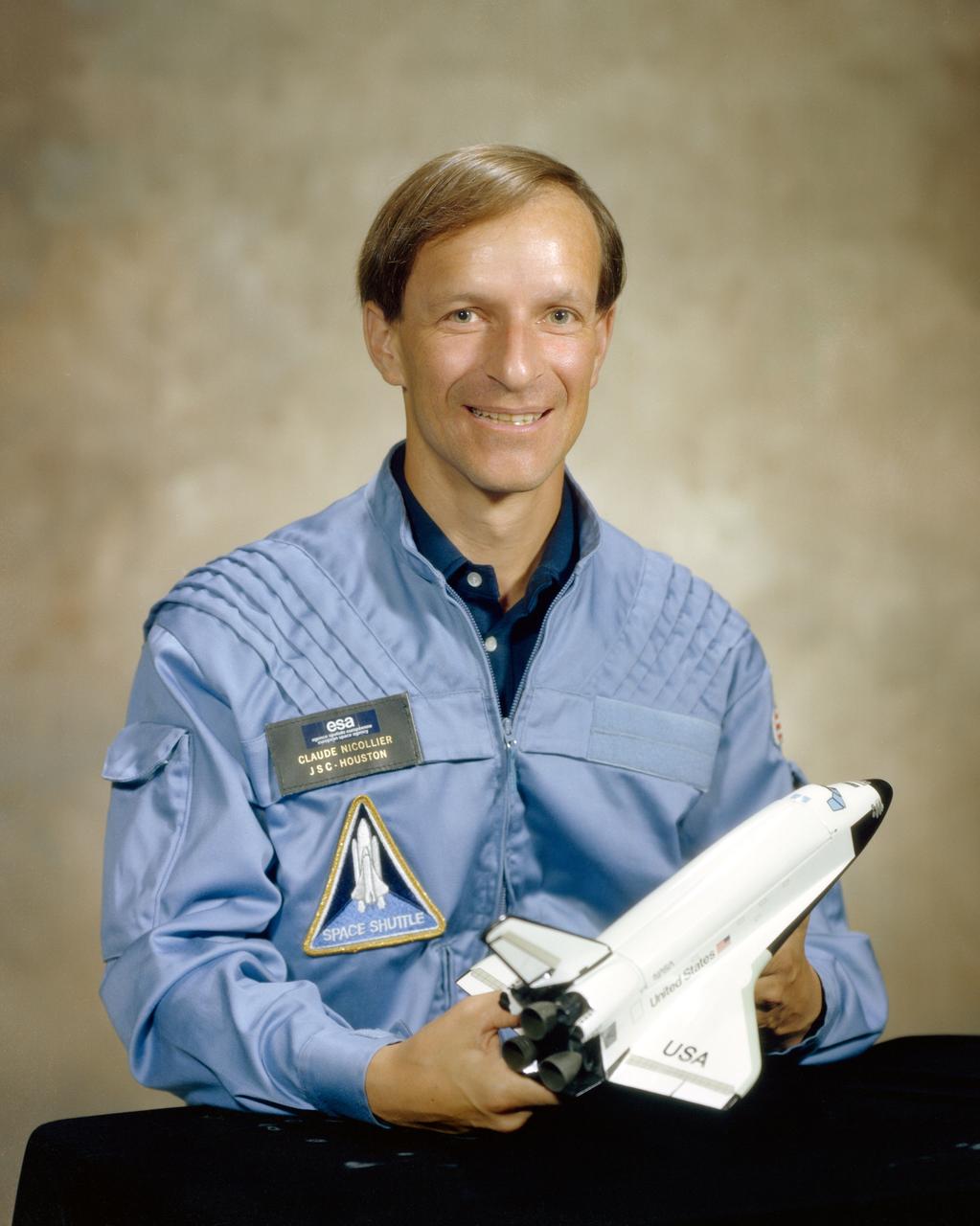

S81-33467 ( July 1981) --- Astronaut Claude Nicollier, mission specialist. EDITOR'S NOTE: Nicollier is a Swiss scientist, representing the European Space Agency (ESA). He began training at the NASA - Johnson Space Center (JSC) in 1980.
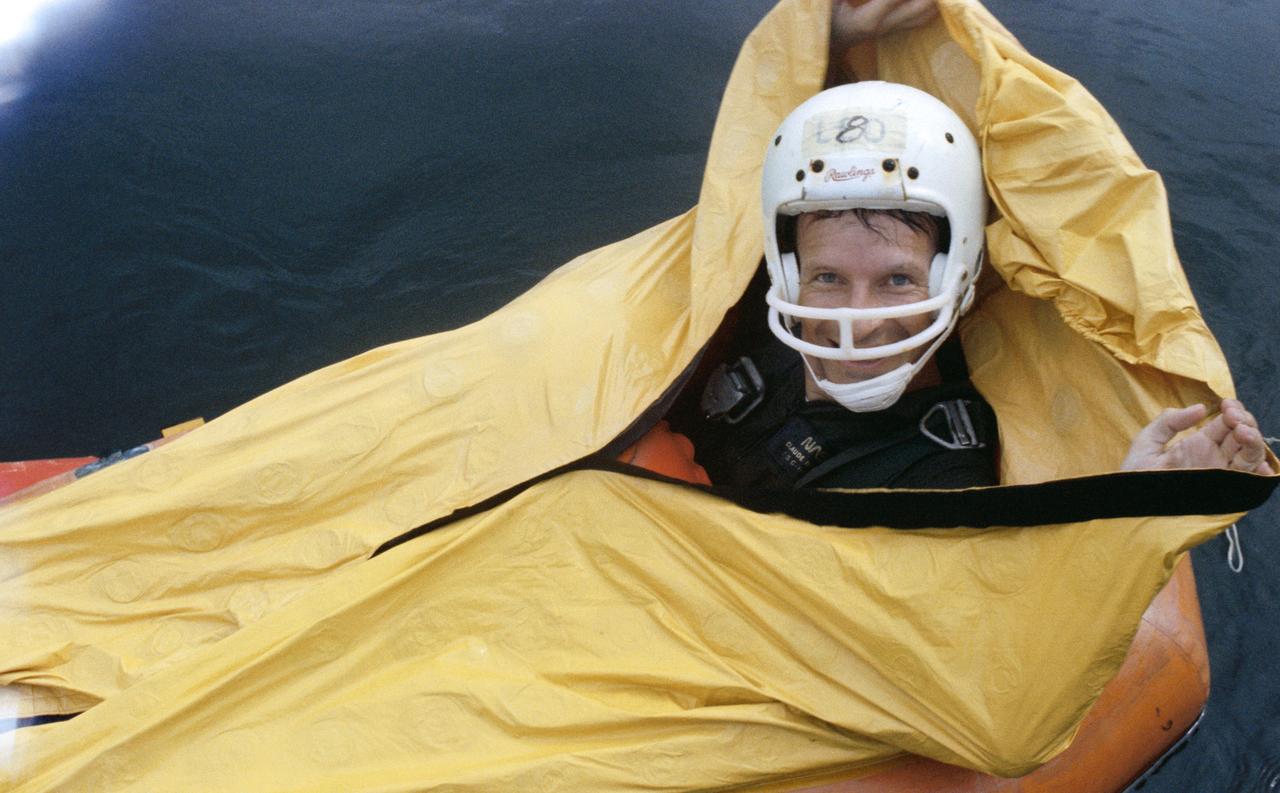

S80-38468 (4 Sept 1980) --- Astronaut Claude Nicollier in water egress training. View is of Nicollier in one-man life raft.
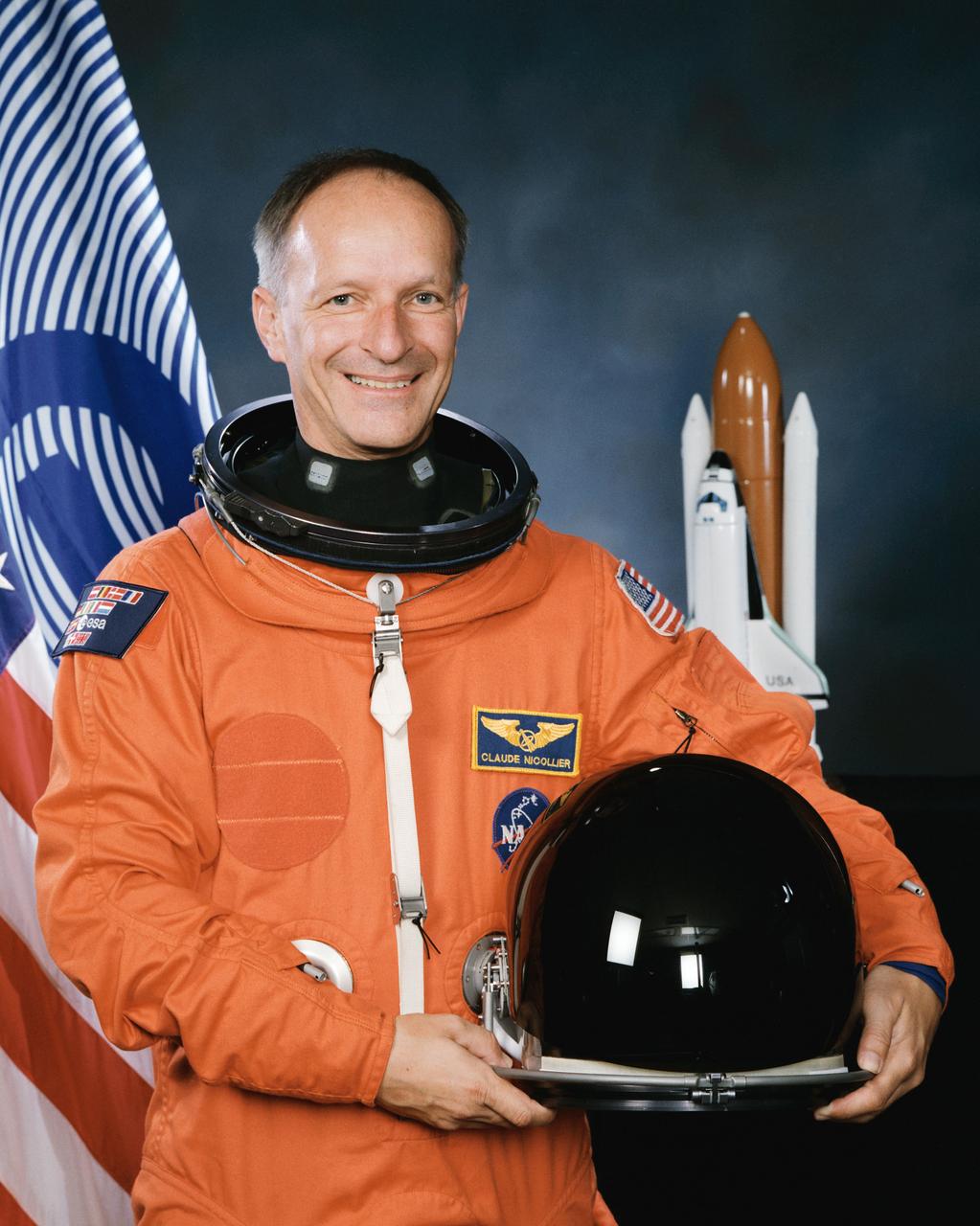

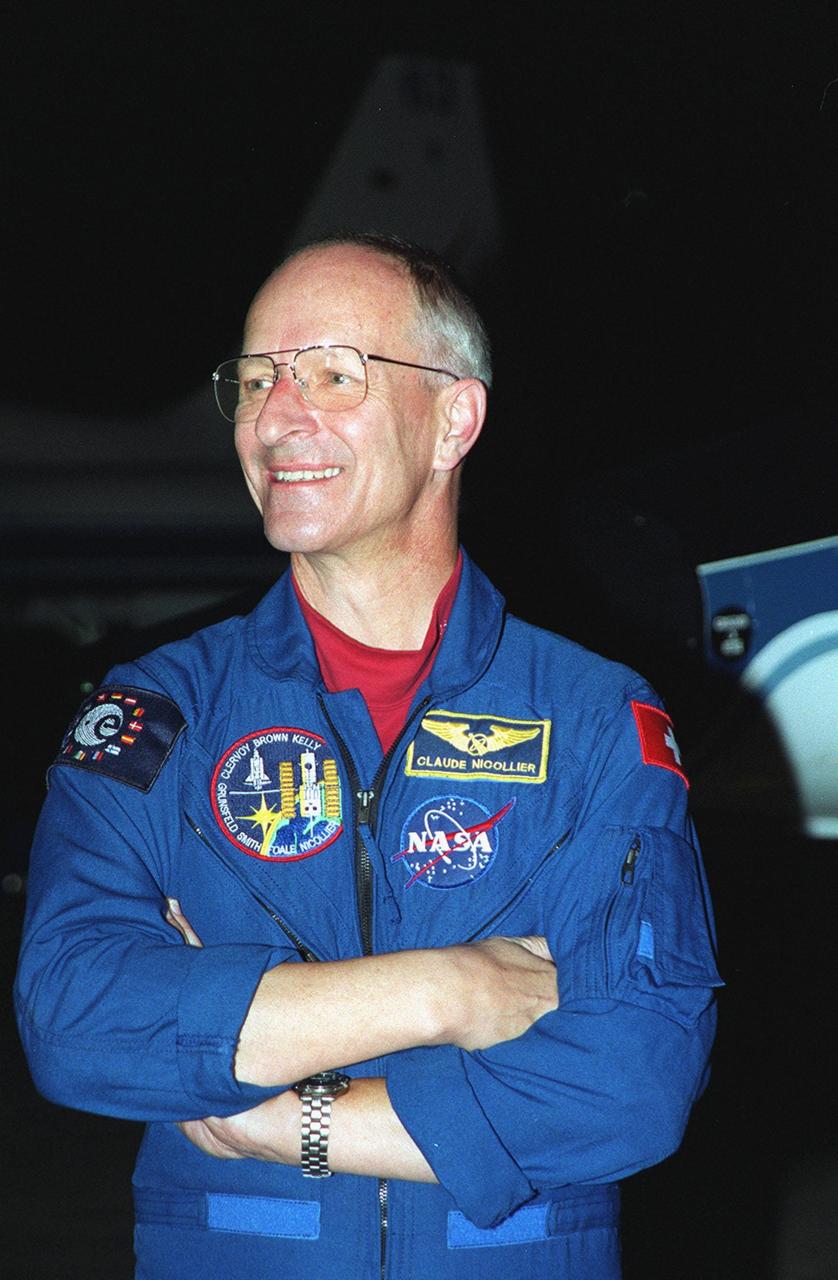
S93-40688 (1993) --- Astronaut Claude Nicollier, representing European Space Agency (ESA).

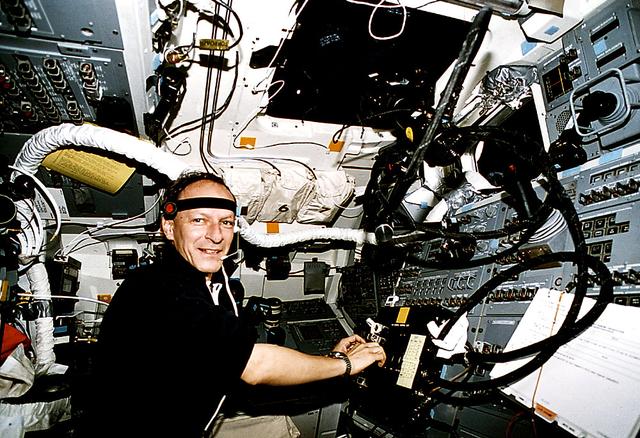
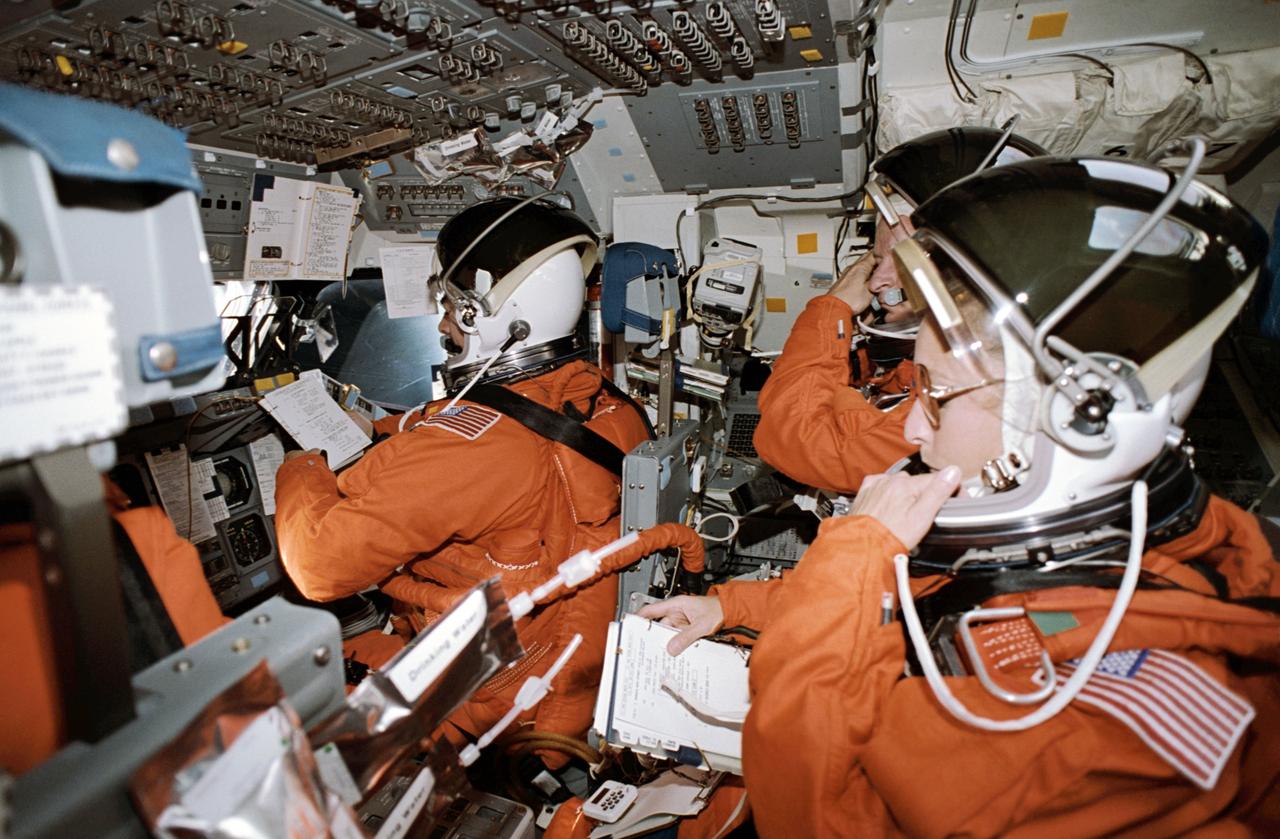
S103-E-5199 (21 December 1999) --- Astronaut Claude Nicollier, mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA), poses near the controls of Discovery's remote manipular system (RMS) robot arm, a system he's worked with on the current flight and on previous missions as well. Nicollier fulfills a different role later in this flight when he dons an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) space suit to participate in one of the telescope-servicing space walks. The photo was recorded with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 11:11:30 GMT, Dec. 21, 1999. This mission offers
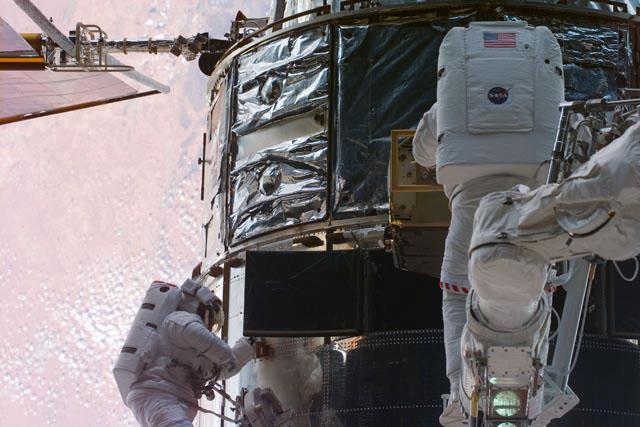

S103-E-5320 (23 December 1999) --- Astronauts C. Michael Foale (left) and Claude Nicollier work on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST)in Discovery's aft cargo bay during their shared space walk to perform servicing tasks on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). A desert area on Earth forms the backdrop for the photo. Nicollier, part of the astronaut corps since 1980, represents the European Space Agency (ESA). Foale, one of NASA's astronauts who had spent several months aboard Russia's Mir Space Station, is an alumnus of the 1987 class of astronaut candidates. The photo was taken with an electronic still camera (ESC).

This Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis (STS-46) onboard photo shows Swiss scientist Claude Nicollier of the European Space Agency (ESA) supporting the Tether Opitical Phenomena (TOP) activities on the flight deck. The Tethered Satellite System (TSS) was a cooperative development effort by the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and NASA made capable of deploying and retrieving a satellite which is attached by a wire tether from distances up to 100 km from the Orbiter. These free-flying satellites are used as observation platforms outside of the Orbiter.
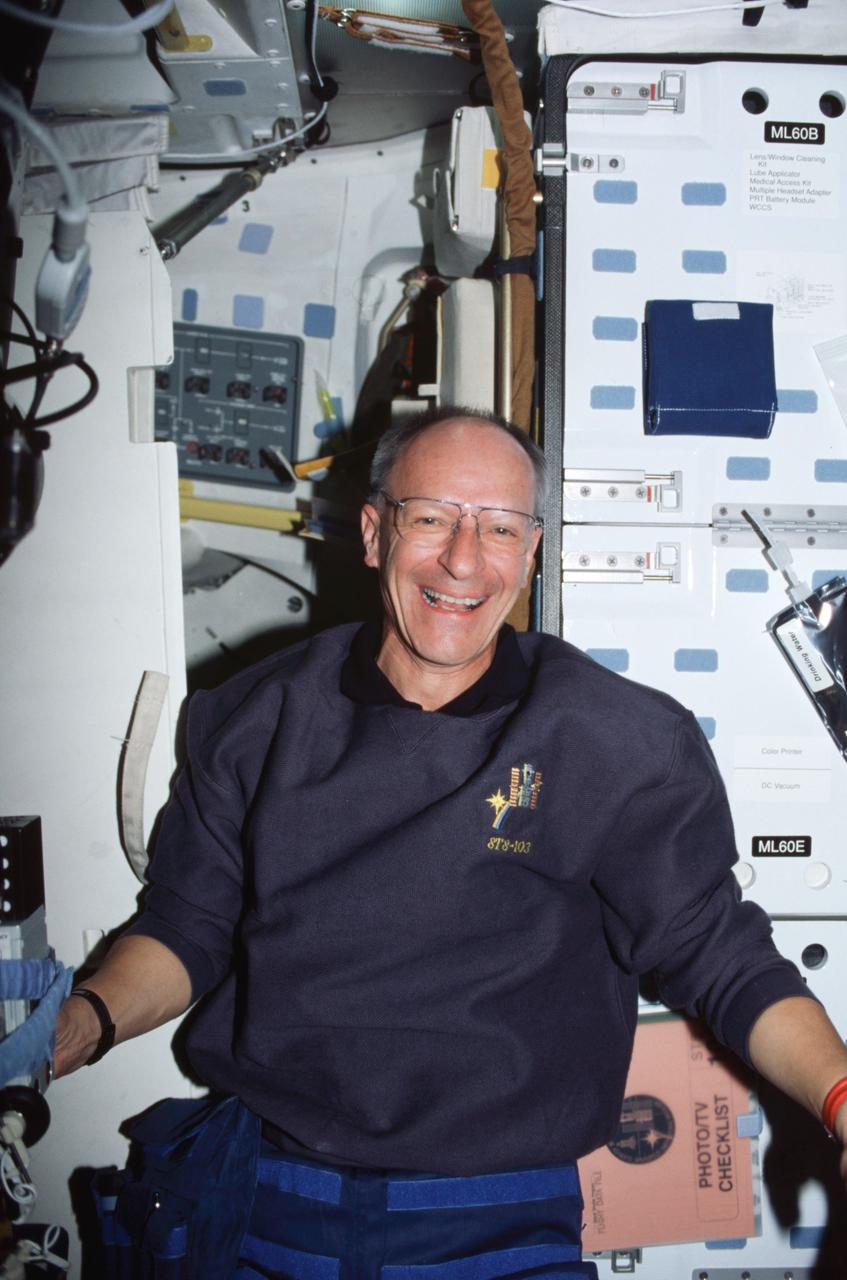

STS103-329-025 (19-27 December 1999) ---.Astronaut Claude Nicollier, mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA), on Discovery's mid deck prior to a space walk in the weightlessness of space.
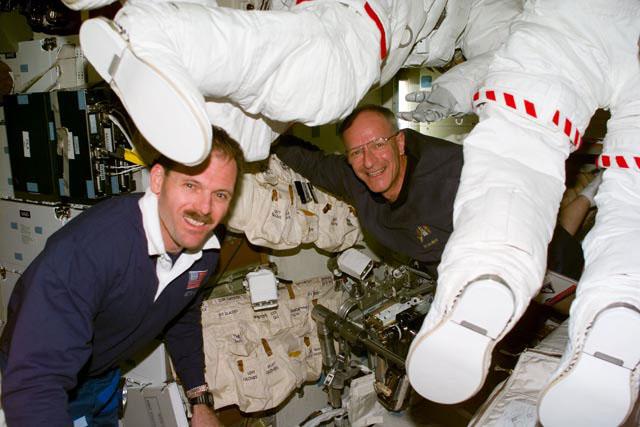

S103-E-5023 (20 December 1999) --- Astronauts Steven L. Smith (foreground) and Claude Nicollier take an early look at their extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) space suits on Discovery's mid deck near the end of their first full day in space. Smith is payload commander and Nicollier, mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA). The two will participate in space walks to service the Hubble Space Telescope later in the week. The photo was recorded with an electronic still camera (ESC) at 21:52.32 GMT, December 20, 1999.

S103-E-5308 (23 Dec. 1999) --- Astronauts C. Michael Foale (left) and Claude Nicollier hover above Discovery's aft cargo bay during their shared spacewalk to perform servicing tasks on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The photo was taken with an electronic still camera (ESC). Photo credit: NASA
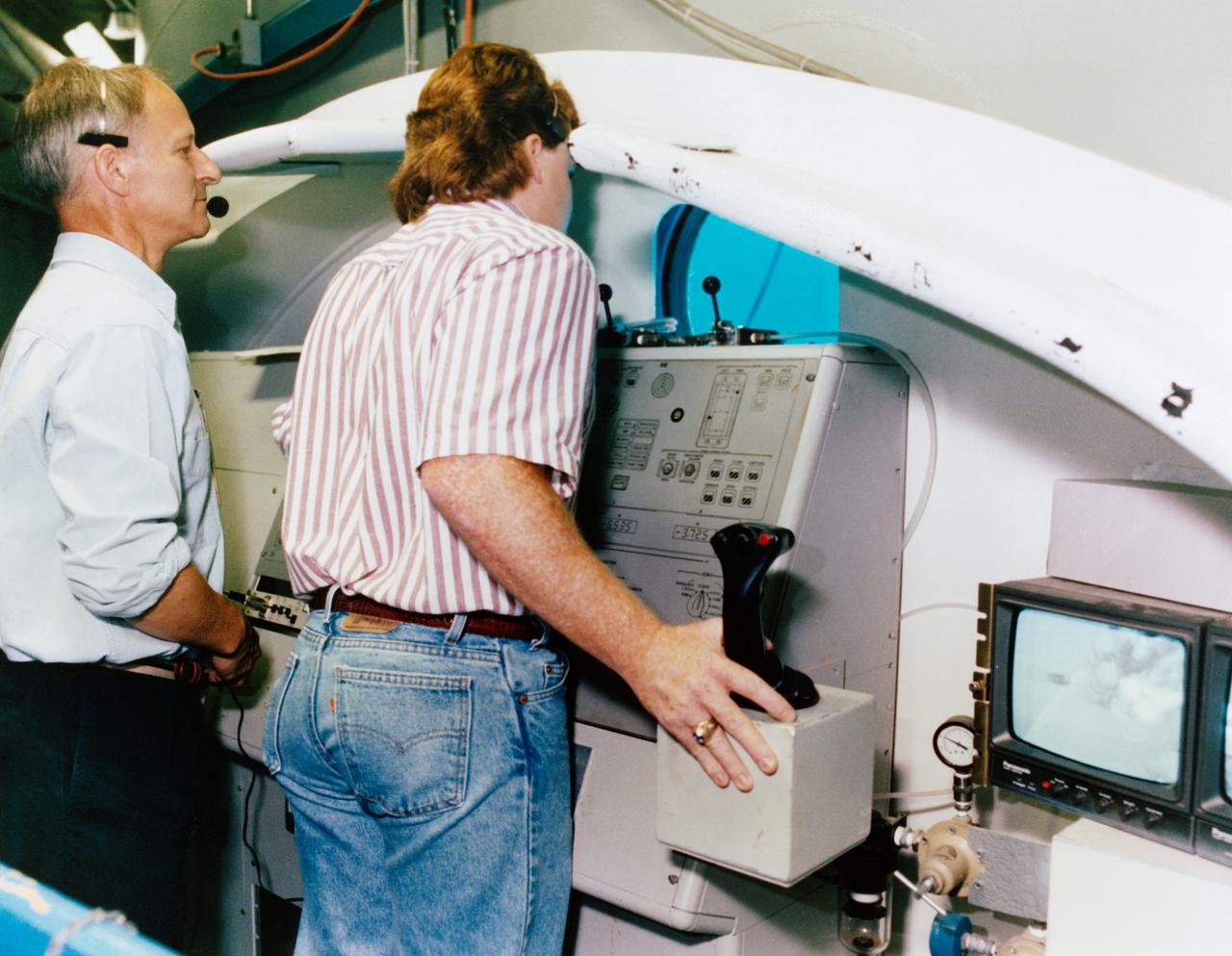

Swiss scientits Claude Nicollier (left), STS-61 mission specialist, waits his turn at the controls for the remote manipulator system (RMS) during a training session in the Neutral Buoyancy Simulator at Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC). Mark Norman of MSFC has control of the RMS in this frame.
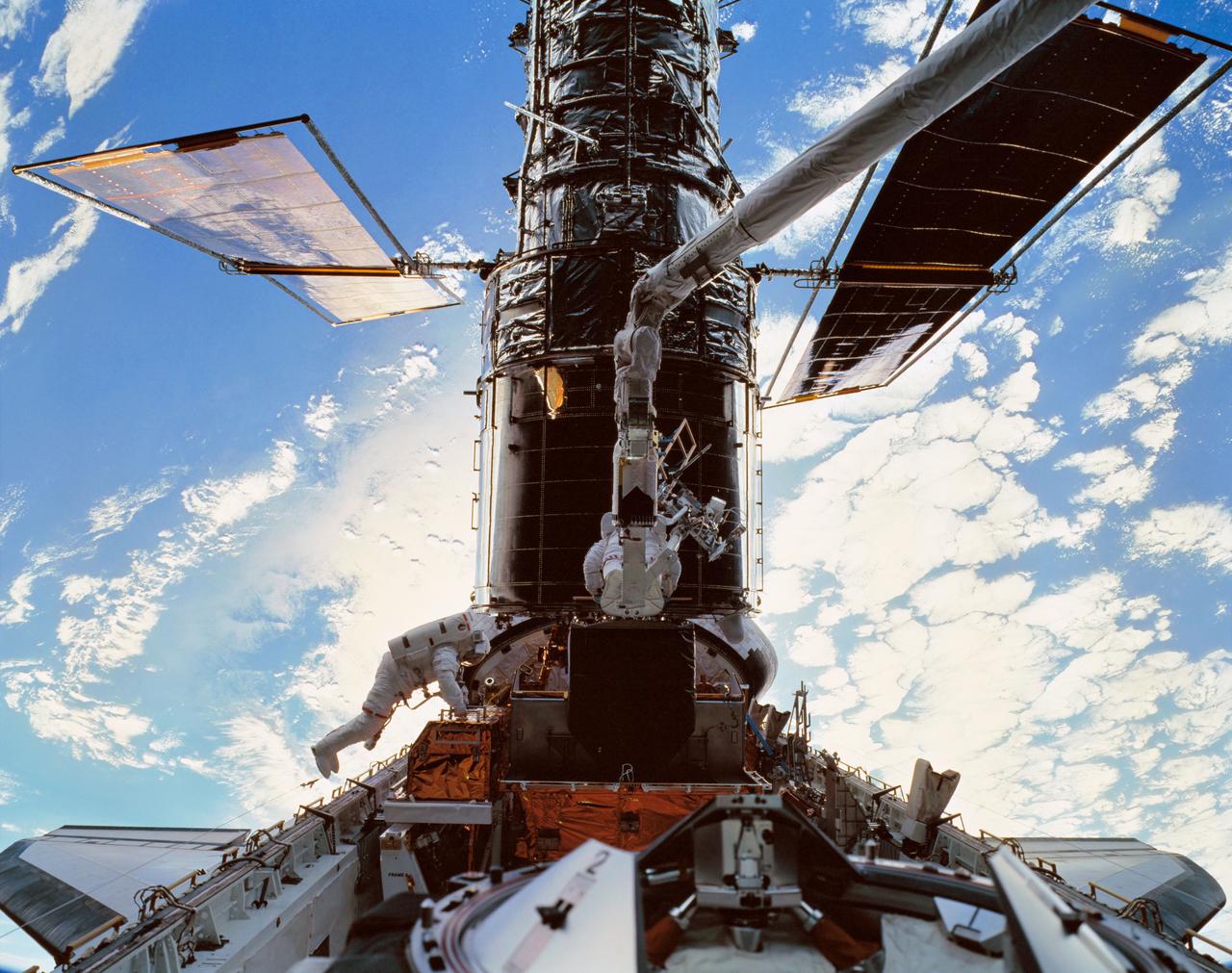

STS103-501-026 (19 - 27 December 1999) --- Astronauts C. Michael Foale, left, and Claude Nicollier (on Discovery's robotic arm) install a Fine Guidance Sensor (FGS) into a protective enclosure in the Shuttle’s payload bay. Foale and Nicollier performed the second of three space walks to service the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) on the STS-103 mission. A large format camera inside Discovery's cabin was used to record this high-resolution image, while the Shuttle was orbiting above ocean and clouds.
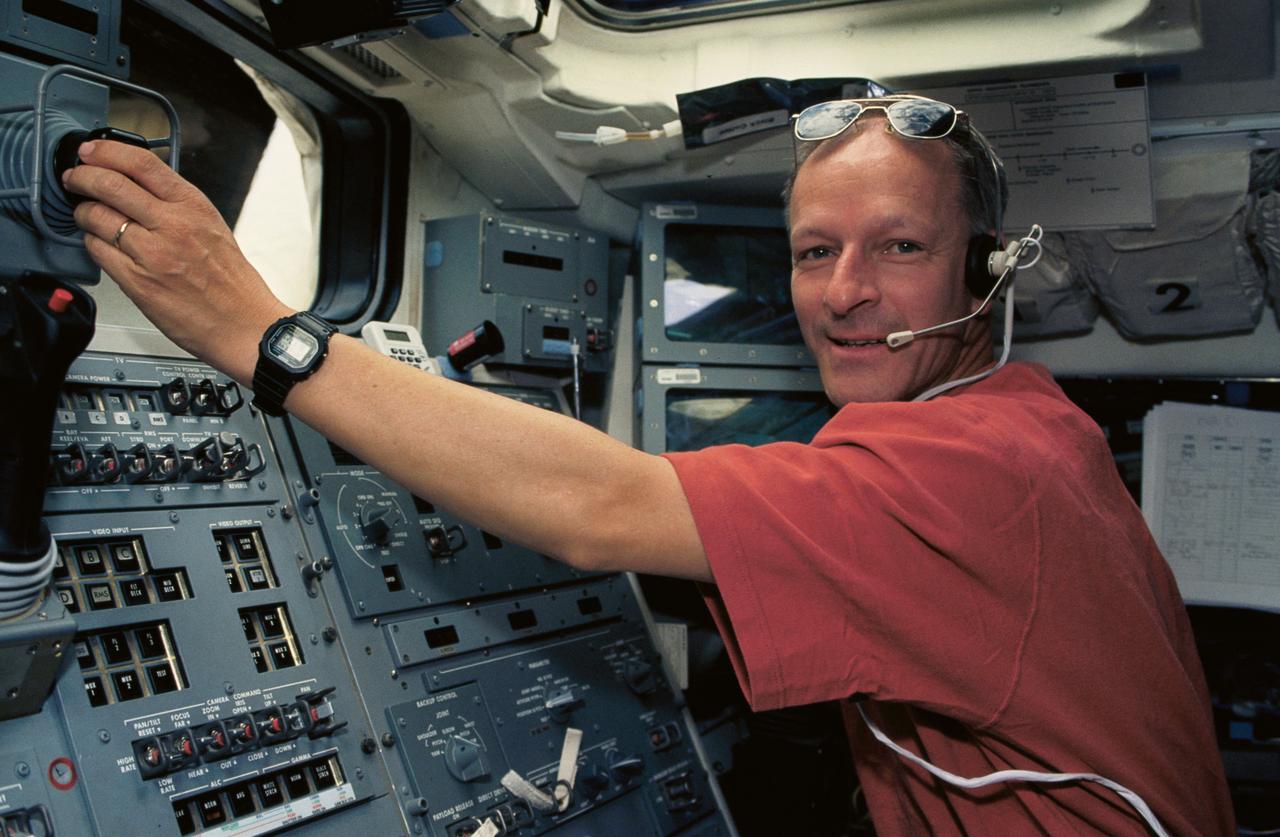

STS061-07-003 (4 Dec 1993) --- Swiss astronaut Claude Nicollier is pictured at the aft flight deck station he occupied during much of the time on NASA's STS-61 mission aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. Among Nicollier's responsibilities were the control of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) during operations with the Hubble Space Telescope (HST).
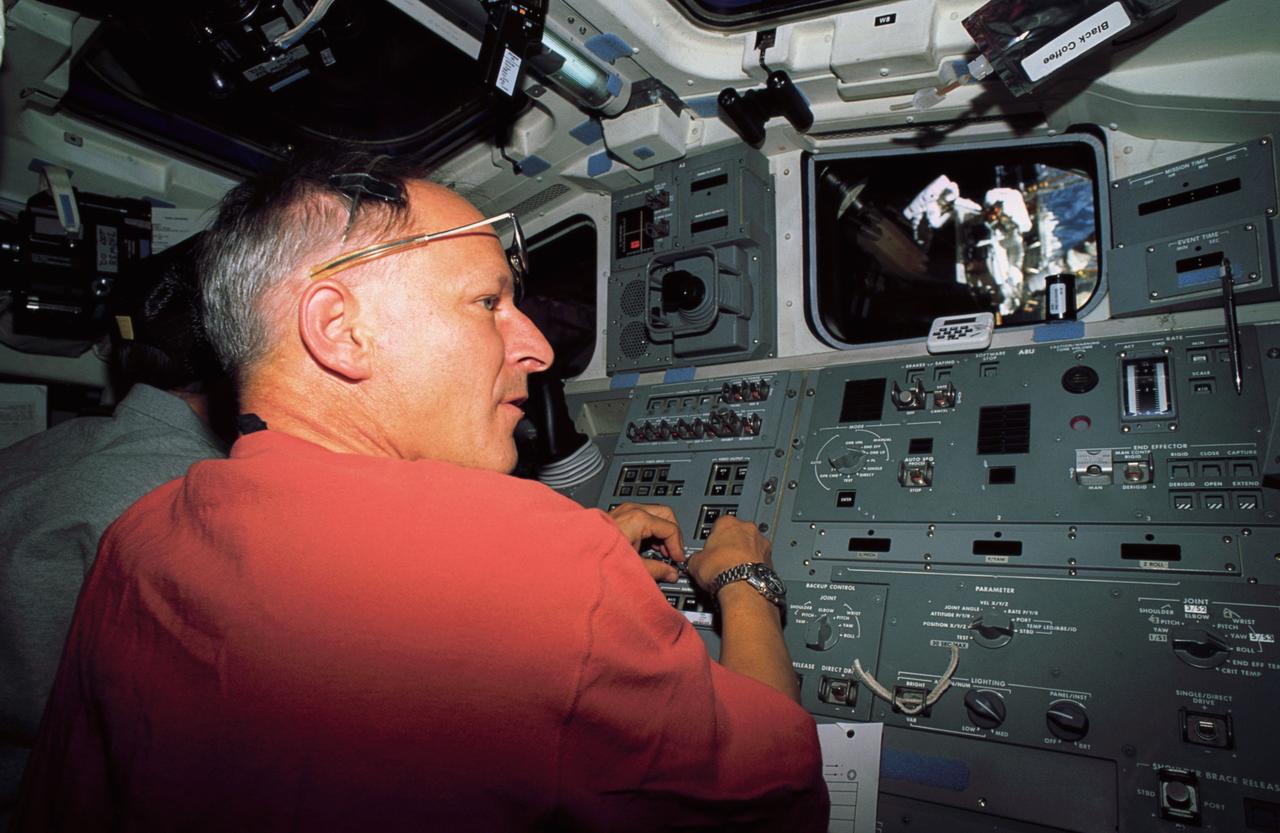

STS061-23-037 (2-13 Dec 1993) --- ESA astronaut Claude Nicollier, mission specialist, is stationed on the Space Shuttle Endeavour's flight deck during one of the five Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing space walks. The controls for the Remote Manipulator System (RMS), which played an important role in the space walks, are left of frame center. Two space walkers can be seen through the aft windows.
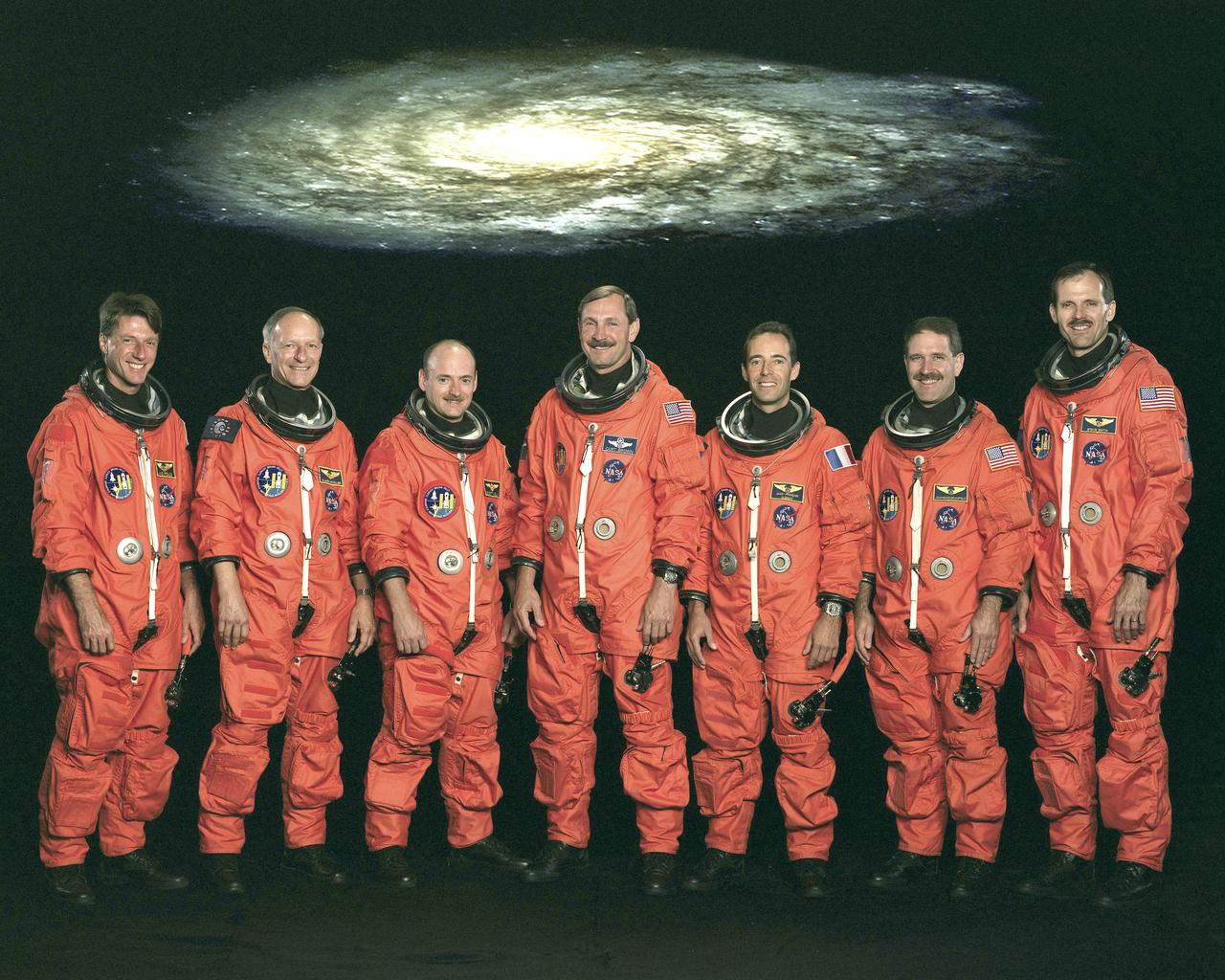

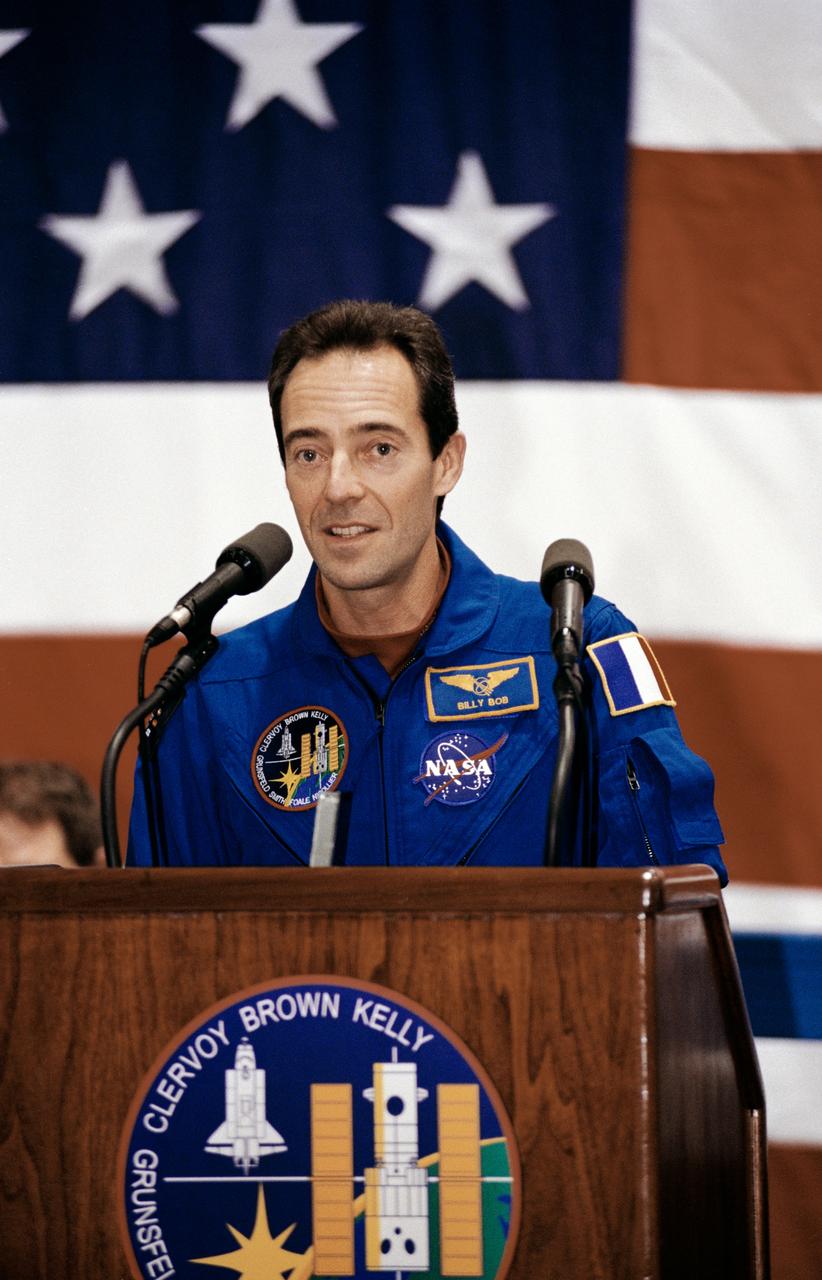
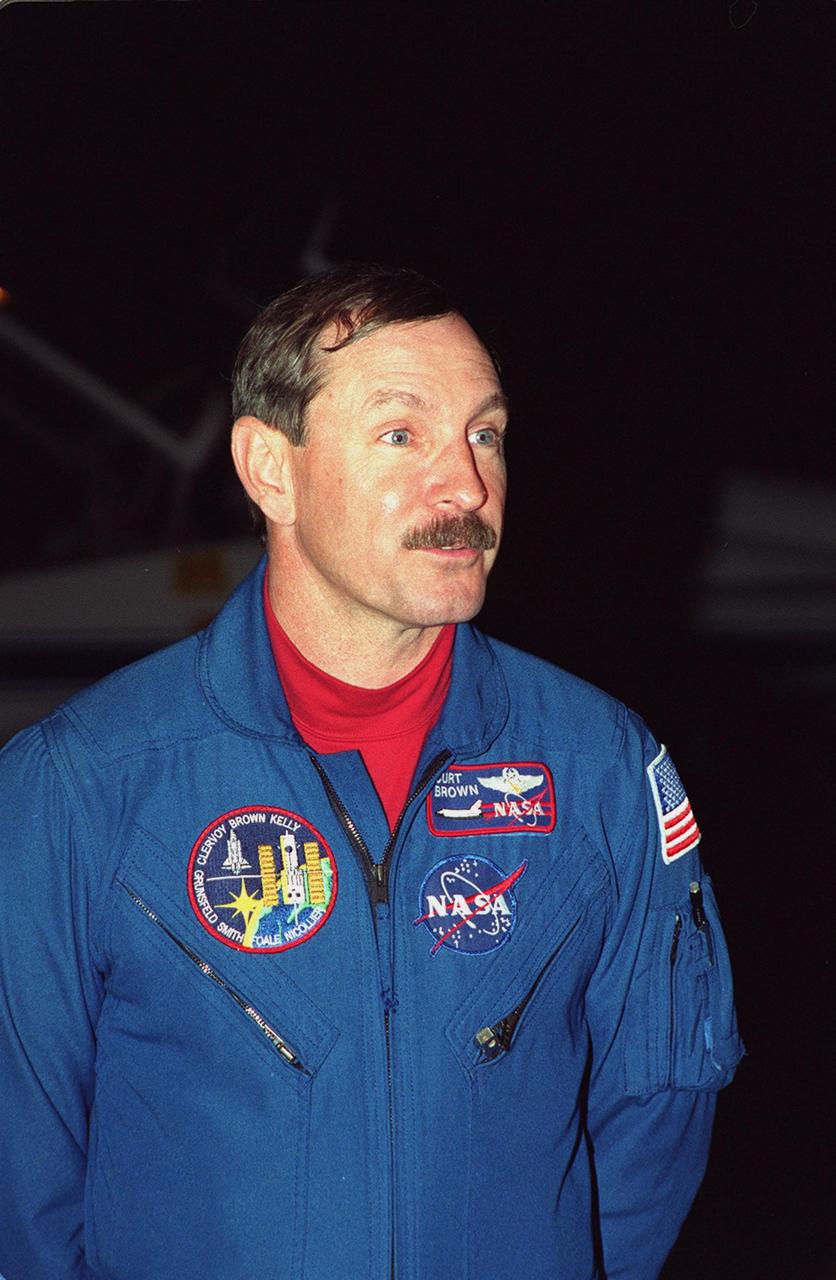
The STS-103 crew portrait includes (from left) C. Michael Foale, mission specialist; Claude Nicollier, mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA) ; Scott J. Kelly, pilot; Curtis L. Brown, commander; and mission specialists Jean-Francois Clervoy (ESA), John M. Grunsfeld, and Steven L. Smith. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery on December 19, 1999 at 6:50 p.m. (CST), the STS-103 mission served as the third Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission.
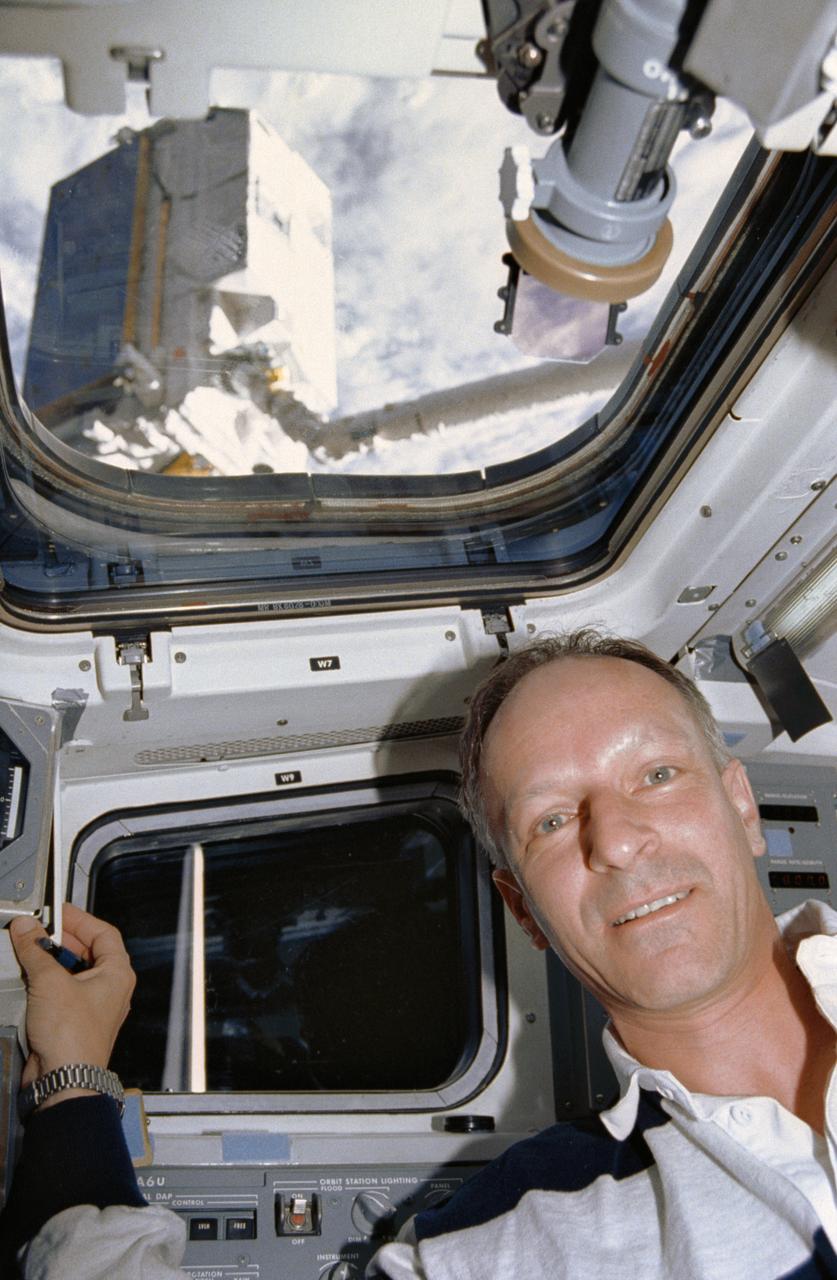

STS046-01-019 (1 Aug 1992) --- Claude Nicollier, representing the European Space Agency (ESA) onboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis for the mission, is seen on the flight deck during pre-deployment operations with the ESA's EURECA satellite. EURECA can be seen on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS). Nicollier was joined by five NASA astronauts and an Italian payload specialist for eight days aboard the Atlantis.
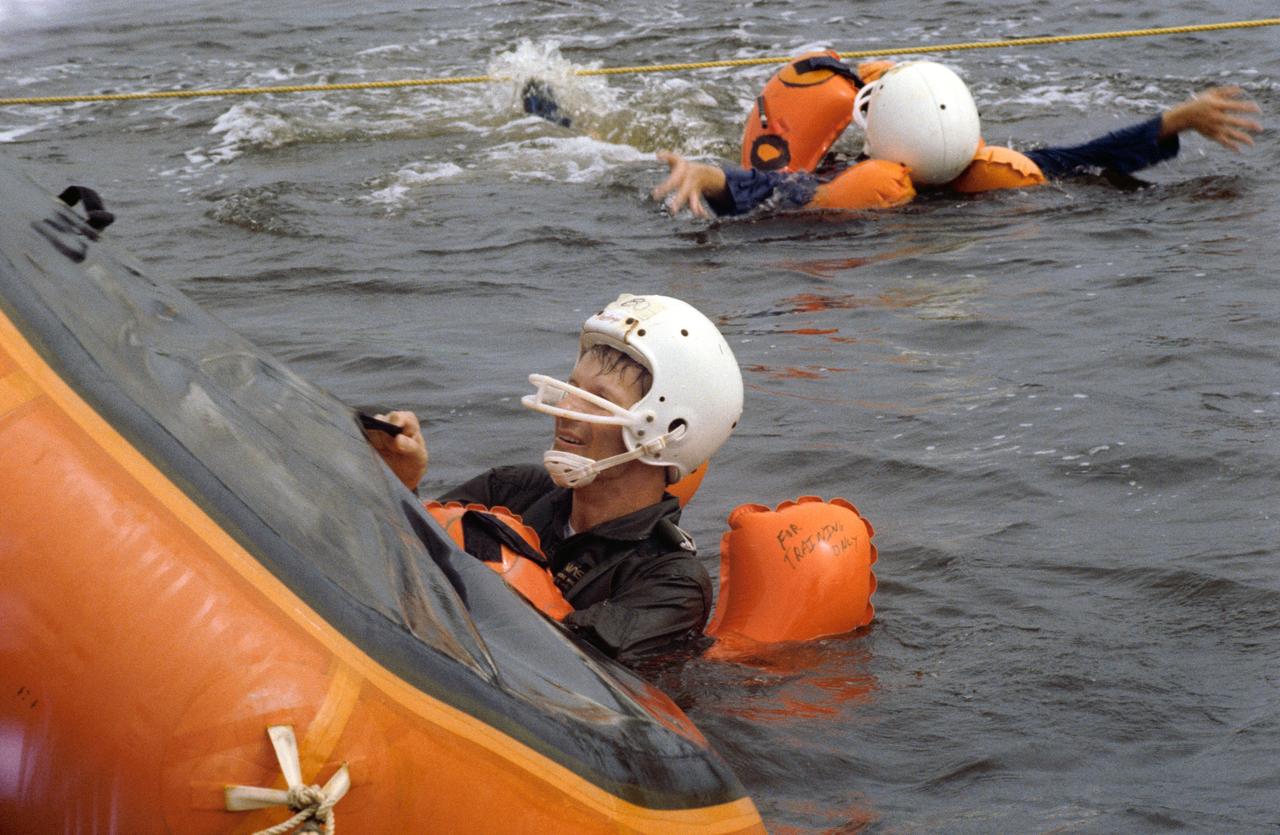

S80-38456 (13 Aug 1980) --- Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, one of two European scientists/Spacelab payload specialist candidates training in the United States along with 19 new NASA astronaut candidates, grabs onto the one-man life raft he is using during a water survival training school attended by several JSC personnel in mid-August. Six of the 19 candidates who had not had this type training before and the two Europeans were joined by a veteran astronaut, training personnel and two NASA physicians on the trip.
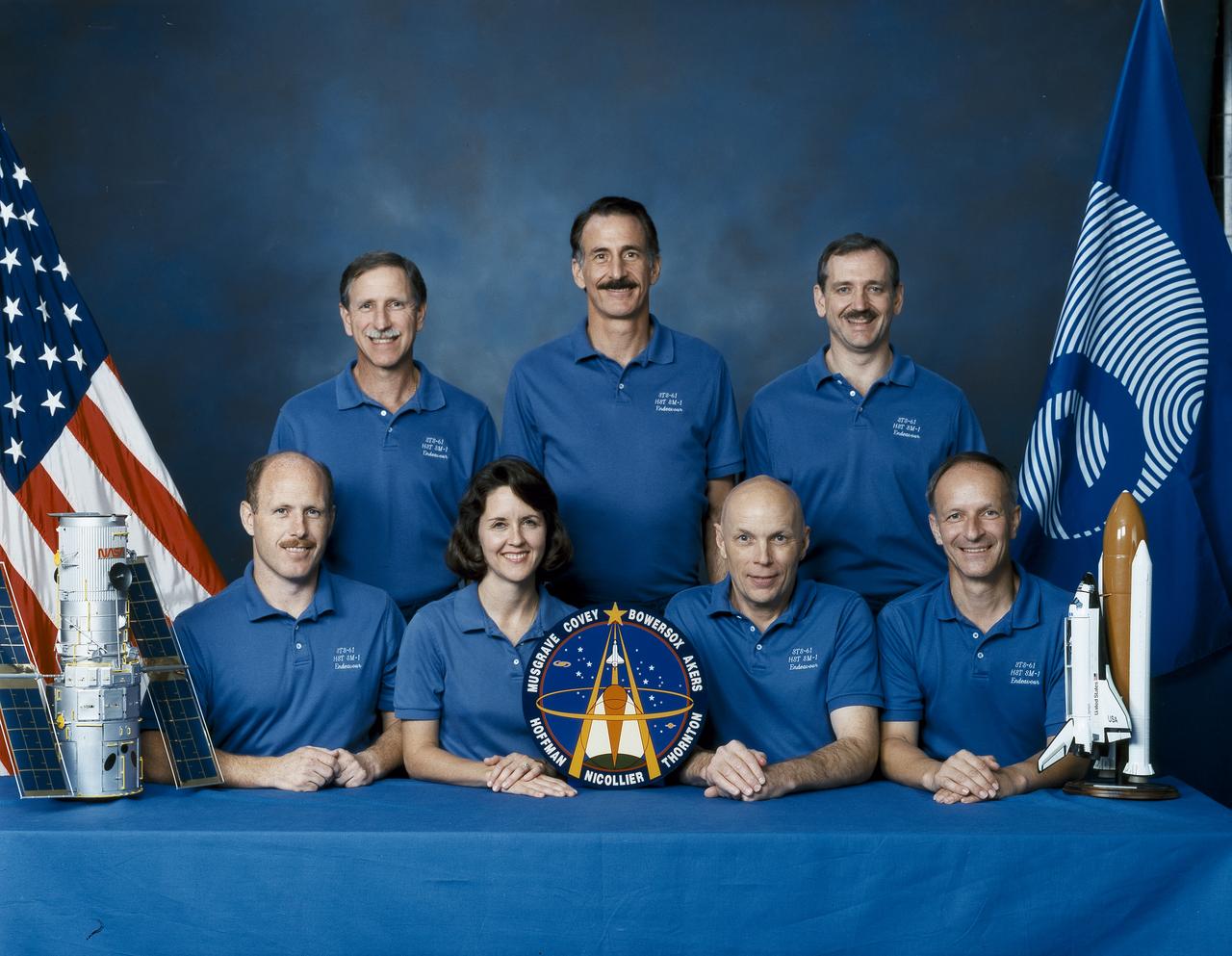

Astronauts included in the STS-61 crew portrait include (standing in rear left to right) Richard O. Covey, commander; and mission specialists Jeffrey A. Hoffman, and Thomas D. Akers. Seated left to right are Kenneth D. Bowersox, pilot; Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialist; F. Story Musgrave, payload commander; and Claude Nicollier, mission specialist. Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavor on December 2, 1993 at 4:27:00 am (EST), the STS-61 mission was the first Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission, and the last mission of 1993.
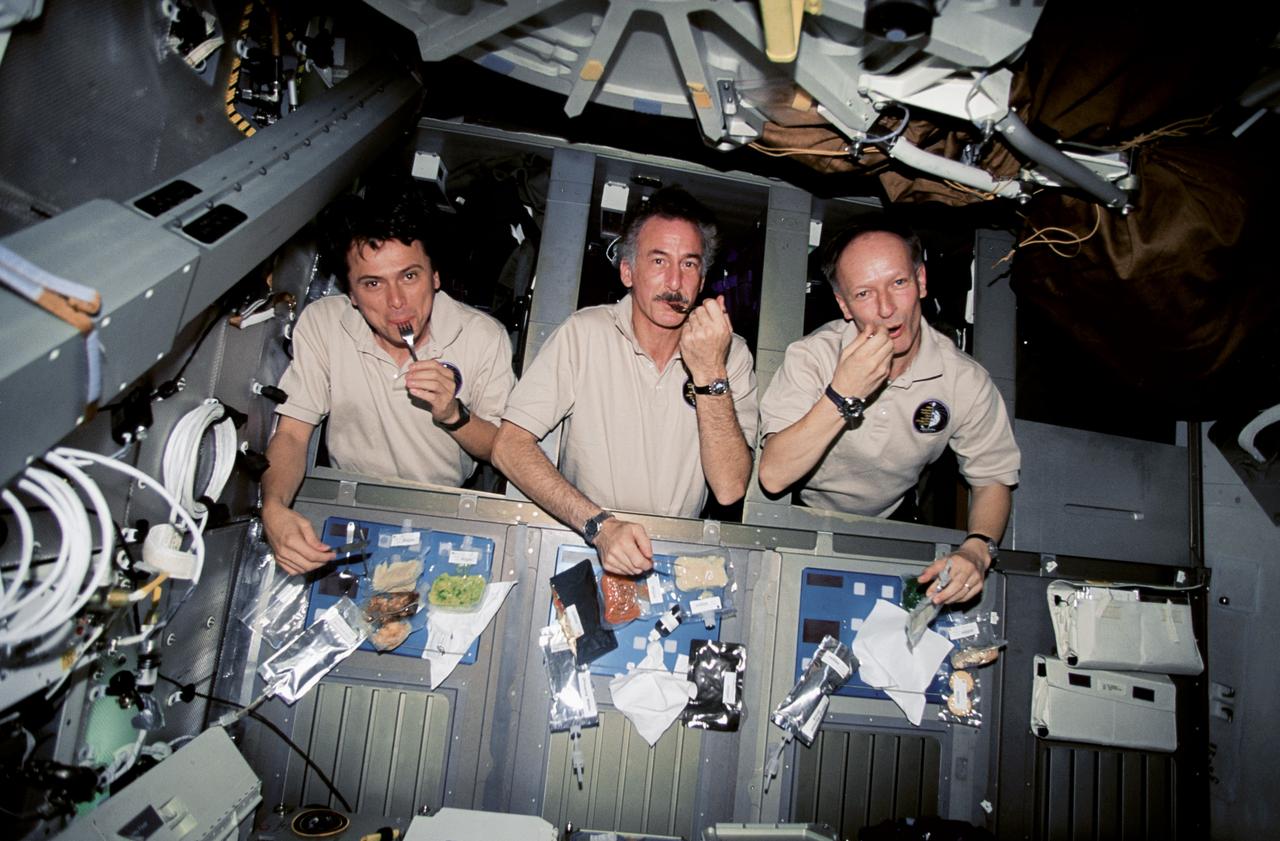

STS075-302-016 (22 Feb.-9 March 1996) --- Soon after reaching Earth orbit, the blue shift team set up what they referred to as a "formal" meal on the space shuttle Columbia's middeck. Left to right are astronauts Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, STS-75 payload commander; Jeffrey A. Hoffman and Claude Nicollier, both mission specialists. Hoffman later told a gathering of Johnson Space Center employees that the meal was accompanied by classical music. Photo credit: NASA or National Aeronautics and Space Administration
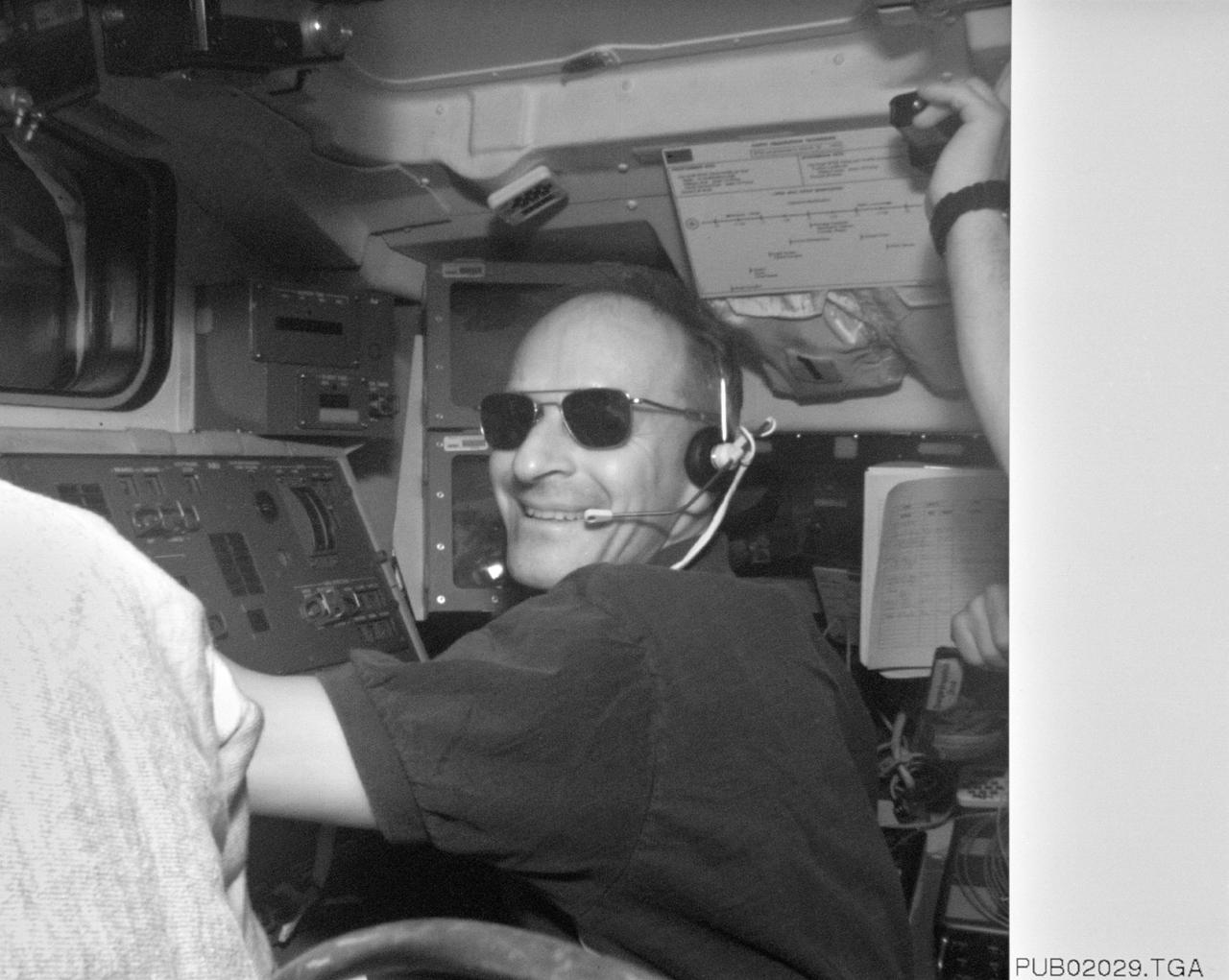

S61-E-006 (5 Dec 1993) --- The robot arm controlling work of Swiss scientist Claude Nicollier was photographed with an Electronic Still Camera (ESC), and down linked to ground controllers soon afterward. With the mission specialist's assistance, Endeavour's crew captured the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) on December 4, 1993. Four of the seven crew members will work in alternating pairs outside Endeavour's shirt sleeve environment to service the giant telescope. Electronic still photography is a relatively new technology which provides the means for a handheld camera to electronically capture and digitize an image with resolution approaching film quality. The electronic still camera has flown as an experiment on several other shuttle missions.
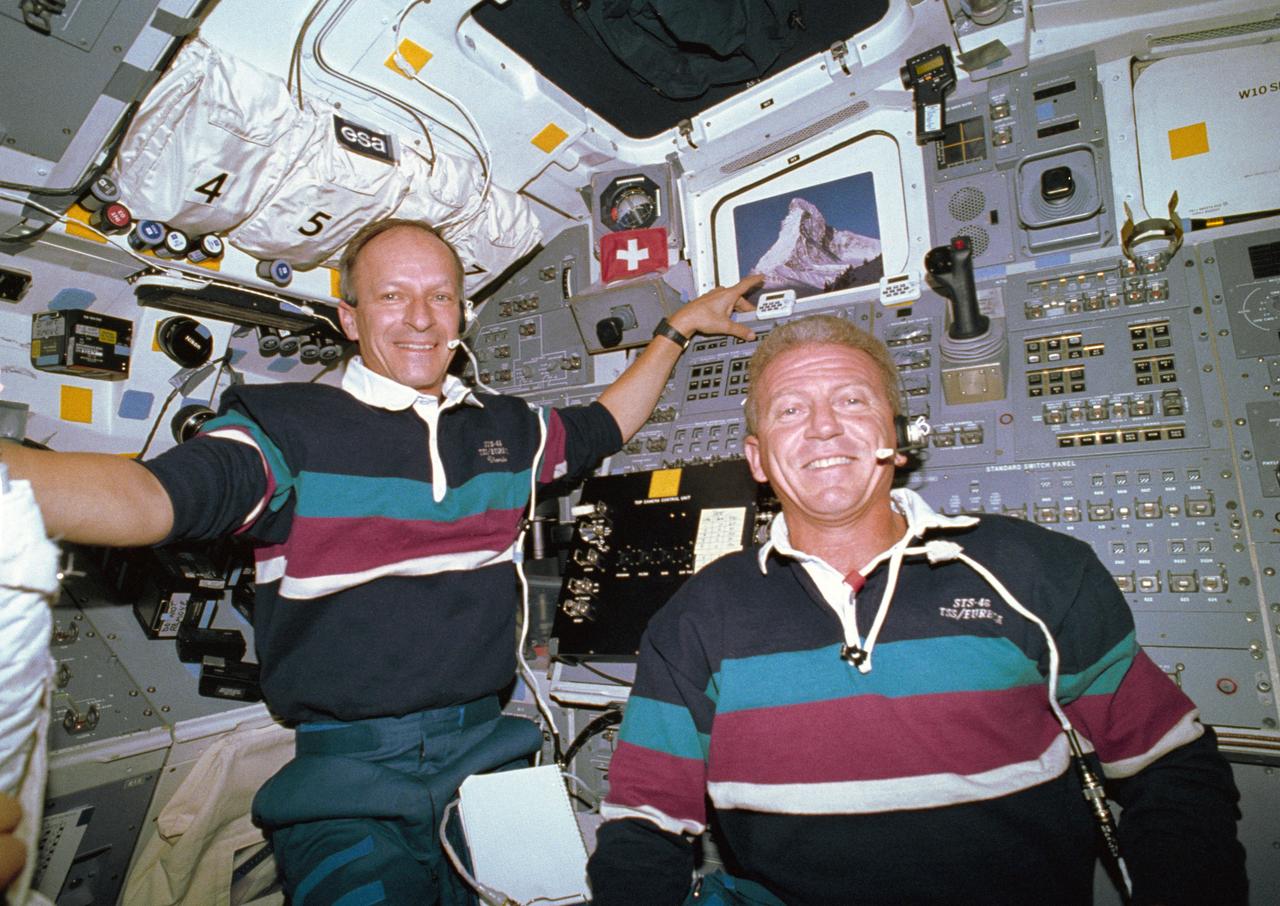

STS046-03-020 (7 Aug 1992) --- With their windows boarded up for specific intravehicular operations, two crew members pose for an in-space portrait. At left, Swiss scientist Claude Nicollier, representing the European Space Agency (ESA), steadies himself near a tiny Swiss flag and a photograph of the Matterhorn, a popular peak on the Swiss-Italian border. Astronaut Loren J. Shriver (right) served as mission commander for the eight-day flight.
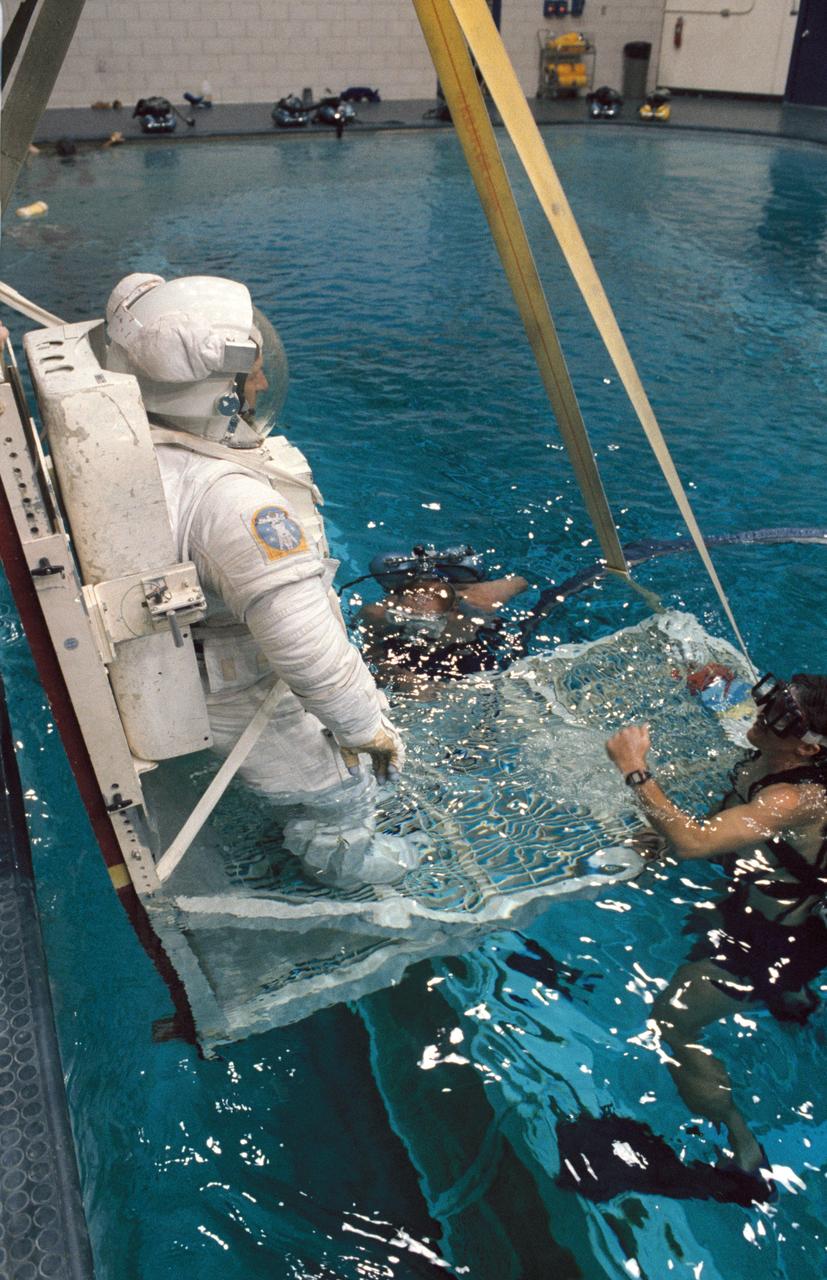
S87-44061 (25 Sept 1987) --- Dr. Claude Nicollier, equipped with a pressurized extravehicular mobility unit (EMU), is in the process of being submerged in the 25-ft. deep pool of JSC's weightless environment training facility (WET-F) for a familiarization session. Dr. Nicollier's suit is weighted to facilitate a neutrally buoyant condition. He is assisted by two SCUBA-equipped divers. Dr. Nicollier, a Swiss scientist assigned to the STS-46 mission as a payload specialist, first came to the Johnson Space Center in July 1980. Along with Dr. Wubbo Ockels, another European Scientist, Dr. Nicollier underwent survival training and other basic astronaut-type training alongside the 1980 class of astronaut candidates. Some photos in this series show Dr. Nicollier in an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU). This is for familiarization purposes only as the scientist is not scheduled for any extravehicular activity.
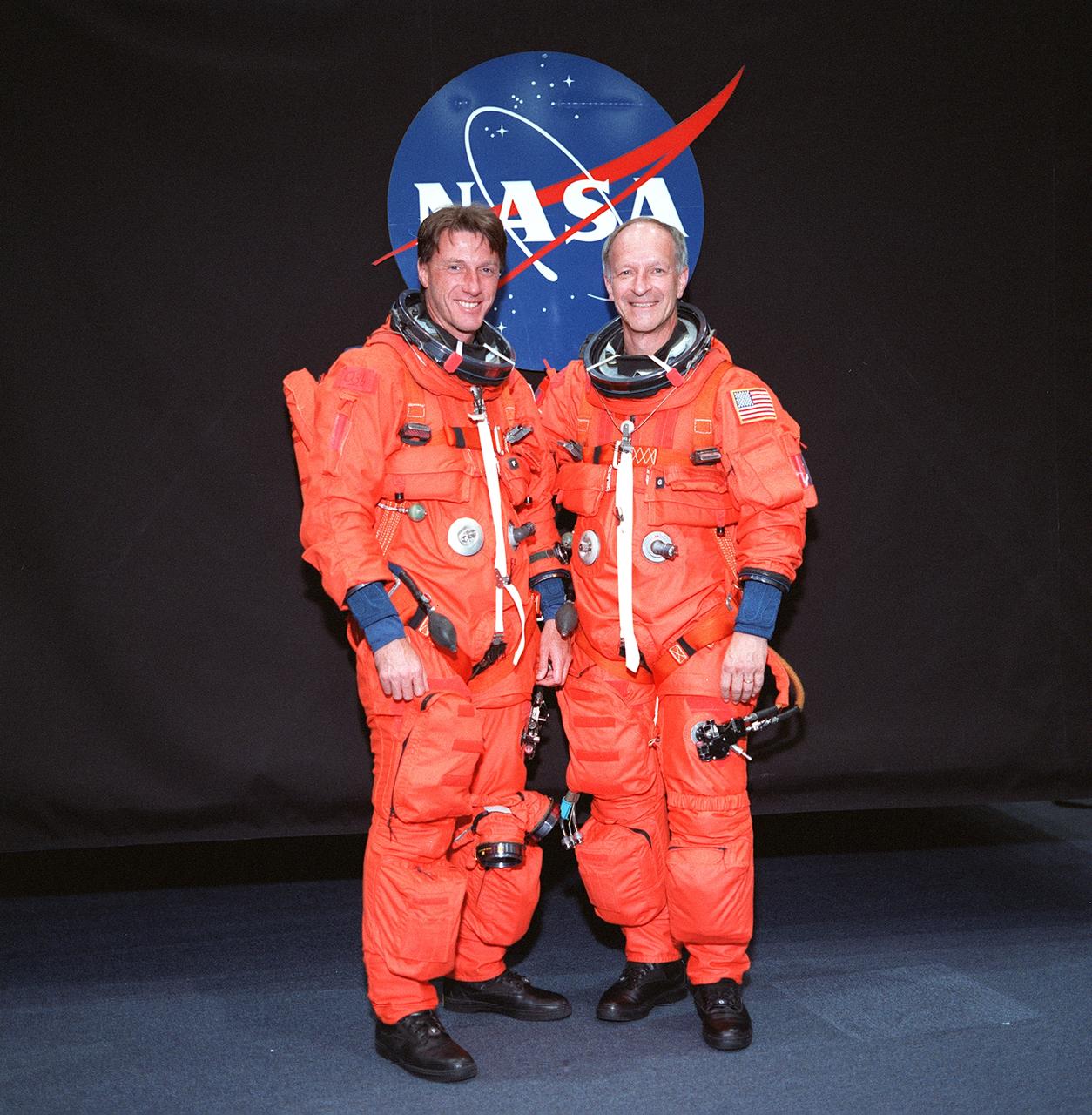

S99-8656 (24 May 1999) --- Astronauts C. Michael Foale, left, and Claude Nicollier, both assigned to EVA duty on the STS-103 crew's upcoming servicing visit to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), pose for an informal portrait in training versions of the launch and entry space garment. Nicollier is one of two astronauts on this crew who represent the European Space Agency (ESA).
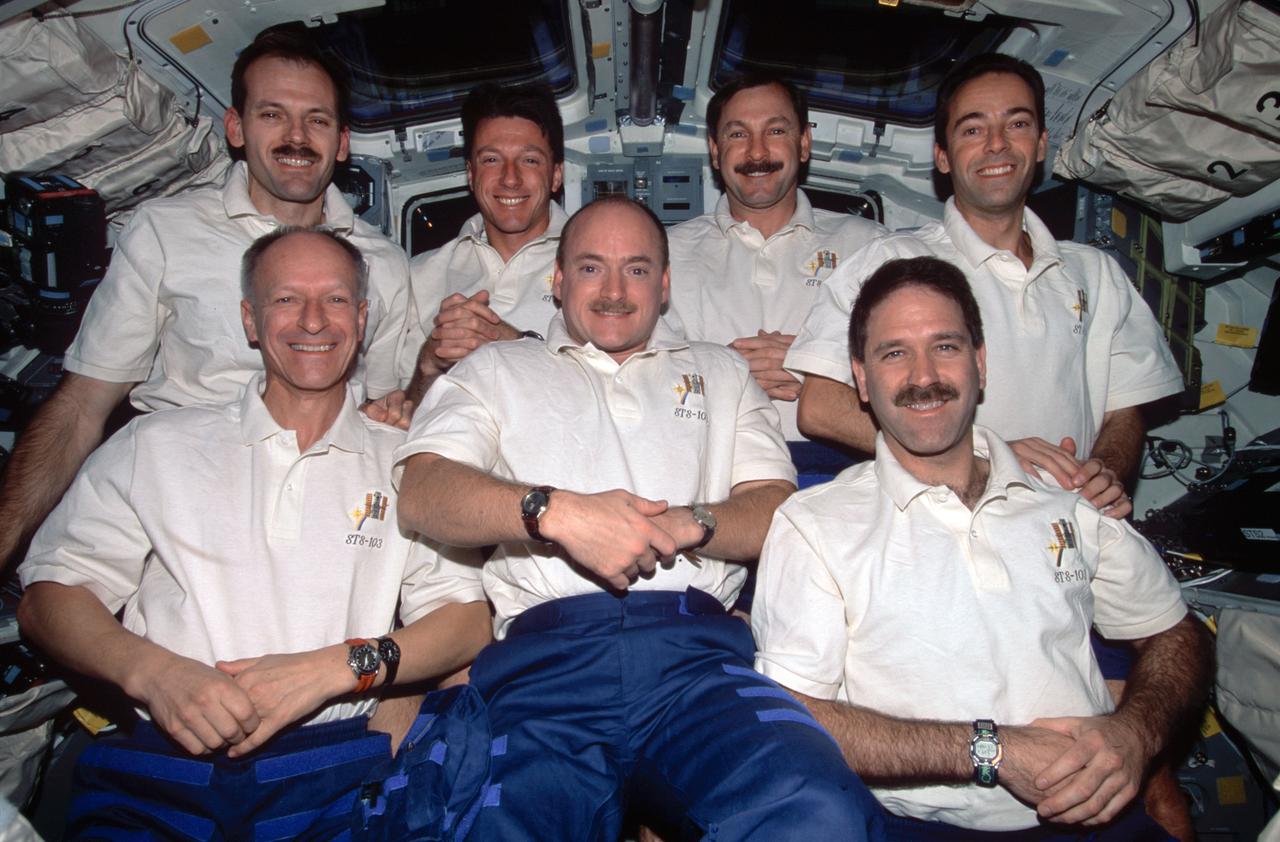

STS103-397-035 (19 - 27 December 1999) --- The seven astronauts aboard the Space Shuttle Discovery for NASA's third servicing visit to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) pose for the traditional inflight crew portrait..In front are, from left, astronauts Claude Nicollier, Scott J. Kelly and John M. Grunsfeld. Behind them are.astronauts Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale, Curtis L. Brown, Jr., and Jean-Francois Clervoy. Nicollier and Clervoy are astronauts from the European Space Agency (ESA).
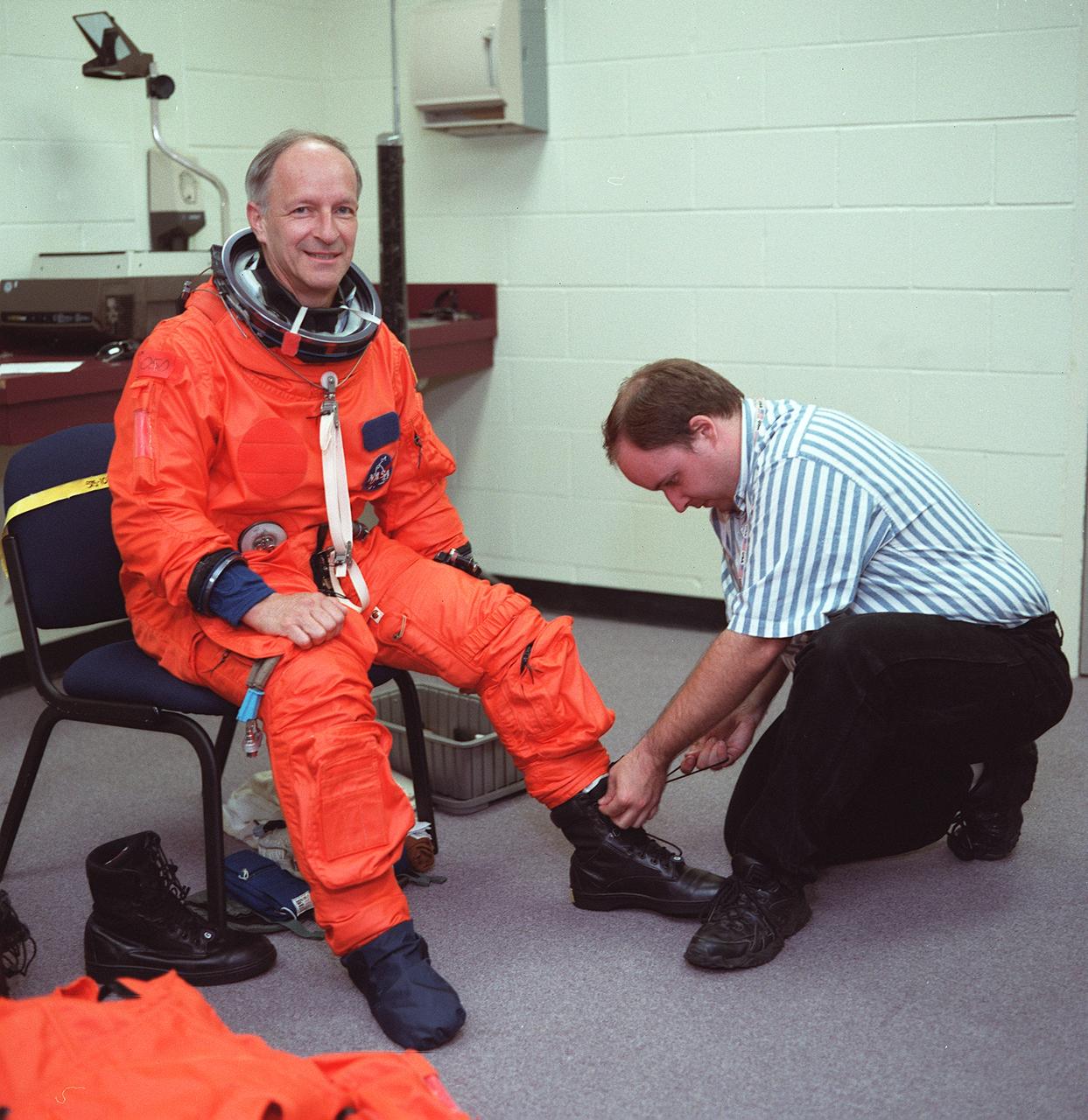

S99-08654 (24 May 1999) --- A suit technician assists astronaut Claude Nicollier, mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA), in readying for a session of emergency bailout training in the Systems Integration Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Nicollier, wearing a training version of the partial-pressure launch and entry garment, and his six STS-103 crew mates are currently in training for the third visit to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) since its 1990 deployment.
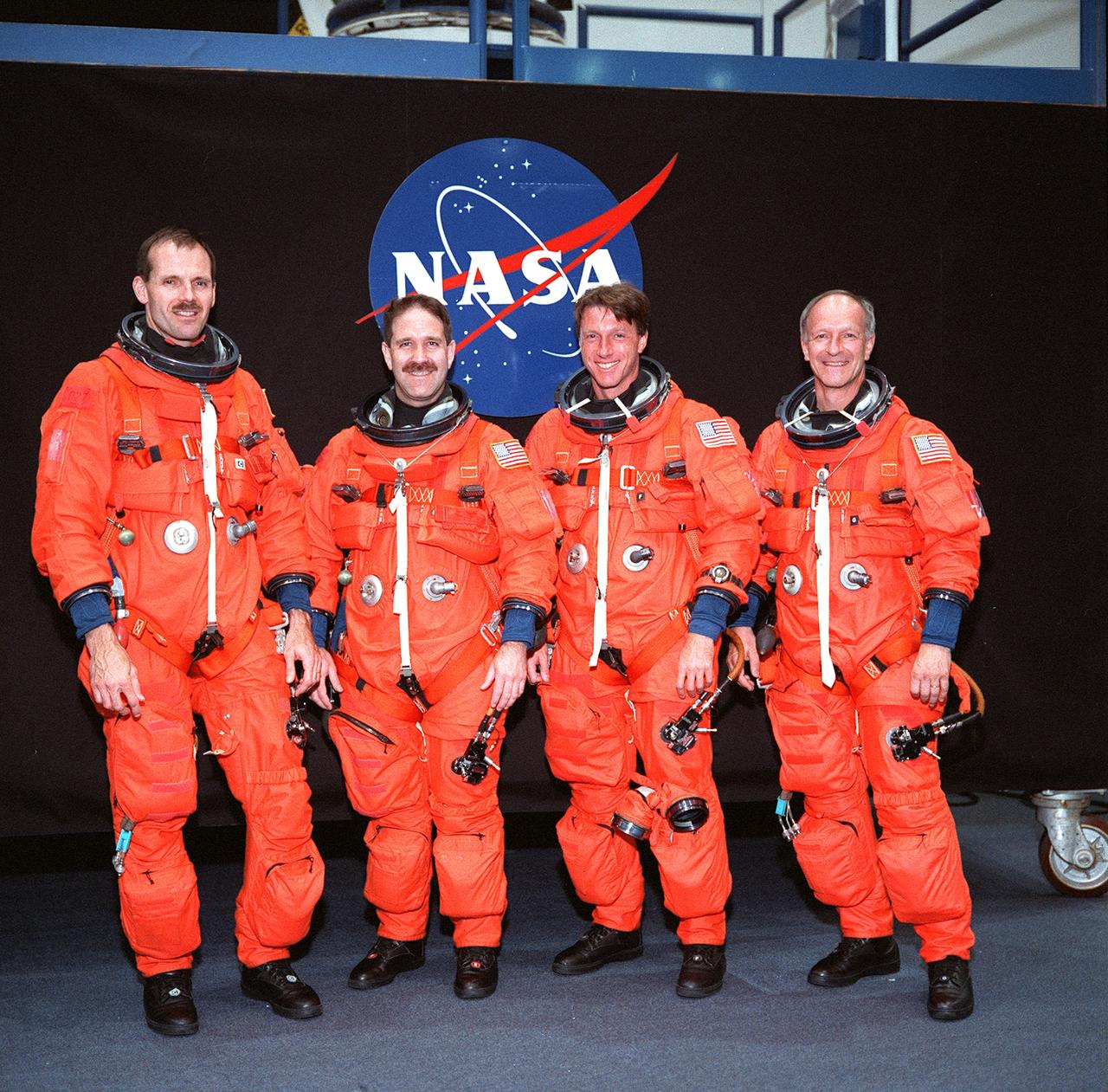

S99-08655 (24 May 1999) --- From the left, astronauts Steven L. Smith, John M. Grunsfeld, C. Michael Foale and Claude Nicollier, all mission specialists, pose for an informal portrait. The STS-103 crew members are wearing training versions of the shuttle partial-pressure launch and entry space garments. Nicollier is one of two astronauts on this flight who represents the European Space Agency (ESA).
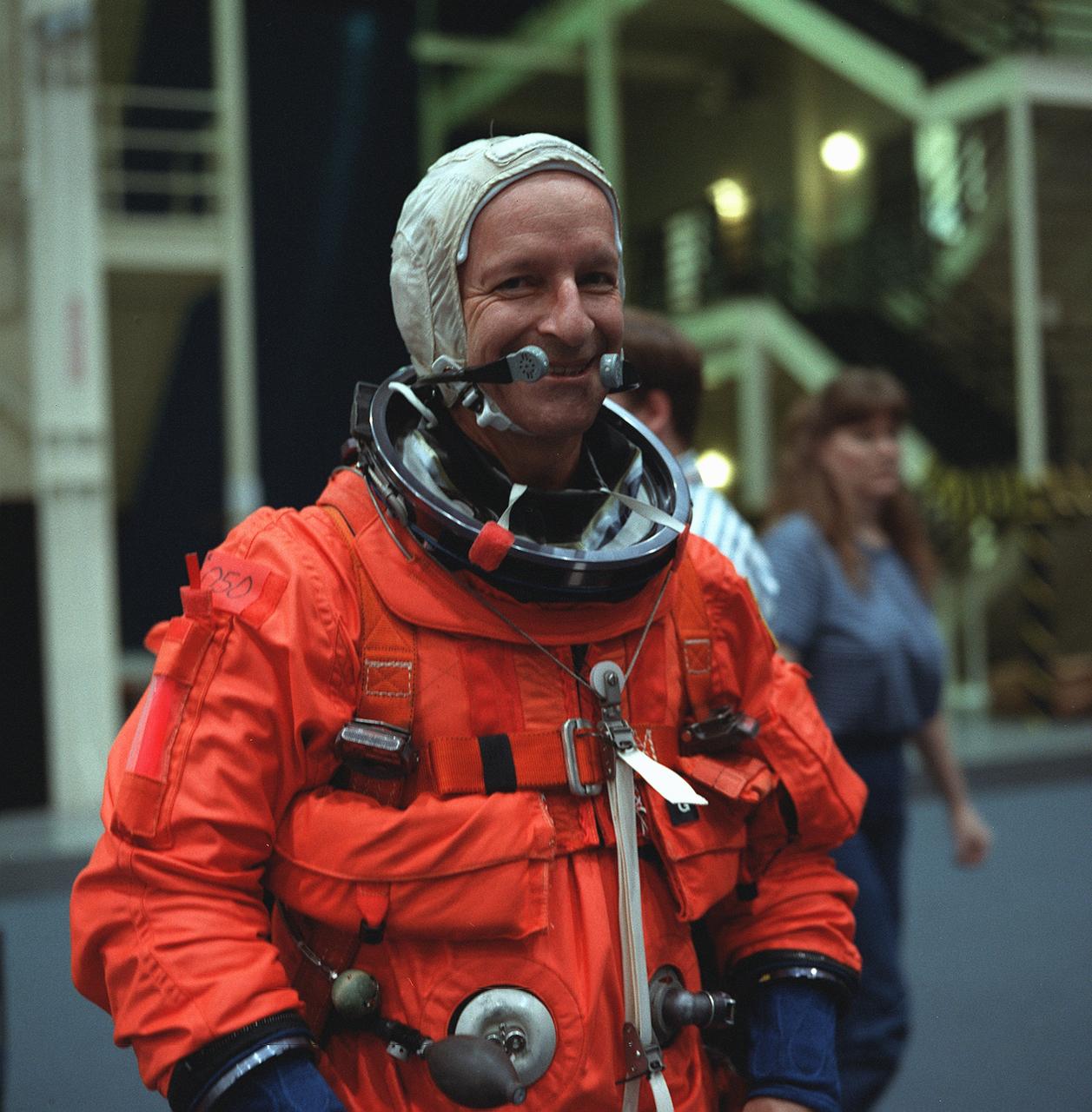

S99-08660 (24 May 1999)--- Astronaut Claude Nicollier, mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA), checks his communications gear prior to a session of emergency bailout training in the Systems Integration Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Nicollier, wearing a training version of the partial-pressure launch and entry garment, and his six STS-103 crew mates are currently in training for the third servicing visit to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) since its 1990 deployment.
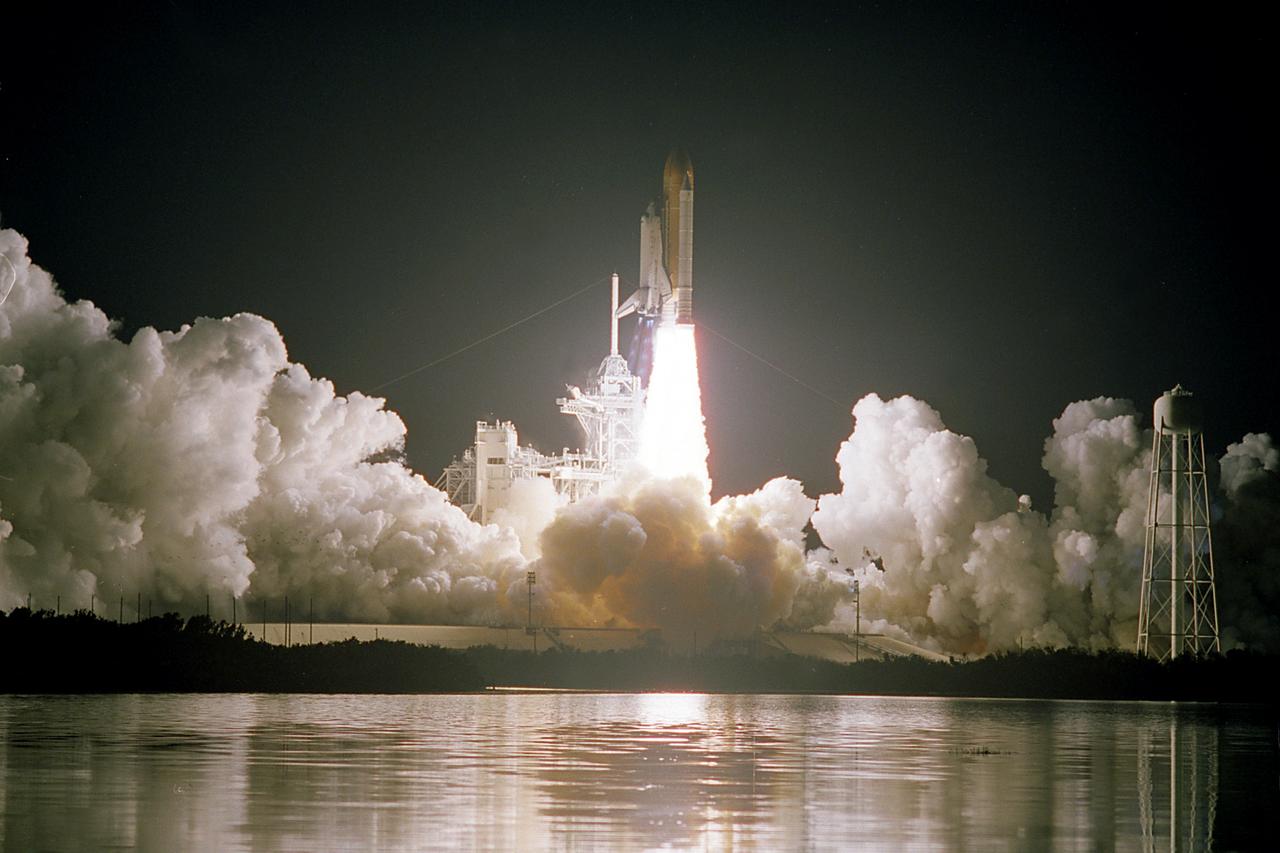

STS103-S-005 (19 December 1999) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery rises into the clear night sky to begin the 96th mission in the STS program. Liftoff occurred at 7:50 p.m. (EST), December 19, 1999, from Launch Pad 39B. Onboard were astronauts Curtis L. Brown, Jr., Scott J. Kelly, Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale, John M. Grunsfeld, Claude Nicollier and Jean-Francois Clervoy. Switzerland's Nicollier and France's Clervoy represent the European Space Agency (ESA).
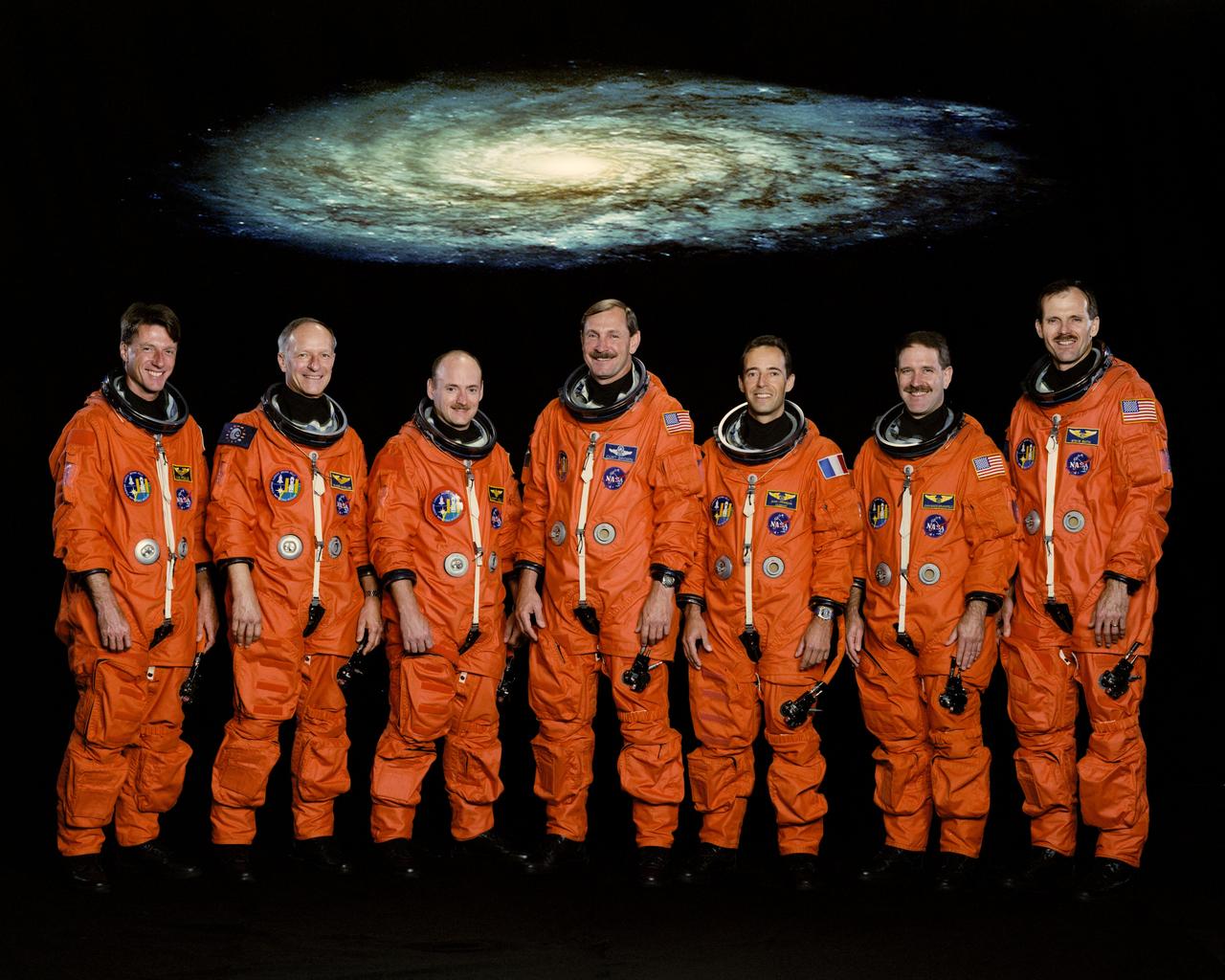

STS103-S-002 (August 1999) --- These seven astronauts have been assigned as crew members for NASA's third servicing mission to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). They are, from the left, astronauts C. Michael Foale, Claude Nicollier, Scott J. Kelly, Curtis L. Brown, Jr., Jean-Francois Clervoy, John M. Grunsfeld and Steven L. Smith. Brown and Kelly are commander and pilot, respectively. All the others are mission specialists (MS), with international MS Nicollier and Clervoy representing the European Space Agency (ESA).
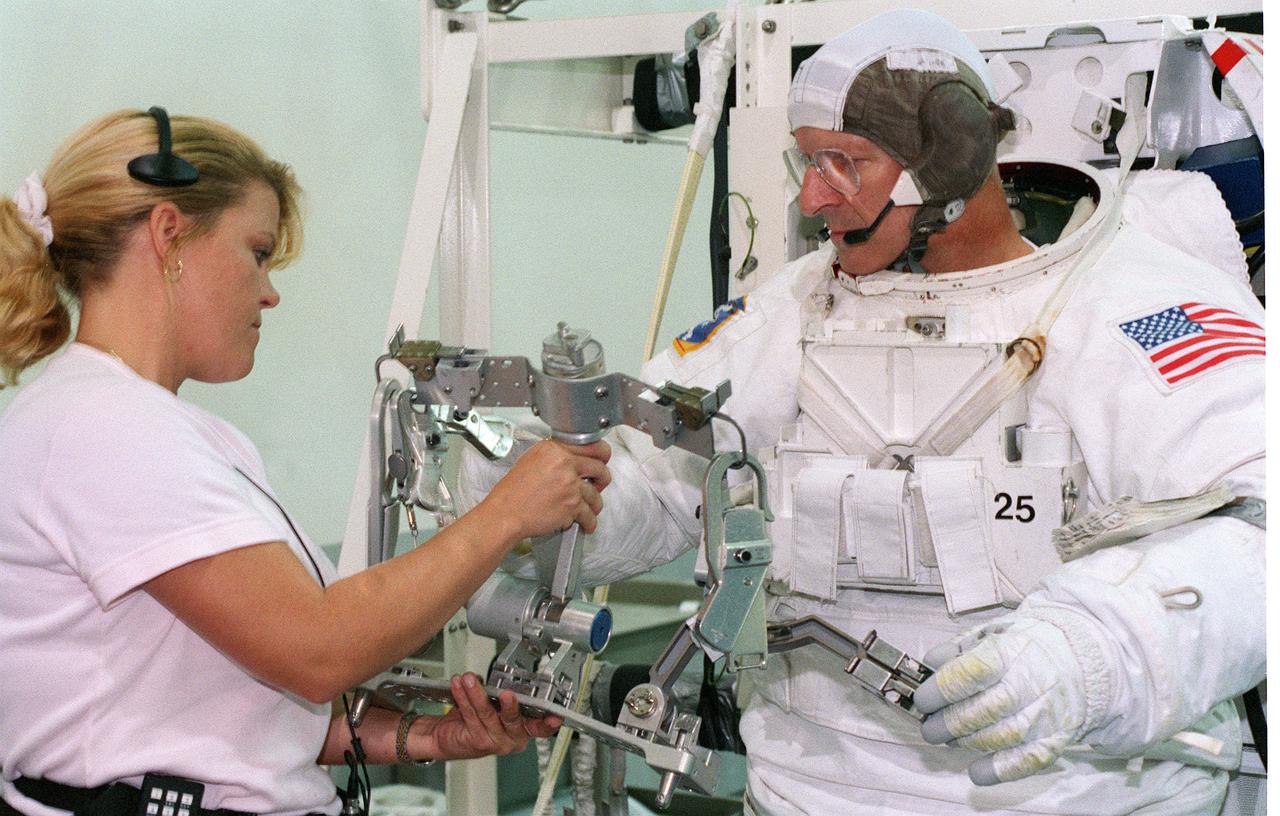

S99-08361 (26 July 1999) --- Astronaut Claude Nicollier, mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA), readies gear for an underwater rehearsal of STS-103 exctravehicular activity (EVA). Nicollier and other astronauts assigned to space walk duty are in training for EVA chores they will handle when they make the third servicing visit to the Earth-orbiting Hubble Space Telescope (HST) since its deployment in April 1990.
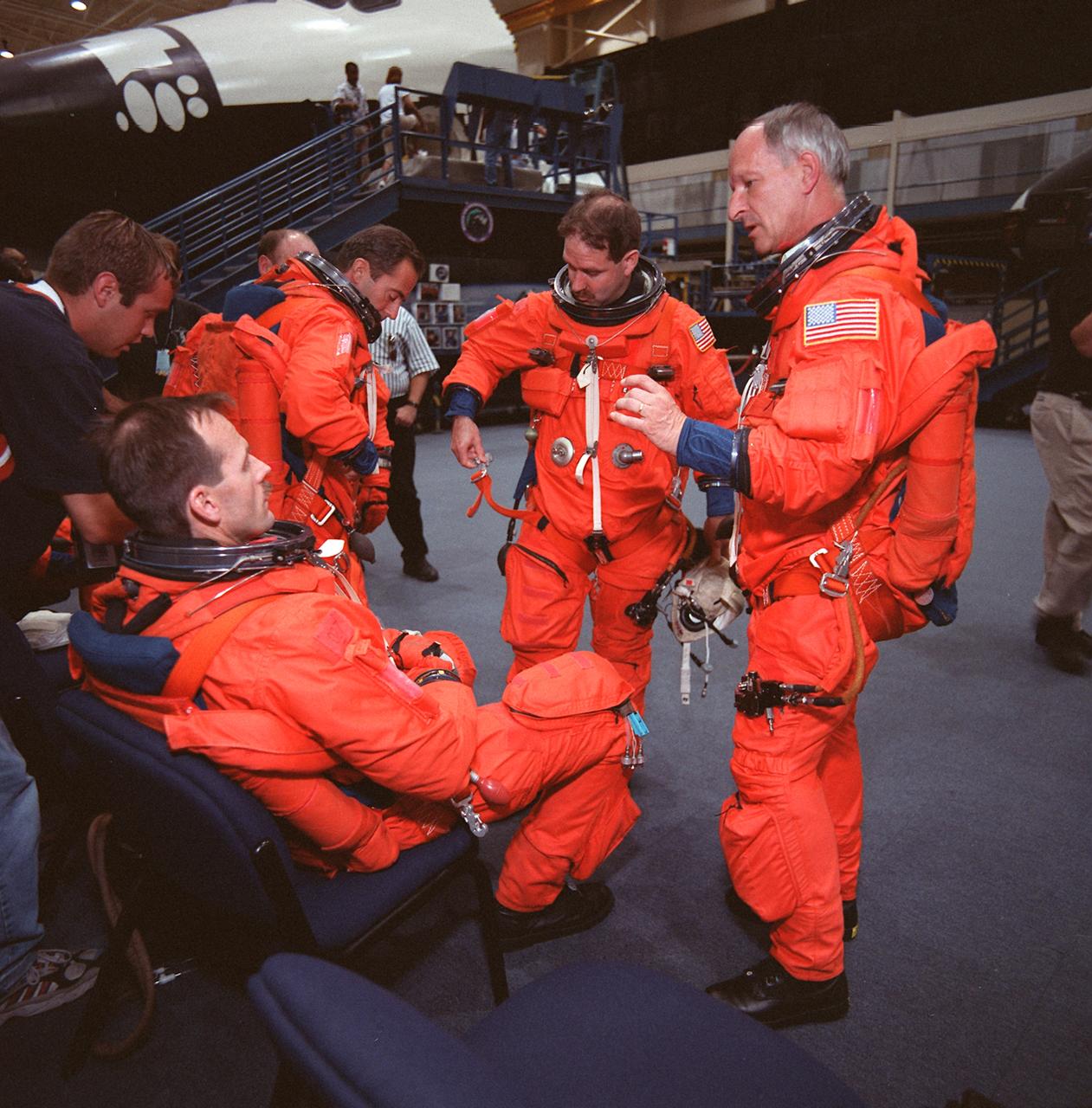

S99-08668 --- Four members of the STS-103 crew prepare their launch and entry suits for a training session on emergency bailout procedures in the Johnson Space Center's Systems Integration Facility. Astronaut Steven L. Smith is seated in the foreground. Others pictured are astronauts Jean-Francois Clervoy, John M. Grunsfeld and Claude Nicollier, all mission specialists. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency (ESA). One of two Crew Compartment Trainers (CCT) is in the background.

S99-16052 (28 December 1999) --- Astronaut Claude Nicollier, a mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA), is greeted at Ellington Field by a sign-bearing group.
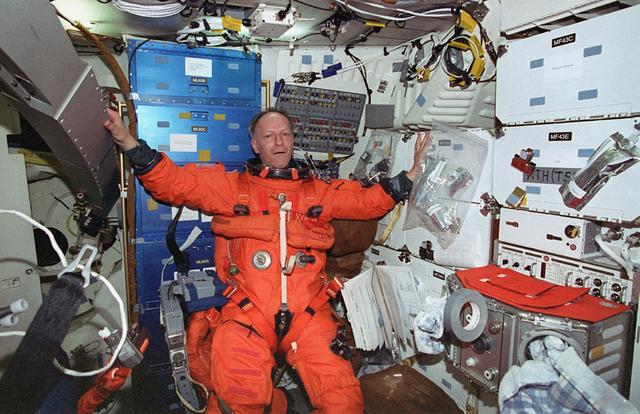

Onboard photo of space shuttle Columbia (STS-75) Swiss crewmember Claude Nicollier with a view of Middeck Glovebox (MGBX) which provides a general-purpose enclosed workspace to carry out small-scale microgravity science experiments.
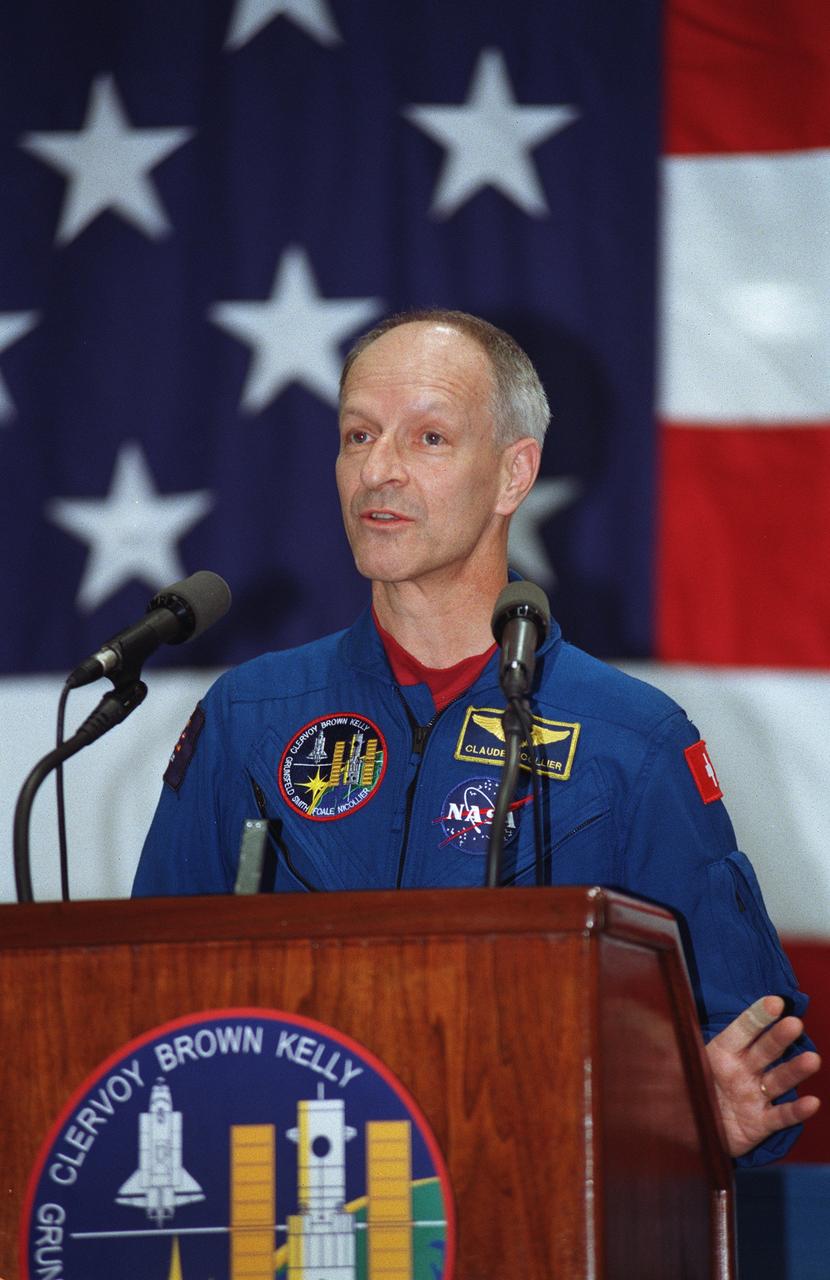

S99-16059 (28 December 1999) --- Astronaut Claude Nicollier, mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA), speaks at crew return ceremony at Ellington Field.
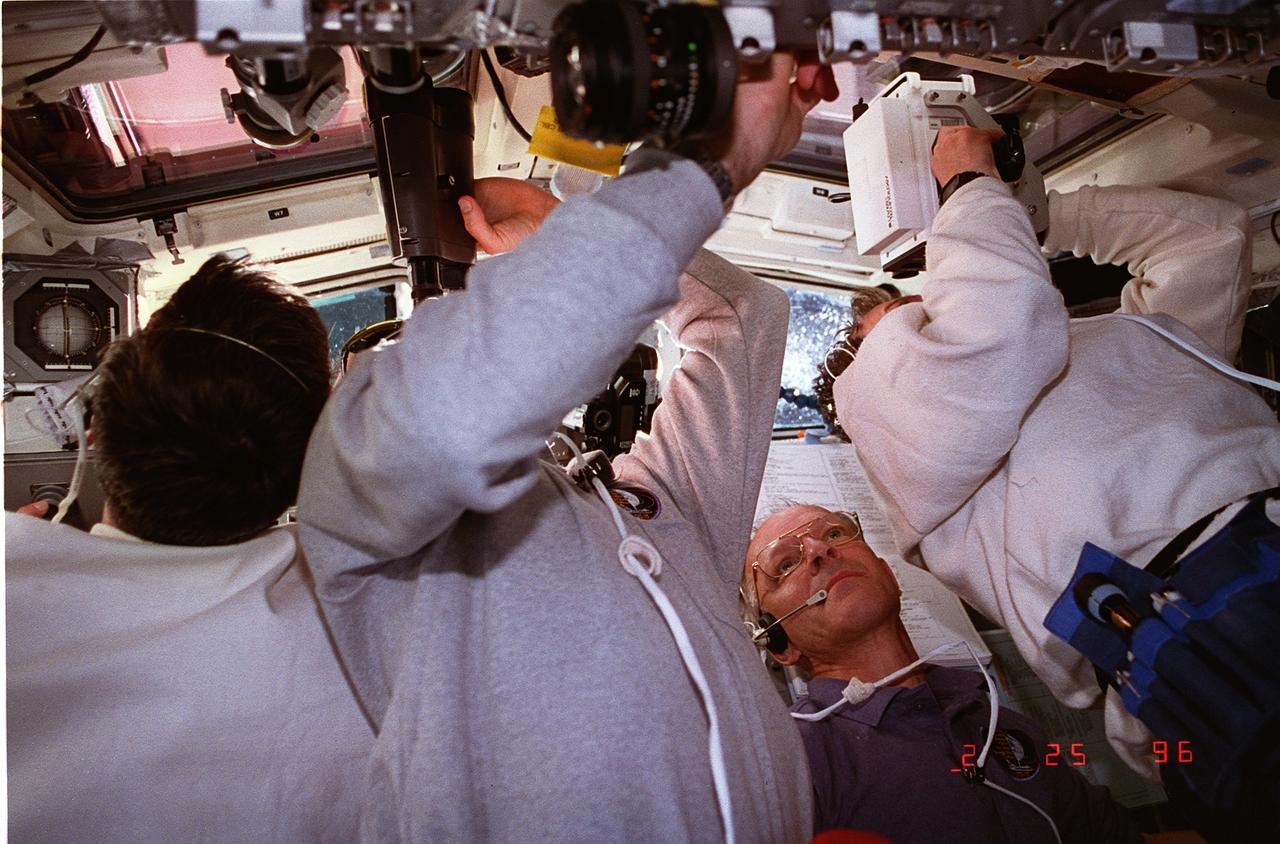

STS075-328-026 (25 Feb. 1996) --- Astronaut Claude Nicollier is the only clearly identifiable crewmember in this scene on the aft flight deck, captured during the busy chores associated with deployment of the Tethered Satellite System (TSS). The seven member crew was launched aboard the space shuttle Columbia on Feb. 22, 1996, and landed on March 9, 1996. Crewmembers were Andrew M. Allen, mission commander; Scott J. Horowitz, pilot; Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, payload commander; and Maurizio Cheli, European Space Agency (ESA); Jeffrey A. Hoffman and Nicollier, ESA, all mission specialists; along with payload specialist Umberto Guidoni of the Italian Space Agency (ASI).
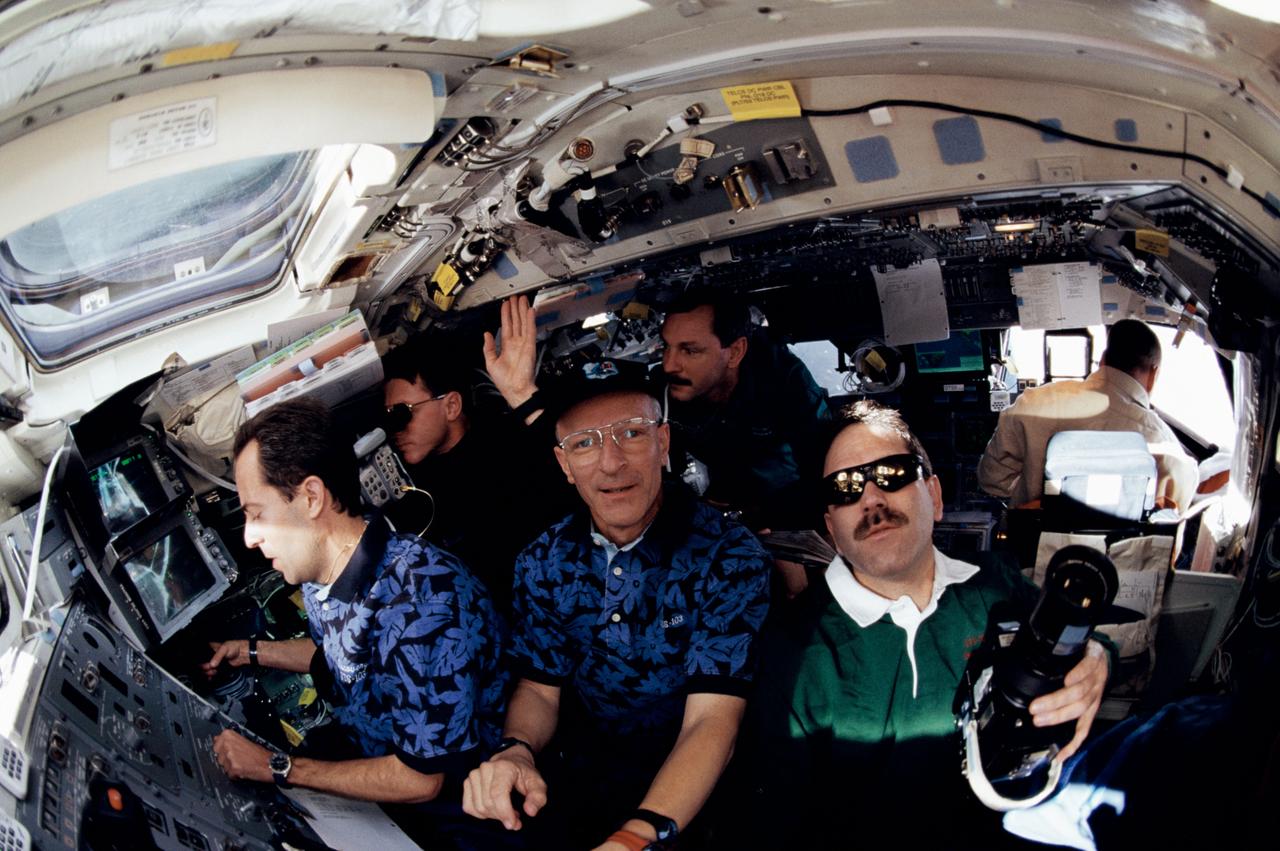

STS103-375-019 (19-27 December 1999) ---.Six members of the STS-103 crew are seen in this "fish-eye" lens scene taken on Discovery's flight deck during the deployment of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). From left are astronauts Jean-Francois Clervoy, C. Michael Foale, Claude Nicollier, Curtis L. Brown, Jr., John M. Grunsfeld and Scott J. Kelly. Brown and Kelly are commander and pilot, respectively. All the others are mission specialists, with international MS Nicollier and Clervoy representing the European Space Agency (ESA). Astronaut Steven L. Smith, payload commander, took the photo.
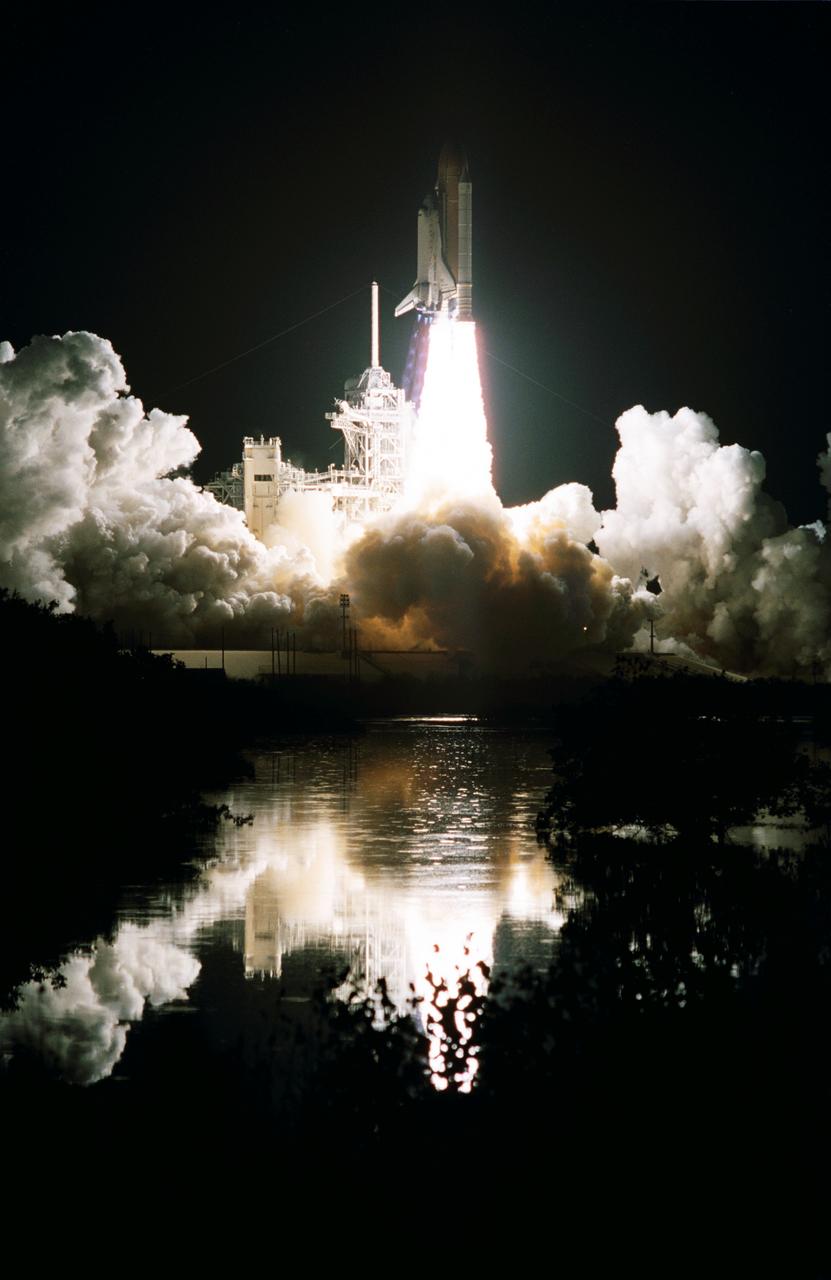

STS103-S-006 (19 December 1999) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery, reflected in nearby water, lifts off into the clear night sky to begin the 96th mission in the STS program. Liftoff occurred at 7:50 p.m. (EST), December 19, 1999, from Launch Pad 39B. Onboard were astronauts Curtis L. Brown, Jr., Scott J. Kelly, Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale, John M. Grunsfeld, Claude Nicollier and Jean-Francois Clervoy. Switzerland's Nicollier and France's Clervoy represent the European Space Agency (ESA).
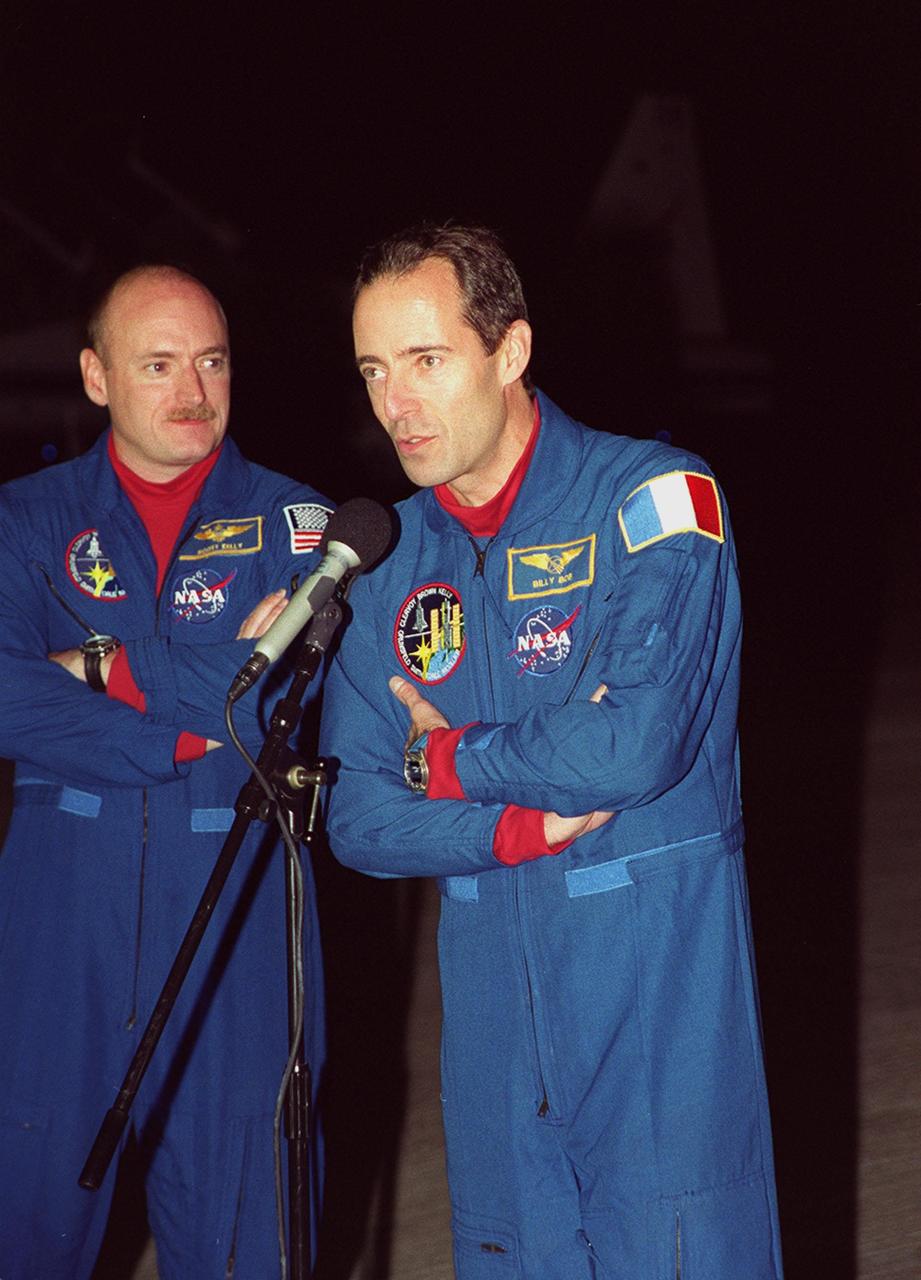

STS-103 Mission Specialist Jean-François Clervoy of France (at microphone) greets the media at the Shuttle Landing Facility as Pilot Scott J. Kelly looks on. The crew arrived at KSC aboard T-38 jets to make final preparations for their launch. The other STS-103 crew members are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr. and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), and Claude Nicollier of Switzerland. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. The mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope a third time, is scheduled for launch Dec. 11 at 12:13 a.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-103 Mission Specialist Claude Nicollier of Switzerland shows his pleasure at being at Kennedy Space Center to make final preparations for his launch. He is accompanied by the other STS-103 crew members: Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy both represent the European Space Agency. The STS-103 mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope a third time, is scheduled for launch Dec. 11 at 12:13 a.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B
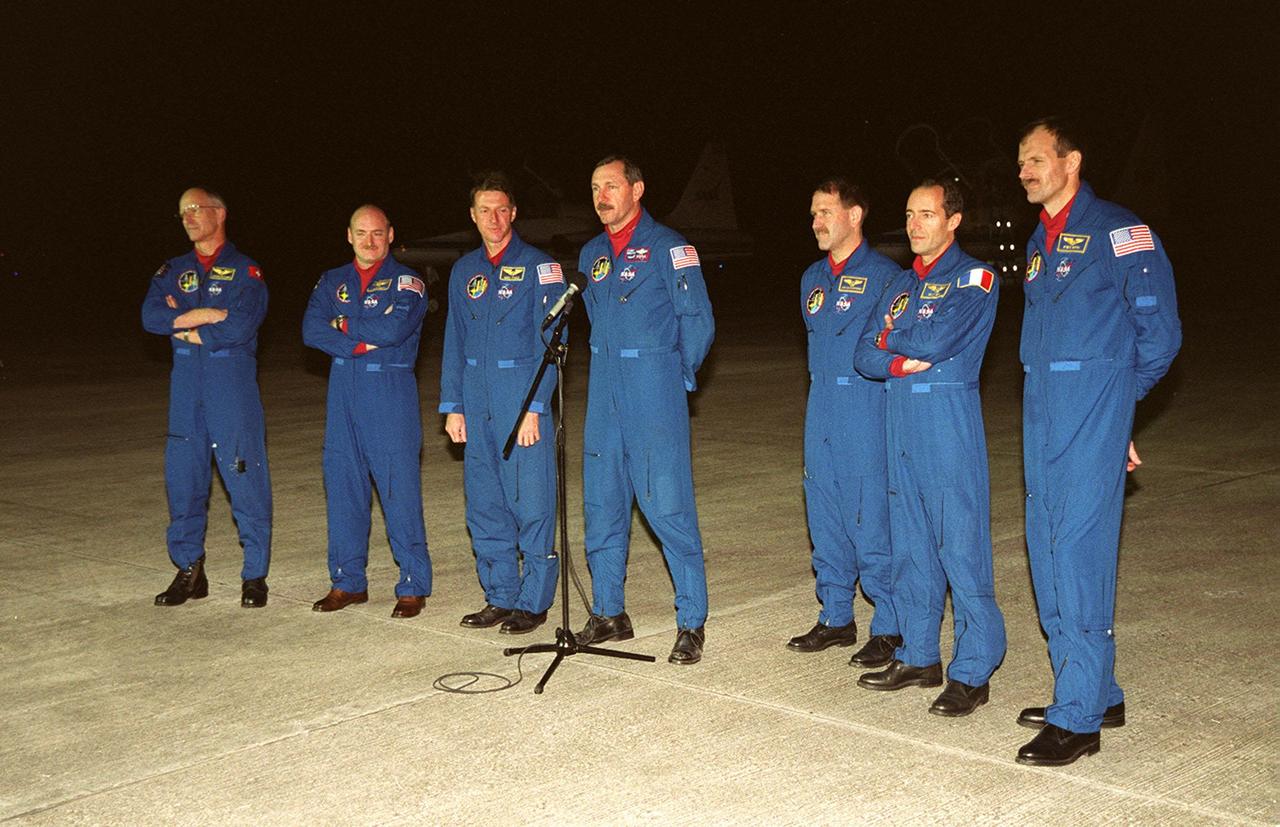

The STS-103 crew greets the media at the Shuttle Landing Facility after arriving aboard T-38 jets to make final preparations for their launch. From left, they are Mission Specialist Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, Pilot Scott J. Kelly, Mission Specialist C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr. (at microphone), and Mission Specialists John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Jean-François Clervoy of France, and Steven L. Smith. Nicollier and Clervoy both represent the European Space Agency. The STS-103 mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope a third time, is scheduled for launch Dec. 11 at 12:13 a.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B
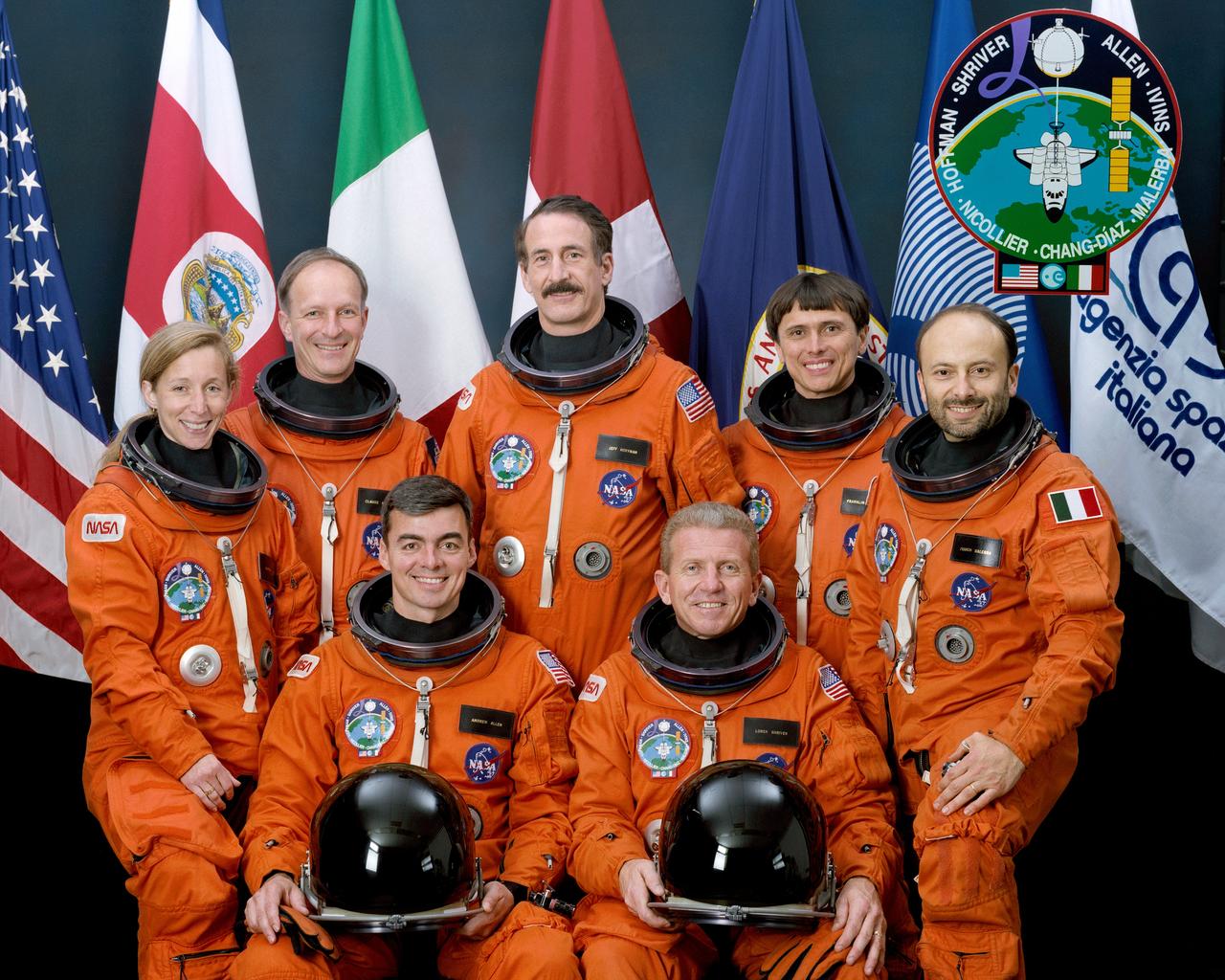

STS046-S-002 (May 1992) --- The crew members assigned to the STS-46 mission pose with seven flags that represent participation on the flight. Loren J. Shriver (right front) is mission commander; Andrew M. Allen (left front) is pilot. Others are (left to right) Marsha S. Ivins, mission specialist; Claude Nicollier, mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA); Jeffrey A. Hoffman, payload commander; Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, mission specialist; and Franco Malerba, flying for the Italian Space Agency (ASI). The flags, left to right, represent the United States of America, Costa Rica (Chang's native country), Italy, Switzerland (Nicollier's homeland), NASA, ESA and ASI.
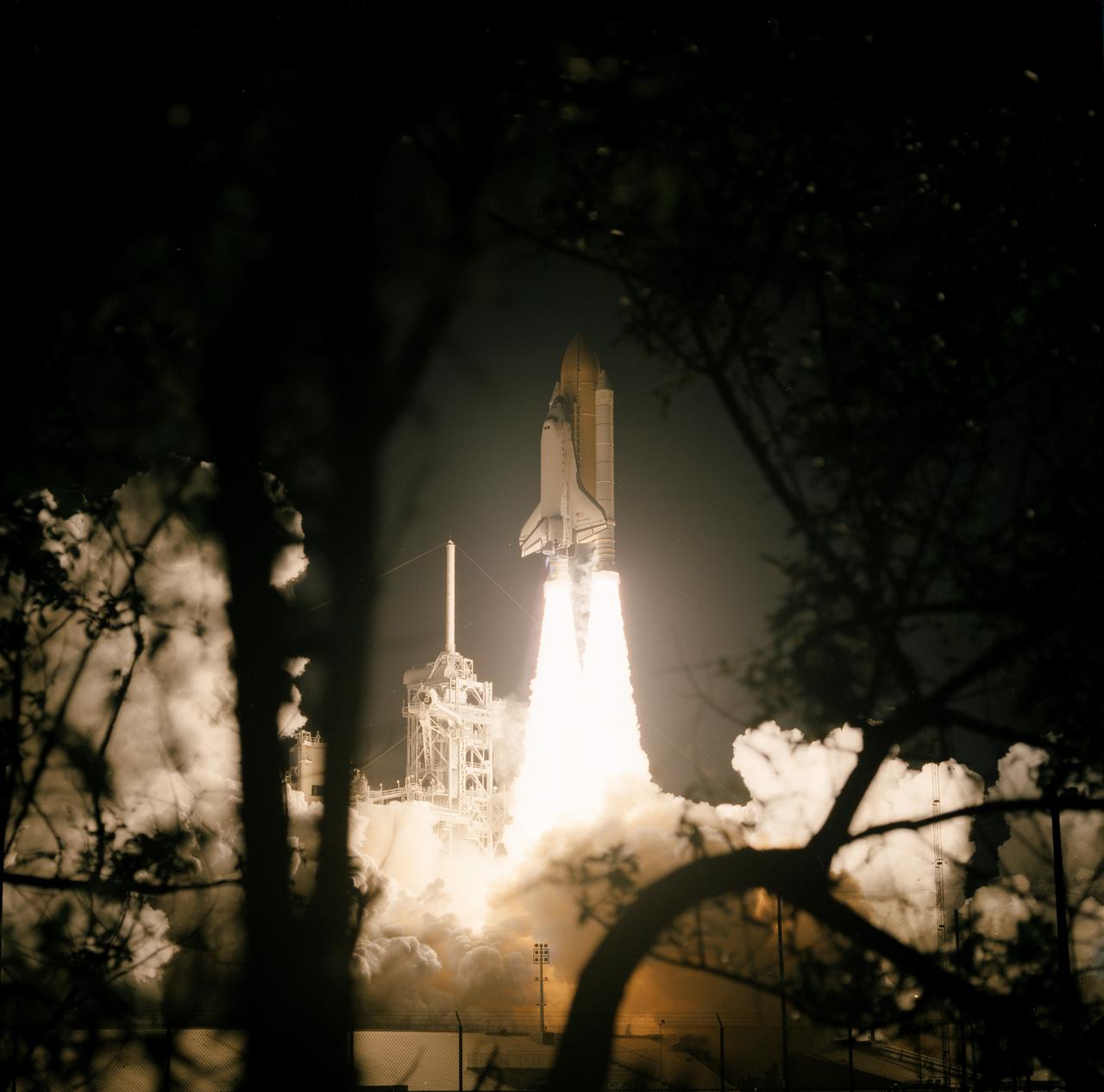

STS103-S-008 (19 December 1999) --- The Space Shuttle Discovery, framed by Florida foliage, clears the launch structure and heads toward the clear night sky to begin the 96th mission in the STS program. Liftoff occurred at 7:50 p.m. (EST), December 19, 1999, from Launch Pad 39B. Onboard were astronauts Curtis L. Brown, Jr., Scott J. Kelly, Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale, John M. Grunsfeld, Claude Nicollier and Jean-Francois Clervoy. Switzerland's Nicollier and France's Clervoy represent the European Space Agency (ESA).
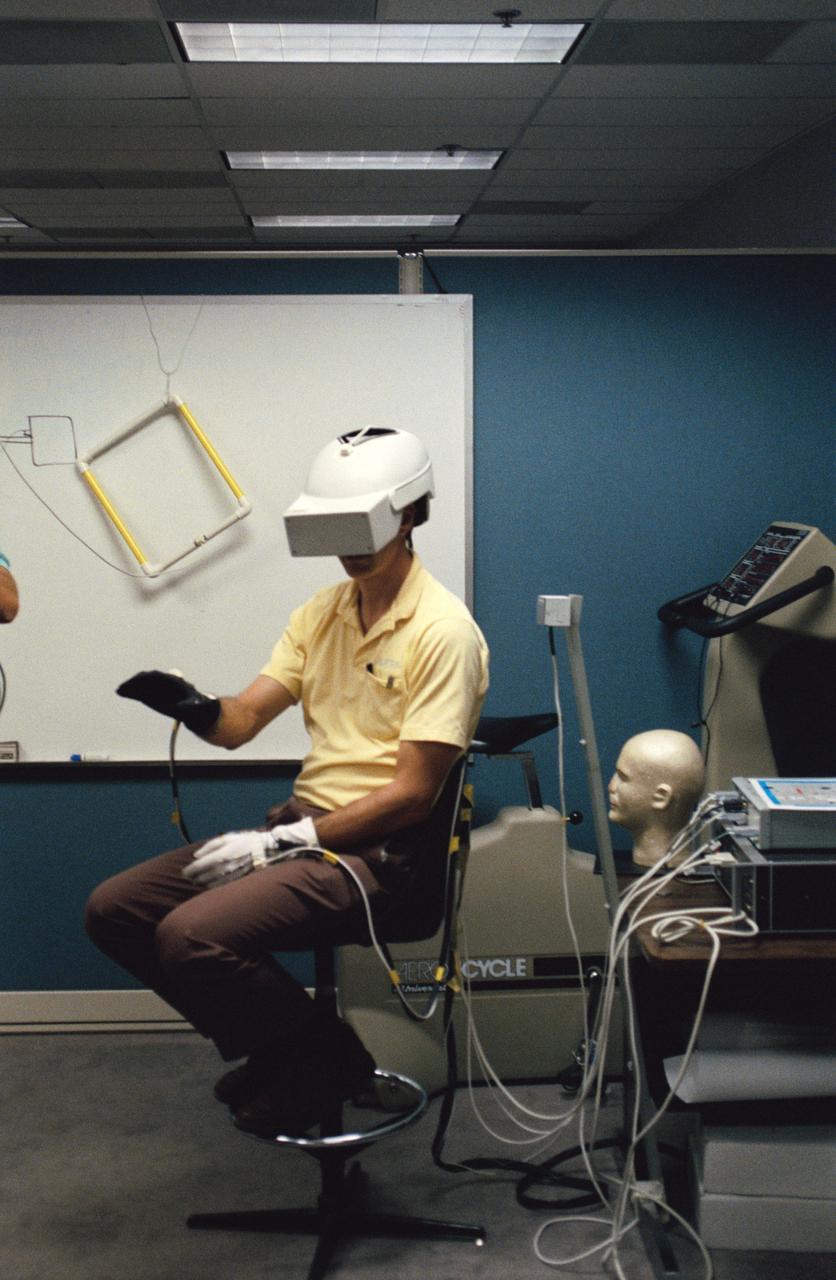
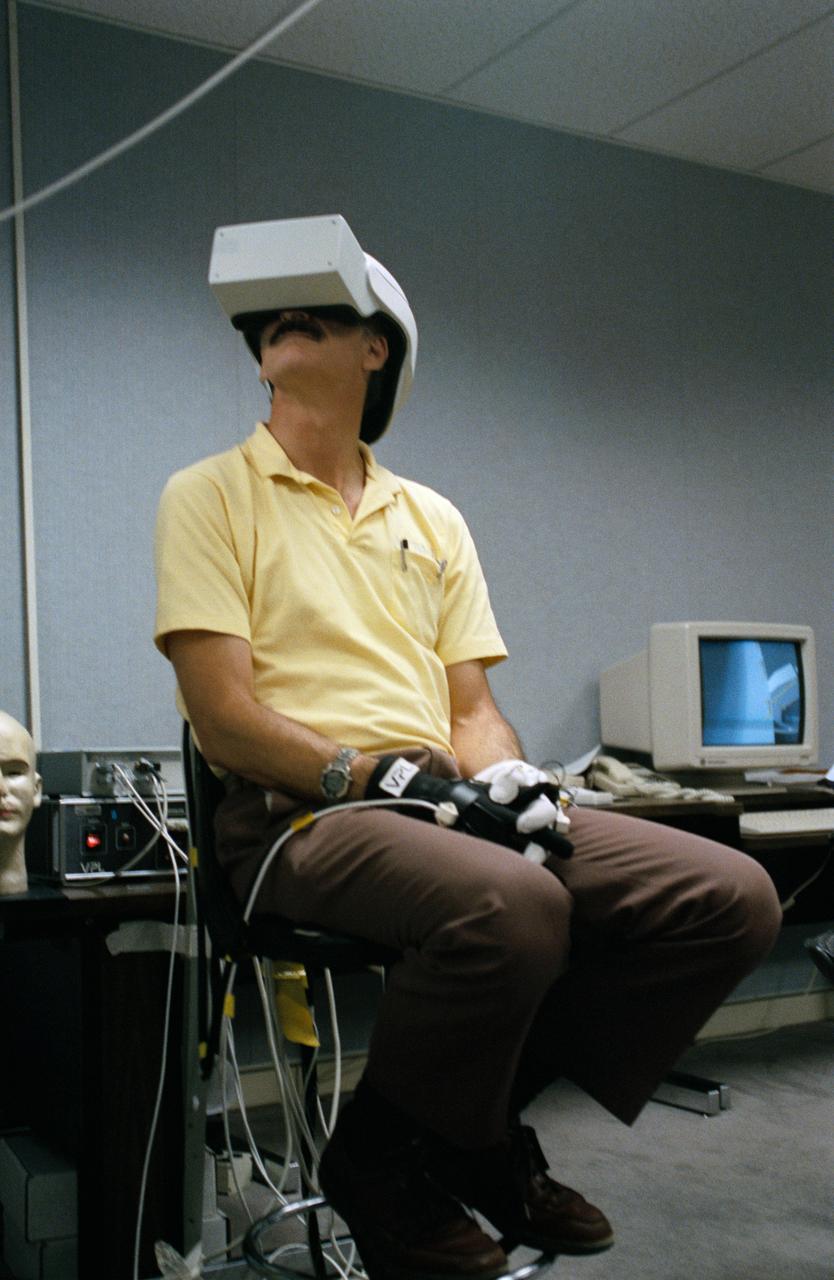
Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).
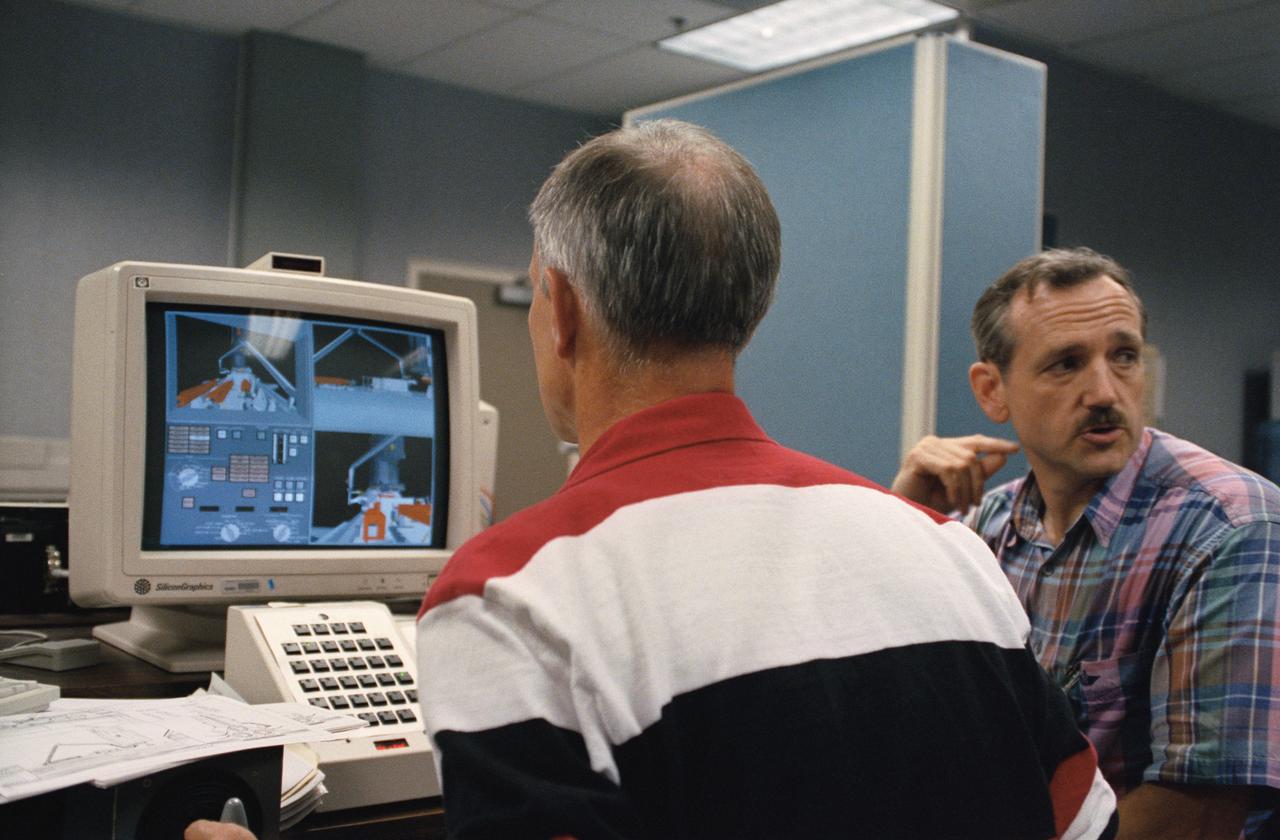

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).
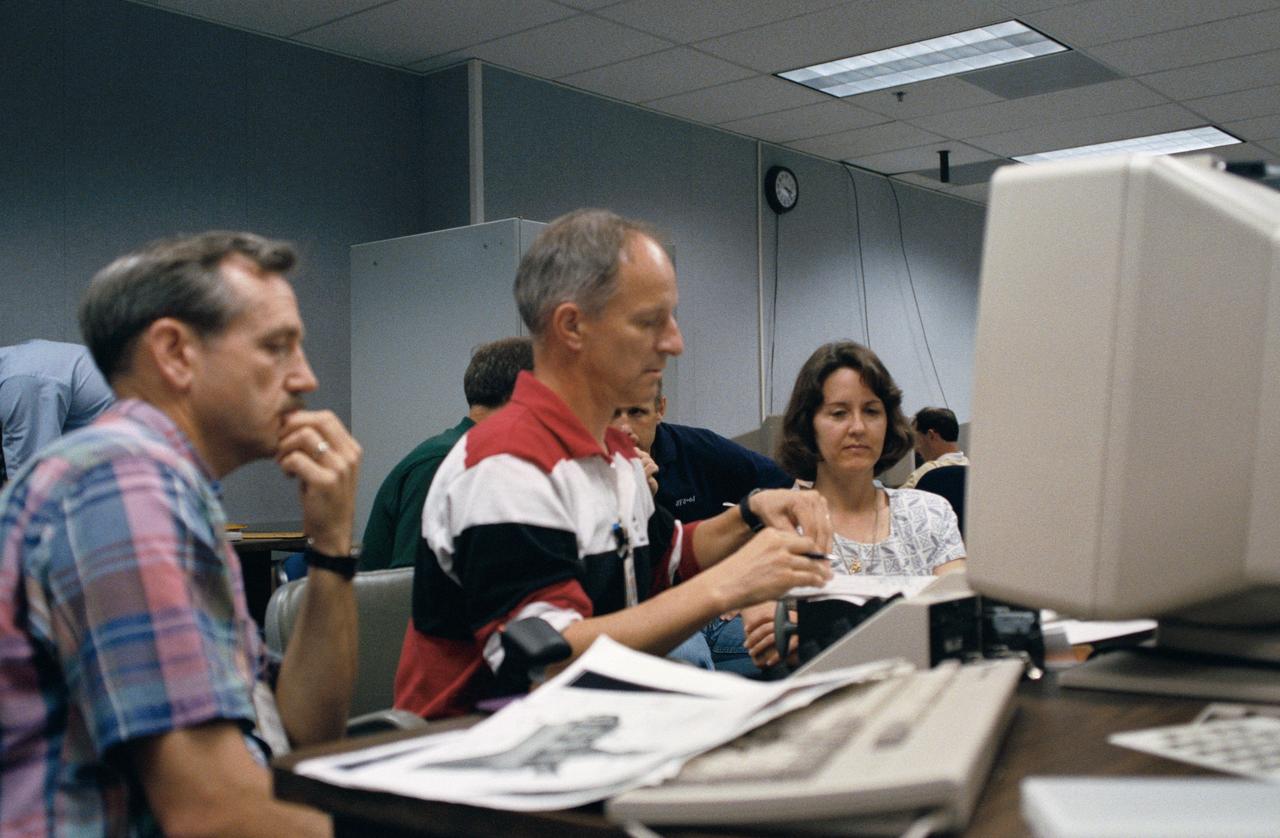

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).
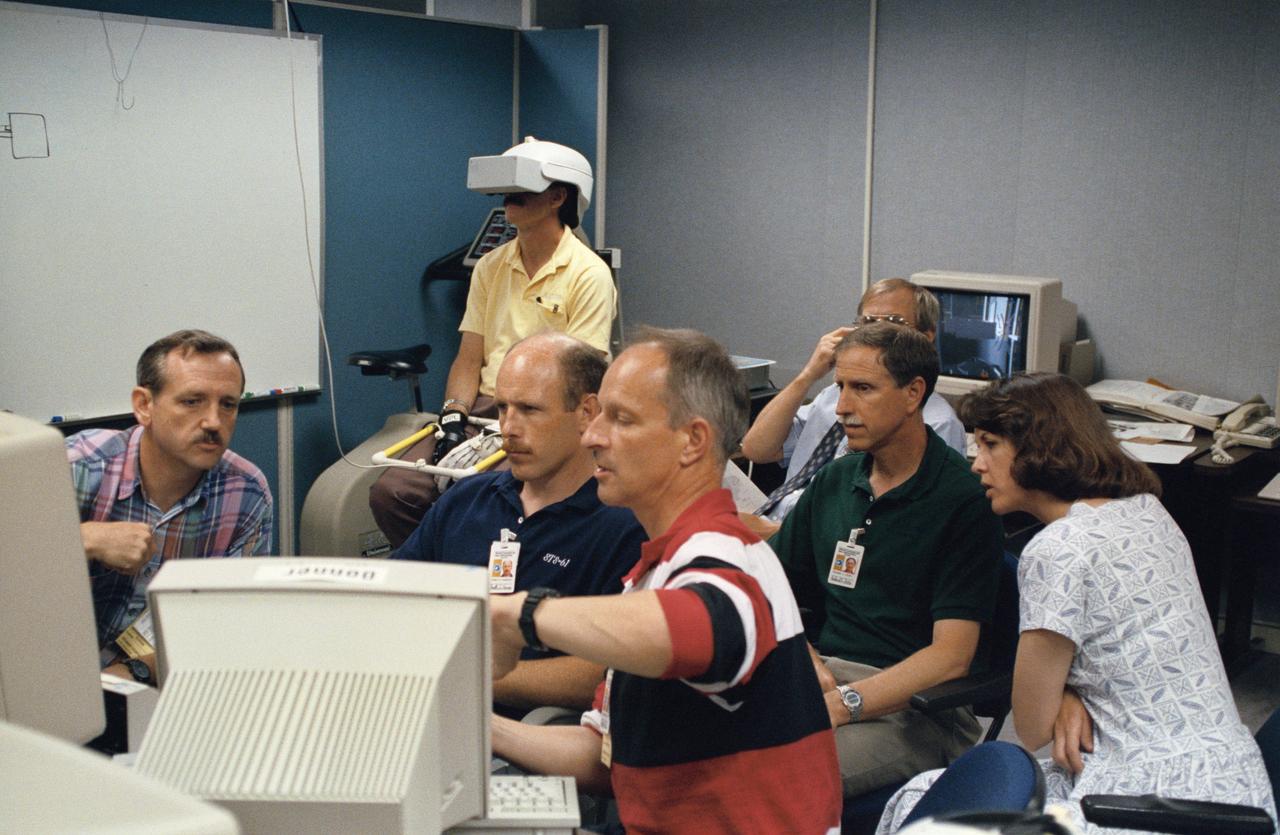

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).
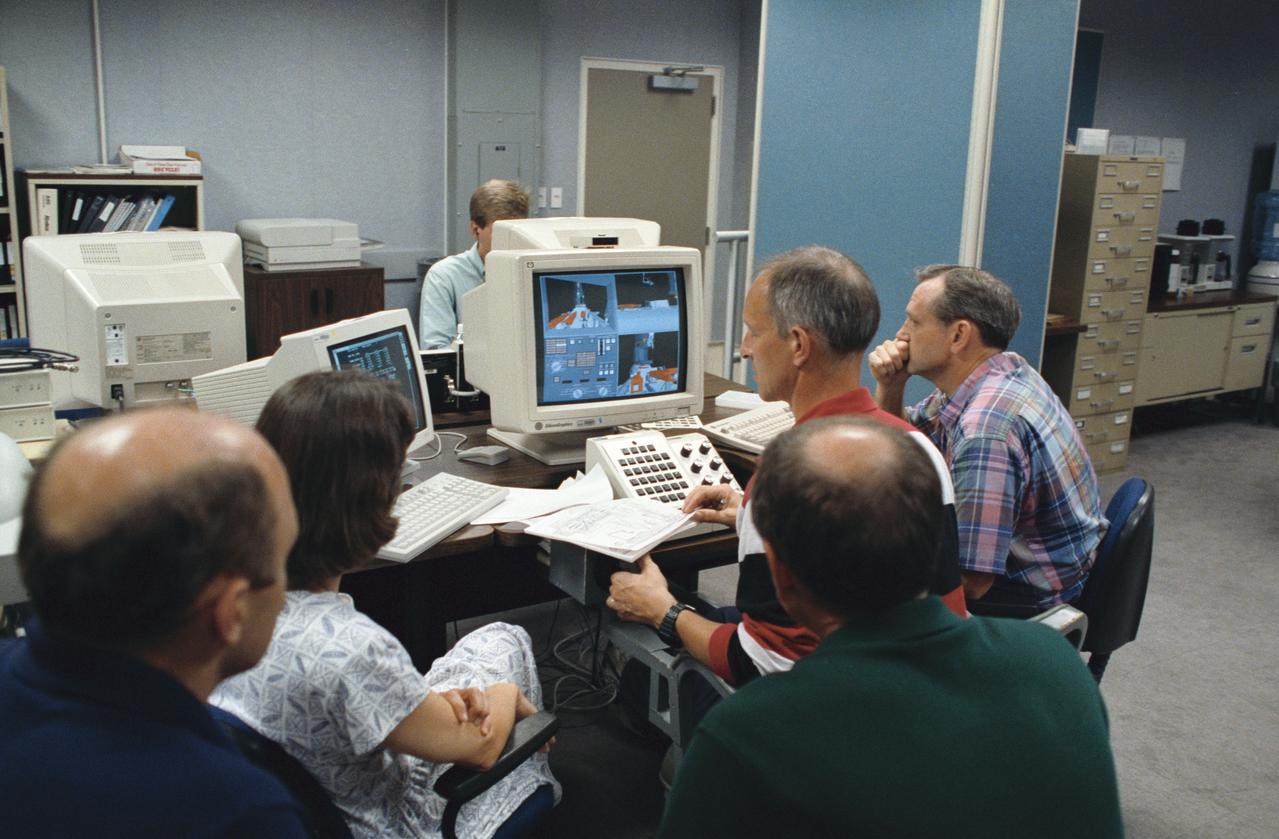

Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman, one of four crewmembers for STS-61 that will conduct scheduled spacewalks during the flight, wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers are utilizing a new virtual reality training aid which assists in refining positioning patterns for Space Shuttle Endeavour's Remote Manipulator System (RMS) (36890); Astronaut Claude Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Thomas D. Akers and Kathryn C. Thornton, mission specialists look on. Nicollier will be responsible for maneuvering the astronauts while they stand in a foot restraint on the end of the RMS arm (36891,36894); Hoffman wears a special helmet and gloves designed to assist in proper positioning near the telescope while on the end of the robot arm (35892); Nicollier looks at a computer display of the Shuttle's robot arm movements as Akers looks on (36893); While (l-r) Astronauts Kenneth Bowersox, Kathryn Thornton, Richard O. Covey and Thomas D. Akers watch, Nicollier moves the Robot arm to desired locations in the Shuttle's payload bay using the Virtual Reality program (36895); Bowersox takes his turn maneuvering the RMS while mission specialist Hoffman, wearing the Virtual Reality helmet, follows his own progress on the end of the robot arm. Crewmembers participating during the training session are (l-r) Astronauts Akers, Hoffman, Bowersox, Nicollier, Covey, and Thornton. In the background, David Homan, an engineer in the JSC Engineering Directorate's Automation and Robotics Division, looks on (36896).

Photographic documentation showing STS-103 crew return at bldg. 990, Ellington Field. Views include: Mission Specialist (MS) John M. Grunsfeld at podium (16048); MS Jean-Francois Clervoy at podium (16049); Grunsfeld signs autographs (16050); woman and child (16051); MS Claude Nicollier meets his Swiss-American fan club (16052); Clervoy holds child (16053); mission commander Curtis L. Brown signs autographs (16054, 16057); MS E. Michael Foale signs autographs (16055); MS and Payload Commander (PLC) Steven L. Smith kneels and holds child (16056); overall view of stage showing Brown at podium with crew seated behind him; from left to right: Nicollier, pilot Scott J. Kelly, Clervoy, Grunsfeld, Mr. George Abbey (JSC director), Foale and Smith (16058); Nicollier at podium (16059); Mr. George Abbey at the podium (16060): Foale ath the podium (16061); Kelly signs autographs (16062).
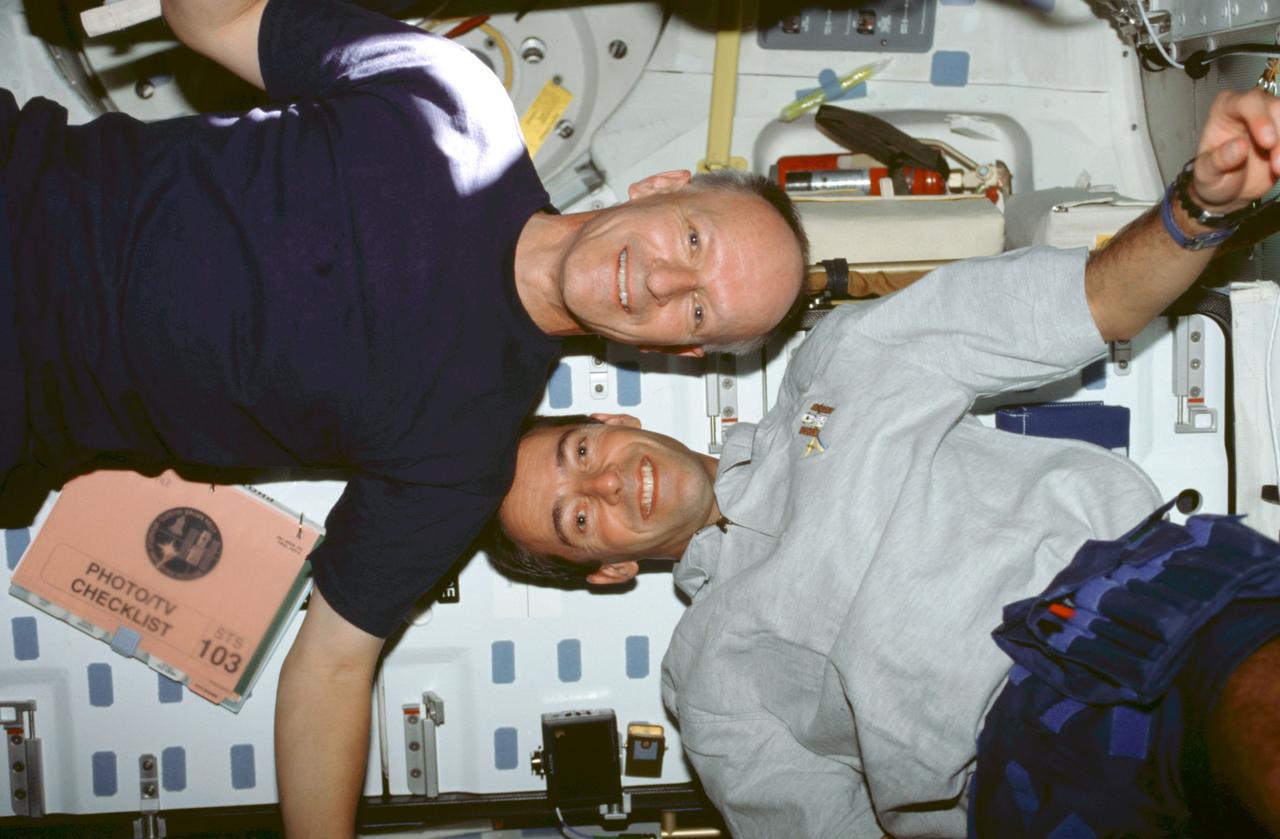

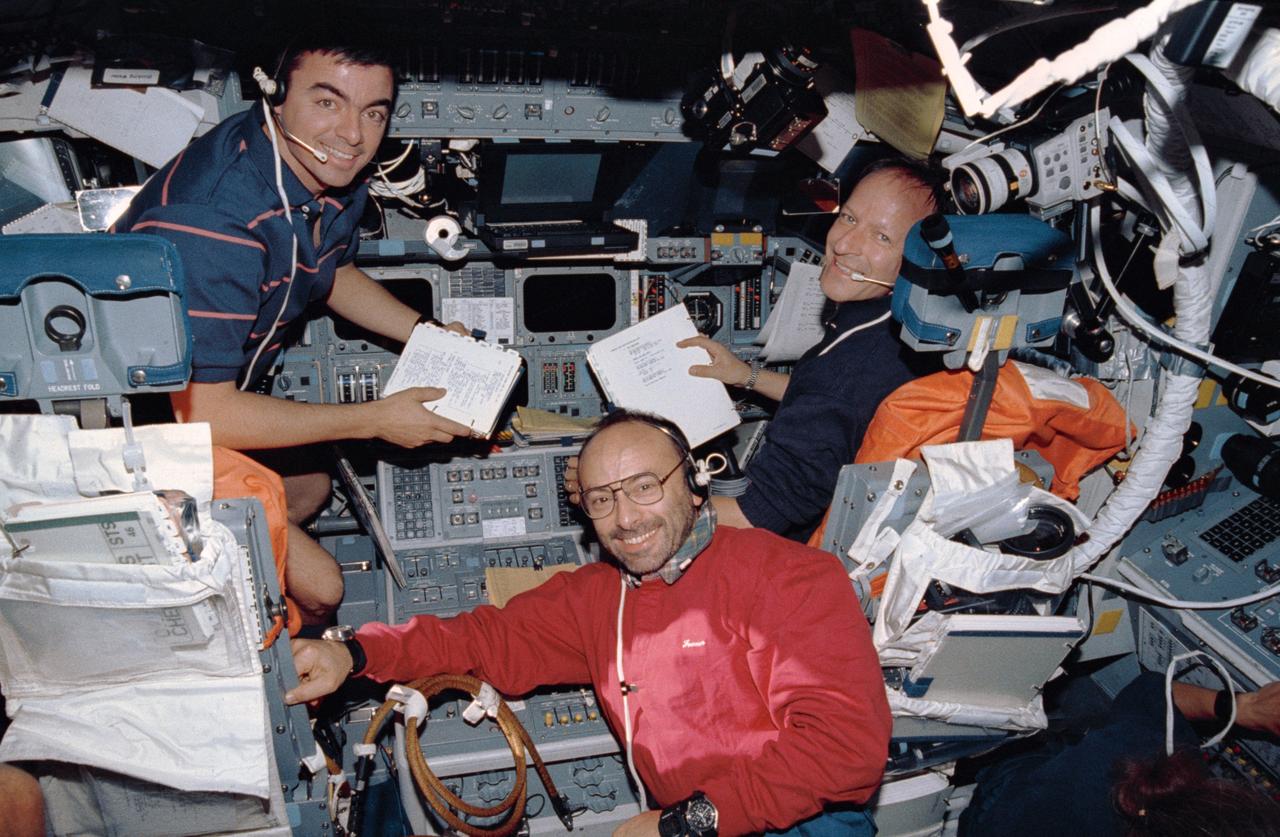
STS103-378-005 (19-27 December 1999) ---.Astronauts Claude Nicollier (left) and.Jean-Francois Clervoy, mission specialists representing the European Space Agency (ESA), move about on Discovery's mid deck in a manner they could not duplicate in Earth-bound training. A photography/television checklist floats nearby.
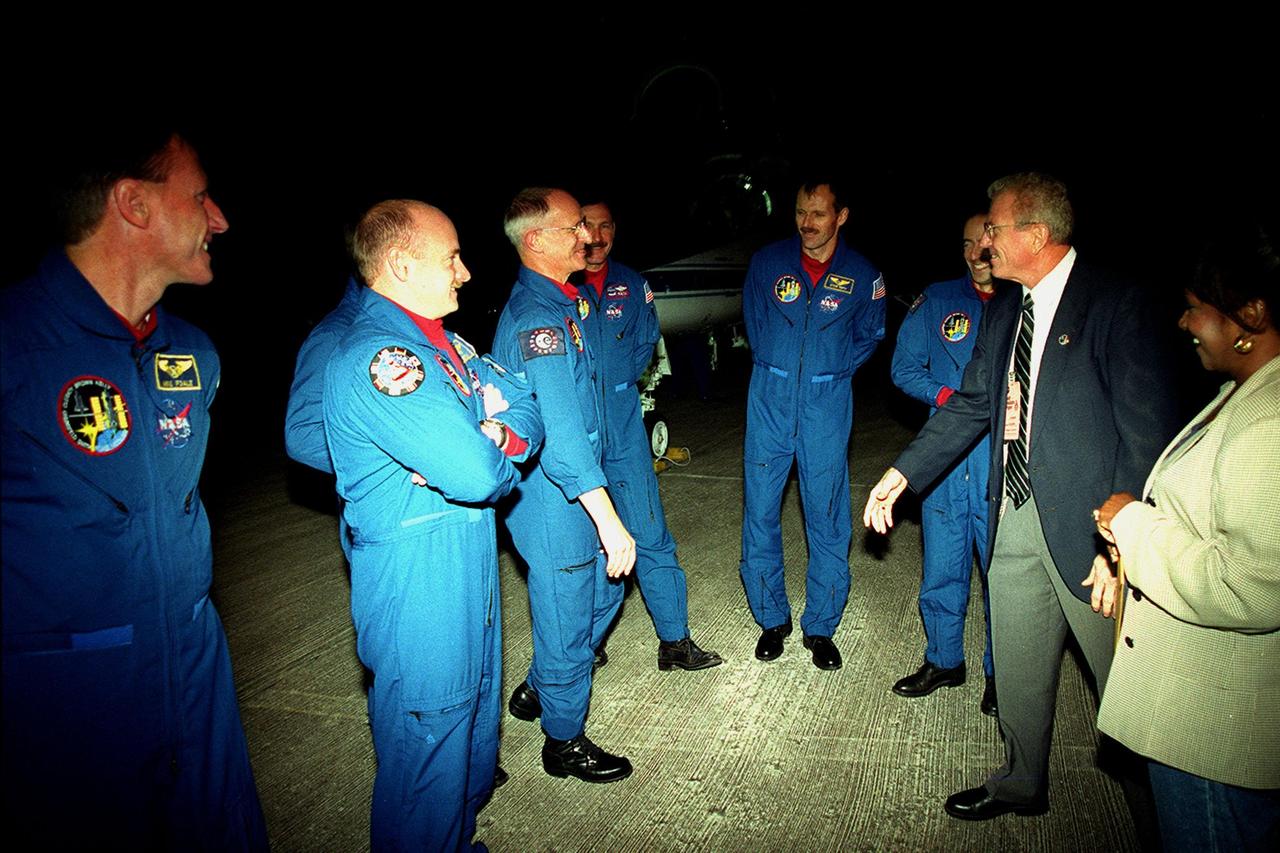

At the Shuttle Landing Facility, the STS-103 crew is greeted by Loren Shriver, Deputy Director for Launch and Payload Processing, upon their arrival aboard T-38 jets to make final preparations for launch. From left are Mission Specialist C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), Pilot Scott J. Kelly, Mission Specialist John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.) (hidden behind Kelly), Mission Specialist Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Mission Specialist Steven L. Smith, Mission Specialist Jean-François Clervoy of France, Loren Shriver, and Delores Green with KSC's Astronaut Office. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. Shriver was the commander of the STS-31 crew which originally deployed the telescope in April of 1990. The STS-103 mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope a third time, is scheduled for launch Dec. 11 at 12:13 a.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B
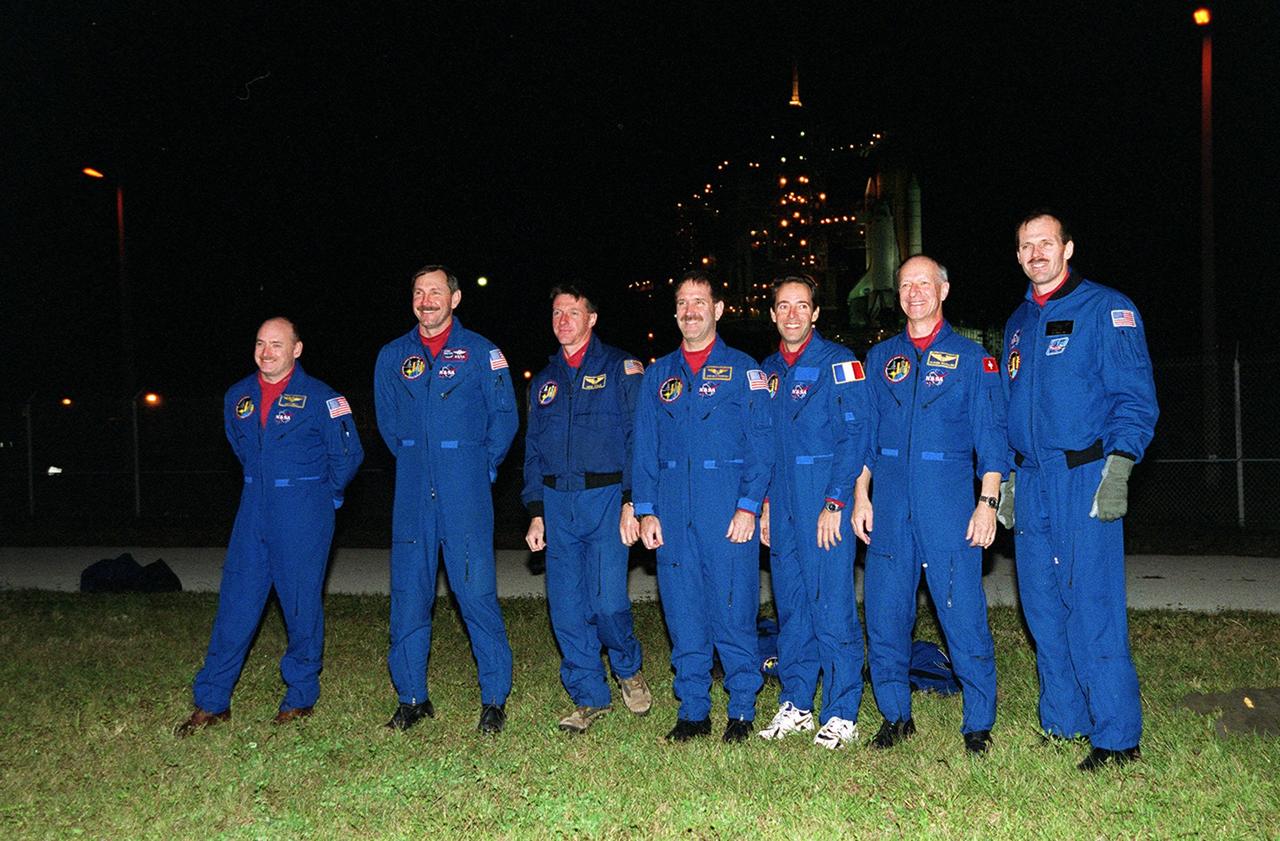

The STS-103 crew address family and friends at Launch Pad 39B. From left to right are Pilot Scott J. Kelly, Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., and Mission Specialists C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Jean-François Clervoy of France , Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Steven L. Smith. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. In the background is Space Shuttle Discovery, alongside the lighted Fixed Service Structure. The STS-103 mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is scheduled for launch Dec. 17 at 8:47 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. Mission objectives include replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. The mission is expected to last about 8 days and 21 hours. Discovery is expected to land at KSC Sunday, Dec. 26, at about 6:25 p.m. EST
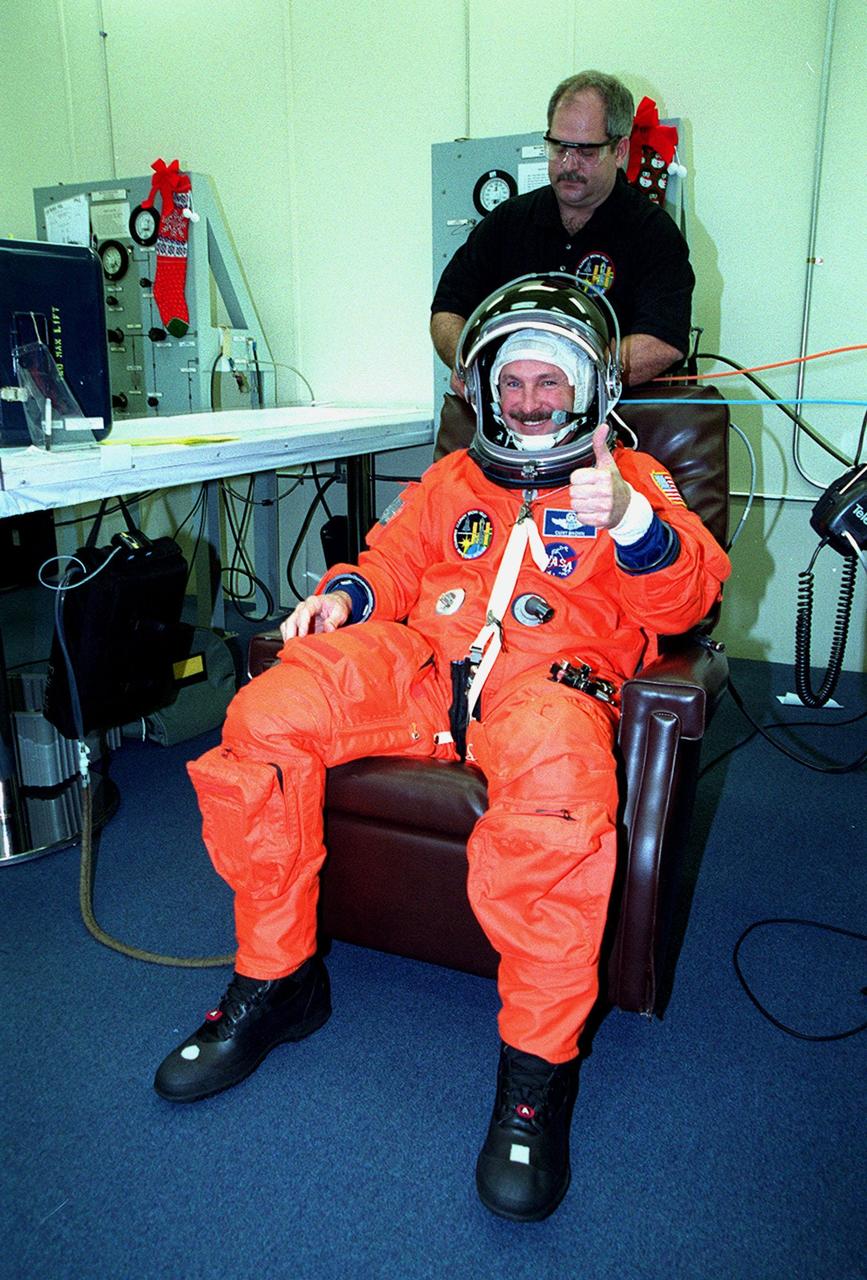

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-103 Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr. signals he's ready for launch while having his launch and entry suit checked by a suit technician. Other crew members are Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michel Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. The STS-103 mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is scheduled for launch Dec. 17 at 8:47 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. Mission objectives include replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. After the 8-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Sunday, Dec. 26, at about 6:30 p.m. EST

STS075-S-004 (22 Feb. 1996) --- The space shuttle Columbia clears the tower to begin the mission. The liftoff occurred on schedule at 3:18:00 p.m. (EST), Feb. 22, 1996. Visible at left is the White Room on the orbiter access arm through which the flight crew had entered the orbiter. Onboard Columbia for the scheduled two-week mission were astronauts Andrew M. Allen, commander; Scott J. Horowitz, pilot; Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, payload commander; and astronauts Maurizio Cheli, Jeffrey A. Hoffman and Claude Nicollier, along with payload specialist Umberto Guidoni. Cheli and Nicollier represent the European Space Agency (ESA), while Guidoni represents the Italian Space Agency (ASI).

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-103 Mission Specialist Jean-François Clervoy of France has donned his launch and entry suit and is ready for launch. Other crew members are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michel Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), and Claude Nicollier of Switzerland. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. The STS-103 mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is scheduled for launch Dec. 17 at 8:47 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. Mission objectives include replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. After the 8-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Sunday, Dec. 26, at about 6:30 p.m. EST
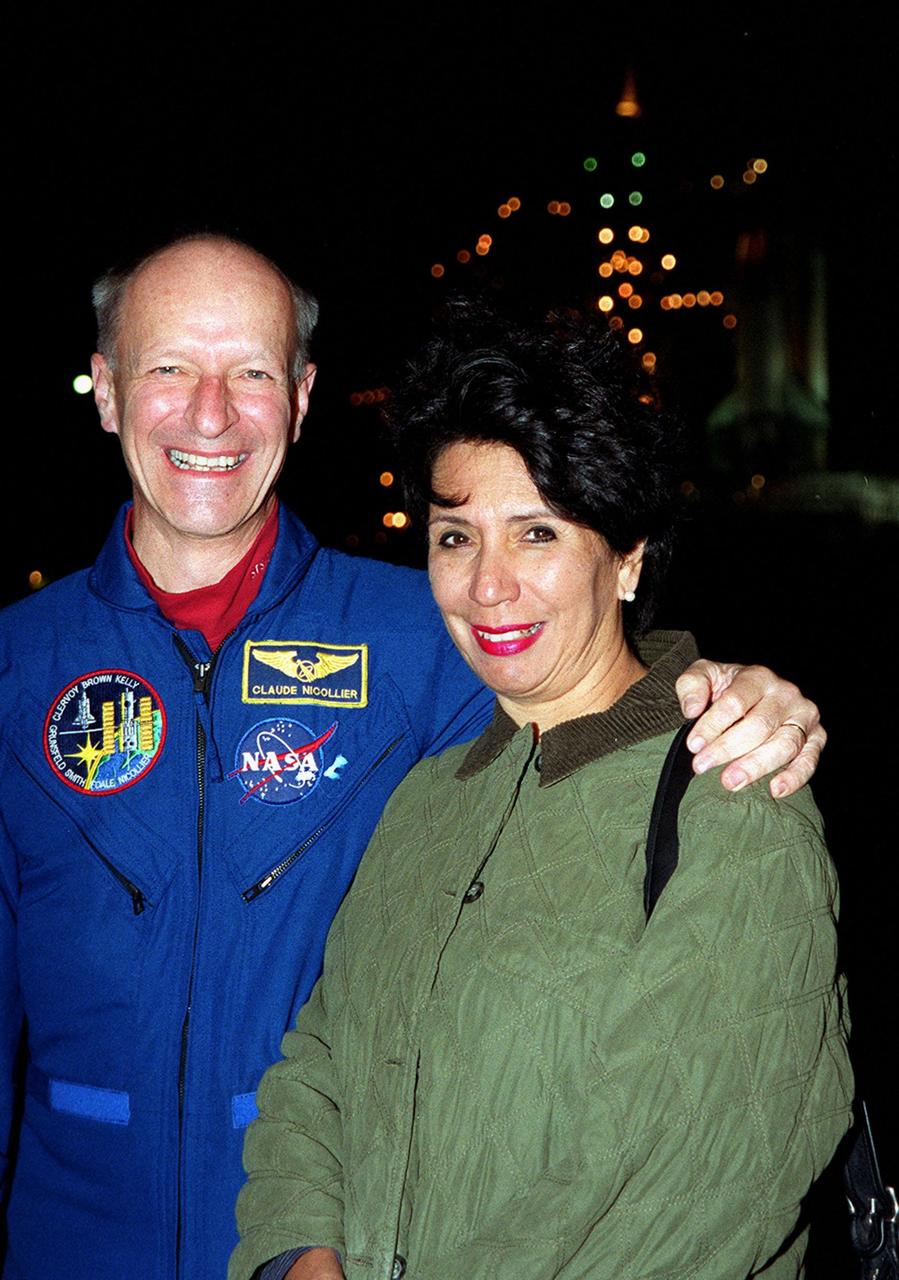

STS-103 Mission Specialist Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and his wife, Susana, pose at Launch Pad 39B during a meeting of the STS-103 crew with their family and friends. Nicollier is with the European Space Agency. The lights in the background are on the Fixed Service Structure next to Space Shuttle Discovery. The mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is scheduled for launch Dec. 17 at 8:47 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. Mission objectives include replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. The mission is expected to last about 8 days and 21 hours. Discovery is expected to land at KSC Sunday, Dec. 26, at about 6:25 p.m. EST

Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr. smiles on his arrival at the Shuttle Landing Facility aboard a T-38 jet aircraft. He joins other crew members Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France, for pre-launch preparations on mission STS-103 aboard Space Shuttle Discovery. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. The mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is scheduled for launch Dec. 11 at 12:13 a.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 20, at 9:21 p.m. EST
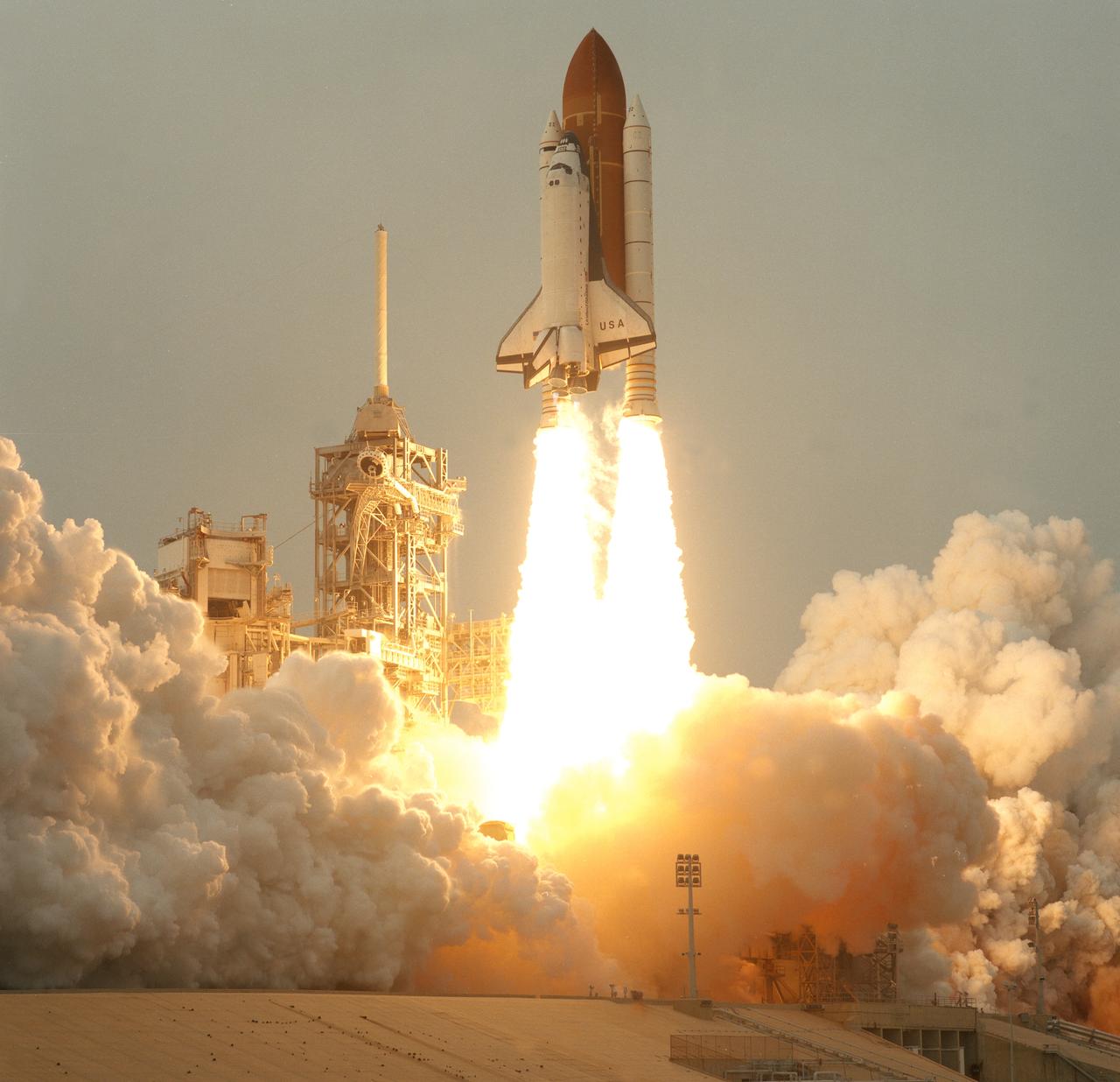

STS075-S-007 (22 Feb. 1996) --- A remote camera at Launch Pad 39B, at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC), recorded this profile view of the space shuttle Columbia as it cleared the tower to begin the mission. The liftoff occurred on schedule at 3:18:00 p.m. (EST), Feb. 22, 1996. Onboard Columbia for the scheduled two-week mission were astronauts Andrew M. Allen, commander; Scott J. Horowitz, pilot; Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, payload commander; and astronauts Maurizio Cheli, Jeffrey A. Hoffman and Claude Nicollier, along with payload specialist Umberto Guidoni. Cheli and Nicollier represent the European Space Agency (ESA), while Guidoni represents the Italian Space Agency (ASI).
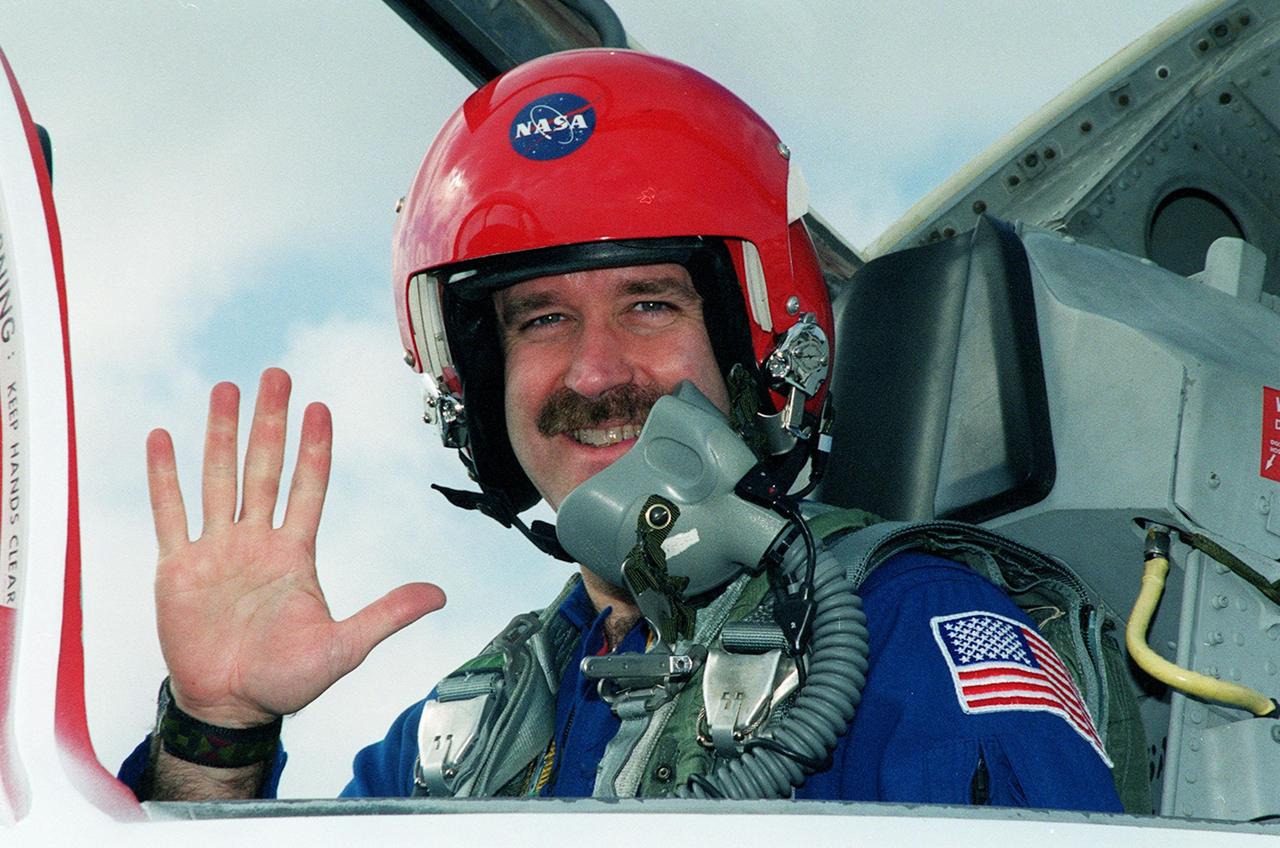

STS-103 Mission Specialist John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.) waves from the rear seat of a T-38 training jet before beginning practice flights. He joins other crew members Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France, for pre-launch preparations on mission STS-103 aboard Space Shuttle Discovery. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. The mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is scheduled for launch Dec. 16 at 9:18 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. The mission is expected to last about 9 days and 21 hours. Discovery is expected to land at KSC Sunday, Dec. 26, at 6:56 p.m. EST
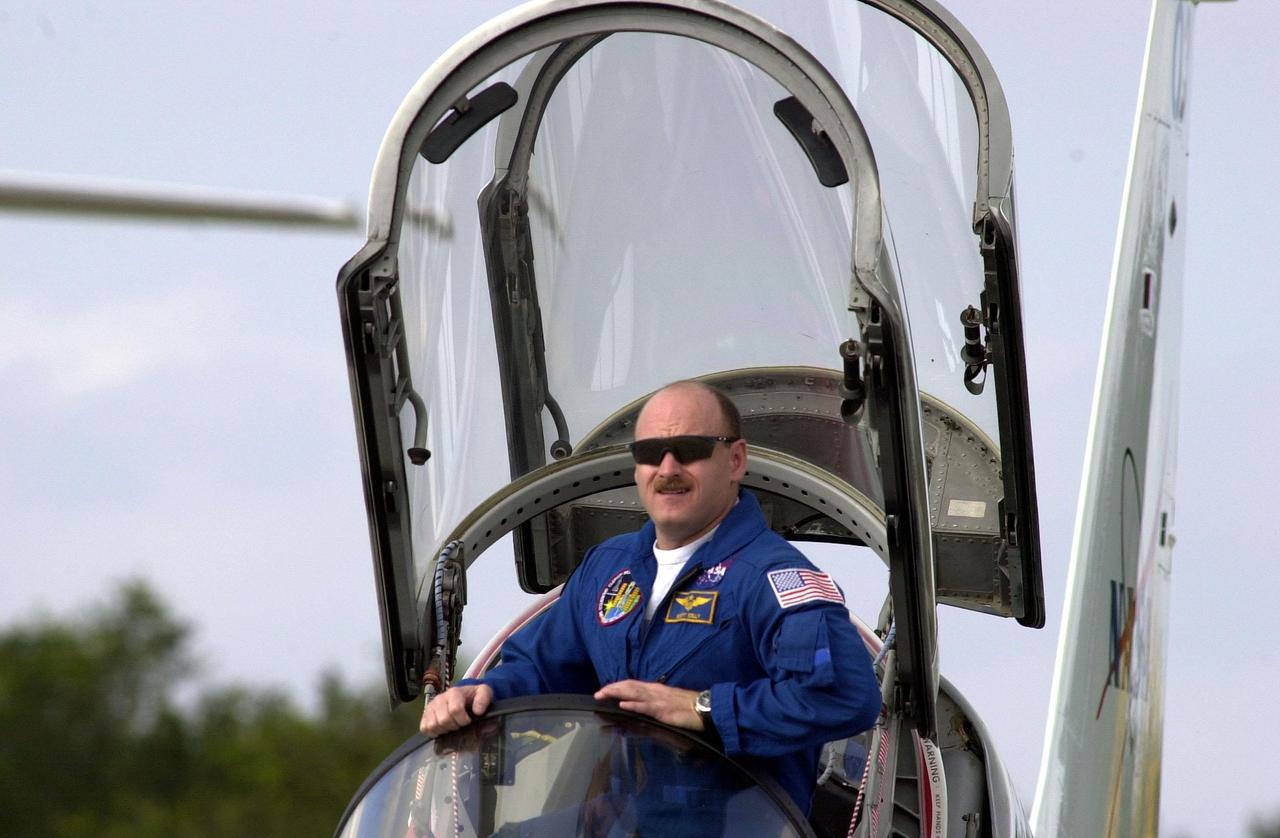

STS-103 Pilot Scott J. Kelly settles into the cockpit of a T-38 training jet for practice flights. He joins other crew members Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr. and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France, for pre-launch preparations on mission STS-103 aboard Space Shuttle Discovery. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. The mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is scheduled for launch Dec. 16 at 9:18 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. The mission is expected to last about 9 days and 21 hours. Discovery is expected to land at KSC Sunday, Dec. 26, at 6:56 p.m. EST

In the Operations and Checkout Building, the STS-103 crew are all smiles as they gather for breakfast before suiting up for launch. From left are Mission Specialists Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), Pilot Scott J. Kelly, Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., and Mission Specialists Jean-Francois Clervoy of France, John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.) and Steven L. Smith. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. The STS-103 mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is scheduled for launch Dec. 17 at 8:47 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. Mission objectives include replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. The mission is expected to last about 8 days and 21 hours. Discovery is expected to land at KSC Sunday, Dec. 26, at about 6:30 p.m. EST
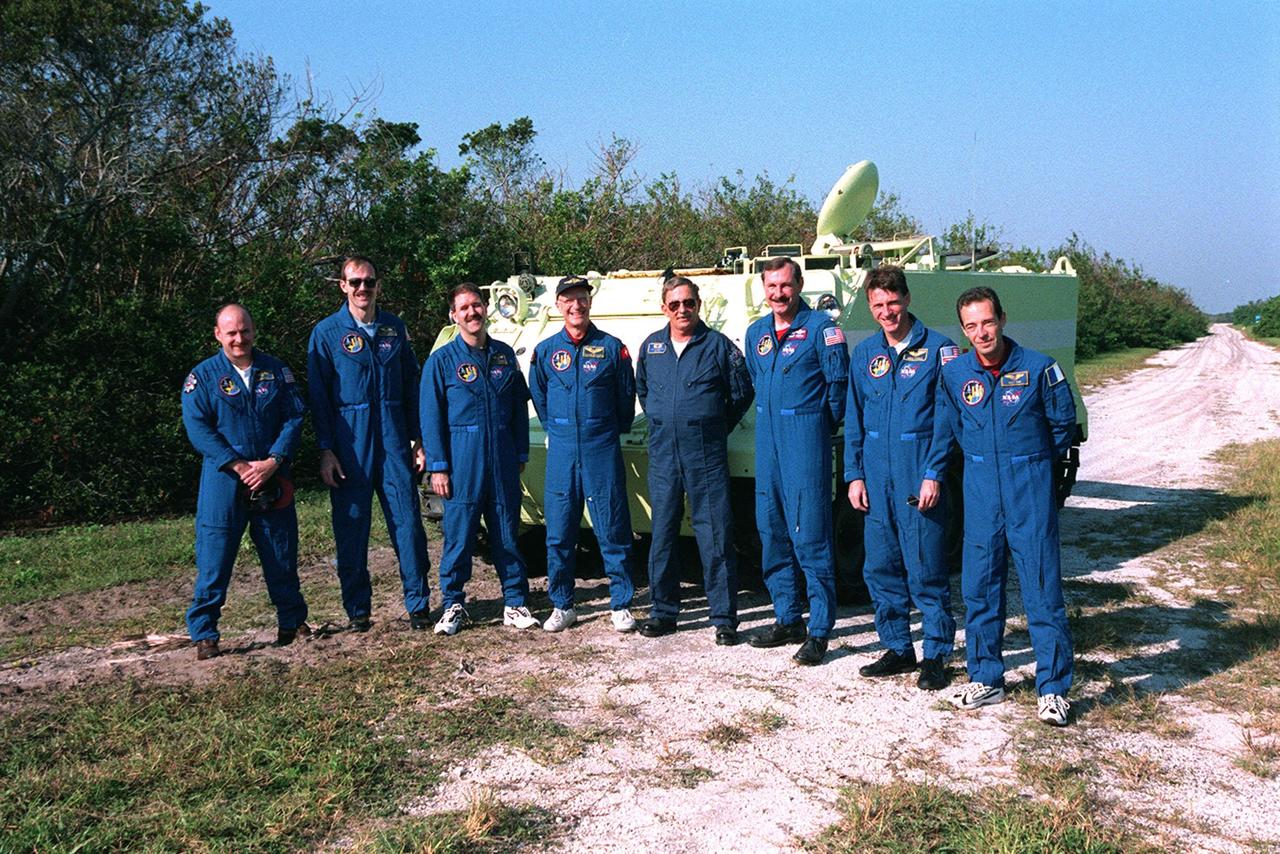

The STS-103 crew pose for photographers following Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) emergency egress training on the small armored personnel carrier behind them. Standing left to right are Pilot Scott J. Kelly, Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, their trainer on the carrier Capt. George Hoggard of the KSC/CCAS Fire Department, Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., and Mission Specialists C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.) and Jean-Francois Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. The TCDT also provides simulated countdown exercises and opportunities to inspect the mission payloads in the orbiter's payload bay. STS-103 is a "call-up" mission due to the need to replace and repair portions of the Hubble Space Telescope. Four EVA's are planned to make the necessary repairs and replacements on the telescope. The mission is targeted for launch Dec. 6 at 2:37 a.m. EST
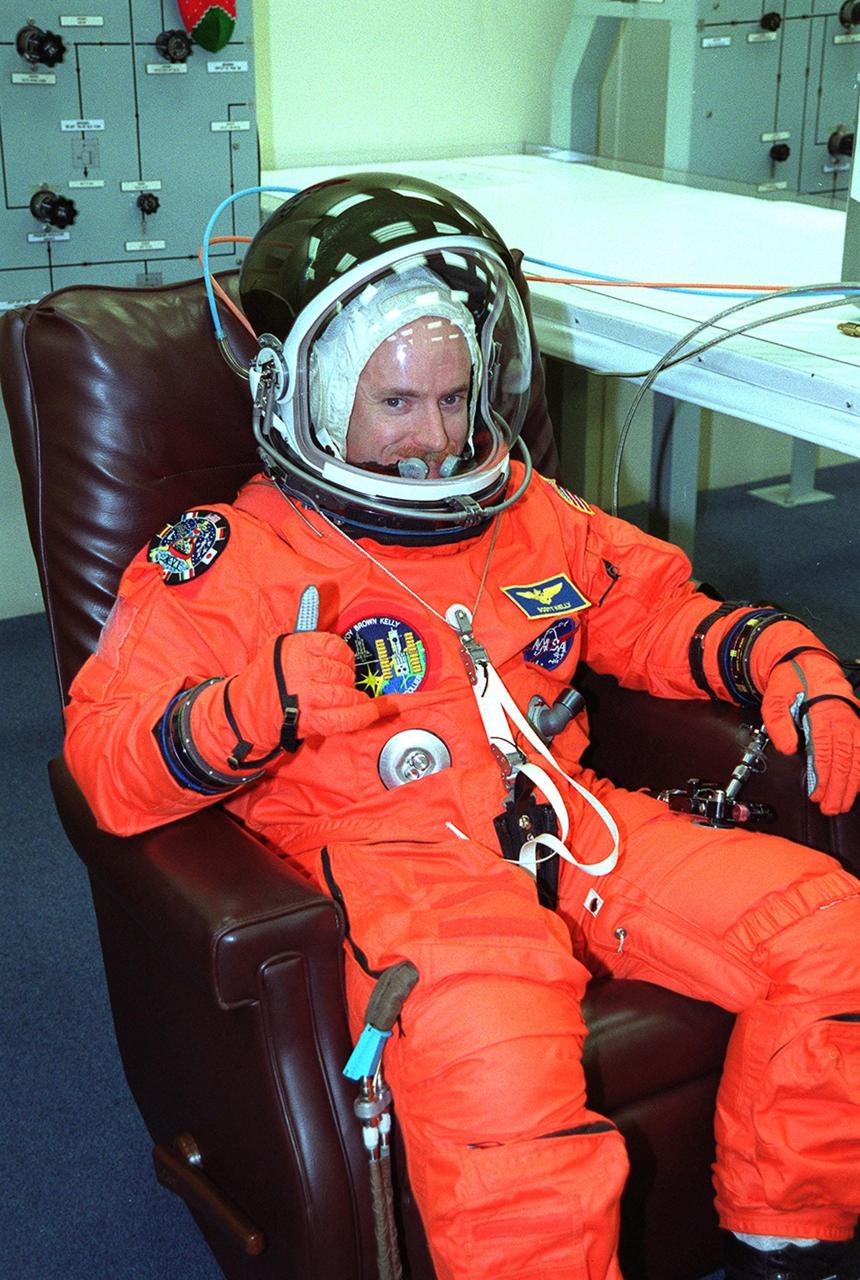

STS-103 Pilot Scott J. Kelly signals he is ready for launch after suiting up in the Operations and Checkout Building. Other crew members are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr. and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michel Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Jean-François Clervoy of France and Claude Nicollier of Switzerland. Clervoy and Nicollier are with the European Space Agency. The STS-103 mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is scheduled for launch Dec. 17 at 8:47 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. Mission objectives include replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. After the 8-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Sunday, Dec. 26, at about 6:30 p.m. EST
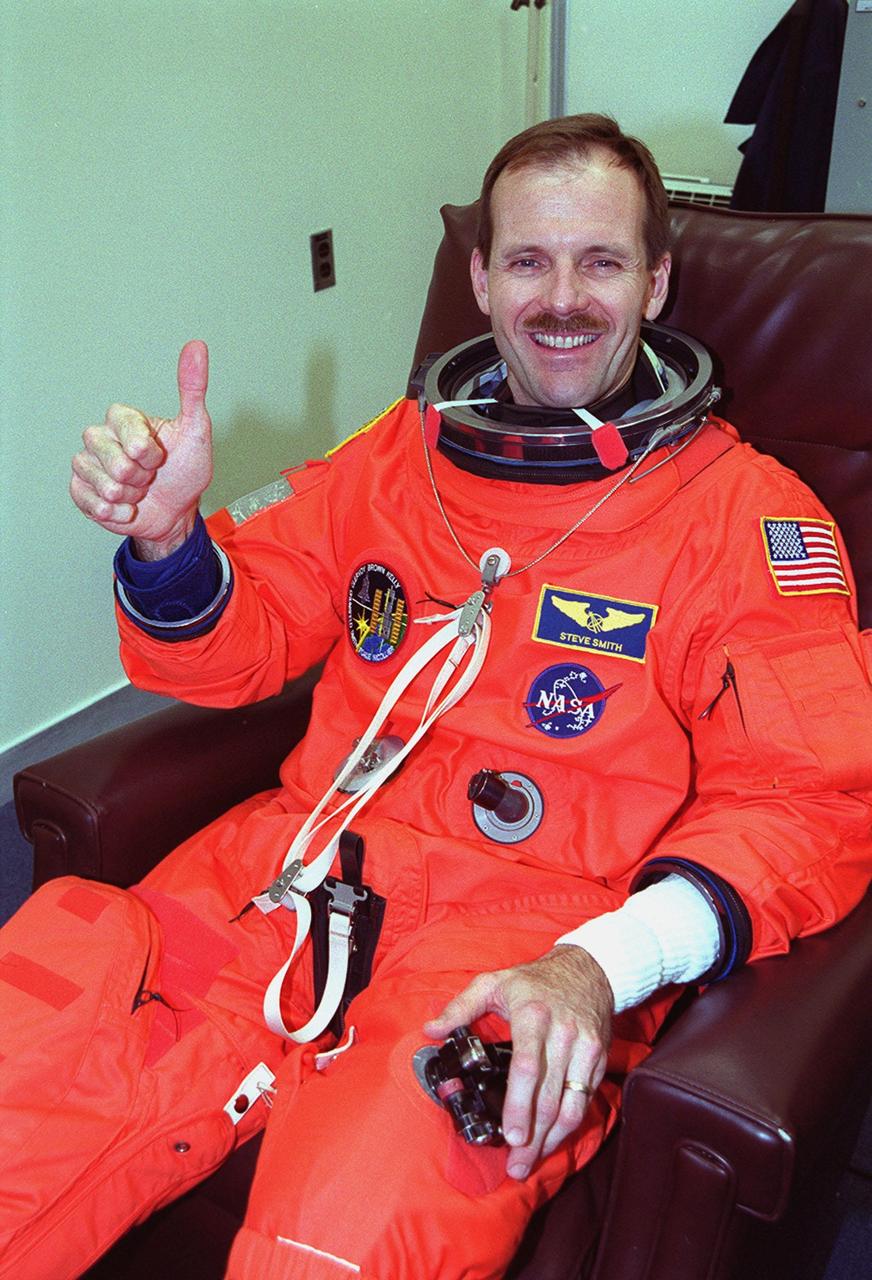

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-103 Mission Specialist Steven L. Smith signals he is suited up and ready for launch. Other crew members are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists C. Michel Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Jean-François Clervoy of France and Claude Nicollier of Switzerland. Clervoy and Nicollier are with the European Space Agency. The STS-103 mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is scheduled for launch Dec. 17 at 8:47 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. Mission objectives include replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. After the 8-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Sunday, Dec. 26, at about 6:30 p.m. EST
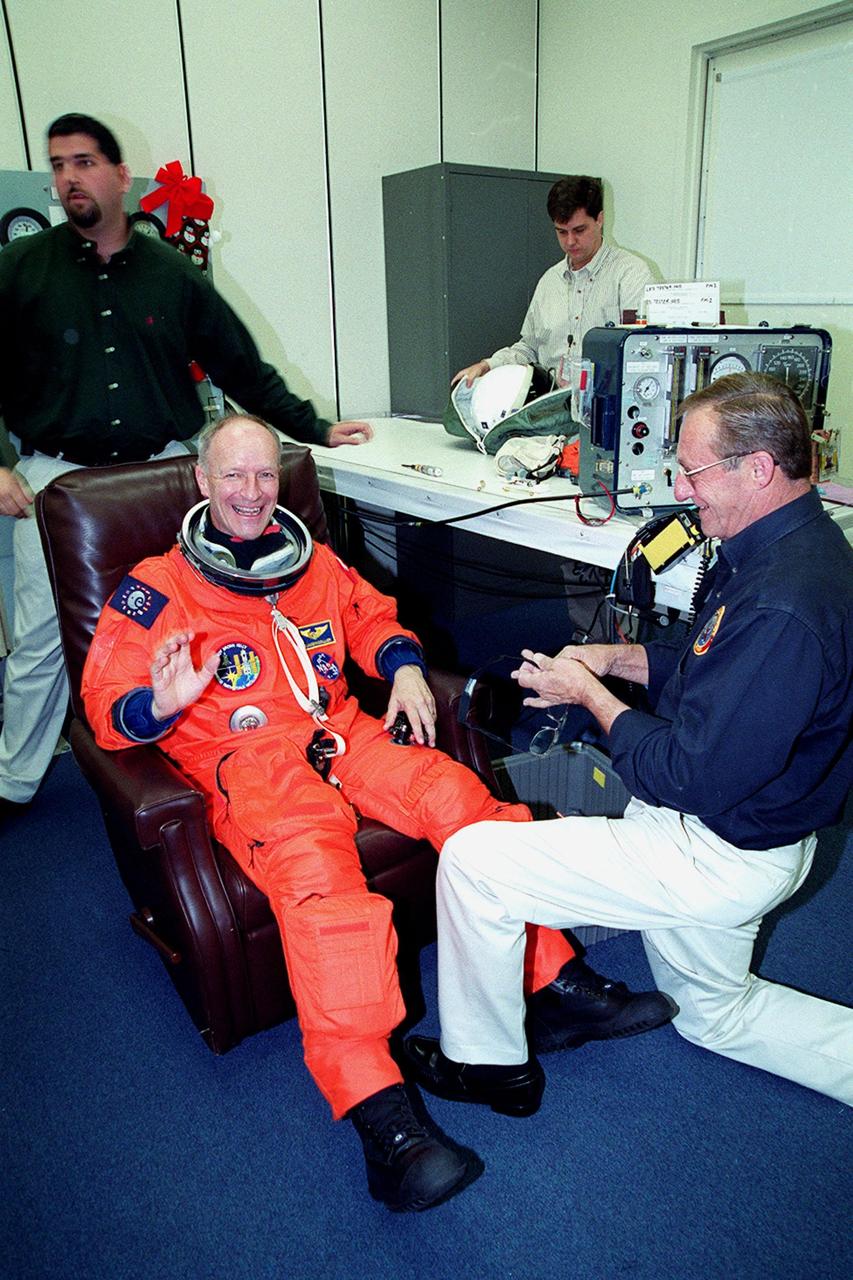

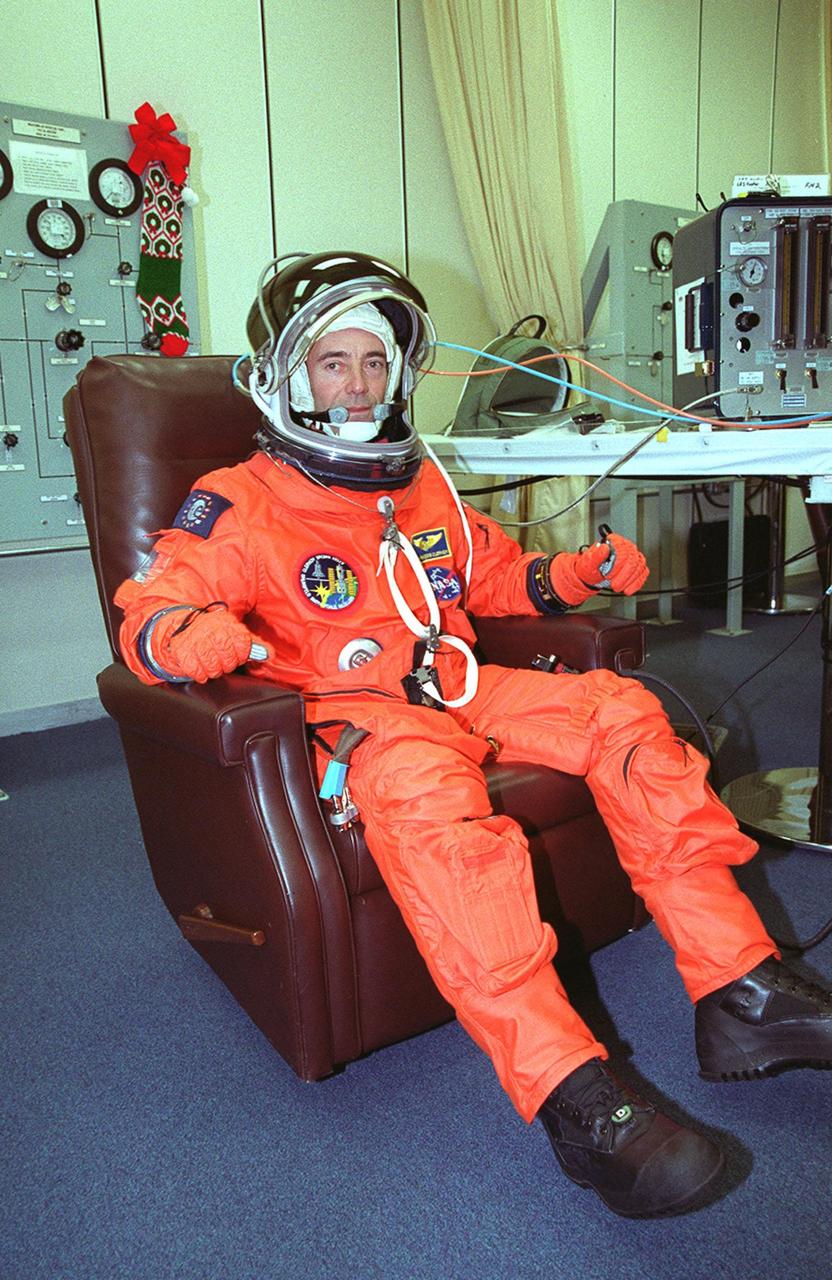
In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-103 Mission Specialist Claude Nicollier of Switzerland waves while having his launch and entry suit checked by a suit techician during final launch preparations. Other crew members are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.) and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. The STS-103 mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is scheduled for launch Dec. 17 at 8:47 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. Mission objectives include replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. After the 8-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Sunday, Dec. 26, at about 6:30 p.m. EST
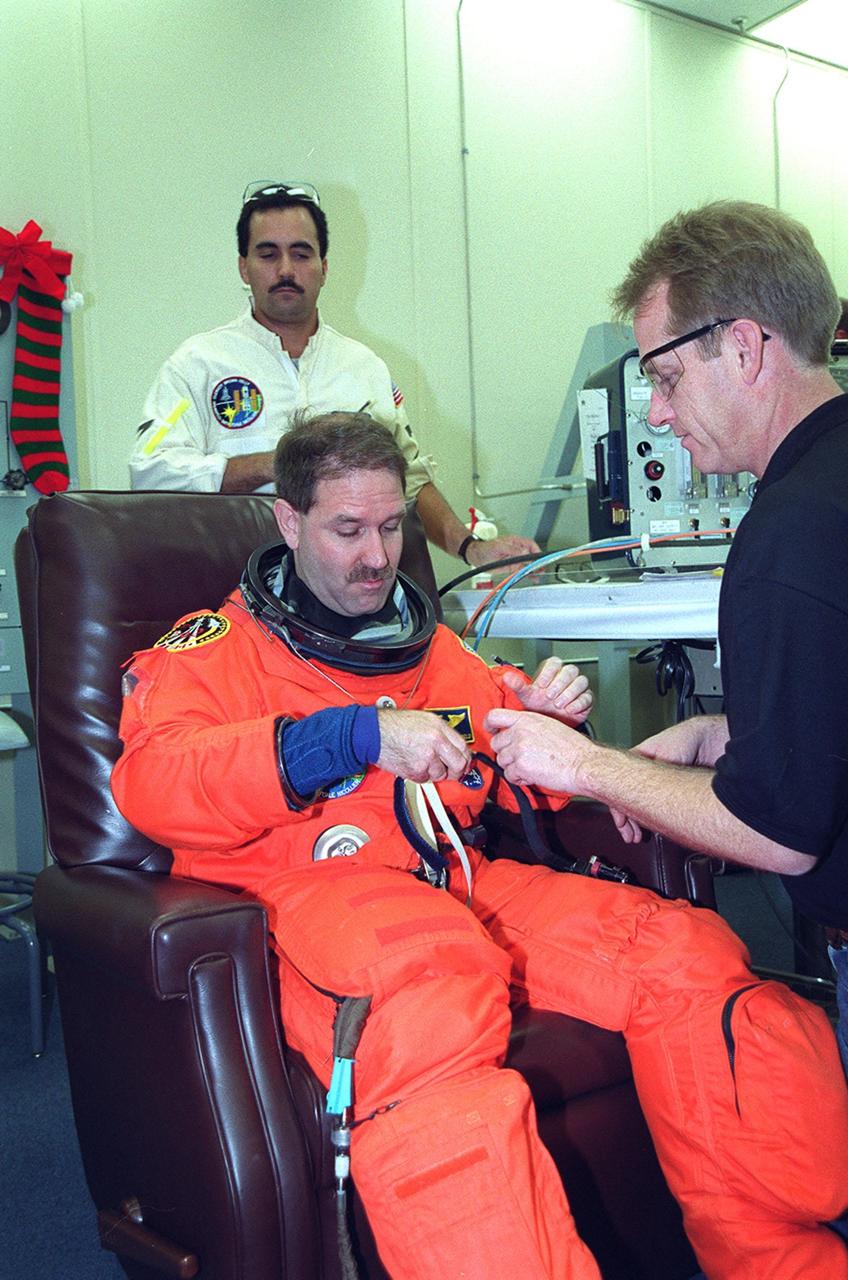

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-103 Mission Specialist John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.) is assisted by a suit technician in donning his launch and entry suit during final launch preparations. Other crew members are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. The STS-103 mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is scheduled for launch Dec. 17 at 8:47 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. Mission objectives include replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. After the 8-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Sunday, Dec. 26, at about 6:30 p.m. EST
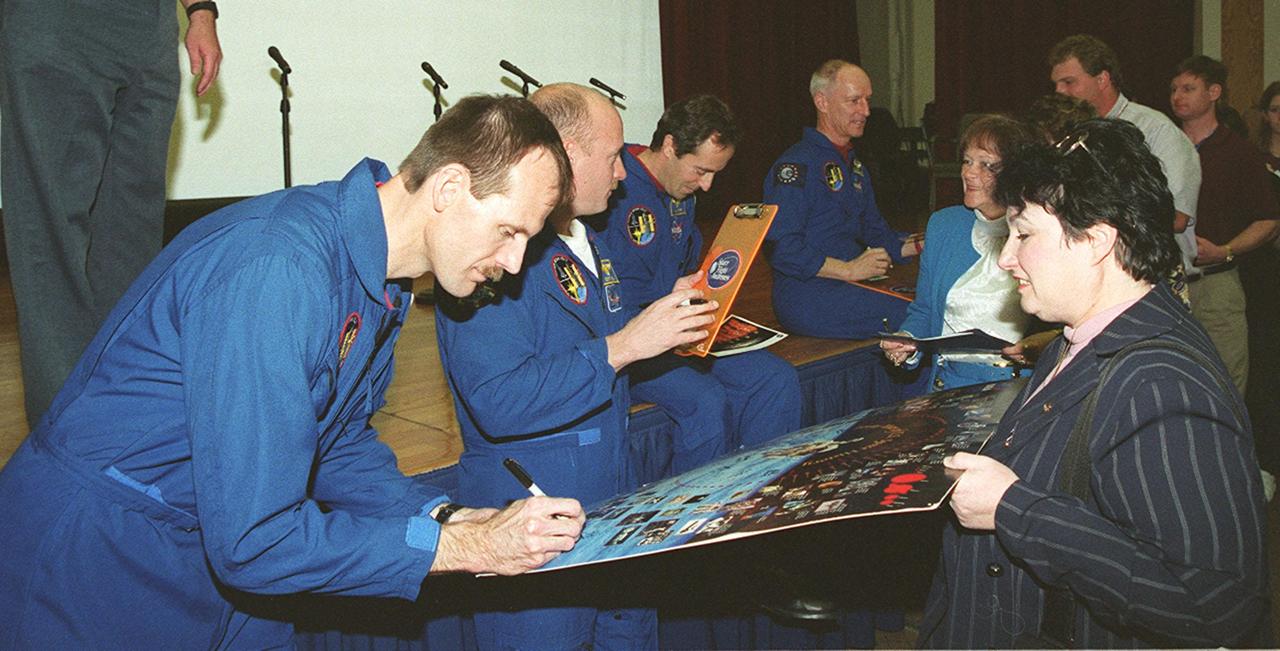

After a presentation at KSC for employees and VIPs about their mission, STS-103 crew members sign autographs. From left are Mission Specialist Steven Smith, Pilot Scott Kelly, and Mission Specialists Jean-Francois Clervoy and Claude Nicollier. The STS-103 mission, servicing the Hubble Space Telescope, included three space walks. STS-103 launched Dec. 19, 1999, and landed Dec. 27, 1999

STS061-23-005 (8 Dec 1993) --- Three members of the STS-61 crew prepare covers to be placed on magnetometers near the top of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Left to right are Richard O. Covey, mission commander; Kenneth D. Bowersox, pilot and Claude Nicollier, mission specialist. On the following day, astronauts Jeffrey A. Hoffman and F. Story Musgrave placed the covers on the magnetometers as they wrapped up five days of servicing on HST.

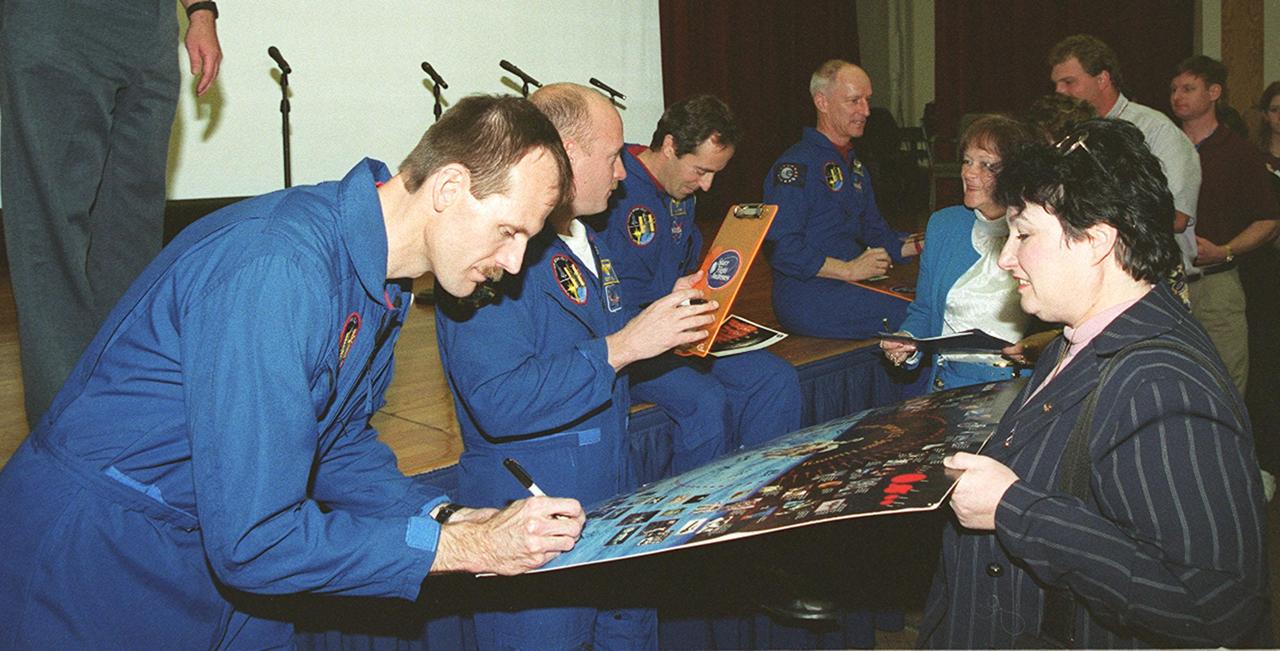
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After a presentation at KSC for employees and VIPs about their mission, STS-103 crew members sign autographs. From left are Mission Specialists Claude Nicollier and Jean-Francois Clervoy, Pilot Scott Kelly and Mission Specialist Steven Smith. The STS-103 mission, servicing the Hubble Space Telescope, included three spacewalks. STS-103 launched Dec. 19, 1999, and landed Dec. 27, 1999.

After a presentation at KSC for employees and VIPs about their mission, STS-103 crew members sign autographs. From left are Mission Specialist Steven Smith, Pilot Scott Kelly, and Mission Specialists Jean-Francois Clervoy and Claude Nicollier. The STS-103 mission, servicing the Hubble Space Telescope, included three space walks. STS-103 launched Dec. 19, 1999, and landed Dec. 27, 1999

STS046-05-019 (31 July-8 Aug 1992) --- The "blue-shift" crew members pose on the flight deck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Atlantis. Left to right are Andrew M. Allen, pilot; Franco Malerba, representing the Italian Space Agency (ASI) and Swiss scientist Claude Nicollier, representing the European Space Agency (ESA).

STS046-19-037 (8 Aug 1992) --- Having completed eight days in Earth-orbit, the crew members prepare for their brief journey home. Left to right are Andrew M. Allen, pilot; Claude Nicollier, mission specialist representing the European Space Agency (ESA); and Marsha S. Ivins, mission specialist. Just out of frame, at left, is Loren J. Shriver, mission commander, who guided the Space Shuttle Atlantis in for its Kennedy Space Center (KSC), Florida landing.
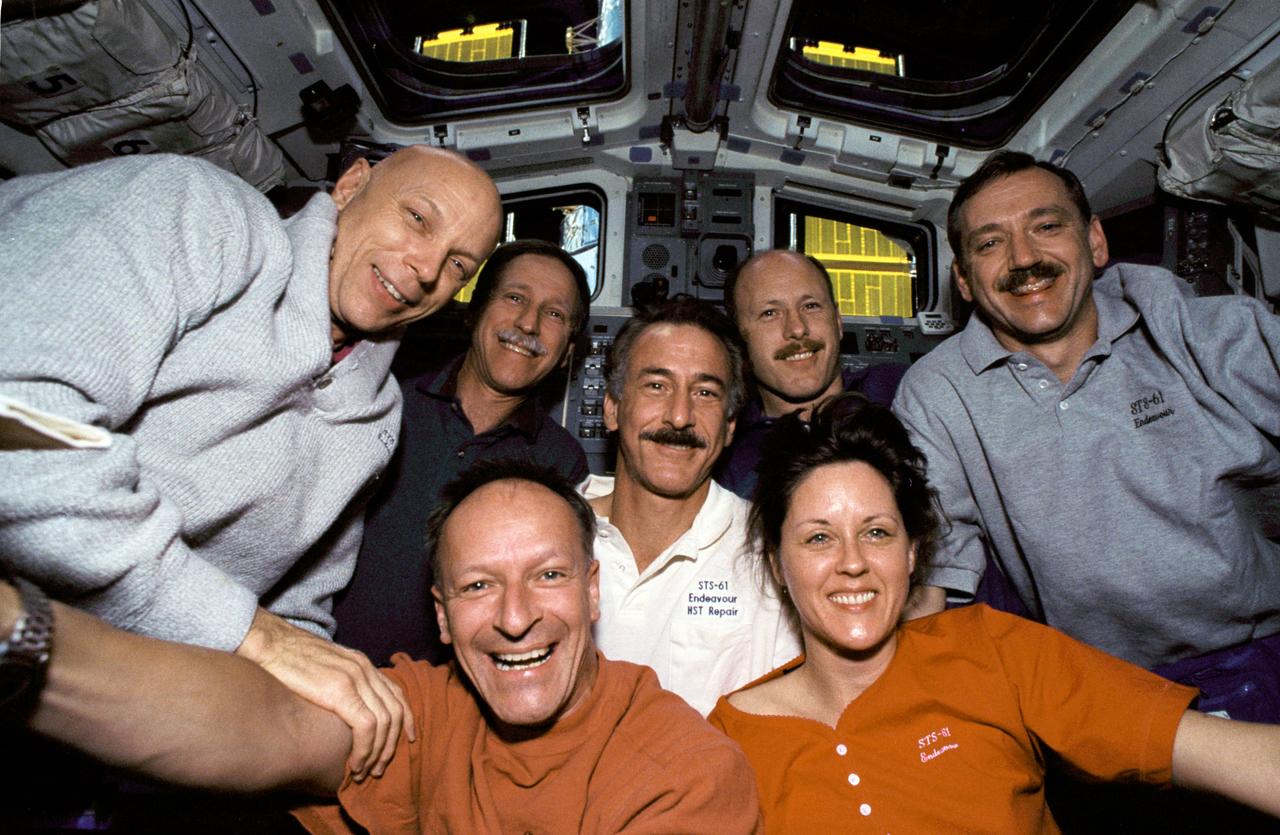

STS061-05-031 (2-13 Dec 1993) --- With the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) berthed in Endeavour's cargo bay, crew members for the STS-61 mission pause for a crew portrait on the flight deck. Left to right are F. Story Musgrave, Richard O. Covey, Claude Nicollier, Jeffrey A. Hoffman, Kenneth D. Bowersox, Kathryn C. Thornton and Thomas D. Akers.
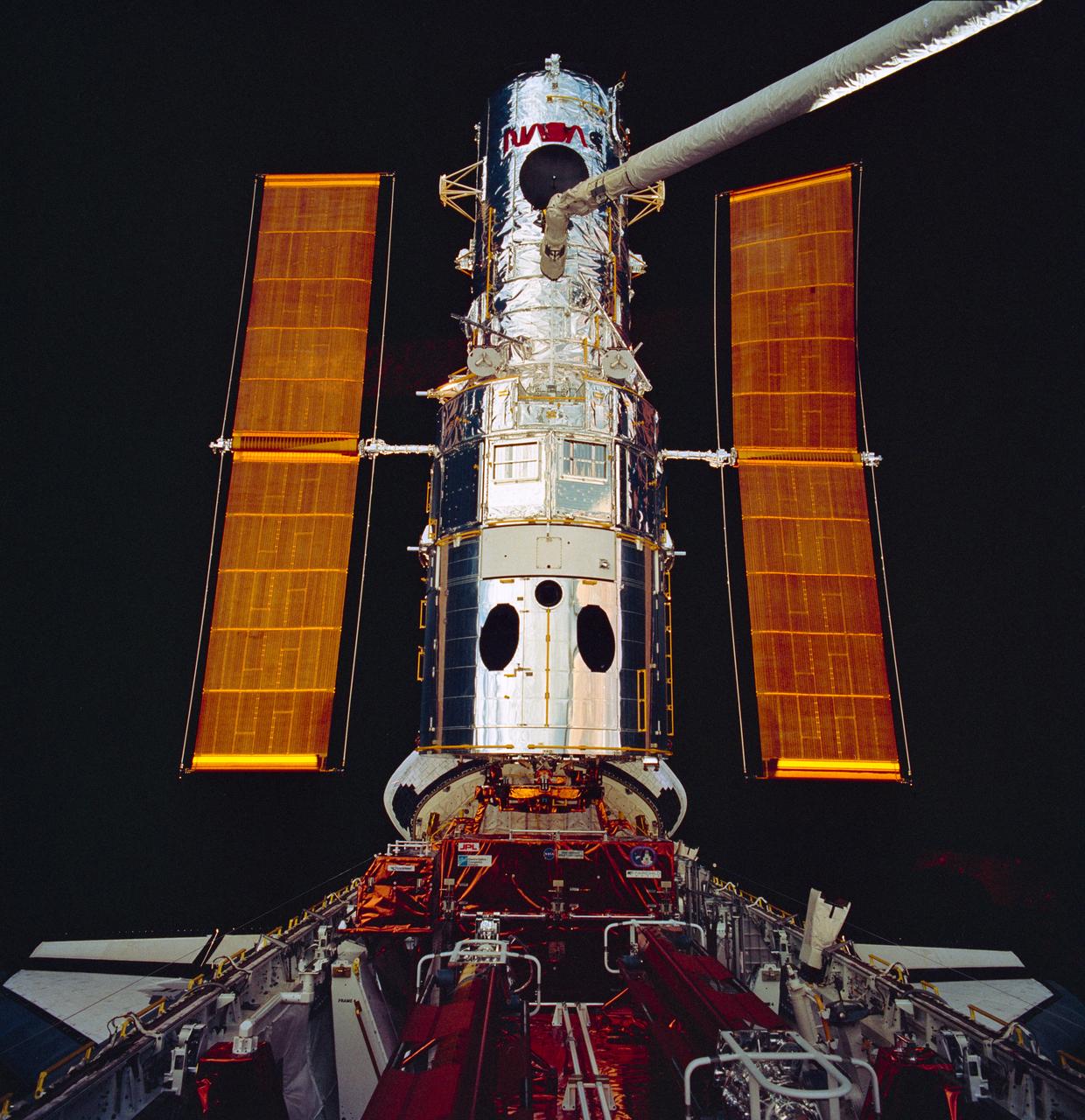

STS061-79-072 (4 Dec 1993) --- The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is backdropped against the blackness of space in this 70mm frame recorded during a video survey of the spacecraft following the telescope's recent berthing in the Space Shuttle Endeavour's cargo bay. European Space Agency (ESA) scientist Claude Nicollier controlled the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm slowly so that mounted TV cameras could show flight controllers the various areas on the telescope.
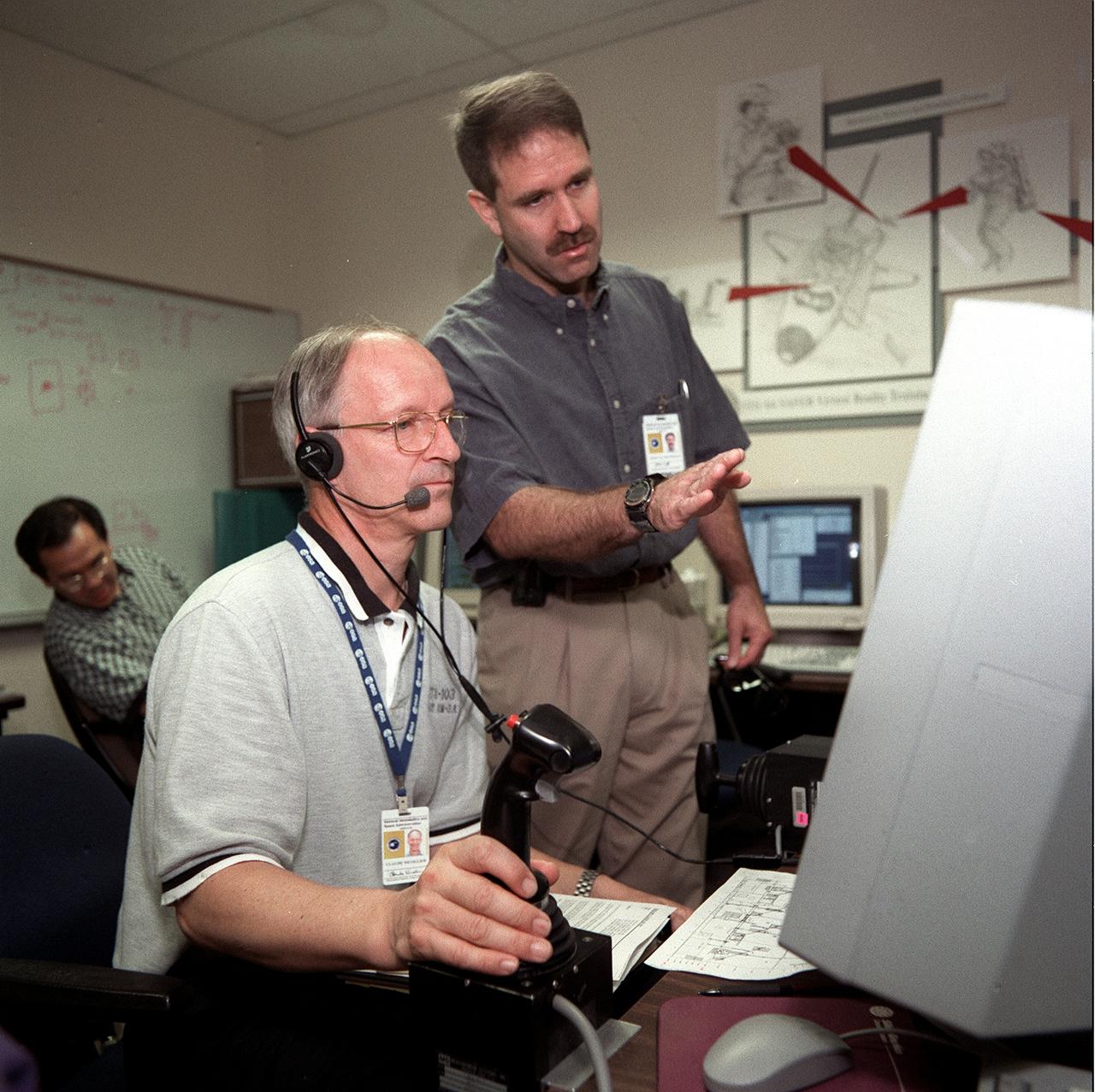

S99-05679 (24 May 1999) --- Astronauts Claude Nicollier (seated), representing the European Space Agency (ESA), and John M. Grunsfeld use virtual reality hardware to rehearse some of their duties for the upcoming STS-103 mission, NASA's third servicing visit to the Earth-orbiting Hubble Space Telescope (HST). The two mission specialists will be joined by five other astronauts, including a second ESA representative, for the STS-103 mission, scheduled for autumn of this year.
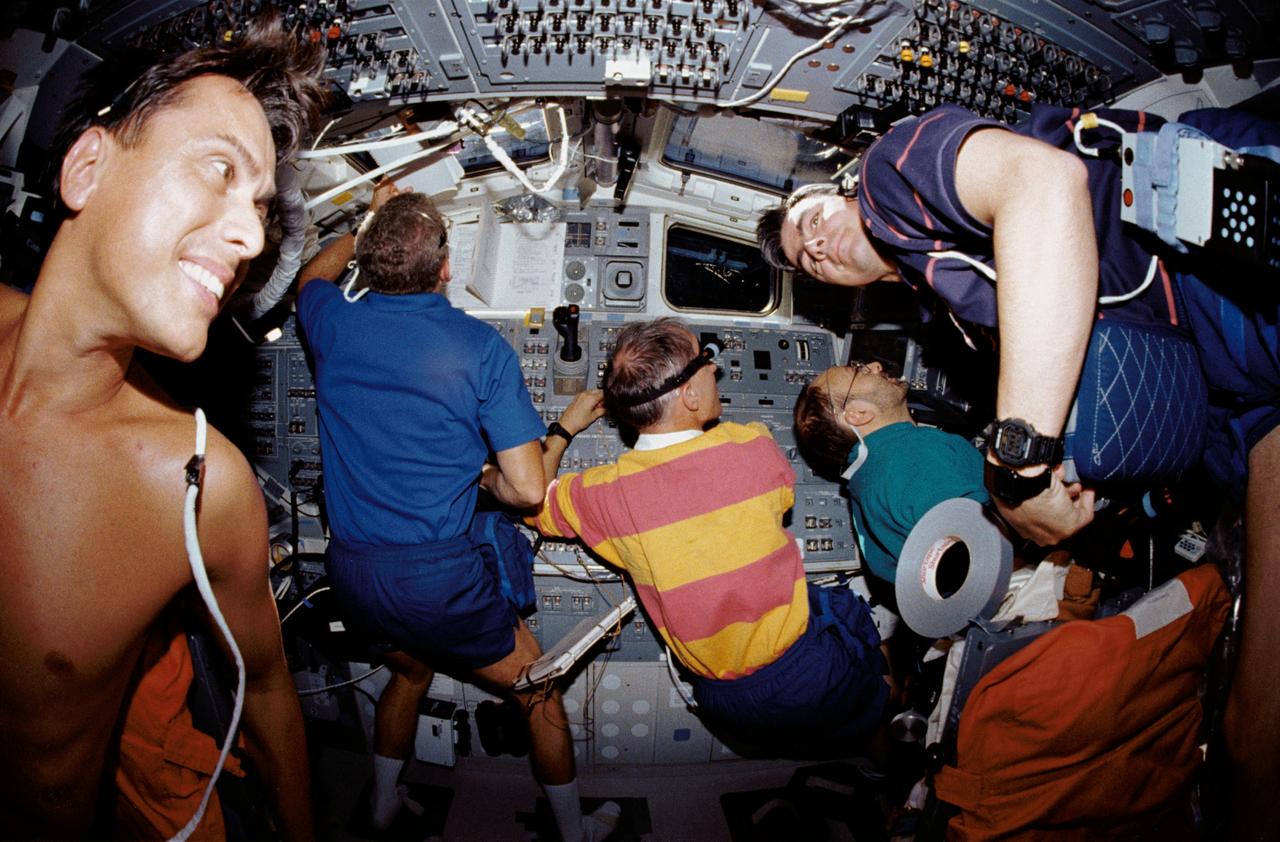

STS046-14-013 (4 Aug. 1992) --- Five of the seven crew members squeezed into this busy scene on the Space Shuttle Atlantis' flight deck during operations with the Tethered Satellite System (TSS). Pictured are, left to right, Franklin R. Chang-Diaz, Loren J. Shriver, Claude Nicollier, Franco Malerba and Andrew M. Allen. Not pictured are astronauts Jeffrey A. Hoffman and Marsha S. Ivins. Mission specialist Ivins used a 35mm camera with a 16mm lens to take this picture.
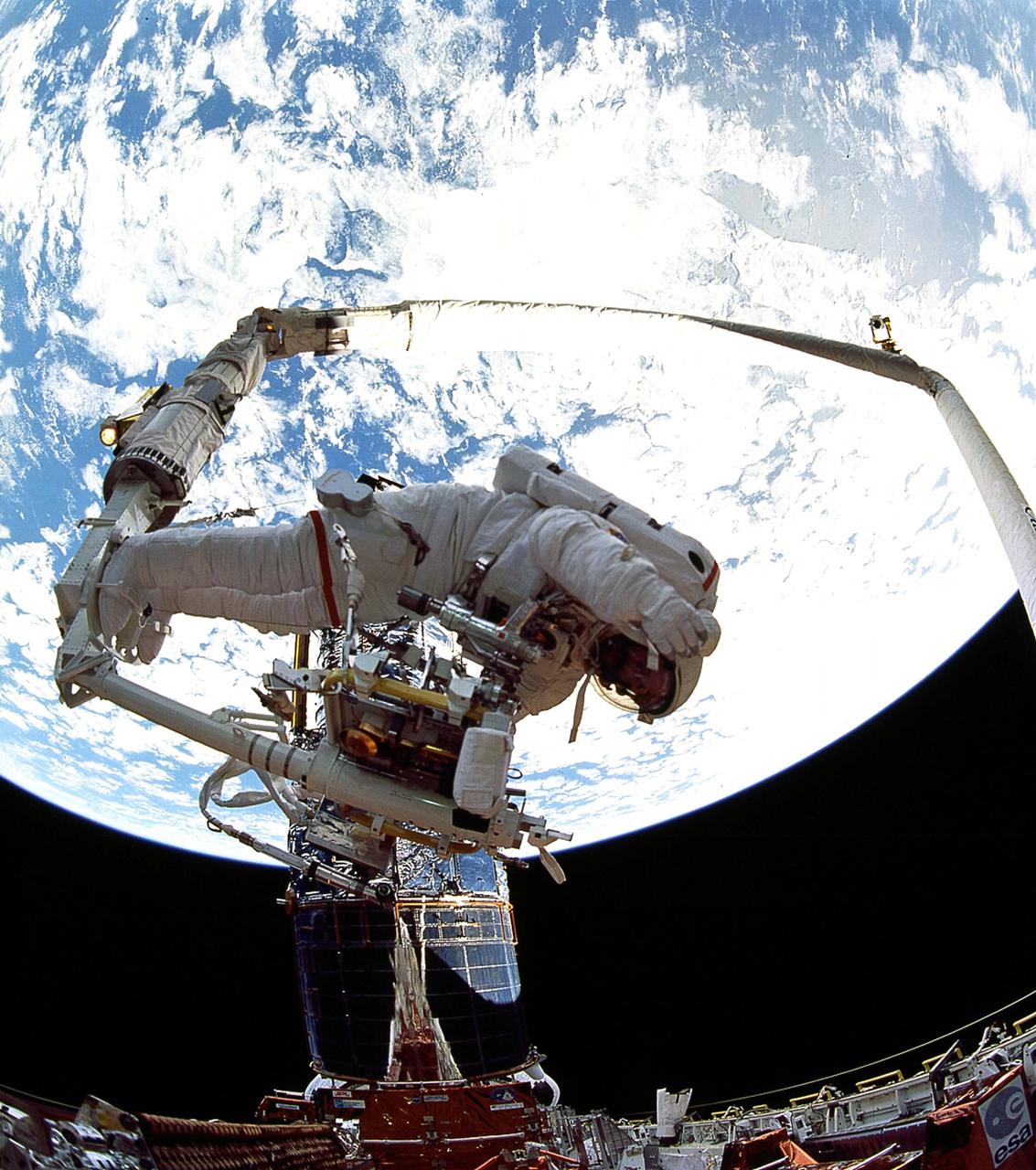

STS061-105-026 (7 Dec. 1993) --- Astronaut Jeffrey A. Hoffman signals directions to European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Claude Nicollier, as the latter controls the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm during the third of five Extravehicular Activities (EVA) on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission. Astronauts Hoffman and F. Story Musgrave earlier changed out the Wide Field\Planetary Camera (WF\PC).
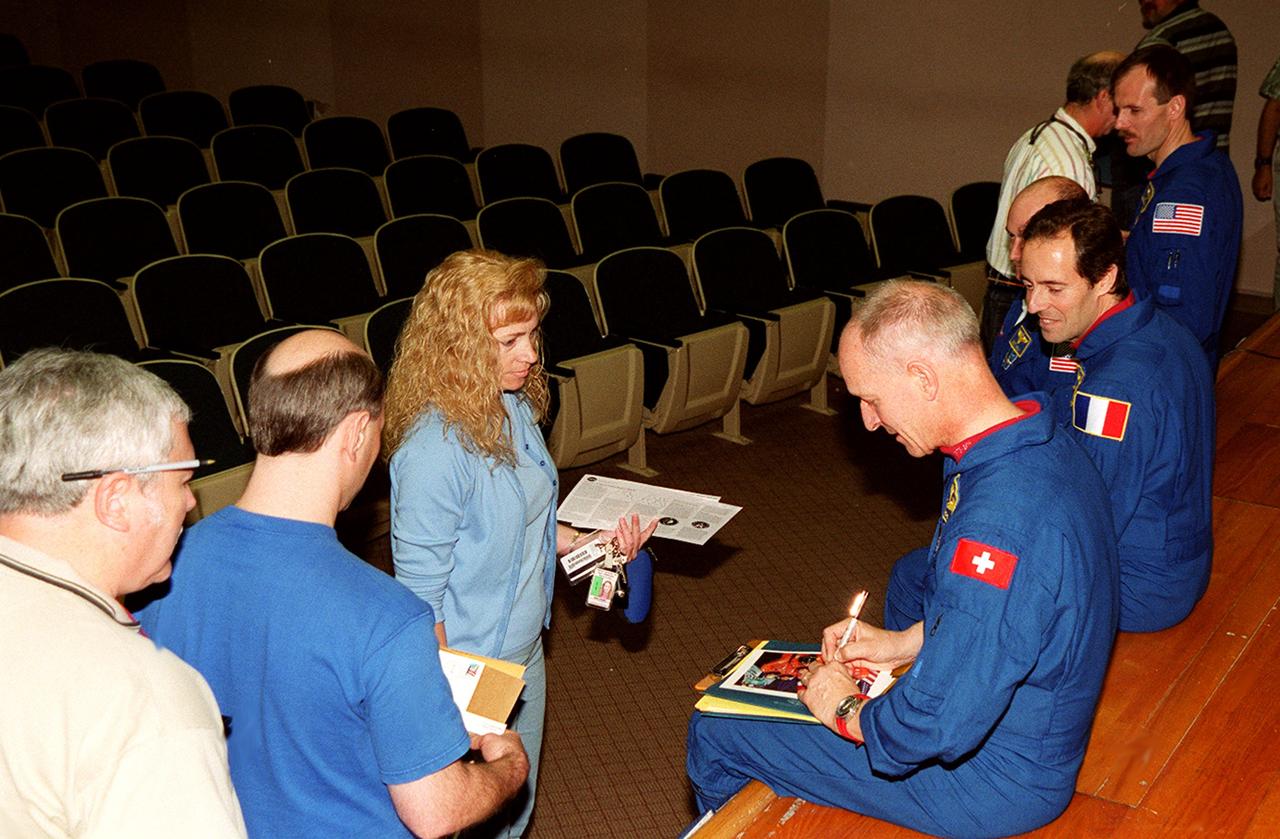

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After a presentation at KSC for employees and VIPs about their mission, STS-103 crew members sign autographs. From left are Mission Specialists Claude Nicollier and Jean-Francois Clervoy, Pilot Scott Kelly and Mission Specialist Steven Smith. The STS-103 mission, servicing the Hubble Space Telescope, included three spacewalks. STS-103 launched Dec. 19, 1999, and landed Dec. 27, 1999.
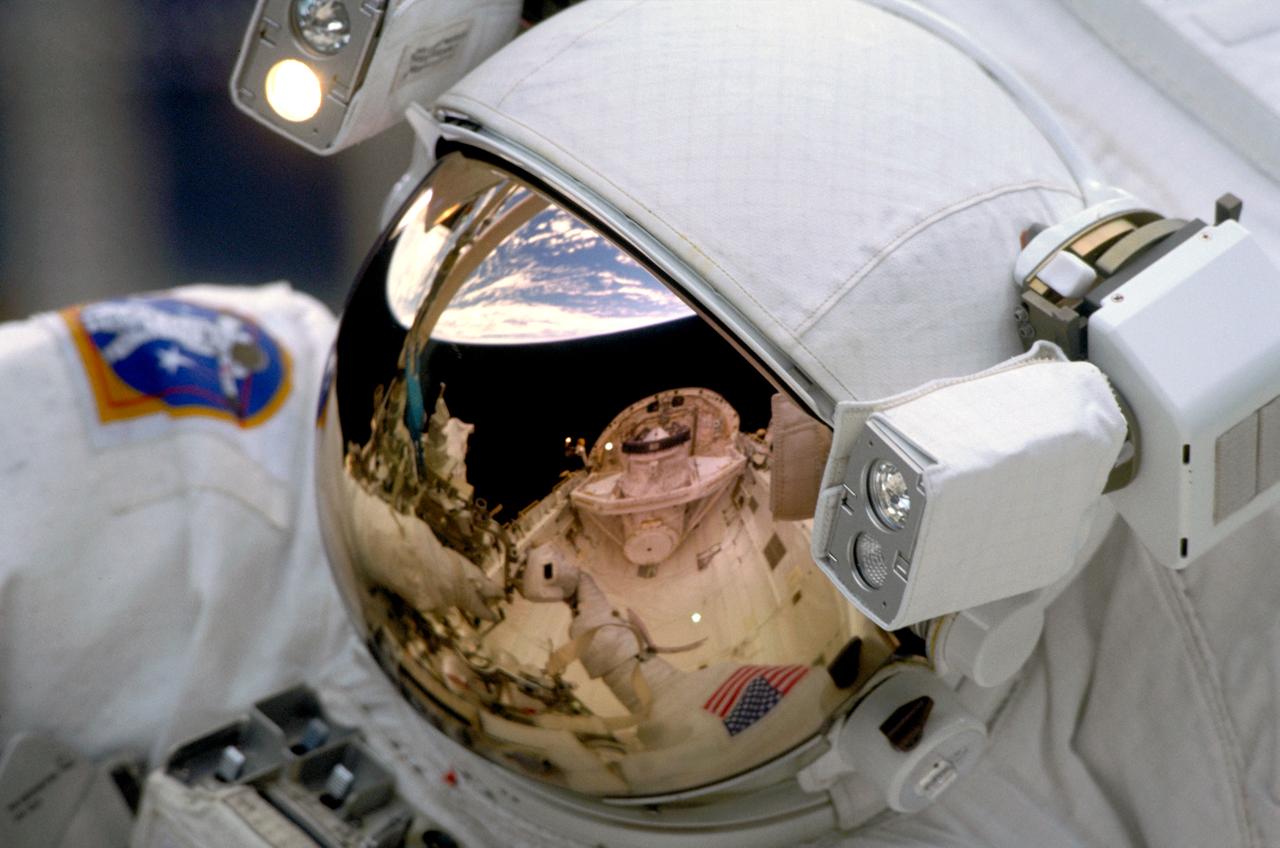

STS103-302-002 (19- 27 December 1999)---.The Space Shuttle Discovery's Cargo Bay and Crew Module, and the Earth's horizon are reflected in the helmet visor of one of the space walking astronauts on STS-103..Astronauts Steven L. Smith, John M. Grunsfeld, C. Michael Foale and Claude Nicollier participated in three days of.extravehicular activity on the NASA's third servicing visit to the Hubble Space Telescope (HST).
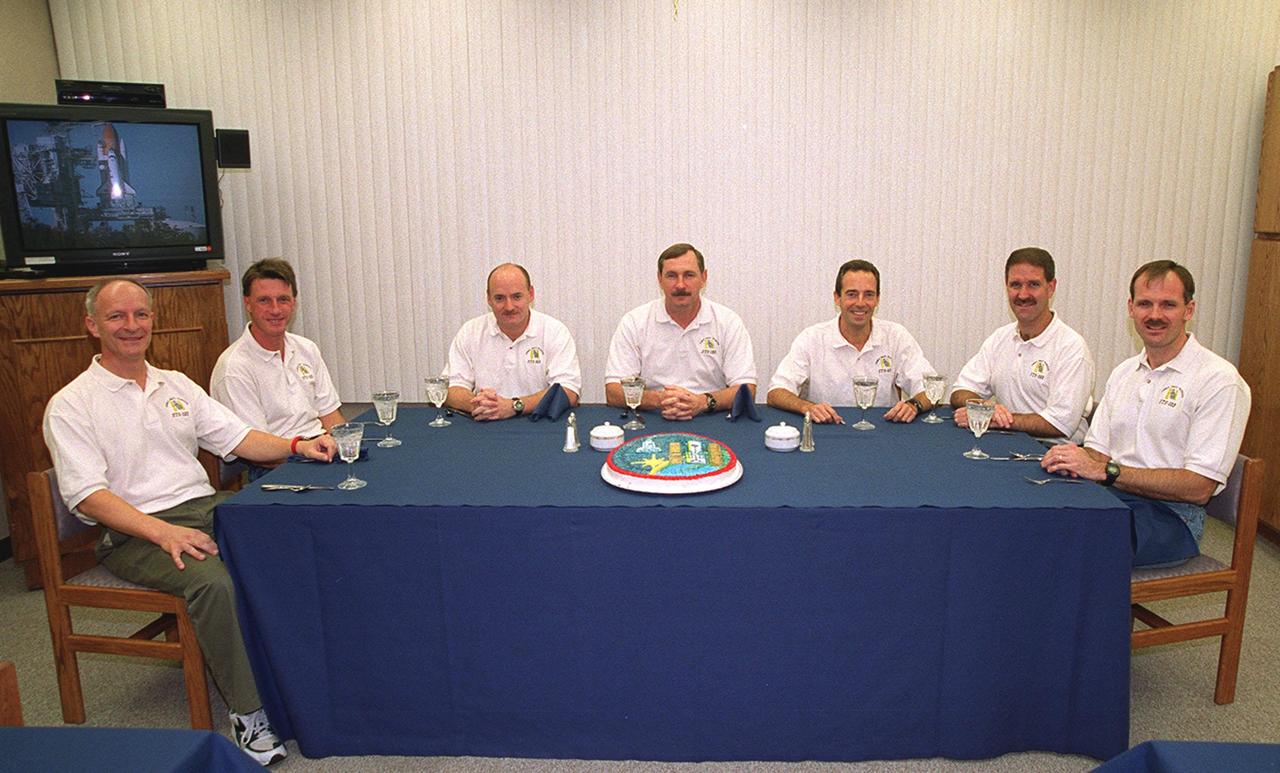

For the second time in two days, the STS-103 crew have breakfast before suiting up for launch. From left are Mission Specialists Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), Pilot Scott J. Kelly, Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., and Mission Specialists Jean-Francois Clervoy of France, John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.) and Steven L. Smith. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. The previous launch attempt on Dec. 17 was scrubbed about 8:52 p.m. due to numerous violations of weather launch commit criteria at KSC. The mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is now scheduled for launch Dec. 19 at 7:50 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. Mission objectives include replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST
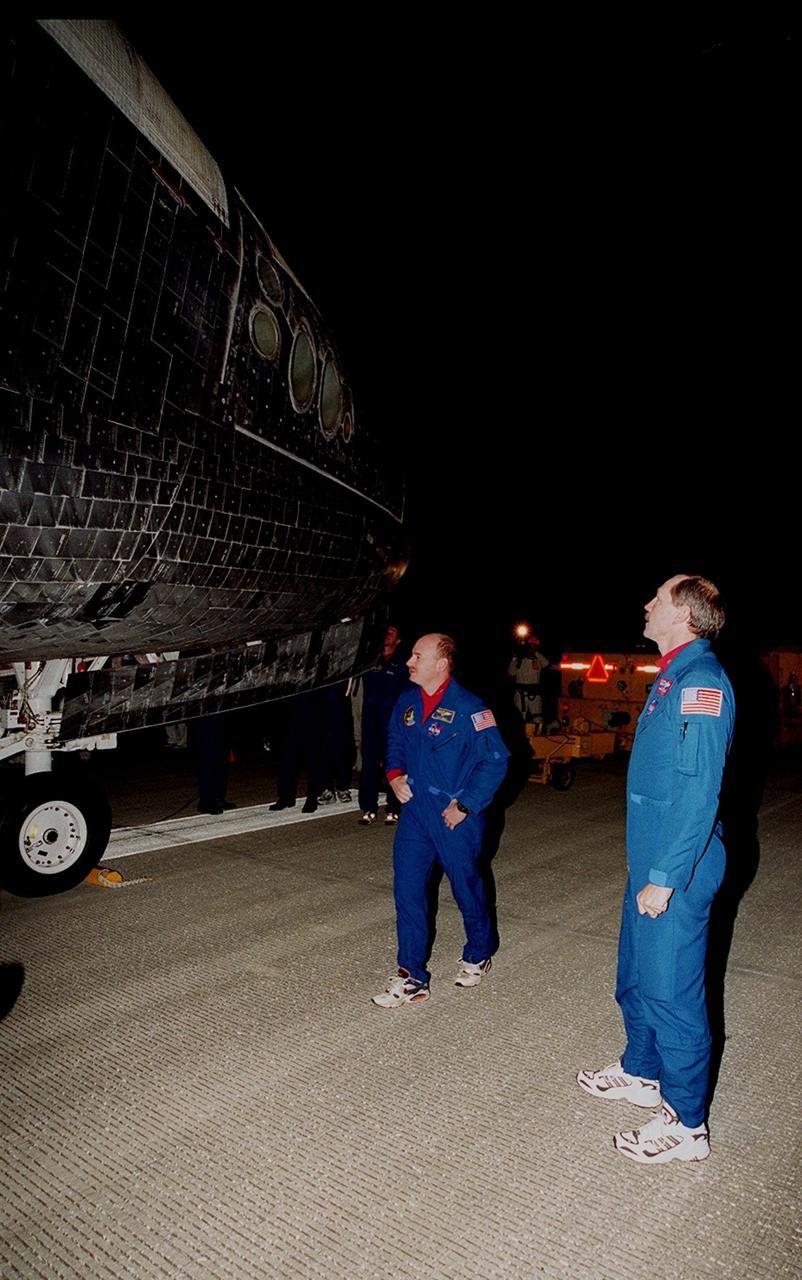

After landing at the Shuttle Landing Facility, STS-103 Pilot Scott J. Kelly (left) and Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr. (right) look at the tiles on orbiter Discovery. They and other crew members Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Jean-Francois Clervoy of France and Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, completed a successful eight-day mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope, spending the Christmas holiday in space in order to accomplish their mission before the end of 1999. During the mission, Discovery's four space-walking astronauts, Smith, Foale, Grunsfeld and Nicollier, spent 24 hours and 33 minutes upgrading and refurbishing Hubble, making it more capable than ever to renew its observations of the universe. Mission objectives included replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. Hubble was released from the end of Discovery's robot arm on Christmas Day. Main gear touchdown was at 7:00:47 p.m. EST. Nose gear touchdown occurred at 7:00:58 p.m. EST and wheel stop at 7:01:34 p.m. EST. This was the 96th flight in the Space Shuttle program and the 27th for the orbiter Discovery. The landing was the 20th consecutive Shuttle landing in Florida and the 13th night landing in Shuttle program history
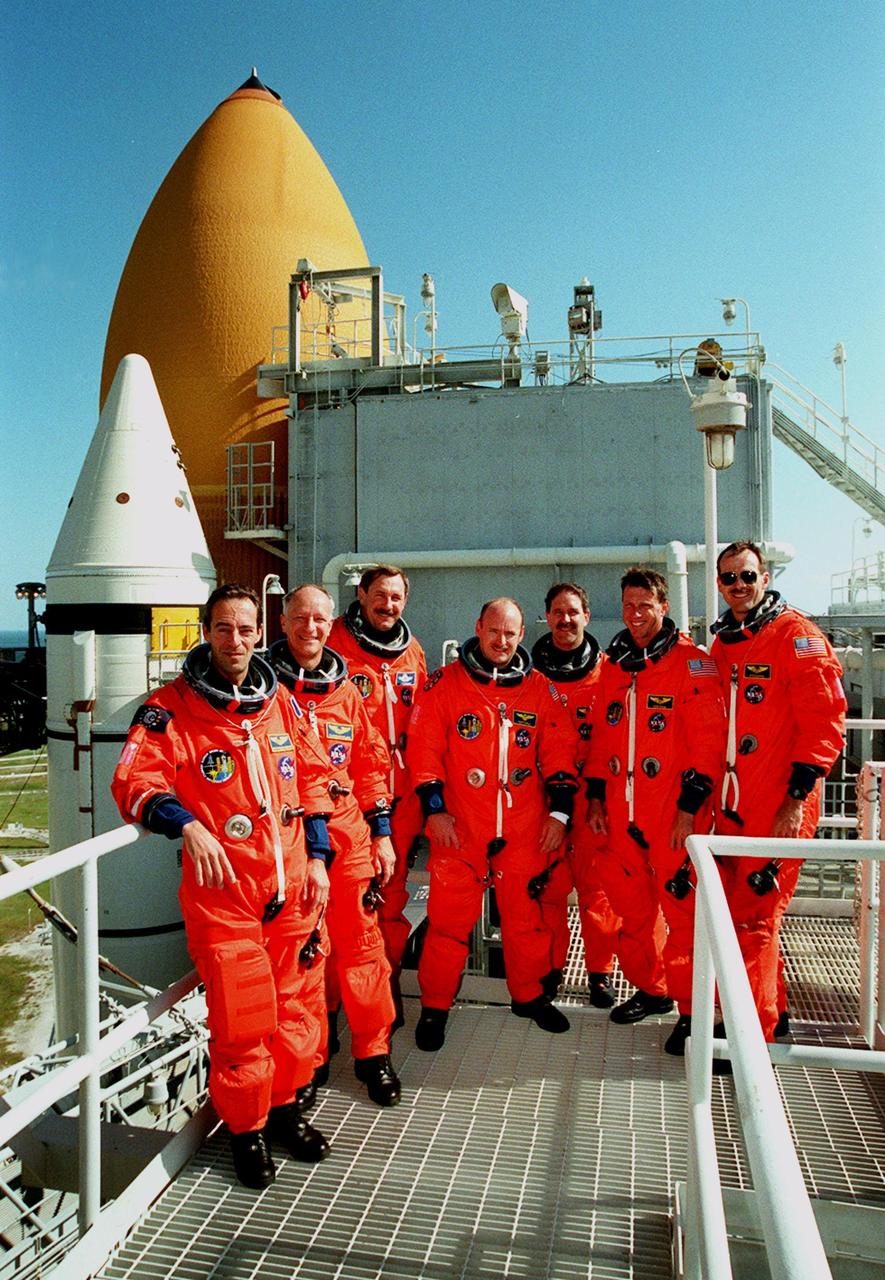

Taking a break during emergency egress training at Launch Pad 39B are (left to right) STS-103 Mission Specialists Jean-François Clervoy of France, Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly, and Mission Specialists John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.) and Steven L. Smith. Clervoy and Nicollier are with the European Space Agency. The training is part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities that also include opportunities to inspect the mission payloads in the orbiter's payload bay and simulated countdown exercises. STS-103 is a "call-up" mission due to the need to replace and repair portions of the Hubble Space Telescope, including the gyroscopes that allow the telescope to point at stars, galaxies and planets. The STS-103 crew will be replacing a Fine Guidance Sensor, an older computer with a new enhanced model, an older data tape recorder with a solid-state digital recorder, a failed spare transmitter with a new one, and degraded insulation on the telescope with new thermal insulation. The crew will also install a Battery Voltage/Temperature Improvement Kit to protect the spacecraft batteries from overcharging and overheating when the telescope goes into a safe mode. Four EVA's are planned to make the necessary repairs and replacements on the telescope. The mission is targeted for launch Dec. 6 at 2:37 a.m. EST
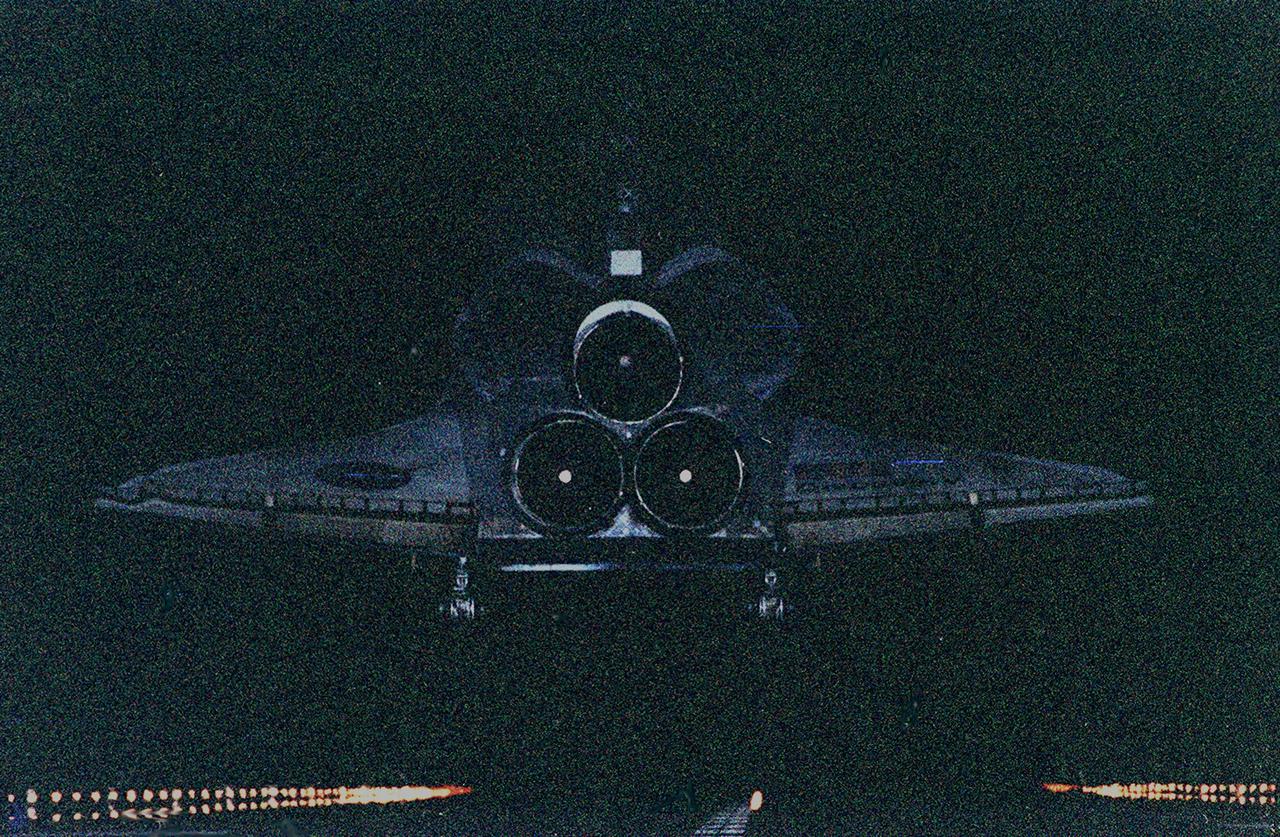
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- The orbiter Discovery looks like a blue ghost as it drops from the darkness onto lighted runway 33 at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility. After traveling more than 3,267,000 miles on a successful eight-day mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope, the orbiter touches down at 7:00:47 p.m. EST. Aboard are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly, and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France, who spent the Christmas holiday in space in order to accomplish their mission before the end of 1999. During the mission, Discovery's four space-walking astronauts, Smith, Foale, Grunsfeld and Nicollier, spent 24 hours and 33 minutes upgrading and refurbishing Hubble, making it more capable than ever to renew its observations of the universe. Mission objectives included replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. Hubble was released from the end of Discovery's robot arm on Christmas Day. This was the 96th flight in the Space Shuttle program and the 27th for the orbiter Discovery. The landing was the 20th consecutive Shuttle landing in Florida and the 13th night landing in Shuttle program history
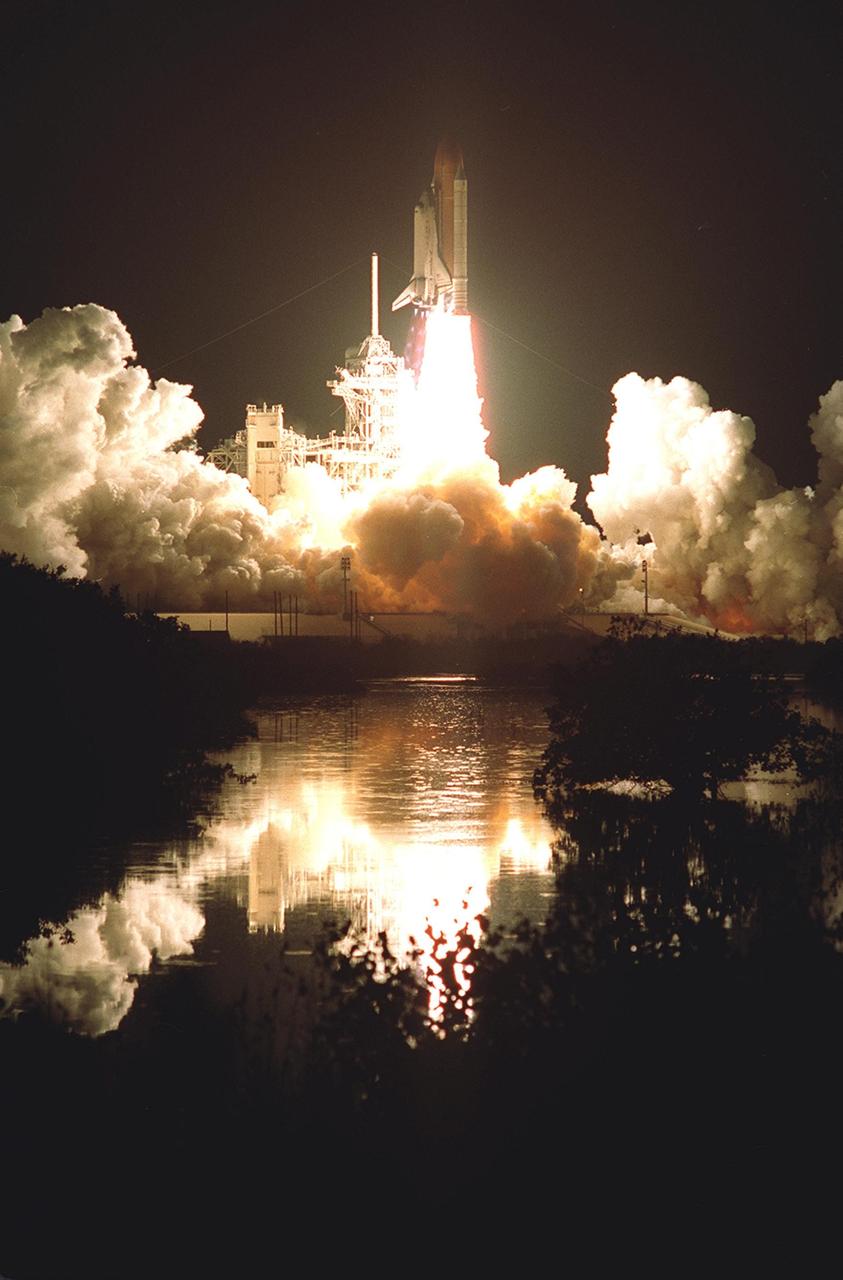

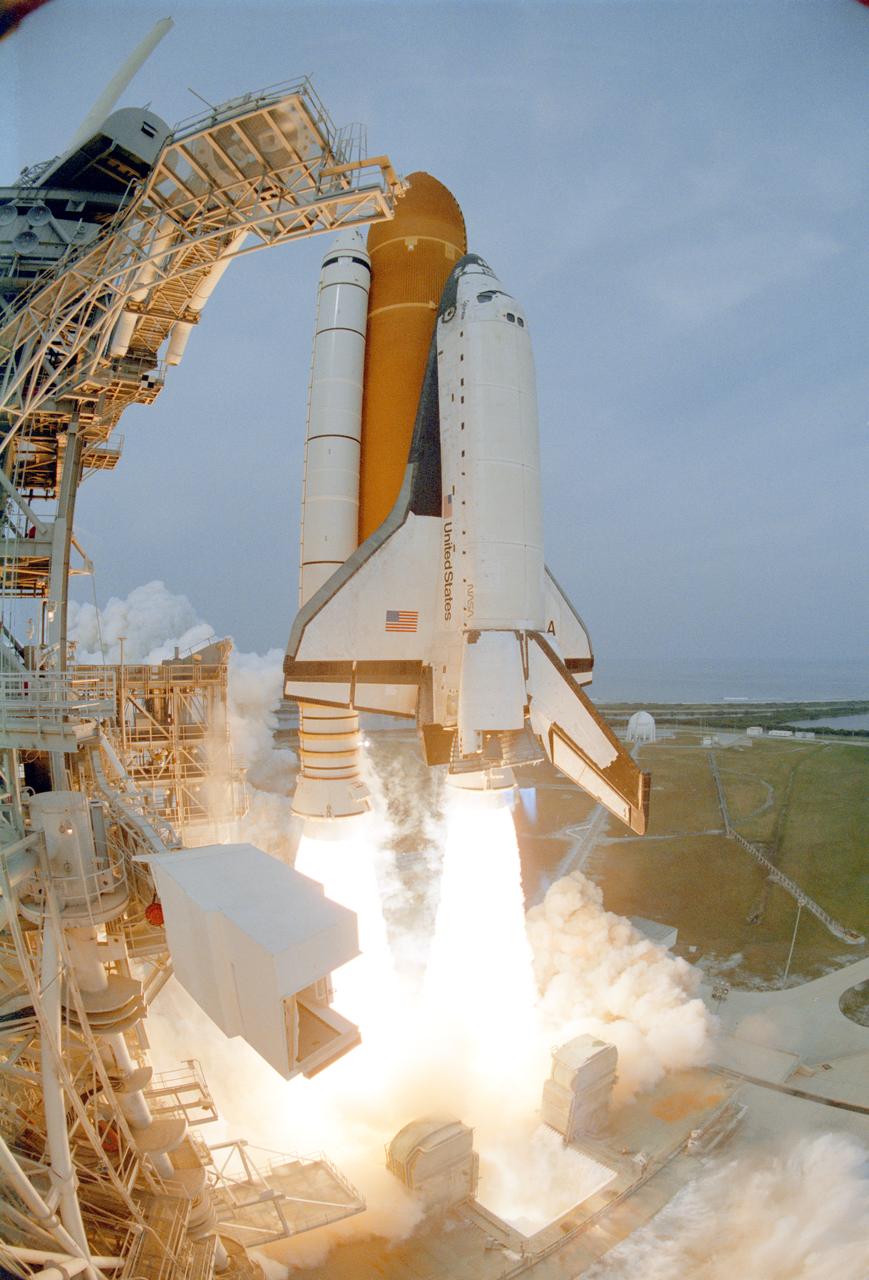
Turning night into day, the brilliance of Space Shuttle Discovery's launch is reflected in the waters nearby. Liftoff occurred at 7:50 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. On board are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. STS-103 is a Hubble Servicing Mission, with three planned space walks designed to install new equipment and replace old. The primary objective is to replace the gyroscopes that make up the three Rate Sensor Units. Extravehicular activities include installing a new computer, changing out one of the Fine Guidance Sensors, replacing a tape recorder with a new solid state recorder, and installing a voltage/temperature improvement kit, and begin repairing the insulation on the telescope's outer surface. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST. This is the 27th flight of Discovery and the 96th mission in the Space Shuttle Program. It is the third launch at Kennedy Space Center in 1999
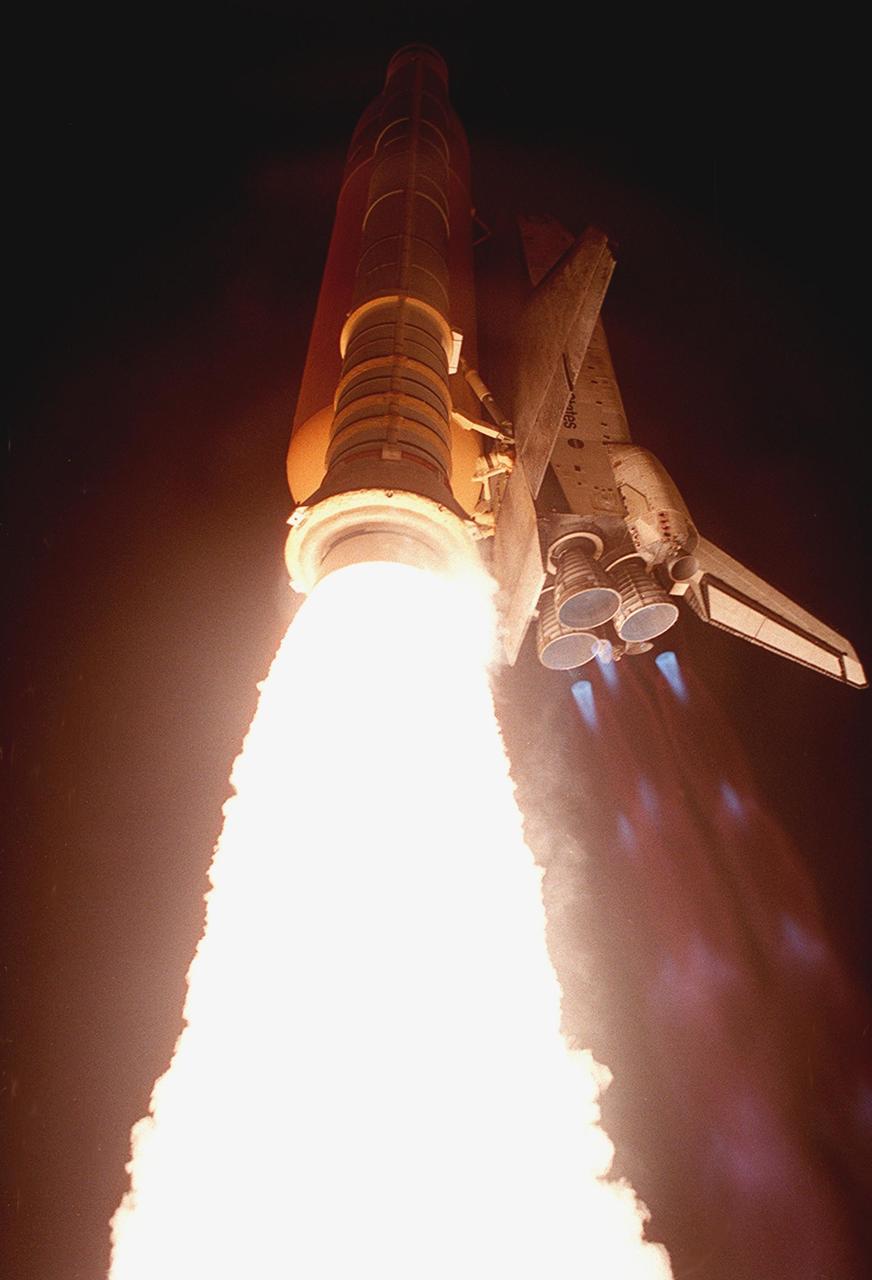

Like a roman candle, Space Shuttle Discovery roars into the clear night sky trailing brilliant exhaust from the solid rocket boosters (center) and blue mach diamonds from the main engine nozzles. Liftoff occurred at 7:50 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. On board are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. STS-103 is a Hubble Servicing Mission, with three planned space walks designed to install new equipment and replace old. The primary objective is to replace the gyroscopes that make up the three Rate Sensor Units. Extravehicular activities include installing a new computer, changing out one of the Fine Guidance Sensors, replacing a tape recorder with a new solid state recorder, and installing a voltage/temperature improvement kit, and begin repairing the insulation on the telescope's outer surface. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST. This is the 27th flight of Discovery and the 96th mission in the Space Shuttle Program. It is the third launch at Kennedy Space Center in 1999
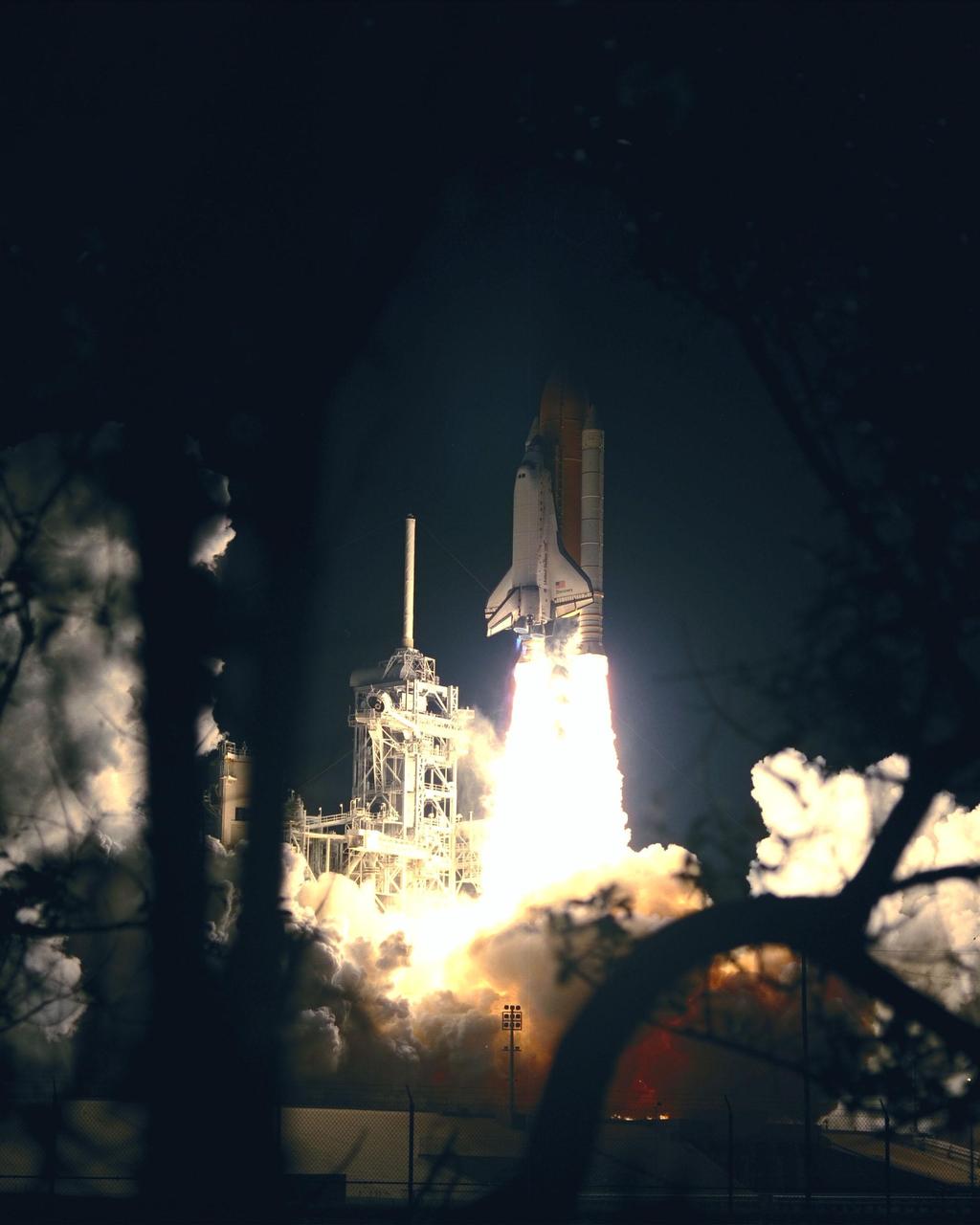

The successful liftoff of Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-103 illuminates the night sky. Liftoff occurred at 7:50 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. On board are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. STS-103 is a Hubble Servicing Mission, with three planned space walks designed to install new equipment and replace old. The primary objective is to replace the gyroscopes that make up the three Rate Sensor Units. Extravehicular activities include installing a new computer, changing out one of the Fine Guidance Sensors, replacing a tape recorder with a new solid state recorder, and installing a voltage/temperature improvement kit, and begin repairing the insulation on the telescope's outer surface. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST. This is the 27th flight of Discovery and the 96th mission in the Space Shuttle Program. It is the third launch at Kennedy Space Center in 1999

(Nikon camera D1 test)Amid billows of smoke and steam, Space Shuttle Discovery lights up the clear night sky as it lifts off on time at 7:50:00.069 EST from Launch Pad 39B on mission STS-103. On board are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. STS-103 is a Hubble Servicing Mission, with three planned space walks designed to install new equipment and replace old. The primary objective is to replace the gyroscopes that make up the three Rate Sensor Units. Extravehicular activities include installing a new computer, changing out one of the Fine Guidance Sensors, replacing a tape recorder with a new solid state recorder, and installing a voltage/temperature improvement kit, and begin repairing the insulation on the telescope's outer surface. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST. This is the 27th flight of Discovery and the 96th mission in the Space Shuttle Program. It is the third launch at Kennedy Space Center in 1999
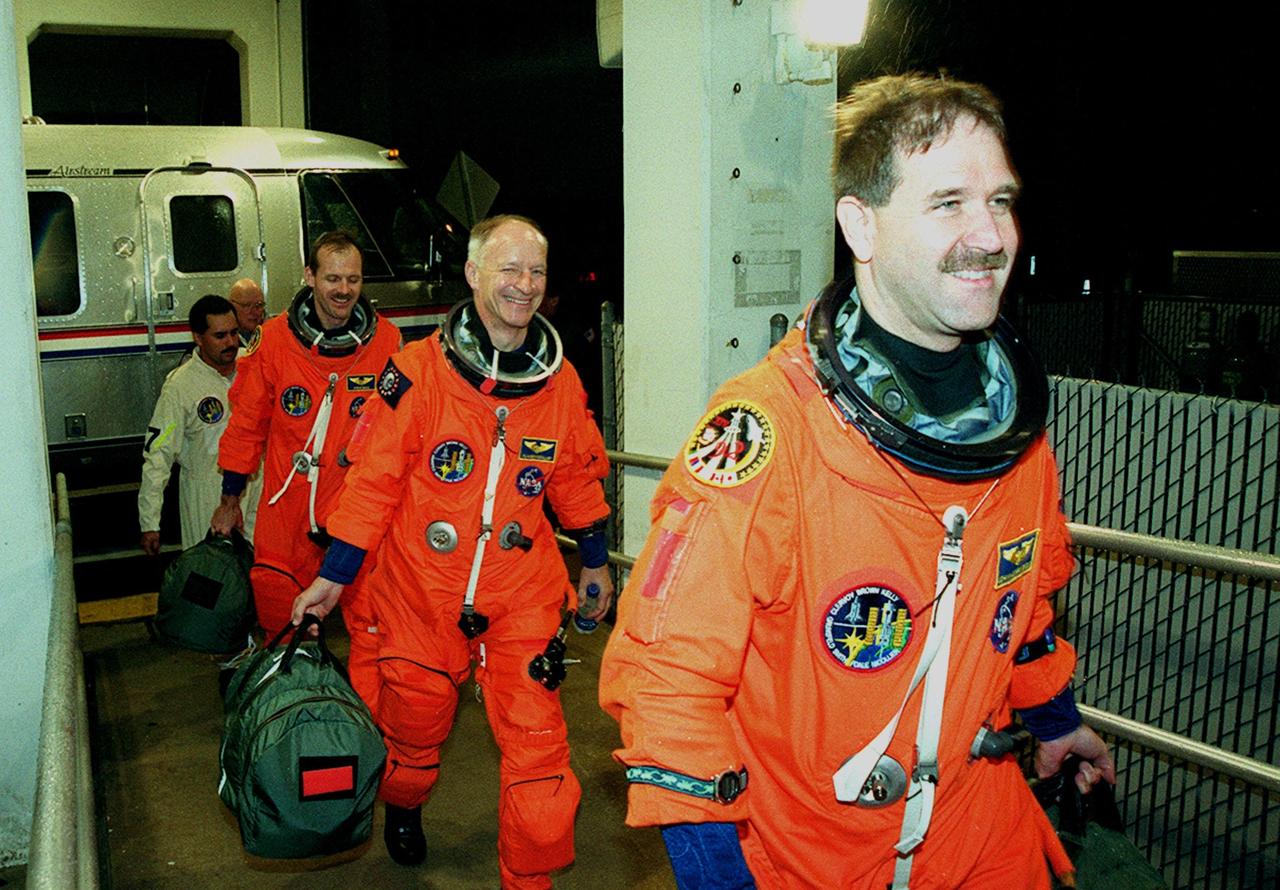

STS-103 crew members head back to the Operations and Checkout Building after the launch of Space Shuttle Discovery was scrubbed due to unfavorable weather conditions. In the lead (right) is Mission Specialist John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), followed by Mission Specialists Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Steven L. Smith. . Other crew members are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly, and Mission Specialists C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.) and Jean-Francois Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. The STS-103 mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is rescheduled for launch Dec. 18 at 8:21 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. Mission objectives include replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Sunday, Dec. 26, at about 6:00 p.m. EST
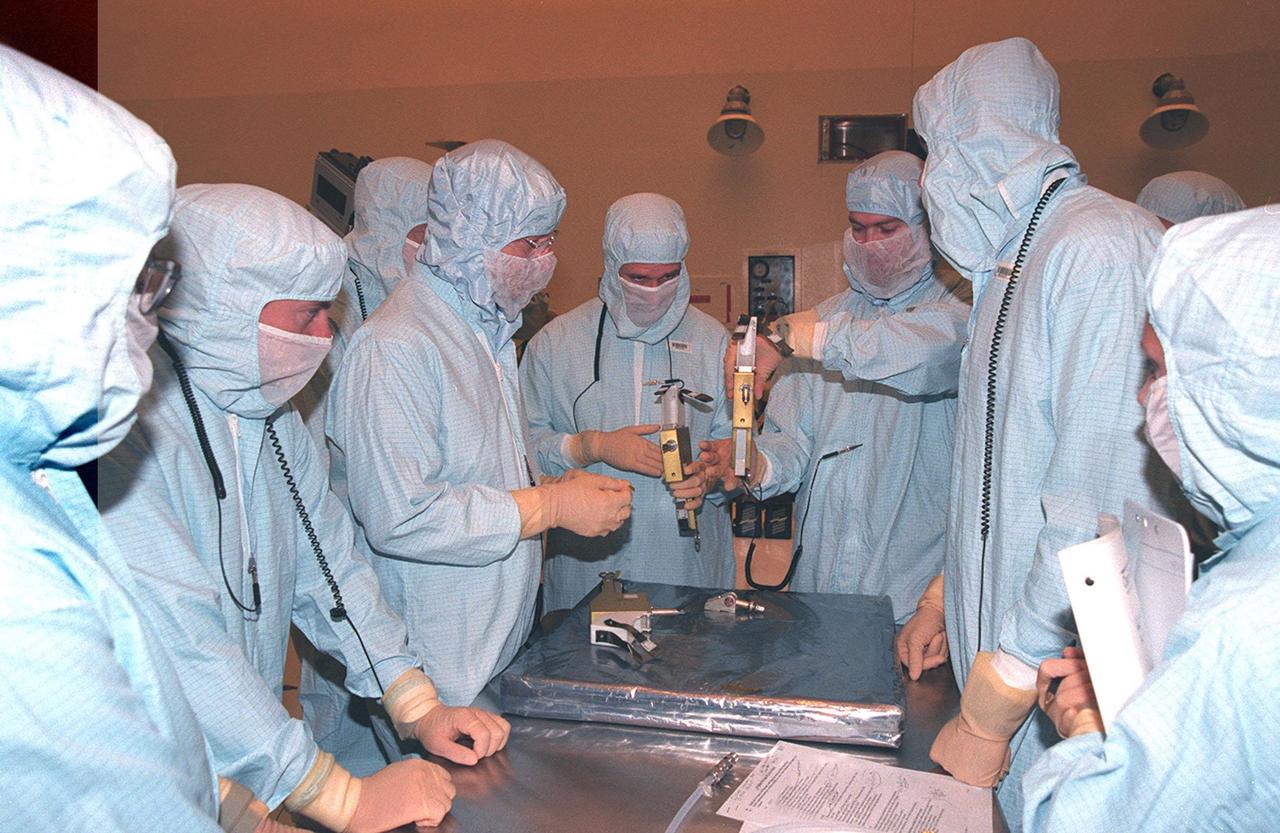

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, the STS-103 crew look over equipment to be used during their mission. The seven-member crew, taking part in a Crew Equipment Interface Test, are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly, and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. Mission STS-103 is a "call-up" due to the need to replace portions of the pointing system, the gyros, which have begun to fail on the Hubble Space Telescope. Although Hubble is operating normally and conducting its scientific observations, only three of its six gyroscopes are working properly. The gyroscopes allow the telescope to point at stars, galaxies and planets. The STS-103 crew will not only replace gyroscopes, it will also replace a Fine Guidance Sensor and an older computer with a new enhanced model, an older data tape recorder with a solid state digital recorder, a failed spare transmitter with a new one, and degraded insulation on the telescope with new thermal insulation. The crew will also install a Battery Voltage/Temperature Improvement Kit to protect the spacecraft batteries from overcharging and overheating when the telescope goes into a safe mode. The scheduled launch date in October is under review
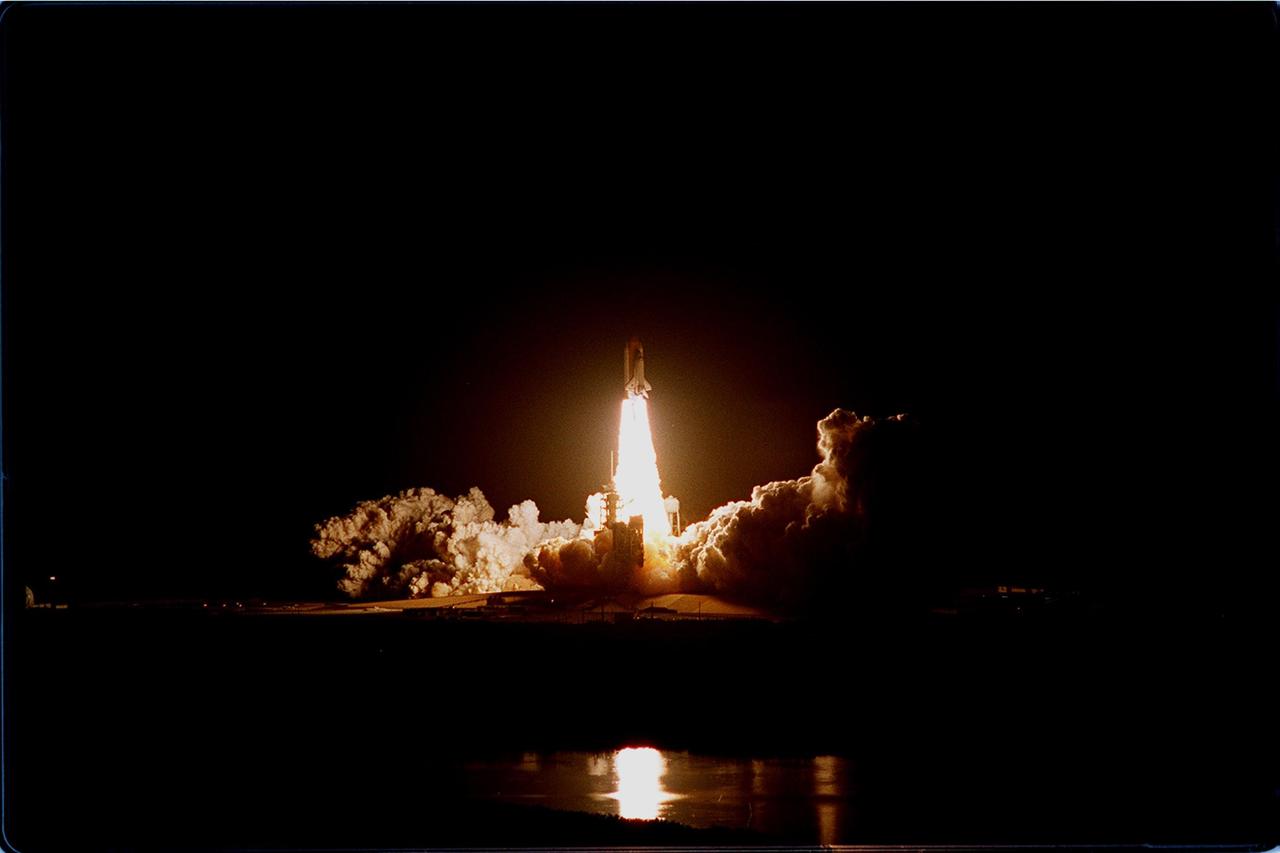

Viewed from the roof of the Vehicle Assembly Building more than 3 miles away, the launch of Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-103 emblazes the night sky. Liftoff occurred at 7:50 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. On board are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. STS-103 is a Hubble Servicing Mission, with three planned space walks designed to install new equipment and replace old. The primary objective is to replace the gyroscopes that make up the three Rate Sensor Units. Extravehicular activities include installing a new computer, changing out one of the Fine Guidance Sensors, replacing a tape recorder with a new solid state recorder, and installing a voltage/temperature improvement kit, and begin repairing the insulation on the telescope's outer surface. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is targeted to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST. This is the 27th flight of Discovery and the 96th mission in the Space Shuttle Program. It is the third launch at Kennedy Space Center in 1999
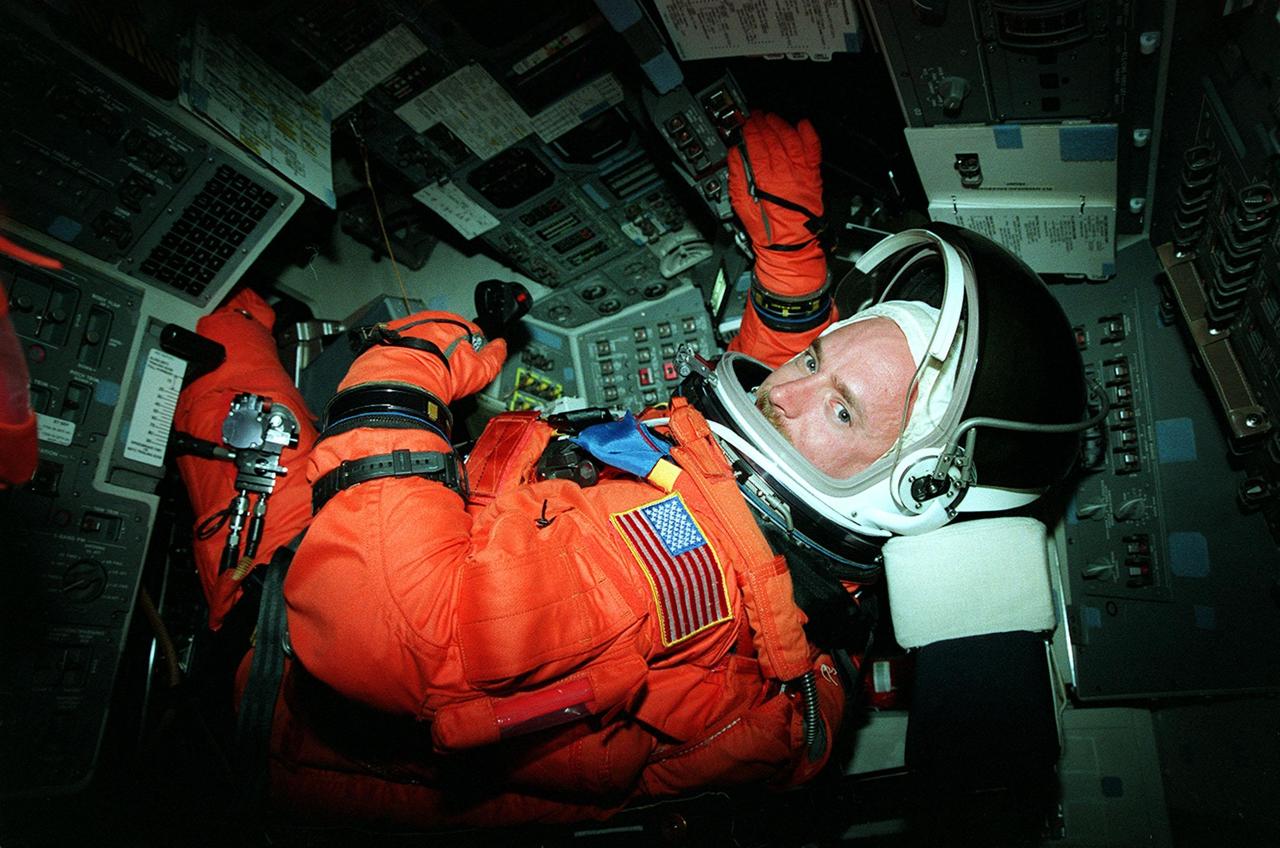

Seated in the orbiter Discovery for a simulated countdown exercise is STS-103 Pilot Scott J. Kelly. The simulation is part of Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test (TCDT) activities. The TCDT also provides the crew with emergency egress training and opportunities to inspect their mission payload in the orbiter's payload bay. Other crew members taking part in the TCDT are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Jean-François Clervoy of France, and Claude Nicollier of Switzerland. Clervoy and Nicollier are with the European Space Agency. STS-103 is a "call-up" mission due to the need to replace and repair portions of the Hubble Space Telescope, including the gyroscopes that allow the telescope to point at stars, galaxies and planets. The STS-103 crew will be replacing a Fine Guidance Sensor, an older computer with a new enhanced model, an older data tape recorder with a solid-state digital recorder, a failed spare transmitter with a new one, and degraded insulation on the telescope with new thermal insulation. The crew will also install a Battery Voltage/Temperature Improvement Kit to protect the spacecraft batteries from overcharging and overheating when the telescope goes into a safe mode. Four EVA's are planned to make the necessary repairs and replacements on the telescope. The mission is targeted for launch Dec. 6 at 2:37 a.m. EST
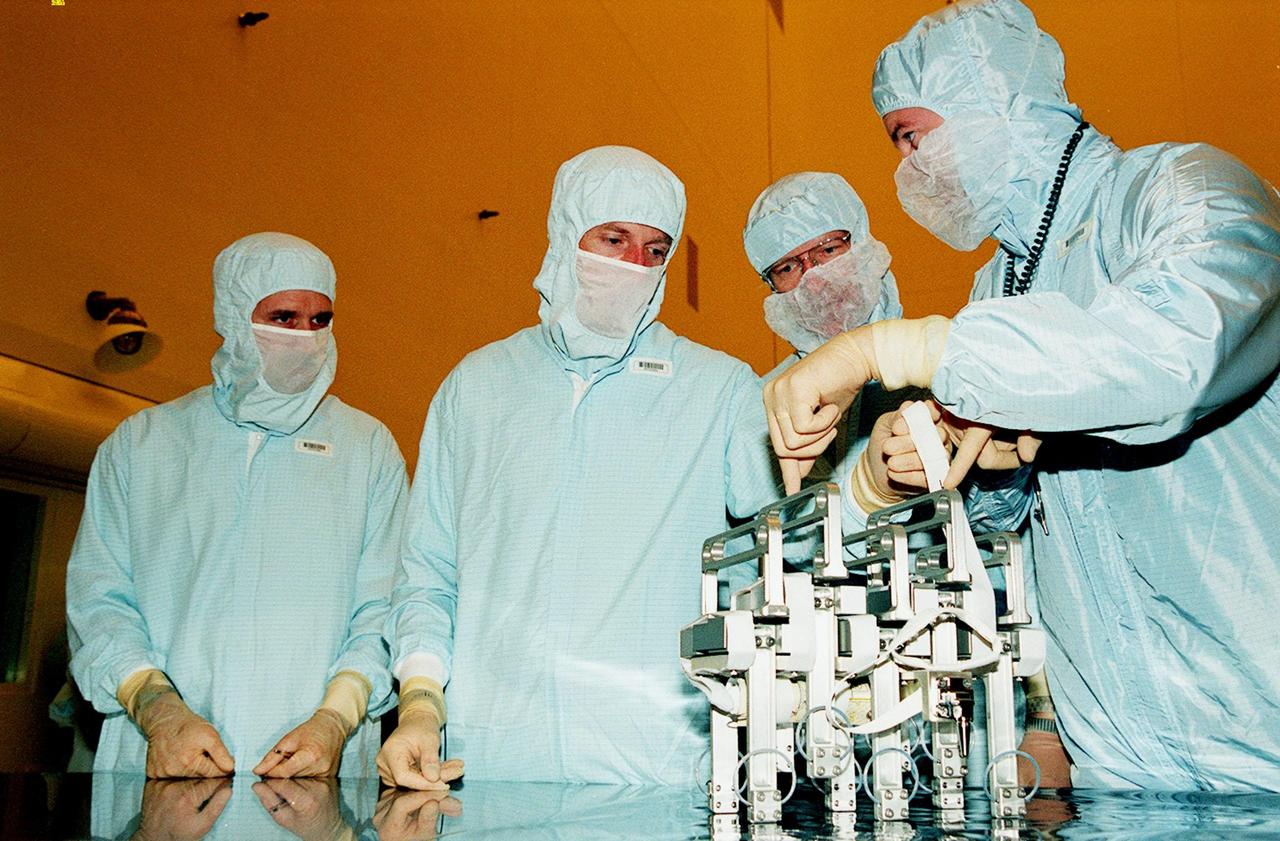

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, members of the STS-103 crew get instructions on use of rib clamps for the Shield Shell Replacement Fabric (SSRF) task on repair of the Hubble Space Telescope. The seven-member crew are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly, and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. Mission STS-103 is a "call-up" due to the need to replace portions of the pointing system, the gyros, which have begun to fail on the Hubble Space Telescope. Although Hubble is operating normally and conducting its scientific observations, only three of its six gyroscopes are working properly. The gyroscopes allow the telescope to point at stars, galaxies and planets. The STS-103 crew will not only replace gyroscopes, it will also replace a Fine Guidance Sensor, an older computer with a new enhanced model, an older data tape recorder with a solid state digital recorder, a failed spare transmitter with a new one, and degraded insulation on the telescope with new thermal insulation. The crew will also install a Battery Voltage/Temperature Improvement Kit to protect the spacecraft batteries from overcharging and overheating when the telescope goes into a safe mode. The scheduled launch date in October is under review
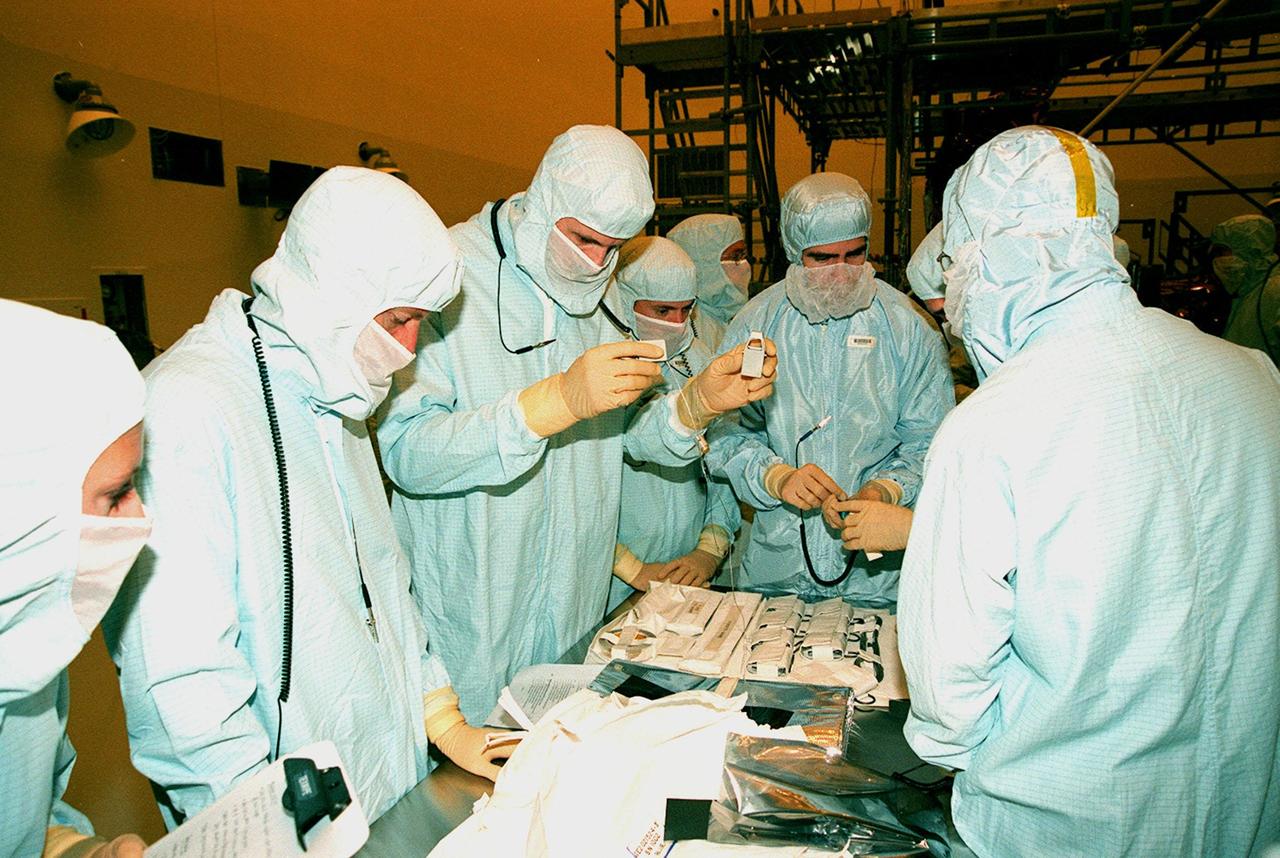

In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, members of the STS-103 crew look at some of the equipment to be used during their mission. The seven-member crew are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly, and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. Mission STS-103 is a "call-up" due to the need to replace portions of the pointing system, the gyros, which have begun to fail on the Hubble Space Telescope. Although Hubble is operating normally and conducting its scientific observations, only three of its six gyroscopes are working properly. The gyroscopes allow the telescope to point at stars, galaxies and planets. The STS-103 crew will not only replace gyroscopes, it will also replace a Fine Guidance Sensor and an older computer with a new enhanced model, an older data tape recorder with a solid state digital recorder, a failed spare transmitter with a new one, and degraded insulation on the telescope with new thermal insulation. The crew will also install a Battery Voltage/Temperature Improvement Kit to protect the spacecraft batteries from overcharging and overheating when the telescope goes into a safe mode. The scheduled launch date in October is under review
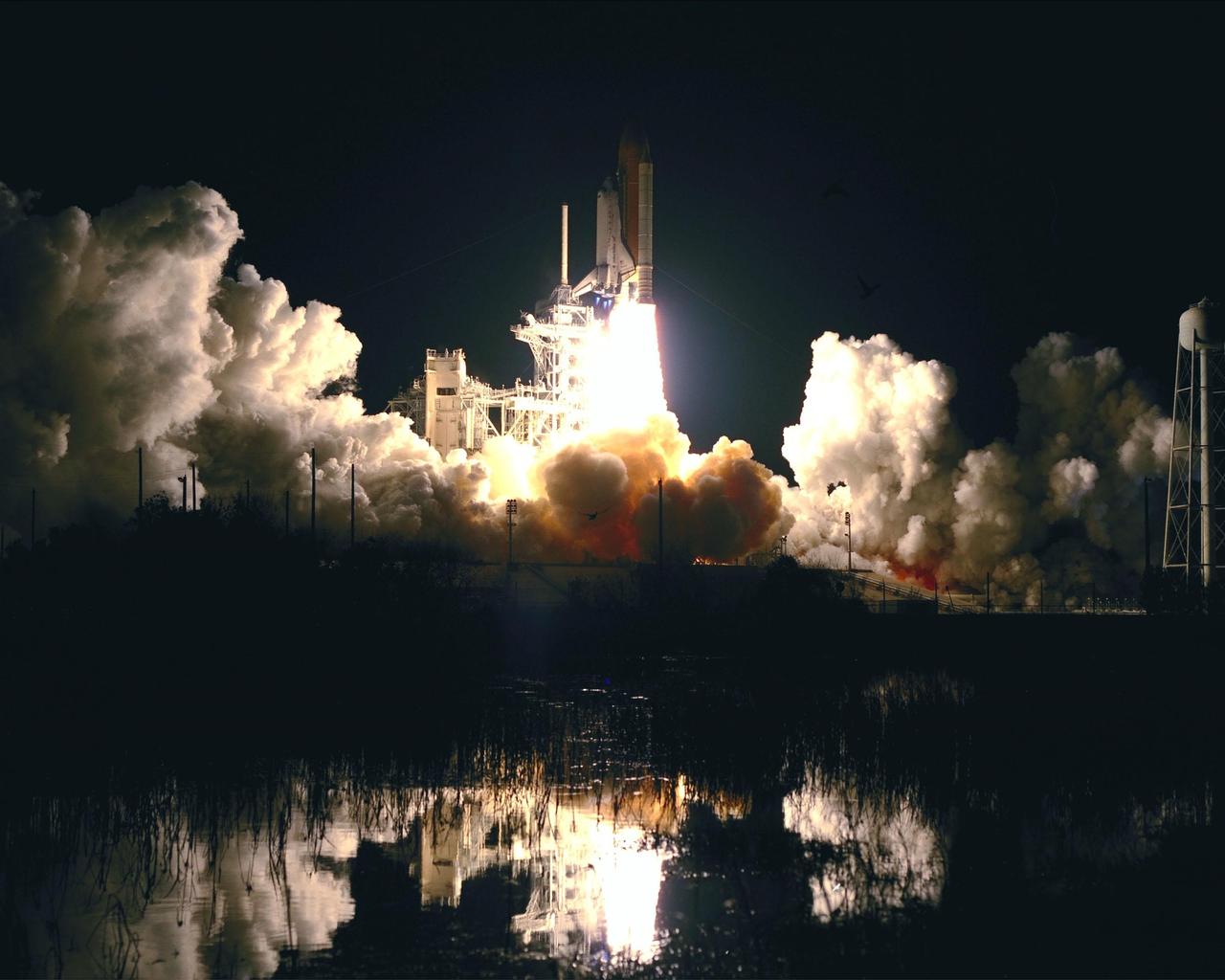

Brilliant light from the successful liftoff of Space Shuttle Discovery on mission STS-103 illuminates the night sky and the nearby waters. Liftoff occurred at 7:50 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. On board are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. STS-103 is a Hubble Servicing Mission, with three planned space walks designed to install new equipment and replace old. The primary objective is to replace the gyroscopes that make up the three Rate Sensor Units. Extravehicular activities include installing a new computer, changing out one of the Fine Guidance Sensors, replacing a tape recorder with a new solid state recorder, and installing a voltage/temperature improvement kit, and begin repairing the insulation on the telescope's outer surface. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST. This is the 27th flight of Discovery and the 96th mission in the Space Shuttle Program. It is the third launch at Kennedy Space Center in 1999

After donning his launch and entry suit, a grinning STS-103 Mission Specialist Claude Nicollier of Switzerland signals he is ready for the second launch attempt of Space Shuttle Discovery. The previous launch attempt on Dec. 17 was scrubbed about 8:52 p.m. due to numerous violations of weather launch commit criteria at KSC. Nicollier and fellow crew members Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.) and Jean-Francois Clervoy of France are scheduled to lift off at 7:50 p.m. EST Dec. 19 on mission STS-103, servicing the Hubble Space Telescope. Objectives for the nearly eight-day mission include replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST
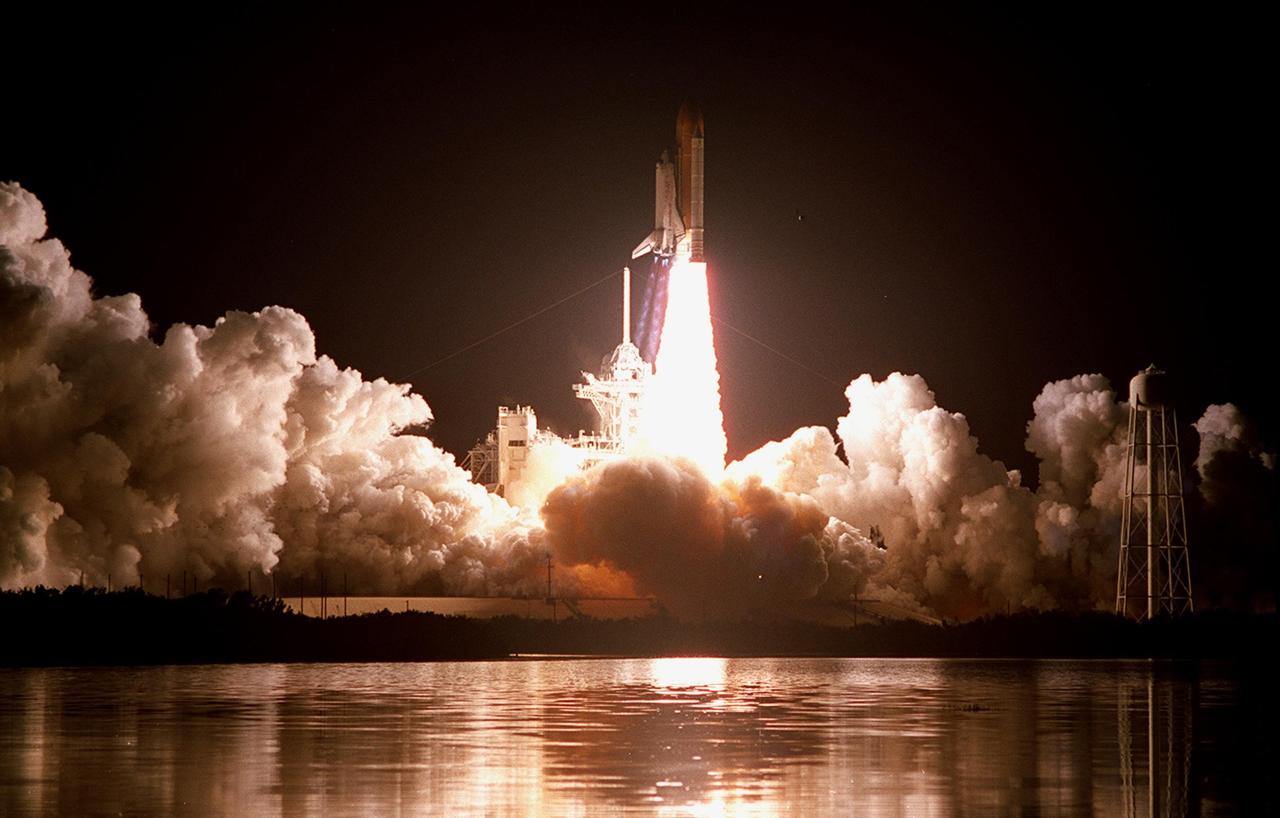

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- As if spawned by the clouds of smoke and steam below, the Space Shuttle Discovery shoots into the night sky on mission STS-103. The brilliant light creates a reflection of the launch in the water nearby. Liftoff occurred at 7:50 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. On board are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. STS-103 is a Hubble Servicing Mission, with three planned space walks designed to install new equipment and replace old. The primary objective is to replace the gyroscopes that make up the three Rate Sensor Units. Extravehicular activities include installing a new computer, changing out one of the Fine Guidance Sensors, replacing a tape recorder with a new solid state recorder, and installing a voltage/temperature improvement kit, and begin repairing the insulation on the telescope's outer surface. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST. This is the 27th flight of Discovery and the 96th mission in the Space Shuttle Program. It is the third launch at Kennedy Space Center in 1999

In the Operations and Checkout Building, STS-103 Mission Specialist C. Michel Foale (Ph.D.) smiles as a suit technician helps him don his launch and entry suit during final launch preparations. Other crew members are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. The STS-103 mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is scheduled for launch Dec. 17 at 8:47 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. Mission objectives include replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. After the 8-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Sunday, Dec. 26, at about 6:30 p.m. EST.is expected to land at KSC Sunday, Dec. 26, at about 6:30 p.m. EST

During a Crew Equipment Interface Test, STS-103 Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr. (left) and Pilot Scott J. Kelly look at a replacement computer for the Hubble Space Telescope. The payload hardware is in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. Other members of the crew are Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland, and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. Mission STS-103 is a "call-up" due to the need to replace portions of the pointing system, the gyros, which have begun to fail on the Hubble Space Telescope. Although Hubble is operating normally and conducting its scientific observations, only three of its six gyroscopes are working properly. The gyroscopes allow the telescope to point at stars, galaxies and planets. The STS-103 crew will not only replace gyroscopes, it will also replace a Fine Guidance Sensor and an older computer with the new enhanced model, an older data tape recorder with a solid state digital recorder, a failed spare transmitter with a new one, and degraded insulation on the telescope with new thermal insulation. The crew will also install a Battery Voltage/Temperature Improvement Kit to protect the spacecraft batteries from overcharging and overheating when the telescope goes into a safe mode. The scheduled launch date in October is under review

Turning night into day for a few moments while belching clouds of smoke and steam, Space Shuttle Discovery hurtles into the black sky on mission STS-103. The successful liftoff occurred at 7:50 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 39B. On board are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. STS-103 is a Hubble Servicing Mission, with three planned space walks designed to install new equipment and replace old. The primary objective is to replace the gyroscopes that make up the three Rate Sensor Units. Extravehicular activities include installing a new computer, changing out one of the Fine Guidance Sensors, replacing a tape recorder with a new solid state recorder, and installing a voltage/temperature improvement kit, and begin repairing the insulation on the telescope's outer surface. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is targeted to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST. This is the 27th flight of Discovery and the 96th mission in the Space Shuttle Program. It is the third launch at Kennedy Space Center in 1999
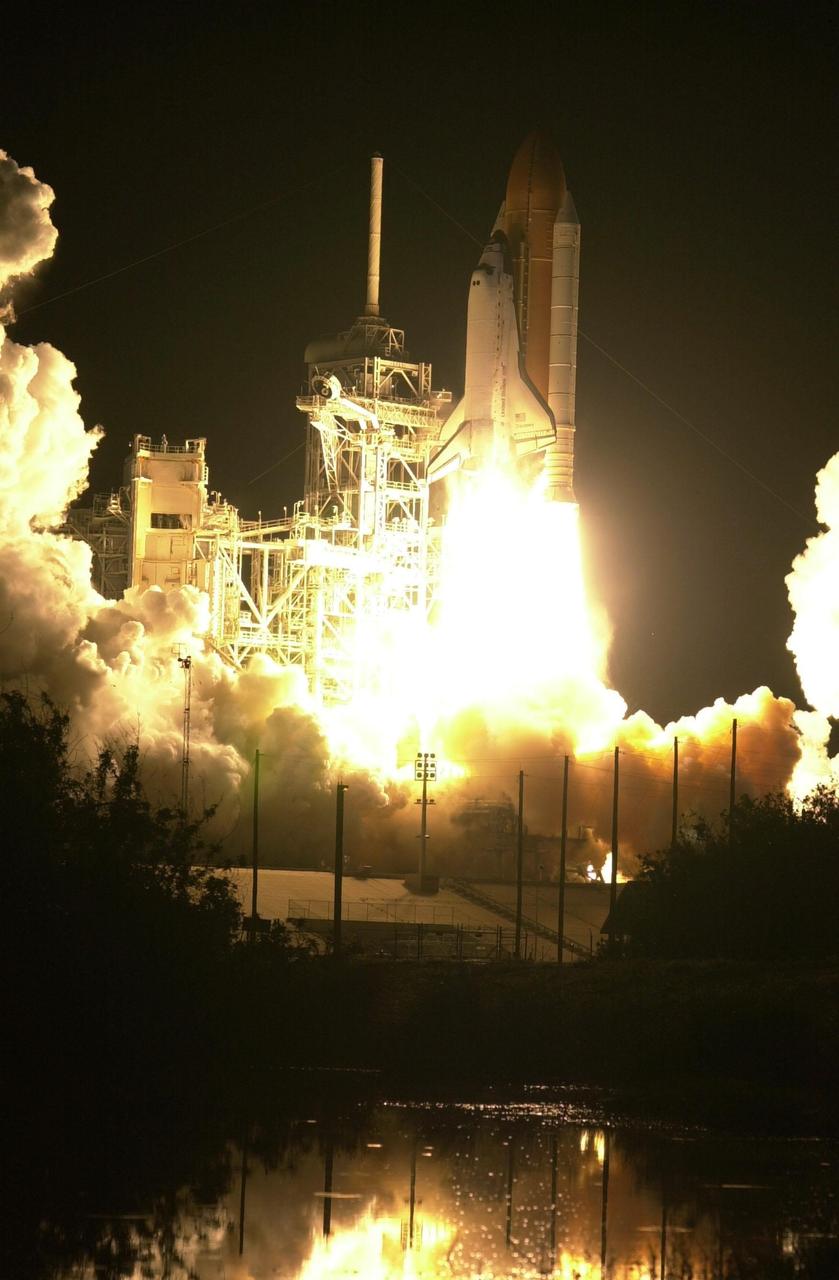

(Nikon camera D1 test)The blazing light of Space Shuttle Discovery's launch turns night into day at Launch Pad 39B. The successful liftoff occurred on time at 7:50:00.069 EST from Launch Pad 39B on mission STS-103. On board are Commander Curtis L. Brown Jr., Pilot Scott J. Kelly and Mission Specialists Steven L. Smith, C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), John M. Grunsfeld (Ph.D.), Claude Nicollier of Switzerland and Jean-François Clervoy of France. Nicollier and Clervoy are with the European Space Agency. STS-103 is a Hubble Servicing Mission, with three planned space walks designed to install new equipment and replace old. The primary objective is to replace the gyroscopes that make up the three Rate Sensor Units. Extravehicular activities include installing a new computer, changing out one of the Fine Guidance Sensors, replacing a tape recorder with a new solid state recorder, and installing a voltage/temperature improvement kit, and begin repairing the insulation on the telescope's outer surface. After the 7-day, 21-hour mission, Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST. This is the 27th flight of Discovery and the 96th mission in the Space Shuttle Program. It is the third launch at Kennedy Space Center in 1999