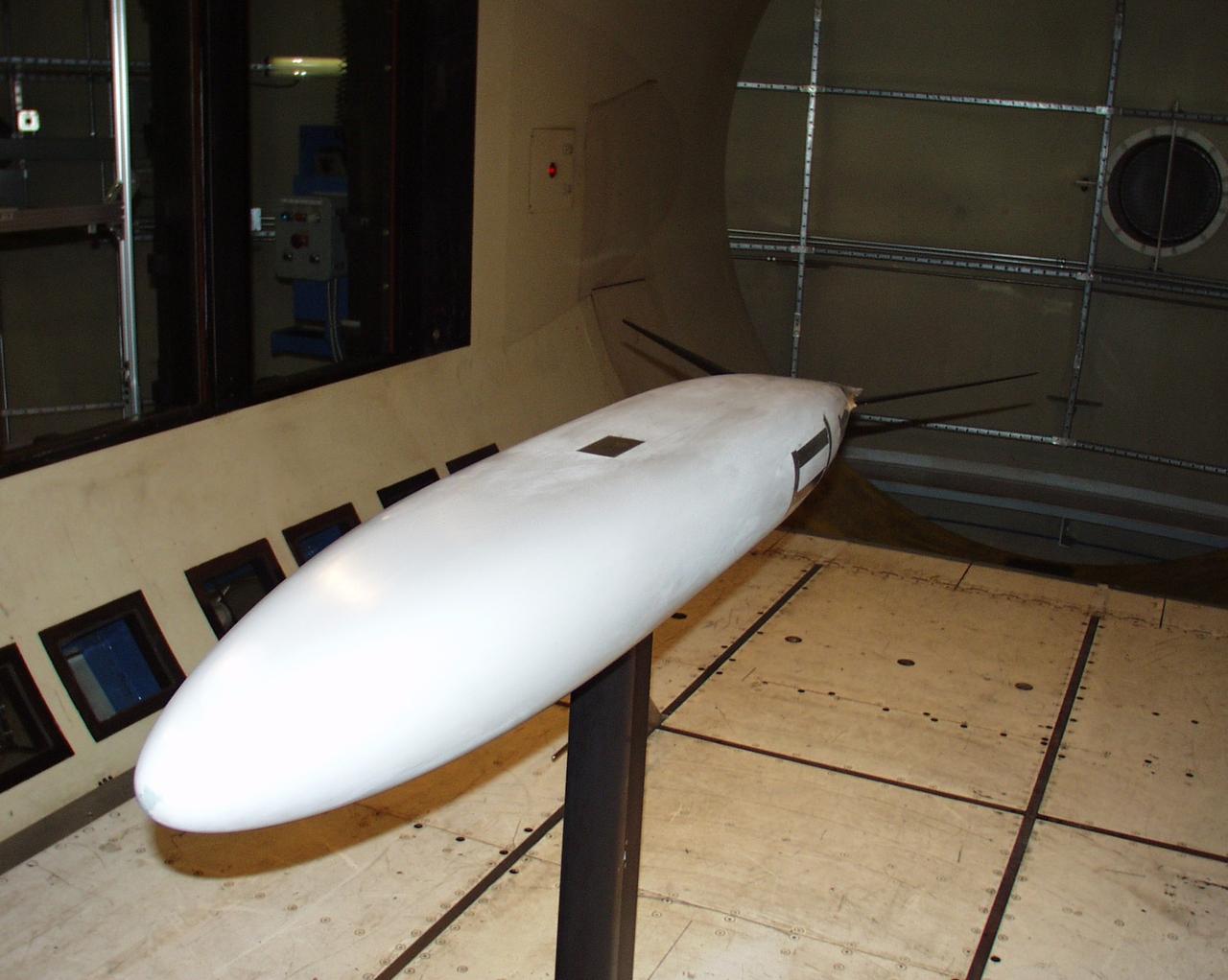

One World Challenge: boat hull configuration optimization test 12-0095 in Ames 12ft pressure wind tunnel. (Three phase Dec 2000 thru May 2002 - America Cup Sailing)

One World Challenge: boat hull configuration optimization test 12-0095 in Ames 12ft pressure wind tunnel. (Three phase Dec 2000 thru May 2002 - America Cup Sailing)
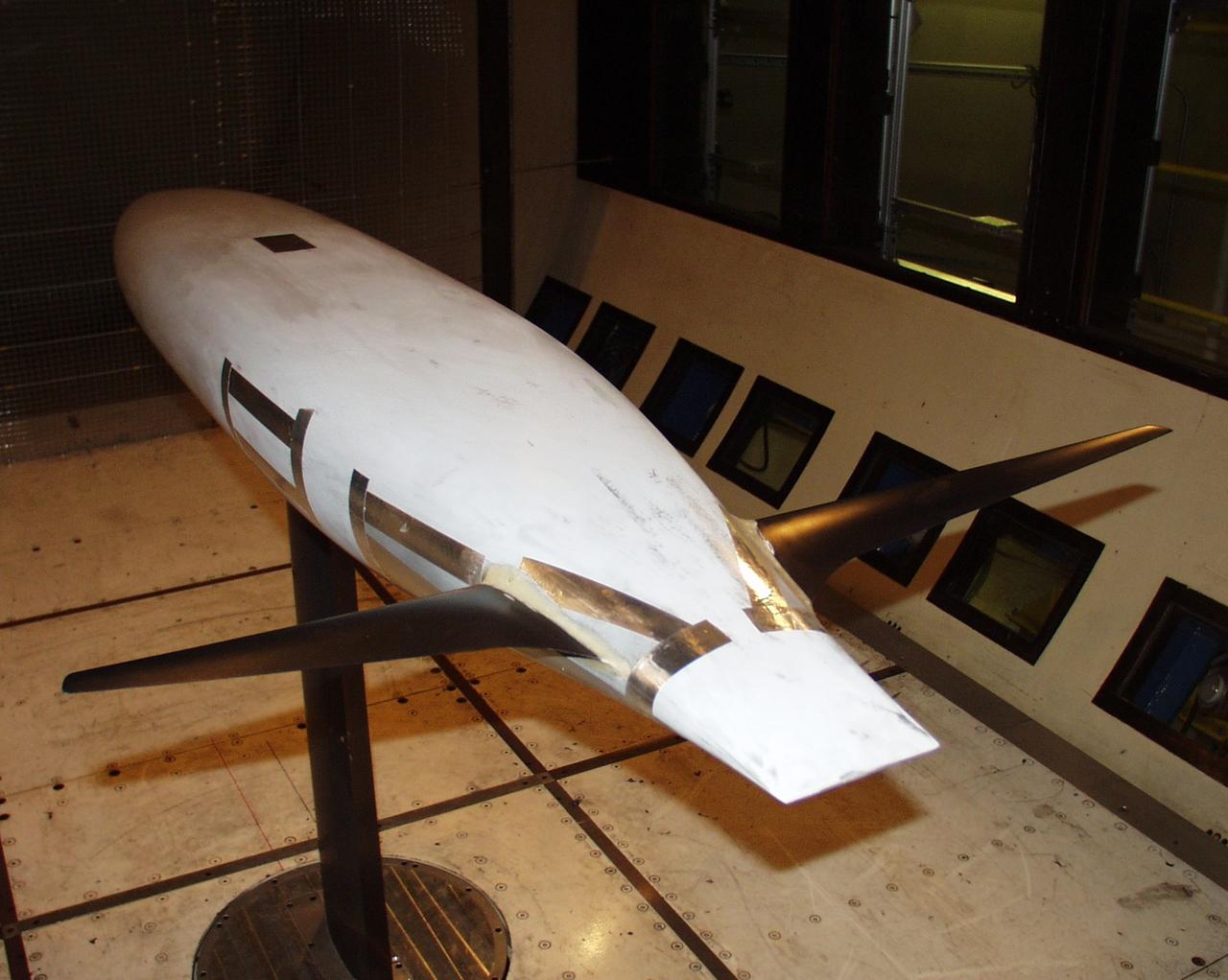

One World Challenge: boat hull configuration optimization test 12-0095 in Ames 12ft pressure wind tunnel. (Three phase Dec 2000 thru May 2002 - America Cup Sailing)
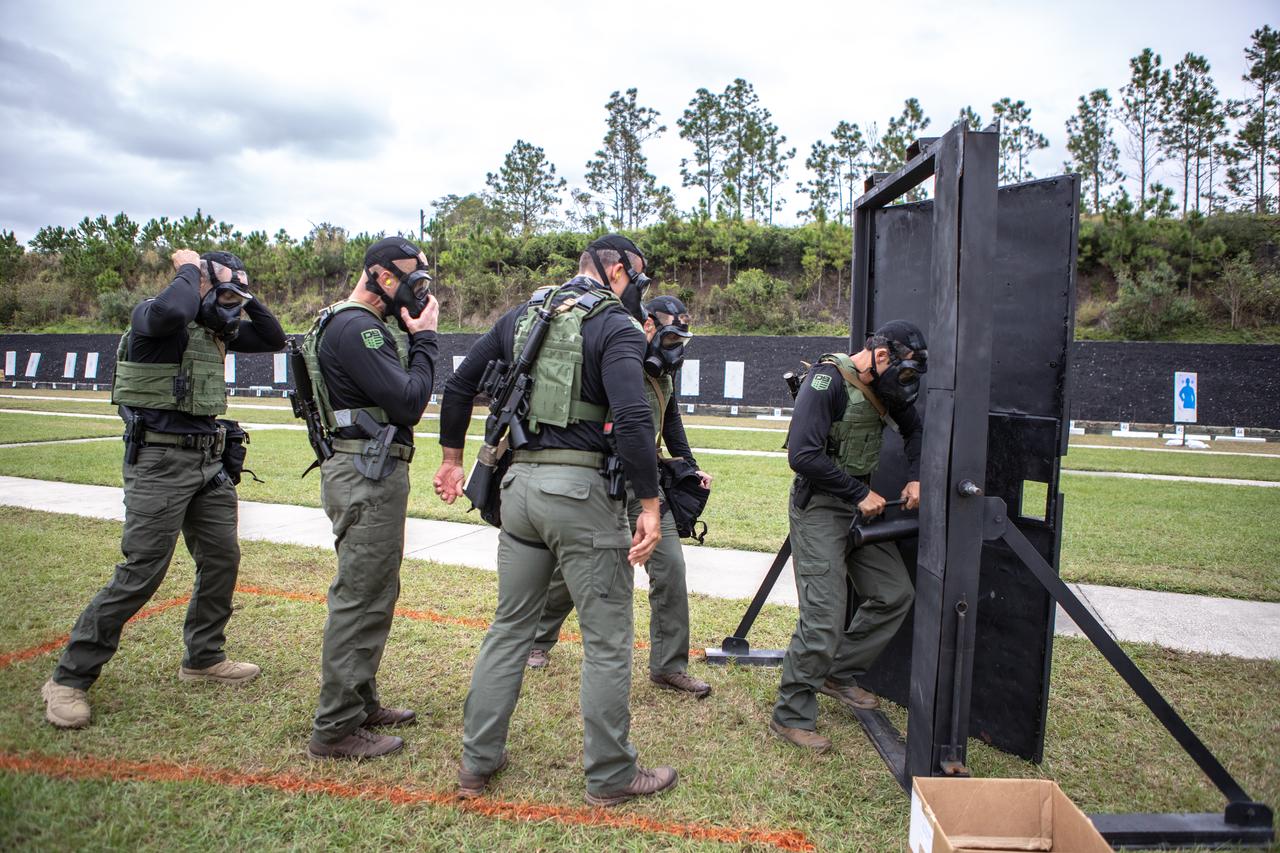

Members of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Emergency Response Team break through a barricade during one of the tactical challenges at the 37th Annual SWAT Round-Up International at the Lawson Lamar Firearms and Tactical Training Center in Orlando, Florida. The competition was held Nov. 10 to 15, 2019, and featured five different tactical challenges. Kennedy's ERT members exchanged best practices and competed with more than 50 teams from the U.S. and around the world.
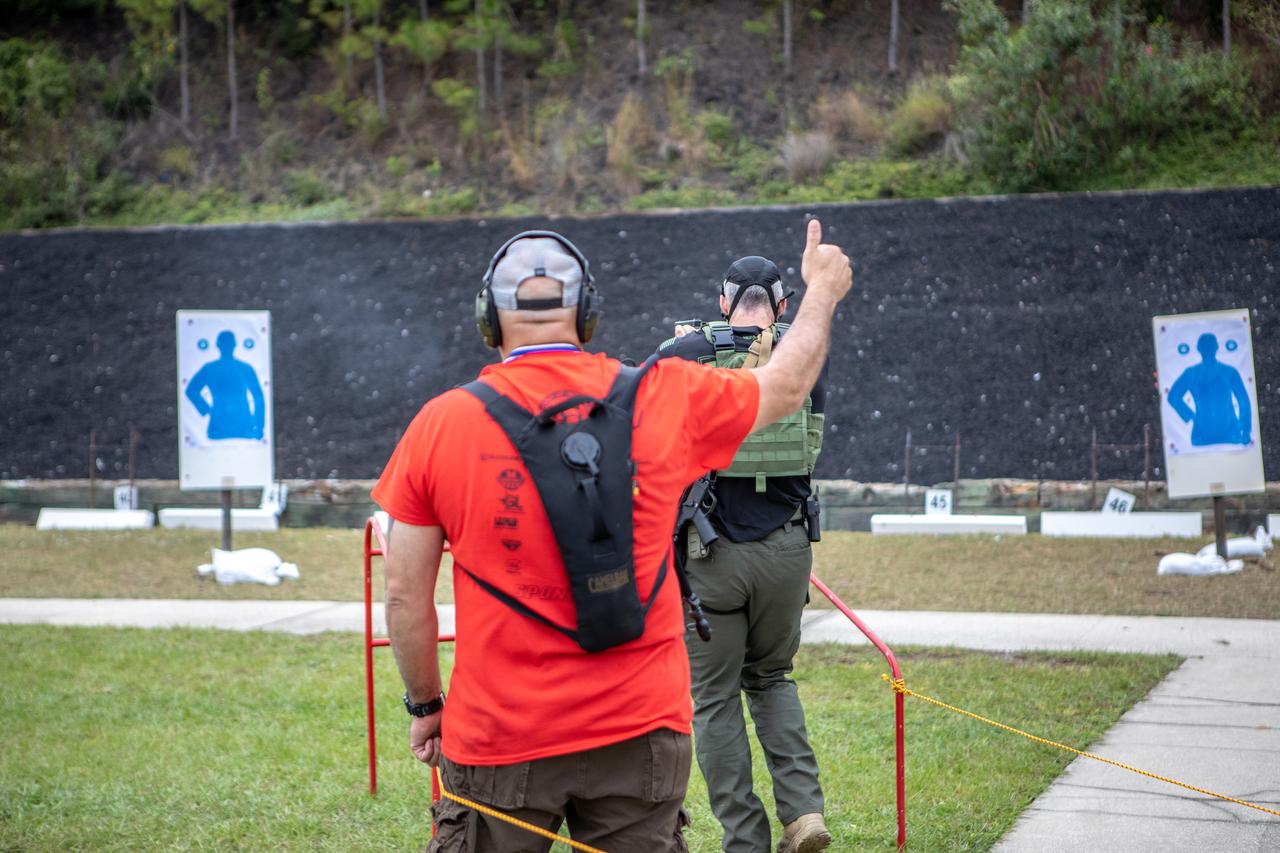

A member of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Emergency Response Team waits for the signal from the judge and then takes aim to shoot at a target with a handgun during one of the tactical challenges at the 35th Annual SWAT Round-up International at the Lawson Lamar Firearms and Tactical Training Center in Orlando, Florida. The competition was held Nov. 10 to 15, 2019, and featured five different tactical challenges. Kennedy's ERT members exchanged best practices and competed with more than 50 teams from the U.S. and around the world.
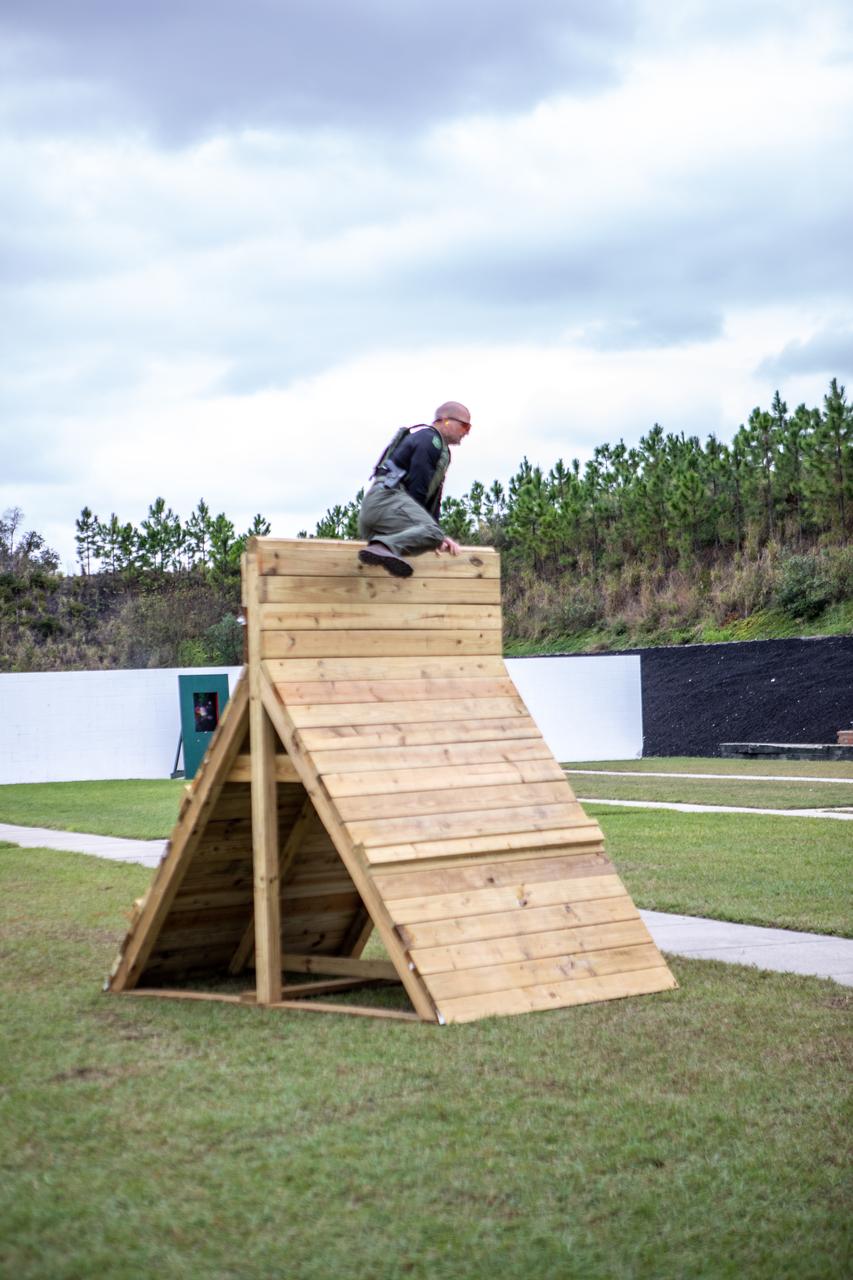

A member of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Emergency Response Team scales over a wall during one of the tactical challenges at the 37th Annual SWAT Round-Up International at the Lawson Lamar Firearms and Tactical Training Center in Orlando, Florida. The competition was held Nov. 10 to 15, 2019, and featured five different tactical challenges. Kennedy's ERT members exchanged best practices and competed with more than 50 teams from the U.S. and around the world.
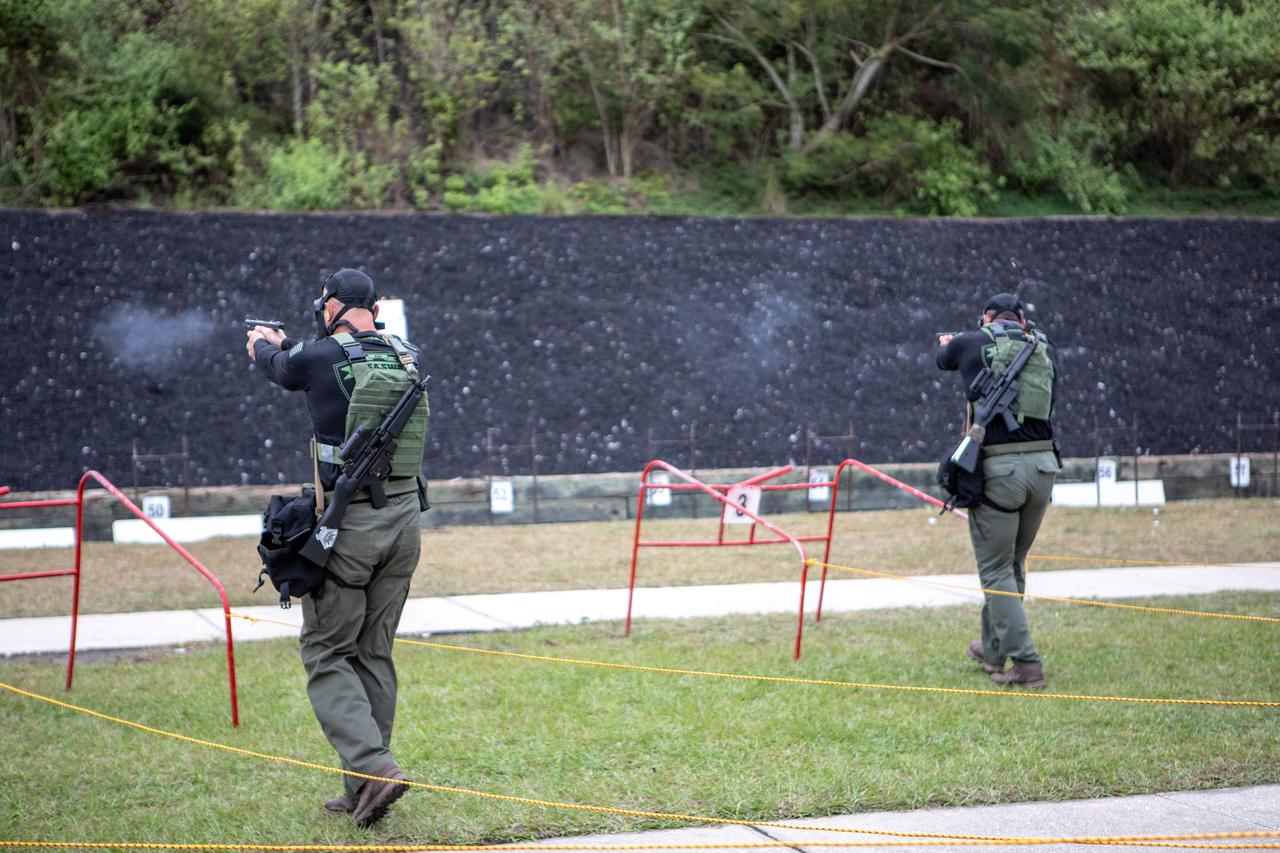

Members of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Emergency Response Team shoot at targets using handguns during one of the tactical challenges at the 37th Annual SWAT Round-Up International at the Lawson Lamar Firearms and Tactical Training Center in Orlando, Florida. The competition was held Nov. 10 to 15, 2019, and featured five different tactical challenges. Kennedy's ERT members exchanged best practices and competed with more than 50 teams from the U.S. and around the world.
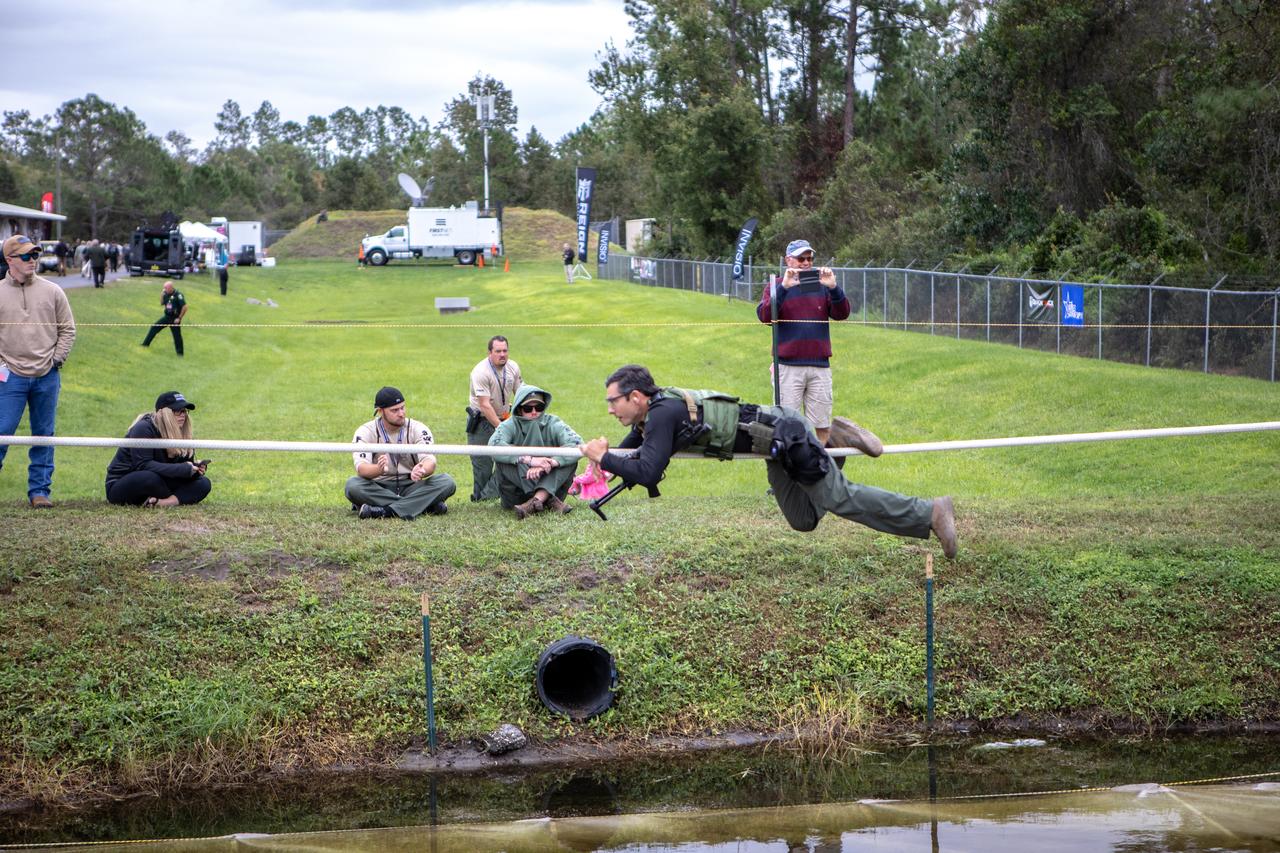

A member of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Emergency Response Team works his way along a rope above water during one of the tactical challenges at the 37th Annual SWAT Round-Up International at the Lawson Lamar Firearms and Tactical Training Center in Orlando, Florida. The competition was held Nov. 10 to 15, 2019, and featured five different tactical challenges. Kennedy's ERT members exchanged best practices and competed with more than 50 teams from the U.S. and around the world.
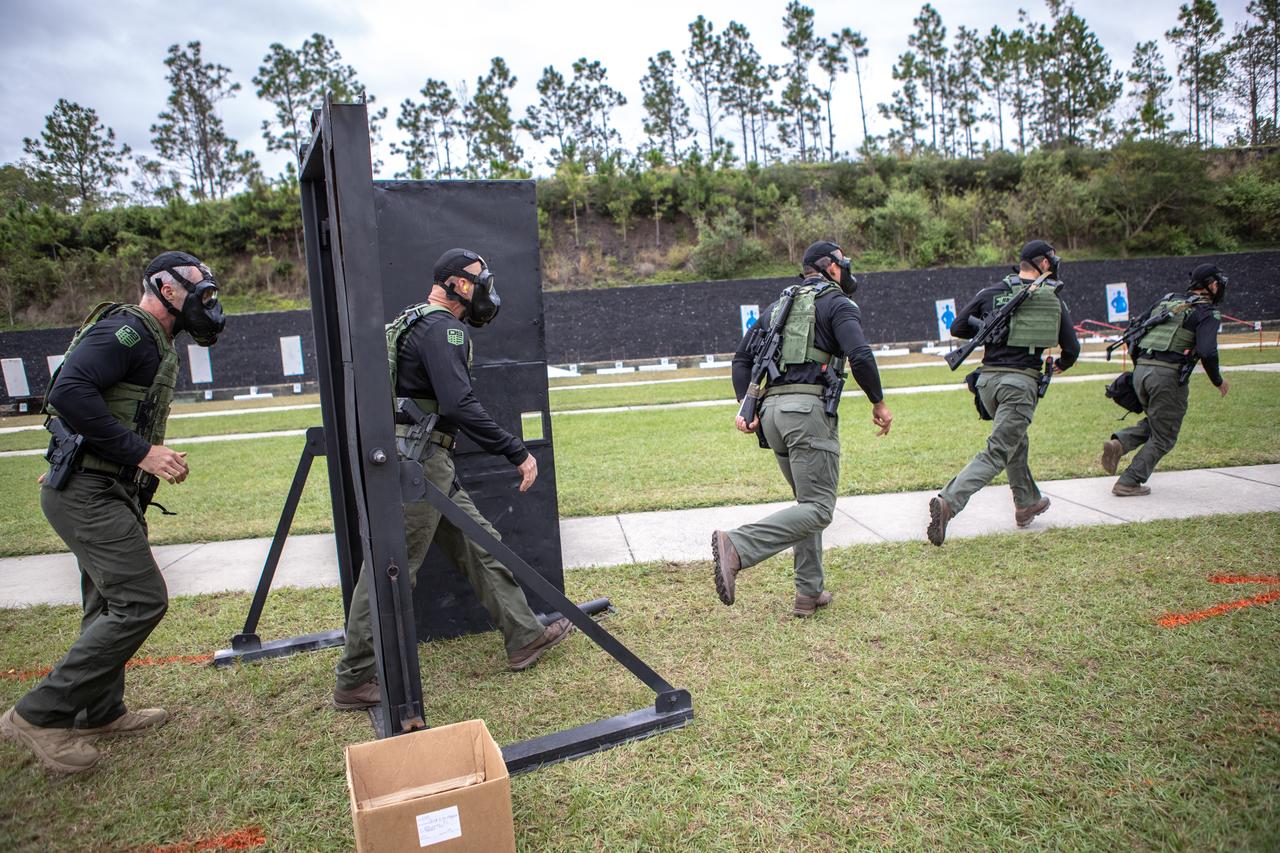

Members of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Emergency Response Team break through a barricade and run through to the other side during one of the tactical challenges at the 37th Annual SWAT Round-Up International at the Lawson Lamar Firearms and Tactical Training Center in Orlando, Florida. The competition was held Nov. 10 to 15, 2019, and featured five different tactical challenges. Kennedy's ERT members exchanged best practices and competed with more than 50 teams from the U.S. and around the world.
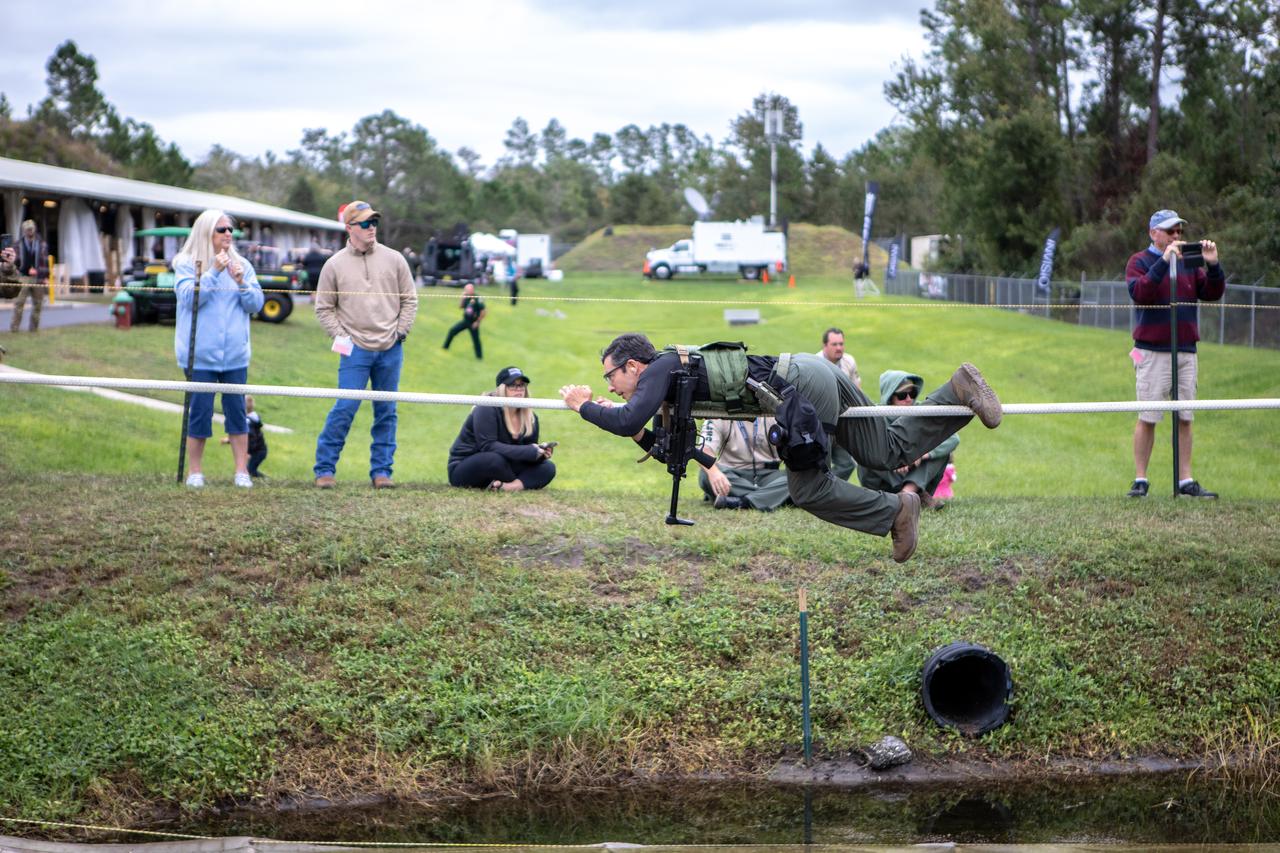

A member of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Emergency Response Team works his way along a rope above water during one of the tactical challenges at the 37th Annual SWAT Round-Up International at the Lawson Lamar Firearms and Tactical Training Center in Orlando, Florida. The competition was held Nov. 10 to 15, 2019, and featured five different tactical challenges. Kennedy's ERT members exchanged best practices and competed with more than 50 teams from the U.S. and around the world.
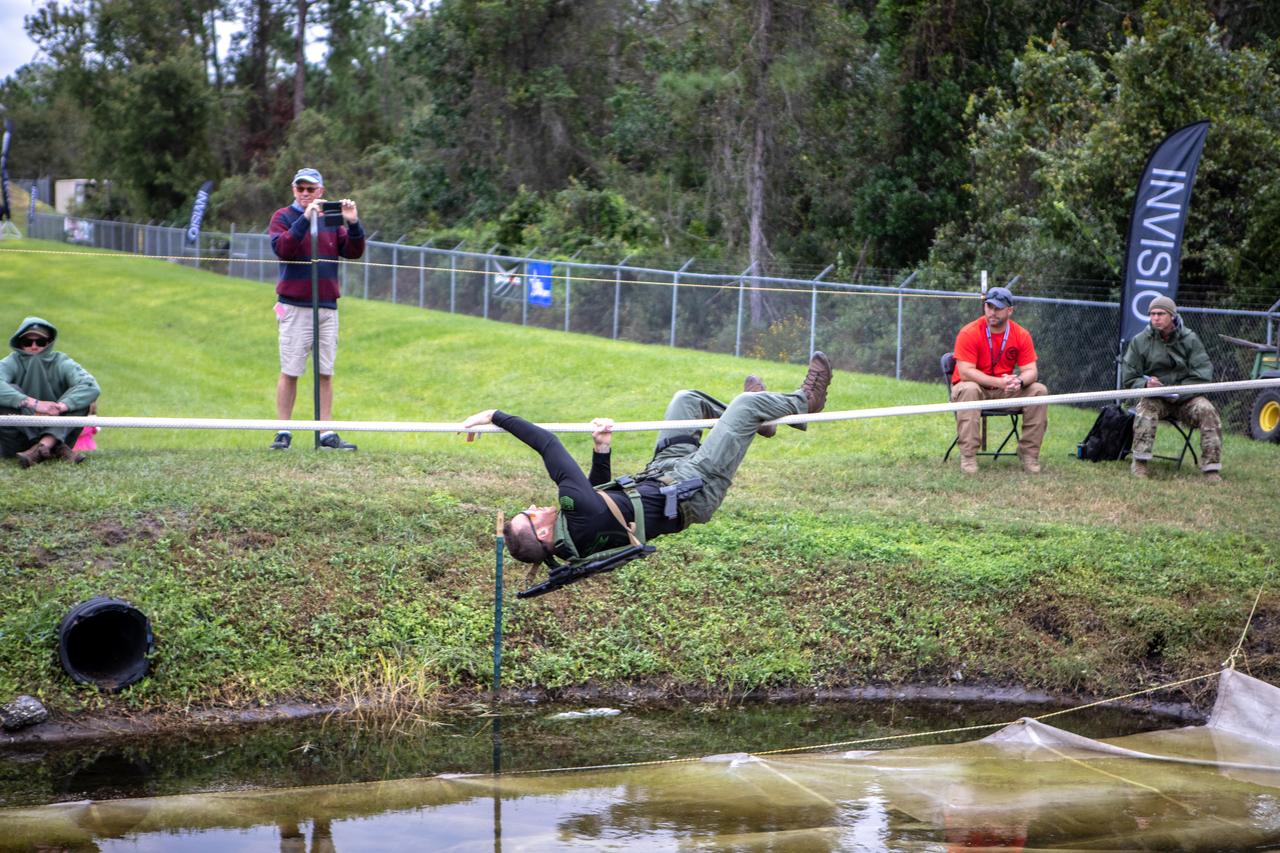

A member of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Emergency Response Team switches position as he works his way along a rope above water during one of the tactical challenges at the 37th Annual SWAT Round-Up International at the Lawson Lamar Firearms and Tactical Training Center in Orlando, Florida. The competition was held Nov. 10 to 15, 2019, and featured five different tactical challenges. Kennedy's ERT members exchanged best practices and competed with more than 50 teams from the U.S. and around the world.
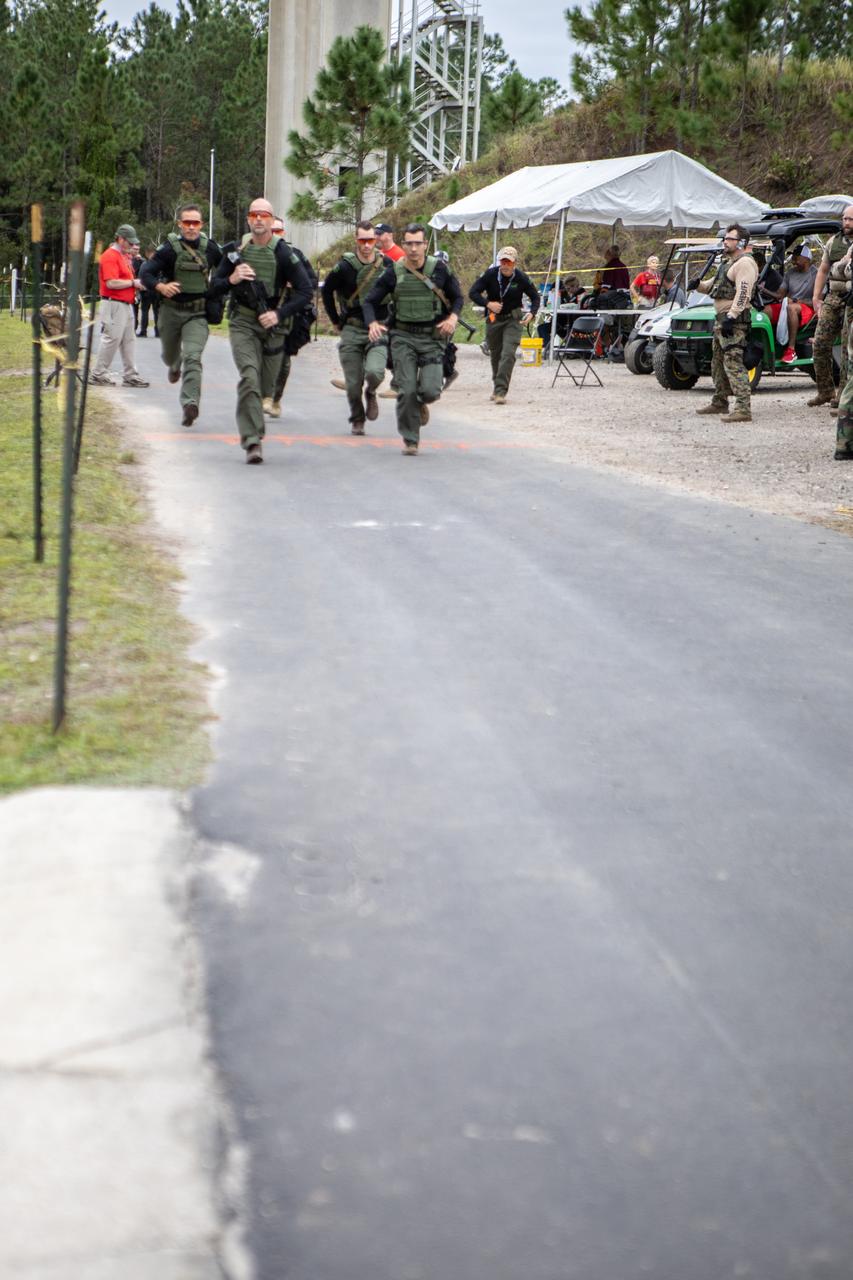

Members of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Emergency Response Team run during one of the tactical challenges at the 37th Annual SWAT Round-Up International at the Lawson Lamar Firearms and Tactical Training Center in Orlando, Florida. The competition was held Nov. 10 to 15, 2019, and featured five different tactical challenges. Kennedy's ERT members exchanged best practices and competed with more than 50 teams from the U.S. and around the world.
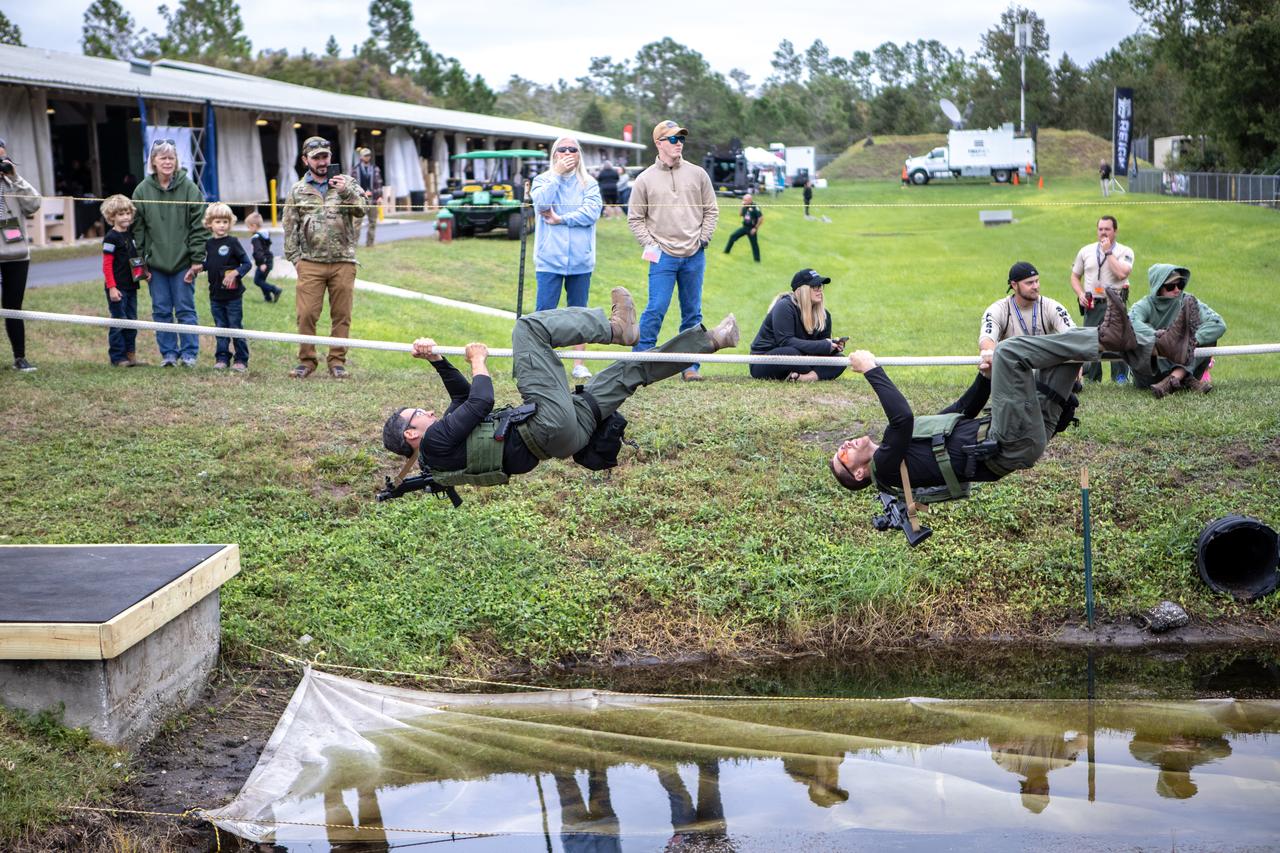

Members of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Emergency Response Team work their way along a rope above water during one of the tactical challenges at the 37th Annual SWAT Round-Up International at the Lawson Lamar Firearms and Tactical Training Center in Orlando, Florida. The competition was held Nov. 10 to 15, 2019, and featured five different tactical challenges. Kennedy's ERT members exchanged best practices and competed with more than 50 teams from the U.S. and around the world.
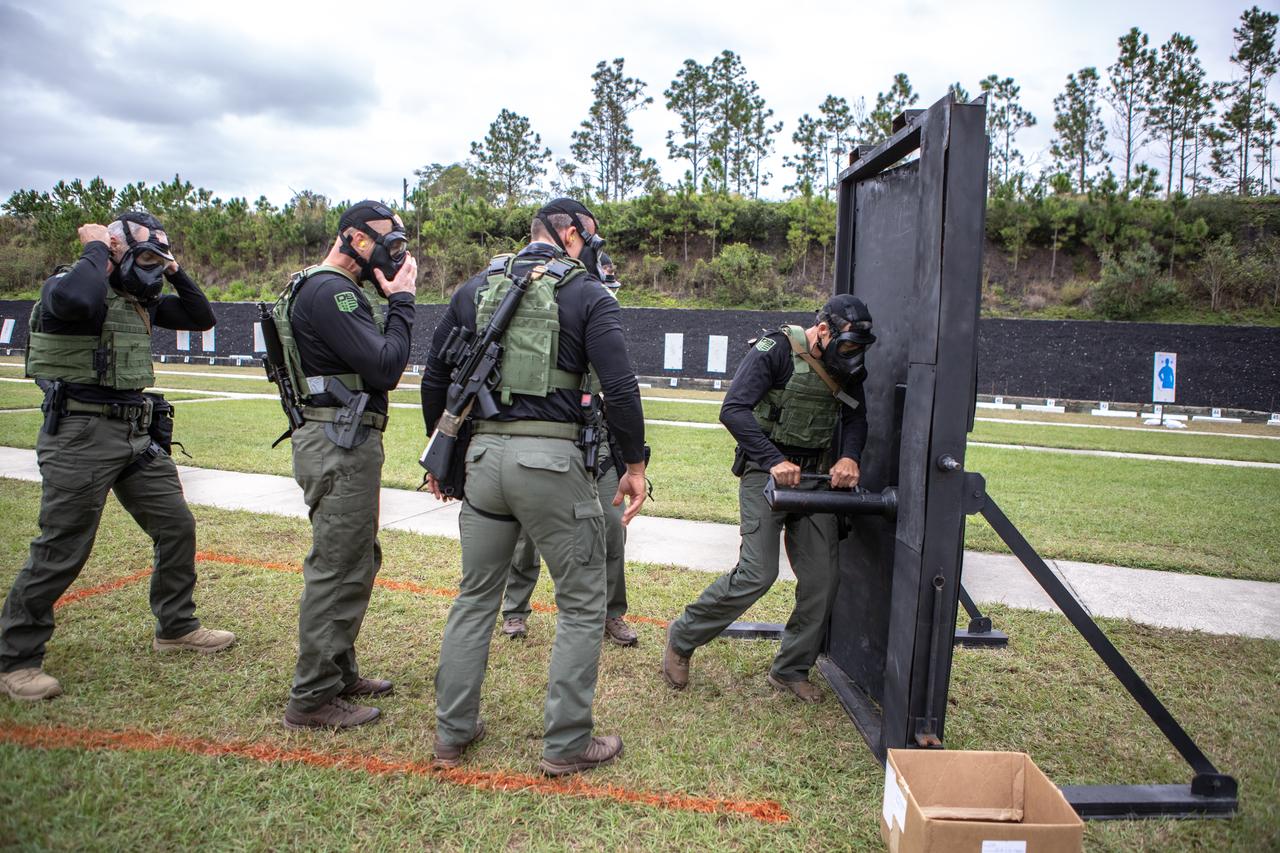

Members of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Emergency Response Team prepare to break through a barricade during one of the tactical challenges at the 37th Annual SWAT Round-Up International at the Lawson Lamar Firearms and Tactical Training Center in Orlando, Florida. The competition was held Nov. 10 to 15, 2019, and featured five different tactical challenges. Kennedy's ERT members exchanged best practices and competed with more than 50 teams from the U.S. and around the world.
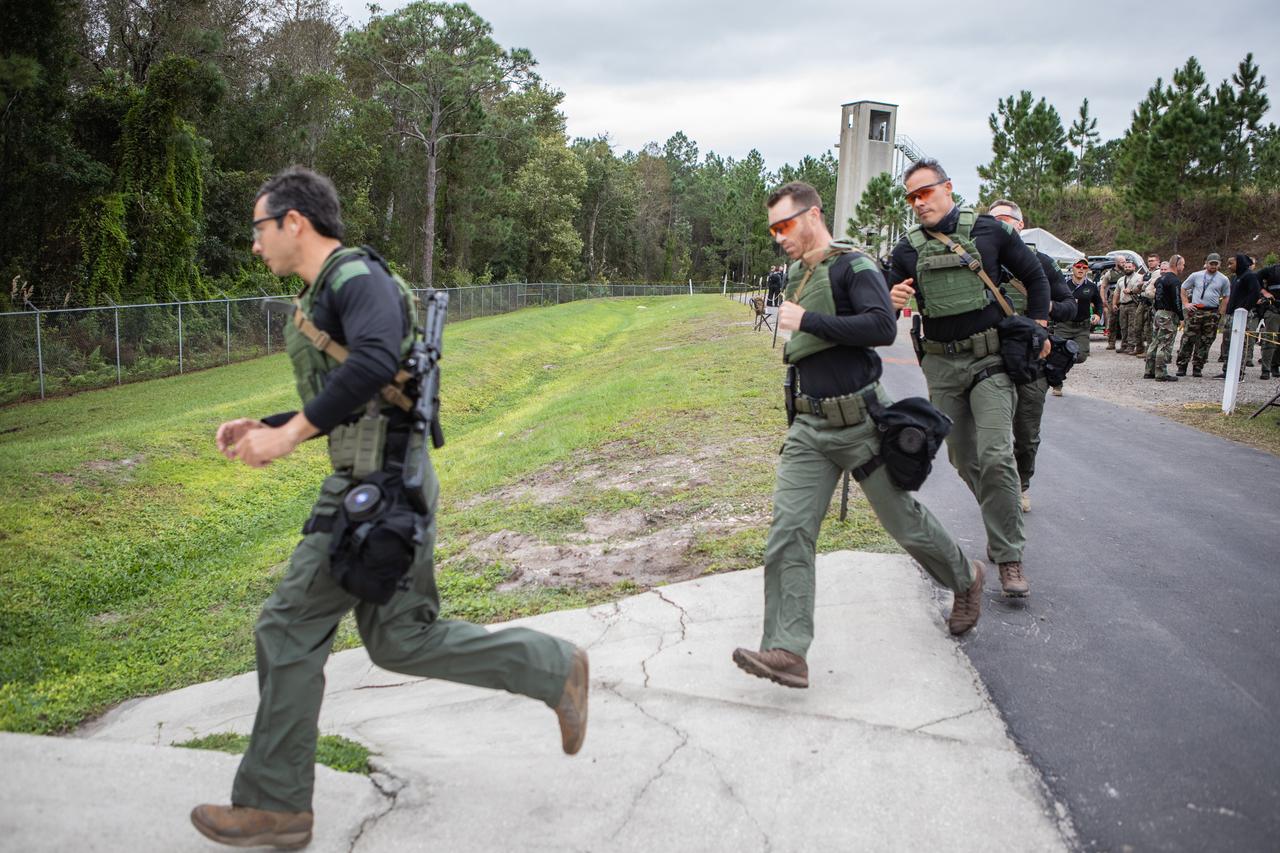

Members of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Emergency Response Team run during one of the tactical challenges at the 37th Annual SWAT Round-Up International at the Lawson Lamar Firearms and Tactical Training Center in Orlando, Florida. The competition was held Nov. 10 to 15, 2019, and featured five different tactical challenges. Kennedy's ERT members exchanged best practices and competed with more than 50 teams from the U.S. and around the world.
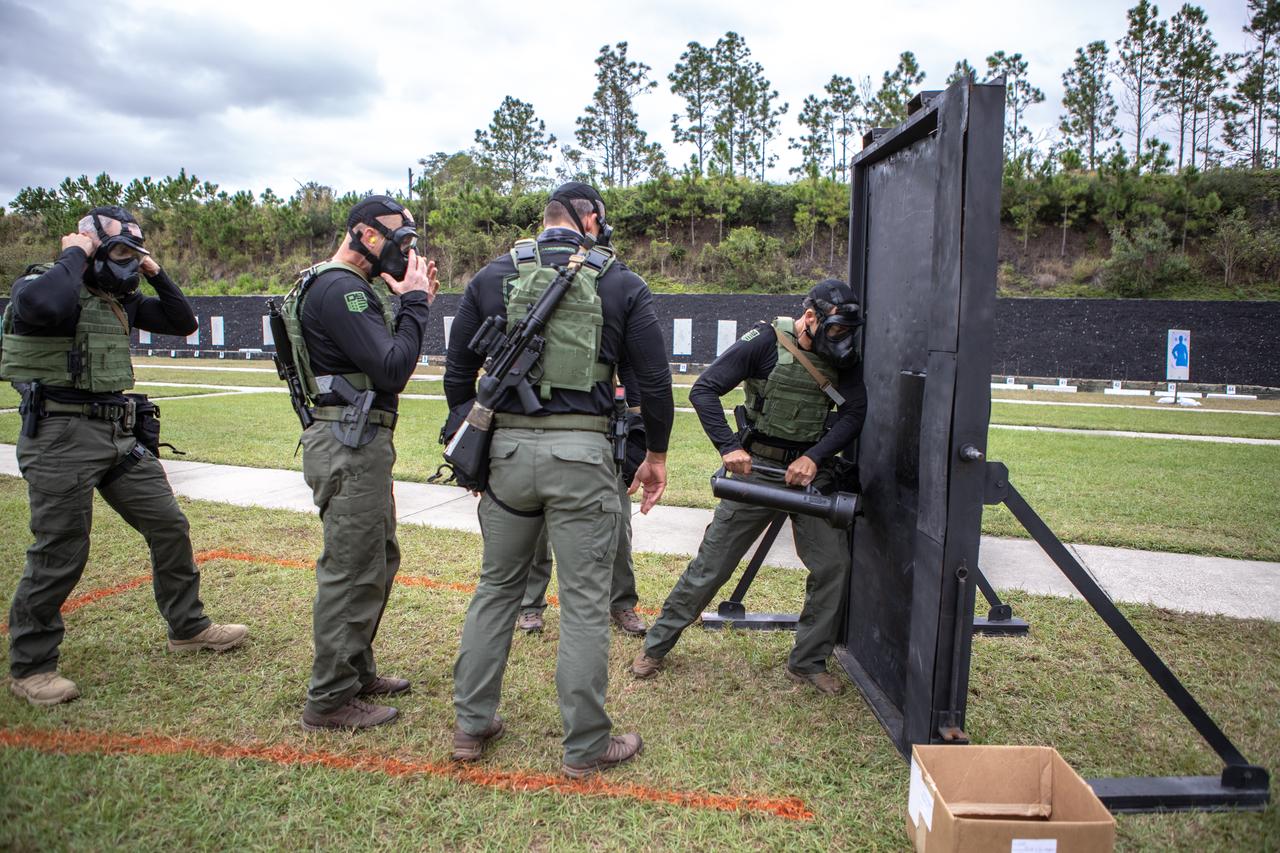

Members of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Emergency Response Team prepare to break through a barricade during one of the tactical challenges at the 37th Annual SWAT Round-Up International at the Lawson Lamar Firearms and Tactical Training Center in Orlando, Florida. The competition was held Nov. 10 to 15, 2019, and featured five different tactical challenges. Kennedy's ERT members exchanged best practices and competed with more than 50 teams from the U.S. and around the world.
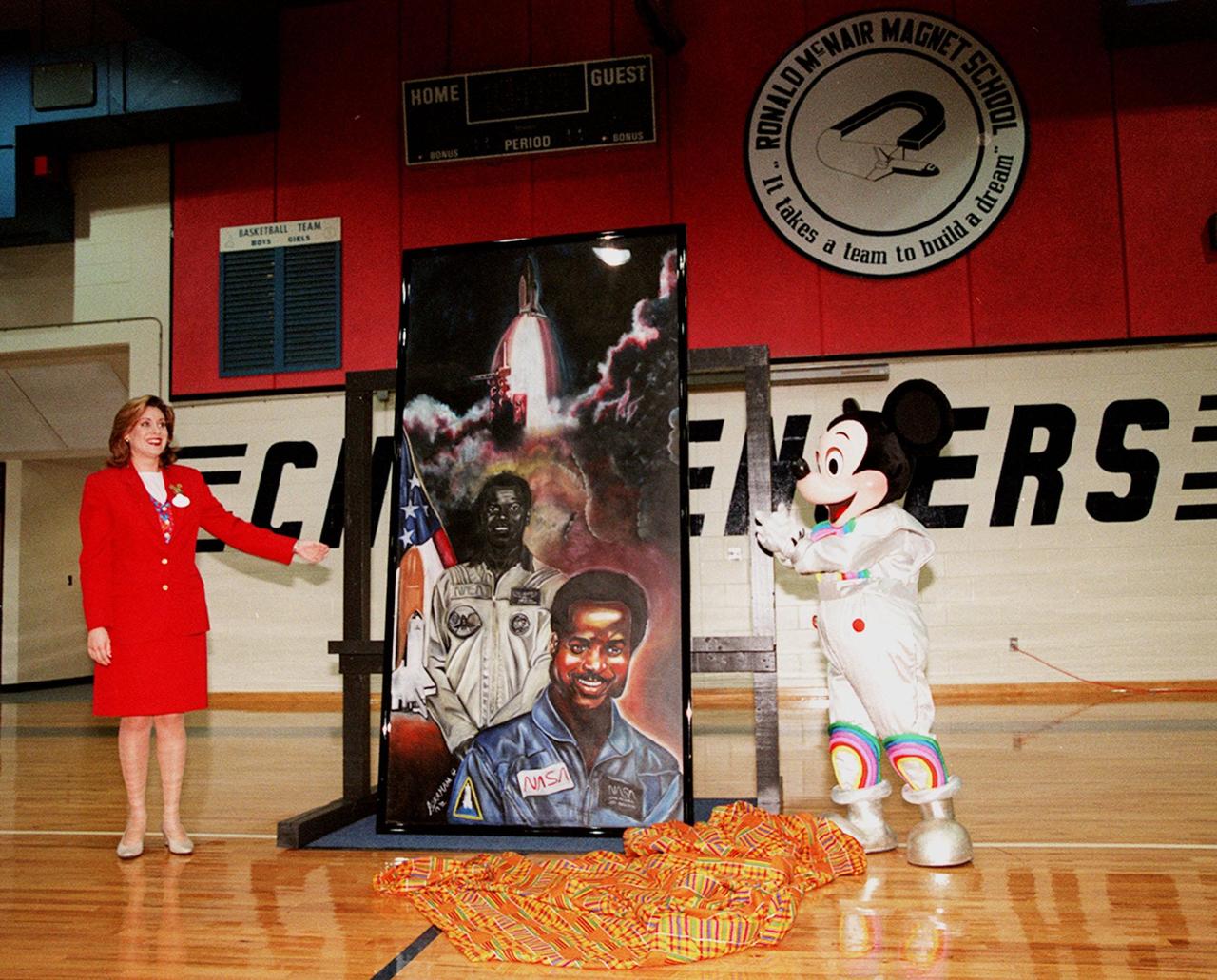

In the gymnasium of Ronald McNair Magnet School in Cocoa, Fla., Ms. Maria Rodriguez, an Walt Disney World Ambassador, and Mickey Mouse pose with a portrait of NASA astronaut Ronald McNair. The portrait was presented to the school by Walt Disney World during a tribute to McNair. The school had previously been renamed for the fallen astronaut, who was one of a crew of seven who lost their lives during an accident following launch of the Space Shuttle Challenger in January 1986
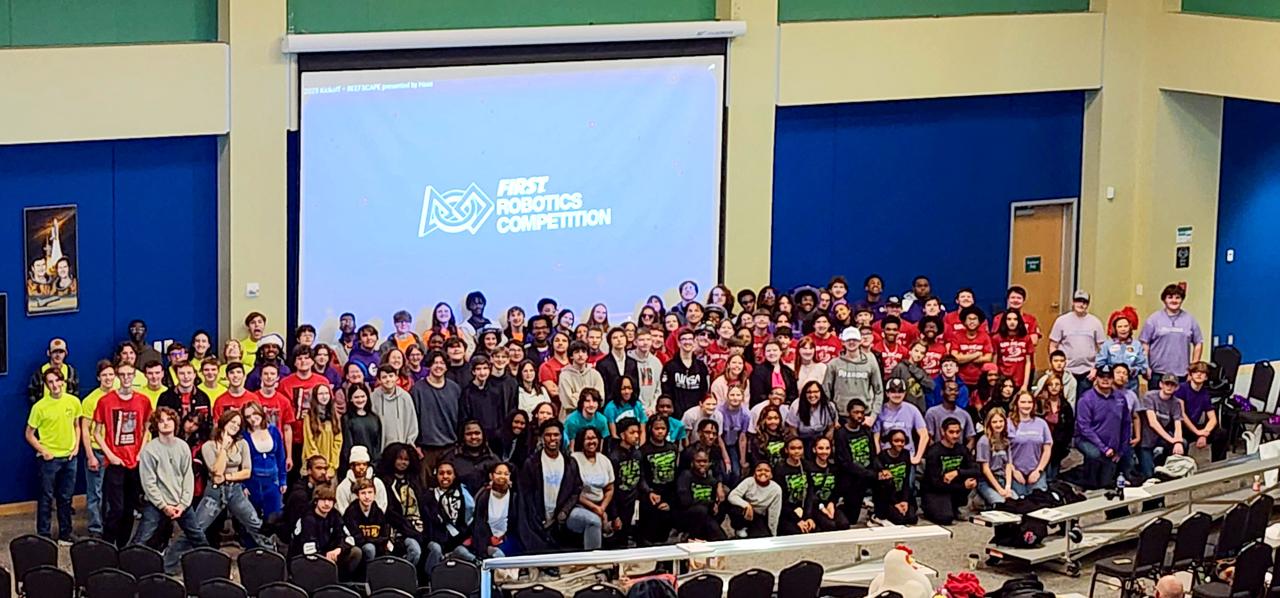

The NASA ASTRO CAMP® Community Partners (ACCP) program hosted a FIRST® Robotics Competition 2025 season kickoff event Jan. 4 at INFINITY Science Center, the official visitor center of NASA’s Stennis Space Center. NASA representatives welcomed competition teams as the event revealed the challenge for the new season. Teams will use engineering skills during the REEFSCAPE℠ challenge to strengthen one of the ocean’s most diverse habitats to build a better world. The third annual FIRST (For the Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology) Robotics Magnolia Regional, a NASA-sponsored event, is scheduled for March 13-15 in Laurel, Mississippi, at the South Mississippi Fairgrounds. The regional competition will serve as a championship-qualifying event for teams to compete in Houston in the world championship event in April. FIRST Robotics is described as the ultimate sport of the mind as teams concentrate and share in the excitement of success.
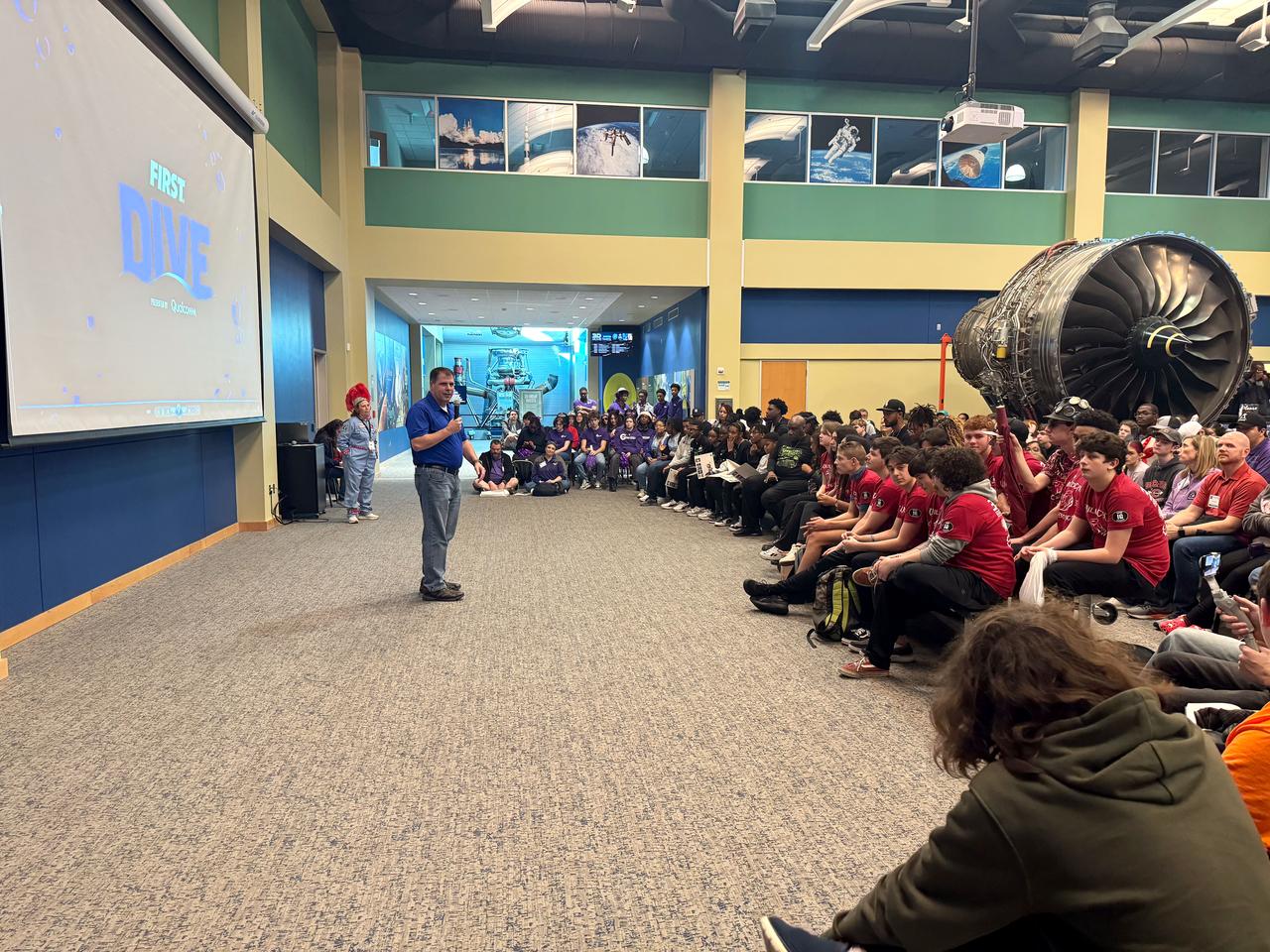

The NASA ASTRO CAMP® Community Partners (ACCP) program hosted a FIRST® Robotics Competition 2025 season kickoff event Jan. 4 at INFINITY Science Center, the official visitor center of NASA’s Stennis Space Center. NASA representatives welcomed competition teams as the event revealed the challenge for the new season. Teams will use engineering skills during the REEFSCAPE℠ challenge to strengthen one of the ocean’s most diverse habitats to build a better world. The third annual FIRST (For the Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology) Robotics Magnolia Regional, a NASA-sponsored event, is scheduled for March 13-15 in Laurel, Mississippi, at the South Mississippi Fairgrounds. The regional competition will serve as a championship-qualifying event for teams to compete in Houston in the world championship event in April. FIRST Robotics is described as the ultimate sport of the mind as teams concentrate and share in the excitement of success.
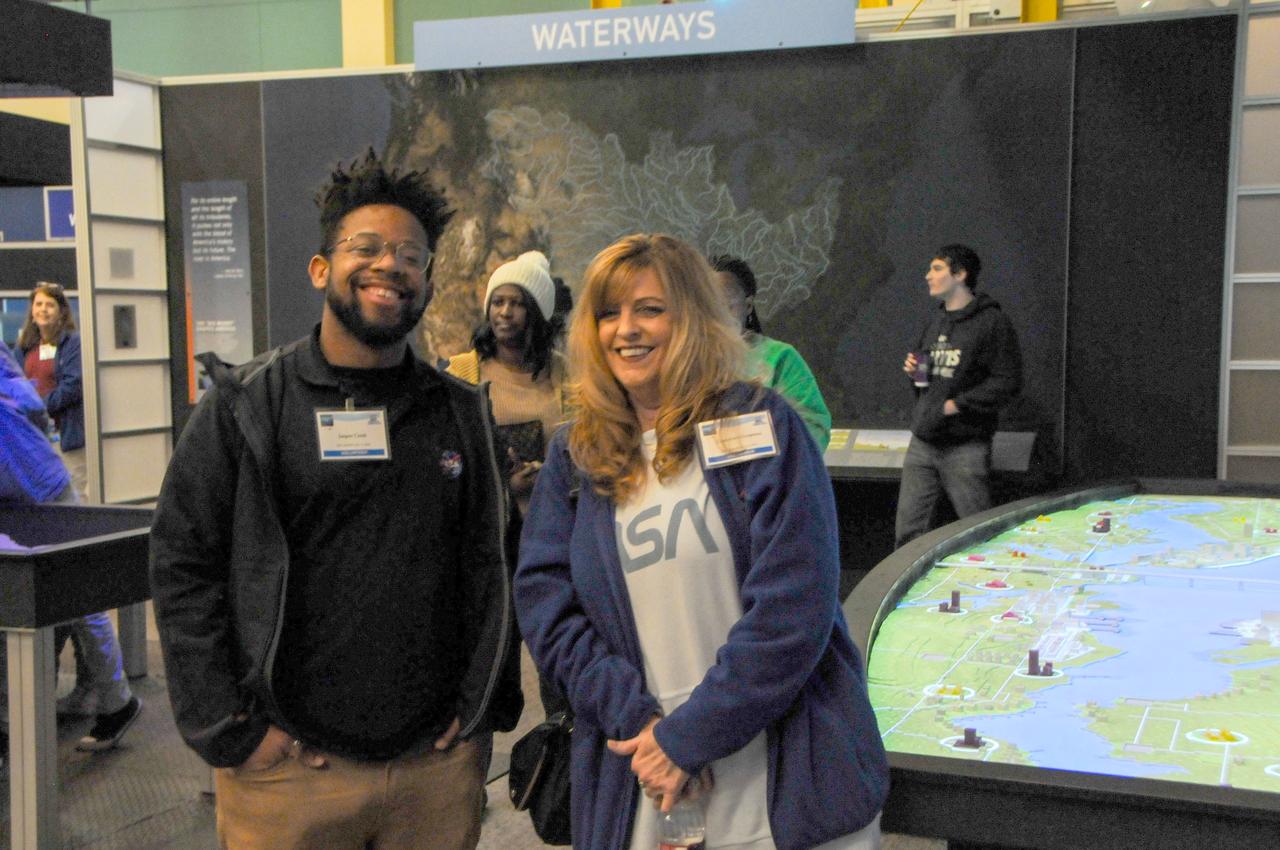

The NASA ASTRO CAMP® Community Partners (ACCP) program hosted a FIRST® Robotics Competition 2025 season kickoff event Jan. 4 at INFINITY Science Center, the official visitor center of NASA’s Stennis Space Center. NASA representatives welcomed competition teams as the event revealed the challenge for the new season. Teams will use engineering skills during the REEFSCAPE℠ challenge to strengthen one of the ocean’s most diverse habitats to build a better world. The third annual FIRST (For the Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology) Robotics Magnolia Regional, a NASA-sponsored event, is scheduled for March 13-15 in Laurel, Mississippi, at the South Mississippi Fairgrounds. The regional competition will serve as a championship-qualifying event for teams to compete in Houston in the world championship event in April. FIRST Robotics is described as the ultimate sport of the mind as teams concentrate and share in the excitement of success.
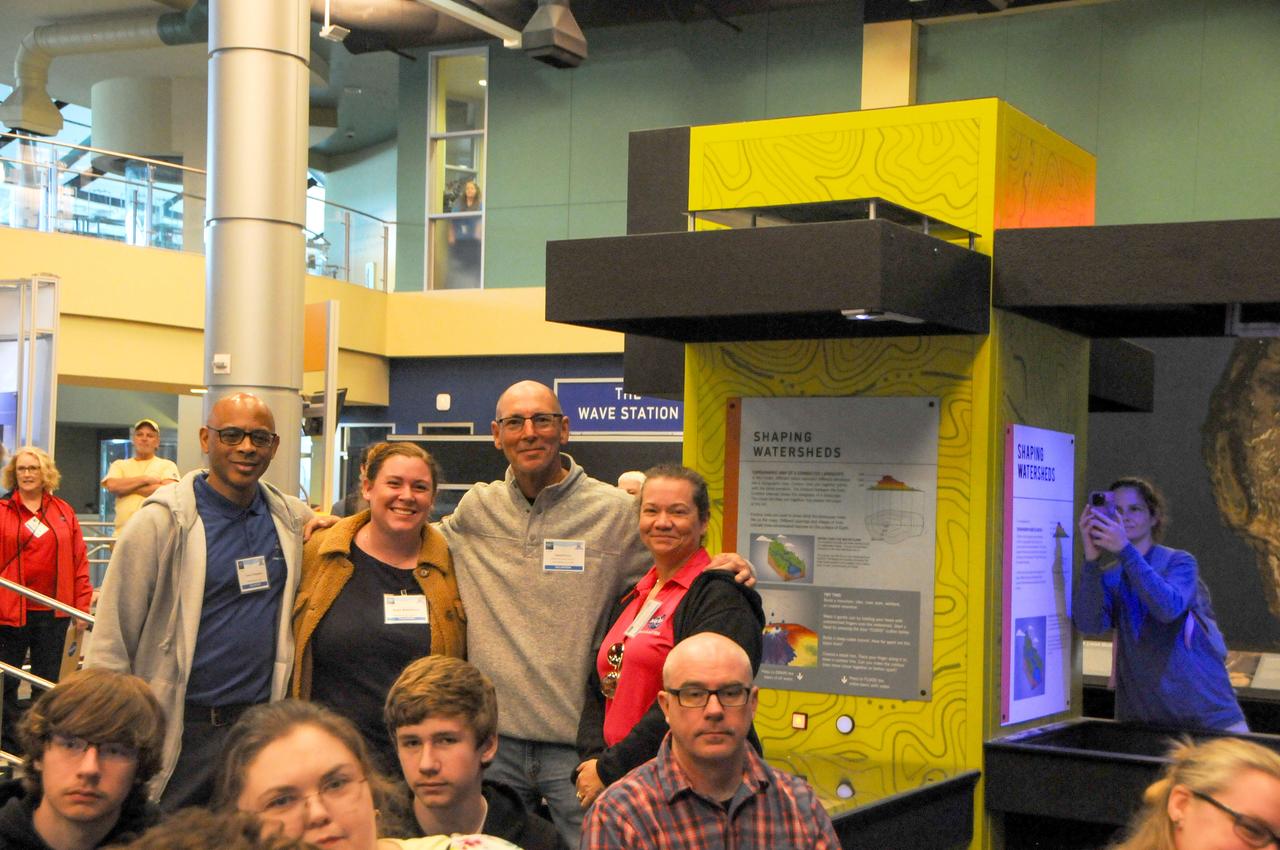

The NASA ASTRO CAMP® Community Partners (ACCP) program hosted a FIRST® Robotics Competition 2025 season kickoff event Jan. 4 at INFINITY Science Center, the official visitor center of NASA’s Stennis Space Center. NASA representatives welcomed competition teams as the event revealed the challenge for the new season. Teams will use engineering skills during the REEFSCAPE℠ challenge to strengthen one of the ocean’s most diverse habitats to build a better world. The third annual FIRST (For the Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology) Robotics Magnolia Regional, a NASA-sponsored event, is scheduled for March 13-15 in Laurel, Mississippi, at the South Mississippi Fairgrounds. The regional competition will serve as a championship-qualifying event for teams to compete in Houston in the world championship event in April. FIRST Robotics is described as the ultimate sport of the mind as teams concentrate and share in the excitement of success.
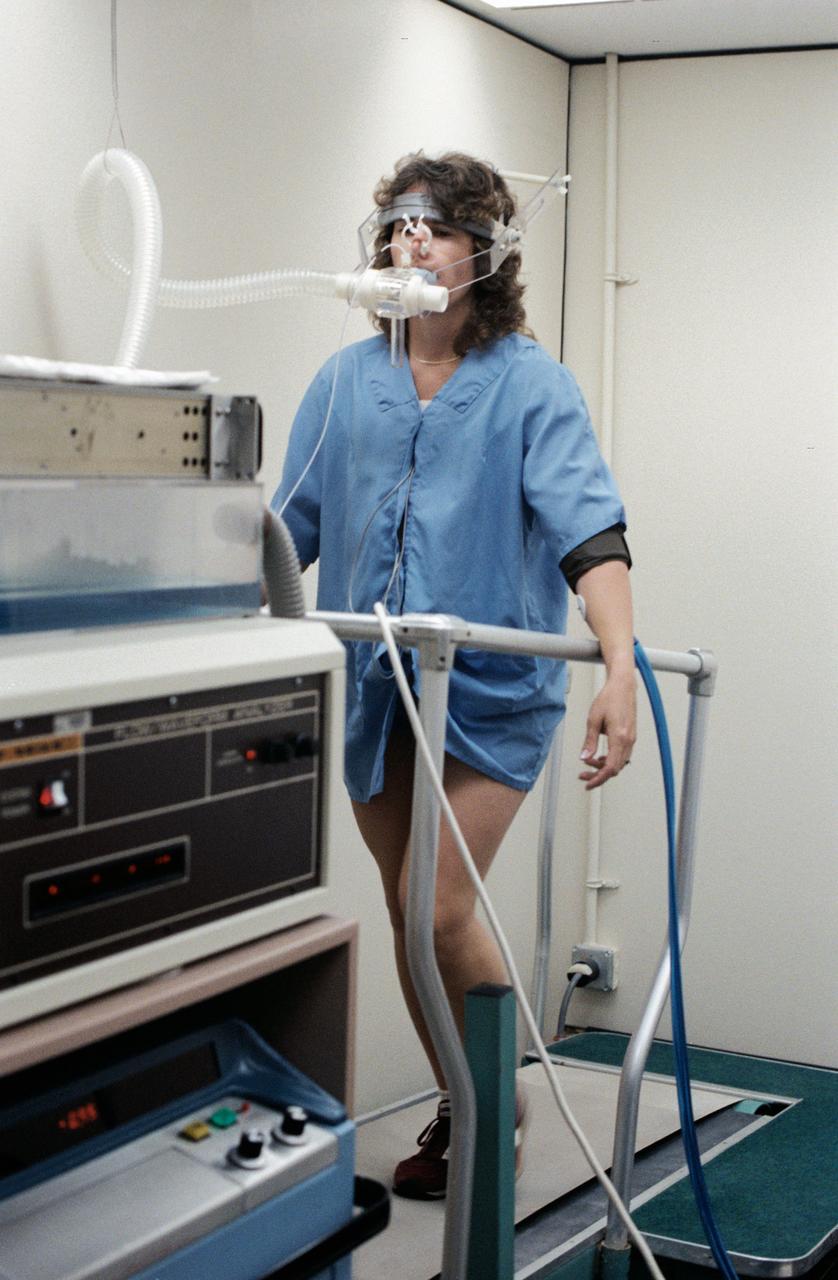
S85-37165 (8-12 July 1985) -- Sharon C. (Christa) McAuliffe of Concord High, Concord, New Hampshire, runs in place on treadmill to test physiological responses at Johnson Space Center. Christa McAuliffe was eventually chosen as the first Teacher in Space and was a member of the seven-member Challenger shuttle crew which died tragically in the explosion of the spacecraft during the launch of STS-51L from the Kennedy Space Center about 11:40 a.m., EST, on Jan. 28, 1986. The explosion occurred 73 seconds into the flight as a result of a leak in one of two Solid Rocket Boosters that ignited the main liquid fuel tank. The crew members of the Challenger represented a cross-section of the American population in terms of race, gender, geography, background, and religion. The explosion became one of the most significant events of the 1980s, as billions around the world saw the accident on television and empathized with any one of the several crew members killed. Photo credit: NASA
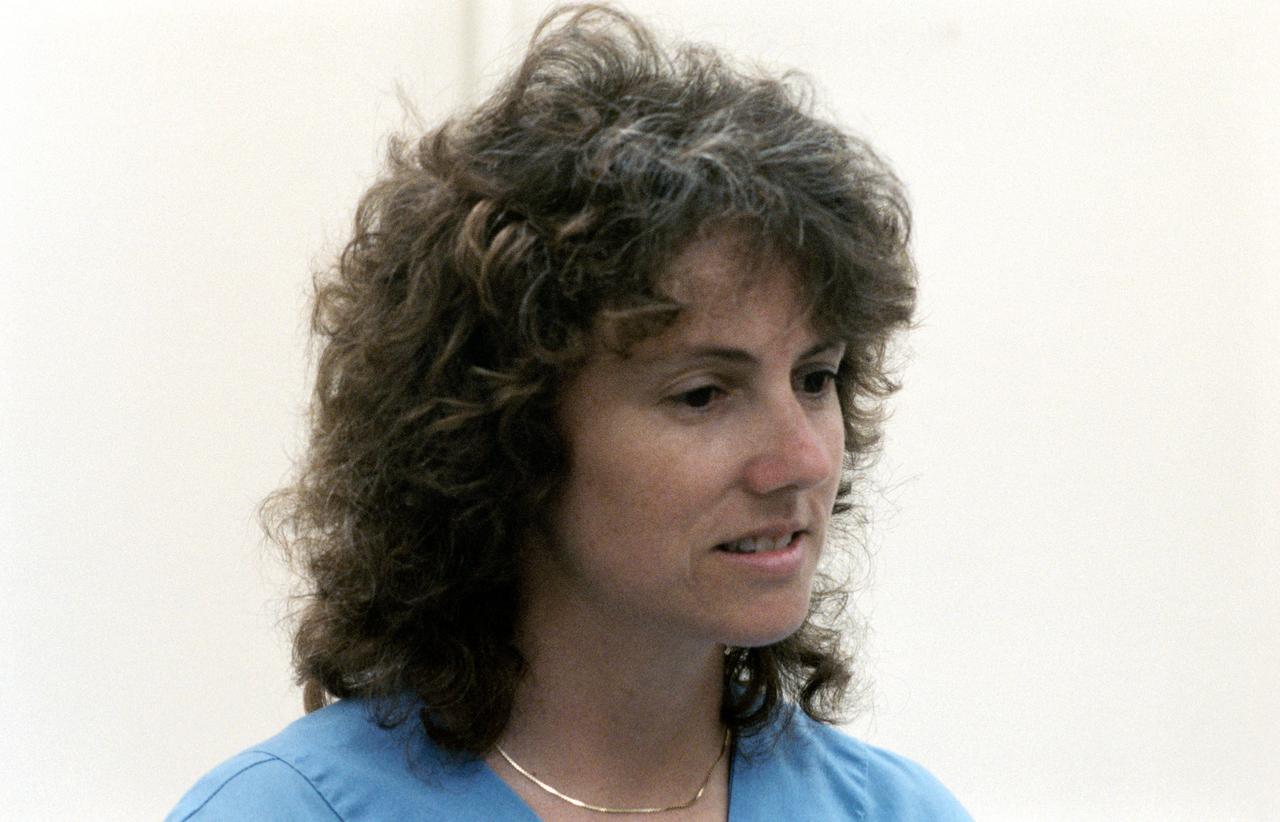

S85-37164 (8-12 July 1985) --- Sharon C. (Christa) McAuliffe of Concord High, Concord, New Hampshire, talks to the media at Johnson Space Center. Christa McAuliffe was eventually chosen as the first Teacher in Space and was a member of the seven-member Challenger shuttle crew which died tragically in the explosion of the spacecraft during the launch of STS-51L from the Kennedy Space Center about 11:40 a.m., EST, on Jan. 28, 1986. The explosion occurred 73 seconds into the flight as a result of a leak in one of two Solid Rocket Boosters that ignited the main liquid fuel tank. The crew members of the Challenger represented a cross-section of the American population in terms of race, gender, geography, background, and religion. The explosion became one of the most significant events of the 1980s, as billions around the world saw the accident on television and empathized with any one of the several crew members killed. Photo credit: NASA
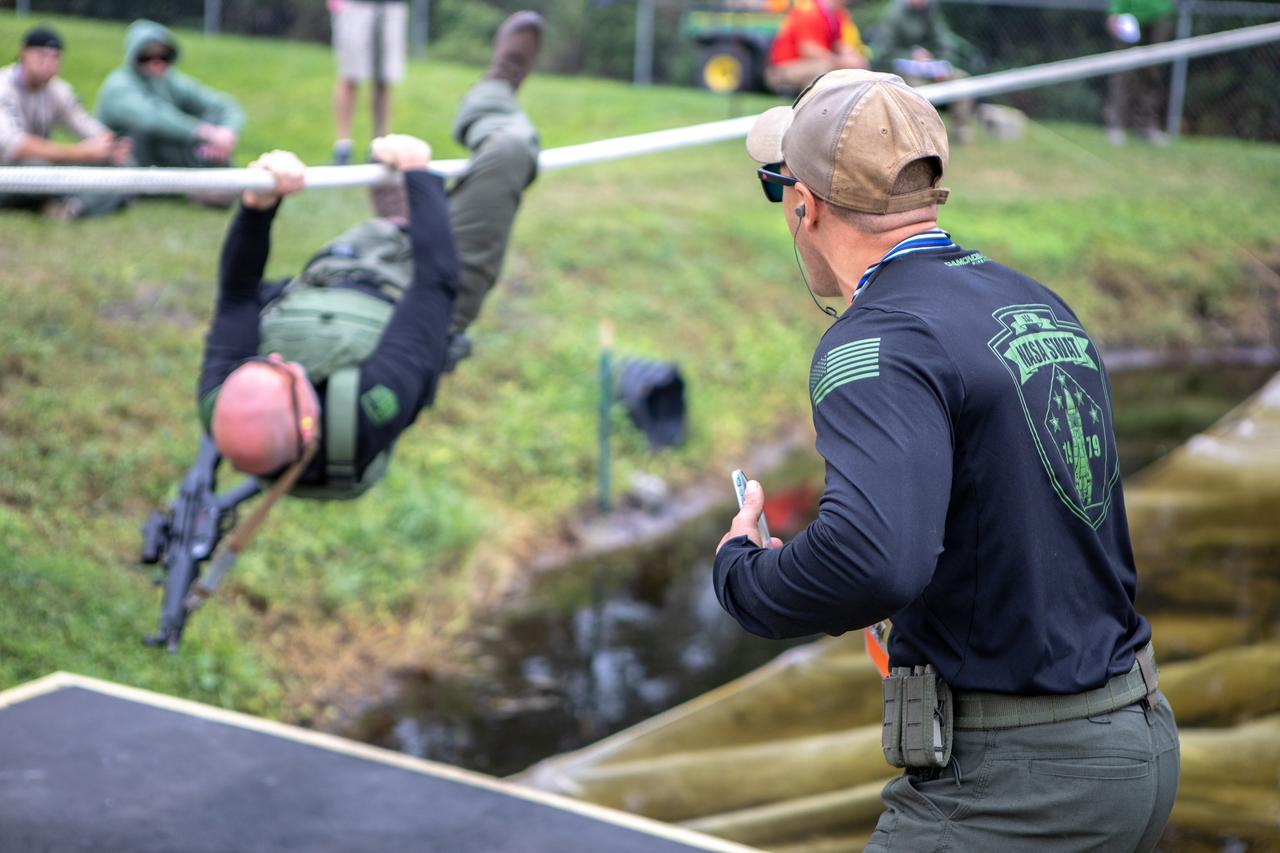

A member of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Emergency Response Team switches position as he works his way along a rope above water during one of the tactical challenges at the 37th Annual SWAT Round-Up International at the Lawson Lamar Firearms and Tactical Training Center in Orlando, Florida. His ERT teammate cheers him on. The competition was held Nov. 10 to 15, 2019, and featured five different tactical challenges. Kennedy's ERT members exchanged best practices and competed with more than 50 teams from the U.S. and around the world.
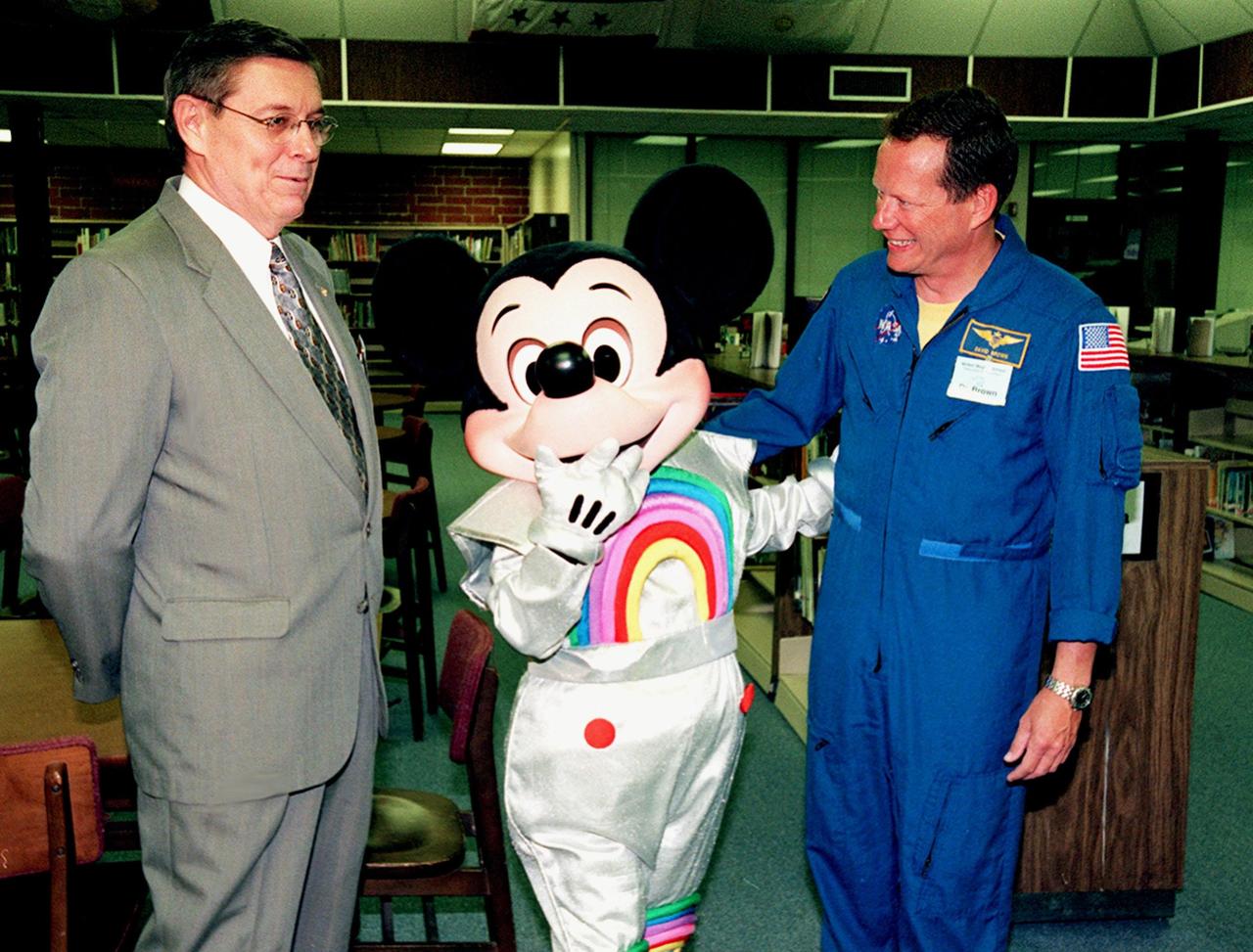

Dr. David Sawyer (left), Superintendent of the Brevard County School District, Mickey Mouse, and Dr. David Brown, a NASA astronaut, attend a tribute to NASA astronaut Ronald McNair held in the gymnasium of Ronald McNair Magnet School in Cocoa, Fla. During the tribute, Walt Disney World presented a portrait of McNair to the school, which had previously been renamed for the fallen astronaut. McNair was one of a crew of seven who lost their lives during an accident following launch of the Space Shuttle Challenger in January 1986
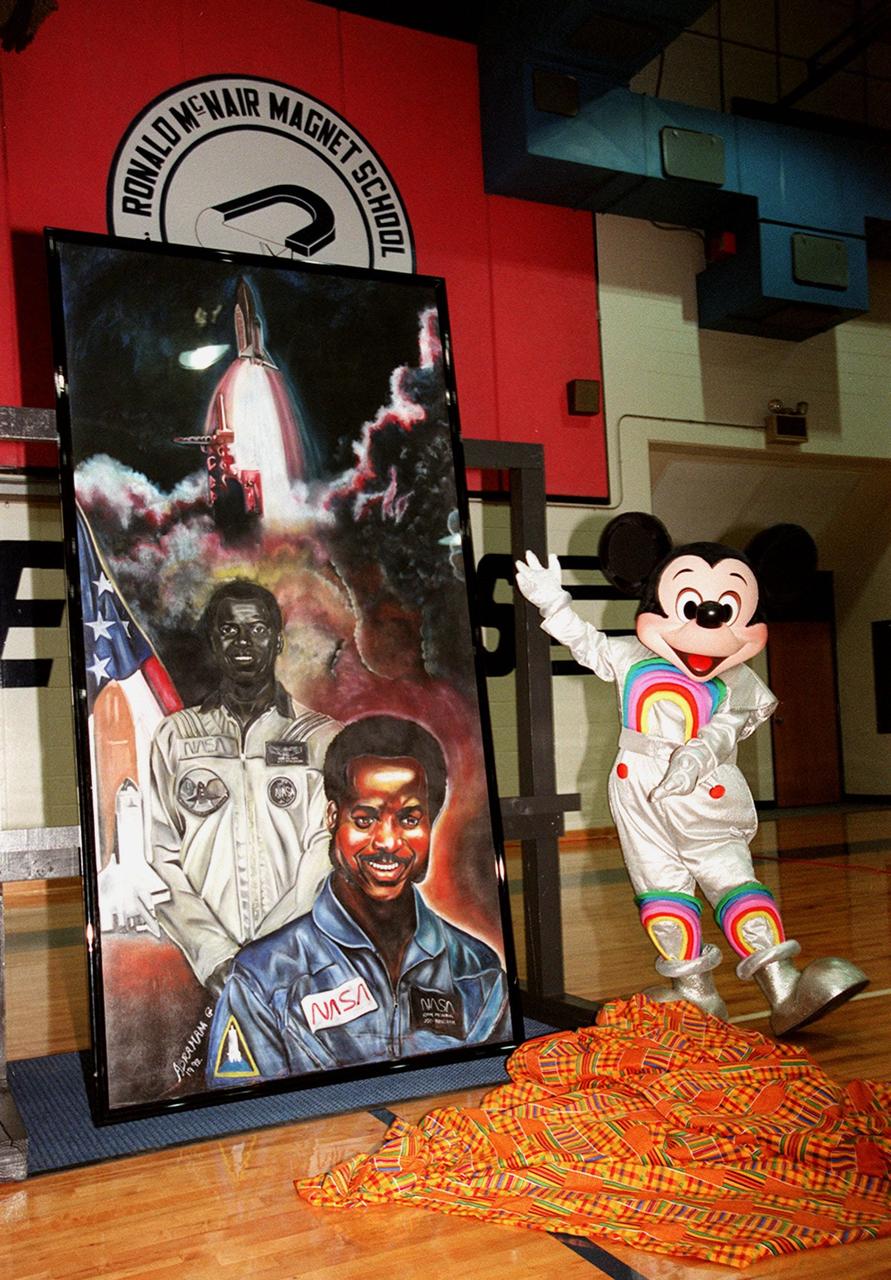

In the gymnasium of Ronald McNair Magnet School in Cocoa, Fla., Mickey Mouse poses with a portrait of NASA astronaut Ronald McNair. The portrait was presented to the school by Walt Disney World during a tribute to McNair. The school had previously been renamed for the fallen astronaut who was one of a crew of seven who lost their lives during an accident following launch of the Space Shuttle Challenger in January 1986
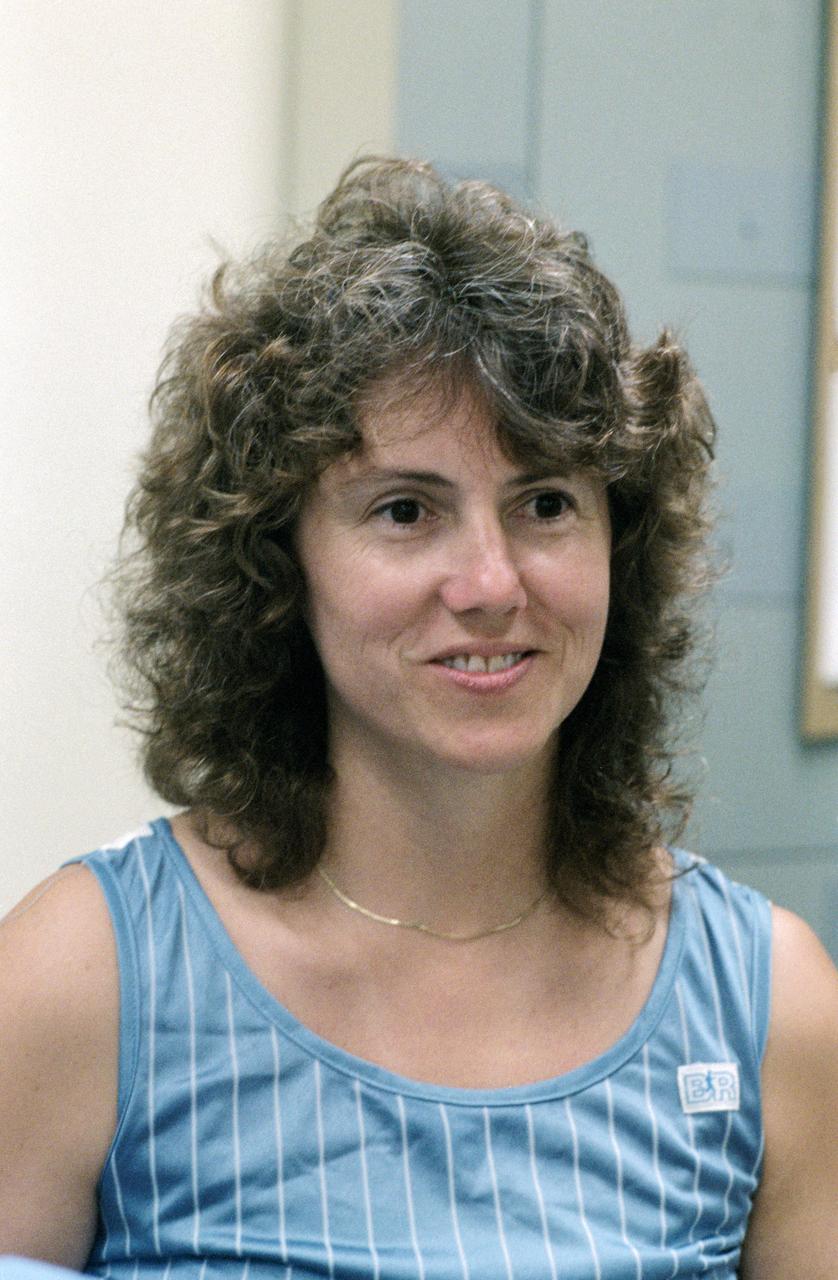
S85-37677 (8-12 July 1985) --- Sharon C. (Christa) McAuliffe of Concord High, Concord, New Hampshire, talks to nurse during physiological testing on first day at Johnson Space Center (JSC). Christa McAuliffe was eventually chosen as the first Teacher in Space and was a member of the seven-member Challenger shuttle crew which died tragically in the explosion of the spacecraft during the launch of STS-51L from the Kennedy Space Center about 11:40 a.m., EST, on Jan. 28, 1986. The explosion occurred 73 seconds into the flight as a result of a leak in one of two Solid Rocket Boosters that ignited the main liquid fuel tank. The crew members of the Challenger represented a cross-section of the American population in terms of race, gender, geography, background, and religion. The explosion became one of the most significant events of the 1980s, as billions around the world saw the accident on television and empathized with any one of the several crew members killed. Photo credit: NASA
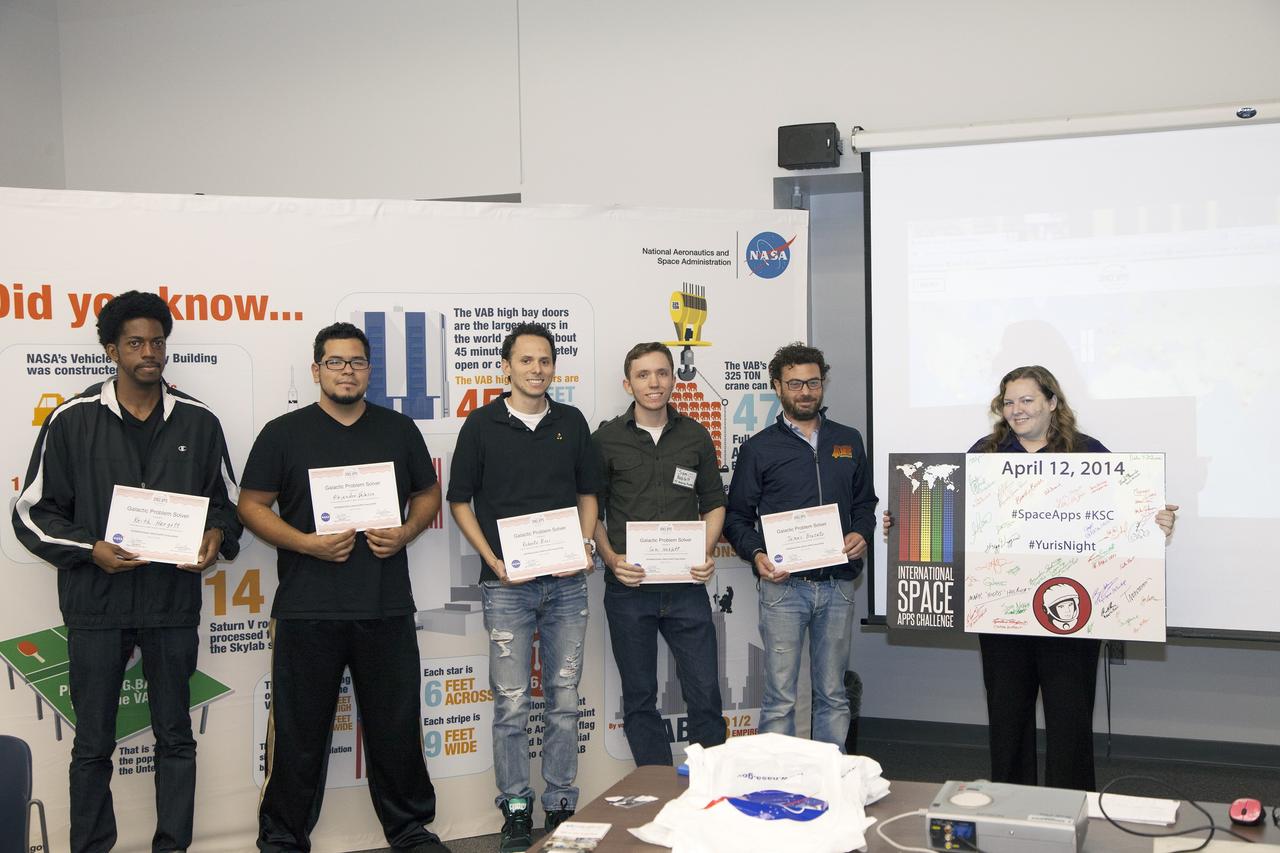

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Members of the winning teams in the International Space Apps Challenge display their Galactic Problem Solver certificates. From left are SpaceWear team members Keith Hargett and Alejandro Velasco, and Astronaut Resource Managing System team members Roberto Ricci, Sam Neblett, and James Brucato. Caley Burke, the NASA event organizer lead, is at right. Kennedy Space Center hosted one of the over 90 locations around the world where participants congregated for the attempt to design innovative solutions for global challenges over a 48-hour period. This year's development marathon focused on five NASA mission areas: Asteroids, Earth Watch, Human Spaceflight, Robotics, and Technology in Space. Three of this year’s challenges were developed by KSC employees: Space Wearables: Fashion Designer to Astronauts, Growing Food for a Martian Table, and Asteroid Prospector. The winners selected in 2014 at Kennedy were Astronaut Resource Managing System, or ARMS, for Best Use of Data and SpaceWear for Best Use of Hardware. ARMS also took the People's Choice Award. For more information, visit https://2014.spaceappschallenge.org. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
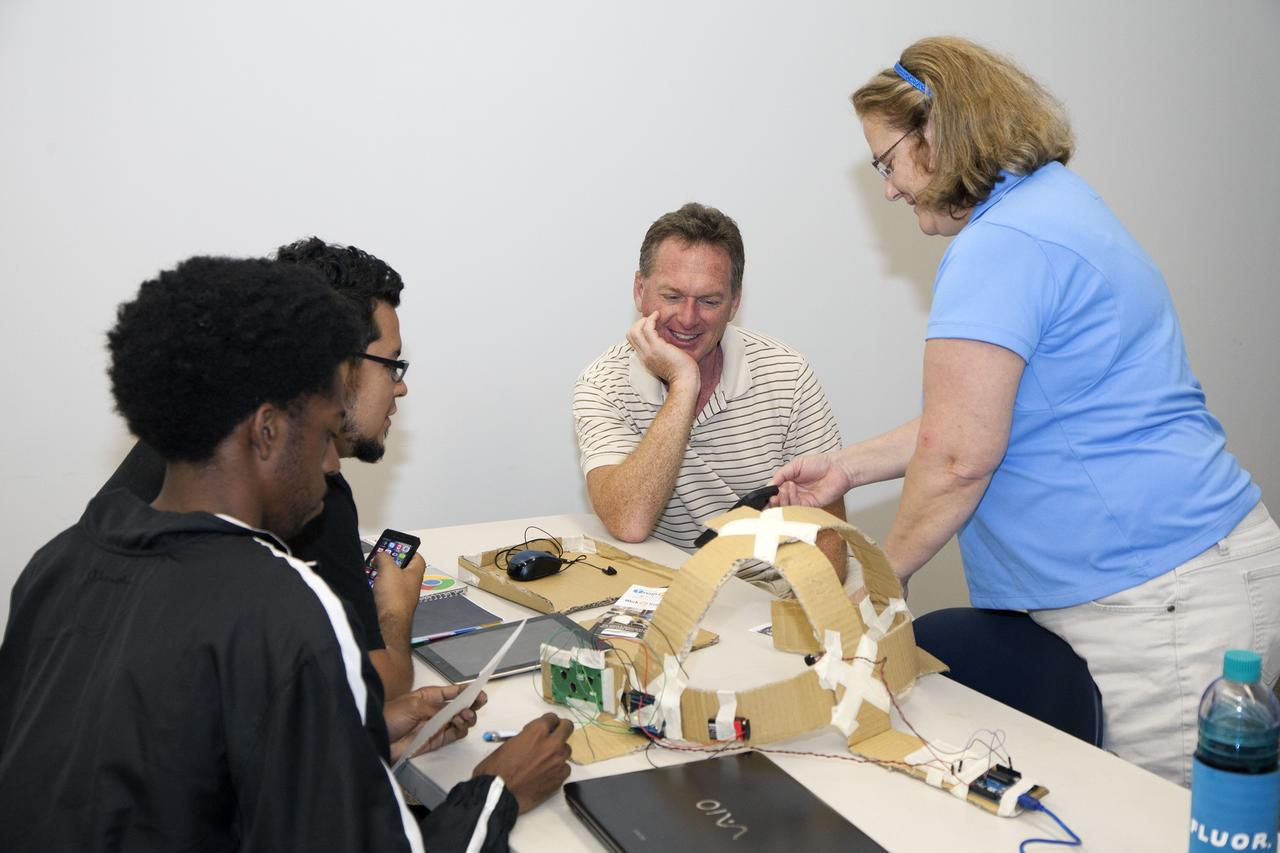

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - SpaceWear team members Keith Hargett, left, and Alejandro Velasco demonstrate their entry in the International Space Apps Challenge to NASA Ground Systems Development and Operation Program Manager Michael Bolger and NASA's Lisa Singleton in the Center for Space Education at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Kennedy Space Center hosted one of the over 90 locations around the world where participants congregated for the attempt to design innovative solutions for global challenges over a 48-hour period. This year's development marathon focused on five NASA mission areas: Asteroids, Earth Watch, Human Spaceflight, Robotics, and Technology in Space. Three of this year’s challenges were developed by KSC employees: Space Wearables: Fashion Designer to Astronauts, Growing Food for a Martian Table, and Asteroid Prospector. The winners selected in 2014 at Kennedy were Astronaut Resource Managing System, or ARMS, for Best Use of Data and SpaceWear for Best Use of Hardware. ARMS also took the People's Choice Award. For more information, visit https://2014.spaceappschallenge.org. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
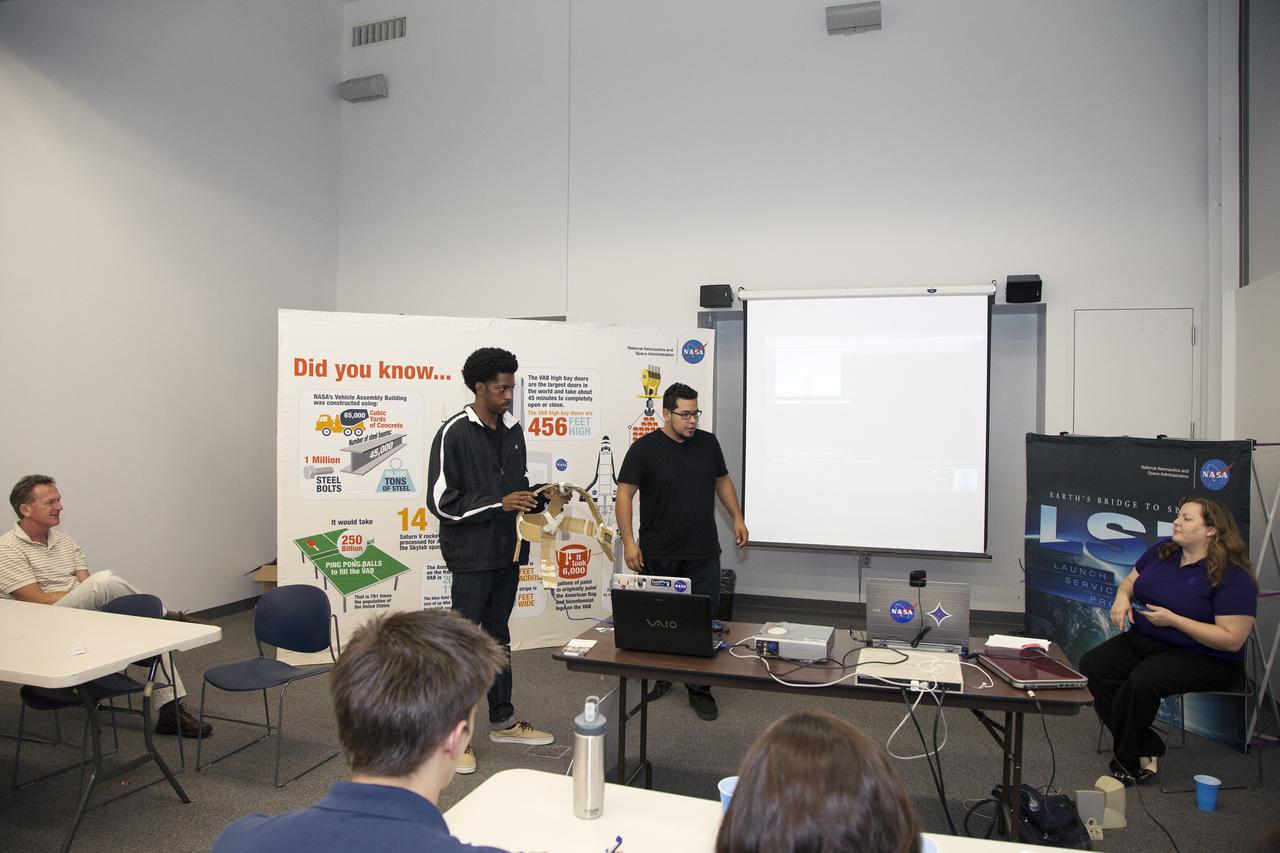

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - SpaceWear team members Keith Hargett, left, and Alejandro Velasco explain their entry in the International Space Apps Challenge to an audience in the Center for Space Education at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. In the audience at left is NASA Ground Systems Development and Operations Program Manager Michael Bolger. Caley Burke, the NASA event organizer lead, is at right. Kennedy Space Center hosted one of the over 90 locations around the world where participants congregated for the attempt to design innovative solutions for global challenges over a 48-hour period. This year's development marathon focused on five NASA mission areas: Asteroids, Earth Watch, Human Spaceflight, Robotics, and Technology in Space. Three of this year’s challenges were developed by KSC employees: Space Wearables: Fashion Designer to Astronauts, Growing Food for a Martian Table, and Asteroid Prospector. The winners selected in 2014 at Kennedy were Astronaut Resource Managing System, or ARMS, for Best Use of Data and SpaceWear for Best Use of Hardware. ARMS also took the People's Choice Award. For more information, visit https://2014.spaceappschallenge.org. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - SpaceWear team members Keith Hargett, left, and Alejandro Velasco participate in the International Space Apps Challenge in the Center for Space Education at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Kennedy Space Center hosted one of the over 90 locations around the world where participants congregated for the attempt to design innovative solutions for global challenges over a 48-hour period. This year's development marathon focused on five NASA mission areas: Asteroids, Earth Watch, Human Spaceflight, Robotics, and Technology in Space. Three of this year’s challenges were developed by KSC employees: Space Wearables: Fashion Designer to Astronauts, Growing Food for a Martian Table, and Asteroid Prospector. The winners selected in 2014 at Kennedy were Astronaut Resource Managing System, or ARMS, for Best Use of Data and SpaceWear for Best Use of Hardware. ARMS also took the People's Choice Award. For more information, visit https://2014.spaceappschallenge.org. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Astronaut Resource Managing System team members Sam Neblett of KSC Technik Inc., left, and Roberto Ricci participate in the International Space Apps Challenge in the Center for Space Education at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida. Kennedy Space Center hosted one of the over 90 locations around the world where participants congregated for the attempt to design innovative solutions for global challenges over a 48-hour period. This year's development marathon focused on five NASA mission areas: Asteroids, Earth Watch, Human Spaceflight, Robotics, and Technology in Space. Three of this year’s challenges were developed by KSC employees: Space Wearables: Fashion Designer to Astronauts, Growing Food for a Martian Table, and Asteroid Prospector. The winners selected in 2014 at Kennedy were Astronaut Resource Managing System, or ARMS, for Best Use of Data and SpaceWear for Best Use of Hardware. ARMS also took the People's Choice Award. For more information, visit https://2014.spaceappschallenge.org. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

"When I left college, I went to go work in investment banking on Wall Street. It was one of these experiences where people said, ‘that’s the most awesome job ever. How did you manage to do that?’ But once I was inside that world, I felt very disconnected from people. I felt like the world was passing me by while I was inside cars going to business meetings and dinners. And I really wasn’t interacting with people, or understanding the challenges they were going through. So I applied to a number of medical schools. Once I got my letters of acceptance, I just chose one and I went. Then I felt like I was really doing what I wanted to do. I had a tremendous experience in my training and my classes. I just felt like, ‘wow. This is what I’m meant to do.’ Everybody has their thing. Everybody has a place where they shine. And for me, it’s being a physician, helping people heal, solving medical problems. Helping people feel better in their own bodies, no matter what that looks like." NASA Headquarters Medical Director, Dr. Andrea Fore, poses for a portrait while working from home during the COVID-19 pandemic, Monday, July 13, 2020 in Maryland. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
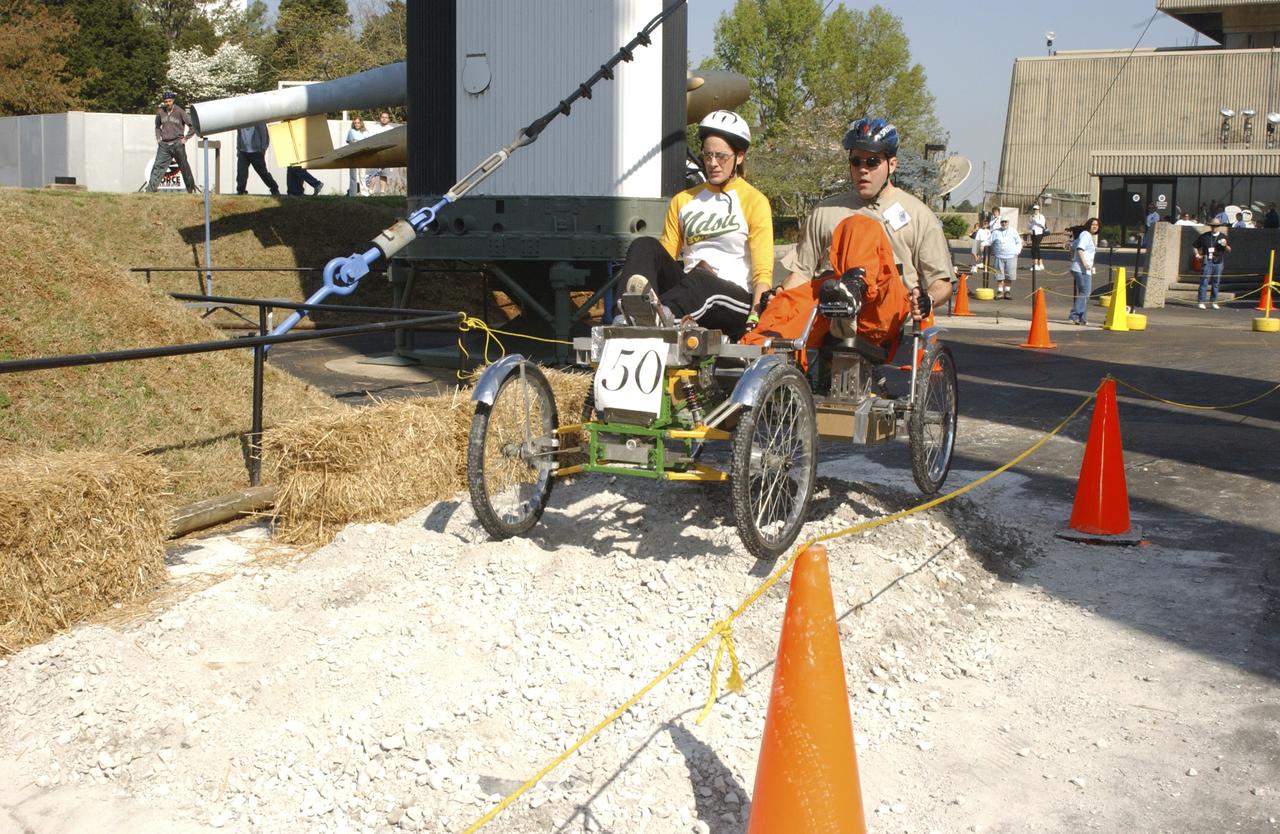

Students from across the United States and as far away as Puerto Rico came to Huntsville, Alabama for the 10th annual Great Moonbuggy Race at the U.S. Space Rocket Center. Sixty-eight teams, representing high schools and colleges from all over the United States, and Puerto Rico, raced human powered vehicles over a lunar-like terrain. Vehicles powered by two team members, one male and one female, raced one at a time over a half-mile obstacle course of simulated moonscape terrain. The competition is inspired by development, some 30 years ago, of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), a program managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The LRV team had to design a compact, lightweight, all-terrain vehicle that could be transported to the Moon in the small Apollo spacecraft. The Great Moonbuggy Race challenges students to design and build a human powered vehicle so they will learn how to deal with real-world engineering problems similar to those faced by the actual NASA LRV team. In this photograph, Team No. 1 from North Dakota State University in Fargo conquers one of several obstacles on their way to victory. The team captured first place honors in the college level competition.
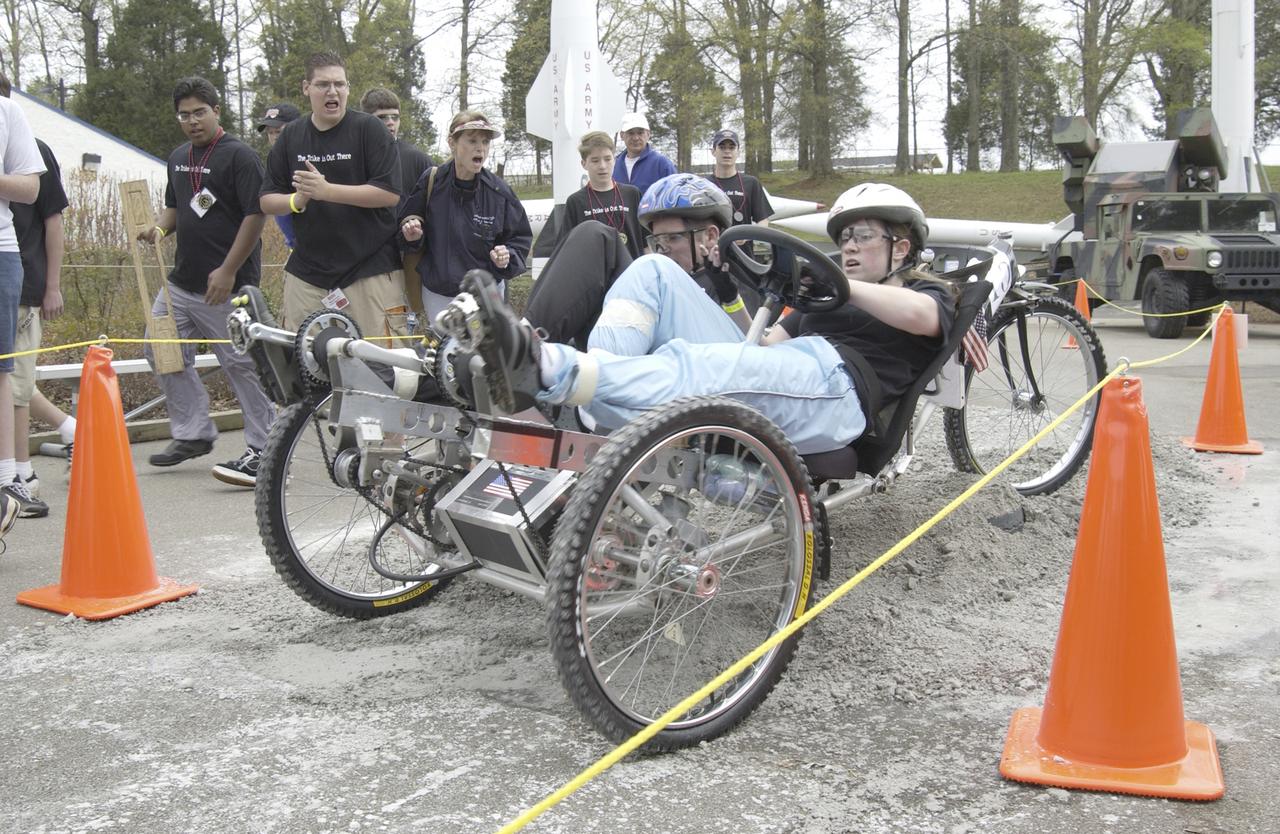

Students from across the United States and as far away as Puerto Rico and South America came to Huntsville, Alabama for the 9th annual Great Moonbuggy Race at the U.S. Space Rocket Center. Seventy-seven teams, representing high schools and colleges from 21 states, Puerto Rico, and Columbia, raced human powered vehicles over a lunar-like terrain. In this photograph, the New Orleans area schools team #2 from New Orleans, Louisiana maneuvers through an obstacle course. The team captured second place in the high school division competition. Vehicles powered by two team members, one male and one female, raced one at a time over a half-mile obstacle course of simulated moonscape terrain. The competition is inspired by the development, some 30 years ago, of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), a program managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The LRV team had to design a compact, lightweight, all-terrain vehicle that could be transported to the Moon in the small Apollo spacecraft. The Great Moonbuggy Race challenges students to design and build a human powered vehicle so they will learn how to deal with real-world engineering problems, similar to those faced by the actual NASA LRV team.
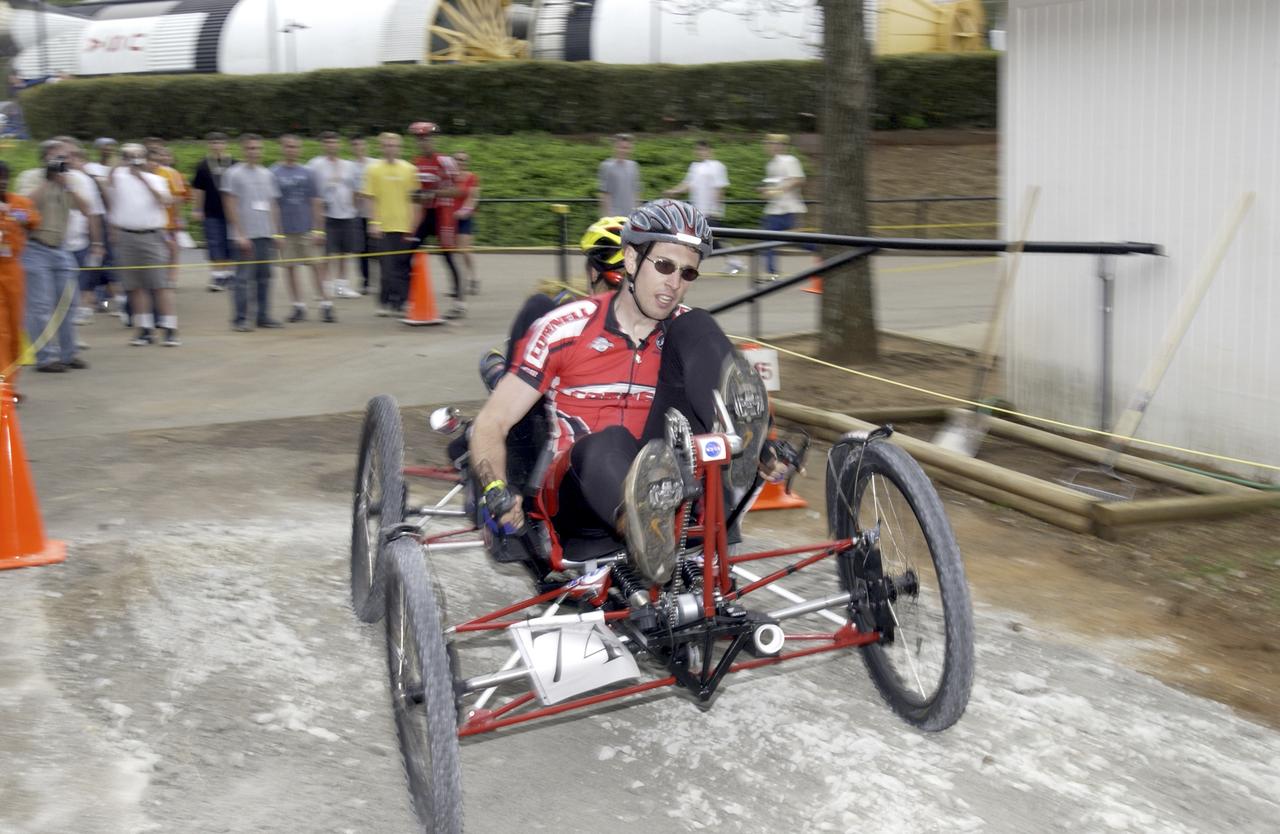

Students from across the United States and as far away as Puerto Rico and South America came to Huntsville, Alabama for the 9th annual Great Moonbuggy Race at the U.S. Space Rocket Center. Seventy-seven teams, representing high schools and colleges from 21 states, Puerto Rico, and Columbia, raced human powered vehicles over a lunar-like terrain. A team from Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, took the first place honor in the college division. In this photograph, the Cornell #1 team, the collegiate first place winner, maneuvers their vehicle through the course. Vehicles powered by two team members, one male and one female, raced one at a time over a half-mile obstacle course of simulated moonscape terrain. The competition is inspired by development, some 30 years ago, of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), a program managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The LRV team had to design a compact, lightweight, all-terrain vehicle that could be transported to the Moon in the small Apollo spacecraft. The Great Moonbuggy Race challenges students to design and build a humanpowered vehicle so they will learn how to deal with real-world engineering problems similar to those faced by the actual NASA LRV team.
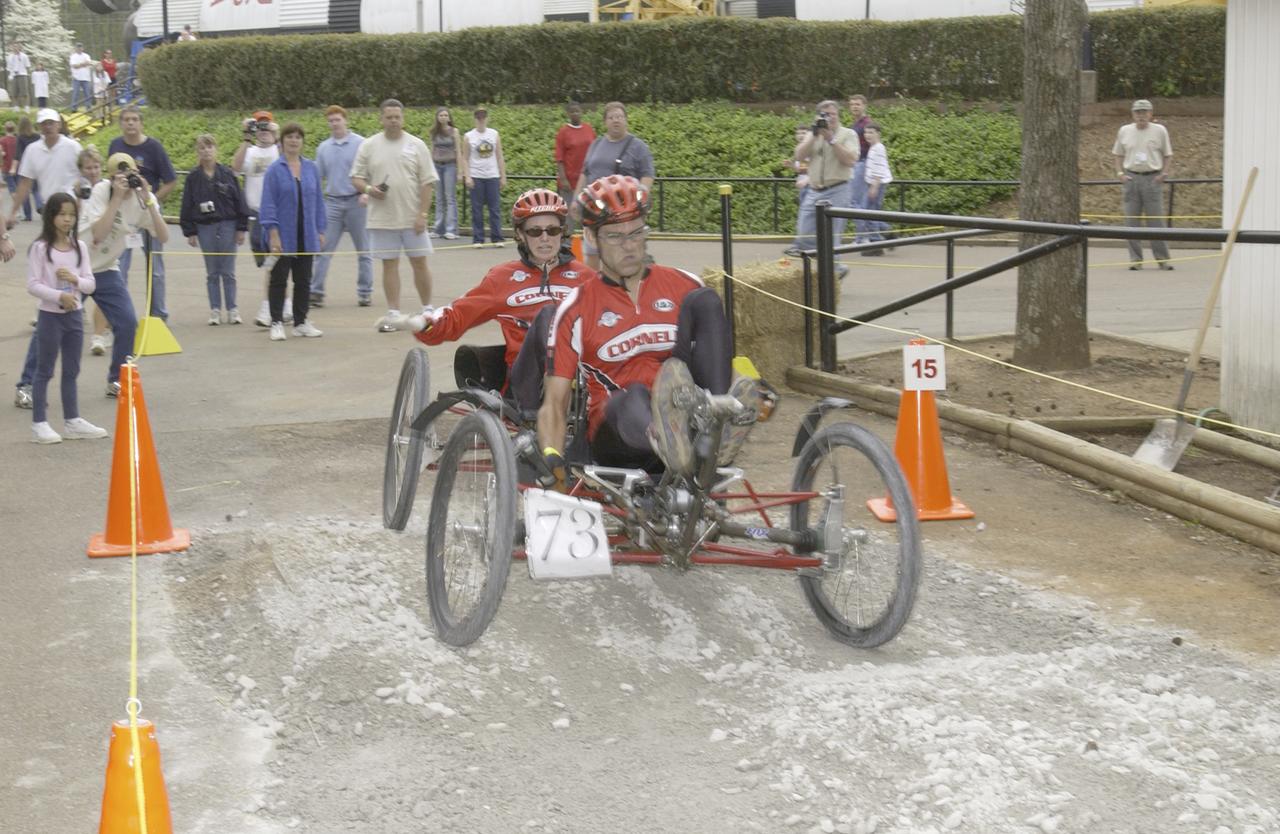

Students from across the United States and as far away as Puerto Rico and South America came to Huntsville, Alabama for the 9th annual Great Moonbuggy Race at the U.S. Space Rocket Center. Seventy-seven teams, representing high schools and colleges from 21 states, Puerto Rico, and Columbia, raced human powered vehicles over a lunar-like terrain. A team from Cornell University in Ithaca, New York, took the first place honor in the college division. This photograph shows the Cornell #2 team driving their vehicle through the course. The team finished the race in second place in the college division. Vehicles powered by two team members, one male and one female, raced one at a time over a half-mile obstacle course of simulated moonscape terrain. The competition is inspired by development, some 30 years ago, of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV), a program managed by the Marshall Space Flight Center. The LRV team had to design a compact, lightweight, all-terrain vehicle, that could be transported to the Moon in the small Apollo spacecraft. The Great Moonbuggy Race challenges students to design and build a human powered vehicle so they will learn how to deal with real-world engineering problems, similar to those faced by the actual NASA LRV team.
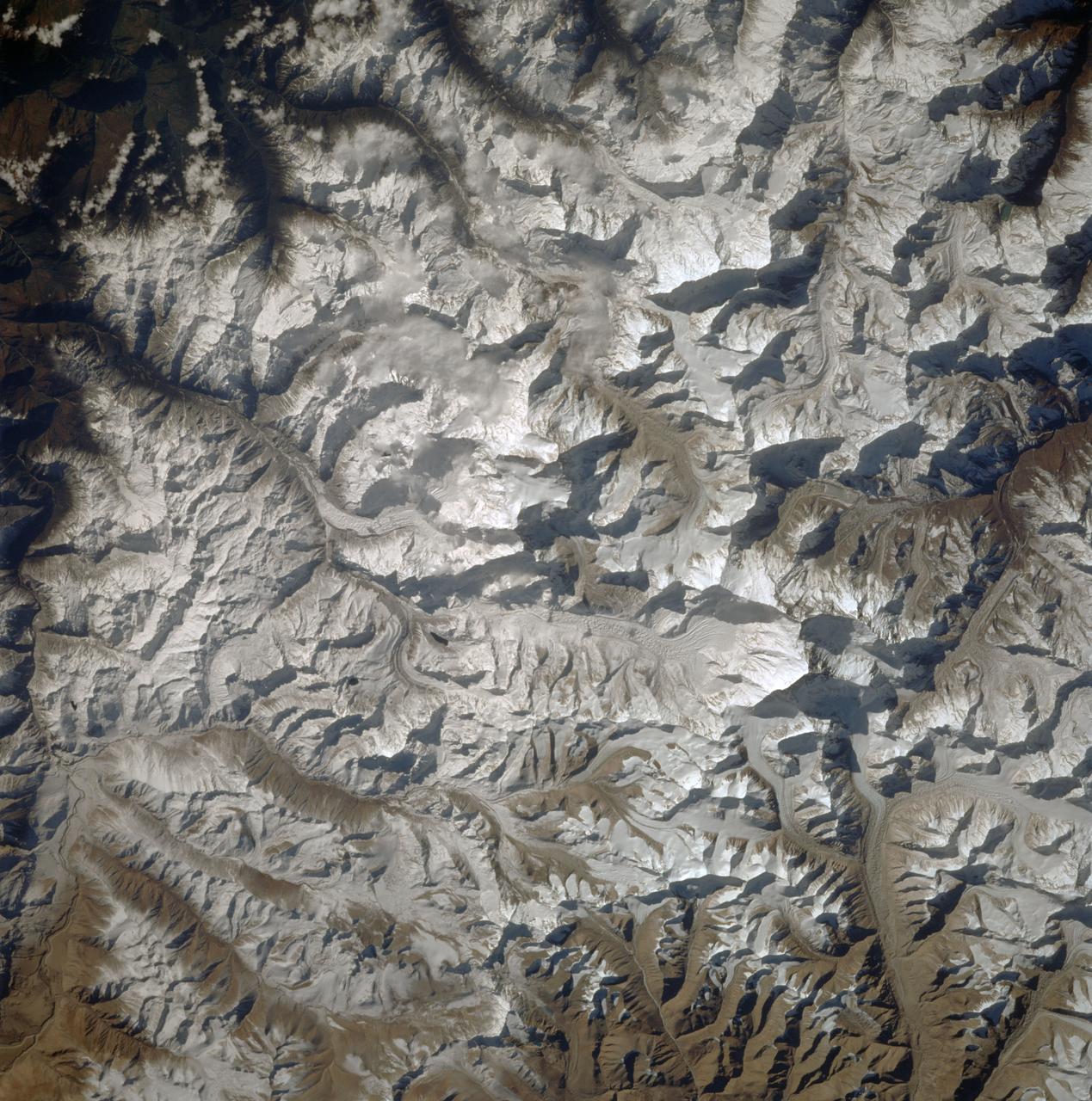

STS087-716-080 (19 November – 5 December 1997) --- Featured in this view is Mount Everest. It is called “Sagarmatha” in Nepal and “Qomolangma Feng” Qomolangma in China (both names meaning “Goddess Mother of the World”), but is known to the western world as Mount Everest. At an altitude of 29,028 feet (8,848 meters) the summit of tallest mountain on Earth (above sea level) reaches two-thirds of the way through the atmosphere. Situated on the border between Nepal and China (27°59’N, 86°56’E), Mount Everest with its low oxygen levels, powerful winds, and extremely cold temperatures has captured the imagination of adventuresome men and women. Sir Edmund Hillary and Tenzing Norgay were the first persons to surmount Mount Everest in 1953. While climbing Everest can be challenging, it can also be tragic. On May 10, 1996, after reaching the summit and descending to camp, several climbers were trapped by a severe and sudden storm. A total of eight people died, making this day the deadliest single tragedy in the history of Mount Everest. This picture is one of the 70mm Earth observations visuals used by the crew at its post flight presentation events.
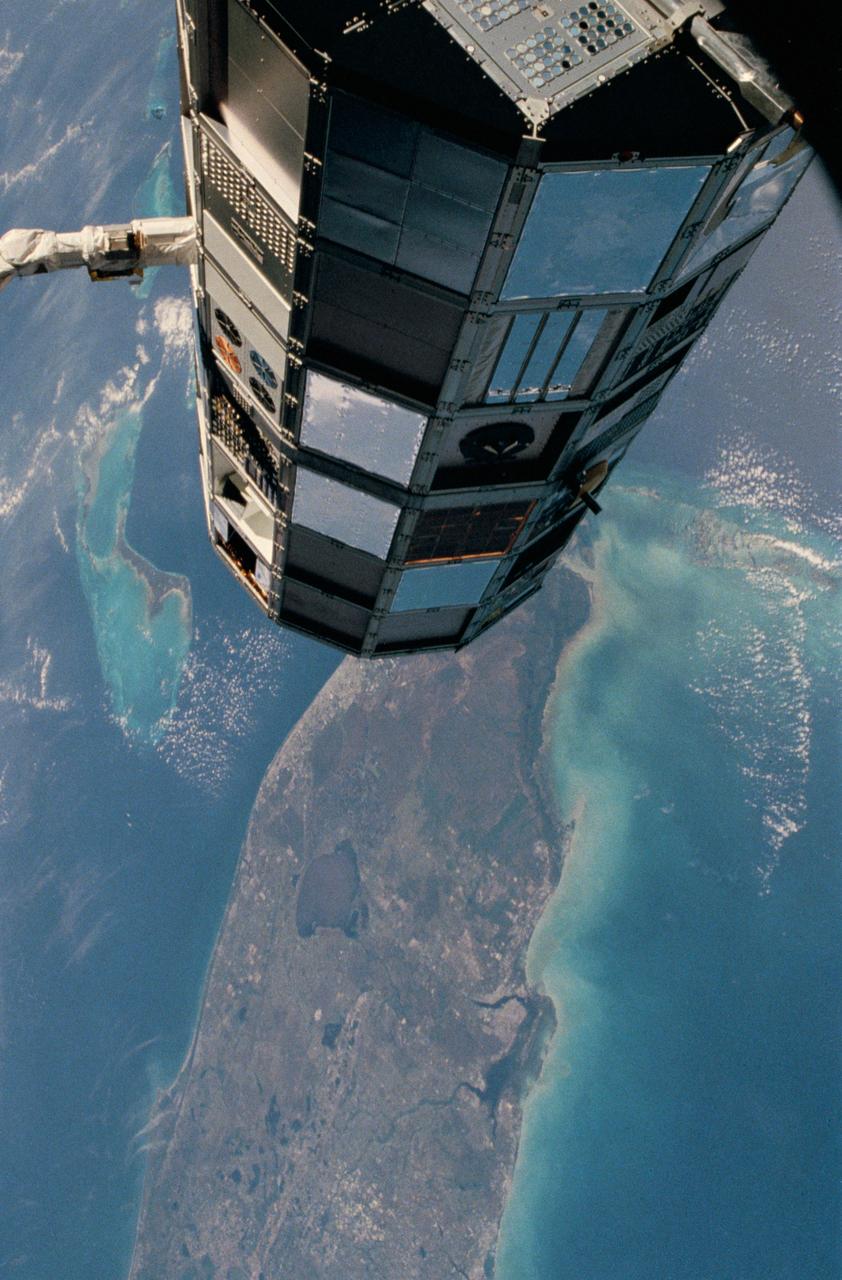

41C-02-067 (6-13 April 1984) --- One of the first major accomplishments of Flight 41-C?s crew aboard the Challenger was to place this giant satellite into Earth orbit. Still attached to the remote manipulator system (RMS) end effector, the Long-Duration Exposure Facility (LDEF) is backdropped against Florida, the Bahama Bank, the Gulf of Mexico and Atlantic waters. The multi-colored cylinder carries 50-odd passive scientific experiments representing 194 investigators from around world. The LDEF program is directed by the Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. The facility will be retrieved in a little less than a year by a Space Shuttle crew. This frame was one of the visuals used by the 41-C astronauts for their April 24, 1984 post-flight press conference. Cape Canaveral, where this seven-day mission got its start, and Lake Okeechobee, are easily recognized in the frame, photographed shortly before 11:30 a.m. (CST), April 7, 1984.
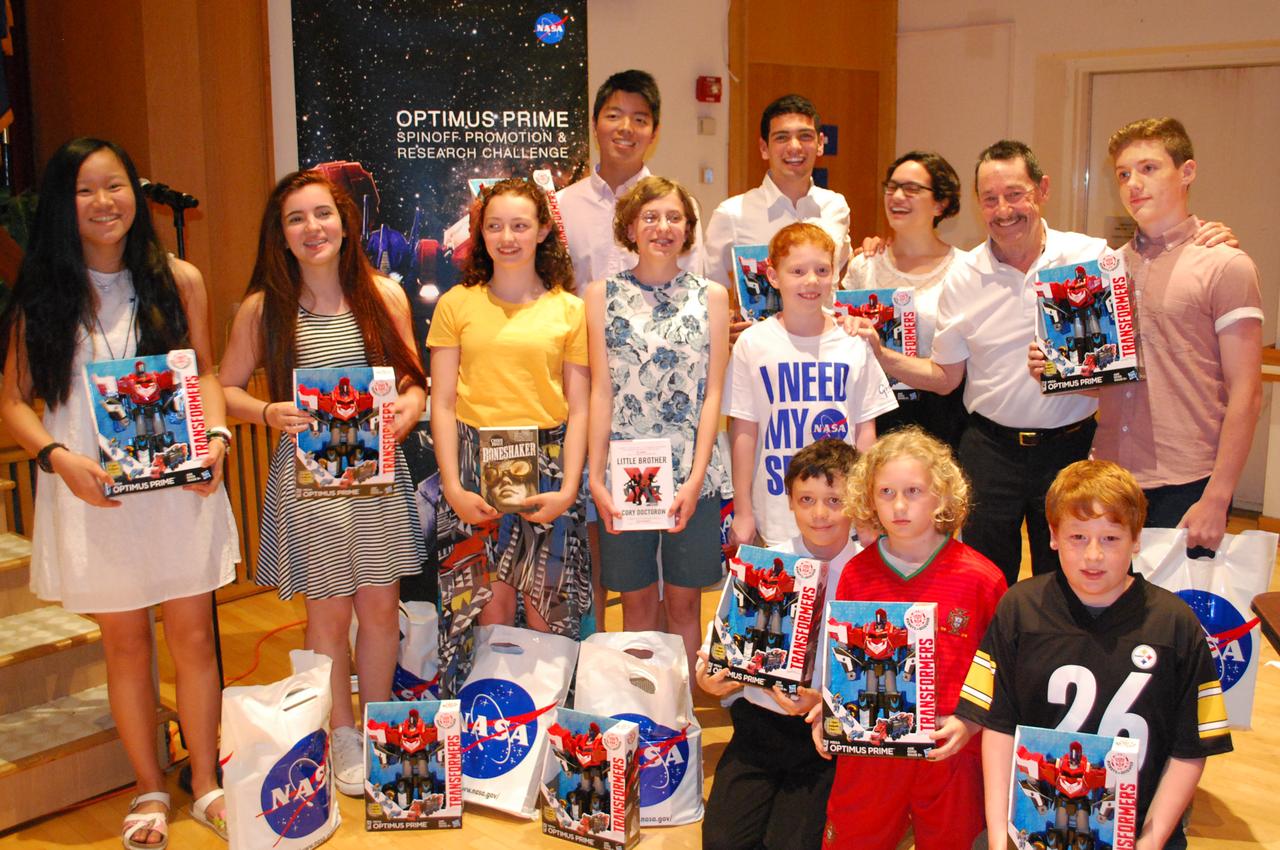

From June 28 through 30, 2016, the OPTIMUS PRIME Spinoff Promotion and Research Challenge (OPSPARC) gave the contest’s winning students the opportunity to explore NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Three teams of students from elementary, middle and high school won the contest by creating the most popular ideas to use NASA technology in new and innovative ways. The students used an online platform called Glogster to make posters about their ideas, and the general public voted for their favorites. Sophia Sheehan won the elementary school prize for her invention of the “blow coat,” which would be powered by solar panels and blow warm air into winter coats, helping people in her hometown of Chicago stay warm in the winter. Heidi Long, Aubrey Nesti, Katherine Valbuena and Jasmine Wu won in the middle school category for their idea called Tent-cordion, which would use spacesuit and satellite insulation materials in a foldable tent to house refugees and the homeless. Finally, Jake Laddis, Alex Li, Isaac Wecht and Isabel Wecht won in the high school category for their idea to use James Webb Space Telescope sunshield technology to shield houses from summer heat and reduce the need for air conditioning around the world. The high school winners also had the opportunity to compete in the NASA InWorld challenge, sponsored by the James Webb Space Telescope project, and continued developing their idea in a virtual world and gaming environment. During their three-day workshop at Goddard, the students toured the center, met with scientists and engineers, took a look at the James Webb Space Telescope in Goddard’s clean room, and even made their own videos in Goddard’s TV studio. One of the students talked about how the experience inspired her. Read more: <a href="http://go.nasa.gov/298fGdQ" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/298fGdQ</a>
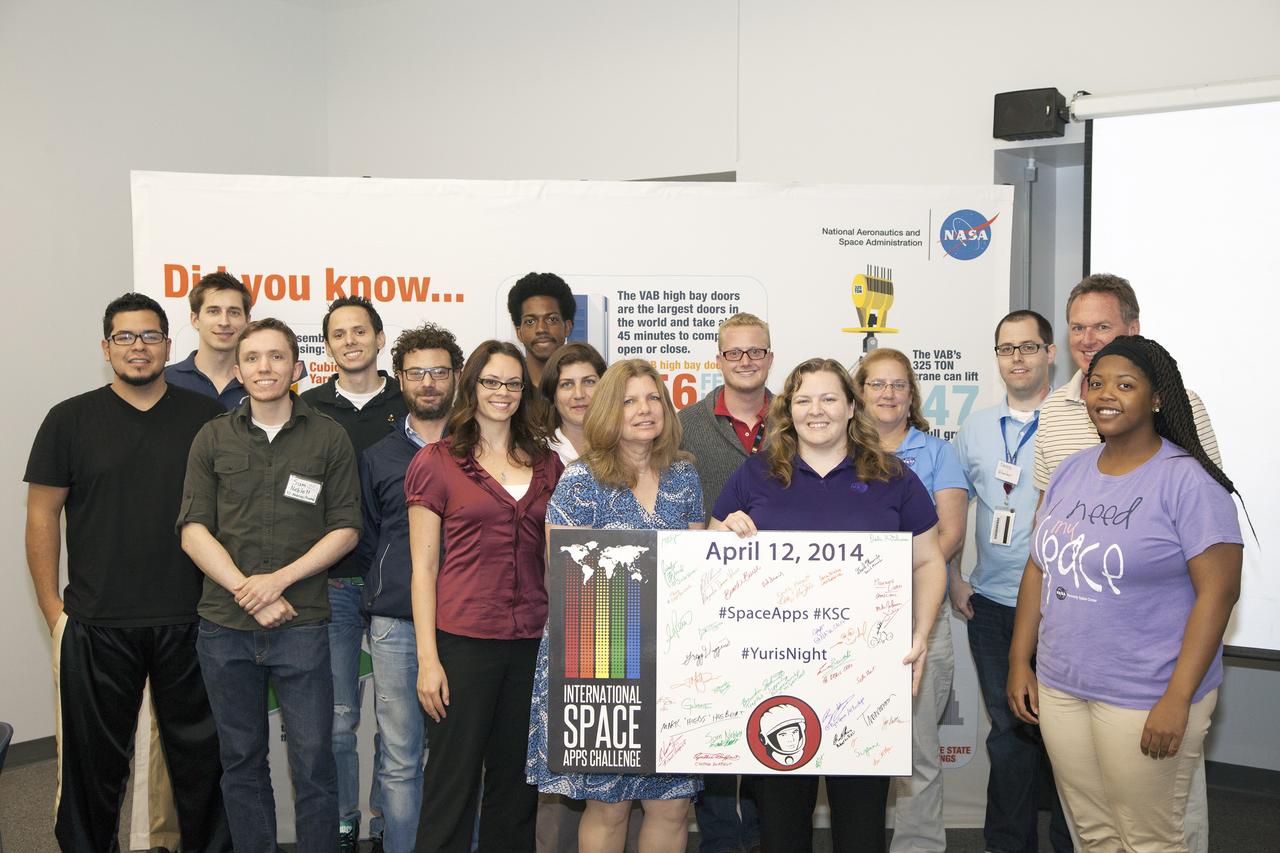

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Members of the winning Astronaut Resource Managing System and SpaceWear teams in the International Space Apps Challenge pose for a group portrait with the NASA volunteers, judges and event organizers. From left are Alejandro Velasco, NASA's Justin Treptow, Sam Neblett, Roberto Ricci, James Brucato, NASA's Suzanne Plantec, Keith Hargett, NASA's Cynthia Duffaut, NASA's Launa Maier, event organizer James Wood, event organizer lead Caley Burke, NASA's Lisa Singleton, event organizer David Miranda, NASA Ground Systems Development and Operation Program Manager Michael Bolger and NASA intern Brandi Burse. Kennedy Space Center hosted one of the over 90 locations around the world where participants congregated for the attempt to design innovative solutions for global challenges over a 48-hour period. This year's development marathon focused on five NASA mission areas: Asteroids, Earth Watch, Human Spaceflight, Robotics, and Technology in Space. Three of this year’s challenges were developed by KSC employees: Space Wearables: Fashion Designer to Astronauts, Growing Food for a Martian Table, and Asteroid Prospector. The winners selected in 2014 at Kennedy were Astronaut Resource Managing System, or ARMS, for Best Use of Data and SpaceWear for Best Use of Hardware. ARMS also took the People's Choice Award. For more information, visit https://2014.spaceappschallenge.org. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Operations Support Building (OSB) II at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of the many speakers discusses innovative ideas with NASA and partners during a three-day LAUNCH: Energy forum Nov. 11-13. This third in a series of forums is part of an ongoing initiative to identify, showcase and support innovative approaches to sustainability challenges. LAUNCH allows NASA to propel innovative solutions that help those outside the agency make the connection between our lives on Earth and how we live and work in space. Through the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)'s involvement, LAUNCH places a special emphasis on accelerating innovations poised for large scale impact in improving the lives of people in the developing world. During the forum, 10 international participants will showcase new innovations that could address energy problems on Earth and in space. NASA, USAID, Nike Inc., and the U.S. Department of State are LAUNCH founding partners. The partners all contributed to planning the forum, selecting innovators and recruiting other event participants. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
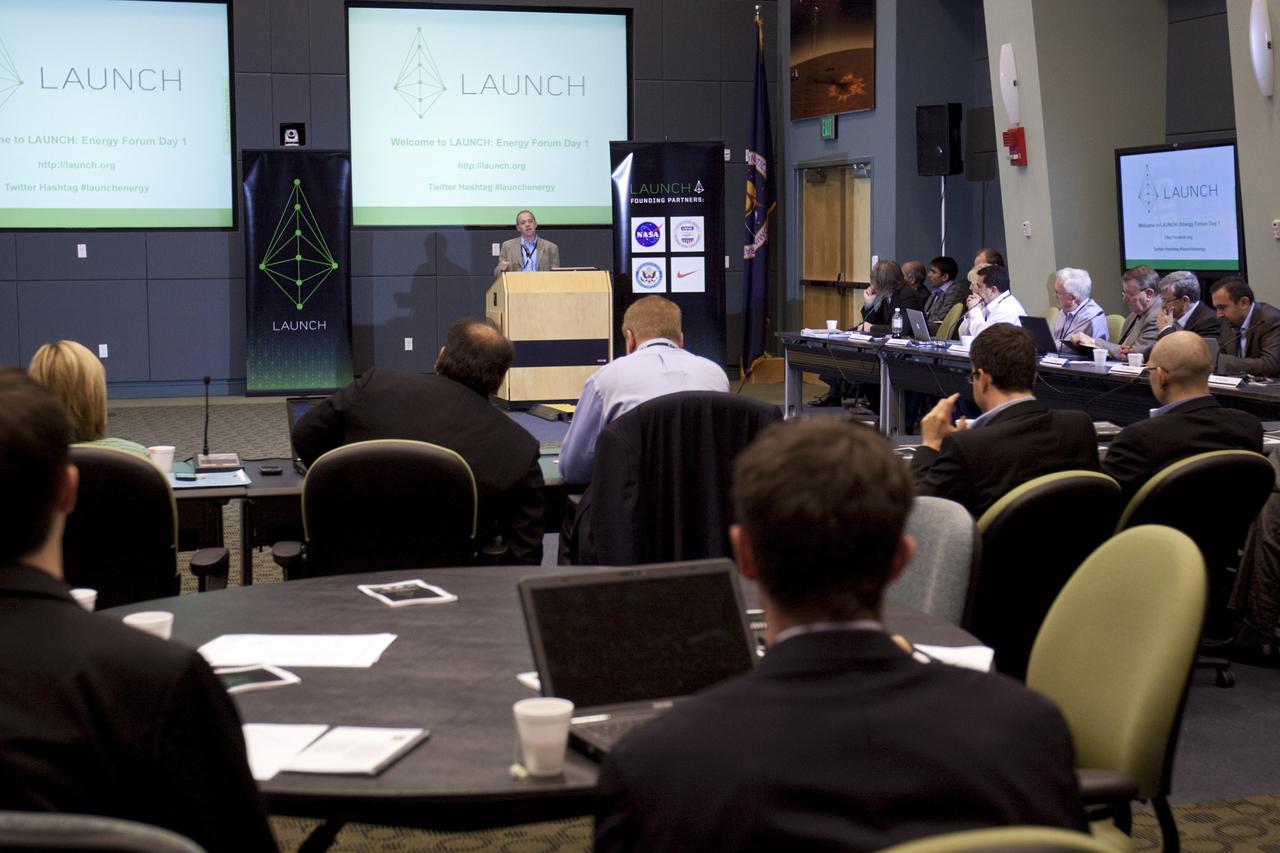

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Operations Support Building (OSB) II at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of the many speakers discusses innovative ideas with NASA and partners during a three-day LAUNCH: Energy forum Nov. 11-13. This third in a series of forums is part of an ongoing initiative to identify, showcase and support innovative approaches to sustainability challenges. LAUNCH allows NASA to propel innovative solutions that help those outside the agency make the connection between our lives on Earth and how we live and work in space. Through the U.S. Agency for International Development (USAID)'s involvement, LAUNCH places a special emphasis on accelerating innovations poised for large scale impact in improving the lives of people in the developing world. During the forum, 10 international participants will showcase new innovations that could address energy problems on Earth and in space. NASA, USAID, Nike Inc., and the U.S. Department of State are LAUNCH founding partners. The partners all contributed to planning the forum, selecting innovators and recruiting other event participants. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
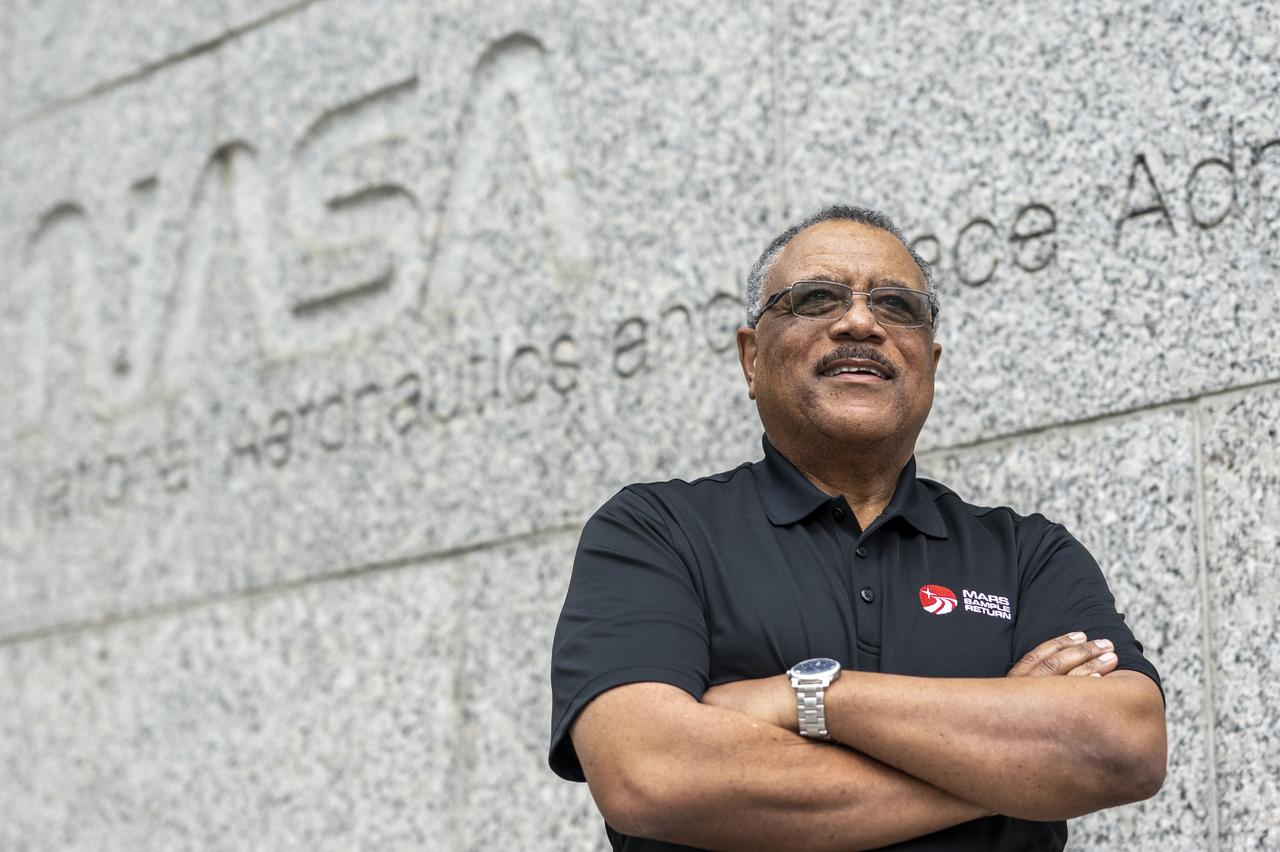

ÒIf you just invest a little time and a little effort in people, you will get so much more back. Not only will you feel good about it and get satisfaction above and beyond anything you can imagine, but the task or the mission you are trying to accomplish will also benefit tremendously. IÕve seen this happen many times when I have given someone an assignment. I am careful not to restrict their creativity. Often, theyÕre able to accomplish the task or mission better than I expected. ÒMy brotherÕs a professional artist, and I learned that from him. If you tell an artist what to paint, they will paint it. But, if you tell them what youÕre looking for, theyÕll paint that Ð and thereÕs a difference. People appreciate that, the openness to be able to create. Another big one is that thereÕs no such thing as a perfect person. So, the day you start thinking everythingÕs going to be perfect, you are in trouble. ÒI remember when I went on my first visit to NASAÕs Jet Propulsion Laboratory to talk about the Mars Sample Return campaign. I sat down with the communications team and said, ÔLook, if you are thinking we are going to do this perfectly and everythingÕs going to go as smoothly as it can, I want to change that mindset right now. We are going to have our challenges. But it is our job to work through those challenges, that is how we succeed. ÒI believe that whenever I am in a leadership position it is my call, my responsibility to create an environment in which all who work around me can be at their most efficient. I have been in situations before in which coworkers have said, ÔThat could not have turned out any better.Õ I believe you have to create the environment in which people can thrive and be their best. ThatÕs a big deal to me and I want people to treat me that way too. IÕve always felt from before I was a teenager that if I do something good, it will go to the next person and the next person, and before you know it, it goes around the world and comes back to me. I have truly believed that all my life, and I still think that today.Ó Dewayne Washington, Mars Sample Return Senior Communications Manager, poses for a portrait, Wednesday, Jan. 25, 2023, at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. Photo Credit: (NASA/Keegan Barber)
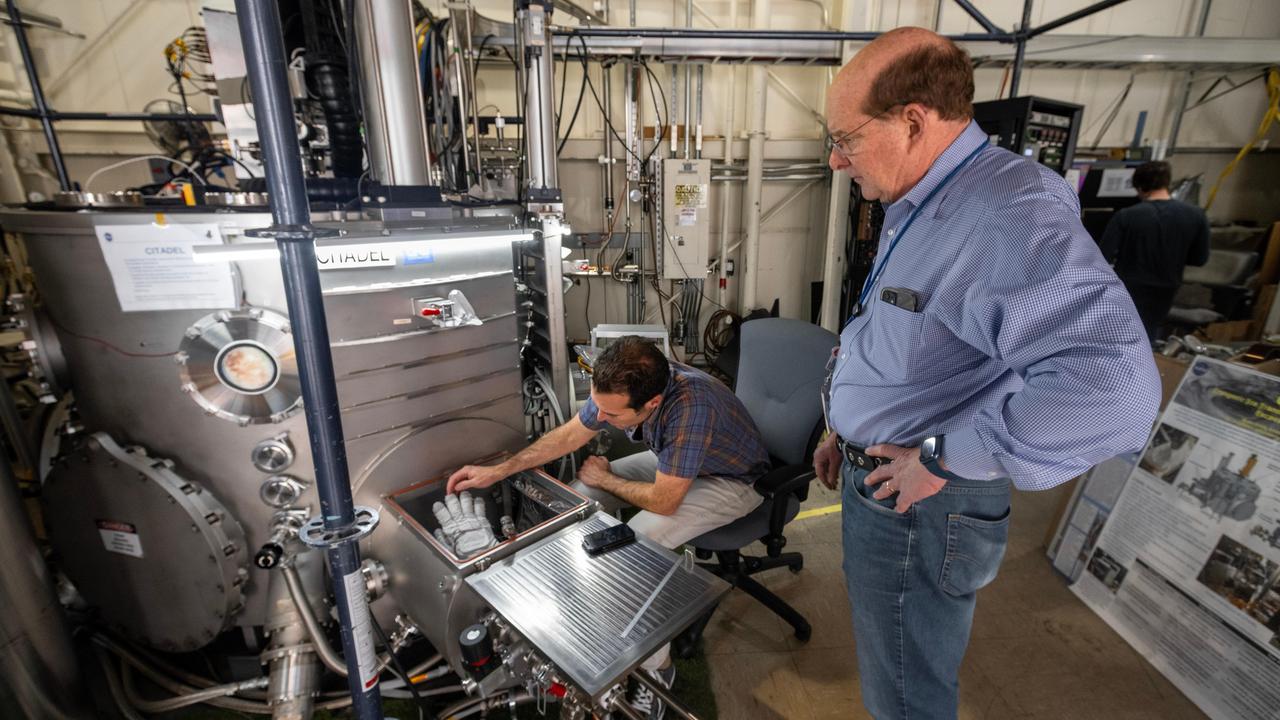

Spacesuit engineer Shane McFarland, left, of the Advanced Suit Team at NASA's Johnson Space Center prepares an astronaut glove for thermal vacuum testing inside a chamber at the agency's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Nov. 1, 2023. Tim Brady of the NASA Engineering and Safety Center (NESC), which spearheaded the glove testing campaign, looks on as McFarland positions the glove in a load lock – one of four small drawer-like chambers through which test materials are inserted into the larger main chamber of a facility called CITADEL (Cryogenic Ice Testing, Acquisition Development, and Excavation Laboratory). The glove was tested at vacuum and temperatures as low as minus 352 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 213 degrees Celsius) – temperatures as frigid as those Artemis III astronauts could experience on the Moon's South Pole. Built to prepare potential future robotic spacecraft for the frosty, low-pressure conditions on ocean worlds like Jupiter's frozen moon Europa, CITADEL has also proven key to evaluating how astronaut gloves and boots hold up in extraordinary cold. The NASA Engineering and Safety Center spearheaded a glove testing campaign in CITADEL from October 2023 to March 2024. Part of a spacesuit design called the Extravehicular Mobility Unit, the gloves tested in the chamber are the sixth version of a glove NASA began using in the 1980s. The testing in CITADEL showed that the legacy glove would not meet thermal requirements in the more challenging lunar South Pole environment. In addition to spotting vulnerabilities with existing suits, the CITADEL experiments will help NASA develop this unique test capability and prepare criteria for standardized, repeatable, and inexpensive test methods for the next-generation lunar suit being built by Axiom Space. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26591
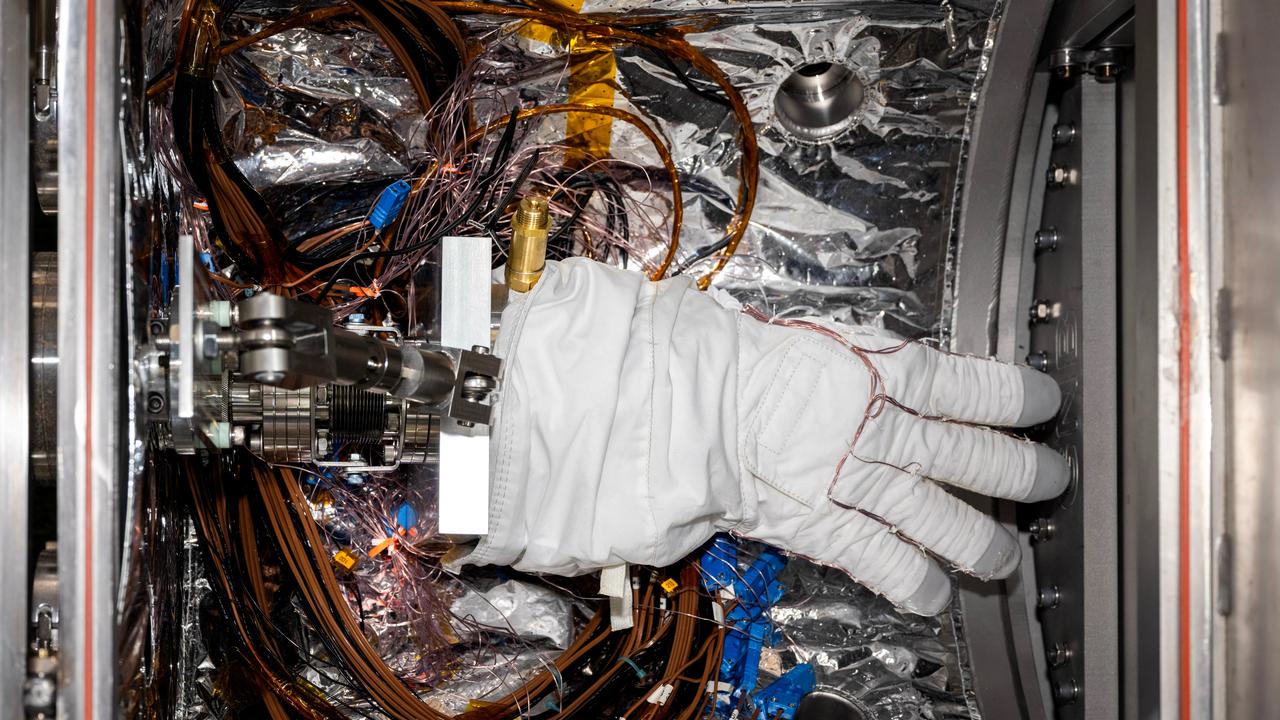

An astronaut glove designed for use during spacewalks on the International Space Station is prepared for thermal vacuum testing inside a chamber at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Nov. 1, 2023. The glove lies in a load lock, one of four small drawer-like chambers through which test materials are inserted into the larger main chamber of a facility called CITADEL (Cryogenic Ice Testing, Acquisition Development, and Excavation Laboratory). The glove was tested at vacuum and temperatures as low as minus 352 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 213 degrees Celsius) – temperatures as frigid as those Artemis III astronauts could experience on the Moon's South Pole. Built to prepare potential future robotic spacecraft for the frosty, low-pressure conditions on ocean worlds like Jupiter's frozen moon Europa, CITADEL has also proven key to evaluating how astronaut gloves and boots hold up in extraordinary cold. The NASA Engineering and Safety Center spearheaded a glove testing campaign in CITADEL from October 2023 to March 2024. Part of a spacesuit design called the Extravehicular Mobility Unit, the gloves tested in the chamber are the sixth version of a glove NASA began using in the 1980s. The testing in CITADEL showed that the legacy glove would not meet thermal requirements in the more challenging lunar South Pole environment. In addition to spotting vulnerabilities with existing suits, the CITADEL experiments will help NASA develop this unique test capability and prepare criteria for standardized, repeatable, and inexpensive test methods for the next-generation lunar suit being built by Axiom Space. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA26430
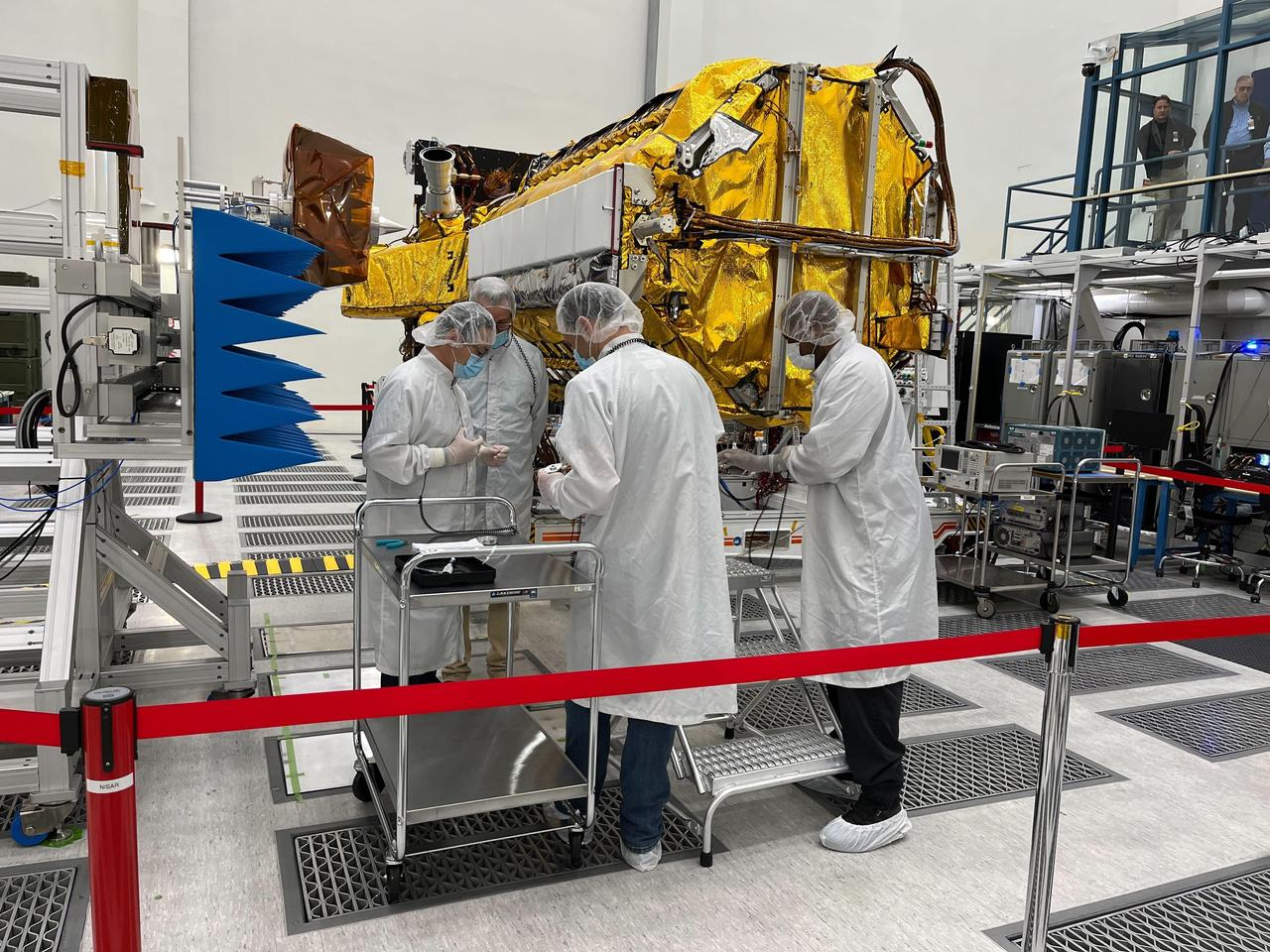

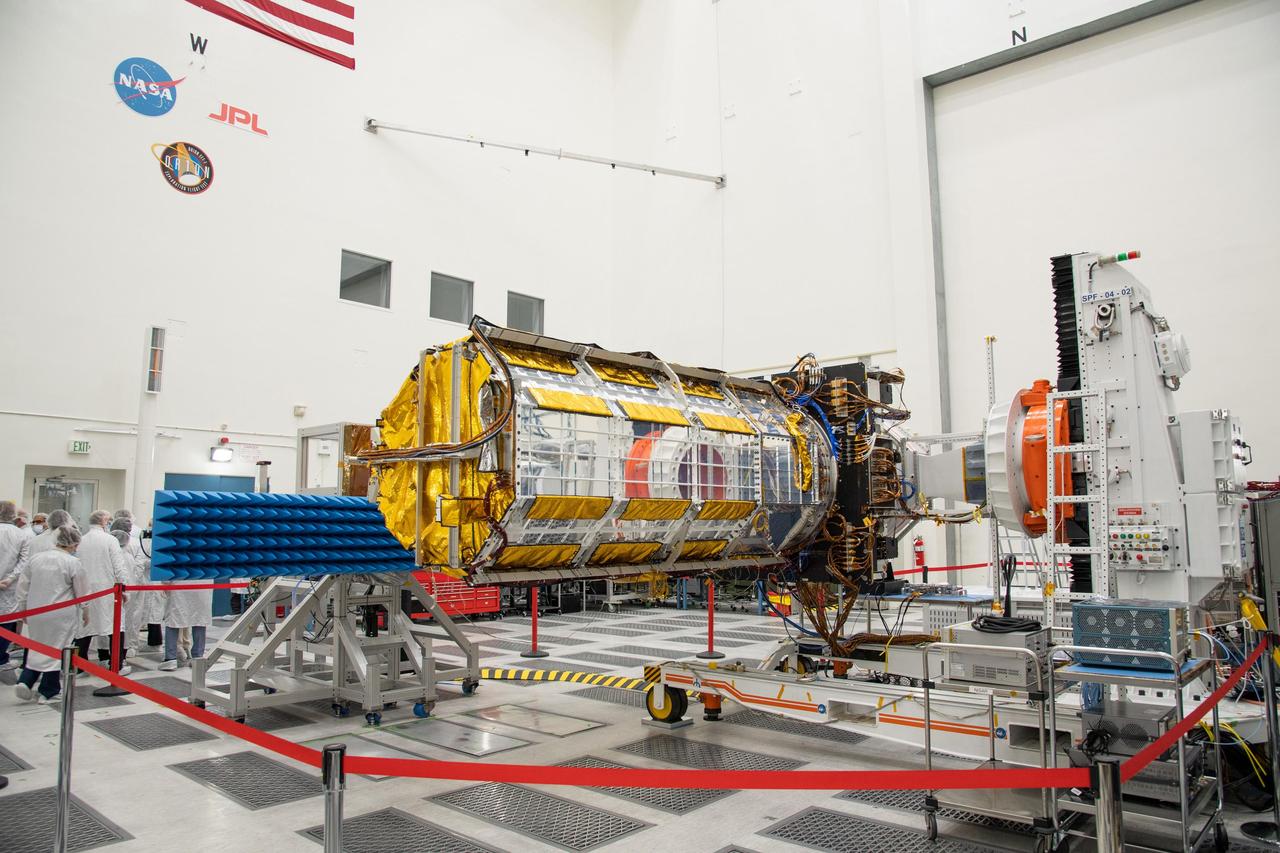
Engineers and technicians from NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory work on the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) science instrument payload in a clean room at JPL on Feb. 3, 2023. The payload is scheduled to ship to India in March 2023. The NISAR mission – a joint effort between NASA and ISRO – will measure changes to Earth's land ice surfaces down to fractions of an inch. Data collected by this satellite will help researchers monitor a wide range of changes critical to life on Earth in unprecedented detail. This includes spotting warning signs of imminent volcanic eruptions, helping to monitor groundwater supplies, tracking the melt rate of ice sheets tied to sea level rise, and observing shifts in the distribution of vegetation around the world. The data will inform humanity's responses to urgent challenges posed by natural disasters and climate change, and help communities prepare for and manage hazards. There are two instruments on the satellite that will send and receive radar signals to and from Earth's surface to make the mission's measurements. An L-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR), which uses a signal wavelength of around 9 inches (24 centimeters), and an S-band SAR with a signal wavelength of nearly 5 inches (12 centimeters). Both will bounce their microwave signal off of the planet's surface and record how long it takes the signal to make one roundtrip, as well as the strength of that return signal. This enables the researchers to calculate the distance from the spacecraft to Earth's surface and thereby determine how the land or ice is changing. An antenna reflector nearly 40 feet (12 meters) in diameter, supported by a deployable boom, will focus the microwave signals sent and received by the SARs. JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, leads the U.S. component of NISAR and is providing the mission's L-band SAR instrument. NASA is also providing the radar reflector antenna, the deployable boom, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder, and payload data subsystem. ISRO is providing the spacecraft bus, the S-band SAR, the launch vehicle, and associated launch services and satellite mission operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25771

NASA's NISAR Project Manager Phil Barela (with hands raised) speaks with Indian Space Research Organisation Chairman S. Somanath about the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) science instrument payload in a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Feb. 3, 2023. Somanath was among a group of visitors to the facility that included officials from NASA, ISRO, and the Indian Embassy. The NISAR mission – a joint effort between NASA and ISRO – will measure changes to Earth's land ice surfaces down to fractions of an inch. Data collected by this satellite will help researchers monitor a wide range of changes critical to life on Earth in unprecedented detail. This includes spotting warning signs of imminent volcanic eruptions, helping to monitor groundwater supplies, tracking the melt rate of ice sheets tied to sea level rise, and observing shifts in the distribution of vegetation around the world. The data will inform humanity's responses to urgent challenges posed by natural disasters and climate change, and help communities prepare for and manage hazards. There are two instruments on the satellite that will send and receive radar signals to and from Earth's surface to make the mission's measurements. An L-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR), which uses a signal wavelength of around 9 inches (24 centimeters), and an S-band SAR with a signal wavelength of nearly 5 inches (12 centimeters). Both will bounce their microwave signal off of the planet's surface and record how long it takes the signal to make one roundtrip, as well as the strength of that return signal. This enables the researchers to calculate the distance from the spacecraft to Earth's surface and thereby determine how the land or ice is changing. An antenna reflector nearly 40 feet (12 meters) in diameter, supported by a deployable boom, will focus the microwave signals sent and received by the SARs. JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, leads the U.S. component of NISAR and is providing the mission's L-band SAR instrument. NASA is also providing the radar reflector antenna, the deployable boom, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder, and payload data subsystem. ISRO is providing the spacecraft bus, the S-band SAR, the launch vehicle, and associated launch services and satellite mission operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25598
![This image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope, shows the wispy filamentary structure of Henize 206, is a four-color composite mosaic created by combining data from an infrared array camera IRAC. The LMC is a small satellite galaxy gravitationally bound to our own Milky Way. Yet the gravitational effects are tearing the companion to shreds in a long-playing drama of 'intergalactic cannibalism.' These disruptions lead to a recurring cycle of star birth and star death. Astronomers are particularly interested in the LMC because its fractional content of heavy metals is two to five times lower than is seen in our solar neighborhood. [In this context, 'heavy elements' refer to those elements not present in the primordial universe. Such elements as carbon, oxygen and others are produced by nucleosynthesis and are ejected into the interstellar medium via mass loss by stars, including supernova explosions.] As such, the LMC provides a nearby cosmic laboratory that may resemble the distant universe in its chemical composition. The primary Spitzer image, showing the wispy filamentary structure of Henize 206, is a four-color composite mosaic created by combining data from an infrared array camera (IRAC) at near-infrared wavelengths and the mid-infrared data from a multiband imaging photometer (MIPS). Blue represents invisible infrared light at wavelengths of 3.6 and 4.5 microns. Note that most of the stars in the field of view radiate primarily at these short infrared wavelengths. Cyan denotes emission at 5.8 microns, green depicts the 8.0 micron light, and red is used to trace the thermal emission from dust at 24 microns. The separate instrument images are included as insets to the main composite. An inclined ring of emission dominates the central and upper regions of the image. This delineates a bubble of hot, x-ray emitting gas that was blown into space when a massive star died in a supernova explosion millions of years ago. The shock waves from that explosion impacted a cloud of nearby hydrogen gas, compressed it, and started a new generation of star formation. The death of one star led to the birth of many new stars. This is particularly evident in the MIPS inset, where the 24-micron emission peaks correspond to newly formed stars. The ultraviolet and visible-light photons from the new stars are absorbed by surrounding dust and re-radiated at longer infrared wavelengths, where it is detected by Spitzer. This emission nebula was cataloged by Karl Henize (HEN-eyes) while spending 1948-1951 in South Africa doing research for his Ph.D. dissertation at the University of Michigan. Henize later became a NASA astronaut and, at age 59, became the oldest rookie to fly on the Space Shuttle during an eight-day flight of the Challenger in 1985. He died just short of his 67th birthday in 1993 while attempting to climb the north face of Mount Everest, the world's highest peak. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05517](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/PIA05517/PIA05517~medium.jpg)
This image from NASA Spitzer Space Telescope, shows the wispy filamentary structure of Henize 206, is a four-color composite mosaic created by combining data from an infrared array camera IRAC. The LMC is a small satellite galaxy gravitationally bound to our own Milky Way. Yet the gravitational effects are tearing the companion to shreds in a long-playing drama of 'intergalactic cannibalism.' These disruptions lead to a recurring cycle of star birth and star death. Astronomers are particularly interested in the LMC because its fractional content of heavy metals is two to five times lower than is seen in our solar neighborhood. [In this context, 'heavy elements' refer to those elements not present in the primordial universe. Such elements as carbon, oxygen and others are produced by nucleosynthesis and are ejected into the interstellar medium via mass loss by stars, including supernova explosions.] As such, the LMC provides a nearby cosmic laboratory that may resemble the distant universe in its chemical composition. The primary Spitzer image, showing the wispy filamentary structure of Henize 206, is a four-color composite mosaic created by combining data from an infrared array camera (IRAC) at near-infrared wavelengths and the mid-infrared data from a multiband imaging photometer (MIPS). Blue represents invisible infrared light at wavelengths of 3.6 and 4.5 microns. Note that most of the stars in the field of view radiate primarily at these short infrared wavelengths. Cyan denotes emission at 5.8 microns, green depicts the 8.0 micron light, and red is used to trace the thermal emission from dust at 24 microns. The separate instrument images are included as insets to the main composite. An inclined ring of emission dominates the central and upper regions of the image. This delineates a bubble of hot, x-ray emitting gas that was blown into space when a massive star died in a supernova explosion millions of years ago. The shock waves from that explosion impacted a cloud of nearby hydrogen gas, compressed it, and started a new generation of star formation. The death of one star led to the birth of many new stars. This is particularly evident in the MIPS inset, where the 24-micron emission peaks correspond to newly formed stars. The ultraviolet and visible-light photons from the new stars are absorbed by surrounding dust and re-radiated at longer infrared wavelengths, where it is detected by Spitzer. This emission nebula was cataloged by Karl Henize (HEN-eyes) while spending 1948-1951 in South Africa doing research for his Ph.D. dissertation at the University of Michigan. Henize later became a NASA astronaut and, at age 59, became the oldest rookie to fly on the Space Shuttle during an eight-day flight of the Challenger in 1985. He died just short of his 67th birthday in 1993 while attempting to climb the north face of Mount Everest, the world's highest peak. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA05517

Officials from NASA, the Indian Space Research Organisation, and the Indian Embassy, grouped at left, visit a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California on Feb. 3, 2023, to view the scientific instrument payload for the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) mission. The payload is scheduled to be shipped to India in March 2023. The NISAR mission – a joint effort between NASA and ISRO – will measure changes to Earth's land ice surfaces down to fractions of an inch. Data collected by this satellite will help researchers monitor a wide range of changes critical to life on Earth in unprecedented detail. This includes spotting warning signs of imminent volcanic eruptions, helping to monitor groundwater supplies, tracking the melt rate of ice sheets tied to sea level rise, and observing shifts in the distribution of vegetation around the world. The data will inform humanity's responses to urgent challenges posed by natural disasters and climate change, and help communities prepare for and manage hazards. There are two instruments on the satellite that will send and receive radar signals to and from Earth's surface to make the mission's measurements. An L-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR), which uses a signal wavelength of around 9 inches (24 centimeters), and an S-band SAR with a signal wavelength of nearly 5 inches (12 centimeters). Both will bounce their microwave signal off of the planet's surface and record how long it takes the signal to make one roundtrip, as well as the strength of that return signal. This enables the researchers to calculate the distance from the spacecraft to Earth's surface and thereby determine how the land or ice is changing. An antenna reflector nearly 40 feet (12 meters) in diameter, supported by a deployable boom, will focus the microwave signals sent and received by the SARs. JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, leads the U.S. component of NISAR and is providing the mission's L-band SAR instrument. NASA is also providing the radar reflector antenna, the deployable boom, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder, and payload data subsystem. ISRO is providing the spacecraft bus, the S-band SAR, the launch vehicle, and associated launch services and satellite mission operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25599

Officials from NASA, the Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO), and the Embassy of India hold a send-off ceremony for the NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar (NISAR) science instrument payload on Feb. 3, 2023, outside a clean room at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California. The payload is scheduled to be shipped to India in March. Pictured left to right: Karen St. Germain, director, Earth Science Division, NASA; Mitra Dutta, NISAR program executive, NASA; Sripriya Ranganathan, ambassador and deputy chief of mission, Indian Embassy; Larry James, deputy director, JPL; Bhavya Lal, associate administrator for technology, policy, and strategy, NASA; Jim Graf, director, Earth Science and Technology Directorate, JPL; S. Somanath, chairman, ISRO; Laurie Leshin, director, JPL; Krunal Joshi, counselor, space and ISRO technical liaison officer, Indian Embassy; M. Sankaran, director, U R Rao Satellite Centre, ISRO; Shantanu Bhatawdekar, scientific secretary, ISRO; Paul Rosen, NISAR project scientist, JPL; CV Shrikant, NISAR project director, ISRO; Phil Barela, NISAR project manager, JPL; and Gerald Bawden, NISAR program scientist, NASA. NISAR – a joint effort between NASA and ISRO – will measure changes to Earth's land ice surfaces down to fractions of an inch. Data collected by this satellite will help researchers monitor a wide range of changes critical to life on Earth in unprecedented detail. This includes spotting warning signs of imminent volcanic eruptions, helping to monitor groundwater supplies, tracking the melt rate of ice sheets tied to sea level rise, and observing shifts in the distribution of vegetation around the world. The data will inform humanity's responses to urgent challenges posed by natural disasters and climate change, and help communities prepare for and manage hazards. There are two instruments on the satellite that will send and receive radar signals to and from Earth's surface to make the mission's measurements. An L-band synthetic aperture radar (SAR), which uses a signal wavelength of around 9 inches (24 centimeters), and an S-band SAR with a signal wavelength of nearly 5 inches (12 centimeters). Both will bounce their microwave signal off of the planet's surface and record how long it takes the signal to make one roundtrip, as well as the strength of that return signal. This enables the researchers to calculate the distance from the spacecraft to Earth's surface and thereby determine how the land or ice is changing. An antenna reflector nearly 40 feet (12 meters) in diameter, supported by a deployable boom, will focus the microwave signals sent and received by the SARs. JPL, which is managed for NASA by Caltech in Pasadena, leads the U.S. component of NISAR and is providing the mission's L-band SAR instrument. NASA is also providing the radar reflector antenna, the deployable boom, a high-rate communication subsystem for science data, GPS receivers, a solid-state recorder, and payload data subsystem. ISRO is providing the spacecraft bus, the S-band SAR, the launch vehicle, and associated launch services and satellite mission operations. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25600