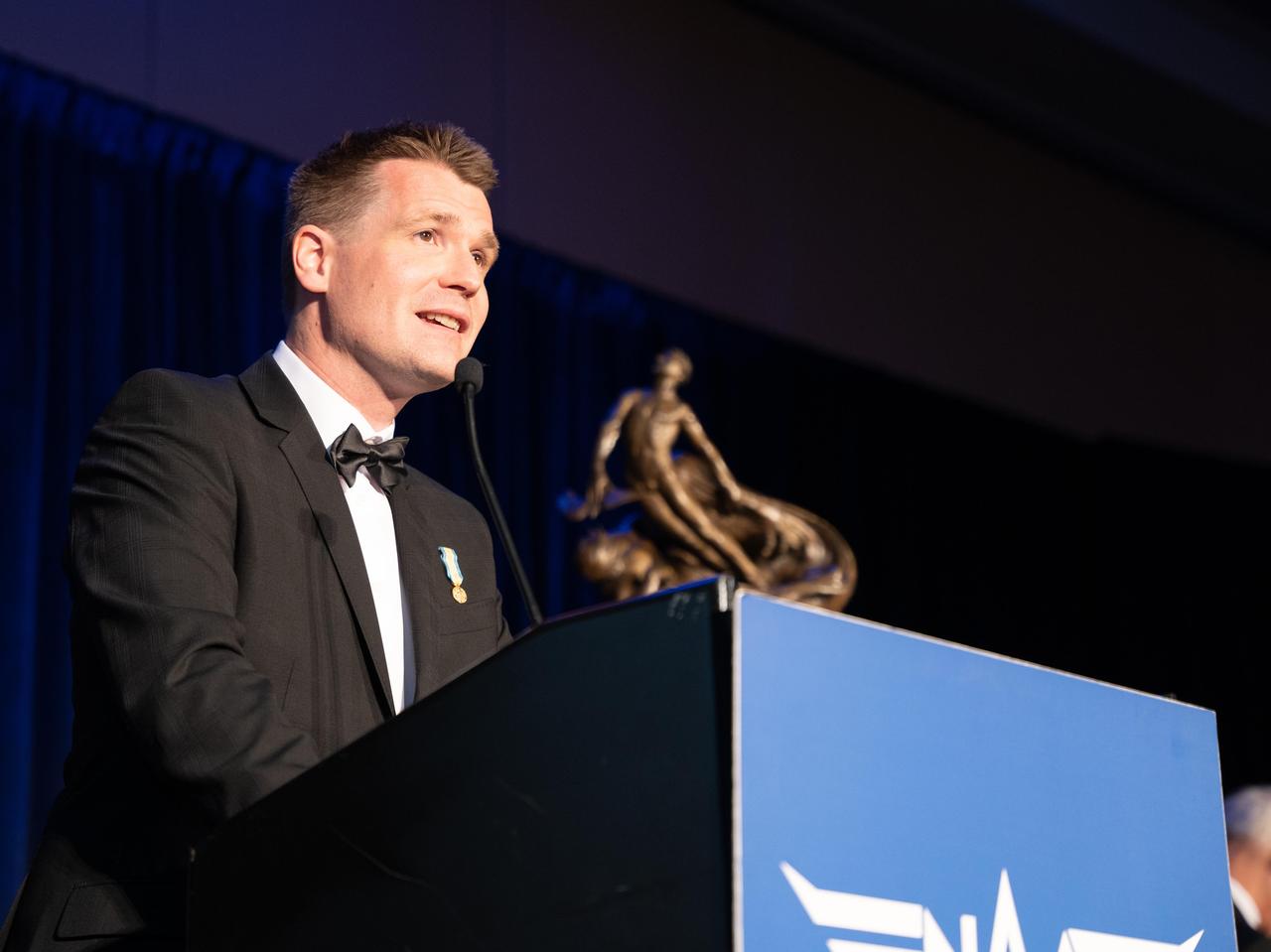

The chief pilot for NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter, Håvard Grip, speaks at the Robert J. Collier Dinner in Washington on June 9, 2022. The Ingenuity Mars Helicopter team was awarded the 2021 Collier Trophy "for the first powered, controlled flight of an aircraft on another planet, thereby opening the skies of Mars and other worlds for future scientific discovery and exploration," the award citation states. This historic trophy – which is on permanent display at the Smithsonian Air and Space Museum in Washington – is awarded annually by the National Aeronautic Association "for the greatest achievement in aeronautics or astronautics in America, with respect to improving the performance, efficiency, and safety of air or space vehicles, the value of which has been thoroughly demonstrated by actual use during the preceding year." https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25216
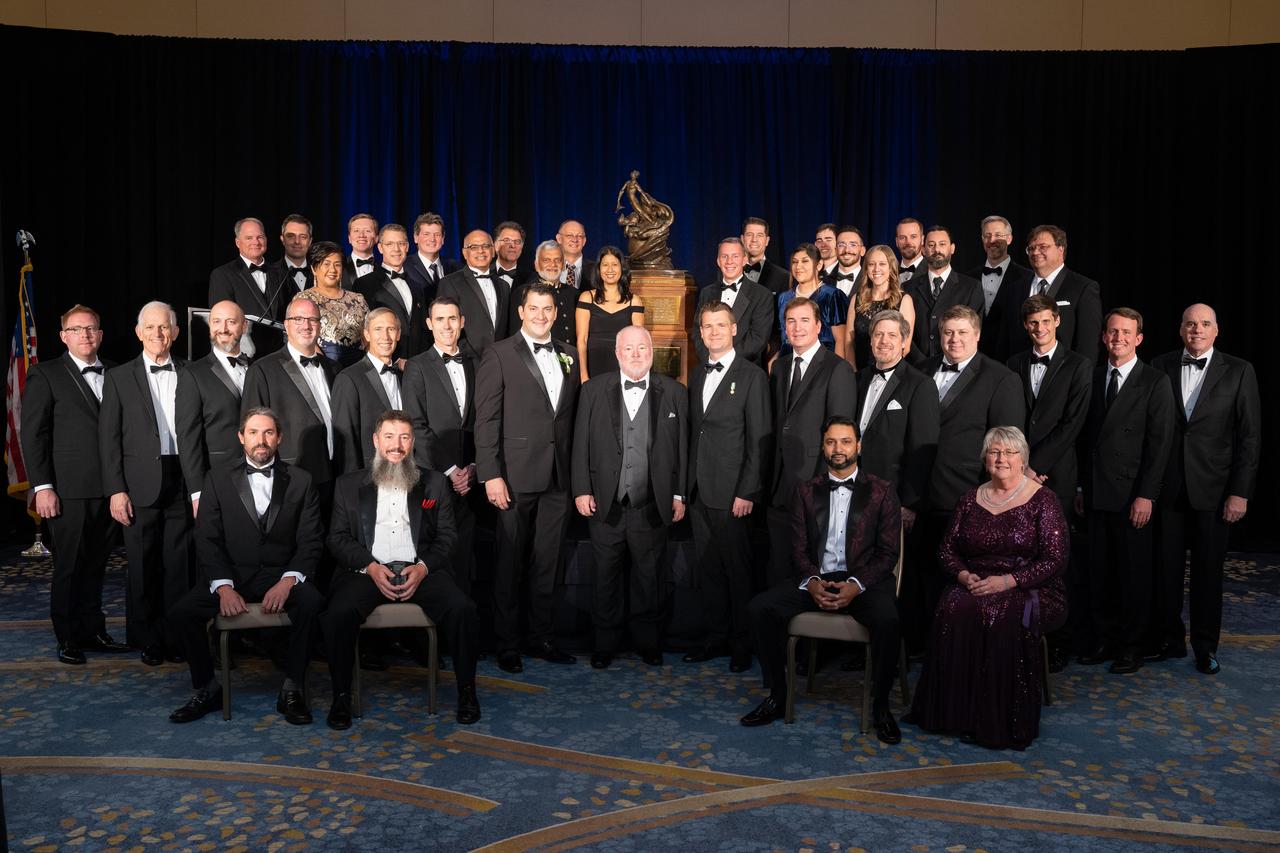

Members of NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter team are pictured with the Collier Trophy during the Robert J. Collier Dinner in Washington on June 9, 2022. The team was awarded the 2021 Collier Trophy "for the first powered, controlled flight of an aircraft on another planet, thereby opening the skies of Mars and other worlds for future scientific discovery and exploration," the award citation states. This historic trophy – which is on permanent display at the Smithsonian Air and Space Museum in Washington – is awarded annually by the National Aeronautic Association "for the greatest achievement in aeronautics or astronautics in America, with respect to improving the performance, efficiency, and safety of air or space vehicles, the value of which has been thoroughly demonstrated by actual use during the preceding year." https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25324
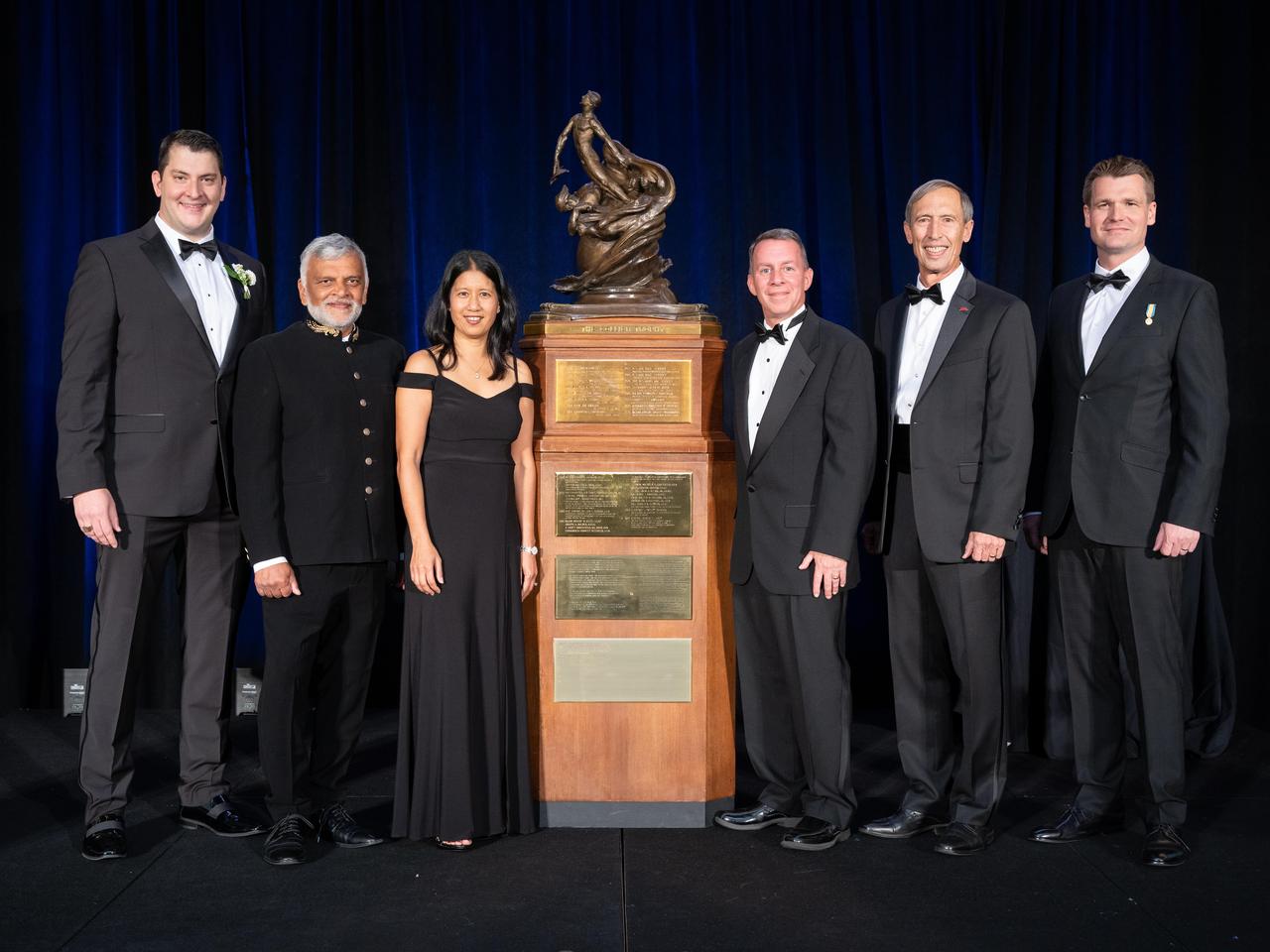

Members of NASA's Ingenuity Mars Helicopter team stand next to the Collier Trophy during the Robert J. Collier Dinner in Washington on June 9, 2022. The team was awarded the 2021 Collier Trophy "for the first powered, controlled flight of an aircraft on another planet, thereby opening the skies of Mars and other worlds for future scientific discovery and exploration," the award citation states. From left to right: Teddy Tzanetos, Ingenuity team lead at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory; Bob Balaram, Ingenuity emeritus chief engineer at JPL; MiMi Aung, former Ingenuity project manager at JPL; Bobby Braun, former director for Planetary Science at JPL; Larry James, deputy director at JPL; Håvard Grip, Ingenuity chief pilot at JPL. This historic trophy – which is on permanent display at the Smithsonian Air and Space Museum in Washington – is awarded annually by the National Aeronautic Association "for the greatest achievement in aeronautics or astronautics in America, with respect to improving the performance, efficiency, and safety of air or space vehicles, the value of which has been thoroughly demonstrated by actual use during the preceding year." https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25323
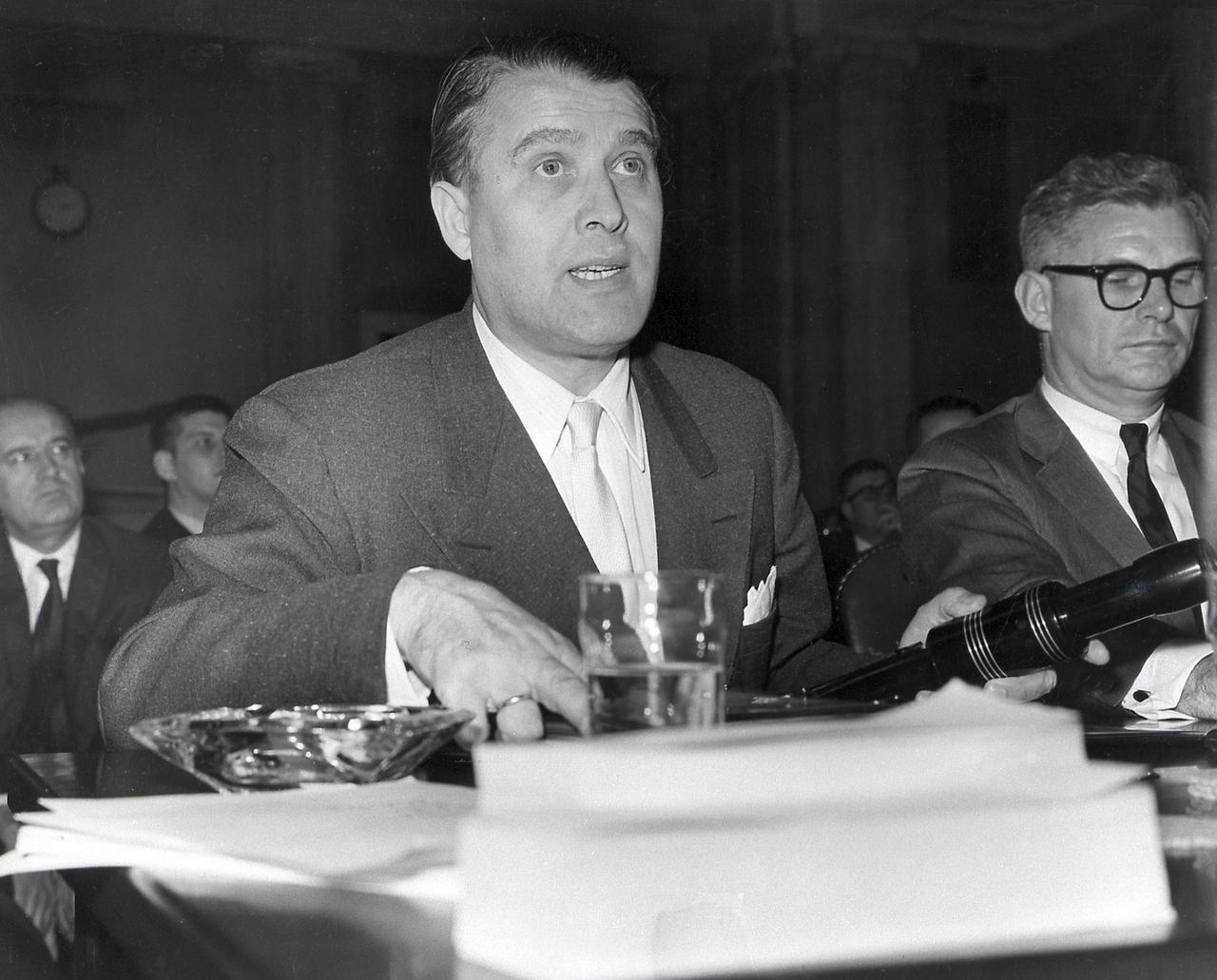

Dr. von Braun, Director of the Marshall Space Flight Center, spoke of the progress in the Saturn Program during his appearance before the Senate Committee on Aeronautical and Space Sciences. He was accompanied by Dr. Robert C. Seamans, Jr., Associate Administrator of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
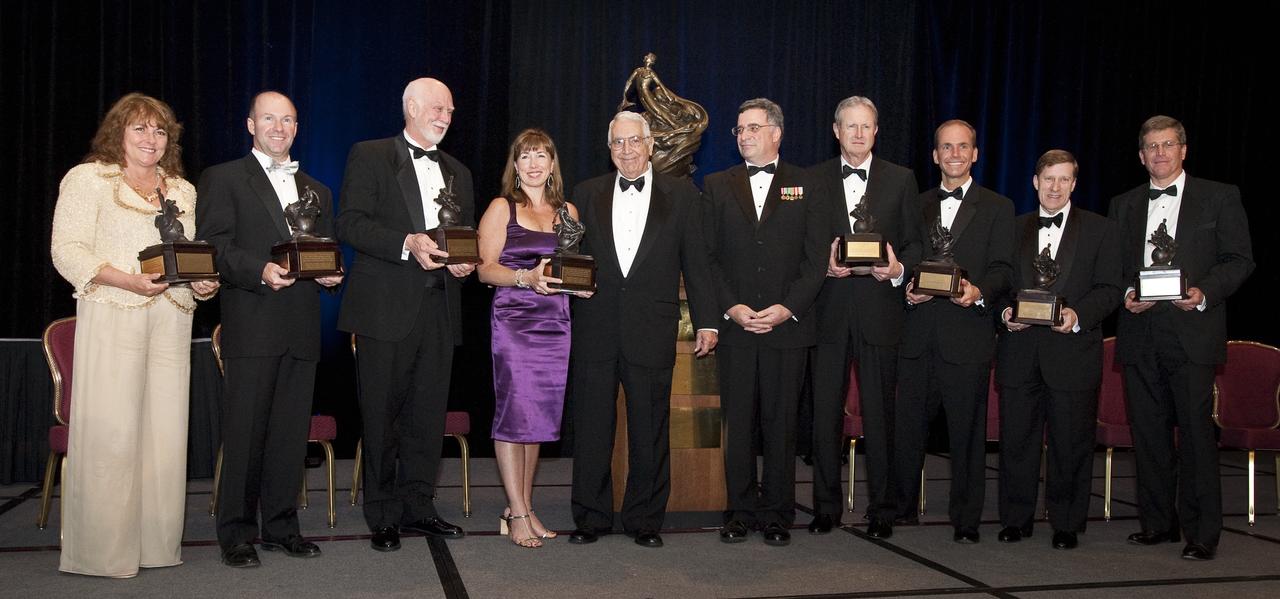

NASA and the International Space Station (ISS) team is selected as the recipient of the 2009 Robert J. Collier Trophy on Thursday, May 13, 2010, in Arlington, VA. Lori Garver, fourth from left, Deputy Administrator of NASA accepts the Collier Trophy on behalf of NASA. The ISS Team nomination consisted NASA, The Boeing Company, Draper Laboratory, Honeywell, Lockheed Martin Corporation, United Space Alliance, and United Technologies/Hamilton Sunstrand. Seen from left are: Virginia Barnes, President and CEO, United Space Alliance; Alain Bellemare, President, United Technologies/Hamilton Sunstrand; James Crocker, VP and GM, Sensing & Exploration, Lockheed Martin; Lori Garver; Wayne Boyne, Chairman, National Aeronautic Association; Jonathan Gaffney, President, National Aeronautic Association; Jim Albaugh, Executive VP of The Boeing Company, President and CEO of Boeing Commercial Airplanes; Dennis Muilenberg, Executive Vice President, The Boeing Company, President and CEO, Boeing Defense, Space and Security; James Shields, President and CEO, Draper Laboratory and Dave Douglas, Vice President, Space, Missiles and Munitions, Honeywell. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
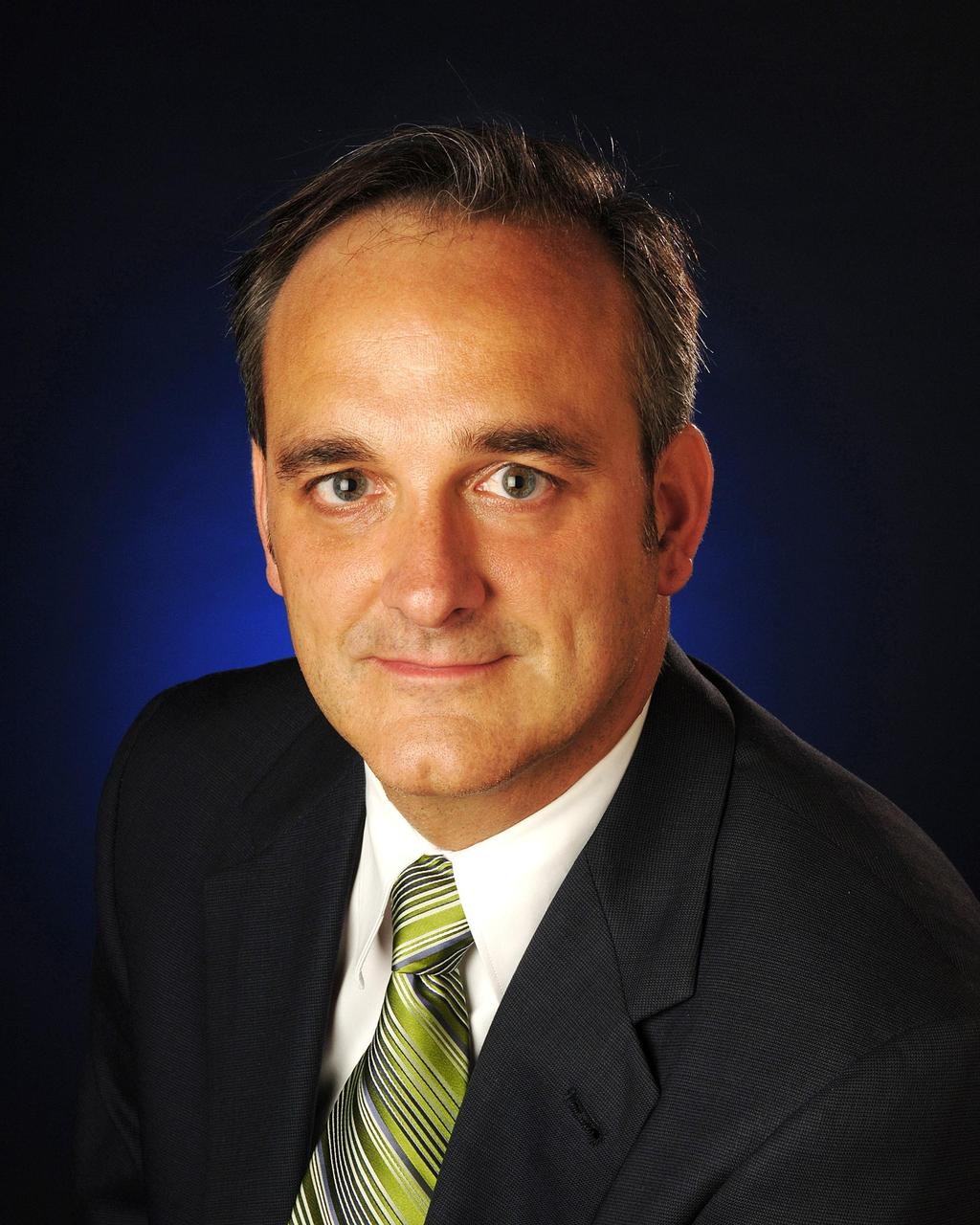

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Official portrait of Rex Geveden, NASA Associate Administrator. Rex Geveden is the associate administrator of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. In this position, he is responsible for all technical operations of the Agency. He works directly with the Administrator to develop strategy and policy and has direct oversight of all NASA’s programs and field centers. Photo credit: NASA/Bill Ingalls.
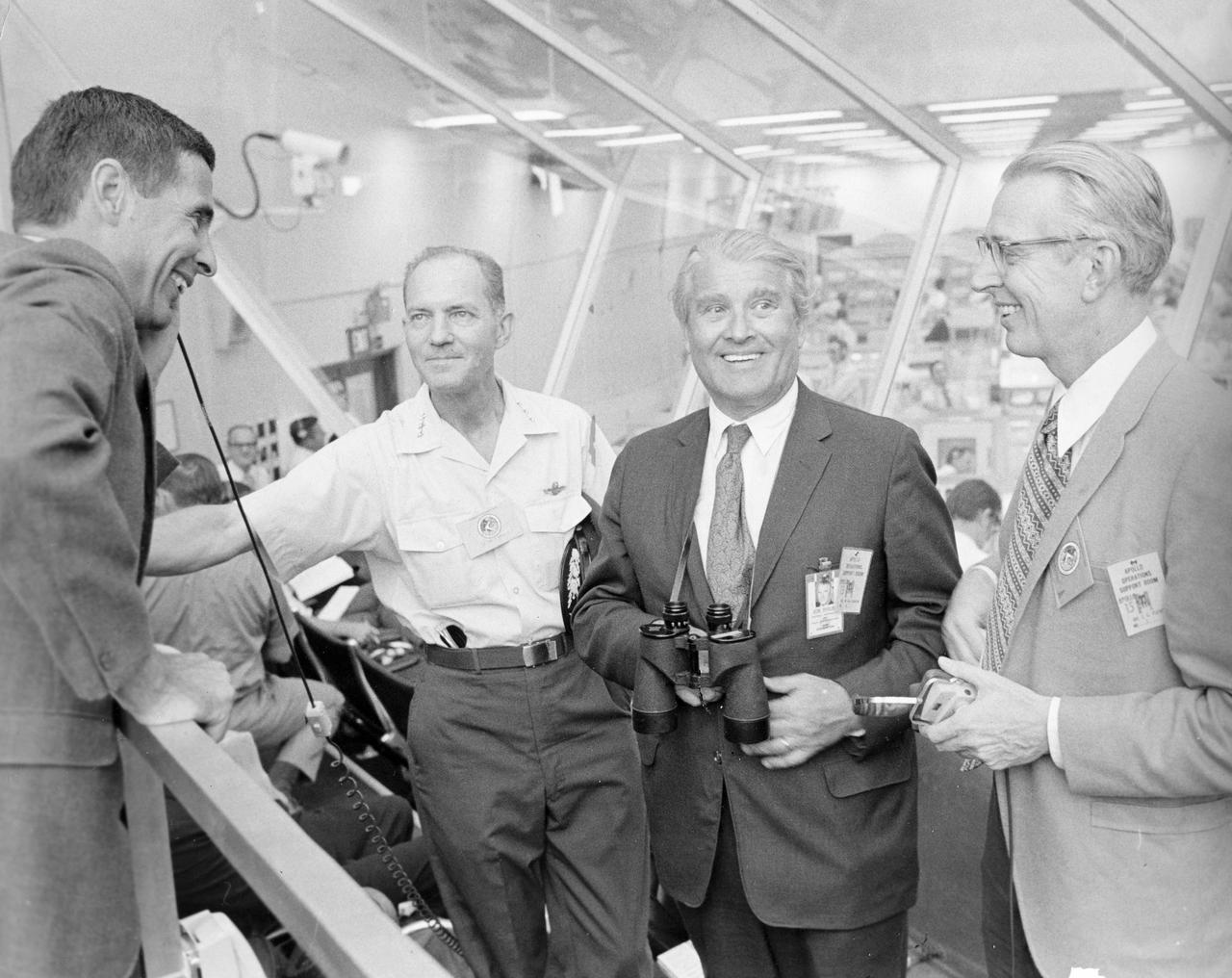

During the Apollo 15 pre-launch activity in the launch control center's firing room 1 at Kennedy Space Center, the then recently appointed NASA Administrator, Dr. James C. Fletcher (right) speaks with (Left to right) William Anders, executive secretary of the National Aeronautics and Space Council; Lt. General Sam Phillips, former Apollo Program Director; and Dr. Wernher von Braun, NASA's Deputy Associate Administrator for planning.
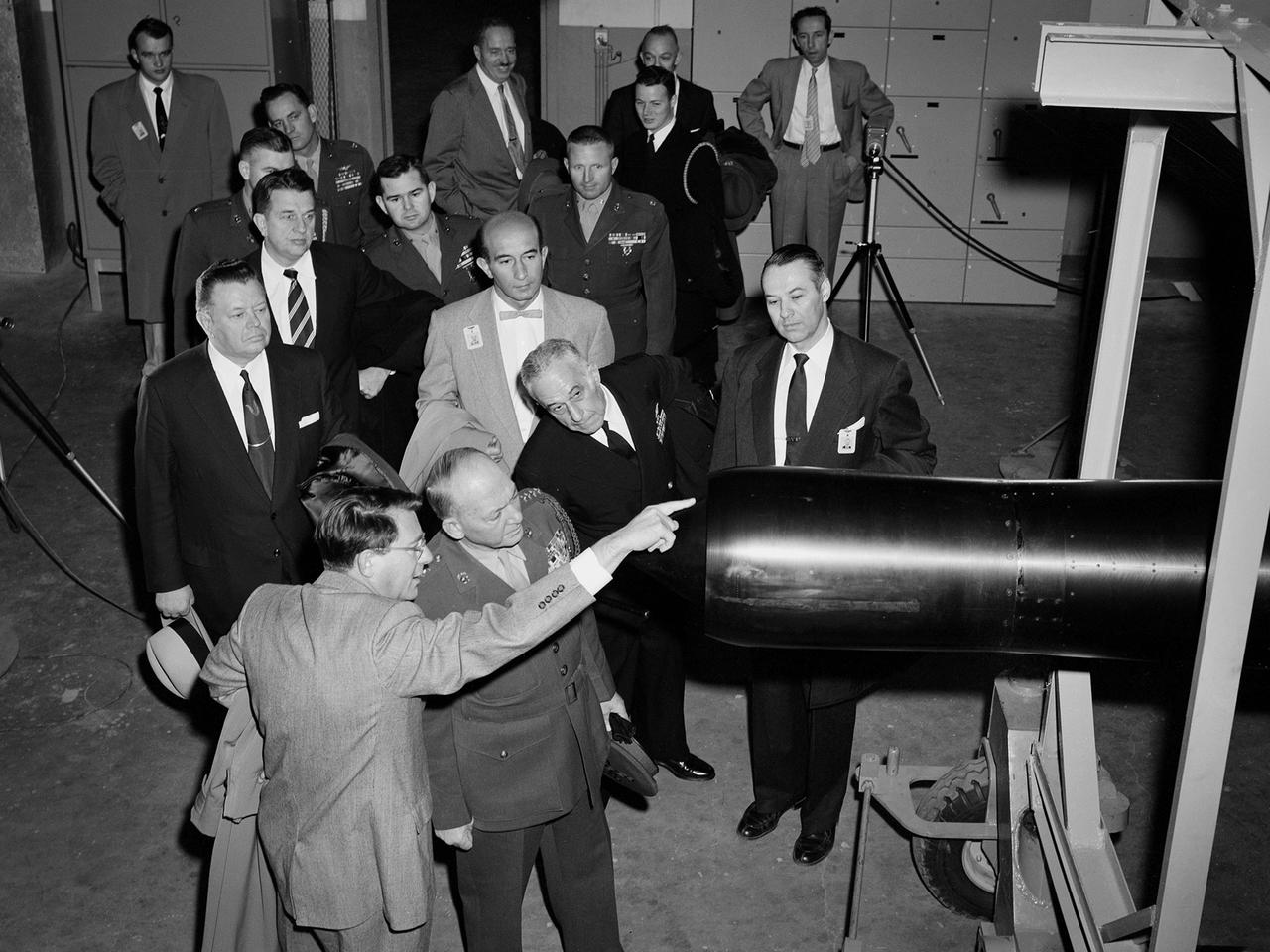

Abe Silverstein, Associate Director of the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory, provides a personal tour of the new 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel for US Senator George Bender (hat in hand) and General Lemuel Shepherd. Shepherd was Commandant of the Marine Corps and had served in World War I, World War II, and the Korean War. The general was accompanied by Admiral Herbert Leary, in dark uniform. Bender was a Republican Senator from Ohio. Behind Bender is President of the Cleveland Chamber of Commerce Curtis Smith. NACA Lewis managers Eugene Manganiello and Wilson Hunter assist with the tour. Abe Silverstein oversaw all research at the laboratory. Upon taking his post in 1952 he reorganized the research staff and began shifting the focus away from airbreathing aircraft engines to new fields such as high energy fuels, electric propulsion, and nuclear power and propulsion. He was an early advocate of the NACA’s involvement in the space program and crucial to the founding of National Aeronautics and Space Administration in 1958. Silverstein began his career helping design and conduct research in the Full Scale Tunnel in 1929 at the Langley Memorial Aeronautical Laboratory. Silverstein advocated a series of increasingly large supersonic wind tunnels after the war, culminating in the 10- by 10.
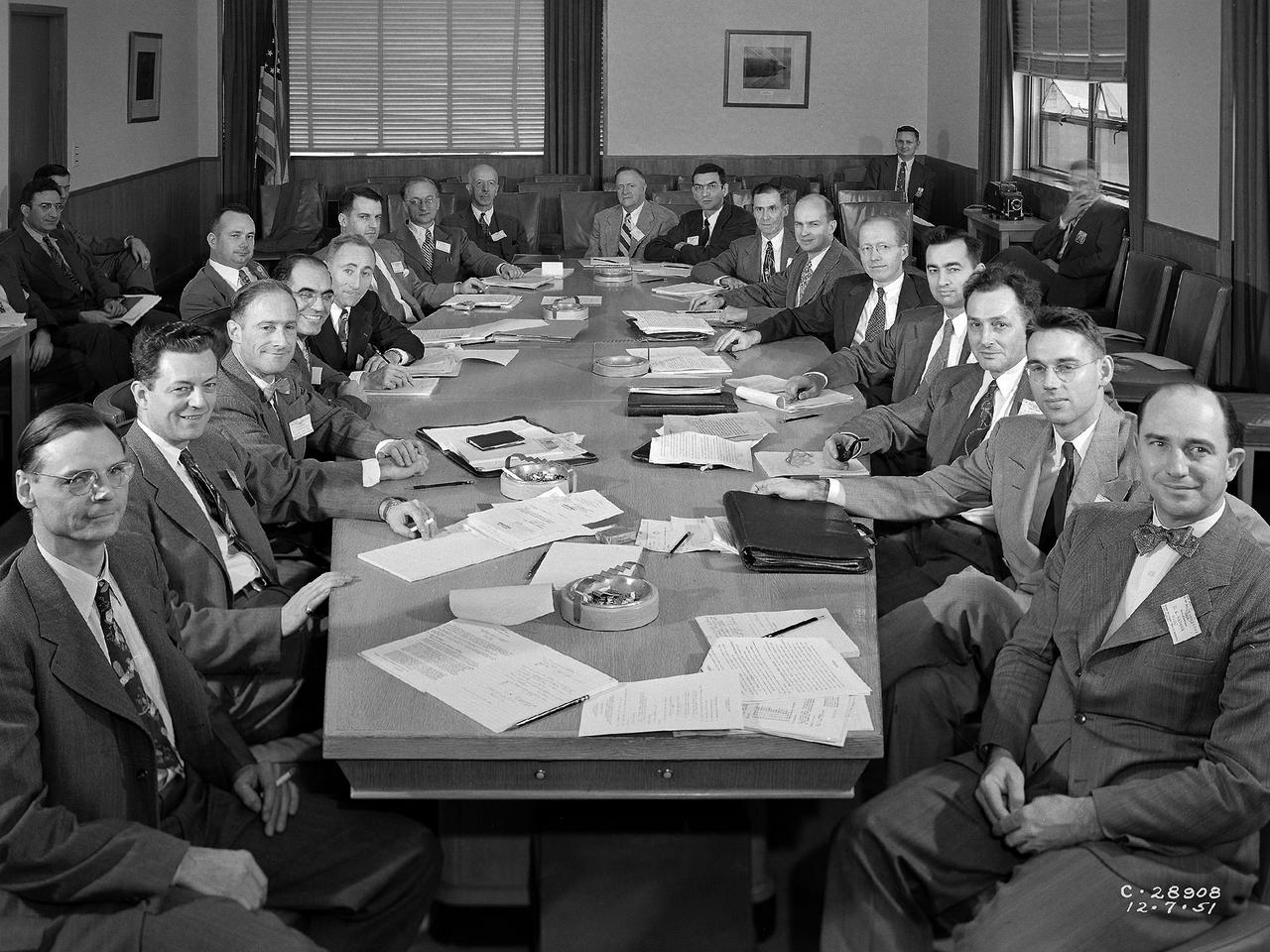

The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Subcommittee on Combustion holds a meeting at Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in Cleveland, Ohio. The NACA was managed by committees that included members of their own staff along with representatives from industry, the military, other government agencies, and universities. The 17-person Executive Committee was the NACA’s primary administrative body. They met several times a year at the NACA headquarters office in Washington DC to discuss broad issues confronting the US aeronautical community. Jerome Hunsaker, head of the Department of Aeronautical Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, served as the NACA chairman from 1941 to 1956. George Lewis was not a member of the Executive Committee but served a key role as the NACA’s Director of Aeronautical Research. The NACA’s organizational chart also included 11 technical committees, several of which had specialized subcommittees. There were over 100 different subcommittees between World War I and 1958. The number of active subcommittees varied over the years. Most existed only for a few years, but some continued for over a decade. The subcommittees met three or four times per year, often at the laboratory most closely associated with the area of research. A team of laboratory researchers presented briefings on their recent activities and plans for the future. The Subcommittee on Combustion existed from 1945 to the NACA’s demise in 1958.
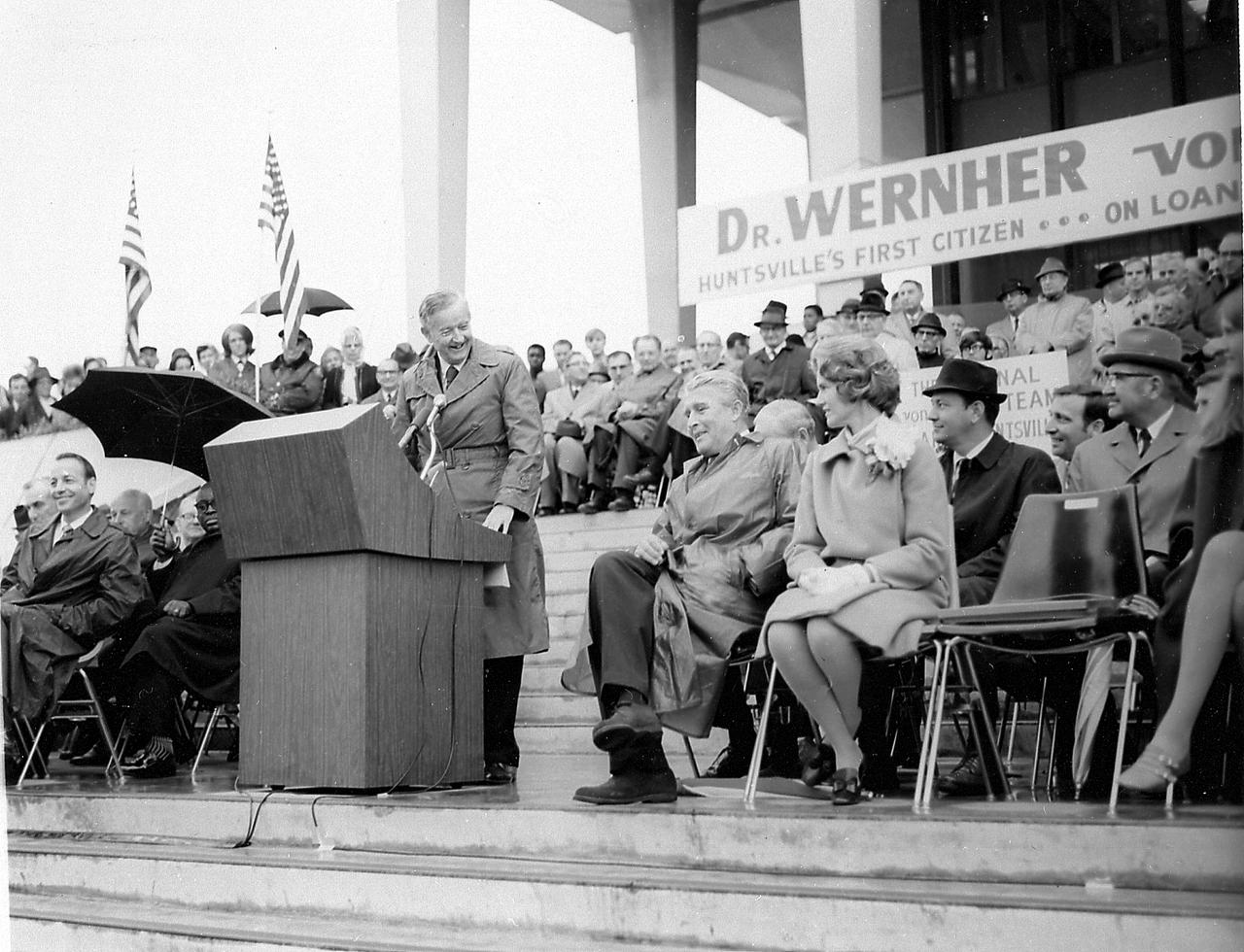

Prior to MSFC (Marshall Space Flight Center) Director, Dr. von Braun's transfer to NASA Headquarters where he had been appointed Deputy Associate Administrator for Plarning, he was honored during a series of events recognizing his contribution to the space effort during his career in Huntsville, Alabama. In this photo at the Madison County Courthouse, Dr. von Braun is shown seated next to his wife, Maria, as U.S. Senator John Sparkman comments on his career in Huntsville, Alabama, where he worked for both the Army and NASA (National Aeronautic Space Administration).

Acting NASA Associate Administrator for Human Exploration and Operations, Ken Bowersox, left, Cristina Chaplain, director, Contracting and National Security Acquisitions, U.S. Government Accountability Office (GAO), center, and Doug Cooke, owner, Cooke Concepts and Solutions, right, testify during a Space and Aeronautics Subcommittee of the House Science, Space, and Technology Committee hearing titled, “Developing Core Capabilities for Deep Space Exploration: An Update on NASA's SLS, Orion, and Exploration Ground Systems," Wednesday, September 18, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
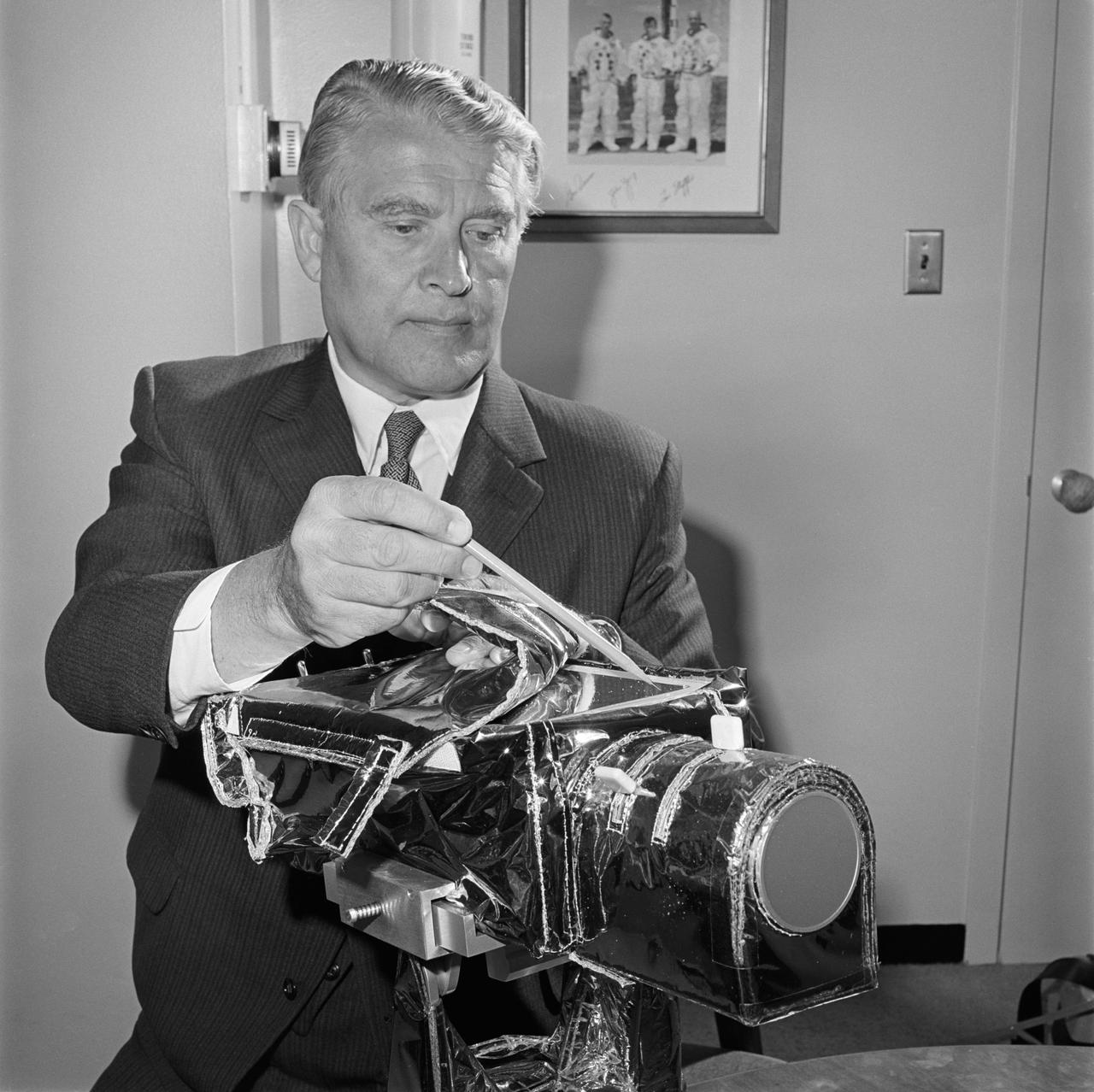

S71-35169 (June 1971) --- The color television camera for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) Apollo 15 lunar landing mission is examined by NASA's Deputy Associate Director Dr. Wernher von Braun. The camera will be mounted on the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) and will be operated by the flight crew astronauts, David R. Scott and James B. Irwin, or by ground command from the Mission Control Center (MCC) in Houston during the three lunar traverses. It will also be used to show the astronauts whenever they leave the LRV, and for the first time it will make possible the viewing of the Lunar Module (LM) ascent stage as it lifts off the moon.

Lori Garver, left, Deputy Administrator of NASA, speaks at the Annual Collier Dinner on Thursday, May 13, 2010 in Arlington, VA. NASA and the International Space Station team is the winner of the 2009 Robert J. Collier Trophy. The Collier Trophy is awarded annually for the greatest achievement in aeronautics or astronautics in America. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Lori Garver, Deputy Administrator of NASA, speaks at the Annual Collier Dinner on Thursday, May 13, 2010 in Arlington, VA. NASA and the International Space Station team is the winner of the 2009 Robert J. Collier Trophy. The Collier Trophy is awarded annually for the greatest achievement in aeronautics or astronautics in America. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
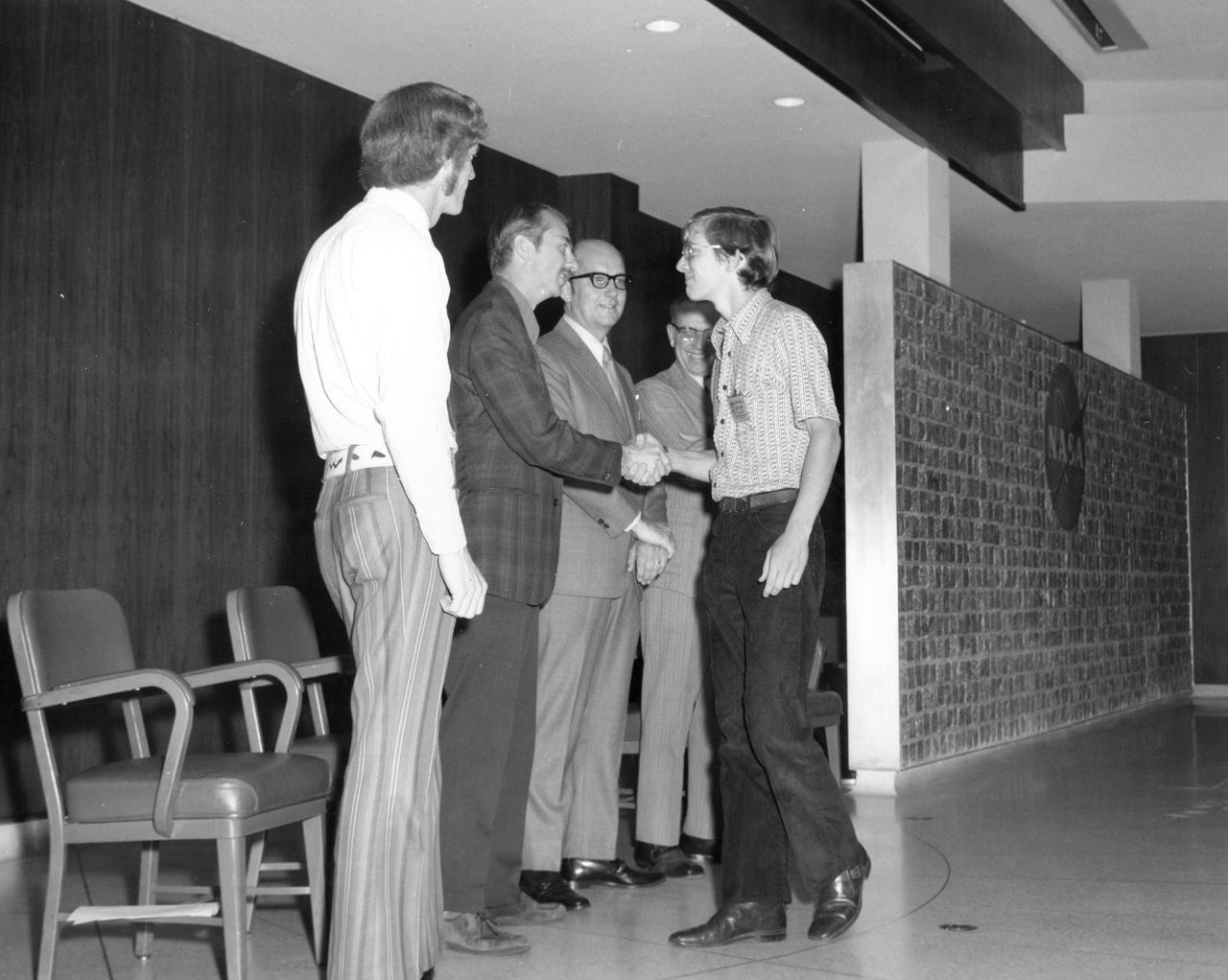

Downey, California high school student, Donald W. Shellack, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Shellack was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.

Atlanta, Georgia high school student, Neal W. Shannon, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Shannon was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
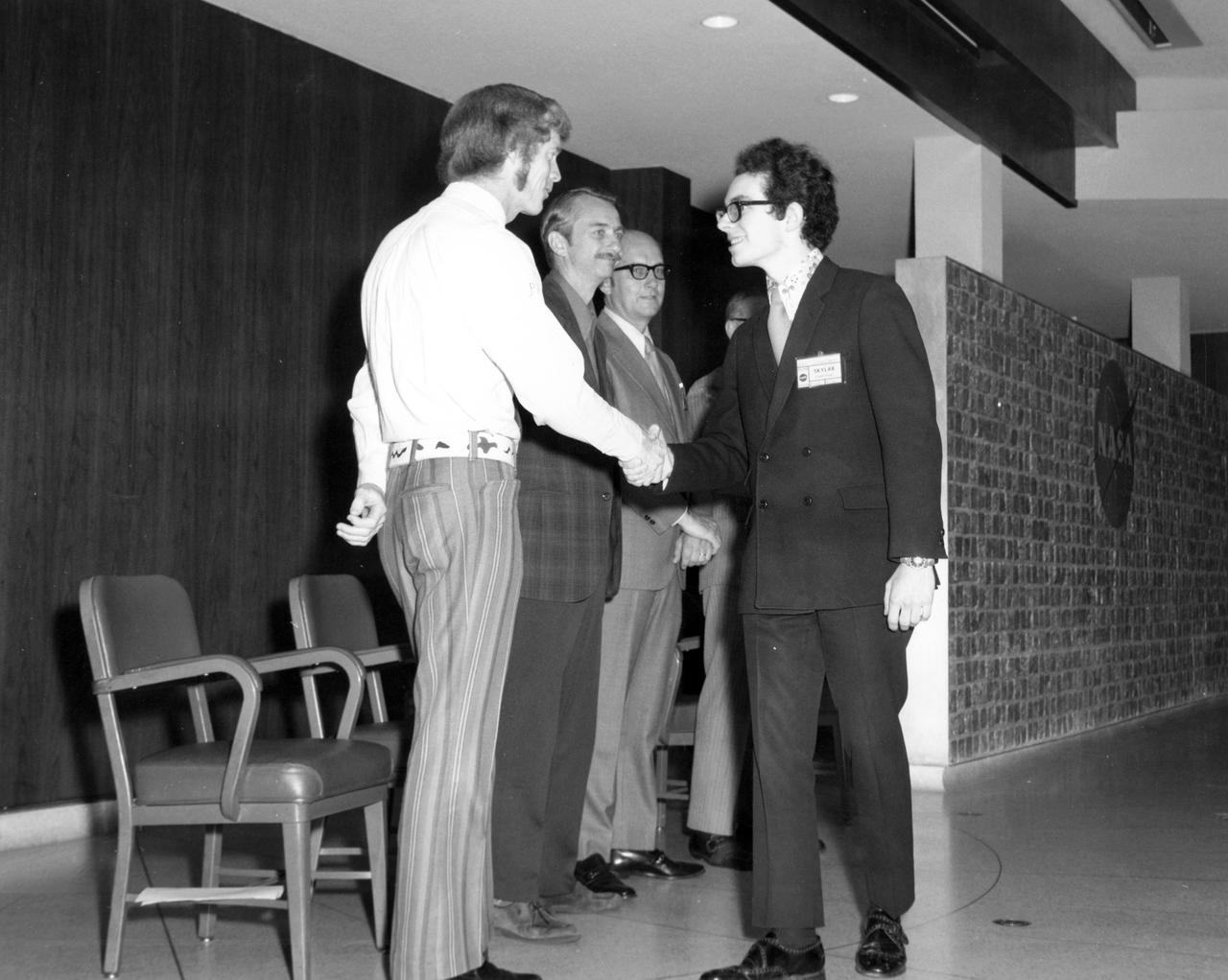

Berkley, Michigan high school student, Kirk M. Sherhart, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Sherhart was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
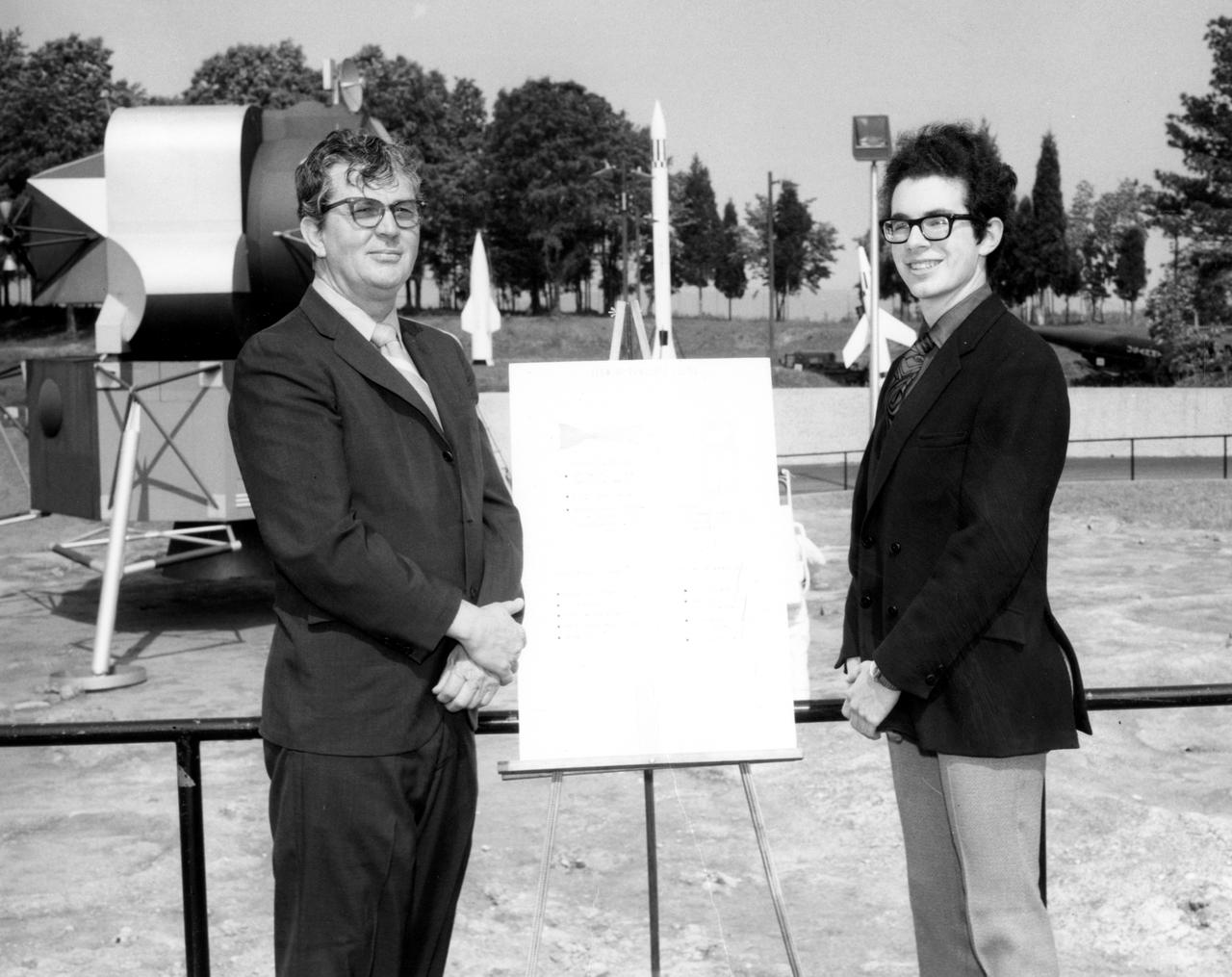

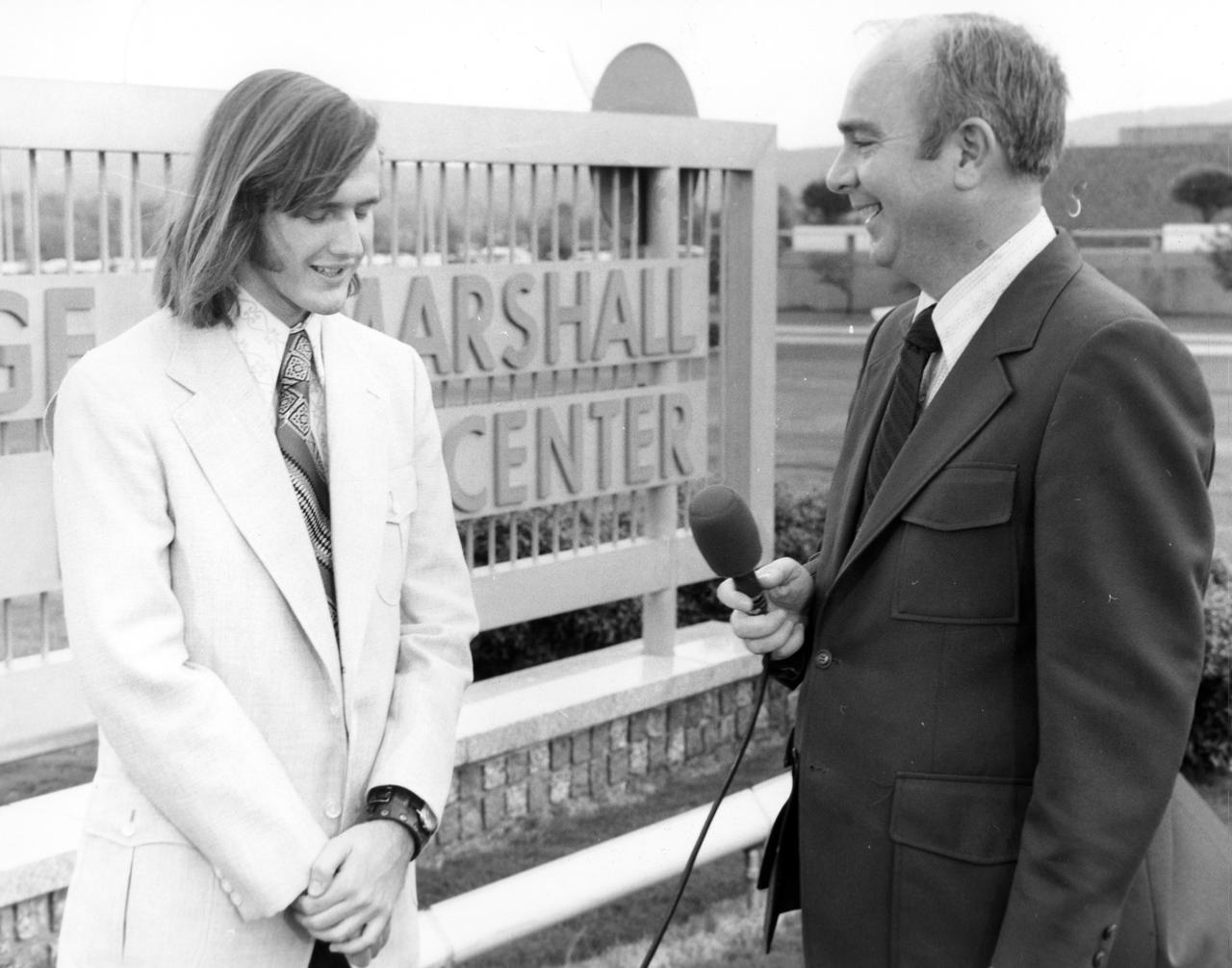
Kirk M. Sherhart, high school student from Berkley, Michigan, discussed a his proposed Skylab experiment with Dr. Robert Head of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) during his visit to the center. The lunar surface scene in the background is one of many space exhibits at the Alabama Space and Rocket Center in nearby Huntsville, Alabama. Sherhart was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
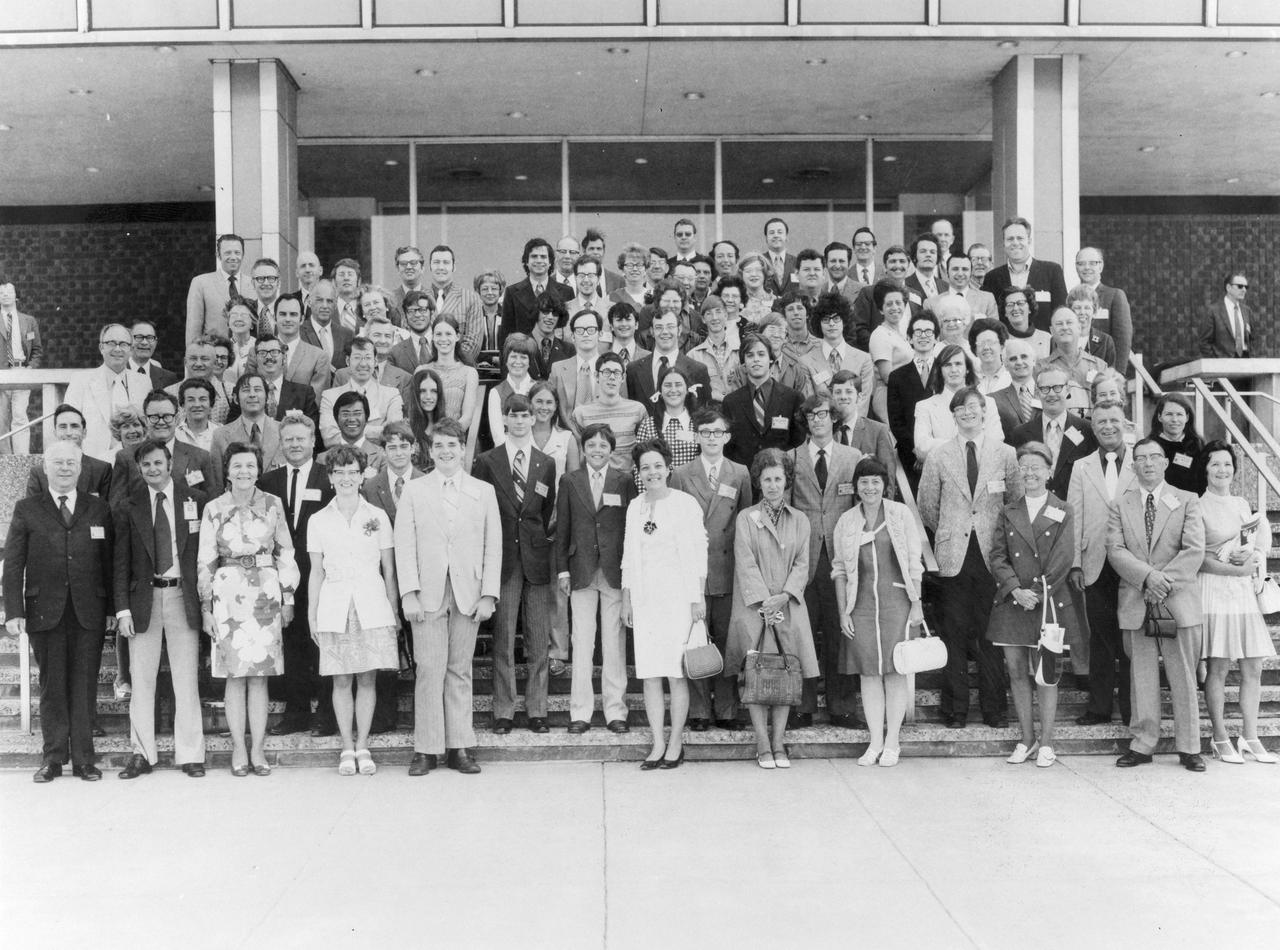

One of the most successful of the Skylab educational efforts was the Skylab Student Project. A nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) in which secondary students were encouraged to submit proposals for experiments to be conducted on Skylan in Earth orbit the following year. After the official announcement of this project, over 4,000 students responded with 3,409 proposals. The winning 25 students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), the lead center for Skylab, where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment. This photograph is a group shot of the 25 winners, parents, and sponsors when they met for the first time on the steps of Building 4200 at MSFC in the Spring of 1972.
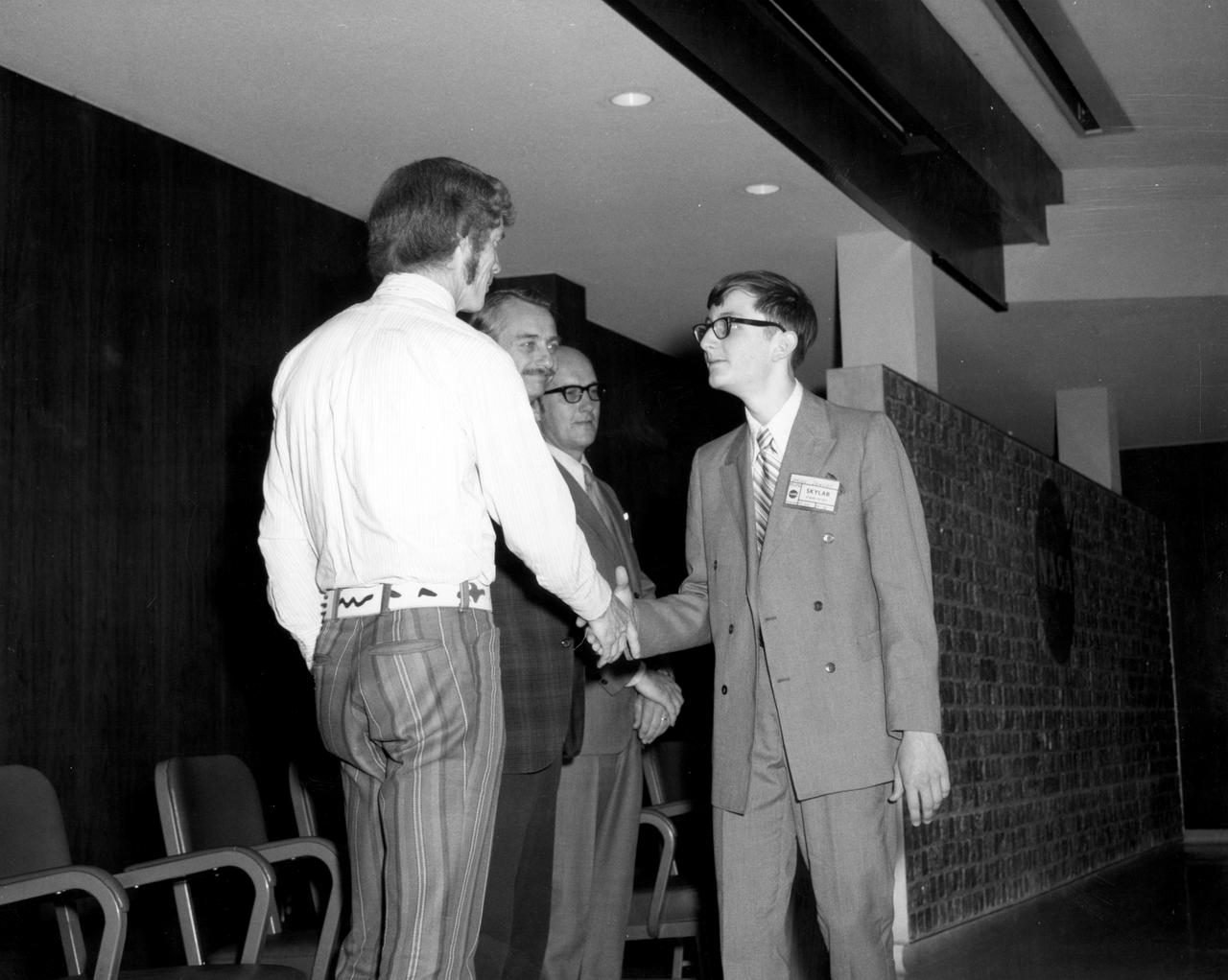

Youngstown, Ohio high school student, W. Brian Dunlap, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Dunlap was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.

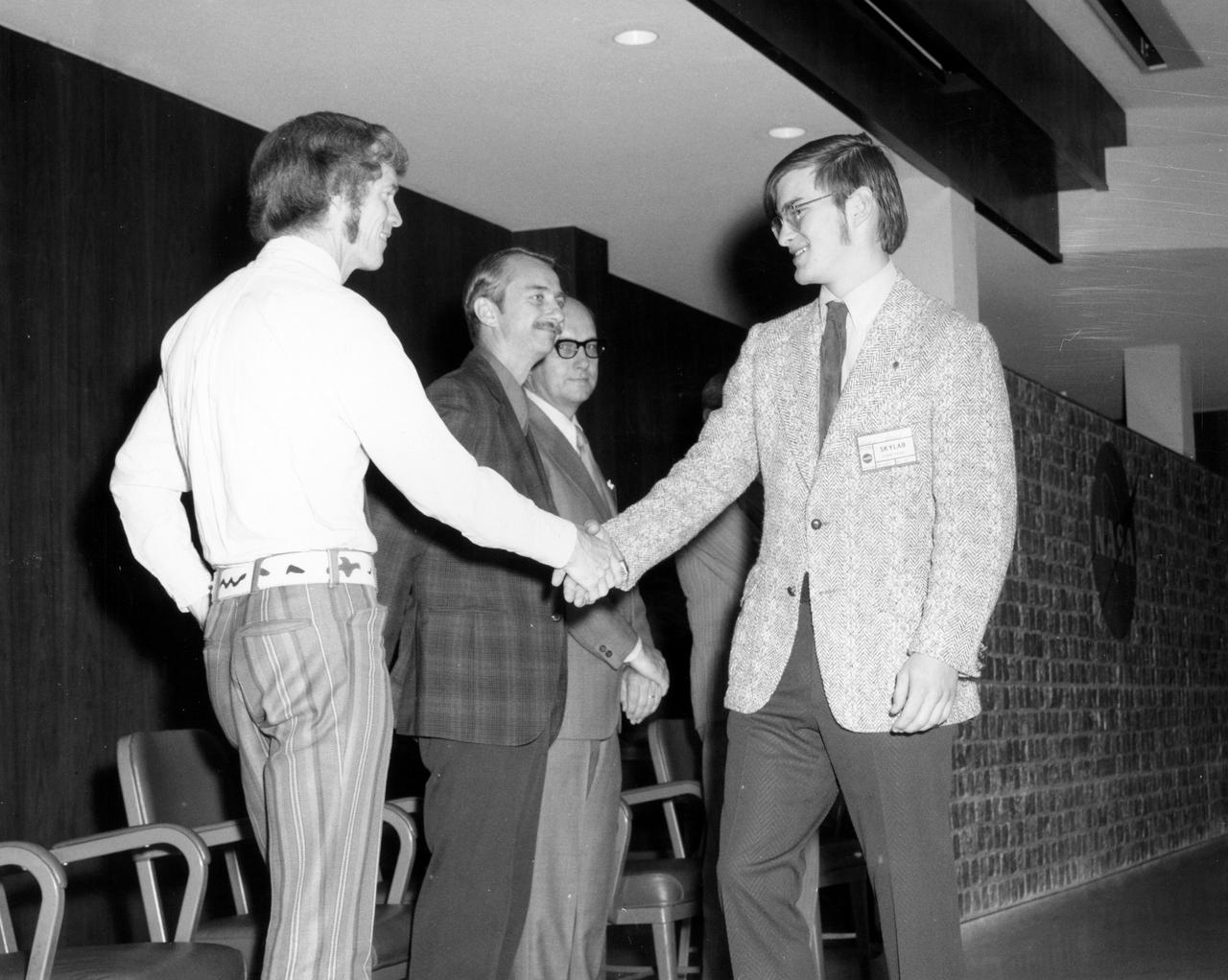
Westbury, New York high school student, Keith L.Stein , is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Stein was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.

Houston, Texas high school student, Kathy L. Jackson, is greeted by astronauts Russell L. Schweickart (left) and Owen K. Garriott (center), and Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew during a tour of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Jackson was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.

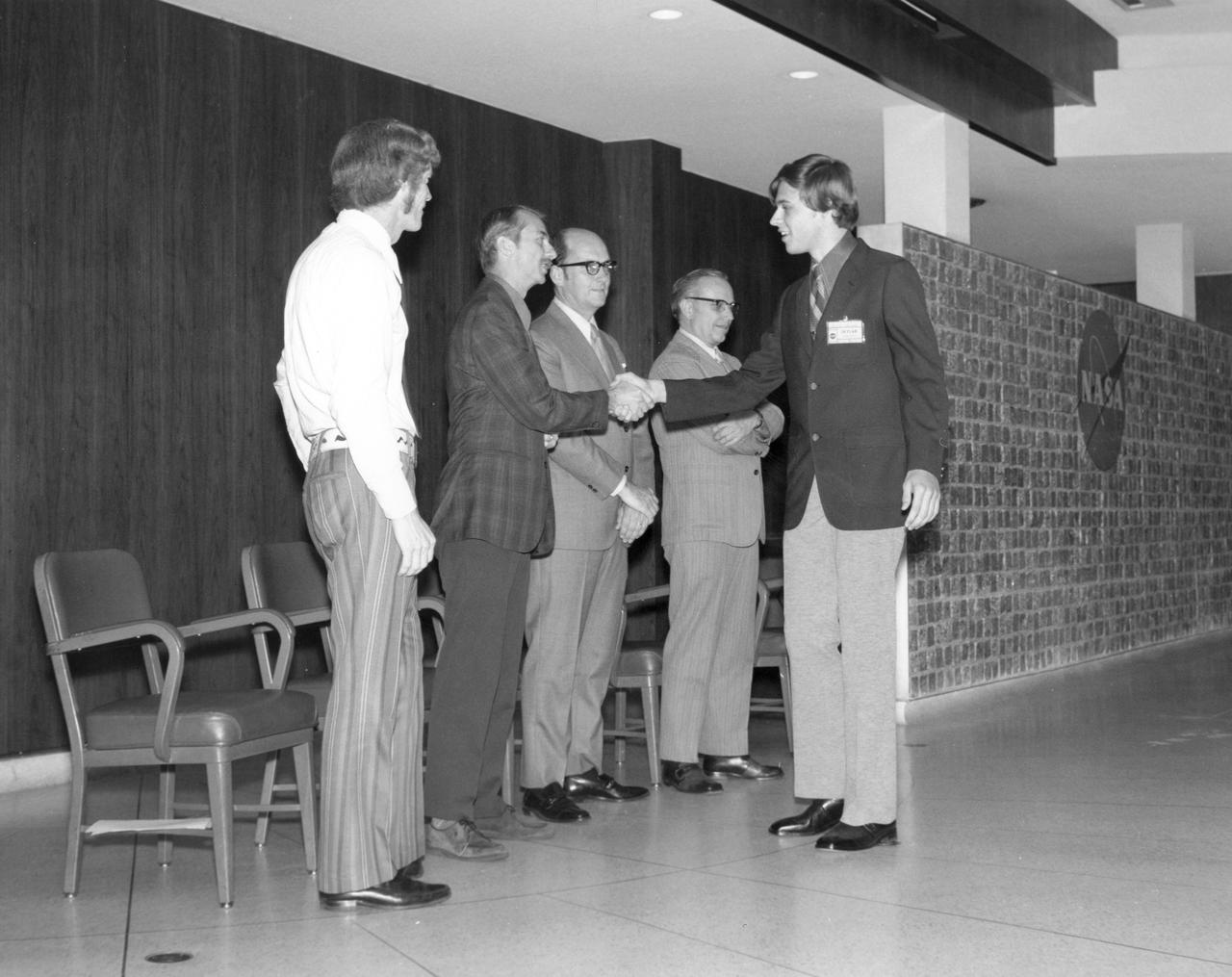
Bayport, New York high school student, James E. Healy, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Healy was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.

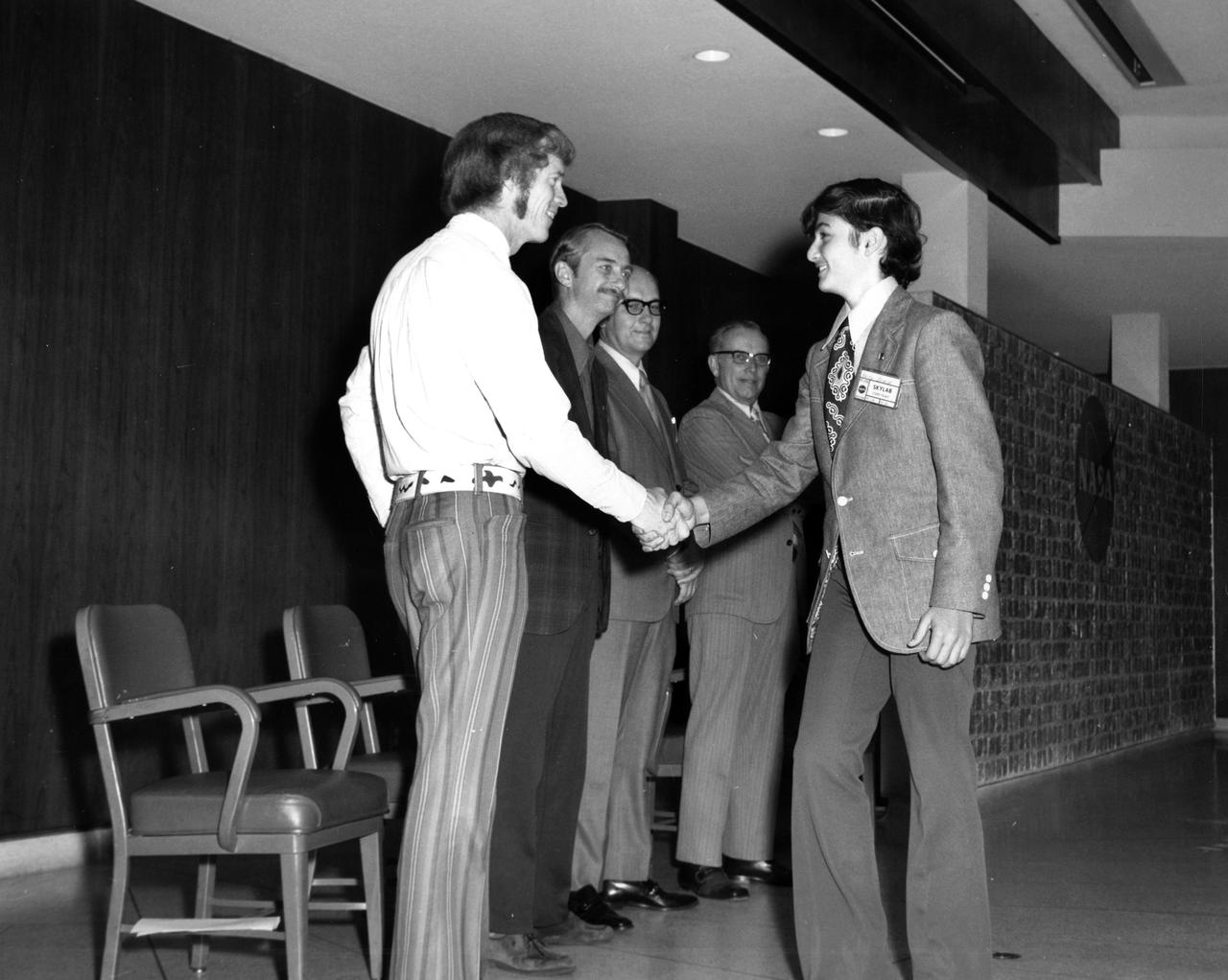
Garland, Texas high school student, Keith D. McGee, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. McGee was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab Mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
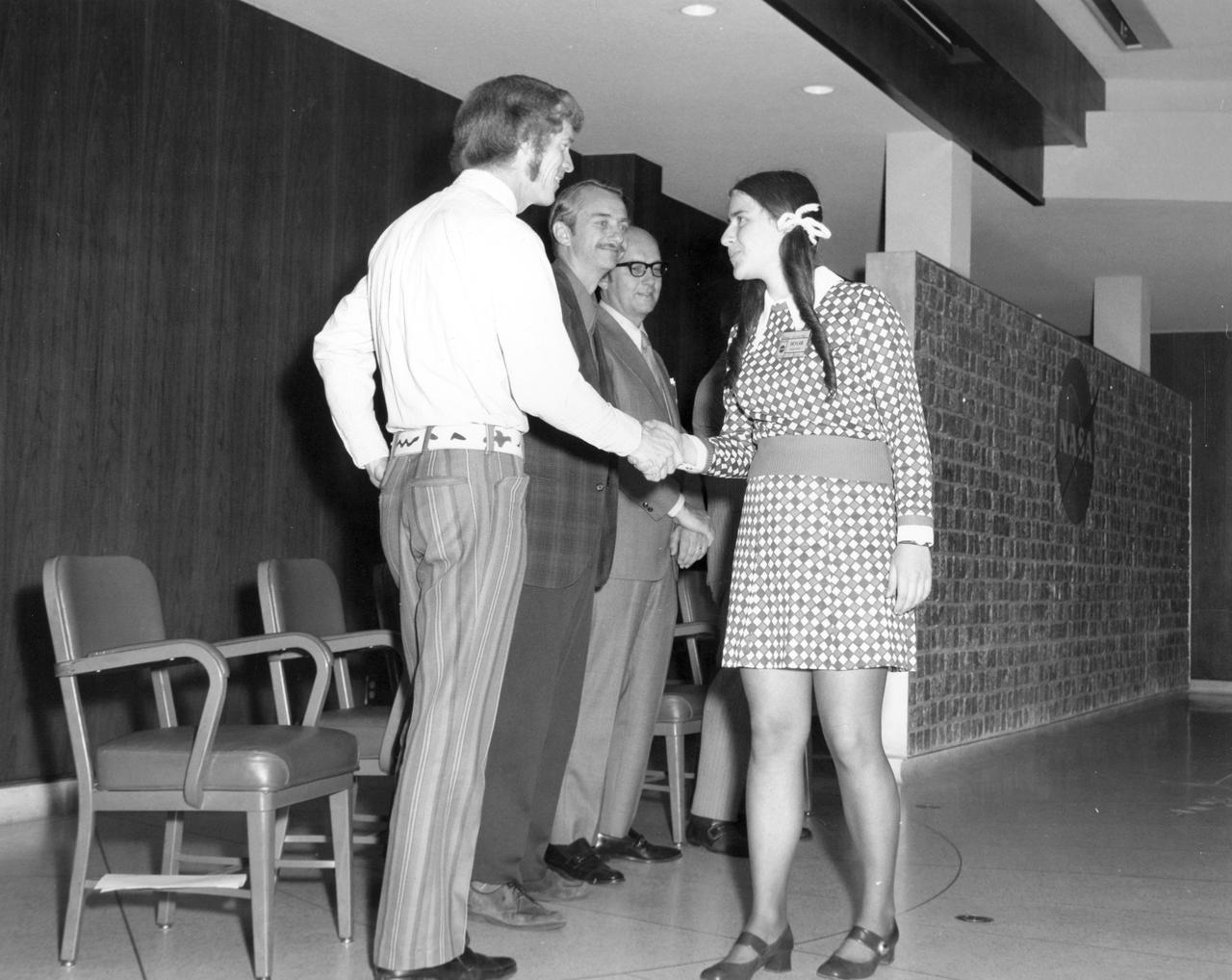

Berkley, California high school student, Jeanne L. Leventhal, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; and Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew during a tour of MSFC. Leventhal was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
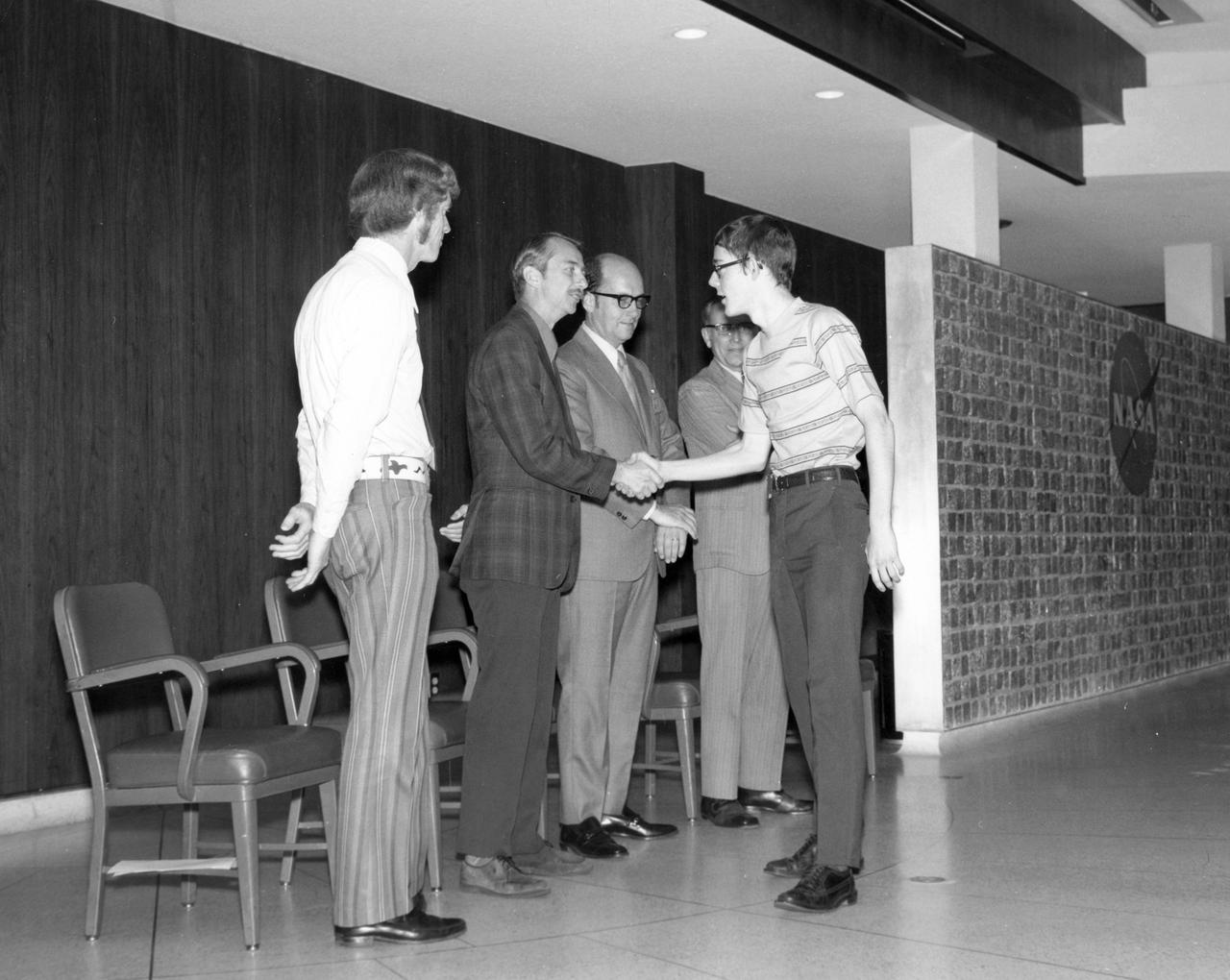

St. Paul, Minnesota high school student, Roger Johnston, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Johnston was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
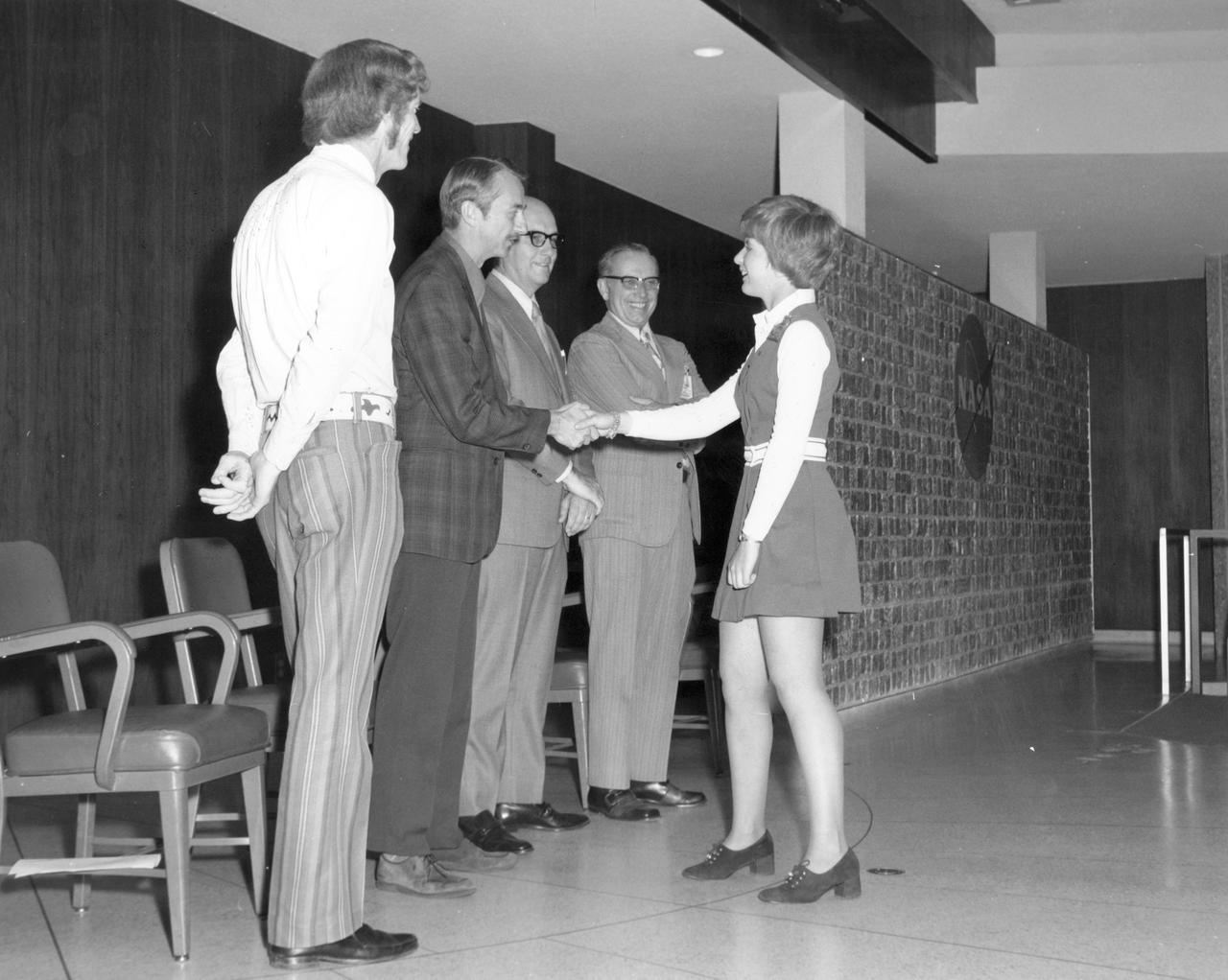

Littleton, Colorado high school student, Cheryl A. Peltz, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Peltz was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
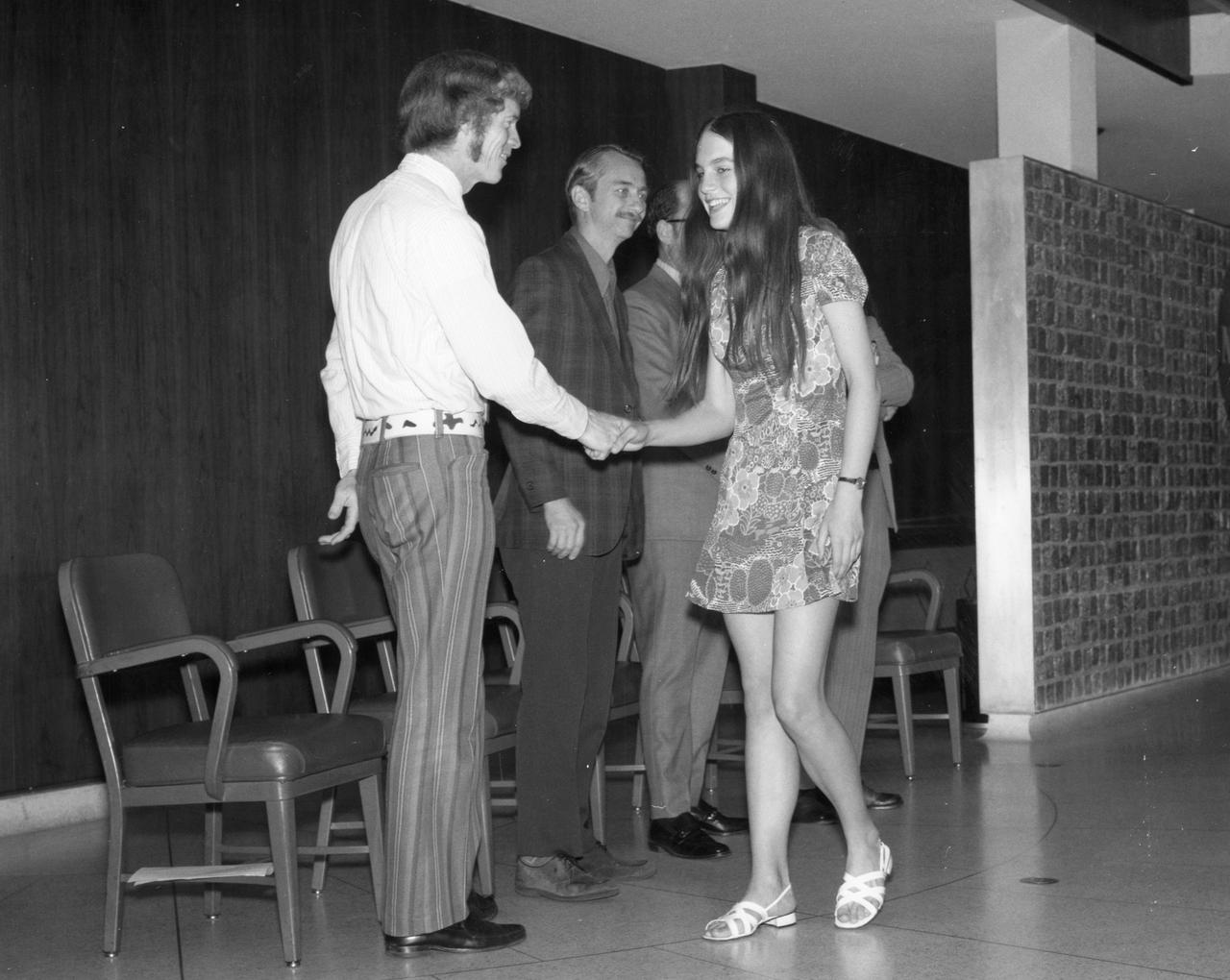

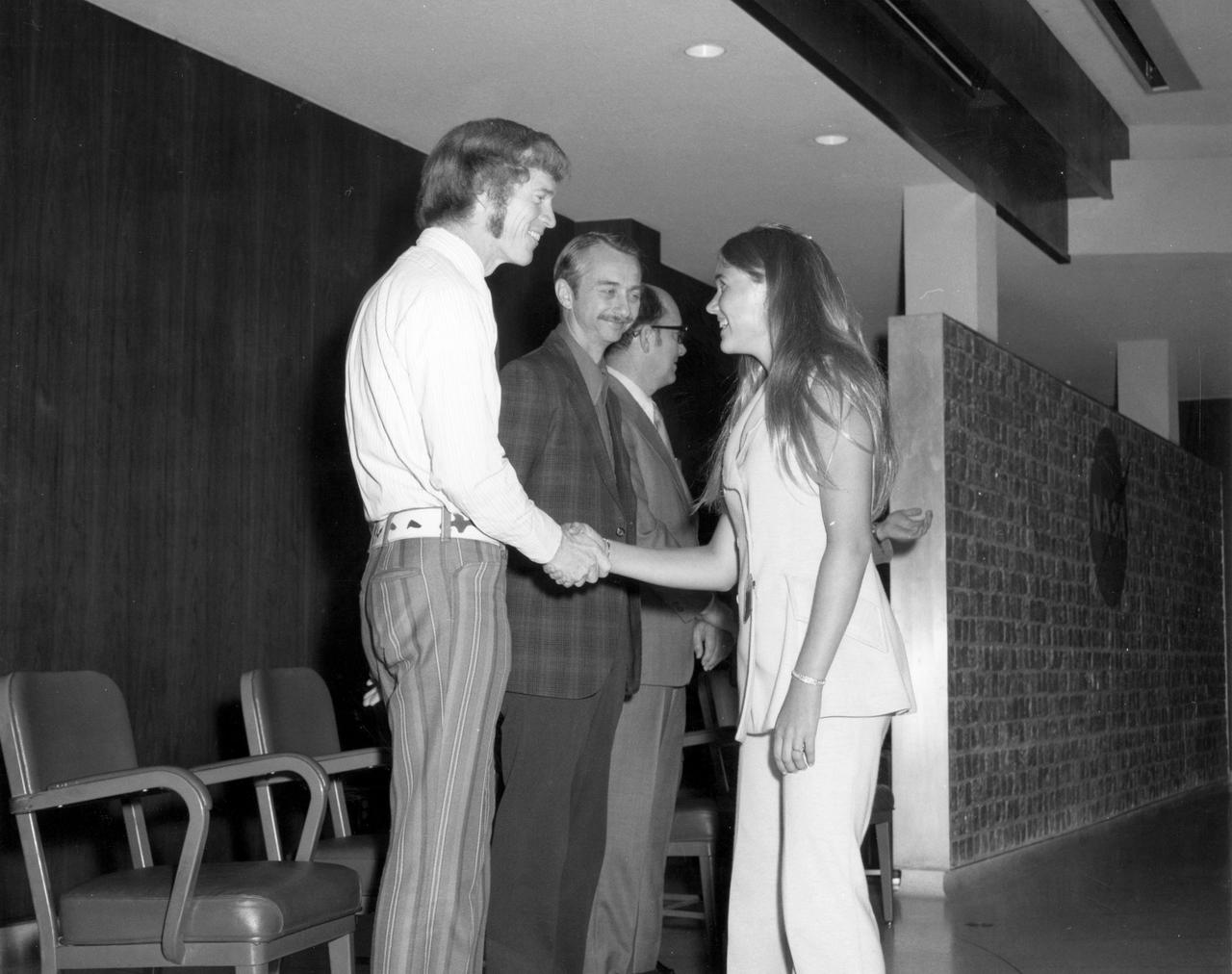
Princeton, New Jersey high school student, Alison Hopfield, is greeted by astronauts Russell L. Schweickart (left) and Owen K. Garriott (center) during a tour of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Hopfield was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
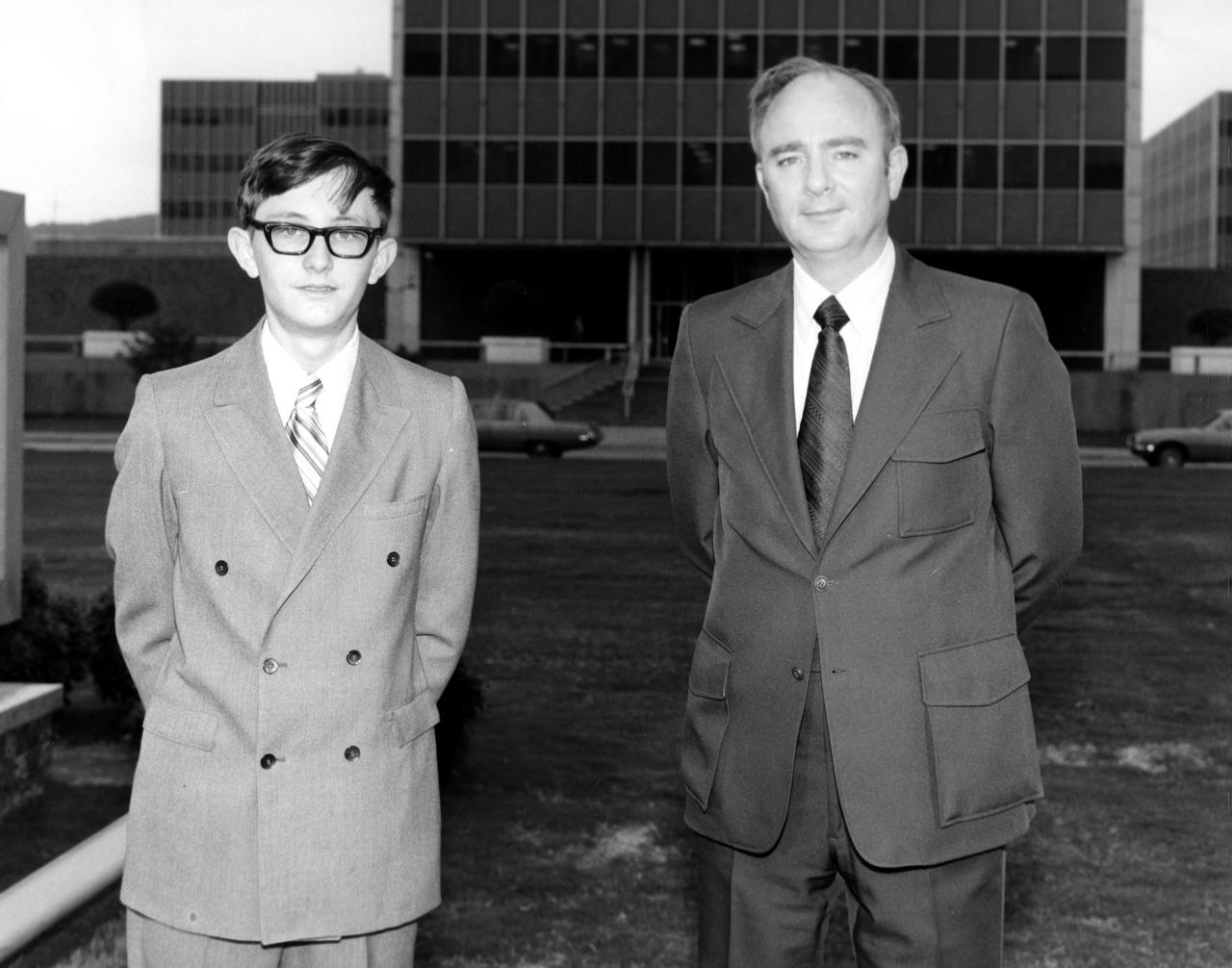

W. Brain Dunlap (left), high school student from Youngstown, Ohio, is pictured here with Harry Coons of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) during a visit to the center. Dunlap was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
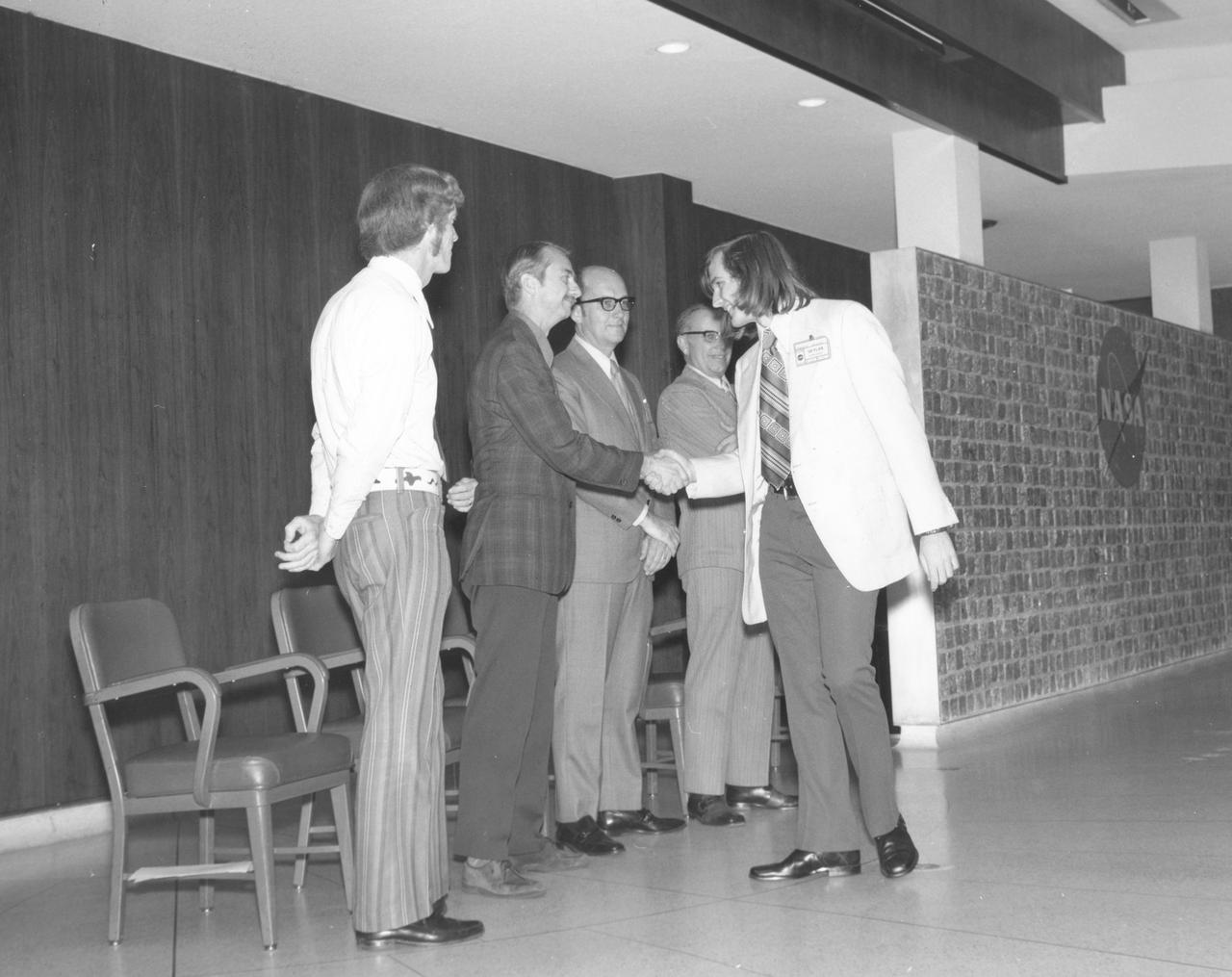

Springfield, Massachusetts high school student, Gregory A. Merkel, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Merkel was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab Mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
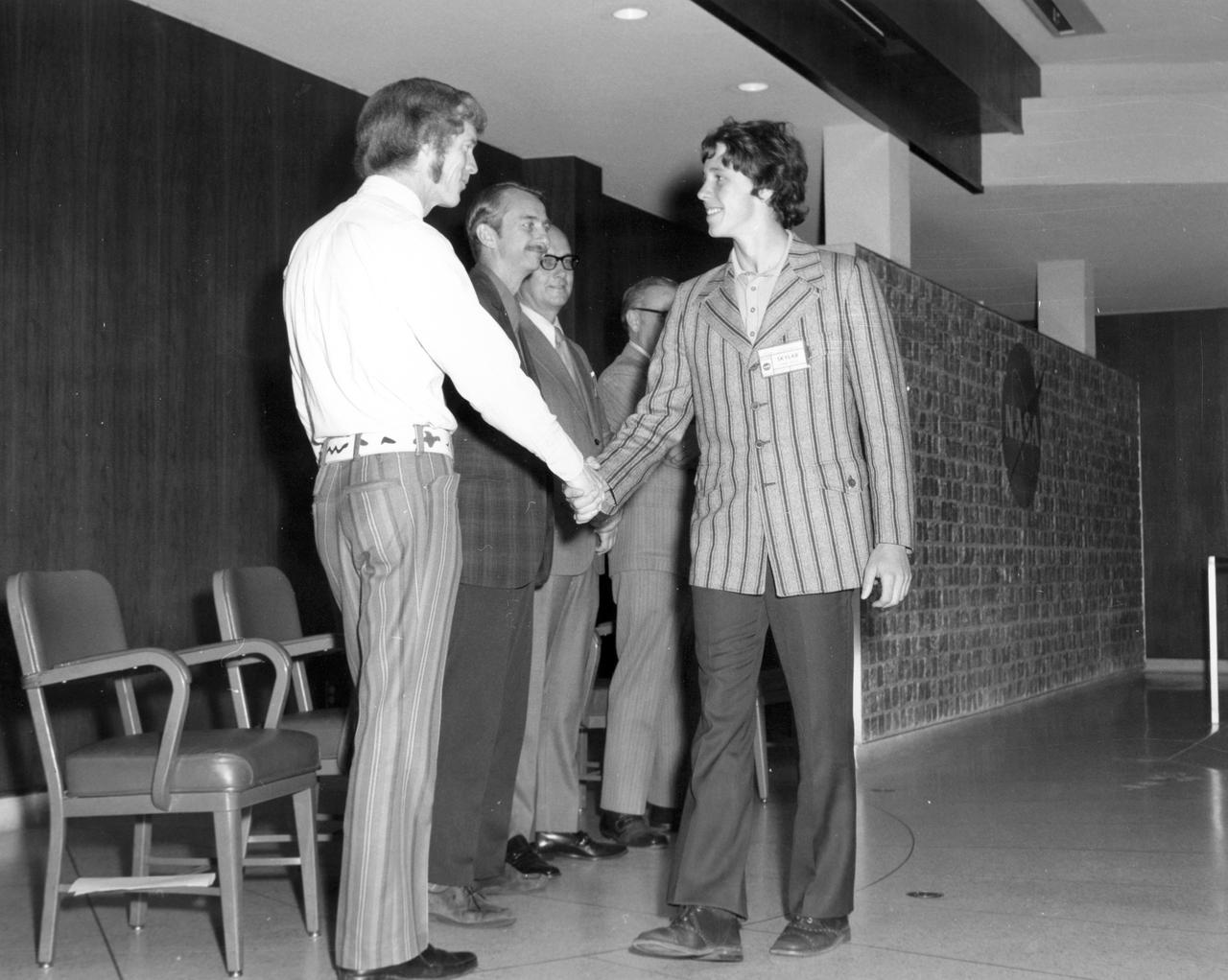

Oshkosh, Wisconsin high school student, Joe B. Zmolek, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Zmolek was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
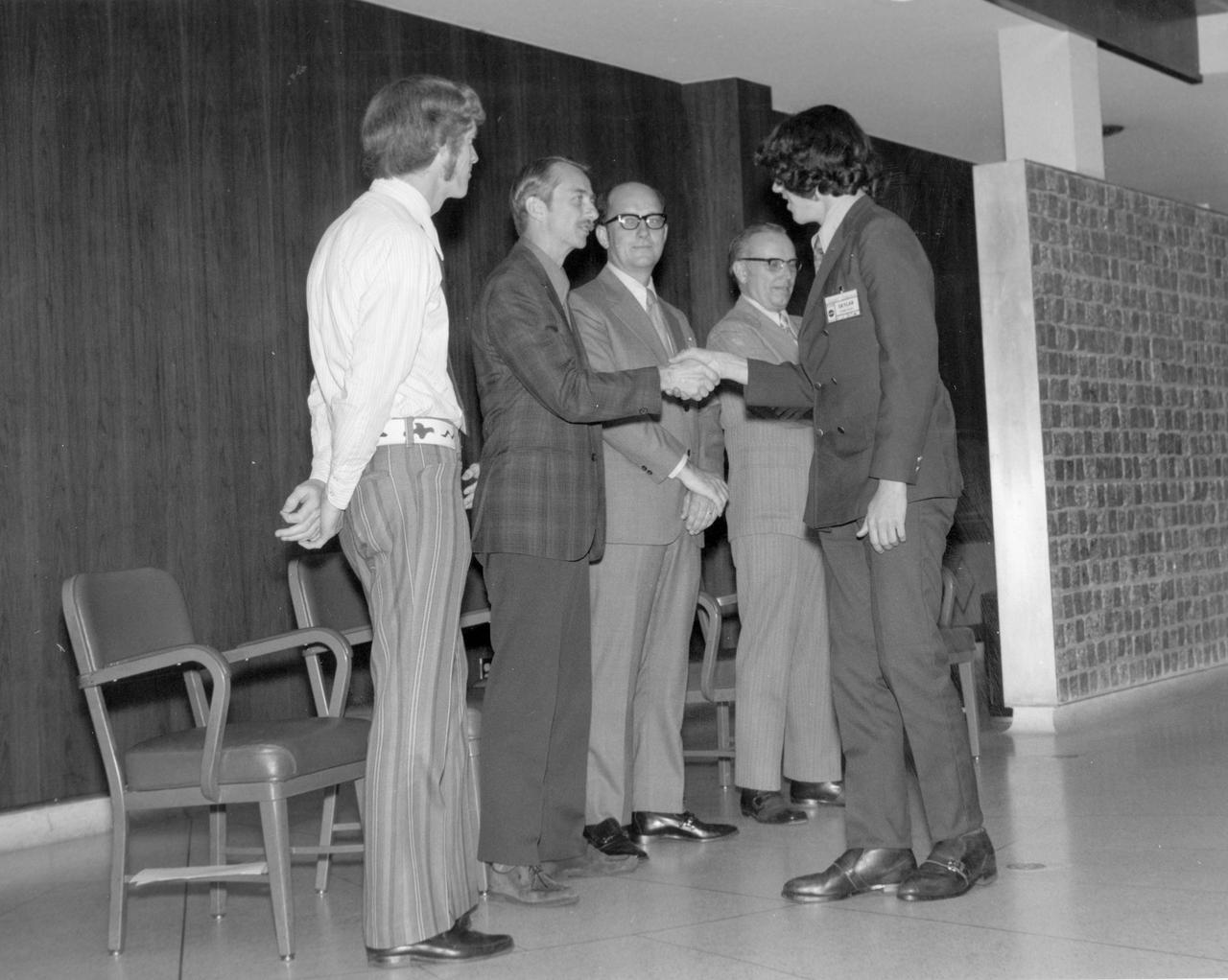

North Rochester, New York high school student, Robert L. Staehle, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Staehle was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
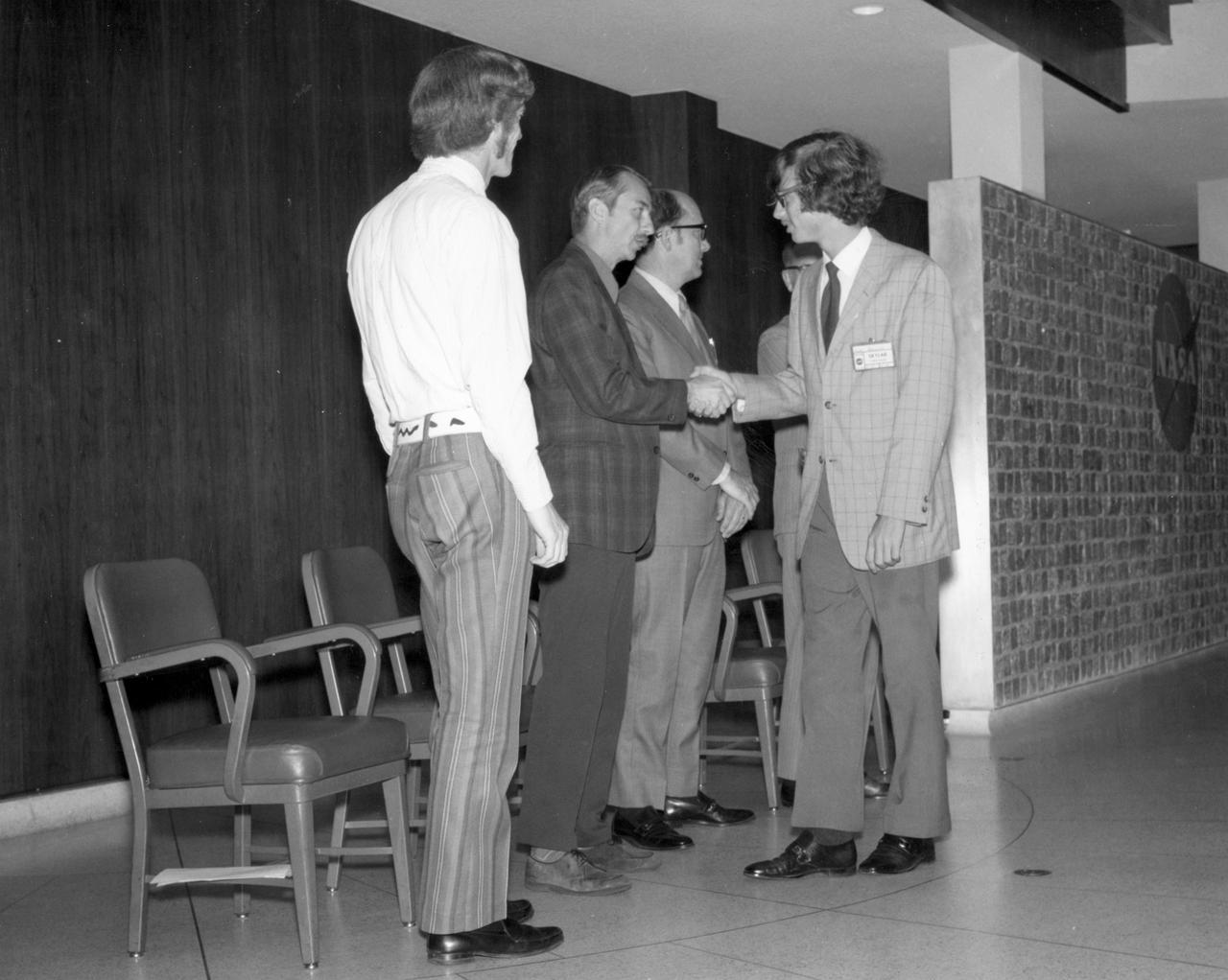

Aiea, Hawaii high school student, John C. Hamilton, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Hamilton was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.

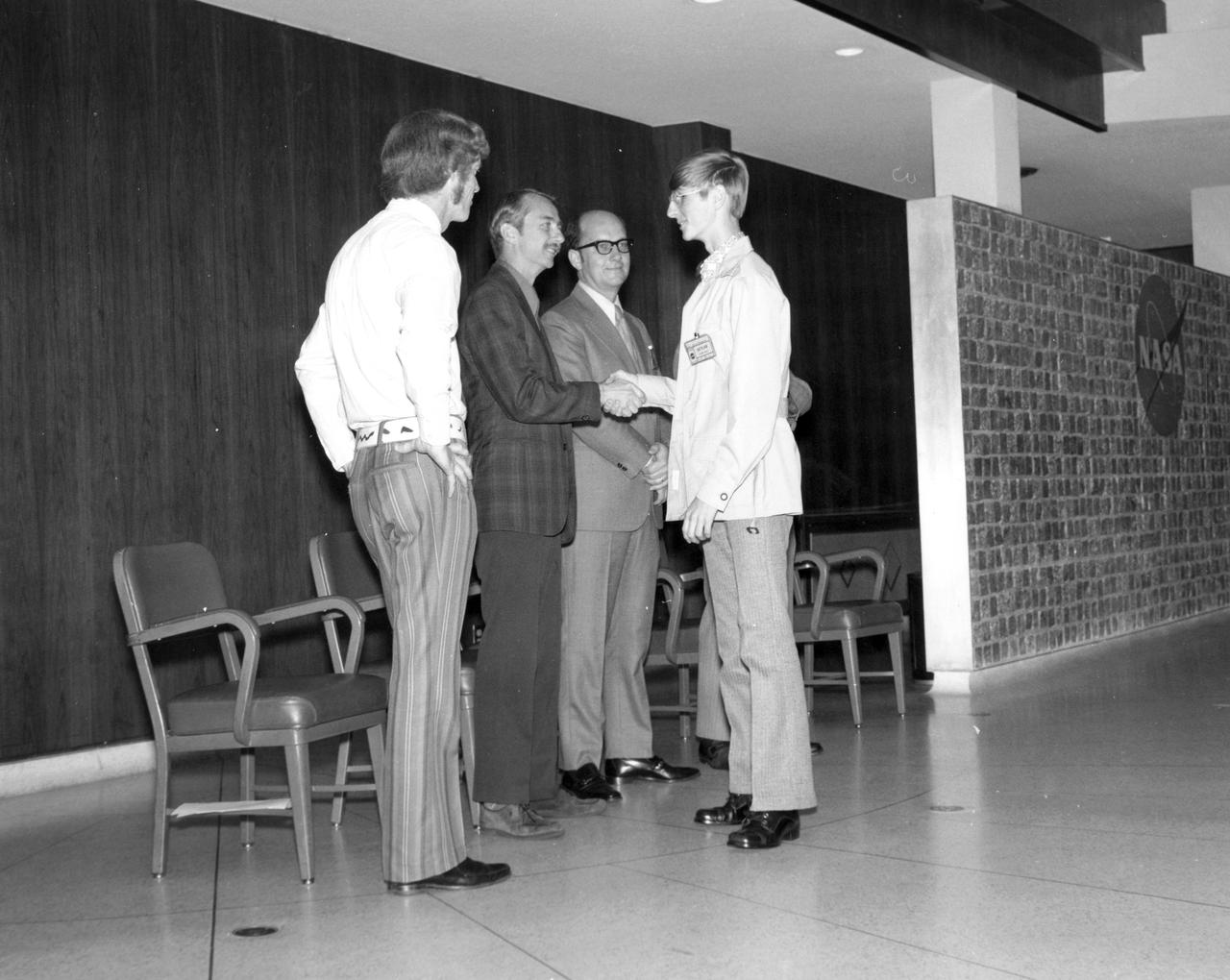
Gregory A. Merkel (left), high school student from Springfield, Massachusetts, is pictured here with Harry Coons of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) during a visit to the center. Merkel was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.

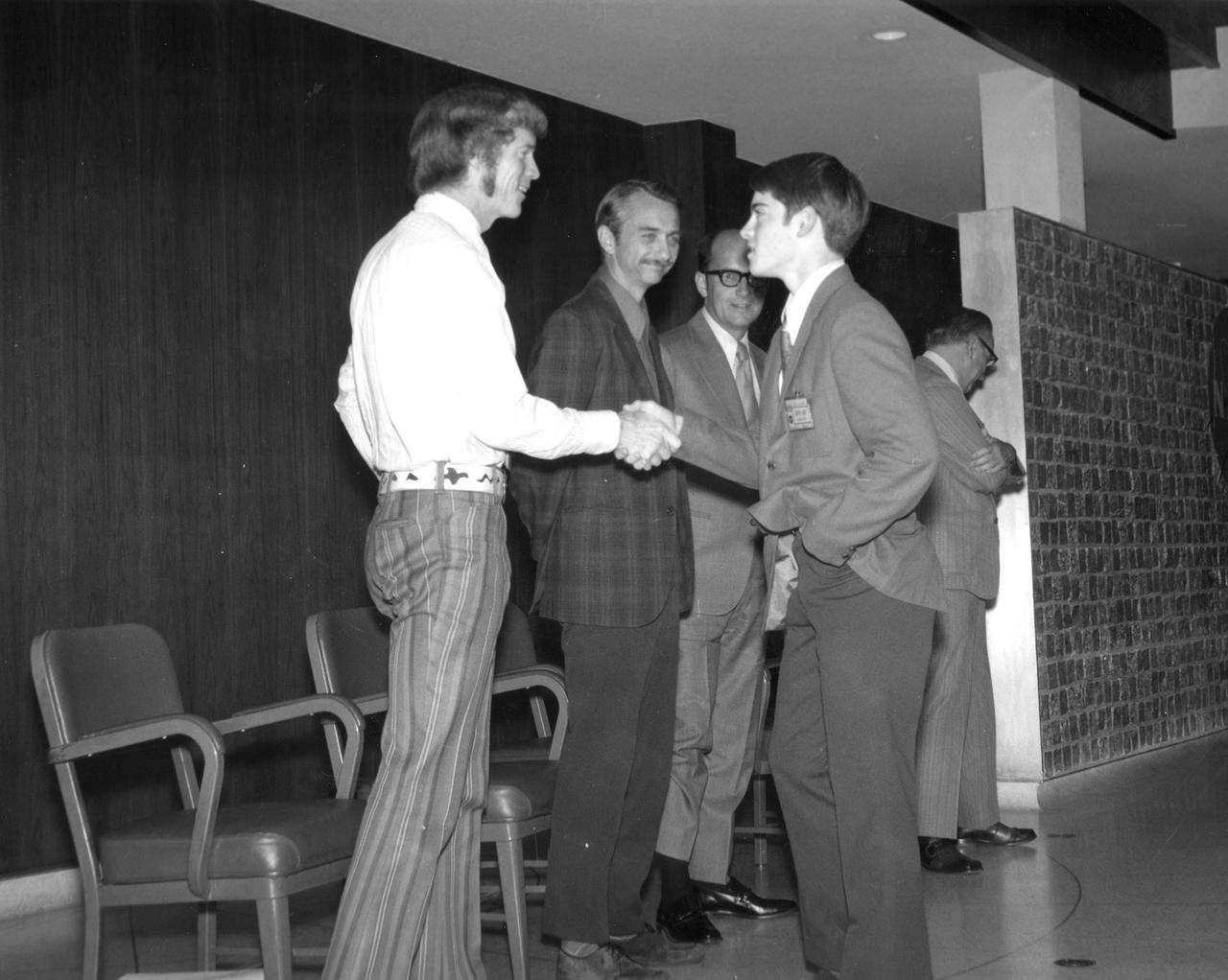
West Point, Nebraska high school student, Joel C. Wordekemper, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Wordekemper was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.

Silverton, Oregon high school student, Daniel C. Bochsler, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Bochsler was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
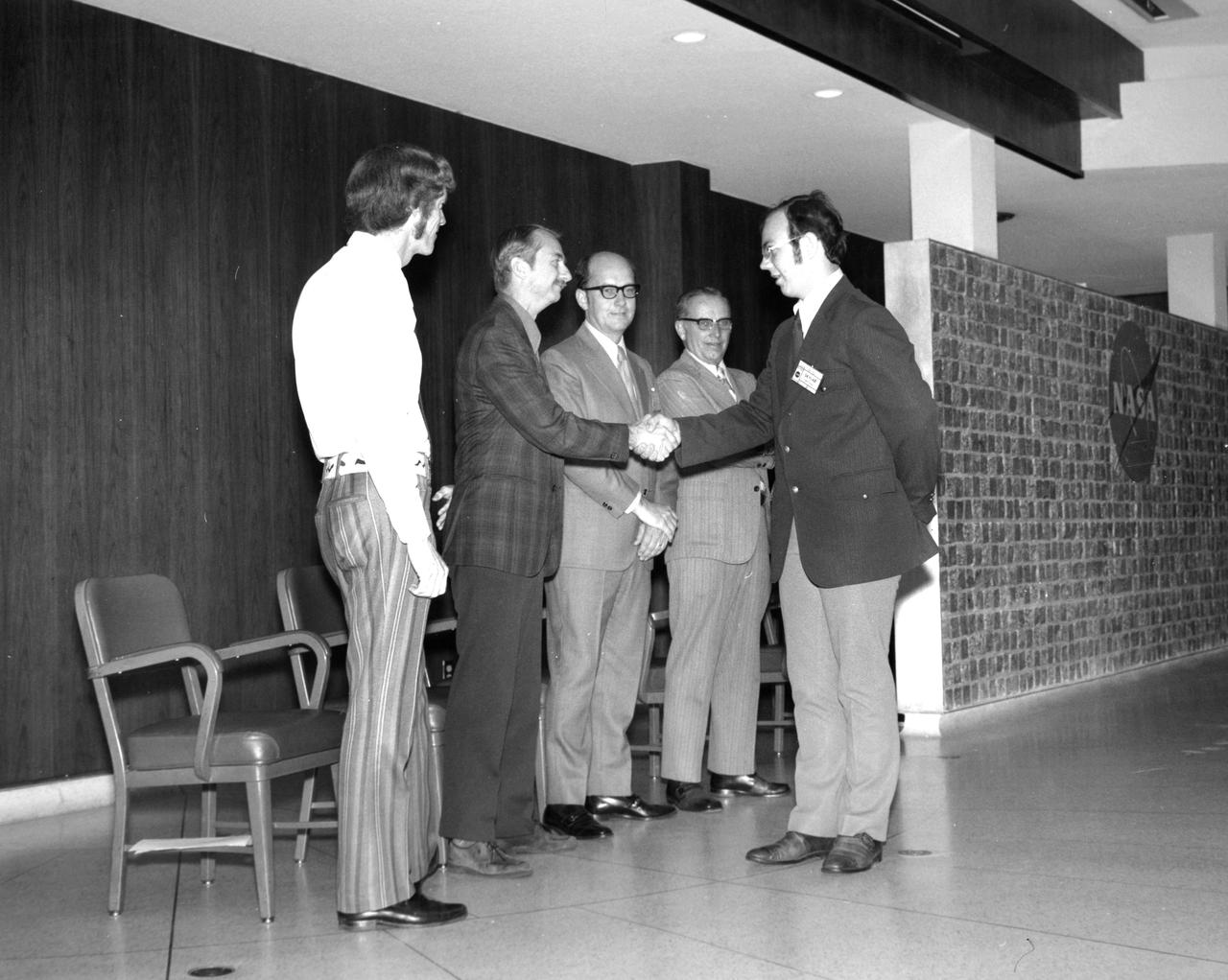

Baton Rouge, Louisiana high school student, Joe W. Reihs, is greeted by (left to right): Astronauts Russell L. Schweickart, and Owen K. Garriott; Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Skylab Program Manager, Leland Belew; and MSFC Director of Administration and Technical Services, David Newby, during a tour of MSFC. Reihs was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
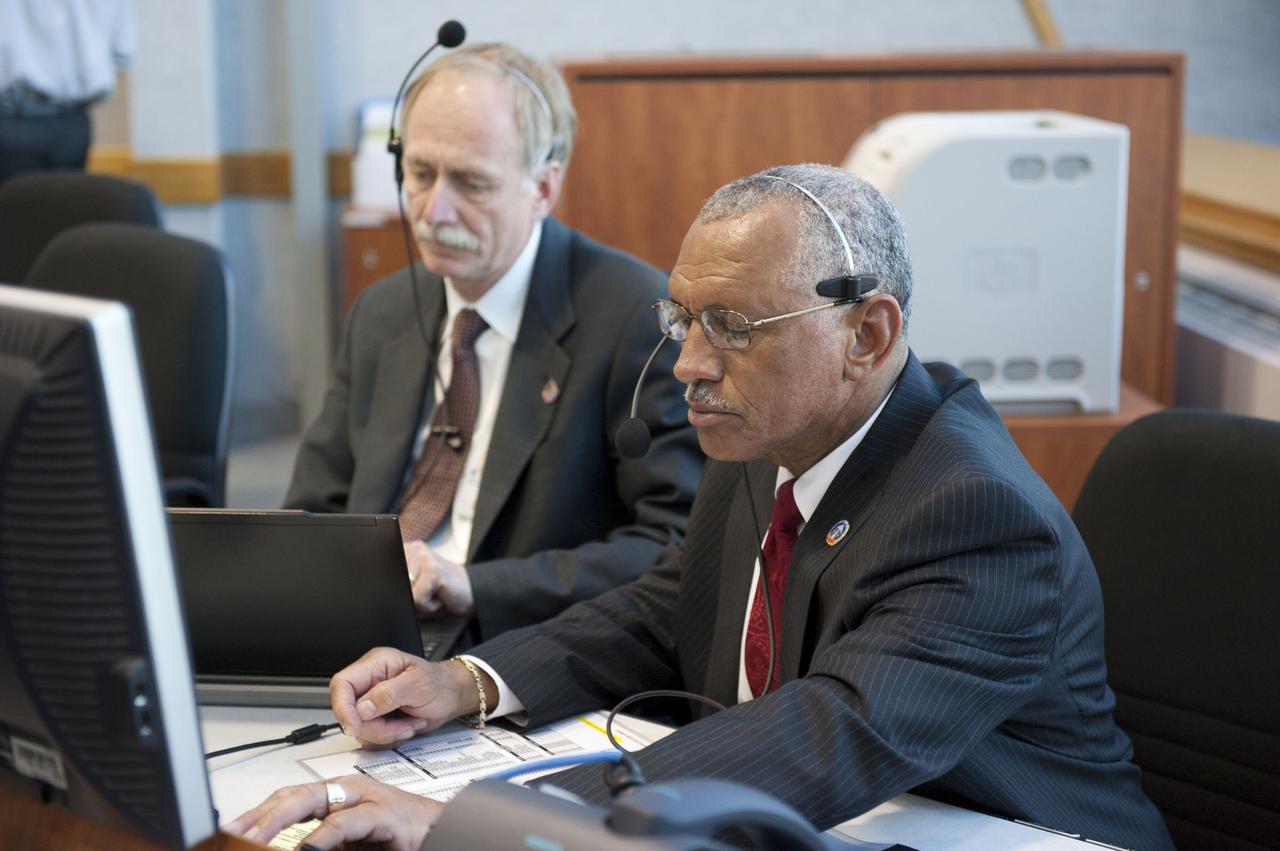

STS133-S-061 (24 Feb. 2011) --- In Firing Room 4 of the Launch Control Center at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden (foreground) and Associate Administrator for Space Operations Bill Gerstenmaier monitor the countdown to launch of space shuttle Discovery on its STS-133 mission to the International Space Station. Discovery and its six-member crew are on a mission to deliver the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. Discovery is making its 39th mission and is scheduled to be retired following STS-133. This is the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
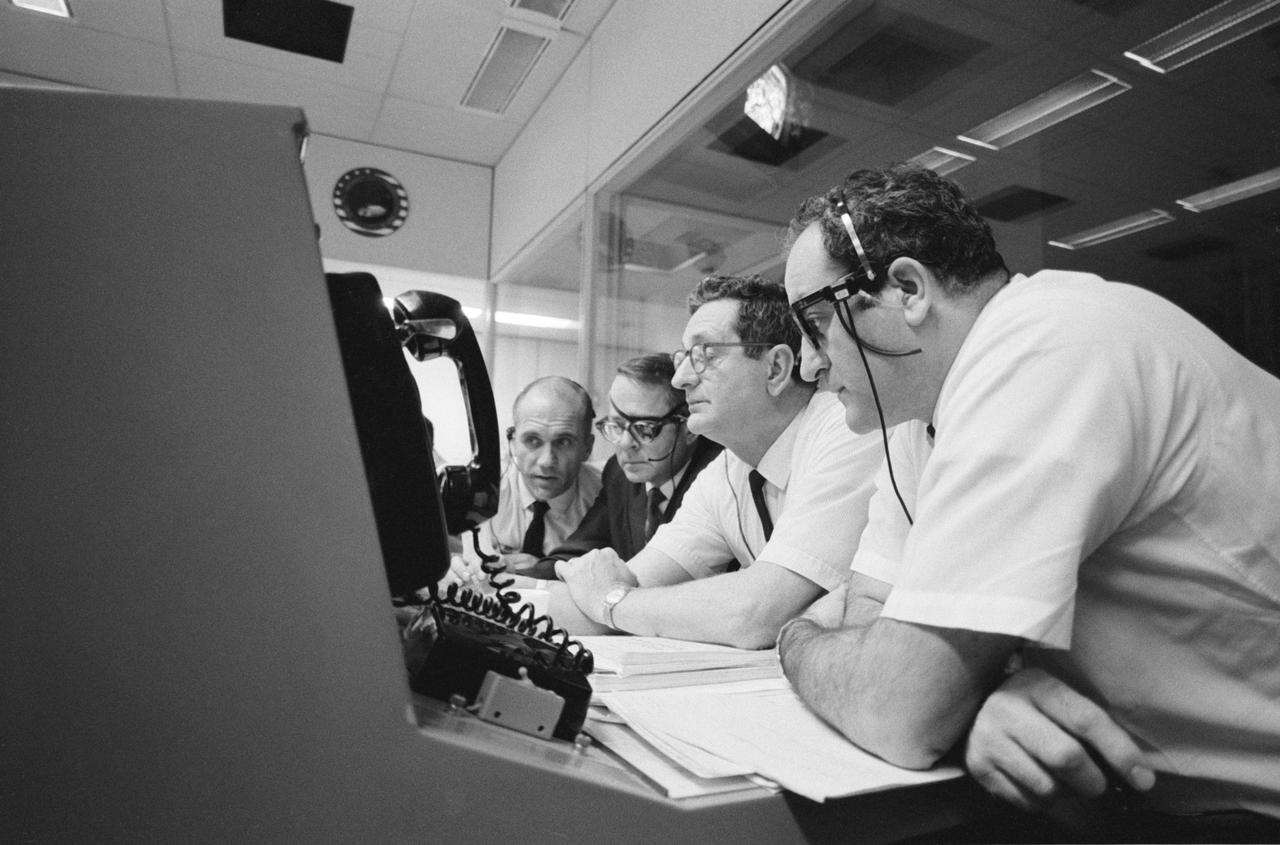

S70-35096 (16 April 1970) --- As the problem-plagued Apollo 13 crewmen entered their final 24 hours in space, several persons important to the mission remained attentive at consoles in the Mission Operations Control Room of the Mission Control Center at Manned Spacecraft Center. Among those monitoring communications and serving in supervisory capacities were these four officials from National Aeronautics and Space Administration Headquarters, Washington, D.C.: (from left) Thomas H. McMullen, Office of Manned Space Flight, who served as Shift 1 mission director; Dale Myers, associate administrator, Manned Space Flight; Chester M. Lee of the Apollo Program Directorate, OMSF, Apollo 13 mission director; and Dr. Rocco A. Petrone, Apollo program director, OMSF.
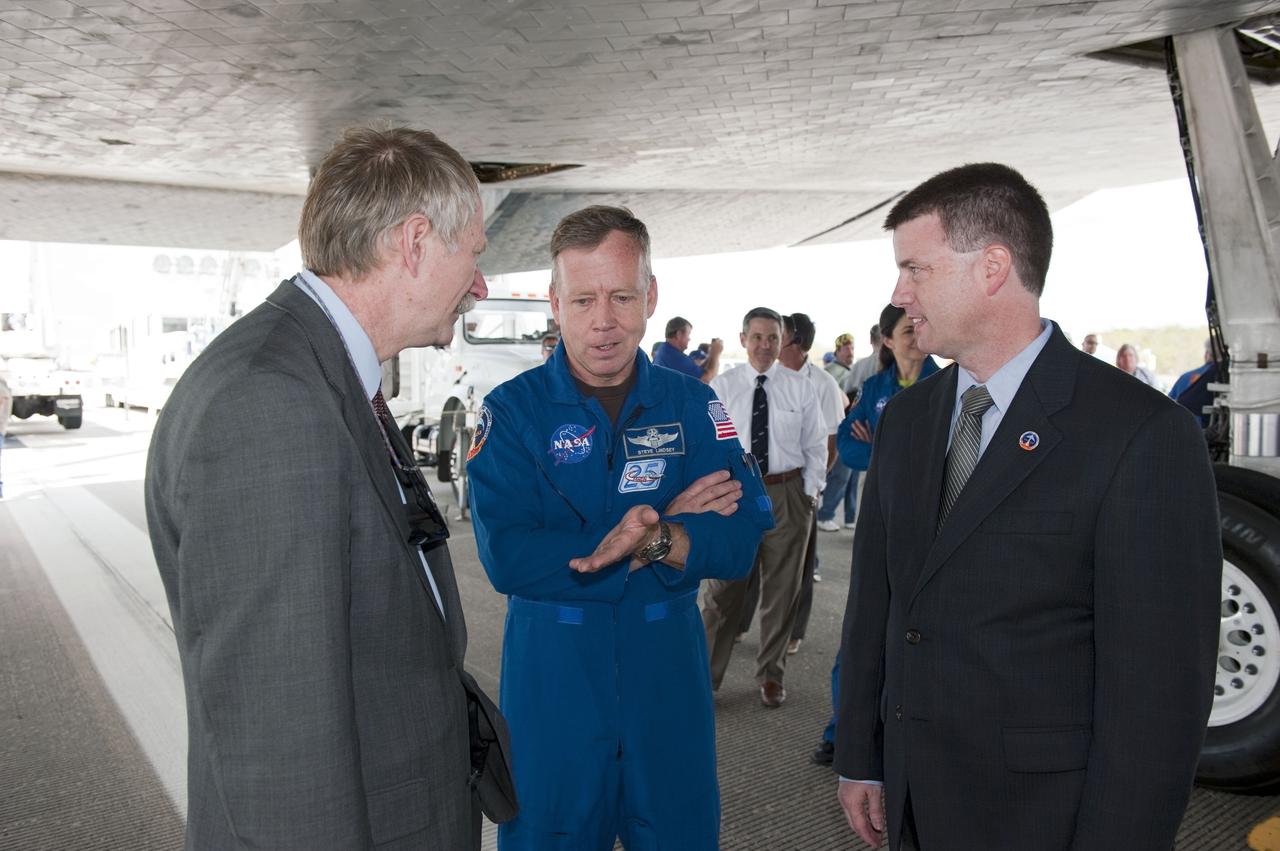

STS133-S-150 (9 March 2011) --- Associate Administrator for Space Operations Bill Gerstenmaier, left, astronaut Steve Lindsey, STS-133 commander, and Space Shuttle Launch Integration Manager Mike Moses talk about Lindsey's recent 13-day, 5.3-million-mile mission to the International Space Station aboard space shuttle Discovery. The STS-133 crew landed at 11:57 a.m. (EST) on March 9, 2011, on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. STS-133 delivered the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. STS-133 was Discovery's 39th and final mission. This was the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
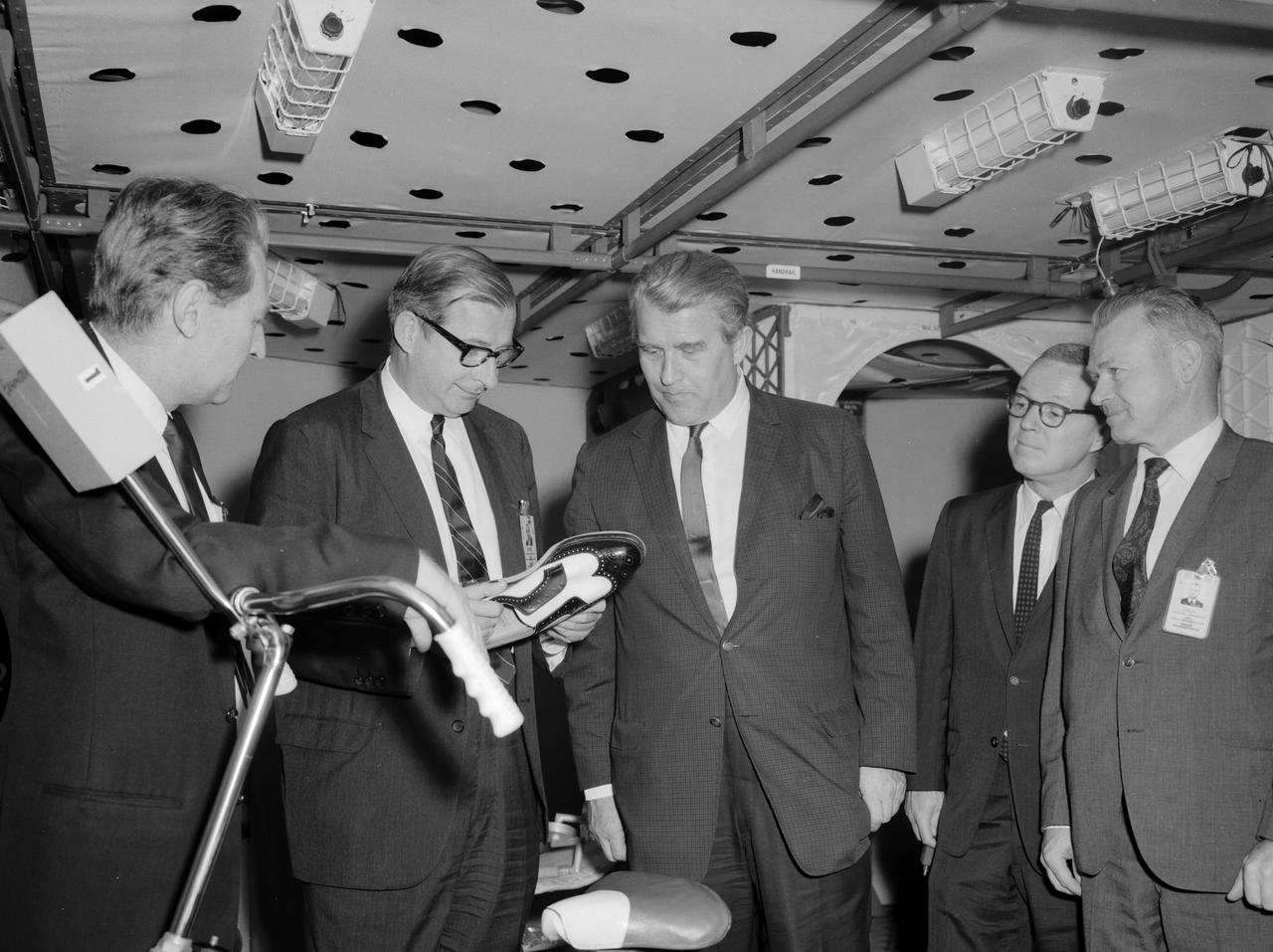

Pictured from the left, in the Saturn I mockup, are: William Brooksbank, Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) Propulsion and Vehicle Engineering Laboratory; Dr. Thomas O. Paine, Deputy Administrator of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA); Dr. Wernher von Braun, MSFC director; Colonel Clare F. Farley, executive officer of the Office of the Administrator; and Charles J. Donlan, newly appointed deputy associate administrator for Manned Space Flight, technical. The party examined an ordinary man’s shoe (held by Paine) outfitted for use in the Saturn I Workshop. The shoe had a unique fastener built into the sole to allow an astronaut to move about the workshop floor and to remain in one position if he desired. Dr. Paine and his party indulged in a two-day tour at the Marshall Space Flight Center getting acquainted with Marshall personnel and programs. It was Paine’s first visit to the center since assuming the NASA post on February 1, 1968.

NASA Associate Administrator, Human Exploration and Operations William Gerstenmaier, left, NASA Special Assistant to the Administrator Mark Sirangelo, Director, Cornell Center for Astrophysics and Planetary Science, Co-Chair of the Former Committee on Human Spaceflight, National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine Dr. Jonathan Lunine, Chair, Aerospace Safety Advisory Panel Dr. Patricia Sanders, and, President, Faulconer Consulting Group, LLC Mr. Walt Faulconer, right, are seen during a House Subcommittee on Space and Aeronautics hearing titled "Keeping our sights on Mars: A Review of NASA's Deep Space Exploration Programs and Lunar Proposal", Wednesday, May 8, 2019 at the Rayburn House Office Building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

STS064-16-031 (19-20 Sept. 1994) --- On the space shuttle Discovery's middeck, astronaut Carl J. Meade checks a hose associated with the new Simplified Aid for EVA Rescue (SAFER) system prior to a Extravehicular Activity (EVA) that tested SAFER. On the Sept. 16, 1994 EVA, astronauts Meade and Mark C. Lee took turns using the SAFER hardware. The test of SAFER is the first phase of a larger SAFER program whose objectives are to establish a common set of requirements for both space shuttle and space station program needs, develop a flight demonstration of SAFER, validate system performance and, finally, develop a production version of SAFER for the shuttle and station programs. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration

S70-35748 (20 April 1970) --- Dr. Donald K. Slayton (center foreground), MSC director of flight crew operations, talks with Dr. Wernher von Braun (right), famed rocket expert, at an Apollo 13 postflight debriefing session. The three crewmen of the problem-plagued Apollo 13 mission (left to right) in the background are astronauts James A Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. The apparent rupture of oxygen tank number two in the Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) and the subsequent damage forced the three astronauts to use the Lunar Module (LM) as a "lifeboat" to return home safely after their moon landing was canceled. Dr. von Braun is the deputy associate administrator for planning of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
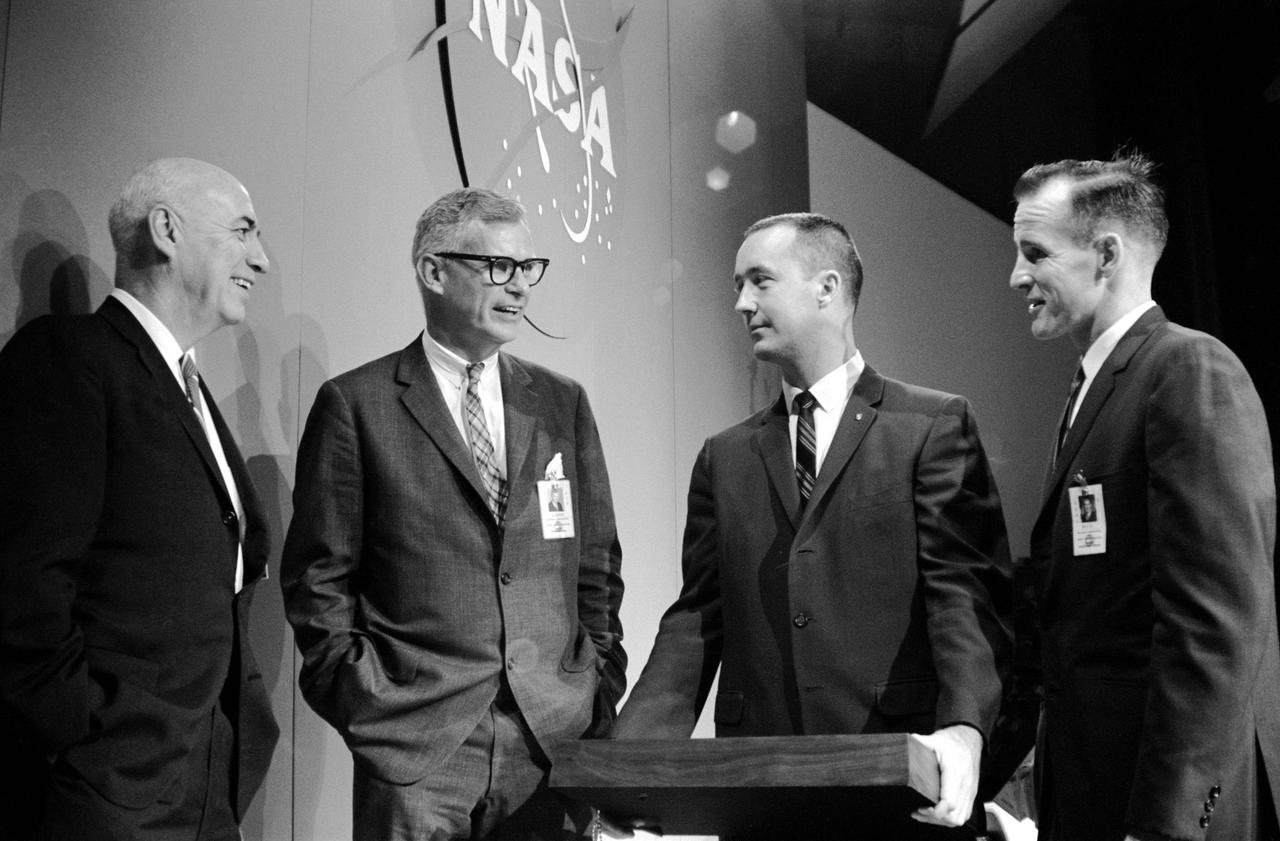

S65-33352 (11 June 1965) --- The Gemini-4 prime crew pose with two NASA officials after a press conference in the MSC auditorium. Left to right, are Dr. Robert R. Gilruth, MSC director; Dr. Robert C. Seamans Jr., associate administrator, National Aeronautics and Space Administration; astronaut James A. McDivitt, command pilot of the Gemini-4 flight; and astronaut Edward H. White II, pilot of the mission. The two astronauts had just returned to Houston following their debriefings at Cape Kennedy. The Gt-4 liftoff was at 10:16 a.m. (EST) on June 3, 1965. Time of splashdown ending the four-day, 62-revolution mission was at 12:12 p.m. on June 7, 1965.
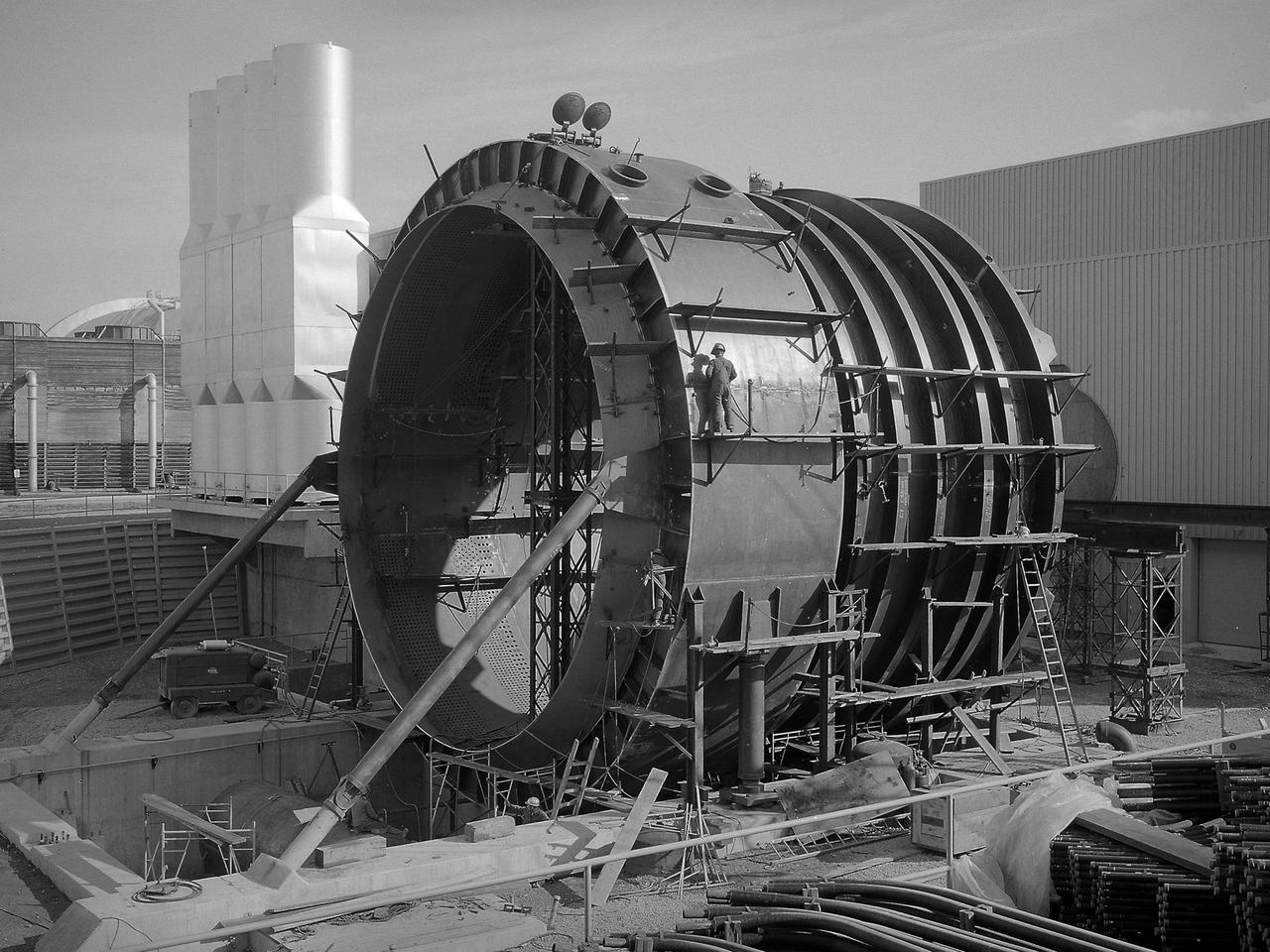

The 50-foot diameter primary cooler for the new Propulsion Systems Laboratory No. 3 and 4 facility constructed at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. In 1968, 20 years after planning began for the original Propulsion Systems Laboratory test chambers, No. 1 and 2, NASA Lewis began preparations to add two additional and more powerful chambers. The move coincided with the center’s renewed focus on aeronautics in 1966. The new 40-foot long and 24-foot diameter chambers were capable of testing engines twice as powerful any then in existence and significantly larger than those in the original two test chambers. After exiting the engine nozzle, the hot exhaust air passed through a 17-foot diameter water exhaust duct and the 50-foot diameter primary cooler. Twenty-seven hundred water-filled tubes inside the cooler reduced the temperature of the air flow as it passed between the tubes from 3000 to 600 °F. A spray cooler further reduced the temperature of the gases to 150 °F before they were sent to the Central Air Building. Excavations for the new facility were completed by October 1967, and the shell of the building was completed a year later. In September 1968, work began on the new test chambers and associated infrastructure. Construction was completed in late 1972, and the first test was scheduled for February 1973.
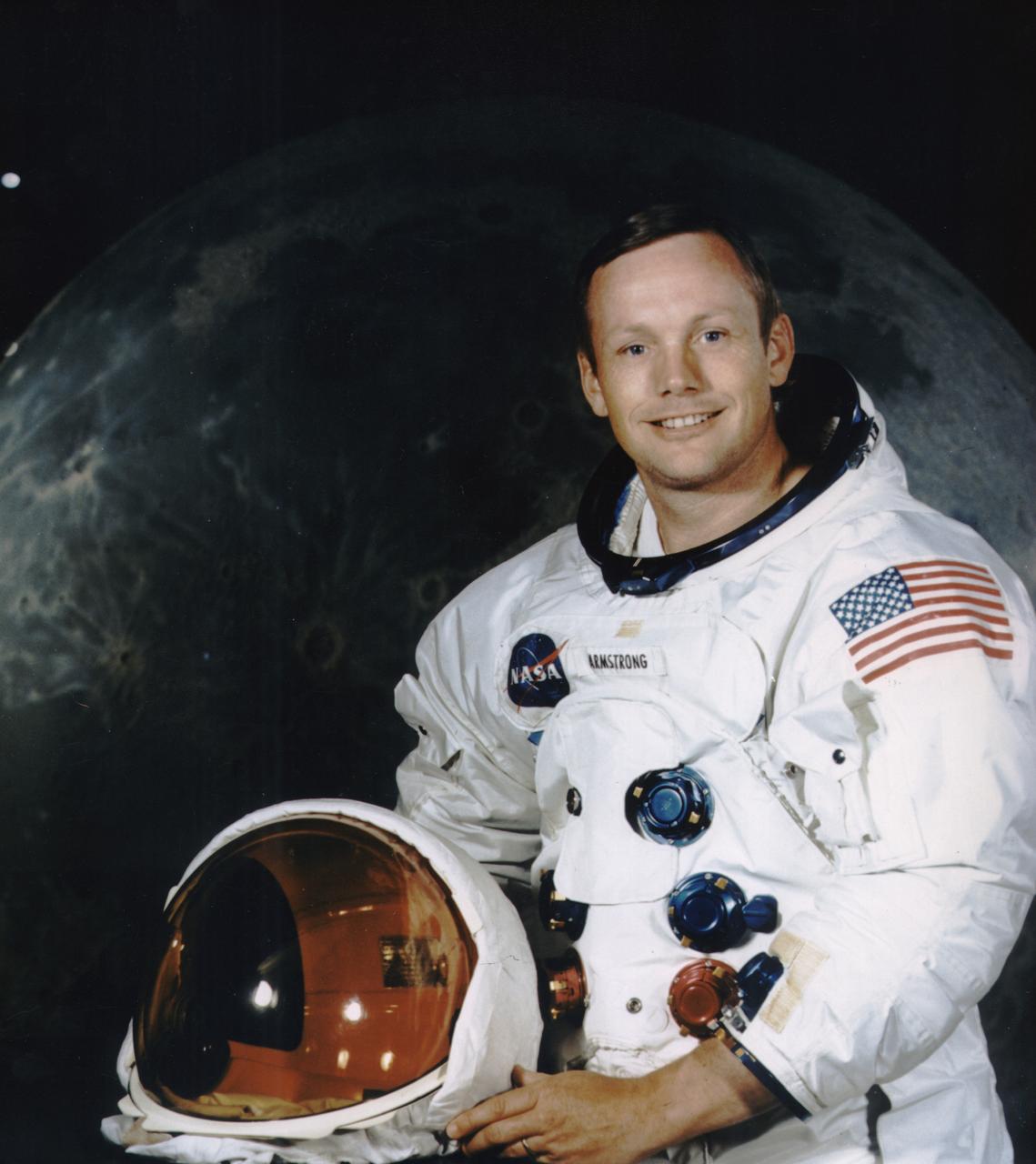

Neil Armstrong, donned in his space suit, poses for his official Apollo 11 portrait. Armstrong began his flight career as a naval aviator. He flew 78 combat missions during the Korean War. Armstrong joined the NASA predecessor, NACA (National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics), as a research pilot at the Lewis Laboratory in Cleveland and later transferred to the NACA High Speed Flight Station at Edwards AFB, California. He was a project pilot on many pioneering high speed aircraft, including the 4,000 mph X-15. He has flown over 200 different models of aircraft, including jets, rockets, helicopters, and gliders. In 1962, Armstrong was transferred to astronaut status. He served as command pilot for the Gemini 8 mission, launched March 16, 1966, and performed the first successful docking of two vehicles in space. In 1969, Armstrong was commander of Apollo 11, the first manned lunar landing mission, and gained the distinction of being the first man to land a craft on the Moon and the first man to step on its surface. Armstrong subsequently held the position of Deputy Associate Administrator for Aeronautics, NASA Headquarters Office of Advanced Research and Technology, from 1970 to 1971. He resigned from NASA in 1971.
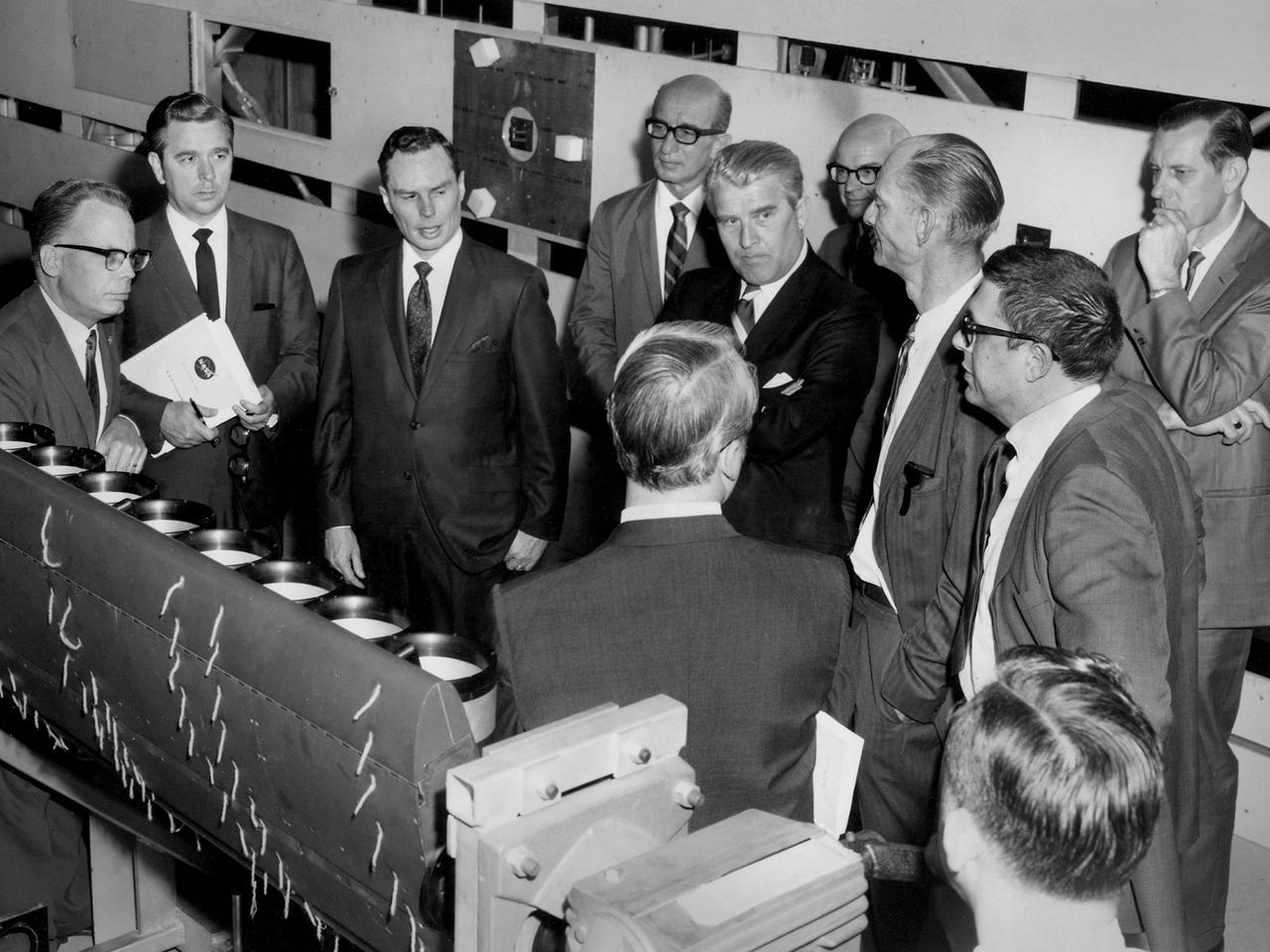

Werner von Braun, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Deputy Associate Administrator for Planning, among a group from Headquarters touring the Lewis Research Center in Cleveland, Ohio. Lewis Special Projects Chief Newell Sanders, left, describes a Short Takeoff and Landing wing-propulsion model. Lewis had recently converted the return leg of its 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel into the 9- by 15-Foot Low Speed Wind Tunnel to investigate Vertical and Short Takeoff and Landing propulsion systems. Gathered from the left near Sanders are James Daniels, Headquarters Executive Secretary; Oran Hicks, Acting Associate Administrator for the Headquarters Office of Advanced Research and Technology; Eugene Manganiello, Lewis Deputy Director; von Braun; Dr. Walter Olson, Lewis Assistant Director; Bruce Lundin, Lewis Director and Dr. Bernard Lubarsky, Lewis Assistant Director. Just months before this photograph, NASA asked von Braun to give up his post as Director of the Marshall Space Flight Center after nearly ten years in order to head up the strategic planning effort for the agency from Washington DC. Von Braun retired from NASA two years later.
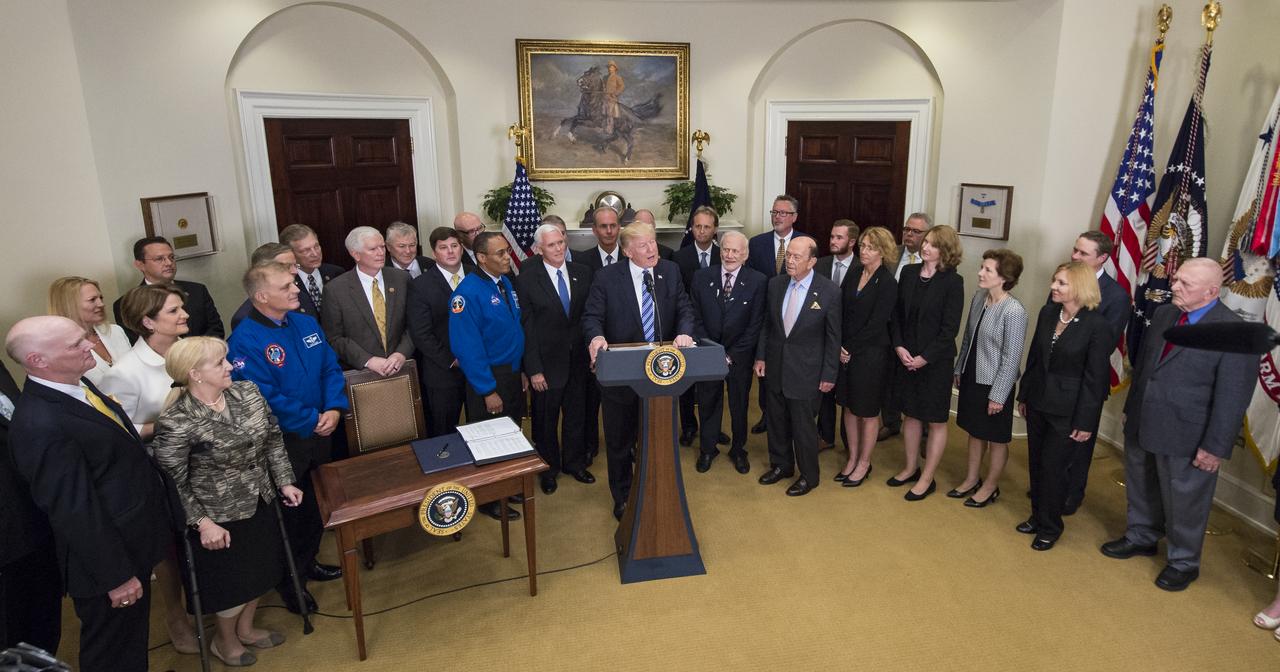

President Donald Trump, center, speaks before signing an Executive Order to reestablish the National Space Council, alongside members of the Congress, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, and Commercial Space Companies in the Roosevelt room of the White House in Washington, Friday, June 30, 2017. Vice President Mike Pence, also in attendance, will chair the council. Also pictured are, Rep. Bill Posey, R-Florida, Rep. Lamar Smith, R-Texas, Rep. John Culberson, R-Texas, Rep. Steven Palazzo, R-Miss., Rep. Brian Babin, R-Texas, Rep. Mo Brooks, R-Alabama, Rep. Dana Rohrbacher, R-California, Former Rep. Bob Walker, R-Pennsylvania, Sandy Magnus, executive director, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, David Melcher, executive director, Aerospace Industries Association, Tory Bruno, CEO, United Launch Alliance, Michal Riley, CEO, AMRO Fabricating Corporation, John Couch, president, Futuramic, Mike Cain, owner, Cain Tubular Products, Mary Lynne Dittmar, executive director, Coalition for Deep Space Exploration, Dennis Muilenburg, CEO Boeing Company, Marilyn Hewson, CEO, Lockheed Martin, Wes Bush, CEO, Northrop Grumman, retired NASA astronaut Buzz Aldrin, NASA astronaut Alvin Drew, retired NASA astronaut David Wolf, Apollo 13 flight director, Gene Kranz, Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross, Under Secretary of the Air Force Lisa Disbrow, and Acting Deputy Director of National Intelligence, Dawn Eilengerger. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
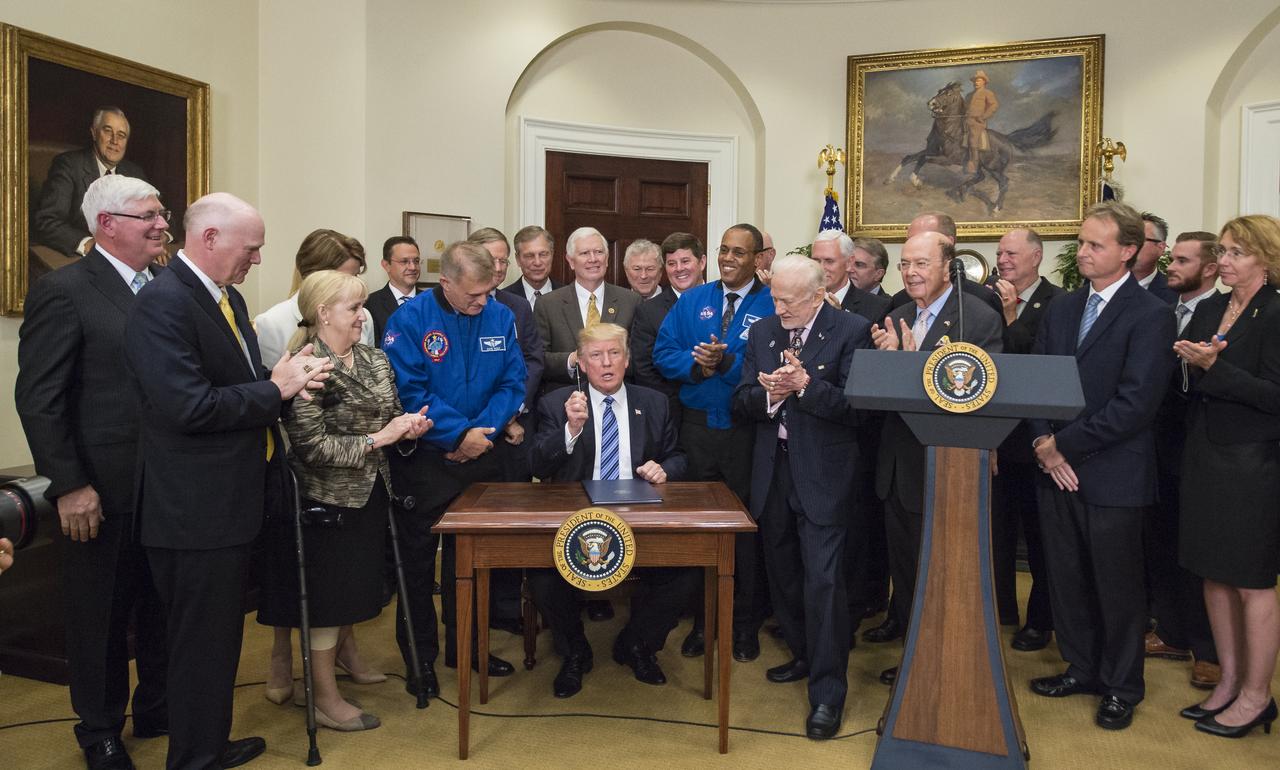

President Donald Trump, center, asks who should receive the pen after signing an Executive Order to reestablish the National Space Council, alongside members of the Congress, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, and Commercial Space Companies in the Roosevelt room of the White House in Washington, Friday, June 30, 2017. Retired astronaut Buzz Aldrin was given the pen. Also pictured are, Vice President Mike Pence, Rep. Bill Posey, R-Florida, Rep. Lamar Smith, R-Texas, Rep. John Culberson, R-Texas, Rep. Steven Palazzo, R-Miss., Rep. Brian Babin, R-Texas, Rep. Mo Brooks, R-Alabama, Rep. Dana Rohrbacher, R-California, Former Rep. Bob Walker, R-Pennsylvania, Sandy Magnus, executive director, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, David Melcher, executive director, Aerospace Industries Association, Tory Bruno, CEO, United Launch Alliance, Michal Riley, CEO, AMRO Fabricating Corporation, John Couch, president, Futuramic, Mike Cain, owner, Cain Tubular Products, Mary Lynne Dittmar, executive director, Coalition for Deep Space Exploration, Dennis Muilenburg, CEO Boeing Company, Marilyn Hewson, CEO, Lockheed Martin, Wes Bush, CEO, Northrop Grumman, NASA Astronaut Alvin Drew, retired NASA astronaut David Wolf, Apollo 13 flight director, Gene Kranz, Secretary of Commerce Wilbur Ross, Under Secretary of the Air Force Lisa Disbrow, and Acting Deputy Director of National Intelligence, Dawn Eilengerger. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
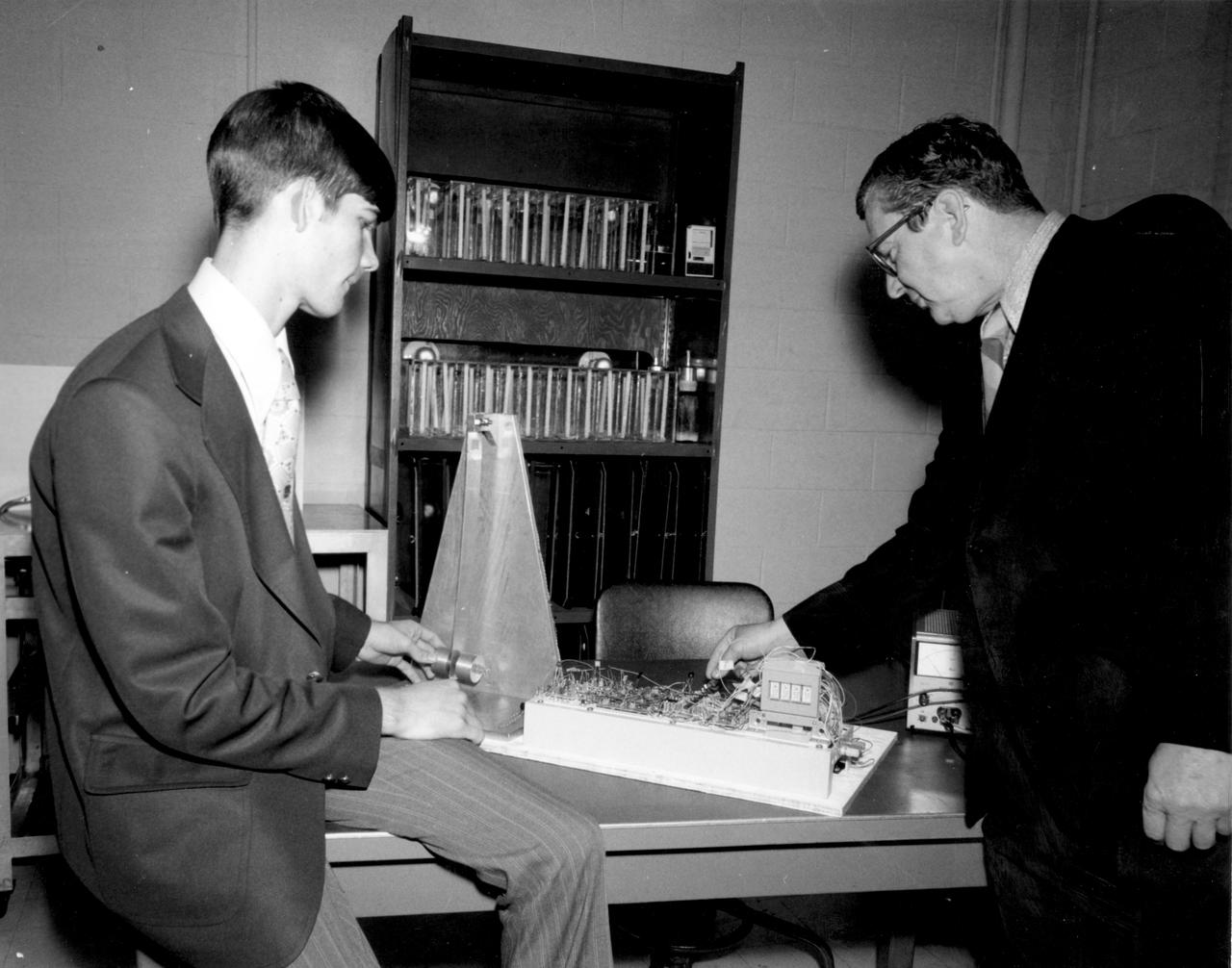

Rockford, Illinois high school student, Vincent Converse (left), and Robert Head of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), check out the equipment to be used in conducting the student’s experiment aboard the Skylab the following year. His experiment, “Zero Gravity Mass Measurement” used a simple leaf spring with the mass to be weighed attached to the end. An electronic package oscillated the spring at a specific rate and the results were recorded electronically. Converse was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC two months earlier where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
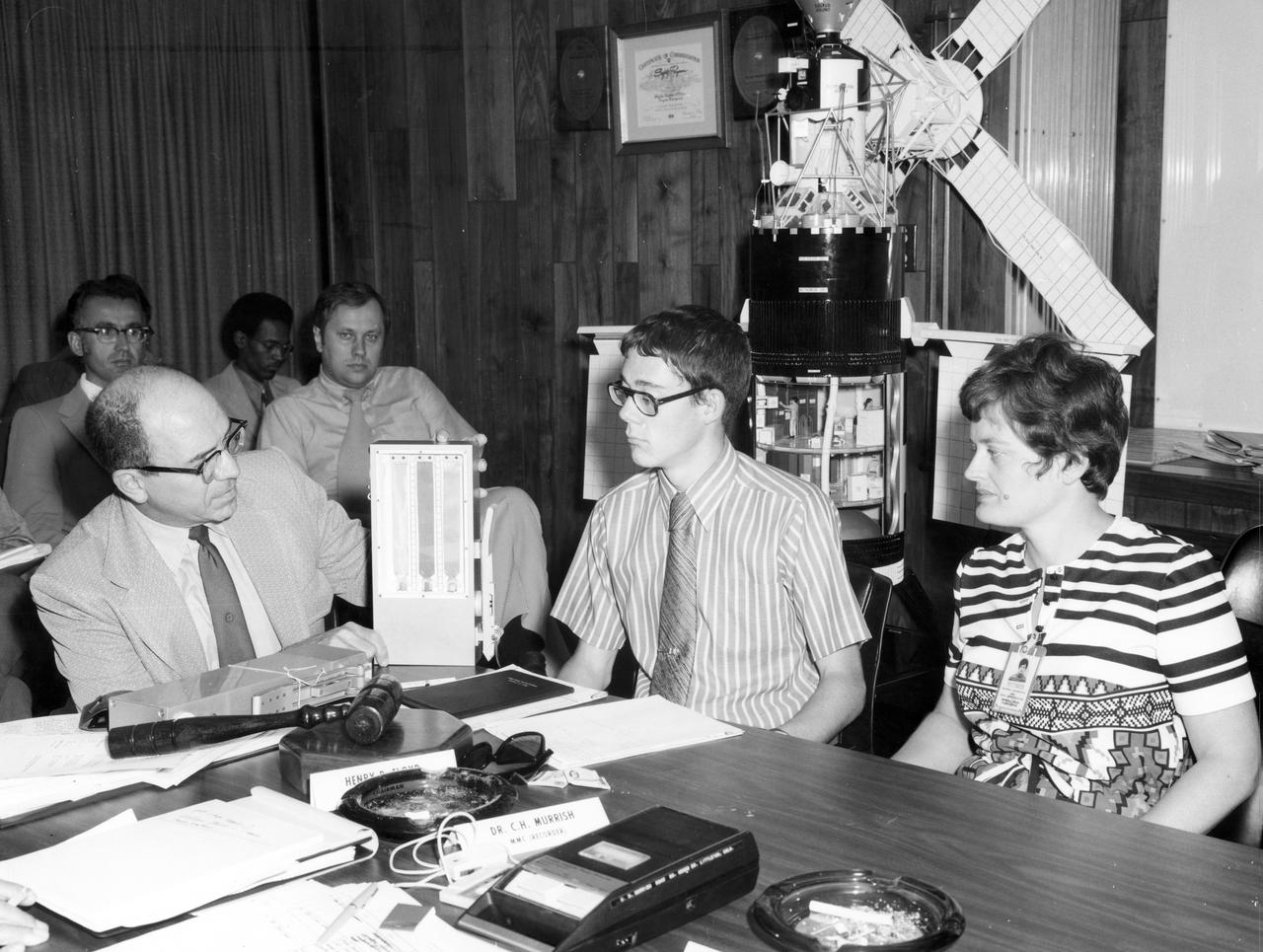

St. Paul Minnesota high school student, Roger Johnston (center), Gene Vacca (left) of NASA Headquarters, and Ann Whitaker of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) discuss the equipment to be used for the student’s experiment, “Capillary Action Studies in a State of Free Fall”, to be performed aboard the Skylab the following year. Johnston was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC two months earlier where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment. The equipment for the experiments was manufactured at MSFC.
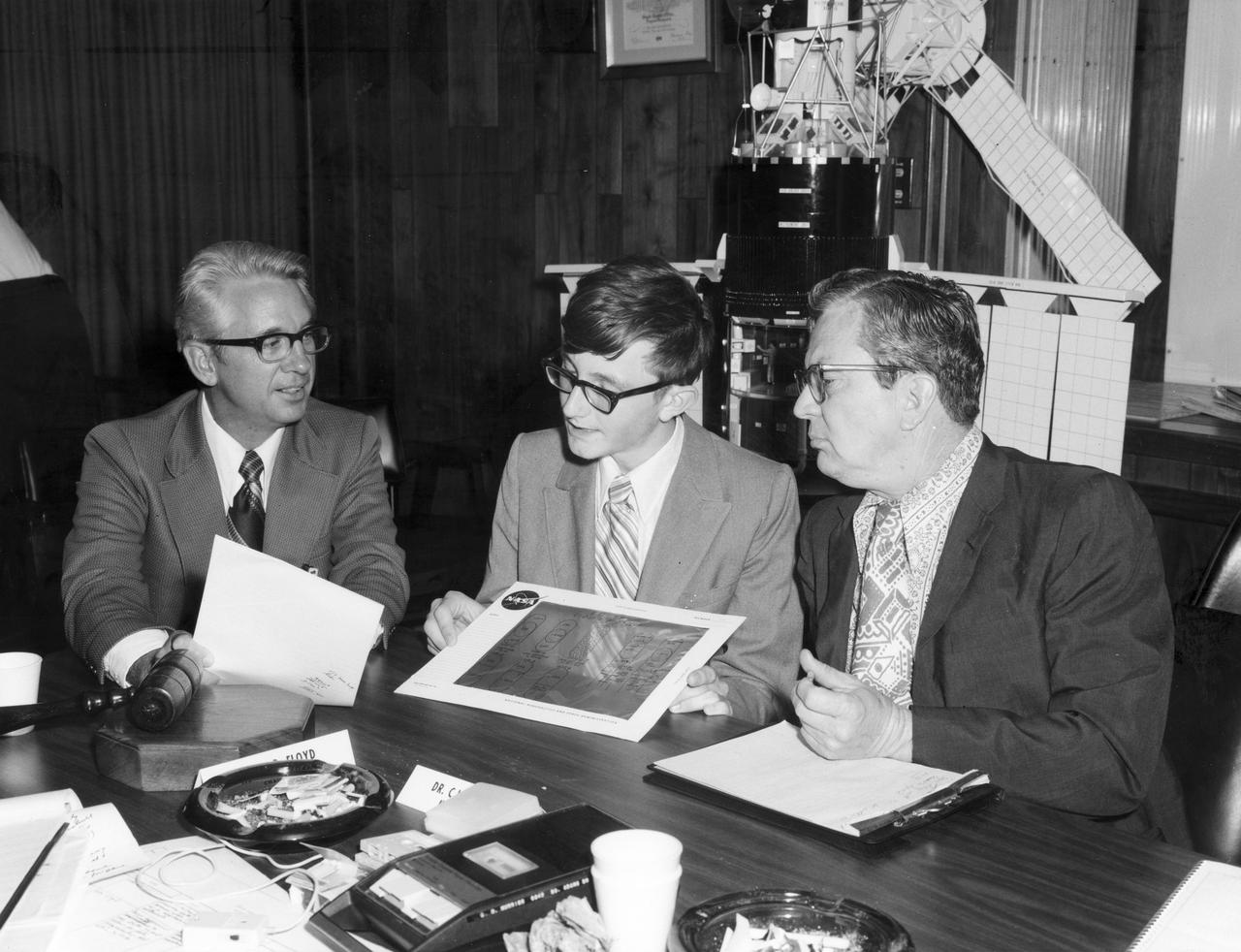

Youngstown, Ohio high school student, W. Brian Dunlap (center), discusses with Dr. Robert Head (right), and Henry Floyd, both of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), his experiment to be performed aboard the Skylab the following year. His experiment, “Wave Motion Trough A Liquid in Zero Gravity” used a container attached to the end of a leaf spring which was oscillated at specific rates using two thickness differentiated types of liquids. Dunlap was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment. The equipment for the experiments was manufactured at MSFC.
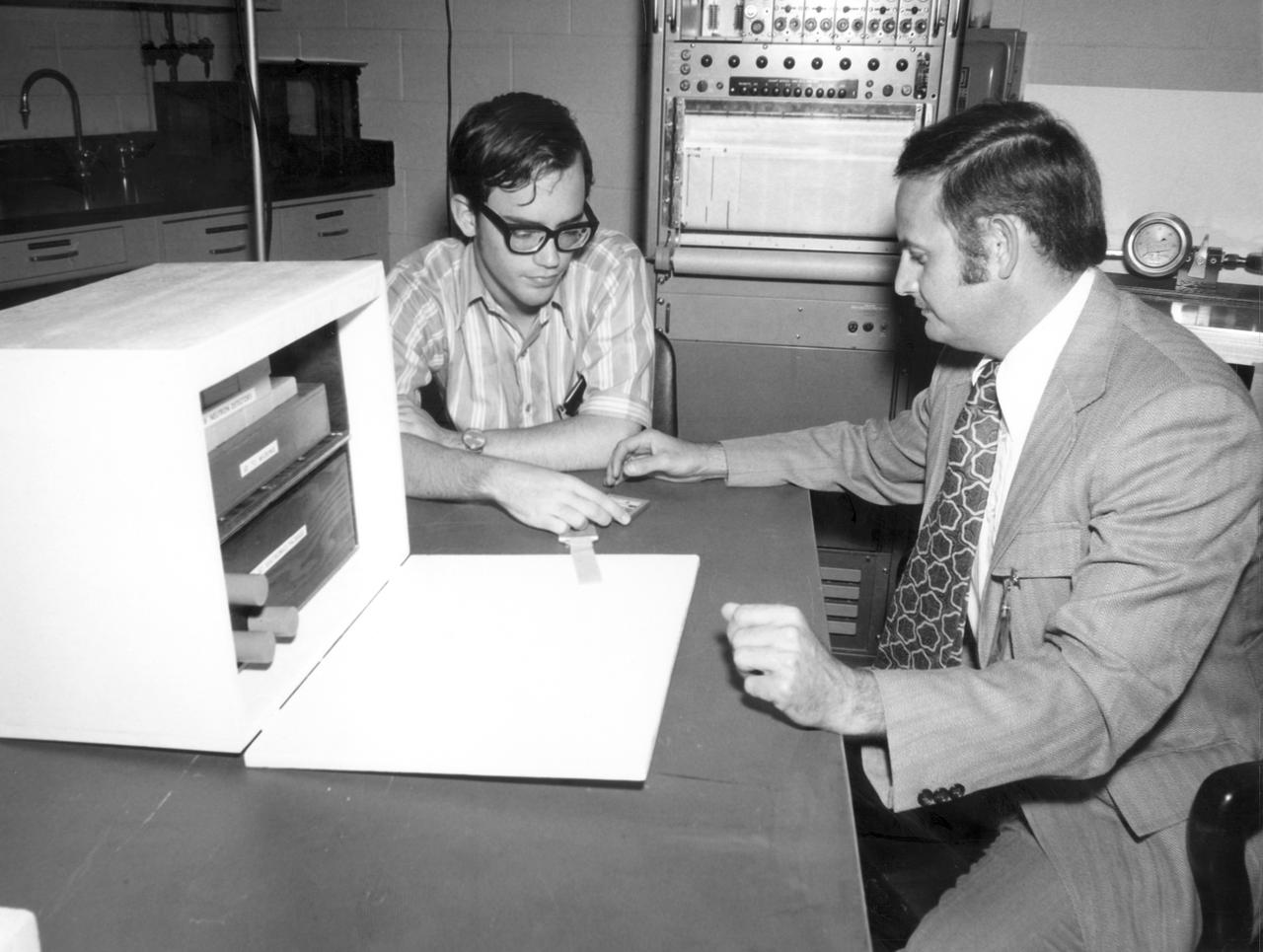

San Antonio, Texas high school student, Terry C. Quist (left), and Dr. Raymond Gause of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), discuss the student’s experiment to be performed aboard the Skylab the following year. His experiment, “Earth Orbital Neutron Analysis” required detectors such as the one he is examining in this photo. The detector was to be attached to a water tank in Skylab. Neutrons striking the detectors left traces that were brought out by a chemical etching process after the Skylab mission. Quist’s experiment seeked to record neutron hits, count them, and determine their direction. This information was to help determine the source of neutrons in the solar system. Quist was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC two months earlier where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment. The equipment for the experiments was manufactured at MSFC.
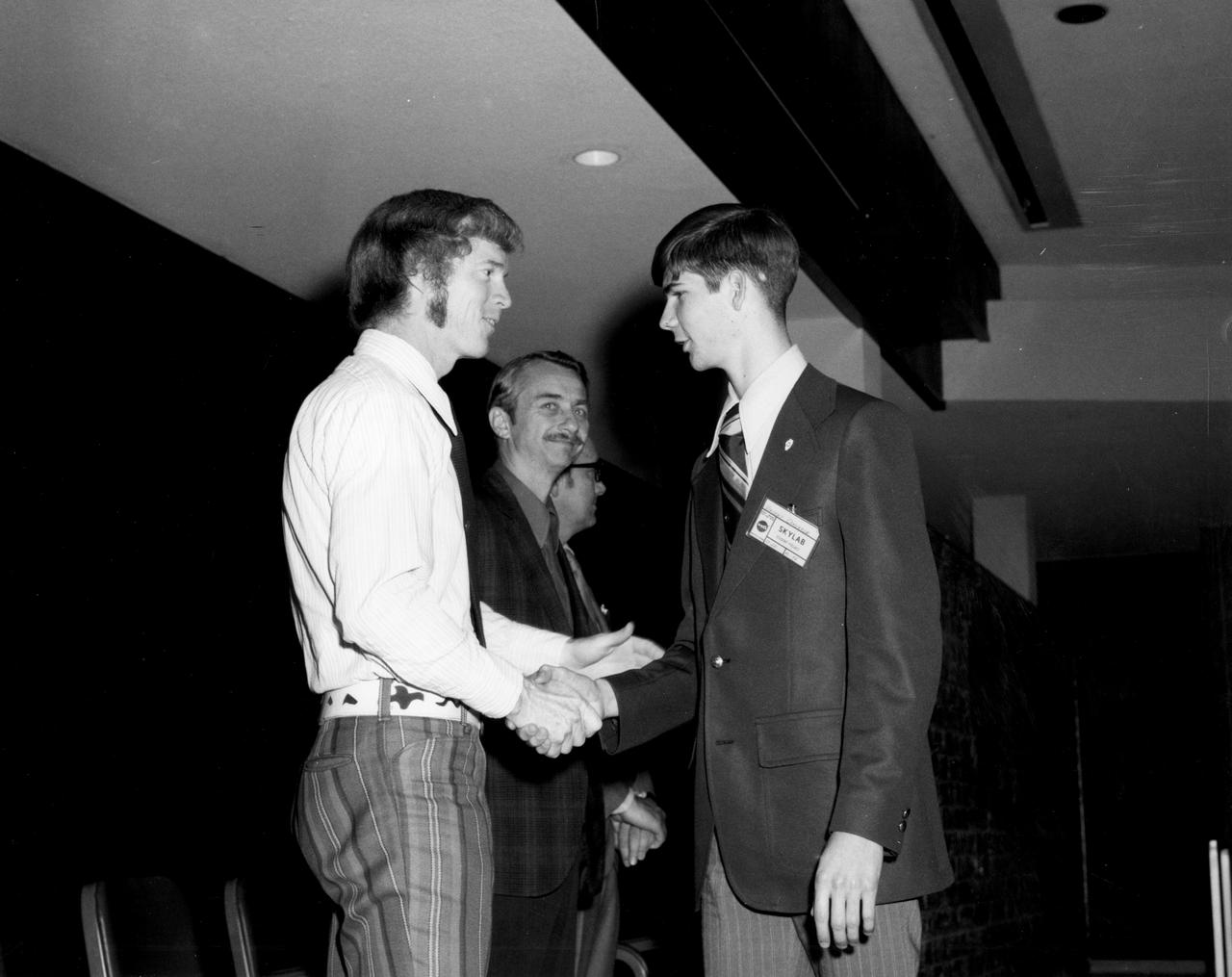

Rockford, Illinois high school student, Vincent Converse (right), is greeted by astronauts Russell L. Schweickart and Owen K. Garriott during a tour of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Converse was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. His experiment, “Zero Gravity Mass Measurement” used a simple leaf spring with the mass to be weighed attached to the end. An electronic package oscillated the spring at a specific rate and the results were recorded electronically. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipme
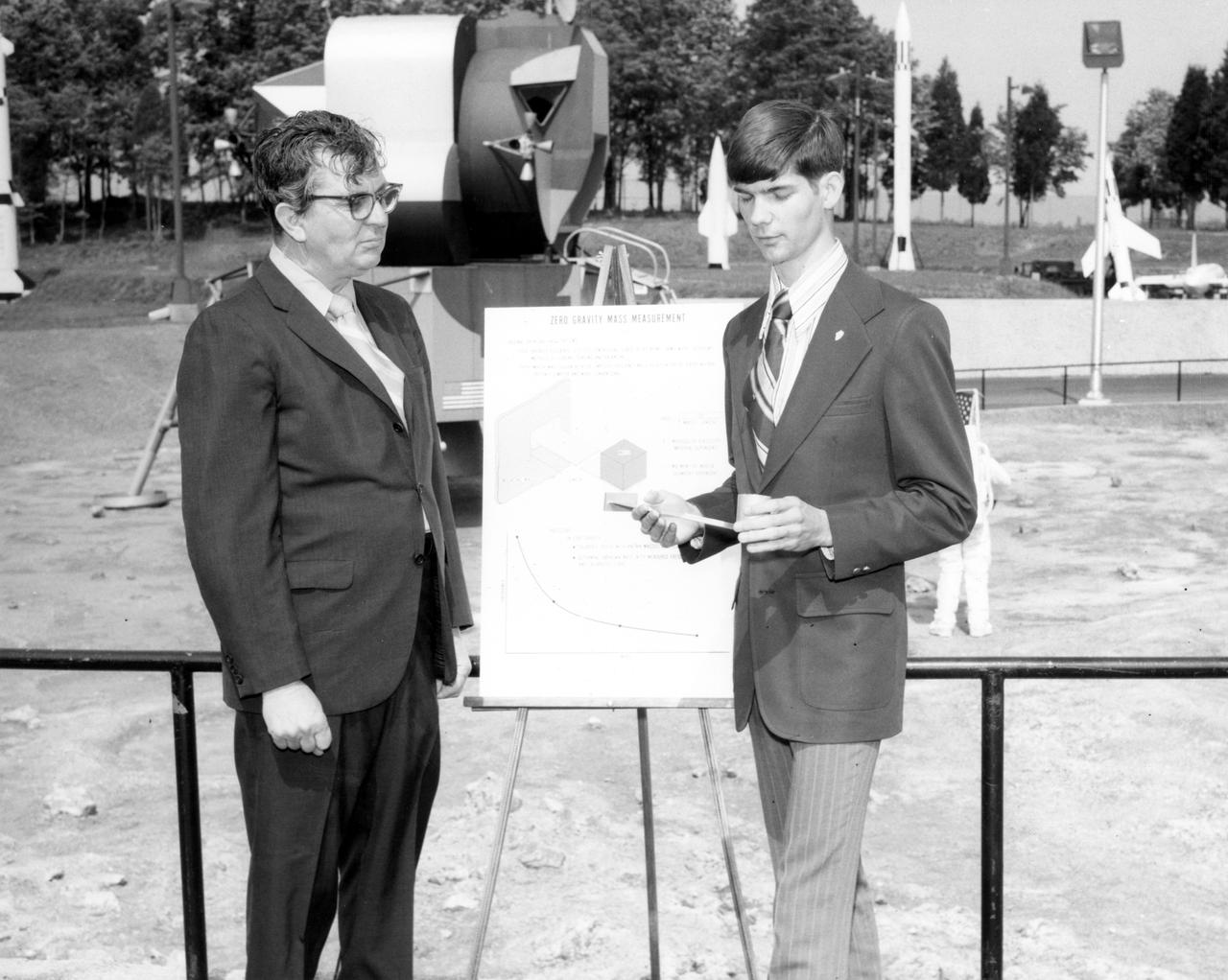

Vincent W. Converse, high school student from Rockford, Illinois, discussed a mass measurement device he proposed for the Skylab mission with Dr. Robert Head of the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) during his visit to the center. The lunar surface scene in the background is one of many space exhibits at the Alabama Space and Rocket Center in nearby Huntsville, Alabama. Converse was among 25 winners of a contest in which some 3,500 high school students proposed experiments for the following year’s Skylab mission. The nationwide scientific competition was sponsored by the National Science Teachers Association and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The winning students, along with their parents and sponsor teachers, visited MSFC where they met with scientists and engineers, participated in design reviews for their experiments, and toured MSFC facilities. Of the 25 students, 6 did not see their experiments conducted on Skylab because the experiments were not compatible with Skylab hardware and timelines. Of the 19 remaining, 11 experiments required the manufacture of additional equipment.
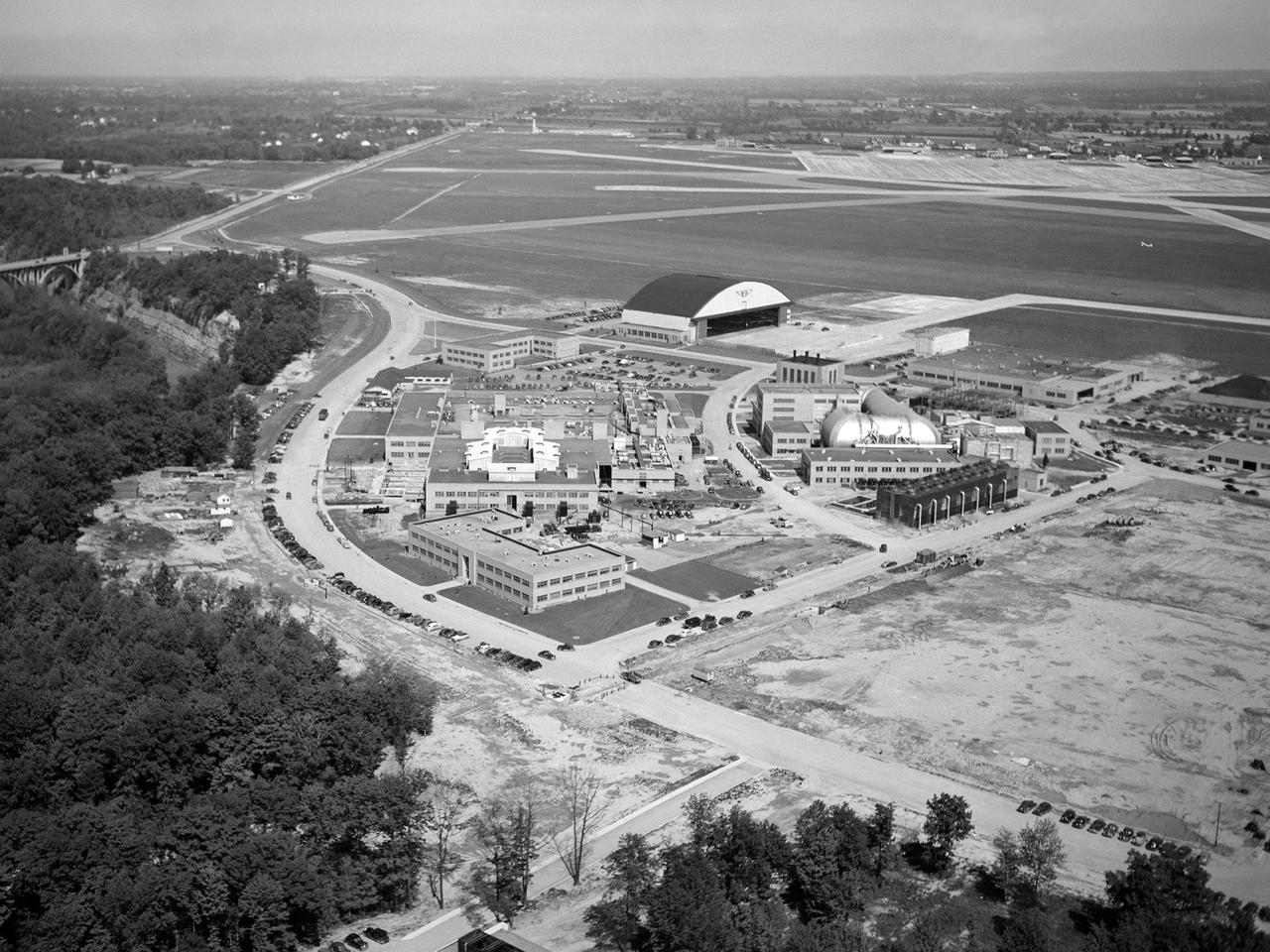

The National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in Cleveland, Ohio as seen from the west in May 1946. The Cleveland Municipal Airport is located directly behind. The laboratory was built in the early 1940s to resolve problems associated with aircraft engines. The initial campus contained seven principal buildings: the Engine Research Building, hangar, Fuels and Lubricants Building, Administration Building, Engine Propeller Research Building, Altitude Wind Tunnel, and Icing Research Tunnel. These facilities and their associated support structures were located within an area occupying approximately one-third of the NACA’s property. After World War II ended, the NACA began adding new facilities to address different problems associated with the newer, more powerful engines and high speed flight. Between 1946 and 1955, four new world-class test facilities were built: the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel, the Propulsion Systems Laboratory, the Rocket Engine Test Facility, and the 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel. These large facilities occupied the remainder of the NACA’s semicircular property. The Lewis laboratory expanded again in the late 1950s and early 1960s as the space program commenced. Lewis purchased additional land in areas adjacent to the original laboratory and acquired a large 9000-acre site located 60 miles to the west in Sandusky, Ohio. The new site became known as Plum Brook Station.
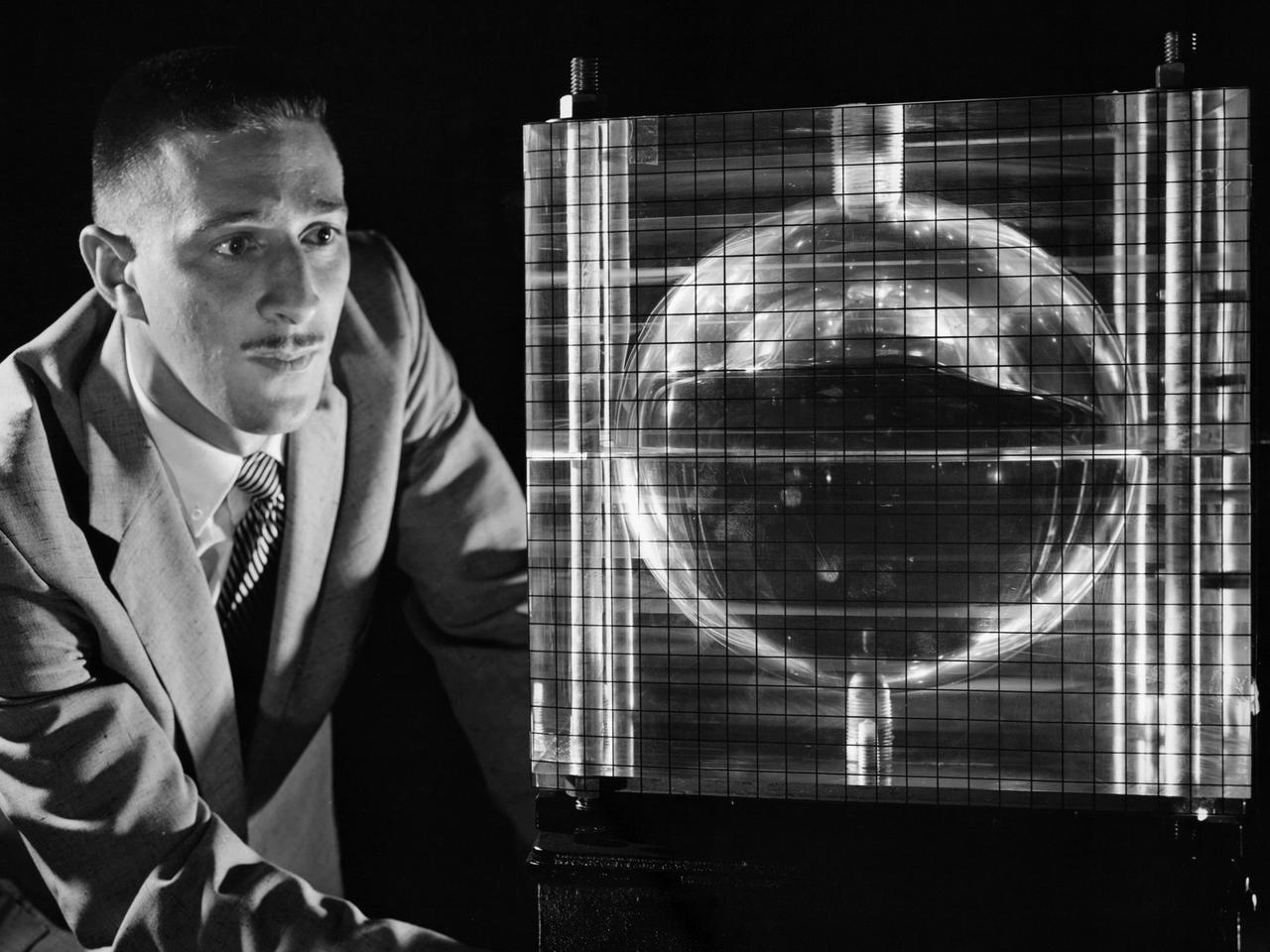

Andy Stofan views a small-scale tank built to study the sloshing characteristics of liquid hydrogen at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. Stofan was tasked with the study of propellant motion, or sloshing, in space vehicle propellant tanks. At the time, there was little knowledge of the behavior of fluids in microgravity or the effects of the launch on the propellant’s motion. Sloshing in the tank could alter a spacecraft’s trajectory or move the propellant away from the turbopump. Stofan became an expert and authored numerous technical reports on the subject. Stofan was assigned to the original Centaur Project Office in 1962 as a member of the Propellant Systems Section. Stofan was instrumental in solving a dynamic instability problem on the Centaur vehicle and served as the systems engineer for the development of the Centaur propellant utilization system. The solution was also applied to the upper-stages of Saturn. In 1966, Stofan was named Head of the Propellant Systems Section. Stofan continued rising through the managerial ranks at Lewis. In 1967 he became Project Manager of a test program that successfully demonstrated the use of a pressurization system for the Centaur vehicle; in 1969 the Assistant Project Manager on the Improved Centaur project; in 1970 Manager of the Titan/Centaur Project Office; in 1974 Director of the Launch Vehicles Division. In 1978, Stofan was appointed Deputy Associate Administrator for the Headquarters Office of Space Science. In 1982, he was named Director of Lewis Research Center.
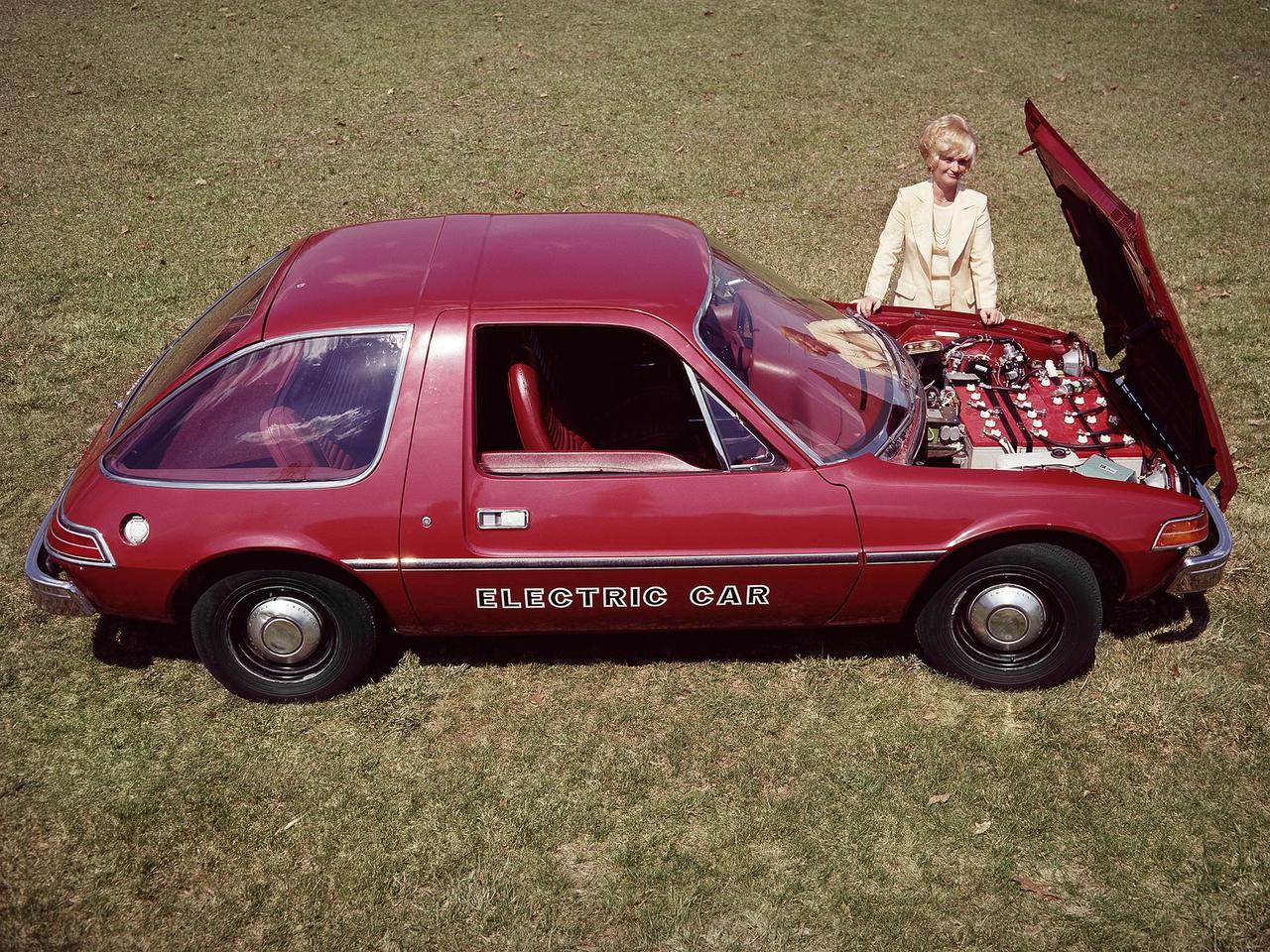

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center tested 16 commercially-manufactured electric vehicles, including this modified Pacer, during the mid-1970s. The Electric Vehicle Project was just one of several energy-related programs that Lewis and the Energy Research and Development Administration (ERDA) undertook in the mid-1970s. NASA and ERDA embarked on this program in 1976 to determine the state of the current electric vehicle technology. As part of the project, Lewis tested a fleet composed of every commercially available electric car. The Cleveland-area Electric Vehicle Associates modified an American Motors Pacer vehicle to create this Change-of-Pace Coupe. It was powered by twenty 6-volt batteries whose voltage could be varied by a foot control. The tests analyzed the vehicle’s range, acceleration, coast-down, braking, and energy consumption. Some of the vehicles had analog data recording systems to measure the battery during operation and sensors to determine speed and distance. Lewis researchers found that the vehicle performance varied significantly from model to model. In general, the range, acceleration, and speed were lower than conventional vehicles. They also found that traditional gasoline-powered vehicles were as efficient as the electric vehicles. The researchers concluded, however, that advances in battery technology and electric drive systems would significantly improve the performance and efficiency.

National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) engineer Robert Jeracki prepares a Hamilton Standard SR-1 turboprop model in the test section of the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the Lewis Research Center. Lewis researchers were analyzing a series of eight-bladed propellers in their wind tunnels to determine their operating characteristics at speeds up to Mach 0.8. The program, which became the Advanced Turboprop, was part of a NASA-wide Aircraft Energy Efficiency Program which was designed to reduce aircraft fuel costs by 50 percent. The ATP concept was different from the turboprops in use in the 1950s. The modern versions had at least eight blades and were swept back for better performance. After Lewis researchers developed the advanced turboprop theory and established its potential performance capabilities, they commenced an almost decade-long partnership with Hamilton Standard to develop, verify, and improve the concept. A series of 24-inch scale models of the SR-1 with different blade shapes and angles were tested in Lewis’ wind tunnels. A formal program was established in 1978 to examine associated noise levels, aerodynamics, and the drive system. The testing of the large-scale propfan was done on test rigs, in large wind tunnels, and, eventually, on aircraft.
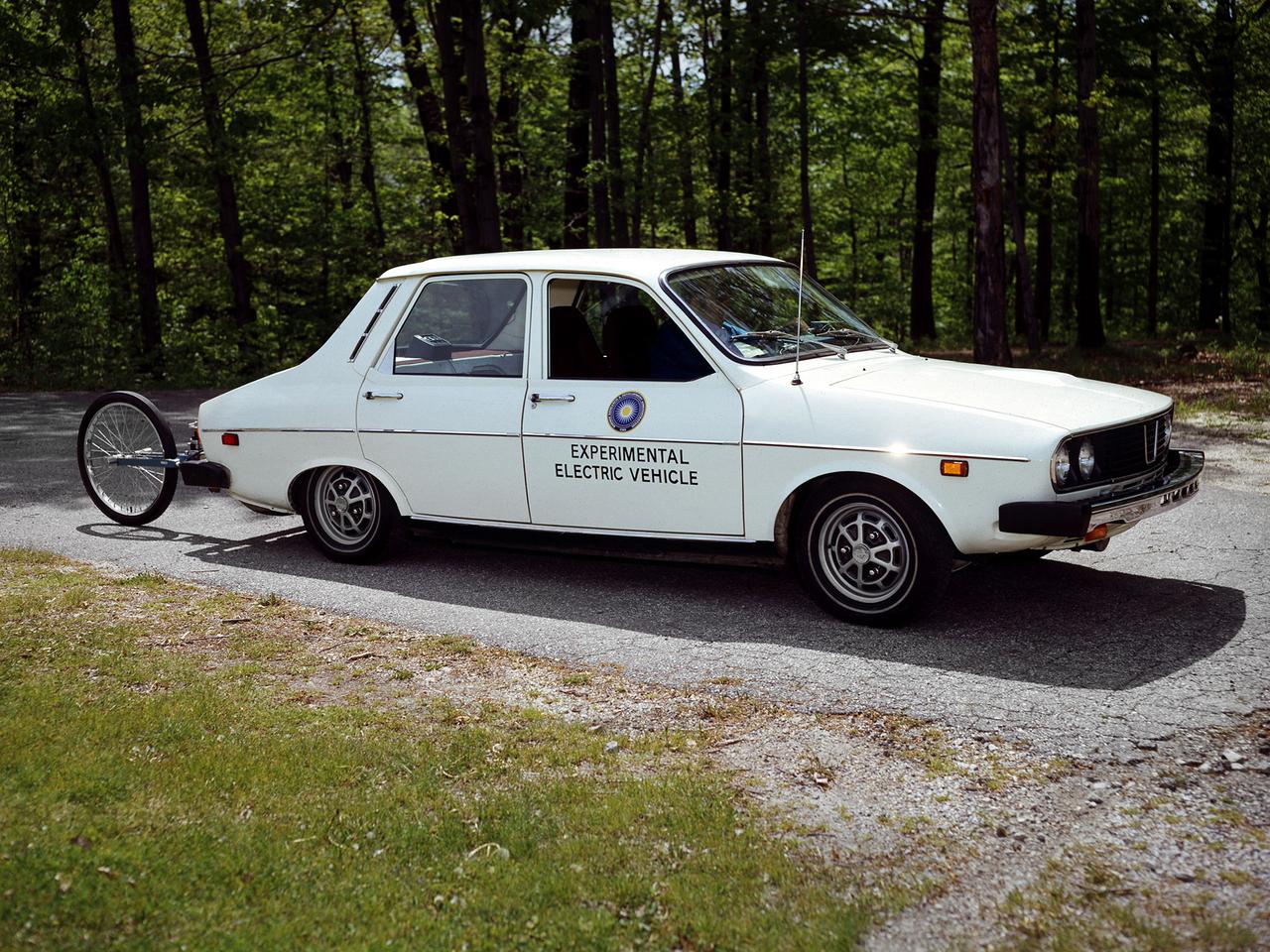

The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center tested 16 commercially-manufactured electric vehicles, including this Metro, during the mid-1970s. Lewis and the Energy Research and Development Administration (ERDA) engaged in several energy-related programs in the mid-1970s, including the Electric Vehicle Project. NASA and ERDA undertook the program in 1976 to determine the state of the current electric vehicle technology. As part of the project, Lewis and ERDA tested every commercially available electric car model. Electric Vehicle Associates, located in a Cleveland suburb, modified a Renault 12 vehicle to create this Metro. Its 1040-pound golfcart-type battery provided approximately 106 minutes of operation. The tests analyzed the vehicle’s range, acceleration, coast-down, braking, and energy consumption. Some of the vehicles had analog data recording systems to measure the battery during operation and sensors to determine speed and distance. The researchers found the performance of the different vehicles varied significantly. In general, the range, acceleration, and speed were lower than that found on conventional vehicles. They also found that traditional gasoline-powered vehicles were as efficient as the electric vehicles. The researchers concluded, however, that advances in battery technology and electric drive systems would significantly improve efficiency and performance.
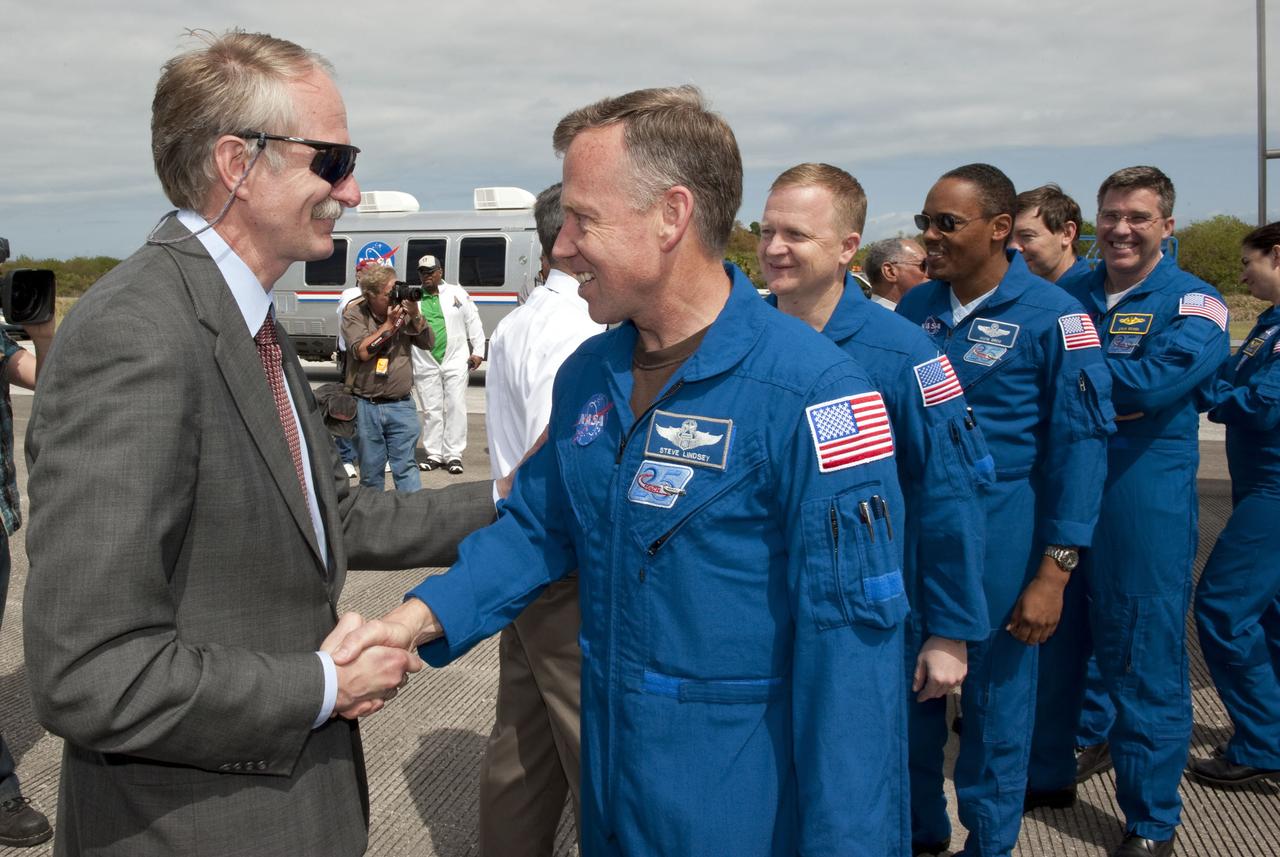

STS133-S-139 (9 March 2011) --- Bill Gerstenmaier, associate administrator for Space Operations, greets the STS-133 crew members as they exit the crew transport vehicle after landing at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida aboard space shuttle Discovery. Leading the crew is astronaut Steve Lindsey, commander; followed by astronauts Eric Boe, pilot; Alvin Drew, Steve Bowen, Michael Barratt and Nicole Stott, all mission specialists. Touchdown on the Shuttle Landing Facility's Runway 15 was at 11:57 a.m. (EST) on March 9, 2011, bringing an end to the 13-day STS-133 mission to the International Space Station. Discovery and its six-member crew delivered the Permanent Multipurpose Module, packed with supplies and critical spare parts, as well as Robonaut 2, the dexterous humanoid astronaut helper, to the orbiting outpost. STS-133 was Discovery's 39th and final mission. This was the 133rd Space Shuttle Program mission and the 35th shuttle voyage to the space station. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
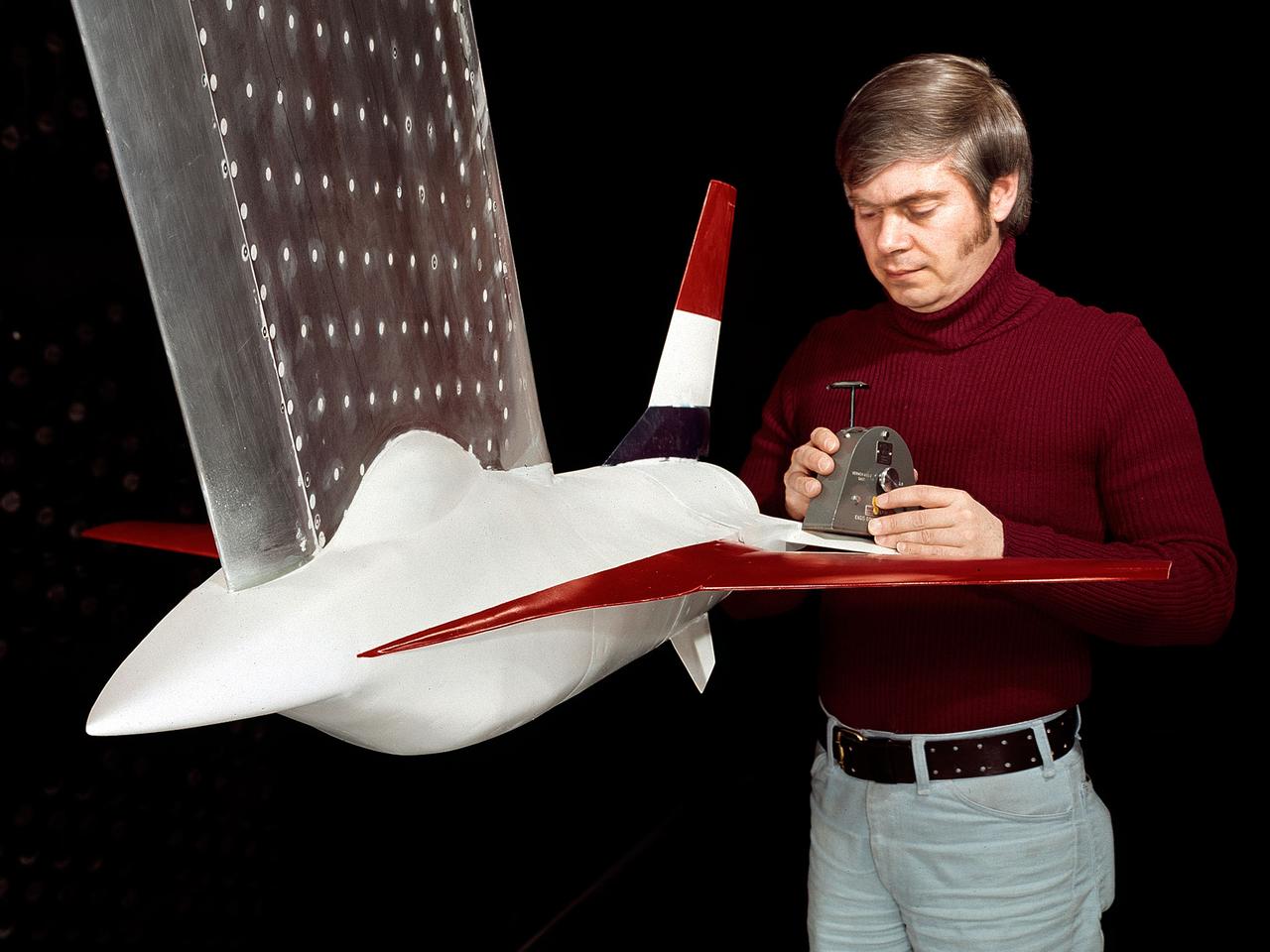

A model of the General Dynamics YF-16 Fighting Falcon in the test section of the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) Lewis Research Center. The YF-16 was General Dynamics response to the military’s 1972 request for proposals to design a new 20,000-pound fighter jet with exceptional acceleration, turn rate, and range. The aircraft included innovative design elements to help pilots survive turns up to 9Gs, a new frameless bubble canopy, and a Pratt and Whitney 24,000-pound thrust F-100 engine. The YF-16 made its initial flight in February 1974, just six weeks before this photograph, at Edwards Air Force Base. Less than a year later, the Air Force ordered 650 of the aircraft, designated as F-16 Fighting Falcons. The March and April 1974 tests in the 8- by 6-foot tunnel analyzed the aircraft’s fixed-shroud ejector nozzle. The fixed-nozzle area limited drag, but also limited the nozzle’s internal performance. NASA researchers identified and assessed aerodynamic and aerodynamic-propulsion interaction uncertainties associated the prototype concept. YF-16 models were also tested extensively in the 11- by 11-Foot Transonic Wind Tunnel and 9- by 7-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at Ames Research Center and the 12-Foot Pressure Wind Tunnel at Langley Research Center.
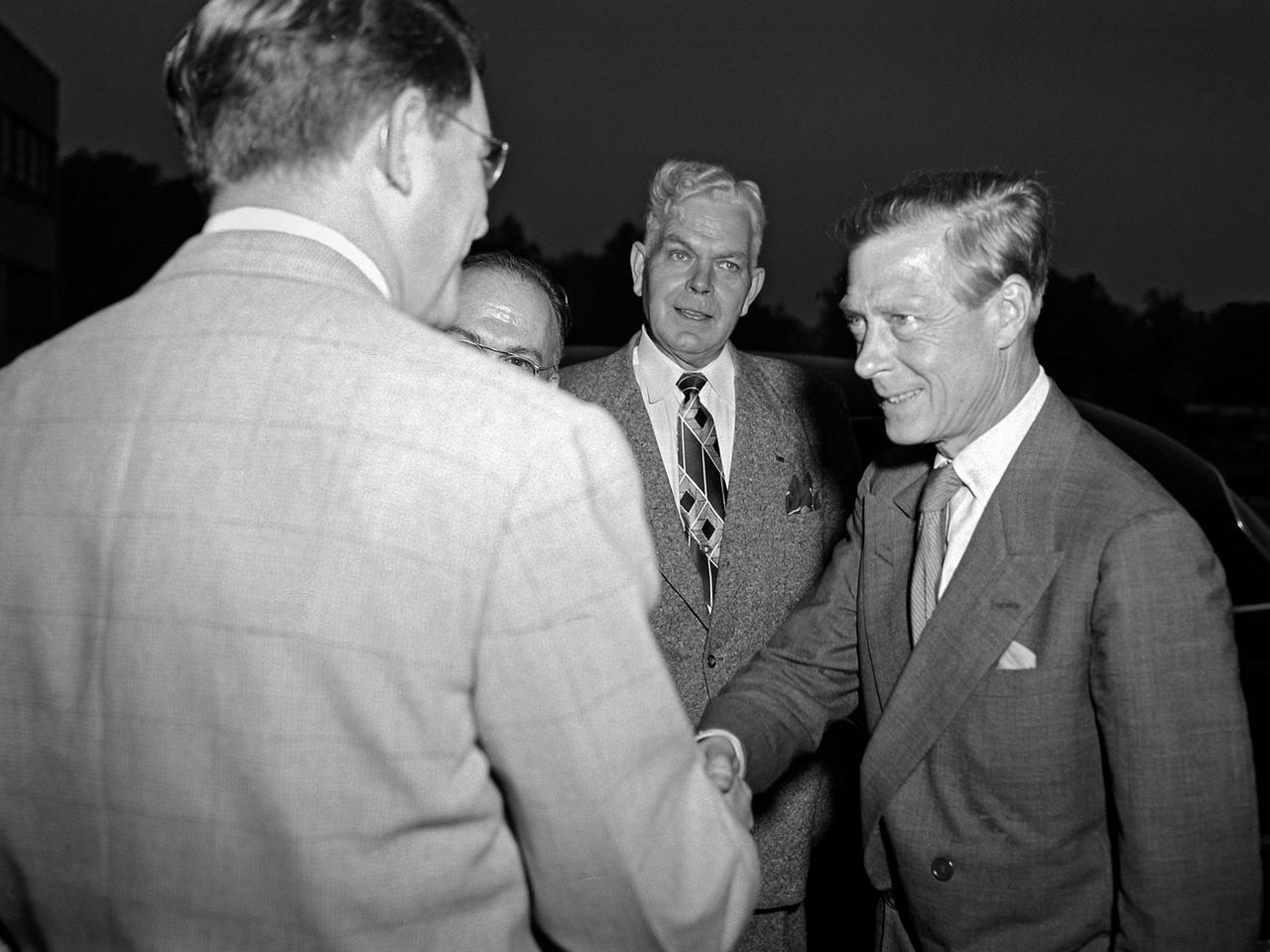

Edward Saxe-Coburg-Gotha, the Duke of Windsor, visits the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory in Cleveland, Ohio. He is seen in this photograph shaking hands with Associate Director Abe Silverstein. Lewis Director Ray Sharp is in the background. Cleveland mayor Thomas Burke and other local officials were also on hand to greet Edward. Silverstein led the group on a tour of Lewis’ new 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel where the Duke inquired about the operation of the facility’s flexible walls, the types of components tested, and the generation of airflow. The Duke was in town in 1951 to promote his new autobiography, A King’s Story, at the American Booksellers Convention. Edward had assumed the British throne in January 1936, only to renounce the position less than a year later to controversially marry Wallis Simpson. Ongoing concerns over the couple’s relationship to the German government resulted in his World War II assignment to the Bahamas. Edward spent the remainder of his life in France.
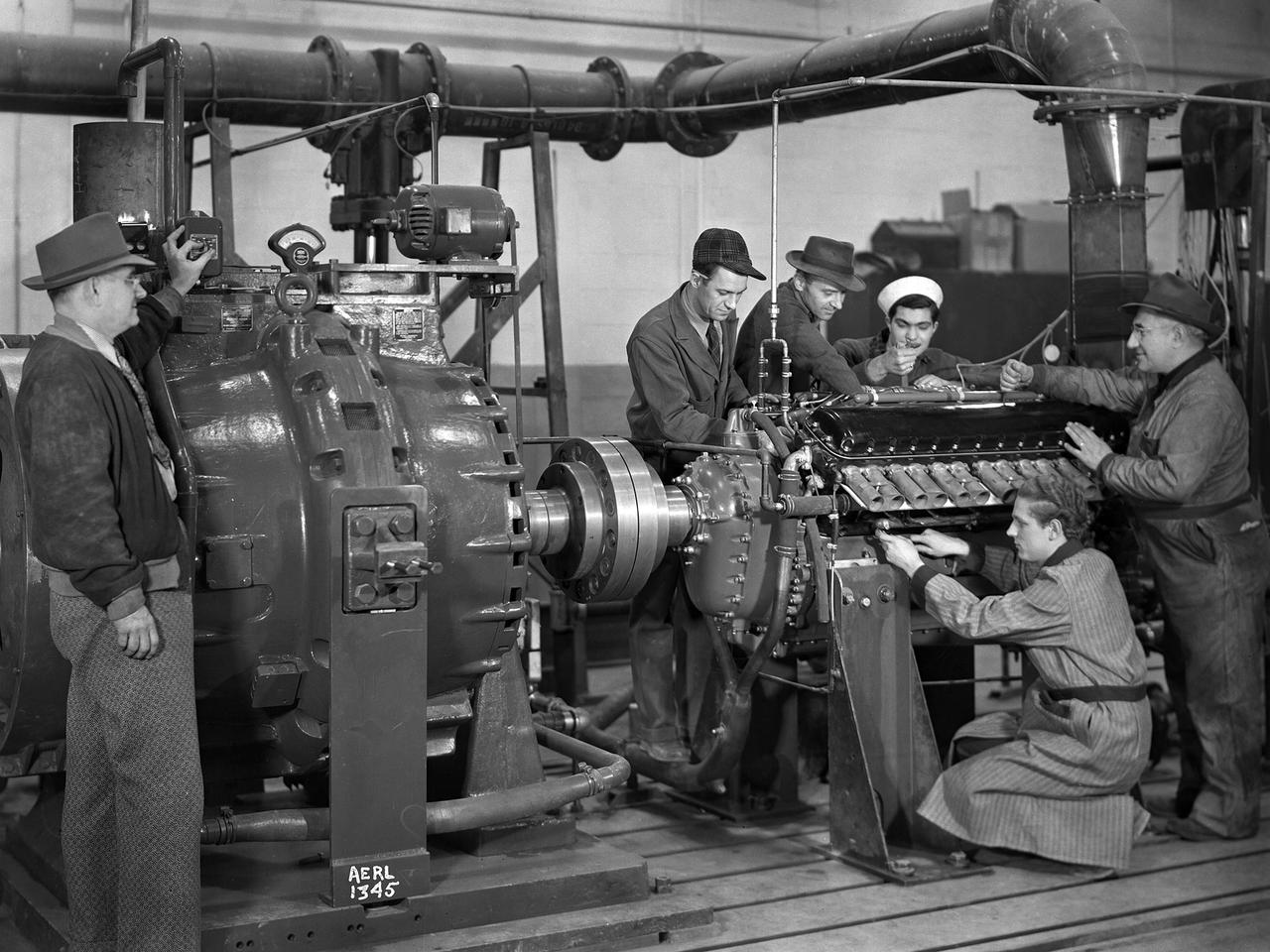
The first research assignment specifically created for the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics’ (NACA) new Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory was the integration of a supercharger into the Allison V–1710 engine. The military was relying on the liquid-cooled V–1710 to power several types of World War II fighter aircraft and wanted to improve the engine's speed and altitude performance. Superchargers forced additional airflow into the combustion chamber, which increased the engine’s performance resulting in greater altitudes and speeds. They also generated excess heat that affected the engine cylinders, oil, and fuel. In 1943 the military tasked the new Aircraft Engine Research Laboratory to integrate the supercharger, improve the cooling system, and remedy associated engine knock. Three Allison engines were provided to the laboratory’s research divisions. One group was tasked with improving the supercharger performance, another analyzed the effect of the increased heat on knock in the fuel, one was responsible for improving the cooling system, and another would install the new components on the engine with minimal drag penalties. The modified engines were installed on this 2000-horsepower dynamotor stand in a test cell within the Engine Research Building. The researchers could run the engine at different temperatures, fuel-air ratios, and speeds. When the modifications were complete, the improved V–1710 was flight tested on a P–63A Kingcobra loaned to the NACA for this project.
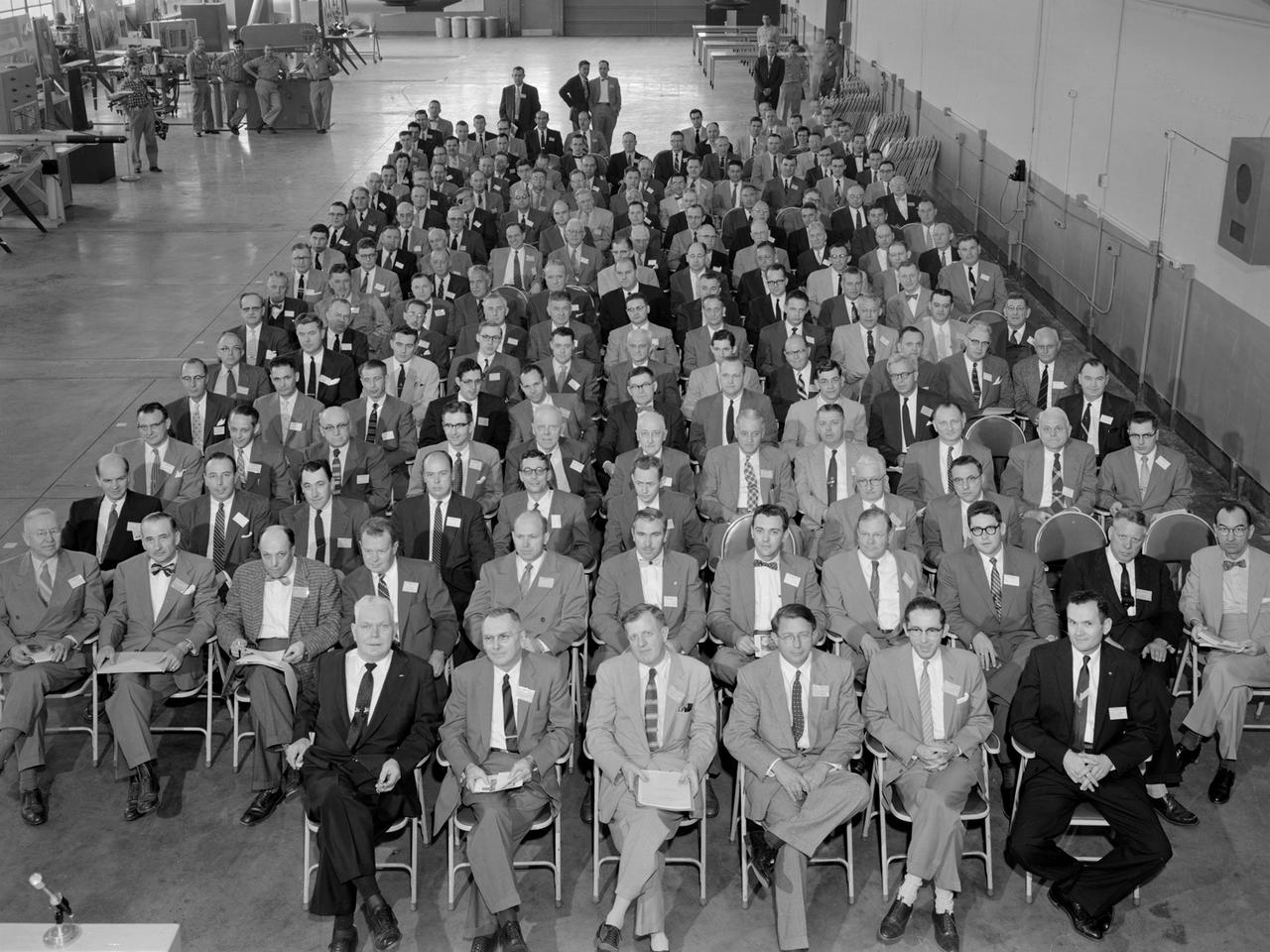

Attendees listen during the May 22, 1956 Inspection of the new 10- by 10-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The facility, known at the time as the Lewis Unitary Plan Tunnel, was in its initial stages of operation. The $33 million 10- by 10 was the most powerful wind tunnel in the nation. Over 150 guests from industry, other NACA laboratories, and the media attended the event. The speakers, from left to right in the front row, addressed the crowd before the tour. Lewis Director Raymond Sharp began the event by welcoming the visitors to the laboratory. NACA Director Hugh Dryden discussed Congress’ Unitary Plan Act and its effect on the creation of the facility. Lewis Associate Director Abe Silverstein discussed the need for research tools and the 10- by 10’s place among the NACA’s other research facilities. Lewis Assistant Director Eugene Wasielewski described the detailed design work that went into the facility. Carl Schueller, Chief of the 10- by 10, described the tunnel’s components and how the facility operated. Robert Godman led the tour afterwards. The 10- by 10 can test engines up to five feet in diameter at supersonic speeds and simulated altitudes of 30 miles. Its main purpose is to investigate problems relating to engine inlet and outlet geometry, engine matching and interference effects, and overall drag. The tunnel’s 250,000-horsepower electric motor drive, the most powerful of its kind in the world, creates air speeds between Mach 2.0 and 3.5.
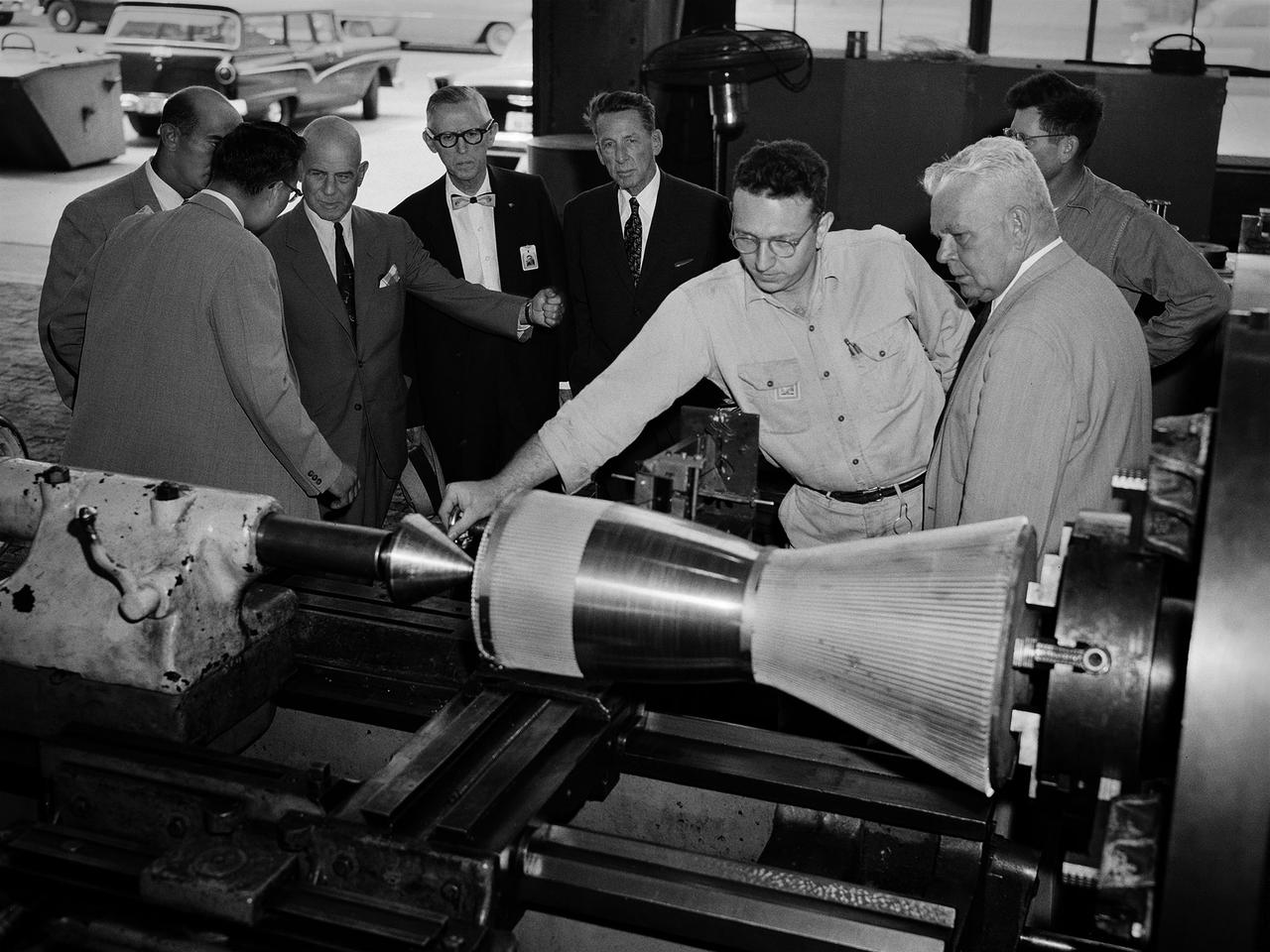

National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Chairman James Doolittle and Thompson Products Chairman of the Board Frederick Crawford receive a tour of the Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory during the last few months of the NACA. Lewis mechanic Leonard Tesar demonstrates the machining of a 20,000-pound thrust rocket engine for the group in the Fabrication Shop. From left to right, Associate Director Eugene Manganiello, researcher Edward Baehr, Doolittle, NACA Executive Secretary John Victory, Crawford, Tesar, Lewis Director Raymond Sharp, and mechanic Curtis Strawn. Doolittle began his career as a test pilot and air racer. In 1942 he famously flew a B-25 Mitchell on a daring raid over Tokyo. Doolittle also worked with the aviation industry on the development of aircraft fuels and instrumentation. After the war he served as vice president of Shell Oil and as a key government advisor. In this capacity he also served on the NACA’s Executive Committee for a number of years and served as its Chairman in 1957 and 1958. Tesar was a supervisor at the Sheet Metal Shop in the Fabrication Building. He joined the laboratory in 1948 and enrolled in their Apprentice Program. He graduated from the school three years later as an aviation metalsmith. The Fabrication Branch created a wide variety of hardware for the laboratory’s research projects. Requests from research divisions ranged from sheetmetal manufacturing for aircraft to fabrication of rocket engines. Tesar retired in 1982 after 37 years of service.
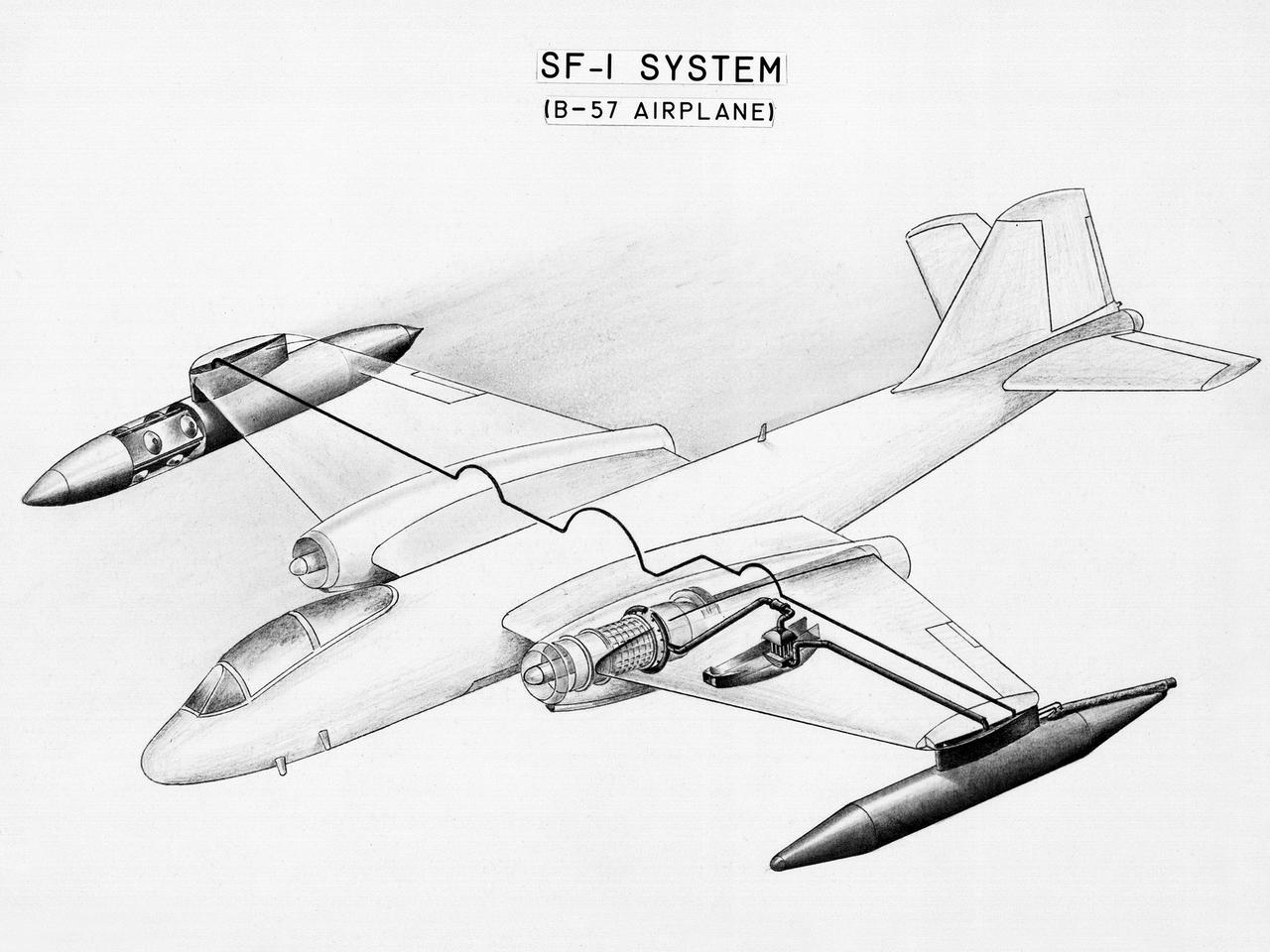
This diagram shows a hydrogen fuel system designed by researchers at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory and installed on a Martin B-57B Canberra aircraft. Lewis researchers accelerated their studies of high energy propellants in the early 1950s. In late 1954, Lewis researchers studied the combustion characteristics of gaseous hydrogen in a turbojet combustor. It was found that the hydrogen provided a very high efficiency. Almost immediately thereafter, Associate Director Abe Silverstein became focused on the possibilities of hydrogen for aircraft propulsion. That fall, Silverstein secured a contract to work with the air force to examine the practicality of liquid hydrogen aircraft. A B-57B Canberra was obtained by the air force especially for this project, referred to as Project Bee. The aircraft was powered by two Wright J65 engines, one of which was modified so that it could be operated using either traditional or liquid hydrogen propellants. The engine and its liquid hydrogen fuel system were tested extensively in the Altitude Wind Tunnel and the Four Burner Area test cells in 1955 and 1956. A B-57B flight program was planned to test the system on an actual aircraft. The aircraft would take off using jet fuel, switch to liquid hydrogen while over Lake Erie, then after burning the hydrogen supply switch back to jet fuel for the landing. The third test flight, in February 1957, was a success, and the ensuing B-57B flights remain the only demonstration of hydrogen-powered aircraft.
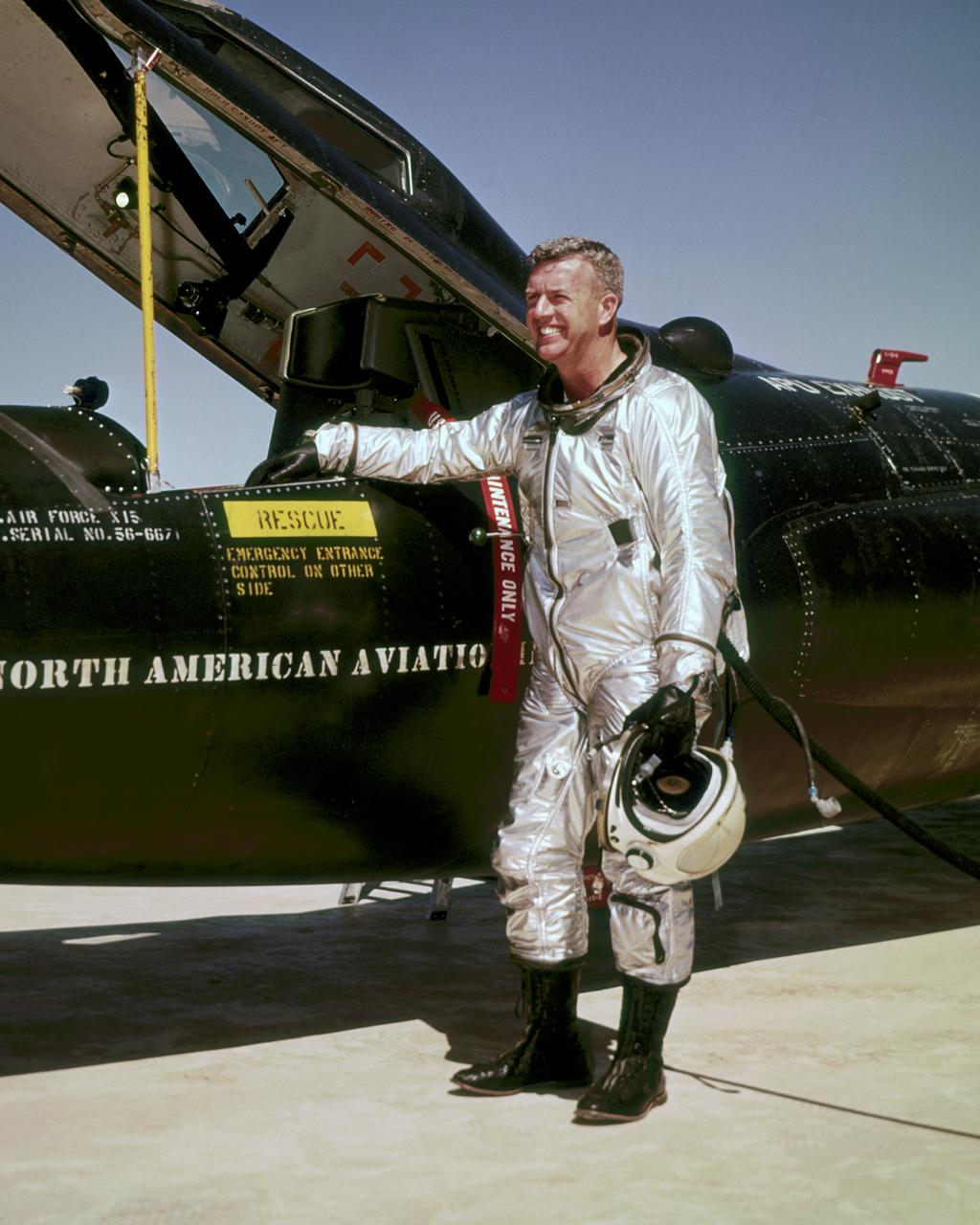

Joseph A. Walker was a Chief Research Pilot at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center during the mid-1960s. He joined the NACA in March 1945, and served as project pilot at the Edwards flight research facility on such pioneering research projects as the D-558-1, D-558-2, X-1, X-3, X-4, X-5, and the X-15. He also flew programs involving the F-100, F-101, F-102, F-104, and the B-47. Walker made the first NASA X-15 flight on March 25, 1960. He flew the research aircraft 24 times and achieved its fastest speed and highest altitude. He attained a speed of 4,104 mph (Mach 5.92) during a flight on June 27, 1962, and reached an altitude of 354,300 feet on August 22, 1963 (his last X-15 flight). He was the first man to pilot the Lunar Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) that was used to develop piloting and operational techniques for lunar landings. Walker was born February 20, 1921, in Washington, Pa. He lived there until graduating from Washington and Jefferson College in 1942, with a B.A. degree in Physics. During World War II he flew P-38 fighters for the Air Force, earning the Distinguished Flying Cross and the Air Medal with Seven Oak Clusters. Walker was the recipient of many awards during his 21 years as a research pilot. These include the 1961 Robert J. Collier Trophy, 1961 Harmon International Trophy for Aviators, the 1961 Kincheloe Award and 1961 Octave Chanute Award. He received an honorary Doctor of Aeronautical Sciences degree from his alma mater in June of 1962. Walker was named Pilot of the Year in 1963 by the National Pilots Association. He was a charter member of the Society of Experimental Test Pilots, and one of the first to be designated a Fellow. He was fatally injured on June 8, 1966, in a mid-air collision between an F-104 he was piloting and the XB-70.
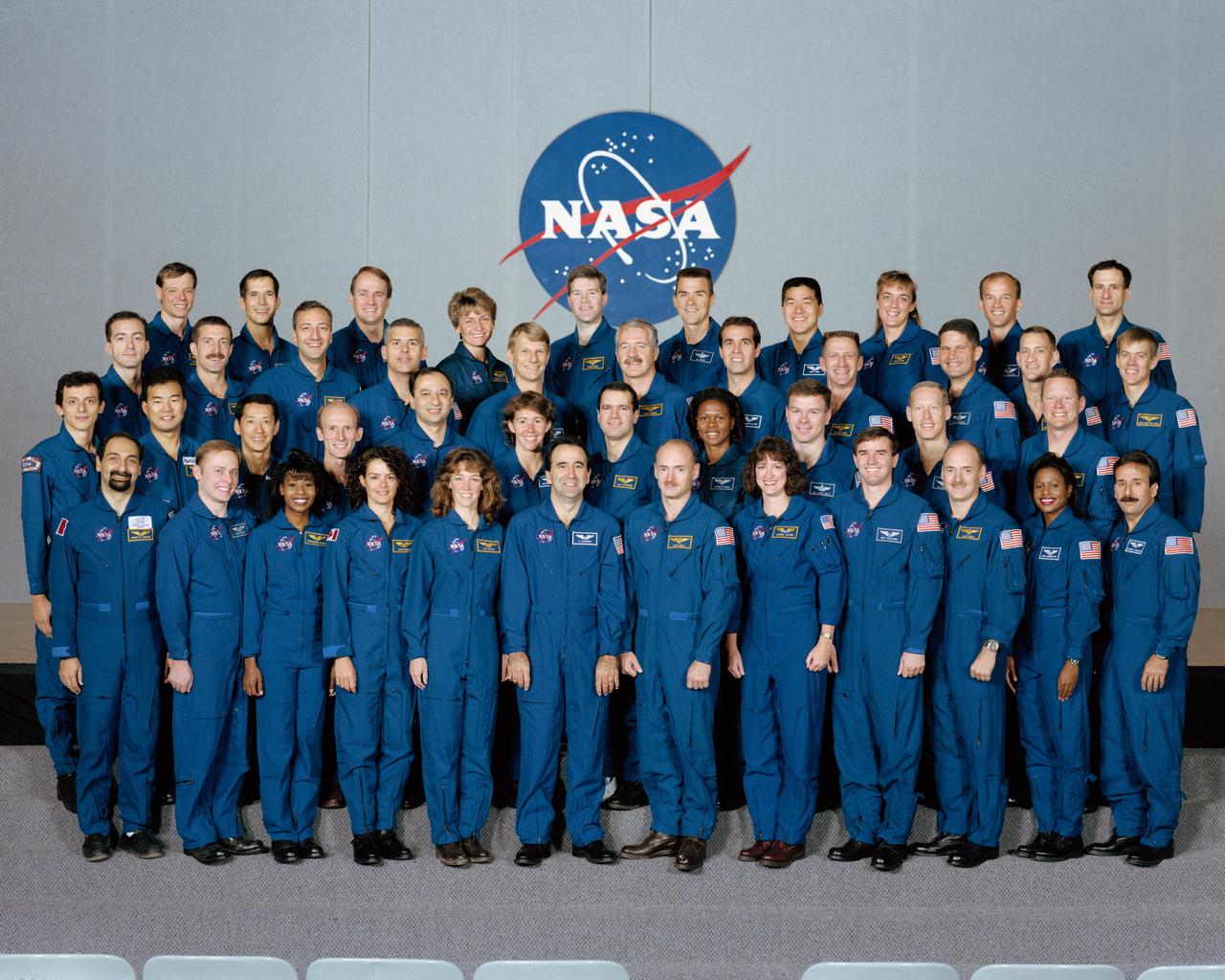

S96-18546 (5 Nov. 1996) --- Following their selection from among 2,400 applicants, the 44 astronaut candidates begin a lengthy period of training and evaluation at NASA's Johnson Space Center as they gather for their group portrait. This year?s class is the largest in the history of space shuttle astronauts and their early program predecessors. Ten pilots and 25 mission specialists make up the internationally diverse class. The international trainees represent the Canadian, Japanese, Italian, French, German and European space agencies. Back row ? from the left, Christer Fuglesang, John Herrington, Steve MacLean, Peggy Whitson, Stephen Frick, Duane Carey, Daniel Tani, Heidemarie Stefanyshyn-Piper, Jeffrey Williams and Donald Pettit. Second to back row ? from the left, Philippe Perrin, Daniel Burbank, Michael Massimino, Lee Morin, Piers Sellers, John Phillips, Richard Mastraccio, Christopher Loria, Paul Lockhart, Charles Hobaugh and William McCool. Second to front row ? from the left, Pedro Duque, Soichi Noguchi, Mamoru Mohri, Gerhard Thiele, Mark Polansky, Sandra Magnus, Paul Richards, Yvonne Cagle, James Kelly, Patrick Forrester and David Brown. Front row ? from the left, Umberto Guidoni, Edward Fincke, Stephanie Wilson, Julie Payette, Lisa Nowak, Fernando Caldeiro, Mark Kelly, Laurel Clark, Rex Walheim, Scott Kelly, Joan Higginbotham and Charles Camarda. Guidoni represents the Italian Space Agency (ASI). Fuglesang and Duque represent the European Space Agency (ESA). Mohri and Noguchi represent the Japanese Space Agency (NASDA). MacLean and Payette are with the Canadian Space Agency. Perrin is associated with the French Space Agency (CNES) and Thiele represents the German Space Agency (DARA). Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
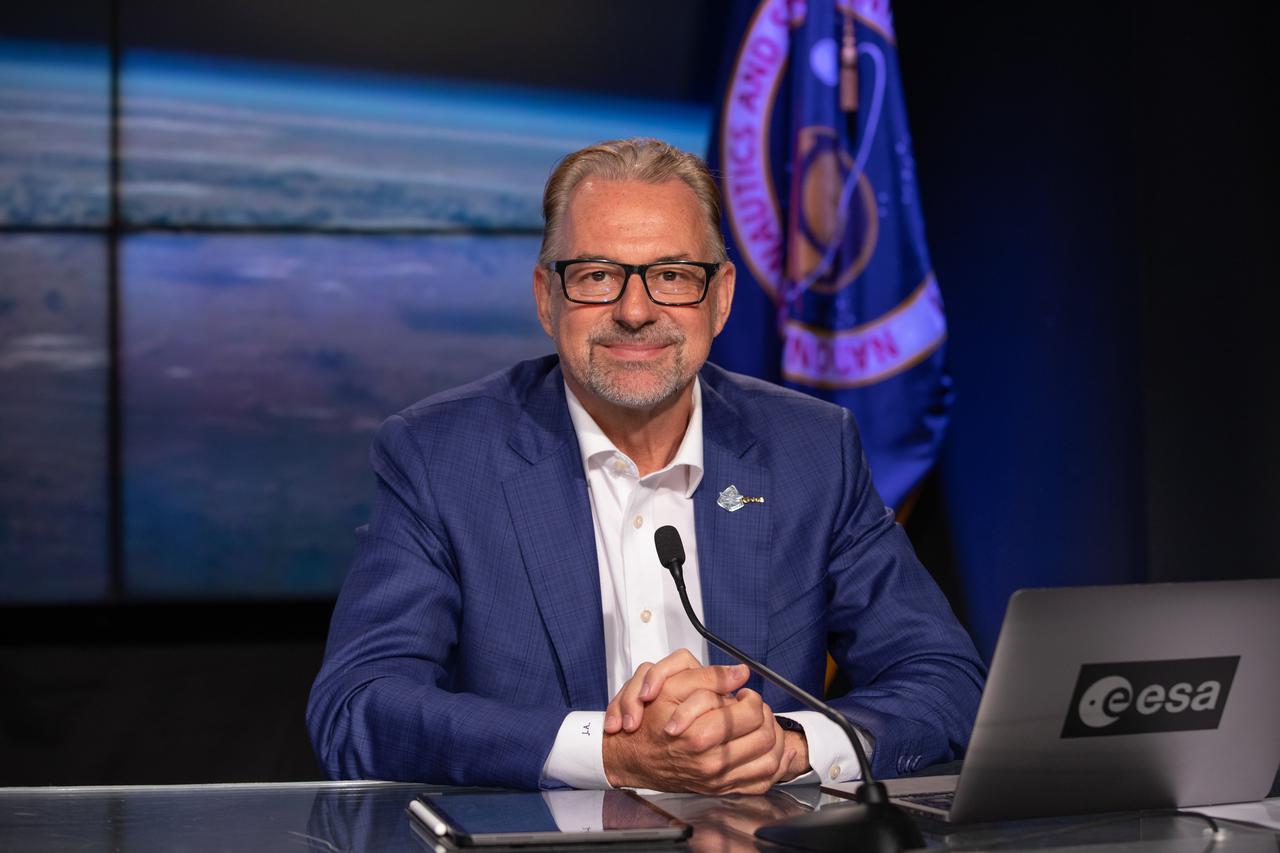

Josef Aschbacher, director general, ESA (European Space Agency), is introduced during a Crew-4 press briefing April 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of the agency’s SpaceX Crew-4 launch. Crew-4 is the fourth crew rotation flight to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The SpaceX Crew Dragon capsule will launch atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A to the space station on Wednesday, April 27, at 3:52 a.m. EDT.
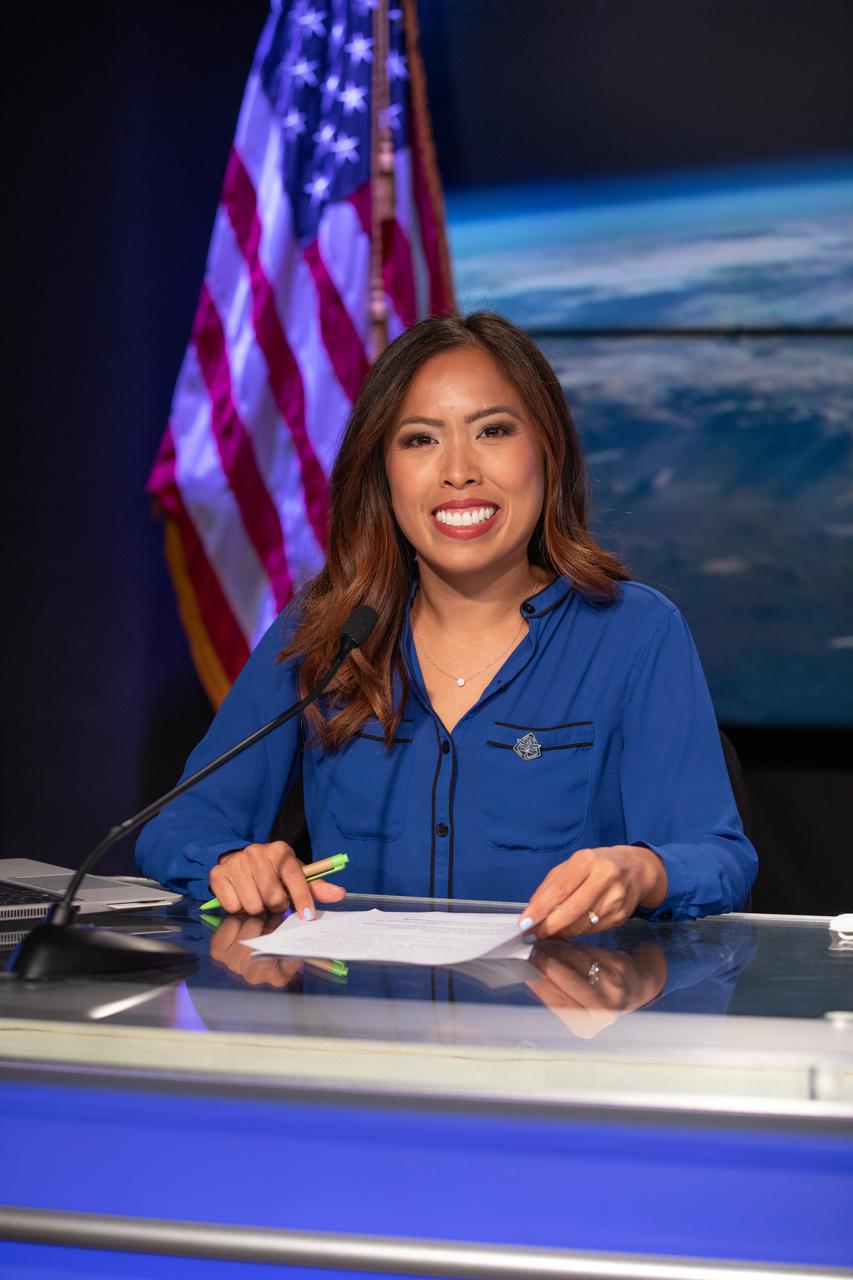

Megan Cruz, NASA Communications, moderates a Crew-4 press briefing April 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of the agency’s SpaceX Crew-4 launch. Crew-4 is the fourth crew rotation flight to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. The SpaceX Crew Dragon capsule will launch atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket from Launch Complex 39A to the space station on Wednesday, April 27, at 3:52 a.m. EDT.
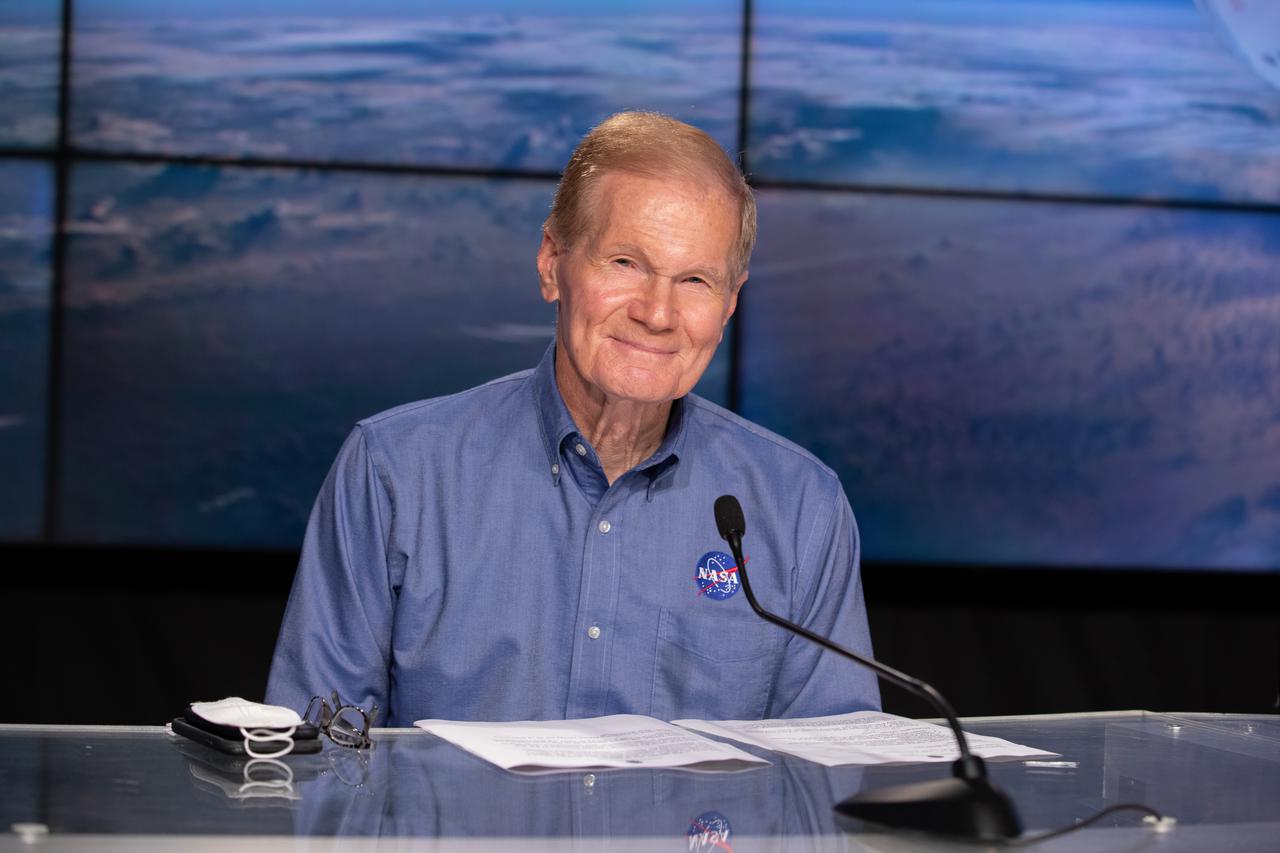

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson is introduced during a Crew-4 press briefing April 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of the agency’s SpaceX Crew-4 launch. NASA astronauts Kjell Lindgren, Bob Hines, and Jessica Watkins, along with ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti, will launch aboard the SpaceX Crew Dragon, named Freedom by the Crew-4 crew, atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket on April 27, 2022, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 3:52 a.m. EDT from Pad 39A.
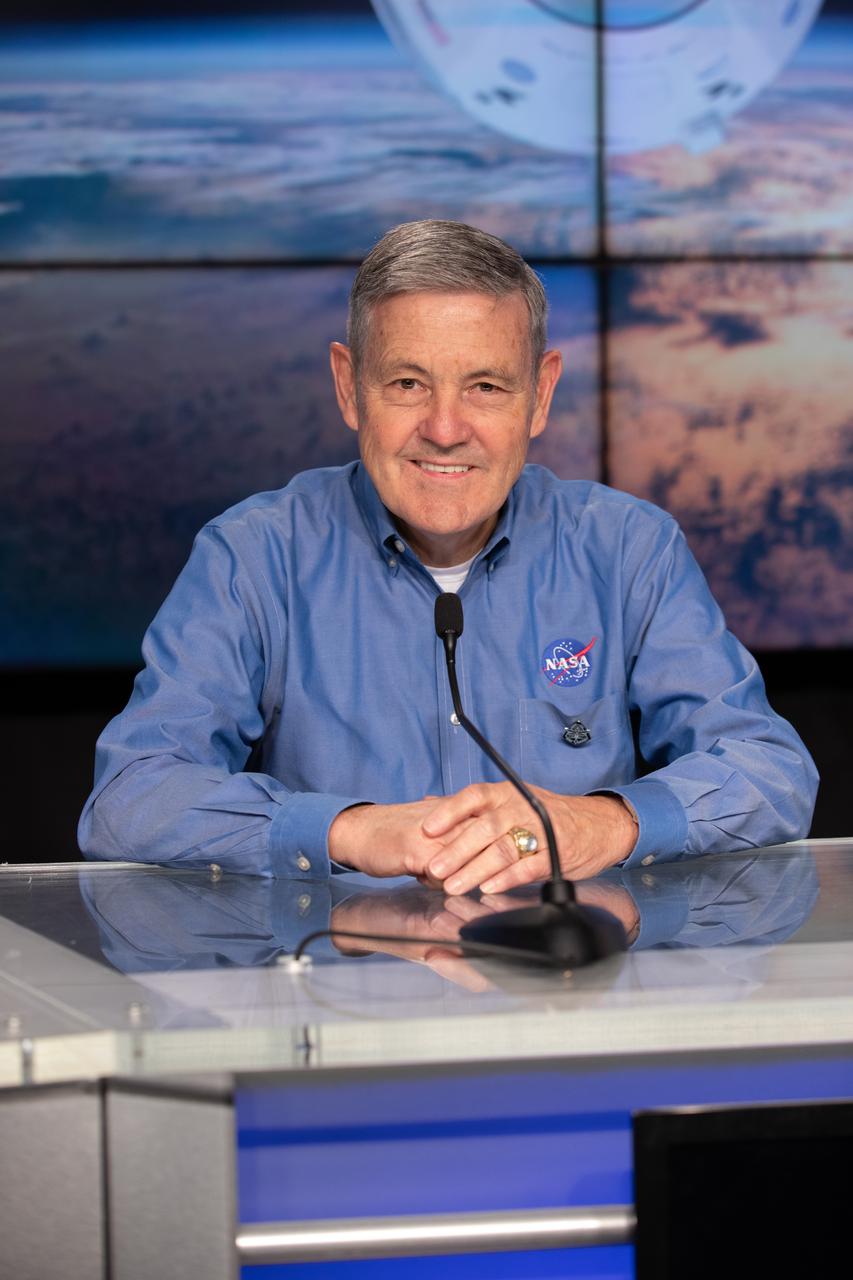

NASA Associate Administrator Bob Cabana is introduced during a Crew-4 press briefing April 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of the agency’s SpaceX Crew-4 launch. NASA astronauts Kjell Lindgren, Bob Hines, and Jessica Watkins, along with ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti, will launch aboard the SpaceX Dragon, named Freedom by the Crew-4 crew, atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket on April 27, 2022, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 3:52 a.m. EDT from Pad 39A.

Heidi Parris, associate program scientist for the International Space Station Program, NASA Johnson, is introduced during a Crew-4 press briefing April 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of the agency’s SpaceX Crew-4 launch. NASA astronauts Kjell Lindgren, Bob Hines, and Jessica Watkins, along with ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti, will launch aboard the SpaceX Dragon, named Freedom by the Crew-4 crew, atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket on April 27, 2022, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 3:52 a.m. EDT from Pad 39A.
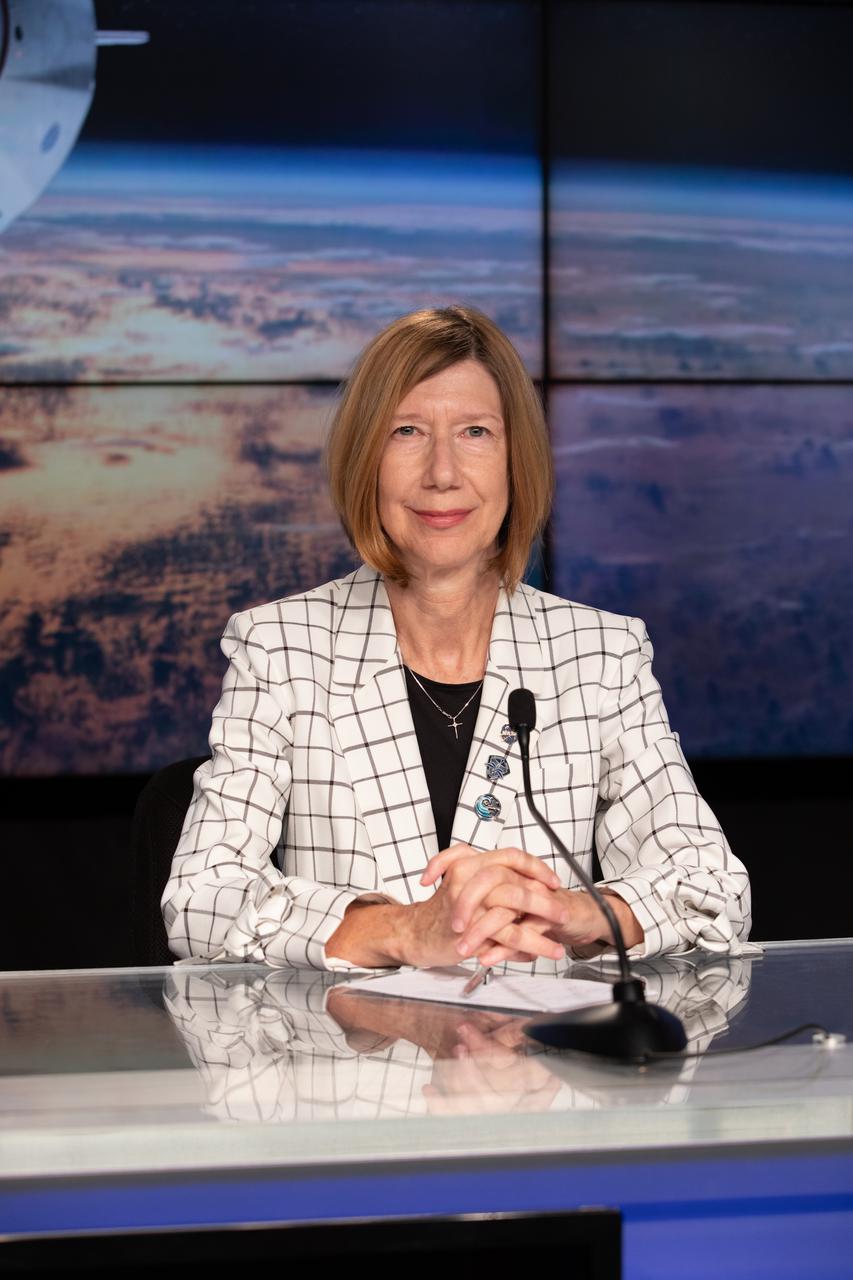

Kathryn Lueders, associate administrator, Space Operations Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters in Washington, is introduced during a Crew-4 press briefing April 26, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida ahead of the agency’s SpaceX Crew-4 launch. NASA astronauts Kjell Lindgren, Bob Hines, and Jessica Watkins, along with ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti, will launch aboard the SpaceX Dragon, named Freedom by the Crew-4 crew, atop the company’s Falcon 9 rocket on April 27, 2022, to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for 3:52 a.m. EDT from Pad 39A.

Crewmates for NASA’s SpaceX Crew-7 mission to the International Space Station walk along the runway at the Launch and Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Aug. 20, 2023. From left, JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Satoshi Furukawa, Roscosmos cosmonaut Konstantin Borisov, NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Andreas Mogensen will launch aboard a SpaceX Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket at 3:49 a.m. EDT Friday, Aug. 25, 2023, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.

The SpaceX Crew-3 astronauts wave to family and friends after walking out through the double doors below the Neil A. Armstrong Building’s Astronaut Crew Quarters at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on launch day, Nov. 10, 2021. They will make their way to the customized Tesla Model X cars that will take them to their spacecraft at Launch Complex 39A. From left are Matthias Maurer, ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut and mission specialist, and NASA astronauts Tom Marshburn; pilot; Raja Chari, commander; and Kayla Barron, mission specialist. The Falcon 9 rocket with Crew Dragon Endurance will launch the four-person crew to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Crew-3 is scheduled to launch at 9:03 p.m. EST from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy.

Seen here is a close-up view of stickers for NASA’s SpaceX Crew-3, Crew-4, and Crew-5 missions that were placed on one of the Tesla Model X cars that carry astronauts from the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building to Launch Complex 39A at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. NASA’s SpaceX Crew-5 astronauts participated in a countdown dress rehearsal on Oct. 2, 2022, in preparation for the upcoming Crew-5 launch. SpaceX’s Crew Dragon Endurance spacecraft will carry NASA astronauts Nicole Aunapu Mann and Josh Cassada, Roscosmos cosmonaut Anna Kikina, and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Koichi Wakata to the International Space Station for a science expedition mission as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Liftoff of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for noon EDT on Oct. 5, 2022, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.

Andrey Fedyaev, Roscosmos cosmonaut and mission specialist for Crew-6, checks his SpaceX spacesuit inside the crew suit-up room in the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a countdown dress rehearsal on Feb. 23, 2023, to prepare for the upcoming Crew-6 launch. Fedyaev, along with NASA astronaut Stephen Bowen, spacecraft commander; NASA astronaut Warren “Woody” Hoburg, pilot; and Sultan Alneyadi, UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut and mission specialist will launch to the International Space Station aboard the Crew Dragon Endeavour on a SpaceX Falcon 9. Launch is targeted for 1:45 a.m. EST on Feb. 27 from Launch Complex 39A. Crew-6 is the sixth crew rotation mission with SpaceX to the station, and the seventh flight of Dragon with people as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
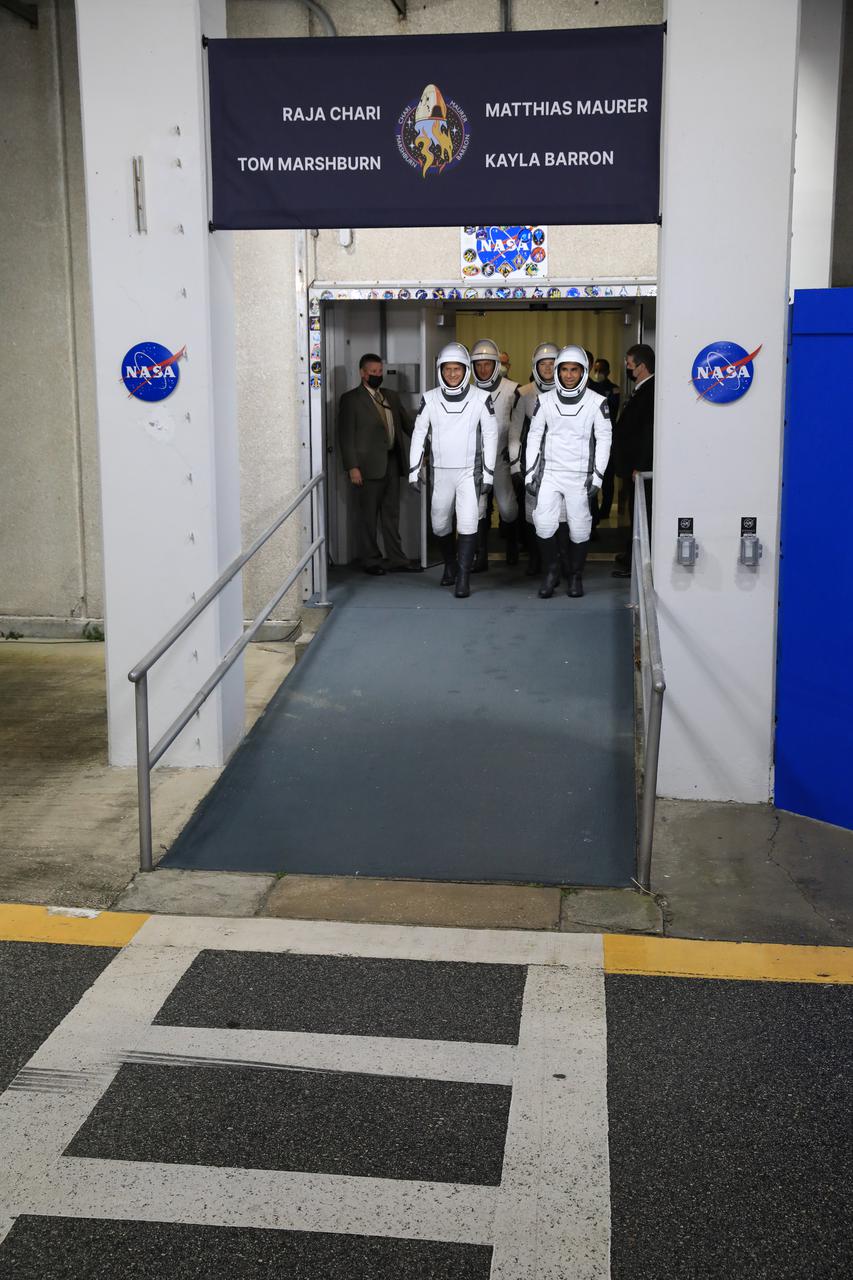

The SpaceX Crew-3 astronauts walk out through the double doors below the Neil A. Armstrong Building’s Astronaut Crew Quarters at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 10, 2021. They will make their way to the customized Tesla Model X cars that will take them to their spacecraft at Launch Complex 39A. In front, from left, are NASA astronauts Tom Marshburn, pilot, and Raja Chari, commander. Behind them, from left, are Matthias Maurer, ESA (European Space Agency astronaut) and mission specialist; and NASA astronaut Kayla Barron, mission specialist. The Falcon 9 rocket with Crew Dragon Endurance will launch the four-person crew to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Crew-3 is scheduled to launch at 9:03 p.m. EST from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy.
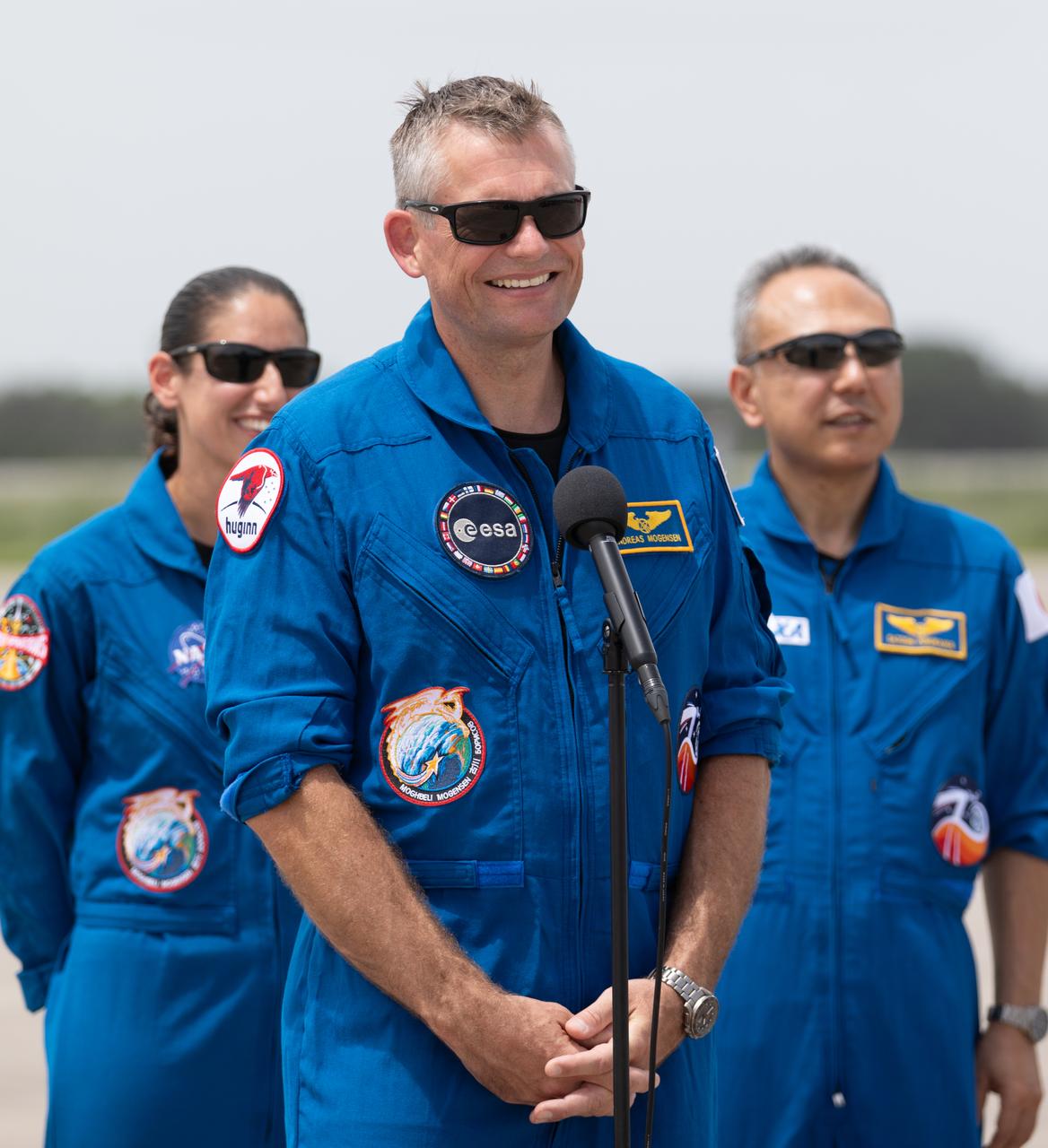

ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Andreas Mogensen addresses members of the news media during NASA’s SpaceX Crew-7 crew arrival event at the Launch and Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Aug. 20, 2023. In the background, from left, is NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Satoshi Furukawa. Liftoff for the Crew-7 mission is targeted for 3:49 a.m. EDT Friday, Aug. 25, 2023, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
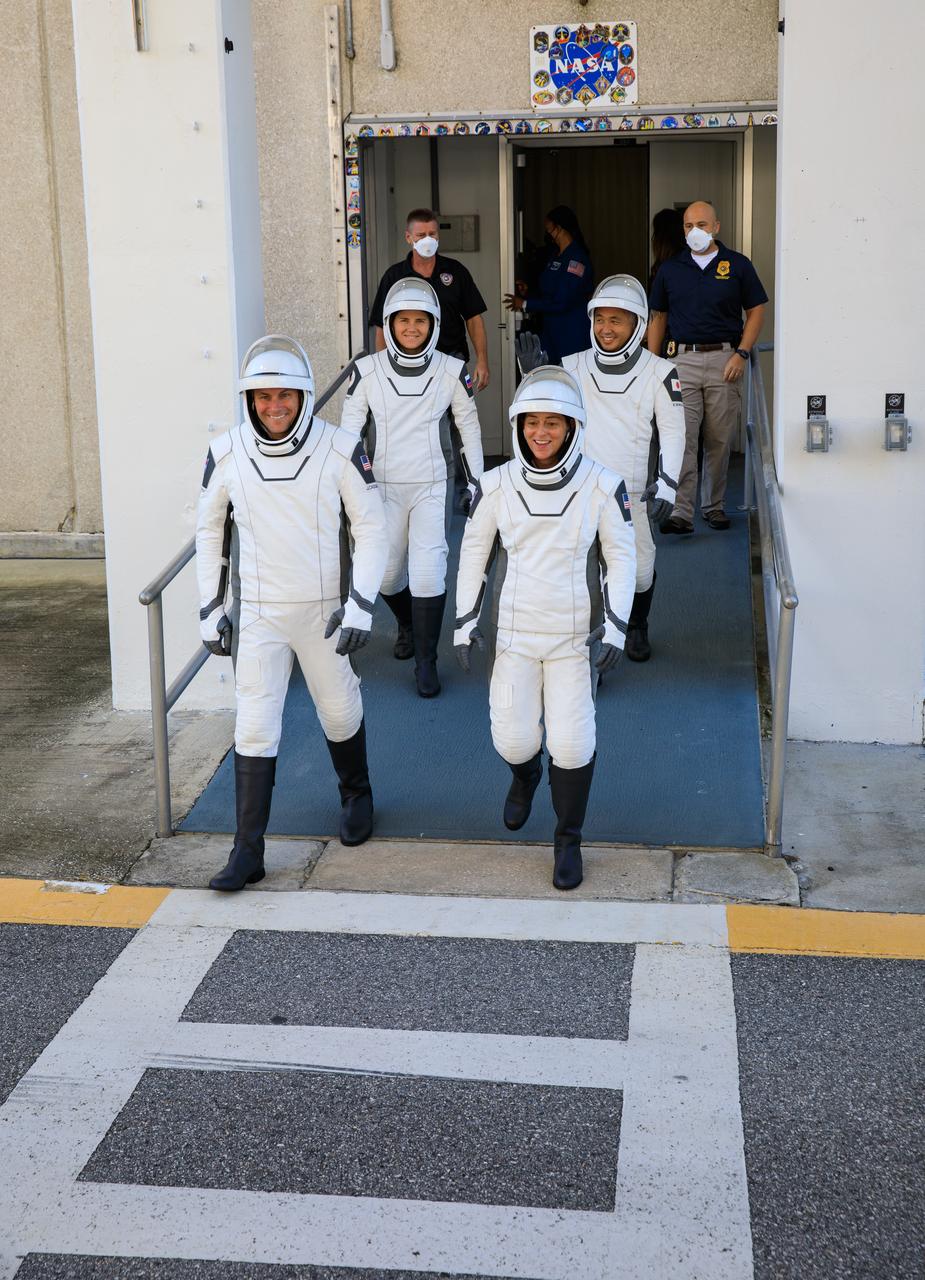

NASA’s SpaceX Crew-5 astronauts walk out of the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a countdown dress rehearsal on Oct. 2, 2022, to prepare for the upcoming Crew-5 launch. In front are NASA astronauts Josh Cassada (left) and Nicole Aunapu Mann, and behind them are Roscosmos cosmonaut Anna Kikina (left) and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Koichi Wakata. The crew will launch to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s Crew Dragon Endurance spacecraft for a science expedition mission as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Liftoff of SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for noon EDT on Oct. 5, 2022, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
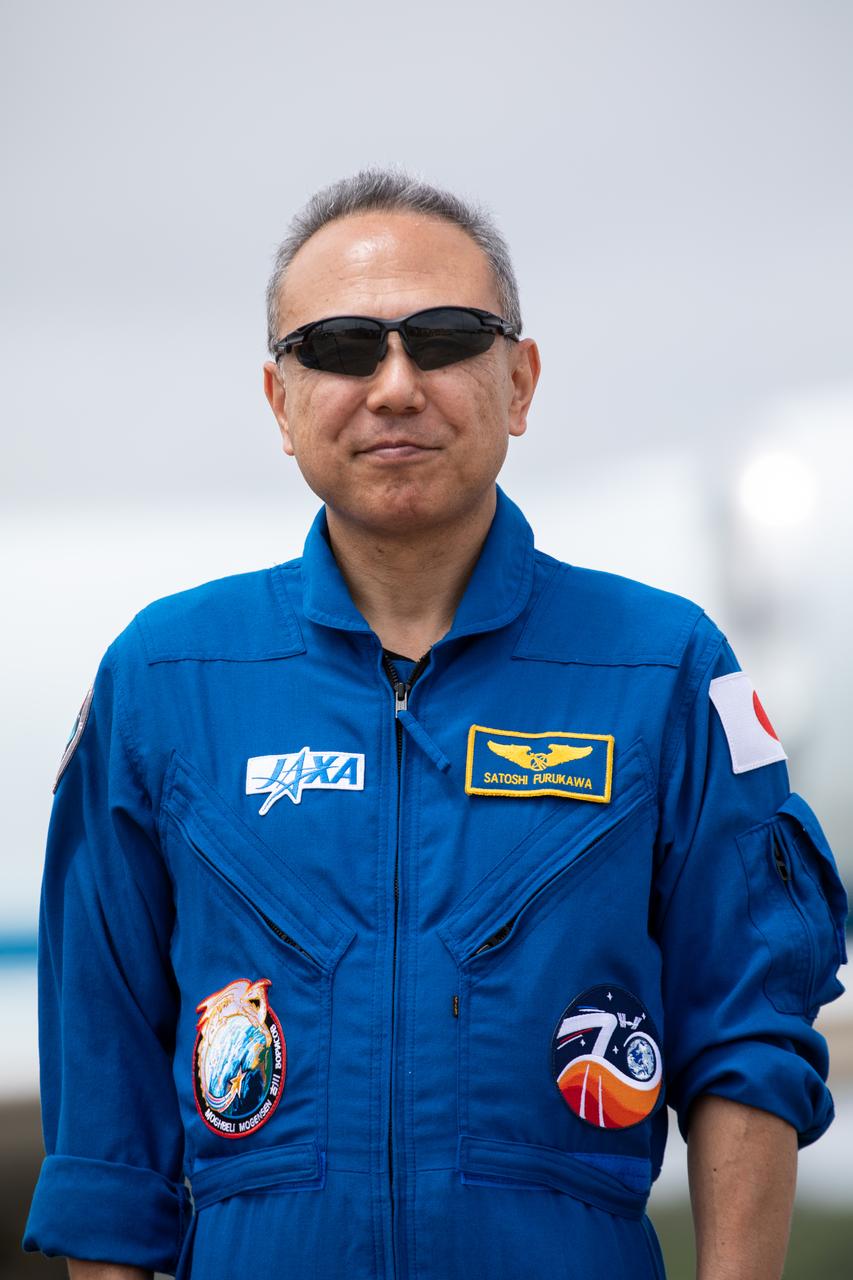

NASA’s SpaceX Crew-7 crew member and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Satoshi Furukawa smiles to the crowd after arriving at the Launch and Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida – along with the rest of his crewmates – on Sunday, Aug. 20, 2023. Crew-7 will launch to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft on the company’s Falcon 9 rocket. Liftoff is targeted for 3:49 a.m. EDT Friday, Aug. 25, 2023, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
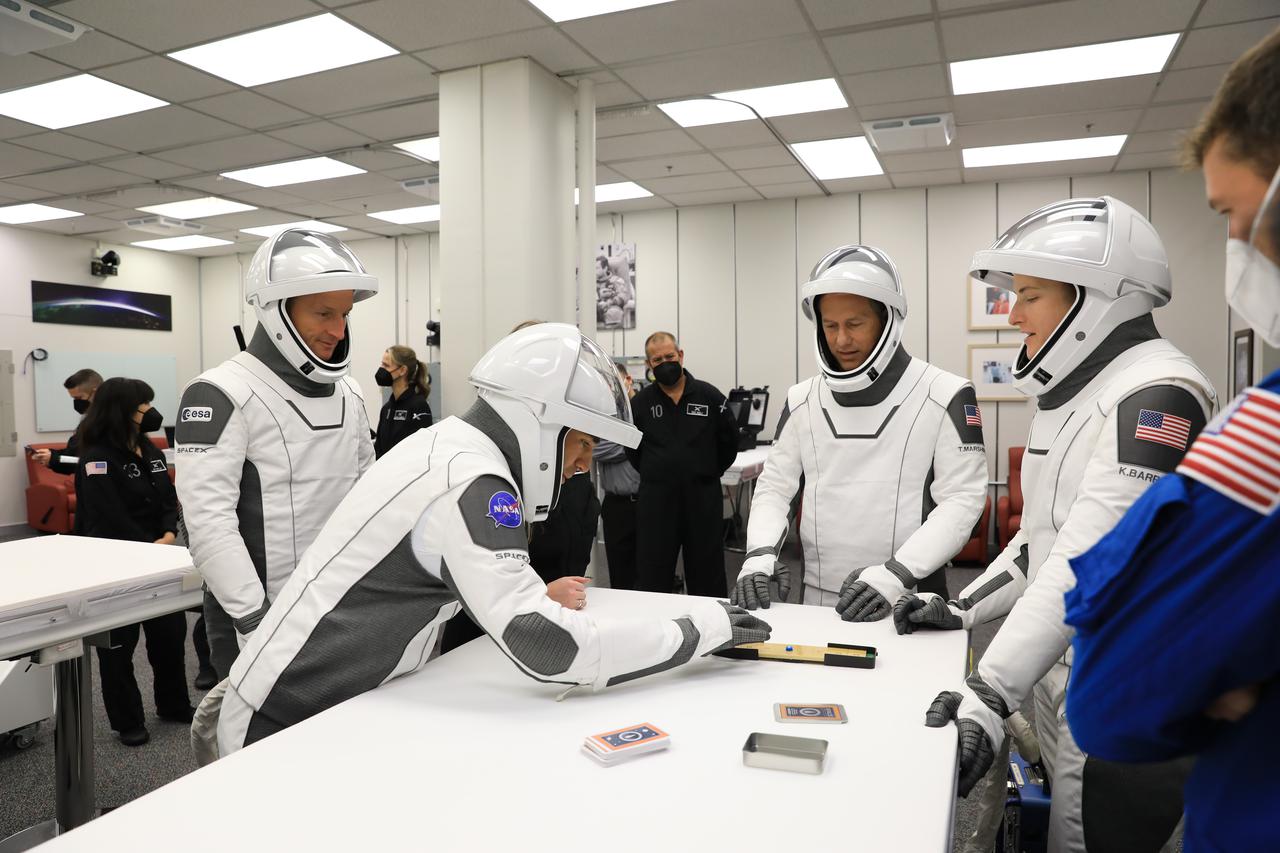

NASA SpaceX Crew-3 mission astronauts play a game while inside the suit-up room in the Astronaut Crew Quarters at Kennedy Space Center’s Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on launch day, Nov. 10, 2021. The Falcon 9 rocket with Crew Dragon Endurance will launch Crew-3 astronauts Raja Chari, Thomas Marshburn, Kayla Barron and Matthias Maurer to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Crew-3 is scheduled to launch at 9:03 p.m. EST from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy.
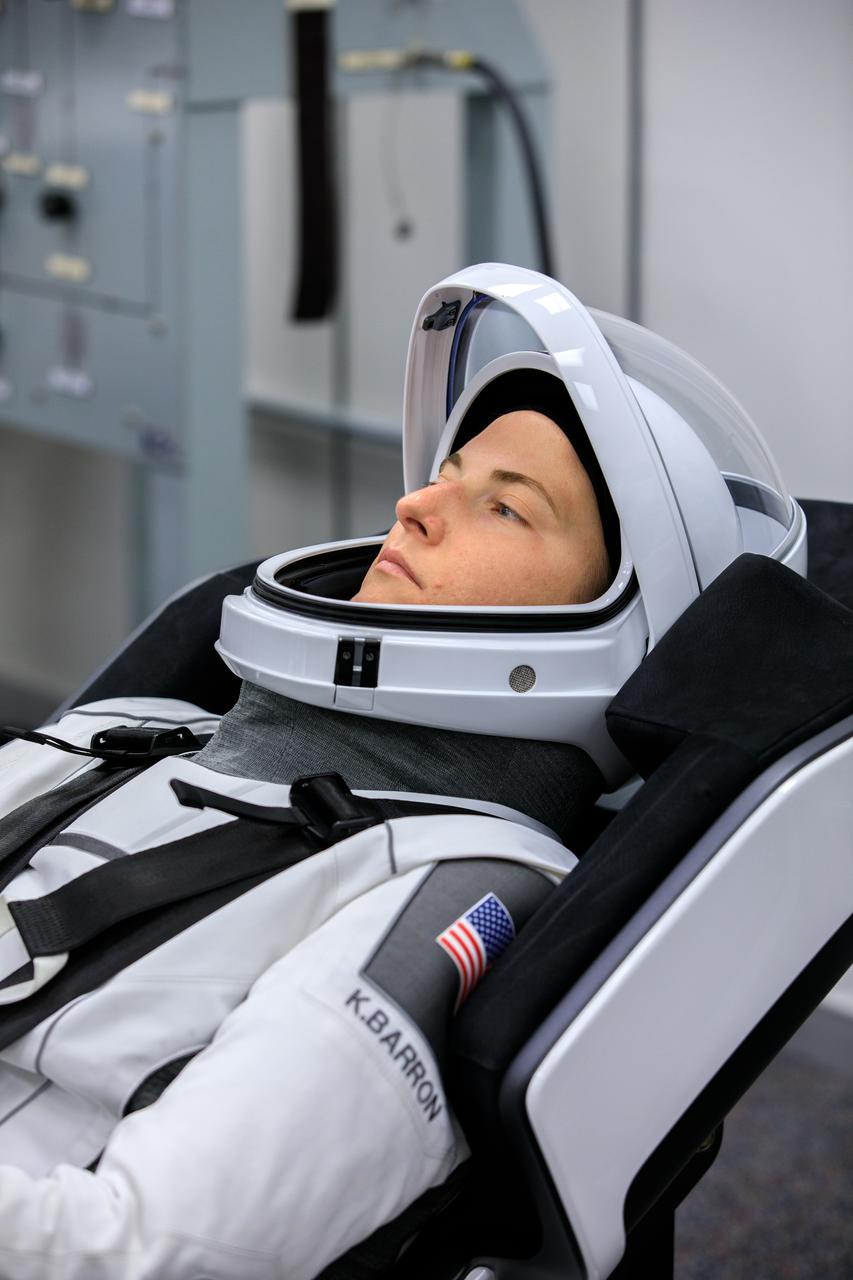

NASA SpaceX Crew-3 mission astronauts are in the suit-up room in the Astronaut Crew Quarters inside Kennedy Space Center’s Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on launch day, Nov. 10, 2021. A team of SpaceX suit technicians will help them as they put on their custom-fitted spacesuits and check the suits for leaks. In view is NASA astronaut Kayla Barron, mission specialist. The Falcon 9 rocket with Crew Dragon Endurance will launch the four-person crew to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Crew-3 is scheduled to launch at 9:03 p.m. EST from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy.

Deputy Chief Scientist of NASA’s Human Research Program Kristin Fabre participates in a social media panel discussion inside the John Holliman Auditorium of the News Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 28, 2024, ahead of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-8 mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff of the eighth crew rotation mission with SpaceX to the station and the ninth flight of Dragon with people as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A is targeted for 12:04 a.m. on Friday, March 1.

A postlaunch news conference is hosted at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Saturday, Sept. 28, 2024, following the launch of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission. Participants include Derrol Nail, NASA Communications; NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Melroy; Ken Bowersox, associate administrator, NASA’s Space Operations Mission Directorate; Dana Hutcherson, deputy manager, NASA’s Commercial Crew Program; Dina Contella, deputy manager, NASA’s International Space Station Program; Sarah Walker, director, Dragon Mission Management, SpaceX. NASA astronaut Nick Hague and Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov launched to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket from nearby Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station at 1:17 p.m. EDT on the ninth crew rotation mission with SpaceX to the space station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
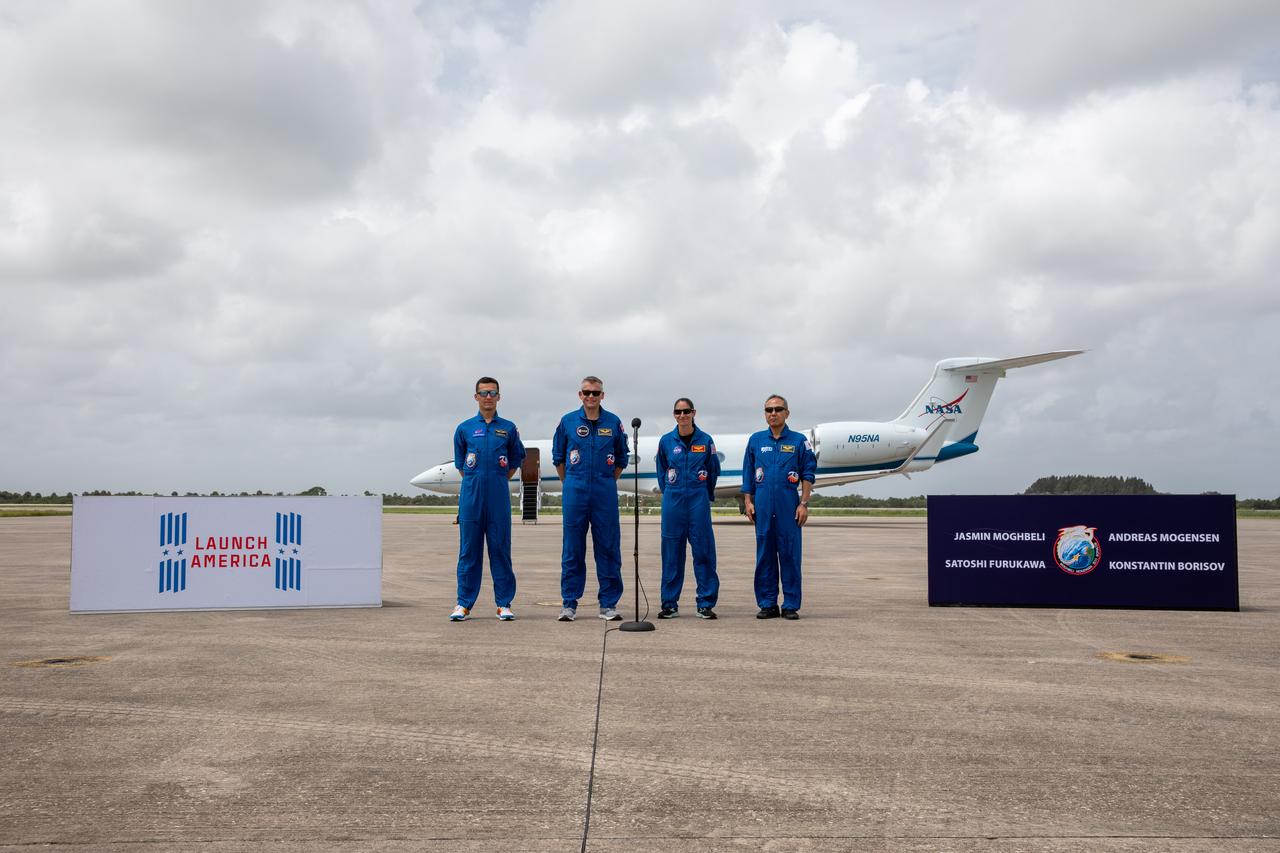

Crew members for NASA’s SpaceX Crew-7 mission to the International Space Station arrive at the Launch and Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Aug. 20, 2023. From left, Roscosmos cosmonaut Konstantin Borisov, ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Andreas Mogensen, NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli, and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Satoshi Furukawa stand before members of the news media. Liftoff of the Crew-7 mission is targeted for 3:49 a.m. EDT Friday, Aug. 25, 2023, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
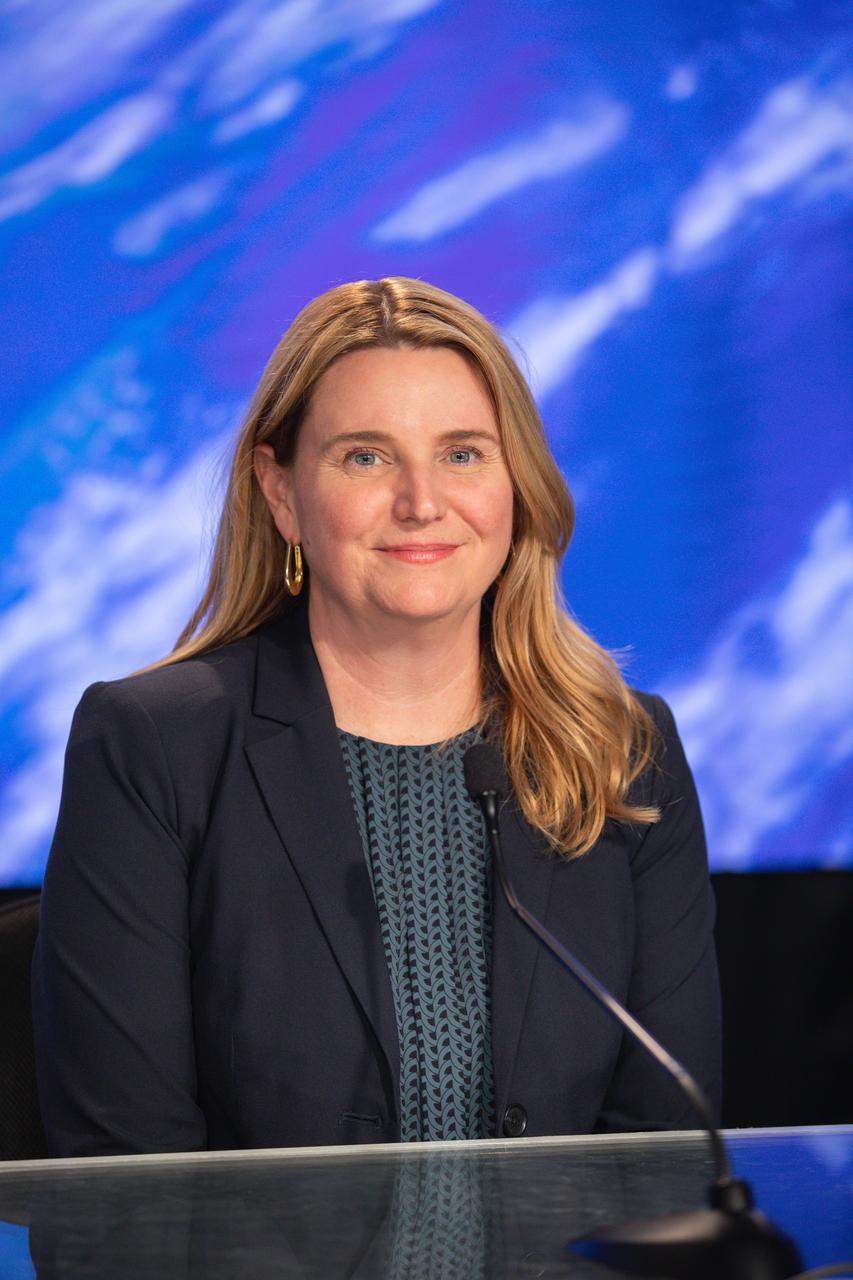

Jennifer Buchli, chief scientist, NASA’s International Space Station Program, participates in an International Space Station 101 Panel Livestream inside the John Holliman Auditorium of the News Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Sept. 27, 2024, ahead of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff of the ninth crew rotation mission with SpaceX to the space station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program is targeted for 1:17 p.m. EDT Sept. 28, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.

NASA’s SpaceX Crew-4 flag is raised near the News Center countdown clock at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 19, 2022. The SpaceX Falcon 9 with Crew Dragon, named Freedom by the Crew-4 crew, atop is scheduled to lift off Saturday, April 23, 2002, at 5:26 p.m. EDT, from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy. Dragon will carry NASA astronauts Kjell Lindgren, Bob Hines, and Jessica Watkins, and ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Samantha Cristoforetti to the International Space Station as part of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program.

A social media panel discussion takes place inside the John Holliman Auditorium of the News Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Wednesday, Feb. 28, 2024, ahead of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-8 mission to the International Space Station. Participants, from left to right are Jasmine Hopkins, NASA Communications; NASA Associate Administrator Jim Free; Carla Koch, mission manager of NASA’s Commercial Crew Program; Jennifer Buchli, chief scientist, International Space Station; Kristin Fabre, deputy chief scientist of NASA’s Human Research Program; and Patrick O’Neill, public affairs and outreach lead of the ISS National Laboratory. Liftoff of the eighth crew rotation mission with SpaceX to the station and the ninth flight of Dragon with people as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A is targeted for 12:04 a.m. on Friday, March 1.
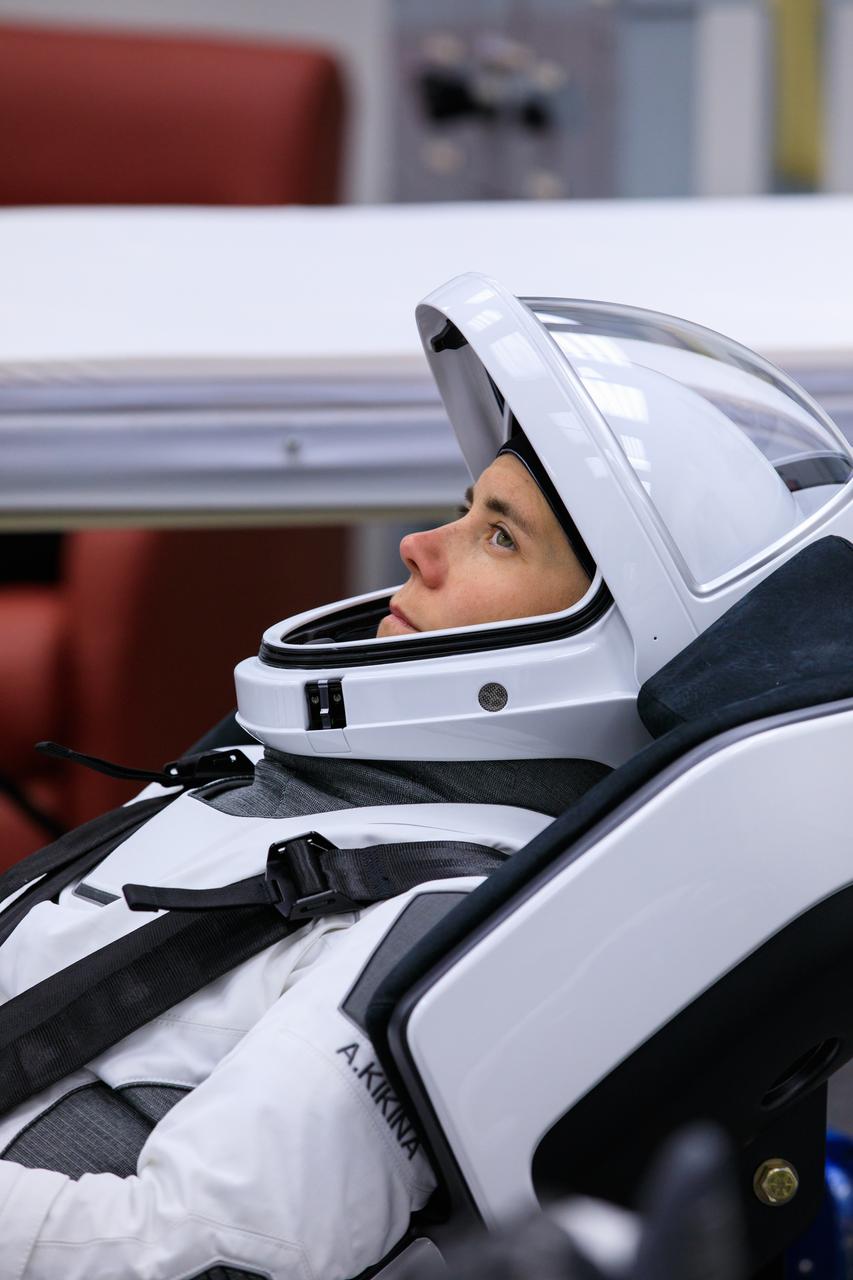

Roscosmos cosmonaut Anna Kikina is seated inside the crew suit-up room in the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a countdown dress rehearsal on Oct. 2, 2022. Kikina, along with NASA astronauts Josh Cassada and Nicole Aunapu Mann, and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Koichi Wakata will launch to the International Space Station on NASA’s SpaceX Crew-5 mission as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program. Liftoff of SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket and Crew Dragon Endurance spacecraft is targeted for noon EDT on Oct. 5, 2022, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.
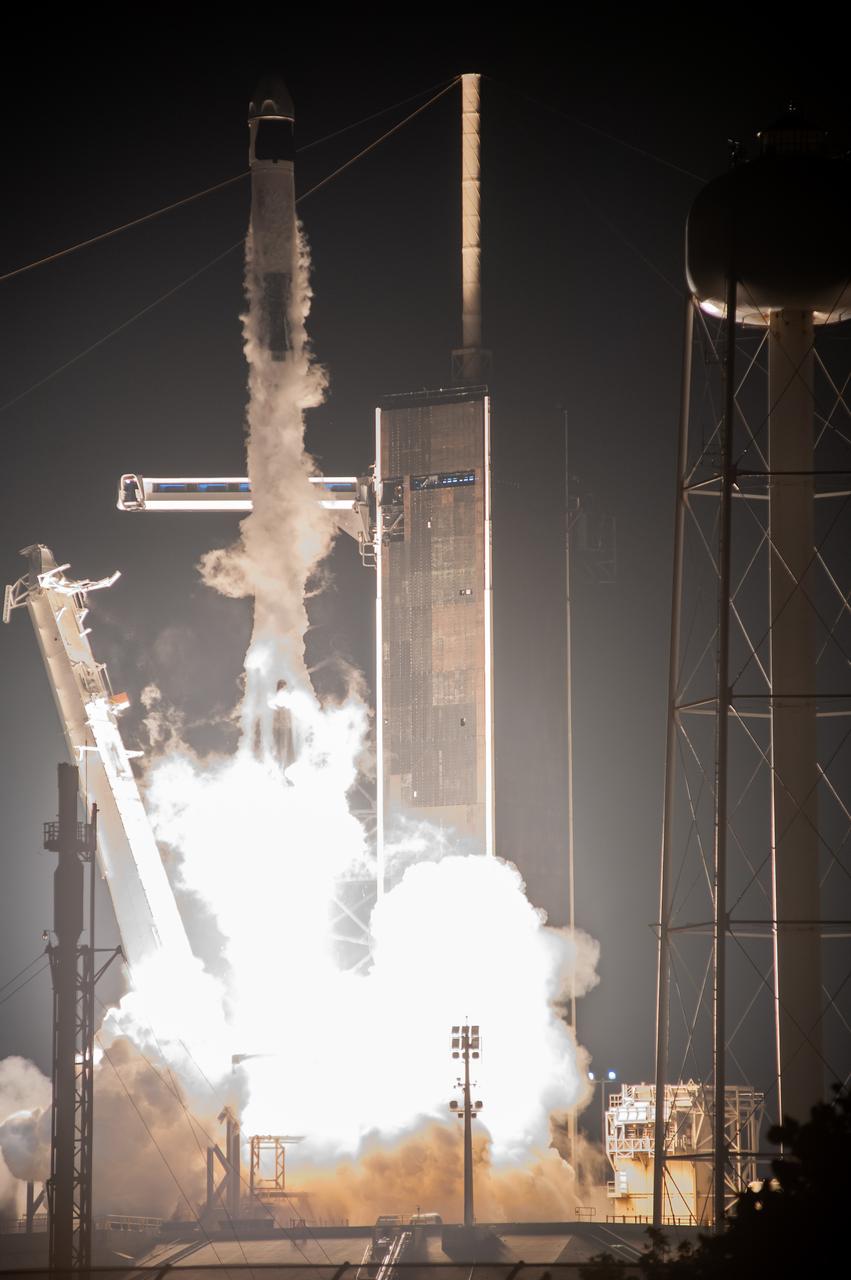

A SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket lifts off the pad at Launch Complex 39A at 12:34 a.m. EST on March 2, 2023 carrying the Dragon spacecraft Endeavour for NASA’s Crew-6 mission to the International Space Station. Aboard Dragon are NASA astronauts, Stephen Bowen, spacecraft commander, and Woody Hoburg, pilot, along with mission specialists Sultan Alneyadi, UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut, and Andrey Fedyaev, Roscosmos cosmonaut. Crew-6 is the sixth crew rotation mission with SpaceX to the station, and the seventh flight of Dragon with people as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.

NASA Associate Administrator Jim Free addresses the media during a prelaunch news conference at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Sept. 27, 2024, ahead of the agency’s SpaceX Crew-9 launch. NASA astronaut Nick Hague and Roscosmos cosmonaut Aleksandr Gorbunov will launch to the International Space Station aboard SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft and Falcon 9 rocket. Launch is targeted for 1:17 p.m. EDT Sept. 28, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. Crew-9 is the ninth crew rotation mission with SpaceX to the space station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
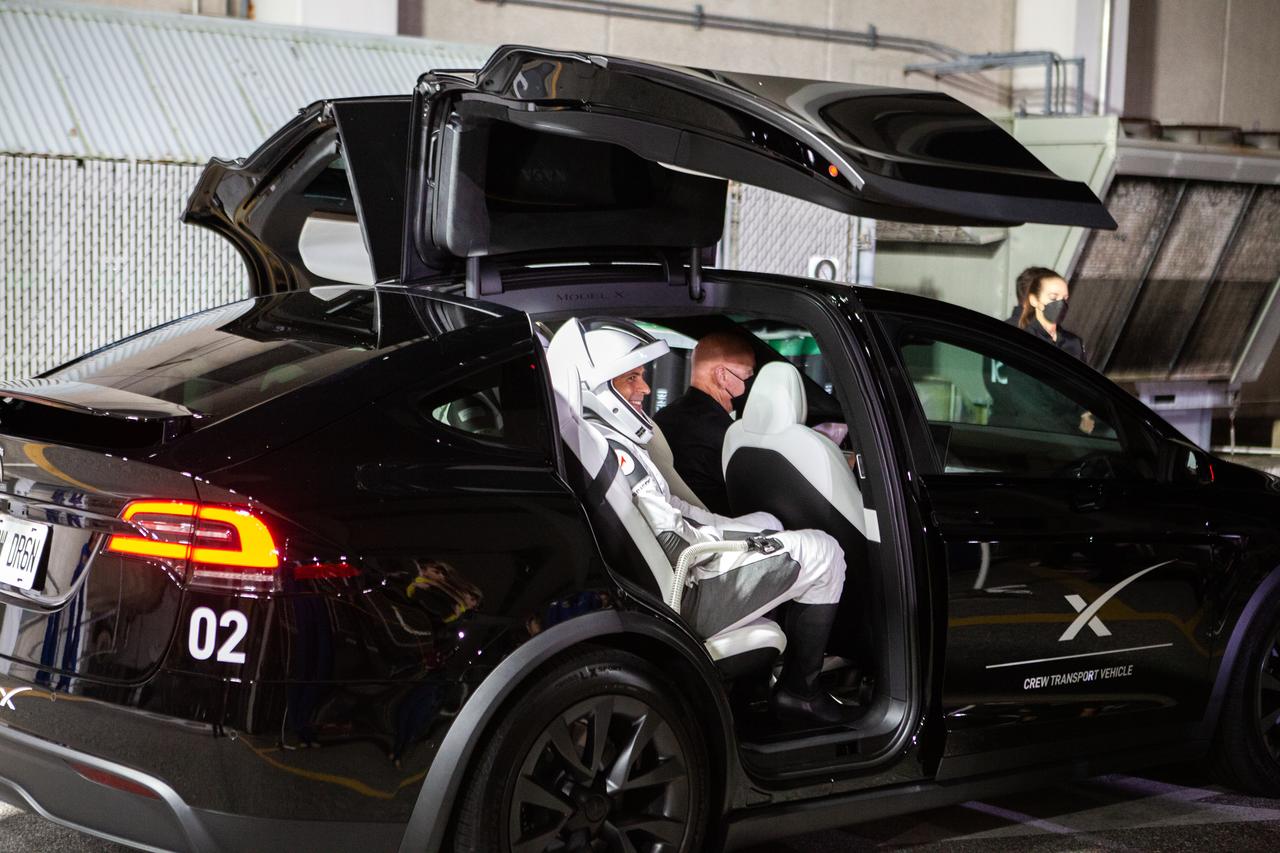

In view outside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 1, 2023, SpaceX Crew-6 astronauts board the first of two Tesla vehicles that will transport NASA’s them to Launch Complex 39A for launch to the International Space Station. Launch of the Dragon spacecraft Endeavour atop the Falcon 9 rocket is targeted for 12:34 a.m. EST on March 2 from Launch Complex 39A. Crew-6 is the sixth crew rotation mission with SpaceX to the station, and the seventh flight of Dragon with people as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.
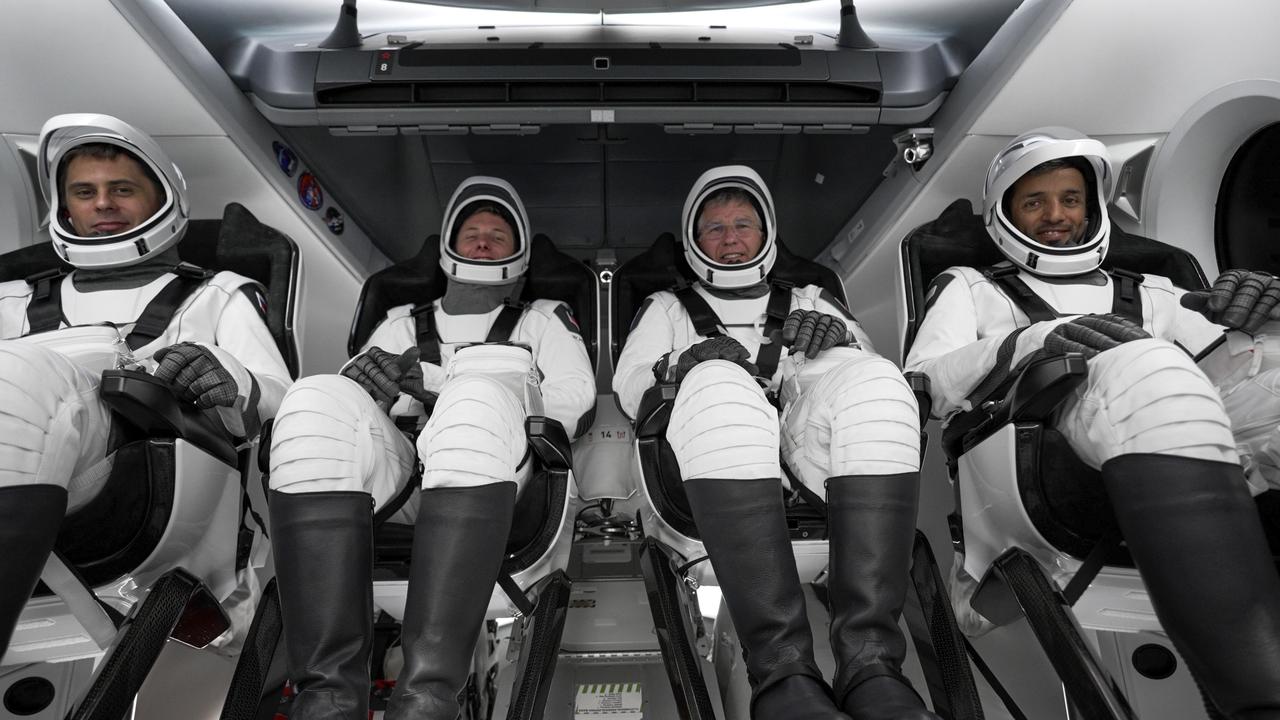

NASA’s SpaceX Crew-6 astronauts are secured in their seats inside the Dragon spacecraft Endeavour. From left are Andrey Fedyaev, Roscosmos cosmonaut and mission specialist; NASA astronaut Warren “Woody” Hoburg, pilot; NASA astronaut Stephen Bowen, spacecraft commander; and Sultan Alneyadi, UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut and mission specialist. The Crew-6 astronauts will launch to the International Space Station aboard the Crew Dragon Endeavour on a SpaceX Falcon 9. Launch was targeted for 1:45 a.m. EST on Feb. 27 from Launch Complex 39A, but was scrubbed for the day. Crew-6 is the sixth crew rotation mission with SpaceX to the station, and the seventh flight of Dragon with people as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program.

John Posey, Dragon engineer, NASA’s Commercial Crew Program, participates in an International Space Station 101 Panel Livestream inside the John Holliman Auditorium of the News Center at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Friday, Sept. 27, 2024, ahead of NASA’s SpaceX Crew-9 mission to the International Space Station. Liftoff of the ninth crew rotation mission with SpaceX to the space station as part of the agency’s Commercial Crew Program is targeted for 1:17 p.m. EDT Sept. 28, 2024, from Space Launch Complex-40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.

Crew members for NASA’s SpaceX Crew-7 mission to the International Space Station arrive at the Launch and Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Sunday, Aug. 20, 2023. From left, Roscosmos cosmonaut Konstantin Borisov, ESA (European Space Agency) astronaut Andreas Mogensen, NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli, and JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) astronaut Satoshi Furukawa stand before members of the news media. Liftoff of the Crew-7 mission is targeted for 3:49 a.m. EDT Friday, Aug. 25, 2023, from Kennedy’s Launch Complex 39A.

NASA SpaceX Crew-3 mission astronauts play a game while inside the suit-up room in the Astronaut Crew Quarters at Kennedy Space Center’s Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on launch day, Nov. 10, 2021. The Falcon 9 rocket with Crew Dragon Endurance will launch Crew-3 astronauts Raja Chari, Thomas Marshburn, Kayla Barron and Matthias Maurer to the International Space Station for NASA’s Commercial Crew Program. Crew-3 is scheduled to launch at 9:03 p.m. EST from Launch Complex 39A at Kennedy.