
The two pots in this image are a composite of two images of asteroid 2002 JF56 taken on June 11 and June 12, 2006, with the Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera component of the New Horizons Ralph imager.
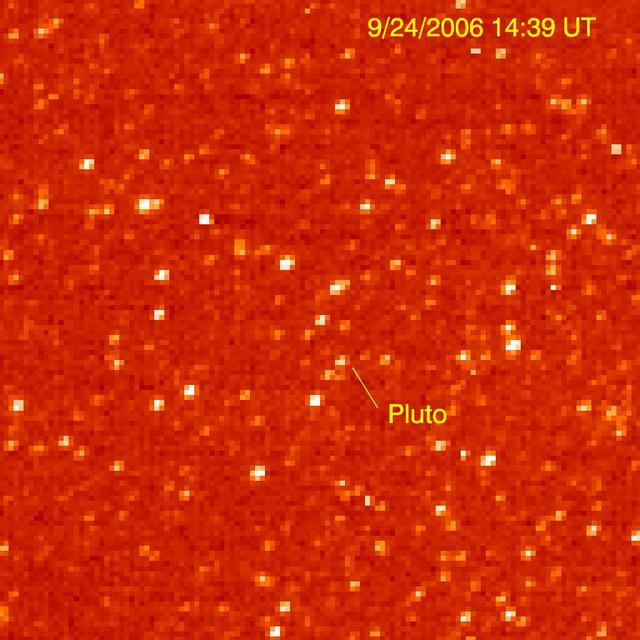

The Long Range Reconnaissance Imager on NASA New Horizons acquired images of the Pluto field three days apart in late September 2006, in order to see Pluto motion against a dense background of stars.
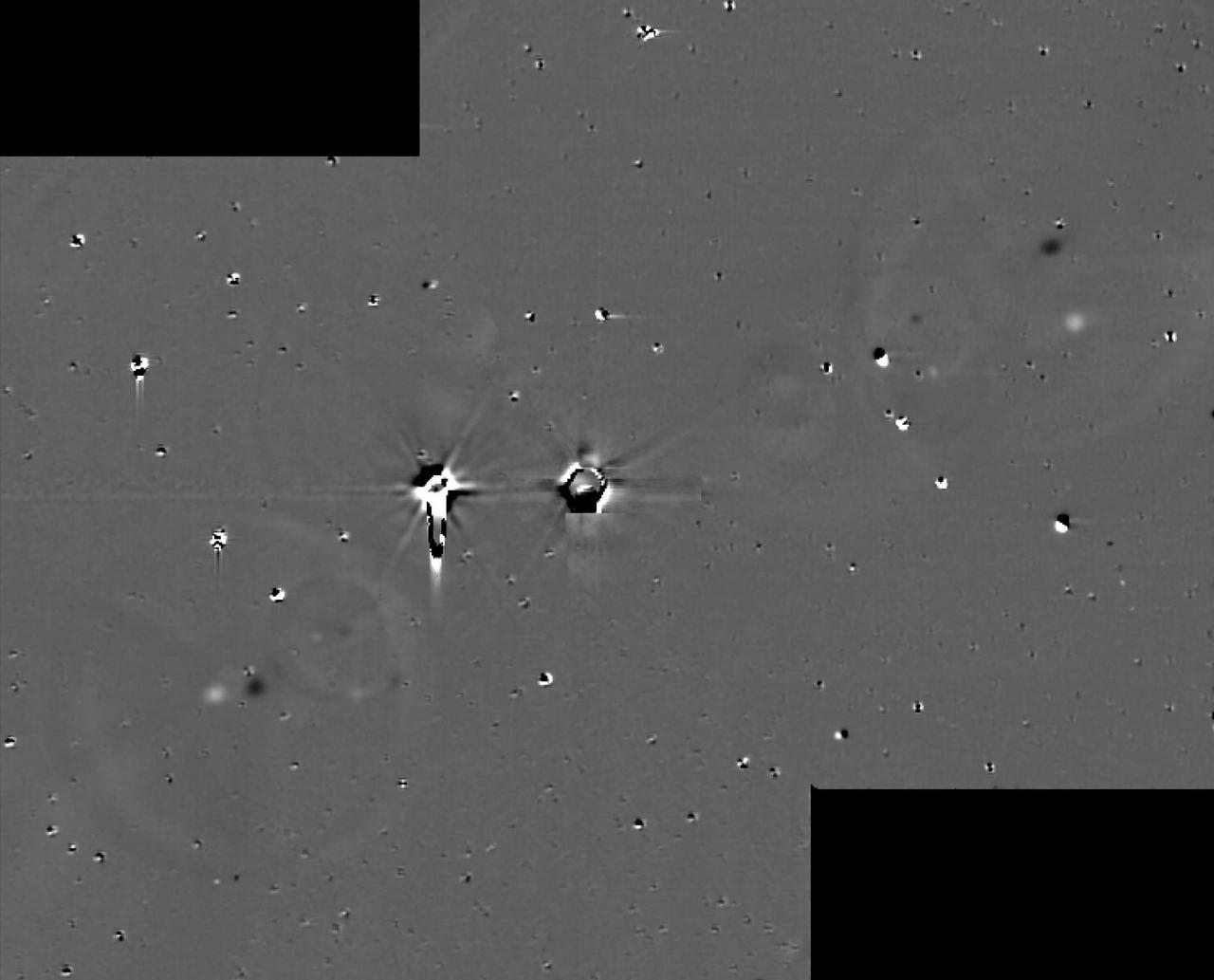
This illustration shows some of the final images used to determine that the coast is clear for New Horizons' flight through the Pluto system. These images show the difference between two sets of 48 combined 10-second exposures with New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) camera, taken at 8:40 UTC and 10:25 UTC on June 26, 2015, from a range of 21.5 million kilometers (approximately 13 million miles) to Pluto. The known small moons, Nix, Hydra, Kerberos and Styx, are visible as adjacent bright and dark pairs of dots, due to their motion in the 105 minutes between the two image sets. The images have been extensively processed to remove the glare and "ghosts" (i.e., lens flare) from Pluto and Charon, and also to remove background stars, though many of the brighter stars are imperfectly removed and appear as irregular bright and dark blobs. These and other similar sets of images demonstrate that there are no previously unknown moons brighter than 15 times fainter than Styx (the faintest known moon) in the region outside of Charon's orbit, or brighter than five times fainter than Styx in the region between Charon's orbit and a few thousand kilometers above Pluto's surface. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19695

This frame from a movie is composed of the sharpest views of Pluto that NASA's New Horizons spacecraft obtained during its flyby of the distant planet on July 14, 2015. The pictures are part of a sequence taken near New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto, with resolutions of about 250-280 feet (77-85 meters) per pixel -- revealing features smaller than half a city block on Pluto's diverse surface. The images include a wide variety of spectacular, cratered, mountainous and glacial terrains -- giving scientists and the public alike a breathtaking, super-high resolution window on Pluto's geology. The images form a strip 50 miles (80 kilometers) wide trending from Pluto's jagged horizon about 500 miles (800 kilometers) northwest of the informally named Sputnik Planum, across the al-Idrisi mountains, onto the shoreline of Sputnik Planum and then across its icy plains. They were made with the telescopic Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) aboard New Horizons, over a timespan of about a minute centered on 11:36 UT on July 14 -- just about 15 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto -- from a range of just 10,000 miles (17,000 kilometers). They were obtained with an unusual observing mode; instead of working in the usual "point and shoot," LORRI snapped pictures every three seconds while the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC) aboard New Horizons was scanning the surface. This mode requires unusually short exposures to avoid blurring the images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20202
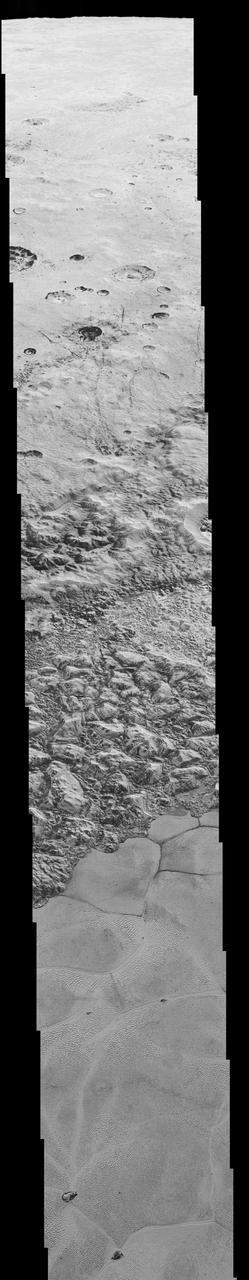
This mosaic is composed of the sharpest views of Pluto that NASA's New Horizons spacecraft obtained during its flyby of the distant planet on July 14, 2015. The pictures are part of a sequence taken near New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto, with resolutions of about 250-280 feet (77-85 meters) per pixel -- revealing features smaller than half a city block on Pluto's diverse surface. The images include a wide variety of spectacular, cratered, mountainous and glacial terrains -- giving scientists and the public alike a breathtaking, super-high resolution window on Pluto's geology. The images form a strip 50 miles (80 kilometers) wide trending from Pluto's jagged horizon about 500 miles (800 kilometers) northwest of the informally named Sputnik Planum, across the al-Idrisi mountains, onto the shoreline of Sputnik Planum and then across its icy plains. They were made with the telescopic Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) aboard New Horizons, over a timespan of about a minute centered on 11:36 UT on July 14 -- just about 15 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto -- from a range of just 10,000 miles (17,000 kilometers). They were obtained with an unusual observing mode; instead of working in the usual "point and shoot," LORRI snapped pictures every three seconds while the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC) aboard New Horizons was scanning the surface. This mode requires unusually short exposures to avoid blurring the images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20201
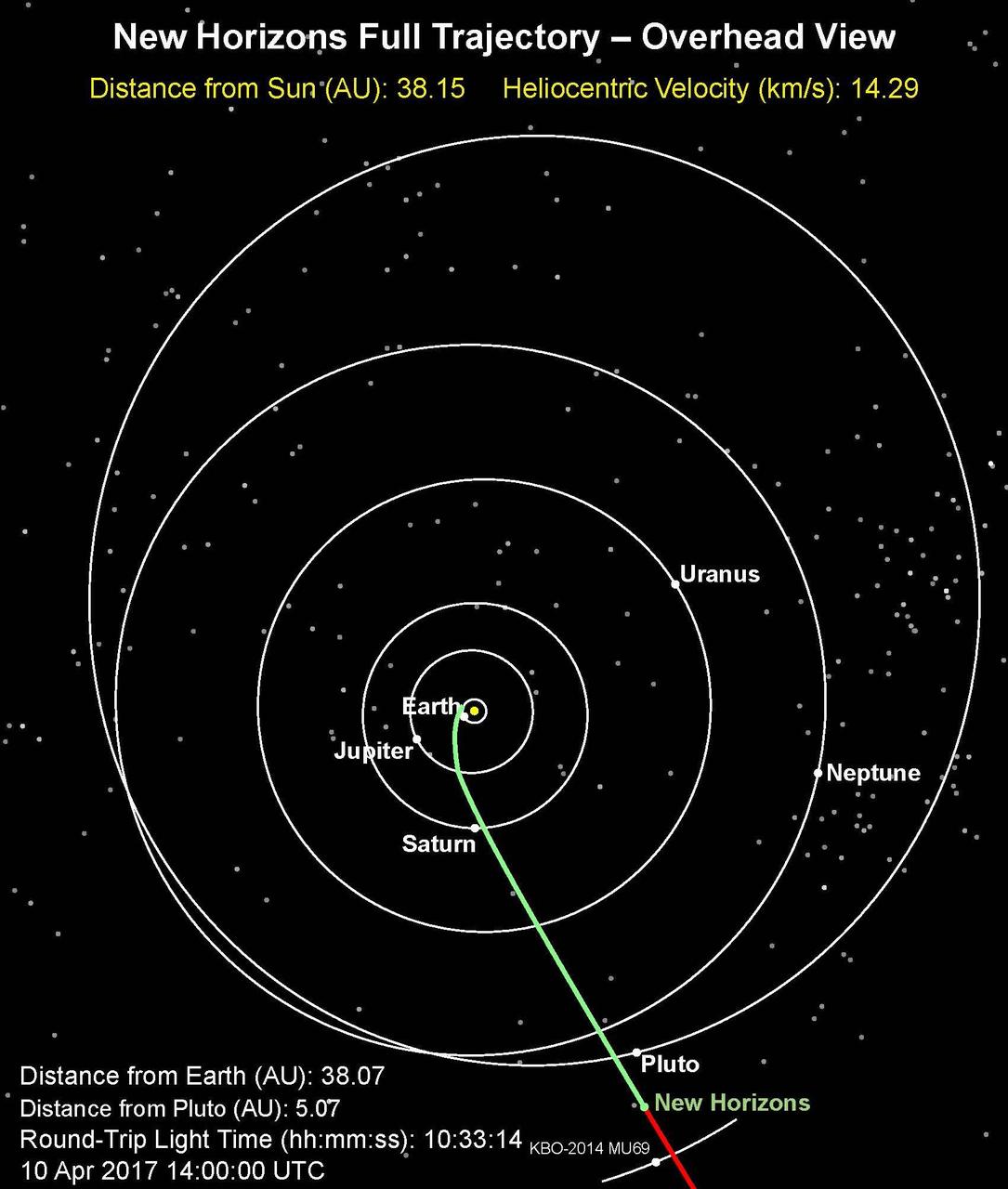
This is an overhead view of NASA's New Horizons full trajectory; the spacecraft has entered a hibernation phase on April 7 that will last until early September. The full article is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21589
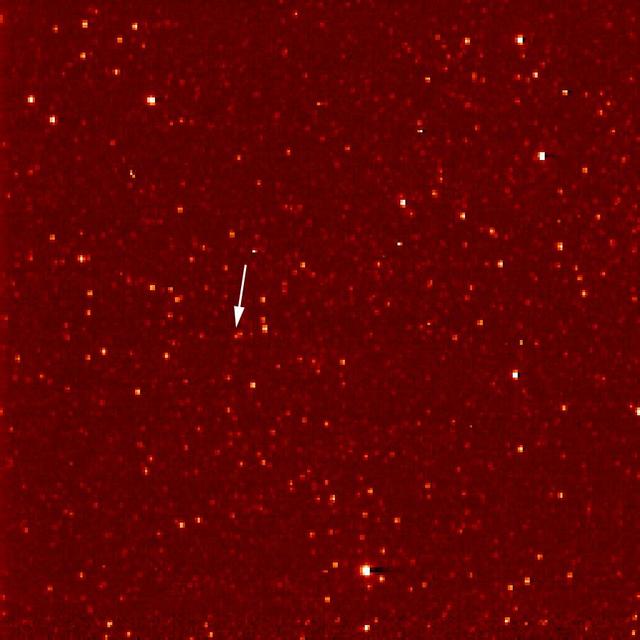

A white arrow marks Pluto in this NASA New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager picture taken Sept. 21, 2006. Pluto is little more than a faint point of light among a dense field of stars.
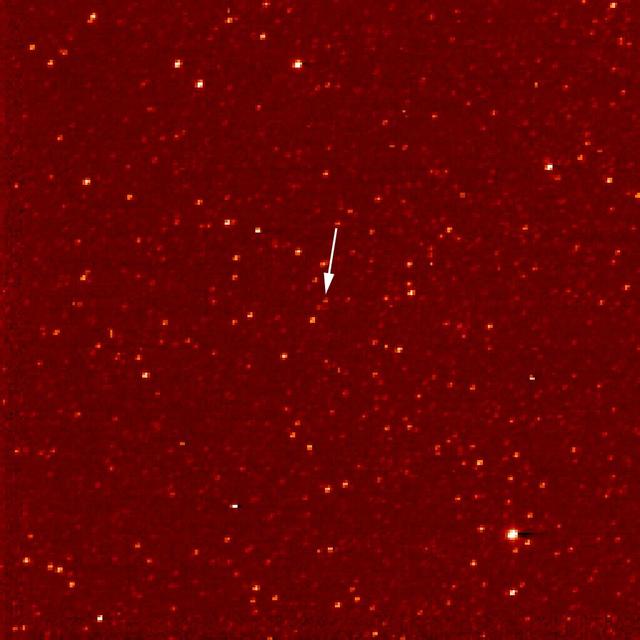

A white arrow marks Pluto in this NASA New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager picture taken Sept. 24, 2006. Pluto is little more than a faint point of light among a dense field of stars.
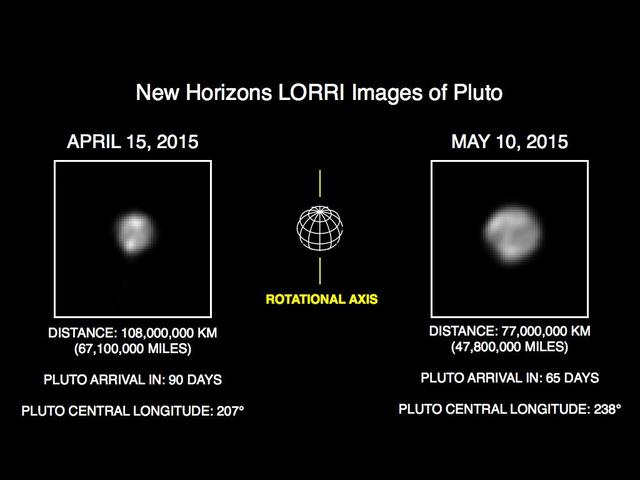
This image of Pluto is part of series of New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager LORRI photos taken May 8-12, 2015; the image at left shows LORRI view of Pluto just one month earlier.
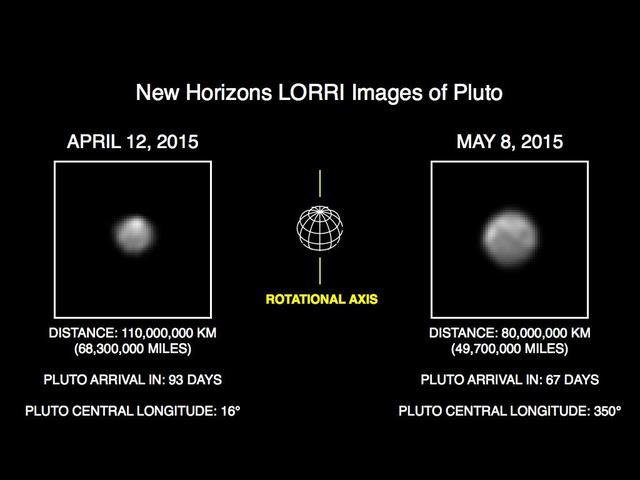
This image of Pluto is part of series of New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager LORRI photos taken May 8-12, 2015; the image at left shows LORRI view of Pluto just one month earlier.

This image of Pluto is part of series of New Horizons Long Range Reconnaissance Imager LORRI photos taken May 8-12, 2015; the image at left shows LORRI view of Pluto just one month earlier.
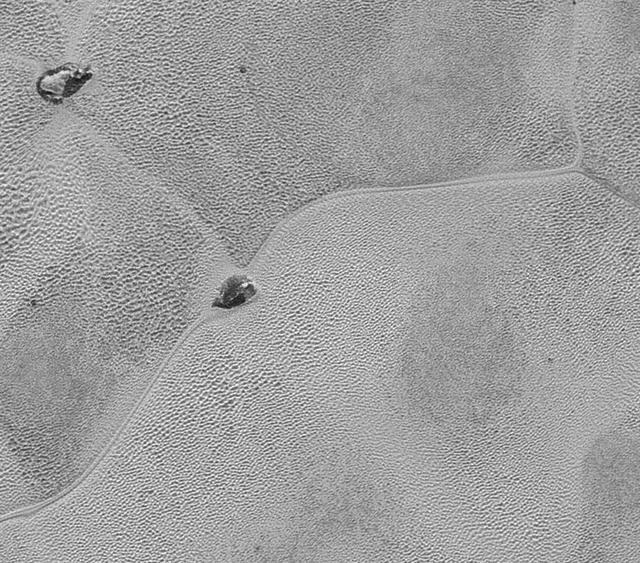

This mosaic strip, extending across the hemisphere that faced the New Horizons spacecraft as it flew past Pluto on July 14, 2015, now includes all of the highest-resolution images taken by the NASA probe.
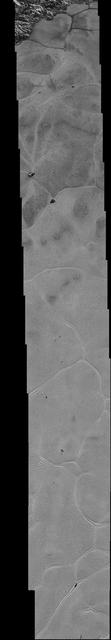
NASA's New Horizons spacecraft continues to transmit the sharpest views of Pluto that it obtained (and recorded) during its flyby of the distant planet on July 14, 2015. The newest image, returned on Dec. 24, 2015, extends New Horizons' highest-resolution swath of Pluto to the very center of the informally named Sputnik Planum, and nearly completes the set of highest-resolution images taken by New Horizons last July. The pictures are part of a sequence taken near New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto, with resolutions of about 250-280 feet (77-85 meters) per pixel -- revealing features smaller than half a city block on Pluto's surface. The images shown here form a strip 50 miles (80 kilometers) wide and more than 400 miles (700 kilometers) long, trending from the northwestern shoreline of Sputnik Planum and out across its icy plains. The images illustrate the polygonal or cellular pattern of the plains, which are thought to result from the convective churning of a deep layer solid, but mobile, nitrogen ice. The surface of Sputnik Planum appears darker toward the shore (at top), possibly implying a change in composition or surface texture. The occasional raised, darker blocks at the cell edges are probably dirty water "icebergs" floating in denser solid nitrogen. The pictures were taken with the telescopic Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) aboard New Horizons, from a range of approximately 10,000 miles (17,000 kilometers) over a timespan of about a minute centered on 11:36 UT on July 14 -- just about 15 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20336

This frame from a movie, which extends across the hemisphere that faced New Horizons spacecraft as it flew past Pluto on July 14, 2015, includes all of the highest-resolution images taken by the NASA probe. With a resolution of about 260 feet (80 meters) per pixel, the movie affords New Horizons scientists and the public the best opportunity to examine the fine details of the various types of terrain the mosaic covers, and determine the processes that formed and shaped them. The view extends from the "limb" of Pluto at the top of the strip, almost to the "terminator" (or day/night line) in the southeast of the encounter hemisphere, seen at the bottom of the strip. The width of the strip ranges from more than 55 miles (90 kilometers) at its northern end to about 45 miles (75 kilometers) at its southern end. The perspective changes greatly along the strip: at its northern end, the view looks out horizontally across the surface, while at its southern end, the view looks straight down onto the surface. This movie pans down the mosaic from top to bottom, offering new views of many of Pluto's distinct landscapes along the way. Starting with hummocky, cratered uplands at top, the view crosses over parallel ridges of the "washboard" terrain; chaotic and angular mountain ranges; the craterless, cellular plains; coarsely "pitted" areas of sublimating nitrogen ice; zones of thin nitrogen ice draped over the topography below; and rugged, dark, mountainous highlands scarred by deep pits. The frames in the movie were obtained by New Horizons' Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) approximately 9,850 miles (15,850 kilometers) from Pluto, about 23 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach. LORRI is only capable of obtaining black-and-white images; all color images are made by the Ralph instrument, which has somewhat lower resolution than LORRI. Movies are available at http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA14457

Artist's impression of NASA's New Horizons spacecraft encountering 2014 MU69, a Kuiper Belt object that orbits one billion miles (1.6 billion kilometers) beyond Pluto, on Jan. 1, 2019. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22190

This image of Pluto and its largest moon, Charon, was taken by the Ralph color imager aboard NASA New Horizons spacecraft on April 9 and downlinked to Earth the following day.
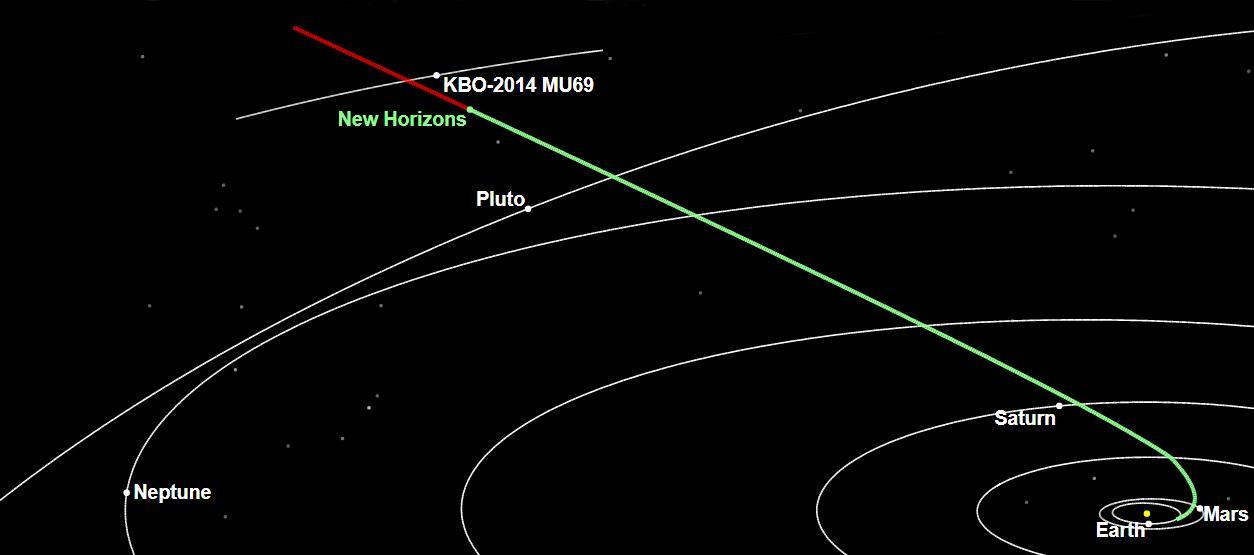
The New Horizons spacecraft is about 300 million miles (483 million kilometers) from 2014 MU69, the Kuiper Belt object it will encounter on Jan. 1, 2019. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22188
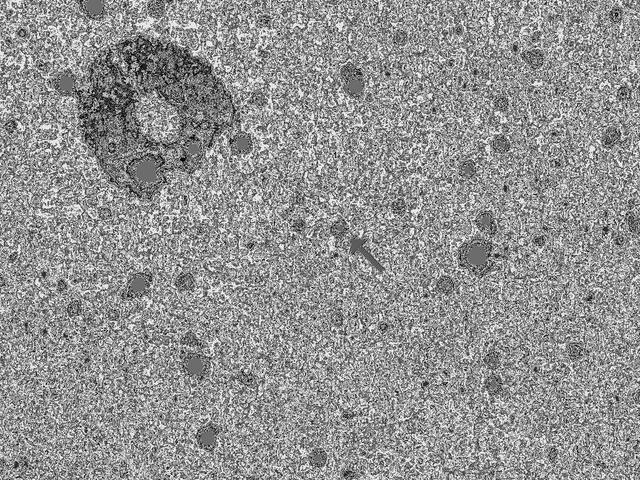
In April 2016, NASA New Horizons spacecraft observed 1994 JR1, a 90-mile 145-kilometer wide Kuiper Belt object KBO orbiting more than 3 billion miles 5 billion kilometers from the sun.

This image shows the results of the New Horizons team first search for potentially hazardous material around Pluto, conducted May 11-12, 2015, from a range of 47 million miles 76 million kilometers.
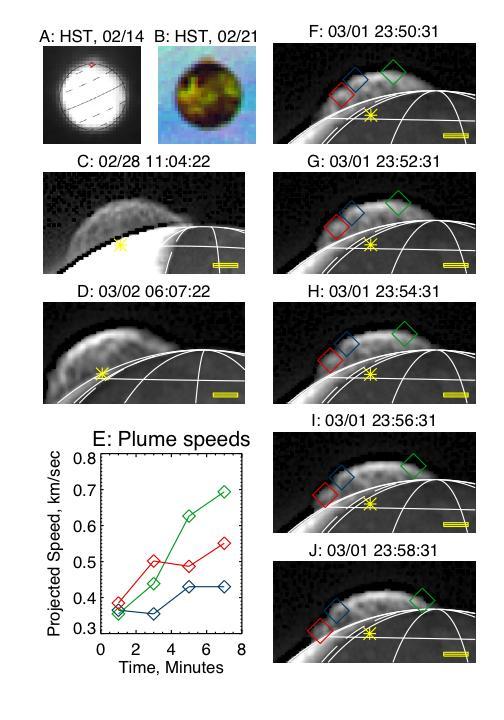
The Tvashtar plume on Io, seen by the Hubble Space Telescope HST and by New Horizons.

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory speaks about new data received from the New Horizons spacecraft during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO and New Horizons project manager Helene Winters of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory discuss the various teams have helped work on New Horizons, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons co-investigator Kelsi Singer of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, and New Horizons science team affiliate Kirby Runyon of John Hopkins discuss the various instruments on the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory high-fives a New Horizons team member after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
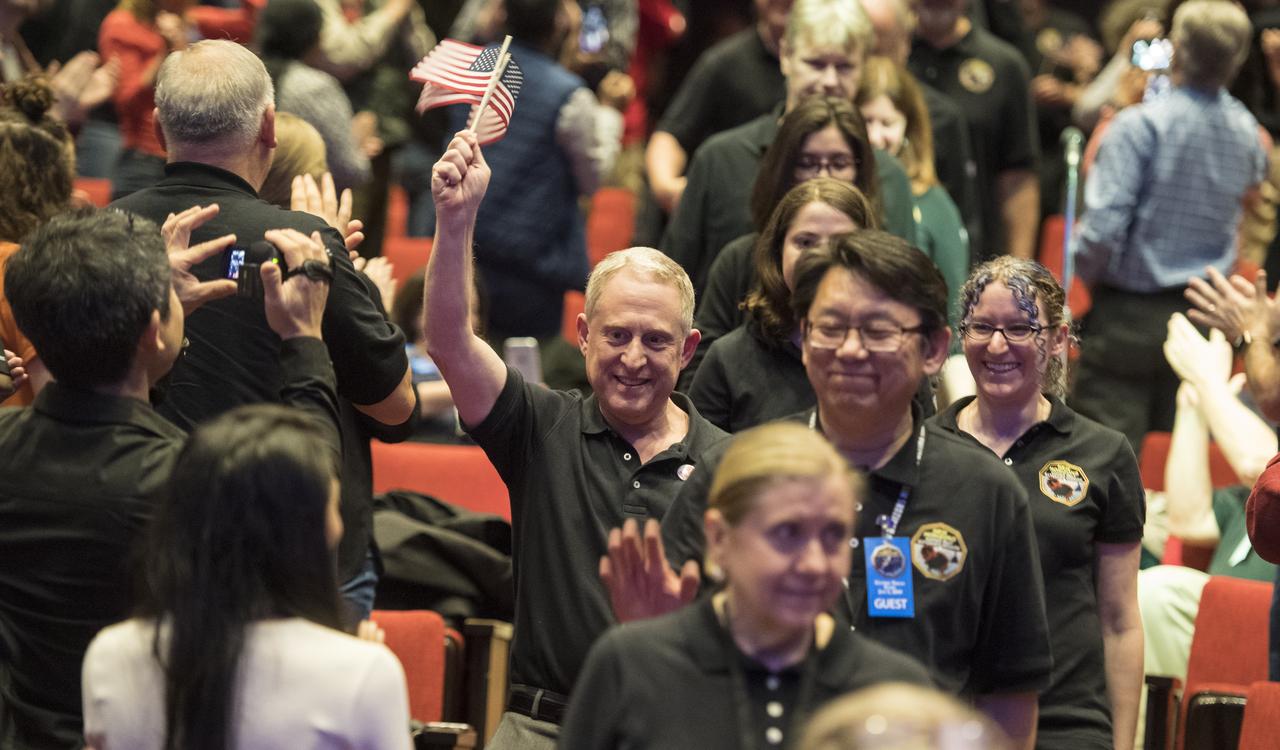

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, is seen with New Horizons team members as they enter the auditorium prior to a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
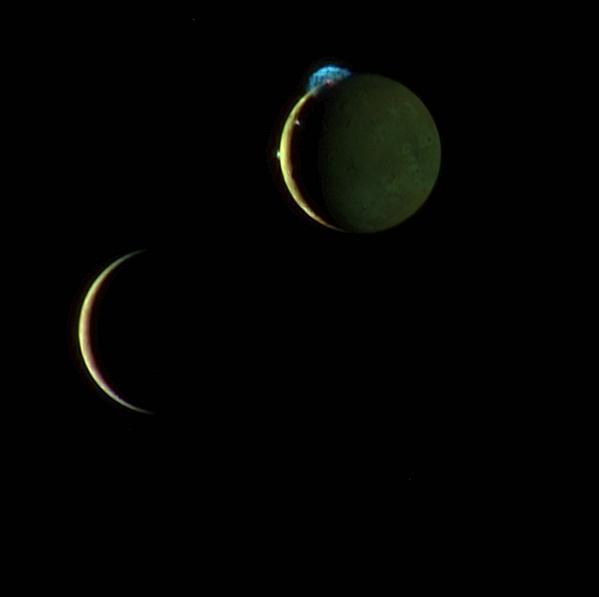

This beautiful image of the crescents of volcanic Io and more sedate Europa is a combination of two New Horizons images taken March 2, 2007, about two days after New Horizons made its closest approach to Jupiter.

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory speaks about the Kuiper Belt during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, speaks at a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory speaks about the Kuiper Belt during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory speaks about the Kuiper Belt during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons project manager Helene Winters of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory speaks at a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, speaks during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons project manager Helene Winters of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory speaks during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons project manager Helene Winters of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory speaks at a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Guests congratulate New Horizons team members after they received signals from the New Horizons spacecraft that it is healthy and it collected data during the fly of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons science team affiliate Kirby Runyon of John Hopkins discuss the various instruments on the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, speaks during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons co-investigator John Spencer of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, speaks about the flyby of Ultima Thule during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
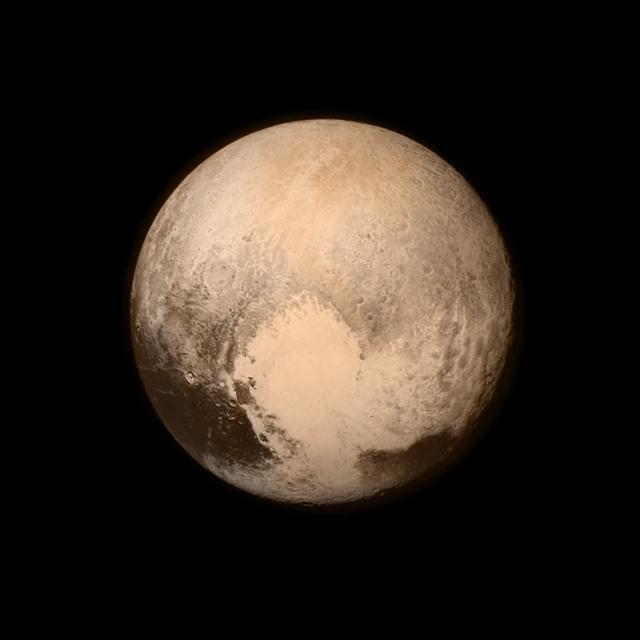

Pluto nearly fills the frame in this image from the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) aboard NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft, taken on July 13, 2015, when the spacecraft was 476,000 miles (768,000 kilometers) from the surface. This is the last and most detailed image sent to Earth before the spacecraft’s closest approach to Pluto on July 14. The color image has been combined with lower-resolution color information from the Ralph instrument that was acquired earlier on July 13. This view is dominated by the large, bright feature informally named the “heart,” which measures approximately 1,000 miles (1,600 kilometers) across. The heart borders darker equatorial terrains, and the mottled terrain to its east (right) are complex. However, even at this resolution, much of the heart’s interior appears remarkably featureless—possibly a sign of ongoing geologic processes. CREDIT: NASA/APL/SwRI <b><a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1L5NU1J" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1L5NU1L" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1L5NU1N" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1L5NWqt" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1L5NWGJ" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b> <b><a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1L5NWGN" rel="nofollow">Credit: NOAA/NASA GOES Project</a></b>

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, right, along with other mission team members and guest watch as Brian May, lead guitarist of the rock band Queen and astrophysicist shows a video with a new song he wrote for the New Horizons mission, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

This dramatic view of the Pluto system is as NASA's New Horizons spacecraft saw it in July 2015. The animation, made with real images taken by New Horizons, begins with Pluto flying in for its close-up on July 14; we then pass behind Pluto and see the atmosphere glow in sunlight before the sun passes behind Pluto's largest moon, Charon. The movie ends with New Horizons' departure, looking back on each body as thin crescents. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19873

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO and New Horizons Mission Operations Manager Alice Bowman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory are seen on a television screen as New Horizons team members and guests cheer as the team receives confirmation from the spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, reads an e-mail sent by Associate Administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen during a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO gives remarks about the New Horizons mission during a briefing discussing small bodies missions, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons co-investigator John Spencer of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO speaks during a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons Mission Operations Manager Alice Bowman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons co-investigator Cathy Olkin of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) speaks about Kuiper Belt object MU69, Ultima Thule, during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons co-investigator John Spencer of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO speaks during a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons co-investigator John Spencer of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO speaks during a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons Mission Operations Manager Alice Bowman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is seen before a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons co-investigator John Spencer of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, right, speaks during a press conference prior to the flyby about the first images received from the New Horizons spacecraft of Ultima Thule that were captured on Dec. 30 as the spacecraft was 1.2 million miles away from Ultima Thule, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons co-investigator John Spencer of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, uses a pen to demonstrate how Ultima Thule might be rotating during a press conference prior to the flyby of the Kuiper Belt object by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO gives remarks about the New Horizons mission during a briefing discussing small bodies missions, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, along with other mission team members, waves American flags as he enters the main auditorium for a press conference, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. The New Horizons team received signals from the spacecraft that it is healthy and it collected data during the fly of Ultima Thule. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons project manager Helene Winters of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory speaks during a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons co-investigator Cathy Olkin of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) speaks about Kuiper Belt object MU69, Ultima Thule, during an overview of the New Horizons Mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons mission systems engineer Chris Hersman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons Mission Operations Manager Alice Bowman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
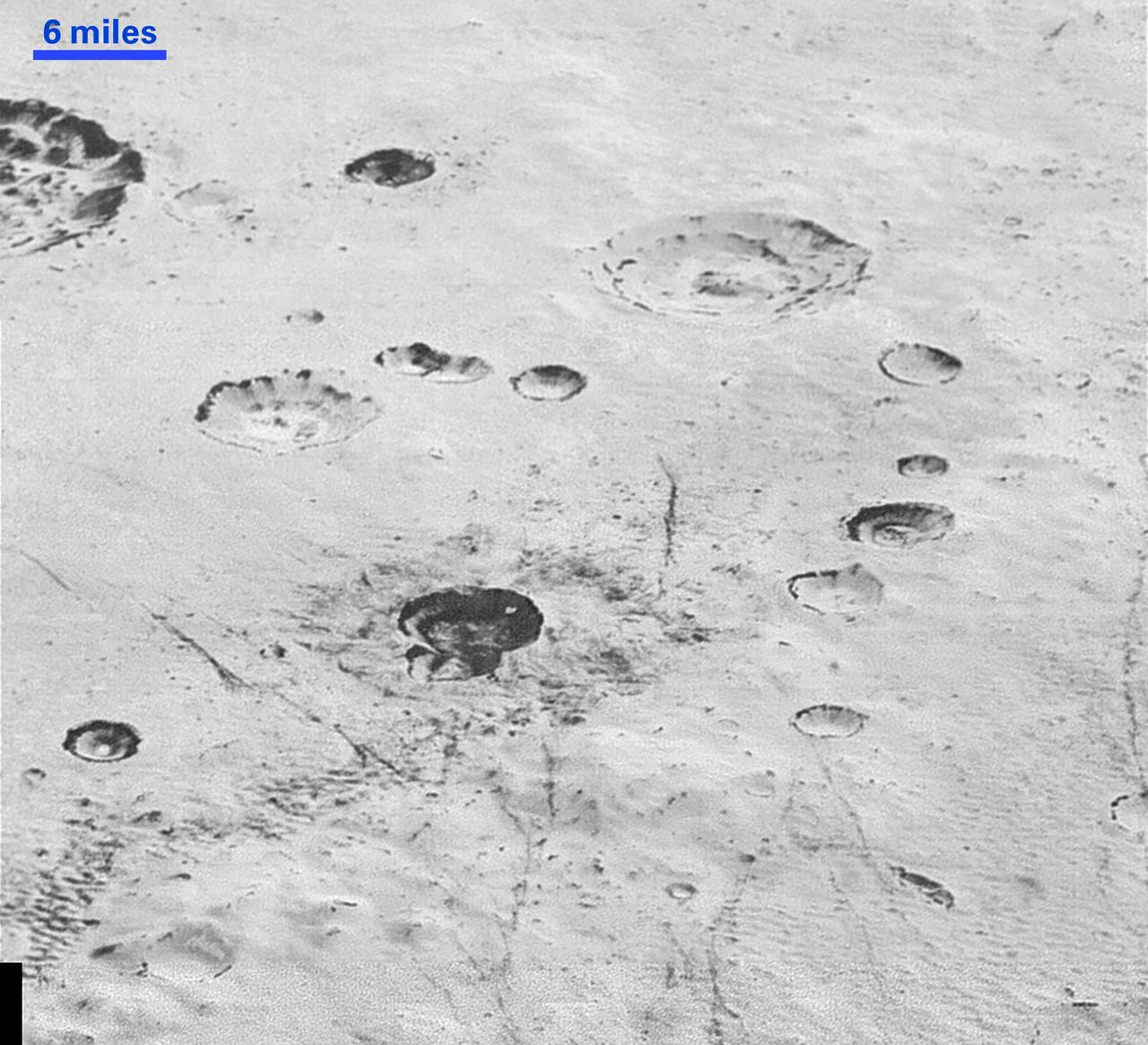

This highest-resolution image from NASA's New Horizons spacecraft reveals new details of Pluto's rugged, icy cratered plains. Notice the layering in the interior walls of many craters (the large crater at upper right is a good example) -- layers in geology usually mean an important change in composition or event but at the moment New Horizons team members do not know if they are seeing local, regional or global layering. The darker crater in the lower center is apparently younger than the others, because dark material ejected from within -- its "ejecta blanket" -- have not been erased and can still be made out. The origin of the many dark linear features trending roughly vertically in the bottom half of the image is under debate, but may be tectonic. Most of the craters seen here lie within the 155-mile (250-kilometer)-wide Burney Basin, whose outer rim or ring forms the line of hills or low mountains at bottom. The basin is informally named after Venetia Burney, the English schoolgirl who first proposed the name "Pluto" for the newly discovered planet in 1930. The top of the image is to Pluto's northwest. These images were made with the telescopic Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) aboard New Horizons, in a timespan of about a minute centered on 11:36 UT on July 14 -- just about 15 minutes before New Horizons' closest approach to Pluto-- from a range of just 10,000 miles (17,000 kilometers). They were obtained with an unusual observing mode; instead of working in the usual "point and shoot," LORRI snapped pictures every three seconds while the Ralph/Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera (MVIC) aboard New Horizons was scanning the surface. This mode requires unusually short exposures to avoid blurring the images. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20200
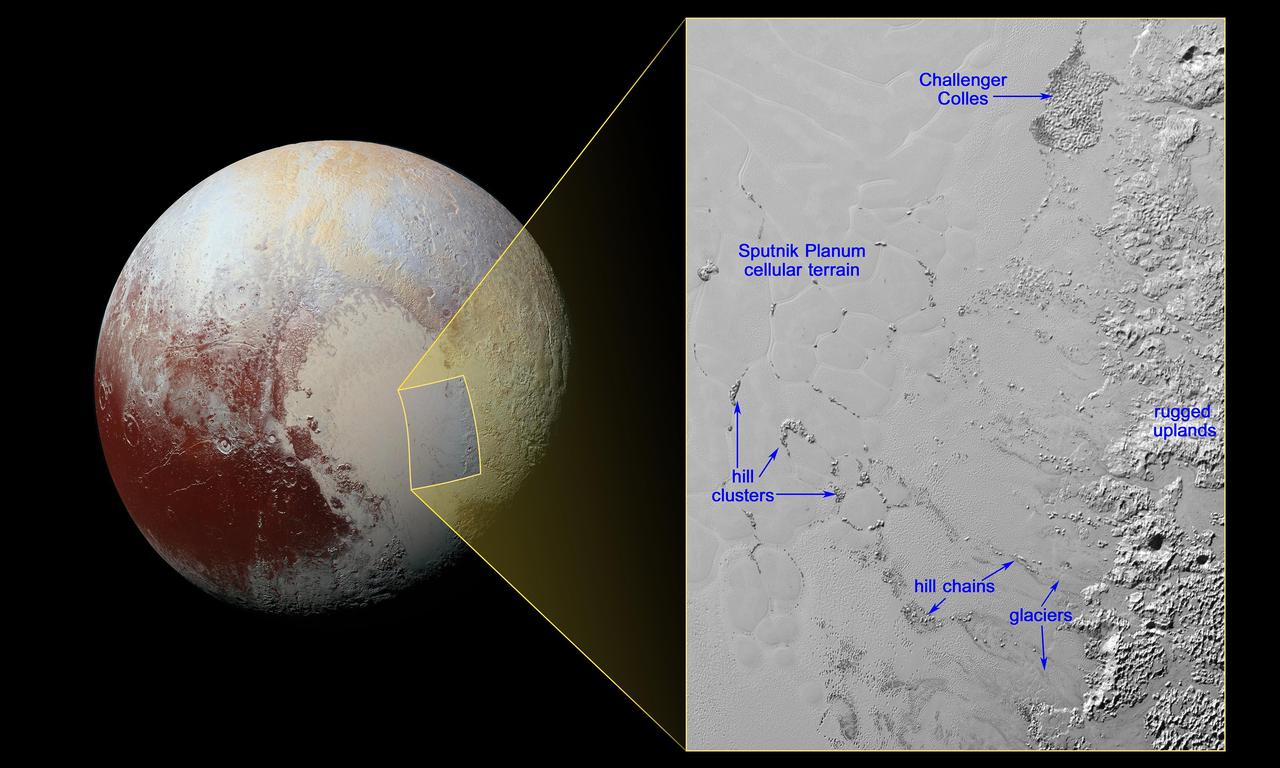
NASA New Horizons spacecraft took this image of Pluto vast nitrogen ice plain informally named Sputnik Planum.
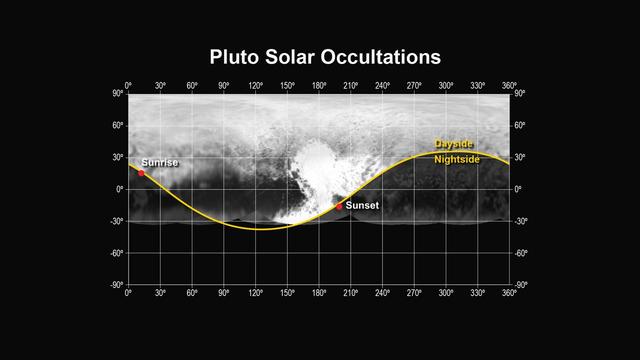
This figure shows the locations of the sunset and sunrise solar occultations observed by the Alice instrument on NASA New Horizons spacecraft.
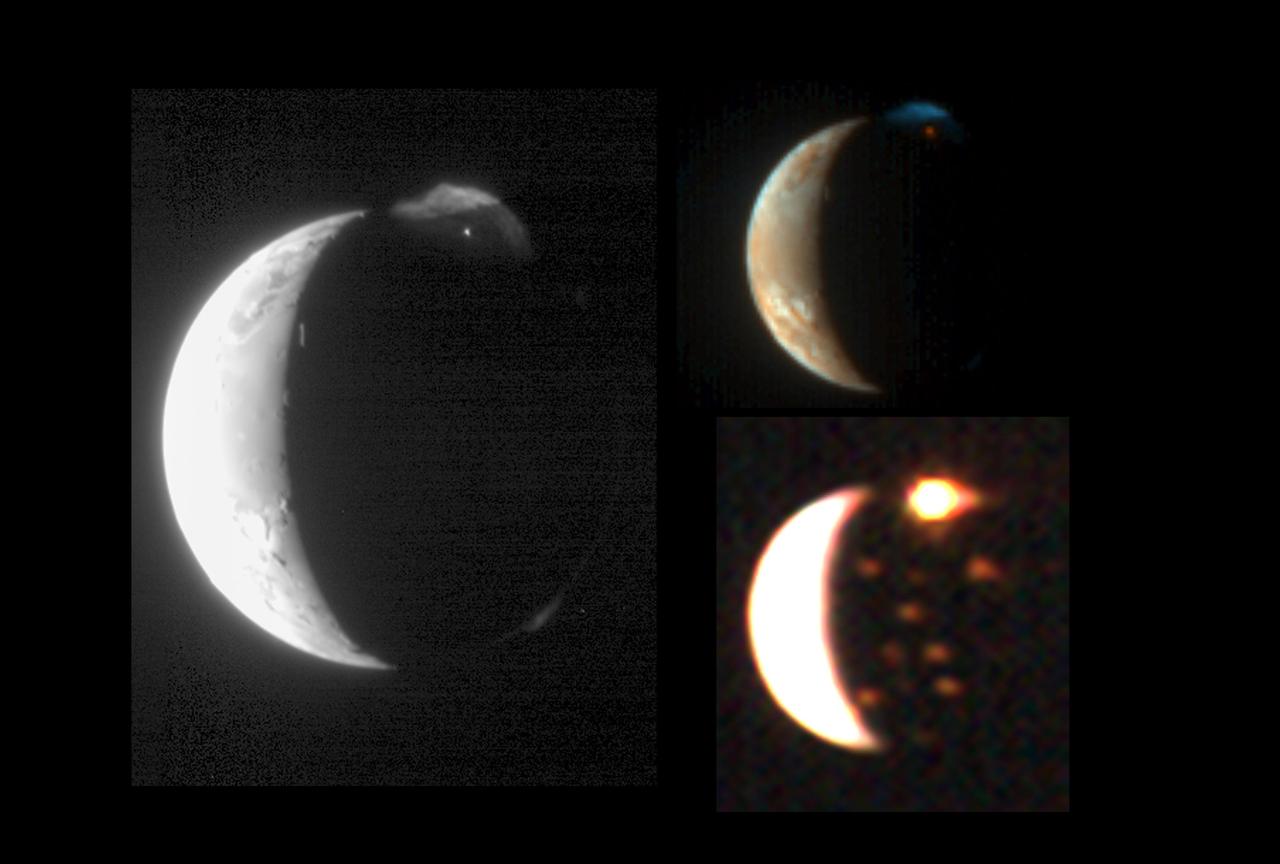

This montage demonstrates New Horizons ability to observe the same target in complementary ways using its diverse suite of instruments.

NASA New Horizons team calibrates the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager LORRI by taking pictures of the open star cluster M7.

This animation of Pluto and its largest moon, Charon, was taken by NASA New Horizons spacecraft as it raced toward Pluto in July 2014.
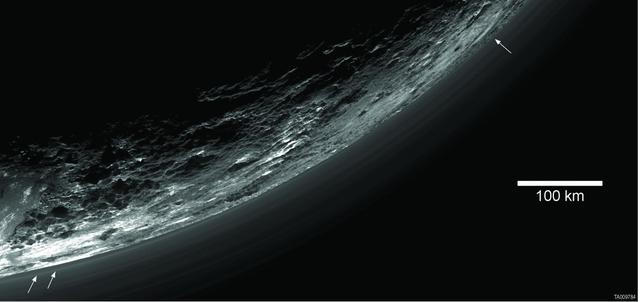
This image of haze layers above Pluto limb was taken by NASA New Horizons spacecraft. About 20 haze layers are seen.

This is a composite of several images taken in several colors by the New Horizons Multispectral Visual Imaging Camera, or MVIC.
A new image of Ultima Thule is seen on a screen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, New Horizons Mission Operations Manager Alice Bowman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, New Horizons mission systems engineer Chris Hersman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, and New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, spoke about the flyby and new pre-flyby information that was downlinked from the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

A new image of Ultima Thule is seen on a screen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, New Horizons Mission Operations Manager Alice Bowman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, New Horizons mission systems engineer Chris Hersman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, and New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, spoke about the flyby and new pre-flyby information that was downlinked from the spacecraft. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Musician Craig Werth introduces a song he made for the New Horizons mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Brian May, lead guitarist of the rock band Queen and astrophysicist shows a video with a new song he wrote for the New Horizons mission, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Guests watch as Brian May, lead guitarist of the rock band Queen and astrophysicist shows a video with a new song he wrote for the New Horizons mission, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

An audience member asks the panelists a question at the "New Horizons: The First Mission to the Pluto System and the Kuiper Belt" Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Monday, August 25, 2014. Scientists discussed how the first images of Pluto and its moons would be captured by the New Horizons spacecraft during a five month long reconnaissance flyby study starting in the summer of 2015. New Horizons launched on January 19, 2006 and is scheduled to make its closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Audience members view slides from a presentation by Dr. Jim Green, Dr. Ed Stone, and Dr. Alan Stern at the "New Horizons: The First Mission to the Pluto System and the Kuiper Belt" Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Monday, August 25, 2014. They discussed how the first images of Pluto and its moons would be captured by the New Horizons spacecraft during a five month long reconnaissance flyby study starting in the summer of 2015. New Horizons launched on January 19, 2006 and is scheduled to make its closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
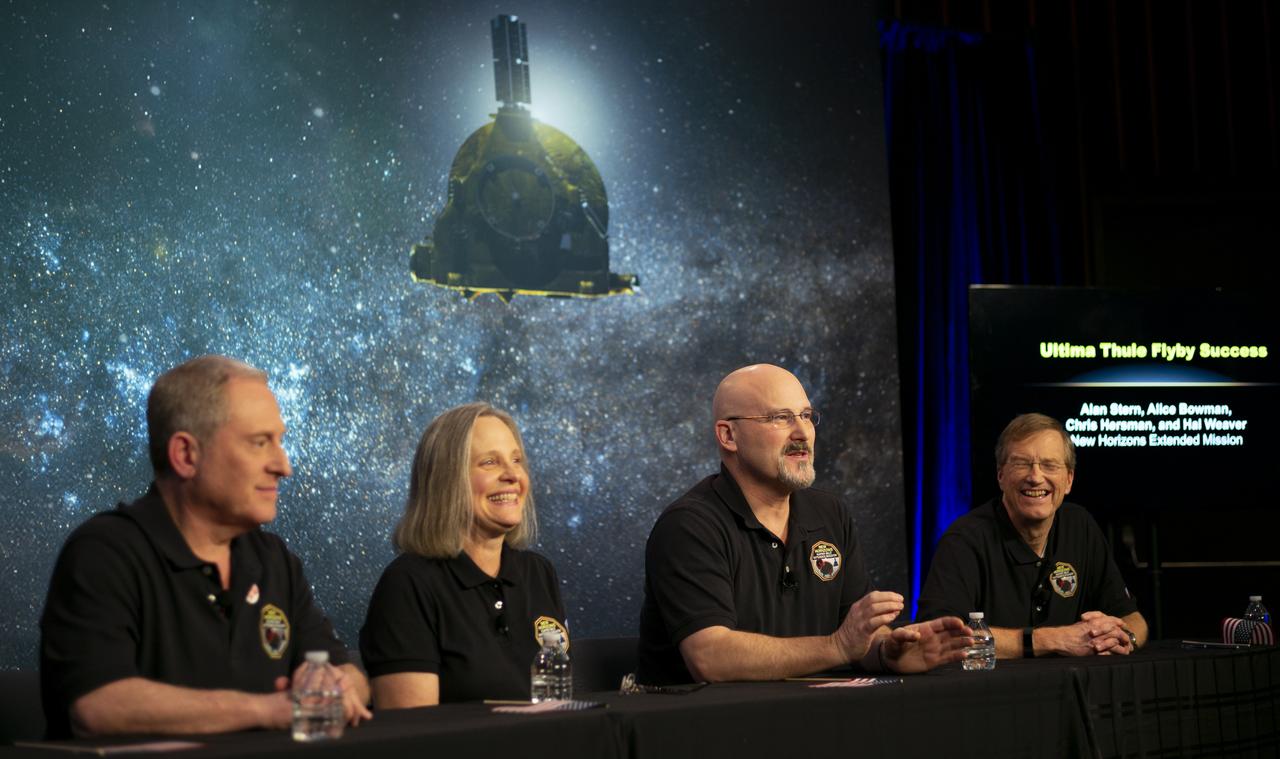

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, left, New Horizons Mission Operations Manager Alice Bowman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, second from left, New Horizons mission systems engineer Chris Hersman of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, second from right, and New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory, right, participate in a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons Mission Systems Engineer Chris Hersman, left, New Horizons Project Manager Helene Winters, and New Horizons Deputy Mission Systems Engineer Gabe Rogers, right, all of the Johns Hopkins Applied Physics Laboratory, wait for a signal from the spacecraft that it is healthy and collected data during the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at the Mission Operations Center of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Dr. Alan Stern, New Horizons principal investigator, speaks on a panel at the "New Horizons: The First Mission to the Pluto System and the Kuiper Belt" Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Monday, August 25, 2014. Scientists discussed how the first images of Pluto and its moons would be captured by the New Horizons spacecraft during a five month long reconnaissance flyby study starting in the summer of 2015. New Horizons launched on January 19, 2006 and is scheduled to make its closest approach to Pluto on July 14, 2015. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
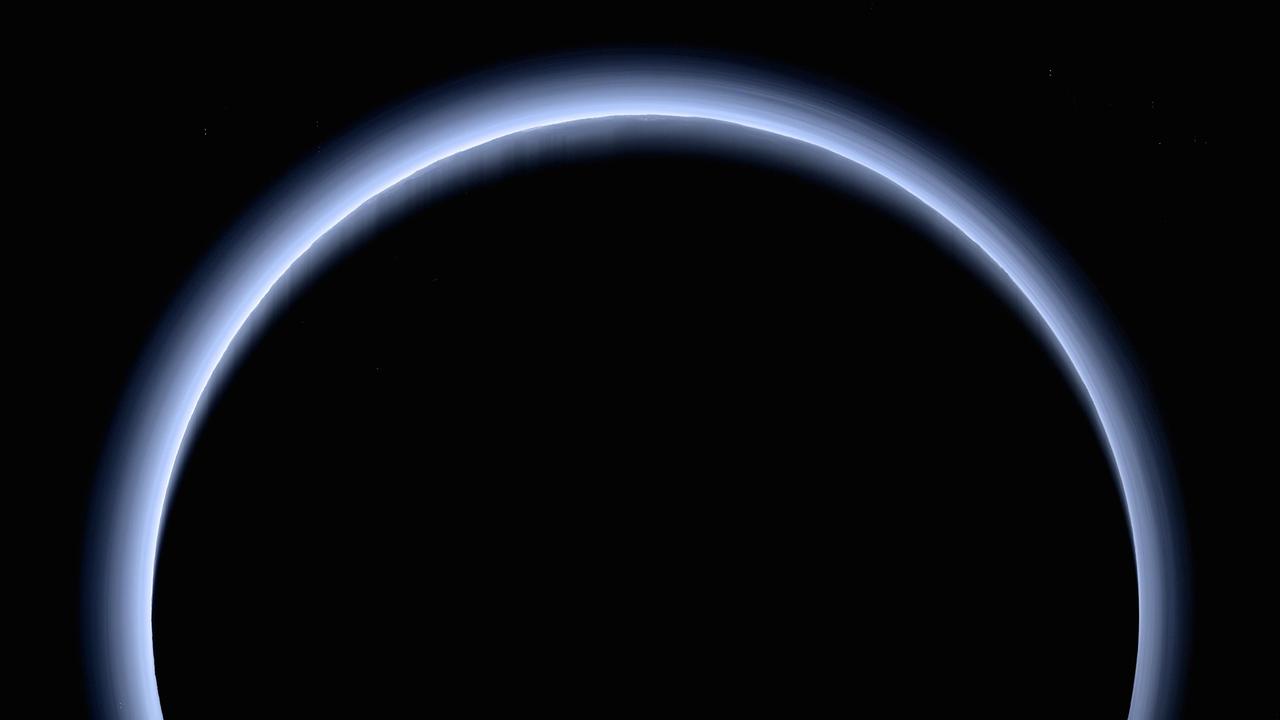

This is the highest-resolution color departure shot of Pluto's receding crescent from NASA's New Horizons spacecraft, taken when the spacecraft was 120,000 miles (200,000 kilometers) away from Pluto. Shown in approximate true color, the picture was constructed from a mosaic of six black-and-white images from the Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI), with color added from a lower resolution Ralph/Multispectral Visible Imaging Camera (MVIC) color image, all acquired between 15:20 and 15:45 UT -- about 3.5 hours after closest approach to Pluto -- on July 14, 2015. The resolution of the LORRI images is about 0.6 miles (1 kilometer) per pixel; the sun illuminates the scene from the other side of Pluto and somewhat toward the top of this image. The image is dominated by spectacular layers of blue haze in Pluto's atmosphere. Scientists believe the haze is a photochemical smog resulting from the action of sunlight on methane and other molecules in Pluto's atmosphere, producing a complex mixture of hydrocarbons such as acetylene and ethylene. These hydrocarbons accumulate into small haze particles, a fraction of a micrometer in size, which preferentially scatter blue sunlight -- the same process that can make haze appear bluish on Earth. As they settle down through the atmosphere, the haze particles form numerous intricate, horizontal layers, some extending for hundreds of miles around large portions of the limb of Pluto. The haze layers extend to altitudes of over 120 miles (200 kilometers). Pluto's circumference is 4,667 miles (7,466 kilometers). Adding to the beauty of this picture are mountains and other topographic features on Pluto's surface that are silhouetted against the haze near the top of the image. Sunlight casts dramatic and beautiful finger-like shadows from many of these features onto the haze (especially on the left, near the 11 o'clock position), forming crepuscular rays like those often seen in Earth's atmosphere near sunrise or sunset. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21590
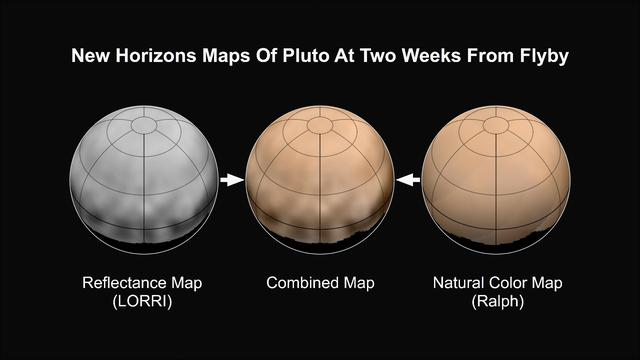
What color is Pluto? The answer, revealed in the first maps made from New Horizons data, turns out to be shades of reddish brown. The mission's first map of Pluto is in approximate true color -- that is, the color you would see if you were riding on New Horizons. At left, a map of Pluto's northern hemisphere composed using high-resolution black-and-white images from New Horizons LORRI instrument. At right is a map of Pluto's colors created using data from the Ralph instrument. In the center is the combined map, produced by merging the LORRI and Ralph data. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19697

New Horizons missions managers including New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO, behind door, wait for a signal from the spacecraft that it is healthy and collected data during the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at the Mission Operations Center of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons principal investigator Alan Stern of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO is seen during a press conference after the team received confirmation from the New Horizons spacecraft that it has completed the flyby of Ultima Thule, Tuesday, Jan. 1, 2019 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

Brian May, lead guitarist of the rock band Queen and astrophysicist discusses the upcoming New Horizons flyby of the Kuiper Belt object Ultima Thule, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Brian May, lead guitarist of the rock band Queen and astrophysicist discusses the upcoming New Horizons flyby of the Kuiper Belt object Ultima Thule, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Associate Administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen is seen during a New Horizons briefing, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Associate Administrator for NASA's Science Mission Directorate Thomas Zurbuchen is seen during a New Horizons briefing, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory gives a talk titled "Pluto Flyby; Summer 2015", Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Geoff Haines-Stiles, writer, producer, director, Passport to Knowledge, discusses documenting the New Horizons mission, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Brian May, lead guitarist of the rock band Queen and astrophysicist discusses the upcoming New Horizons flyby of the Kuiper Belt object Ultima Thule, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory gives a talk titled "Pluto Flyby; Summer 2015", Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory gives a talk titled "Pluto Flyby; Summer 2015", Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Media and guest listen to briefings leading up to the New Horizons spacecraft closest approach to Ultima Thule, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Brian May, lead guitarist of the rock band Queen and astrophysicist discusses the upcoming New Horizons flyby of the Kuiper Belt object Ultima Thule, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons deputy project scientist Cathy Olkin of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO discusses what they hope to learn from the flyby of Ultima Thule, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
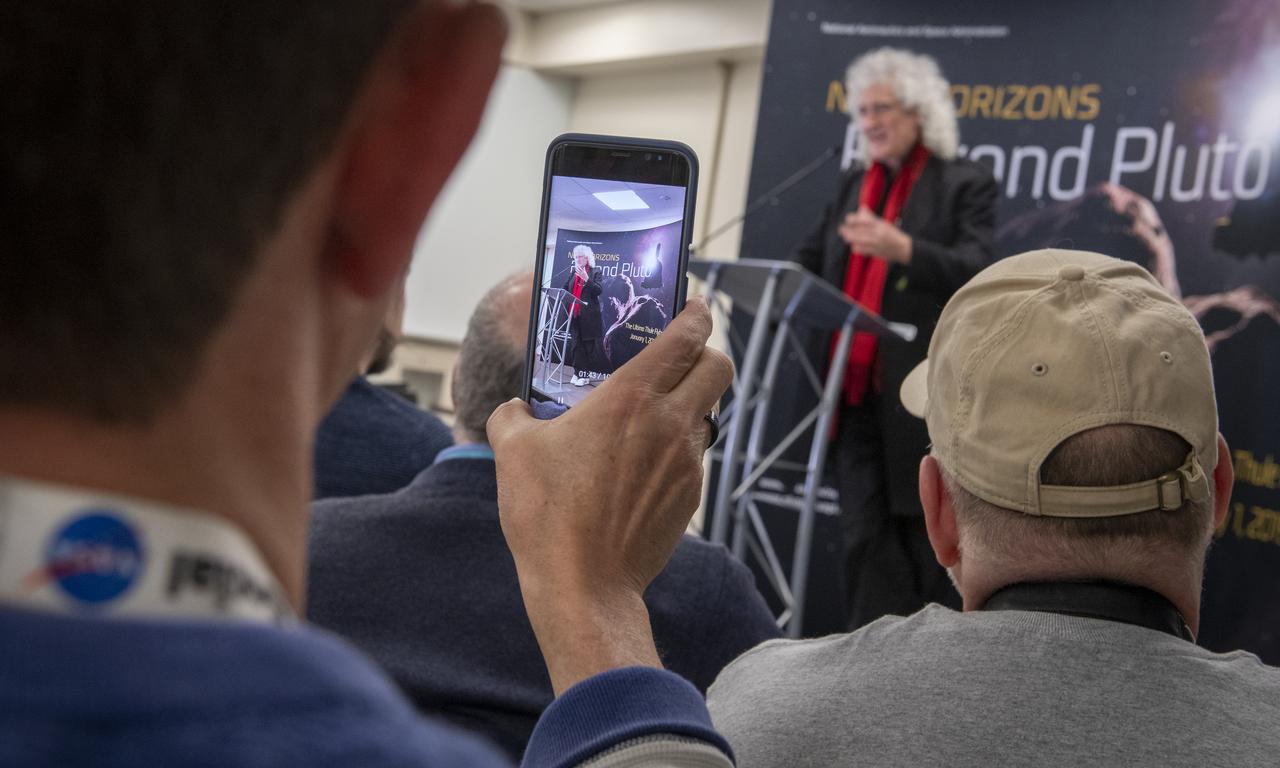

Brian May, lead guitarist of the rock band Queen and astrophysicist discusses the upcoming New Horizons flyby of the Kuiper Belt object Ultima Thule, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Fred Pelletier, lead of the project navigation team at KinetX Inc. in Simi Valley, California, speaks at a press conference prior to the flyby of Ultima Thule by the New Horizons spacecraft, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

New Horizons deputy project scientist John Spencer of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), Boulder, CO discusses what they hope to learn from the flyby of Ultima Thule, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

New Horizons co-investigator Silvia Protopapa of the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) discusses what they hope to learn from the flyby of Ultima Thule, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
New Horizons project scientist Hal Weaver of the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory discusses what they hope to learn from the flyby of Ultima Thule, Monday, Dec. 31, 2018 at Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)