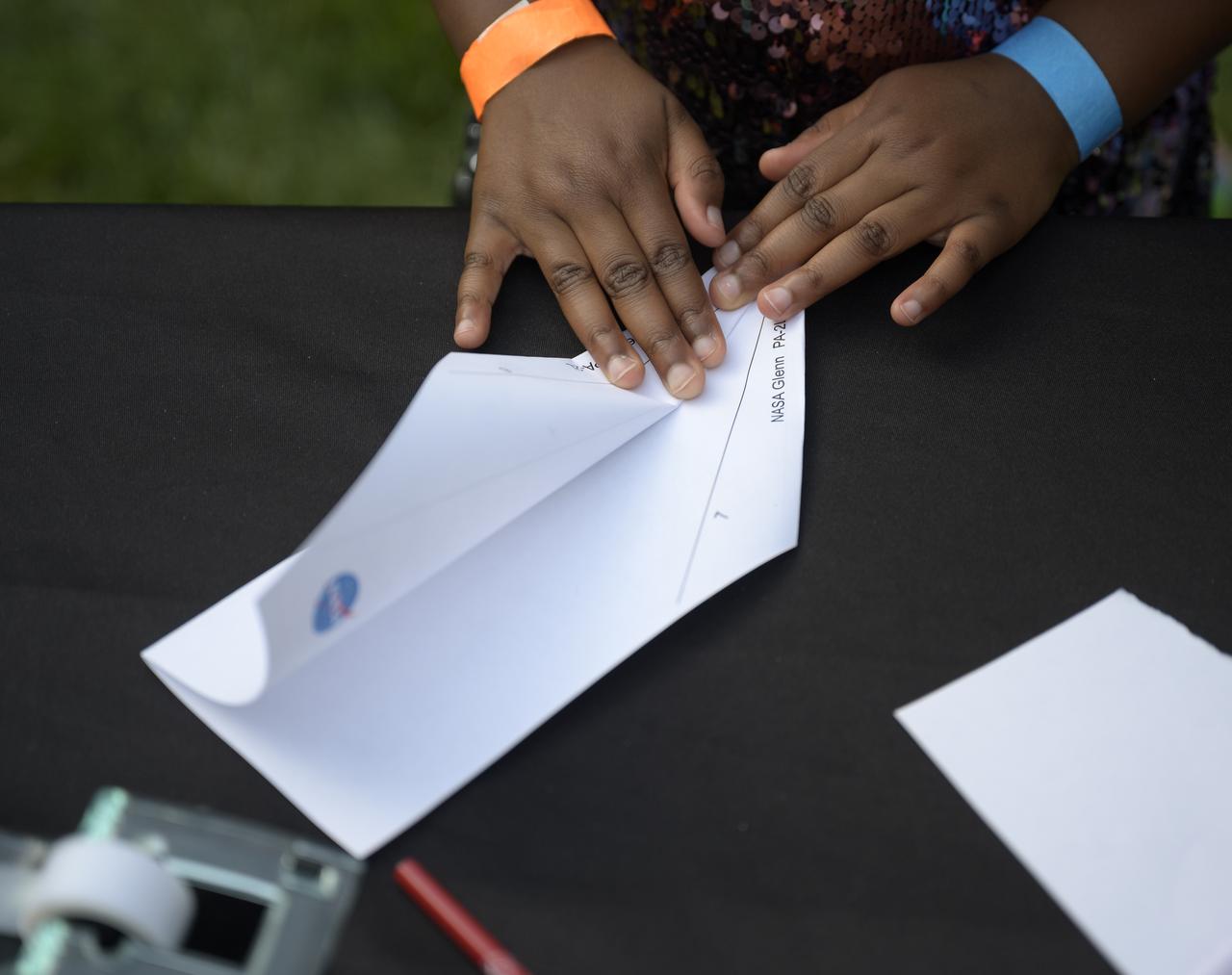

Students work an airplane building hands-on STEM activity on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Students work a straw rocket hands-on STEM activity on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
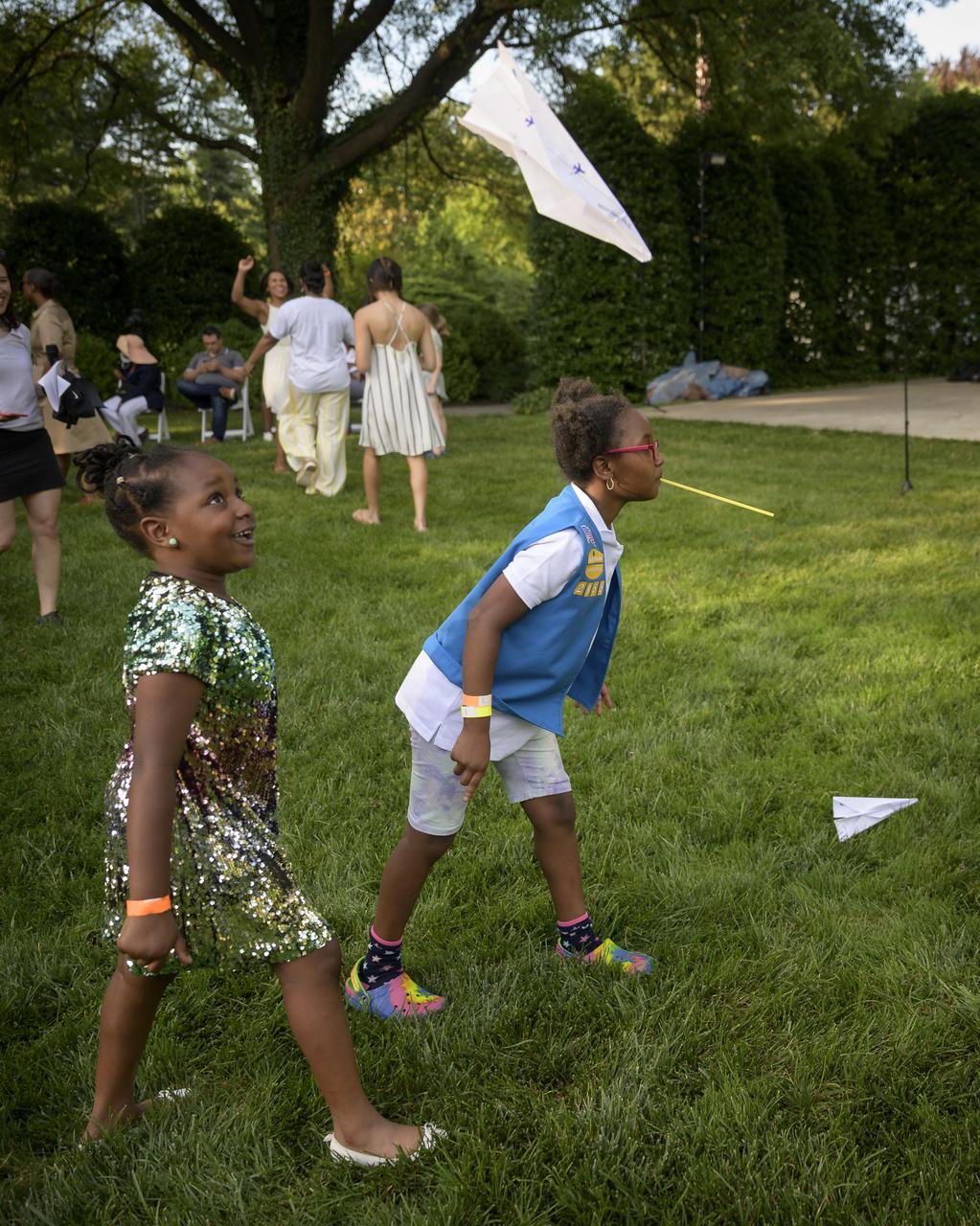
Students test their paper airplanes and straw rockets during a hands-on STEM activity on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
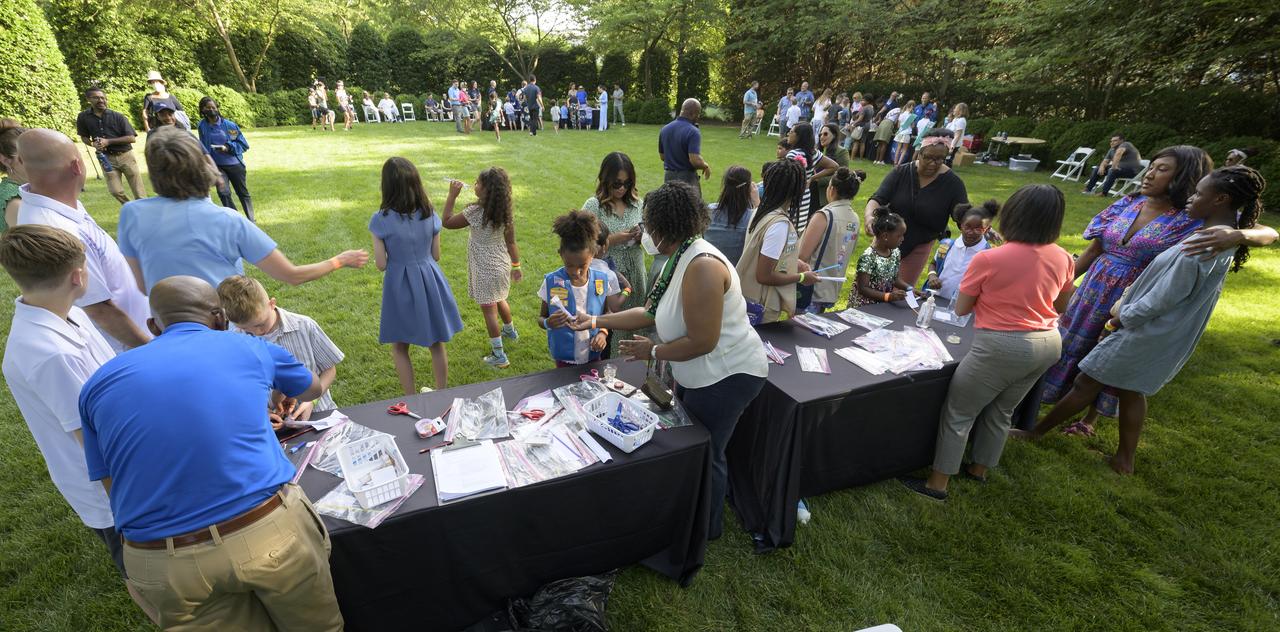

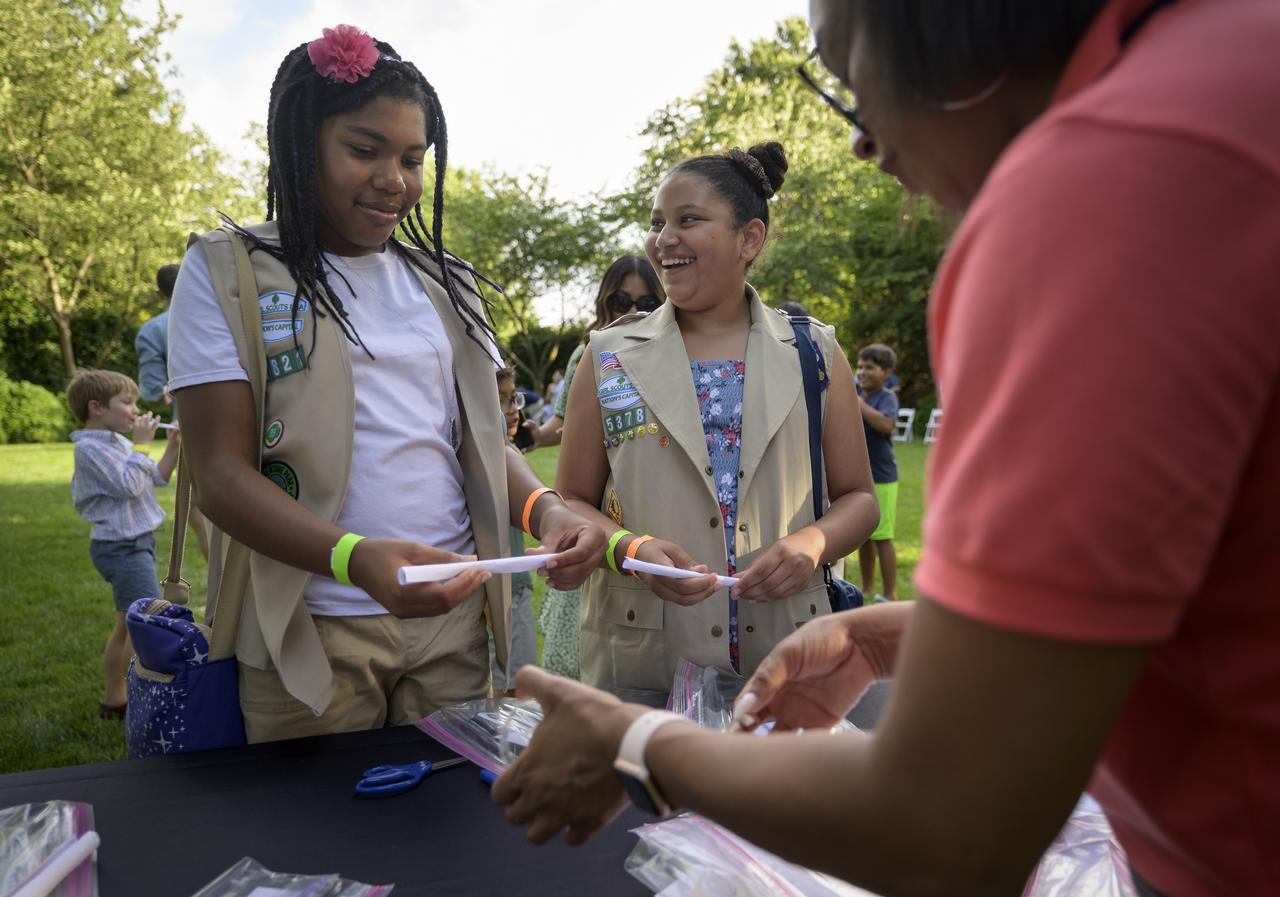
NASA astronauts and volunteers work hands-on STEM activities with students from 4th-8th grade on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
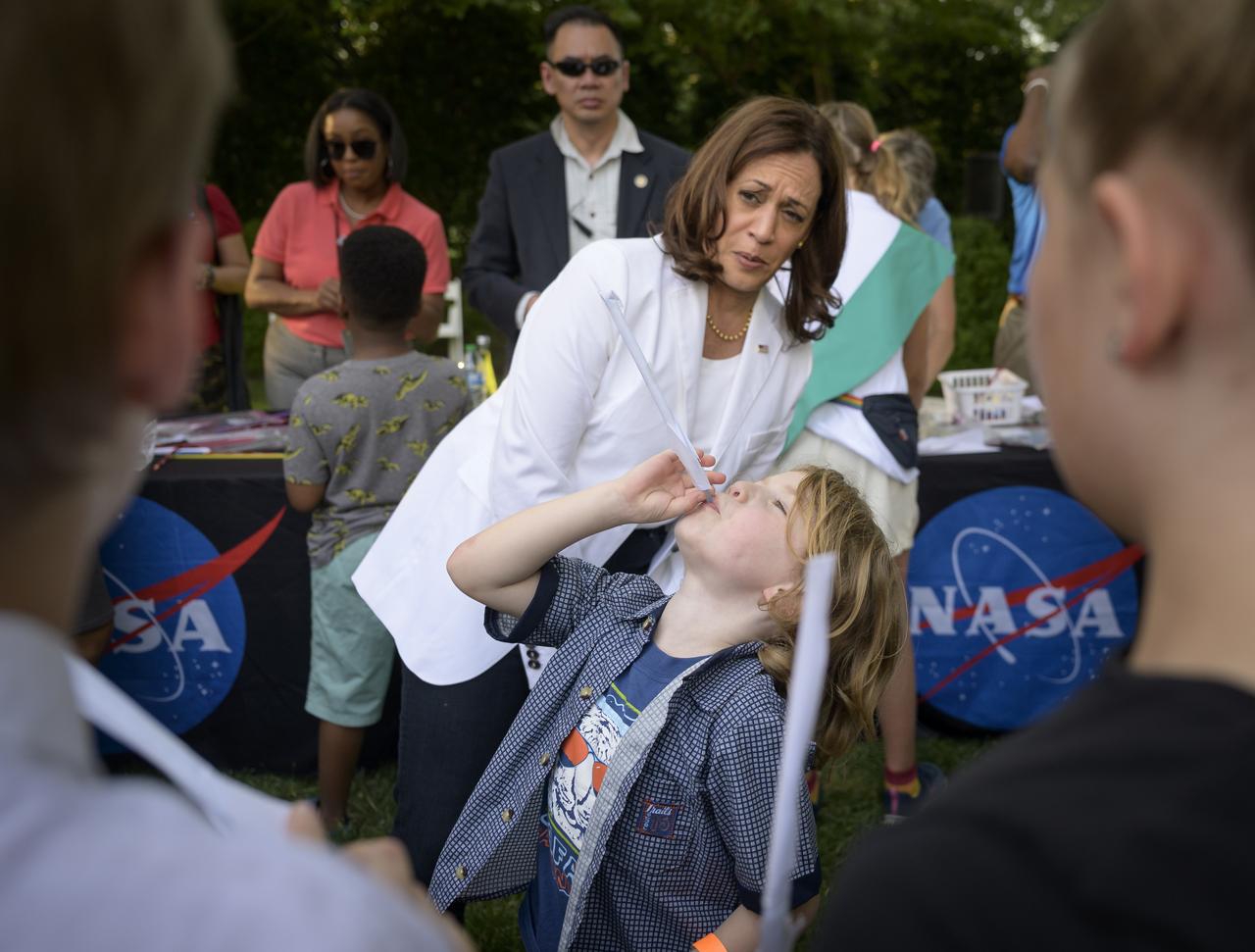

Vice President Kamala Harris interacts with children during hands-on STEM activities on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
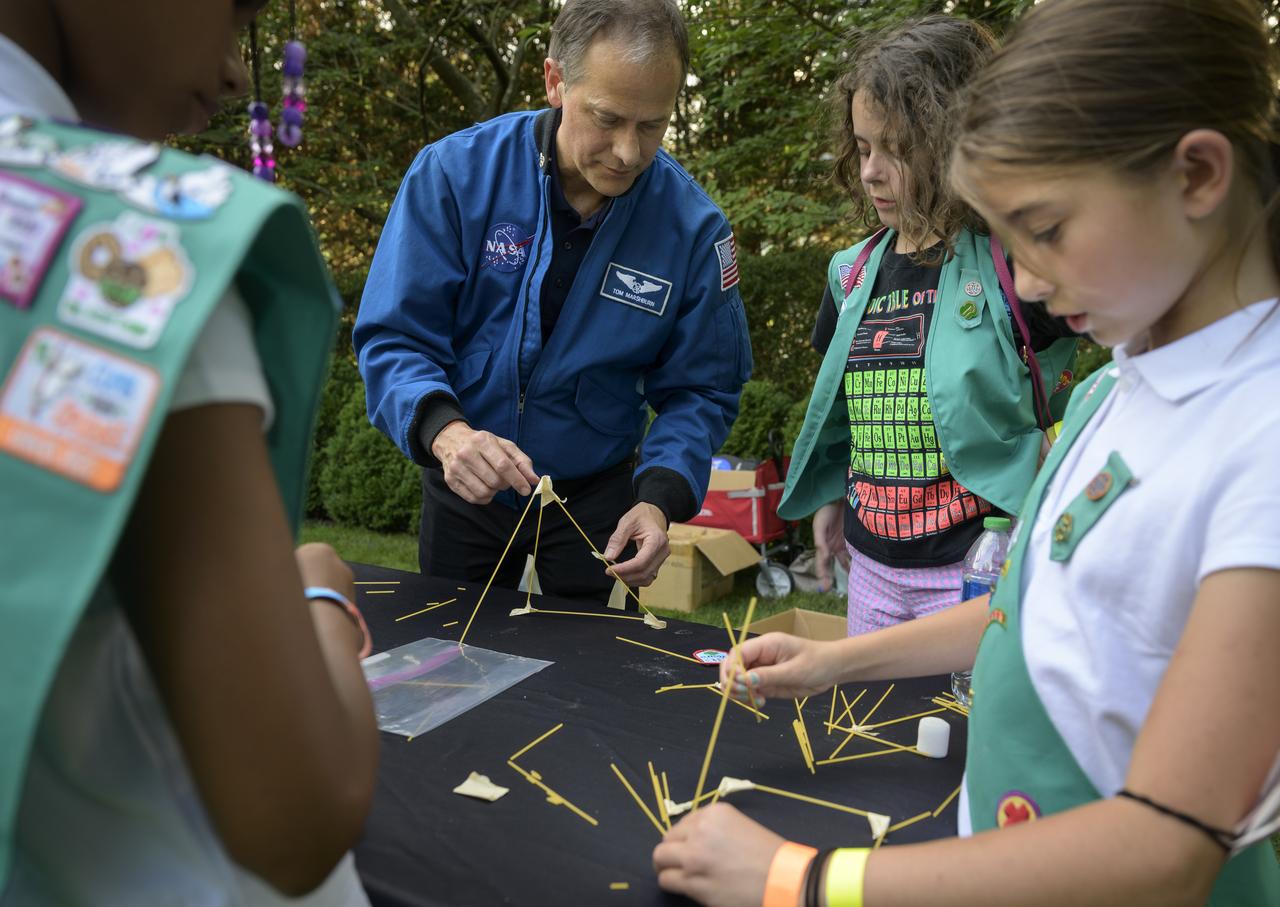

NASA astronaut Tom Marshburn works with students during a hands-on STEM activity on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
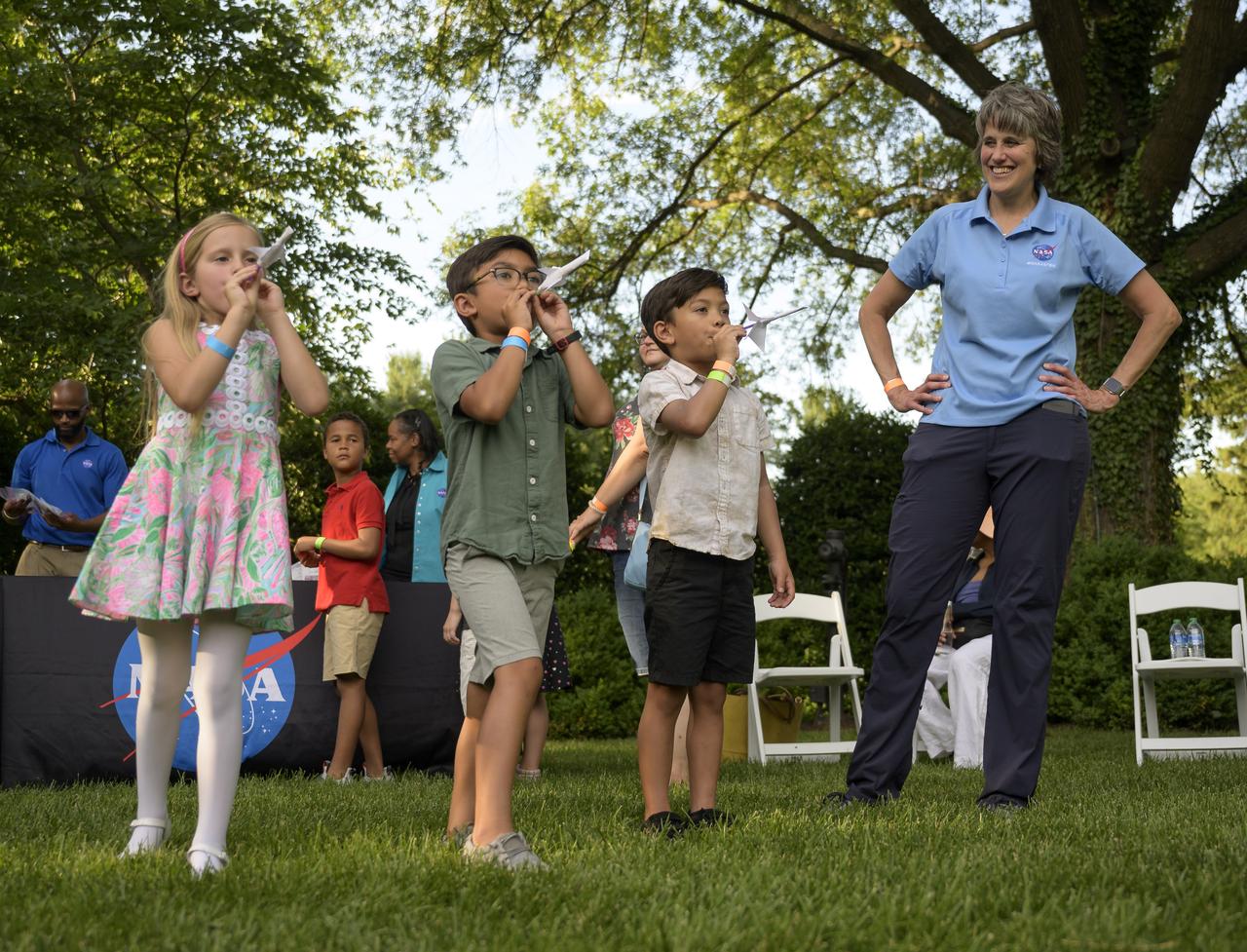
Cindy Hasselbring, NASA K-12 Education Advisor at NASA’s Office of STEM Engagement, works hands-on STEM activities with students from 4th-8th grade on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA astronaut Stephanie Wilson, 2nd from left, works with students during a hands-on STEM activity on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
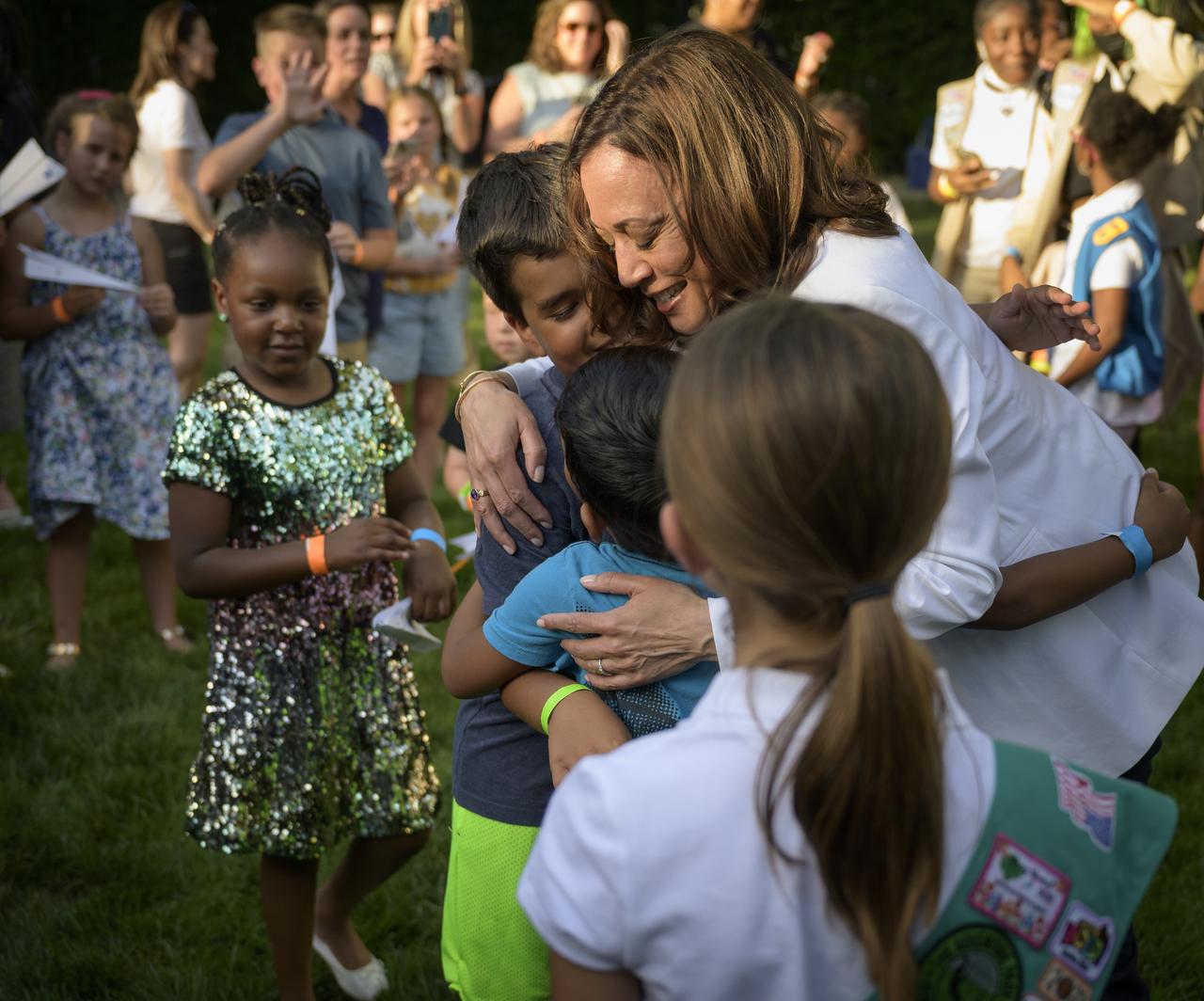
Vice President Kamala Harris hugs children that participated in hands-on STEM activities on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
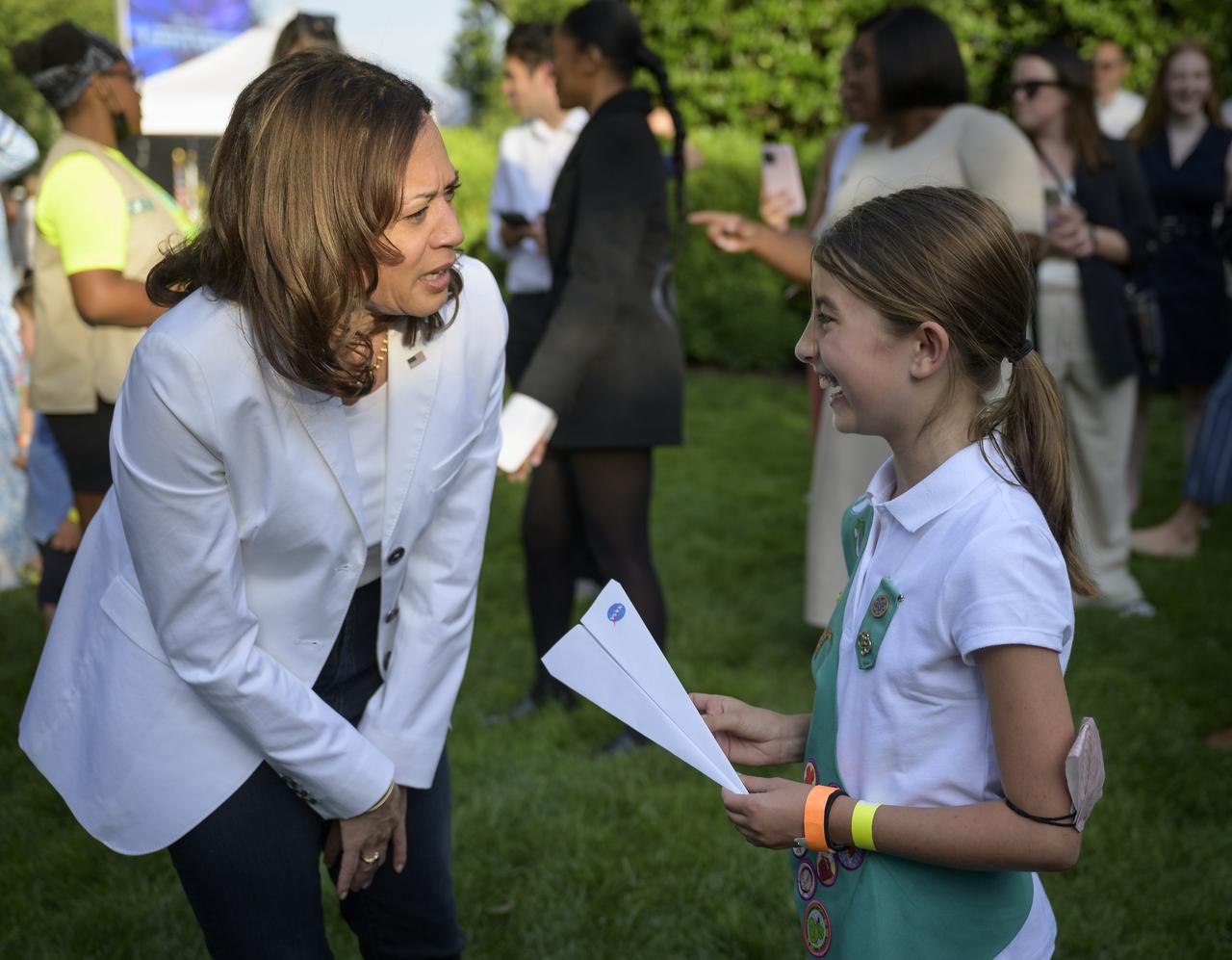

Vice President Kamala Harris talks with children as they participate in hands-on STEM activities on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
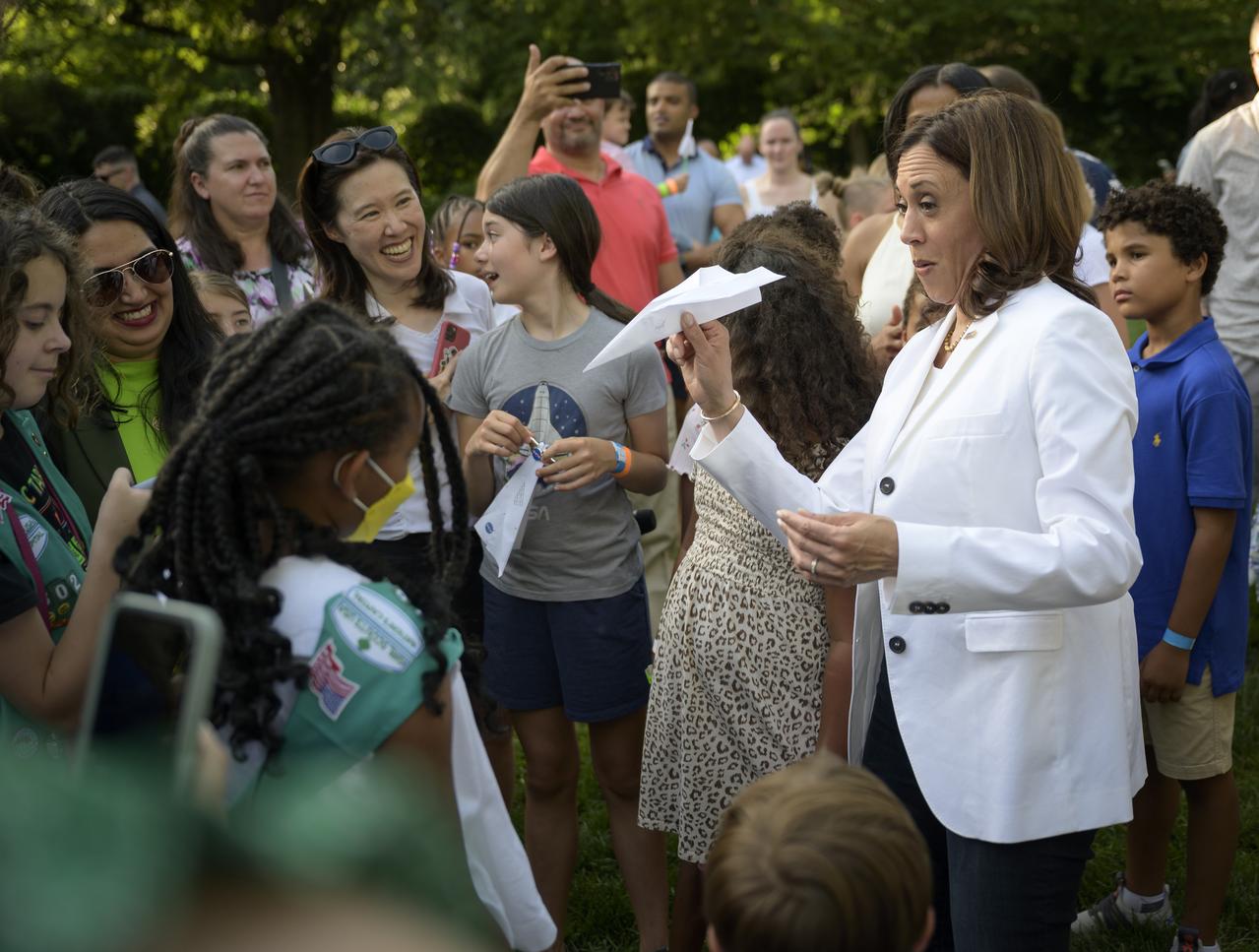
Vice President Kamala Harris interacts with children during hands-on STEM activities on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
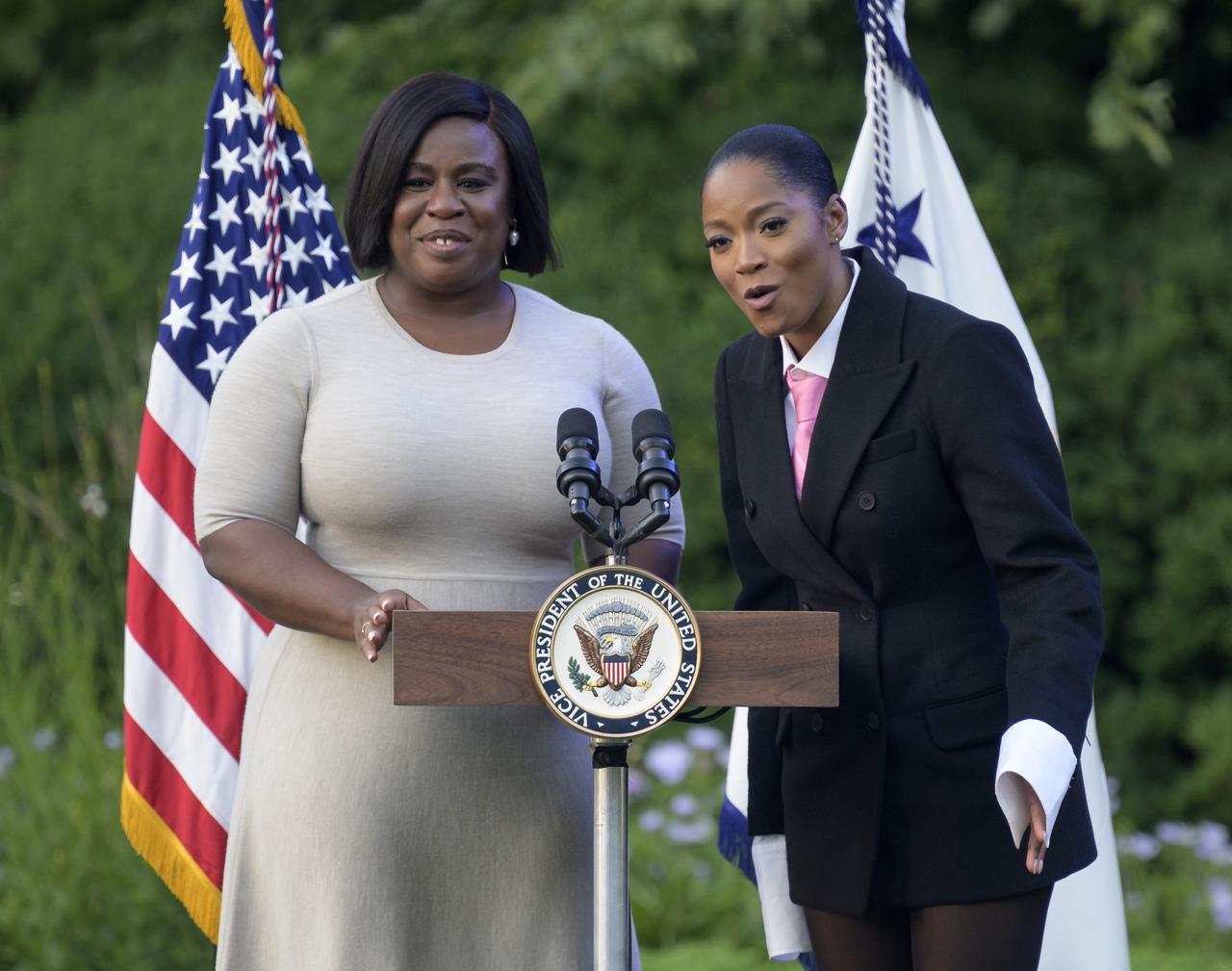

American actresses Uzo Aduba, left, and Keke Palmer give remarks prior to the screening of the movie Lightyear on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. Vice President Kamala Harris and Second Gentleman Doug Emhoff hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
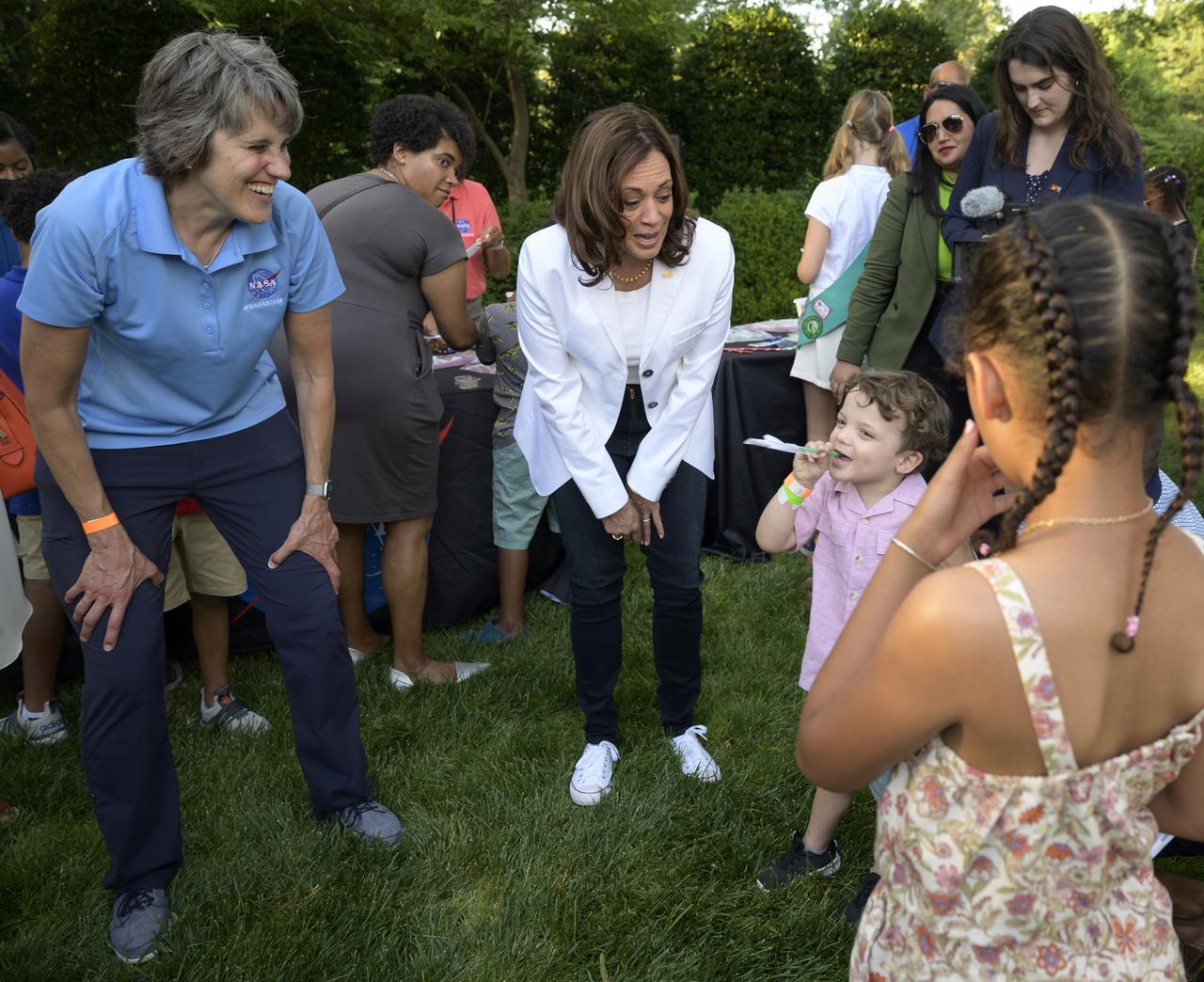
Vice President Kamala Harris interacts with children during hands-on STEM activities on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
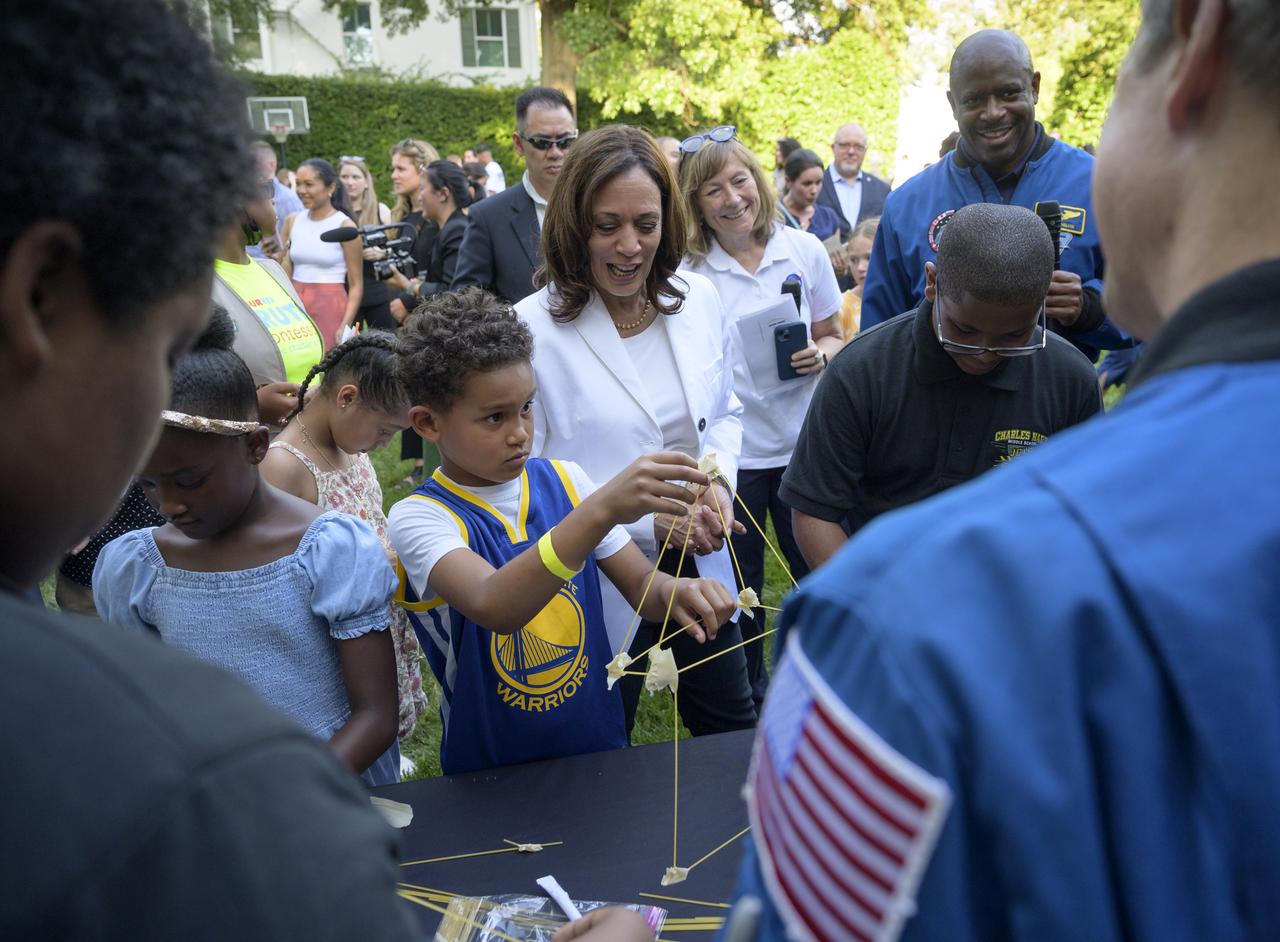

Vice President Kamala Harris interacts with children during hands-on STEM activities on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
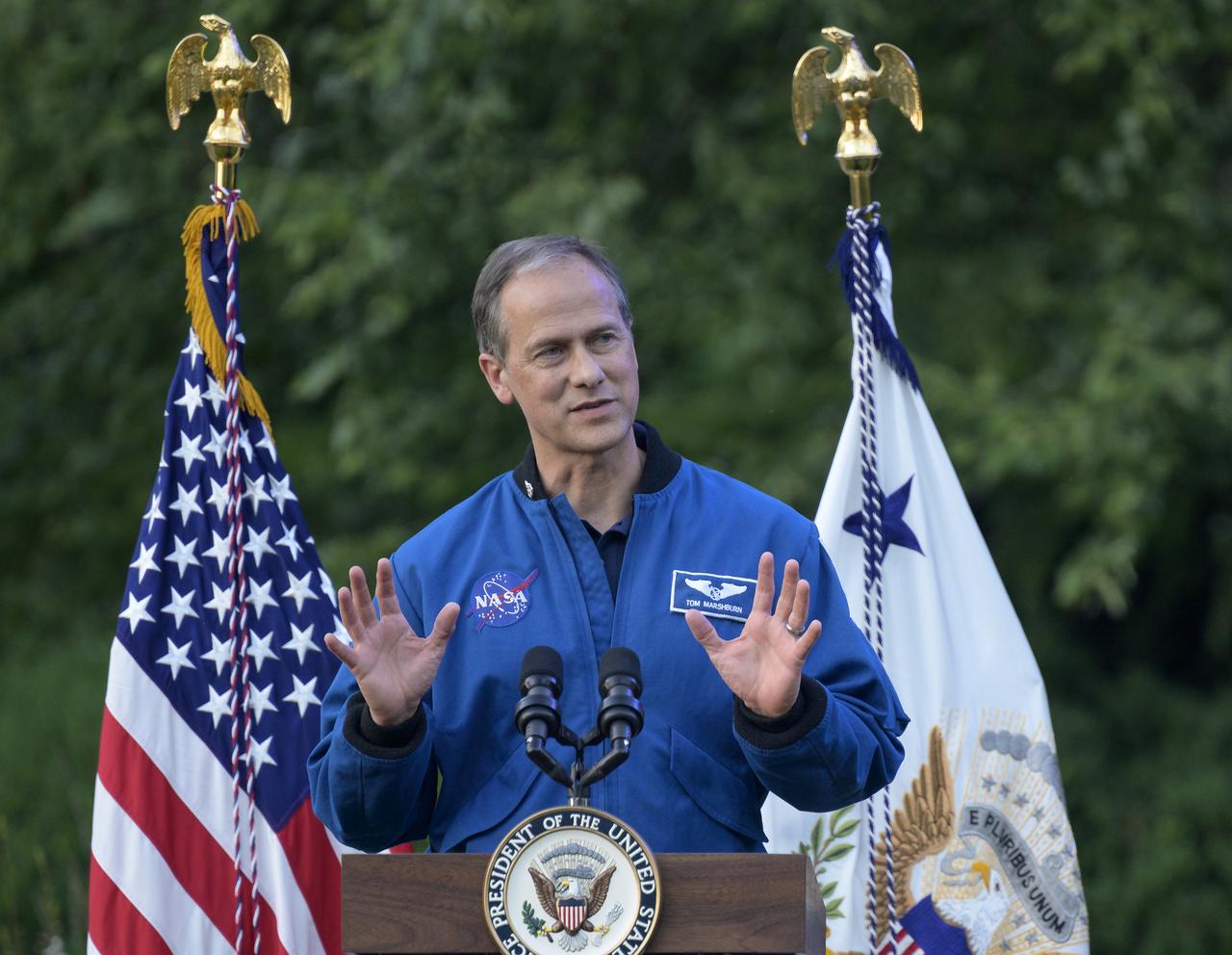

NASA astronaut Tom Marshburn gives remarks prior to the screening of the movie Lightyear on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. Vice President Kamala Harris and Second Gentleman Doug Emhoff hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
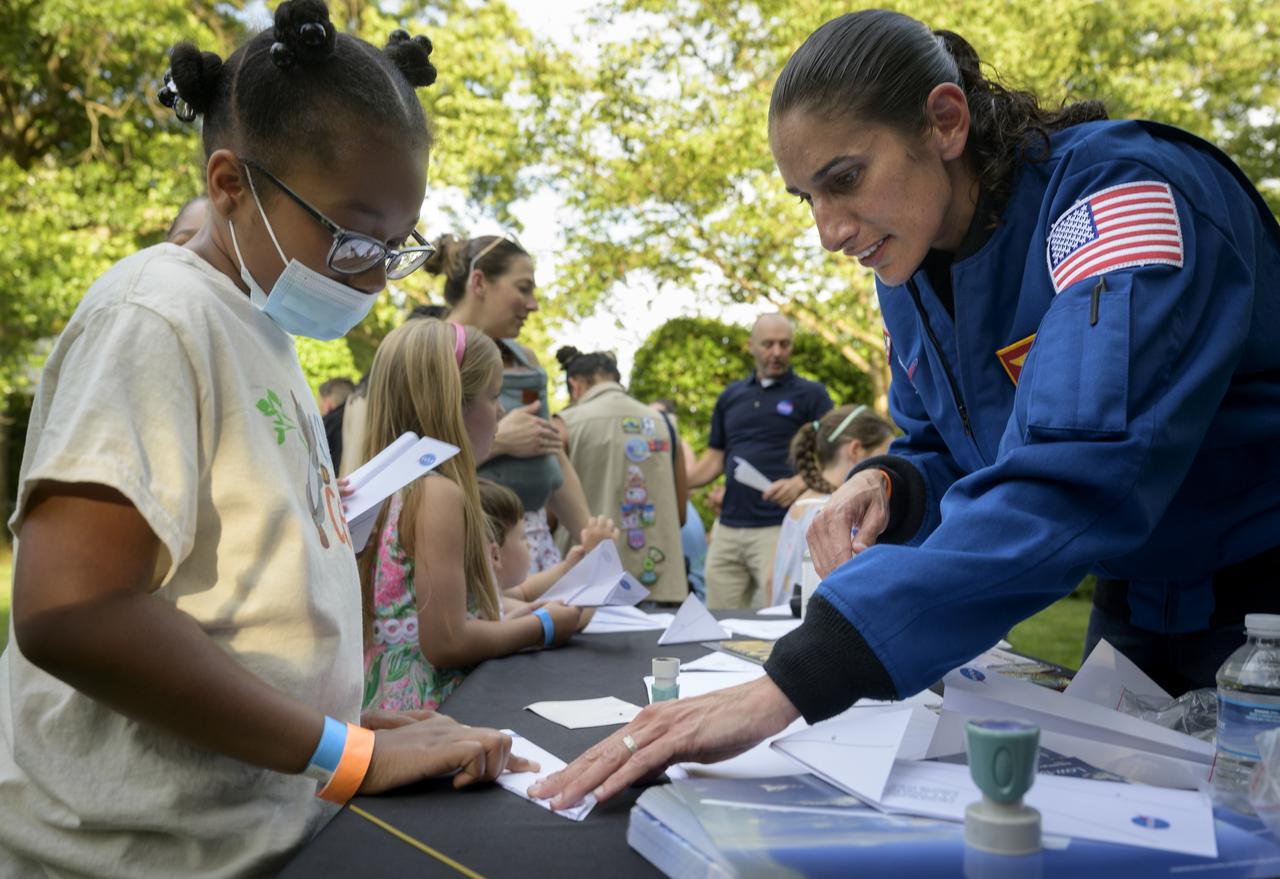

NASA astronaut Jasmin Moghbeli works with students during a hands-on STEM activity on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA astronauts Bob Hines, left, Jessica Watkins, and Kjell Lindgren, give remarks from the International Space Station prior to the screening of the movie Lightyear on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
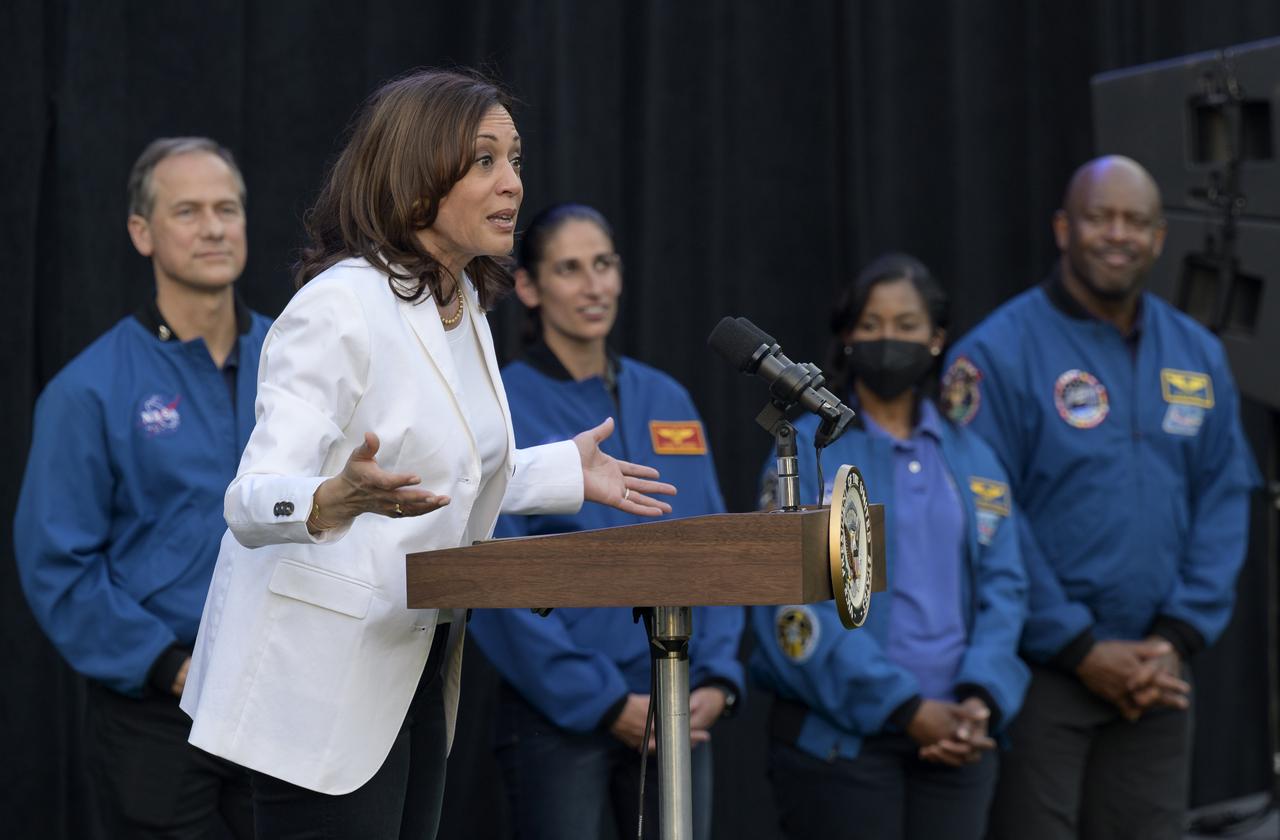

Vice President Kamala Harris gives remarks as NASA astronauts Tom Marshburn, Jasmin Moghbeli, Stephanie Wilson, and Former NASA astronaut Leland Melvin, right, look on prior to the screening of the movie Lightyear on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
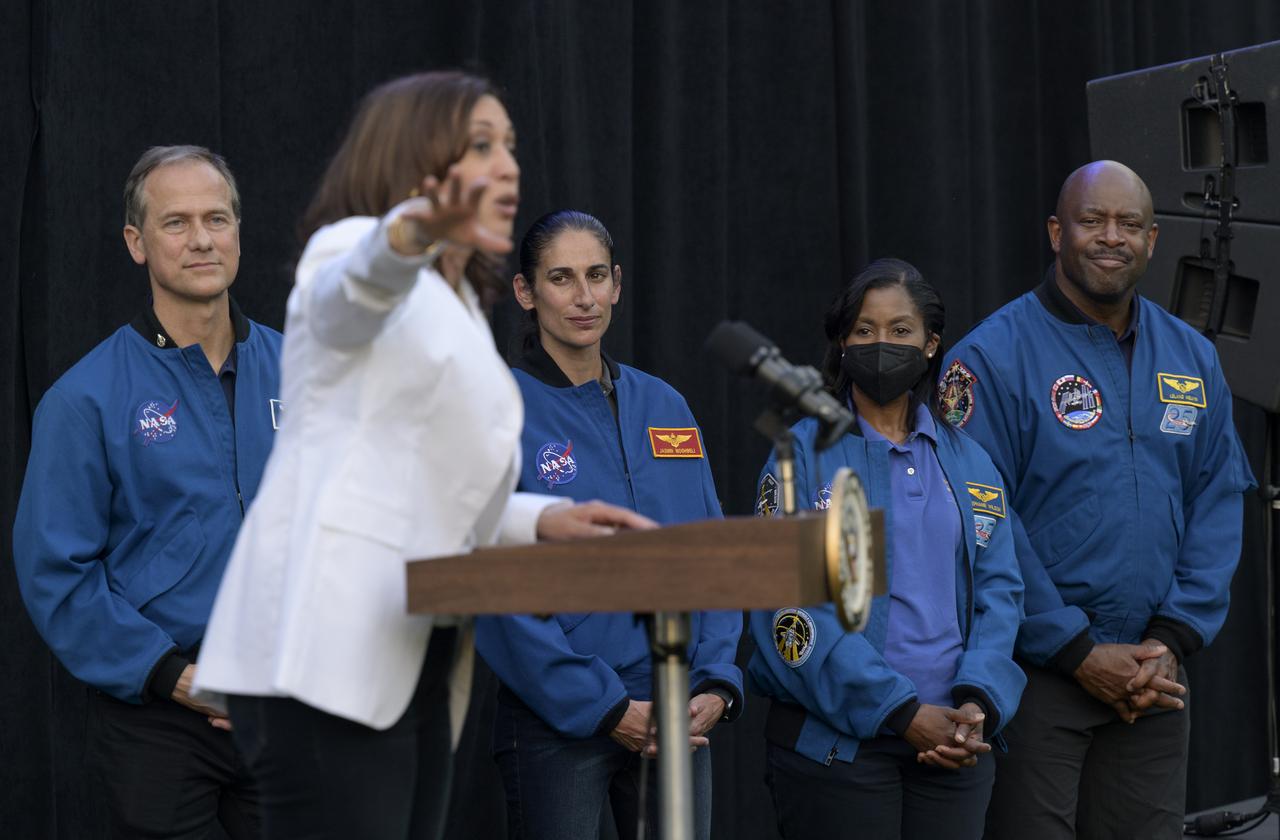

Vice President Kamala Harris gives remarks as NASA astronauts Tom Marshburn, Jasmin Moghbeli, Stephanie Wilson, and Former NASA astronaut Leland Melvin, right, look on prior to the screening of the movie Lightyear on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
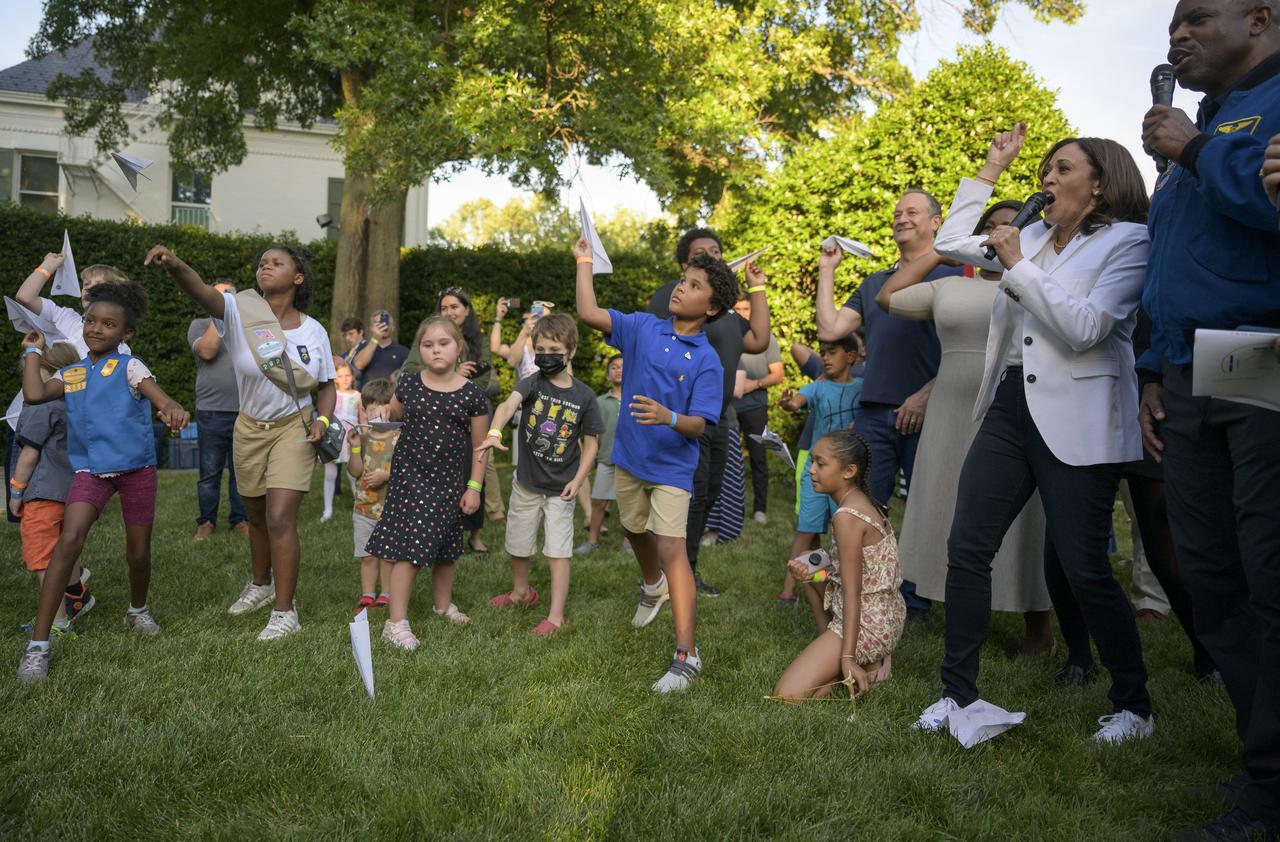
Vice President Kamala Harris counts down for children to throw their paper planes during hands-on STEM activities on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
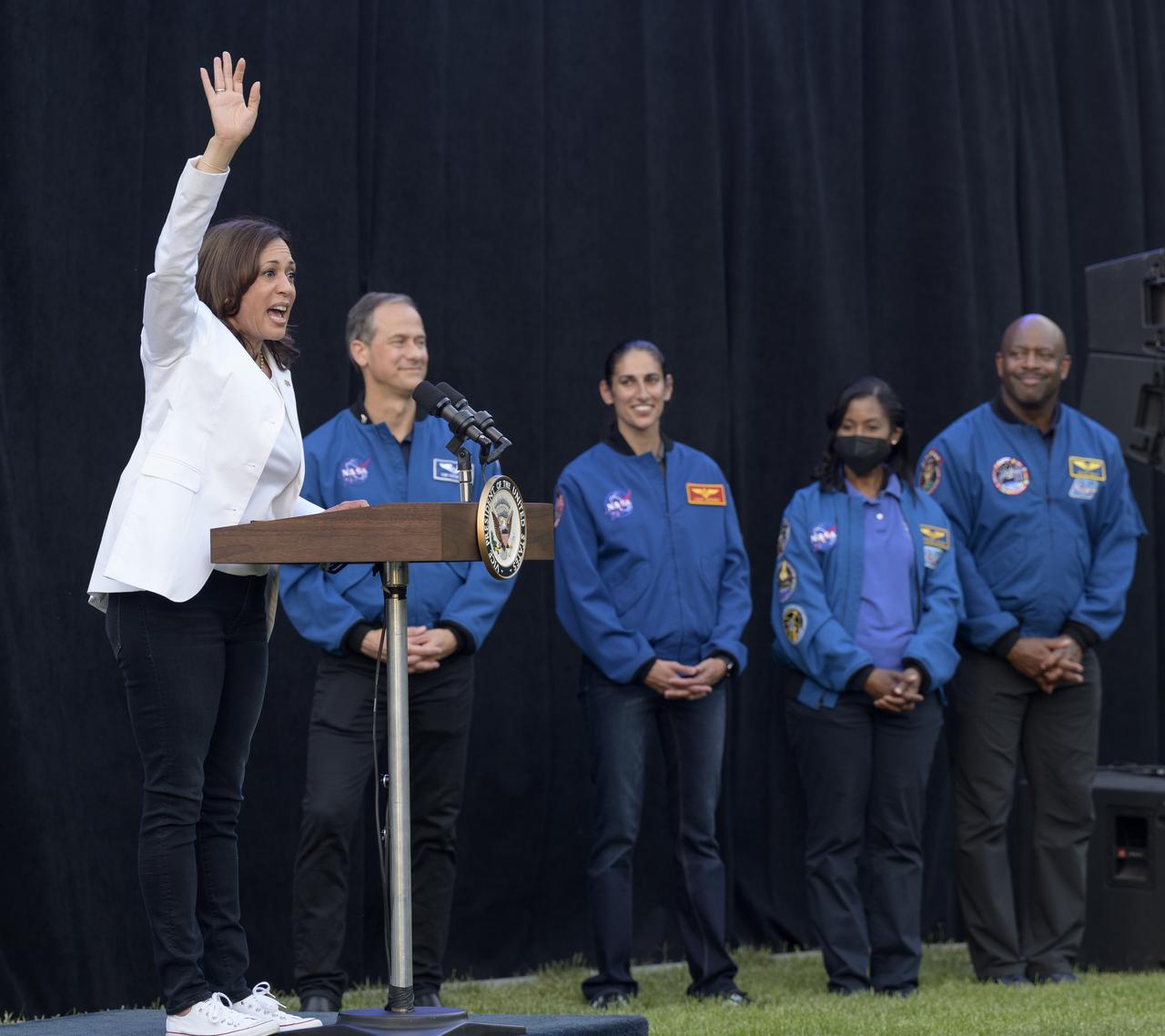

Vice President Kamala Harris gives remarks as NASA astronauts Tom Marshburn, Jasmin Moghbeli, Stephanie Wilson, and Former NASA astronaut Leland Melvin, right, look on prior to the screening of the movie Lightyear on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
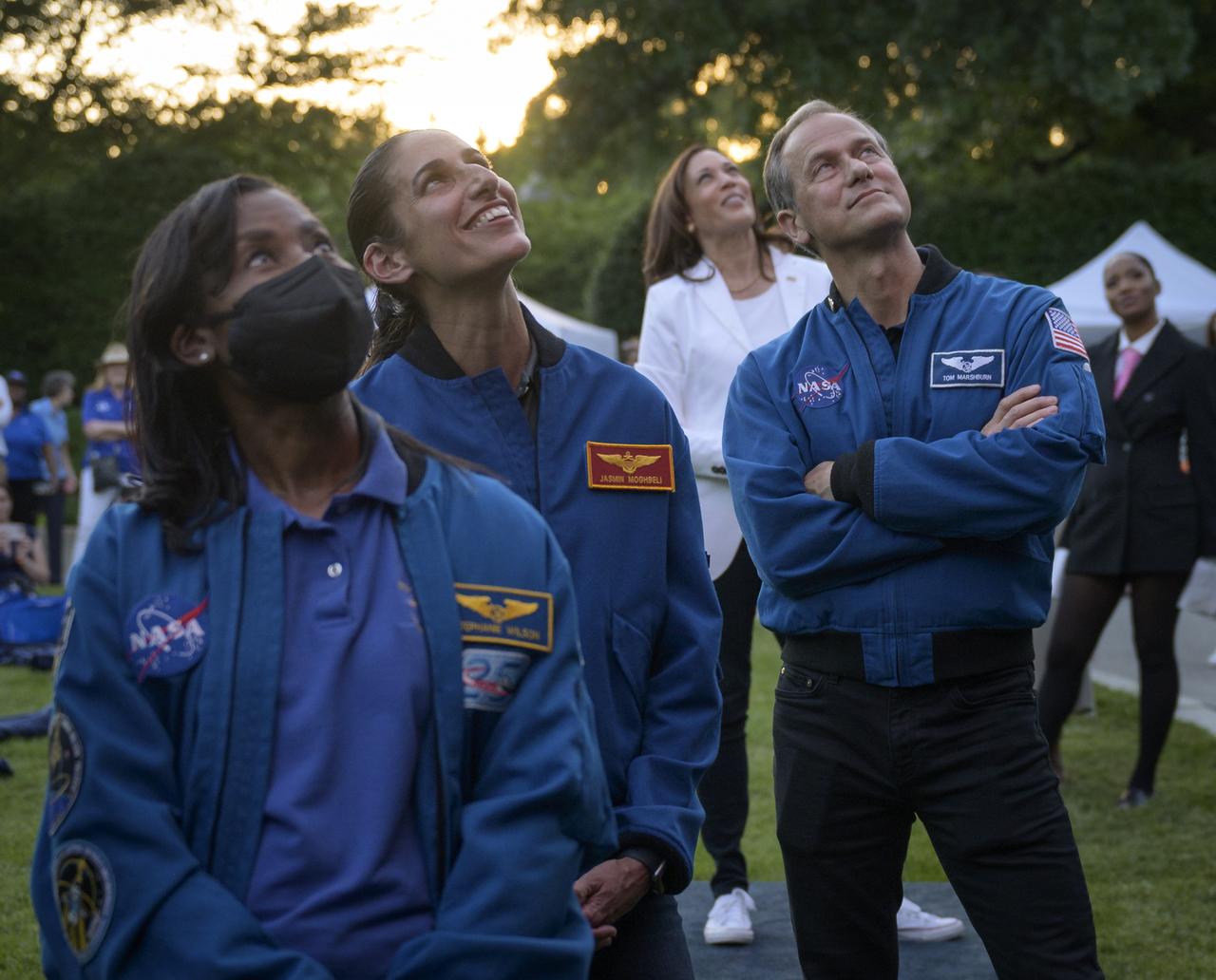

NASA astronauts Stephanie Wilson, left, Jasmin Moghbeli, and Tom Marshburn, along with Vice President Kamala Harris watch a video screen as NASA astronauts onboard the International Space Station give remarks prior to the screening of the movie Lightyear on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
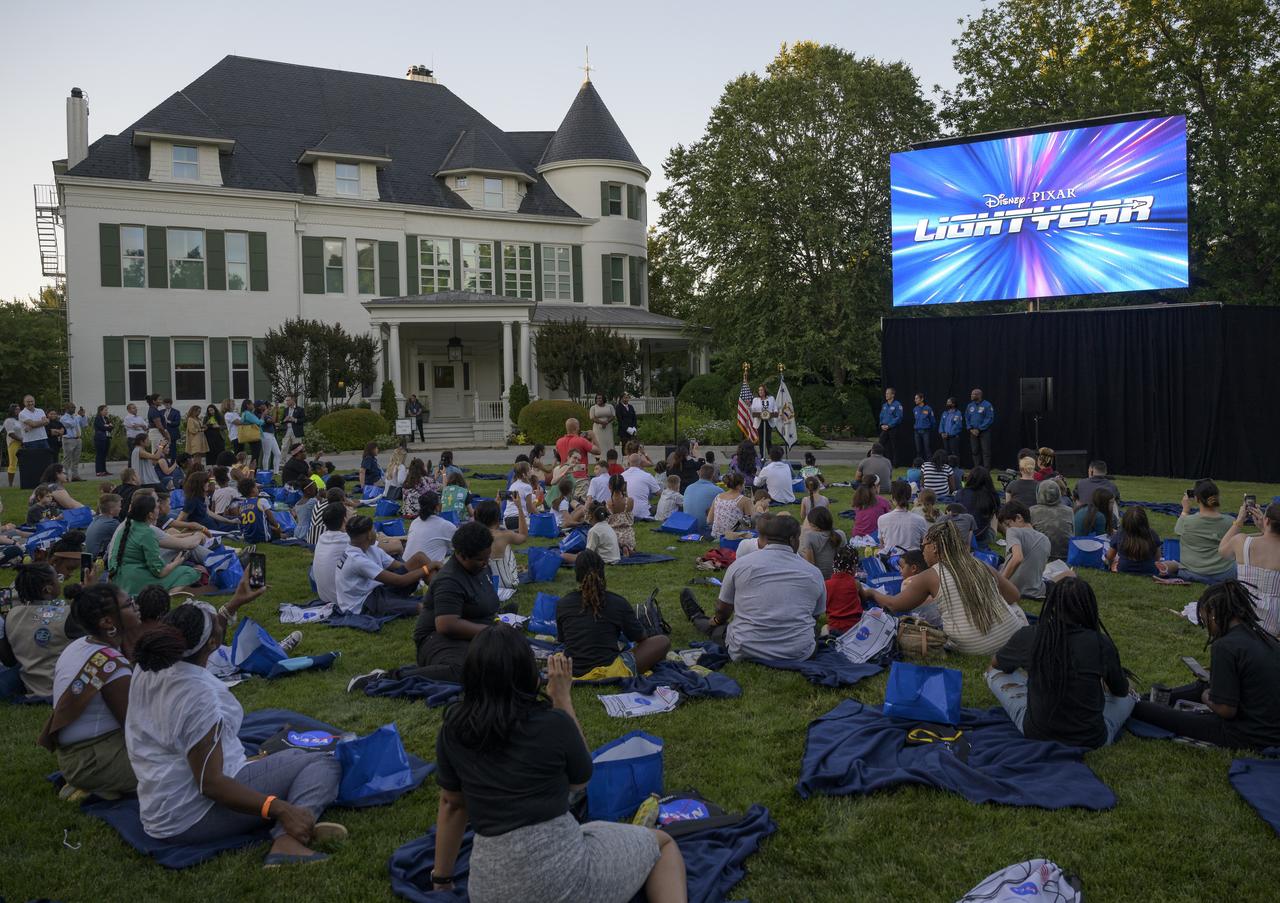

Vice President Kamala Harris gives remarks prior to the screening of the movie Lightyear on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
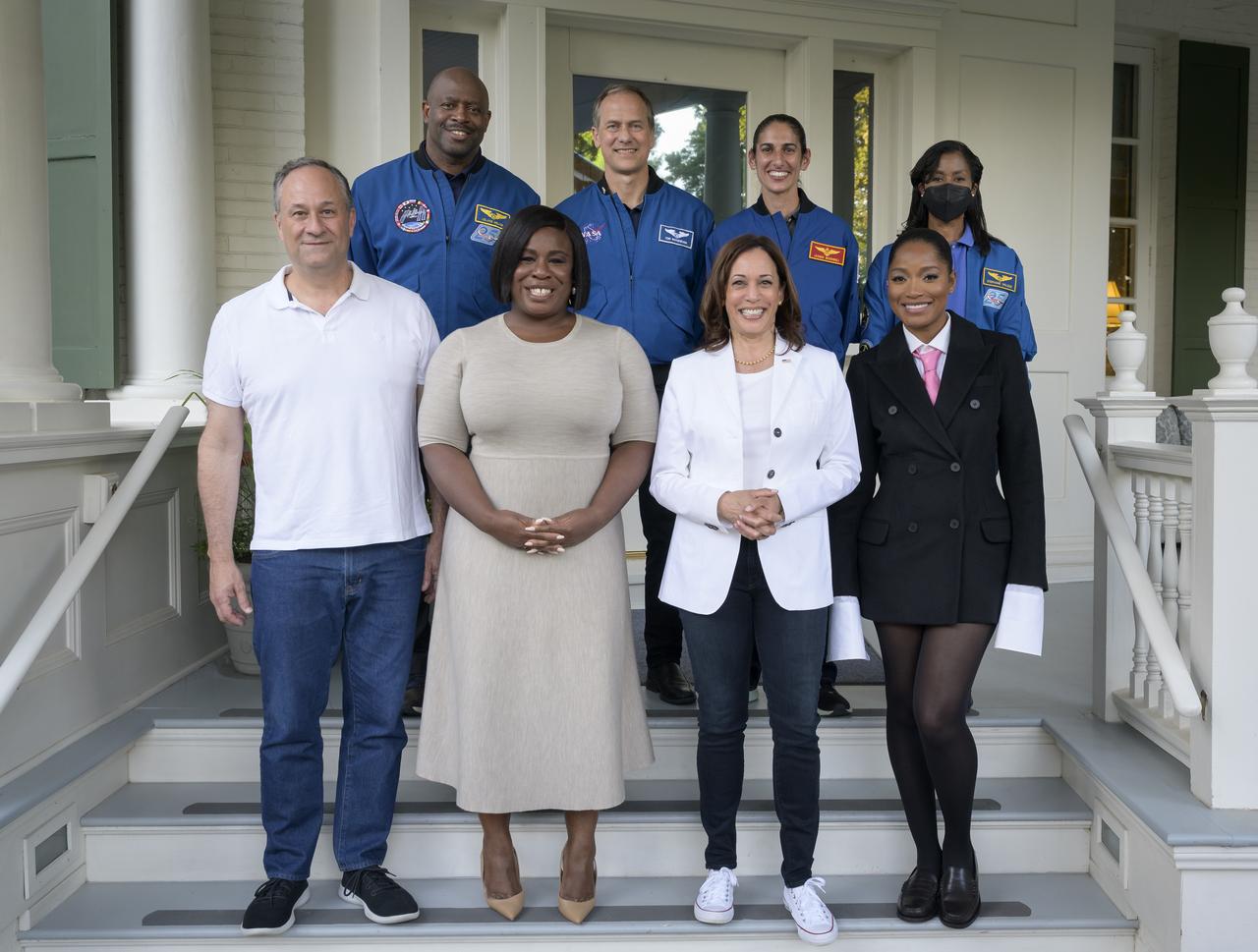

Vice President Kamala Harris and Second Gentleman Doug Emhoff pose for a group photo with Former NASA astronaut Leland Melvin, back left, NASA astronauts Tom Marshburn, Jasmin Moghbeli, and Stephanie Wilson, back right, along with American actress Uzo Aduba, and American actress Keke Palmer, bottom right, after they met with students from 4th-8th grade to work hands-on STEM activities on the grounds of the Vice President's residence at the Naval Observatory, Friday, June 17, 2022, in Washington. The Vice President and Second Gentleman hosted an evening of NASA STEM activities at the Naval Observatory for military families and local STEM students and their families, including a special screening of Disney Pixar’s Lightyear. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
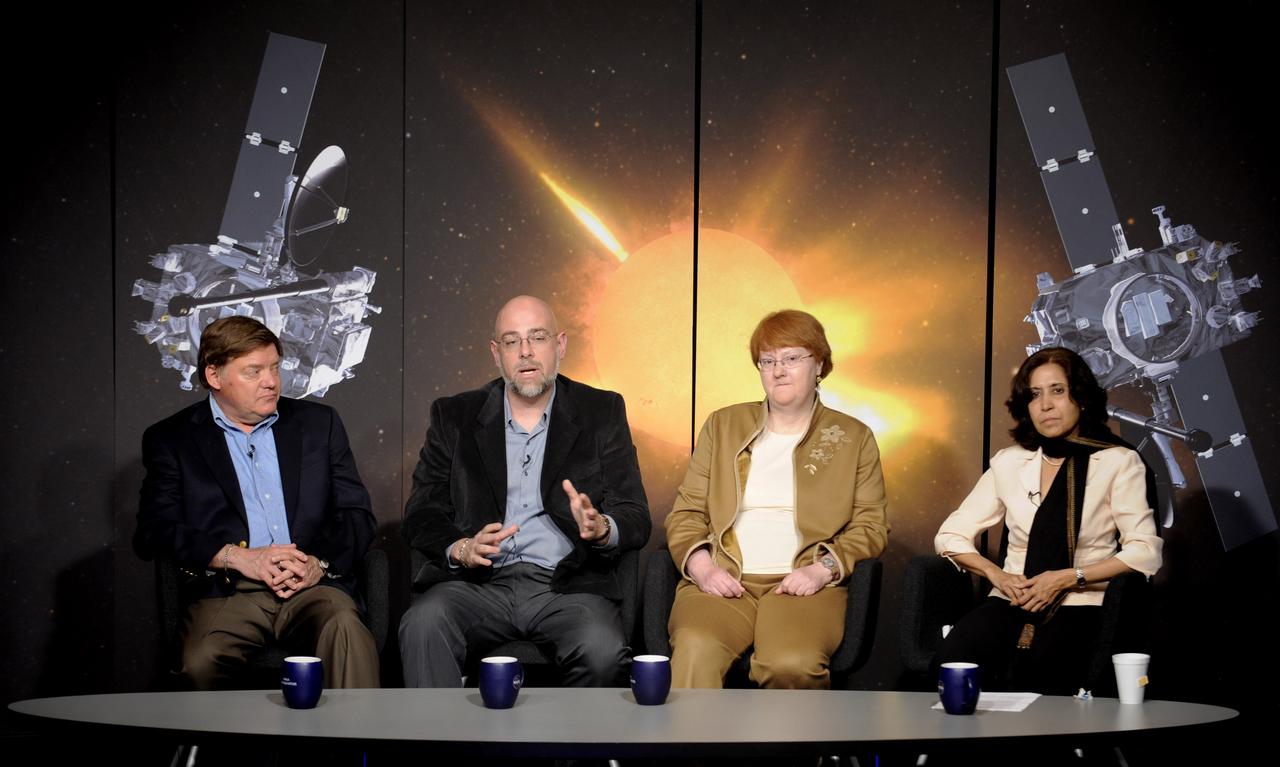

Angelo Vourlidas, project scientist, Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation, at the Naval Research Laboratory, second from left, makes a comment during a Science Update on the STEREO mission at NASA Headquarters in Washington, Tuesday, April 14, 2009, as Michael Kaiser, project scientist, Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) at Goddard Space Flight Center, left, Toni Galvin, principal investigator, Plasma and Superthermal Ion Composition instrument at the University of New Hampshire and Madhulika Guhathakurta, STEREO program scientist, right, look on. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
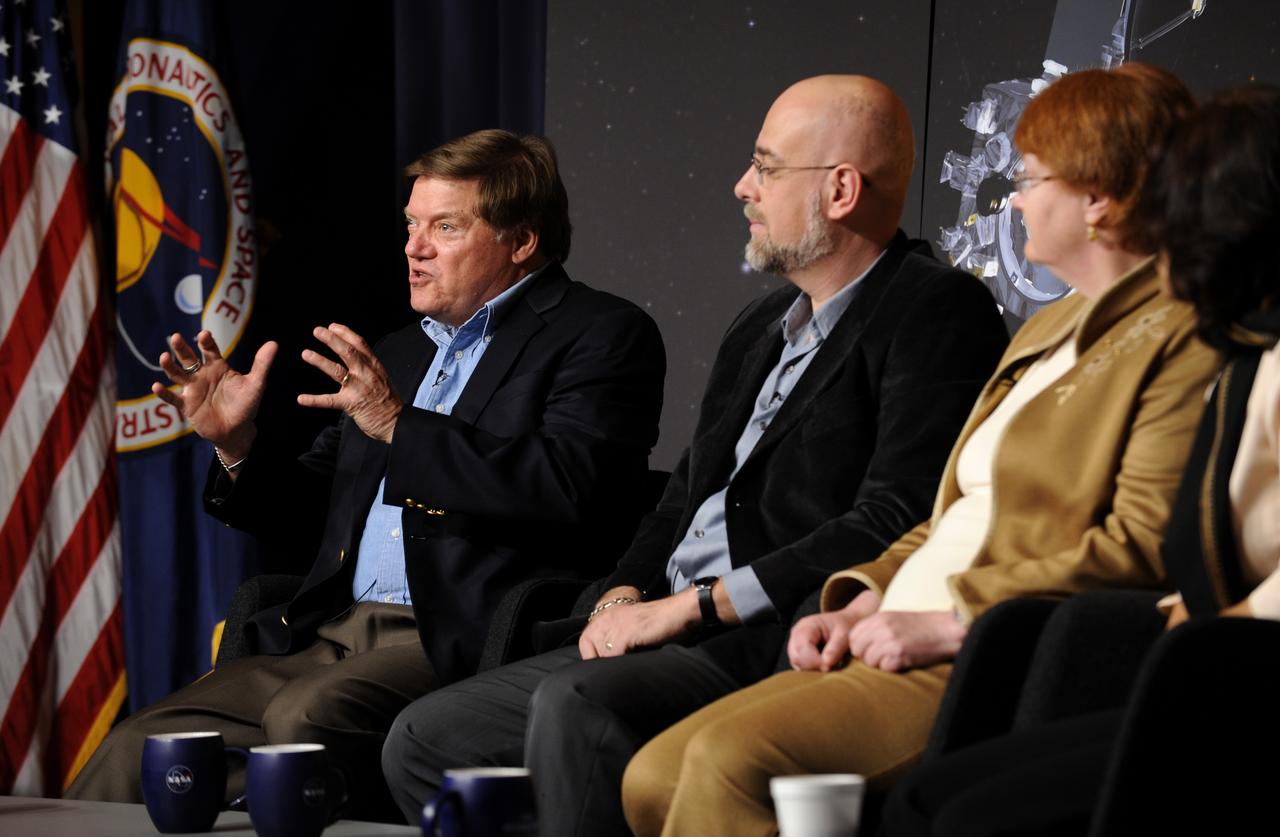

Michael Kaiser, project scientist, Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) at Goddard Space Flight Center, left, makes a point during a Science Update on the STEREO mission at NASA Headquarters in Washington, Tuesday, April 14, 2009, as Angelo Vourlidas, project scientist, Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation, at the Naval Research Laboratory, Toni Galvin, principal investigator, Plasma and Superthermal Ion Composition instrument at the University of New Hampshire and Madhulika Guhathkurta, STEREO program scientist, right, look on. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

Michael Kaiser, project scientist, Solar Terrestrial Relations Observatory (STEREO) at Goddard Space Flight Center, left, makes a comment during a Science Update on the STEREO mission at NASA Headquarters in Washington, Tuesday, April 14, 2009, as Angelo Vourlidas, project scientist, Sun Earth Connection Coronal and Heliospheric Investigation, at the Naval Research Laboratory, second from left, Toni Galvin, principal investigator, Plasma and Superthermal Ion Composition instrument at the University of New Hampshire and Madhulika Guhathakurta, STEREO program scientist, right, look on. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)
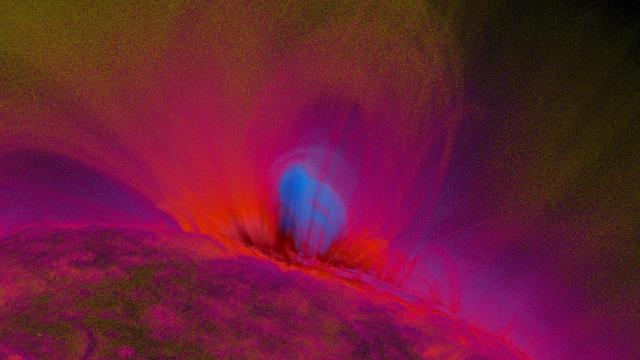
Caption: This is an image of magnetic loops on the sun, captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). It has been processed to highlight the edges of each loop to make the structure more clear. A series of loops such as this is known as a flux rope, and these lie at the heart of eruptions on the sun known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs.) This is the first time scientists were able to discern the timing of a flux rope's formation. (SDO AIA 131 and 171 difference blended image of flux ropes during CME.) Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO ---- On July 18, 2012, a fairly small explosion of light burst off the lower right limb of the sun. Such flares often come with an associated eruption of solar material, known as a coronal mass ejection or CME – but this one did not. Something interesting did happen, however. Magnetic field lines in this area of the sun's atmosphere, the corona, began to twist and kink, generating the hottest solar material – a charged gas called plasma – to trace out the newly-formed slinky shape. The plasma glowed brightly in extreme ultraviolet images from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) aboard NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and scientists were able to watch for the first time the very formation of something they had long theorized was at the heart of many eruptive events on the sun: a flux rope. Eight hours later, on July 19, the same region flared again. This time the flux rope's connection to the sun was severed, and the magnetic fields escaped into space, dragging billions of tons of solar material along for the ride -- a classic CME. "Seeing this structure was amazing," says Angelos Vourlidas, a solar scientist at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C. "It looks exactly like the cartoon sketches theorists have been drawing of flux ropes since the 1970s. It was a series of figure eights lined up to look like a giant slinky on the sun." <b>To read more about this new discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14UHsTt" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14UHsTt</a> </b>

Caption: This is an image of magnetic loops on the sun, captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). It has been processed to highlight the edges of each loop to make the structure more clear. A series of loops such as this is known as a flux rope, and these lie at the heart of eruptions on the sun known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs.) This is the first time scientists were able to discern the timing of a flux rope's formation. (SDO AIA 131 and 171 difference blended image of flux ropes during CME.) Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO ---- On July 18, 2012, a fairly small explosion of light burst off the lower right limb of the sun. Such flares often come with an associated eruption of solar material, known as a coronal mass ejection or CME – but this one did not. Something interesting did happen, however. Magnetic field lines in this area of the sun's atmosphere, the corona, began to twist and kink, generating the hottest solar material – a charged gas called plasma – to trace out the newly-formed slinky shape. The plasma glowed brightly in extreme ultraviolet images from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) aboard NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and scientists were able to watch for the first time the very formation of something they had long theorized was at the heart of many eruptive events on the sun: a flux rope. Eight hours later, on July 19, the same region flared again. This time the flux rope's connection to the sun was severed, and the magnetic fields escaped into space, dragging billions of tons of solar material along for the ride -- a classic CME. "Seeing this structure was amazing," says Angelos Vourlidas, a solar scientist at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C. "It looks exactly like the cartoon sketches theorists have been drawing of flux ropes since the 1970s. It was a series of figure eights lined up to look like a giant slinky on the sun." <b>To read more about this new discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14UHsTt" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14UHsTt</a> </b>
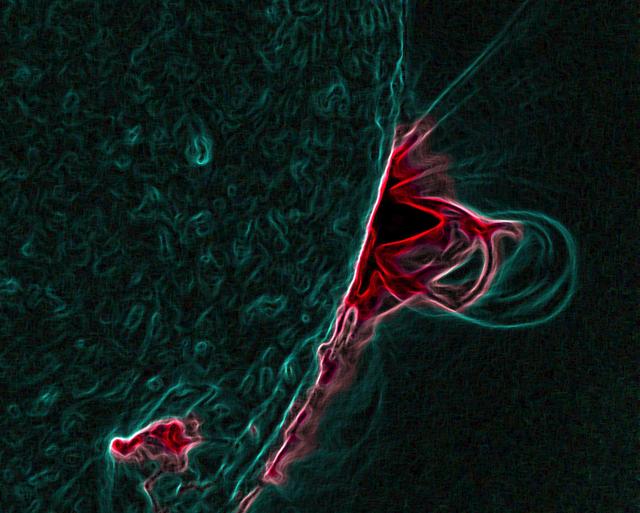
Caption: This is an image of magnetic loops on the sun, captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory on July 18, 2012. It has been processed to highlight the edges of each loop to make the structure more clear. A series of loops such as this is known as a flux rope, and these lie at the heart of eruptions on the sun known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs.) This is the first time scientists were able to discern the timing of a flux rope's formation. Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO ---- On July 18, 2012, a fairly small explosion of light burst off the lower right limb of the sun. Such flares often come with an associated eruption of solar material, known as a coronal mass ejection or CME – but this one did not. Something interesting did happen, however. Magnetic field lines in this area of the sun's atmosphere, the corona, began to twist and kink, generating the hottest solar material – a charged gas called plasma – to trace out the newly-formed slinky shape. The plasma glowed brightly in extreme ultraviolet images from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) aboard NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and scientists were able to watch for the first time the very formation of something they had long theorized was at the heart of many eruptive events on the sun: a flux rope. Eight hours later, on July 19, the same region flared again. This time the flux rope's connection to the sun was severed, and the magnetic fields escaped into space, dragging billions of tons of solar material along for the ride -- a classic CME. "Seeing this structure was amazing," says Angelos Vourlidas, a solar scientist at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C. "It looks exactly like the cartoon sketches theorists have been drawing of flux ropes since the 1970s. It was a series of figure eights lined up to look like a giant slinky on the sun." <b>To read more about this new discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14UHsTt" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14UHsTt</a> </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Caption: This is an image of magnetic loops on the sun, captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). It has been processed to highlight the edges of each loop to make the structure more clear. A series of loops such as this is known as a flux rope, and these lie at the heart of eruptions on the sun known as coronal mass ejections (CMEs.) This is the first time scientists were able to discern the timing of a flux rope's formation. (Blended 131 Angstrom and 171 Angstrom images of July 19, 2012 flare and CME.) Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center/SDO ---- On July 18, 2012, a fairly small explosion of light burst off the lower right limb of the sun. Such flares often come with an associated eruption of solar material, known as a coronal mass ejection or CME – but this one did not. Something interesting did happen, however. Magnetic field lines in this area of the sun's atmosphere, the corona, began to twist and kink, generating the hottest solar material – a charged gas called plasma – to trace out the newly-formed slinky shape. The plasma glowed brightly in extreme ultraviolet images from the Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA) aboard NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO) and scientists were able to watch for the first time the very formation of something they had long theorized was at the heart of many eruptive events on the sun: a flux rope. Eight hours later, on July 19, the same region flared again. This time the flux rope's connection to the sun was severed, and the magnetic fields escaped into space, dragging billions of tons of solar material along for the ride -- a classic CME. "Seeing this structure was amazing," says Angelos Vourlidas, a solar scientist at the Naval Research Laboratory in Washington, D.C. "It looks exactly like the cartoon sketches theorists have been drawing of flux ropes since the 1970s. It was a series of figure eights lined up to look like a giant slinky on the sun." <b>To read more about this new discovery go to: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/14UHsTt" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/14UHsTt</a> </b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
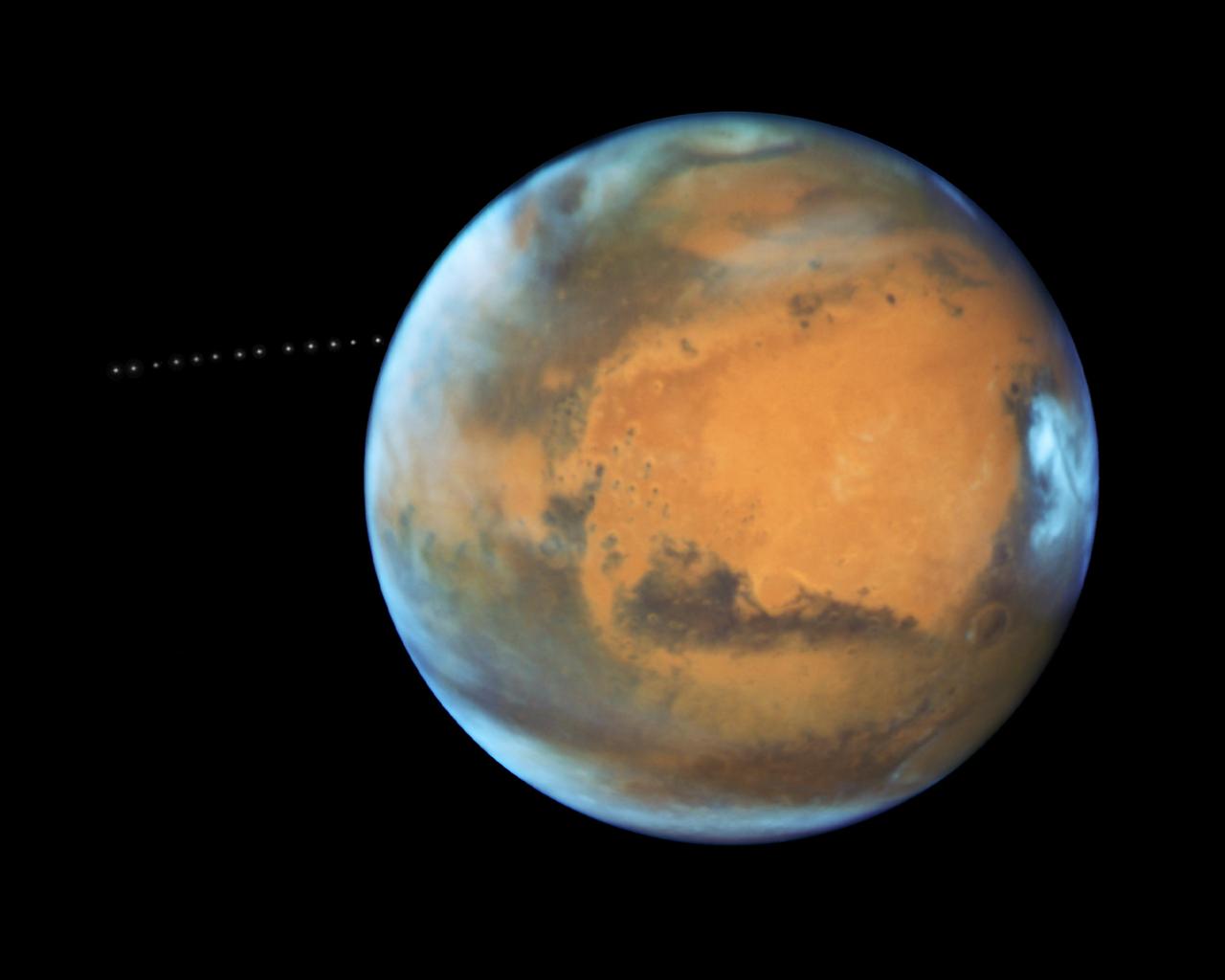
The sharp eye of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has captured the tiny moon Phobos during its orbital trek around Mars. Because the moon is so small, it appears star-like in the Hubble pictures. Over the course of 22 minutes, Hubble took 13 separate exposures, allowing astronomers to create a time-lapse video showing the diminutive moon's orbital path. The Hubble observations were intended to photograph Mars, and the moon's cameo appearance was a bonus. A football-shaped object just 16.5 miles by 13.5 miles by 11 miles, Phobos is one of the smallest moons in the solar system. It is so tiny that it would fit comfortably inside the Washington, D.C. Beltway. The little moon completes an orbit in just 7 hours and 39 minutes, which is faster than Mars rotates. Rising in the Martian west, it runs three laps around the Red Planet in the course of one Martian day, which is about 24 hours and 40 minutes. It is the only natural satellite in the solar system that circles its planet in a time shorter than the parent planet's day. About two weeks after the Apollo 11 manned lunar landing on July 20, 1969, NASA's Mariner 7 flew by the Red Planet and took the first crude close-up snapshot of Phobos. On July 20, 1976 NASA's Viking 1 lander touched down on the Martian surface. A year later, its parent craft, the Viking 1 orbiter, took the first detailed photograph of Phobos, revealing a gaping crater from an impact that nearly shattered the moon. Phobos was discovered by Asaph Hall on August 17, 1877 at the U.S. Naval Observatory in Washington, D.C., six days after he found the smaller, outer moon, named Deimos. Hall was deliberately searching for Martian moons. Both moons are named after the sons of Ares, the Greek god of war, who was known as Mars in Roman mythology. Phobos (panic or fear) and Deimos (terror or dread) accompanied their father into battle. Close-up photos from Mars-orbiting spacecraft reveal that Phobos is apparently being torn apart by the gravitational pull of Mars. The moon is marred by long, shallow grooves that are probably caused by tidal interactions with its parent planet. Phobos draws nearer to Mars by about 6.5 feet every hundred years. Scientists predict that within 30 to 50 million years, it either will crash into the Red Planet or be torn to pieces and scattered as a ring around Mars. Orbiting 3,700 miles above the Martian surface, Phobos is closer to its parent planet than any other moon in the solar system. Despite its proximity, observers on Mars would see Phobos at just one-third the width of the full moon as seen from Earth. Conversely, someone standing on Phobos would see Mars dominating the horizon, enveloping a quarter of the sky. From the surface of Mars, Phobos can be seen eclipsing the sun. However, it is so tiny that it doesn't completely cover our host star. Transits of Phobos across the sun have been photographed by several Mars-faring spacecraft. The origin of Phobos and Deimos is still being debated. Scientists concluded that the two moons were made of the same material as asteroids. This composition and their irregular shapes led some astrophysicists to theorize that the Martian moons came from the asteroid belt. However, because of their stable, nearly circular orbits, other scientists doubt that the moons were born as asteroids. Such orbits are rare for captured objects, which tend to move erratically. An atmosphere could have slowed down Phobos and Deimos and settled them into their current orbits, but the Martian atmosphere is too thin to have circularized the orbits. Also, the moons are not as dense as members of the asteroid belt. Phobos may be a pile of rubble that is held together by a thin crust. It may have formed as dust and rocks encircling Mars were drawn together by gravity. Or, it may have experienced a more violent birth, where a large body smashing into Mars flung pieces skyward, and those pieces were brought together by gravity. Perhaps an existing moon was destroyed, reduced to the rubble that would become Phobos. Hubble took the images of Phobos orbiting the Red Planet on May 12, 2016, when Mars was 50 million miles from Earth. This was just a few days before the planet passed closer to Earth in its orbit than it had in the past 11 years. A time-lapse video captures a portion of the path that tiny Phobos takes around Mars. Over the course of 22 minutes, Hubble snapped 13 separate exposures of the little Martian moon. The video can be viewed at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21837