
Jonah Saunders, Electrical Engineering Pathways Intern, poses in front of Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 17, 2023.

Jonah Saunders, Electrical Engineering Pathways Intern, poses in front of Vehicle Assembly Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on April 17, 2023.
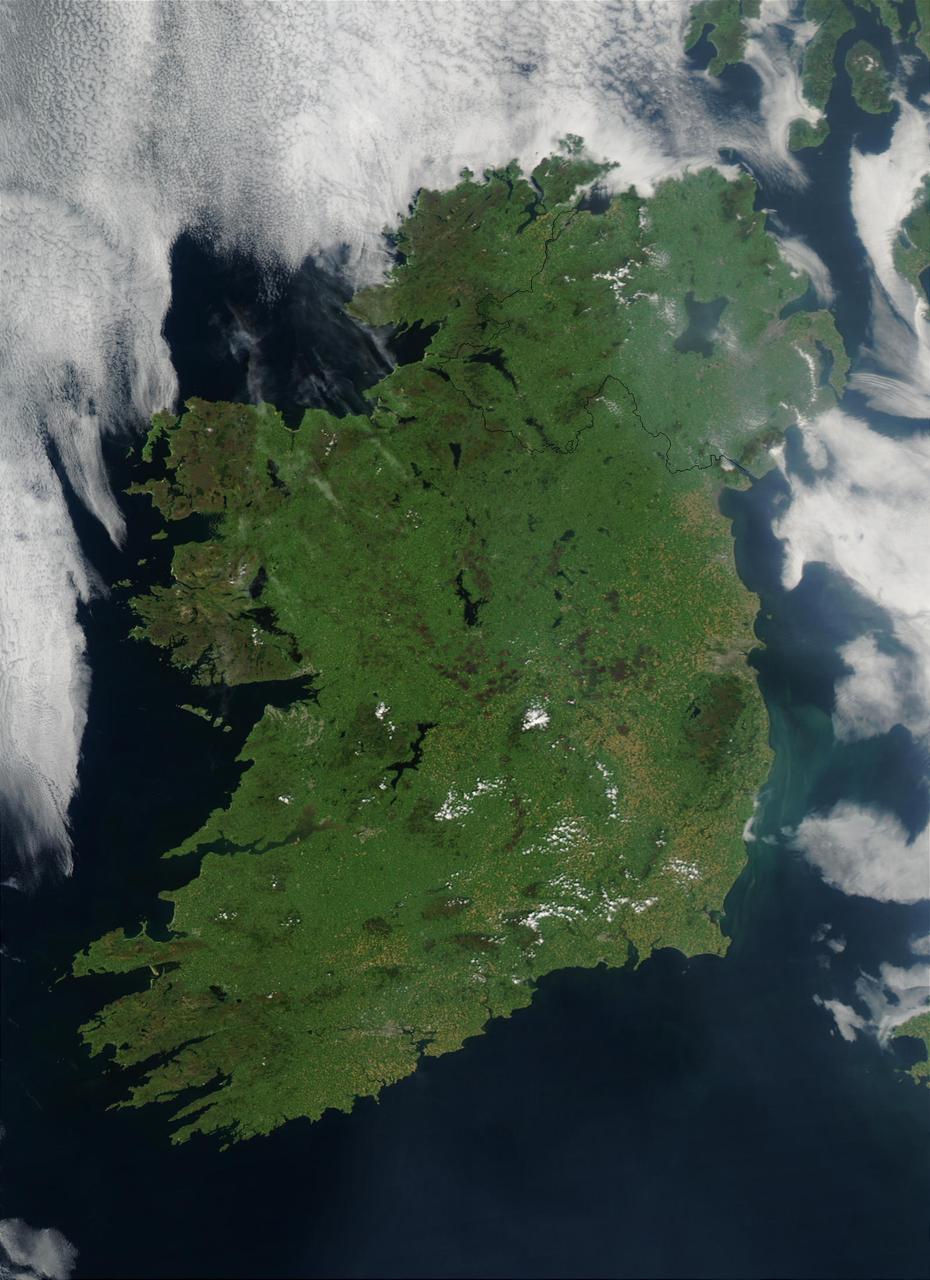

On August 7, 2003, the NASA Aqua MODIS instrument acquired this image of Ireland on the first day this summer that most of the island hasn´t been completely obscured by cloud cover. Called the Emerald Isle for a good reason, Ireland is draped in vibrant shades of green amidst the blue Atlantic Ocean and Celtic (south) and Irish (east) Seas. Faint ribbons of blue-green phytoplankton drift in the waters of the Celtic Sea, just south of Dublin. Dublin itself appears as a large grayish-brown spot on the Republic of Ireland´s northeastern coast. This large capital city (population 1.12 million) sits on the River Liffey, effectively splitting the city in half. Northern Ireland´s capital city, Belfast, also sits on a river: the River Lagan. This city, though its population is only a fifth of the size of Dublin´s, is also clearly visible in the image as a grayish-brown spot on the coast of the Irish Sea. Sensor Aqua/MODIS Credit Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team, NASA/GSFC For more information go to: <a href="http://visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_rec.php?id=5744" rel="nofollow">visibleearth.nasa.gov/view_rec.php?id=5744</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a><b> </b></b>
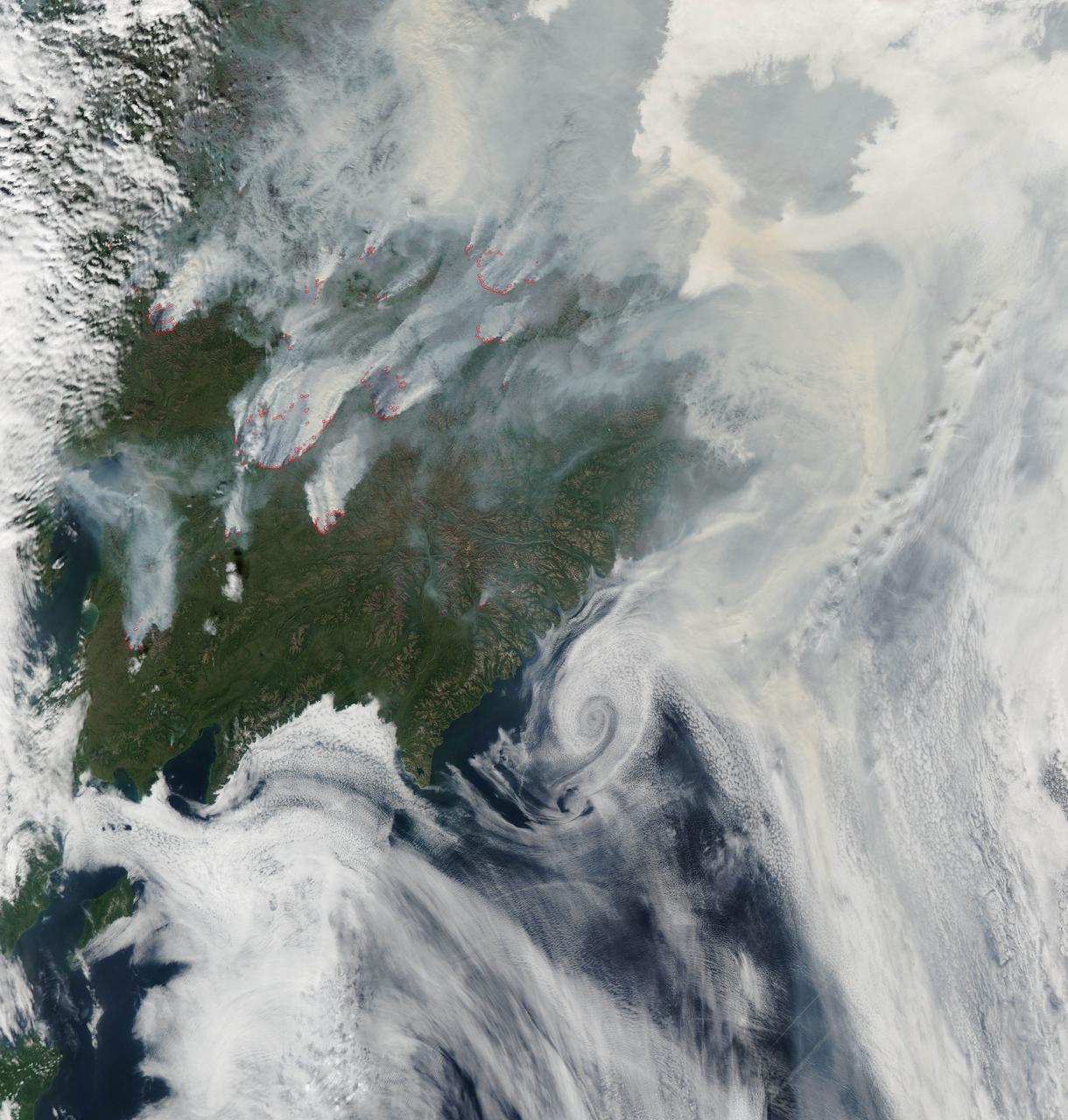
NASA image acquired August 1, 2010 Intense fires continued to burn in the boreal forests of eastern Siberia on August 1, 2010. The fires are outlined in red in this image, acquired by the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer (MODIS) on NASA’s Aqua satellite. The fires span the borders of Russia’s Chukotskiy, Magadan, and Koryakskiy provinces. Burning in coniferous (evergreen) forests, the fires blanketed northeastern Siberia with thick brown smoke. The smoke hugs the ground near the fires, filling valleys, and soars over clouds farther away from the flames. On August 1, the smoke flowed north from the fires and over the Arctic Ocean. A wide view of the Arctic shows the smoke crossing the Bering Strait and clouding skies over northern Alaska. This image is available in additional resolutions from the MODIS Rapid Response Team here: <a href="http://rapidfire.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/?2010213-0801/Russia.A2010213.0045.2km.jpg" rel="nofollow">rapidfire.sci.gsfc.nasa.gov/gallery/?2010213-0801/Russia....</a> To view more images from this event go to: <a href="http://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/event.php?id=44561" rel="nofollow">earthobservatory.nasa.gov/NaturalHazards/event.php?id=44561</a> NASA image courtesy Jeff Schmaltz, MODIS Rapid Response Team at NASA GSFC. Caption by Holli Riebeek Instrument: Aqua - MODIS <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> is home to the nation's largest organization of combined scientists, engineers and technologists that build spacecraft, instruments and new technology to study the Earth, the sun, our solar system, and the universe. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a><b></b></b>
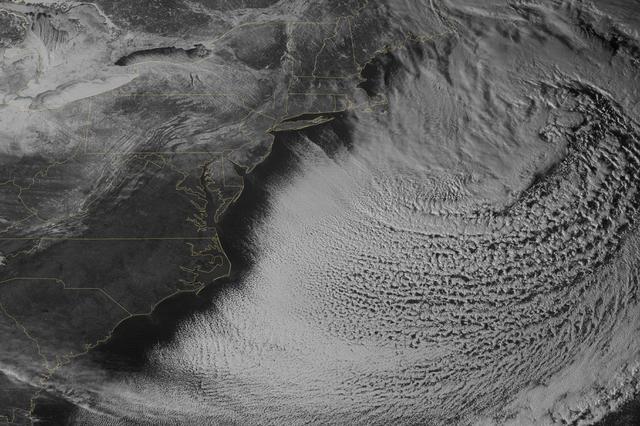
Yet another potent winter storm battered the northeastern United States on February 14-15, 2015. The nor'easter brought 12 to 20 inches (30 to 50 centimeters) of snow across much of eastern New England, along with tropical storm force winds over 60 miles (100 kilometers) per hour. The latest snowfall pushed Boston to its highest monthly total on record—58 inches and counting—and its third highest yearly snow total. This image was acquired by the GOES-East weather satellite at 3:45 p.m. Eastern Standard Time (20:45 Universal Time) on February 15, 2015, as the storm was mostly out to sea. Note the comma-like shape of the nor'easter, which spawned blizzard conditions at coastal locations. The official meteorological definition of a blizzard is three consecutive hours of falling or blowing snow with winds gusting above 35 miles (56 kilometers) per hour and visibility below one-fourth of a mile (0.4 kilometers). As of February 17, the snow depth near Boston was greater than in all but two reported locations in Alaska. It was significantly higher than the notoriously snowy states of Michigan, Wisconsin, and Minnesota. Only Buffalo, New York, had a higher snow pack. On February 16-17, more snow and ice fell across the eastern United States from northern Mississippi all the way to Maine. Read more: <a href="http://1.usa.gov/19wR4LI" rel="nofollow">1.usa.gov/19wR4LI</a> Via: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> GOES image courtesy of the NASA/NOAA GOES Project Science team. Terra MODIS image by Jeff Schmaltz, LANCE/EOSDIS Rapid Response at NASA Goddard Space Flight Center. Caption by Mike Carlowicz. <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
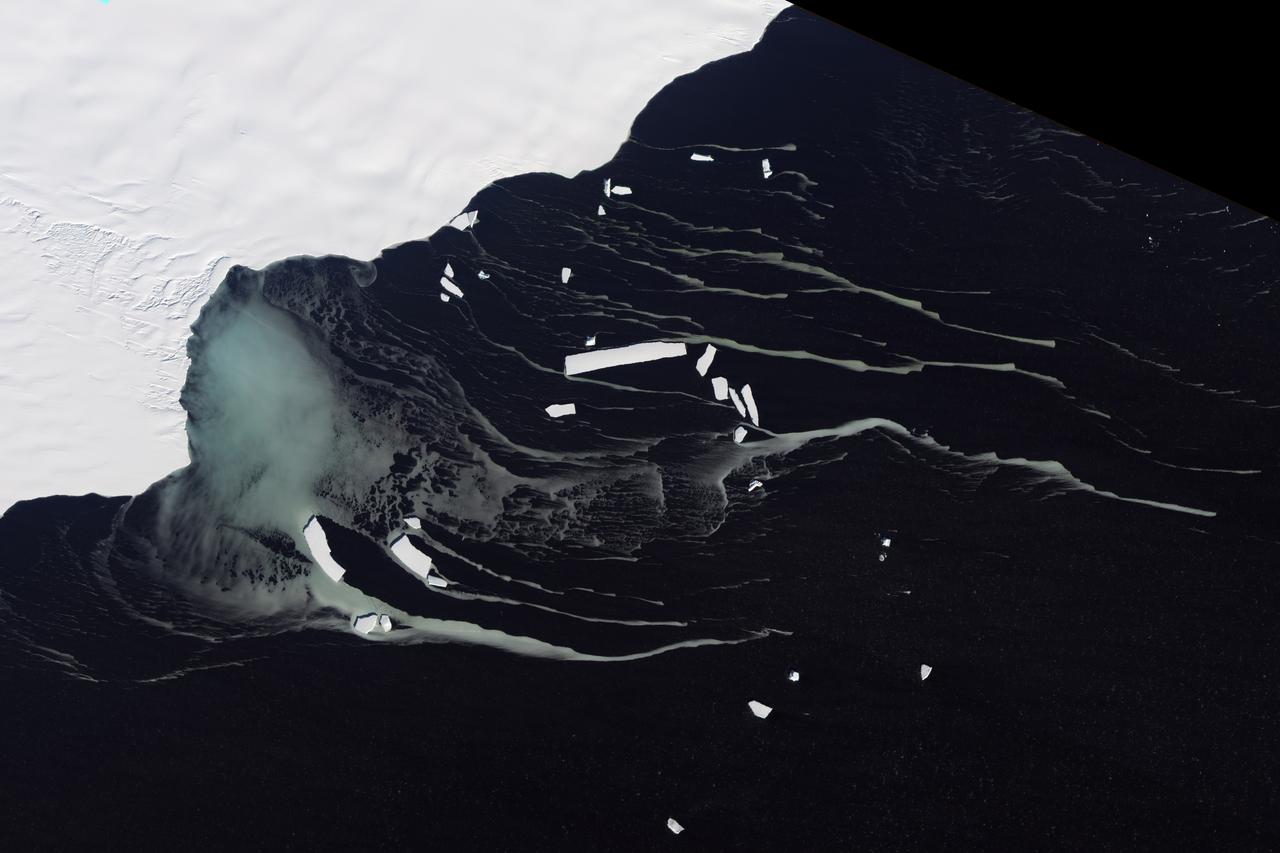
Off the northeastern edge of Antarctica’s Amery Ice Shelf lies Mackenzie Bay, which was painted with a ghostly blue-green mass in early February 2012. Similarly colored tendrils also streamed northward across the ocean, their flow sometimes interrupted by icebergs. Multiple factors might account for the ghostly shapes, including low-lying clouds or katabatic winds—downslope winds blowing toward the coast, which can freeze the water at the ocean surface. But an intriguing and perhaps more likely explanation involves processes occurring below the ice shelf. An ice shelf is a thick slab of ice often fed by glaciers attached to the coastline. The shelf floats on the ocean surface, with seawater circulating underneath. Like most ice shelves, the Amery is very thick in the upstream area near the shore. It thins significantly as it stretches northward away from the continent. Water at depth is subject to much greater pressure than water at the surface, and one effect of this intense pressure is that it effectively lowers the freezing point. So water circulating at depth beneath the Amery Ice Shelf may be slightly below the temperature at which it would normally begin to freeze. As some that water wells up along the underbelly of the shelf, the pressure is reduced and the water begins to freeze even though the temperature may not change. As it freezes, this deep-ocean water forms needle-like crystals known as frazil. The crystals are only 3 to 4 millimeters (0.12 to 0.16 inches) wide, but a sufficient concentration of frazil can change the appearance of the water. A frazil-rich plume probably accounts for the blue-green waters off the Amery Ice Shelf in the image above. Modeling of ocean circulation beneath the shelf indicates just such a plume emerging in that location. Frazil-rich water explains the plume, and wind transport of the surface water explains the long streams extending northward. As the sub-iceshelf water mixes with surface water around the Antarctic coastline, the frazil is gradually melted and the streams disappear. The Advanced Land Imager (ALI) on NASA’s Earth Observing-1 (EO-1) satellite captured this natural-color image of Mackenzie Bay and the ice shelf on February 12, 2012. NASA Earth Observatory image created by Jesse Allen and Robert Simmon, using EO-1 ALI data provided courtesy of the NASA EO-1 team. Caption by Michon Scott with information from Helen A. Fricker, Scripps Institution of Oceanography; Robert Massom, Australian Antarctic Division; Ben Galton-Fenzi, University of Tasmania, Australia; and Florence Fetterer, Walt Meier, and Ted Scambos, National Snow and Ice Data Center. Credit: <b><a href="http://www.earthobservatory.nasa.gov/" rel="nofollow"> NASA Earth Observatory</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b> Instrument: EO-1 - ALI