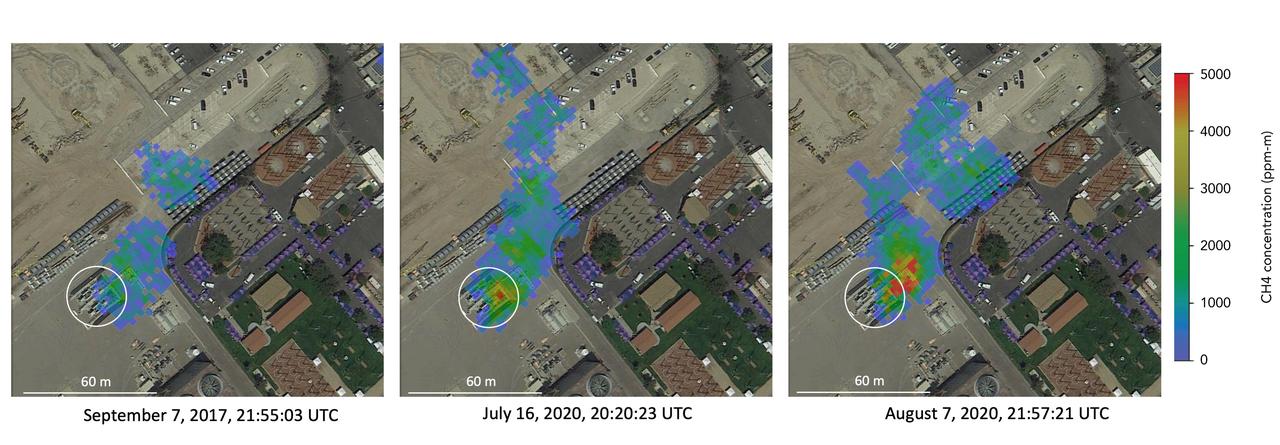
Atmospheric methane is a potent greenhouse gas and an important contributor to air quality. Future instruments on orbiting satellites can help improve our understanding of important methane emission sources. NASA conducts periodic methane studies using the next-generation Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer (AVIRIS-NG) instrument. These studies are determining the locations and magnitudes of the largest methane emission sources across California, including those associated with landfills, refineries, dairies, wastewater treatment plants, oil and gas fields, power plants, and natural gas infrastructure. These three images show concentrations of methane in a natural gas plume relative to background air measured by AVIRIS-NG, overlaid on true-color land surface images (source: Google Earth). The aircraft was flying at an altitude of about 10,000 feet (3,000 meters) above ground level and the AVIRIS-NG image pixels are each about 10 feet (3 meters) across. The plume shape varies with changing emission rate, wind speed and direction. The methane plume originates from a compressor — circled in each image — at Valley Generating Station, a natural gas-fired power plant near Los Angeles. The color scale indicates the concentration of methane in each pixel relative to background methane concentrations in the surrounding atmosphere. The plume was initially detected by a single overflight in September 2017 but assumed at the time to be due to normal operations (intermittent venting). The plume was detected by AVIRIS-NG again on six flights in July-August 2020. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24019
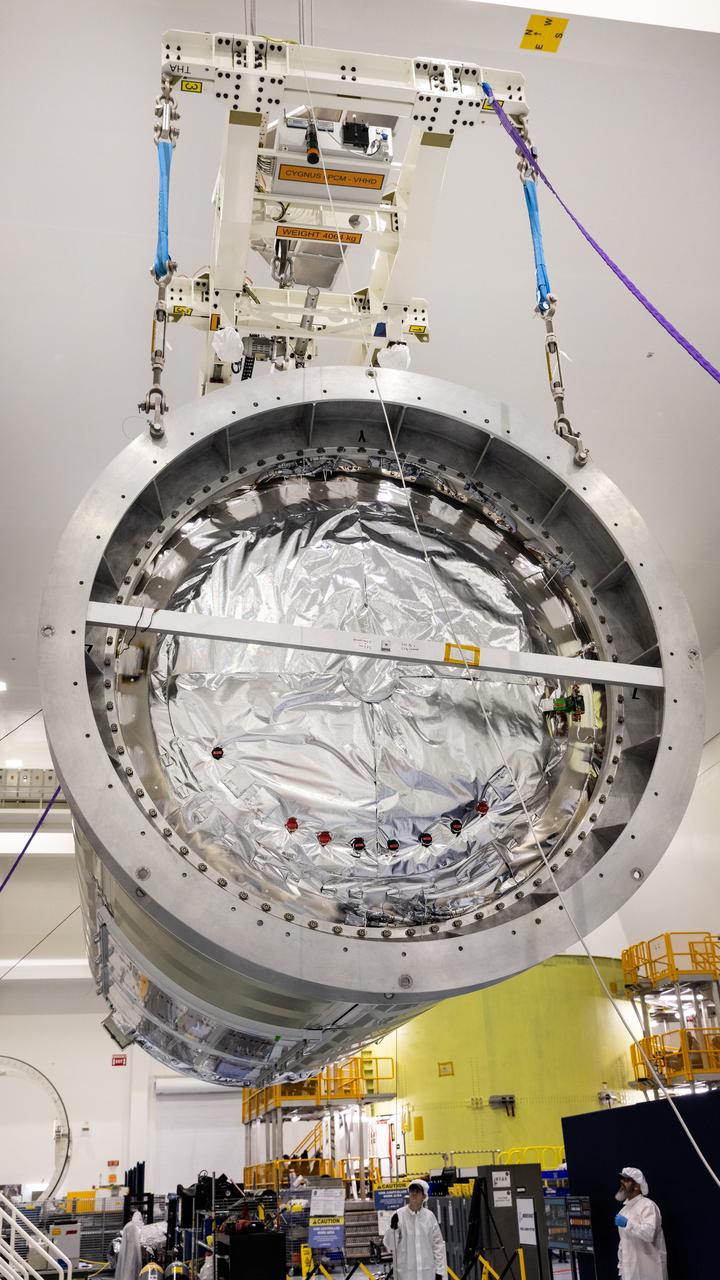
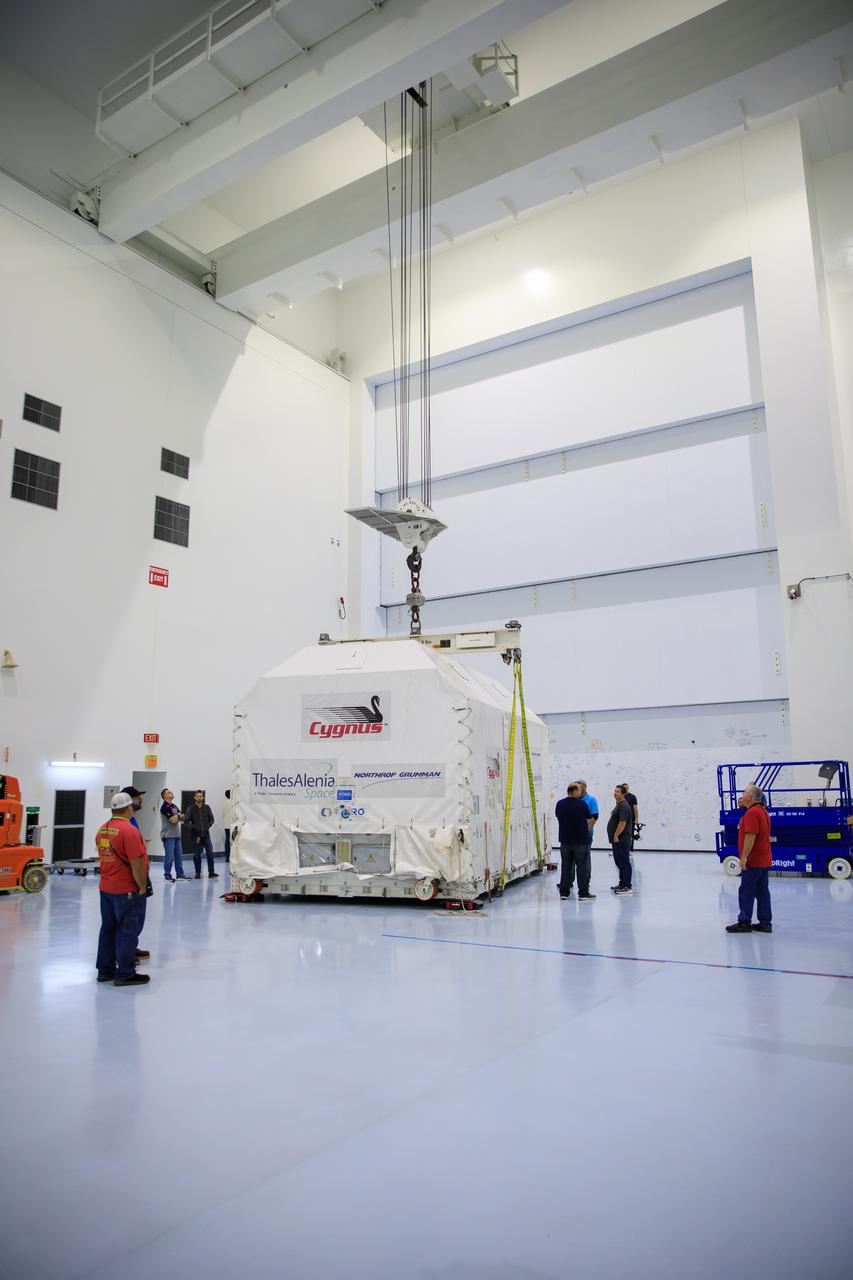
Technicians use a crane to lift Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft’s pressurized cargo module out of the shipping container on Thursday, July 10, 2025, inside the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new extended Cygnus capsule, scheduled to launch no earlier than fall 2025, will carry supplies, food, and scientific experiments for crew members at the International Space Station as part of the company’s 23rd cargo resupply mission.
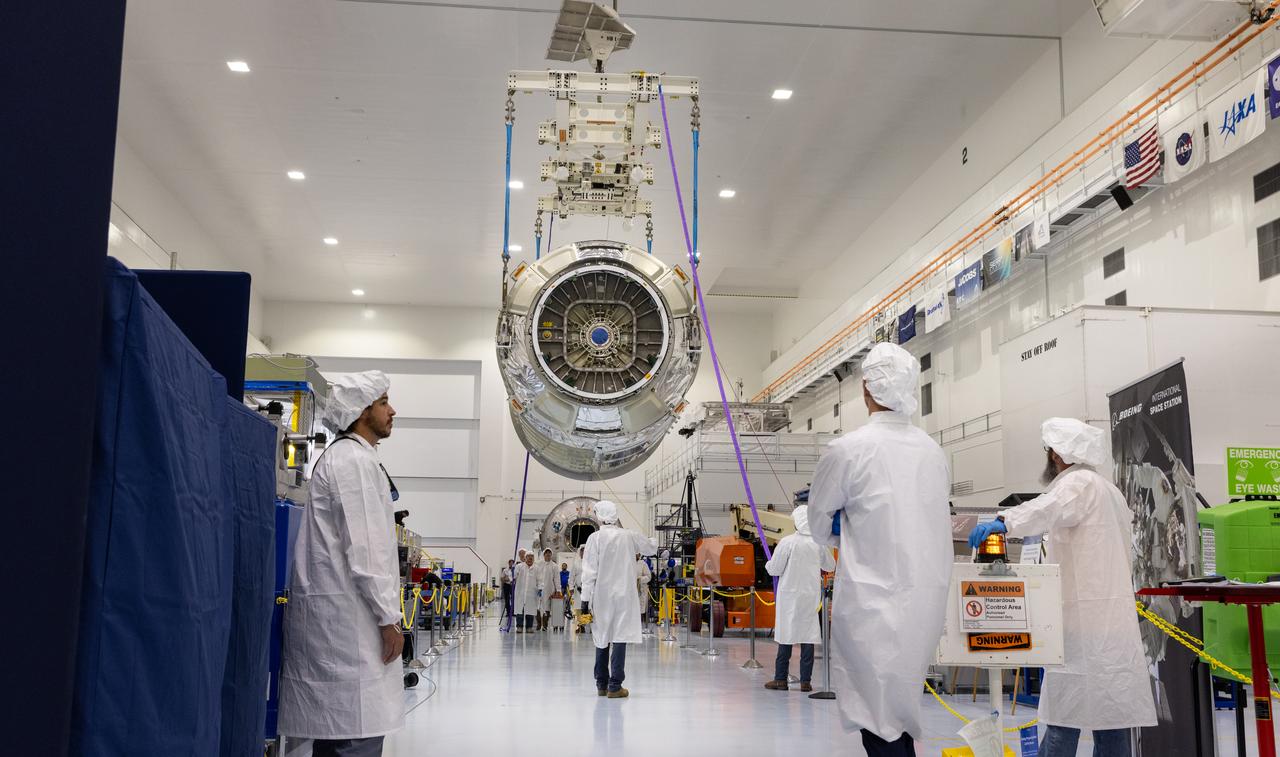

Technicians use a crane to lift Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft’s pressurized cargo module out of the shipping container on Thursday, July 10, 2025, inside the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new extended Cygnus capsule, scheduled to launch no earlier than fall 2025, will carry supplies, food, and scientific experiments for crew members at the International Space Station as part of the company’s 23rd cargo resupply mission.

Technicians use a crane to lift Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft’s pressurized cargo module out of the shipping container on Thursday, July 10, 2025, inside the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The new extended Cygnus capsule, scheduled to launch no earlier than fall 2025, will carry supplies, food, and scientific experiments for crew members at the International Space Station as part of the company’s 23rd cargo resupply mission.
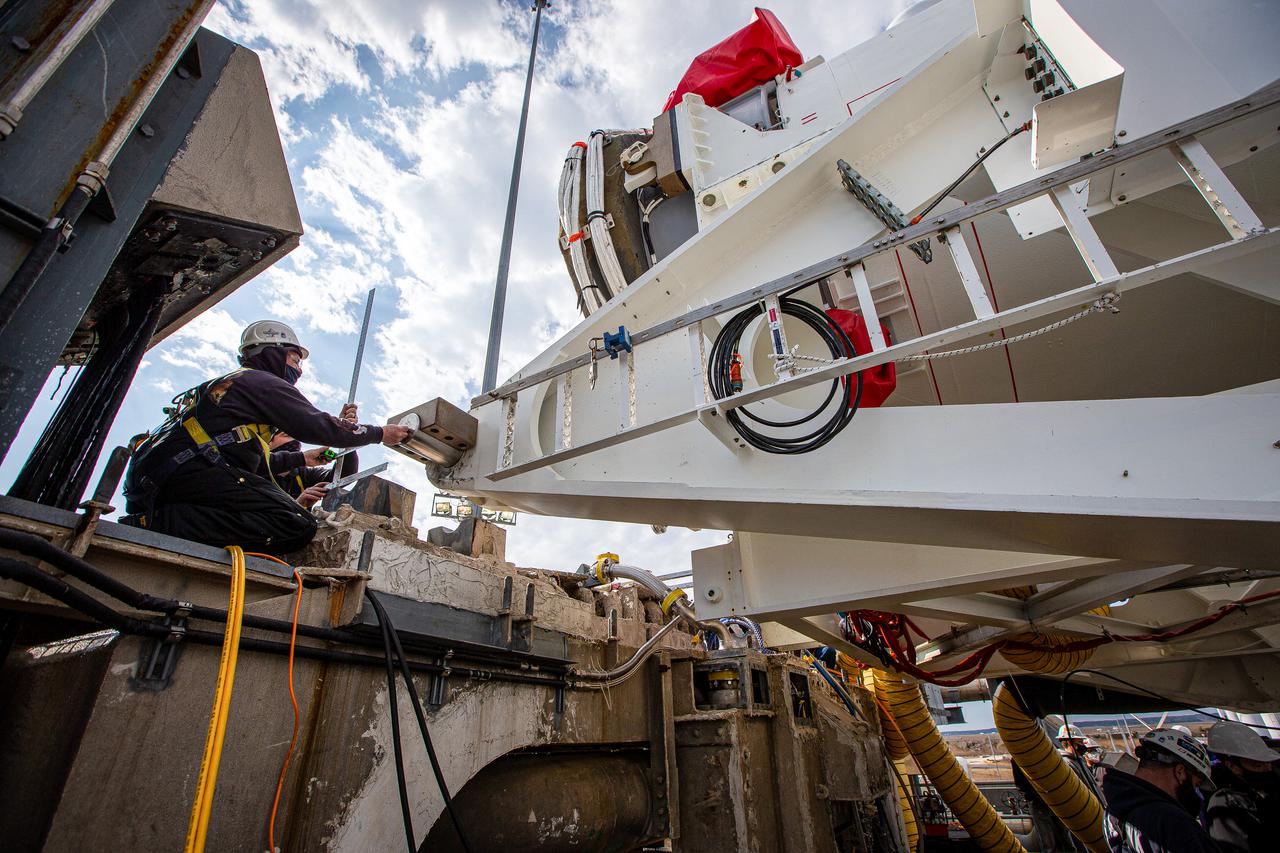

Personnel prepare to mate the Transporter-Erector-Launcher, also called the TEL, carrying a Northrop Grumman Antares rocket to the launch mount on the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport’s Pad 0A at NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The Antares arrived at the launch pad on Tuesday, Feb. 16, in preparation for launch at 12:36 p.m. EST, Feb. 20, 2021. The launch will be Northrop Grumman’s 15th contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA to the International Space Station, carrying about 8,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew. Antares is carrying the company’s CRS-15 Cygnus cargo spacecraft named after NASA mathematician, Katherine Johnson, a Black woman who time and again broke through barriers of gender and race. Photo Credit: (NASA/Patrick Black)
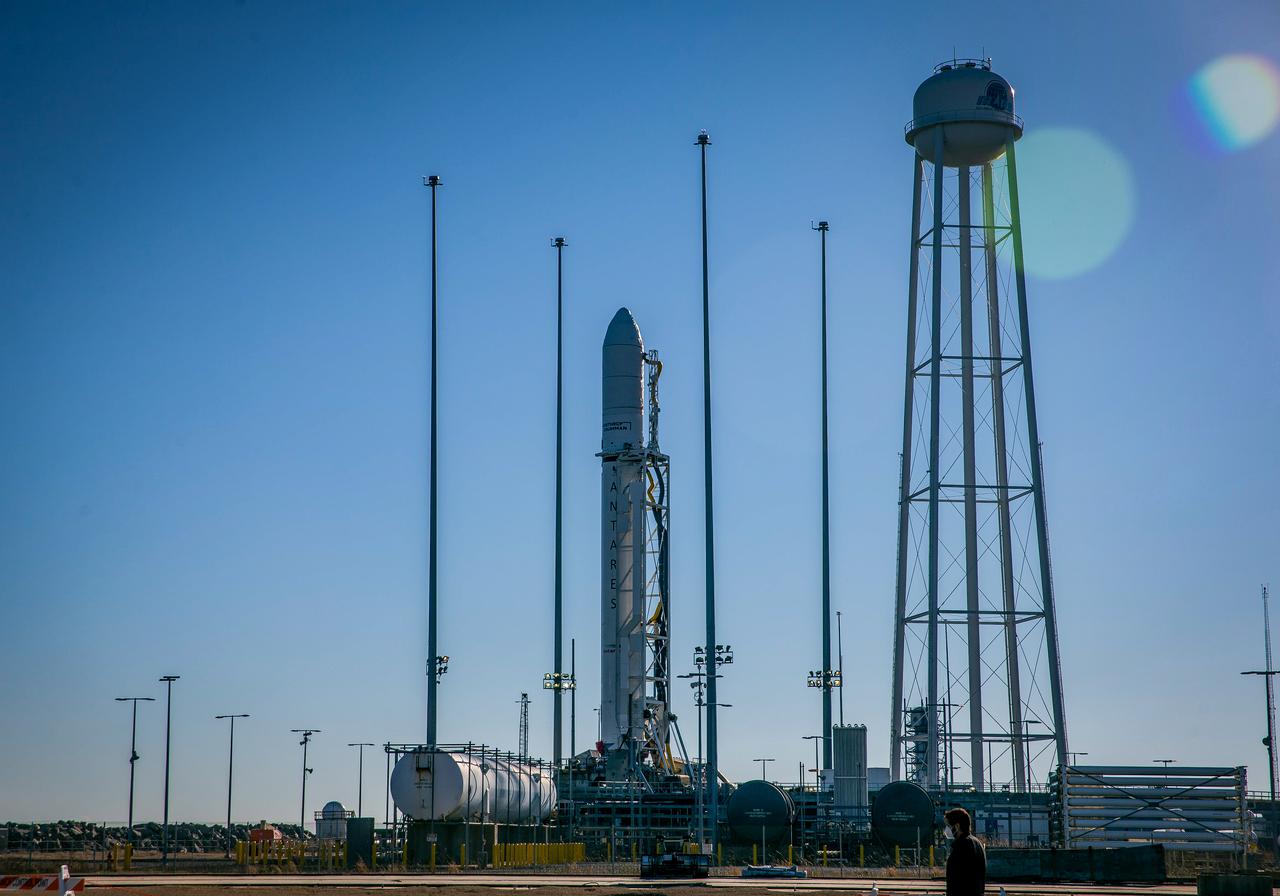

A Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft is in the vertical launch position on the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport’s Pad-0A, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 15th contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA to the International Space Station will deliver about 8,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew. The CRS-15 Cygnus spacecraft is named after NASA mathematician, Katherine Johnson, a Black woman who time and again broke through barriers of gender and race. The launch is scheduled 12:36 p.m. EST, Feb. 20, 2021. Photo Credit: (NASA/Patrick Black)
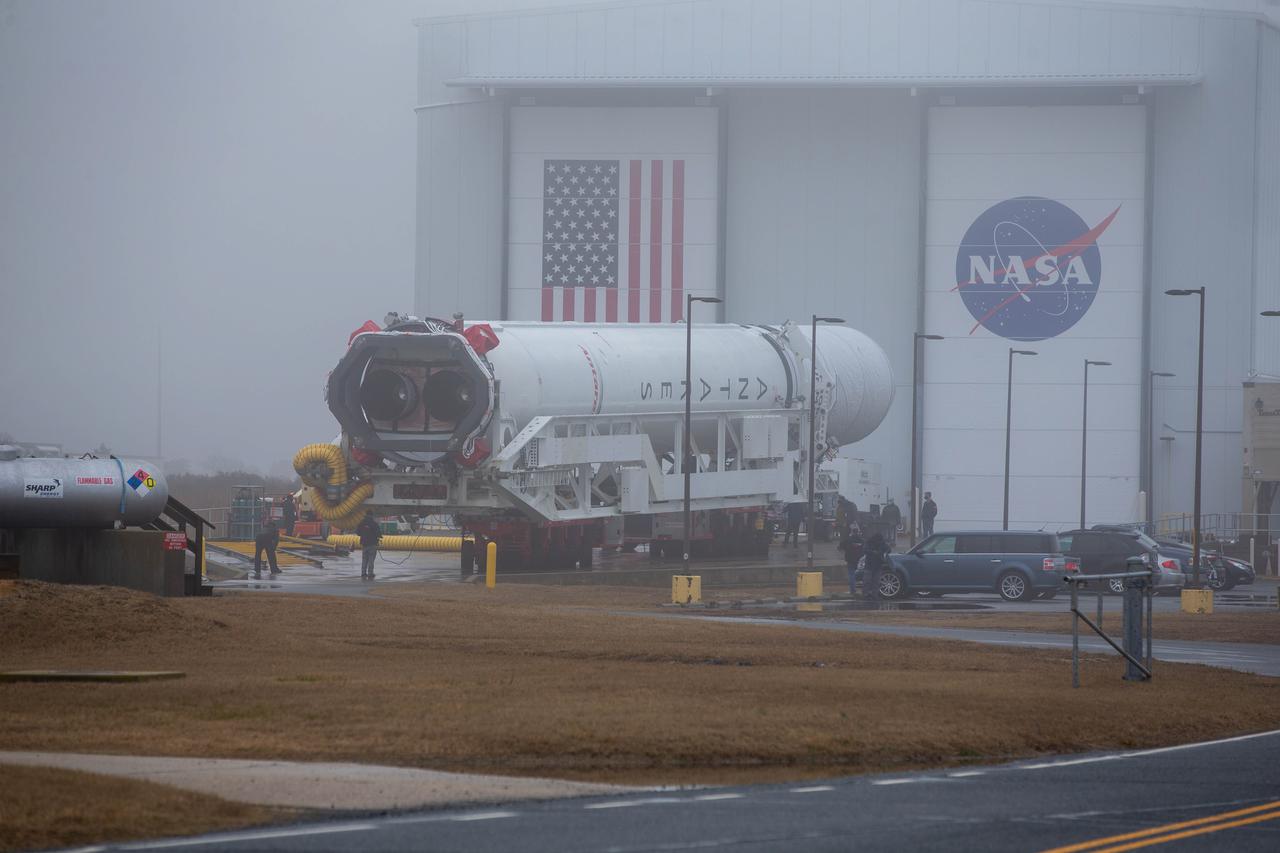

A Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft is seen as it is rolled out of the Horizontal Integration Facility on its way to the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport’s Pad-0A, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 15th contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA to the International Space Station will deliver about 8,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew. The CRS-15 Cygnus spacecraft is named after NASA mathematician, Katherine Johnson, a Black woman who time and again broke through barriers of gender and race. The launch is scheduled for 12:36 p.m. EST, Feb. 20, 2021. Photo Credit: (NASA/Patrick Black)
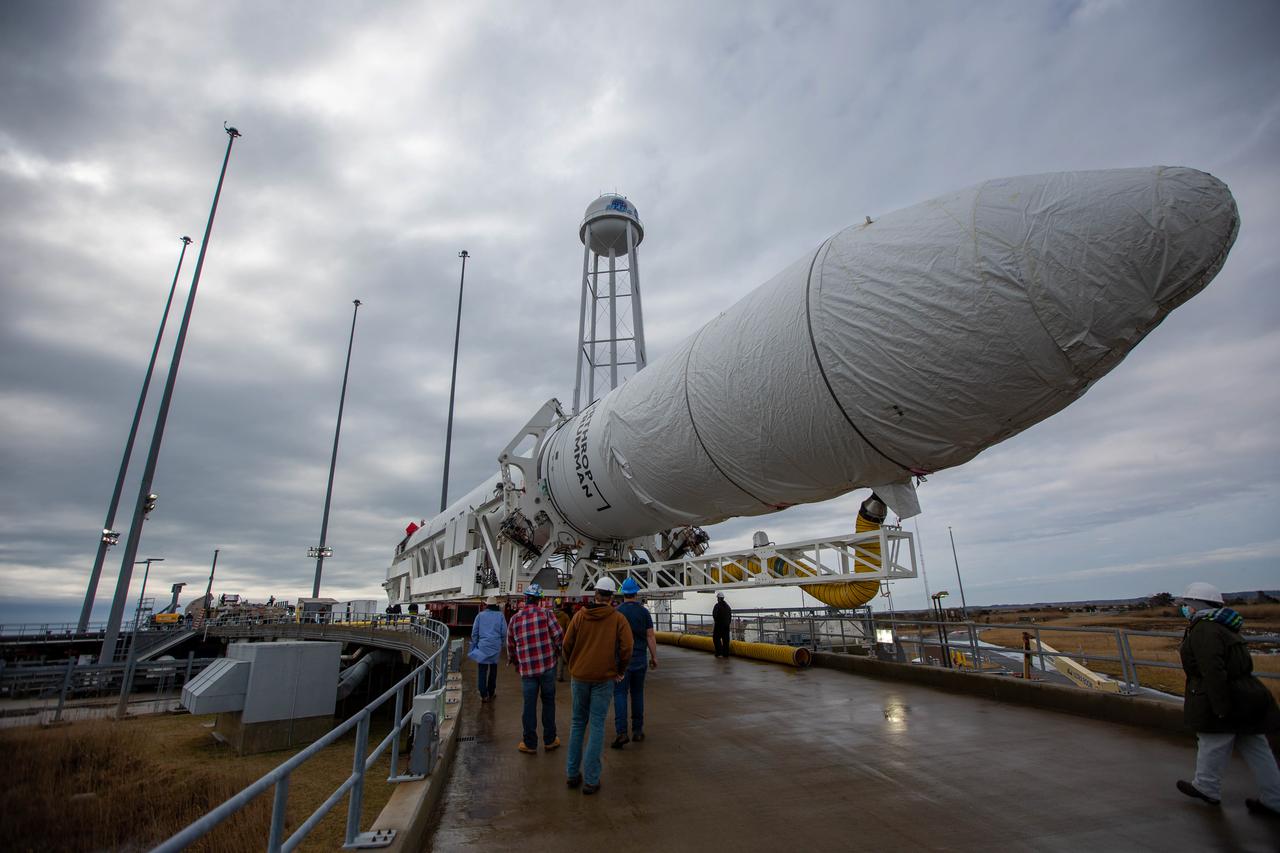

A Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft arrives at the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport’s Pad-0A, Tuesday, Feb. 16, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 15th contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA to the International Space Station will deliver about 8,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew. The CRS-15 Cygnus spacecraft is named after NASA mathematician, Katherine Johnson, a Black woman who time and again broke through barriers of gender and race. The launch is scheduled for 12:36 p.m. EST, Feb. 20, 2021. Photo Credit: (NASA/Patrick Black)
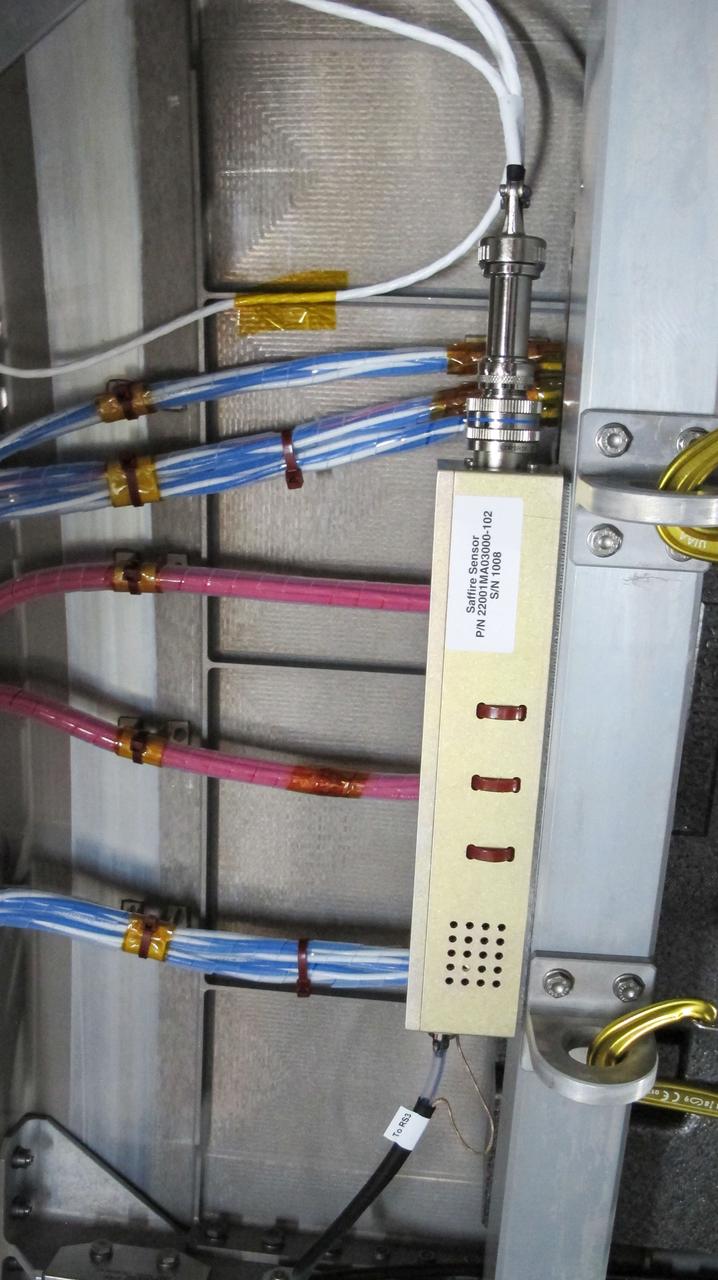
jsc2019e050038 (8/12/2019) --- Photo documentation taken during the NG-12 Crew Equipment Interface Test (CEIT) The view is of a SAFFIRE sensor. The NASA Advanced Exploration Systems program began a project to develop and demonstrate spacecraft fire safety technologies in relevant environments. The keystone of these demonstrations is a large-scale fire safety experiment conducted on an International Space Station (ISS) re-supply vehicle after it has undocked from the ISS and before it enters the atmosphere.
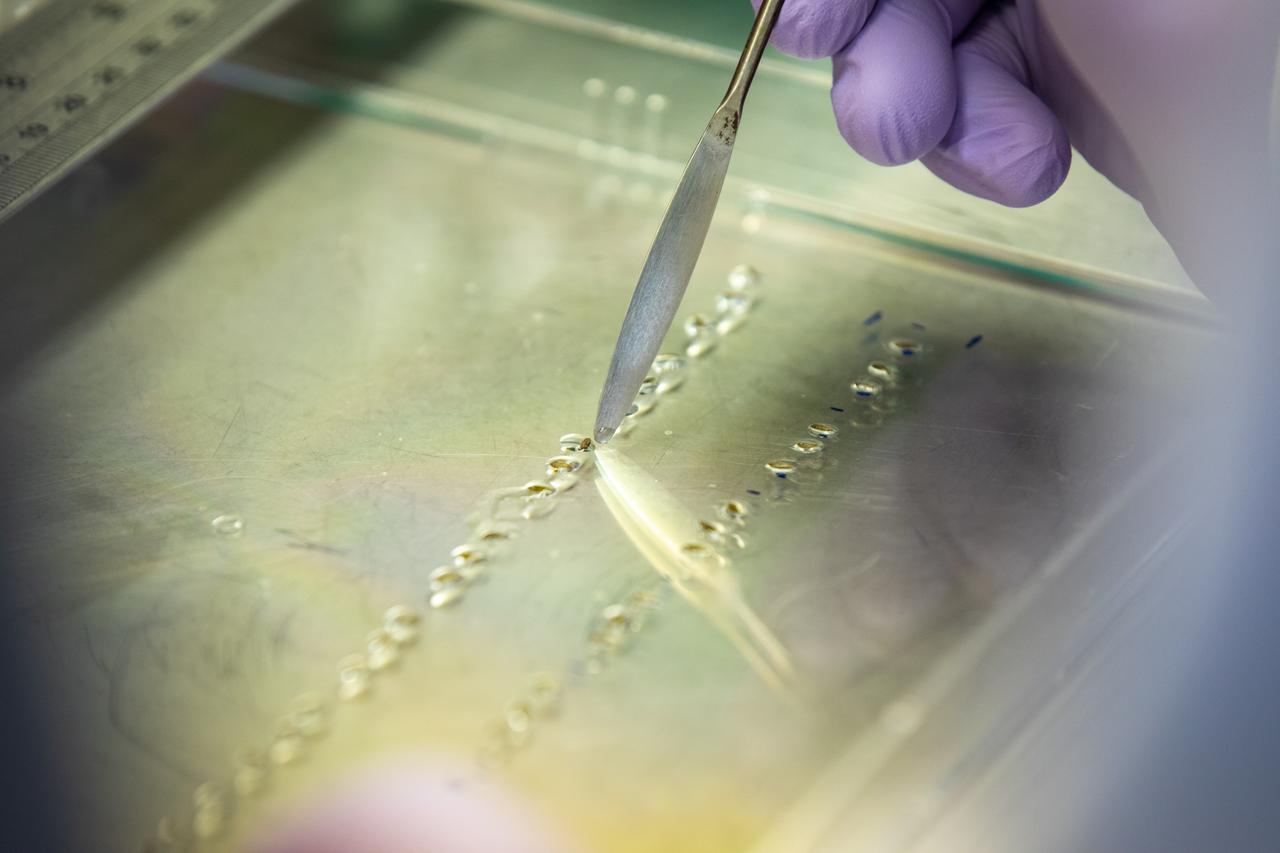
Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a researcher prepares red romaine lettuce seeds in seed film – a new seed handling material– on Jan. 15, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a research scientist glues red romaine lettuce seeds to a sheet of seed film – a new seed handling material – on Jan. 15, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.

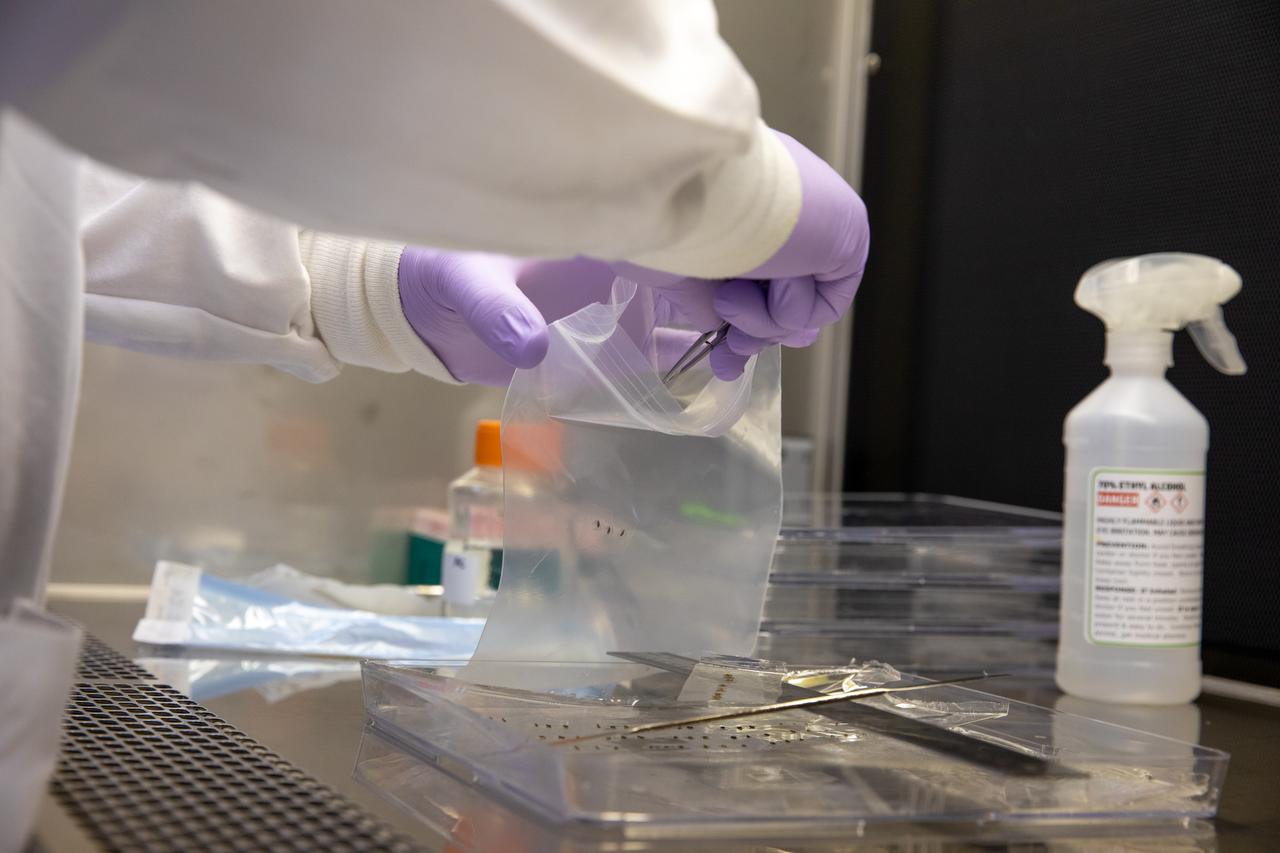
A research scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida cuts strips of seed film – a new seed handling material containing red romaine lettuce seeds – inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 16, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.

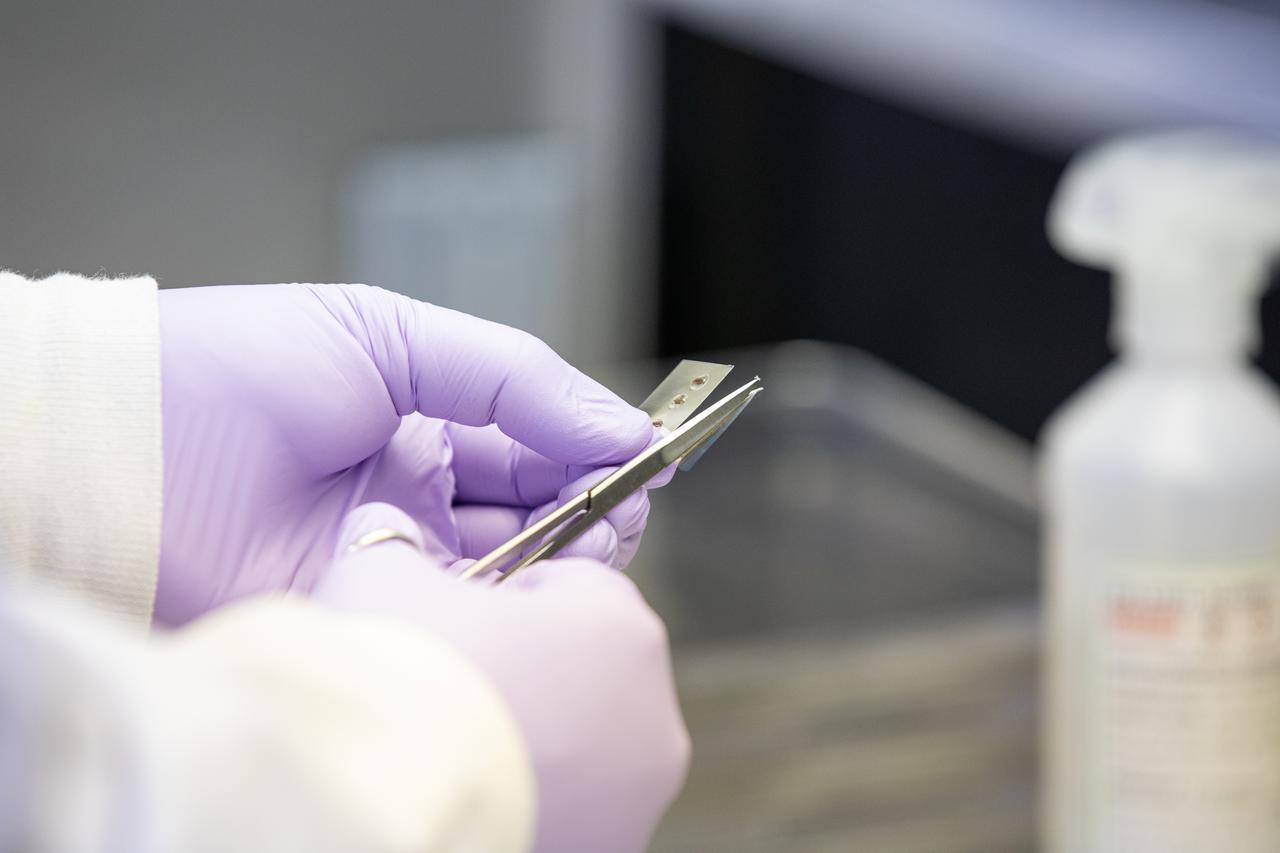
A research scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida cuts and stores strips of seed film – a new seed handling material containing red romaine lettuce seeds – inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 16, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.

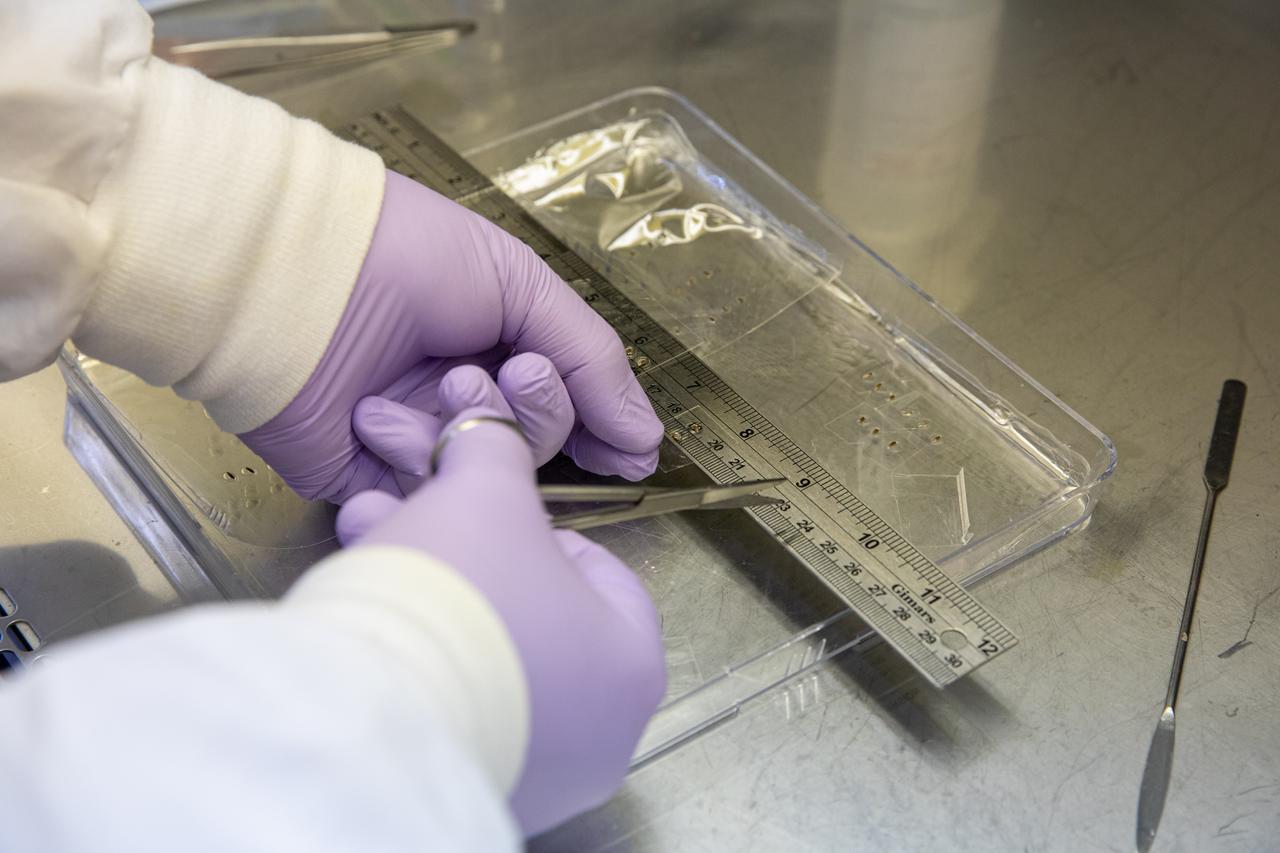
Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, red romaine lettuce seeds are affixed to seed film – a new seed handling material – on Jan. 15, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.

A research scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida cuts strips of seed film – a new seed handling material containing red romaine lettuce seeds – inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 16, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
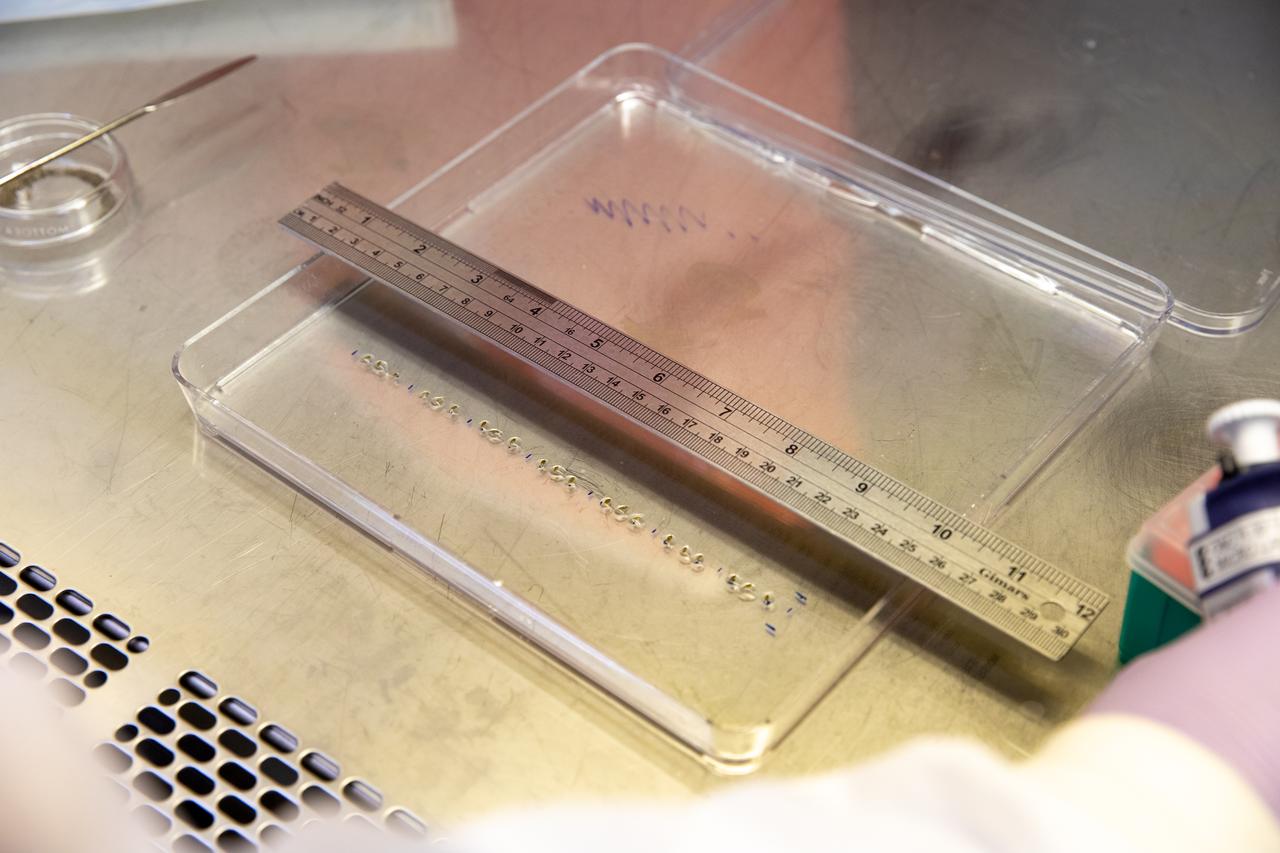

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, red romaine lettuce seeds are measured before being placed in seed film – a new seed handling material – on Jan. 15, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
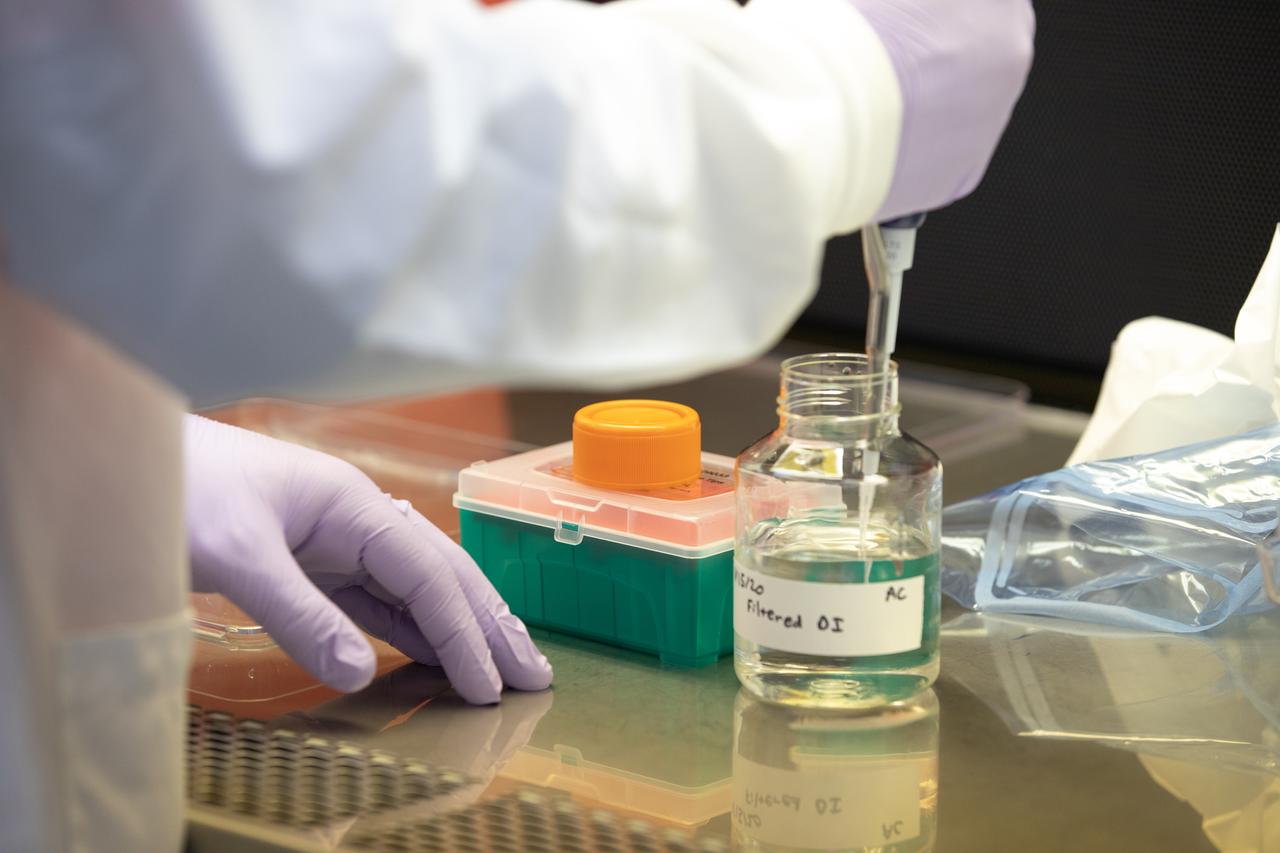

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a research scientist is preparing to glue red romaine lettuce seeds to a sheet of seed film – a new seed handling material – on Jan. 15, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
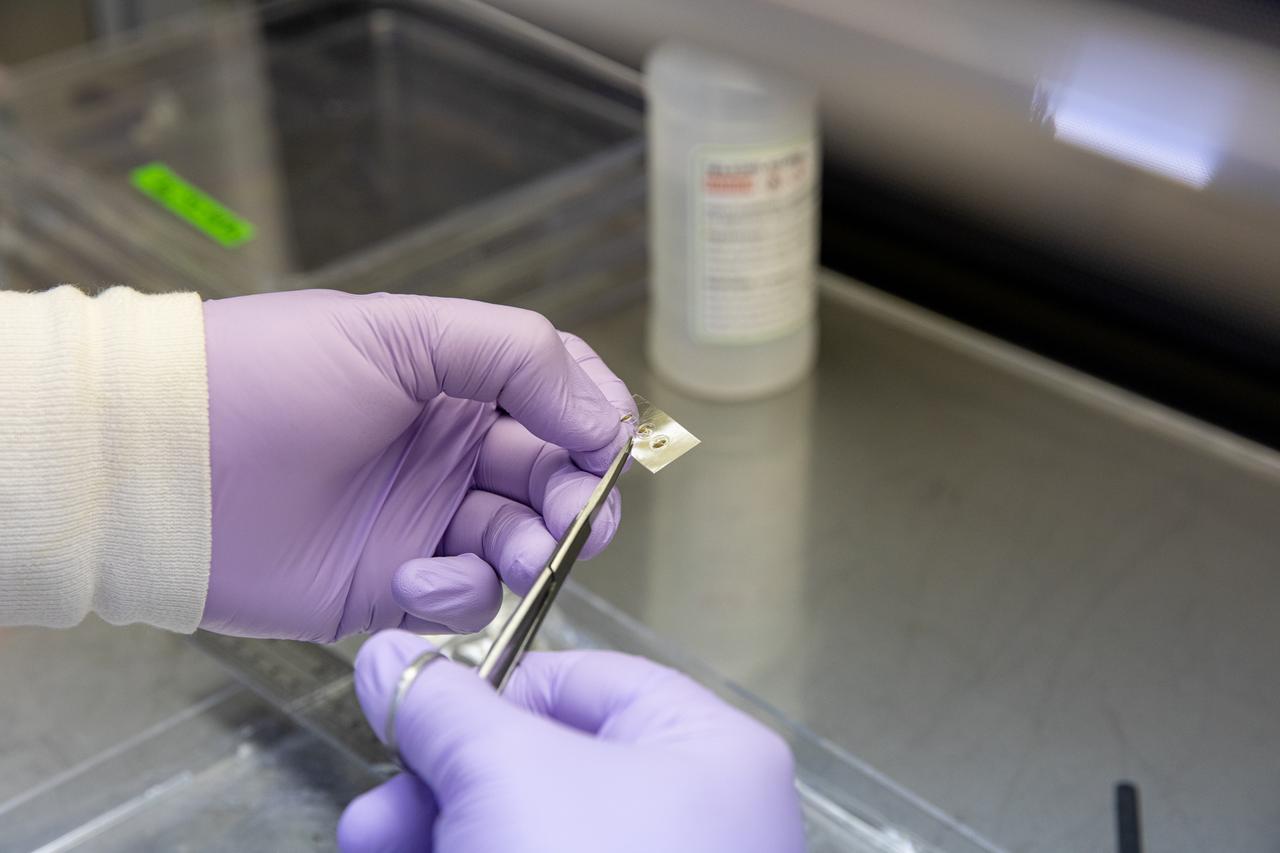
A research scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida cuts strips of seed film – a new seed handling material containing red romaine lettuce seeds – inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 16, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
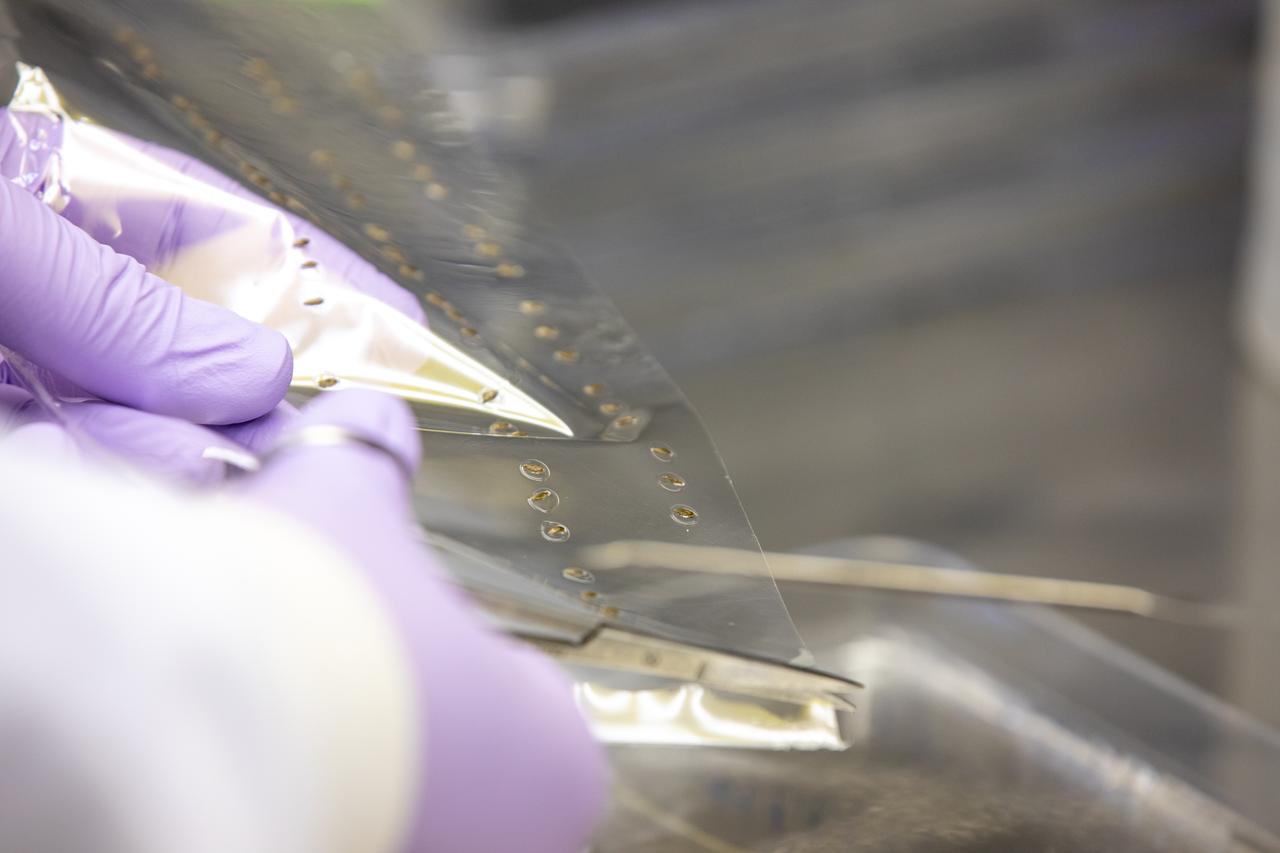
A research scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida cuts strips of seed film – a new seed handling material containing red romaine lettuce seeds – inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 16, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
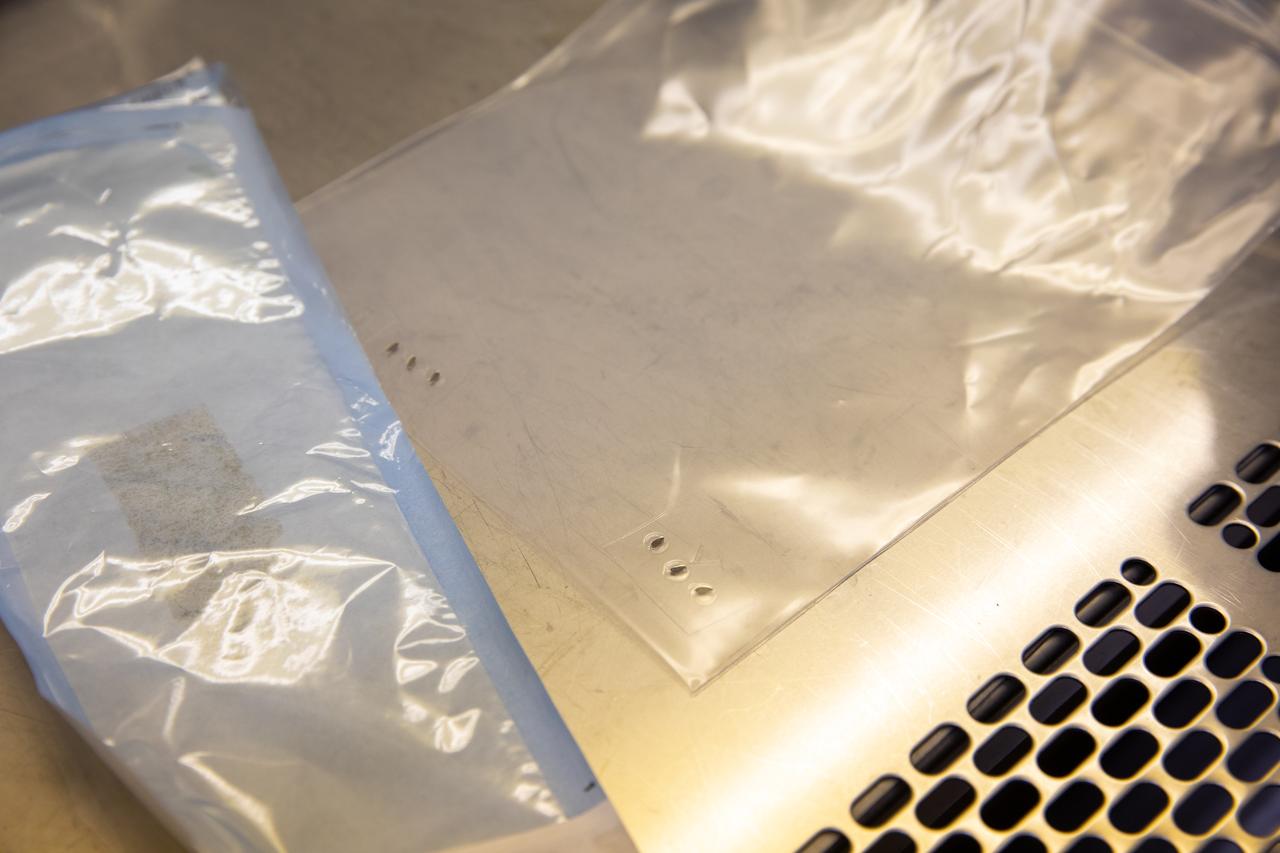

Strips of seed film – a new seed handling material containing red romaine lettuce seeds – are photographed inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 16, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
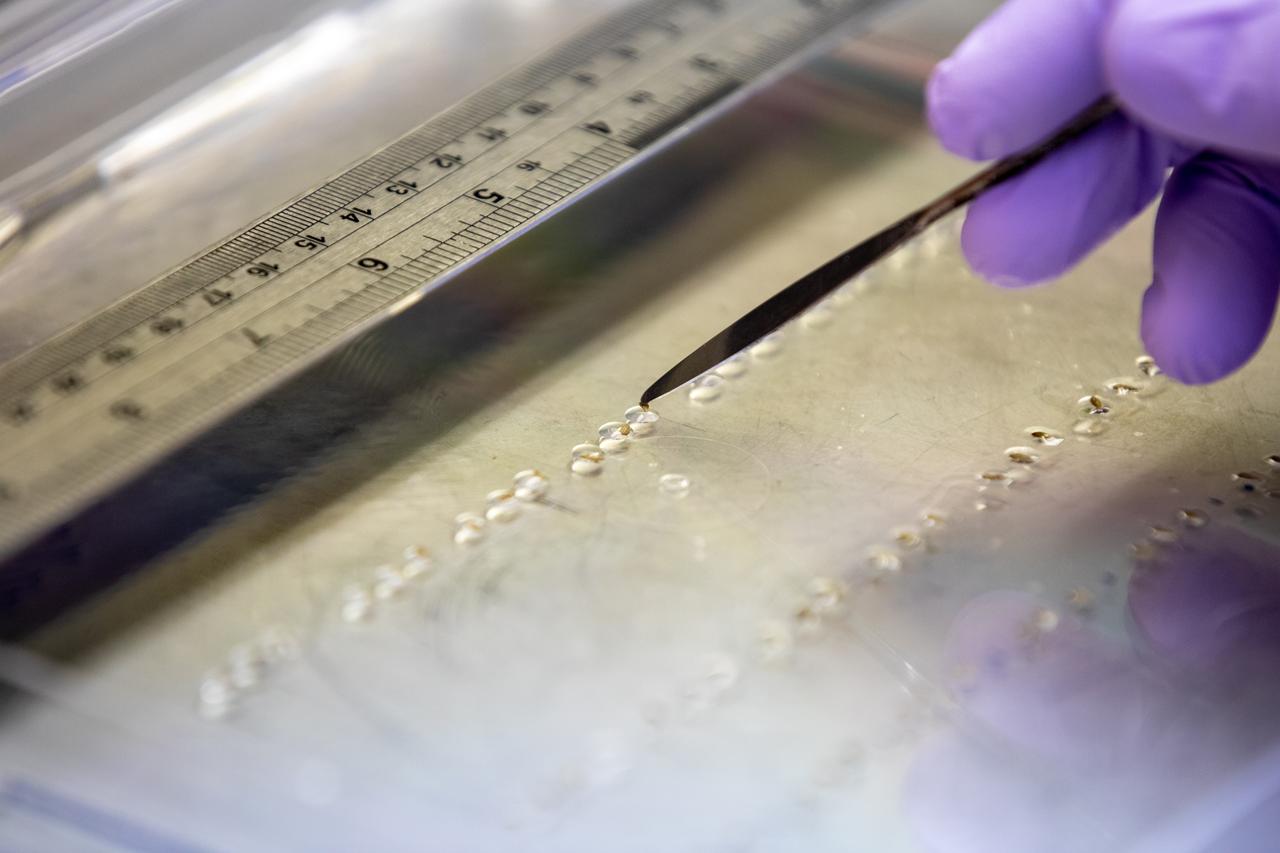
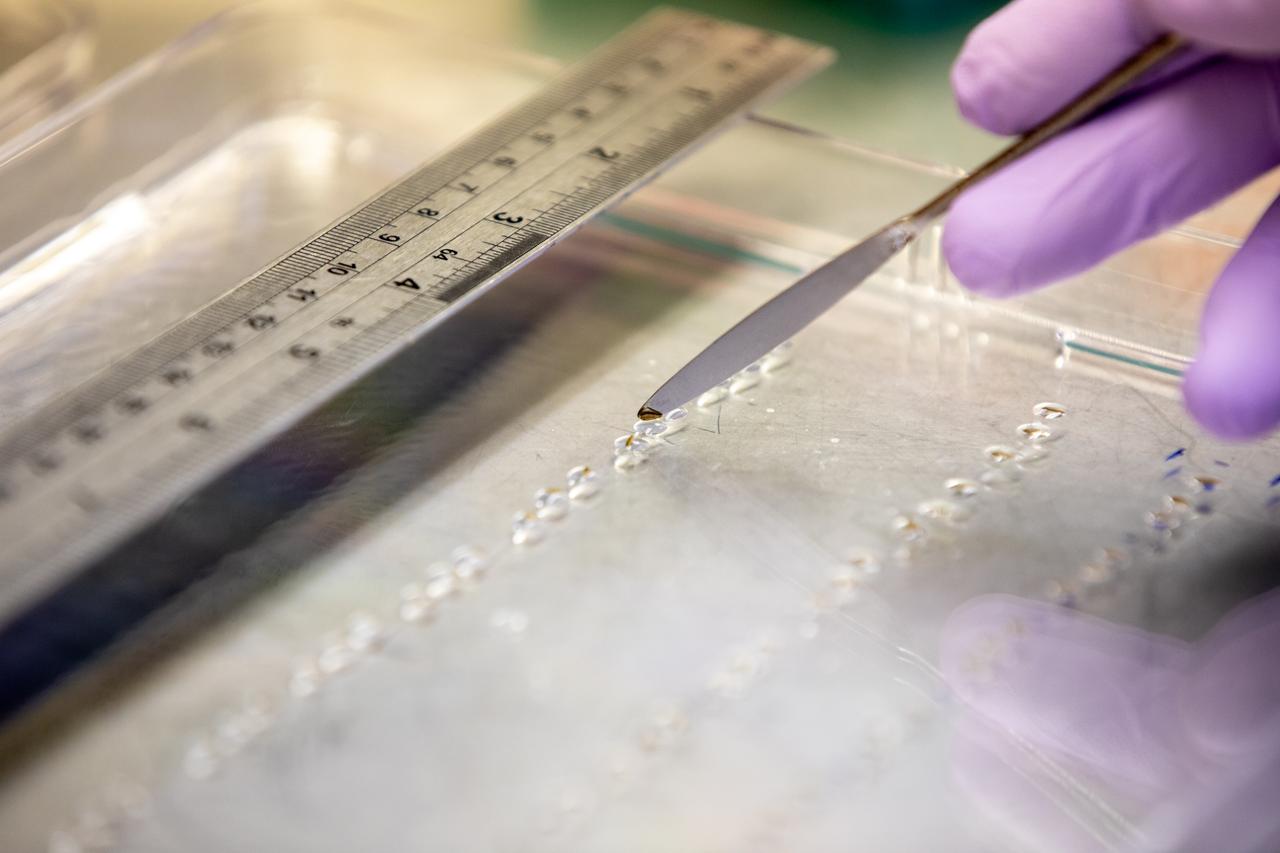
Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, red romaine lettuce seeds are affixed to seed film – a new seed handling material – on Jan. 15, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
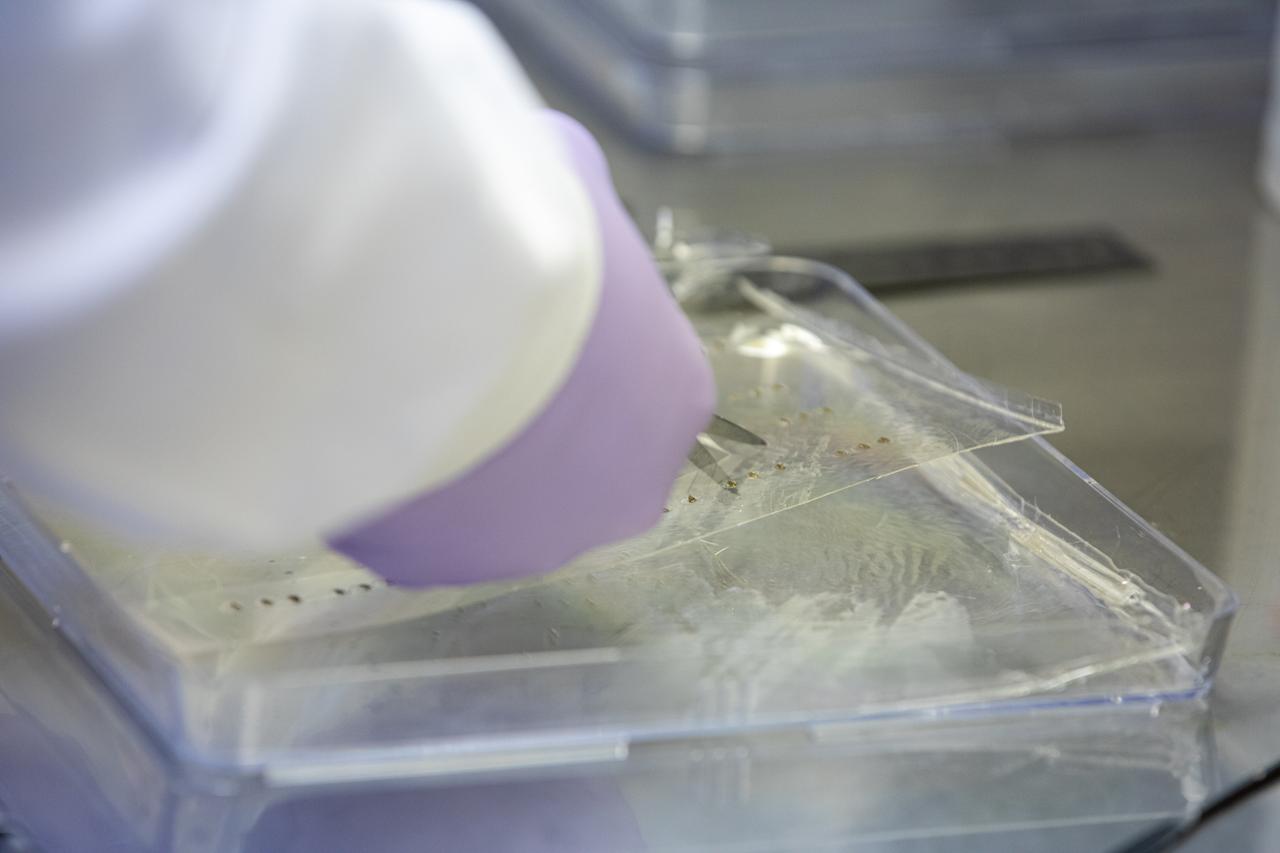
A research scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida cuts strips of seed film – a new seed handling material containing red romaine lettuce seeds – inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 16, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
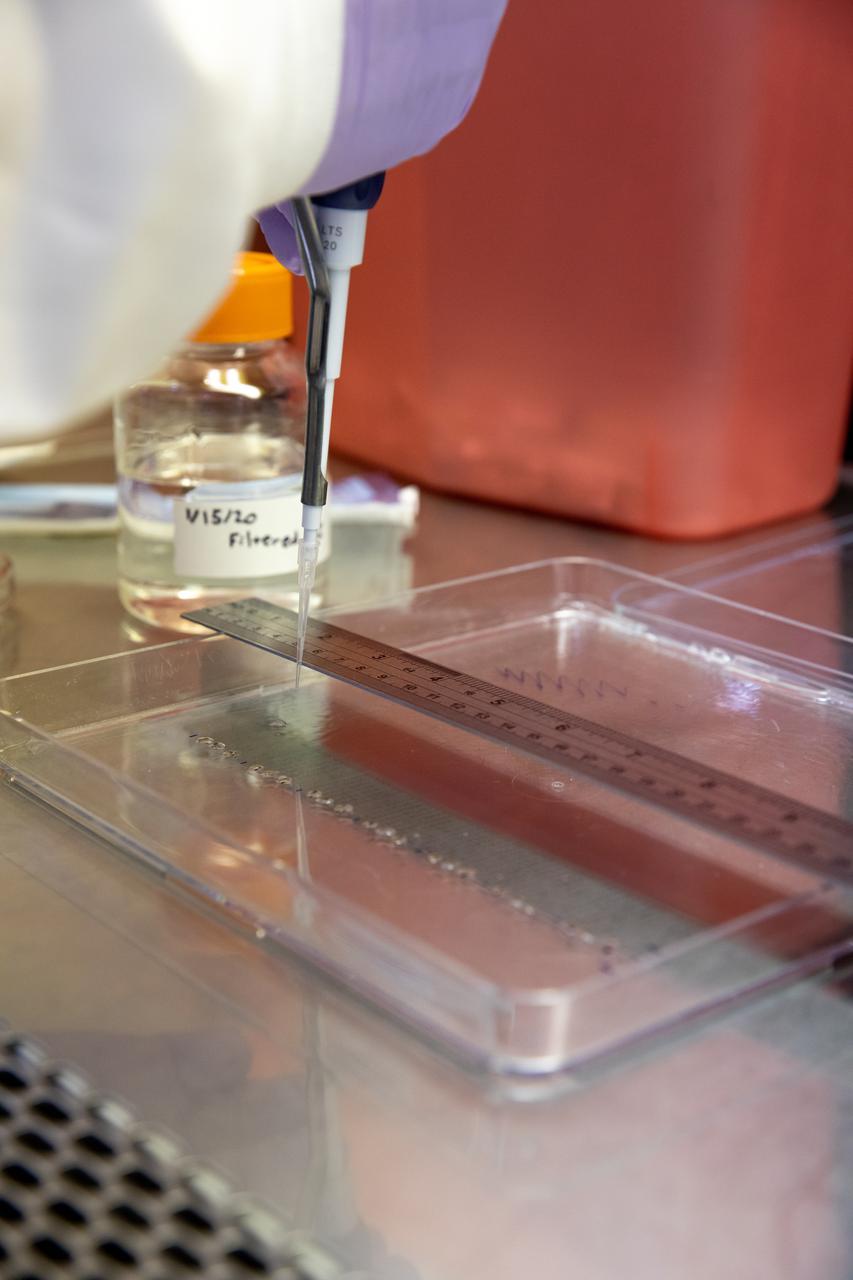

Aaron Curry, a research scientist with the Laboratory Support Services and Operations (LASSO) contract at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida affixes red romaine lettuce seeds to a sheet of seed film – a new seed handling material – inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 15, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
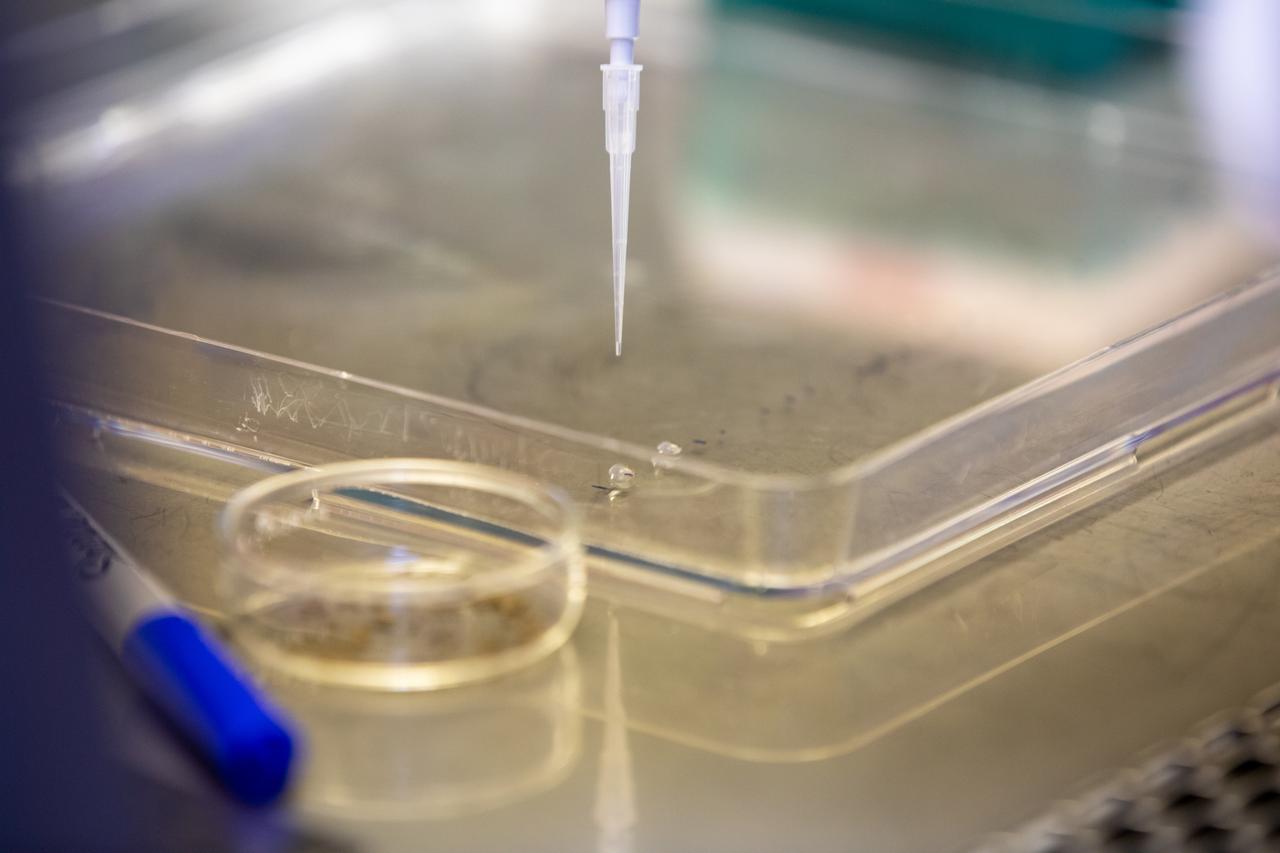
Aaron Curry, a research scientist with the Laboratory Support Services and Operations (LASSO) contract at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida affixes red romaine lettuce seeds to a sheet of seed film – a new seed handling material – inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 15, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
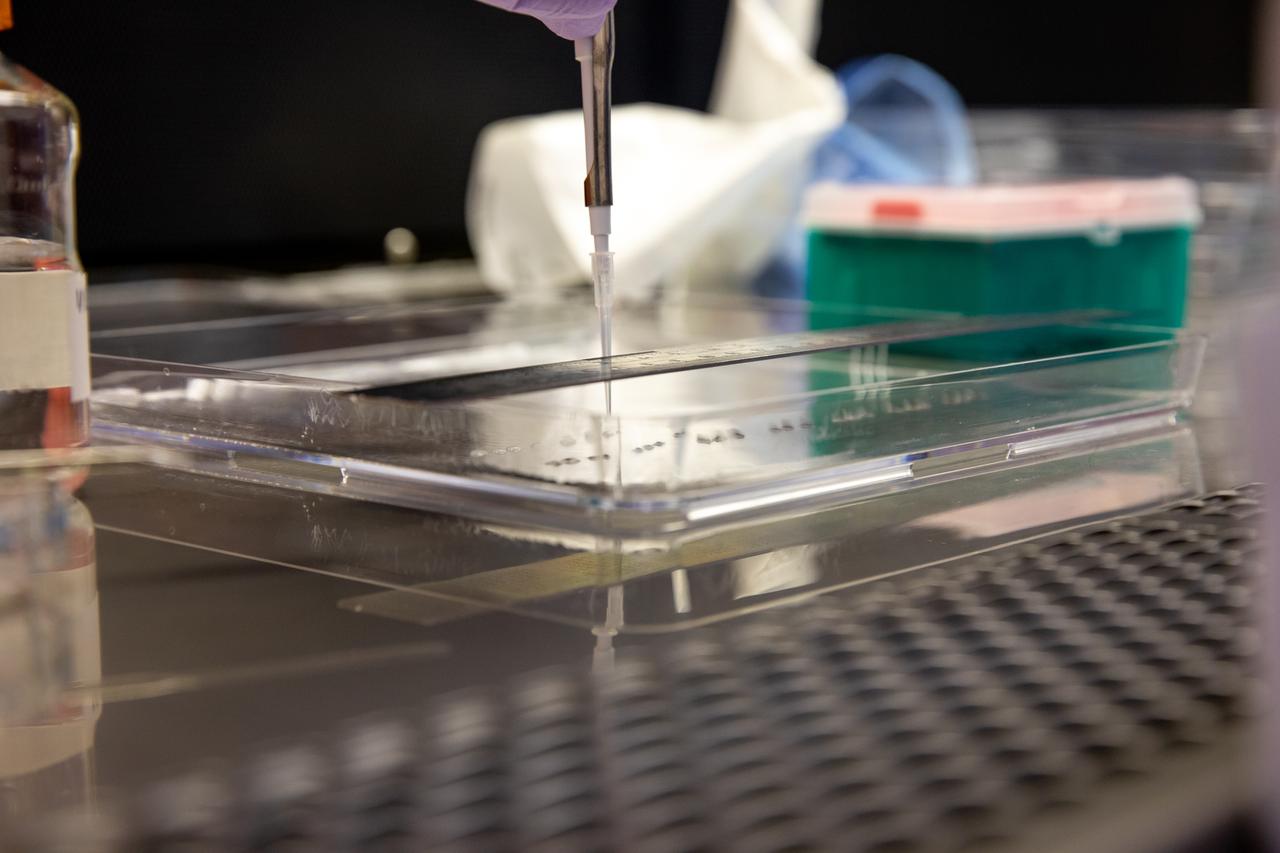
Aaron Curry, a research scientist with the Laboratory Support Services and Operations (LASSO) contract at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida affixes red romaine lettuce seeds to a sheet of seed film – a new seed handling material – inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 15, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
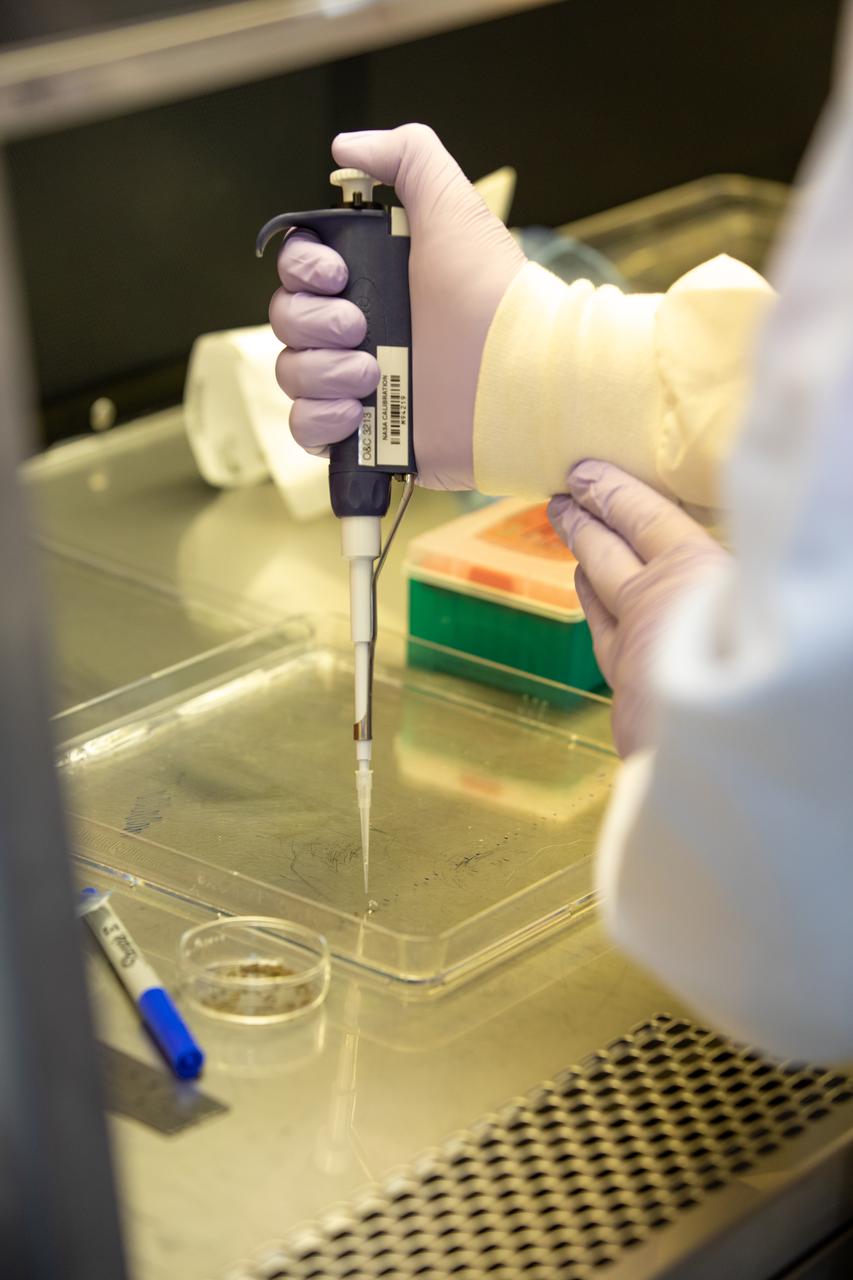

Aaron Curry, a research scientist with the Laboratory Support Services and Operations (LASSO) contract at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida affixes red romaine lettuce seeds to a sheet of seed film – a new seed handling material – inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 15, 2020. The seed film is being prepared for the VEG-03 J experiment that will fly to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. This seed film experiment involves crew aboard the orbiting laboratory planting the seeds into plant pillows – a common method used to grow plants in space – themselves for the first time ever. The water-soluble, dissolving film addresses the challenge of handling seeds in a microgravity environment and also can be used to deliver fertilizers and other beneficial substances that help plants grow. NG-13 is scheduled to launch from the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
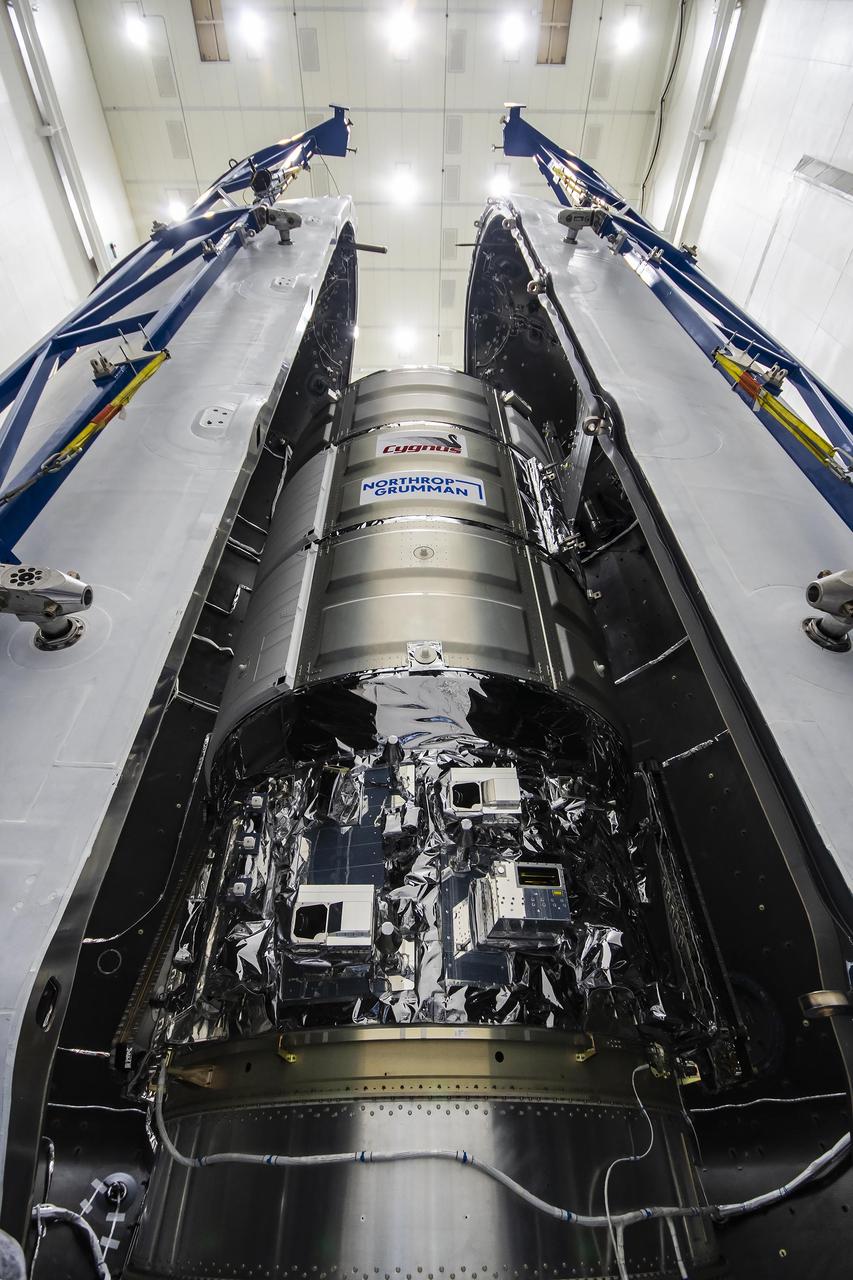

On Wednesday, Jan. 24, 2024, the Northrop Grumman Cygnus resupply spacecraft is seen being encapsulated inside the SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing as it prepares to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida for the 20th Northrop Grumman commercial resupply services for NASA. The mission will carry 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment to the International Space Station to support the agency’s Expedition 70 crew. Liftoff is scheduled no earlier than 12:07 p.m. EST Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024.

On Tuesday, July 30, 2024, the Northrop Grumman Cygnus resupply spacecraft is seen being encapsulated inside the SpaceX Falcon 9 payload fairing as it prepares to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida for the 21st Northrop Grumman commercial resupply services for NASA. The mission will carry 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment to the International Space Station. Liftoff is scheduled for no earlier than 11:29 a.m. EDT Saturday, Aug. 3.
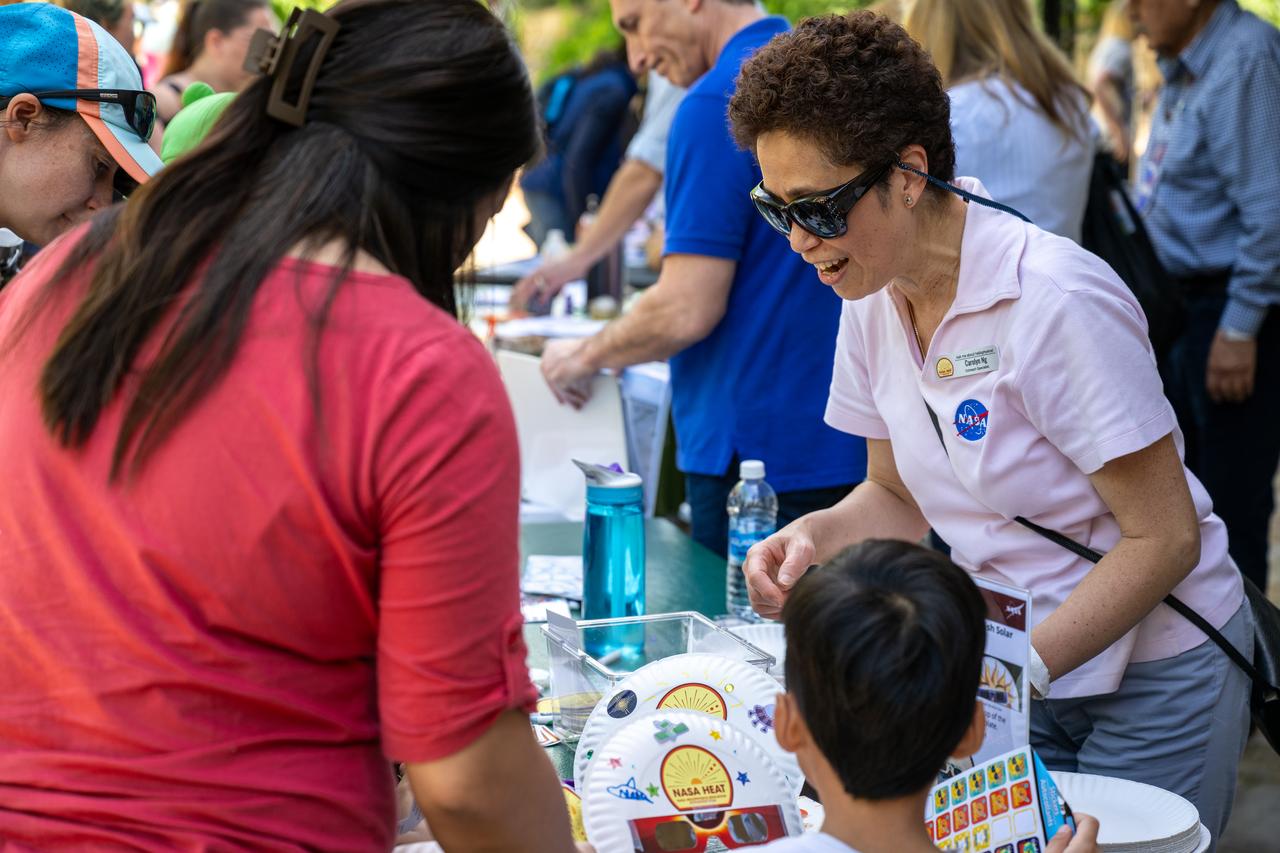

NASA Principal Scientist Carolyn Ng speaks to guests about the upcoming total solar eclipse at the Dallas Arboretum, Sunday, April 7, 2024, in Dallas, Texas. On Monday, April 8, a total solar eclipse will sweep across a narrow portion of the North American continent from Mexico’s Pacific coast to the Atlantic coast of Newfoundland, Canada, while a partial solar eclipse will be visible across the entire North American continent along with parts of Central America and Europe. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
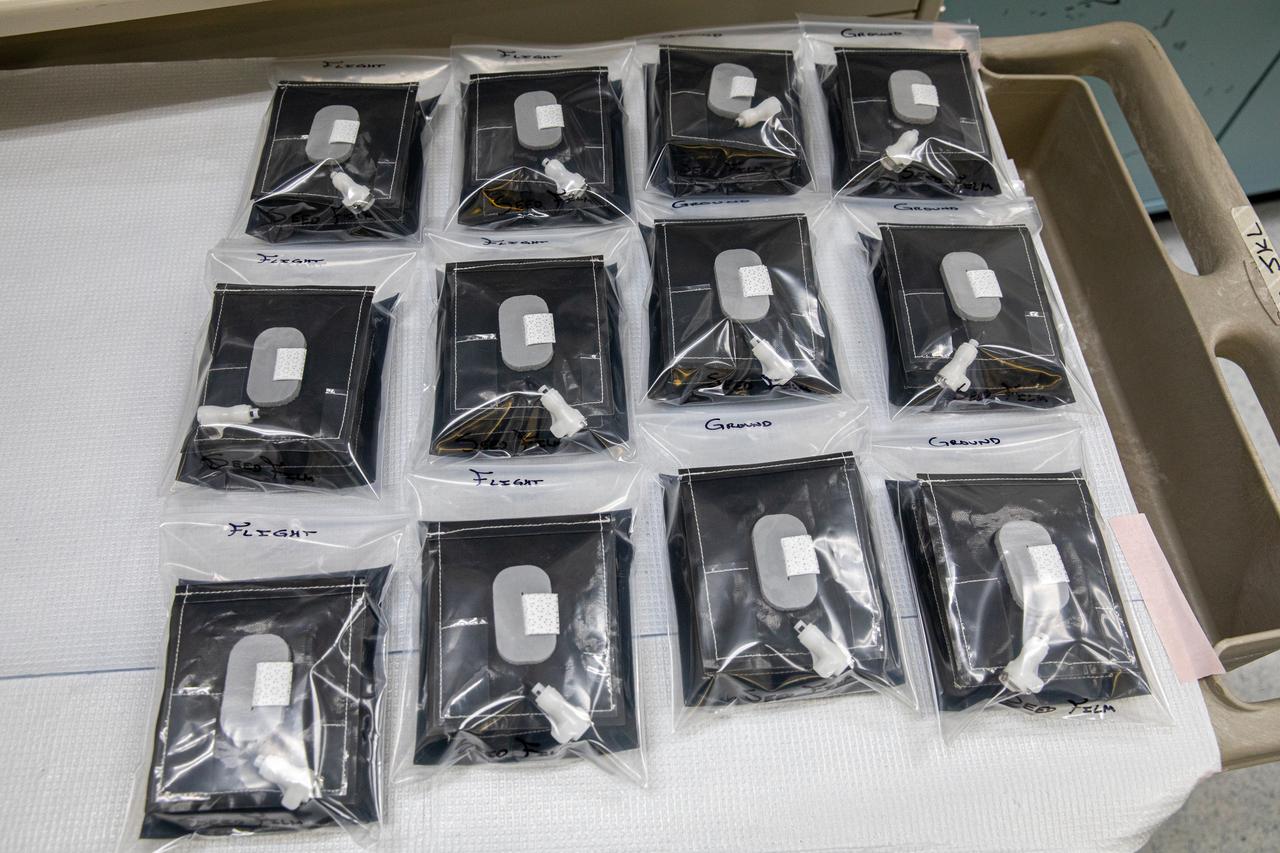

On Jan. 21, 2020, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, plant pillows are packaged for their upcoming flight to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
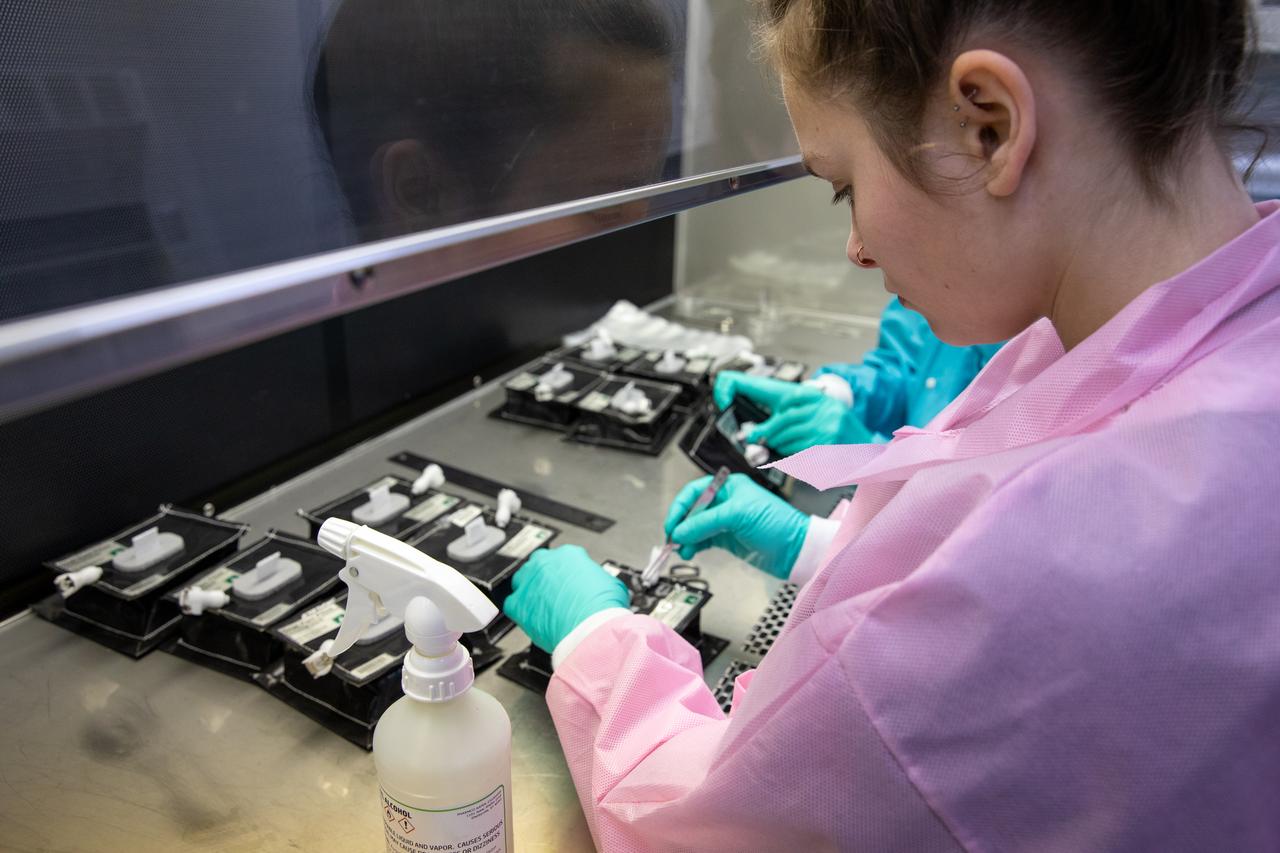

On Jan. 21, 2020, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, intern Emily Kennebeck prepares plant pillows for their flight to the International Space Station. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
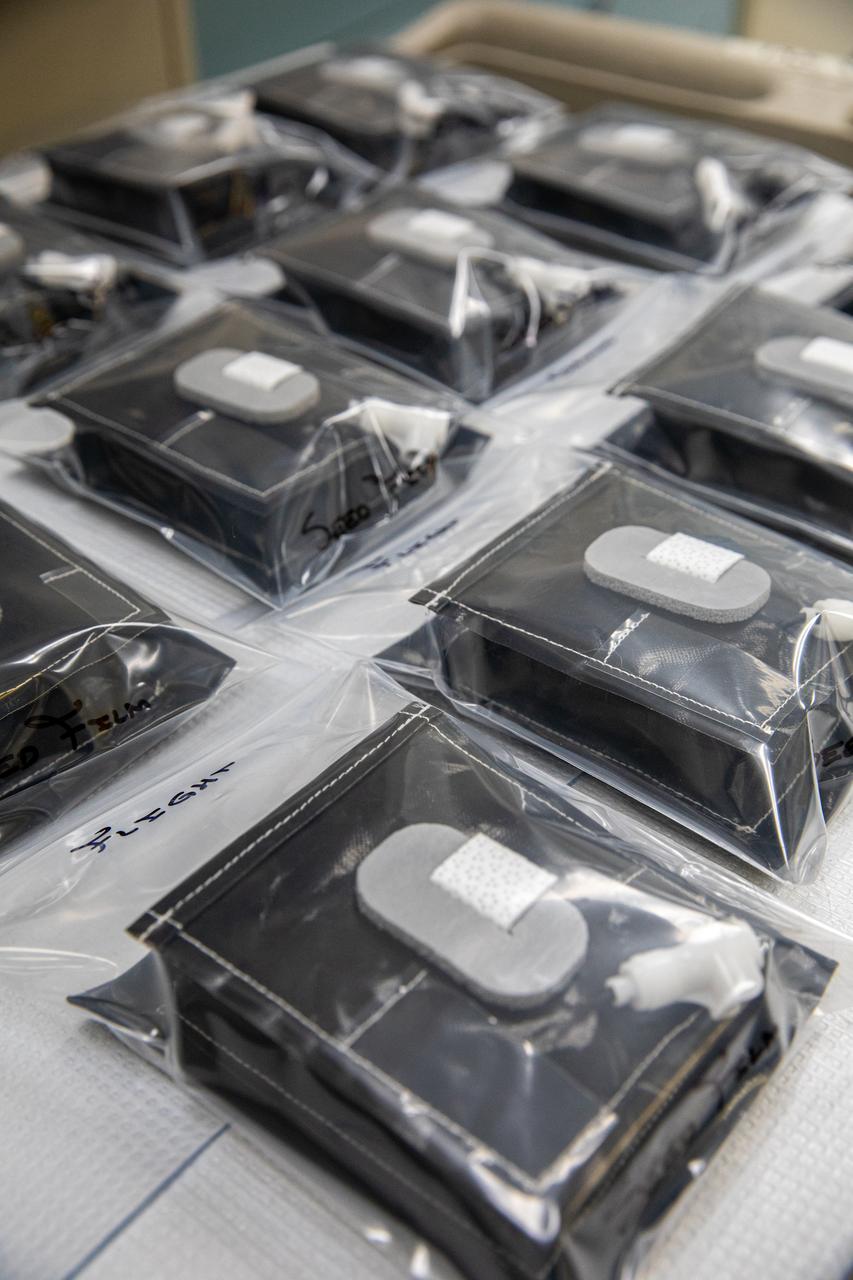

On Jan. 21, 2020, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, plant pillows are packaged for their upcoming flight to the International Space Station on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
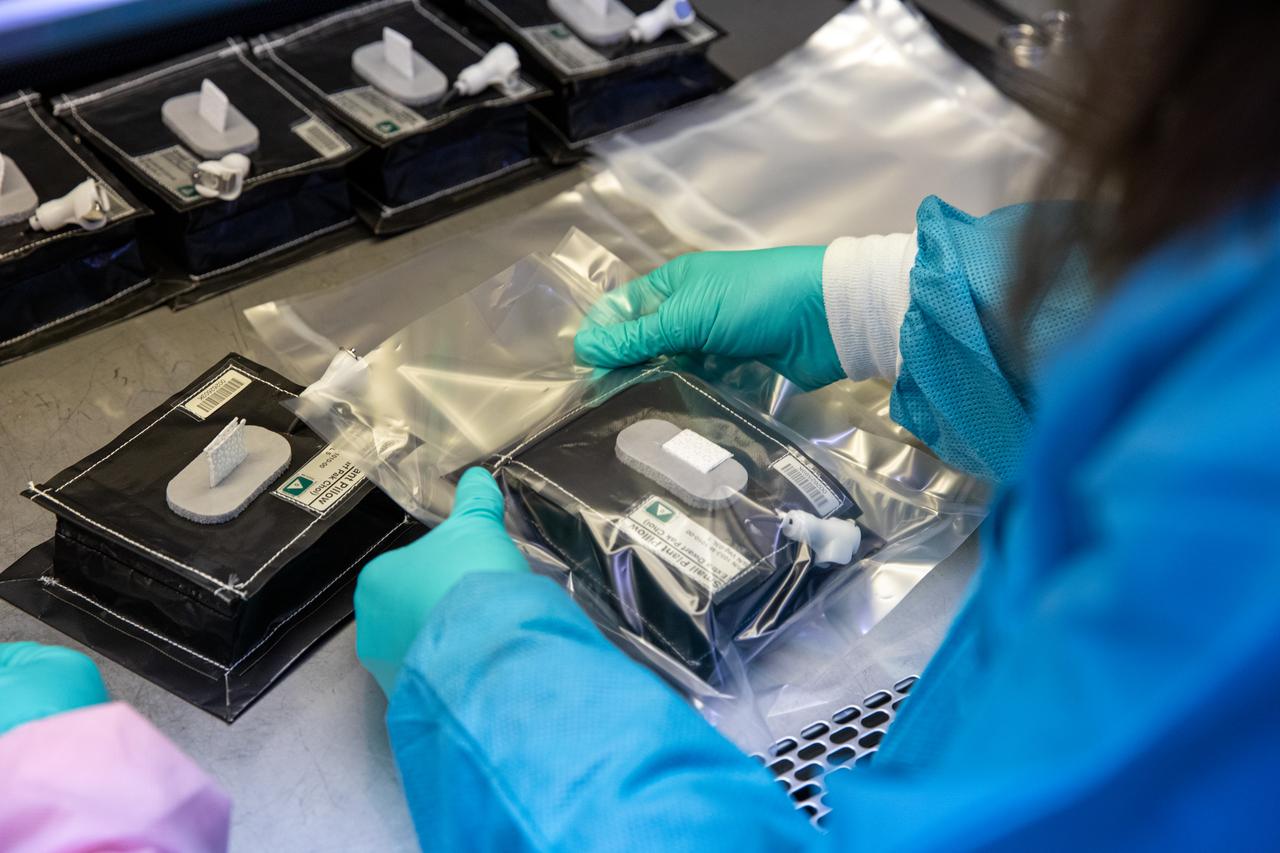

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 21, 2020, Jess Bunchek, a pseudonaut and associate scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares plant pillows for their flight to the International Space Station. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
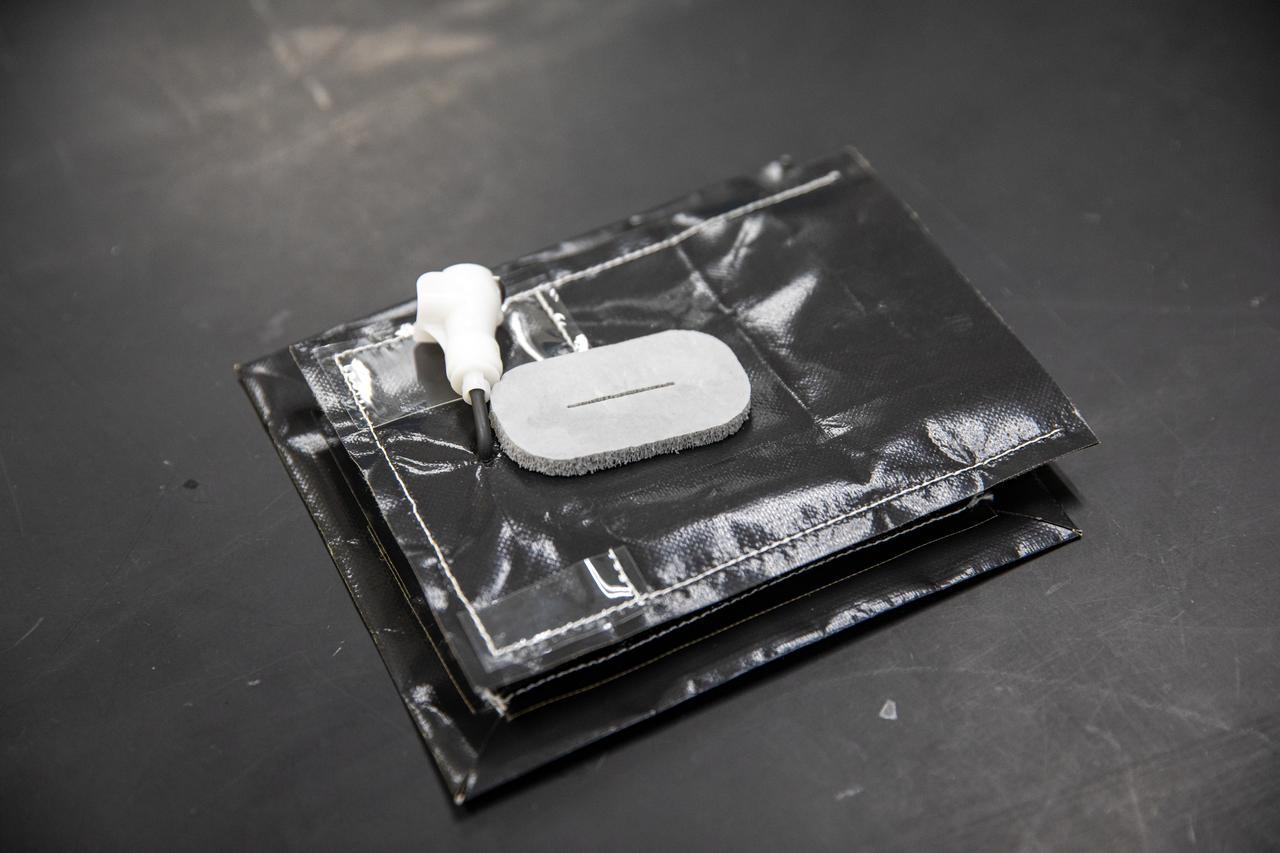

A plant pillow is photographed inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 21, 2020, prior to being packaged for flight to the International Space Station. A number of plant pillows are being prepped to fly to the orbiting laboratory on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are ready for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
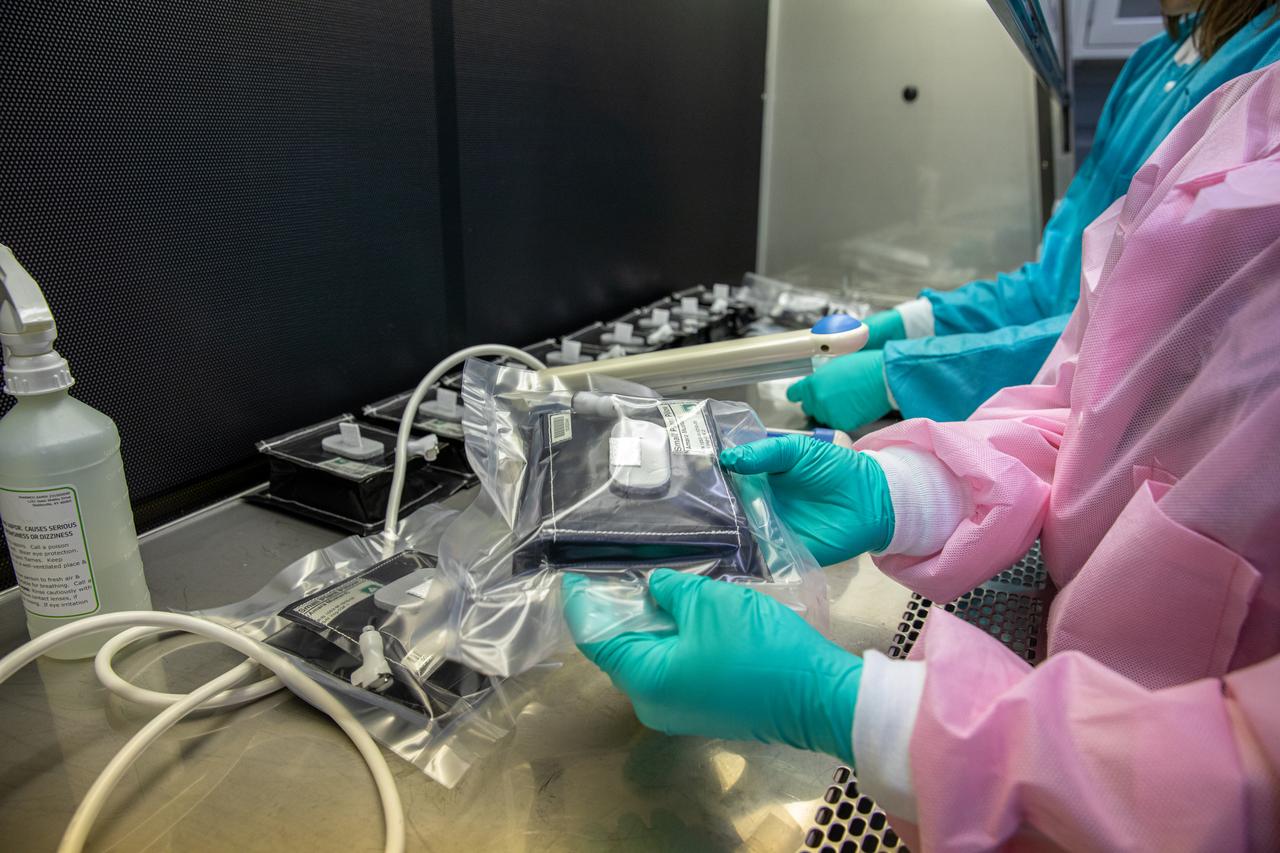

On Jan. 21, 2020, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, intern Emily Kennebeck prepares plant pillows for their upcoming flight to the International Space Station. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
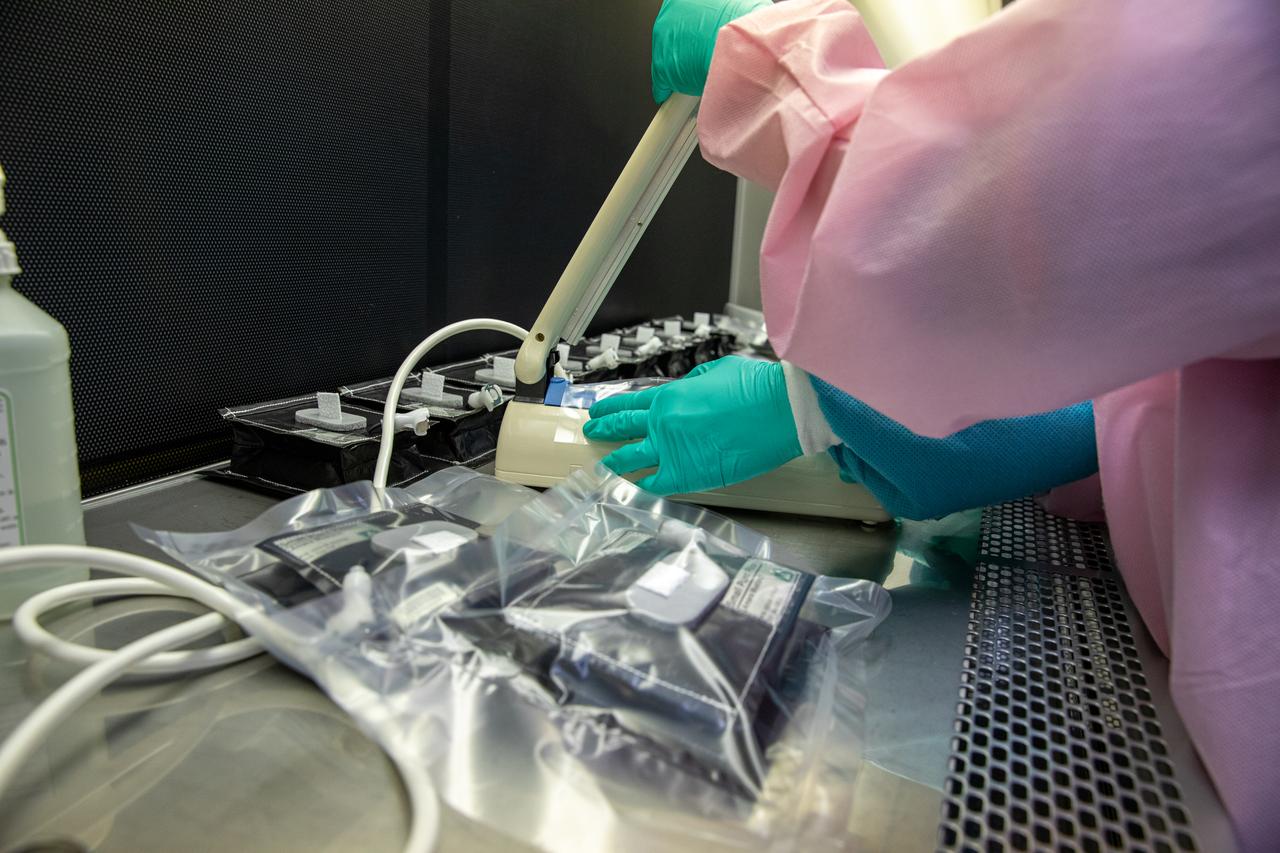

On Jan. 21, 2020, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, intern Emily Kennebeck prepares plant pillows for their upcoming flight to the International Space Station. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
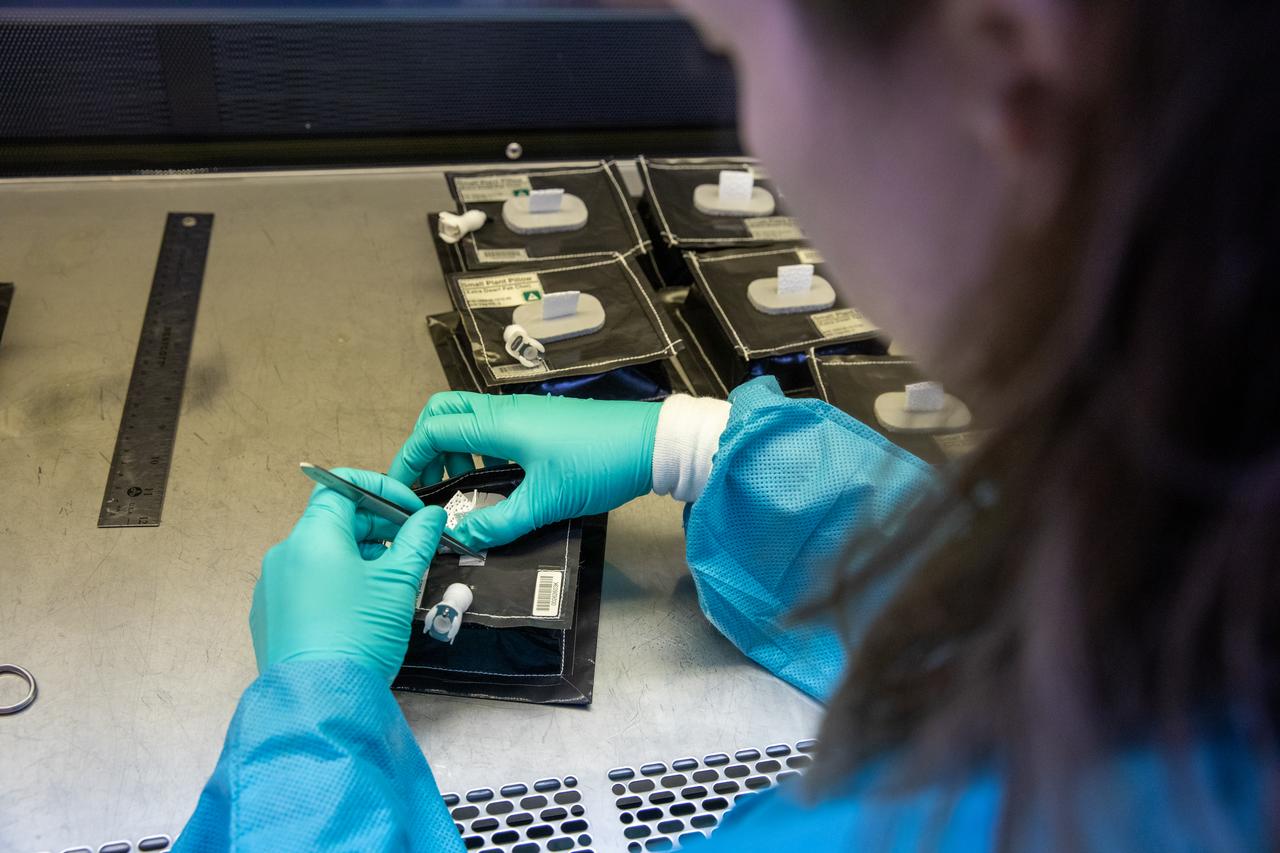

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 21, 2020, Jess Bunchek, a pseudonaut and associate scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares plant pillows for their flight to the International Space Station. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
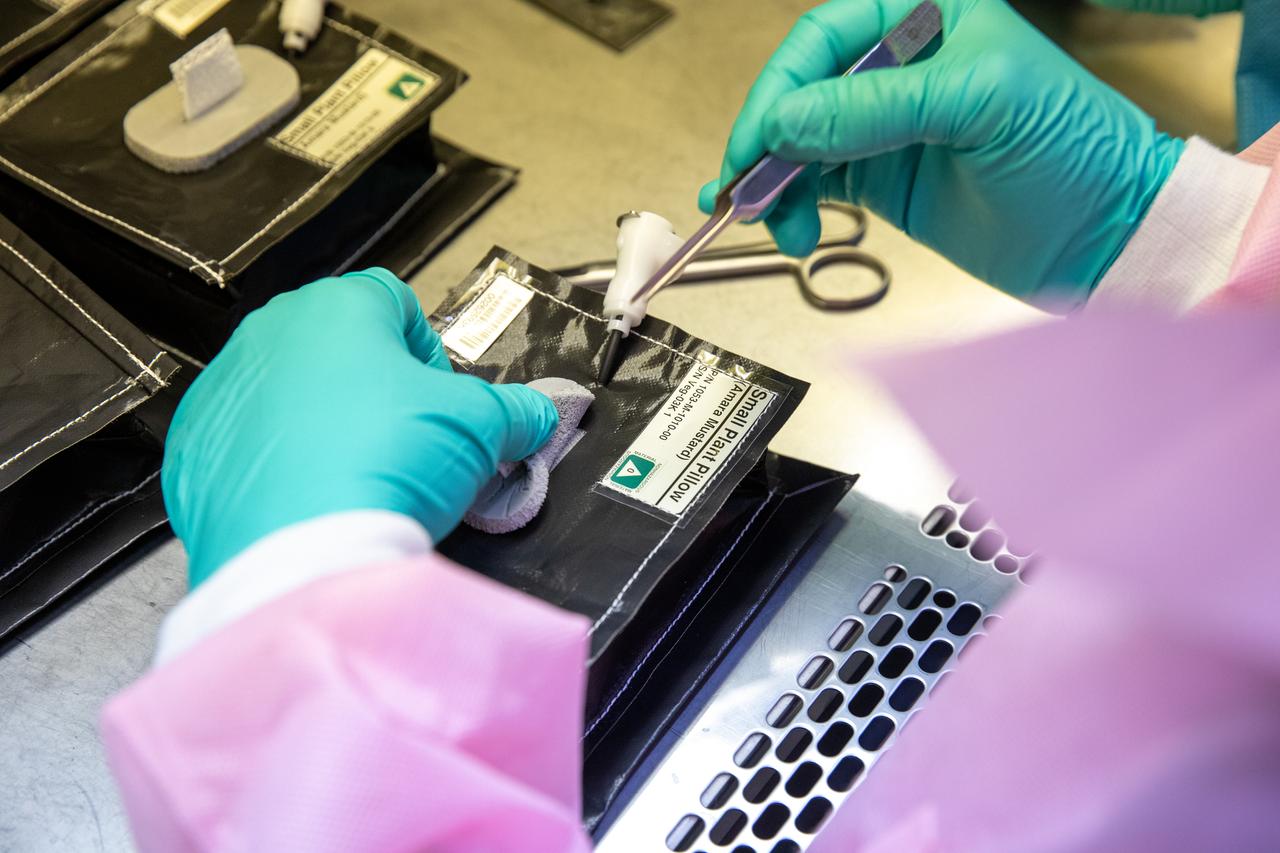

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 21, 2020, Emily Kennebeck, an intern at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares plant pillows for their flight to the International Space Station. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
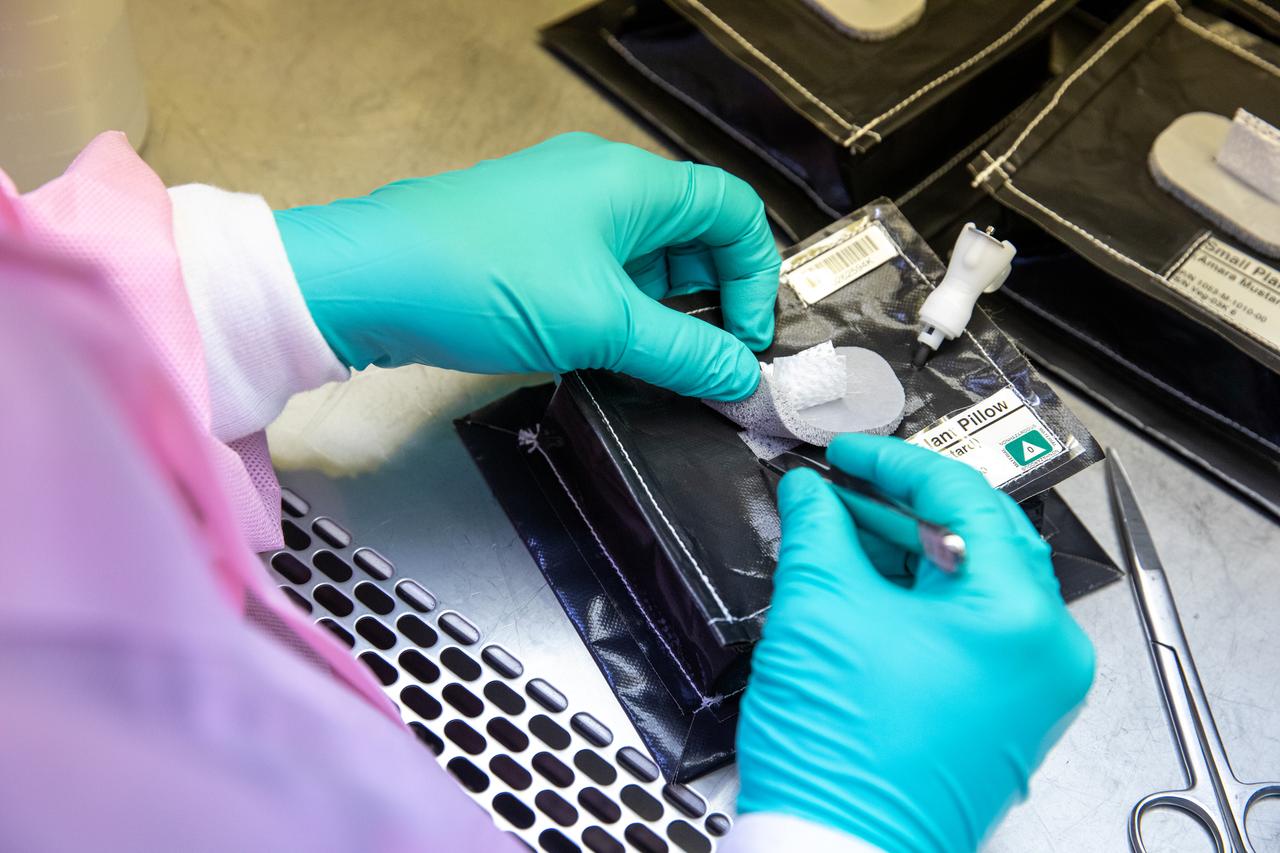

On Jan. 21, 2020, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, intern Emily Kennebeck prepares plant pillows for their flight to the International Space Station. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
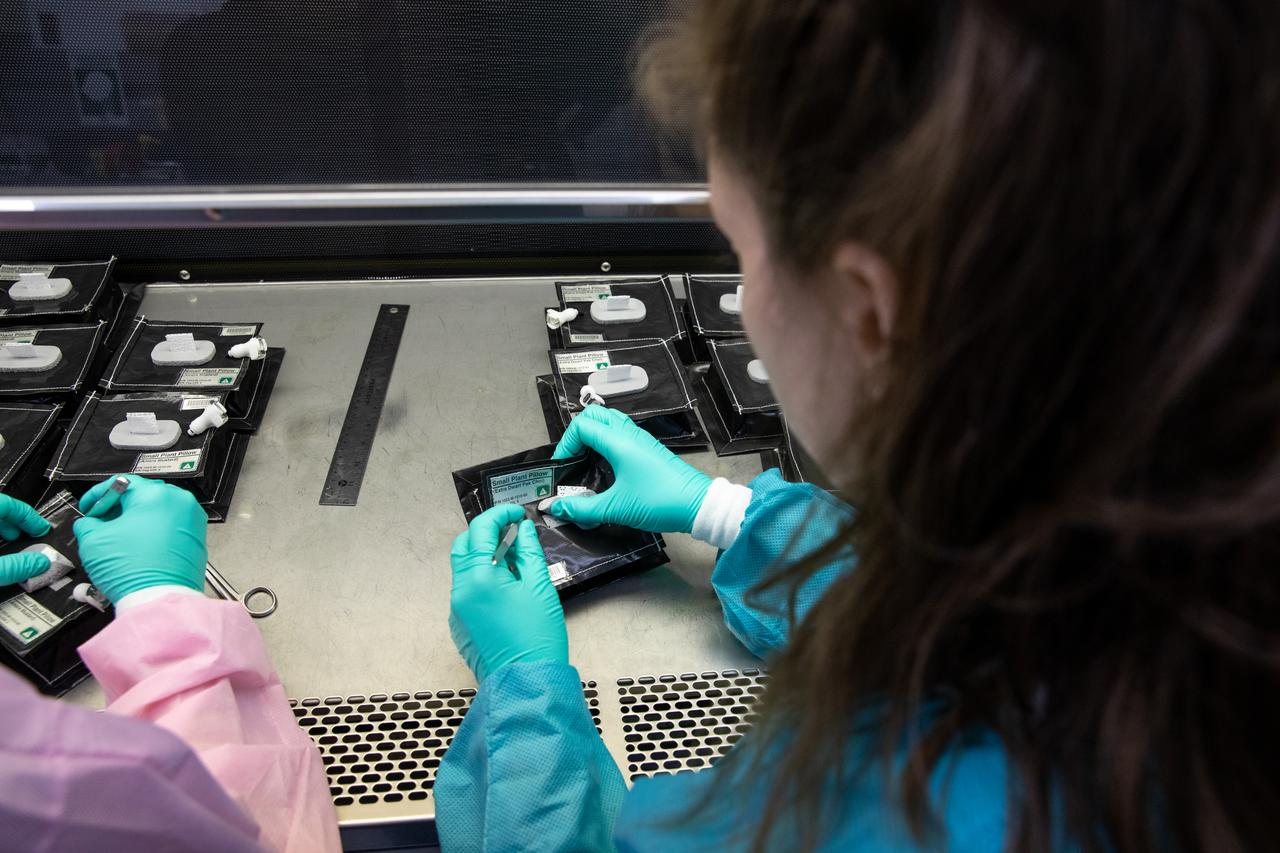

Inside the Space Station Processing Facility on Jan. 21, 2020, Jess Bunchek, a pseudonaut and associate scientist at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, prepares plant pillows for their flight to the International Space Station. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
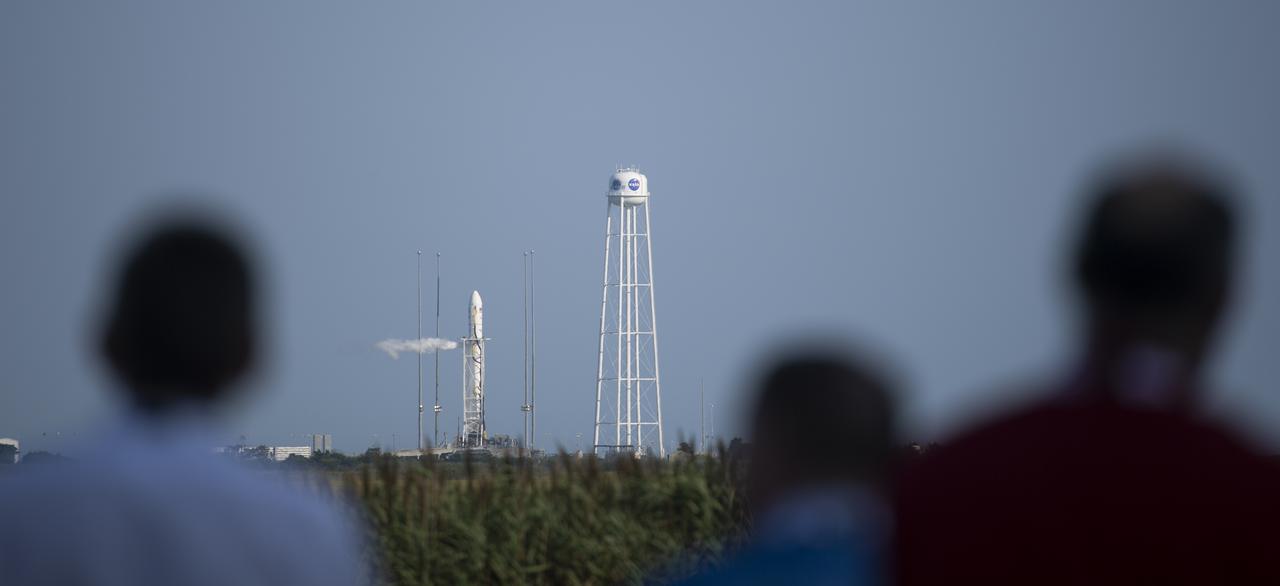

A Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft is seen on Pad-0A of the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport prior to launch, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 16th contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA launched at 6:01 p.m. EDT and will deliver nearly 8,200 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the International Space Station and its crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky}
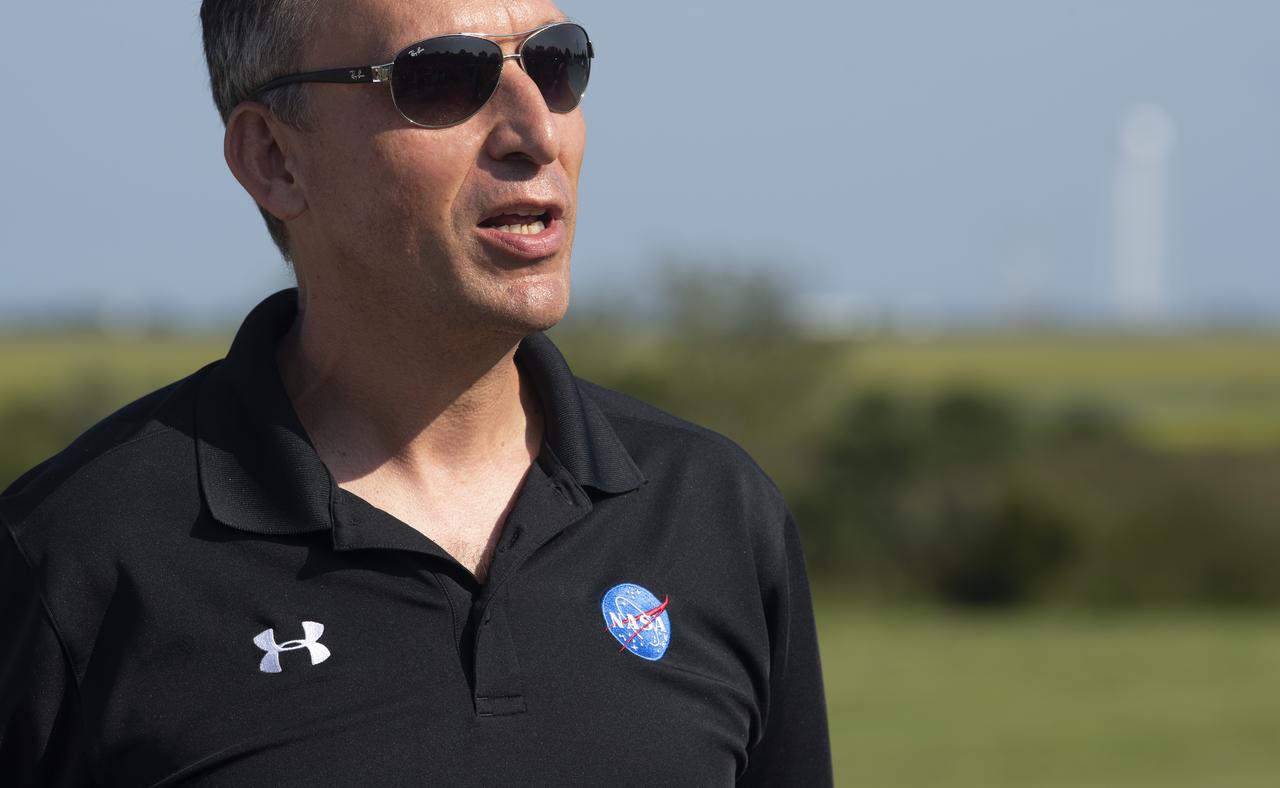

Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, speaks to members of the media prior to the launch of a Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 16th contracted cargo resupply mission for NASA launched at 6:01 p.m. EDT and will deliver nearly 8,200 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the International Space Station and its crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
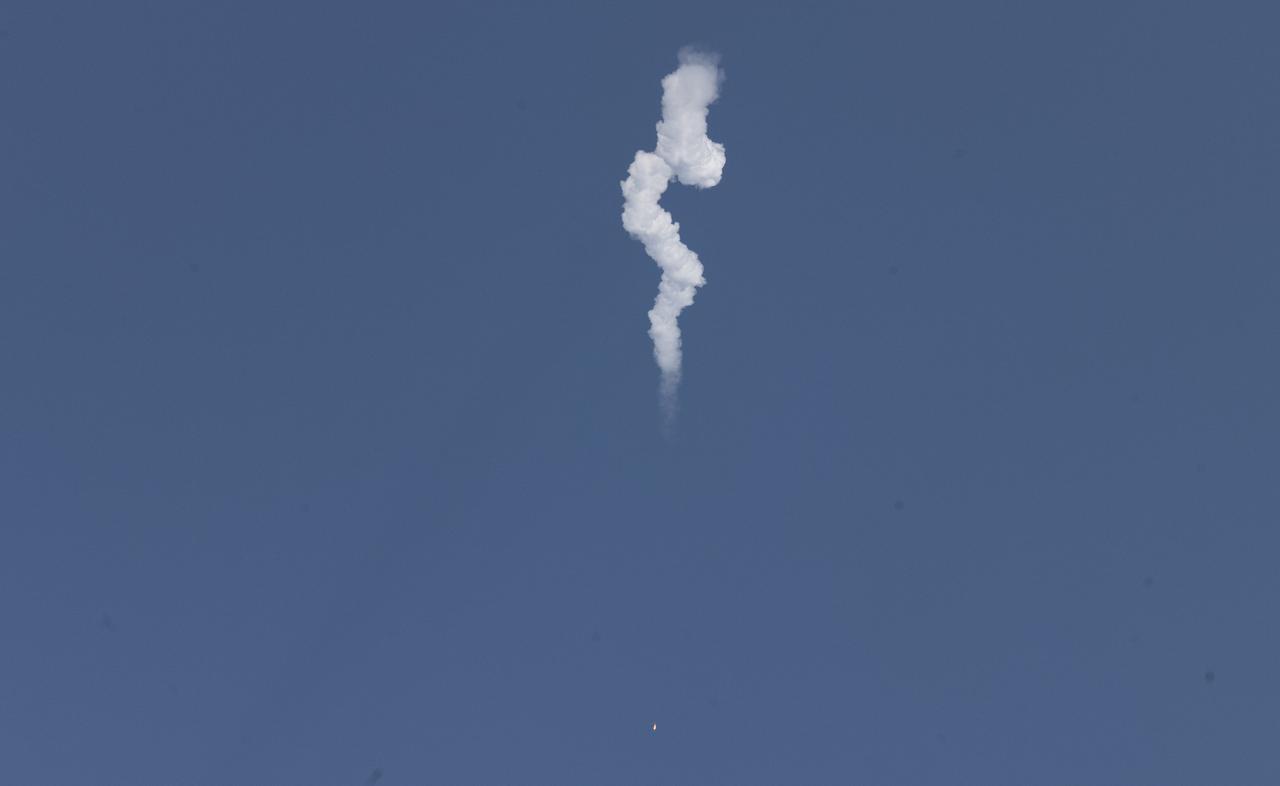

A Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft launches from Pad-0A of the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 16th contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA will deliver nearly 8,200 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the International Space Station and its crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky}
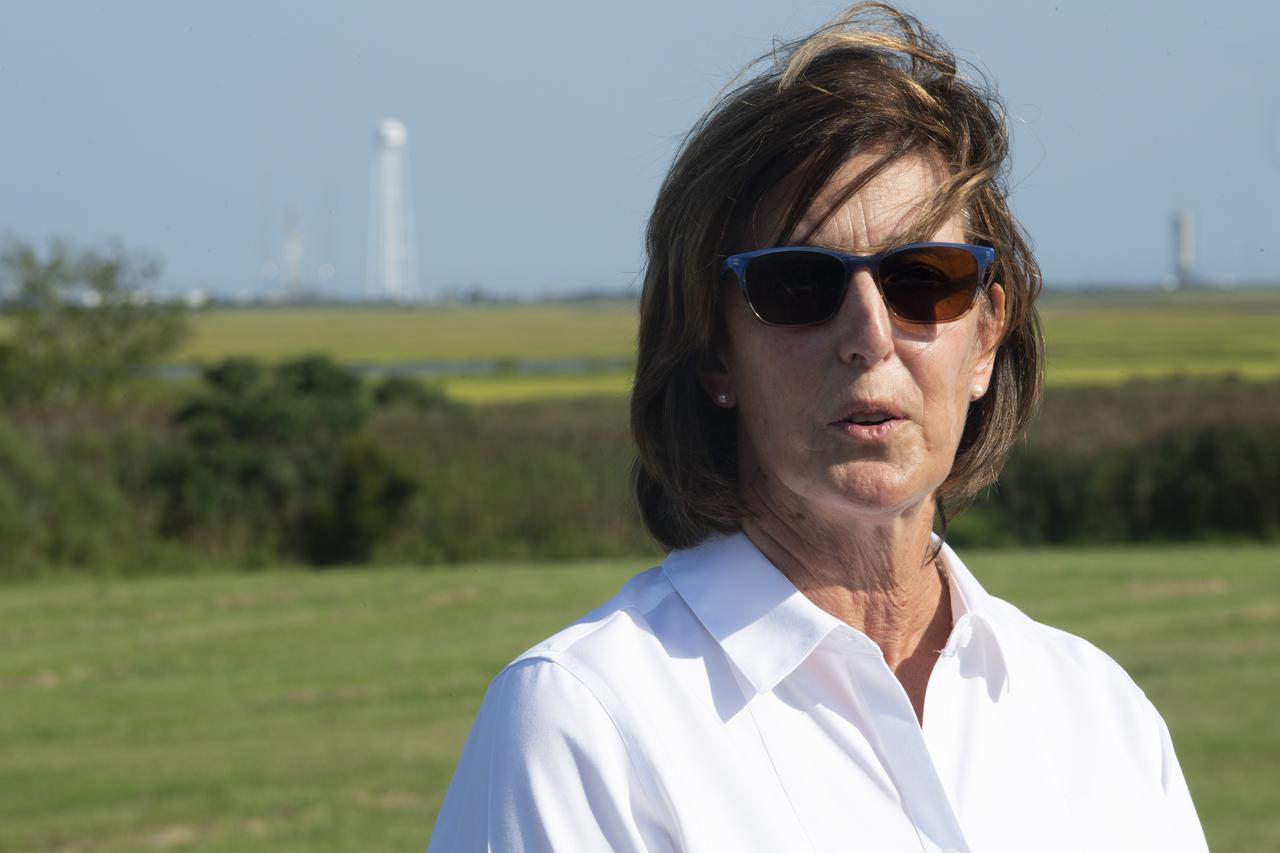

Robyn Gatens, director of NASA’s International Space Station Division, speaks to members of the media prior to the launch of a Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 16th contracted cargo resupply mission for NASA launched at 6:01 p.m. EDT and will deliver nearly 8,200 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the International Space Station and its crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
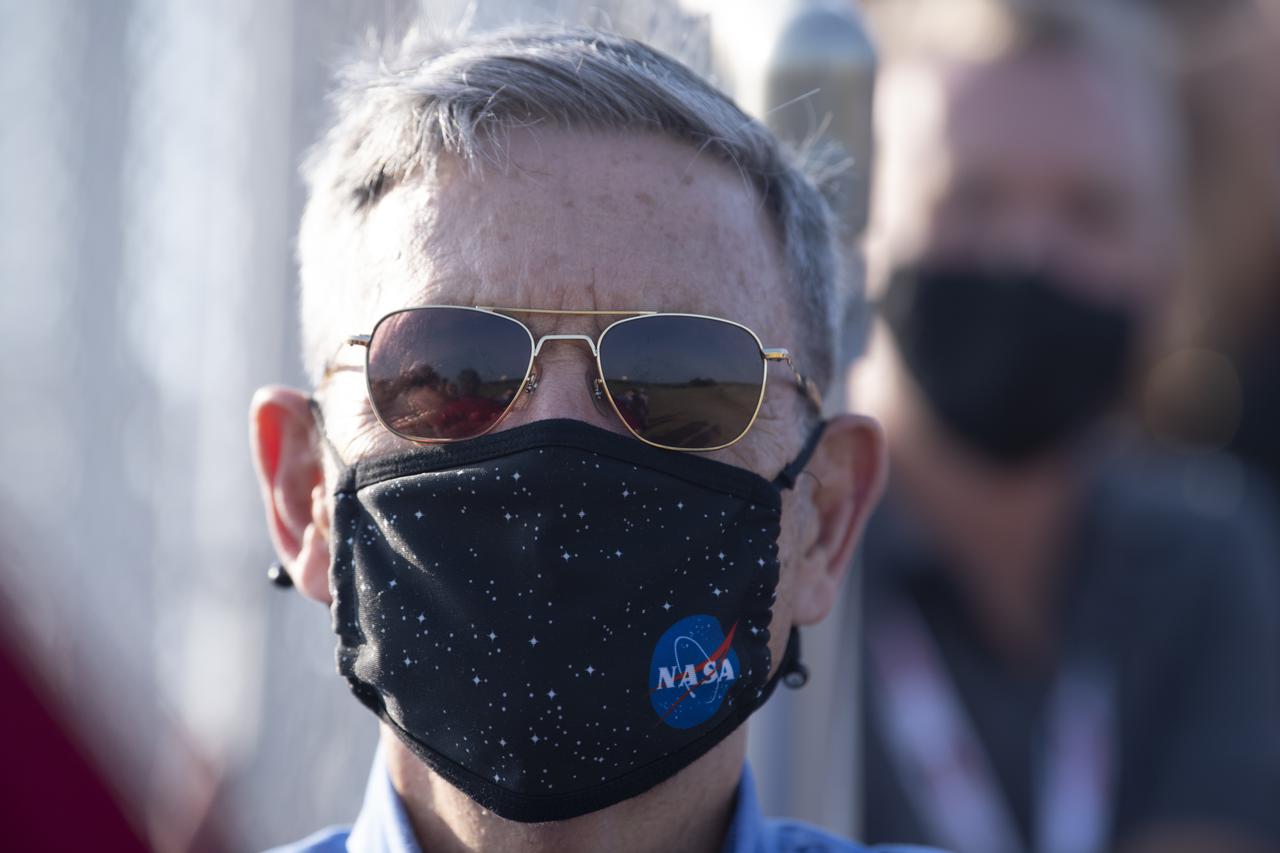

Bob Cabana, NASA associate administrator, watches the launch of a Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft launches from Pad-0A of the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 16th contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA will deliver nearly 8,200 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the International Space Station and its crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky}
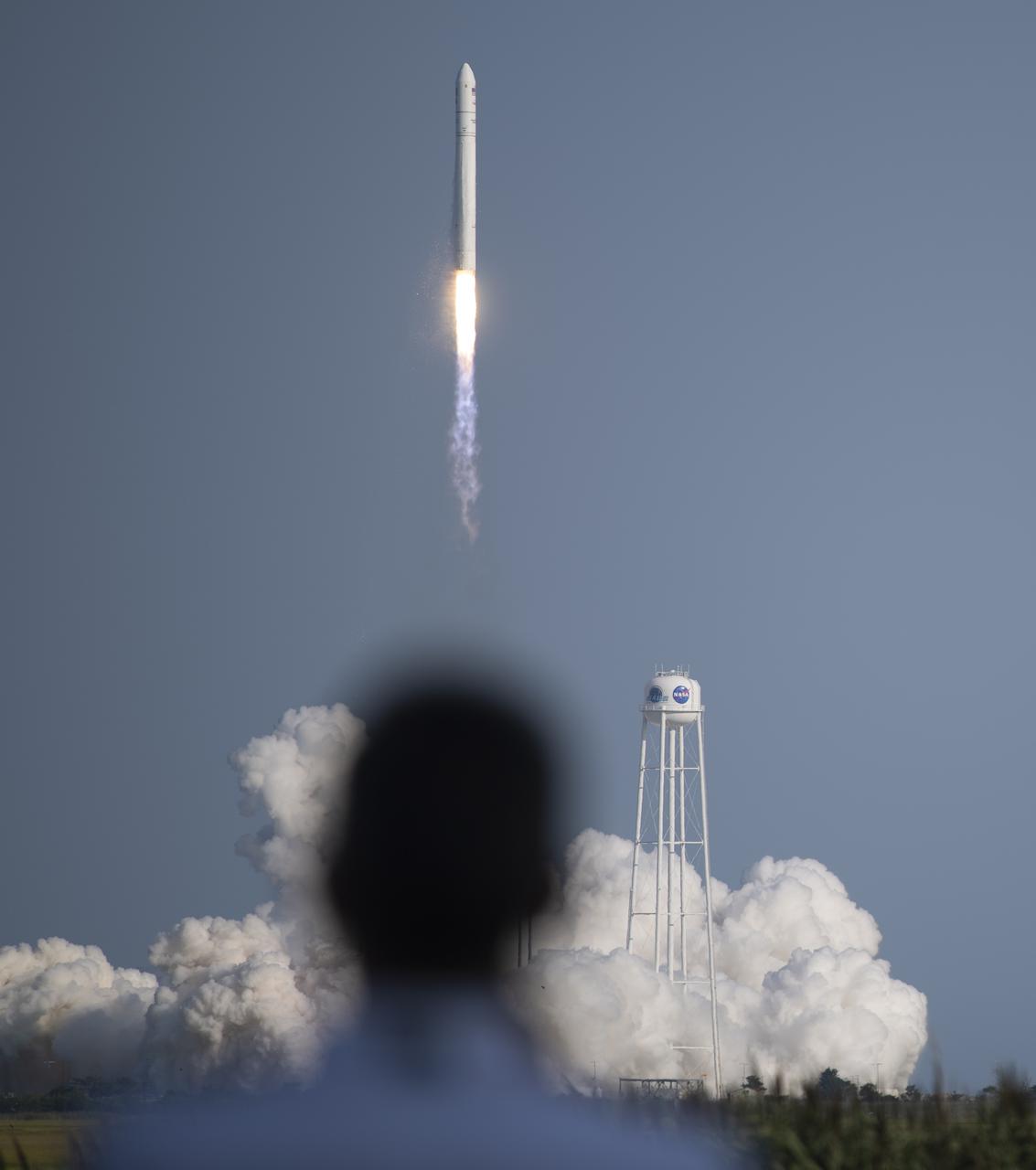

A Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft launches from Pad-0A of the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 16th contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA will deliver nearly 8,200 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the International Space Station and its crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
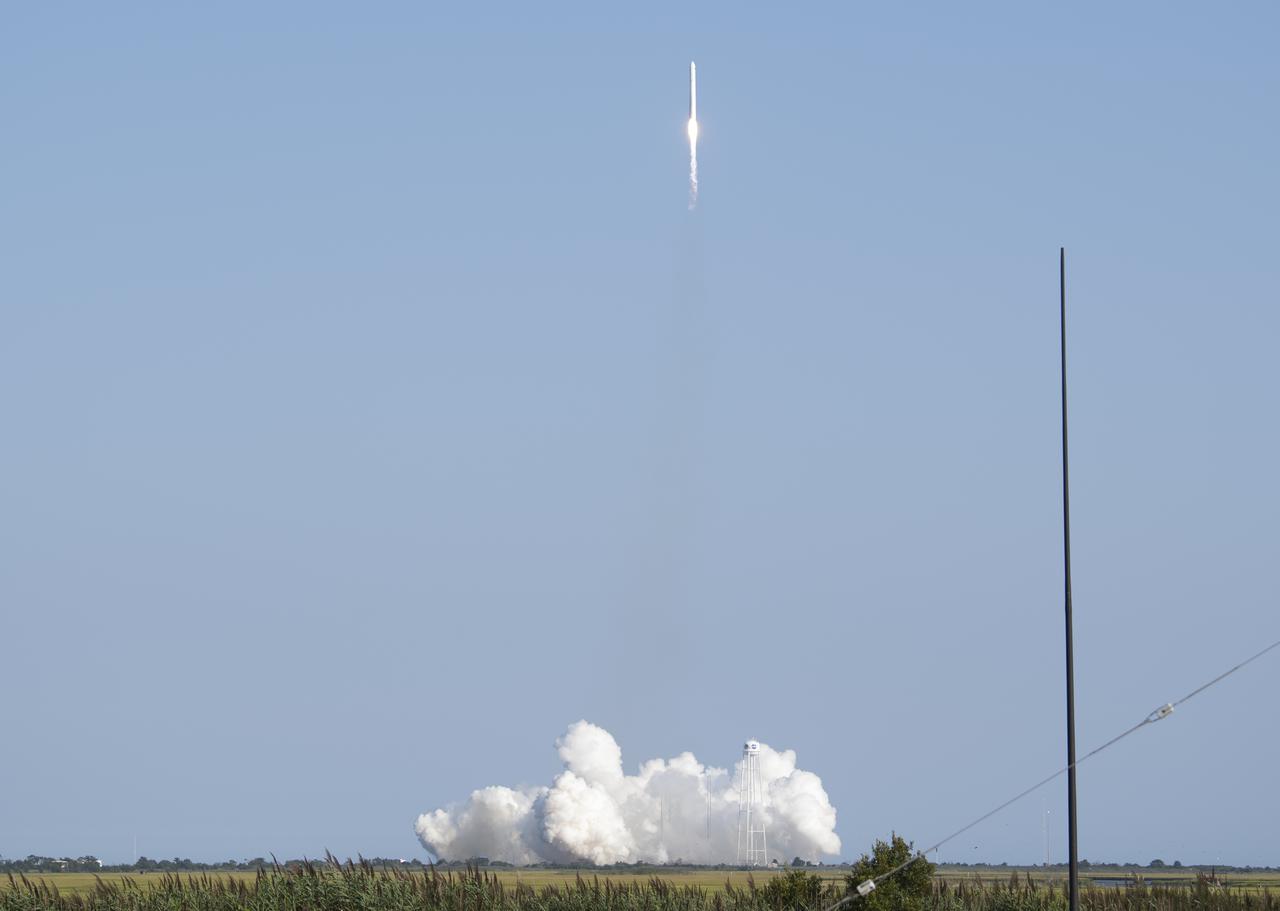

A Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft launches from Pad-0A of the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 16th contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA will deliver nearly 8,200 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the International Space Station and its crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky}

NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy, center, watches as a Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft launches from Pad-0A of the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 16th contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA will deliver nearly 8,200 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the International Space Station and its crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
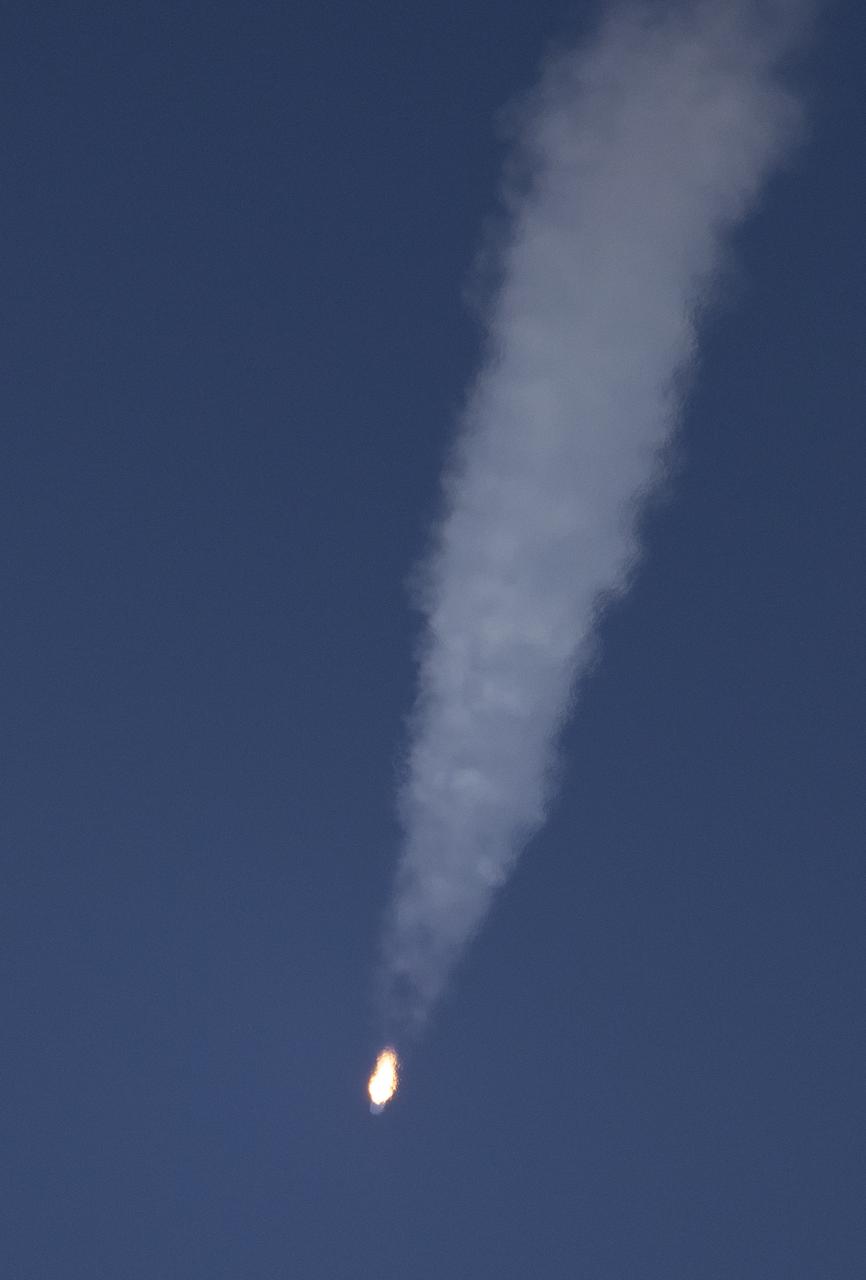

A Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft launches from Pad-0A of the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 16th contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA will deliver nearly 8,200 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the International Space Station and its crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky}
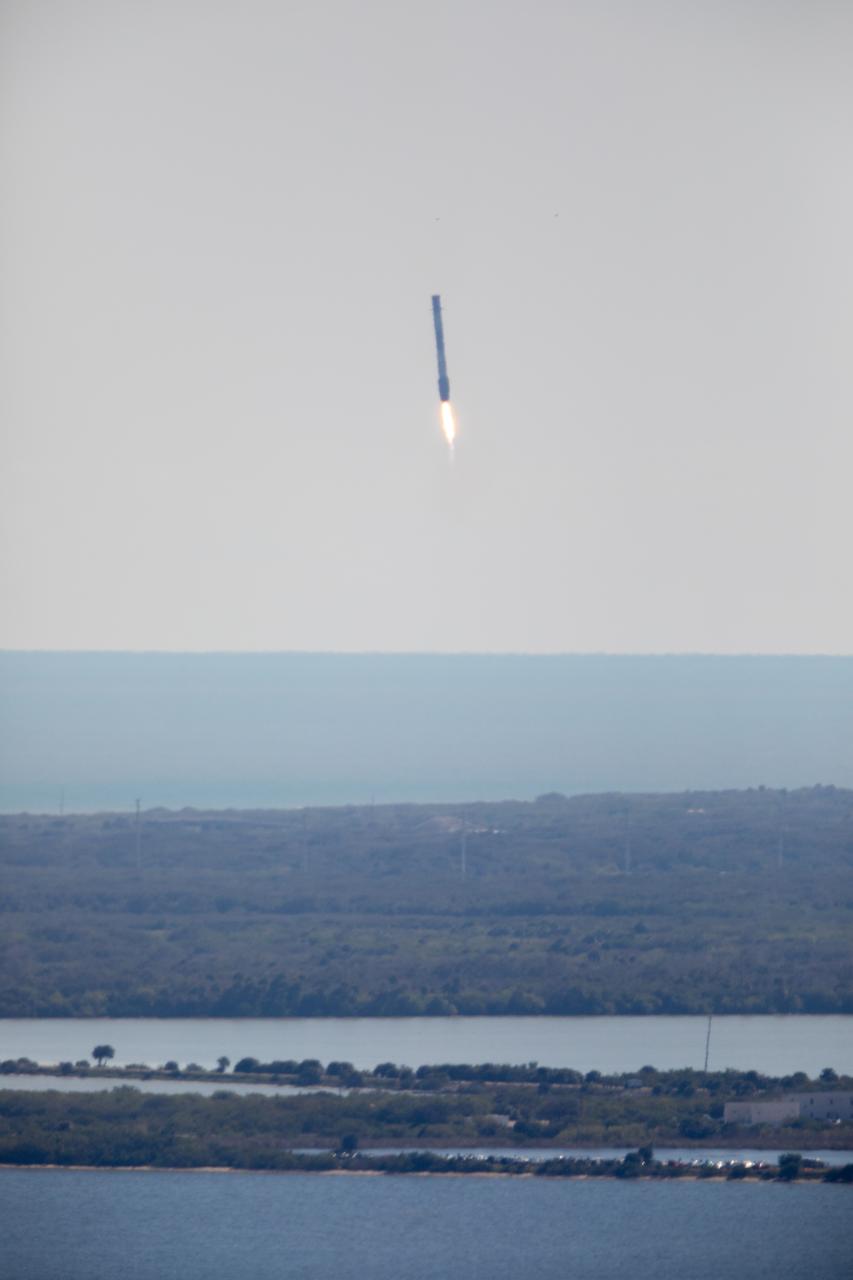

Following liftoff of Northrup Grumman's 20th commercial resupply services mission for NASA, the first stage of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket returns to Landing Zone 1. Launch of Northrop Grumman's Cygnus resupply spacecraft atop Falcon 9 occurred at 12:07 p.m. EST on Tuesday, Jan. 30 from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
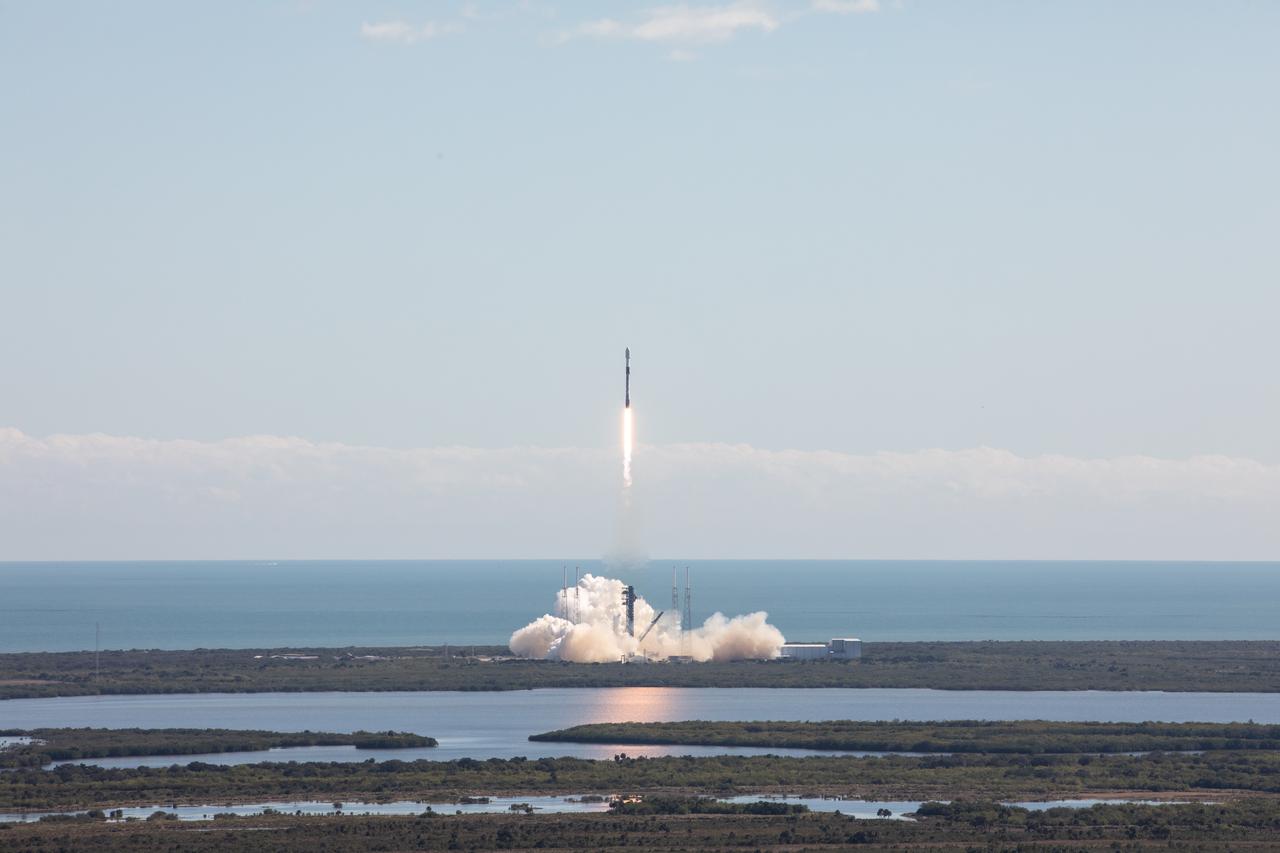

A successful liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida as Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, heads to the International Space Station for the 20th Northrop Grumman resupply mission on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The spacecraft is expected to reach the space station Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024, bringing 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment for the international crew.

A successful liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida as Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, heads to the International Space Station for the 20th Northrop Grumman resupply mission on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The spacecraft is expected to reach the space station Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024, bringing 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment for the international crew.
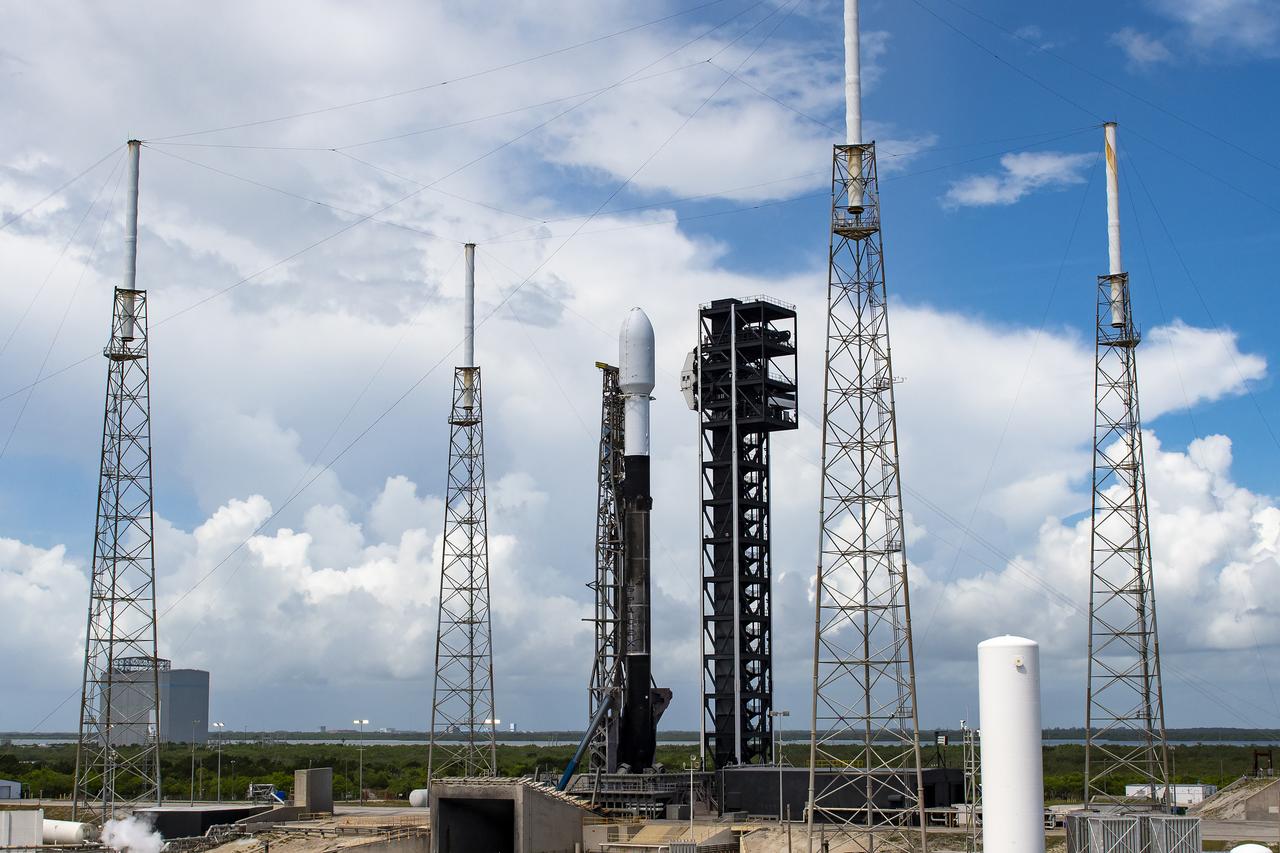

A Northrop Grumman Cygnus resupply spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, stands tall at Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Sunday, Aug. 4, 2024, in preparation for a launch to the International Space Station. Cygnus will deliver 8,200 pounds of scientific investigations and cargo to the international crew.
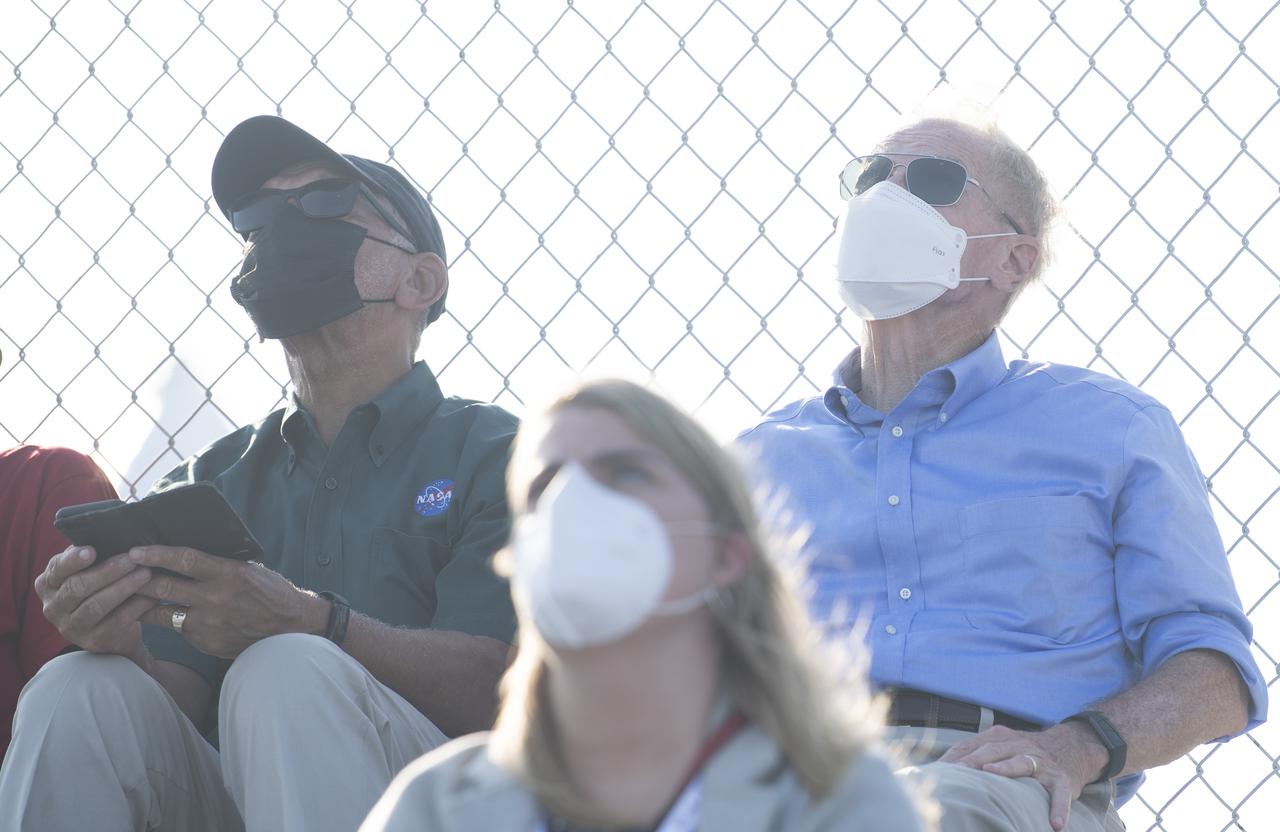

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, right, and former NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, watch as a Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft launches from Pad-0A of the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 16th contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA will deliver nearly 8,200 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the International Space Station and its crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky}
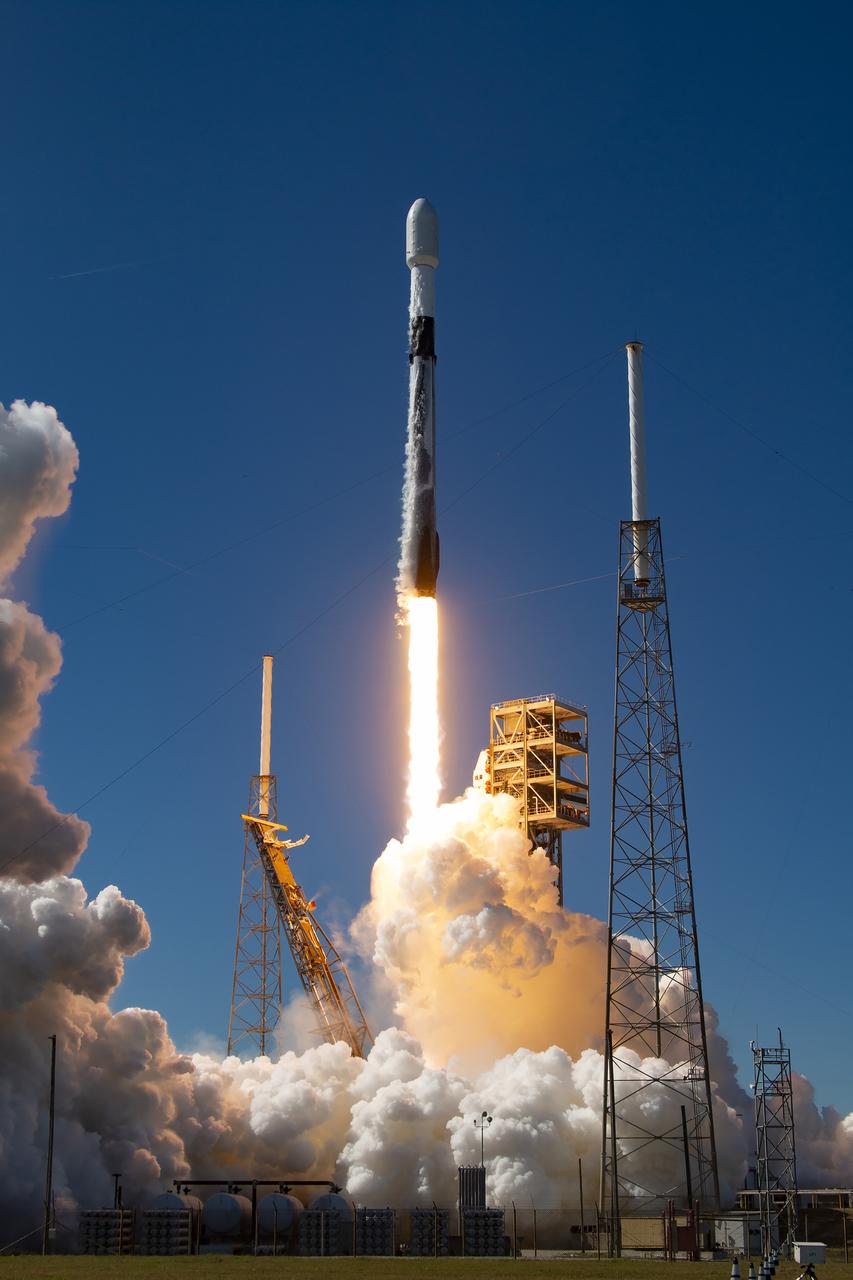

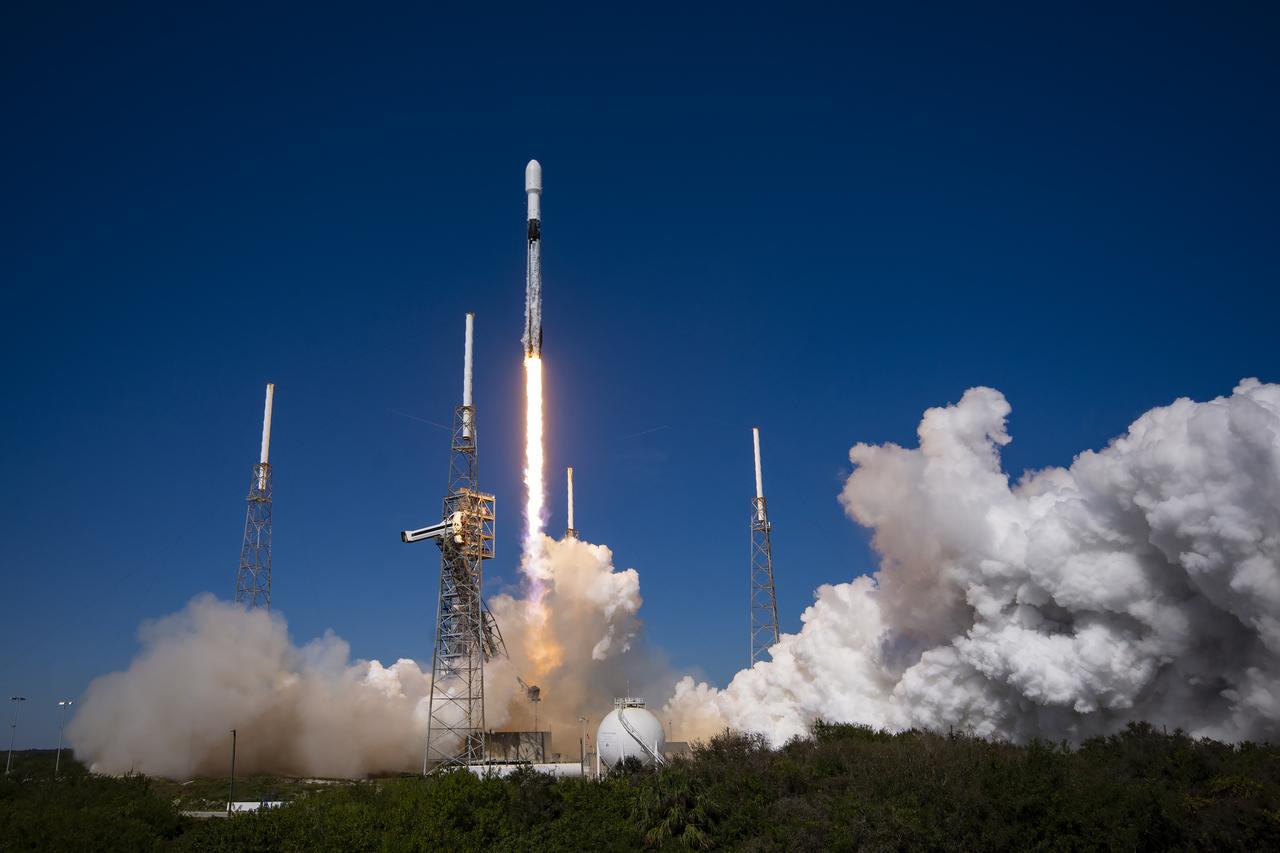
A successful liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida as Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, heads to the International Space Station for the 20th Northrop Grumman resupply mission on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The spacecraft is expected to reach the space station Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024, bringing 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment for the international crew.

Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft, atop a SpaceX 9 Falcon rocket, soars from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024, for 20th Northrop Grumman commercial resupply mission for NASA. The spacecraft will bring 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment to the International Space Station including tests of a 3D metal printer, semiconductor manufacturing, and thermal protection systems. The Cygnus spacecraft is expected to reach the space station Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024, where it will remain until its expected departure in May.

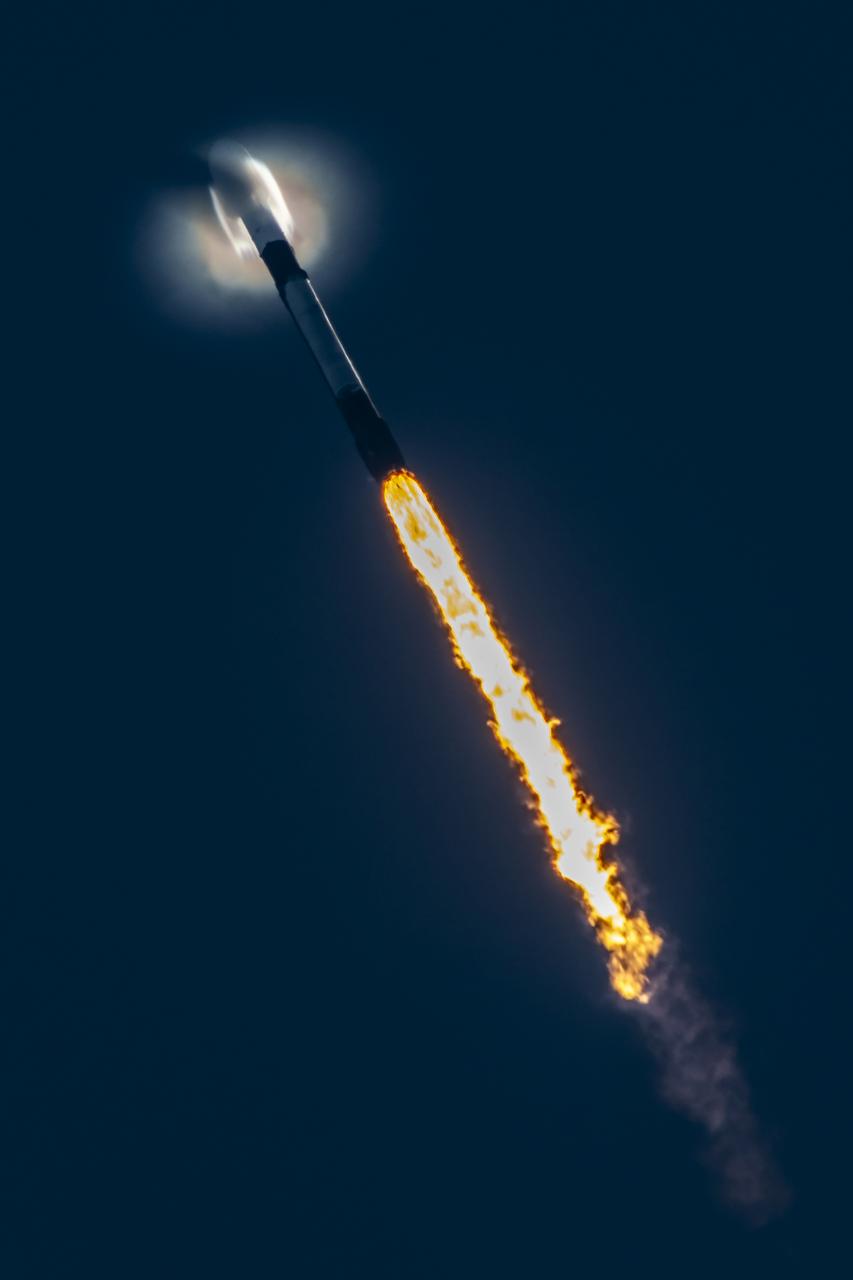
A successful liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida as Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, heads to the International Space Station for the 21st Northrop Grumman resupply mission on Sunday, Aug. 4, 2024. The spacecraft is expected to reach the space station Tuesday, Aug. 6, bringing 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment for the international crew.
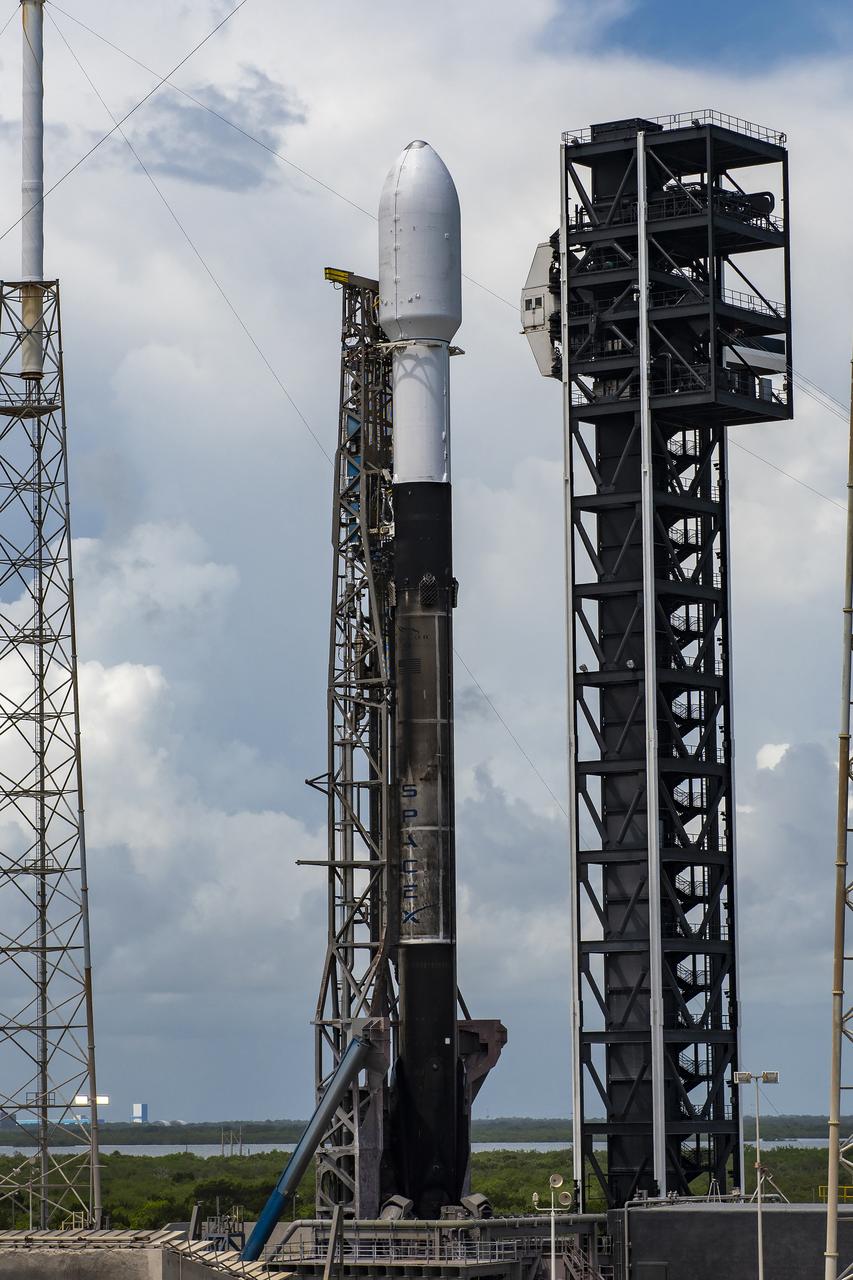

A Northrop Grumman Cygnus resupply spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, stands tall at Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Sunday, Aug. 4, 2024, in preparation for a launch to the International Space Station. Cygnus will deliver 8,200 pounds of scientific investigations and cargo to the international crew.
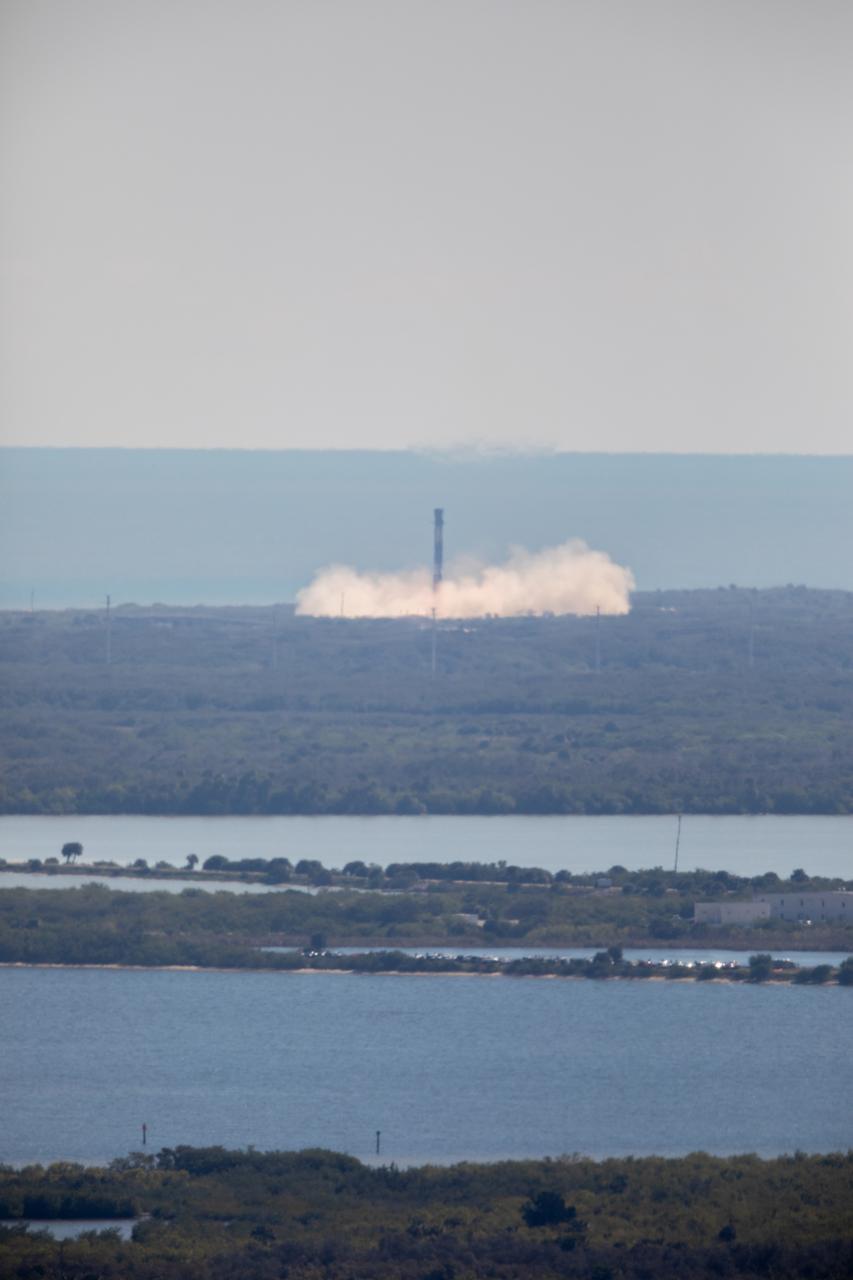

Following liftoff of Northrup Grumman's 20th commercial resupply services mission for NASA, the first stage of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket returns to Landing Zone 1. Launch of Northrop Grumman's Cygnus resupply spacecraft atop Falcon 9 occurred at 12:07 p.m. EST on Tuesday, Jan. 30 from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
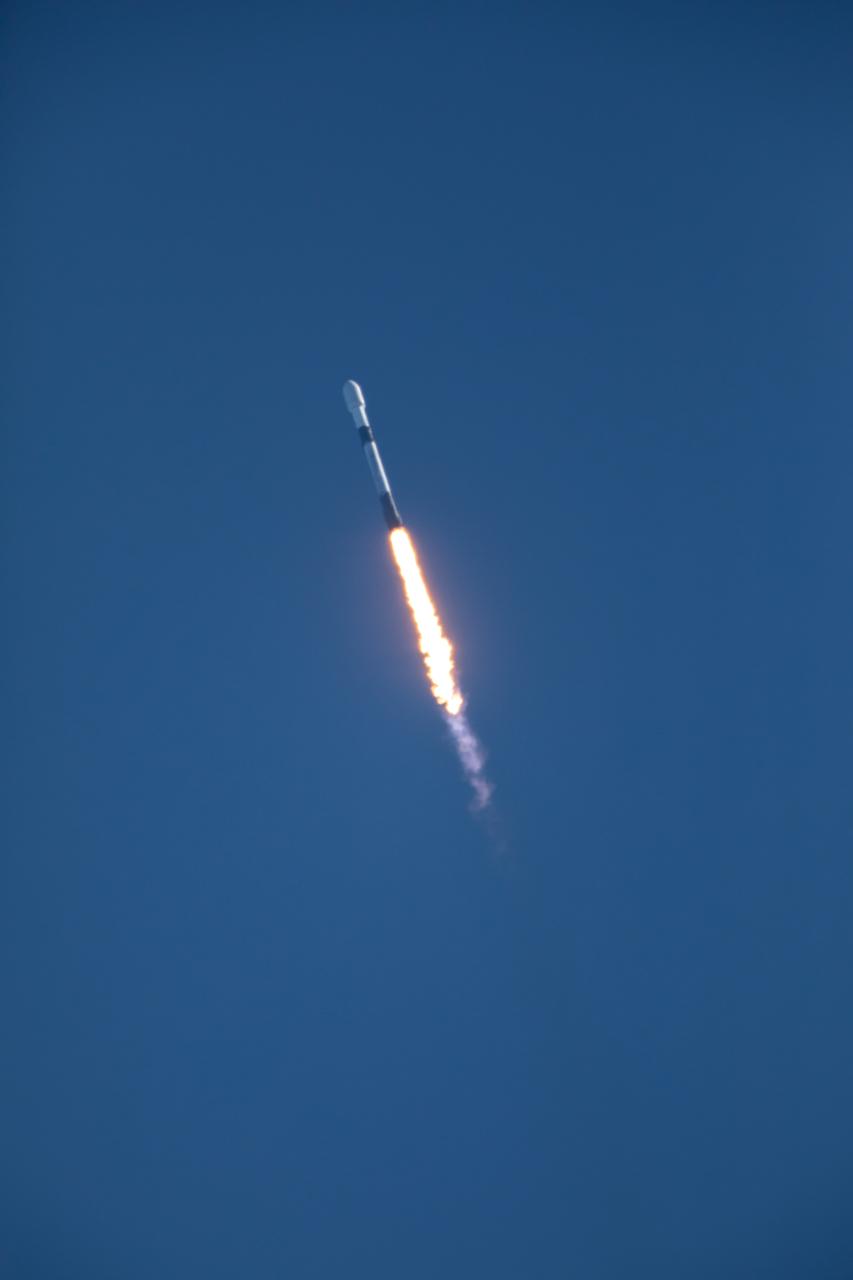

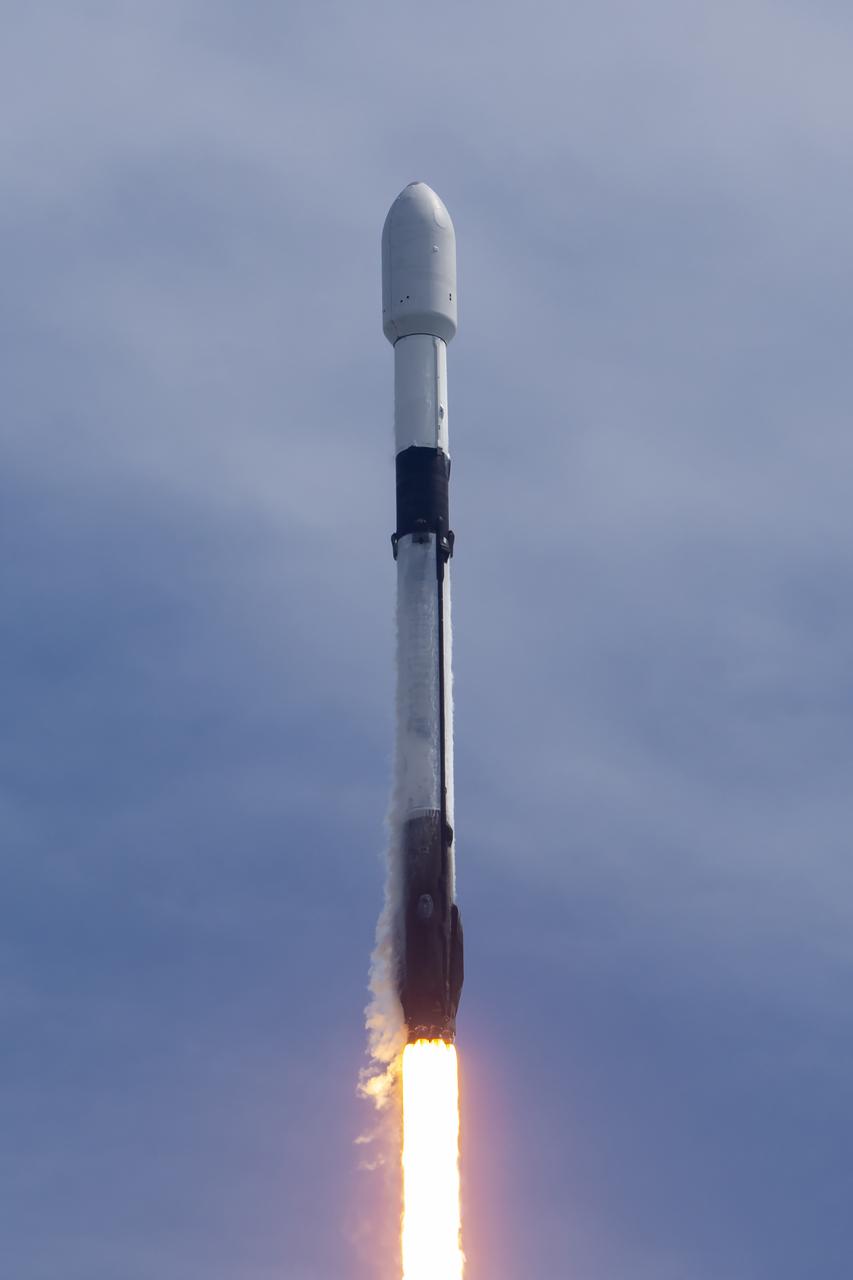
Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft, atop a SpaceX 9 Falcon rocket, soars from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024, for the 20th Northrop Grumman commercial resupply mission for NASA. The spacecraft will bring 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment to the International Space Station including tests of a 3D metal printer, semiconductor manufacturing, and thermal protection systems. The Cygnus spacecraft is expected to reach the space station Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024, where it will remain until its expected departure in May.
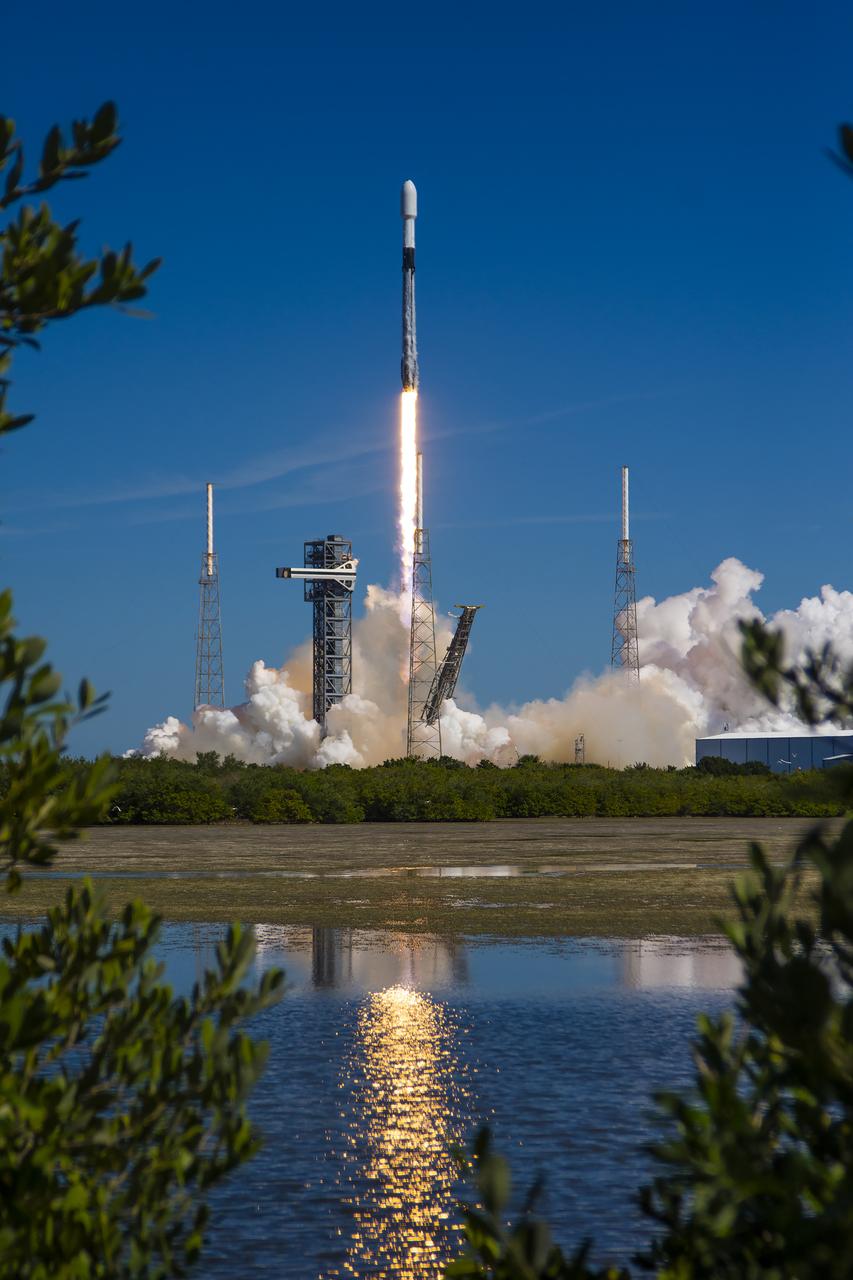

A successful liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida as Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, heads to the International Space Station for the 20th Northrop Grumman resupply mission on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The spacecraft is expected to reach the space station Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024, bringing 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment for the international crew.
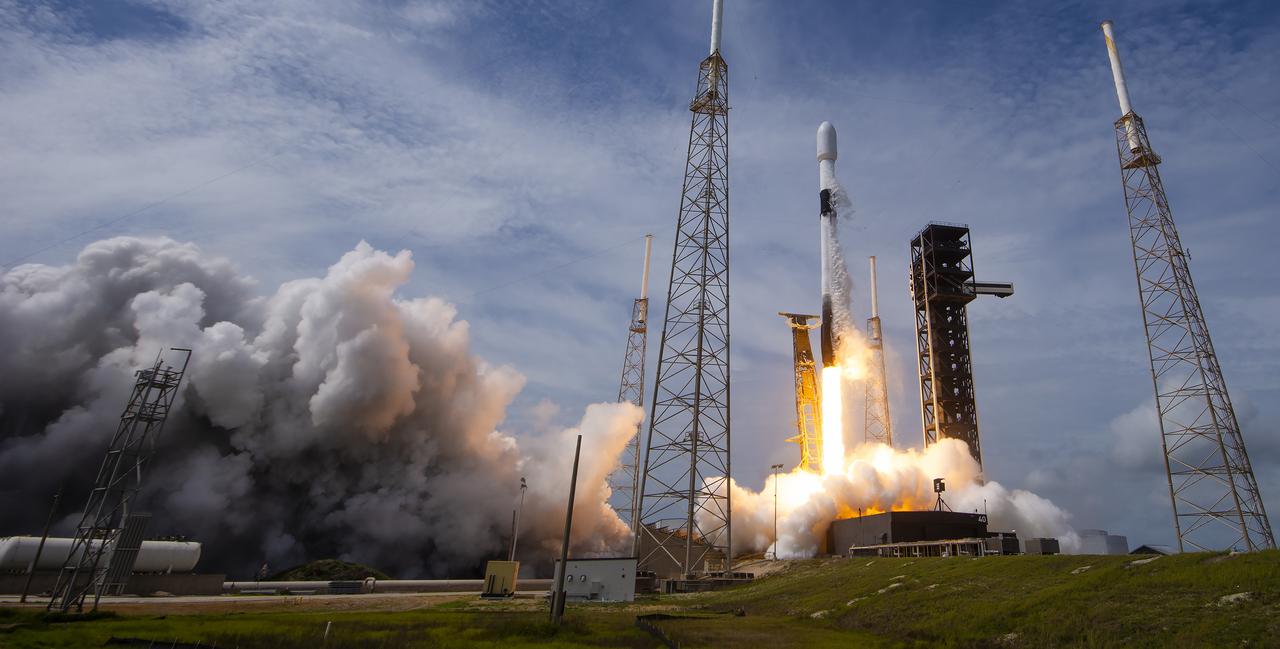

Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, soars from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Sunday, Aug. 4, 2024, for the 21st Northrop Grumman commercial resupply mission for NASA. The spacecraft is expected to reach the space station Tuesday, Aug. 6, bringing 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment for the international crew.

Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, soars from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Sunday, Aug. 4, 2024, for the 21st Northrop Grumman commercial resupply mission for NASA. The spacecraft is expected to reach the space station Tuesday, Aug. 6, bringing 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment for the international crew.
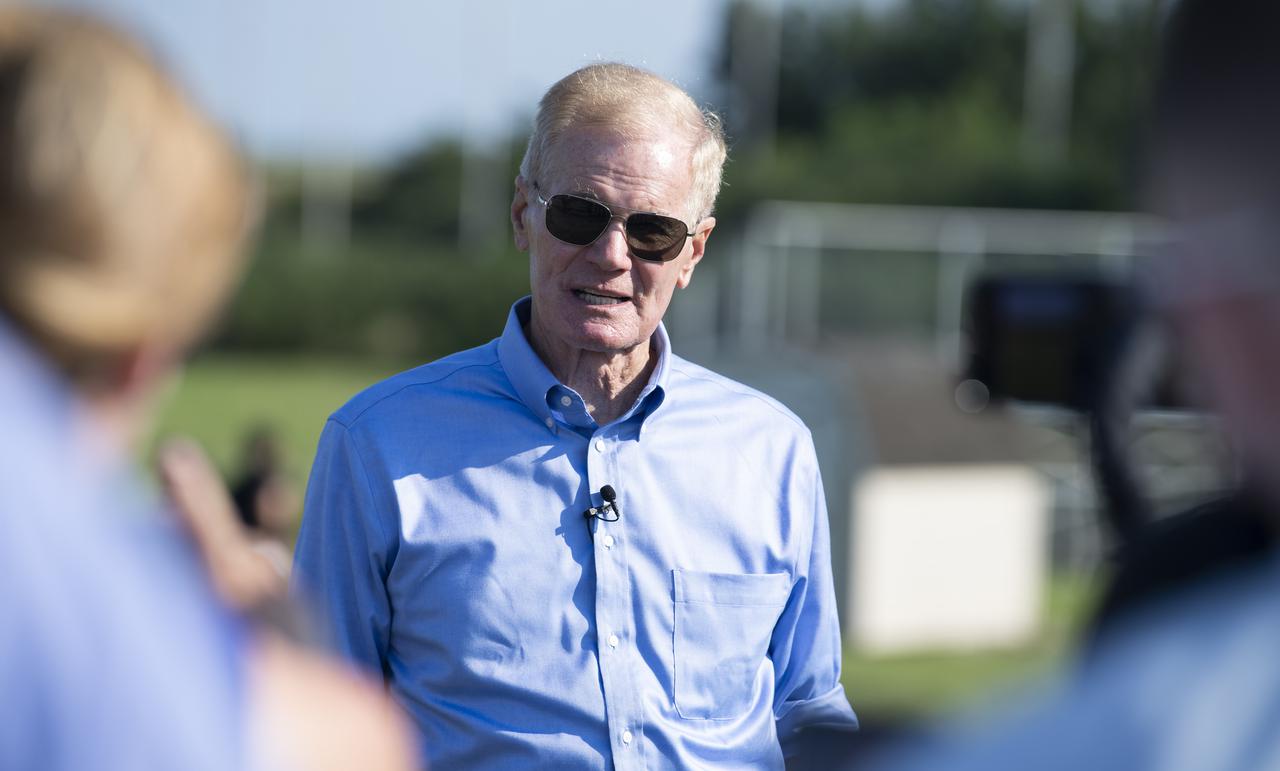

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson speaks to members of the media prior to the launch of a Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 16th contracted cargo resupply mission for NASA launched at 6:01 p.m. EDT and will deliver nearly 8,200 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the International Space Station and its crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky}
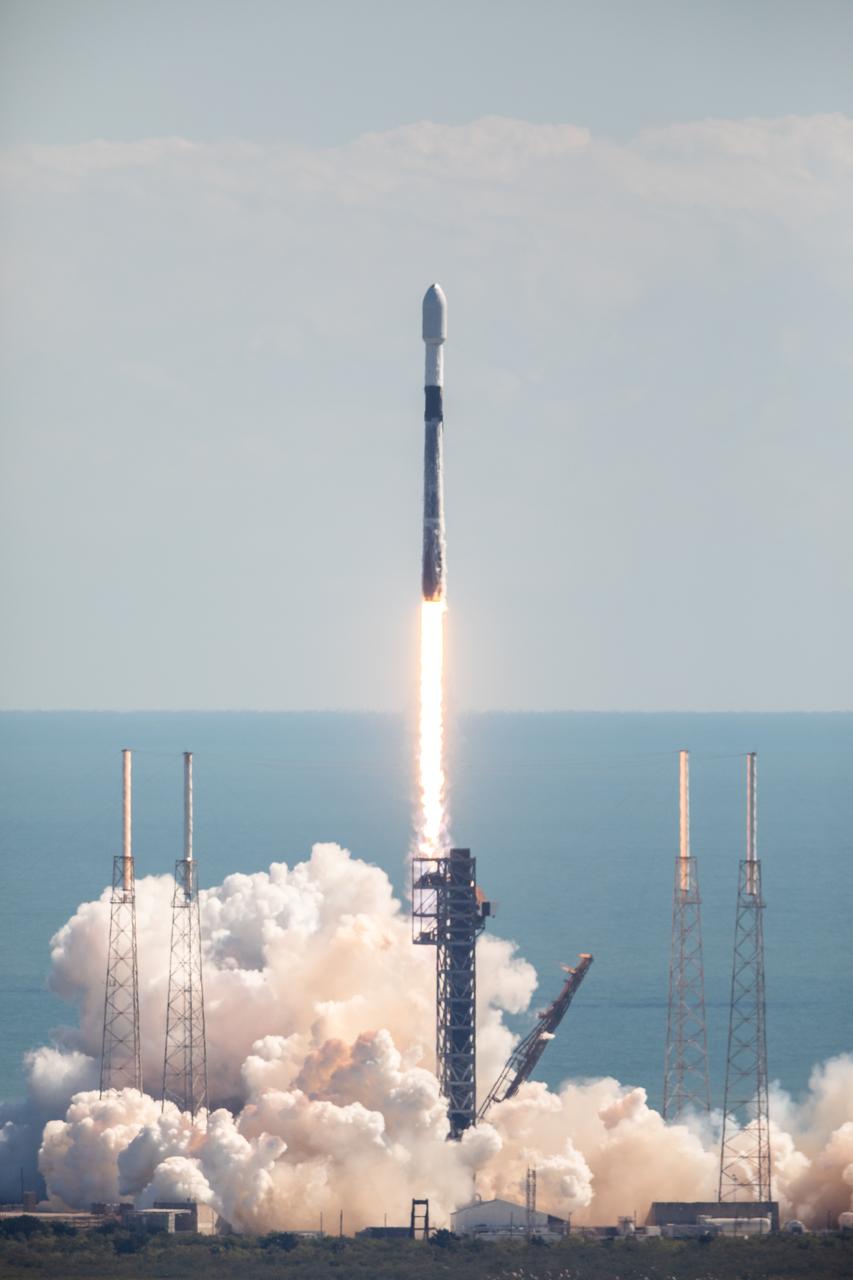

A successful liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida as Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, heads to the International Space Station for the 20th Northrop Grumman resupply mission on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The spacecraft is expected to reach the space station Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024, bringing 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment for the international crew.
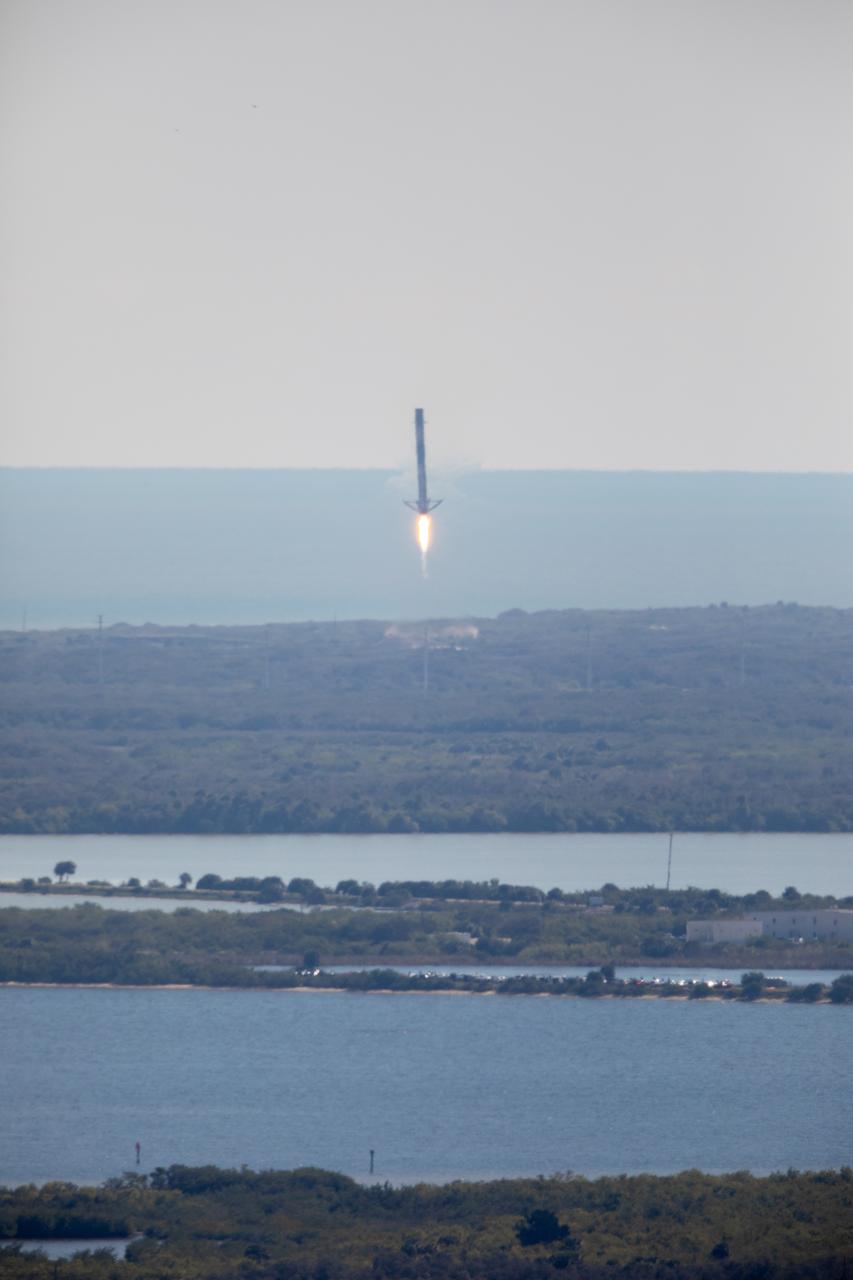

Following liftoff of Northrup Grumman's 20th commercial resupply services mission for NASA, the first stage of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket returns to Landing Zone 1. Launch of Northrop Grumman's Cygnus resupply spacecraft atop Falcon 9 occurred at 12:07 p.m. EST on Tuesday, Jan. 30 from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.

Robyn Gatens, director of NASA’s International Space Station Division, left, Thomas Zurbuchen, associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate, second from left, NASA Administrator Bill Nelson, second from right, and Bob Cabana, NASA associate administrator, right, speak to members of the media prior to the launch of a Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 16th contracted cargo resupply mission for NASA launched at 6:01 p.m. EDT and will deliver nearly 8,200 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the International Space Station and its crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
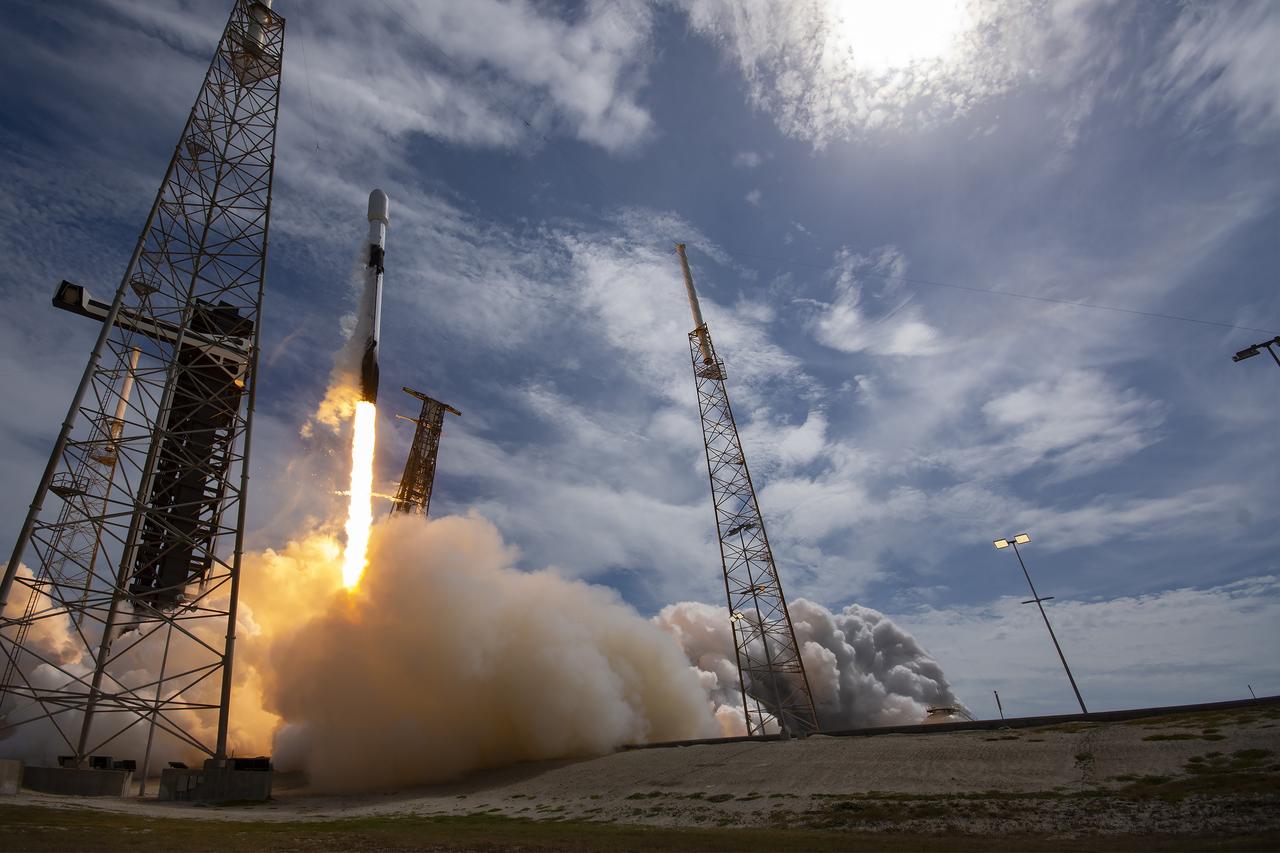

Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft, atop a SpaceX 9 Falcon rocket, soars from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Sunday, Aug. 4, 2024, for the 21st Northrop Grumman commercial resupply mission for NASA. The spacecraft is expected to reach the space station Tuesday, Aug. 6, bringing 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment for the international crew.
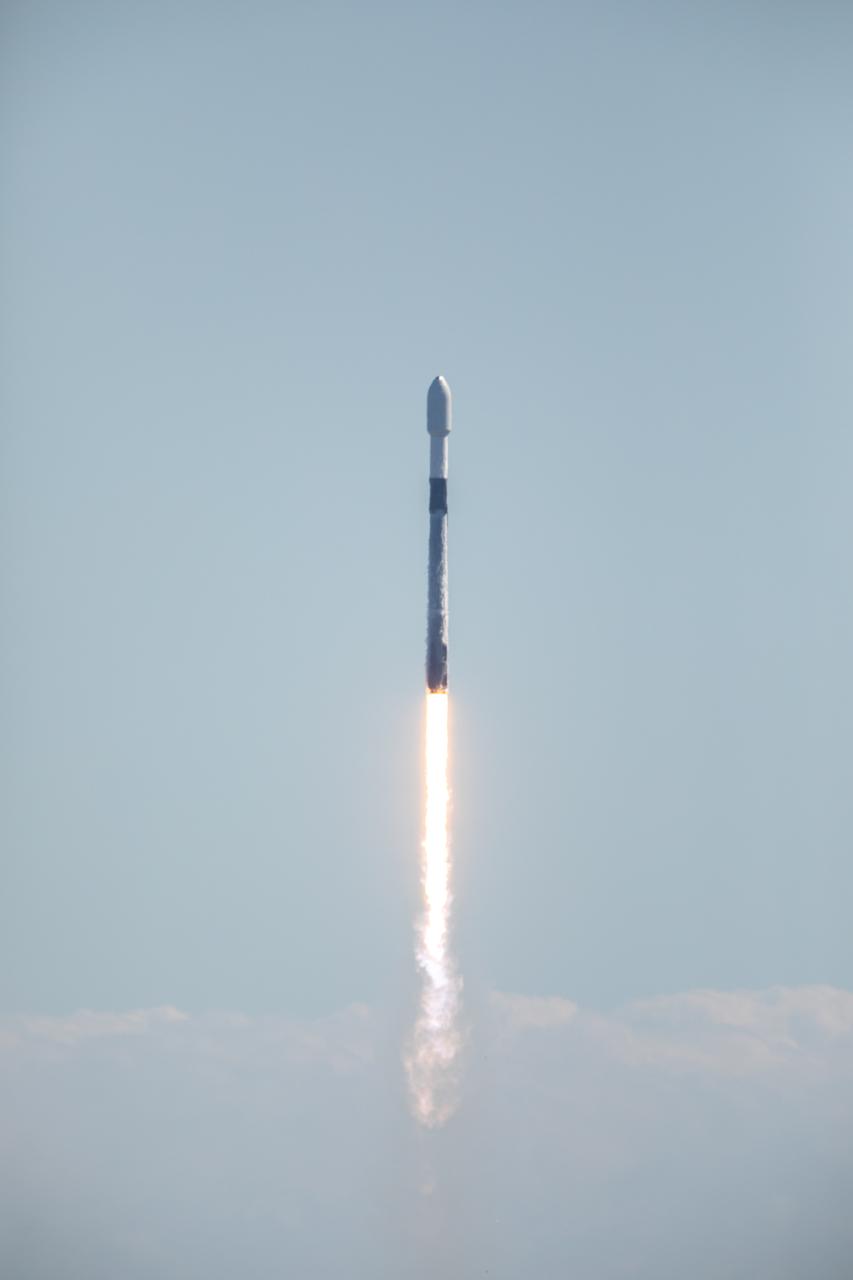

Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft, atop a SpaceX 9 Falcon rocket, soars from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024, for the 20th Northrop Grumman commercial resupply mission for NASA. The spacecraft will bring 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment to the International Space Station including tests of a 3D metal printer, semiconductor manufacturing, and thermal protection systems. The Cygnus spacecraft is expected to reach the space station Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024, where it will remain until its expected departure in May.
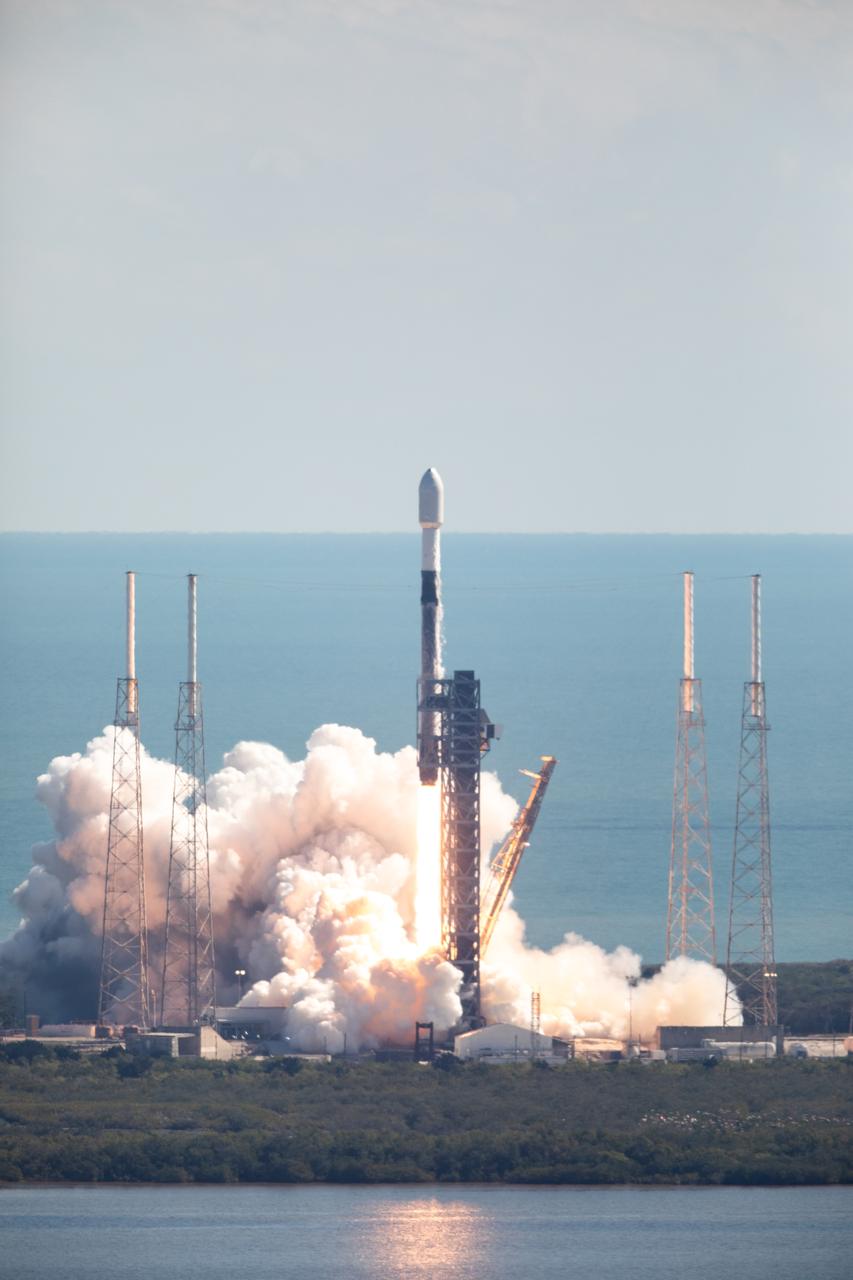

A successful liftoff from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida as Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, heads to the International Space Station for the 20th Northrop Grumman resupply mission on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024. The spacecraft is expected to reach the space station Thursday, Feb. 1, 2024, bringing 8,200 pounds of science investigations, supplies, and equipment for the international crew.
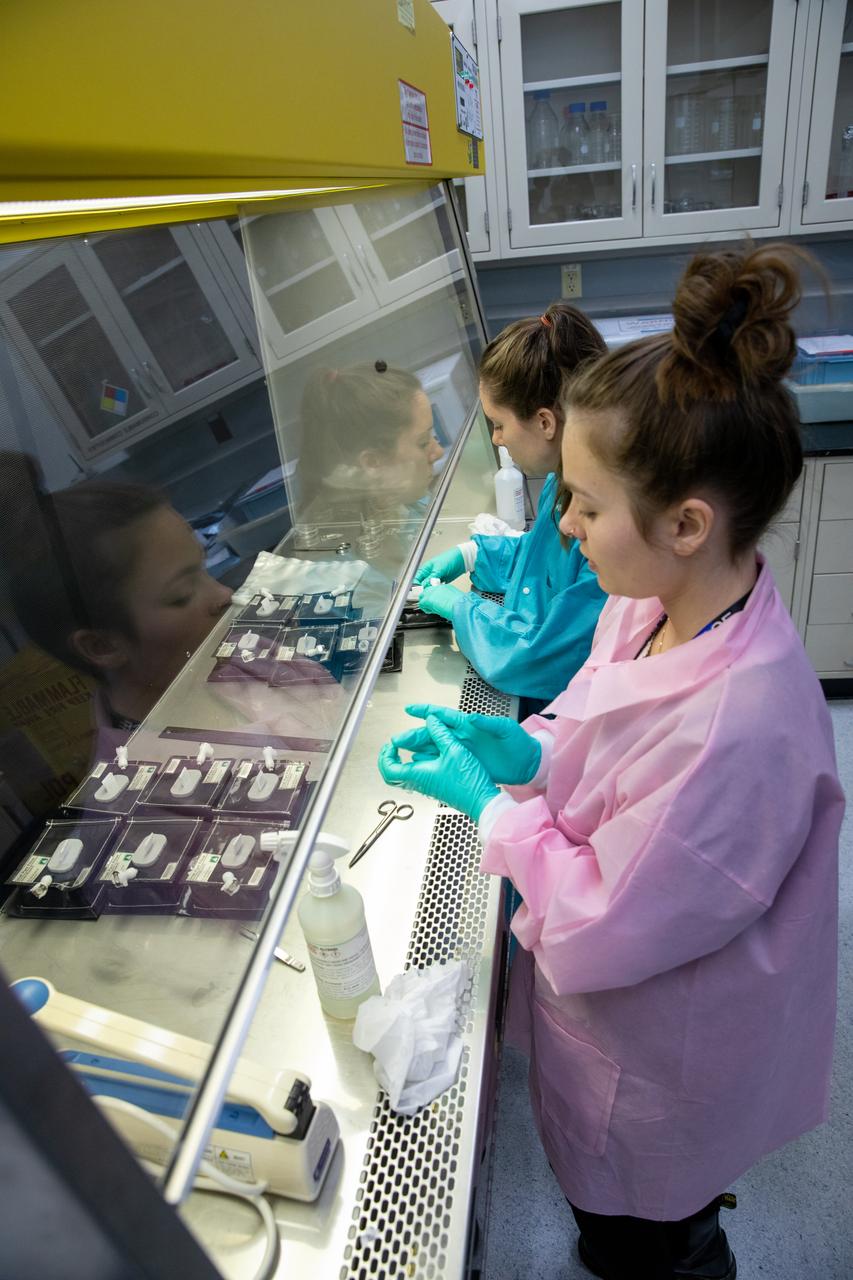

On Jan. 21, 2020, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, intern Emily Kennebeck (left) and Jess Bunchek, a pseudonaut and associate scientist, prepare plant pillows for their flight to the International Space Station. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
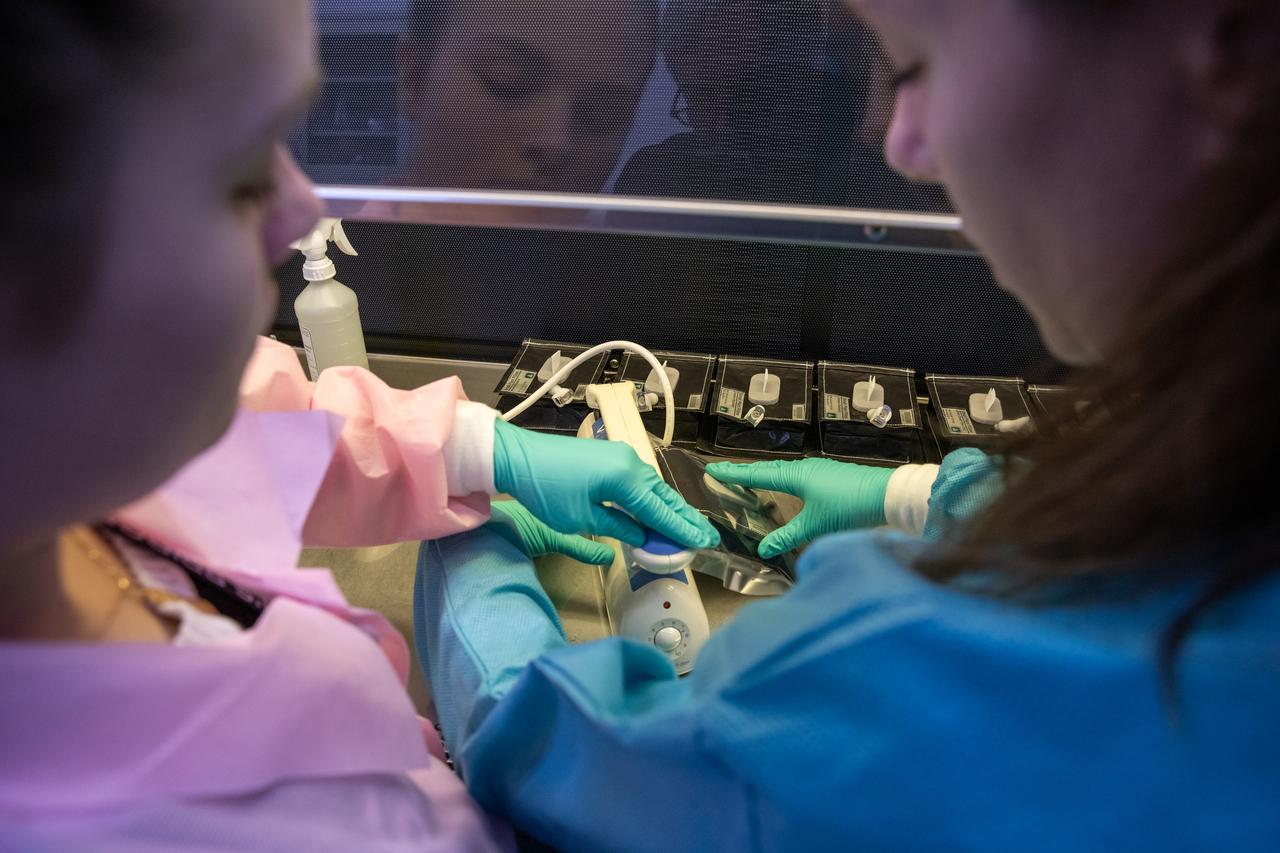
On Jan. 21, 2020, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, intern Emily Kennebeck (left) and Jess Bunchek, a pseudonaut and associate scientist, prepare plant pillows for their upcoming flight to the International Space Station. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m.
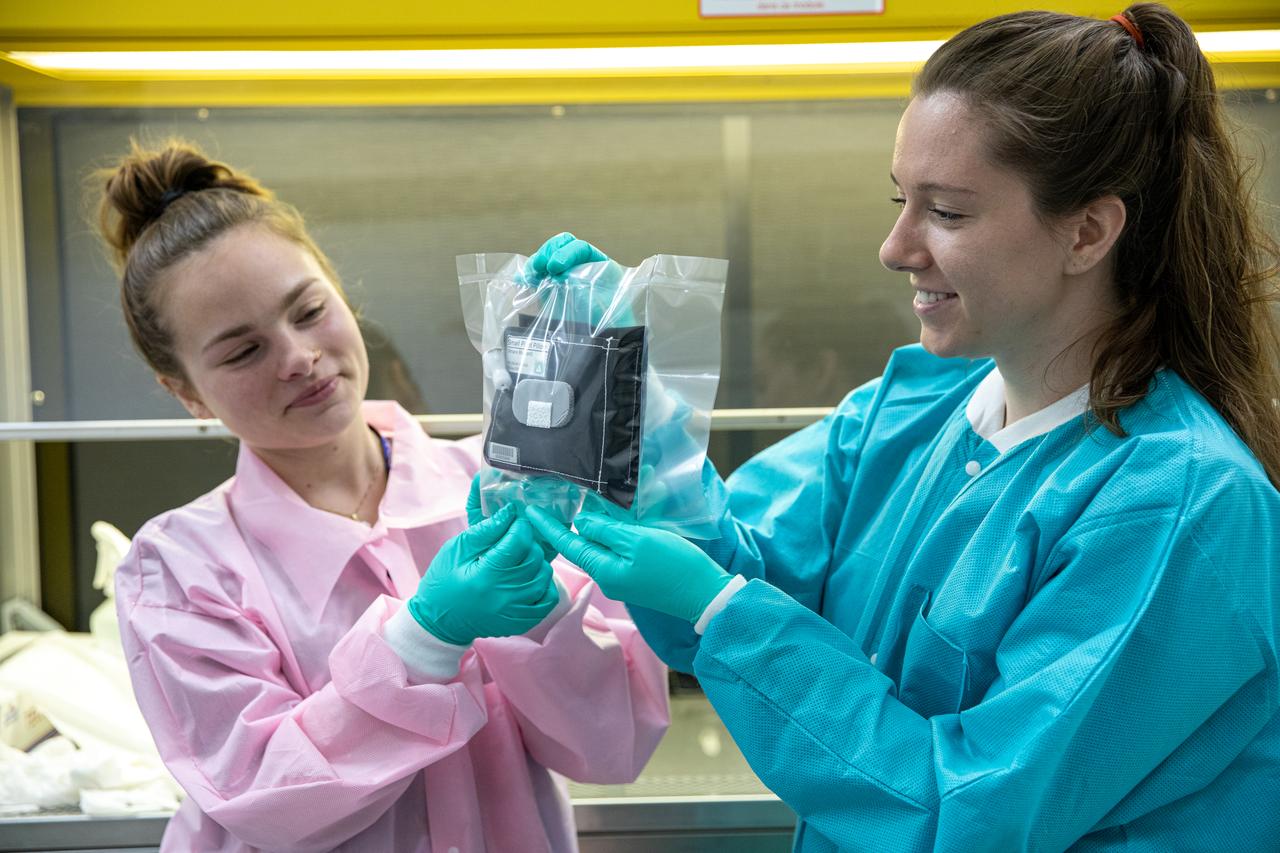

On Jan. 21, 2020, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, intern Emily Kennebeck (left) and Jess Bunchek, a pseudonaut and associate scientist, prepare plant pillows for their upcoming flight to the International Space Station. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
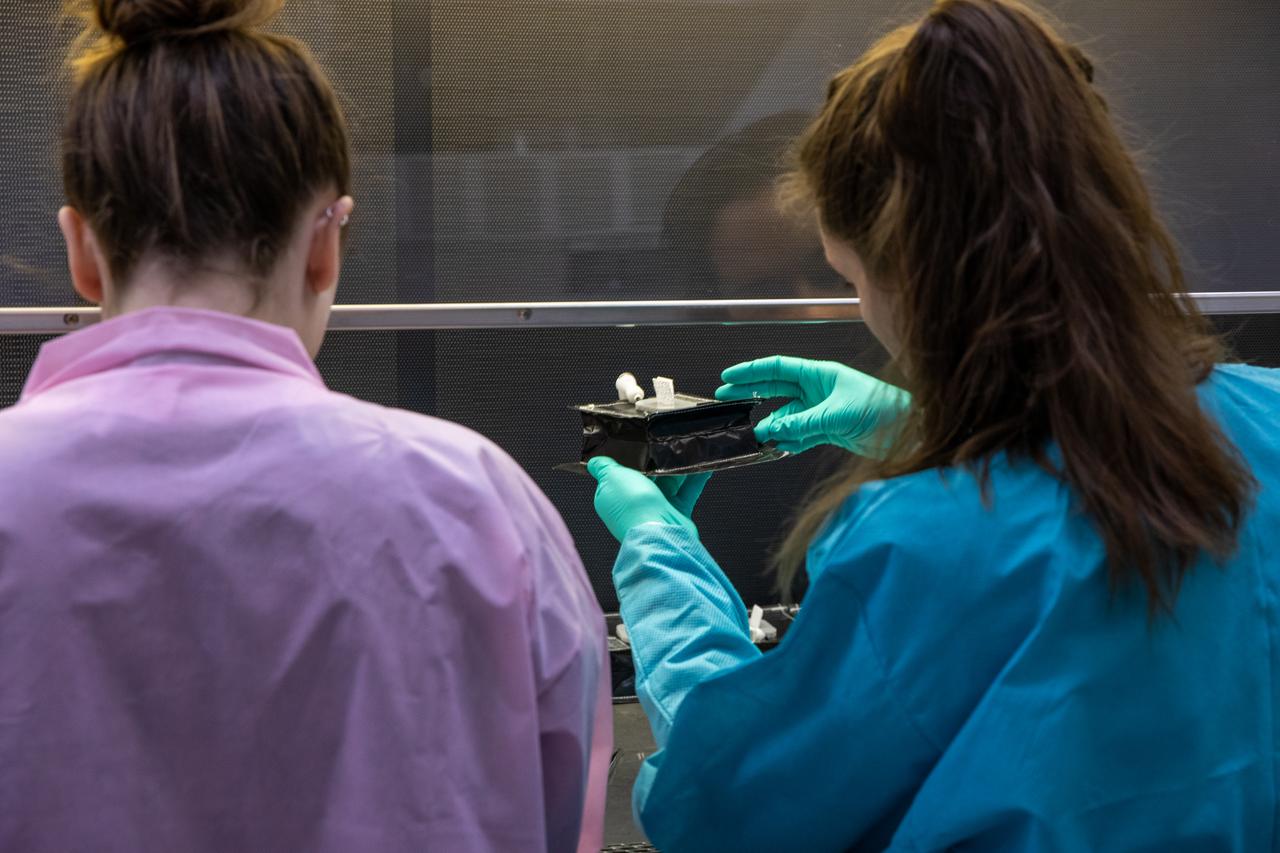

On Jan. 21, 2020, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, intern Emily Kennebeck (left) and Jess Bunchek, a pseudonaut and associate scientist, prepare plant pillows for their flight to the International Space Station. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
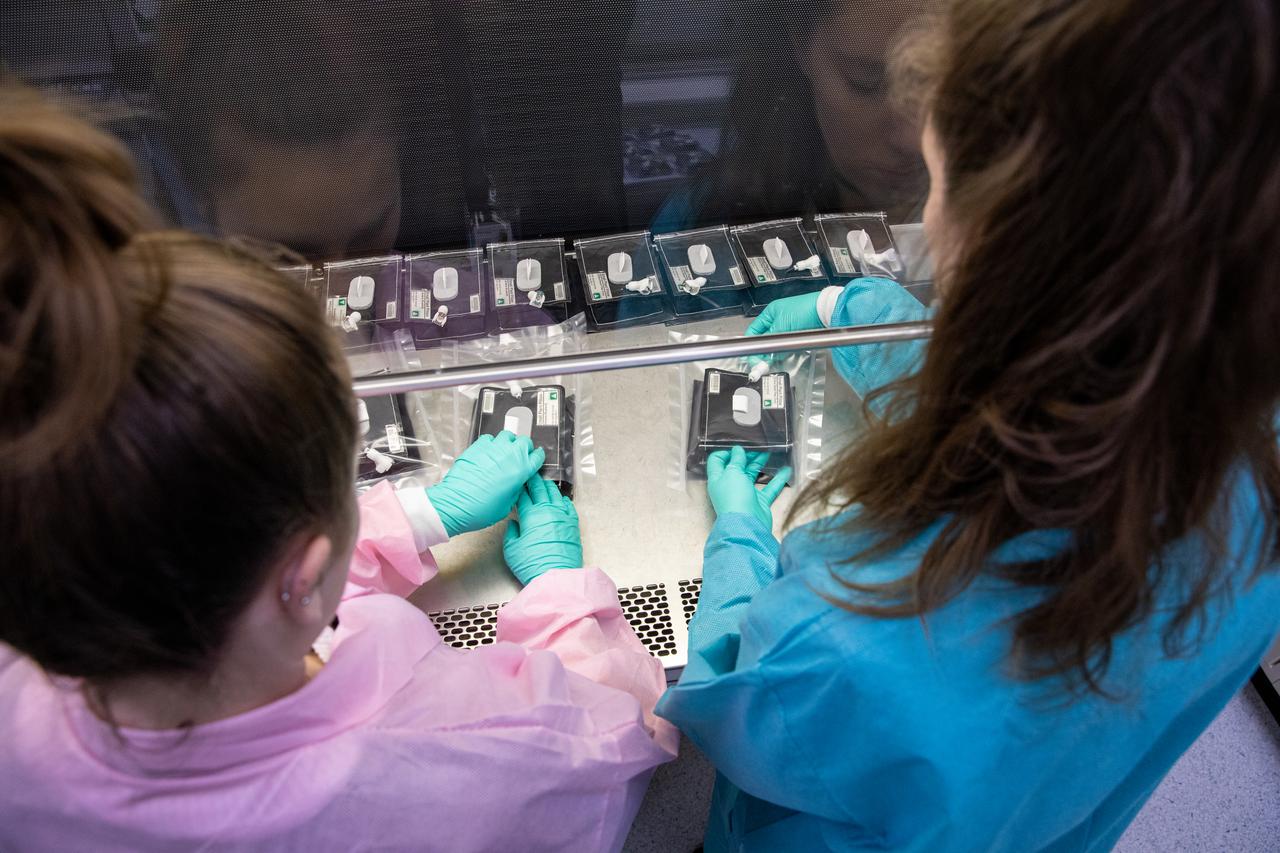

On Jan. 21, 2020, inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, intern Emily Kennebeck (left) and Jess Bunchek, a pseudonaut and associate scientist, prepare plant pillows for their upcoming flight to the International Space Station. The pillows, which are a common method used to grow plants in space, are being sent to the orbiting laboratory on Northrop Grumman’s 13th resupply services (NG-13) mission for a series of VEG-03 experiments that will study the growth of three types of leafy greens in a microgravity environment. Once the pillows are assembled and packaged for flight, they will be transported to the agency’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia, where liftoff will occur. NG-13 is scheduled to launch on Feb. 9, 2020, at 5:39 p.m. EST.
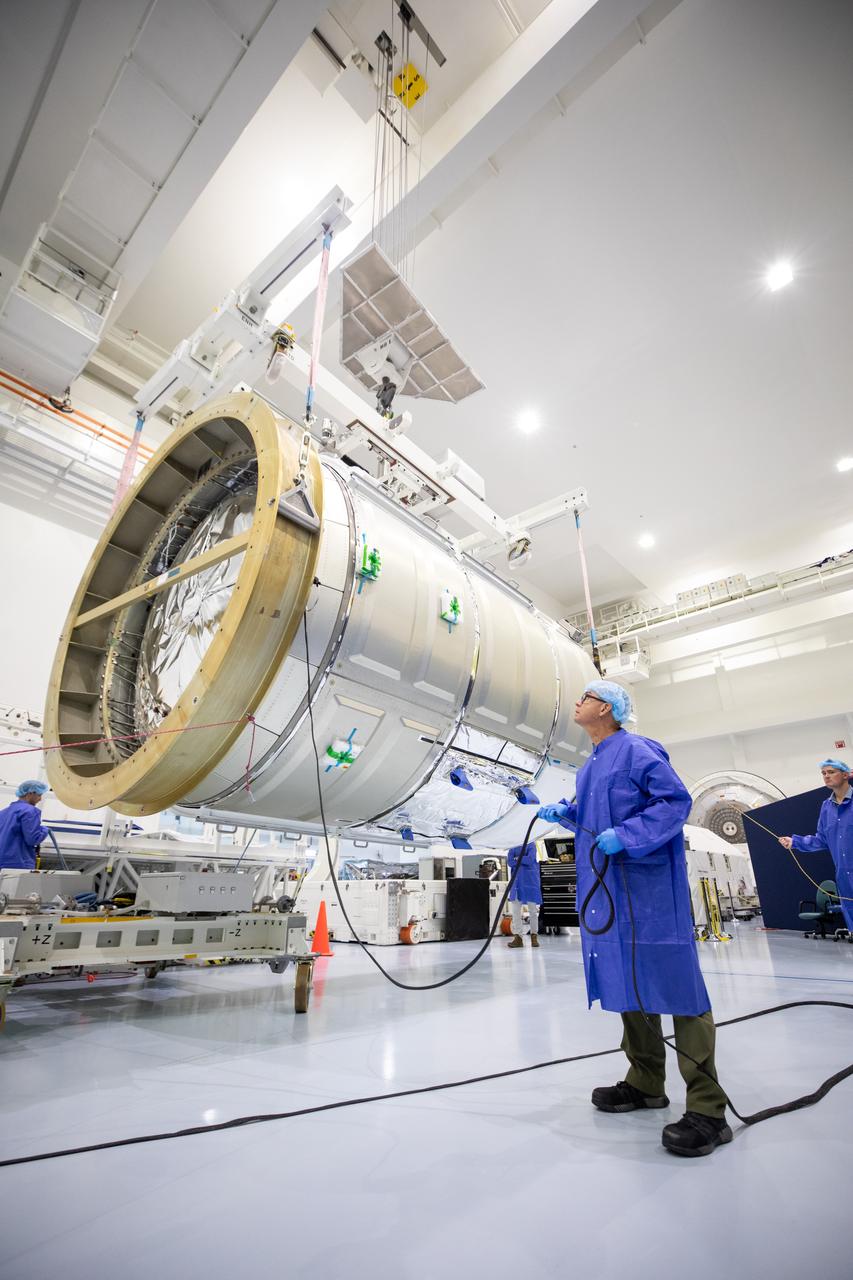

The Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft’s pressurized cargo module (PCM) for the company’s 20th commercial resupply mission is lifted and moved by crane inside the high bay in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 18, 2023. The next step is vehicle processing for the mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, will be from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40.
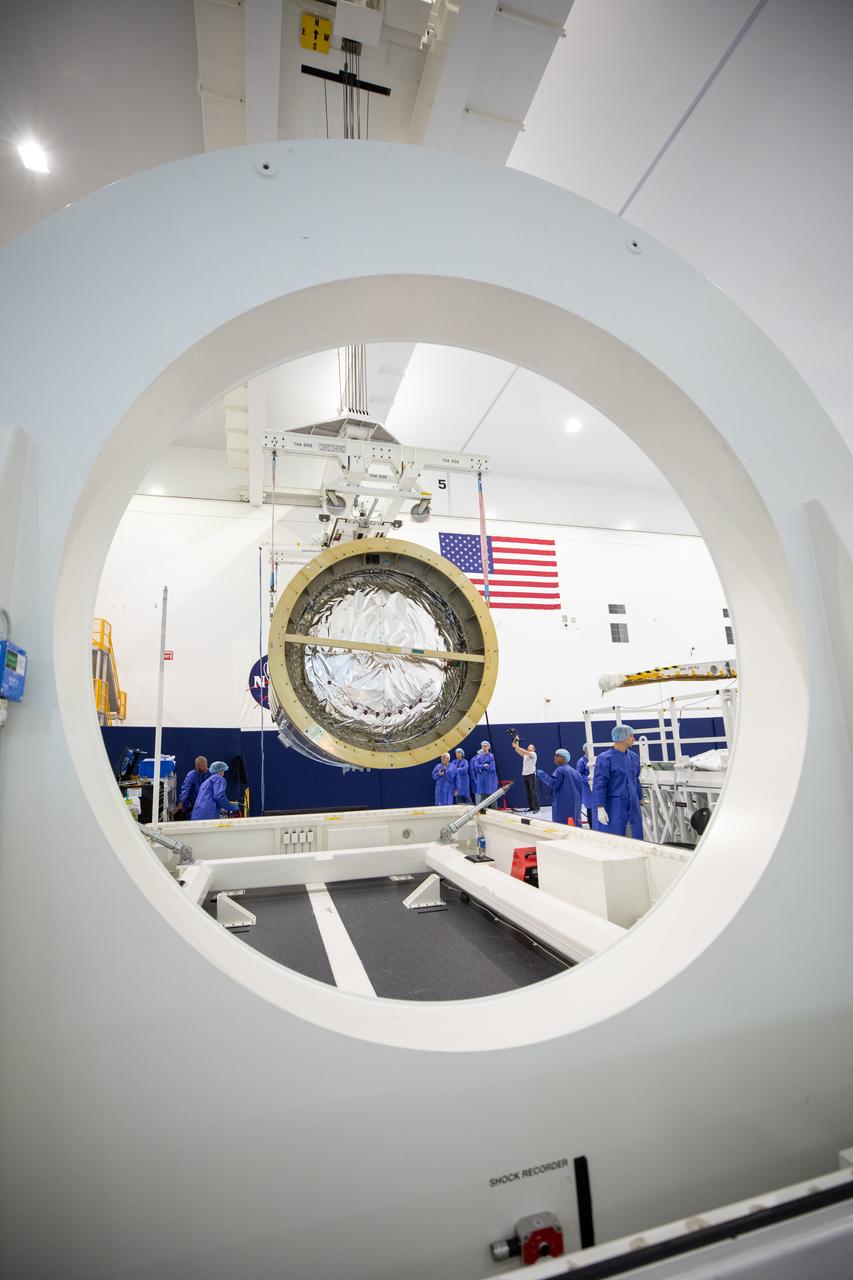

The Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft’s pressurized cargo module (PCM) for the company’s 20th commercial resupply mission is lifted and moved by crane inside the high bay in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 18, 2023. The next step is vehicle processing for the mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, will be from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40.
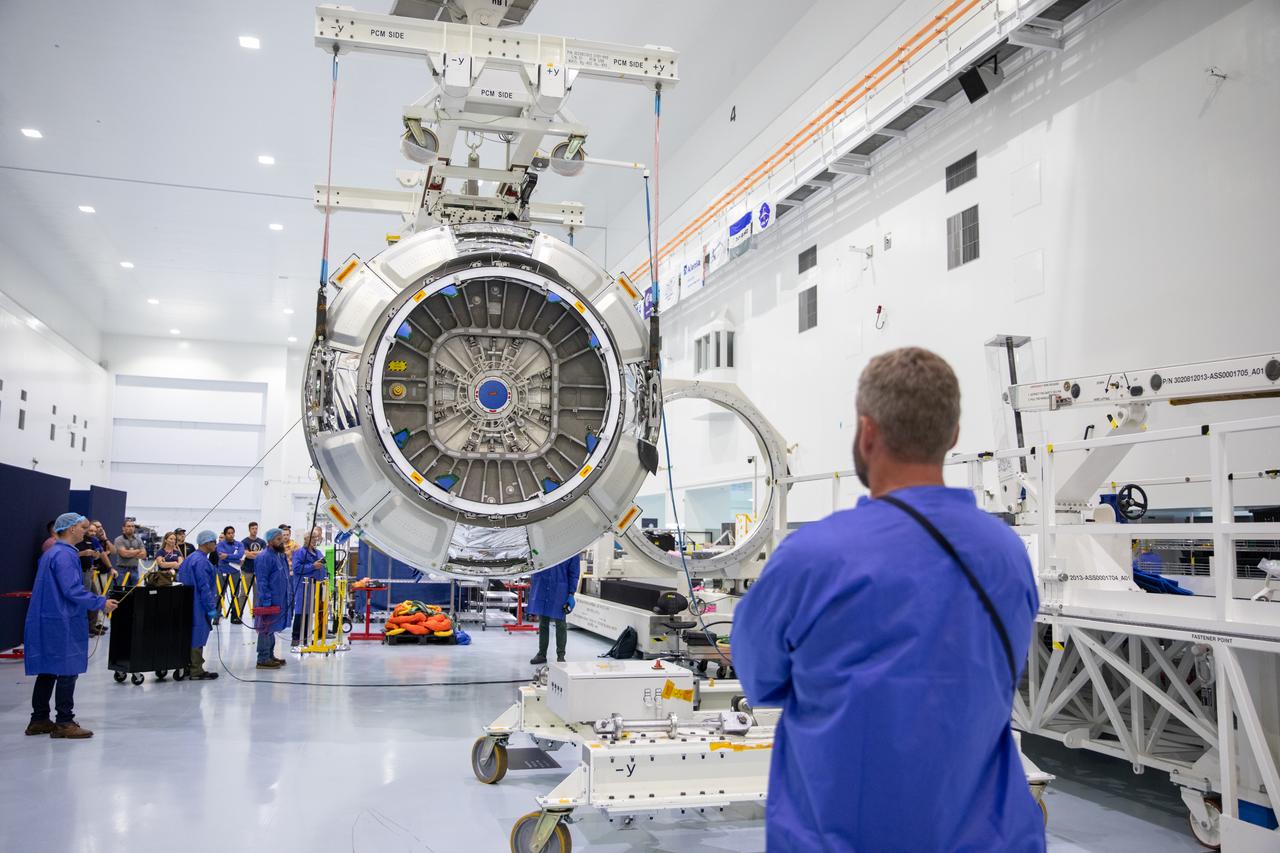

The Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft’s pressurized cargo module (PCM) for the company’s 20th commercial resupply mission is lifted and moved by crane inside the high bay in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 18, 2023. The next step is vehicle processing for the mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, will be from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40.
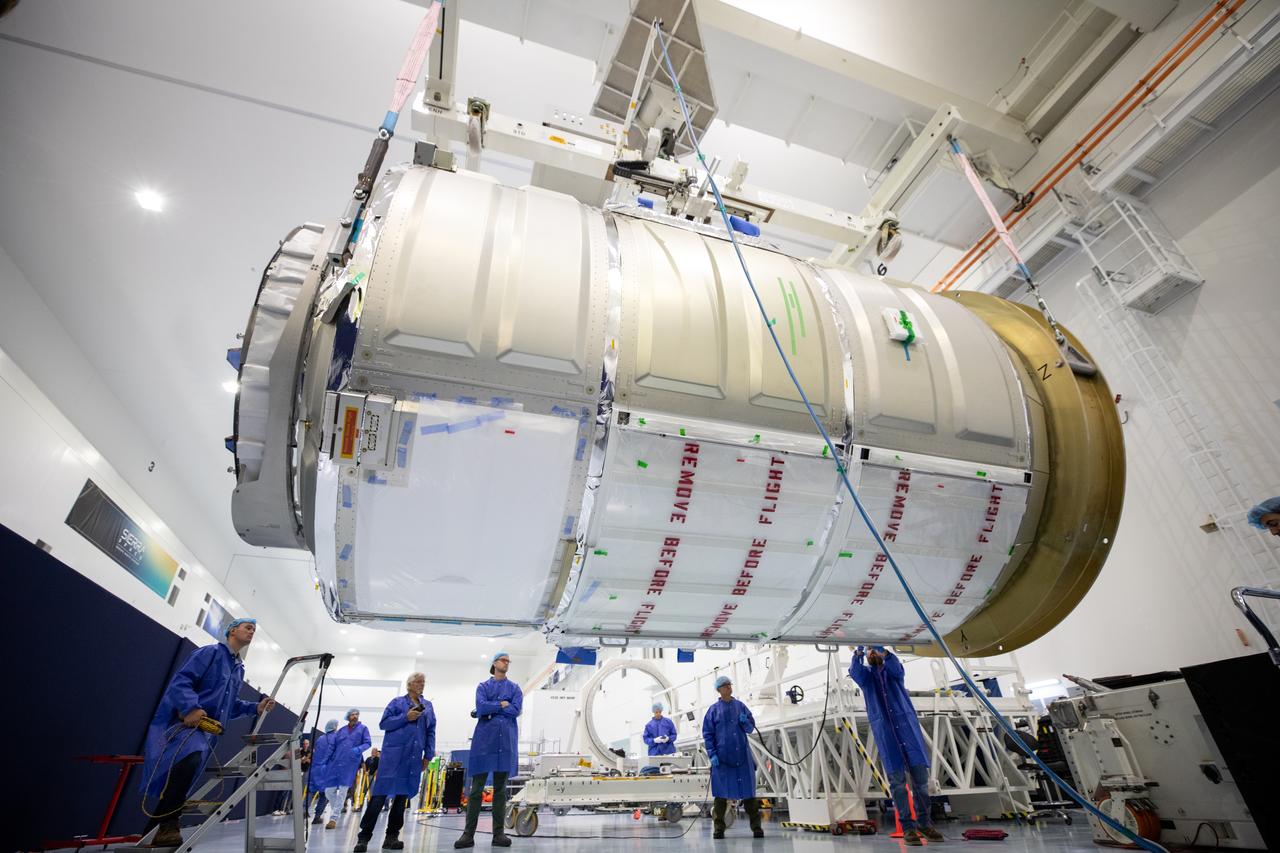

The Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft’s pressurized cargo module (PCM) for the company’s 20th commercial resupply mission is lifted and moved by crane inside the high bay in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 18, 2023. The next step is vehicle processing for the mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, will be from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40.
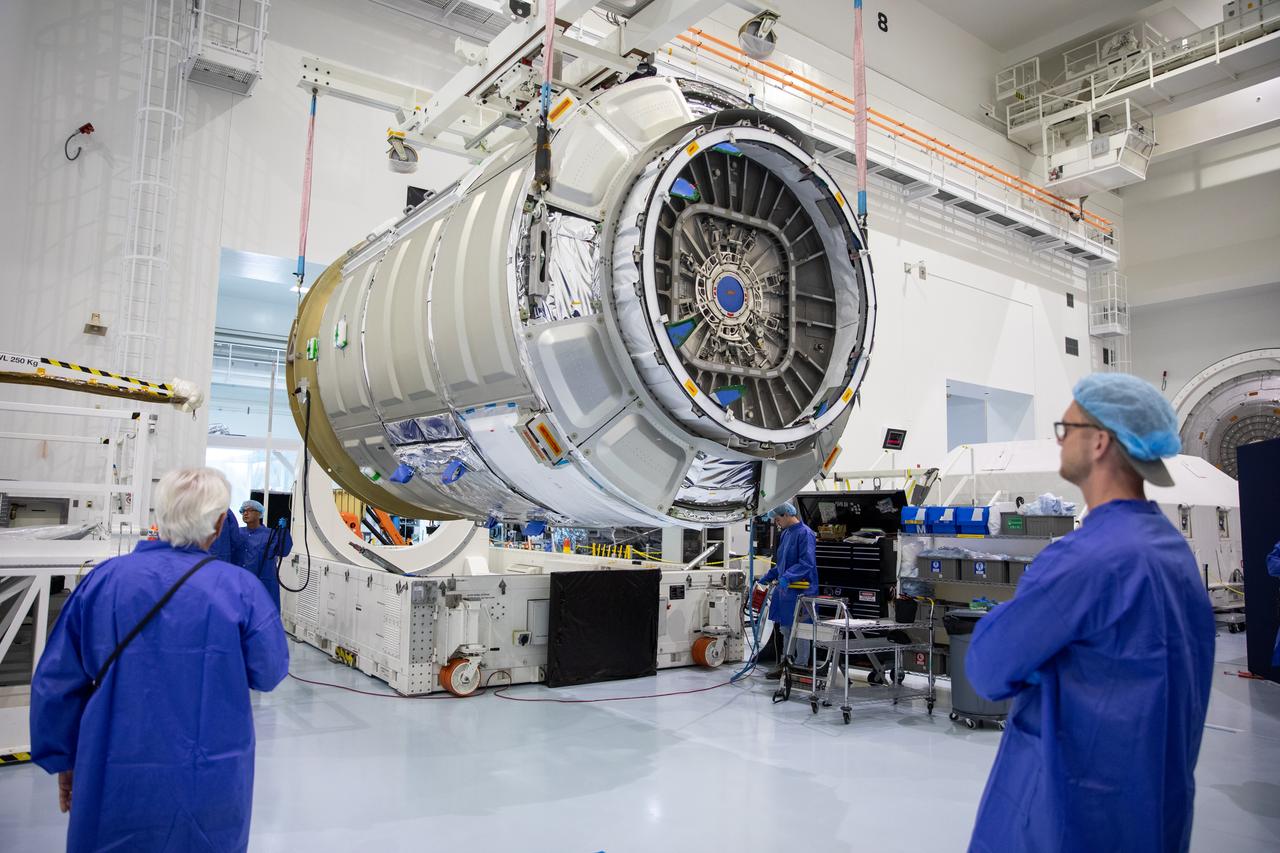

The Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft’s pressurized cargo module (PCM) for the company’s 20th commercial resupply mission is lifted and moved by crane inside the high bay in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 18, 2023. The next step is vehicle processing for the mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, will be from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40.
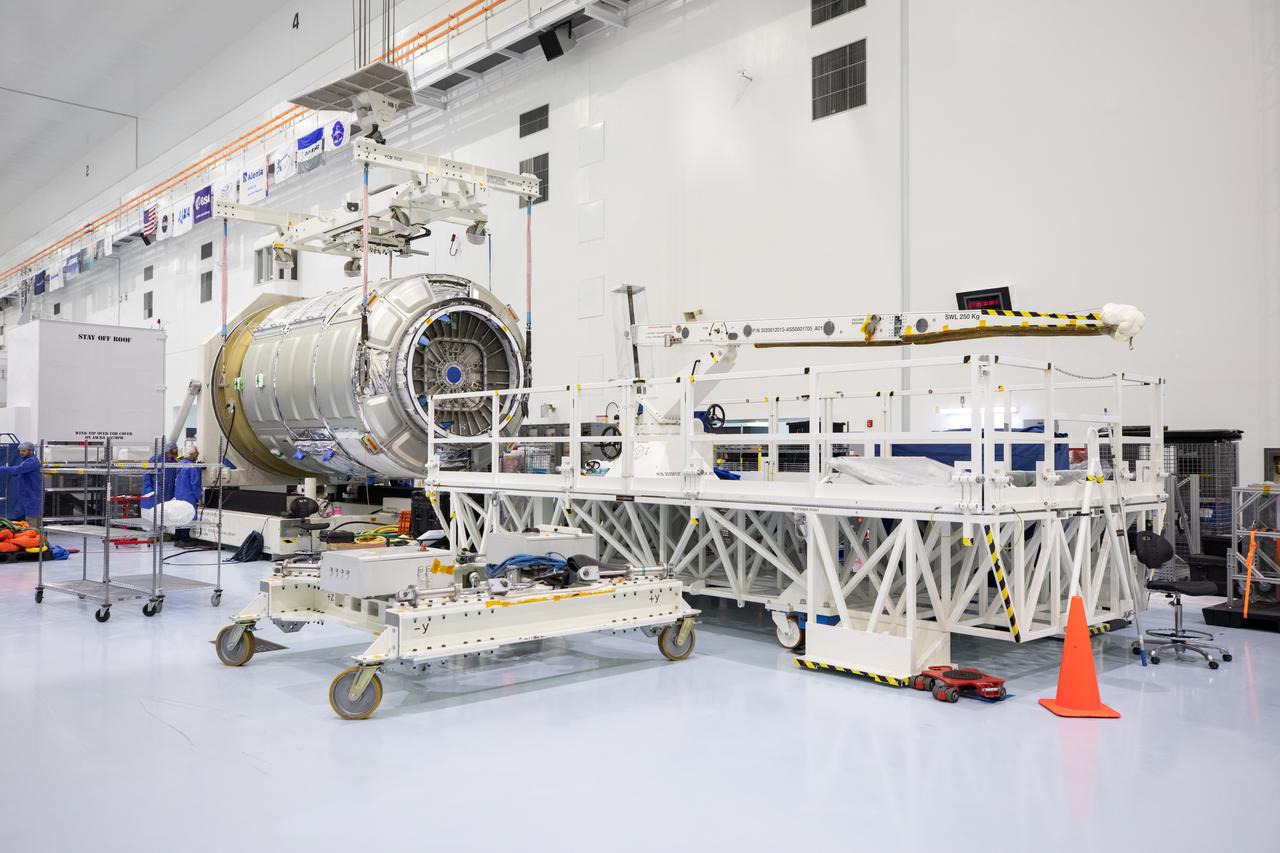

The Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft’s pressurized cargo module (PCM) for the company’s 20th commercial resupply mission is lifted and moved by crane inside the high bay in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 18, 2023. The next step is vehicle processing for the mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, will be from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40.
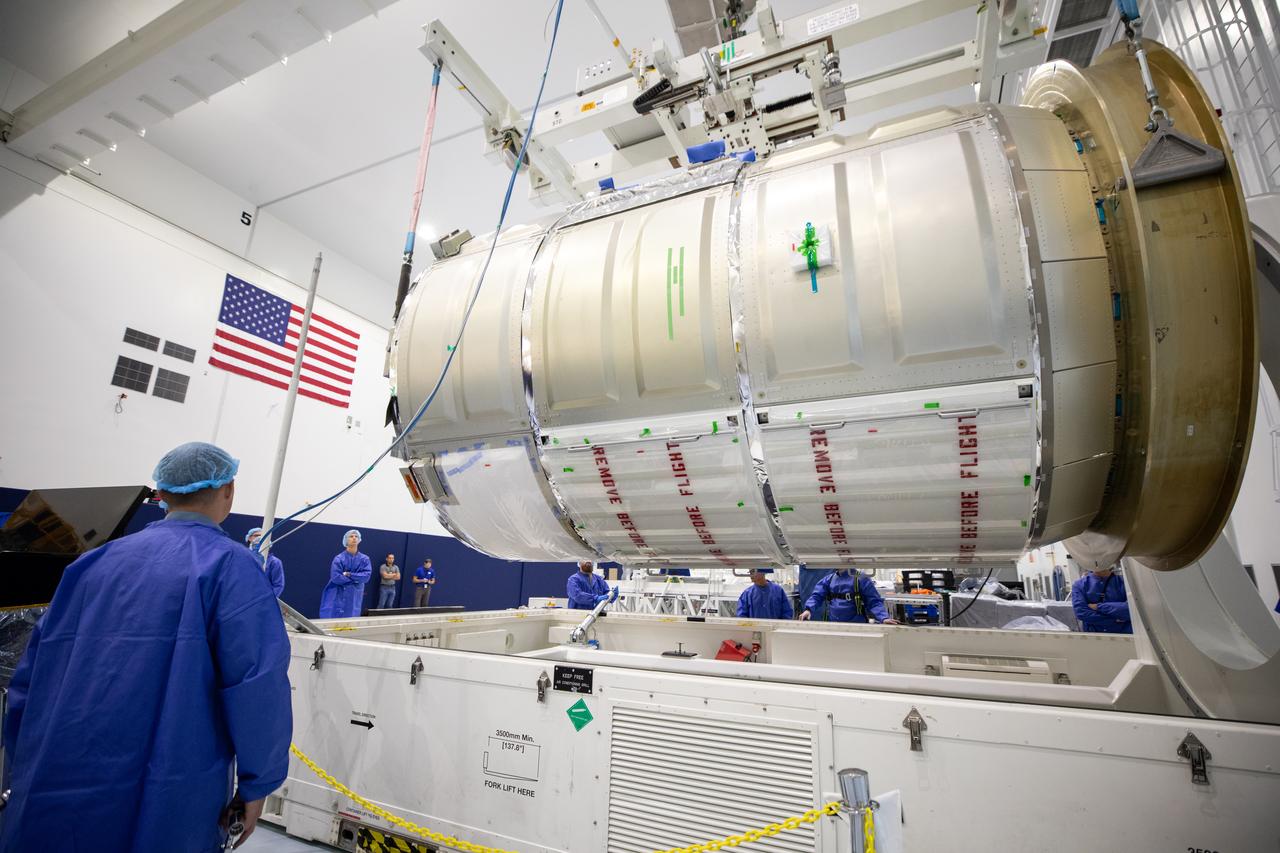

The Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft’s pressurized cargo module (PCM) for the company’s 20th commercial resupply mission is lifted and moved by crane inside the high bay in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Sept. 18, 2023. The next step is vehicle processing for the mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff, aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, will be from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40.
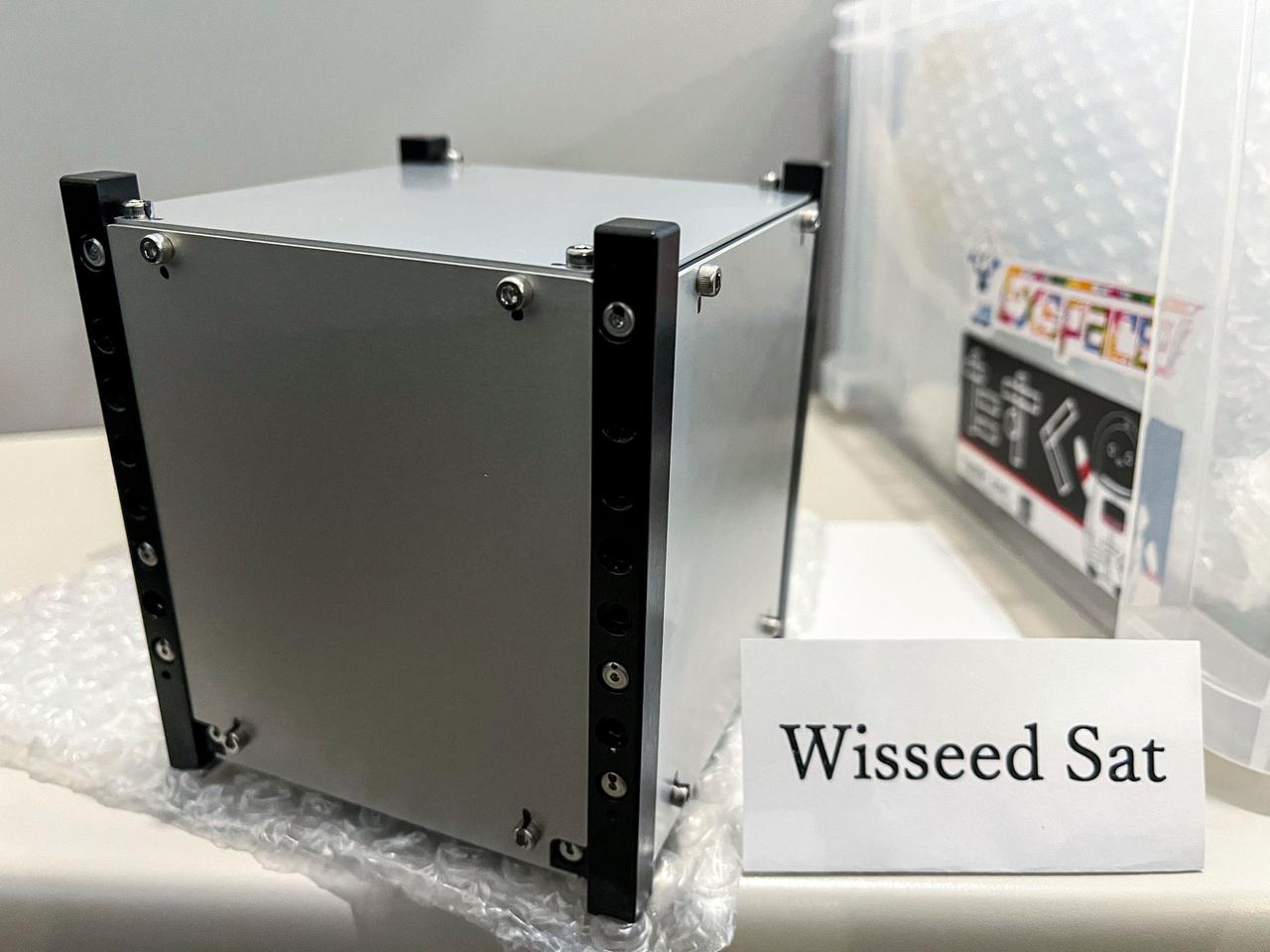

jsc2024e043927 (3/5/2024) --- The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Wisseed CubeSat is shown from the front. It is deployed on the J-SSOD-31 mission, and launched on NG-21. Image courtesy of Task Inc. and Exspace Inc.
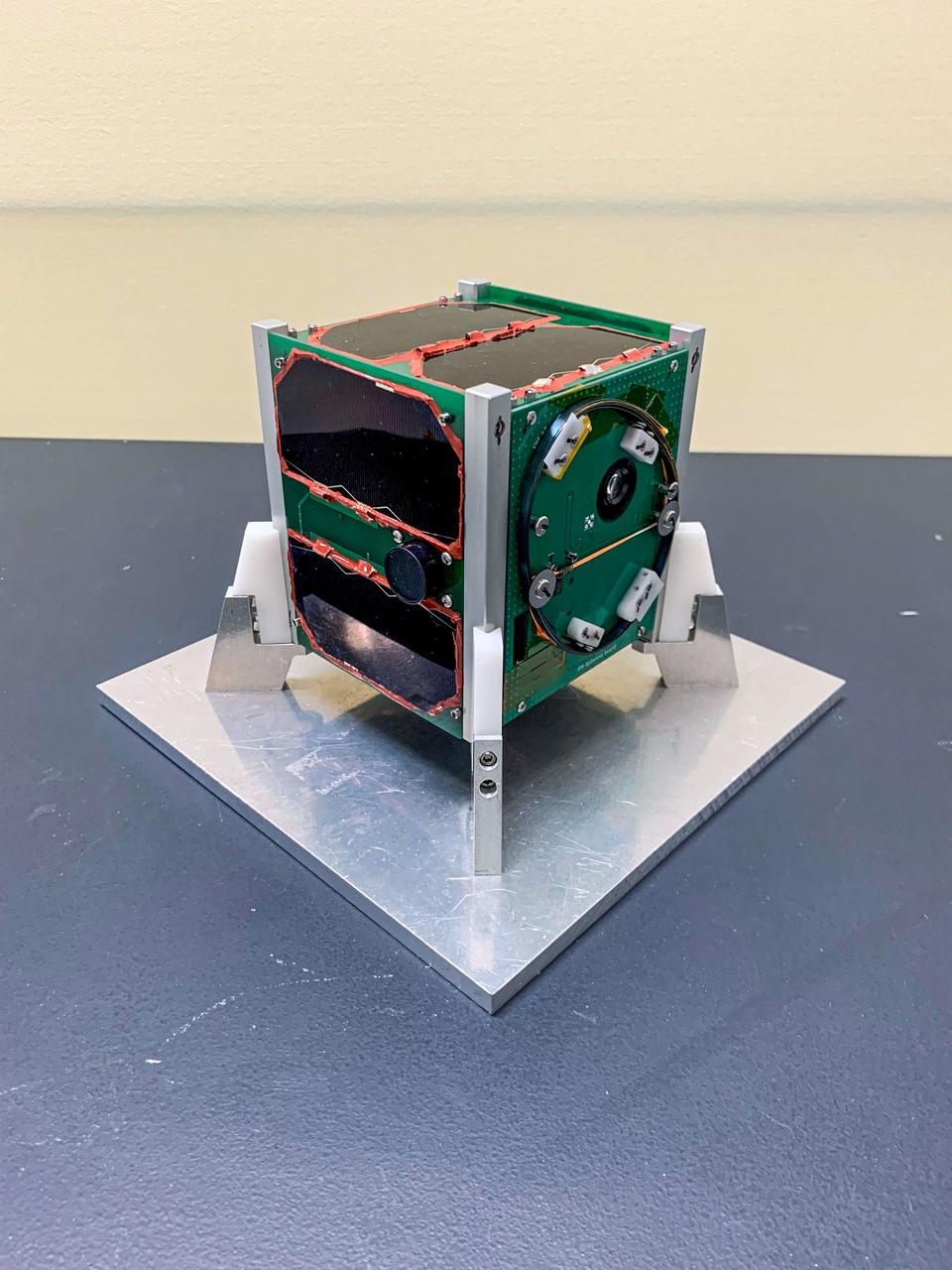
jsc2024e043925 (3/23/2024) ---The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) SaganSat0 CubeSat is deployed on the J-SSOD-31 mission and launched on NG-21. Image courtesy of Saga Prefectural Space and Science Museum.
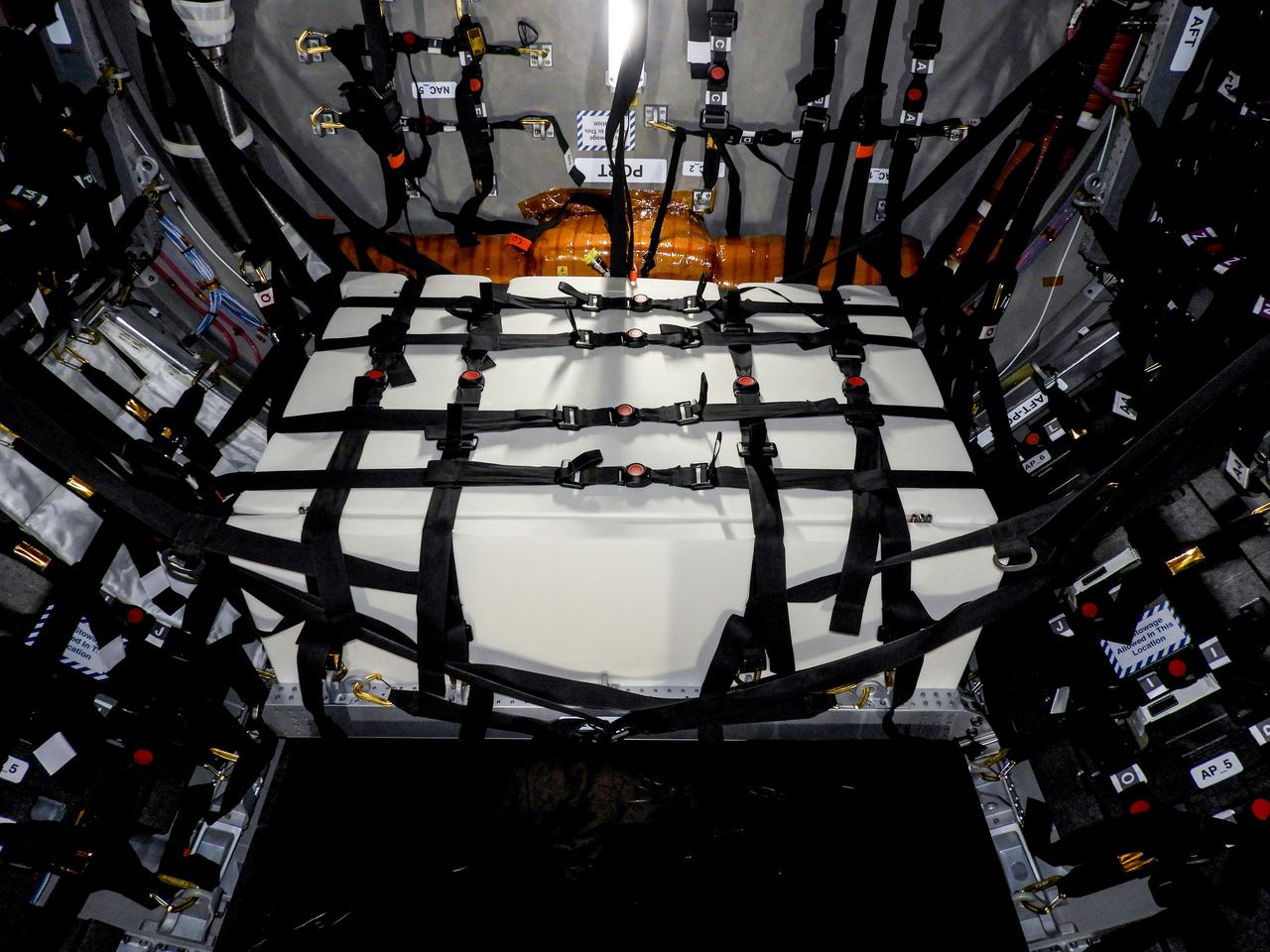
jsc2023e046377 (12/14/2019) --- A view of the Spacecraft Fire Safety Experiments (Saffire) VI experiment hardware, loaded inside the Northrop Grumman (NG) Cygnus cargo vehicle for the 19th NG resupply mission to the International Space Station. Saffire is a series of experiments to investigate how fire spreads on a variety of combustible materials in the microgravity environment. The experiments are ignited in the Cygnus cargo spacecraft after it departs the space station and before it reenters the Earth's atmosphere. Saffire-VI builds on prior results to test flammability at different oxygen levels and aims to further knowledge of realistic flame spread to aid the development of fire safety equipment and strategies for future spacecraft.
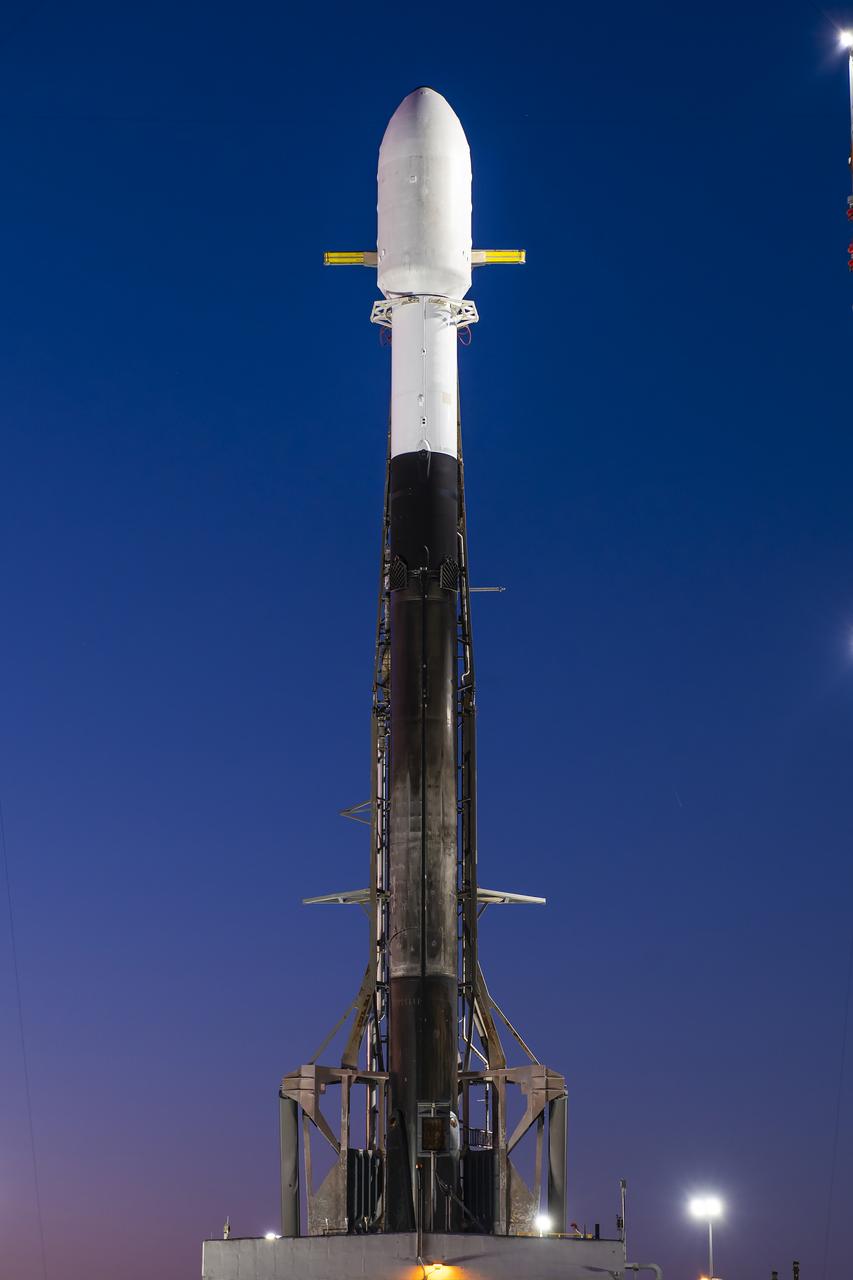

A Northrop Grumman Cygnus resupply spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, stands tall at sunrise at Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024, in preparations for a launch to the International Space Station. Northrop Grumman’s 20th commercial resupply mission includes multiple science investigations, such as tests of a 3D metal printer, semiconductor manufacturing, and thermal protection systems for reentry to Earth to support the agency’s Expedition 70 crew. Liftoff is scheduled for 12:07p.m. EST Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024.
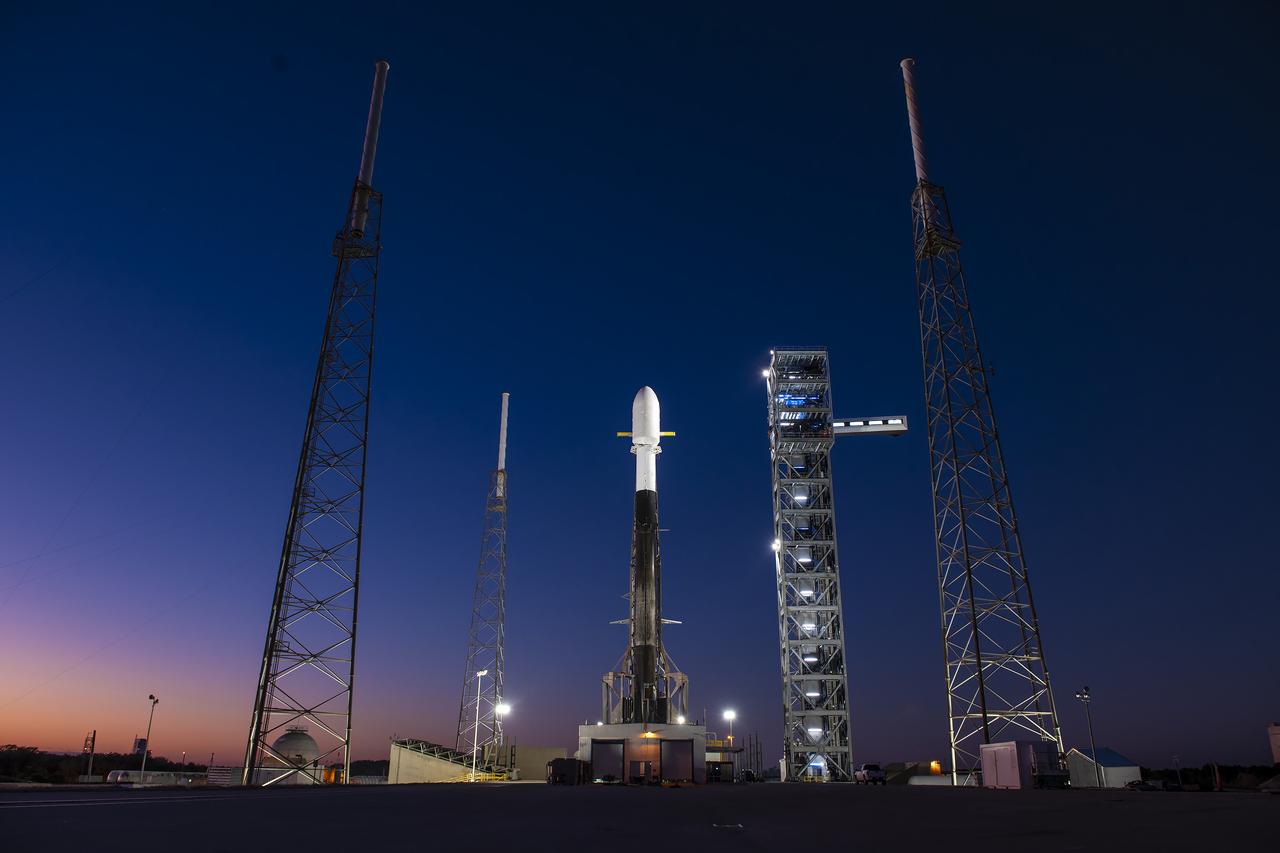

A Northrop Grumman Cygnus resupply spacecraft, atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket, stands tall at sunrise at Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida on Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024, in preparations for a launch to the International Space Station. Northrop Grumman’s 20th commercial resupply mission includes multiple science investigations, such as tests of a 3D metal printer, semiconductor manufacturing, and thermal protection systems for reentry to Earth to support the agency’s Expedition 70 crew. Liftoff is scheduled for 12:07p.m. EST Tuesday, Jan. 30, 2024.
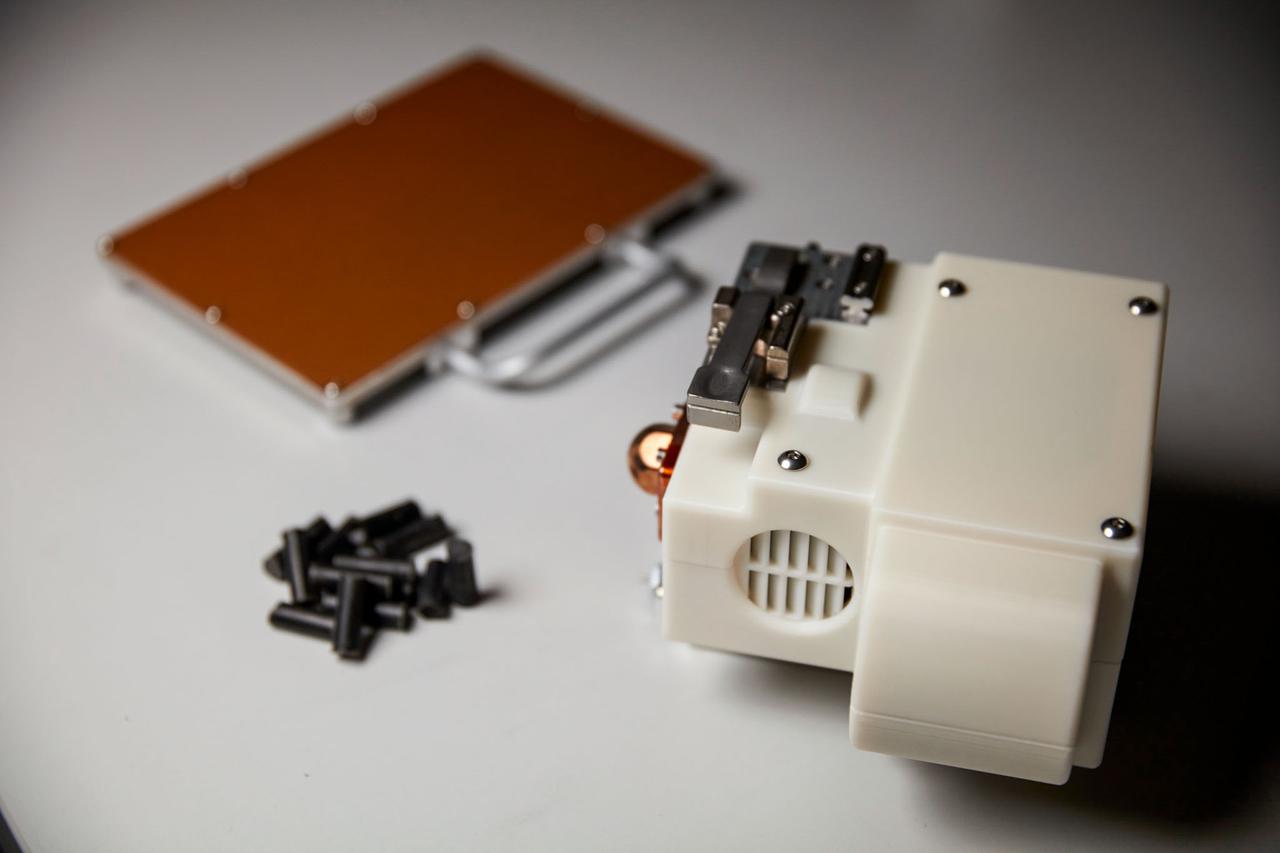

jsc2021e031161 (7/22/2021) --- A preflight view of the Redwire Regolith Print (RRP) facility suite launching aboard NG-16, including the RRP print heads, plates and lunar regolith simulant feedstock Photo courtesy of Redwire Space.
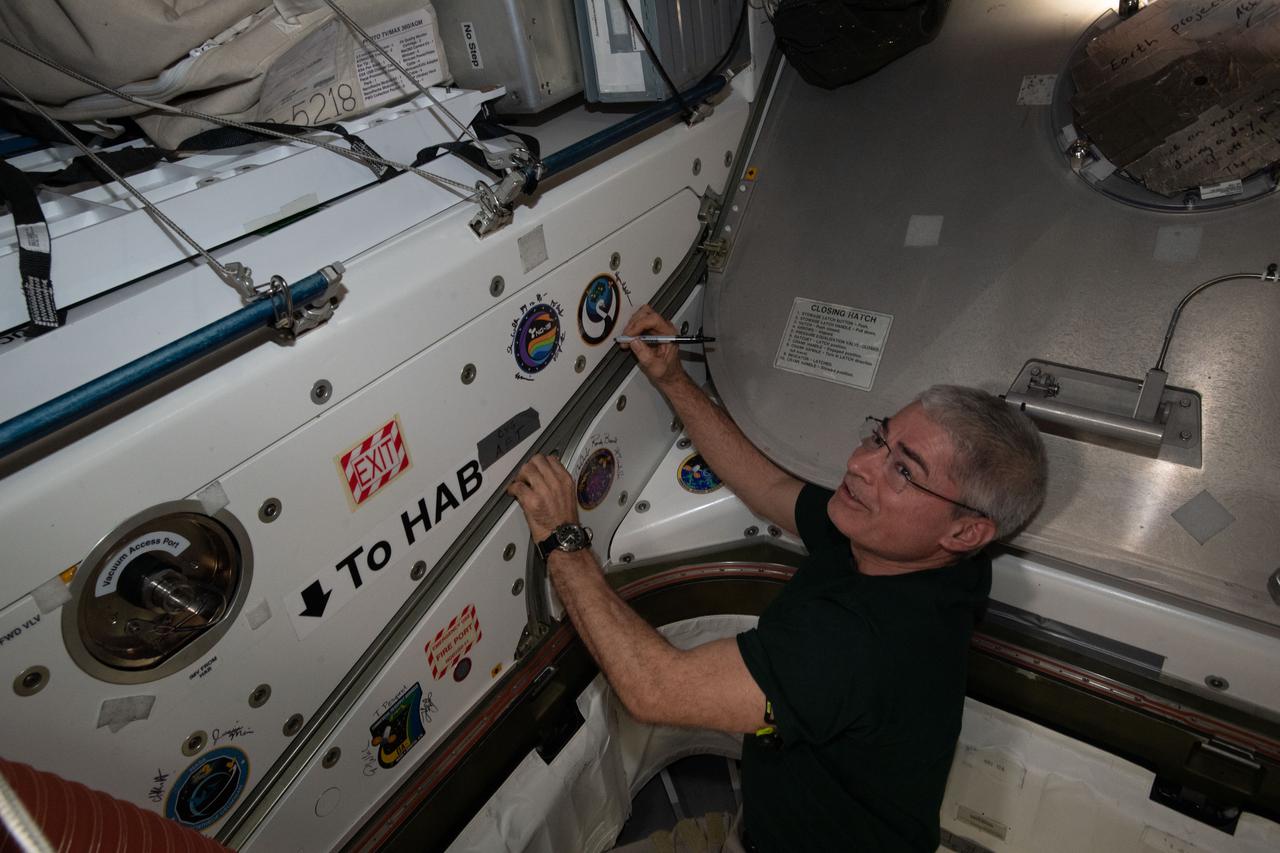

iss065e389501 (Sept. 17, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Mark Vande Hei signs his name around the Northrop Grumman-16 (NG-16) mission insignia sticker affixed to the vestibule in between the Unity module and the Cygnus space freighter.
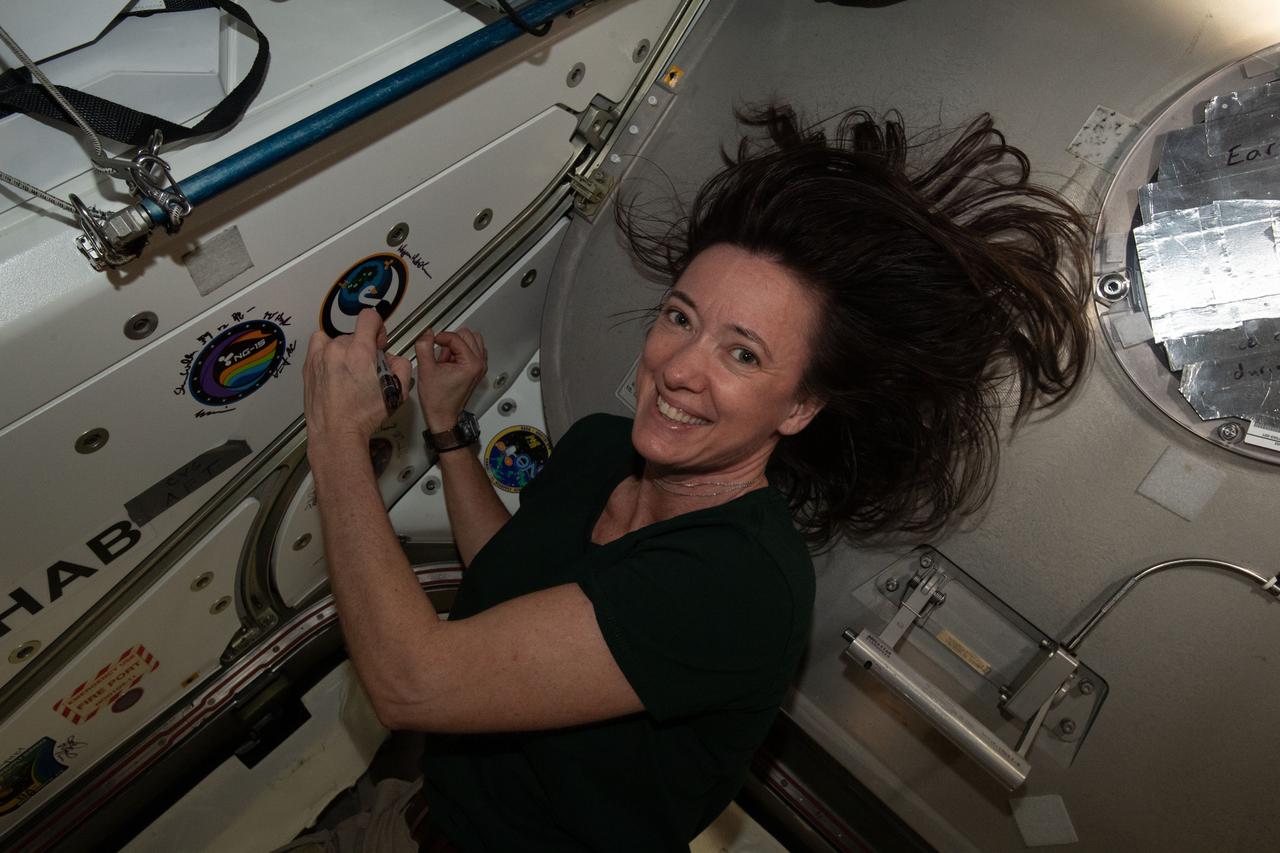

iss065e389491 (Sept. 17, 2021) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 65 Flight Engineer Megan McArthur signs her name around the Northrop Grumman-16 (NG-16) mission insignia sticker affixed to the vestibule in between the Unity module and the Cygnus space freighter.
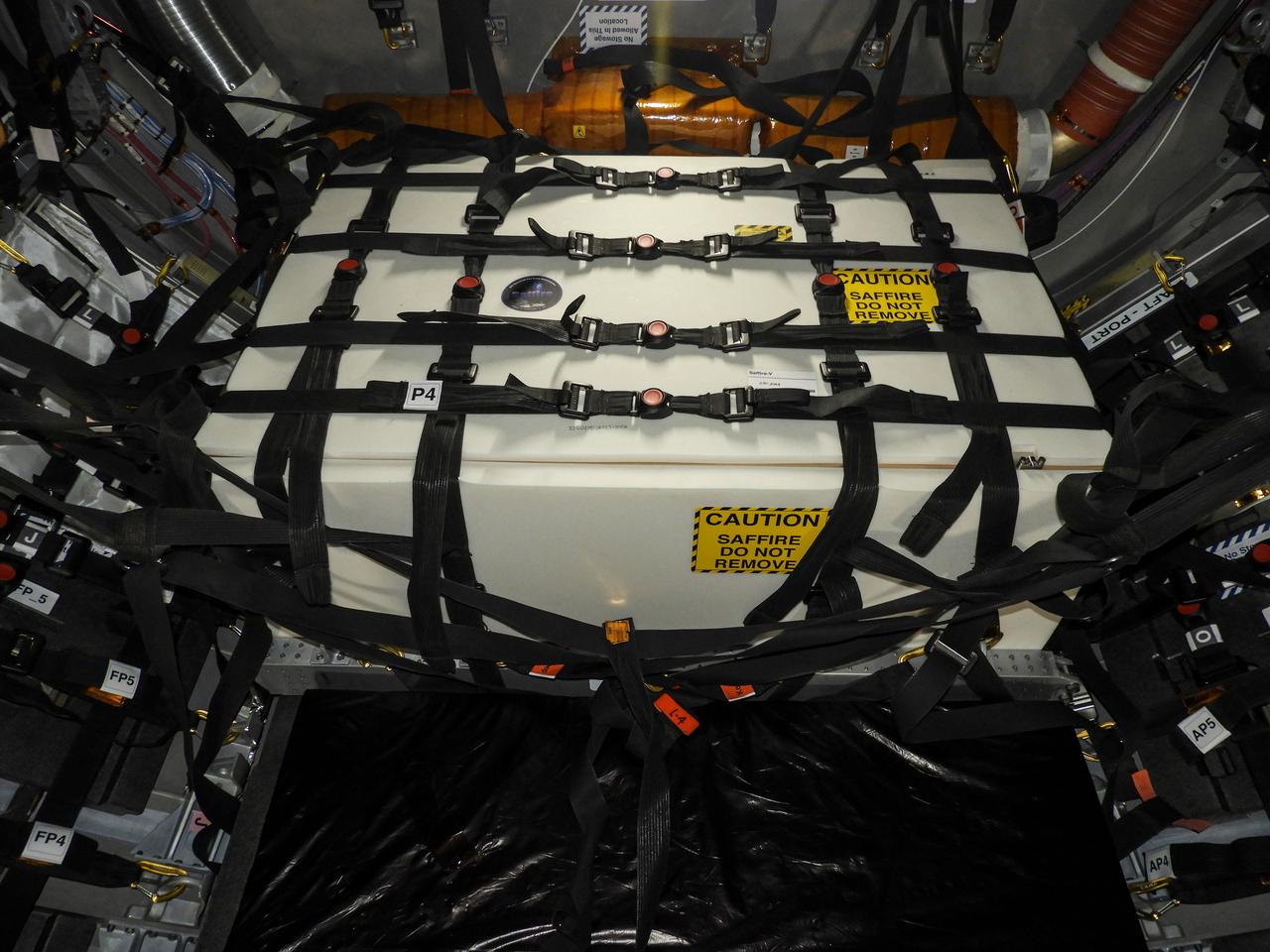

jsc2020e043815 (Sept. 10, 2020) --- A view of the Spacecraft Fire Safety Experiments (Saffire) V experiment hardware, loaded inside the Northrop Grumman(NG) Cygnus cargo vehicle for the 14th NG resupply mission to the International Space Station. Saffire is a series of experiments to investigate how fire spreads on a variety of combustible materials in the microgravity environment. The experiments are ignited in Cygnus cargo spacecraft after it departs the space station and before it reenters the Earth's atmosphere. Studying the development and growth of fire in a re-supply cargo vehicle eliminates the risk of exposure to humans in an occupied spacecraft. Understanding how fire behaves in microgravity, and how different materials propagate flames in space is immensely important for the development of future crew spacecraft.
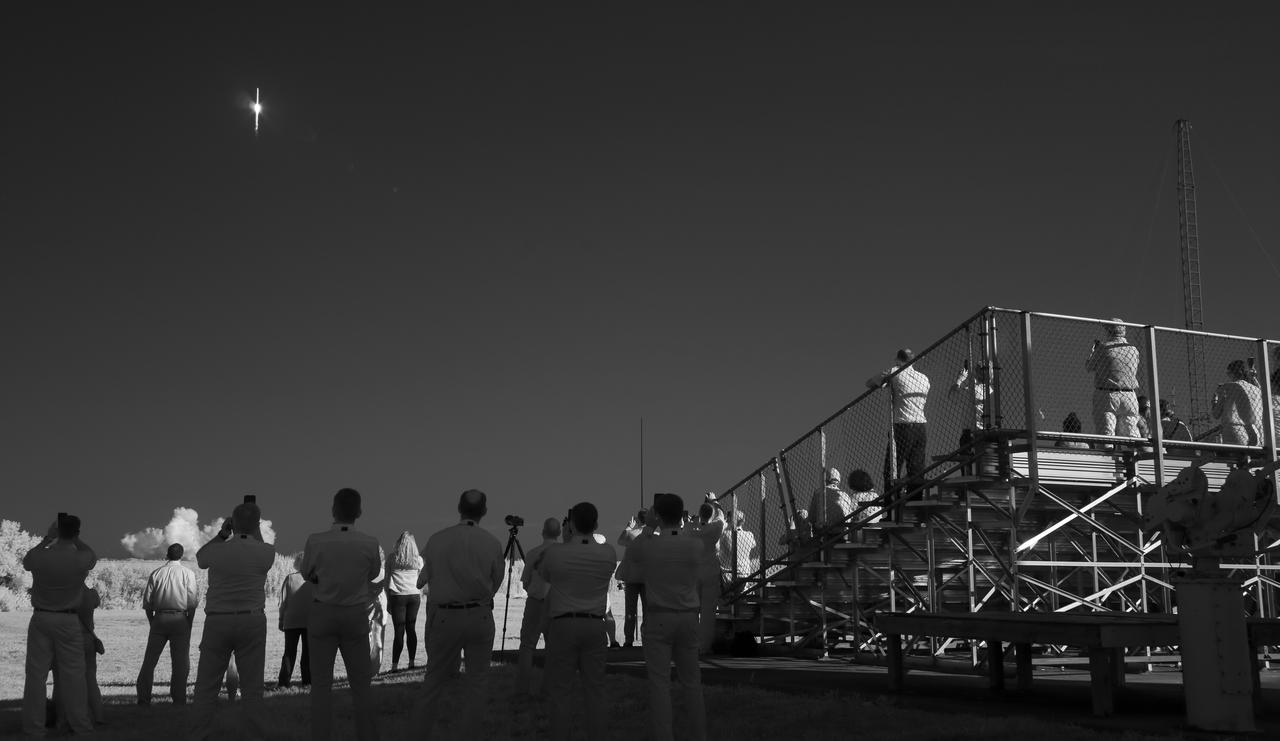

In this black and white infrared image, a Northrop Grumman Antares rocket carrying a Cygnus resupply spacecraft launches from Pad-0A of the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport, Tuesday, Aug. 10, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman’s 16th contracted cargo resupply mission with NASA will deliver nearly 8,200 pounds of science and research, crew supplies and vehicle hardware to the International Space Station and its crew. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
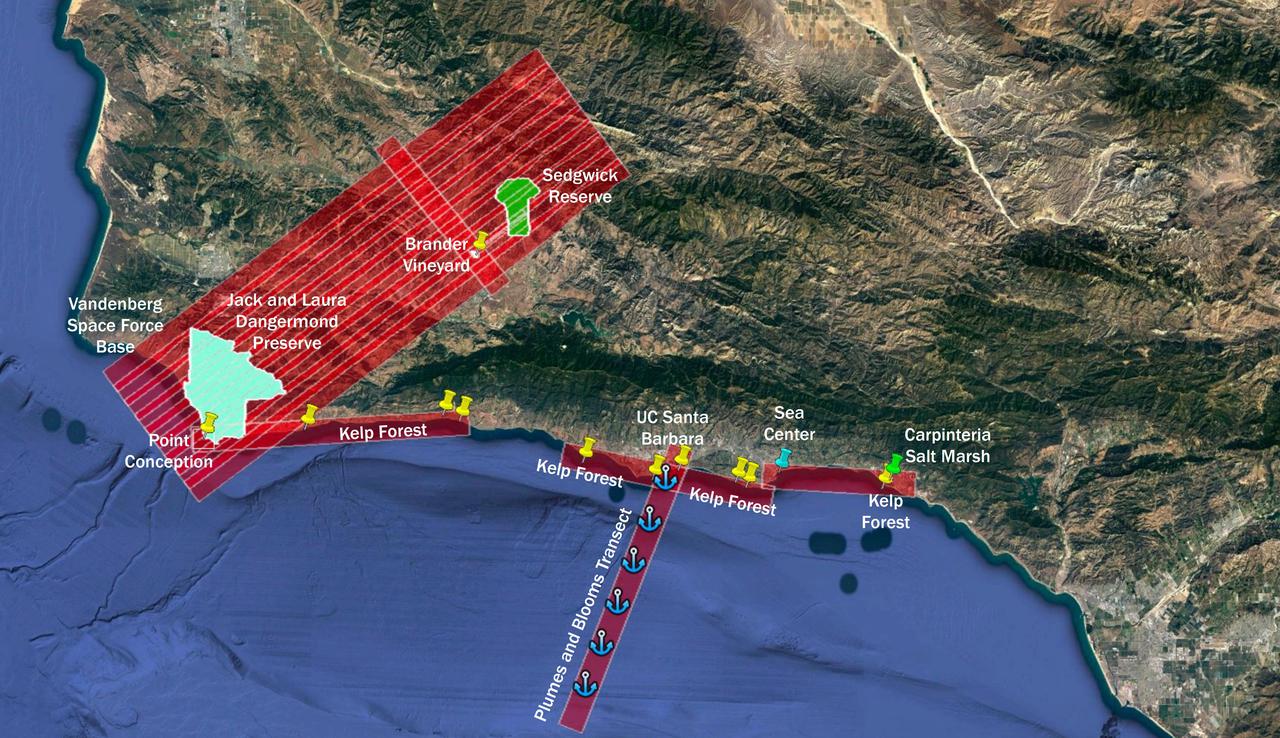
The Surface Biology and Geology High-Frequency Time Series (SHIFT) campaign employs a research plane carrying the AVIRIS-NG (Airborne Visible/Infrared Imaging Spectrometer-Next Generation) instrument. From late February to late May 2022, the plane is collecting spectral data of land and aquatic plant communities over a 640-square-mile (1,656-square-kilometer) study area in Santa Barbara County and the nearby ocean. SHIFT is jointly led by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, the University of California, Santa Barbara (UCSB), and The Nature Conservancy. The aerial portion of SHIFT flies on an approximately weekly basis over the study area, which includes the Jack and Laura Dangermond Preserve, owned by The Nature Conservancy, and the Sedgwick Reserve, operated by UCSB. SHIFT combines the ability of airborne science instruments to gather data over widespread areas with the more concentrated observations scientists conduct in the field to study the functional characteristics, health, and resilience of plant communities. The sampling and analysis done by researchers on the ground and in the ocean is intended to validate data taken by AVIRIS-NG and help scientists design data collection and processing algorithms for NASA's proposed Surface Biology and Geology (SBG) mission, which would launch no earlier than 2028. The data is also intended to support the research and conservation objectives of The Nature Conservancy, which owns the Dangermond Preserve, and UCSB, which operates the Sedgwick Reserve, another nature preserve within the study area. More than 60 scientists from institutions around the U.S. have indicated they intend to use the SHIFT data in their research. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25144
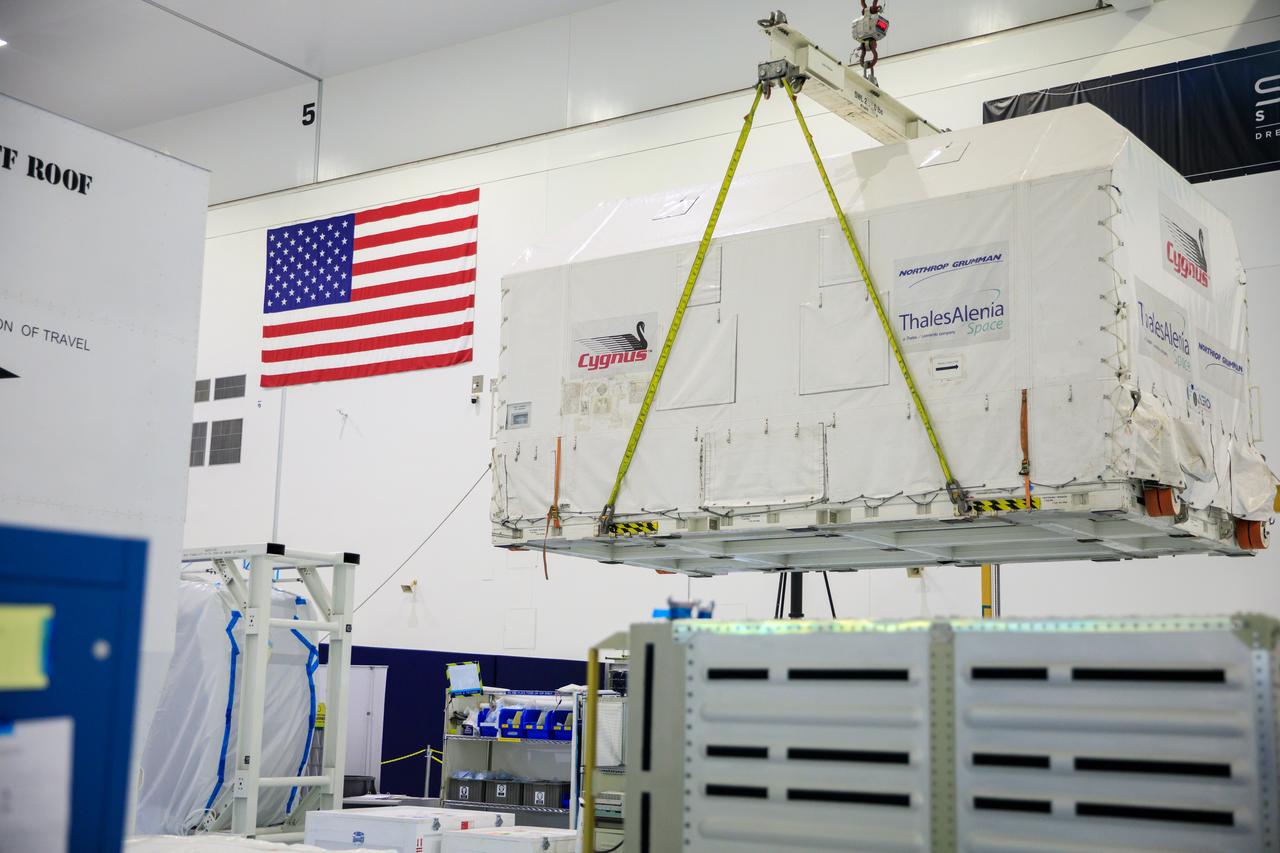

The Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft’s pressurized cargo module (PCM) for the company’s 20th commercial resupply mission is moved by crane in its environmentally controlled shipping container in to the Space Station Processing Facility’s high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 2, 2023. Cygnus will launch later this year atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40 to the International Space Station. Cygnus will undergo prelaunch processing at Kennedy before it is transported to SpaceX’s integration facility.

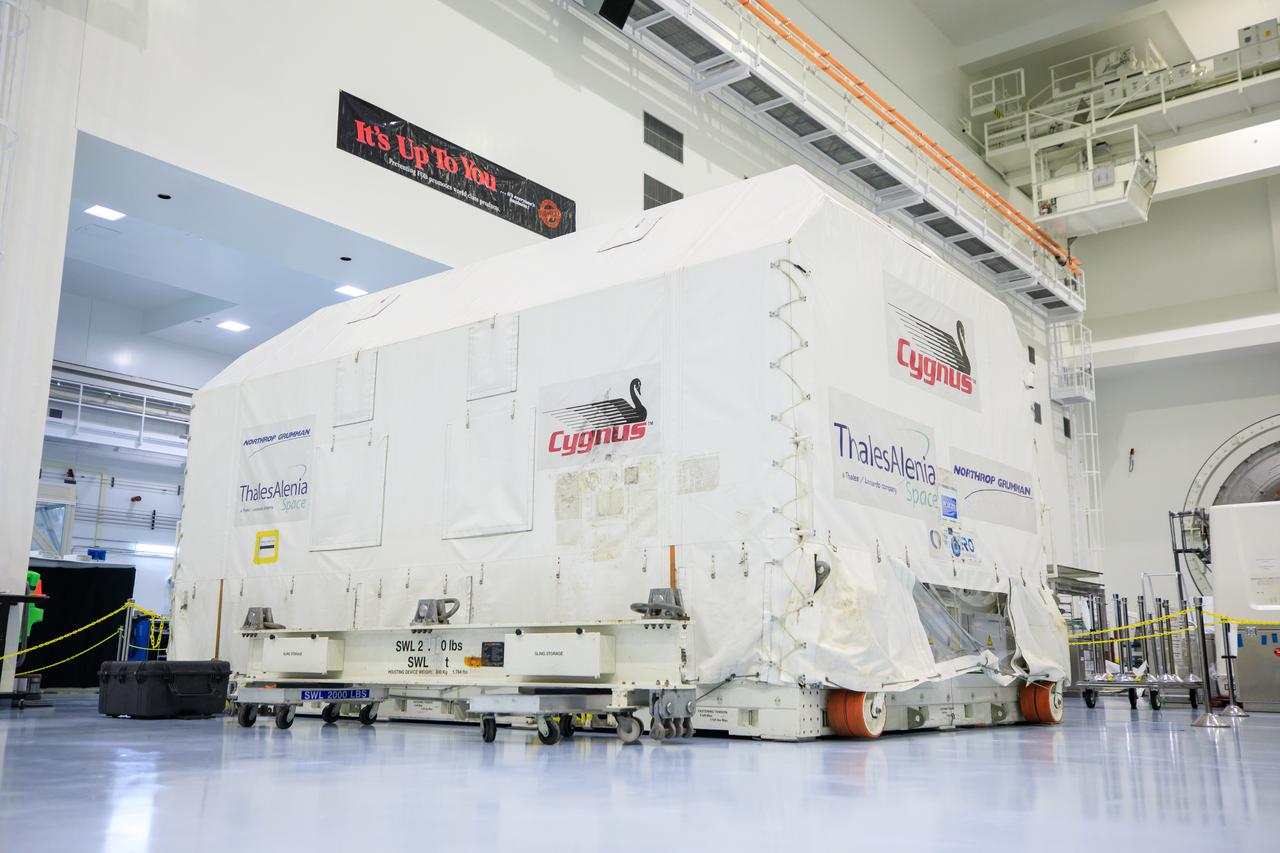
The Cygnus pressurized cargo module for Northrop Grumman’s 20th commercial resupply mission is lowered by crane in its carrier and secured onto a transport base inside the low bay in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 2, 2023. Cygnus will launch later this year atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40 to the International Space Station. Cygnus will undergo prelaunch processing at Kennedy before it is transported to SpaceX’s integration facility.

Northrop Grumman’s Cygnus pressurized cargo module for the company’s 20th commercial resupply mission arrives in its environmentally controlled shipping container inside the high bay in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 2, 2023. Cygnus will launch later this year atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40 to the International Space Station. Cygnus will undergo prelaunch processing at Kennedy before it is transported to SpaceX’s integration facility.
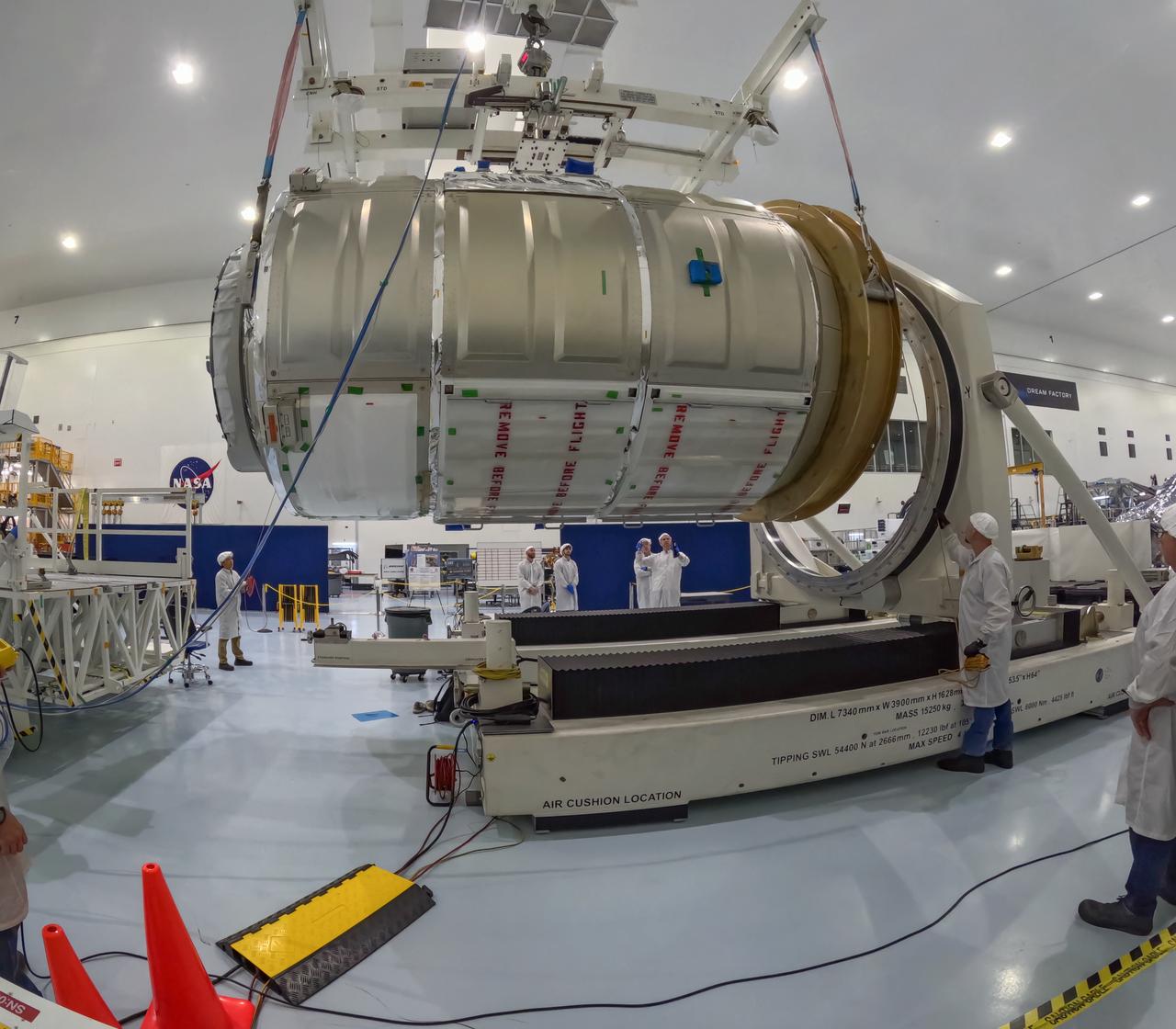

The Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft’s pressurized cargo module for the company’s 21st commercial resupply mission is lifted and moved by a crane inside the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, June 1, 2024, as prelaunch processing operations continue. The Cygnus spacecraft will launch to the International Space Station aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station.
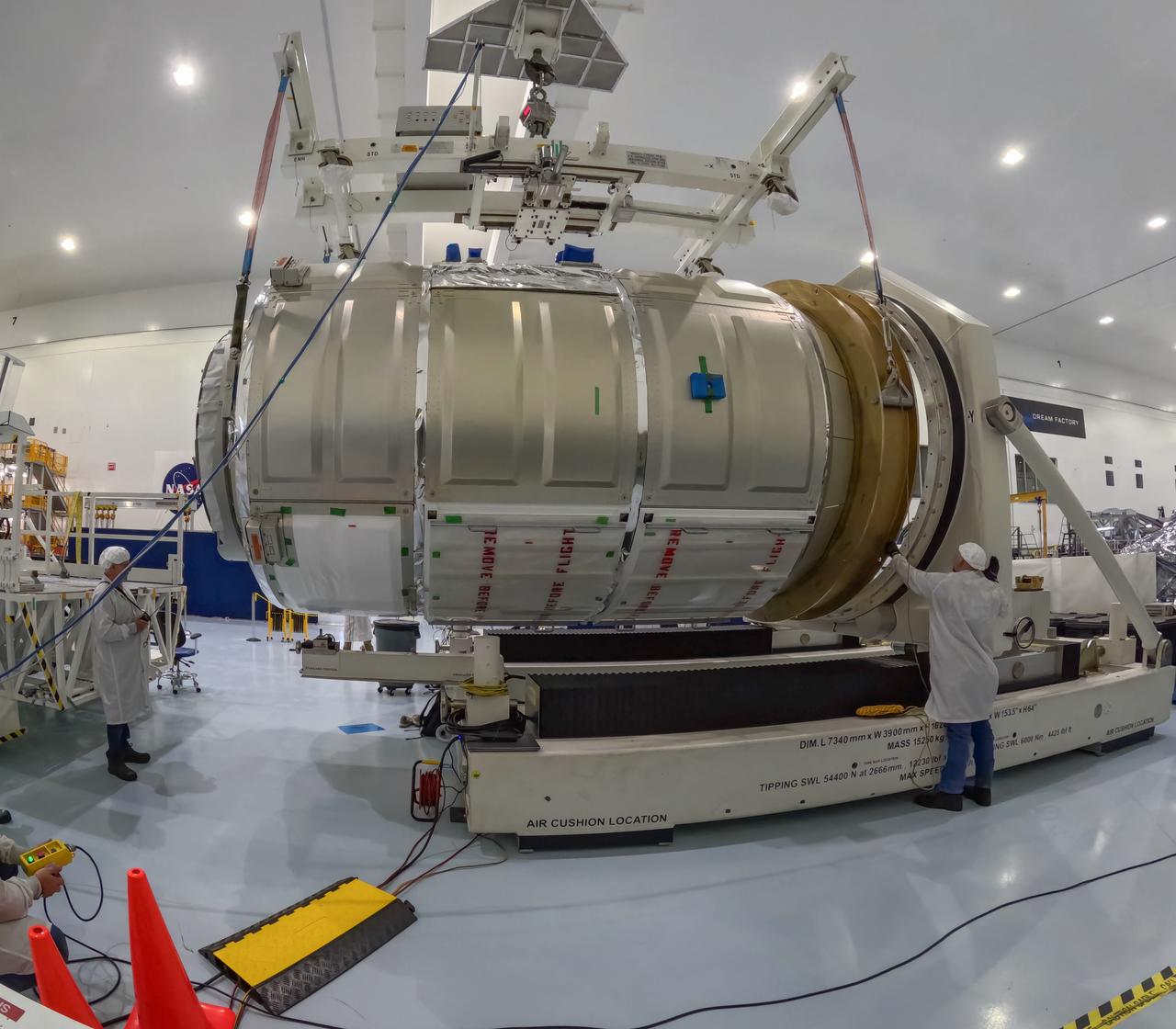

The Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft’s pressurized cargo module for the company’s 21st commercial resupply mission is lifted and moved by a crane inside the Space Systems Processing Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, June 1, 2024, as prelaunch processing operations continue. The Cygnus spacecraft will launch to the International Space Station aboard a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station.
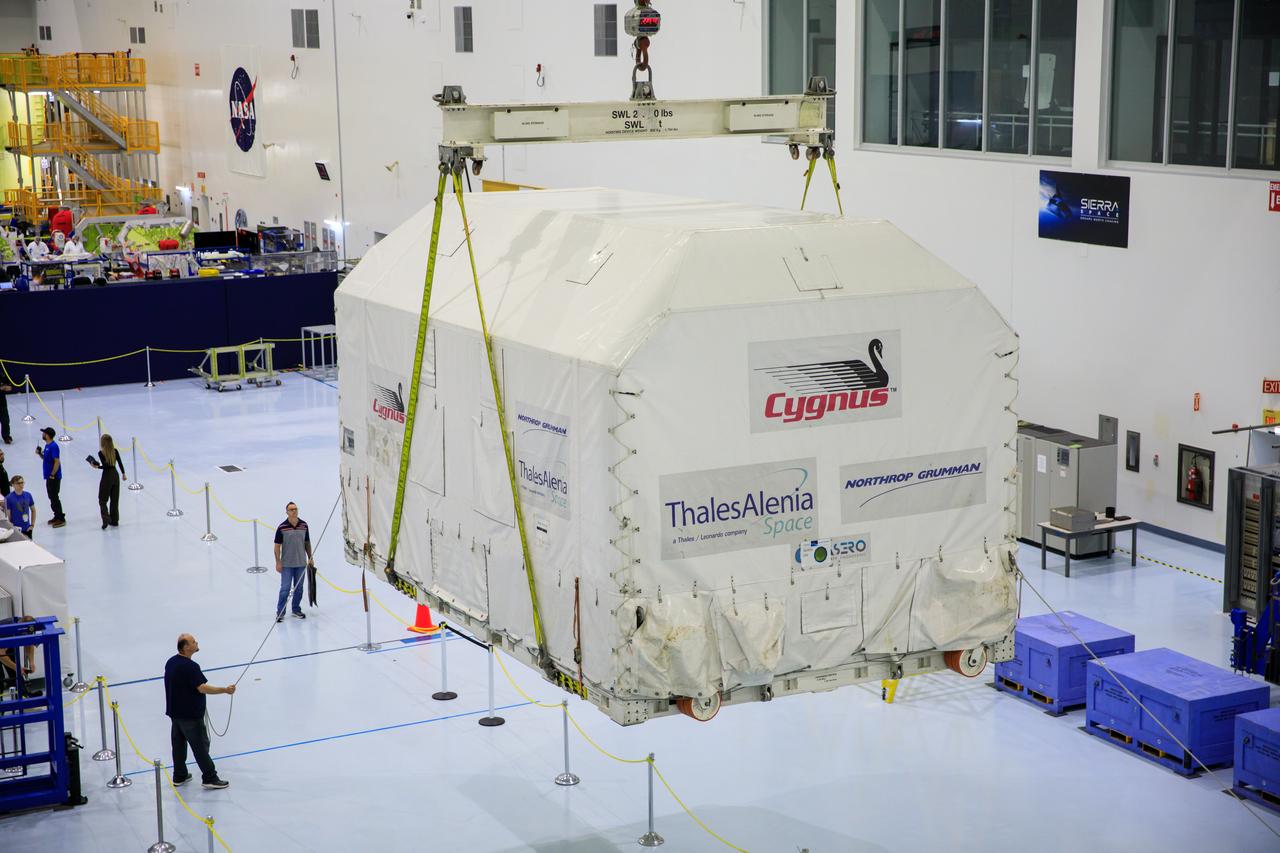

A crane is used to lift the Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft's pressurized cargo module (PCM) off a flatbed truck after arrival at the Space Station Processing Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 2, 2023. The PCM is sealed in an environmentally controlled shipping container. Cygnus will launch later this year atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40 to the International Space Station. Cygnus will undergo prelaunch processing at Kennedy before it is transported to SpaceX’s integration facility.
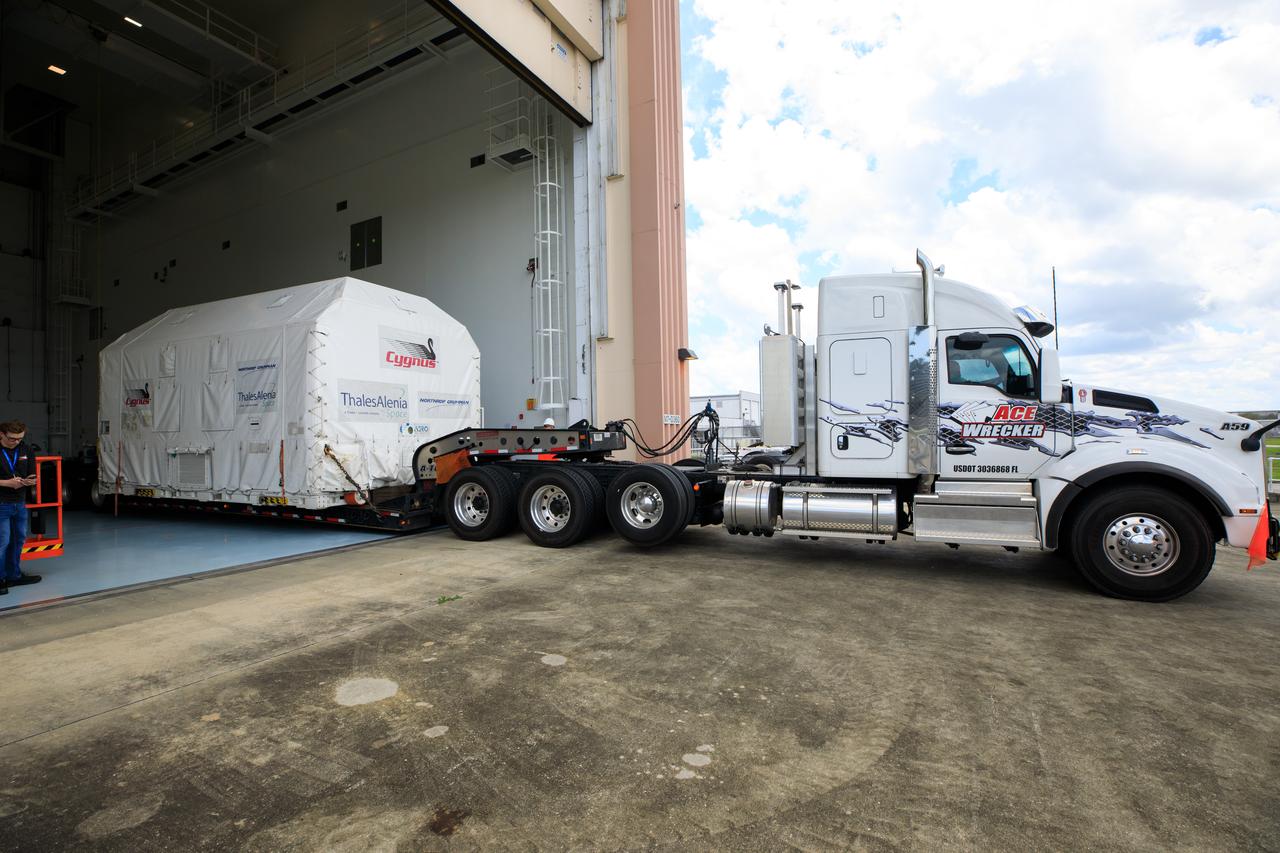

The Northrop Grumman Cygnus spacecraft's pressurized cargo module (PCM) arrives at the Space Station Processing Facility of NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 2, 2023. The PCM is sealed in an environmentally controlled shipping container, pulled in by truck on a flatbed trailer. Cygnus will launch later this year atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 40 to the International Space Station. Cygnus will undergo prelaunch processing at Kennedy before it is transported to SpaceX’s integration facility.