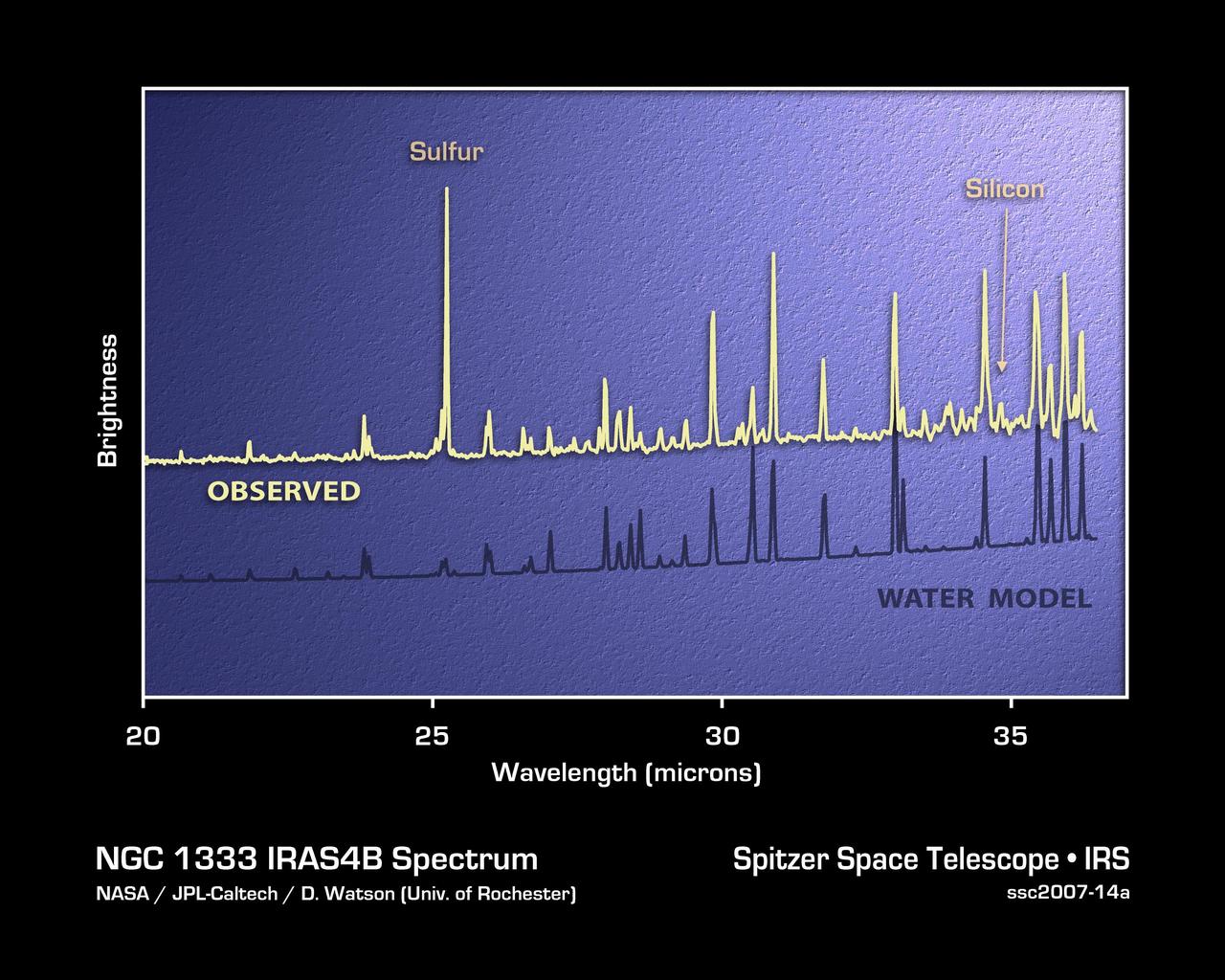
This plot of infrared data, called a spectrum, shows the strong signature of water vapor deep within the core of an embryonic star system, called NGC 1333-IRAS 4B. The data were captured by NASA Spitzer Space Telescope.
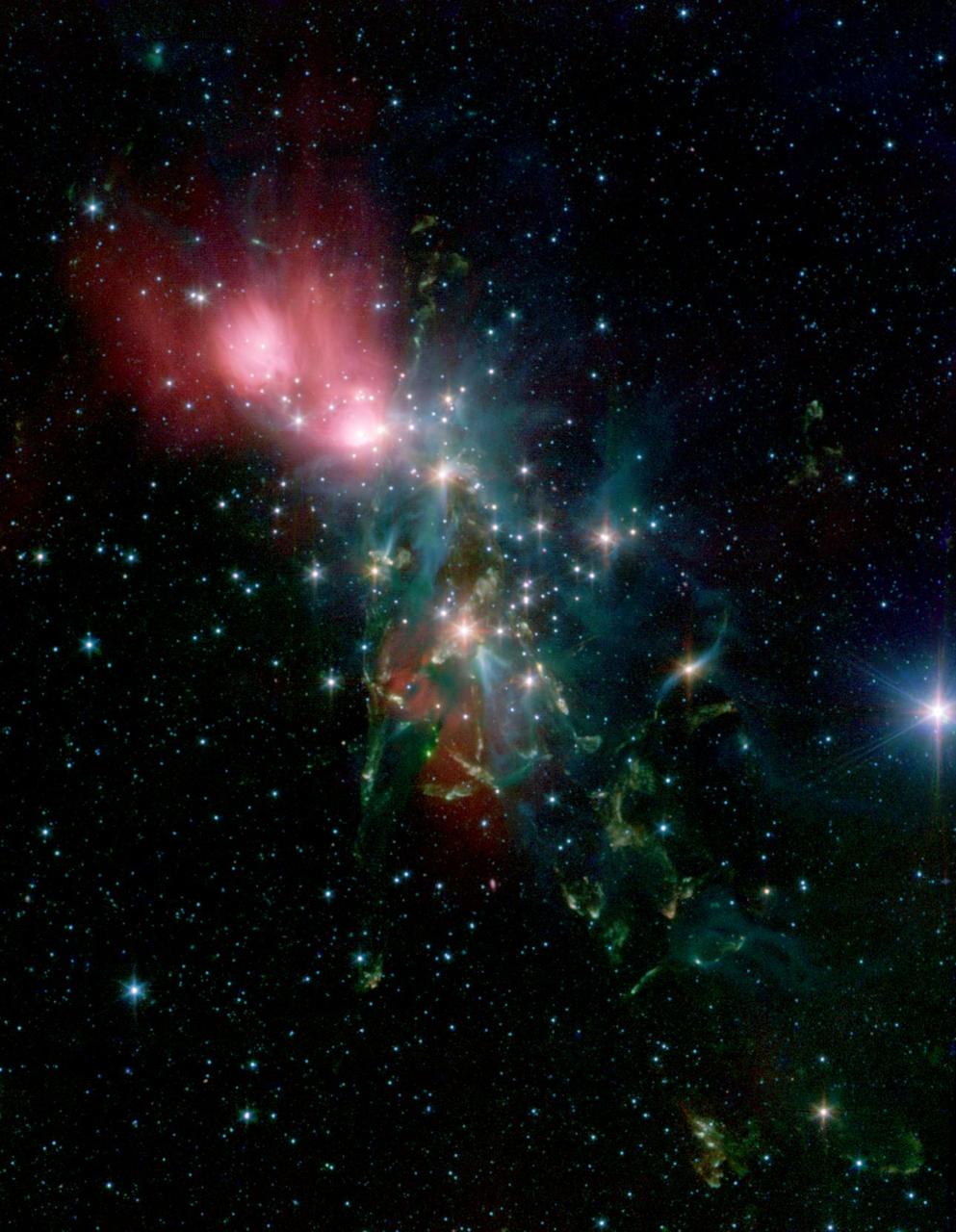

Located 1,000 light years from Earth in the constellation Perseus, a reflection nebula called NGC 1333 epitomizes the beautiful chaos of a dense group of stars being born. This image is from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope.

This diagram illustrates the earliest journeys of water in a young, forming star system. NASA Spitzer Space Telescope was able to probe a crucial phase of this stellar evolution.
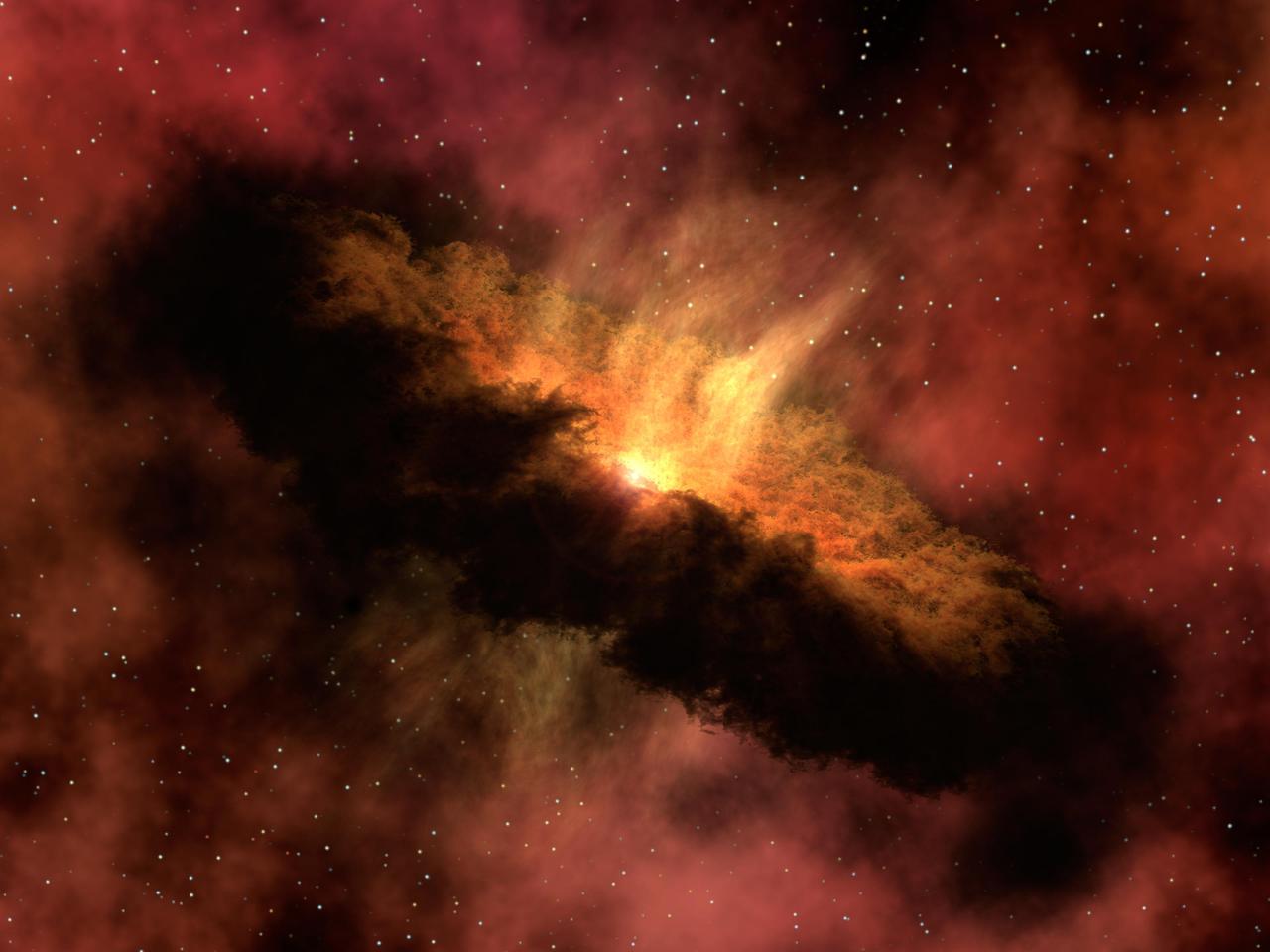

NASA Spitzer Space Telescope observed a fledgling solar system like the one depicted in this artist concept, and discovered deep within it enough water vapor to fill the oceans on Earth five times.

This new composite image of stellar cluster NGC 1333 combines X-rays from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory (pink); infrared data from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope (red); and optical data from the Digitized Sky Survey and the National Optical Astronomical Observatories' Mayall 4-meter telescope on Kitt Peak near Tucson, Arizona. The Chandra data reveal 95 young stars glowing in X-ray light, 41 of which had not been seen previously using Spitzer because they lacked infrared emission from a surrounding disk. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19347

In this image, the NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has captured the smoking gun of a newborn star, the Herbig–Haro objects numbered 7 to 11 (HH 7–11). These five objects, visible in blue in the top center of the image, lie within NGC 1333, a reflection nebula full of gas and dust found about a thousand light-years away from Earth. Bright patches of nebulosity near newborn stars, Herbig-Haro objects like HH 7–11 are transient phenomena. Traveling away from the star that created them at a speed of up to about 150,000 miles per hour, they disappear into nothingness within a few tens of thousands of years. The young star that is the source of HH 7–11 is called SVS 13, and all five objects are moving away from SVS 13 toward the upper left. The current distance between HH 7 and SVS 13 is about 20,000 times the distance between Earth and the Sun. Herbig–Haro objects are formed when jets of ionized gas ejected by a young star collide with nearby clouds of gas and dust at high speeds. The Herbig-Haro objects visible in this image are no exception to this and were formed when the jets from the newborn star SVS 13 collided with the surrounding clouds. These collisions created the five brilliant clumps of light within the reflection nebula.