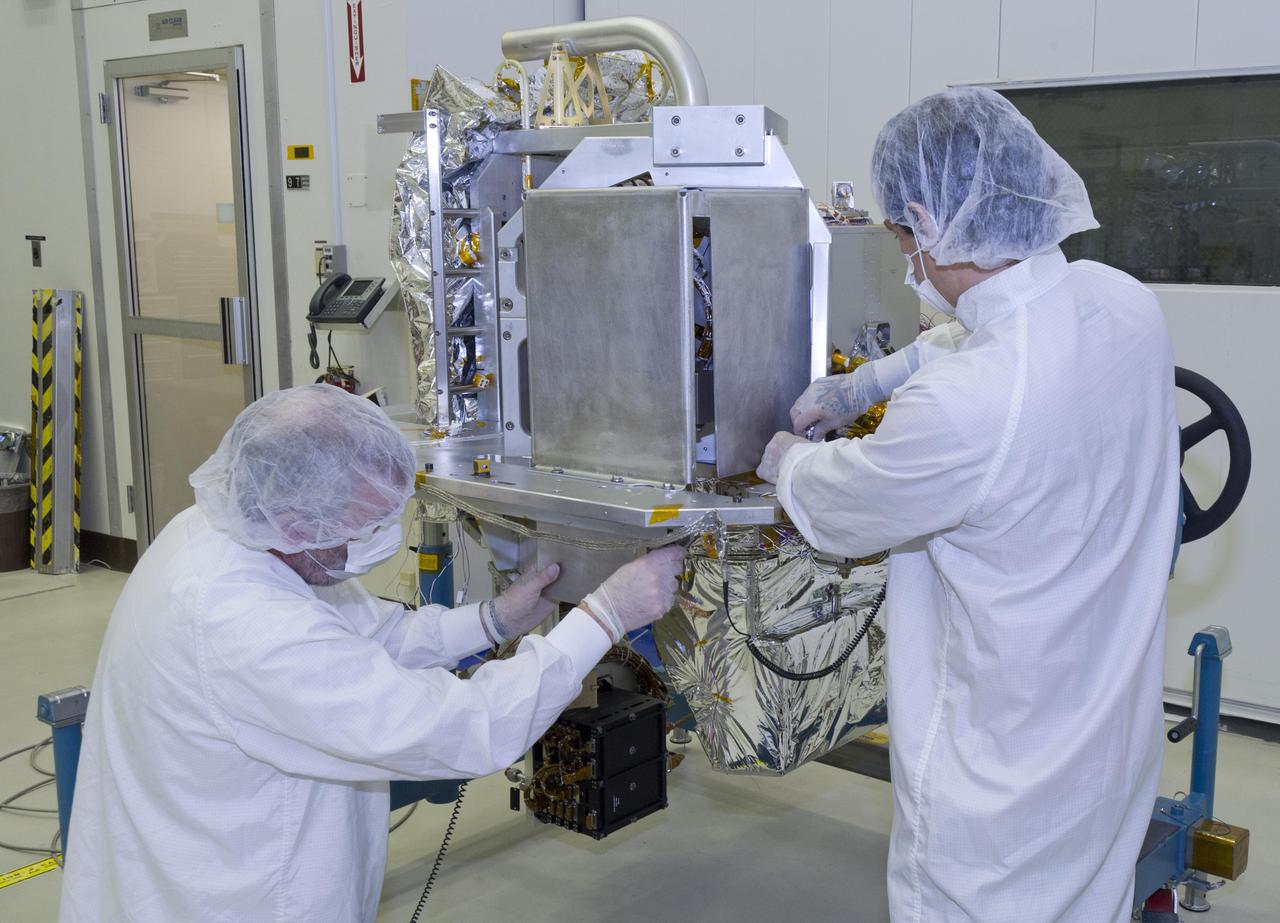

Technicians prep NASA OCO-2 instrument for shipping at Jet Propulsion Lab in Pasadena, Ca.

Technicians prep NASA OCO-2 instrument for shipping at Jet Propulsion Lab in Pasadena, Ca. Animation available in More Details.

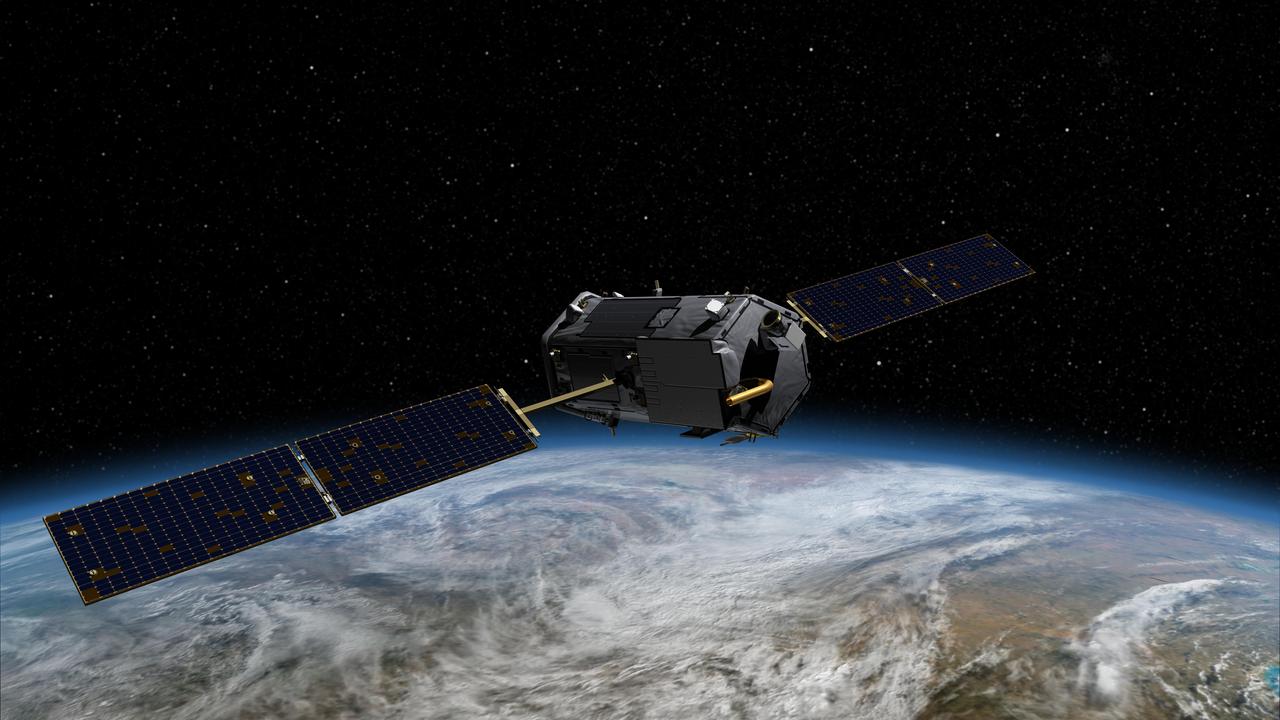
Artist rendering of NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory OCO-2, one of five new NASA Earth science missions set to launch in 2014, and one of three managed by JPL.
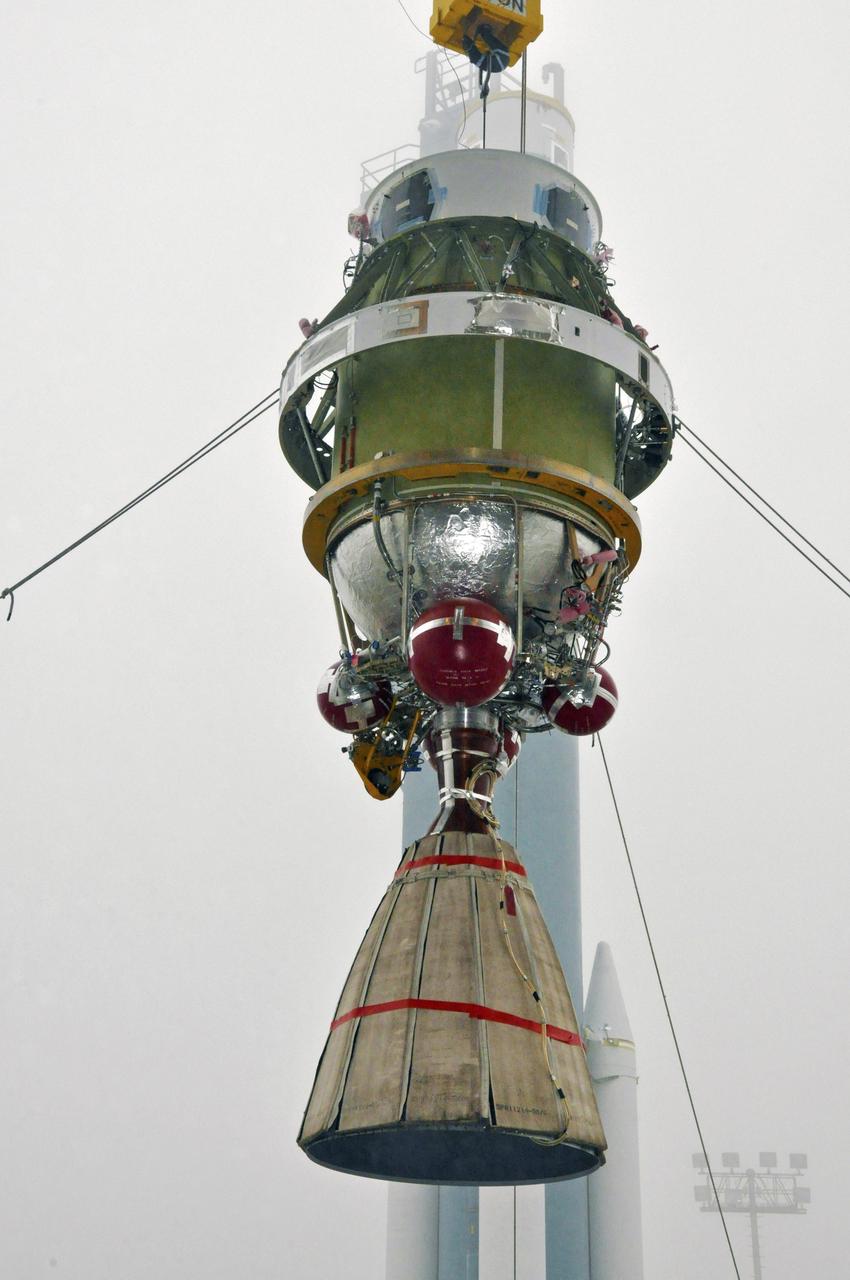

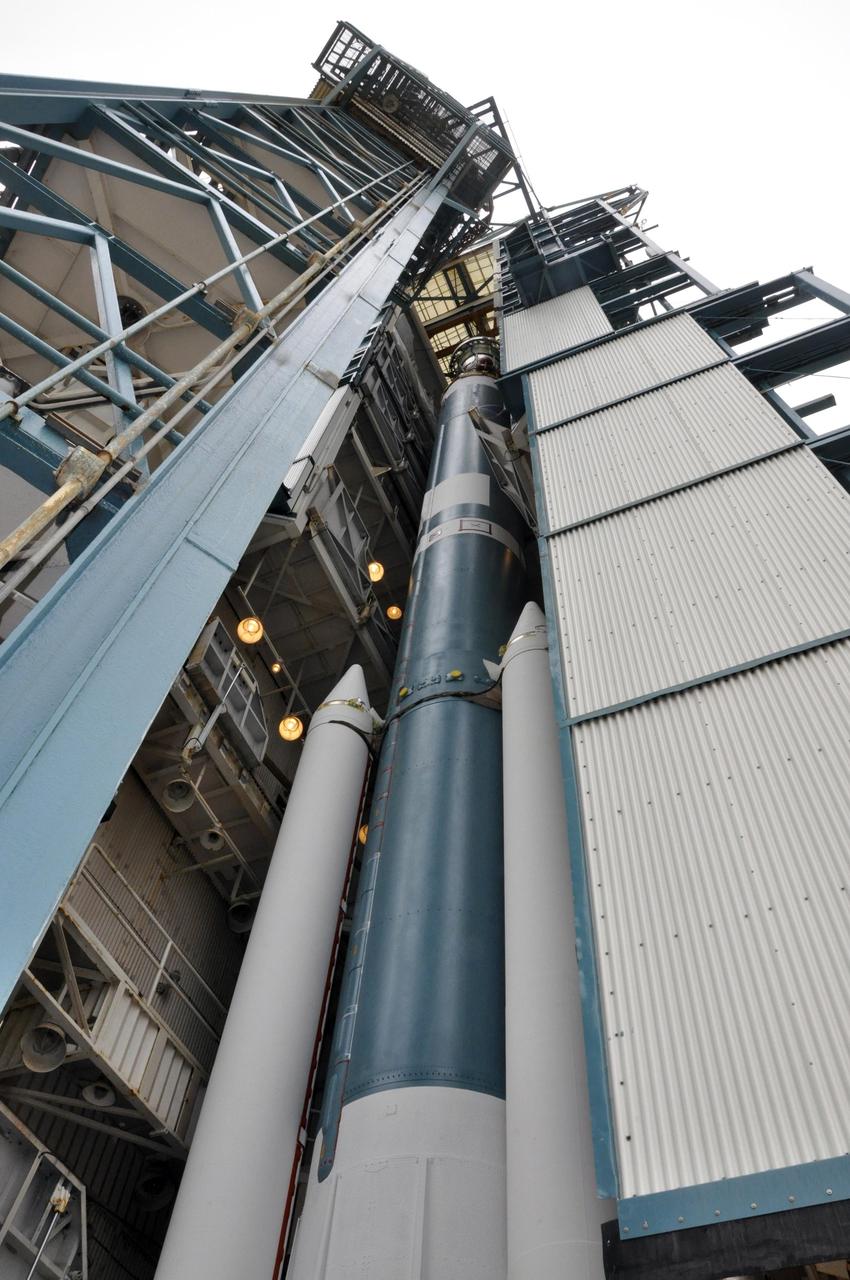
The Delta II second stage for NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted to the top of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
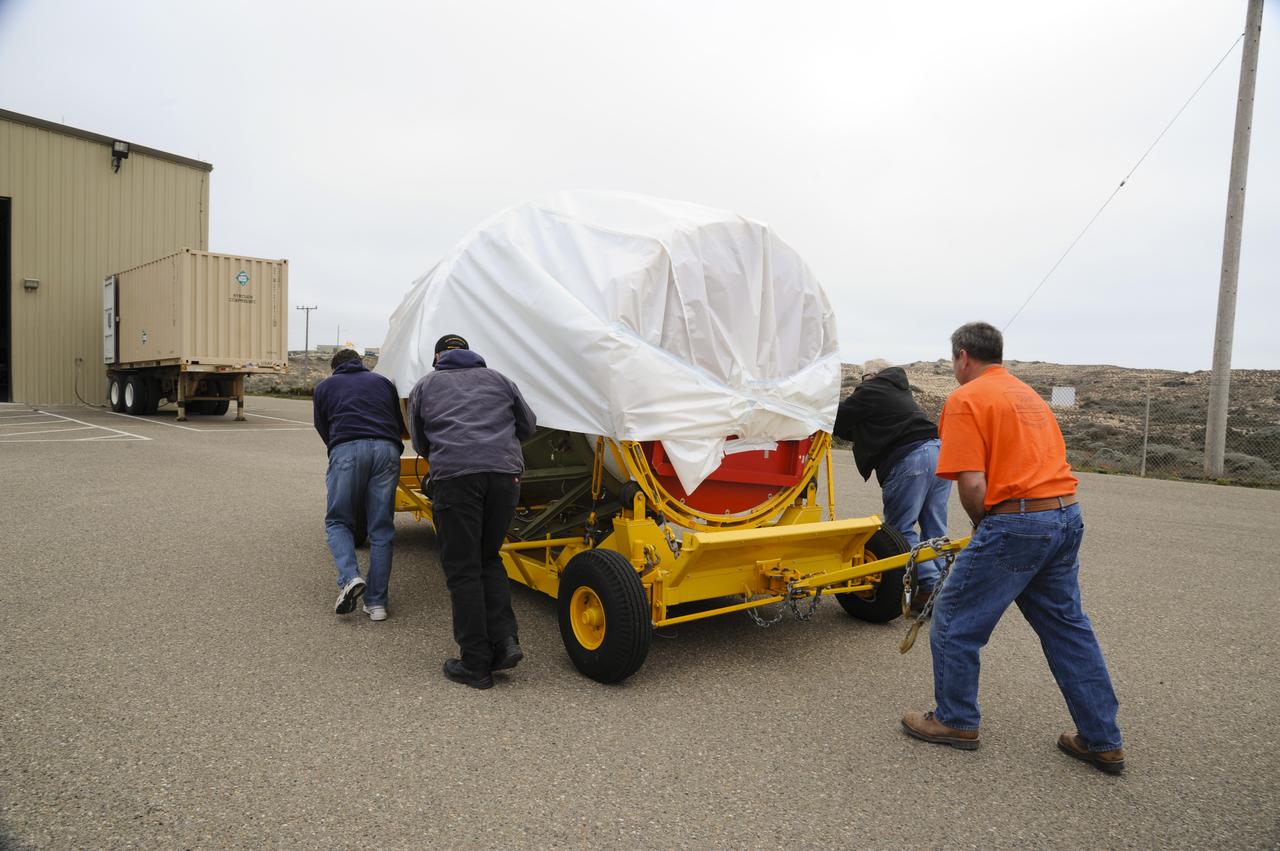

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers push the second stage for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, toward the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The rocket's second stage will insert OCO-2 into a polar Earth orbit. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Arron Tauman, 30th Space Wing, VAFB
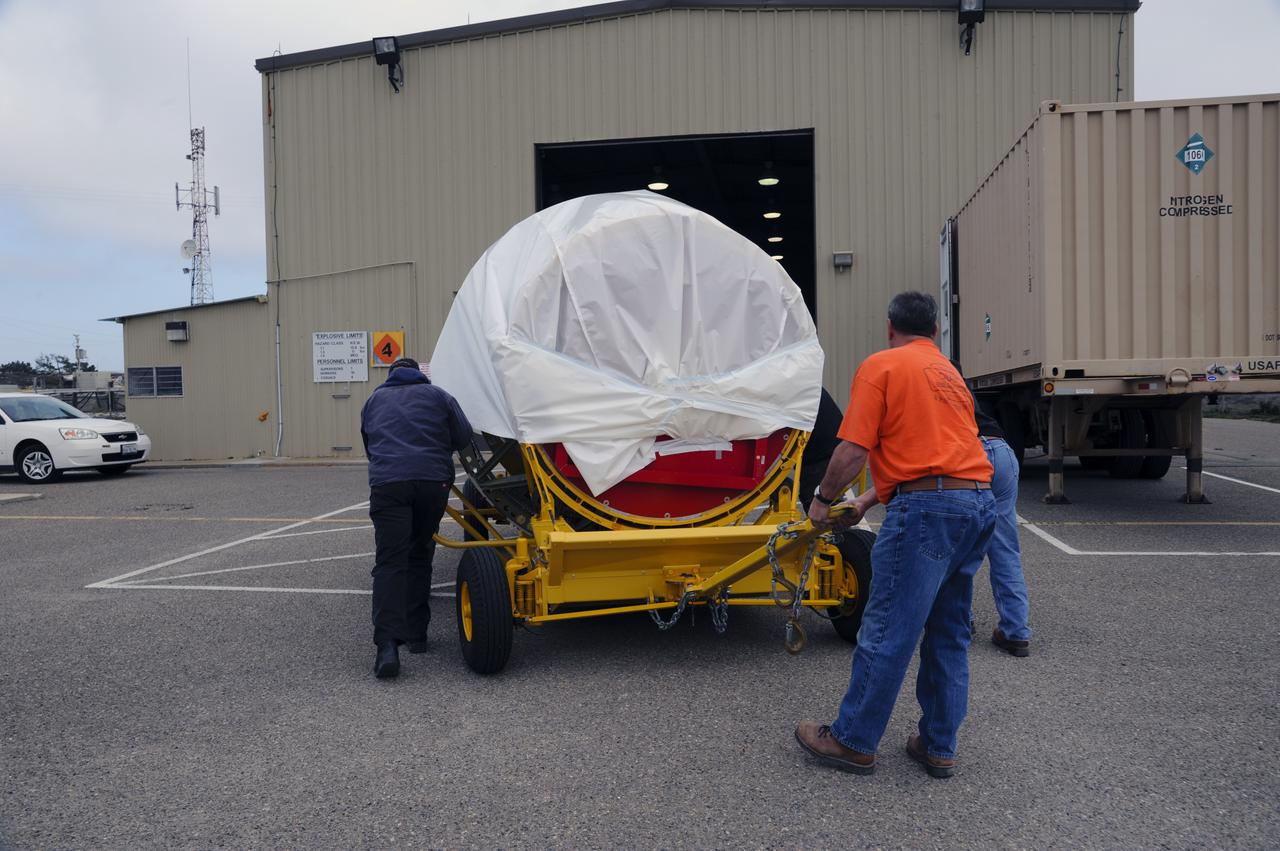

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers guide the second stage for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The rocket's second stage will insert OCO-2 into a polar Earth orbit. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Arron Tauman, 30th Space Wing, VAFB
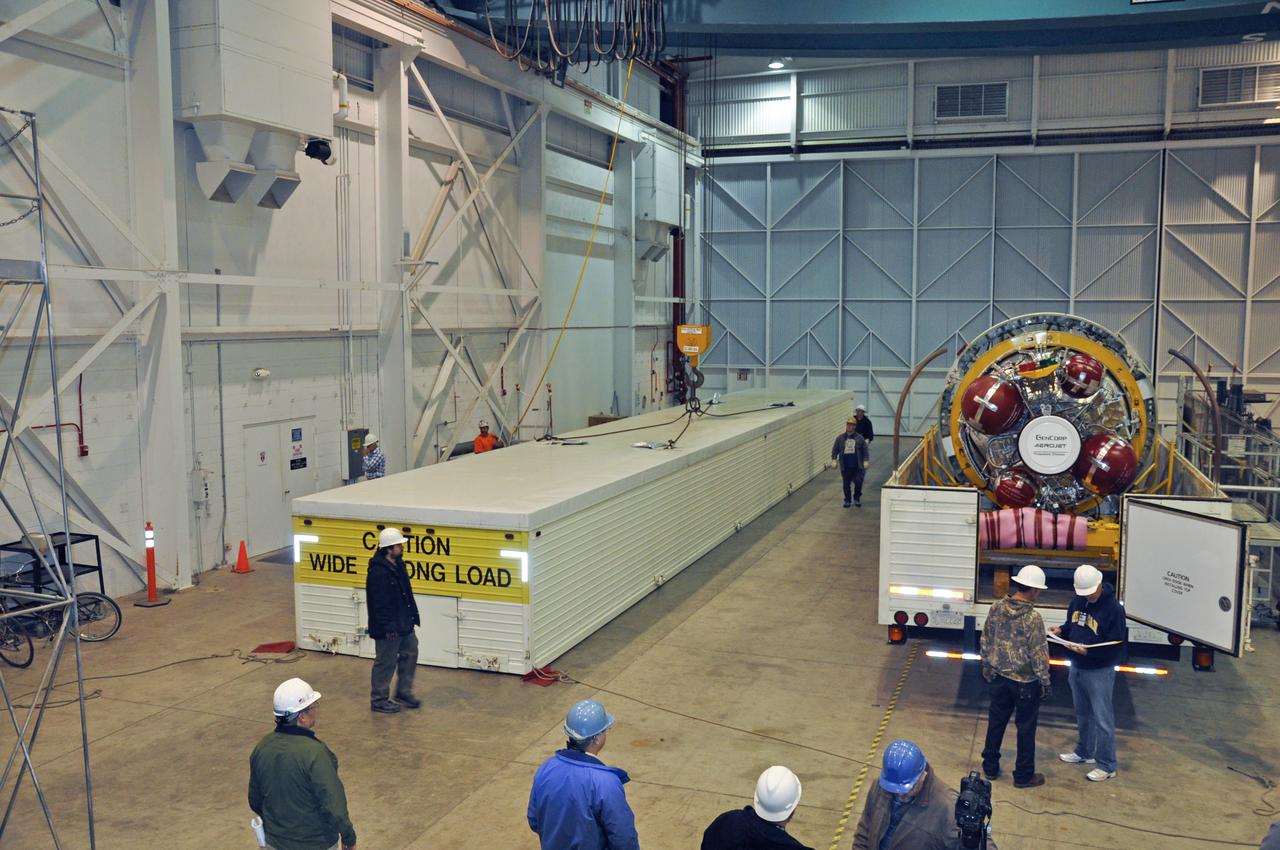

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers prepare to lift the second stage for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, from its transportation trailer in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The rocket's second stage will insert OCO-2 into a polar Earth orbit. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
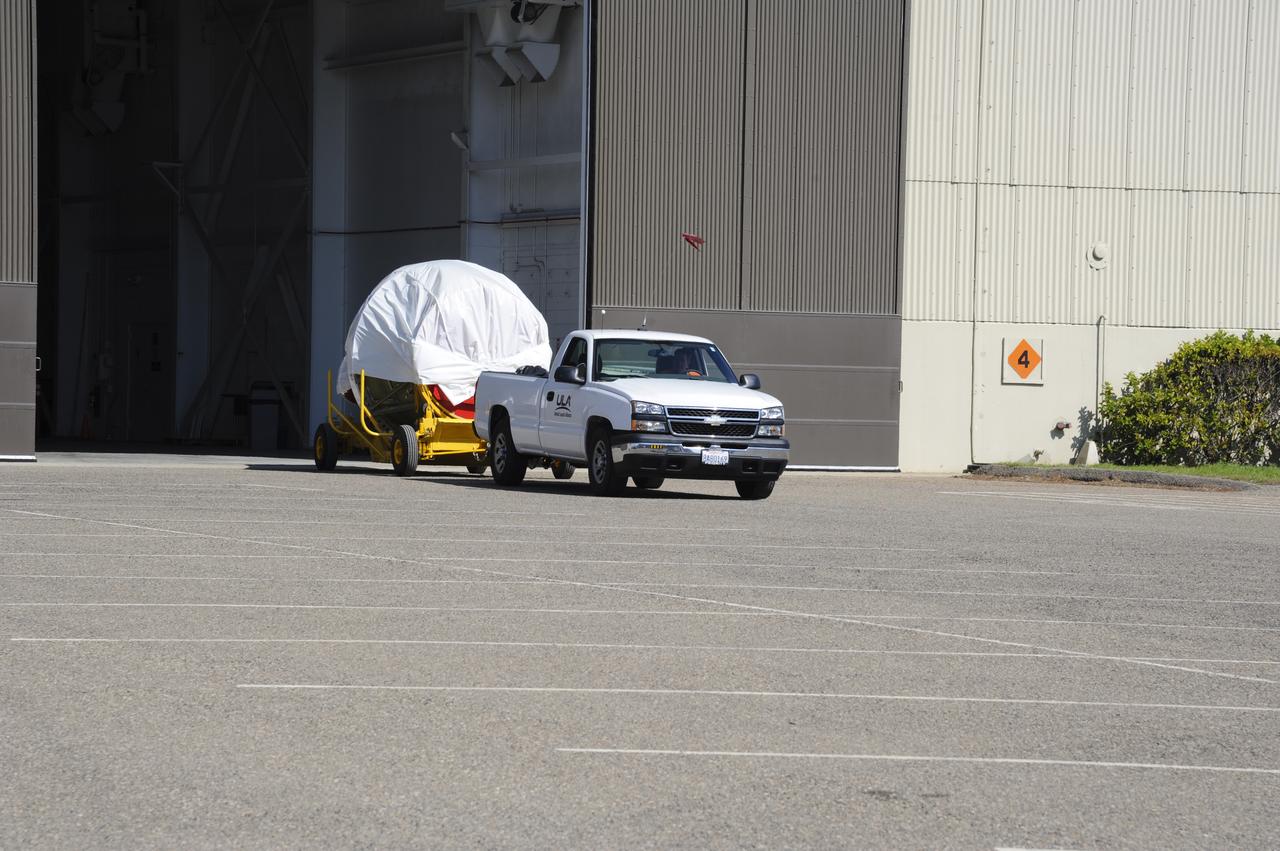

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The second stage for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is being towed from the Building 836 hangar to the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The rocket's second stage will insert OCO-2 into a polar Earth orbit. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Arron Tauman, 30th Space Wing, VAFB
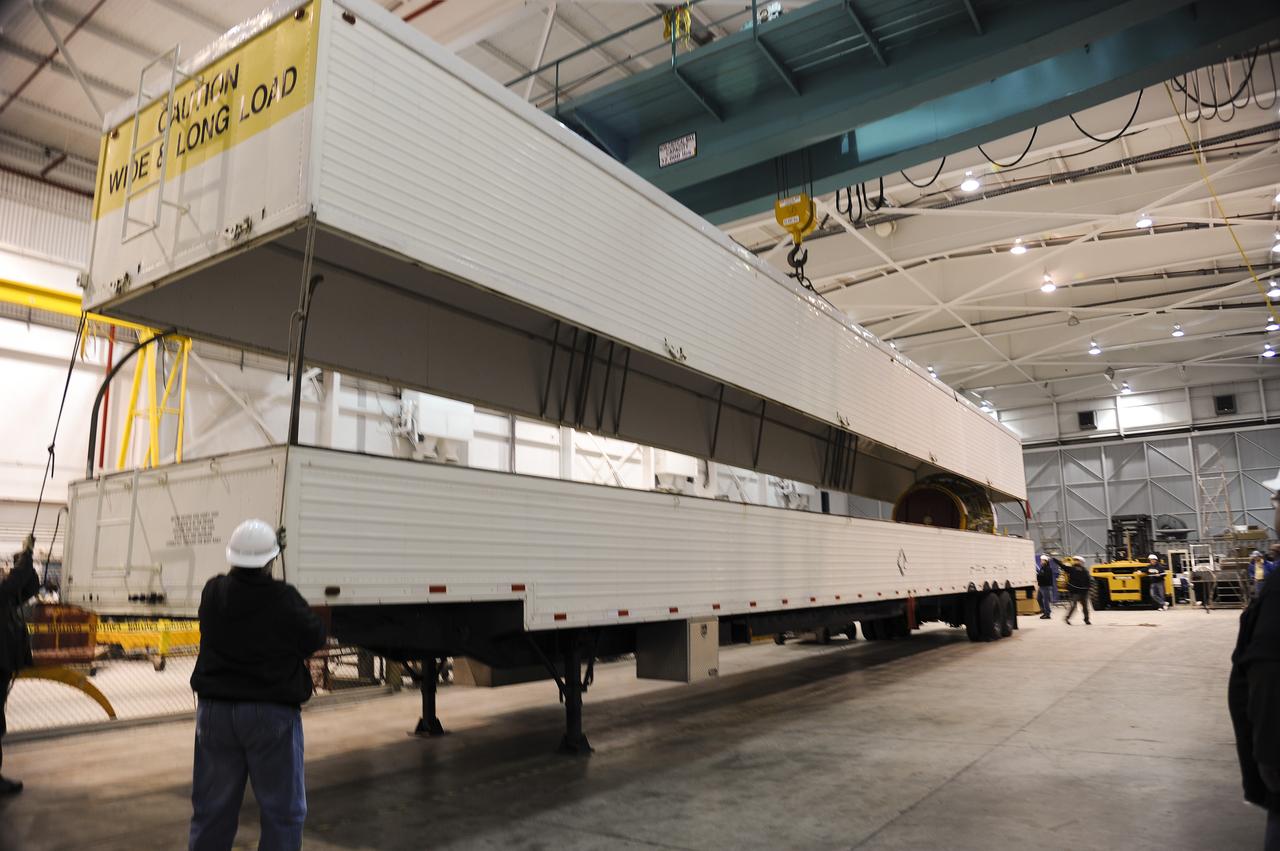

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – As the cover of the transportation trailer is lifted in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the second stage for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, comes into view. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The rocket's second stage will insert OCO-2 into a polar Earth orbit. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Arron Tauman, 30th Space Wing, VAFB
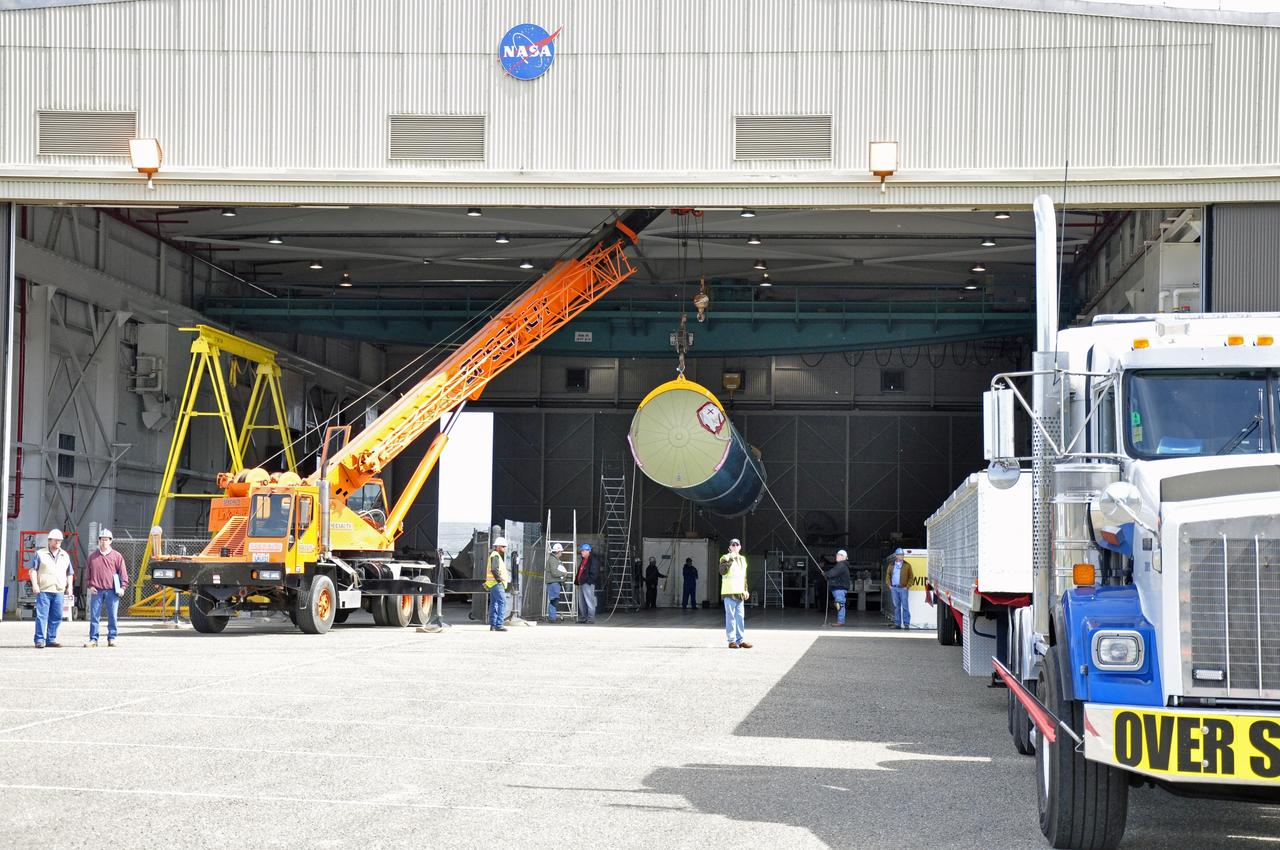

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is suspended midair during its transfer from its transportation trailer to a transportation hardware cradle in the Building 836 hangar at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, rests on a transportation hardware cradle in the Building 836 hangar at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California awaiting installation on the pad. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
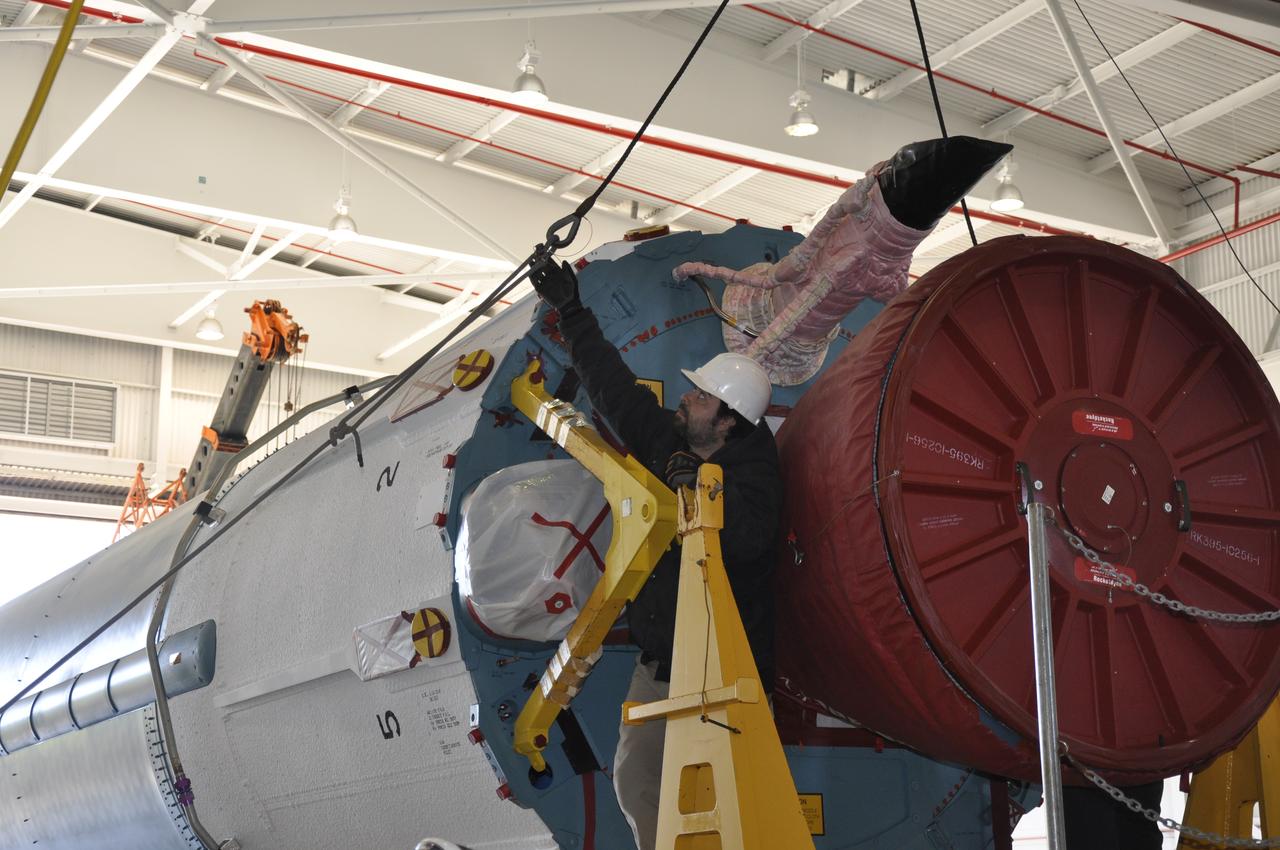

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lowered onto a transportation hardware cradle in the Building 836 hangar at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
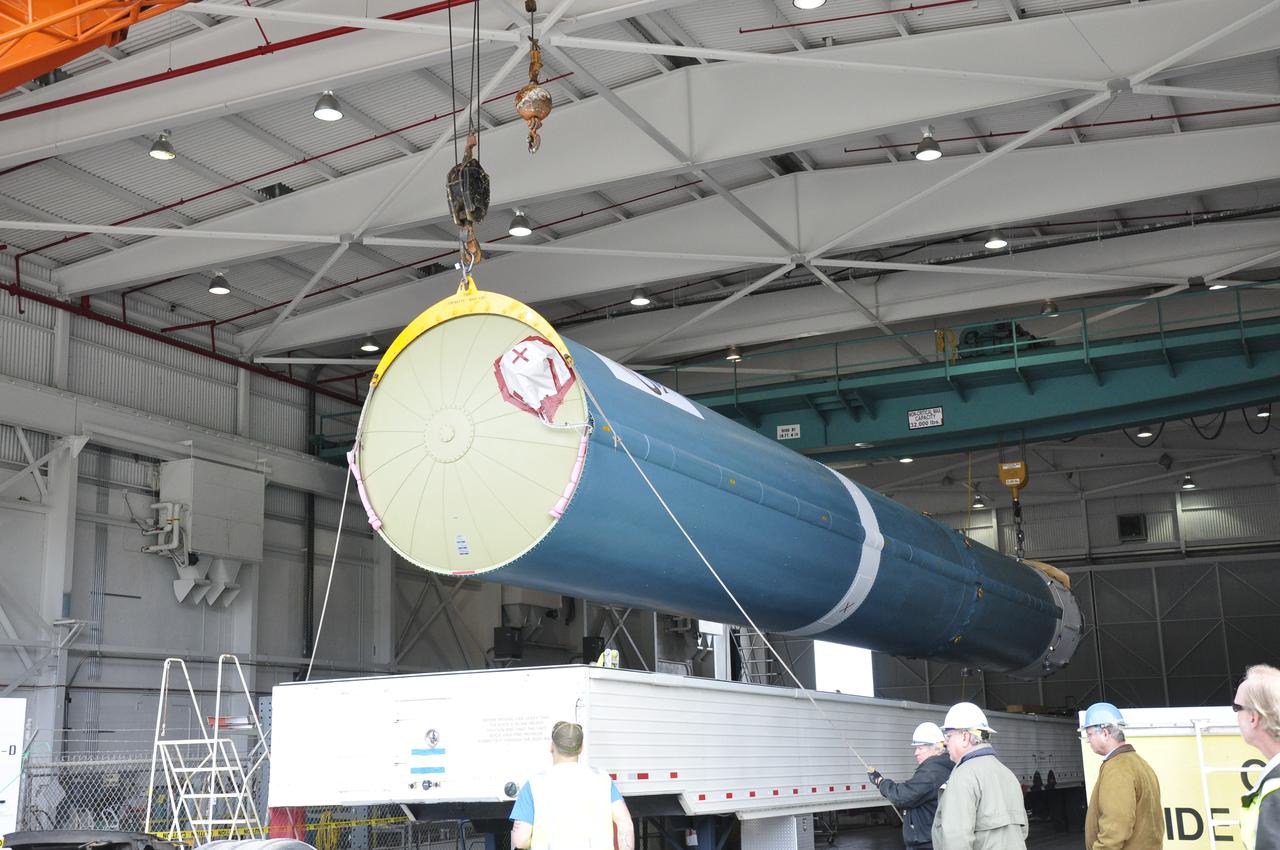

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted from its transportation trailer in the Building 836 hangar at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
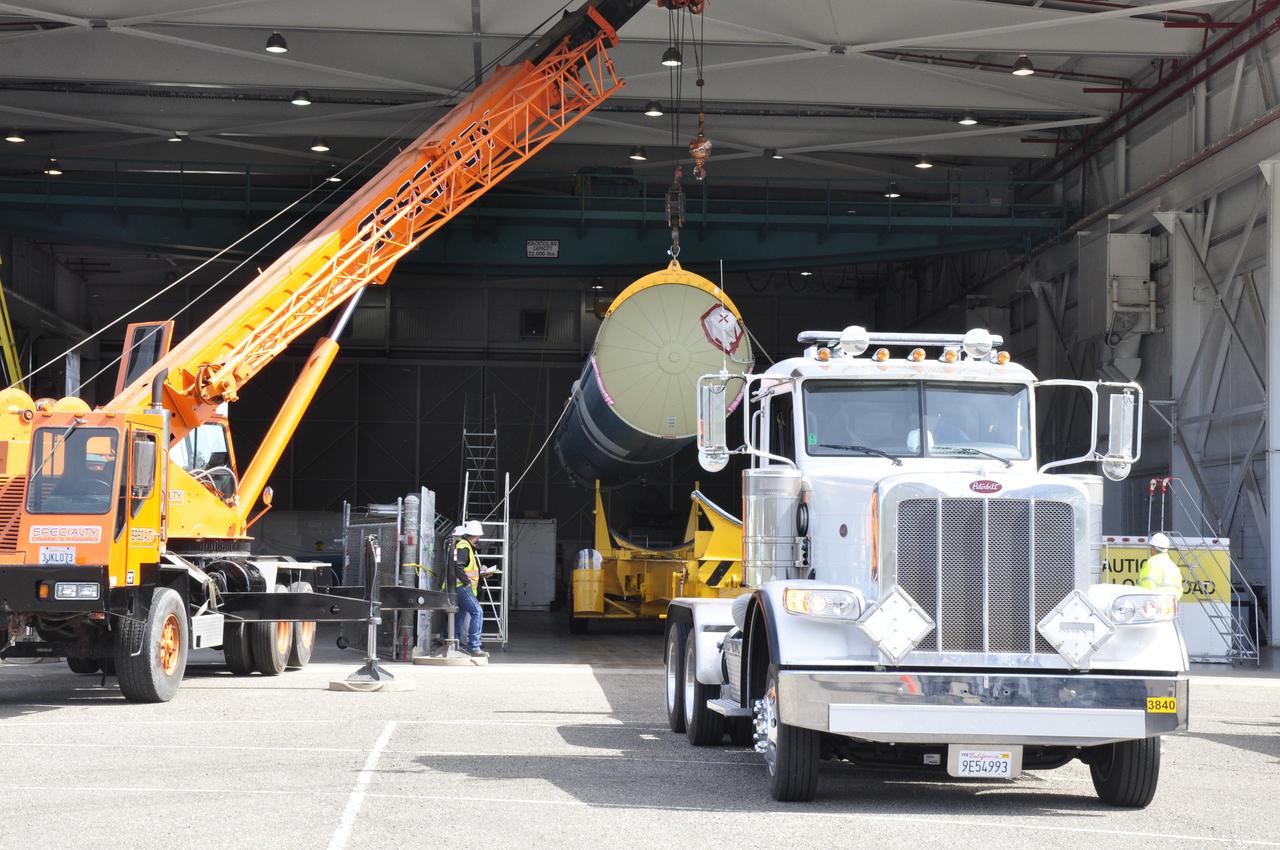

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A mobile crane is enlisted to lift NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, from its transportation trailer in the Building 836 hangar at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
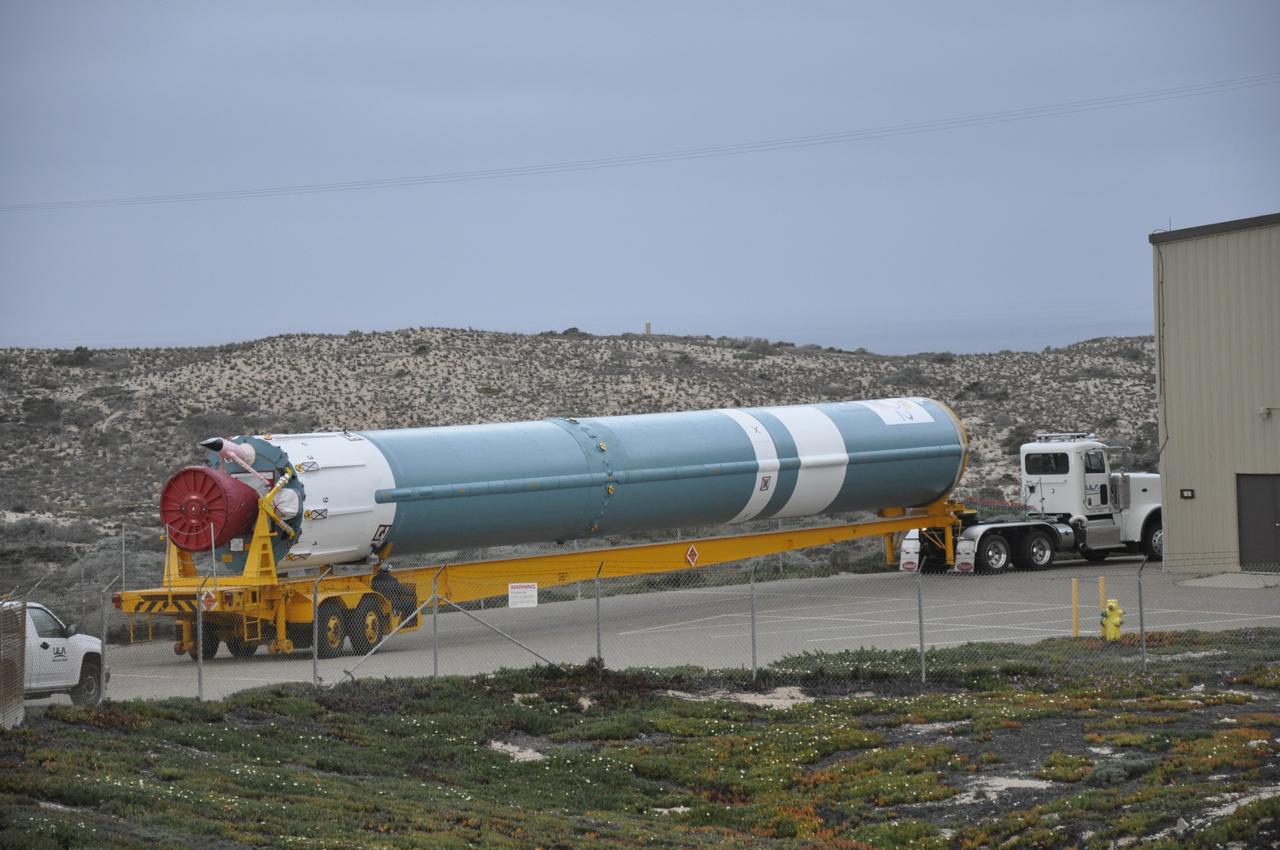

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, secured in a transportation hardware cradle, is towed to the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
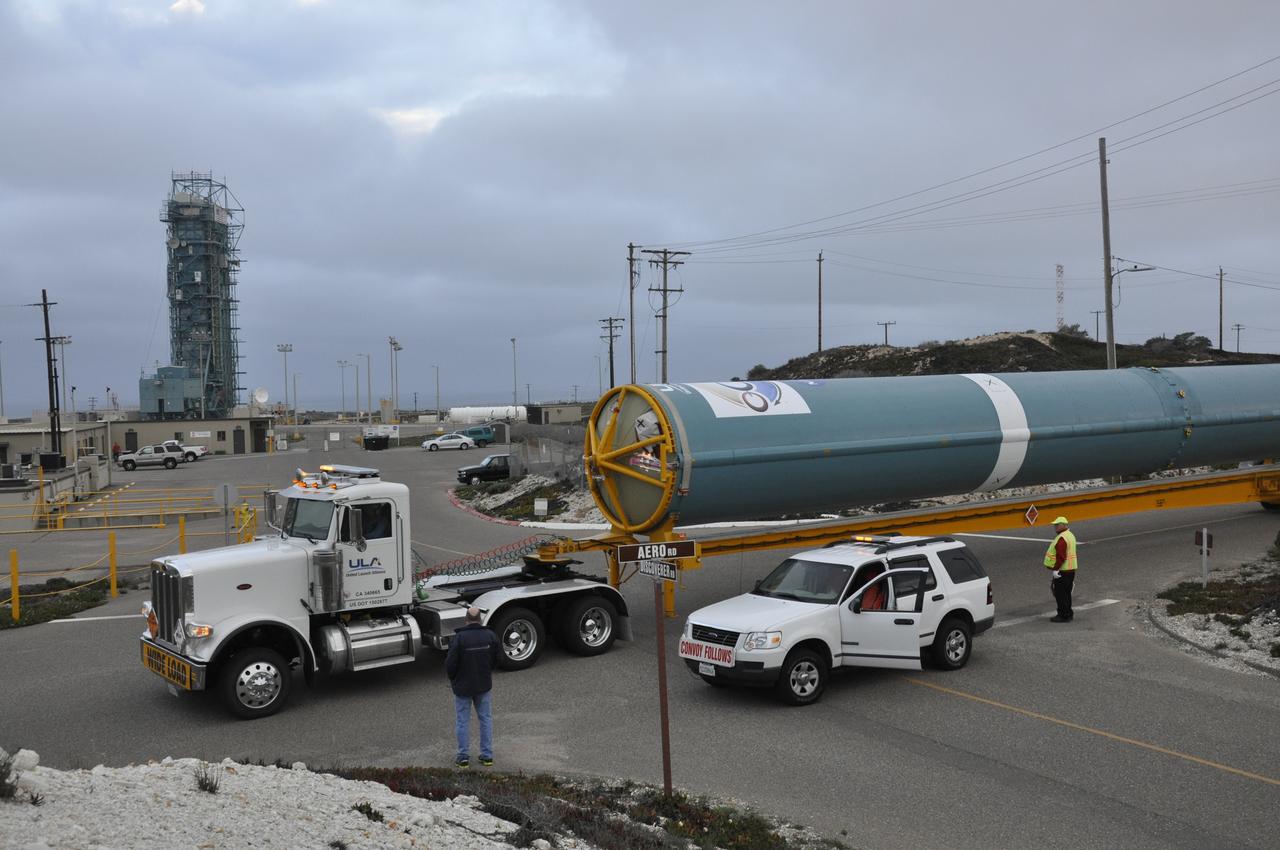

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, arrives at the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, and its transportation hardware cradle roll into the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
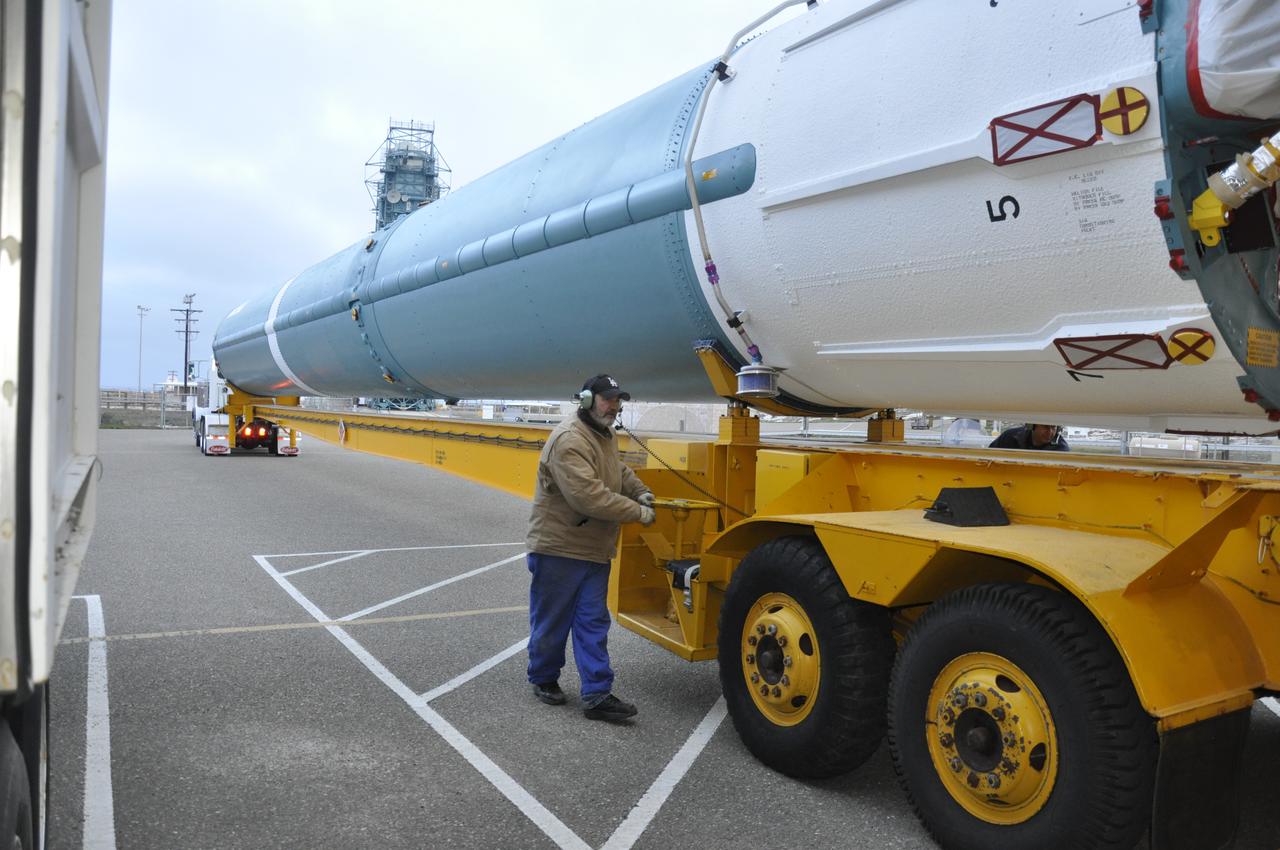

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A worker surveys the Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, secured in a transportation hardware cradle, that he delivered to the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
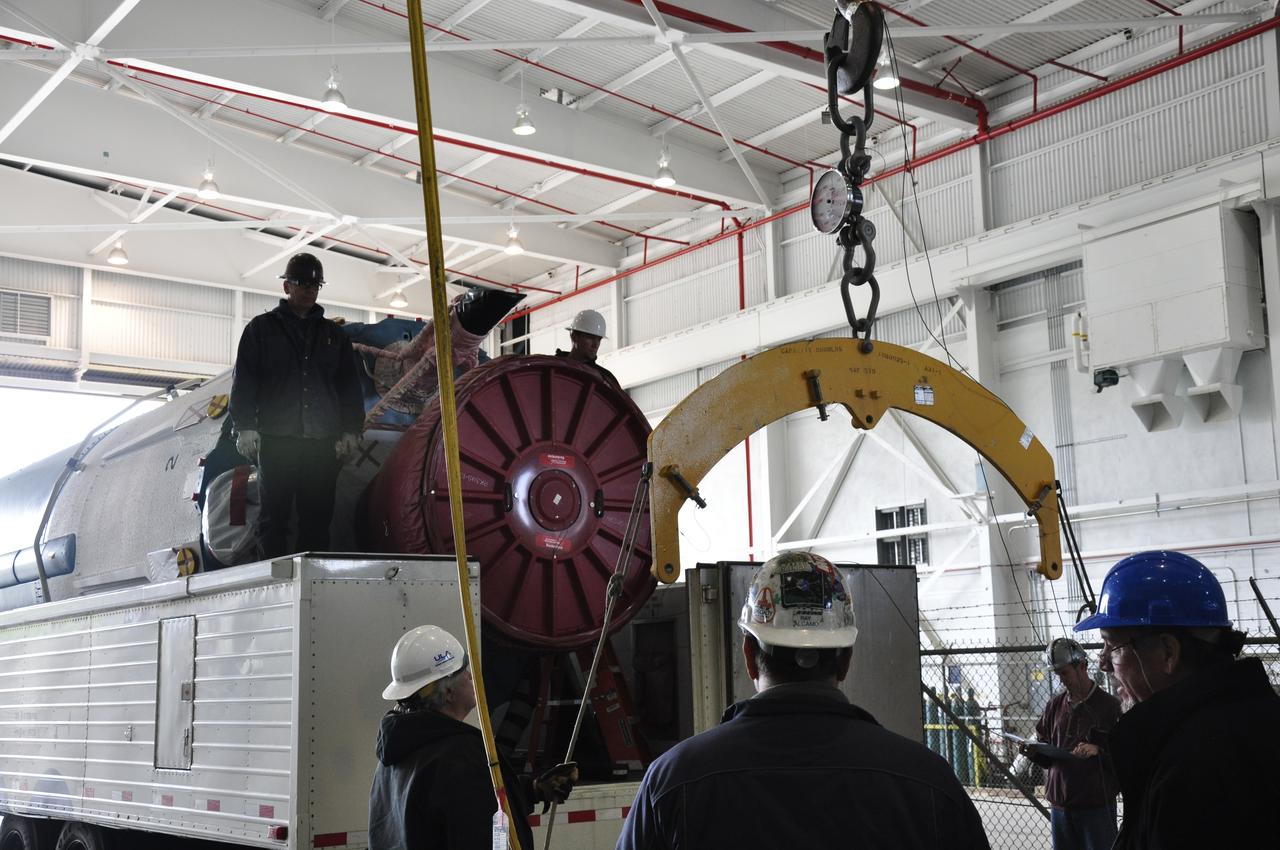

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers prepare to lift the Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, from its transportation trailer in the Building 836 hangar at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
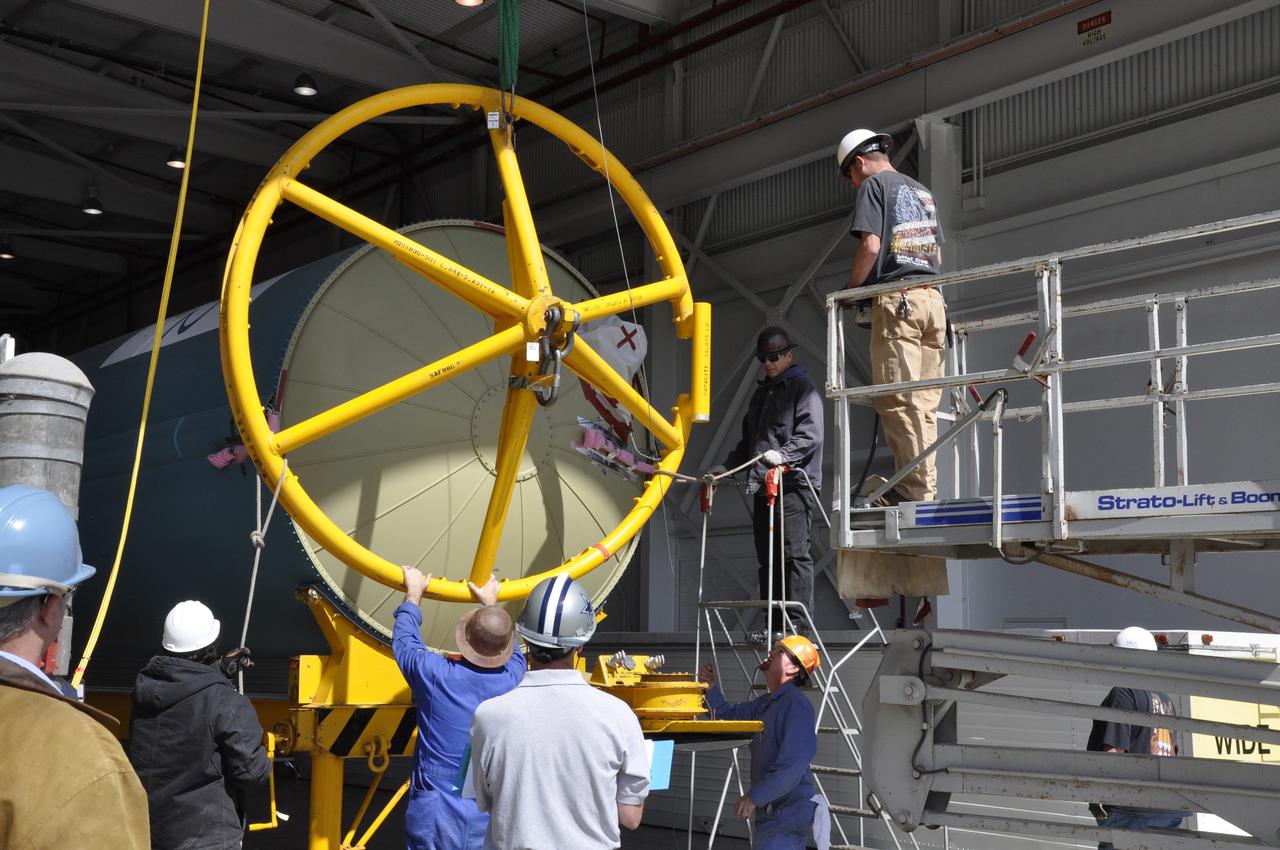

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers secure the Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, onto a transportation hardware cradle in the Building 836 hangar at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
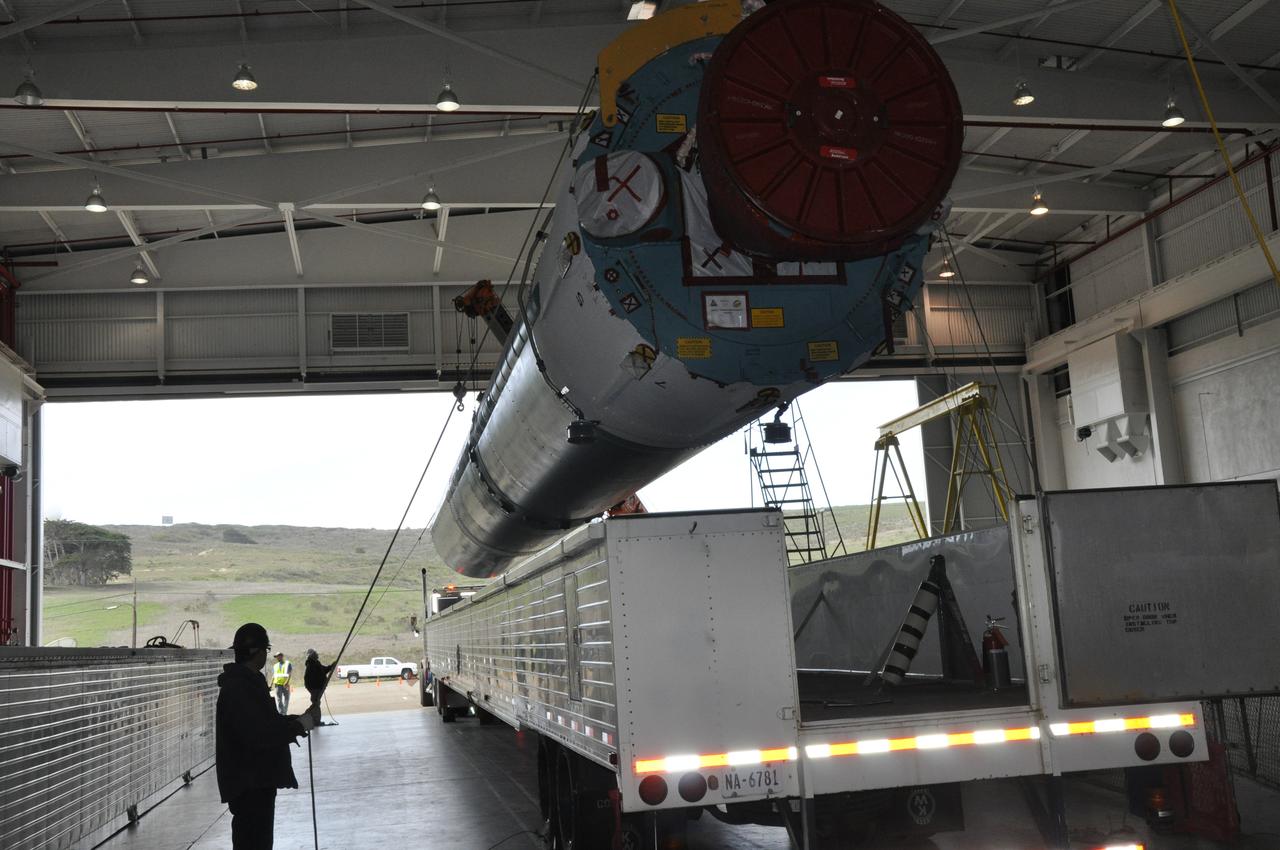

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers steady the Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, as it is lifted from its transportation trailer in the Building 836 hangar at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is positioned inside the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
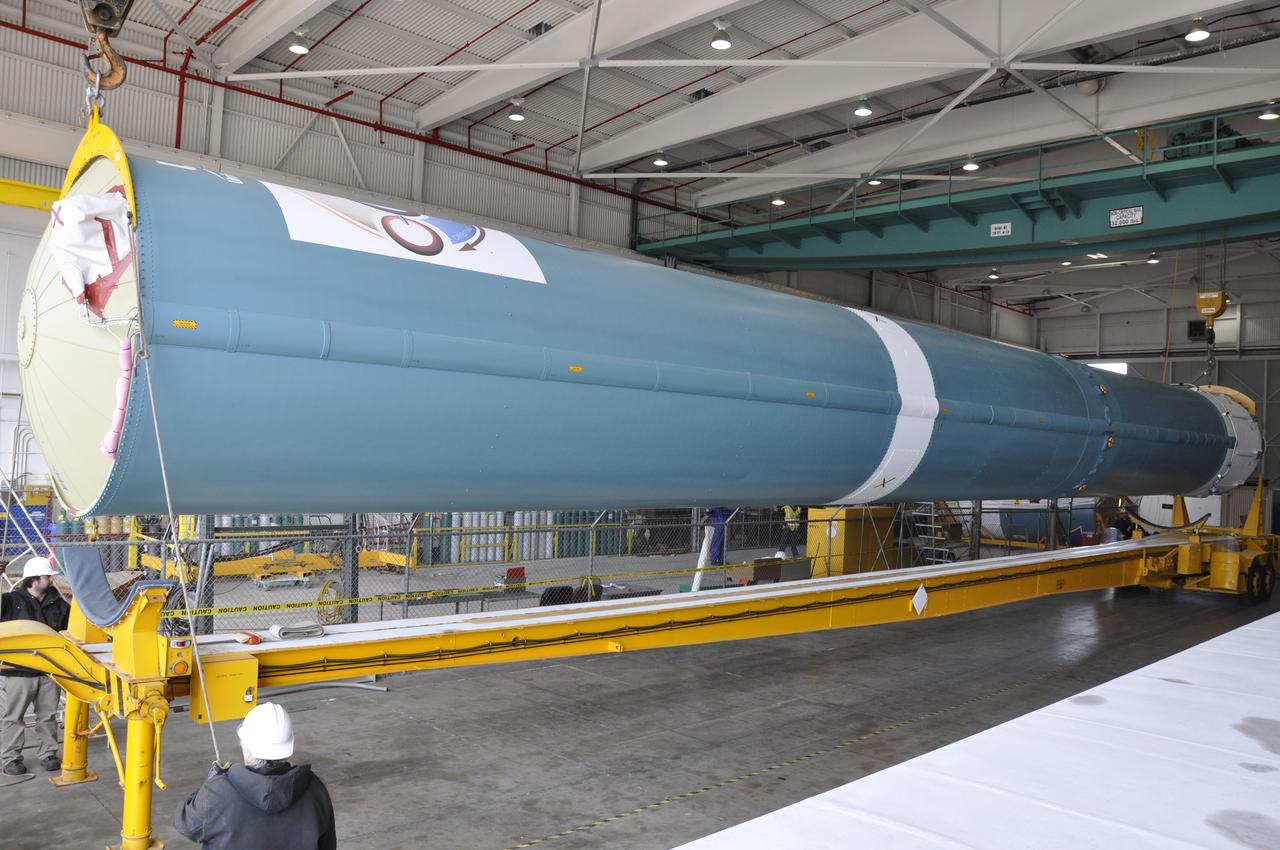

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lowered onto a transportation hardware cradle in the Building 836 hangar at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A worker maneuvers the transporter towing the Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, at the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
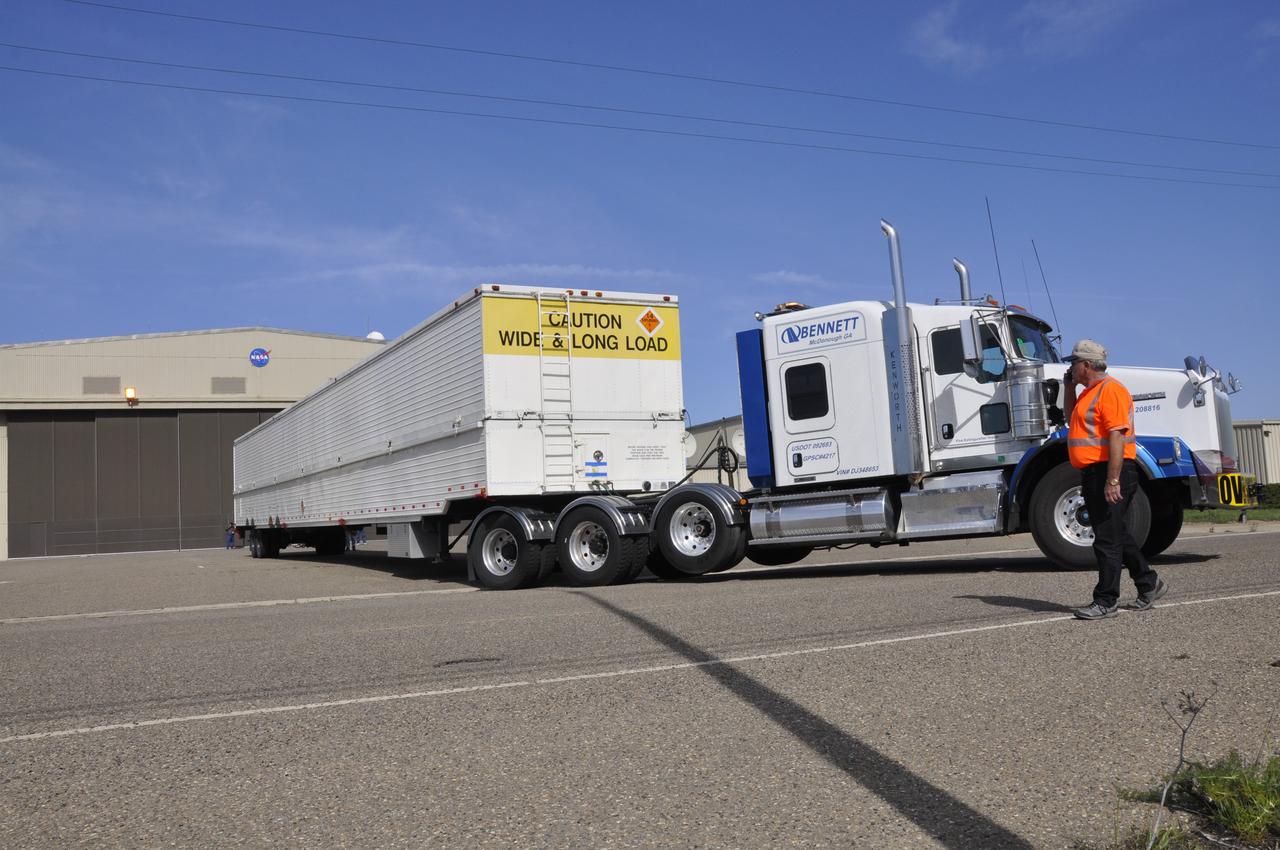

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The truck transporting the Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, backs toward the Building 836 hangar at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
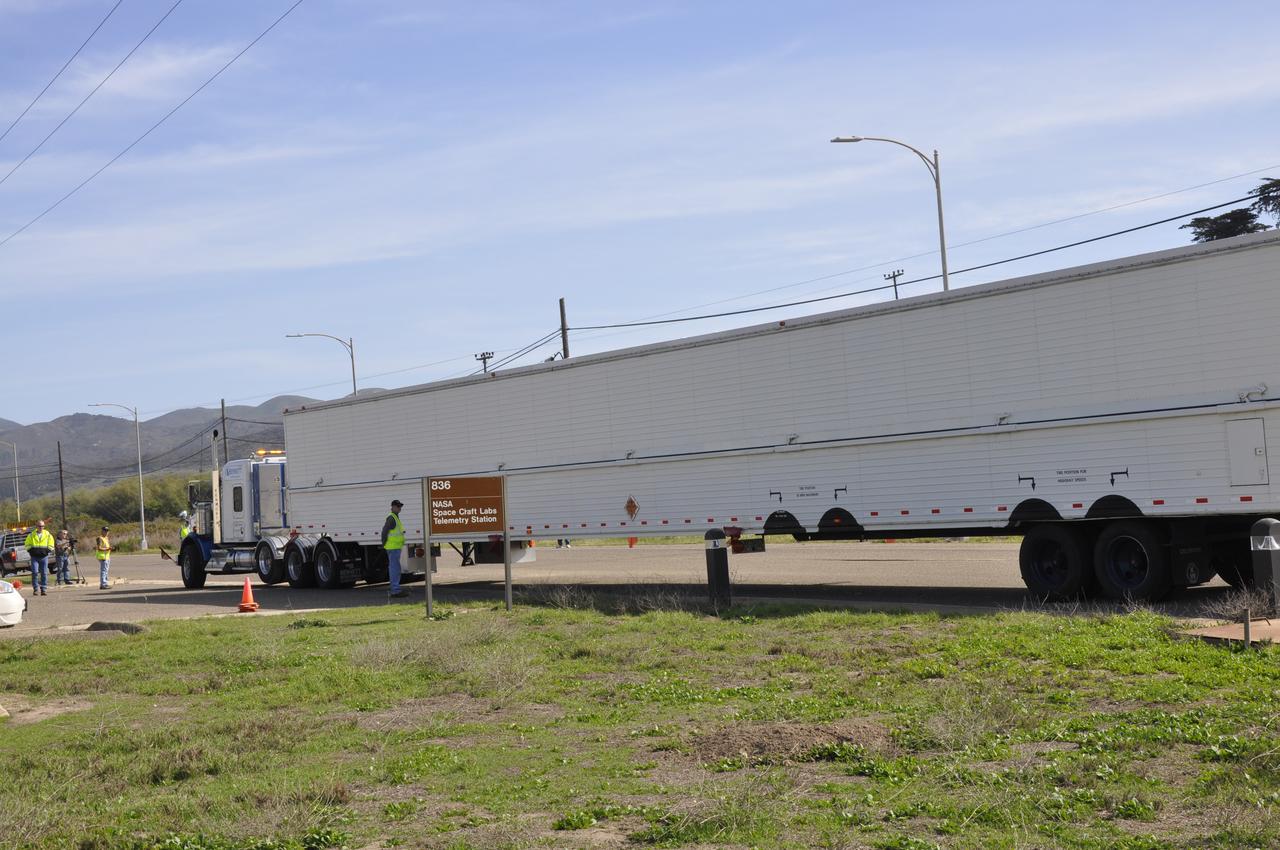

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The truck transporting the Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, arrives outside the Building 836 hangar at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
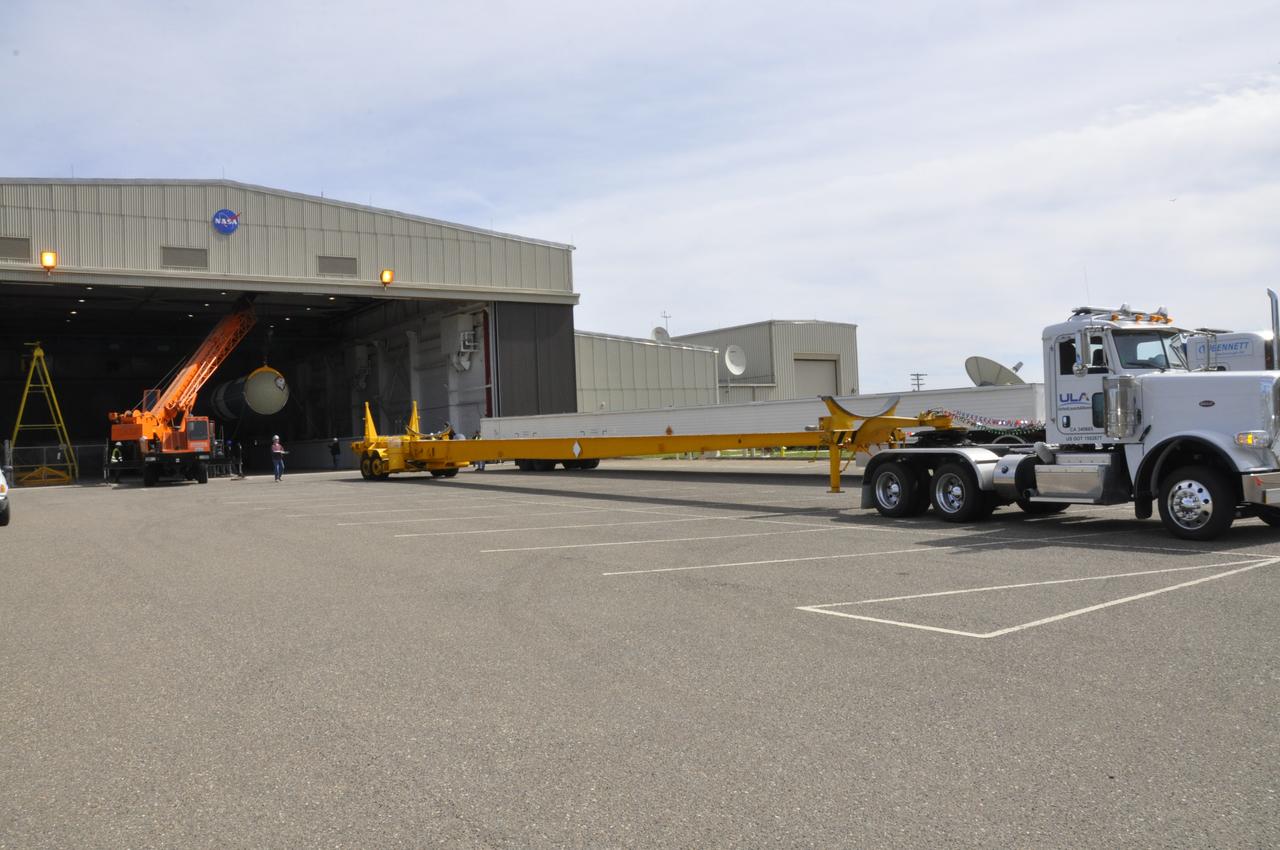

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – It's mission accomplished for the transportation trailer that delivered NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, to the Building 836 hangar at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
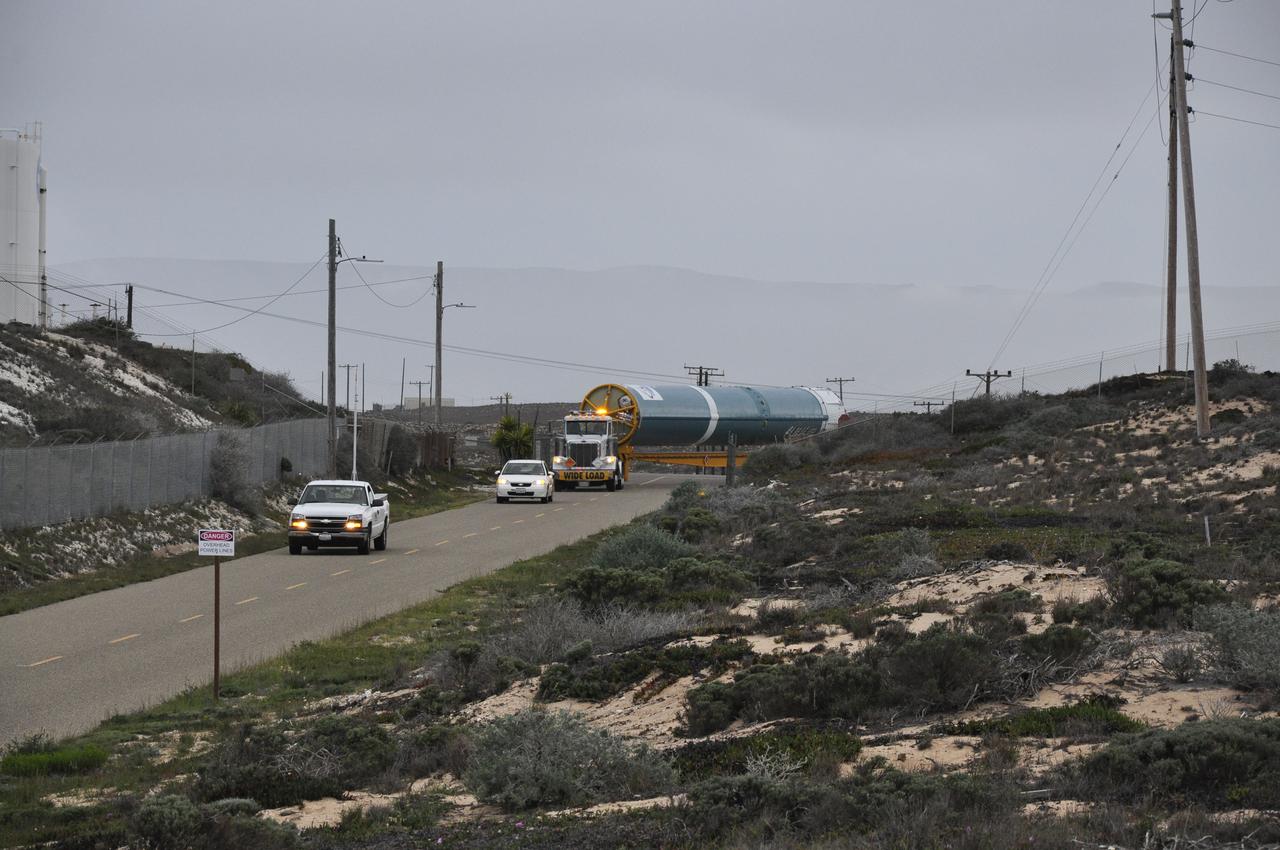

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is towed to the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
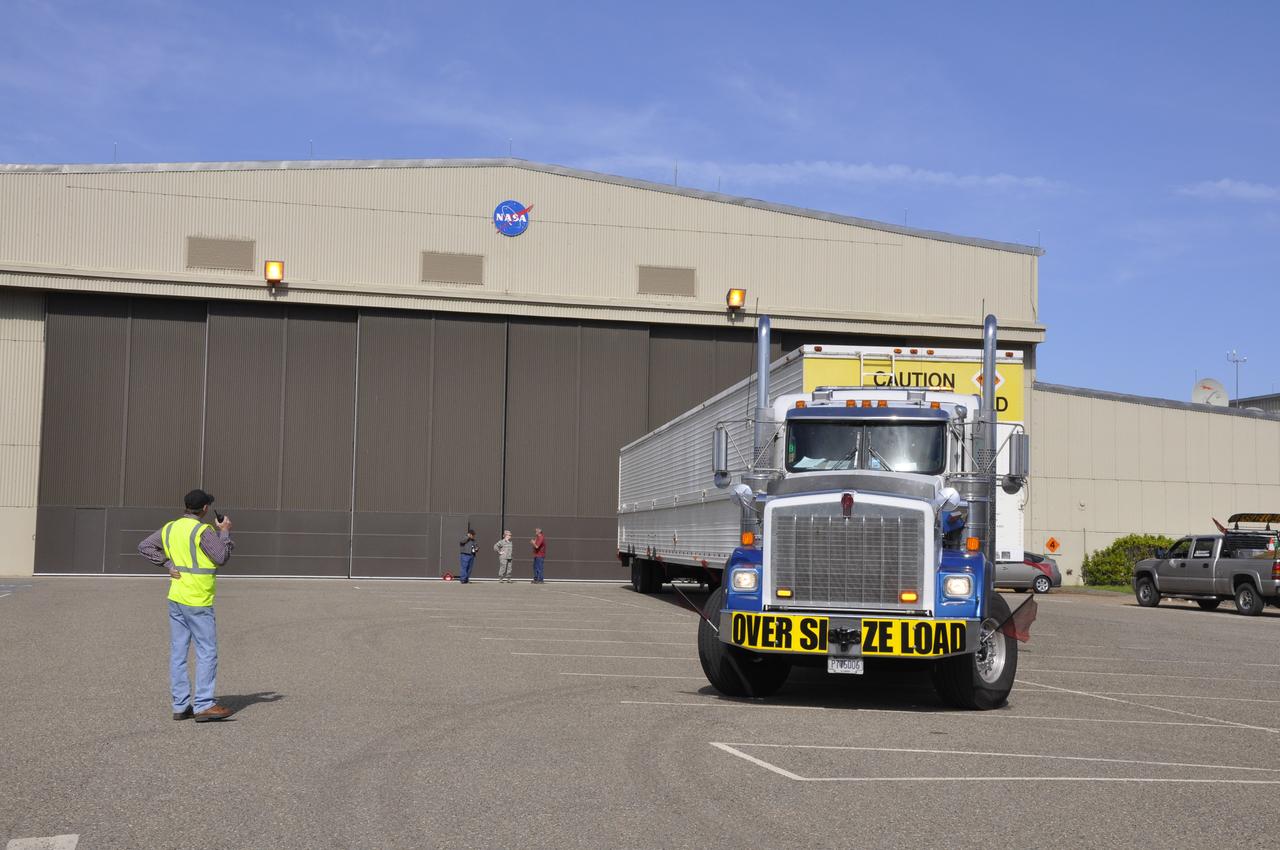

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Preparations are underway to offload the Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into the Building 836 hangar at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
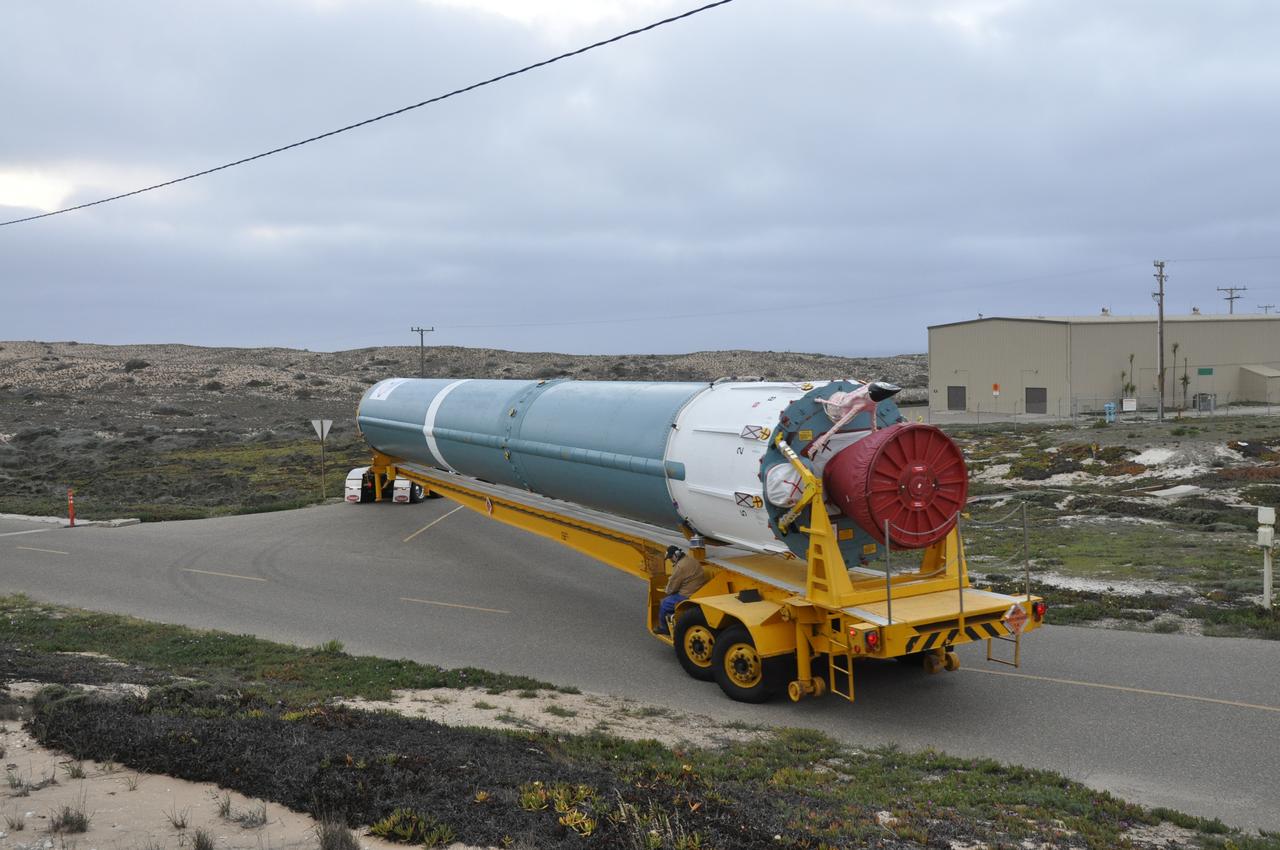

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, arrives at the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
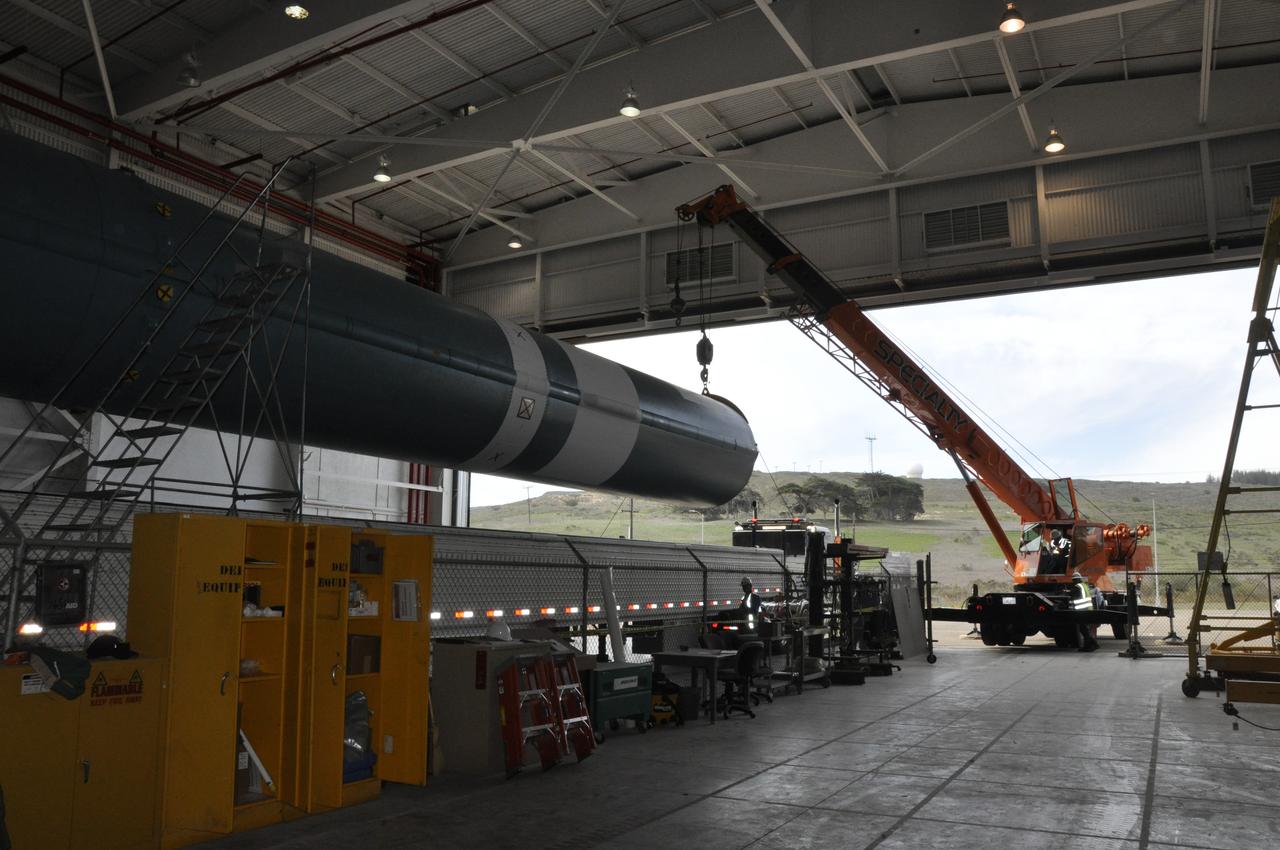

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The Delta first-stage booster for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is suspended above its transportation trailer in the Building 836 hangar at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
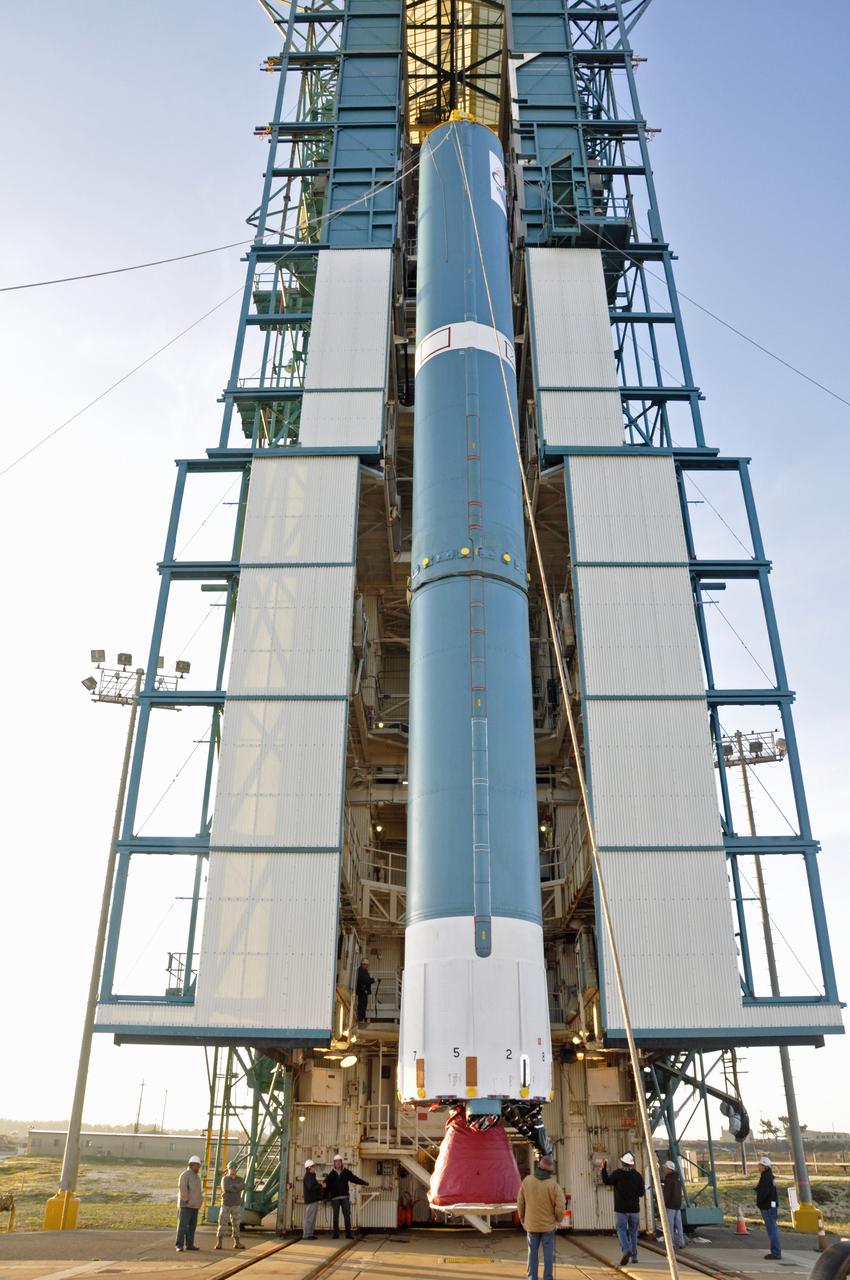

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted into the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
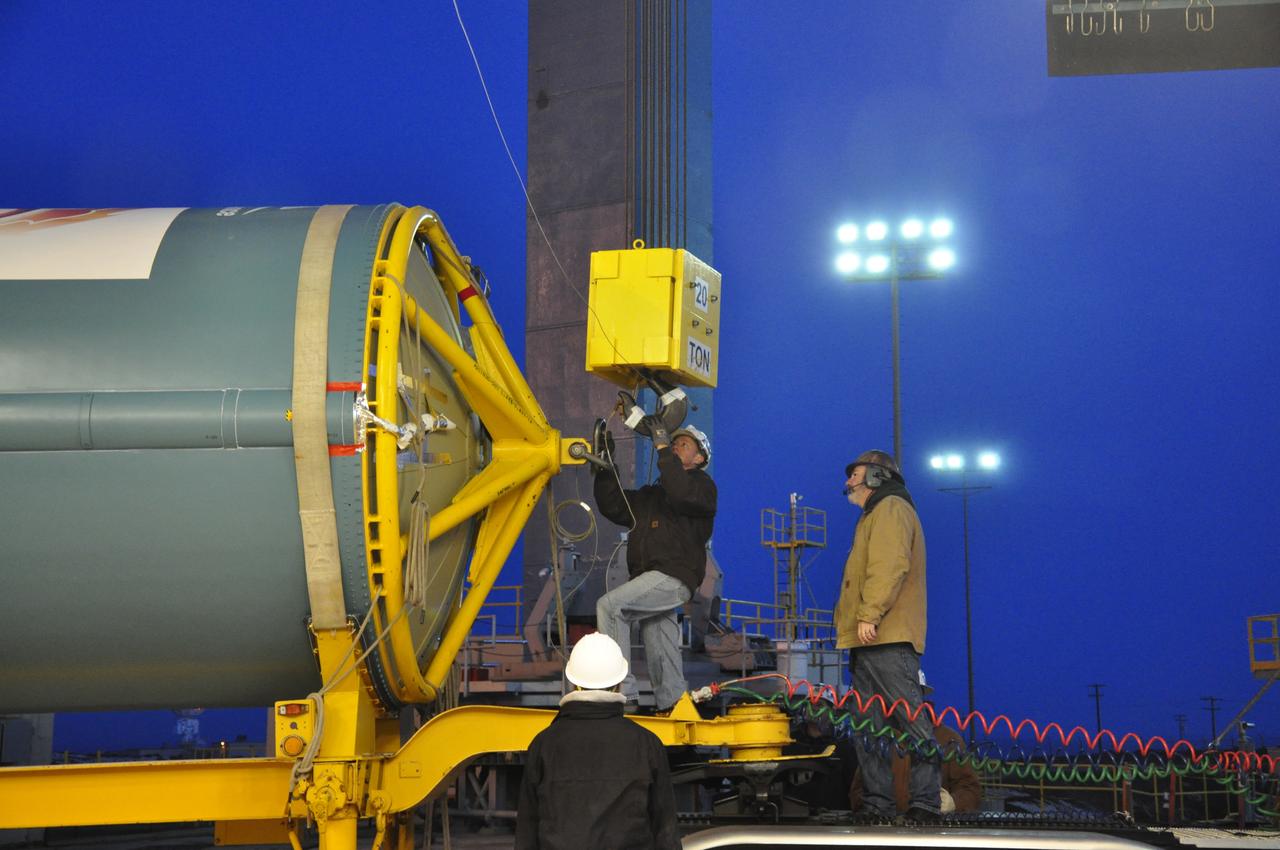

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers attach the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, to a lifting device at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
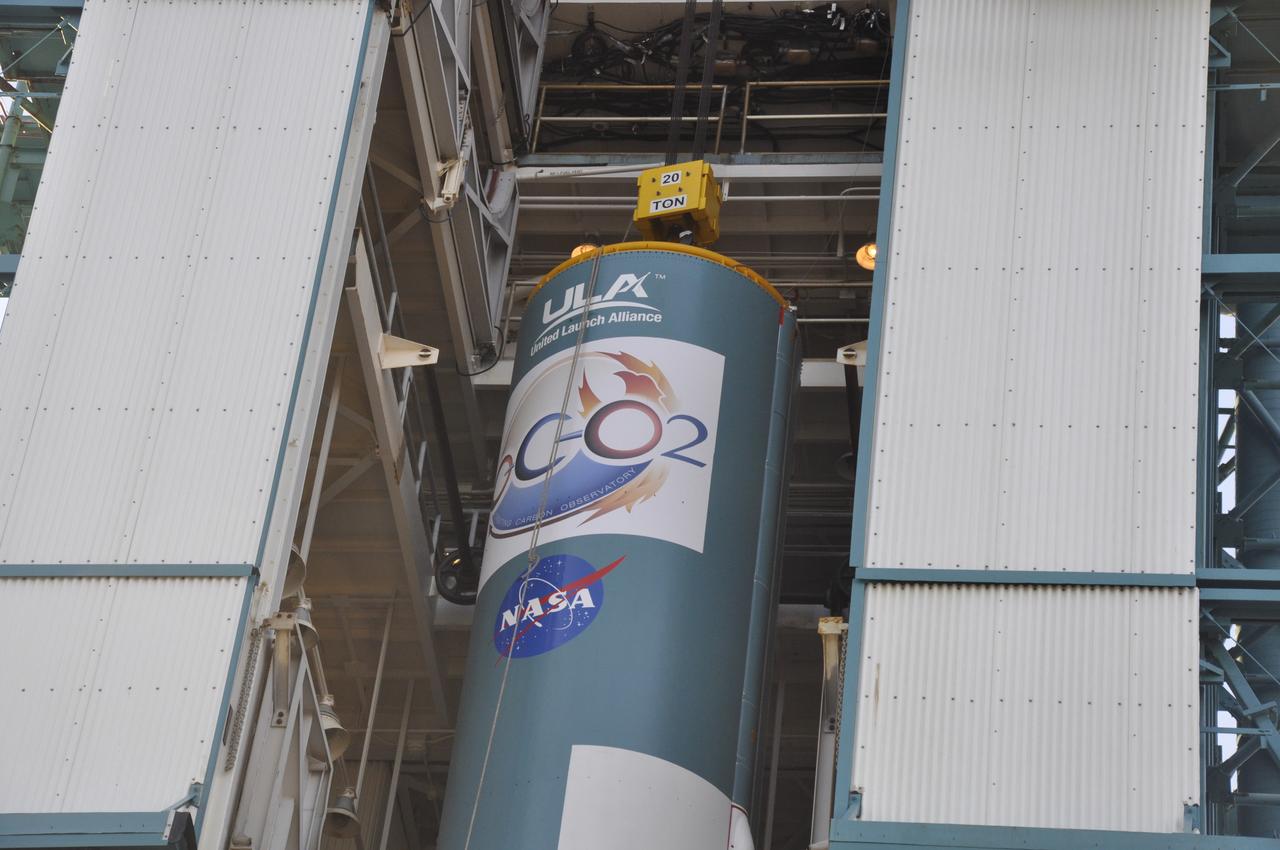

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is transferred into the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
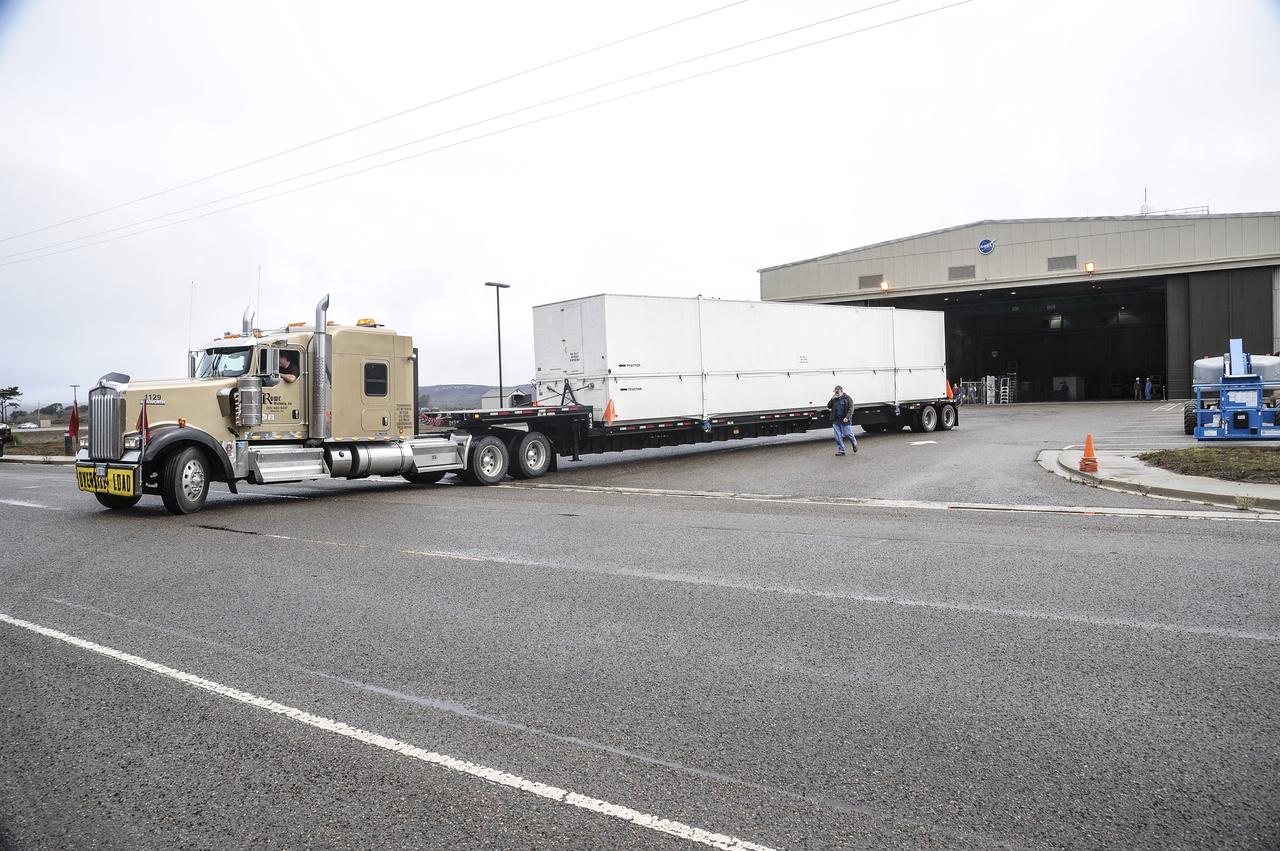

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, arrives at the Building 836 hangar on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Jeremy Moore, 30th Space Wing, VAFB
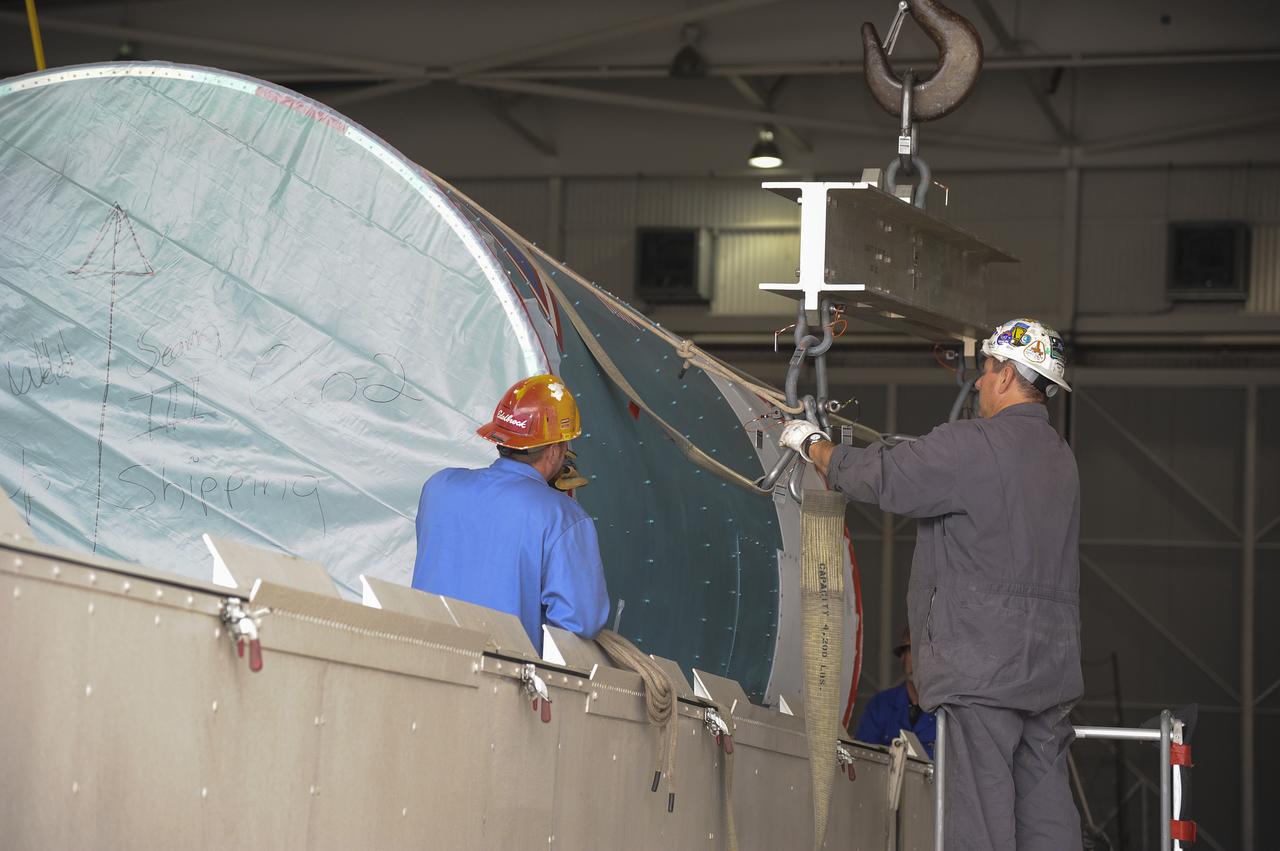

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers attach the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, to a lifting device in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Jeremy Moore, 30th Space Wing, VAFB
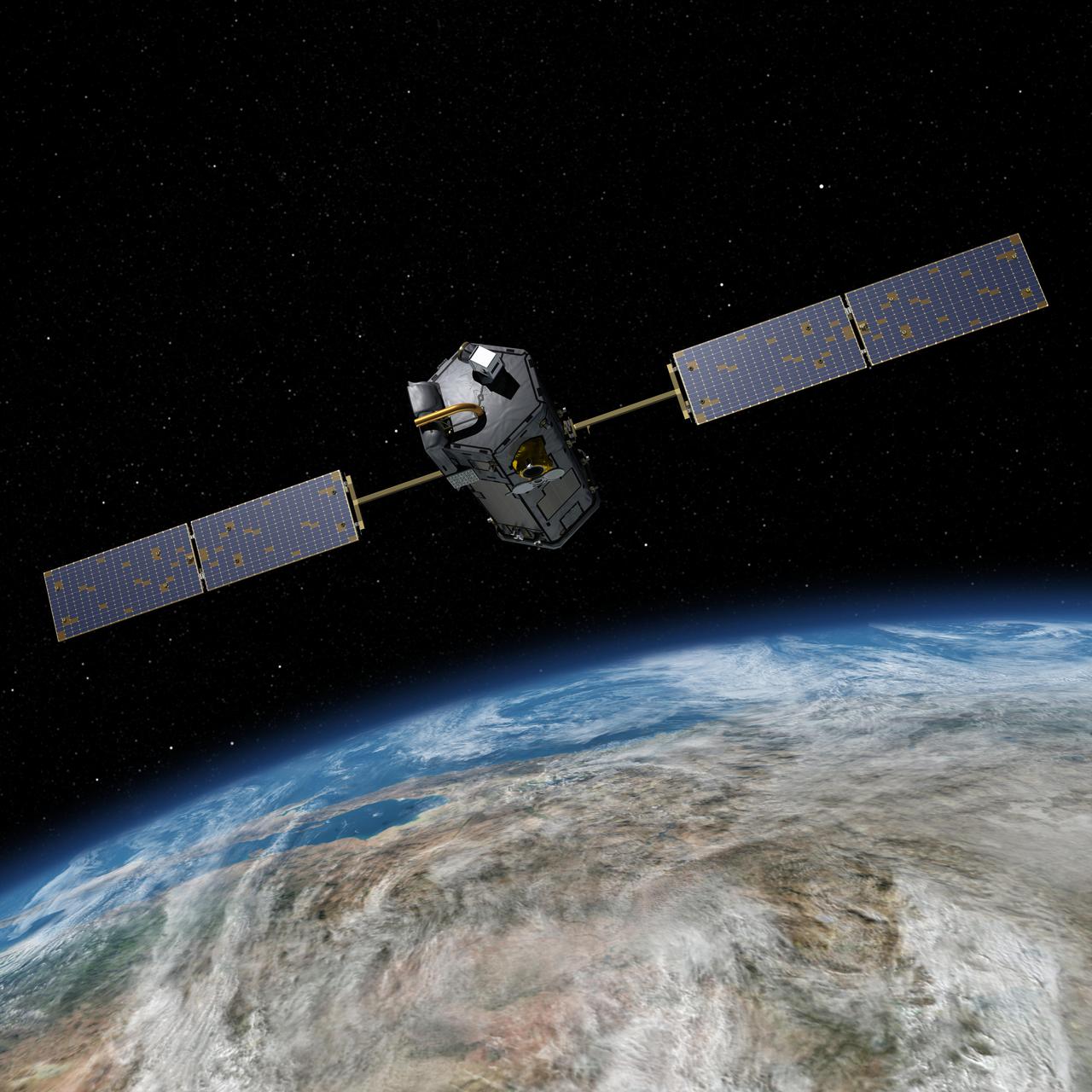

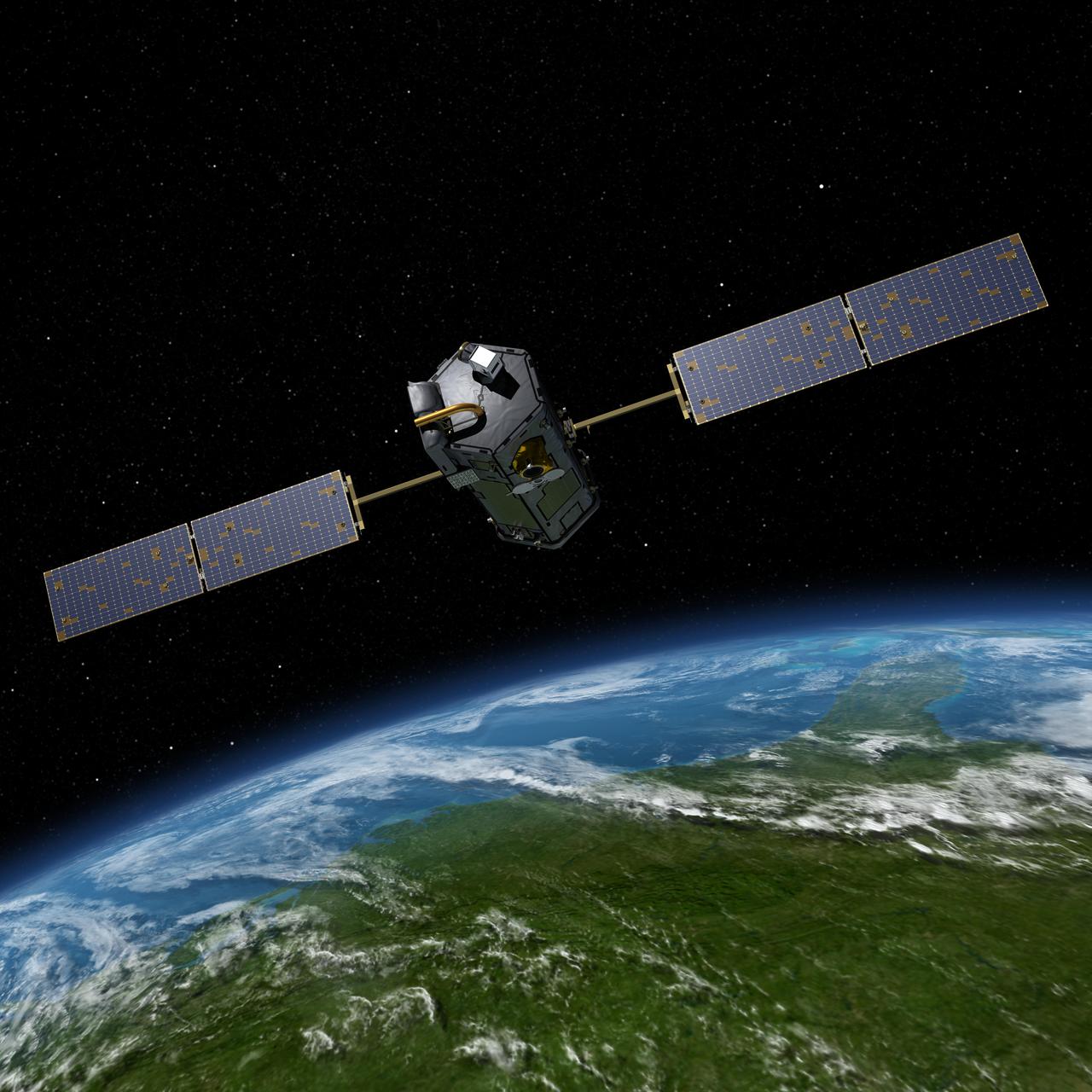
This most recent artist rendering shows NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory OCO-2, one of five new NASA Earth science missions set to launch in 2014, and one of three managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory JPL.
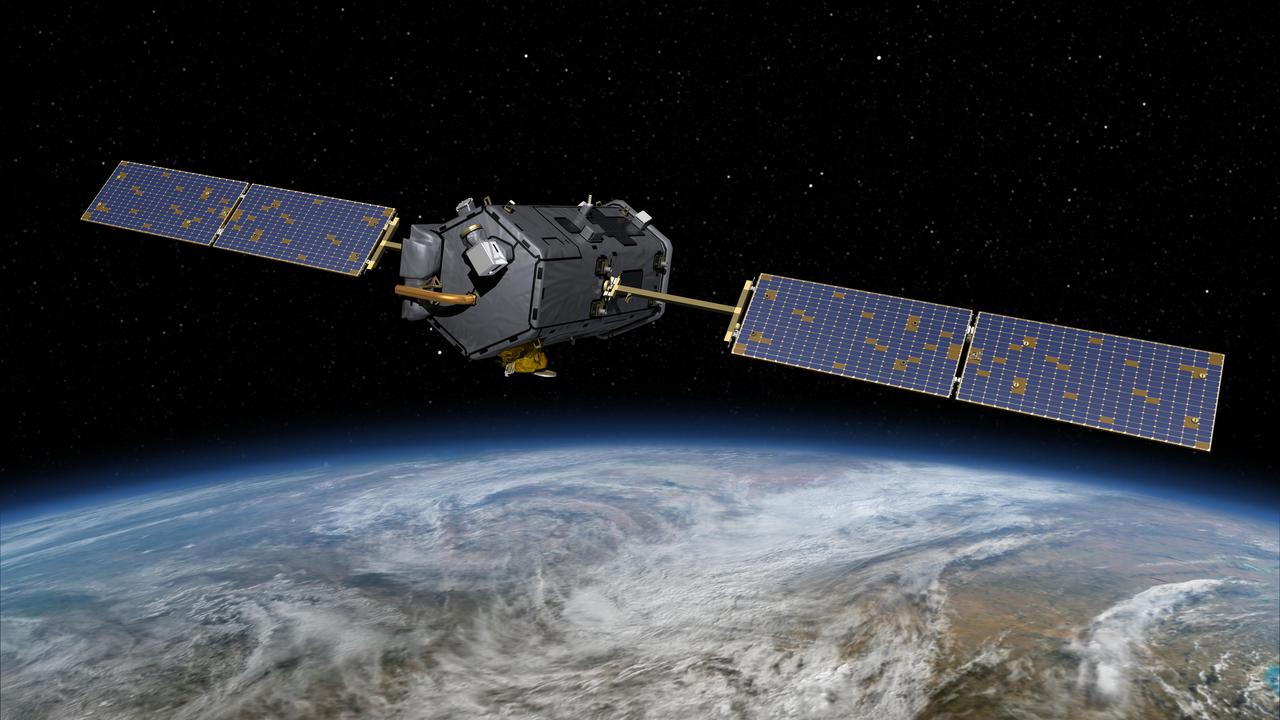

This most recent artist rendering shows NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory OCO-2, one of five new NASA Earth science missions set to launch in 2014, and one of three managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory JPL.
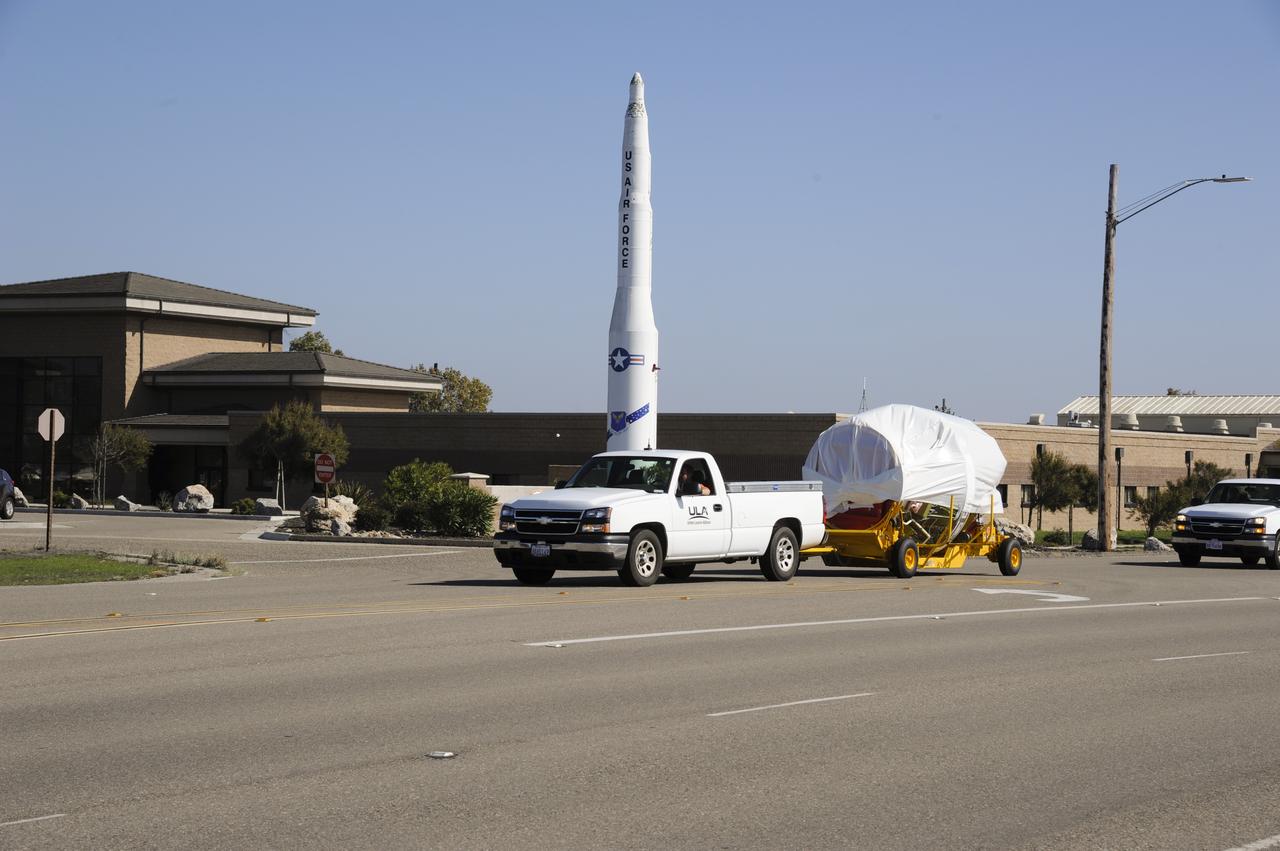

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The second stage for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, passes a static display of a U.S. Air Force Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile on its move from the Building 836 hangar to the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The rocket's second stage will insert OCO-2 into a polar Earth orbit. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Arron Tauman, 30th Space Wing, VAFB
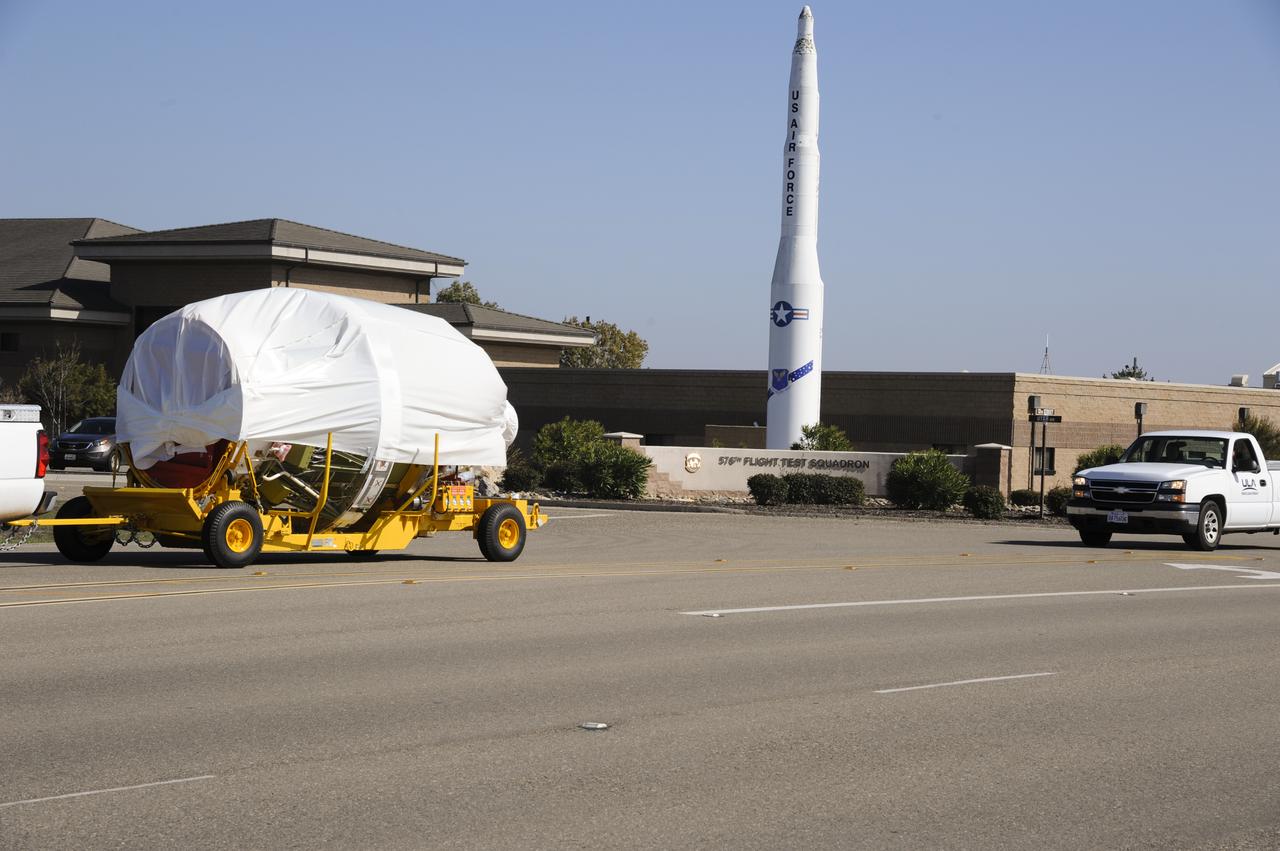

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The second stage for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, passes a static display of a U.S. Air Force Minuteman III intercontinental ballistic missile on its move from the Building 836 hangar to the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in July. The rocket's second stage will insert OCO-2 into a polar Earth orbit. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Arron Tauman, 30th Space Wing, VAFB
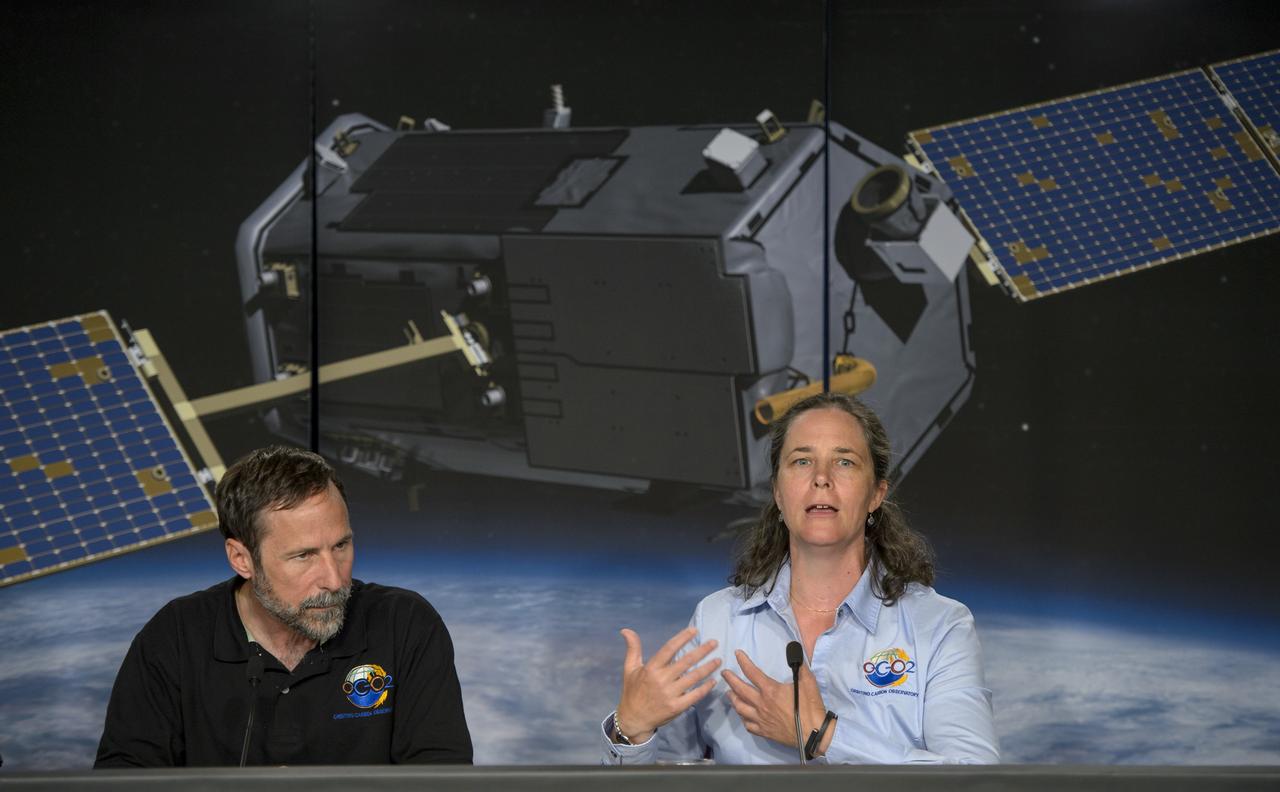

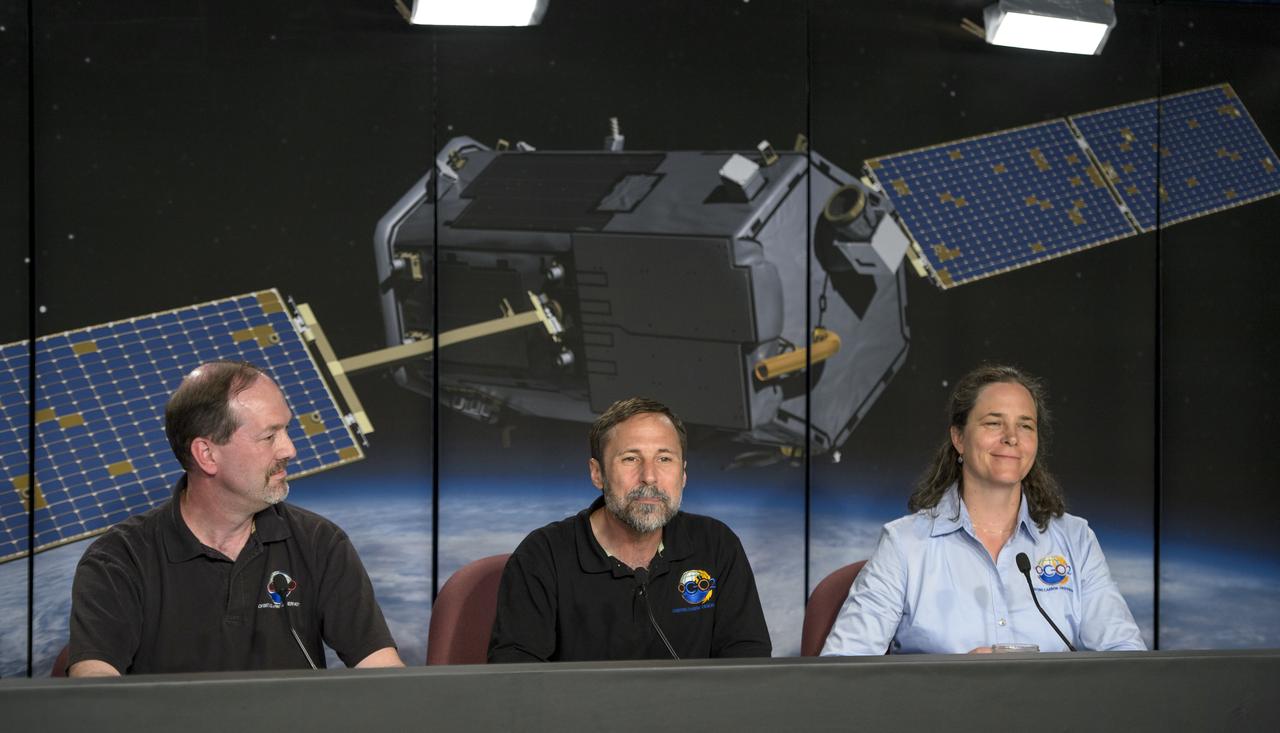
Dave Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader, JPL, left, and Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist, JPL, are seen during a science briefing ahead of the planned launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
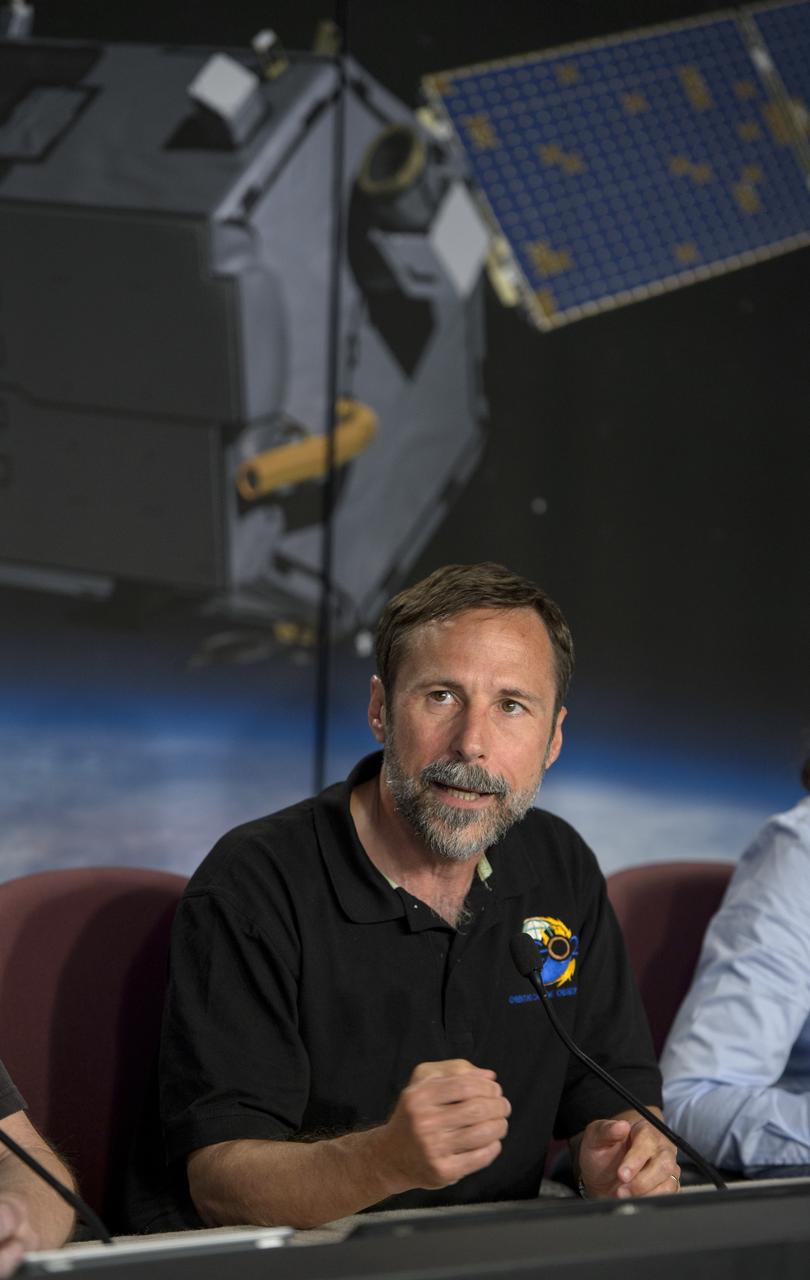

Dave Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader, JPL talks during an Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) science briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
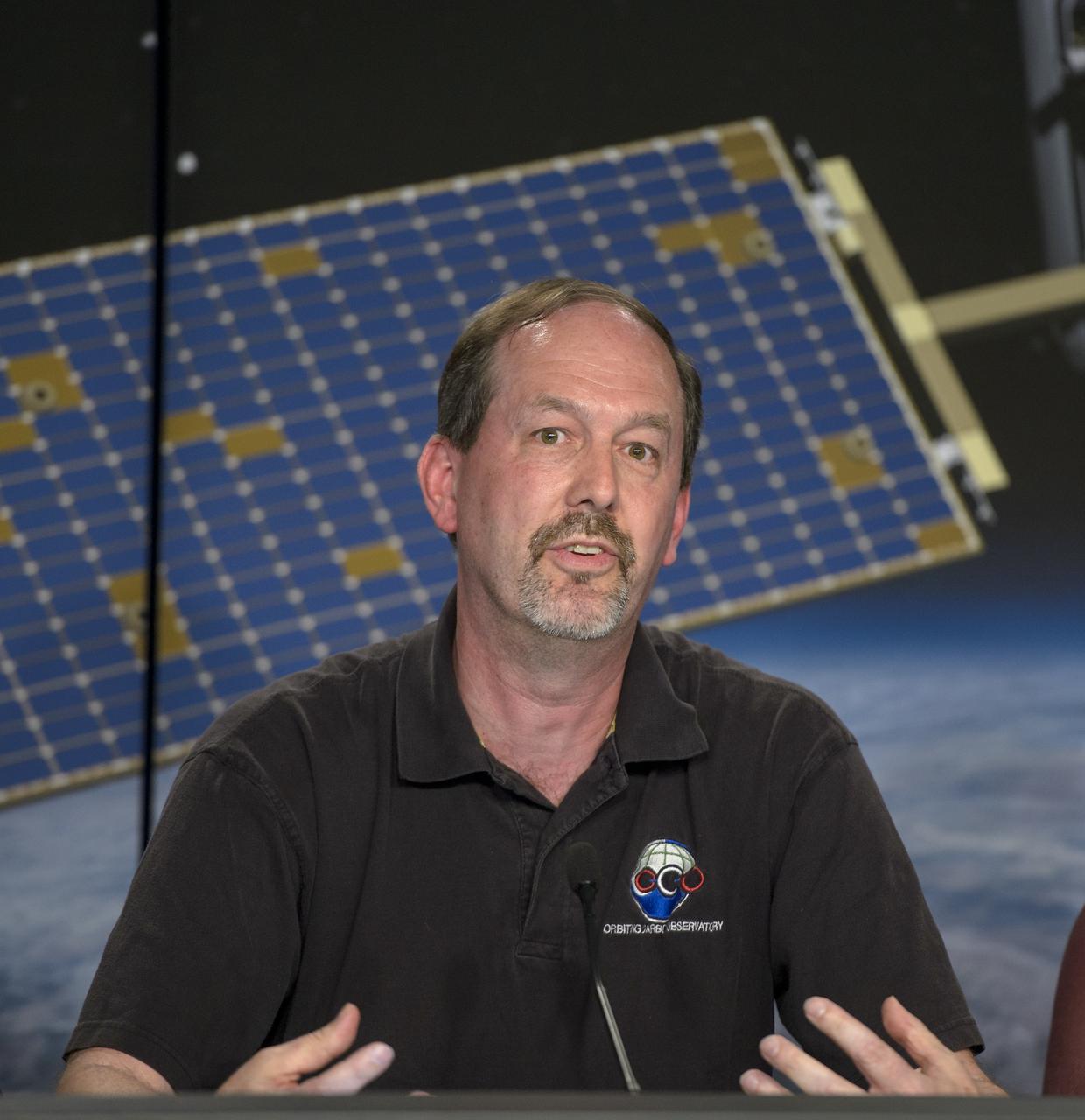

Ken Jucks, OCO-2 program scientist, NASA Headquarters talks during an Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) science briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Ken Jucks, OCO-2 program scientist, NASA Headquarters talks during an Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) science briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
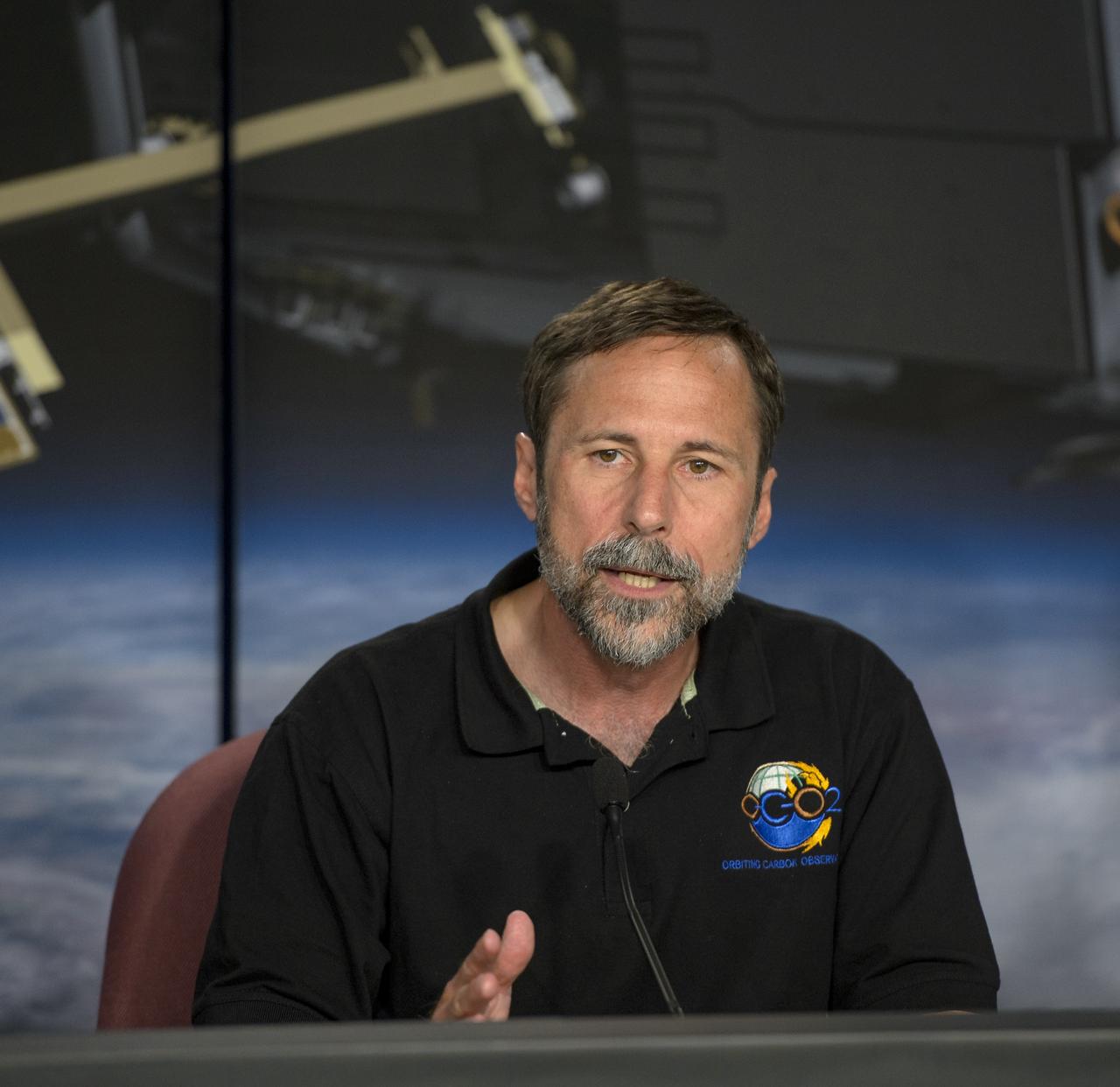

Dave Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader, JPL talks during an Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) science briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
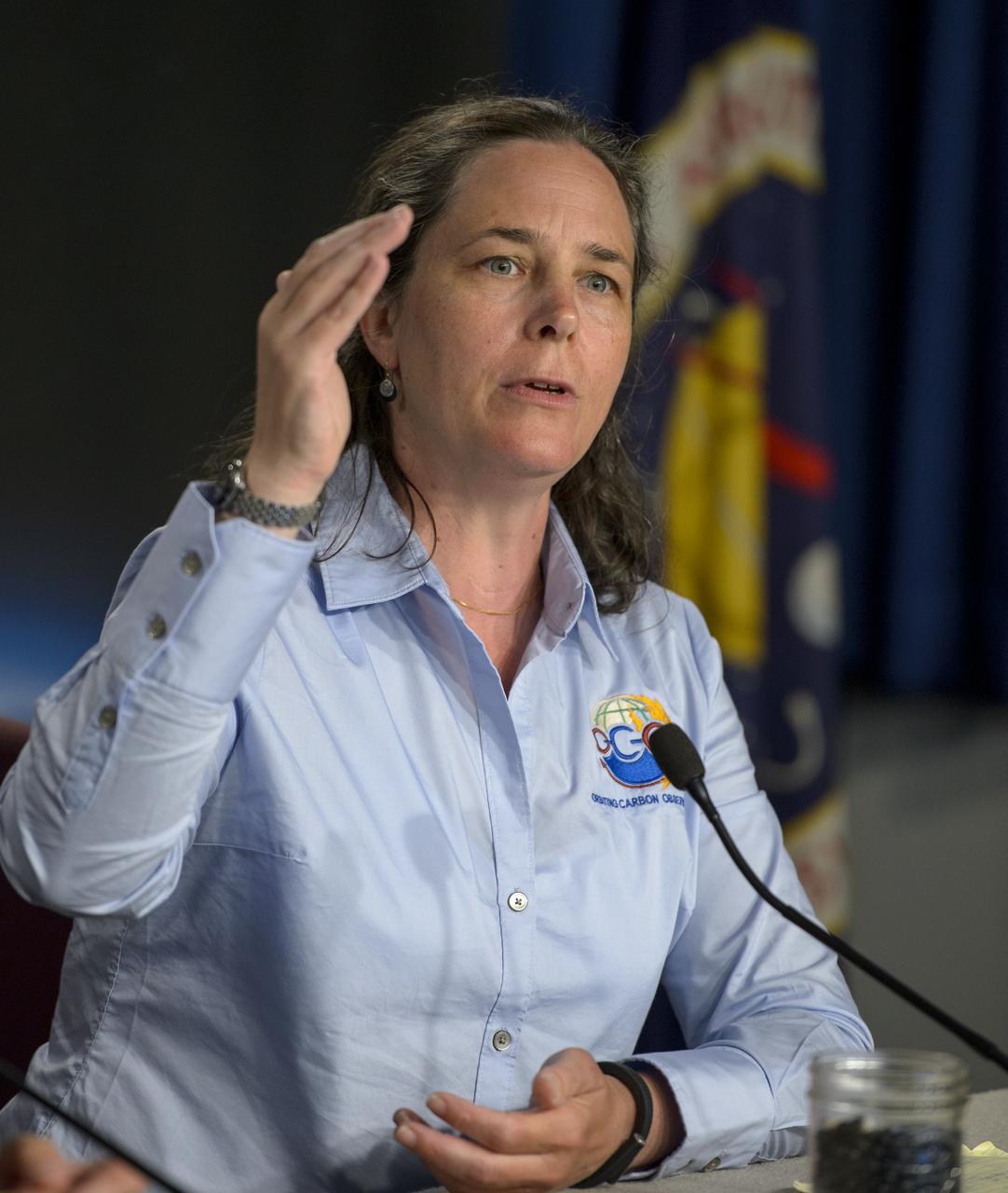

Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist, JPL talks during an Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) science briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
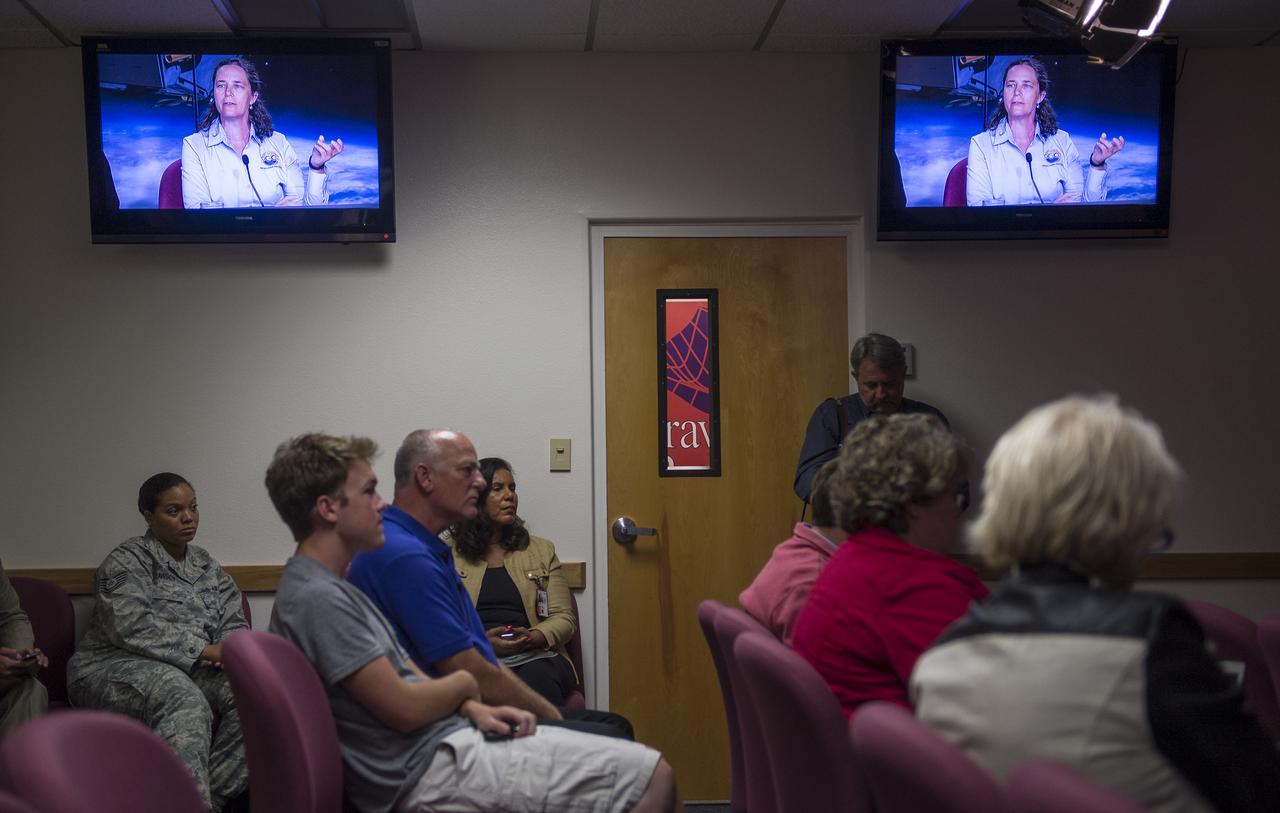

Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist, JPL is seen talking on the monitors during an Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) science briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
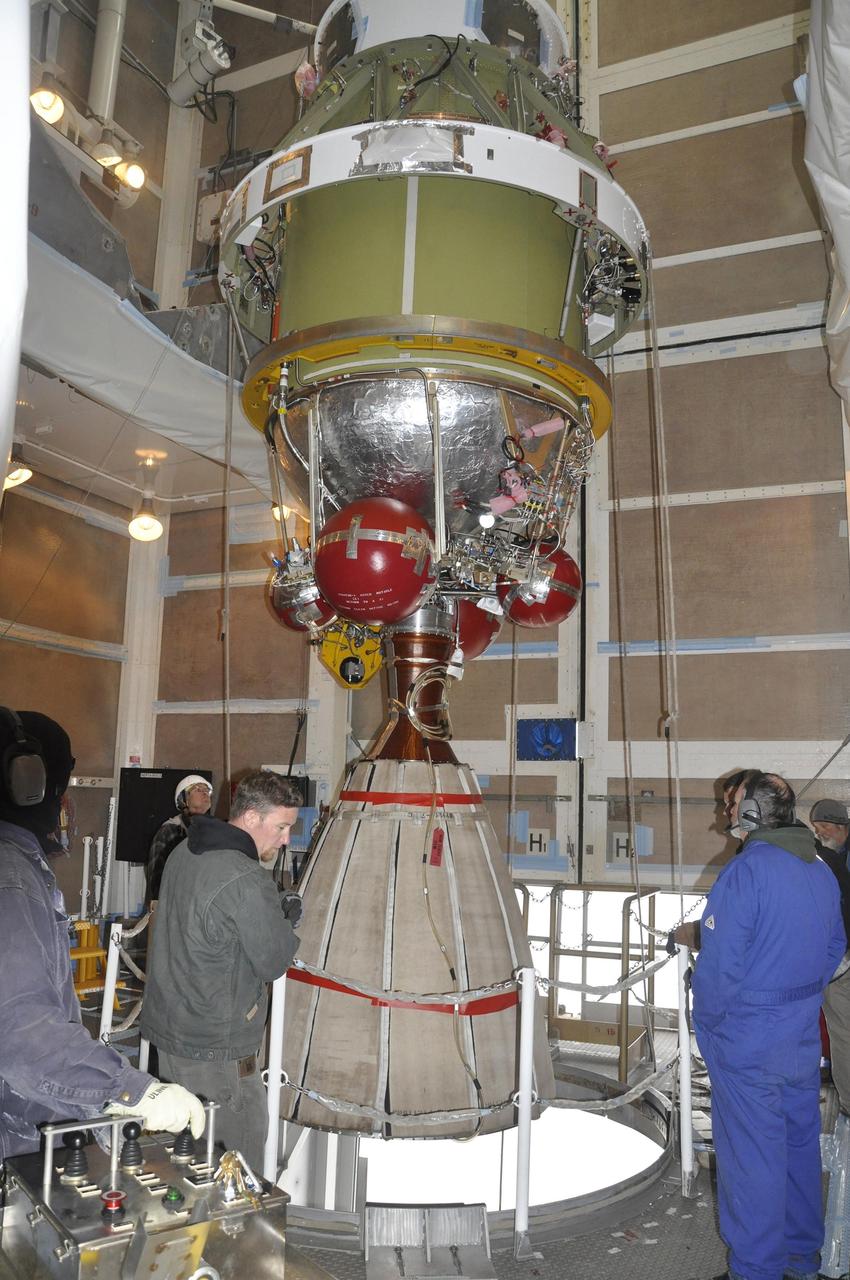

Workers monitor the Delta II second stage for NASA OCO-2, as it is lifted into position for mating with the rocket first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
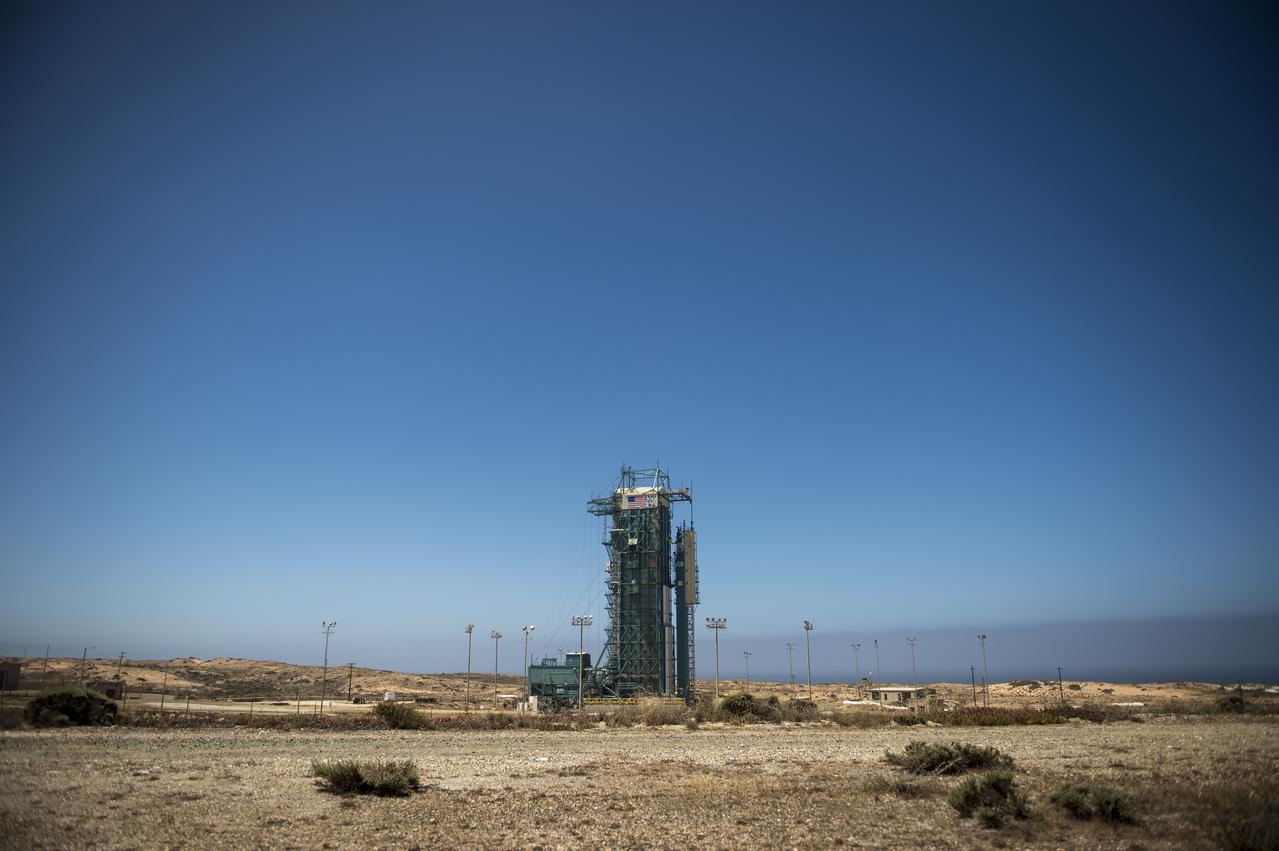

The launch gantry, surrounding the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard, is seen at the Space Launch Complex 2, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

The launch gantry, surrounding the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard, is seen at the Space Launch Complex 2, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

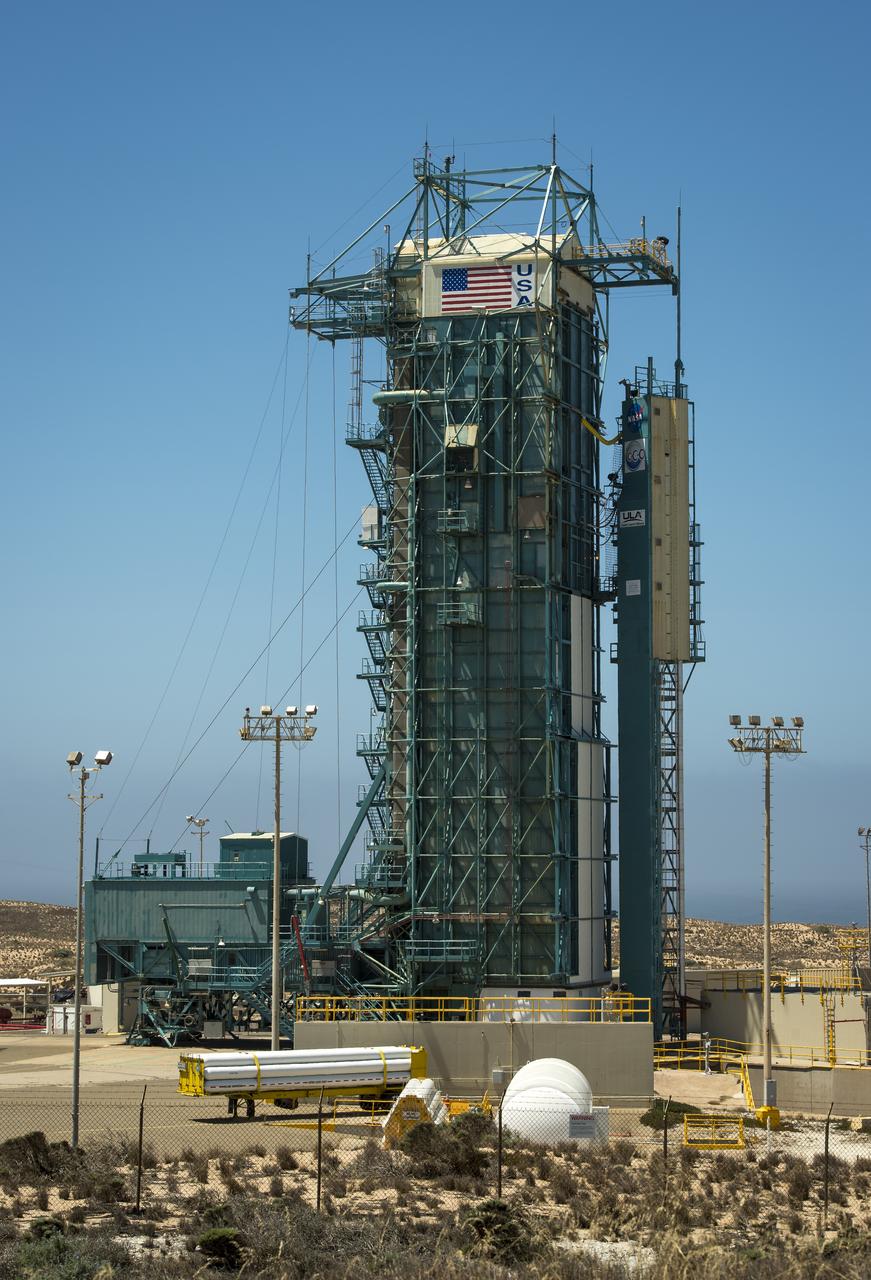
The upper levels of the launch gantry, surrounding the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard, are seen at the Space Launch Complex 2, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
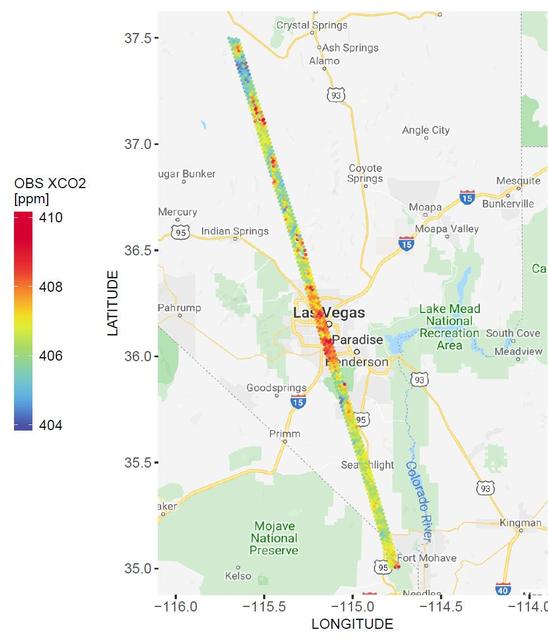
A spatial map of the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) present in columns of the atmosphere below NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite as it flew over Las Vegas on Feb. 8, 2018. Warmer colors over the city center indicate higher amounts of carbon dioxide. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23781
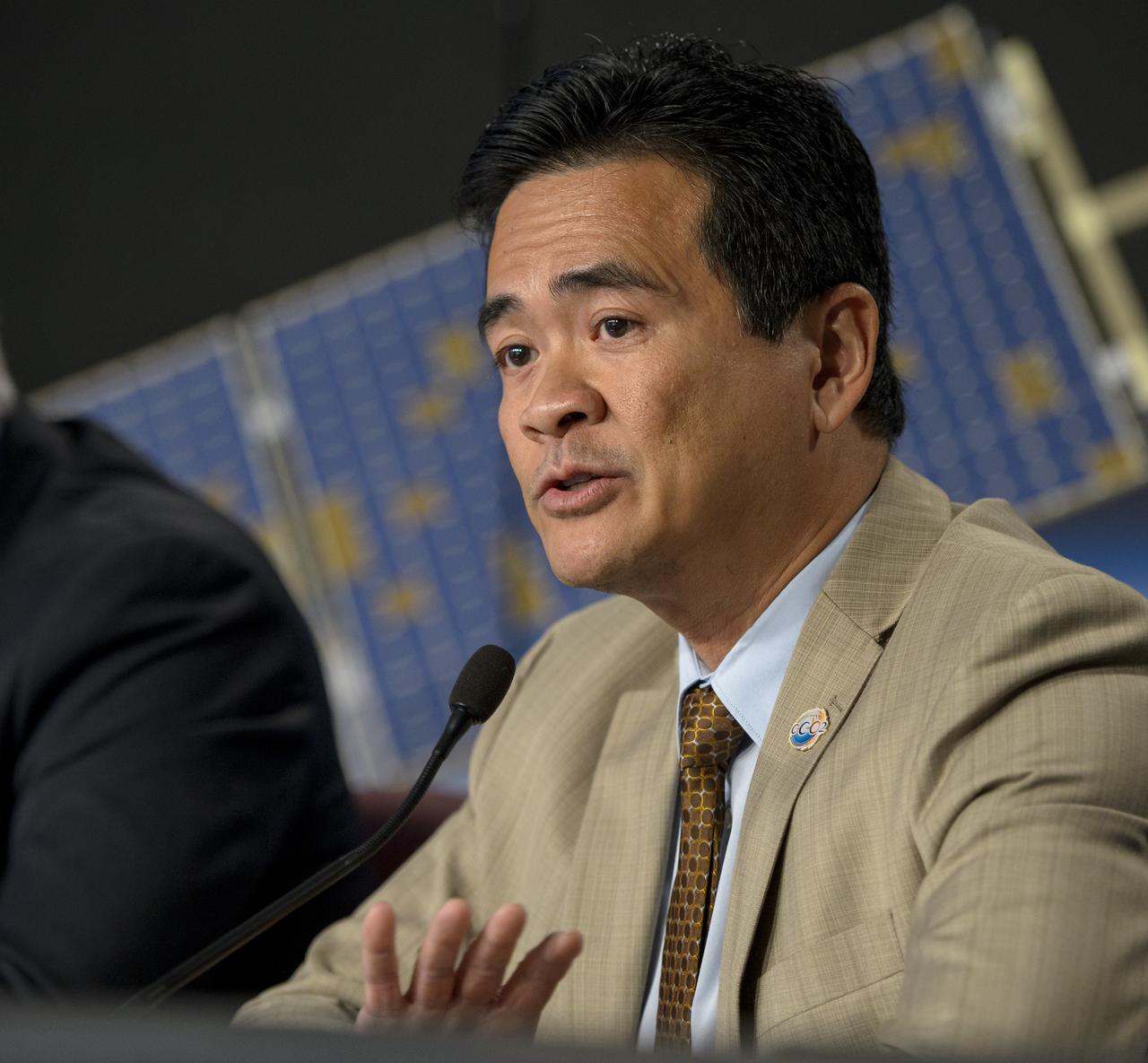

Ralph Basilio, OCO-2 project manager, JPL, discusses the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Ralph Basilio, OCO-2 project manager, JPL, discusses the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
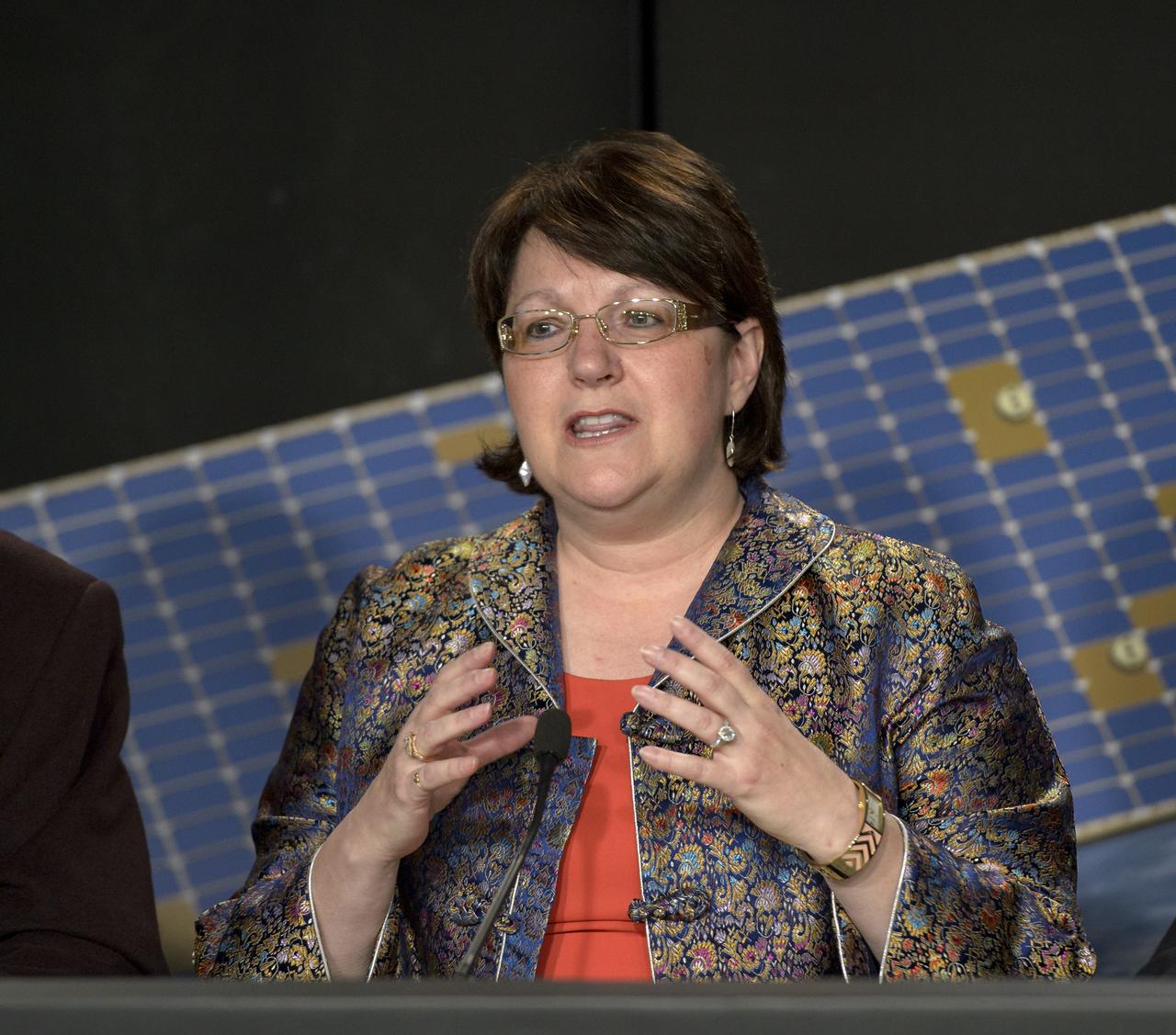

Betsy Edwards, OCO-2 program executive, NASA Headquarters, discusses the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

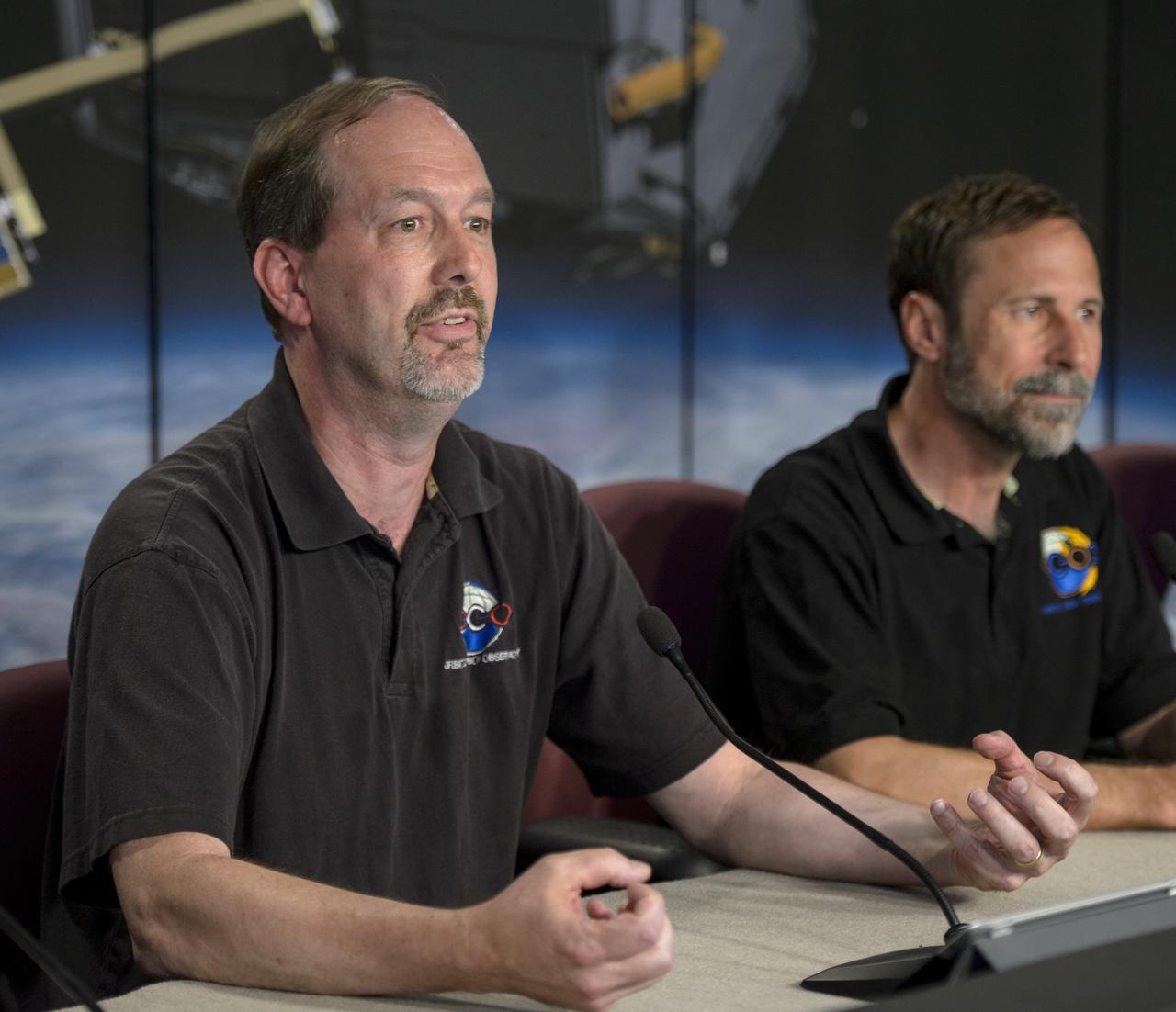
Ken Jucks, OCO-2 program scientist, NASA Headquarters, left, Dave Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader, JPL, and Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist, JPL, right, give a science briefing ahead of the planned launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

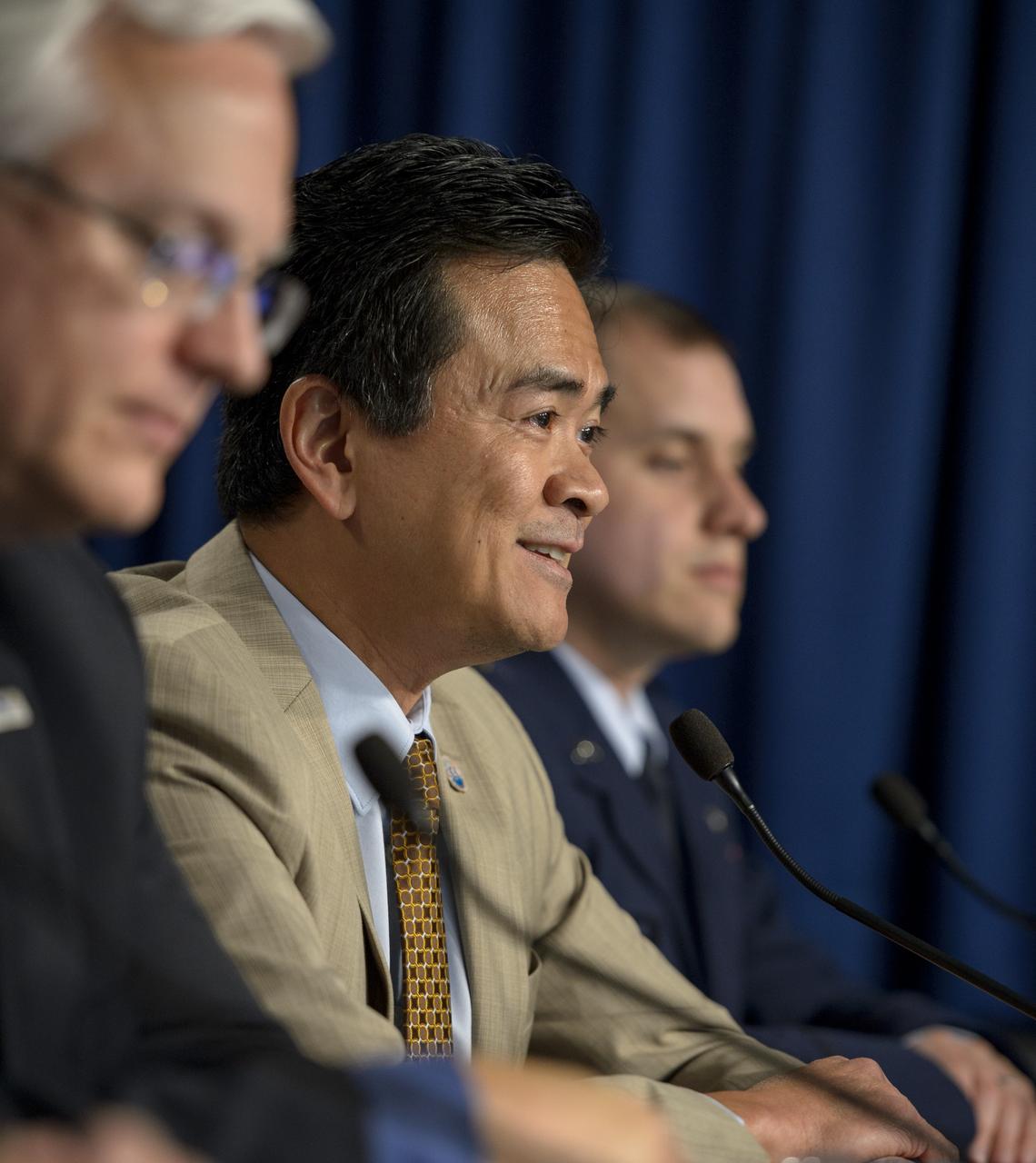
Ken Jucks, OCO-2 program scientist, NASA Headquarters, left, Dave Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader, JPL, and Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist, JPL, right, give a science briefing ahead of the planned launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
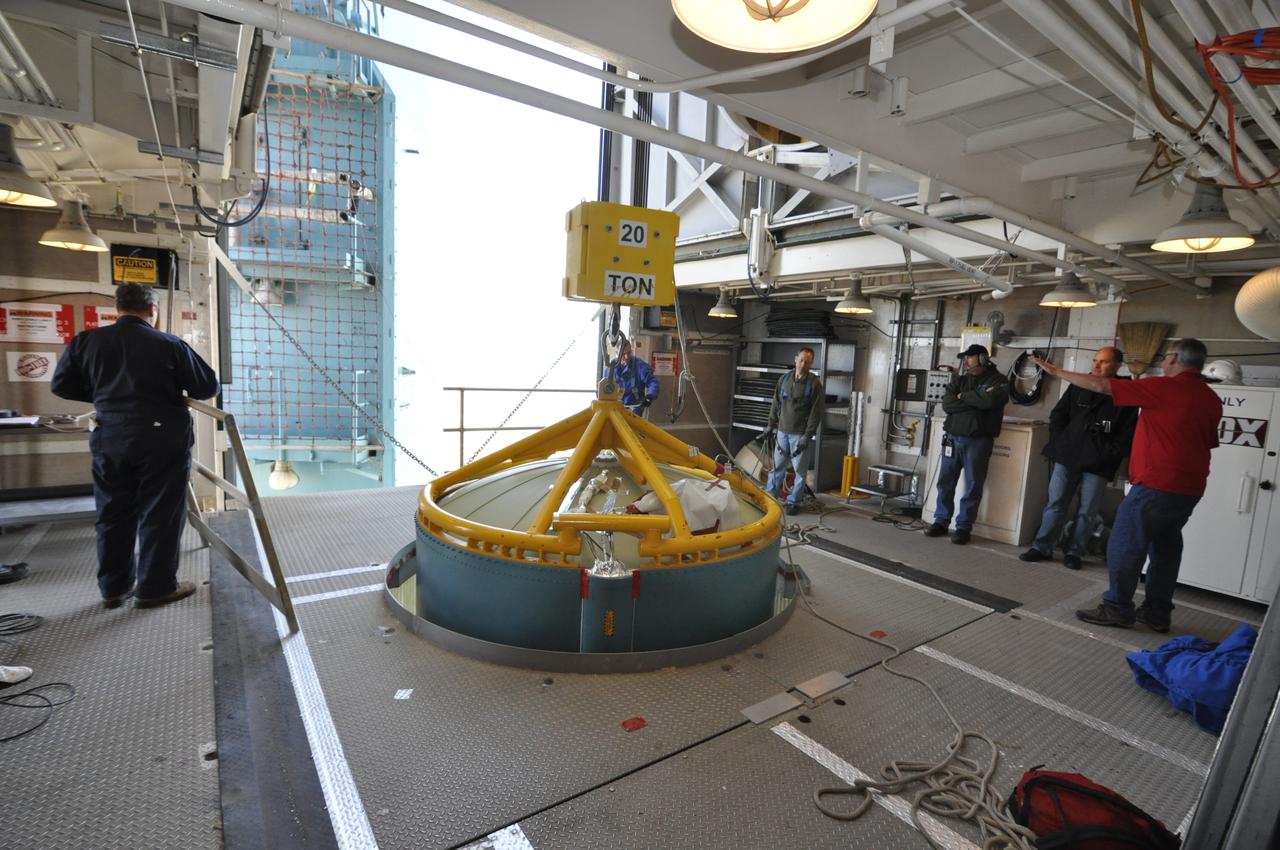

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Work platforms are moved into place around the upper end of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, in the environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
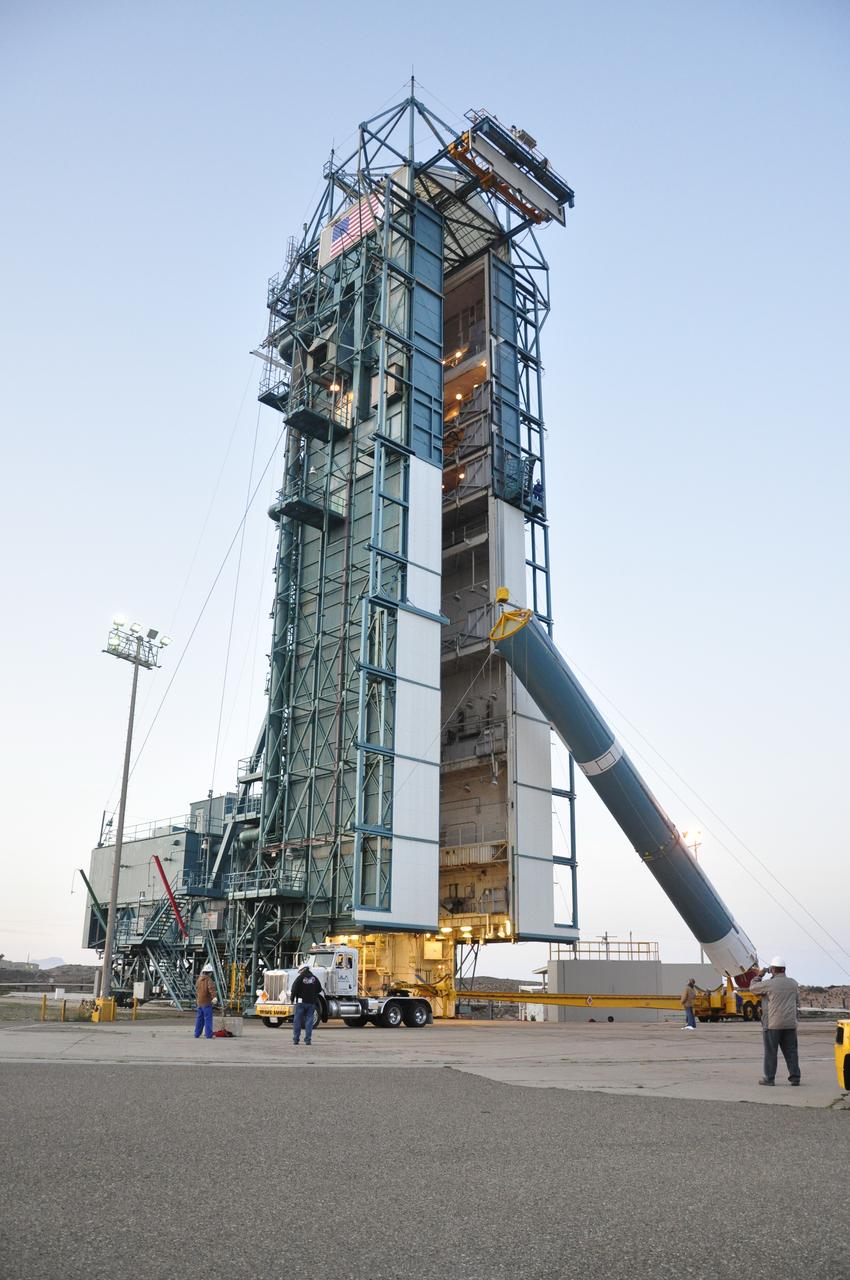

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted into a vertical position beside the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Preparations are underway to transport the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, from the Horizontal Processing Facility to the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
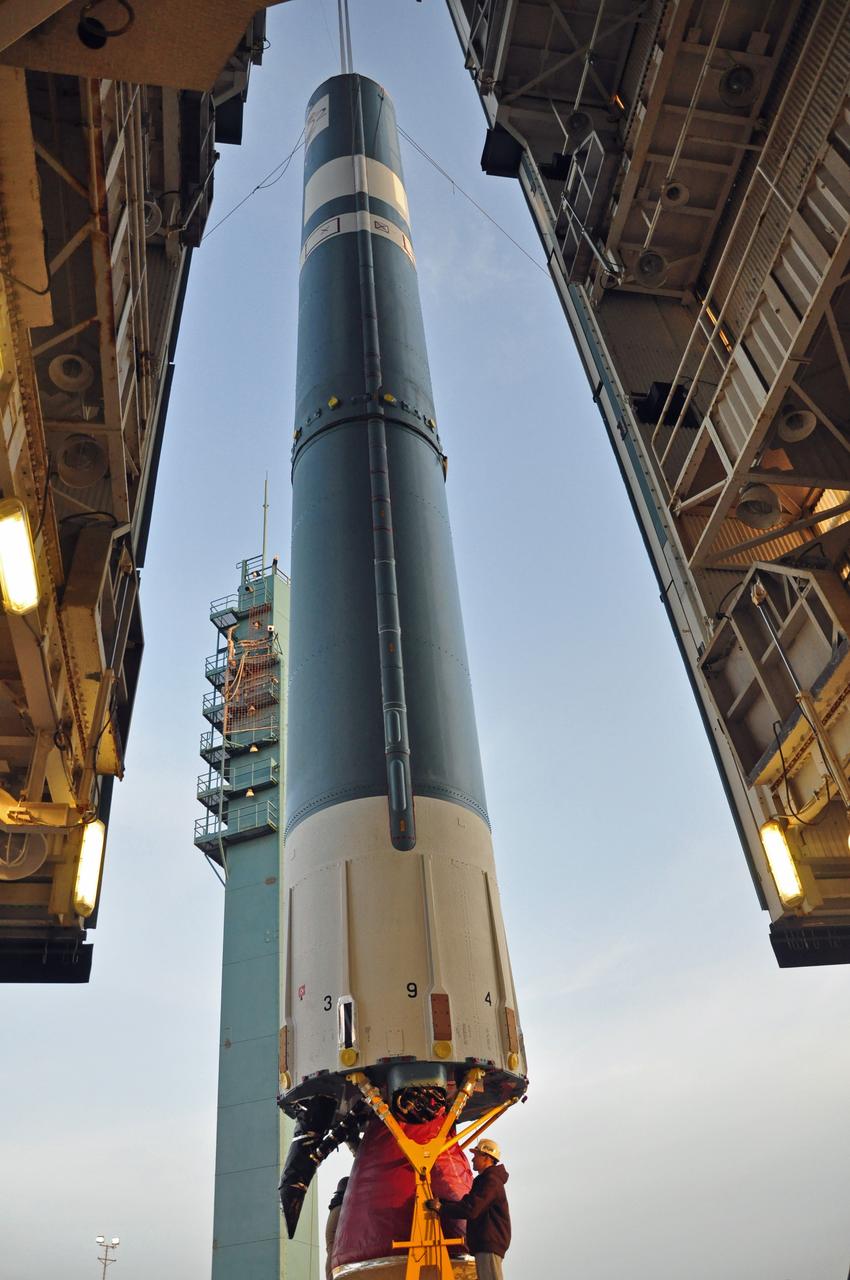

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted from its transporter beside the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
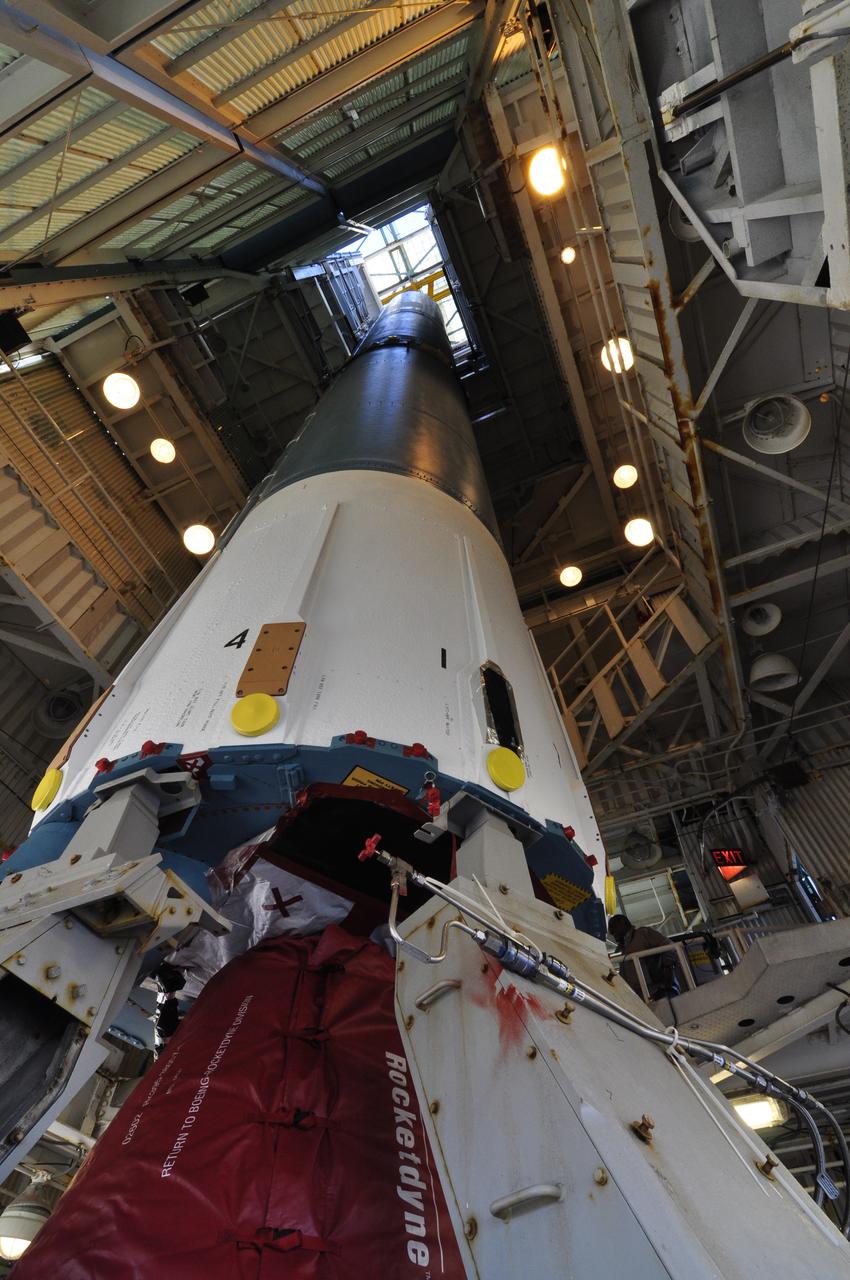

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is positioned onto a launch stand in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
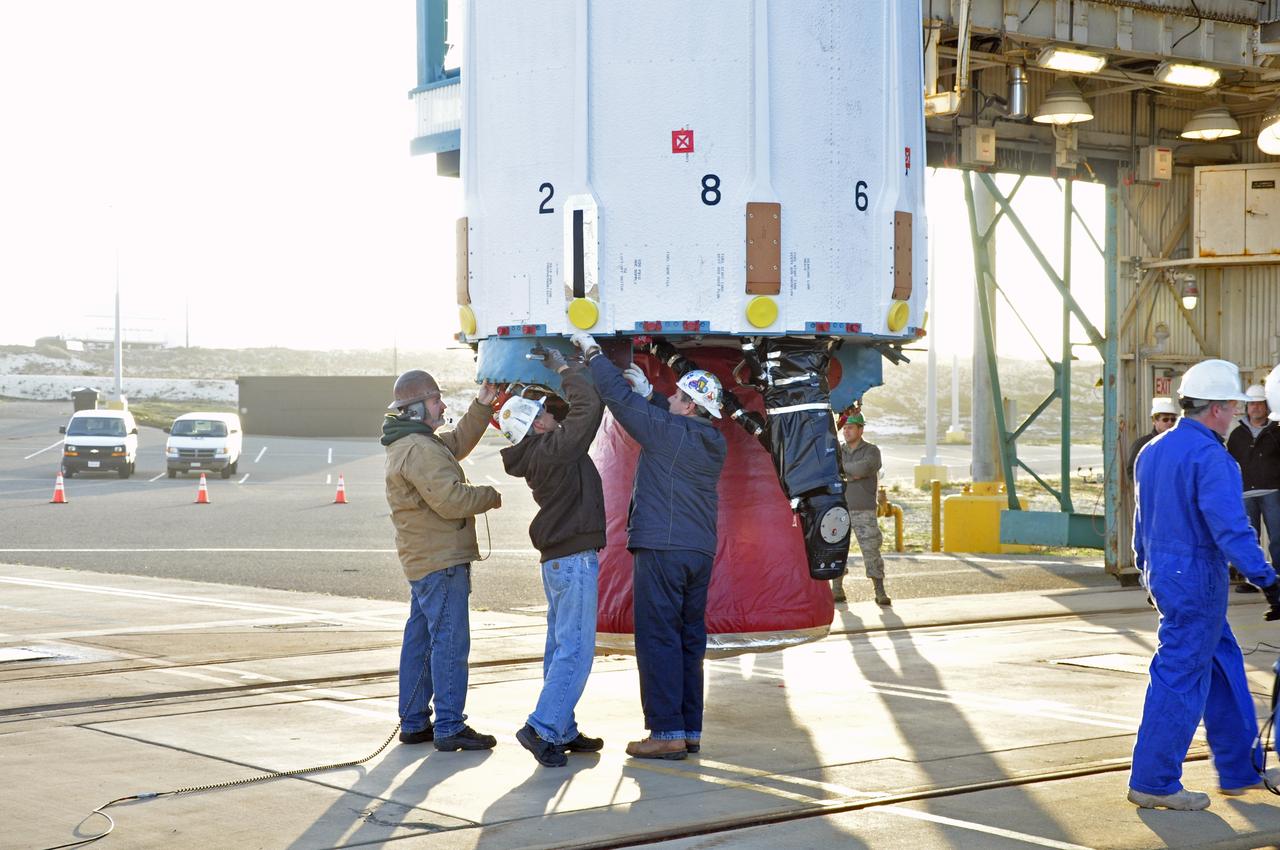

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers prepare the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, for its lift into the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
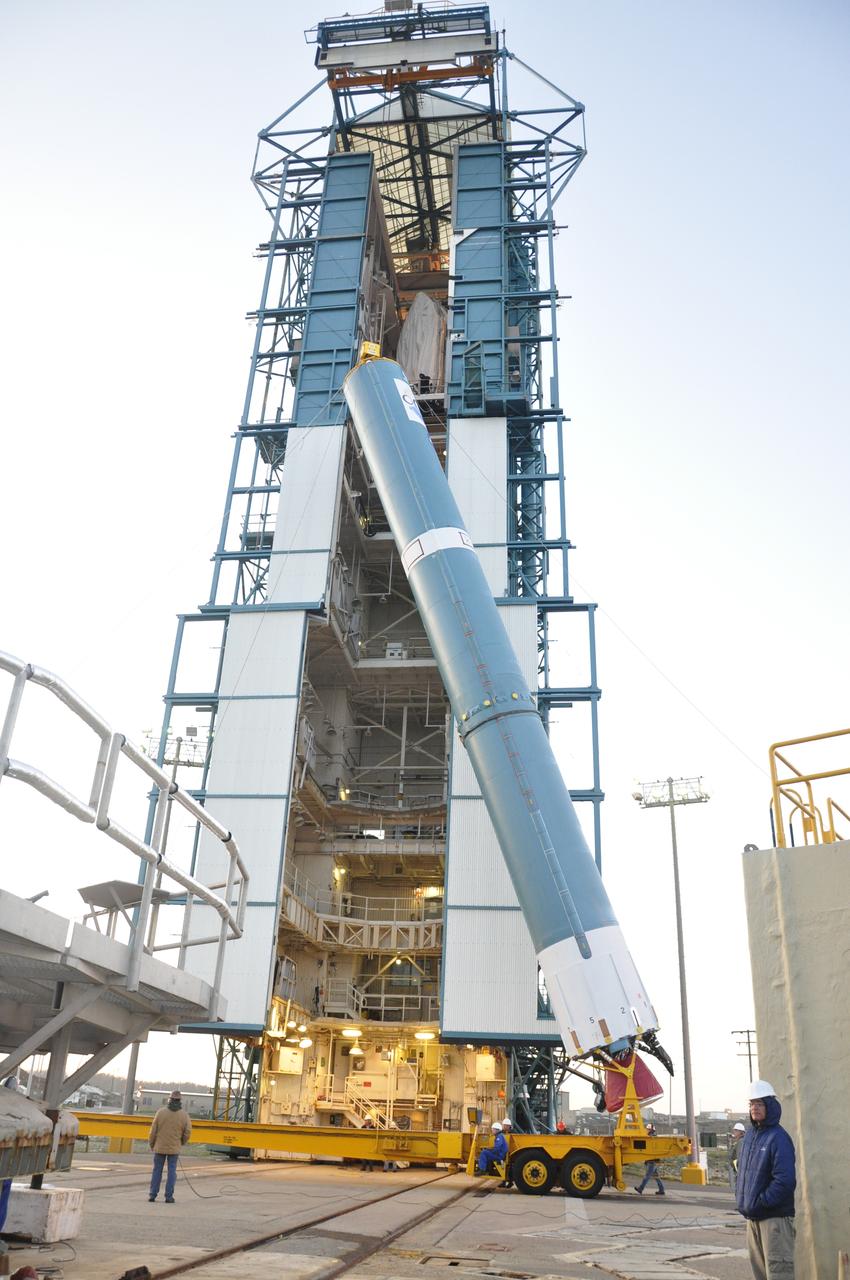

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted into a vertical position beside the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
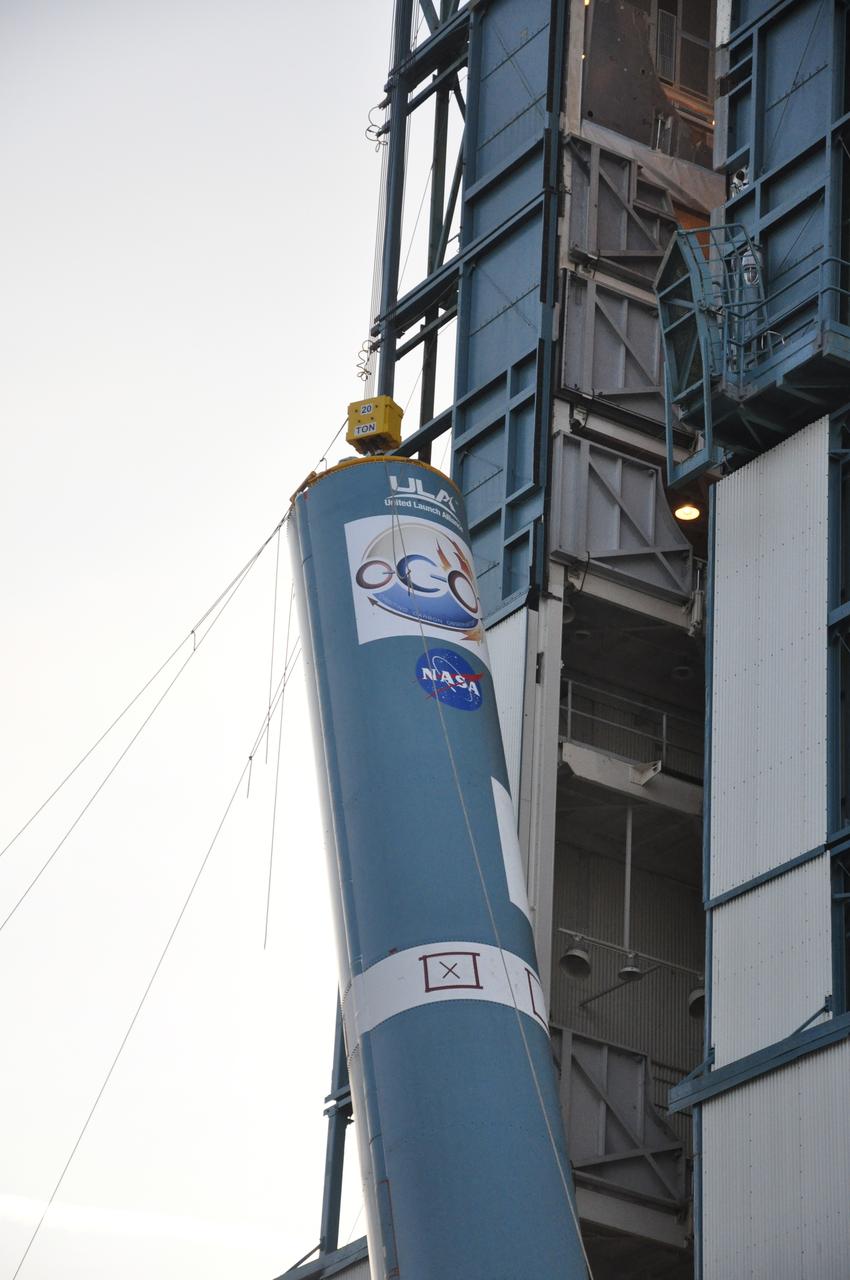

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Preparations are underway to lift the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
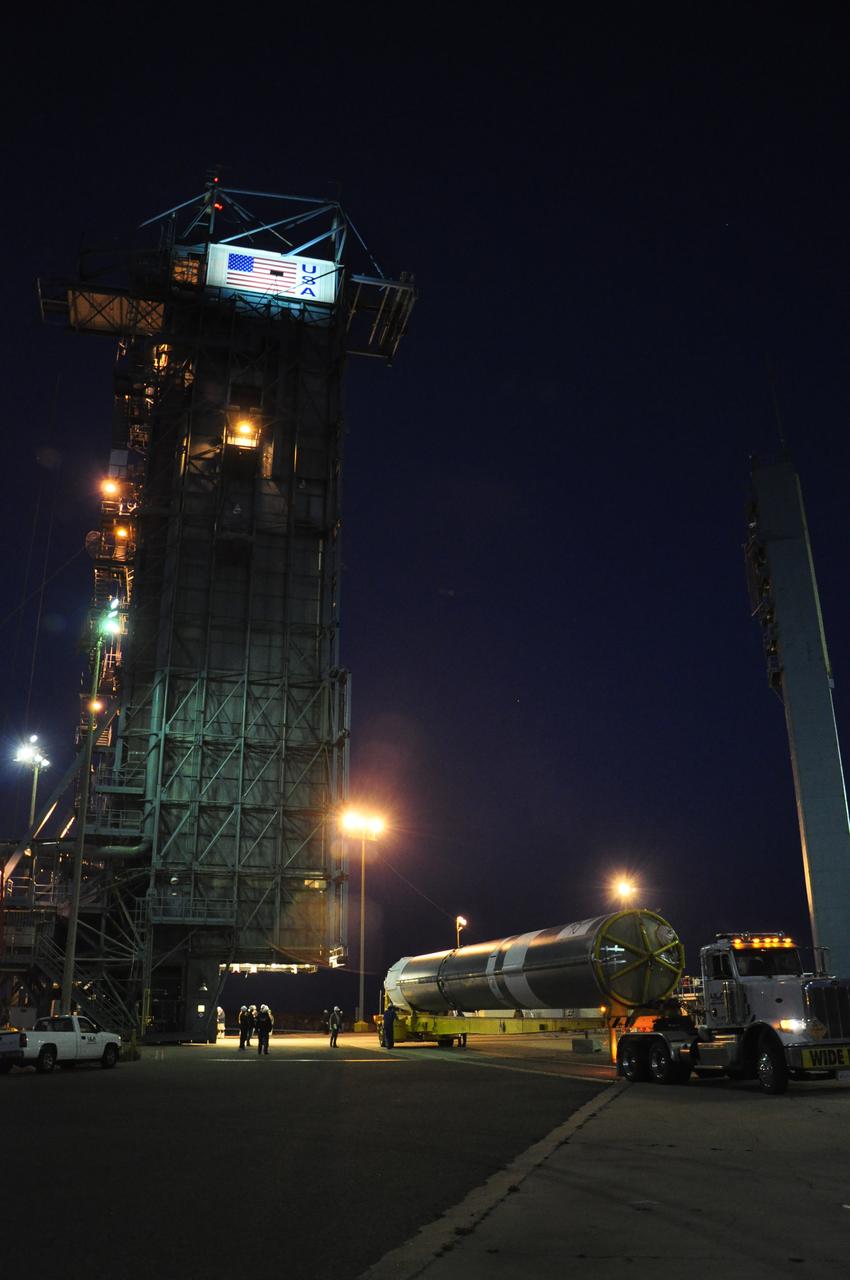

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is positioned next to the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

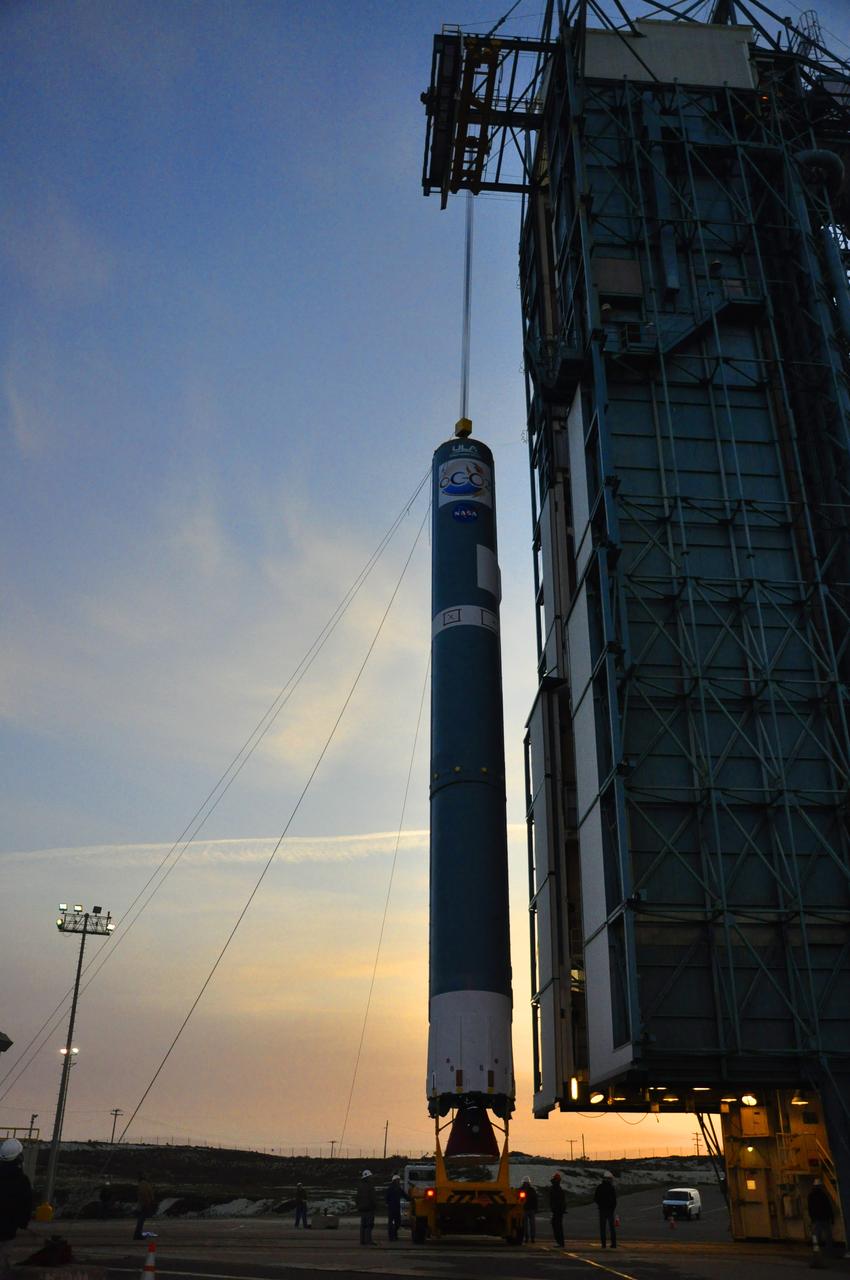
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers secure the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, onto a launch stand in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
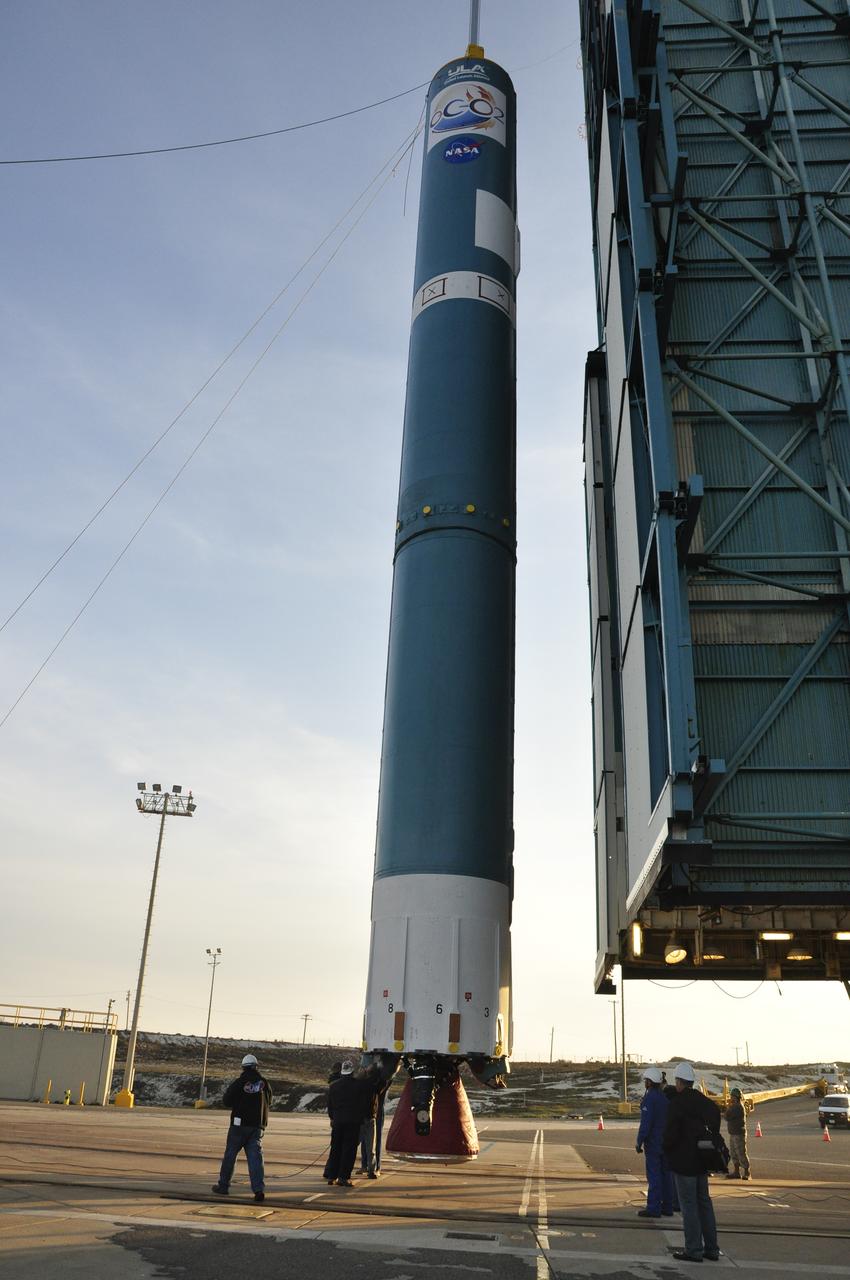

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, hangs in a vertical position beside the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted from its transporter beside the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

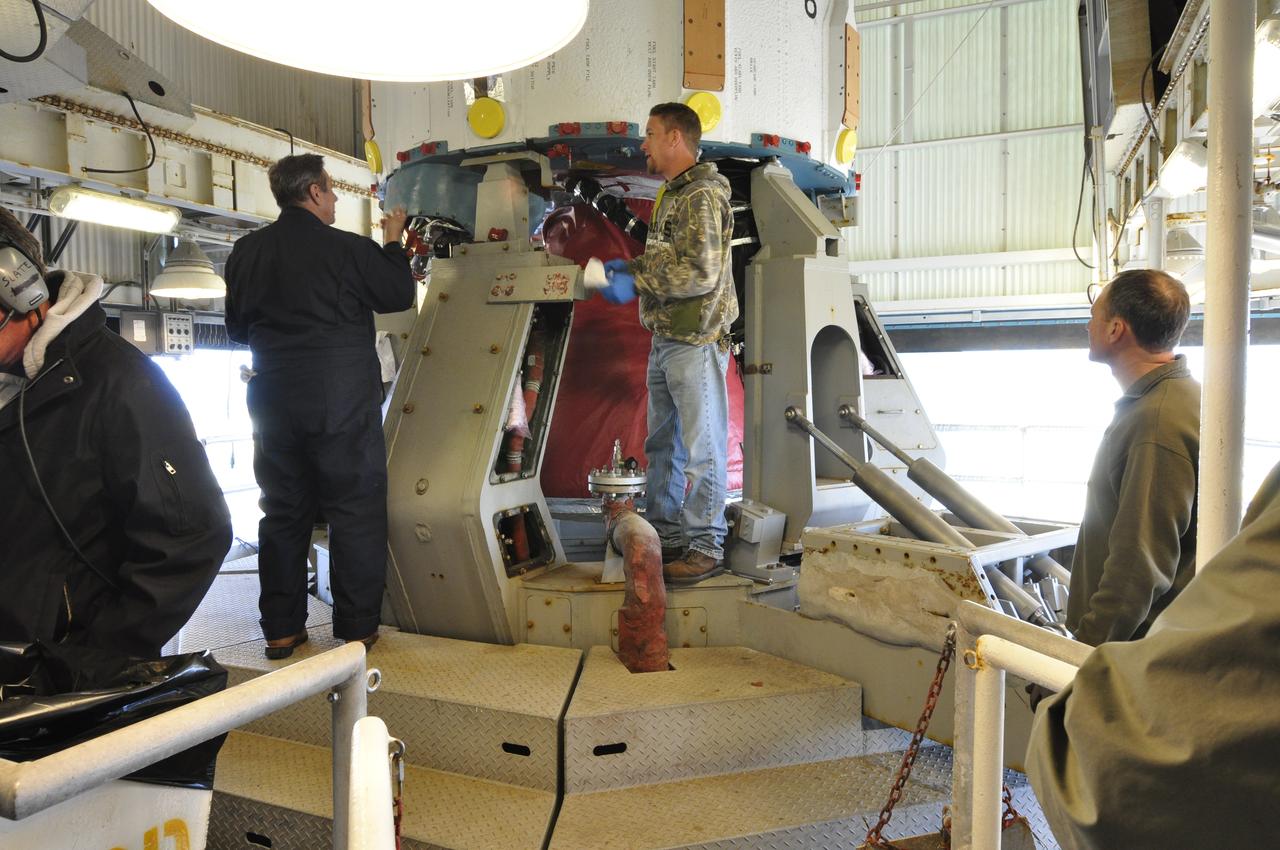
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers in the environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California steady the upper end of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, as work platforms move into position around it. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers monitor the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, as it is lifted from its transporter beside the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
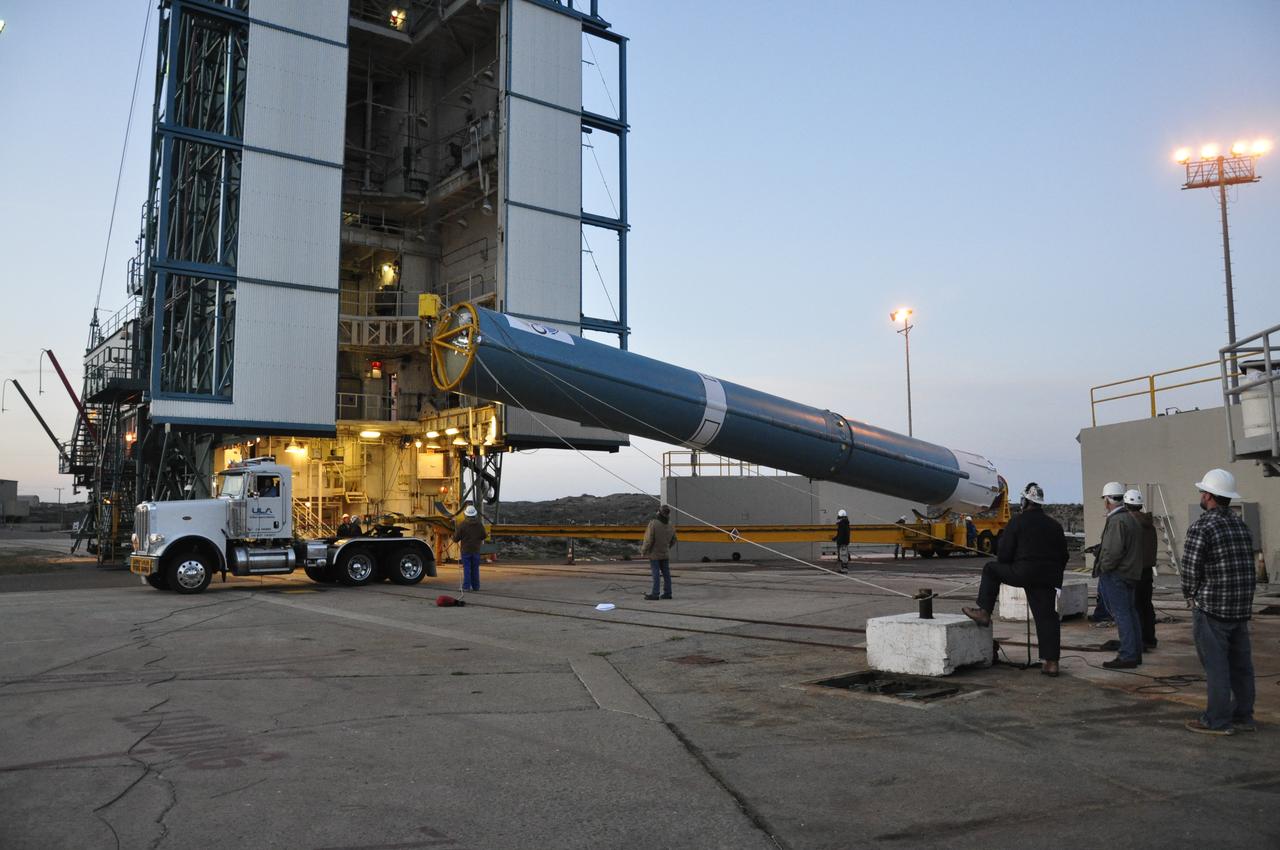

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted into a vertical position beside the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
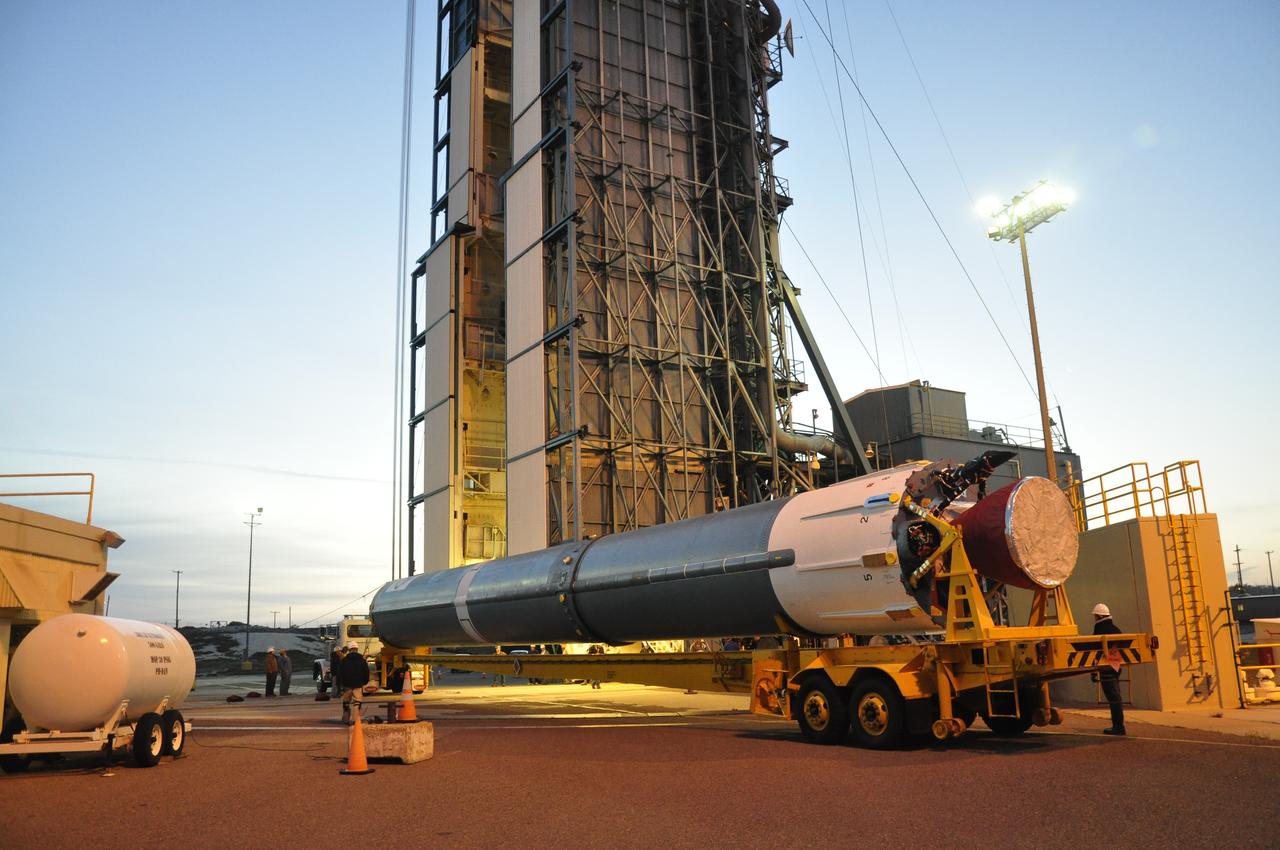

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Preparations are underway to lift the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
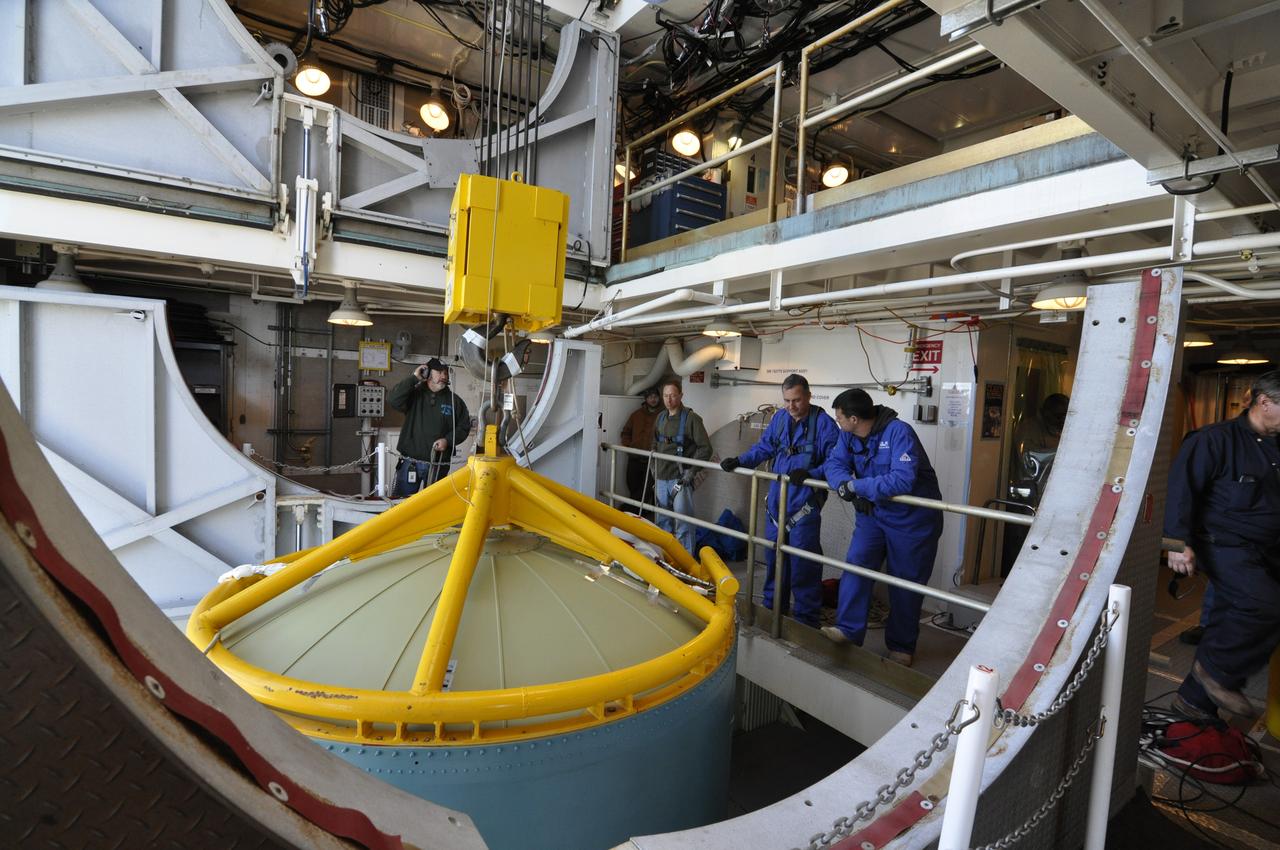

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers in the environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California prepare to release the upper end of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, from the lifting device. Launch is scheduled for July 2014. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
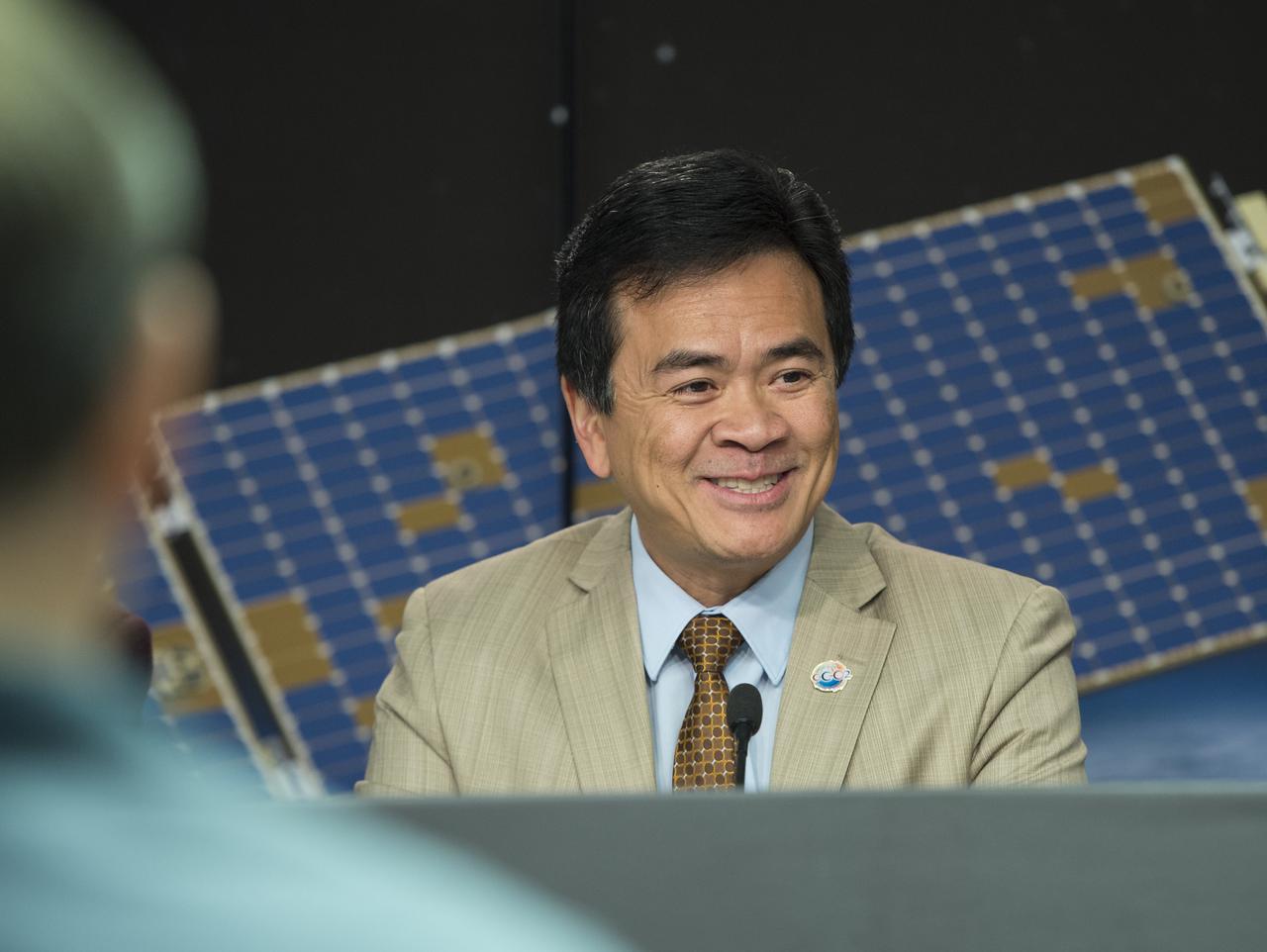
Ralph Basilio, OCO-2 project manager, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, discusses the successful launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Wednesday, July 2, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
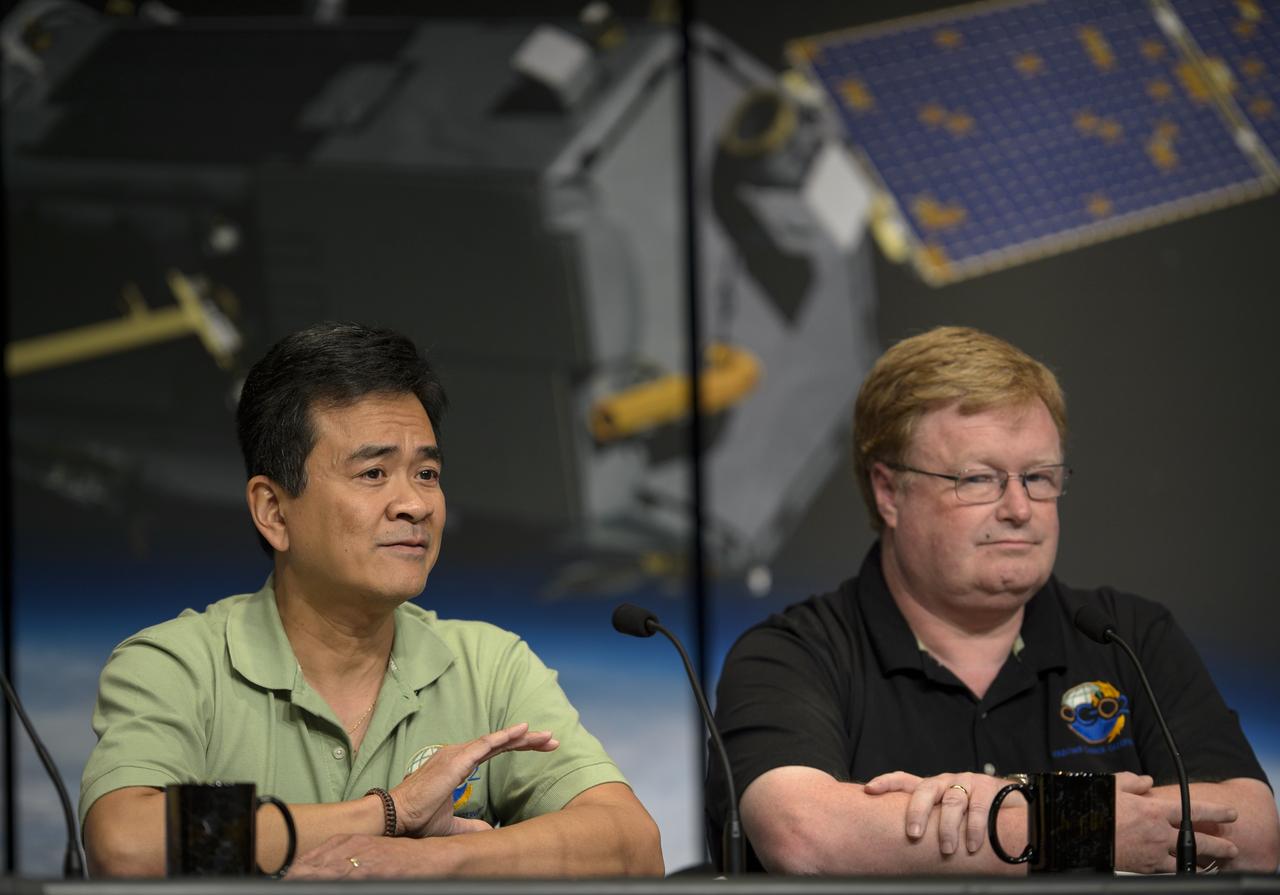
Ralph Basilio, OCO-2 project manager with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, left, and Mike Gunson, OCO-2 project scientist at JPL, discuss the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Thursday, June 12, 2014, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Its mission is to measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
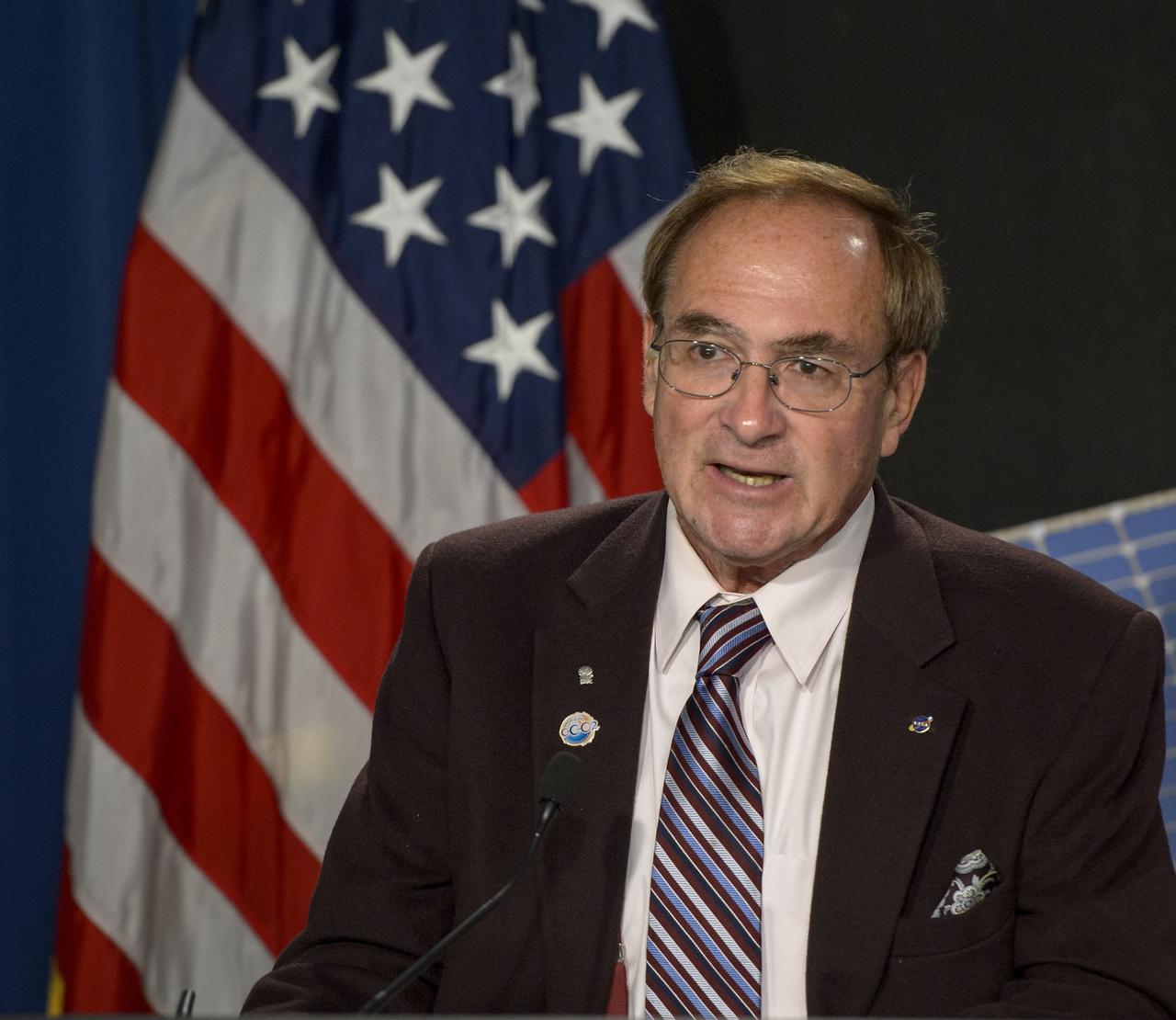

NASA Kennedy Space Center Public Affairs Officer George Diller, moderates a briefing ahead of the planned launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
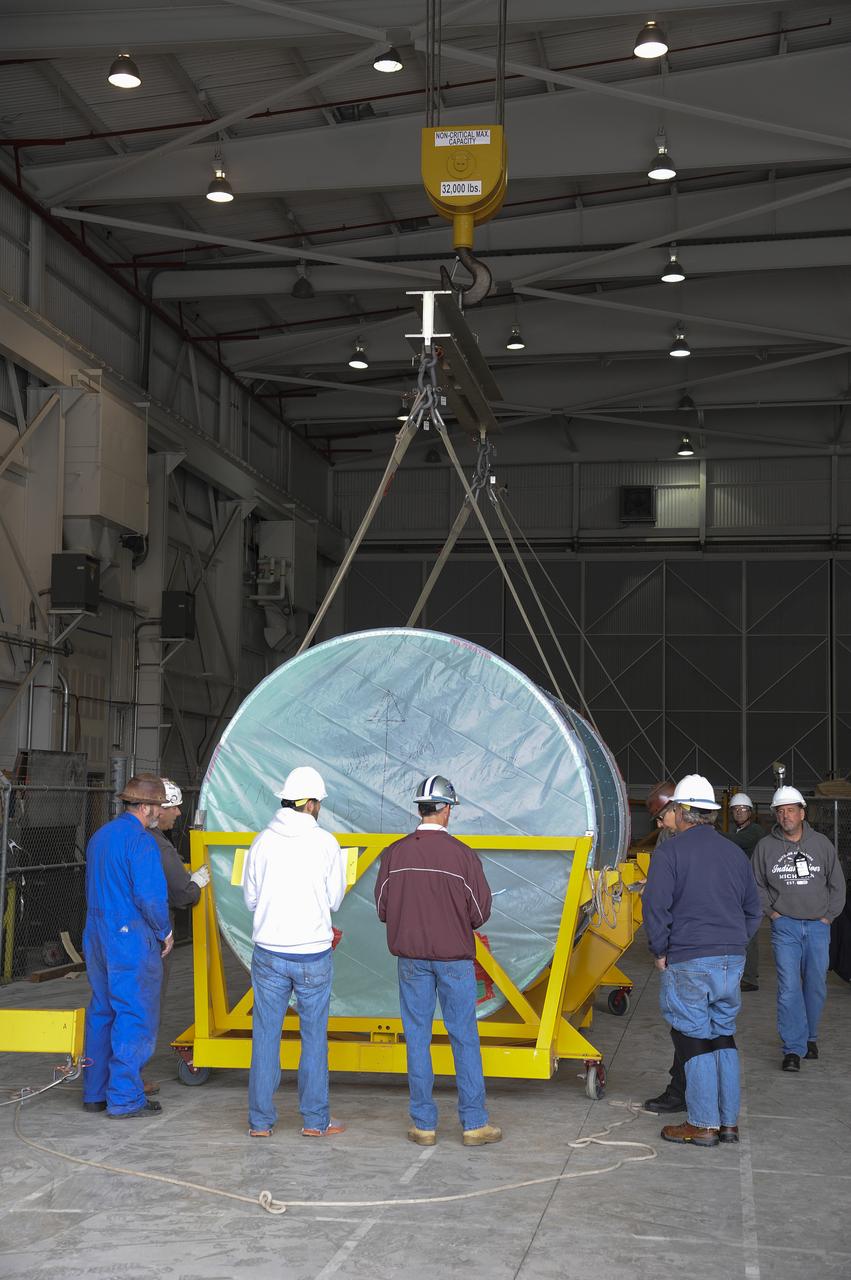

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers lower the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into a transportation hardware cradle in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Jeremy Moore, 30th Space Wing, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers lift the interstage adapter, or ISA, for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, from its transportation trailer in the high bay of the Building 836 hangar on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The ISA is the interface between the Delta II first and second stages. The second stage engine fits within the ISA. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Jeremy Moore, 30th Space Wing, VAFB
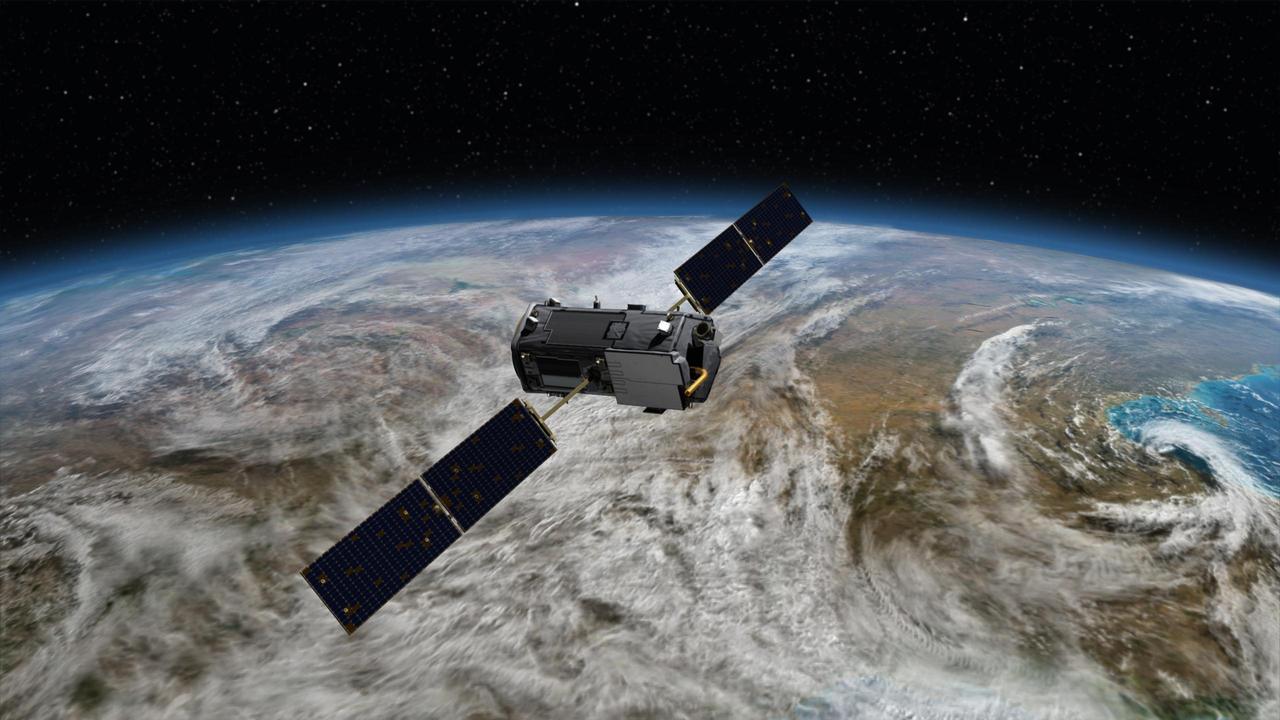

Artist rendering of NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory OCO-2, one of five new NASA Earth science missions set to launch in 2014, and one of three managed by JPL.

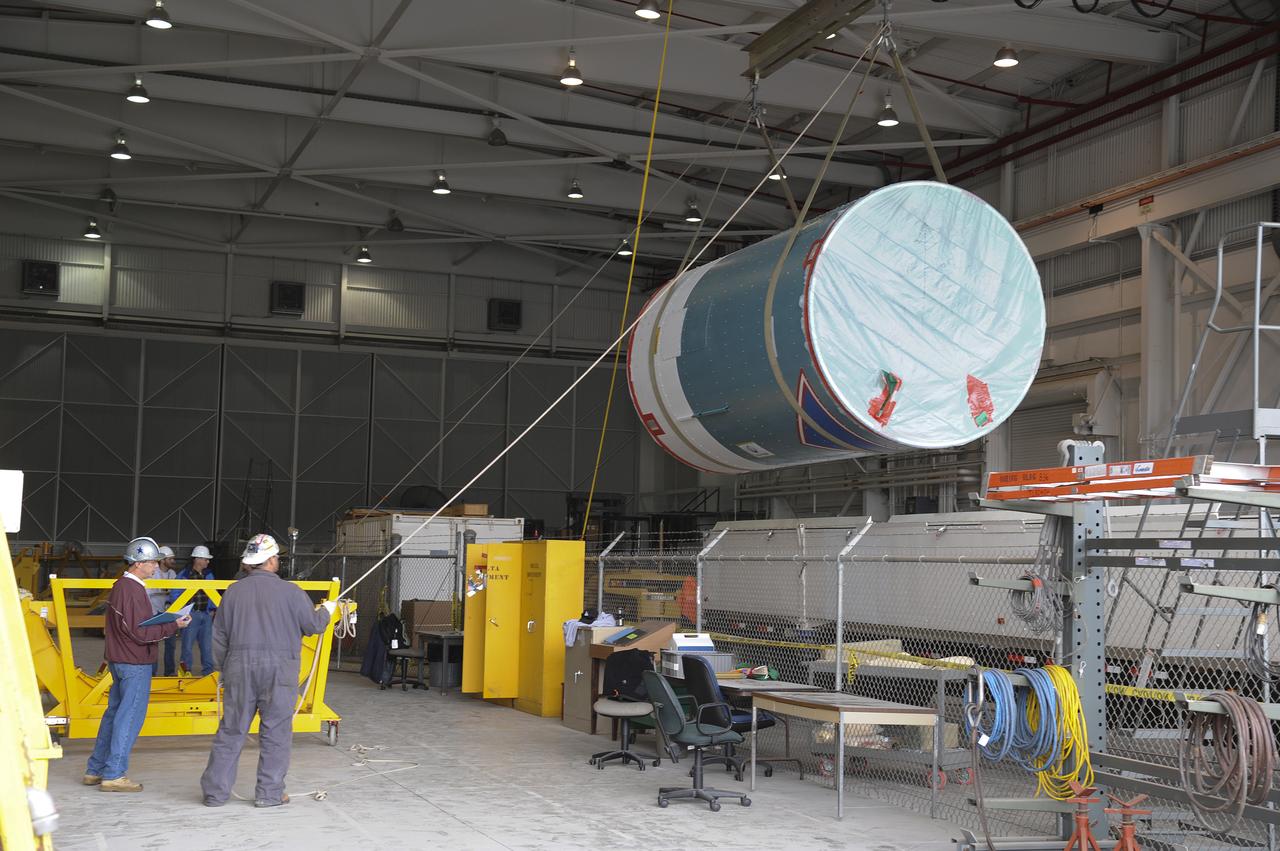
The Delta II second stage for NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is positioned atop the rocket first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
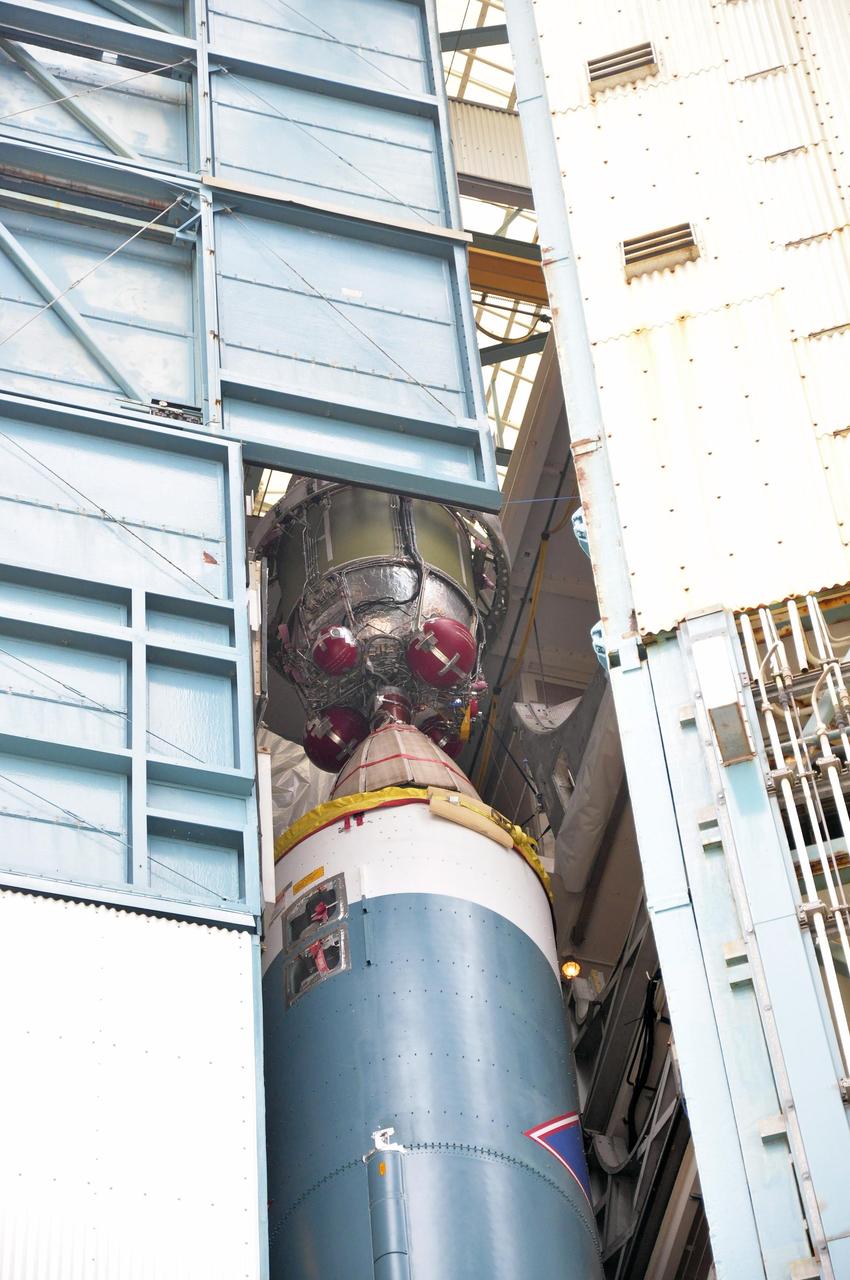

The Delta II second stage for NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, makes contact with the rocket first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
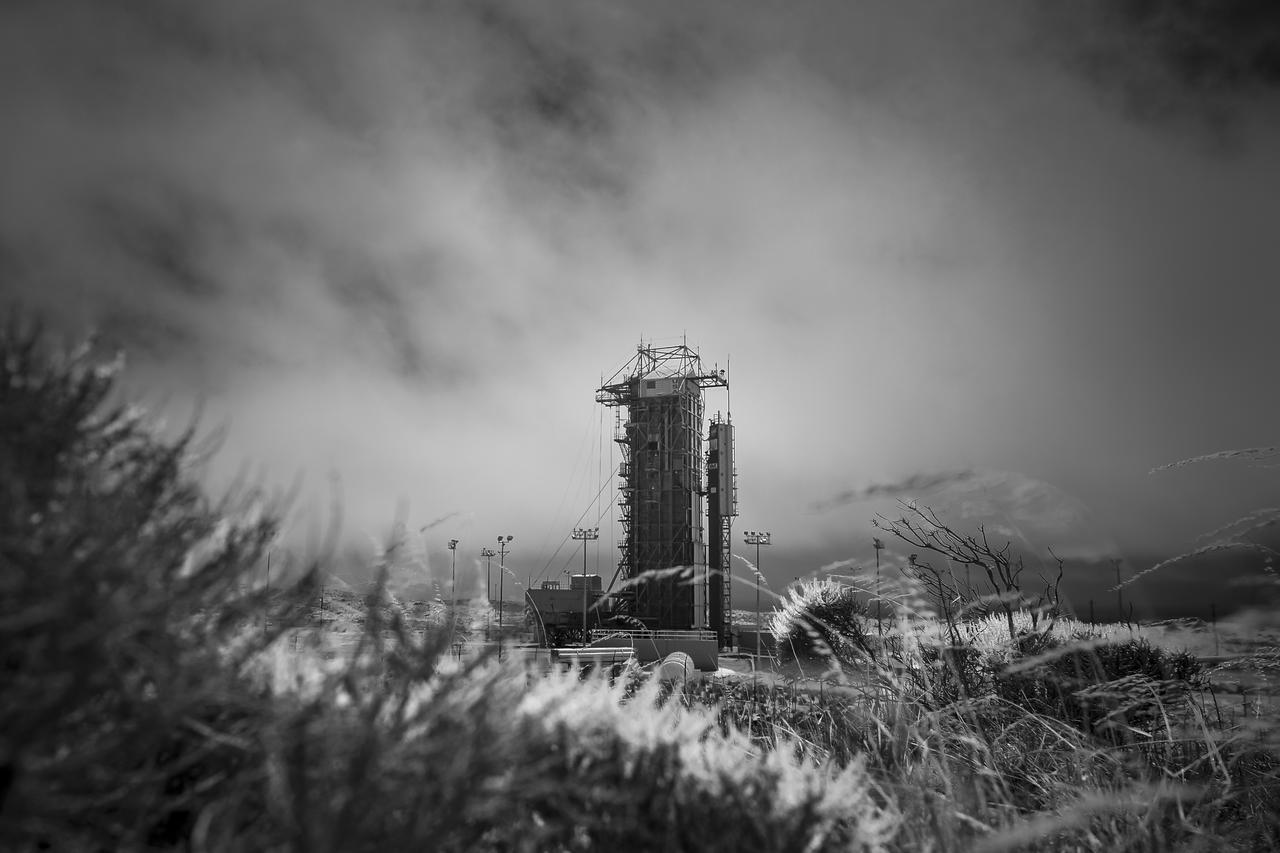

The launch gantry, surrounding the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard, is seen in this black and white infrared view at Space Launch Complex 2, Friday, June 27, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
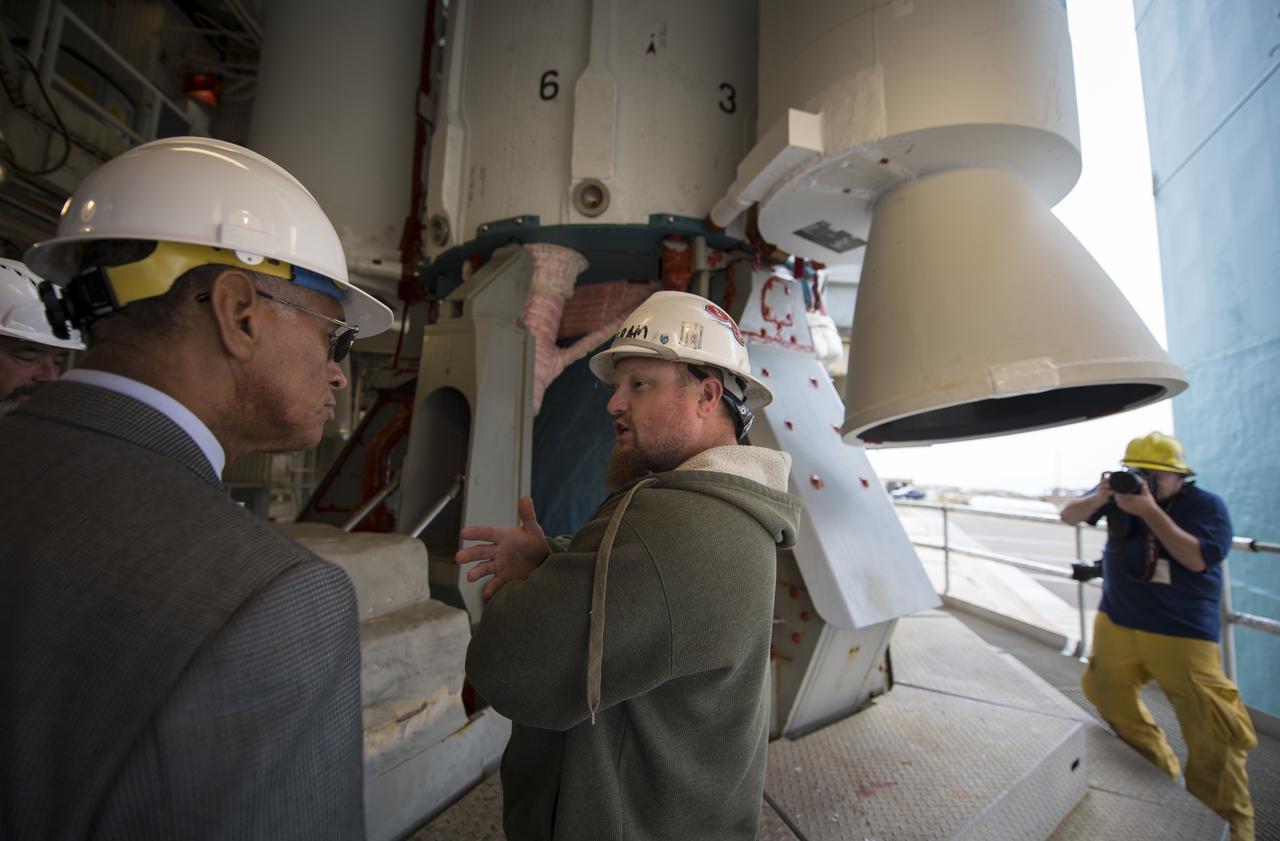

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, talks with an engineer at the base of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard, Monday, June 30, 2014, Space Launch Complex 2, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

From left, NASA Kennedy Space Center Public Affairs Officer George Diller, Ken Jucks, OCO-2 program scientist, NASA Headquarters, Dave Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader, JPL, and Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist, JPL, give a science briefing ahead of the planned launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
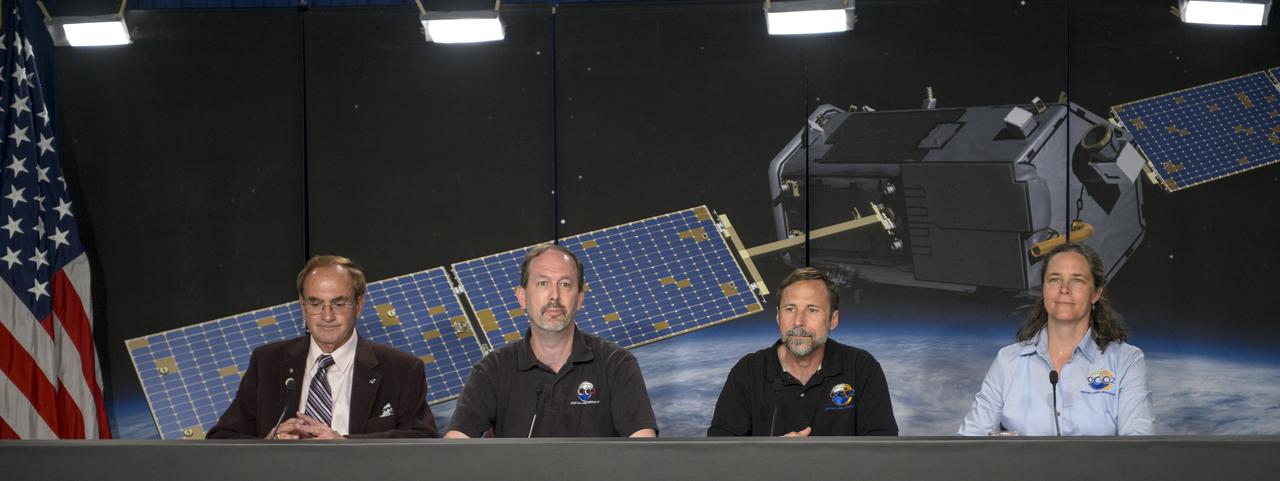

From left, NASA Kennedy Space Center Public Affairs Officer George Diller, Ken Jucks, OCO-2 program scientist, NASA Headquarters, Dave Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader, JPL, and Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist, JPL, give a science briefing ahead of the planned launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Headquarters Public Affairs Officer Steve Cole, standing, moderates a Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) briefing with (from left), Betsy Edwards, OCO-2 program executive with the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, Ralph Basilio, OCO-2 project manager with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, Mike Gunson, OCO-2 project scientist with JPL, and Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist JPL, , Thursday, June 12, 2014, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. OCO-2, NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, is set for a July 1, 2014 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Its mission is to measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
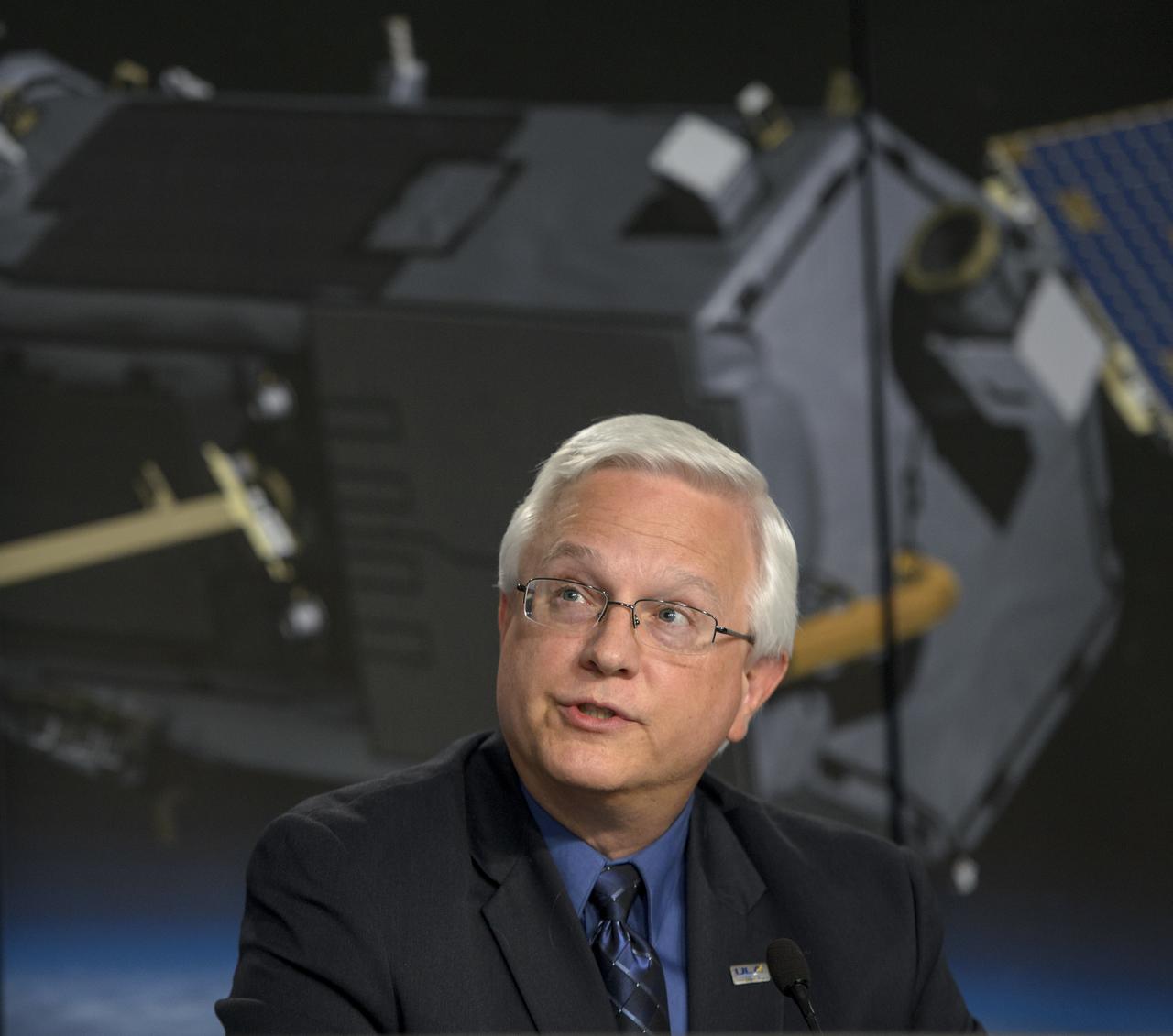

Vern Thorp, United Launch Alliance program manager, NASA missions, discusses the launch of NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) onboard a ULA Delta II rocket, during a press briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
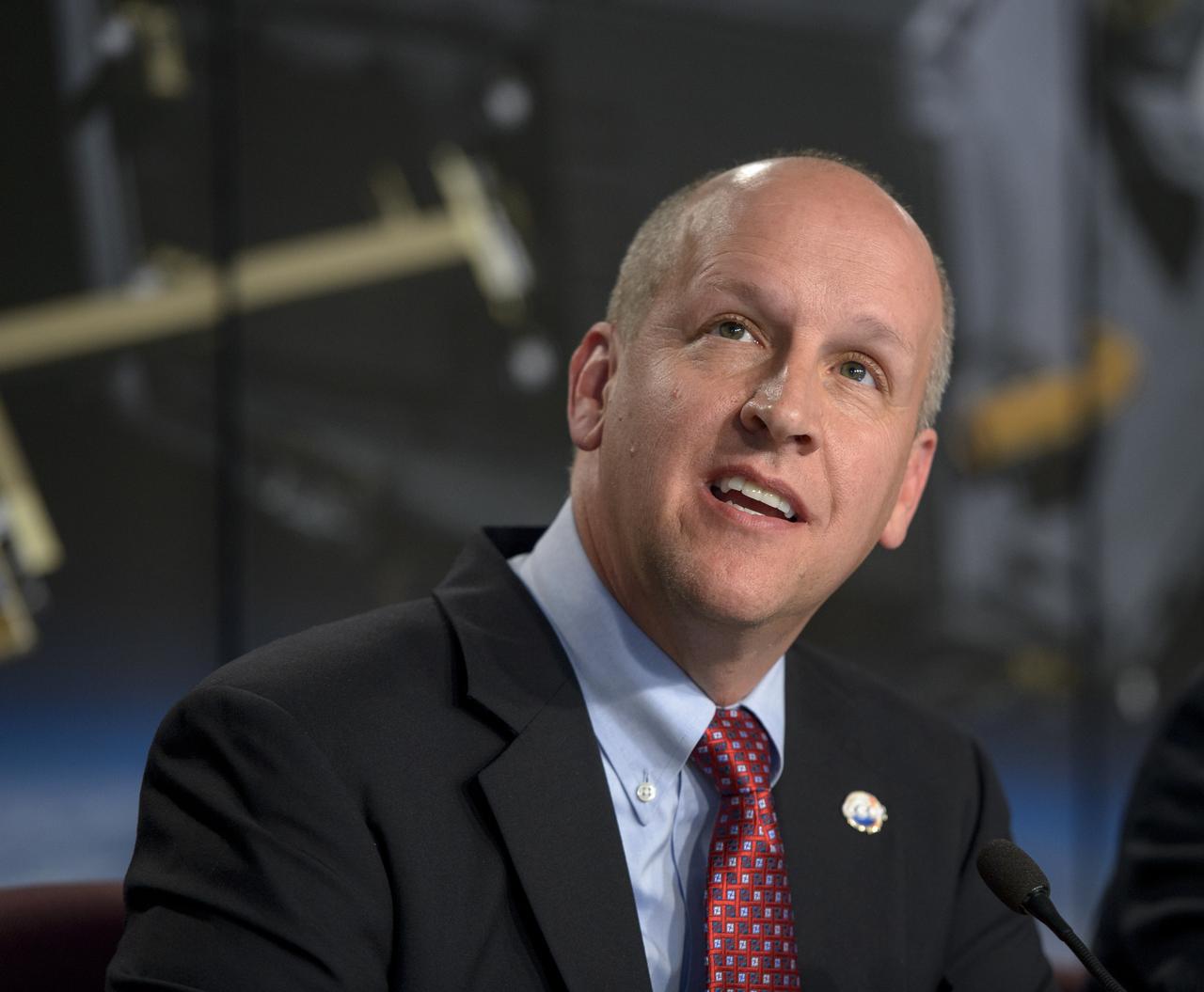

Tim Dunn, NASA launch director, Kennedy Space Center, discusses the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
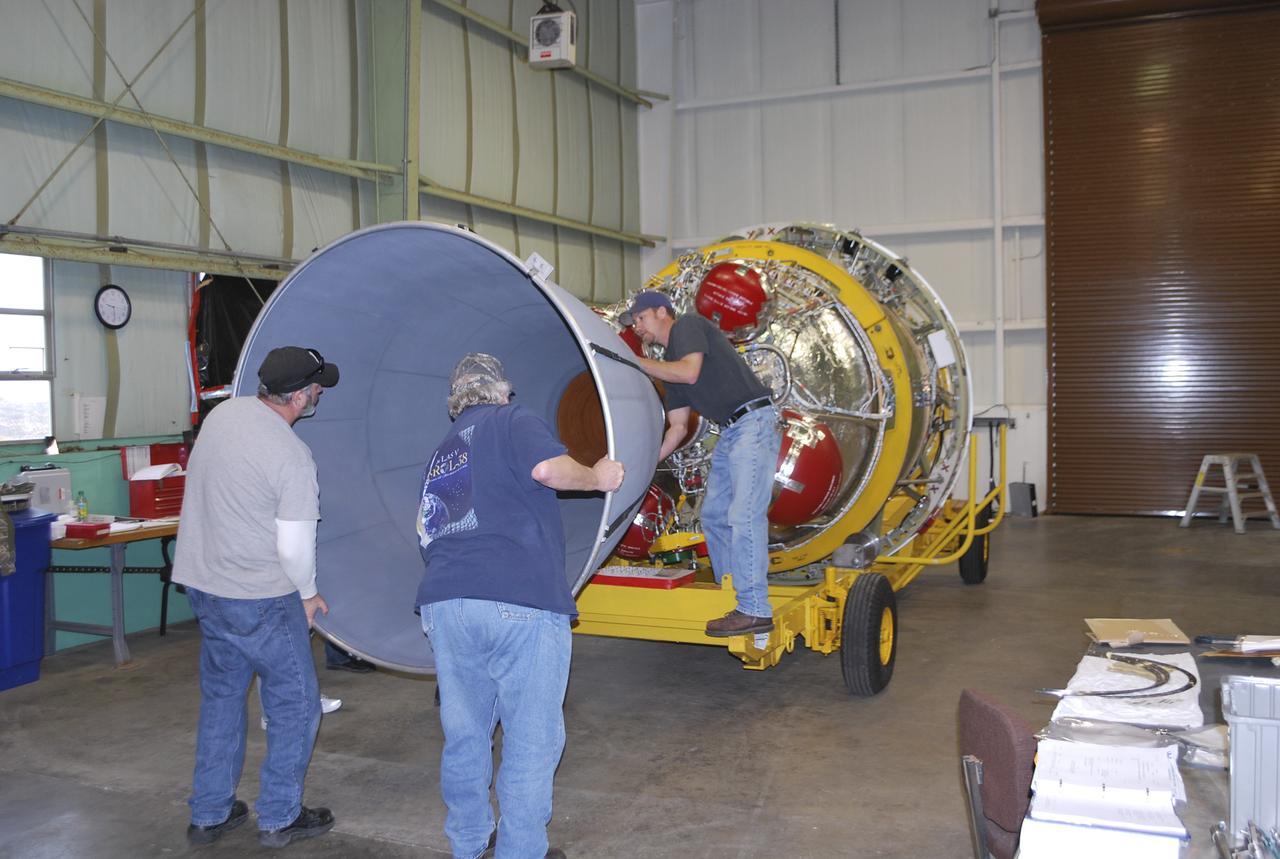

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – In the Horizontal Processing Facility at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the engine bell is installed around the second-stage nozzle of the Delta II rocket for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2. OCO-2 is scheduled to launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The rocket's second stage will insert OCO-2 into a polar Earth orbit. OCO-2 will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

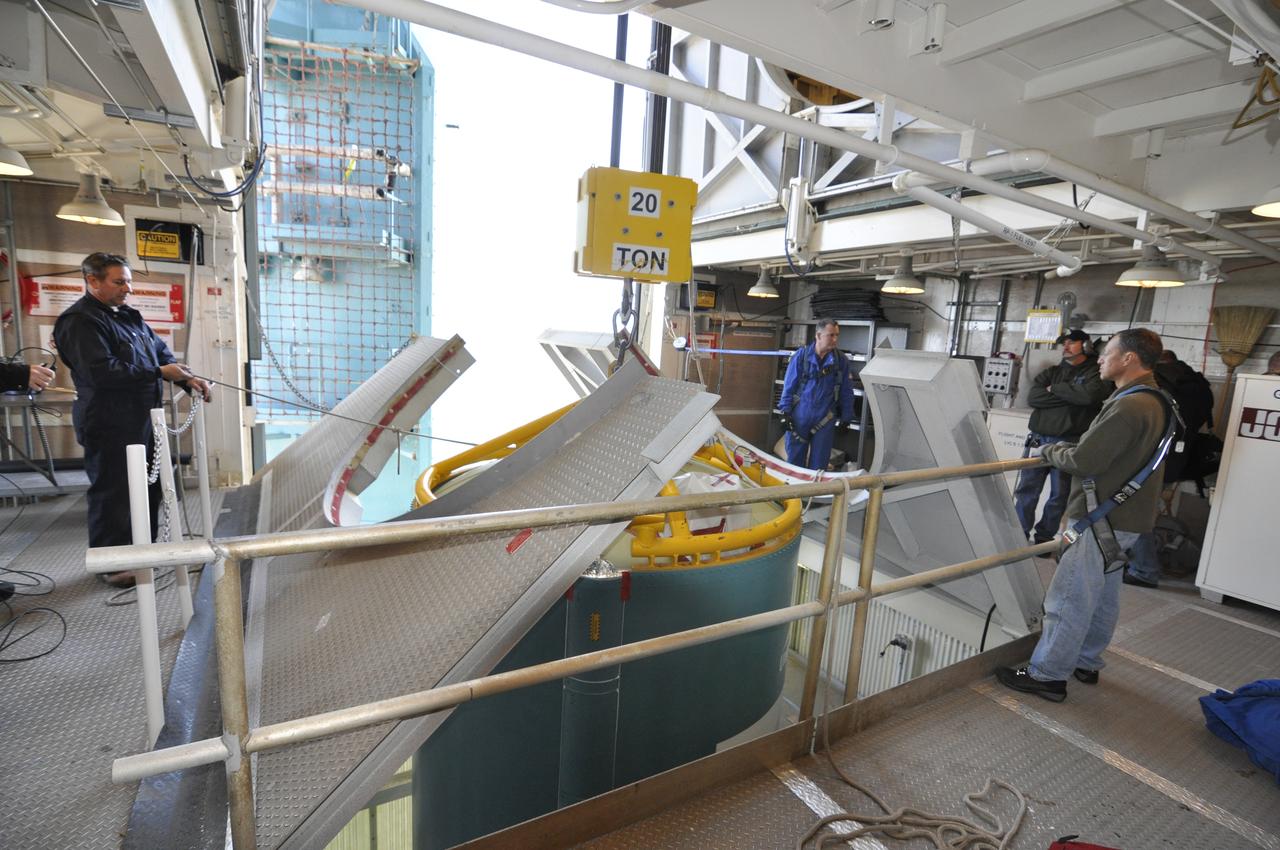
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Both halves of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, are delivered to Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations have begun to hoist the sections of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the pad's tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
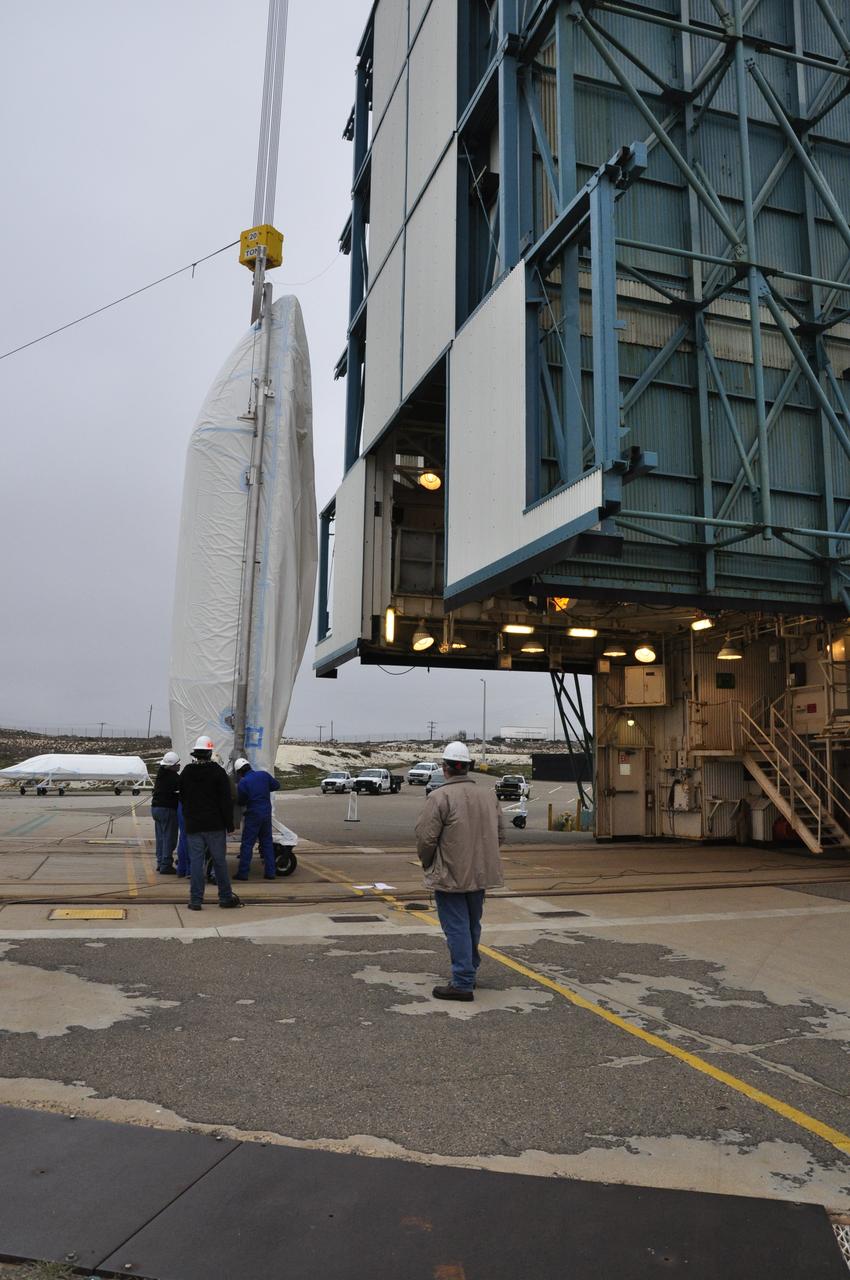

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – A crane is employed to lift half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into a vertical position at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to hoist this section of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

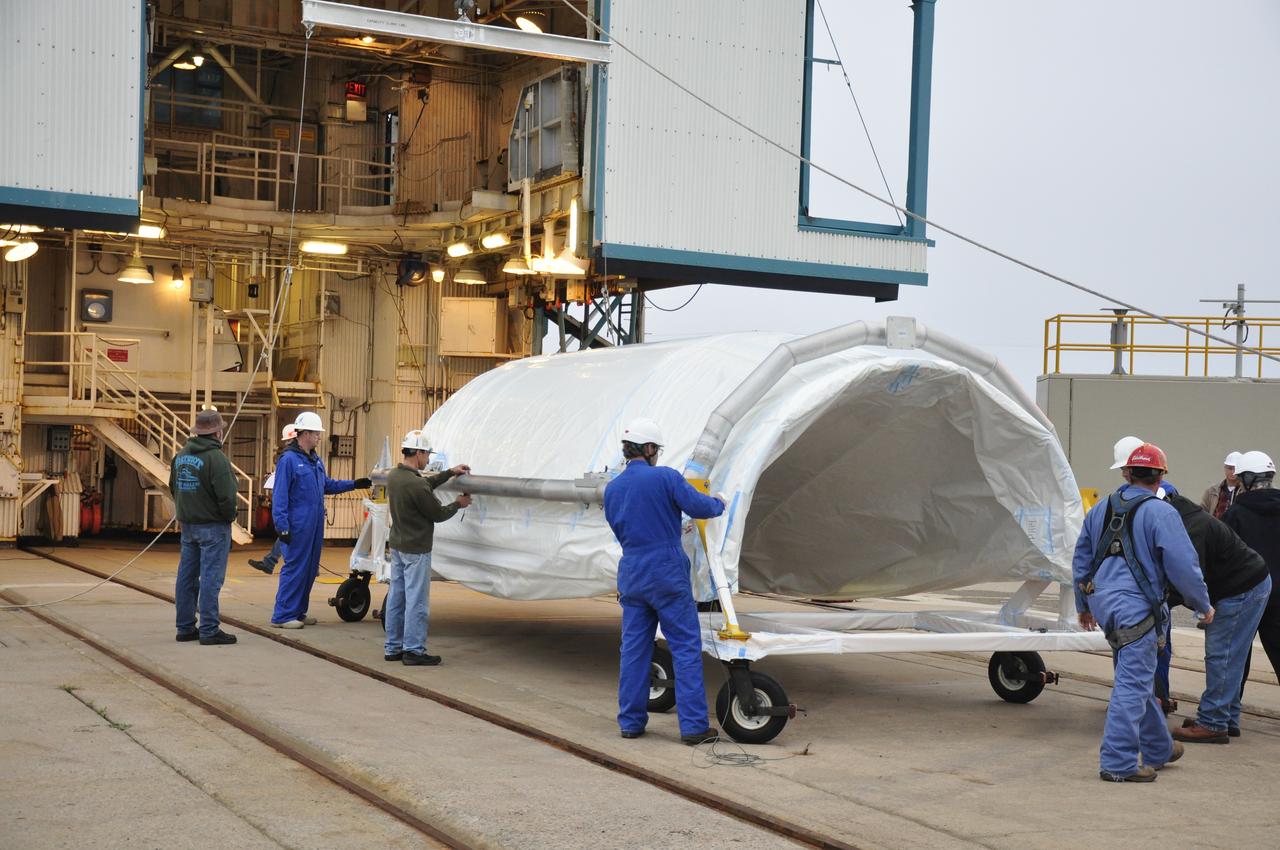
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is transferred through the portal into the environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the Delta II launcher at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
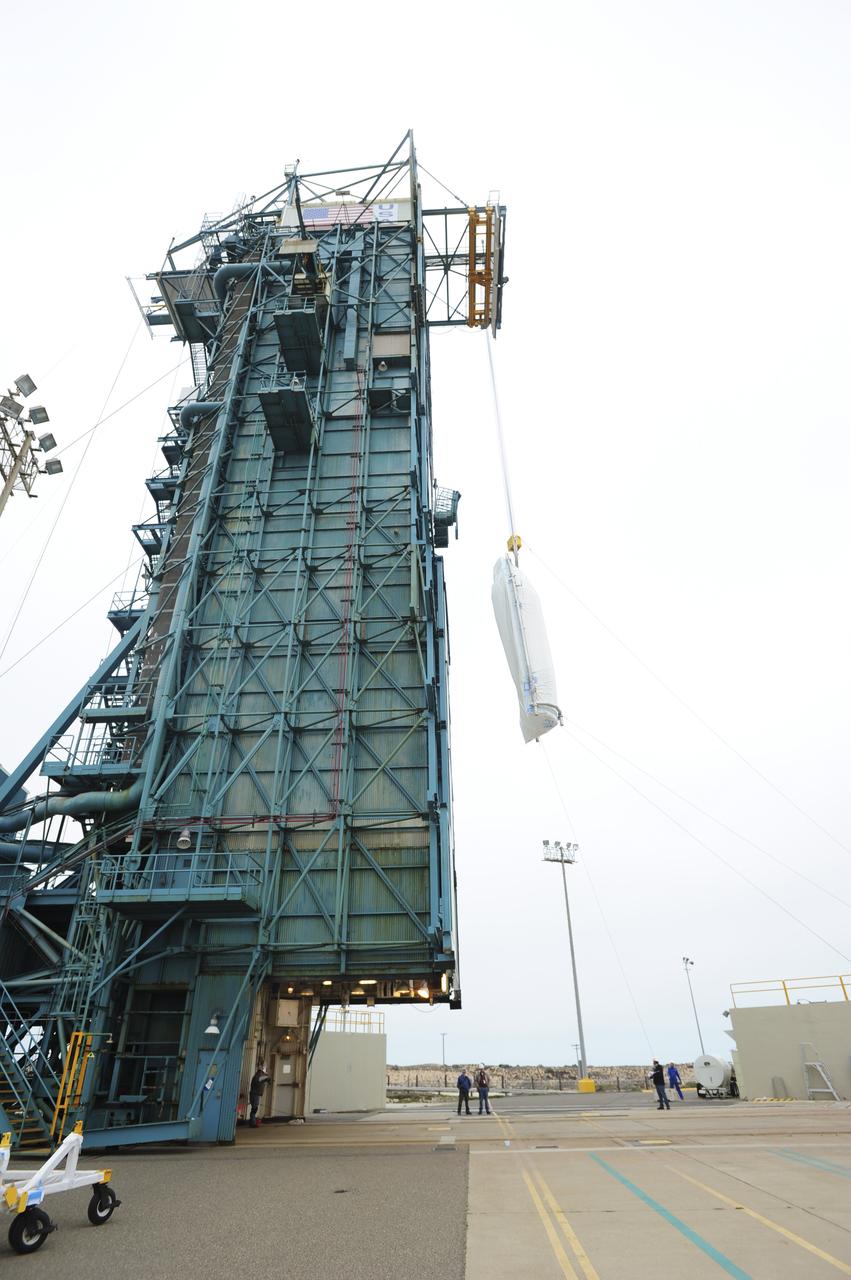

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted up the side of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California toward the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/30th Space Wing, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers remove the protective wrap from half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, newly arrived at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations are underway to hoist this section of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
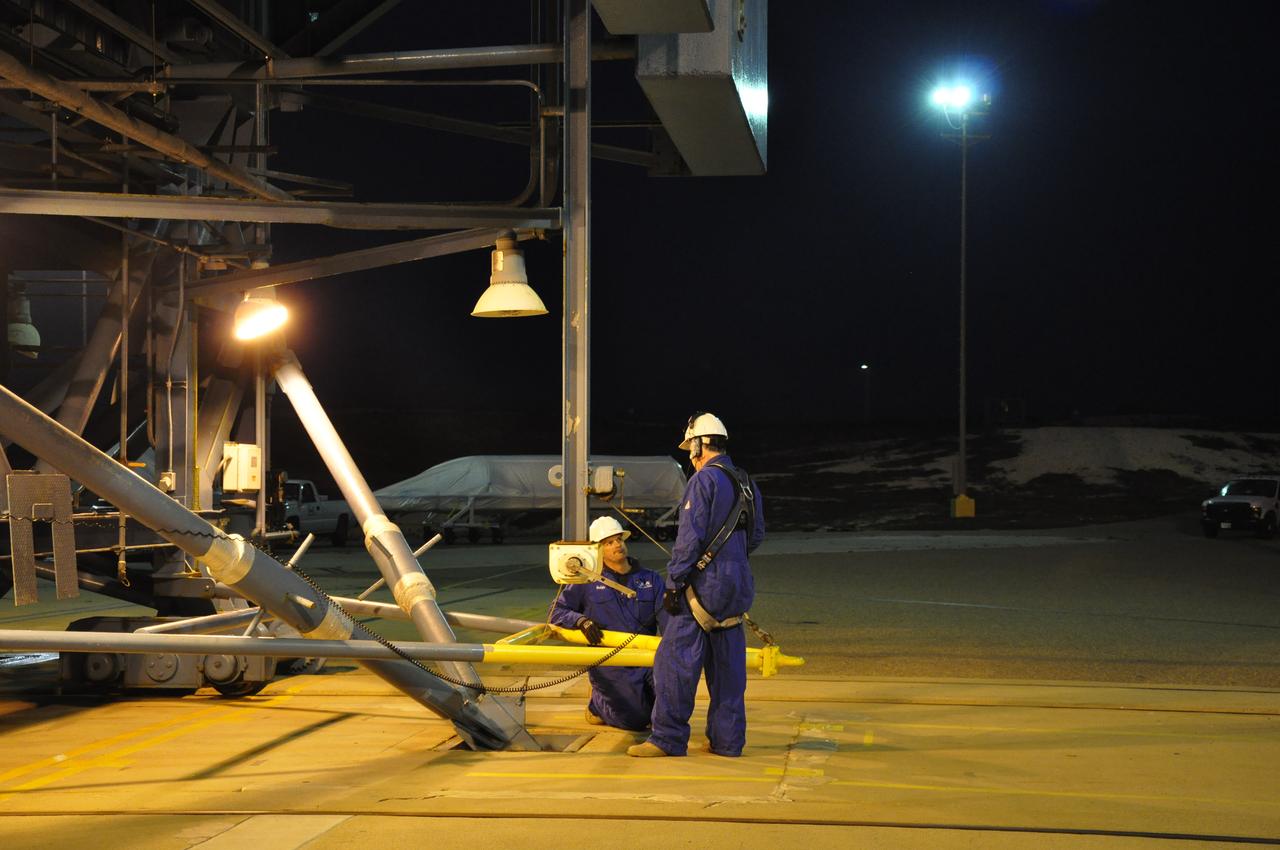

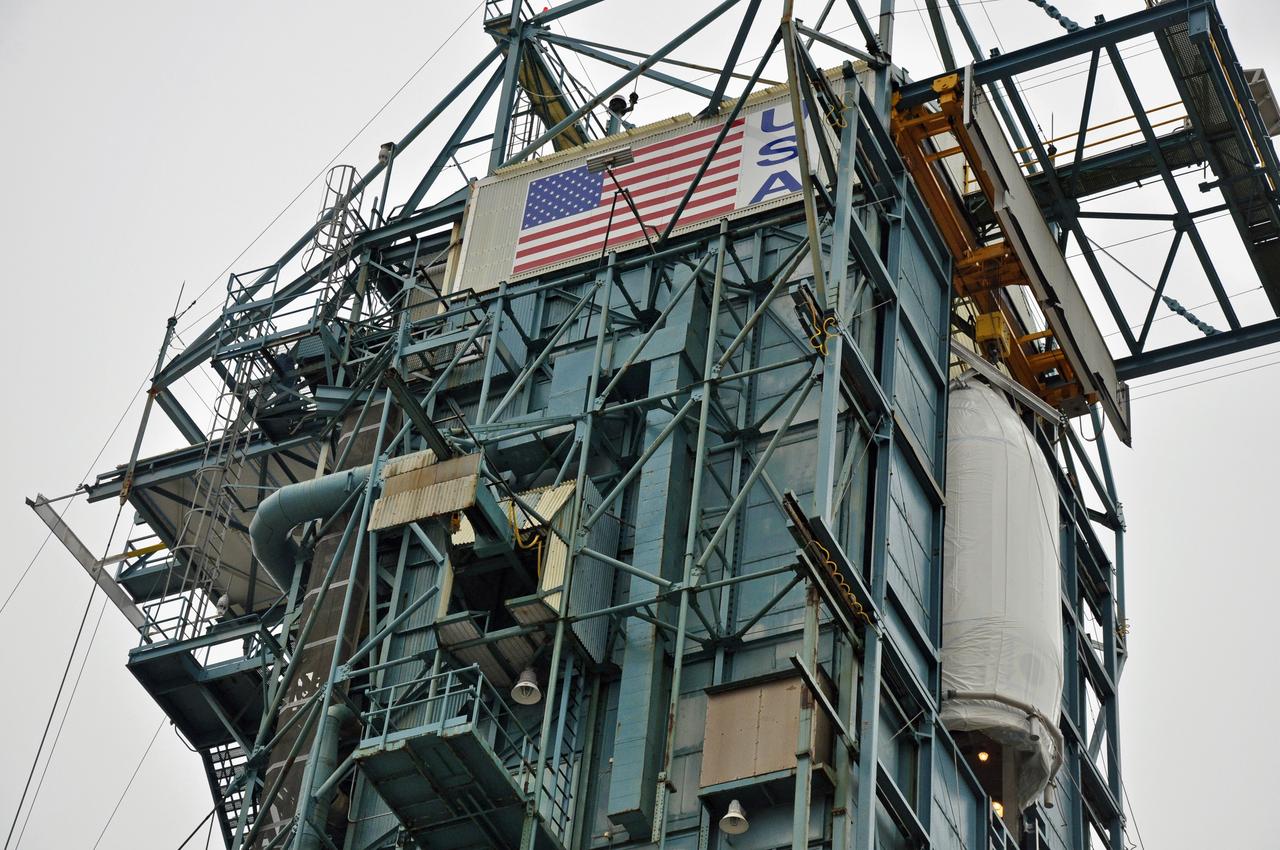
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – At Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers prepare to hoist the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, seen in the background, into the gantry's environmental enclosure, or clean room, following the rollback of the mobile service tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The mobile service tower is rolled away from the Delta II launcher at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California in preparation for hoisting the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into the gantry's environmental enclosure, or clean room. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
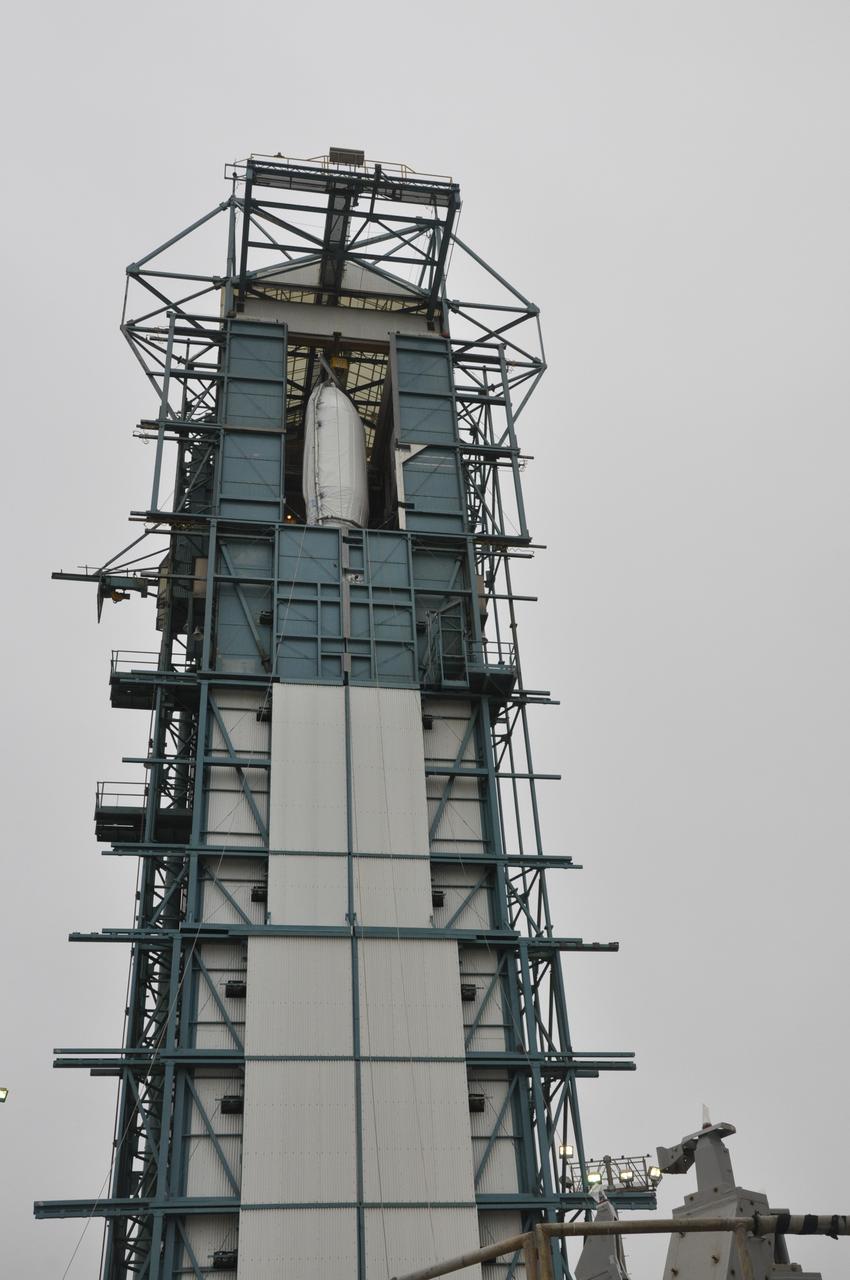

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is positioned into the environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the Delta II launcher at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
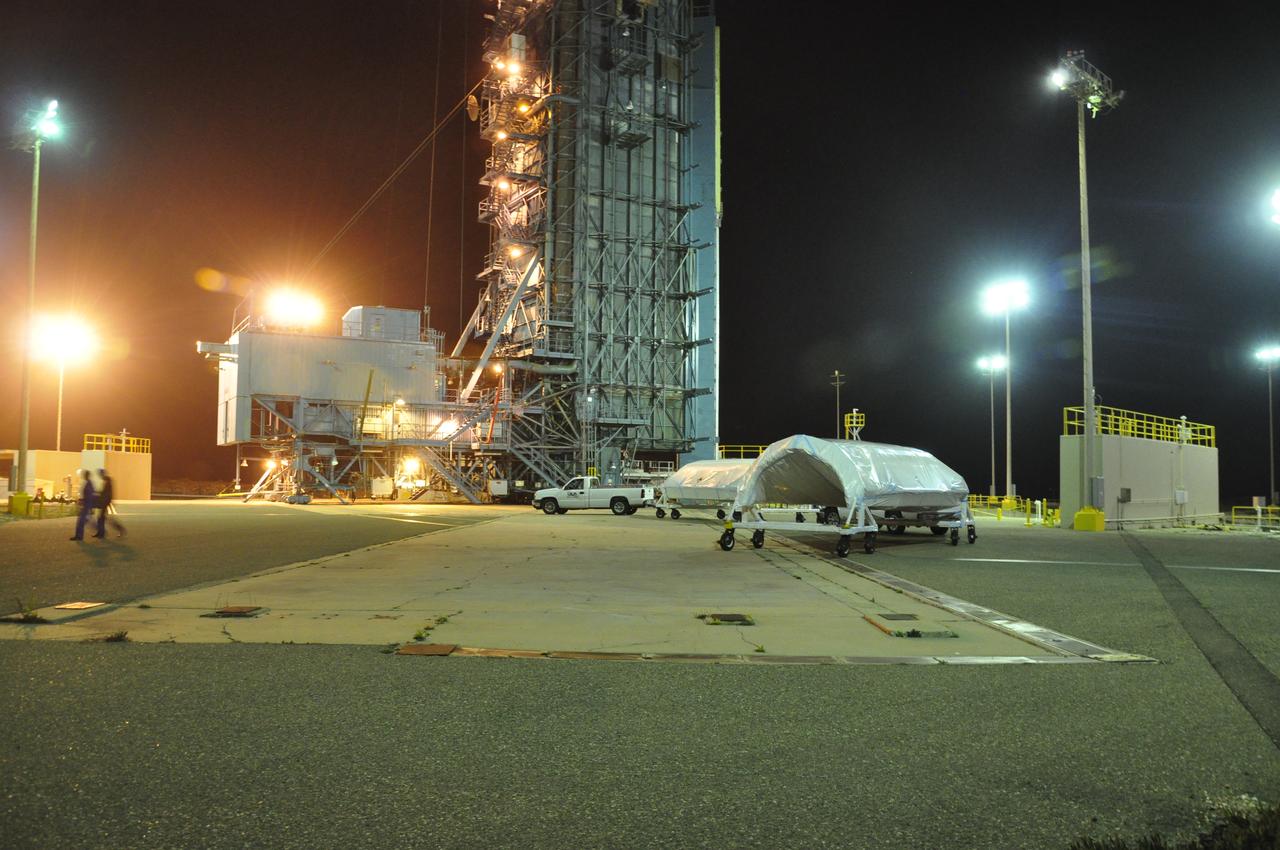

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Both halves of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, arrive at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Operations have begun to hoist the sections of the fairing into the Delta II launcher's environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the pad's tower. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
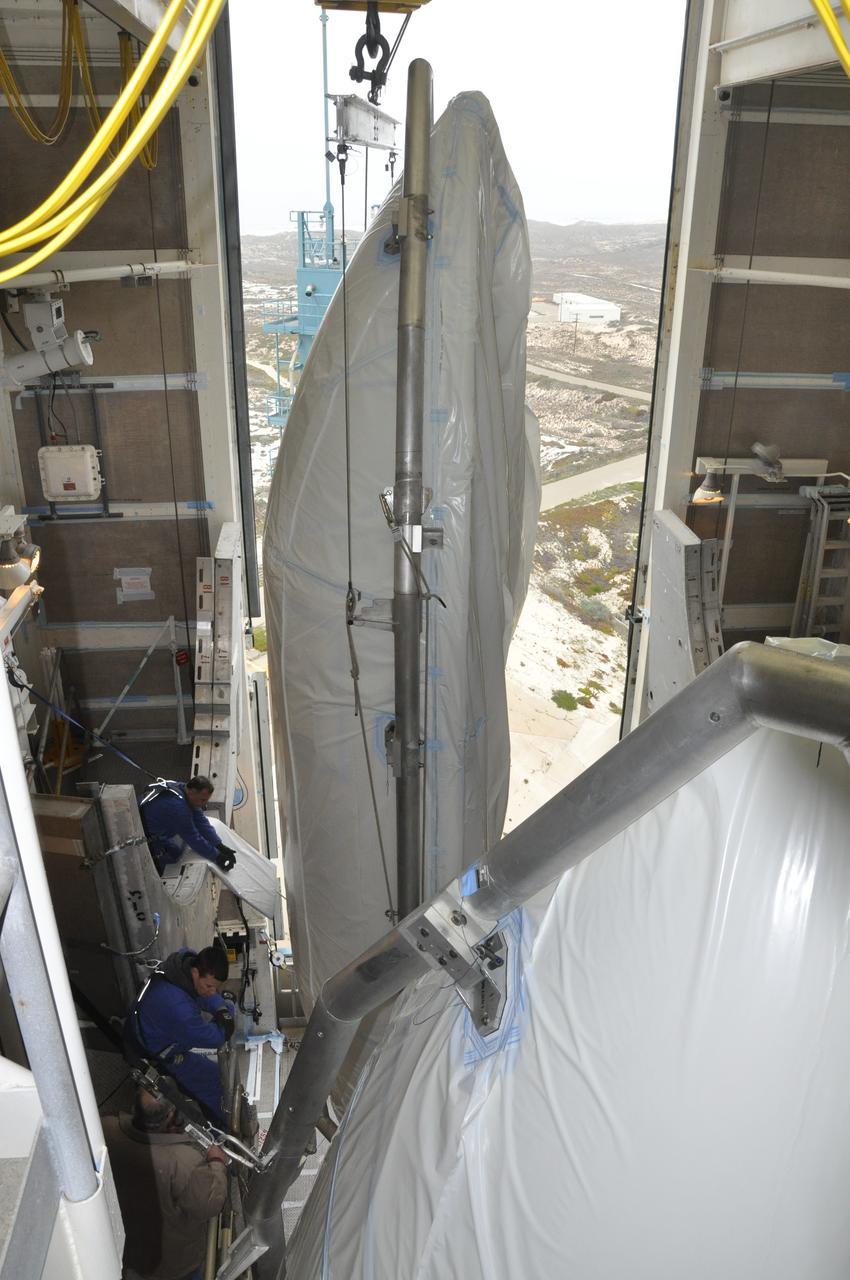

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Workers transfer half of the fairing for NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, into the environmental enclosure, or clean room, at the top of the Delta II launcher at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. The fairing will protect OCO-2 during launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket from Space Launch Complex 2 in July. The observatory will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere and provide scientists with a better idea of the chemical compound's impacts on climate change. Scientists will analyze this data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important atmospheric gas. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://oco.jpl.nasa.gov. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin