
President Barack Obama delivers remarks at the National Medals of Science and National Medals of Technology and Innovation Awards Ceremony, Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, was awarded the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor, at the ceremony. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

President Barack Obama delivers remarks at the National Medals of Science and National Medals of Technology and Innovation Awards Ceremony, Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, was awarded the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor, at the ceremony. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

President Barack Obama delivers remarks at the National Medals of Science and National Medals of Technology and Innovation Awards Ceremony, Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, was awarded the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor, at the ceremony. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

President Barack Obama delivers remarks at the National Medals of Science and National Medals of Technology and Innovation Awards Ceremony, Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, was awarded the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor, at the ceremony. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
President Barack Obama delivers remarks at the National Medals of Science and National Medals of Technology and Innovation Awards Ceremony, Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, was awarded the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor, at the ceremony. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
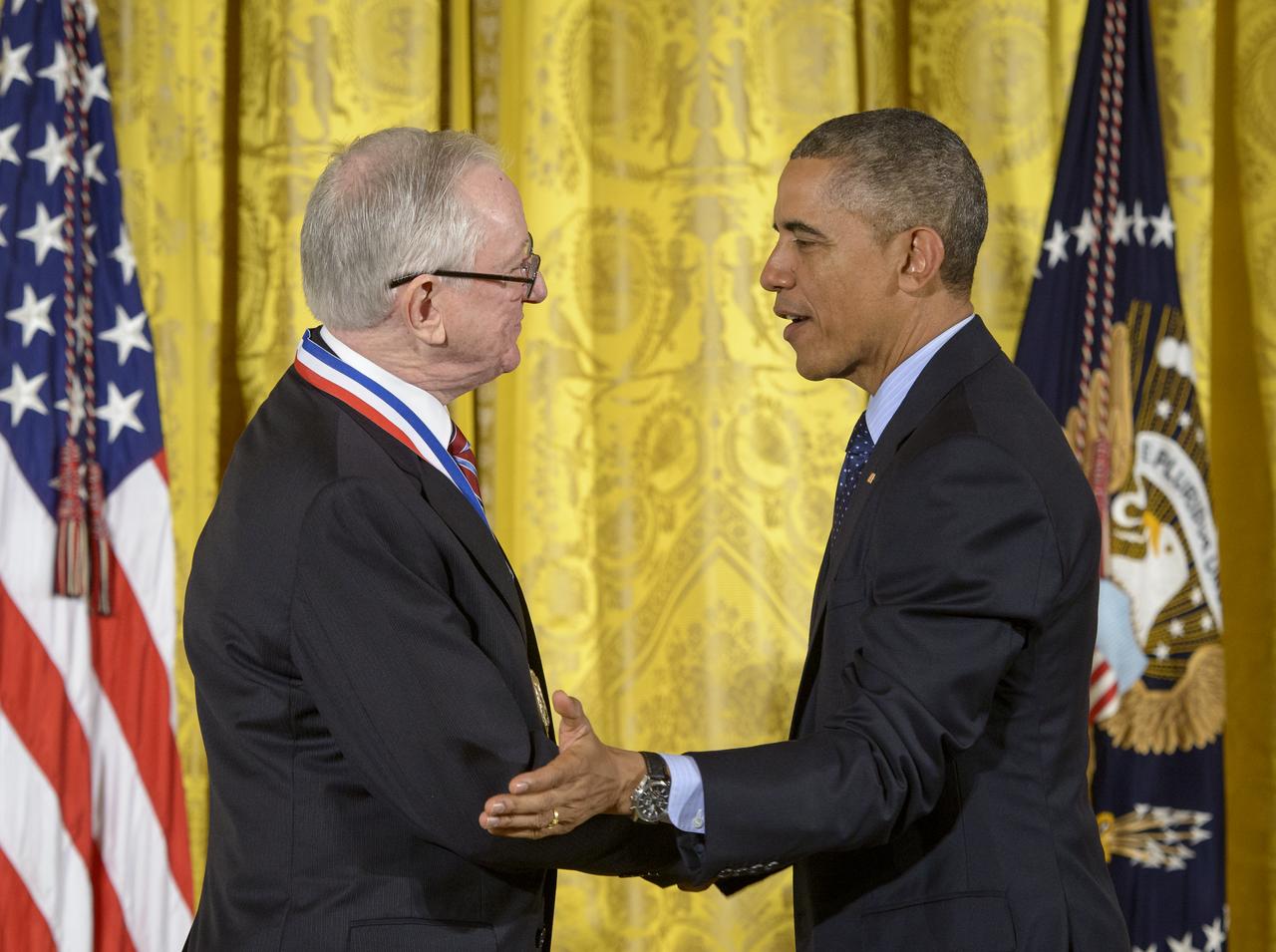

President Barack Obama congratulates MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, after awarding him the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor,Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 during a ceremony in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

President Barack Obama, right, and MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, listen as a citation is read prior to the President bestowing the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor to Solomon, Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 during a ceremony in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
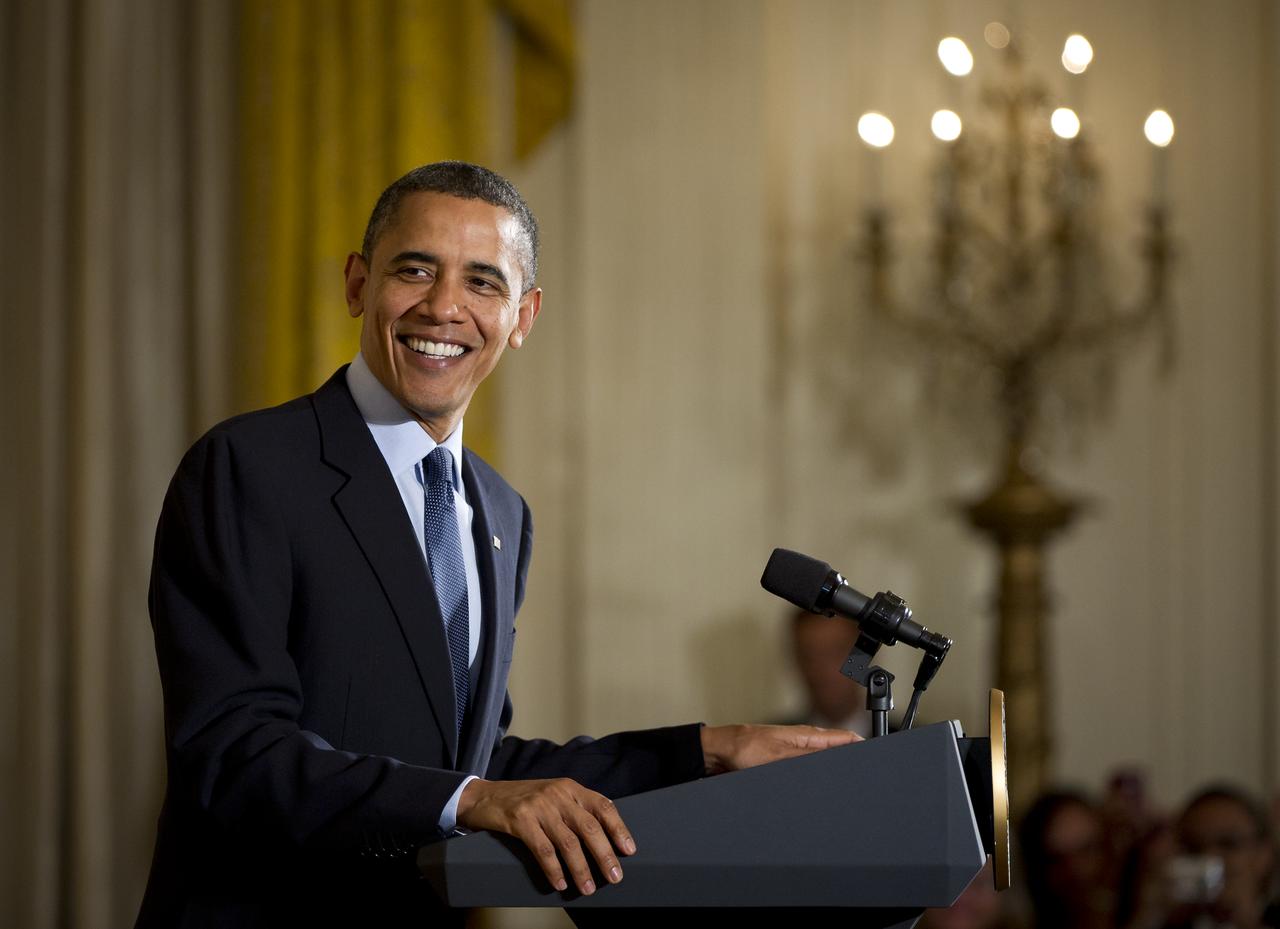

U.S. President Barack Obama smiles during a ceremony for recipients of the National Medal of Science and the National Medal of Technology and Innovation, the highest honors bestowed by the United States government on scientists, engineers, and inventors, at the White House in Washington, Wednesday, Nov. 17, 2010. Amongst those in attendance where NASA Administrator Charles Bolden and NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
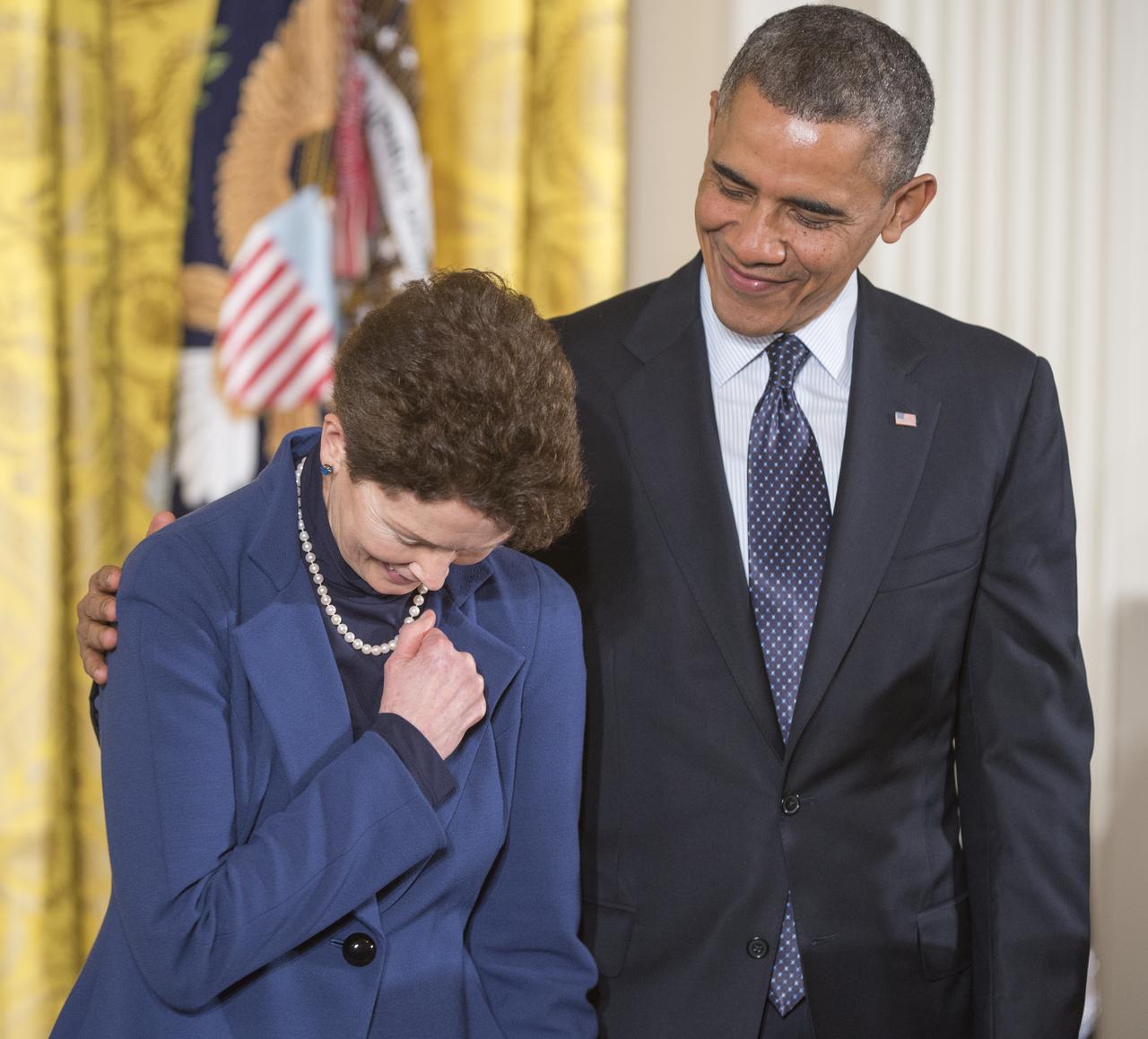

Tam O'Shaughnessy, Sally Ride's life partner and chair, board of directors of Sally Ride Science, is seen with President Barack Obama as she prepares to accept the Presidential Medal of Freedom on behalf of Dr. Ride, Wednesday, Nov. 20, 2013 at the White House in Washington. Sally Ride, who was awarded the Medal of Freedom posthumously, was the first American female astronaut to travel to space. As a role model to generations of young women, she advocated passionately for science education, stood up for racial and gender equality in the classroom, and taught students from every background that there are no limits to what they can accomplish. The Medal of Freedom is our Nation’s highest civilian honor, presented to individuals who have made especially meritorious contributions to the security or national interests of the United States, to world peace, or to cultural or other significant public or private endeavors. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)

Tam O'Shaughnessy, Sally Ride's life partner and chair, board of directors of Sally Ride Science, is seen with President Barack Obama as she prepares to accept the Presidential Medal of Freedom on behalf of Dr. Ride, Wednesday, Nov. 20, 2013 at the White House in Washington. Sally Ride, who was awarded the Medal of Freedom posthumously, was the first American female astronaut to travel to space. As a role model to generations of young women, she advocated passionately for science education, stood up for racial and gender equality in the classroom, and taught students from every background that there are no limits to what they can accomplish. The Medal of Freedom is our Nation’s highest civilian honor, presented to individuals who have made especially meritorious contributions to the security or national interests of the United States, to world peace, or to cultural or other significant public or private endeavors. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
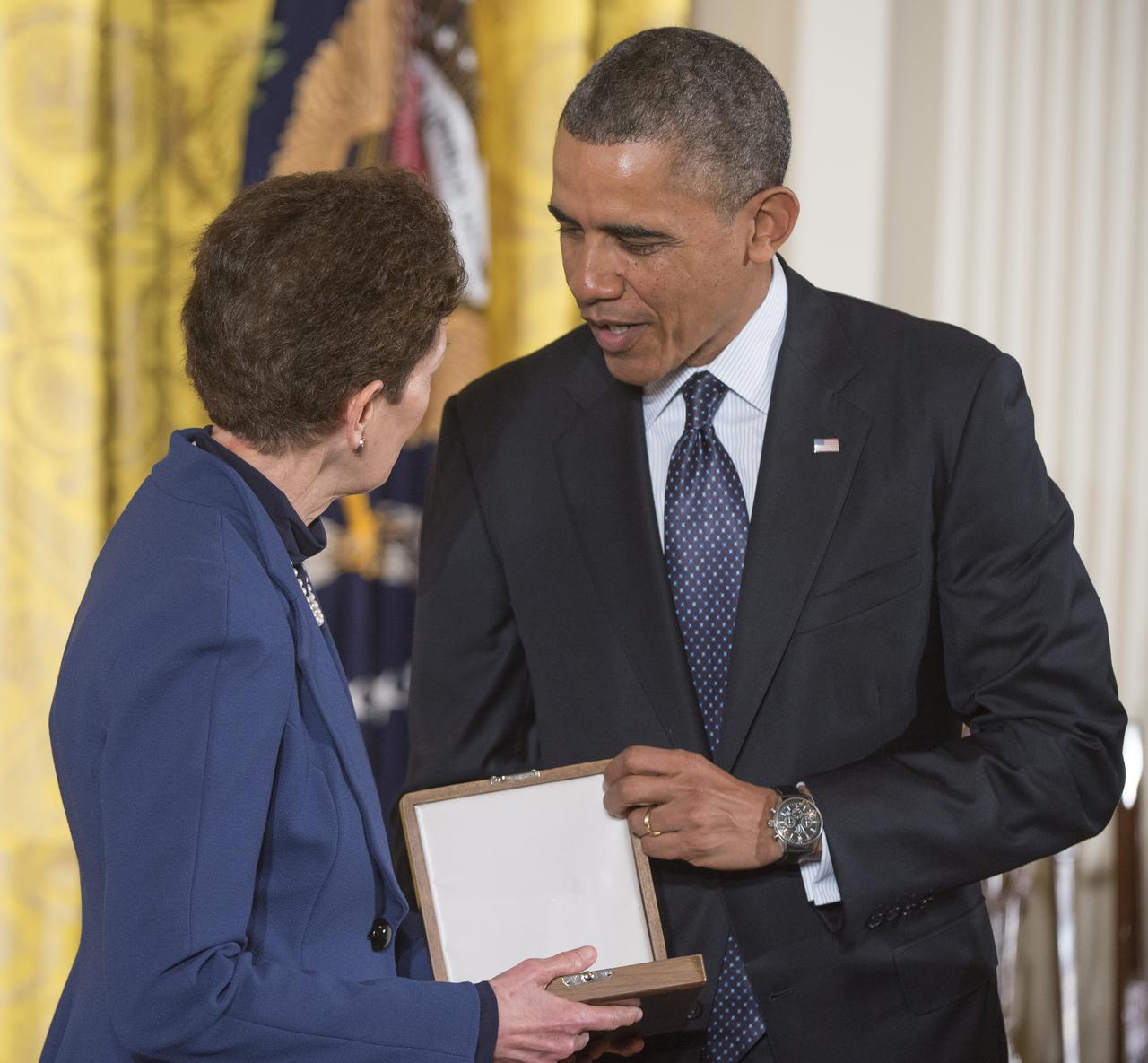

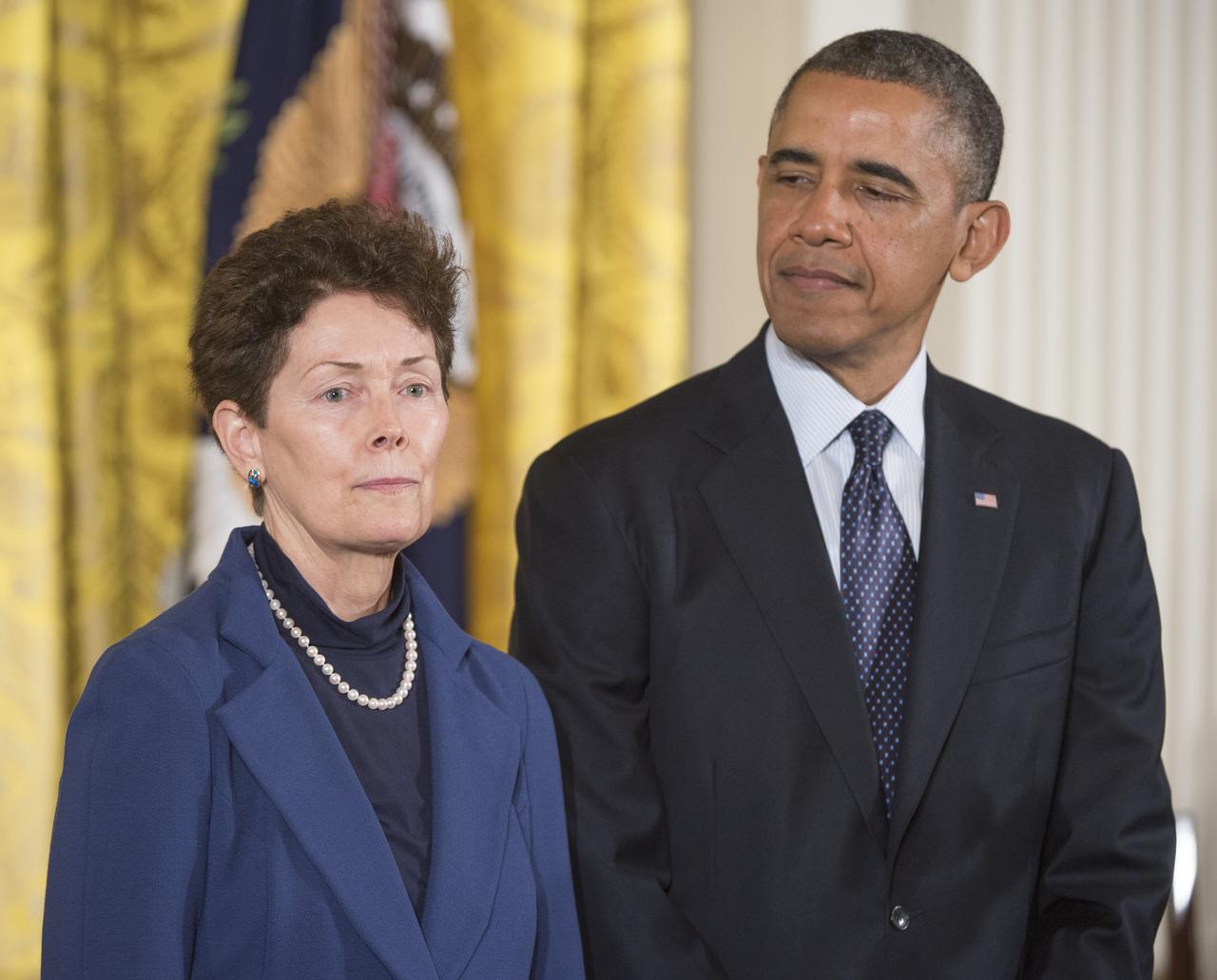
Tam O'Shaughnessy, Sally Ride's life partner and chair, board of directors of Sally Ride Science, is seen with President Barack Obama as she accepts the Presidential Medal of Freedom on behalf of Dr. Ride, Wednesday, Nov. 20, 2013 at the White House in Washington. Sally Ride, who was awarded the Medal of Freedom posthumously, was the first American female astronaut to travel to space. As a role model to generations of young women, she advocated passionately for science education, stood up for racial and gender equality in the classroom, and taught students from every background that there are no limits to what they can accomplish. The Medal of Freedom is our Nation’s highest civilian honor, presented to individuals who have made especially meritorious contributions to the security or national interests of the United States, to world peace, or to cultural or other significant public or private endeavors. Photo Credit: (NASA/Carla Cioffi)
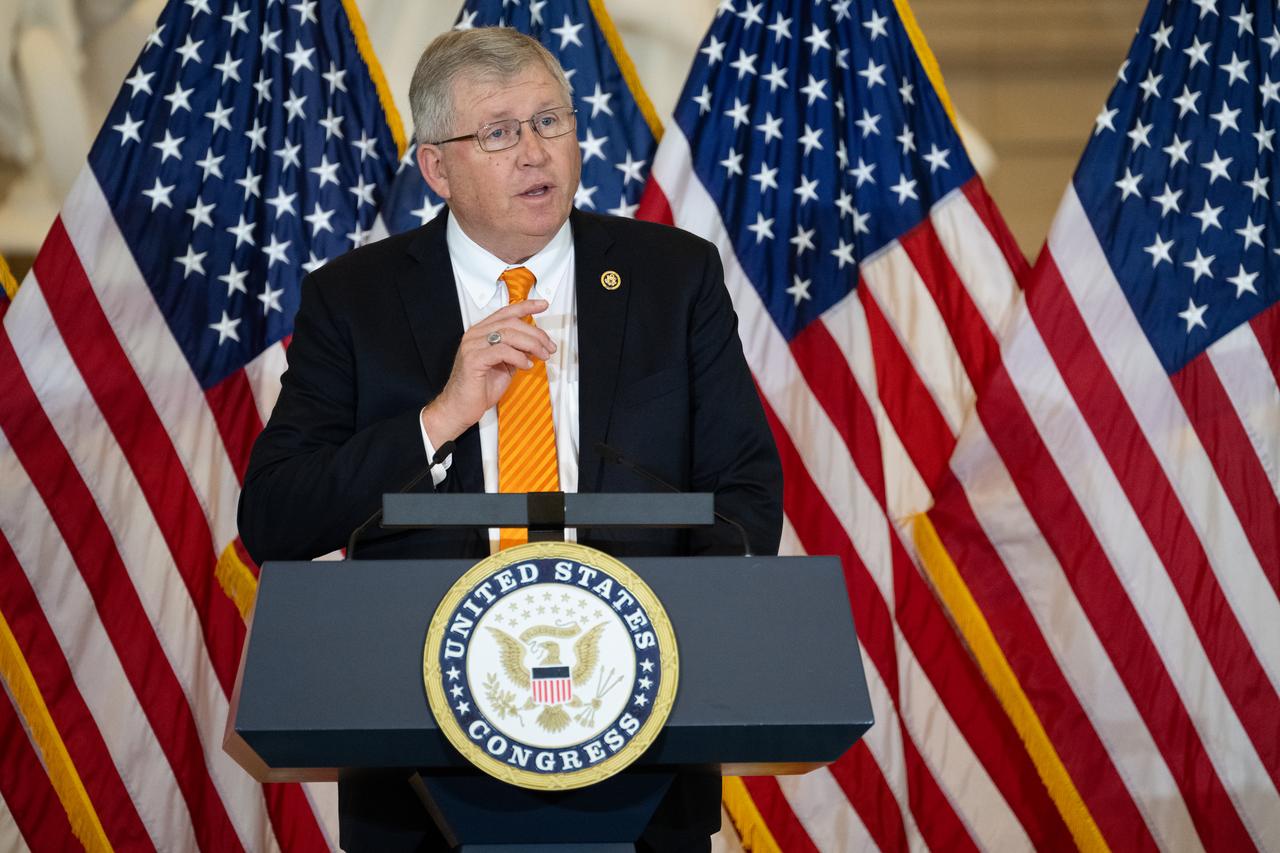

Rep. Frank Lucas, (R-OK) Chairman of the House Committee on Science, Space, and Technology, deliveres remarks during a Congressional Gold Medal ceremony recognizing NASA’s Hidden Figures, Wednesday, Sept. 18, 2024, in Emancipation Hall at the U.S. Capitol in Washington. Congressional Gold Medals were awarded to Katherine Johnson, Dr. Christine Darden, Dorothy Vaughan, and Mary W. Jackson in recognition of their service to the United States as well as a Congressional Gold Medal in recognition of all the women who served as computers, mathematicians, and engineers at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics and NASA between the 1930s and 1970s. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
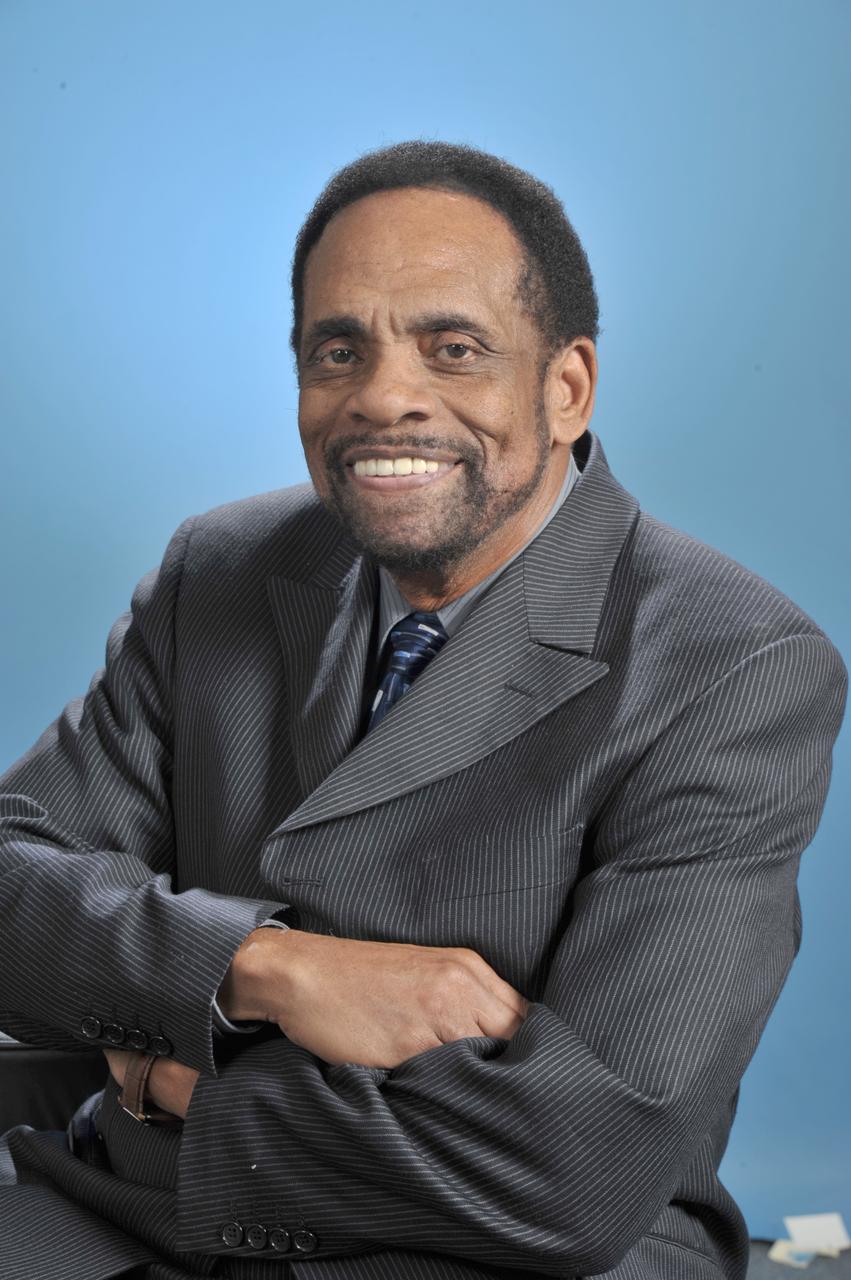

George Edward Alcorn, a pioneering African American physicist and engineer, is credited with dozens of inventions over the course of a distinguished career in private industry and at NASA, for which he earned eight patents. Alcorn joined Goddard Space Flight Center in 1978 and held numerous leadership roles in both research and administration until his retirement in 2012. One of Alcorn’s signature accomplishments at NASA was developing a smaller, more sensitive X-ray spectrometer, changing the way scientists were able to use the powerful tool in deep space exploration missions. His tool, which uses thermomigration of aluminum, can gather information about remote solar systems; for the invention, Alcorn was honored as the NASA Goddard Inventor of the Year in 1984. In addition to his groundbreaking contributions as an inventor and innovator, Alcorn also championed efforts to hire more women and minorities at Goddard, for which he was honored with the NASA Equal Opportunity Medal, and taught students at Howard University and the University of the District of Columbia. He also founded the Saturday Academy, an honors program in math and science for underserved middle school students. He earned many accolades over the years from NASA and beyond. These include, in 2010, the Robert H. Goddard Award for Merit, for his outstanding innovation and significant contributions to space science, technology, and NASA programs, as well as recognition in 1994 at Howard University’s Heritage of Greatness awards ceremony. He was also inducted into the National Inventor’s Hall of Fame in 2015. Alcorn passed away in 2024 at the age of 84.
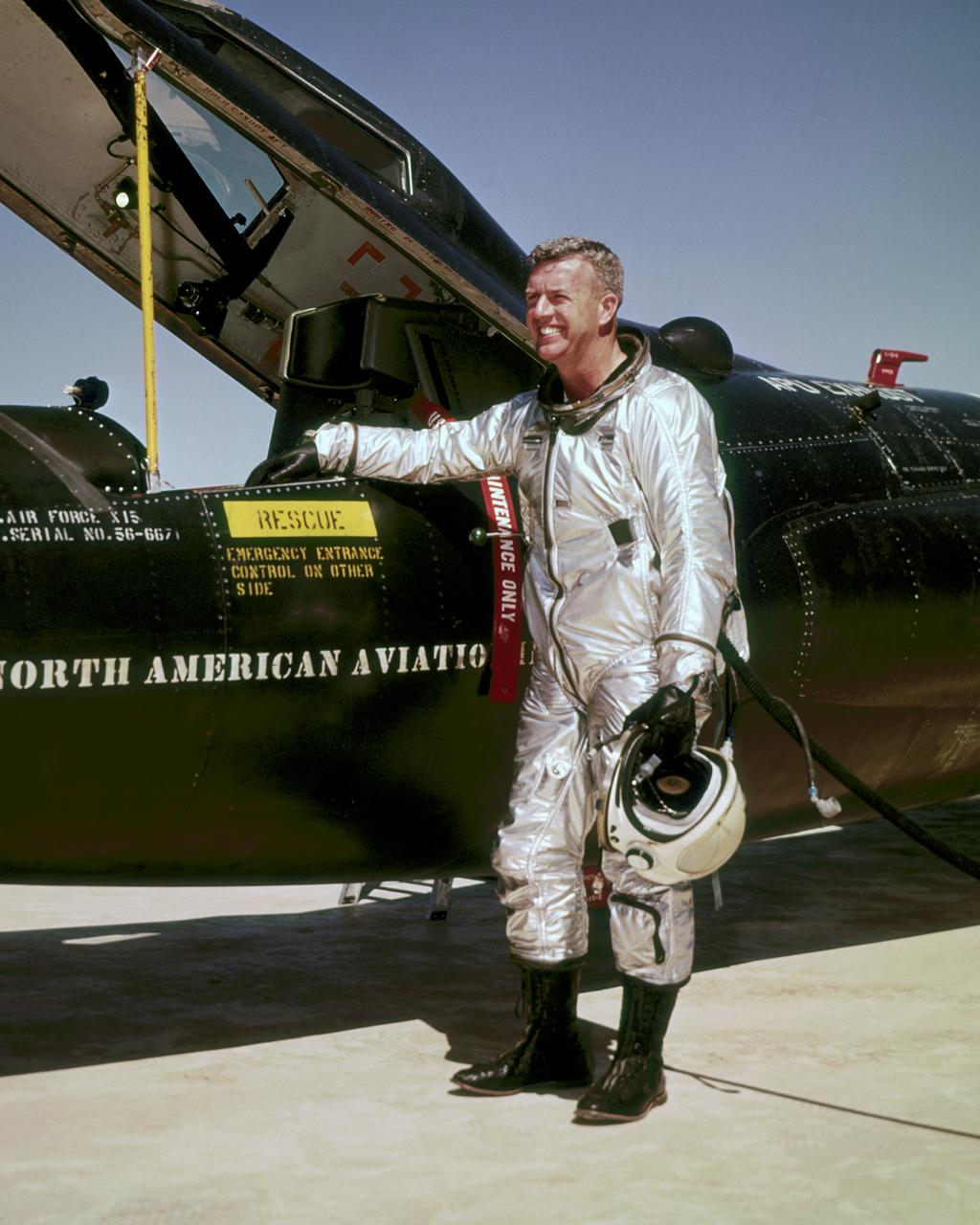

Joseph A. Walker was a Chief Research Pilot at the NASA Dryden Flight Research Center during the mid-1960s. He joined the NACA in March 1945, and served as project pilot at the Edwards flight research facility on such pioneering research projects as the D-558-1, D-558-2, X-1, X-3, X-4, X-5, and the X-15. He also flew programs involving the F-100, F-101, F-102, F-104, and the B-47. Walker made the first NASA X-15 flight on March 25, 1960. He flew the research aircraft 24 times and achieved its fastest speed and highest altitude. He attained a speed of 4,104 mph (Mach 5.92) during a flight on June 27, 1962, and reached an altitude of 354,300 feet on August 22, 1963 (his last X-15 flight). He was the first man to pilot the Lunar Landing Research Vehicle (LLRV) that was used to develop piloting and operational techniques for lunar landings. Walker was born February 20, 1921, in Washington, Pa. He lived there until graduating from Washington and Jefferson College in 1942, with a B.A. degree in Physics. During World War II he flew P-38 fighters for the Air Force, earning the Distinguished Flying Cross and the Air Medal with Seven Oak Clusters. Walker was the recipient of many awards during his 21 years as a research pilot. These include the 1961 Robert J. Collier Trophy, 1961 Harmon International Trophy for Aviators, the 1961 Kincheloe Award and 1961 Octave Chanute Award. He received an honorary Doctor of Aeronautical Sciences degree from his alma mater in June of 1962. Walker was named Pilot of the Year in 1963 by the National Pilots Association. He was a charter member of the Society of Experimental Test Pilots, and one of the first to be designated a Fellow. He was fatally injured on June 8, 1966, in a mid-air collision between an F-104 he was piloting and the XB-70.