
Nili Patera
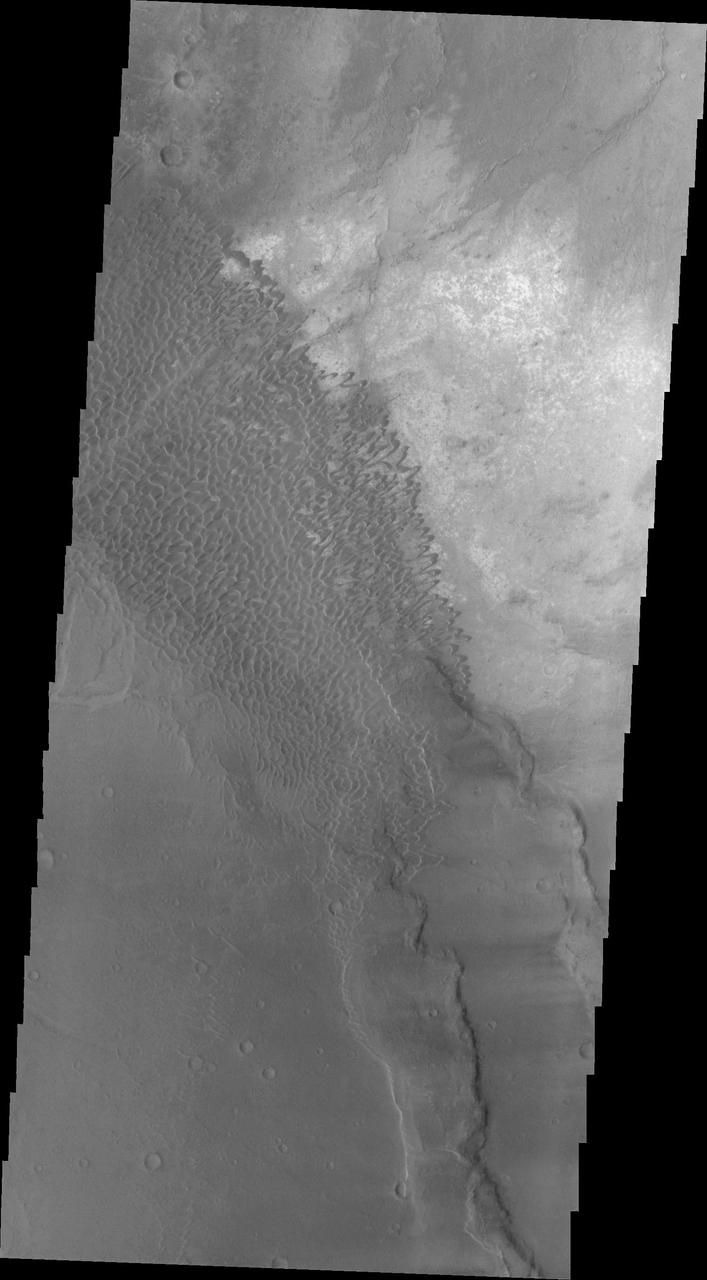

Nili Patera Dunes
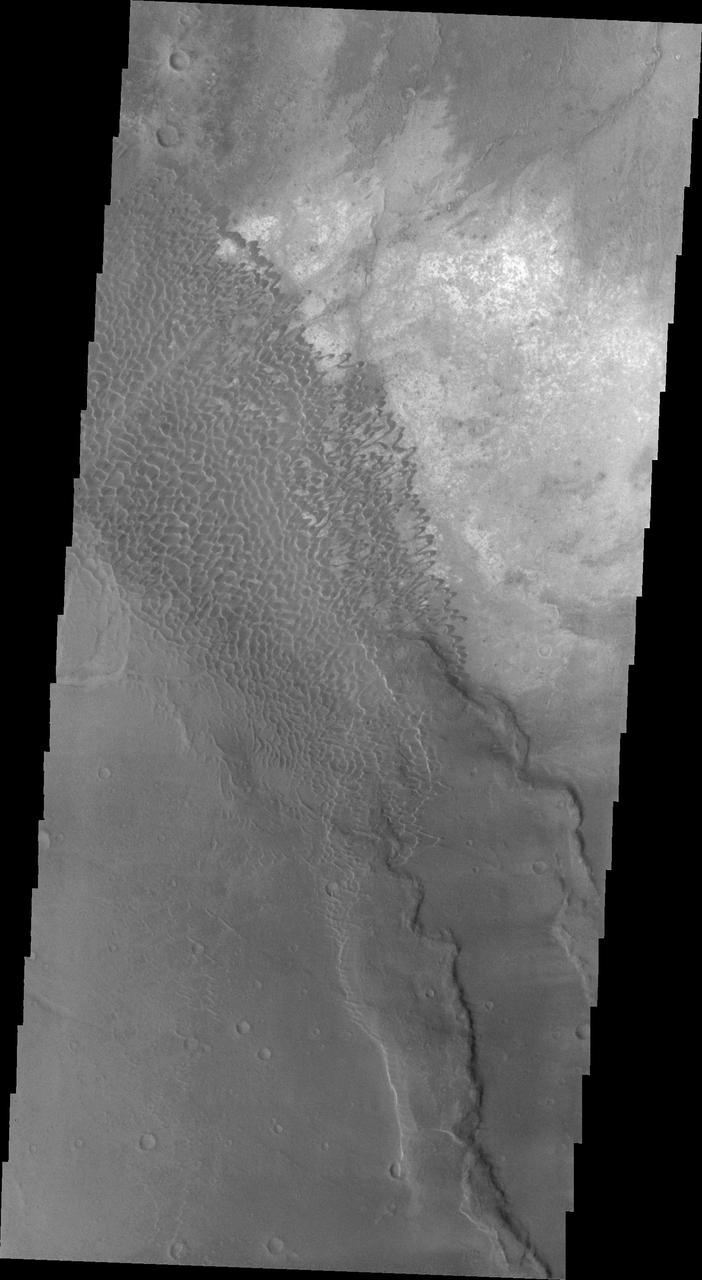

Nili Patera Dunes

Nili Patera Dunes
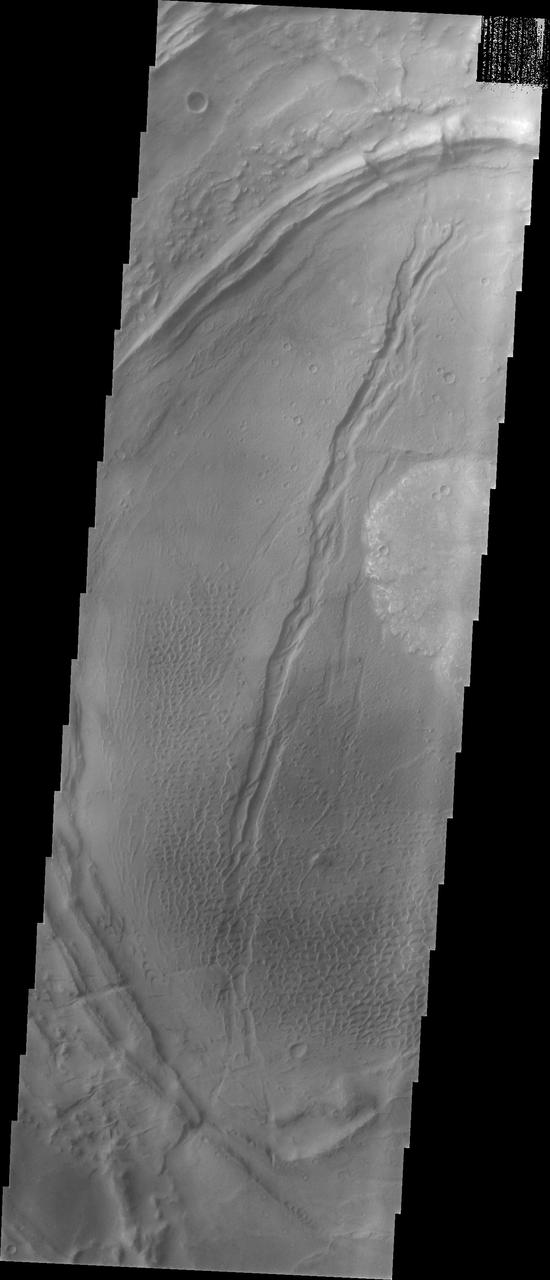

Nili Patera Dune Field
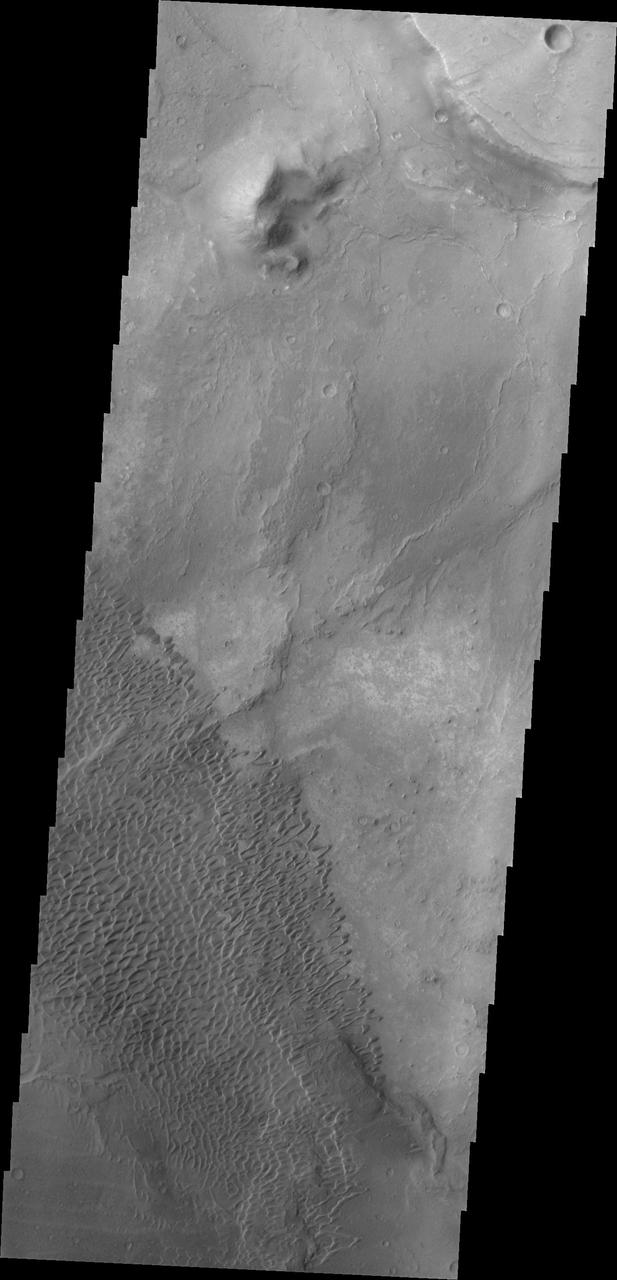

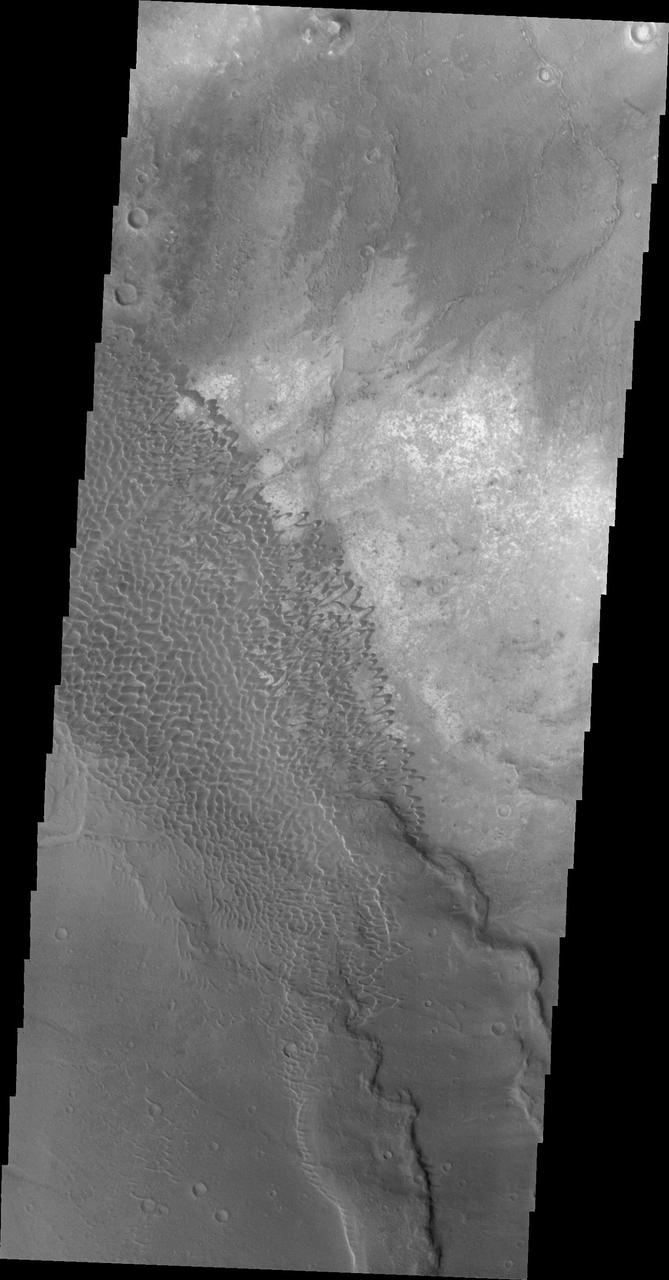
The dunes in this image from NASA Mars Odyssey are located in Nili Patera, one of the two patera of Syrtis Major Planum.

This 2001 Mars Odyssey image shows the dune field in Nili Patera.
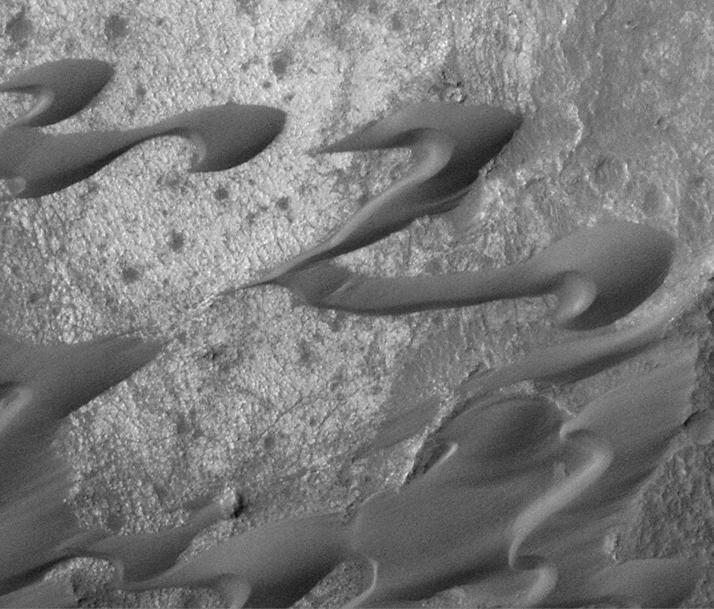
Sand Dunes of Nili Patera, Syrtis Major

Today's VIS image shows part of Nili Patera. Nili Patera is the northern caldera in the immense volcanic complex of Syrtis Major Planum. The dunes are moving westward across the top of these ancient volcanic flows. Orbit Number: 90030 Latitude: 8.95316 Longitude: 67.1774 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2022-04-01 09:05 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25468

This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows the dune field on the floor of Nili Patera.

Individual sand dunes are visible in this image of Nili Patera taken by NASA Mars Odyssey.

These dunes are moving along the hard volcanic surface Nili Patera in Syrtis Major. This image was captured by NASA Mars Odyssey.

The individual dunes in this image from NASA Mars Odyssey are moving along a hard surface in Nili Patera.

Dunes appear on the floor of Nili Patera, one of the two volcanic calderas of Syrtis Major in this image taken by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey.

Nili Patera is one of the most active dune fields on Mars. Continuously monitored by the HiRise instrument onboard NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, a new image is acquired about every six weeks.
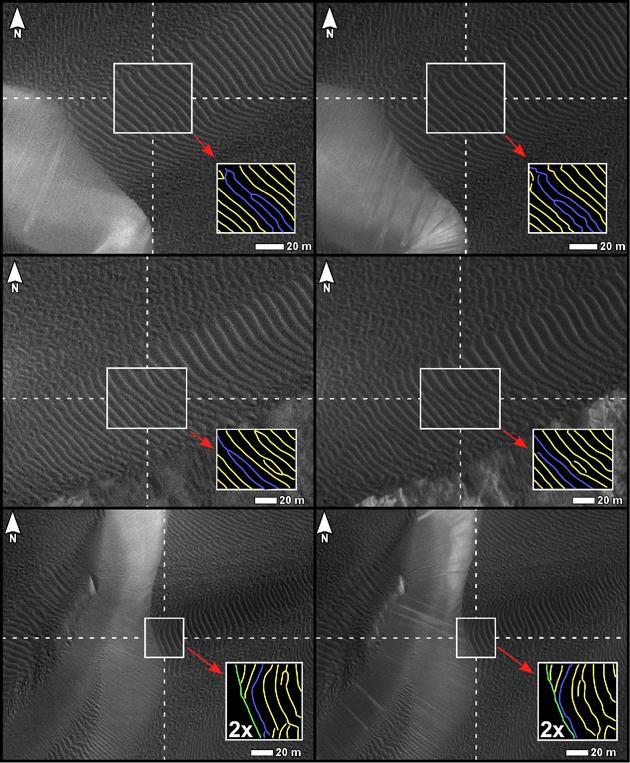
Three pairs of before and after images from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter illustrate movement of ripples on dark sand dunes in the Nili Patera region of Mars.

The THEMIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows Nili Patera and the dunes located in the patera. Orbit Number: 19306 Latitude: 8.80756 Longitude: 67.4616 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2006-04-22 00:12. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20230

The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. This false color image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows part of Nili Patera.

Two pairs of side-by-side, before and after images from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter illustrate changes in the shape of edges of dark sand dunes in the Nili Patera region of Mars.

Nili Patera is a region on Mars in which dunes and ripples are moving rapidly. HiRISE continues to monitor this area every couple of months to see changes over seasonal and annual time scales as seen by NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter.
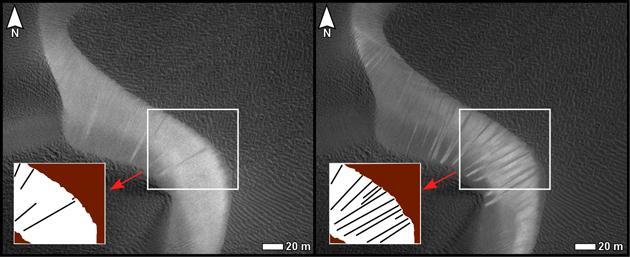
Before and after images from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter illustrate occurrence of new streaks on the slip face of a dark sand dune in the Nili Patera region of Mars.
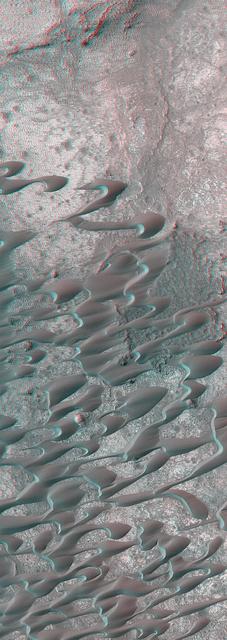
This stereo image mosaic from NASA Mars Global Surveyor is of a field of dunes located in Nili Patera, a volcanic depression in central Syrtis Major. 3D glasses are necessary to view this image.
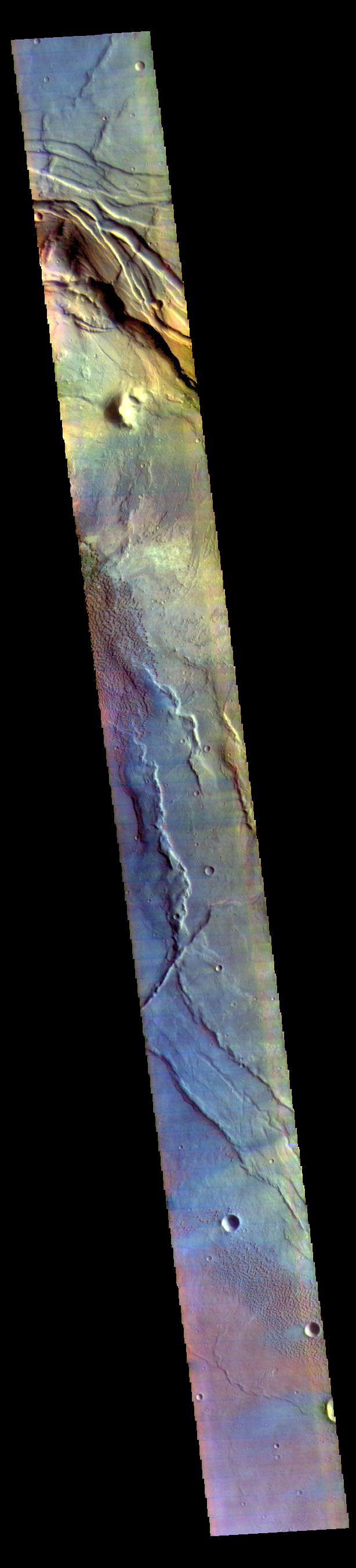
Today's false color image is located at Nili Patera in Syrtis Major Planum. There are regions of small dunes towards the top and the bottom of the image. The wide range of colors indicate the complexity of surface materials in this area. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Orbit Number: 61810 Latitude: 8.37503 Longitude: 67.4659 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2015-11-20 04:48 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23071
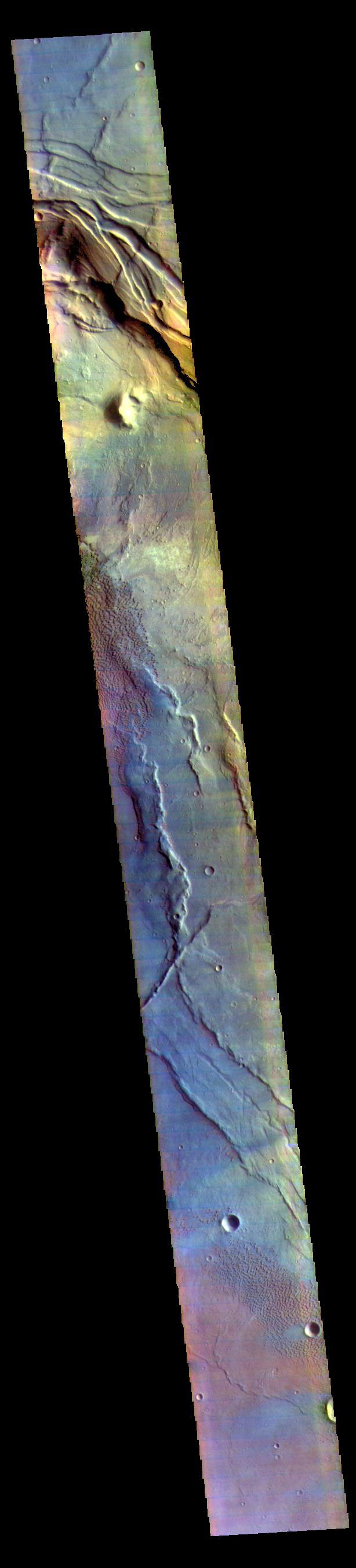
This false color image covers the region from Nili Patera at the top of the frame to the dunes near Meroe Patera (which is off the bottom of the image). High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 61810 Latitude: 8.37503 Longitude: 67.4659 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2015-11-20 04:48 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22015
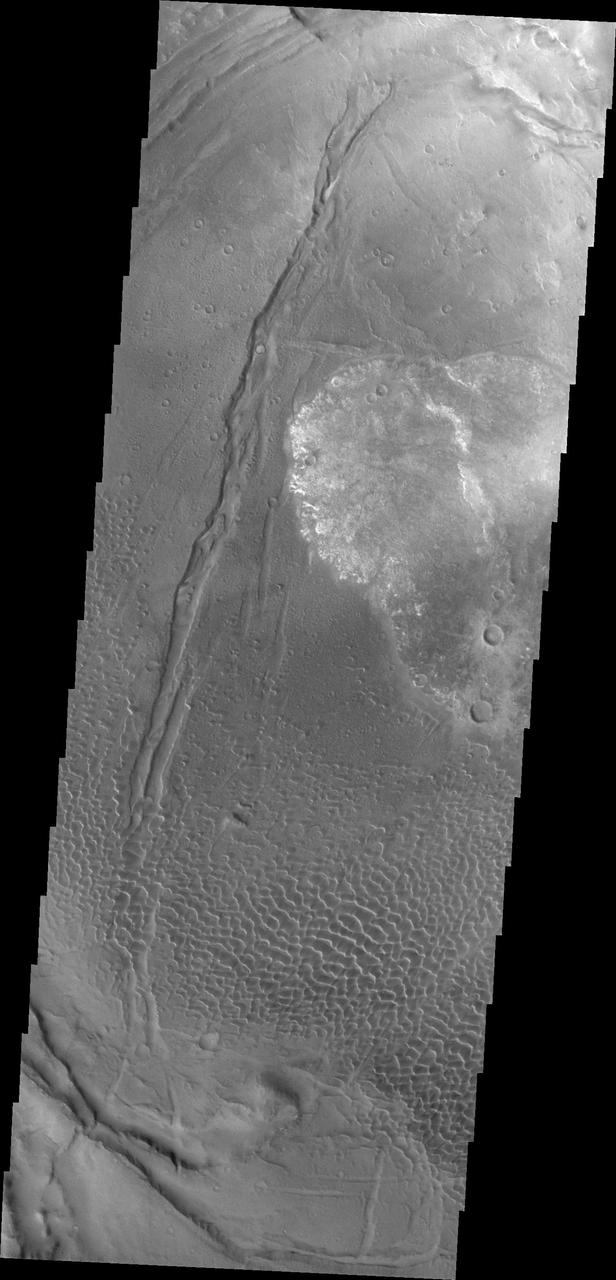

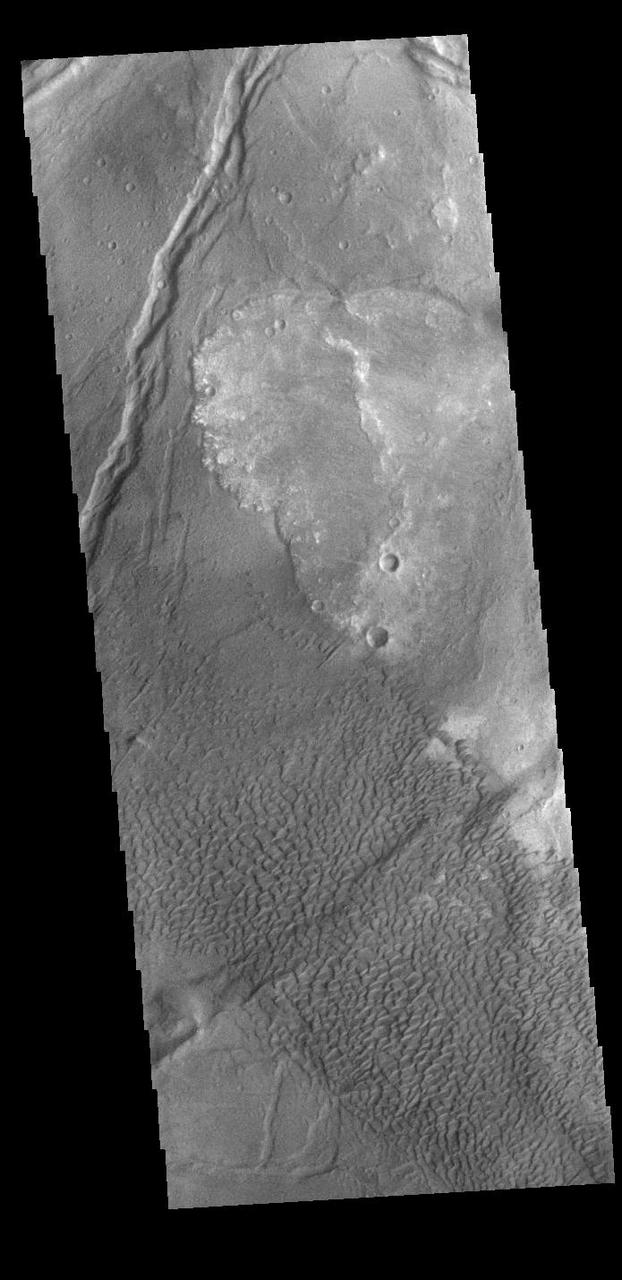
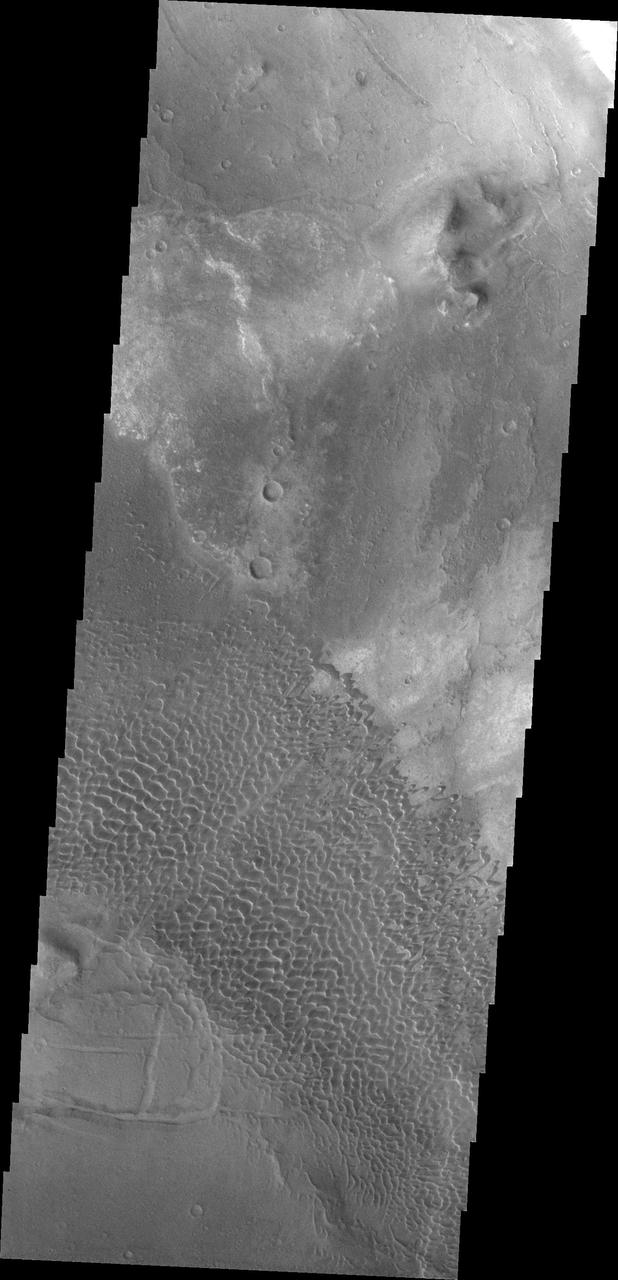
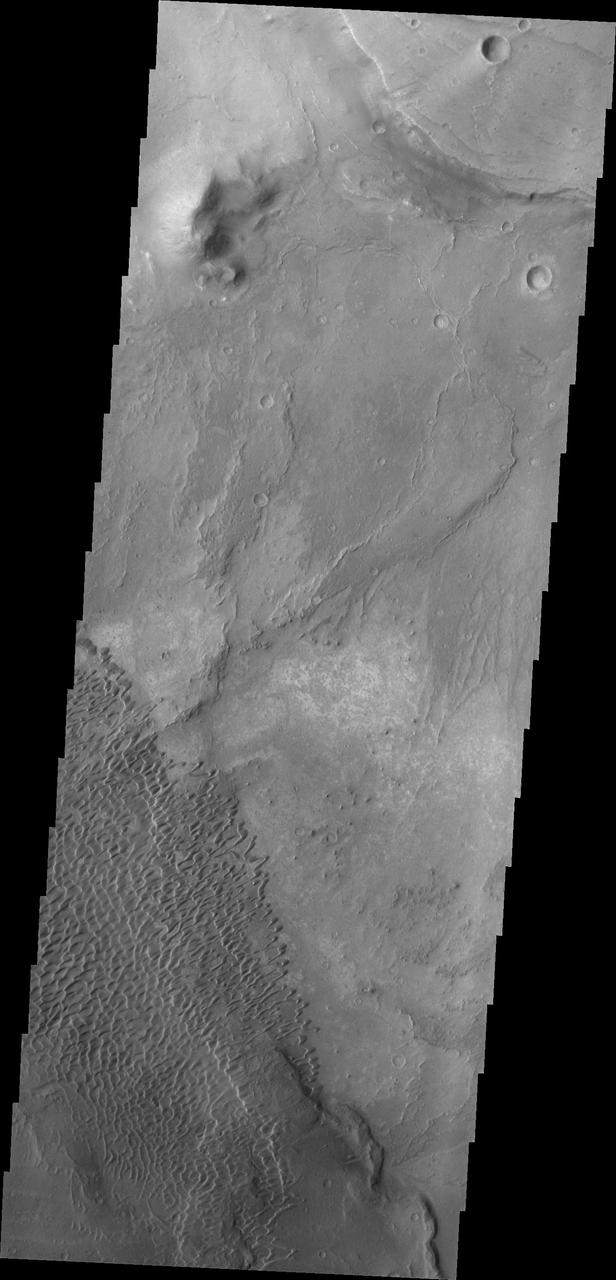
This image shows part of the Nili Patera dune field. High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 42079 Latitude: 8.99242 Longitude: 67.1173 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2011-06-10 03:08 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22007
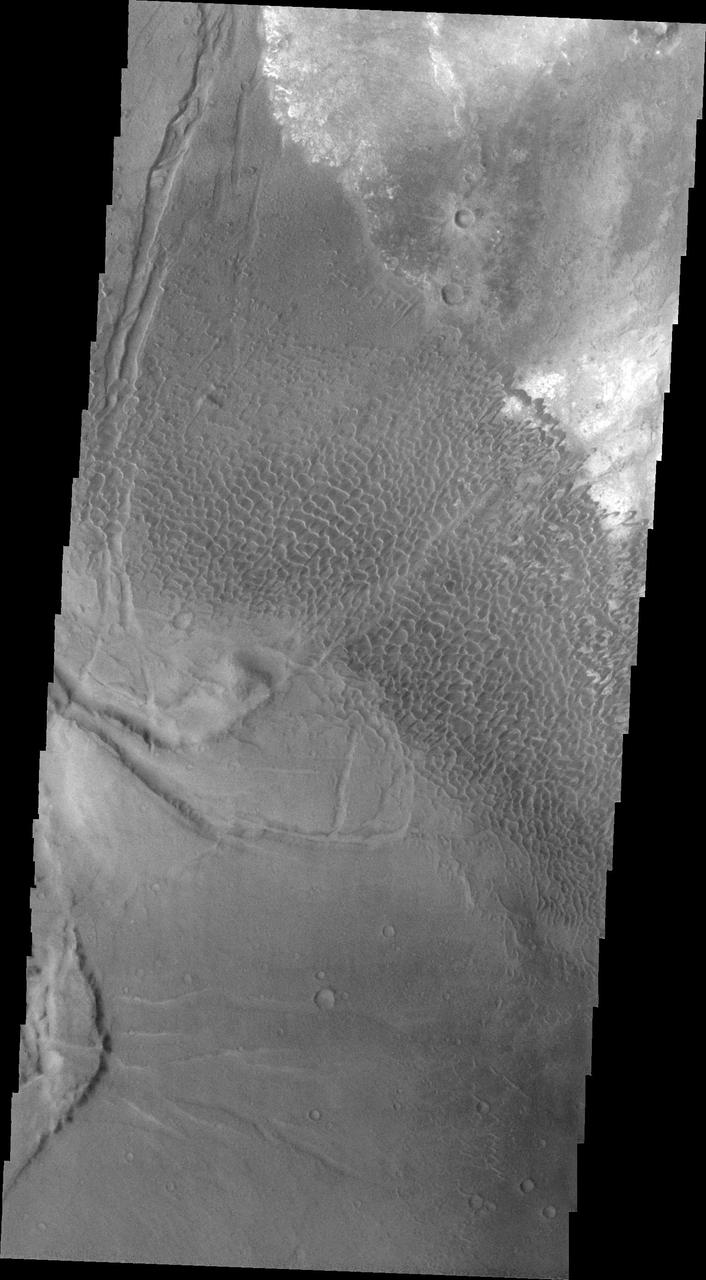

This image shows part of the Nili Patera dune field. High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 34554 Latitude: 8.70872 Longitude: 67.1631 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2009-09-28 12:58 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22002
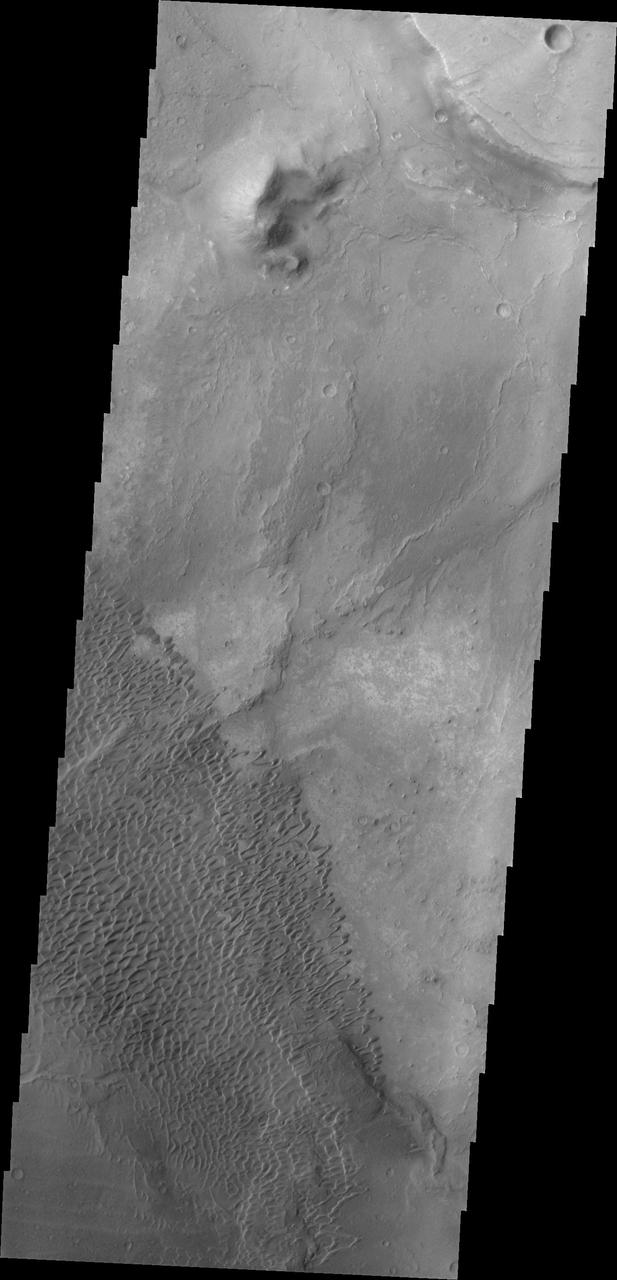

This image shows part of the Nili Patera dune field. High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 38248 Latitude: 8.87797 Longitude: 67.3841 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2010-07-29 16:30 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22004

This is a false color image of part of the Nili Patera dune field. High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 19306 Latitude: 8.80756 Longitude: 67.4616 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2006-04-22 00:12 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22008
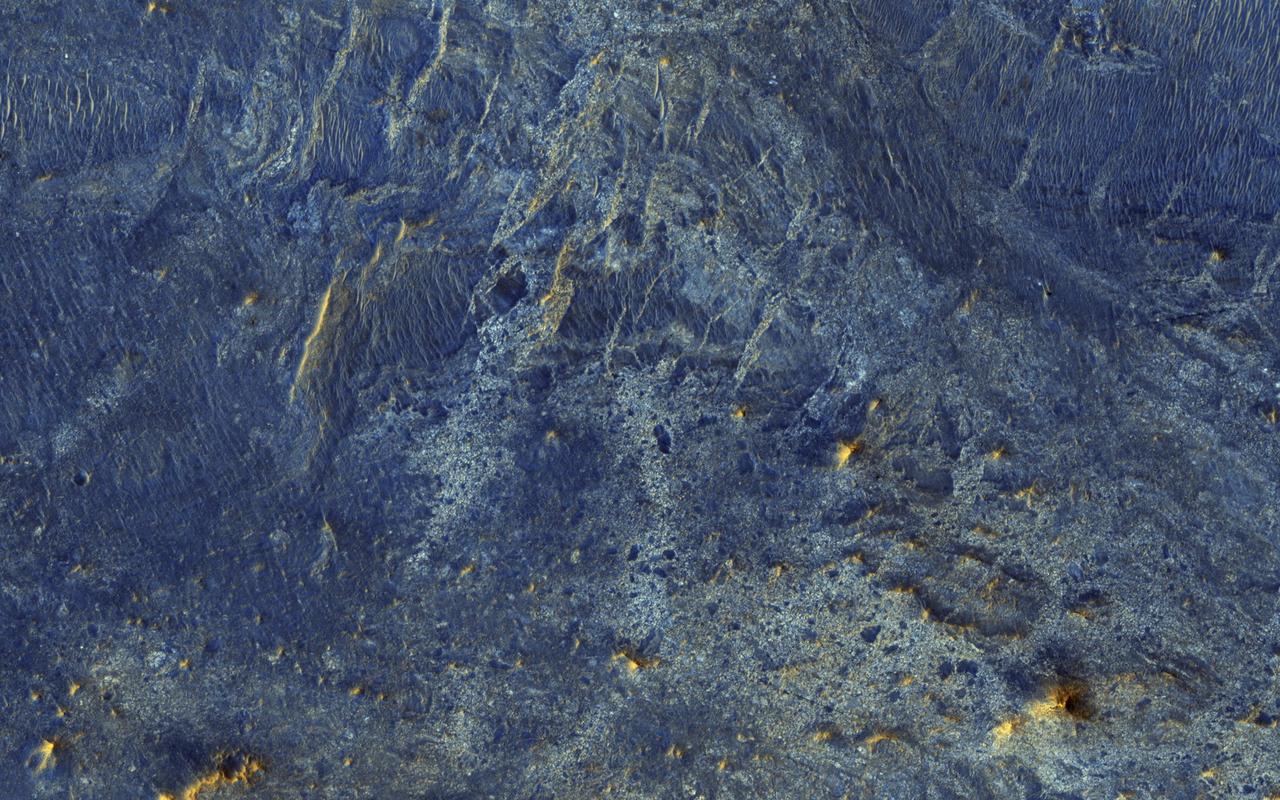

There have been several proposals to send people to Mars but not land them on the surface. Instead, they would either fly by Mars once and return to Earth, or orbit Mars for a period of time. Would they at least get spectacular naked-eye views of the Martian surface? Some parts of Mars would be interesting: for example the polar ice caps, and the bright (dust-covered) regions would be seen reasonably well, although the color is very uniform. The dark (low reflectance) regions of Mars are some of the most interesting and important regions studied by our orbiters and rovers, but they would appear very bland to humans outside of the planet's atmosphere. This is because the thin atmosphere of Mars is quite bright and dusty, so when looking at dark surface areas, most of what you would see is scattered light from the atmospheric dust, and the surface would have a very low contrast. It would also appear reddish, even if the surface materials are not reddish, from the scattered light. Here is an example from the Nili Patera region of Mars, a candidate future landing site. At the top is an approximation of the natural color as seen by people with normal color vision -- almost no surface detail is visible. In the middle is the standard HiRISE IRB color product, consisting of the infrared, red, and blue-green images displayed as red, green, and blue, respectively, and with a min-max stretch applied to each color. In other words, the darkest pixel in the entire image is set to black, the brightest pixel is set to white, and all others are linearly interpolated. At bottom is an enhanced color product, in which each bandpass is given a linear stretch for the local subimage, sometimes saturating a small percentage of data to black or white to give the rest of the scene more contrast, followed by color saturation enhancement. Now we can see a diversity of colors that distinguish different surface units: dust, sand, and rocks with different minerals. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21040
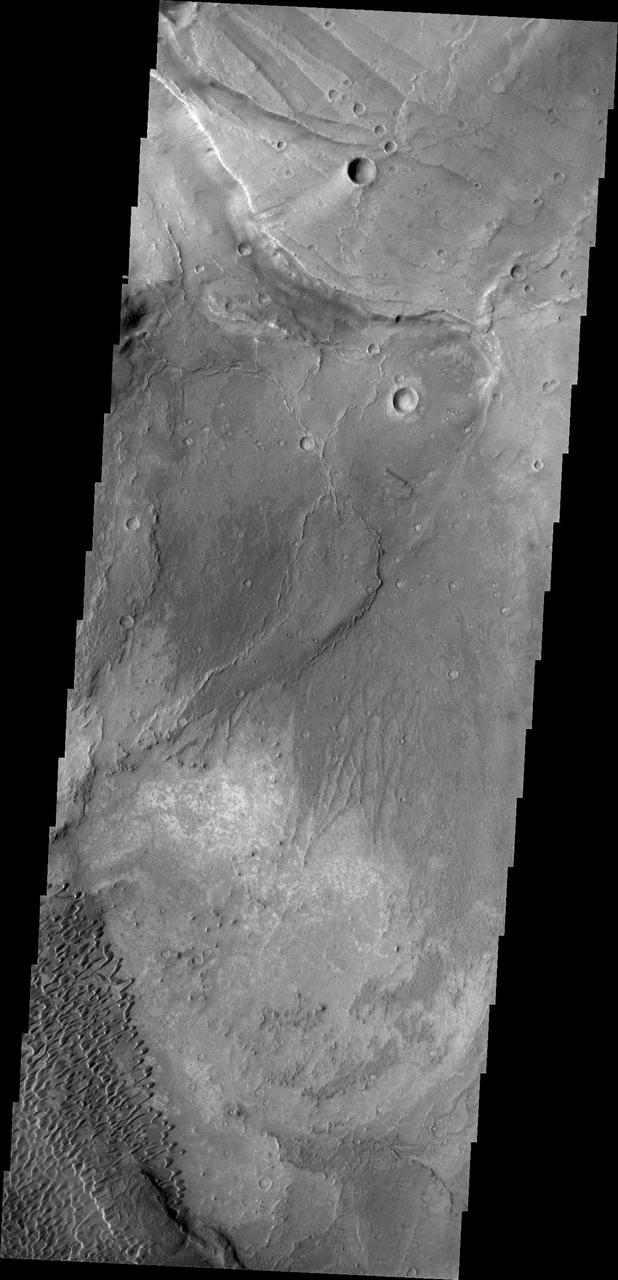

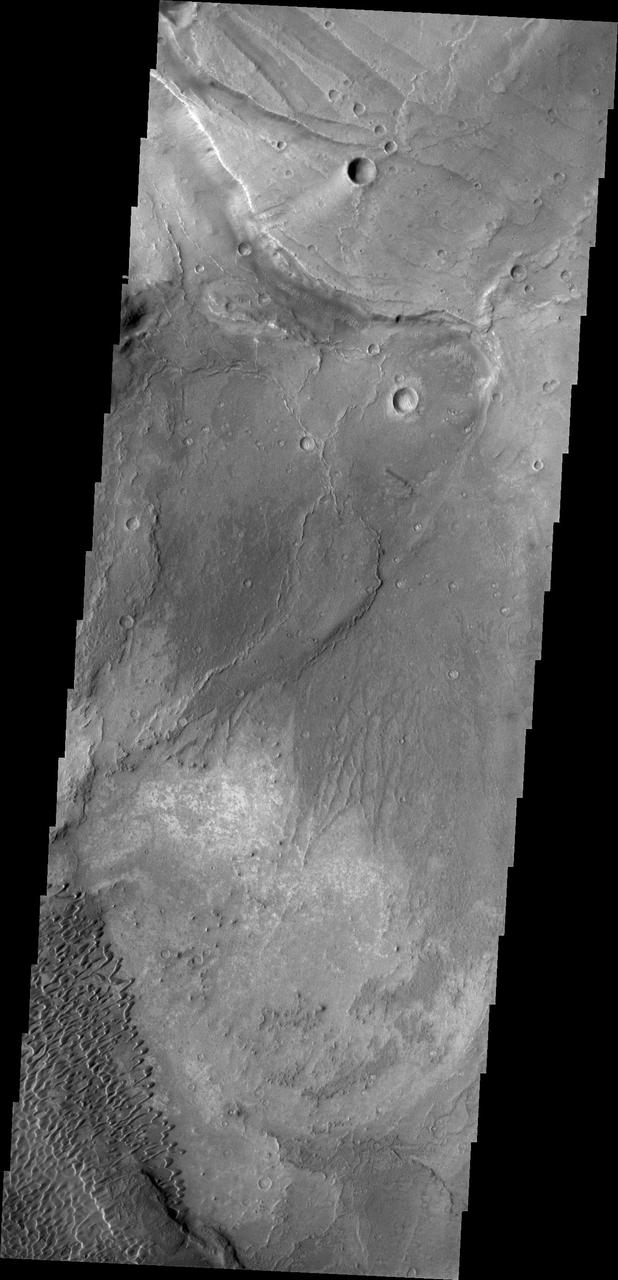
This image shows part of the Nili Patera dune field. High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 39109 Latitude: 8.96069 Longitude: 67.5169 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2010-10-08 14:02 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22006
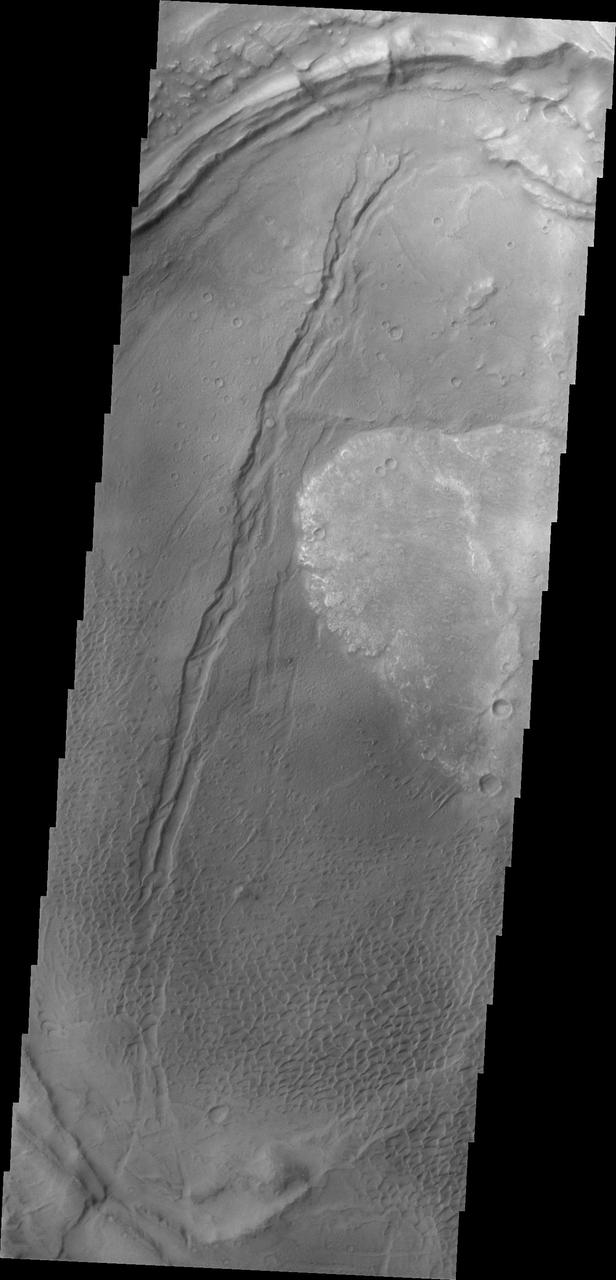

This image shows part of the Nili Patera dune field. High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 37075 Latitude: 9.03973 Longitude: 67.1106 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2010-04-24 02:29 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22003
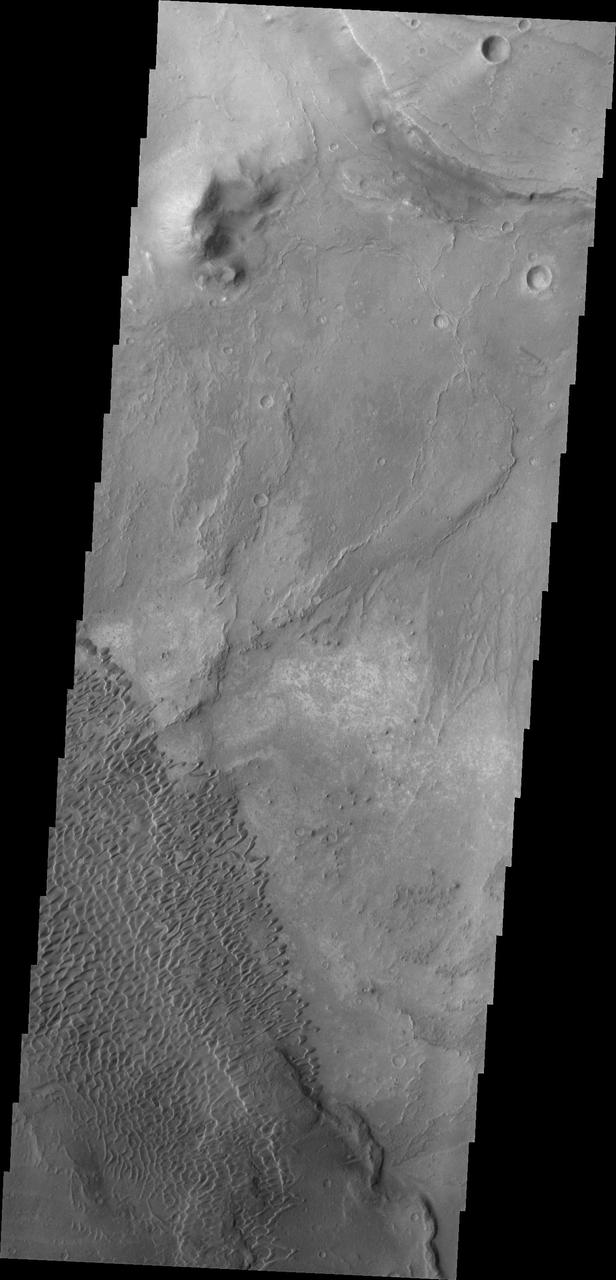

This image shows part of the Nili Patera dune field. High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 38822 Latitude: 8.88015 Longitude: 67.4268 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2010-09-14 22:51 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22005
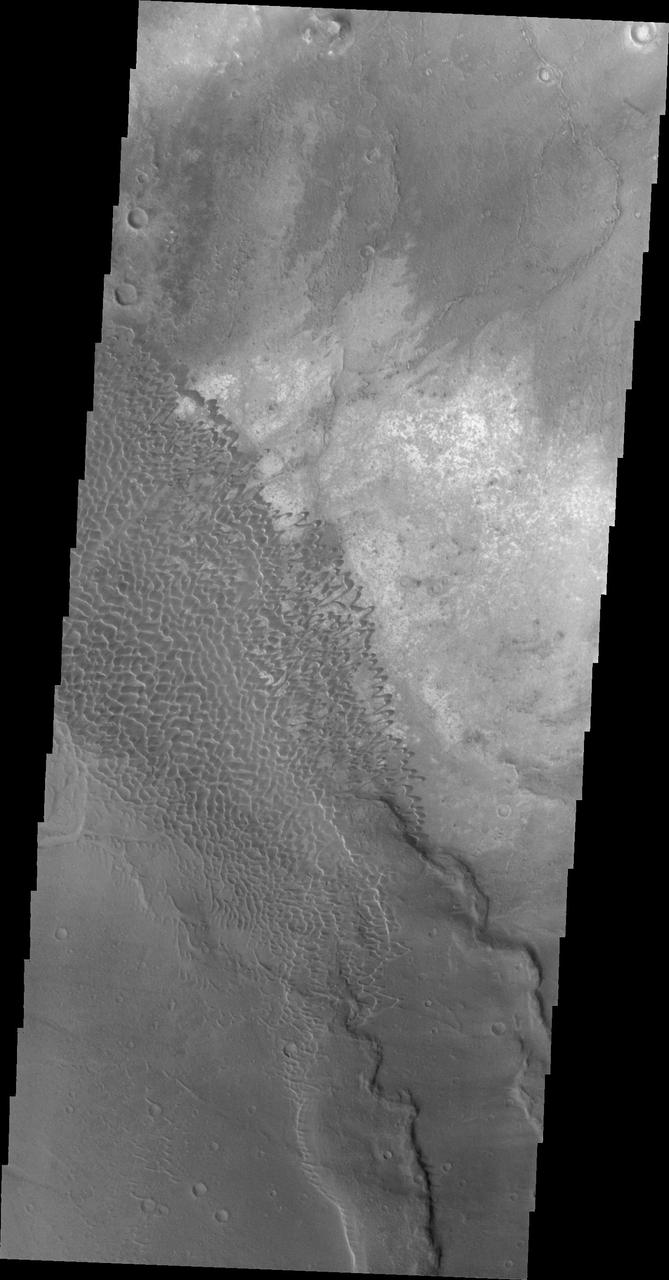

This image shows part of the Nili Patera dune field. High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 33668 Latitude: 8.71491 Longitude: 67.3706 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2009-07-17 14:09 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22001

This is a false color image of part of the Nili Patera dune field. High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 48021 Latitude: 8.95091 Longitude: 67.3366 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2012-10-11 05:22 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22009

The windstreaks in this image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft are located in Syrtis Major Planum between Nili and Meroe Paterae.
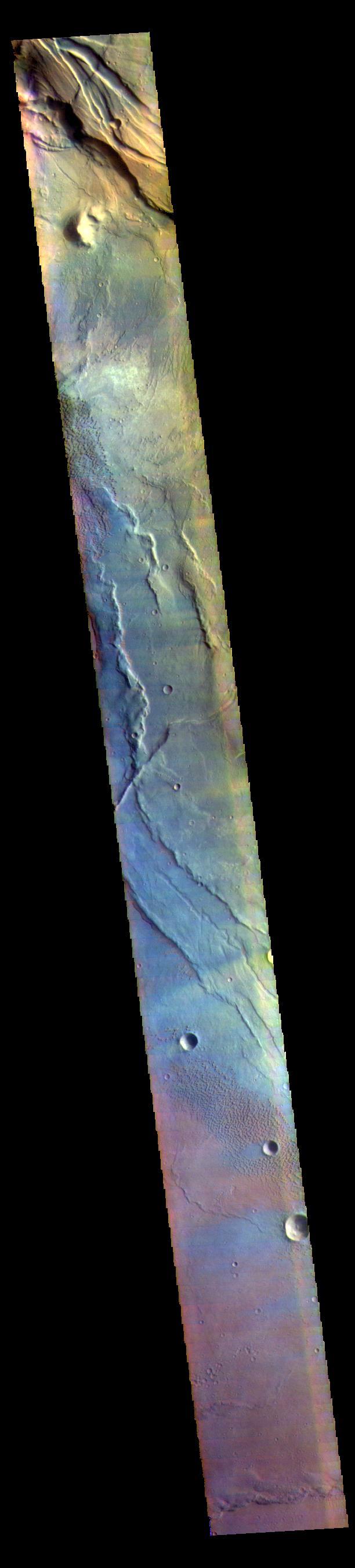

This VIS image is located in the center of Syrtis Major Planum. At the top of the image is Nili Patera, a volcanic summit. The sand dunes located near Nili Patera are visible on the left side of the image. The bottom of the image is just west of Meroe Patera. Dunes located between Nili and Meroe are visible towards the bottom of the image. Winds in the region have created the dunes, but also many windstreaks on the downward side of craters in the image. Wind streaks indicate the direction of the wind. In this region the winds are blowing from east to west. The THEMIS VIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Orbit Number: 62072 Latitude: 7.99408 Longitude: 67.5512 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2015-12-11 18:39 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23095
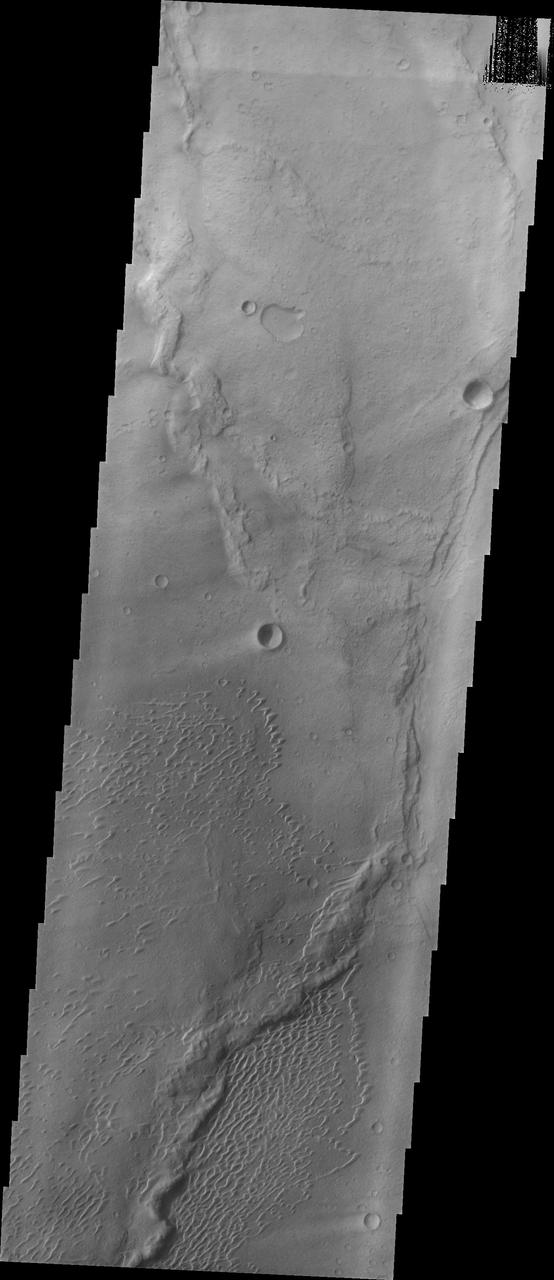

his image shows part of the dune field near Meroe Patera. High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 11606 Latitude: 7.06099 Longitude: 68.2238 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2004-07-27 00:59 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22012
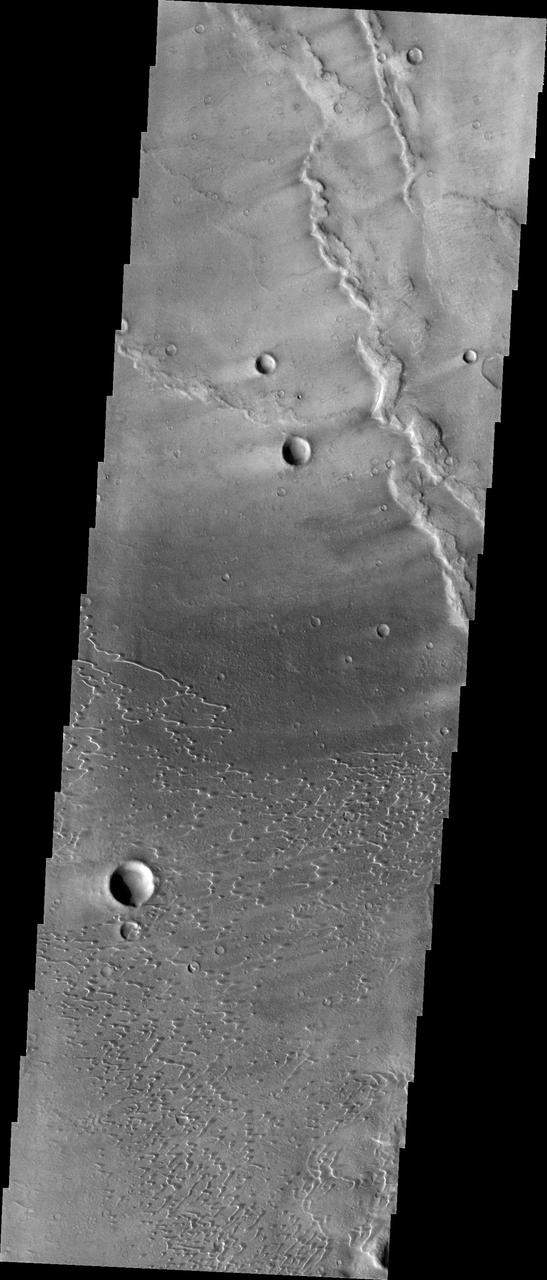

Context image This image shows part of the dune field near Meroe Patera. High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 8536 Latitude: 7.10227 Longitude: 68.0484 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2003-11-17 06:40 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22011

This image shows part of the dune field near Meroe Patera. High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 48870 Latitude: 6.6541 Longitude: 68.1311 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2012-12-20 02:19 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22014
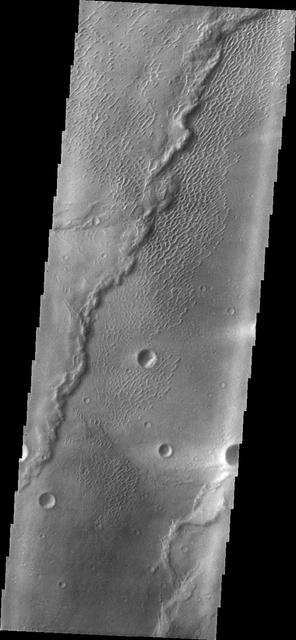
This image shows part of the dune field near Meroe Patera. High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 28341 Latitude: 6.34784 Longitude: 68.078 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2008-05-04 22:05 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22013
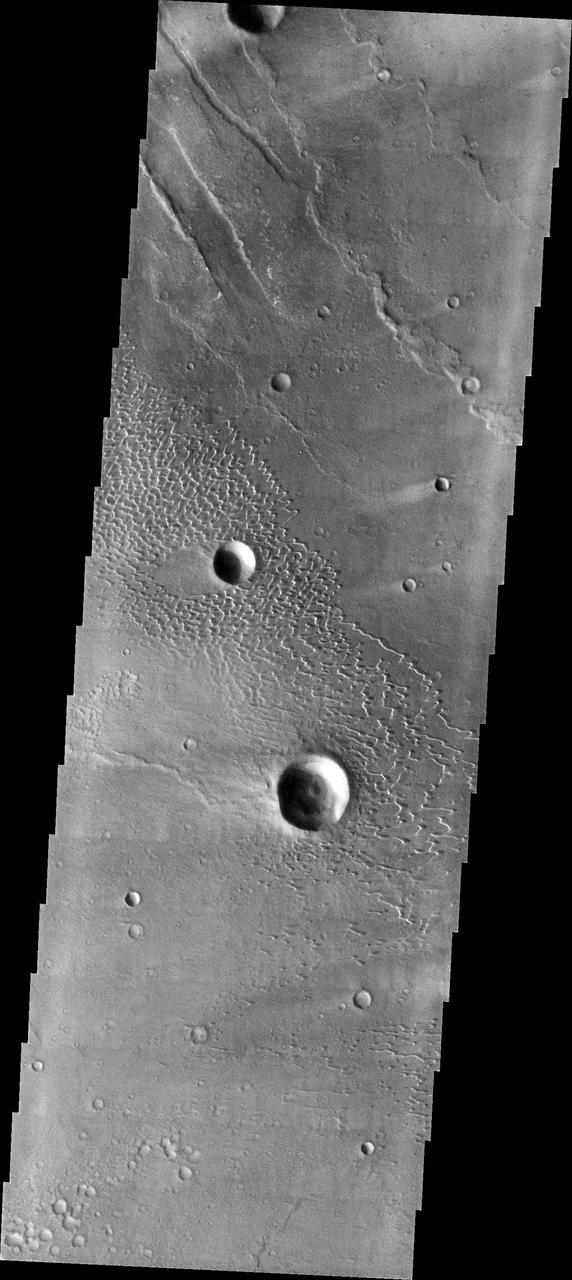
This image shows part of the dune field near Meroe Patera. High resolution imaging by other spacecraft has revealed that the dunes in this region are moving. Winds are blowing the dunes across a rough surface of regional volcanic lava flows. The paterae are calderas on the volcanic complex called Syrtis Major Planum. Dunes are found in both Nili and Meroe Paterae and in the region between the two calderas. The Odyssey spacecraft has spent over 15 years in orbit around Mars, circling the planet more than 69000 times. It holds the record for longest working spacecraft at Mars. THEMIS, the IR/VIS camera system, has collected data for the entire mission and provides images covering all seasons and lighting conditions. Over the years many features of interest have received repeated imaging, building up a suite of images covering the entire feature. From the deepest chasma to the tallest volcano, individual dunes inside craters and dune fields that encircle the north pole, channels carved by water and lava, and a variety of other feature, THEMIS has imaged them all. For the next several months the image of the day will focus on the Tharsis volcanoes, the various chasmata of Valles Marineris, and the major dunes fields. We hope you enjoy these images! Orbit Number: 8149 Latitude: 7.17974 Longitude: 67.7955 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2003-10-16 10:14 https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22010
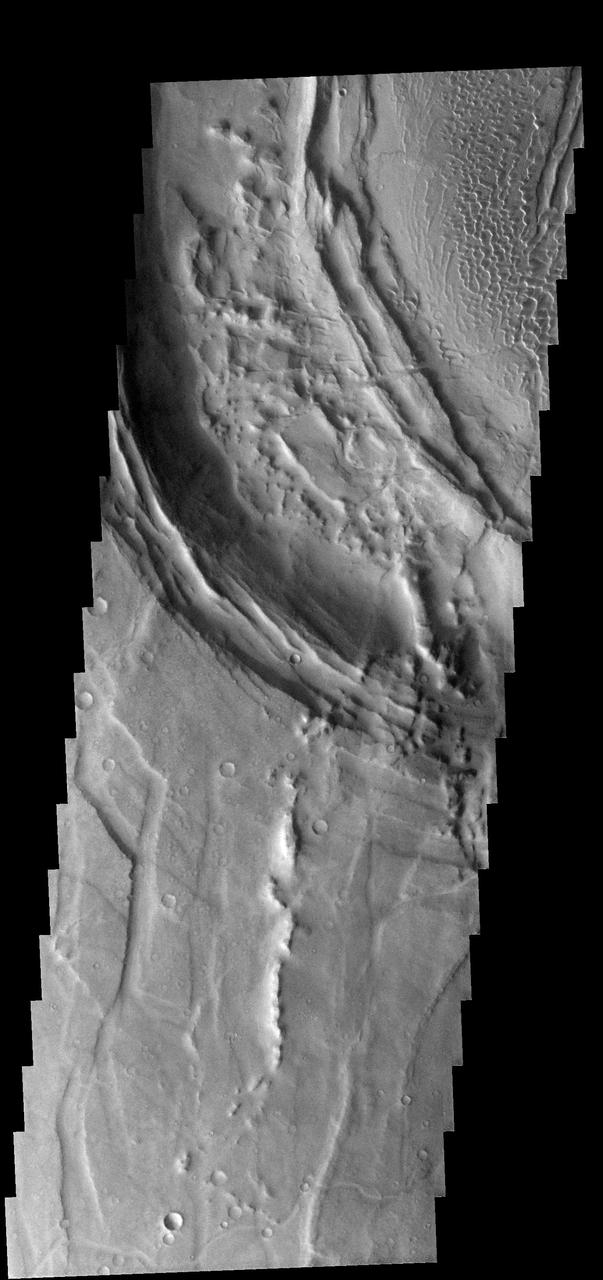

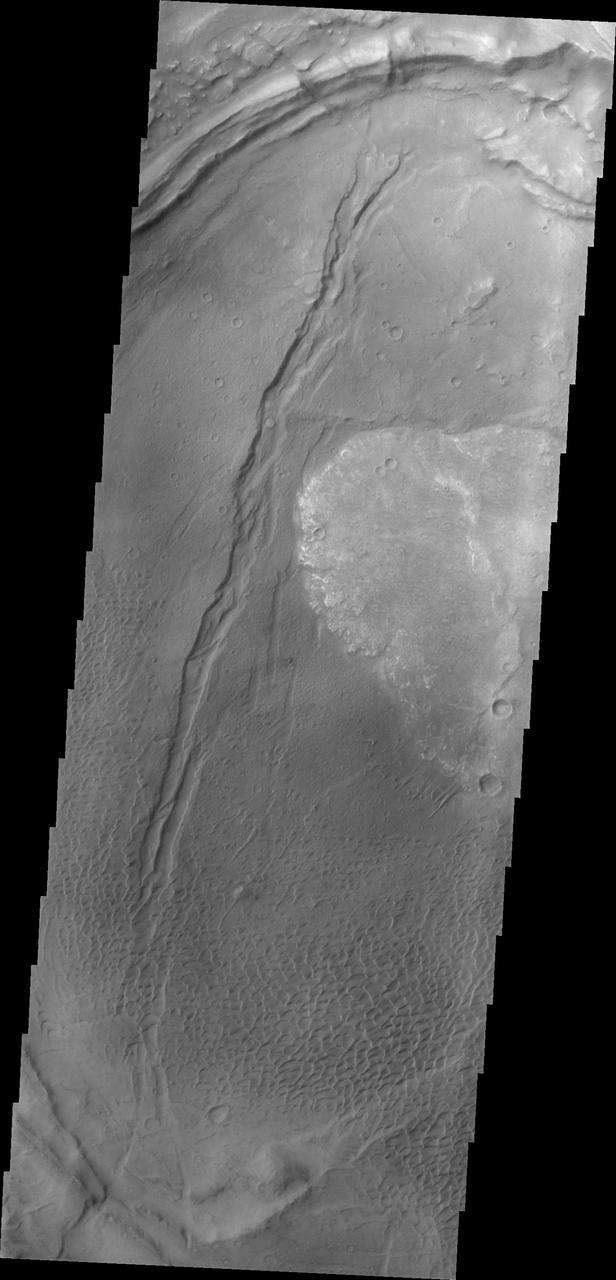
This image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows part of the caldera rim of Nili Patera. Dunes are located within the caldera.

The upper portion of this map is from an observation by the Context Camera on NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter of a field of dark sand dunes in the Nili Patera region of Mars.

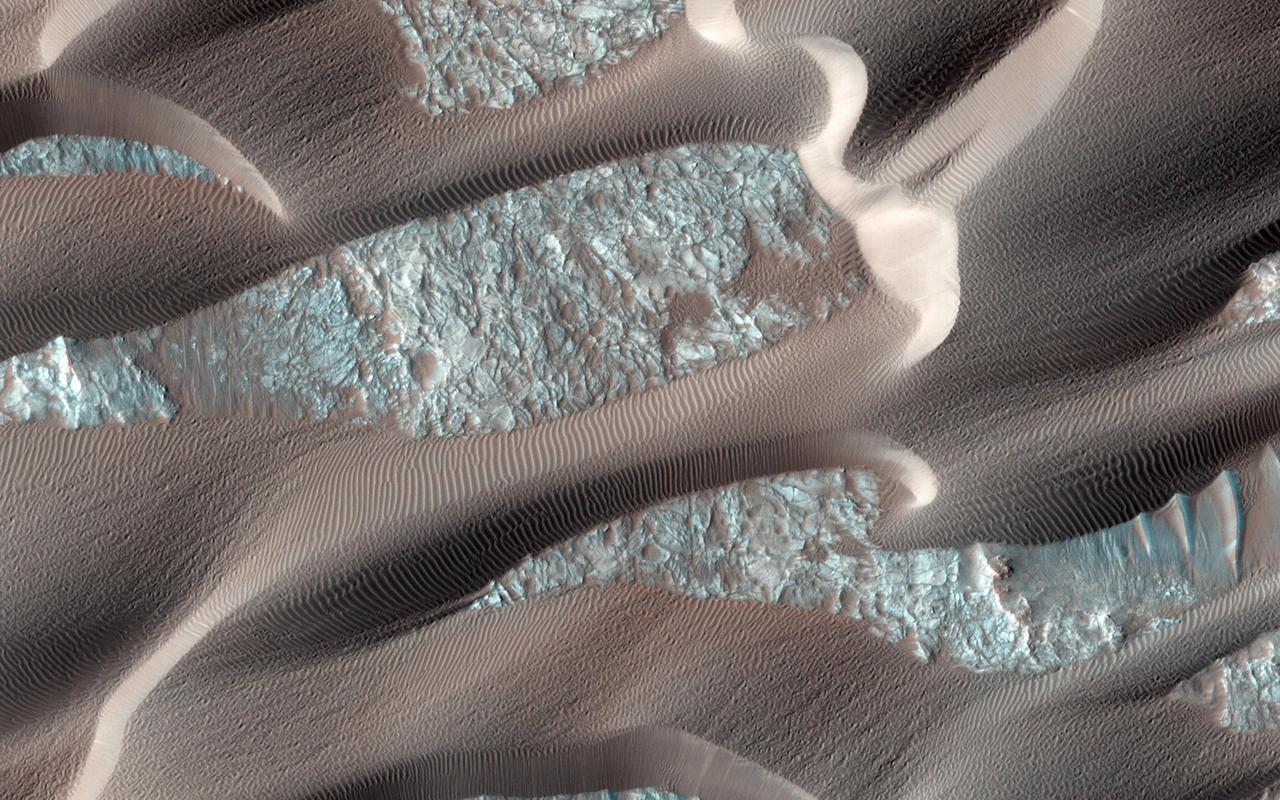
This false color image from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter indicates that the volcanic cone in the Nili Patera caldera on Mars has hydrothermal mineral deposits on the southern flanks and nearby terrains.
The THEMIS camera contains 5 filters. The data from different filters can be combined in multiple ways to create a false color image. These false color images may reveal subtle variations of the surface not easily identified in a single band image. Today's false color image shows part of Syrtis Major Planum, between Nili Patera and Meroe Patera. Orbit Number: 43352 Latitude: 8.2378 Longitude: 67.7675 Instrument: VIS Captured: 2011-09-22 22:16 http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20988

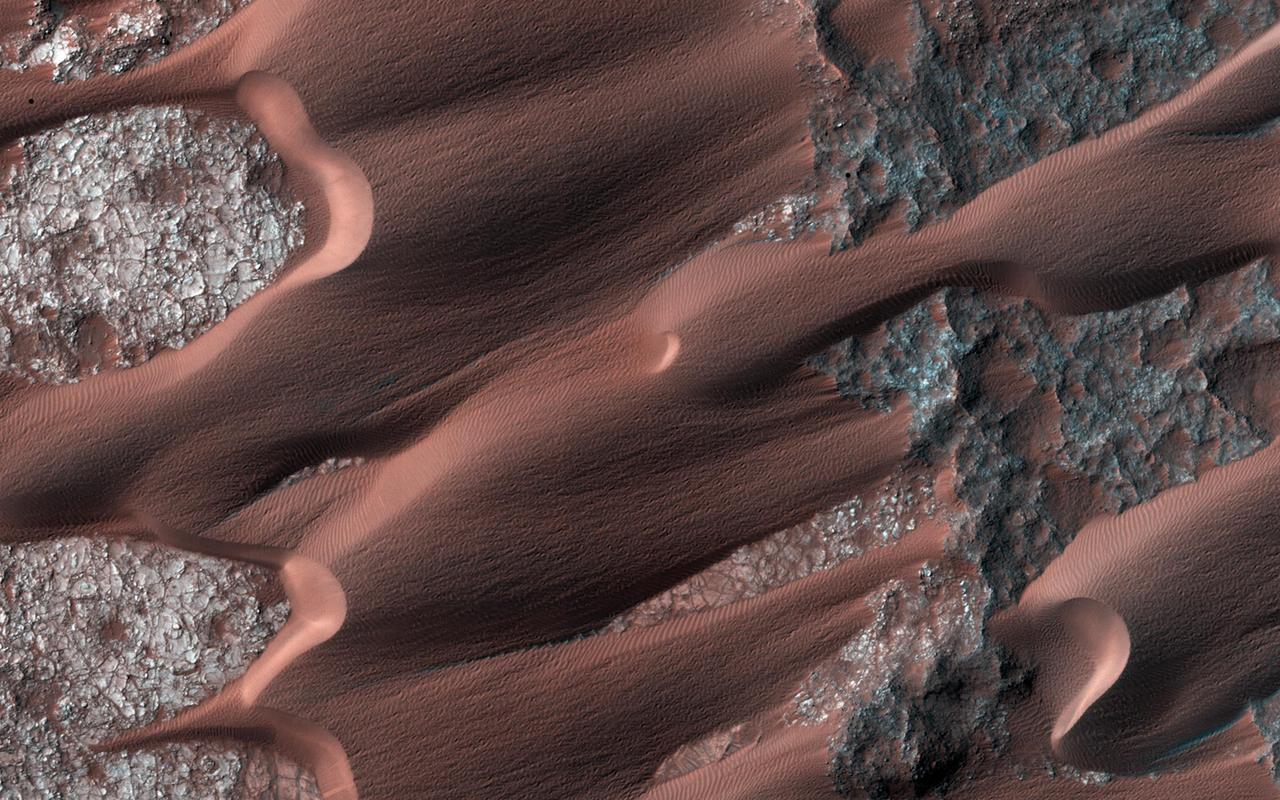
In this image many sand dunes are visible. They have an elongated crescent form and are called "barchan dunes." They are formed by the continuous action of the wind, blowing in the same direction, giving this particular shape. The orientation of these dunes tell us that the prevailing wind blows from the right to the left (east to west). The wind is continuously moving sand grains up the longer dune slope, towards the top. The small ripples on the slope are caused by this movement. When the sand grains arrive at the top, they fall down the steeper and shorter slope, which as a consequence, has no ripples. It is this gradual sand movement that causes the dunes to slowly move over time. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23056
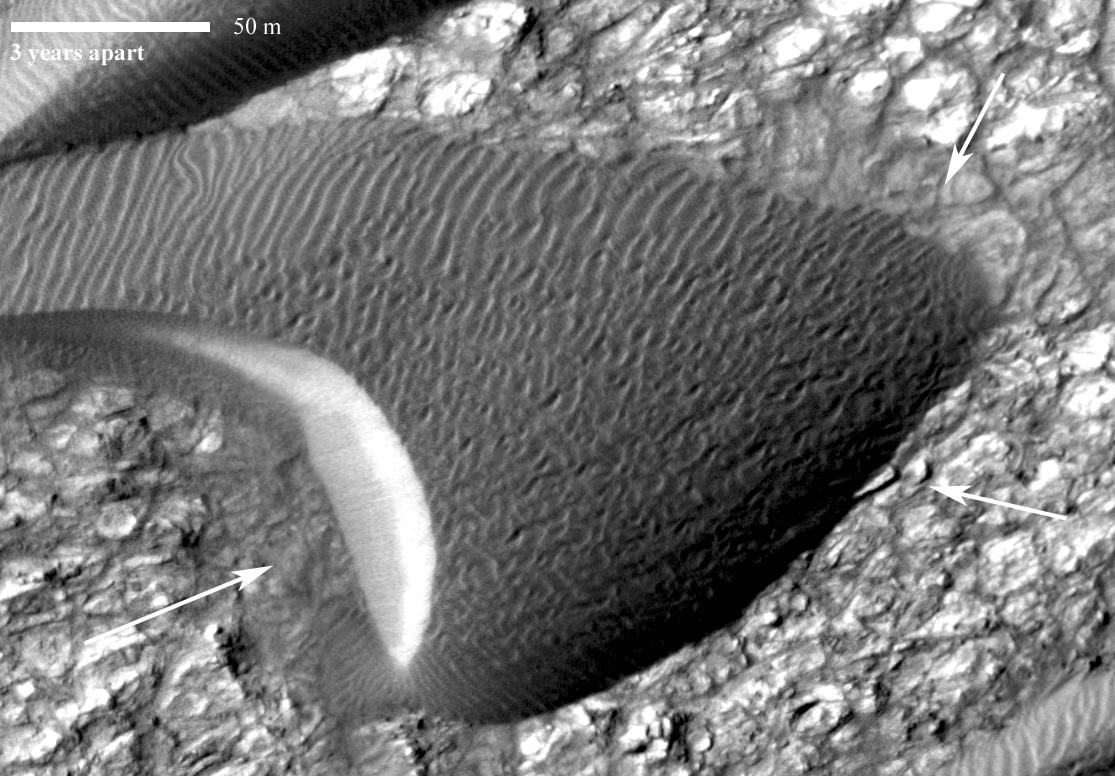

This image, from an animation from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter shows a dark, rippled sand dune overlying bright-toned rock.

This image, one of two from a two-image animation from NASA Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, shows movement of ripples covering a sand dune on Mars.
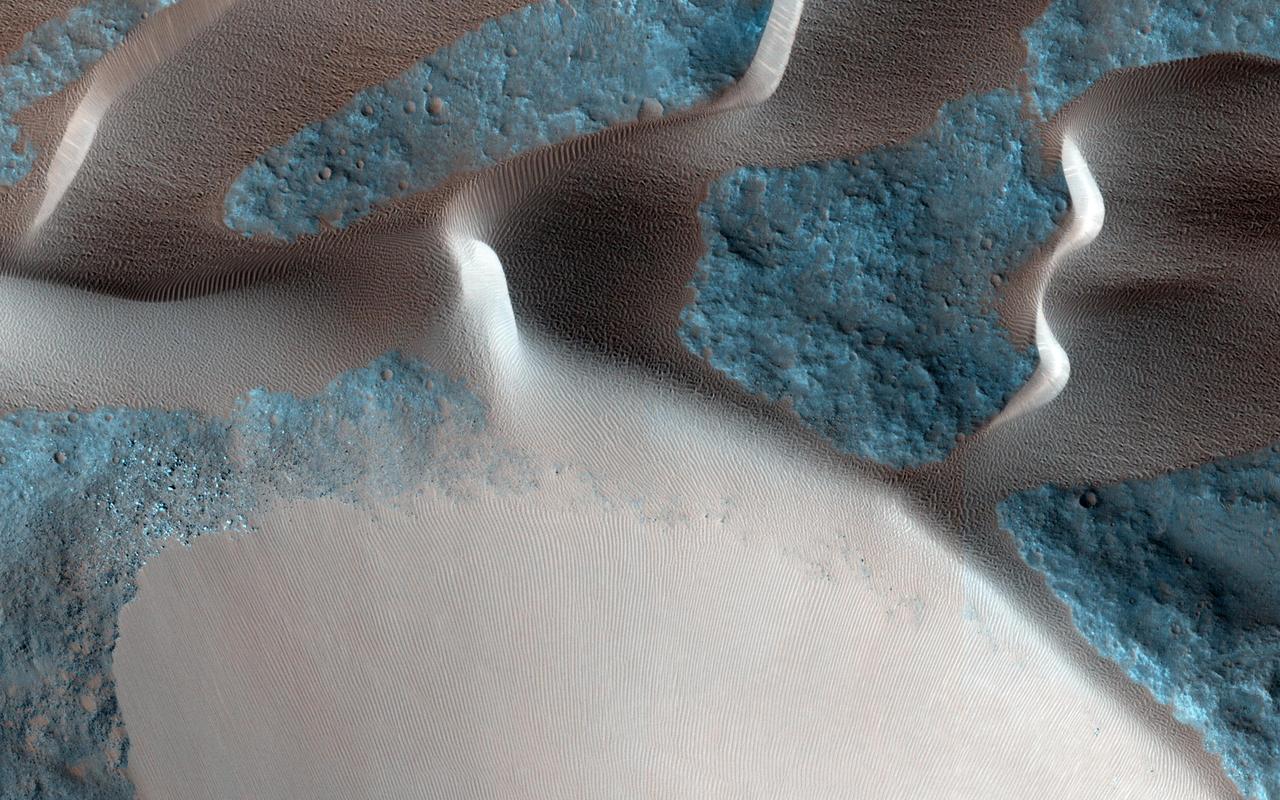

One of the major extended-mission objectives for HiRISE has been to re-image parts of the surface to look for changes. Such observations can tell us what processes are active today. This image was acquired as part of a series to look for sand movement in Meroe Patera, not far from the active sand dunes of Nili Patera. Our image shows that sand dunes are missing downwind (to the left) of a crater near the center of the observation, because sand falls into the crater and is trapped. Zooming in on the sand-coated crater wall and comparing it with older images revealed a surprise: several major sand flows slumped down into the crater (towards the upper left), leaving small ridges (called "levees") along their path and rounded piles of sand at the end. What caused these slumps? Dry ice, which is thought to cause flows in some gullies and the North polar dunes, does not occur this close to the equator. There is no sign of recurring slope lineae, the leading candidates for liquid on the Martian surface. Instead, it is most likely that these were dry flows. They are far larger than the avalanches commonly seen on sand dunes, typified by the shorter light streaks visible in the lower left part of the "after" image, so they might have been triggered by a Mars-quake or an unusually strong wind. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19305