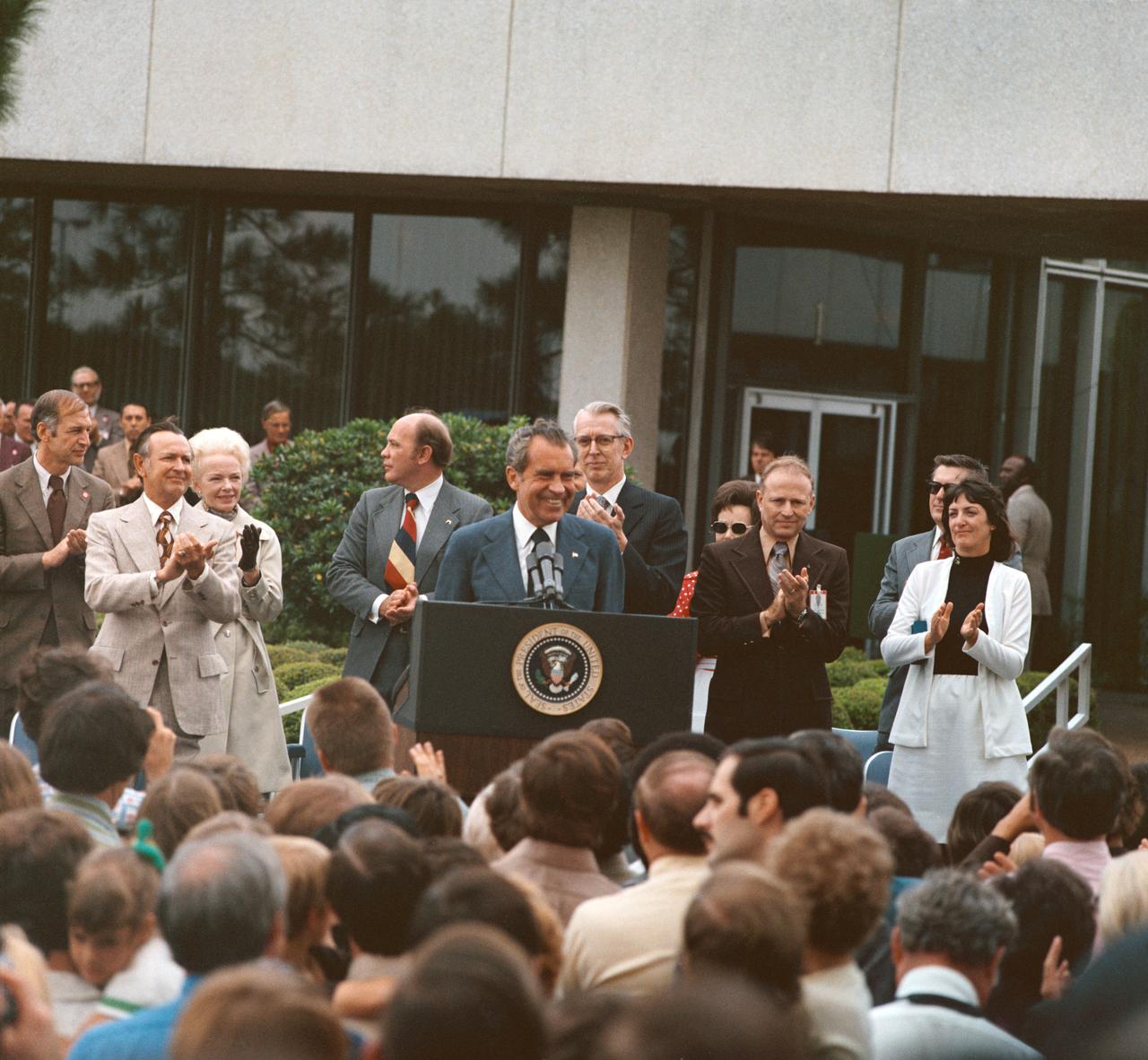

Five (5) views of President Richard M. Nixon during his visit to the JSC. These views show the President as he addresses a crowd of employees and visitors outside of Building 1 Auditorium. Dr. Christopher C. Kraft, Fletcher, and Astronaut Gerald Carr, with Pete Clements, George Abbey, and Jack Waite in the background is also seen with the President. 1. Pres. Richard M. Nixon 2. Dr. Christopher C. Kraft JSC, HOUSTON, TX
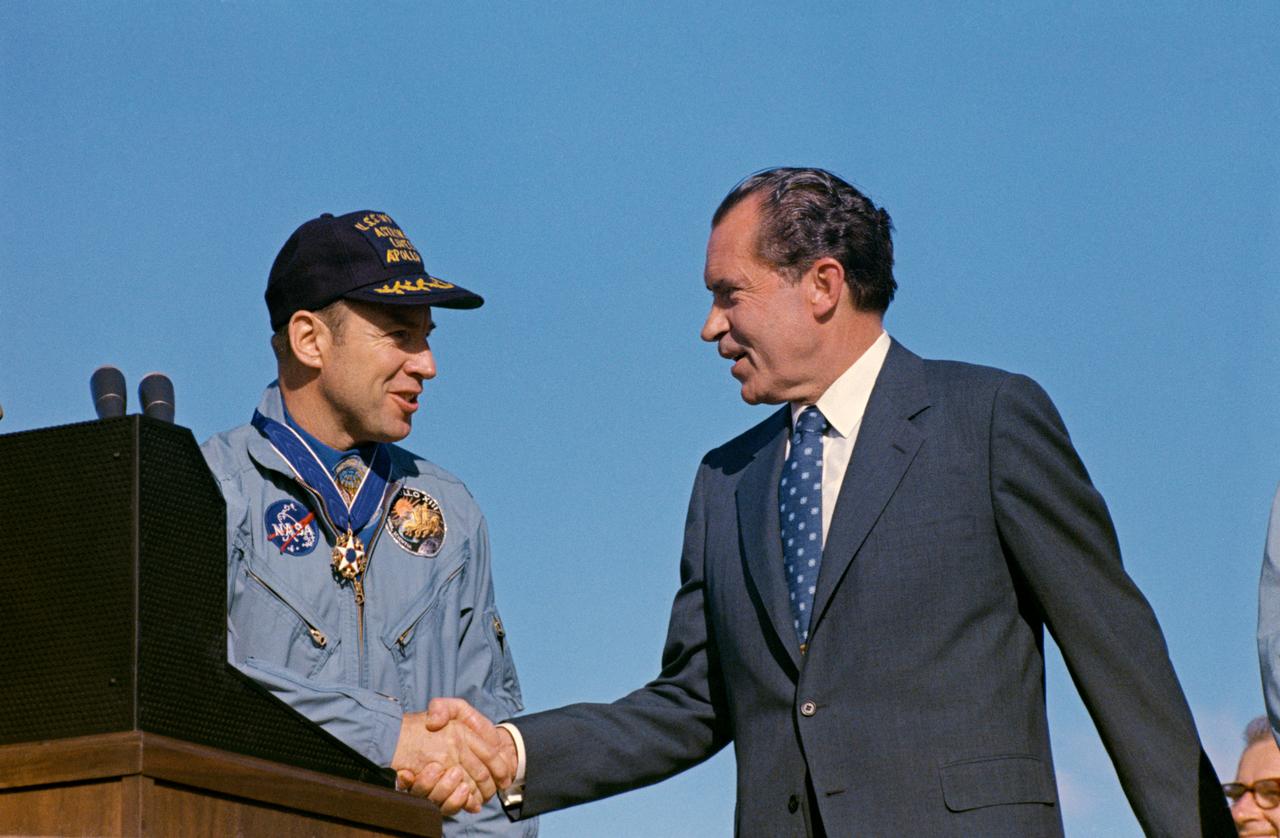

S70-15506 (18 April 1970) --- President Richard M. Nixon and astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., Apollo 13 commander, shake hands at special ceremonies at Hickam Air Force Base, Hawaii. President Nixon was in Hawaii to present the Apollo 13 crew with the Presidential Medal of Freedom, the nation's highest civilian honor. The wives of astronauts Lovell and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot; and the parents of astronaut John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, flew with the Chief Executive to Hickam Air Force Base. The Apollo 13 splashdown occurred at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, a day and a half prior to the awards ceremony.
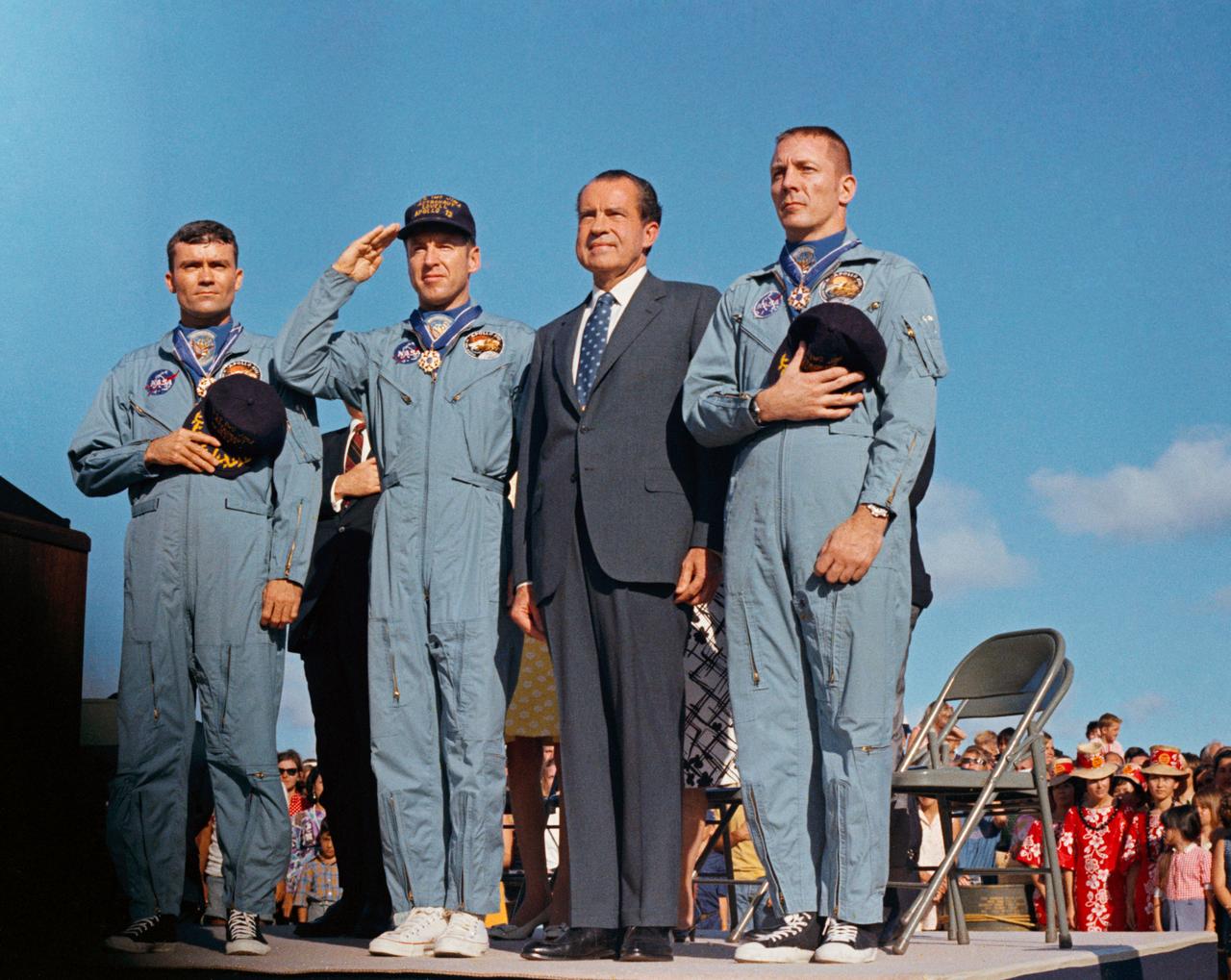

S70-15526 (18 April 1970) --- President Richard M. Nixon and the Apollo 13 crew members pay honor to the United States flag during the post-mission ceremonies at Hickam Air Force Base, Hawaii. Astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., (United States Navy Captain, salutes the flag) commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot (right); and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot (left), were presented the Presidential Medal of Freedom by the Chief Executive. The Apollo 13 splashdown occurred at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, about a day and a half prior to the award presentation.
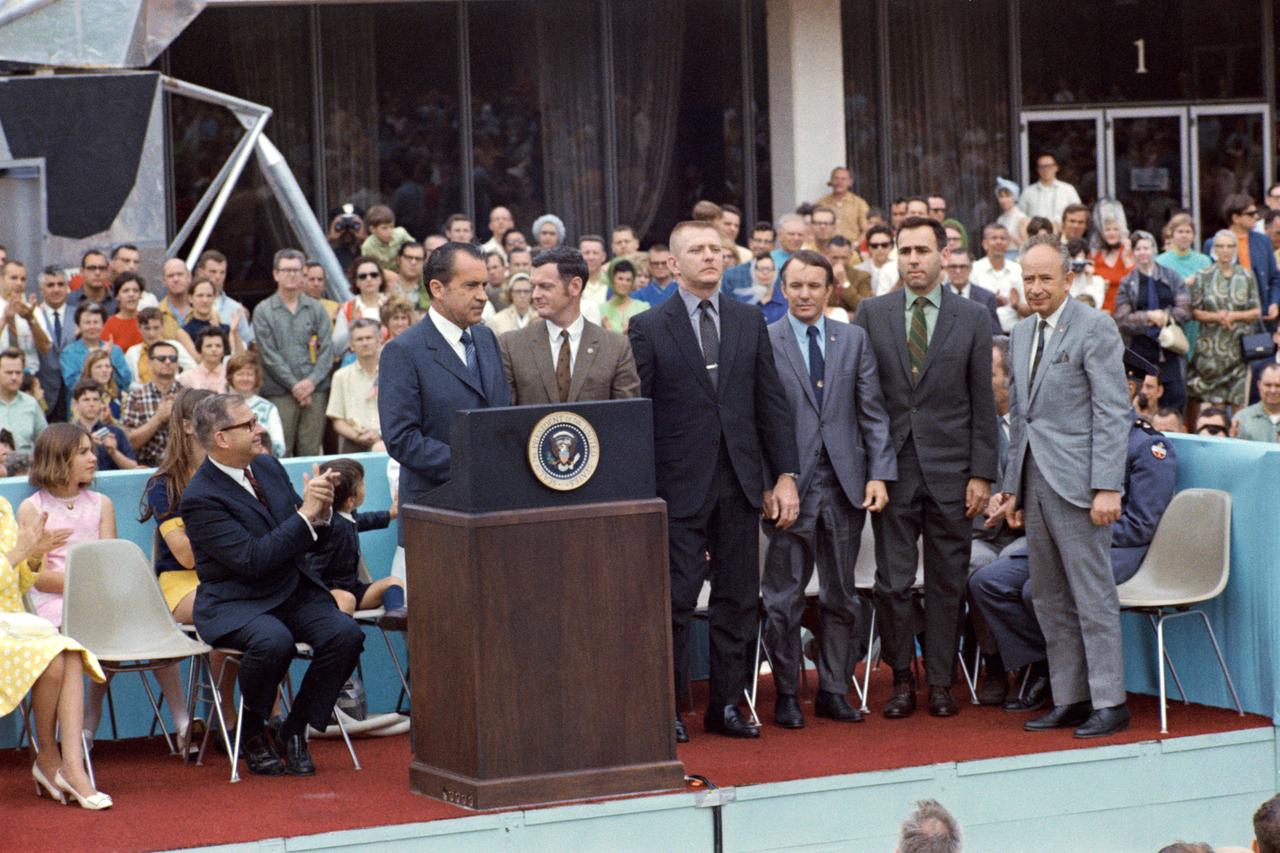

S70-35600 (18 April 1970) --- President Richard M. Nixon introduces Sigurd A. Sjoberg (far right), director of Flight Operations at Manned Spacecraft Center, and the four Apollo 13 flight directors during the President?s post-mission visit to the Manned Spacecraft Center. The flight directors are, from left to right, Glynn S. Lunney, Eugene A. Kranz, Gerald D. Griffin and Milton L. Windler. Dr. Thomas O. Paine, Administrator, National Aeronautics and Space Administration, is seated at left. President Nixon was on the site to present the Presidential Medal of Freedom - the nation?s highest civilian honor -to the Apollo 13 Mission Operations Team.
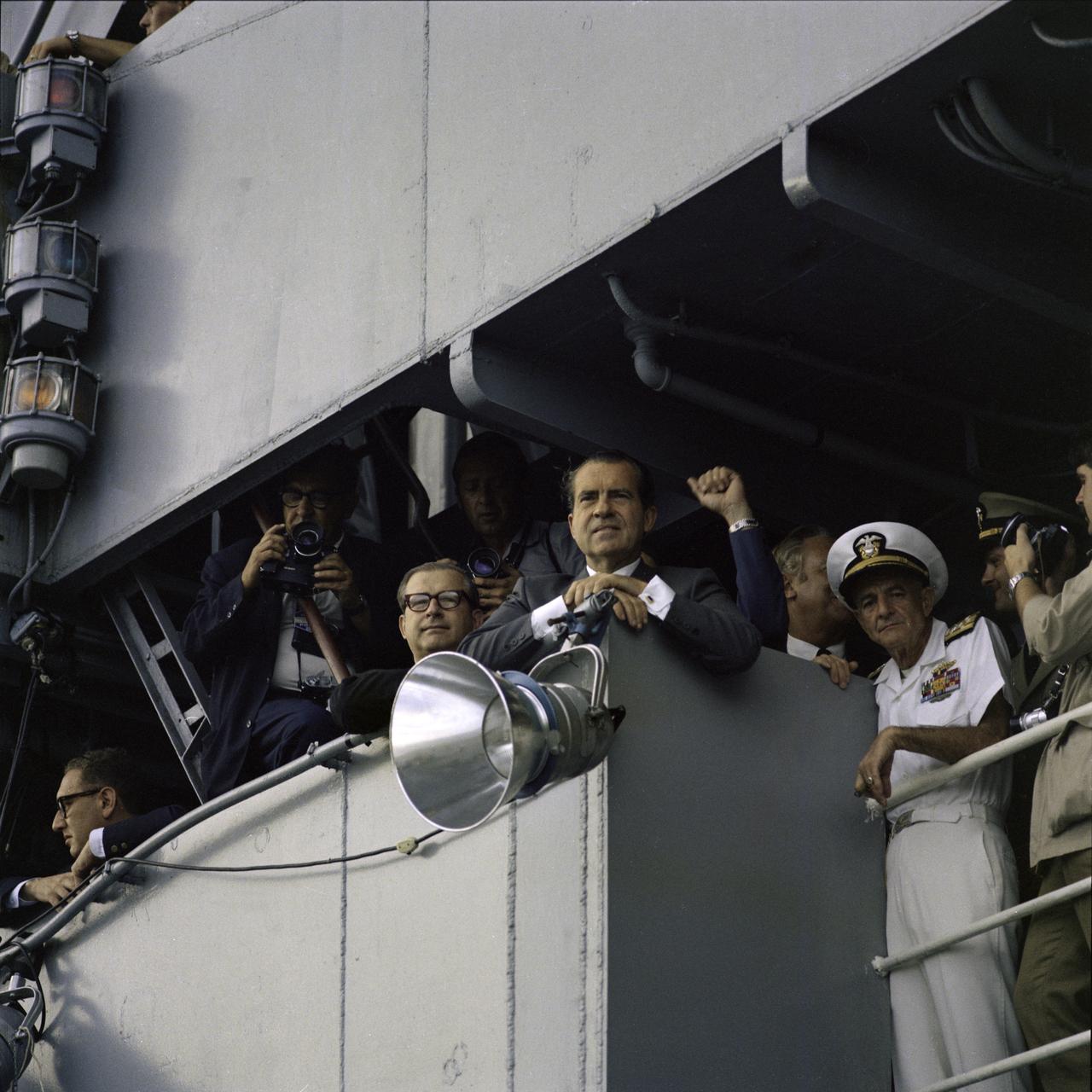

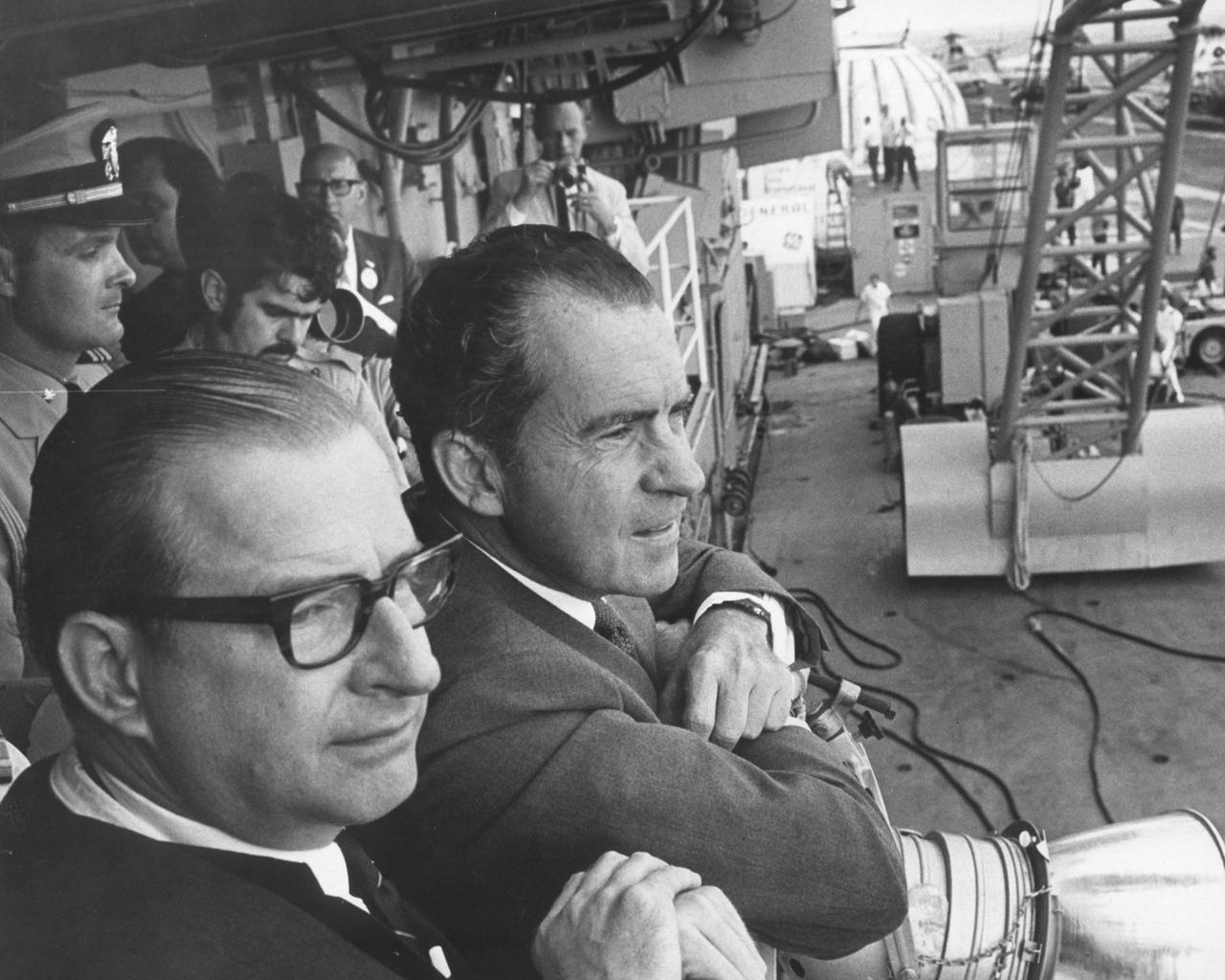
S69-21736 (24 July 1969) --- President Richard M. Nixon photographed on the deck of the USS Hornet, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission, awaiting the Apollo 11 crew arrival. Apollo 11 splashed down at 11:40 a.m. (EDT), July 24, 1969, about 812 nautical miles southwest of Hawaii.

On June 4, 1974, 5 years after the successful Apollo 11 lunar landing mission, commander Neil Armstrong (right) presented a plaque to U.S. President Richard Milhous Nixon (left) on behalf of all people who had taken part in the space program. In making the presentation, Armstrong said “Mr. President, you have proclaimed this week to be United States Space week in conjunction with the fifth anniversary of our first successful landing on the Moon. It is my privilege to represent my colleagues, the crewmen of projects Mercury, Gemini, Apollo, and Skylab, and the men and women of NASA, and the hundreds of thousands of Americans from across the land who contributed so mightily to the success of our efforts in space in presenting this plaque which bears the names of each individual who has had the privilege of representing this country” in a space flight. The presentation was made at the California white house in San Clemente.
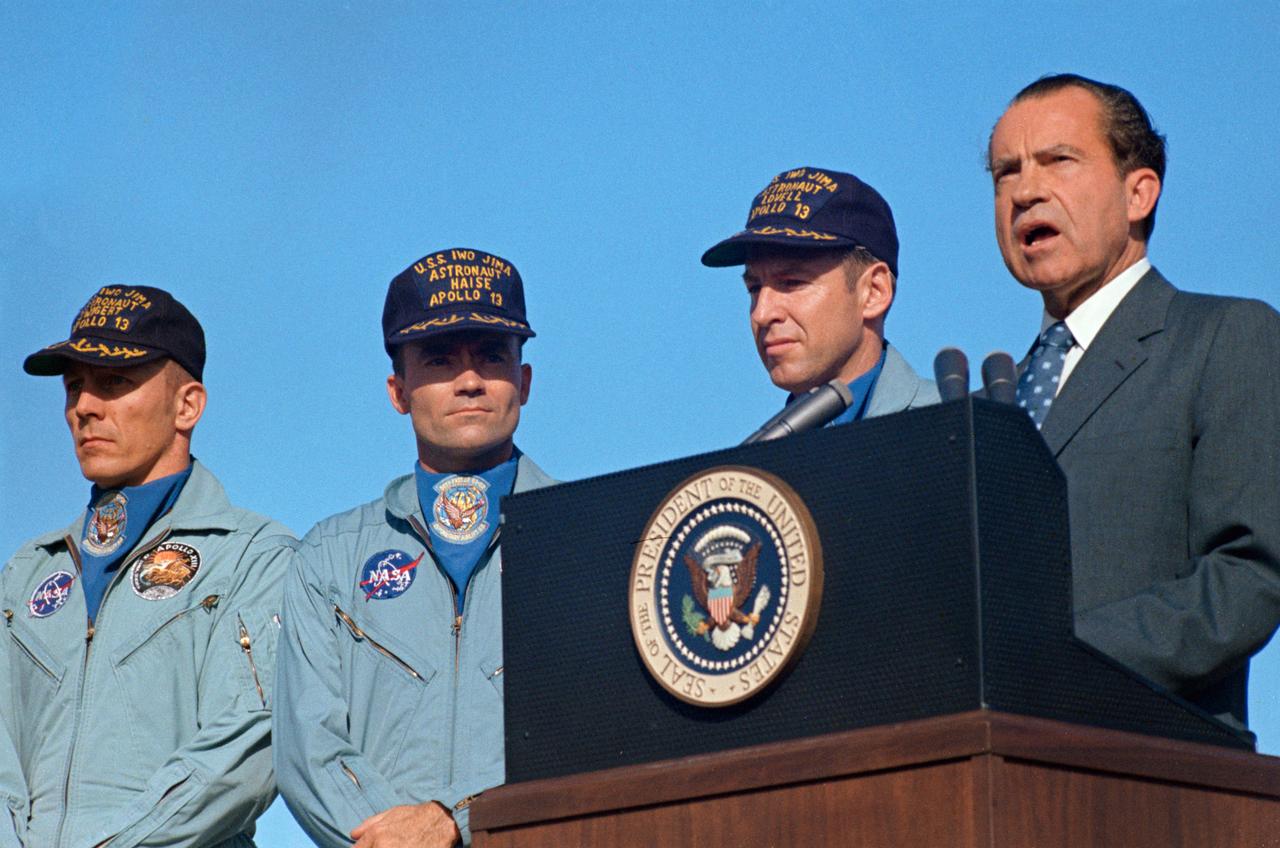

S70-15511 (19 April 1970) --- President Richard M. Nixon speaks at Hickham Air Force Base prior to presenting the nation's highest civilian award to the Apollo 13 crew. Receiving the Presidential Medal of Freedom were astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., (next to the Chief Executive), commander; John L. Swigert Jr. (left), command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. Wives of Lovell and Haise and the parents of Swigert accompanied the President to Hawaii. The Apollo 13 splashdown occurred at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST), April 17, 1970, about a day and a half prior to the Hickam Air Force Base ceremonies.

APOLLO 11 RECOVERY = RECOVERY OF C/M; ARRIVAL OF PRES. NIXON; NIXON GREETS ASTROS; ASTROS. TRANSFER FROM HELICOPTER TO MQF
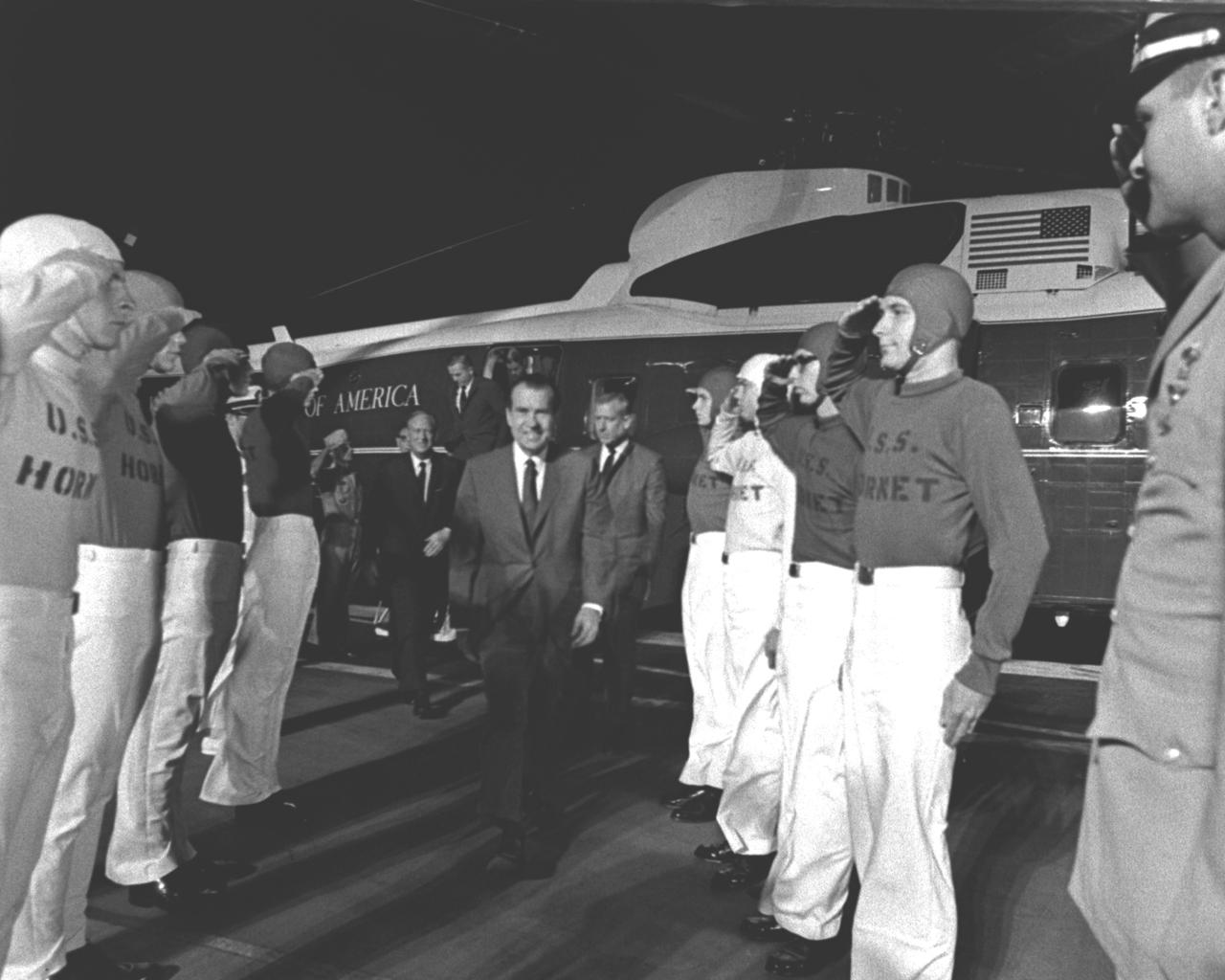

U.S. President Richard Milhous Nixon (center), is saluted by the honor guard of flight deck crewmen when he arrives aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, prime recovery ship for the Apollo 11 mission, to watch recovery operations and welcome the astronauts home. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) for 21 days following the mission. The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun.

Dr. Thomas Paine, NASA administrator (left) and U.S. President Richard Milhous Nixon wait aboard the recovery ship, the U.S.S. Hornet, for splashdown of the Apollo 11 in the Pacific Ocean. Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man crew. The crew was taken to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF). The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via a Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was taken to safety aboard the USS Hornet, where they were quartered in a mobile quarantine facility. Shown here is the Apollo 11 crew inside the quarantine facility as prayer is offered by Lt. Commander John Pirrto, USS Hornet Chaplain accompanied by U.S. President Richard Nixon (front right). With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
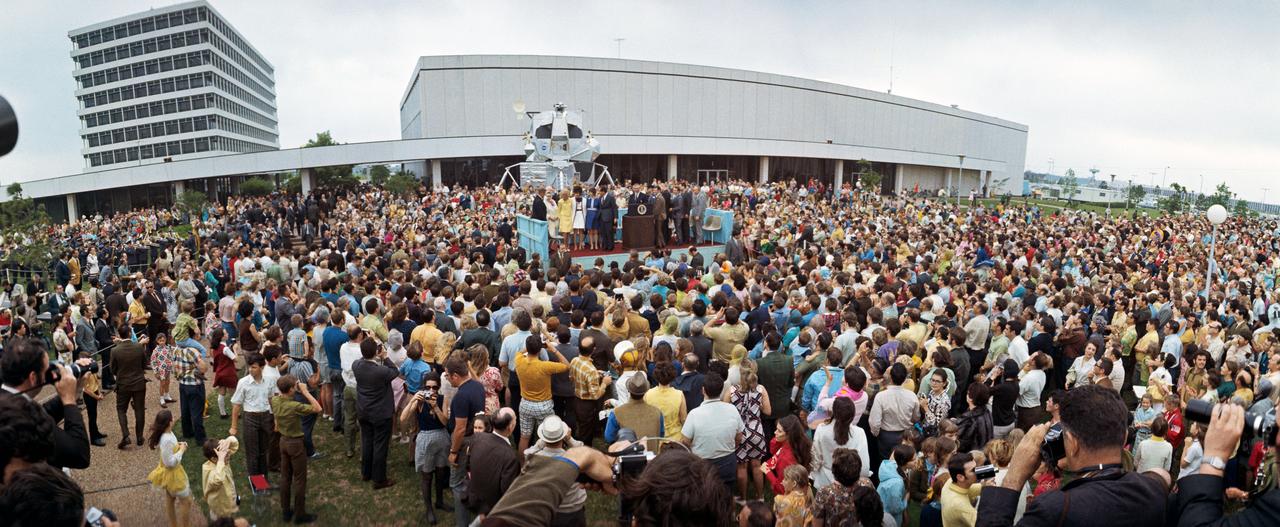

S70-35601 (18 April 1970) --- A wide-angle, overall view of the large crowd of people who were on hand to see President Richard M. Nixon present the Presidential Medal of Freedom to the Apollo 13 Mission Operations Team. The honor is the nation's highest civilian award. A temporary speaker's platform was erected beside Building 1 for the occasion.
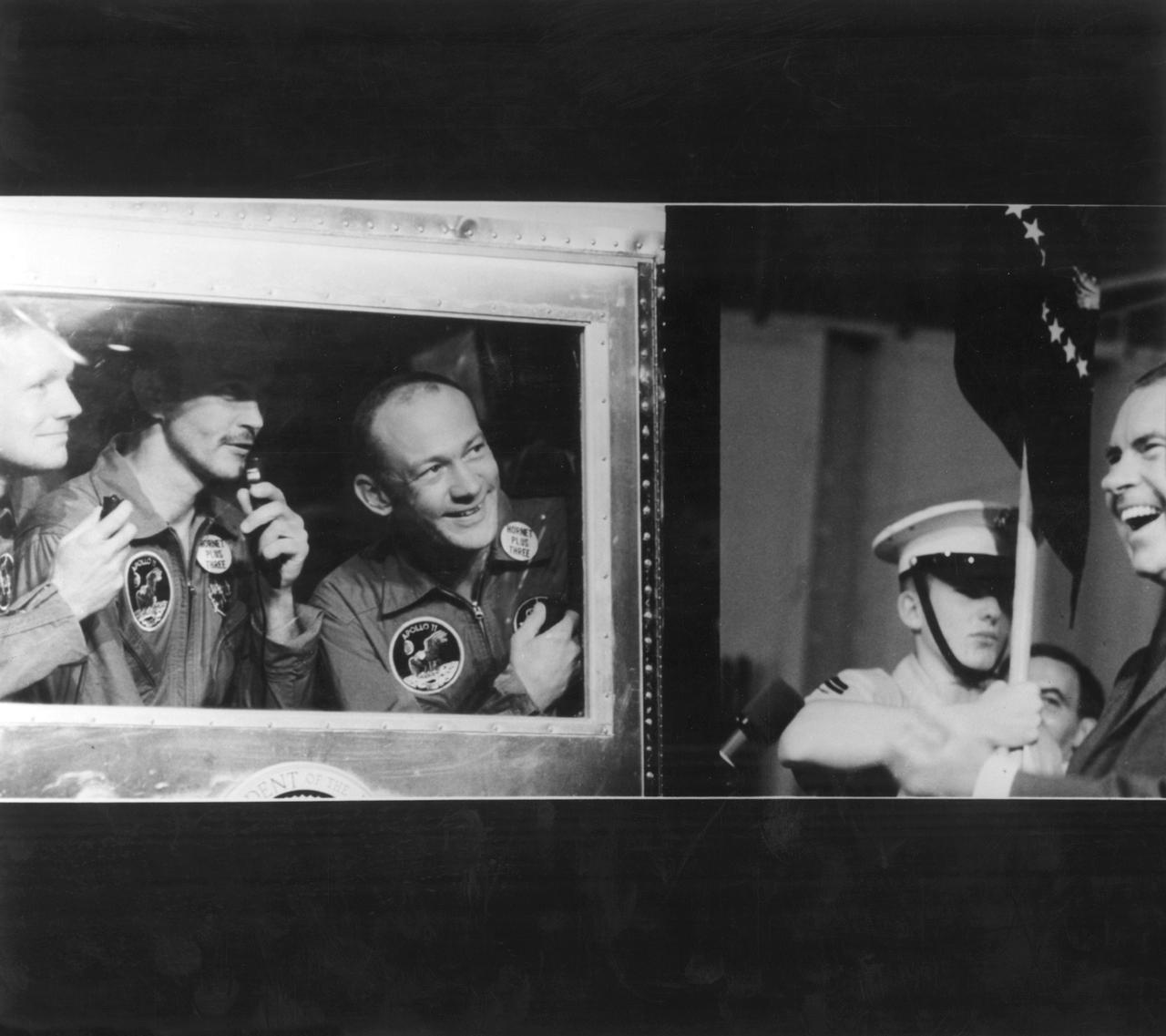

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) for 21 days. Here, U.S. President Richard Milhous Nixon gets a good laugh at something being said by Astronaut Collins (center) as astronauts Armstrong (left), and Aldrin (right) listen. The president was aboard the recovery vessel awaiting return of the astronauts. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
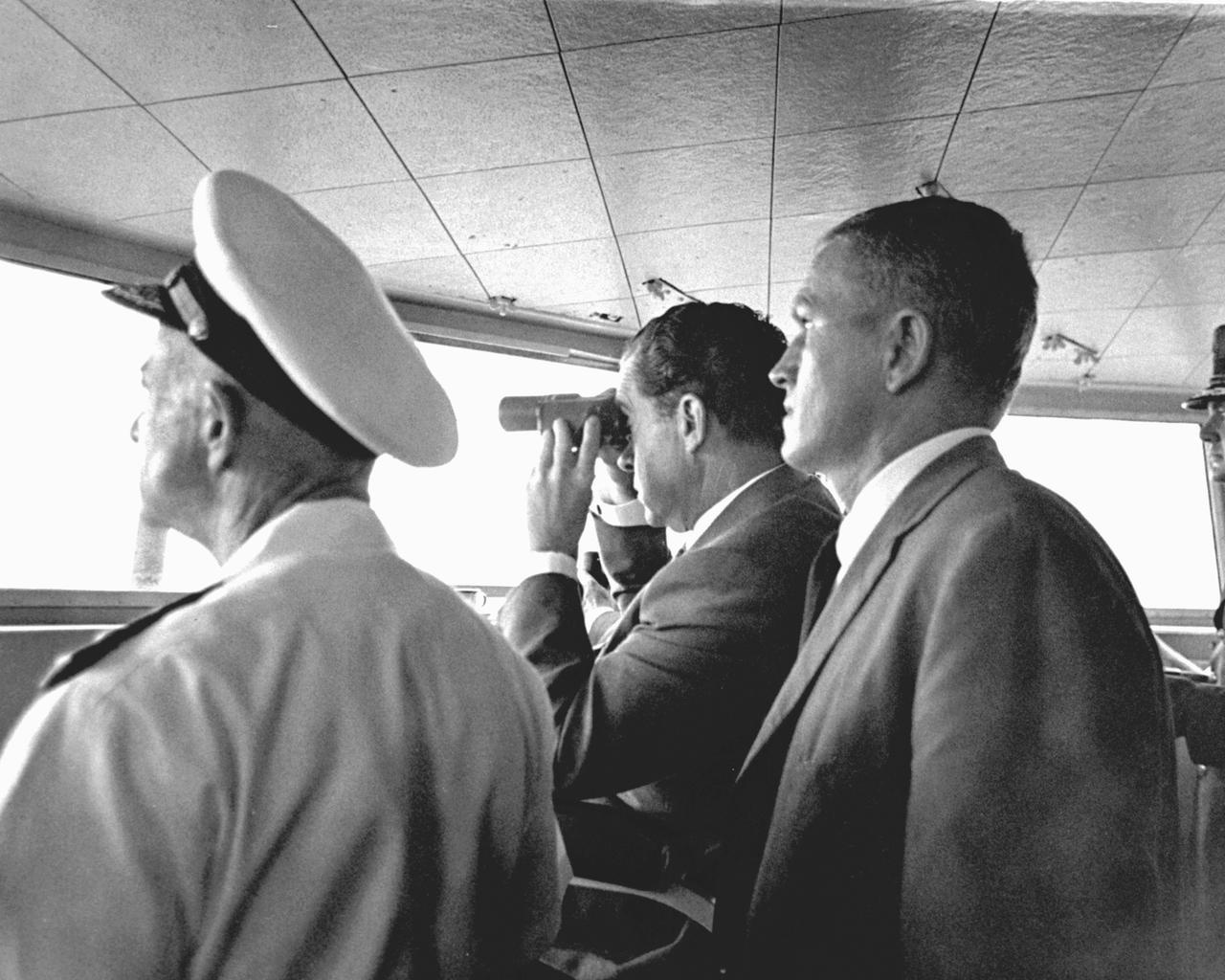

U.S. President Richard Milhous Nixon (center), aboard the U.S.S. Hornet aircraft carrier, used binoculars to watch the Apollo 11 Lunar Mission Recovery. Standing next to the President is astronaut Frank Borman, Apollo 8 Commander. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) for 21 days post mission. The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
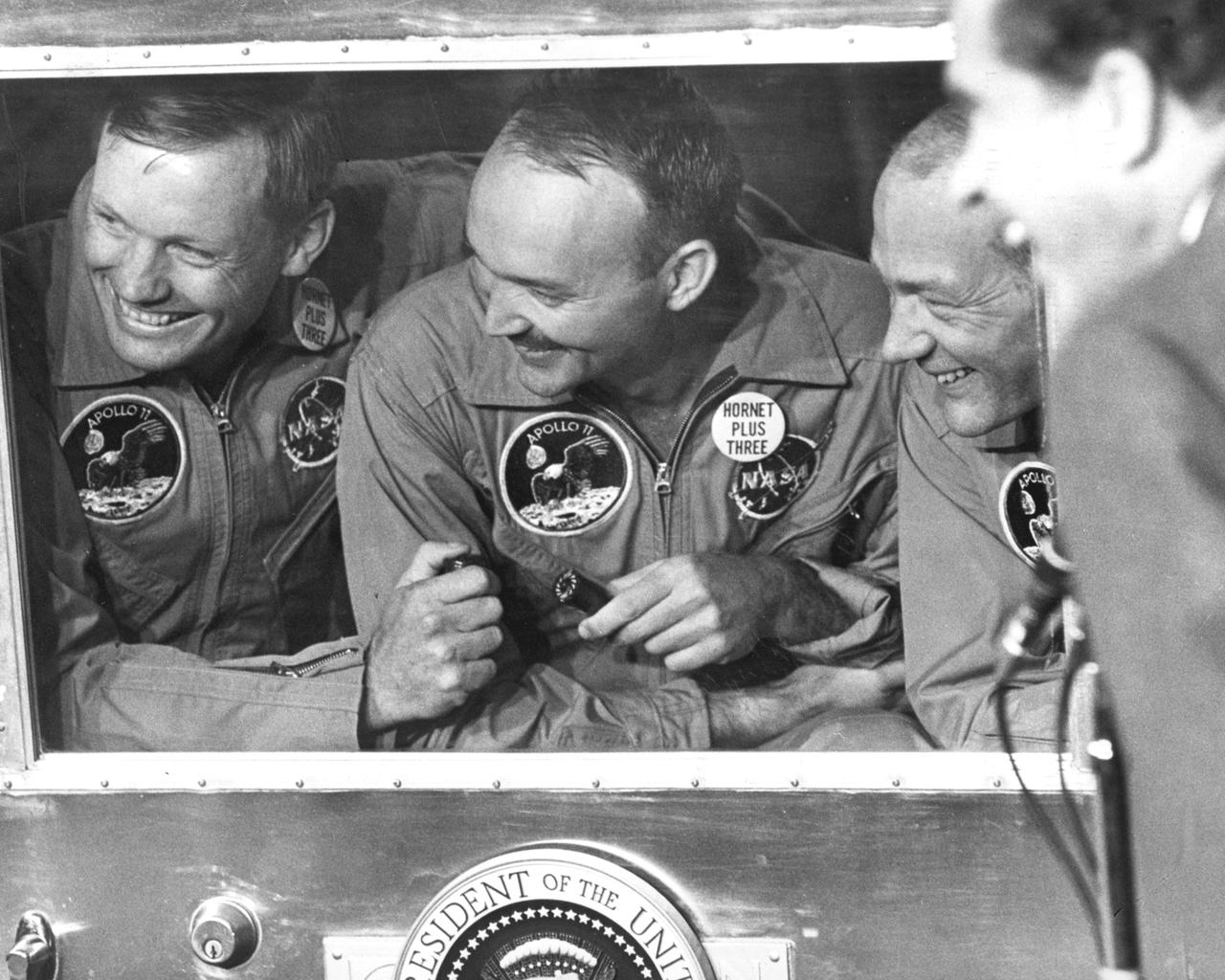

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF). Here the quarantined Apollo 11 crew members (l to r) Armstrong, Collins, and Aldrin, and U.S. President Richard Milhous Nixon share laughs over a comment made by fellow astronaut Frank Borman, Apollo 8 commander. The president was aboard the recovery vessel awaiting return of the astronauts. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
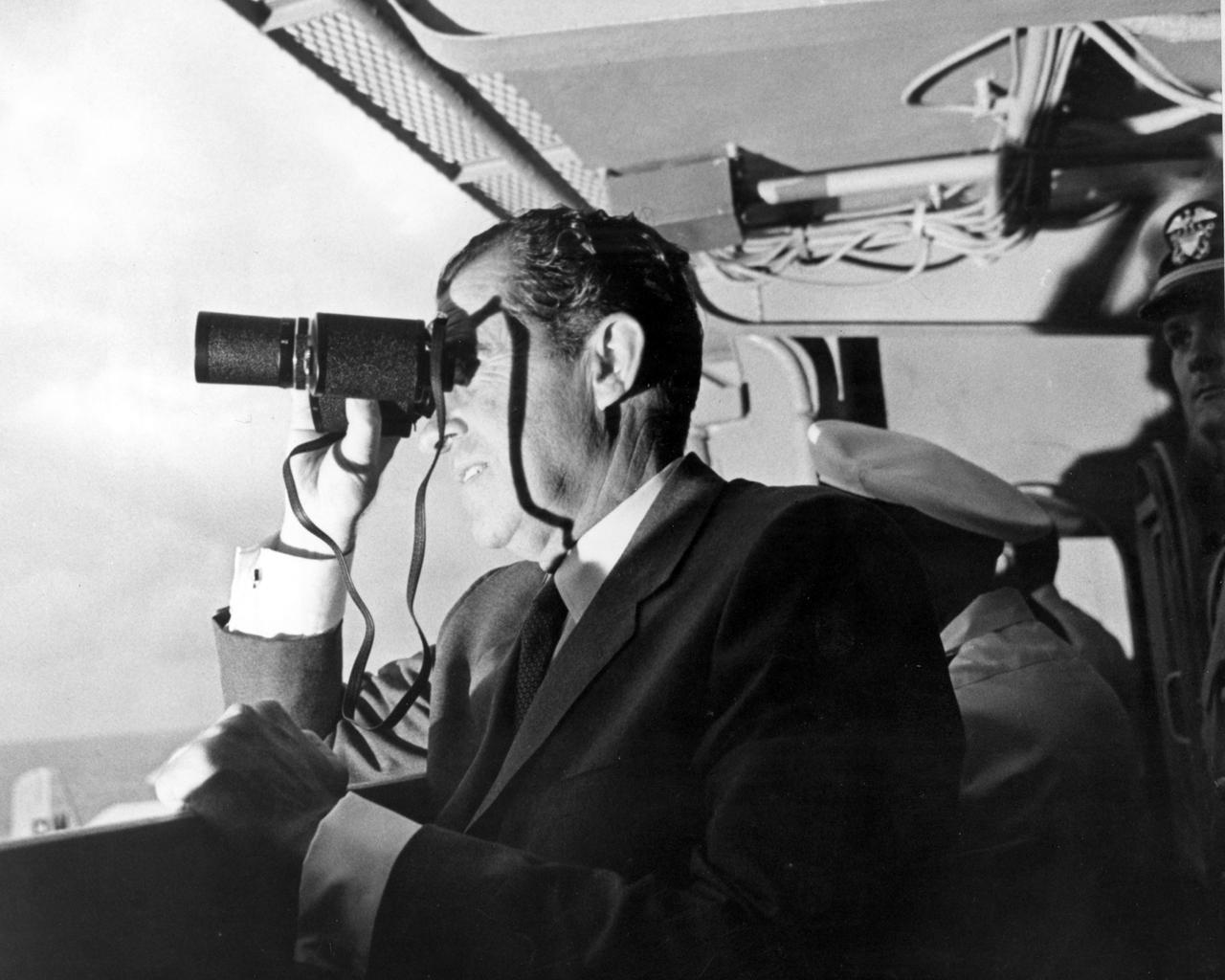

U.S. President Richard Milhous Nixon, aboard the U.S.S. Hornet aircraft carrier, used binoculars to watch the Apollo 11 Lunar Mission recovery. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) for 21 days post mission. The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
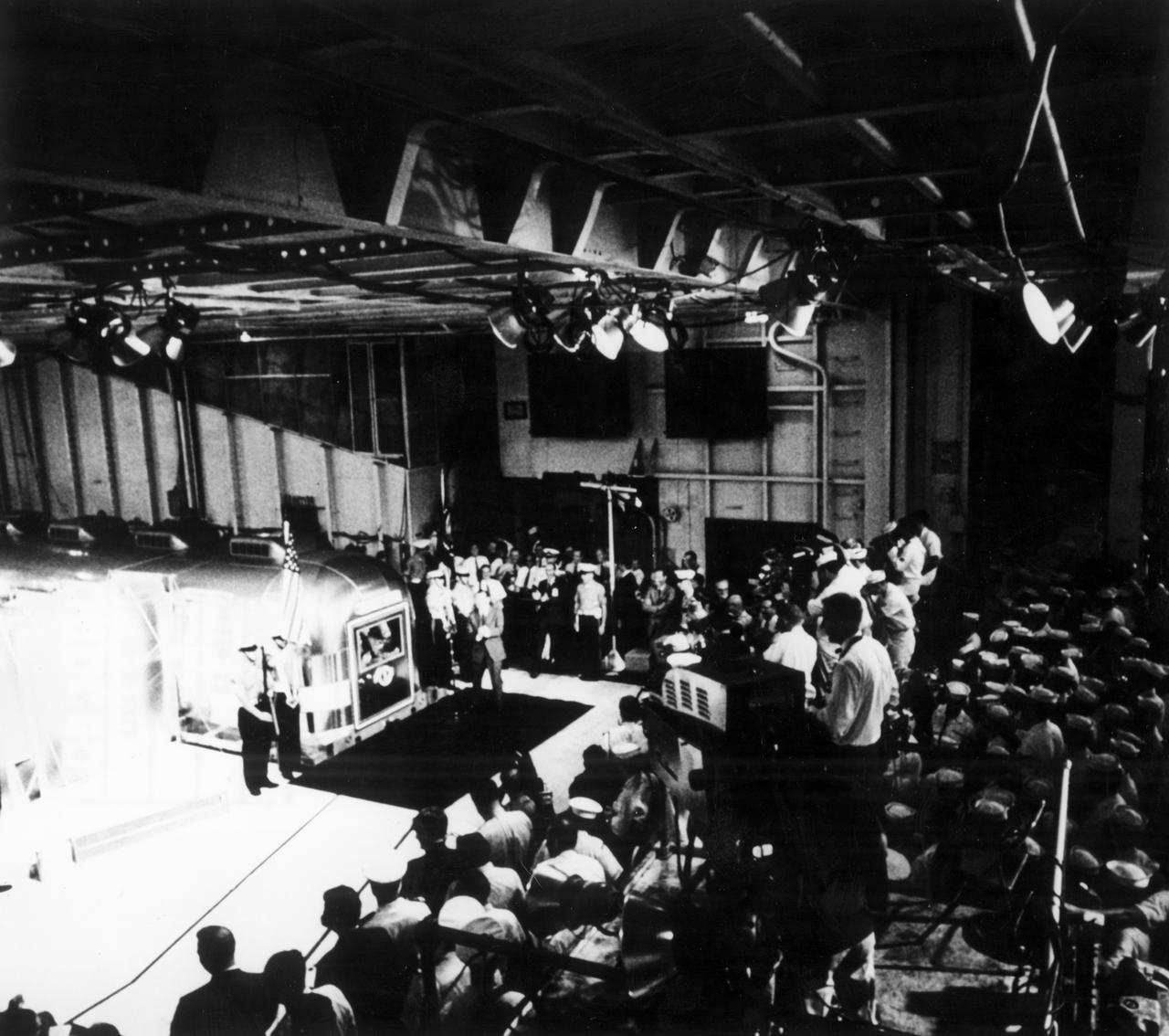

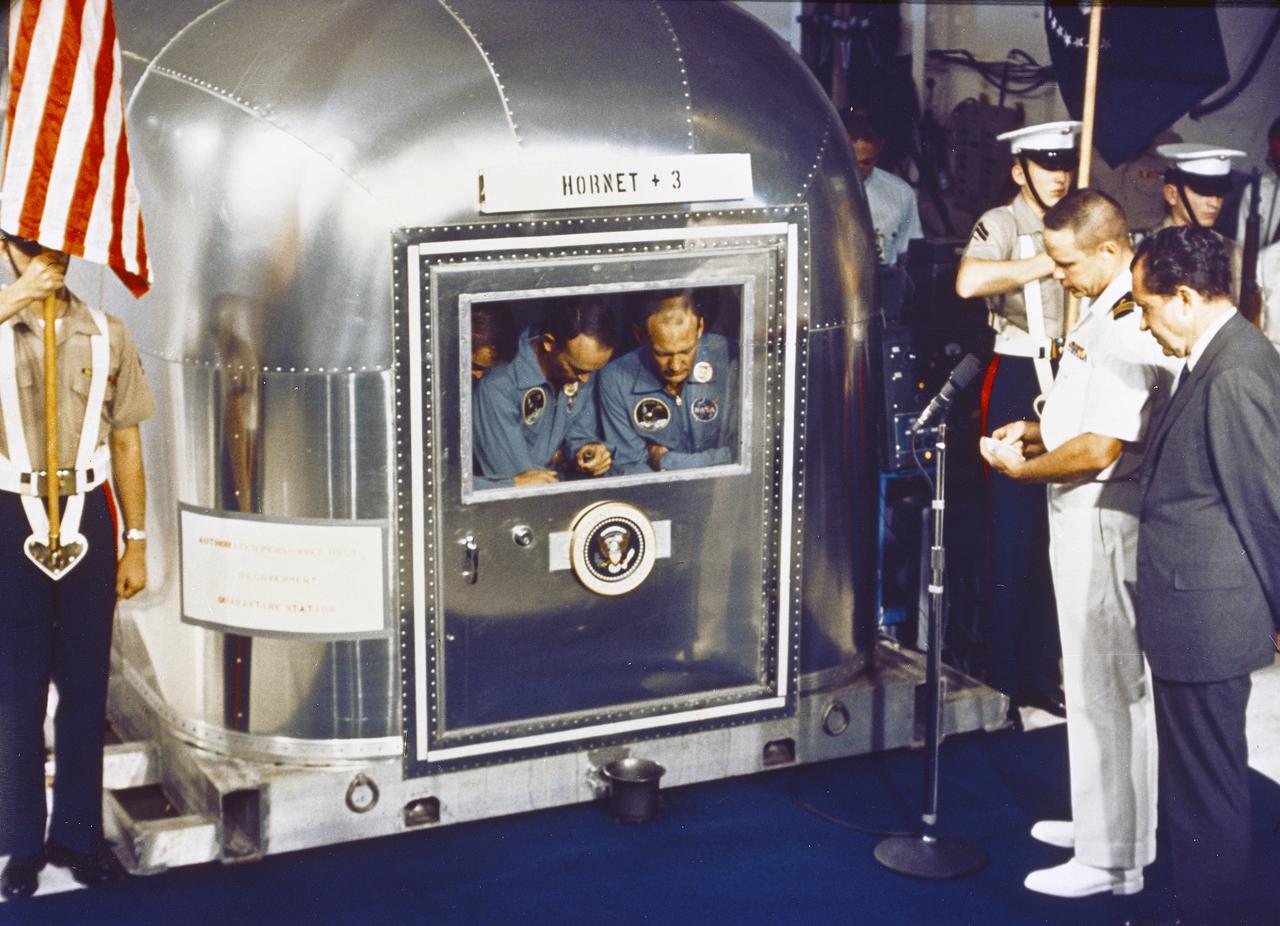
The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. Aboard the space craft were astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet recovery ship, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF). In this photograph, the U.S.S. Hornet crew looks on as the quarantined Apollo 11 crew is addressed by U.S. President Richard Milhous Nixon via microphone and intercom. The president was aboard the recovery vessel awaiting return of the astronauts. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
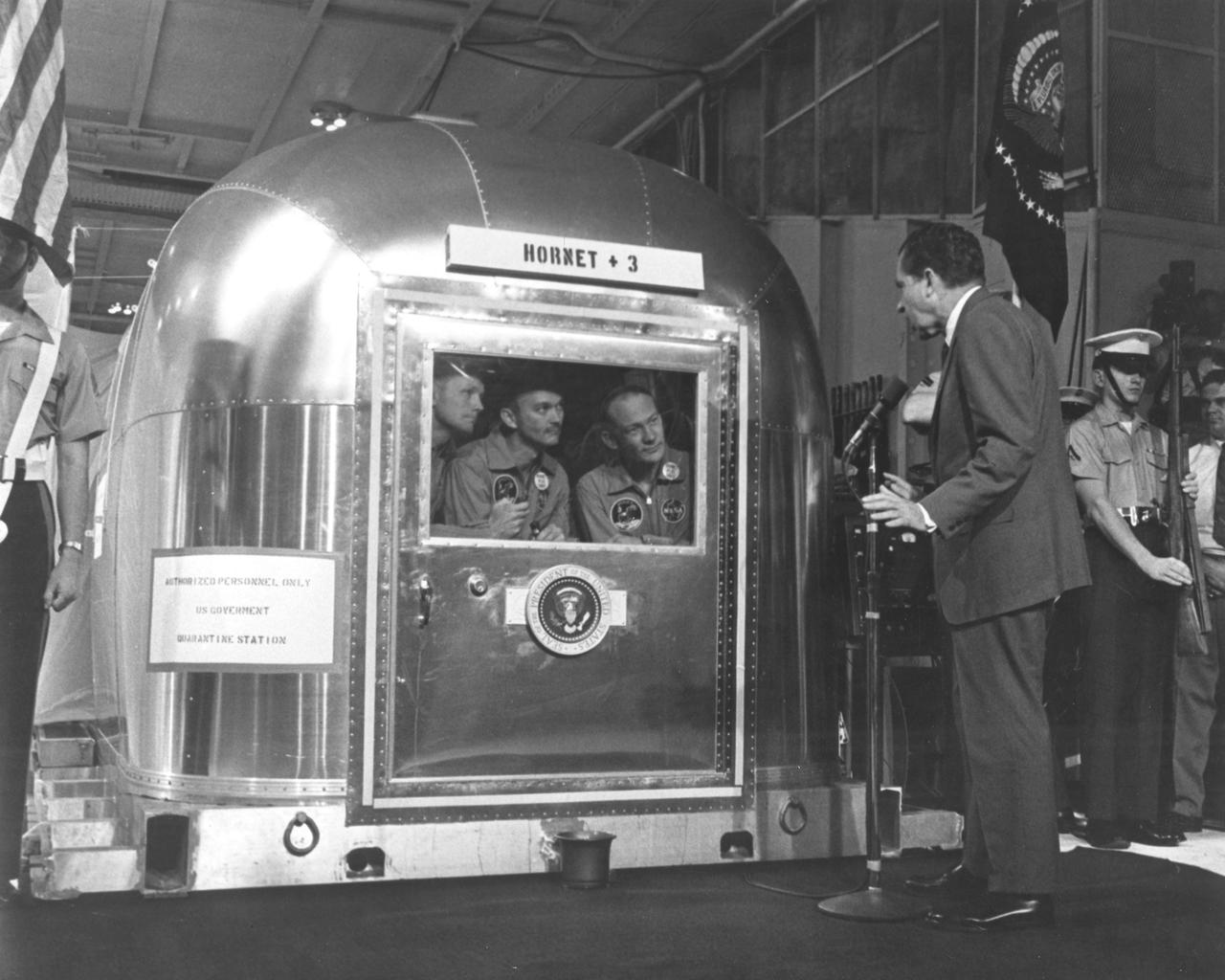

The Apollo 11 mission, the first manned lunar mission, launched from the Kennedy Space Center, Florida via the Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The Saturn V vehicle was developed by the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) under the direction of Dr. Wernher von Braun. Aboard were Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot. The CM, piloted by Michael Collins remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, named “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Aldrin, landed on the Moon. Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Edwin (Buzz) Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. The recovery operation took place in the Pacific Ocean where Navy para-rescue men recovered the capsule housing the 3-man Apollo 11 crew. The crew was airlifted by helicopter and taken to safety aboard the U.S.S. Hornet, where they were quartered in a Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF). Shown here are the Apollo 11 crew members (L to R) Neil Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Edwin Aldrin inside the MQF as U.S. President Richard Milhous Nixon speaks to them via intercom. The president was aboard the recovery vessel awaiting return of the astronauts. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
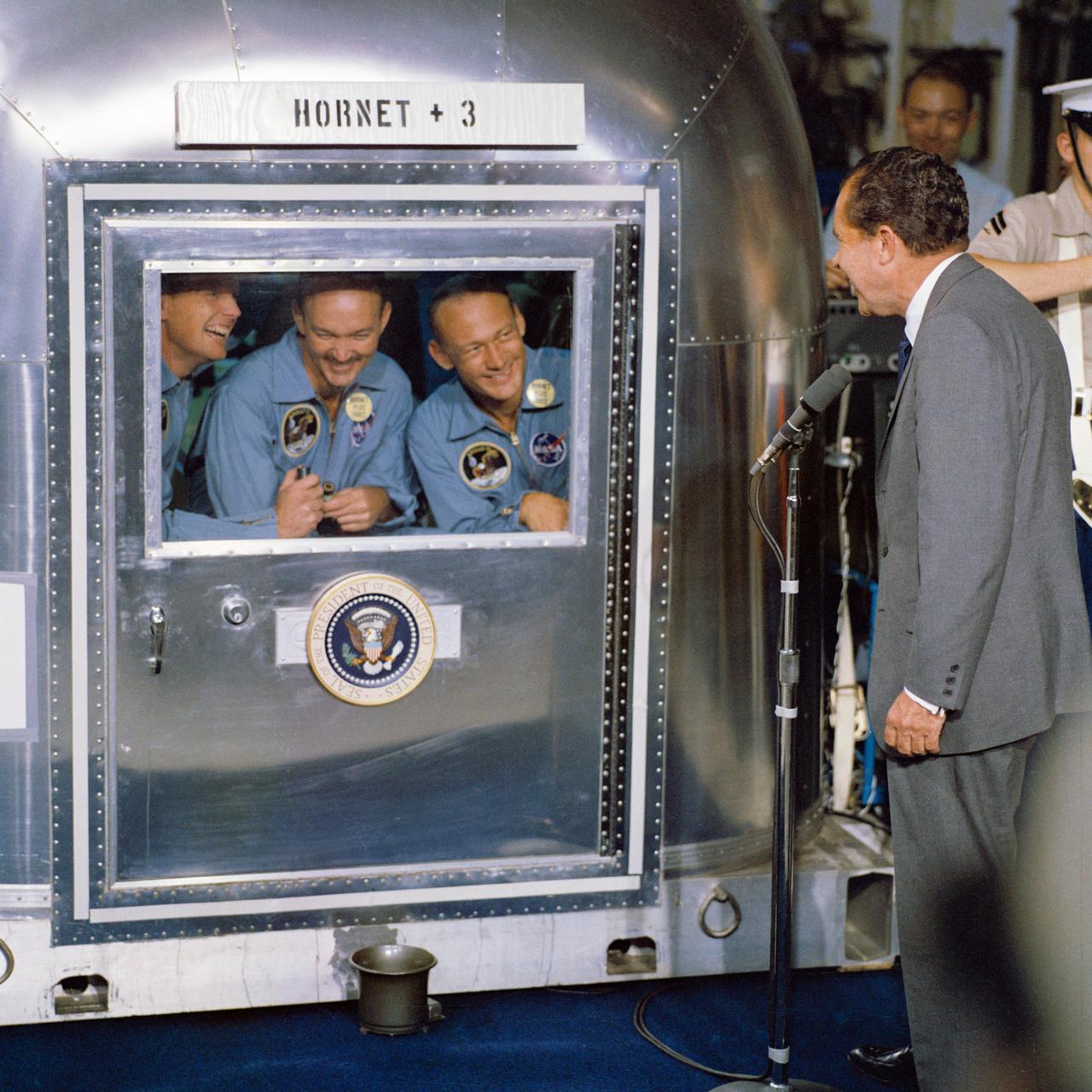

S69-21365 (24 July 1969) --- United States President Richard M. Nixon was in the central Pacific recovery area to welcome the Apollo 11 astronauts aboard the USS Hornet, prime recovery ship for the historic Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. Already confined to the Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF) are (left to right) Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, command module pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., lunar module pilot. Apollo 11 splashed down at 11:49 a.m. (CDT), July 24, 1969, about 812 nautical miles southwest of Hawaii and only 12 nautical miles from the USS Hornet. The three crewmen will remain in the MQF until they arrive at the Manned Spacecraft Center's (MSC) Lunar Receiving Laboratory (LRL). While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Collins remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit. Photo credit: NASA

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - President Richard M. Nixon greets crowd gathered to watch the Apollo 12 launch at Kennedy Space Center.
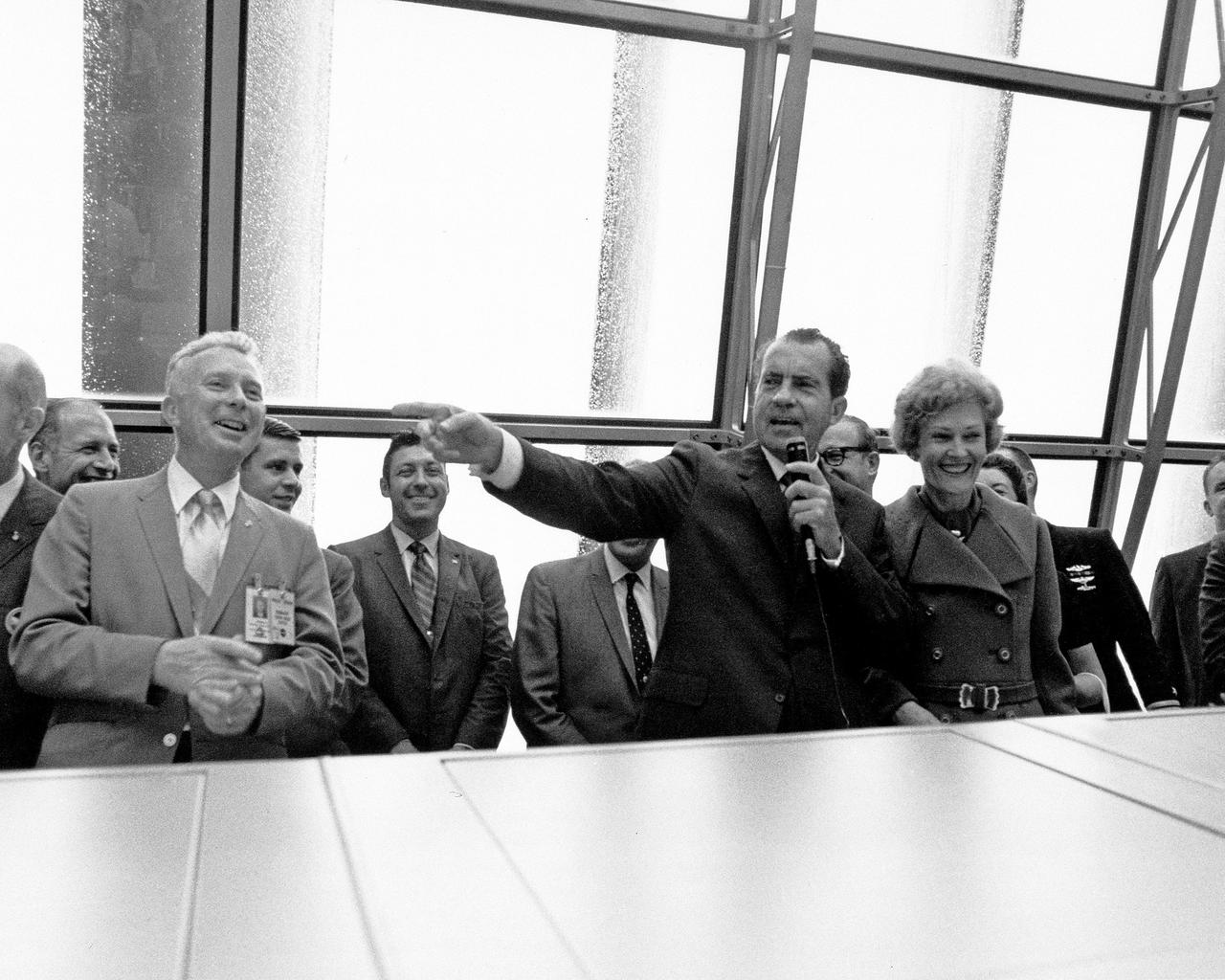

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- At the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, President Richard M. Nixon speaks in the Launch Control Center after the successful liftoff of the Apollo 12 space vehicle, which sent astronauts Charles Conrad, Jr., Richard F. Gordon and Alan Bean on the first leg of their lunar landing mission. With the President are Paul Donnelly, Launch Operations manager, on the left, and First Lady Pat Nixon, on the right. Photo Credit: NASA
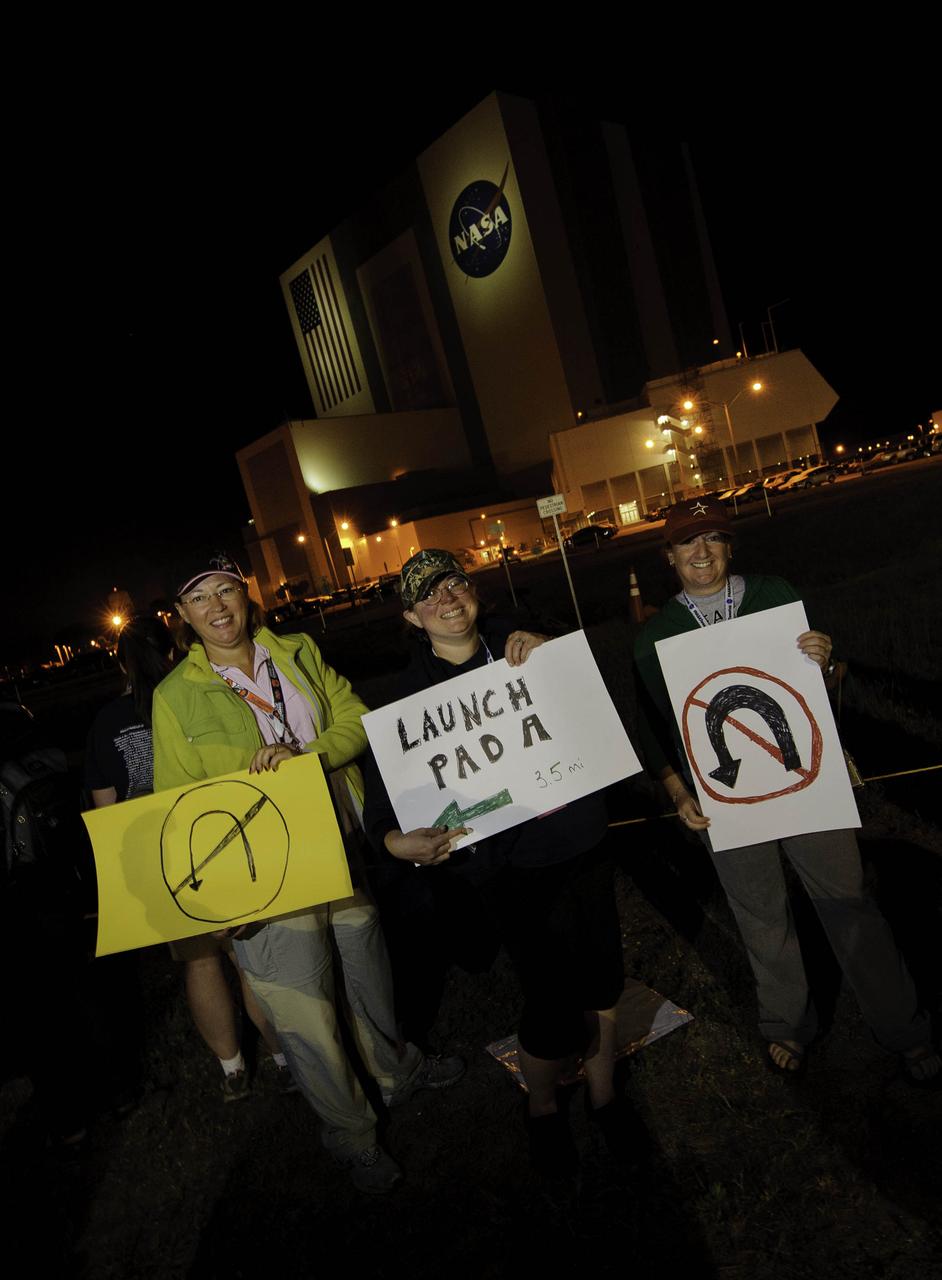
NASA Twitter followers from left; Leigh Checkman (@liprap), Barbara Nixon (@BarbaraNixon), and Beth Schaefer (@boonbeth), hold up signs just before the Astrovan, carrying the STS-134 crew out to launch pad 39a passed by, early Monday, May 16, 2011, at Kennedy Space Center in Cape Canaveral, Fla. During the 16-day mission, Endeavour, with Commander Mark Kelly, Pilot Gregory H. Johnson, Mission Specialists Michael Fincke, Greg Chamitoff, Andrew Feustel and European Space Agency astronaut Robert Vittori will deliver the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer (AMS) and spare parts including two S-band communications antennas, a high-pressure gas tank and additional spare parts for Dextre. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

Cassini project scientist at JPL, Linda Spilker, left, Cassini interdisciplinary Titan scientist at Cornell University, Jonathan Lunine, second from left, Cassini Composite Infrared Spectrometer(CIRS) Instrument deputy principle investigator Connor Nixon, second from right, and Cassini assistant project science systems engineer Morgan Cable, right, participate in a Cassini science panel discussion during the Cassini NASA Social, Thursday, Sept. 14, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
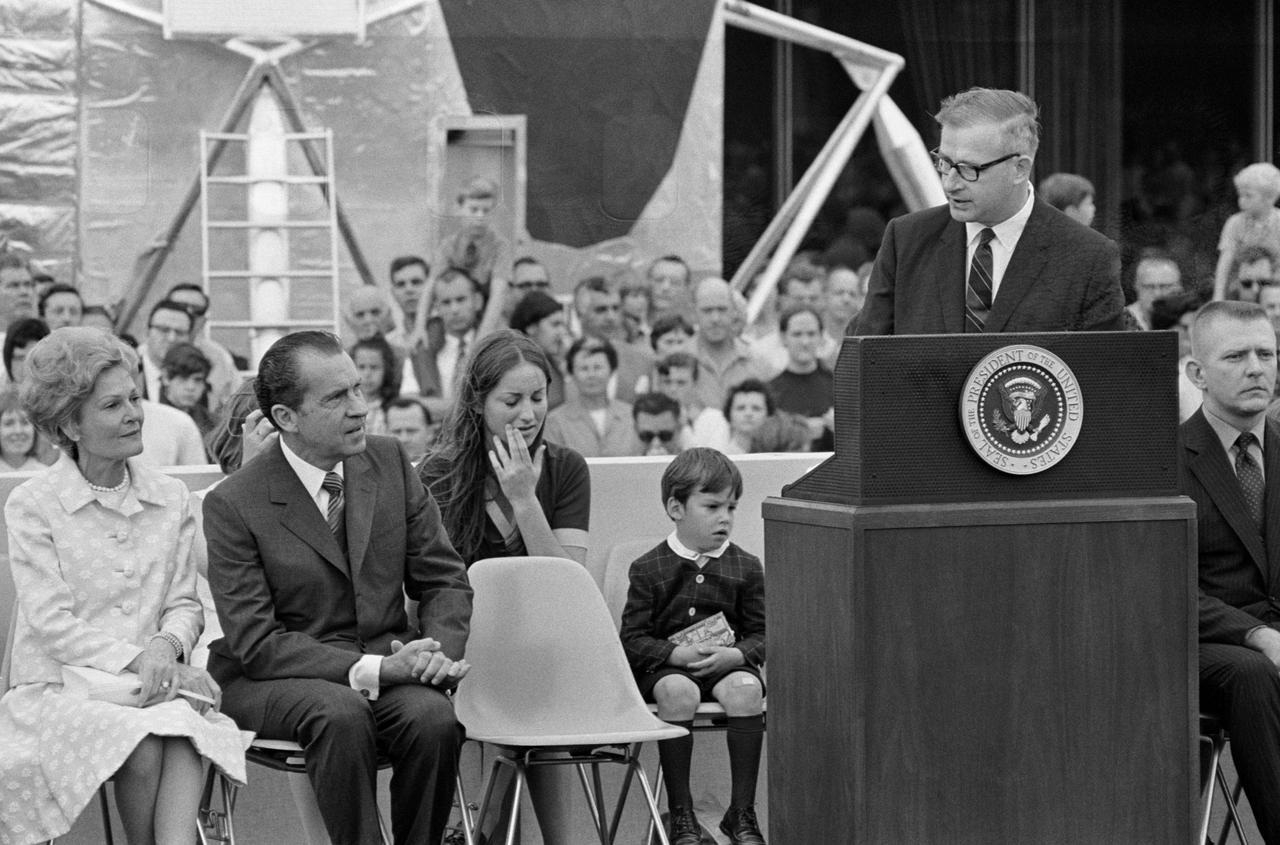

S70-35595 (18 April 1970) --- President Richard M. Nixon is welcomed to Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) and introduced by Dr. Thomas O. Paine, Administrator, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA). The First Lady is at extreme left. Others on the speakers platform in this view are Barbara and Jeffrey C. Lovell, children of astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander; and Eugene F. Kranz (extreme right), one of four flight directors on duty around the clock during the mission. President Nixon was on the site to present the Presidential Medal of Freedom to the Apollo 13 Mission Operations Team.
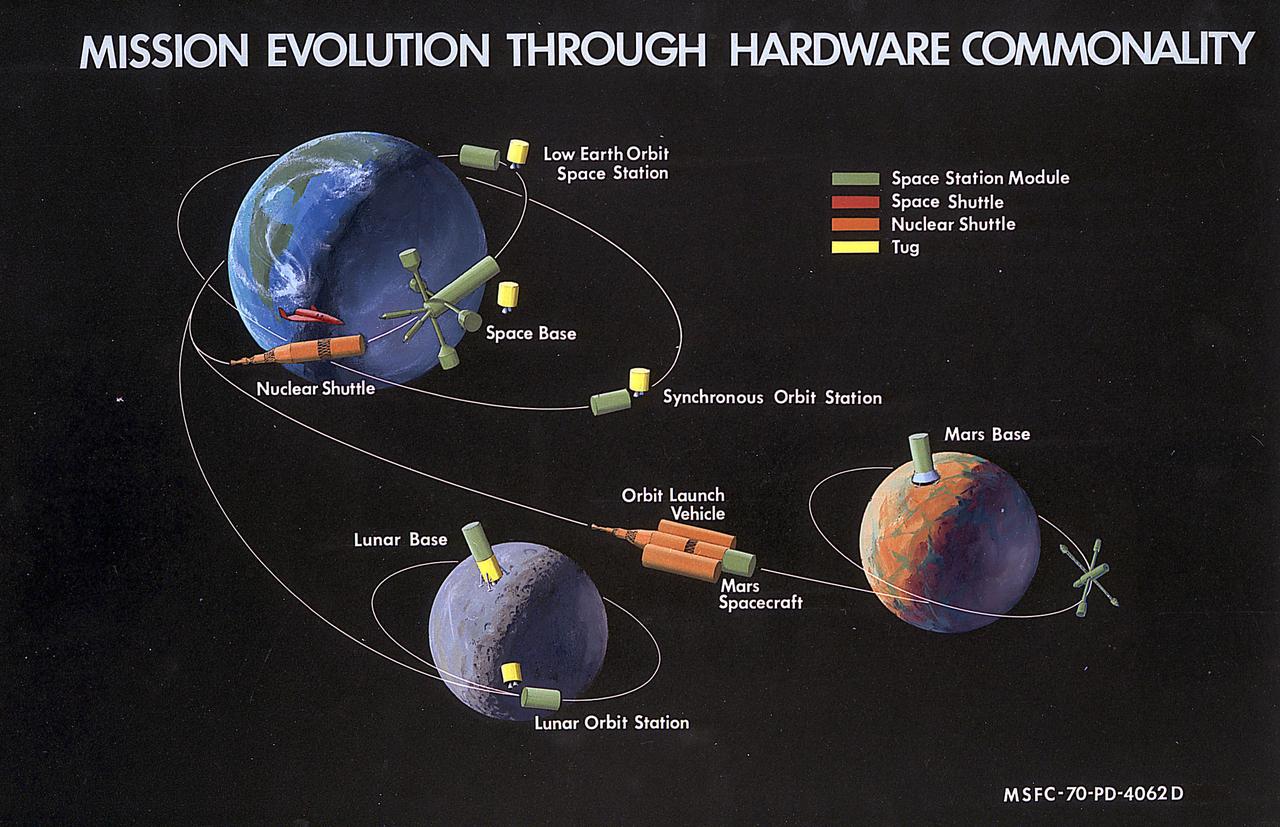
In this artist's concept from 1970, propulsion concepts such as the Nuclear Shuttle and Space Tug are shown in conjunction with other proposed spacecraft. As a result of the recommendations from President Nixon's Space Task Group for more commonality and integration in the American space program, Marshall Space Flight engineers studied many of the spacecraft depicted here.

S70-35562 (April 1970) --- A photographic replica of the Presidential Medal of Freedom Award which President Richard M. Nixon presented to the Apollo 13 Missions Operations Team (MOT). The presentation was made by the Chief Executive during a visit to the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) in April 1970.
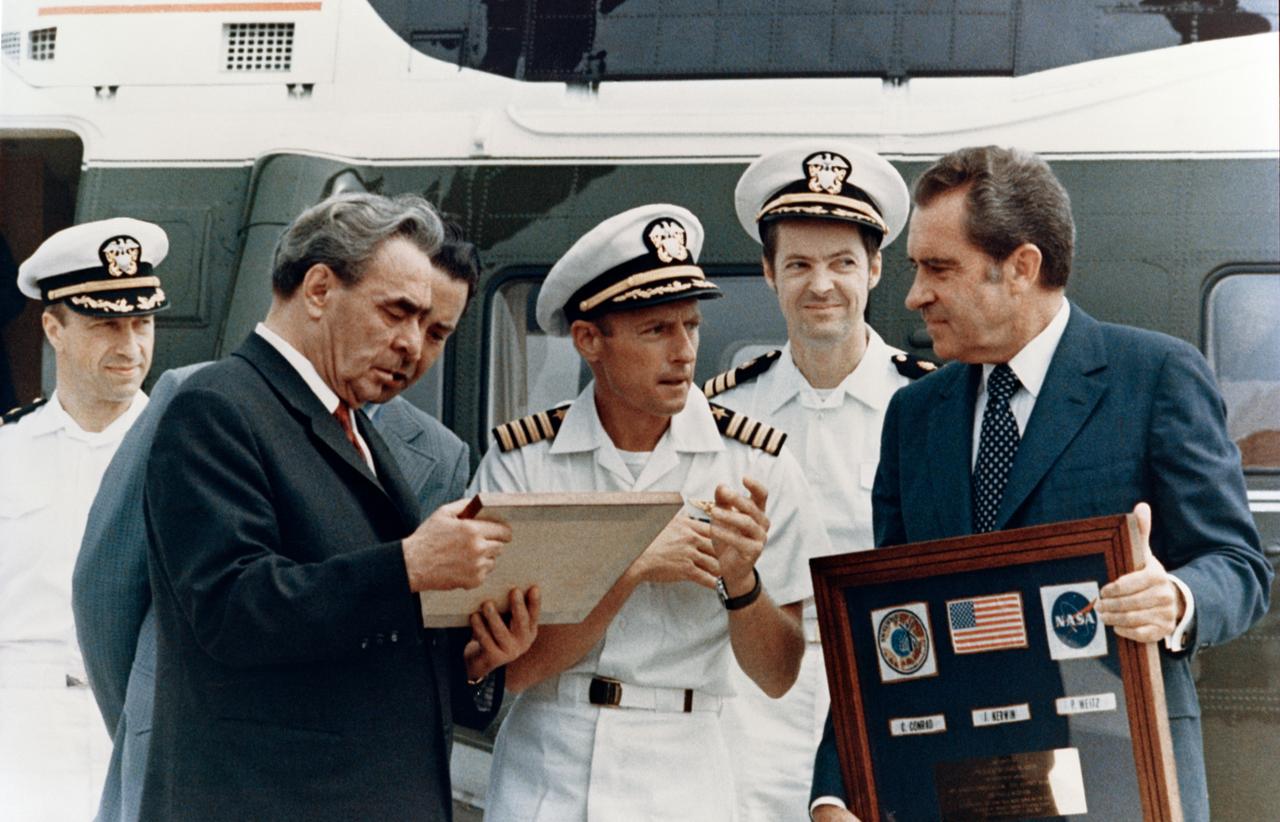

S73-30889 (June 1973) --- Leonid I. Breznev, General Secretary of the Communist Party, Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, and President Richard M. Nixon, during ceremonies at the Western White House in San Clemente, California, examine plaques presented by Skylab astronauts Charles Conrad Jr., center; Joseph P. Kerwin, second from right; and Paul J. Weitz, left. Photo credit: NASA
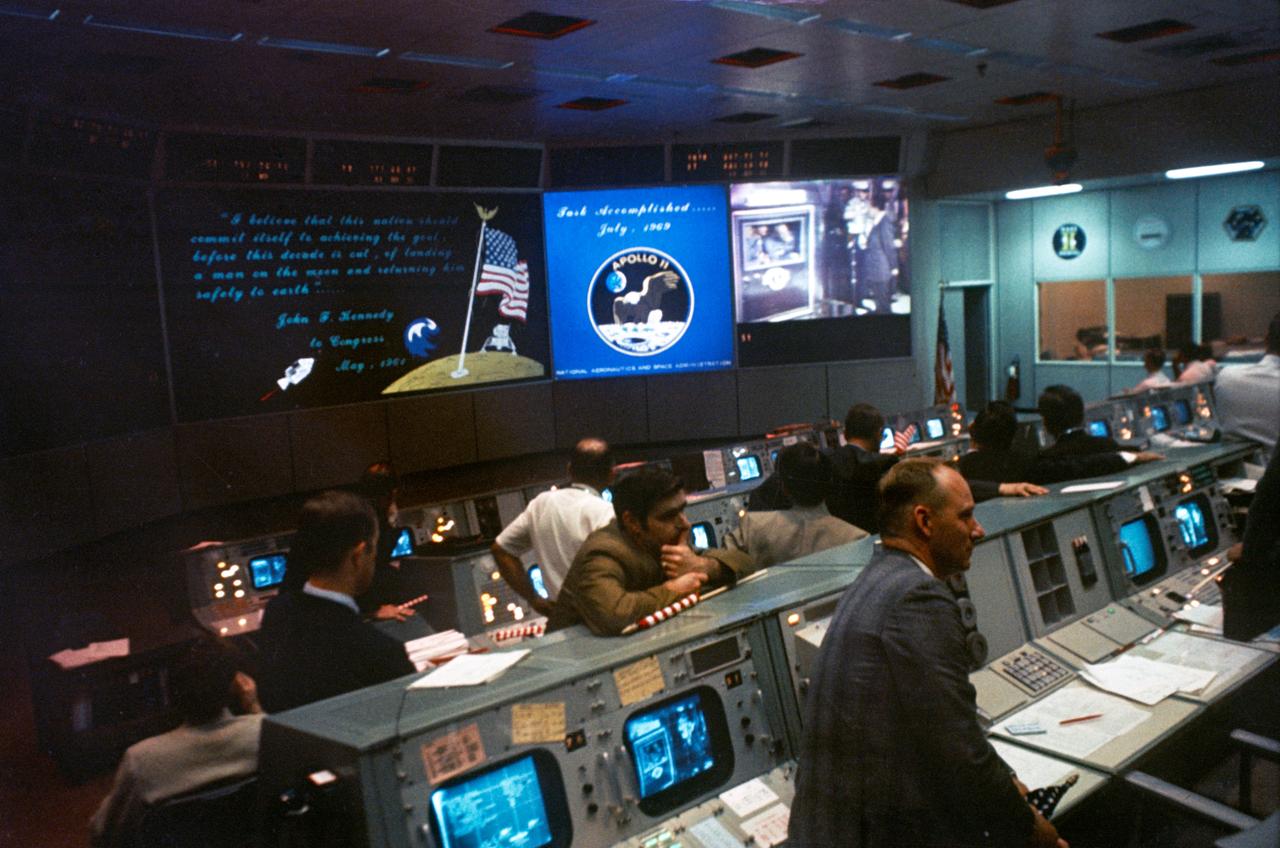

S69-40301 (24 July 1969) --- Overall view of the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) in the Mission Control Center (MCC), Building 30, Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC), at the conclusion of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. The television monitor shows President Richard M. Nixon greeting the Apollo 11 astronauts aboard the USS Hornet in the Pacific recovery area. Astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, Michael Collins, and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. are inside the Mobile Quarantine Facility (MQF).
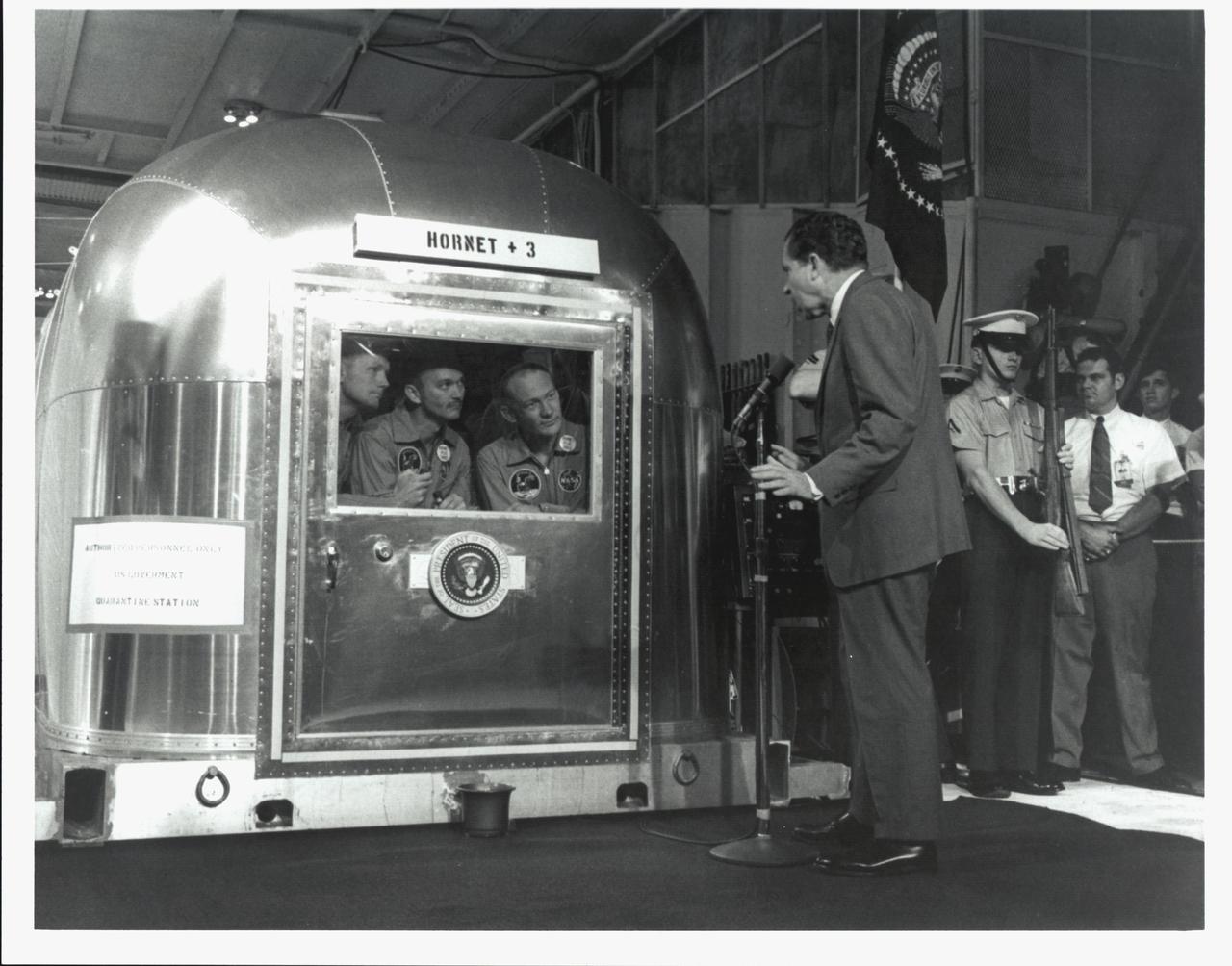

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Apollo 11 astronauts, left to right, Neil A. Armstrong, Michael Collins and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., inside the Mobile Quarantine Facility aboard the USS Hornet, listen to President Richard M. Nixon as he welcomes them back to Earth and for a job well done. The astronauts, after their first manned mission to the Moon, splashed down in the Pacific Ocean at 12:50 p.m. EDT about 900 miles southwest of Hawaii.

As a result of the recommendations from President Nixon's Space Task Group, Marshall Space Flight Center engineers studied various ways to enhance commonality and integration in the American space program. This artist's concept from 1969 shows a possible spacecraft configuration for a marned Mars mission. In this mode, two planetary vehicles, each powered by a Nuclear Shuttle, are joined together during the flight and rotated to provide artificial gravity for crew members.
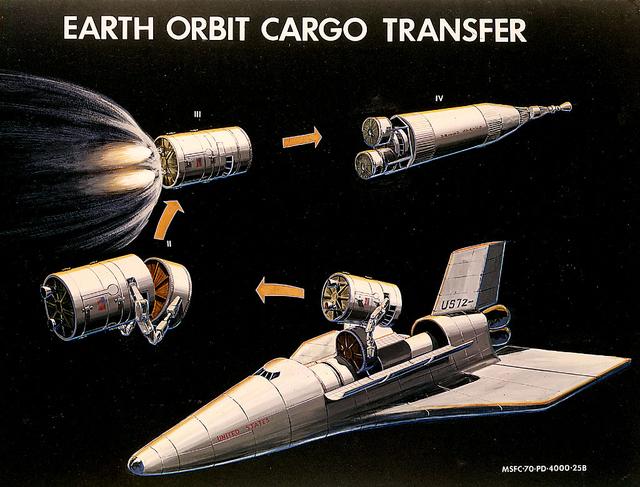

This 1969 artist's concept illustrates the use of three major elements of NASA's Integrated program, as proposed by President Nixon's Space Task Group. In Phases I and II, a Space Tug with a manipulator-equipped crew module removes a cargo module from an early Space Shuttle Orbiter and docks with it. In Phases III and IV, the Space Tug with attached cargo module flys toward a Nuclear Shuttle. As a result of the Space Task Group's recommendations for more commonality and integration in the American space program, Marshall Space Flight Center engineers studied many of the spacecraft depicted here.

S70-15501 (17 April 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., Apollo 13 mission commander, reads a newspaper account of the safe recovery of the problem plagued mission. Lovell is on board the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for Apollo 13, which was on a course headed for Pago Pago. From Pago Pago the astronauts flew to Hickam Air Force Base, Hawaii, where they were presented the Presidential Medal of Freedom by President Richard M. Nixon. Other Apollo 13 crew members were astronauts John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
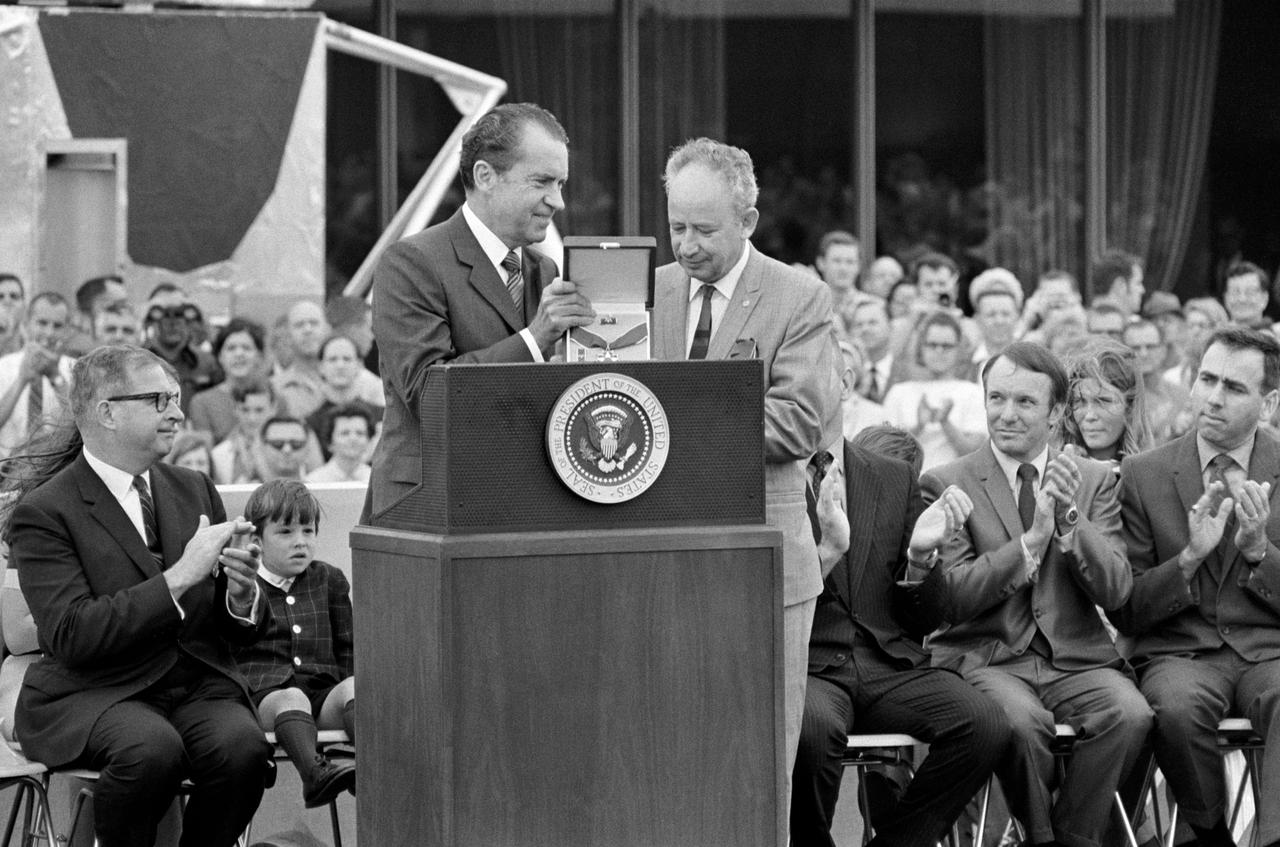

S70-35594 (18 April 1970) --- President Richard M. Nixon presents the Presidential Medal of Freedom to the Apollo 13 Mission Operations Team at Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Accepting for the team is Sigurd A. Sjoberg, director of Flight Operations at MSC. Dr. Thomas O. Paine, Administrator, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), is at left. Also seen here on the speaker's platform are Jeffrey C. Lovell, son of astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., commander of the Apollo 13 mission; Gerald D. Griffin (second from right) and Milton L. Windler, two of four flight directors who worked around the clock during the mission.

Space Shuttle Orbiters: From its establishment in 1958, NASA studied aspects of reusable launch vehicles and spacecraft that could return to earth. On January 5, 1972, President Richard Nixon announced that the United States would develop the space shuttle, a delta-winged orbiter about the size of a DC-9 aircraft. Between the first launch on April 12, 1981, and the final landing on July 21, 2011, NASA's space shuttle fleet -- Columbia, Challenger, Discovery, Atlantis and Endeavour – launched on 135 missions, helped construct the International Space Station and inspired generations. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
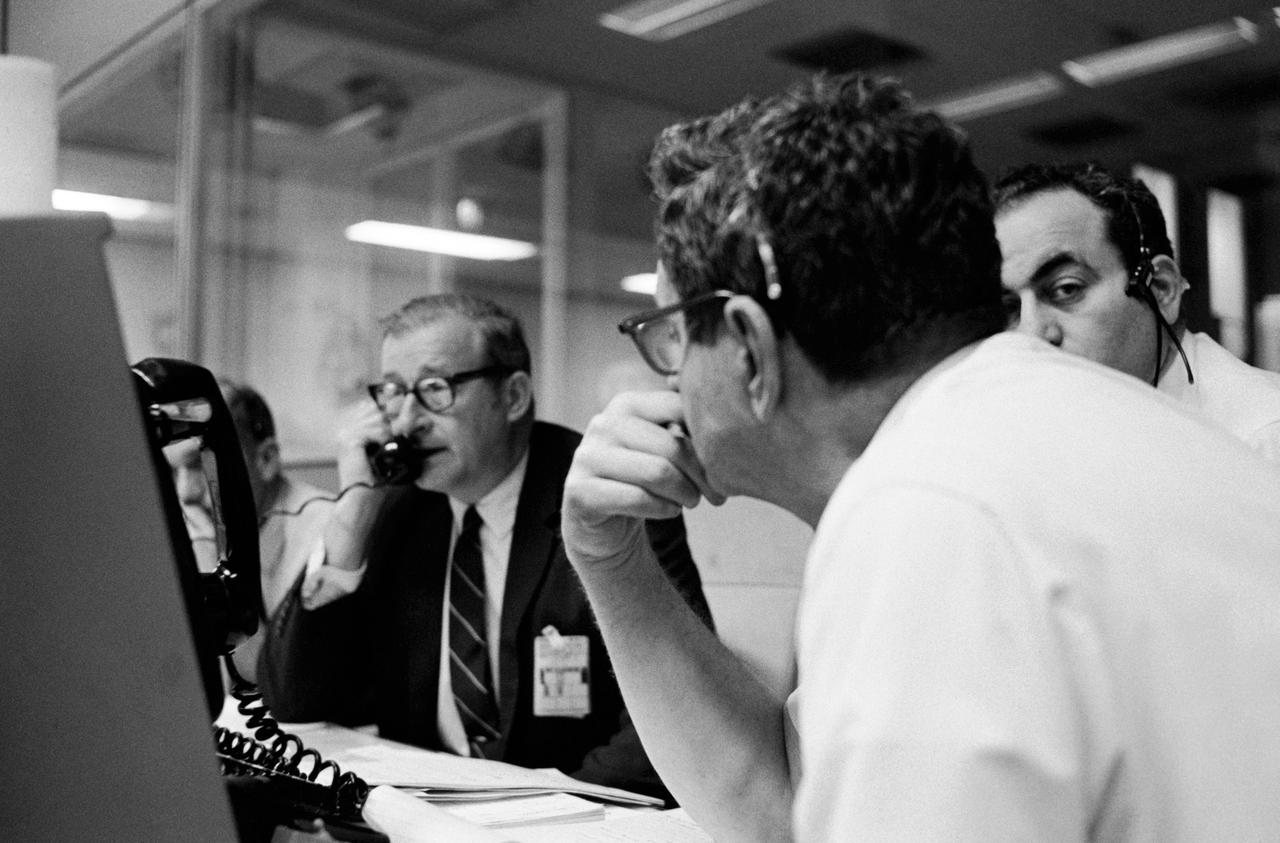

S70-34903 (14 April 1970) --- Dr. Thomas O. Paine, Administrator, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), talks on the telephone to President Richard M. Nixon. Dr. Paine is seated at his console in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) at the Mission Control Center (MCC), Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Also pictured are Dr. Rocco Petrone, Apollo program director, Office Manned Spaceflight, NASA Headquarters (facing camera); and Chester M. Lee, Apollo mission director, Office of Manned Spaceflight, NASA Headquarters (HQ). Dr. Paine and the President were discussing the revised Apollo 13 flight plan following discovery of an oxygen cell failure in the Apollo 13 spacecraft several hours earlier.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — Christine Nixon (left), principal of Warrington Middle School in Pensacola, Fla., joins Kennedy Space Center Jim Kennedy and the school’s NASA Explorer School team to recognize the new partnership with NASA. Kennedy is visiting the school to share the vision for space exploration with the next generation. He is talking with students about our destiny as explorers, NASA’s stepping stone approach to exploring Earth, the moon, Mars and beyond, how space impacts our lives, and how people and machines rely on each other in space. NES establishes a three-year partnership annually between NASA and 50 NASA Explorer School teams, consisting of teachers and education administrators from diverse communities nationwide. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — During kickoff of the NASA Explorer School program at Warrington Middle School in Pensacola, Fla., Center Director Jim Kennedy talks to students and faculty. Seated at left is Christine Nixon, principal of Warrington Middle School. Joining Kennedy for the event was NASA aerospace specialist Les Gold, NASA official Gregg Buckingham, and astronaut Alan Poindexter. Kennedy is visiting the school to share the vision for space exploration with the next generation. He is talking with students about our destiny as explorers, NASA’s stepping stone approach to exploring Earth, the moon, Mars and beyond, how space impacts our lives, and how people and machines rely on each other in space. NES establishes a three-year partnership annually between NASA and 50 NASA Explorer School teams, consisting of teachers and education administrators from diverse communities nationwide. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
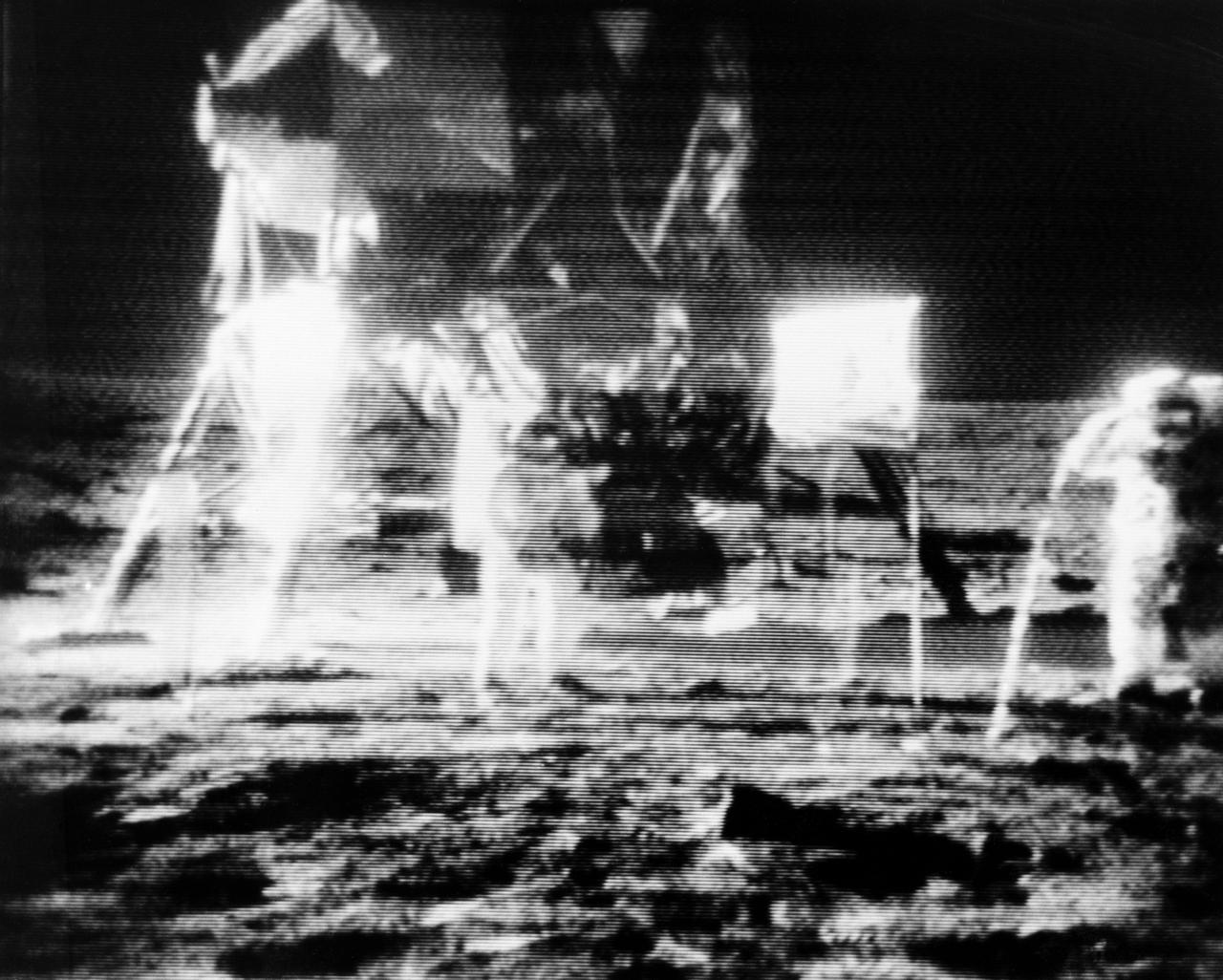

S69-39562 (20 July 1969) --- Astronauts Neil A. Armstrong (center), commander; and Edwin E. Aldrin Jr. (right), lunar module pilot, are seen standing near their Lunar Module (LM) in this black and white reproduction taken from a telecast by the Apollo 11 lunar surface camera during the Apollo 11 extravehicular activity (EVA). This picture was made from a televised image received at the Deep Space Network (DSN) tracking station at Goldstone, California. United States President Richard M. Nixon had just spoken to the two astronauts by radio. Aldrin, a Colonel in the United States Air Force, is saluting the Commander-in-Chief. While astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin descended in the LM "Eagle" to explore the Sea of Tranquility region of the moon, astronaut Michael Collins, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "Columbia" in lunar orbit.

Presidential Visits to Kennedy Space Center: All the U. S. presidents shown here were in office at the time they visited KSC. President Dwight D. Eisenhower, 02/10/1960 President Lyndon B. Johnson visited twice, 09/14/1964 and 09/27/1966 President Richard M. Nixon viewed the Apollo 12 launch on 11/14/1969 President Jimmy Carter came to KSC on 10/01/1978 President William J. Clinton viewed the STS-95 launch on 10/29/1998 and President Barack H. Obama visited KSC twice, 04/15/2010 and 04/29/2011. Poster designed by Kennedy Space Center Graphics Department/Greg Lee. Credit: NASA
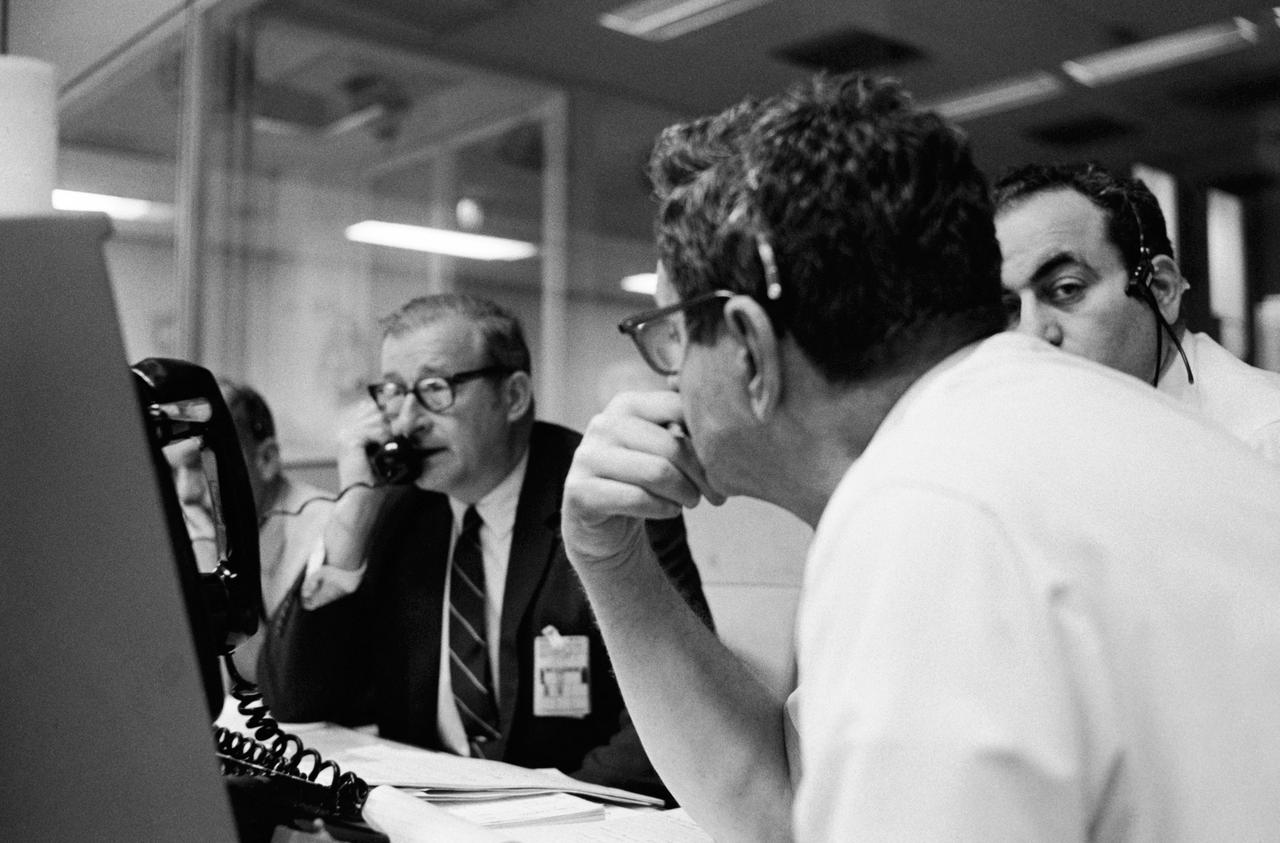

S70-34903 (14 April 1970) --- Dr. Thomas O. Paine, Administrator, National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA), talks on the telephone to President Richard M. Nixon. Dr. Paine is seated at his console in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) at the Mission Control Center (MCC), Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Also pictured are Dr. Rocco Petrone, Apollo program director, Office Manned Spaceflight, NASA Headquarters (facing camera); and Chester M. Lee, Apollo mission director, Office of Manned Spaceflight, NASA Headquarters (HQ). Dr. Paine and the President were discussing the revised Apollo 13 flight plan following discovery of an oxygen cell failure in the Apollo 13 spacecraft several hours earlier.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — Christine Nixon (left), principal of Warrington Middle School in Pensacola, Fla., is presented a banner recognizing the school’s new partnership with NASA as a NASA Explorer School. At far right is NASA official Gregg Buckingham, who was joined by Center Director Jim Kennedy and astronaut Alan Poindexter for this kickoff event at the school. Kennedy is visiting the school to share the vision for space exploration with the next generation. He is talking with students about our destiny as explorers, NASA’s stepping stone approach to exploring Earth, the moon, Mars and beyond, how space impacts our lives, and how people and machines rely on each other in space. NES establishes a three-year partnership annually between NASA and 50 NASA Explorer School teams, consisting of teachers and education administrators from diverse communities nationwide. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

NASA Social attendees are seen during a science panel discussion with Cassini project scientist at JPL, Linda Spilker, Cassini interdisciplinary Titan scientist at Cornell University, Jonathan Lunine, Cassini Composite Infrared Spectrometer(CIRS) Instrument deputy principle investigator Connor Nixon, and Cassini assistant project science systems engineer Morgan Cable, Thursday, Sept. 14, 2017 at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California. Since its arrival in 2004, the Cassini-Huygens mission has been a discovery machine, revolutionizing our knowledge of the Saturn system and captivating us with data and images never before obtained with such detail and clarity. On Sept. 15, 2017, operators will deliberately plunge the spacecraft into Saturn, as Cassini gathered science until the end. The “plunge” ensures Saturn’s moons will remain pristine for future exploration. During Cassini’s final days, mission team members from all around the world gathered at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California, to celebrate the achievements of this historic mission. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — Christine Nixon, principal of Warrington Middle School in Pensacola, Fla., introduces guests on stage to the audience of students and faculty. The occasion is the kickoff of the NASA Explorer School program at the school. Among those seated on stage are Jim Paul, superintendent of Escambia County Schools; Denise Jamison, the school’s NASA Team facilitator; Les Gold, NASA aerospace specialist; Gregg Buckingham, NASA official; Jim Kennedy, director of Kennedy Space Center; Charles Baire, District representative, representing Congressman Jeff Miller; Letitia Wheeler, student at Warrington Middle School; and Alan Poindexter, NASA astronaut. Kennedy is visiting the school to share the vision for space exploration with the next generation. He is talking with students about our destiny as explorers, NASA’s stepping stone approach to exploring Earth, the moon, Mars and beyond, how space impacts our lives, and how people and machines rely on each other in space. NES establishes a three-year partnership annually between NASA and 50 NASA Explorer School teams, consisting of teachers and education administrators from diverse communities nationwide. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
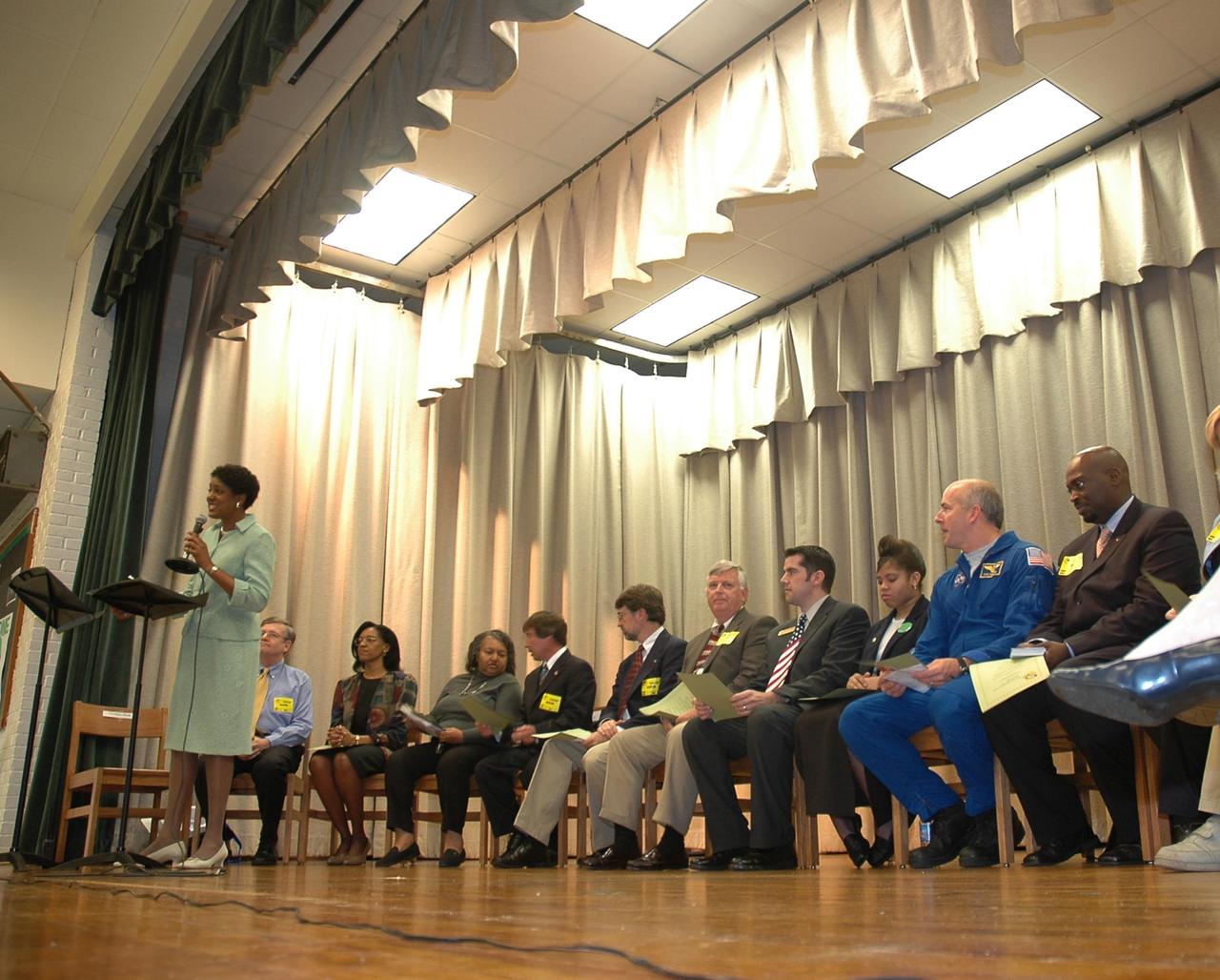

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. — Christine Nixon, principal of Warrington Middle School in Pensacola, Fla., introduces guests on stage to the audience of students and faculty. The occasion is the kickoff of the NASA Explorer School (NES) program at the school. Seated on stage are (from left) Jim Paul, superintendent of Escambia County Schools; a school official; Denise Jamison, the school’s NASA Team facilitator; Les Gold, NASA aerospace specialist; Gregg Buckingham, NASA official; Jim Kennedy, director of Kennedy Space Center; Charles Baire, District representative, representing Congressman Jeff Miller; Letitia Wheeler, student at Warrington Middle School; Alan Poindexter, NASA astronaut; and Clarence Bostic, NES coordinator. Kennedy is visiting the school to share the vision for space exploration with the next generation. He is talking with students about our destiny as explorers, NASA’s stepping stone approach to exploring Earth, the moon, Mars and beyond, how space impacts our lives, and how people and machines rely on each other in space. NES establishes a three-year partnership annually between NASA and 50 NASA Explorer School teams, consisting of teachers and education administrators from diverse communities nationwide. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

Millions of people on Earth watched via television as a message for all mankind was delivered to the Mare Tranquilitatis (Sea of Tranquility) region of the Moon during the historic Apollo 11 mission, where it still remains today. This photograph is a reproduction of the commemorative plaque that was attached to the leg of the Lunar Module (LM), Eagle, engraved with the following words: “Here men from the planet Earth first set foot upon the Moon July, 1969 A.D. We came in peace for all of mankind.” It bears the signatures of the Apollo 11 astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin, Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot along with the signature of the U.S. President Richard M. Nixon. The Apollo 11 mission launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The CM, “Columbia”, piloted by Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon. On July 20, 1969, Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
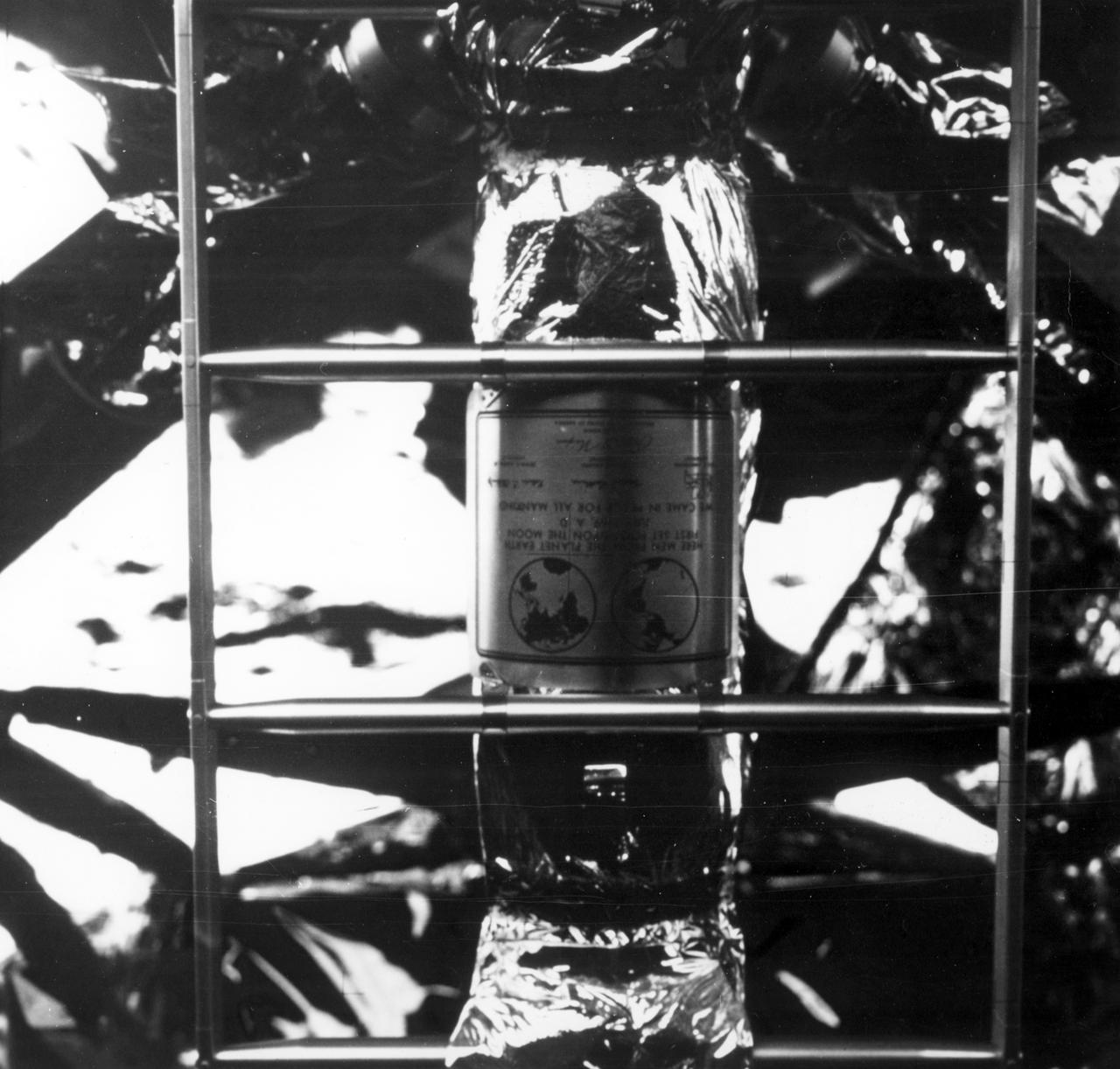

Millions of people on Earth watched via television as a message for all mankind was delivered to the Mare Tranquilitatis (Sea of Tranquility) region of the Moon during the historic Apollo 11 mission, where it still remains today. This commemorative plaque, attached to the leg of the Lunar Module (LM), Eagle, is engraved with the following words: “Here men from the planet Earth first set foot upon the Moon July, 1969 A.D. We came in peace for all of mankind.” It bears the signatures of the Apollo 11 astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin, Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot along with the signature of the U.S. President Richard M. Nixon. The Apollo 11 mission launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The CM, “Columbia”, piloted by Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon. On July 20, 1969, Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.

Millions of people on Earth watched via television as a message for all mankind was delivered to the Mare Tranquilitatis (Sea of Tranquility) region of the Moon during the historic Apollo 11 mission, where it still remains today. A commemorative plaque was attached to the leg of the Lunar Module (LM), Eagle, engraved with the following words: “Here men from the planet Earth first set foot upon the Moon July, 1969 A.D. We came in peace for all of mankind.” It bears the signatures of the Apollo 11 astronauts Neil A. Armstrong, commander; Michael Collins, Command Module (CM) pilot; and Edwin E. Aldrin, Jr., Lunar Module (LM) pilot along with the signature of the U.S. President Richard M. Nixon. The plaque, as shown here, covered with protective steel for the launch and journey to the moon, was uncovered by crew members after landing. The Apollo 11 mission launched from the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida via the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) developed Saturn V launch vehicle on July 16, 1969 and safely returned to Earth on July 24, 1969. The CM, “Columbia”, piloted by Collins, remained in a parking orbit around the Moon while the LM, “Eagle’’, carrying astronauts Armstrong and Aldrin, landed on the Moon. On July 20, 1969, Armstrong was the first human to ever stand on the lunar surface, followed by Aldrin. During 2½ hours of surface exploration, the crew collected 47 pounds of lunar surface material for analysis back on Earth. With the success of Apollo 11, the national objective to land men on the Moon and return them safely to Earth had been accomplished.
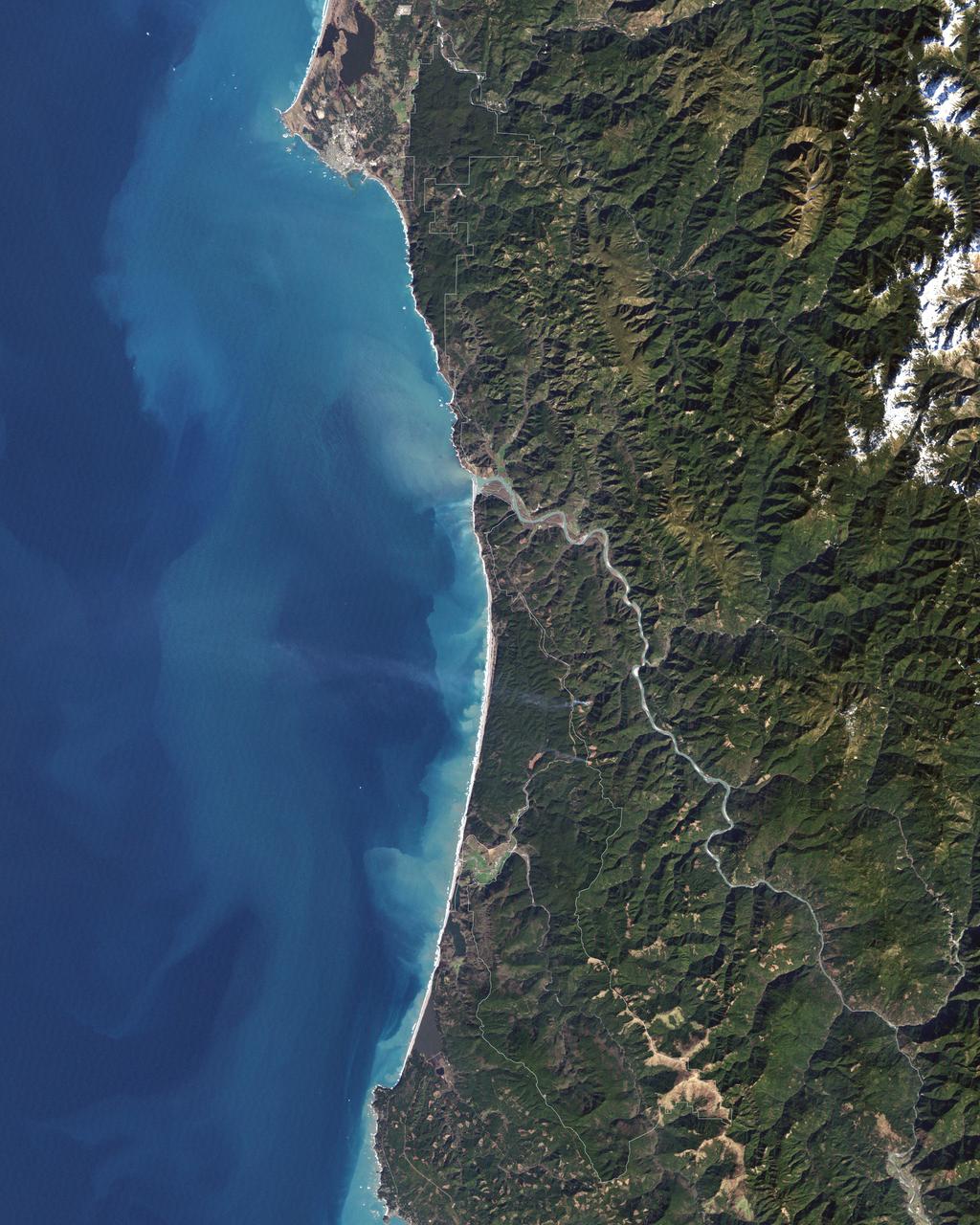

In 1968, after state parks had already been established in northern California, the U.S. Congress established Redwood National Park. This new park supplemented protected lands in the region, and in 1994, state and federal authorities agreed to jointly manage the area’s public lands. On February 6, 2003, the Enhanced Thamatic Mapper Plus on NASA’s Landsat 7 satellite captured this true-color image of the southern end of Redwood National Park - a thin coastal corridor connects the northern and southern ends of the park system. Along the coast, sandy beaches appear off-white, and sediments form swirls of pale blue in the darker blue sea. Inland, the park is dominated by green vegetation, with isolated patches of gray-beige rock. This image of the Redwood National Park includes two stands of trees: Lady Bird Johnson Grove and Tall Trees Grove. The first grove was dedicated to the former first lady by President Richard Nixon in August 1969. The second grove became the focus of efforts to protect the surrounding area from logging. Two waterways appear in this image: Redwood Creek and Klamath River. The more conspicuous Klamath River flows through the park system’s midsection (north of the area pictured here). Redwood Creek flows through the southern portion of the park system. Both waterways have carved gorges through the mountainous landscape. Redwood National and State Parks occupy an area considered to be the most seismically active in the United States. The frequent seismic activity has led to shifting waterways, landslides, and rapid erosion along the coastline. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/2bRlryv" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2bRlryv</a> Credit: NASA/Landsat7 <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>