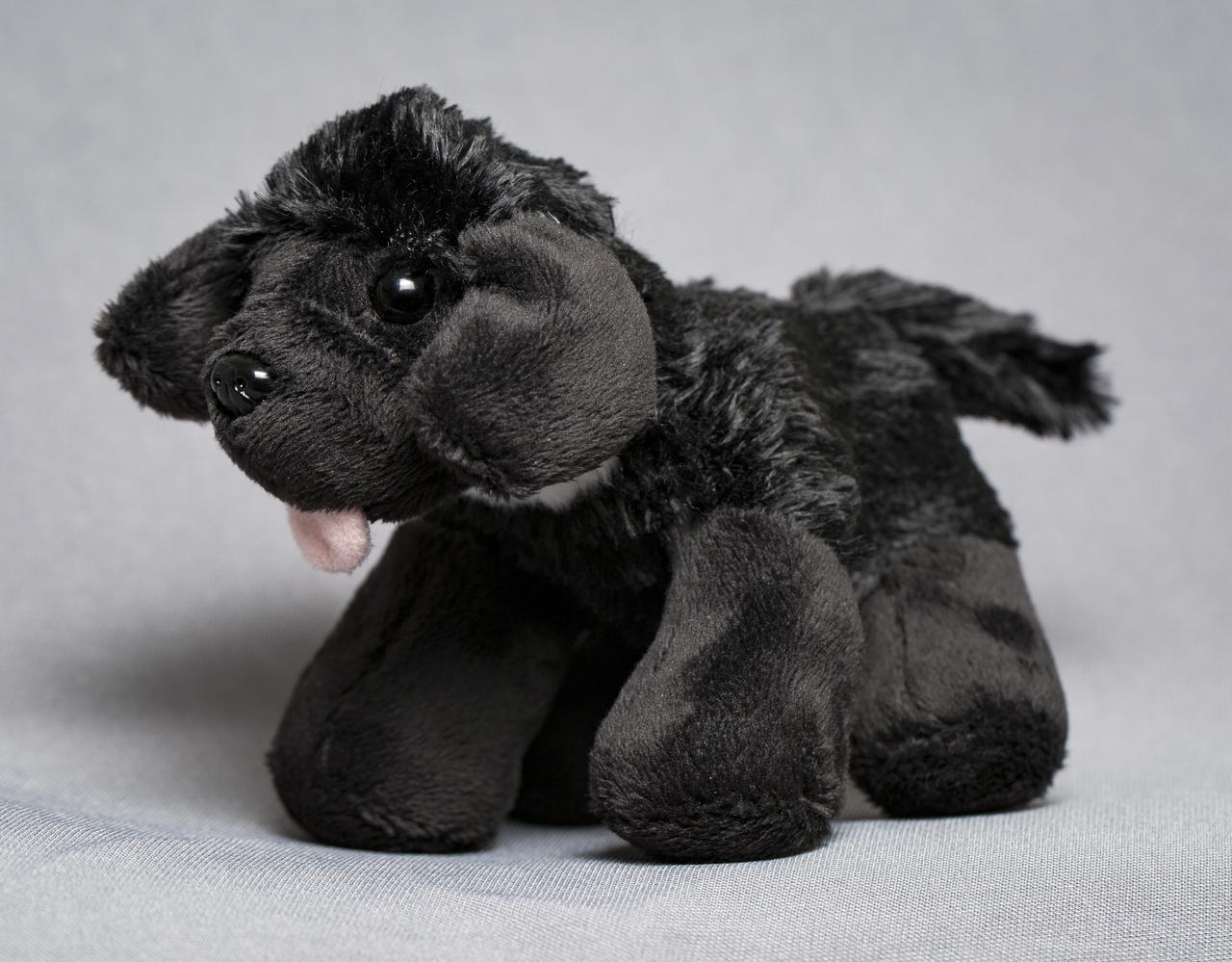

A toy dog named Seaman Jr., representing the Newfoundland that accompanied Lewis and Clark on their historic expedition in the 1800's, is seen here, Thursday, May 3, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Seaman Jr. is headed to the International Space Station this summer to help celebrate NASA’s 60th Anniversary and the National Trail System’s 50th anniversary. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

A toy dog named Seaman Jr., representing the Newfoundland that accompanied Lewis and Clark on their historic expedition in the 1800's, is seen here, Thursday, May 3, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Seaman Jr. is headed to the International Space Station this summer to help celebrate NASA’s 60th Anniversary and the National Trail System’s 50th anniversary. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
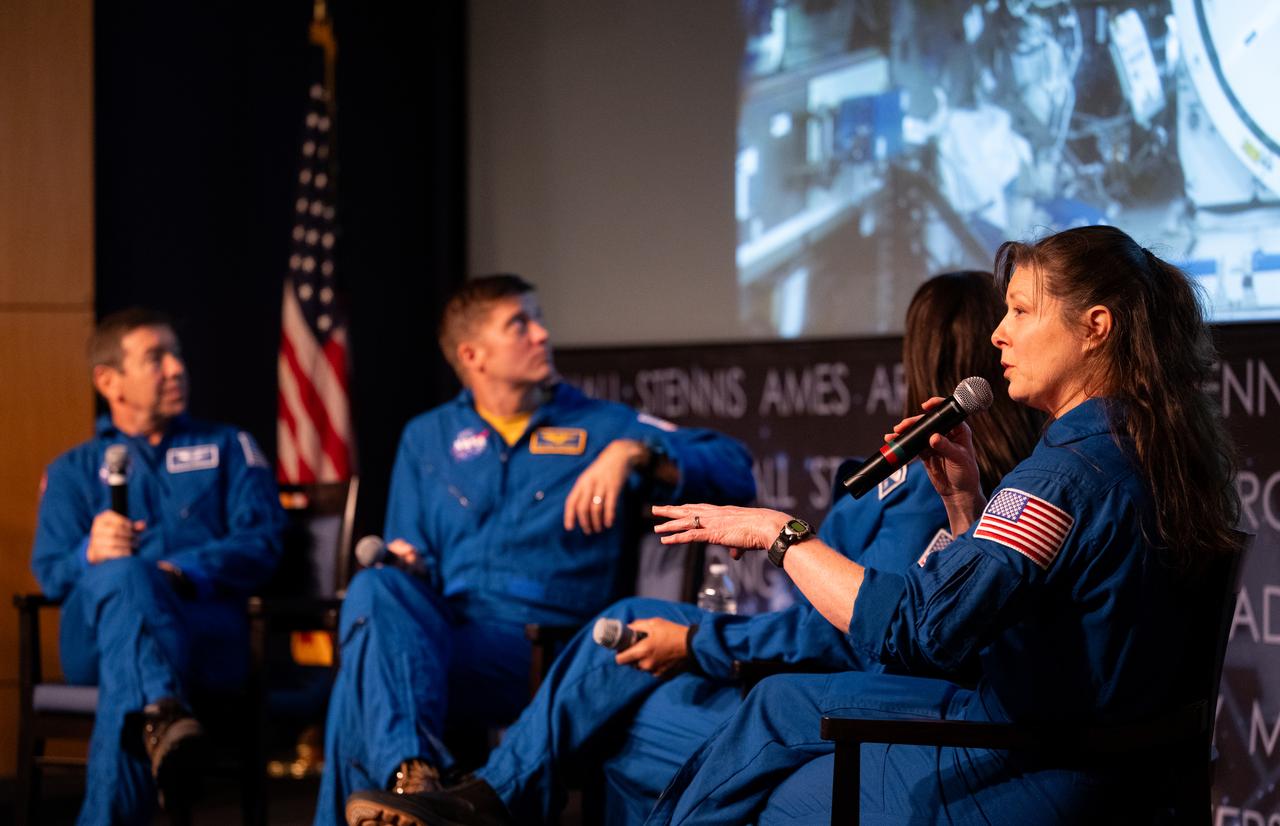

Expedition 71 NASA astronaut Tracy Dyson, speaks to delegates of the U. S. Senate Youth Program alongside fellow Expedition 71 crewmates Michael Barratt, Matthew Dominick, and Jeanette Epps, Wednesday, March 5, 2025 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters Building in Washington. Dominick, Epps, Barratt, and Dyson served as part of Expedition 71 aboard the International Space Station. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
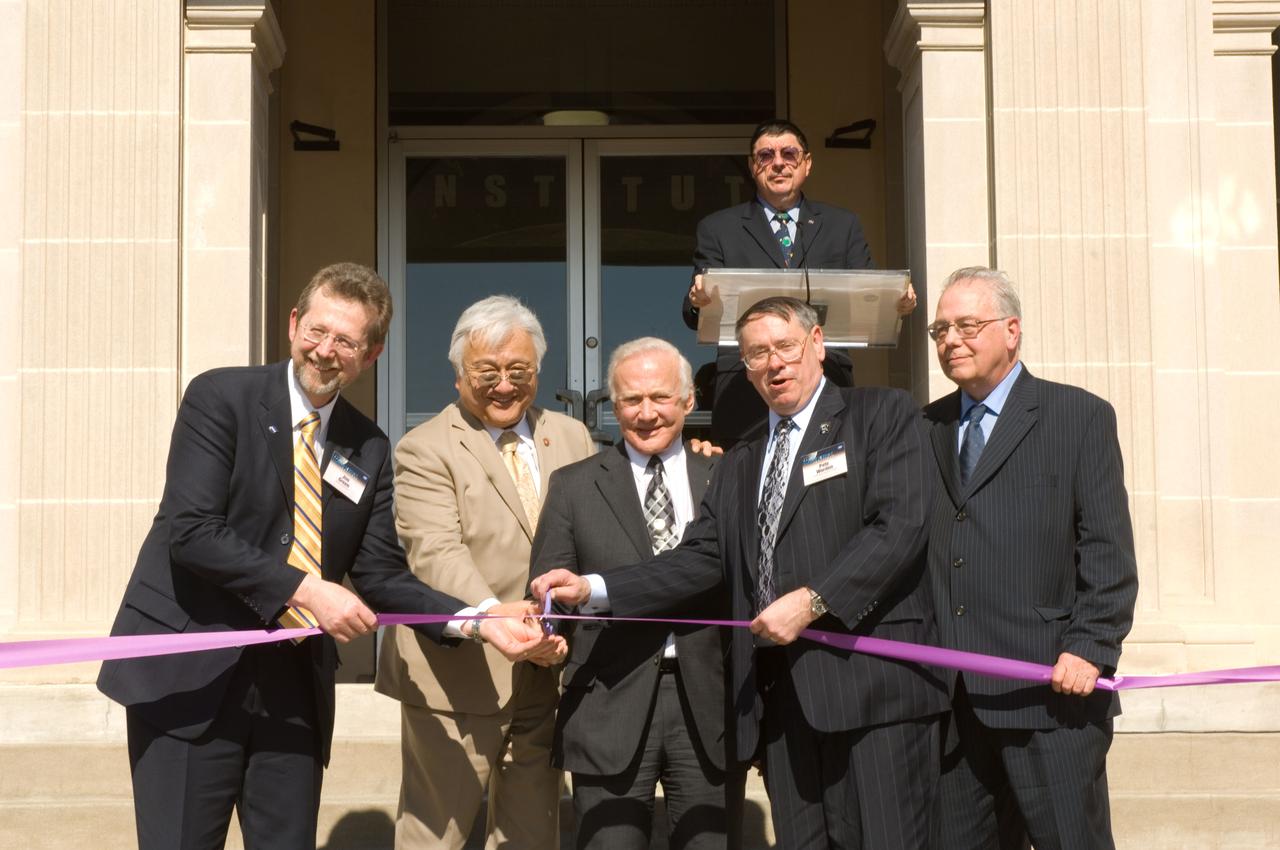

Lunar Science Institute (LSI) Grand Opening. Ribbon Cutting, L-R: James Green, Director, Planetary Programs, NASA Headquarters, Mike Honda, U.S. Congressman,15th District, Apollo Astronaut Buzz Aldrin, S. Pete Worden, Director, NASA Ames Research Center, David Morrison, Interiu Director, NASA Lunar Science Institute. David Morse at podium.

A toy dog named Seaman Jr., representing the Newfoundland that accompanied Lewis and Clark on their historic expedition in the 1800's, is seen here, Thursday, May 3, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Seaman Jr. is headed to the International Space Station this summer to help celebrate NASA’s 60th Anniversary and the National Trail System’s 50th anniversary. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
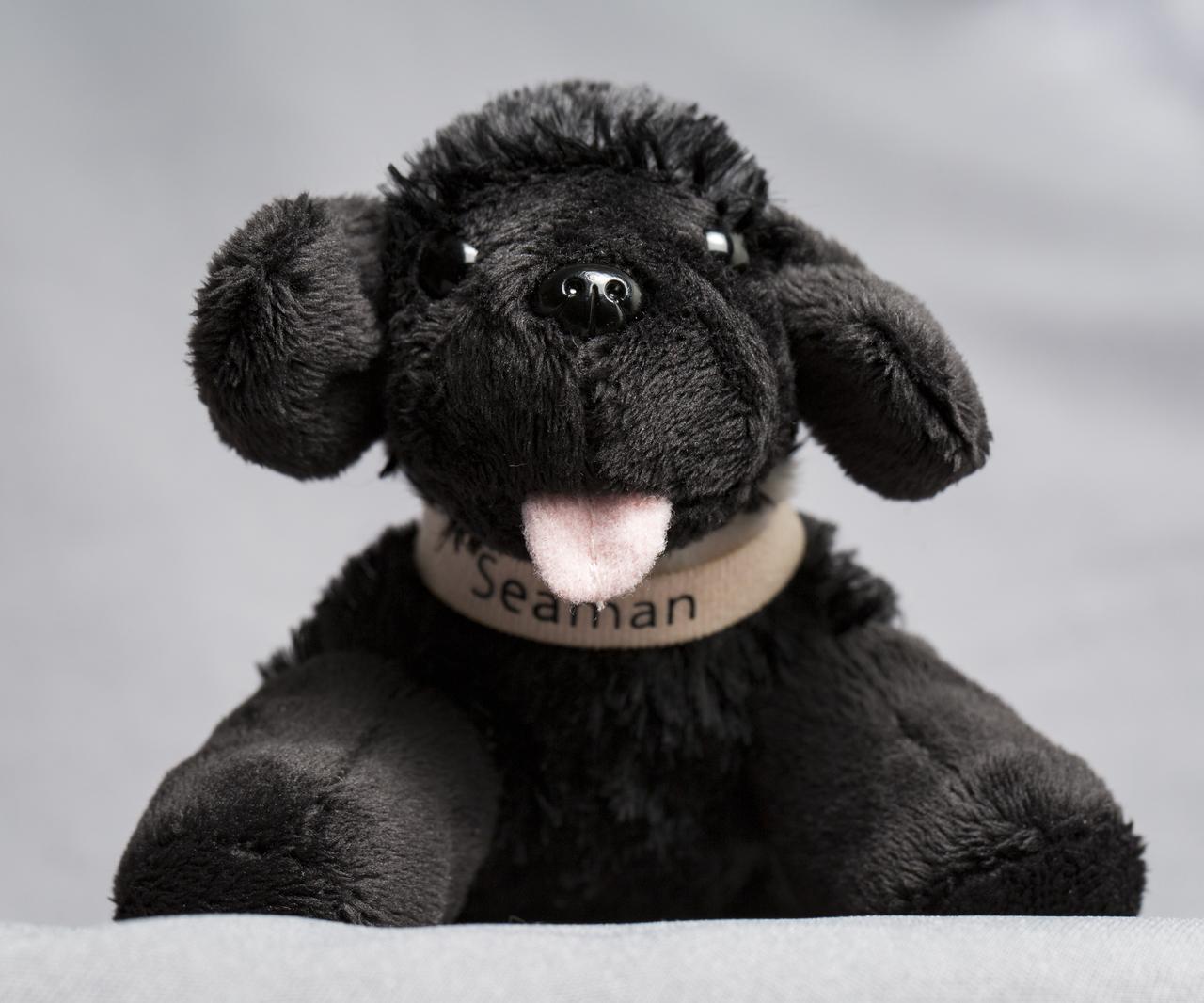

A toy dog named Seaman Jr., representing the Newfoundland that accompanied Lewis and Clark on their historic expedition in the 1800's, is seen here, Thursday, May 3, 2018 at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Seaman Jr. is headed to the International Space Station this summer to help celebrate NASA’s 60th Anniversary and the National Trail System’s 50th anniversary. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

WASHINGTON, D.C.---S&T Partnership Forum In-Space Assembly Technical Interchange Meeting-On September 6th 2017, many of the United States government experts on In-Space Assembly met at the U.S. Naval Research Lab to discuss both technology development and in-space applications that would advance national capabilities in this area. Expertise from NASA, USAF, NRO, DARPA and NRL met in this meeting which was coordinated by the NASA Headquarters, Office of the Chief Technologist. This technical interchange meeting was the second meeting of the members of this Science and Technology Partnership Forum.
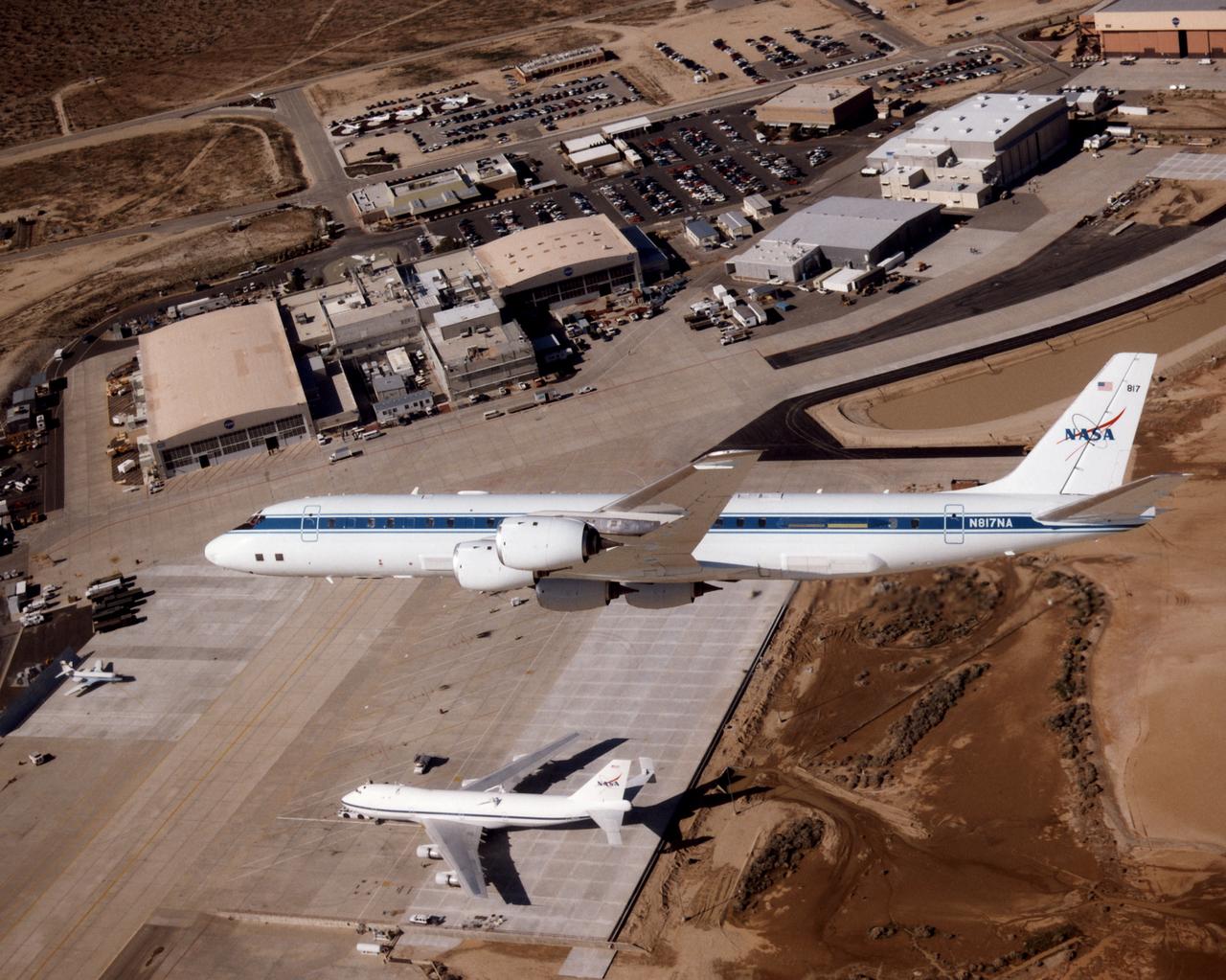

The DC-8 aircraft is seen making a banking turn high above the NASA Dryden ramp. This view of the DC-8's left side reveals some of the modifications necessary for particular on-board experiments. To the right of the DC-8 is the edge of Rogers Dry Lake. Above the aircraft's forward fuselage is the Dryden Flight Research Center headquarters building, while other NASA facilities extend down the flightline to the right. Below the DC-8 is the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA), on which are visible attachment points for the Shuttle Orbiter.
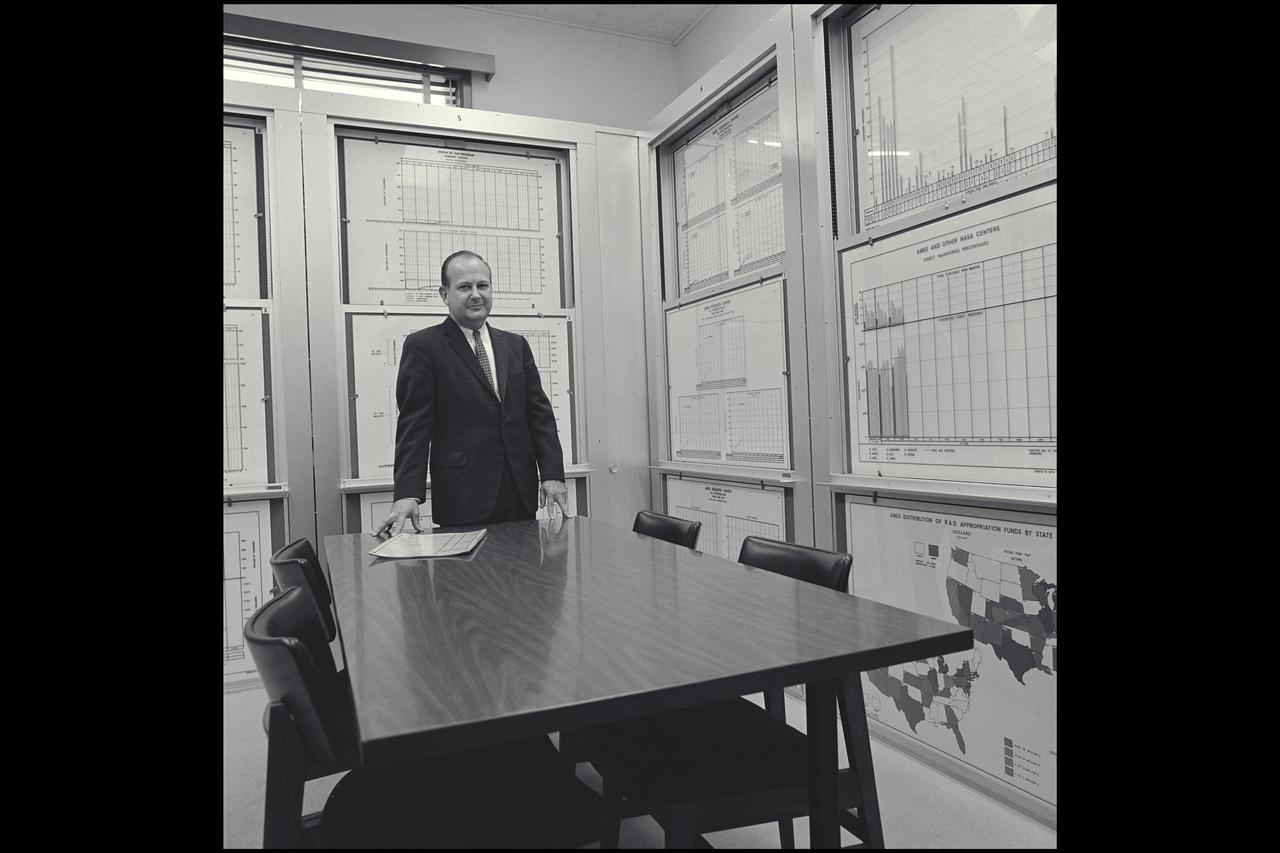

Management process invaded Ames as the Center shifted from NACA to NASA oversight. Ames constructed a review room in its headquarters building where, in the graphical style that prevailed in the 1960's, Ames leadership could review progress against schedule, budget and performance measures. Shown, in October 1965 is Merrill Mead chief of Ames' program and resources office. (for H Julian Allen Retirement album)

Russian Scientists from the Commission of Interplanetary Travel of the Soviet Academy of Science November 21,1959 Left to right: Front row: Yury S. Galkin, Anatoly A. Blagonravov, and Prof. Leonid I. Sedov (Chair of the Commission for Interplanetary Travel)-Soviet Academy of Science, Leninski Gory, Moscow, Russia Dr. H.J. E. Reid and Floyd L. Thompson Langley Research Center. Second row: Boris Kit Translator, Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. Eugene C. Draley and Laurence K. Loftin, Jr. -Langley Research Center Arnold W. Frutkin and Harold R. Lawrence NASA Headquarters. Back row: T.Melvin Butler-Langley Research Center John W. Townsend Goddard Space Flight Center, NASA, Washington D.C., and George M. Low NASA Headquarters.
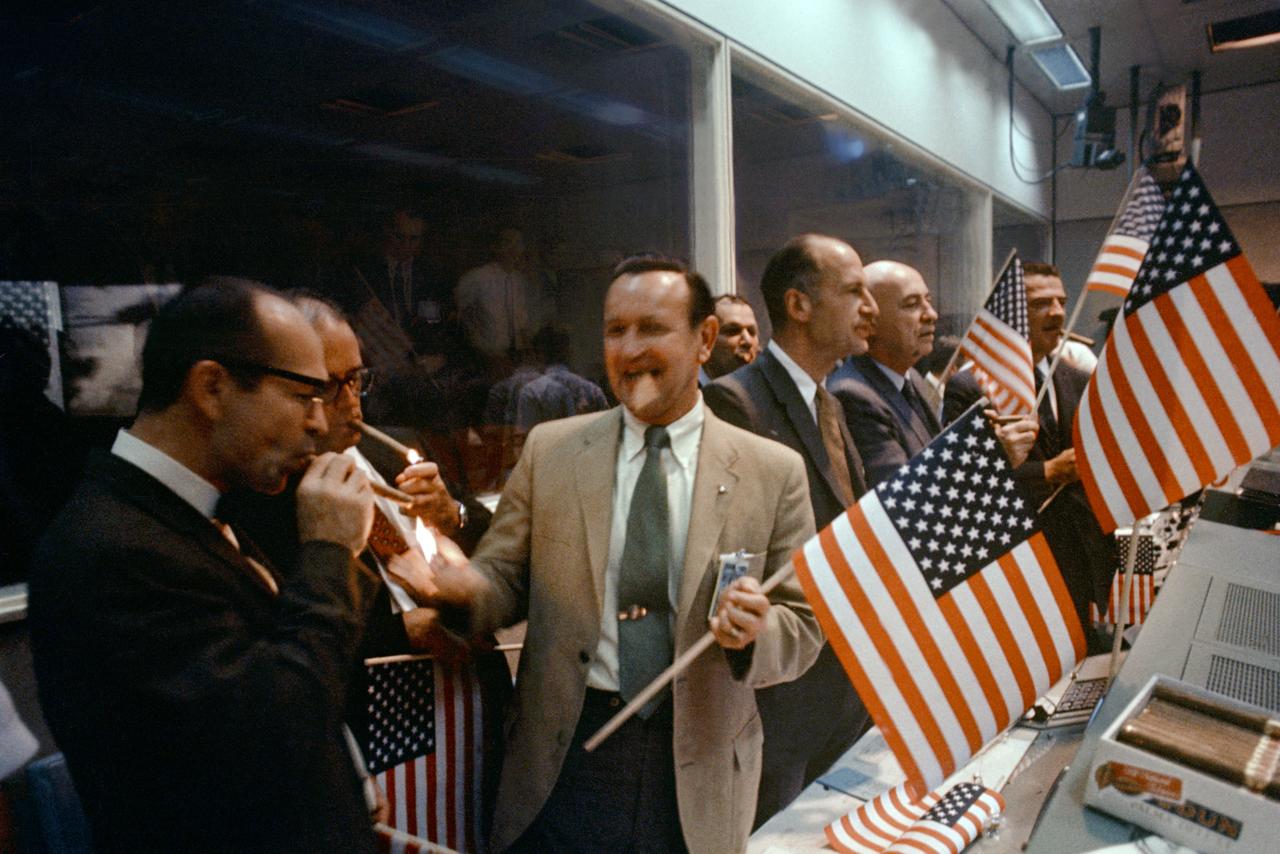

S69-40302 (24 July 1969) --- A group of NASA and Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) officials join in with the flight controllers in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center (MCC), Building 30, in celebrating the successful conclusion of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. From left foreground are Dr. Maxime A. Faget, MSC Director of Engineering and Development; George S. Trimble, MSC Deputy Director; Dr. Christopher C. Kraft Jr., MSC Director of Flight Operations; Julian Scheer (in back), Assistant Administrator, Office of Public Affairs, NASA Headquarters; George M. Low, Manager, Apollo Spacecraft Program, MSC; Dr. Robert R. Gilruth, MSC Director; and Charles W. Mathews, Deputy Associate Administrator, Office of Manned Space Flight, NASA Headquarters.
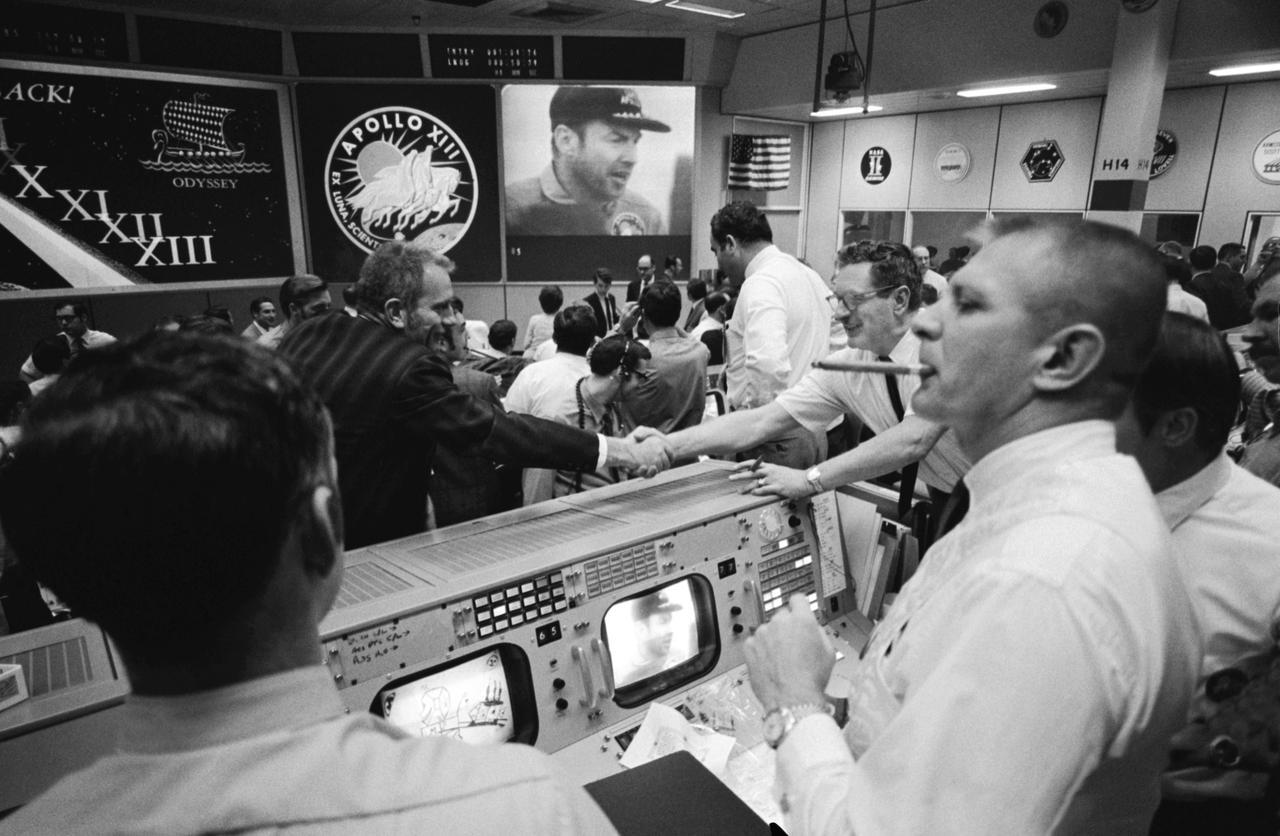

S70-35145 (17 April 1970) --- Overall view of Mission Operations Control Room in Mission Control Center at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) during the ceremonies aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission. Dr. Donald K. Slayton (in black shirt, left of center), director of Flight Crew Operations at MSC, and Chester M. Lee of the Apollo Program Directorate, Office of Manned Space Flight, NASA Headquarters, shake hands, while Dr. Rocco A. Petrone, Apollo program director, Office of Manned Space Flight, NASA Headquarters (standing, near Lee), watches the large screen showing astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., Apollo 13 commander, during the onboard ceremonies. In the foreground, Glynn S. Lunney (extreme left) and Eugene F. Kranz (smoking a cigar), two Apollo 13 flight directors, view the activity from their consoles.
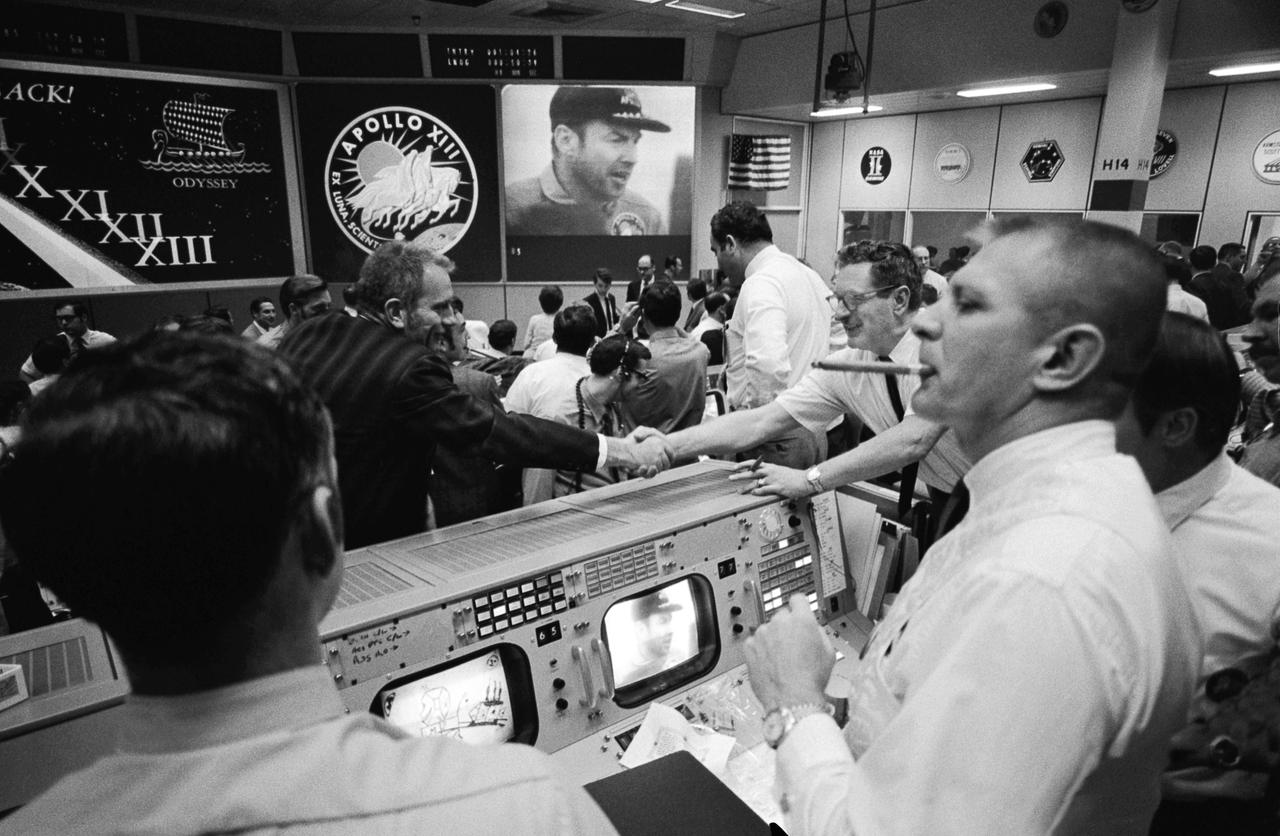

S70-35145 (17 April 1970) --- Overall view of Mission Operations Control Room in Mission Control Center at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) during the ceremonies aboard the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 13 mission. Dr. Donald K. Slayton (in black shirt, left of center), director of Flight Crew Operations at MSC, and Chester M. Lee of the Apollo Program Directorate, Office of Manned Space Flight, NASA Headquarters, shake hands, while Dr. Rocco A. Petrone, Apollo program director, Office of Manned Space Flight, NASA Headquarters (standing, near Lee), watches the large screen showing astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., Apollo 13 commander, during the onboard ceremonies. In the foreground, Glynn S. Lunney (extreme left) and Eugene F. Kranz (smoking a cigar), two Apollo 13 flight directors, view the activity from their consoles.

Teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Crew 1 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center in Huntsville, Alabama. SpaceX will launch a Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA astronauts aboard the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station on Nov. 14, 2020. The Marshall team is supporting flight control teams working with NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, and SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, as they monitor the different phases of the upcoming mission. Engineers and technicians at Marshall will use headsets and loops to communicate with the multiple locations on console for the launch. The Crew 1 flight is part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The Crew 1 astronauts will arrive at the space station for docking a short time later at 4:20 a.m. on Sunday, Nov. 15 to join Expedition 64 for a six-month science mission.
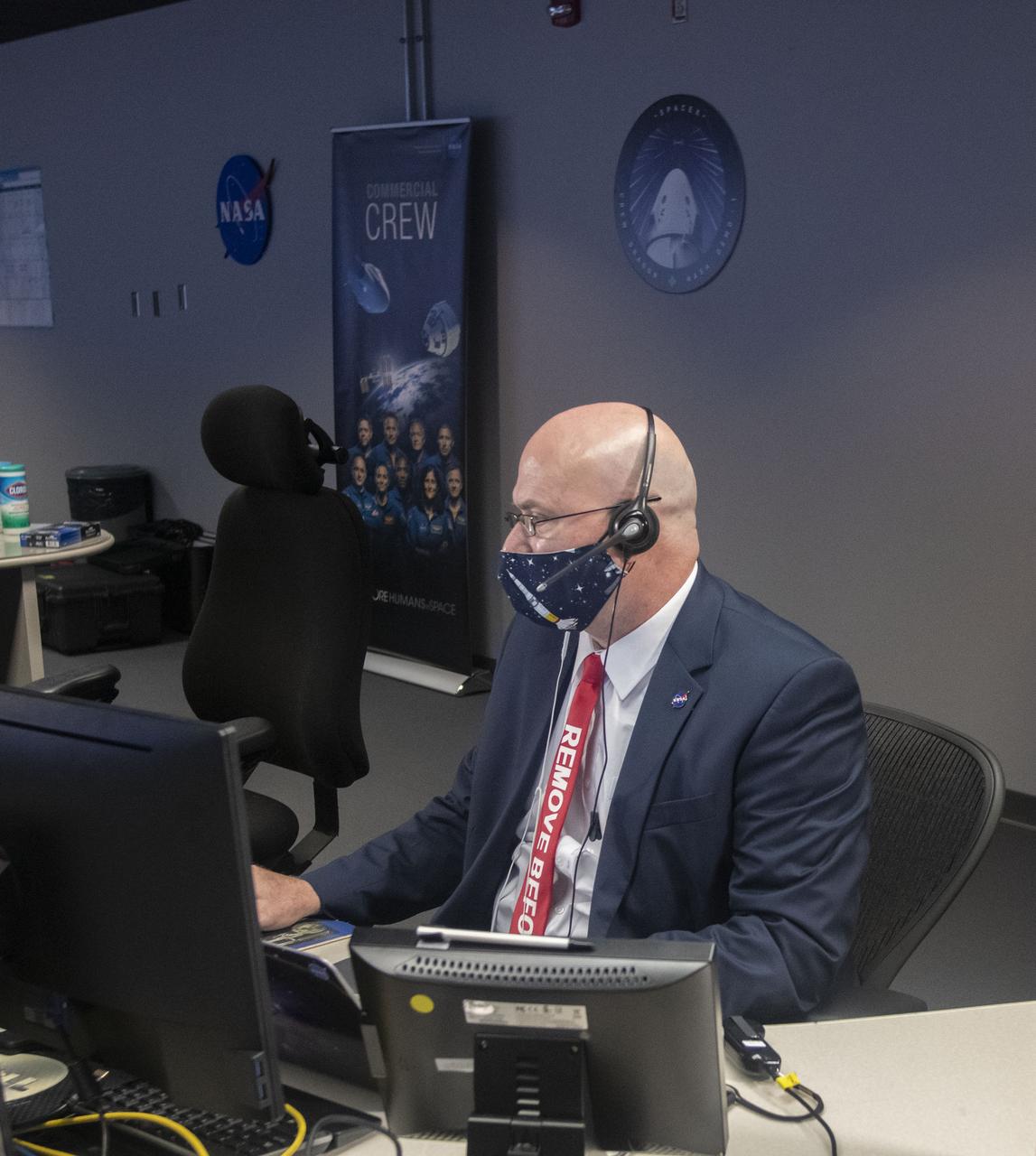

Teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Crew 1 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center in Huntsville, Alabama. SpaceX will launch a Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA astronauts aboard the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station on Nov. 14, 2020. The Marshall team is supporting flight control teams working with NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, and SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, as they monitor the different phases of the upcoming mission. Engineers and technicians at Marshall will use headsets and loops to communicate with the multiple locations on console for the launch. The Crew 1 flight is part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The Crew 1 astronauts will arrive at the space station for docking a short time later at 4:20 a.m. on Sunday, Nov. 15 to join Expedition 64 for a six-month science mission.
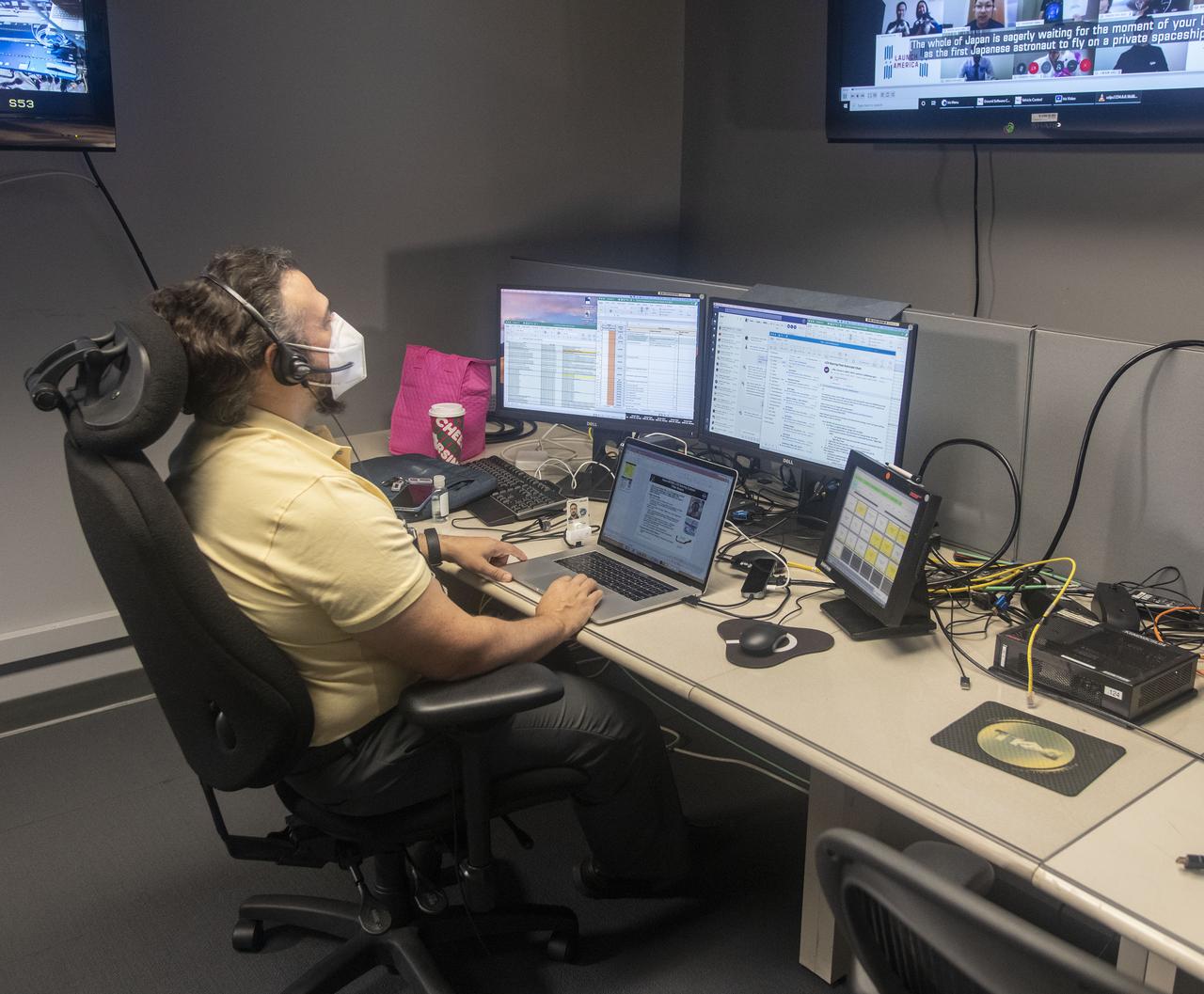

Teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Crew 1 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center in Huntsville, Alabama. SpaceX will launch a Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA astronauts aboard the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station on Nov. 14, 2020. The Marshall team is supporting flight control teams working with NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, and SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, as they monitor the different phases of the upcoming mission. Engineers and technicians at Marshall will use headsets and loops to communicate with the multiple locations on console for the launch. The Crew 1 flight is part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The Crew 1 astronauts will arrive at the space station for docking a short time later at 4:20 a.m. on Sunday, Nov. 15 to join Expedition 64 for a six-month science mission.
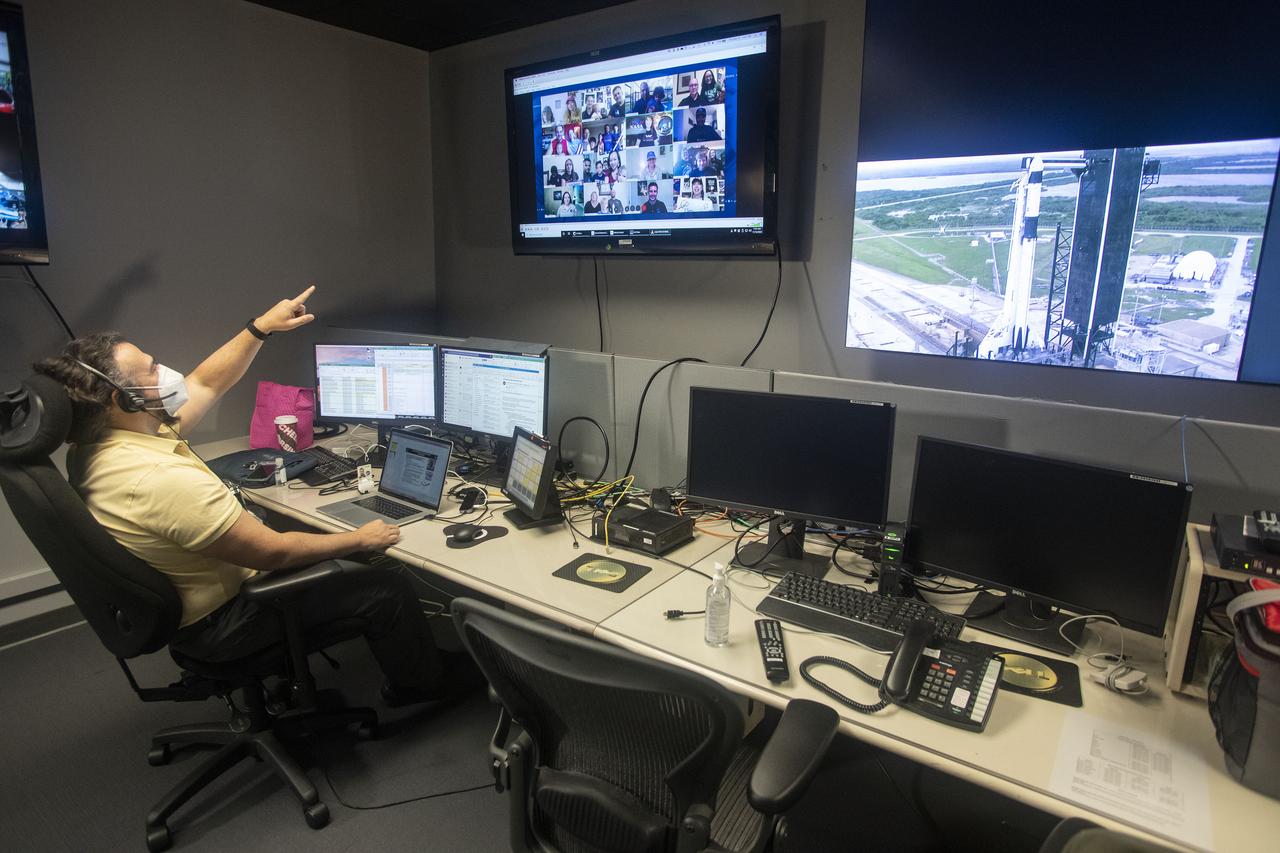

Teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Crew 1 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center in Huntsville, Alabama. SpaceX will launch a Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA astronauts aboard the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station on Nov. 14, 2020. The Marshall team is supporting flight control teams working with NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, and SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, as they monitor the different phases of the upcoming mission. Engineers and technicians at Marshall will use headsets and loops to communicate with the multiple locations on console for the launch. The Crew 1 flight is part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The Crew 1 astronauts will arrive at the space station for docking a short time later at 4:20 a.m. on Sunday, Nov. 15 to join Expedition 64 for a six-month science mission.
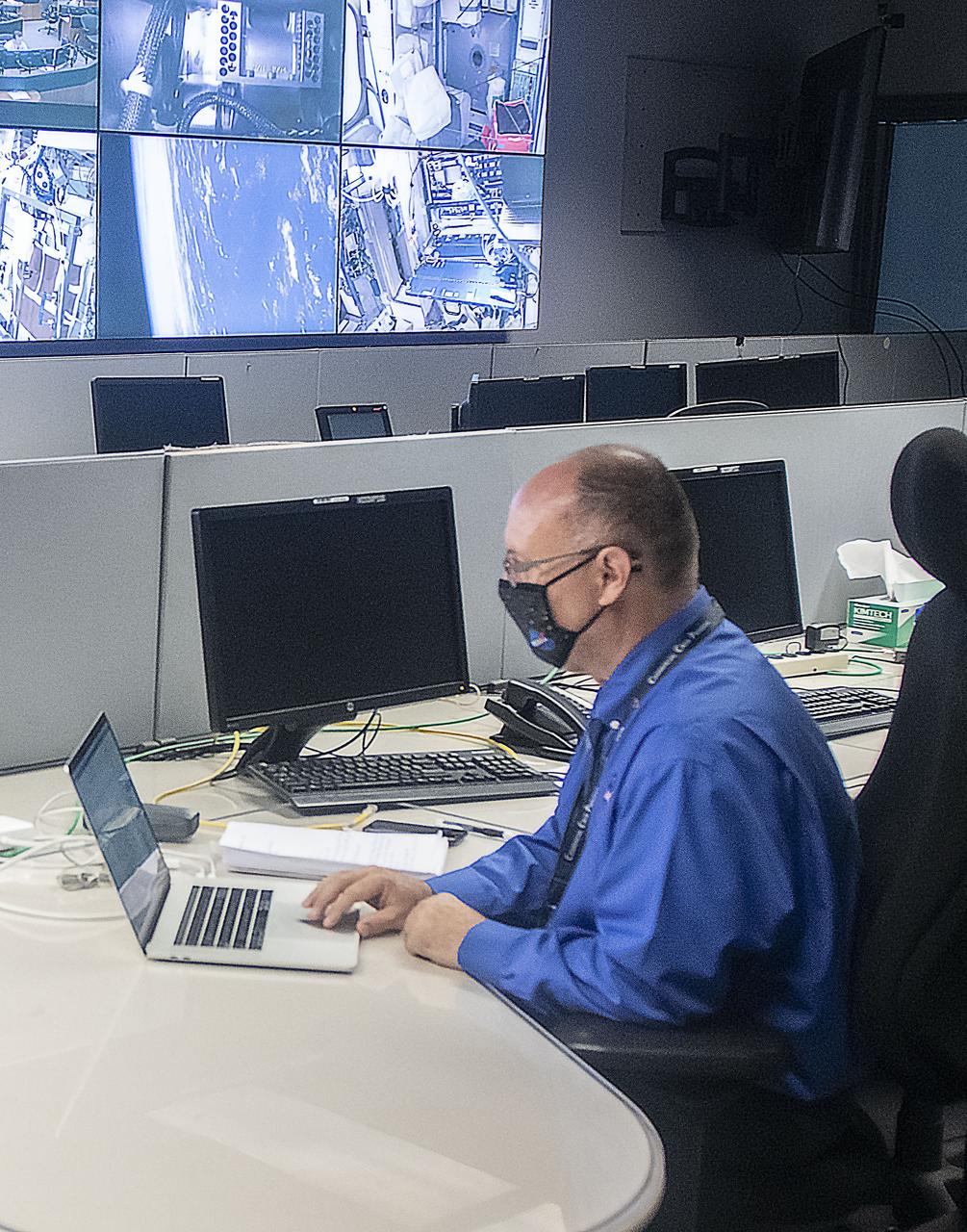

Teams at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center help monitor launch conditions for the Crew 1 mission from the Huntsville Operations Support Center in Huntsville, Alabama. SpaceX will launch a Falcon 9 rocket carrying NASA astronauts aboard the company’s Crew Dragon spacecraft to the International Space Station on Nov. 14, 2020. The Marshall team is supporting flight control teams working with NASA’s Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas, NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Florida, and SpaceX headquarters in Hawthorne, California, as they monitor the different phases of the upcoming mission. Engineers and technicians at Marshall will use headsets and loops to communicate with the multiple locations on console for the launch. The Crew 1 flight is part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The Crew 1 astronauts will arrive at the space station for docking a short time later at 4:20 a.m. on Sunday, Nov. 15 to join Expedition 64 for a six-month science mission.
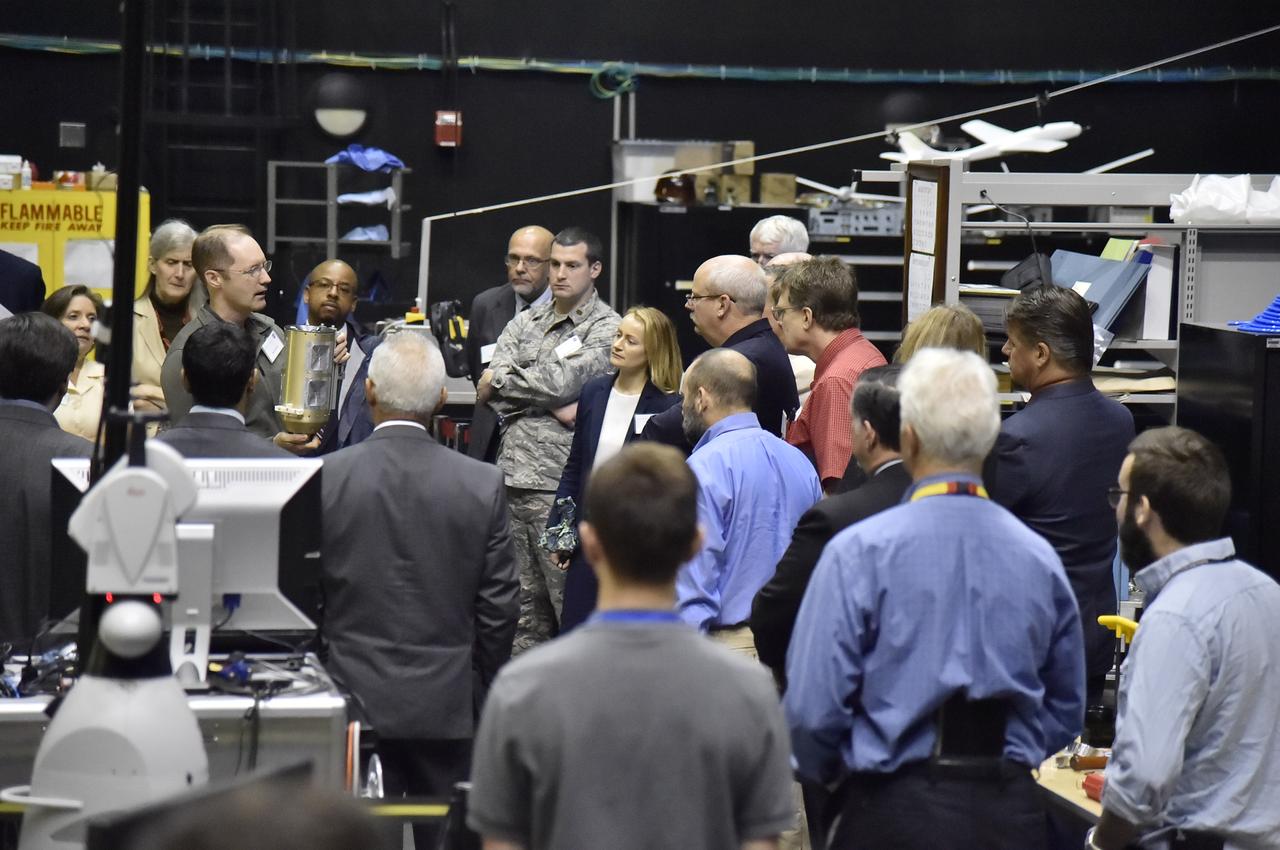

WASHINGTON, D.C.---S&T Partnership Forum In-Space Assembly Technical Interchange Meeting-On September 6th 2017, many of the United States government experts on In-Space Assembly met at the U.S. Naval Research Lab to discuss both technology development and in-space applications that would advance national capabilities in this area. Expertise from NASA, USAF, NRO, DARPA and NRL met in this meeting which was coordinated by the NASA Headquarters, Office of the Chief Technologist. This technical interchange meeting was the second meeting of the members of this Science and Technology Partnership Forum. Glen Henshaw of Code 8231 talks to the group in the Space Robotics Lab.

S65-62062 (12 Dec. 1965) --- Discussing the scrubbing of the planned National Aeronautics and Space Administration?s Gemini-6 spaceflight are (from left) William C. Schneider (standing), deputy director, Gemini Program Office of Manned Spaceflight, NASA Headquarters, Washington, D.C.; Eugene F. Kranz (seated), white team flight director; Christopher C. Kraft Jr., red team flight director; and John D. Hodge, blue team flight director. The Gemini-6 mission has been rescheduled for Dec. 15, 1965. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
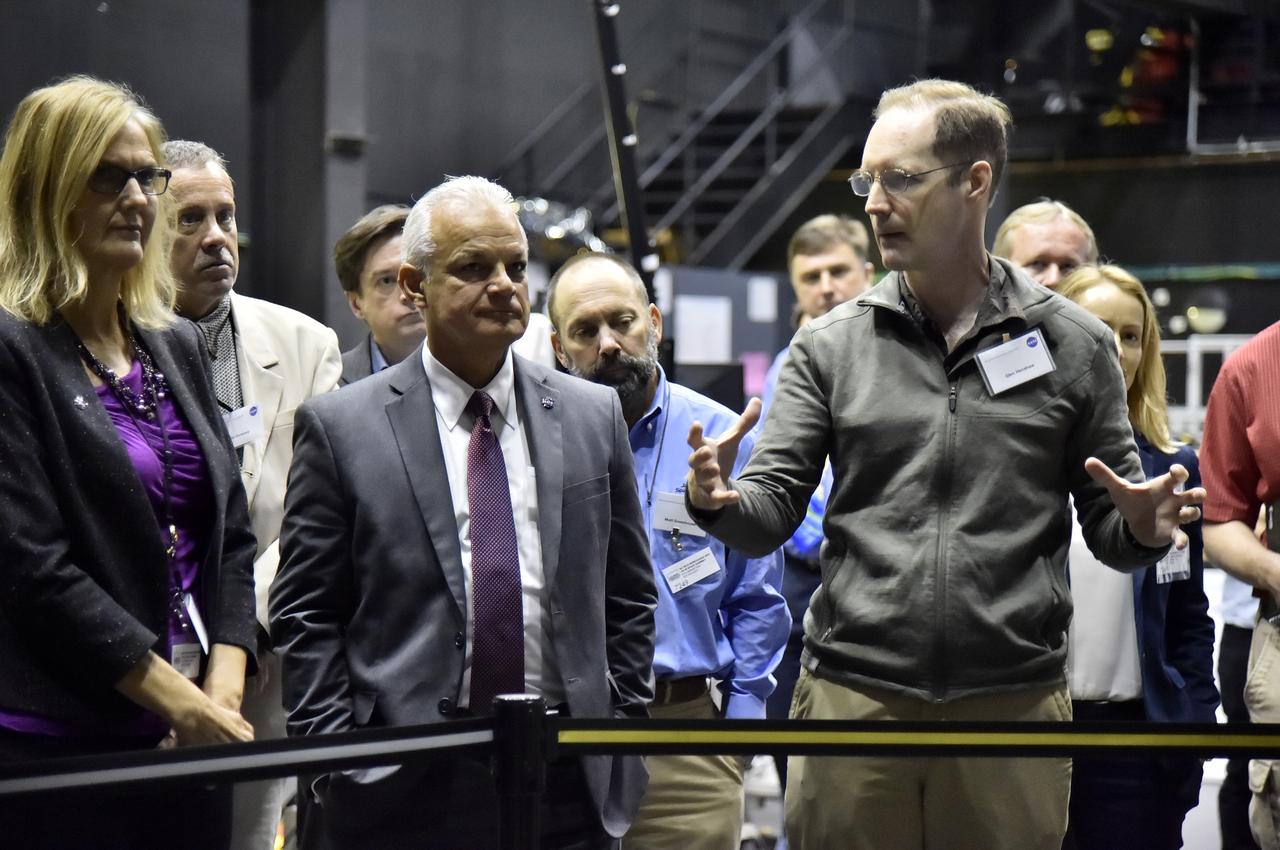

WASHINGTON, D.C.---S&T Partnership Forum In-Space Assembly Technical Interchange Meeting-On September 6th 2017, many of the United States government experts on In-Space Assembly met at the U.S. Naval Research Lab to discuss both technology development and in-space applications that would advance national capabilities in this area. Expertise from NASA, USAF, NRO, DARPA and NRL met in this meeting which was coordinated by the NASA Headquarters, Office of the Chief Technologist. This technical interchange meeting was the second meeting of the members of this Science and Technology Partnership Forum. Glen Henshaw of Code 8231 talks to the group in the Space Robotics Lab.
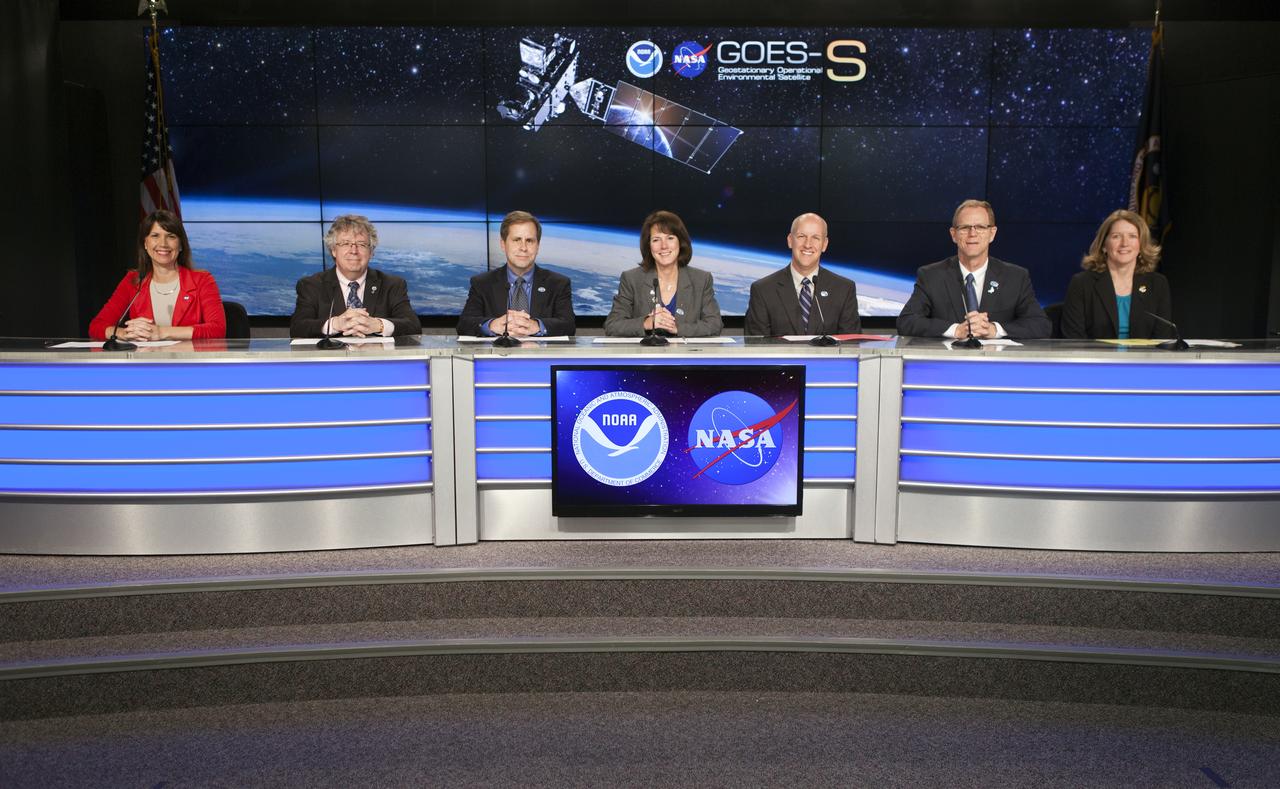

In the Kennedy Space Center's Press Site auditorium, NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the media at a prelaunch news conference about National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's, or NOAA's, Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite, or GOES-S. Participants from left are: Tori McLendon of NASA Communications; Stephen Volz, director for Satellite and Information Services for NOAA; Tim Walsh, acting GOES-R System Program director for NOAA; Sandra Smalley, director of the Joint Agency Satellite Division at NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C.; Tim Dunn, NASA launch director at Kennedy; Scott Messer, manager of NASA Programs for United launch Alliance; and Kathy Winters, launch weather officer for the U.S. Air Force 45th Weather Squadron at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The GOES series of satellites will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to lift off at 5:02 p.m. EST on March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
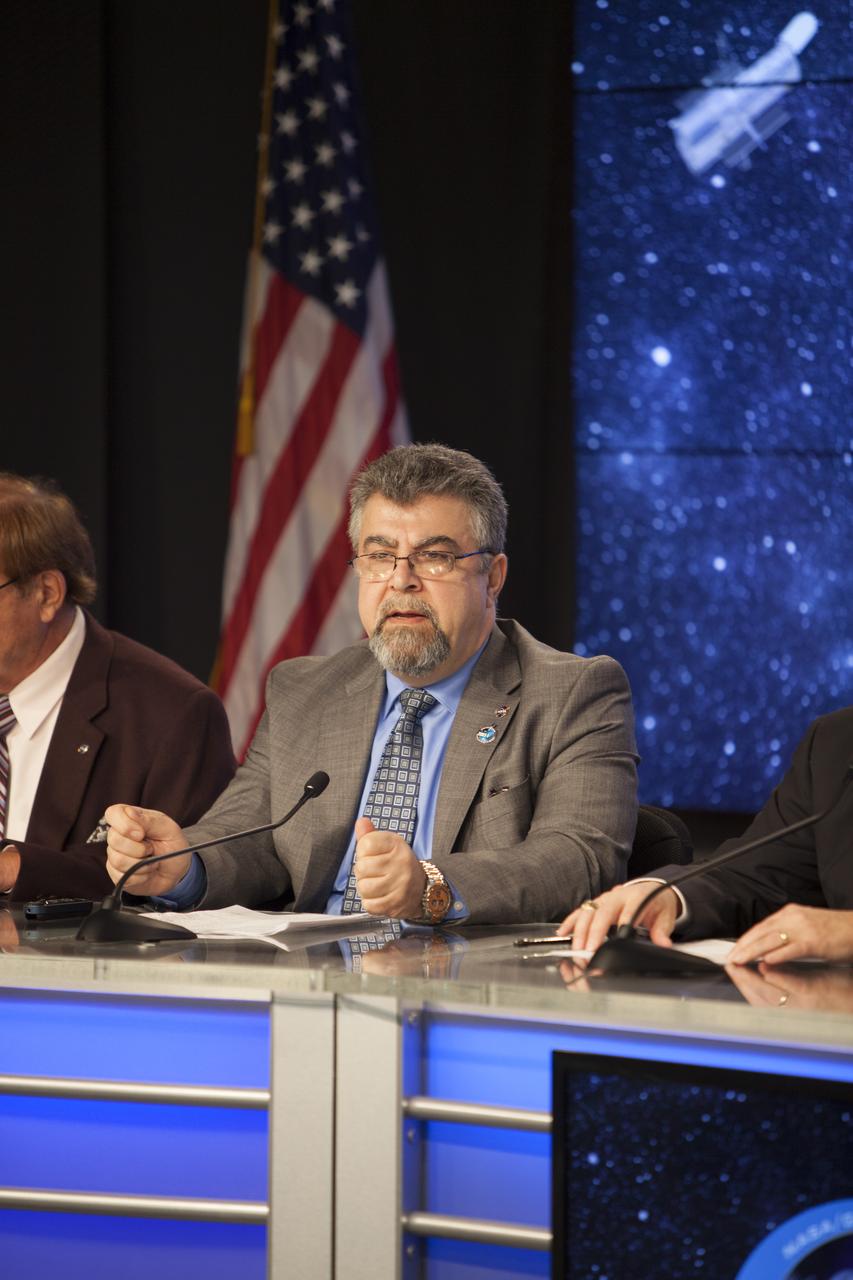

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – During a news conference at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, agency and contractor officials discussed preparations for the launch of NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft. Participants included Badri Younes, deputy associate administrator, Space Communications and Navigation SCaN NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C. The TDRS-L spacecraft is the second of three new satellites designed to ensure vital operational continuity for NASA by expanding the lifespan of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System TDRSS fleet, which consists of eight satellites in geosynchronous orbit. The spacecraft provide tracking, telemetry, command and high bandwidth data return services for numerous science and human exploration missions orbiting Earth. These include NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and the International Space Station. TDRS-L has a high-performance solar panel designed for more spacecraft power to meet the growing S-band communications requirements. TDRSS is one of NASA Space Communication and Navigation’s SCaN three networks providing space communications to NASA’s missions. For more information more about TDRS-L, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/tdrs To learn more about SCaN, visit: www.nasa.gov/scan Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the media at a prelaunch news conference for the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1. Participants, from left, are Tori McLendon of NASA Communications, Steve Volz, director of NOAA’s Satellite and Information Service, Greg Mandt, director of the NOAA Joint Polar Satellite System Program, Sandra Smalley, director of the Joint Agency Satellite Division at NASA Headquarters, Omar Baez, NASA launch director, Scott Messer, United Launch Alliance program manager for NASA missions, and U. S. Air Force Capt. Ross Malugani, launch weather officer at Vandenberg's 30th Space Wing. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2 at 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
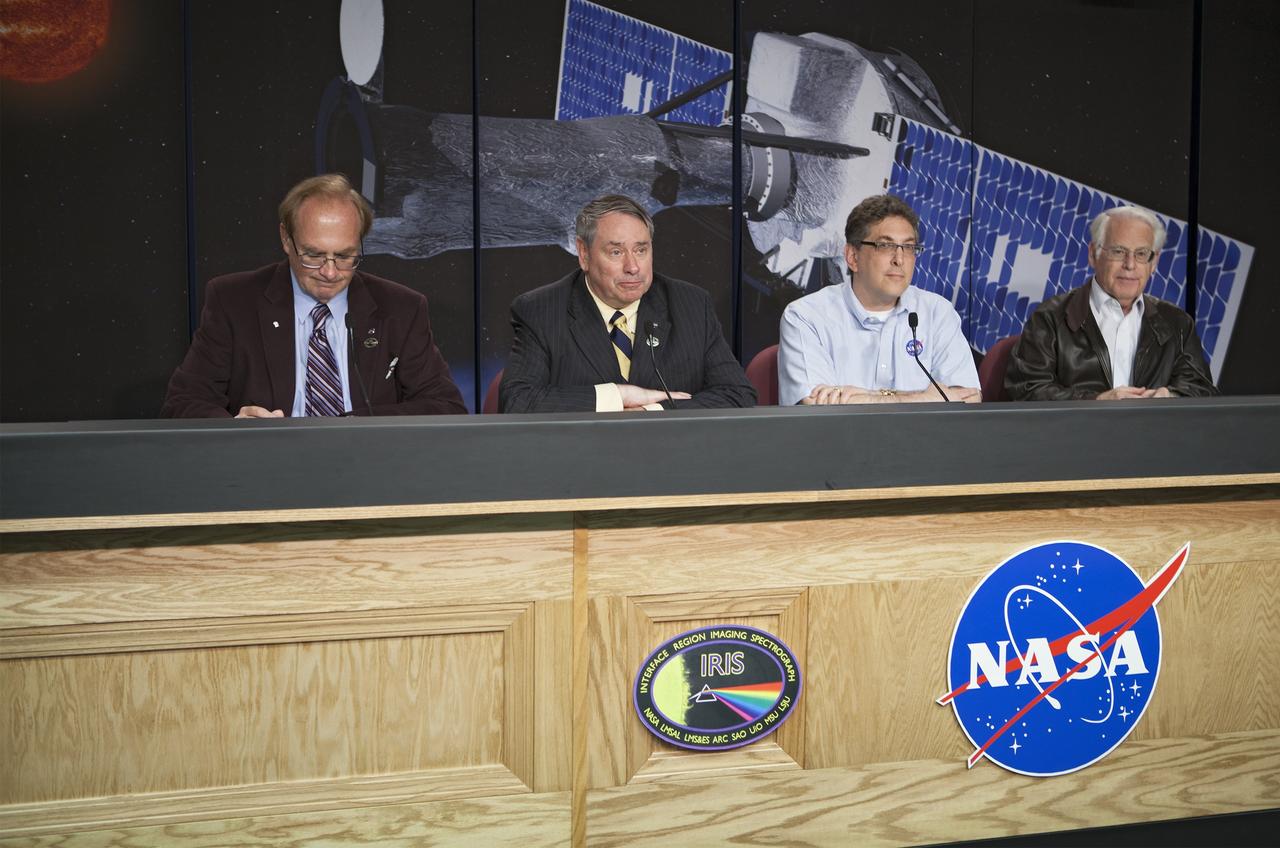

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA hosted a prelaunch mission briefing on the Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph, or IRIS, solar observatory scheduled to launch on a Pegasus XL rocket. Participating in the news conference are George Diller, NASA Public Affairs, Dr. S. Pete Worden, director of NASA's Ames Research Center in Calif., Jeffrey Newmark, IRIS Program scientist at NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C., and Alan Title, IRIS principal investigator with Lockheed Martin. Scheduled for launch from Vandenberg on June 26, 2013, IRIS will open a new window of discovery by tracing the flow of energy and plasma through the chromospheres and transition region into the sun’s corona using spectrometry and imaging. The IRIS mission will observe how solar material moves, gathers energy and heats up as it travels through a largely unexplored region of the solar atmosphere. The interface region, located between the sun's visible surface and upper atmosphere, is where most of the sun's ultraviolet emission is generated. These emissions impact the near-Earth space environment and Earth's climate. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/iris Photo credit: NASA/ Daniel Casper

Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA and industry leaders speak to members of the media at a prelaunch news conference for the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1. Participants, from left, are Greg Mandt, director of the NOAA Joint Polar Satellite System Program, Sandra Smalley, director of the Joint Agency Satellite Division at NASA Headquarters, Omar Baez, NASA launch director, Scott Messer, United Launch Alliance program manager for NASA missions, and U. S. Air Force Capt. Ross Malugani, launch weather officer at Vandenberg's 30th Space Wing. Built by Ball Aerospace and Technologies Corp. of Boulder, Colorado, JPSS is the first in a series four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled to take place from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex 2 at 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
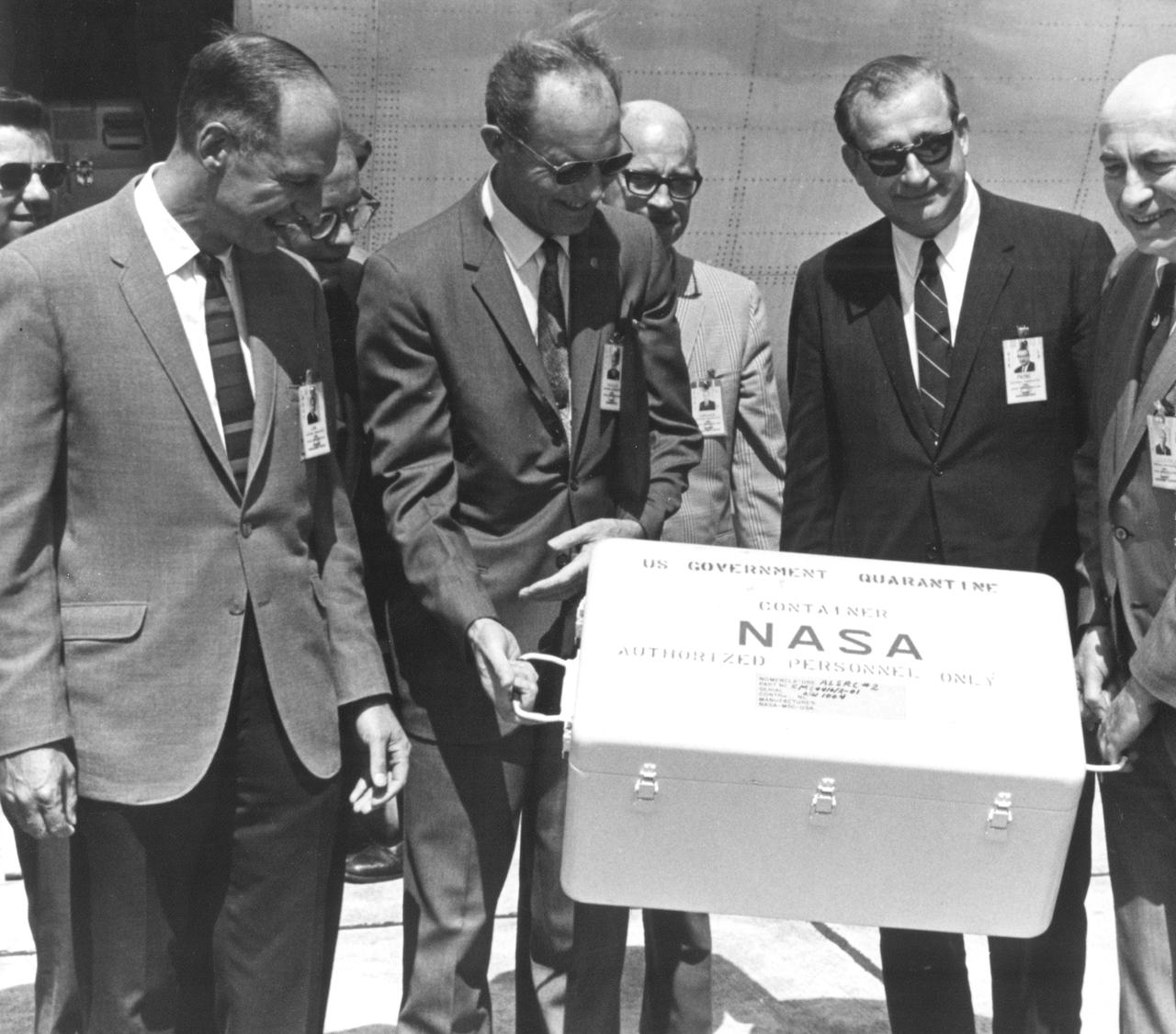

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. This photograph was taken as the mission’s first loaded sample return container arrived at Ellington Air Force Base by air from the Pacific recovery area. The rock box was immediately taken to the Lunar Receiving Laboratory at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) in Houston, Texas. Happily posing for the photograph with the rock container are (L-R) Richard S. Johnston (back), special assistant to the MSC Director; George M. Low, MSC Apollo Spacecraft Program manager; George S. Trimble (back), MSC Deputy Director; Lt. General Samuel C. Phillips, Apollo Program Director, Office of Manned Spaceflight at NASA headquarters; Eugene G. Edmonds, MSC Photographic Technology Laboratory; Dr. Thomas O. Paine, NASA Administrator; and Dr. Robert R. Gilruth, MSC Director.
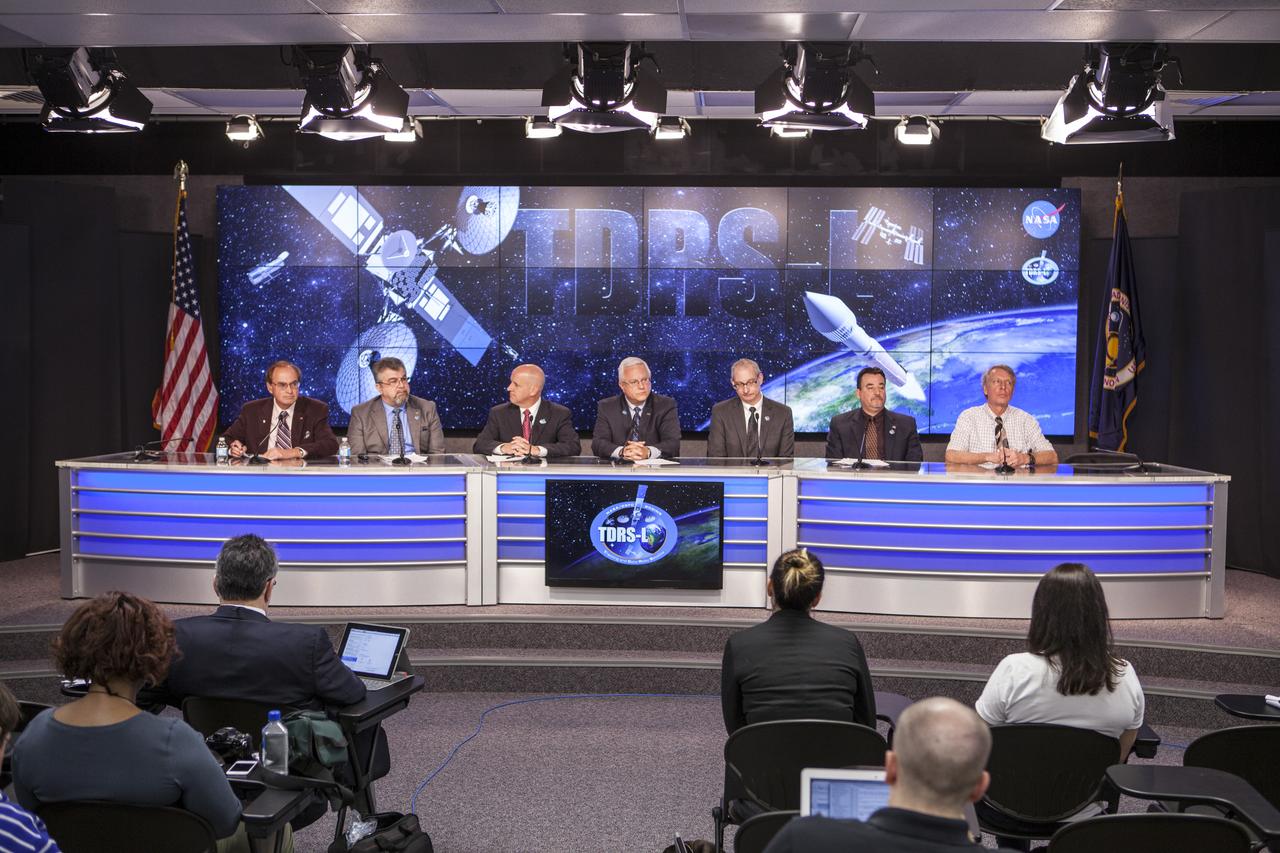

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –During a news conference at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, agency and contractor officials discussed preparations for the launch of NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft. Participating in the briefing, from the left, are George Diller of NASA Public Affairs, Badri Younes, deputy associate administrator, Space Communications and Navigation SCaN NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C., Tim Dunn, NASA launch director at Kennedy, Vernon Thorp, program manager for NASA Missions with United Launch Alliance in Denver, Colo., Jeffrey Gramling, NASA's TDRS-L project manager at the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., Andy Kopito, Civil Space Programs director for Boeing Space & Intelligence Systems in El Segundo, Calif., and Clay Flinn, launch weather officer for the 45th Weather Squadron at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The TDRS-L spacecraft is the second of three new satellites designed to ensure vital operational continuity for NASA by expanding the lifespan of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System TDRSS fleet, which consists of eight satellites in geosynchronous orbit. The spacecraft provide tracking, telemetry, command and high bandwidth data return services for numerous science and human exploration missions orbiting Earth. These include NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and the International Space Station. TDRS-L has a high-performance solar panel designed for more spacecraft power to meet the growing S-band communications requirements. TDRSS is one of NASA Space Communication and Navigation’s SCaN three networks providing space communications to NASA’s missions. For more information more about TDRS-L, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/tdrs To learn more about SCaN, visit: www.nasa.gov/scan Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
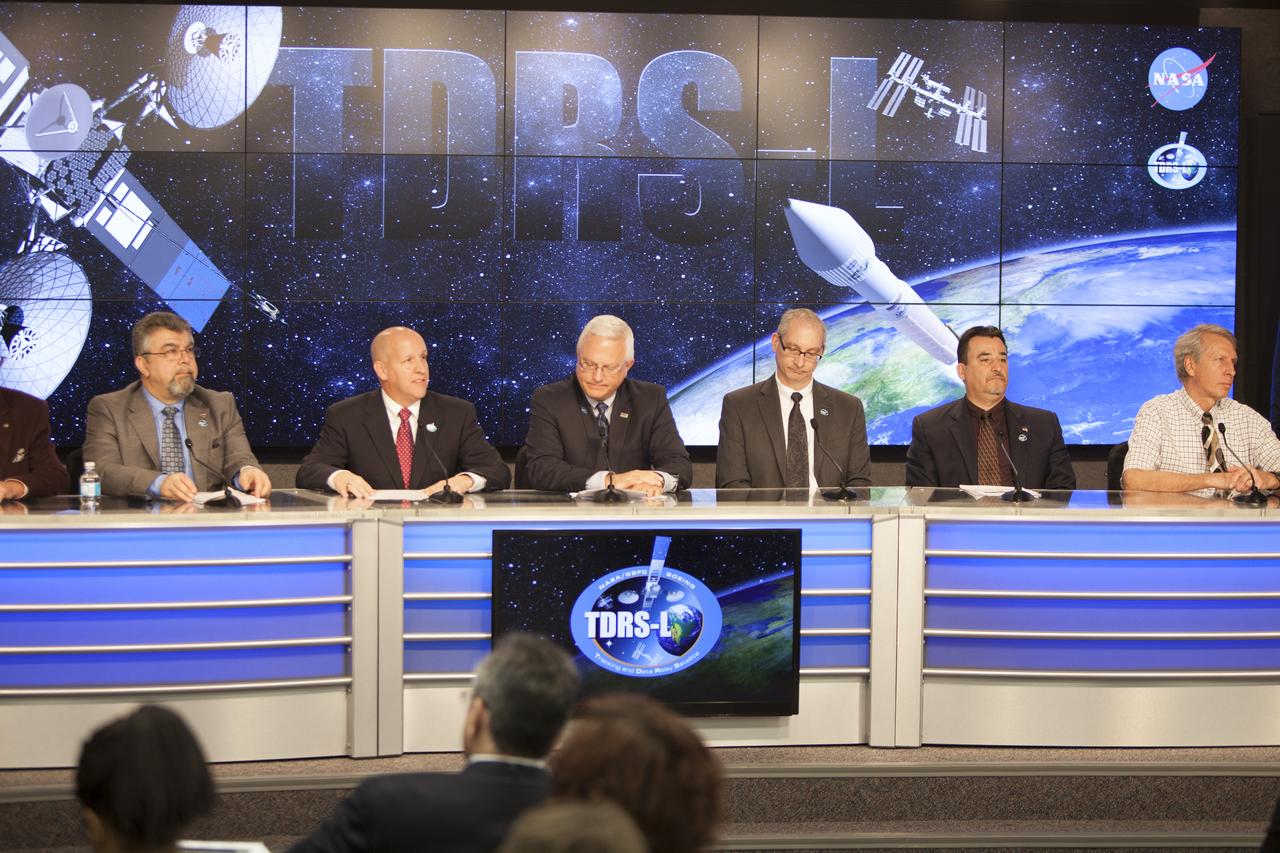

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –During a news conference at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, agency and contractor officials discussed preparations for the launch of NASA's Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft. Participating in the briefing, from the left, are Badri Younes, deputy associate administrator, Space Communications and Navigation SCaN NASA Human Exploration and Operations Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington D.C., Tim Dunn, NASA launch director at Kennedy, Vernon Thorp, program manager for NASA Missions with United Launch Alliance in Denver, Colo., Jeffrey Gramling, NASA's TDRS-L project manager at the Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., Andy Kopito, Civil Space Programs director for Boeing Space & Intelligence Systems in El Segundo, Calif., and Clay Flinn, launch weather officer for the 45th Weather Squadron at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station, Fla. The TDRS-L spacecraft is the second of three new satellites designed to ensure vital operational continuity for NASA by expanding the lifespan of the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite System TDRSS fleet, which consists of eight satellites in geosynchronous orbit. The spacecraft provide tracking, telemetry, command and high bandwidth data return services for numerous science and human exploration missions orbiting Earth. These include NASA's Hubble Space Telescope and the International Space Station. TDRS-L has a high-performance solar panel designed for more spacecraft power to meet the growing S-band communications requirements. TDRSS is one of NASA Space Communication and Navigation’s SCaN three networks providing space communications to NASA’s missions. For more information more about TDRS-L, visit: http://www.nasa.gov/tdrs To learn more about SCaN, visit: www.nasa.gov/scan Photo credit: NASA/Frankie Martin
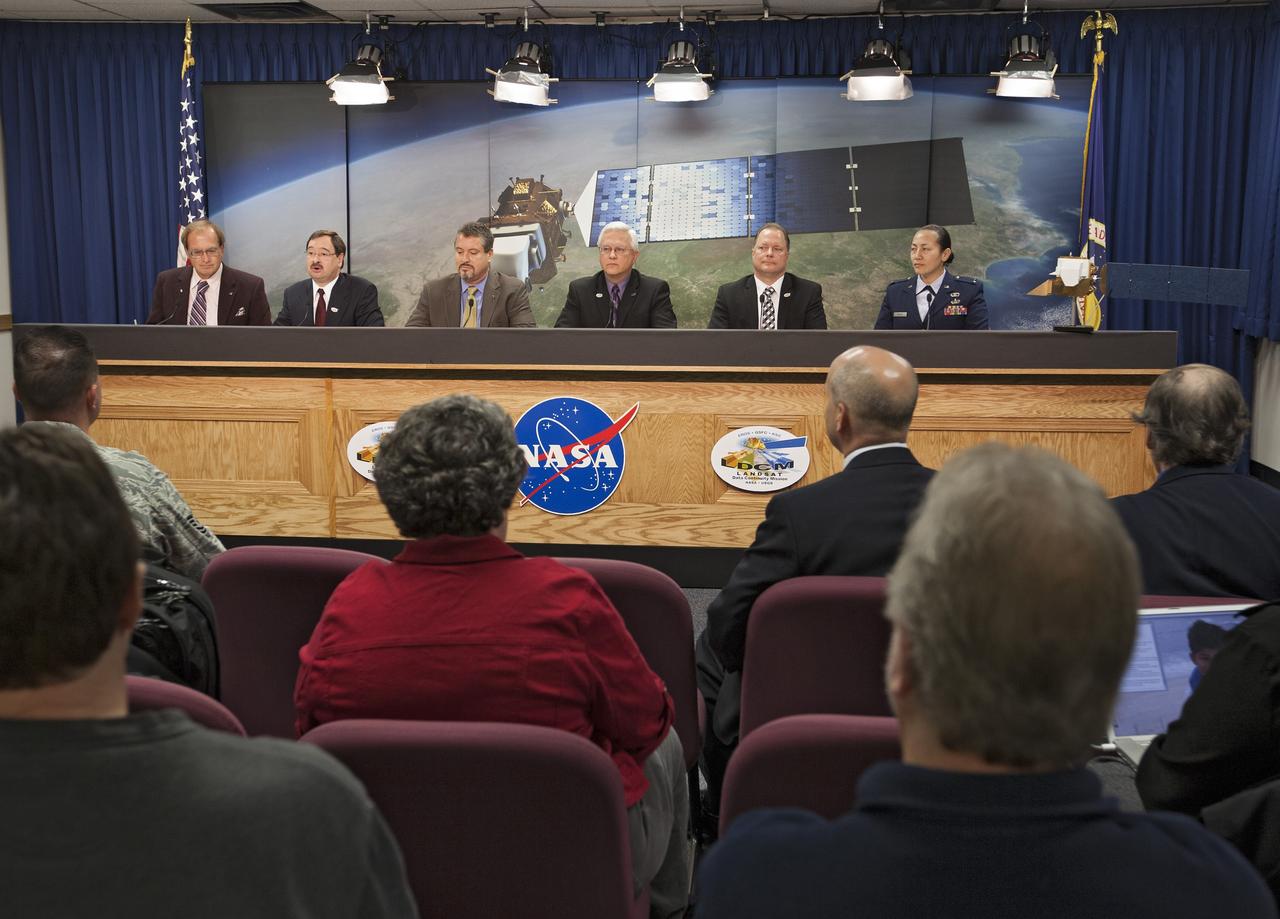

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- Media attend a prelaunch press conference at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to discuss NASA's readiness to launch the Landsat Data Continuity Mission LDCM. From left are George Diller of NASA Public Affairs, LDCM program executive David Jarrett from NASA Headquarters, NASA Launch Director Omar Baez from Kennedy Space Center, United Launch Alliance Program Manager for NASA Missions Vernon Thorp, LDCM Project Manager Ken Schwer from Goddard Space Flight Center, and 1st Lt. Jennifer Kelley, launch weather officer for the 30th Operations Support Squadron at Vandenberg. Launch of LDCM aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Vandenberg's Space Launch Complex-3E is planned for Feb. 11 during a 48-minute launch window that opens at 10:02 a.m. PST, or 1:02 p.m. EST. LDCM is the eighth satellite in the Landsat Program series of Earth-observing missions and will continue the program’s critical role in monitoring, understanding and managing the resources needed for human sustainment, such as food, water and forests. NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md., is responsible for LDCM project management. Orbital Sciences Corp. built the LDCM satellite. NASA's Launch Services Program at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida provides launch management. After launch and the initial checkout phase, the U. S. Geological Survey will take operational control of LDCM, and it will be renamed Landsat 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett