
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center showcased it's various projects for the public in Huntsville, Alabama's Big Spring Park. Exhibits were displayed by all of the various directorates of the Center with employee volunteers explaining all aspects of their projects. Adding to the festivities was the attendance of retired NASA astronaut Robert "Hoot" Gibson. Northrup Grumman employees fire a tethered miniature rocket at NASA Day in the Park.
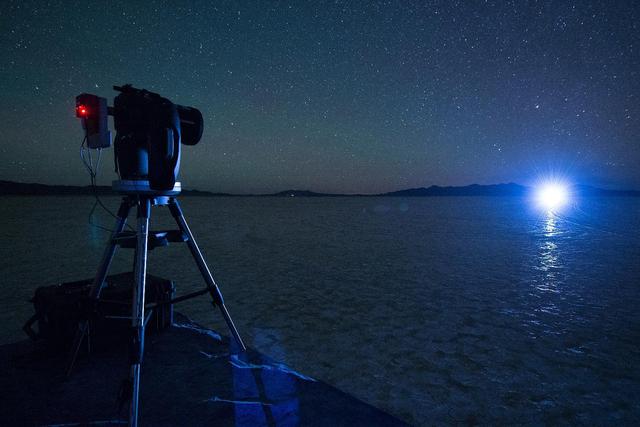

A night test of a small-scale starshade model, in a dry lake bed in central Nevada's Smith Creek by Northrup Grumman, took place in May to June 2014. A telescope points toward a bright light, which in the darkness of the desert mimics the conditions of starlight in space. Other lights, which are up to 10 million times fainter than the light source standing in for the star, represent the reflected light of planets. Telescopes searching for the relatively dim light of an exoplanet next to its much brighter star are faced with a challenge as difficult as searching from Los Angeles for a firefly in New York -- if the firefly is next to the brightness of a lighthouse. The tests by Northrup Grumman determined that a starshade, or external occulter, is capable of blocking starlight to a degree that can indeed reveal the light of a planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20901
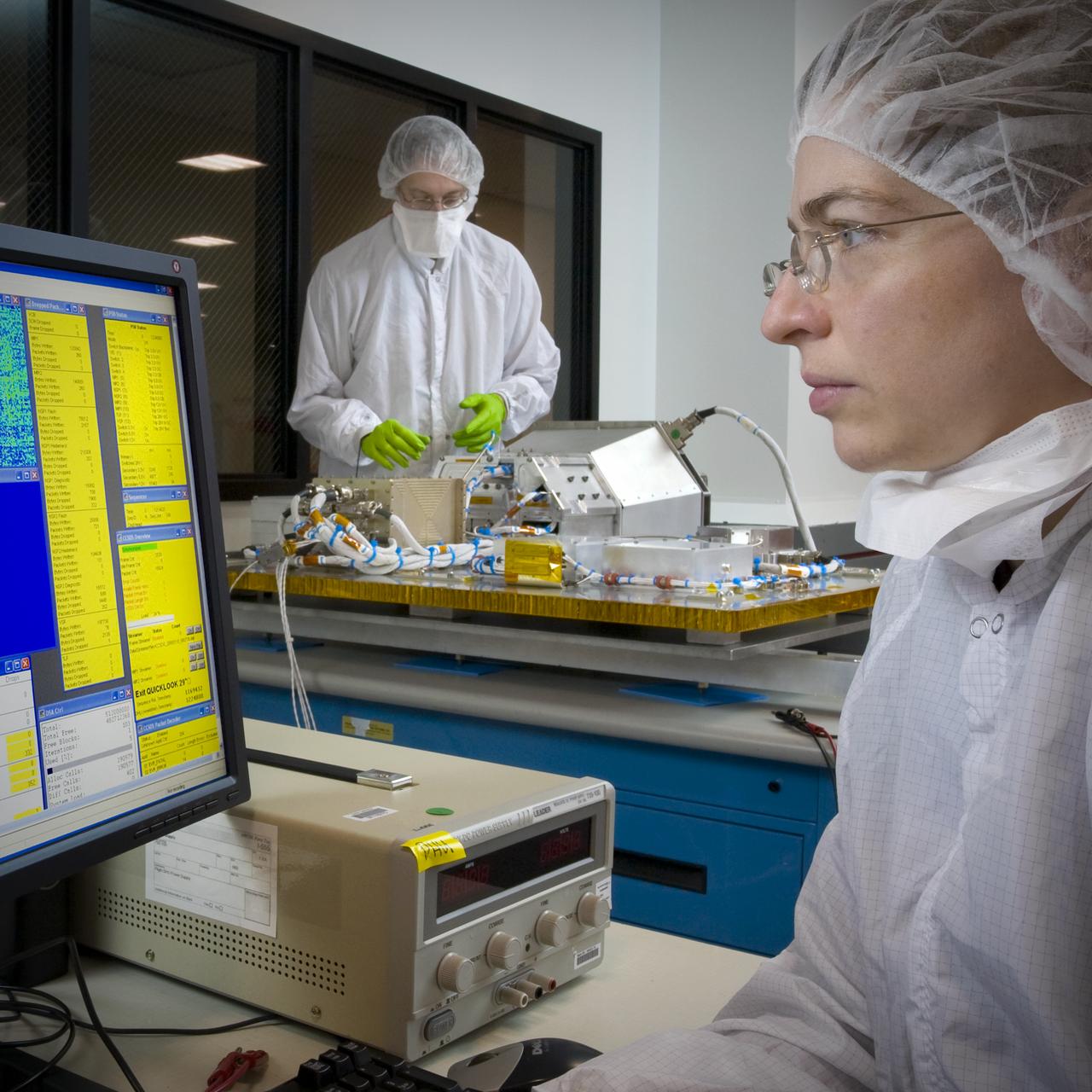

LCROSS leaves Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA clean room post shippment verification tests before being mated to the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbitor (LR0) spacecraft for a piggyback ride to the Moon. With Kim Ennico Ames P.I. and Mark Shirley, Northrup Grumman.
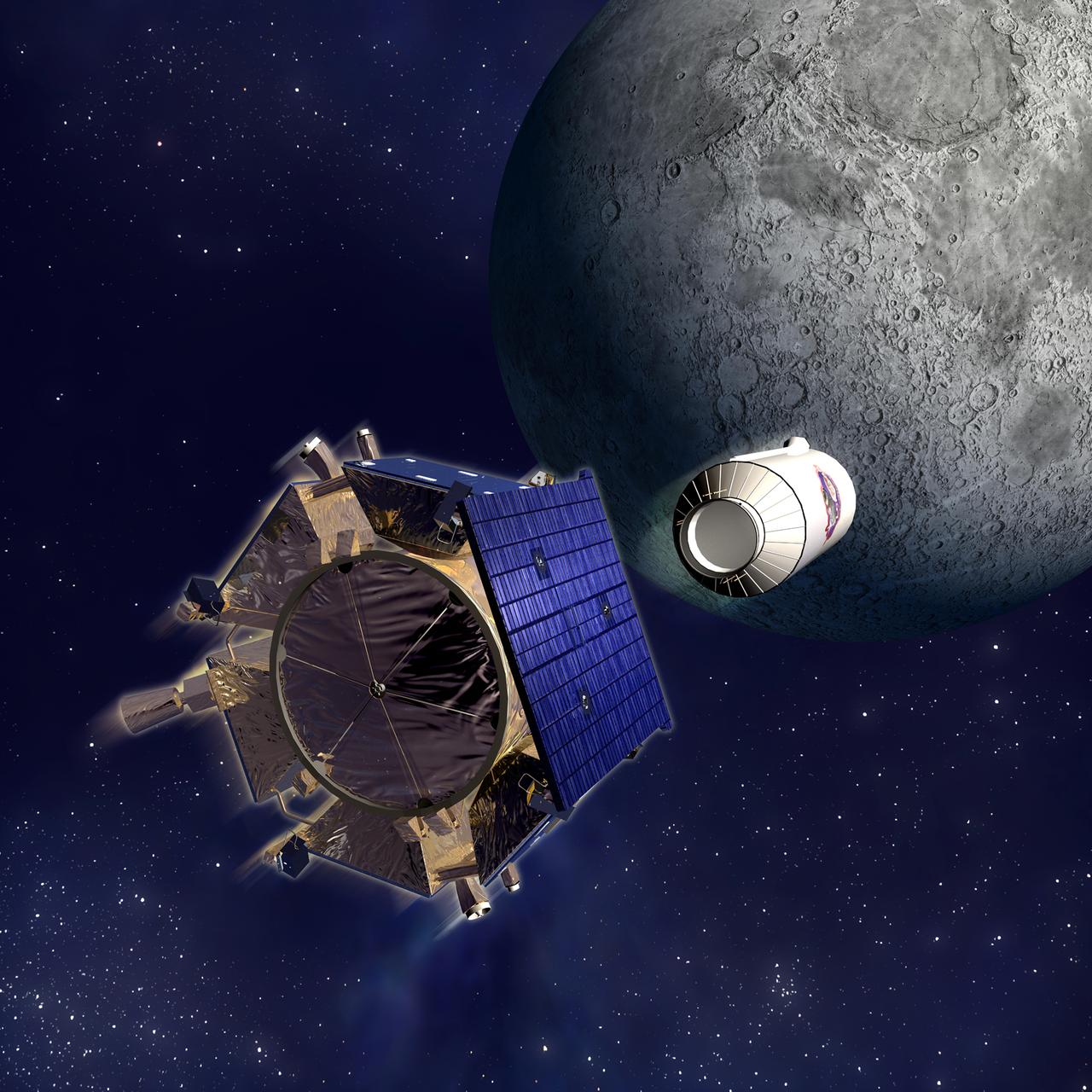
LCROSS artwork. Credit Northrup Grumman Image converted using ifftoany
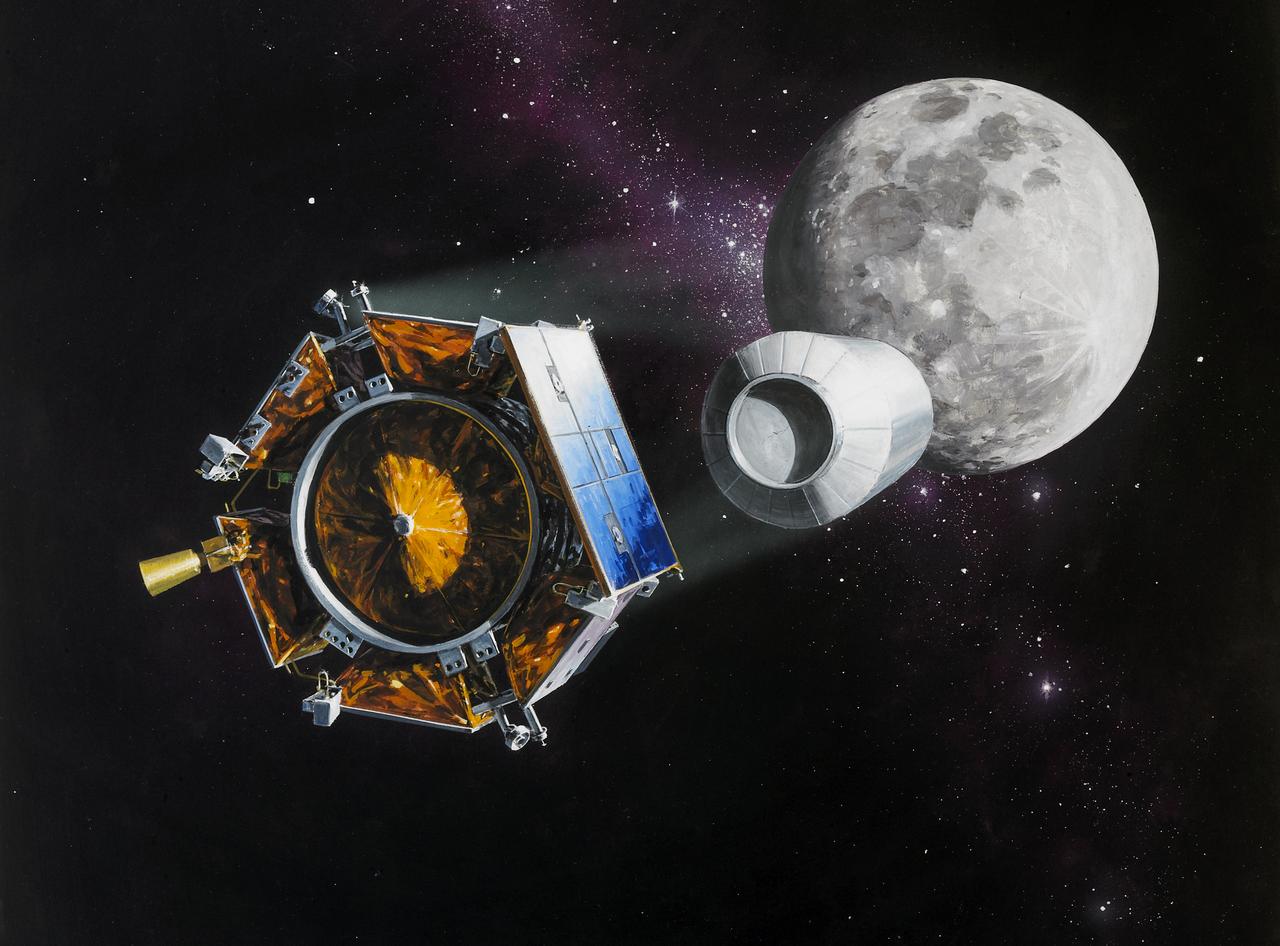

LCROSS impact artwork credit line required Northrup Grumman
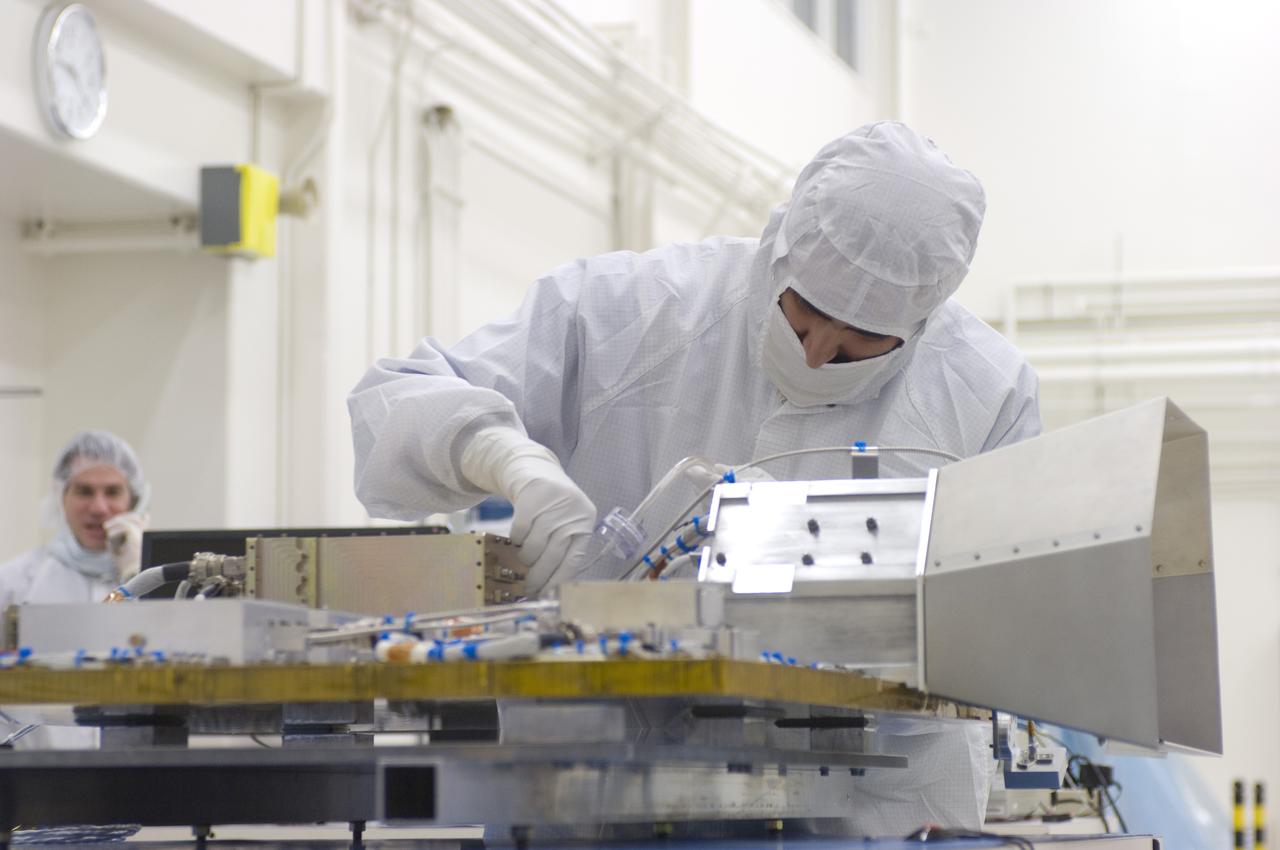

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- cleaning for shipping to Northrup Grumman, Redondo Beach, CA

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240 - cleaning for shippment to Northrup Grumman, Redondo Beach, CA
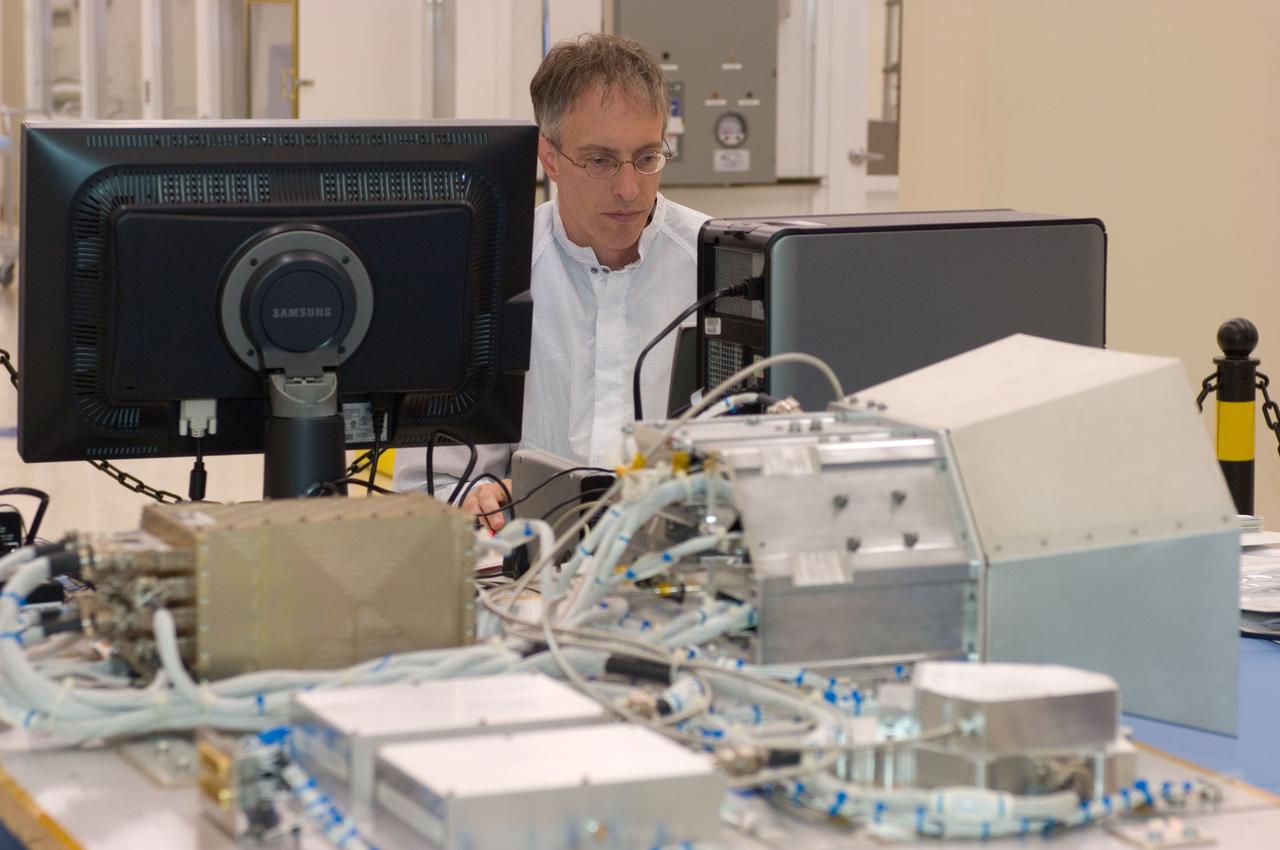

LCROSS flight hardware in clean room at Ames N-240. with Mark Shirley, LCROSS Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA
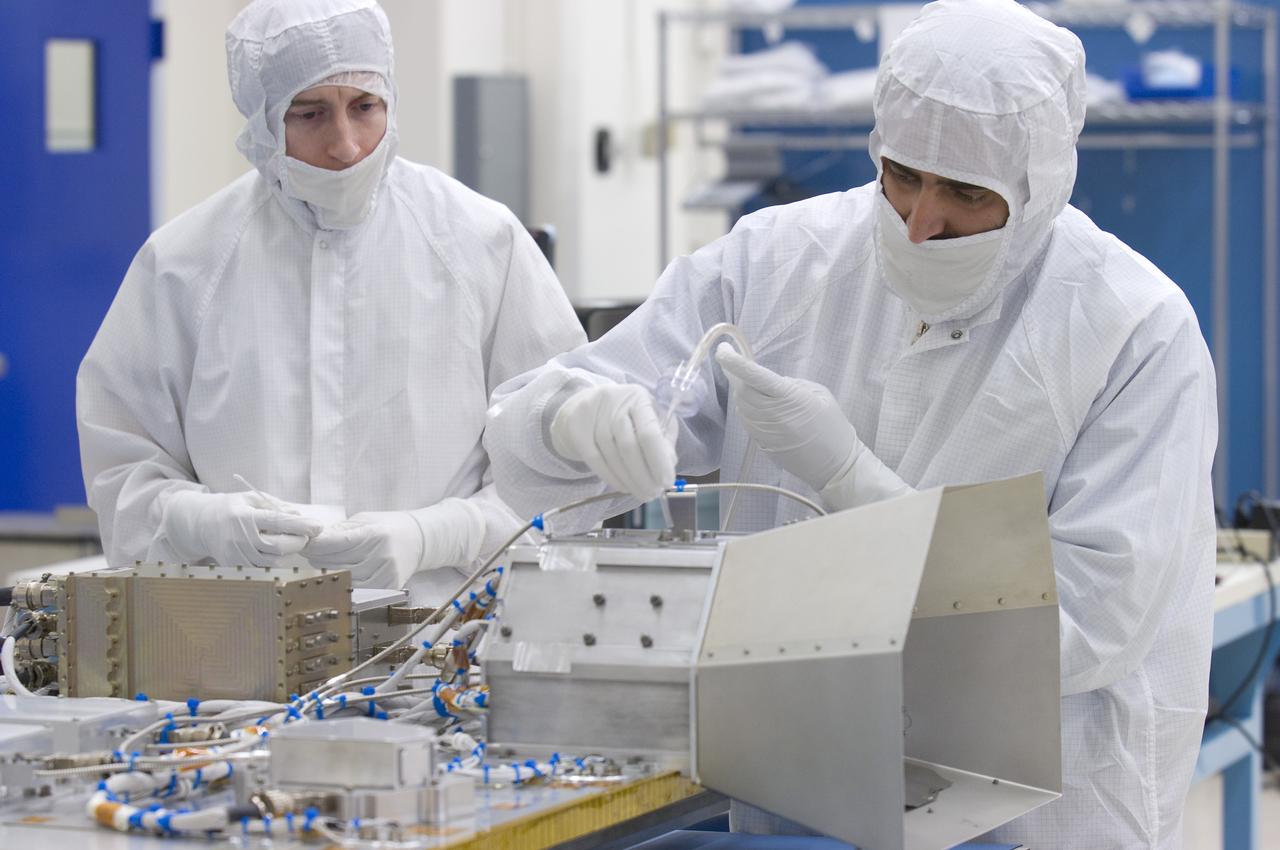

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240 -cleaning for shipping to Northrup Grumman, Redondo Beach, CA.
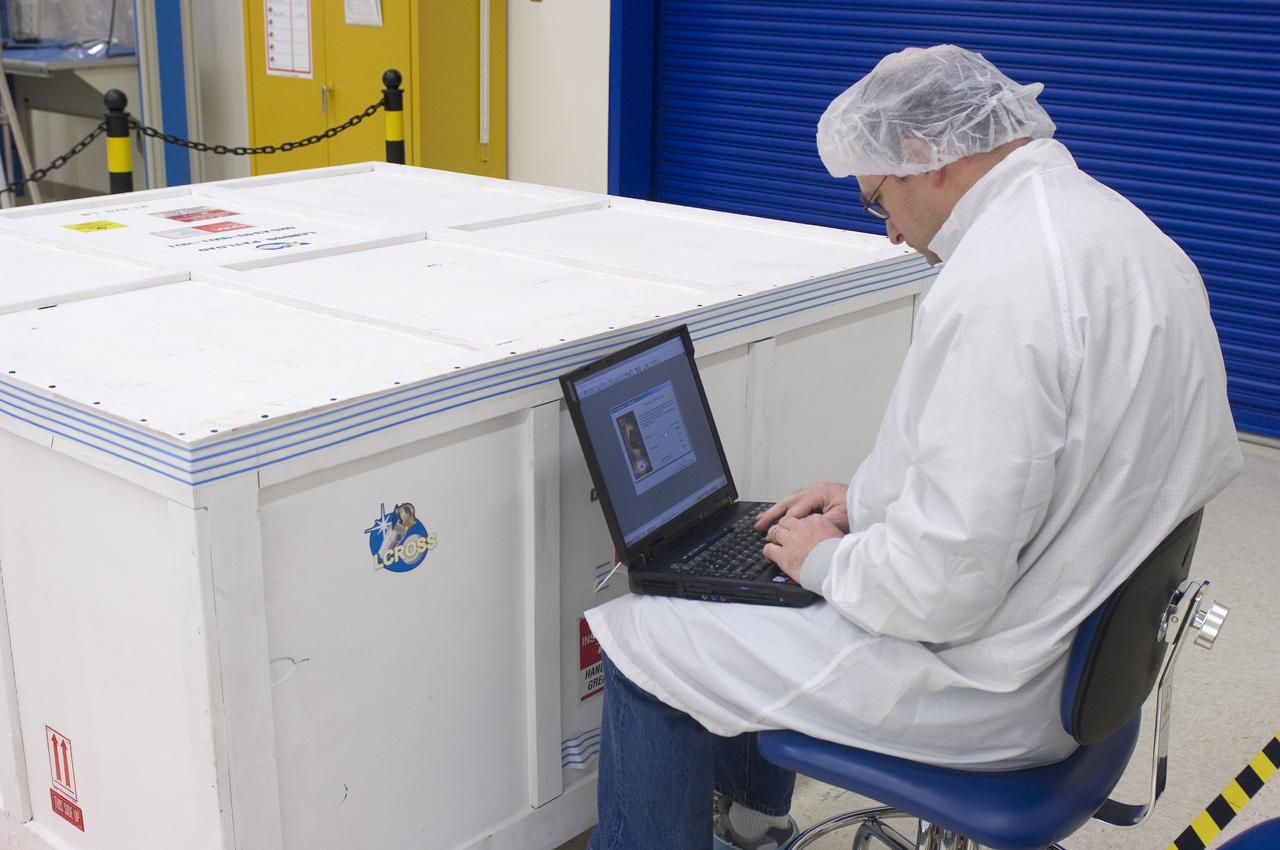

LCROSS - loading onto truck for trip to Northrup Grumman Los Angles, CA for matting with it's Lunar Reconnaissance Orbitor (LR0) spacecraft with Steve Ord
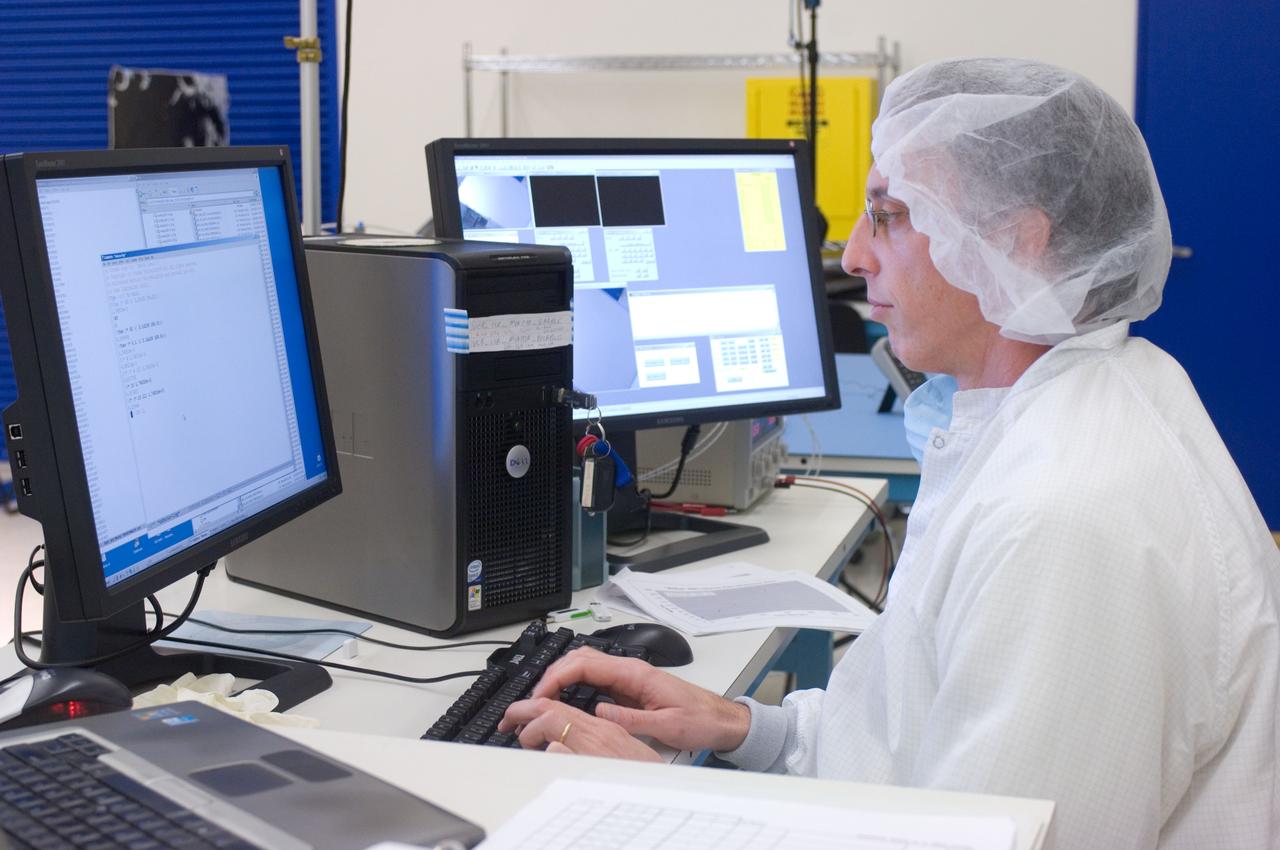

LCROSS in ames clean room N-240 - Calibration and camera chec out with Mark Shirley, Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA

A furled first prototype starshade developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, shown in technology partner Astro Aerospace/Northrup Grumman's facility in Santa Barbara, California, in 2013. This design shows petals that are more extreme in shape, which properly diffracts starlight for smaller telescopes. For launch, the petals of the starshade will be wrapped around the spacecraft, then unfurled into the familiar flower-like design once in space. As shown by this 66-foot (20-meter) model, starshades can come in many shapes and sizes. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20905
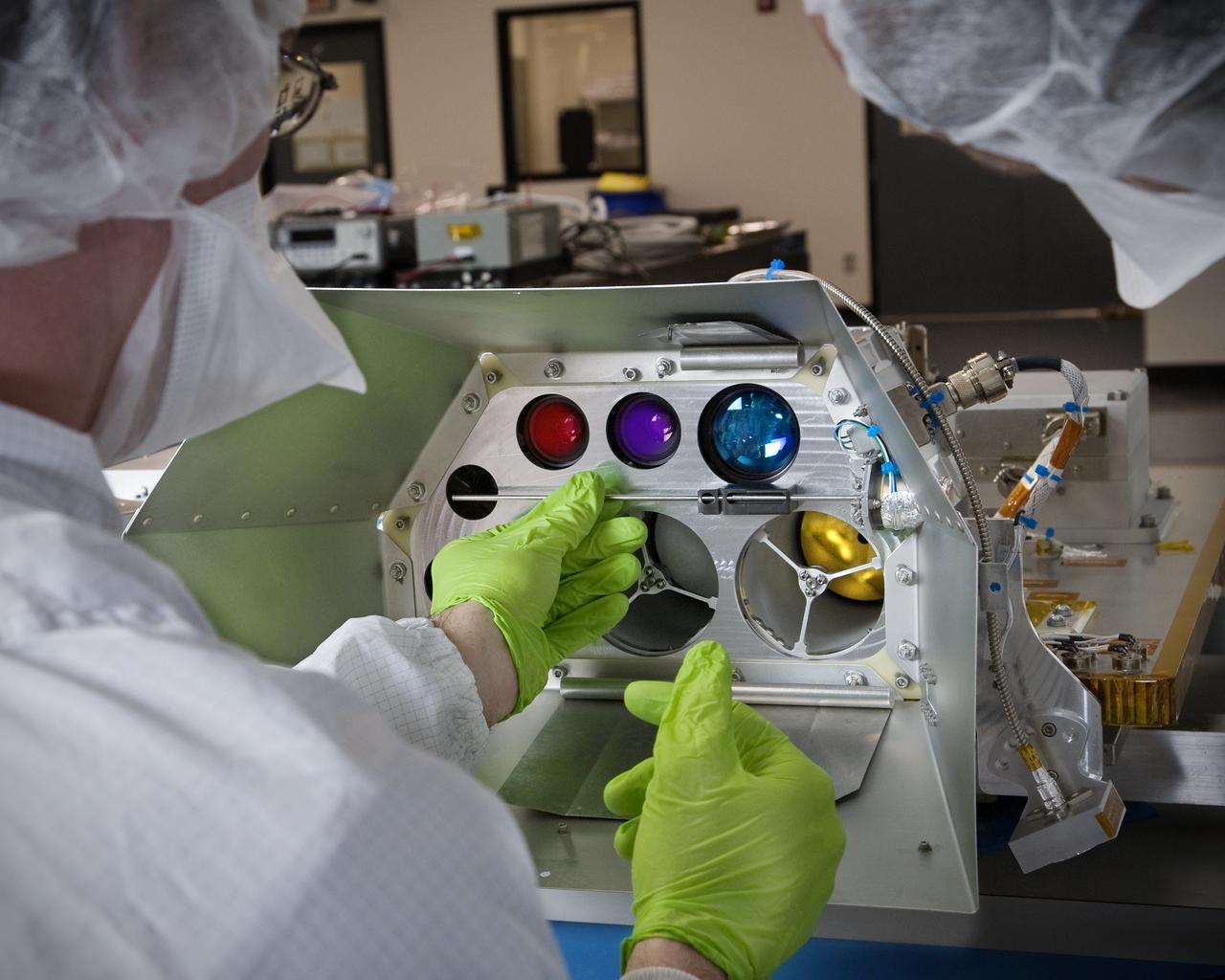

LCROSS leaves Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA clean room post shippment verification tests before being mated to the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbitor (LR0) spacecraft for a piggyback ride to the Moon.
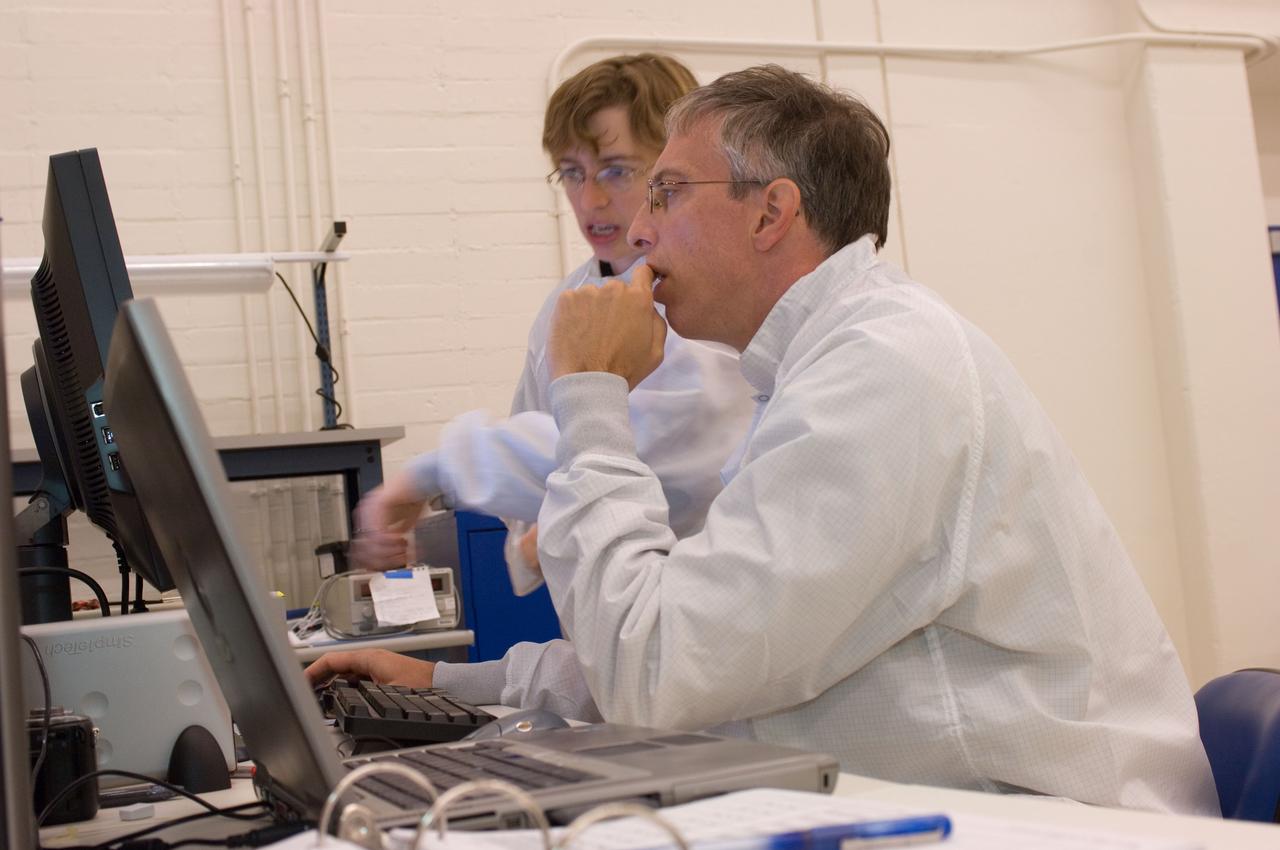

LCROSS flight hardware in clean room at Ames N-240. with Mark Shirley, LCROSS Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA and Kim Ennico, NASA Ames P.I.
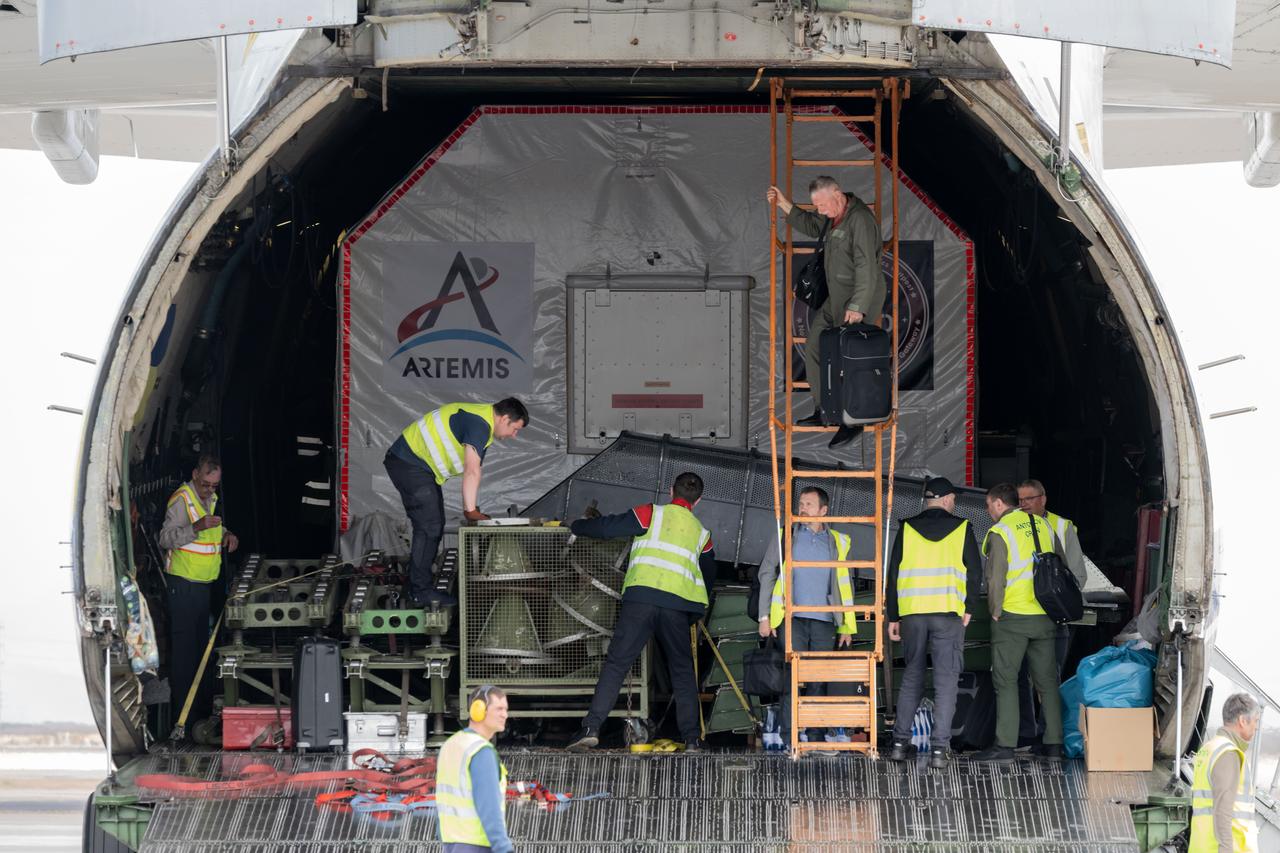

PHOTO DATE: April 01, 2025. LOCATION: Mesa Gateway Airport. SUBJECT: Gateway Habitation and Logistics Outpost (HALO) module delivery to Northrup Grumman Facility in Gilbert, AZ. PHOTO CREDIT: NASA/Josh Valcarcel
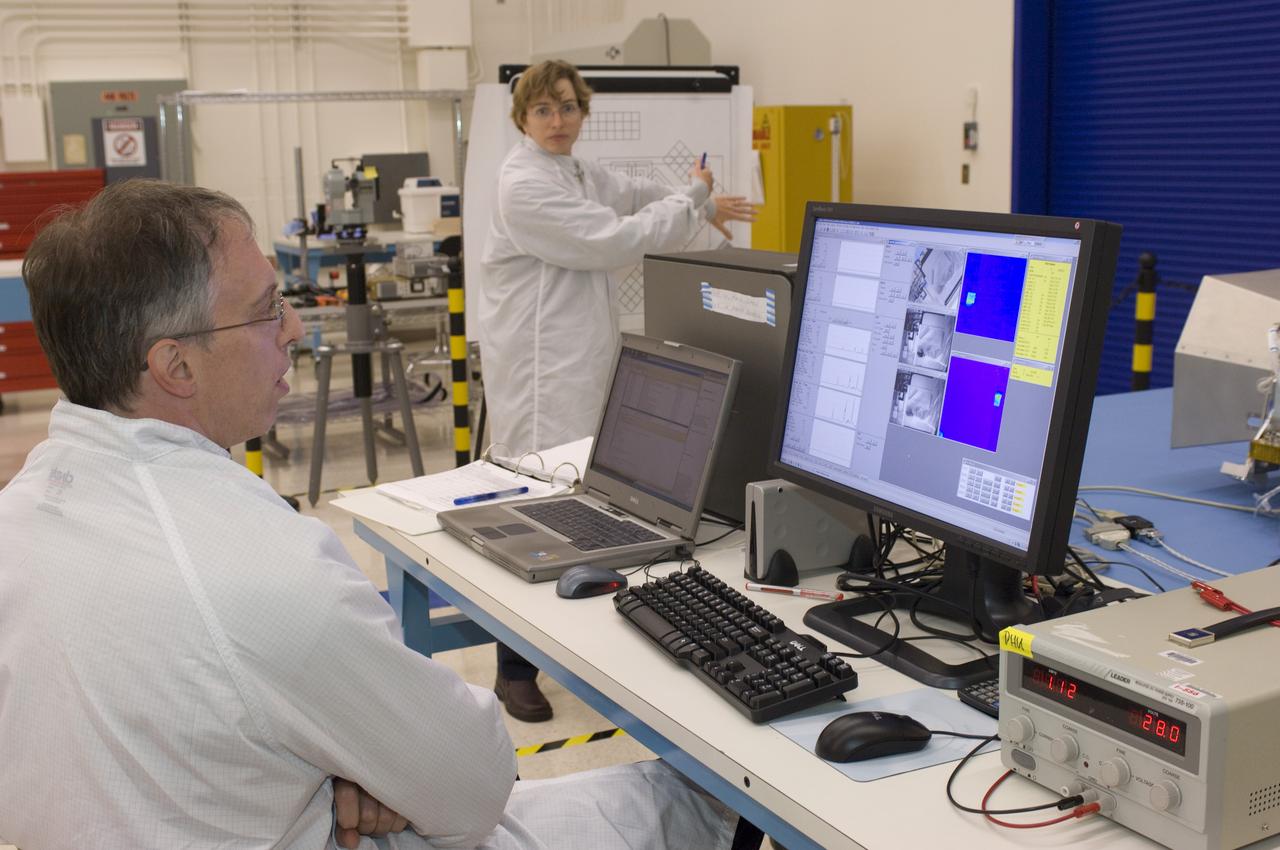

LCROSS flight hardware in clean room at Ames N-240. with Mark Shirley, LCROSS Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA and Kim Ennico, NASA Ames P.I.
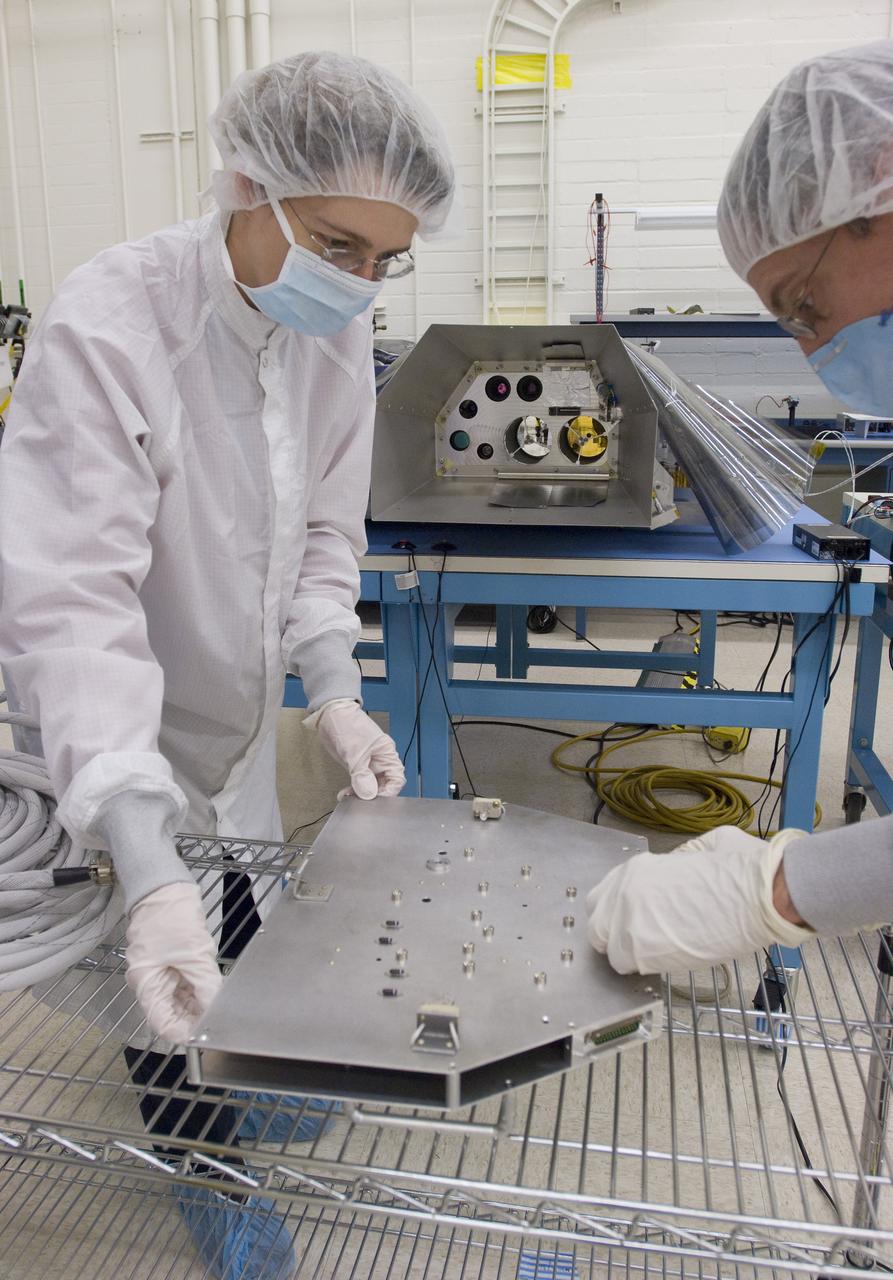

LCROSS in Ames Clean room N-240 - calibration and camera check out wit Kim Ennico (l) and Mark Shirley, Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA remove rear cover
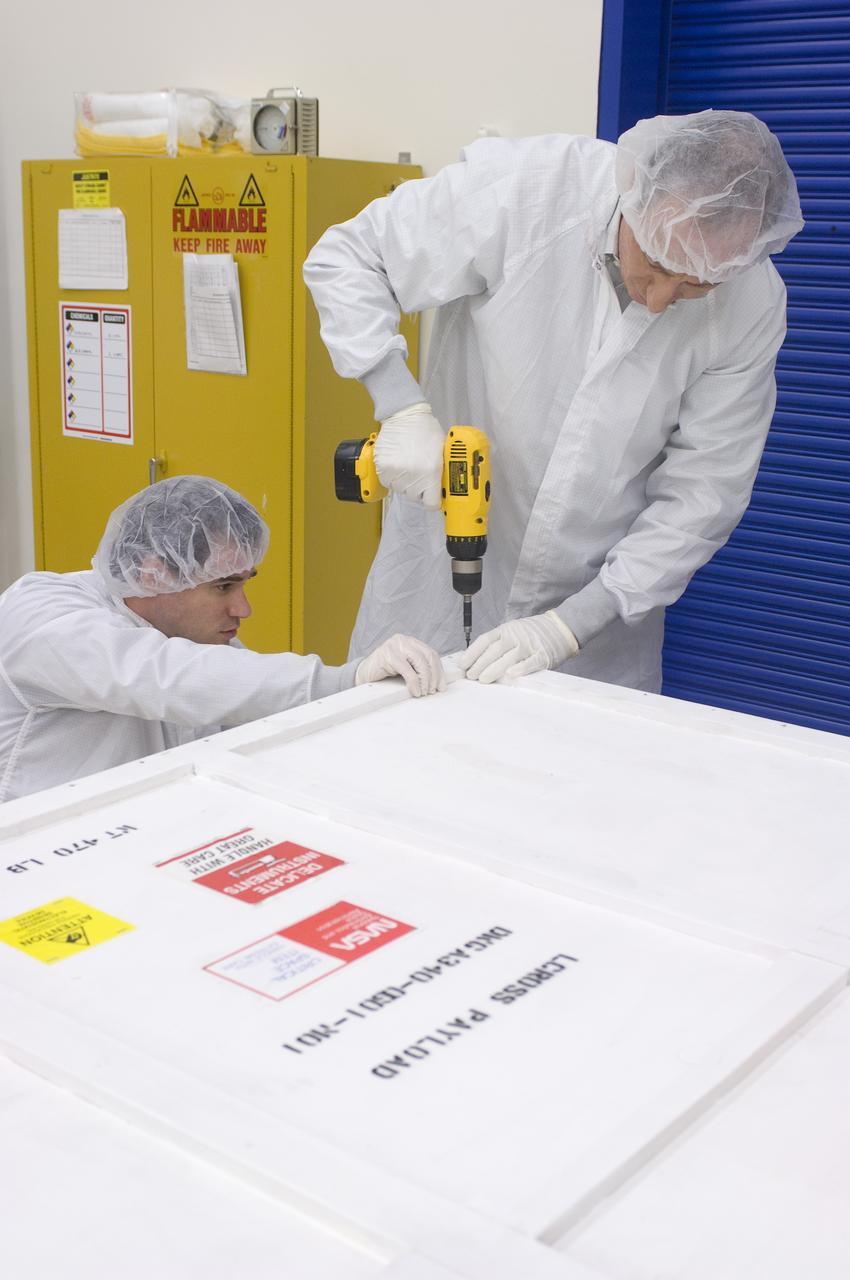

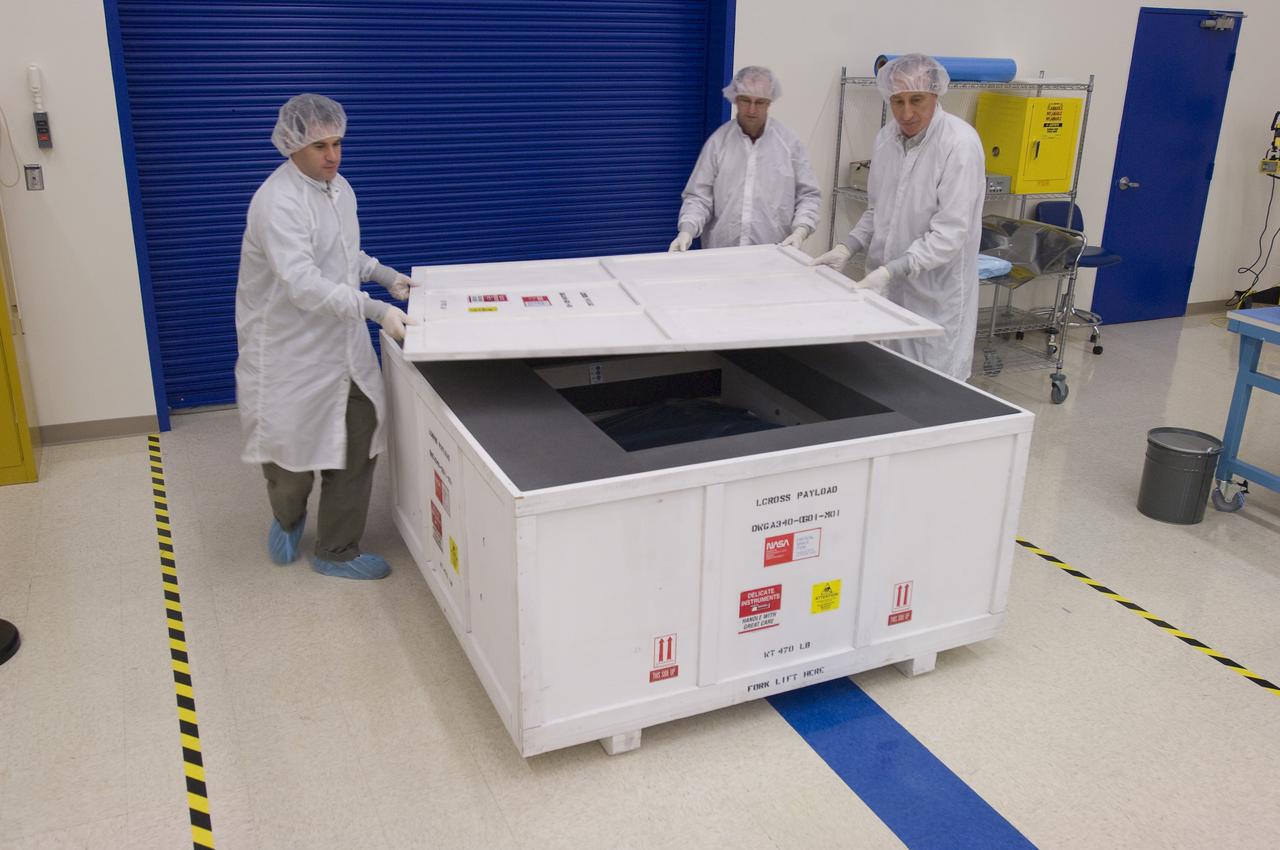
LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- securing special made crate for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft
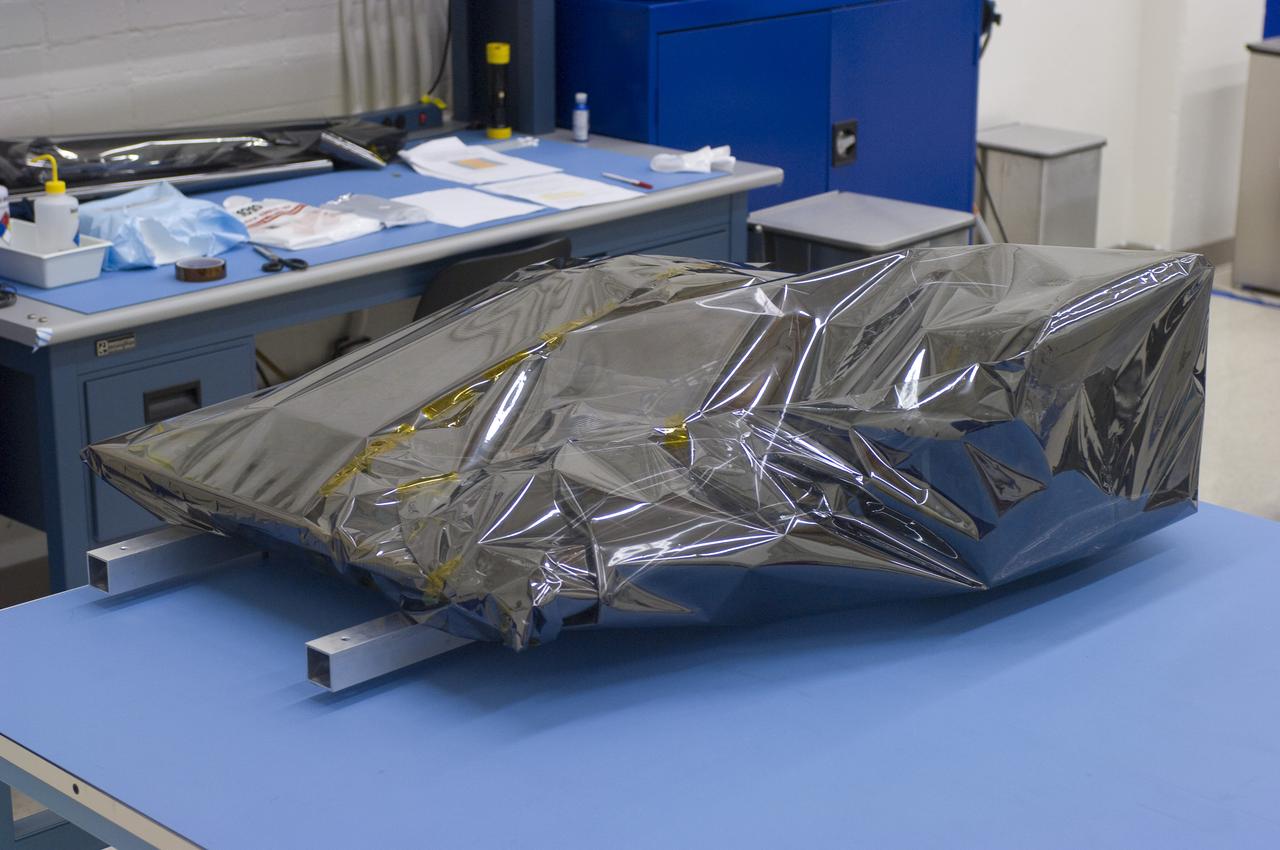

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- wrapped for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft
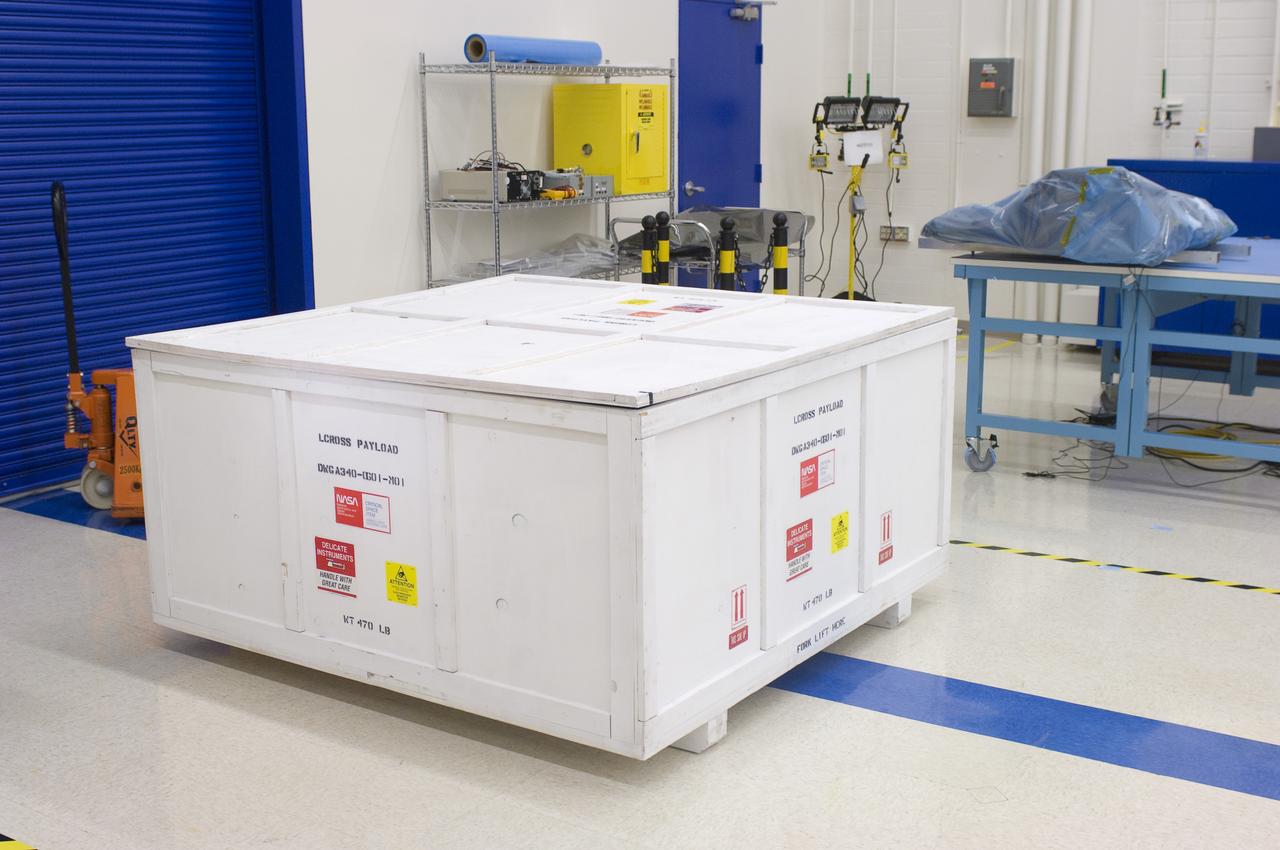

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- special made crate for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft
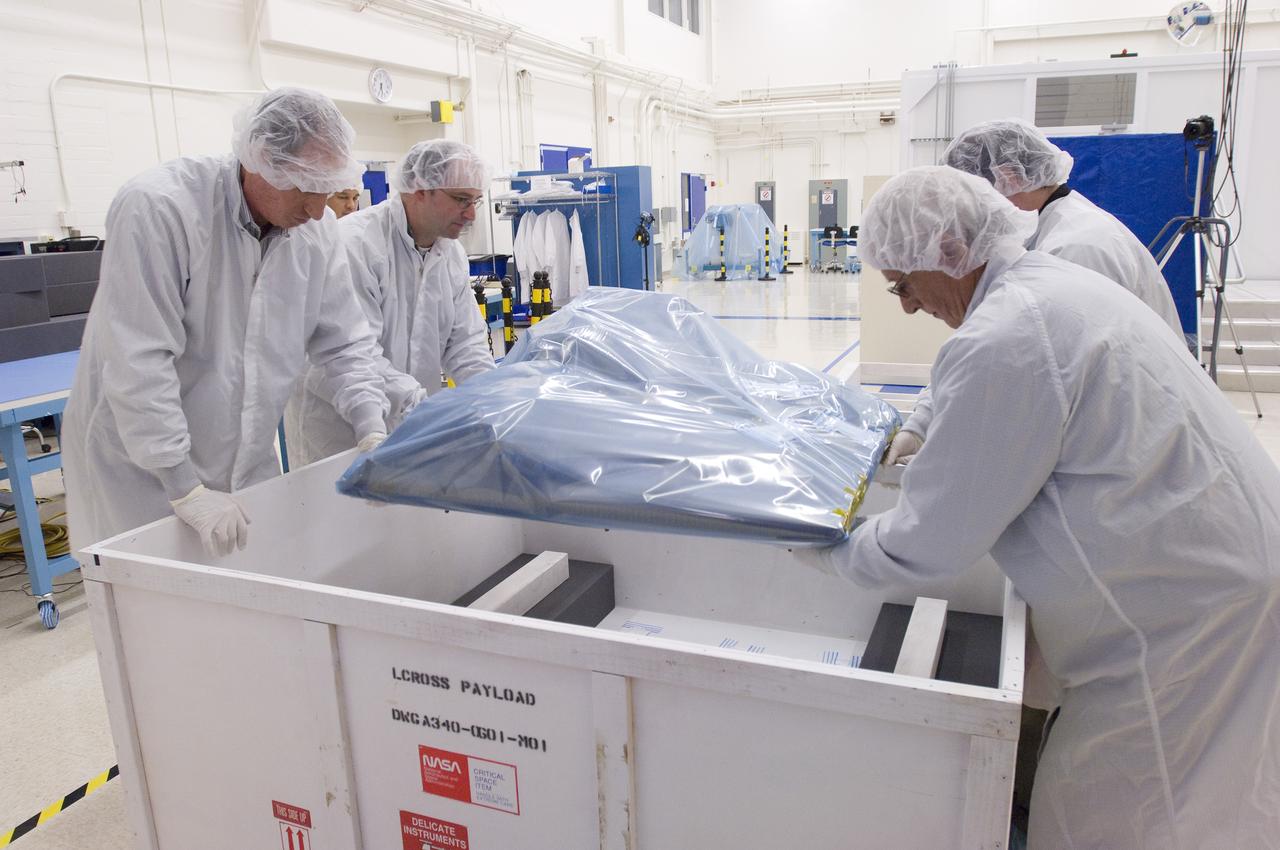

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- packing and crating for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft
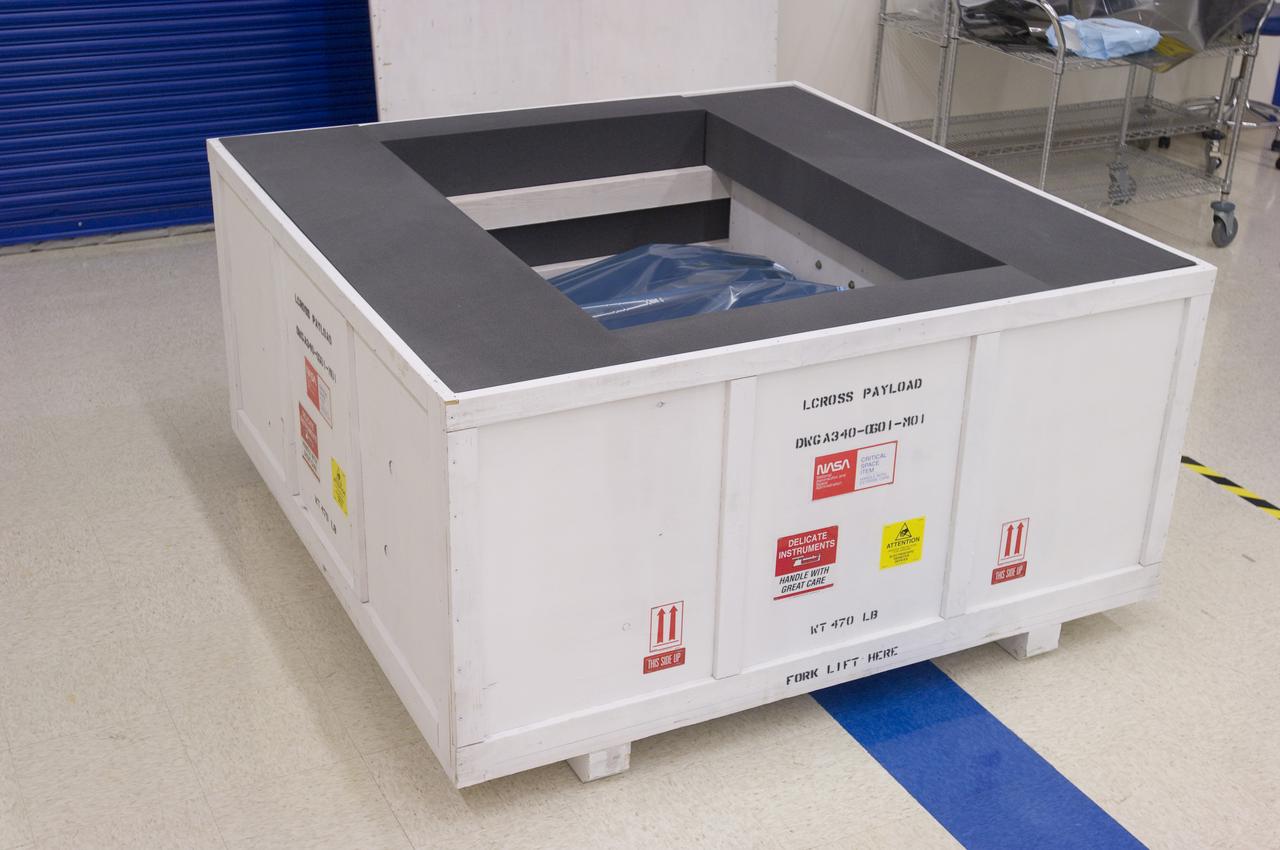

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- packed into a special made crate for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft
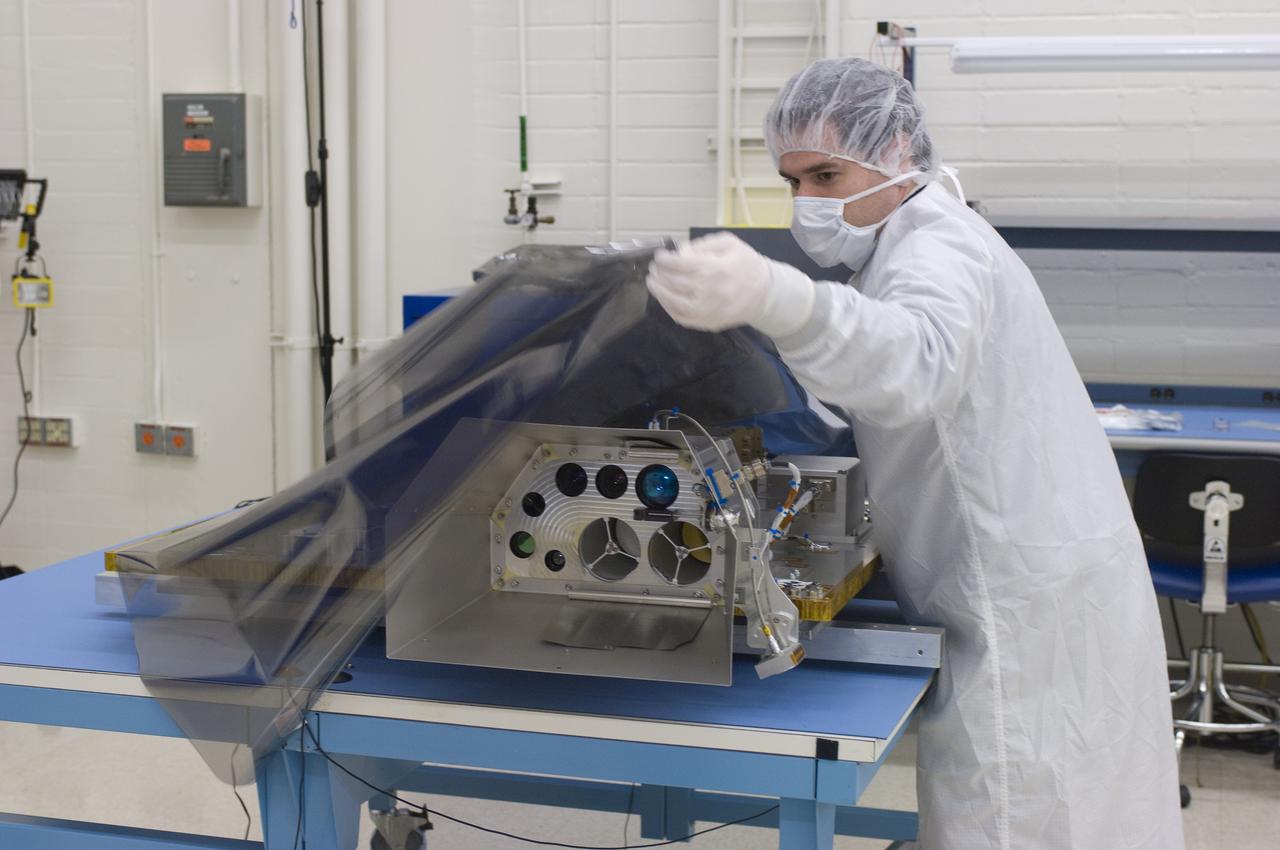

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- cleaning and wrapping for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft (with Tony Colaprete)
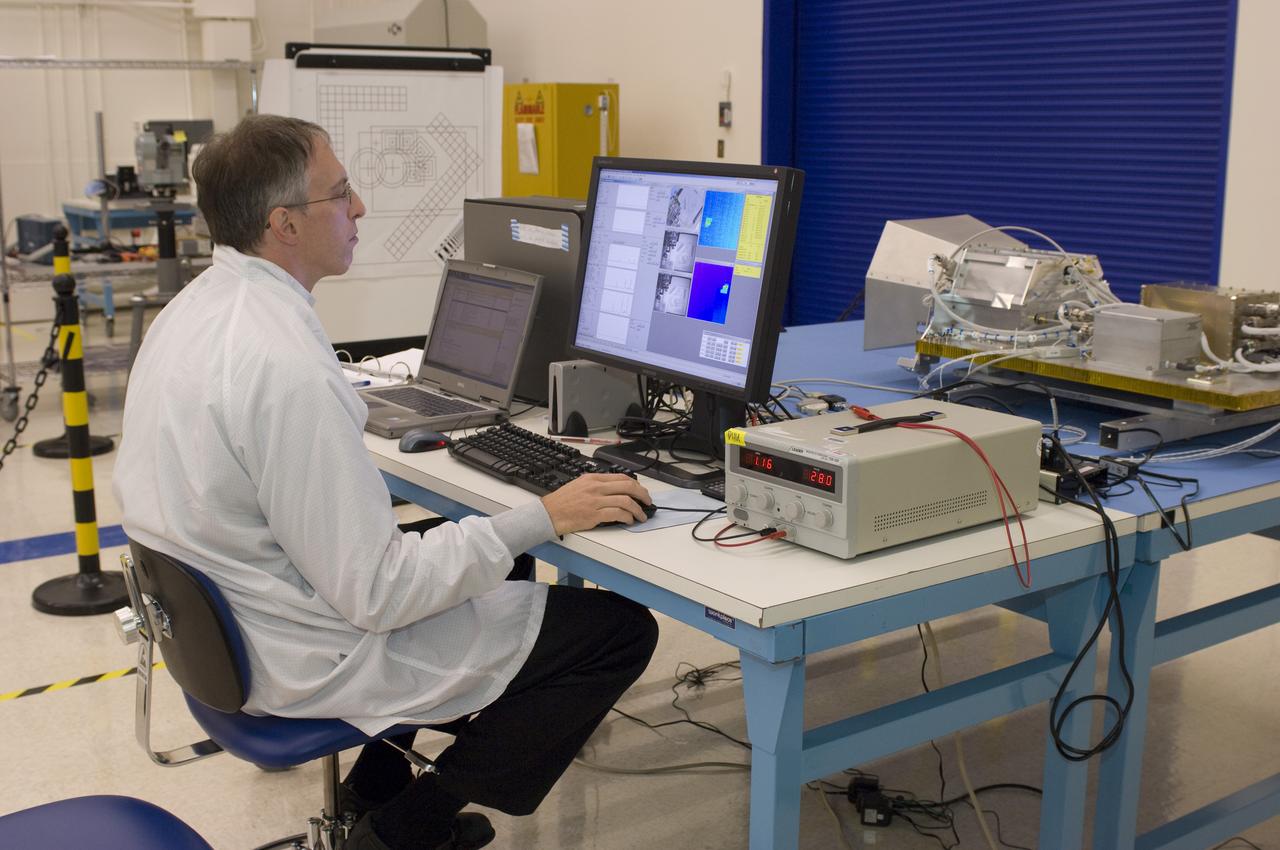

LCROSS flight hardware in clean room at Ames N-240. with P.I.'s and EEL personnel preforming various tests with Mark Shirley, LCROSS Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA

The first prototype starshade developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, shown in technology partner Astro Aerospace/Northrup Grumman's facility in Santa Barbara, California, in 2013. As shown by this 66 foot (20-meter) model, starshades can come in many shapes and sizes. This design shows petals that are more extreme in shape which properly diffracts starlight for smaller telescopes. Each petal is covered in a high-performance plastic film that resembles gold foil. On a starshade ready for launch, the thermal gold foil will only cover the side of the petals facing away from the telescope, with black on the other, so as not to reflect other light sources such as the Earth into its camera. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20906
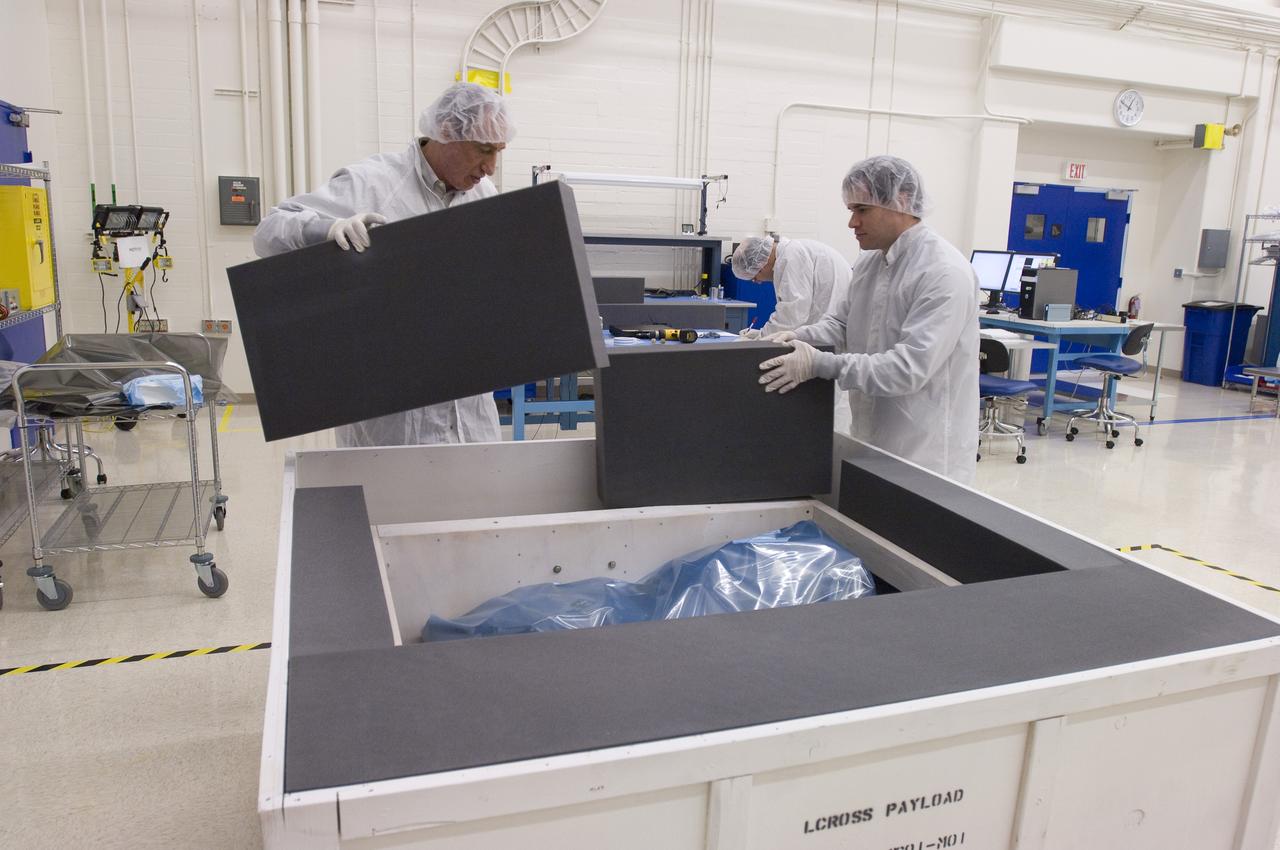

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- packing into a special made crate for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft (Tony Colaprete (r) LCROSS P.I.)
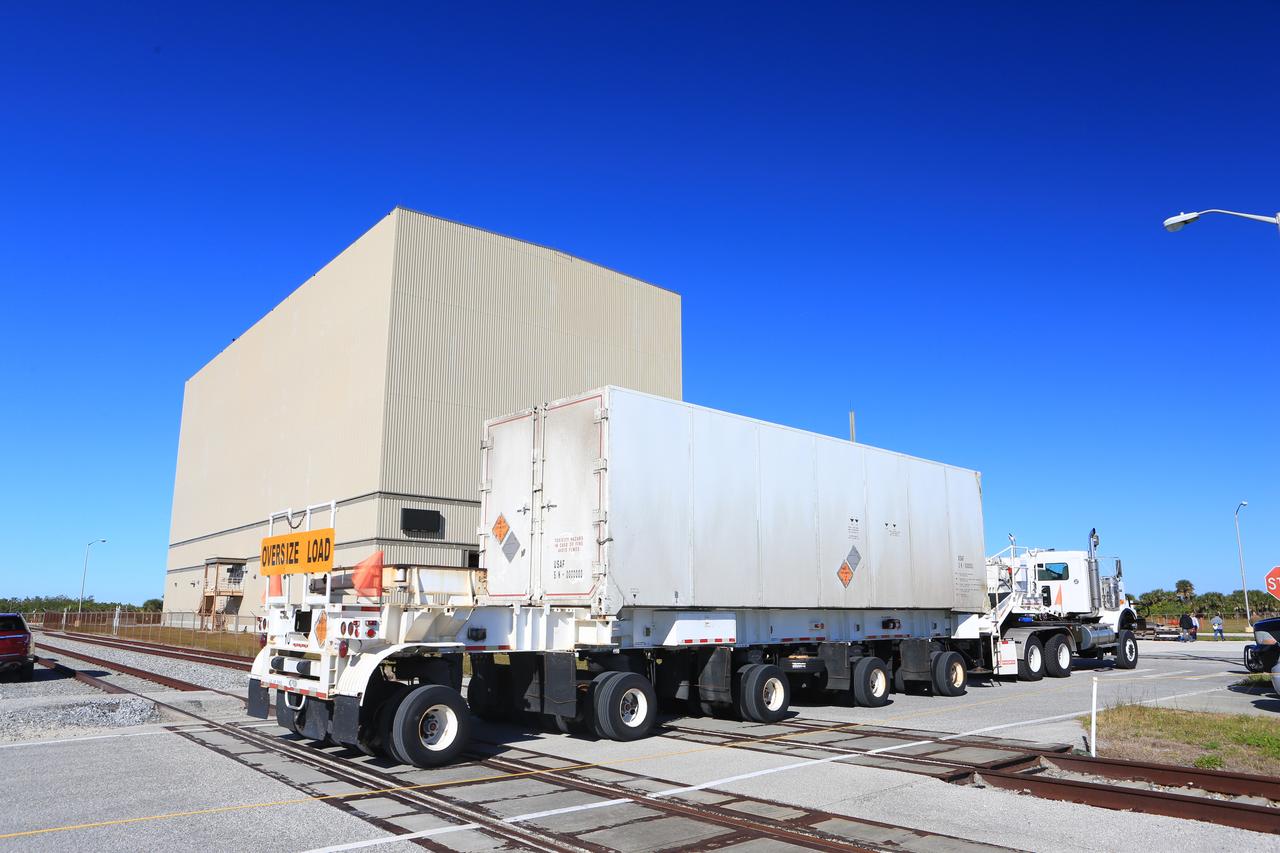

The Northrup Grumman SR118 for Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) which is loaded with propellants moves from the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) to the Rotation Protection and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center for continued flight processing on Jan. 29, 2019.
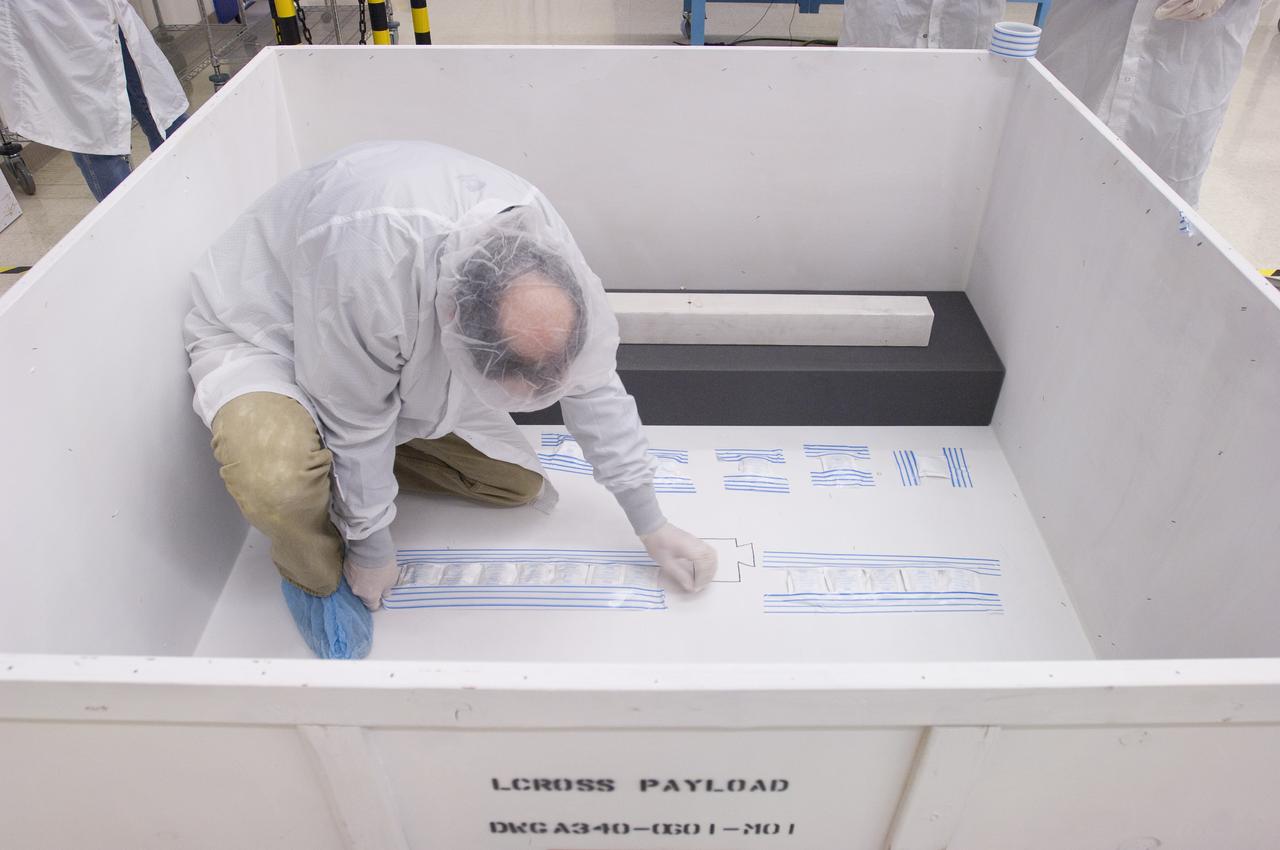

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- Steve Ord inspects special made crate for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft

LCROSS leaves Ames clean room to be loaded onto a truck for trip to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA for further calibration and verification tests before being mated to the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbitor (LR0) spacecraft for a piggyback ride to the Moon.
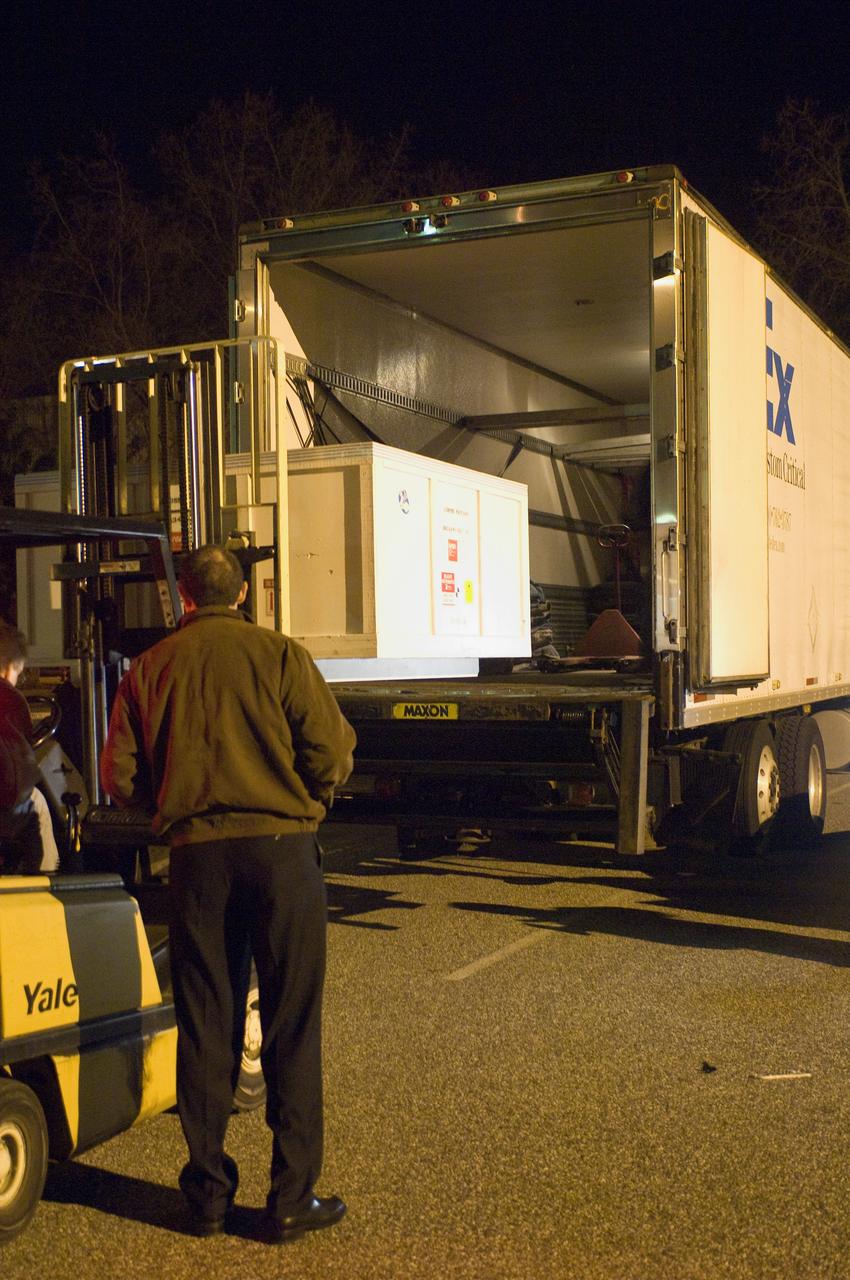

LCROSS leaves Ames clean room and is loaded onto a truck for trip to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA for further calibration and verification tests before being mated to the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbitor (LR0) spacecraft for a piggyback ride to the Moon.
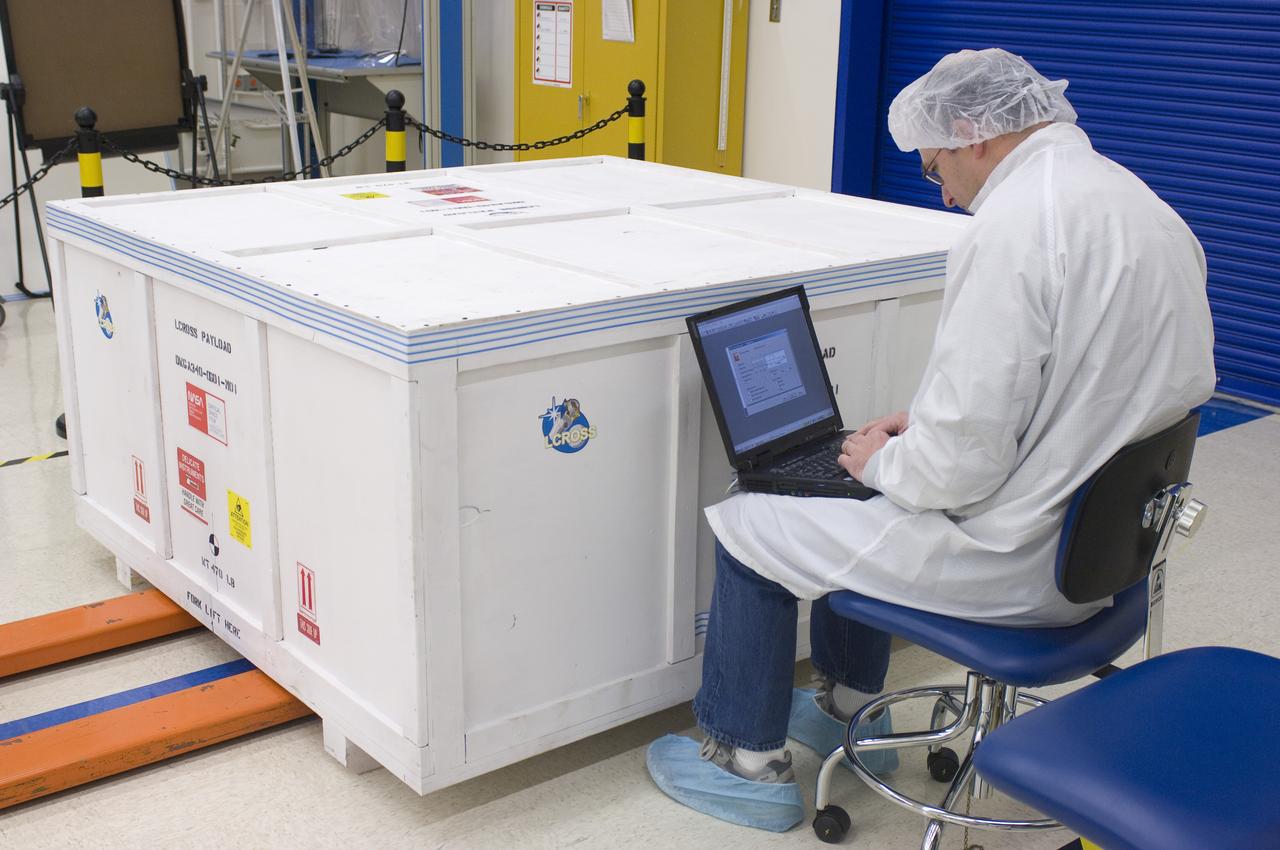

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- securing the special made crate for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft with Steve Ord, Ames Project Management Office
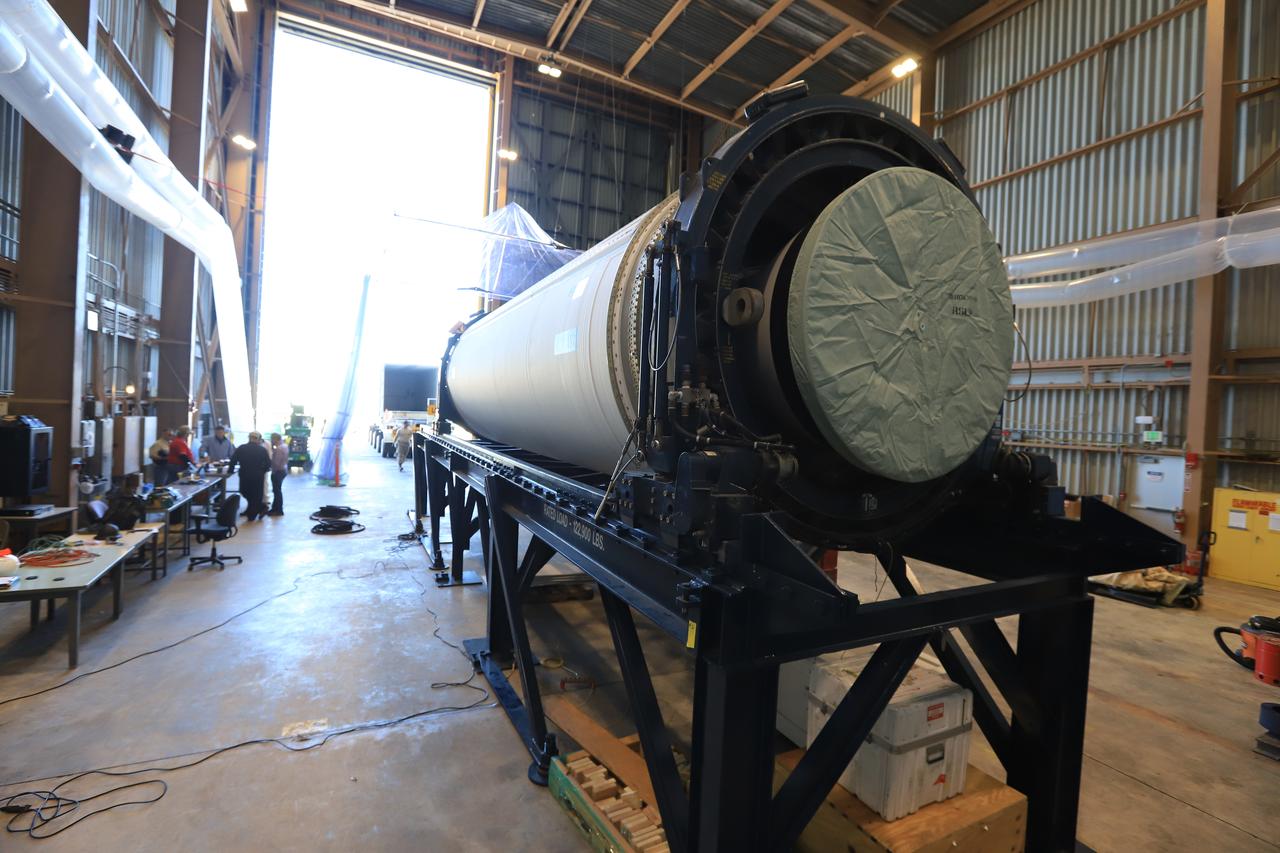

The Northrup Grumman SR118 for Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) which is loaded with propellants moves from the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) to the Rotation Protection and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center for continued flight processing on Jan. 29, 2019.
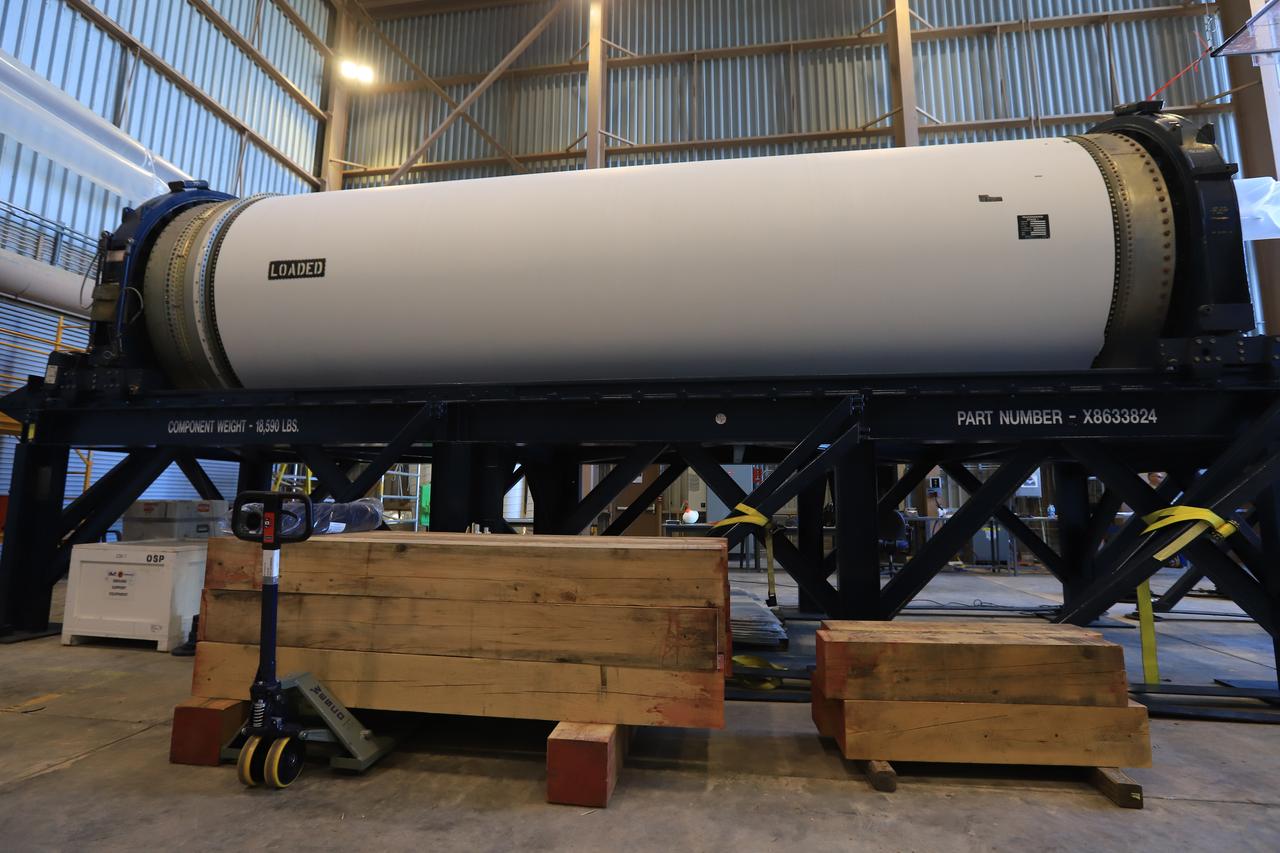

The Northrup Grumman SR118 for Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) which is loaded with propellants moves from the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) to the Rotation Protection and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center for continued flight processing on Jan. 29, 2019.
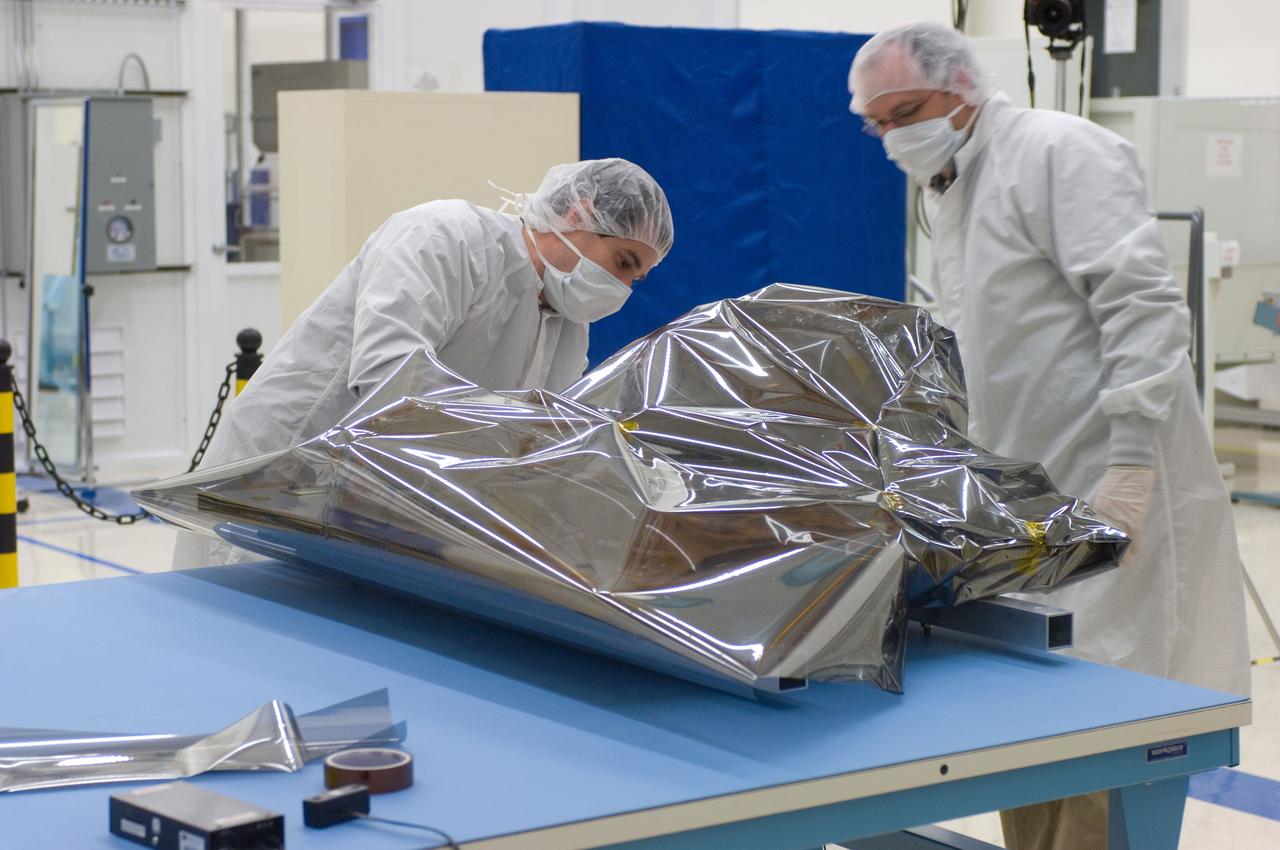

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- cleaning and wrapping for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft (with Steve Ord, Project Management Division (l) and Tony Colaprete (r) LCROSS P.I.)

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- cleaning and wrapping for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft (with Steve Ord, Project Management Division (l) and Tony Colaprete (r) LCROSS P.I.)
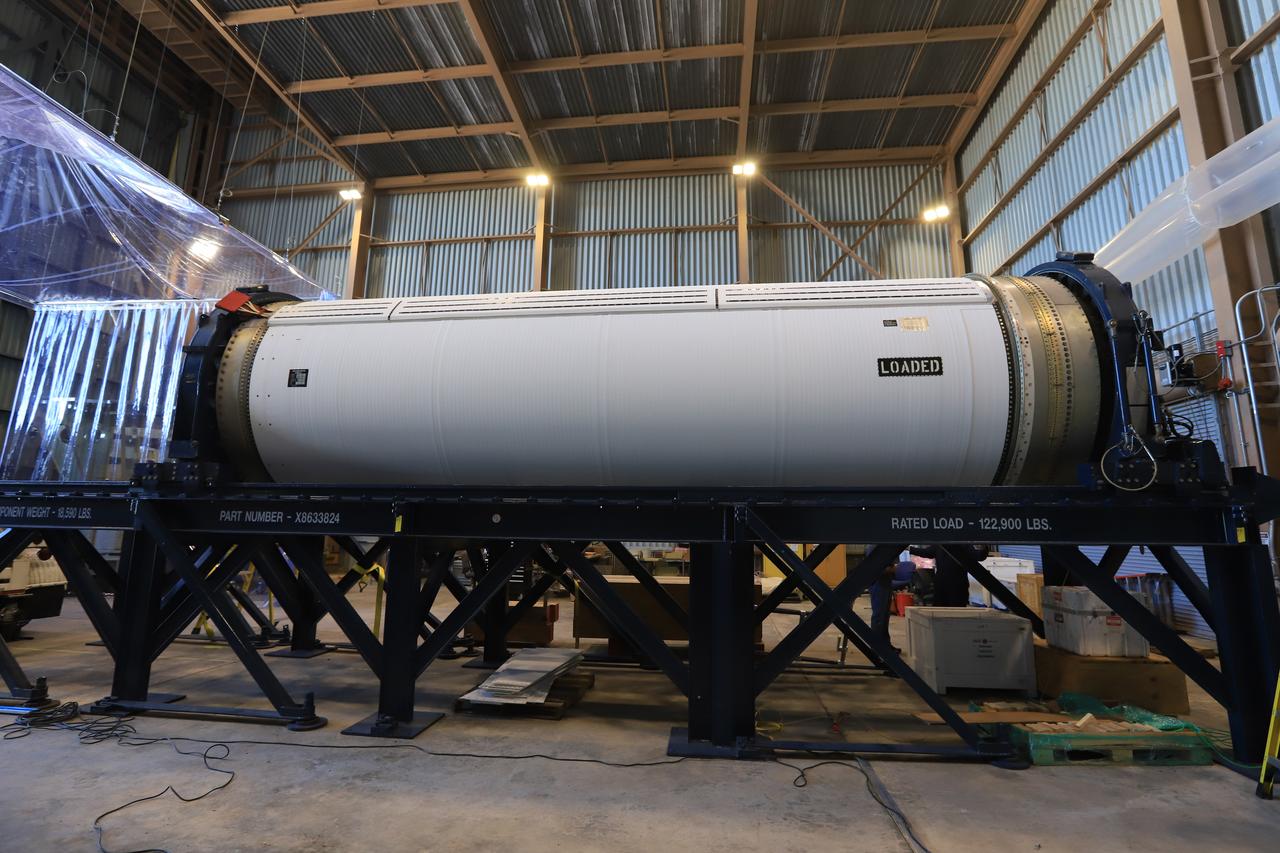

The Northrup Grumman SR118 for Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) which is loaded with propellants moves from the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) to the Rotation Protection and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center for continued flight processing on Jan. 29, 2019.

iss069e004683 (April 20, 2023) --- The Northrup Grumman Cygnus space freighter is pictured in the grip of the Canadarm2 robotic arm while attached to the Unity module's Earth-facing port. The International Space Station was soaring into an orbital sunset 266 miles above the Indian Ocean in between South Africa and Antarctica at the time of this photograph.

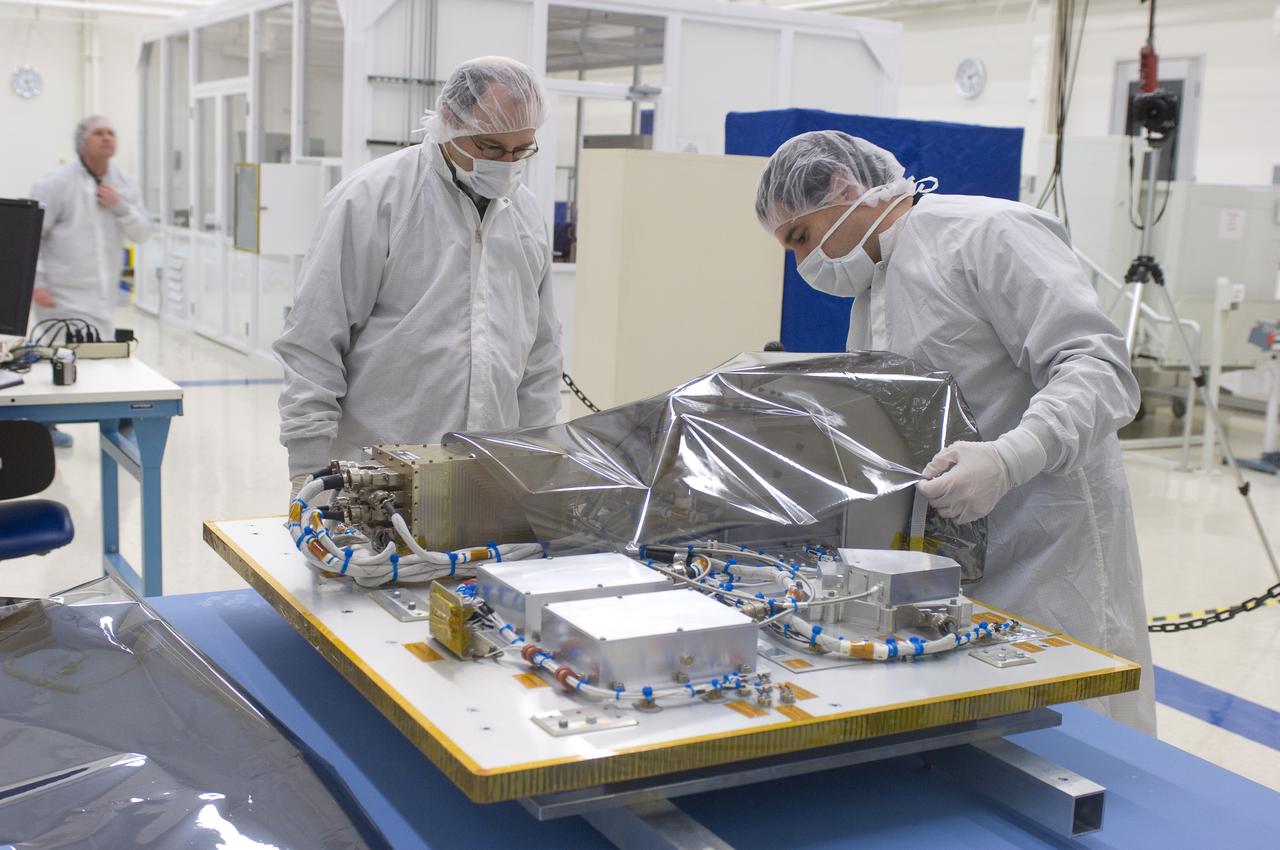
LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- securing special made crate for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft (with Tony Colaprete (l) LCROSS P.I. Steve Ord, Project Management Division (c) ) and Unknown)
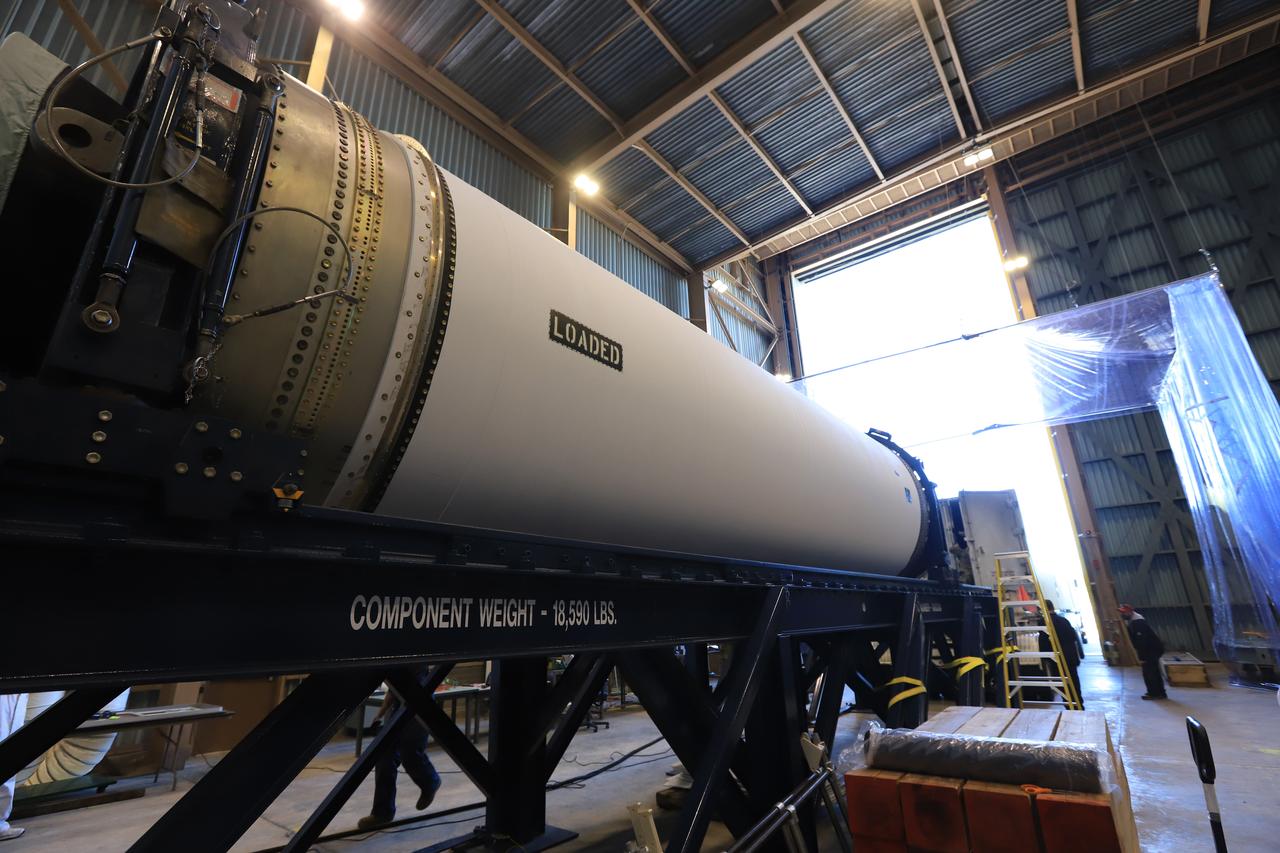

The Northrup Grumman SR118 for Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) which is loaded with propellants moves from the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) to the Rotation Protection and Surge Facility at Kennedy Space Center for continued flight processing on Jan. 29, 2019.
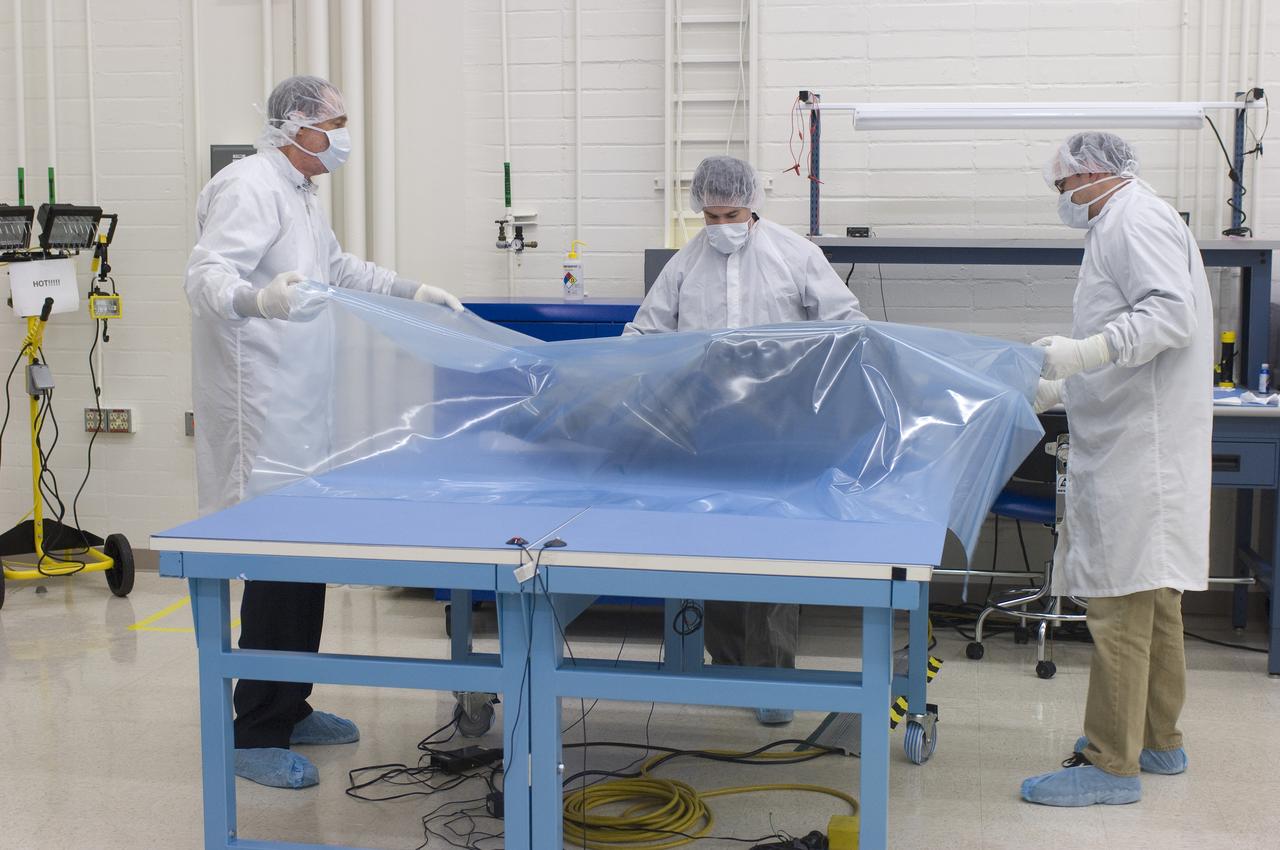

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- wrapping for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft (with Steve Ord, Project Management Division (l) and Tony Colaprete (r), LCROSS P.I.)
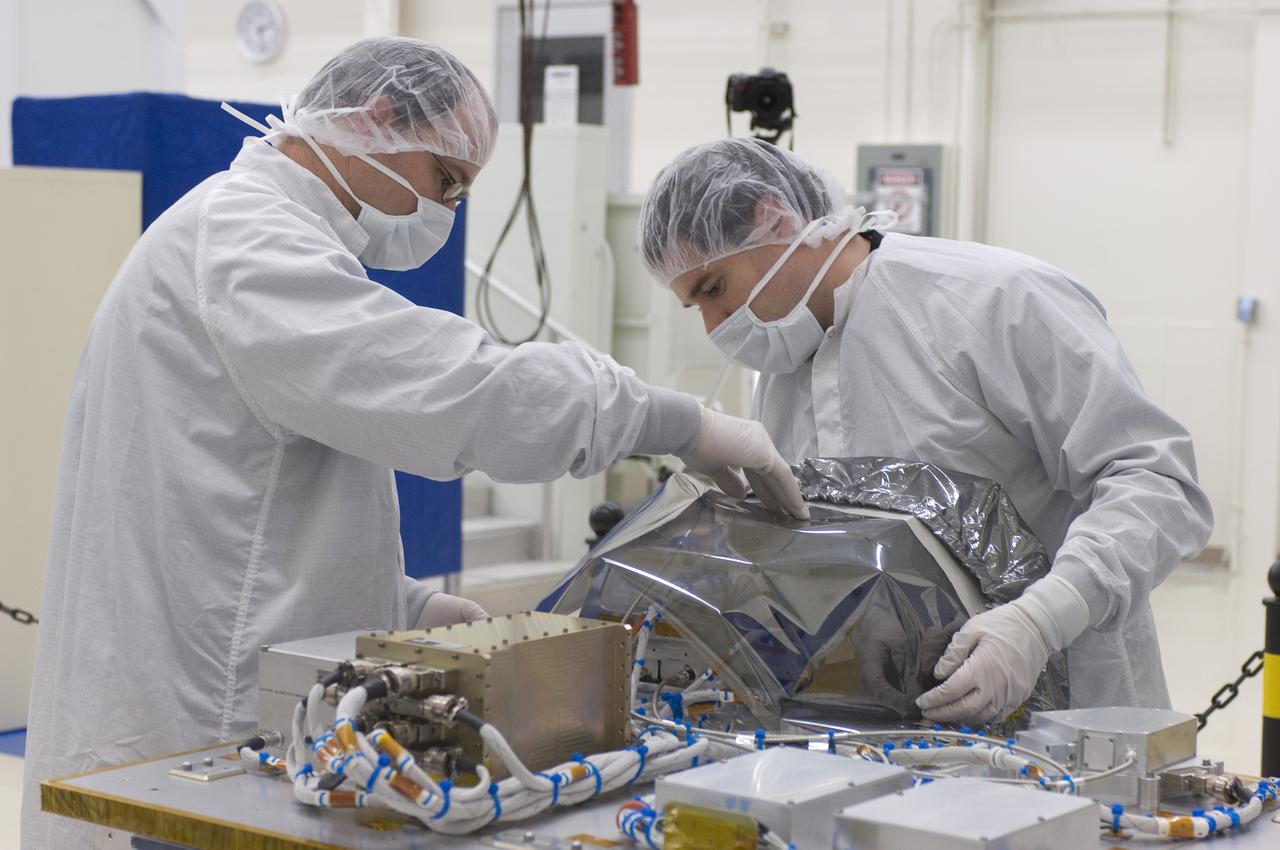

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- cleaning and wrapping for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft (with Steve Ord, Project Management Division (l) and Tony Colaprete (r) LCROSS P.I.)
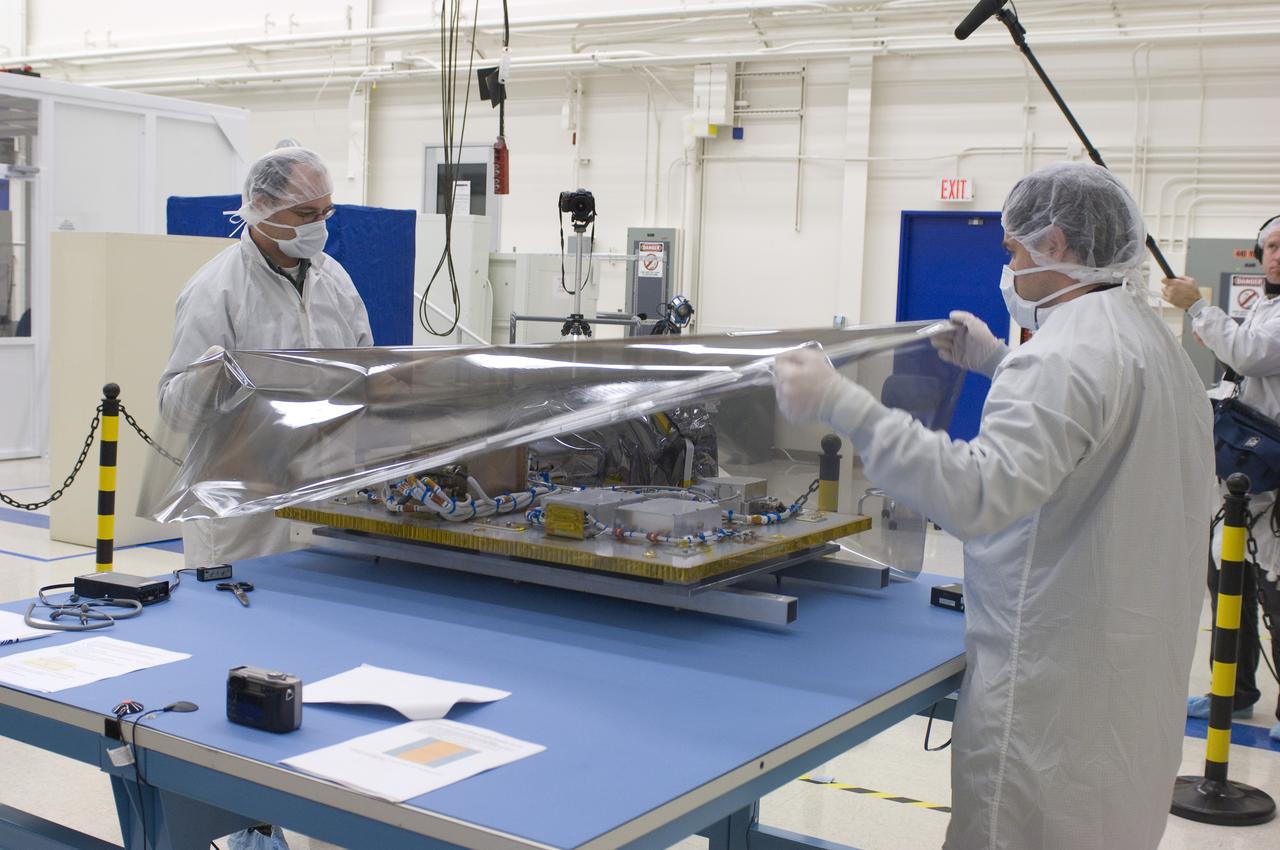

LCROSS in Ames clean room N-240- cleaning and wrapping for transfer to Northrup Grumman Redondo Beach, CA where more calibration will be done before finally being sent for mating with the LRO spacecraft (with Steve Ord, Project Management Division (l) and Tony Colaprete (r) LCROSS P.I.)
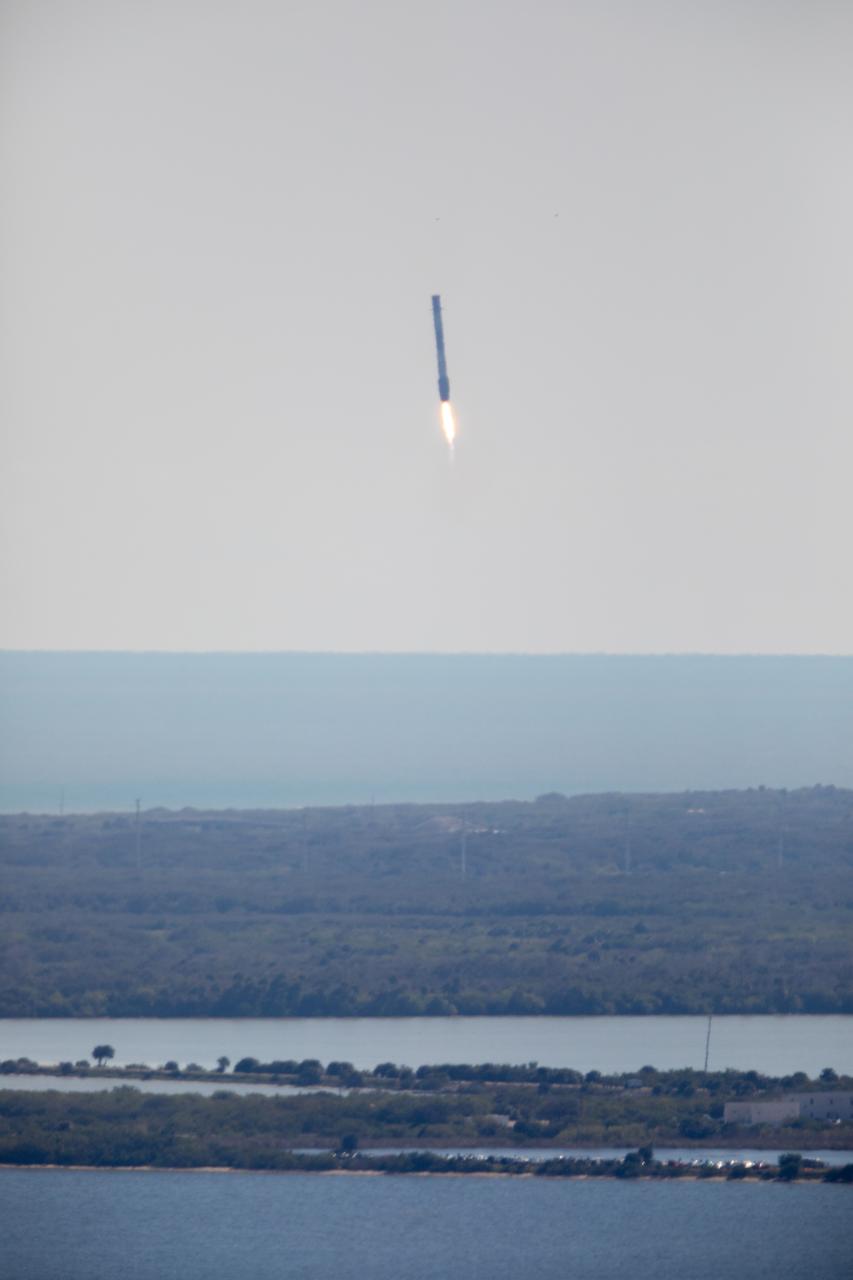

Following liftoff of Northrup Grumman's 20th commercial resupply services mission for NASA, the first stage of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket returns to Landing Zone 1. Launch of Northrop Grumman's Cygnus resupply spacecraft atop Falcon 9 occurred at 12:07 p.m. EST on Tuesday, Jan. 30 from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
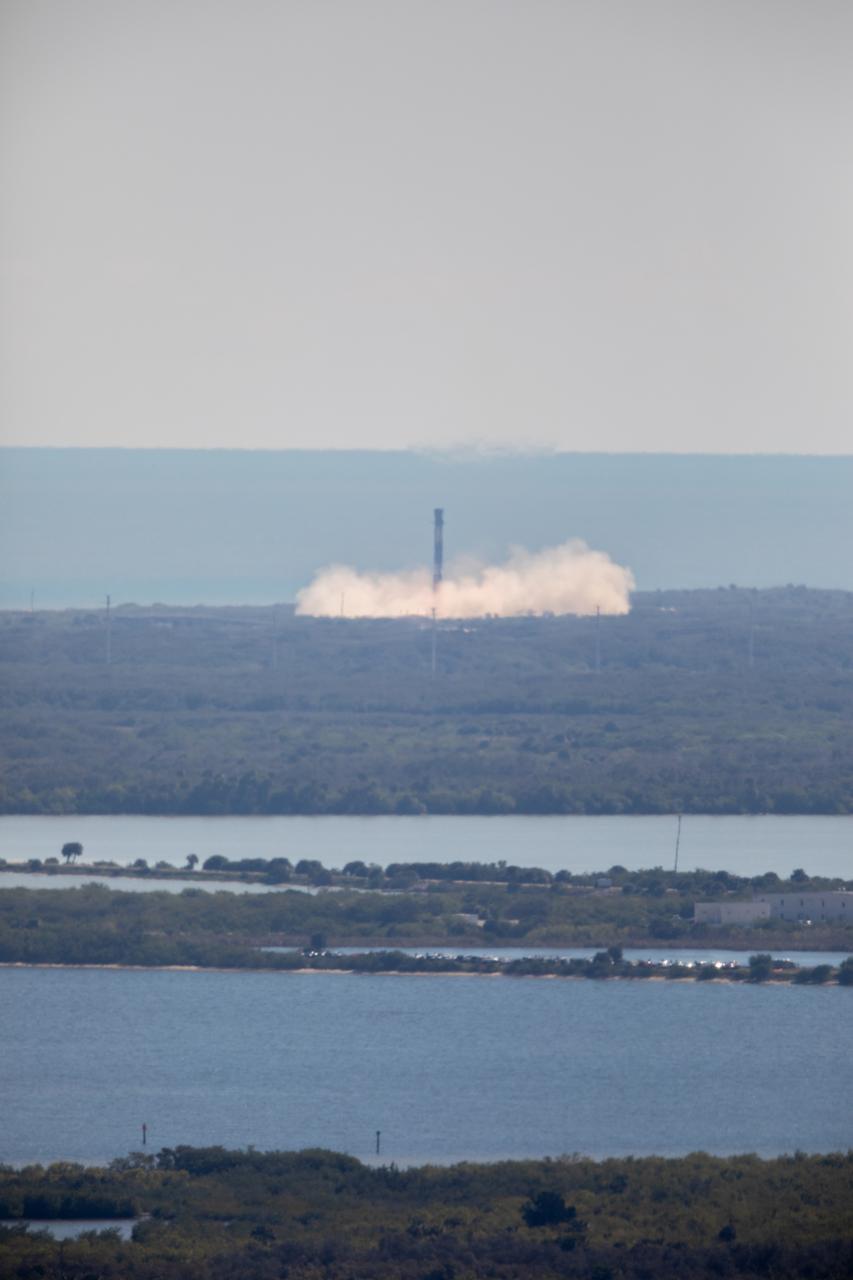

Following liftoff of Northrup Grumman's 20th commercial resupply services mission for NASA, the first stage of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket returns to Landing Zone 1. Launch of Northrop Grumman's Cygnus resupply spacecraft atop Falcon 9 occurred at 12:07 p.m. EST on Tuesday, Jan. 30 from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
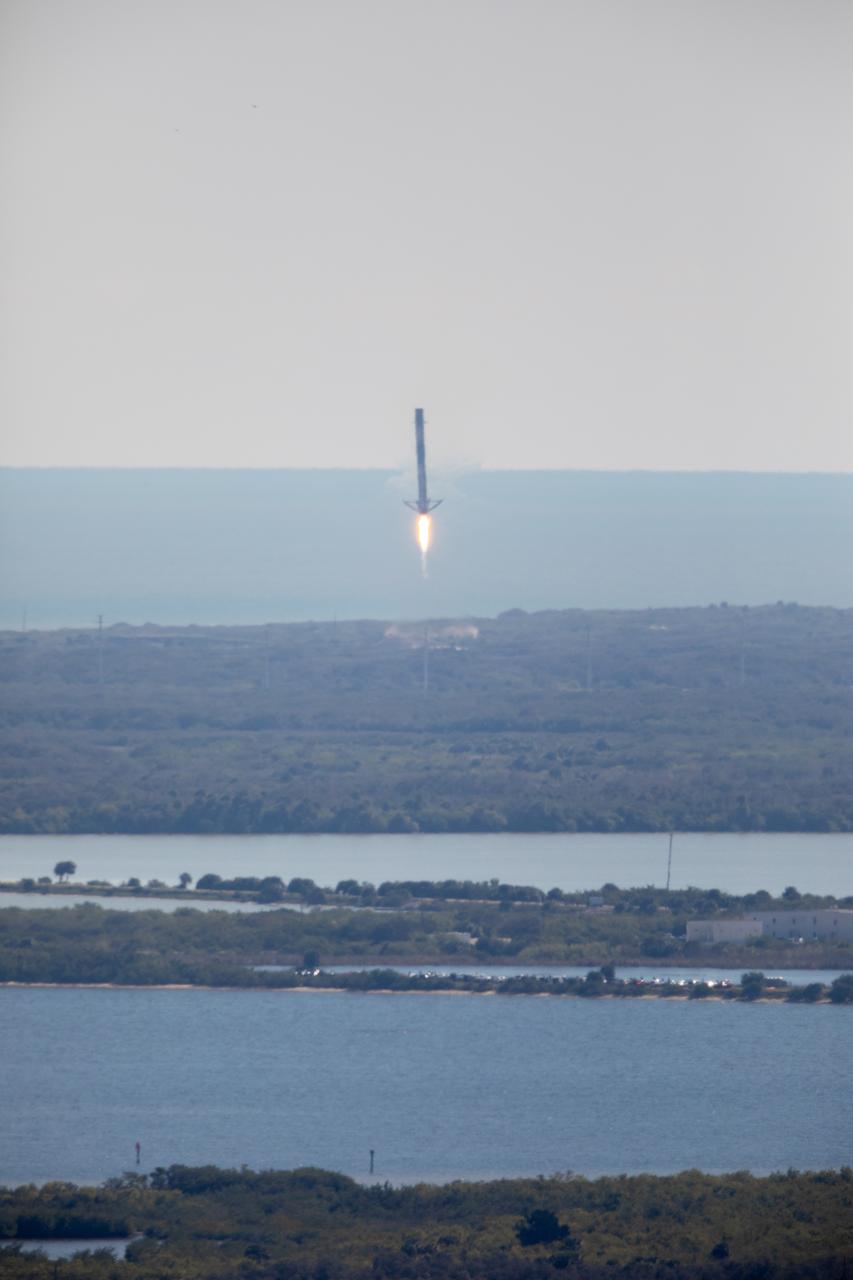

Following liftoff of Northrup Grumman's 20th commercial resupply services mission for NASA, the first stage of a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket returns to Landing Zone 1. Launch of Northrop Grumman's Cygnus resupply spacecraft atop Falcon 9 occurred at 12:07 p.m. EST on Tuesday, Jan. 30 from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida.
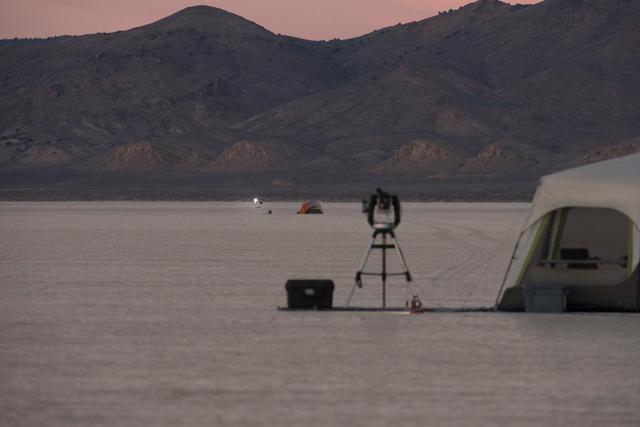

A test of a small-scale starshade model in a dry lake bed in central Nevada's Smith Creek by Northrup Grumman in May-June 2014. A telescope points toward a bright light, which mimics the conditions of starlight in space. Other lights, which are up to 10 million times fainter than the light source standing in for the star, represent the reflected light of planets. Telescopes searching for the relatively dim light of an exoplanet next to its much bright star are faced with a challenge as difficult as searching from Los Angeles for a firefly in New York– if the firefly is also beside a lighthouse. These tests determined that a starshade, or external occulter, is indeed capable of blocking starlight to a degree that reveals the light of a planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20908
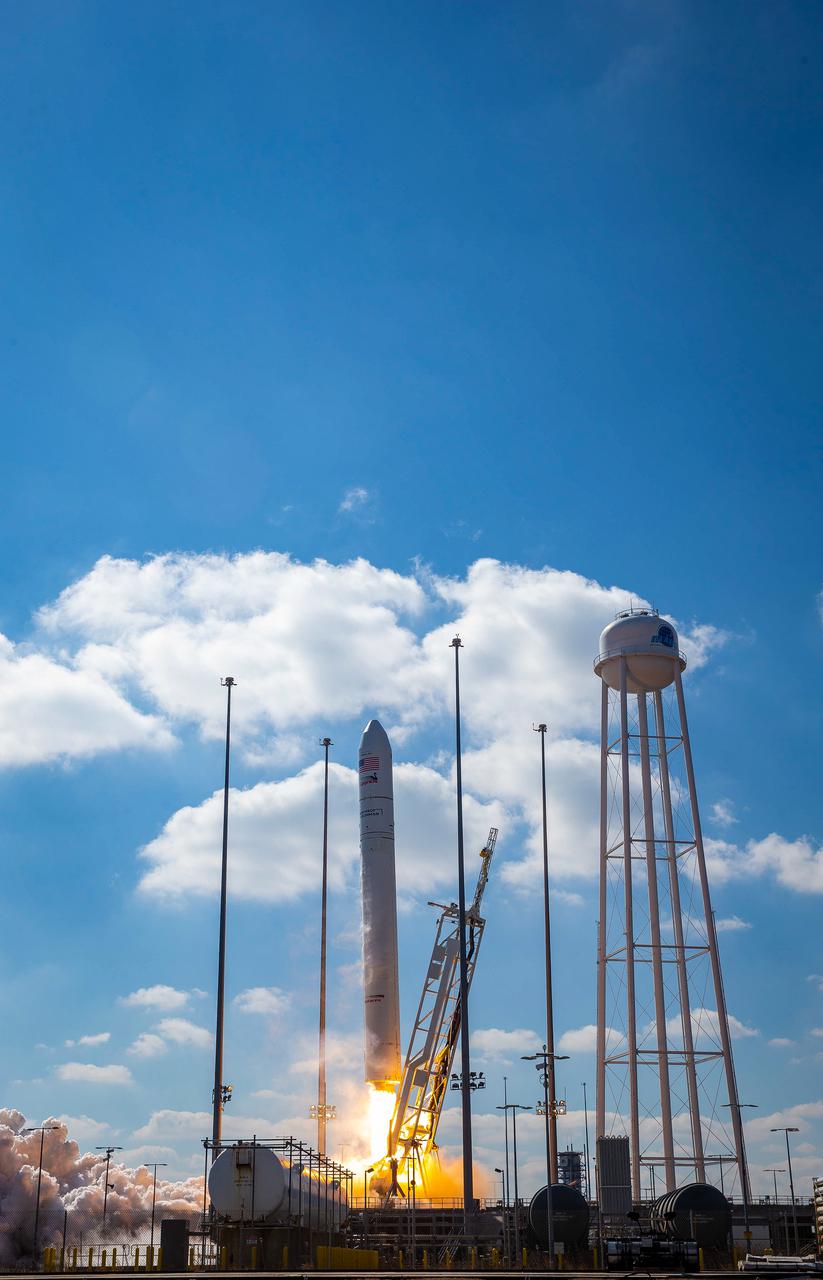

The Northrop Grumman Antares rocket, with Cygnus resupply spacecraft aboard, launches from Pad-0A, Saturday, Feb. 20, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman's 15th contracted cargo resupply mission for NASA to the International Space Station will deliver about 8,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies, and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew. Photo Credit: NASA's Wallops Flight Facility/Patrick Black
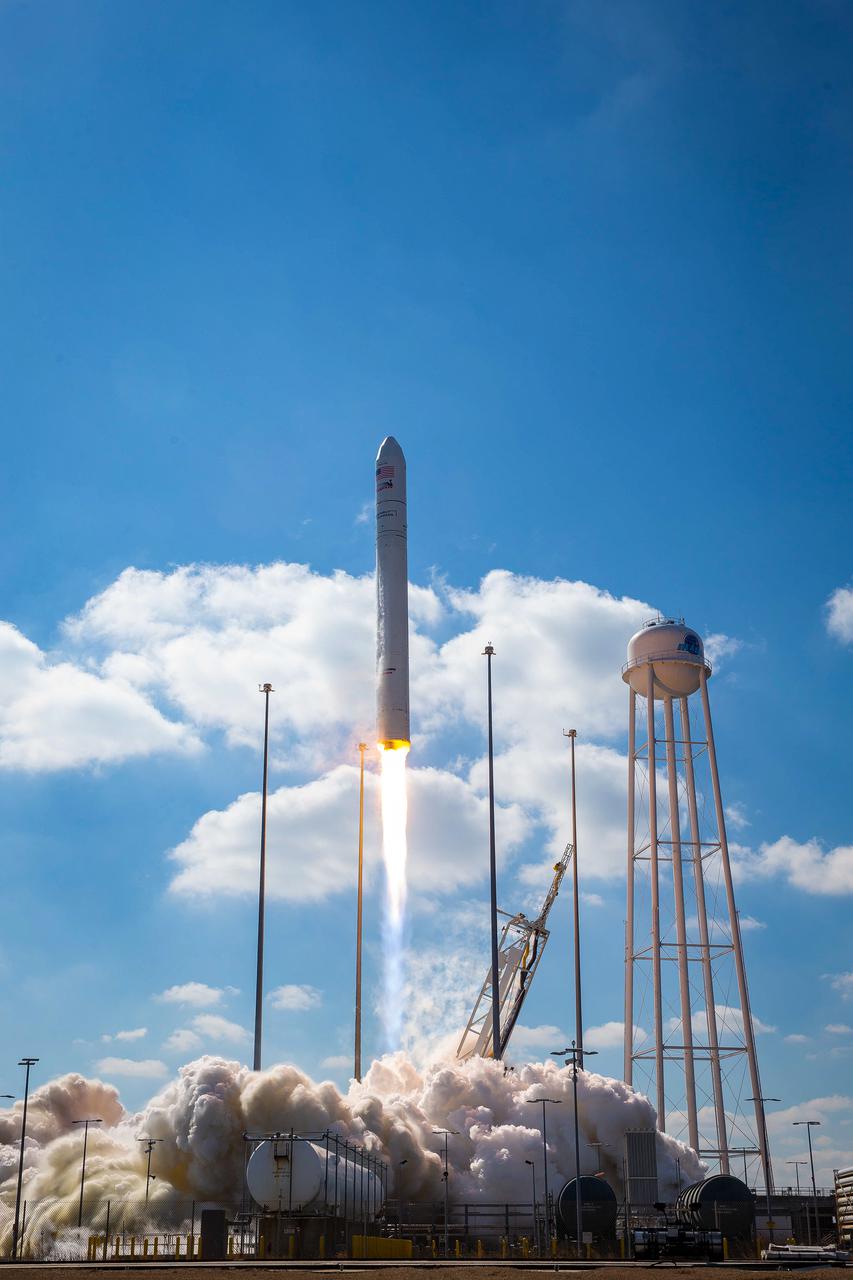

The Northrop Grumman Antares rocket, with Cygnus resupply spacecraft aboard, launches from Pad-0A, Saturday, Feb. 20, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman's 15th contracted cargo resupply mission for NASA to the International Space Station will deliver about 8,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies, and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew. Photo Credit: NASA's Wallops Flight Facility/Patrick Black

The Northrop Grumman Antares rocket, with Cygnus resupply spacecraft aboard, launches from Pad-0A, Saturday, Feb. 20, 2021, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. Northrop Grumman's 15th contracted cargo resupply mission for NASA to the International Space Station will deliver about 8,000 pounds of science and research, crew supplies, and vehicle hardware to the orbital laboratory and its crew. Photo Credit: NASA's Wallops Flight Facility/Patrick Black
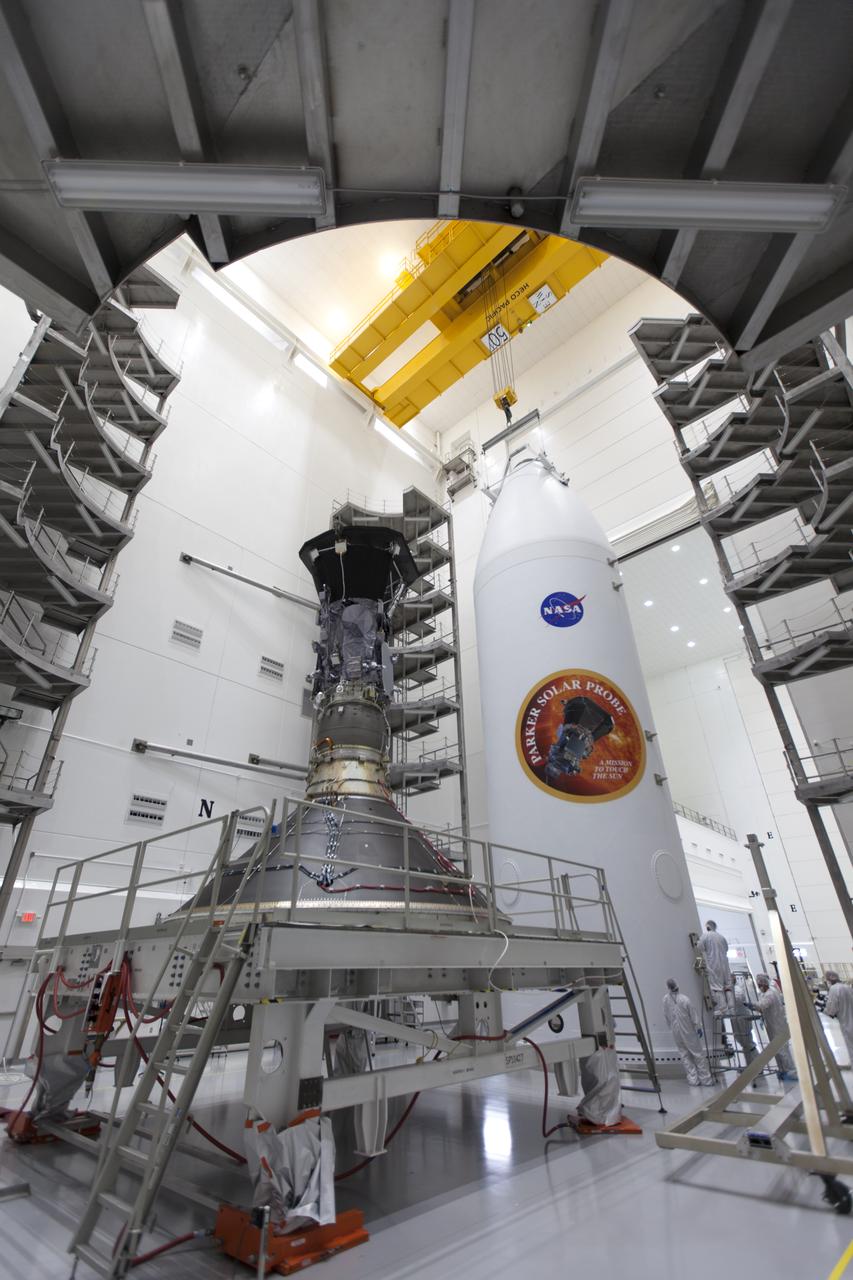

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Monday, July 16, 2018, NASA's Parker Solar Probe is prepared for encapsulation in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler, Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection
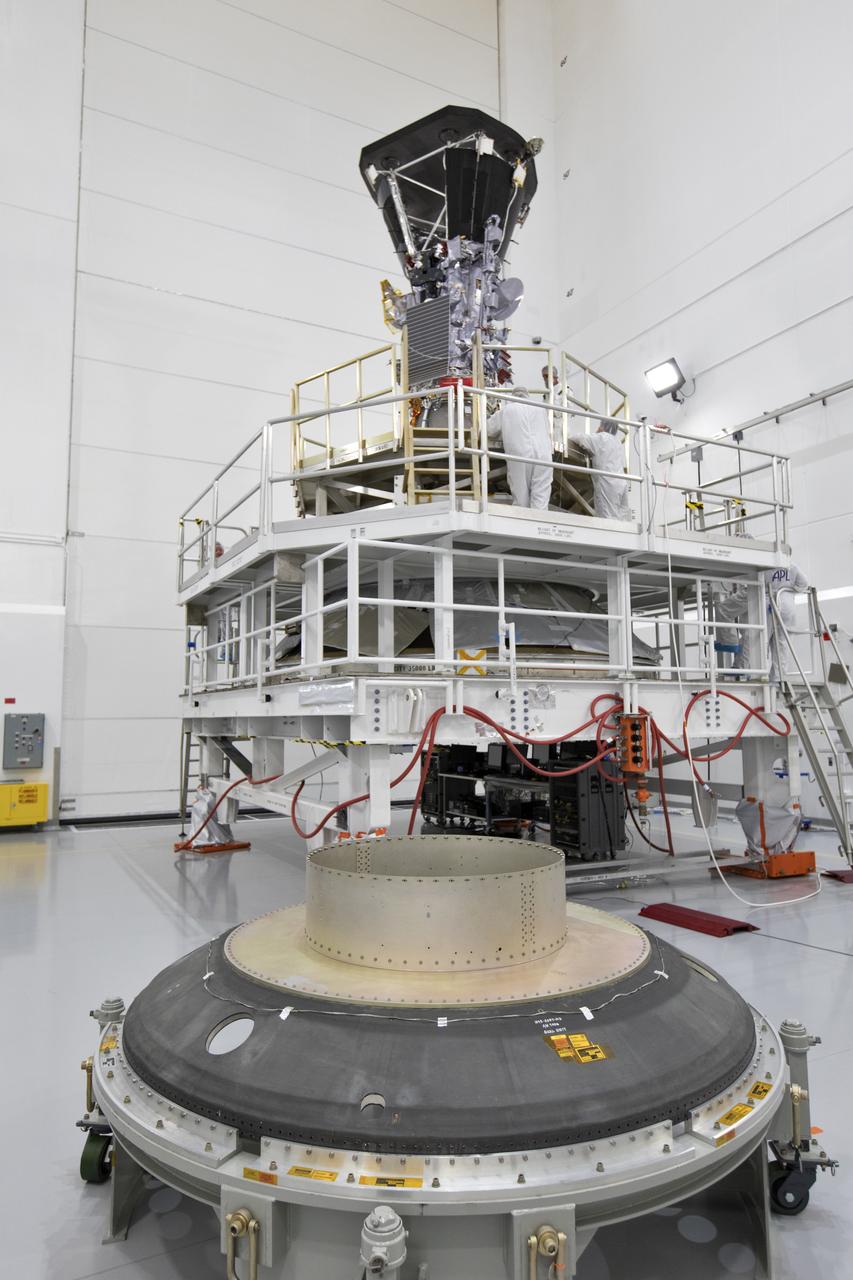

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, July 11, 2018, technicians and engineers mate NASA's Parker Solar Probe to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
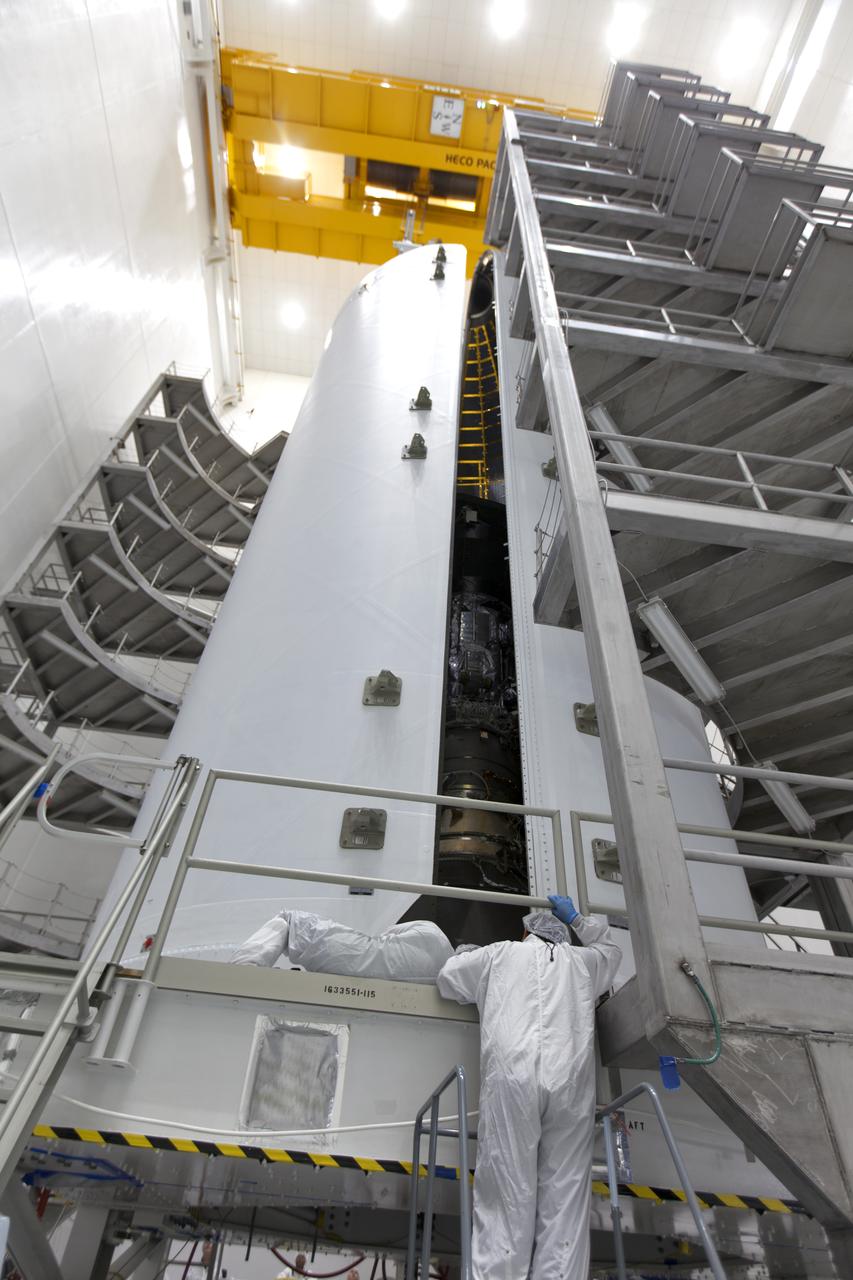

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Thursday, July 19, 2018, technicians and engineers encapsulate NASA's Parker Solar Probe in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler, Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
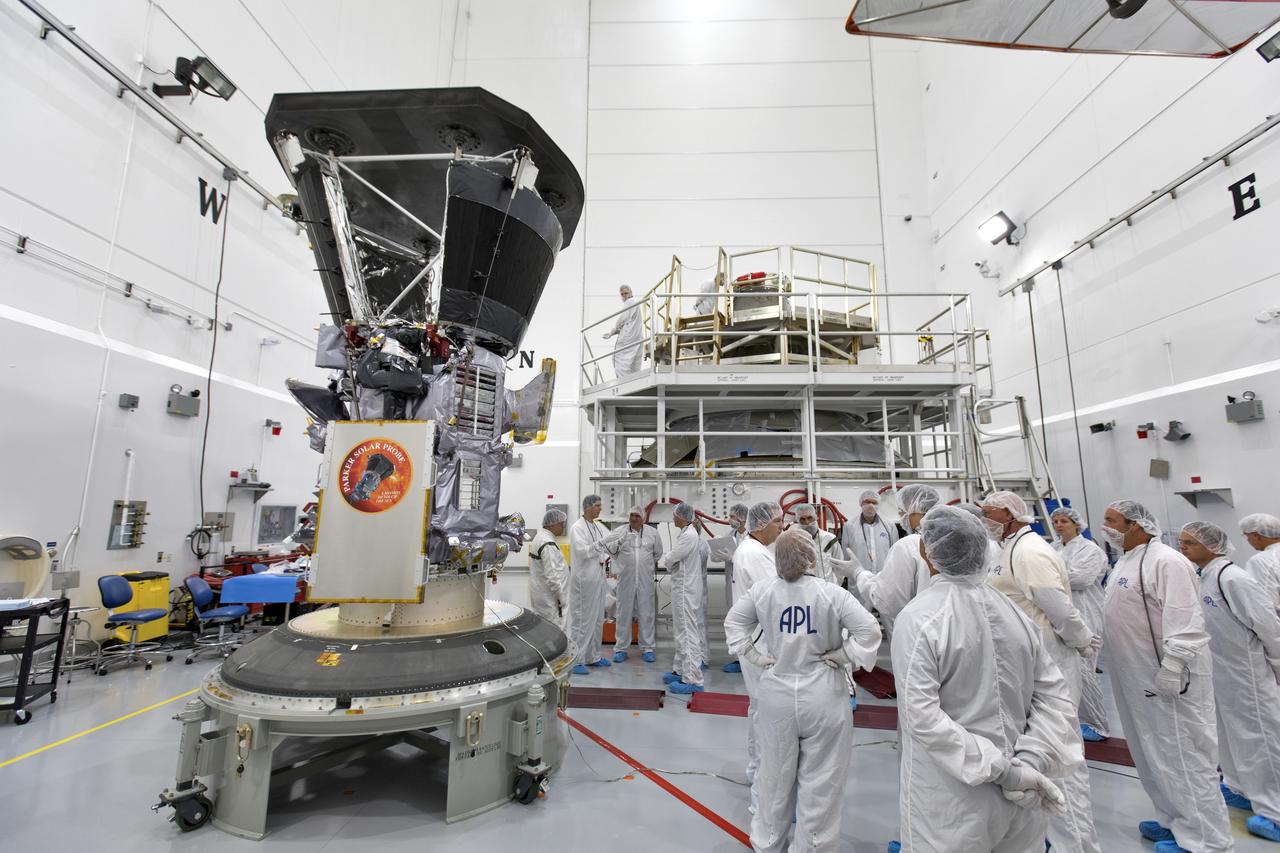

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, July 11, 2018, technicians and engineers prepare to mate NASA's Parker Solar Probe to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
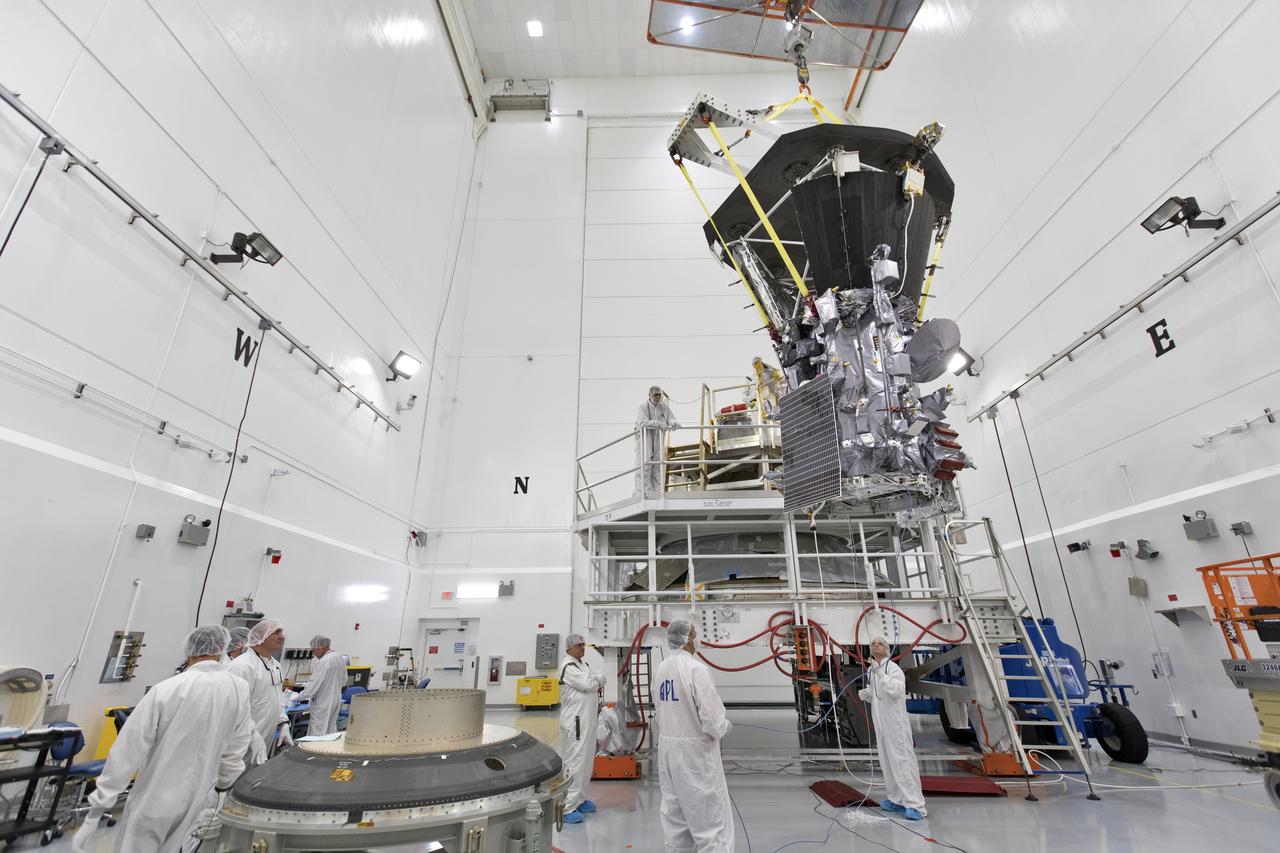

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, July 11, 2018, technicians and engineers use a crane to move NASA's Parker Solar Probe into position for mating to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
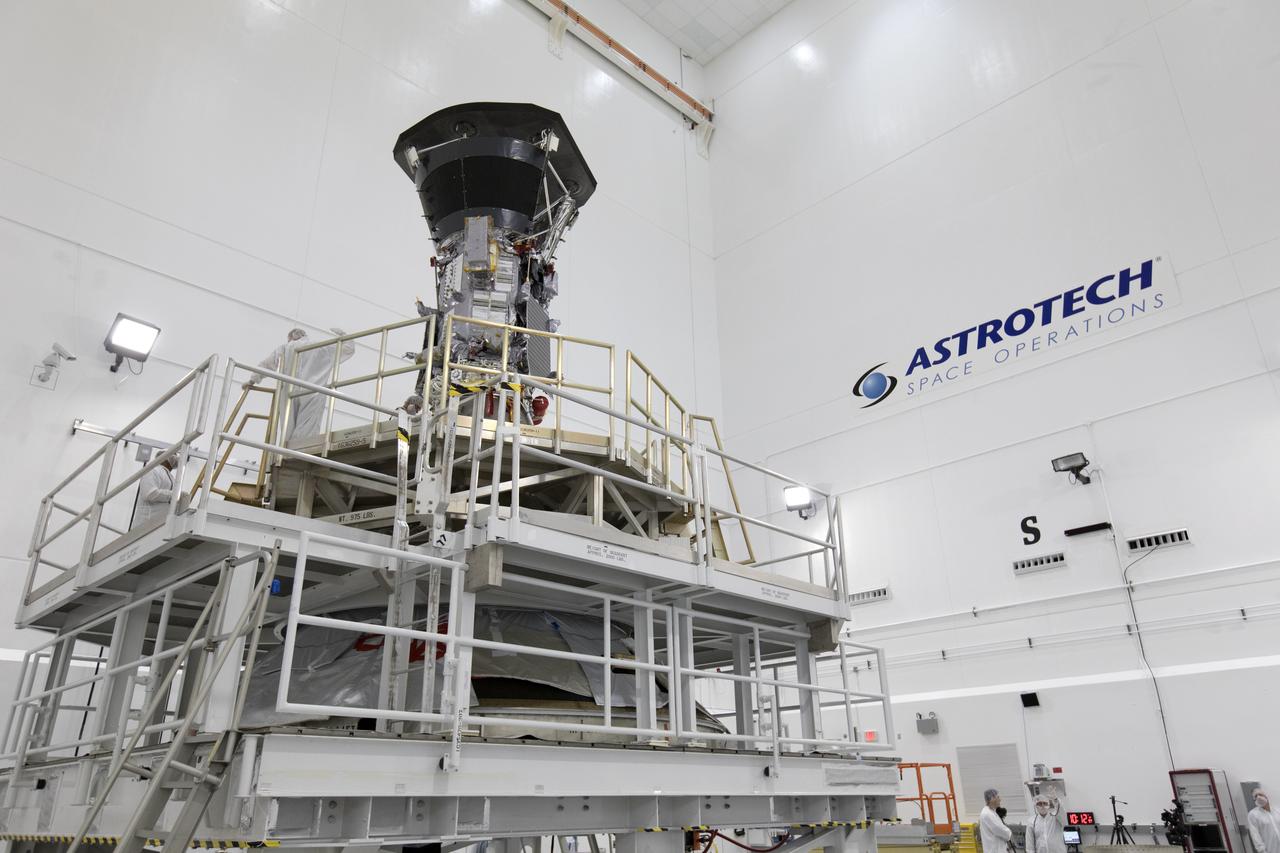

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, July 11, 2018, technicians and engineers mate NASA's Parker Solar Probe to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Thursday, July 19, 2018, technicians and engineers encapsulate NASA's Parker Solar Probe in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler, Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
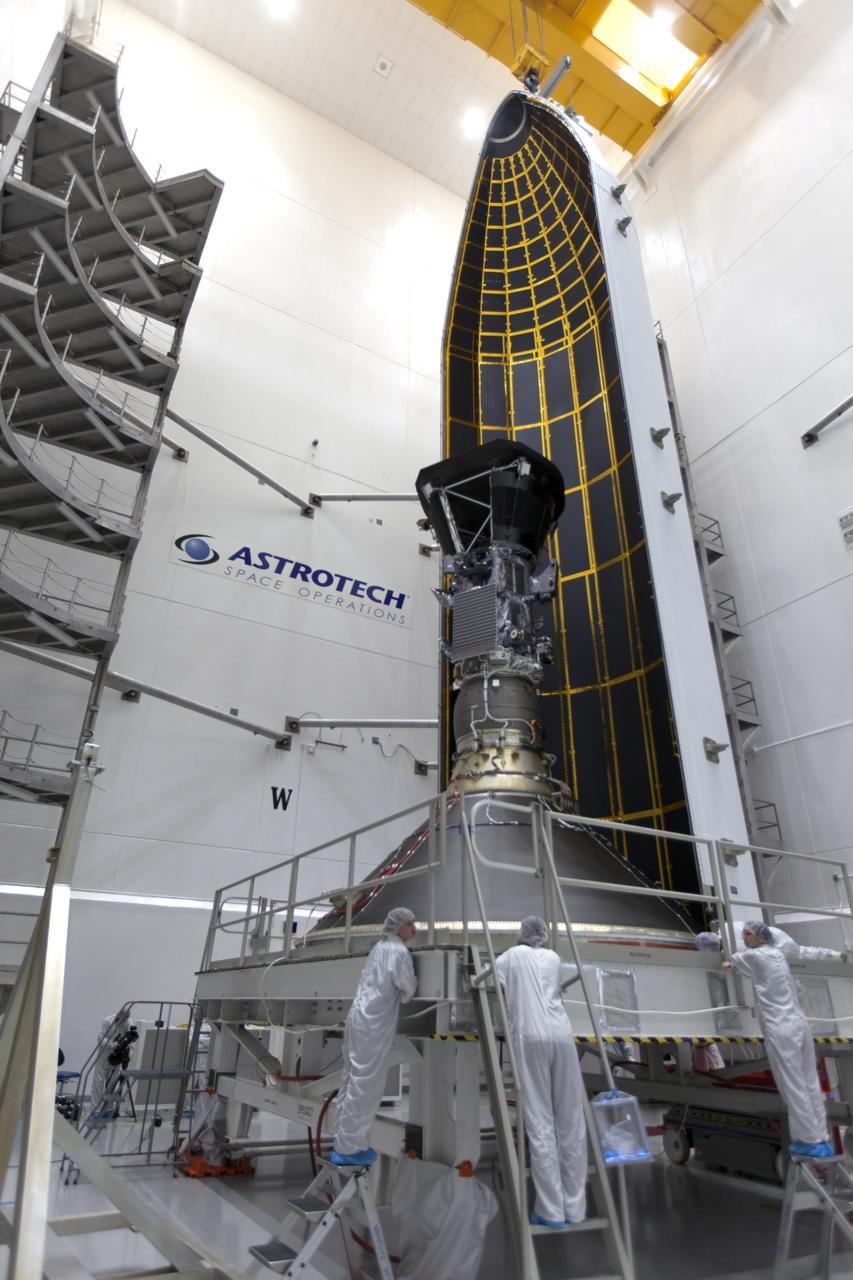

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Monday, July 16, 2018, technicians and engineers encapsulate NASA's Parker Solar Probe in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler, Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
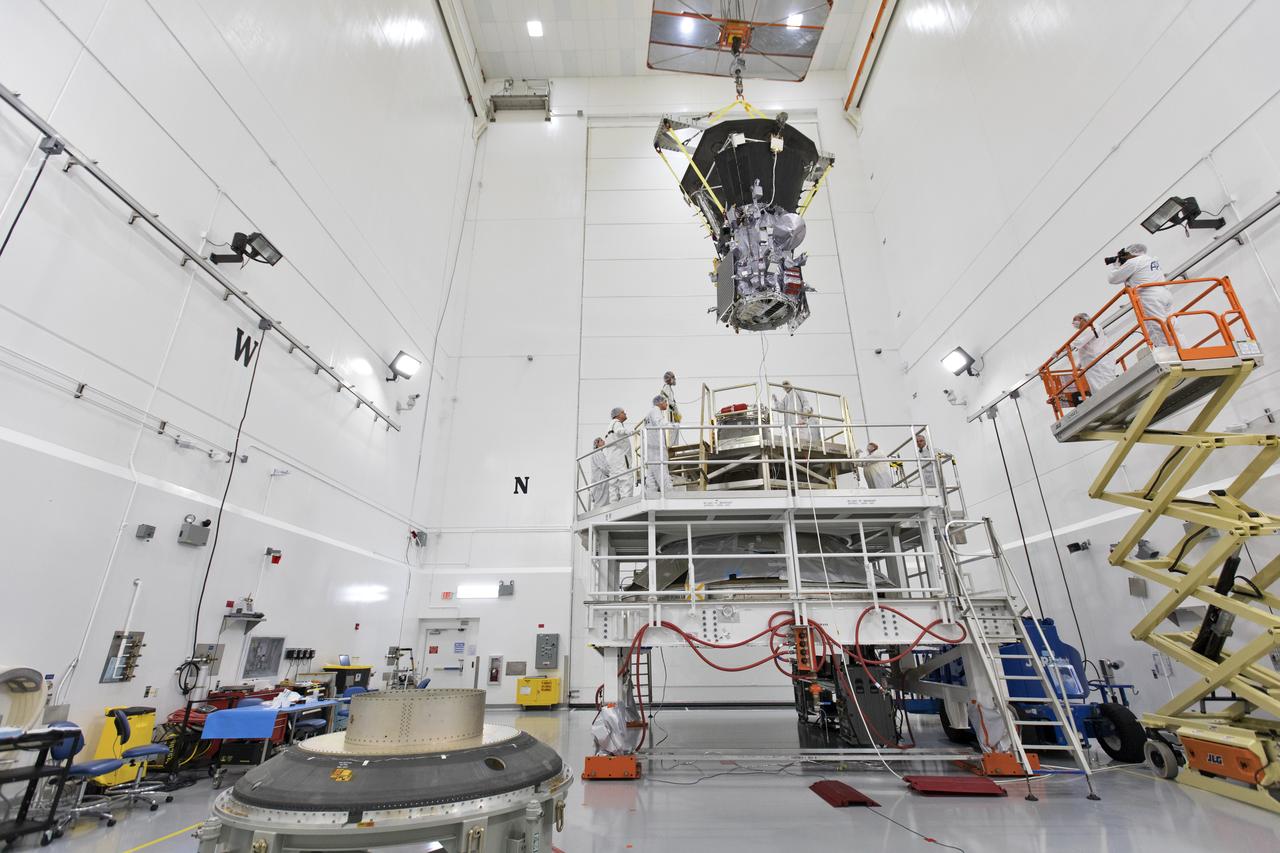

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, July 11, 2018, technicians and engineers use a crane to move NASA's Parker Solar Probe into position for mating to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
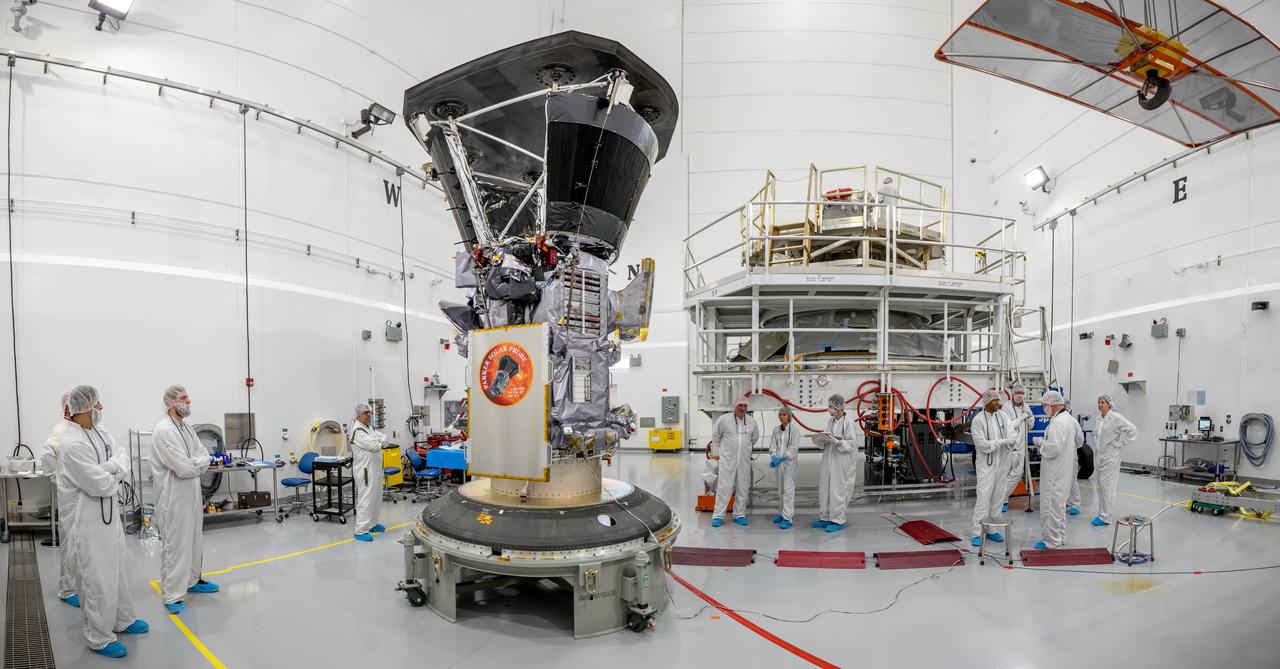

In a wide-angle view at the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, July 11, 2018, technicians and engineers prepare to mate NASA's Parker Solar Probe to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, July 11, 2018, technicians and engineers prepare to mate NASA's Parker Solar Probe to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
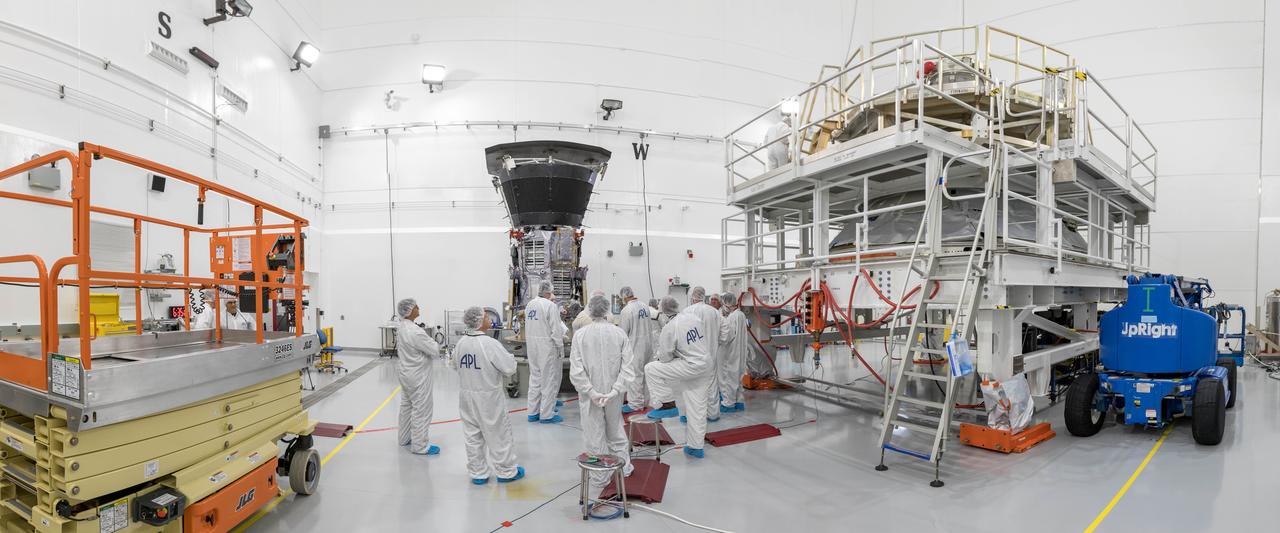

In a wide-angle view at the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, July 11, 2018, technicians and engineers prepare to mate NASA's Parker Solar Probe to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
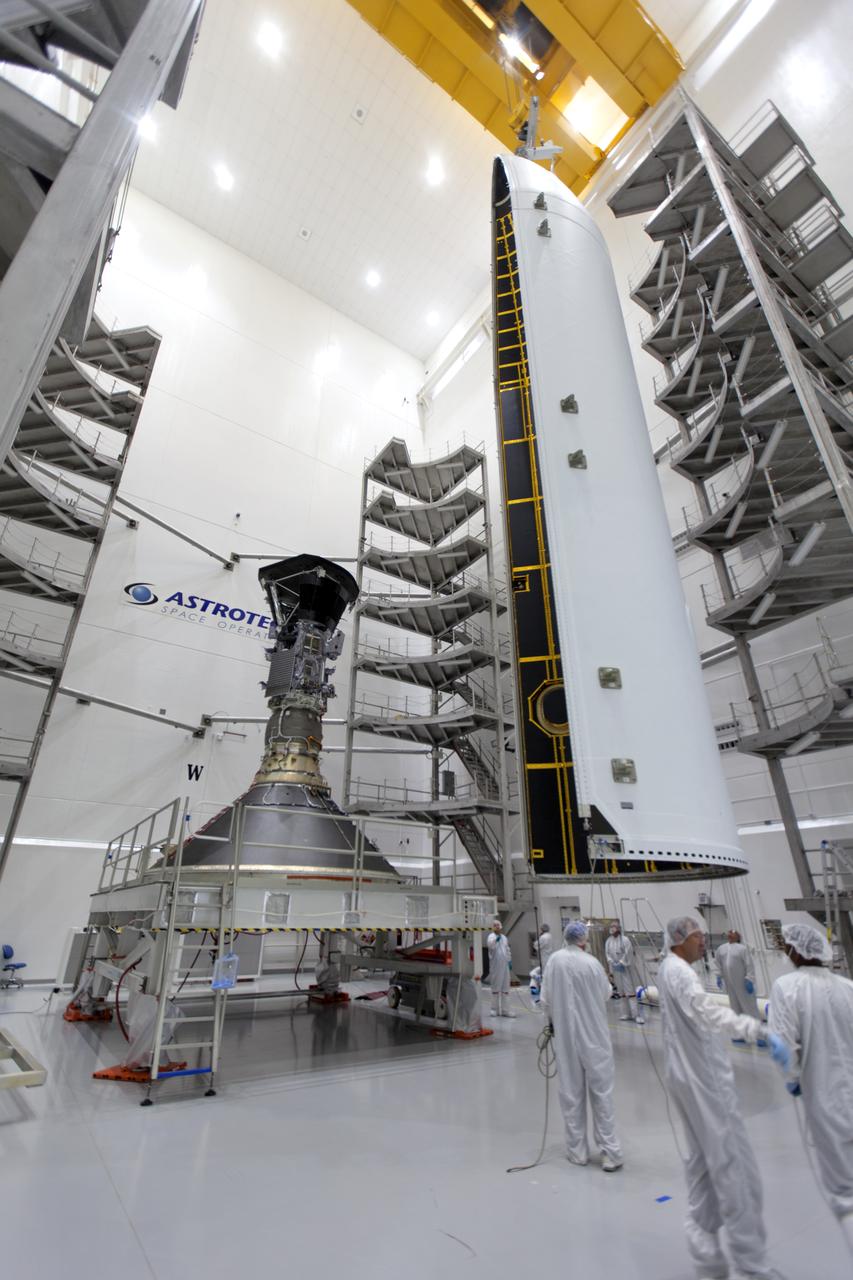

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Monday, July 16, 2018, technicians and engineers prepare NASA's Parker Solar Probe for encapsulation in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler, Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
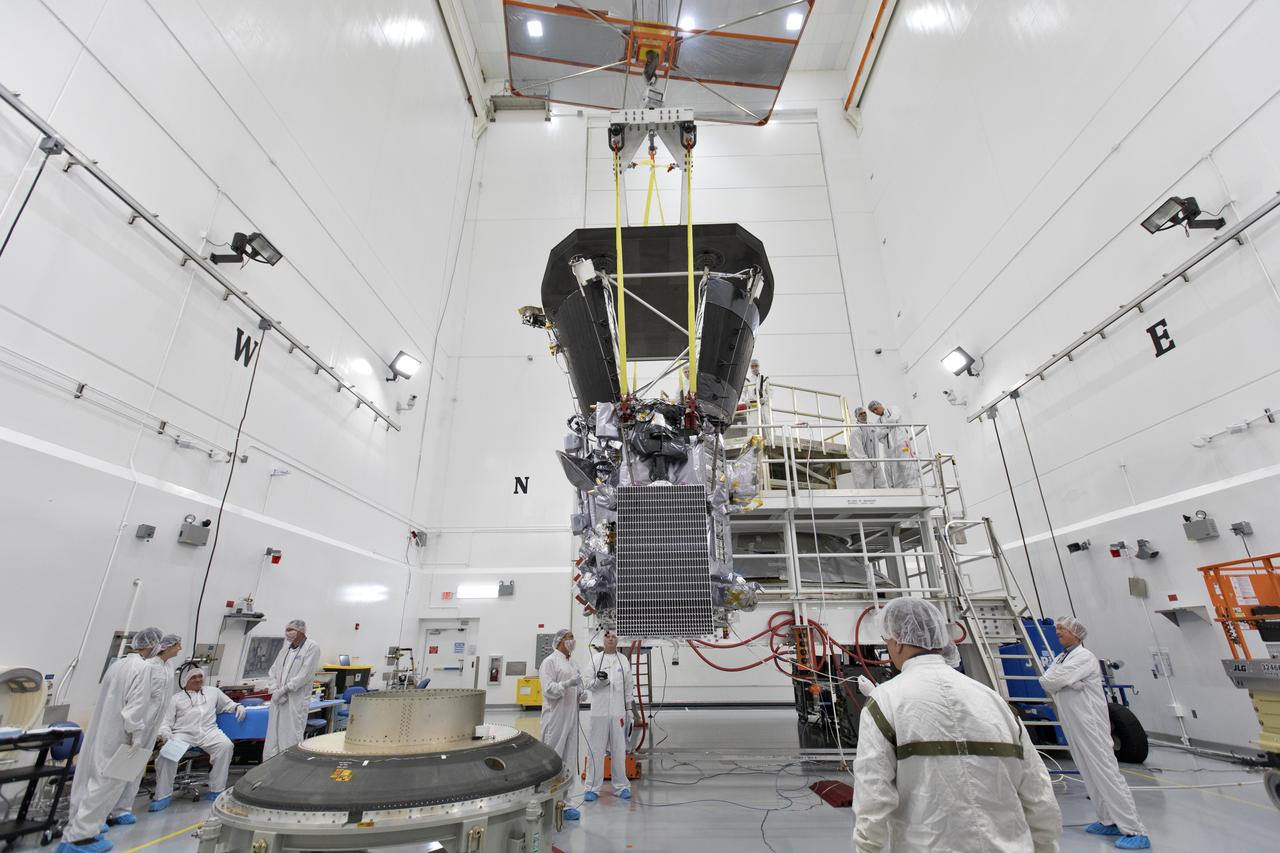

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, July 11, 2018, technicians and engineers use a crane to move NASA's Parker Solar Probe into position for mating to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
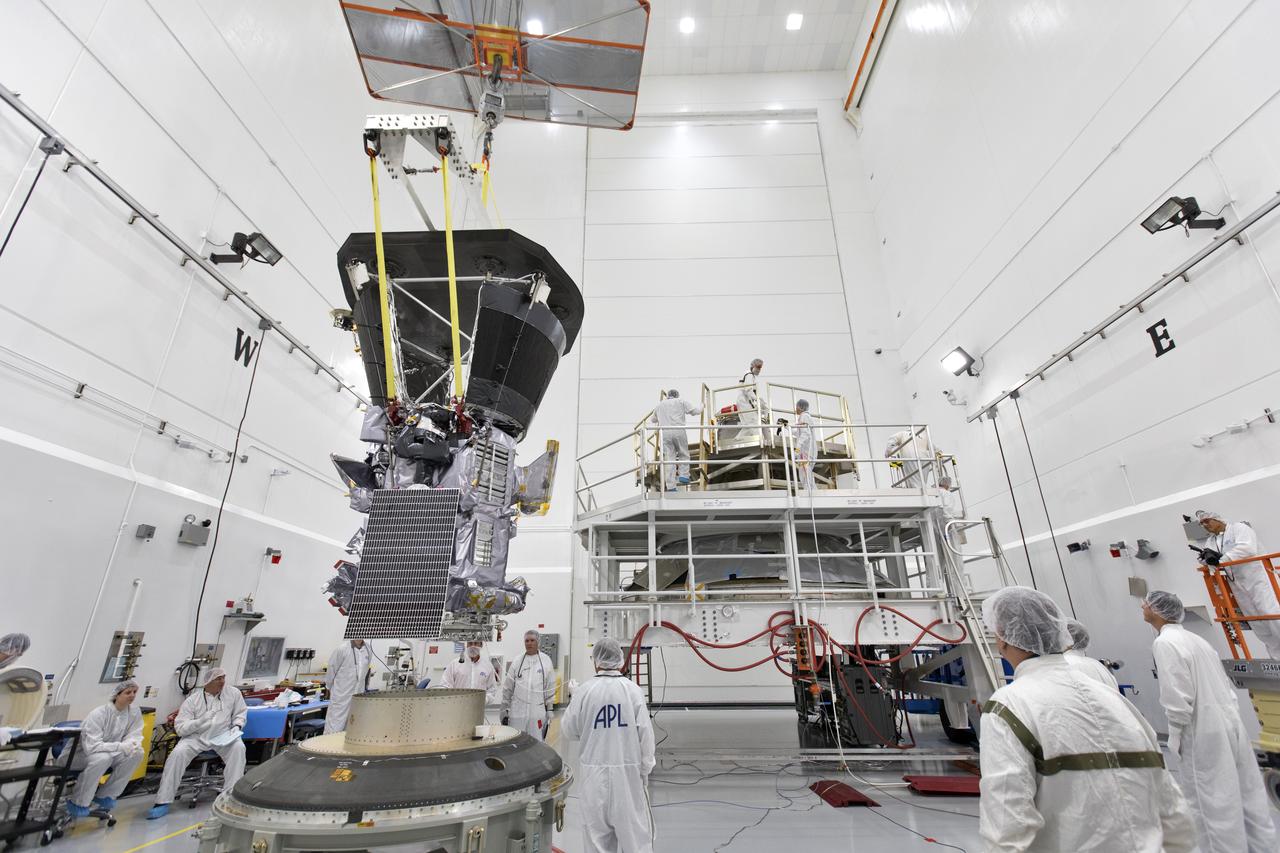

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, July 11, 2018, technicians and engineers use a crane to move NASA's Parker Solar Probe into position for mating to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
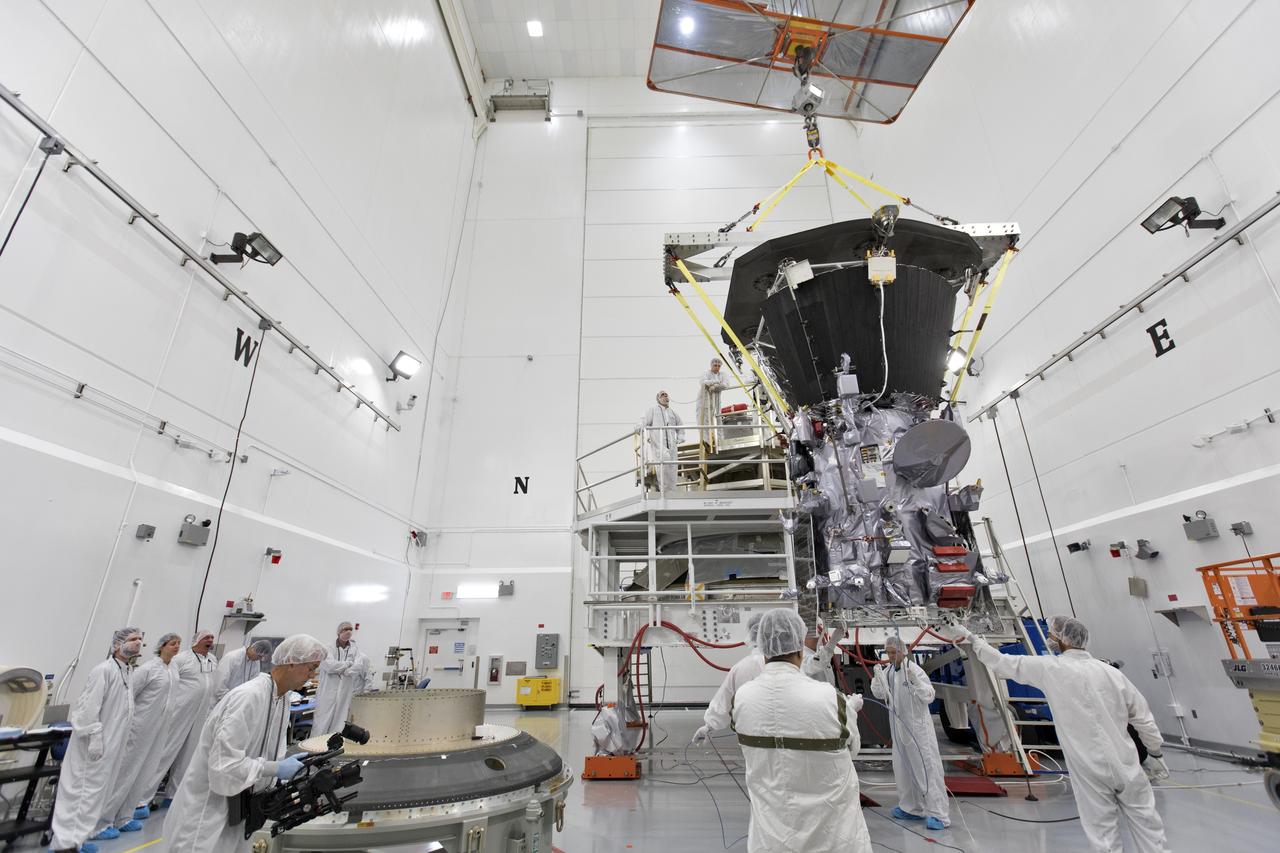

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, July 11, 2018, technicians and engineers use a crane to move NASA's Parker Solar Probe into position for mating to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
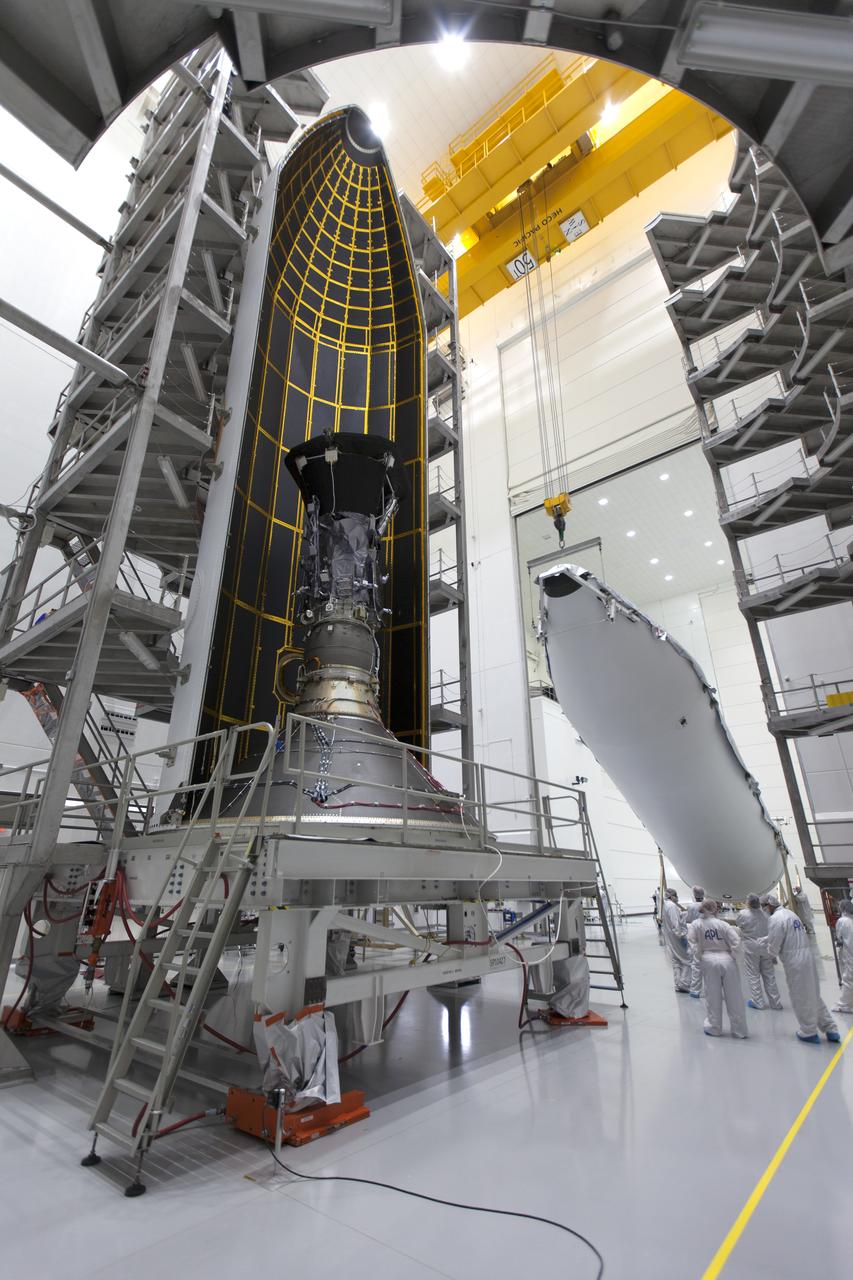

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Thursday, July 19, 2018, NASA's Parker Solar Probe is being encapsulated in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler, Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
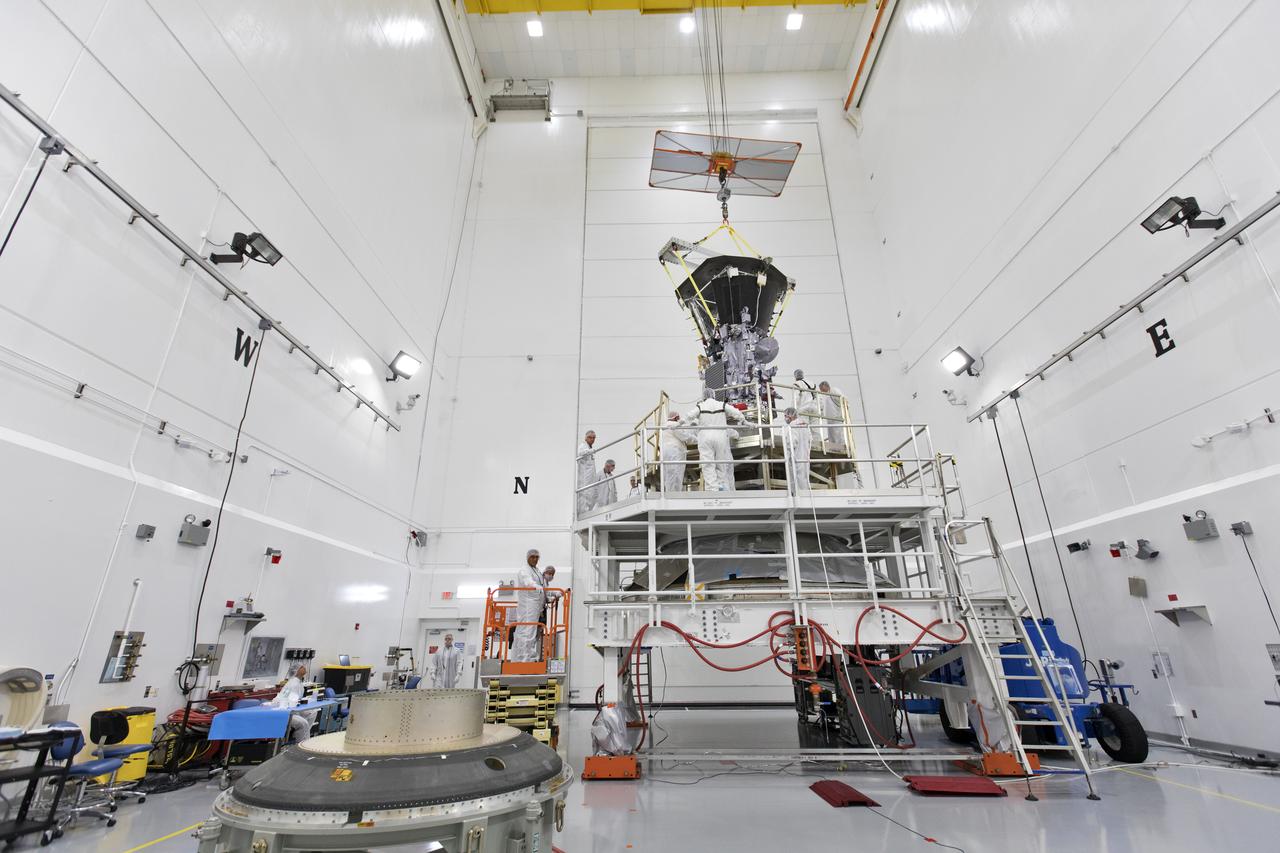

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, July 11, 2018, technicians and engineers use a crane to move NASA's Parker Solar Probe into position for mating to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
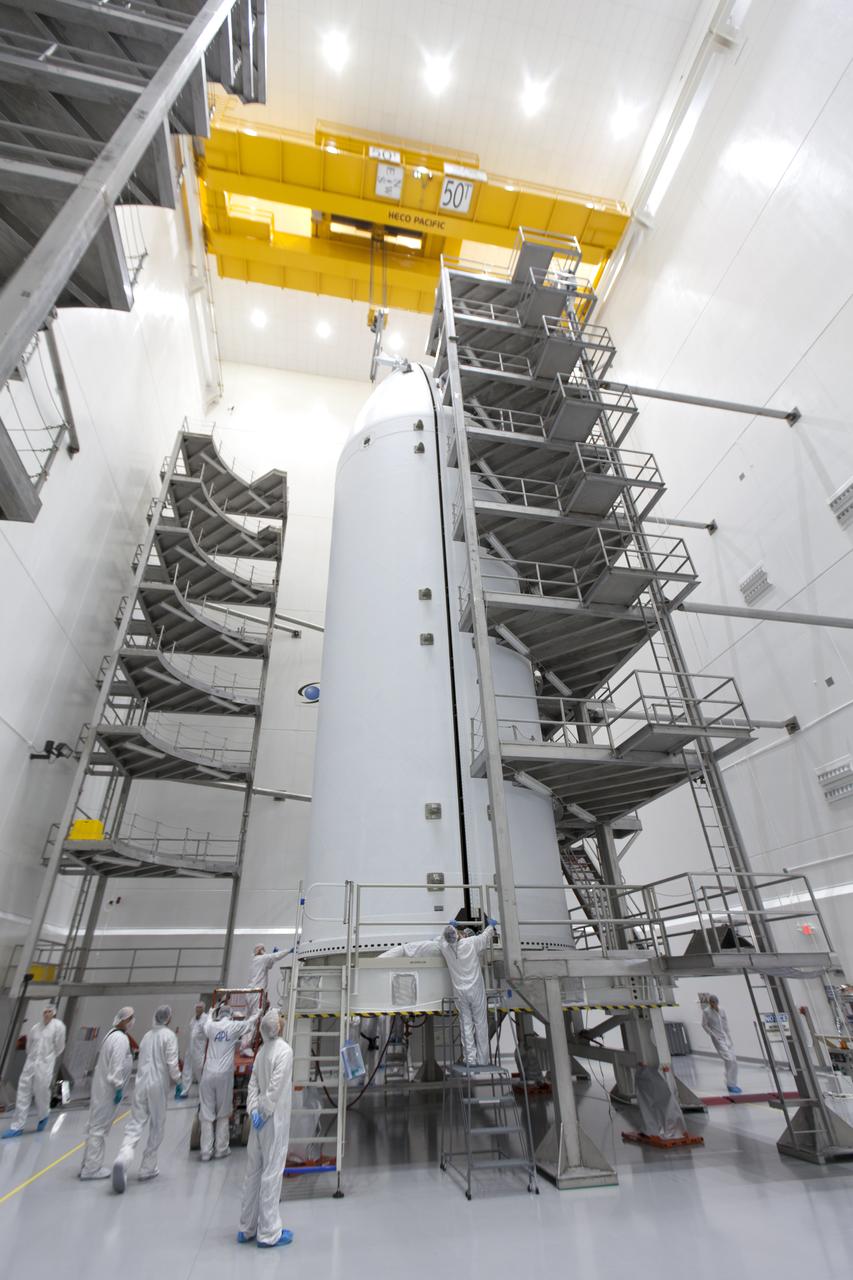

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Thursday, July 19, 2018, technicians and engineers have encapsulated NASA's Parker Solar Probe in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler, Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
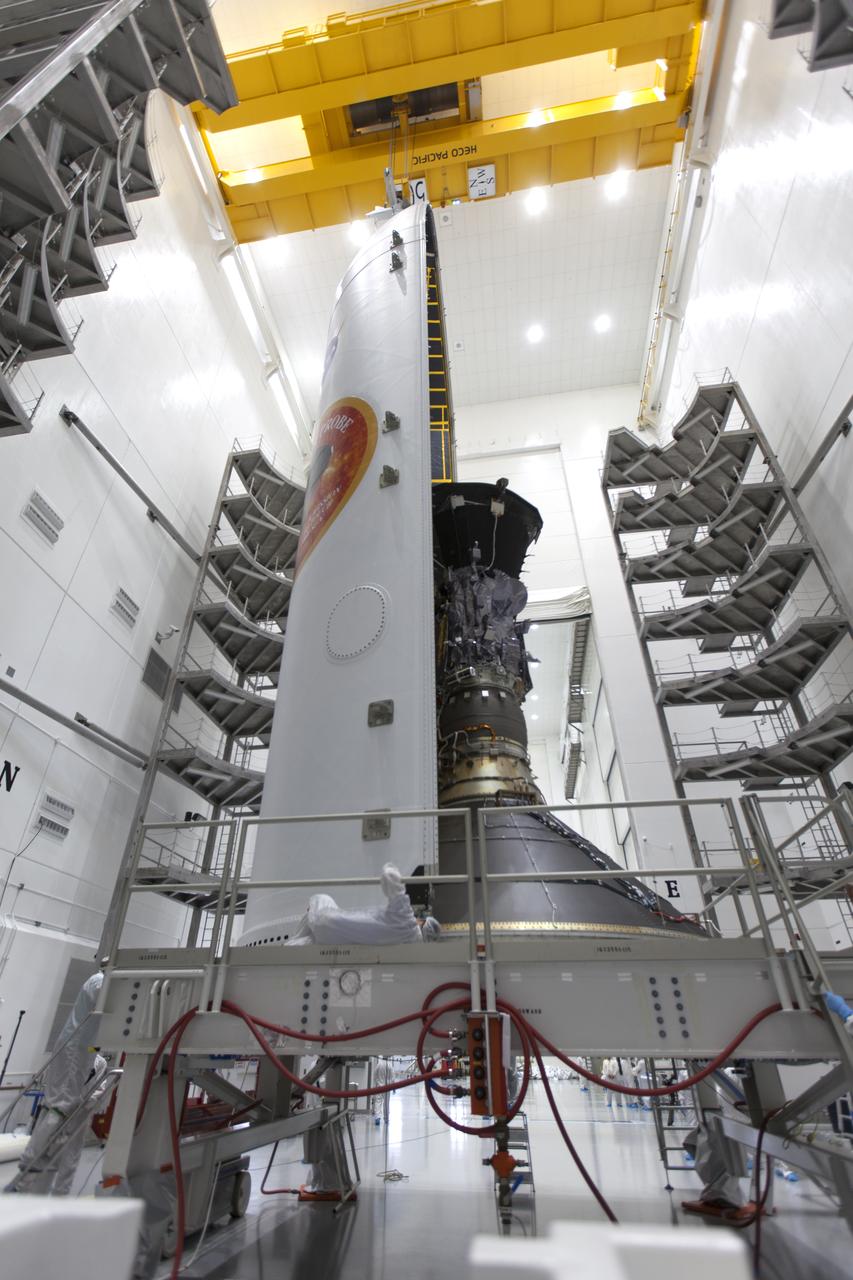

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Monday, July 16, 2018, NASA's Parker Solar Probe is being encapsulated in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler, Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
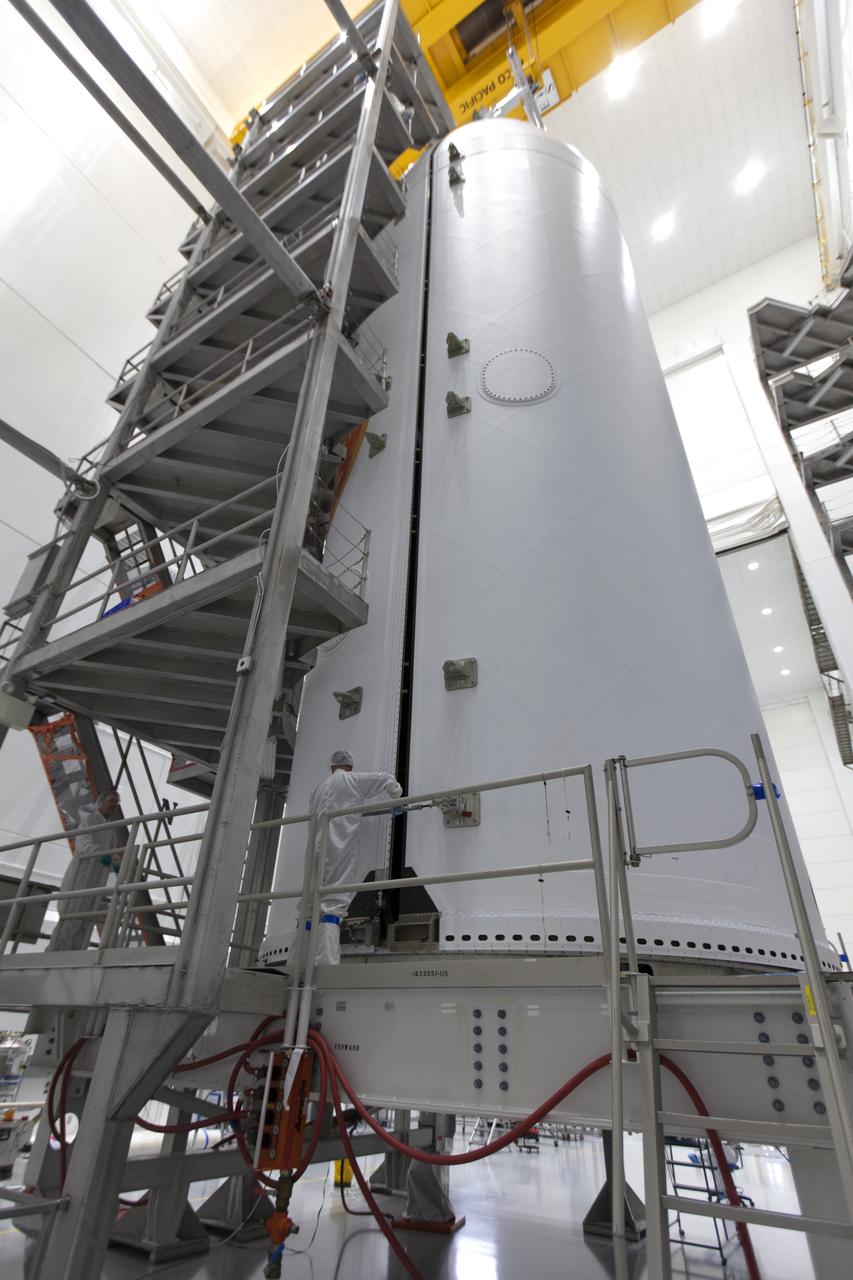

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Thursday, July 19, 2018, NASA's Parker Solar Probe has been encapsulated in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler, Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
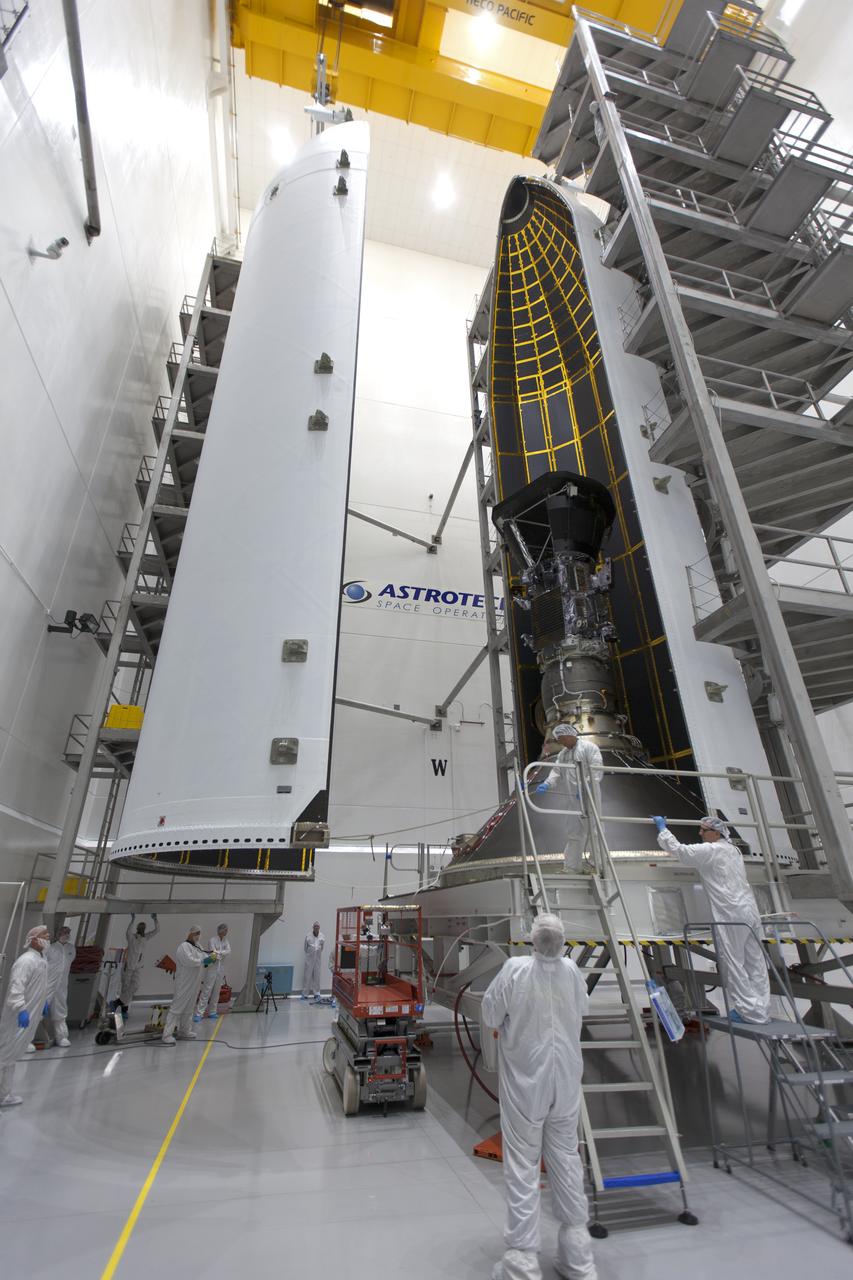

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Thursday, July 19, 2018, technicians and engineers encapsulate NASA's Parker Solar Probe in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler, Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
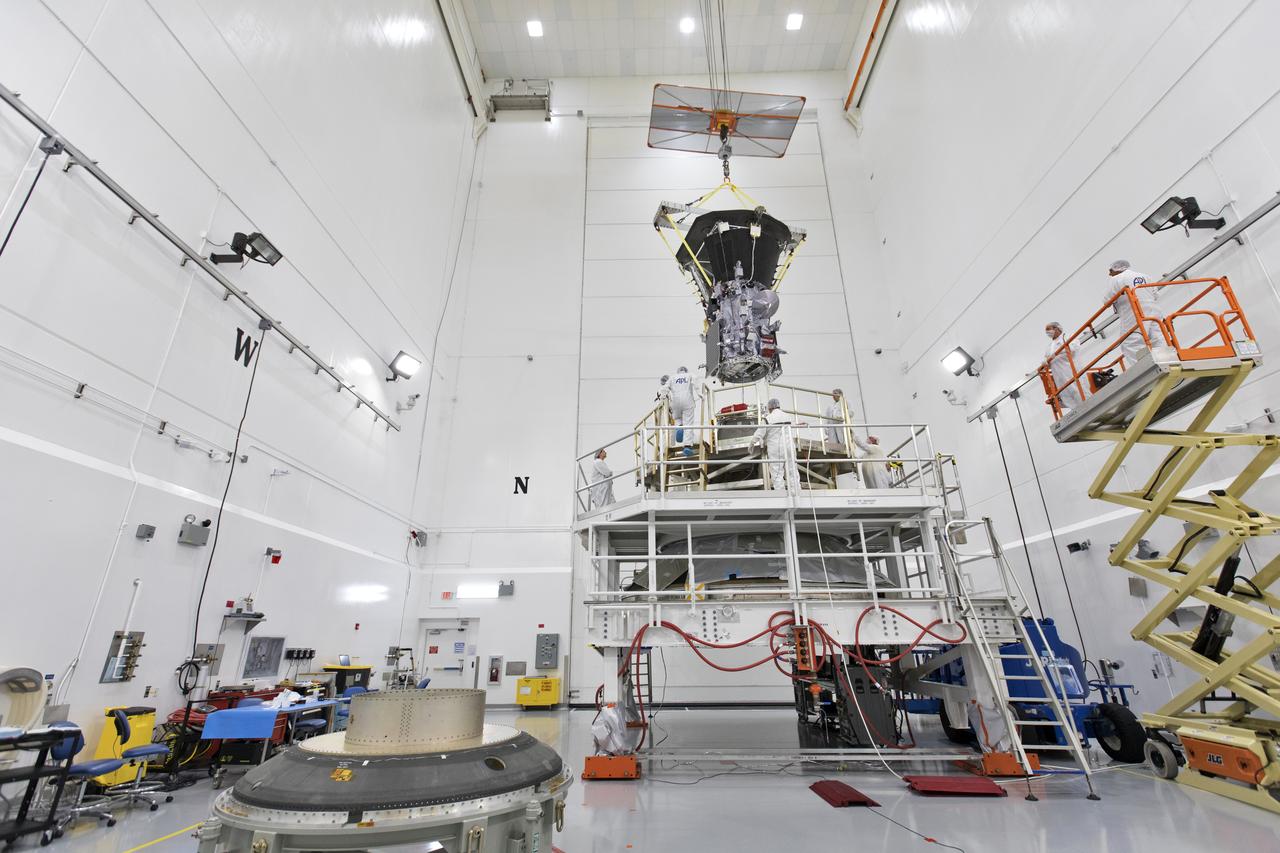

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, July 11, 2018, technicians and engineers use a crane to move NASA's Parker Solar Probe into position for mating to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
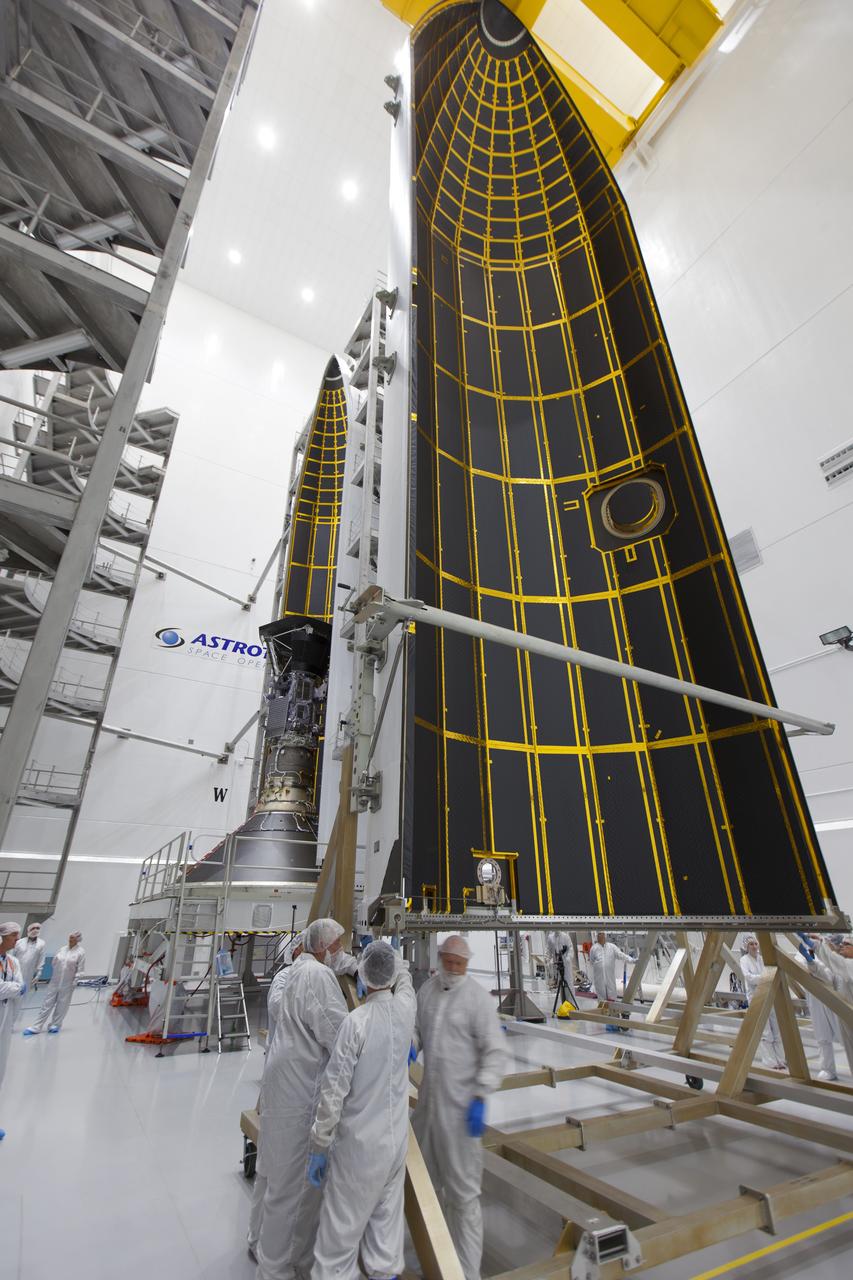

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Thursday, July 19, 2018, technicians and engineers encapsulate NASA's Parker Solar Probe in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler, Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
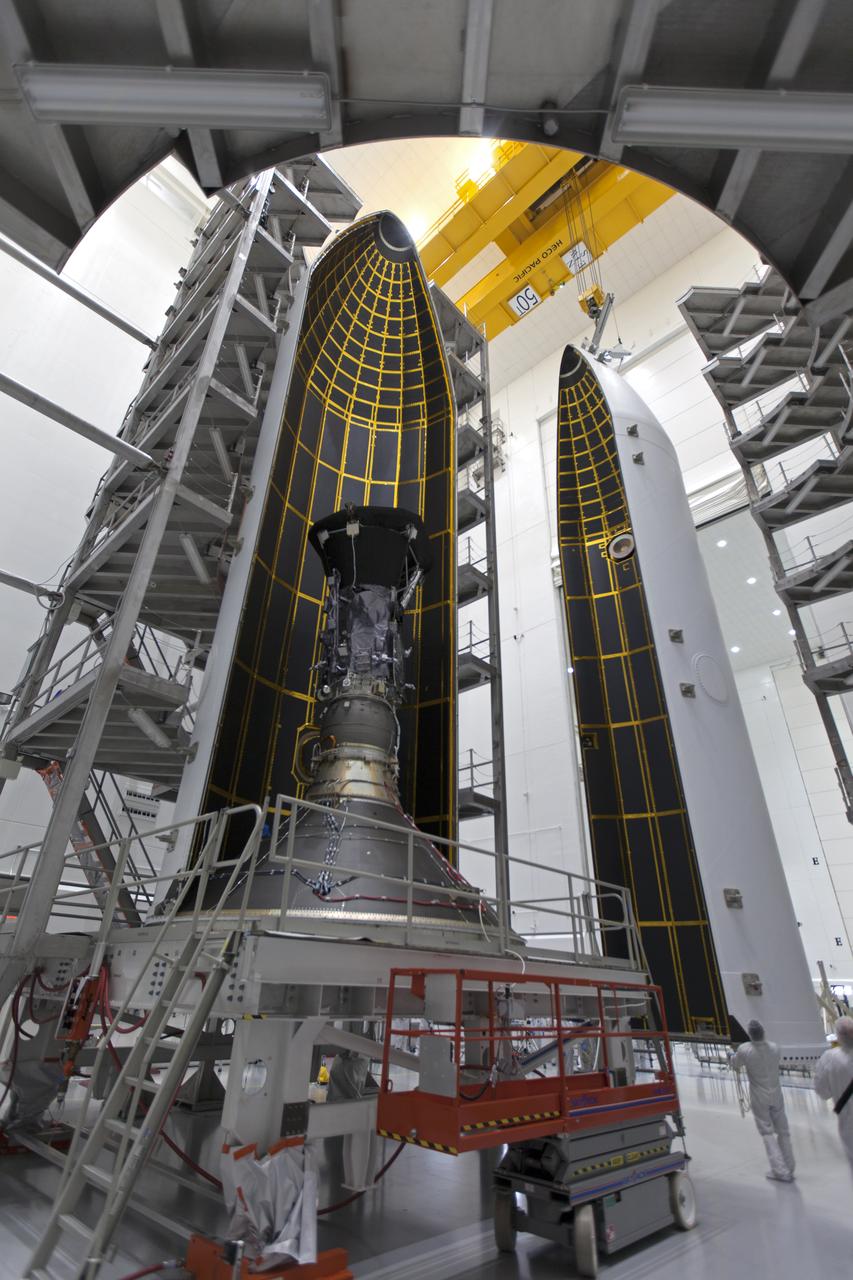

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Thursday, July 19, 2018, NASA's Parker Solar Probe is being encapsulated in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler, Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
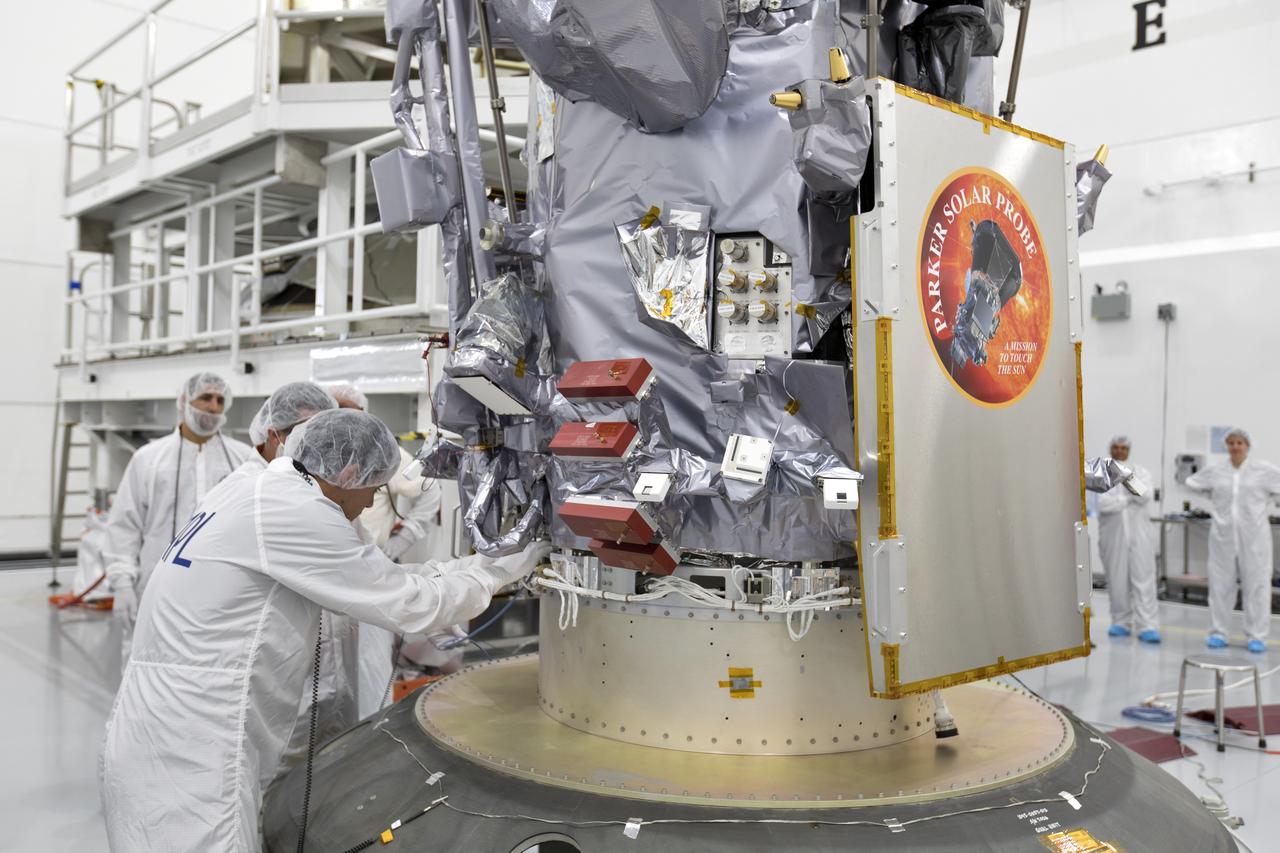

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Wednesday, July 11, 2018, technicians and engineers prepare to mate NASA's Parker Solar Probe to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
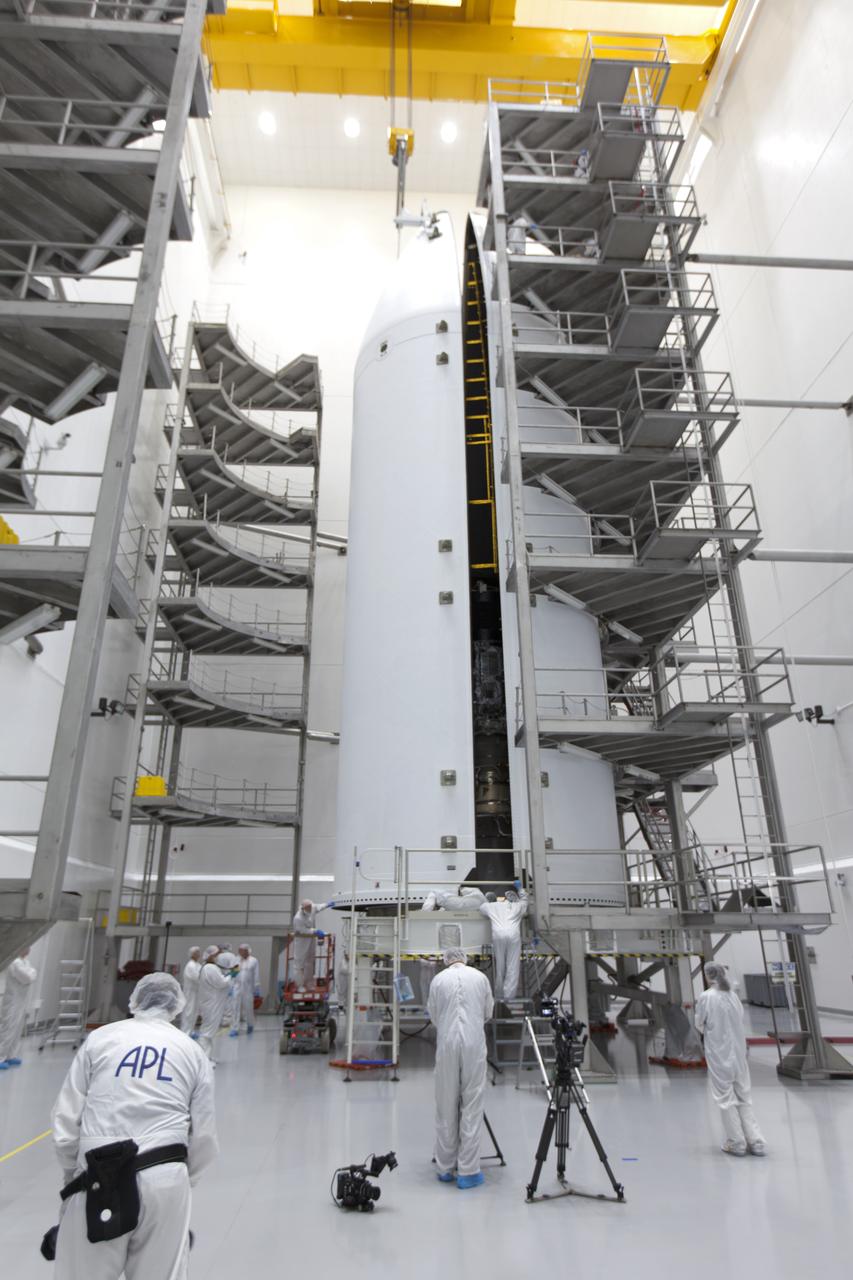

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Thursday, July 19, 2018, technicians and engineers encapsulate NASA's Parker Solar Probe in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
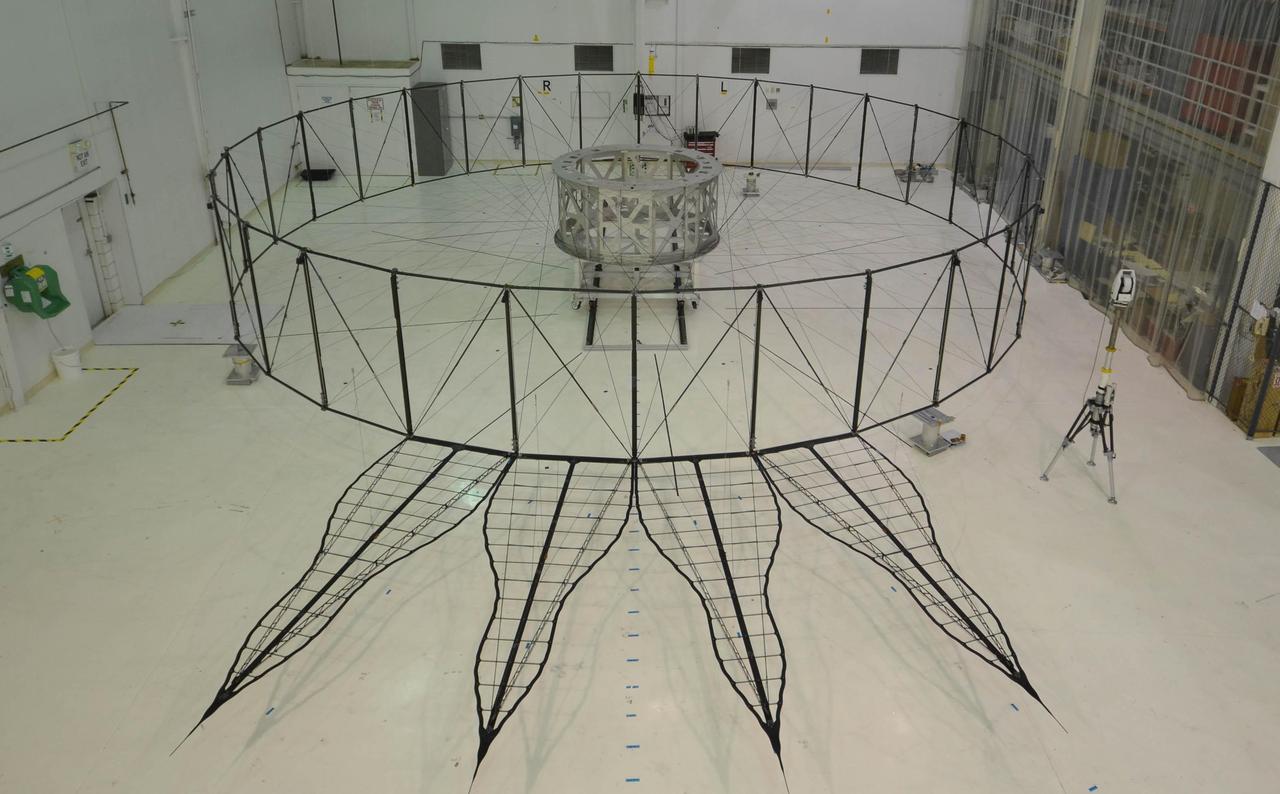
This image shows the bare bones of the first prototype starshade by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory, Pasadena, California. The prototype was shown in technology partner Astro Aerospace/Northrup Grumman's facility in Santa Barbara, California in 2013. In order for the petals of the starshade to diffract starlight away from the camera of a space telescope, they must be deployed with accuracy once the starshade reaches space. The four petals pictured in the image are being measured for this positional accuracy with a laser. As shown by this 66-foot (20-meter) model, starshades can come in many shapes and sizes. This design shows petals that are more extreme in shape which properly diffracts starlight for smaller telescopes. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20903
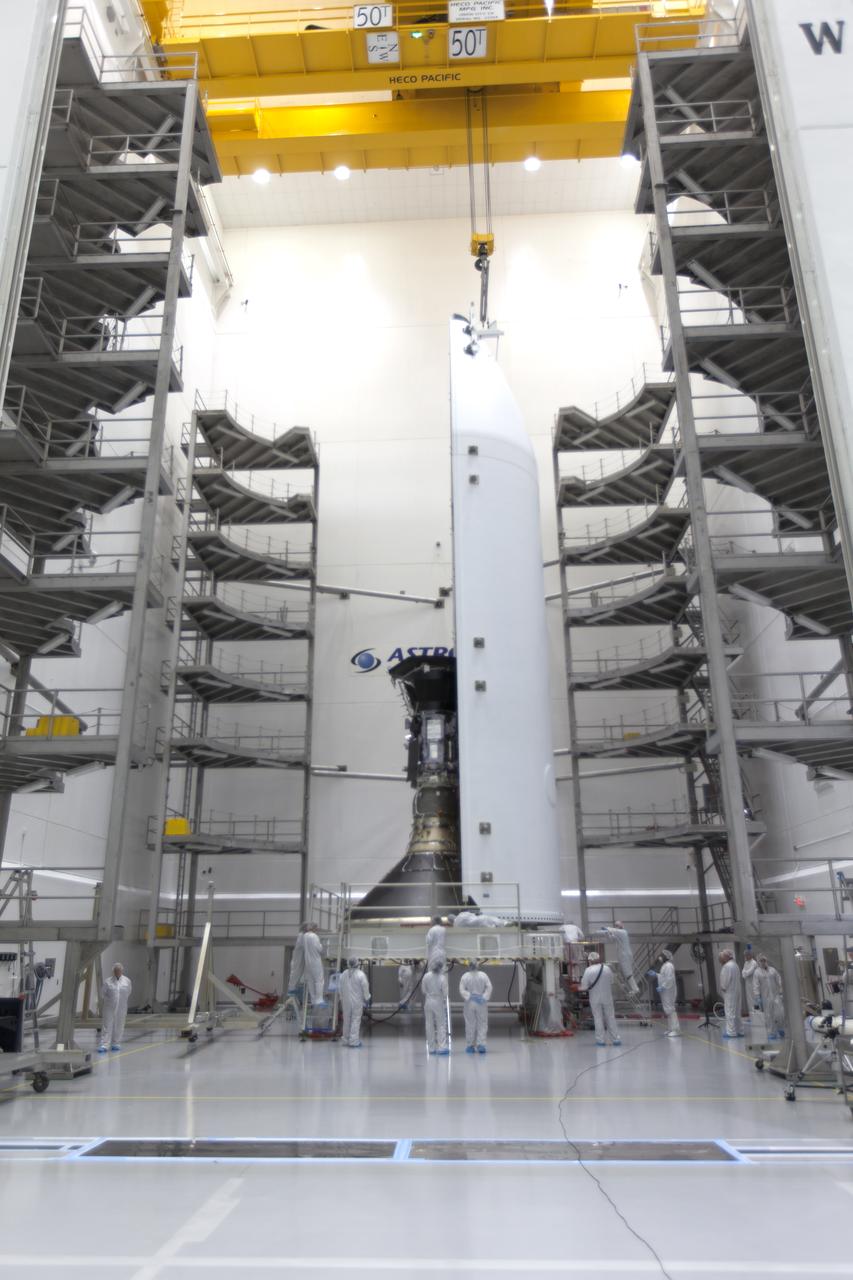

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Monday, July 16, 2018, technicians and engineers encapsulate NASA's Parker Solar Probe in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler, Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
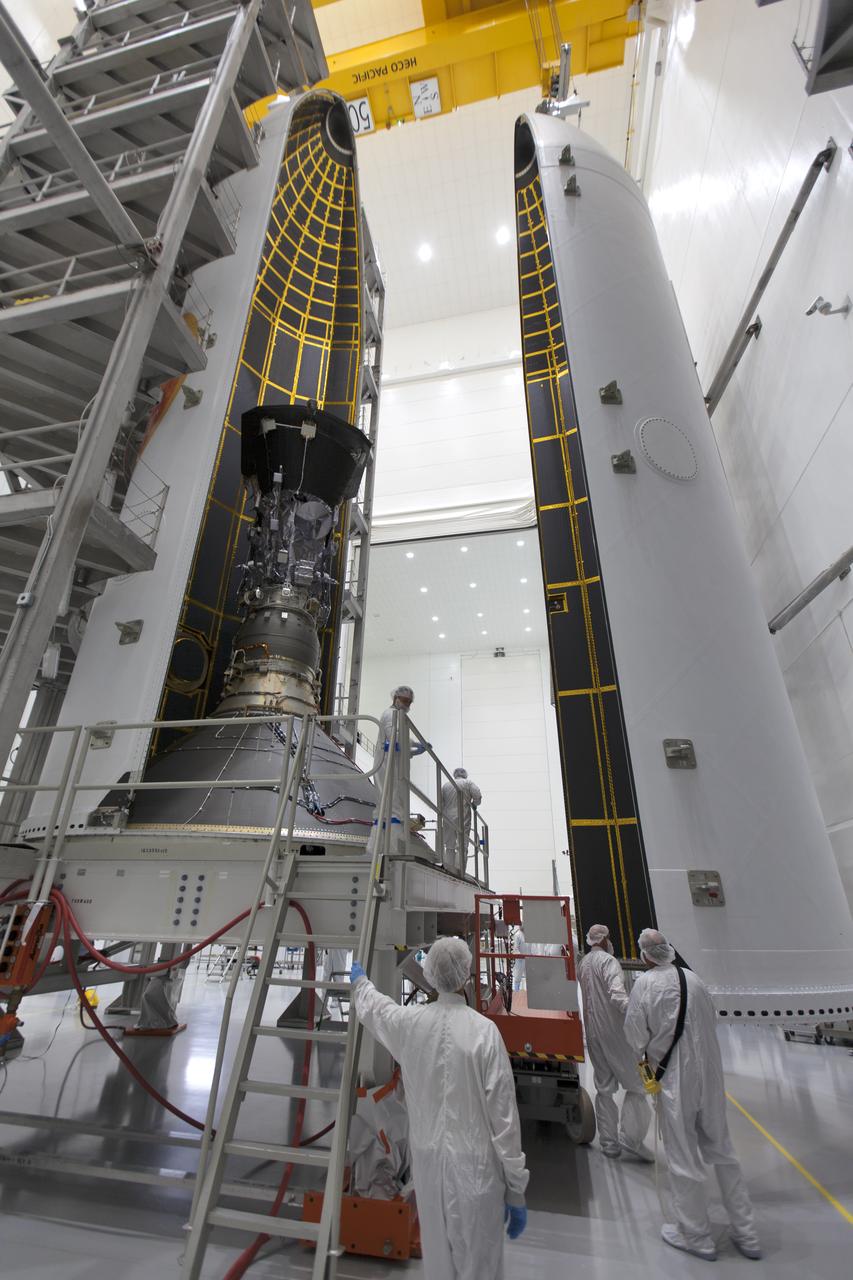

In the Astrotech processing facility in Titusville, Florida, near NASA's Kennedy Space Center, on Thursday, July 19, 2018, technicians and engineers encapsulate NASA's Parker Solar Probe in its payload fairing. The spacecraft is mated to its third stage, built and tested by Northrup Grumman in Chandler, Arizona. The Parker Solar Probe will launch on a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The mission will perform the closest-ever observations of a star when it travels through the Sun's atmosphere, called the corona. The probe will rely on measurements and imaging to revolutionize our understanding of the corona and the Sun-Earth connection.
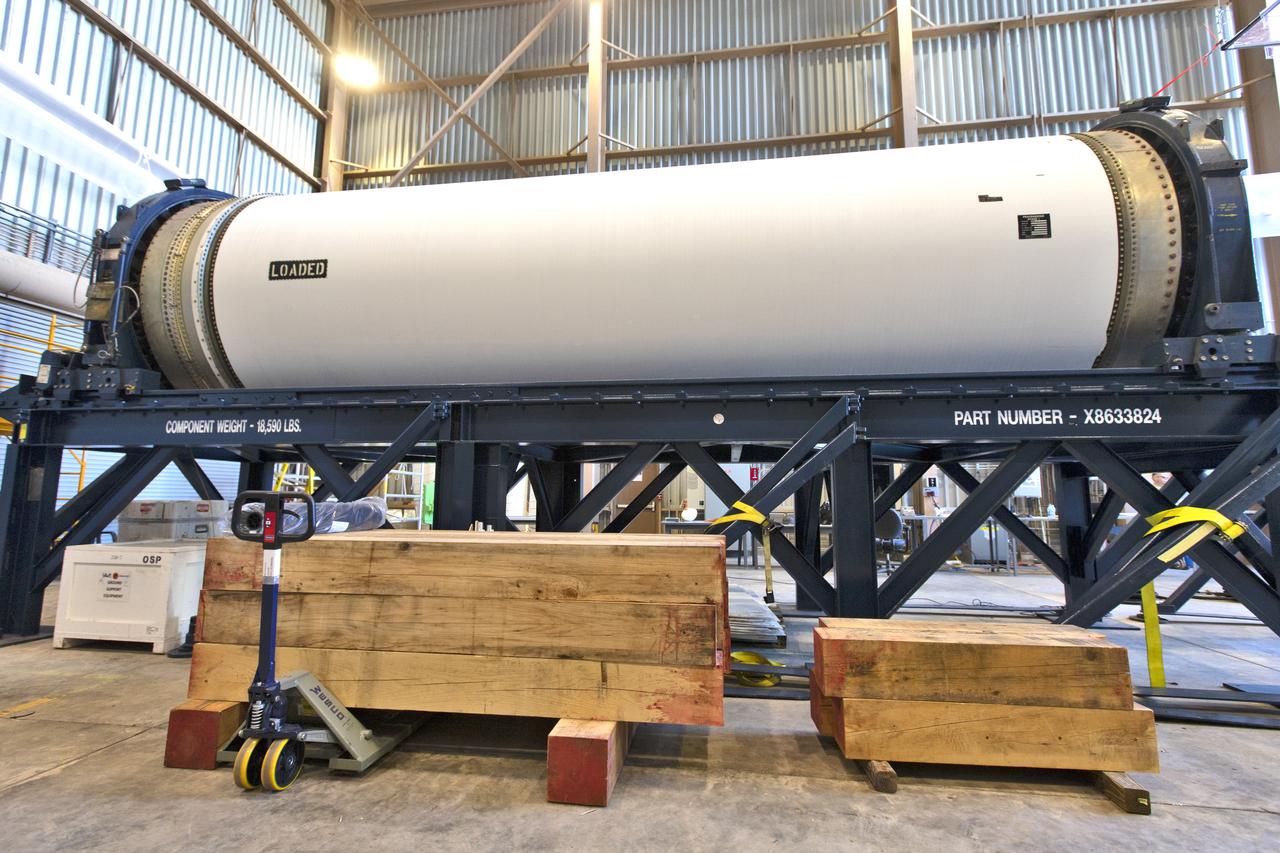

The Northrop Grumman-provided ascent test booster for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 29, 2019. The booster will be outfitted for flight. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the Launch Abort System, scheduled for April 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.

The Northrop Grumman-provided ascent test booster for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 29, 2019. The booster will be outfitted for flight. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the Launch Abort System, scheduled for April 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.

The Northrop Grumman-provided ascent test booster for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 29, 2019. The booster will be outfitted for flight. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the Launch Abort System, scheduled for April 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
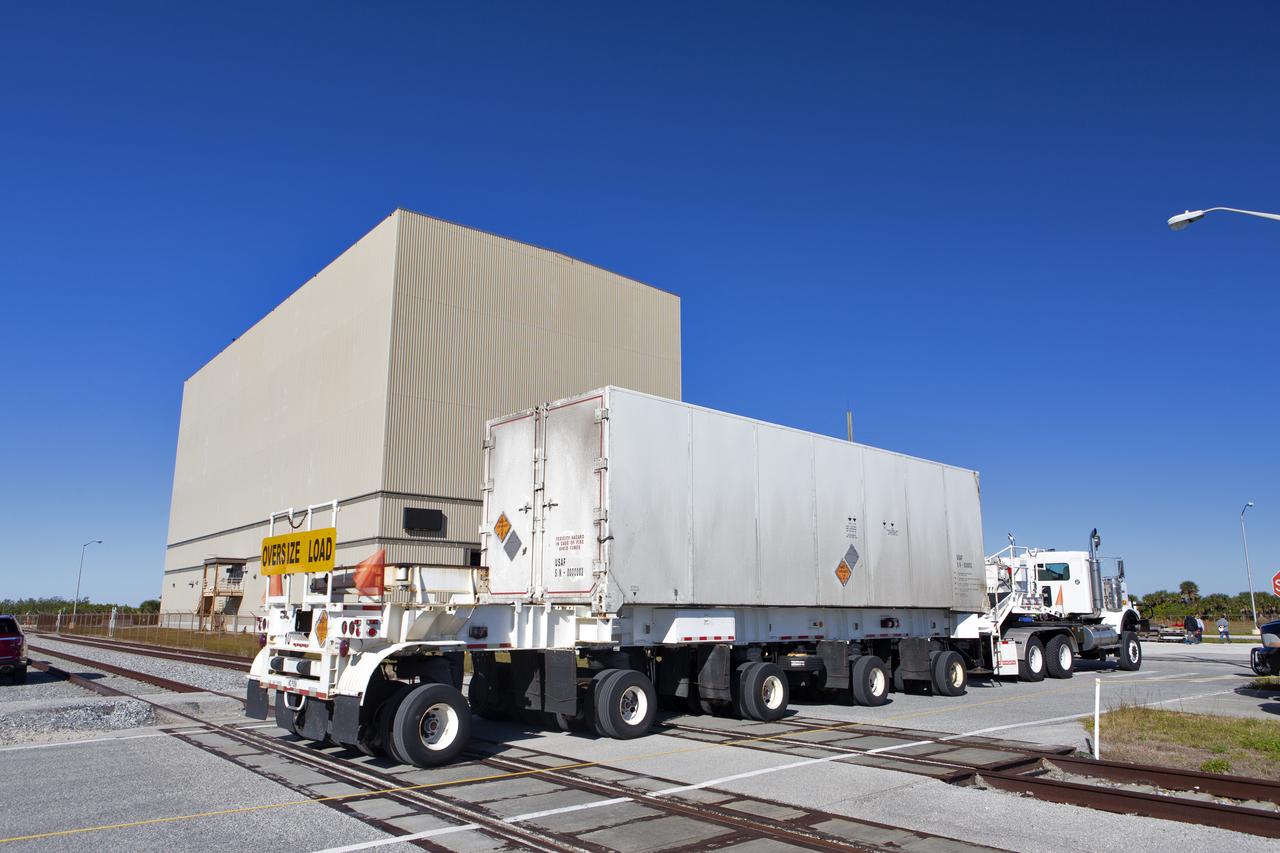

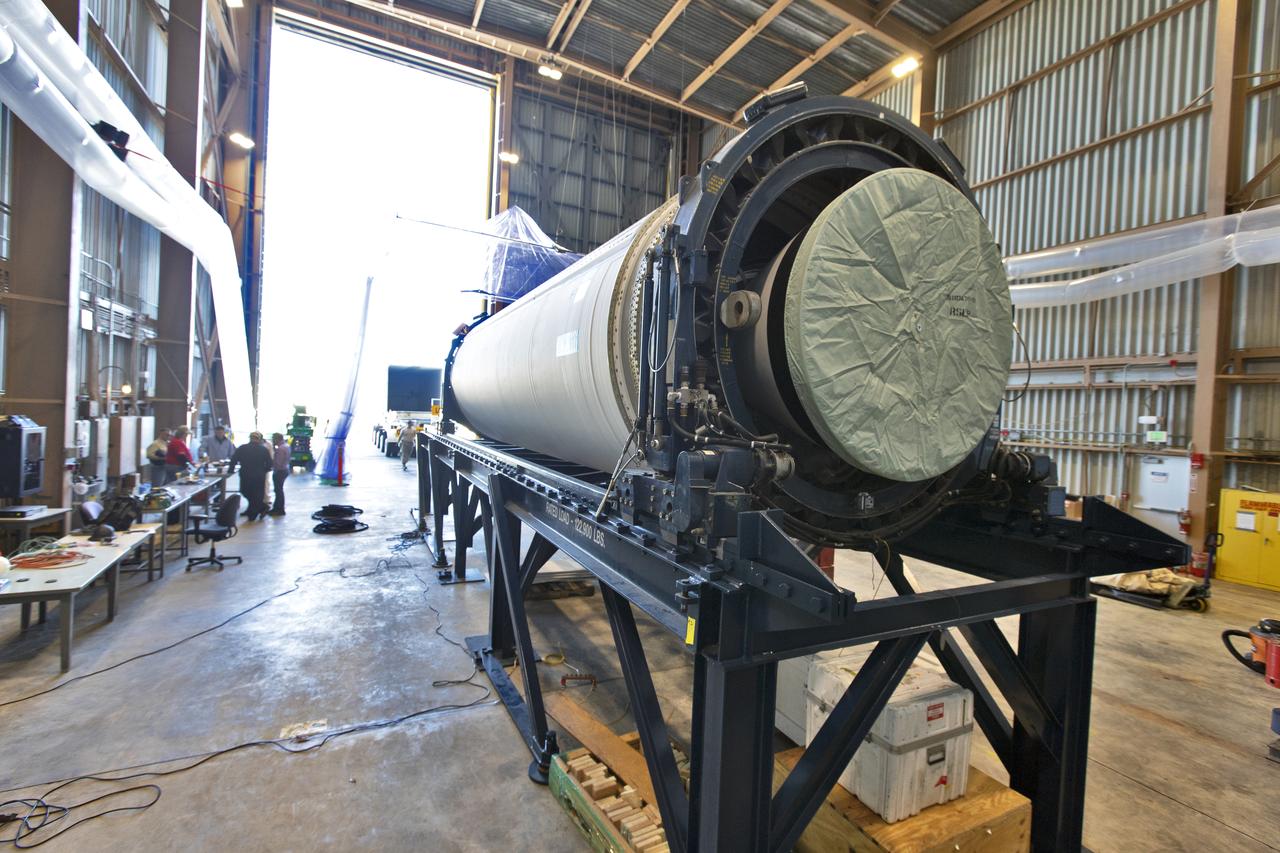
A heavy transport truck containing the Northrop Grumman-provided ascent test booster for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test, arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 29, 2019. The booster will be unloaded and moved into the RPSF where it will be outfitted for flight. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the Launch Abort System, scheduled for April 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
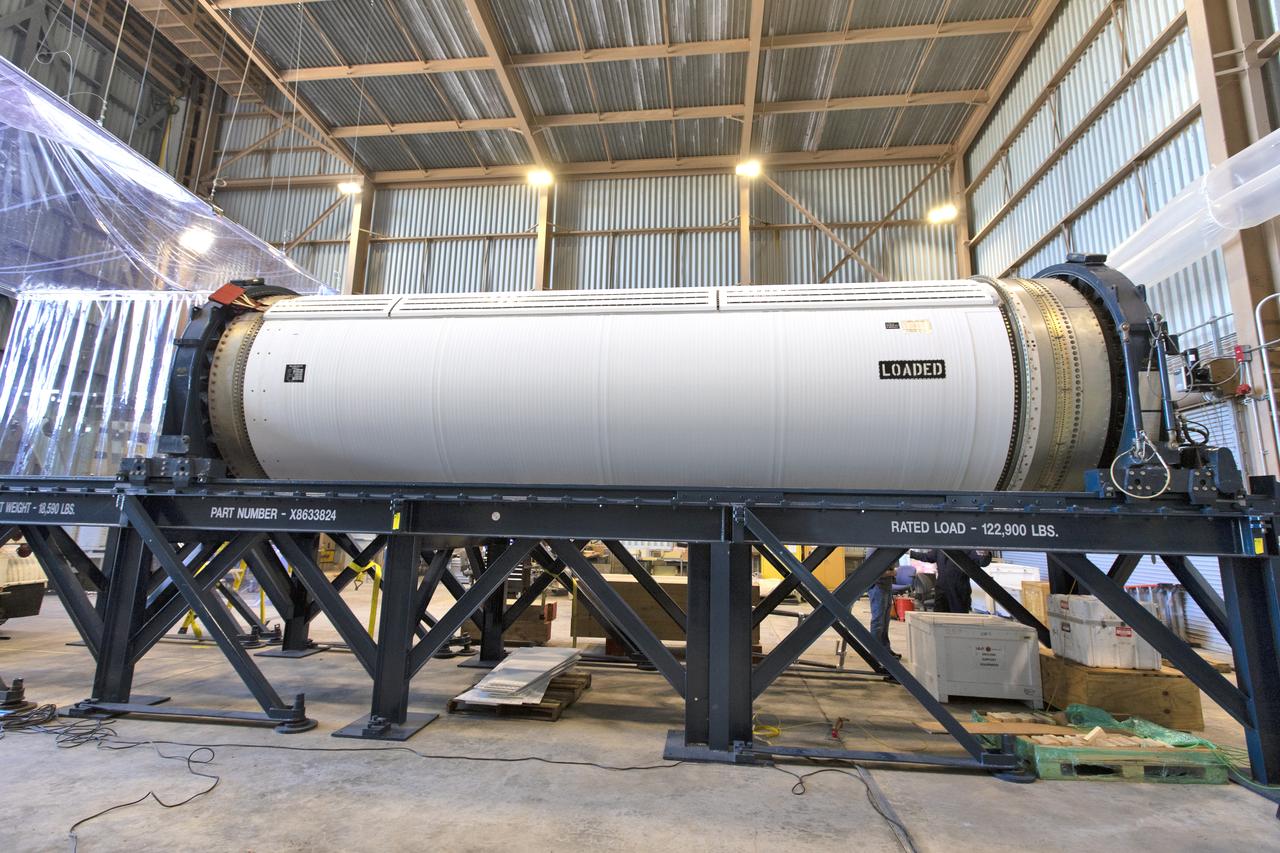

The Northrop Grumman-provided ascent test booster for the Orion Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) Flight Test is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Jan. 29, 2019. The booster will be outfitted for flight. AA-2 is a full-stress test of the Launch Abort System, scheduled for April 2019. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
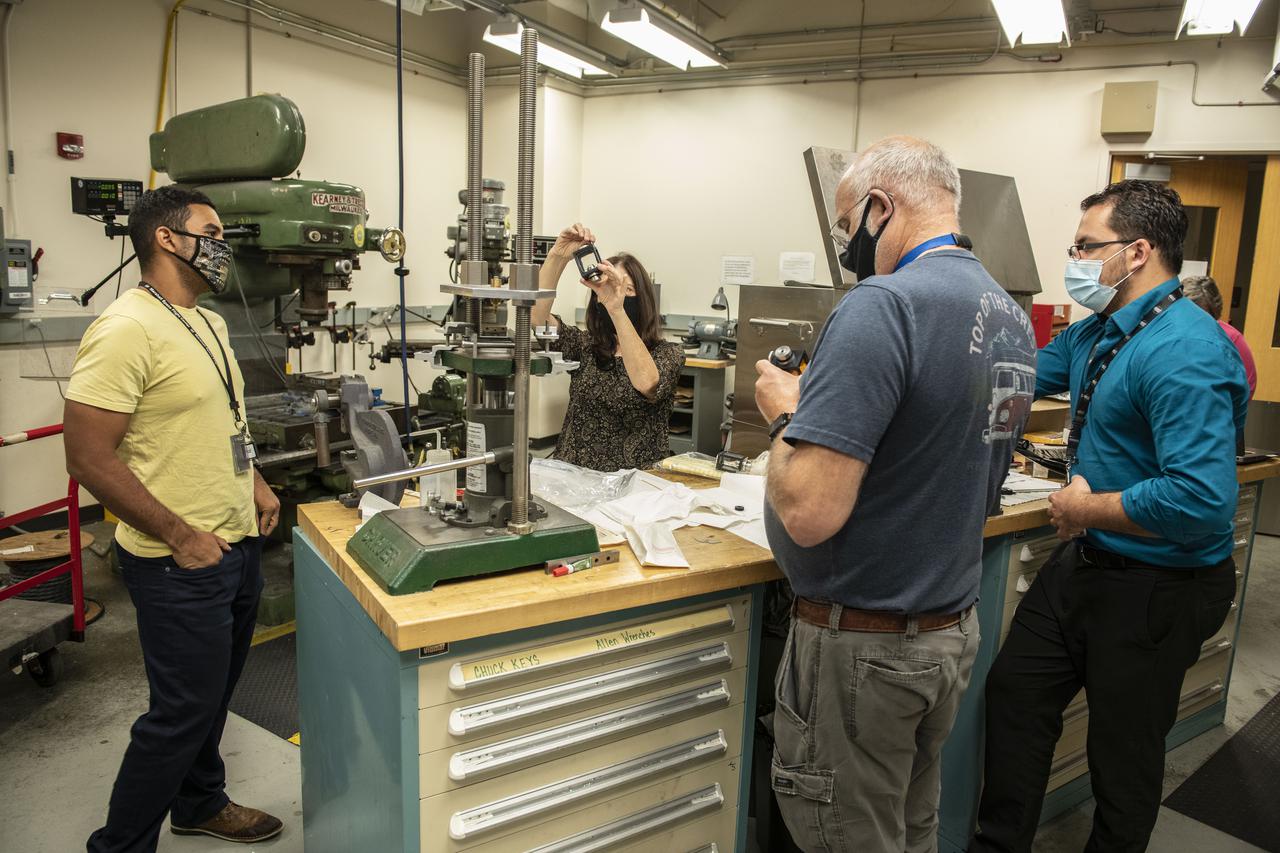

Scientists at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, clean equipment and prepare for shipment of the ring sheared drop payload currently set for launch on Northrop Grumman 16 the first week in August, 2021. The payload studies the formation of potentially destructive amyloid fibrils, or protein clusters, like those found in the brain tissue of patients battling neurodegenerative diseases. Such illnesses may damage neurons, the drivers of the human nervous system. Experimentation in microgravity provides the opportunity to study amyloid fibril formation in conditions more analogous to those found in the human body than can be studied in a ground-based laboratory environment.
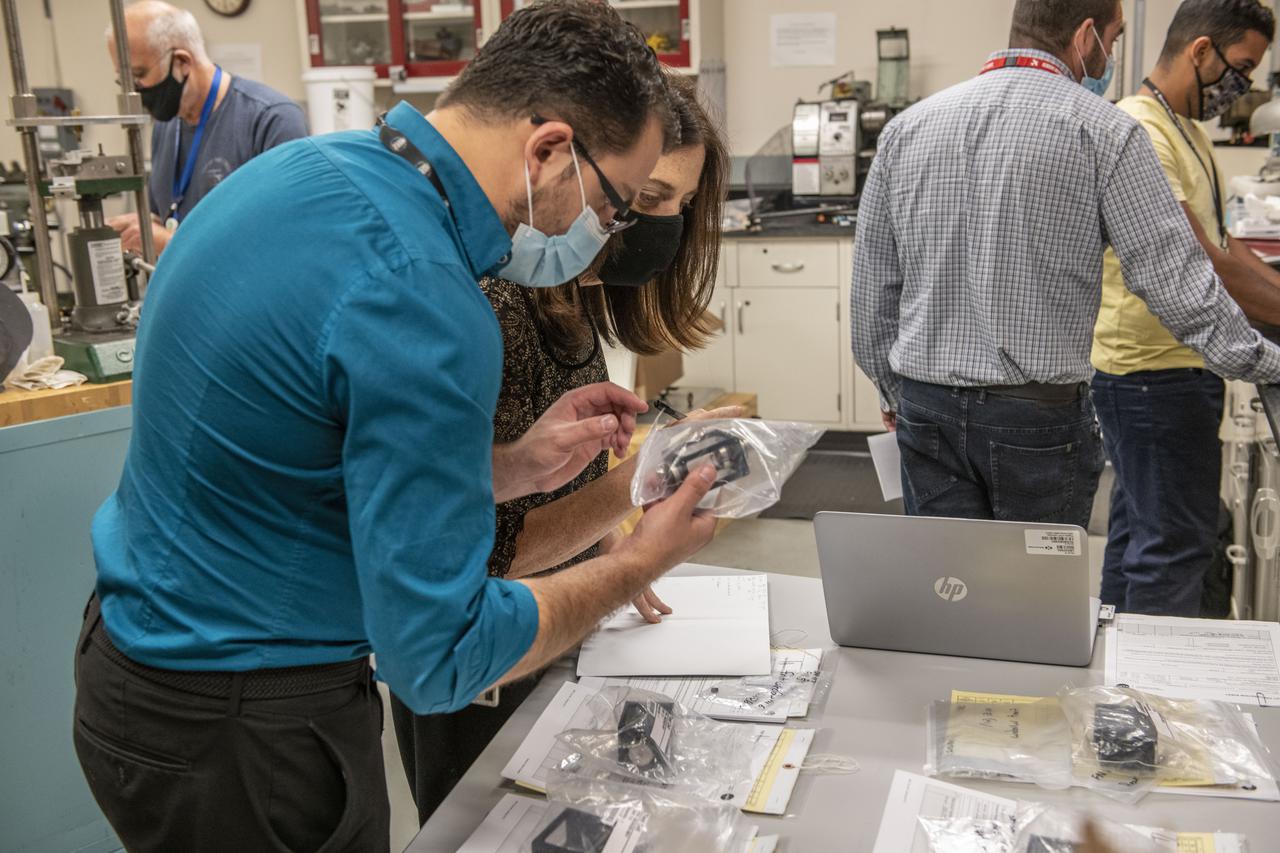

Scientists at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, clean equipment and prepare for shipment of the ring sheared drop payload currently set for launch on Northrop Grumman 16 the first week in August, 2021. The payload studies the formation of potentially destructive amyloid fibrils, or protein clusters, like those found in the brain tissue of patients battling neurodegenerative diseases. Such illnesses may damage neurons, the drivers of the human nervous system. Experimentation in microgravity provides the opportunity to study amyloid fibril formation in conditions more analogous to those found in the human body than can be studied in a ground-based laboratory environment.

Scientists at NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, clean equipment and prepare for shipment of the ring sheared drop payload currently set for launch on Northrop Grumman 16 the first week in August, 2021. The payload studies the formation of potentially destructive amyloid fibrils, or protein clusters, like those found in the brain tissue of patients battling neurodegenerative diseases. Such illnesses may damage neurons, the drivers of the human nervous system. Experimentation in microgravity provides the opportunity to study amyloid fibril formation in conditions more analogous to those found in the human body than can be studied in a ground-based laboratory environment.
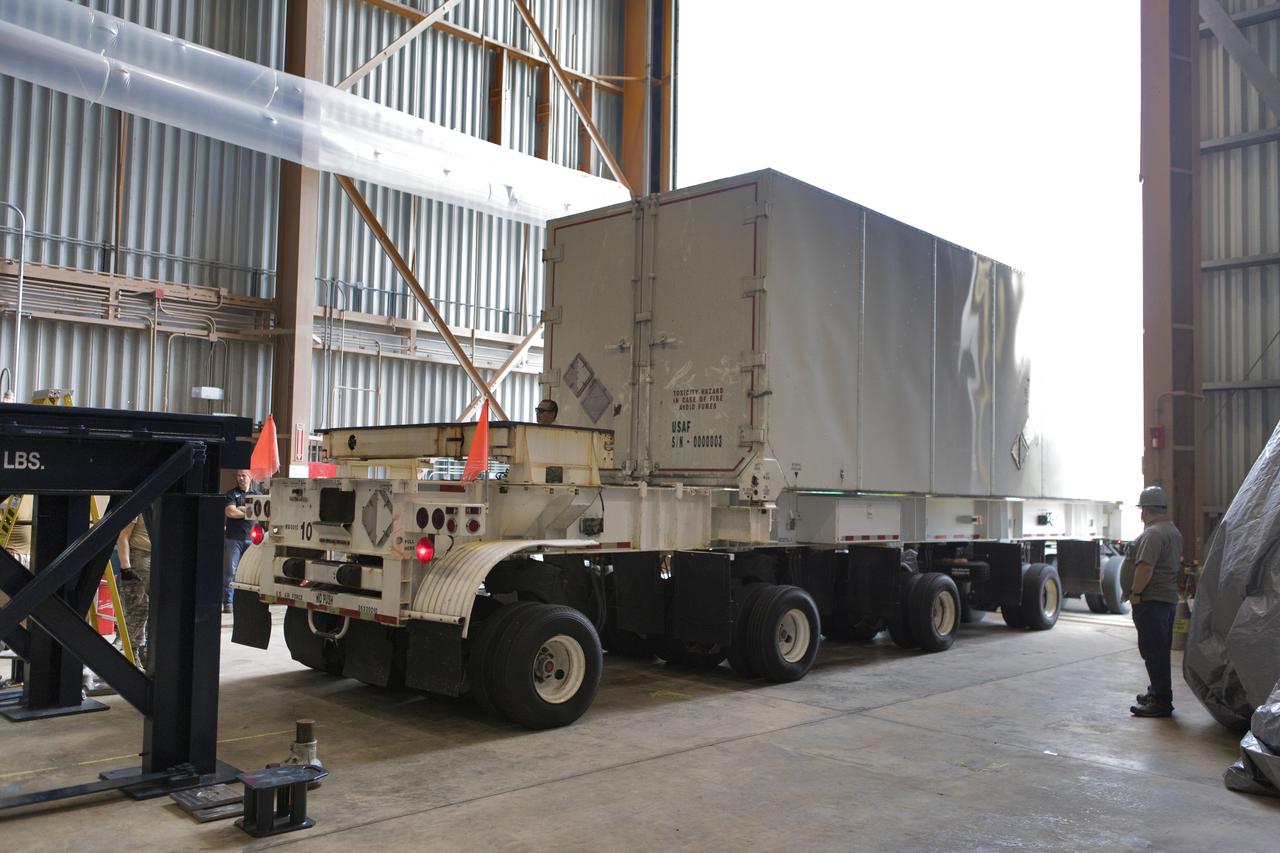

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
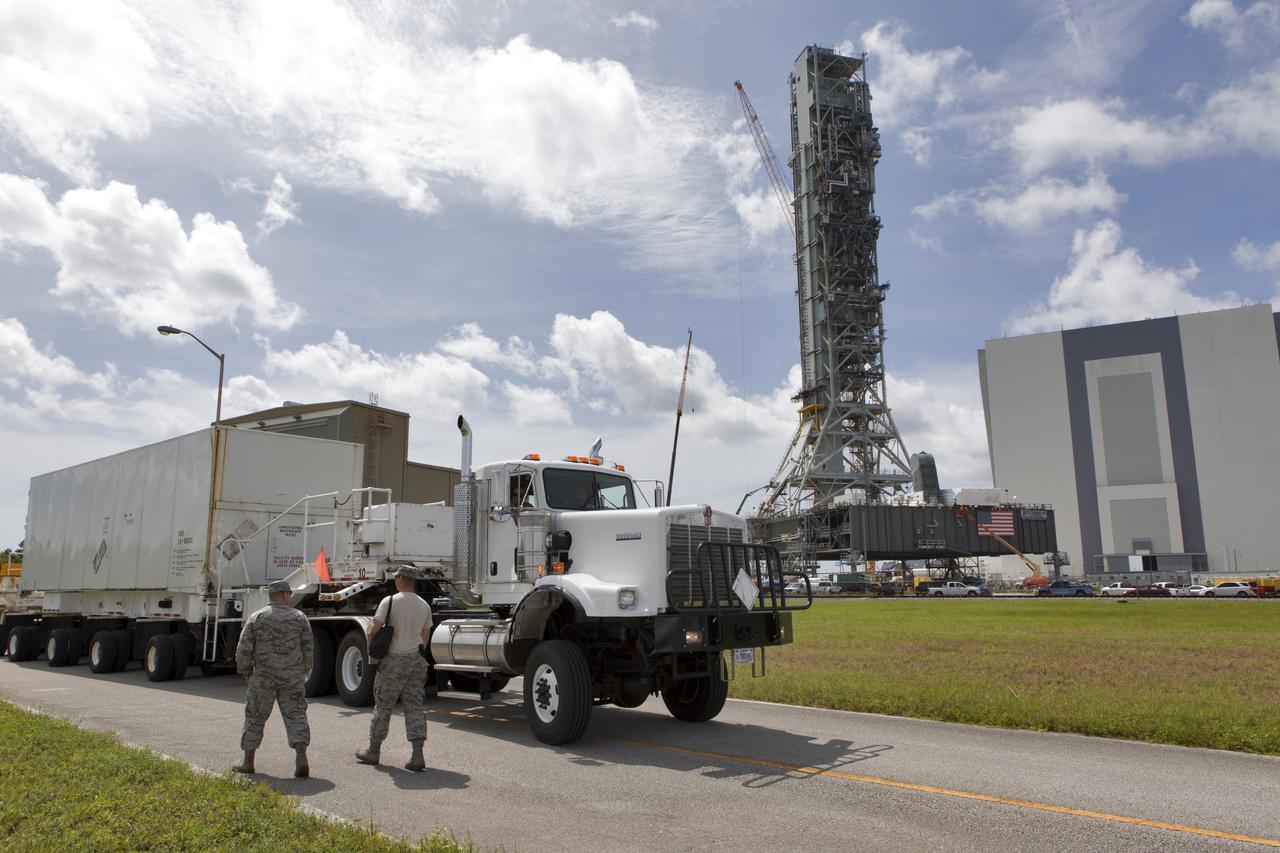

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
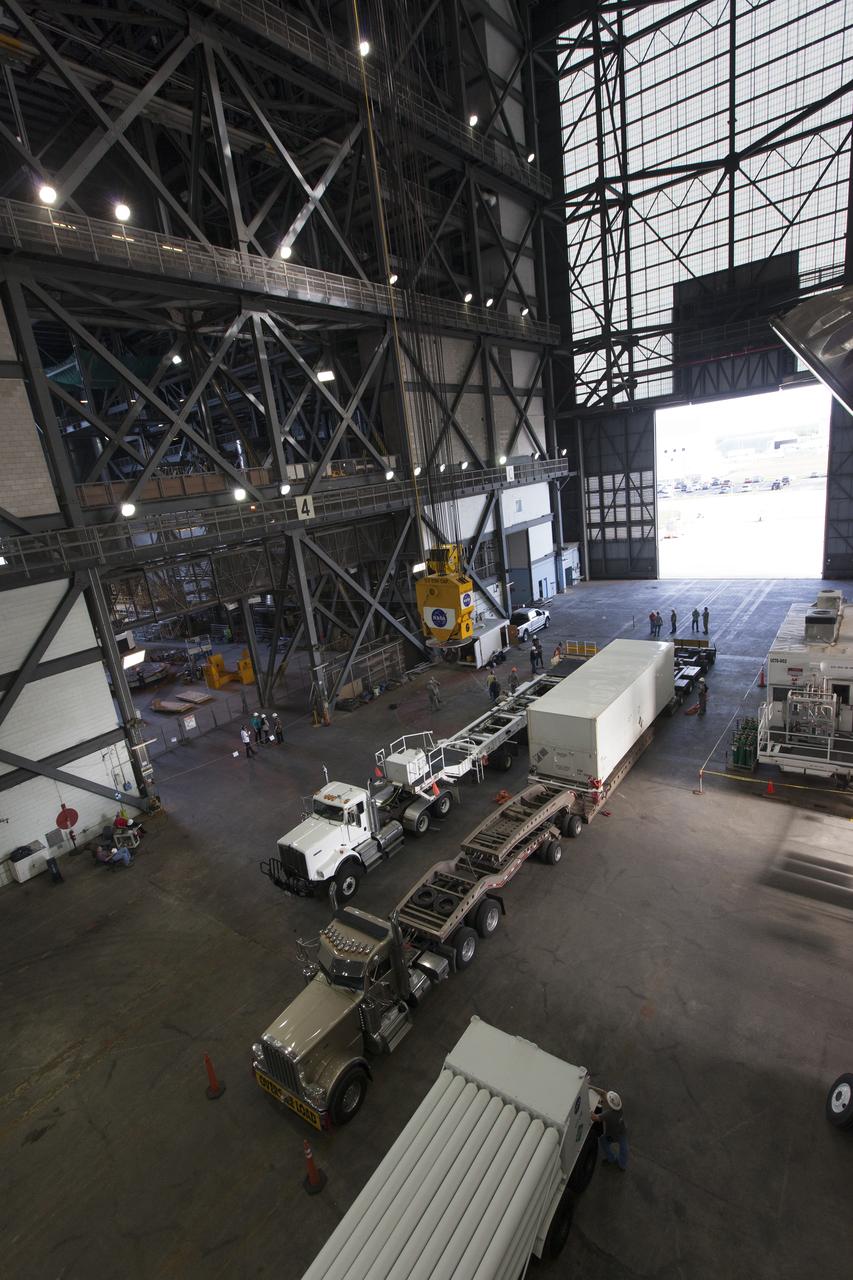

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in its shipping container in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be transferred to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
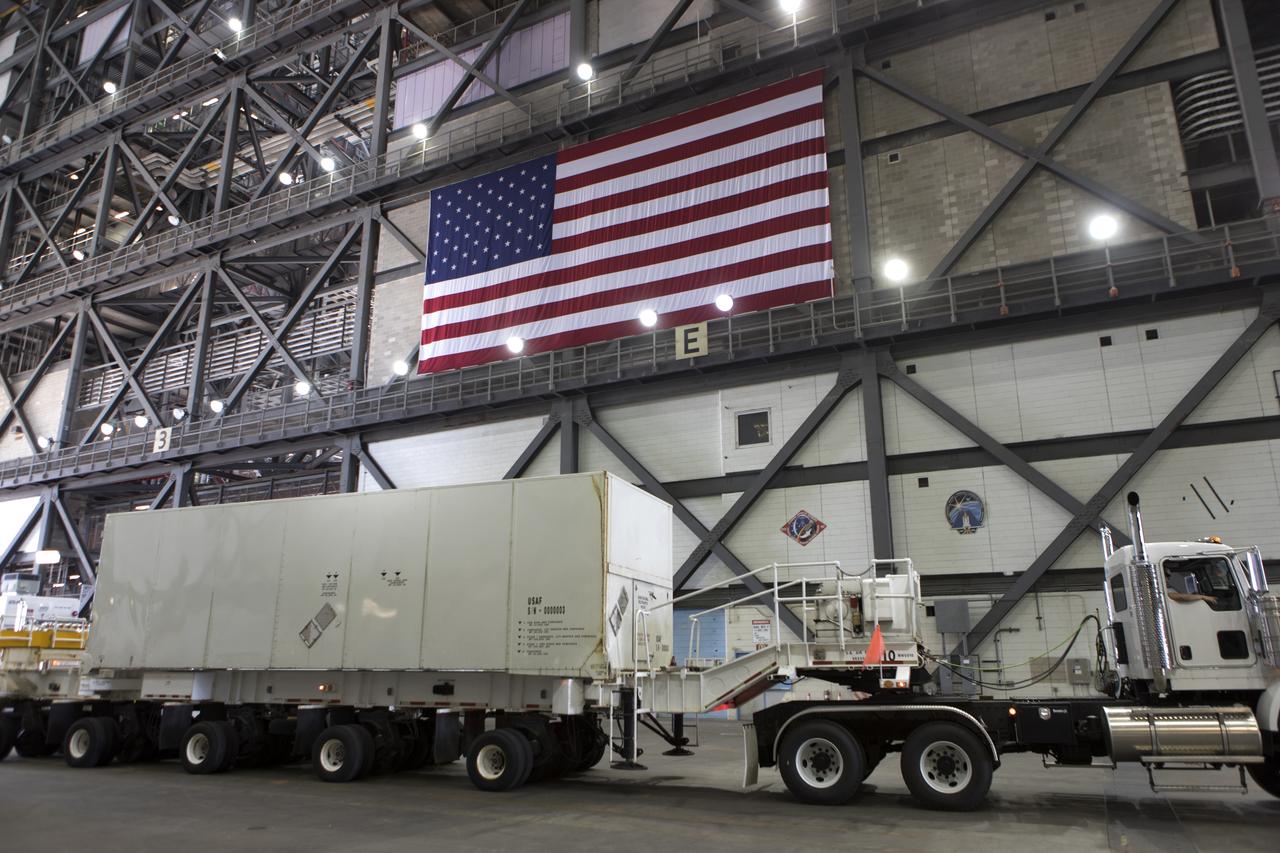

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) will be moved from the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
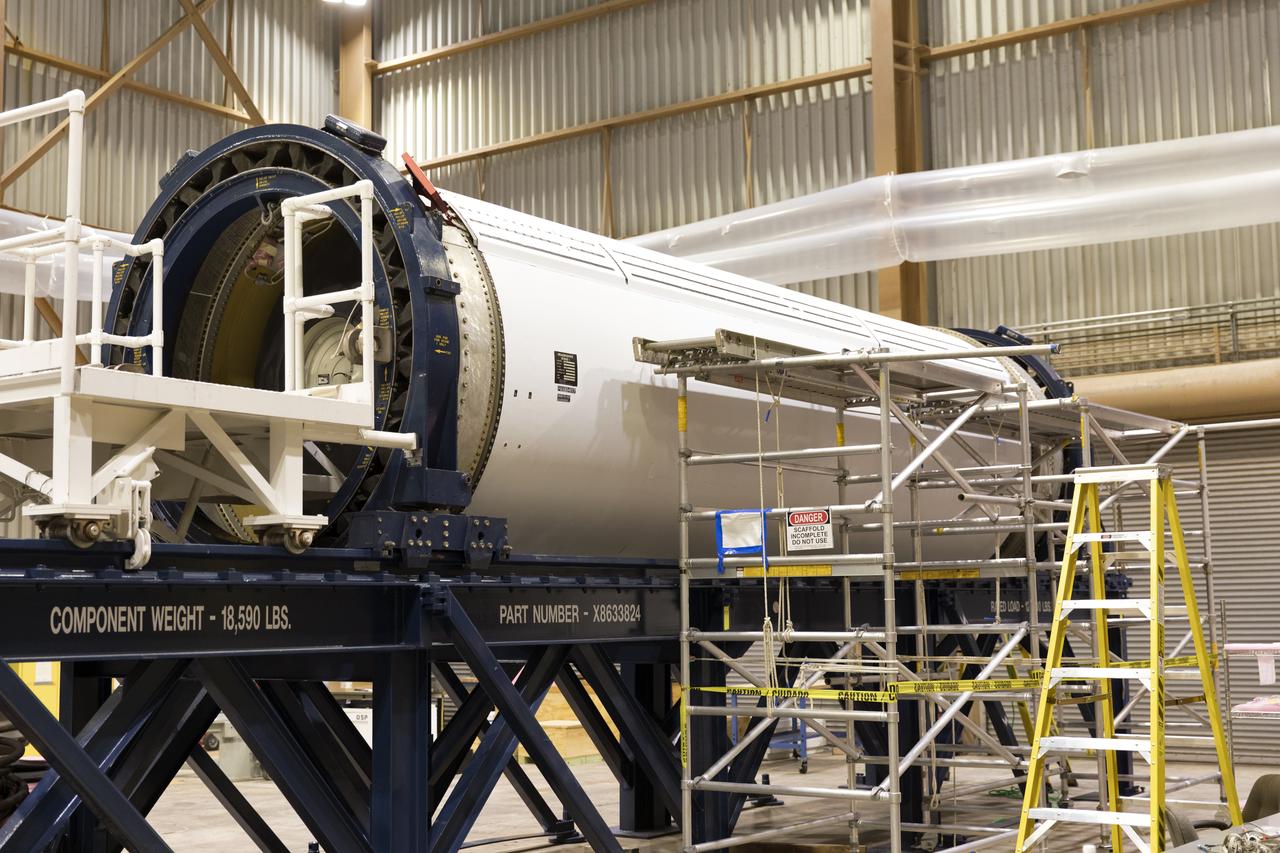

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
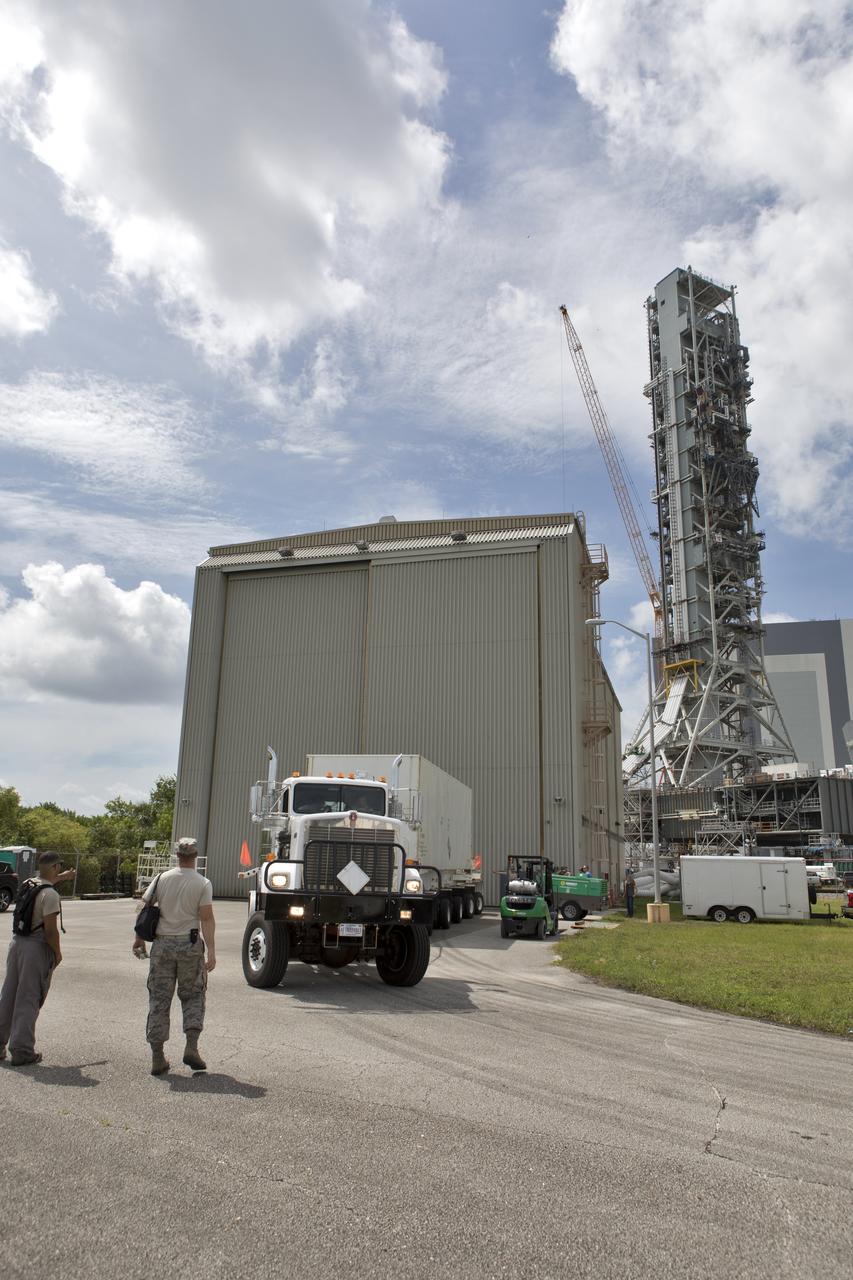

Secured on a flatbed transporter in its shipping container, the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives at the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility (RPSF) on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In the RPSF the motor will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
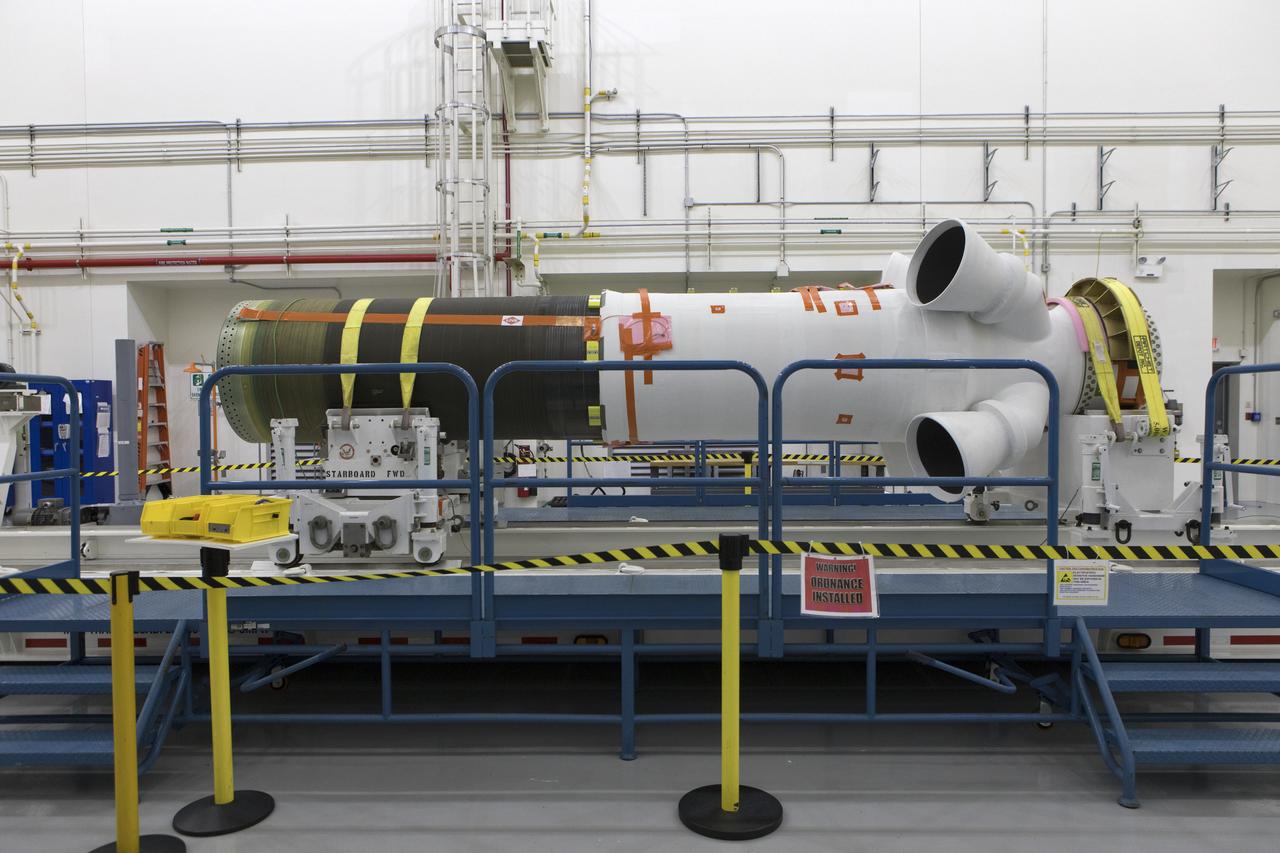

The abort motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Launch Abort System Facility on Aug. 28, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This motor will be used for flight during a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. The abort motor is what will activate to pull the Orion crew module away during the event of an emergency during ascent. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
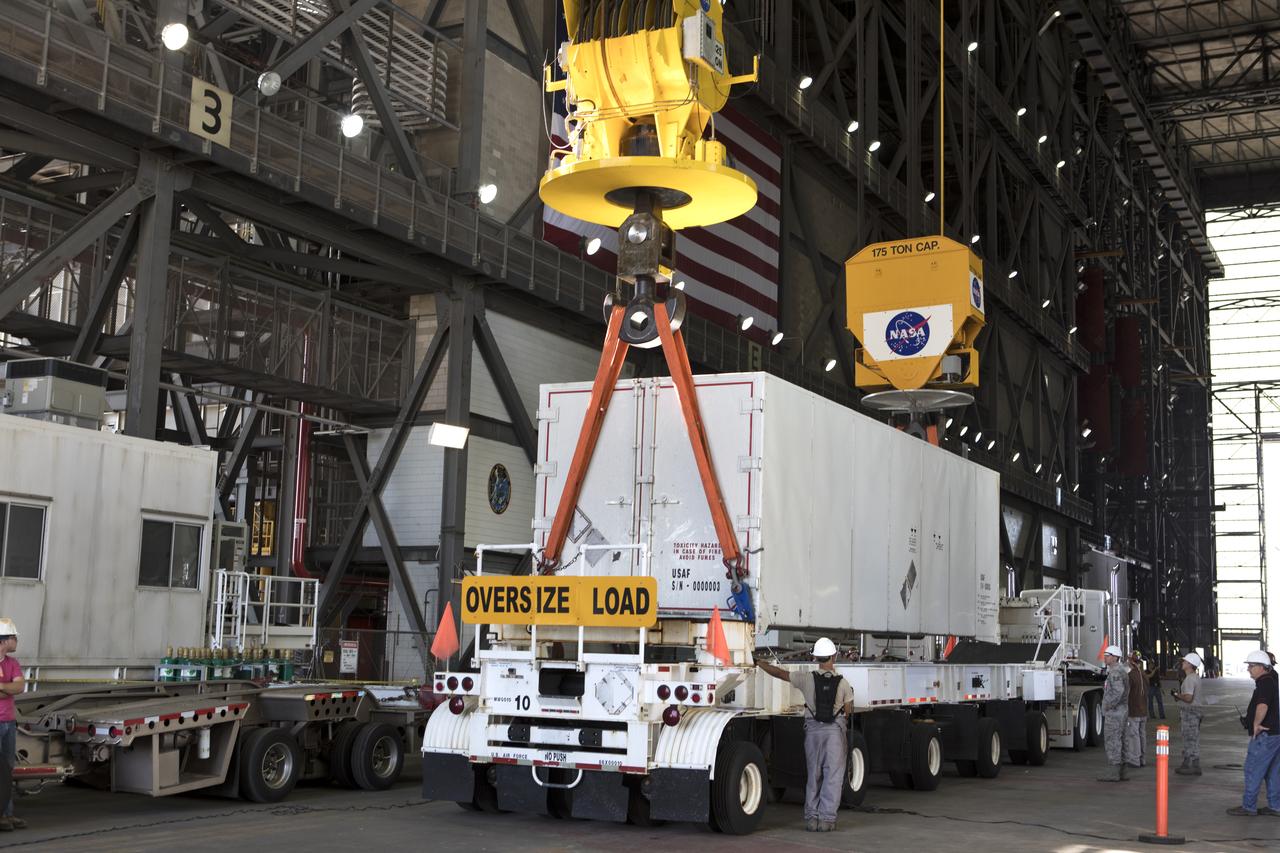

In the transfer aisle inside the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers the shipping container with the ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) inside onto another transporter on July 20, 2018. The container will be moved to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch SMC/LEXO, are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
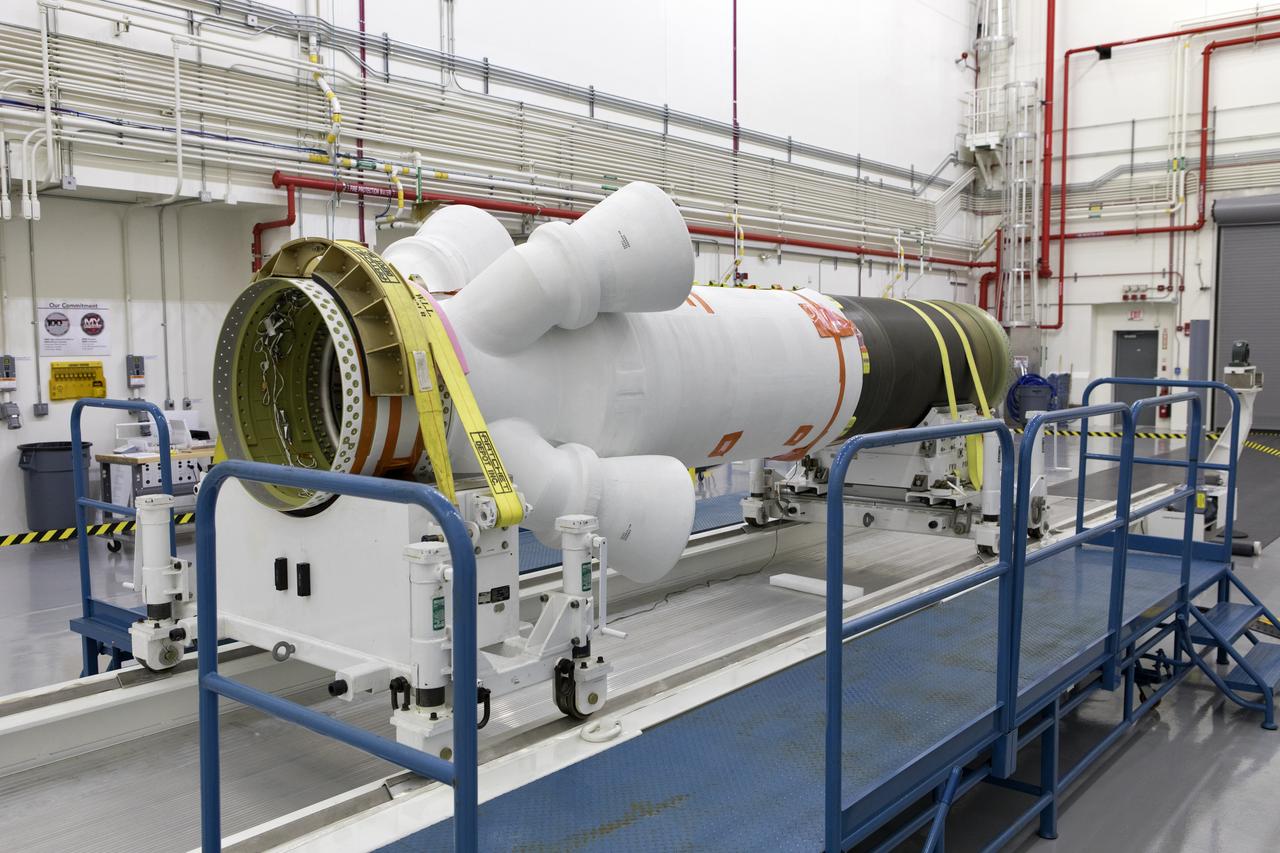

The abort motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Launch Abort System Facility on Aug. 28, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This motor will be used for flight during a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. The abort motor is what will activate to pull the Orion crew module away during the event of an emergency during ascent. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
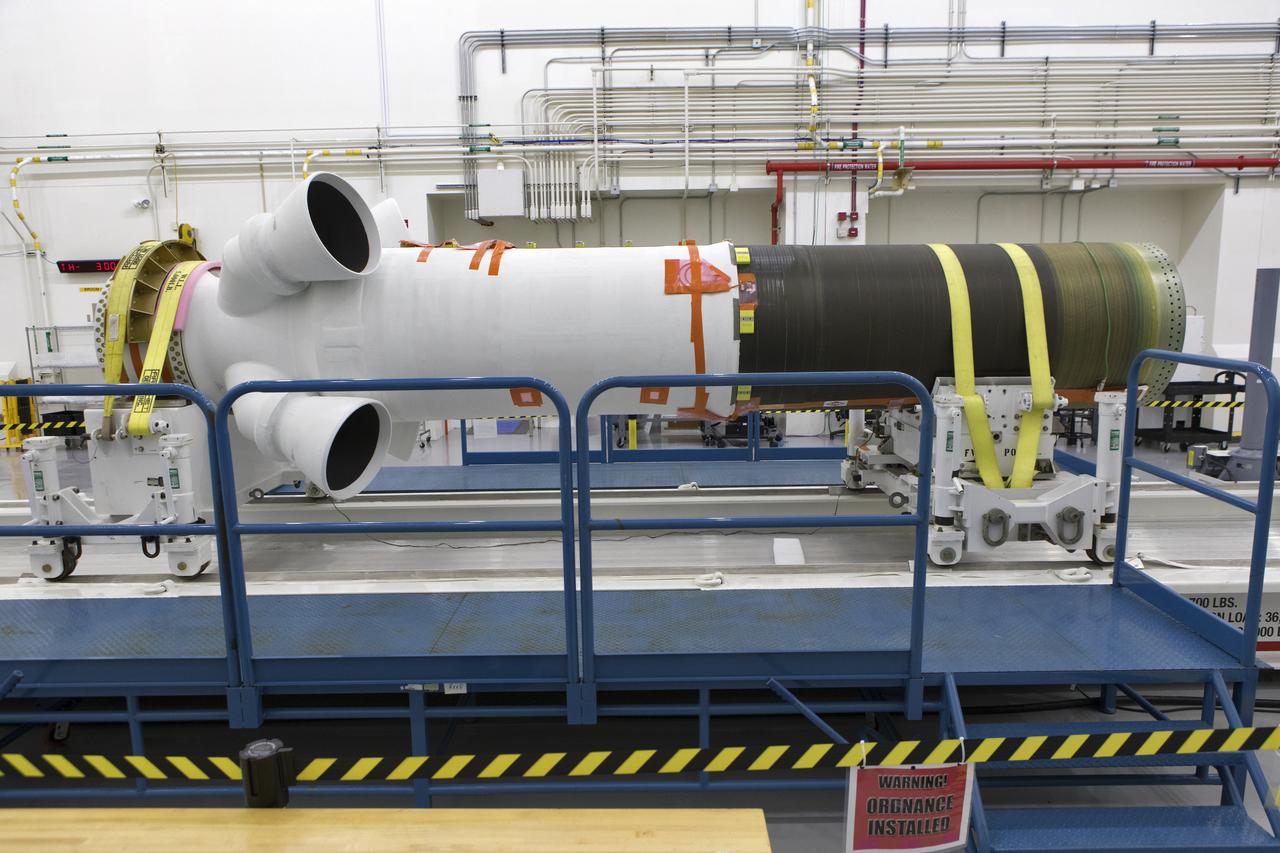
The abort motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Launch Abort System Facility on Aug. 28, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. This motor will be used for flight during a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. The abort motor is what will activate to pull the Orion crew module away during the event of an emergency during ascent. AA-2 will launch from Space Launch Complex 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing flight operations for AA-2.
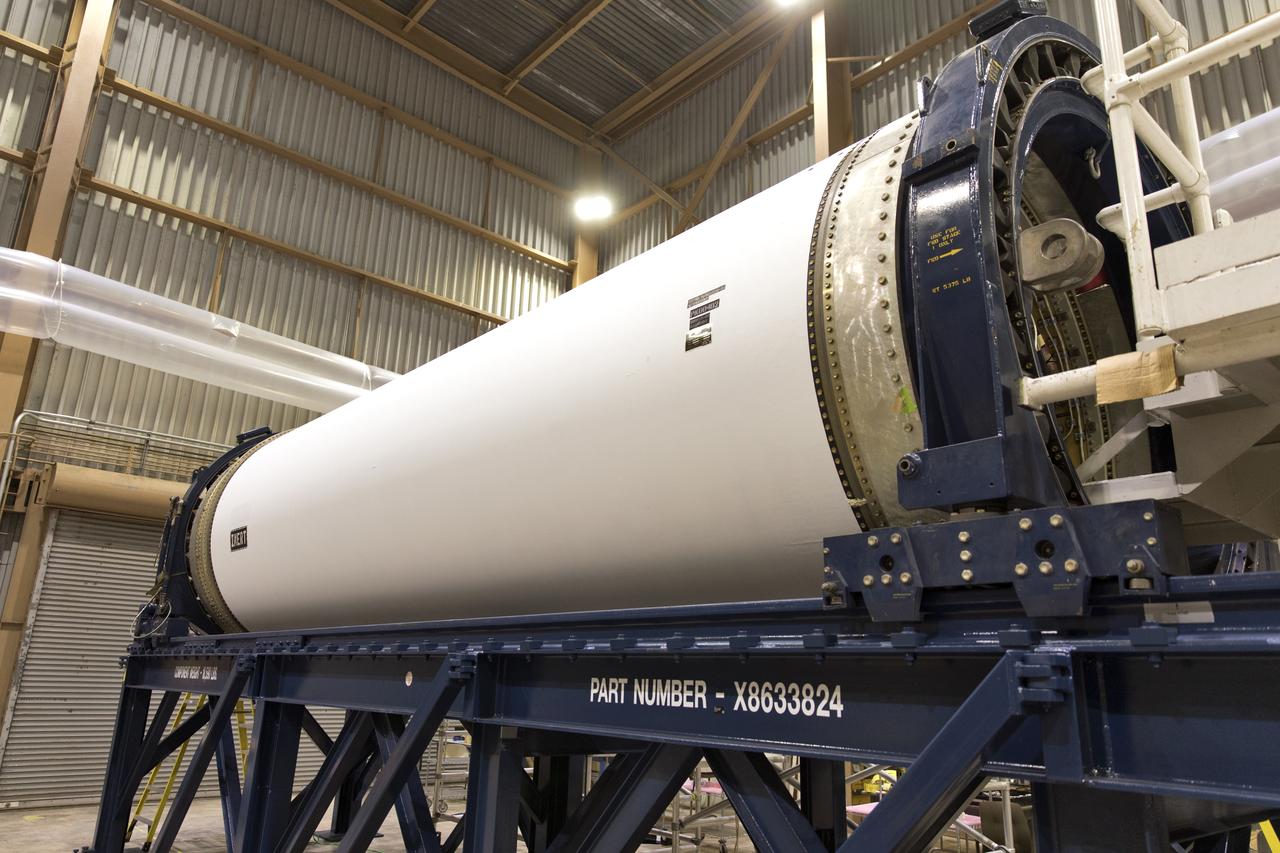

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
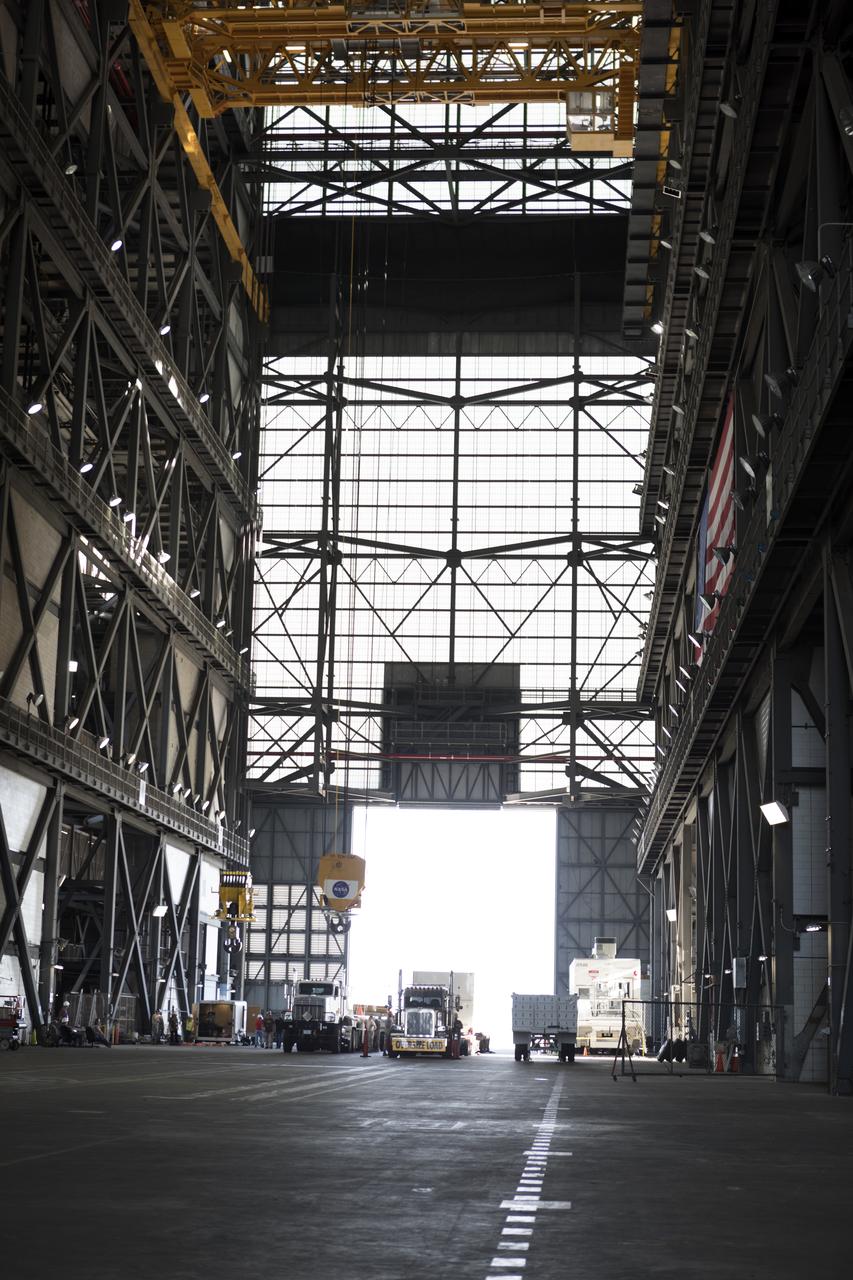

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) arrives by flatbed truck in its shipping container in the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building on July 20, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be transferred to the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility where it will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.
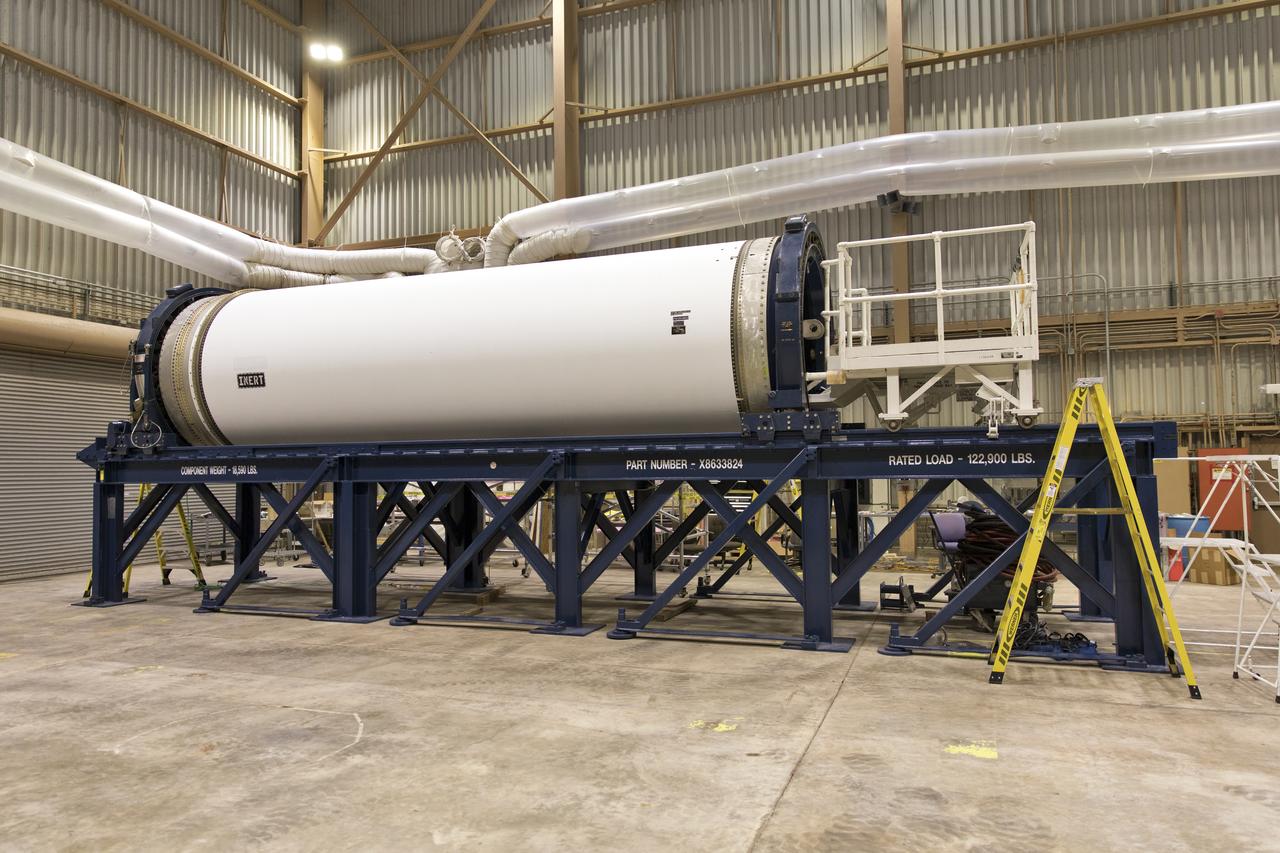

The ground test motor for Orion's Launch Abort System (LAS) is secured on a work stand inside the Rotation, Processing and Surge Facility on July 31, 2018, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. It will be inspected and prepared for transport to Space Launch Complex 46 (SLC-46) at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mechanical fit testing. This inert motor will not be used for flight, but will be used to certify flight hardware assembly in preparation for a full-stress test of the LAS, called Ascent Abort-2 (AA-2) flight test, scheduled for April 2019. During the test, the booster will launch from SLC 46, carrying a fully functional LAS and a 22,000-pound Orion test vehicle to an altitude of 31,000 feet and traveling at more than 1,000 miles an hour. The test will verify the LAS can steer the crew module and astronauts aboard to safety in the event of an issue with the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket when the spacecraft is under the highest aerodynamic loads it will experience during a rapid climb into space. NASA's Orion and Exploration Ground Systems programs and their contractors from Jacob's and Northrup Grumman in conjunction with the Air Force Space and Missile Center's Launch Operations branch are performing the pathfinding exercises and flight operations for AA-2.