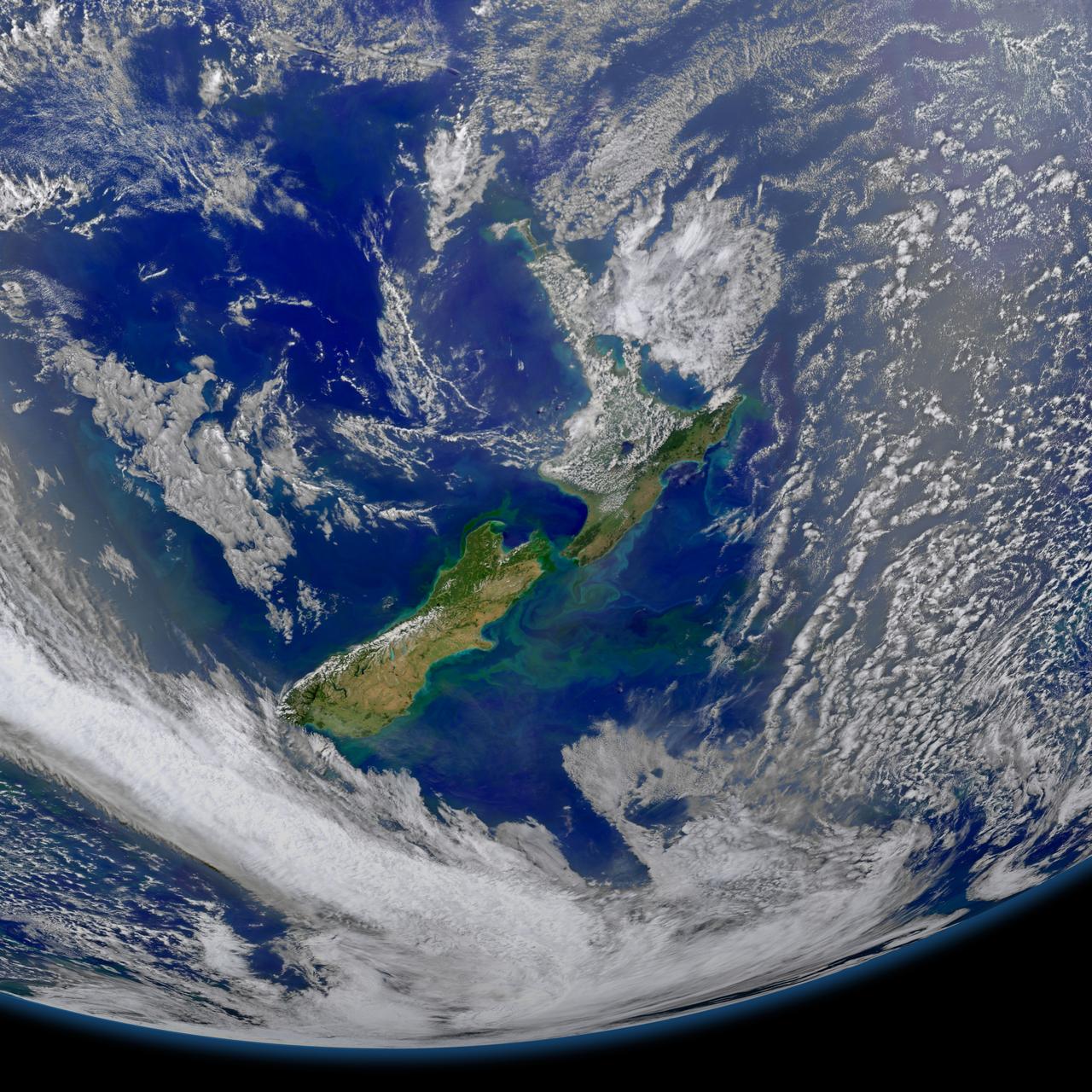

This image taken from the Suomi NPP satellite's VIIRS instrument of New Zealand was collected on January 9, 2015 when the phytoplankton were blooming — particularly to the east of the islands and along the Chatham Rise. Derived from the Greek words phyto (plant) and plankton (made to wander or drift), phytoplankton are microscopic organisms that live in watery environments, both salty and fresh. Credit: NASA/Goddard/NPP <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
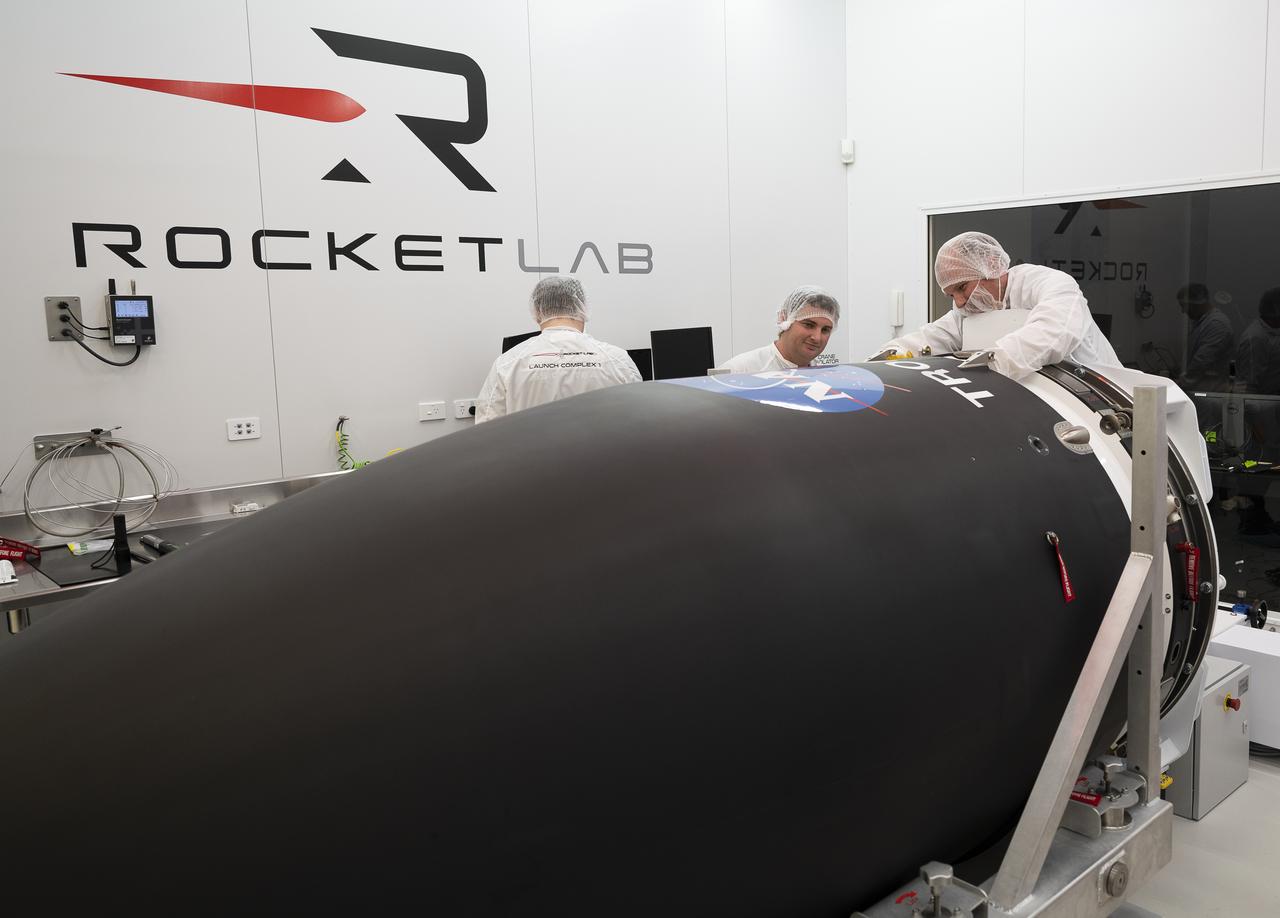

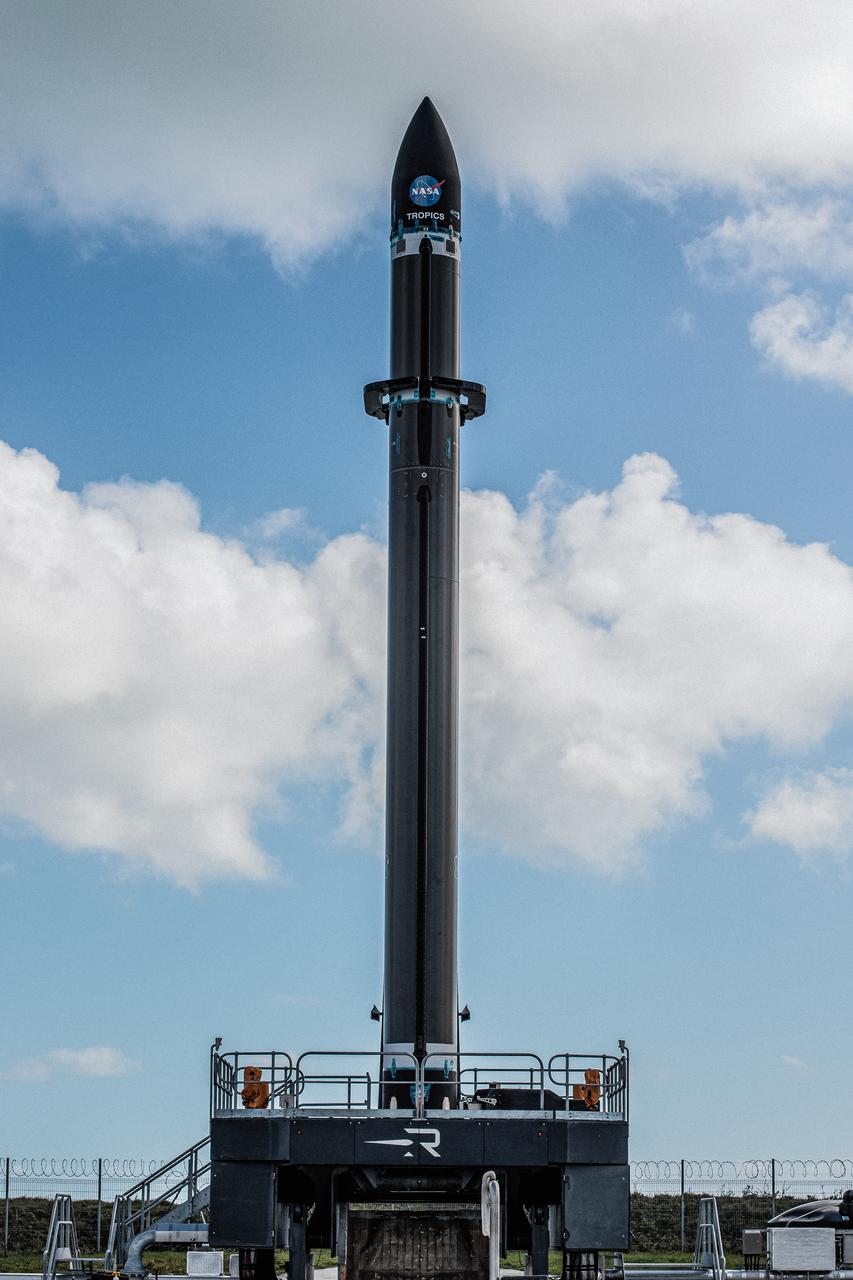
NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are encapsulated inside Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Technicians prepare NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats for encapsulation in Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
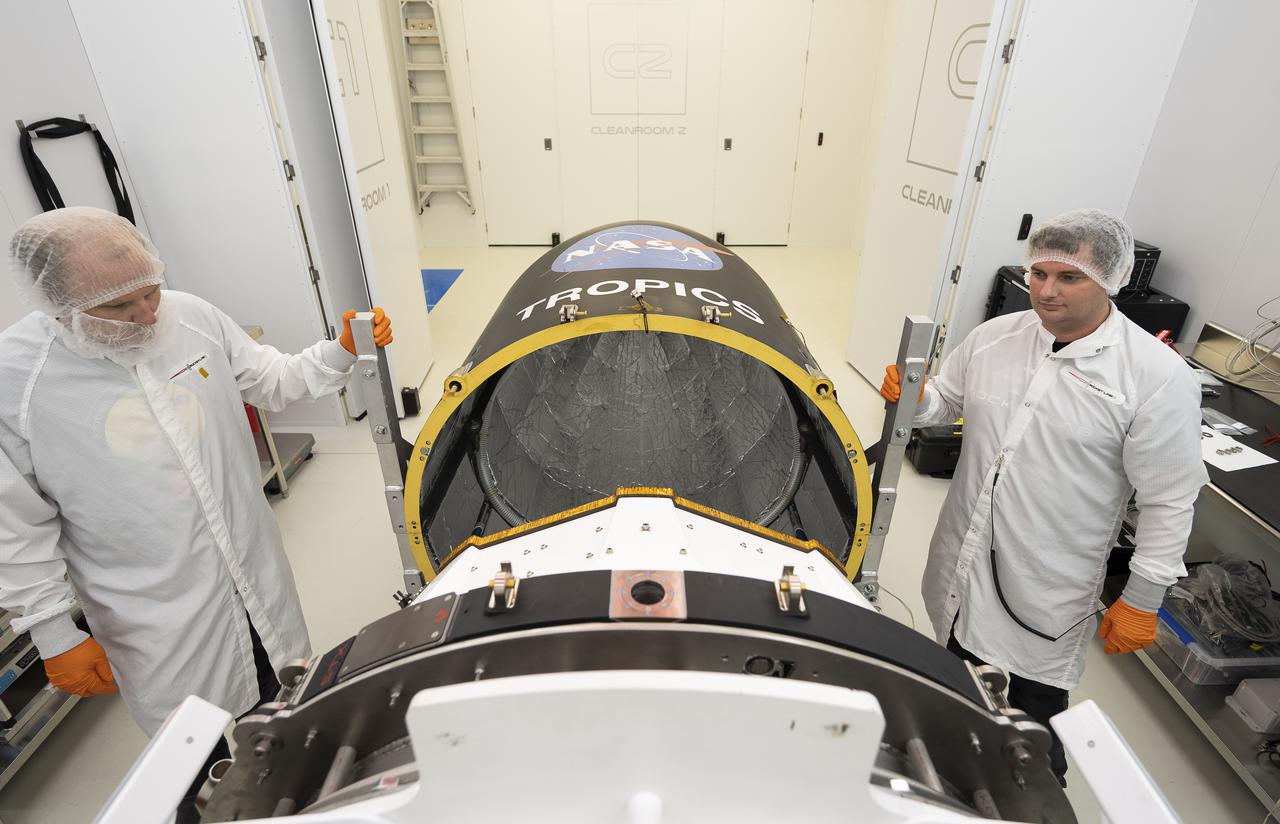

Technicians place NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats in Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing in a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing is in view inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Technicians check Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron payload fairing is in view inside a processing facility near Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats have been encapsulated inside the payload fairing. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

The Banks Peninsula, New Zealand was created by volcanic activity in the Miocene epoch about 10 million years ago. This image is from NASA Terra spacecraft.
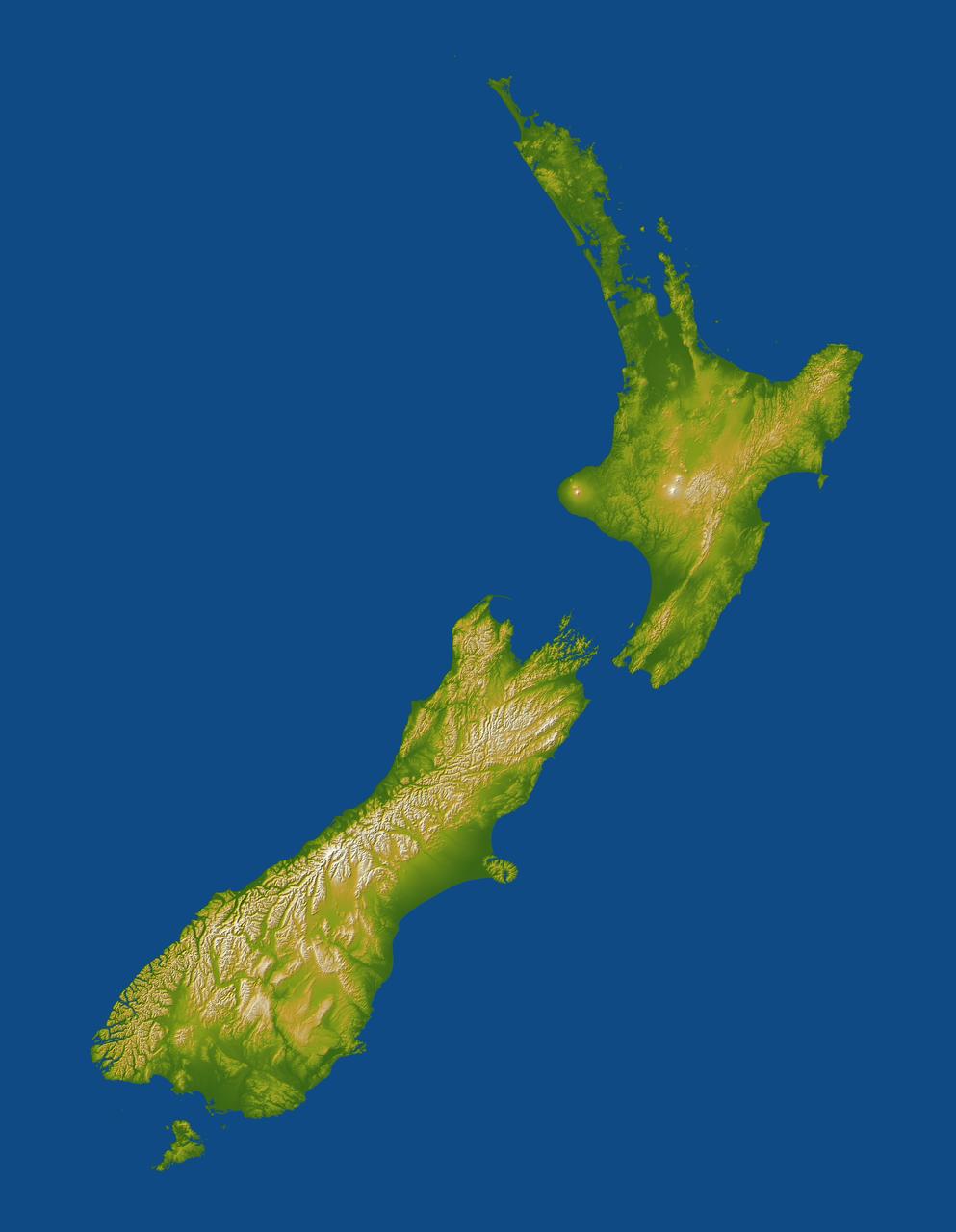
New Zealand straddles the juncture of the Indo-Australian and Pacific tectonic plates, two of Earth major crustal plates.
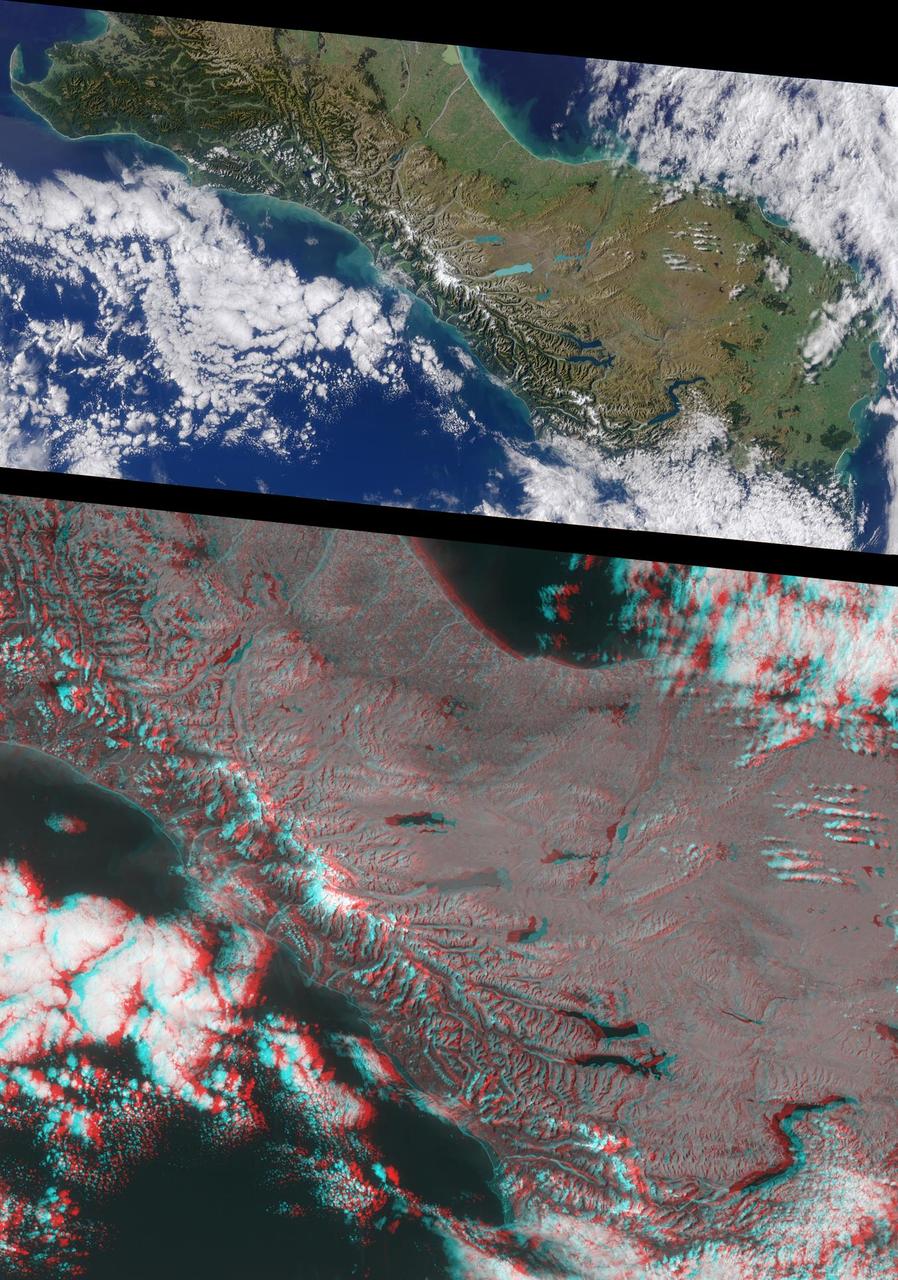
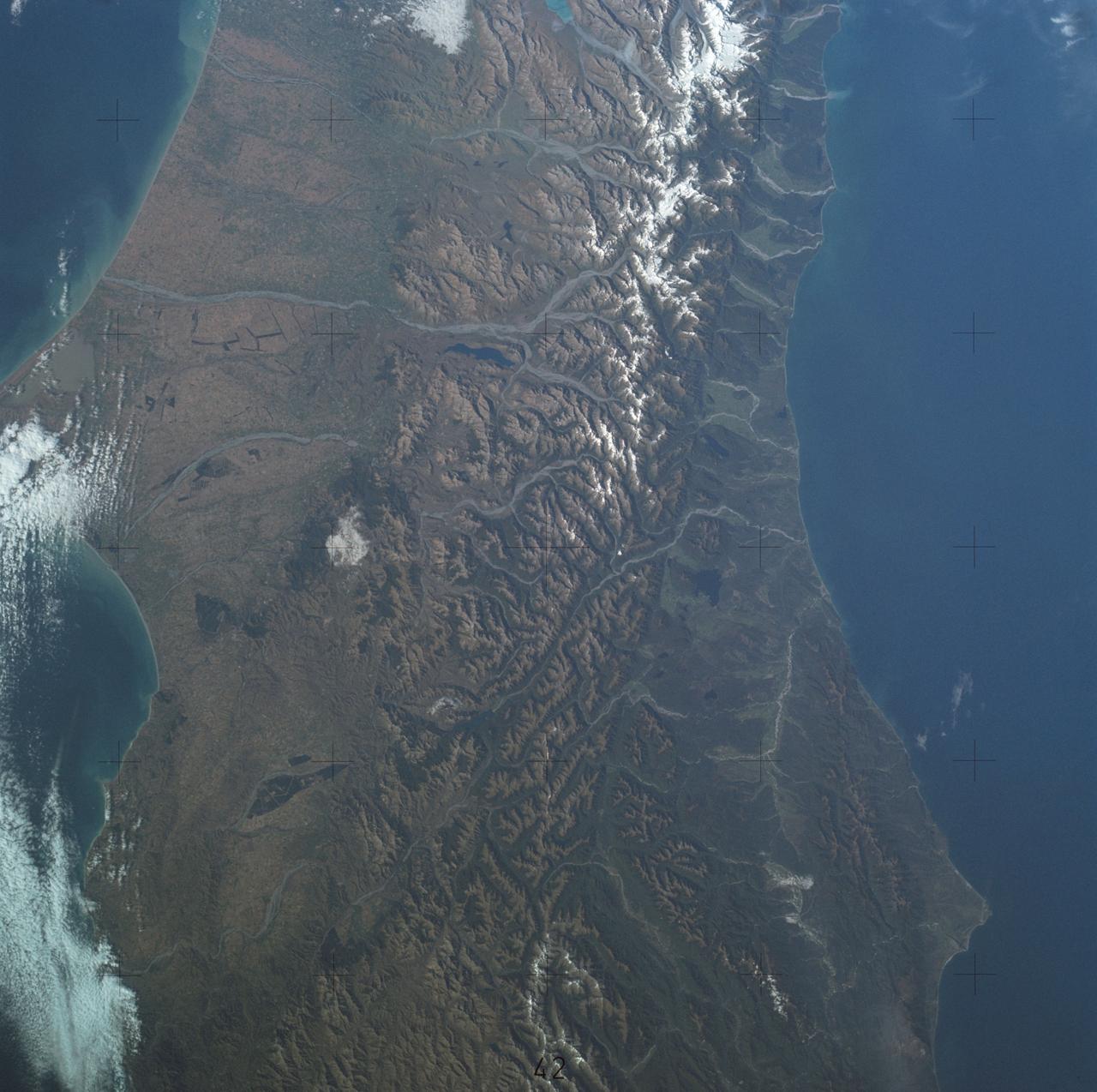
This anaglyph from the MISR instrument aboard NASA Terra spacecraft shows the rugged Southern Alps extending some 650 kilometers along the western side of New Zealand South Island. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
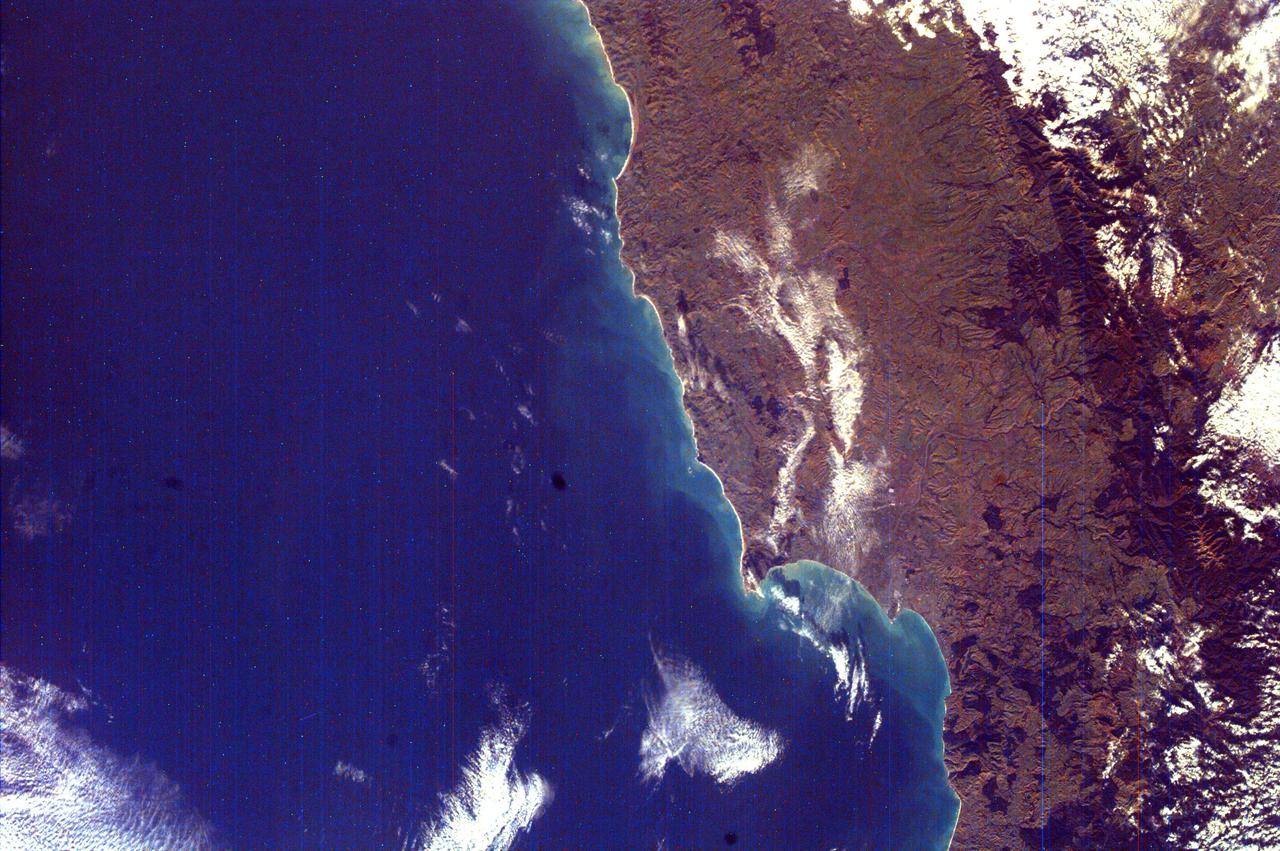

This image from NASA EarthKAM is of Hawke Bay, one of the 12 local government regions of eastern North Island, New Zealand. It includes larger cities, such as Hastings and Napier.
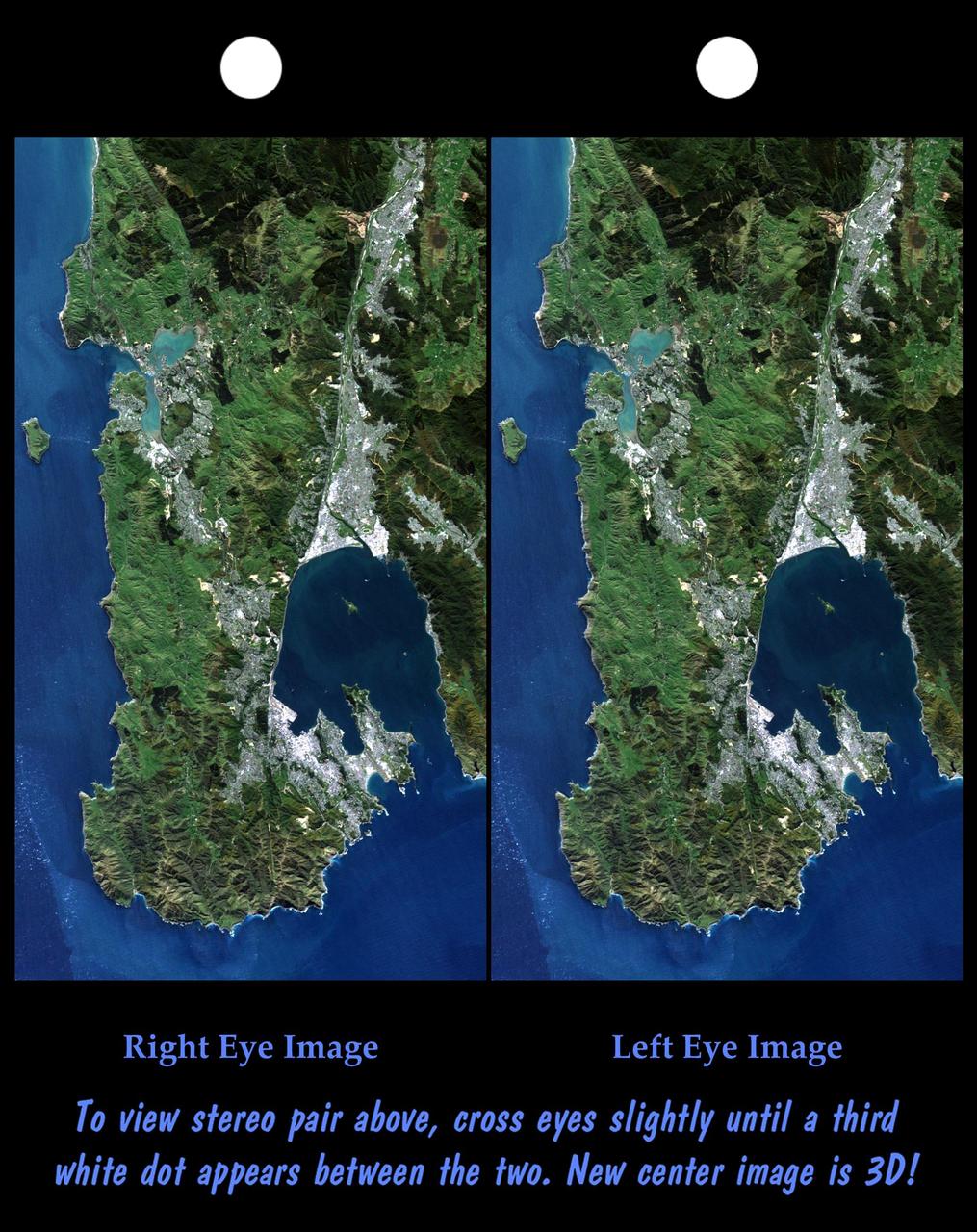

Wellington, the capital city of New Zealand, is located on the shores of Port Nicholson, a natural harbor at the south end of North Island. The city was founded in 1840 by British emigrants and now has a regional population of more than 400,000 residents.
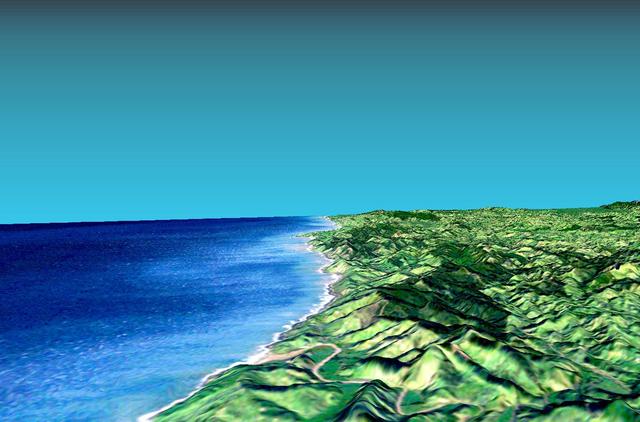

This 3-D perspective view looks south along the southeast coast of the North Island of New Zealand. The capital city of Wellington is off the right side of the image.
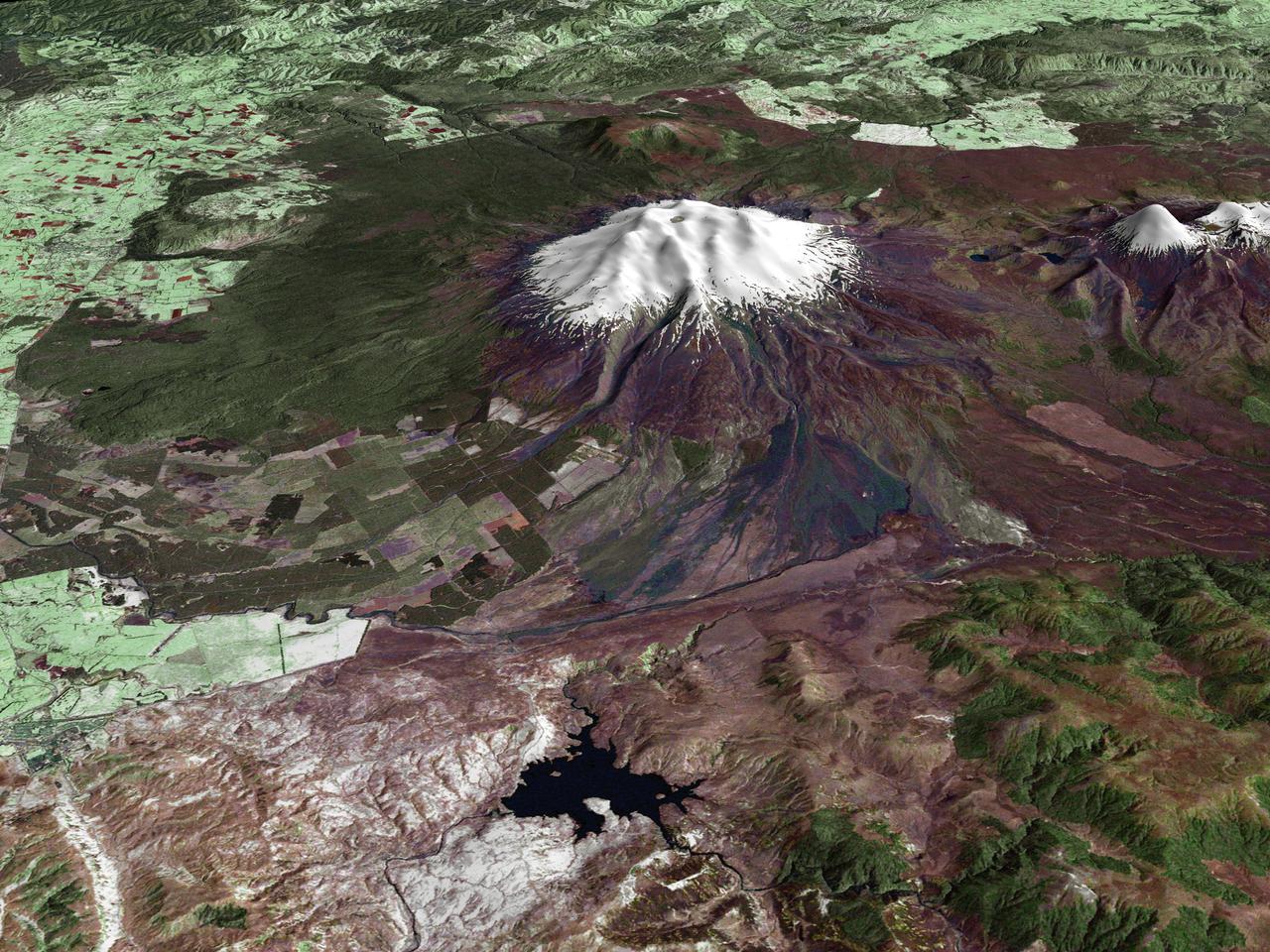
All around the world, people live in places where the threat of natural disaster is high. On the North Island of New Zealand, the Mount Ruapehu volcano is just such a threat. A towering, active stratovolcano (the classic cone-shaped volcano), snow-capped Ruapehu Volcano is pictured in this enhanced-color image. The image is made from topography data collected by the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour, launched on February 11, 2000, and imagery collected by the Landsat satellite on October 23, 2002. Ruapehu is one of New Zealand’s most active volcanoes, with ten eruptions since 1861. The eruptions aren’t the only threat from the volcano, however. Among the most serious threats is a volcanic mudflow called a lahar. In between eruptions, a lake forms in the volcano’s caldera from melting snow. If a previous eruption has deposited a dam of ash, rocks and mud in the lake’s natural overflow point, then the lake becomes dangerously full, held back only by the temporary dam. In this scene, the lake is nestled among the ridges at the top of the volcano. Eventually, the dam gives way and a massive flow of mud and debris churns down the mountain toward farmland and towns below. Scientists estimate that Ruapehu has experienced 60 lahars in the last 150 years. A devastating lahar in 1953 killed more than 150 people, who died when a passenger train plunged into a ravine when a railroad bridge was taken out by the lahar. The flank of the volcano below the lake is deeply carved by the path of previous lahars; the gouge can be seen just left of image center. Currently scientists in the region are predicting that the lake will overflow in a lahar sometime in the next year. There is great controversy about how to deal with the threat. News reports from the region indicate that the government is planning to invest in a high-tech warning system that will alert those who might be affected well in advance of any catastrophic release. Others feel that the government should combat the threat through engineering at the top of the mountain, for example, by undertaking a controlled release of the lake. Credit Landsat data provided courtesy of the University of Maryland Global Land Cover Facility Landsat processing by Laura Rocchio, Landsat Project Science Office SRTM 3-arcsecond elevation data courtesy of SRTM Team NASA/JPL/NIMA Visualization created by Earth Observatory staff. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>
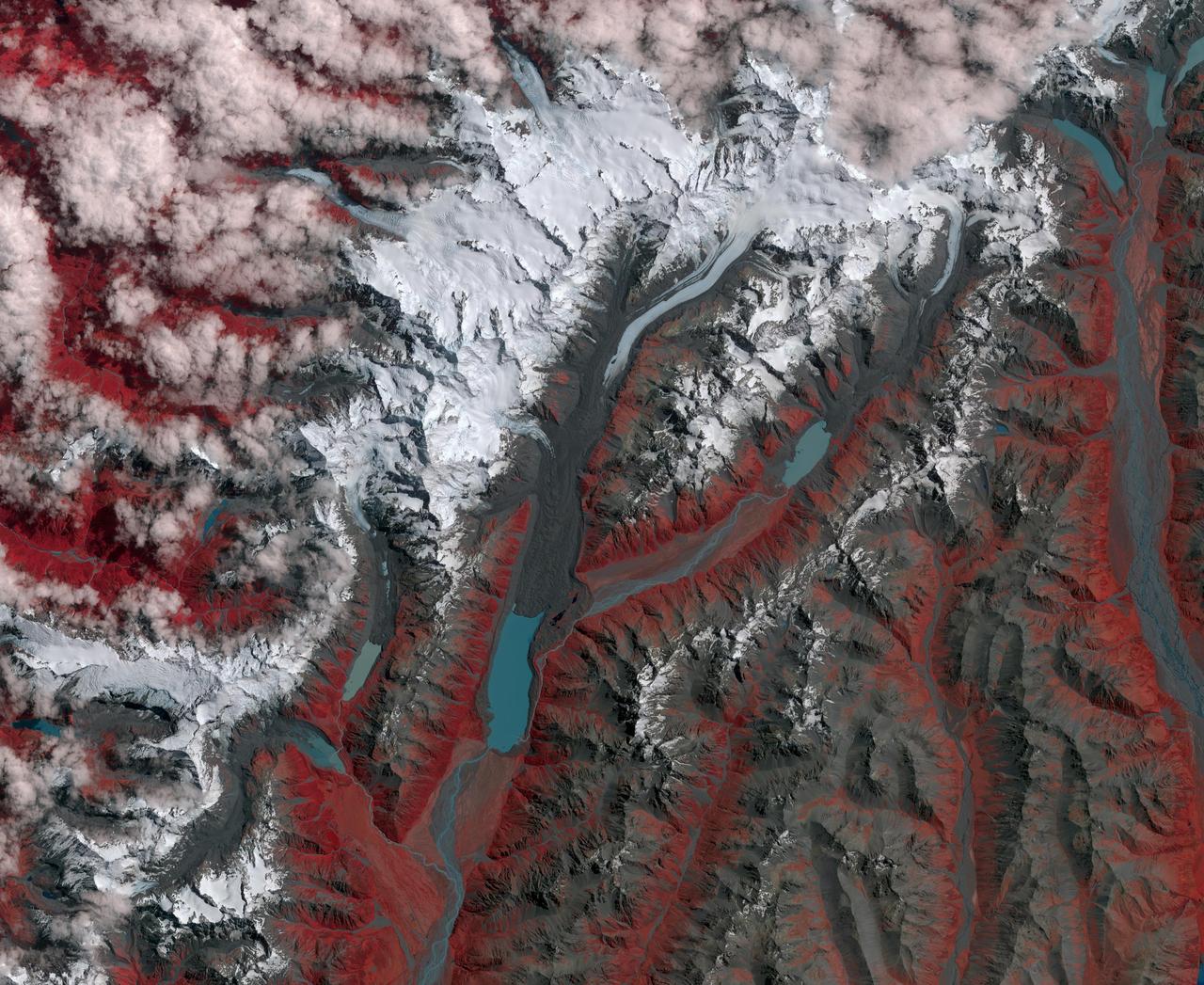

New Zealand contains over 3,000 glaciers, most of which are in the Southern Alps on the South Island. Since 1890, the glaciers have been retreating, with short periods of small advances, as shown in this image from NASA Terra spacecraft. The image cover an area of 39 by 46 km, and are located at 43.7 degrees south, 170 degrees east. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21509
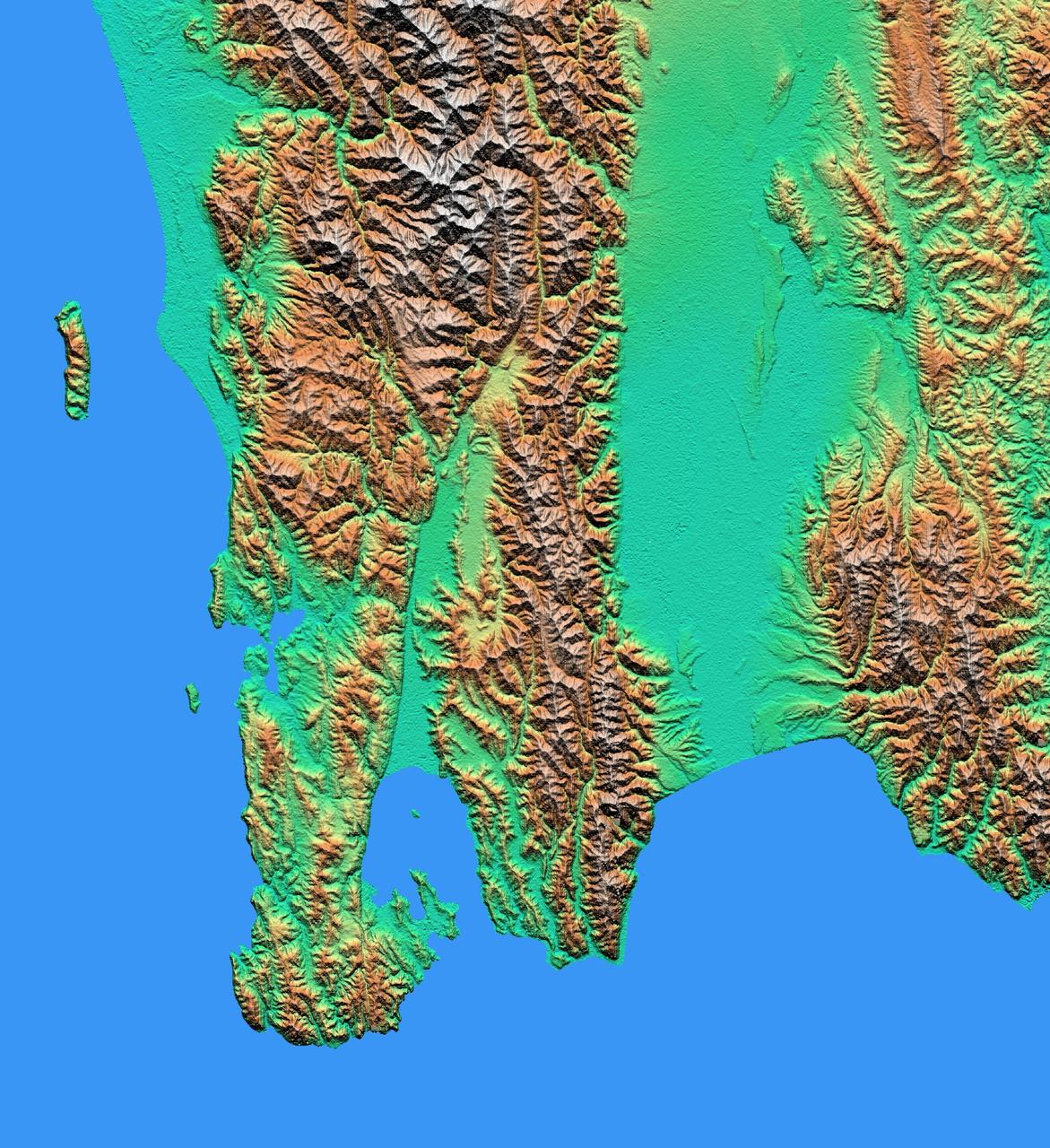
The topography of New Zealand North Island is rich in seismic features: The sharp line cutting through the city of Wellington on the left side of the large bay on the bottom coast is the active Wellington Fault.
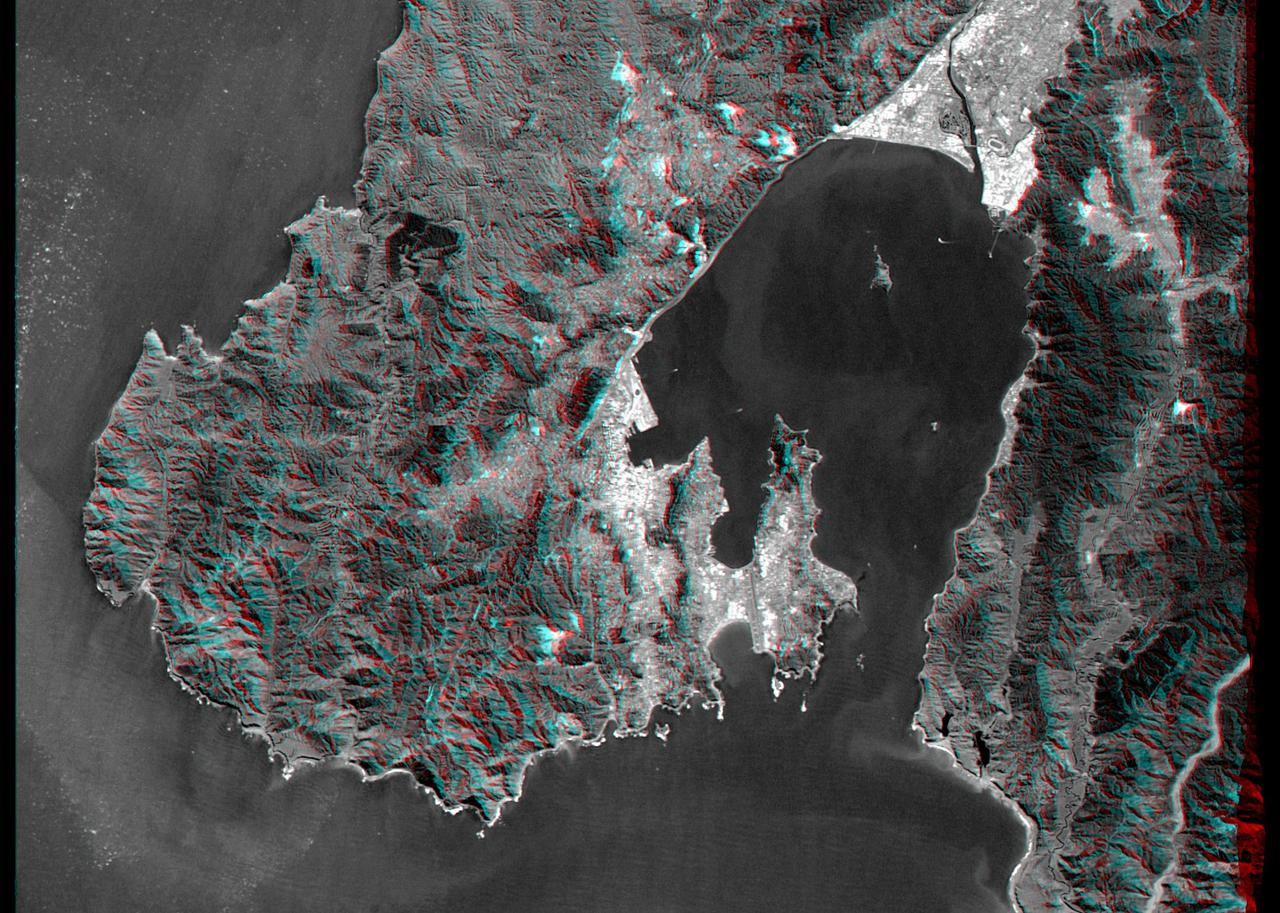

This anaglyph, from NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, is of Wellington, the capital city of New Zealand, located on the shores of Port Nicholson, a natural harbor. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
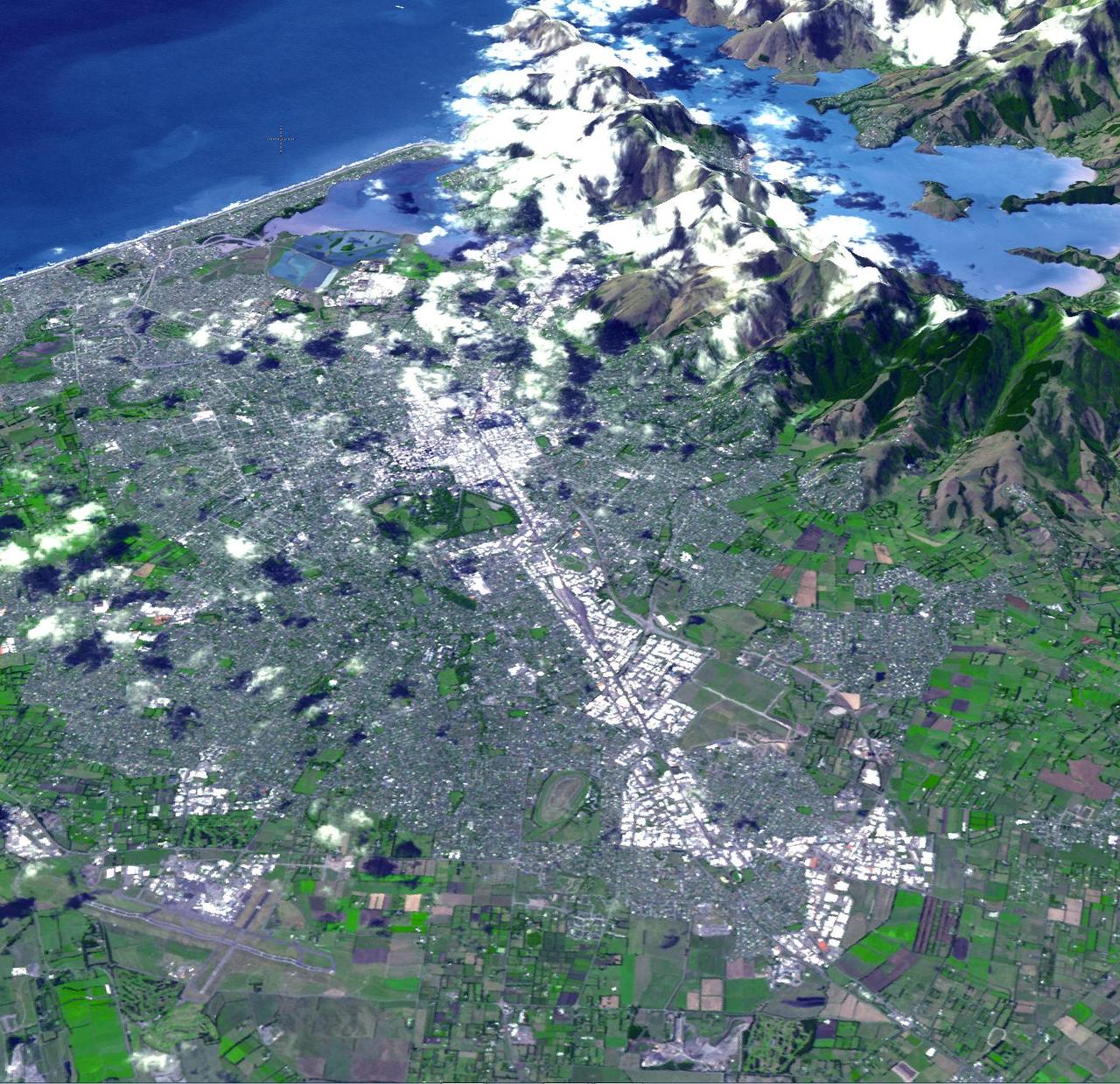
On Feb. 23, 2011, NASA Terra spacecraft imaged the Christchurch region on New Zealand South Island; this region was rocked by a powerful magnitude 6.3 earthquake.

A rainbow frames the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy 747SP during its first Southern Hemisphere deployment in Christchurch, New Zealand, in July 2013.
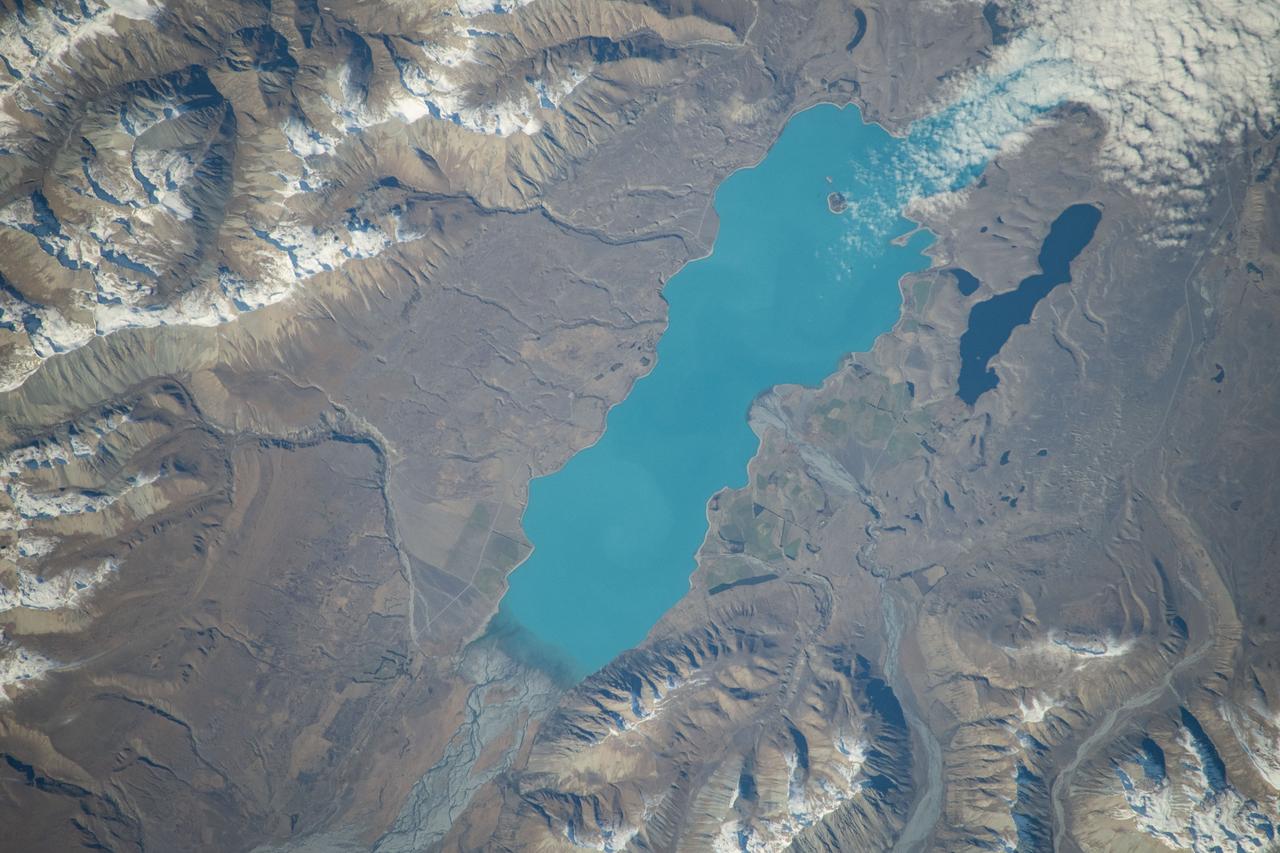

iss071e051532 (May 5, 2024) -- Lake Tekapo's turquoise color contrasts against the surrounding mountains as the International Space Station orbited 266 miles above New Zealand's South Island. Fed by the Godley River, it's one of three nearly parallel lakes in the Mackenzie Basin. Next to it lies Lake Alexandria.
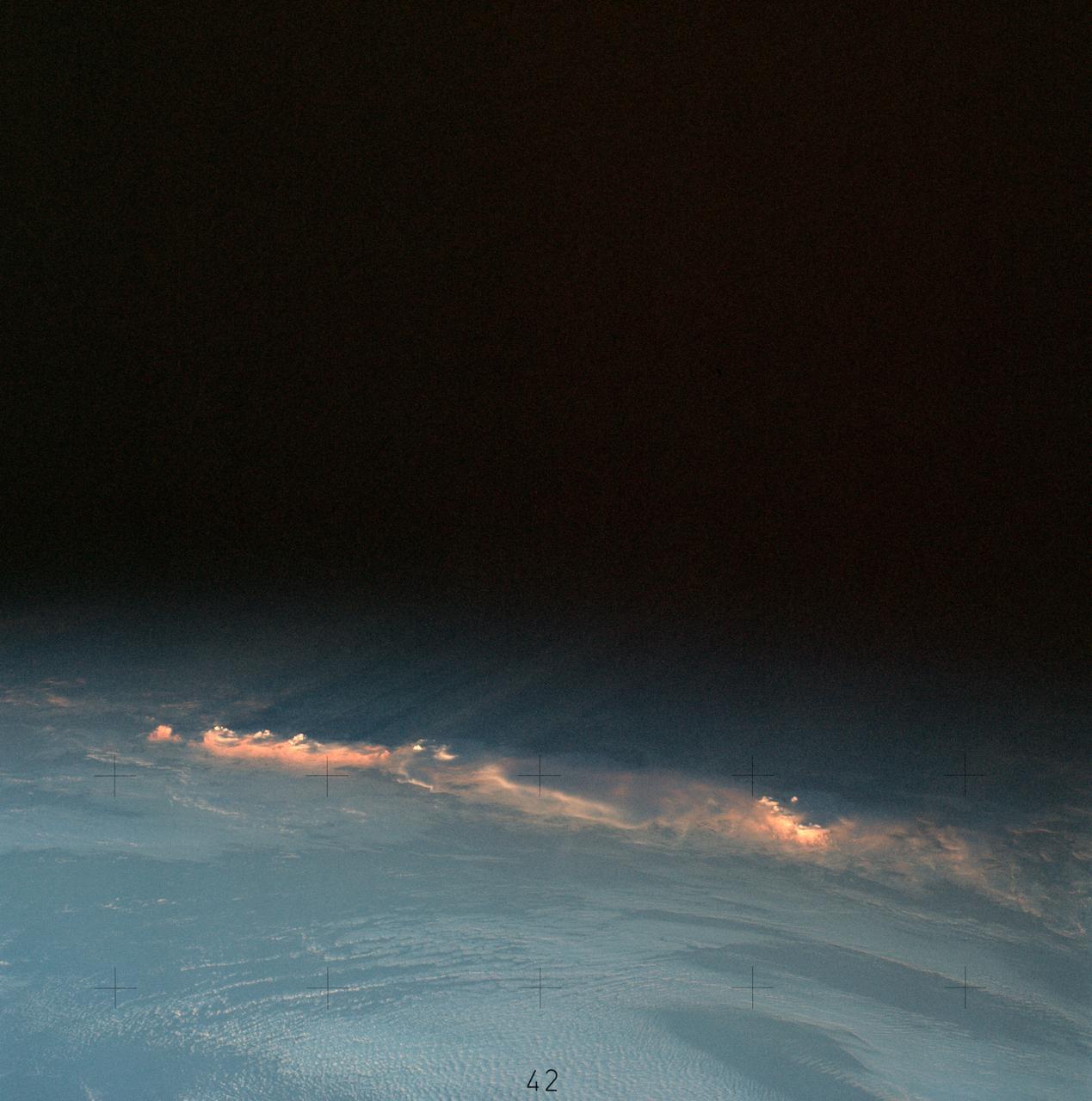

SL4-137-3566 (12 Dec. 1973) --- A group of clouds near New Zealand, as photographed from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit by one of the Skylab 4 crew members. The camera used was a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad with SO-368 medium speed Ektachrome. This picture shows vividly how low sun angles enhance relief, giving these clouds a three-dimensional appearance. In addition to being "pretty," this photograph can be used to study the line of storms seen here at sunset. Relative heights of individuals cells can be measured, as well as their relation to the surrounding clouds. Photo credit: NASA

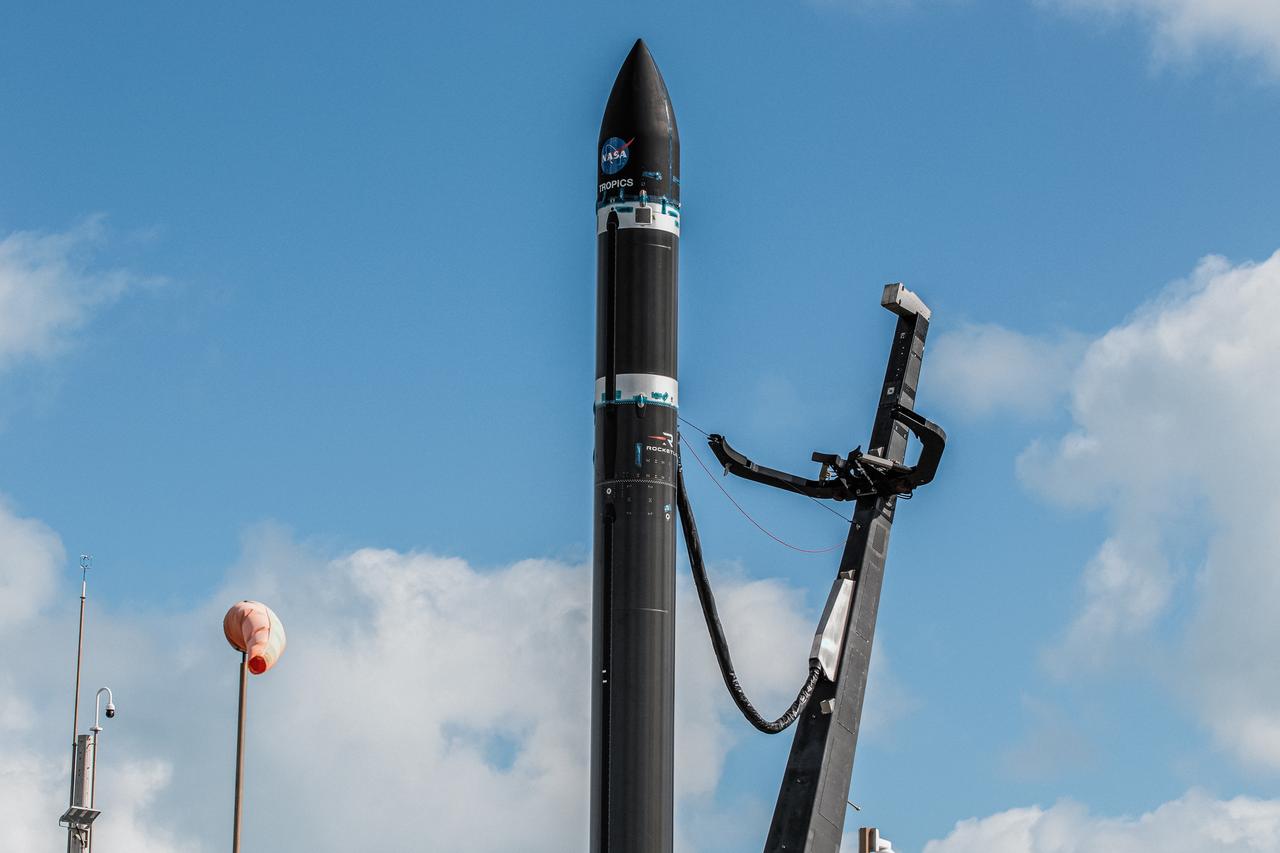
Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
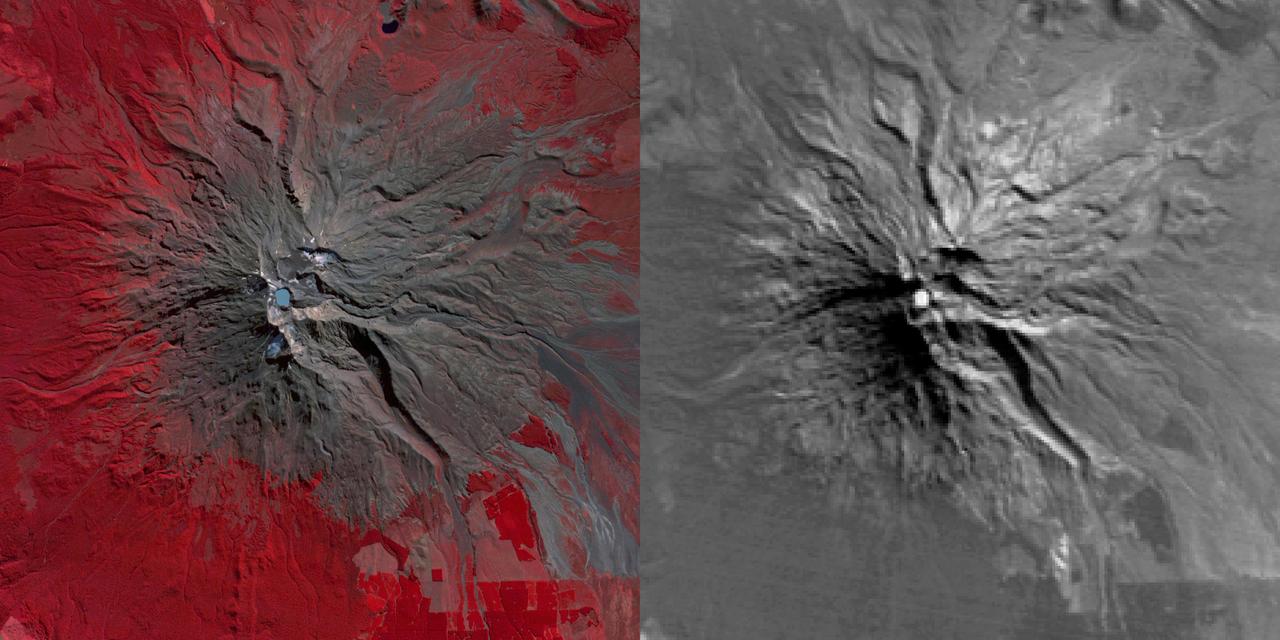

NASA Terra spacecraft reveals signs of life in New Zealand Mount Ruapehu Volcano which has been on a level 1 volcanic alert for some time, indicating minor volcanic unrest.
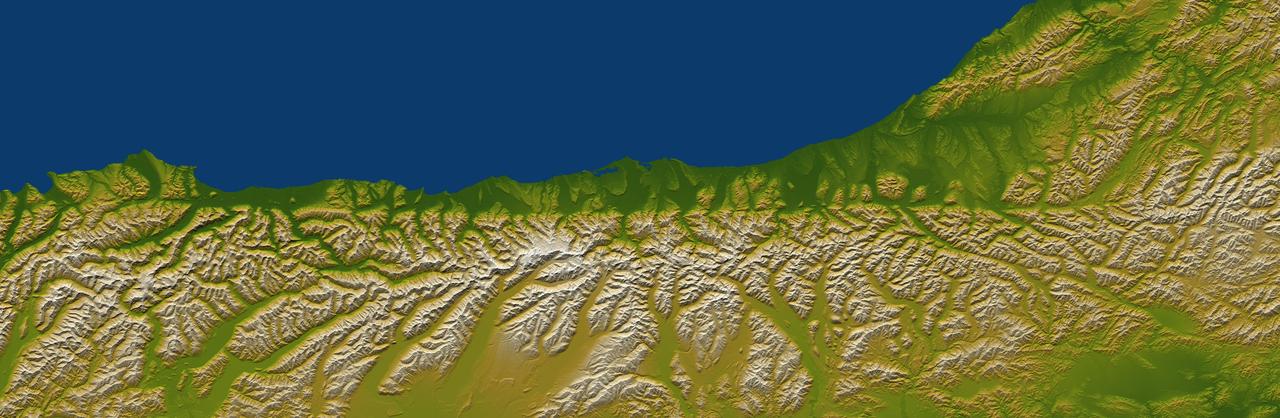
The Alpine fault runs parallel to, and just inland of, much of the west coast of New Zealand South Island. This view was created from the near-global digital elevation model produced by NASA Shuttle Radar Topography Mission SRTM.
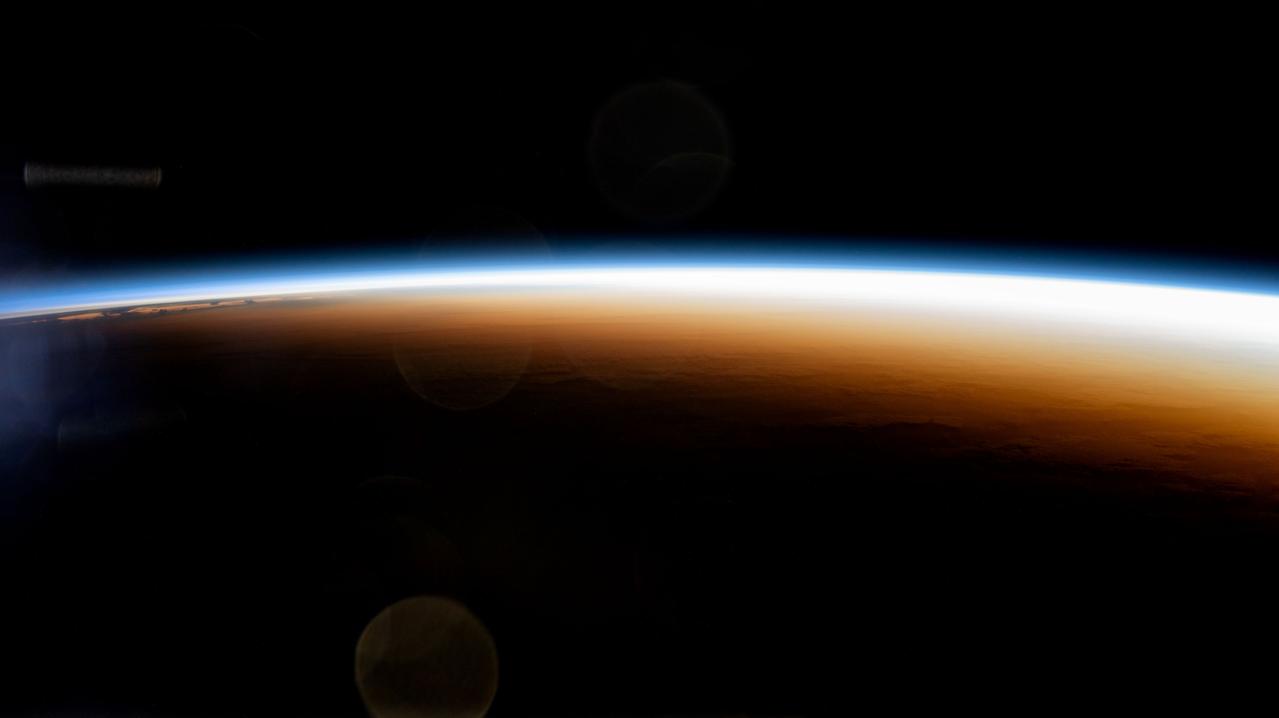

iss071e439624 (Aug. 6, 2024) --- An orbital sunrise colorfully illuminates the Earth's atmosphere and highlights the boundary between night and day, also known as the terminator, in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 267 miles above the Pacific Ocean north of Auckland, New Zealand.

SL4-137-3700 (22 Dec. 1973) --- A near vertical view of a portion of South Island, New Zealand, as see from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. This picture was taken by one of the Skylab 4 crew members with a handheld 70mm Hasselblad camera using a 100mm lens. The picture should be held with the largest body of water (Tasman Sea) on the left. Cape Foulwind is at the upper left. The City of Christchurch is under clouds at the center right margin. Note the movement of sediment by alongshore currents, especially on the east (right) side of the island. The Alpine Fault, which is part of the circum-Pacific volcanic-tectonic belt, is clearly visible on the left (west) side of the island. The fault line is marked by a scarp, which appears very distinct from orbital altitude. Differences in topography and vegetation on either side of the fault are also sharp. Streams change direction at the fault line, and the change in slope at the fault line is evident in the widening of stream channels. The left side of the fault has moved northeast (upward) relative to the right side; some stream offsets indicate the direction of relative movement, but others are controlled by local topography. The Alpine Fault, which also transects New Zealand's North Island, was photographed and described more than a dozen times by the Skylab 4 crewmen. The circum-Pacific volcanic-tectonic belt is a feature of the Earth's crust which is related to sea floor spreading and continental drift. Though the Alpine Fault is sharply delineated in this photograph, other major crustal features are subtle that their existence was unknown before their observation from orbit. The distance from top to bottom is about 290 kilometers (175 miles). Photo credit: NASA
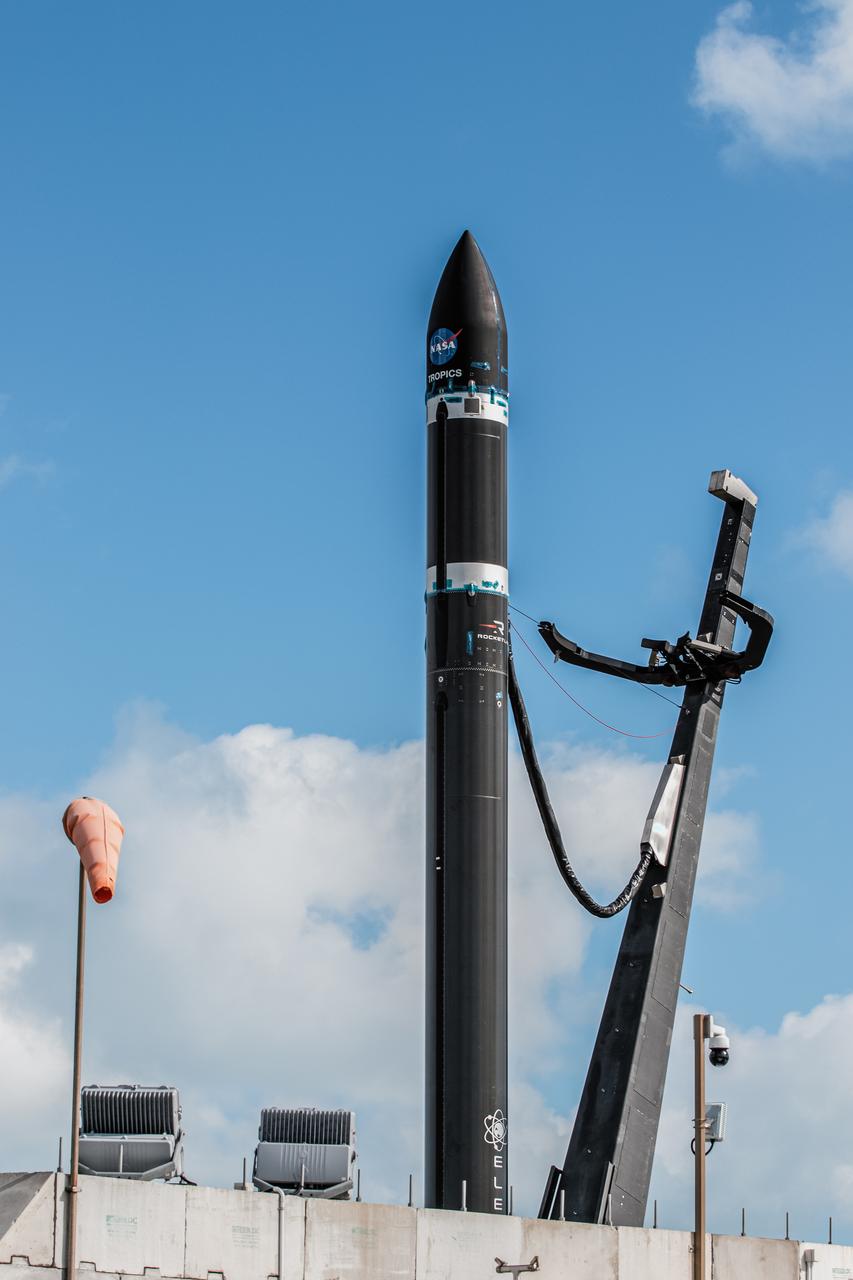

With the umbilical tower in view, Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.

With the umbilical tower in view, Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats are secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. TROPICS is scheduled to launch on Monday, May 1, at 1 a.m. New Zealand time from Launch Complex 1, Pad B. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
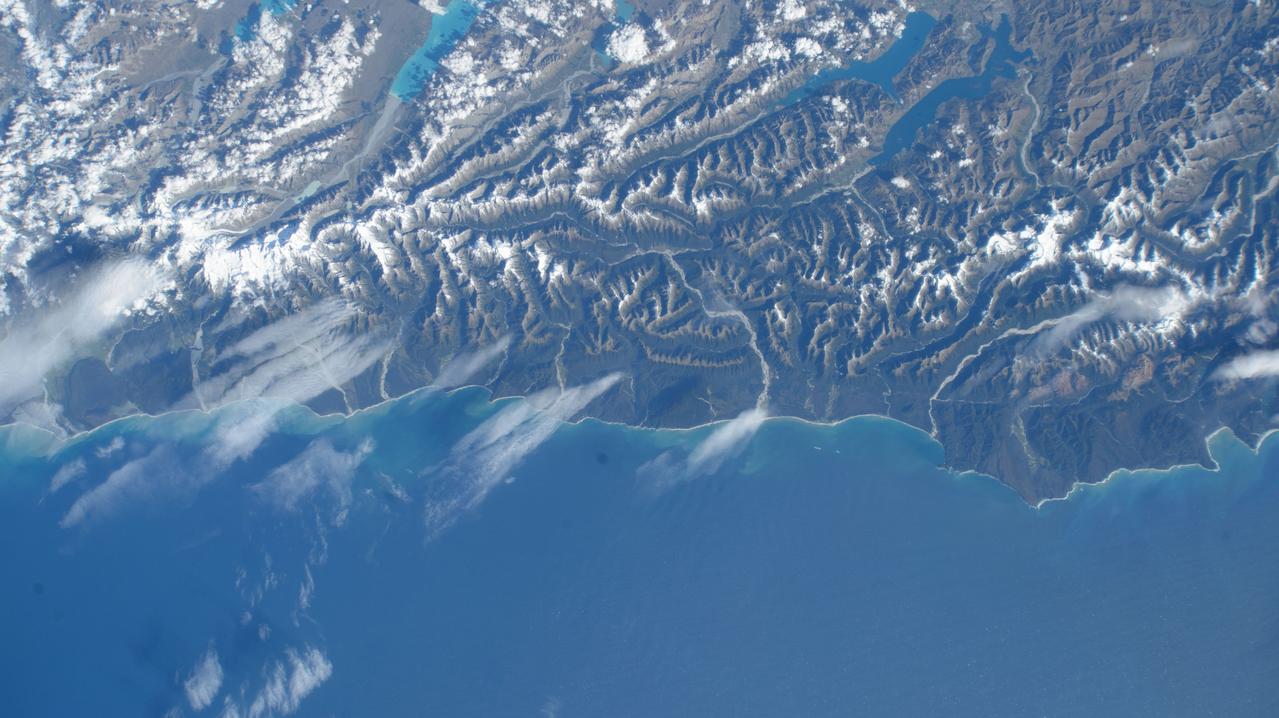

iss072e424419 (Jan. 4, 2025) --- The Tasman Sea coast on New Zealand's South Island, with Mount Aspiring National Park in the Southern Alps, is pictured from the International Space Station as it orbited 267 miles above.

Caption: A NASA Super Pressure Balloon with the COSI payload is ready for launch from McMurdo, Antarctica. Credit: NASA More info: NASA’s globetrotting Balloon Program Office is wrapping up its 2014-2015 Antarctic campaign while prepping for an around-the-world flight launching out of Wanaka, New Zealand, in March. After 16 days, 12 hours, and 56 minutes of flight, operators successfully conducted a planned flight termination of the Suborbital Polarimeter for Inflation Dust and the Epoch of Reionization (SPIDER) mission Saturday, Jan. 18, the final mission of the campaign. Other flights in the 2014-2015 Antarctic campaign included the Antarctic Impulsive Transient Antenna (ANITA-III) mission as well as the Compton Spectrometer and Imager (COSI) payload flown on the developmental Super Pressure Balloon (SPB). ANITA-III successfully wrapped up Jan. 9 after 22 days, 9 hours, and 14 minutes of flight. Flight controllers terminated the COSI flight 43 hours into the mission after detecting a small gas leak in the balloon. Crews are now working to recover all three instruments from different locations across the continent. The 6,480-pound SPIDER payload is stationary at a position about 290 miles from the United Kingdom’s Sky Blu Logistics Facility in Antarctica. The 4,601 pound ANITA-III payload, located about 100 miles from Australia’s Davis Station, and the 2,866 pound COSI payload, located about 340 miles from the United States McMurdo Station both had numerous key components recovered in the past few days. Beginning in late January, the Balloon Program Office will deploy a team to Wanaka, New Zealand, to begin preparations for an SPB flight, scheduled to launch in March. The Program Office seeks to fly the SPB more than 100 days, which would shatter the current flight duration record of 55 days, 1 hour, and 34 minutes for a large scientific balloon. “We’re looking forward to the New Zealand campaign and hopefully a history-making flight with the Super Pressure Balloon,” said Debbie Fairbrother, NASA’s Balloon Program Office Chief. Most scientific balloons see altitude variances based on temperature changes in the atmosphere at night and during the day. The SPB is capable of missions on the order of 100 days or more at constant float altitudes due to the pressurization of the balloon. “Stable, long-duration flights at near-space altitudes above more than 99 percent of the atmosphere are highly desirable in the science community, and we’re ready to deliver,” said Fairbrother. In addition to the SPB flight in March, the Balloon Program Office has 10 more balloon missions planned through September 2015 to include scheduled test flights of the Low-Density Supersonic Decelerator, which is testing new technologies for landing larger, heavier payloads on Mars. NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility manages the agency’s Scientific Balloon Program with 10 to 15 flights each year from launch sites worldwide. The balloons are massive in volume; the average-sized balloon could hold the volume of nearly 200 blimps. Previous work on balloons have contributed to confirming the Big Bang Theory. For more information on NASA’s Scientific Balloon Program, see: <a href="http://sites.wff.nasa.gov/code820/index.html" rel="nofollow">sites.wff.nasa.gov/code820/index.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
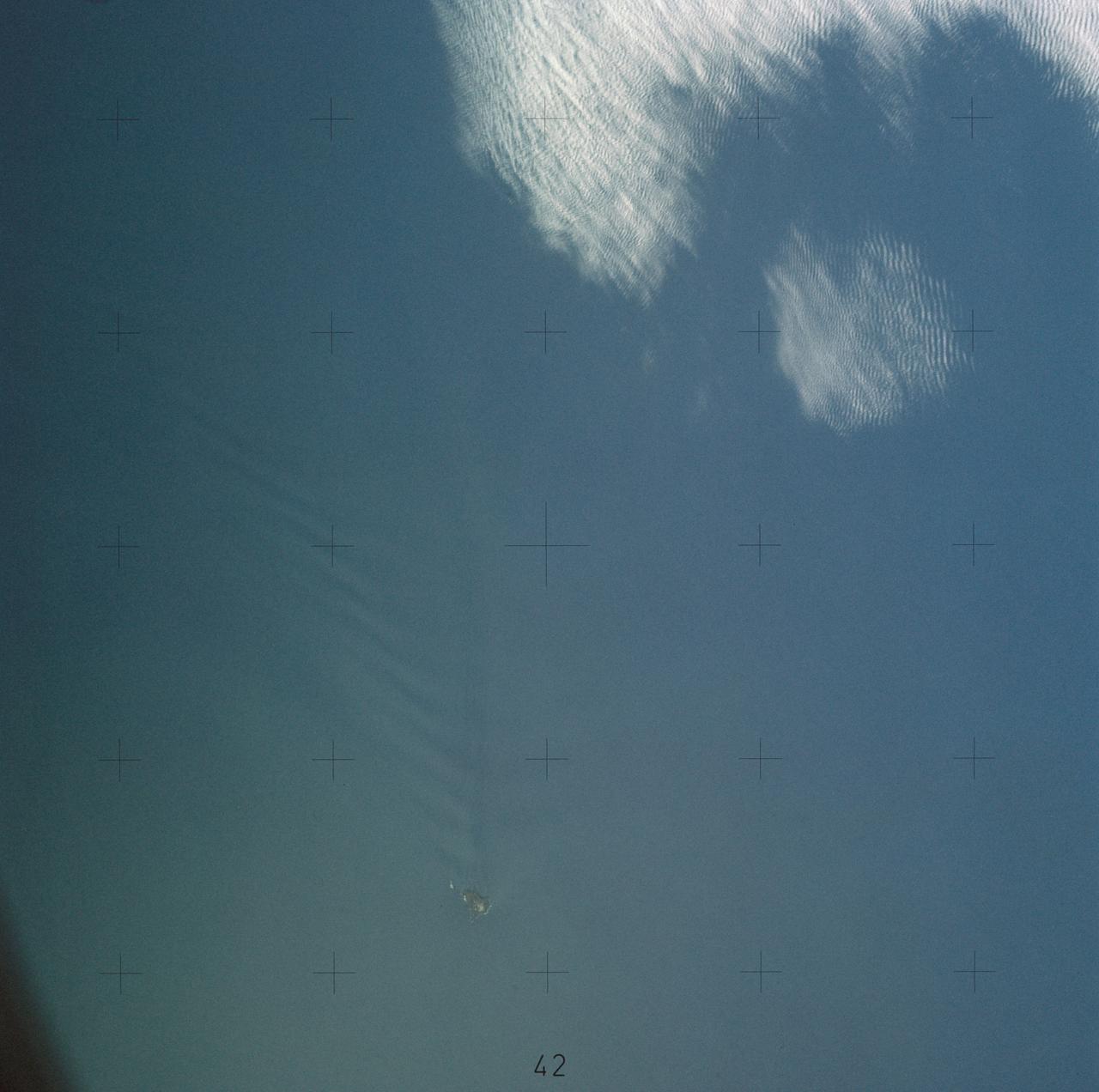

SL4-137-3655 (16 Dec. 1973) --- An island wake produced by the Antipodes Islands in the ocean current south of New Zealand is seen in this photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. A Skylab 4 crewmen took the picture with a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad camera. The bow wave pattern is quite evident and can be used to determine the current speed from the angle of the bow wave if the propagation speed of the surface wave is known. Also, evident is the darker band extending downstream from the island tens of miles. This is the actual wake of the island. The existence of water color differences from within to outside a turbulent island wake may indicate a temperature difference, with cooler water being stirred to the surface in the wake. This temperature difference could be used to drive a thermo-electric type generator to reduce small islands' dependence on imported oil for power generation. Photo credit: NASA
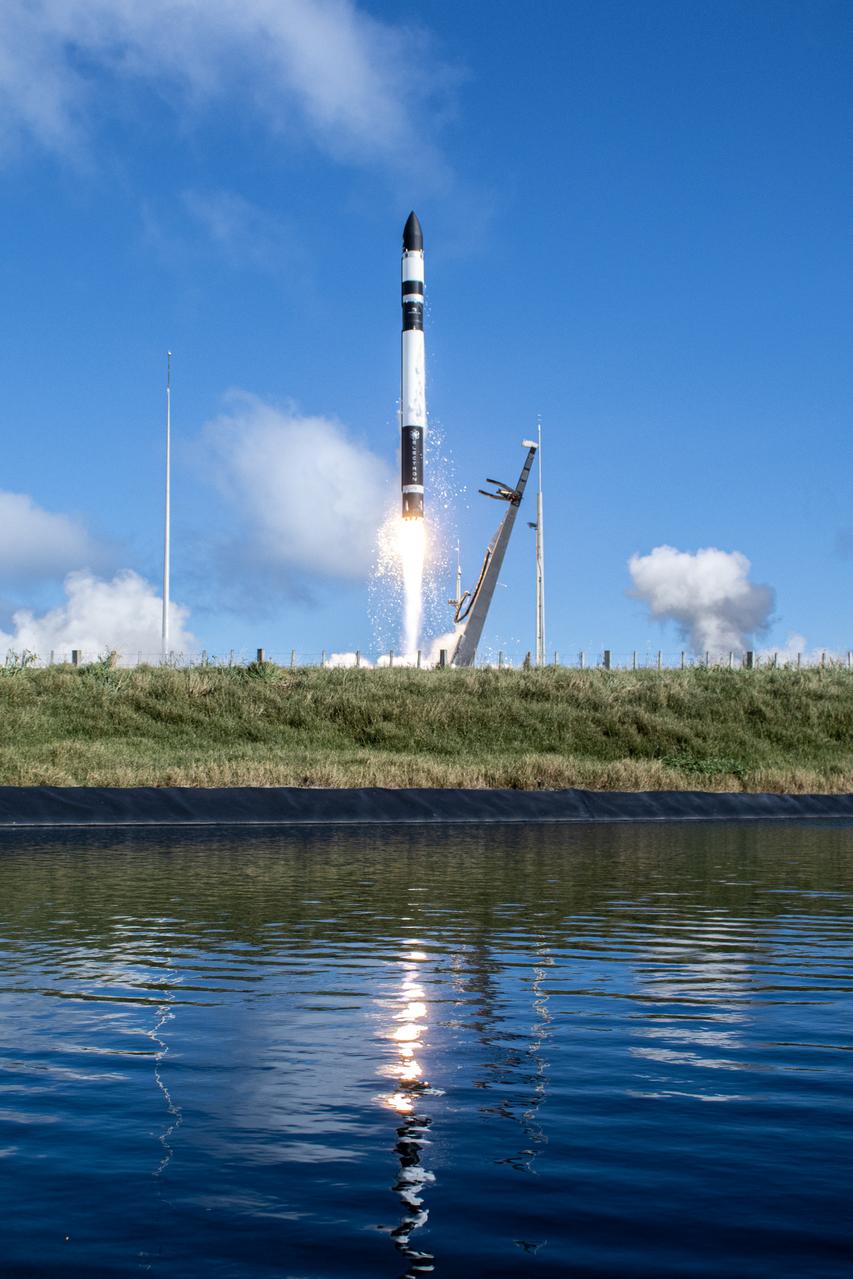

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
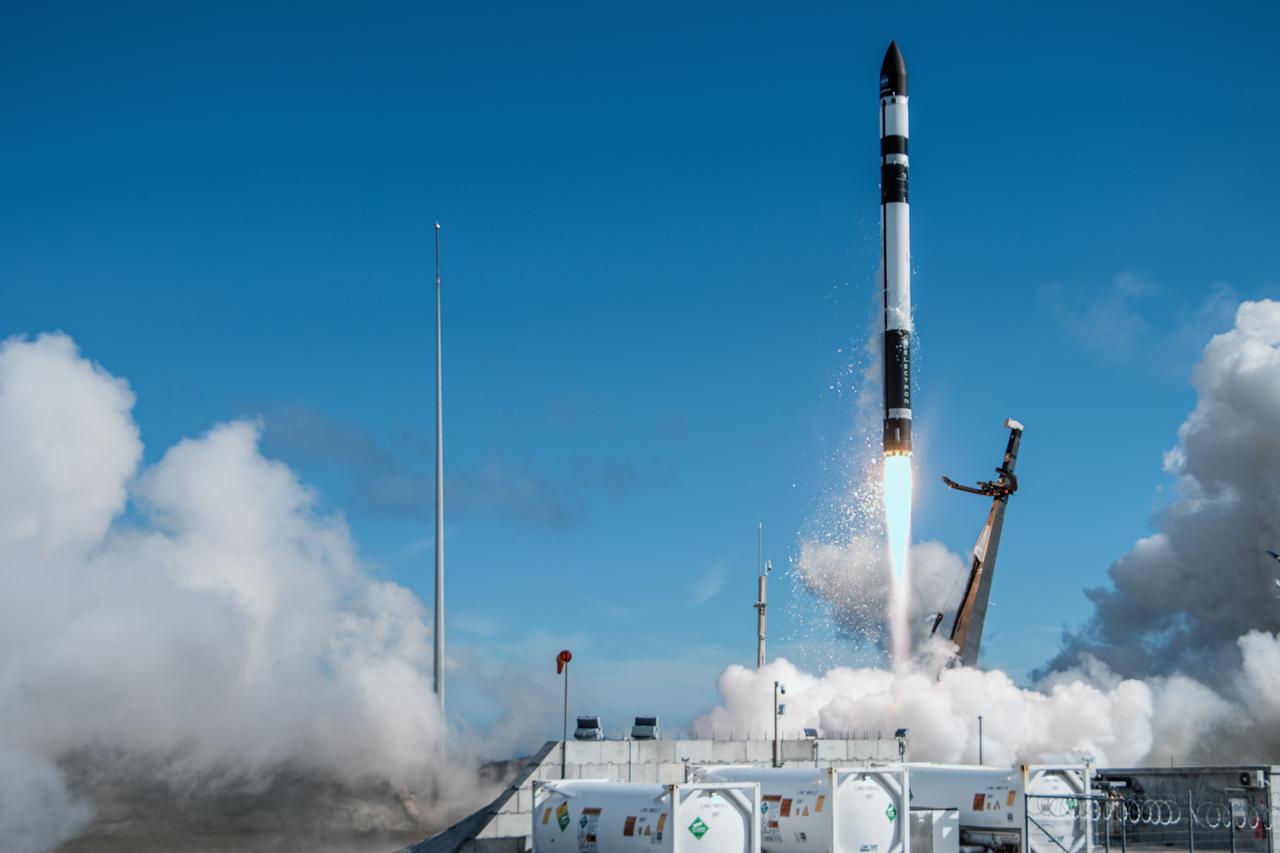

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
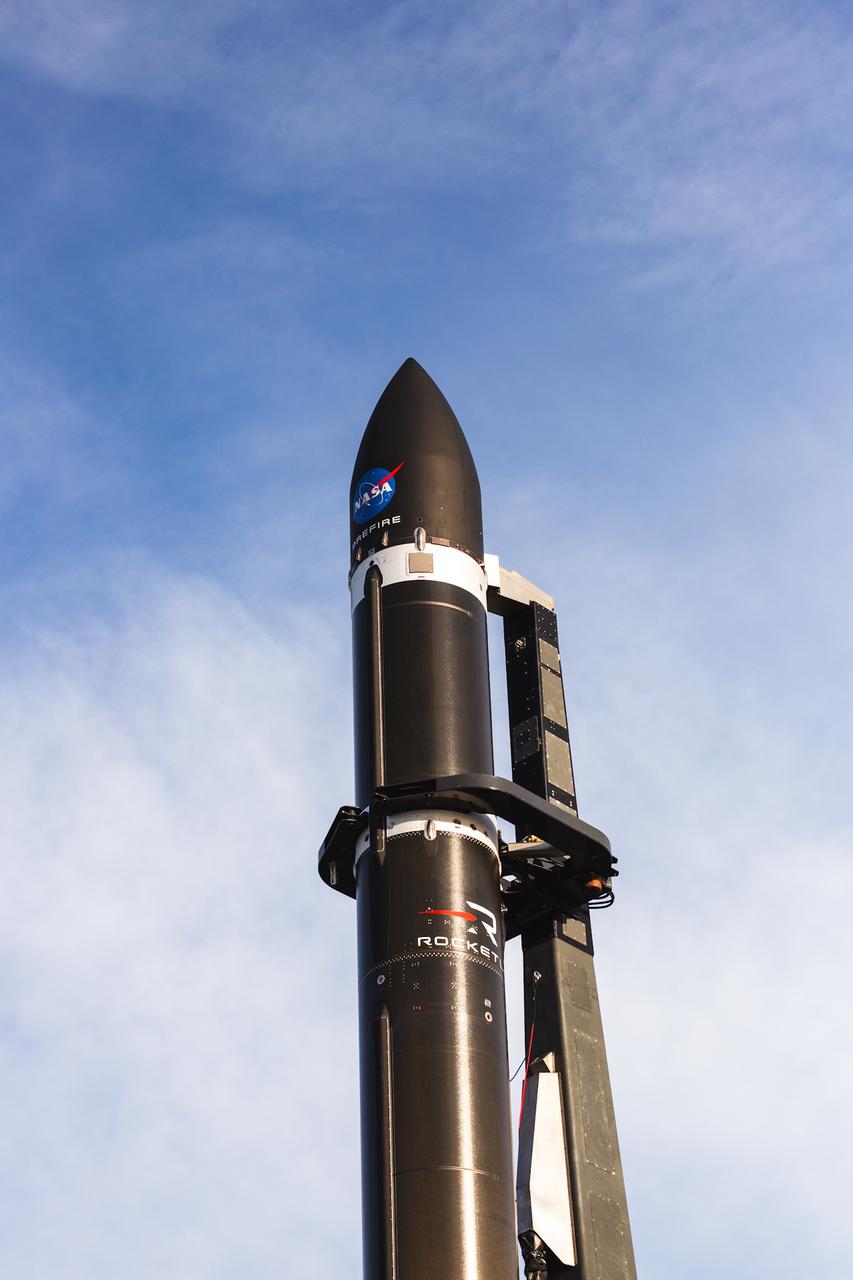

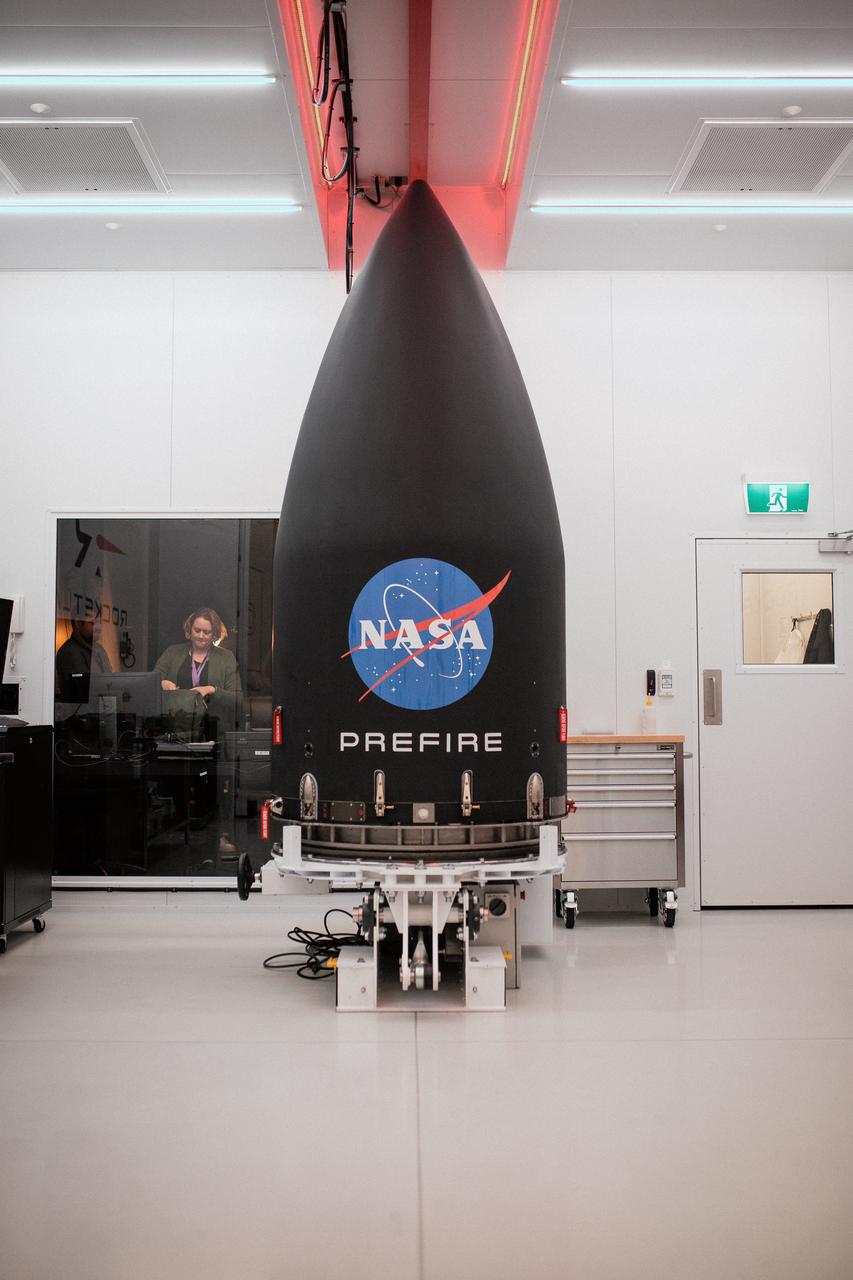
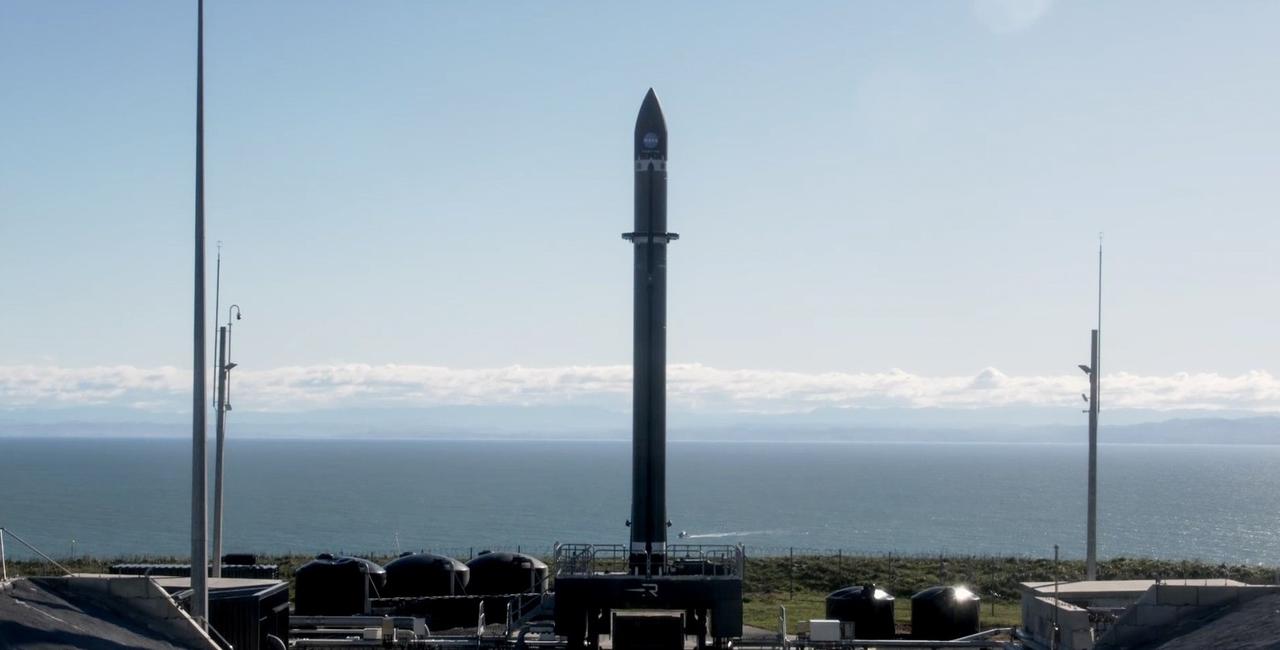
Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” is vertical on the pad awaiting liftoff at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, ahead of NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission Wednesday, June 5, 2024. The mission, the second of two launches for NASA’S PREFIRE, features two identical 6U CubeSats in asynchronous, near-polar orbits, will study how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
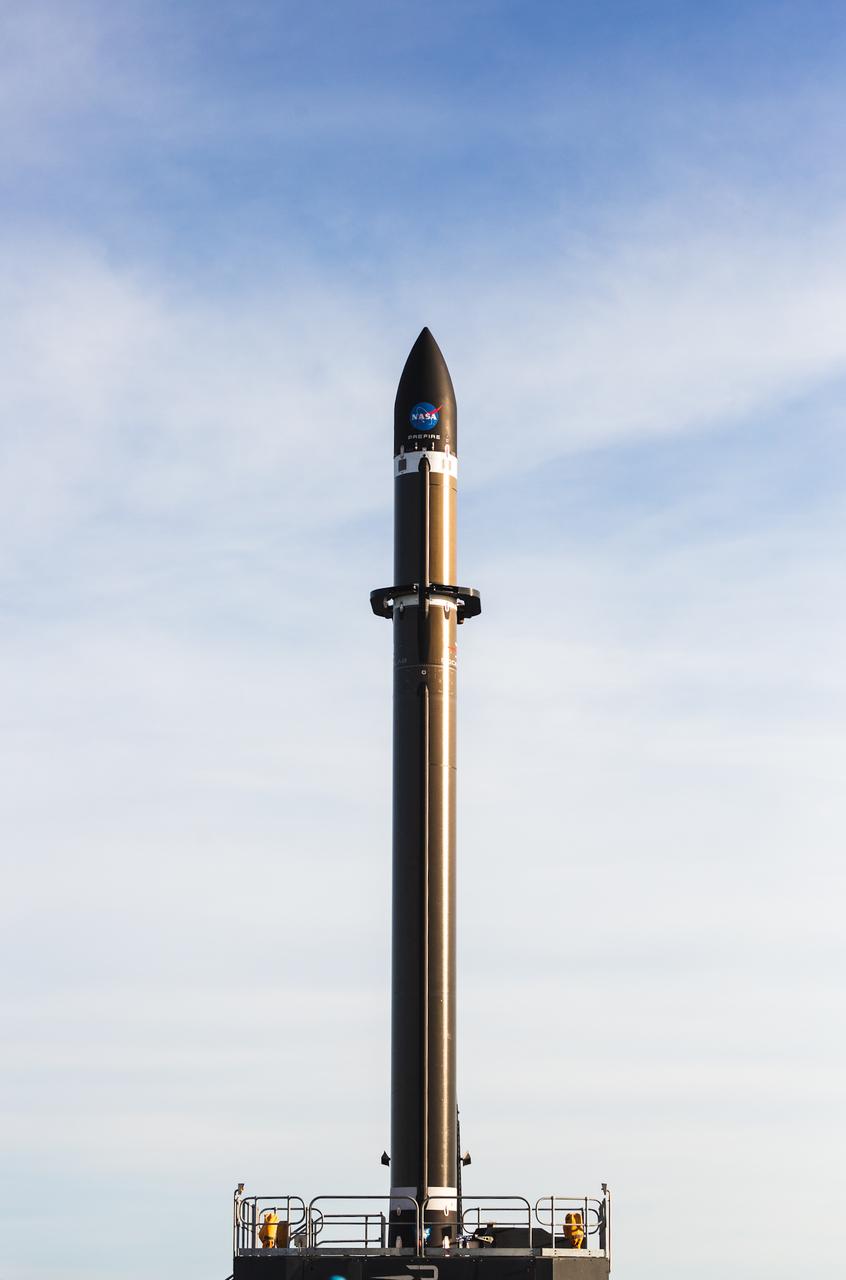

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” is vertical on the pad awaiting liftoff at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, ahead of NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission Wednesday, June 5, 2024. The mission, the second of two launches for NASA’S PREFIRE, features two identical 6U CubeSats in asynchronous, near-polar orbits, will study how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.

This high-dynamic range (HDR) photo of the Stratospheric Observatory for Infrared Astronomy (SOFIA) was captured just before sunset at the Christchurch International Airport in Christchurch, New Zealand while aircraft crews were preparing for a nighttime observation flight.
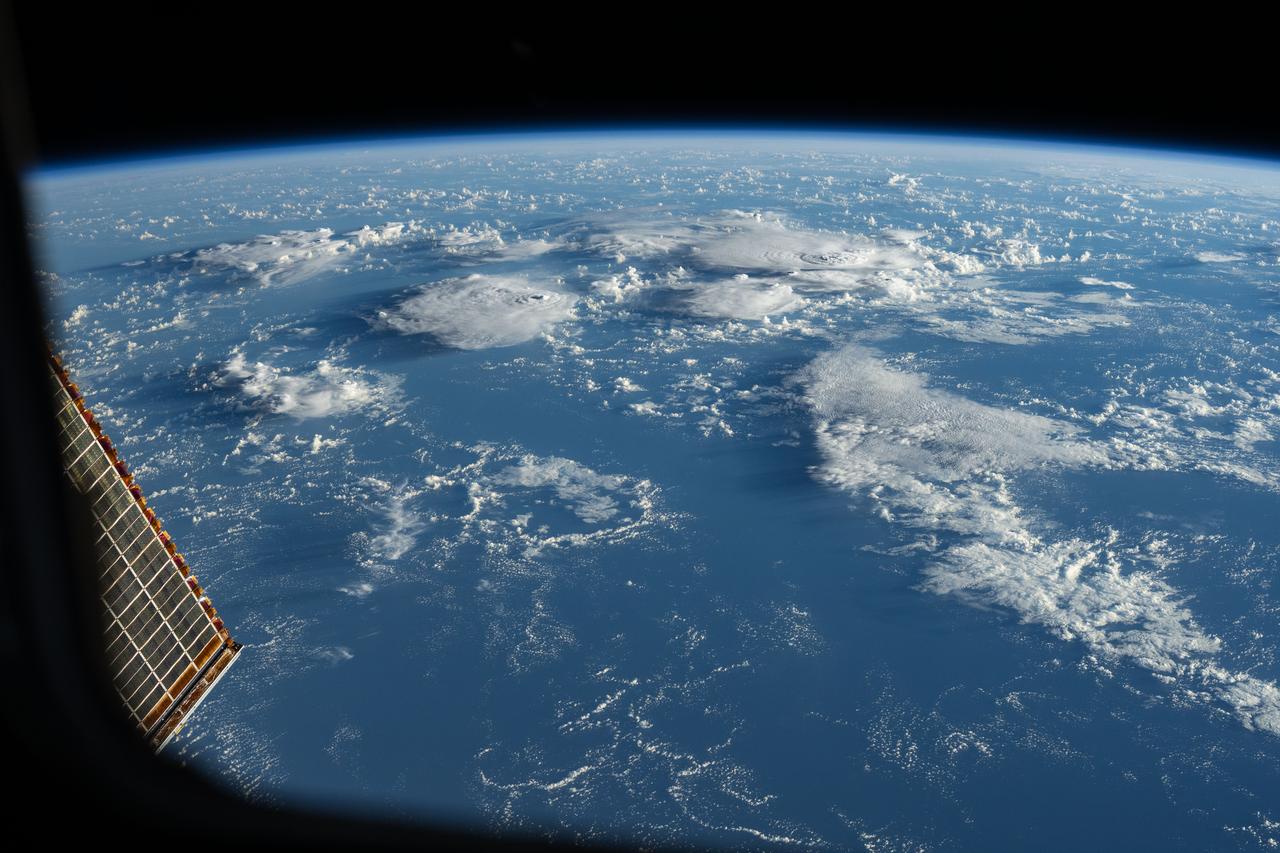

iss072e617674 (Feb. 1, 2025) --- Storm clouds rise above the South Pacific Ocean northwest of New Zealand in this photograph from the International Space Station as it orbited 264 miles above.
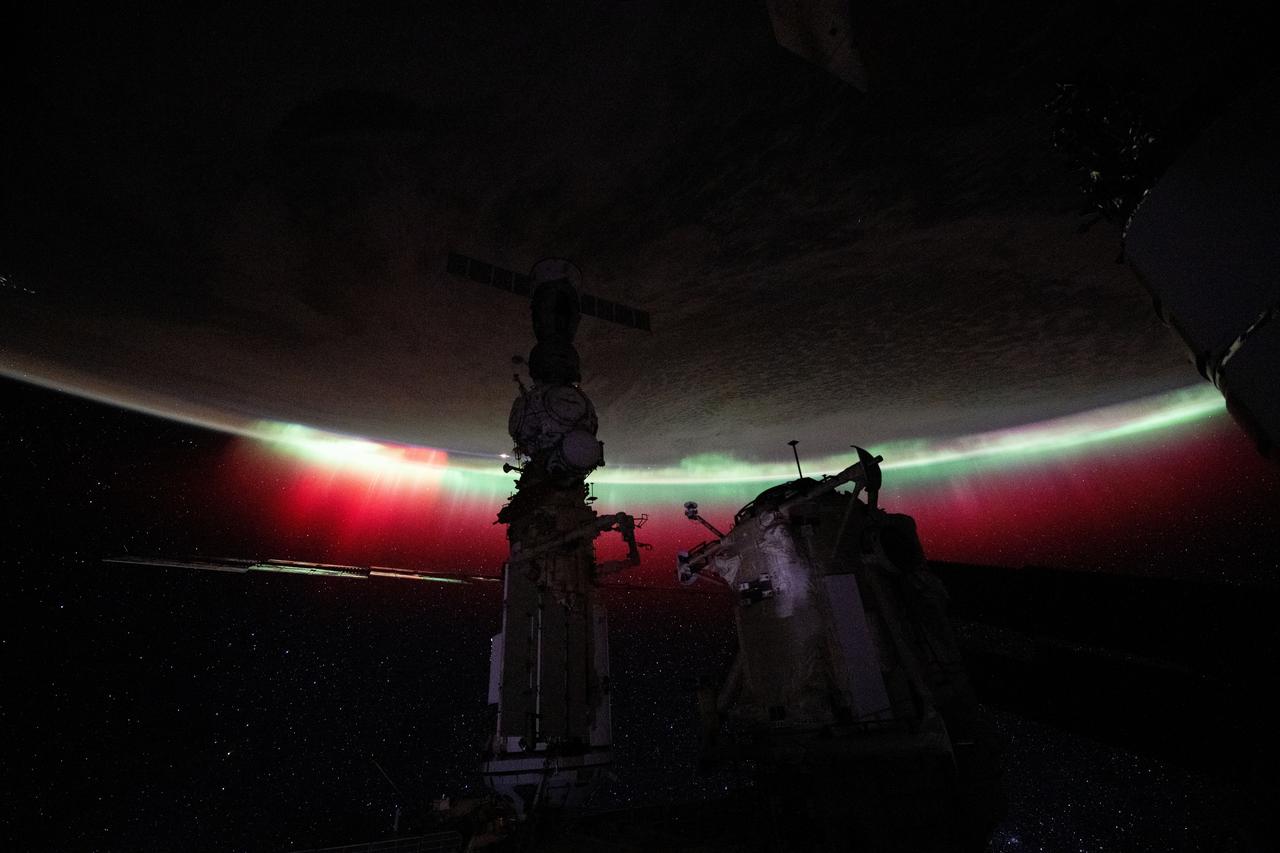

iss071e560367 (Aug. 11, 2024) -- A vibrant green and red aurora shimmers through orbital nighttime as the International Space Station soared 268 miles above New Zealand.
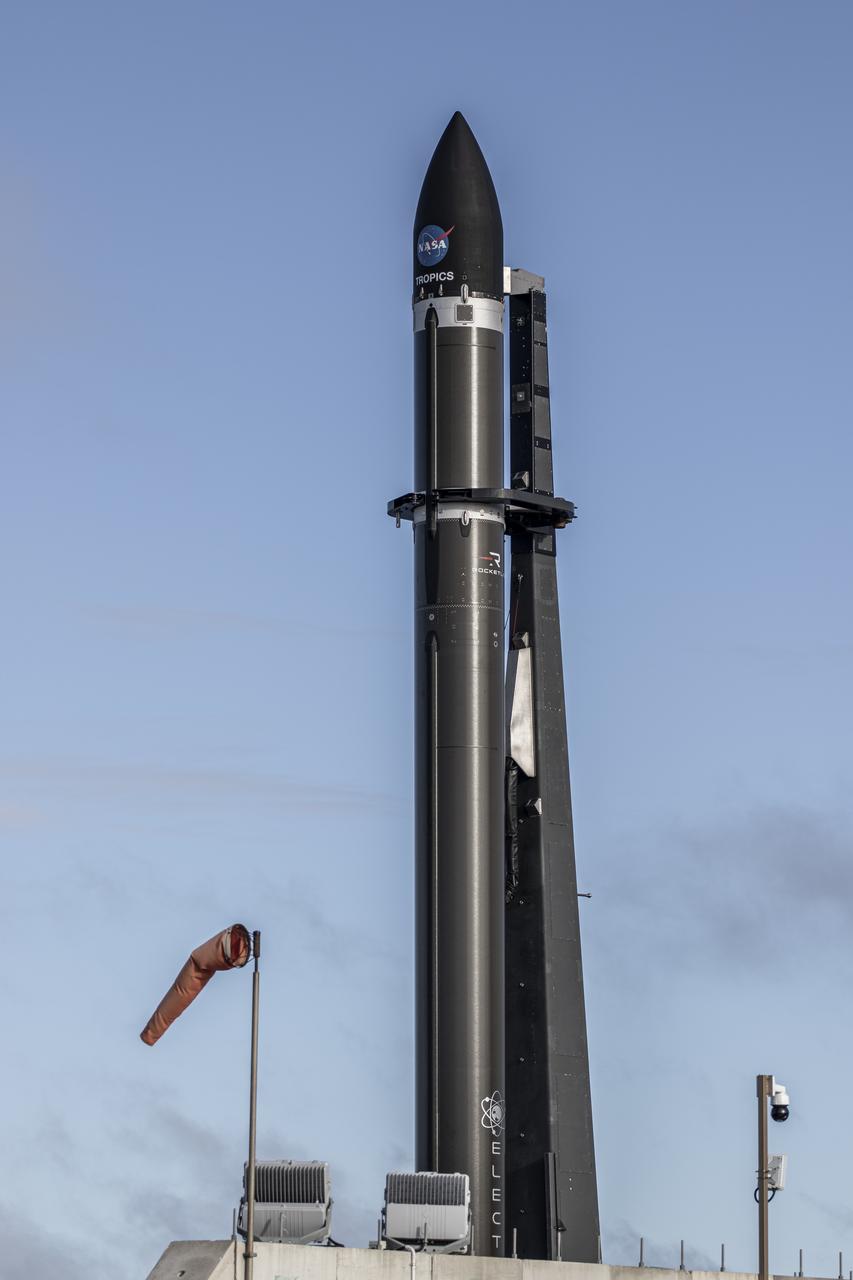

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket is poised for launch atop Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand. Launch time is May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT). The Electron rocket is carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
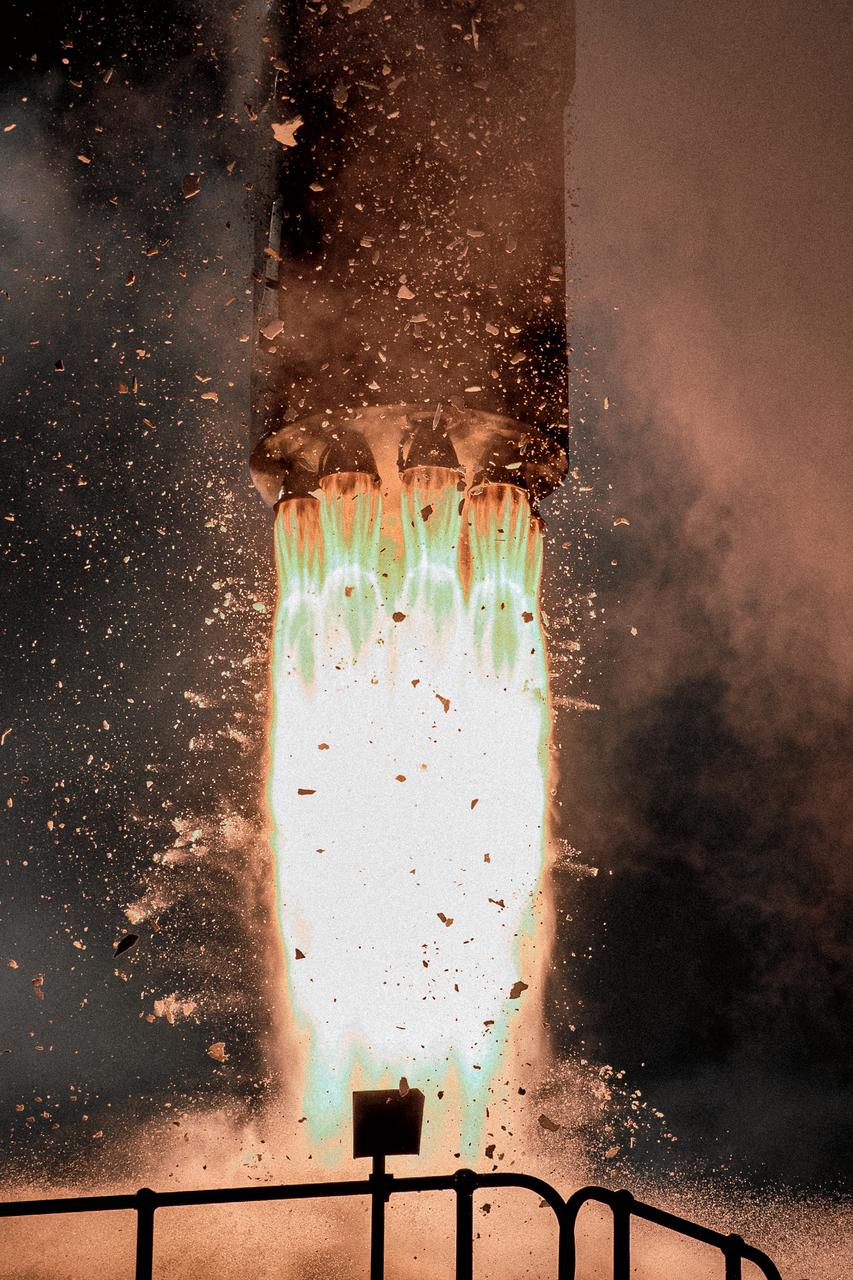

The engines of the first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignite as the rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
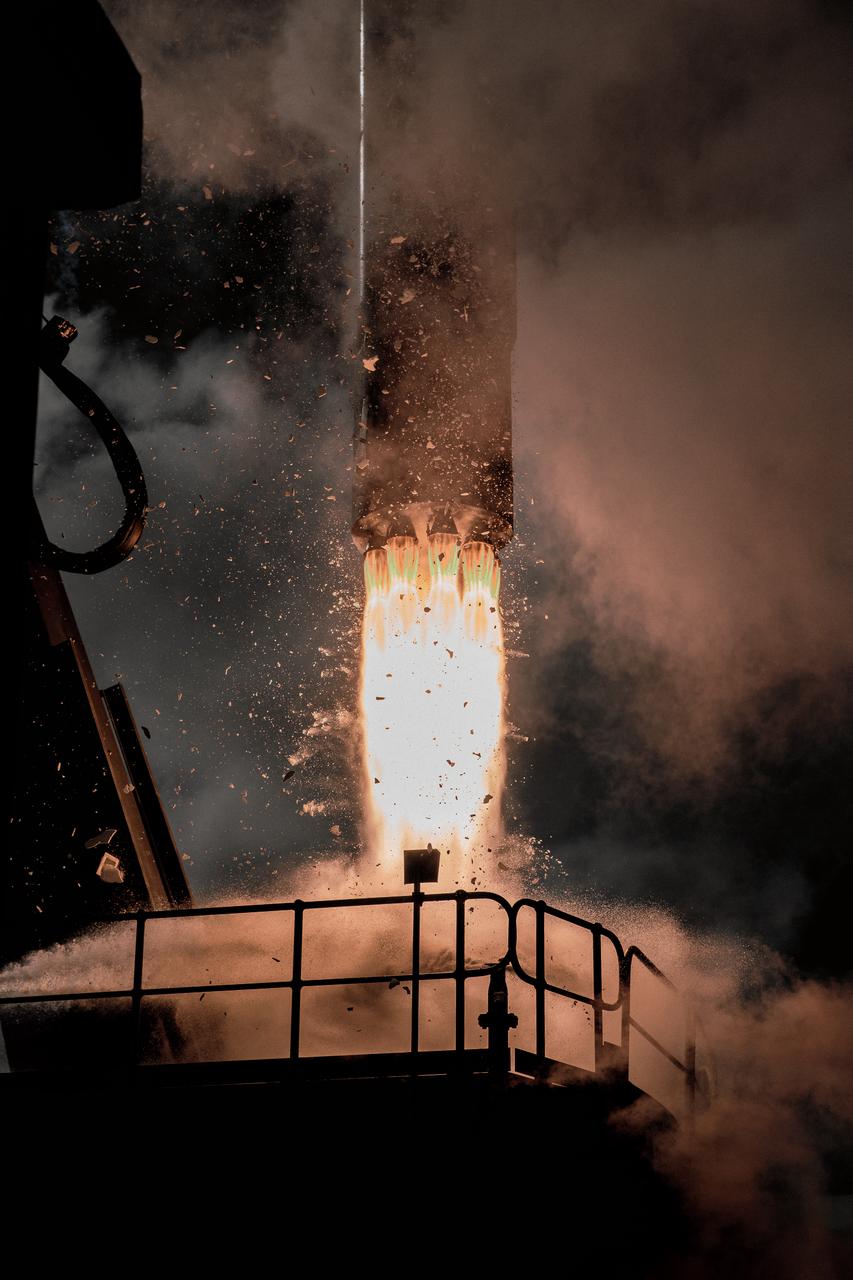

The engines of the first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignite as the rocket lifts off Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
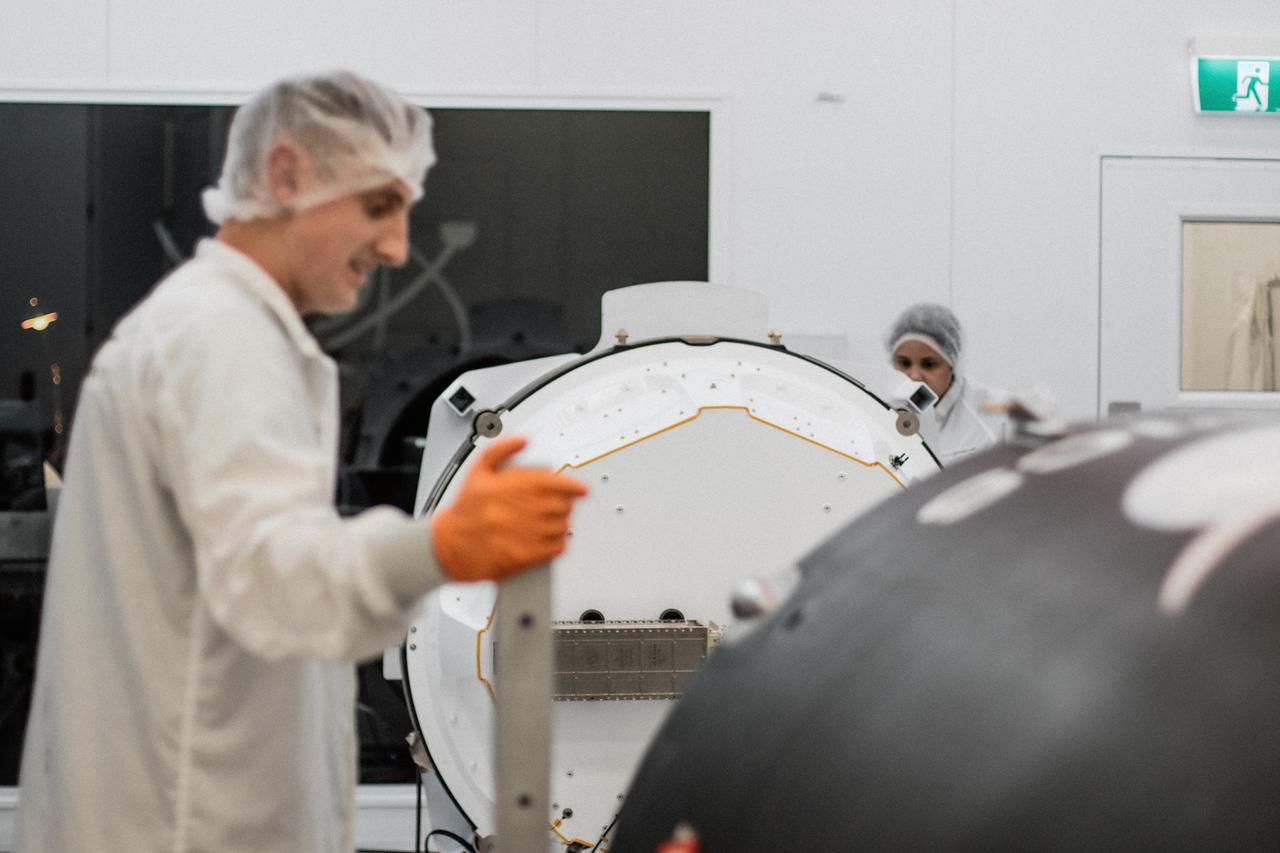

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
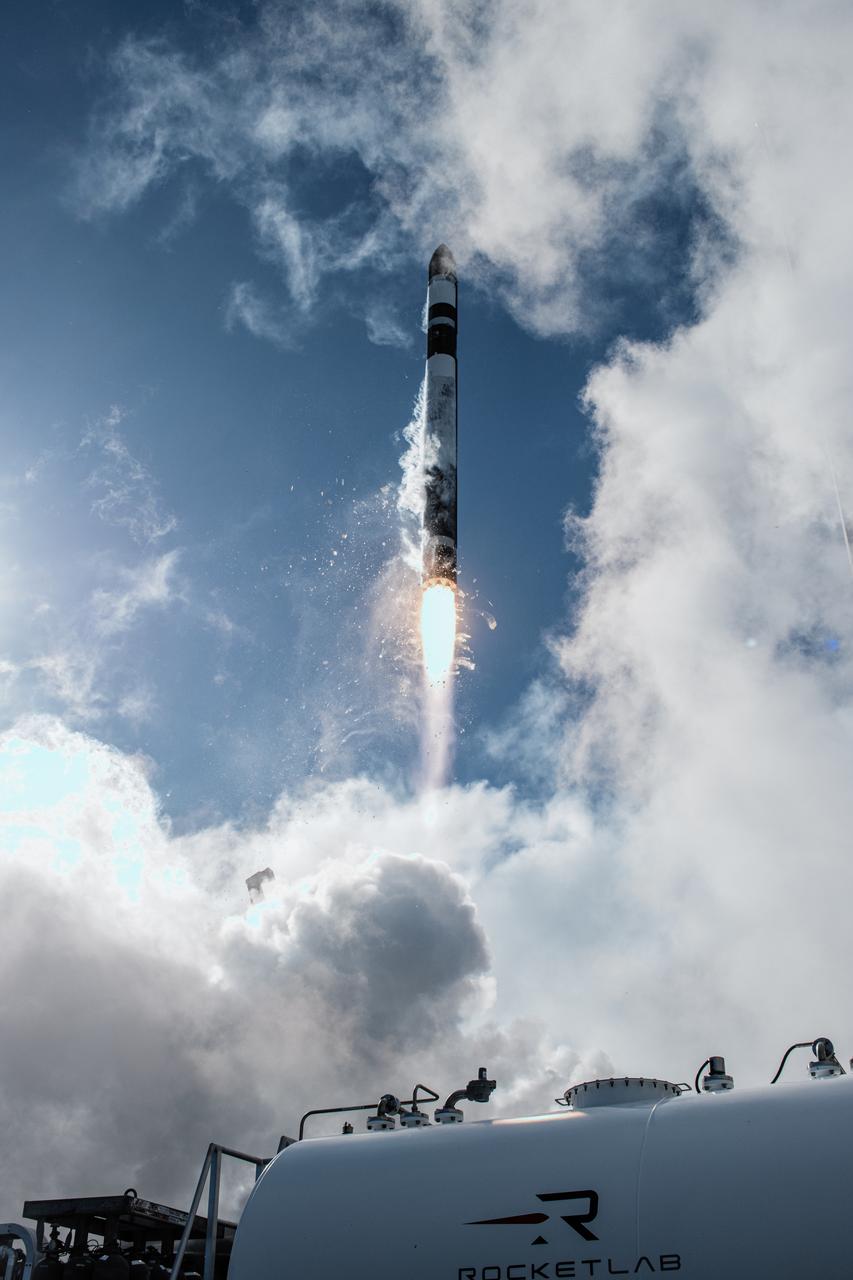

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket soars upward after liftoff from Launch Complex 1, Pad B, in Māhia, New Zealand on May 8 at 1 p.m. New Zealand time (May 7 at 9 p.m. EDT), carrying two NASA CubeSats designed to study tropical cyclones, including hurricanes and typhoons. NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
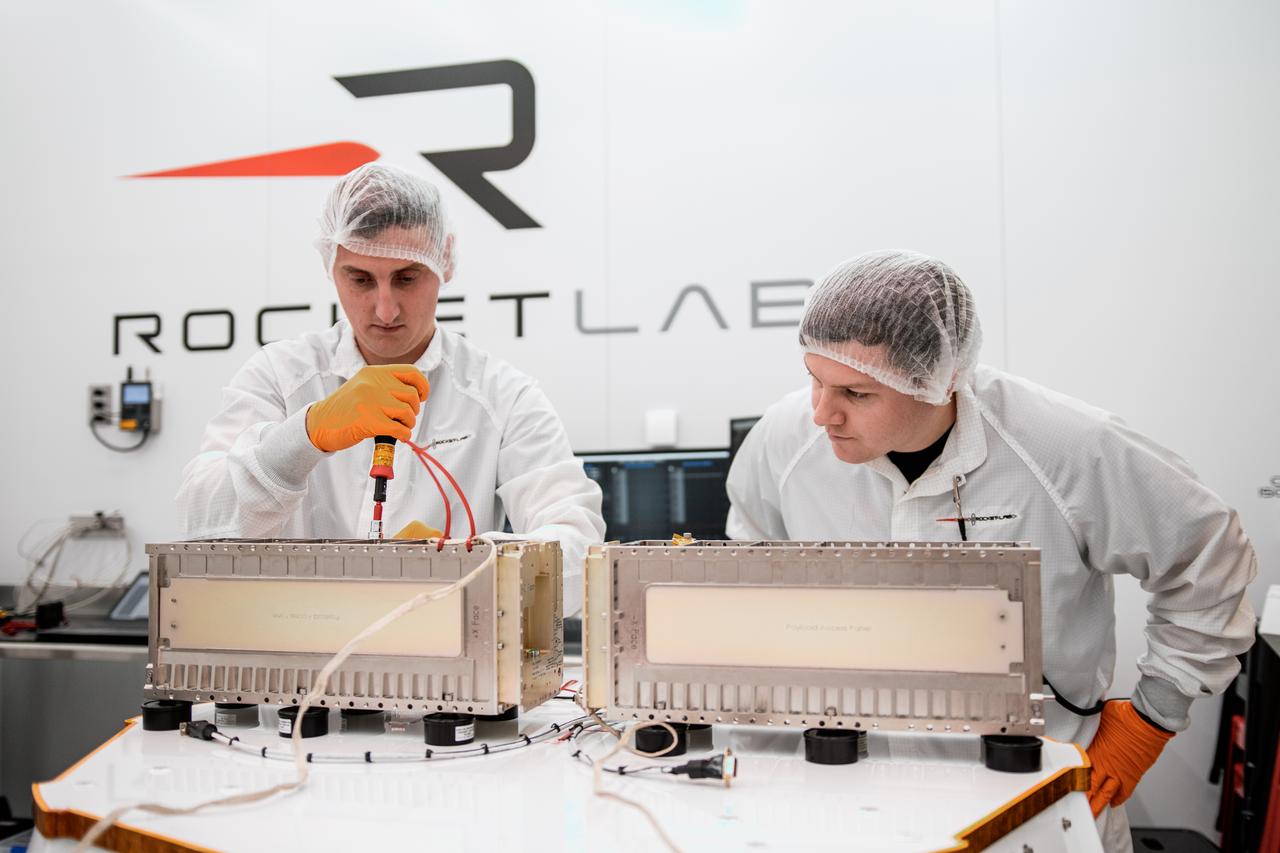

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
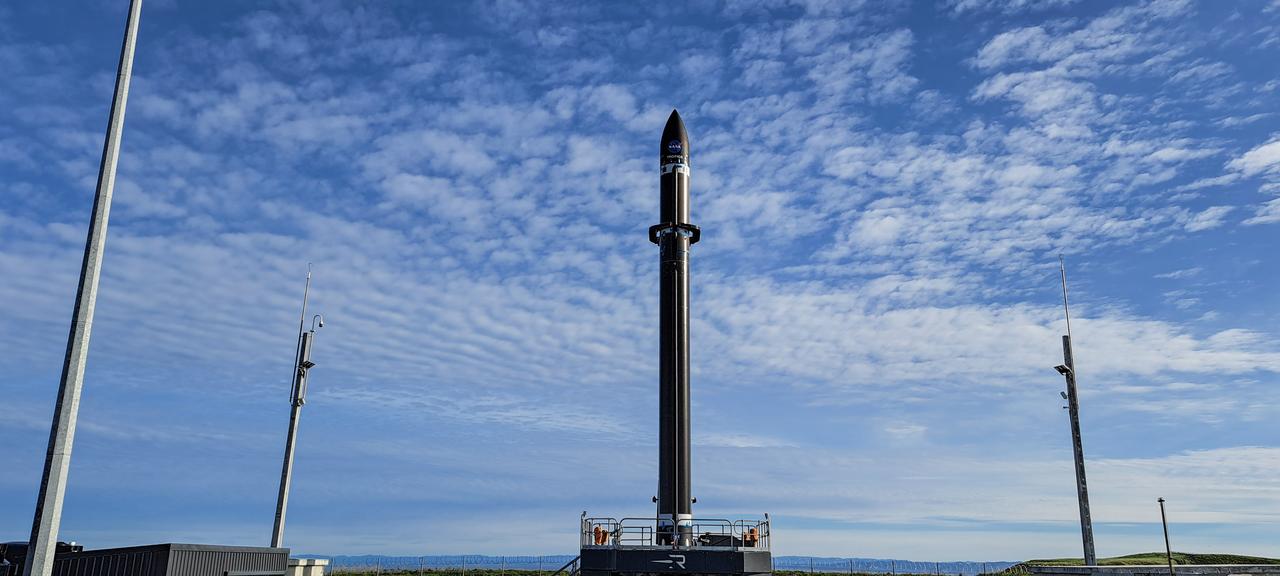

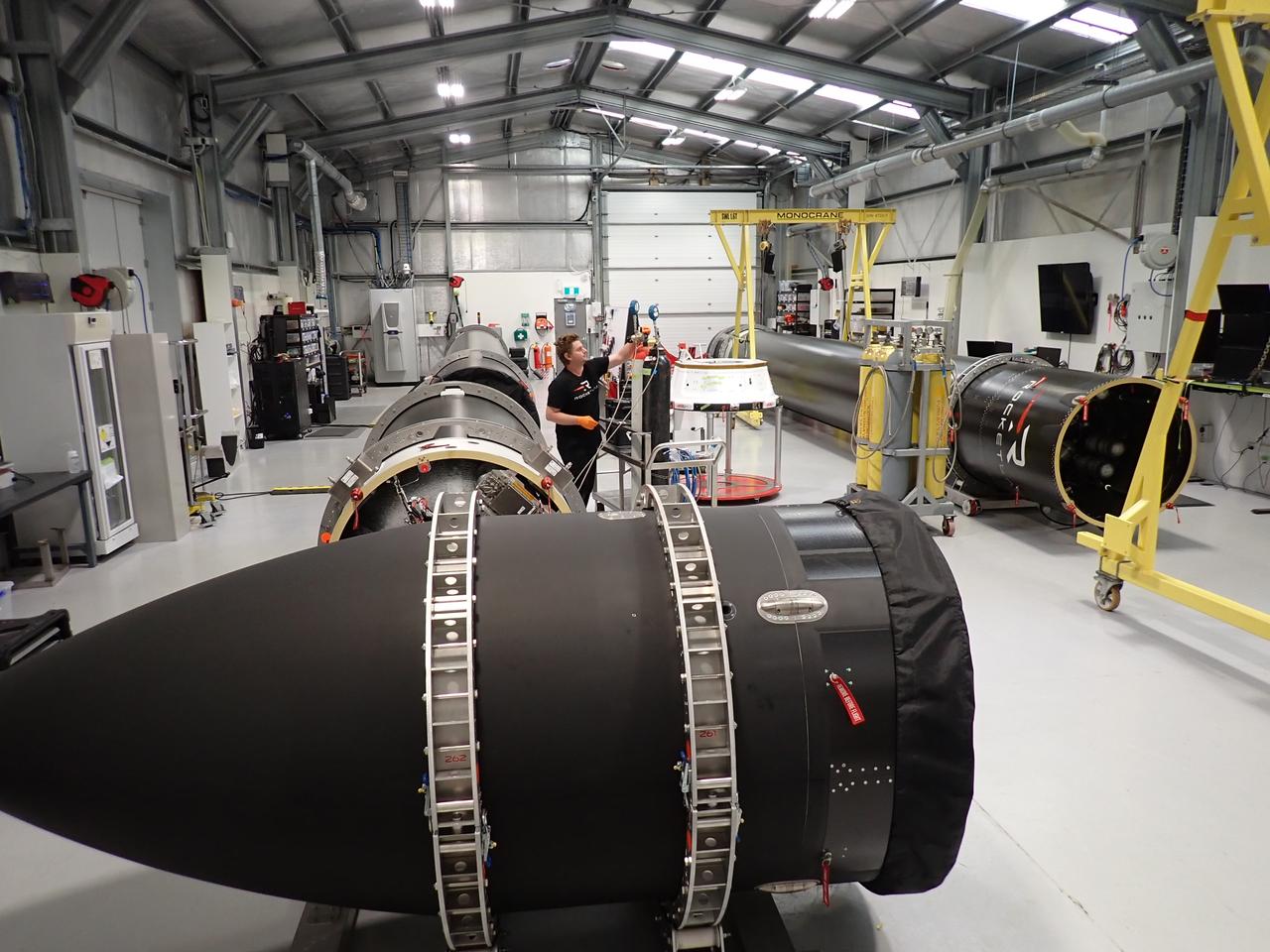
Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, during a May 18, 2023, wet dress rehearsal for NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), to launch the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.

Two CubeSats are encapsulated at the Rocket Lab facility in Mahia, New Zealand, on April 24, 2023, in preparation for NASA’s second TROPICS (Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), for liftoff of the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
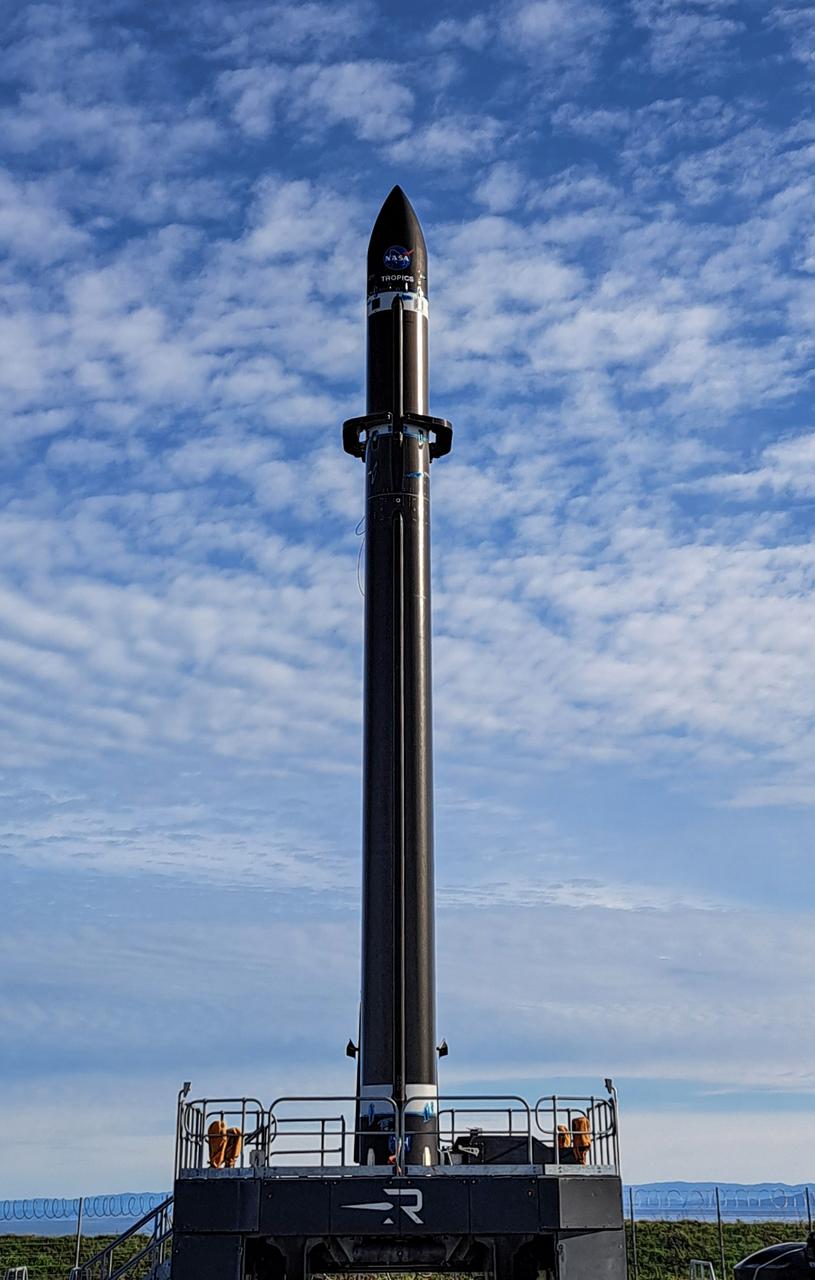

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, during a May 18, 2023, wet dress rehearsal for NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) launch. After successfully launching the first pair of small satellites earlier this month from New Zealand, NASA and Rocket Lab are targeting no earlier than 12 a.m. EDT Thursday, May 25 (4 p.m. NZST), to launch the second pair of storm tracking CubeSats into orbit. NASA will use TROPICS to study tropical cyclones as part of the agency’s Earth Venture Class missions.
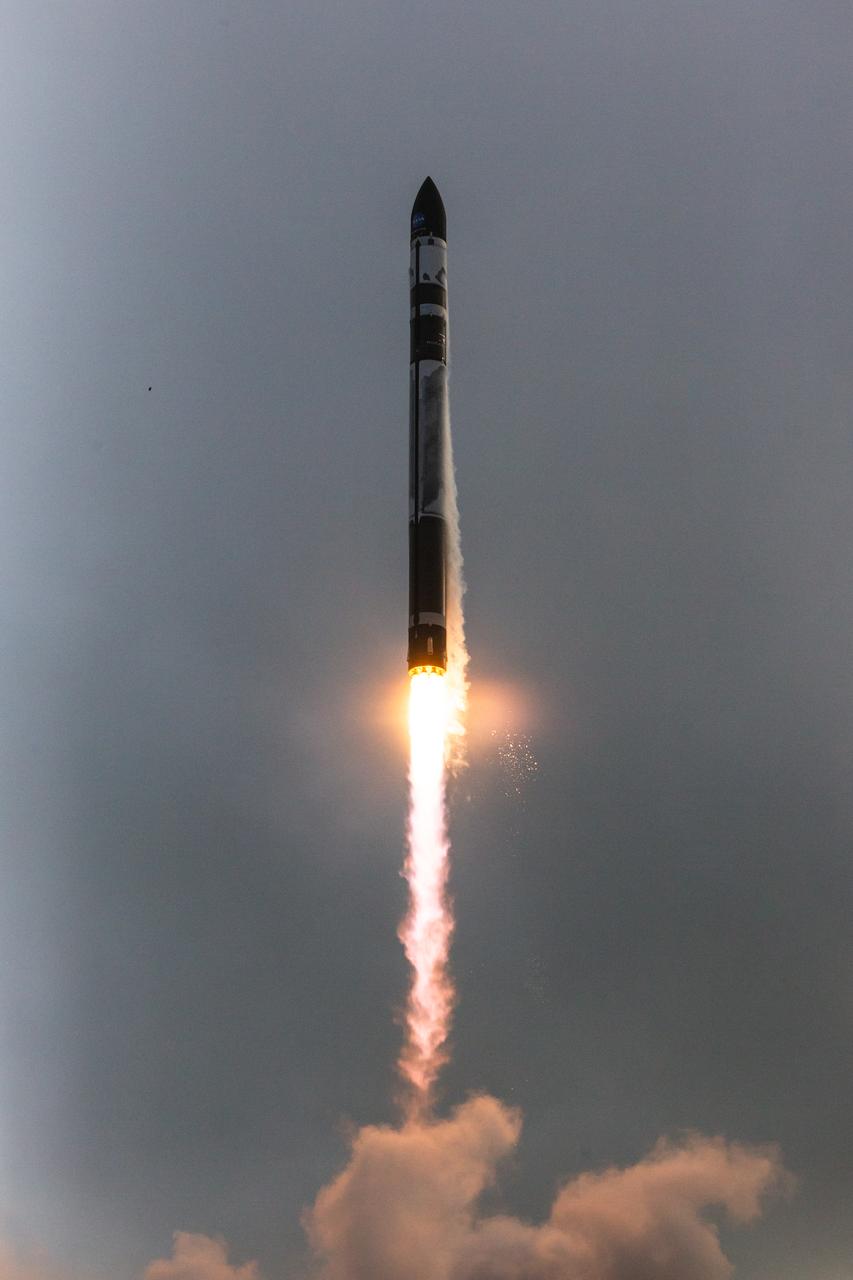

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 3:15 p.m. NZST Wednesday, June 5, 2024 (11:15 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 4), on the second of two launches for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment). The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
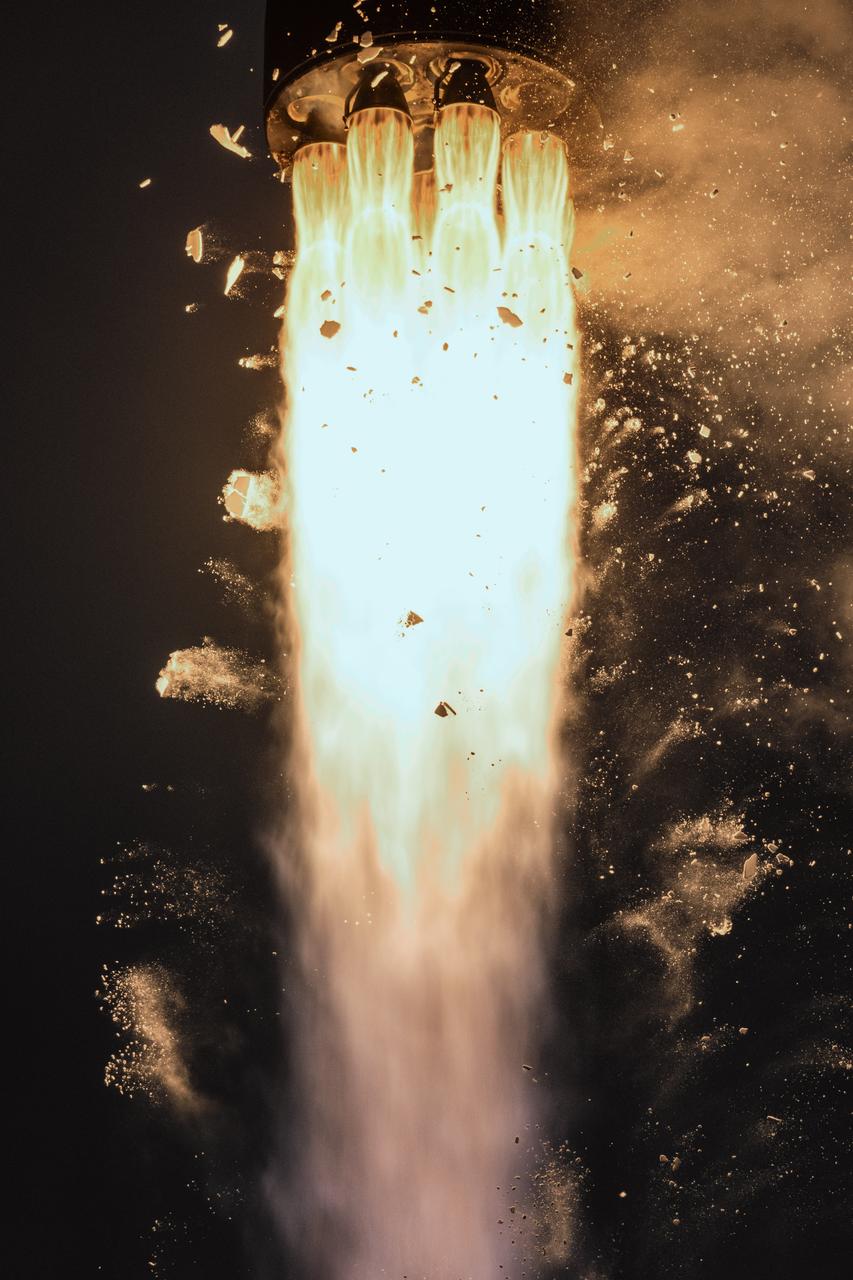

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 3:15 p.m. NZST Wednesday, June 5, 2024 (11:15 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 4), on the second of two launches for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment). The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
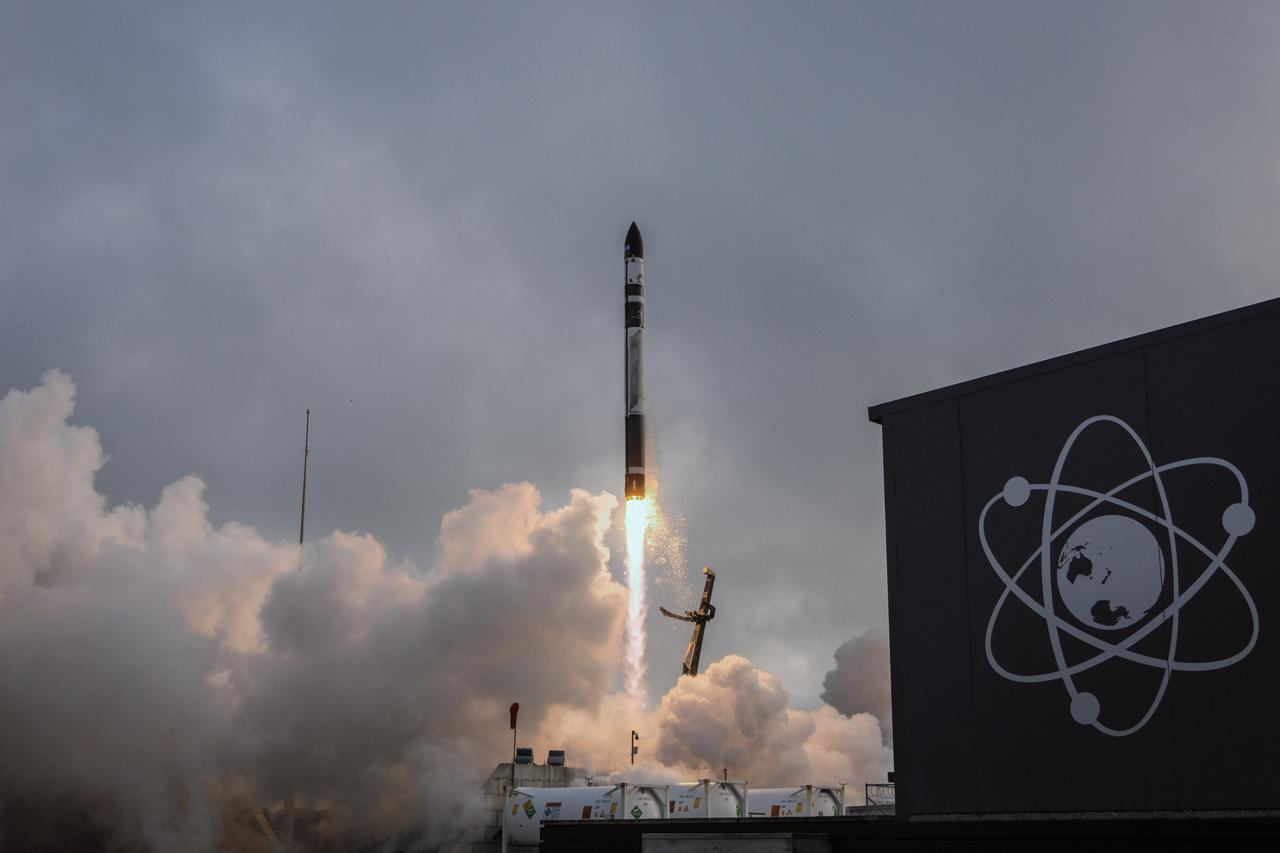

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket called “PREFIRE and Ice,” lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 3:15 p.m. NZST Wednesday, June 5, 2024 (11:15 p.m. EDT, Tuesday, June 4), on the second of two launches for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment). The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
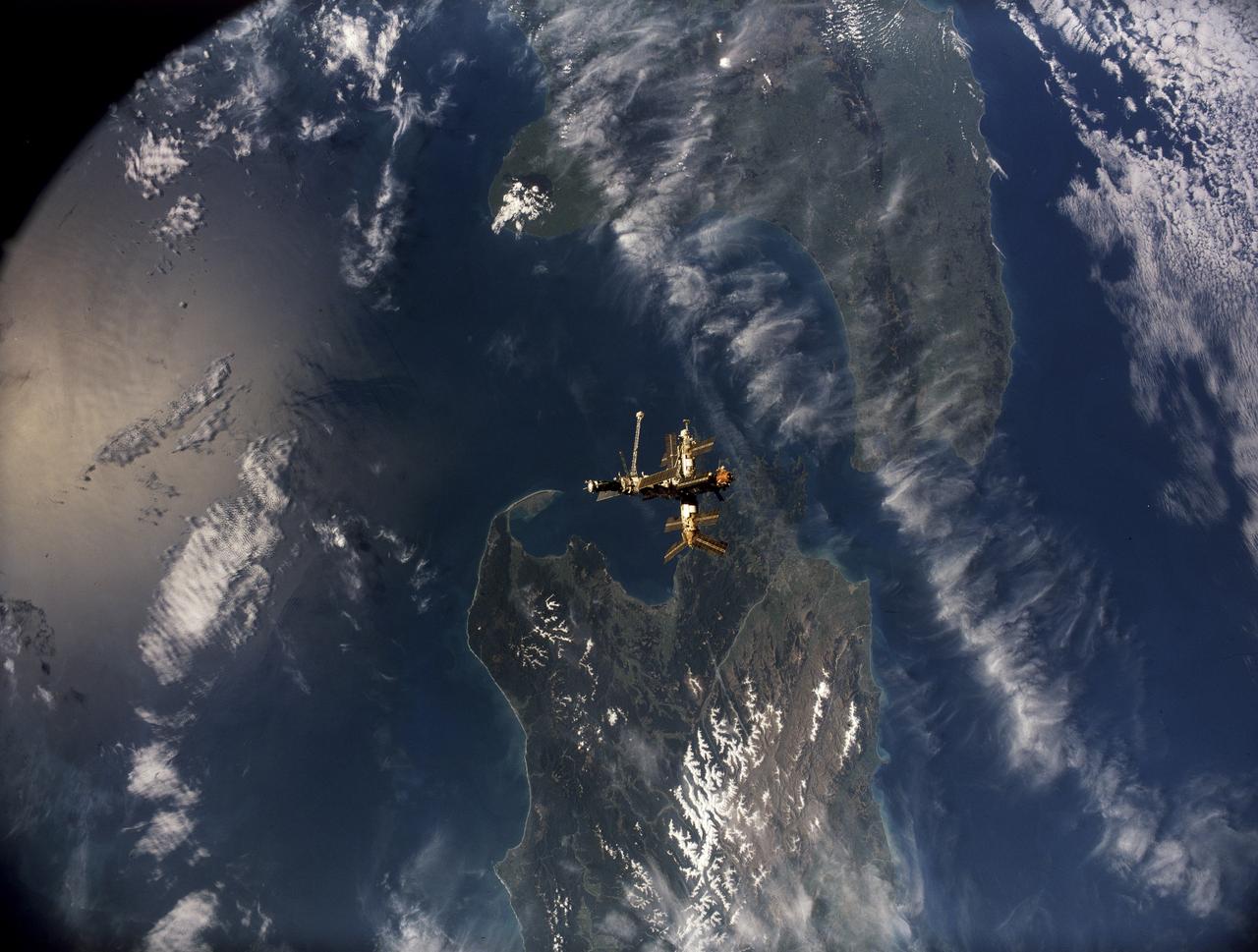

STS079-S-105 (16-26 Sept. 1996) --- Following undocking from the space shuttle Atlantis, Russia's Mir Space Station is backdropped over parts of both of New Zealand's main islands in this motion picture frame. Mt. Egmont and Cook Strait are geologic features that can be easily delineated in the image. During the STS-79 mission, the crew used an IMAX camera to document Intravehicular Activities (IVA) aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis and the various Mir modules, as well as to record both docking and undocking activities through Atlantis' windows. NASA has flown IMAX camera systems on many Shuttle missions, including a special cargo bay camera's coverage of other recent Shuttle-Mir rendezvous and/or docking missions.

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off Launch Complex-1 at Māhia Peninsula in New Zealand carrying NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites-19 (ELaNa-19) payload. Liftoff occurred at 6:33 a.m. UTC on Dec. 17 (1:33 p.m. EST on Dec. 16). The liftoff marks the first flight of a payload under NASA’s Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS). Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to provide increased access to space specifically for these small spacecraft, called CubeSats.
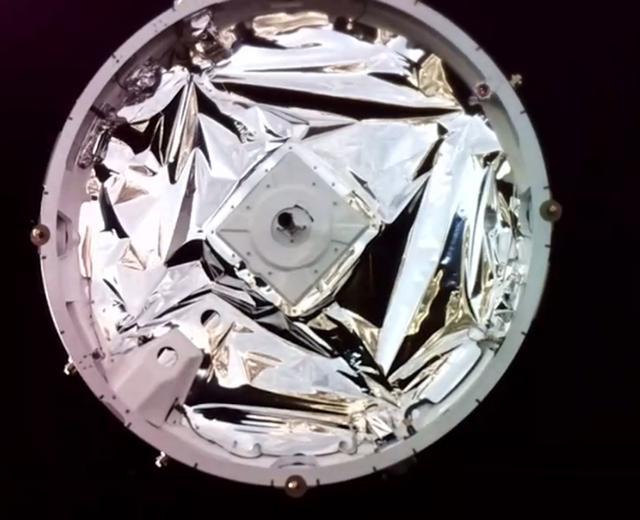

NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites-19 (ELaNa-19) payload after separation from a Rocket Lab Electron rocket after successful liftoff from Launch Complex-1 at Māhia Peninsula in New Zealand. Launched at 6:33 a.m. UTC on Dec. 17 (1:33 p.m. EST on Dec 16), this marks the first flight of a payload under NASA’s Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS). Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to provide increased access to space specifically for payloads like this, carrying small spacecraft called CubeSats. The successful launch and deployment officially begins the venture-class era.
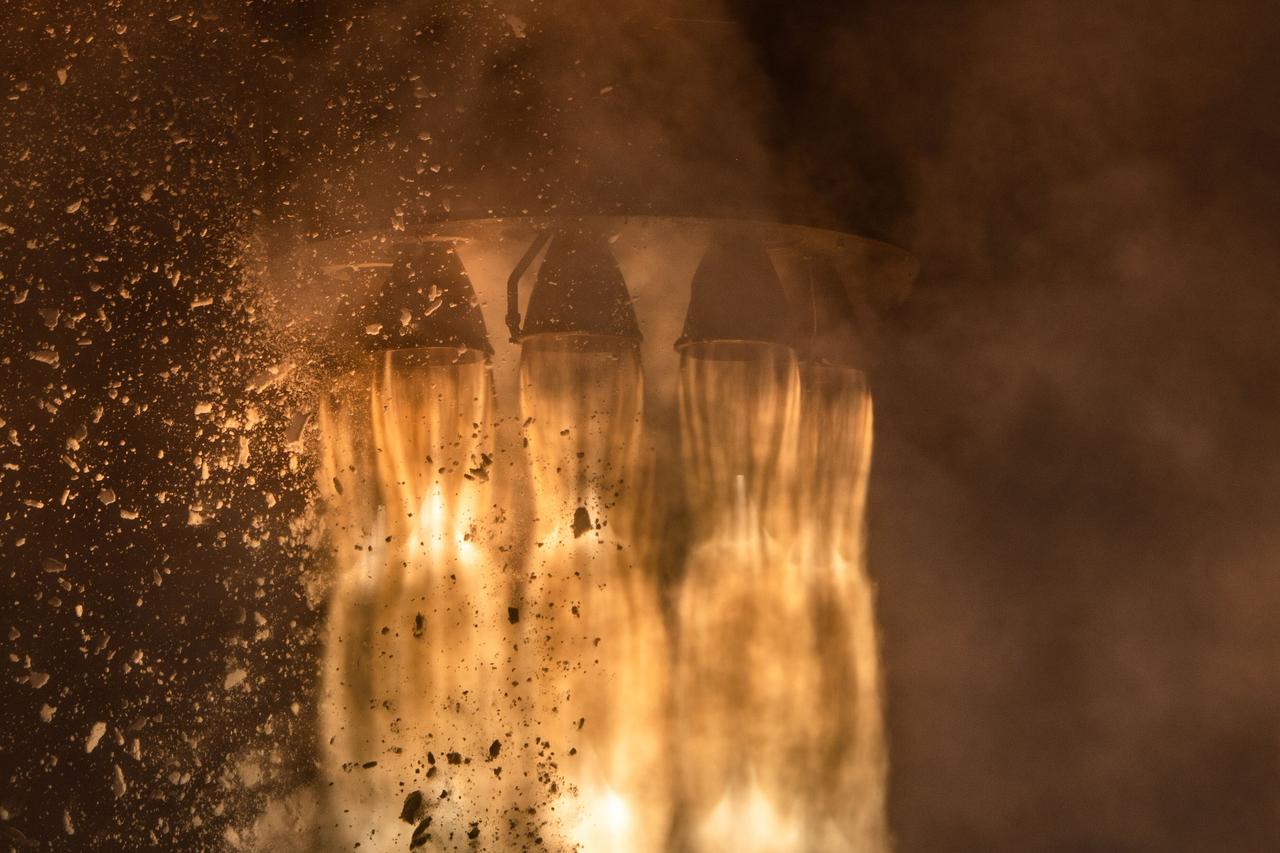
A Rocket Lab Electron rocket’s nine first-stage Rutherford engines ignite as NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites-19 (ELaNa-19) payload lifts off at 6:33 a.m. UTC on Dec. 17 (1:33 p.m. EST on Dec. 16) from Launch Complex-1, located at Māhia Peninsula in New Zealand. The liftoff marks the first flight of a payload under NASA’s Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS). Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to provide increased access to space specifically for these small spacecraft, called CubeSats.
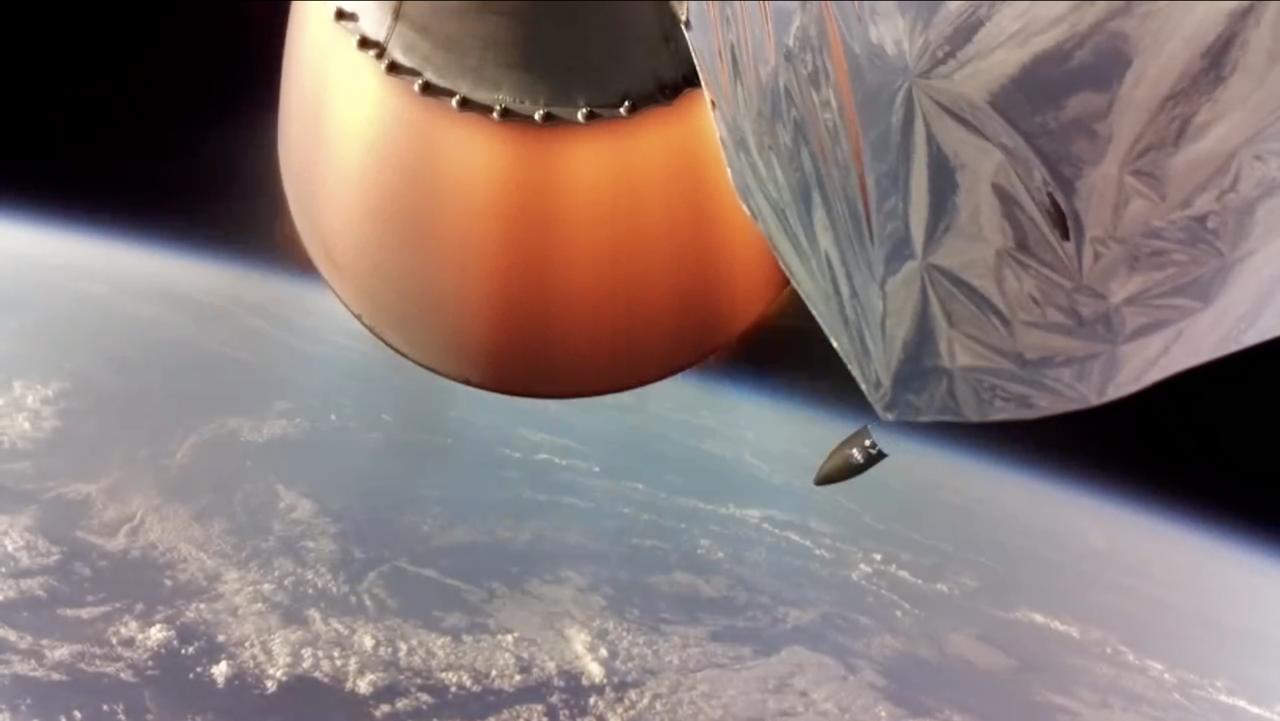

NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellites-19 (ELaNa-19) payload separates from the upper stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket after successful liftoff from Launch Complex-1 at Māhia Peninsula in New Zealand. Launched at 6:33 a.m. UTC on Dec. 17 (1:33 p.m. EST on Dec. 16), this marks the first flight of a payload under NASA’s Venture Class Launch Services (VCLS). Managed by NASA’s Launch Services Program at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, VCLS was developed to provide increased access to space specifically for these small spacecraft, called CubeSats.

After years of tests and development, NASA’s Balloon Program team is on the cusp of expanding the envelope in high-altitude, heavy-lift ballooning with its super pressure balloon (SPB) technology. NASA’s scientific balloon experts are in Wanaka, New Zealand, prepping for the fourth flight of an 18.8 million-cubic-foot (532,000 cubic-meter) balloon, with the ambitious goal of achieving an ultra-long-duration flight of up to 100 days at mid-latitudes. Launch of the pumpkin-shaped, football stadium-size balloon is scheduled for sometime after April 1, 2016, from Wanaka Airport, pending final checkouts and flight readiness of the balloon and supporting systems. Once launched, the SPB, which is made from 22-acres of polyethylene film – similar to a sandwich bag, but stronger and more durable – will ascend to a nearly constant float altitude of 110,000 feet (33.5 km). The balloon will travel eastward carrying a 2,260-pound (1,025 kg) payload consisting of tracking, communications and scientific instruments. NASA expects the SPB to circumnavigate the globe once every one to three weeks, depending on wind speeds in the stratosphere. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1p56xKR" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1p56xKR</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

After years of tests and development, NASA’s Balloon Program team is on the cusp of expanding the envelope in high-altitude, heavy-lift ballooning with its super pressure balloon (SPB) technology. NASA’s scientific balloon experts are in Wanaka, New Zealand, prepping for the fourth flight of an 18.8 million-cubic-foot (532,000 cubic-meter) balloon, with the ambitious goal of achieving an ultra-long-duration flight of up to 100 days at mid-latitudes. Launch of the pumpkin-shaped, football stadium-size balloon is scheduled for sometime after April 1, 2016, from Wanaka Airport, pending final checkouts and flight readiness of the balloon and supporting systems. Once launched, the SPB, which is made from 22-acres of polyethylene film – similar to a sandwich bag, but stronger and more durable – will ascend to a nearly constant float altitude of 110,000 feet (33.5 km). The balloon will travel eastward carrying a 2,260-pound (1,025 kg) payload consisting of tracking, communications and scientific instruments. NASA expects the SPB to circumnavigate the globe once every one to three weeks, depending on wind speeds in the stratosphere. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/1p56xKR" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/1p56xKR</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
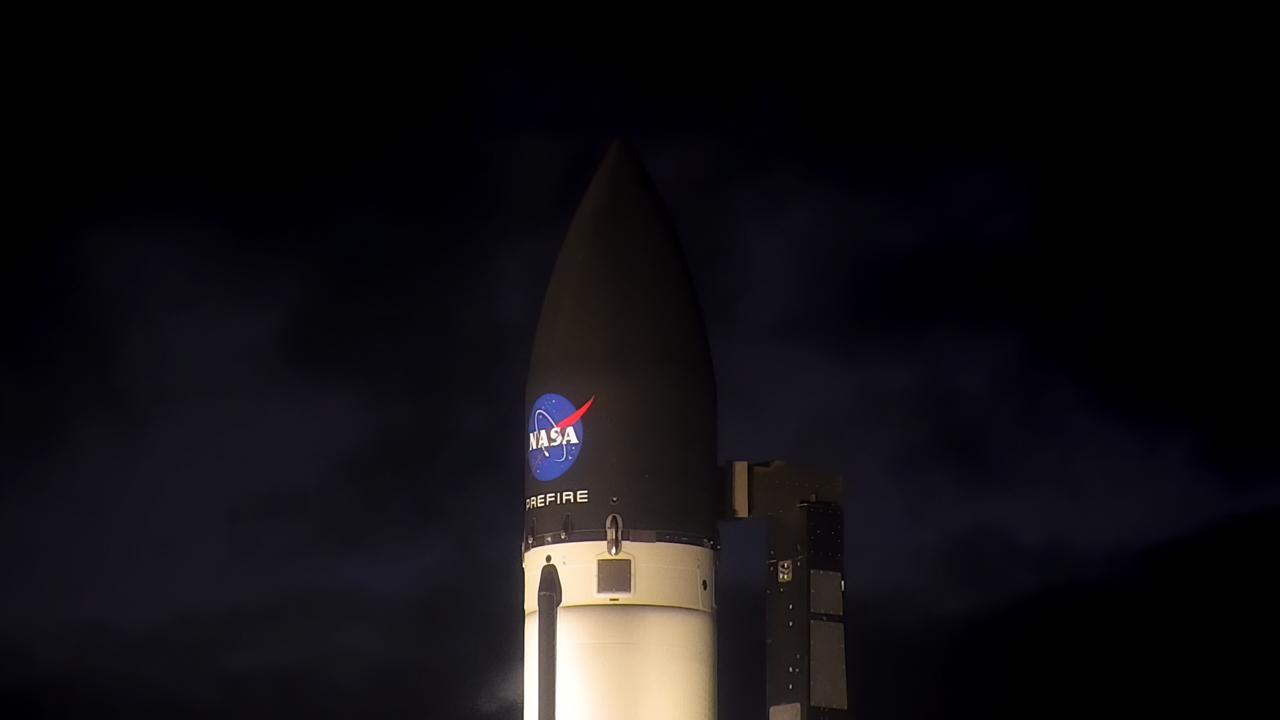

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad Saturday, May 25, 2024, at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the first of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the first CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” occurred at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT).
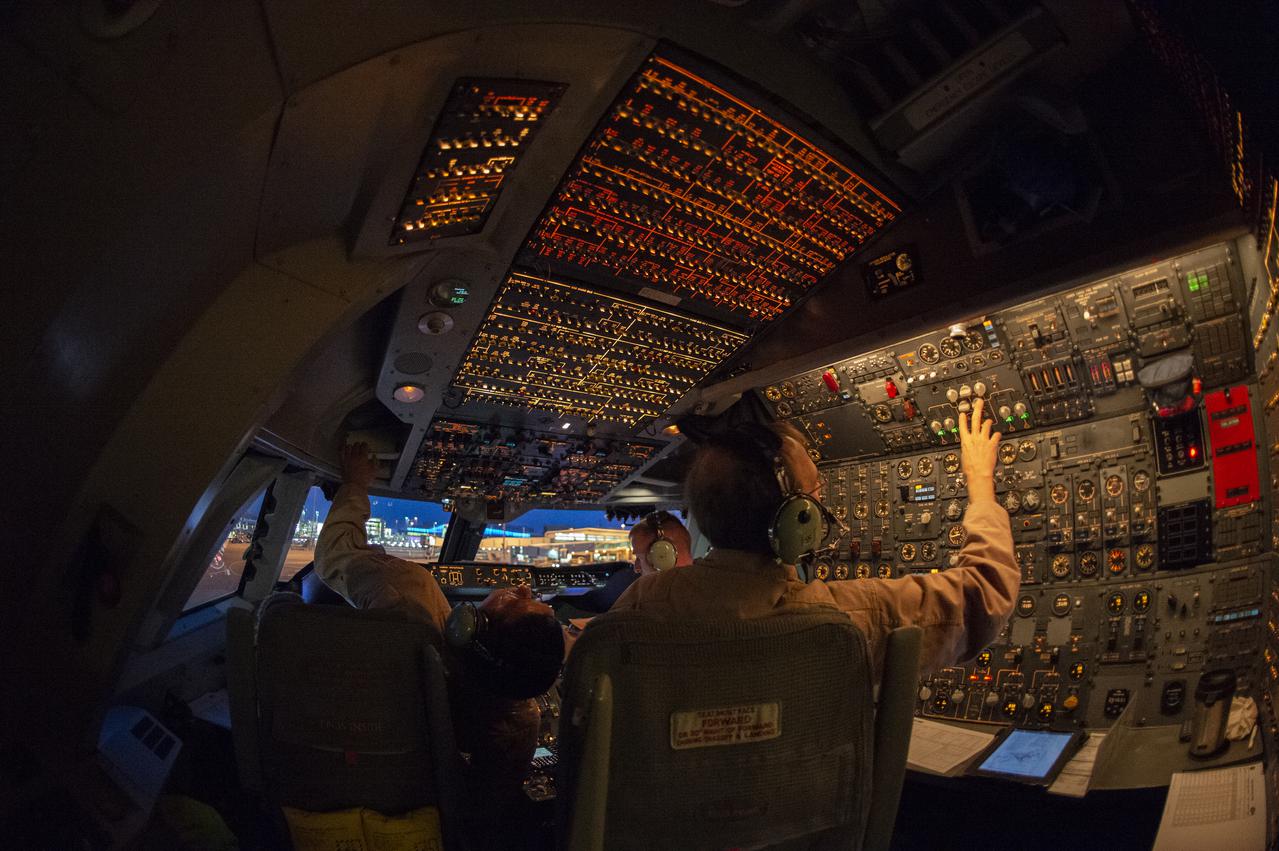

SOFIA’s flight crew prepare to takeoff from the U.S. Antarctic Program facility at Christchurch International Airport in Christchurch, New Zealand, to observe the Southern Hemisphere’s skies. Pilot: Manny Antimisiaris, Co-Pilot: Jim Less, Flight Engineer: Marty Trout
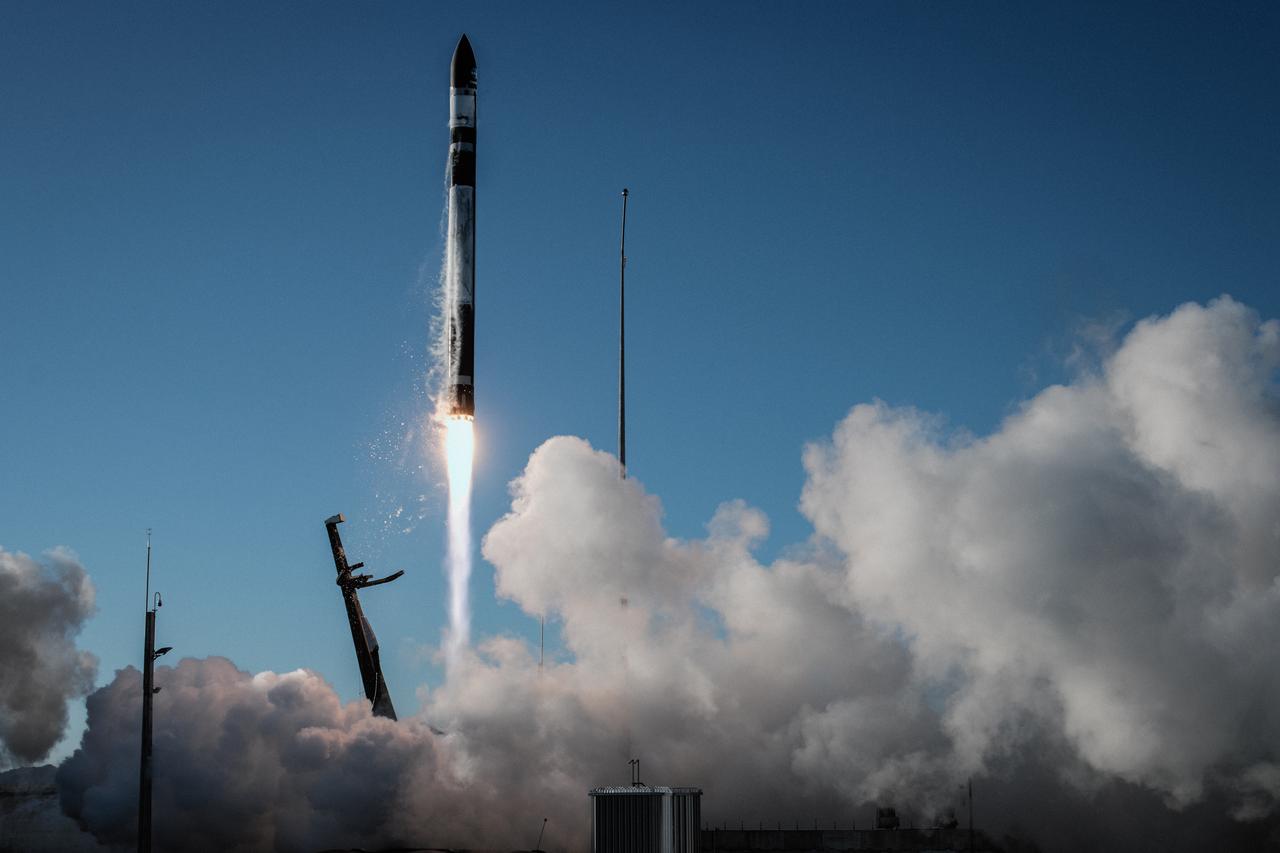

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket soars upward after liftoff from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
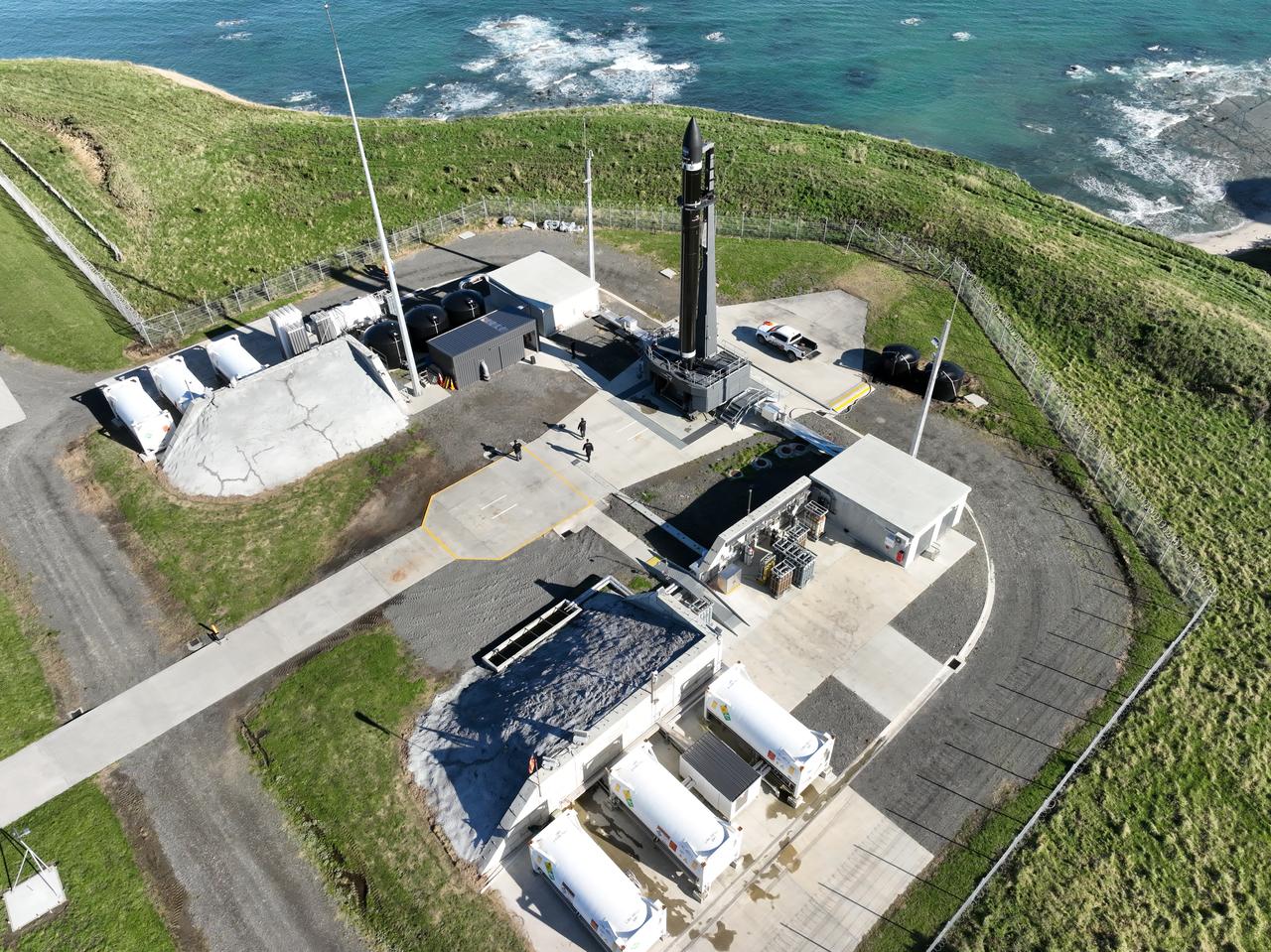

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
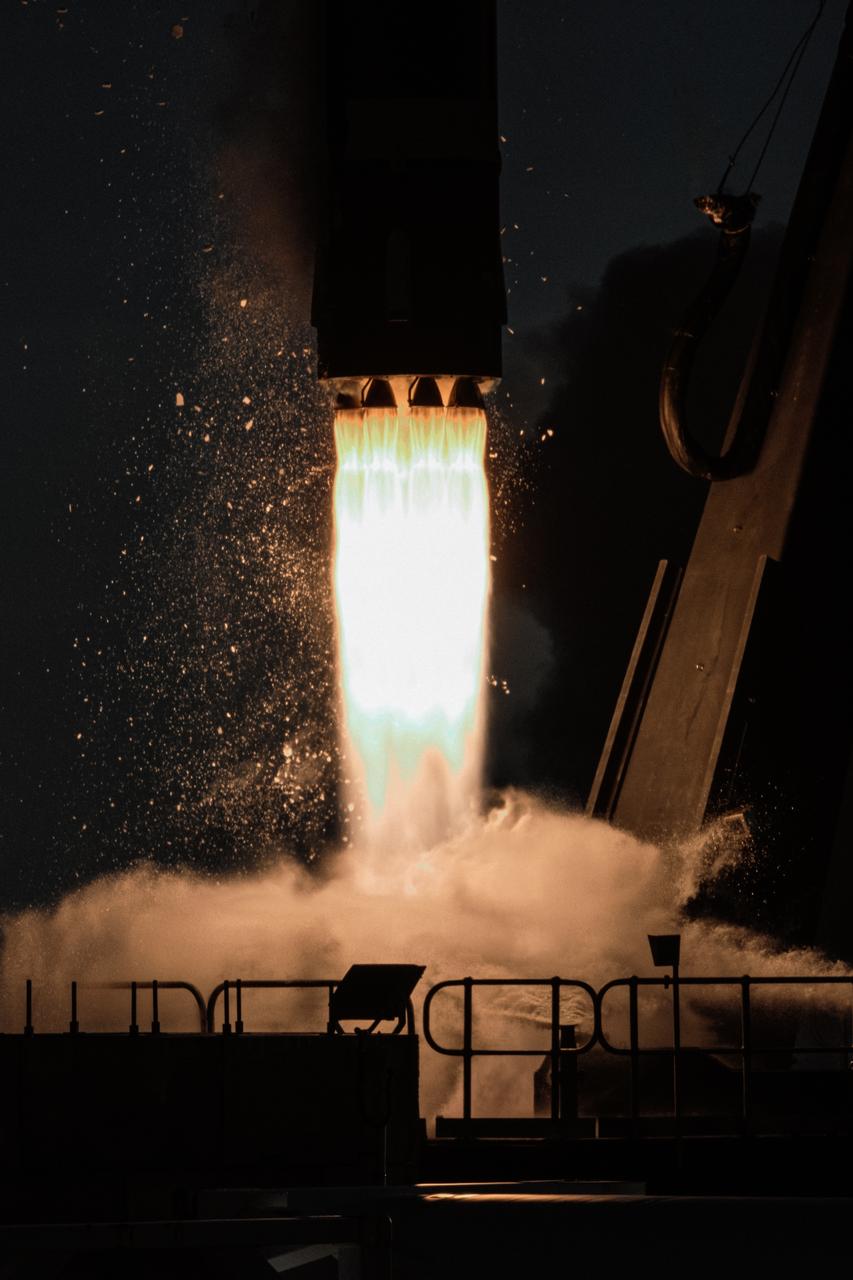

The first stage of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket ignites at liftoff from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
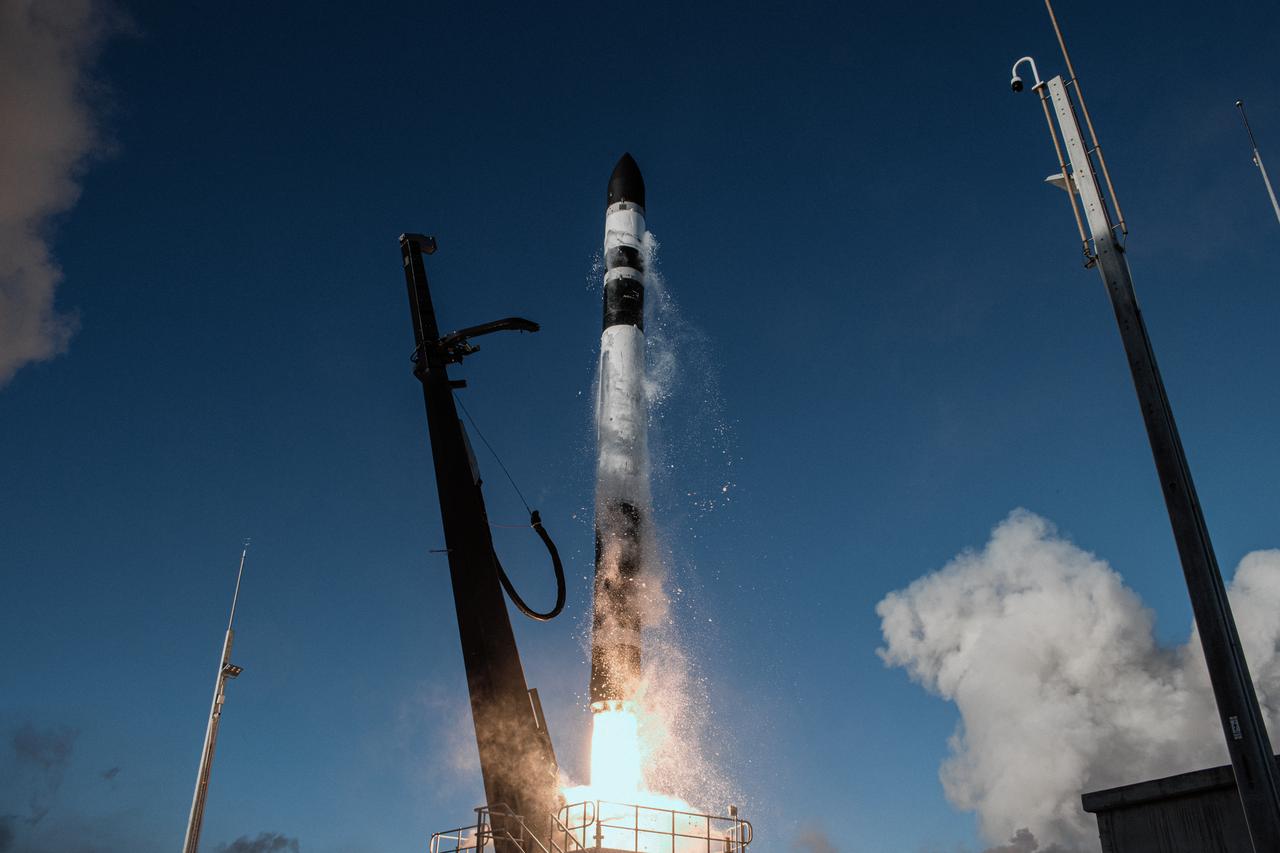

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
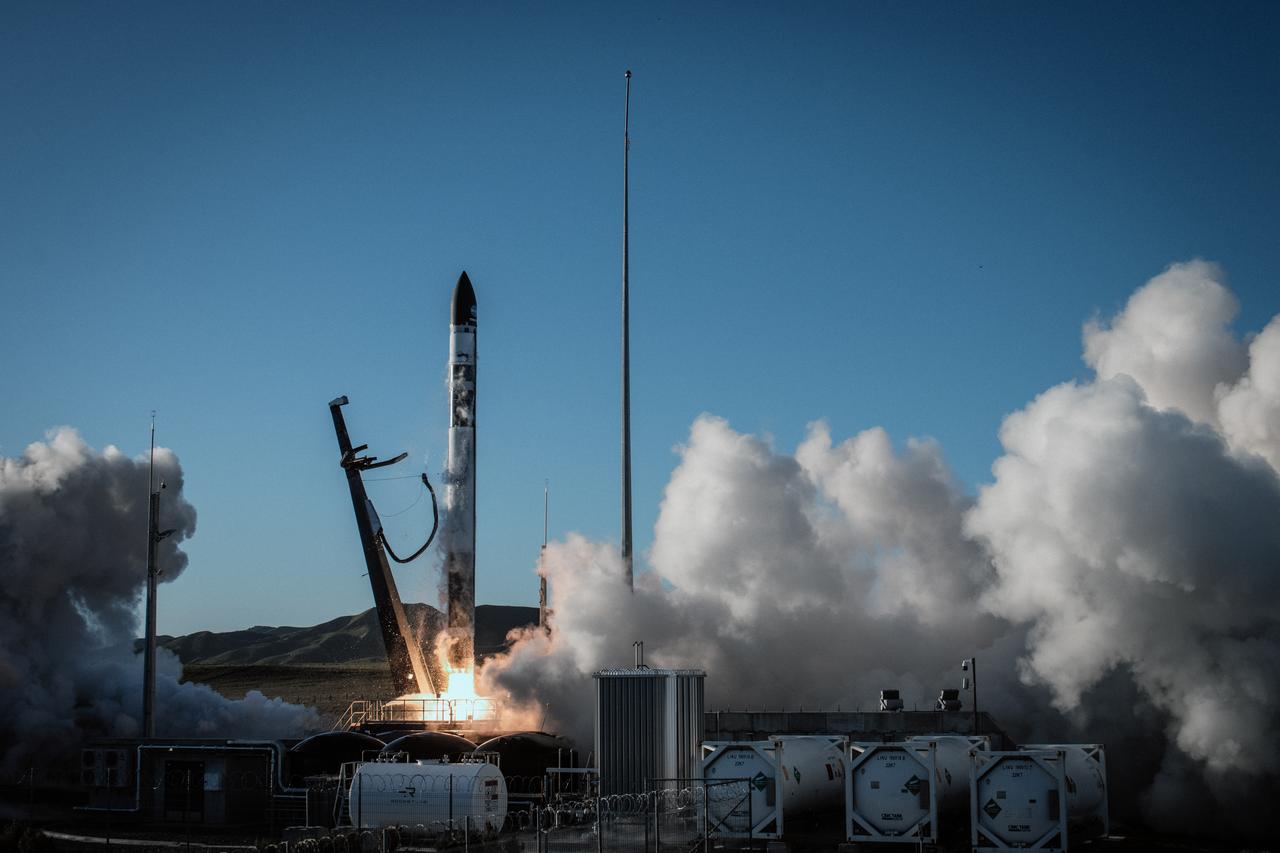

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, at 11:46 p.m. EDT on Thursday, May 25 (3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26) carrying the final pair of NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
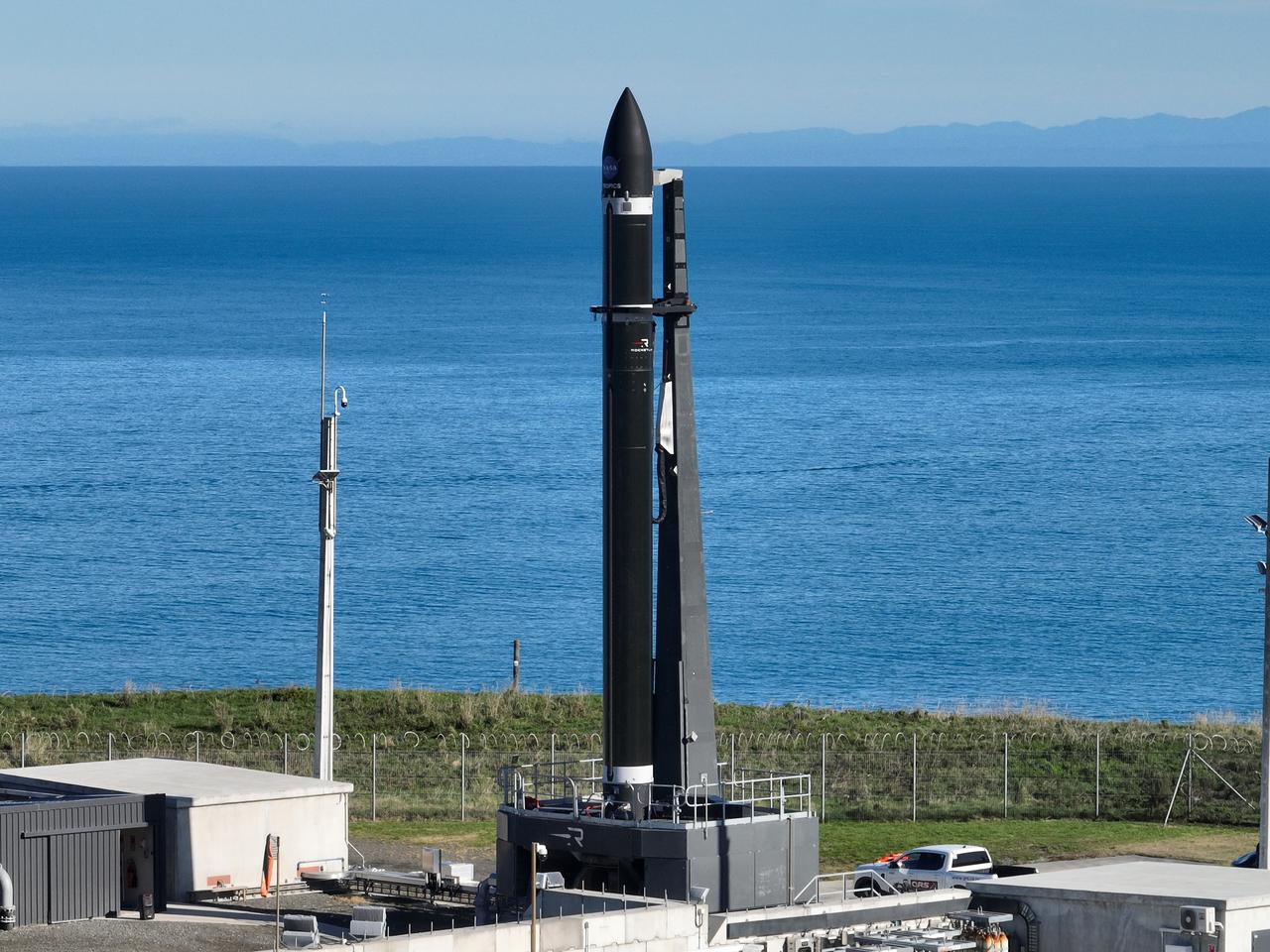

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
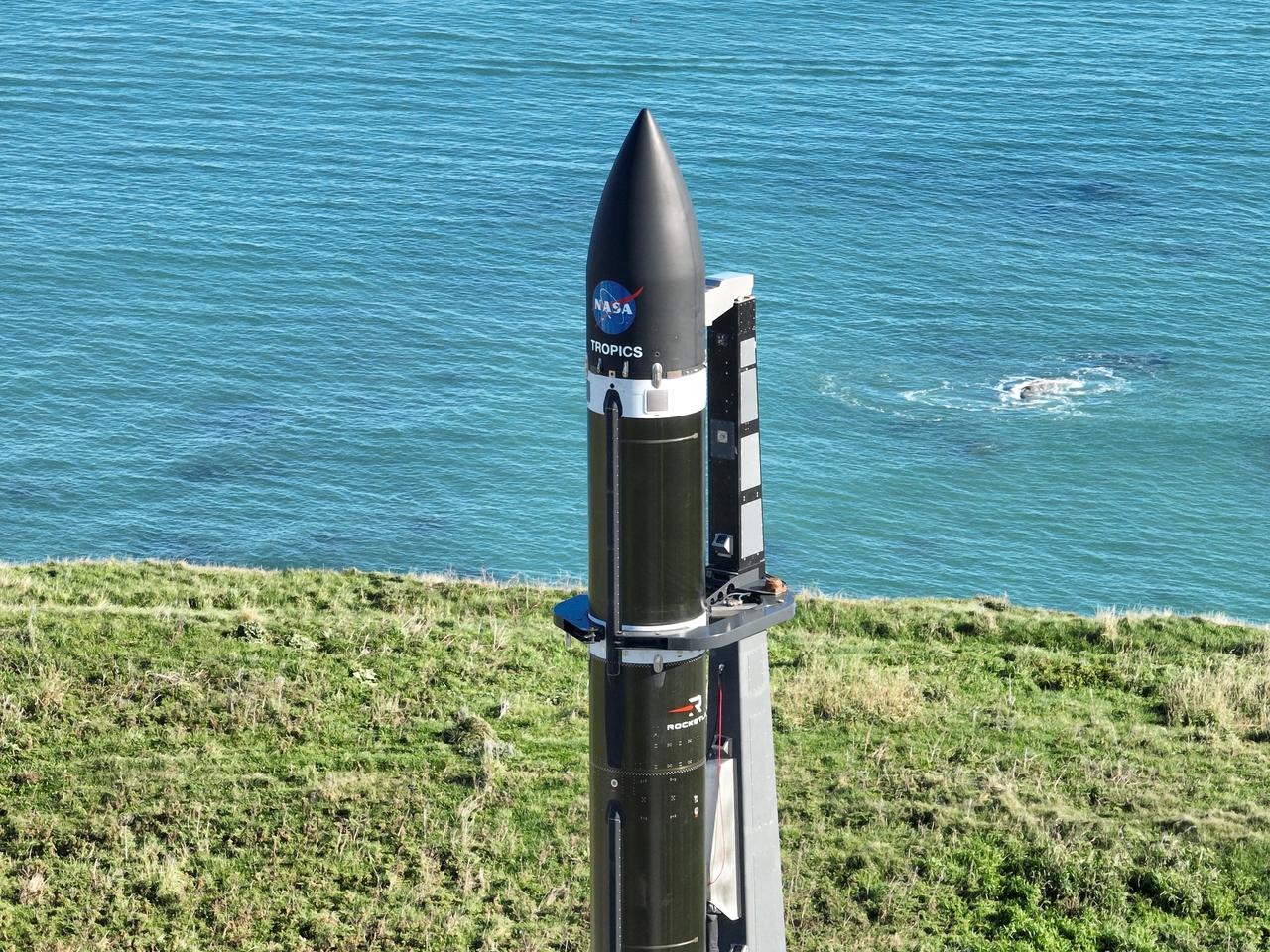

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
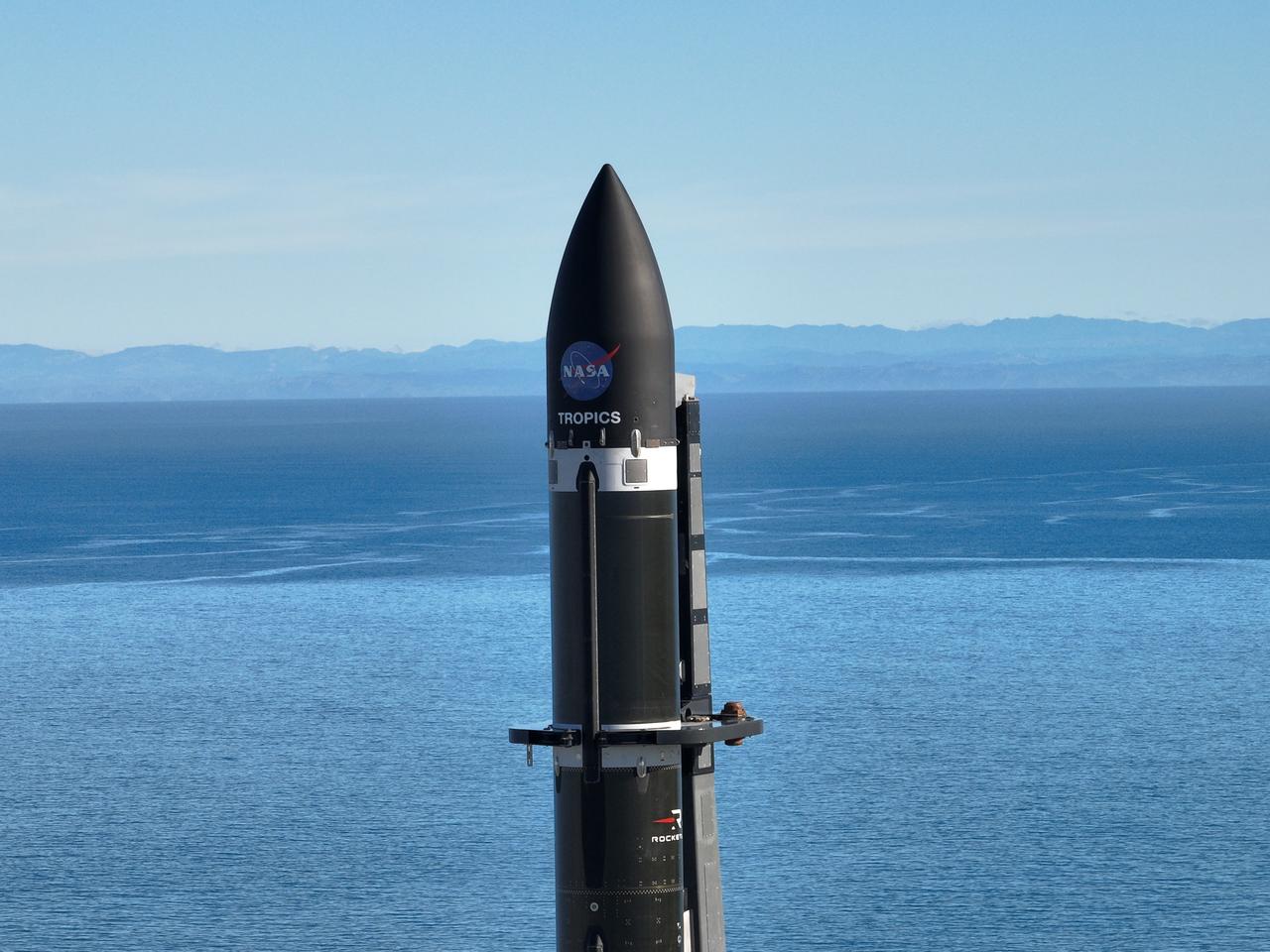

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket stands on Pad B, Launch Complex 1, in Māhia, New Zealand, just ahead of liftoff at 3:46 p.m. NZST Friday, May 26, with NASA’s Time-Resolved Observations of Precipitation structure and storm Intensity with a Constellation of Smallsats (TROPICS) CubeSats secured in the payload fairing atop the rocket. The successful launch placed the final pair of TROPICS CubeSats into orbit, completing the constellation. TROPICS will provide data on temperature, precipitation, water vapor, and clouds by measuring microwave frequencies, providing insight into storm formation and intensification.
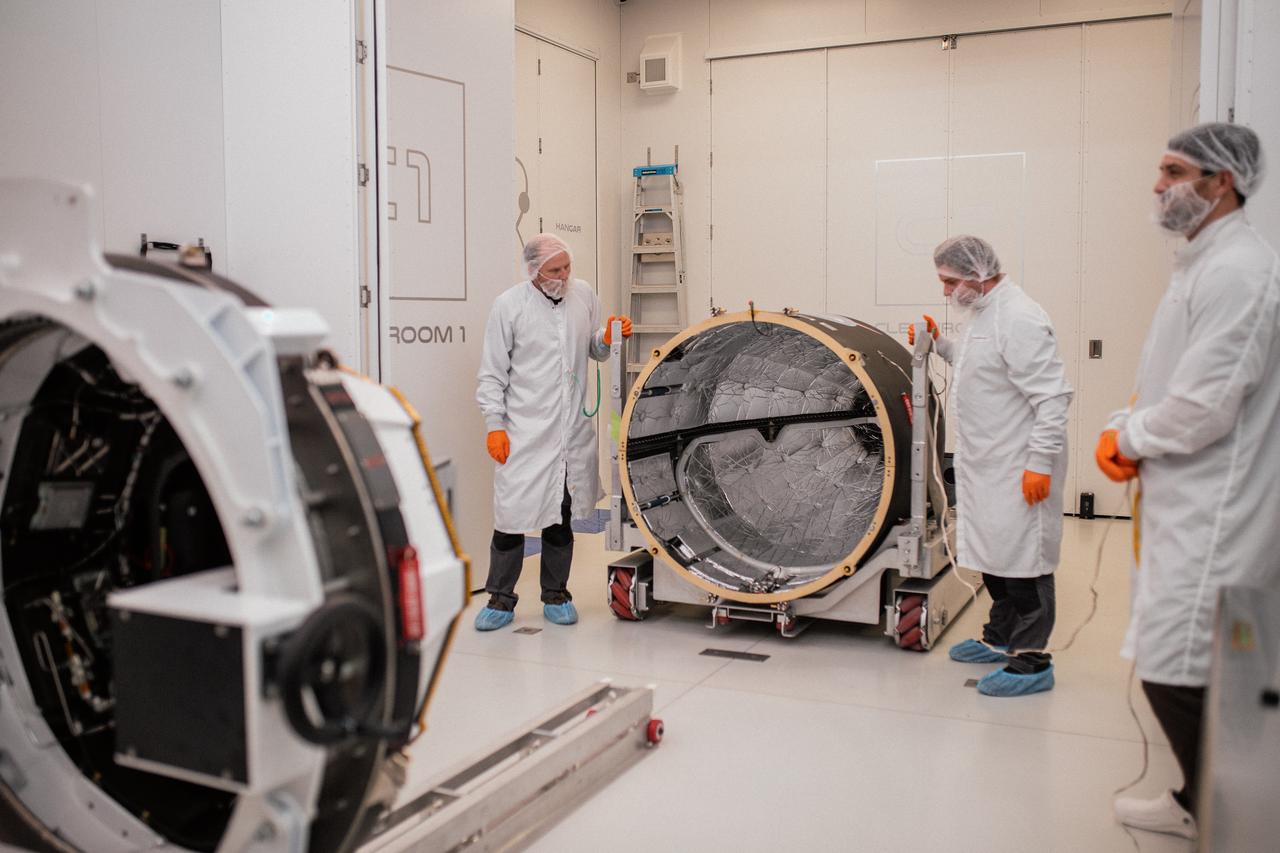

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
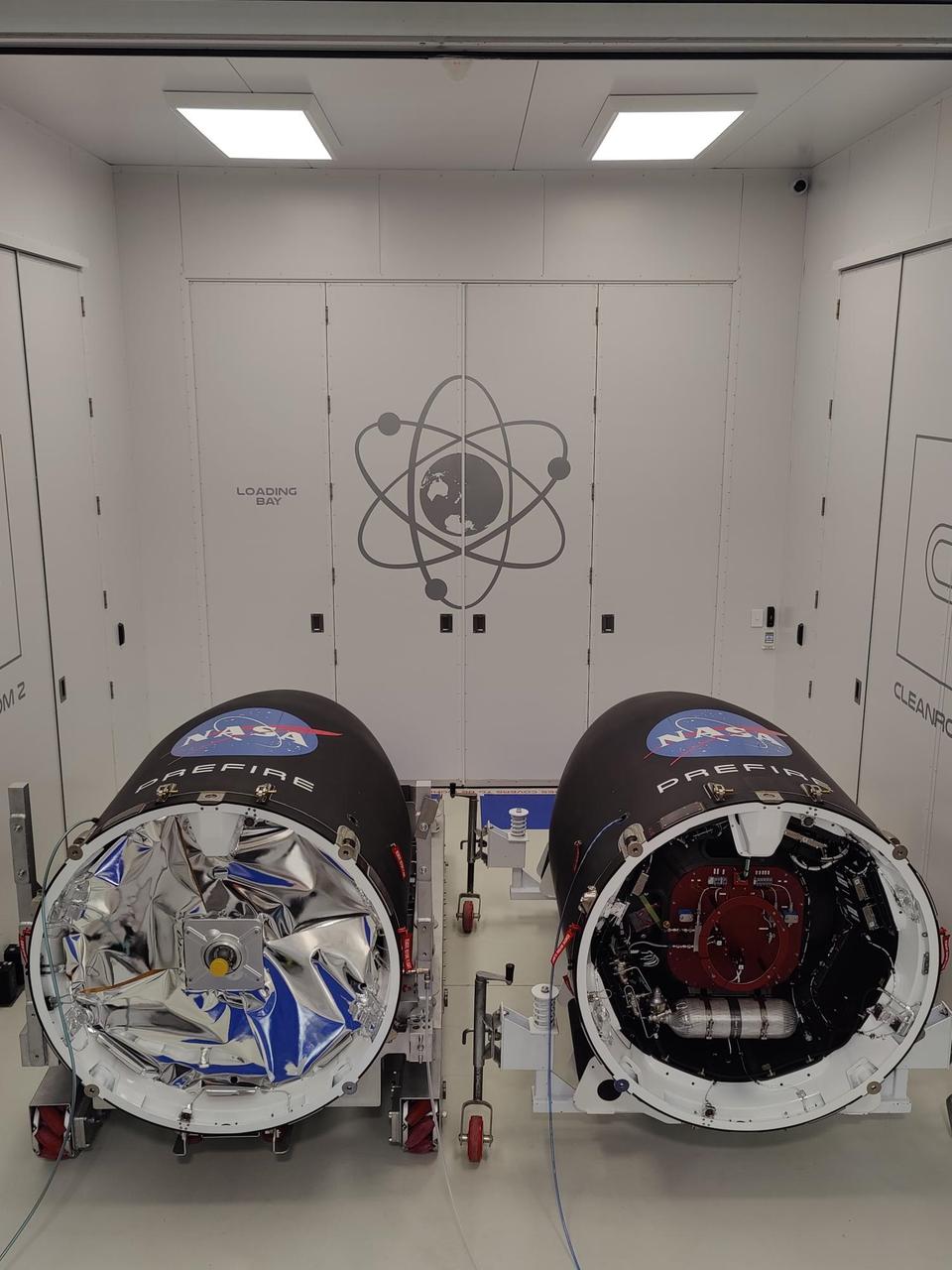

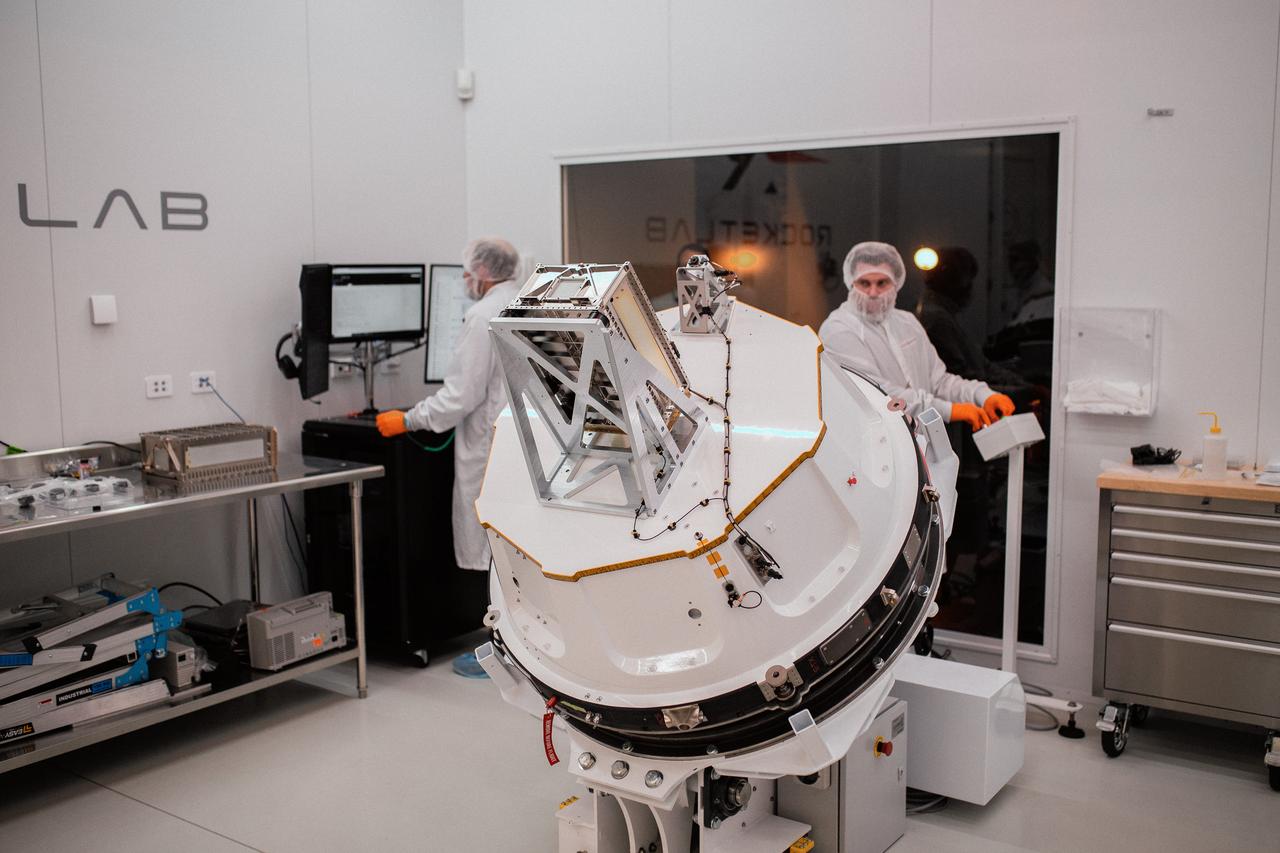
NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) CubeSats are encapsulated inside Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairings on Tuesday, May 21, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.
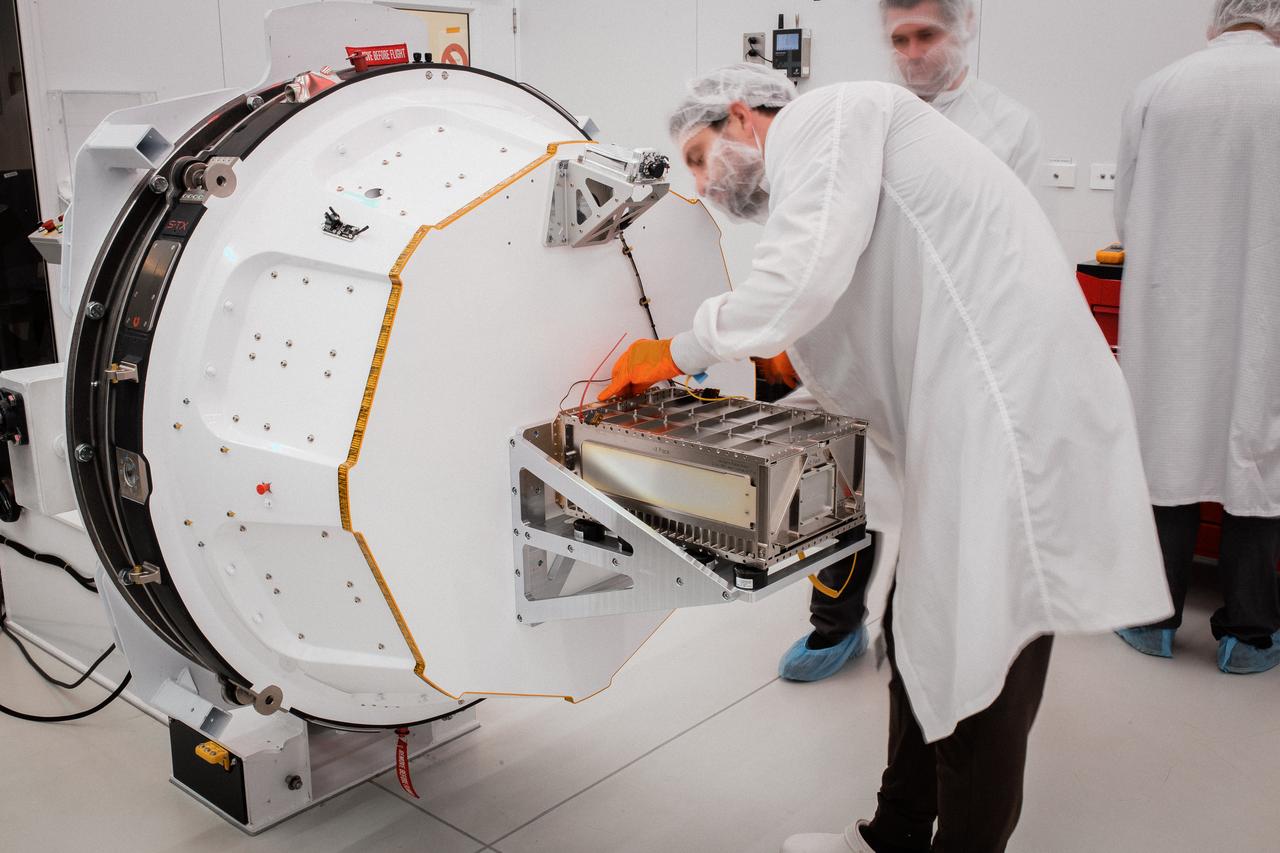

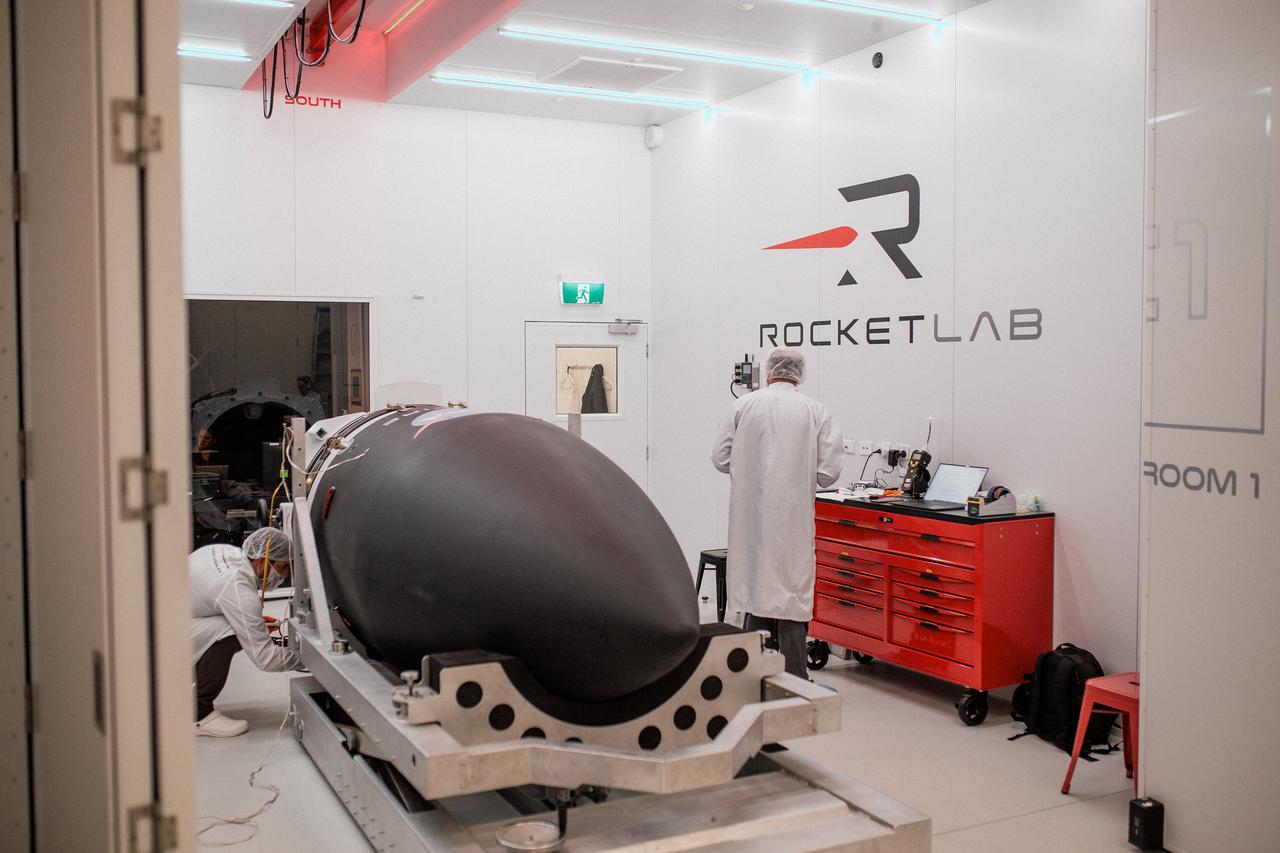
Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.

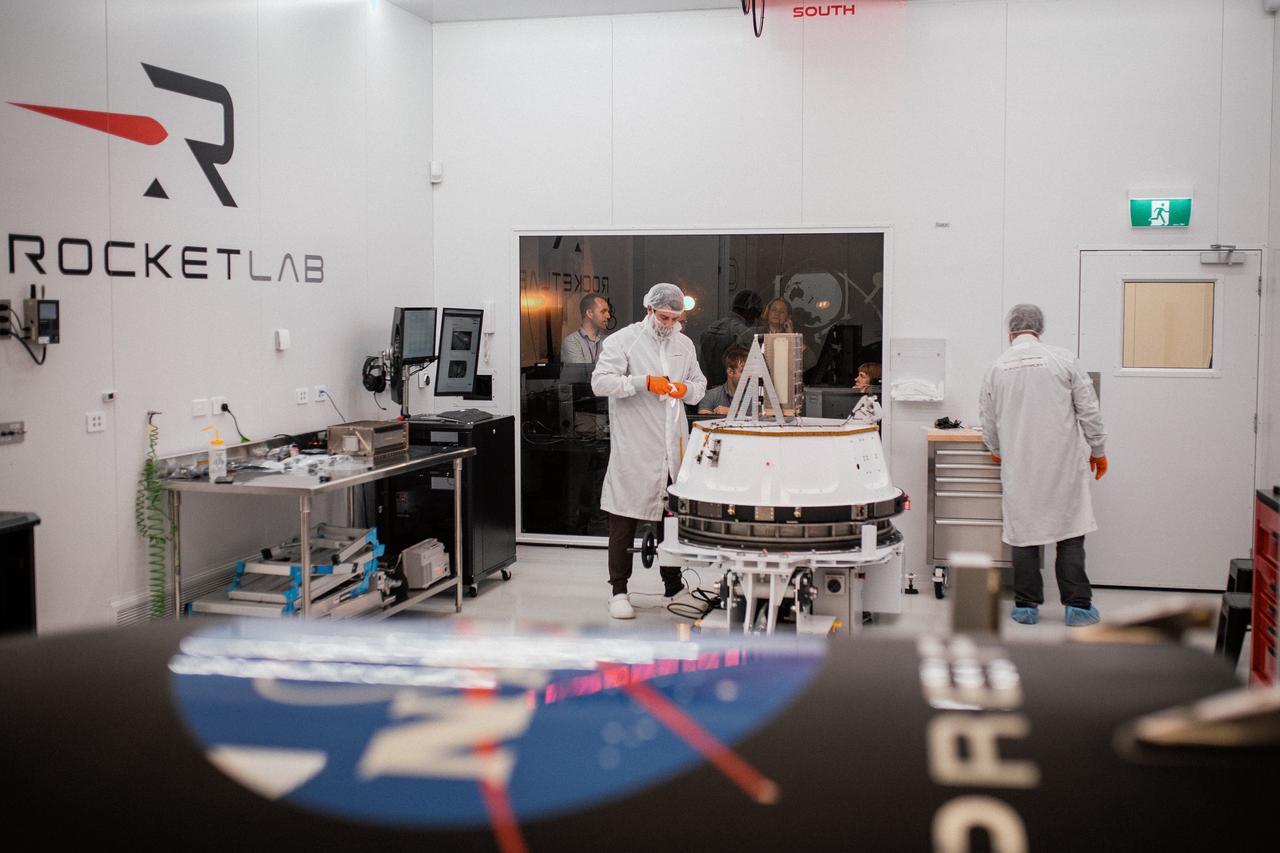
Technicians process NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) ahead of integration with a Rocket Lab Electron rocket on Thursday, May 2, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.

Technicians integrate NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) payload inside the Rocket Lab Electron rocket payload fairing on Wednesday, May 15, 2024, at the company’s facility in New Zealand. The agency’s PREFIRE mission to study heat loss to space in Earth’s polar regions will launch two CubeSats on two different flights aboard Rocket Lab's Electron rockets from the company’s Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand.

This image from NASA Terra spacecraft shows Macquarie Island which lies halfway between New Zealand and Antarctica, and is part of Tasmania.
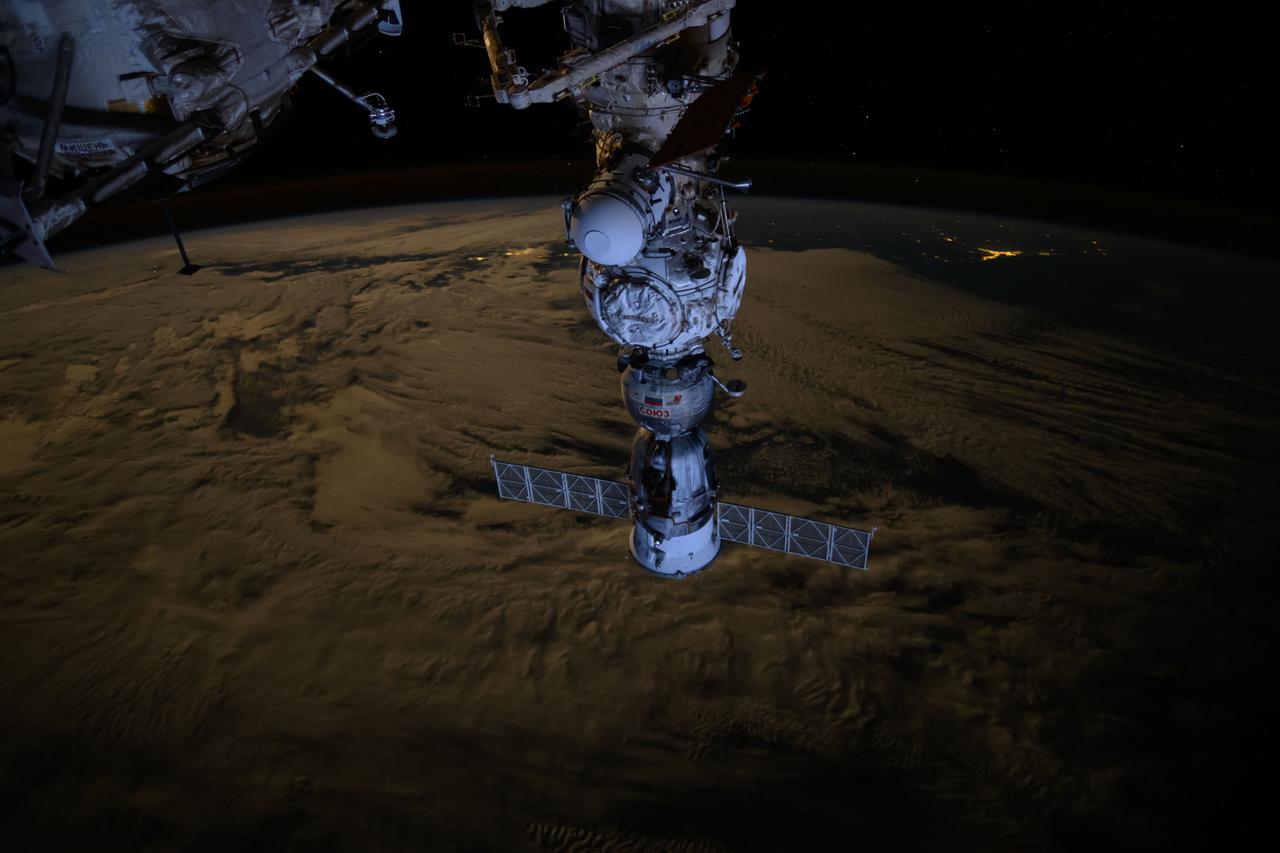

iss071e365226 (July 19, 2024) --- The Soyuz MS-25 crew ship is picture docked to the Prichal docking module as the International Space Station orbited 271 miles above the Tasman Sea off the coast of New Zealand.

SOFIA at nighttime in New Zealand.

SOFIA at nighttime in New Zealand.
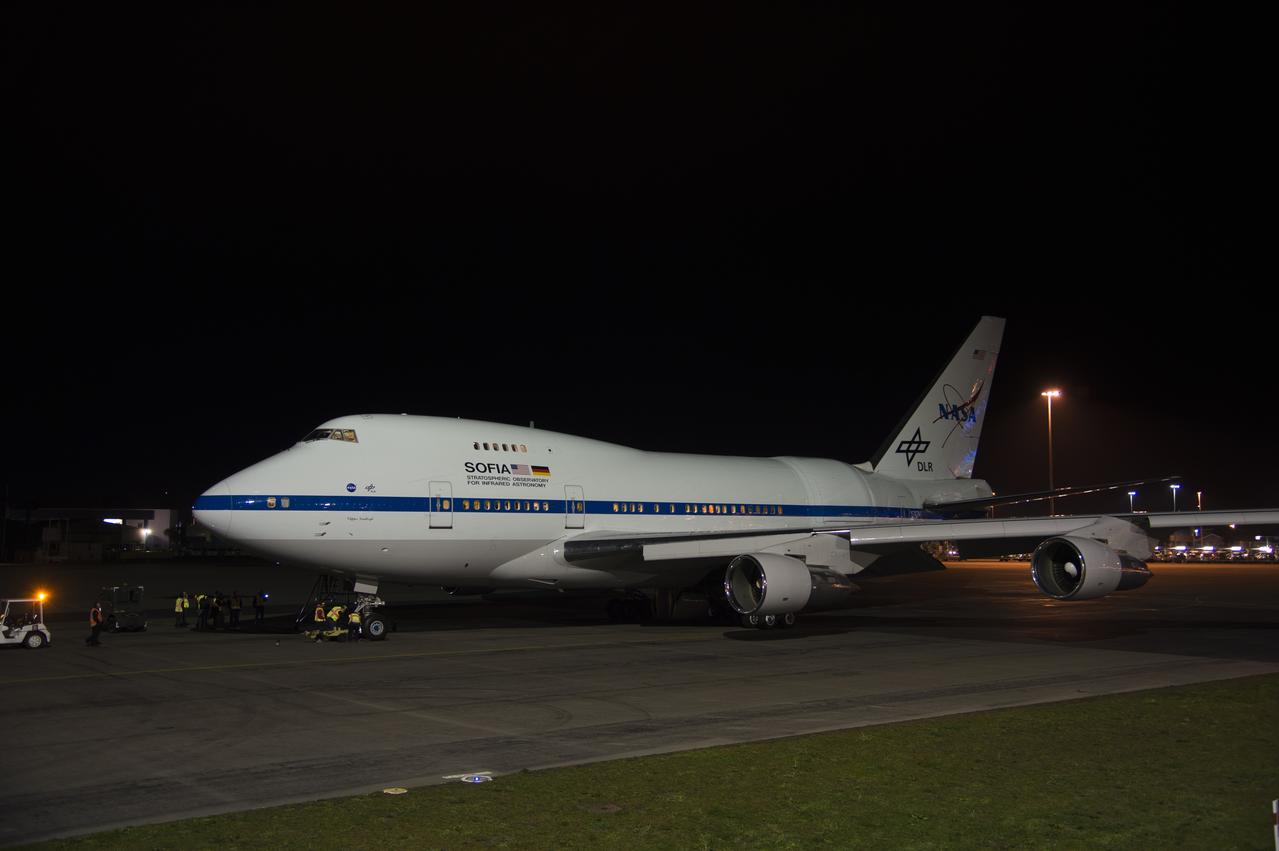

SOFIA at nighttime in New Zealand.
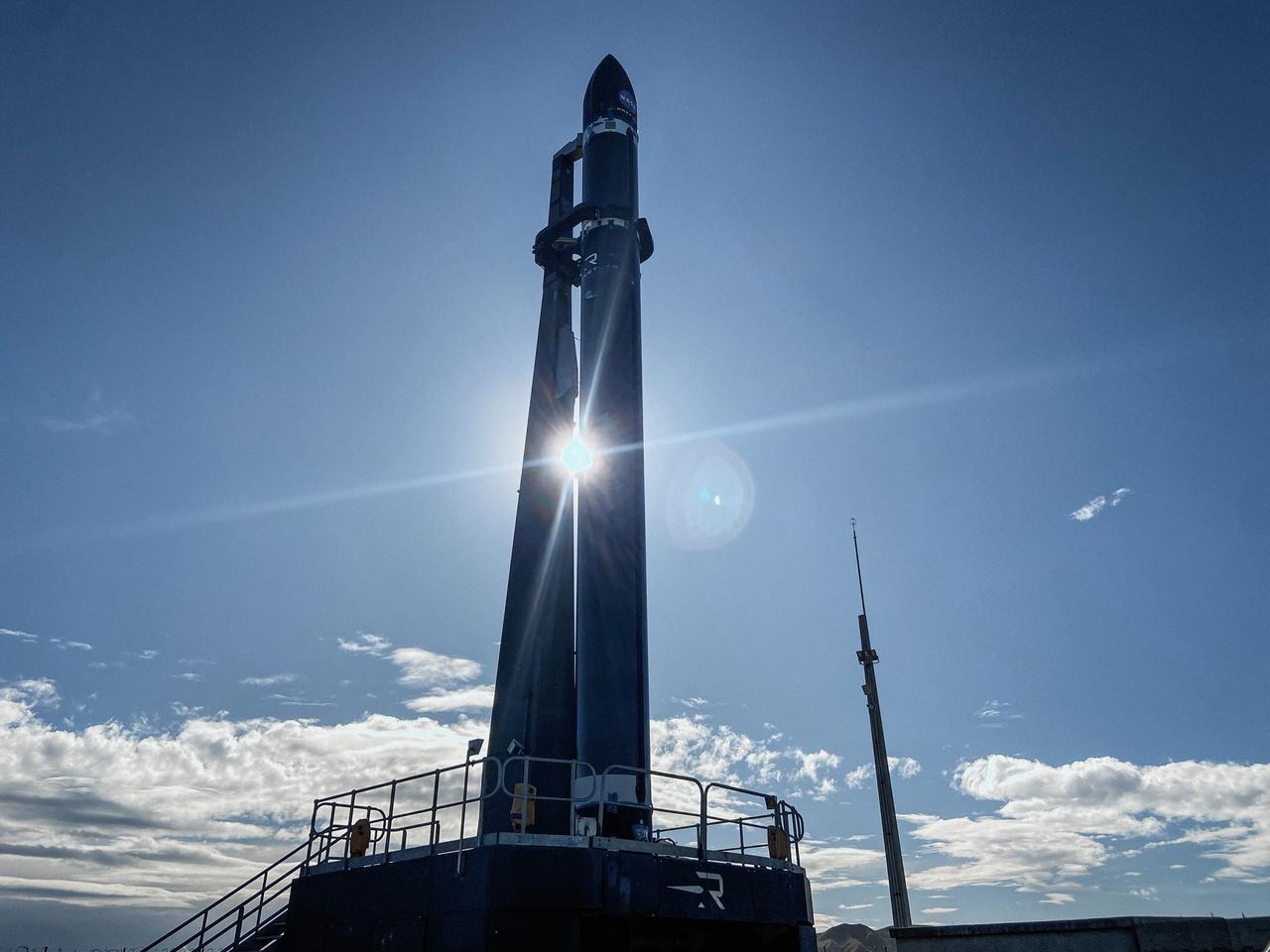

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the second of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the second CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “PREFIRE and Ice” was targeted for Saturday, June 1, 2024, but was scrubbed for the day.

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the second of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the second CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “PREFIRE and Ice” was targeted for Saturday, June 1, 2024, but was scrubbed for the day.
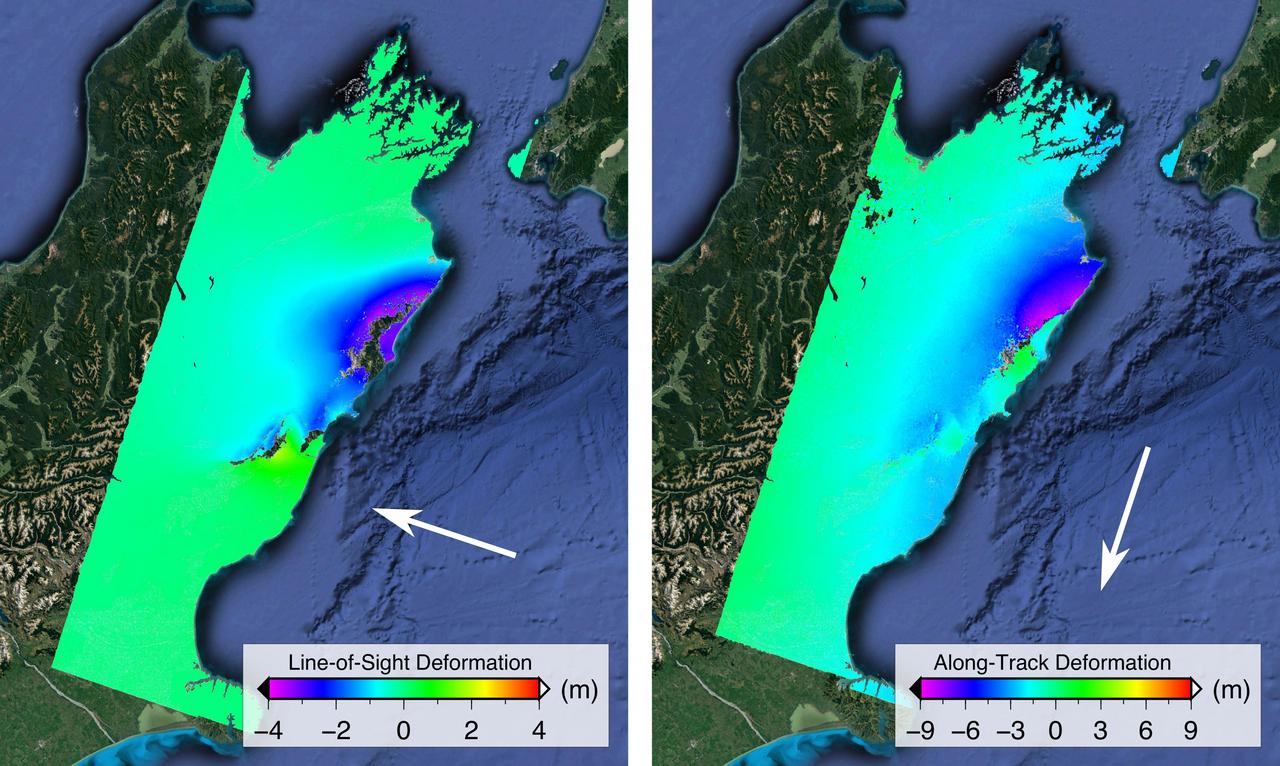
NASA and its partners are contributing important observations and expertise to the ongoing response to the Nov. 14, 2016, magnitude 7.8 Kaikoura earthquake in New Zealand. This shallow earthquake was so complex and unusual, it is likely to change how scientists think about earthquake hazards in plate boundary zones around the world. Scientists with the Advanced Rapid Imaging and Analysis project (ARIA), a collaboration between NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, and Caltech in Pasadena, analyzed interferometric synthetic aperture radar images from the PALSAR-2 instrument on the ALOS-2 satellite operated by the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) to calculate maps of the deformation of Earth's surface caused by the quake. Two maps show motion of the surface in two different directions. Each false-color map shows the amount of permanent surface movement caused almost entirely by the earthquake, as viewed by the satellite, during a 28-day interval between two ALOS-2 wide-swath images acquired on Oct. 18 and Nov. 15, 2016. In these two new maps made from the wide-swath images, the colors of the surface displacements are proportional to the surface motion. The wide-swath images cover the entire 106-mile (170-kilometer) length of the complex set of earthquake ruptures. The arrows show the direction of the radar motion measurement. In the left image, the blue and purple tones show the areas where the land around the Kaikoura peninsula in the Marlborough region of New Zealand's South Island has moved toward the satellite by up to 13.2 feet (4 meters), both eastward and upward. In the right image, the blue and purple tones show the areas that moved to the north by up to 30 feet (9 meters) and green tones show the area that moved to the south. The sharp line of color change is across the Kekerengu Fault, which had the largest amount of motion in the earthquake. Field studies found maximum rupture at the surface was measured at 39 feet (12 meters) of horizontal displacement. Several other faults have sharp color changes due to smaller amounts of motion, with a total of at least 12 faults rupturing in this single large earthquake. Areas without color have snow, heavy vegetation or open water that prevents the radar measurements from being coherent between satellite images – a required condition to measure ground displacement. Scientists use these maps to build detailed models of the fault slip at depth and associated land movements to better understand the impact on future earthquake activity. The PALSAR-2 data were provided by JAXA through the Committee on Earth Observation Satellites (CEOS) and through scientific research projects. The background image is from Google Earth. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21210

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad Saturday, May 25, 2024, at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the first of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the first CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” occurred at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT).
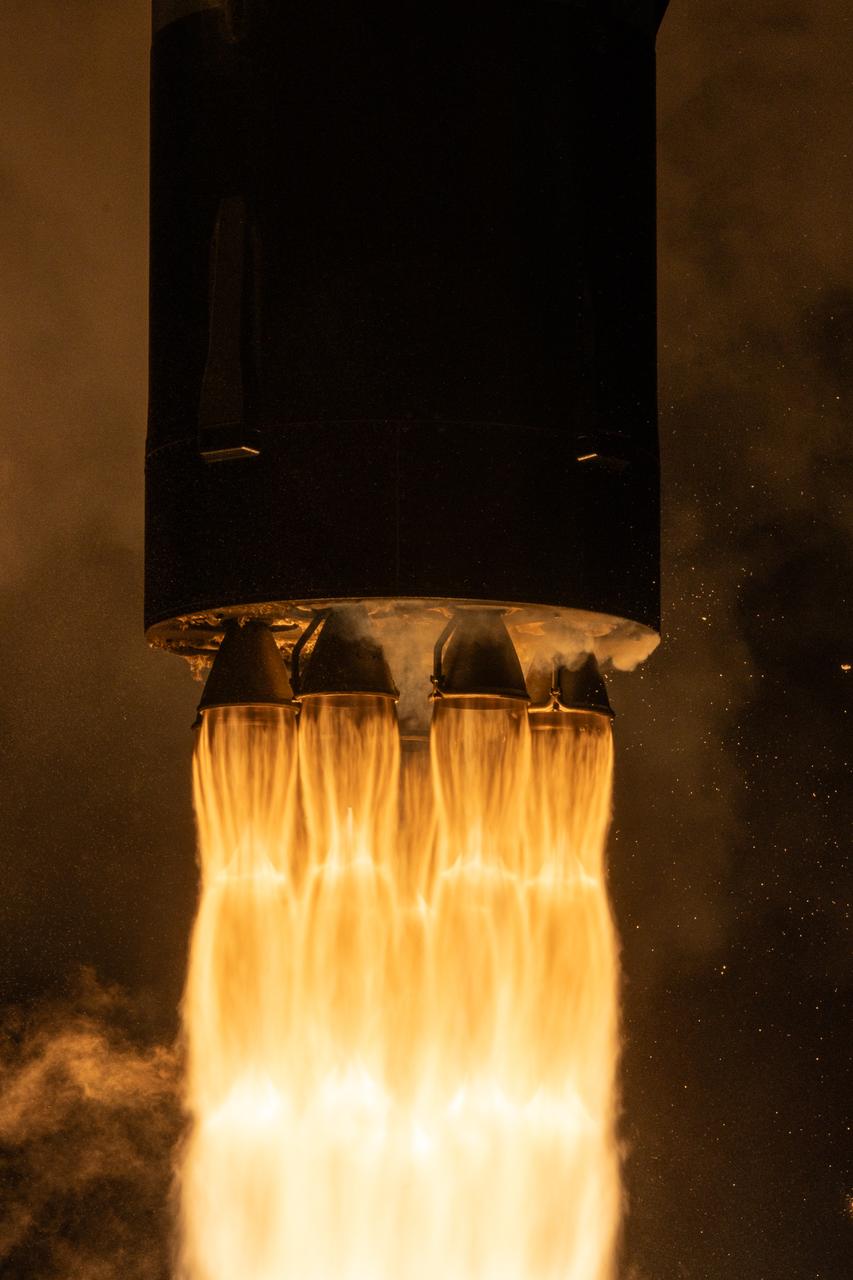

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT) Saturday, May 25, 2024, on the first of two launches which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission. The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.

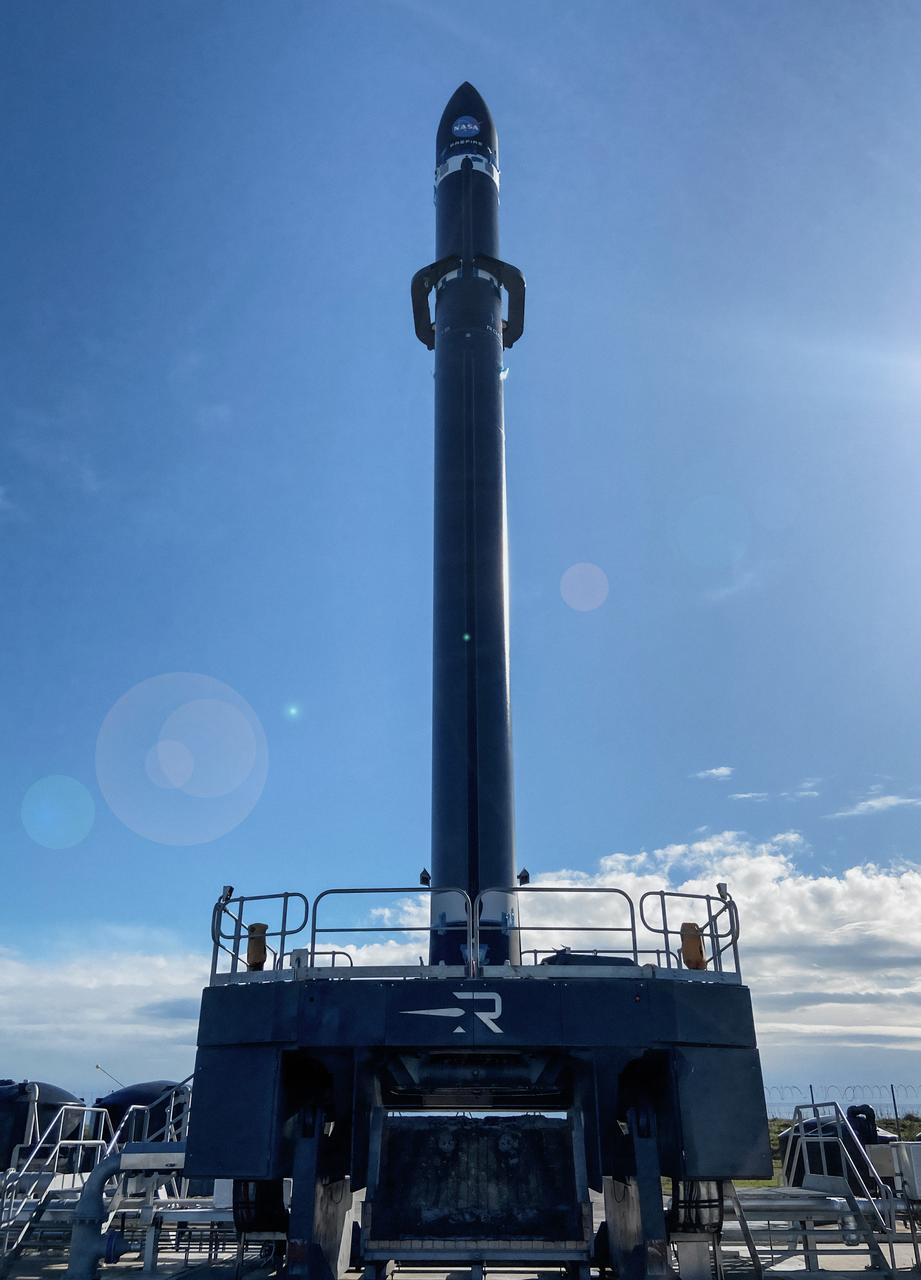
Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad Saturday, May 25, 2024, at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the first of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the first CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” occurred at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT).
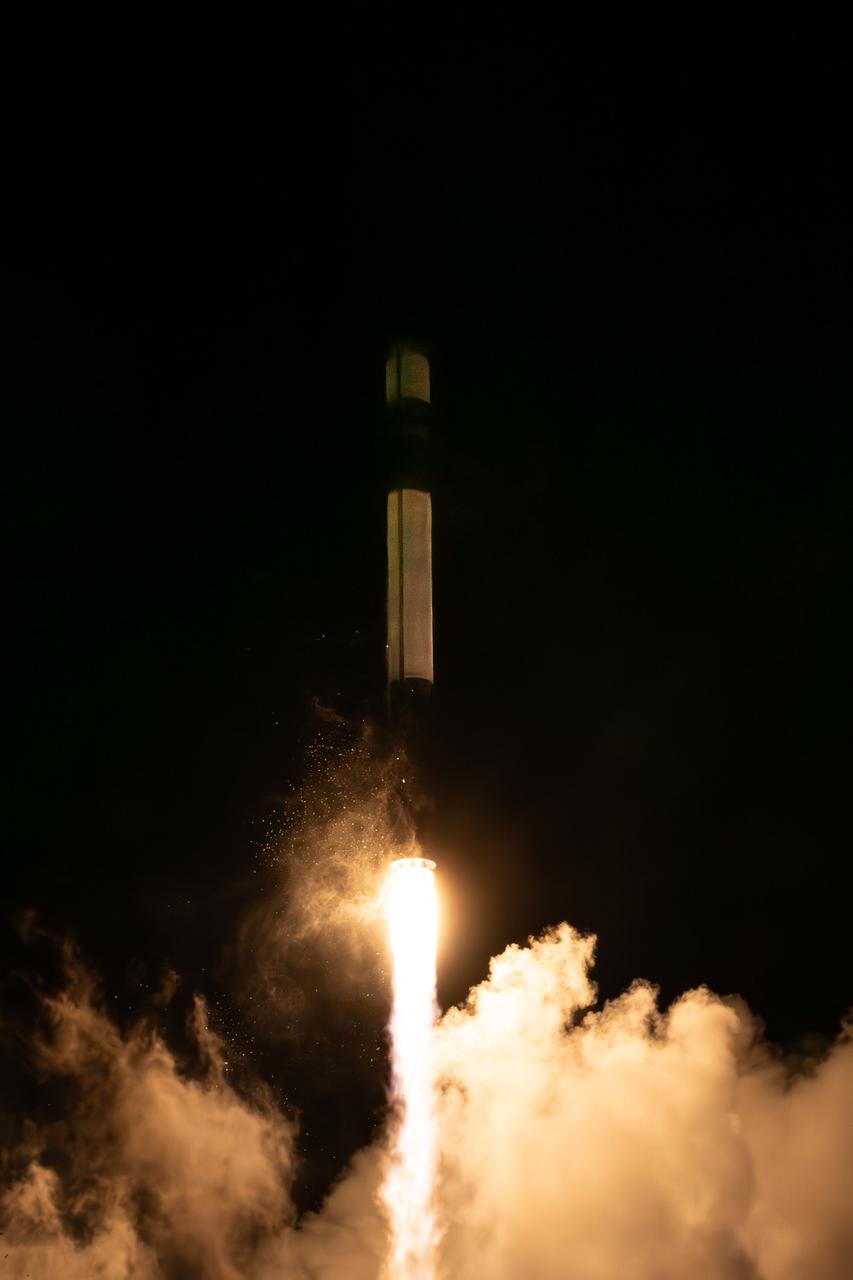

A Rocket Lab Electron rocket lifts off from Launch Complex 1 in Māhia, New Zealand at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT) Saturday, May 25, 2024, on the first of two launches which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission. The PREFIRE mission, expected to last at least 10 months, consists of sending two CubeSats to asynchronous, near-polar orbits, to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica.
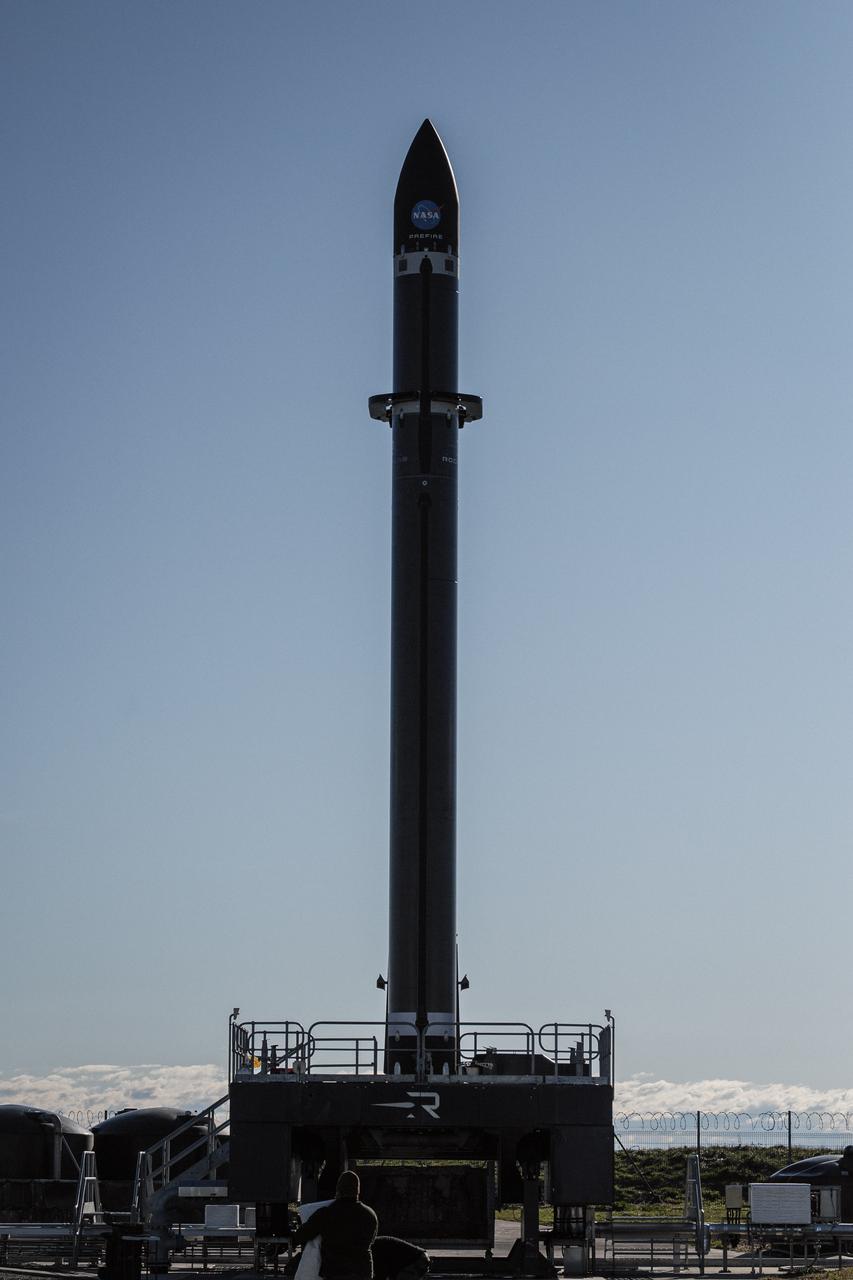

Rocket Lab’s Electron rocket is vertical on the pad Saturday, May 25, 2024, at Launch Complex 1 in Mahia, New Zealand, loaded with the first of two identical 6U CubeSats for NASA’s PREFIRE (Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment) mission to help close a gap in our understanding of how much of Earth’s heat is lost to space from the Arctic and Antarctica. Liftoff of the first CubeSat launch, which Rocket Lab named “Ready, Aim, PREFIRE,” occurred at 7:41 p.m. NZST (3:41 a.m. EDT).
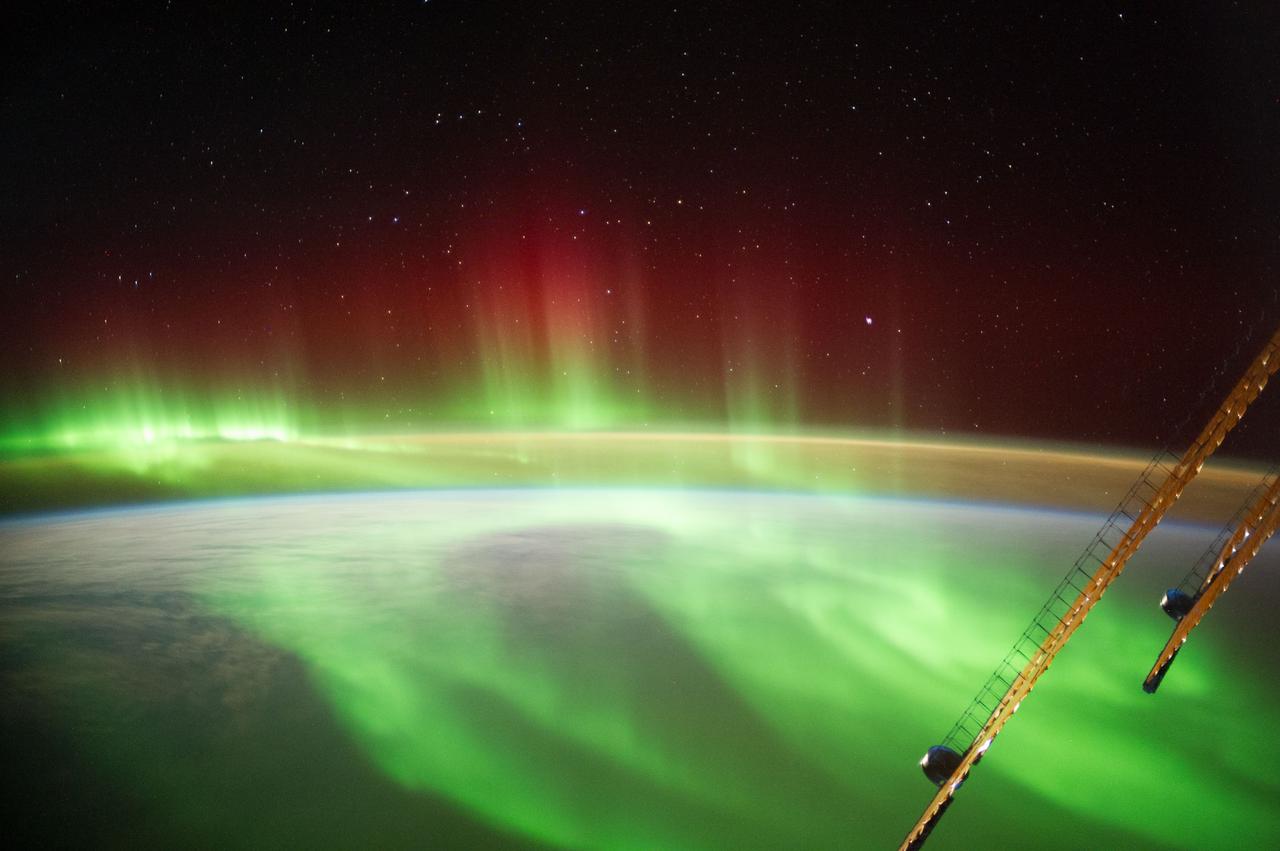

Earth observation taken by the Expedition 40 crew aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Folder labels this as: TL Aurora w New Zealand at end.
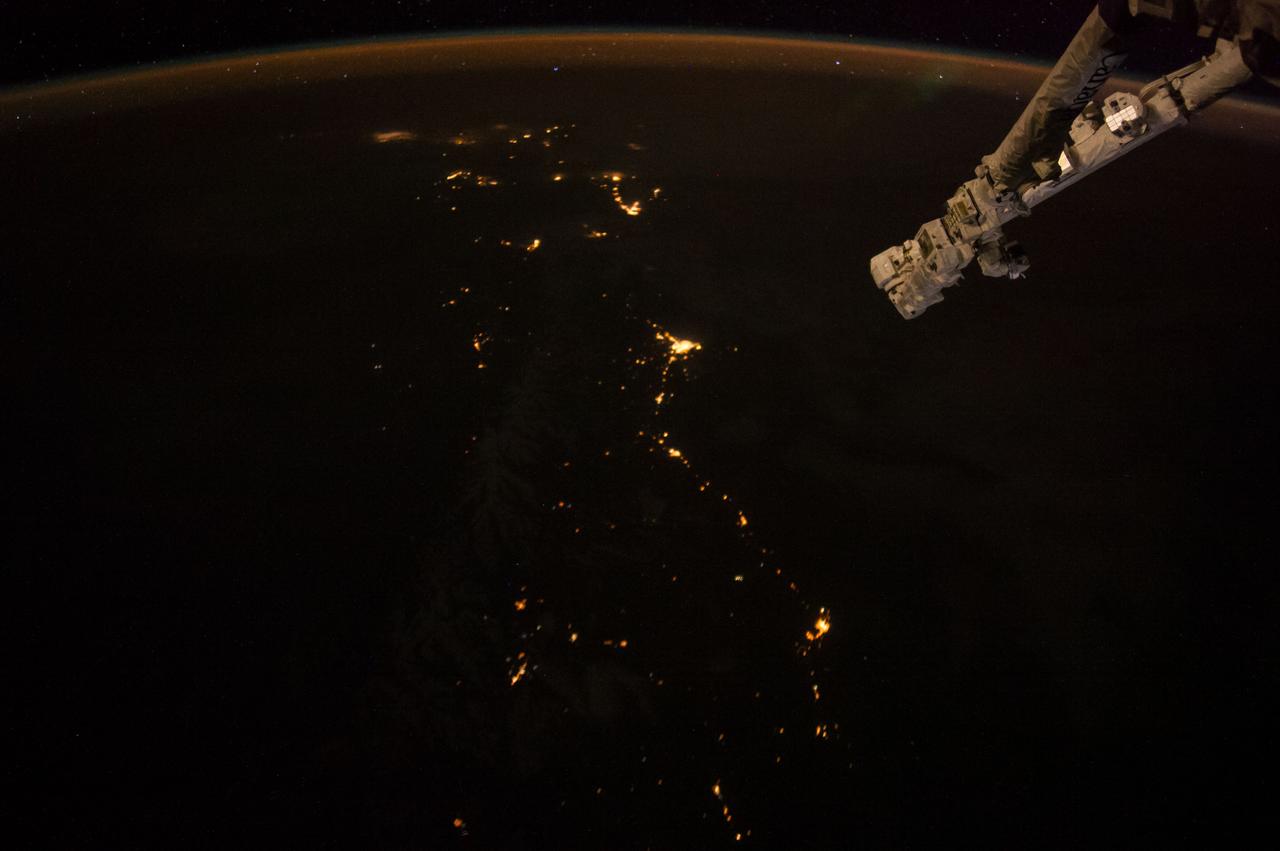

Earth Observation taken during a night pass by the Expedition 40 crew aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Folder lists this as: New Zealand night pass.
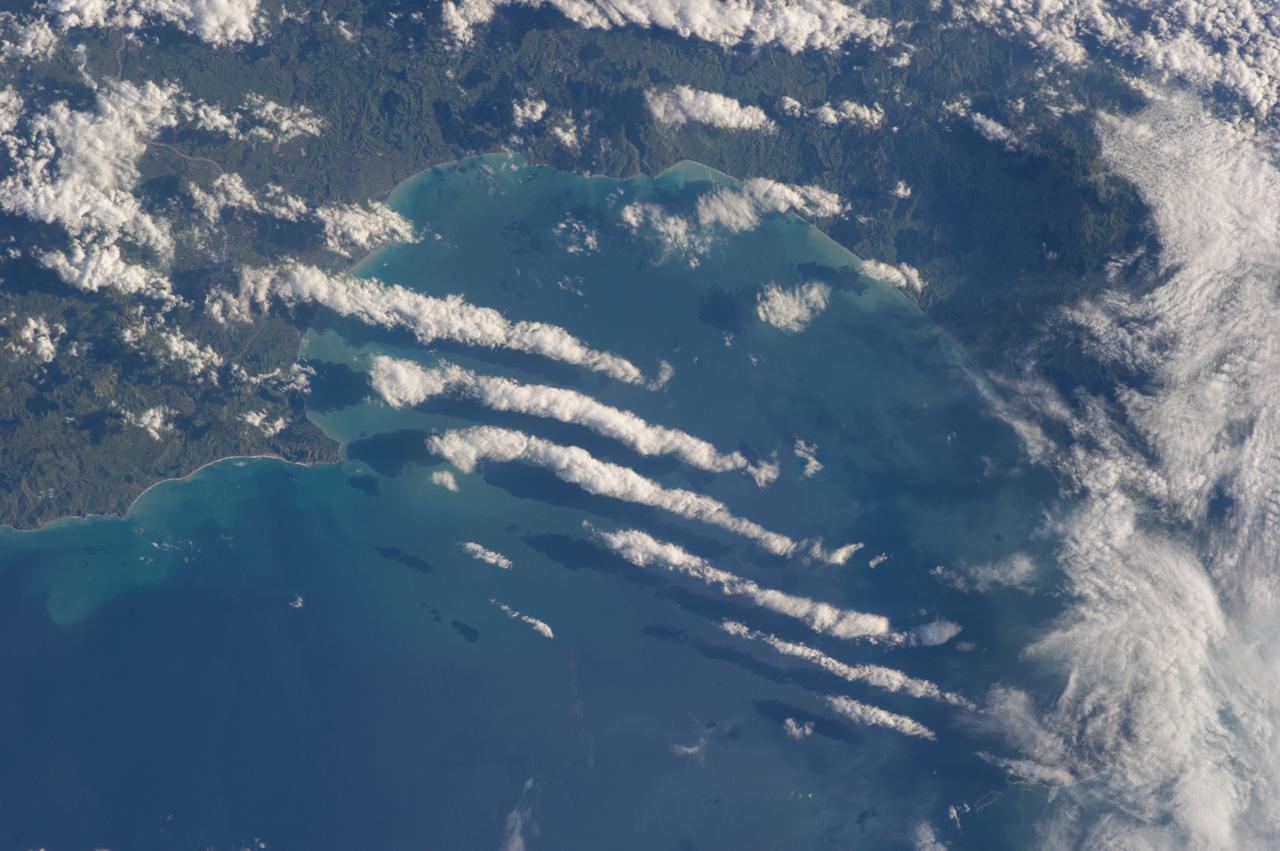

Earth Observation taken during a day pass by the Expedition 40 crew aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Folder lists this as: New Zealand.

iss063e046732 (July 14, 2020) --- The sun's glint beams on the South Pacific Ocean as the International Space Station orbited just off the coast of Auckland, New Zealand.

Earth Observation taken during a day pass by the Expedition 40 crew aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Folder lists this as: New Zealand.

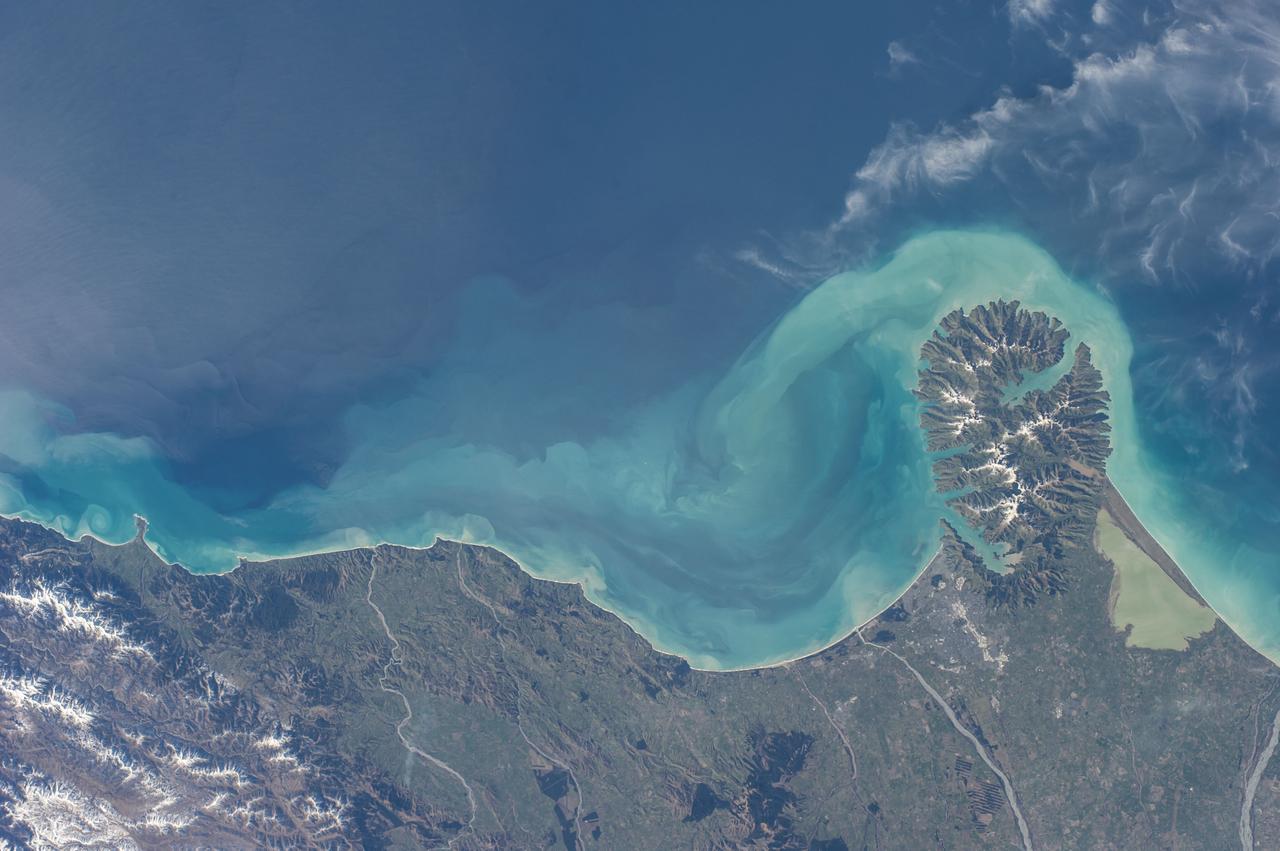
Earth Observation taken during a day pass by the Expedition 40 crew aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Folder lists this as: New Zealand.
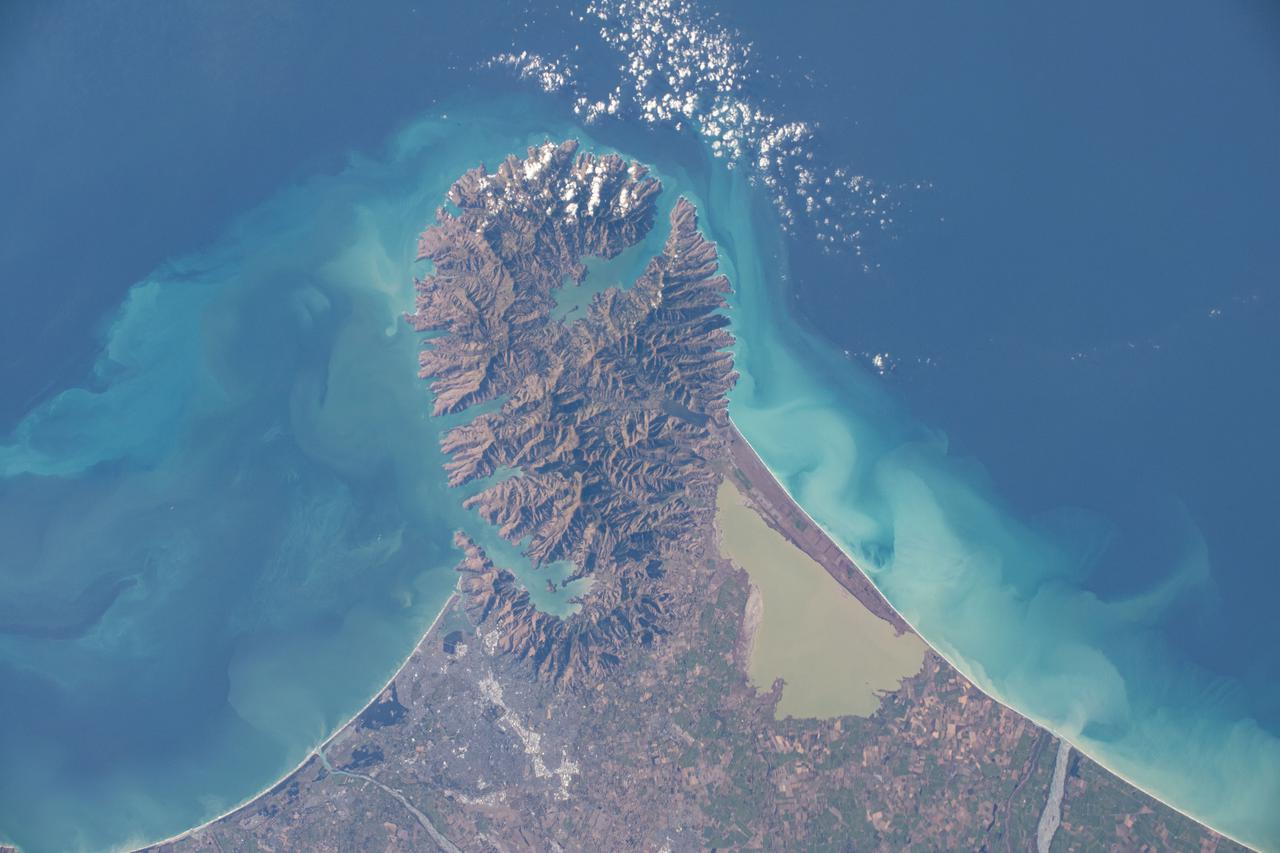

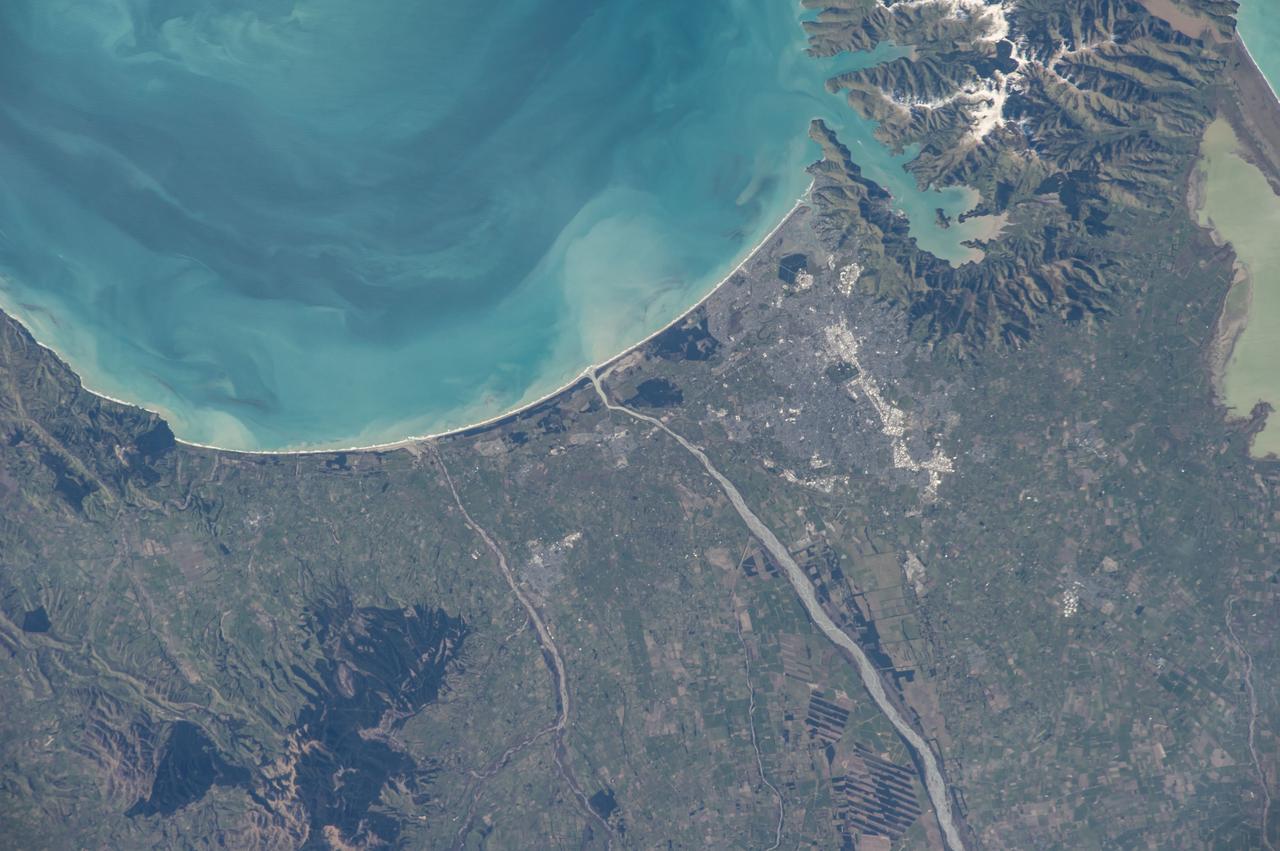
iss064e044628 (March 18, 2021) --- Christchurch, New Zealand, is pictured on the coast of Pegasus Bay as the International Space Station orbited 271 miles above the South Pacific.
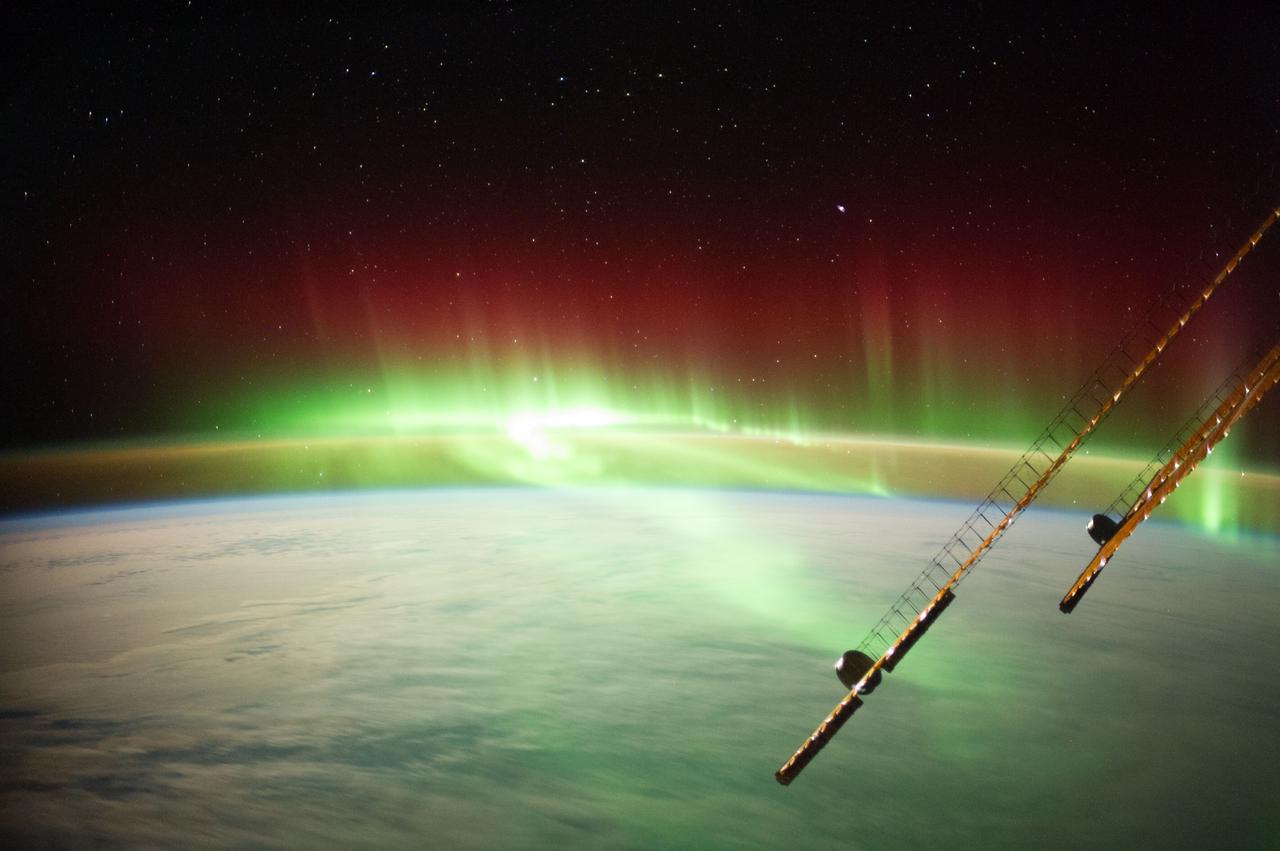

Earth observation taken by the Expedition 40 crew aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Folder labels this as: TL Aurora w New Zealand at end.
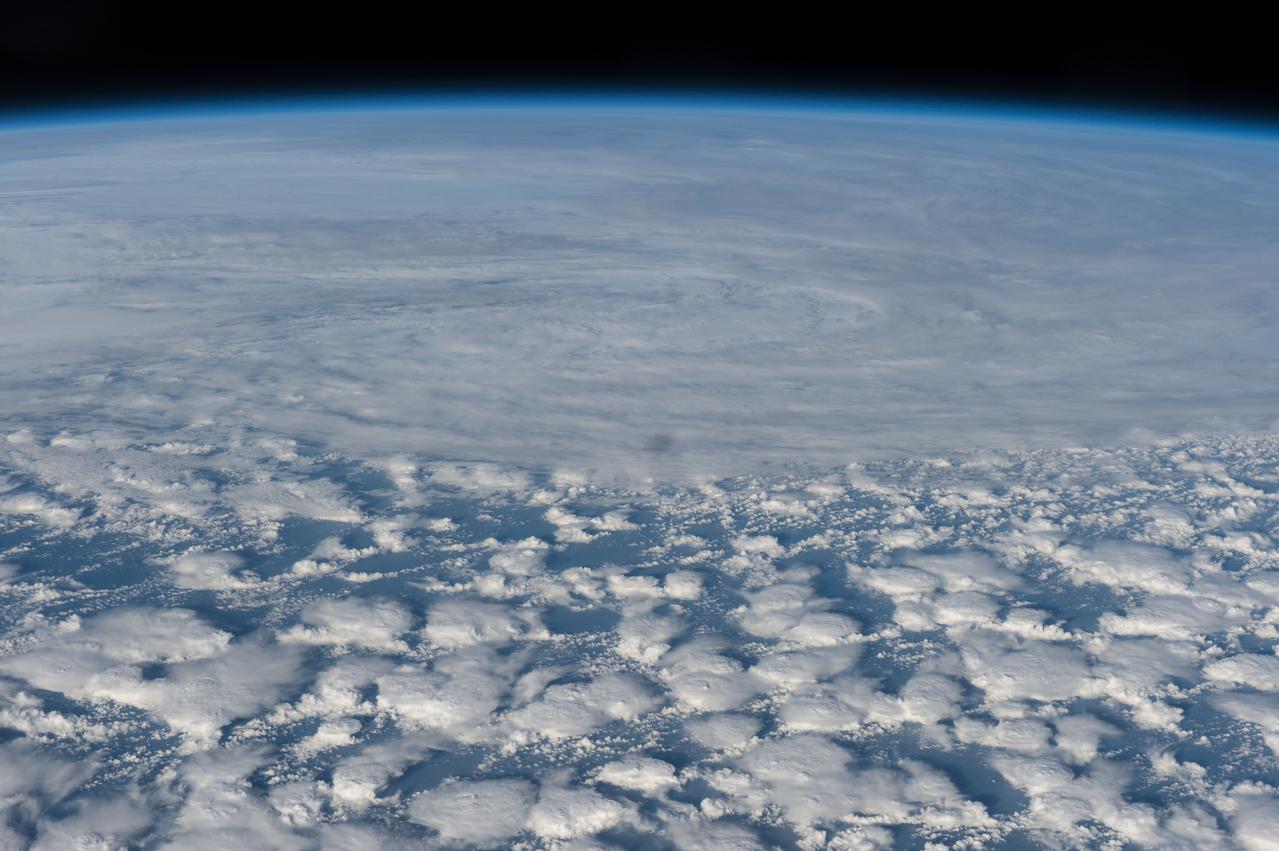

iss050e066032 (03/27/2017) --- Cyclone Debbie over Australia as seen by members of Expedition 50 aboard the International Space Station on Mar 27, 2017. After devastating Australia over the last days of March the massive category four cyclone lashed New Zealand closing motorways and causing a major landslip. The storm hit parts of New Zealand still recovering from a devastating earthquake four months ago.
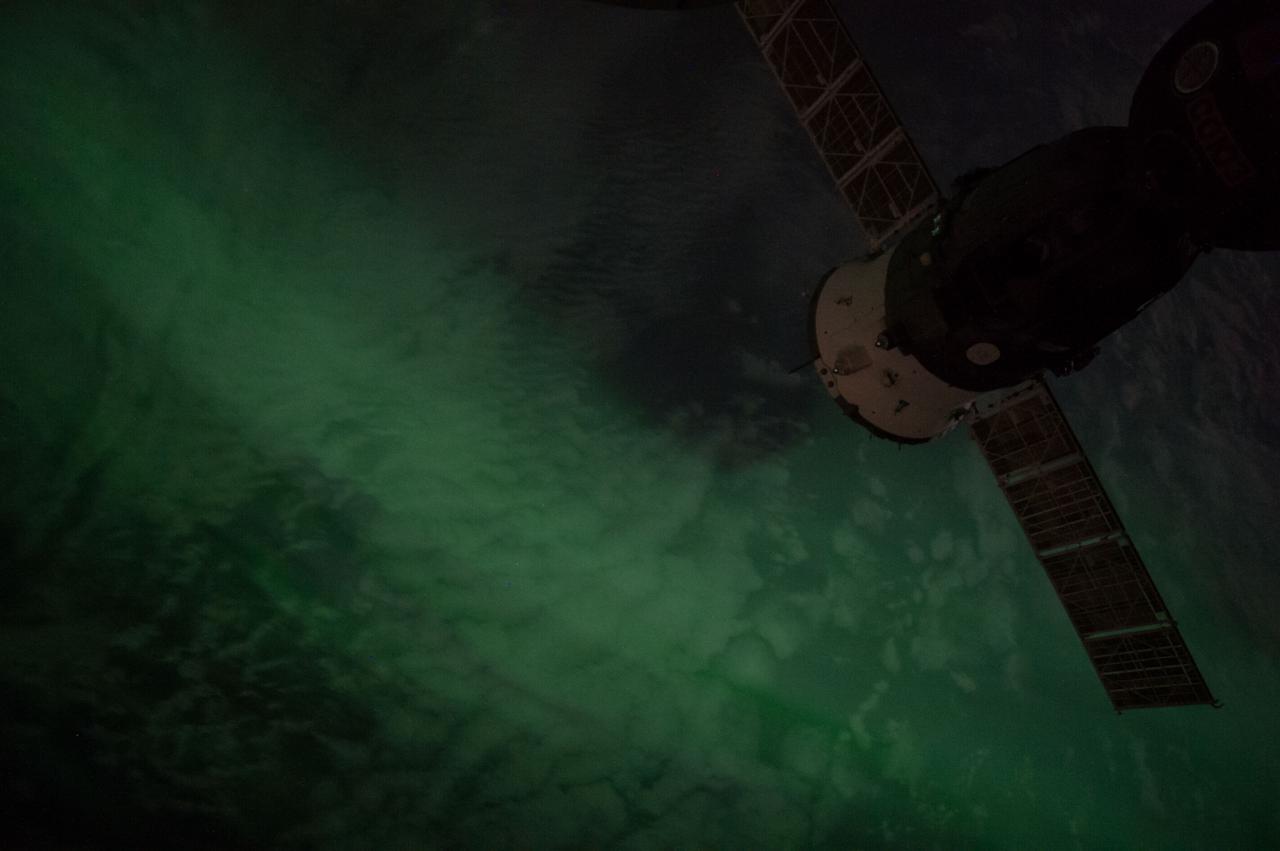

Earth Observation taken during a night pass by the Expedition 40 crew aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Folder lists this as: New Zealand Aurora night pass. On crewmember's Flickr page - Look straight down into an aurora.