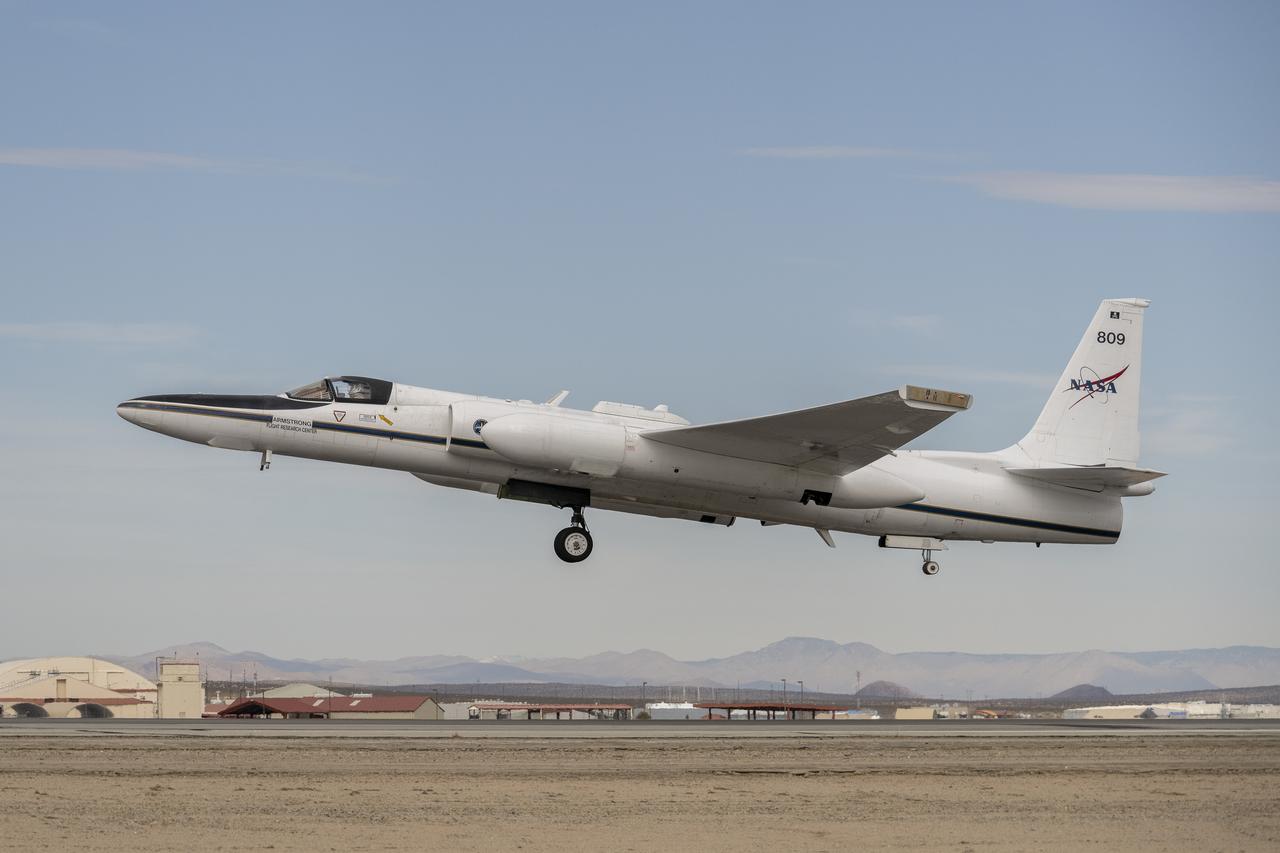

A team of experts wrap up science flights on the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California after the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Pilot Tim Williams ascends the ER-2 on the runway for one of the final science flights validating satellite-borne data. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
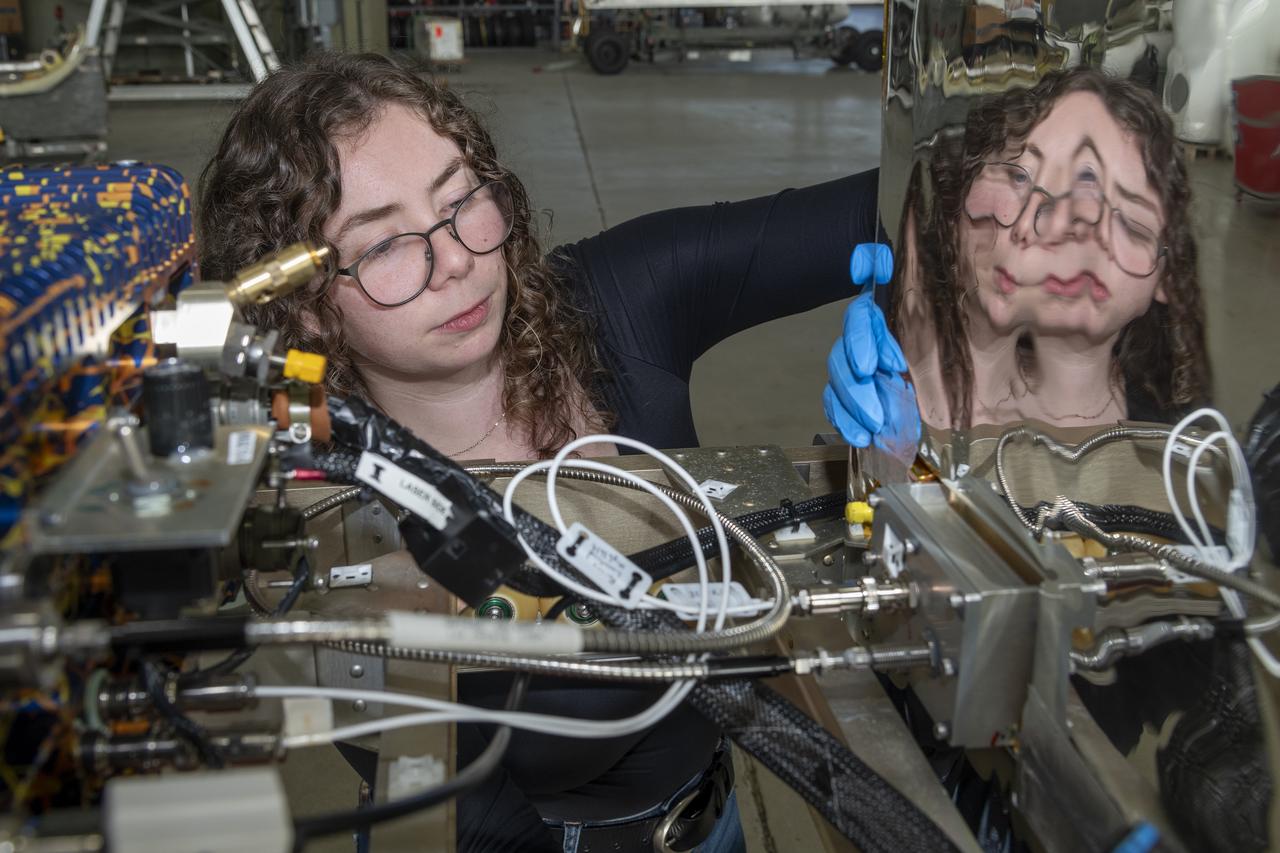
A team of experts prepares the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California for the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Researcher Jennifer Moore checks the cabling on the Roscoe instrument which flew at high altitudes on the ER-2. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
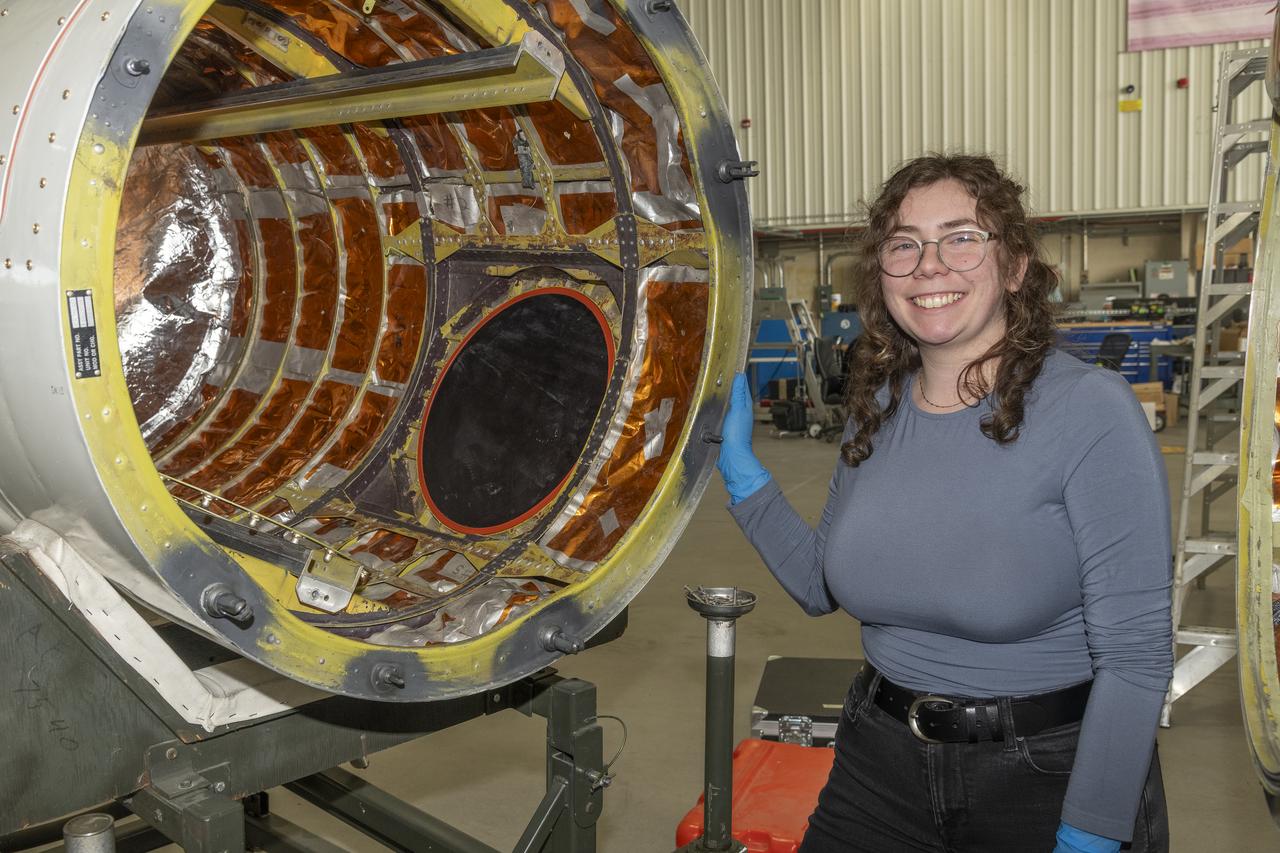

A team of experts prepares the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California for the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Researcher Jennifer Moore from NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center smiles beside the ER-2 aircraft’s forebody pod where the Cloud Physics Lidar (CPL) instrument will be installed. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
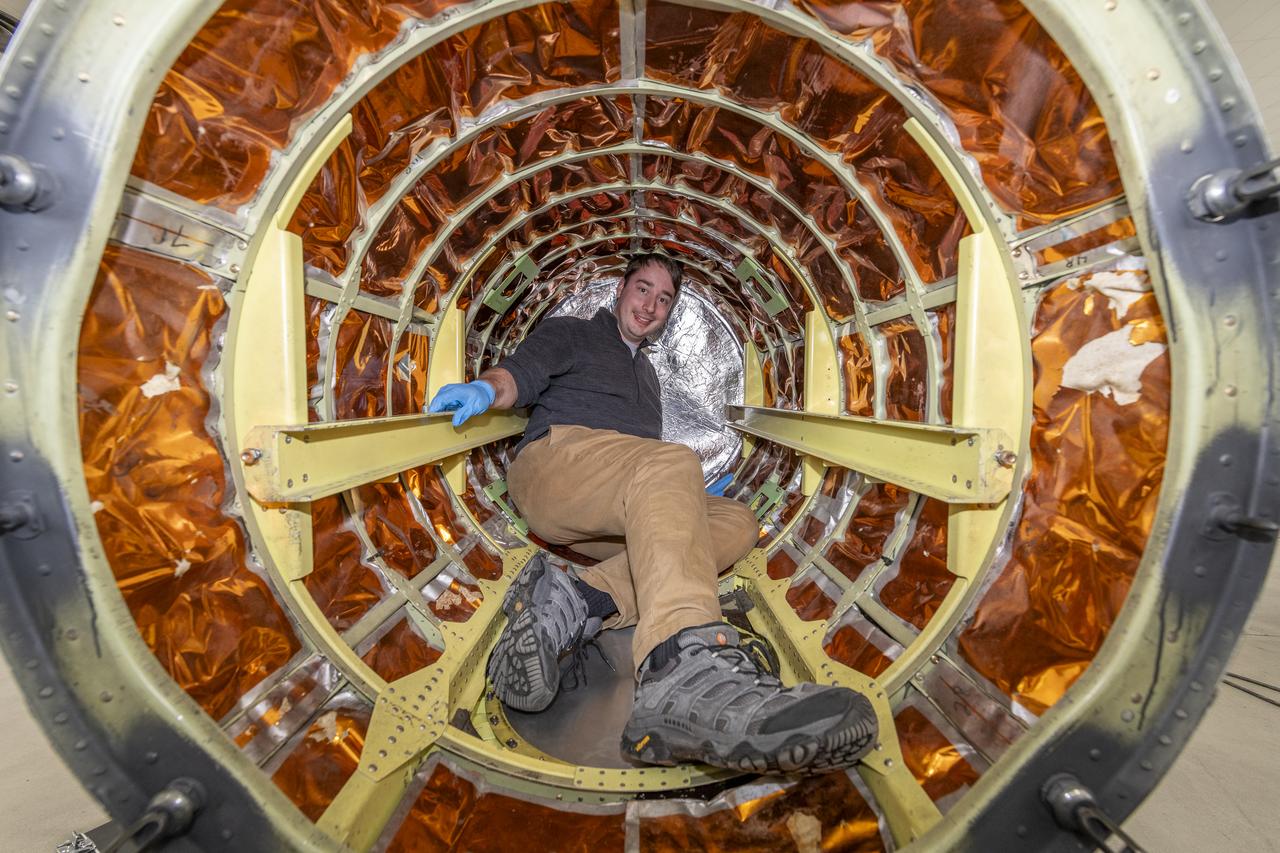

A team of experts prepares the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California for the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Researcher Grant Finneman from the University of Iowa installs the insulations at the front of the ER-2 forebody pod where the Cloud Physics Lidar (CPL) flies. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
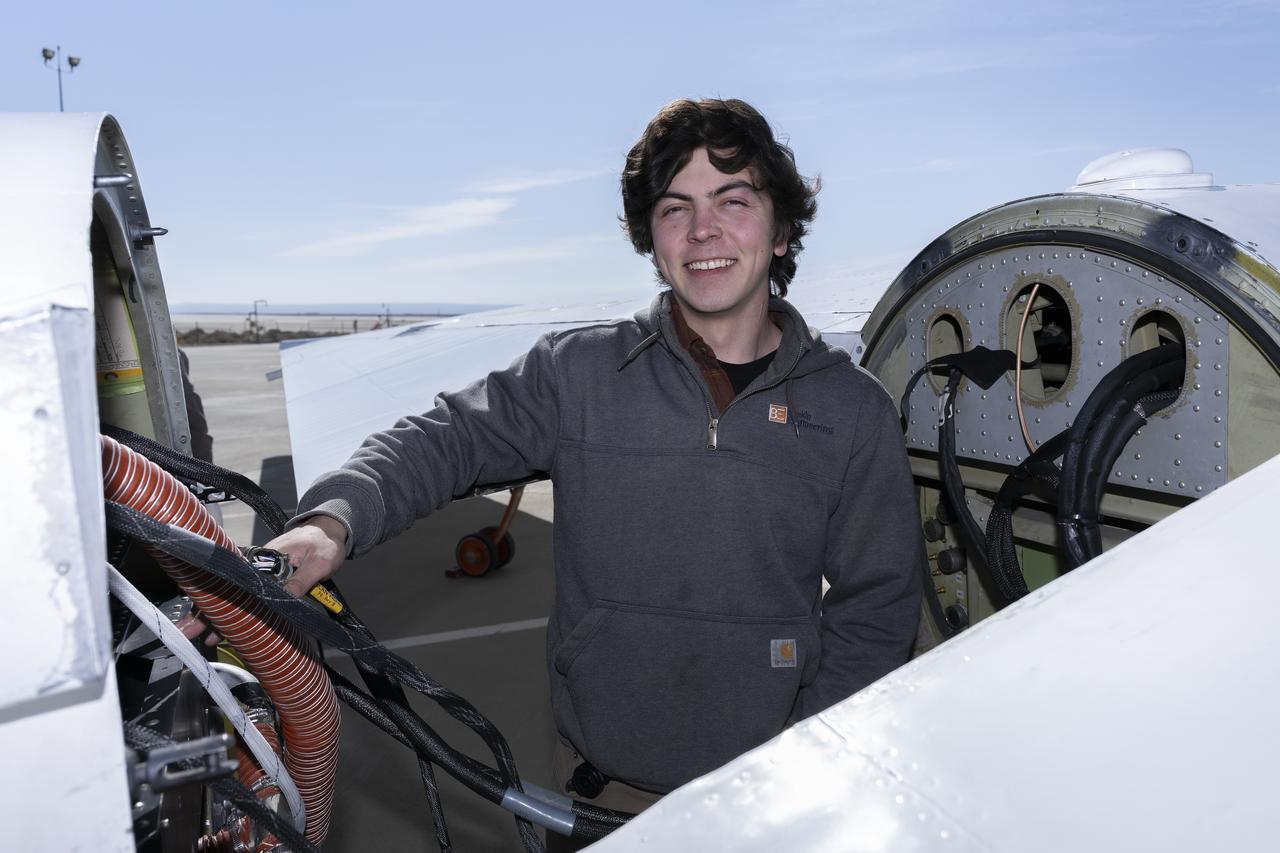

A team of experts wrap up science flights on the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California after the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Nikolas Gibson from NASA Ames Research Center integrates the enhanced MODIS Airbrone Simulator (eMAS) instrument onto the ER-2. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
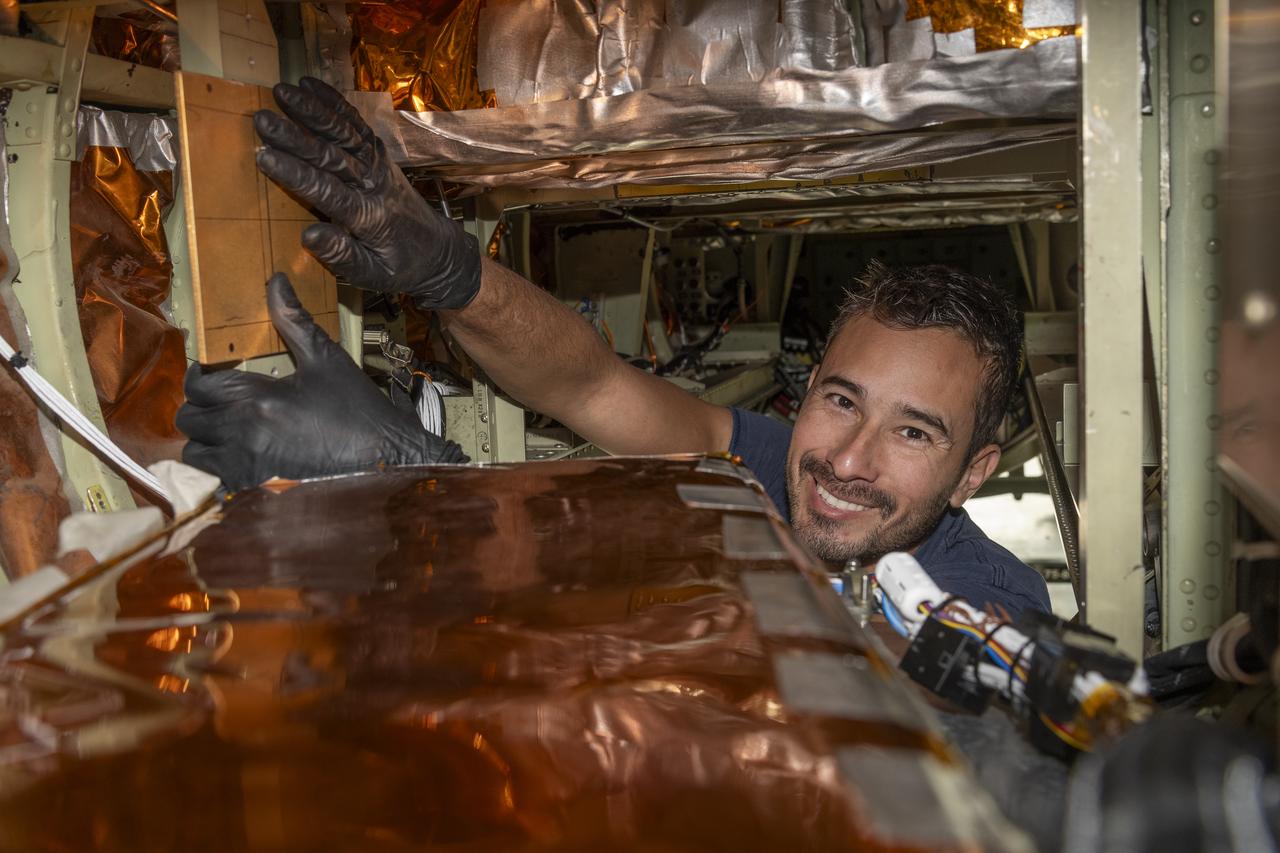

A team of experts prepares the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California for the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Aircraft mechanic Darick Alvarez-Alonzo installs a satellite-simulating instrument which will fly at high altitudes on the ER-2 to validate satellite-borne data. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
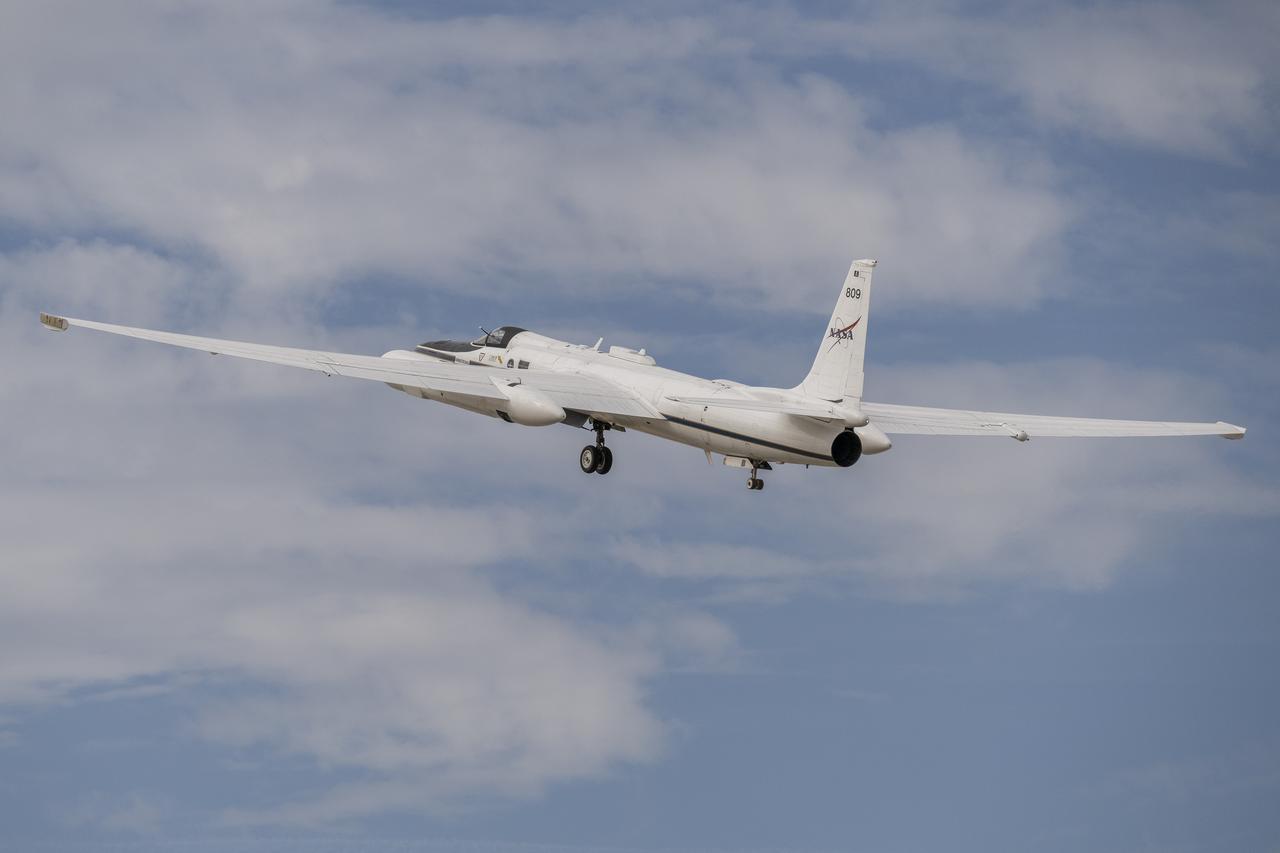

A team of experts wrap up science flights on the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California after the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Pilot Tim Williams ascends the ER-2 to higher skies for one of the final science flights validating satellite-borne data. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
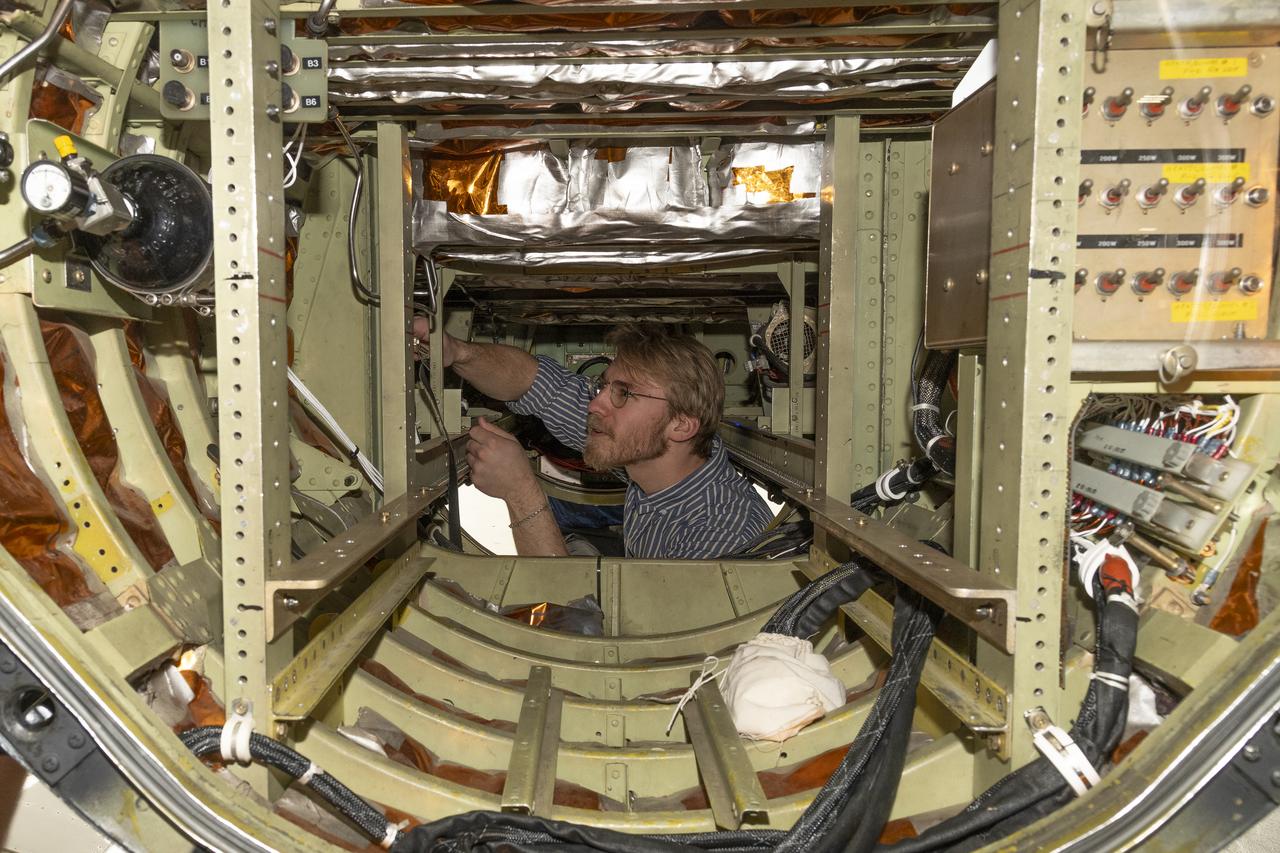

A team of experts prepares the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California for the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Researcher Jackson Begolka from the University of Iowa examines the instrument connectors in the ER-2 onboard the ER-2, which flies at high altitudes to validate satellite-borne data. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.
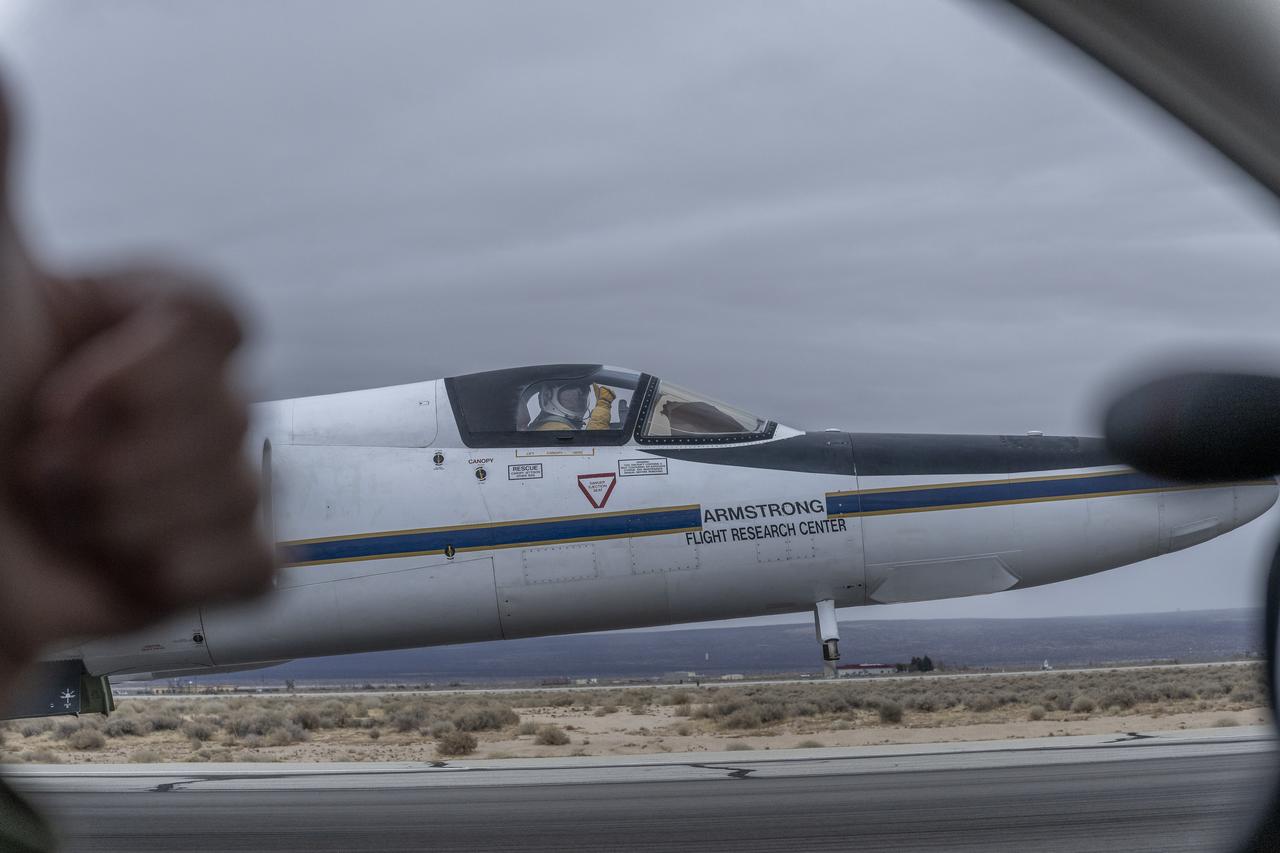

A team of experts wrap up science flights on the ER-2 aircraft at Armstrong Flight Research Center in Edwards, California after the GSFC Lidar Observation and Validation Experiment (GLOVE) in February 2025. Pilot Kirt Stallings ascends the ER-2 on the runway for one of the final science flights validating satellite-borne data. As a collaboration between engineers, scientists, and aircraft professionals, GLOVE aims to improve satellite data products for Earth Science applications.