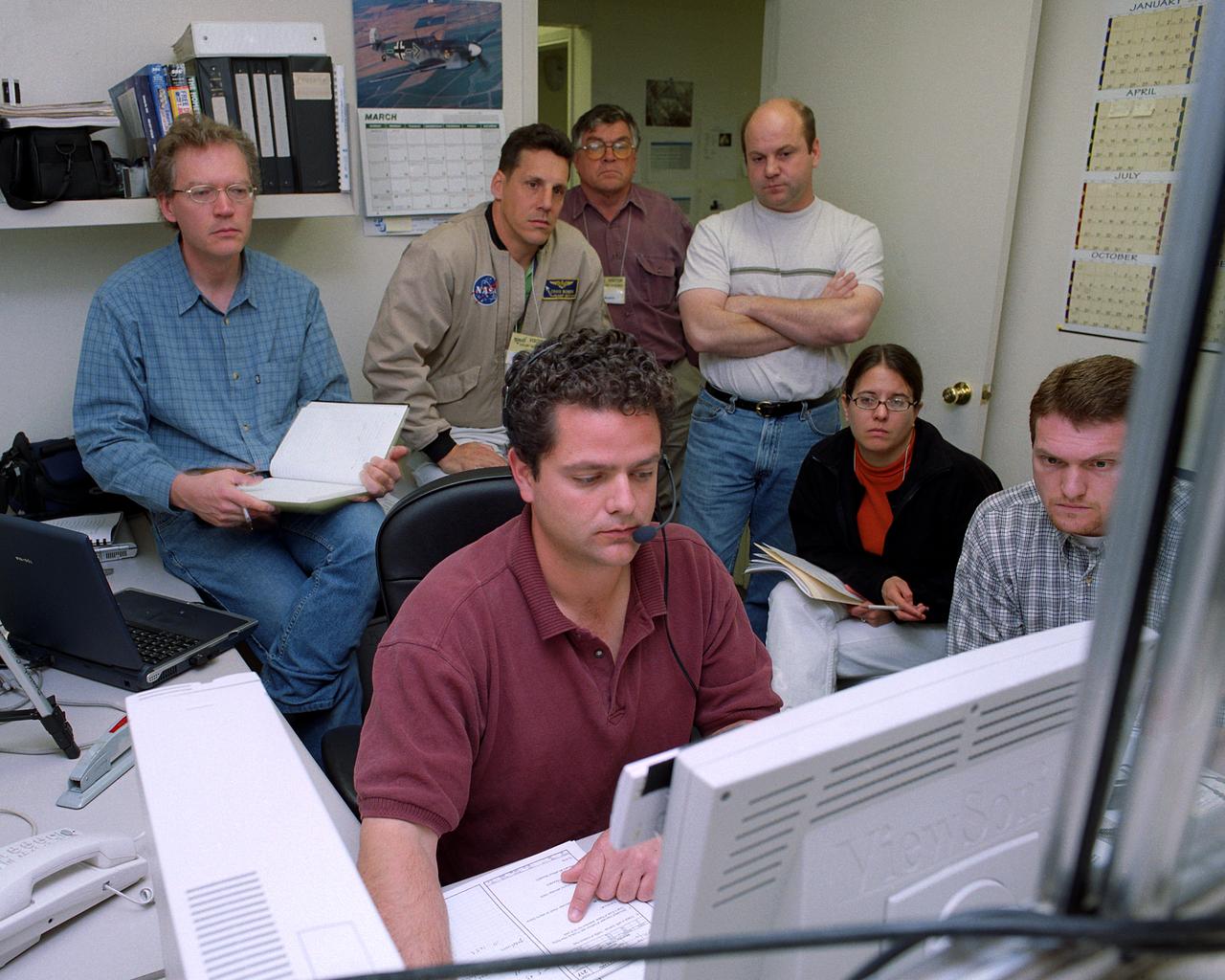

Proteus DSA control room in Mojave, CA (L to R) Jean-Pierre Soucy; Amphitech International Software engineer Craig Bomben; NASA Dryden Test Pilot Pete Siebold; (with headset, at computer controls) Scaled Composites pilot Bob Roehm; New Mexico State University (NMSU) UAV Technical Analysis Application Center (TAAC) Chuck Coleman; Scaled Composites Pilot Kari Sortland; NMSU TAAC Russell Wolfe; Modern Technology Solutions, Inc. Scaled Composites' unique tandem-wing Proteus was the testbed for a series of UAV collision-avoidance flight demonstrations. An Amphitech 35GHz radar unit installed below Proteus' nose was the primary sensor for the Detect, See and Avoid tests.
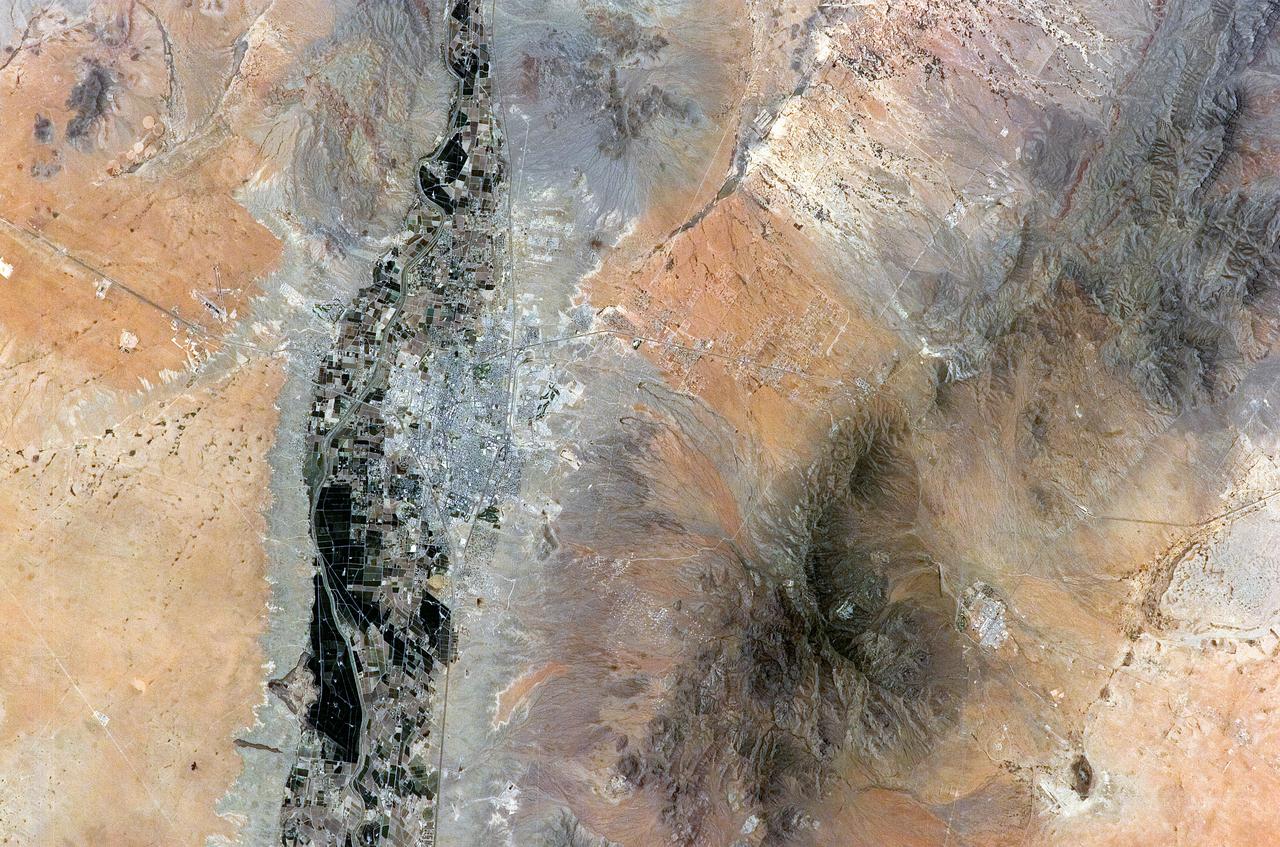

ISS011-E-08410 (9 June 2005) --- Las Cruces, New Mexico is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 11 crewmember on the International Space Station. The city of Las Cruces is located within the Rio Grande Rift, a large geological feature that extends from Colorado southward into Mexico. According to NASA geologists, rifting usually heralds the breakup of continental landmasses, such as the separation of South America and Africa to form the southern Atlantic Ocean during the Mesozoic Era. The Rift is marked by a series of depressions (known as graben) caused by the subsidence of crustal blocks between parallel faults as the continental crust is pulled apart by tectonic forces. These graben are frequently marked by uplifted rocks along bounding faults — the striking Organ Mountains to the east of Las Cruces are one such uplifted fault block. While separation of the continental crust is no longer occurring, the Rio Grande Rift is still considered active as evidenced by frequent low-intensity earthquakes and hot springs to the north of Las Cruces. The modern city of Las Cruces — the seat of Doña Ana County and home to New Mexico State University — is undergoing rapid urban expansion due to influx of new residents attracted to the climate and landscape. The current urban area (gray to white region at image center) contrasts sharply with agricultural lands (dark green and grey brown) located along the Rio Grande River and the surrounding desert valley floor to the northeast and southwest (brown, blue gray and tan areas).

This photograph shows the Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory being released from the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis during the STS-35 mission in April 1991. The GRO reentered the Earth's atmosphere and ended its successful mission in June 2000. For nearly 9 years, GRO's Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE), designed and built by the Marshall Space Flight Center, kept an unblinking watch on the universe to alert scientist to the invisible, mysterious gamma-ray bursts that had puzzled them for decades. By studying gamma-rays from objects like black holes, pulsars, quasars, neutron stars, and other exotic objects, scientists could discover clues to the birth, evolution, and death of star, galaxies, and the universe. The gamma-ray instrument was one of four major science instruments aboard the Compton. It consisted of eight detectors, or modules, located at each corner of the rectangular satellite to simultaneously scan the entire universe for bursts of gamma-rays ranging in duration from fractions of a second to minutes. In January 1999, the instrument, via the Internet, cued a computer-controlled telescope at Las Alamos National Laboratory in Los Alamos, New Mexico, within 20 seconds of registering a burst. With this capability, the gamma-ray experiment came to serve as a gamma-ray burst alert for the Hubble Space Telescope, the Chandra X-Ray Observatory, and major gound-based observatories around the world. Thirty-seven universities, observatories, and NASA centers in 19 states, and 11 more institutions in Europe and Russia, participated in BATSE's science program.

This photograph shows the Compton Gamma-Ray Observatory (GRO) being deployed by the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis during the STS-37 mission in April 1991. The GRO reentered Earth atmosphere and ended its successful mission in June 2000. For nearly 9 years, the GRO Burst and Transient Source Experiment (BATSE), designed and built by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), kept an unblinking watch on the universe to alert scientists to the invisible, mysterious gamma-ray bursts that had puzzled them for decades. By studying gamma-rays from objects like black holes, pulsars, quasars, neutron stars, and other exotic objects, scientists could discover clues to the birth, evolution, and death of stars, galaxies, and the universe. The gamma-ray instrument was one of four major science instruments aboard the Compton. It consisted of eight detectors, or modules, located at each corner of the rectangular satellite to simultaneously scan the entire universe for bursts of gamma-rays ranging in duration from fractions of a second to minutes. In January 1999, the instrument, via the Internet, cued a computer-controlled telescope at Las Alamos National Laboratory in Los Alamos, New Mexico, within 20 seconds of registering a burst. With this capability, the gamma-ray experiment came to serve as a gamma-ray burst alert for the Hubble Space Telescope, the Chandra X-Ray Observatory, and major gound-based observatories around the world. Thirty-seven universities, observatories, and NASA centers in 19 states, and 11 more institutions in Europe and Russia, participated in the BATSE science program.

The Proteus high-altitude aircraft at Sunset
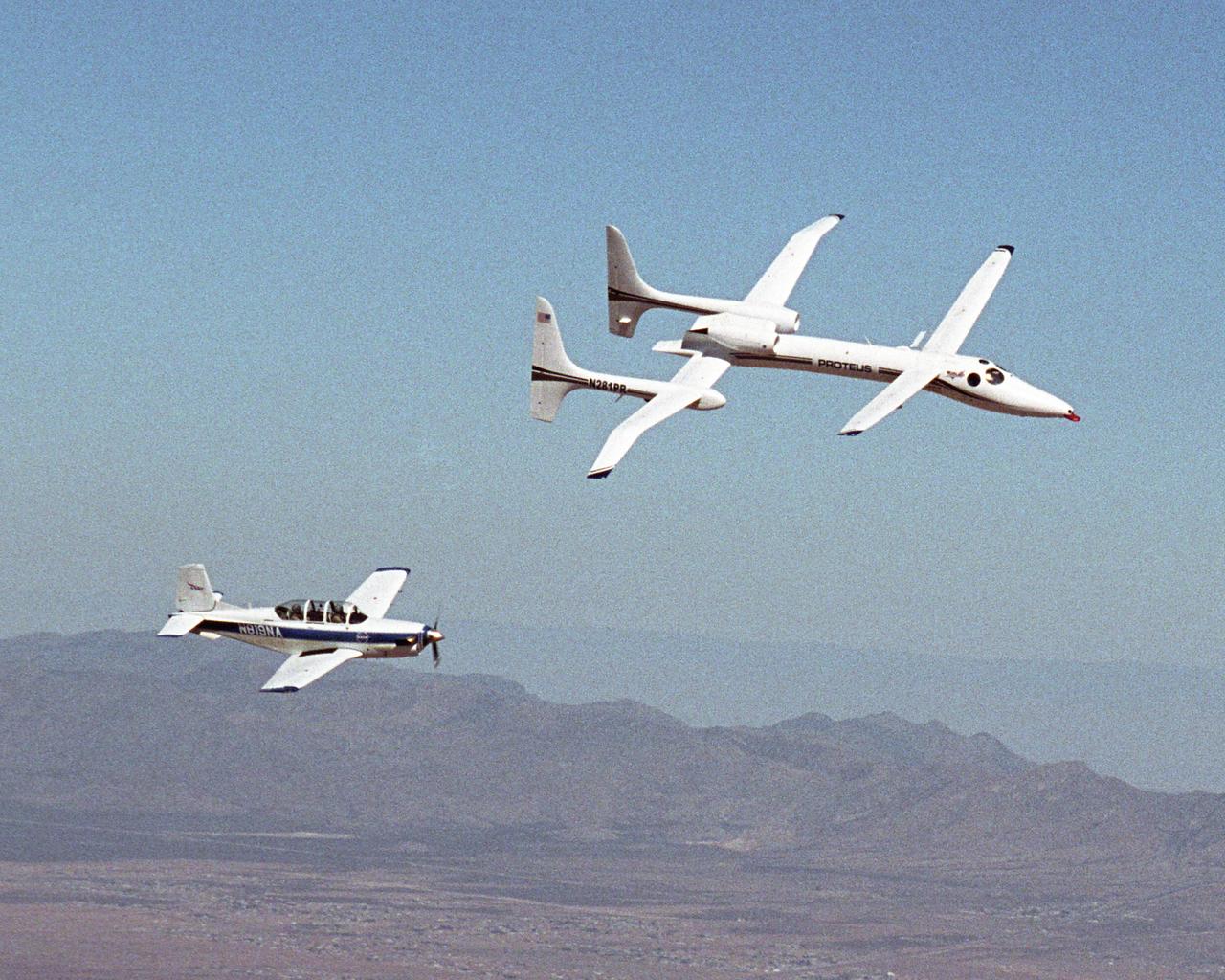

The Proteus aircraft and NASA Dryden's T-34 in flight over Las Cruces, New Mexico.
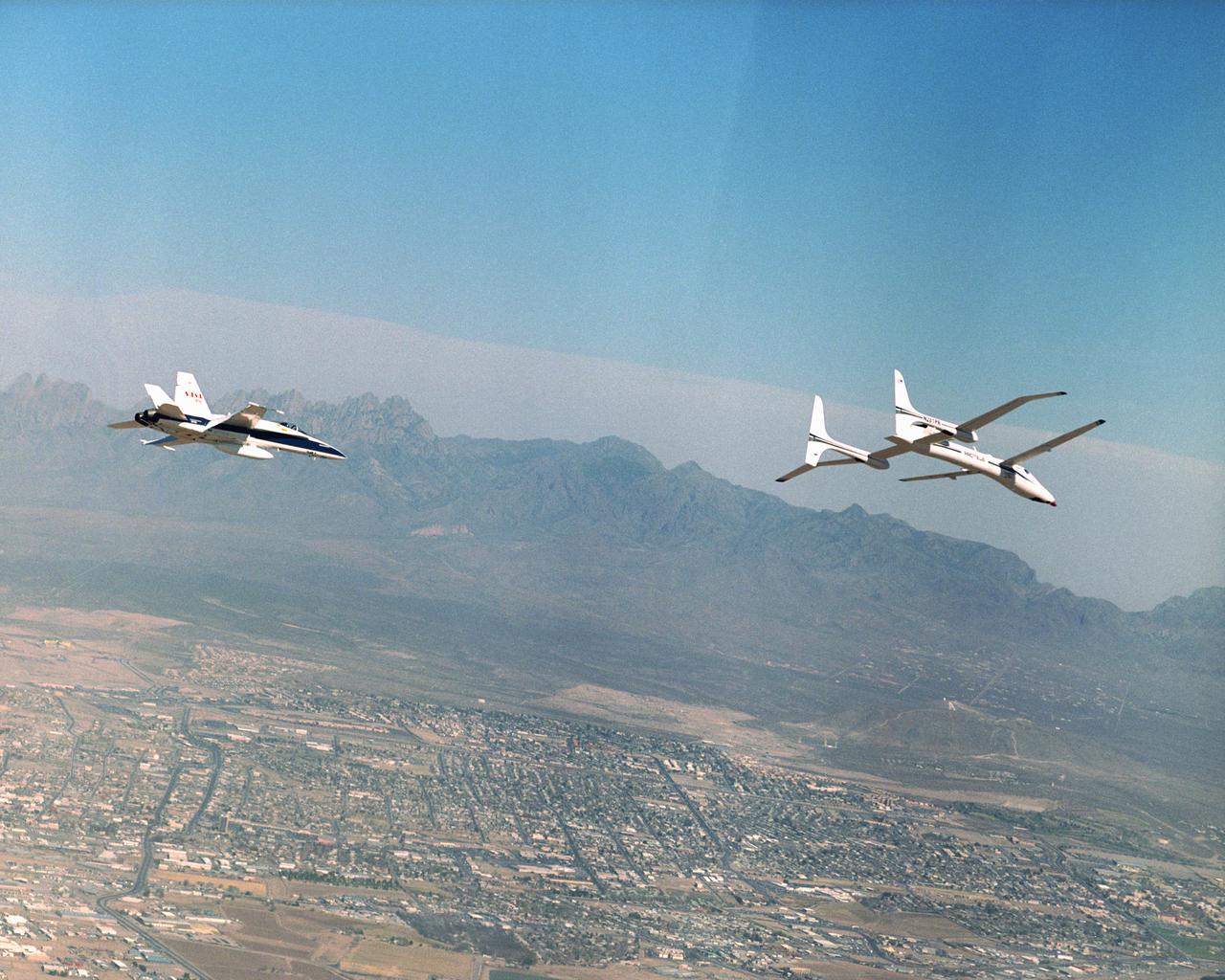

Proteus and an F/A-18 Hornet from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center are seen here in flight over Las Cruces, New Mexico.
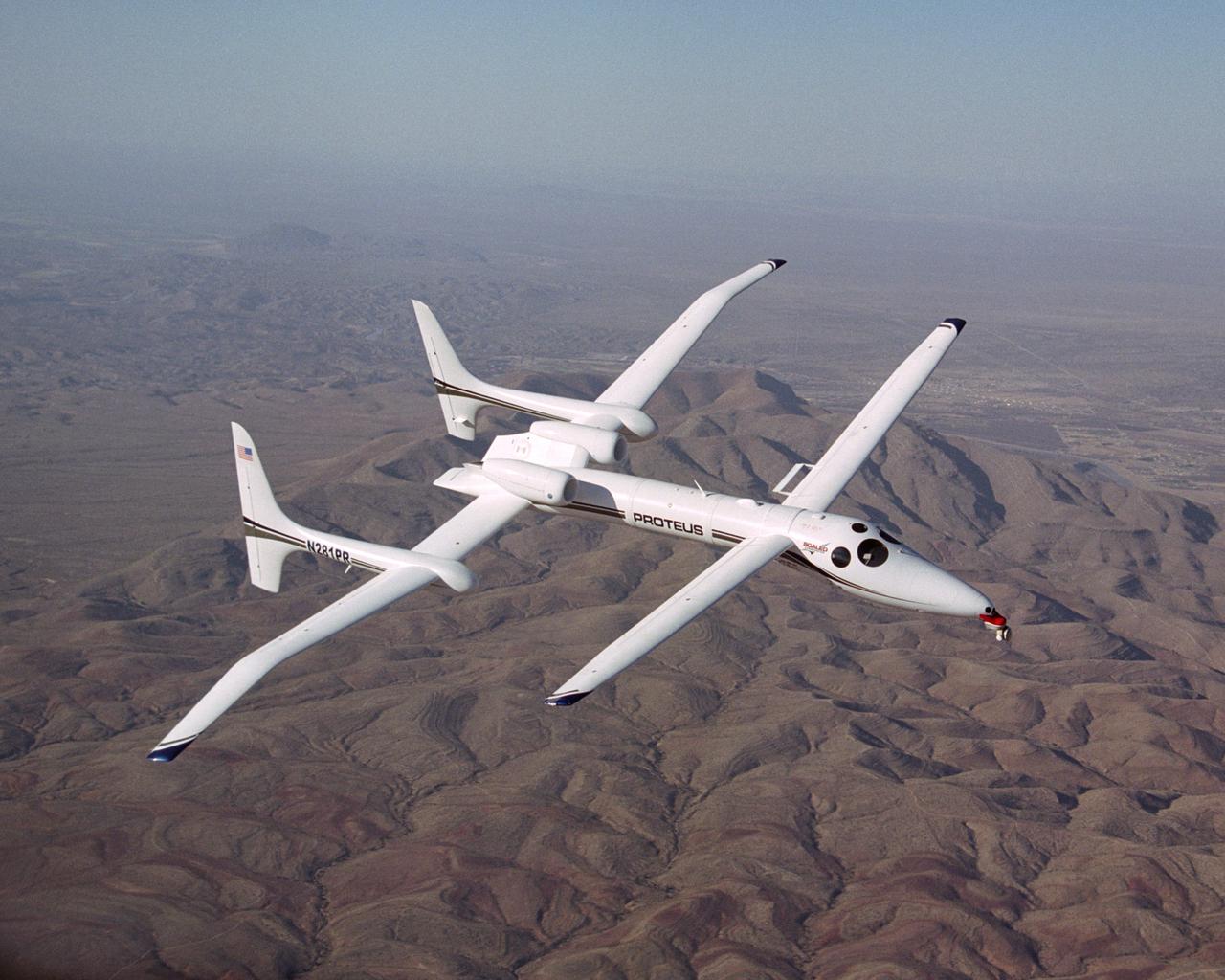

Proteus in flight over mountains near Las Cruces, New Mexico.
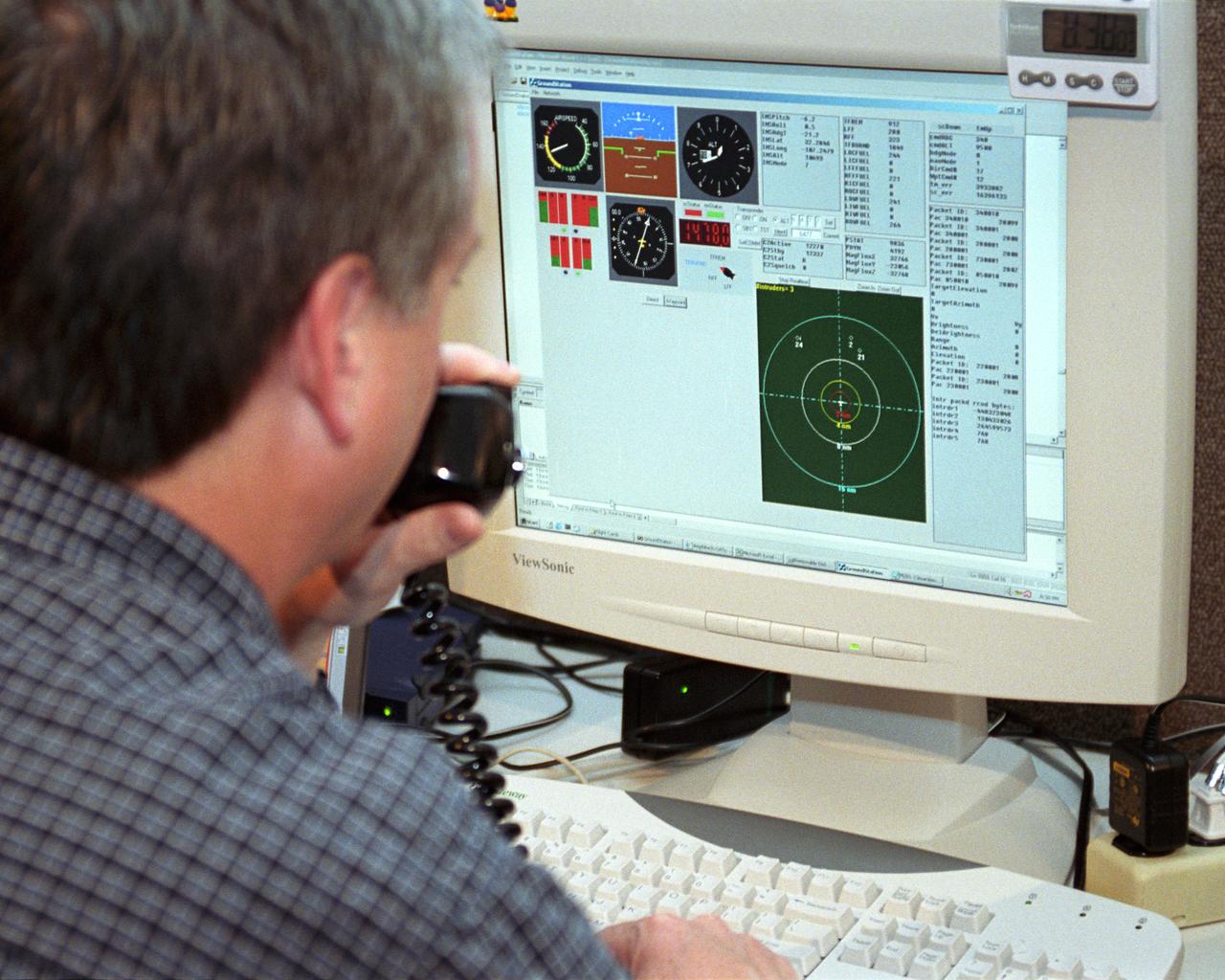

Scaled Composites' Doug Shane examines the screen of his ground control station during tests in New Mexico. Shane used this configuration as the ground control station to remotely pilot the Proteus aircraft during a NASA sponsored series of tests.
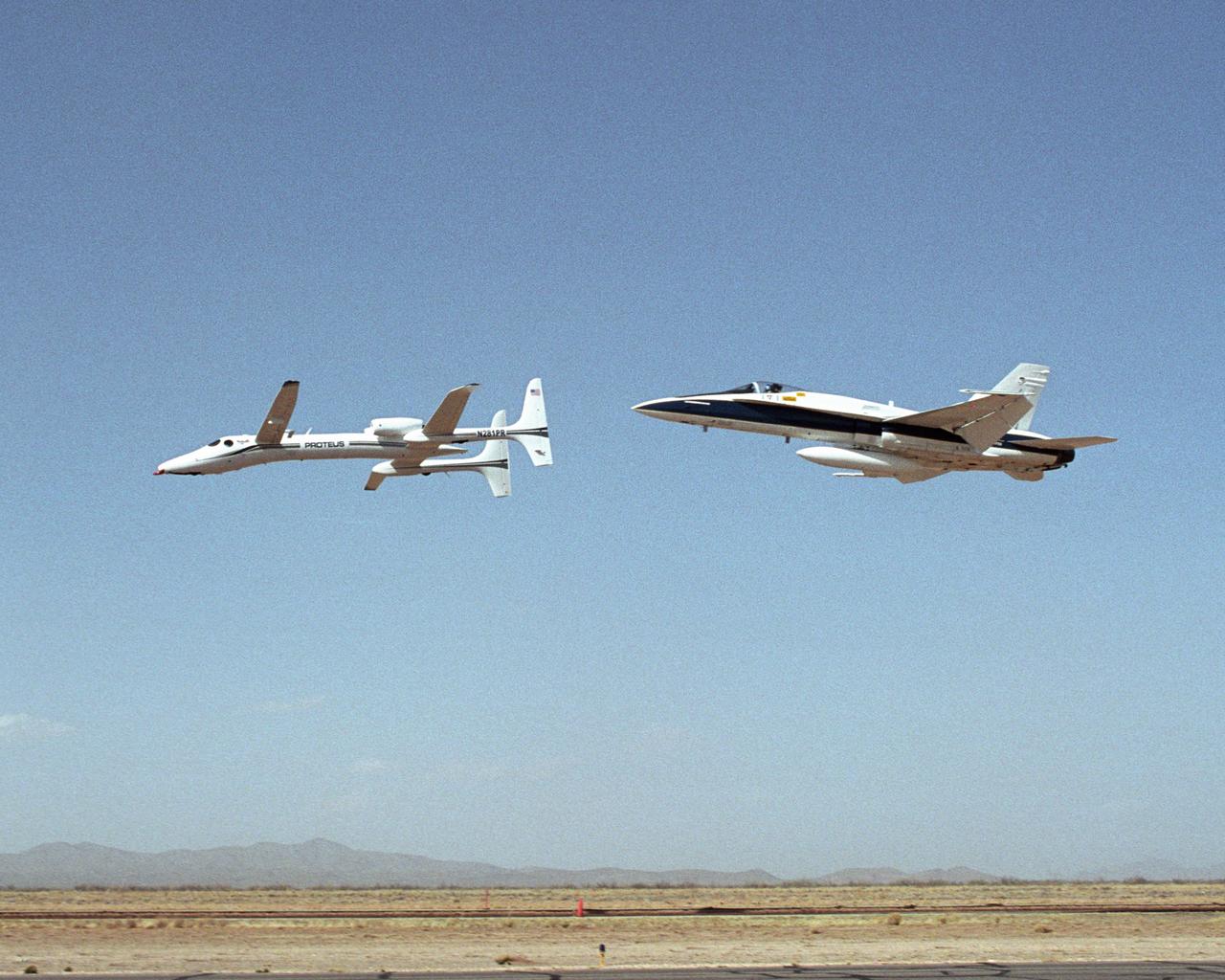

Scaled Composites' Proteus aircraft and an F/A-18 Hornet from NASA's Dryden Flight Research Center during a low-level flyby at Las Cruces Airport in New Mexico.

Proteus aircraft low-level flyby at Las Cruces Airport.
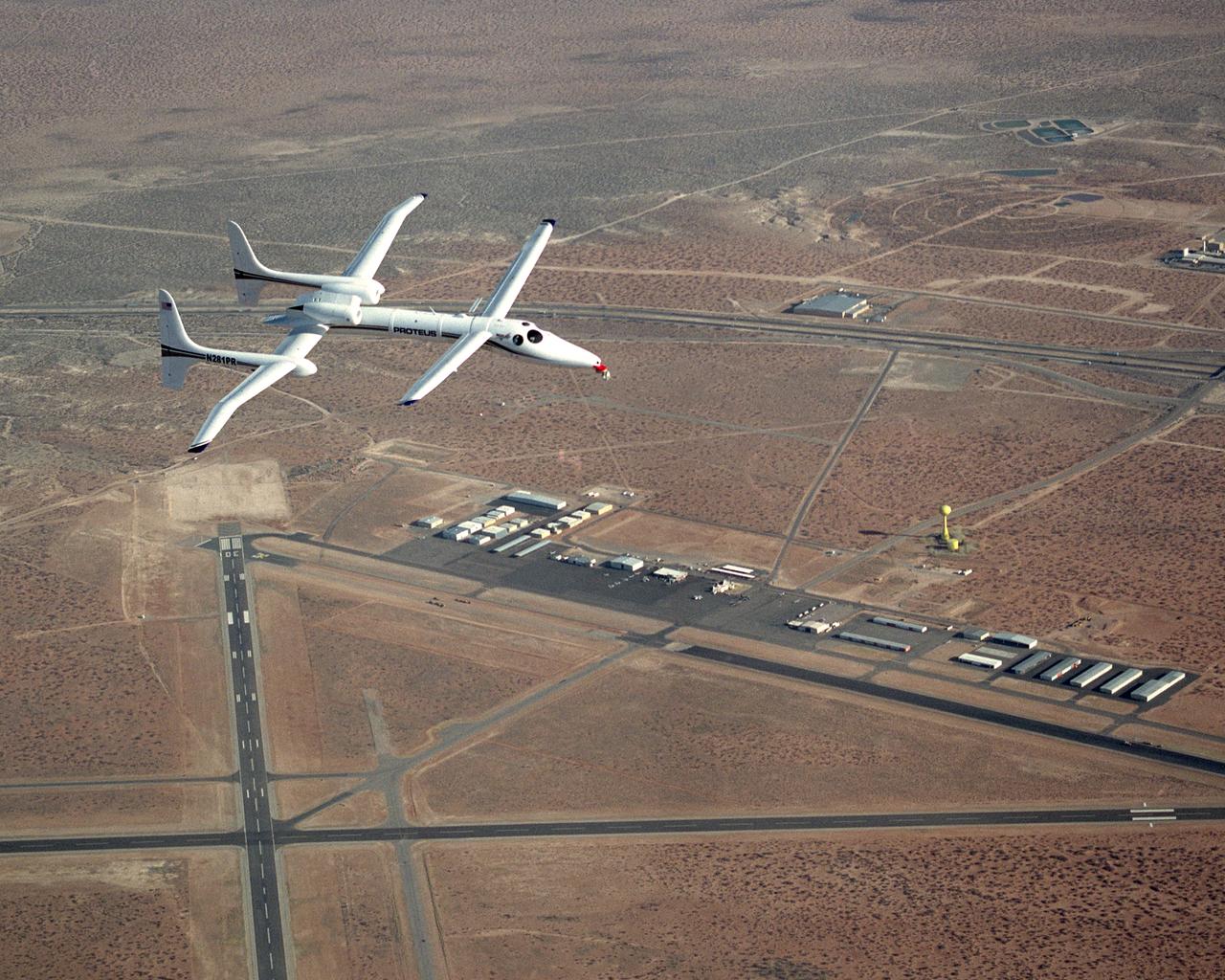

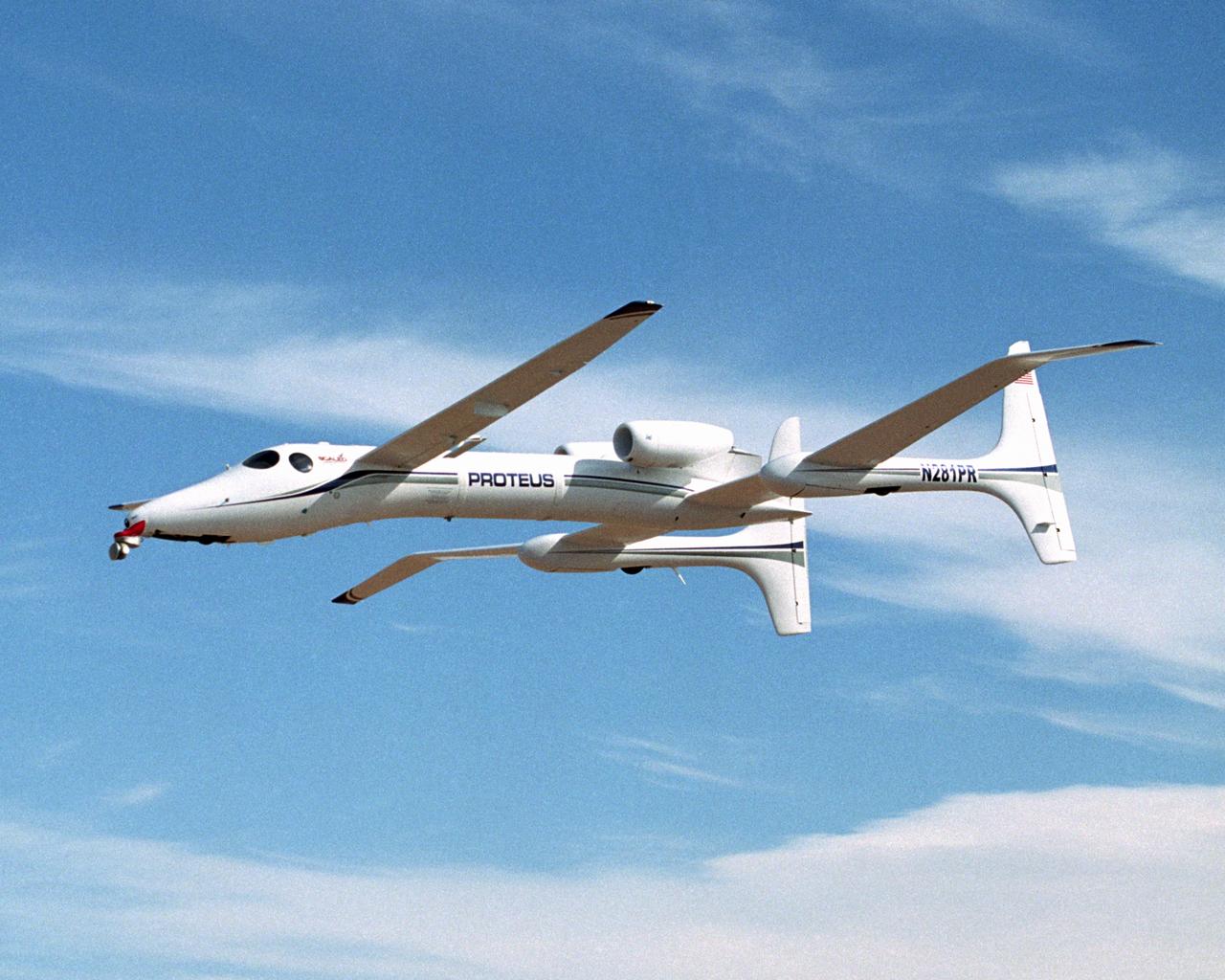
Proteus aircraft over Las Cruces International Airport in New Mexico.
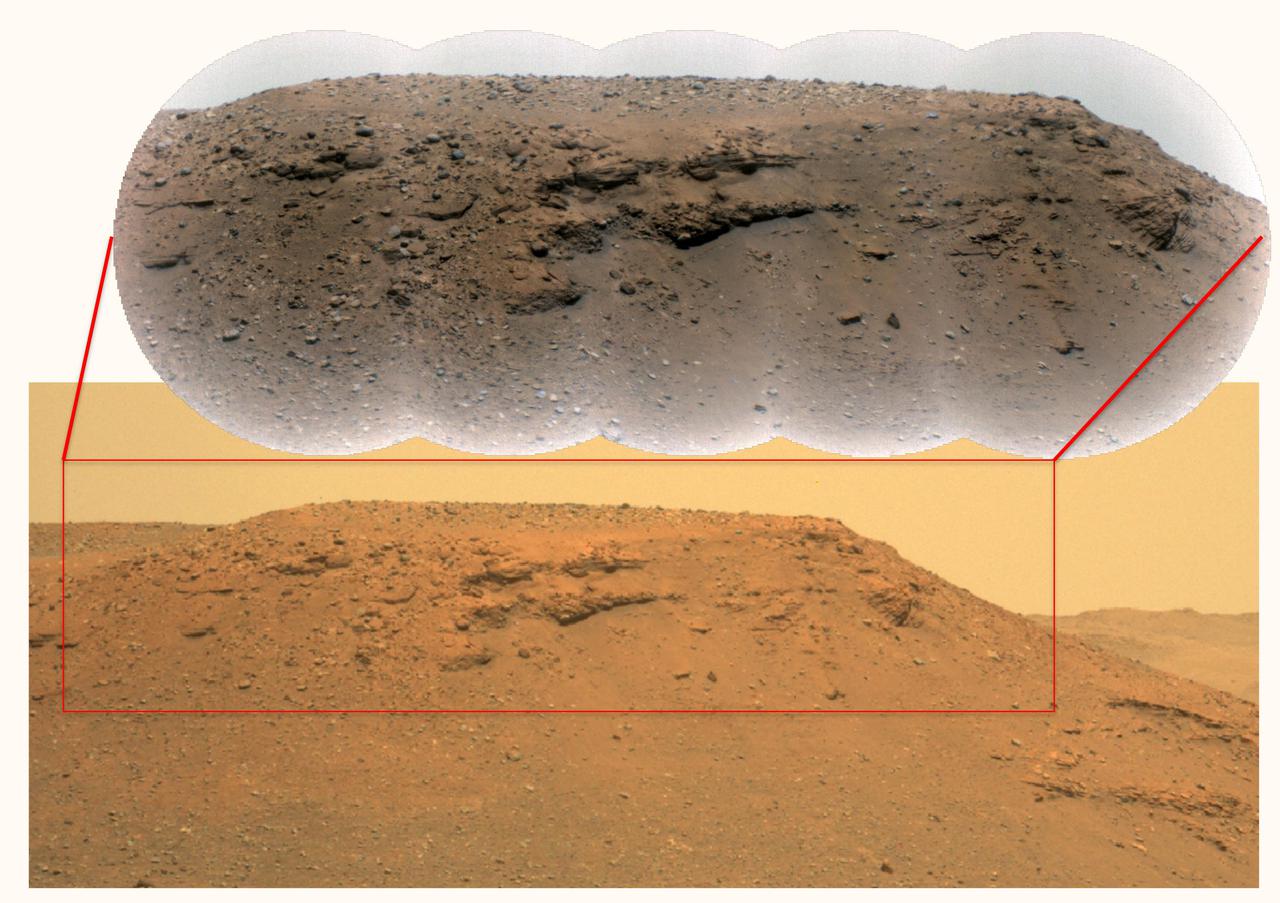
This composite image of the "Delta Scarp" in Mars' Jezero Crater was generated using data from two imagers aboard NASA's Perseverance rover. Taken by the rover's Mastcam-Z, the bottom image shows both the base and plateau of the escarpment. The inset above, created from a mosaic of five Remote Microscopic Imager (RMI) pictures, zooms in on a 377-foot-wide (115-meter-wide) portion of the scarp, allowing closer inspection of some of its intriguing geologic features. Part of the rover's SuperCam instrument, the RMI is able to spot an object the size of a softball from nearly a mile away, allowing scientists to take images of details from a long distance. It also provides fine details of nearby targets zapped by SuperCam's laser. SuperCam is led by Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico, where the instrument's Body Unit was developed. That part of the instrument includes several spectrometers, control electronics and software. The Mast Unit was developed and built by several laboratories of the CNRS (French National Centre for Scientific Research) and French universities under the contracting authority of CNES. Arizona State University in Tempe leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24684
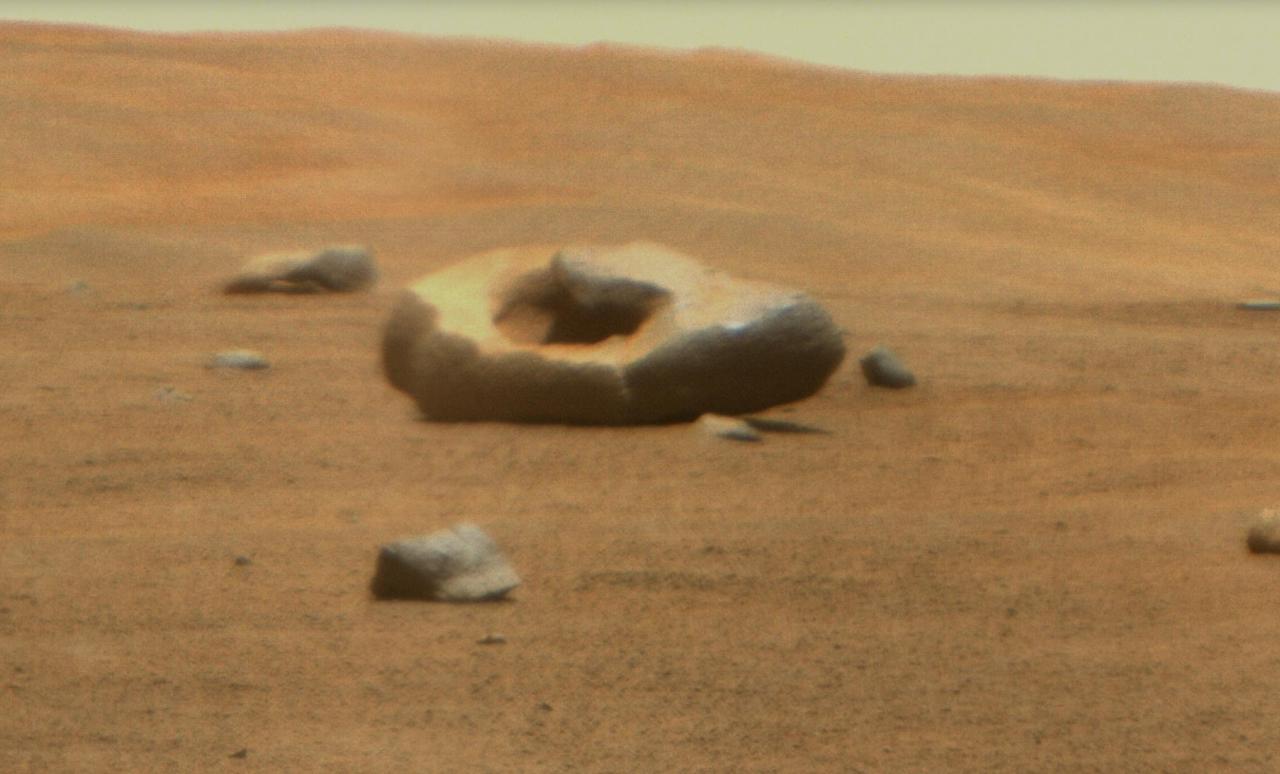

NASA's Perseverance Mars rover captured this doughnut-shaped rock in Jezero Crater from about 328 feet (100 meters) away using its Remote Microscopic Imager (RMI), part of the SuperCam instrument, on June 22, 2023, the 832nd Martian day, or sol, of the mission. Oddly shaped rocks aren't uncommon, either on Earth or Mars; they're often formed over eons as winds sandblast rock faces. This particular rock may have formed after a smaller rock (or multiple rocks) eroded near its center. That left behind a cavity that was later enlarged by the wind. Figure A shows the same rock in its broader context, when it was first spotted by the rover's Mastcam-Z instrument from about 1,312 feet (400 meters away) on April 15, 2023, the 765th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. SuperCam is led by Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico, where the instrument's body unit was developed. That part of the instrument includes several spectrometers as well as control electronics and software. The mast unit, including RMI, was developed and built by several laboratories of the CNRS (the French research center) and French universities under the contracting authority of Centre National d'Études Spatiales (CNES), the French space agency. Arizona State University leads the operations of the Mastcam-Z instrument, working in collaboration with Malin Space Science Systems in San Diego, on the design, fabrication, testing, and operation of the cameras, and in collaboration with the Niels Bohr Institute of the University of Copenhagen on the design, fabrication, and testing of the calibration targets. A key objective for Perseverance's mission on Mars is astrobiology, including the search for signs of ancient microbial life. The rover will characterize the planet's geology and past climate, pave the way for human exploration of the Red Planet, and be the first mission to collect and cache Martian rock and regolith (broken rock and dust). Subsequent NASA missions, in cooperation with ESA (European Space Agency), would send spacecraft to Mars to collect these sealed samples from the surface and return them to Earth for in-depth analysis. The Mars 2020 Perseverance mission is part of NASA's Moon to Mars exploration approach, which includes Artemis missions to the Moon that will help prepare for human exploration of the Red Planet. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25916
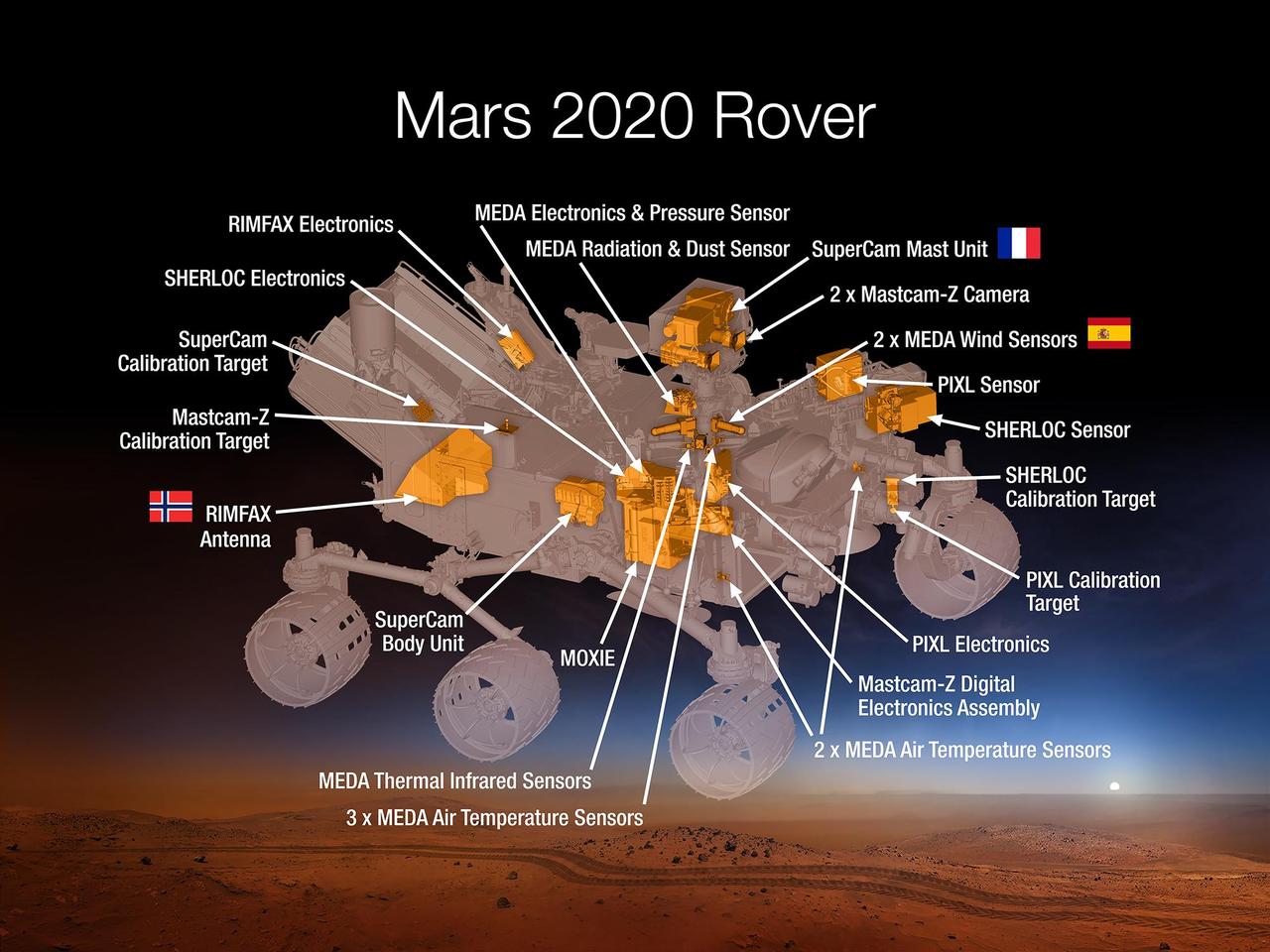
This 2015 diagram shows components of the investigations payload for NASA's Mars 2020 rover mission. Mars 2020 will re-use the basic engineering of NASA's Mars Science Laboratory to send a different rover to Mars, with new objectives and instruments, launching in 2020. The rover will carry seven instruments to conduct its science and exploration technology investigations. They are: Mastcam-Z, an advanced camera system with panoramic and stereoscopic imaging capability and the ability to zoom. The instrument also will determine mineralogy of the Martian surface and assist with rover operations. The principal investigator is James Bell, Arizona State University in Tempe. SuperCam, an instrument that can provide imaging, chemical composition analysis, and mineralogy. The instrument will also be able to detect the presence of organic compounds in rocks and regolith from a distance. The principal investigator is Roger Wiens, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Los Alamos, New Mexico. This instrument also has a significant contribution from the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales, Institut de Recherche en Astrophysique et Planétologie (CNES/IRAP) France. Planetary Instrument for X-ray Lithochemistry (PIXL), an X-ray fluorescence spectrometer that will also contain an imager with high resolution to determine the fine-scale elemental composition of Martian surface materials. PIXL will provide capabilities that permit more detailed detection and analysis of chemical elements than ever before. The principal investigator is Abigail Allwood, NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California. Scanning Habitable Environments with Raman & Luminescence for Organics and Chemicals (SHERLOC), a spectrometer that will provide fine-scale imaging and uses an ultraviolet (UV) laser to determine fine-scale mineralogy and detect organic compounds. SHERLOC will be the first UV Raman spectrometer to fly to the surface of Mars and will provide complementary measurements with other instruments in the payload. SHERLOC includes a high-resolution color camera for microscopic imaging of Mars' surface. The principal investigator is Luther Beegle, JPL. The Mars Oxygen ISRU Experiment (MOXIE), an exploration technology investigation that will produce oxygen from Martian atmospheric carbon dioxide. The principal investigator is Michael Hecht, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts. Mars Environmental Dynamics Analyzer (MEDA), a set of sensors that will provide measurements of temperature, wind speed and direction, pressure, relative humidity and dust size and shape. The principal investigator is Jose Rodriguez-Manfredi, Centro de Astrobiologia, Instituto Nacional de Tecnica Aeroespacial, Spain. The Radar Imager for Mars' Subsurface Experiment (RIMFAX), a ground-penetrating radar that will provide centimeter-scale resolution of the geologic structure of the subsurface. The principal investigator is Svein-Erik Hamran, the Norwegian Defence Research Establishment, Norway. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19672
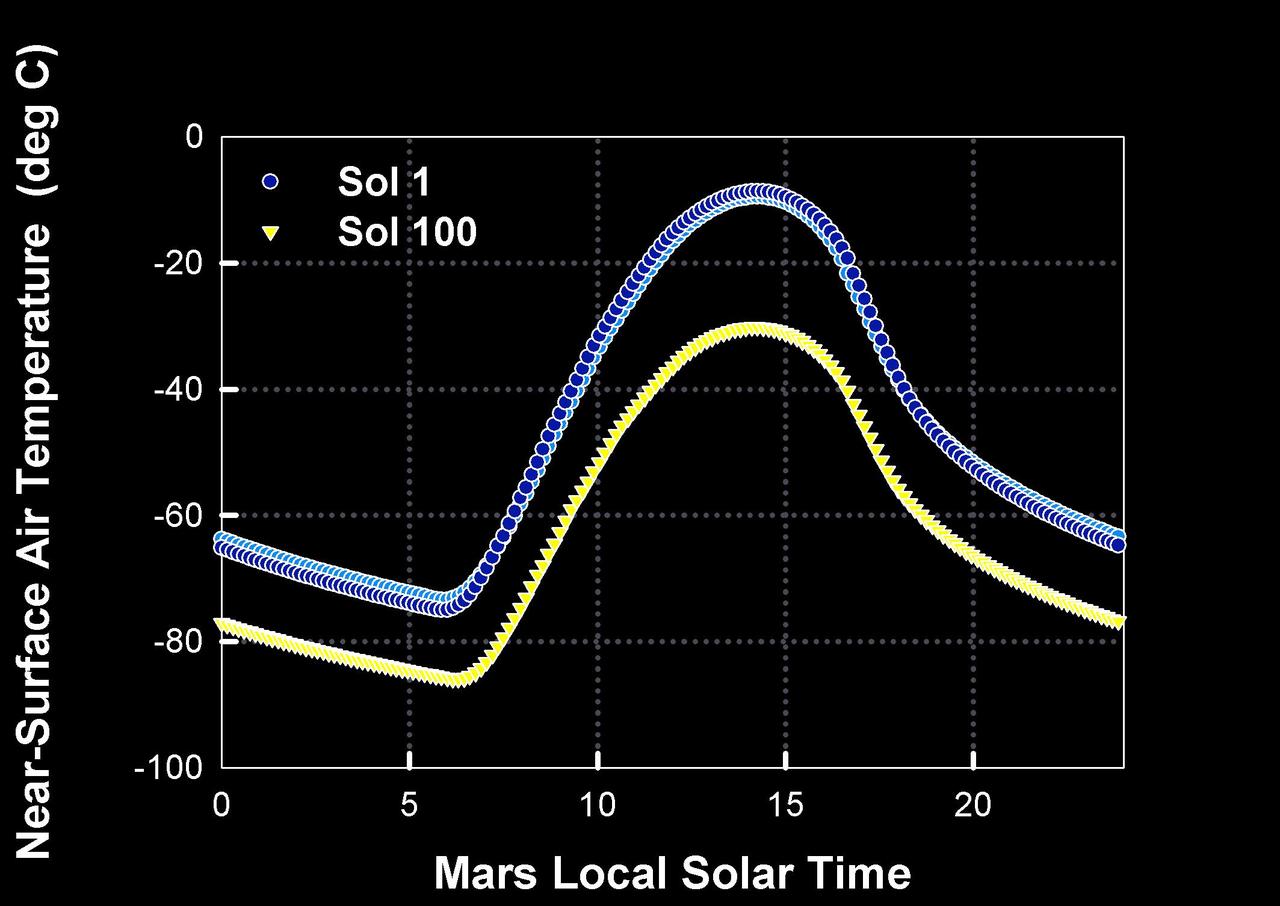
How Warm is Mars?
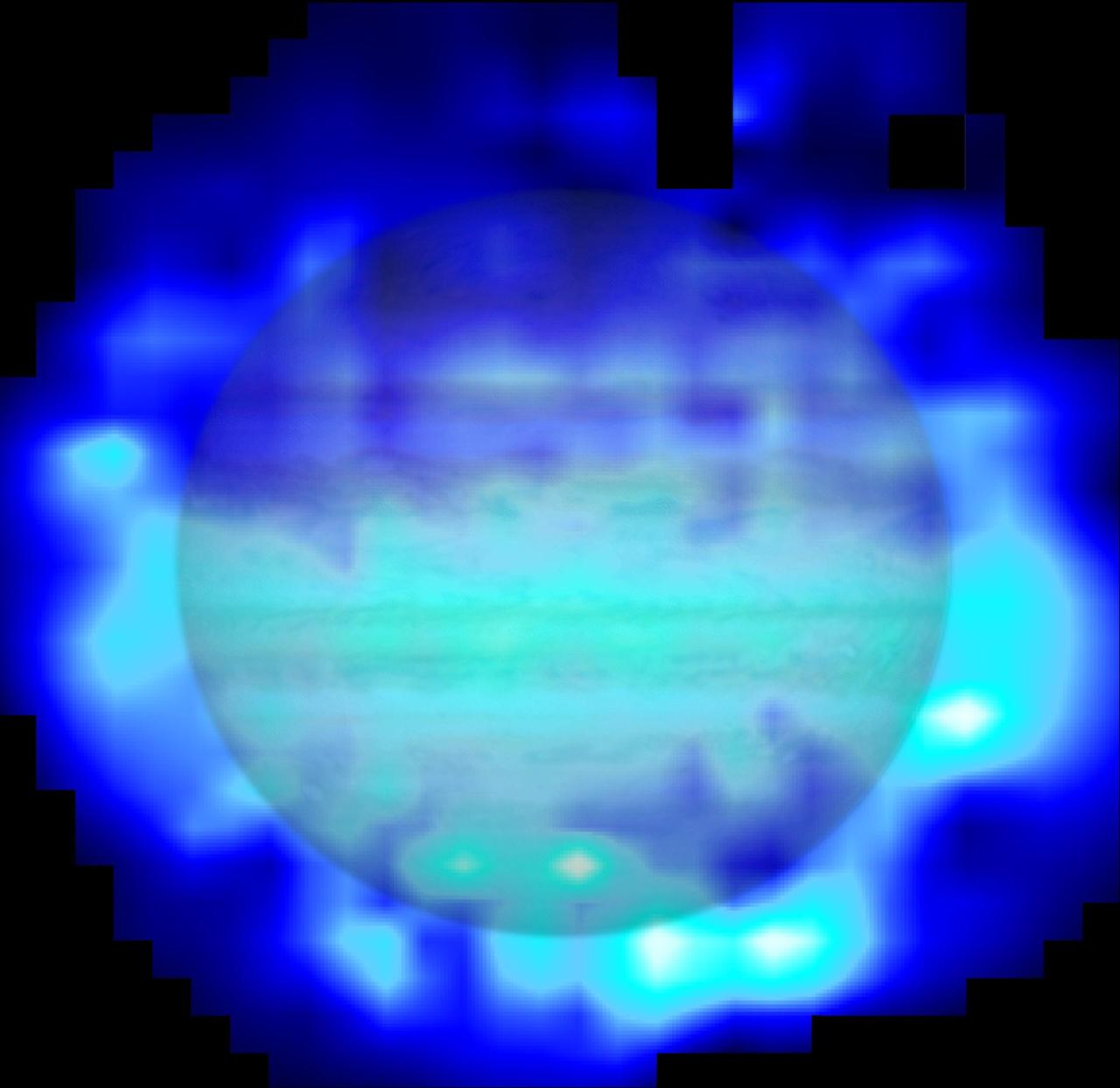
This map shows the distribution of water in the stratosphere of Jupiter as measured with the Herschel space observatory. White and cyan indicate highest concentration of water, and blue indicates lesser amounts.