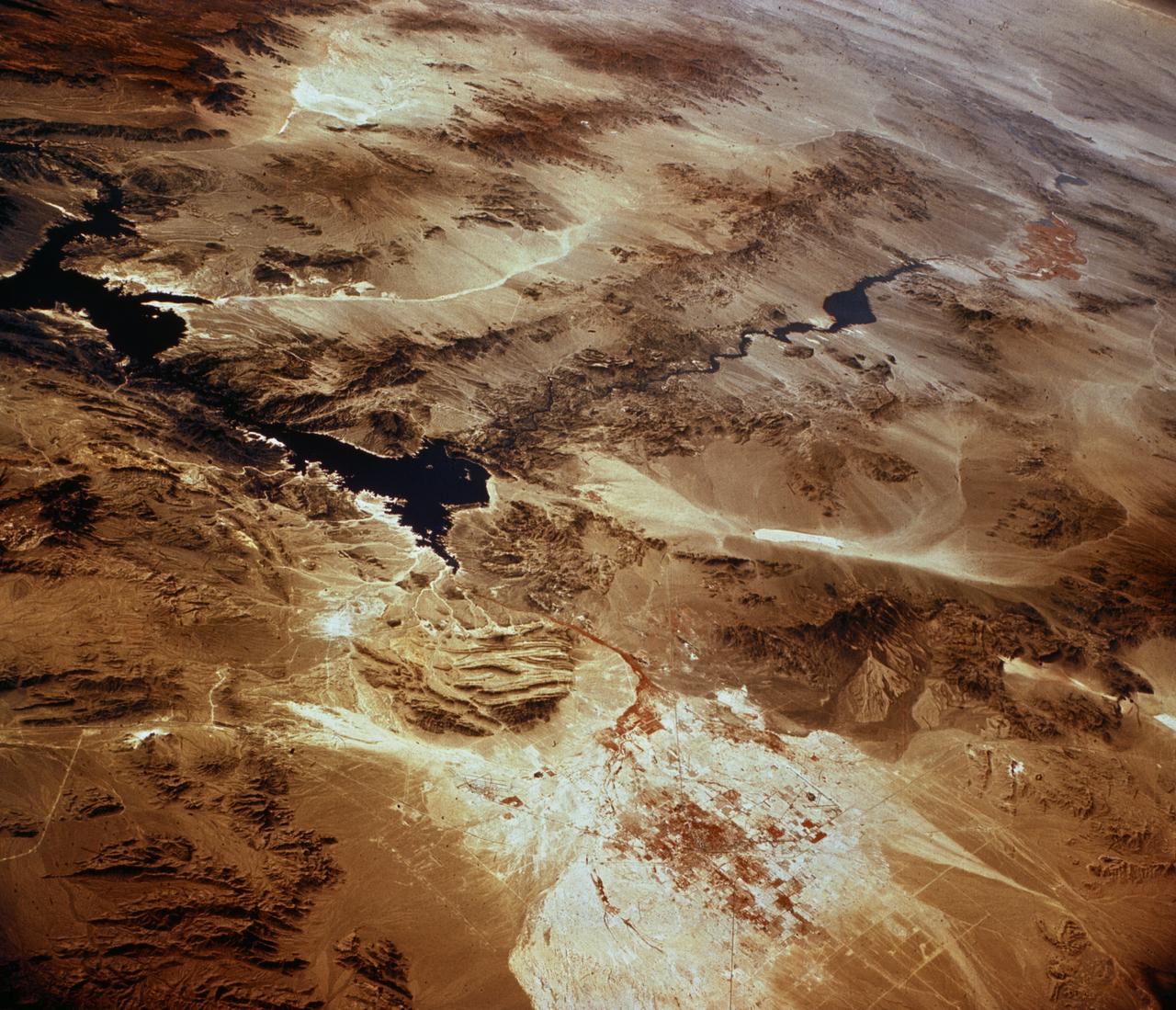

Southwestern US, with Las Vegas, NV in foreground, taken by X-15 Hycon HR-236 Camera during flt. 2-39-70 on June 27, 1965.
![jsc2022e057892 (5/12/2022) --- The SpaceOMIX team traveling to Space Applications Services, Brussels, Belgium for sample integration [Credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/jsc2022e057892/jsc2022e057892~medium.jpg)
jsc2022e057892 (5/12/2022) --- The SpaceOMIX team traveling to Space Applications Services, Brussels, Belgium for sample integration [Credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]
![jsc2022e057886 (5/12/2022) --- ICE Cubes mission control centre at the Space Applications Services, Brussels, Belgium [credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/jsc2022e057886/jsc2022e057886~medium.jpg)
jsc2022e057886 (5/12/2022) --- ICE Cubes mission control centre at the Space Applications Services, Brussels, Belgium [credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]
![jsc2022e057891 (5/13/2022) --- A view of two samples from the onboard camera to the mission control centre and personal computer screen [Credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/jsc2022e057891/jsc2022e057891~medium.jpg)
jsc2022e057891 (5/13/2022) --- A view of two samples from the onboard camera to the mission control centre and personal computer screen [Credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]
![jsc2022e057894 (5/13/2022) --- Views of the Maltese Biocube based on the ICE Cubes platform by Belgian company Space Applications Services [Credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/jsc2022e057894/jsc2022e057894~medium.jpg)
jsc2022e057894 (5/13/2022) --- Views of the Maltese Biocube based on the ICE Cubes platform by Belgian company Space Applications Services [Credit: Space Applications Services, NV/SA]
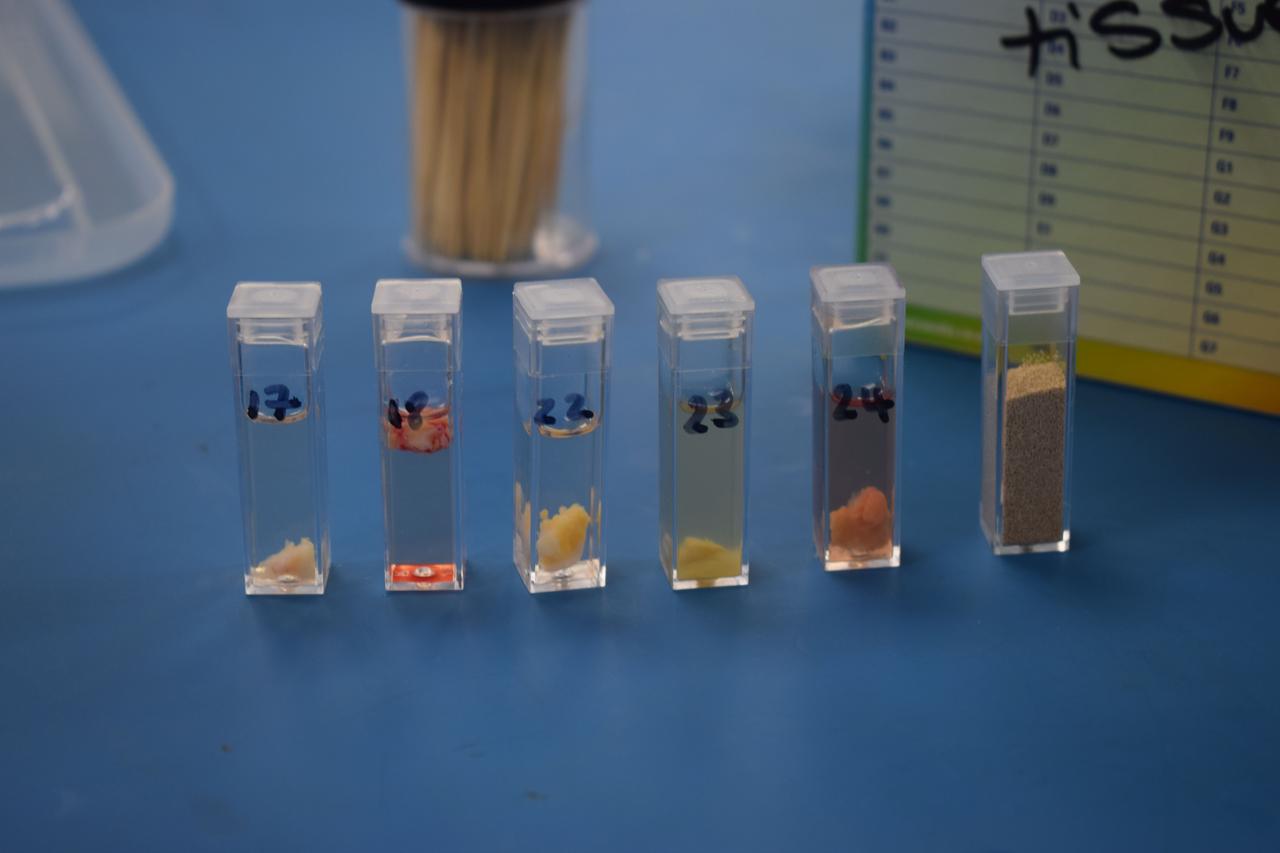

jsc2022e057883 (5/12/2022) --- A close up view of six sample cuvettes that are planned to hold five human skin tissue and microbiome samples from Diabetic Foot Ulcer patients and one yeast sample from Malta. This is part of the Follow-up Study of Human Skin Tissue Microbiome Studies and Yeast Cells in Space (Ice Cubes #9.2 – Maleth 2) investigation. Image courtesy of Space Applications Services, NV/SA.
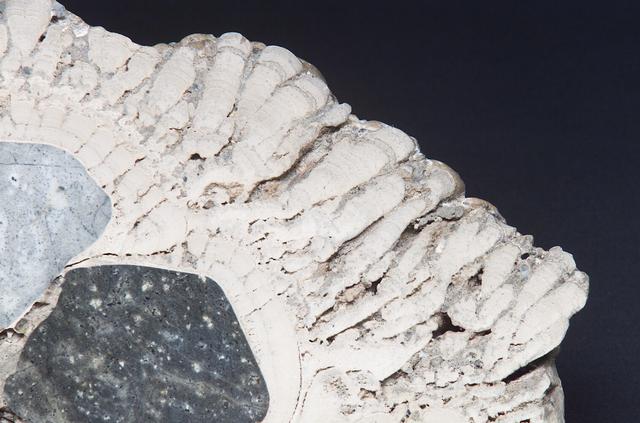

Microbial Mats study: close up of a section of a Stomatolite from Walker Lake, NV
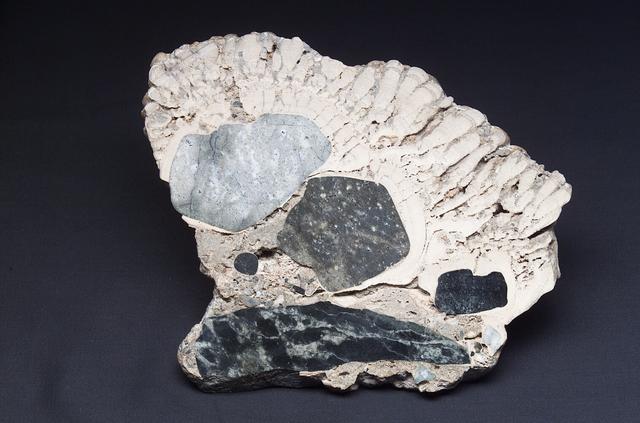

Microbial Mats study: close up of a section of a Stomatolite from Walker Lake, NV
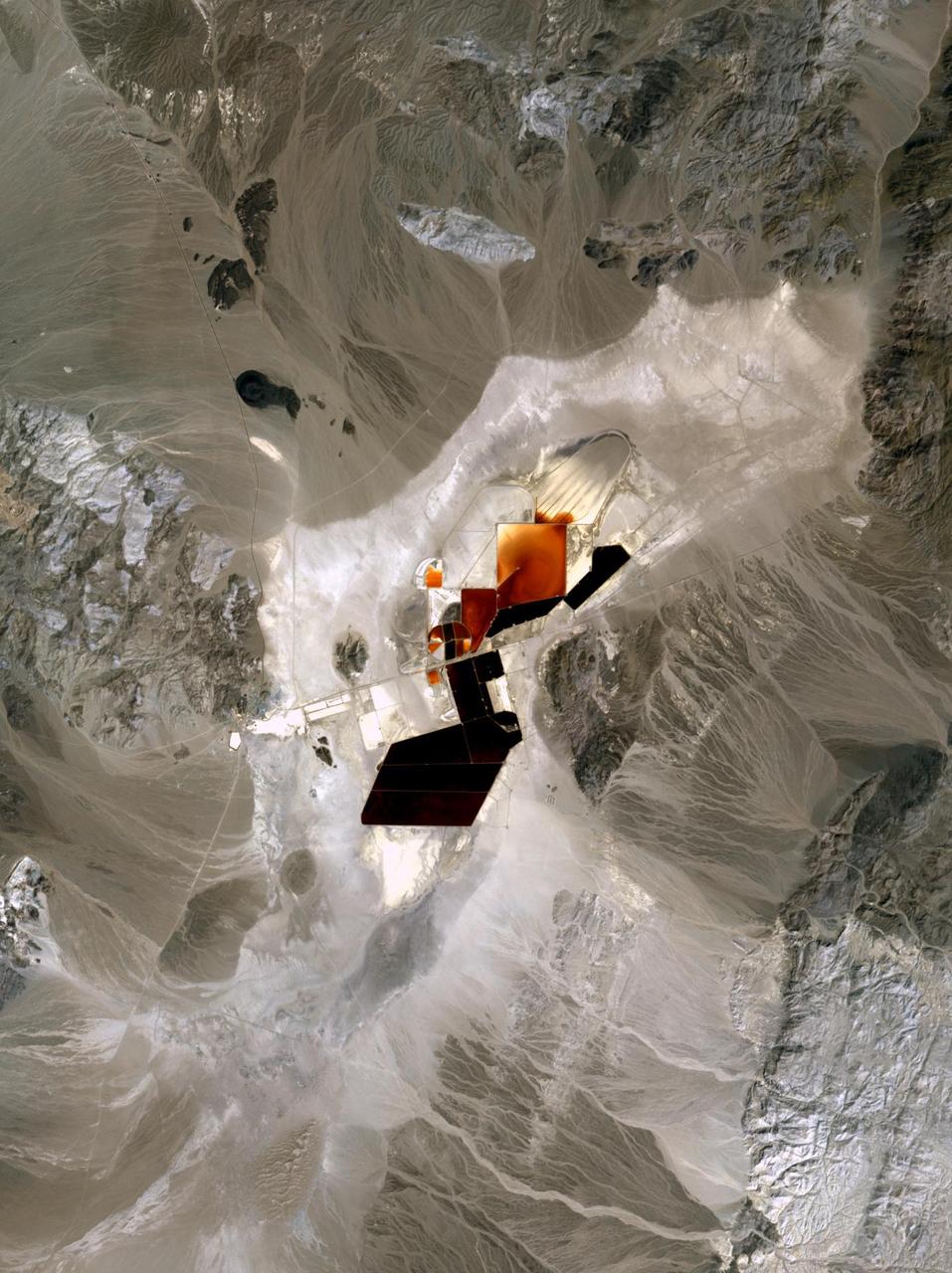

In Clayton Valley, Nevada, lithium has been produced since 1966. Currently it is produced by pumping lithium-rich brine to the surface to evaporate, or processed through direct lithium extraction. About 5,000 metric tons of lithium carbonate are produced annually at Nevada's only lithium-producing site. In the future, newly discovered deposits will produce more lithium than any other state. The image was acquired April 23, 2023, covers an area of 21.5 by 28.8 km, and is located at 37.75 degrees north, 117.6 degrees west. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26505
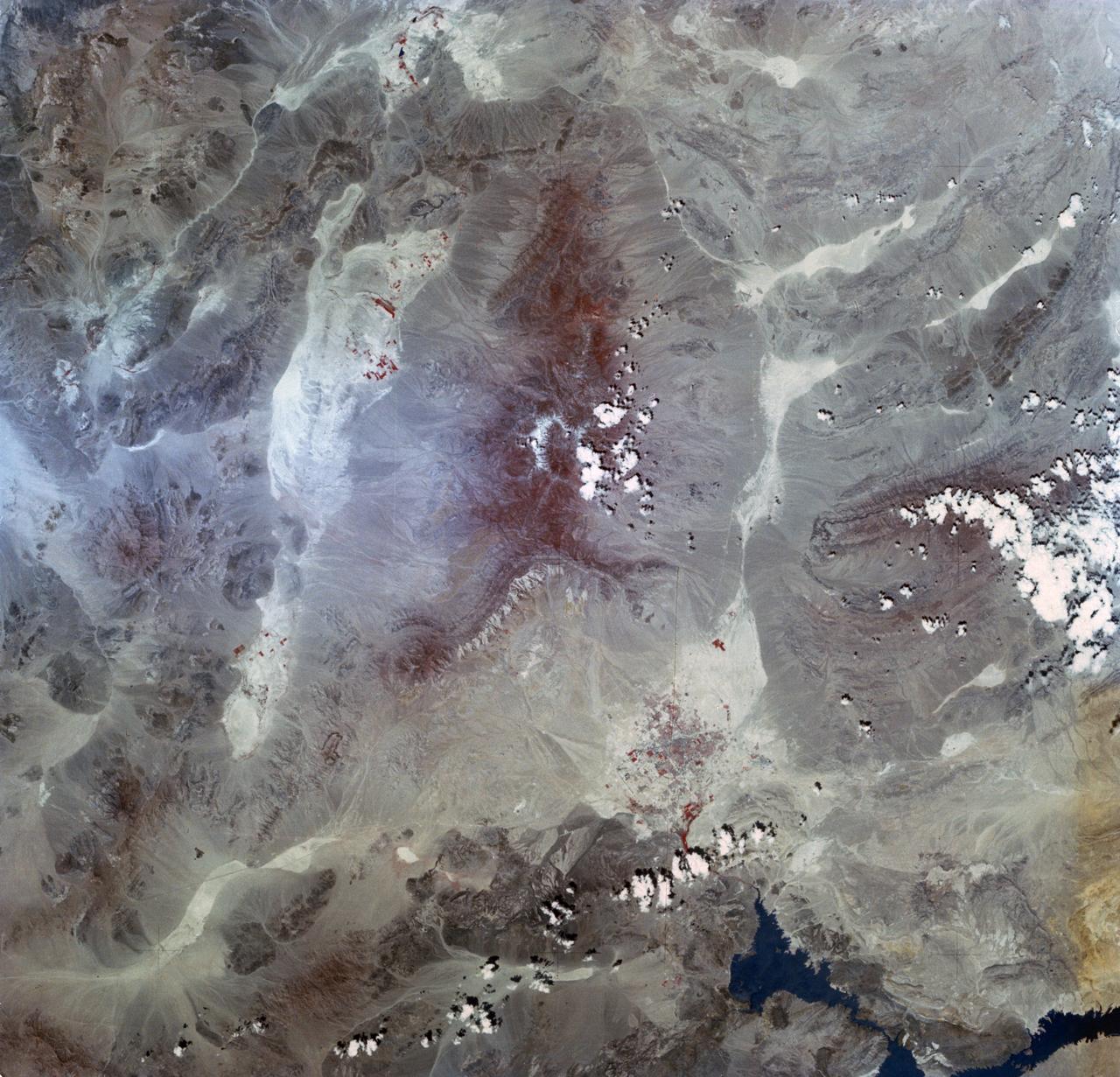

SL2-03-192 (22 June 1973) --- Lake Mead, Nevada, (36.0N, 114.5E) where the water from the Colorado River empties after it's 273 mile journey through the Grand Canyon of Arizona is the subject of this photo. Other features of interest are Hoover Dam on the south shore of Lake Mead where cheap hydroelectric power is secondary to the water resources made available in this northern desert region and the resort city of Las Vegas, just to the west of Lake Mead. In this harsh desert environment, color infrared photography readily penetrates haze, detects and portrays vegetation as shades of red. Photo credit: NASA
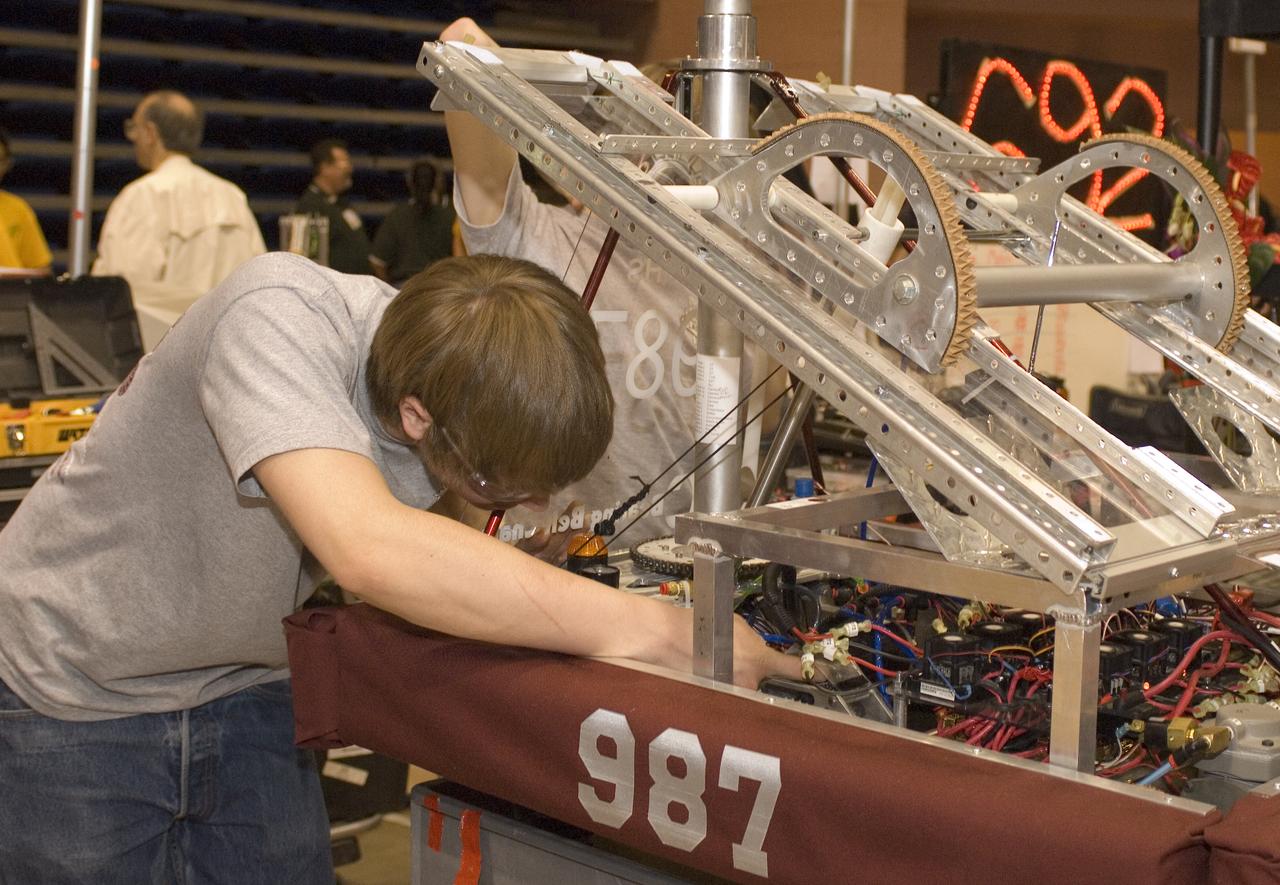

Silicon Valley FIRST Regional Robotics competition: HIGHROLLERS - TEAM 987 - Bearing Belt Chain/Alcoa Fastening Systems/VSR Lock/NASA/Summerlin Children's Forum & Cimarron-Memorial High School, Las Vegas, Nevada (NV)

Caroline Kennedy, center, is recognized by U.S. Vice President Joe Biden, left, Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid (D-NV), second from left, former U.S. Labor Secretary Elaine Chao, and U.S. Senator John Kerry (D-MA), right, at an event recognizing the 50th anniversary of the inauguration of John F. Kennedy as President of the United States, Thursday, Jan. 20, 2011 in the rotunda at the U.S. Capitol. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
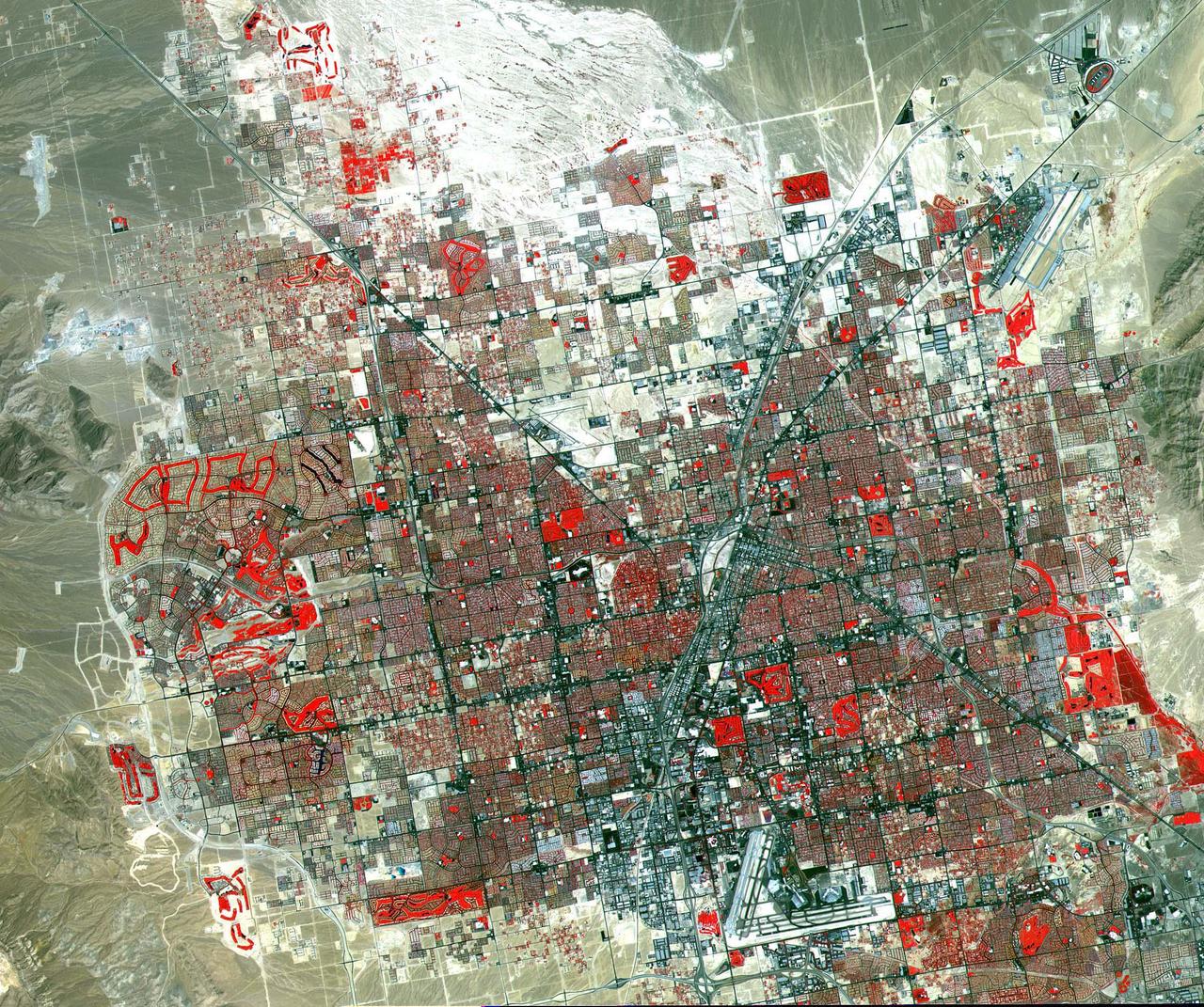
This image of Las Vegas, NV was acquired on August, 2000 and covers an area 42 km (25 miles) wide and 30 km (18 miles) long. The image displays three bands of the reflected visible and infrared wavelength region, with a spatial resolution of 15 m. McCarran International Airport to the south and Nellis Air Force Base to the NE are the two major airports visible. Golf courses appear as bright red areas of worms. The first settlement in Las Vegas (which is Spanish for The Meadows) was recorded back in the early 1850s when the Mormon church, headed by Brigham Young, sent a mission of 30 men to construct a fort and teach agriculture to the Indians. Las Vegas became a city in 1905 when the railroad announced this city was to be a major division point. Prior to legalized gambling in 1931, Las Vegas was developing as an agricultural area. Las Vegas' fame as a resort area became prominent after World War II. The image is located at 36.1 degrees north latitude and 115.1 degrees west longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA11096
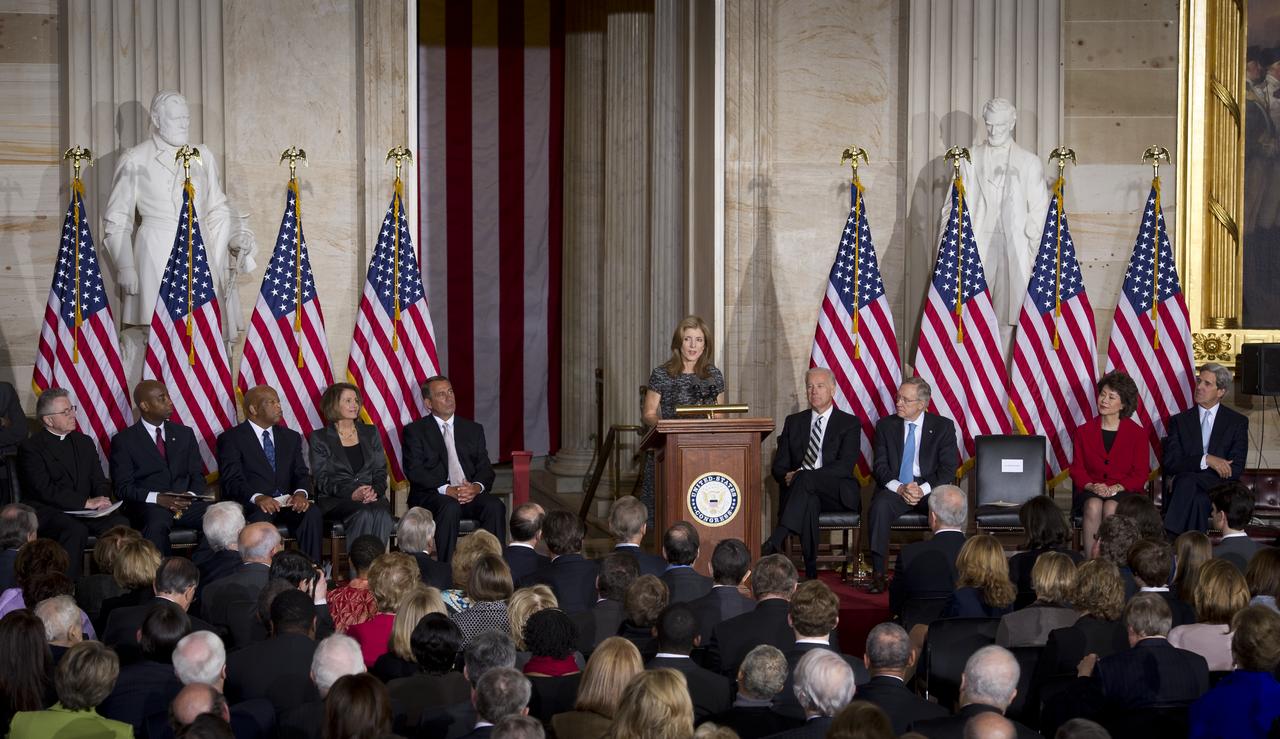

Caroline Kennedy speaks at an event recognizing the 50th anniversary of the inauguration of John F. Kennedy as President of the United States, Thursday, Jan. 20, 2011 in the rotunda at the U.S. Capitol. Also participating in the event, seated from left, Reverend Daniel P. Coughlin, Dr. Barry Black, U.S. Congressman John Lewis (D-GA), U.S. House Minority Leader Nancy Pelosi (D-CA), House Speaker John Boehner (R-OH), U.S. Vice President Joe Biden, Senate Majority Leader Harry Reid (D-NV), former U.S. Labor Secretary Elaine Chao, and U.S. Senator John Kerry (D-MA). Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
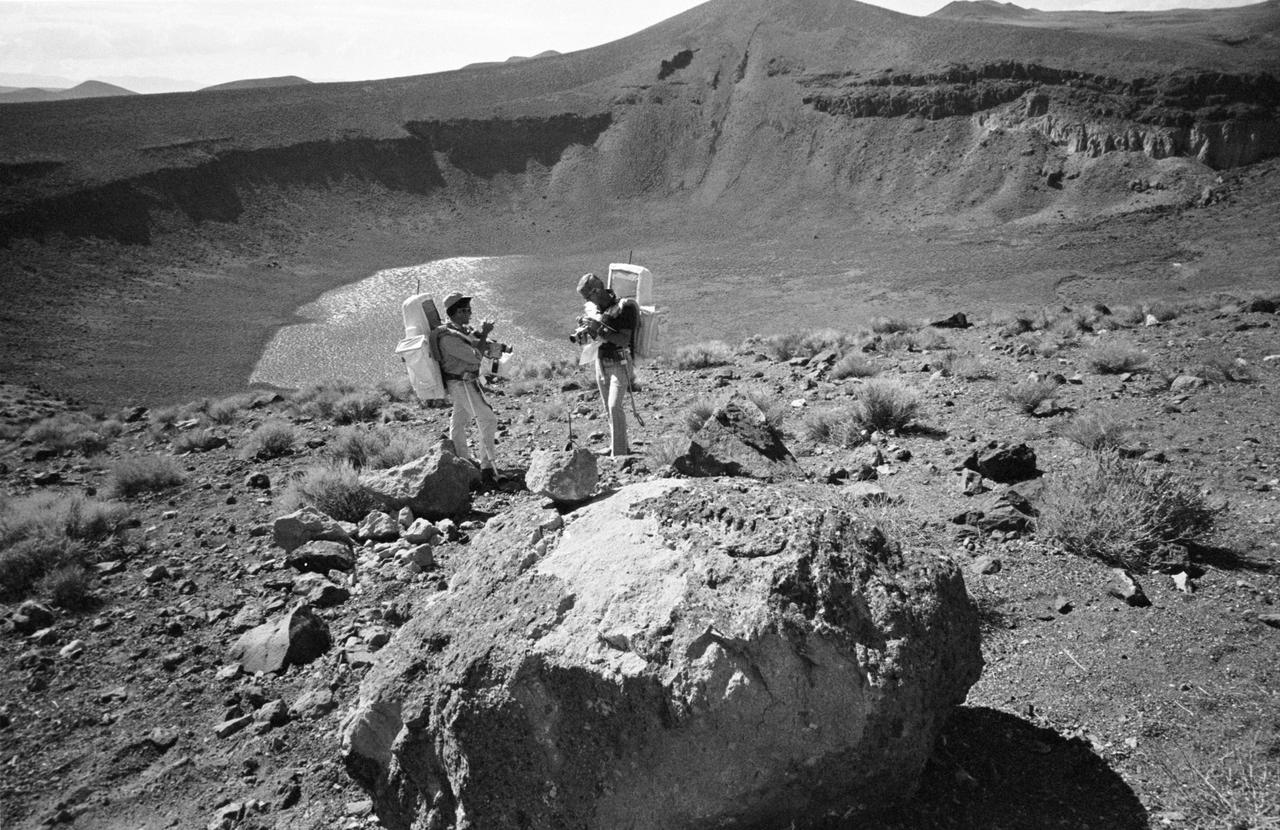

S72-48854 (6 Sept. 1972) --- Two members of the prime crew of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission examine rock specimens during lunar surface extravehicular activity simulation training on a geological field trip to the Pancake Range area of south-central Nevada. They are astronaut Eugene A. Cernan (right), commander; and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot. They are standing on the rim of Lunar Crater, which is about 600 feet deep and five-eighths of a mile in diameter. It is a volcanic crater.
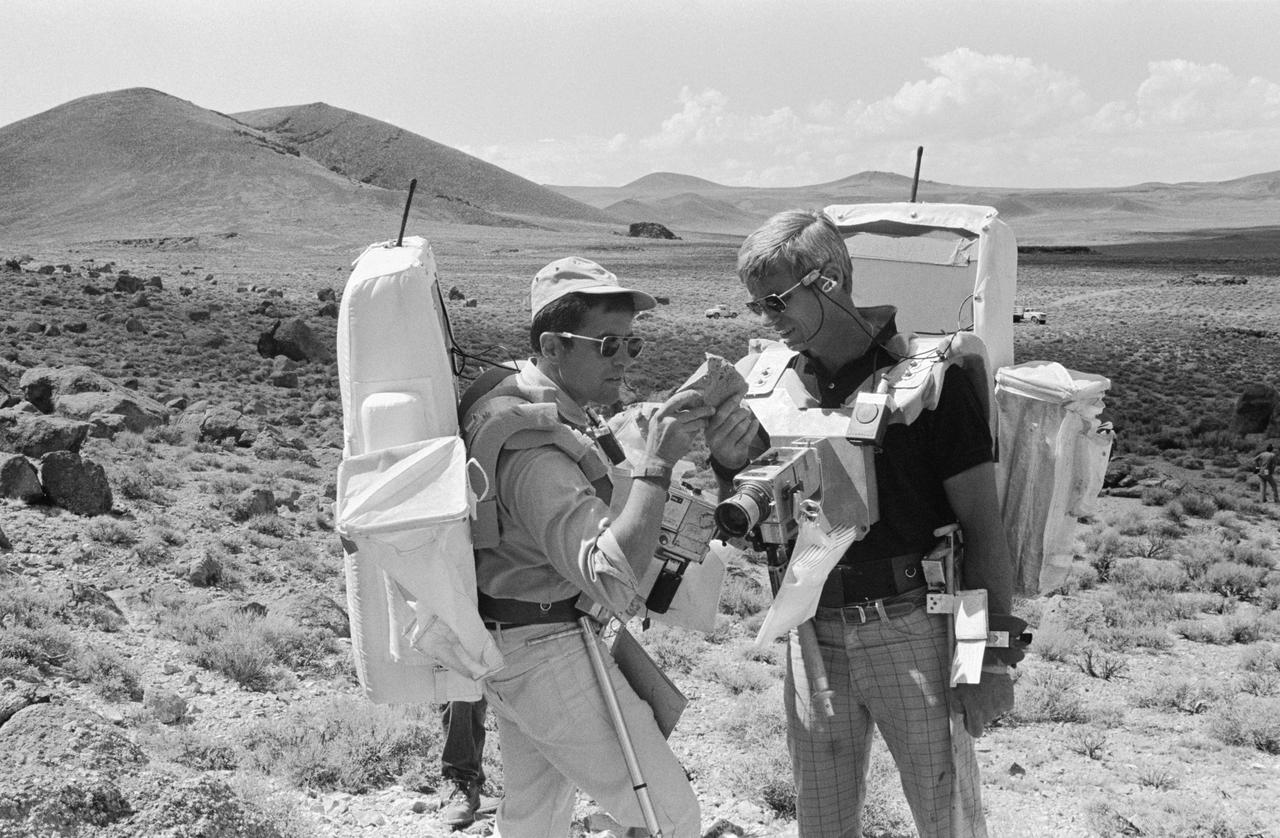

S72-48859 (6 Sept. 1972) --- Two members of the prime crew of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission examine a rock specimen during lunar surface extravehicular activity simulation training on a geological field trip to the Pancake Range area of south-central Nevada. They are astronauts Eugene A. Cernan (right), commander; and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot.
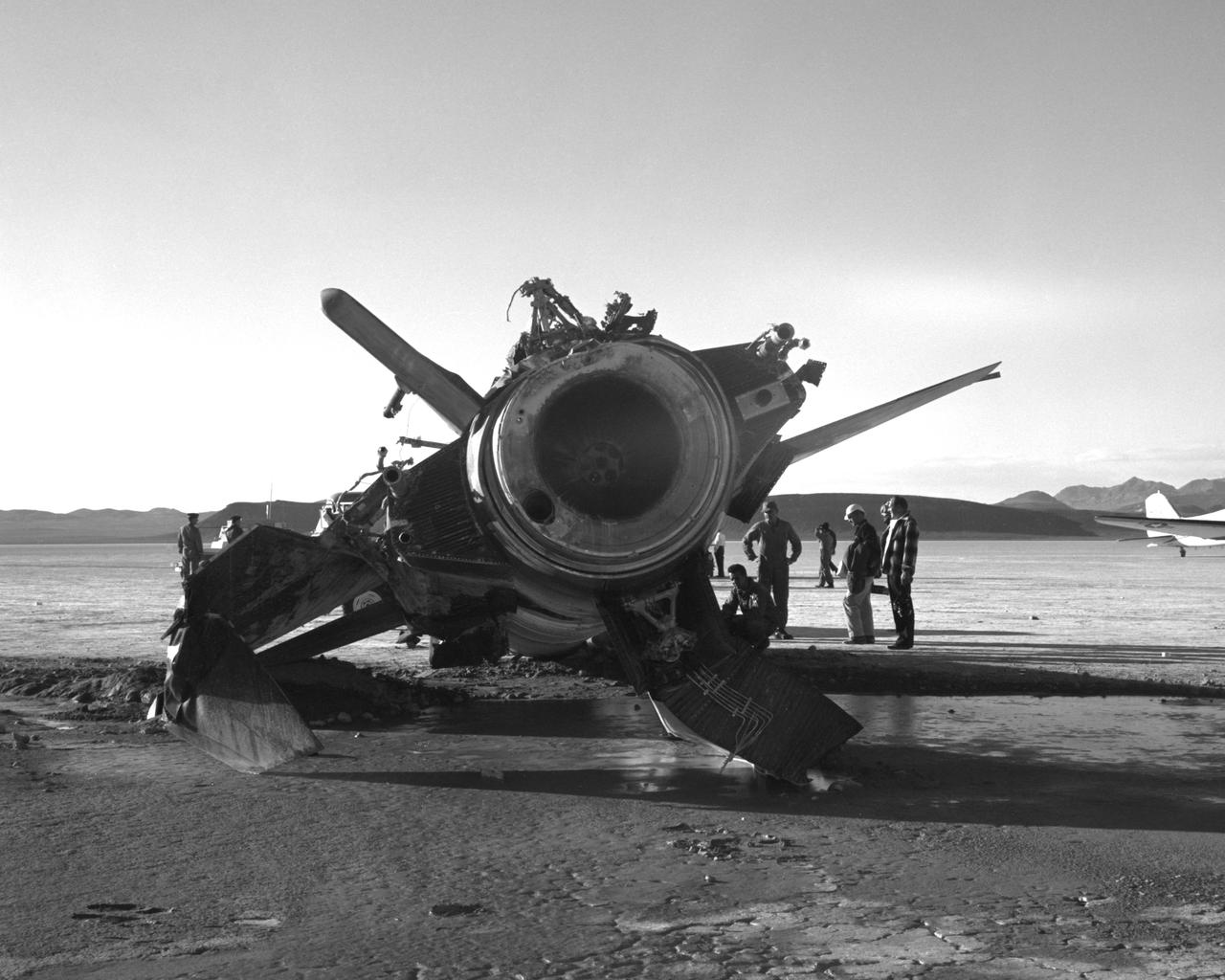

NASA research pilot Jack McKay was injured in a crash landing of the X-15 #2 on November 9, 1962. Following the launch from the B-52 to begin flight 2-31-52, he started the X-15's rocket engine, only to discover that it produced just 30 percent of its maximum thrust. He had to make a high-speed emergency landing on Mud Lake, NV, without flaps but with a significant amount of fuel still in the aircraft. As the X-15 slid across the lakebed, the left skid collapsed; the aircraft turned sideways and flipped onto its back. McKay suffered back injuries but was eventually able to resume X-15 pilot duties, making 22 more flights. The X-15 was sent back to North American Aviation and rebuilt into the X-15A-2.
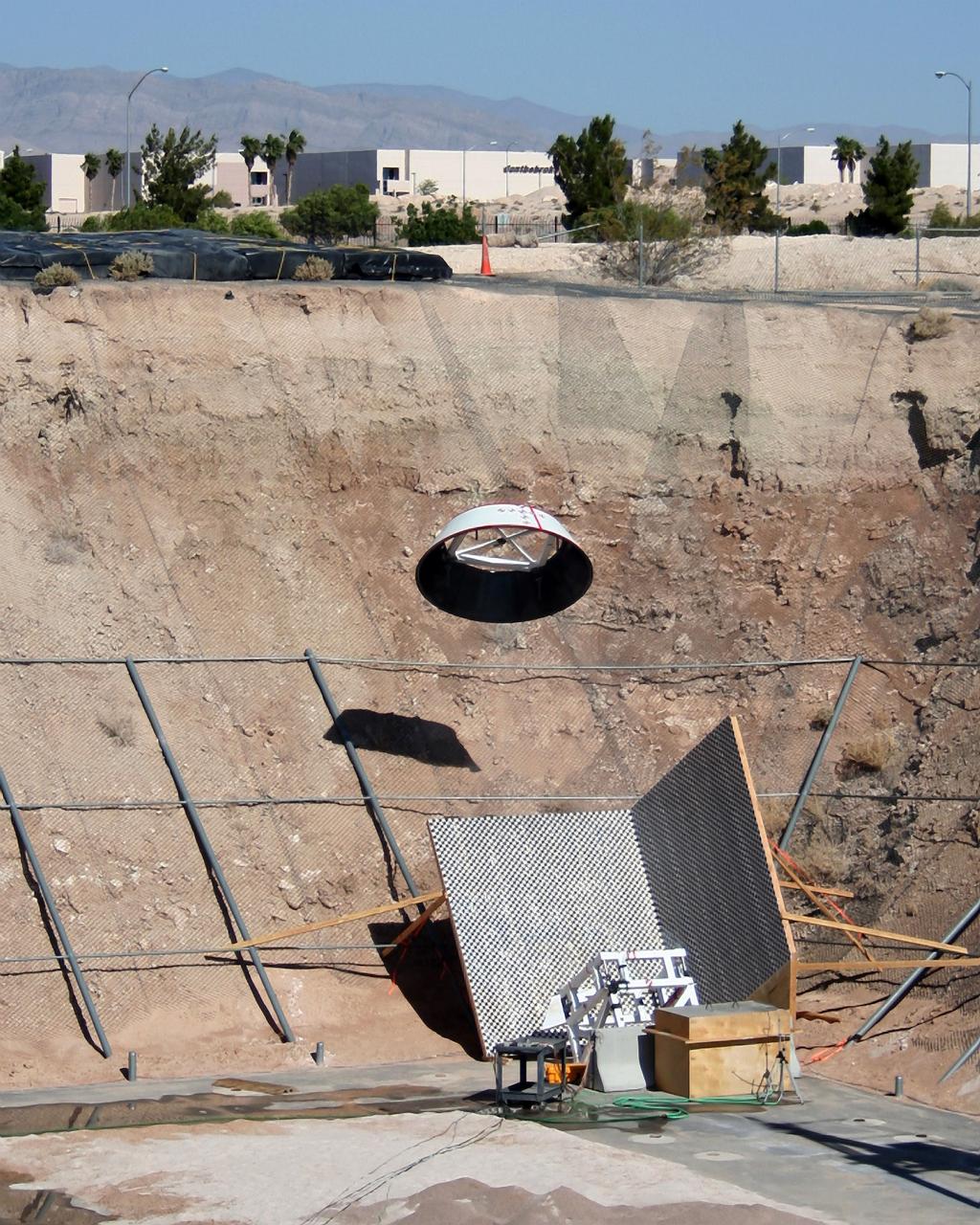

LAS VEGAS -- The Boeing Company tests the forward heat shield FHS jettison system of its CST-100 spacecraft at the Bigelow Aerospace facility in Las Vegas as part of an agreement with NASA's Commercial Crew Program CCP during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities. The FHS will protect the spacecraft's parachutes, rendezvous-and-docking sensor packages, and docking mechanism during ascent and re-entry. During a mission to low Earth orbit, the shield will be jettisoned after re-entry heating, allowing the spacecraft's air bags to deploy for a safe landing. In 2011, NASA selected Boeing for CCDev2 to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also were selected to mature launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, Excalibur Almaz Inc., Blue Origin, Sierra Nevada Corp. SNC, Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Boeing The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is developing the necessary ground systems, infrastructure and operational approaches required to safely process, assemble, transport and launch the next generation of rockets and spacecraft in support of NASA’s exploration objectives. Future work also will replace the antiquated communications, power and vehicle access resources with modern efficient systems. Some of the utilities and systems slated for replacement have been used since the VAB opened in 1965. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/systems/ground/index.html Photo credit: Boeing
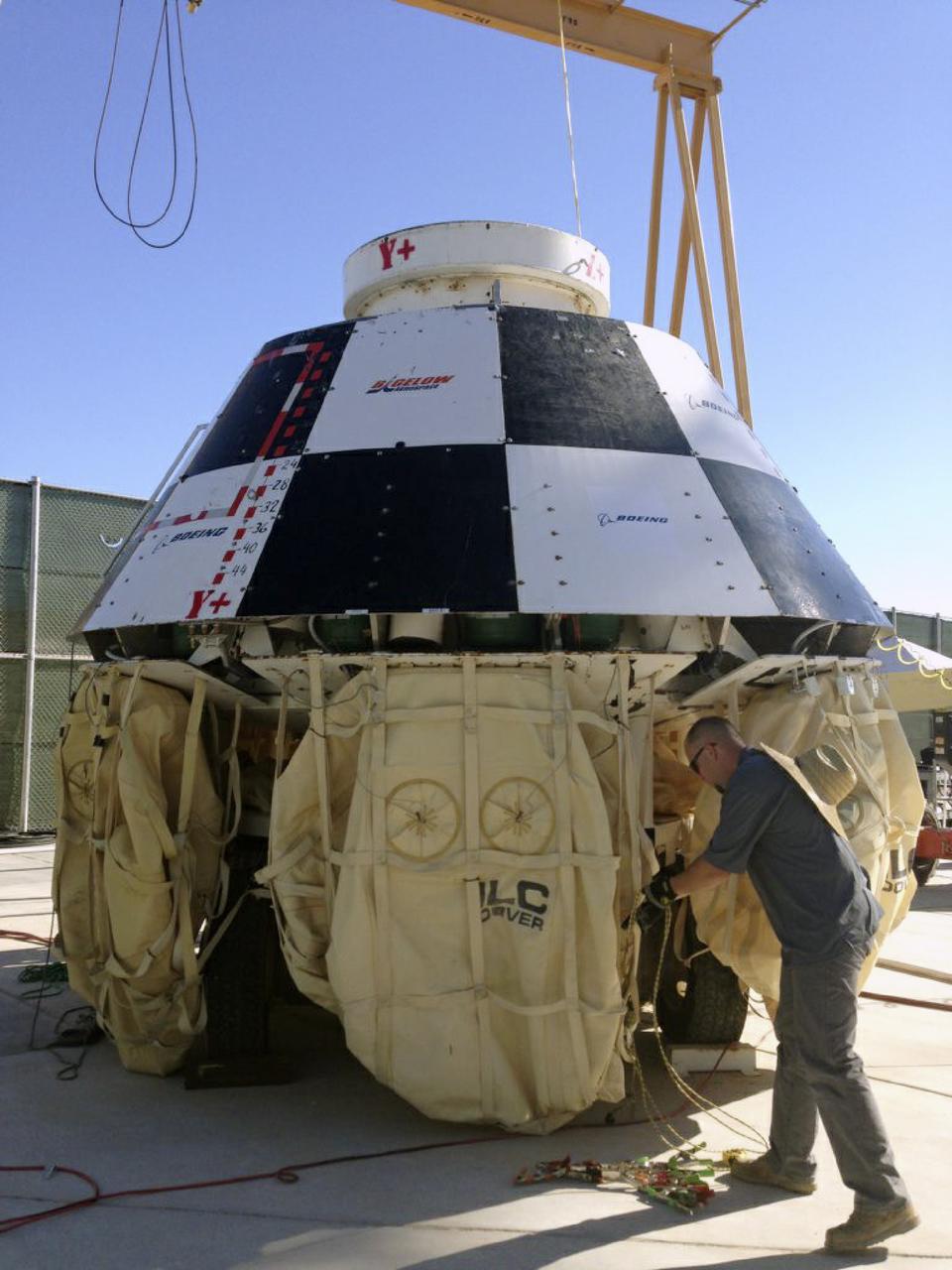

LAS VEGAS, Nev. – An engineer prepares a mock-up of The Boeing Company's CST-100 spacecraft for the third and final series of simulated contingency water landing scenarios at Bigelow Aerospace's headquarters near Las Vegas. The CST-100 is designed for ground landings, but could splash down on the water, if necessary. The tests are part of the company’s ongoing work supporting its funded Space Act Agreement with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative. CCP is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers to low-Earth orbit. Future development and certification initiatives eventually will lead to the availability of human spaceflight services for NASA to send its astronauts to the International Space Station, where critical research is taking place daily. For more information about CCP, go to http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Boeing/Kelly George
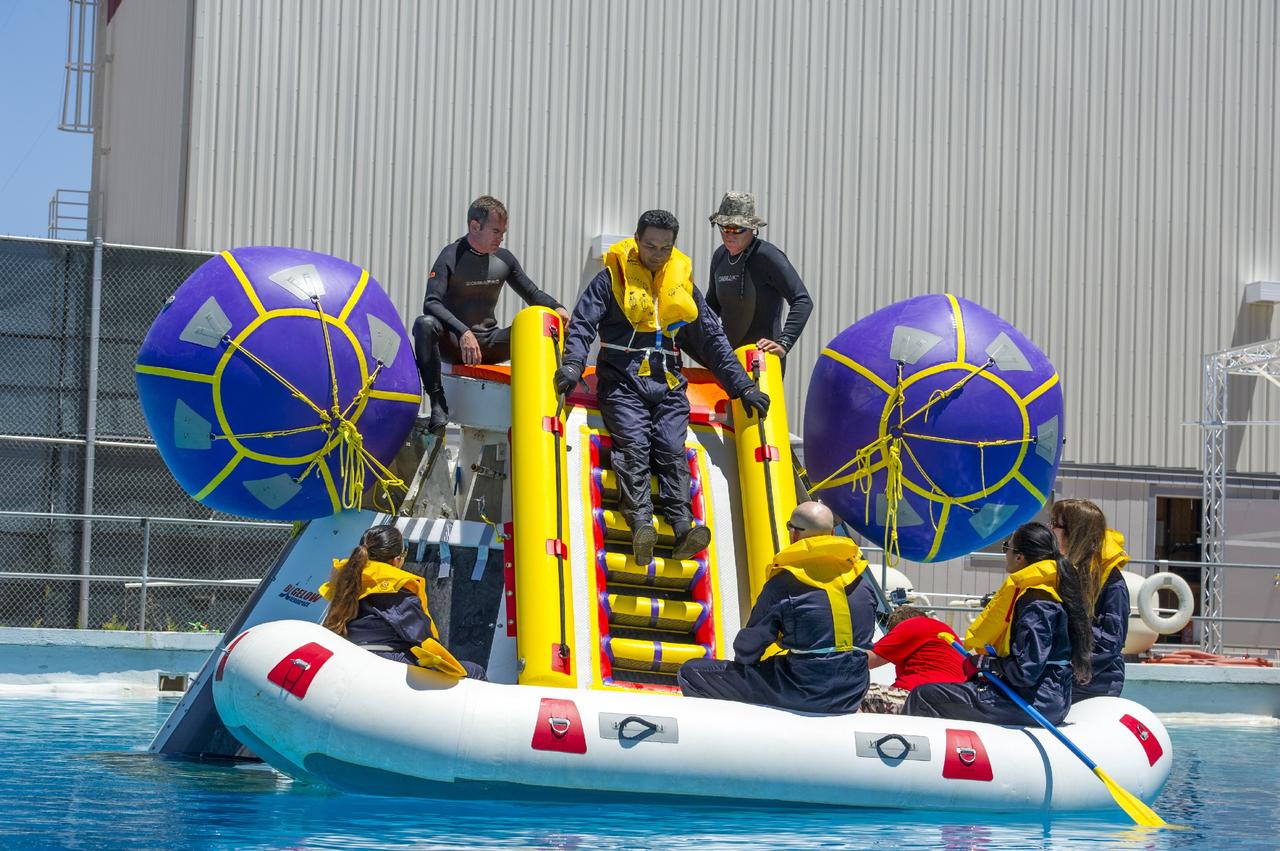

LAS VEGAS, Nev. – The Boeing Company performed simulated contingency water landing scenarios with a mock-up CST-100 spacecraft at Bigelow Aerospace's headquarters near Las Vegas. The CST-100 is designed for ground landings, but could splash down on the water, if necessary. During the water tests, Department of Defense search-and-recovery personnel practiced pulling five Boeing engineers out of the capsule and to safety. The tests are part of the company’s ongoing work supporting its funded Space Act Agreement with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative. CCP is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers to low-Earth orbit. Future development and certification initiatives eventually will lead to the availability of human spaceflight services for NASA to send its astronauts to the International Space Station, where critical research is taking place daily. For more information about CCP, go to http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Boeing
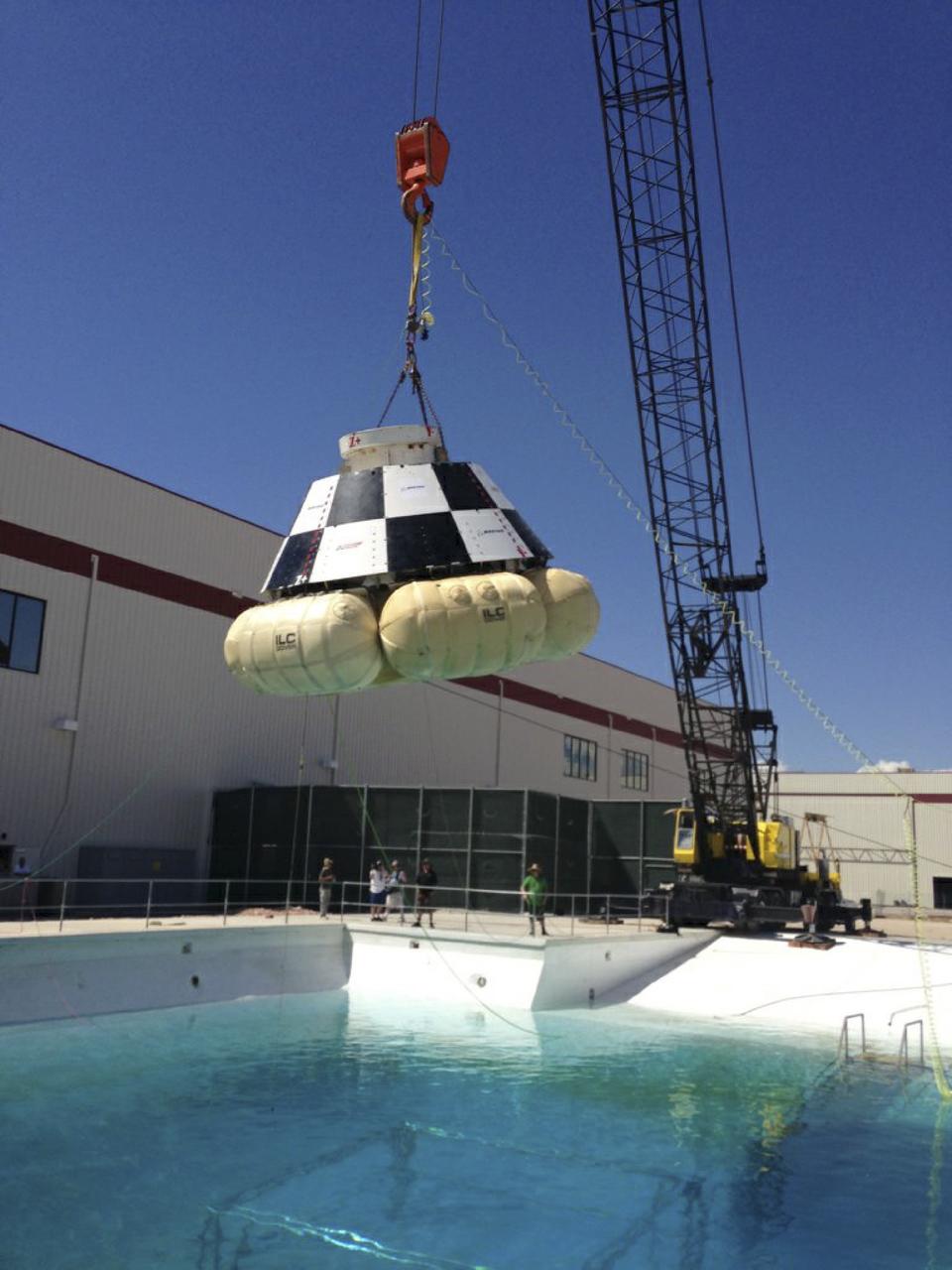

LAS VEGAS, Nev. – A mock-up of The Boeing Company's CST-100 spacecraft is prepared for the third and final series of simulated contingency water landing scenarios at Bigelow Aerospace's headquarters near Las Vegas. The CST-100 is designed for ground landings, but could splash down on the water, if necessary. The tests are part of the company’s ongoing work supporting its funded Space Act Agreement with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative. CCP is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers to low-Earth orbit. Future development and certification initiatives eventually will lead to the availability of human spaceflight services for NASA to send its astronauts to the International Space Station, where critical research is taking place daily. For more information about CCP, go to http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Boeing/Kelly George
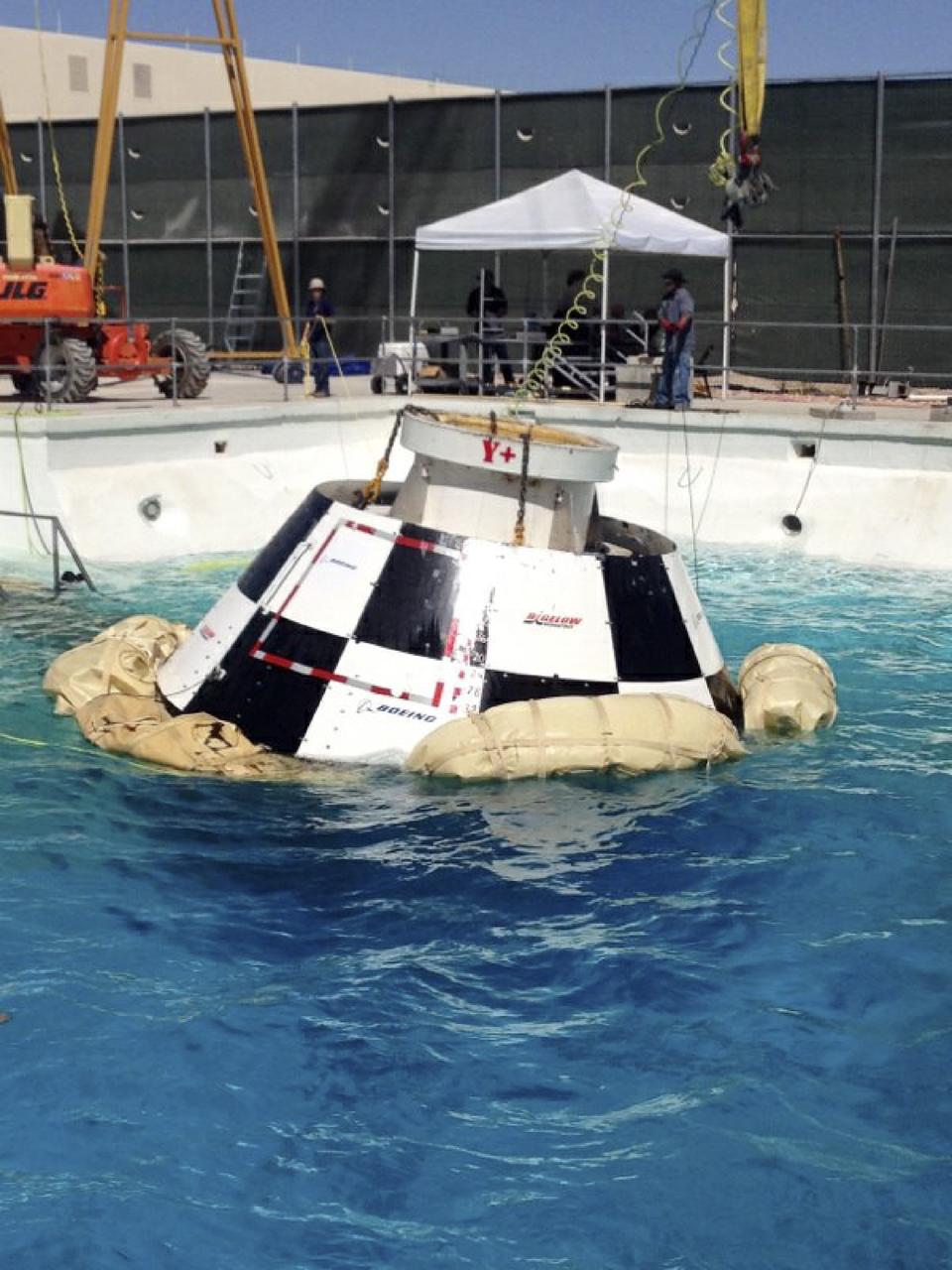

LAS VEGAS, Nev. – A mock-up of The Boeing Company's CST-100 spacecraft floats following the third and final series of simulated contingency water landing scenarios at Bigelow Aerospace's headquarters near Las Vegas. The CST-100 is designed for ground landings, but could splash down on the water, if necessary. The tests are part of the company’s ongoing work supporting its funded Space Act Agreement with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative. CCP is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers to low-Earth orbit. Future development and certification initiatives eventually will lead to the availability of human spaceflight services for NASA to send its astronauts to the International Space Station, where critical research is taking place daily. For more information about CCP, go to http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Boeing/Kelly George
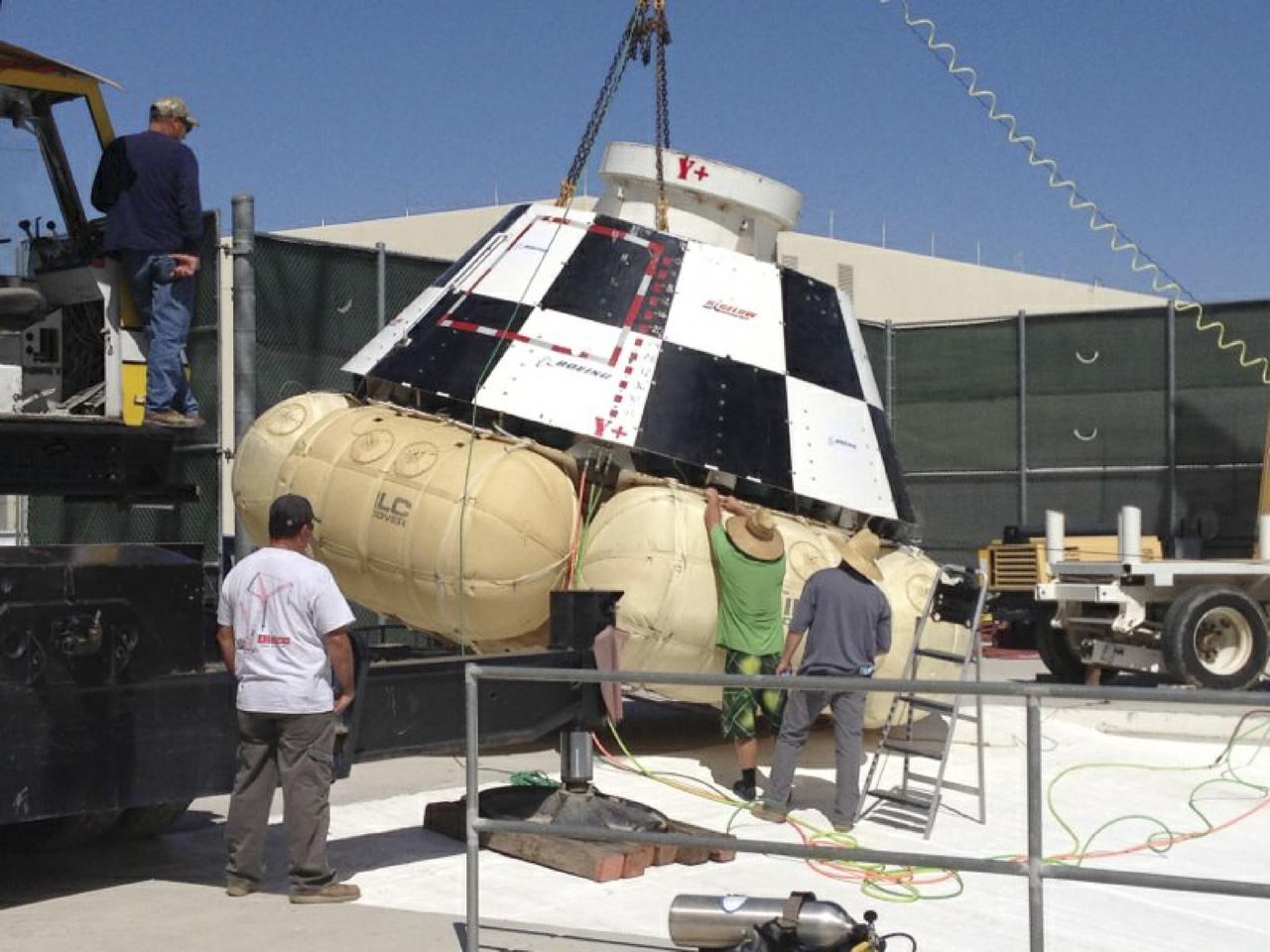

LAS VEGAS, Nev. – Engineers prepare a mock-up of The Boeing Company's CST-100 spacecraft for the third and final series of simulated contingency water landing scenarios at Bigelow Aerospace's headquarters near Las Vegas. The CST-100 is designed for ground landings, but could splash down on the water, if necessary. The tests are part of the company’s ongoing work supporting its funded Space Act Agreement with NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, or CCP, during the Commercial Crew Integrated Capability, or CCiCap, initiative. CCP is intended to lead to the availability of commercial human spaceflight services for government and commercial customers to low-Earth orbit. Future development and certification initiatives eventually will lead to the availability of human spaceflight services for NASA to send its astronauts to the International Space Station, where critical research is taking place daily. For more information about CCP, go to http://www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Photo credit: Boeing/Kelly George
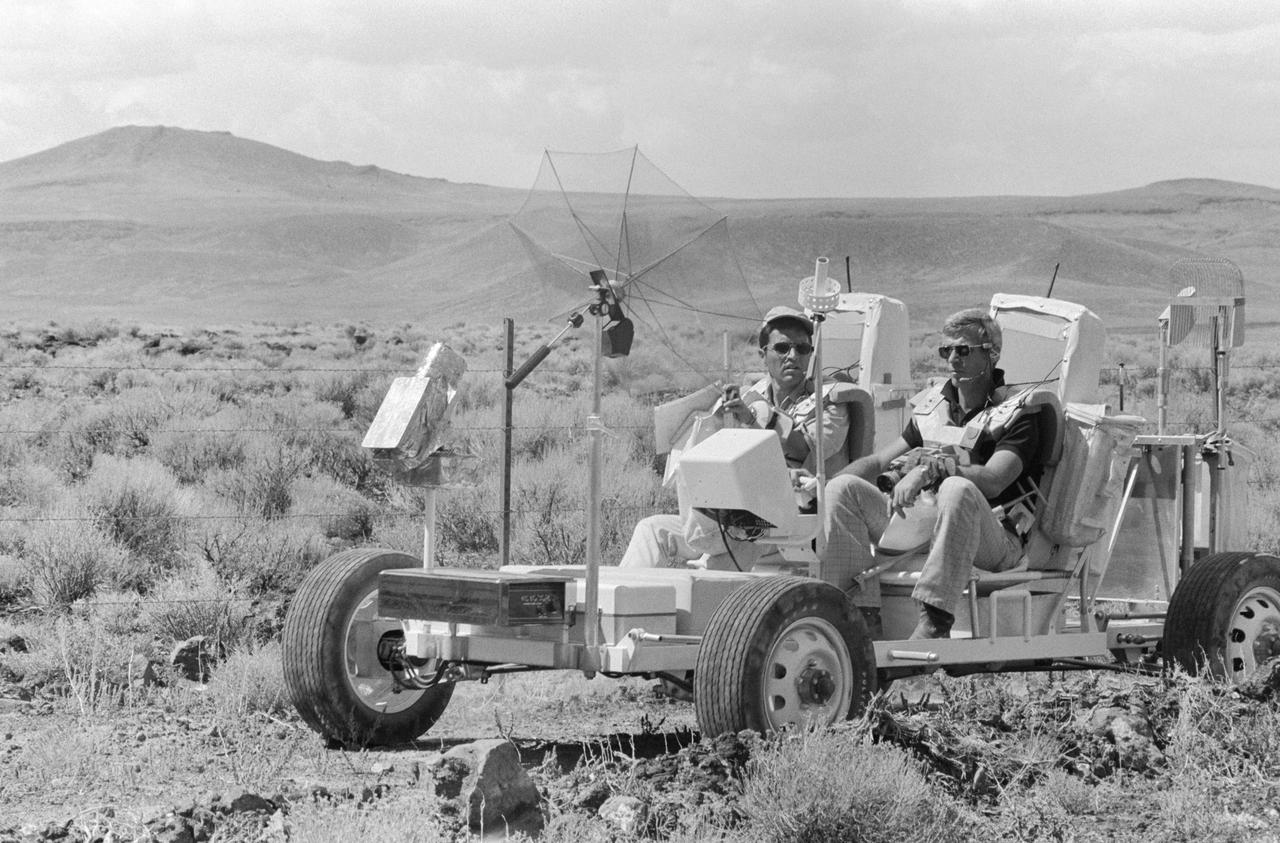

S72-48864 (6 Sept. 1972) --- Two members of the prime crew of the Apollo 17 lunar landing mission ride in a Lunar Roving Vehicle trainer during lunar surface extravehicular activity simulation training in the Pancake Range area of south-central Nevada. They are astronaut Eugene A. Cernan (foreground), commander; and scientist-astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt (on Cernan’s right), lunar module pilot.
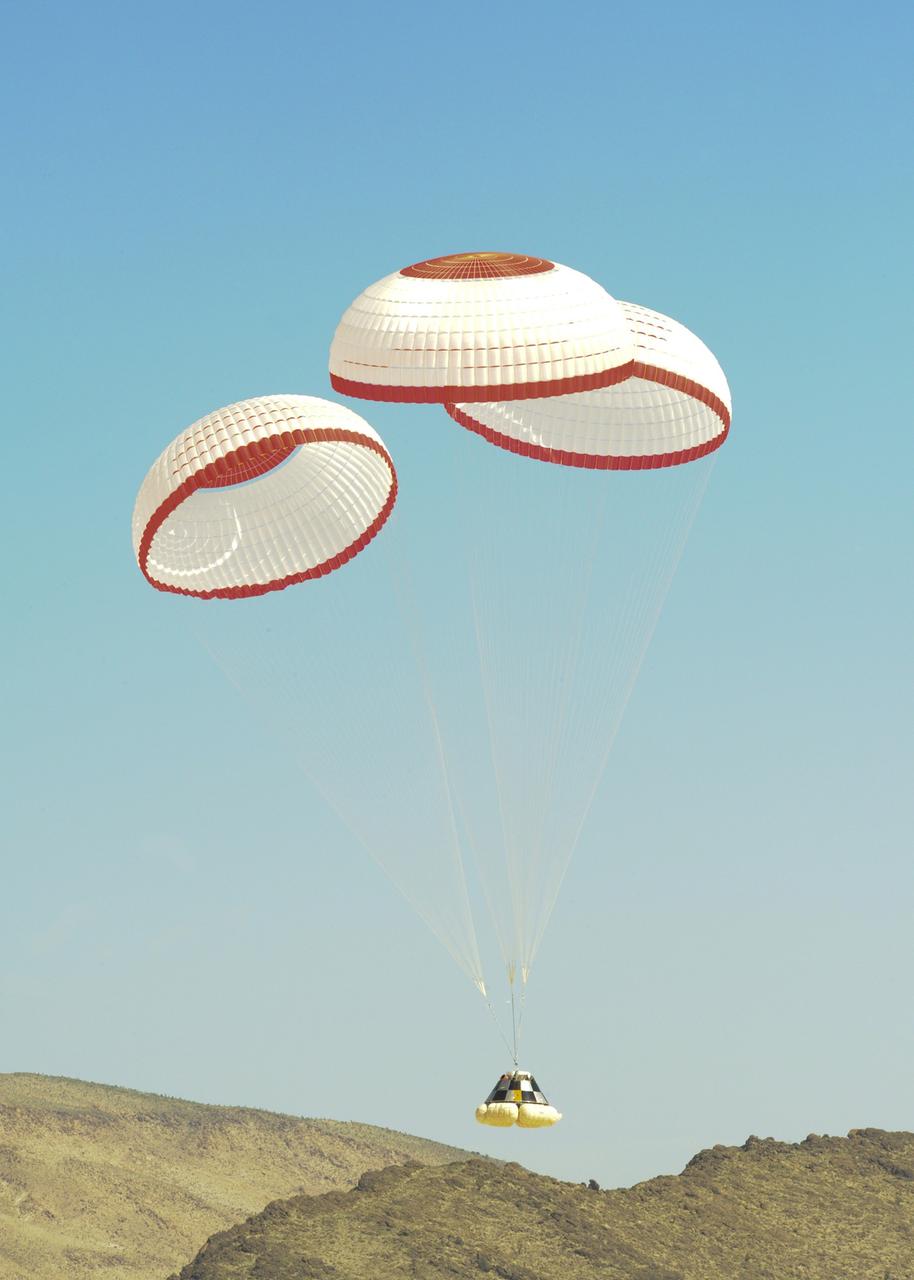

DELAMAR DRY LAKE BED, Nev. – The Boeing Company's CST-100 crew capsule floats to a smooth landing beneath three main parachutes over the Delamar Dry Lake Bed near Alamo, Nev. This is the second parachute test that Boeing performed under its partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program CCP. The first showed the parachute system’s deployment scheme worked and that it could be re-packed and re-used for this second test. In 2011, NASA selected Boeing during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, Excalibur Almaz Inc., Blue Origin, Sierra Nevada, Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Boeing
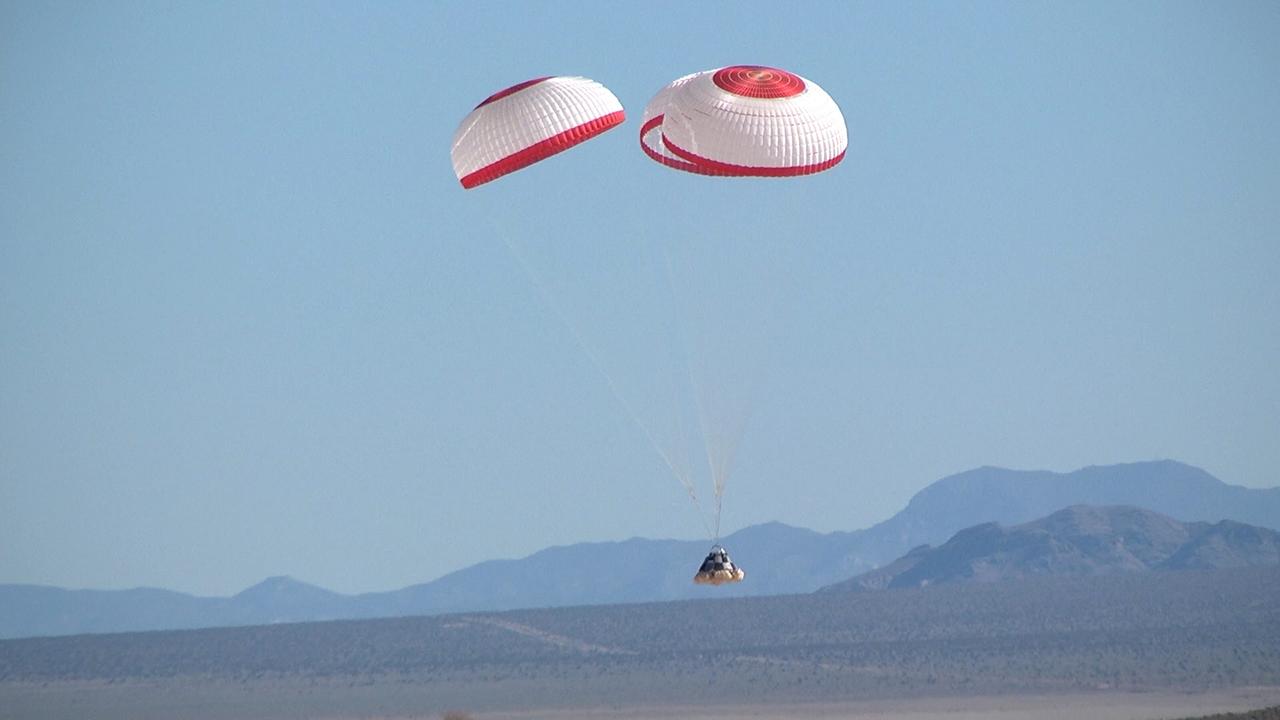

DELAMAR DRY LAKE BED, Nev. -- The Boeing Company's CST-100 boilerplate crew capsule floats toward a smooth landing beneath three main parachutes after being released from an Erickson Sky Crane helicopter at about 11,000 feet above Delamar Dry Lake Bed near Alamo, Nev. This is one of two tests that Boeing will perform for NASA's Commercial Crew Program CCP in order to validate the spacecraft's parachute system architecture and deployment scheme, characterize pyrotechnic shock loads, confirm parachute sizing and design, and identify potential forward compartment packaging and deployment issues. In 2011, NASA selected Boeing during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, Excalibur Almaz Inc., Blue Origin, Sierra Nevada, Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Boeing
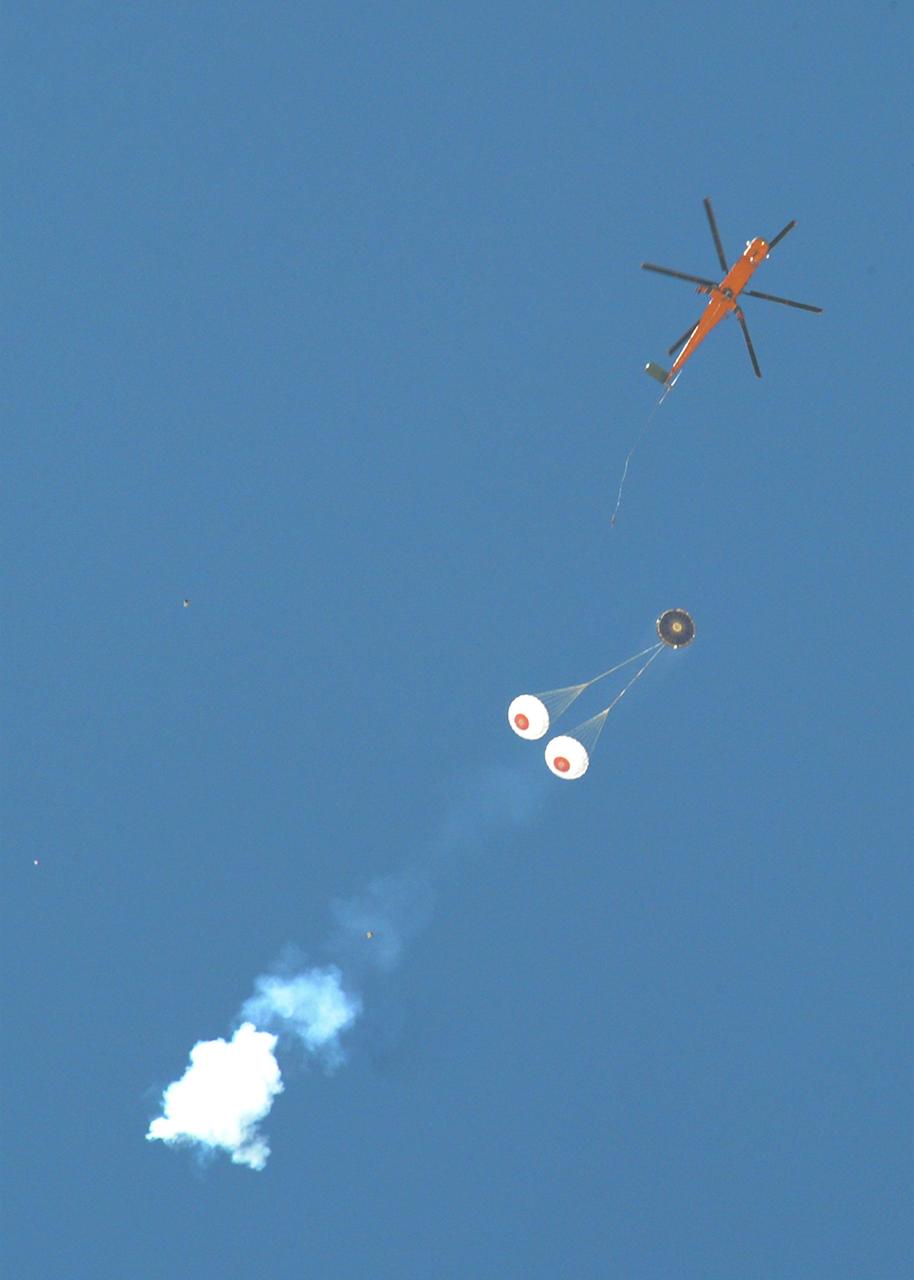

DELAMAR DRY LAKE BED, Nev. – An Erickson Sky Crane helicopter releases The Boeing Company's CST-100 crew capsule over the Delamar Dry Lake Bed near Alamo, Nev., where it floated to a smooth landing beneath its parachute system. This is the second parachute test that Boeing performed under its partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program CCP. The first showed the parachute system’s deployment scheme worked and that it could be re-packed and re-used for this second test. In 2011, NASA selected Boeing during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, Excalibur Almaz Inc., Blue Origin, Sierra Nevada, Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Boeing
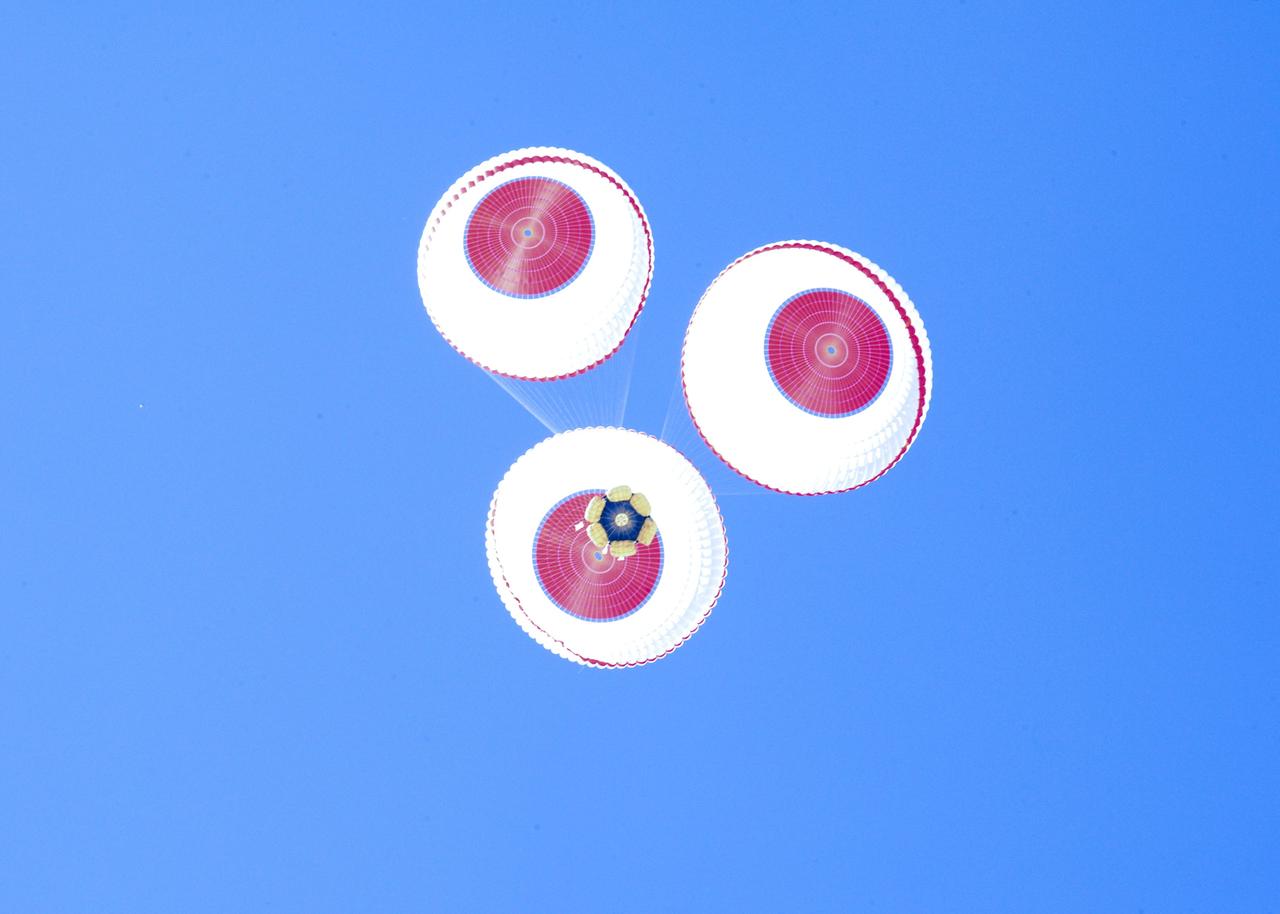

DELAMAR DRY LAKE BED, Nev. – The Boeing Company's CST-100 crew capsule floats to a smooth landing beneath three main parachutes over the Delamar Dry Lake Bed near Alamo, Nev. This is the second parachute test that Boeing performed under its partnership with NASA's Commercial Crew Program CCP. The first showed the parachute system’s deployment scheme worked and that it could be re-packed and re-used for this second test. In 2011, NASA selected Boeing during Commercial Crew Development Round 2 CCDev2) activities to mature the design and development of a crew transportation system with the overall goal of accelerating a United States-led capability to the International Space Station. The goal of CCP is to drive down the cost of space travel as well as open up space to more people than ever before by balancing industry’s own innovative capabilities with NASA's 50 years of human spaceflight experience. Six other aerospace companies also are maturing launch vehicle and spacecraft designs under CCDev2, including Alliant Techsystems Inc. ATK, Excalibur Almaz Inc., Blue Origin, Sierra Nevada, Space Exploration Technologies SpaceX, and United Launch Alliance ULA. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/commercialcrew. Image credit: Boeing
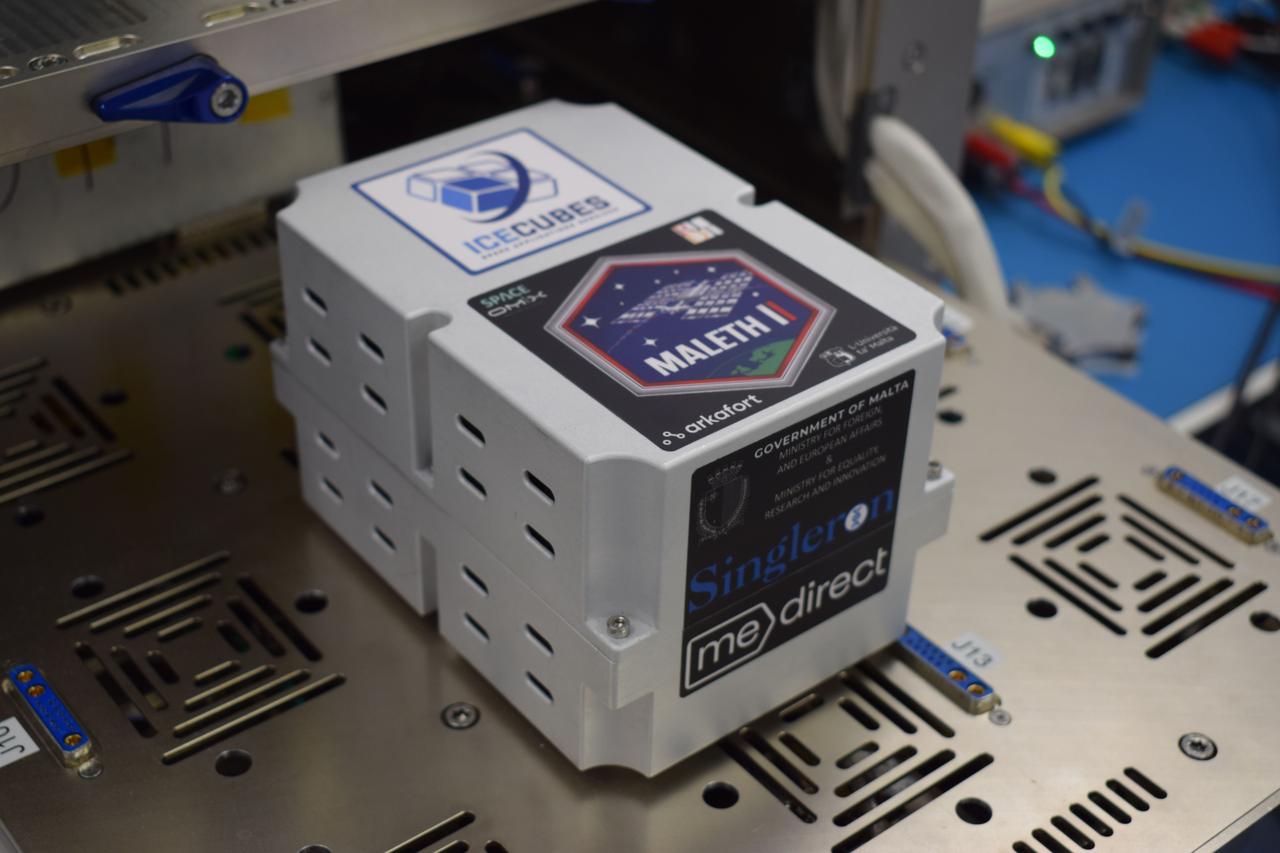

jsc2022e057890 (5/12/2022) --- MALETH II Biocube, based on the ICE Cubes platform by Space Applications Services, that takes Malta’s second space mission samples to the International Space Station. This is part of the Follow-up Study of Human Skin Tissue Microbiome Studies and Yeast Cells in Space (Ice Cubes #9.2 – Maleth 2) investigation. Image courtesy of Glenn Sciortino, Arkafort Ltd.
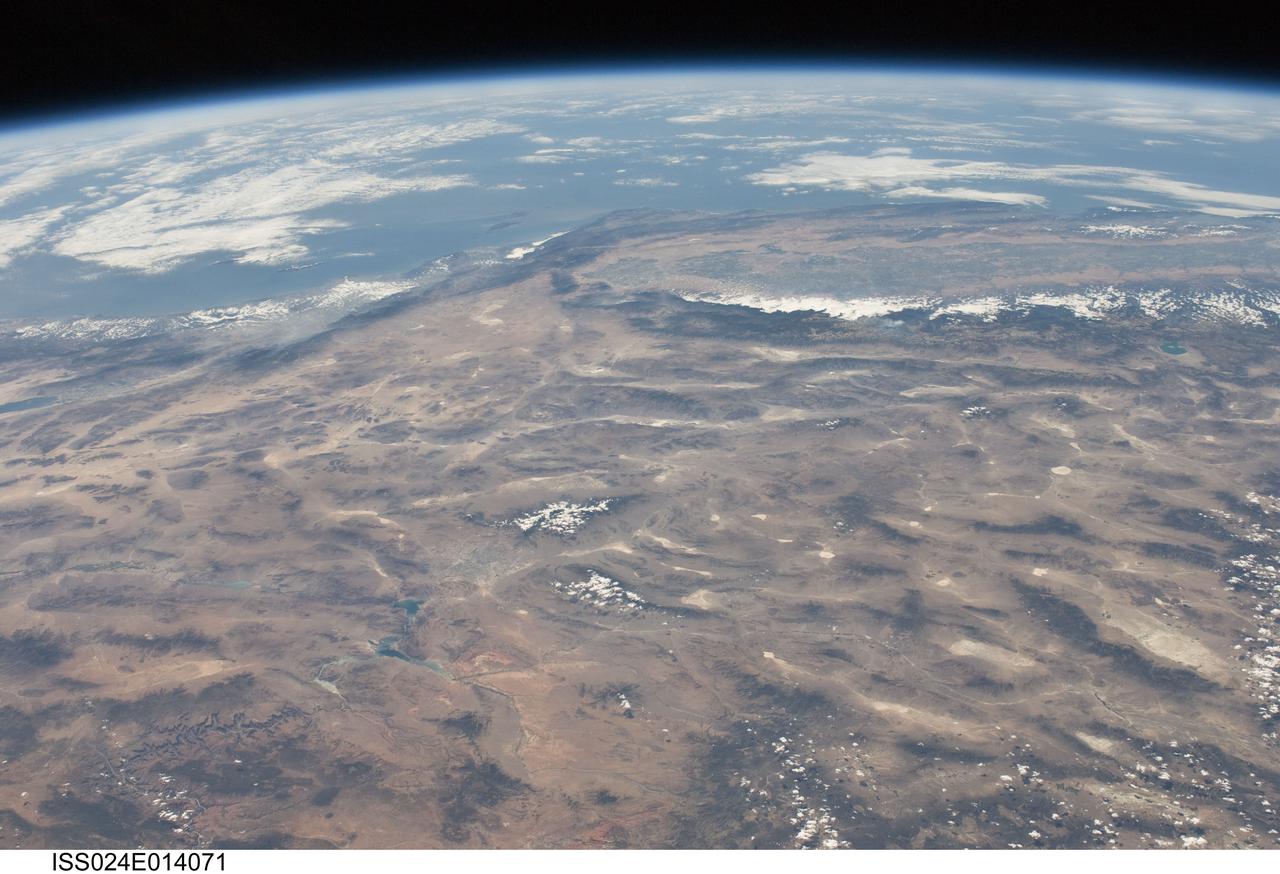

ISS024-E-014071 (9 Sept. 2010) --- This striking panoramic view of the southwestern USA and Pacific Ocean is an oblique image photographed by an Expedition 24 crew member looking outwards at an angle from the International Space Station (ISS). While most unmanned orbital satellites view Earth from a nadir perspective?in other words, collecting data with a ?straight down? viewing geometry?crew members onboard the space station can acquire imagery at a wide range of viewing angles using handheld digital cameras. The ISS nadir point (the point on Earth?s surface directly below the spacecraft) was located in northwestern Arizona, approximately 260 kilometers to the east-southeast, when this image was taken. The image includes parts of the States of Arizona, Nevada, Utah, and California together with a small segment of the Baja California, Mexico coastline at center left. Several landmarks and physiographic features are readily visible. The Las Vegas, NV metropolitan area appears as a gray region adjacent to the Spring Mountains and Sheep Range (both covered by white clouds). The Grand Canyon, located on the Colorado Plateau in Arizona, is visible (lower left) to the east of Las Vegas with the blue waters of Lake Mead in between. The image also includes the Mojave Desert, stretching north from the Salton Sea (left) to the Sierra Nevada mountain range. The Sierra Nevada range is roughly 640 kilometers long (north-south) and forms the boundary between the Central Valley of California and the adjacent Basin and Range. The Basin and Range is so called due to the pattern of long linear valleys separated by parallel linear mountain ranges ? this landscape, formed by extension and thinning of Earth?s crust, is particularly visible at right.