This image from NASA Terra spacecraft shows the Kuk Early Agricultural Site in the western highlands of New Guinea. It is an excellent example of transformation of agricultural practices over time.
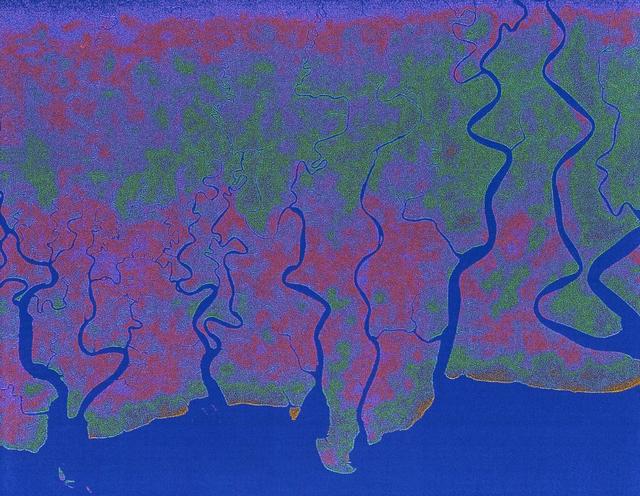

The objective of NASA Shuttle Imaging Radar A SIR-A was to observe the Earth by use of radar imagery, acquire and transmit data of different geologic regions. This is a view of New Guinea in 2000.
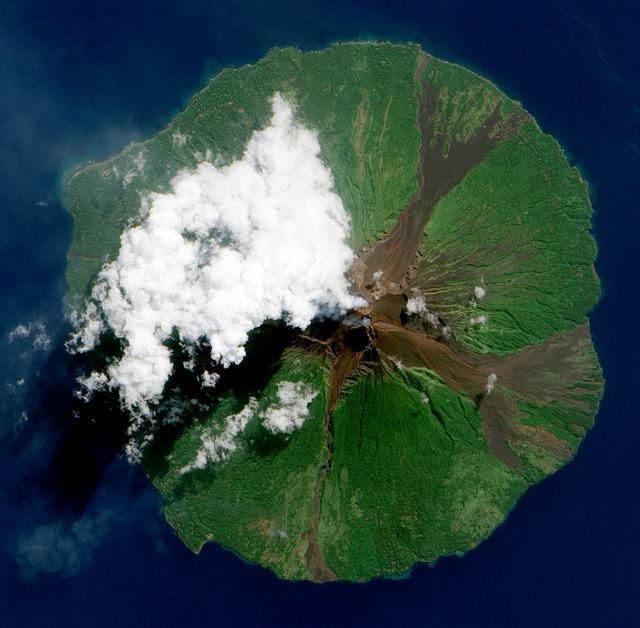

NASA image acquired June 16, 2010. Papua New Guinea’s Manam Volcano released a thin, faint plume on June 16, 2010, as clouds clustered at the volcano’s summit. The Advanced Land Imager (ALI) on NASA’s Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite took this picture the same day. Rivulets of brown rock interrupt the carpet of green vegetation on the volcano’s slopes. Opaque white clouds partially obscure the satellite’s view of Manam. The clouds may result from water vapor from the volcano, but may also have formed independent of volcanic activity. The volcanic plume appears as a thin, blue-gray veil extending toward the northwest over the Bismarck Sea. Located 13 kilometers (8 miles) off the coast of mainland Papua New Guinea, Manam forms an island 10 kilometers (6 miles) wide. It is a stratovolcano. The volcano has two summit craters, and although both are active, most historical eruptions have arisen from the southern crater. NASA Earth Observatory image created by Jesse Allen, using EO-1 ALI data provided courtesy of the NASA EO-1 team. Caption by Michon Scott. Instrument: EO-1 - ALI To view the full image go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=44307&src=nhrss" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/view.php?id=4430...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
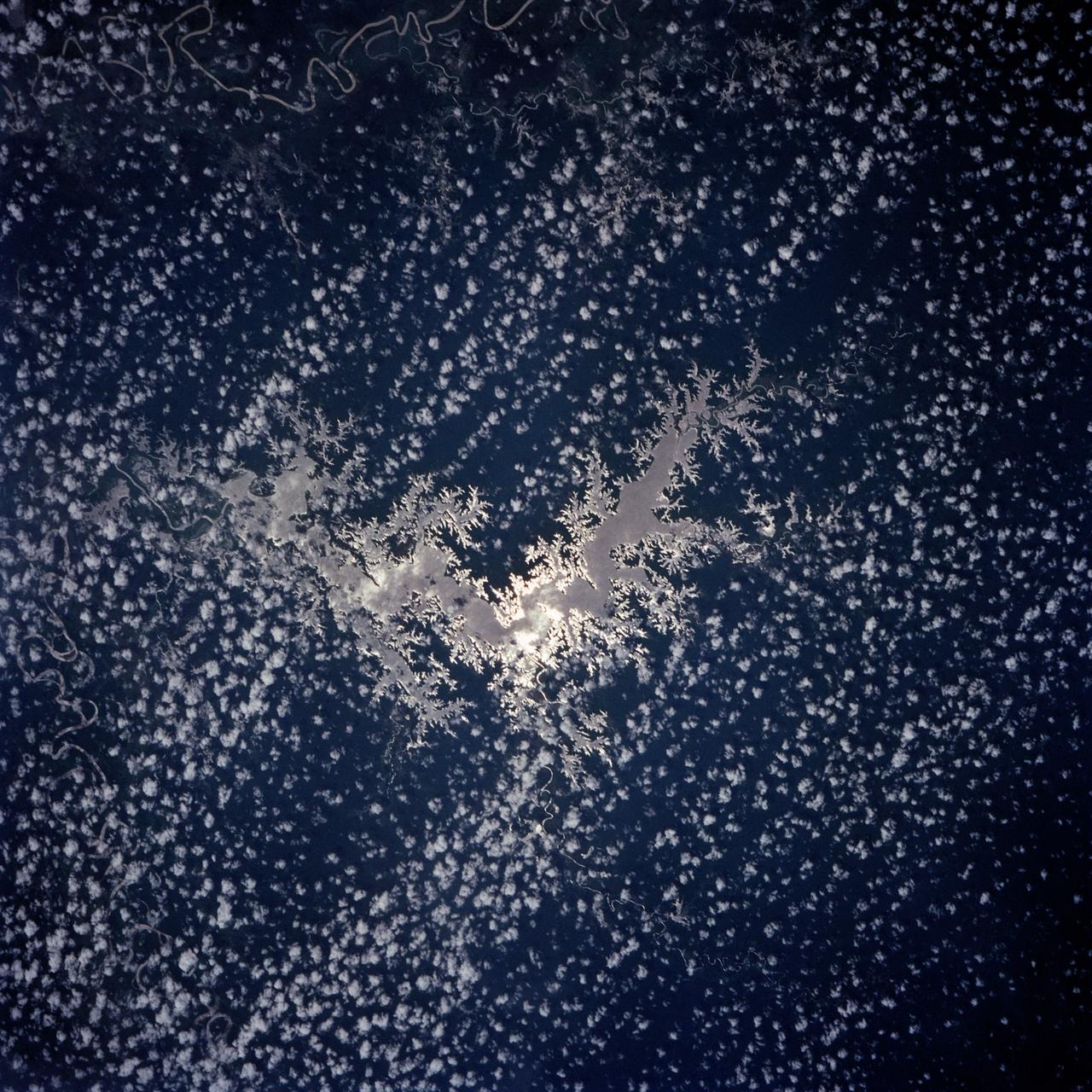

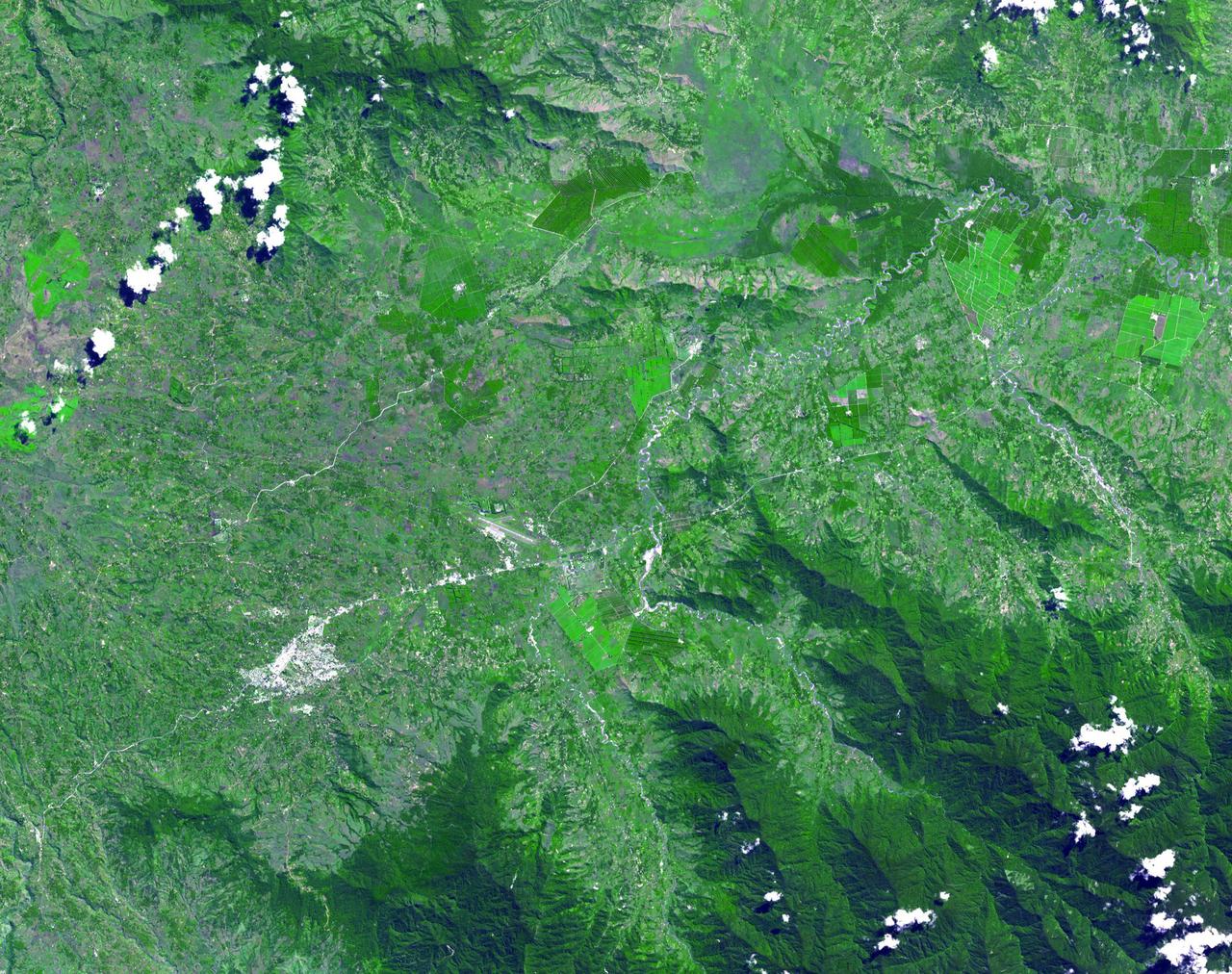
Lake Murray, a manmade reservoir, lies between the Fly and Strickland River Basins, Papua, New Guinea (7.0S, 141.5E). The region, photographed in sunglint, shows the water level in the reservoir and the full extent of the drainage basins of both river systems as the rivers meander through wide alluvial floodplains. Some forest clearing can be seen in places throughout the region, but most of the area remains in closed canopy forest.
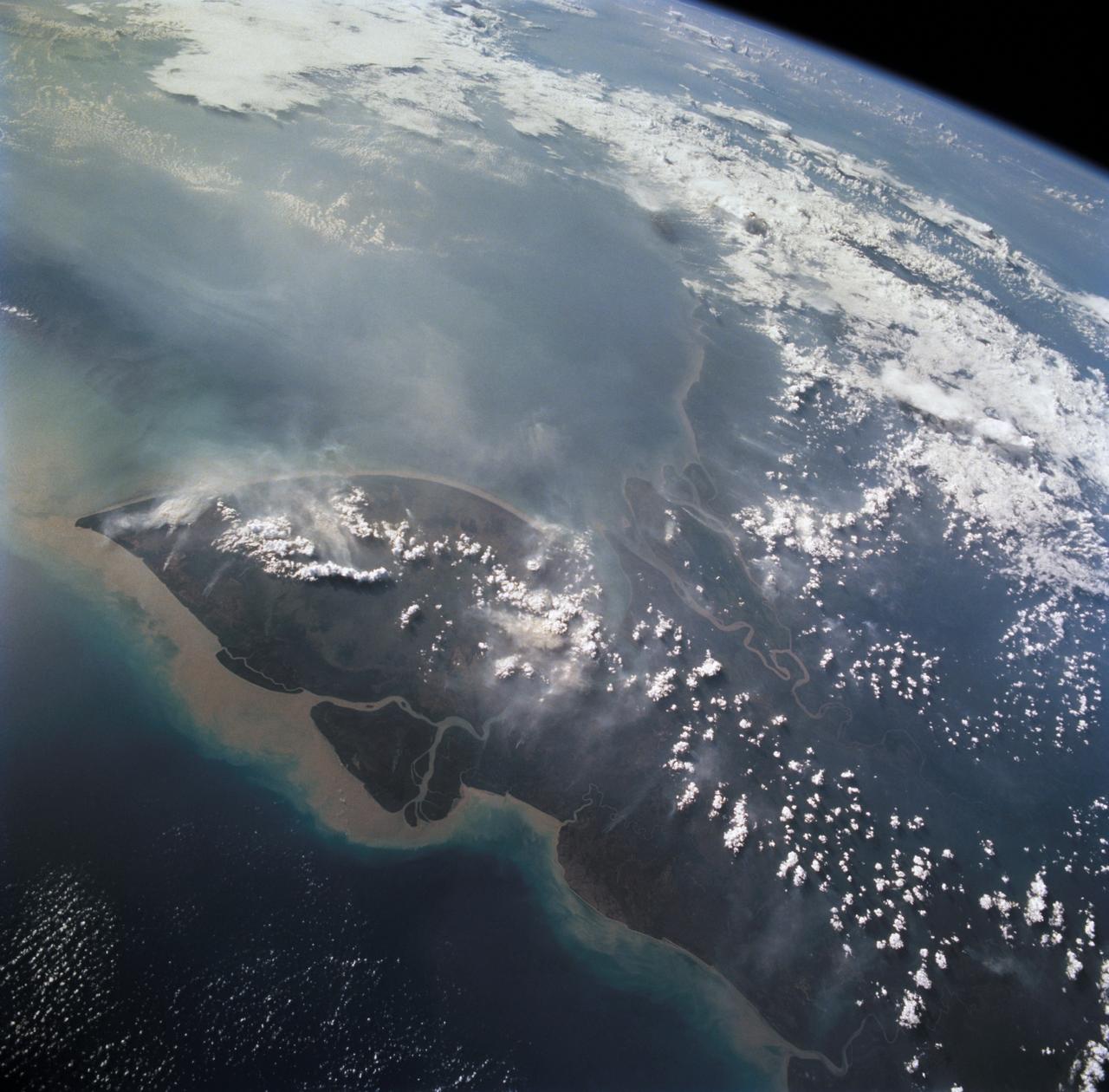

STS068-261-062 (30 September-11 October 1994) --- Vals Cape (left) is the prominent point of the island of New Guinea (Indonesia's Irian Jaya) that juts southwest into the Arafura Sea, pointing towards Australia. The part of New Guinea in this northwest-looking view is entirely low-lying swampland with very low population density. The Digul River, snaking across the middle of the view, drains the high mountain chain, which runs along the spine of the island.
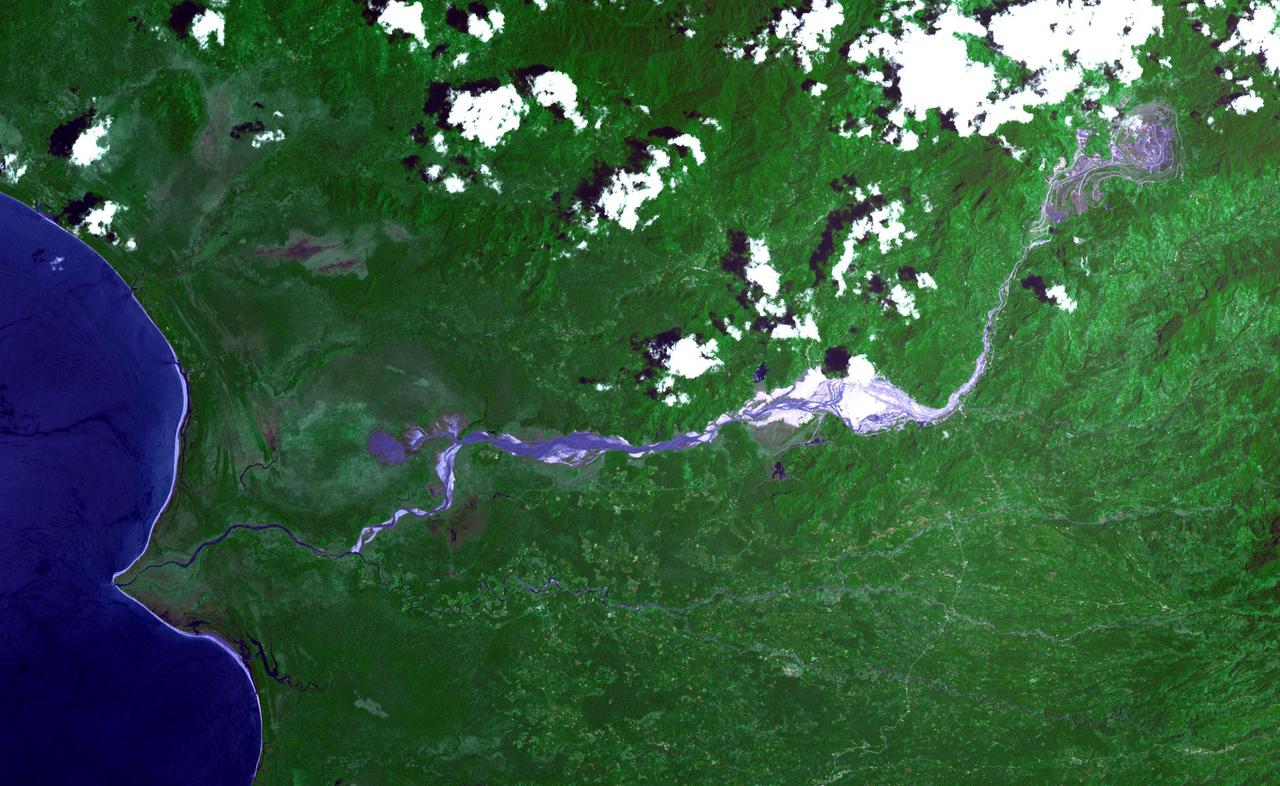

The Panguna copper ore deposit was discovered in 1969 in the Autonomous Region of Bougainville, Papua New Guinea. It has one of the largest reserves in the world, with 1 billion tons of copper and 12 million ounces of gold. In 1989 the then world's largest open pit copper-gold mine closed as a result of conflict between the mine owners and traditional land owners over the profits. The mine owners were also accused of poisoning the entire length of the Jaba River. The image was acquired November 12, 2013, covers an area of 24 by 39 kilometers, and is located at 6.3 degrees south, 155.5 degrees east. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23338
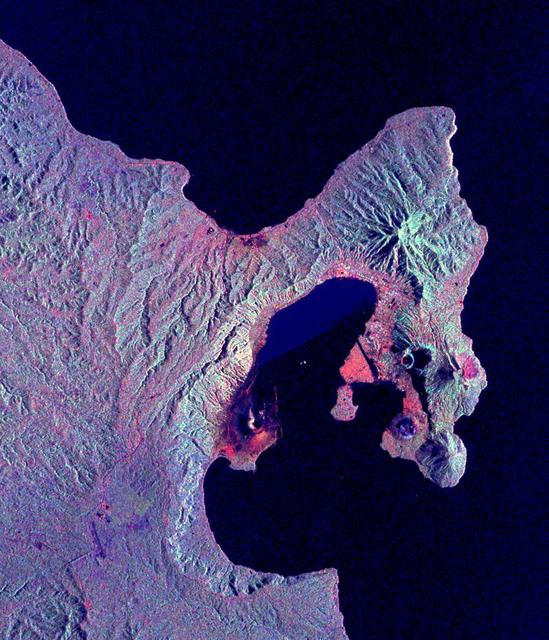

This is a radar image of the Rabaul volcano on the island of New Britain, Papua, New Guinea taken almost a month after its September 19, 1994, eruption that killed five people and covered the town of Rabaul and nearby villages with up to 75 centimeters (30 inches) of ash. More than 53,000 people have been displaced by the eruption. The image was acquired by the Spaceborne Imaging Radar-C/X-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) aboard the space shuttle Endeavour on its 173rd orbit on October 11, 1994. This image is centered at 4.2 degrees south latitude and 152.2 degrees east longitude in the southwest Pacific Ocean. The area shown is approximately 21 kilometers by 25 kilometers (13 miles by 15.5 miles). North is toward the upper right. The colors in this image were obtained using the following radar channels: red represents the L-band (horizontally transmitted and received); green represents the L-band (horizontally transmitted and vertically received); blue represents the C-band (horizontally transmitted and vertically received). Most of the Rabaul volcano is underwater and the caldera (crater) creates Blanche Bay, the semi-circular body of water that occupies most of the center of the image. Volcanic vents within the caldera are visible in the image and include Vulcan, on a peninsula on the west side of the bay, and Rabalanakaia and Tavurvur (the circular purple feature near the mouth of the bay) on the east side. Both Vulcan and Tavurvur were active during the 1994 eruption. Ash deposits appear red-orange on the image, and are most prominent on the south flanks of Vulcan and north and northwest of Tavurvur. A faint blue patch in the water in the center of the image is a large raft of floating pumice fragments that were ejected from Vulcan during the eruption and clog the inner bay. Visible on the east side of the bay are the grid-like patterns of the streets of Rabaul and an airstrip, which appears as a dark northwest-trending band at the right-center of the image. Ashfall and subsequent rains caused the collapse of most buildings in the town of Rabaul. Mudflows and flooding continue to pose serious threats to the town and surrounding villages. Volcanologists and local authorities expect to use data such as this radar image to assist them in identifying the mechanisms of the eruption and future hazardous conditions that may be associated with the vigorously active volcano. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA01767
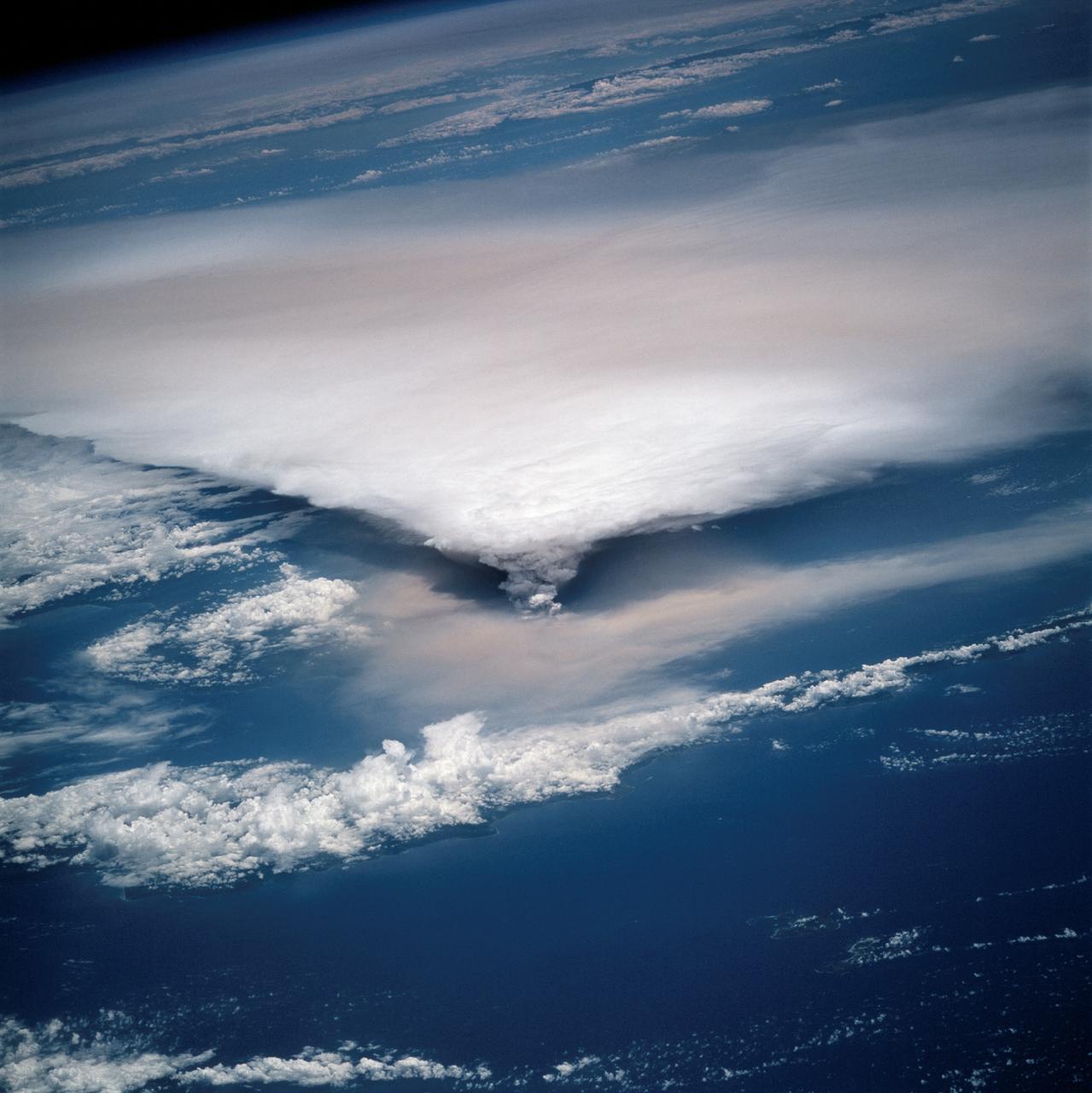

STS064-116-064 (20 Sept. 1994) --- Near the end of the mission, the crew aboard space shuttle Discovery was able to document the beginning of the second day of activity of the Rabaul volcano, on the east end of New Britain. On the morning of Sept. 19, 1994, two volcanic cones on the opposite sides of the 6-kilometer sea crater had begun to erupt with very little warning. Discovery flew just east of the eruption roughly 24 hours after it started and near the peak of its activity. New Ireland, the cloud-covered area in the foreground, lies just east of Rabaul harbor. The eruption, which sent a plume up to over 60,000 feet into the atmosphere, caused over 50,000 people to evacuate the area. Because winds were light at the time of the eruption, most of the ash was deposited in a region within 20 kilometers of the eruption zone. This photo shows the large white billowing eruption plume is carried in a westerly direction by the weak prevailing winds. At the base of the eruption column is a layer of yellow-brown ash being distributed by lower level winds. A sharp boundary moving outward from the center of the eruption in the lower cloud is a pulse of laterally-moving ash which results from a volcanic explosion. Geologists theorize that the large white column and the lower gray cloud are likely from the two main vents on each side of the harbor. The bay and harbor of Rabaul are covered with a layer of ash, possibly partly infilled with volcanic material. Matupit Island and the airport runway have disappeared into the bay. More than a meter of ash has fallen upon the city of Rabaul. Up to five vents were reported to have erupted at once, including the two cones Vulcan and Tavurvur, which are opposites of the harbor as well as new vents below the bay. Half of the Vulcan cone has collapsed into the sea. The extra day in space due to bad weather at the landing site afforded the crew the opportunity for both still and video coverage of the event. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
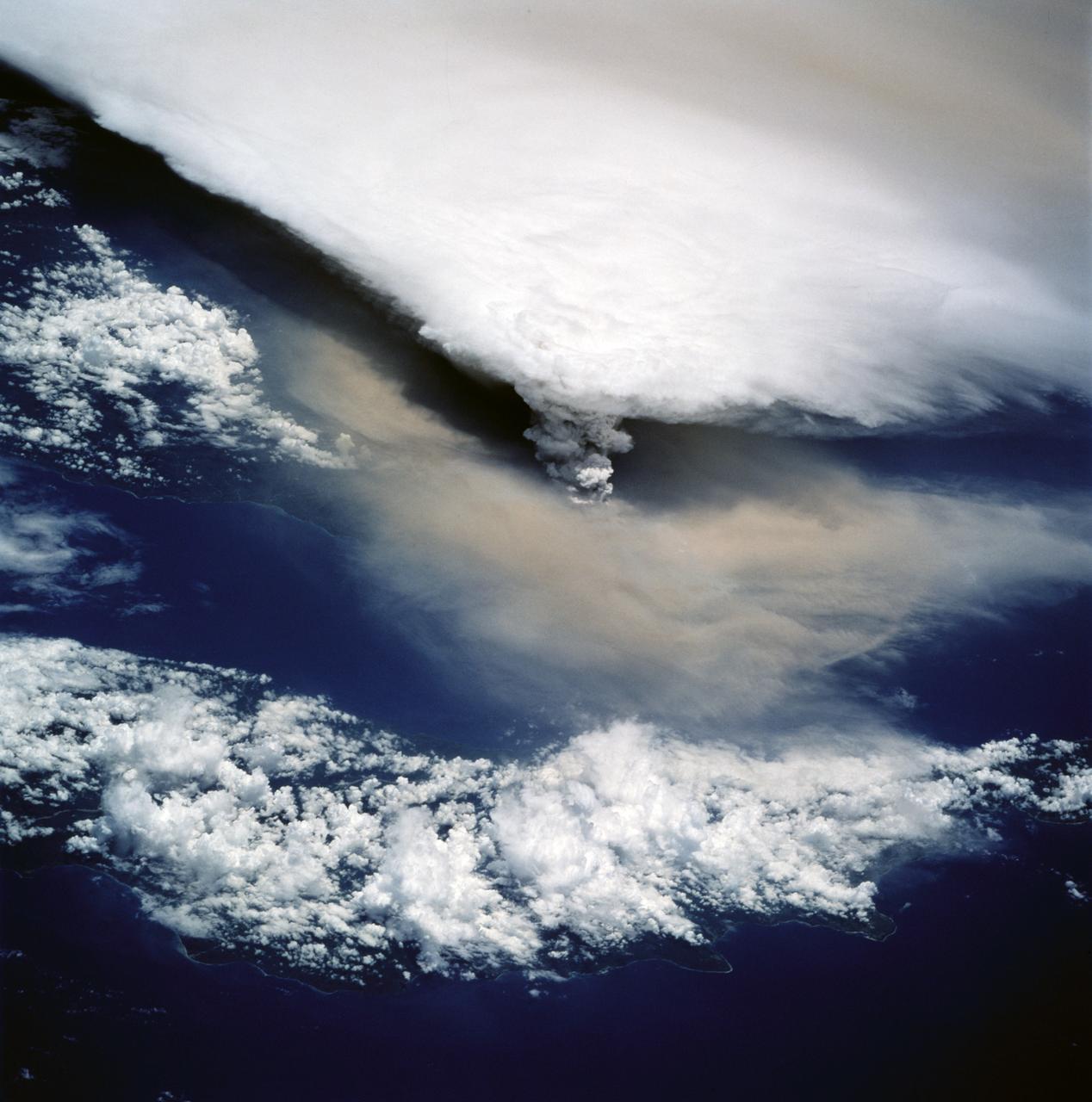

STS064-116-055 (20 Sept. 1994) --- Near the end of its mission, the crew aboard space shuttle Discovery was able to document the beginning of the second day of activity of the Rabaul volcano, on the east end of New Britain. On the morning of Sept. 19, 1994, two volcanic cones on the opposite sides of the 6-kilometer sea crater had begun to erupt with very little warning. Discovery flew just east of the eruption roughly 24 hours after it started and near the peak of its activity. The eruption, which sent a plume up to over 60,000 feet into the atmosphere, caused over 50,000 people to evacuate the area. Because winds were light at the time of the eruption, most of the ash was deposited in a region within 20 kilometers of the eruption zone. This photo shows the large white billowing eruption plume is carried in a westerly direction by the weak prevailing winds. At the base of the eruption column is a layer of yellow-brown ash being distributed by lower level winds. A sharp boundary moving outward from the center of the eruption in the lower cloud is a pulse of laterally-moving ash which results from a volcanic explosion. Geologists theorize that the large white column and the lower gray cloud are likely from the two main vents on each side of the harbor. The cloud-covered island in the foreground is New Ireland. The bay and harbor of Rabaul are covered with a layer of ash, possibly partly infilled with volcanic material. Matupit Island and the airport runway have disappeared into the bay. More than a meter of ash has fallen upon the city of Rabaul. Up to five vents were reported to have erupted at once, including the cones Vulcan and Tavurvur, which are opposites of the harbor as well as new vents below the bay. Half of the Vulcan cone has collapsed into the sea. The extra day in space due to bad weather at the landing site afforded the crew the opportunity for both still and video coverage of the event. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
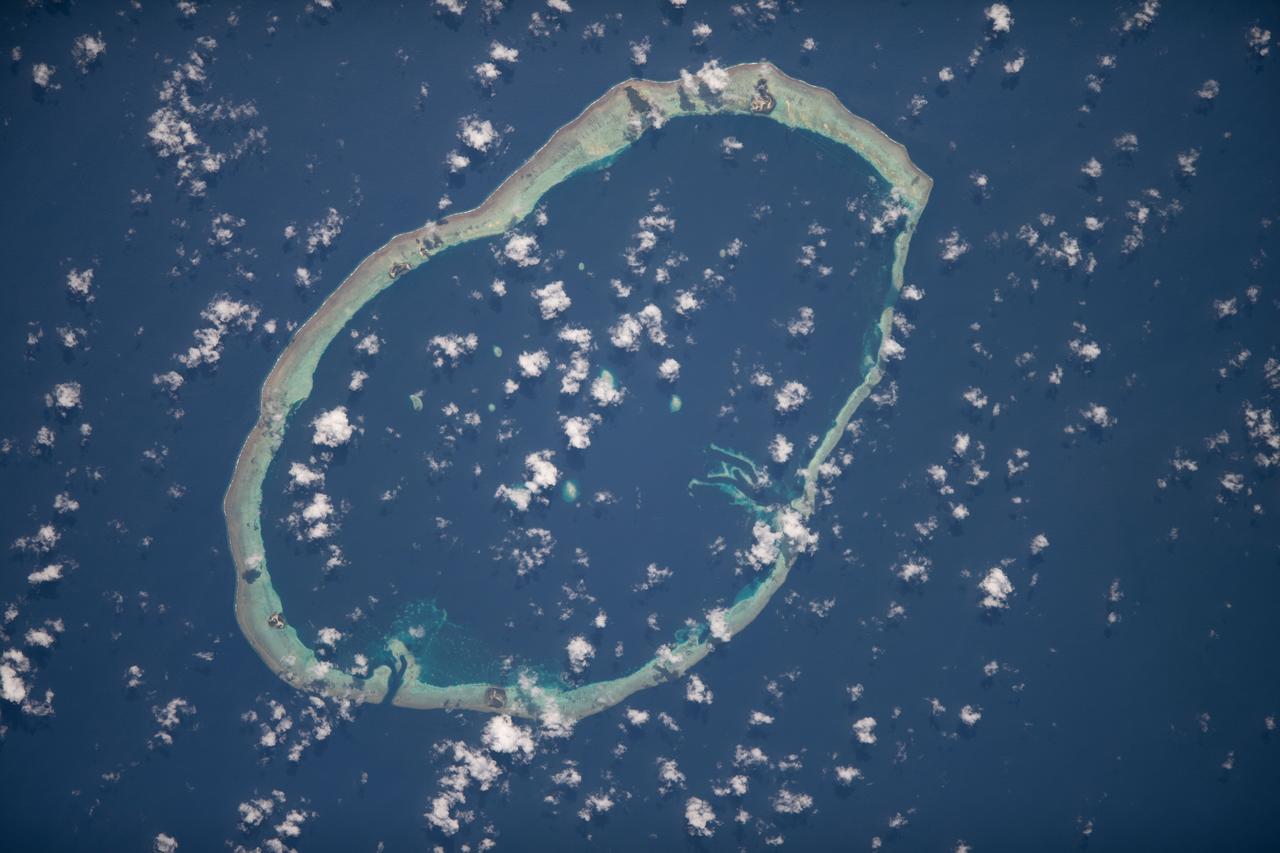

iss068e007434 (Oct. 2, 2022) --- Carteret Atoll, part of the independent nation of Papua New Guinea, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 260 miles above the southwestern Pacific Ocean. Credit: ESA/Samantha Cristoforetti

iss060e022358 (Aug. 4, 2019) --- The Milky Way lights up an orbital night pass as the International Space Station orbited 257 miles above the Coral Sea in between Australia and Papua New Guinea. The atmospheric glow highlights Earth's limb below.
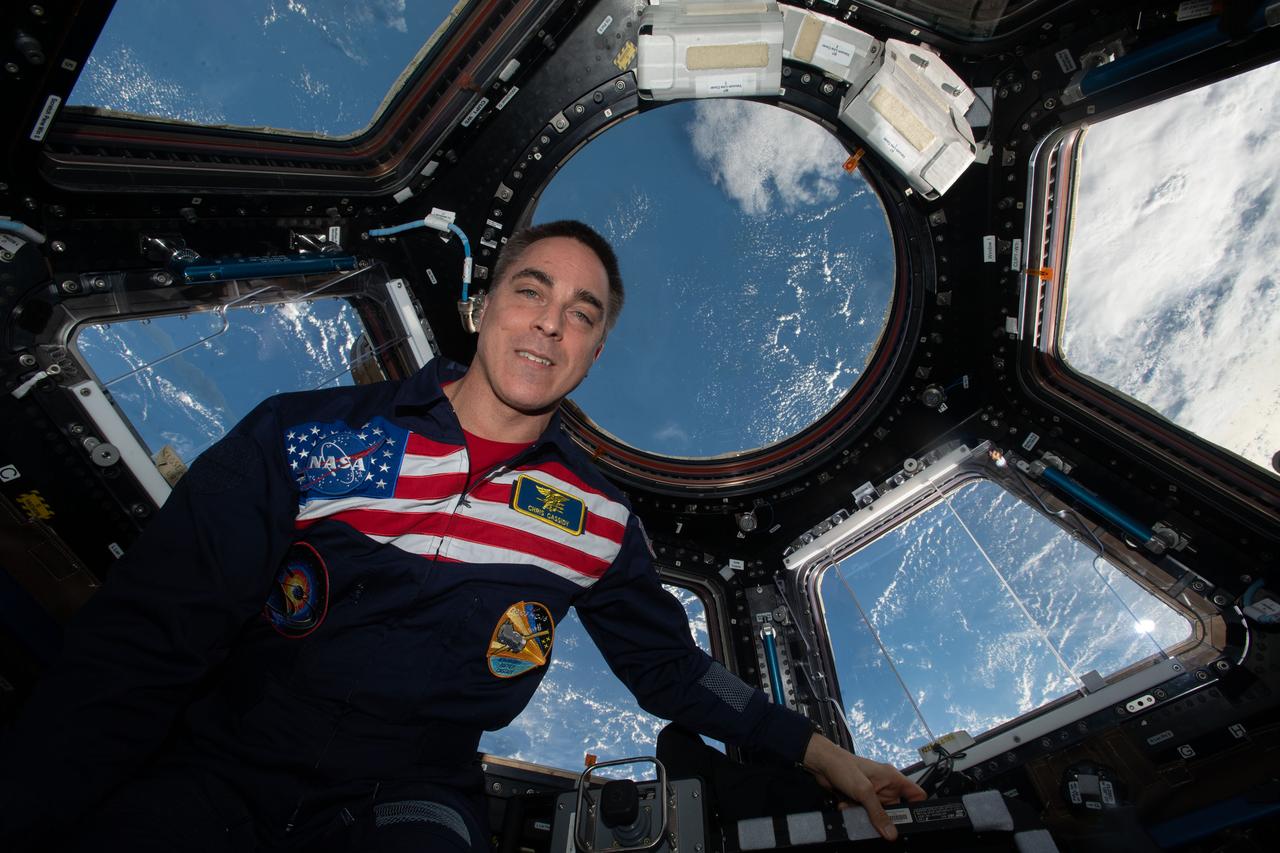

iss063e087971 (Sept. 11, 2020) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 63 Commander Chris Cassidy poses for a portrait wearing his flight suit inside the cupola, the International Space Station's window to the world. The orbiting lab was flying above the Pacific Ocean northeast of Papua New Guinea when this photograph was taken.
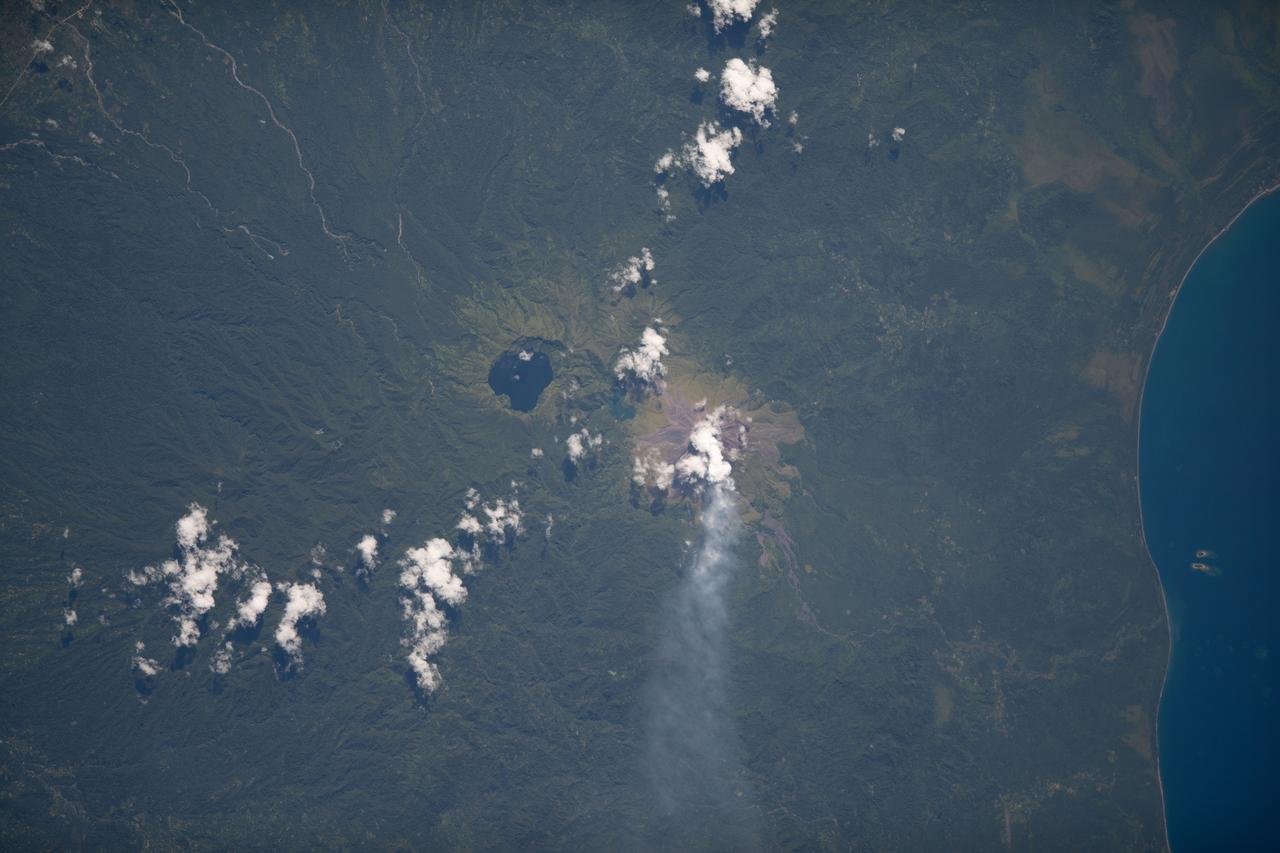

iss068e007429 (Oct. 2, 2022) --- Billy Mitchell Crater Lake and the active volcano Bagana on Papua New Guinea's Bougainville Island are pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 260 miles above the southwestern Pacific Ocean. Credit: ESA/Samantha Cristoforetti
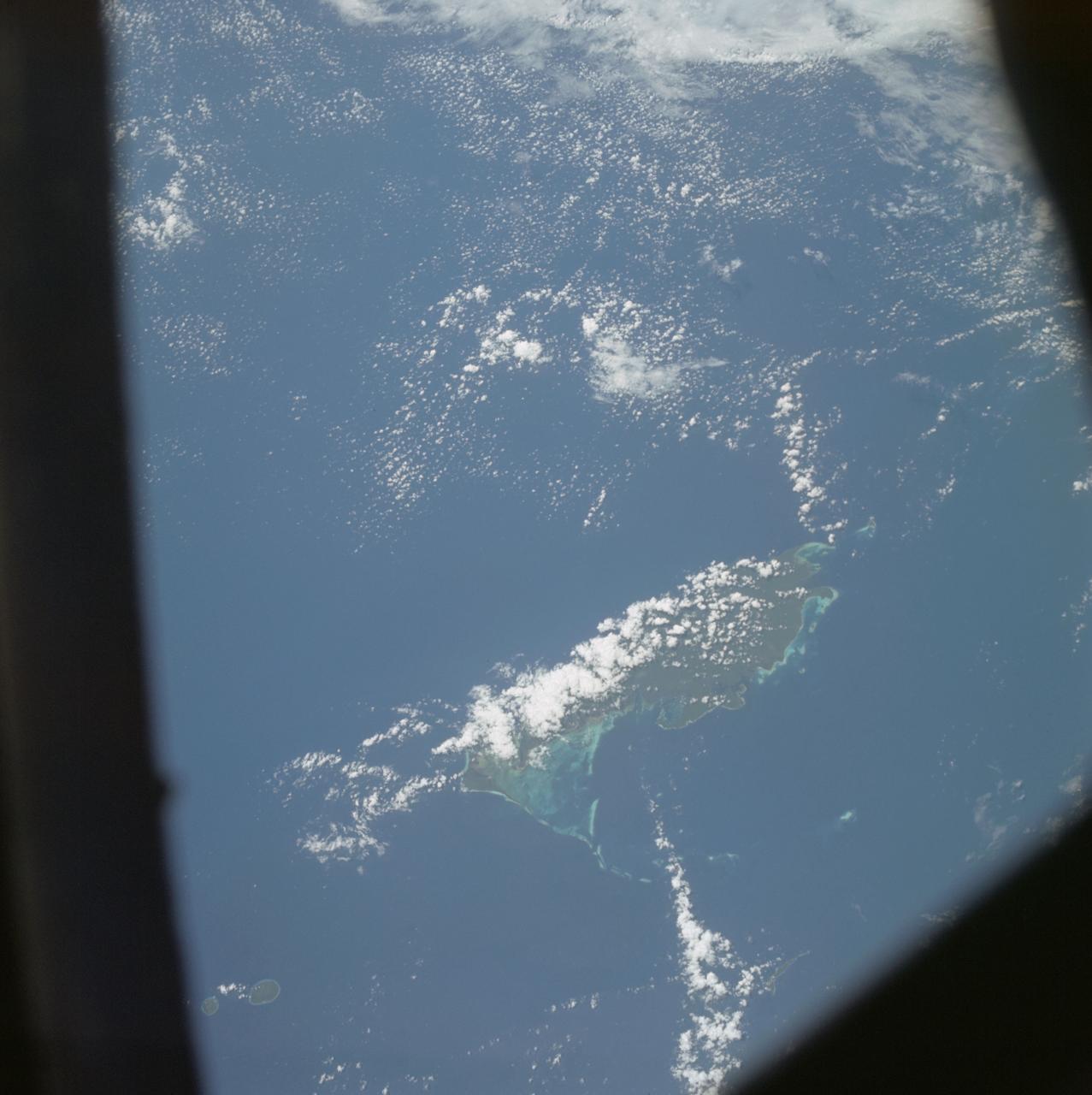

AS07-04-1609 (21 Oct. 1968) --- Woodlark Island in the Solomon Sea, east of New Guinea and northeast of Australia, as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 158th revolution of Earth. Photographed from an altitude of 140 nautical miles, at ground elapsed time of 251 hours and 21 minutes.
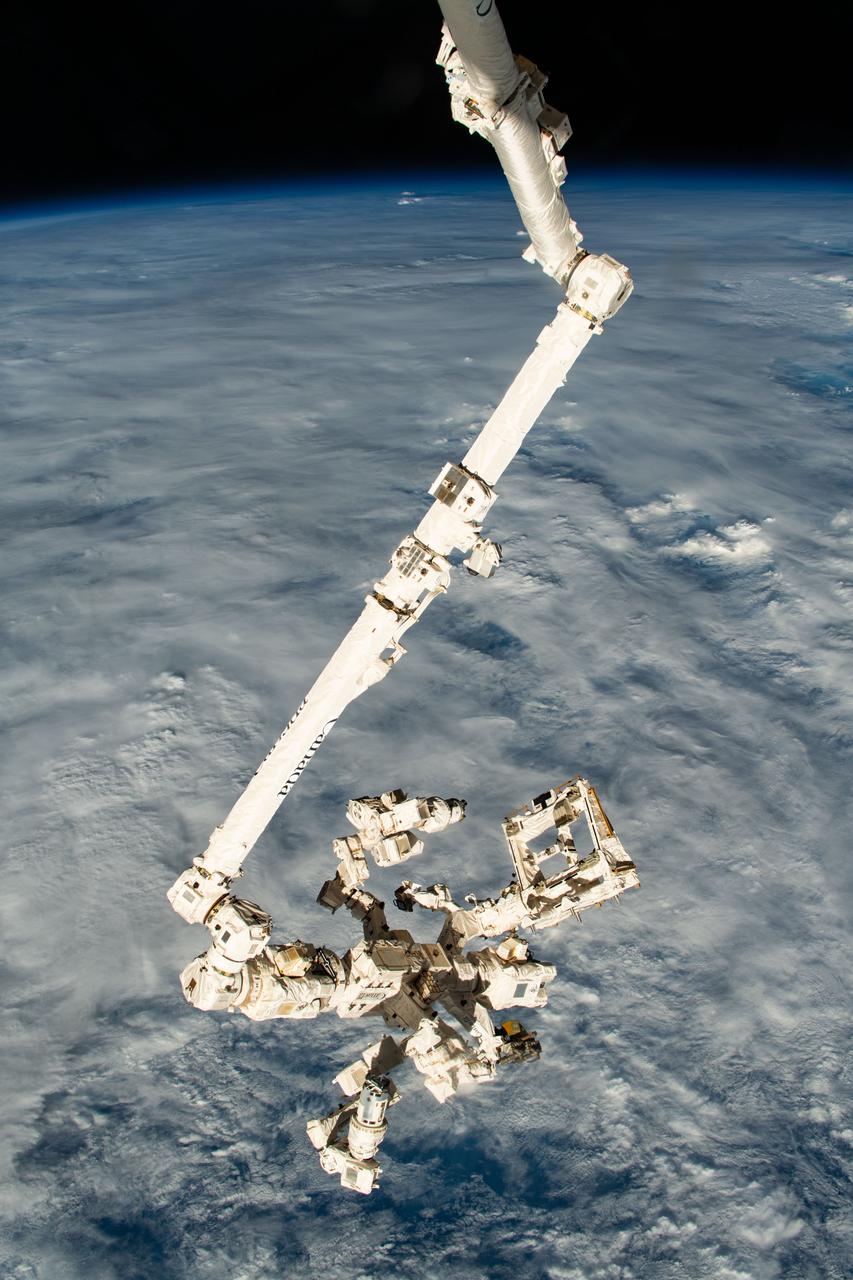

iss070e025899 (Nov. 15, 2023) --- The Canadarm2 robotic arm with its fine-tuned robotic hand, also known as Dextre, attached extends vertically down from the International Space Station as it orbited 261 miles above a cloudy Pacific Ocean north of Papua New Guinea.

iss070e076676 (Jan. 21, 2024) --- This high exposure photograph from the International Space Station shows Earth's atmospheric glow and a starry sky as the orbital complex soared 258 miles above the Pacific Ocean northeast of Papua New Guinea. At left, are the station's Nauka science module and the Prichal docking module, both from Roscosmos.
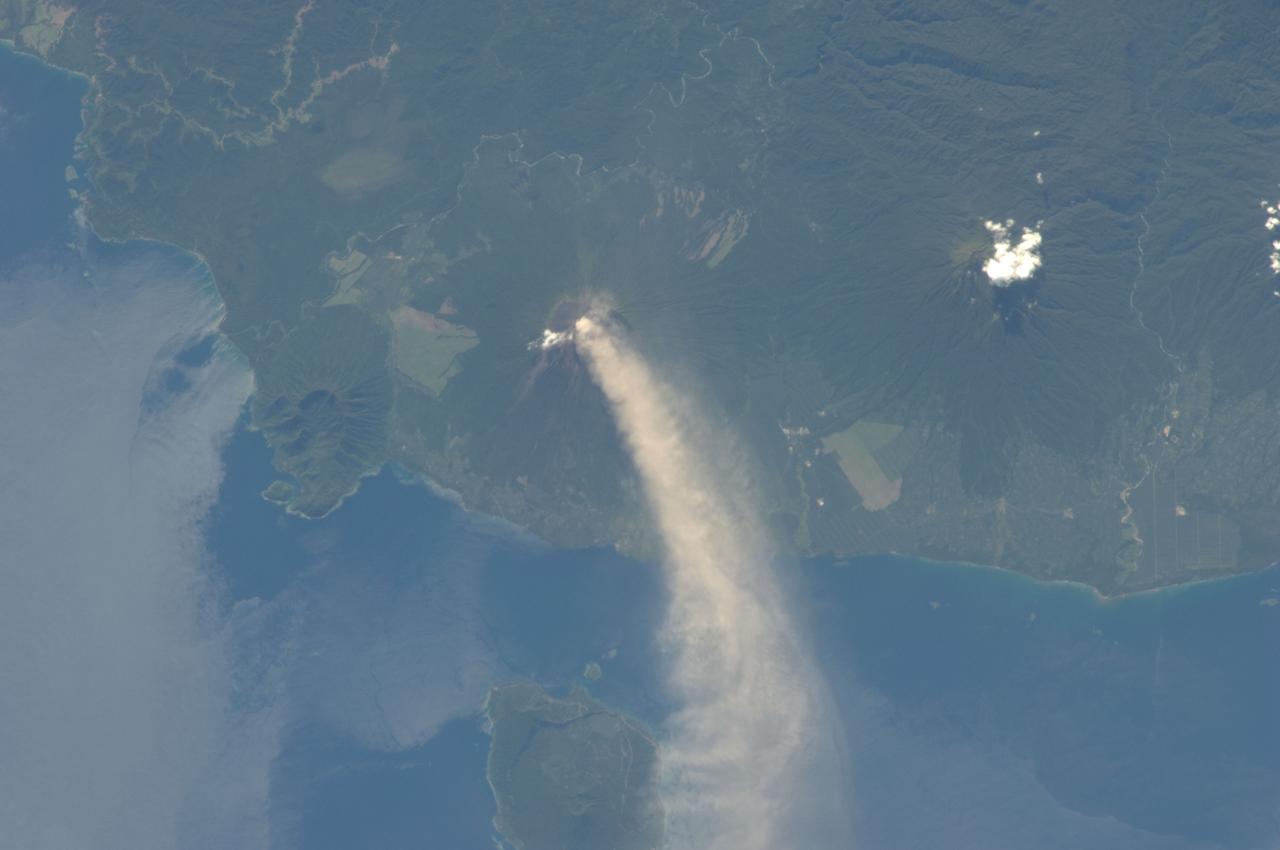

ISS034-E-005496 (30 Nov. 2012) --- An eruption at the Ulawun volcano, New Britain Island, Papua New Guinea is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 34 crew member on the International Space Station. Numerous volcanoes contribute to the landmass of the island of New Britain, the largest in the Bismarck Archipelago of Papua New Guinea. One of the most active of these volcanoes, Ulawun, is also the highest with a summit elevation of 2,334 meters. This photograph was taken during the most recent phase of volcanic activity at Ulawun. A white steam and ash plume extends from the summit crater of the stratovolcano towards the northwest (center; note the image is oriented such that north is towards the lower left). The plume begins to broaden as it passes the southwestern coast of Lolobau Island approximately 23 kilometers downwind from its source. Ulawun volcano is also known as “the Father”, with the Bamus volcano to the southwest also known as “the South Son”. The summit of Bamus is obscured by white cumulus clouds (not of volcanic origin) in this image. While Ulawun has been active since at least 1700, the most recent eruptive activity at Bamus occurred in the late 19th century. A large region of ocean surface highlighted by sunglint – sunlight reflecting off the water surface, lending it a mirror-like appearance– is visible to the north-northeast of Ulawun (lower left).
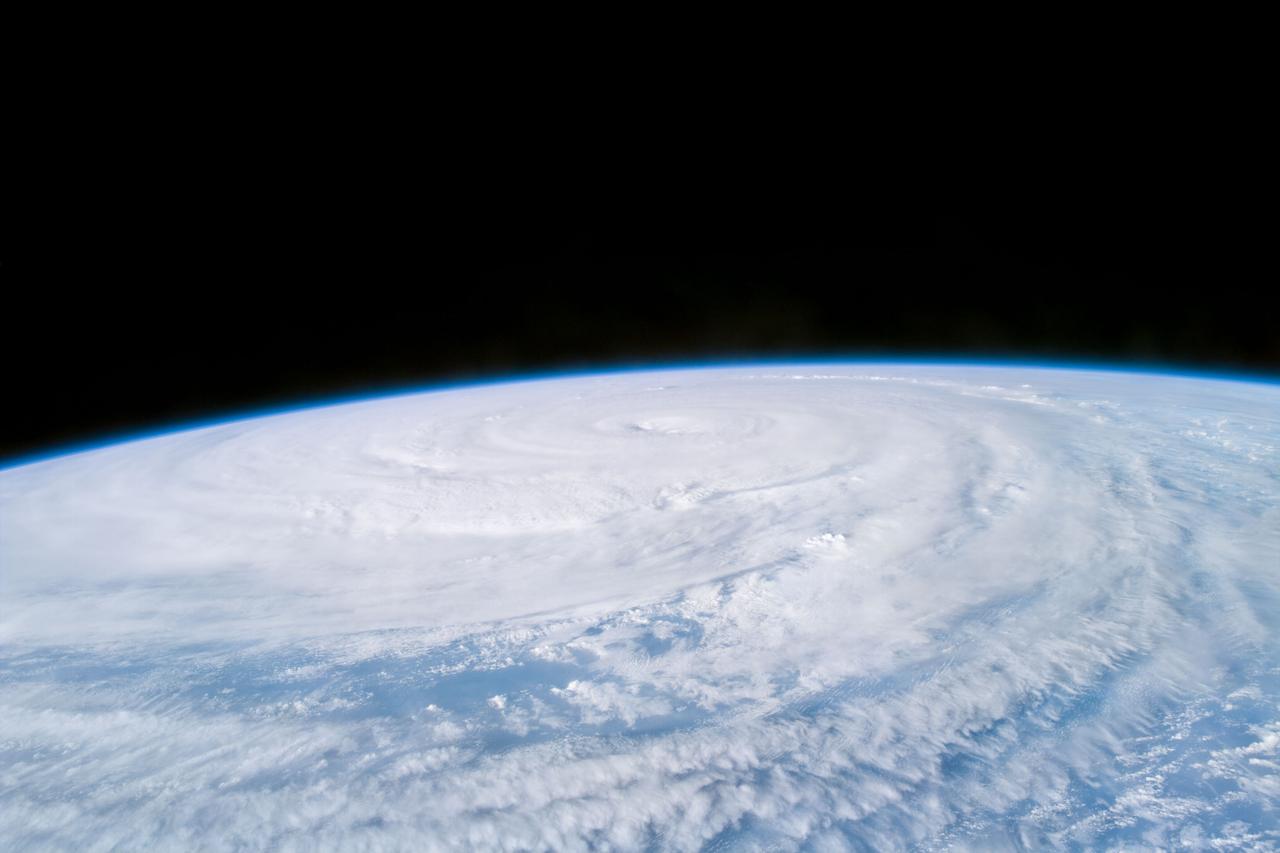

S85-E-5071 (13 August 1997) --- The STS-85 crew members aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery downlinked this oblique, Electronic Still Camera (ESC) view of the Super Typhoon Winnie about halfway between New Guinea and Japan in the Pacific Ocean late evening, August 13, 1997. Maximum sustained winds of 105 knots, gusts up to 130 knots. This photo was taken 14 1/2 hours after STS085-E-5069 was recorded with the same ESC.
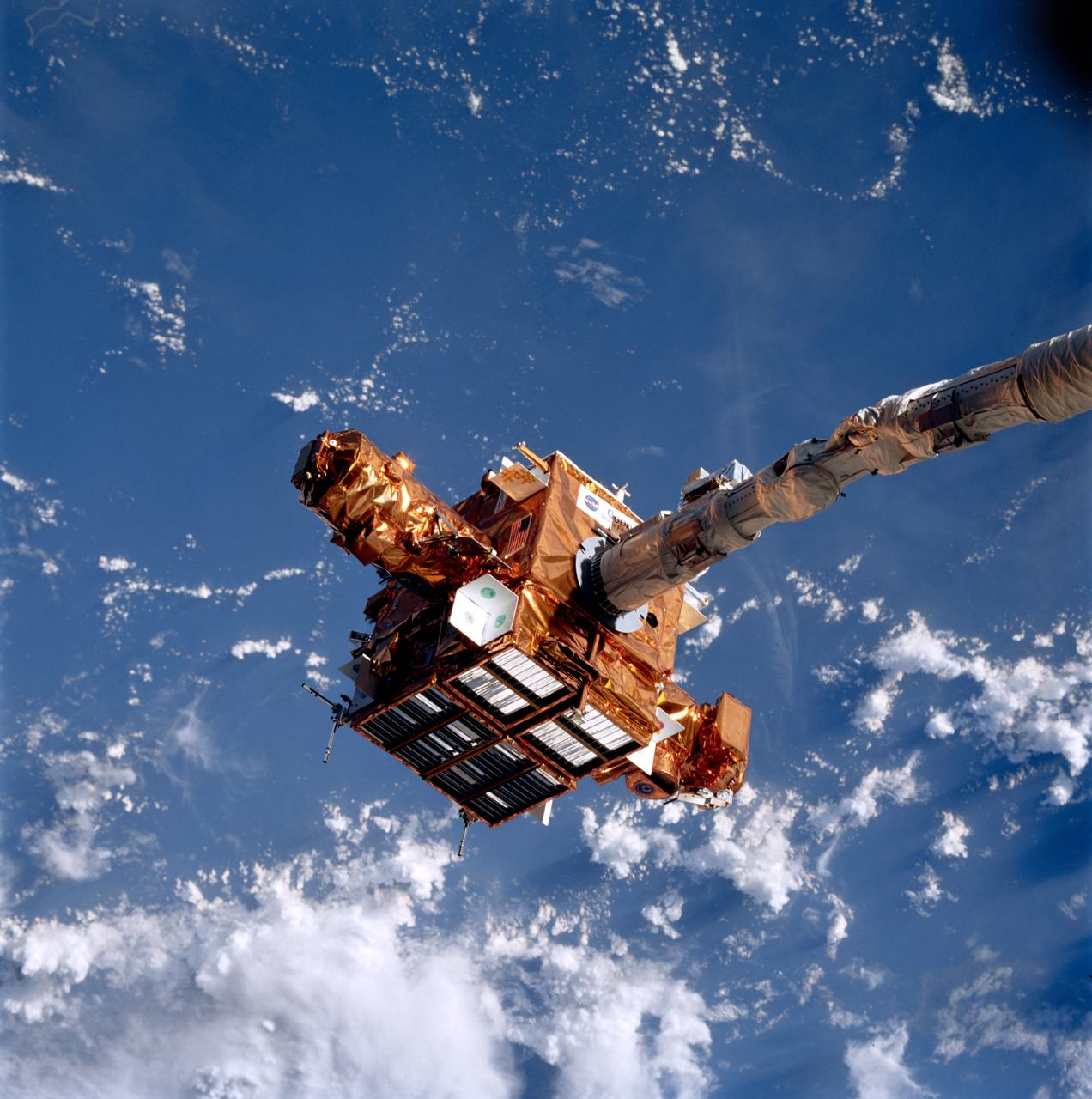

STS087-706-020 (19 November – 5 December 1997) --- The Spartan 201 satellite, held in the grasp of the Space Shuttle Columbia's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, is backdropped over white clouds and blue waters of the Pacific Ocean. Long Island, off the coast of Papua New Guinea, is barely visible in the lower left corner.

S85-E-5092 (14 August 1997) --- Flying directly over the eye just before 3 p.m. (EST), Aug. 15, the STS-85 crew members captured this image of Super Typhoon Winnie. The massive typhoon is located about half way between Japan and New Guinea in the Pacific Ocean. The Canadian-built robot arm of Discovery, being used in operations with CRISTA-SPAS on this mission, is partially visible in left foreground.
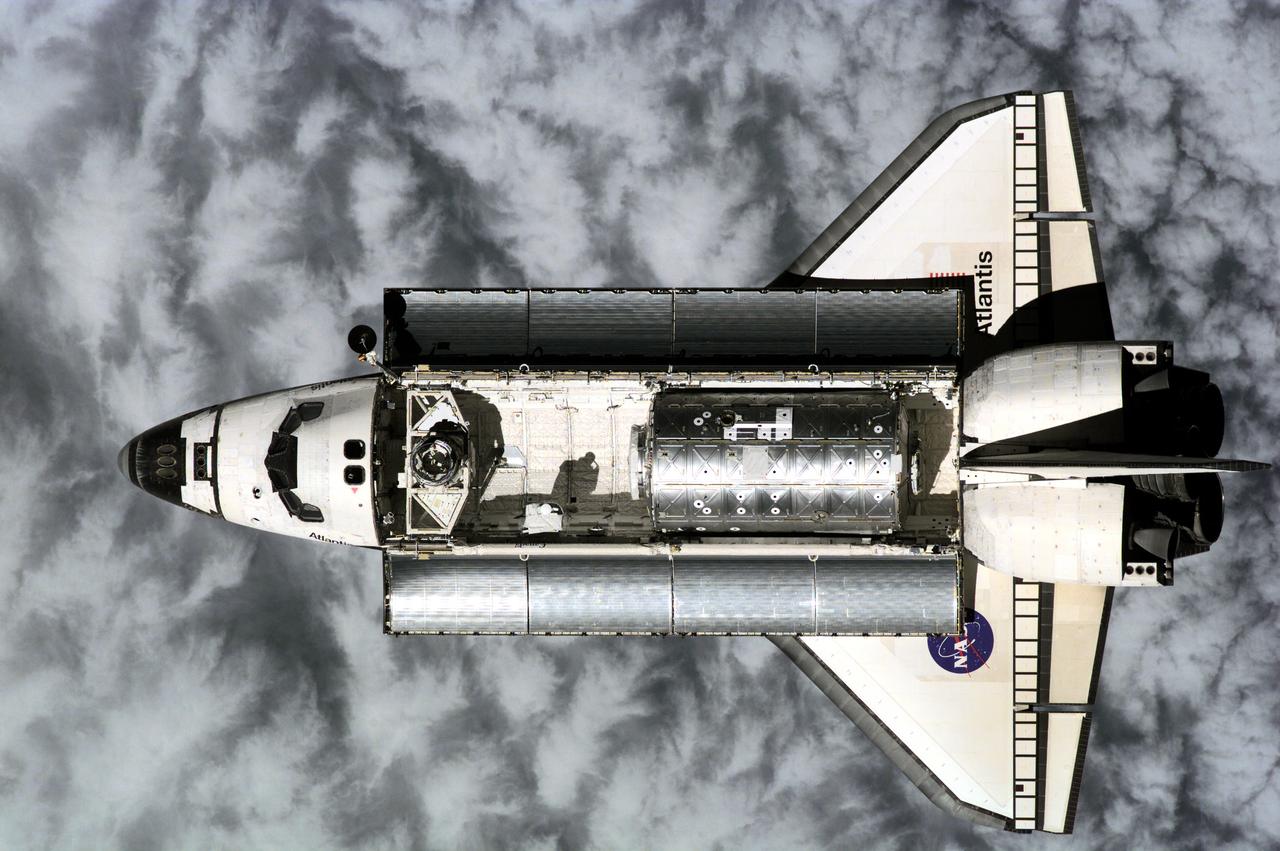
ISS001-E-6128 (9 February 2001) --- Atlantis was photographed from the International Space Station (ISS) prior to link-up with international outpost at 10:50 a.m. (CST), Feb. 9, 2001, as the two craft flew over the Western Pacific northeast of New Guinea. About ninety minutes later, hatches were swung open between Atlantis and the ISS, enabling the STS-98 and station crews to greet each other and transfer critical gear before re-closure later in preparation for the first (Feb. 10) of three planned space walks to help in the installation and hookup of Destiny on the station. The photograph was taken with a digital still camera.
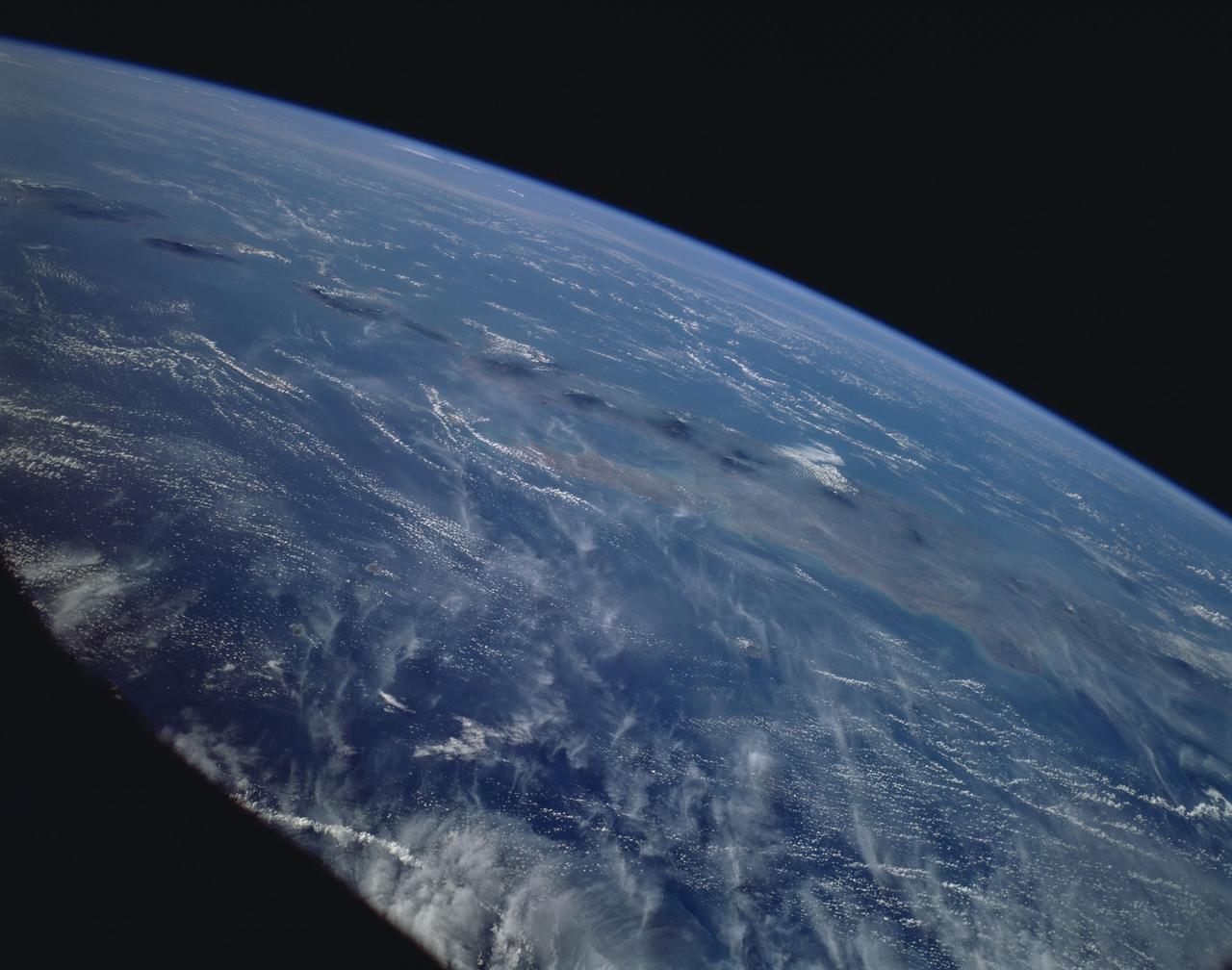

This is a striking, oblique view to the south of the Indonesian islands of Java (right), Bali and Lombok (upper left). The linear array of dark regions across the photo is a chain of volcanoes which make up the back bone of this part of the Indonesian Islands. This chain has been quite active over the past six months. Plumes of steam can be seen rising from the summits of Arjuno (west-central Java) and Merapi (central Java, near the right side of this photo). The region appears hazy due to an extended drought over Indonesia and Australia. Because of drought conditions, huge fires continue to burn over other regions of Indonesia, New Guinea and norther Australia, producing a regional smoke pall.
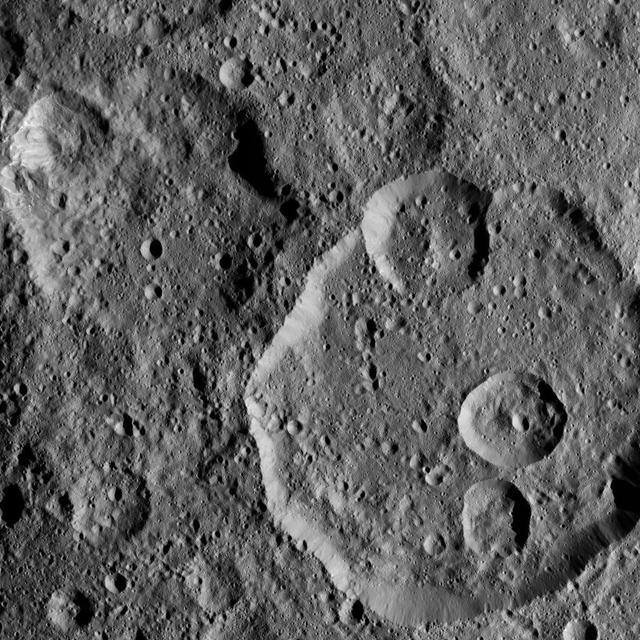
Meanderi Crater on Ceres is seen at lower right in this image from NASA's Dawn spacecraft. Meanderi -- named for the Ngaing goddess (New Guinea) of taro, sugar cane and other foods -- hosts several medium-sized craters within its walls. Meanderi measures 64 miles (103 kilometers) in diameter. The crater is centered at 41 degrees south, 194 degrees east. Dawn took this image on Oct. 26, 2016, during its second extended-mission science orbit (XMO2), from a distance of about 920 miles (1,480 kilometers) above the surface of Ceres. The image resolution is about 460 feet (140 meters) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21248
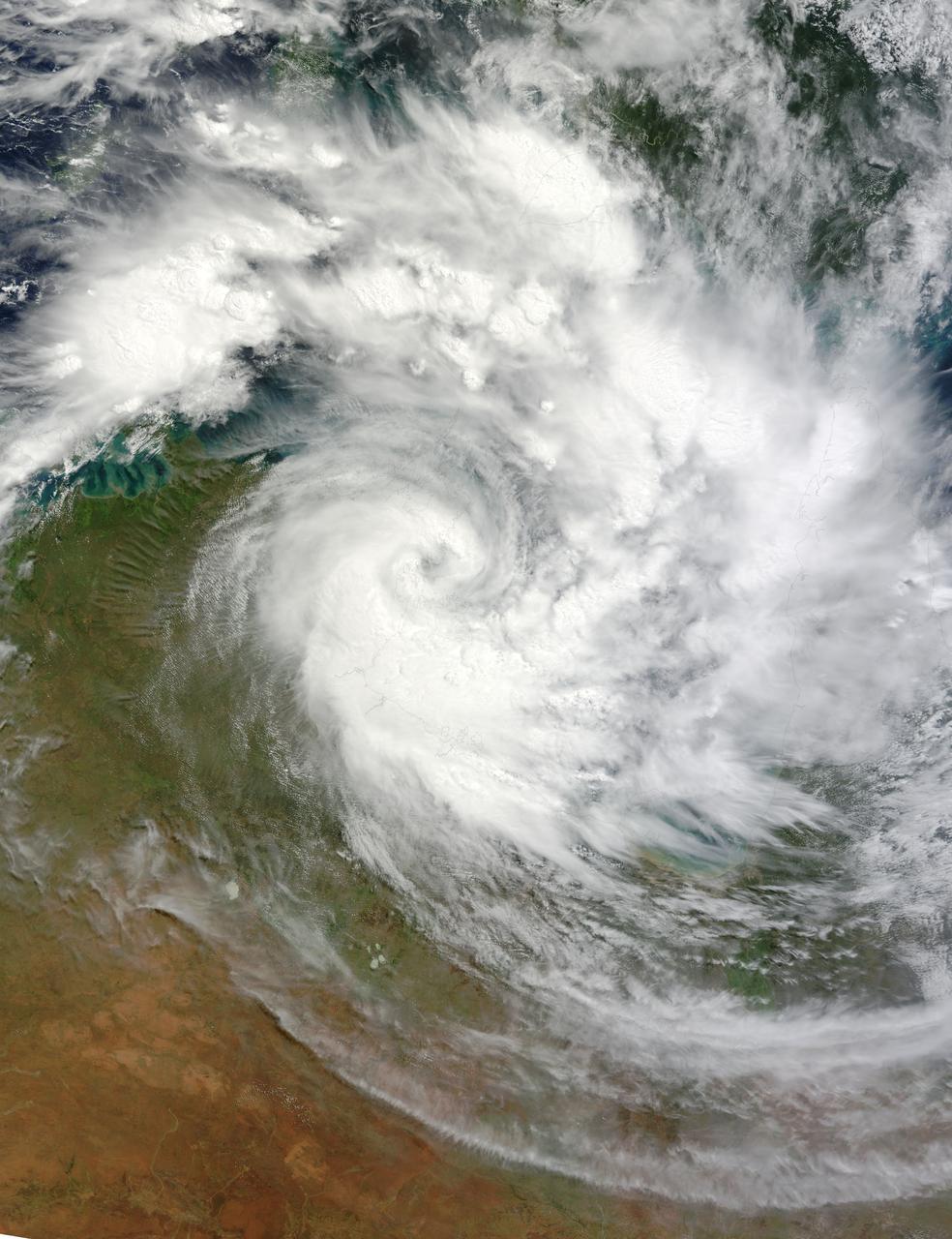

NASA image March 29, 2010 Tropical Cyclone Paul spanned the ocean waters between Australia and New Guinea on March 29, 2010. The MODIS on NASA’s Terra satellite captured this natural-color image the same day. The center of the cyclone is along the coast of Northern Territory’s Arnhem Land. Clouds run counter-clockwise across the Gulf of Carpentaria and Cape York Peninsula, over New Guinea’s Pulau Dolok, and over the Arafura Sea. On March 29, 2010, the U.S. Navy’s Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) reported that Tropical Cyclone Paul storm had maximum sustained winds of 60 knots (110 kilometers per hour) and gusts up to 75 knots (140 kilometers per hour). The storm was located roughly 315 nautical miles (585 kilometers) east of Darwin. The storm had moved slowly toward the southwest over the previous several hours. The JTWC forecast that the storm would likely maintain its current intensity for several more hours before slowly dissipating over land. Credit: NASA/GSFC/Jeff Schmaltz/MODIS To learn more about this image go to: <a href="http://modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/individual.php?db_date=2010-03-30" rel="nofollow">modis.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/individual.php?db_date=2010-0...</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe.
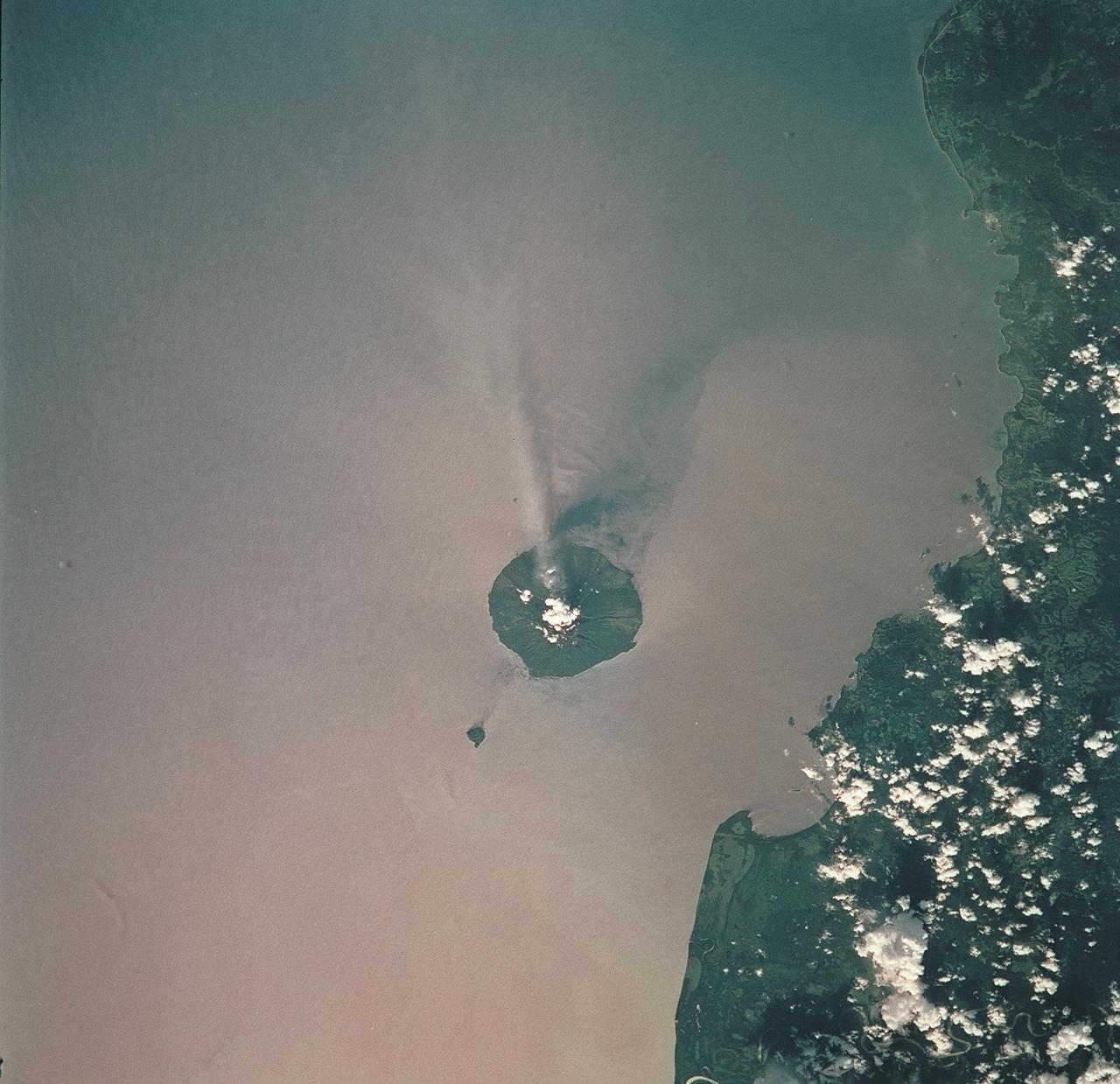

STS093-709-051 (23-27 July 1999) --- The STS-93 astronauts aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia took this picture of the volcanic island of Manam, along the northeast coast of Papua New Guinea. Manam is one in a string of currently active volcanoes called the Bismarck Arc. It is the most active of the group, having begun its present activity in 1994. The plume of steam and ash streaming from its crater extends more than 20 miles into the atmosphere. When the photo was taken, the shuttle was flying over a point located at 12.2 degrees south latitude and 132.0 degrees east longitude. Data back information on the 70mm film lists time and date of the photo as 05:42:31 GMT, July 25, 1999 (orbit 33).
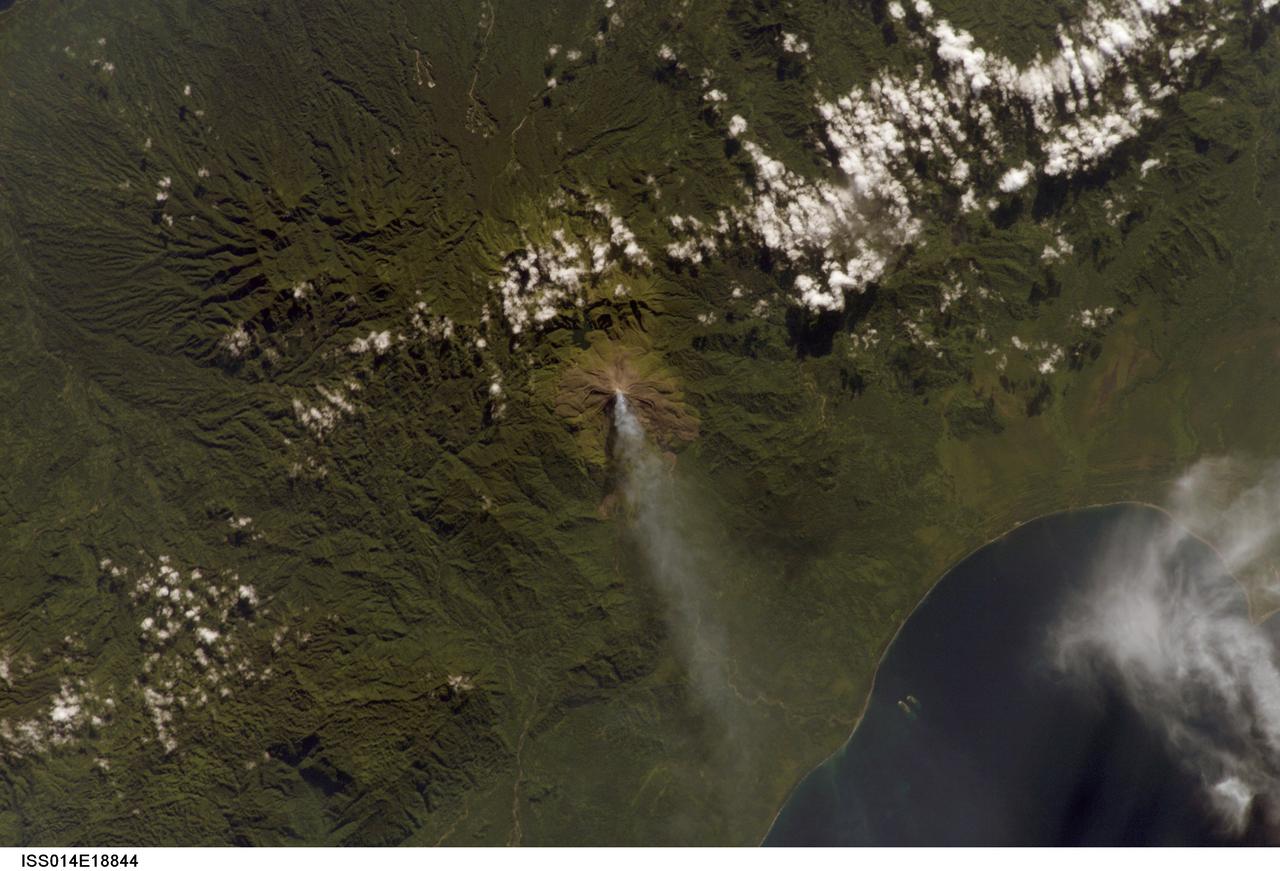

ISS014-E-18844 (2 April 2007) --- A plume at Mt. Bagana, Bougainville Island is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 14 crewmember on the International Space Station. Bougainville Island, part of the Solomon Islands chain to the east of Papua New Guinea, is typical of many Pacific Rim islands in that volcanism has played a large part in both its geological and recorded history. The island hosts three large volcanoes along its northwest-southeast trending axis: Mt. Balbi, Mt. Bagana, and the Mt. Takuan volcanic complex. Mt. Bagana (near center) is the only volcano on the island that has been historically active. Light green stressed vegetation, and brown lobate lava flows mark the 1,750 meter high lava cone of Mt. Bagana within the verdant landscape of Bougainville Island. The eruptive style of the volcano is typically non-explosive, producing thick lobes of andesitic lava that run down the flanks and maintain a dome in the summit crater. Occasional pyroclastic flows have also been noted. The most recent phase of activity, which began on March 7, has been characterized by vapor plumes with occasional ash-producing emissions. This photograph, acquired almost one month (twenty days) after the last reported activity at Bagana, records a diffuse white vapor plume extending west-southwest from the summit. The Solomon Island region experiences other effects due to the geologic setting: earlier this week, a large but shallow earthquake shook the region and induced a tsunami that hit the western part of the Solomon Island chain.