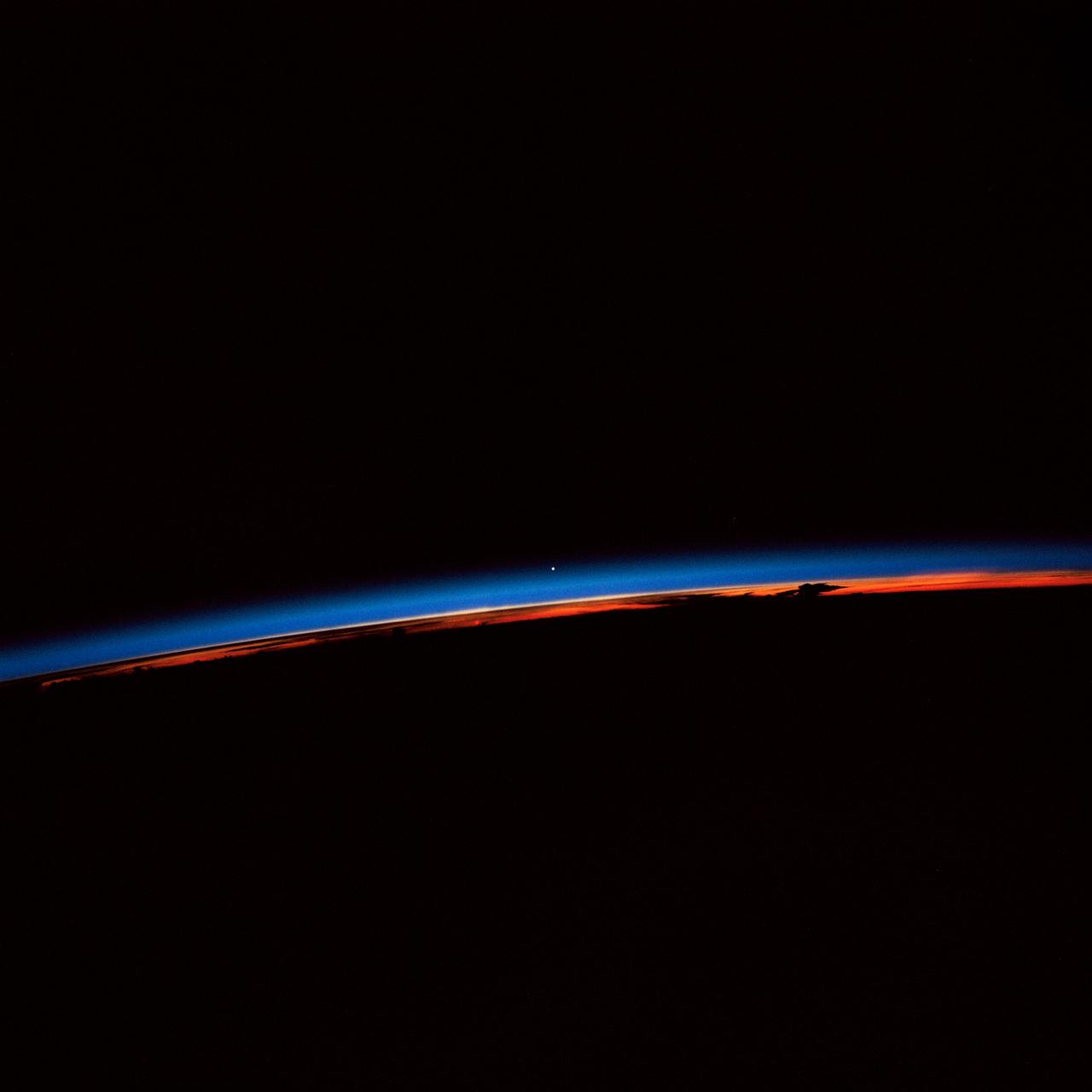

STS-30 Earth observation captured by crewmembers onboard Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104, shows the sunset over the Earth as well as the planet Venus near the center of the frame. Jutting clouds are seen on the horizon, just beneath the blue strip of airglow.
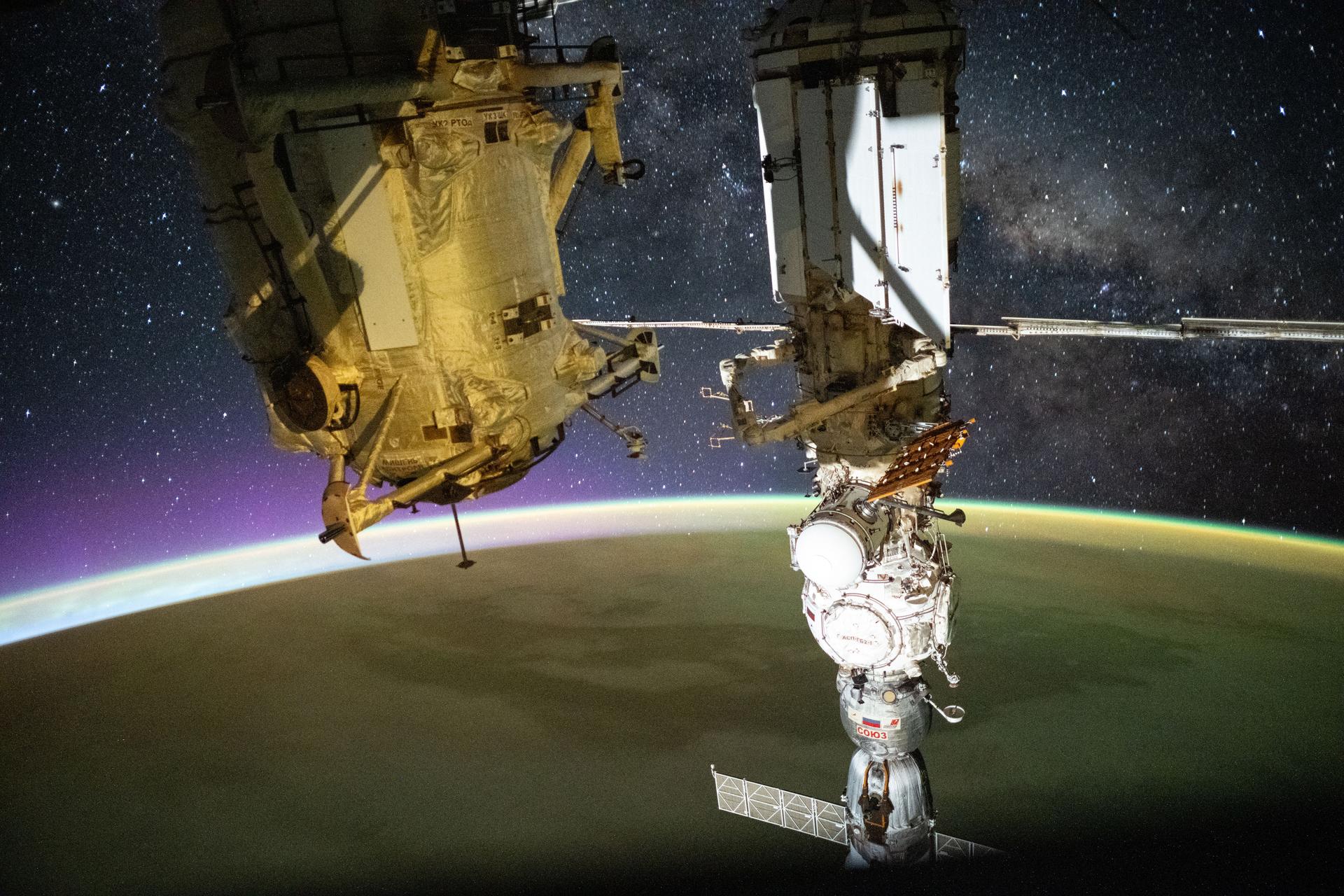

iss073e0880390 (Oct. 13, 2025) --- This long-exposure photograph captures a yellow-green airglow blanketing Earth as an orbital sunrise begins to illuminate the planet’s upper atmosphere. The Milky Way stretches across the star-filled night sky in the background, while the golden-hued Rassvet module and the Soyuz MS-27 crew spacecraft—docked to the Prichal module, itself attached to the Nauka science module—dominate the foreground. The International Space Station was orbiting 268 miles above the South Atlantic Ocean at approximately 2:45 a.m. local time when this photograph was taken.
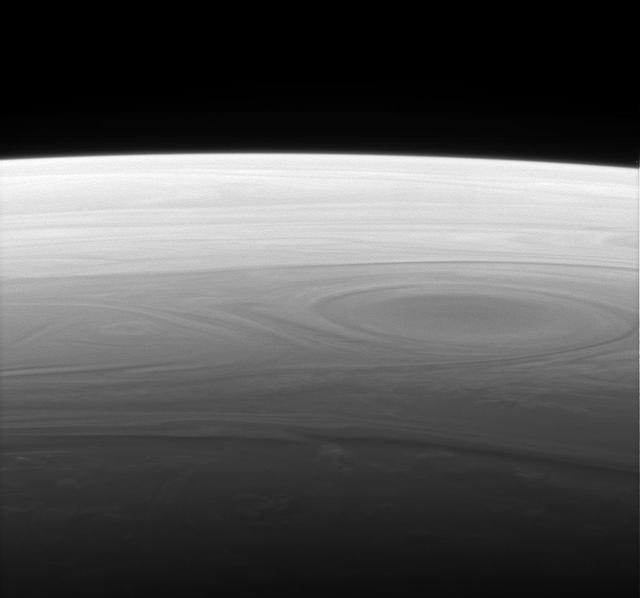
The Cassini spacecraft returns a grand and unique vista of Saturn horizon, reminiscent of the views of our own planet from Earth orbit

This artist concept depicts Kepler-186f, the first validated Earth-size planet to orbit a distant star in the habitable zone, a range of distance from a star where liquid water might pool on the planet surface.

This artist concept depicts the Juno spacecraft which will launch from Earth in 2011 and will arrive at Jupiter in 2016 to study the giant planet from an elliptical, polar orbit.
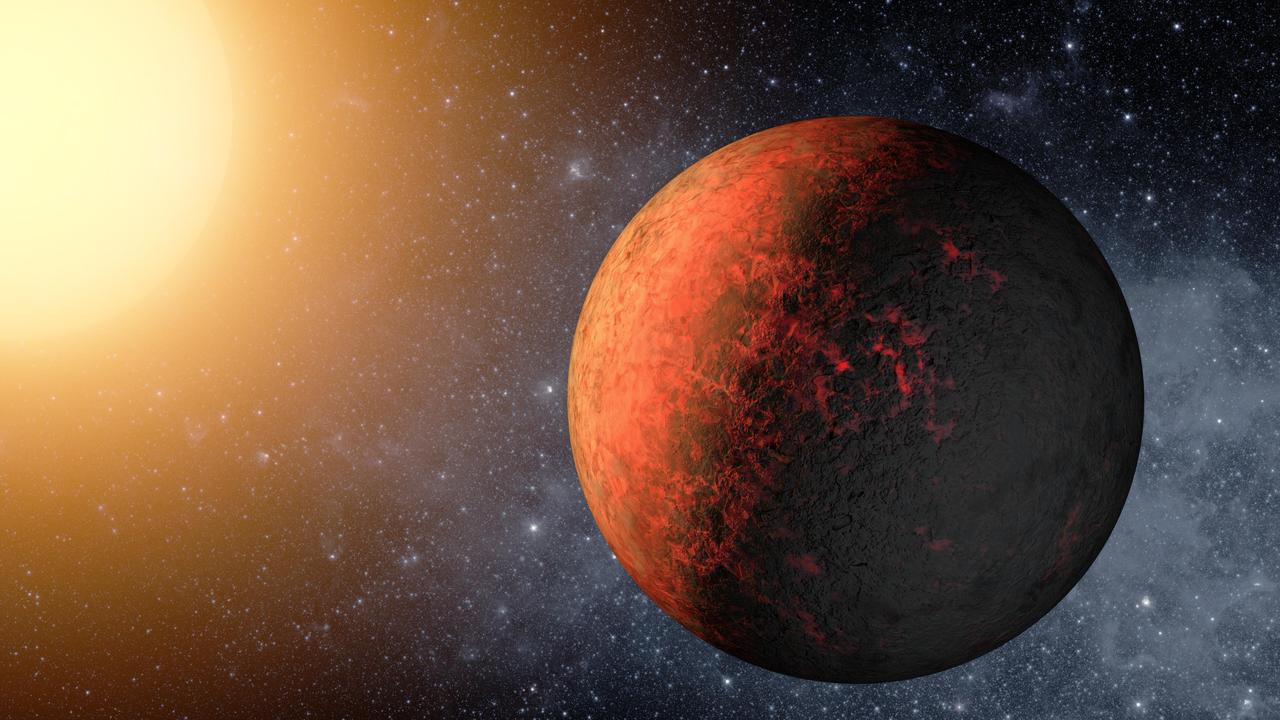
Kepler-20e is the first planet smaller than the Earth discovered to orbit a star other than the sun. A year on Kepler-20e only lasts 6 days, as it is much closer to its host star than the Earth is to the sun.

Kepler data has increased by 20 percent and now totals 2,740 potential planets orbiting 2,036 stars; dramatic increases are seen in the number of Earth-size and super Earth-size candidates discovered.

This artist's concept shows NASA's Kepler Space Telescope on its K2 mission. In July 2016, an international team of astronomers announced they had discovered more than 100 new planets using this telescope. The batch includes four planets in the size range of Earth that are orbiting a single dwarf star, depicted in this illustration. Two of these planets are too hot to support life as we know it, but two are in the star's "habitable" zone, where liquid water could exist on the surface. These small, rocky worlds are far closer to their star than Mercury is to our sun. But because the star is smaller and cooler than ours, its habitable zone is much closer. One of the two planets in the habitable zone, K2-72c, has a "year" about 15 Earth-days long -- the time it takes to complete one orbit. This closer planet is likely about 10 percent warmer than Earth. The slightly more distant planet in the habitable zone, K2-72e, has a year lasting 24 Earth days, and would be about 6 percent colder than Earth. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20698

This illustration shows the seven Earth-size planets of TRAPPIST-1, an exoplanet system about 40 light-years away, based on data current as of February 2018. The image shows the planets' relative sizes but does not represent their orbits to scale. The art highlights possibilities for how the surfaces of these intriguing worlds might look based on their newly calculated properties. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. In the background, slightly distorted versions the familiar constellations of Orion and Taurus are shown as they would appear from the location of TRAPPIST-1 (courtesy of California Academy of Sciences/Dan Tell). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22097

During its flight and lunar orbit, NASA’s Clementine spacecraft returned images of the planet Earth and the Moon. This collection of UVVIS camera Clementine images shows the Earth from the Moon and 3 images of the Earth. The image on the left shows the Earth as seen across the lunar north pole; the large crater in the foreground is Plaskett. The Earth actually appeared about twice as far above the lunar horizon as shown. The top right image shows the Earth as viewed by the UVVIS camera while Clementine was in transit to the Moon; swirling white cloud patterns indicate storms. The two views of southeastern Africa were acquired by the UVVIS camera while Clementine was in low Earth orbit early in the mission. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00432
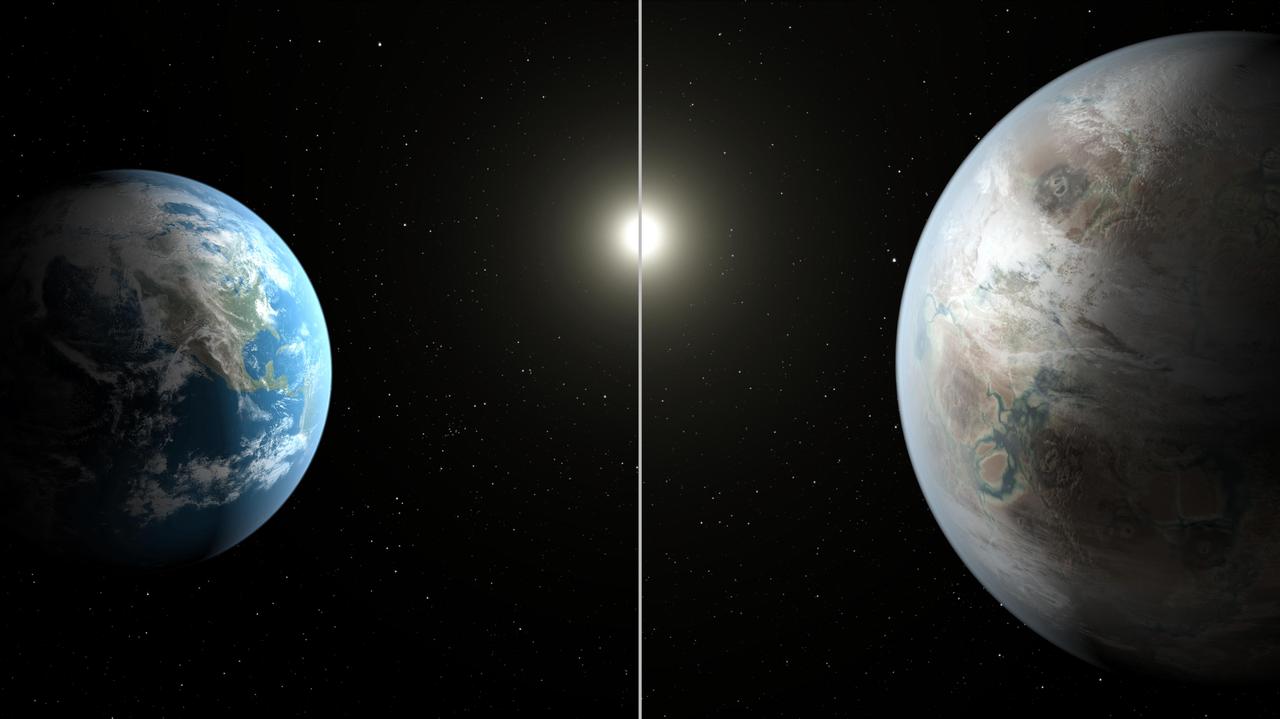
Scientists using data from NASA's Kepler mission have confirmed the first near-Earth-size planet orbiting in the habitable zone of a sun-like star. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures are just right for water to exist in its liquid form. The artist's concept compares Earth (left) to the new planet, called Kepler-452b, which is about 60 percent larger. The illustration represents one possible appearance for Kepler-452b -- scientists do not know whether the planet has oceans and continents like Earth. Both planets orbit a G2-type star of about the same temperature; however, the star hosting Kepler-452b is 6 billion years old, 1.5 billion years older than our sun. As stars age, they become larger, hotter and brighter, as represented in the illustration. Kepler-452b's star appears a bit larger and brighter. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19825

This chart shows, on the top row, artist concepts of the seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 with their orbital periods, distances from their star, radii and masses as compared to those of Earth. On the bottom row, the same numbers are displayed for the bodies of our inner solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The TRAPPIST-1 planets orbit their star extremely closely, with periods ranging from 1.5 to only about 20 days. This is much shorter than the period of Mercury, which orbits our sun in about 88 days. The artist concepts show what the TRAPPIST-1 planetary system may look like, based on available data about their diameters, masses and distances from the host star. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial, according to research published in 2017 in the journal Nature. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21425
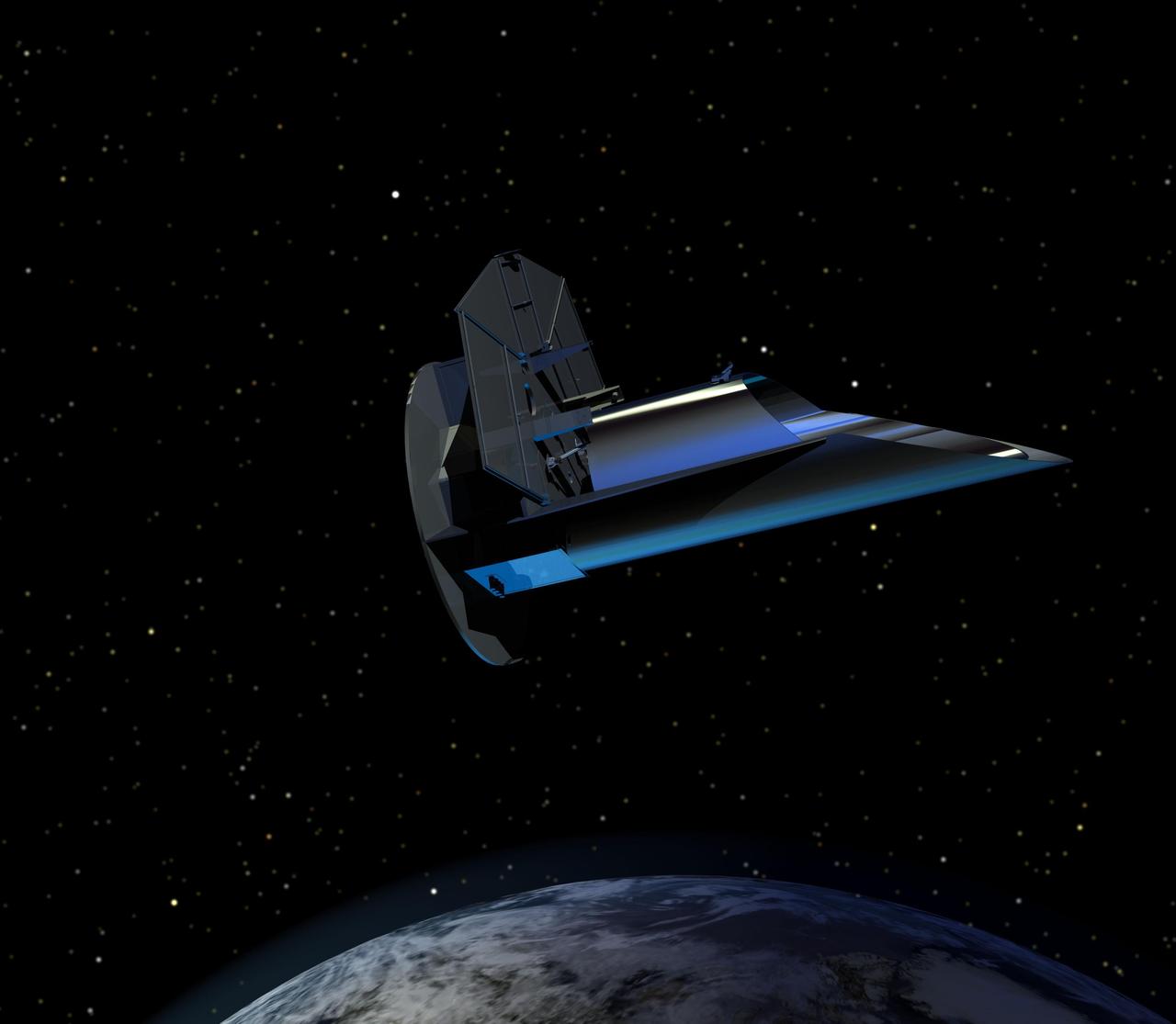

This is an artist rendering of the spacecraft FINESSE orbiting above Earth. Proposed for launch in 2016 as part of NASA Explorers Program, FINESSE would take the first family portrait of extrasolar planets.
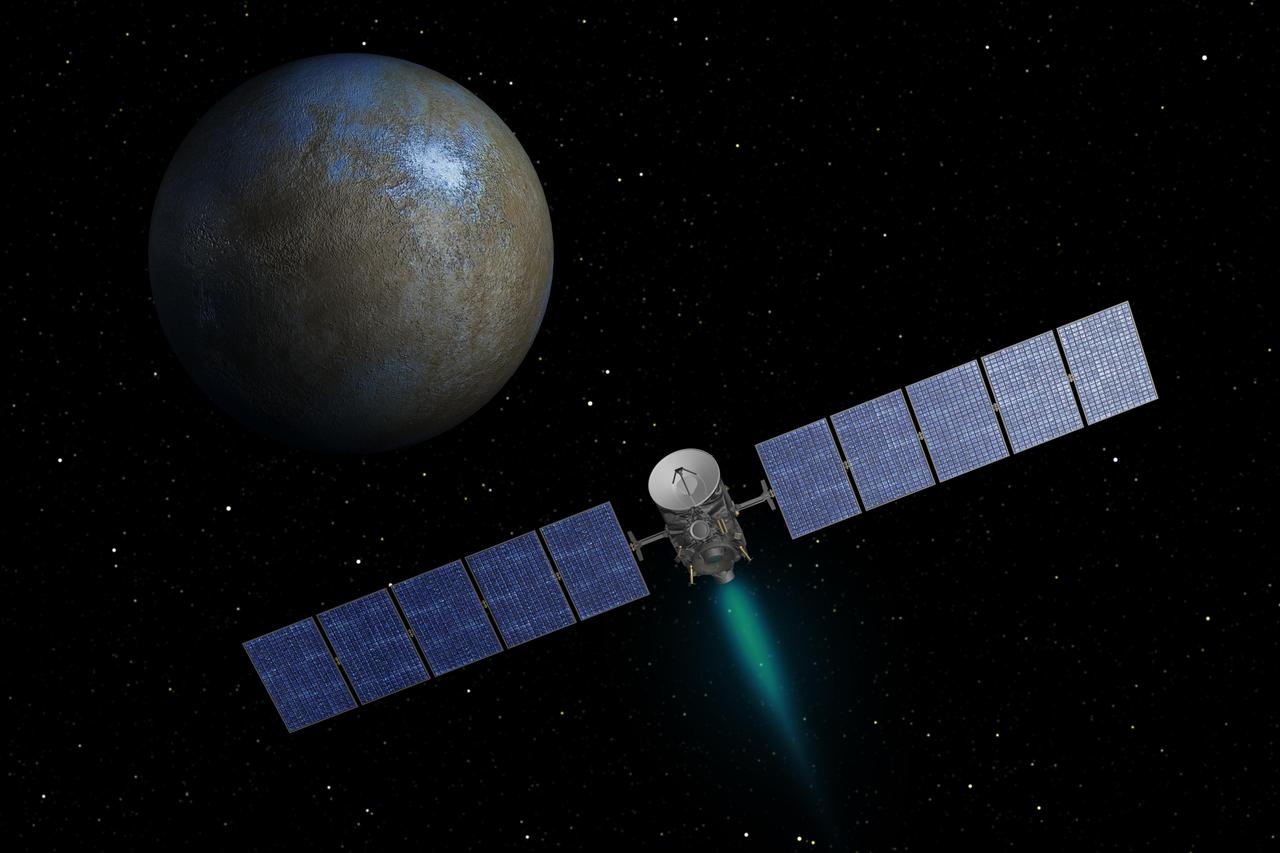

This artist concept shows NASA Dawn spacecraft heading toward the dwarf planet Ceres. When Dawn arrives, it will be the first spacecraft to go into orbit around two destinations in our solar system beyond Earth.
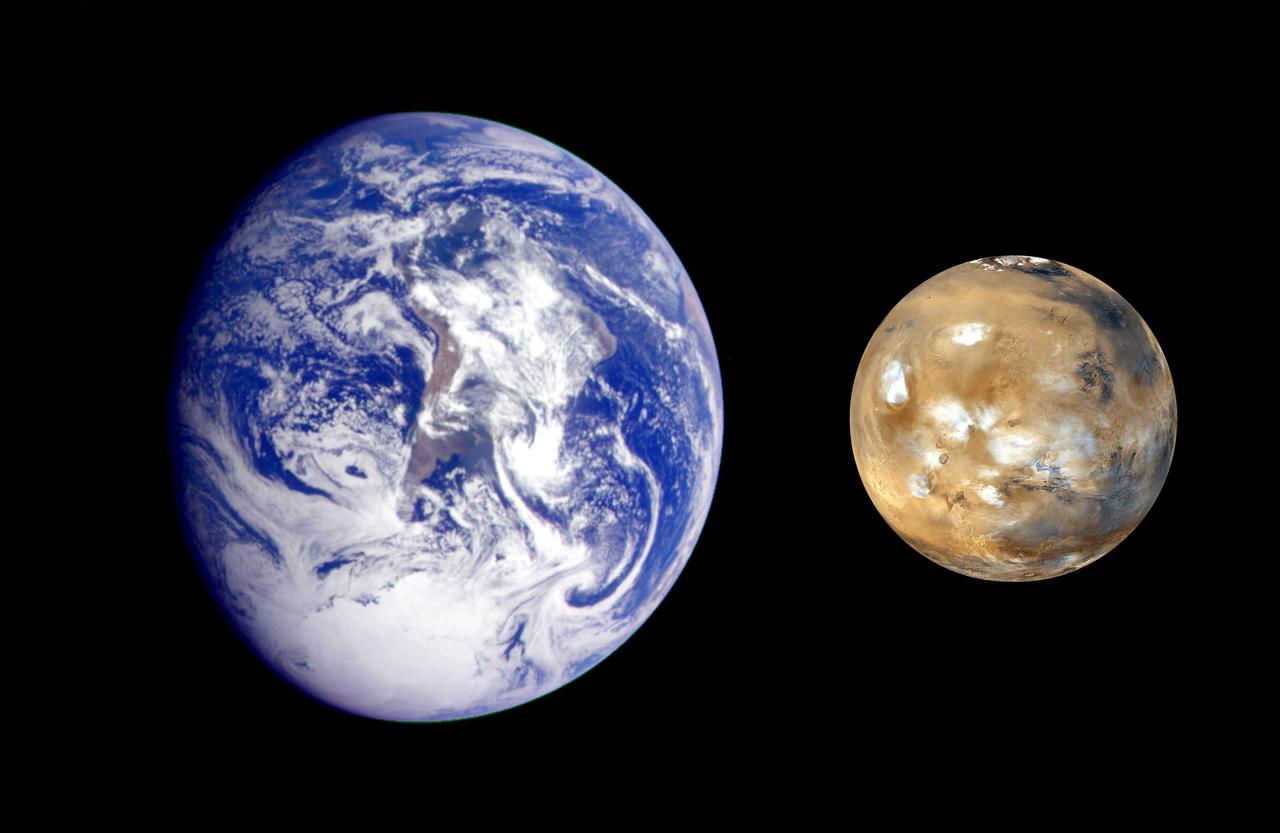

This composite image, from NASA Galileo and Mars Global Survey orbiters, of Earth and Mars was created to allow viewers to gain a better understanding of the relative sizes of the two planets.

This artist's concept appeared on the Feb. 23, 2017 cover of the journal Nature announcing that the TRAPPIST-1 star, an ultra-cool dwarf, has seven Earth-size planets orbiting it. Any of these planets could have liquid water on them. Planets that are farther from the star are more likely to have significant amounts of ice, especially on the side that faces away from the star. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21421

This artist concept depicts 55 Cancri e as it orbits its star. NASA Spitzer Space Telescope has, for the first time, captured the light emanating from a distant super Earth, a planet more massive than Earth but lighter than Neptune.

This chart shows, on the top row, artist concepts of the seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 with their orbital periods, distances from their star, radii, masses, densities and surface gravity as compared to those of Earth. These numbers are current as of February 2018. On the bottom row, the same numbers are displayed for the bodies of our inner solar system: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars. The TRAPPIST-1 planets orbit their star extremely closely, with periods ranging from 1.5 to only about 20 days. This is much shorter than the period of Mercury, which orbits our sun in about 88 days. The masses and densities of the TRAPPIST-1 planets were determined by careful measurements of slight variations in the timings of their orbits using extensive observations made by NASA's Spitzer and Kepler space telescopes, in combination with data from Hubble and a number of ground-based telescopes. These measurements are the most precise to date for any system of exoplanets. In this illustration, the relative sizes of the planets are all shown to scale. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22094
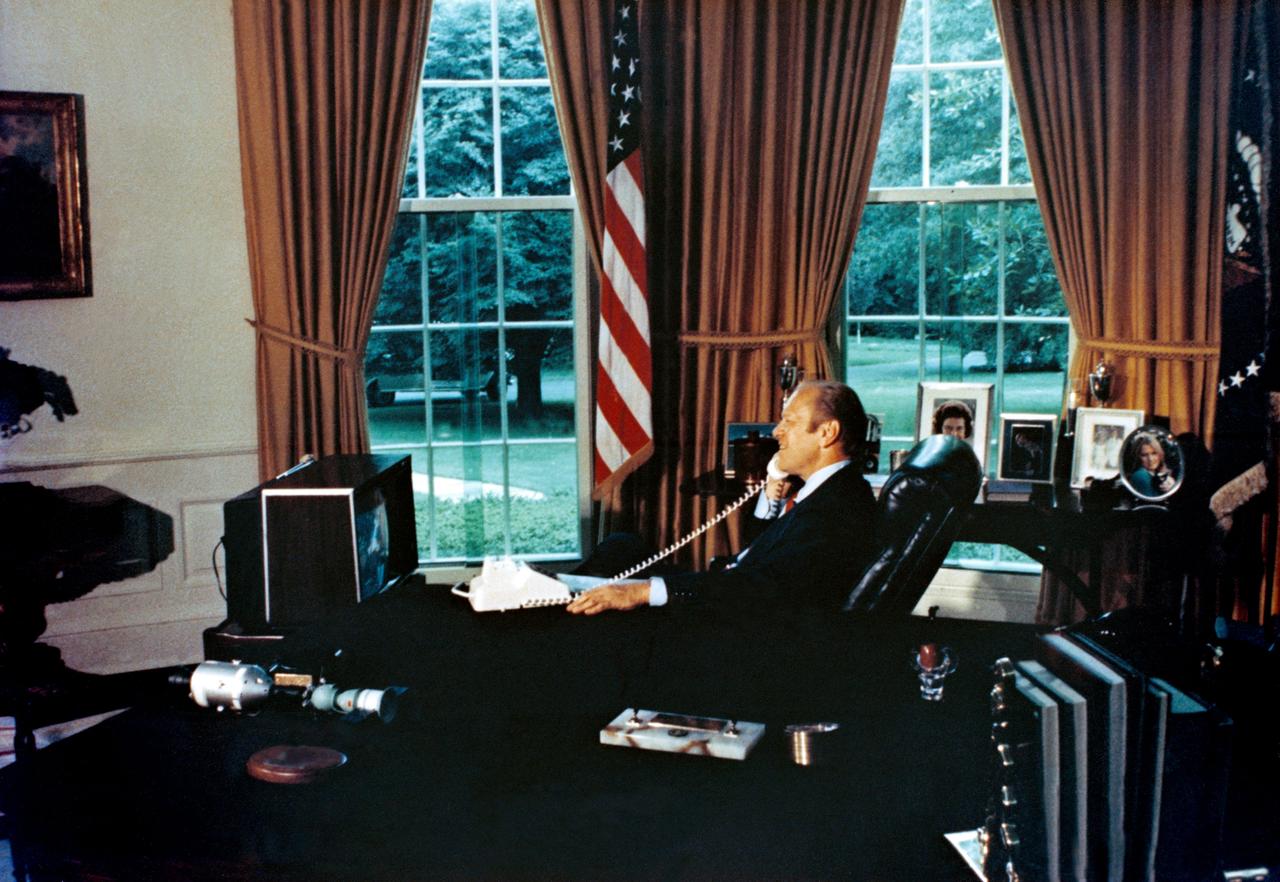

S75-30515 (18 July 1975) --- President Gerald R. Ford watches ASTP crewmen Thomas P. Stafford, Donald K. Slayton and Valeriy N. Kubasov on television as he talks to them via radio-telephone while they orbited Earth on July 18, 1975. The American Apollo spacecraft and Soviet Soyuz spacecraft were docked. The five ASTP crewmen visited each other?s spacecraft while the Soyuz and Apollo were linked in space.

NASA's Polar Radiant Energy in the Far-InfraRed Experiment (PREFIRE) mission will measure the amount of heat Earth emits into space from two of the coldest, most remote regions on the planet. Data from the mission will improve computer models researchers use to predict how Earth's ice, seas, and weather will change in a warming world. This artist's concept depicts one of two PREFIRE CubeSats in orbit around Earth. Earth absorbs a lot of the Sun's energy at the tropics, and weather and ocean currents transport that heat to the poles. Ice, snow, clouds, and other parts of the polar environment emit the heat into space, much of it in the form of far-infrared radiation. The difference between how much heat Earth absorbs at the tropics and then radiates out to space from the Arctic and Antarctic determines the planet's temperature and drives a dynamic system of climate and weather. But far-infrared emissions at the poles have never been systematically measured. This is where PREFIRE comes in. The mission will help researchers gain a clearer understanding of when and where Earth's poles emit far-infrared radiation, as well as how atmospheric water vapor and clouds influence the amount that escapes to space. PREFIRE is composed of two roughly shoebox-size CubeSats outfitted with specialized miniature heat sensors that will give researchers a more accurate picture of how much heat Earth emits into space. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26185
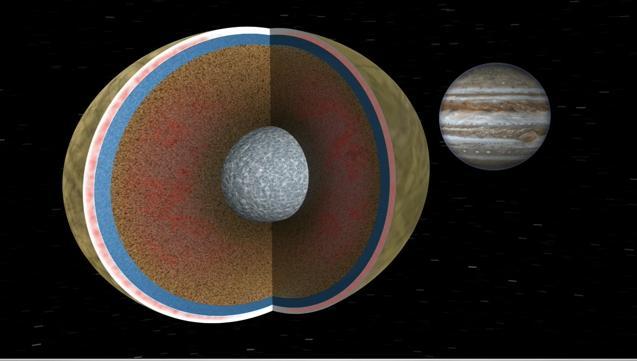
In this image, Europa is seen in a cutaway view through two cycles of its 3.5 day orbit about the giant planet Jupiter. Like Earth, Europa is thought to have an iron core, a rocky mantle and a surface ocean of salty water. Animation available at the Photo
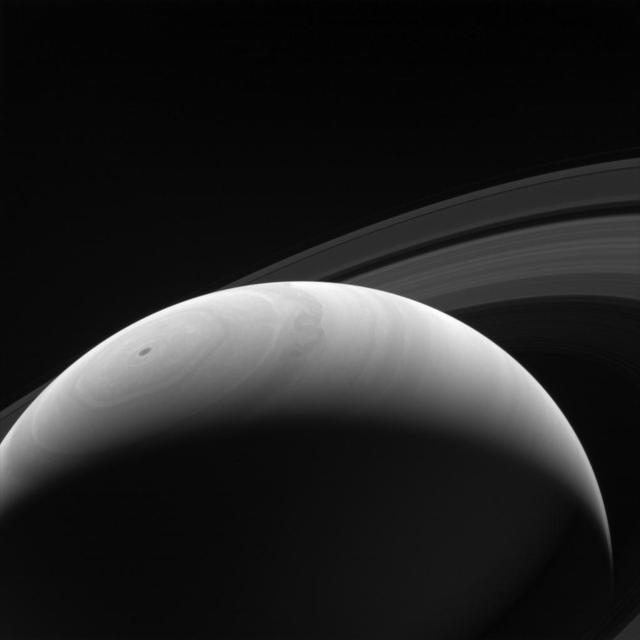

A new day dawns on Saturn as the part of the planet is seen emerging once more into the Sun light by NASA Cassini orbiter. With an estimated rotation period of 10 hours and 40 minutes, Saturn days and nights are much shorter than those on Earth.
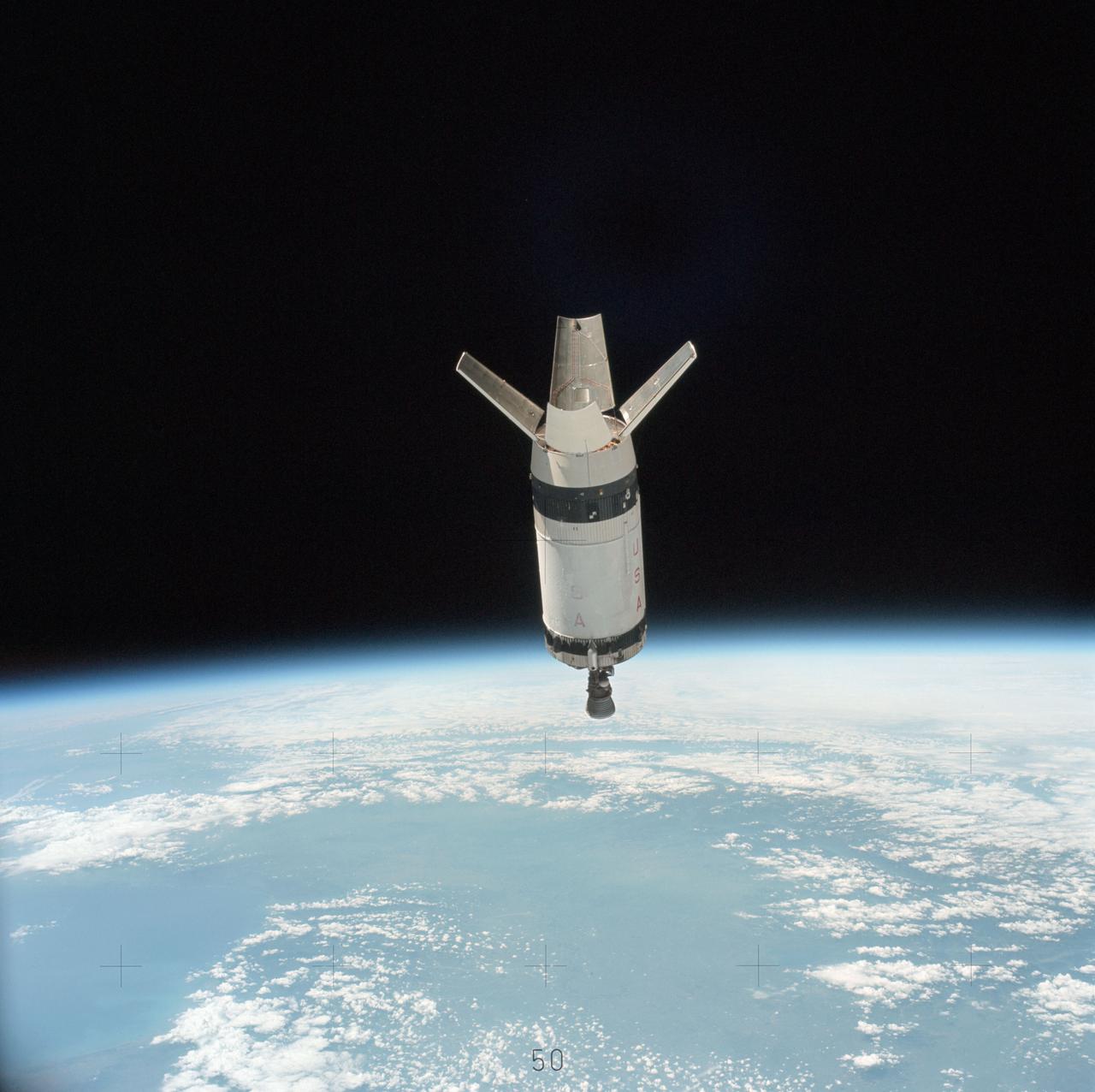

SL3-114-1625 (July-September 1973) --- An excellent view of the expended S-IVB second stage of the Skylab 3/Saturn 1B space vehicle is seen in this photograph taken from the Skylab 3 Command and Service Module (CSM) in Earth orbit. The land mass below is Italy and France, with part of the Mediterranean Sea visible. This photograph was taken with a handheld 70mm Hasselblad camera using a 100mm lens, and medium speed Ektachrome film. Photo credit: NASA
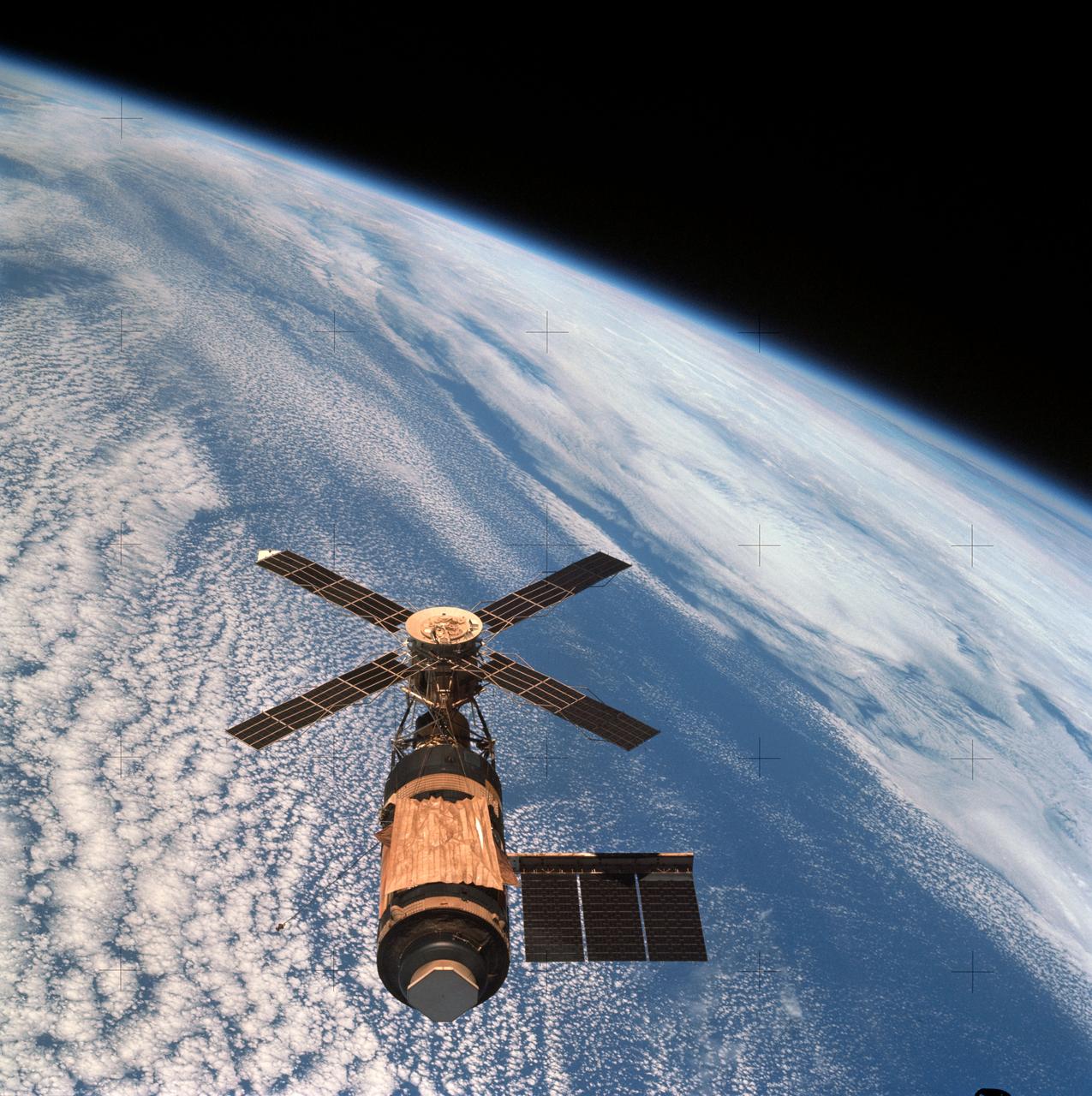

SL4-143-4706 (8 Feb. 1974) --- An overhead view of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit as photographed from the Skylab 4 Command and Service Modules (CSM) during the final fly-around by the CSM before returning home. The space station is contrasted against a cloud-covered Earth. Note the solar shield which was deployed by the second crew of Skylab and from which a micro meteoroid shield has been missing since the cluster was launched on May 14, 1973. The Orbital Workshop (OWS) solar panel on the left side was also lost on workshop launch day. Inside the Command Module (CM) when this picture was made were astronaut Gerald P. Carr, commander; scientist-astronaut Edward G. Gibson, science pilot; and astronaut William R. Pogue, pilot. The crew used a 70mm hand-held Hasselblad camera to take this photograph. Photo credit: NASA
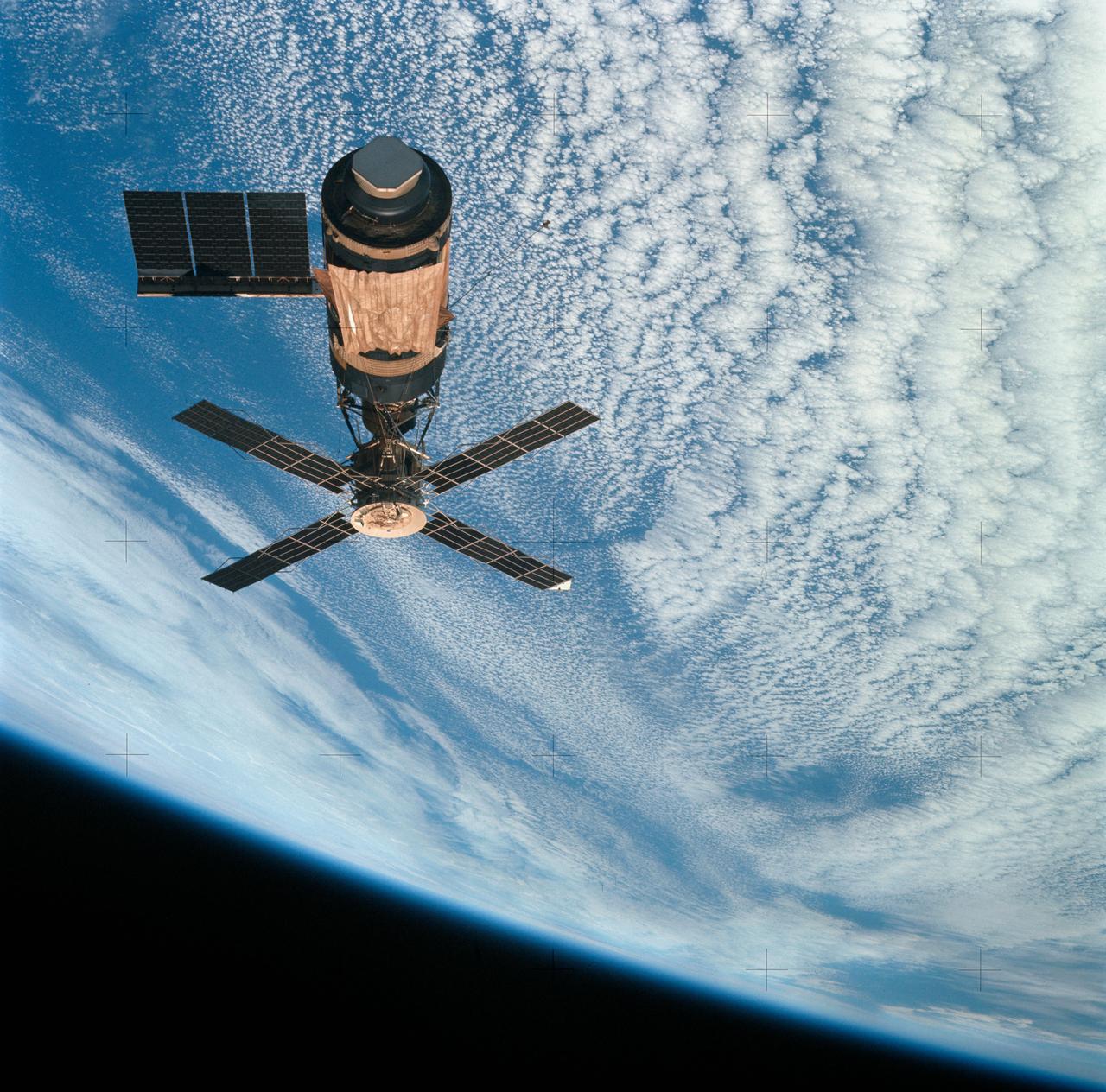

SL4-143-4707 (8 Feb. 1974) --- An overhead view of the Skylab space station cluster in Earth orbit as photographed from the Skylab 4 Command and Service Modules (CSM) during the final fly-around by the CSM before returning home. The space station is contrasted against a cloud-covered Earth. Note the solar shield which was deployed by the second crew of Skylab and from which a micrometeoroid shield has been missing since the cluster was launched on May 14, 1973. The OWS solar panel on the left side was also lost on workshop launch day. Photo credit: NASA
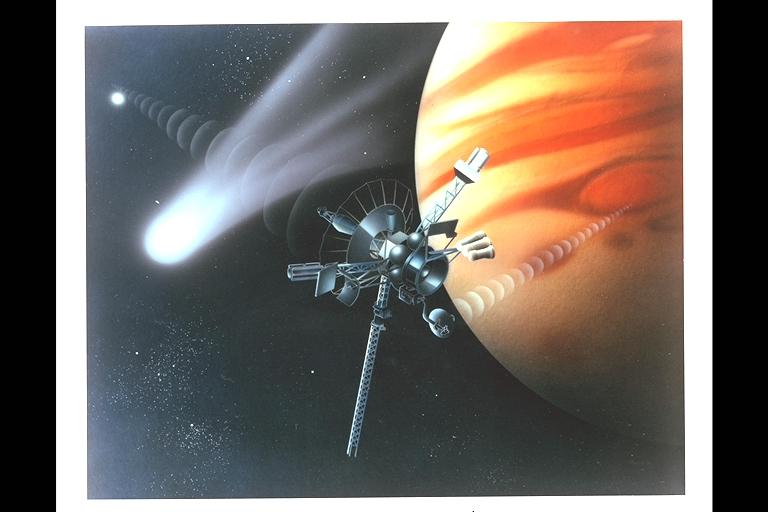
Pioneer Galileo mission trajectory artwork depicting radio signal from Earth to spacecraft to planet and comet crossing spacecrafts' orbit

This illustration shows the seven TRAPPIST-1 planets as they might look as viewed from Earth using a fictional, incredibly powerful telescope. The sizes and relative positions are correctly to scale: This is such a tiny planetary system that its sun, TRAPPIST-1, is not much bigger than our planet Jupiter, and all the planets are very close to the size of Earth. Their orbits all fall well within what, in our solar system, would be the orbital distance of our innermost planet, Mercury. With such small orbits, the TRAPPIST-1 planets complete a "year" in a matter of a few Earth days: 1.5 for the innermost planet, TRAPPIST-1b, and 20 for the outermost, TRAPPIST-1h. This particular arrangement of planets with a double-transit reflect an actual configuration of the system during the 21 days of observations made by NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope in late 2016. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21429

All seven planets discovered in orbit around the red dwarf star TRAPPIST-1 could easily fit inside the orbit of Mercury, the innermost planet of our solar system. In fact, they would have room to spare. TRAPPIST-1 also is only a fraction of the size of our Sun; it isn't much larger than Jupiter. So, the TRAPPIST-1 system's proportions look more like Jupiter and its moons than those of our solar system. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22096
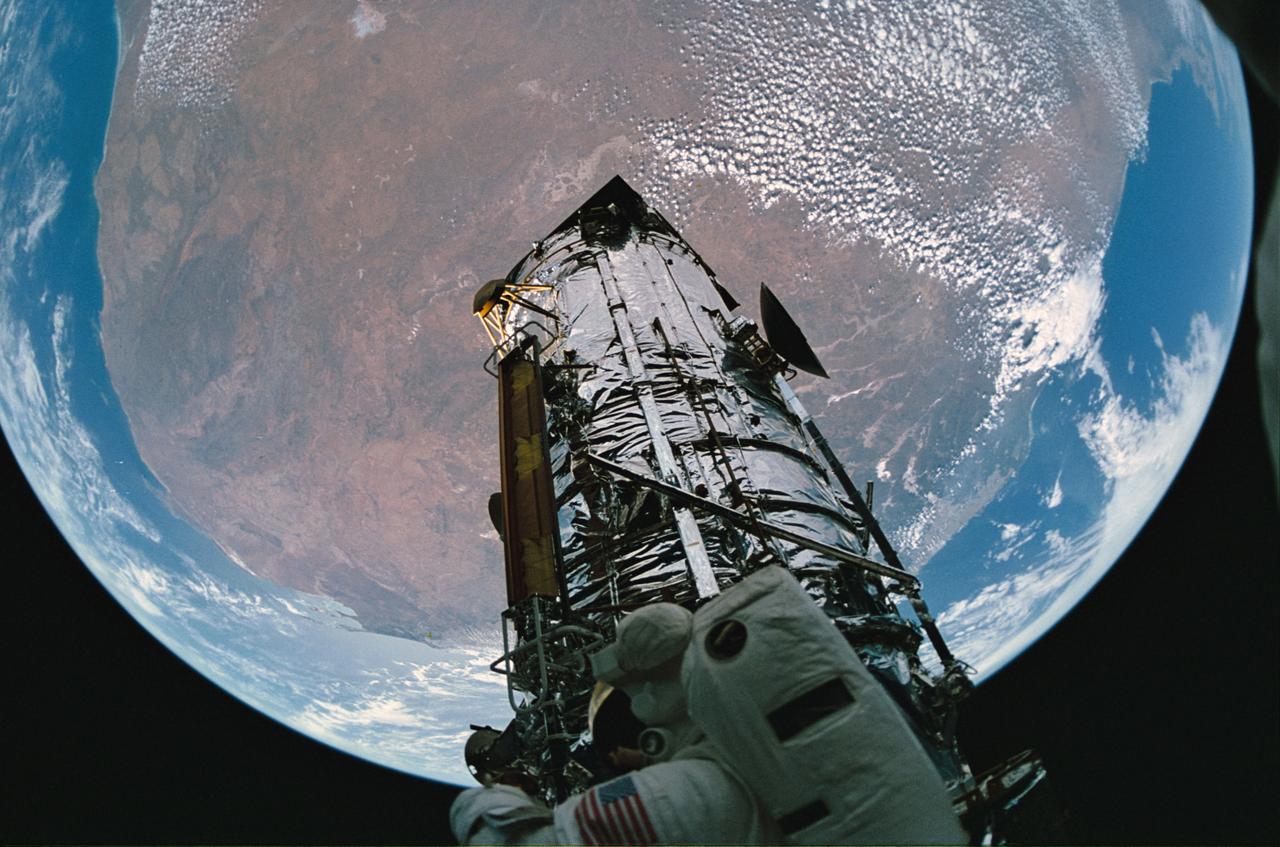

STS061-65-015 (9 Dec 1993) --- A fish-eye lens was used to capture the Hubble Space Telescope (HST), a spherical Earth and Australian landmass with a bit of distortion during the final extravehicular activity (EVA) on the STS-61 HST-servicing mission. Astronaut F. Story Musgrave can be seen at bottom of the frame.
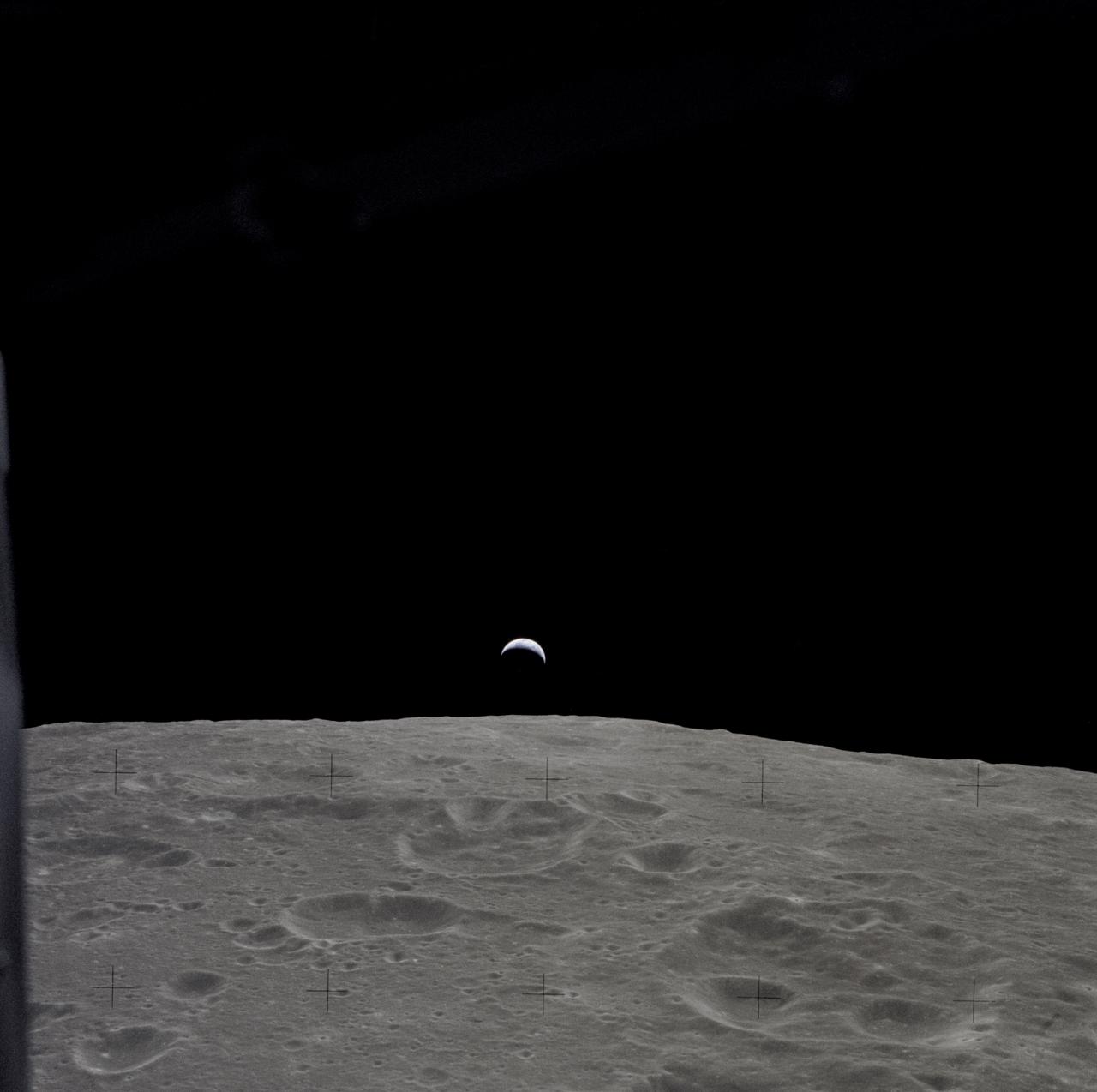

AS12-47-6891 (14-24 Nov. 1969) --- A partially illuminated Earth rises above the lunar horizon in this photograph taken from the Apollo 12 spacecraft in lunar orbit.
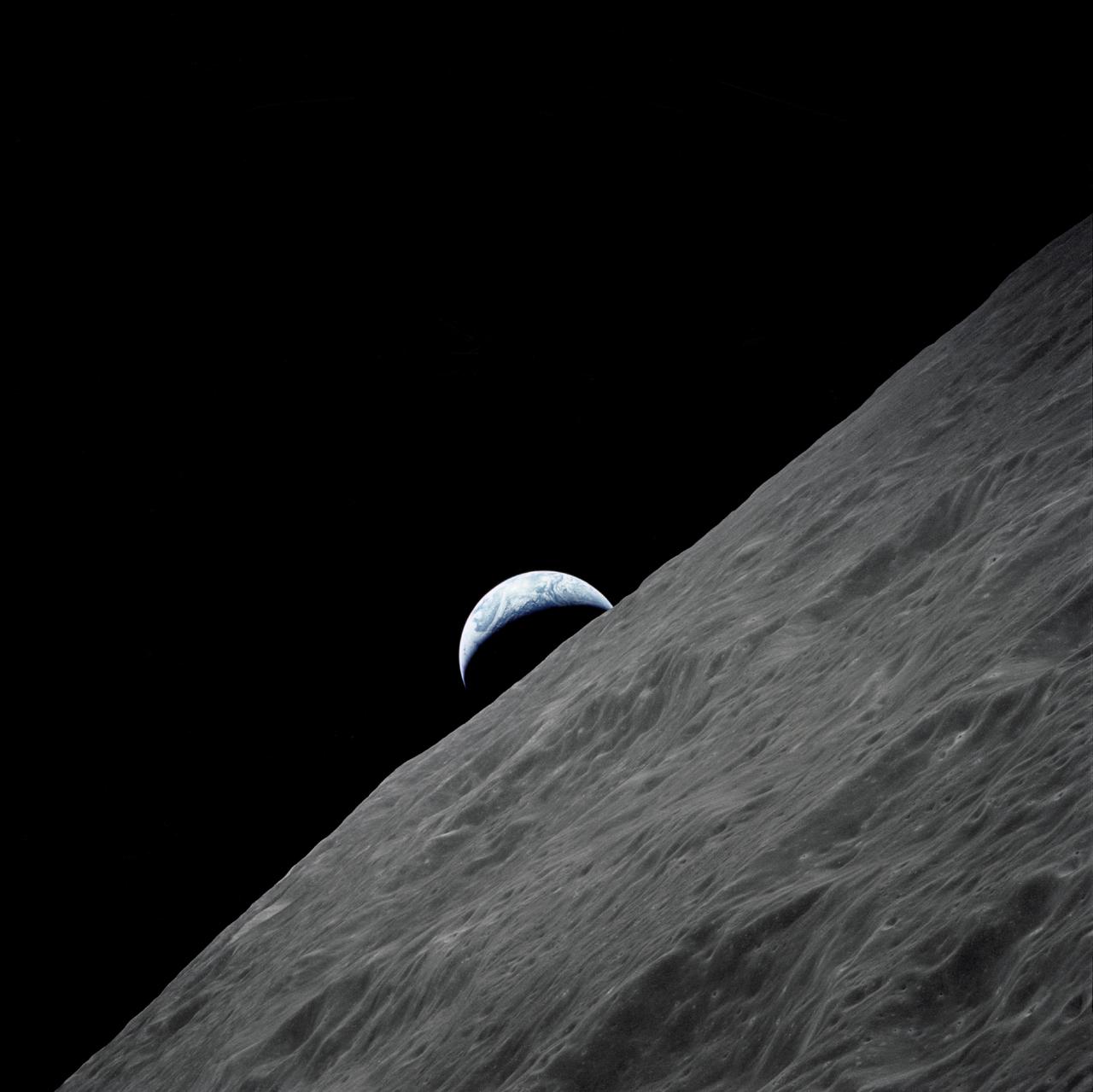

AS17-152-23274 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- The crescent Earth rises above the lunar horizon in this spectacular photograph taken from the Apollo 17 spacecraft in lunar orbit during National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) final lunar landing mission in the Apollo program. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Harrison H. Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the Lunar Module (LM) "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
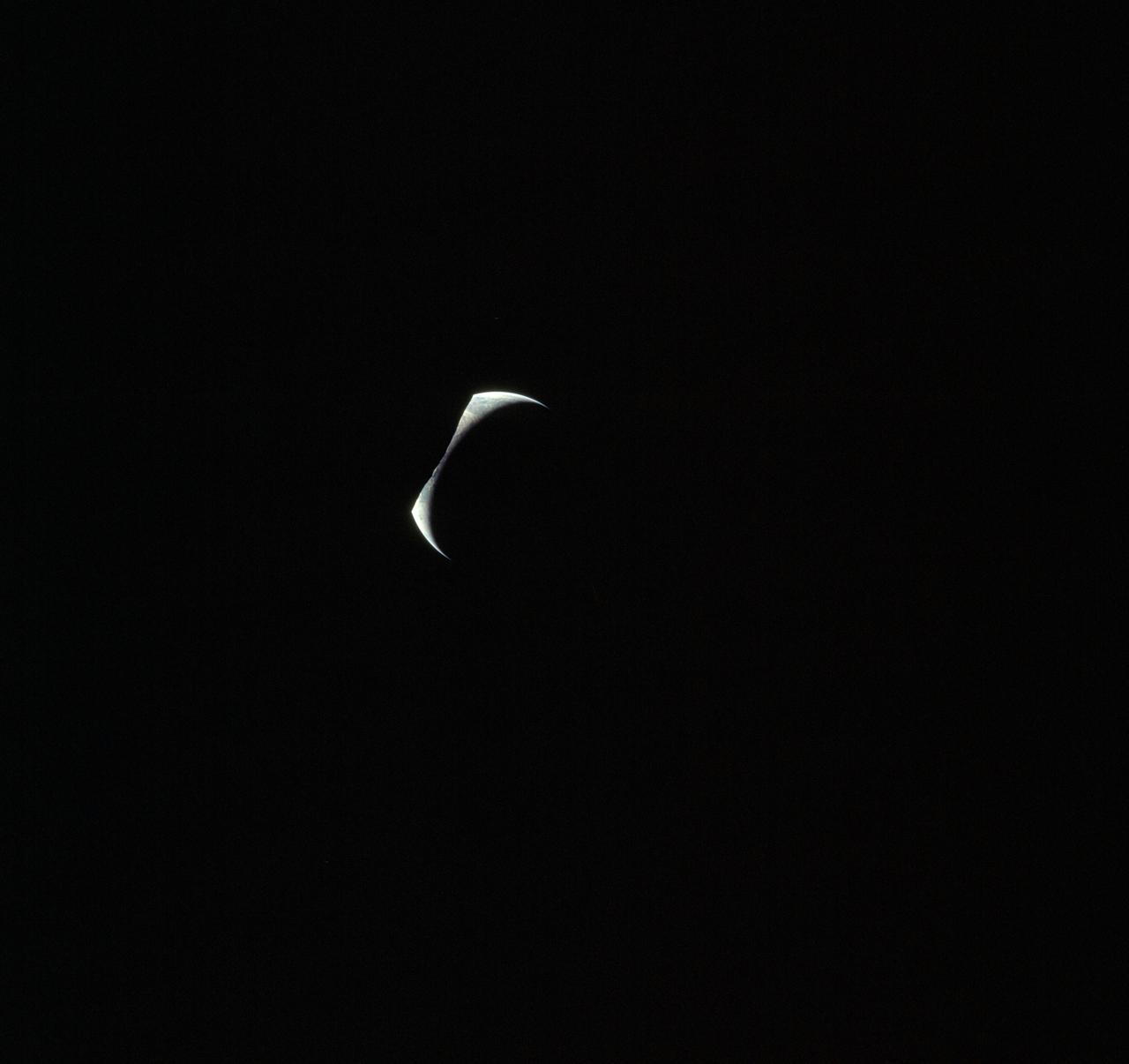
AS17-152-23279 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Eclipsed by the silhouetted horizon of the moon, the crescent Earth appears in the shape of a Viking's headwear in this unusual Apollo 17 photograph. The three astronauts--Eugene A. Cernan, Ronald E. Evans and Harrison H. Schmitt--were just about to begin their journey homeward following the successful lunar landing phase of their mission.
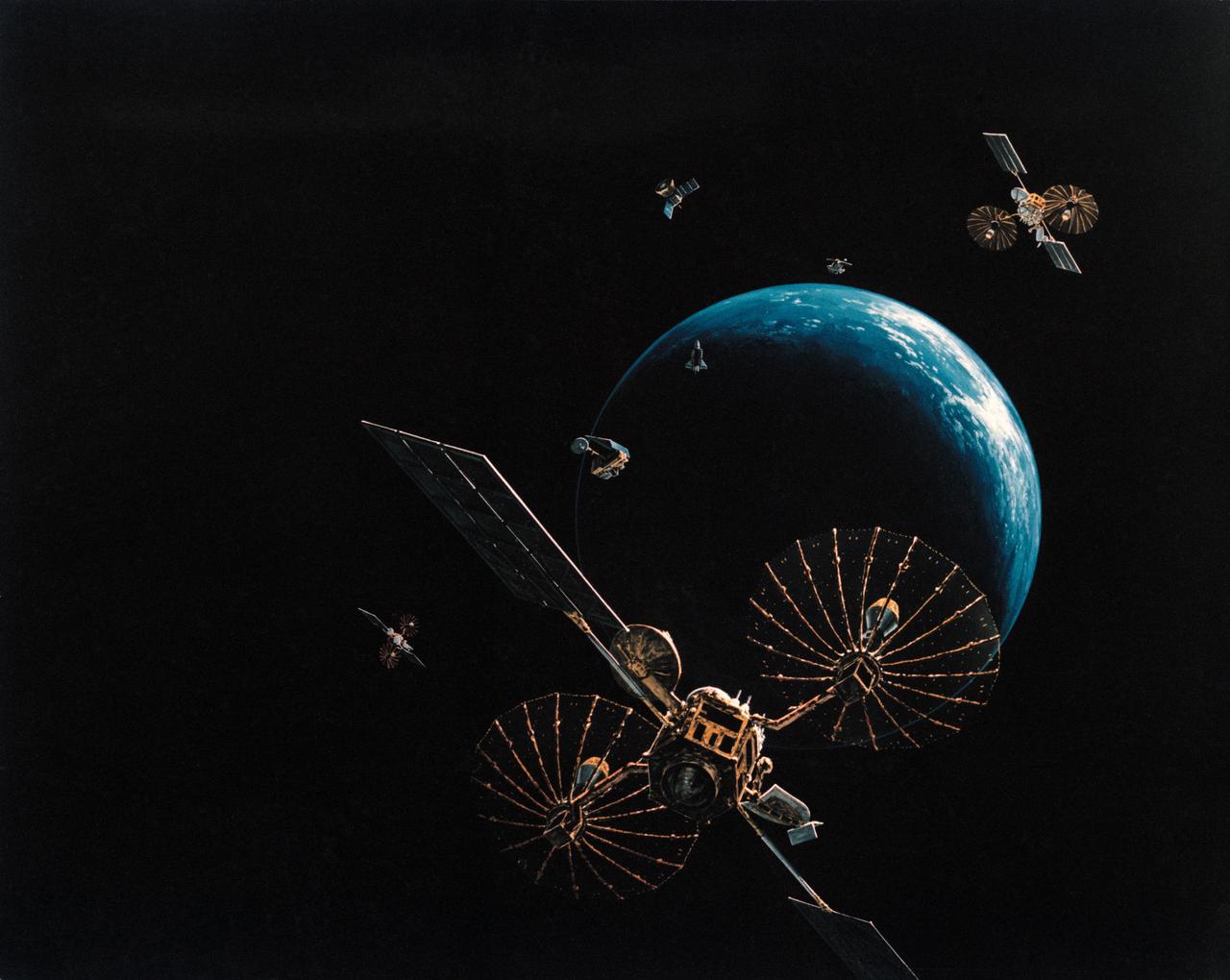

Artist concept shows the Tracking and Data Relay Satellite E (TDRS-E) augmenting a sophisticated TDRS system (TDRSS) communications network after deployment during STS-43 from Atlantis, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104. TDRS, built by TRW, will be placed in a geosynchronous orbit and after onorbit testing, which requires several weeks, will be designated TDRS-5. The communications satellite will replace TDRS-3 at 174 degrees West longitude. The backbone of NASA's space-to-ground communications, the TDRSs have increased NASA's ability to send and receive data to spacecraft in low-earth orbit to more than 85 percent of the time. Before TDRS, NASA relied solely on a system of ground stations that permitted communications only 15 percent of the time. Increased coverage has allowed onorbit repairs, live television broadcast from space and continuous dialogues between astronaut crews and ground control during critical periods such as Space Shuttle landings.

This artist concept shows K2-138, the first multi-planet system discovered by citizen scientists. The central star is slightly smaller and cooler than our Sun. The five known planets are all between the size of Earth and Neptune. Planet b may potentially be rocky, but planets c, d, e, and f likely contain large amounts of ice and gas. All five planets have orbital periods shorter than 13 days and are all incredibly hot, ranging from 800 to 1,800 degrees Fahrenheit. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22088

Of the 1,030 confirmed planets from Kepler, a dozen are less than twice the size of Earth and reside in the habitable zone of their host stars. In this diagram, the sizes of the exoplanets are represented by the size of each sphere. These are arranged by size from left to right, and by the type of star they orbit, from the M stars that are significantly cooler and smaller than the sun, to the K stars that are somewhat cooler and smaller than the sun, to the G stars that include the sun. The sizes of the planets are enlarged by 25 times compared to the stars. The Earth is shown for reference. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19827

How do we find Earth-like planets outside our solar system? One idea is to send a giant structure that blocks starlight so that astronomers can more easily detect orbiting planets. This artist's rendering shows the proposed starshade concept flying in sync with a space telescope. The giant sunflower-like structure would be used to acquire images of Earth-like rocky planets around nearby stars. The proposed starshade could launch together with a telescope. Once in space, it would separate from the rocket and telescope, unfurl its petals, then move into position to block the light of stars. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20911
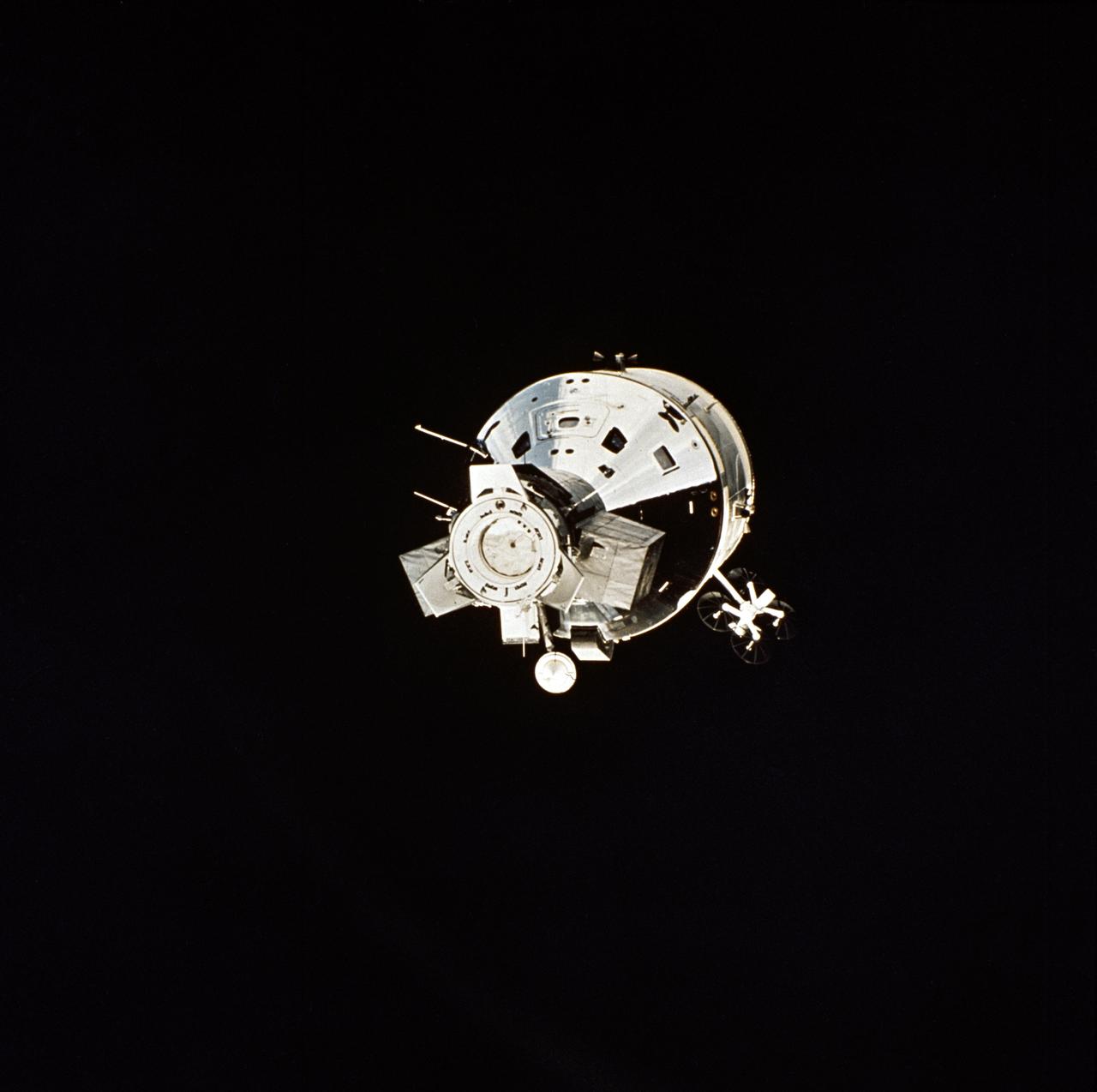

AST-32-2691 (17-19 July 1975) --- The American Apollo spacecraft as seen in Earth orbit from the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The Command/Service Module and Docking Module are contrasted against a black-sky background. This is a near "head on" view of the Apollo. This picture was furnished by the USSR in an exchange of photography taken during the ASTP flight. Note the docking mechanism and docking target on the Docking Module. The four dish-like reflectors of the unified S-band high-gain antenna protrude from the side of the Service Module. The American and Soviet spacecraft were joined together in space for approximately 47 hours on July 17-18-19, 1975. PHOTO COURTESY: USSR ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
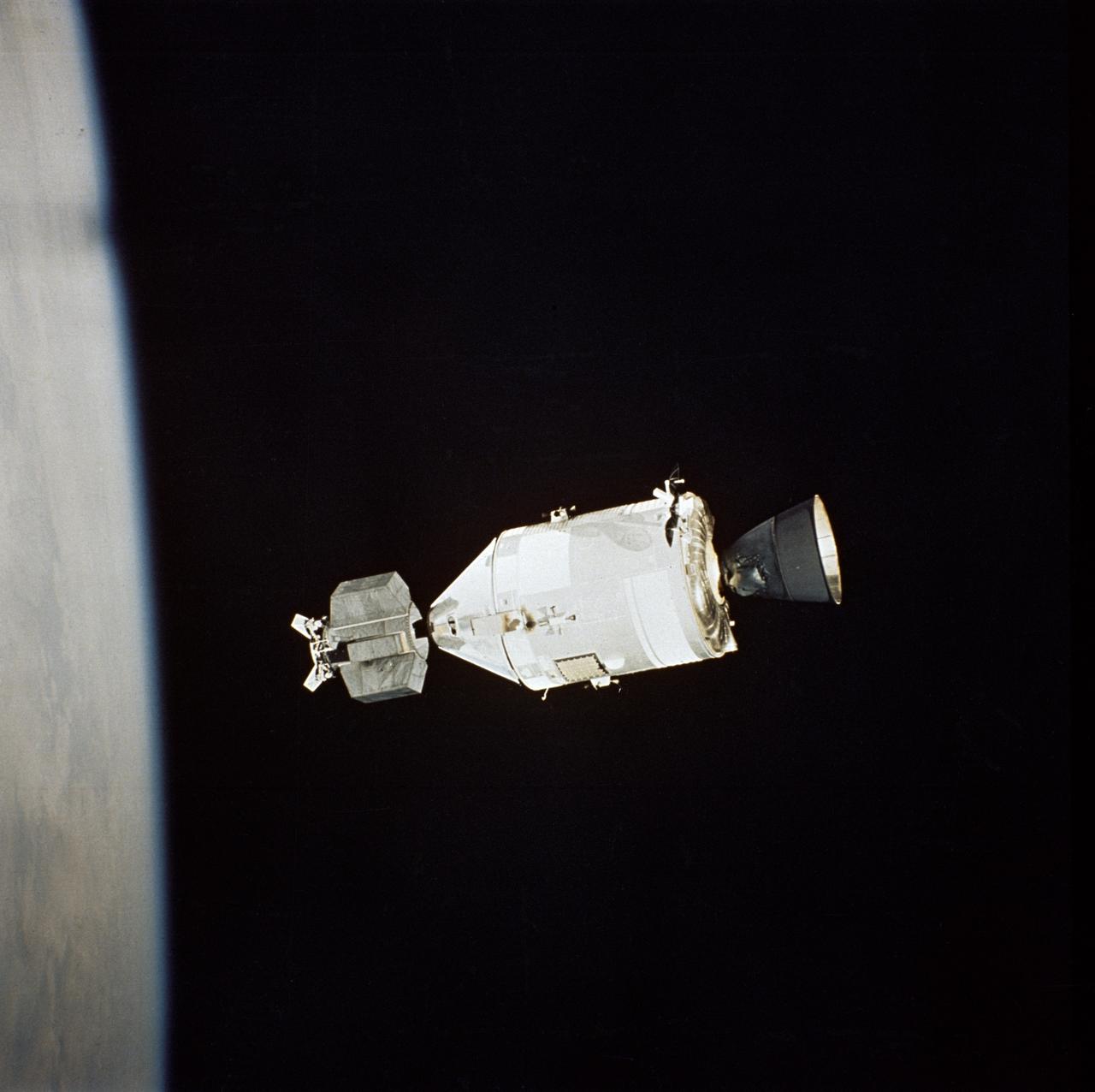

AST-32-2695 (17-19 July 1975) --- The American Apollo spacecraft as seen in Earth orbit from the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The Command/Service Module and Docking Module are contrasted against a black-sky background. The horizon of Earth is below. This picture was furnished by the USSR in an exchange of photography taken during the ASTP flight. The bell-shaped engine nozzle of the service propulsion system protrudes from the rear of the Service Module. Note the docking mechanism on the Docking Module. The American and Soviet spacecraft were joined together in space for approximately 47 hours on July 17-18-19, 1975. PHOTO COURTESY: USSR ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
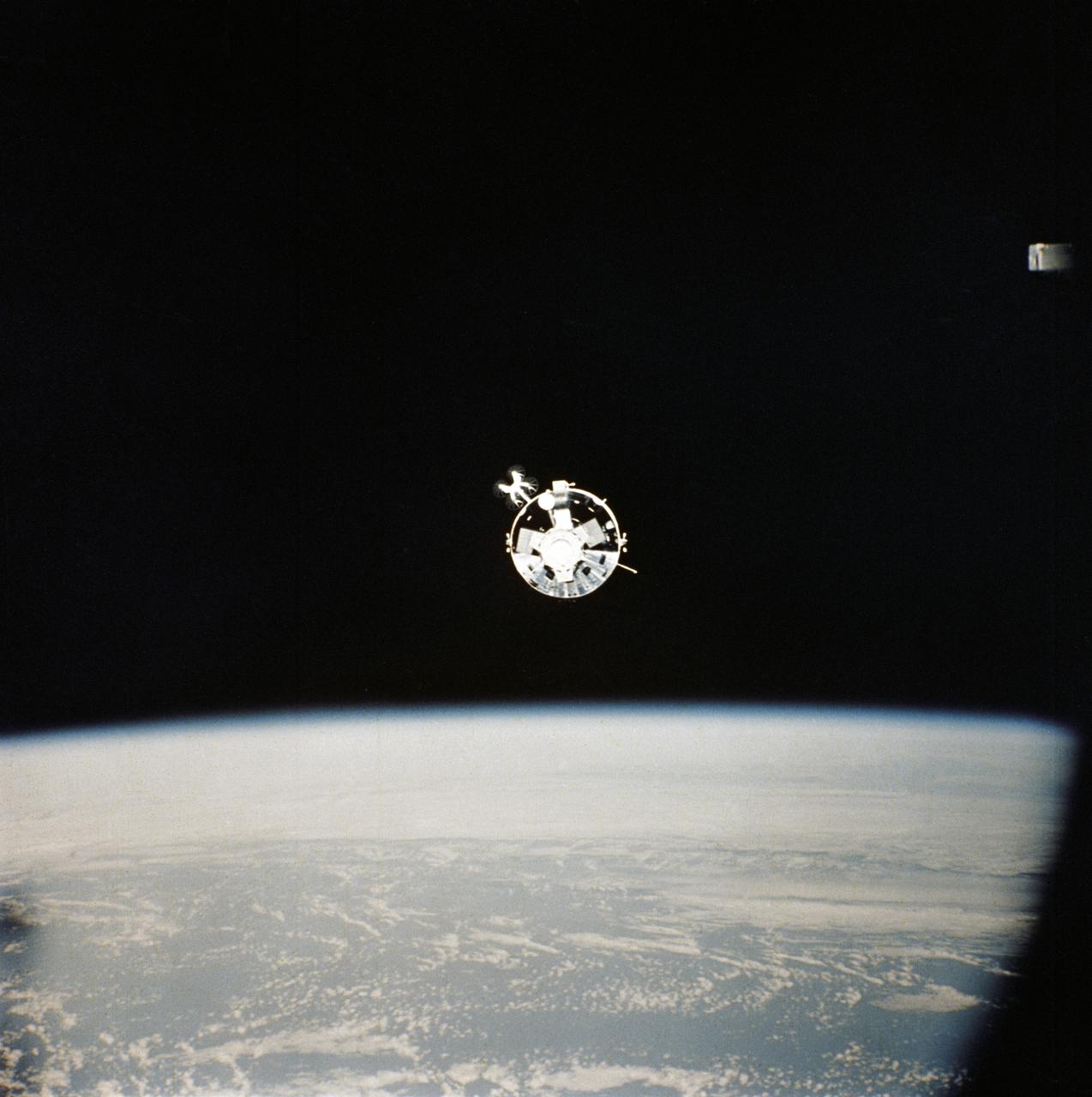

AST-32-2675 (17-19 July 1975) --- The American Apollo spacecraft as seen in Earth orbit from the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project mission. The Command/Service Module and Docking Module are contrasted against a black-sky background. This is a "head on" view of the Apollo. The horizon of Earth is below. This picture was furnished by the USSR in an exchange of photography taken during the ASTP flight. The American and Soviet spacecraft were joined together in space for approximately 47 hours on July 17-18-19, 1975. Note the docking mechanism on the Docking Module. PHOTO COURTESY: USSR ACADEMY OF SCIENCES
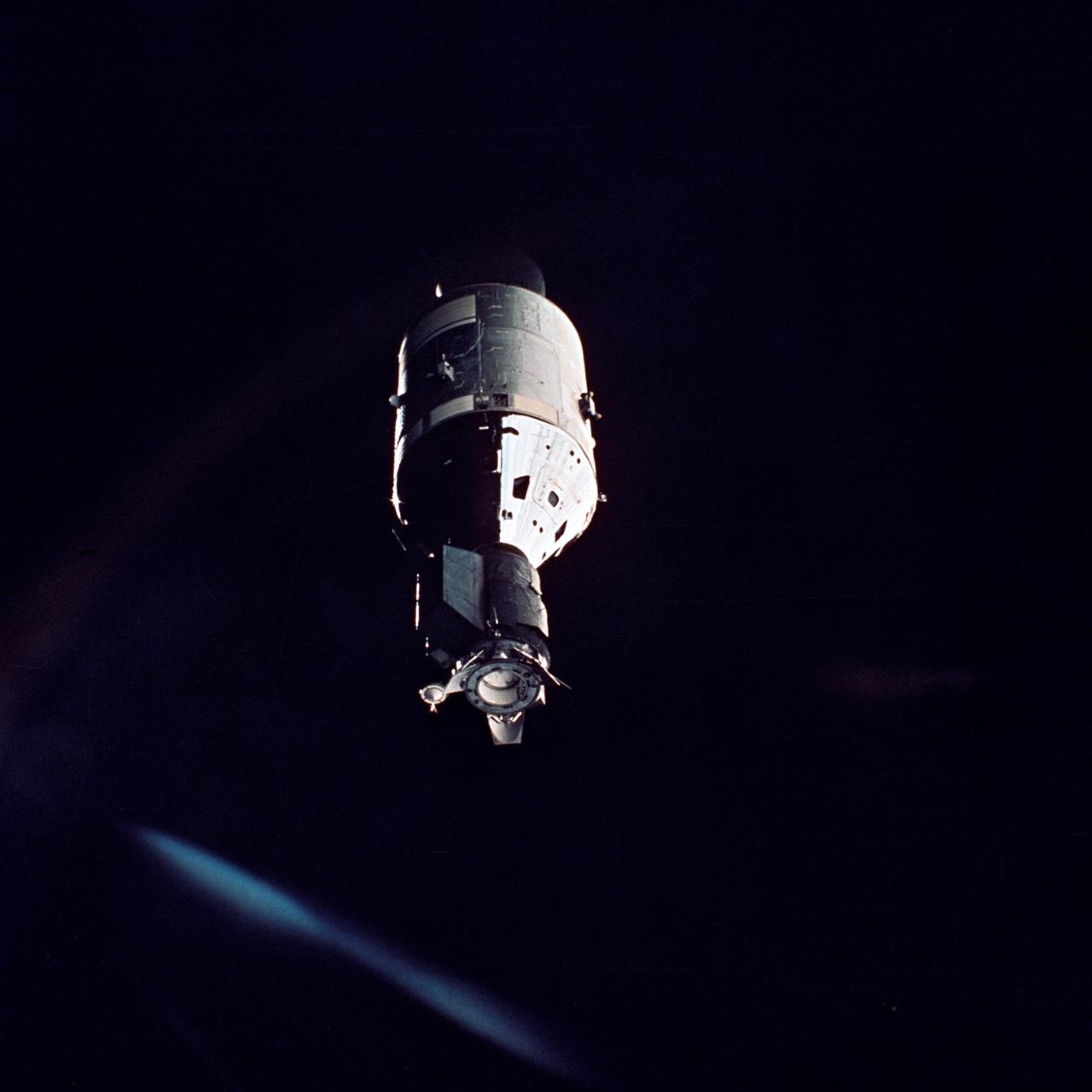

AST-32-2686 (17-19 July 1975) --- The American Apollo spacecraft as seen in Earth orbit from the Soviet Soyuz 19 spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) mission. The Command and Service Module (CSM) and Docking Module (DM) are contrasted against a black-sky background. Light reflected in the camera streaks the image. Note the docking mechanism and docking target on the DM. On the left the bell-shaped engine nozzle of the service propulsion system protrudes from the rear of the Service Module (SM). The American and Soviet spacecraft were joined together in space for approximately 47 hours on July 17, 18, 19, 1975. This picture was furnished by the USSR in an exchange of photography taken during the ASTP flight. The Apollo crew consisted of astronauts Thomas P. Stafford, commander; Donald K. "Deke" Slayton, docking module pilot; and Vance D. Brand, command module pilot. The Soyuz 19 crew consisted of cosmonauts Aleksei A. Leonov, command pilot; and Valeri N. Kubasov, flight engineer.
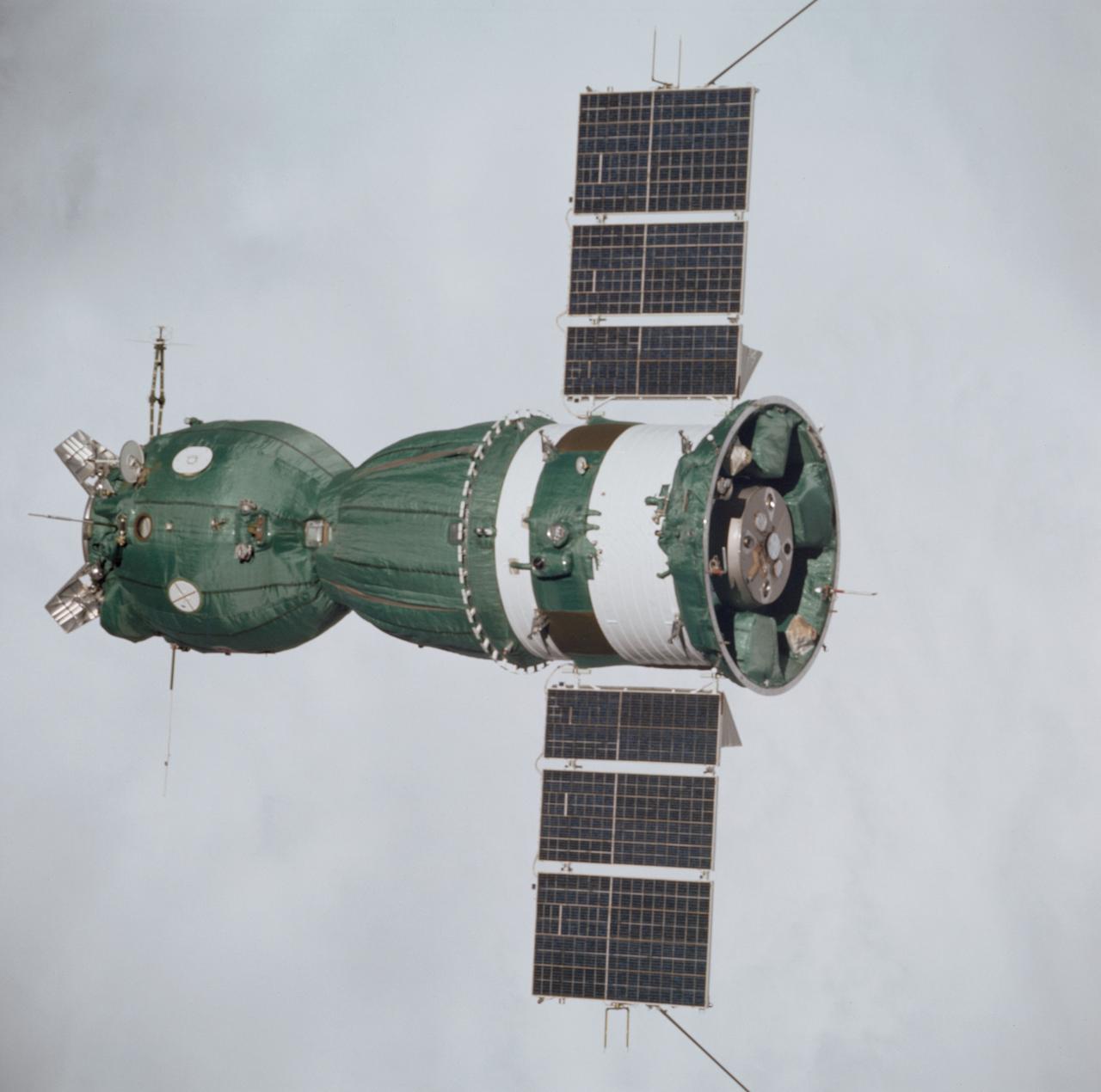

AST-01-056 (18 July 1975) --- An excellent view of the Soviet Soyuz spacecraft in Earth orbit, photographed from the American Apollo spacecraft during the joint U.S.-USSR Apollo-Soyuz Test Project (ASTP) docking mission in Earth orbit. The Soyuz is contrasted against a white-cloud background in this overhead view. The three major components of the Soyuz are the spherical-shaped Orbital Module, the bell-shaped Descent Vehicle and the cylindrical-shaped instrument Assembly Module from which two solar panels protrude. The docking system on the Orbital Module was specially designed to interface with the docking system on the Apollo's Docking Module. The ASTP astronauts and cosmonauts visited each other's spacecraft while the Soyuz and Apollo were docked in Earth orbit for two days. The Apollo crew consisted of astronauts Stafford, commander; Donald K. "Deke" Slayton, docking module pilot; and Vance D. Brand, command module pilot. The Soyuz 19 crew consisted of cosmonauts Leonov, command pilot; and Valeri N. Kubasov, flight engineer.
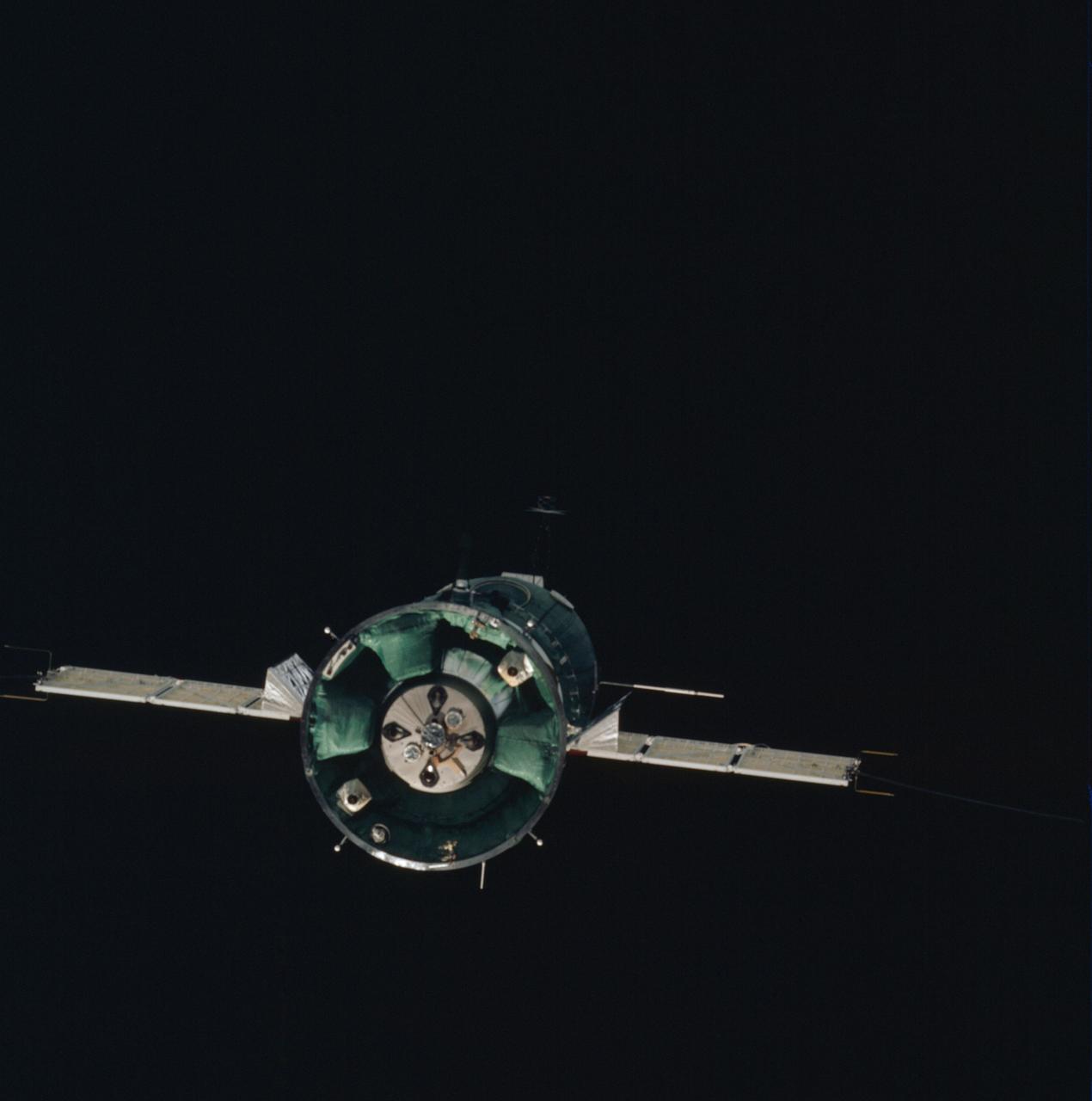

AST-01-053 (17-19 July 1975) --- The Soviet Soyuz spacecraft is contrasted against a black-sky background in this photograph taken in Earth orbit. This view is looking toward the aft end of the Soyuz. Two solar panels protrude out from the spacecraft's Instrument Assembly Module. The ASTP astronauts and cosmonauts visited each other's spacecraft while the Soyuz and Apollo were docked in Earth orbit for two days.

This graph presents measured properties of the seven TRAPPIST-1 exoplanets (labeled b through h), showing how they stack up with one another as well as with Earth and the other inner rocky worlds in our own solar system. The relative sizes of the planets are indicated by the circles. All of the known TRAPPIST-1 planets are larger than Mars, with five of them within 15% of the diameter of Earth. The vertical axis shows the uncompressed densities of the planets. Density, calculated from a planet's mass and volume, is the first important step in understanding its composition. Uncompressed density takes into account that the larger a planet is, the more its own gravity will pack the planet's material together and increase its density. Uncompressed density, therefore, usually provides a better means of comparing the composition of planets. The plot shows that the uncompressed densities of the TRAPPIST-1 planets are similar to one another, suggesting they may have all have a similar composition. The four rocky planets in our own solar system show more variation in density compared to the seven TRAPPIST-1 planets. Mercury, for example, contains a much higher percentage of iron than the other three rocky planets and thus has a much higher uncompressed density. The horizontal axis shows the level of illumination that each planet receives from its host star. The TRAPPIST-1 star is a mere 9% the mass of our Sun, and its temperature is much cooler. But because the TRAPPIST-1 planets orbit so closely to their star, they receive comparable levels of light and heat to Earth and its neighboring planets. The corresponding "habitable zones" — regions where an Earth-like planet could potentially support liquid water on its surface — of the two planetary systems are indicated near the top of the plot. The the two zones do not line up exactly because the cooler TRAPPIST-1 star emitting more of its light in the form of infrared radiation that is more efficiently absorbed by an Earth-like atmosphere. Since it takes less illumination to reach the same temperatures, the habitable zone shifts farther away from the star. The masses and densities of the TRAPPIST-1 planets were determined by measurements of slight variations in the timings of their orbits using extensive observations made by NASA's Spitzer and Kepler space telescopes, in combination with data from Hubble and a number of ground-based telescopes. The latest analysis, which includes Spitzer's complete record of over 1,000 hours of TRAPPIST-1 observations, has reduced the uncertainties of the mass measurements to a mere 3-6%. These are among the most accurate measurements of planetary masses anywhere outside of our solar system. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24371

This illustration shows what the TRAPPIST-1 system might look like from a vantage point near planet TRAPPIST-1f (at right). The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial, according to research published in 2017 in the journal Nature. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. They are likely all tidally locked, meaning the same face of the planet is always pointed at the star, as the same side of our moon is always pointed at Earth. This creates a perpetual night side and perpetual day side on each planet. TRAPPIST-1b and c receive the most light from the star and would be the warmest. TRAPPIST-1e, f and g all orbit in the habitable zone, the area where liquid water is most likely to be detected. But any of the planets could potentially harbor liquid water, depending on their compositions. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21751

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - MESSENGER, a NASA Discovery mission. The MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) mission is a scientific investigation of the planet Mercury. MESSENGER will be launched in the summer of 2004 and will enter Mercury orbit in March of 2011, after one Earth flyby, two flybys of Venus, and three of Mercury along the way. The flyby and orbital phases of the mission will provide global mapping and detailed characterization of the planet's surface, interior, atmosphere and magnetosphere.

This first high-resolution image, taken on the first day of the Artemis I mission, was captured by a camera on the tip of one of Orion’s solar arrays. The spacecraft was 57,000 miles from Earth when the image was captured, and continues to distance itself from planet Earth as it approaches the Moon and distant retrograde orbit.
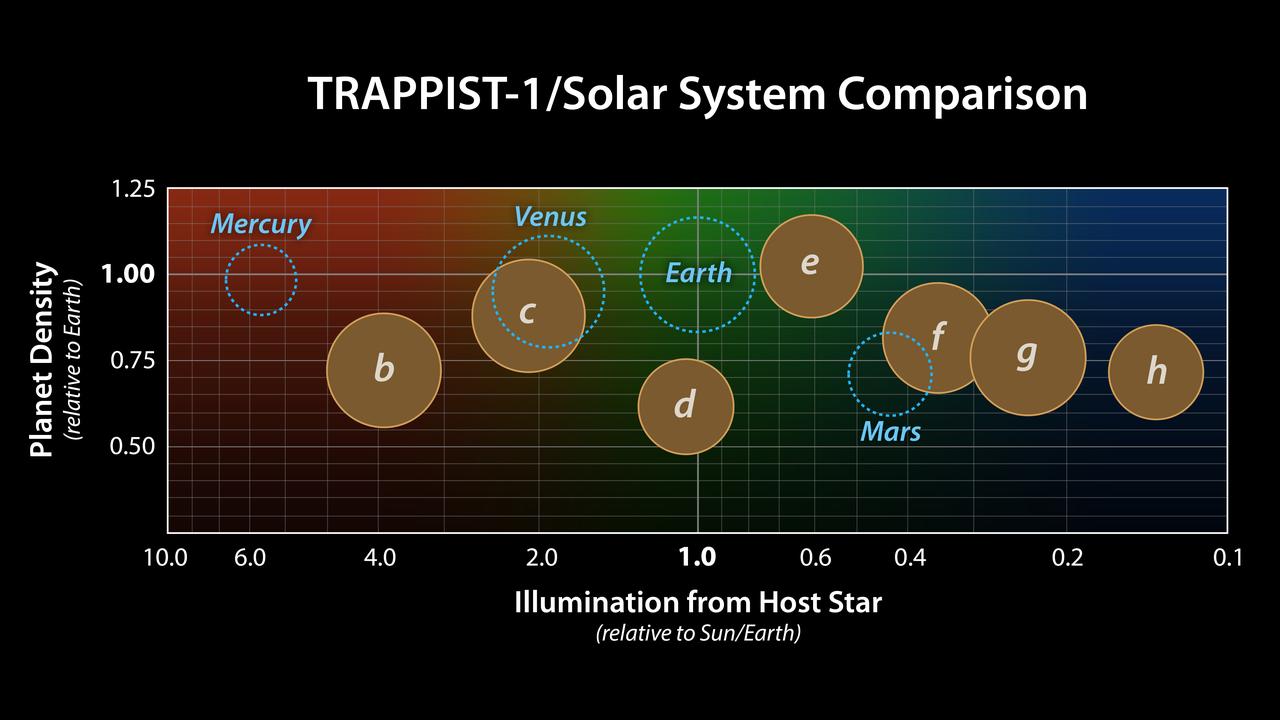
This graph presents known properties of the seven TRAPPIST-1 exoplanets (labeled b through h), showing how they stack up to the inner rocky worlds in our own solar system. The horizontal axis shows the level of illumination that each planet receives from its host star. TRAPPIST-1 is a mere 9 percent the mass of our Sun, and its temperature is much cooler. But because the TRAPPIST-1 planets orbit so closely to their star, they receive comparable levels of light and heat to Earth and its neighboring planets. The vertical axis shows the densities of the planets. Density, calculated based on a planet's mass and volume, is the first important step in understanding a planet's composition. The plot shows that the TRAPPIST-1 planet densities range from being similar to Earth and Venus at the upper end, down to values comparable to Mars at the lower end. The relative sizes of the planets are indicated by the circles. The masses and densities of the TRAPPIST-1 planets were determined by careful measurements of slight variations in the timings of their orbits using extensive observations made by NASA's Spitzer and Kepler space telescopes, in combination with data from Hubble and a number of ground-based telescopes. These measurements are the most precise to date for any system of exoplanets. By comparing these measurements with theoretical models of how planets form and evolve, researchers have determined that they are all rocky in overall composition. Estimates suggest the lower-density planets could have large quantities of water -- as much as 5 percent by mass for TRAPPIST-1d. Earth, in comparison, has only about 0.02 percent of its mass in the form of water. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22095
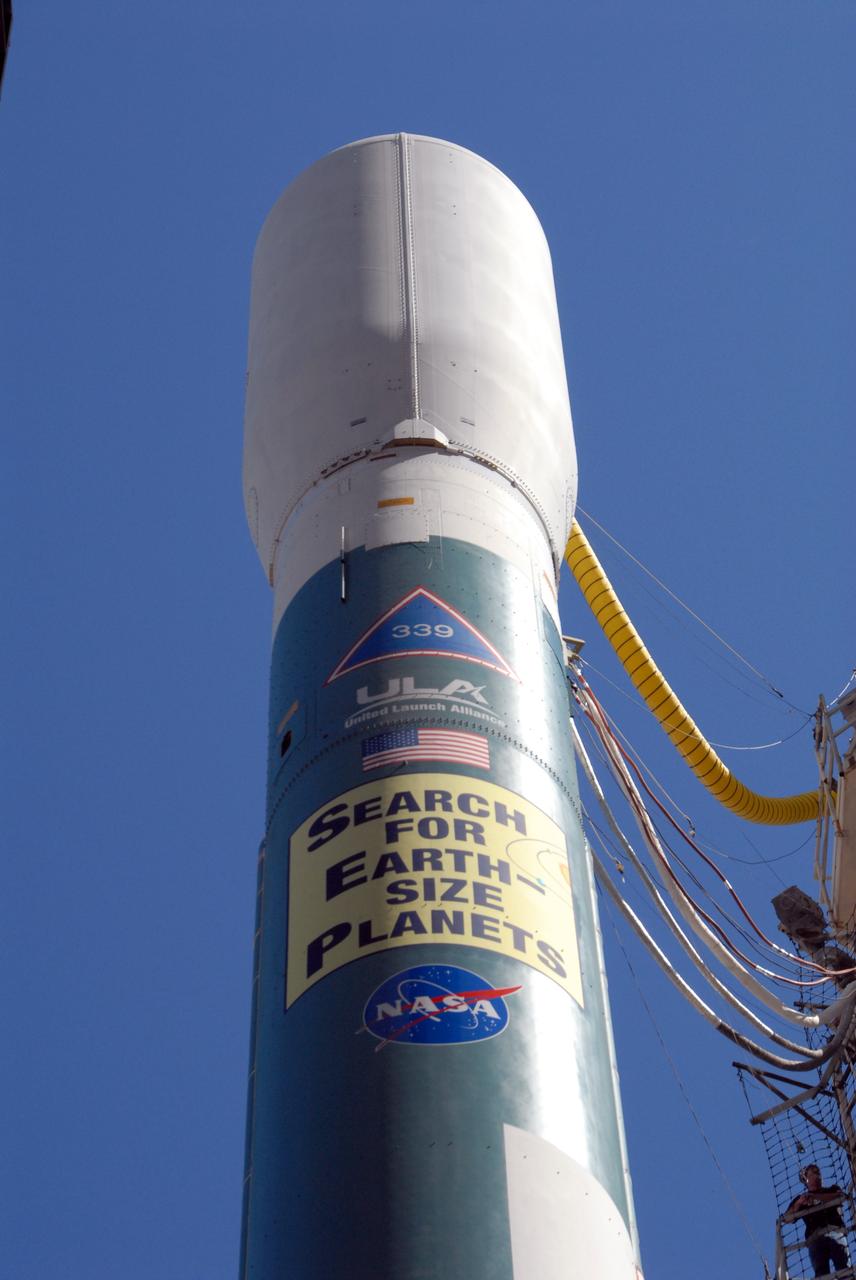

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
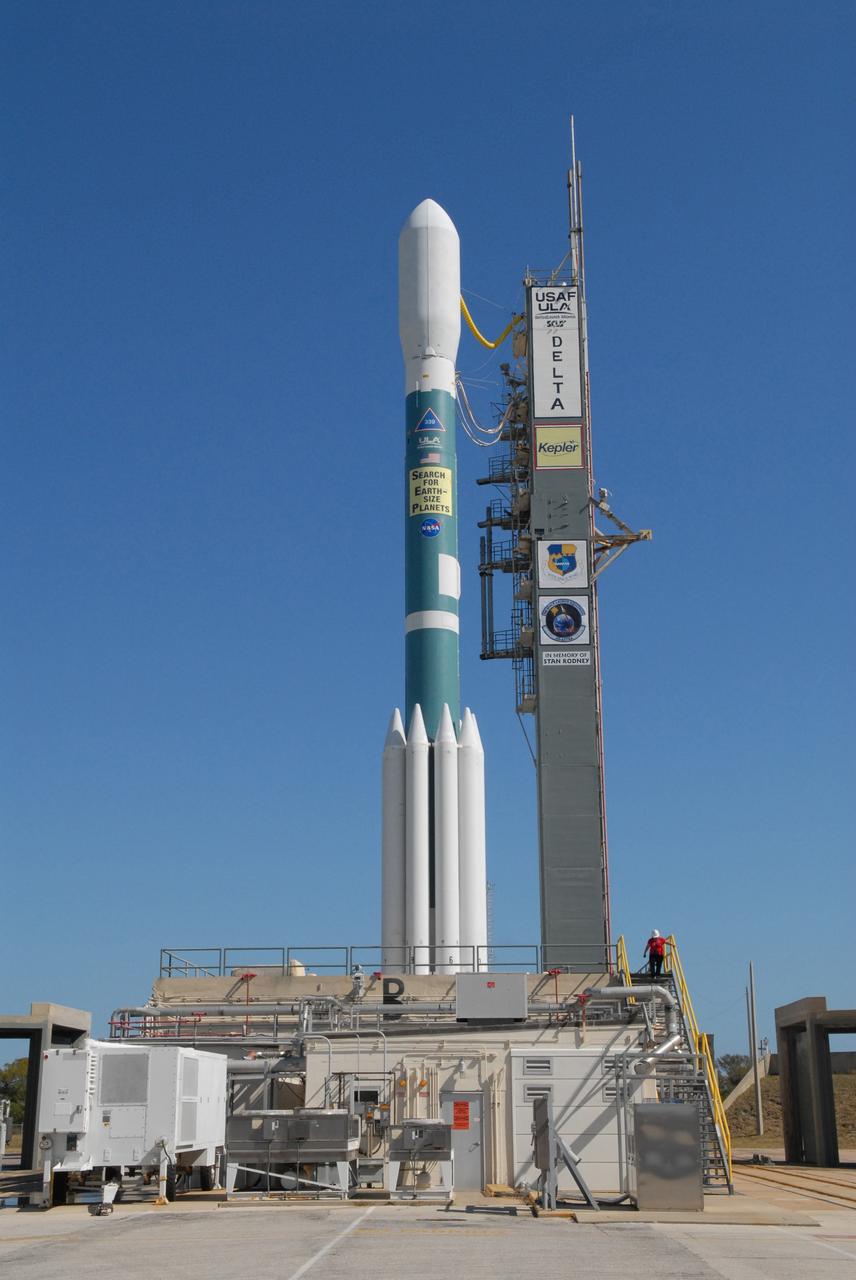

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
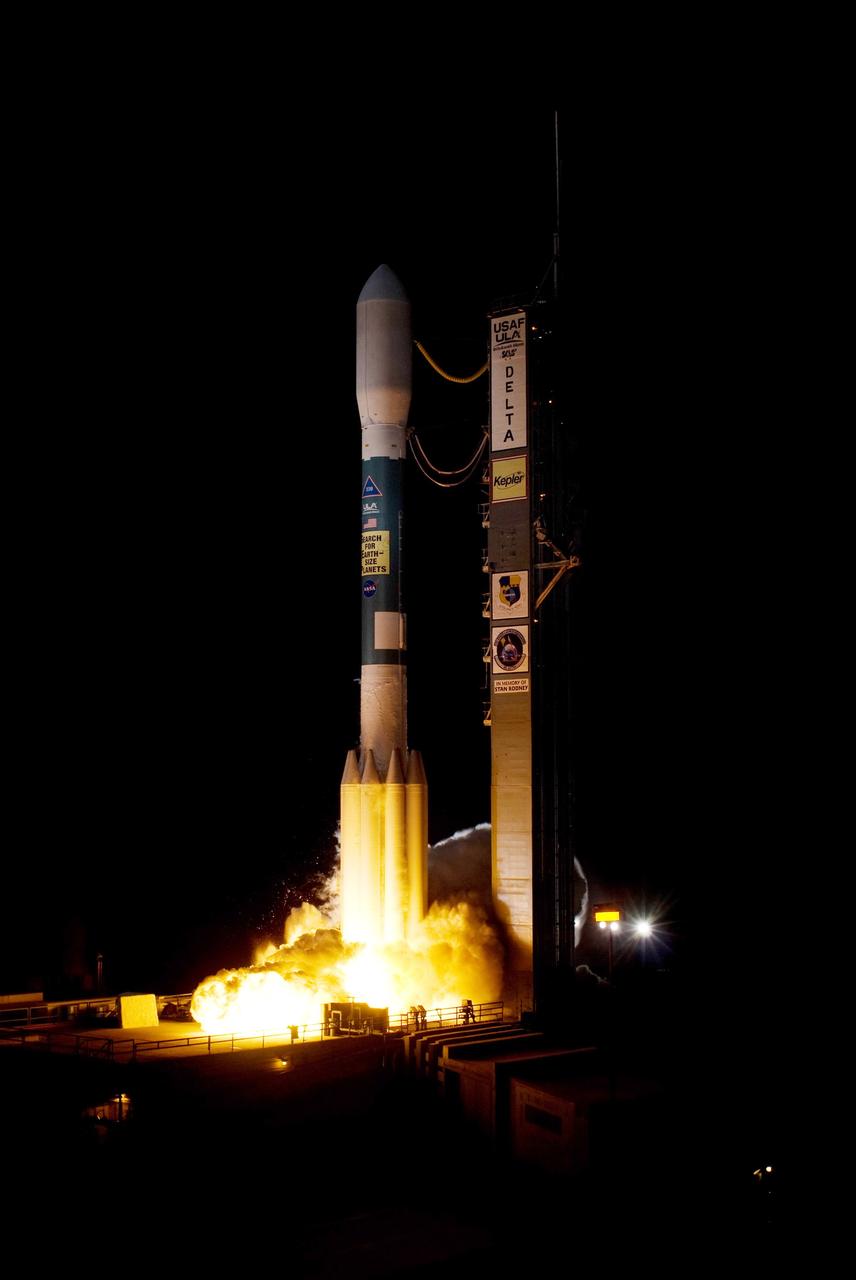

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, the engines on United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket carrying NASA's Kepler spacecraft ignite. Liftoff was on time at 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Tony Gray
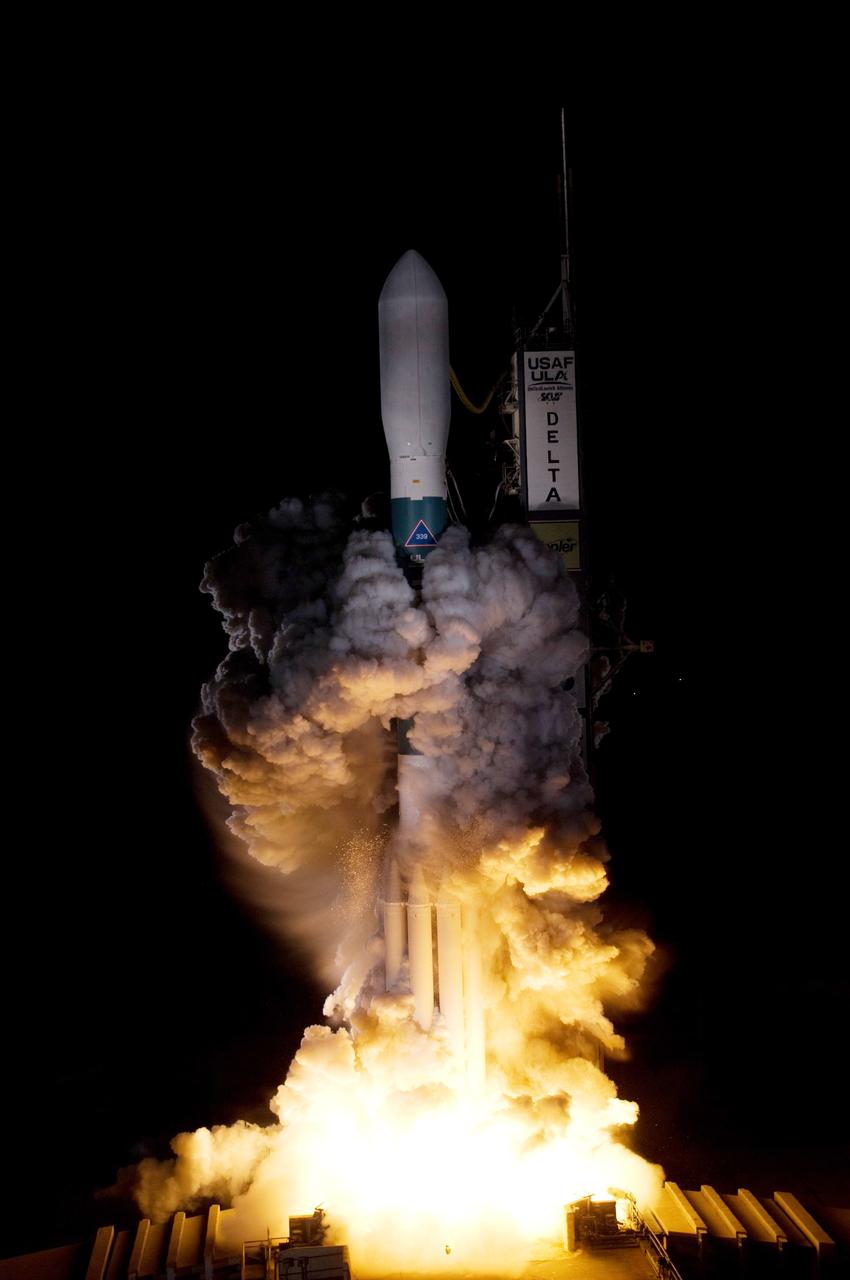

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket carrying NASA's Kepler spacecraft rises through the exhaust cloud created by the firing of the rocket’s engines. Liftoff was on time at 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Regina Mitchell-Ryall, Tom Farrar
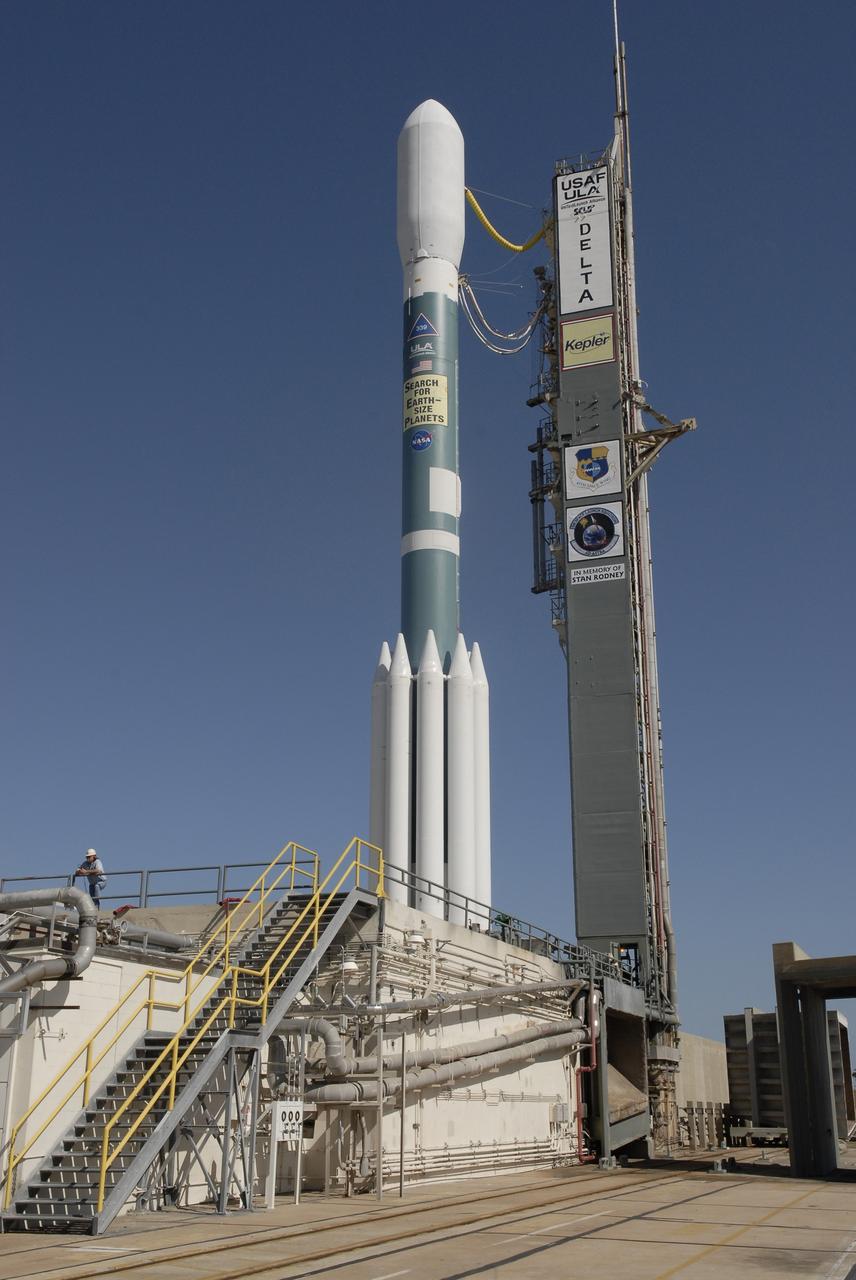

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After rollback of the mobile service tower on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Pad 17-B in Florida, NASA's Kepler spacecraft sits poised for launch atop the United Launch Alliance Delta II 7925 rocket. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
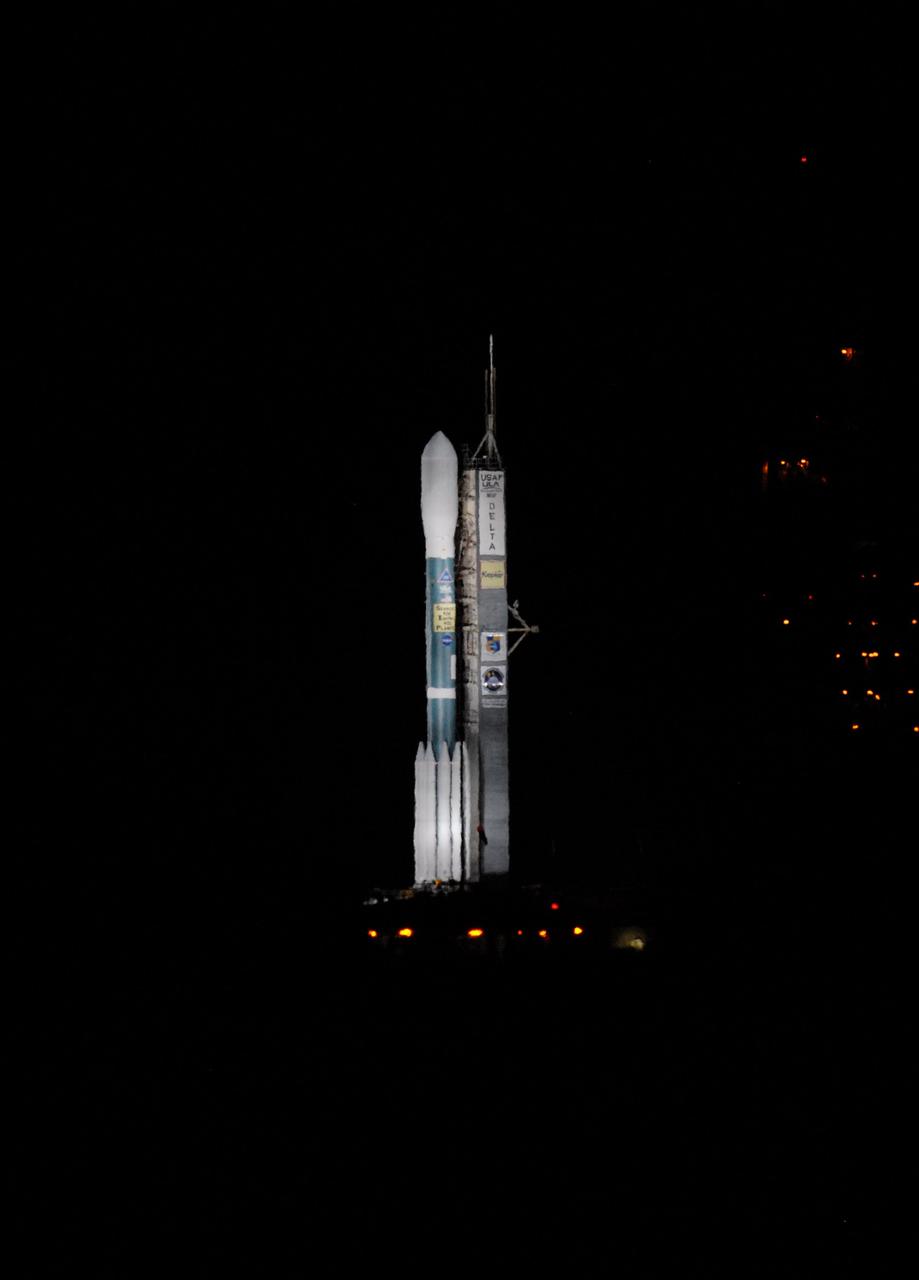

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket, with NASA's Kepler spacecraft aboard, is bathed in light on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida prior to launch. Liftoff is planned for 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
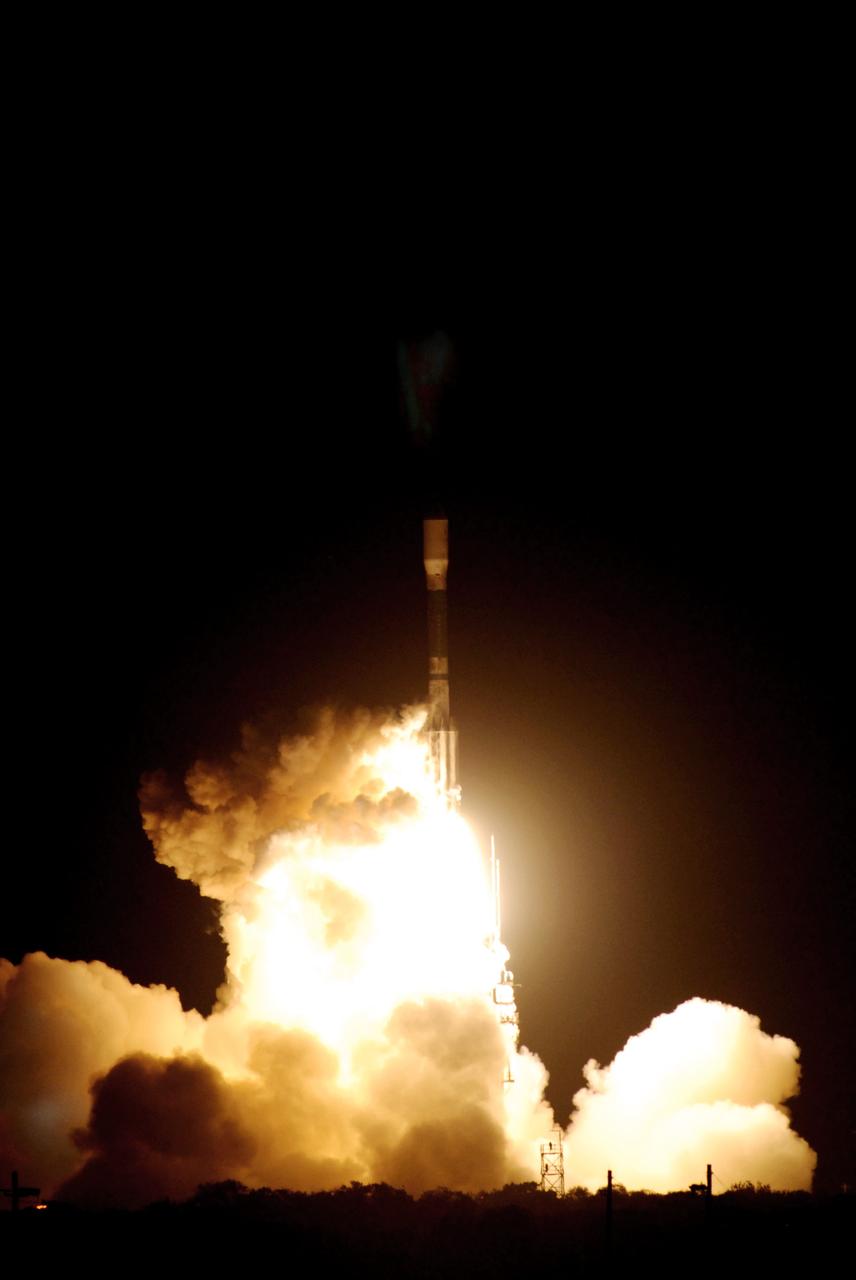

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket roars into the night sky carrying NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Liftoff from Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida was on time at 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
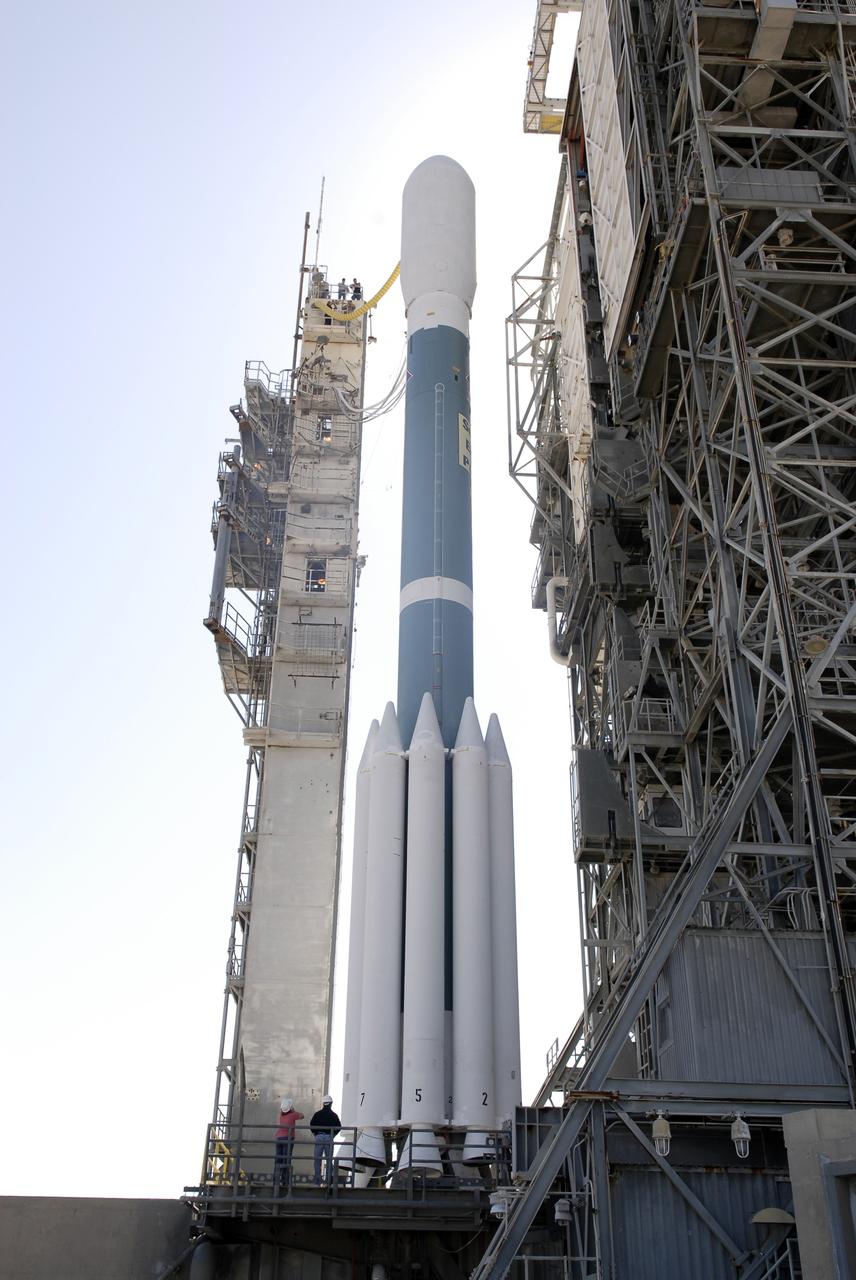

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
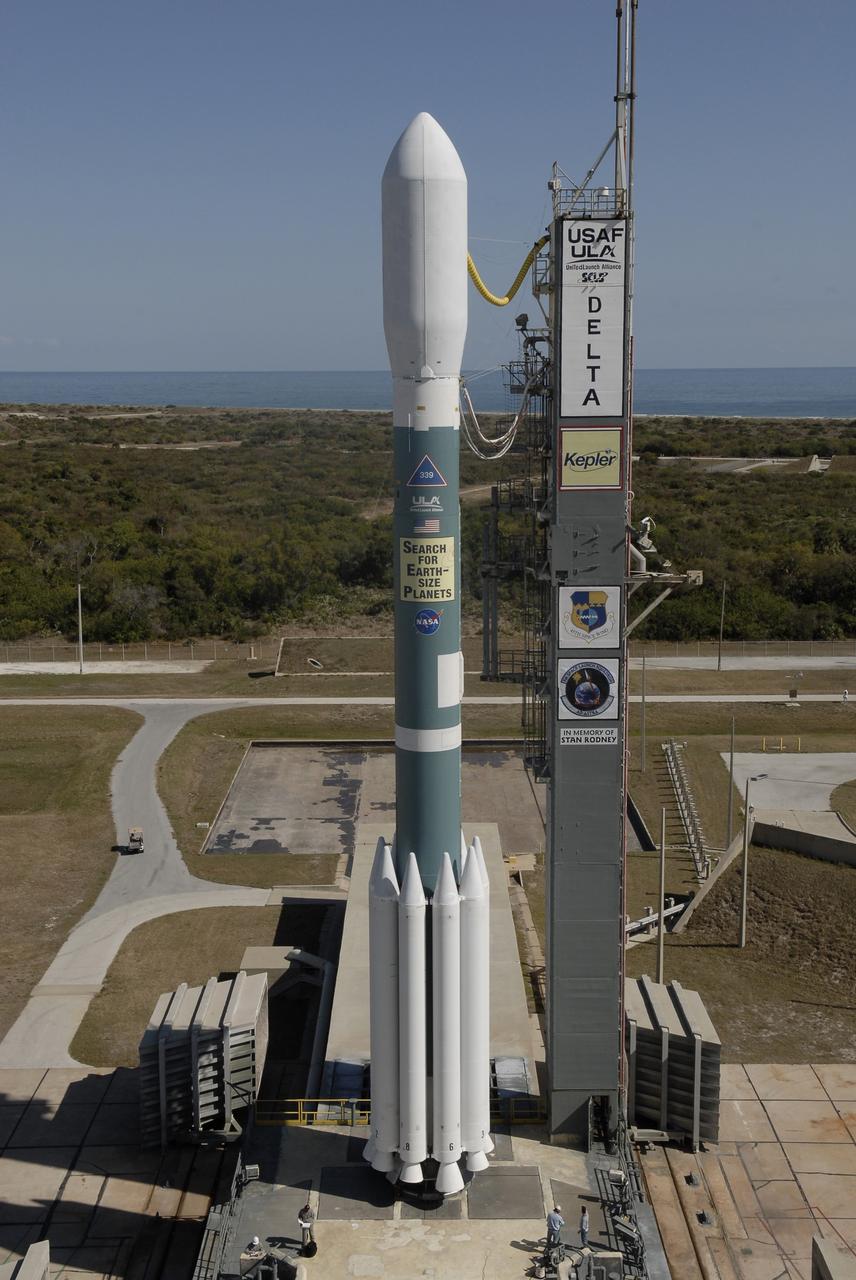

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After rollback of the mobile service tower on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Pad 17-B, in Florida, NASA's Kepler spacecraft sits poised for launch atop the United Launch Alliance Delta II 7925 rocket. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
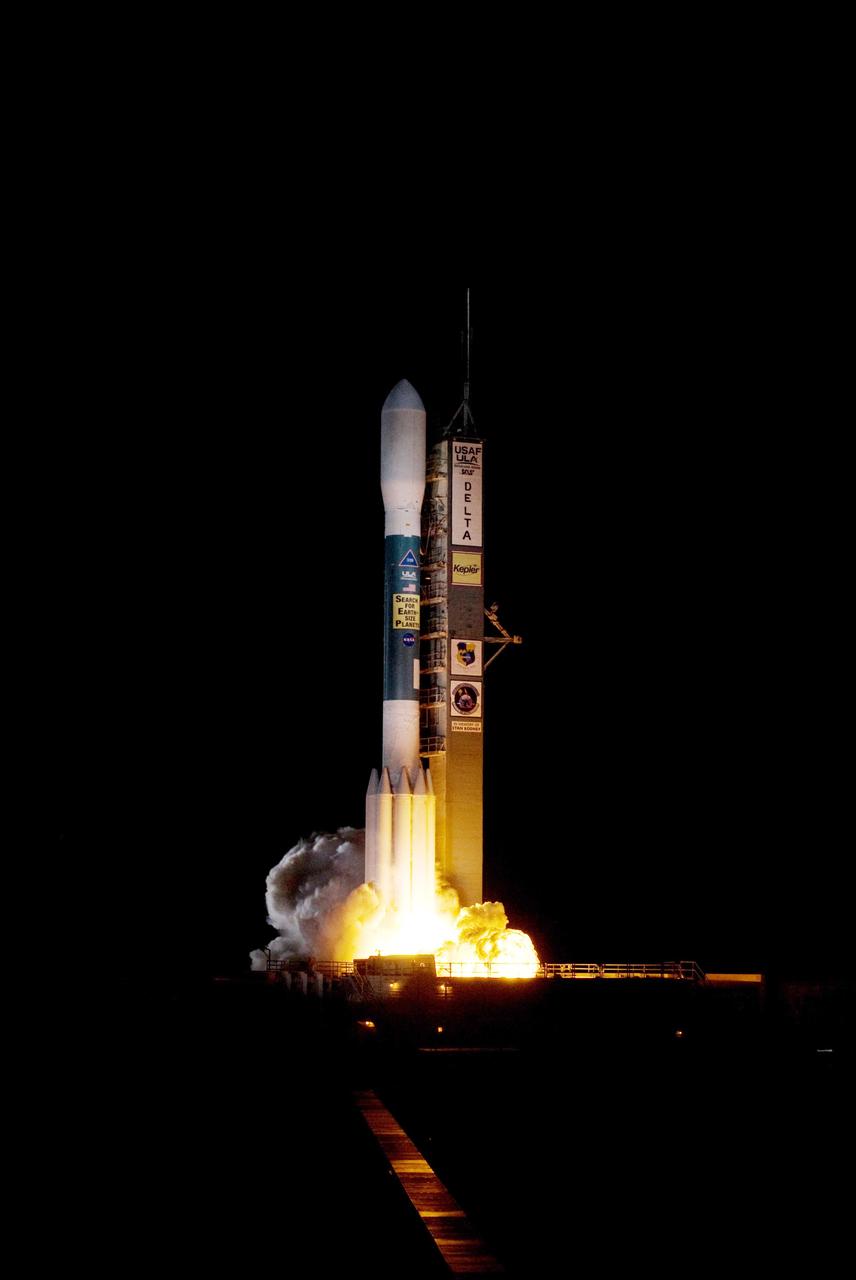

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – On Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida, exhaust clouds cascade around the base of United Launch Alliance's Delta II rocket carrying NASA's Kepler spacecraft as the rocket’s engines ignite. Liftoff was on time at 10:49 p.m. EST. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Sandra Joseph, Kevin O'Connell
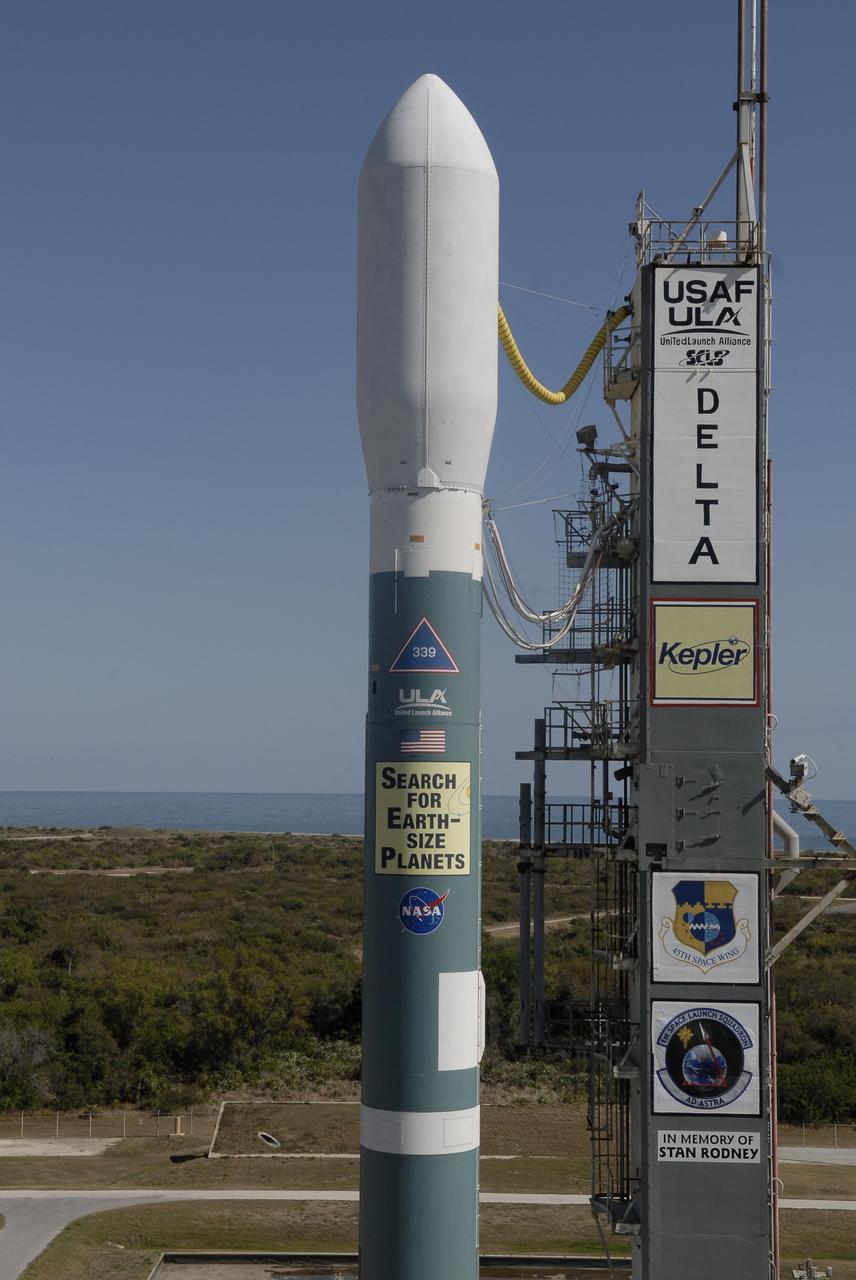

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Against the backdrop of the Atlantic Ocean, the Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
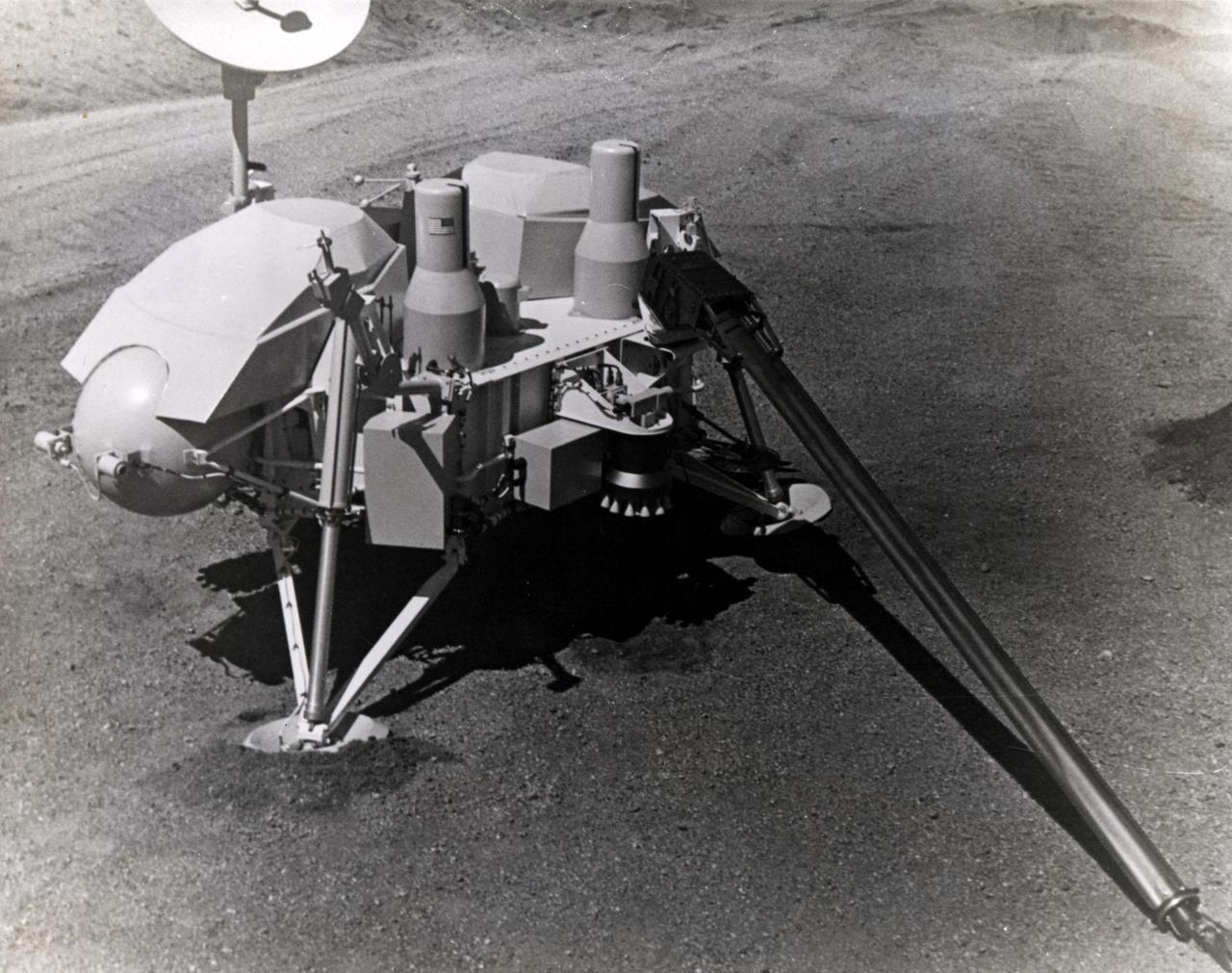
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Viking Project In 1976: NASA will land two automated scientific laboratories on the planet Mars. This pioneering effort to explore in detail the surface of another primary planet in our solar system will be identified by a name that exemplifies the spirit of historic exploration. To accomplish this goal, two spacecraft will be launched from the Kennedy Space Center within a month of another in mid-1975. These spacecraft, each including a lander and an orbiter, will hurtle nearly 460 million miles around the Sun before reaching the red planet. The descent will occur when Mars is about 225 million miles from Earth and nearly on the other side of the Sun. This requires a completely automated de-orbit and landing operation because, at that distance, two-way communication between Mars and Earth takes nearly 45 minutes. Surface science will then commence with principal scientific interest invested in biology, geology and meteorology.
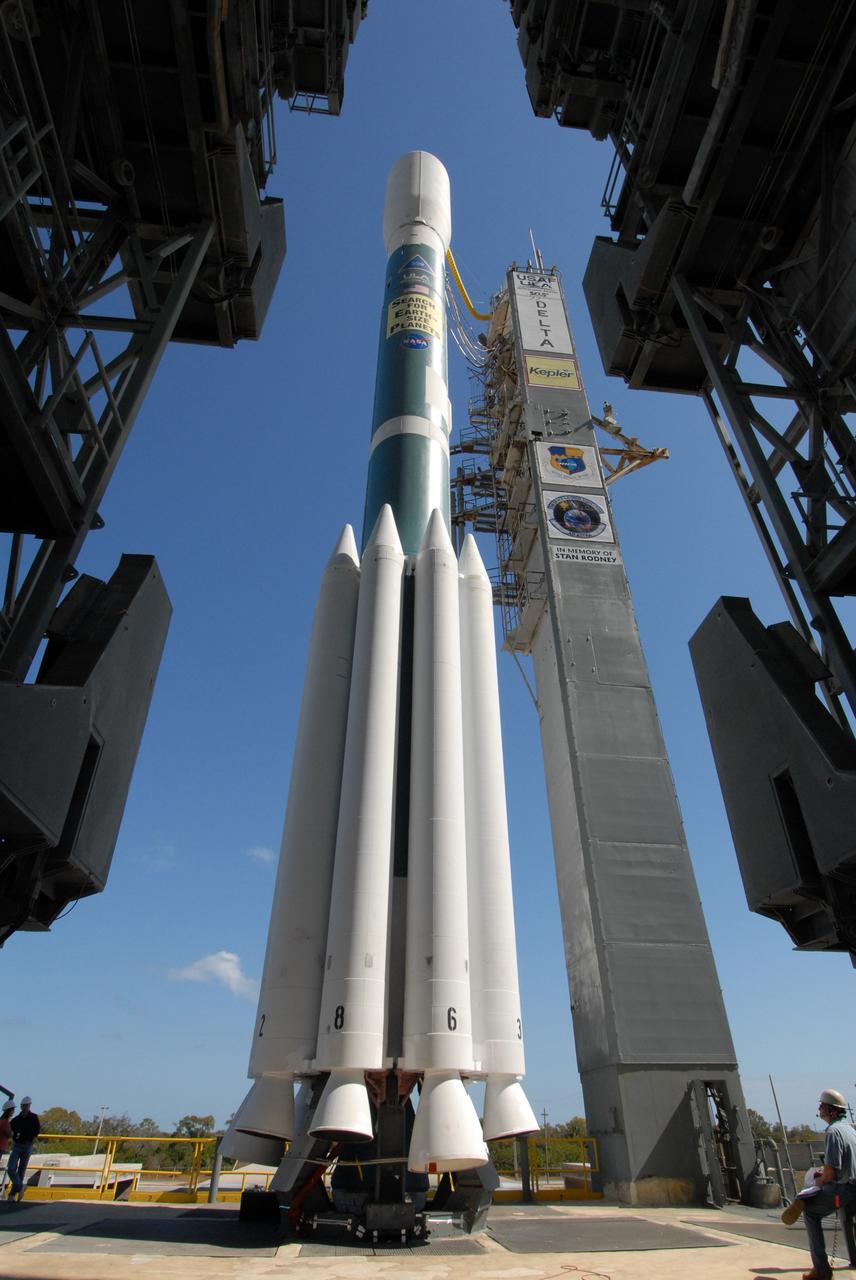

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Delta II 7925 rocket stands ready for launch following rollback of the mobile service tower on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Atop the rocket is NASA's Kepler spacecraft. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
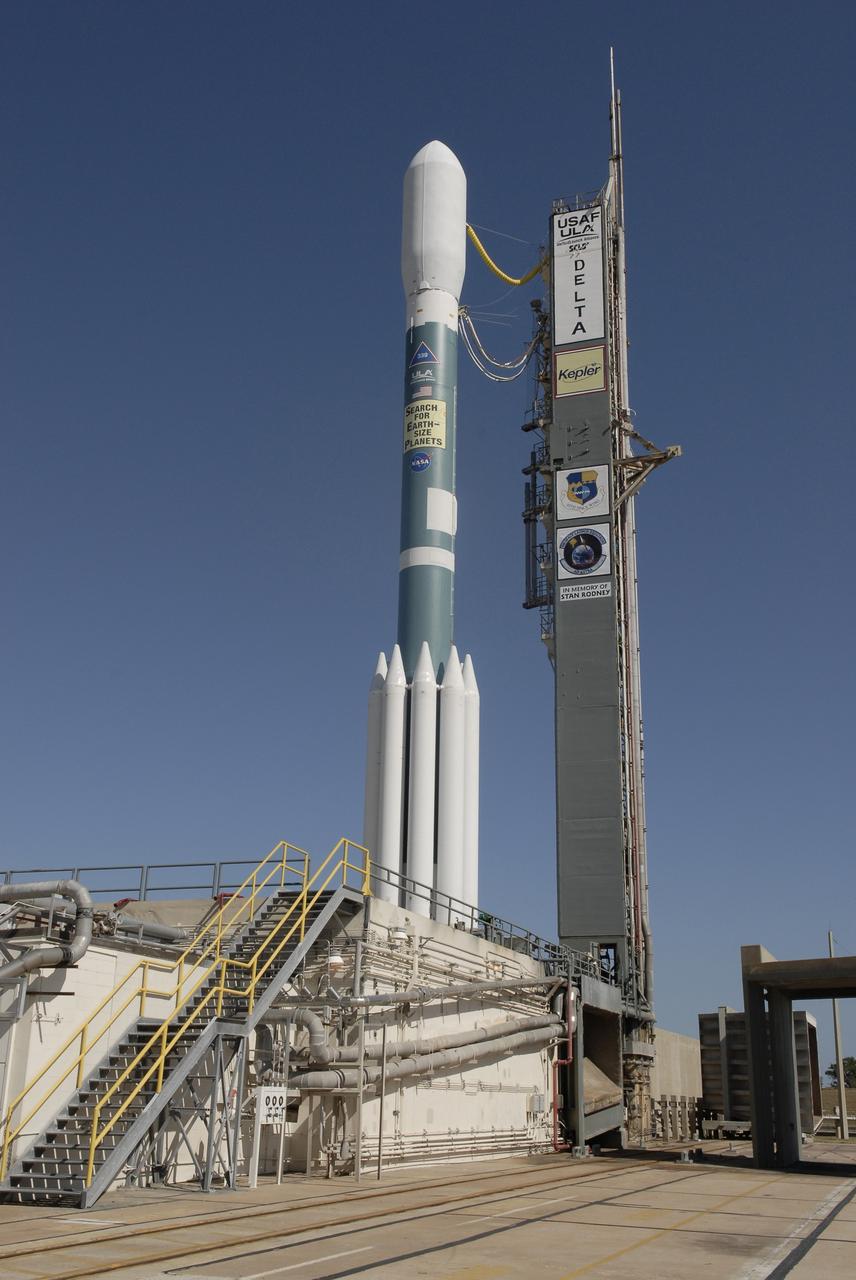

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After rollback of the mobile service tower on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station's Launch Pad 17-B in Florida, NASA's Kepler spacecraft sits poised for launch atop the United Launch Alliance Delta II 7925 rocket. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
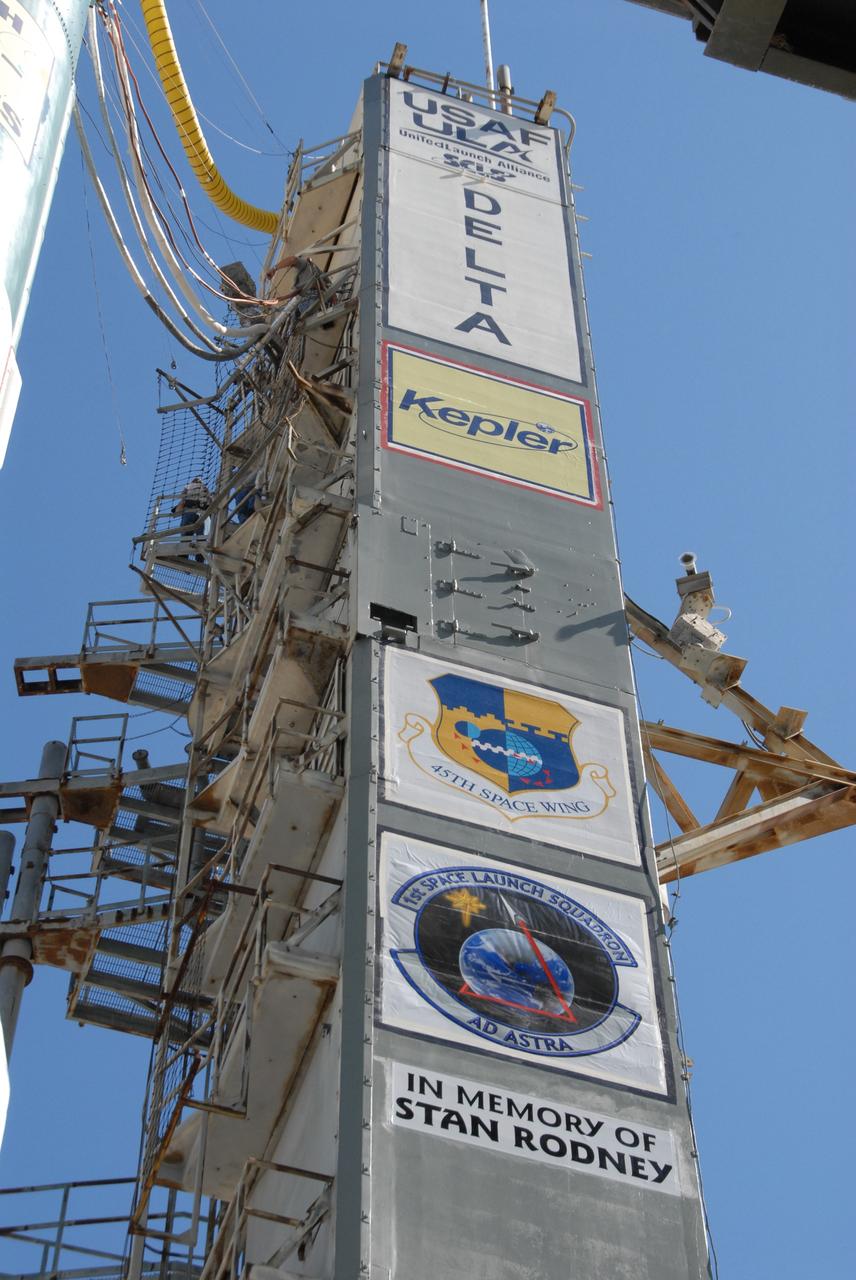

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The gantry on Launch Pad 17-B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida shows the various logos of NASA's Kepler spacecraft launch. Kepler is a spaceborne telescope designed to search the nearby region of our galaxy for Earth-size planets orbiting in the habitable zone of stars like our sun. The habitable zone is the region around a star where temperatures permit water to be liquid on a planet's surface. The challenge for Kepler is to look at a large number of stars in order to statistically estimate the total number of Earth-size planets orbiting sun-like stars in the habitable zone. Kepler will survey more than 100,000 stars in our galaxy. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
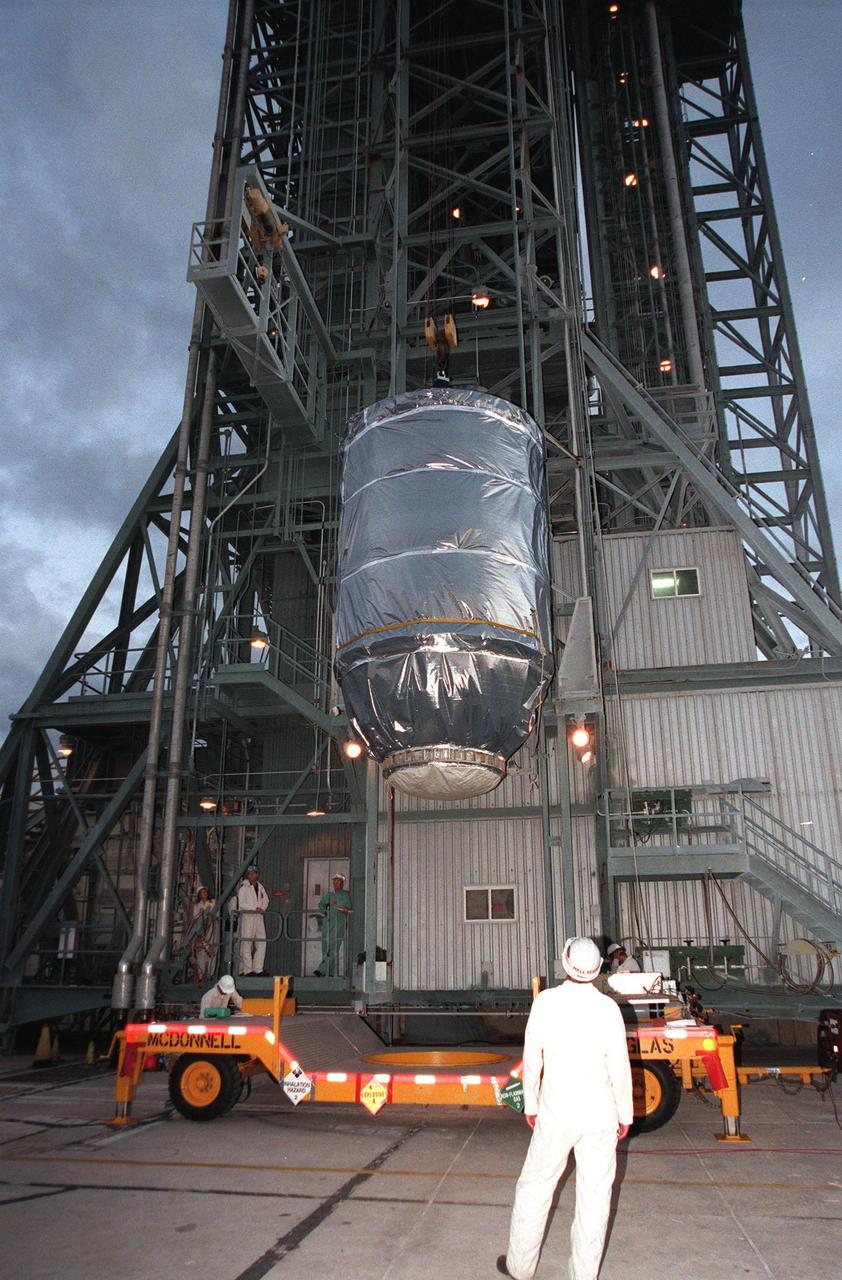

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Wrapped in a protective covering, the Mars Climate Orbiter with its upper stage booster is lifted up at Launch Complex 17, Pad A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, in preparation for mating to the second stage of a Boeing Delta II (7425) rocket. Targeted for liftoff on Dec. 10, 1998, the orbiter will be the first spacecraft to be launched in the pair of Mars ’98 missions. After its arrival at the red planet, the Mars Climate Orbiter will be used primarily to support its companion Mars Polar Lander spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Jan. 3, 1999. The orbiter will then monitor the Martian atmosphere and image the planet’s surface on a daily basis for one Martian year, the equivalent of about two Earth years. The spacecraft will observe the appearance and movement of atmospheric dust and water vapor, and characterize seasonal changes on the planet’s surface
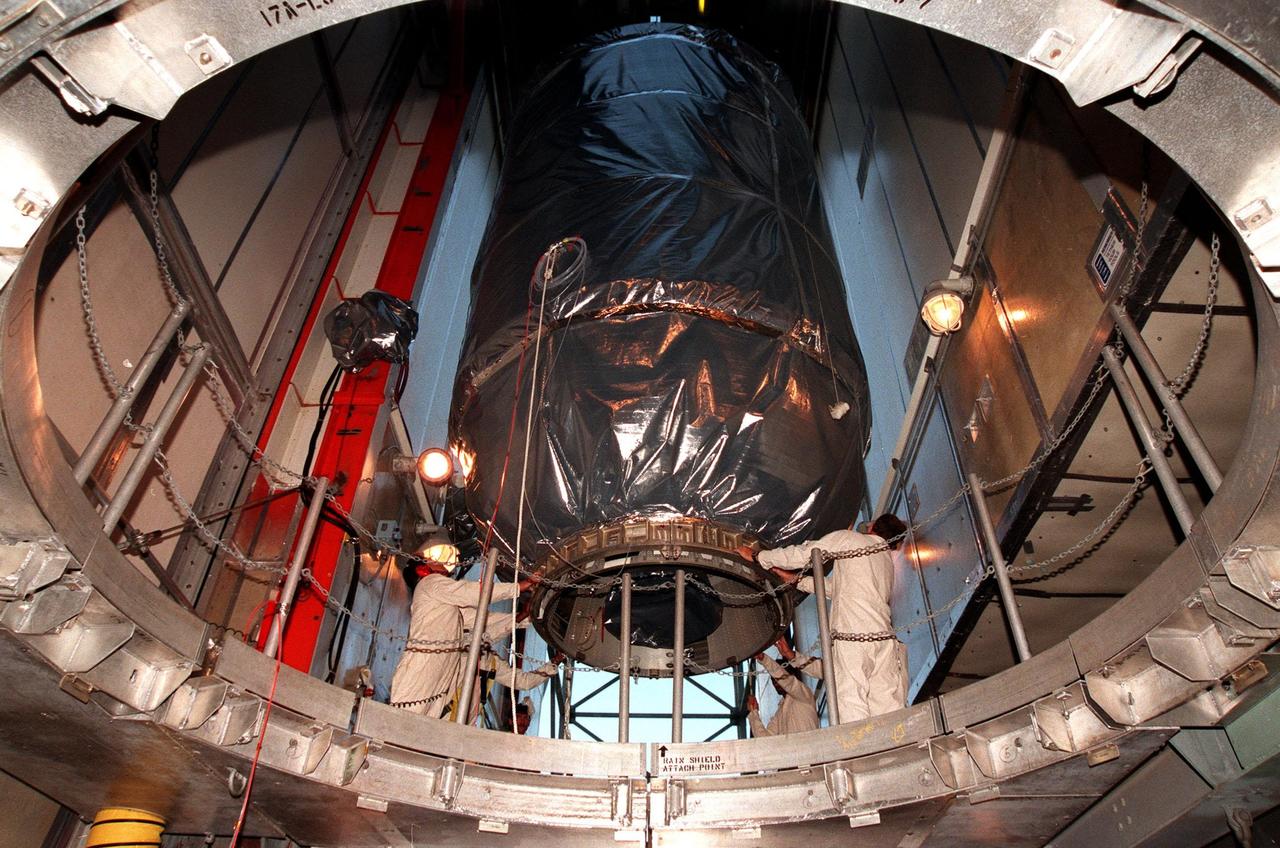

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Wrapped in a protective covering, the Mars Climate Orbiter with its upper stage booster is lowered in preparation for mating to the second stage of a Boeing Delta II (7425) rocket at Launch Complex 17, Pad A, Cape Canaveral Air Station. Targeted for liftoff on Dec. 10, 1998, the orbiter will be the first spacecraft to be launched in the pair of Mars ’98 missions. After its arrival at the red planet, the Mars Climate Orbiter will be used primarily to support its companion Mars Polar Lander spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Jan. 3, 1999. The orbiter will then monitor the Martian atmosphere and image the planet’s surface on a daily basis for one Martian year, the equivalent of about two Earth years. The spacecraft will observe the appearance and movement of atmospheric dust and water vapor, and characterize seasonal changes on the planet’s surface
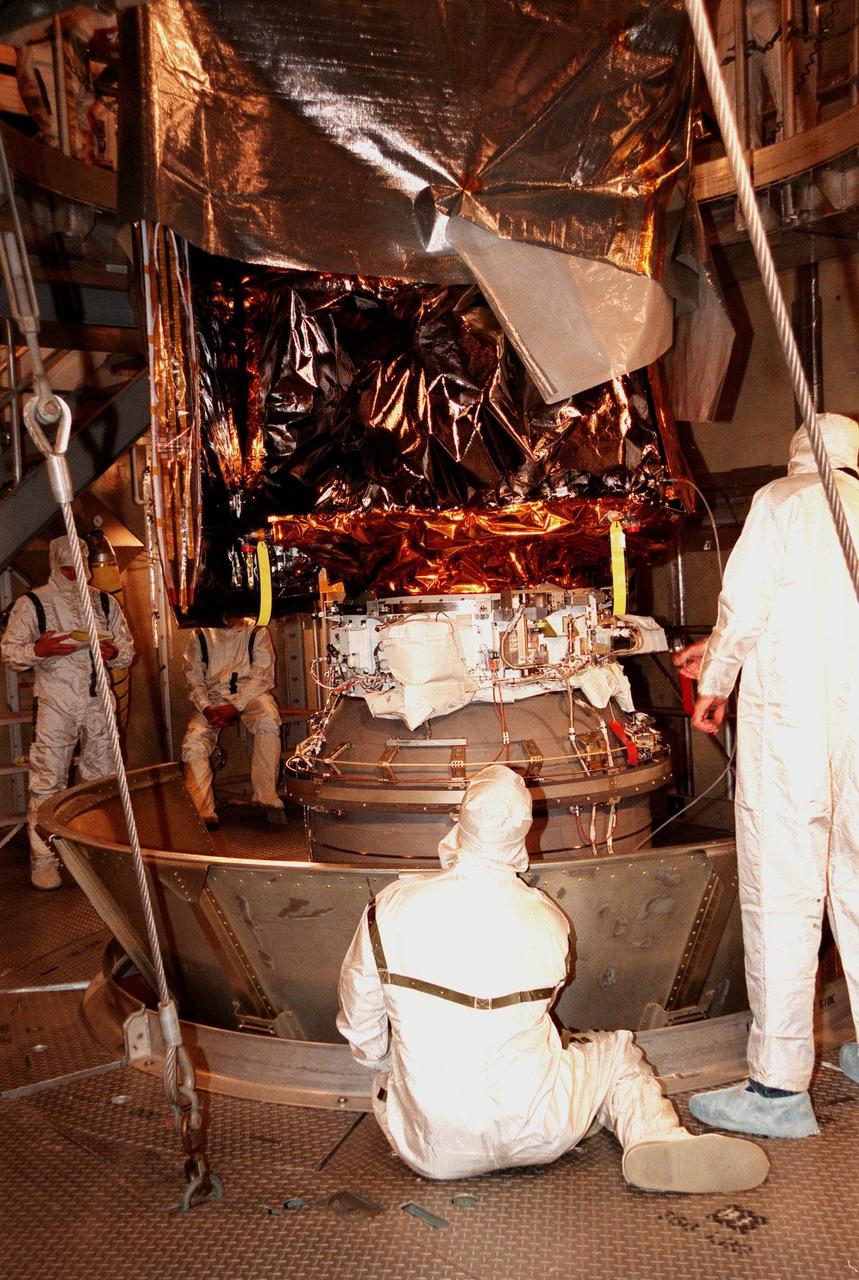

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, workers remove the canister surrounding the Mars Climate Orbiter. Targeted for liftoff on Dec. 10, 1998, aboard a Boeing Delta II (7425) rocket, the orbiter will be the first spacecraft to be launched in the pair of Mars '98 missions. After its arrival at the red planet, the Mars Climate Orbiter will be used primarily to support its companion Mars Polar Lander spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Jan. 3, 1999. The orbiter will then monitor the Martian atmosphere and image the planet's surface on a daily basis for one Martian year, the equivalent of about two Earth years. The spacecraft will observe the appearance and movement of atmospheric dust and water vapor, and characterize seasonal changes on the planet's surface
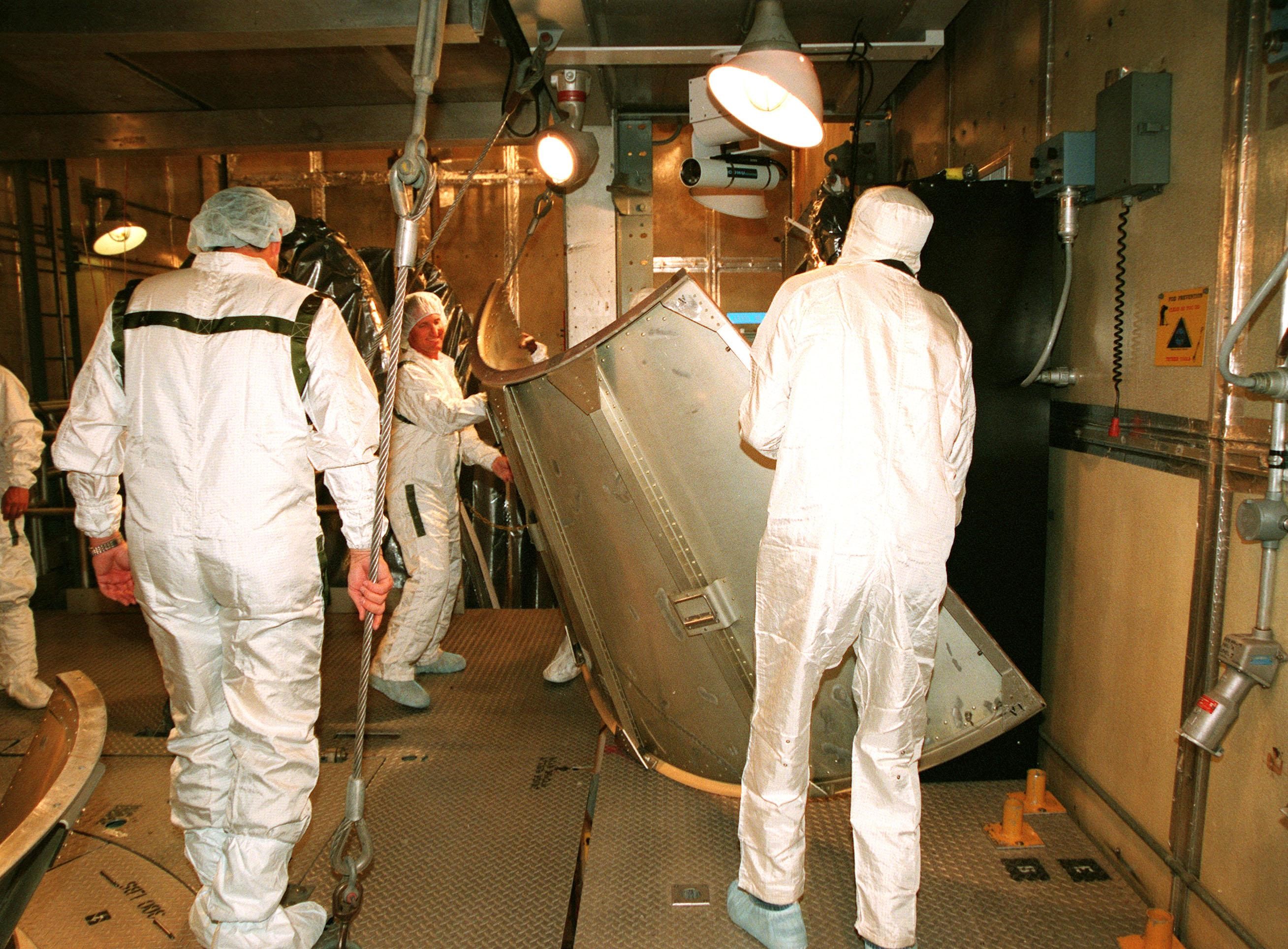

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, workers place aside a piece of the canister surrounding the Mars Climate Orbiter. Targeted for liftoff on Dec. 10, 1998, aboard a Boeing Delta II (7425) rocket, the orbiter will be the first spacecraft to be launched in the pair of Mars '98 missions. After its arrival at the red planet, the Mars Climate Orbiter will be used primarily to support its companion Mars Polar Lander spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Jan. 3, 1999. The orbiter will then monitor the Martian atmosphere and image the planet's surface on a daily basis for one Martian year, the equivalent of about two Earth years. The spacecraft will observe the appearance and movement of atmospheric dust and water vapor, and characterize seasonal changes on the planet's surface
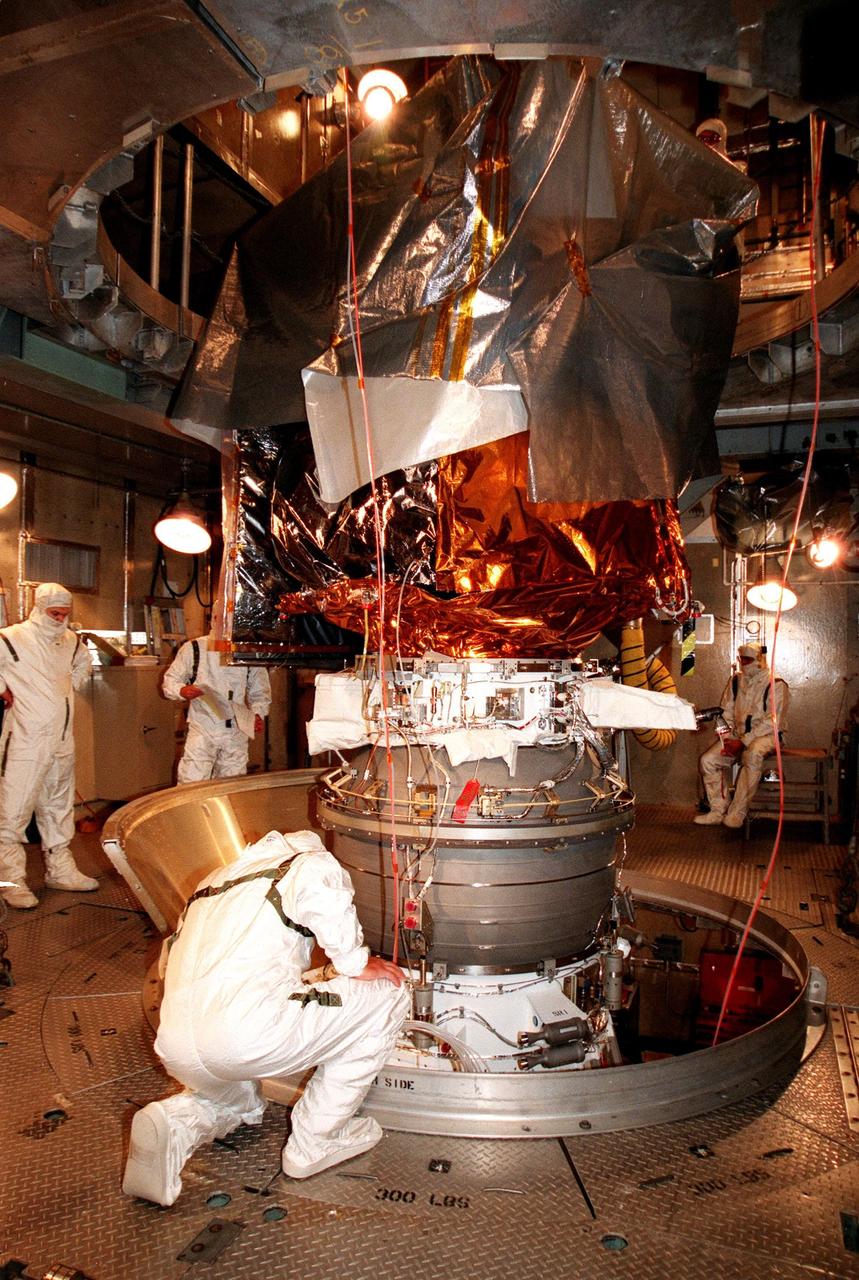

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, workers get ready to remove the last piece of the canister surrounding the Mars Climate Orbiter. Targeted for liftoff on Dec. 10, 1998, aboard a Boeing Delta II (7425) rocket, the orbiter will be the first spacecraft to be launched in the pair of Mars '98 missions. After its arrival at the red planet, the Mars Climate Orbiter will be used primarily to support its companion Mars Polar Lander spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Jan. 3, 1999. The orbiter will then monitor the Martian atmosphere and image the planet's surface on a daily basis for one Martian year, the equivalent of about two Earth years. The spacecraft will observe the appearance and movement of atmospheric dust and water vapor, and characterize seasonal changes on the planet's surface
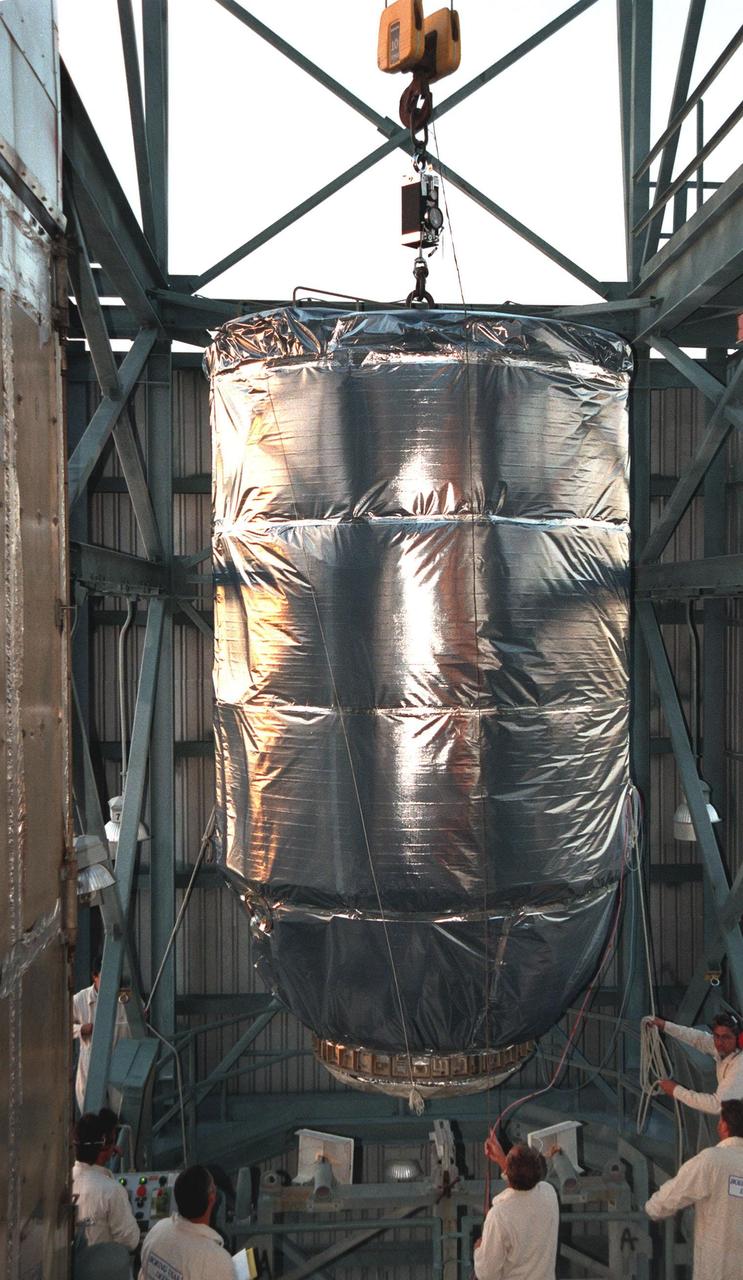

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Wrapped in a protective covering, the Mars Climate Orbiter with its upper stage booster is lifted up at Launch Complex 17, Pad A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, in preparation for mating to the second stage of a Boeing Delta II (7425) rocket. Targeted for liftoff on Dec. 10, 1998, the orbiter will be the first spacecraft to be launched in the pair of Mars ’98 missions. After its arrival at the red planet, the Mars Climate Orbiter will be used primarily to support its companion Mars Polar Lander spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Jan. 3, 1999. The orbiter will then monitor the Martian atmosphere and image the planet’s surface on a daily basis for one Martian year, the equivalent of about two Earth years. The spacecraft will observe the appearance and movement of atmospheric dust and water vapor, and characterize seasonal changes on the planet’s surface
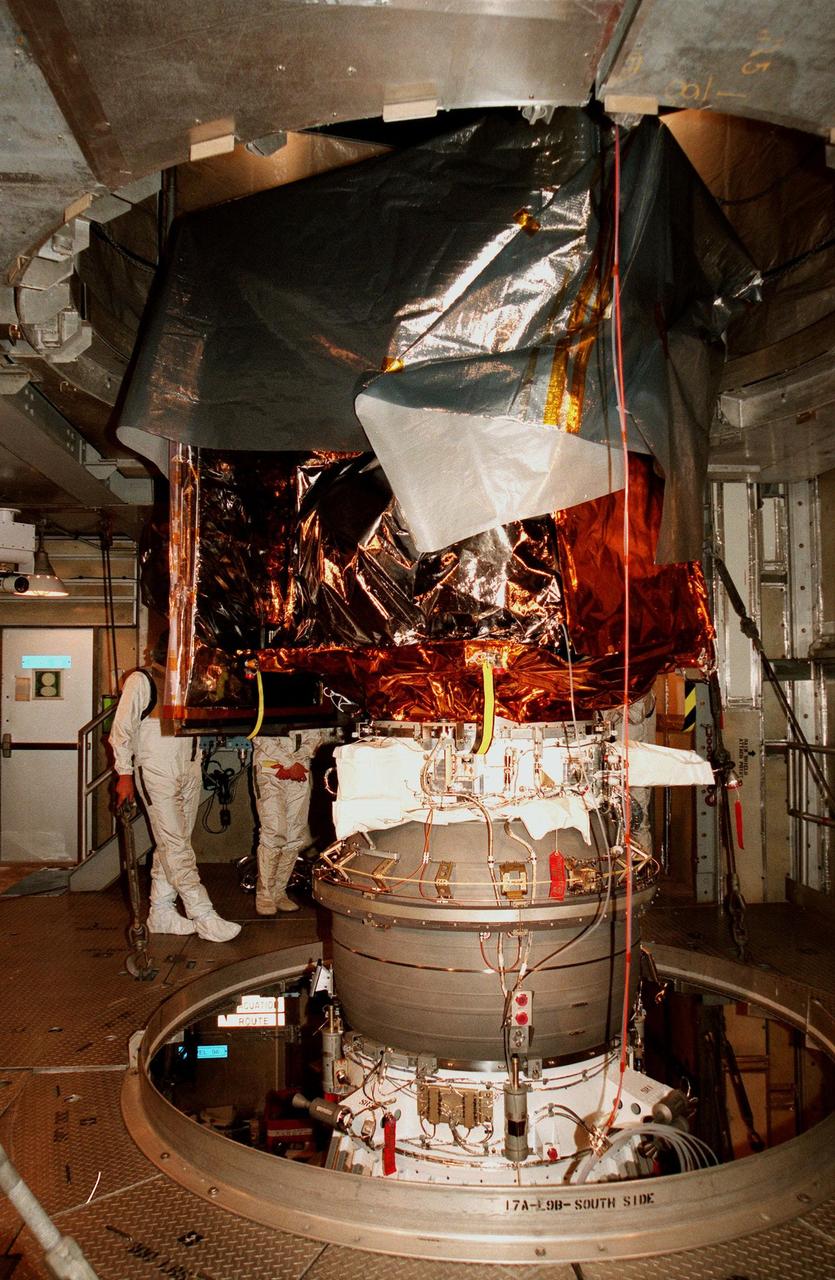

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- At Launch Complex 17A, Cape Canaveral Air Station, the Mars Climate Orbiter is free of the protective canister that surrounded it during the move to the pad. Targeted for liftoff on Dec. 10, 1998, aboard a Boeing Delta II (7425) rocket, the orbiter will be the first spacecraft to be launched in the pair of Mars '98 missions. After its arrival at the red planet, the Mars Climate Orbiter will be used primarily to support its companion Mars Polar Lander spacecraft, scheduled for launch on Jan. 3, 1999. The orbiter will then monitor the Martian atmosphere and image the planet's surface on a daily basis for one Martian year, the equivalent of about two Earth years. The spacecraft will observe the appearance and movement of atmospheric dust and water vapor, and characterize seasonal changes on the planet's surface
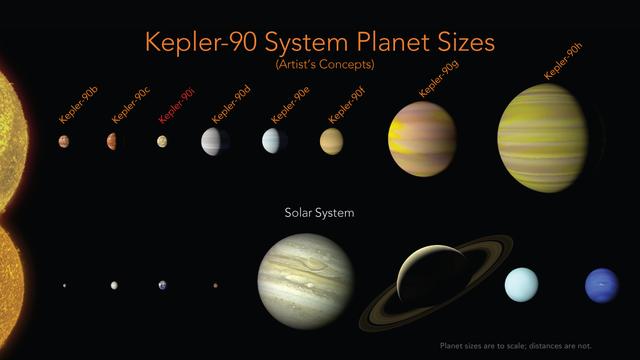
Our solar system now is tied for most number of planets around a single star, with the recent discovery of an eighth planet circling Kepler-90, a Sun-like star 2,545 light years from Earth. The planet was discovered in data from NASA's Kepler Space Telescope. This artist's concept depicts the Kepler-90 system compared with our own solar system. The newly-discovered Kepler-90i -- a sizzling hot, rocky planet that orbits its star once every 14.4 days -- was found using machine learning from Google. Machine learning is an approach to artificial intelligence in which computers "learn." In this case, computers learned to identify planets by finding in Kepler data instances where the telescope recorded changes in starlight caused by planets beyond our solar system, known as exoplanets. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22193

Our solar system now is tied for most number of planets around a single star, with the recent discovery of an eighth planet circling Kepler-90, a Sun-like star 2,545 light years from Earth. The planet was discovered in data from NASA's Kepler Space Telescope. The newly-discovered Kepler-90i -- a sizzling hot, rocky planet that orbits its star once every 14.4 days -- was found using machine learning from Google. Machine learning is an approach to artificial intelligence in which computers "learn." In this case, computers learned to identify planets by finding in Kepler data instances where the telescope recorded changes in starlight caused by planets beyond our solar system, known as exoplanets. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22192
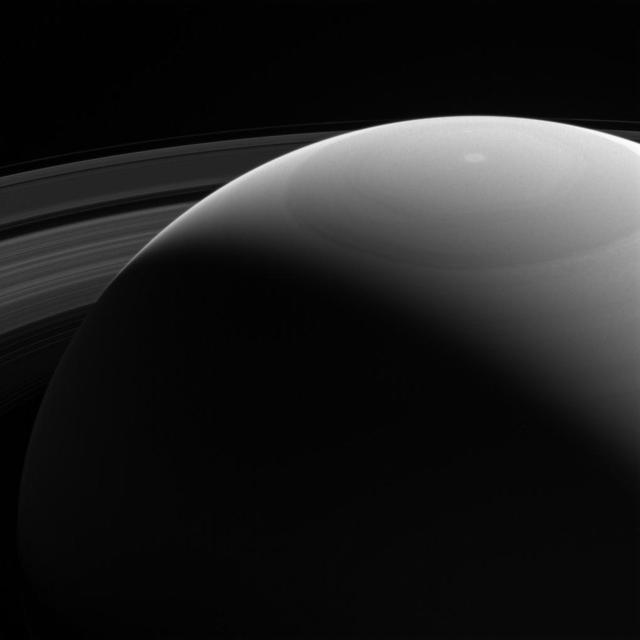

No Earth-based telescope could ever capture a view quite like this. Earth-based views can only show Saturn's daylit side, from within about 25 degrees of Saturn's equatorial plane. A spacecraft in orbit, like Cassini, can capture stunning scenes that would be impossible from our home planet. This view looks toward the sunlit side of the rings from about 25 degrees (if Saturn is dominant in image) above the ring plane. The image was taken in violet light with the Cassini spacecraft wide-angle camera on Oct. 28, 2016. The view was obtained at a distance of approximately 810,000 miles (1.3 million kilometers) from Saturn. Image scale is 50 miles (80 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20517

This STS-68 patch was designed by artist Sean Collins. Exploration of Earth from space is the focus of the design of the insignia, the second flight of the Space Radar Laboratory (SRL-2). SRL-2 was part of NASA's Mission to Planet Earth (MTPE) project. The world's land masses and oceans dominate the center field, with the Space Shuttle Endeavour circling the globe. The SRL-2 letters span the width and breadth of planet Earth, symbolizing worldwide coverage of the two prime experiments of STS-68: The Shuttle Imaging Radar-C and X-Band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SIR-C/X-SAR) instruments; and the Measurement of Air Pollution from Satellites (MAPS) sensor. The red, blue, and black colors of the insignia represent the three operating wavelengths of SIR-C/X-SAR, and the gold band surrounding the globe symbolizes the atmospheric envelope examined by MAPS. The flags of international partners Germany and Italy are shown opposite Endeavour. The relationship of the Orbiter to Earth highlights the usefulness of human space flights in understanding Earth's environment, and the monitoring of its changing surface and atmosphere. In the words of the crew members, the soaring Orbiter also typifies the excellence of the NASA team in exploring our own world, using the tools which the Space Program developed to explore the other planets in the solar system.
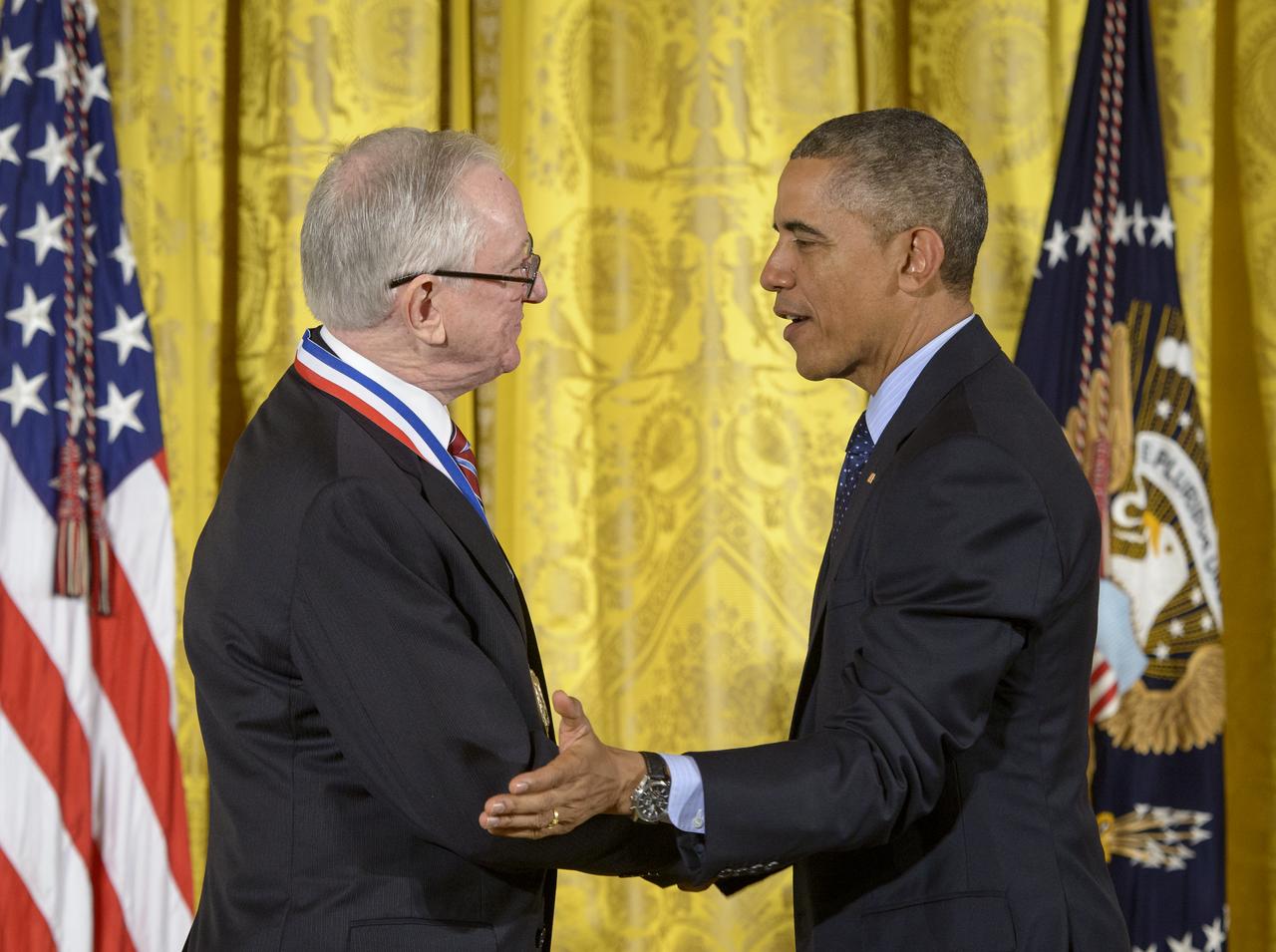

President Barack Obama congratulates MESSENGER Principal Investigator, director of Columbia University's Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, Sean Solomon, after awarding him the National Medal of Science, the nation's top scientific honor,Thursday, Nov. 20, 2014 during a ceremony in the East Room of the White House in Washington. MESSENGER (MErcury Surface, Space ENvironment, GEochemistry, and Ranging) is a NASA-sponsored scientific investigation of the planet Mercury and the first space mission designed to orbit the planet closest to the Sun. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
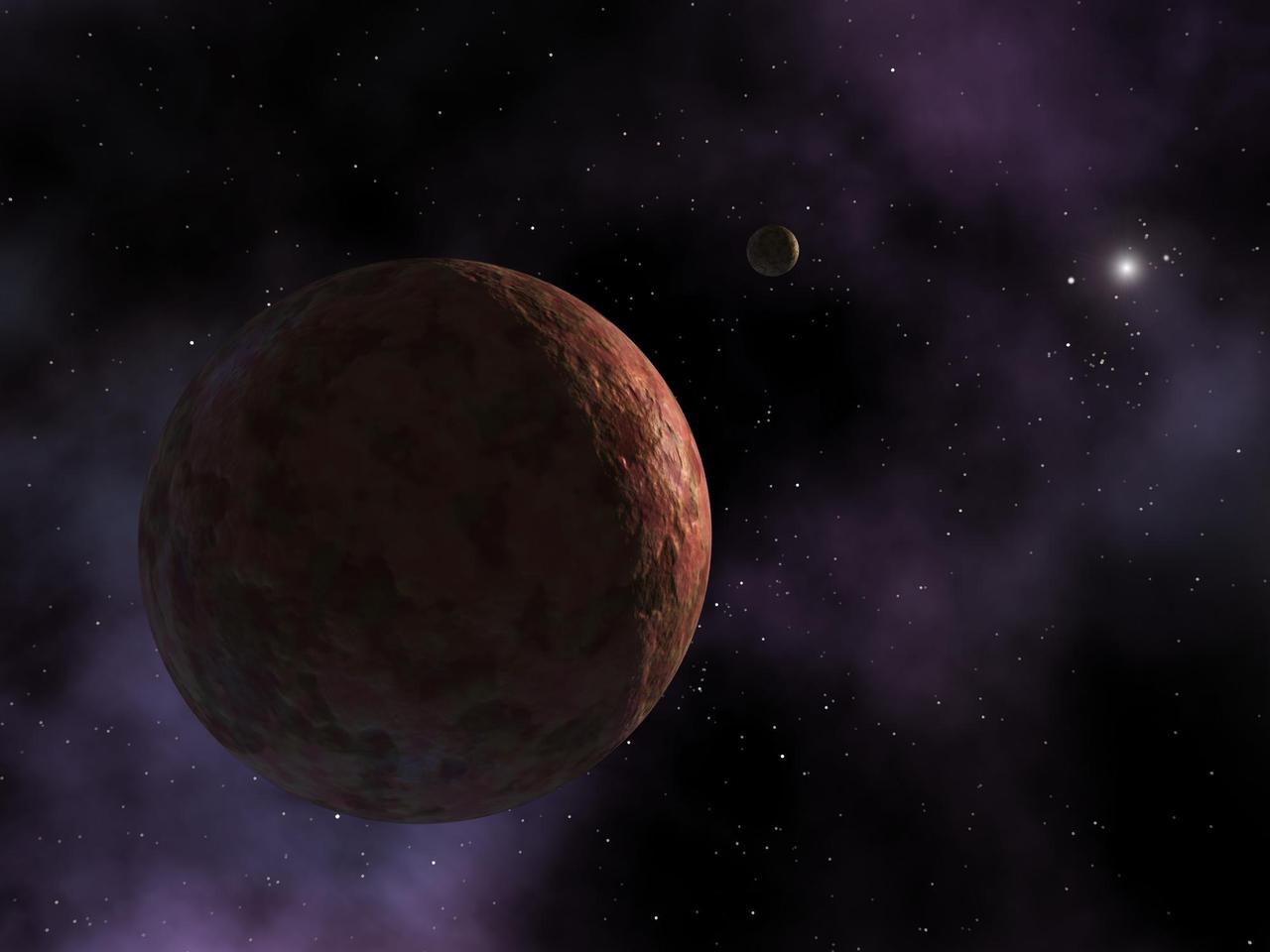

In this artist's visualization, the newly discovered planet-like object, dubbed "Sedna," is shown where it resides at the outer edges of the known solar system. The object is so far away that the Sun appears as an extremely bright star instead of a large, warm disc observed from Earth. All that is known about Sedna's appearance is that it has a reddish hue, almost as red and reflective as the planet Mars. In the distance is a hypothetical small moon, which scientists believe may be orbiting this distant body. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05566

WASP-18b is an exoplanet located 325 light-years from Earth. The planet's mass is 10 times that of Jupiter, and it orbits its star once every 23 hours. A 2017 study found that this planet has a stratosphere that's loaded with carbon dioxide, but has no signs of water. A stratosphere is a layer of atmosphere in which temperature increases with higher altitudes. The study used NASA's Spitzer and Hubble space telescopes. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22087
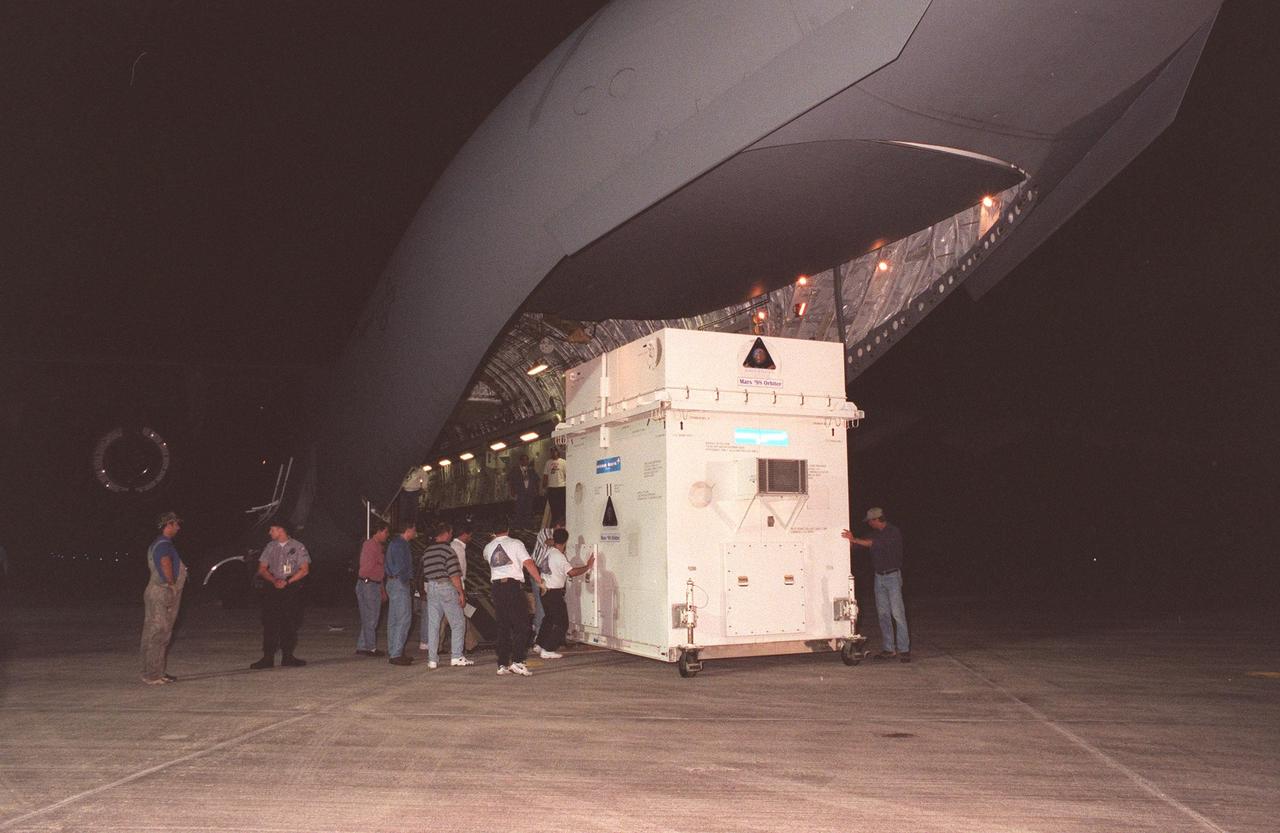

The Mars Climate Orbiter spacecraft arrives at KSC's Shuttle Landing Facility aboard an Air Force C-17 cargo plane early this morning following its flight from the Lockheed Martin Astronautics plant in Denver, Colo. When the spacecraft arrives at the red planet, it will primarily support its companion Mars Polar Lander spacecraft, planned for launch on Jan. 3, 1999. After that, the Mars Climate Orbiter's instruments will monitor the Martian atmosphere and image the planet's surface on a daily basis for one Martian year (1.8 Earth years). It will observe the appearance and movement of atmospheric dust and water vapor, as well as characterize seasonal changes on the surface. The detailed images of the surface features will provide important clues to the planet's early climate history and give scientists more information about possible liquid water reserves beneath the surface. The scheduled launch date for the Mars Climate Orbiter is Dec. 10, 1998, on a Delta II 7425 rocket

The International Space Station (ISS) Expedition 6 crew patch depicts the station orbiting the Earth on its mission of international cooperation and scientific research. The Earth is placed in the center of the patch to emphasize that work conducted aboard this orbiting laboratory is intended to improve life on our home planet. The shape of the Space Station’s orbit symbolizes the role that experience gained from ISS will have on future exploration of our solar system and beyond. The American and Russian flags encircling the Earth represent the native countries of the Expedition 6 crew members, which are just two of the many participant countries contributing to the ISS and committed to the peaceful exploration of space.

The International Space Station (ISS) Expedition 6 crew patch depicts the station orbiting the Earth on its mission of international cooperation and scientific research. The Earth is placed in the center of the patch to emphasize that work conducted aboard this orbiting laboratory is intended to improve life on our home planet. The shape of the Space Station’s orbit symbolizes the role that experience gained from ISS will have on future exploration of our solar system and beyond. The American and Russian flags encircling the Earth represent the native countries of the Expedition 6 crew members, which are just two of the many participant countries contributing to the ISS and committed to the peaceful exploration of space.
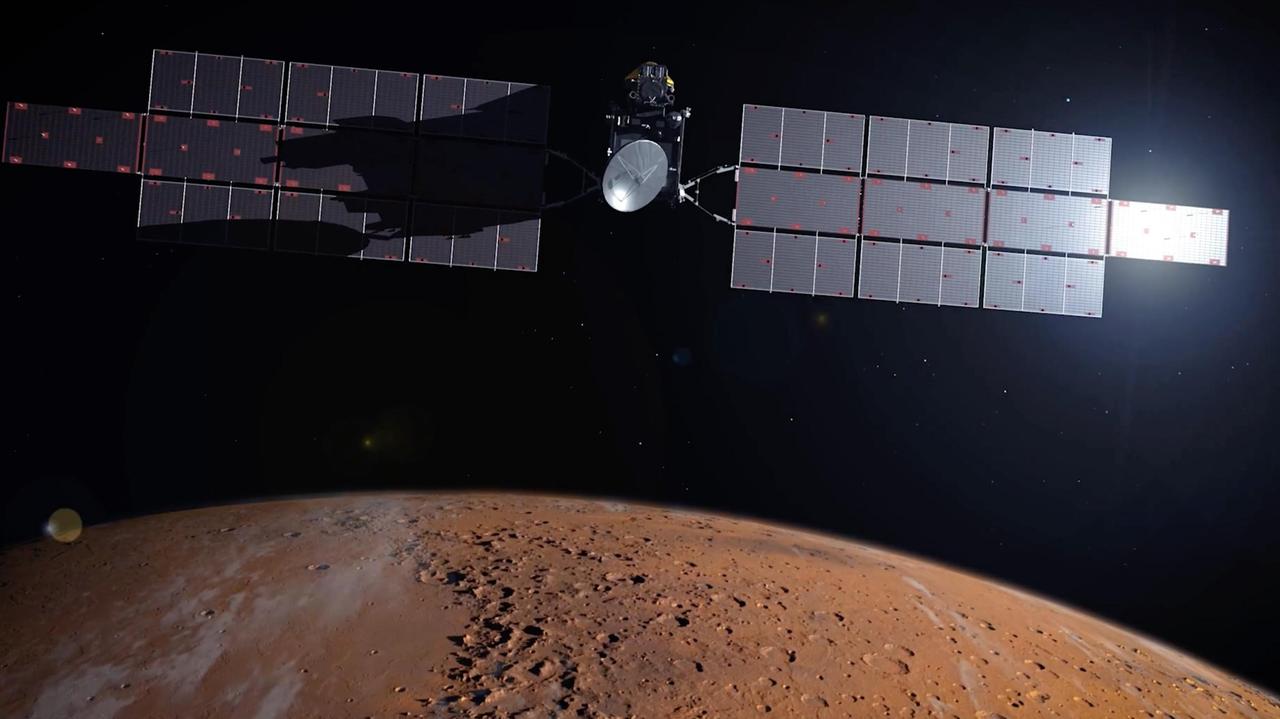

The Earth Return Orbiter (ERO) is one of the flight missions making up the Mars Sample Return campaign to bring martian rock and atmospheric samples back to Earth. This European Space Agency (ESA) orbiter would be the first interplanetary spacecraft to capture samples in orbit and make a return trip between Earth and Mars. ERO would also be the largest spacecraft to orbit the Red Planet. In addition to the rendezvous and return mission, ERO would provide critical Mars-Earth communications coverage for NASA's Perseverance rover and the Sample Retrieval Lander to deliver the martian samples. The Earth Return Orbiter is part of the multi-mission Mars Sample Return campaign being planned by NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA). https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25891
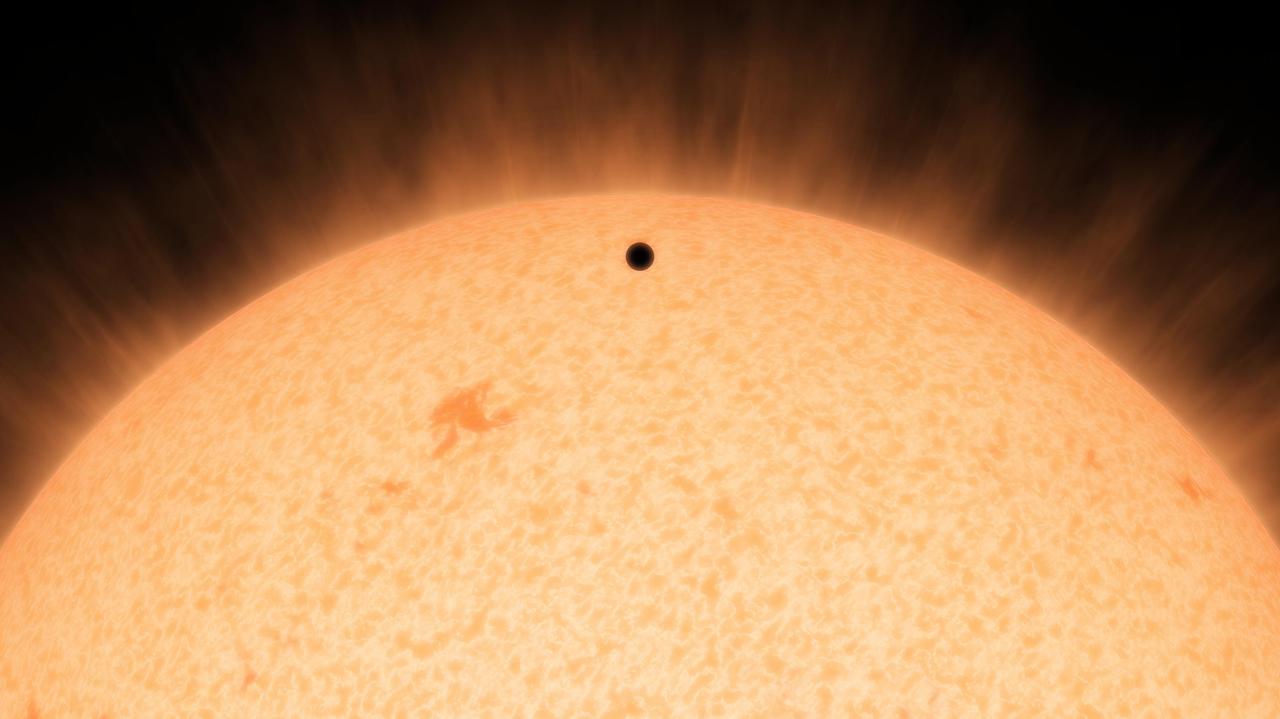

This artist's conception shows the silhouette of a rocky planet, dubbed HD 219134b, as it passes in front of its star. At 21 light-years away, the planet is the closest outside of our solar system that can be seen crossing, or transiting, its star -- a bonus for astronomers because transiting planets make ideal specimens for detailed studies of their atmospheres. It was discovered using the HARPS-North instrument on the Italian 3.6-meter National Galileo Telescope in the Canary Islands, and NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope. The planet, which is about 1.6 times the size of Earth, is also the nearest confirmed rocky planet outside our solar system. It orbits a star that is cooler and smaller than our sun, whipping closely around it in a mere three days. The proximity of the planet to the star means that it would be scorching hot and not habitable. Transiting planets are ideal targets for astronomers wanting to know more about planetary compositions and atmospheres. As a planet passes in front of its star, it causes the starlight to dim, and telescopes can measure this effect. If molecules are present in the planet's atmosphere, they can absorb certain wavelengths of light, leaving imprints in the starlight. This type of technique will be used in the future to investigate potentially habitable planets and search for signs of life. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA19831

This artist's concept shows OGLE-2016-BLG-1195Lb, a planet discovered through a technique called microlensing. The planet was reported in a 2017 study in the Astrophysical Journal Letters. Study authors used the Korea Microlensing Telescope Network (KMTNet), operated by the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute, and NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope, to track the microlensing event and find the planet. Although OGLE-2016-BLG-1195Lb is about the same mass as Earth, and the same distance from its host star as our planet is from our sun, the similarities may end there. This planet is nearly 13,000 light-years away and orbits a star so small, scientists aren't sure if it's a star at all. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21430

ISS048e056981 (0813/2016) --- Sparkling aurora colors of magenta and green color the sky's while the International Space Station orbits above the planet every 90 minutes. SpaceX’s Dragon resupply vehicle is seen docked to the Earth-facing port of the Harmony module.

This artist's concept shows exoplanet Kepler-1649c orbiting around its host red dwarf star. This exoplanet is in its star's habitable zone (the distance where liquid water could exist on the planet's surface) and is the closest to Earth in size and temperature found yet in Kepler's data. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23689
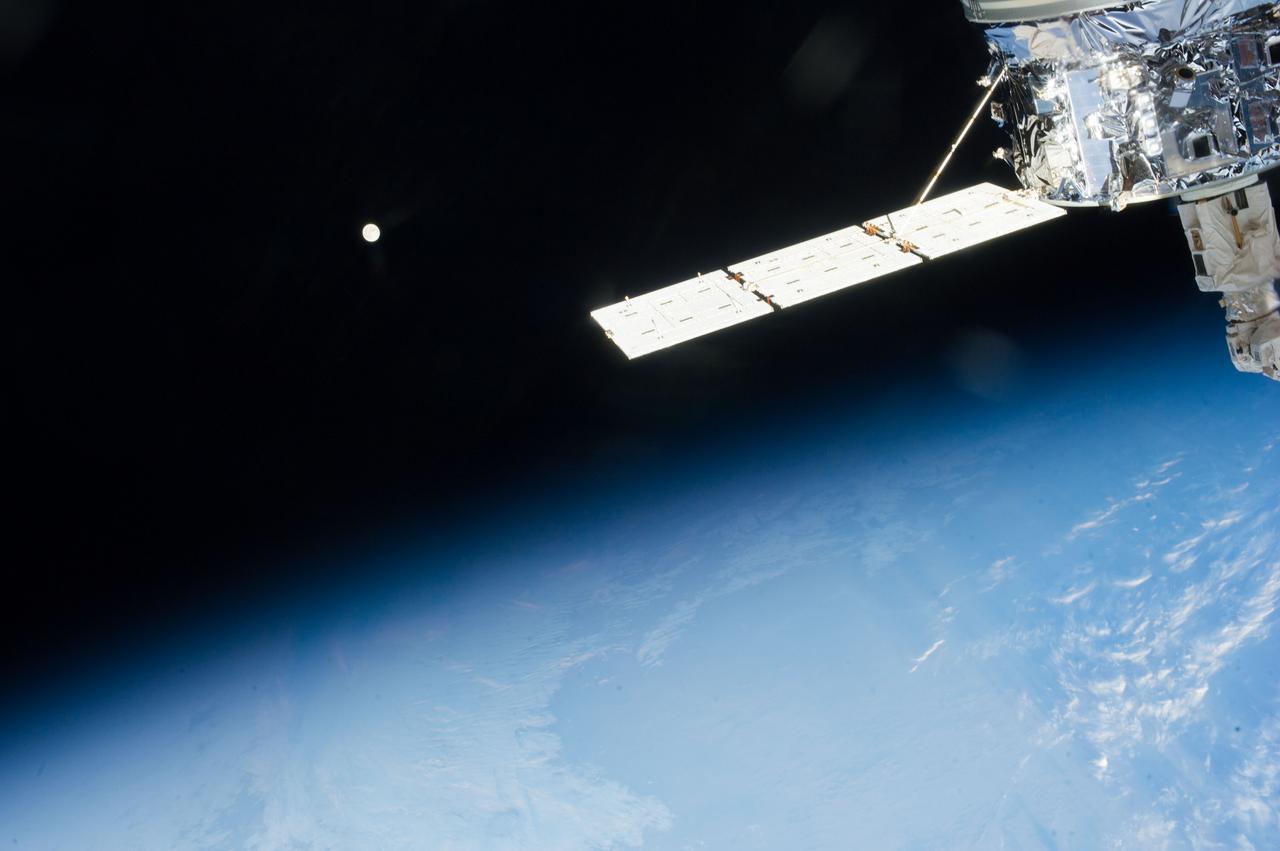

ISS037-E-017169 (19 Oct. 2013) --- The European Space Agency's fourth Automated Transfer Vehicle (ATV-4), also known as the Albert Einstein, is seen in the foreground of an image featuring the home planet and its moon as photographed by one of Expedition 37 crew members aboard the Earth-orbiting International Space Station.
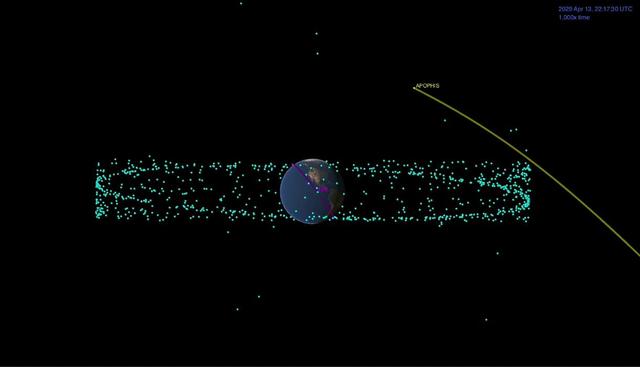
This animation shows the distance between the Apophis asteroid and Earth at the time of the asteroid's closest approach. The blue dots are the many man-made satellites that orbit our planet, and the pink represents the International Space Station. Movie available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23195
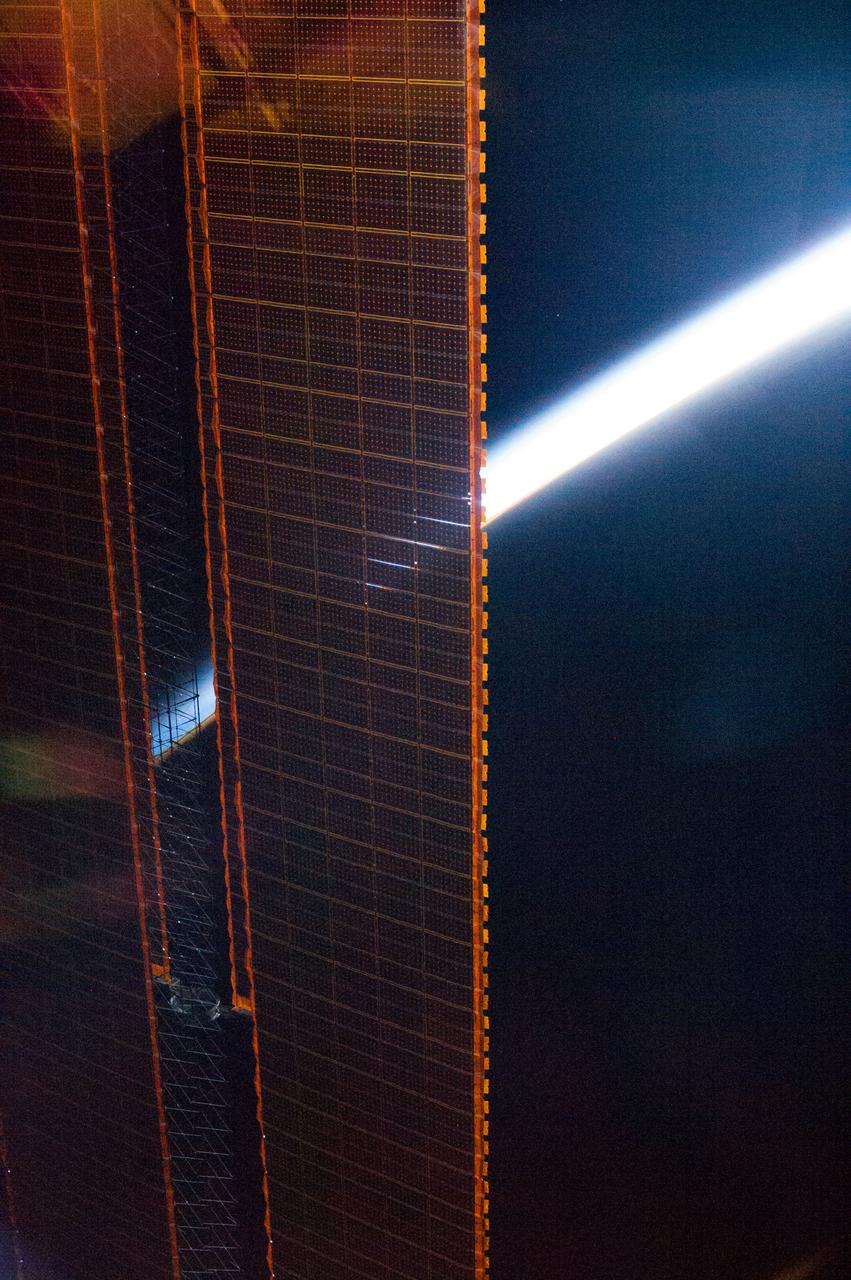

ISS036-E-007619 (13 June 2013) --- To a crew member aboard the International Space Station, the home planet is seen from many different angles and perspectives, as evdenced by this Expedition 36 image of Earth's atmophere partially obscured by one of the orbital outpost's solar panels.

ISS028-E-030096(22 Aug. 2011) --- A last quarter moon appears at the center of this night time photo taken from the International Space Station in Earth orbit on Aug. 22, 2011. A thin line of the planet's atmosphere and a small group of clouds are the other illuminated objects in the picture.
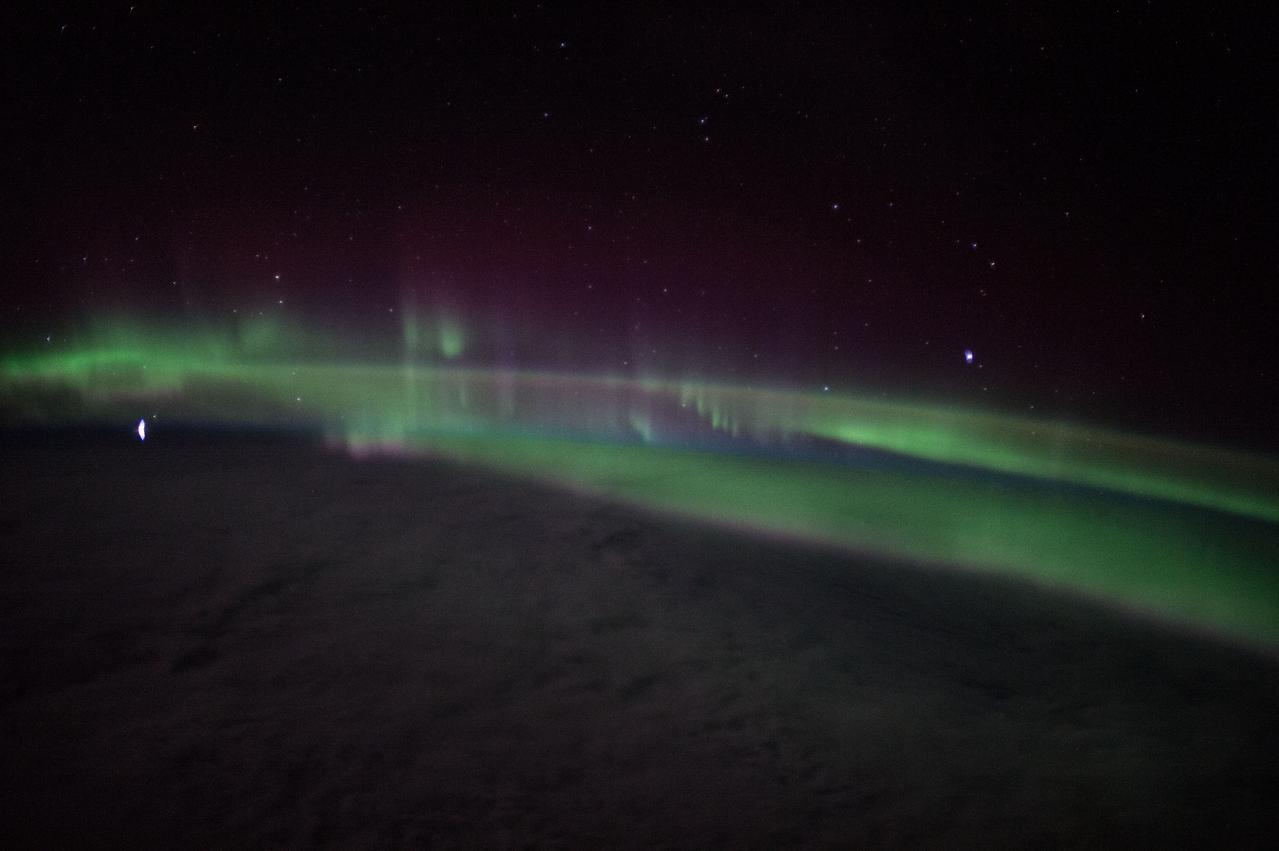

ISS047e000320 (02/17/2016) --- Aurora flashing over the Earth as the International Space Station orbits around the planet. NASA astronaut Tim Kopra sent this mesmerizing image out with the comment " "Stunning #aurora tonight- felt like we were enveloped in green light when we passed through this band @Space_Station". "
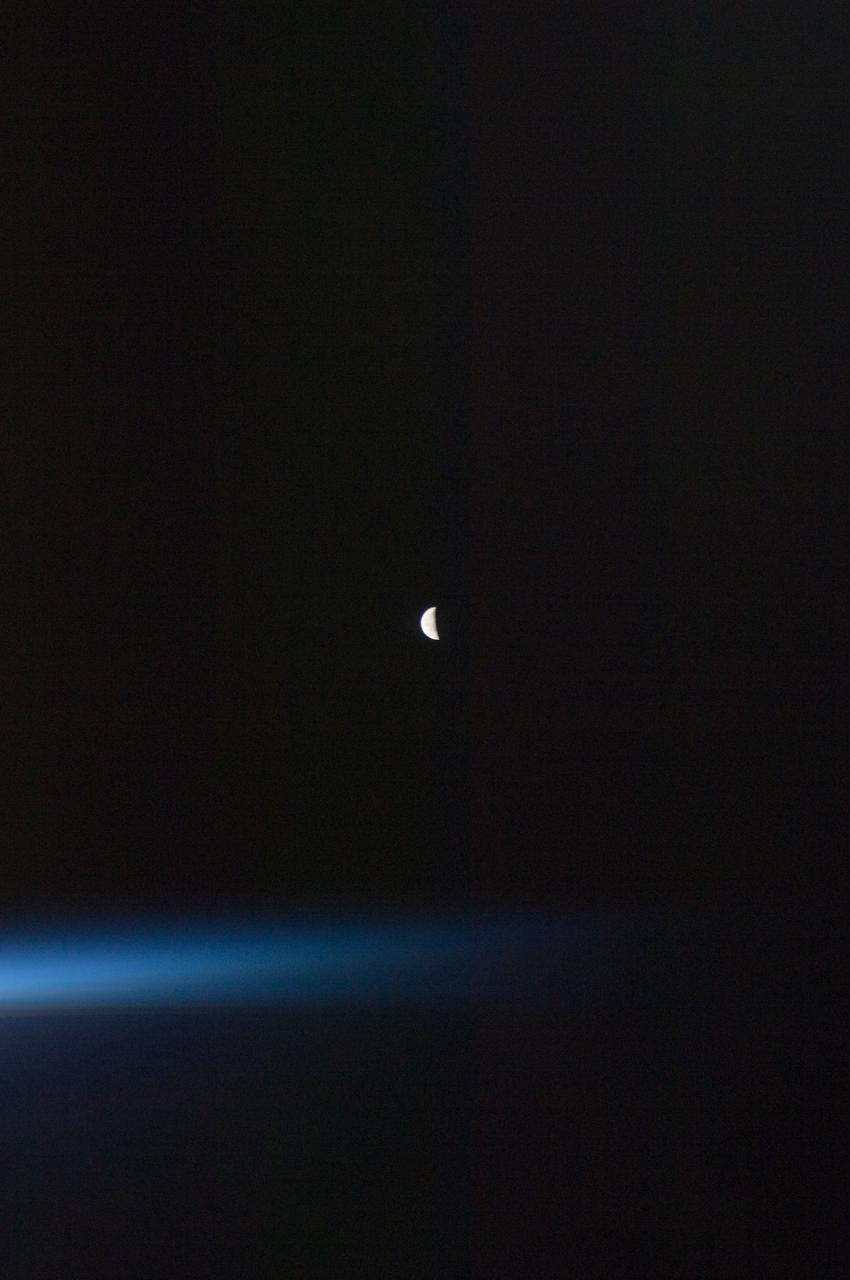

ISS028-E-030098 (22 Aug. 2011) --- A last quarter moon appears at the center of this night time photo taken from the International Space Station in Earth orbit. A thin line of the planet's atmosphere is the other illuminated object in the picture.
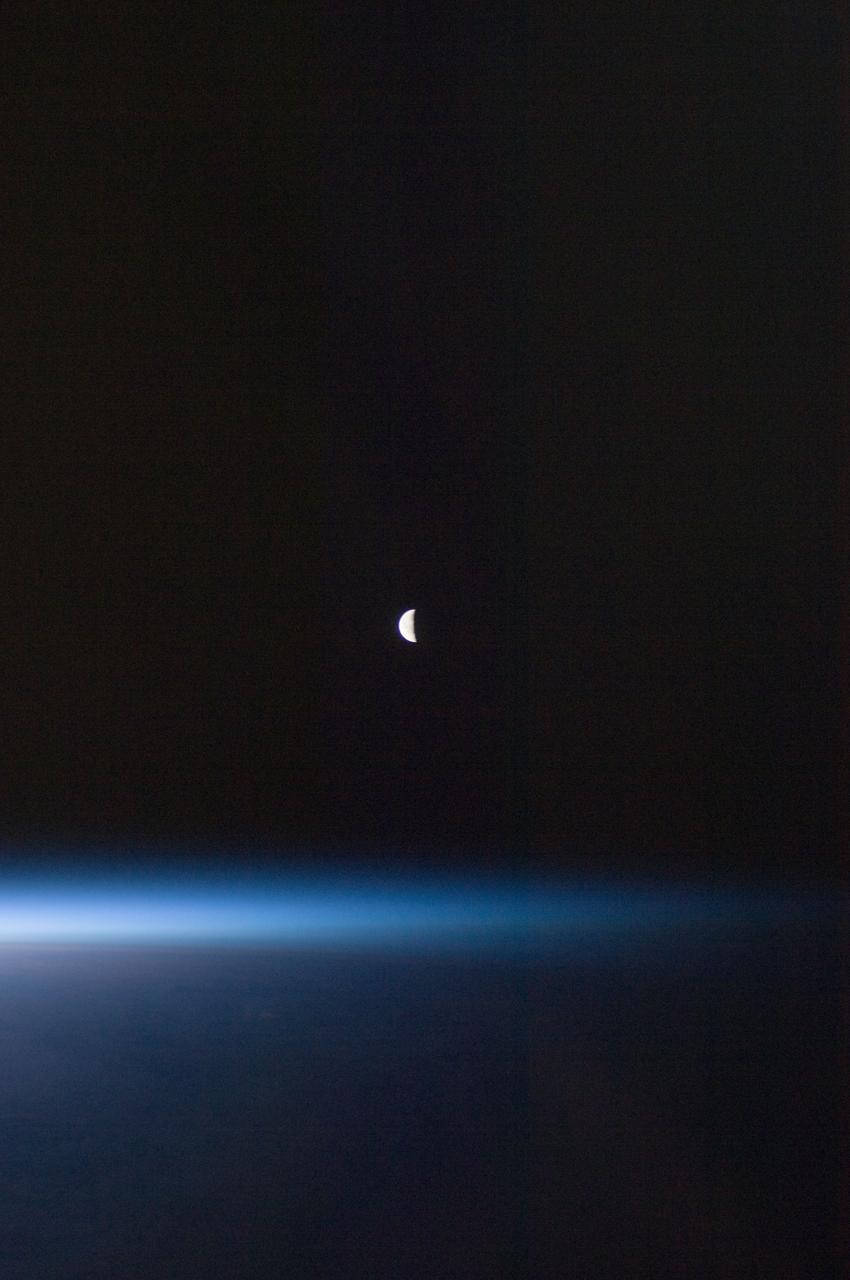

ISS028-E-030097 (22 Aug. 2011) --- A last quarter moon appears at the center of this night time photo taken from the International Space Station in Earth orbit. A thin line of the planet's atmosphere is the other illuminated object in the picture.
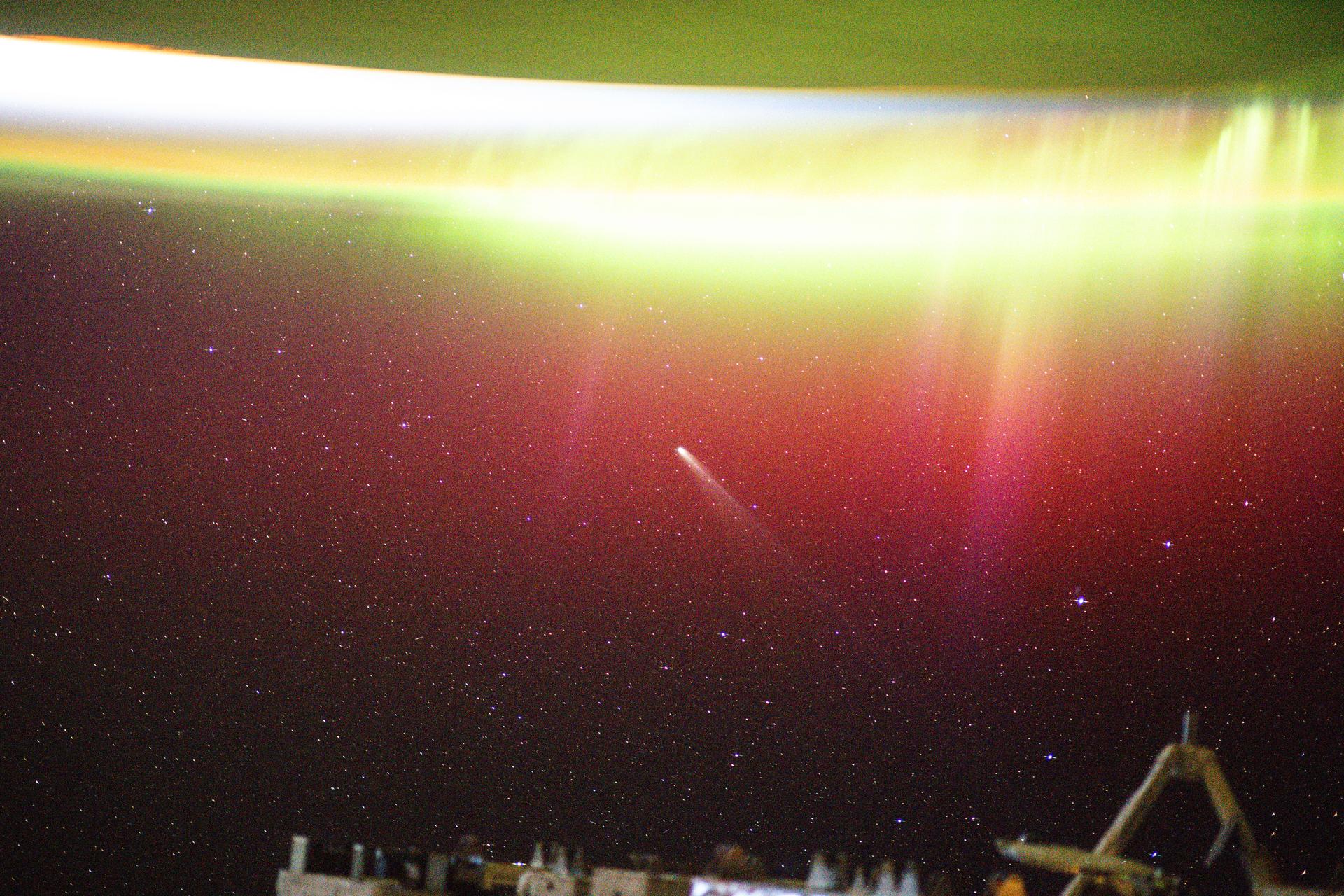

iss073e0981058 (Oct. 24, 2025) --- This long-exposure photograph shows a bright aurora radiating above Earth as Comet Lemmon (C/2025 A6) soared past the planet at a distance of about 57.2 million miles (92.1 million kilometers). The International Space Station was orbiting 263 miles above northern Minnesota at the time of this photograph.

This still from a video shows illustrations of the seven Earth-size planets of TRAPPIST-1, an exoplanet system about 40 light-years away, based on data current as of February 2018. Each planet is shown in sequence, starting with the innermost TRAPPIST-1b and ending with the outermost TRAPPIST-1h. The video presents the planets' relative sizes as well as the relative scale of the central star as seen from each planet. The art highlights possibilities for how the surfaces of these intriguing worlds might look based on their newly calculated properties. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. In the background, slightly distorted versions our familiar constellations, including Orion and Taurus, are shown as they would appear from the location of TRAPPIST-1 (backdrop image courtesy California Academy of Sciences/Dan Tell). An animation is available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22098
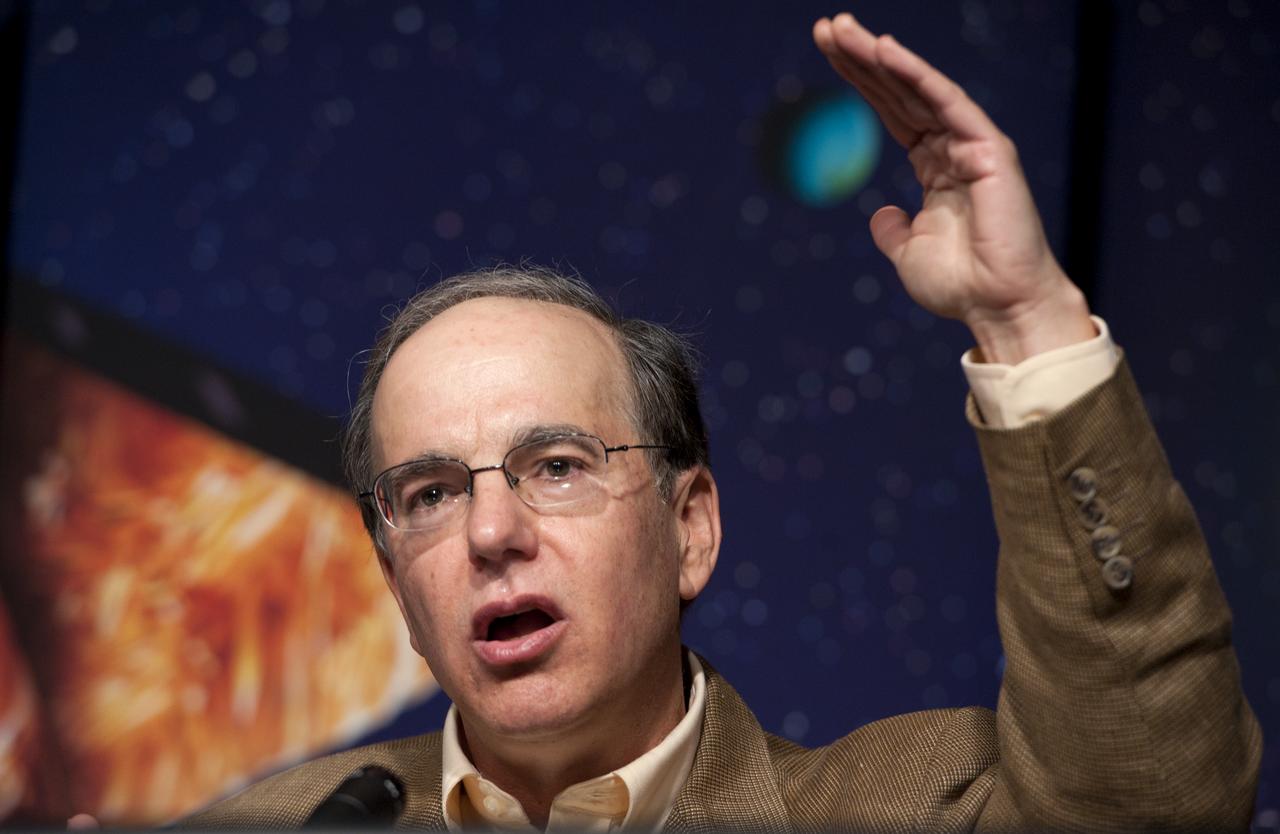

Jack Lissauer, a planetary scientist and a Kepler science team member at NASA's Ames Research Center, speaks during a news conference, Wednesday, Feb. 2, 2010, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Scientists using NASA's Kepler, a space telescope, recently discovered six planets made of a mix of rock and gases orbiting a single sun-like star, known as Kepler-11, which is located approximately 2,000 light years from Earth."It’s amazingly compact, it’s amazingly flat, there’s an amazingly large number of big planets orbiting close to their star - we didn’t know such systems could even exist." Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

Jack Lissauer, a planetary scientist and a Kepler science team member at NASA's Ames Research Center, speaks during a news conference, Wednesday, Feb. 2, 2010, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. Scientists using NASA's Kepler, a space telescope, recently discovered six planets made of a mix of rock and gases orbiting a single sun-like star, known as Kepler-11, which is located approximately 2,000 light years from Earth. "It’s amazingly compact, it’s amazingly flat, there’s an amazingly large number of big planets orbiting close to their star - we didn’t know such systems could even exist," he said. Photo Credit: (NASA/Paul E. Alers)

All seven planets discovered in orbit around the red dwarf star TRAPPIST-1 could easily fit inside the orbit of Mercury, the innermost planet of our solar system. In fact, they would have room to spare. TRAPPIST-1 also is only a fraction of the size of our sun; it isn't much larger than Jupiter. So the TRAPPIST-1 system's proportions look more like Jupiter and its moons than those of our solar system. The seven planets of TRAPPIST-1 are all Earth-sized and terrestrial, according to research published in 2017 in the journal Nature. TRAPPIST-1 is an ultra-cool dwarf star in the constellation Aquarius, and its planets orbit very close to it. The system has been revealed through observations from NASA's Spitzer Space Telescope and the ground-based TRAPPIST (TRAnsiting Planets and PlanetesImals Small Telescope) telescope, as well as other ground-based observatories. The system was named for the TRAPPIST telescope. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21428

Panelists pose for a group photo at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and highlighted how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

Dr. Christopher House, Professor of Geosciences, Pennsylvania State University, speaks on a panel at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and was moderated by Dr. David H. Grinspoon, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute. Six scientists discussed how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
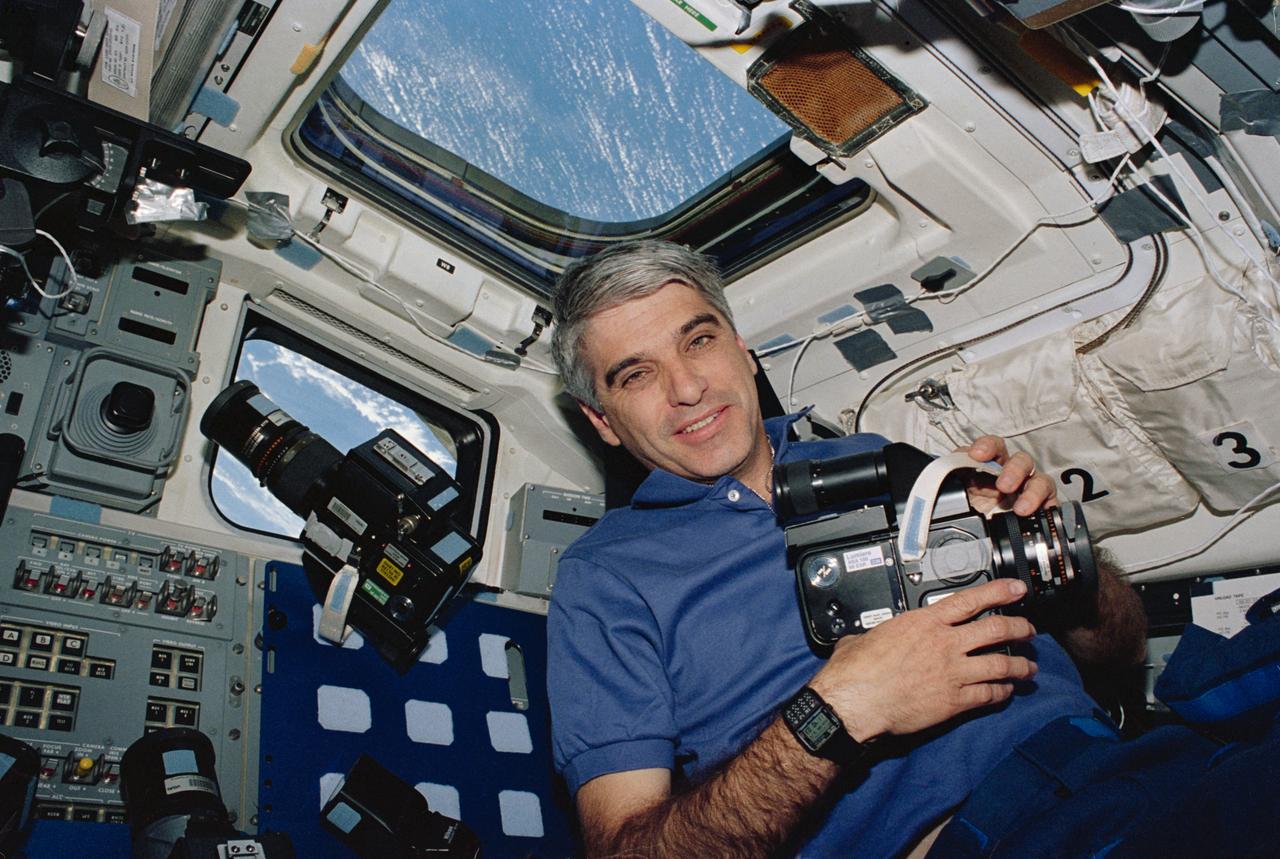

STS059-19-004 (9-20 April 1994) --- Astronaut Sidney M. Gutierrez, mission commander, pauses on the flight deck during Earth observations on the Space Shuttle Endeavour. Gutierrez, who was joined by five other NASA astronauts for 11-days in Earth orbit, holds a 70mm Hasselblad camera. The camera was one of several instruments used during the SRL mission to record an unprecedented compilation of data on planet Earth.

Dr. Timothy Lyons, Professor of Biogeochemistry, UC Riverside, speaks on a panel at the “Ancient Earth, Alien Earths” Event at NASA Headquarters in Washington, DC Wednesday, August 20, 2014. The event was sponsored by NASA, the National Science Foundation (NSF), and the Smithsonian Institution and was moderated by Dr. David H. Grinspoon, Senior Scientist at the Planetary Science Institute. Six scientists discussed how research on early Earth could help guide our search for habitable planets orbiting other stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)