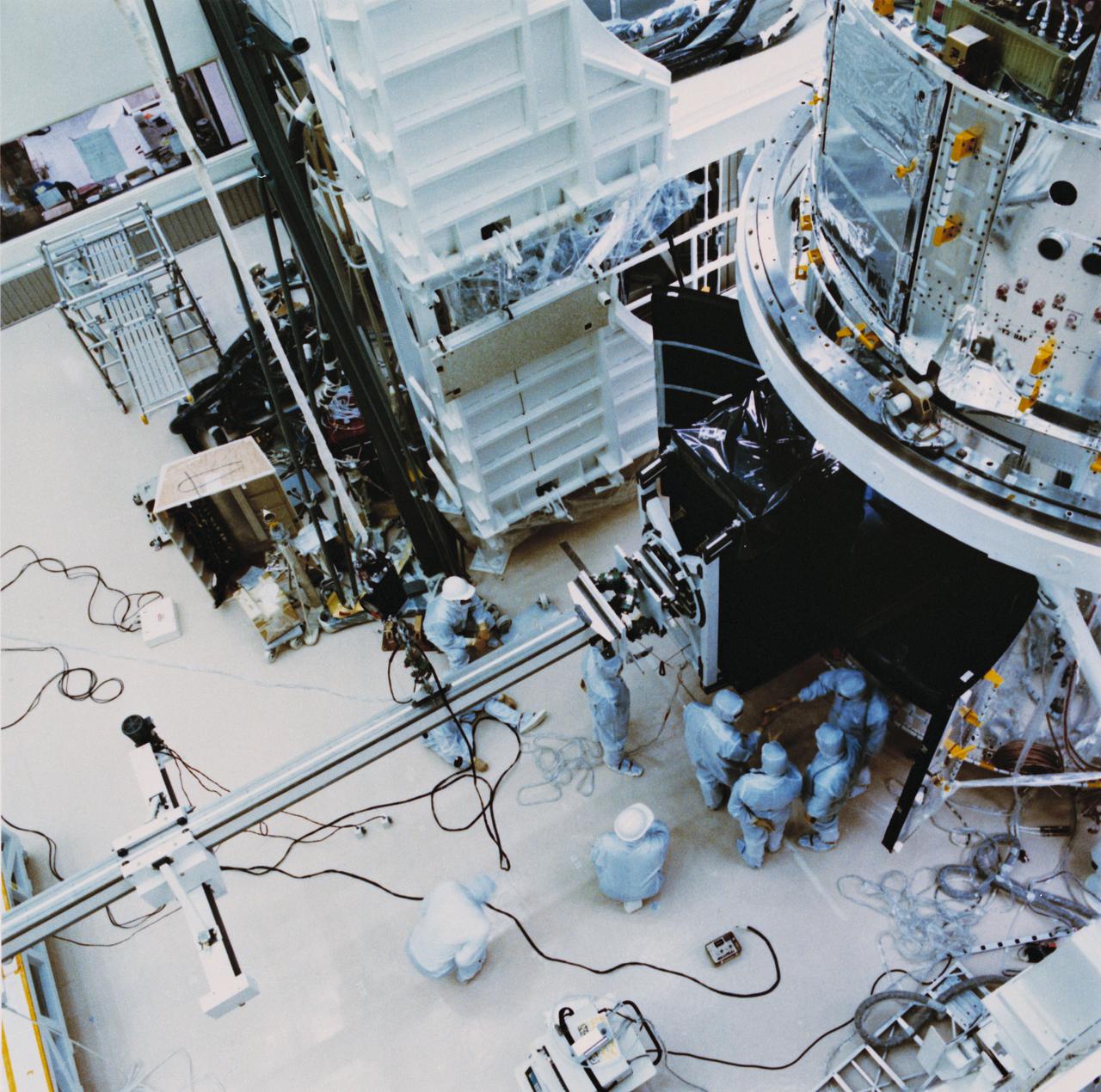

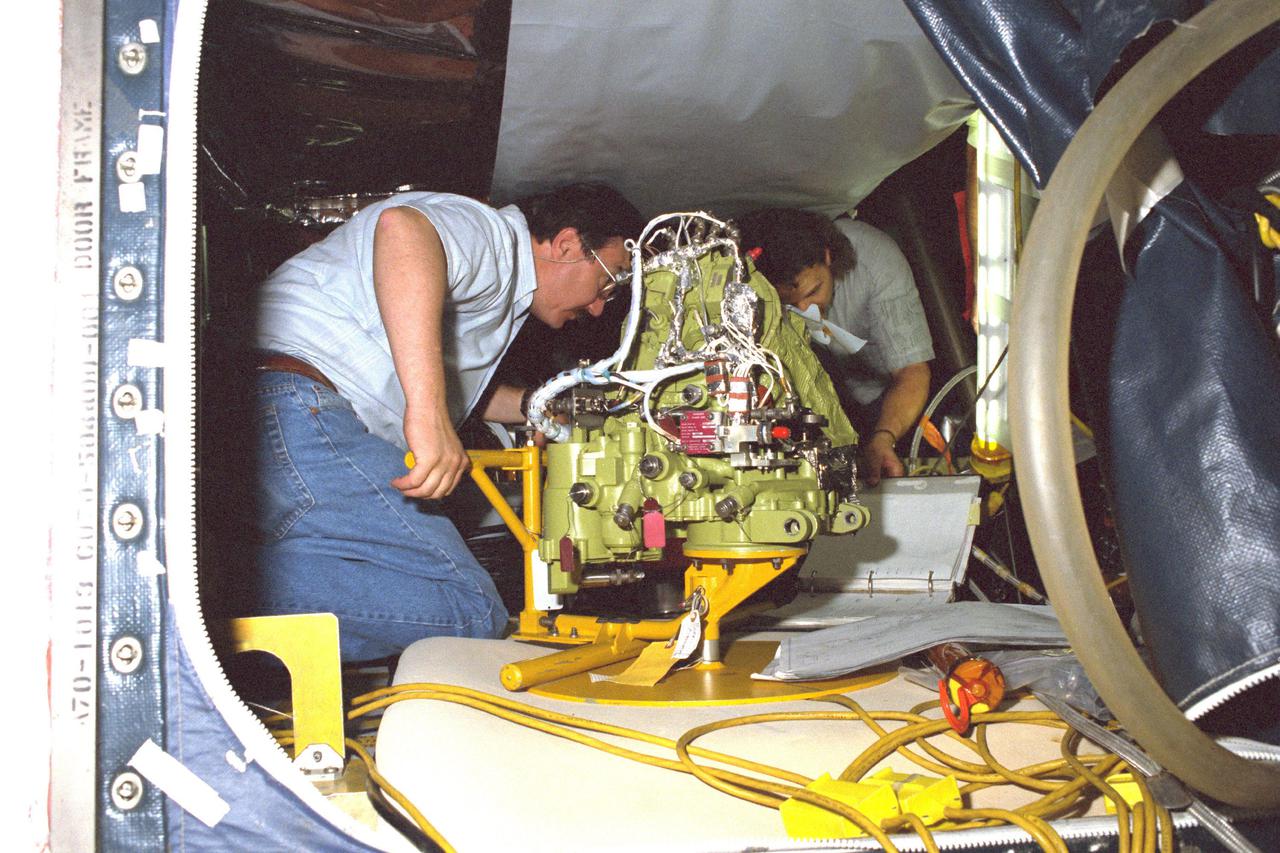
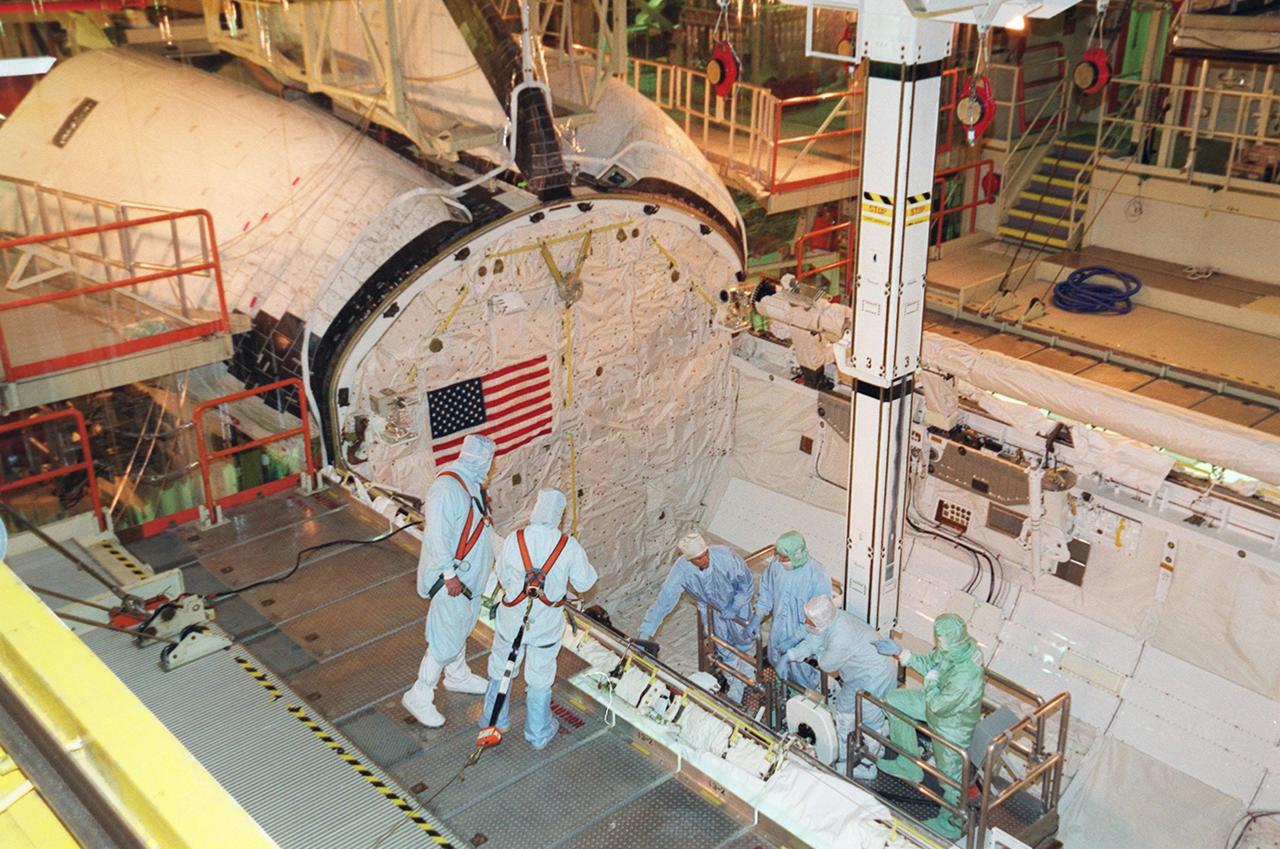
A mechanical arm positions the axial scientific instrument (SI) module (orbital replacement unit (ORU)) just outside the open doors of the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) Support System Module (SSM) as clean-suited technicians oversee the process. HST assembly is being completed at the Lockheed Facility in Sunnyvale, California.
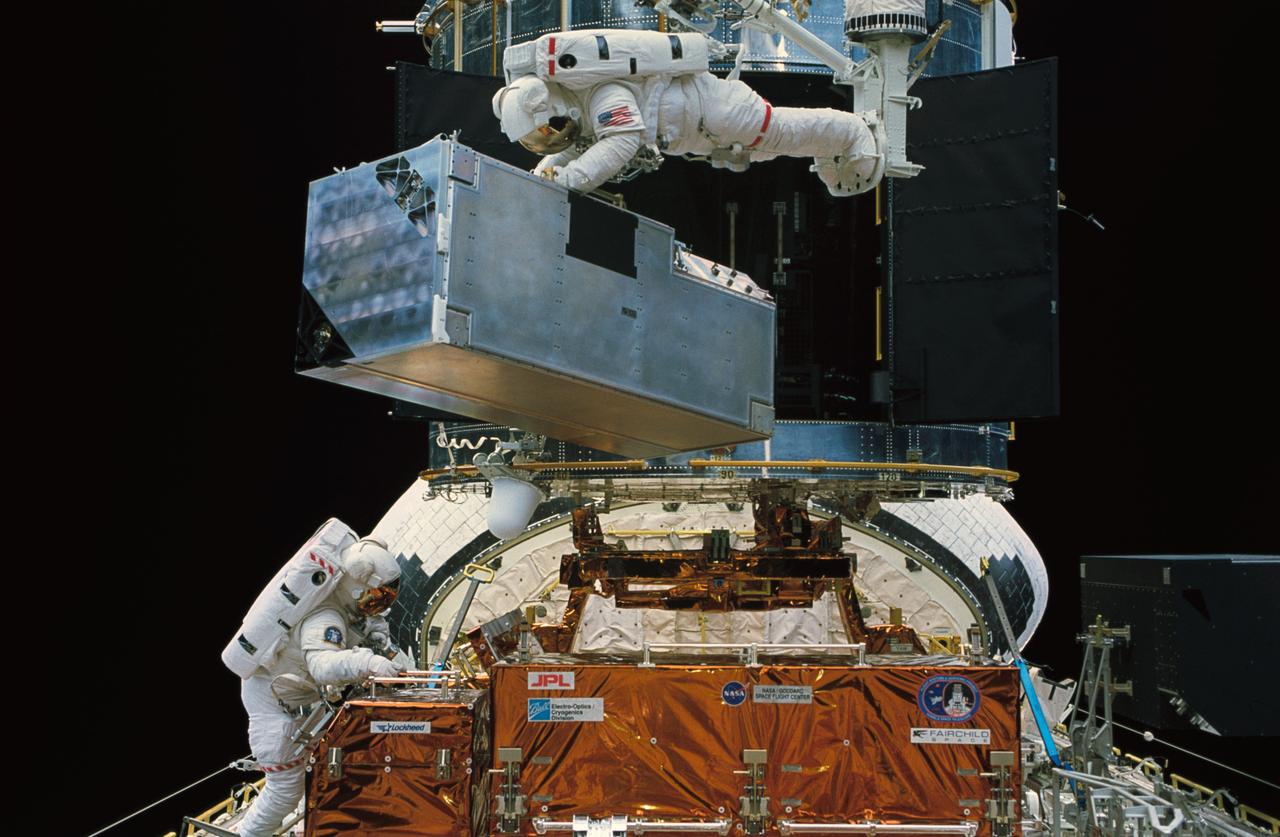
STS061-47-014 (8 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton lifts the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) prior to its installation on the Hubble Space Telescope (HST). Thornton is anchored to a foot restraint on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm. Astronaut Thomas D. Akers, who assisted in the COSTAR installation, is at lower left.
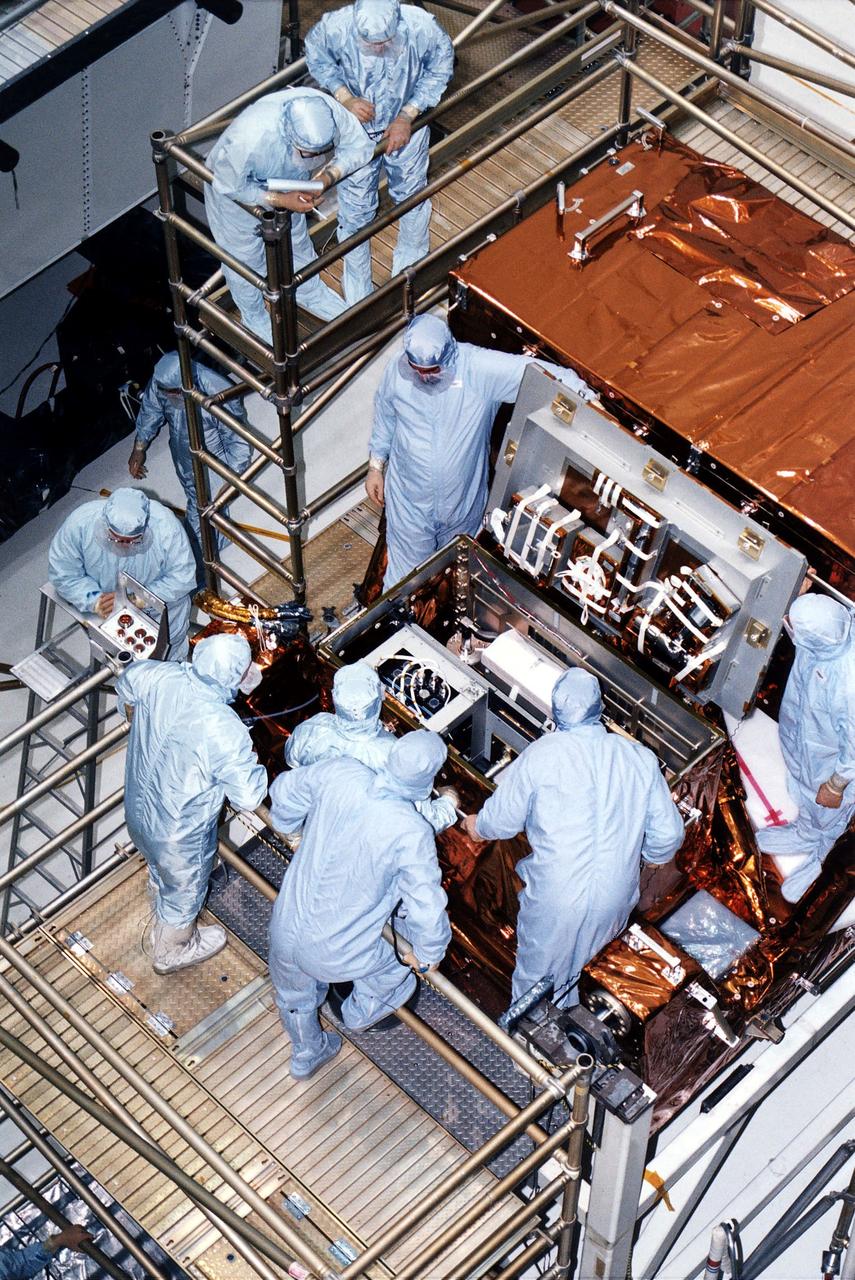

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-82 crew members and workers at KSC's Vertical Processing Facility look at hardware in the Multipurpose ORU (Orbital Replacement Unit) Protective Enclsoure, also called MOPE. The crew is participating in the Crew Equipment Integration Test (CEIT). Liftoff of STS-82, the second Hubble Space Telescope (HST) servicing mission, is scheduled Feb. 11 aboard Discovery with a crew of seven.
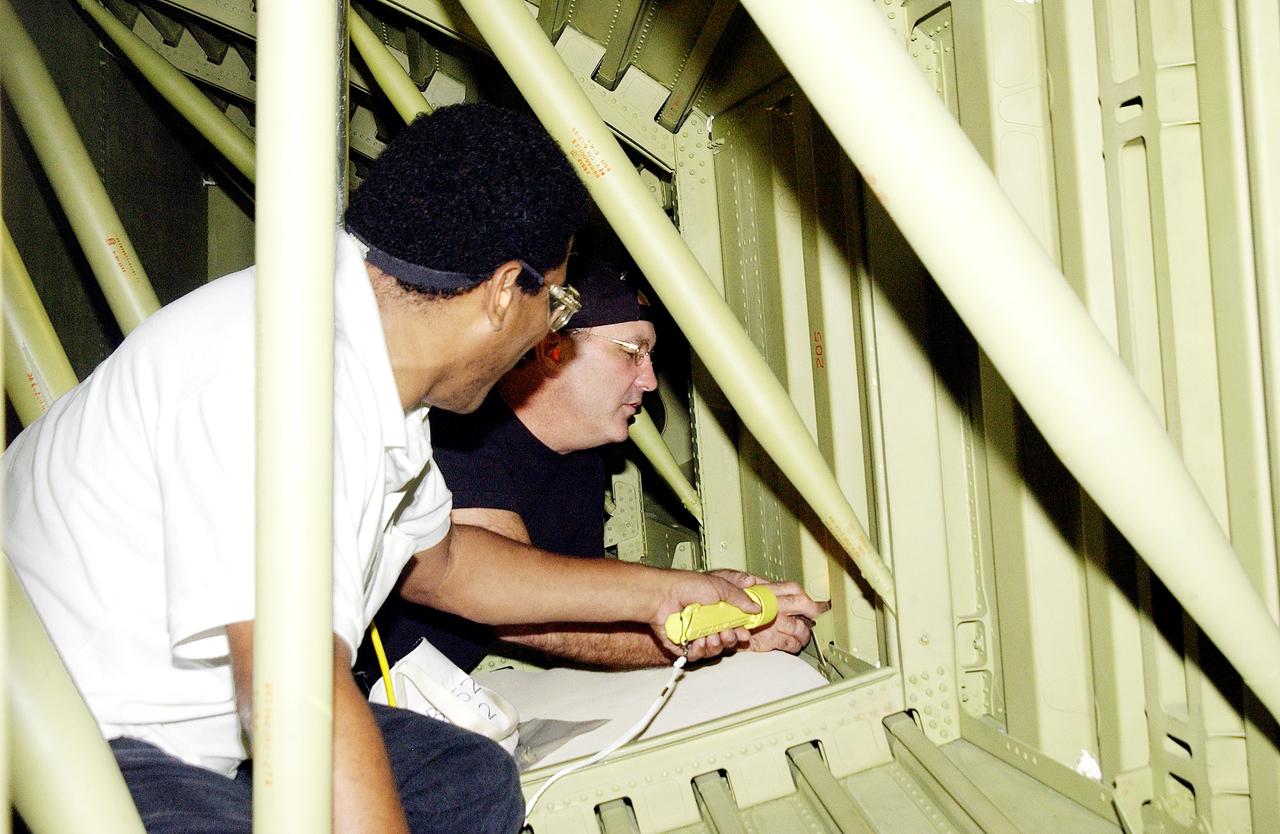

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF), United Space Alliance technicians replace the attachment points for the spars on the interior of a wing of Space Shuttle Atlantis. Reinforced Carbon Carbon (RCC) panels are mechanically attached to the wing with a series of floating joints - spars - to reduce loading on the panels caused by wing deflections. The aluminum and the metallic attachments are protected from exceeding temperature limits by internal insulation. The next launch of Atlantis will be on mission STS-114, a utilization and logistics flight to the International Space Station.
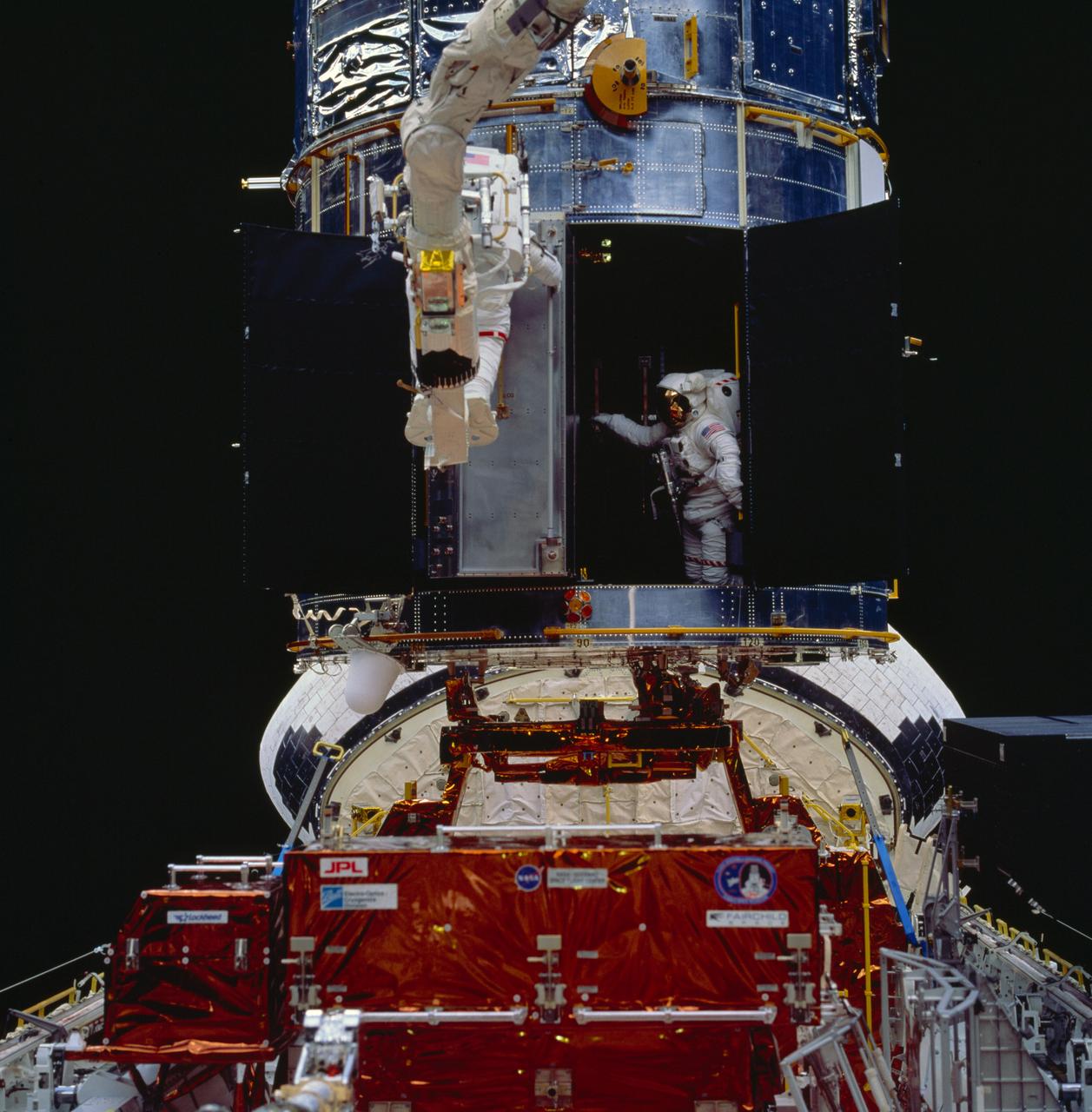

STS061-94-050 (8 Dec 1993) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Akers maneuvers inside the bay which will house the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) while assisting astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton with the installation of the 640-pound instrument. Thornton, anchored on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, is partially visible as she prepares to install the COSTAR, during their extravehicular activity (EVA).
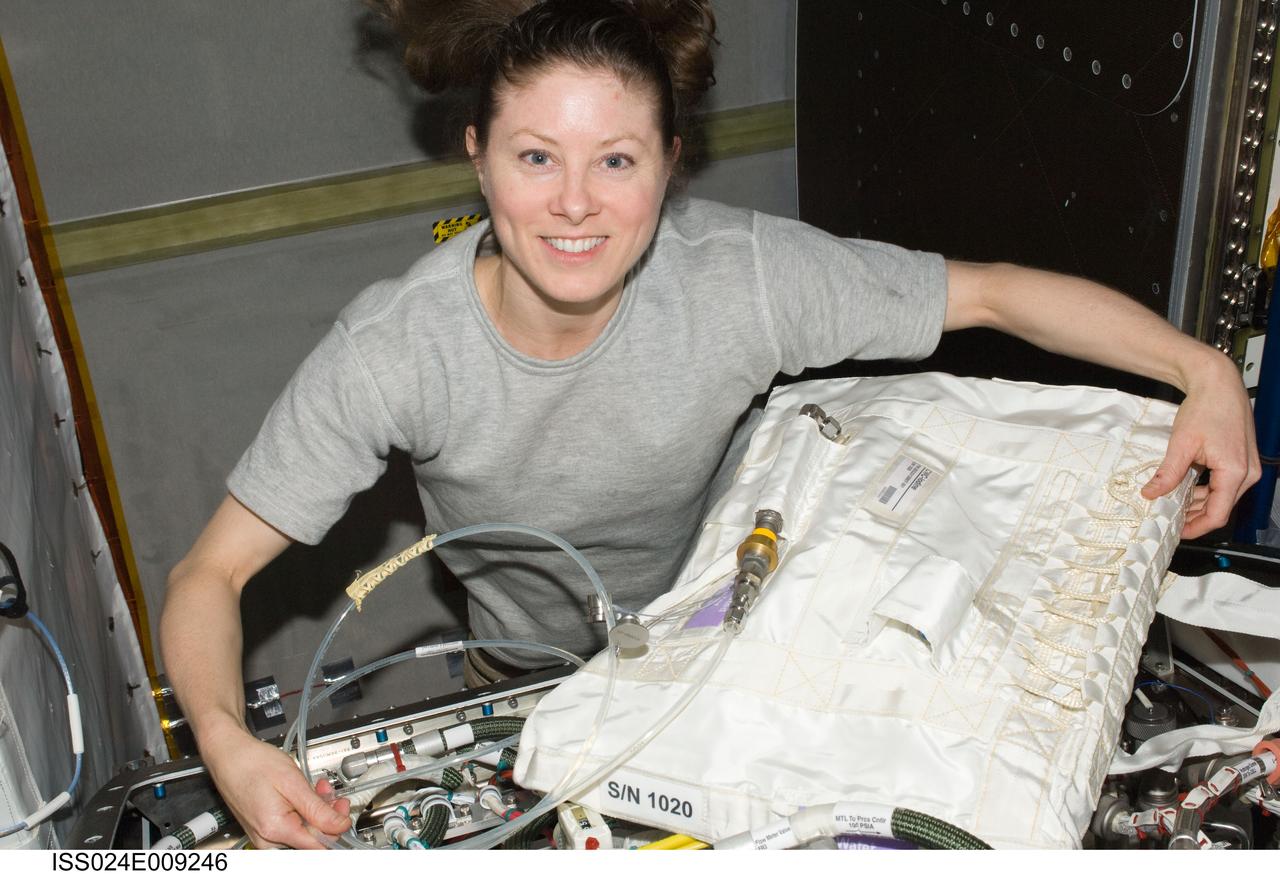

ISS024-E-009246 (21 July 2010) --- NASA astronaut Tracy Caldwell Dyson, Expedition 24 flight engineer, is pictured during troubleshooting operations of the Oxygen Generator System (OGS) hardware and replacement of an H2 (hydrogen) Dome Orbit Replaceable Unit (ORU) in the Destiny laboratory of the International Space Station.
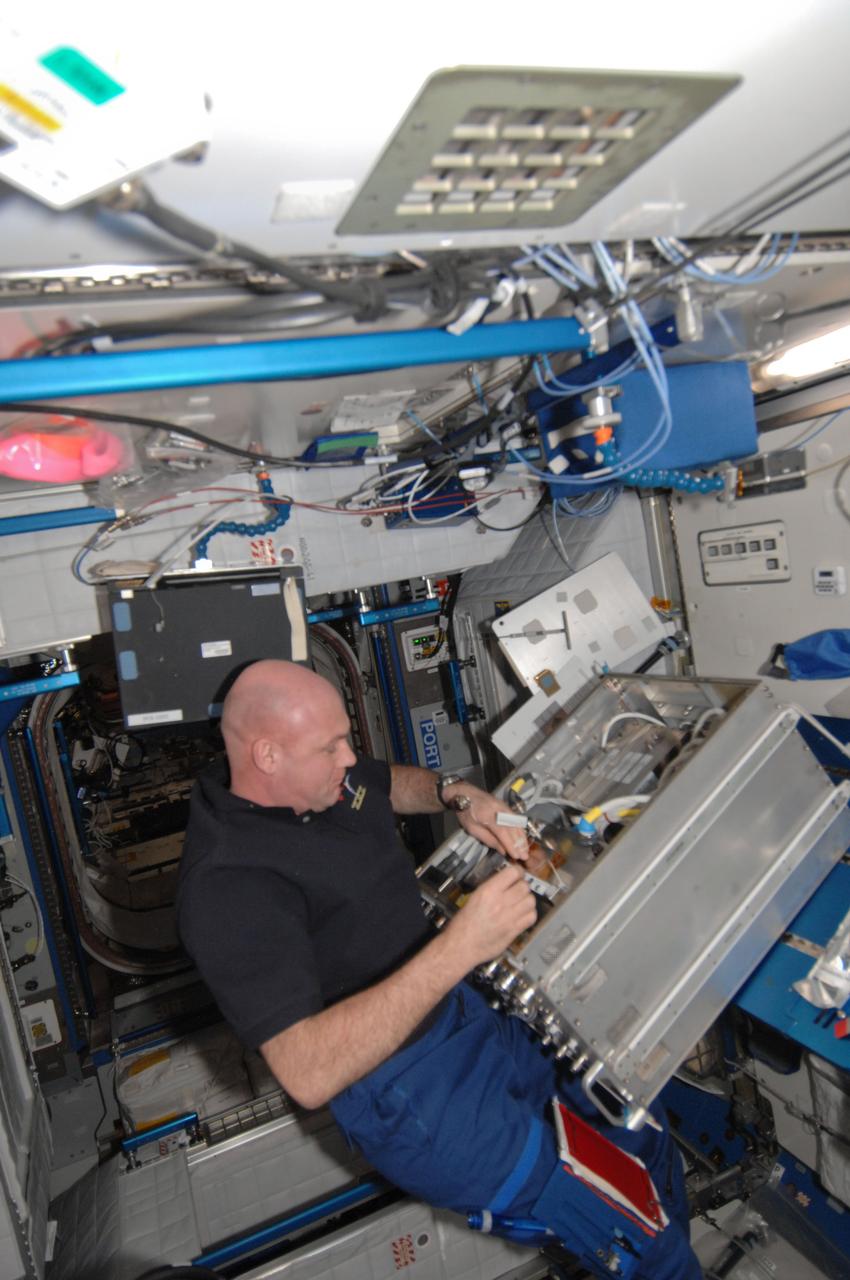

ISS030-E-117367 (31 Jan. 2012) --- European Space Agency astronaut Andre Kuipers, Expedition 30 flight engineer, removes and replaces the Photoacoustic Analyzer Module (PAM) Orbit Replaceable Unit (ORU) of the Pulmonary Function System (PFS) in the Harmony node of the International Space Station.
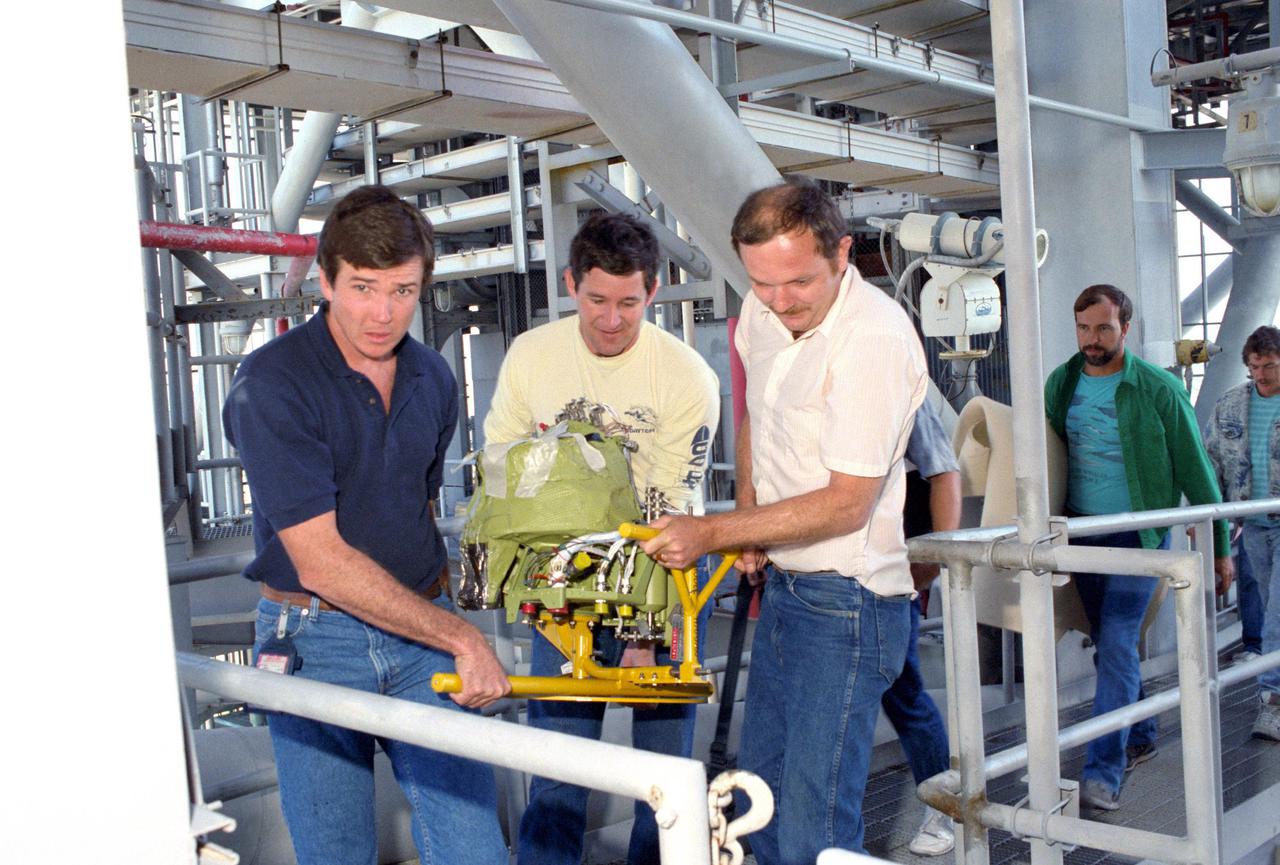

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Technicians at Pad 39-B carry a new Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) to be installed in the orbiter Discovery. It will replace APU #1 that failed during the STS-31 launch attempt on April 10.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Technicians install a new Auxiliary Power Unit (APU) in the aft compartment of the orbiter Discovery at Pad 39-B. The unit replaces APU #1 that failed during the STS-31 countdown on April 10.

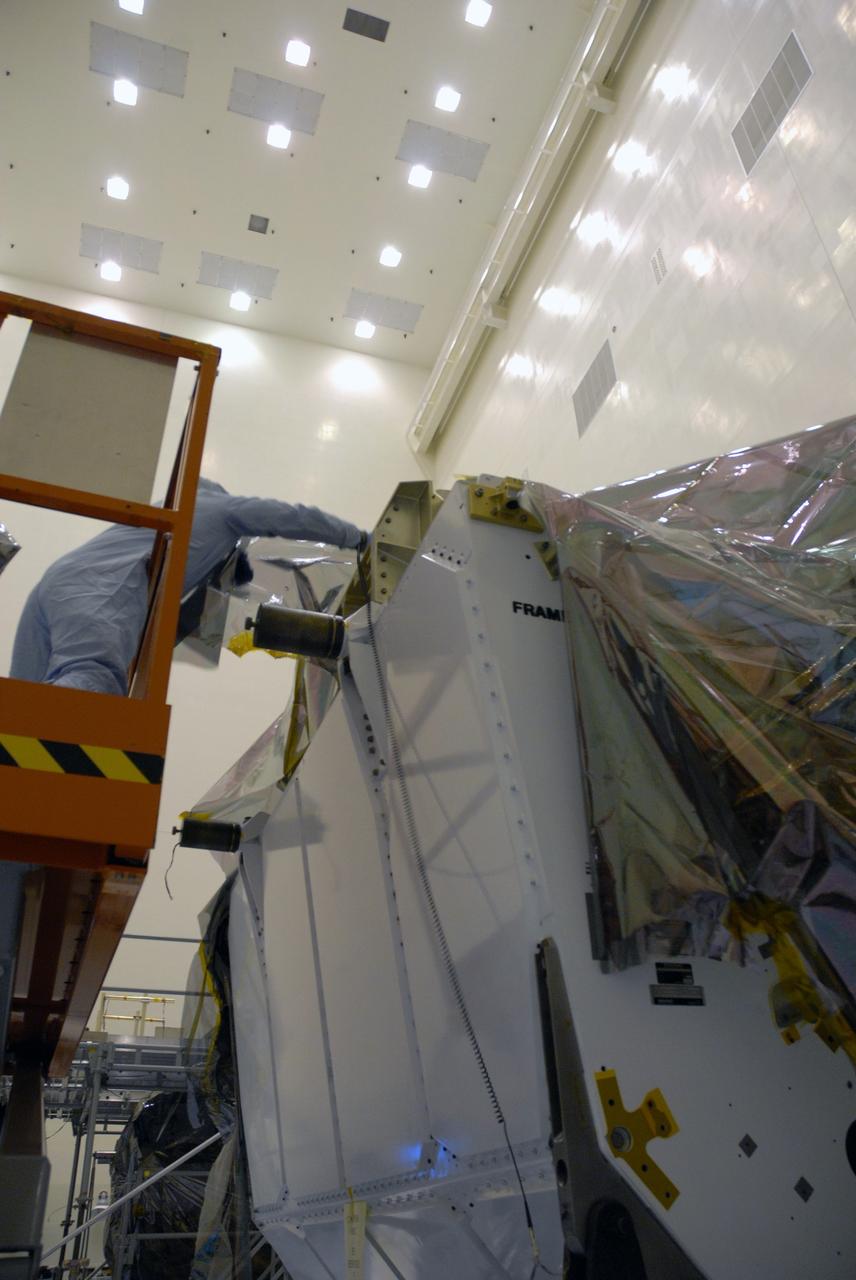
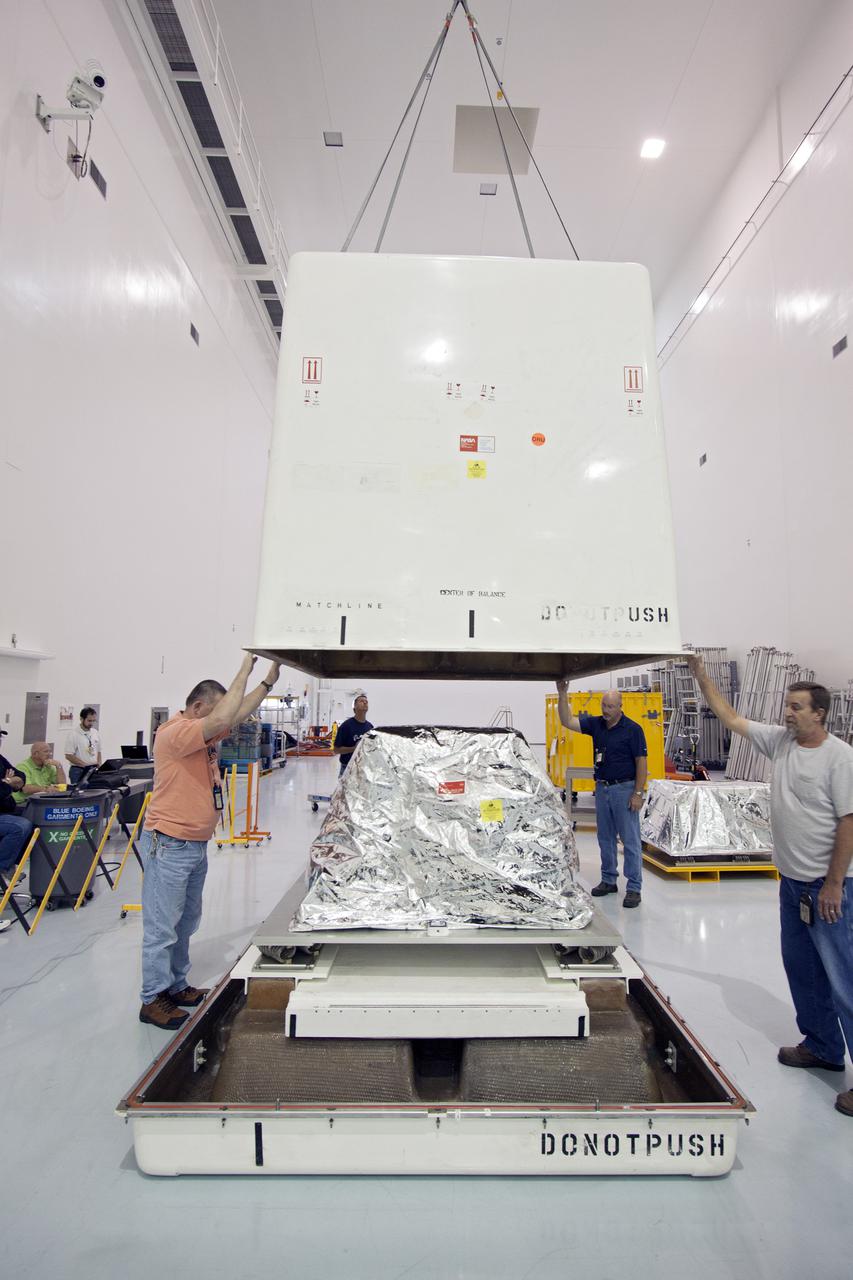
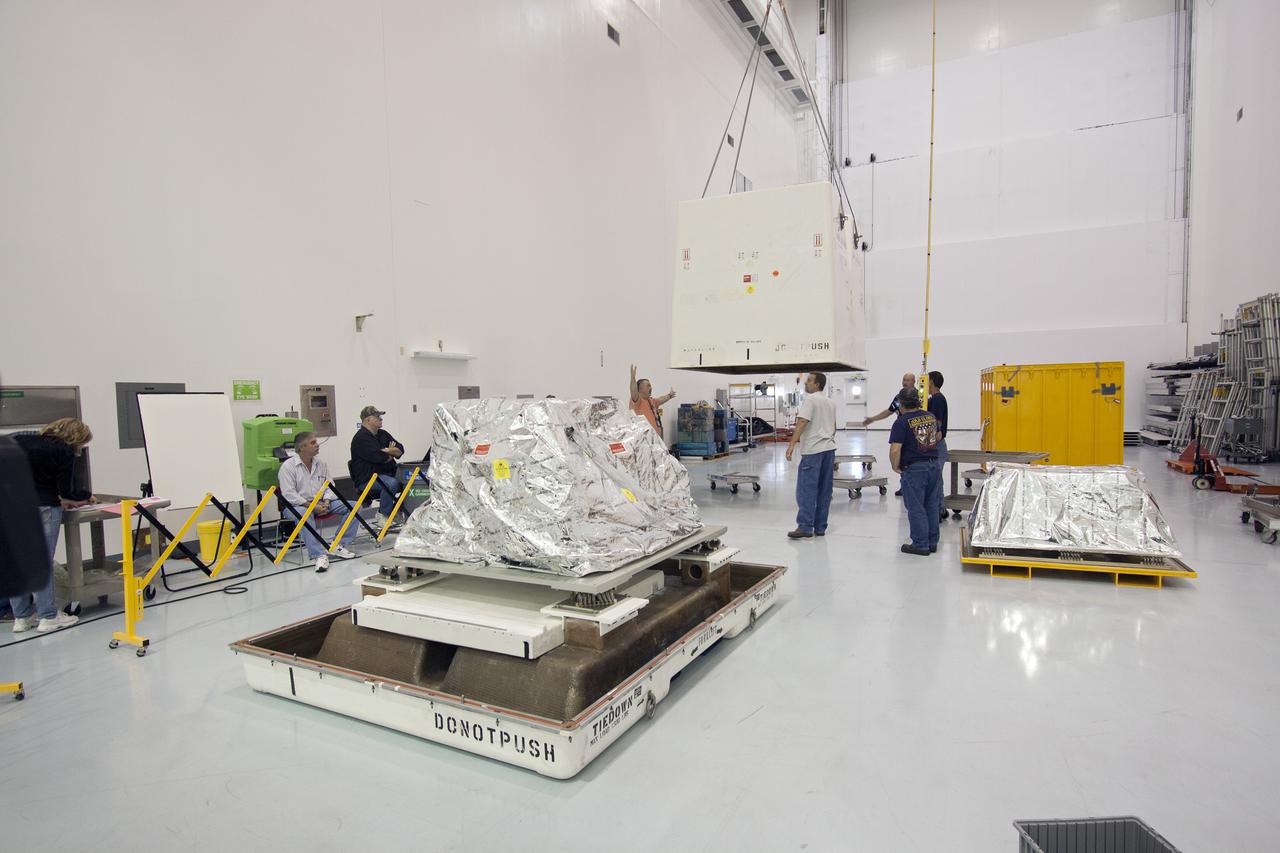
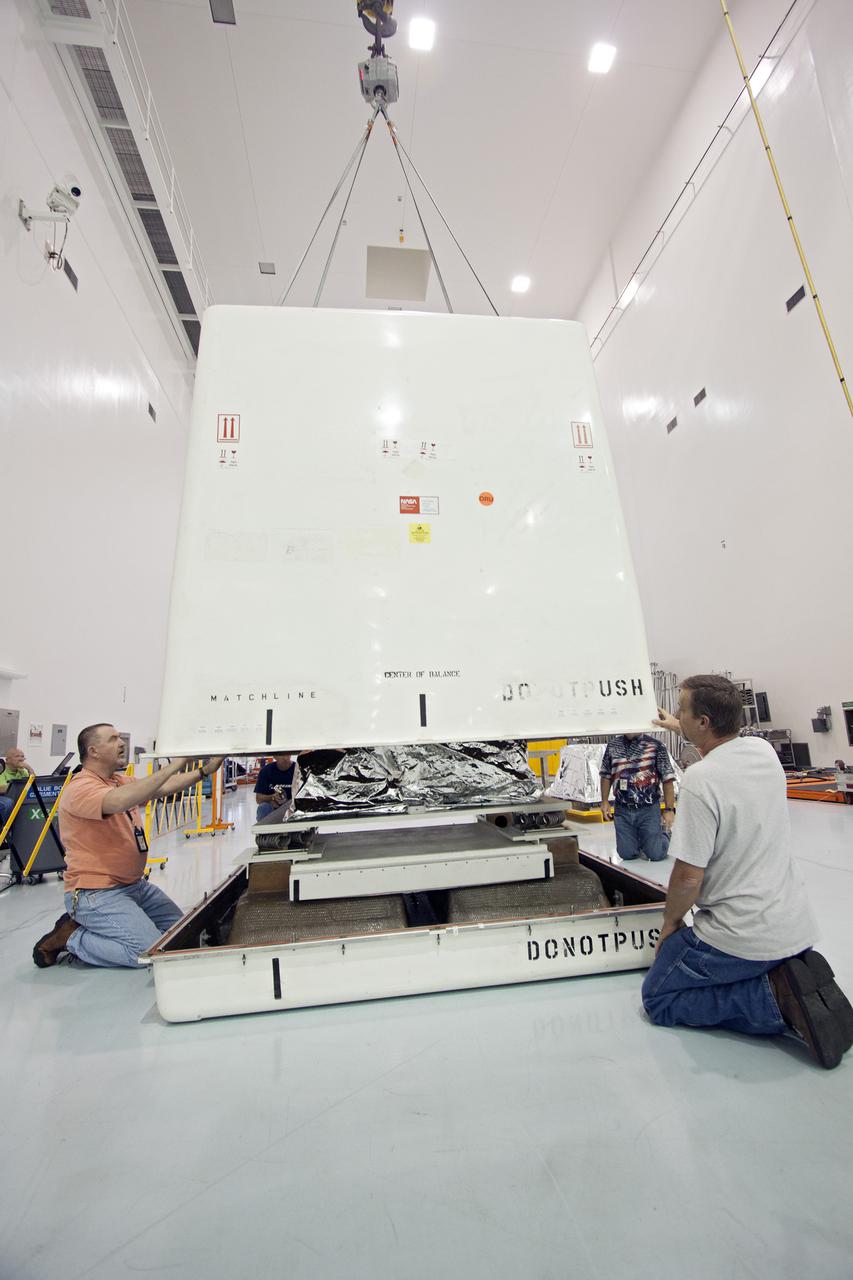
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope is secured on a work platform by workers from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in late July. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

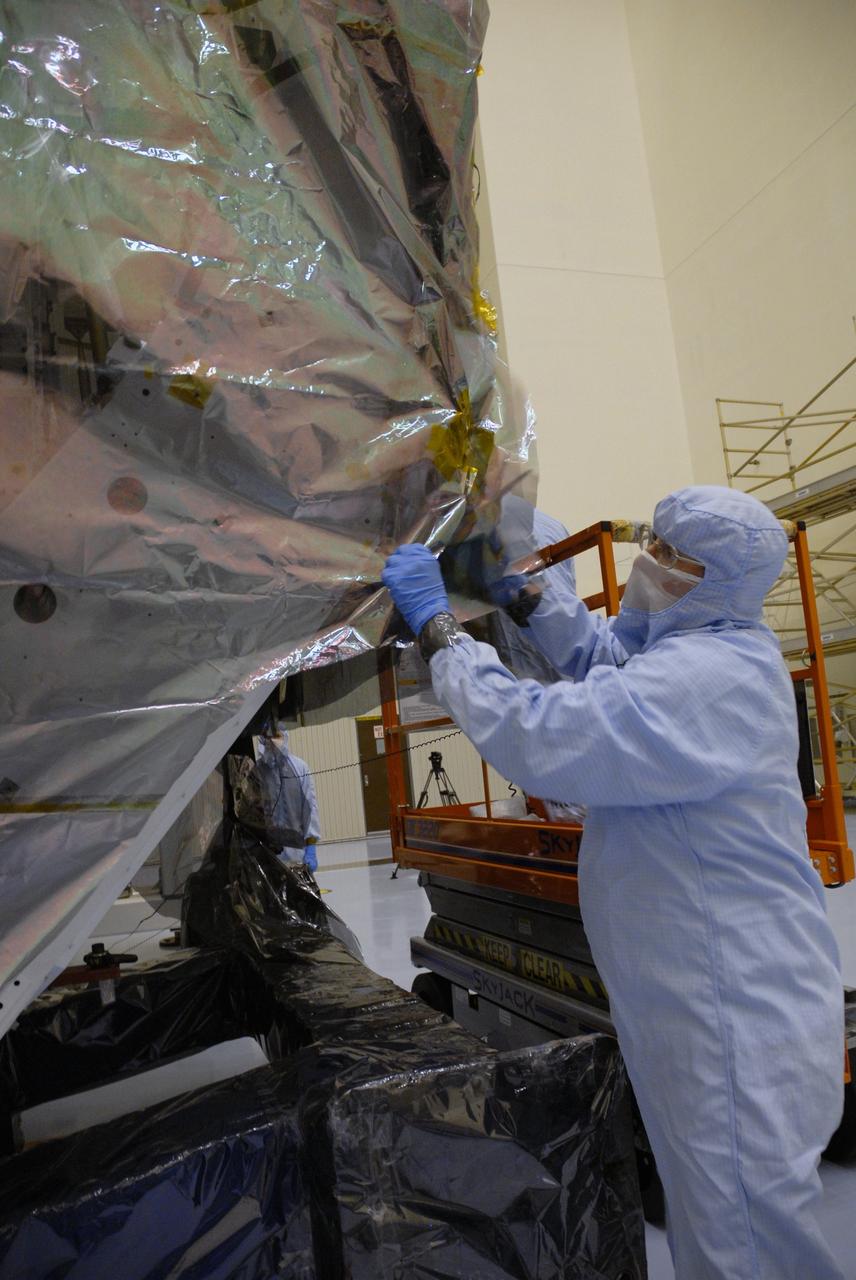
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center removes the protective wrapping from the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in late July. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center removes the protective wrapping from the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in late July. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center cuts away the protective wrapping from the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in late July. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center removes the protective wrapping from the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in late July. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope is lifted from its transportation canister by workers from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in late July. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
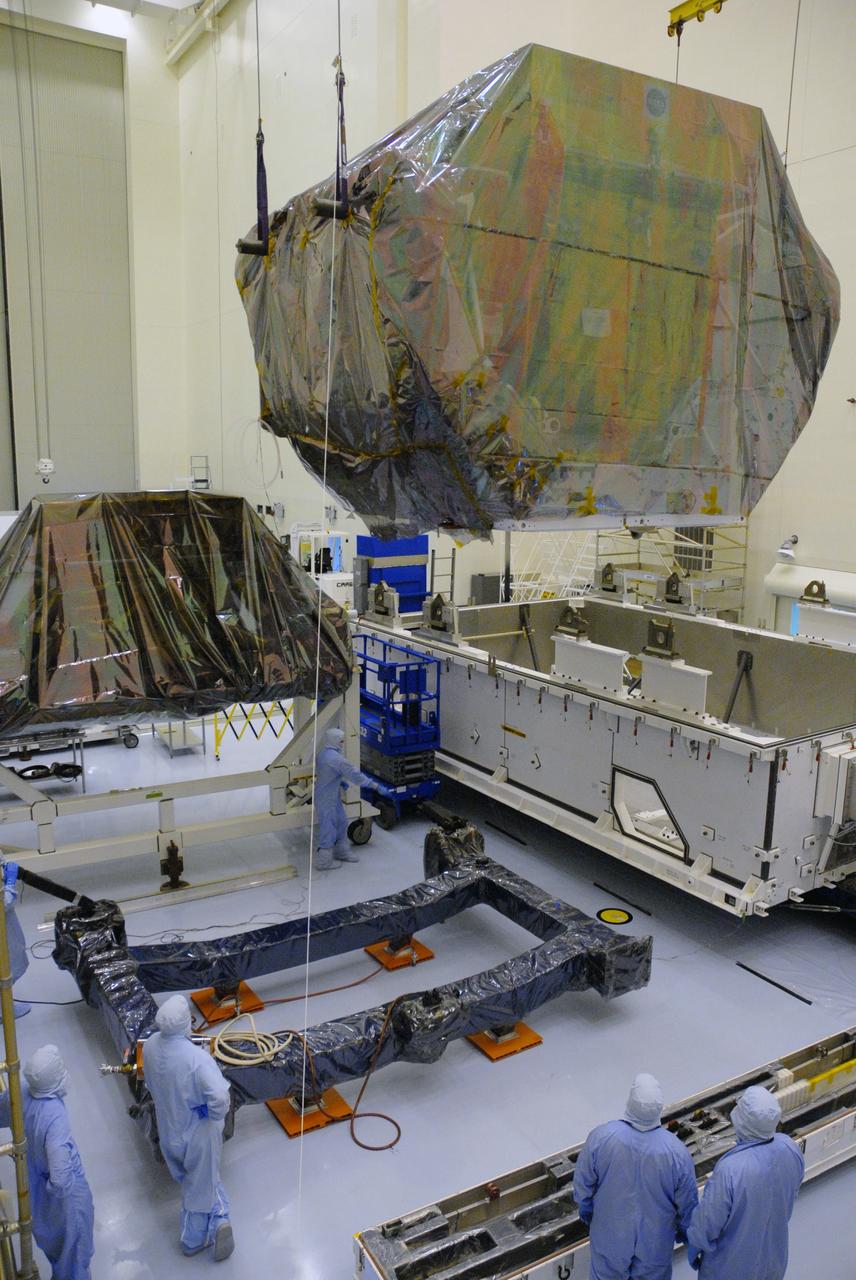

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope is lifted from its transportation canister by workers from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, at ground-level left, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in late July. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope is positioned on a work platform by workers from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in late July. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
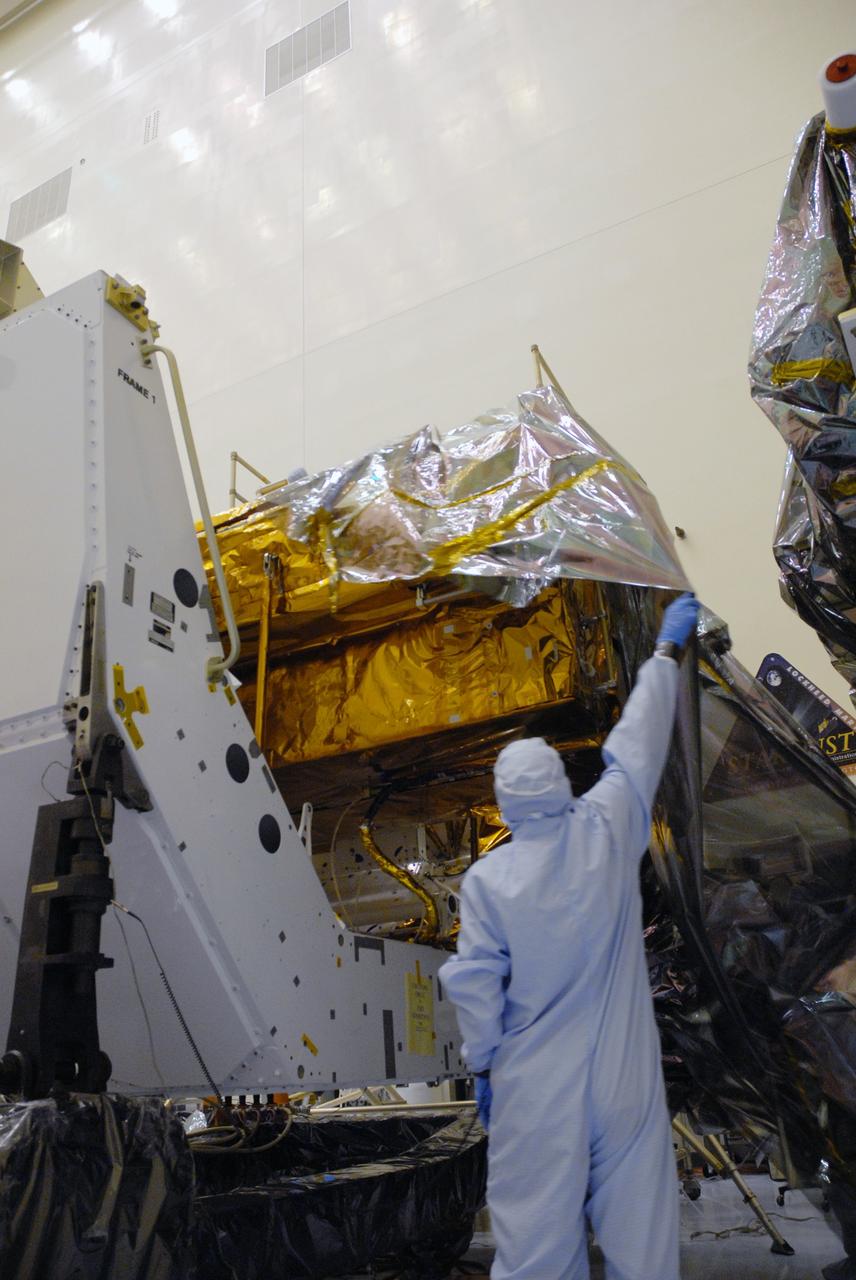

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center removes the protective wrapping from the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in late July. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
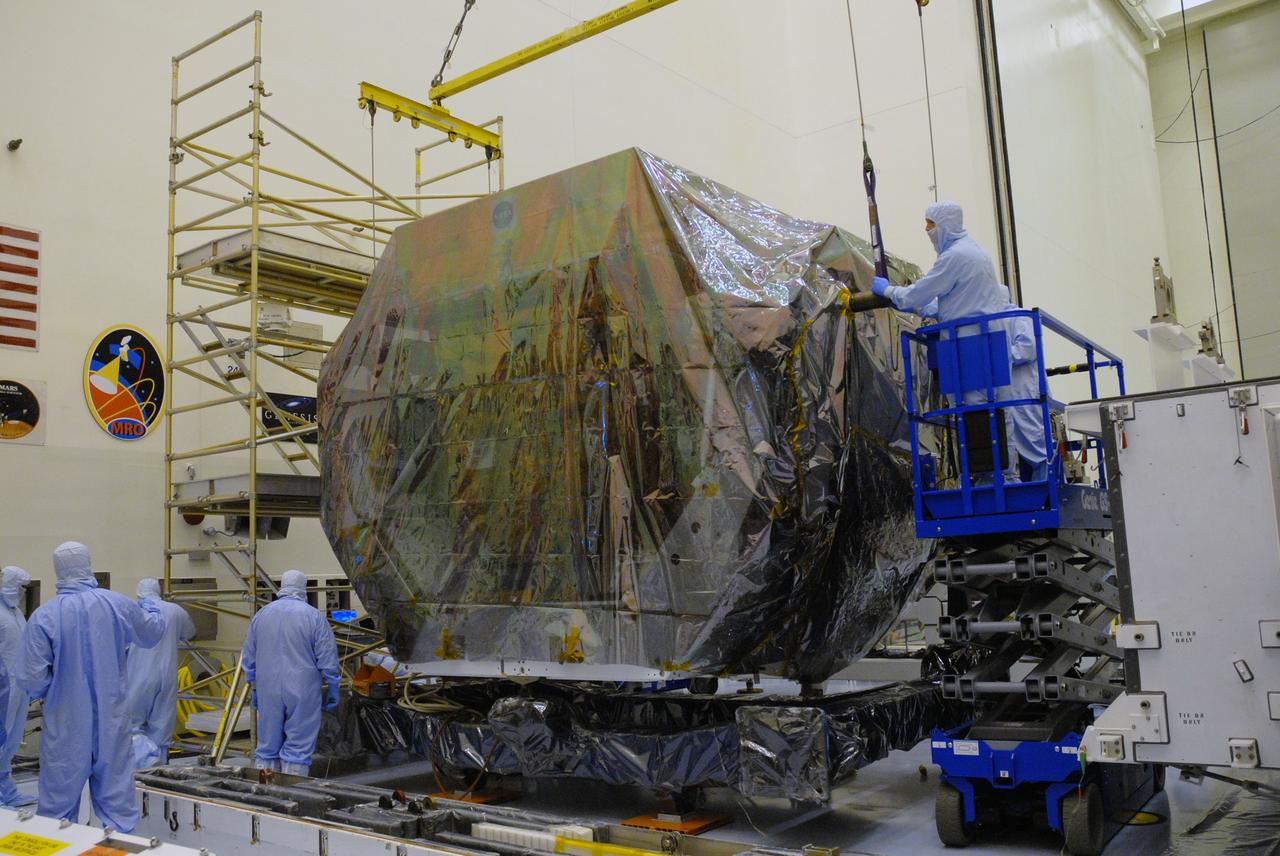

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center begin to remove the protective wrapping from the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in late July. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
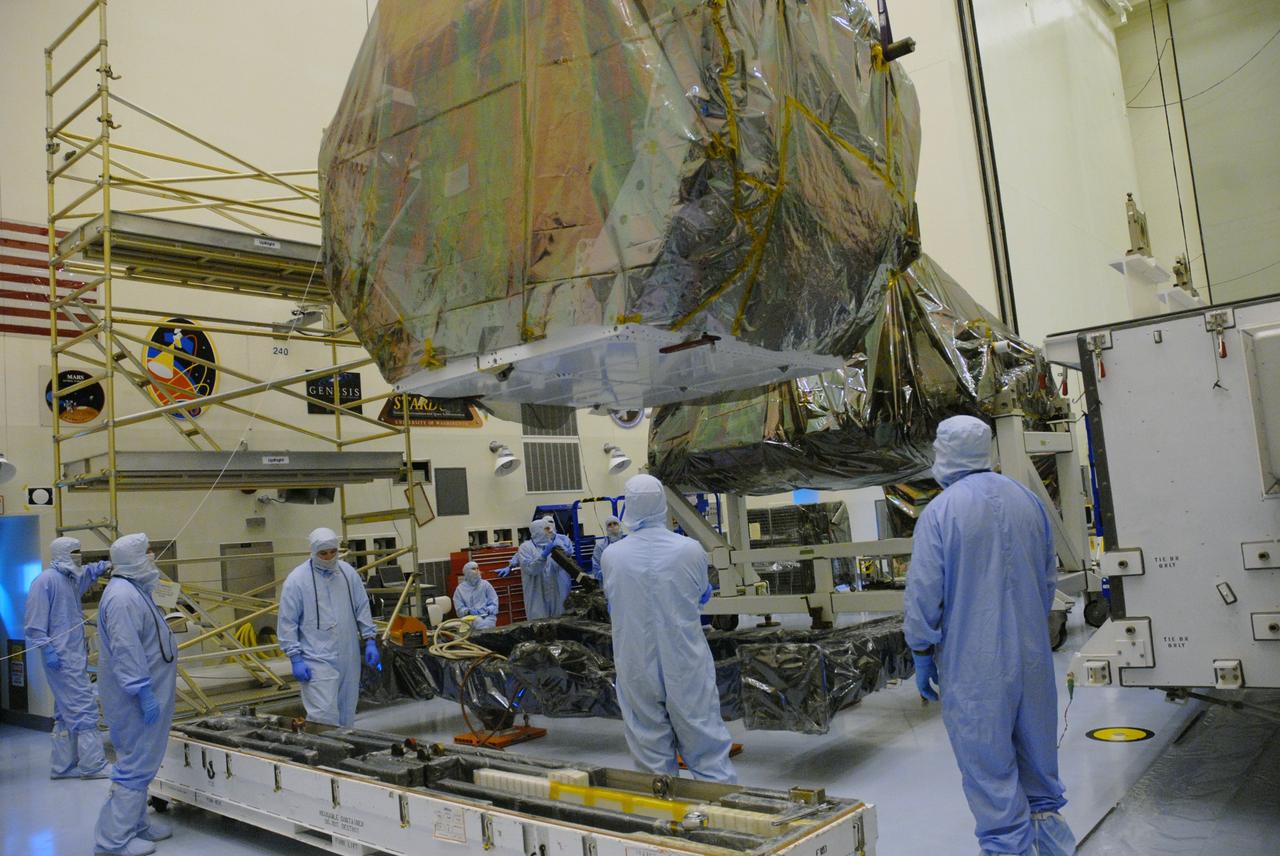

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope is lowered onto a work platform by workers from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, seen behind the ORUC, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in late July. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
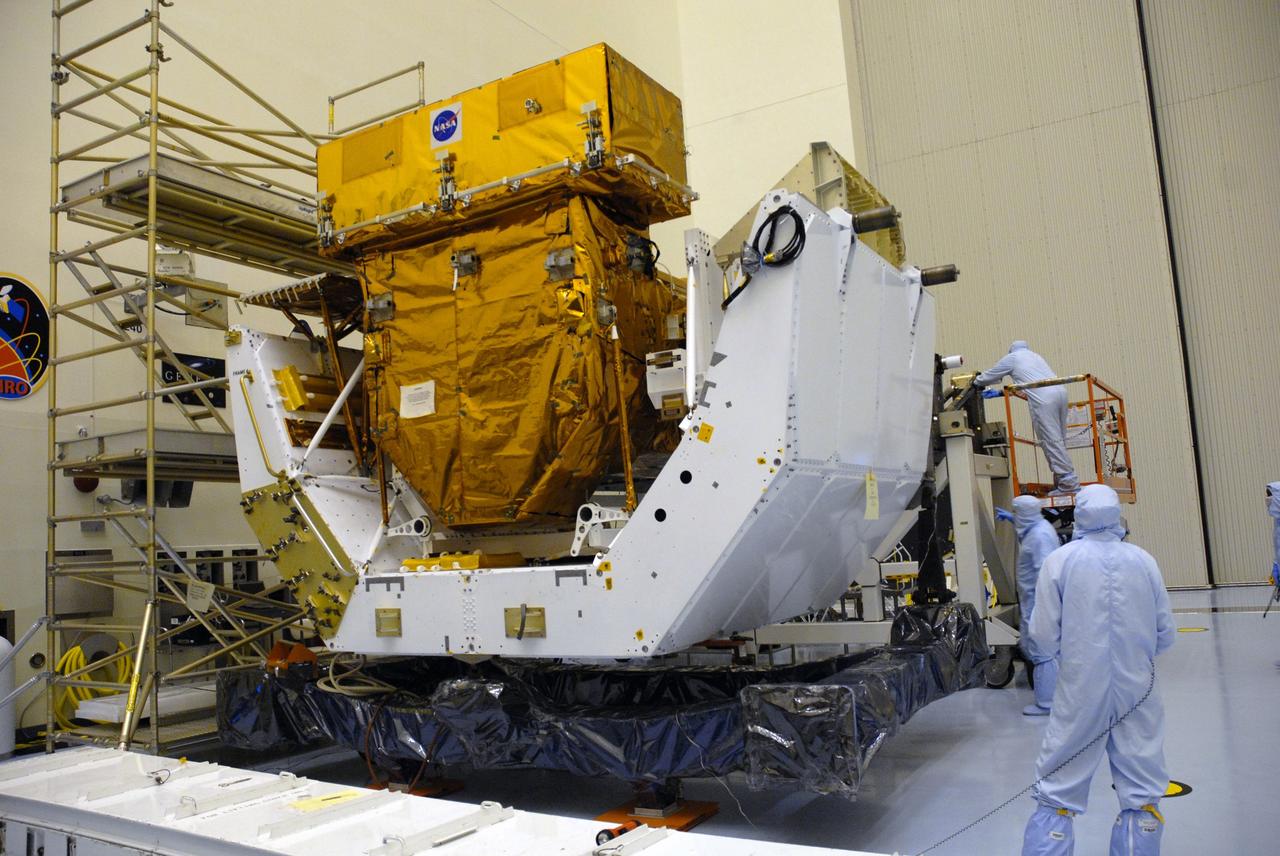

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, for the Hubble Space Telescope is unwrapped and awaits final processing for launch. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in late July. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
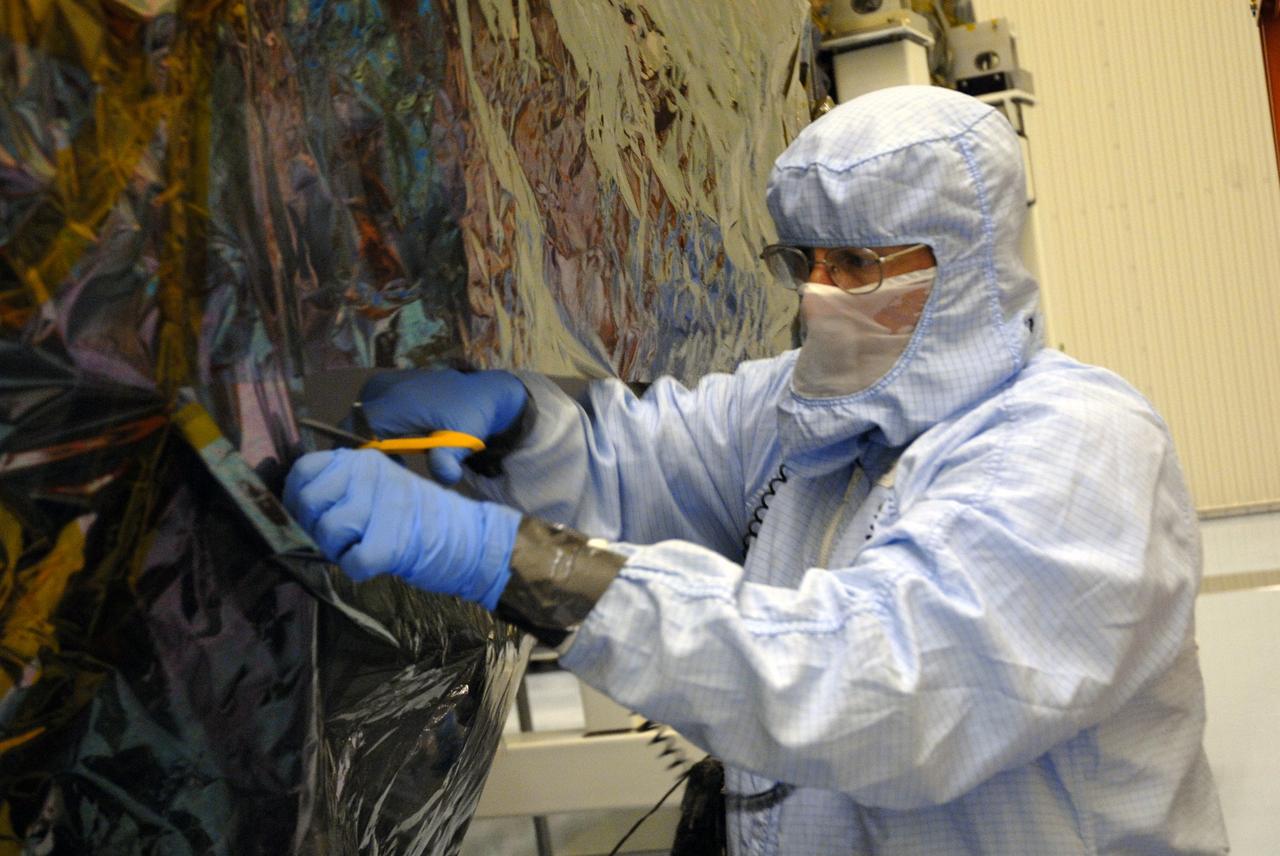

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the high bay of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a worker from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center cuts away the protective wrapping from the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier for the Hubble Space Telescope. The Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, is one of four carriers supporting hardware for space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission to service the telescope. The Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier, or SLIC, and the Flight Support System, or FSS, have also arrived at Kennedy. The Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment carrier will be delivered in late July. The carriers will be prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the Hubble servicing mission, targeted for launch Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
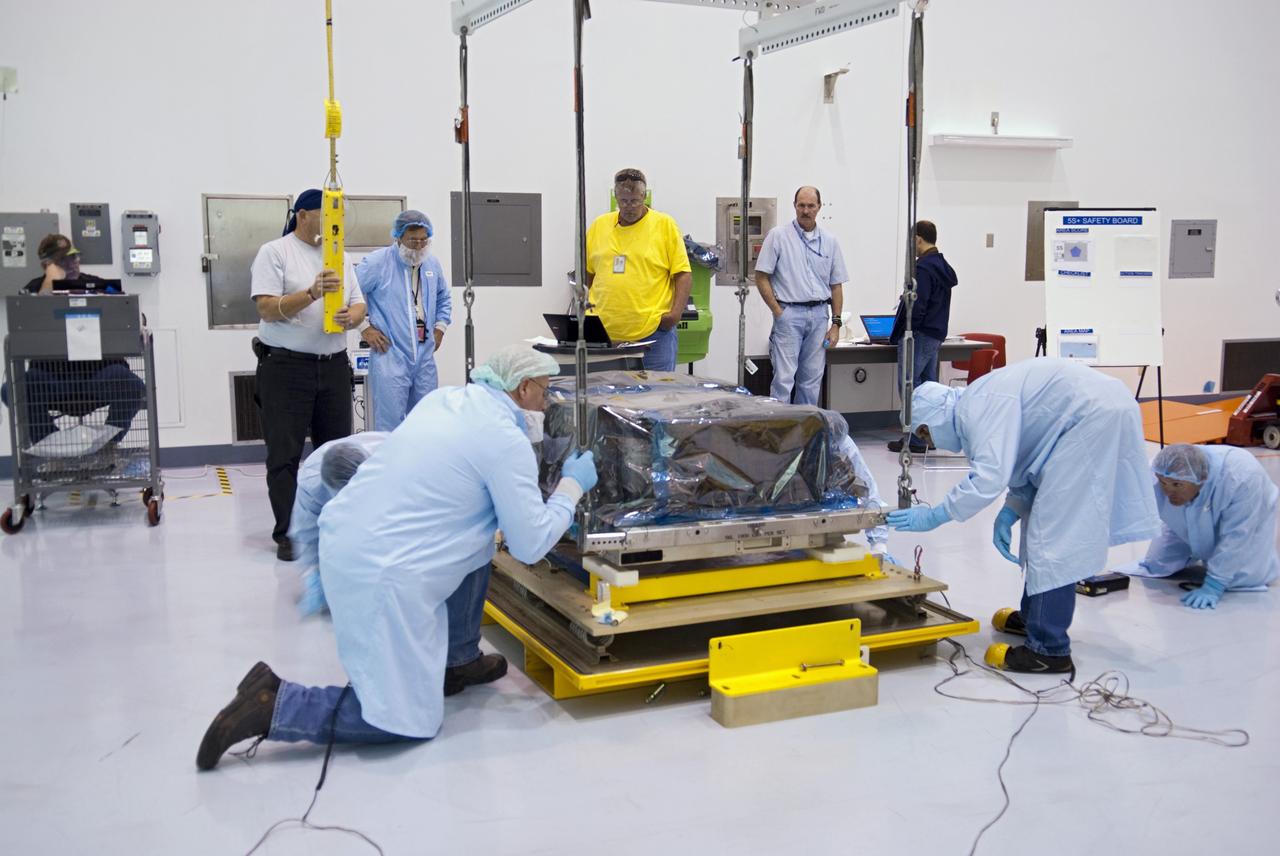

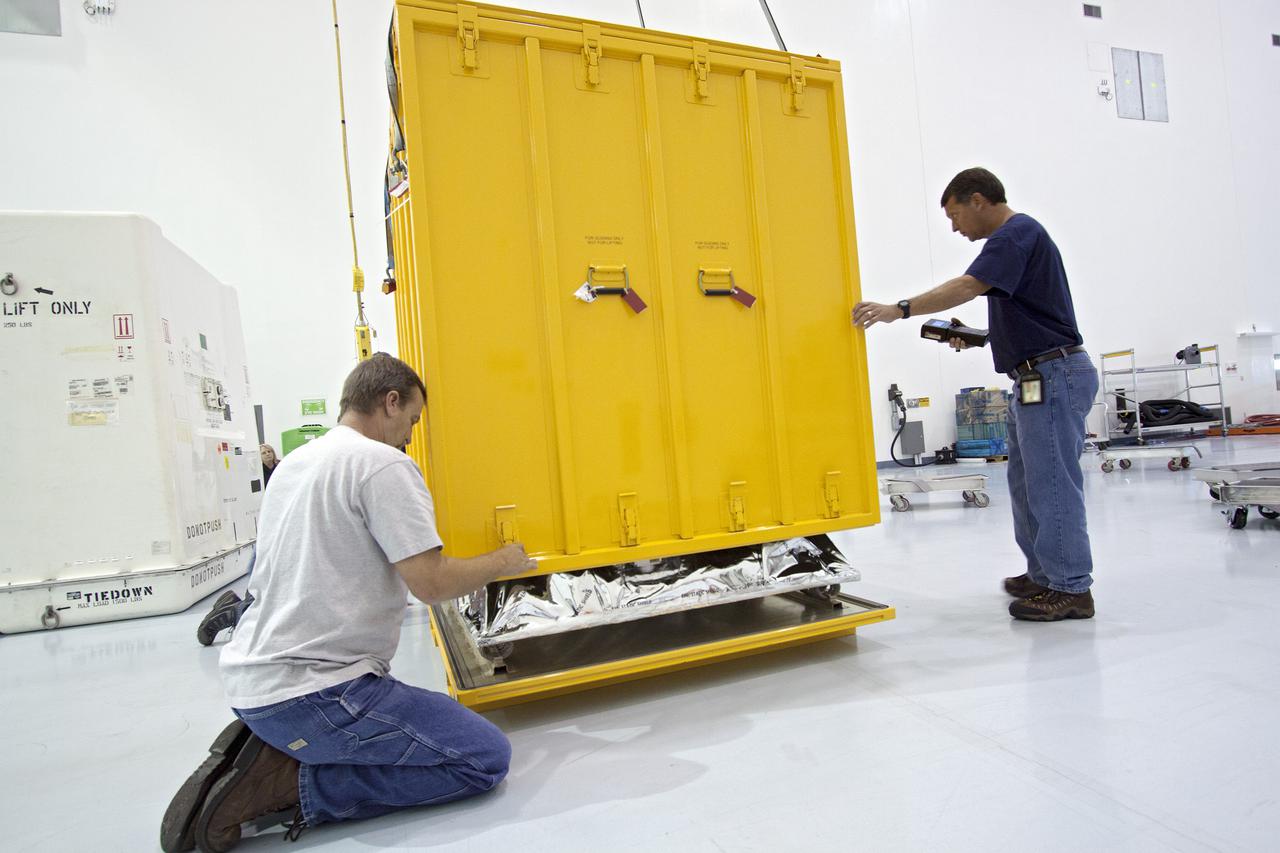
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida position the orbital replacement unit for the space station's main bus switching unit as they prepare to pack the unit in a shipping container. The unit, which was processed at Kennedy, will be shipped to Japan at the beginning of the year for the HTV-4 launch, which is currently scheduled for 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
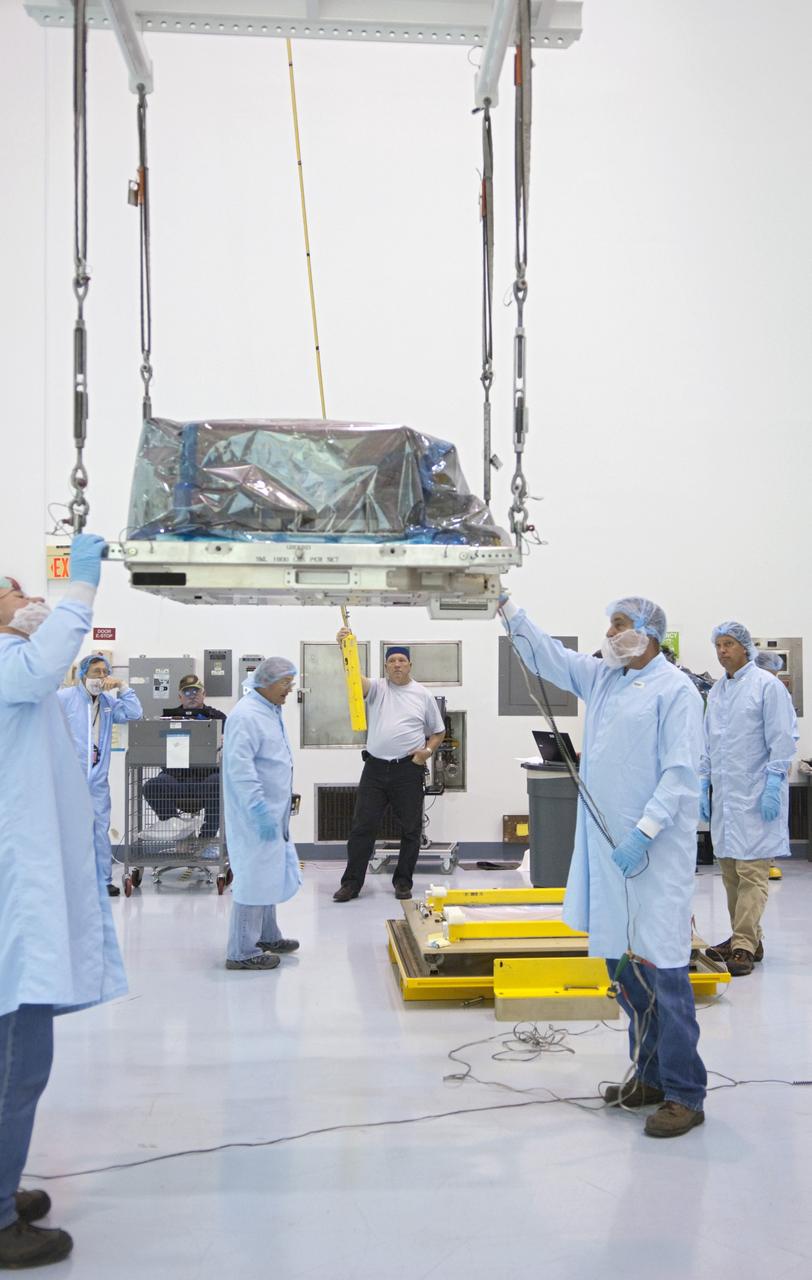

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida lift the orbital replacement unit for the space station's main bus switching unit as they prepare to pack the unit in a shipping container. The unit, which was processed at Kennedy, will be shipped to Japan at the beginning of the year for the HTV-4 launch, which is currently scheduled for 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

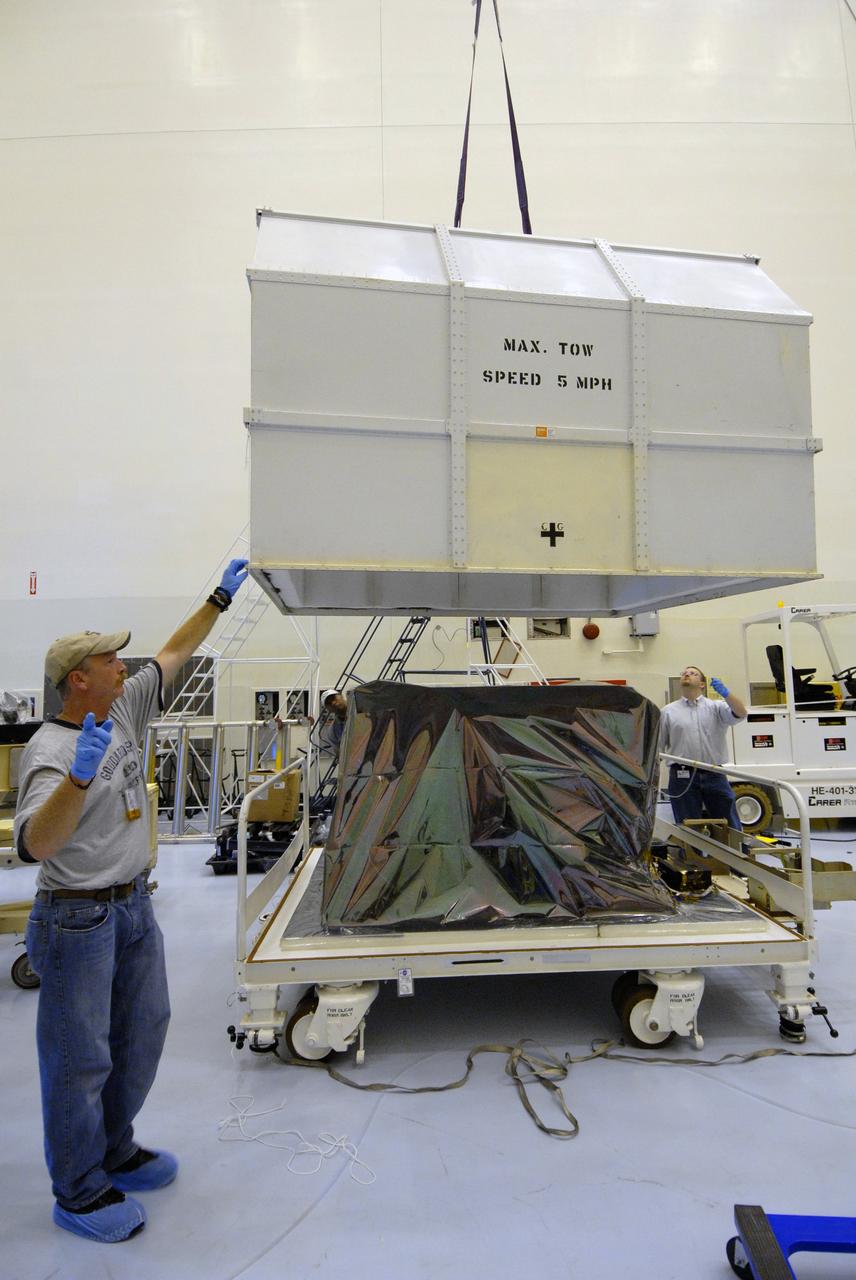
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers begin removing the protective cover from the Hubble Fine Guidance Sensor, or FGS. The FGS will be integrated onto the Orbital Replacement Unit carrier in the clean room of the facility. The sensor will extend the life of the pointing control system on the Hubble Space Telescope. On the mission, this FGS will replace one of the three sensors that is failing and thus outfit the telescope with two completely healthy units, which are needed. A third, older FGS aboard the telescope will provide additional target-pointing efficiency and redundancy. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane begins to lift the Hubble Fine Guidance Sensor, or FGS. The FGS will be integrated onto the Orbital Replacement Unit carrier in the clean room of the facility. The sensor will extend the life of the pointing control system on the Hubble Space Telescope. On the mission, this FGS will replace one of the three sensors that is failing and thus outfit the telescope with two completely healthy units, which are needed. A third, older FGS aboard the telescope will provide additional target-pointing efficiency and redundancy. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Fine Guidance Sensor, or FGS, arrives at NASA's Kennedy Space Center for the STS-125 mission. The FGS will be integrated onto the Orbital Replacement Unit carrier in the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The sensor will extend the life of the pointing control system on the Hubble Space Telescope. On the mission, this FGS will replace one of the three sensors that is failing and thus outfit the telescope with two completely healthy units, which are needed. A third, older FGS aboard the telescope will provide additional target-pointing efficiency and redundancy. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The shipping container holding the Fine Guidance Sensor, or FGS, is moved into the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The FGS will be integrated onto the Orbital Replacement Unit carrier in the clean room of the facility. The sensor will extend the life of the pointing control system on the Hubble Space Telescope. On the mission, this FGS will replace one of the three sensors that is failing and thus outfit the telescope with two completely healthy units, which are needed. A third, older FGS aboard the telescope will provide additional target-pointing efficiency and redundancy. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a crane lifts the cover of the shipping container holding the Fine Guidance Sensor, or FGS. The FGS will be integrated onto the Orbital Replacement Unit carrier in the clean room of the facility. The sensor will extend the life of the pointing control system on the Hubble Space Telescope. On the mission, this FGS will replace one of the three sensors that is failing and thus outfit the telescope with two completely healthy units, which are needed. A third, older FGS aboard the telescope will provide additional target-pointing efficiency and redundancy. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The shipping container holding the Fine Guidance Sensor, or FGS, is moved into the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center. The FGS will be integrated onto the Orbital Replacement Unit carrier in the clean room of the facility. The sensor will extend the life of the pointing control system on the Hubble Space Telescope. On the mission, this FGS will replace one of the three sensors that is failing and thus outfit the telescope with two completely healthy units, which are needed. A third, older FGS aboard the telescope will provide additional target-pointing efficiency and redundancy. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
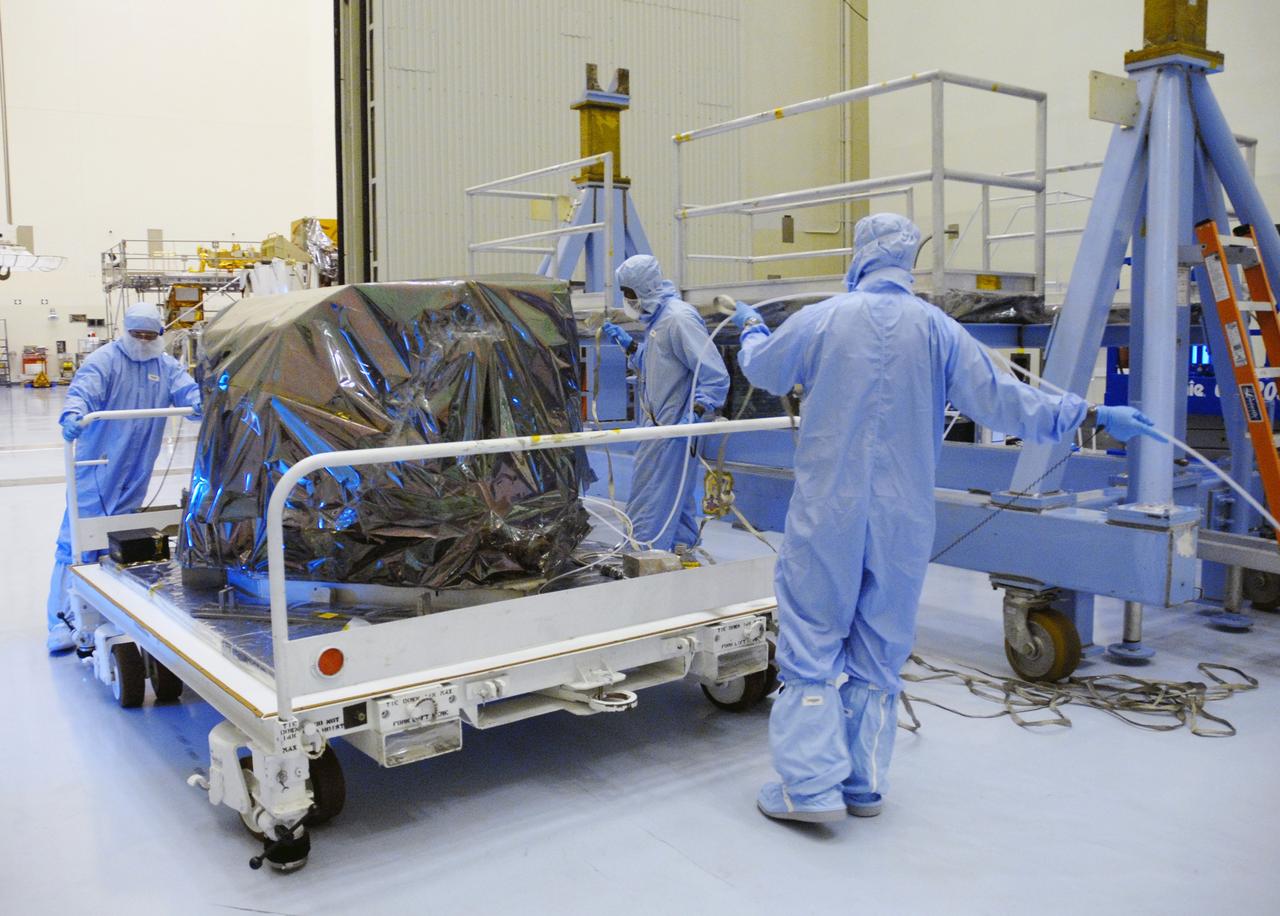

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers move the Hubble Fine Guidance Sensor, or FGS, before removing the protective cover. The FGS will be integrated onto the Orbital Replacement Unit carrier in the clean room of the facility. The sensor will extend the life of the pointing control system on the Hubble Space Telescope. On the mission, this FGS will replace one of the three sensors that is failing and thus outfit the telescope with two completely healthy units, which are needed. A third, older FGS aboard the telescope will provide additional target-pointing efficiency and redundancy. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
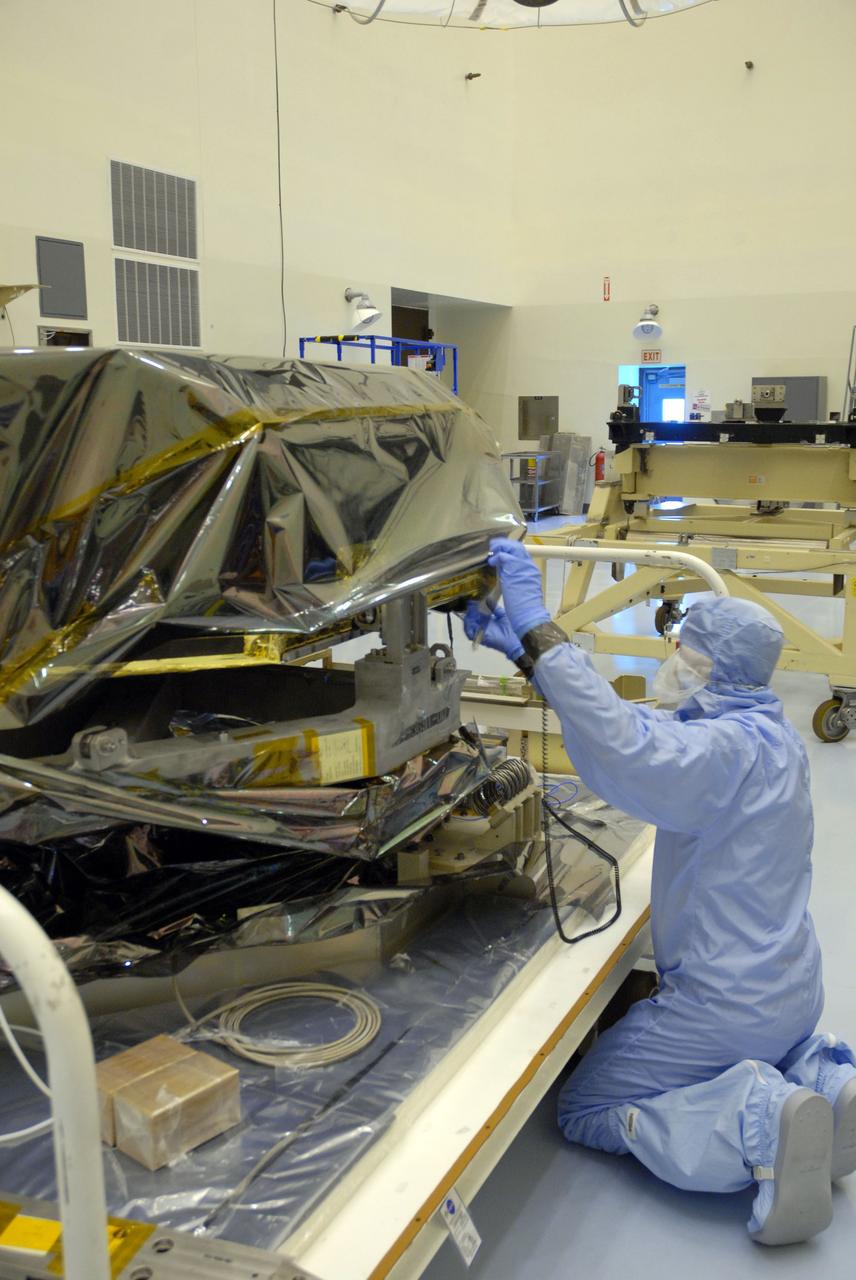

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers prepare to remove the protective cover from the Hubble Fine Guidance Sensor, or FGS. The FGS will be integrated onto the Orbital Replacement Unit carrier in the clean room of the facility. The sensor will extend the life of the pointing control system on the Hubble Space Telescope. On the mission, this FGS will replace one of the three sensors that is failing and thus outfit the telescope with two completely healthy units, which are needed. A third, older FGS aboard the telescope will provide additional target-pointing efficiency and redundancy. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
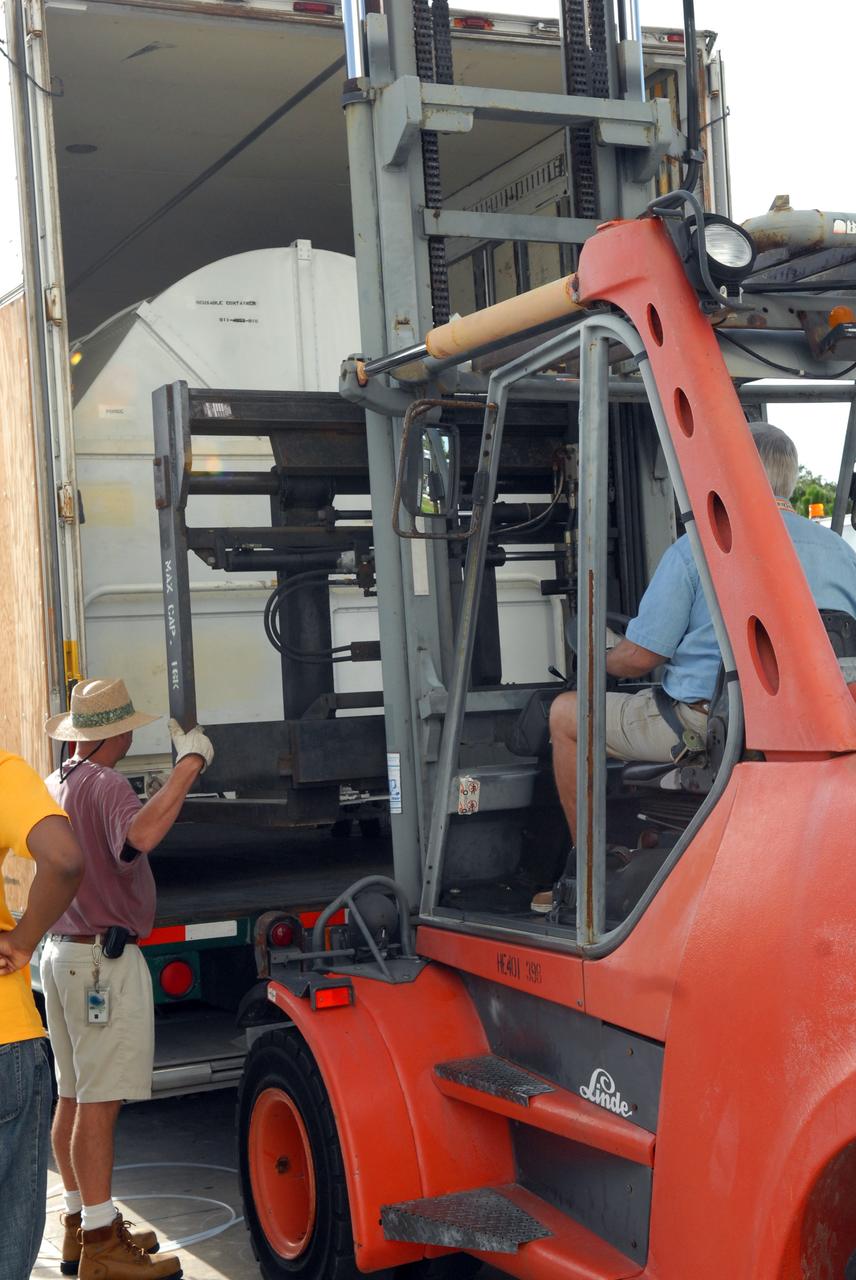

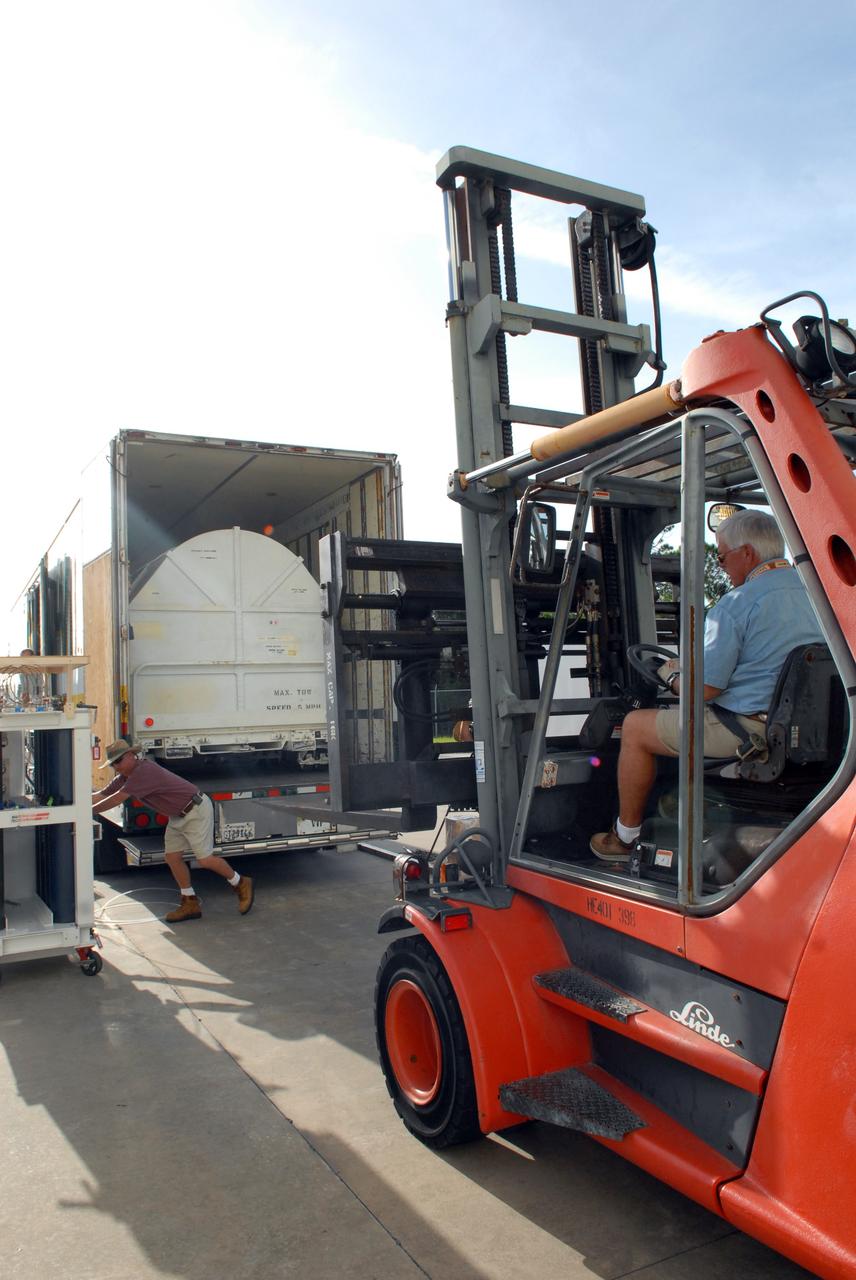
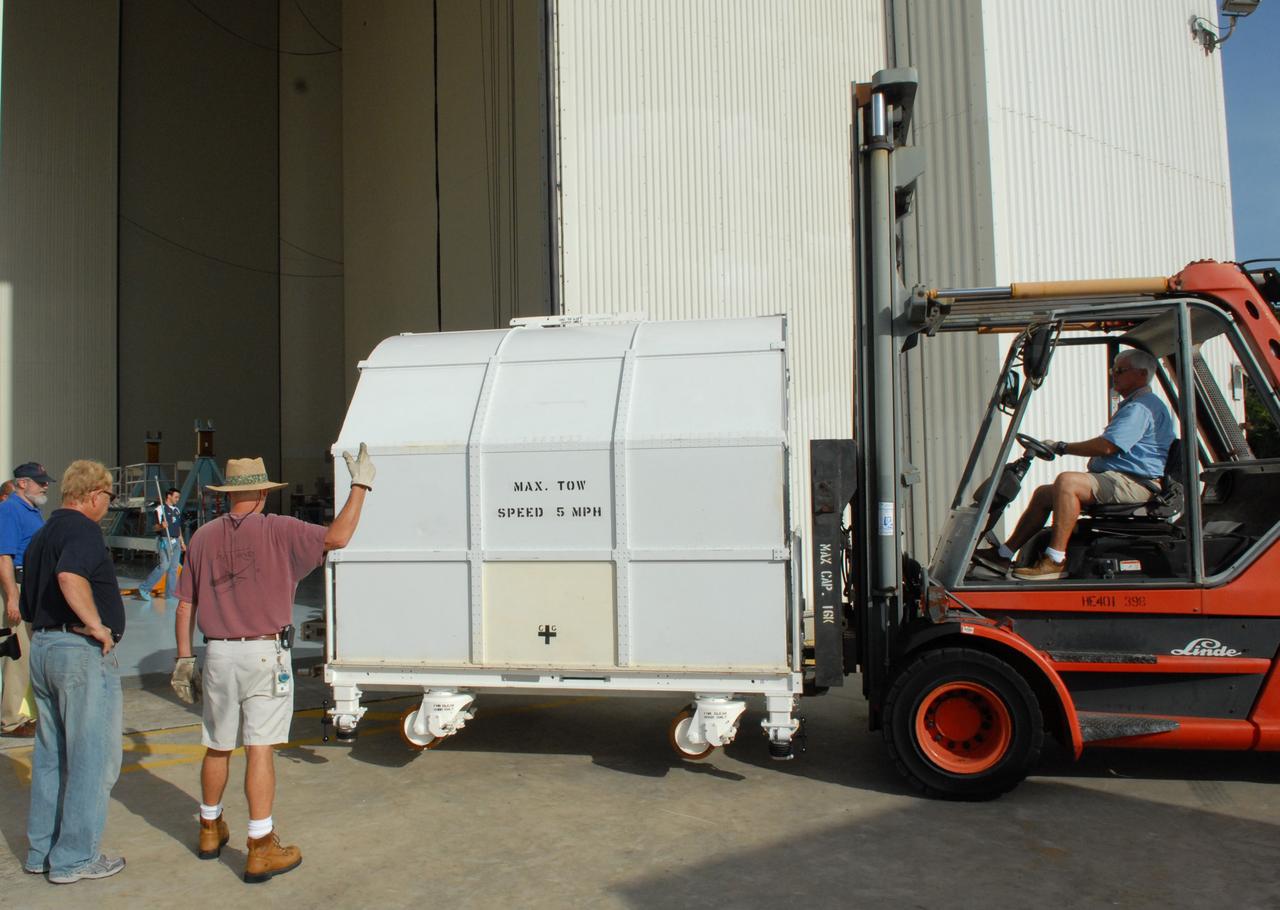
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Fine Guidance Sensor, or FGS, is offloaded from the truck at NASA's Kennedy Space Center for the STS-125 mission. The FGS will be integrated onto the Orbital Replacement Unit carrier in the clean room of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility. The sensor will extend the life of the pointing control system on the Hubble Space Telescope. On the mission, this FGS will replace one of the three sensors that is failing and thus outfit the telescope with two completely healthy units, which are needed. A third, older FGS aboard the telescope will provide additional target-pointing efficiency and redundancy. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
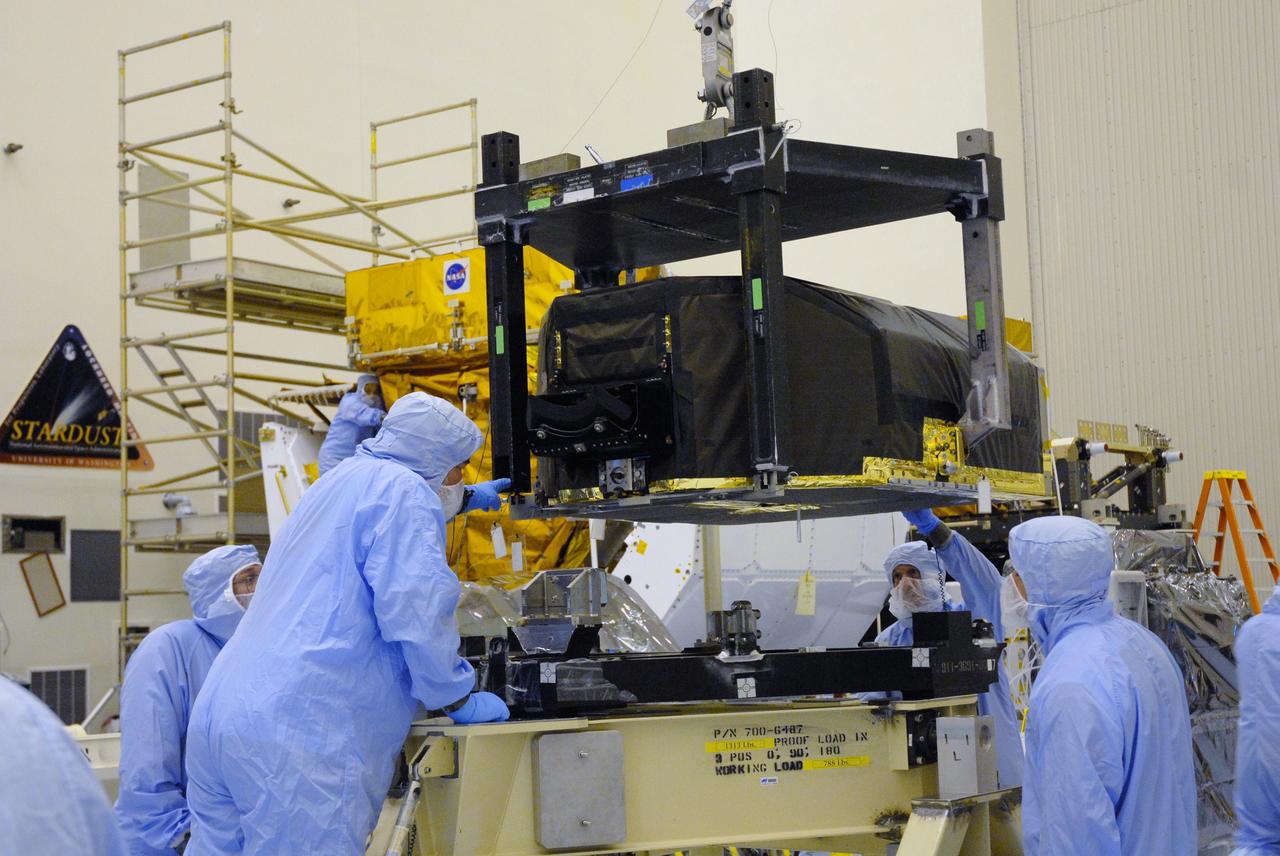

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians watch closely as the Hubble Fine Guidance Sensor, or FGS, is moved to a work stand The FGS will be integrated onto the Orbital Replacement Unit carrier in the clean room of the facility. The sensor will extend the life of the pointing control system on the Hubble Space Telescope. On the mission, this FGS will replace one of the three sensors that is failing and thus outfit the telescope with two completely healthy units, which are needed. A third, older FGS aboard the telescope will provide additional target-pointing efficiency and redundancy. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
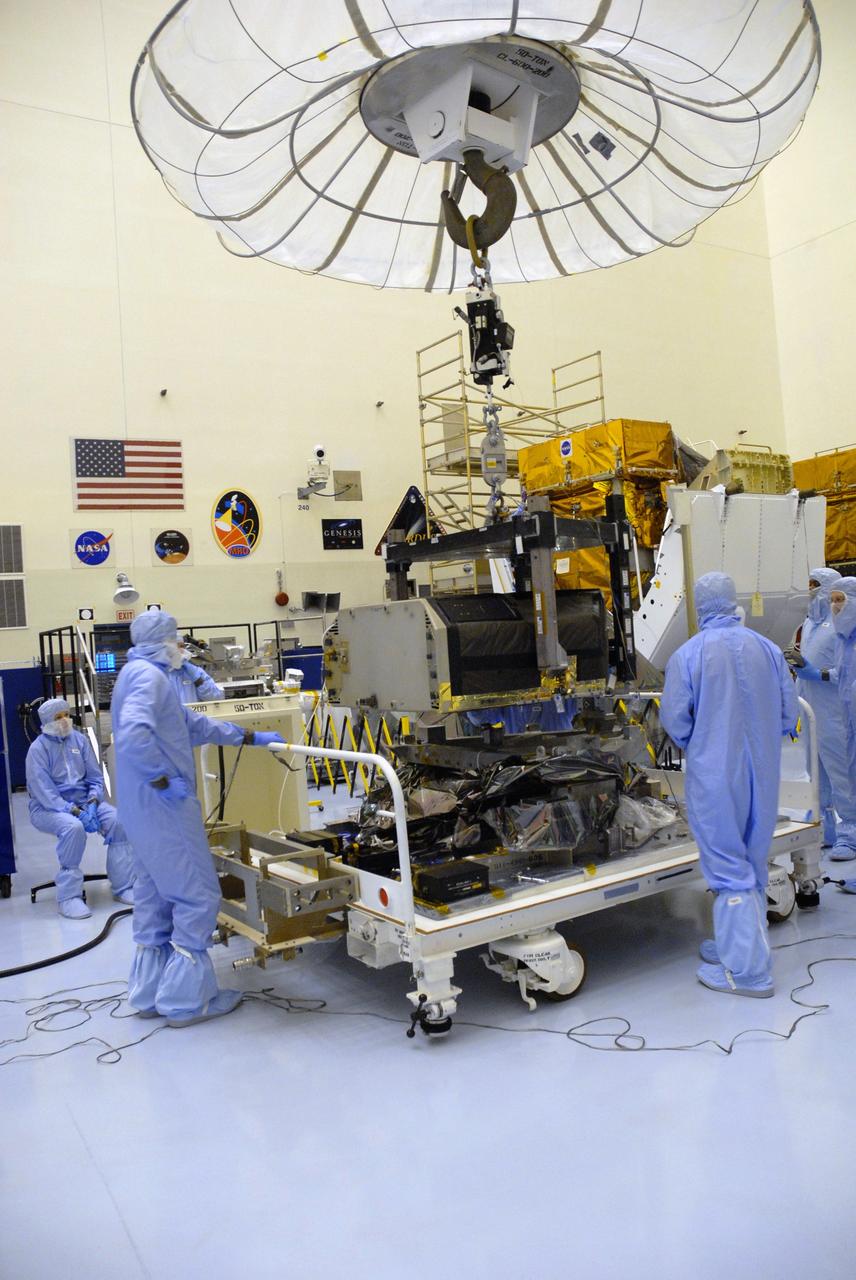

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lifts the Hubble Fine Guidance Sensor, or FGS. The FGS will be integrated onto the Orbital Replacement Unit carrier in the clean room of the facility. The sensor will extend the life of the pointing control system on the Hubble Space Telescope. On the mission, this FGS will replace one of the three sensors that is failing and thus outfit the telescope with two completely healthy units, which are needed. A third, older FGS aboard the telescope will provide additional target-pointing efficiency and redundancy. Space shuttle Atlantis is targeted to launch on the STS-125 mission Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
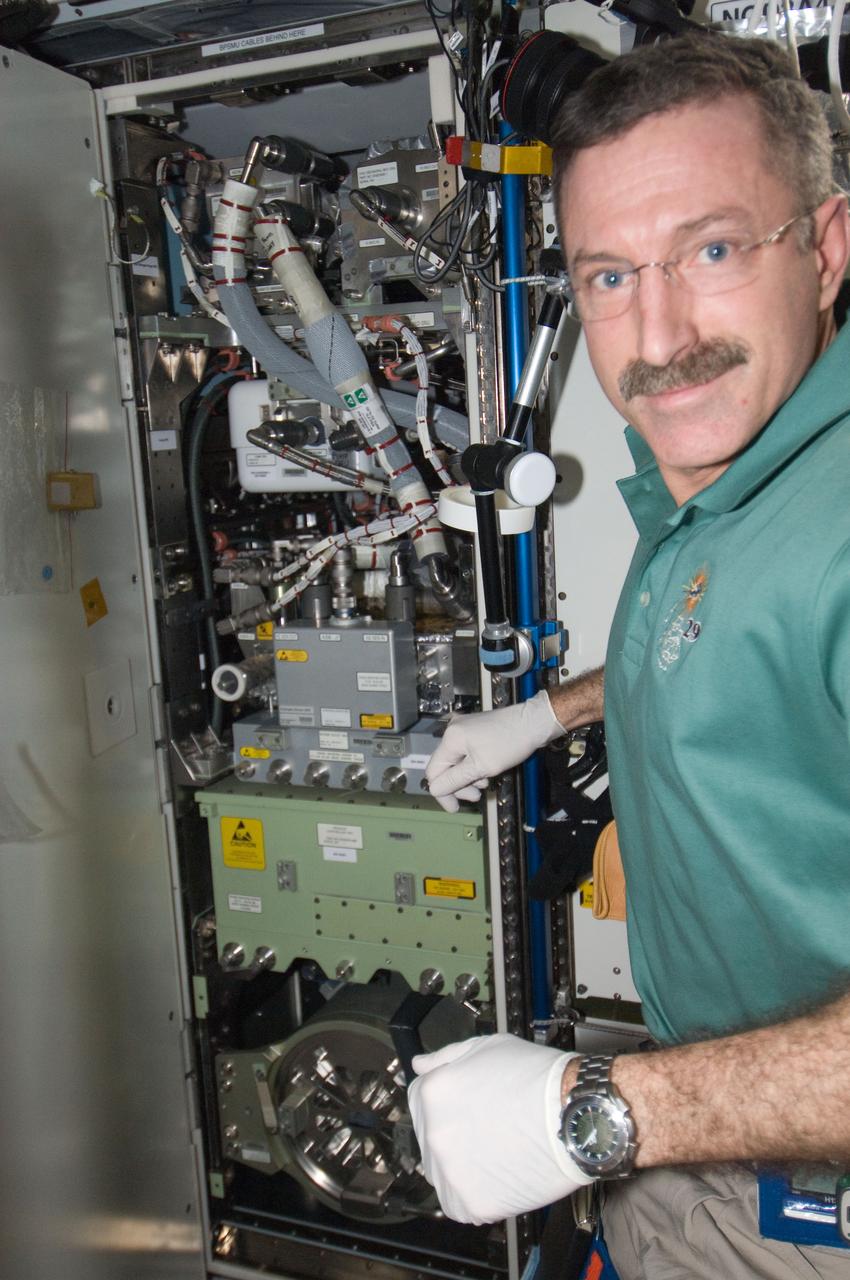

ISS030-E-236919 (18 April 2012) --- NASA astronaut Dan Burbank, Expedition 30 commander, works with the Oxygen Generator System (OGS) rack in the Tranquility node of the International Space Station. Burbank unpowered the OGS, purged the hydrogen sensor Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU) with the Hydrogen Sensor ORU Purge Adapter (HOPA) for return to Earth, and replaced the hydrogen sensor with a new spare, then cleaned the rack Avionics Air Assembly (AAA).
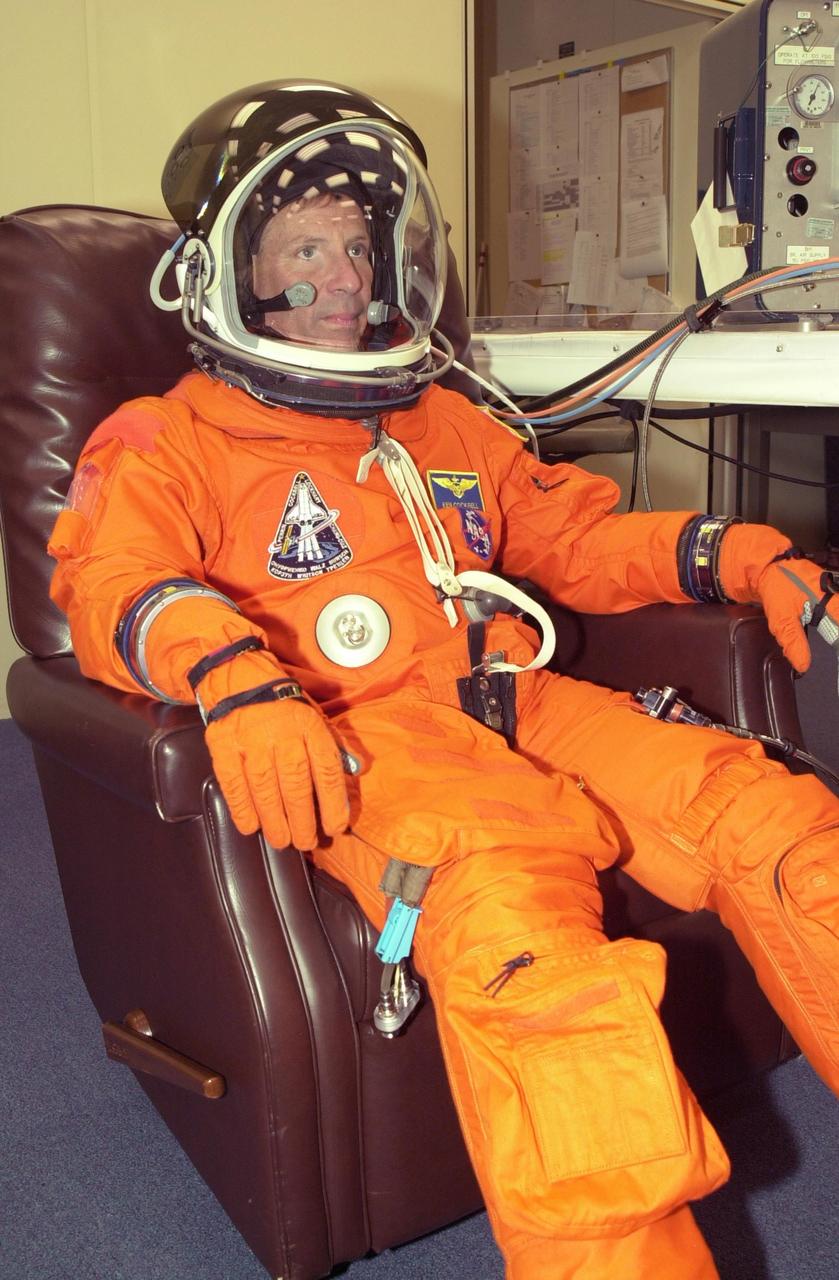

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-111 Commander Kenneth Cockrell has suited up in preparation for a simulated launch countdown at the pad. The simulation is part of STS-111 Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities for the crew and Expedition 5. The payload on the mission to the International Space Station includes the Mobile Base System, an Orbital Replacement Unit and Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. The Expedition 5 crew is traveling on Endeavour to replace the Expedition 4 crew on the Station. Launch of Endeavour is scheduled for May 30, 2002
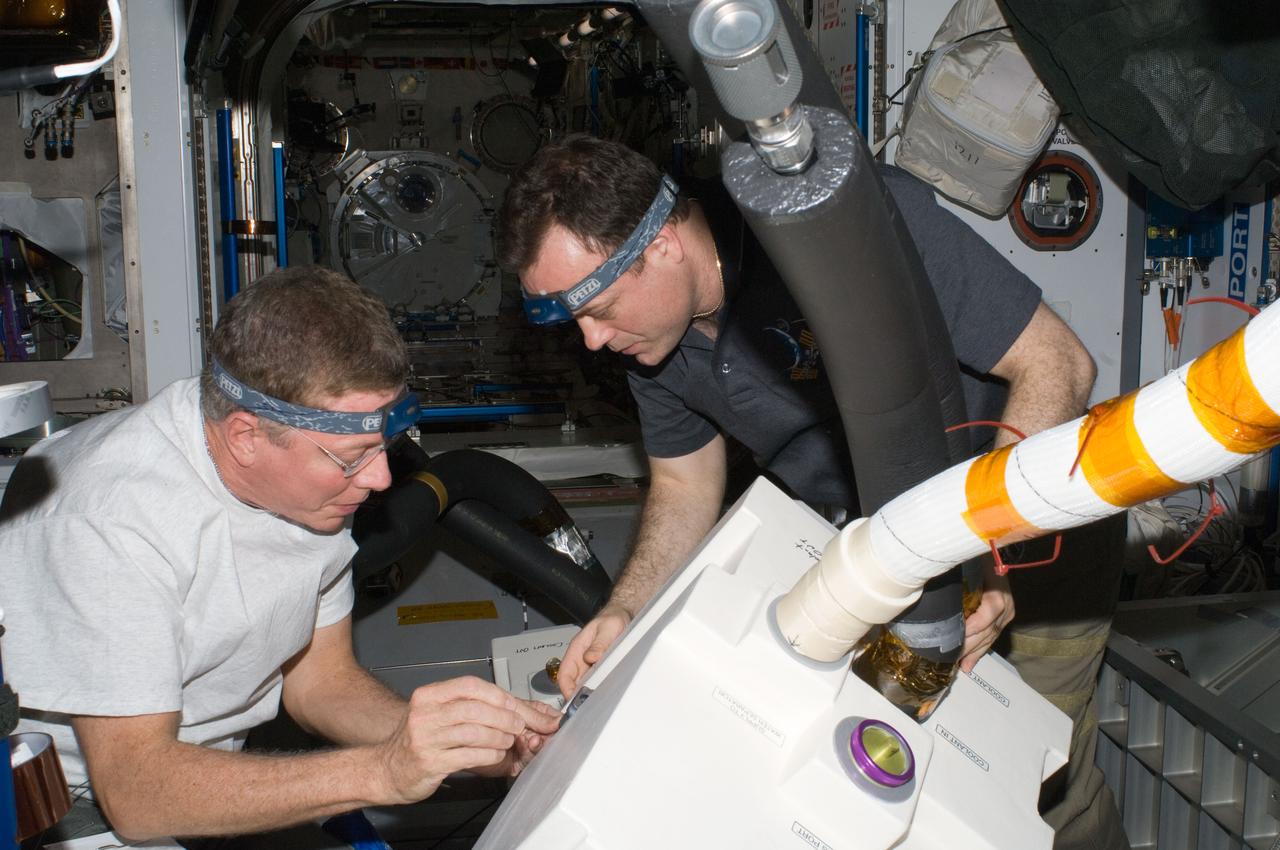

ISS028-E-010781 (30 June 2011) --- NASA astronauts Mike Fossum (left) and Ron Garan, both Expedition 28 flight engineers, perform in-flight maintenance in the Harmony node of the International Space Station. The maintenance involved removing and replacing the failed Common Cabin Air Assembly (CCAA) heat exchanger in the P3 Midbay with a new spare Heat Exchanger Orbit Replaceable Unit (HX ORU) and lines.
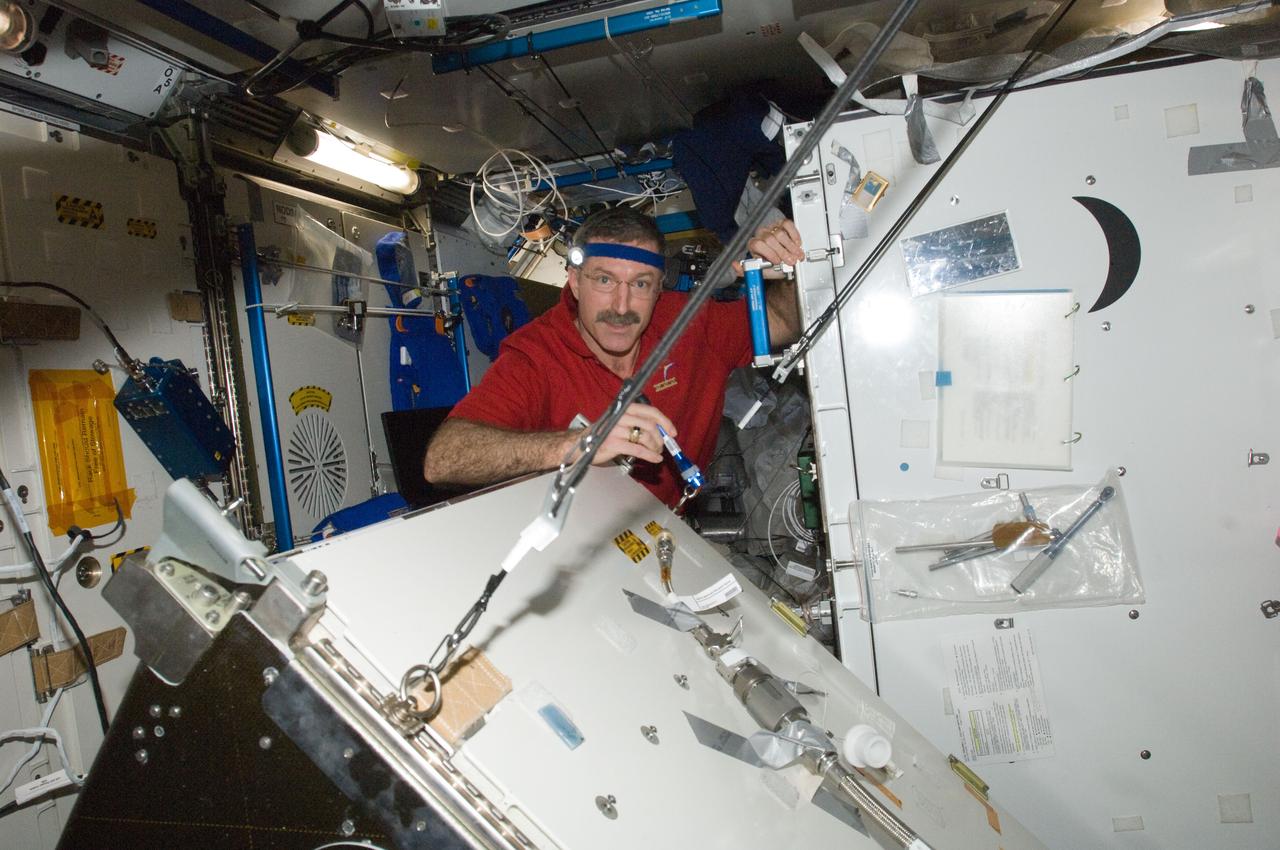

ISS030-E-128752 (8 March 2012) --- NASA astronaut Dan Burbank, Expedition 30 commander, performs part one of the Water Recovery System-1 (WRS-1) repair in the Tranquility node of the International Space Station. Burbank removed and replaced the failed Catalytic Reactor (CR), and installed a temporary filter kit between the new CR and the Microbial Check Valve (MCV) to support a system flush of the new Orbital Replacement Unit (ORU).
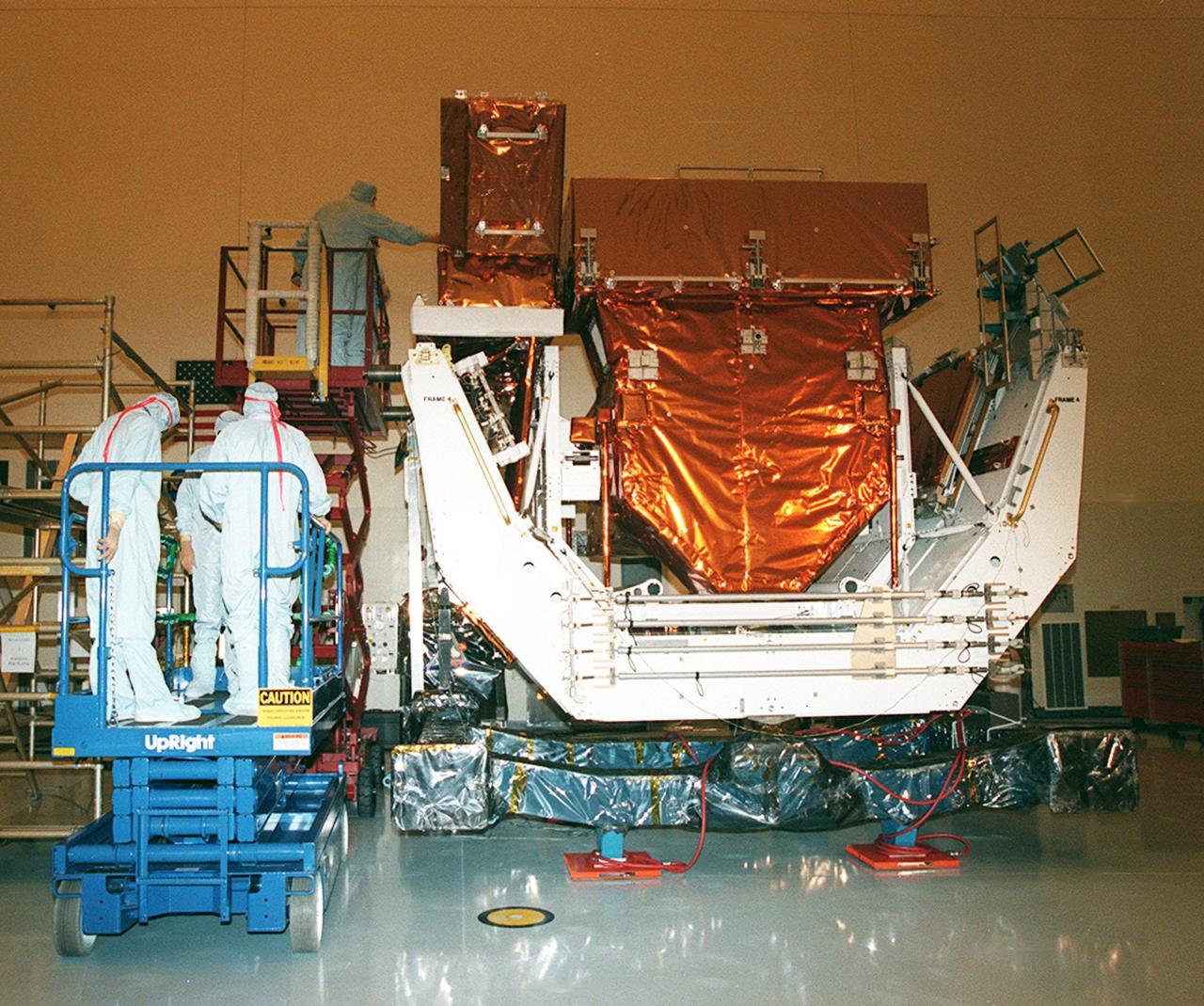
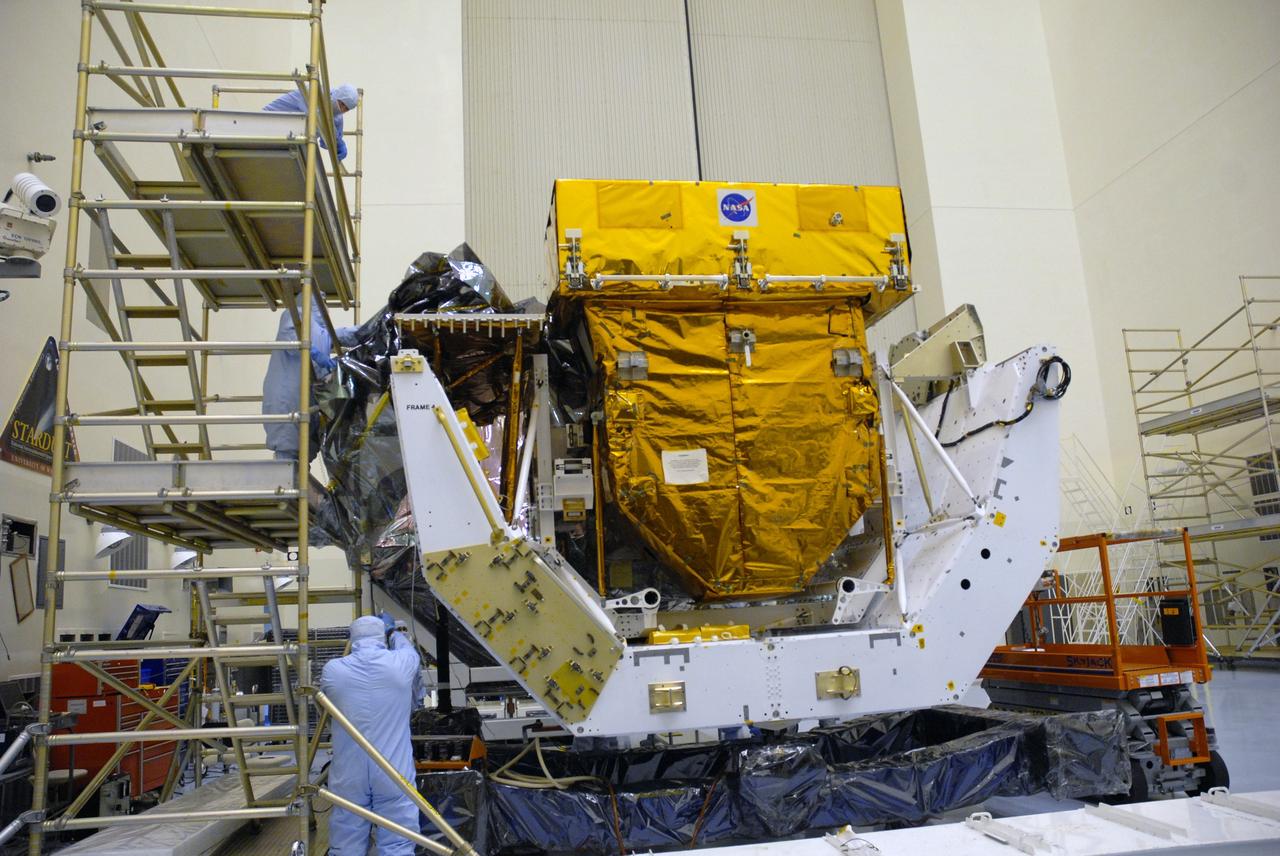
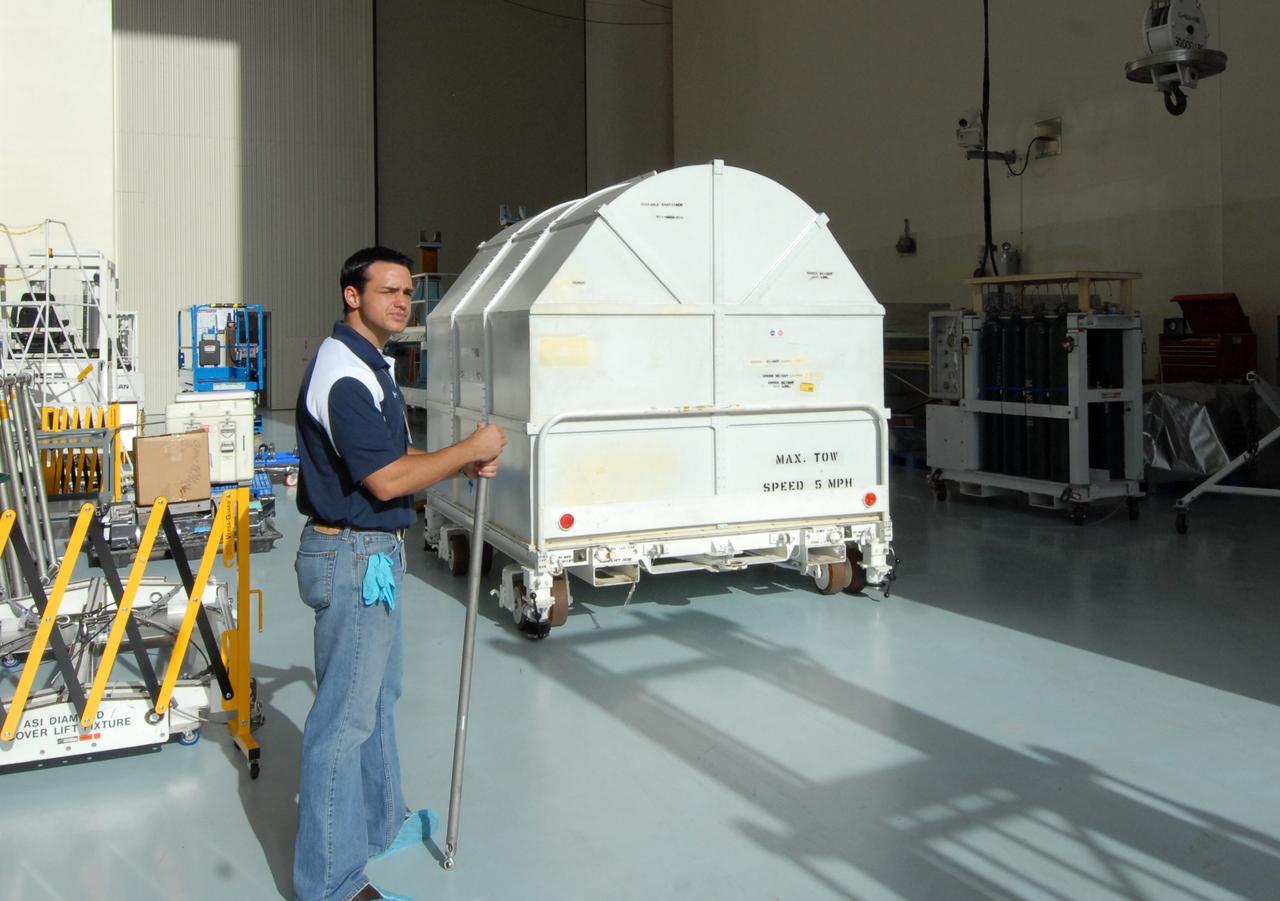
In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility clean room, the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, part of the flight hardware for the Hubble Space Telescope Servicing mission, is on display for media representatives. This mission is designed to replace aging parts on the nine-year-old observatory and to upgrade some of its functioning systems. During the flight, the astronaut crew will replace all six of Hubble's gyroscopes, a fine guidance sensor, the observatory's main computer, and other equipment. The 10-day mission is scheduled to launch no earlier than Dec. 2 at 4:32 a.m. EST from Launch Complex 39
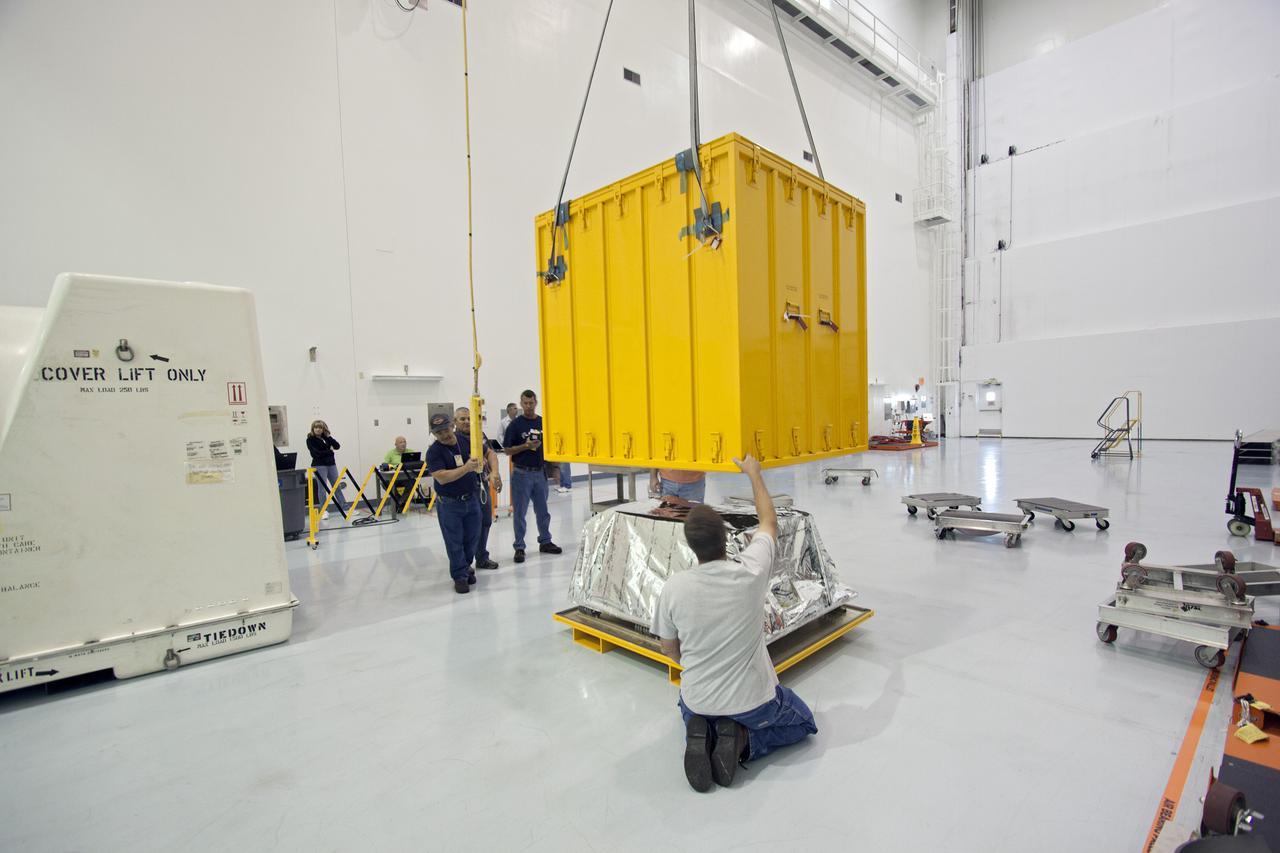

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians lower the cover of a shipping container that will enclose the orbital replacement unit for the space station's main bus switching unit. The unit is one of the payloads processed at Kennedy that will be flown to Japan for the HTV-4 launch to the station, which is currently scheduled for this summer. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
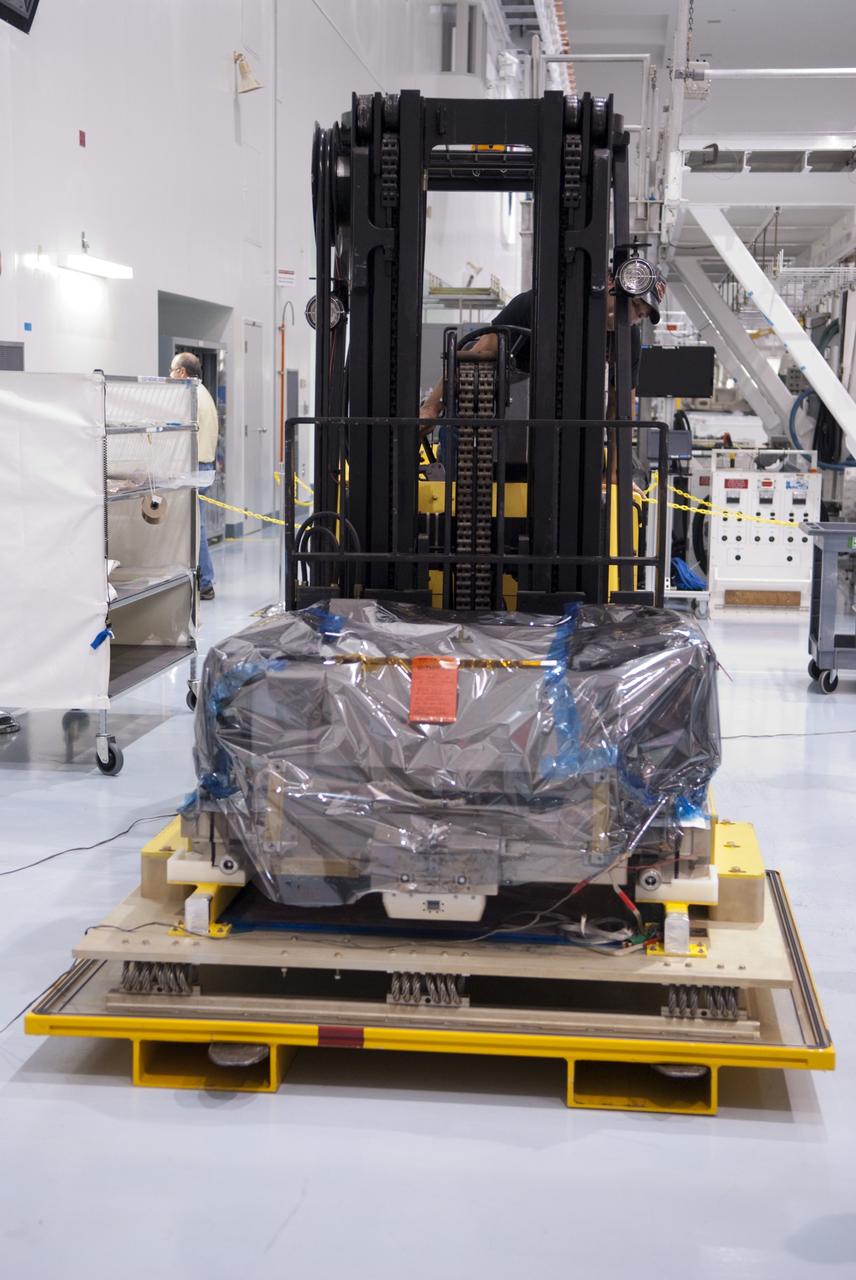

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers have prepared the orbital replacement unit for the space station's main bus switching unit to be placed in a shipping container. The unit, which was processed at Kennedy, will be shipped to Japan at the beginning of the year for the HTV-4 launch, which is currently scheduled for 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians lower the cover of a shipping container that will enclose the orbital replacement unit for the space station's main bus switching unit. The unit is one of the payloads processed at Kennedy that will be flown to Japan for the HTV-4 launch to the station, which is currently scheduled for this summer. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
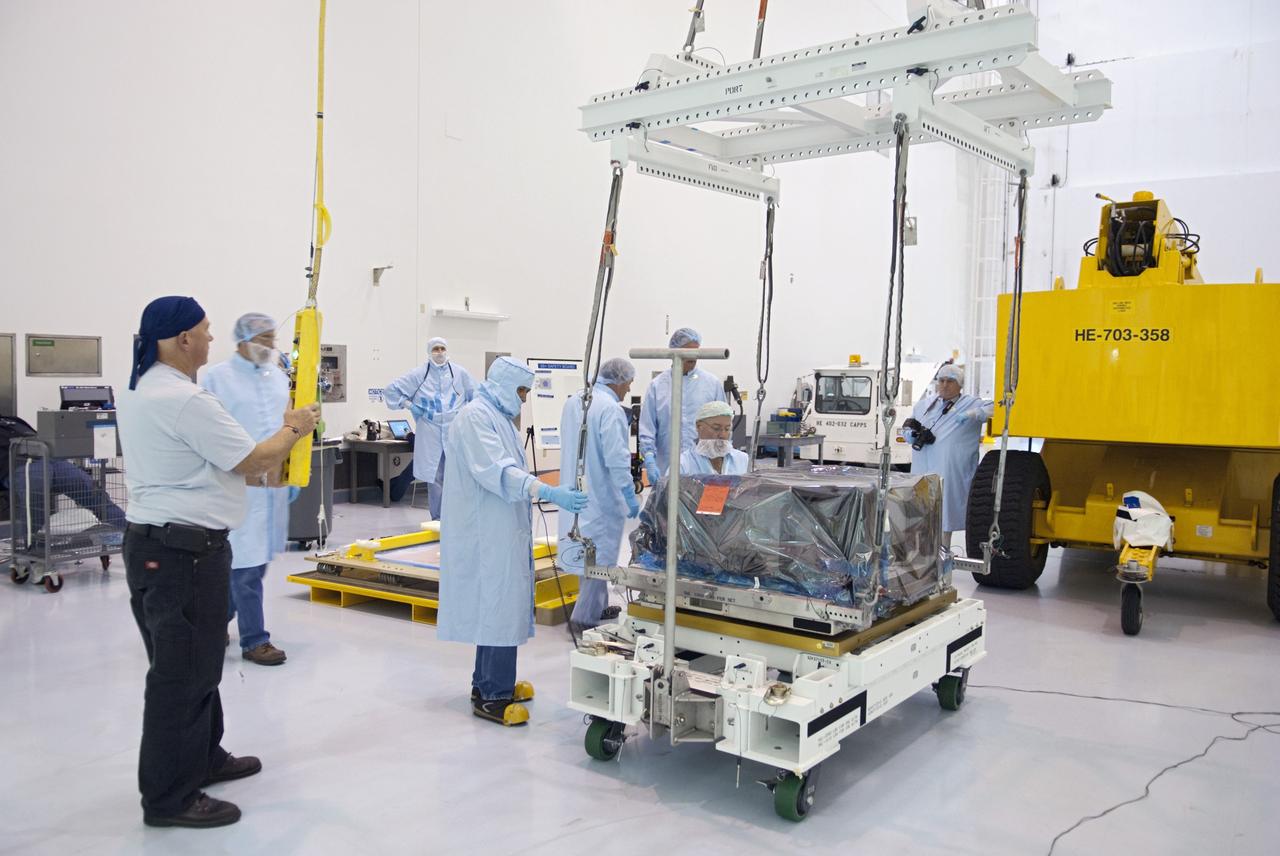

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepare to pack the orbital replacement unit for the space station's main bus switching unit in a shipping container. The unit, which was processed at Kennedy, will be shipped to Japan at the beginning of the year for the HTV-4 launch, which is currently scheduled for 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
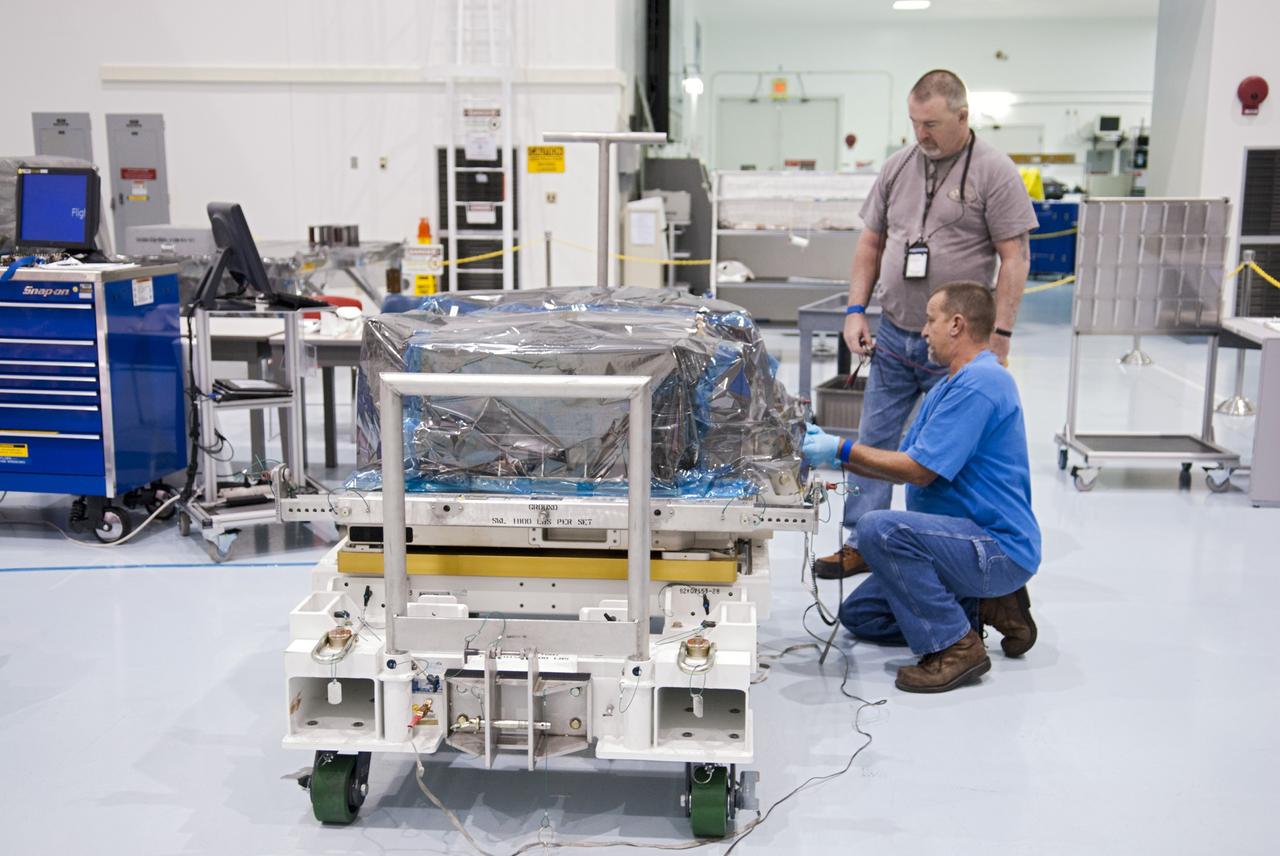

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida prepare to pack the orbital replacement unit for the space station's main bus switching unit in a shipping container. The unit, which was processed at Kennedy, will be shipped to Japan at the beginning of the year for the HTV-4 launch, which is currently scheduled for 2013. Photo credit: NASA/Charisse Nahser
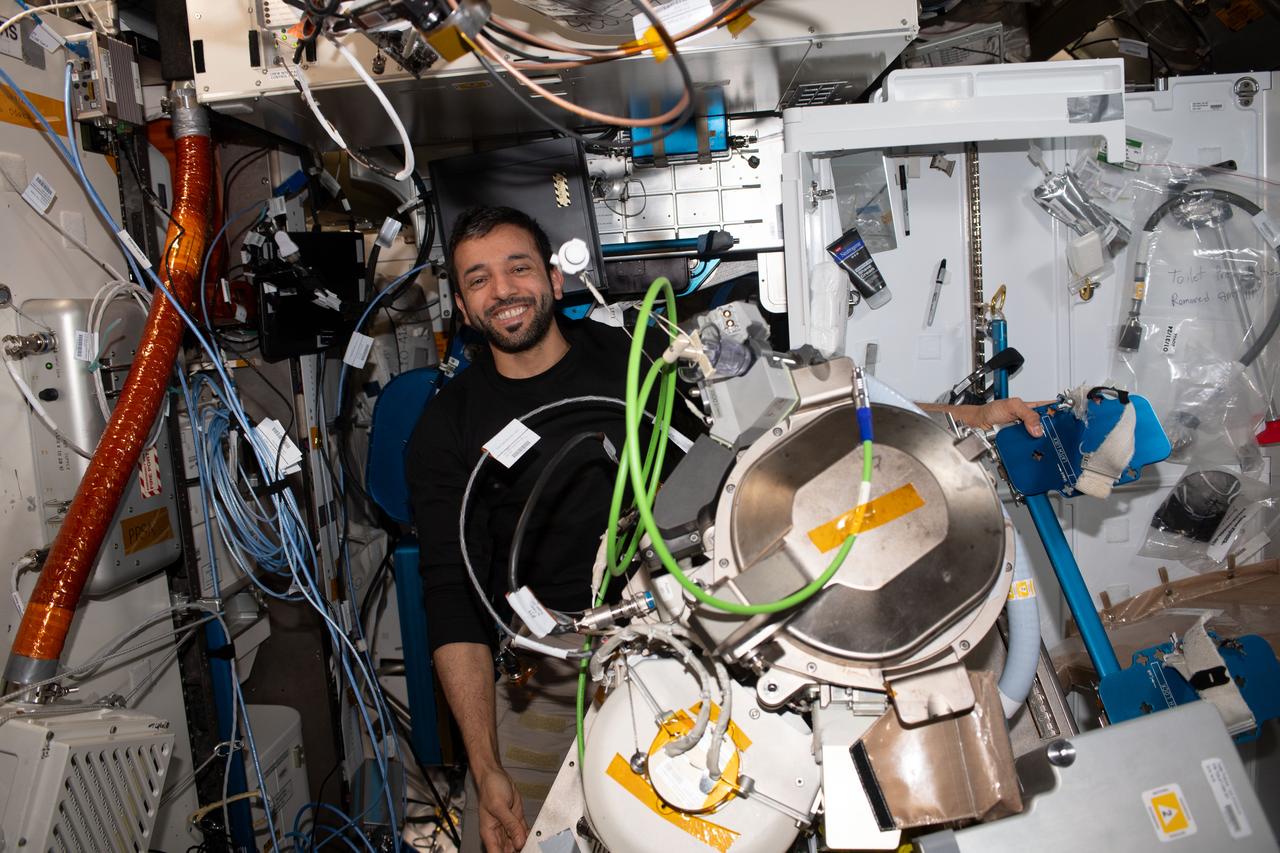

iss069e056737 (Aug. 11, 2023) --- UAE (United Arab Emirates) astronaut and Expedition 69 Flight Engineer Sultan Alneyadi replaces orbital plumbing components in the International Space Station's bathroom, or Waste and Hygiene Compartment, located in the Tranquility module.
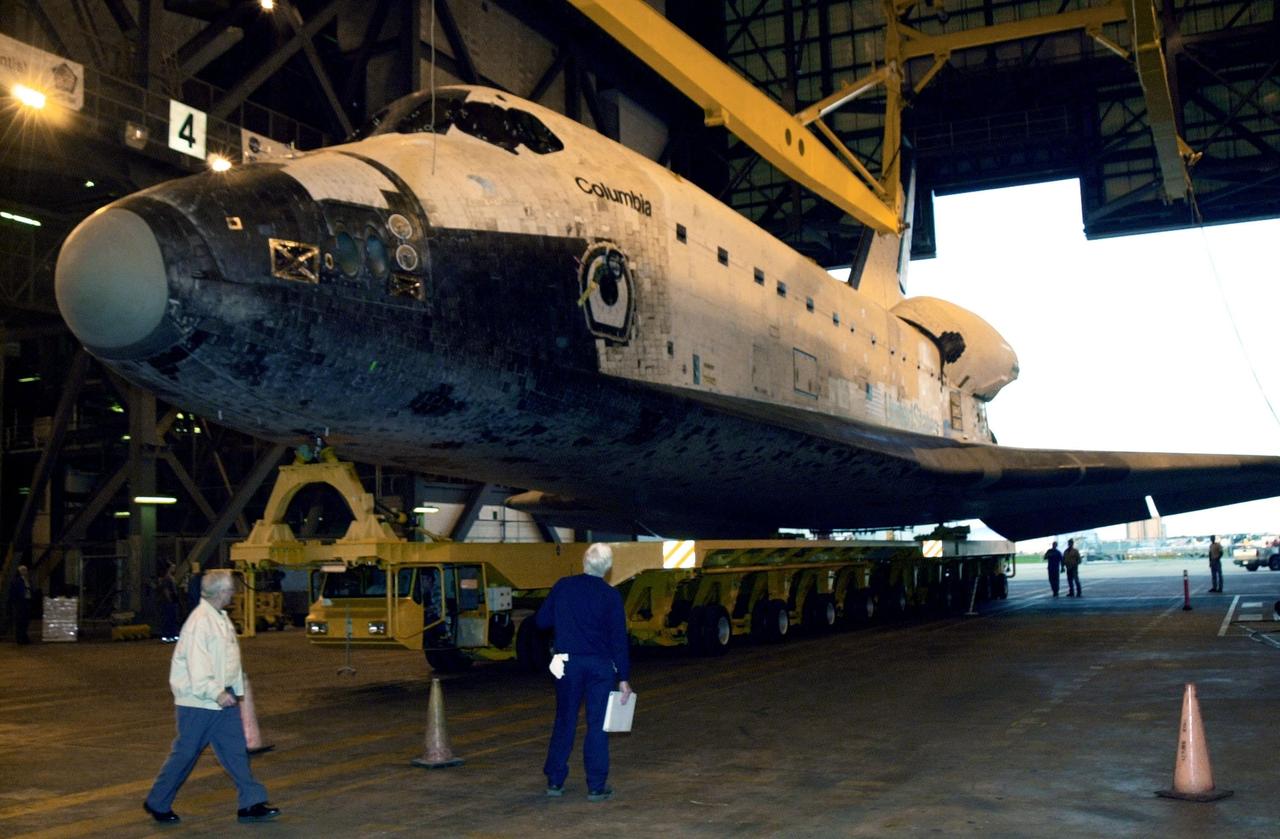

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Vehicle Assembly Building, overhead cranes are lowered toward the orbiter Columbia. The cranes will lift the orbiter to a vertical position for stacking with the external tank and solid rocket boosters. Columbia is scheduled to be launched Feb. 28 on mission STS-109, a Hubble Servicing Mission. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation
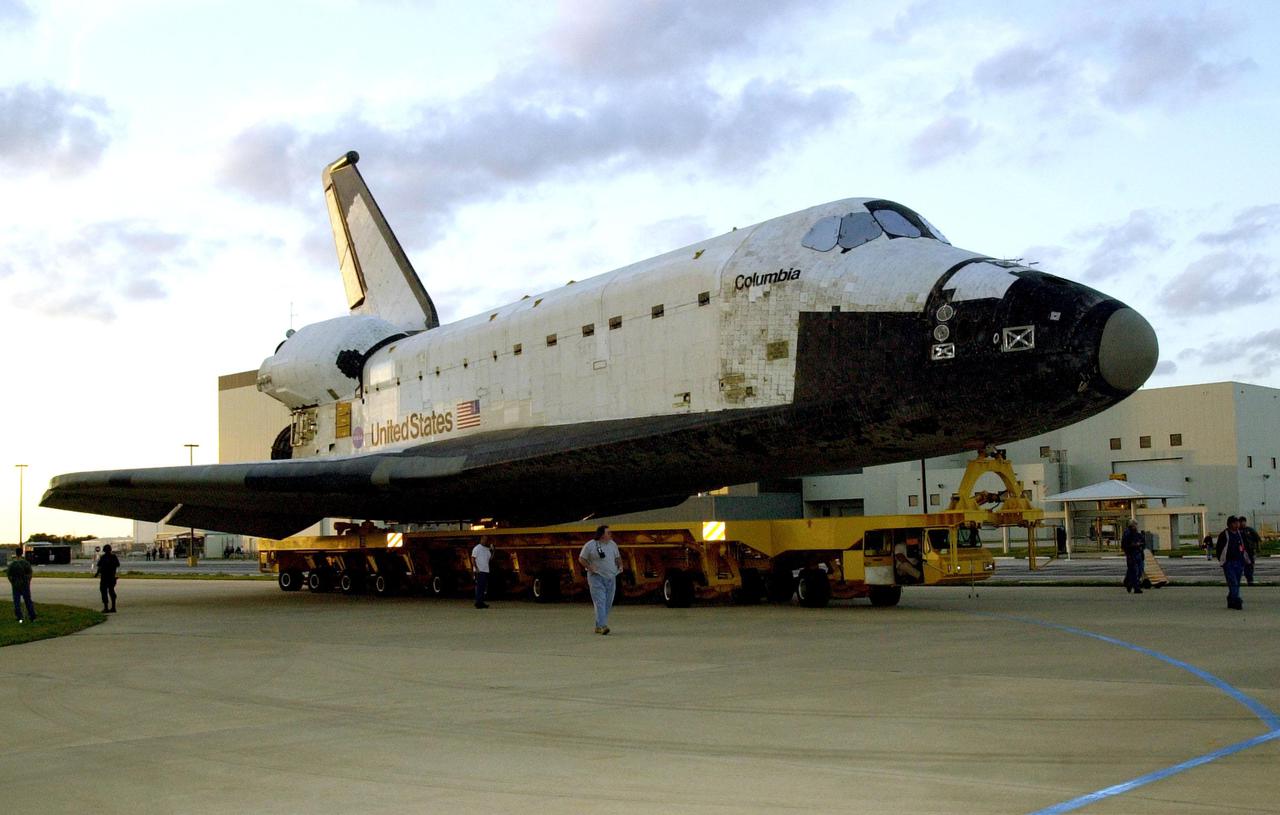

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The orbiter Columbia, atop a transporter, rolls away from the Orbiter Processing Facility on its way to the Vehicle Assembly Building. There it will be mated with the external tank-solid rocket booster stack. Columbia is scheduled to be launched Feb. 28 on mission STS-109, a Hubble Servicing Mission. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. - Members of the STS-109 crew are lowered into the payload bay of orbiter Columbia to check out some of the equipment. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities that include familiarization with the orbiter and equipment. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
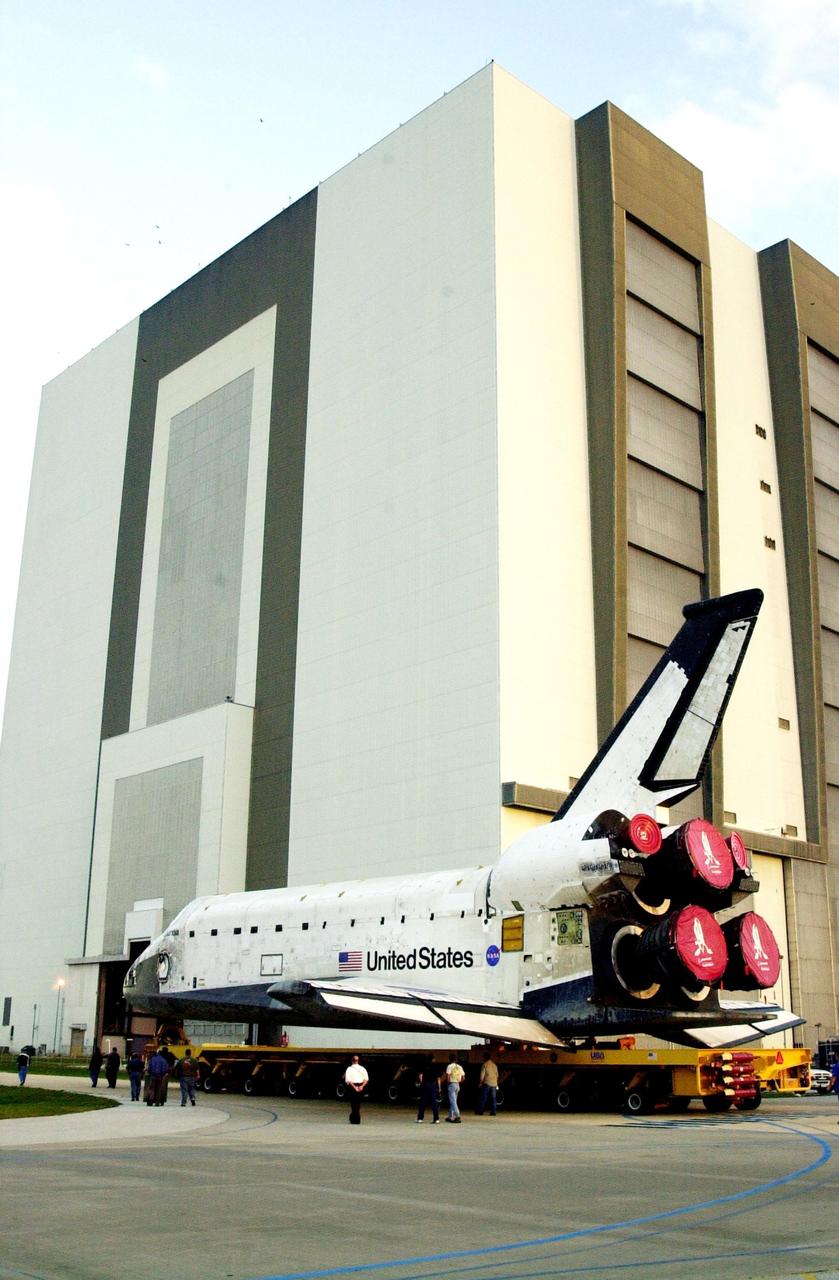

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After leaving the Orbiter Processing Facility, orbiter Columbia rolls toward the Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be mated with the external tank-solid rocket booster stack. Columbia is scheduled to be launched Feb. 28 on mission STS-109, a Hubble Servicing Mission. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation
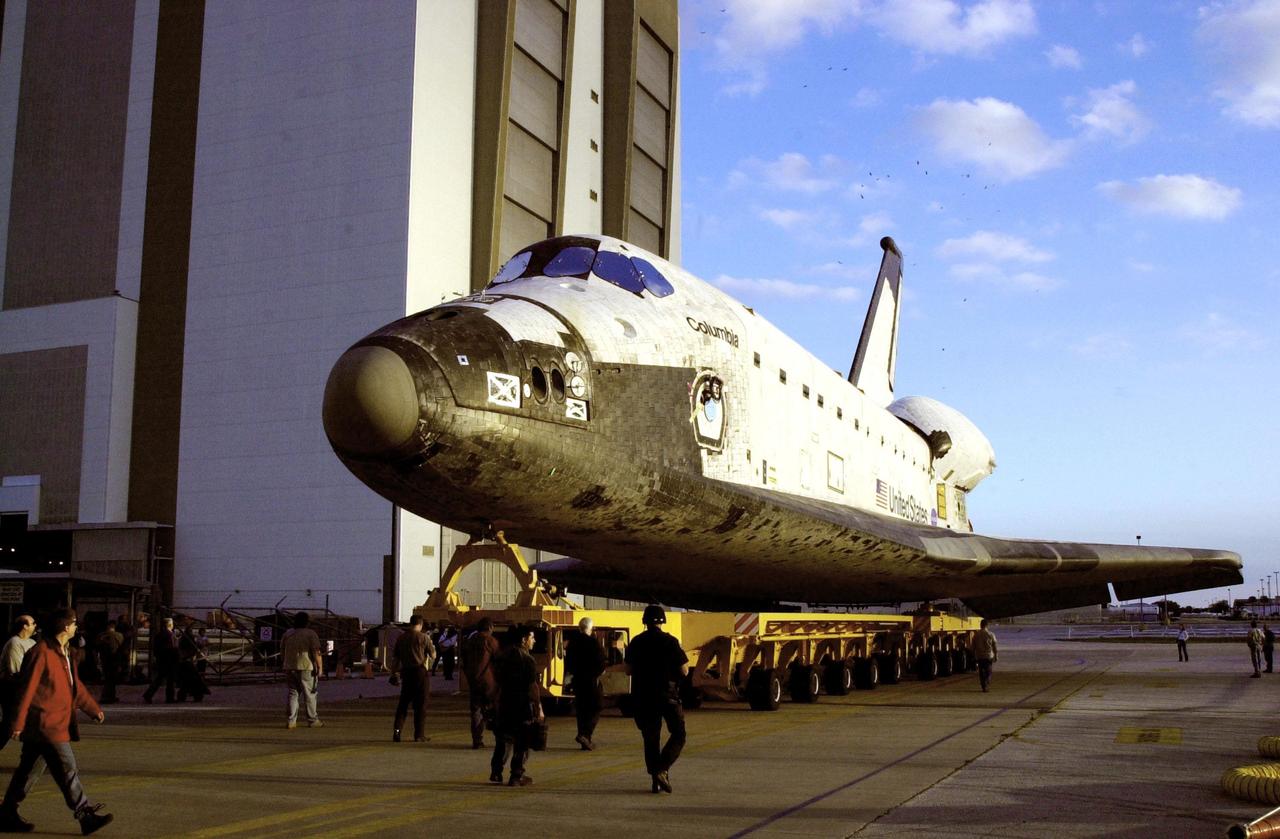

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- After leaving the Orbiter Processing Facility, orbiter Columbia rolls toward the Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be mated with the external tank-solid rocket booster stack. Columbia is scheduled to be launched Feb. 28 on mission STS-109, a Hubble Servicing Mission. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Thermal Protection System Facility, Tim Wright, engineering manager with United Space Alliance, tests a new tile, called "Boeing replacement insulation" or "BRI-18." The new tiles will gradually replace older tiles around main landing gear doors, external tank doors and nose landing gear doors. Currently, 10 tiles have been processed inside the facility. Discovery will receive the first BRI-18 tiles. Technicians inside the Orbiter Processing Facility are performing fit checks and will begin bonding the tiles to the vehicle this month. The raw material is manufactured by The Boeing Company in Huntington Beach, Calif. Replacing older tile with the BRI-18 tile in strategic areas is one of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board's recommendations to strengthen the orbiters. The tiles are more impact resistant than previous designs, enhancing the crew’s safety.
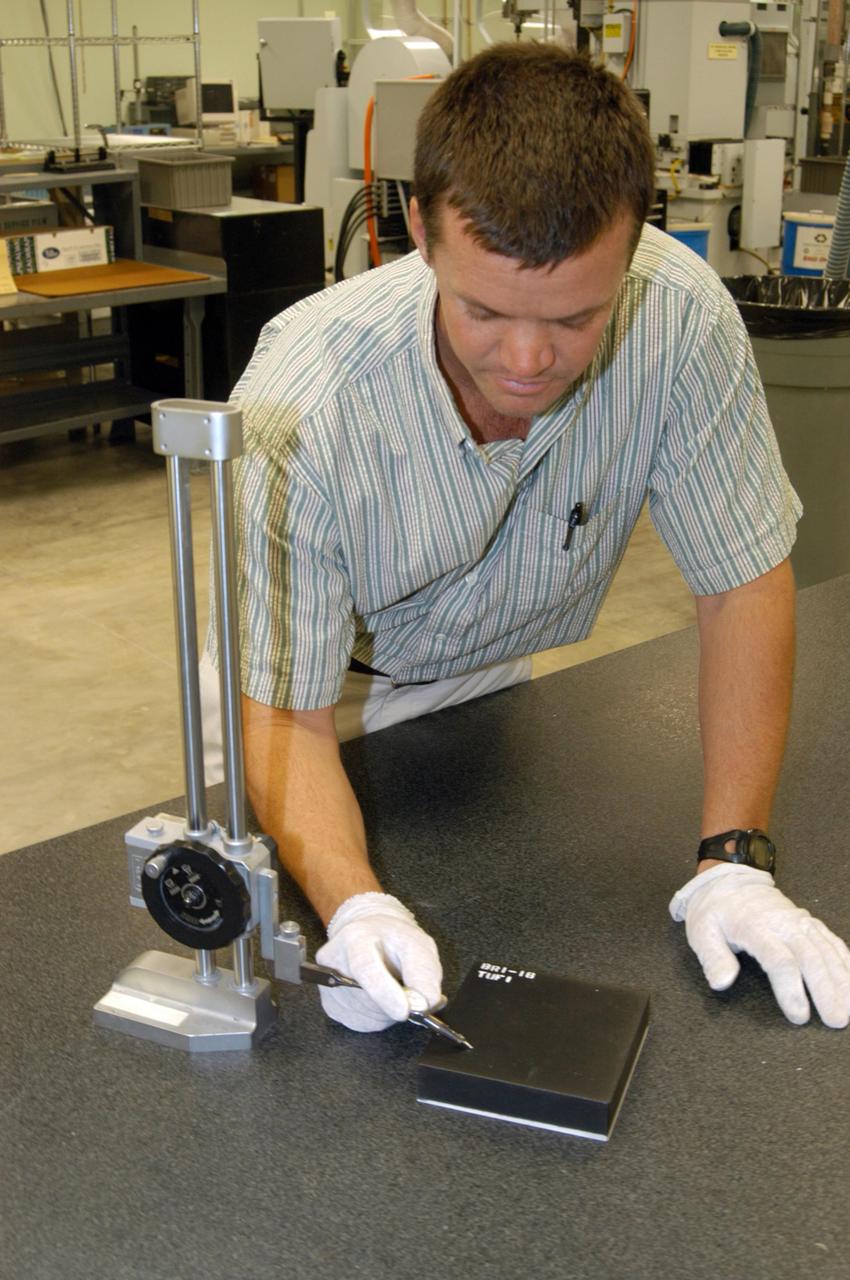

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Thermal Protection System Facility, Tim Wright, engineering manager with United Space Alliance, tests a new tile, called "Boeing replacement insulation" or "BRI-18." The new tiles will gradually replace older tiles around main landing gear doors, external tank doors and nose landing gear doors. Currently, 10 tiles have been processed inside the facility. Discovery will receive the first BRI-18 tiles. Technicians inside the Orbiter Processing Facility are performing fit checks and will begin bonding the tiles to the vehicle this month. The raw material is manufactured by The Boeing Company in Huntington Beach, Calif. Replacing older tile with the BRI-18 tile in strategic areas is one of the Columbia Accident Investigation Board's recommendations to strengthen the orbiters. The tiles are more impact resistant than previous designs, enhancing the crew’s safety.
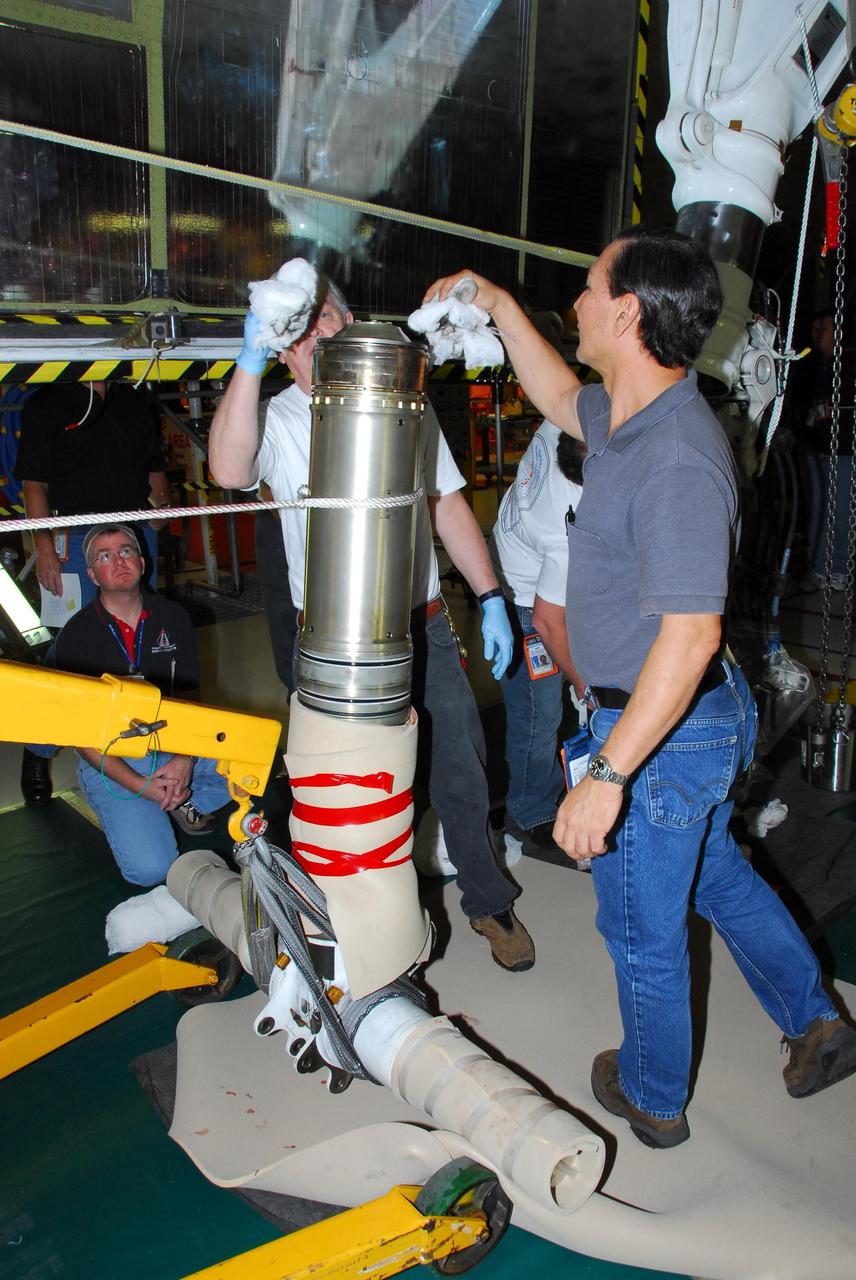

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians work on the starboard landing gear assembly of space shuttle Discovery. They will replace a leaking dynamic seal in Discovery's right main-gear strut. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
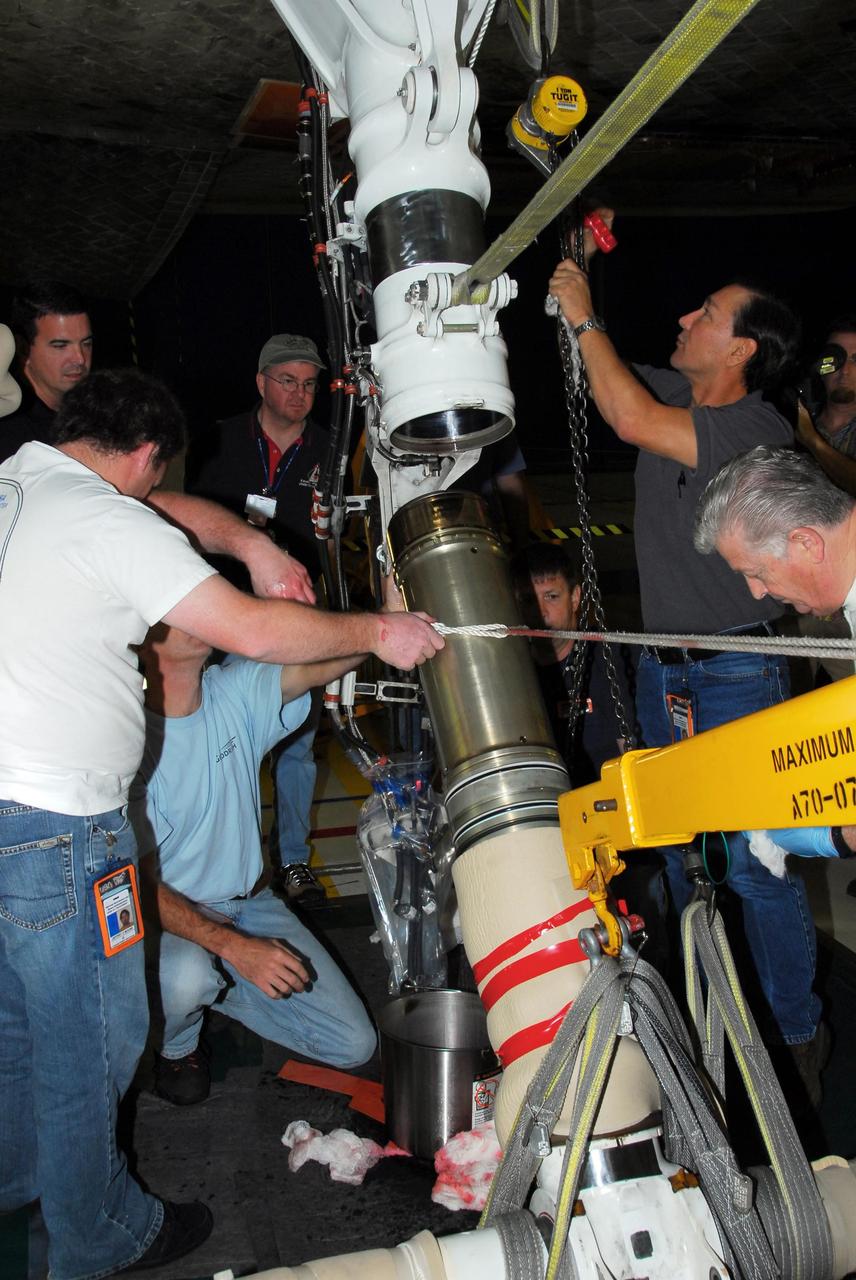

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians work on the starboard landing gear assembly of space shuttle Discovery. They will replace a leaking dynamic seal in Discovery's right main-gear strut. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
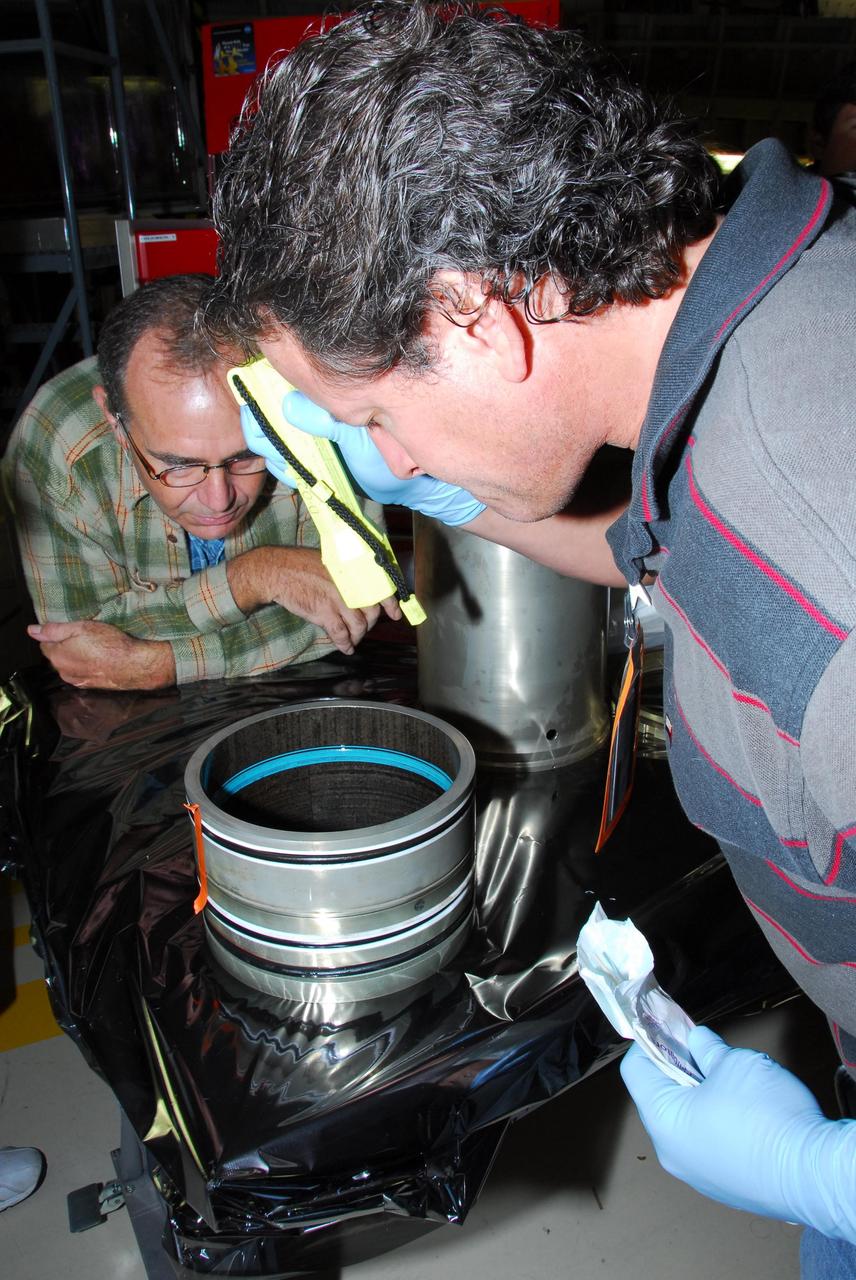

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians look inside part of space shuttle Discovery's right main-gear strut where a leaking seal has been found. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. The seal will be replaced. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
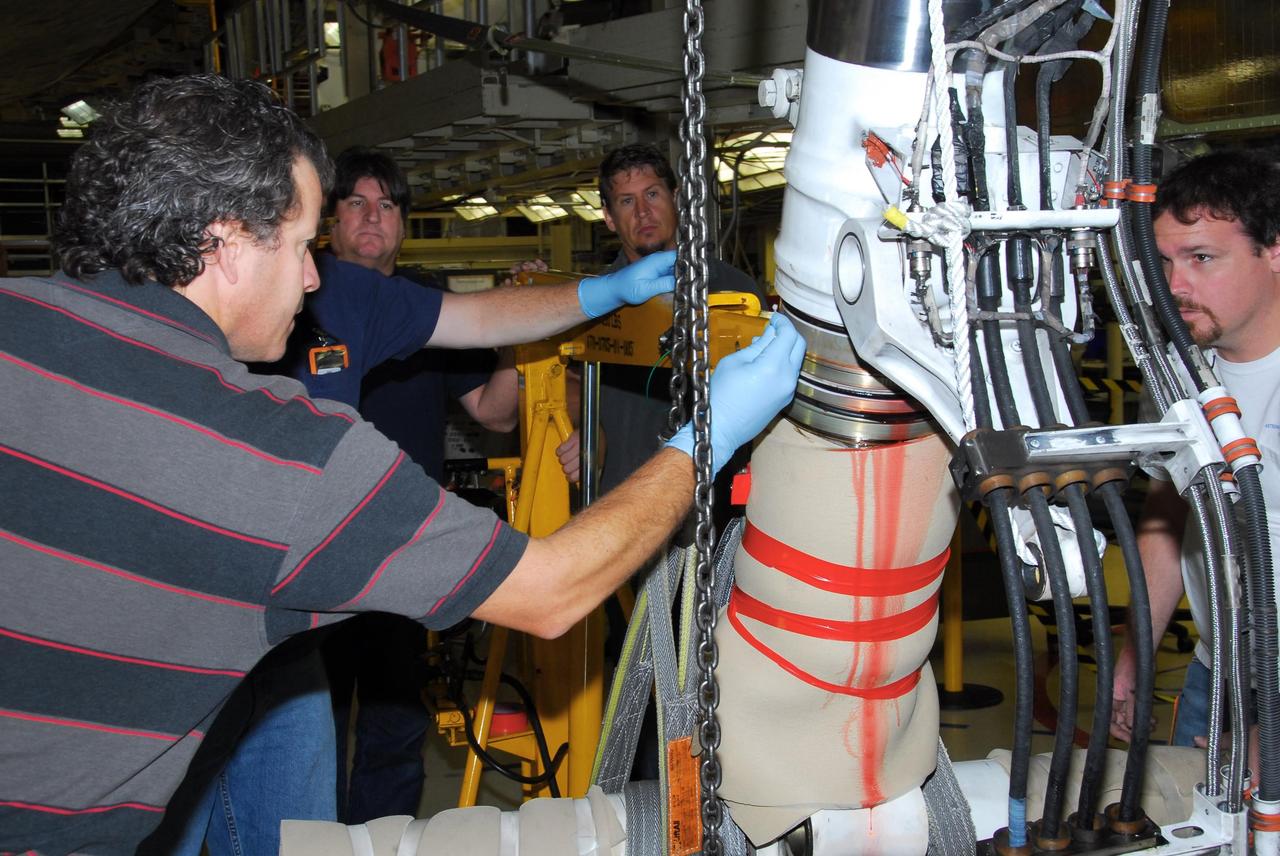

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians begin work on the starboard landing gear assembly of space shuttle Discovery. They will replace a leaking dynamic seal in Discovery's right main-gear strut. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians remove part of space shuttle Discovery's right main-gear strut where a leaking seal has been found. They will replace the seal. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 3, United Space Alliance and B.F. Goodrich technicians begin work on the starboard landing gear assembly of space shuttle Discovery. They will replace a leaking dynamic seal in Discovery's right main-gear strut. The struts act as shock absorbers during the shuttle's landing. Engineers determined the observed leak of hydraulic fluid in the main landing gear strut exceeded specification and could not be reduced to an acceptable rate. Removing the strut and replacing seals require disconnecting and replacing the brakes and tires, disconnecting and reconnecting instruments and other requirements to allow access to the strut. Discovery had been scheduled to roll over Sept. 19 from its processing hangar to the Vehicle Assembly Building. A new rollover date will be set after technicians determine how long replacing the seal will take. Photo credit: NASA/George Shelton
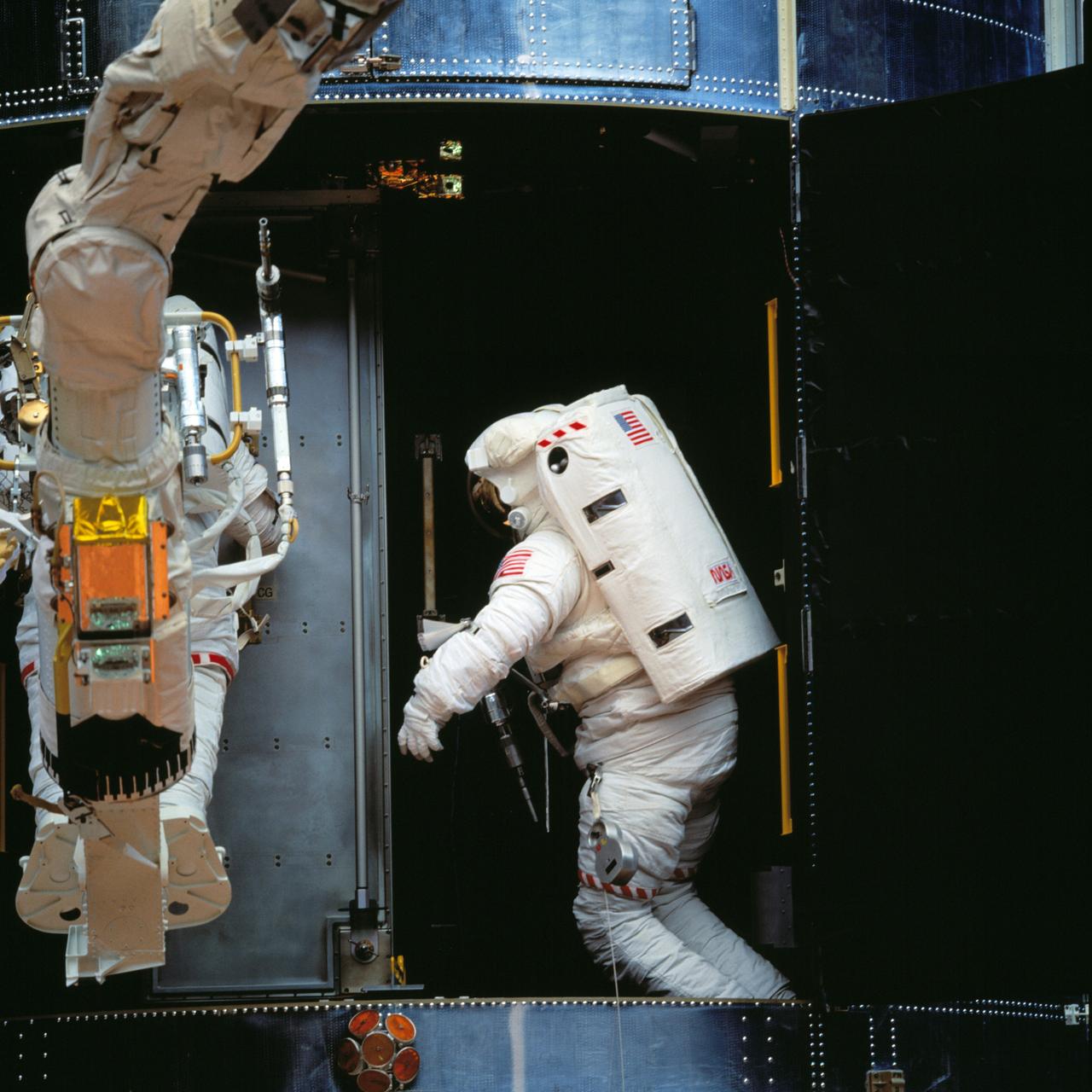
STS061-94-059 (8 Dec. 1993) --- Astronaut Thomas D. Akers maneuvers inside the bay which will house the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR) while assisting astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton with the installation of the 640-pound instrument. Thornton, anchored on the end of the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, is partially visible as she prepares to install the COSTAR.
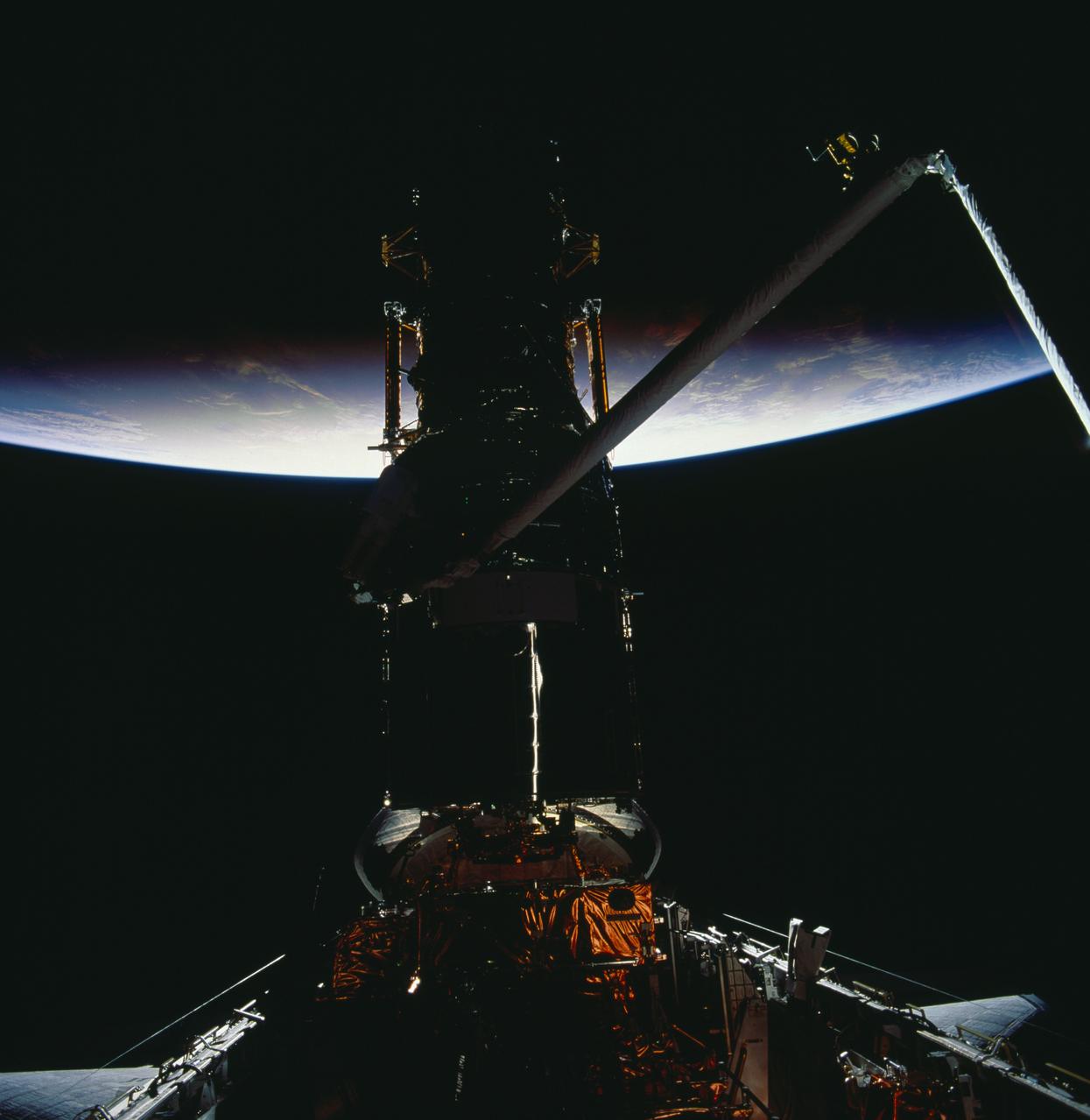

STS061-98-0AR (8 Dec 1993) --- Earth is partially illuminated but the Hubble Space Telescope (HST) and the Space Shuttle Endeavour are still mostly in darkness, in this 70mm frame photographed during the fourth of five space walks. Astronaut Kathryn C. Thornton, barely visible above left center in the frame, works to install the Corrective Optics Space Telescope Axial Replacement (COSTAR).

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians begin to lower the cover of a shipping container that will enclose the orbital replacement unit for the space station's utility transfer assembly. The unit is one of the payloads processed at Kennedy that will be flown to Japan for the HTV-4 launch to the station, which is currently scheduled for this summer. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to lower the cover of a shipping container that will enclose the orbital replacement unit for the space station's utility transfer assembly. The unit is one of the payloads processed at Kennedy that will be flown to Japan for the HTV-4 launch to the station, which is currently scheduled for this summer. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Science Instrument Command and Data Handling Unit, or SIC&DH, is moved toward the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment Carrier in the background, where it will be installed. The SIC&DH will be installed on the Hubble Space Telescope during space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission. This unit will replace the one that suffered a failure aboard the orbiting telescope on Sept. 27, 2008. Atlantis is targeted for launch on May 12. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians help with the installation of the Science Instrument Command and Data Handling Unit, or SIC&DH, on the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment Carrier. The SIC&DH will be installed on the Hubble Space Telescope during space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission. This unit will replace the one that suffered a failure aboard the orbiting telescope on Sept. 27, 2008. Atlantis is targeted for launch on May 12. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
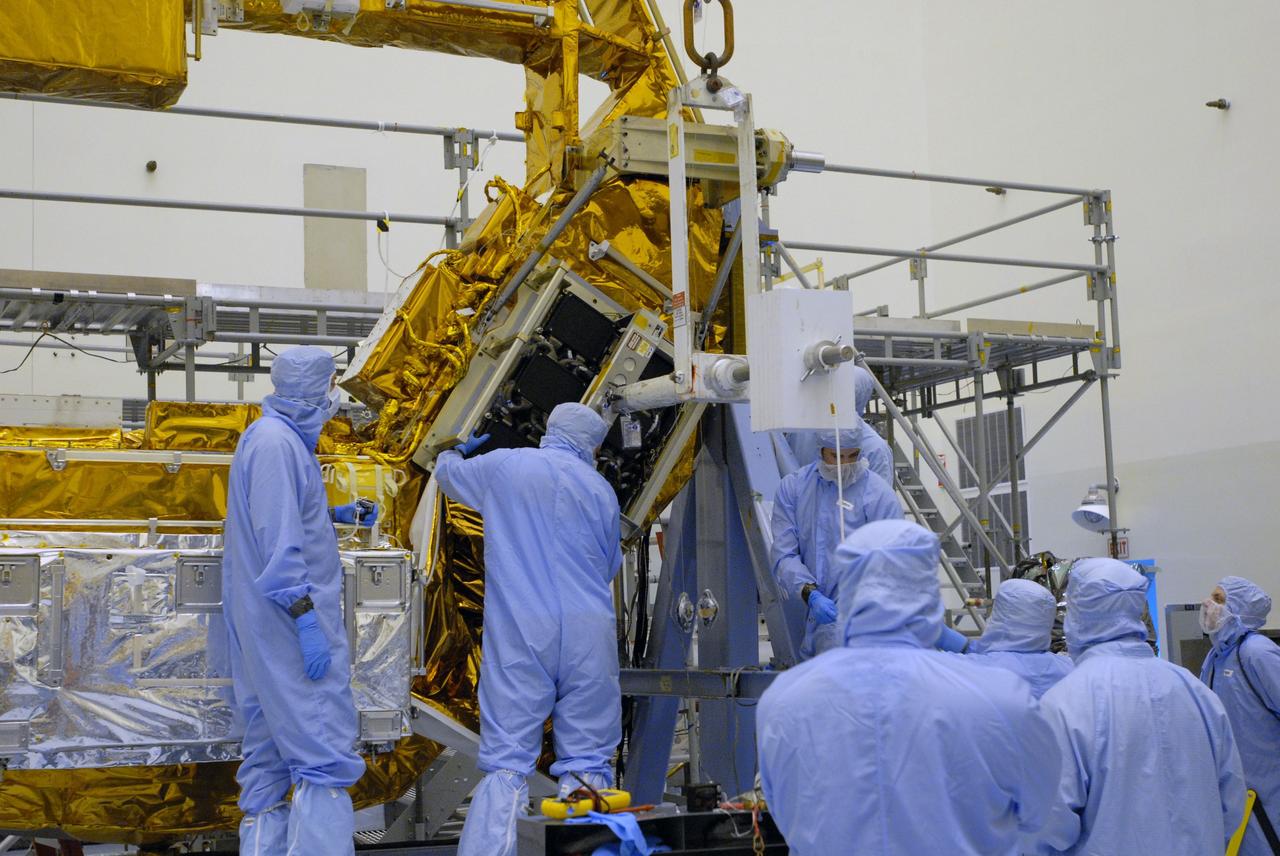

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians help with the installation of the Science Instrument Command and Data Handling Unit, or SIC&DH, on the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment Carrier. The SIC&DH will be installed on the Hubble Space Telescope during space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission. This unit will replace the one that suffered a failure aboard the orbiting telescope on Sept. 27, 2008. Atlantis is targeted for launch on May 12. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
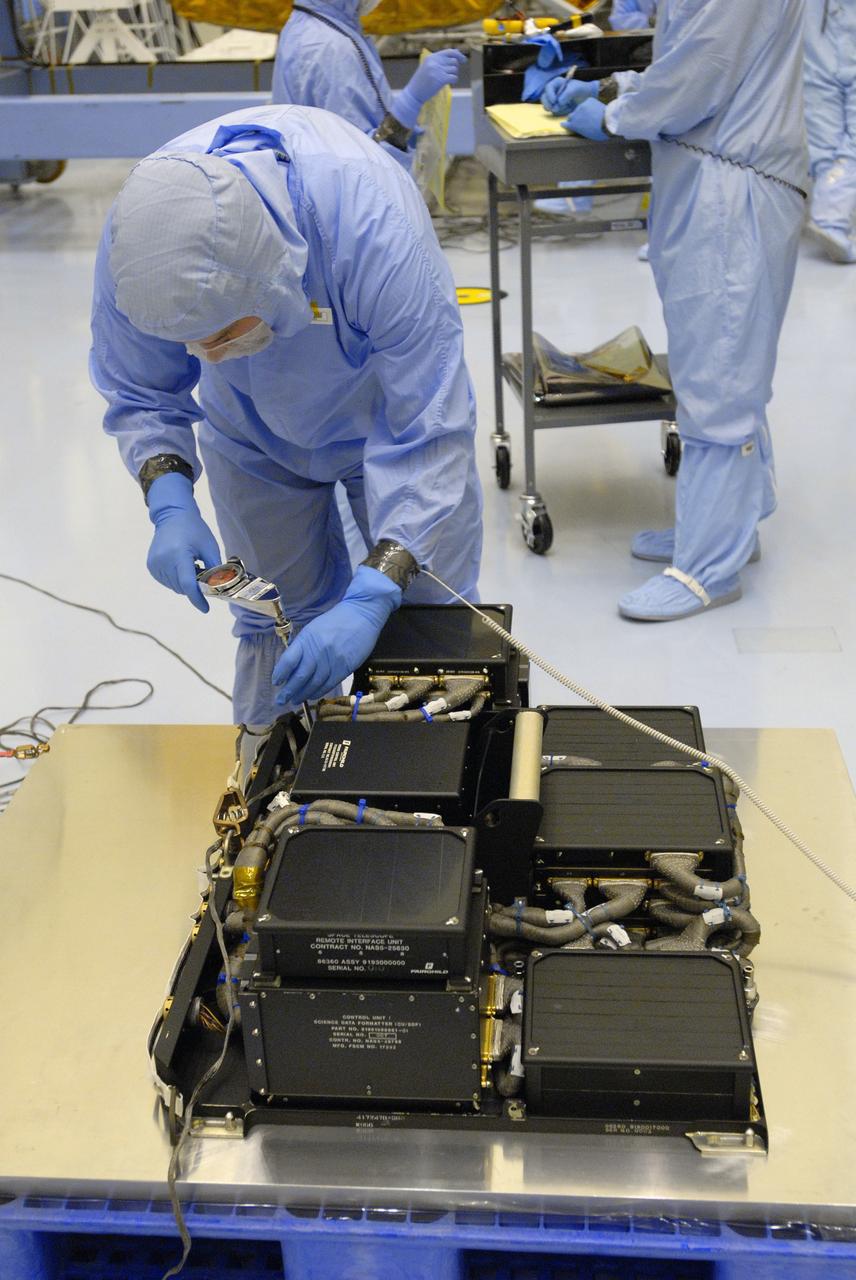

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician prepares the Science Instrument Command and Data Handling Unit, or SIC&DH, for its move to the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment Carrier in the facility. The SIC&DH will be installed on the Hubble Space Telescope during space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission. This unit will replace the one that suffered a failure aboard the orbiting telescope on Sept. 27, 2008. Atlantis is targeted for launch on May 12. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Science Instrument Command and Data Handling Unit, or SIC&DH, is moved toward the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment Carrier in the background, where it will be installed. The SIC&DH will be installed on the Hubble Space Telescope during space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission. This unit will replace the one that suffered a failure aboard the orbiting telescope on Sept. 27, 2008. Atlantis is targeted for launch on May 12. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians check the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment Carrier where the Science Instrument Command and Data Handling Unit, or SIC&DH, is being installed. The SIC&DH will be installed on the Hubble Space Telescope during space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission. This unit will replace the one that suffered a failure aboard the orbiting telescope on Sept. 27, 2008. Atlantis is targeted for launch on May 12. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians look over the Science Instrument Command and Data Handling Unit, or SIC&DH, installed on the Multi-Use Lightweight Equipment Carrier. The SIC&DH will be installed on the Hubble Space Telescope during space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission. This unit will replace the one that suffered a failure aboard the orbiting telescope on Sept. 27, 2008. Atlantis is targeted for launch on May 12. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians finish lowering the cover of a shipping container that will enclose the orbital replacement unit for the space station's utility transfer assembly. The unit is one of the payloads processed at Kennedy that will be flown to Japan for the HTV-4 launch to the station, which is currently scheduled for this summer. Photo credit: NASA_Jim Grossmann
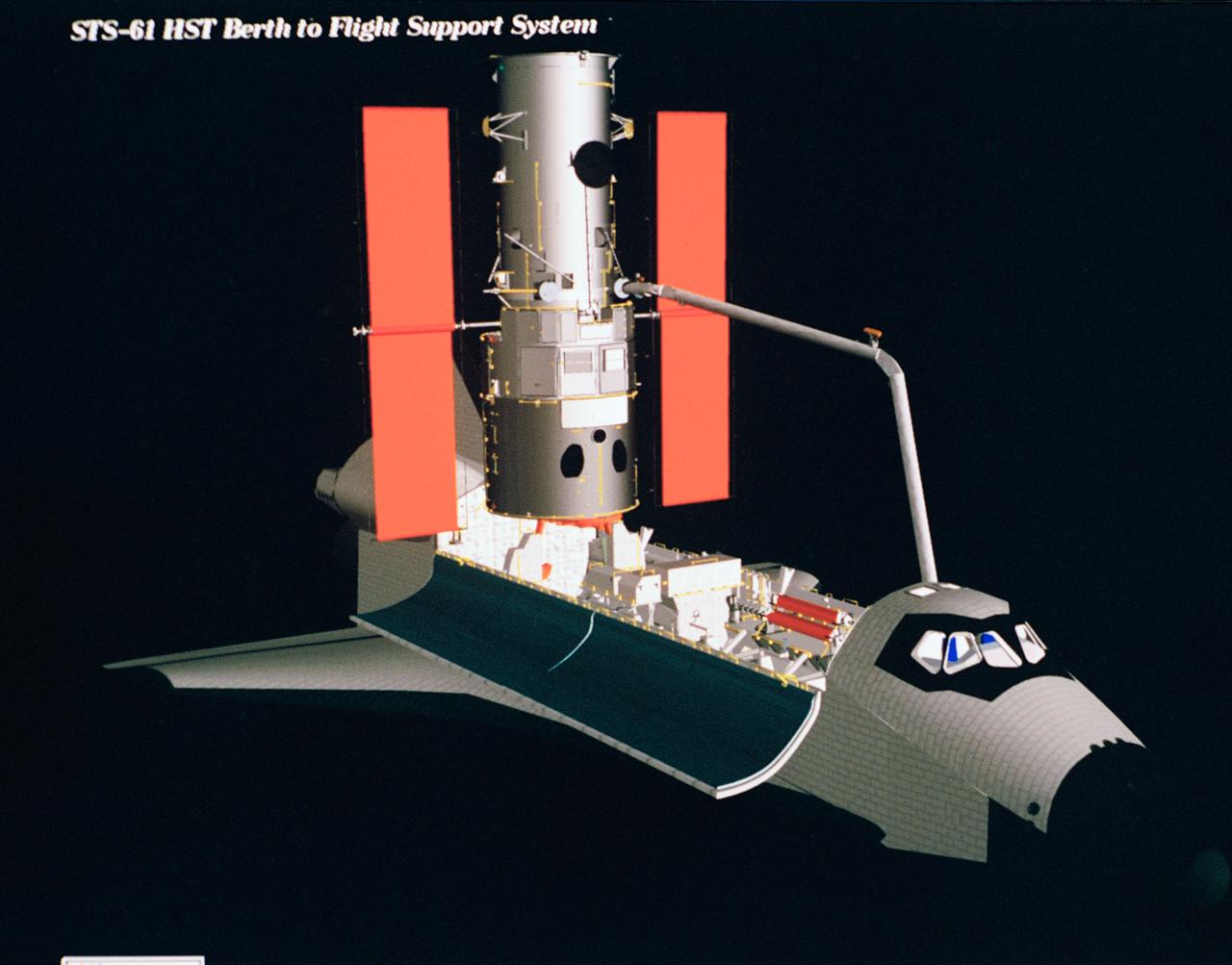
Computer generated scenes depicting the Hubble Space Telescope capture and a sequence of planned events on the planned extravehicular activity (EVA). Scenes include the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm assisting two astronauts changing out the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC) (48699); RMS arm assisting in the temporary mating of the orbiting telescope to the flight support system in Endeavour's cargo bay (48700); Endeavour's RMS arm assisting in the "capture" of the orbiting telescope (48701); Two astronauts changing out the telescope's coprocessor (48702); RMS arm assistign two astronauts replacing one of the telescope's electronic control units (48703); RMS assisting two astronauts replacing the fuse plugs on the telescope's Power Distribution Unit (PDU) (48704); The telescope's High Resolution Spectrograph (HRS) kit is depicted in this scene (48705); Two astronauts during the removal of the high speed photometer and the installation of the COSTAR instrument (48706); Two astronauts, standing on the RMS, during installation of one of the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) (48707); High angle view of the orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour with its cargo bay doors open, revealing the bay's pre-capture configuration. Seen are, from the left, the Solar Array Carrier, the ORU Carrier and the flight support system (48708); Two astronauts performing the replacement of HST's Rate Sensor Units (RSU) (48709); The RMS arm assisting two astronauts with the replacement of the telescope's solar array panels (48710); Two astronauts replacing the telescope's Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) (48711).
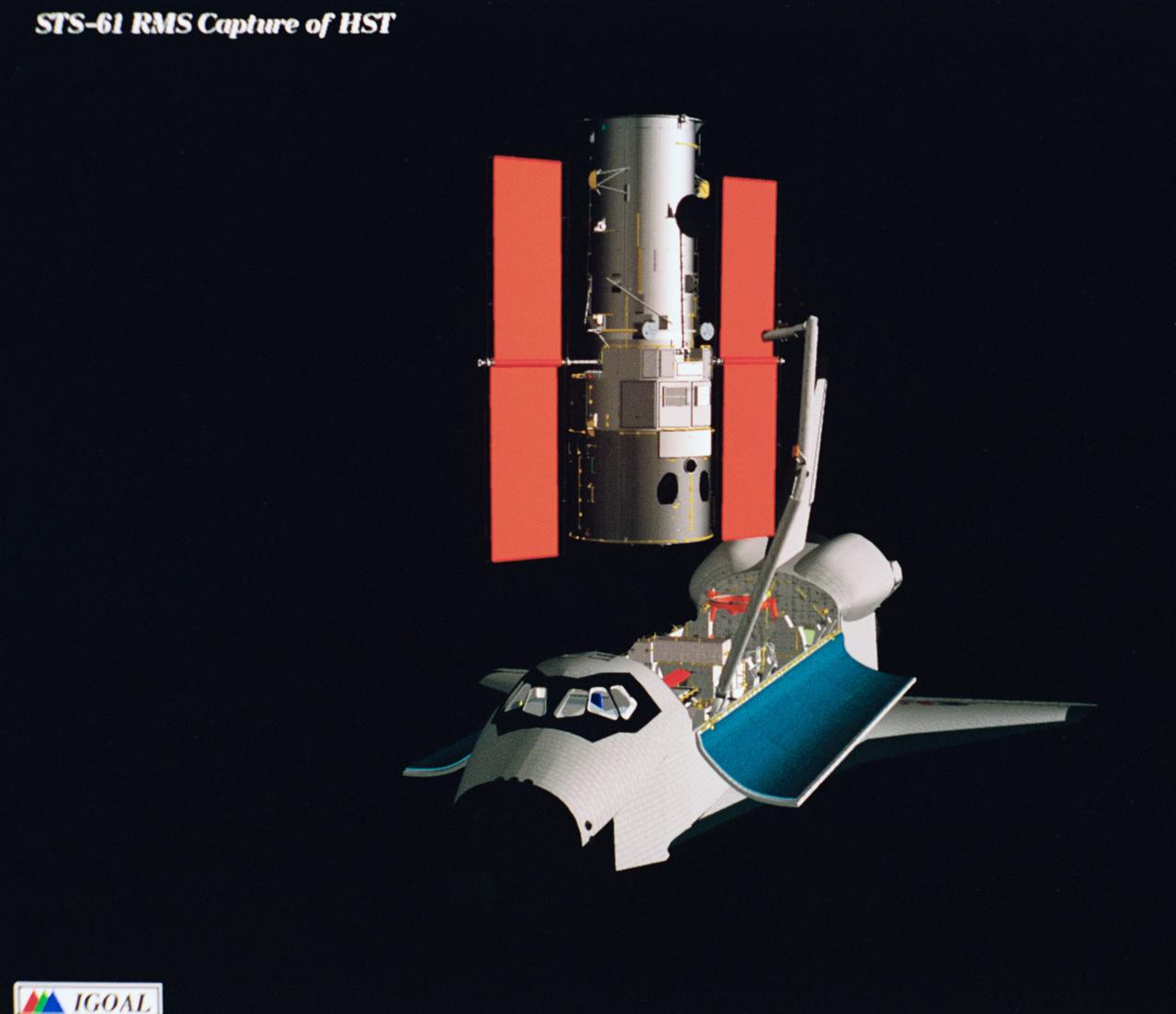
Computer generated scenes depicting the Hubble Space Telescope capture and a sequence of planned events on the planned extravehicular activity (EVA). Scenes include the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm assisting two astronauts changing out the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC) (48699); RMS arm assisting in the temporary mating of the orbiting telescope to the flight support system in Endeavour's cargo bay (48700); Endeavour's RMS arm assisting in the "capture" of the orbiting telescope (48701); Two astronauts changing out the telescope's coprocessor (48702); RMS arm assistign two astronauts replacing one of the telescope's electronic control units (48703); RMS assisting two astronauts replacing the fuse plugs on the telescope's Power Distribution Unit (PDU) (48704); The telescope's High Resolution Spectrograph (HRS) kit is depicted in this scene (48705); Two astronauts during the removal of the high speed photometer and the installation of the COSTAR instrument (48706); Two astronauts, standing on the RMS, during installation of one of the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) (48707); High angle view of the orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour with its cargo bay doors open, revealing the bay's pre-capture configuration. Seen are, from the left, the Solar Array Carrier, the ORU Carrier and the flight support system (48708); Two astronauts performing the replacement of HST's Rate Sensor Units (RSU) (48709); The RMS arm assisting two astronauts with the replacement of the telescope's solar array panels (48710); Two astronauts replacing the telescope's Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) (48711).
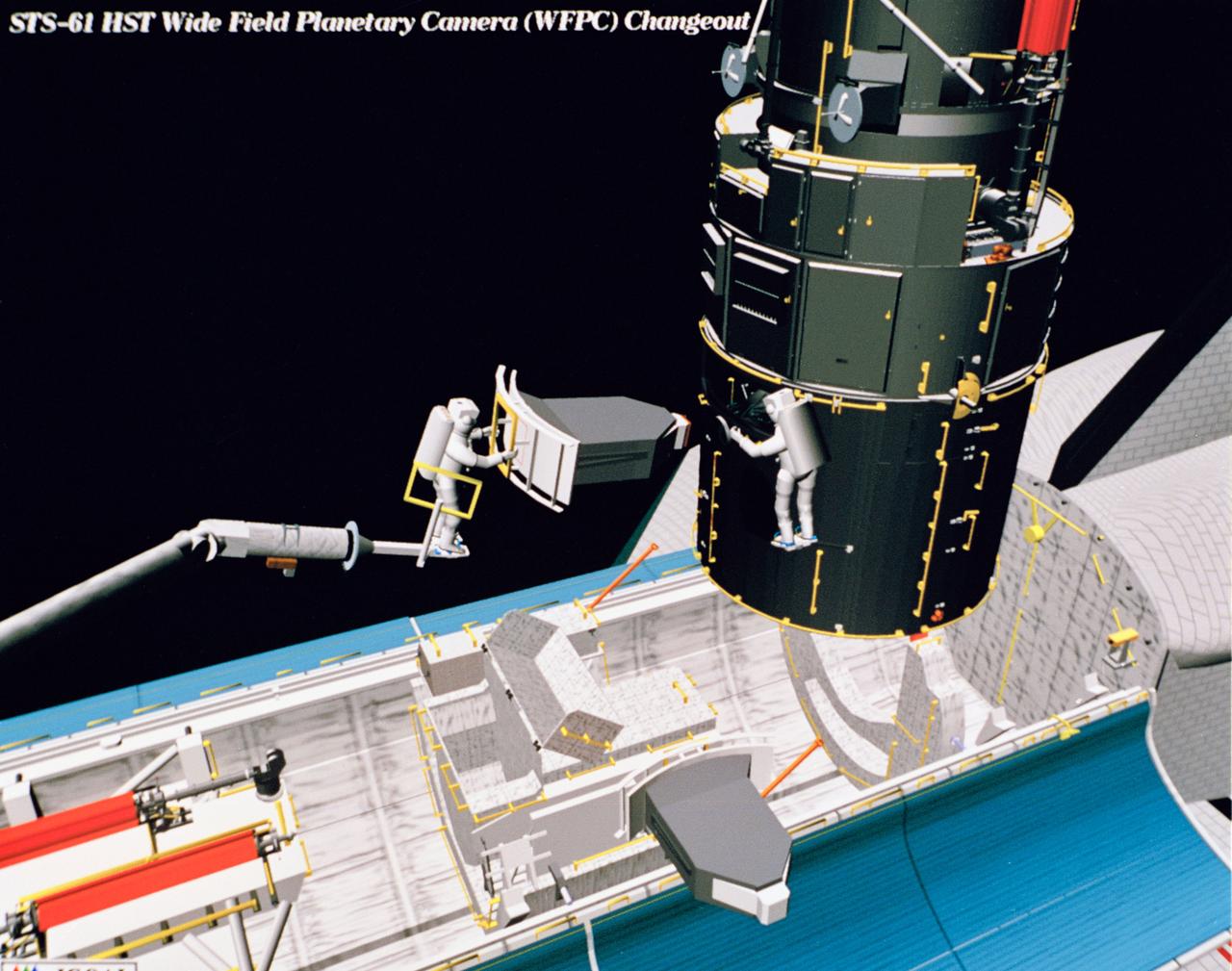
Computer generated scenes depicting the Hubble Space Telescope capture and a sequence of planned events on the planned extravehicular activity (EVA). Scenes include the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm assisting two astronauts changing out the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC) (48699); RMS arm assisting in the temporary mating of the orbiting telescope to the flight support system in Endeavour's cargo bay (48700); Endeavour's RMS arm assisting in the "capture" of the orbiting telescope (48701); Two astronauts changing out the telescope's coprocessor (48702); RMS arm assistign two astronauts replacing one of the telescope's electronic control units (48703); RMS assisting two astronauts replacing the fuse plugs on the telescope's Power Distribution Unit (PDU) (48704); The telescope's High Resolution Spectrograph (HRS) kit is depicted in this scene (48705); Two astronauts during the removal of the high speed photometer and the installation of the COSTAR instrument (48706); Two astronauts, standing on the RMS, during installation of one of the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) (48707); High angle view of the orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour with its cargo bay doors open, revealing the bay's pre-capture configuration. Seen are, from the left, the Solar Array Carrier, the ORU Carrier and the flight support system (48708); Two astronauts performing the replacement of HST's Rate Sensor Units (RSU) (48709); The RMS arm assisting two astronauts with the replacement of the telescope's solar array panels (48710); Two astronauts replacing the telescope's Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) (48711).
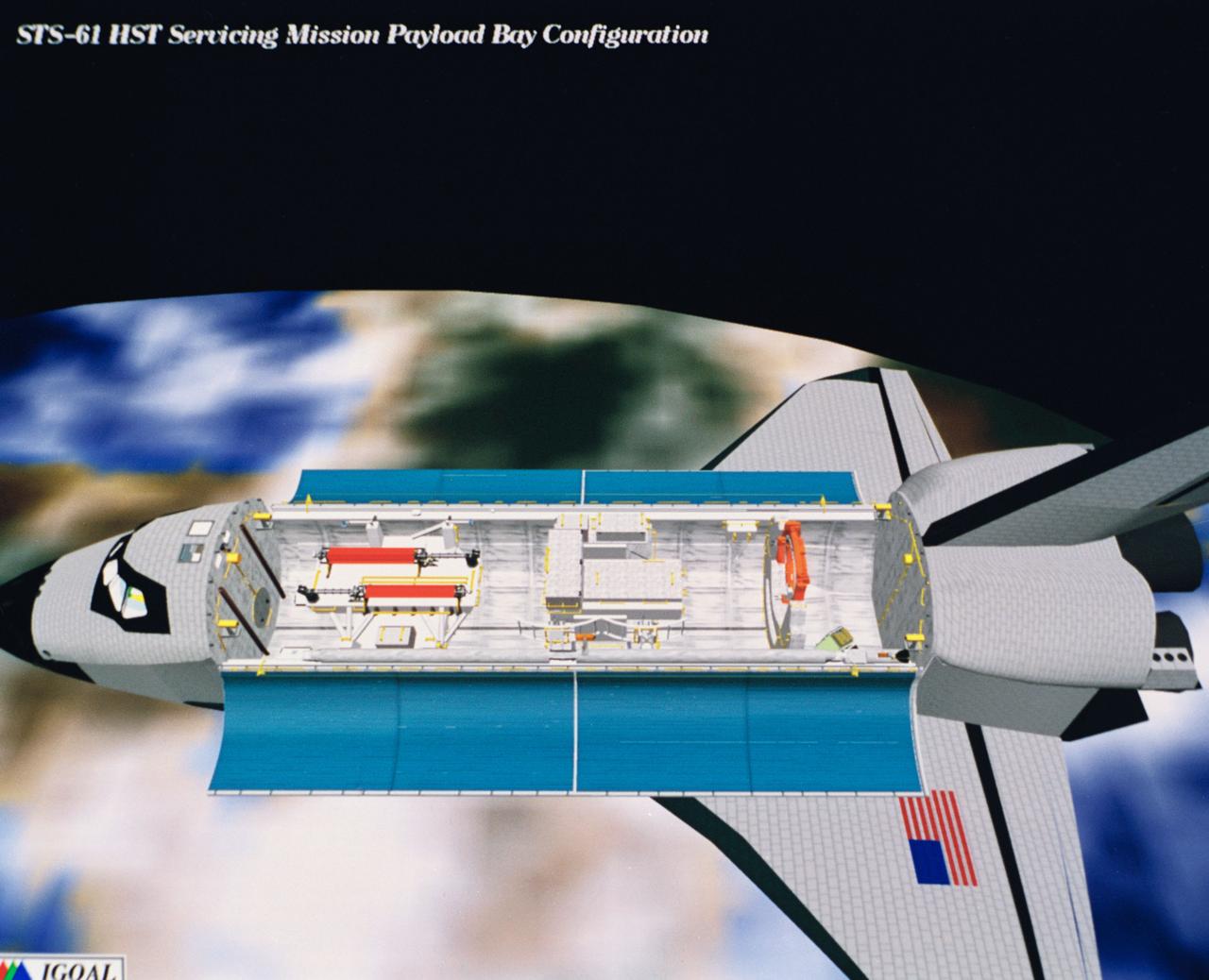
Computer generated scenes depicting the Hubble Space Telescope capture and a sequence of planned events on the planned extravehicular activity (EVA). Scenes include the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm assisting two astronauts changing out the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC) (48699); RMS arm assisting in the temporary mating of the orbiting telescope to the flight support system in Endeavour's cargo bay (48700); Endeavour's RMS arm assisting in the "capture" of the orbiting telescope (48701); Two astronauts changing out the telescope's coprocessor (48702); RMS arm assistign two astronauts replacing one of the telescope's electronic control units (48703); RMS assisting two astronauts replacing the fuse plugs on the telescope's Power Distribution Unit (PDU) (48704); The telescope's High Resolution Spectrograph (HRS) kit is depicted in this scene (48705); Two astronauts during the removal of the high speed photometer and the installation of the COSTAR instrument (48706); Two astronauts, standing on the RMS, during installation of one of the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) (48707); High angle view of the orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour with its cargo bay doors open, revealing the bay's pre-capture configuration. Seen are, from the left, the Solar Array Carrier, the ORU Carrier and the flight support system (48708); Two astronauts performing the replacement of HST's Rate Sensor Units (RSU) (48709); The RMS arm assisting two astronauts with the replacement of the telescope's solar array panels (48710); Two astronauts replacing the telescope's Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) (48711).
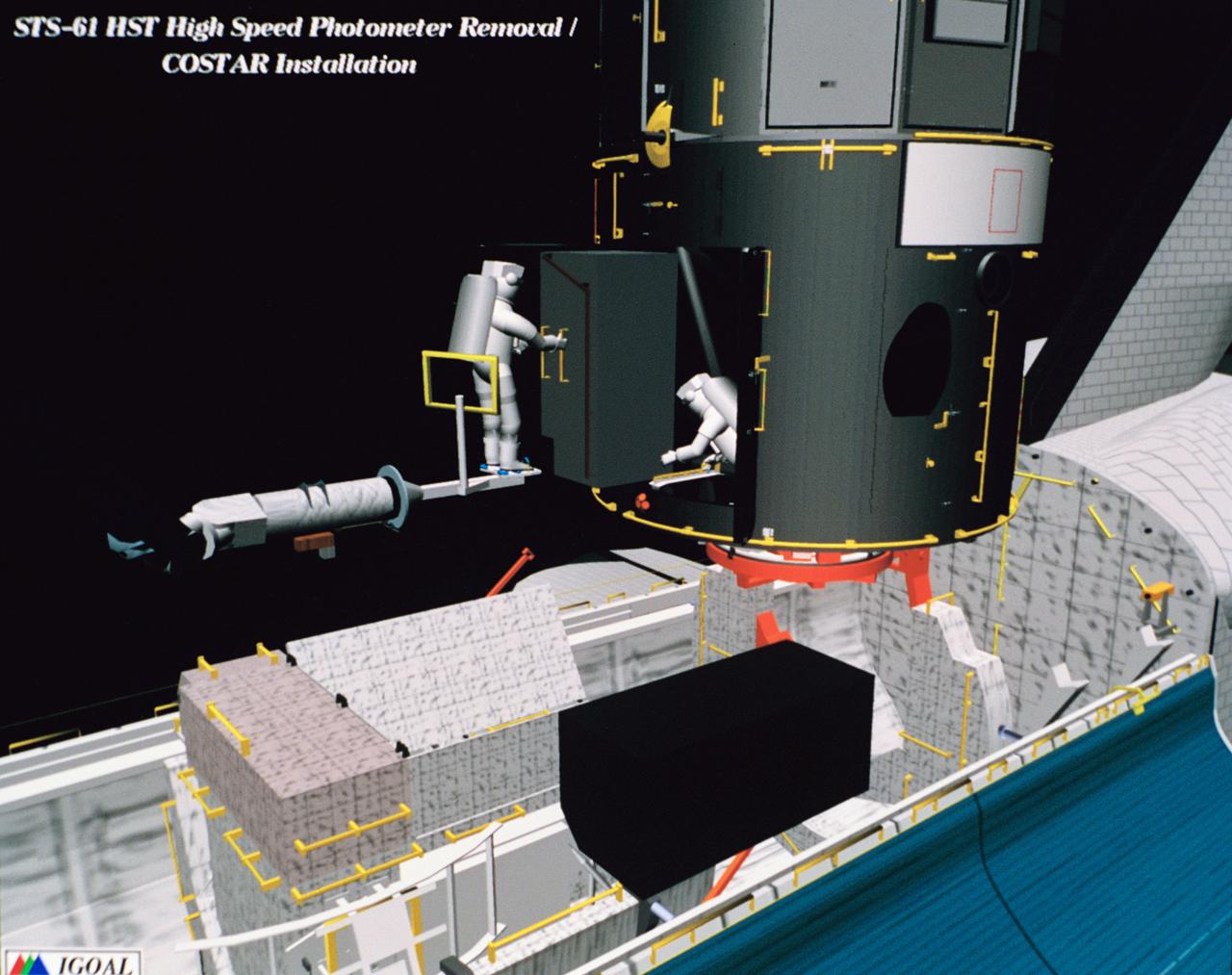
Computer generated scenes depicting the Hubble Space Telescope capture and a sequence of planned events on the planned extravehicular activity (EVA). Scenes include the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm assisting two astronauts changing out the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC) (48699); RMS arm assisting in the temporary mating of the orbiting telescope to the flight support system in Endeavour's cargo bay (48700); Endeavour's RMS arm assisting in the "capture" of the orbiting telescope (48701); Two astronauts changing out the telescope's coprocessor (48702); RMS arm assistign two astronauts replacing one of the telescope's electronic control units (48703); RMS assisting two astronauts replacing the fuse plugs on the telescope's Power Distribution Unit (PDU) (48704); The telescope's High Resolution Spectrograph (HRS) kit is depicted in this scene (48705); Two astronauts during the removal of the high speed photometer and the installation of the COSTAR instrument (48706); Two astronauts, standing on the RMS, during installation of one of the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) (48707); High angle view of the orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour with its cargo bay doors open, revealing the bay's pre-capture configuration. Seen are, from the left, the Solar Array Carrier, the ORU Carrier and the flight support system (48708); Two astronauts performing the replacement of HST's Rate Sensor Units (RSU) (48709); The RMS arm assisting two astronauts with the replacement of the telescope's solar array panels (48710); Two astronauts replacing the telescope's Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) (48711).
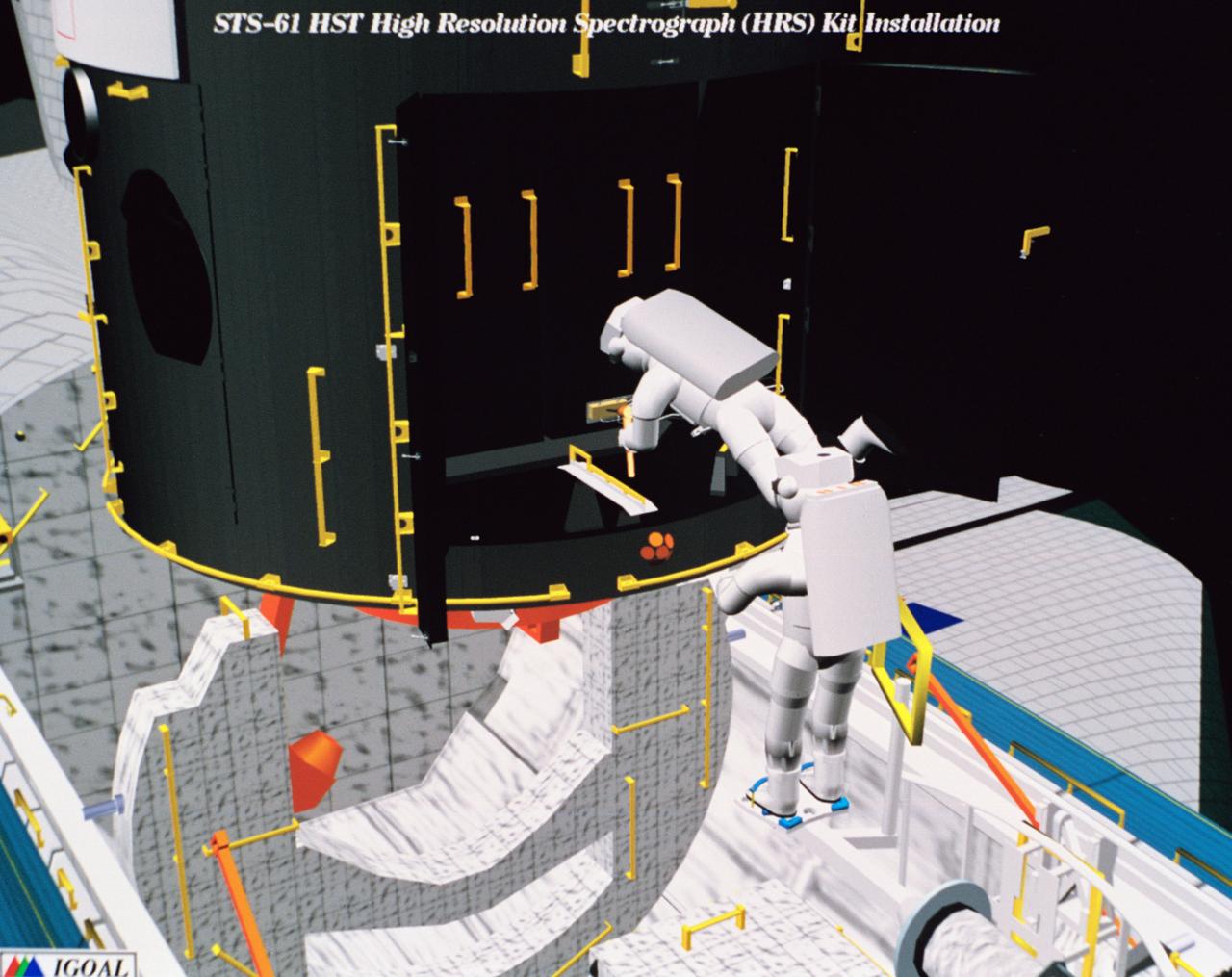
Computer generated scenes depicting the Hubble Space Telescope capture and a sequence of planned events on the planned extravehicular activity (EVA). Scenes include the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm assisting two astronauts changing out the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC) (48699); RMS arm assisting in the temporary mating of the orbiting telescope to the flight support system in Endeavour's cargo bay (48700); Endeavour's RMS arm assisting in the "capture" of the orbiting telescope (48701); Two astronauts changing out the telescope's coprocessor (48702); RMS arm assistign two astronauts replacing one of the telescope's electronic control units (48703); RMS assisting two astronauts replacing the fuse plugs on the telescope's Power Distribution Unit (PDU) (48704); The telescope's High Resolution Spectrograph (HRS) kit is depicted in this scene (48705); Two astronauts during the removal of the high speed photometer and the installation of the COSTAR instrument (48706); Two astronauts, standing on the RMS, during installation of one of the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) (48707); High angle view of the orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour with its cargo bay doors open, revealing the bay's pre-capture configuration. Seen are, from the left, the Solar Array Carrier, the ORU Carrier and the flight support system (48708); Two astronauts performing the replacement of HST's Rate Sensor Units (RSU) (48709); The RMS arm assisting two astronauts with the replacement of the telescope's solar array panels (48710); Two astronauts replacing the telescope's Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) (48711).
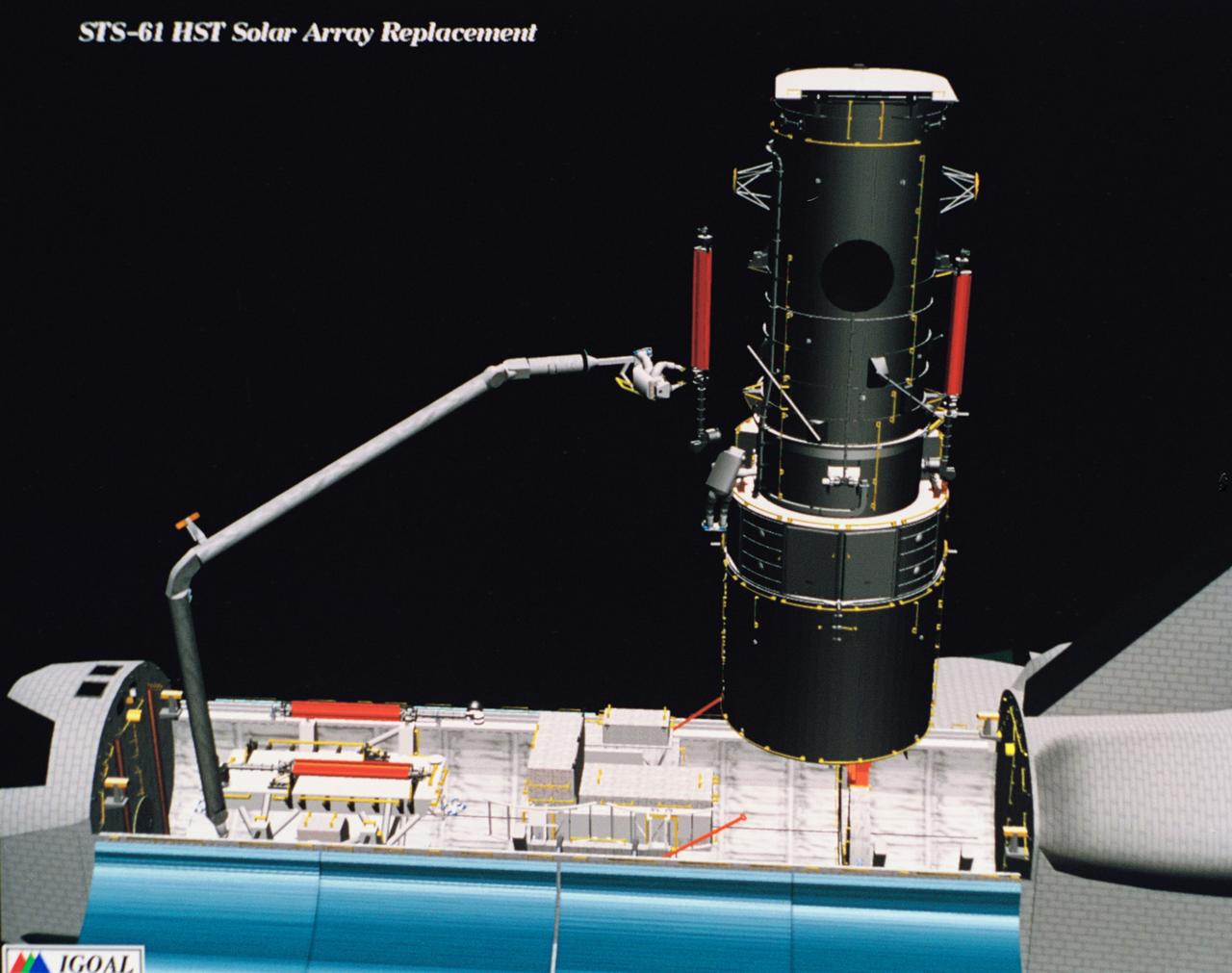
Computer generated scenes depicting the Hubble Space Telescope capture and a sequence of planned events on the planned extravehicular activity (EVA). Scenes include the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm assisting two astronauts changing out the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC) (48699); RMS arm assisting in the temporary mating of the orbiting telescope to the flight support system in Endeavour's cargo bay (48700); Endeavour's RMS arm assisting in the "capture" of the orbiting telescope (48701); Two astronauts changing out the telescope's coprocessor (48702); RMS arm assistign two astronauts replacing one of the telescope's electronic control units (48703); RMS assisting two astronauts replacing the fuse plugs on the telescope's Power Distribution Unit (PDU) (48704); The telescope's High Resolution Spectrograph (HRS) kit is depicted in this scene (48705); Two astronauts during the removal of the high speed photometer and the installation of the COSTAR instrument (48706); Two astronauts, standing on the RMS, during installation of one of the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) (48707); High angle view of the orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour with its cargo bay doors open, revealing the bay's pre-capture configuration. Seen are, from the left, the Solar Array Carrier, the ORU Carrier and the flight support system (48708); Two astronauts performing the replacement of HST's Rate Sensor Units (RSU) (48709); The RMS arm assisting two astronauts with the replacement of the telescope's solar array panels (48710); Two astronauts replacing the telescope's Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) (48711).
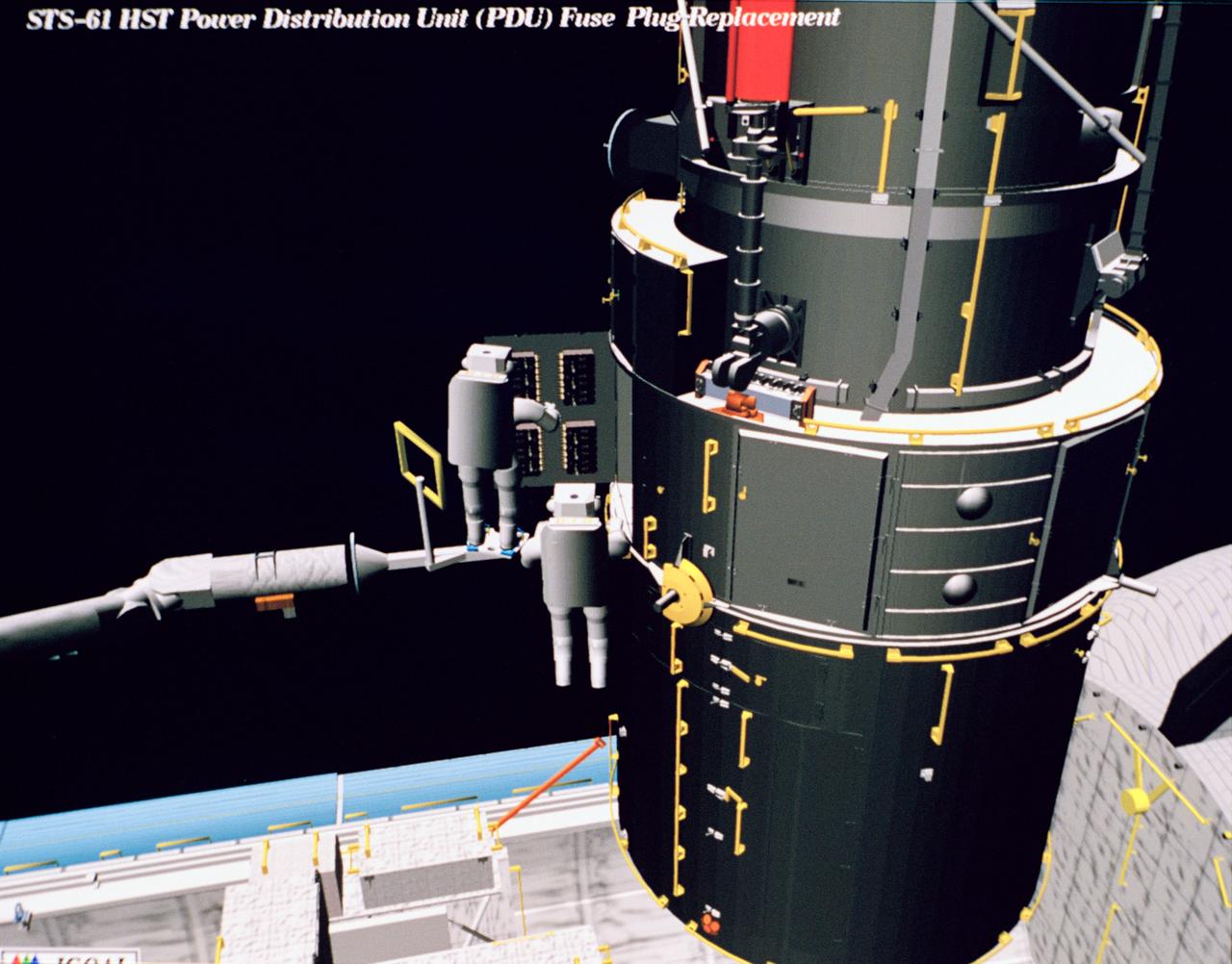
Computer generated scenes depicting the Hubble Space Telescope capture and a sequence of planned events on the planned extravehicular activity (EVA). Scenes include the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm assisting two astronauts changing out the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC) (48699); RMS arm assisting in the temporary mating of the orbiting telescope to the flight support system in Endeavour's cargo bay (48700); Endeavour's RMS arm assisting in the "capture" of the orbiting telescope (48701); Two astronauts changing out the telescope's coprocessor (48702); RMS arm assistign two astronauts replacing one of the telescope's electronic control units (48703); RMS assisting two astronauts replacing the fuse plugs on the telescope's Power Distribution Unit (PDU) (48704); The telescope's High Resolution Spectrograph (HRS) kit is depicted in this scene (48705); Two astronauts during the removal of the high speed photometer and the installation of the COSTAR instrument (48706); Two astronauts, standing on the RMS, during installation of one of the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) (48707); High angle view of the orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour with its cargo bay doors open, revealing the bay's pre-capture configuration. Seen are, from the left, the Solar Array Carrier, the ORU Carrier and the flight support system (48708); Two astronauts performing the replacement of HST's Rate Sensor Units (RSU) (48709); The RMS arm assisting two astronauts with the replacement of the telescope's solar array panels (48710); Two astronauts replacing the telescope's Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) (48711).
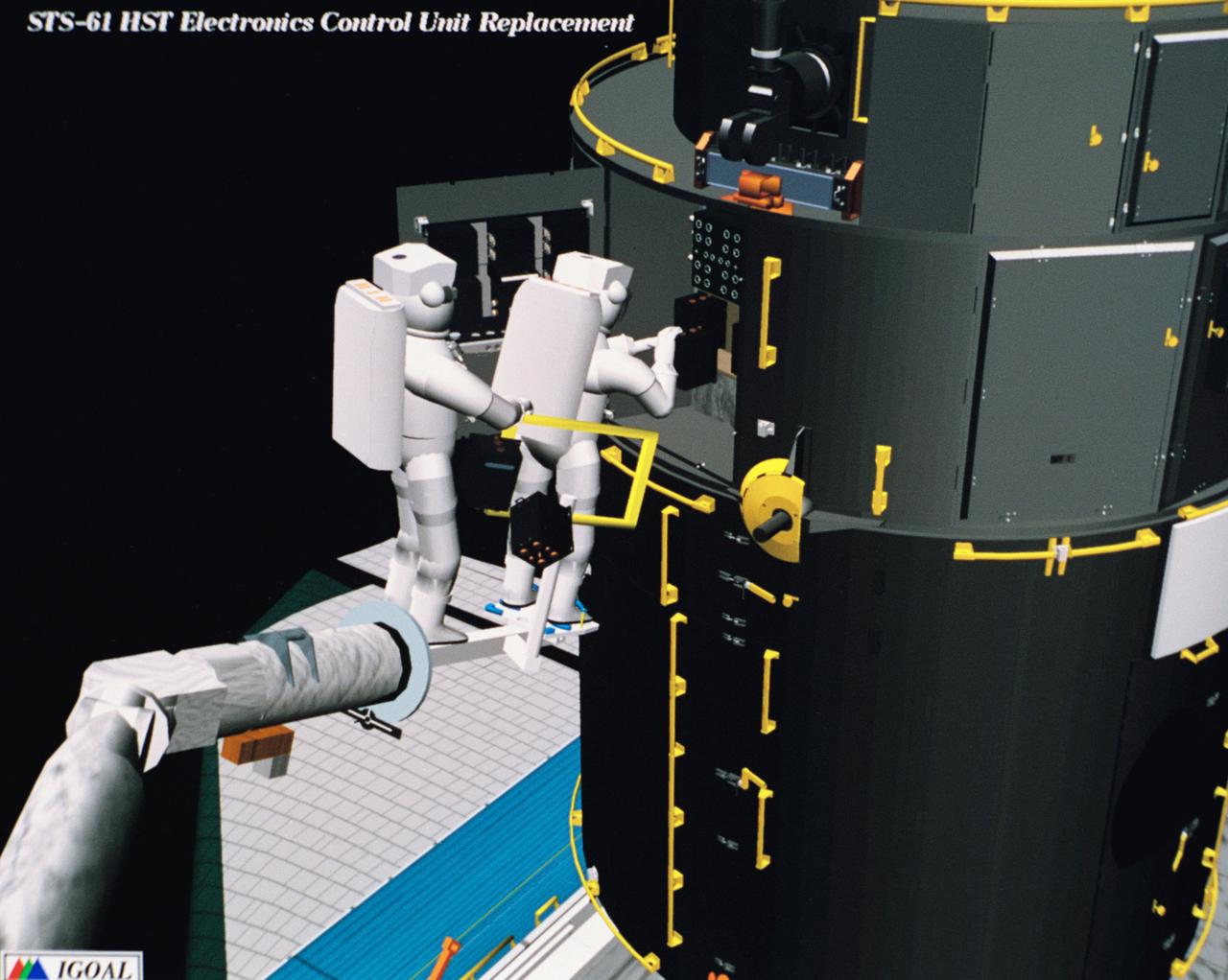
Computer generated scenes depicting the Hubble Space Telescope capture and a sequence of planned events on the planned extravehicular activity (EVA). Scenes include the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm assisting two astronauts changing out the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC) (48699); RMS arm assisting in the temporary mating of the orbiting telescope to the flight support system in Endeavour's cargo bay (48700); Endeavour's RMS arm assisting in the "capture" of the orbiting telescope (48701); Two astronauts changing out the telescope's coprocessor (48702); RMS arm assistign two astronauts replacing one of the telescope's electronic control units (48703); RMS assisting two astronauts replacing the fuse plugs on the telescope's Power Distribution Unit (PDU) (48704); The telescope's High Resolution Spectrograph (HRS) kit is depicted in this scene (48705); Two astronauts during the removal of the high speed photometer and the installation of the COSTAR instrument (48706); Two astronauts, standing on the RMS, during installation of one of the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) (48707); High angle view of the orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour with its cargo bay doors open, revealing the bay's pre-capture configuration. Seen are, from the left, the Solar Array Carrier, the ORU Carrier and the flight support system (48708); Two astronauts performing the replacement of HST's Rate Sensor Units (RSU) (48709); The RMS arm assisting two astronauts with the replacement of the telescope's solar array panels (48710); Two astronauts replacing the telescope's Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) (48711).

Computer generated scenes depicting the Hubble Space Telescope capture and a sequence of planned events on the planned extravehicular activity (EVA). Scenes include the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm assisting two astronauts changing out the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC) (48699); RMS arm assisting in the temporary mating of the orbiting telescope to the flight support system in Endeavour's cargo bay (48700); Endeavour's RMS arm assisting in the "capture" of the orbiting telescope (48701); Two astronauts changing out the telescope's coprocessor (48702); RMS arm assistign two astronauts replacing one of the telescope's electronic control units (48703); RMS assisting two astronauts replacing the fuse plugs on the telescope's Power Distribution Unit (PDU) (48704); The telescope's High Resolution Spectrograph (HRS) kit is depicted in this scene (48705); Two astronauts during the removal of the high speed photometer and the installation of the COSTAR instrument (48706); Two astronauts, standing on the RMS, during installation of one of the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) (48707); High angle view of the orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour with its cargo bay doors open, revealing the bay's pre-capture configuration. Seen are, from the left, the Solar Array Carrier, the ORU Carrier and the flight support system (48708); Two astronauts performing the replacement of HST's Rate Sensor Units (RSU) (48709); The RMS arm assisting two astronauts with the replacement of the telescope's solar array panels (48710); Two astronauts replacing the telescope's Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) (48711).
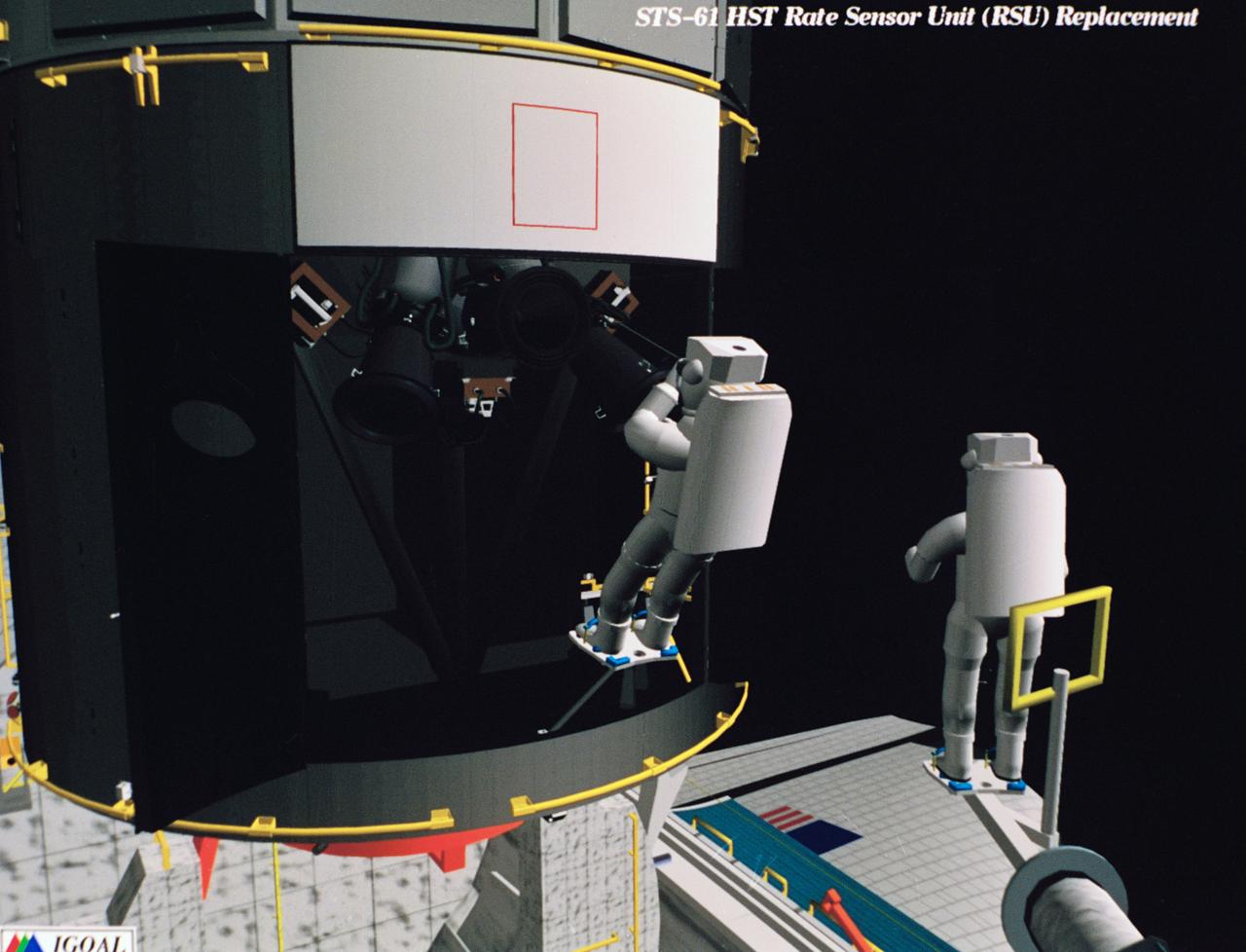

Computer generated scenes depicting the Hubble Space Telescope capture and a sequence of planned events on the planned extravehicular activity (EVA). Scenes include the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm assisting two astronauts changing out the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC) (48699); RMS arm assisting in the temporary mating of the orbiting telescope to the flight support system in Endeavour's cargo bay (48700); Endeavour's RMS arm assisting in the "capture" of the orbiting telescope (48701); Two astronauts changing out the telescope's coprocessor (48702); RMS arm assistign two astronauts replacing one of the telescope's electronic control units (48703); RMS assisting two astronauts replacing the fuse plugs on the telescope's Power Distribution Unit (PDU) (48704); The telescope's High Resolution Spectrograph (HRS) kit is depicted in this scene (48705); Two astronauts during the removal of the high speed photometer and the installation of the COSTAR instrument (48706); Two astronauts, standing on the RMS, during installation of one of the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) (48707); High angle view of the orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour with its cargo bay doors open, revealing the bay's pre-capture configuration. Seen are, from the left, the Solar Array Carrier, the ORU Carrier and the flight support system (48708); Two astronauts performing the replacement of HST's Rate Sensor Units (RSU) (48709); The RMS arm assisting two astronauts with the replacement of the telescope's solar array panels (48710); Two astronauts replacing the telescope's Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) (48711).

Computer generated scenes depicting the Hubble Space Telescope capture and a sequence of planned events on the planned extravehicular activity (EVA). Scenes include the Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm assisting two astronauts changing out the Wide Field/Planetary Camera (WF/PC) (48699); RMS arm assisting in the temporary mating of the orbiting telescope to the flight support system in Endeavour's cargo bay (48700); Endeavour's RMS arm assisting in the "capture" of the orbiting telescope (48701); Two astronauts changing out the telescope's coprocessor (48702); RMS arm assistign two astronauts replacing one of the telescope's electronic control units (48703); RMS assisting two astronauts replacing the fuse plugs on the telescope's Power Distribution Unit (PDU) (48704); The telescope's High Resolution Spectrograph (HRS) kit is depicted in this scene (48705); Two astronauts during the removal of the high speed photometer and the installation of the COSTAR instrument (48706); Two astronauts, standing on the RMS, during installation of one of the Magnetic Sensing System (MSS) (48707); High angle view of the orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour with its cargo bay doors open, revealing the bay's pre-capture configuration. Seen are, from the left, the Solar Array Carrier, the ORU Carrier and the flight support system (48708); Two astronauts performing the replacement of HST's Rate Sensor Units (RSU) (48709); The RMS arm assisting two astronauts with the replacement of the telescope's solar array panels (48710); Two astronauts replacing the telescope's Solar Array Drive Electronics (SADE) (48711).

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-103 Mission Specialist C. Michael Foale (Ph.D.), in his orange launch and entry suit, is assisted by closeout crew members in the White Room before entering the orbiter. At left is United Space Alliance (USA) Orbiter Vehicle Closeout Chief Travis Thompson and USA Mechanical Technician Vinny Defranzo. The White Room is an environmental chamber at the end of the orbiter access arm on the fixed service structure. It provides entry to the orbiter crew compartment. The mission, to service the Hubble Space Telescope, is scheduled to lift off at 7:50 p.m. EST Dec. 19 on mission STS-103, servicing the Hubble Space Telescope. Objectives for the nearly eight-day mission include replacing gyroscopes and an old computer, installing another solid state recorder, and replacing damaged insulation in the telescope. Discovery is expected to land at KSC Monday, Dec. 27, at about 5:24 p.m. EST

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers help guide the Fine Guidance Sensor Scientific Instrument Protective Enclosure, or FSIPE, cover alongside the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, for installation. The ORUC is one of three carriers that are being prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Launch is targeted for Oct. 8. PHoto credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-111 Mission Specialist Philippe Perrin gets ready in his launch and entry suit for a simulated launch countdown at the pad. Perrin is with the French Space Agency. The simulation is part of STS-111 Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities for the STS-111 crew and Expedition 5. The payload on the mission to the International Space Station includes the Mobile Base System, an Orbital Replacement Unit and Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. The Expedition 5 crew is traveling on Endeavour to replace the Expedition 4 crew on the Station. Launch of Endeavour is scheduled for May 30, 2002.
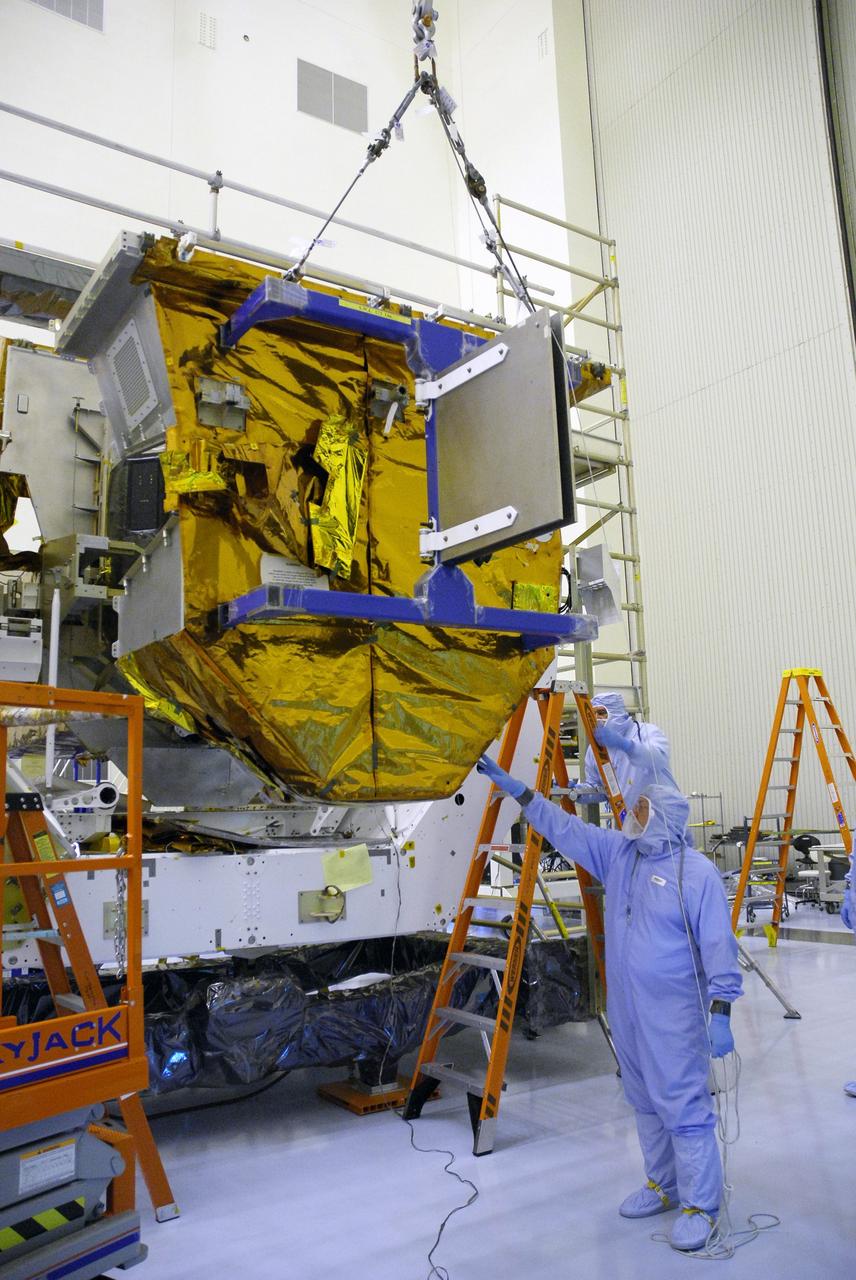

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lowers the Fine Guidance Sensor Scientific Instrument Protective Enclosure, or FSIPE, cover alongside the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, for installation. The ORUC is one of three carriers that are being prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Launch is targeted for Oct. 8. PHoto credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
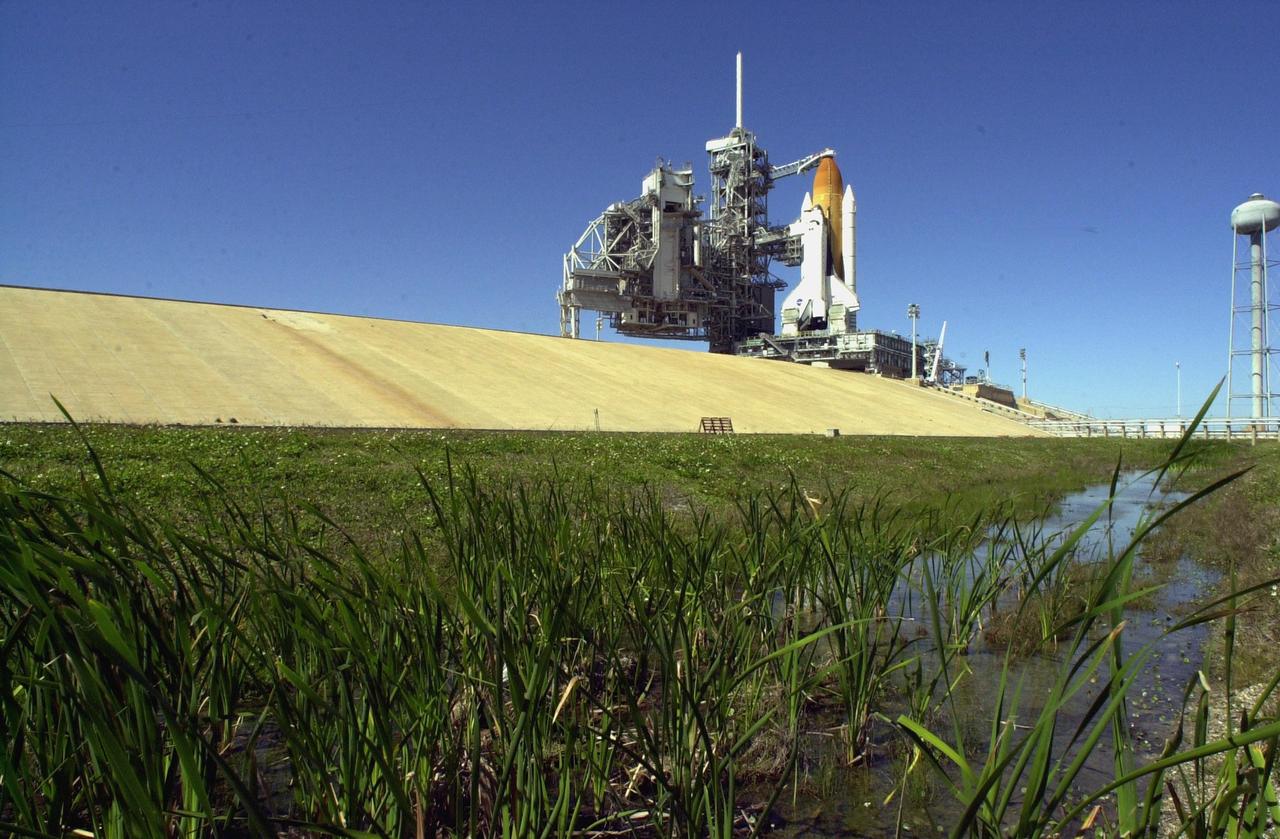

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Rotating Service Structure is rolled back from Space Shuttle Columbia in preparation for launch Feb. 28, 2002, at 6:48 a.m. EST (11:48 GMT) on mission STS-109. In the photo is seen the Orbiter Access Arm stretched to Columbia's cockpit. A Hubble Servicing Mission, the goal of STS-109 is to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the ACS, install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation.
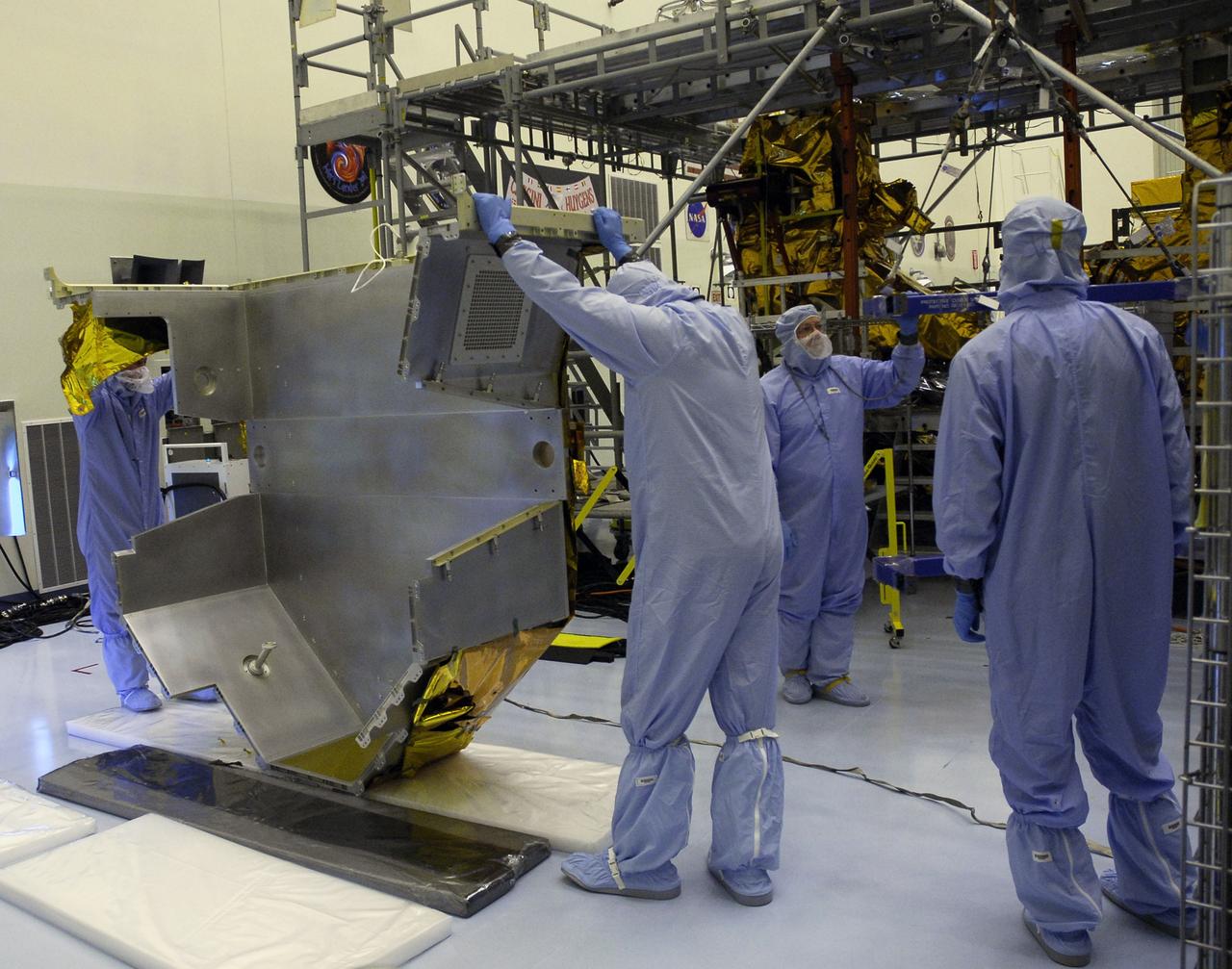

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers lift the Fine Guidance Sensor Scientific Instrument Protective Enclosure, or FSIPE, cover before attaching a crane. The cover will be installed on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC. The ORUC is one of three carriers that are being prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Launch is targeted for Oct. 8. PHoto credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
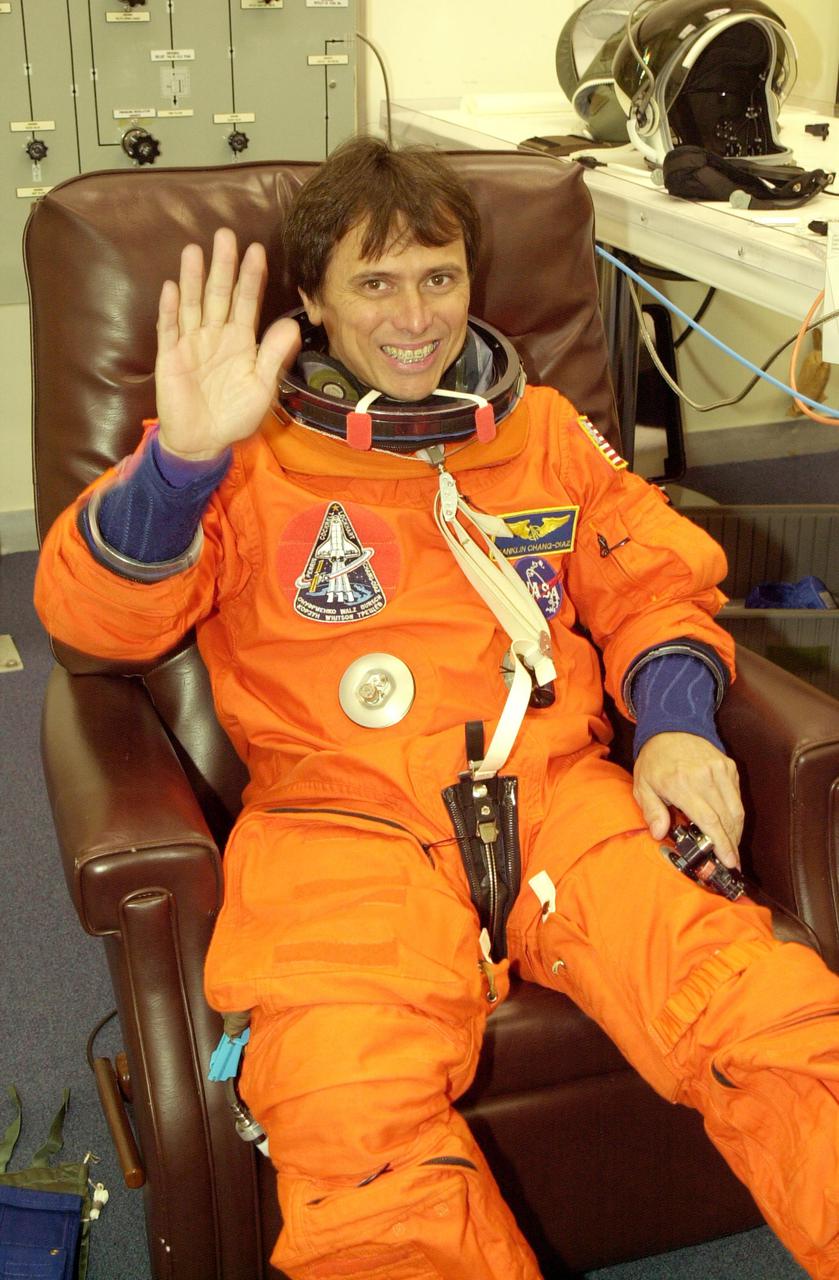

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-111 Mission Specialist Franklin Chang-Diaz waves during suitup, getting ready for a simulated launch countdown at the pad. The simulation is part of STS-111 Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities for the crew and Expedition 5. The payload on the mission to the International Space Station includes the Mobile Base System, an Orbital Replacement Unit and Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. The Expedition 5 crew is traveling on Endeavour to replace the Expedition 4 crew on the Station. Launch of Endeavour is scheduled for May 30, 2002
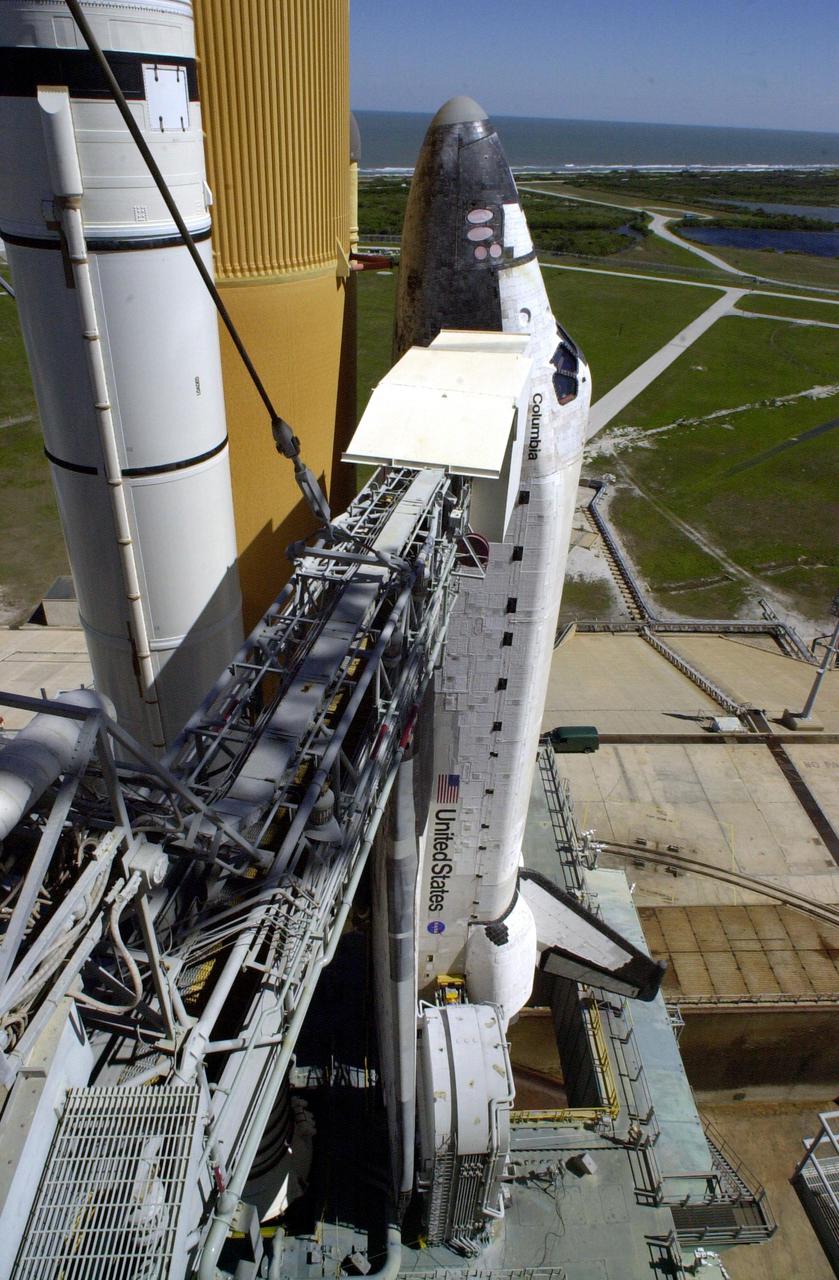

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Rotating Service Structure is rolled back from Space Shuttle Columbia in preparation for launch Feb. 28, 2002, at 6:48 a.m. EST (11:48 GMT) on mission STS-109. In the photo is seen the Orbiter Access Arm stretched to Columbia's cockpit. A Hubble Servicing Mission, the goal is to replace Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replace the Power Control Unit, remove the Faint Object Camera and install the ACS, install the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and install New Outer Blanket Layer insulation.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The orbiter Columbia rolls into the transfer aisle of the Vehicle Assembly Building where it will be mated with the external tank-solid rocket booster stack. Columbia is scheduled to be launched Feb. 28 on mission STS-109, a Hubble Servicing Mission. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the ACS, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation
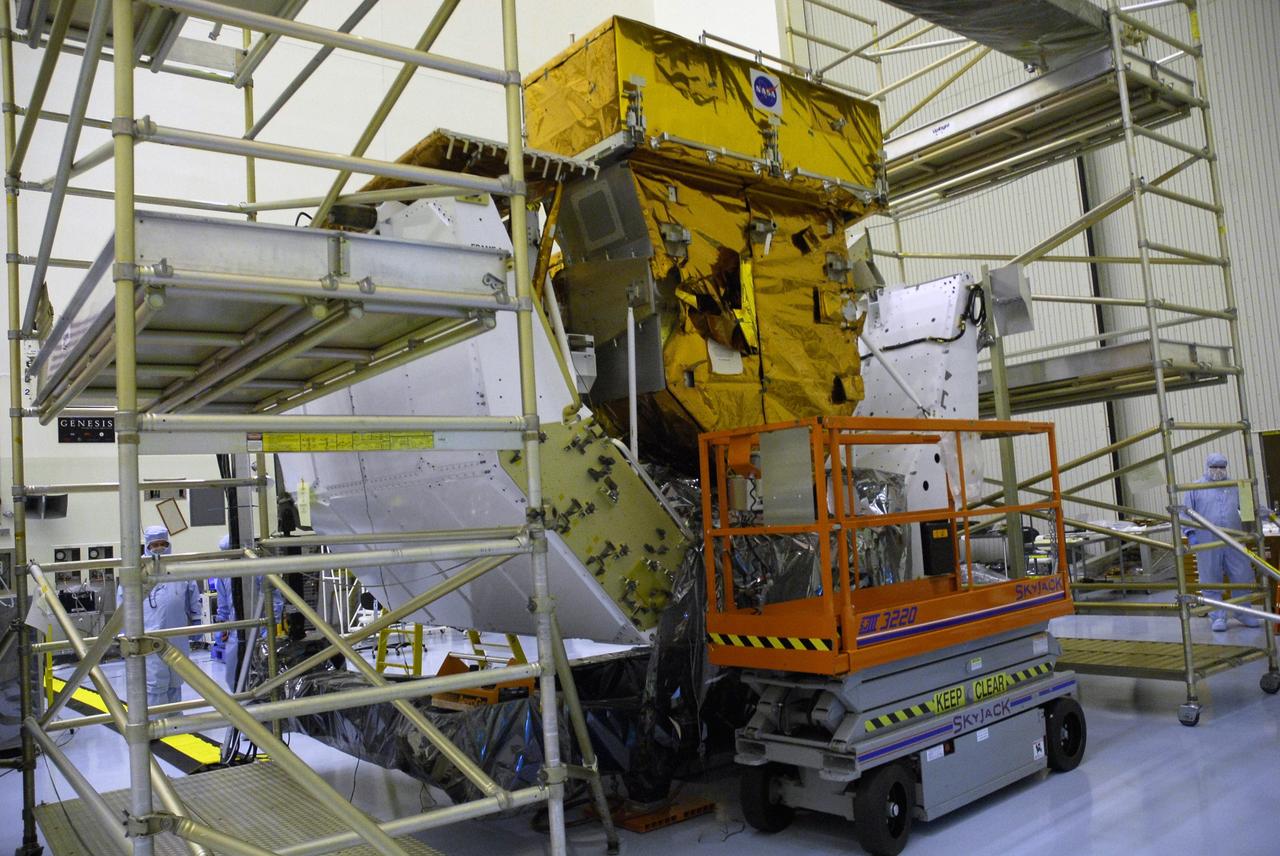

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Fine Guidance Sensor Scientific Instrument Protective Enclosure, or FSIPE, cover has been installed on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC. The ORUC is one of three carriers that are being prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Launch is targeted for Oct. 8. PHoto credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
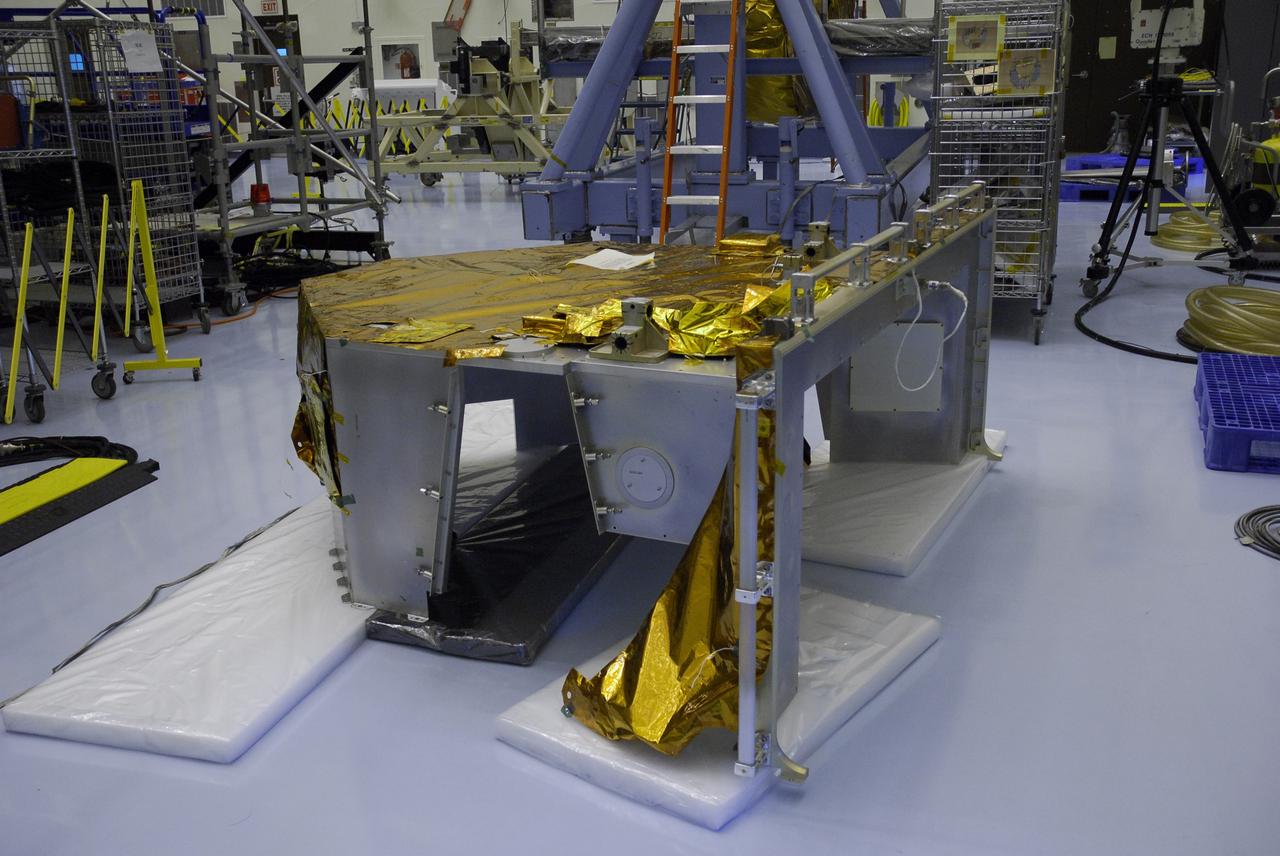

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Fine Guidance Sensor Scientific Instrument Protective Enclosure, or FSIPE, cover awaits a move to be installed on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC. The ORUC is one of three carriers that are being prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Launch is targeted for Oct. 8. PHoto credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
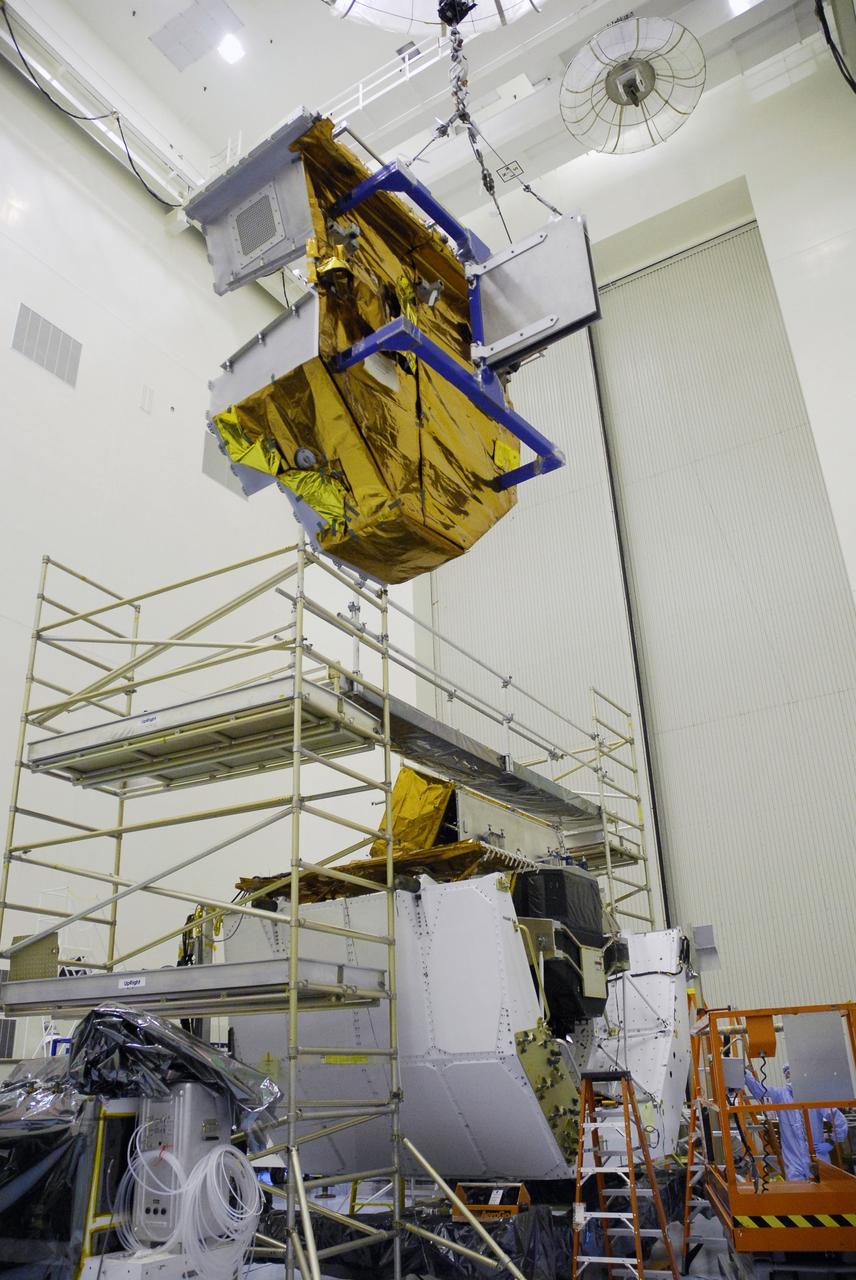

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane moves the Fine Guidance Sensor Scientific Instrument Protective Enclosure, or FSIPE, cover to be installed on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, below. The ORUC is one of three carriers that are being prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Launch is targeted for Oct. 8. PHoto credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
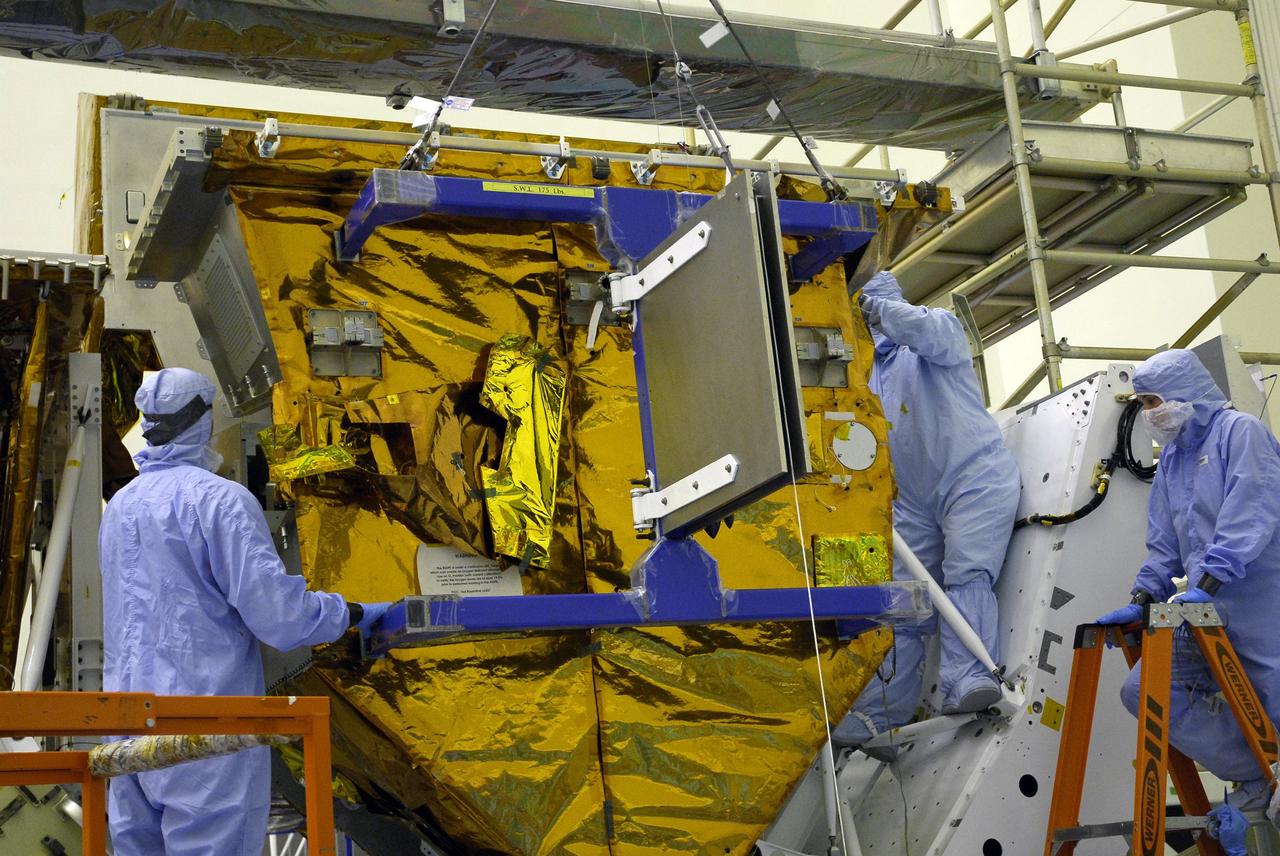

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers help maneuver the Fine Guidance Sensor Scientific Instrument Protective Enclosure, or FSIPE, cover alongside the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, for installation. The ORUC is one of three carriers that are being prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Launch is targeted for Oct. 8. PHoto credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers help maneuver the Fine Guidance Sensor Scientific Instrument Protective Enclosure, or FSIPE, cover into place on the Orbital Replacement Unit Carrier, or ORUC, for installation. The ORUC is one of three carriers that are being prepared for the integration of telescope science instruments, both internal and external replacement components, as well as the flight support equipment to be used by the astronauts during the fifth and final Hubble servicing mission, STS-125. Launch is targeted for Oct. 8. PHoto credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
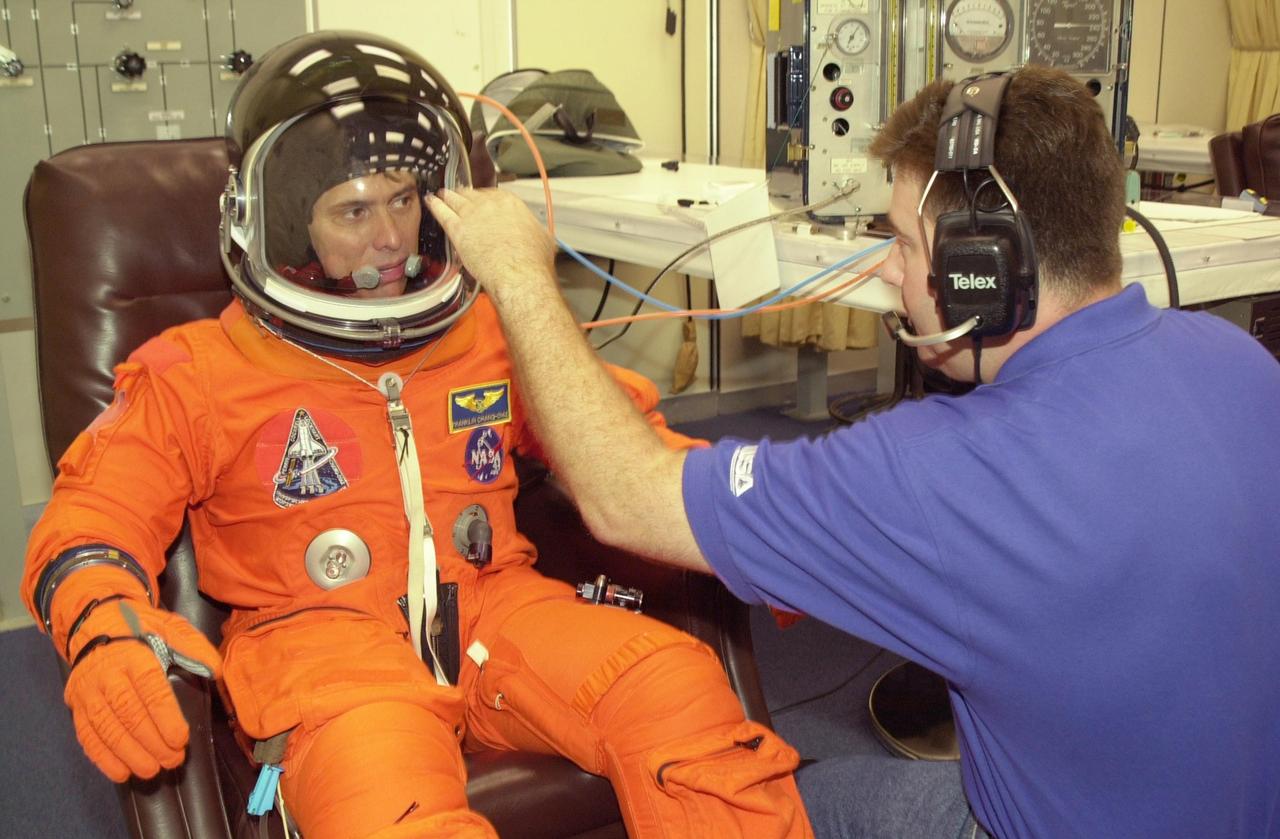

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-111 Mission Specialist Franklin Chang-Diaz gets ready in his launch and entry suit for a simulated launch countdown at the pad. The simulation is part of STS-111 Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities for the crew and Expedition 5. The payload on the mission to the International Space Station includes the Mobile Base System, an Orbital Replacement Unit and Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo. The Expedition 5 crew is traveling on Endeavour to replace the Expedition 4 crew on the Station. Launch of Endeavour is scheduled for May 30, 2002.
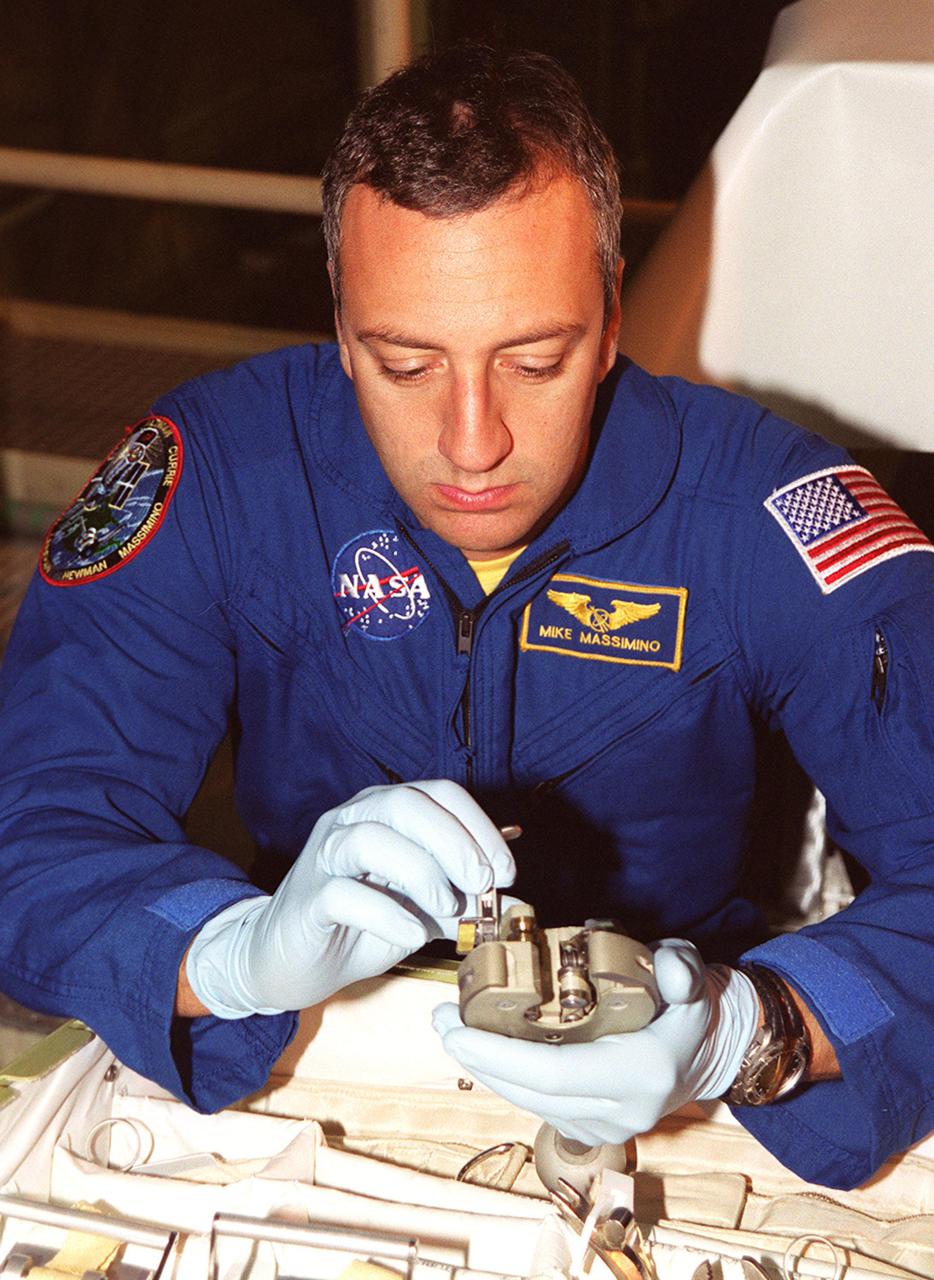

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, Fla. -- STS-109 Mission Specialist Michael Massimino practices on equipment that will be used on the mission. The crew is at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities that include familiarization with the orbiter and equipment. The goal of the mission is to service the HST, replacing Solar Array 2 with Solar Array 3, replacing the Power Control Unit, removing the Faint Object Camera and installing the Advanced Camera for Surveys, installing the Near Infrared Camera and Multi-Object Spectrometer (NICMOS) Cooling System, and installing New Outer Blanket Layer insulation on bays 5 through 8. Mission STS-109 is scheduled for launch Feb. 14, 2002
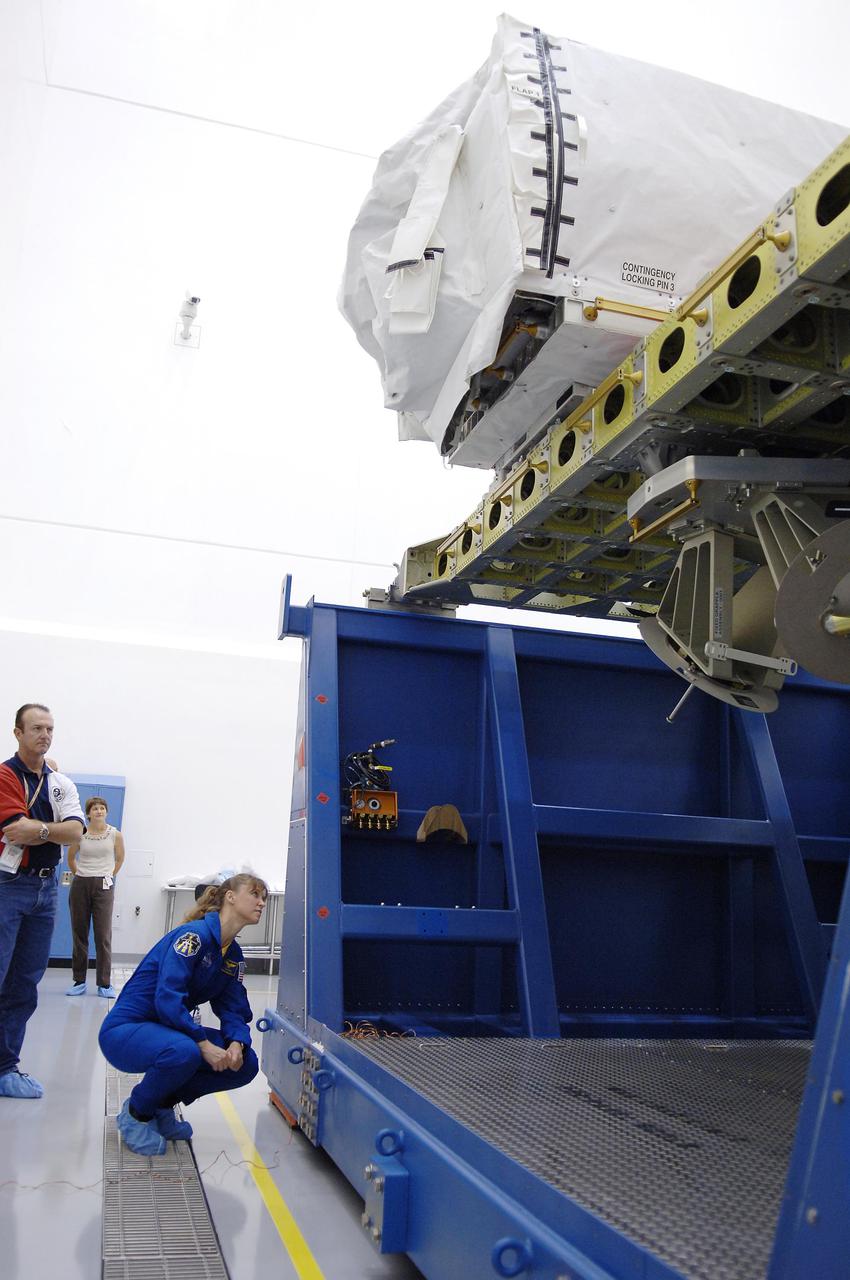

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Fla., STS-121 Mission Specialist Lisa Nowak looks at an orbital replacement unit sitting on the Integrated Cargo Carrier. She and other crew members are at KSC to take part in Crew Equipment Interface Test activities, which provide hands-on experience with equipment they will use on-orbit. STS-121, the second Return to Flight mission, is targeted for launch in a lighted planning window of Sept. 9 to Sept. 25.