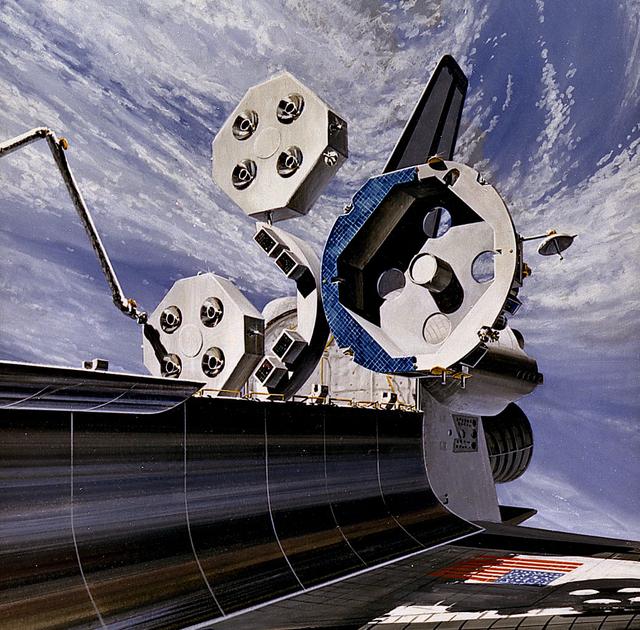
In this 1986 artist's concept, the Orbital Maneuvering Vehicle (OMV), undergoes changeout of the Propulsion Module outside the Space Shuttle Cargo Bay. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center plarners, the OMV would be a remotely-controlled free-flying space tug which would place, rendezvous, dock, and retrieve orbital payloads.
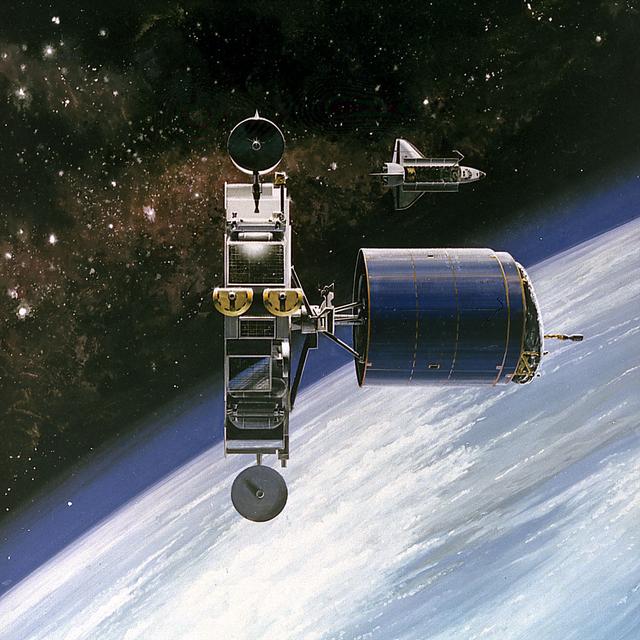

This 1986 artist's concept shows the Orbital Maneuvering Vehicle (OMV) towing a satellite. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center plarners, the OMV would be a remotely-controlled free-flying space tug which would place, rendezvous, dock, and retrieve orbital payloads.
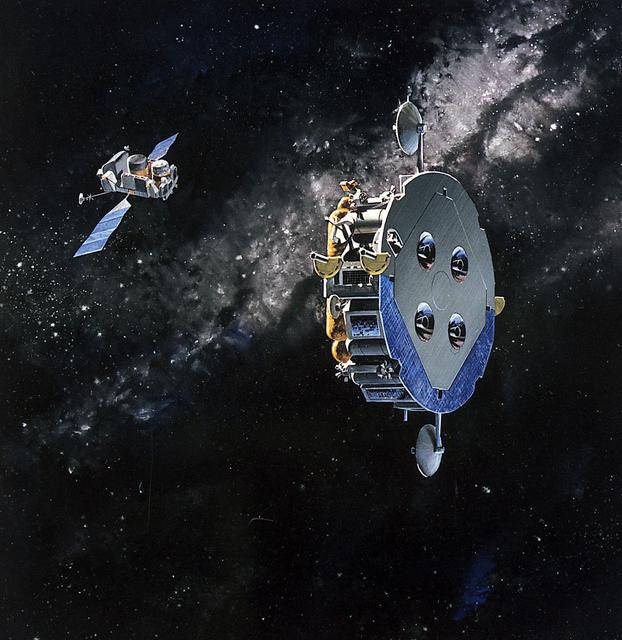

In this 1988 artist's concept, the Orbital Maneuvering Vehicle (OMV), closes in on a satellite. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight plarners, the OMV would be a remotely-controlled free-flying space tug which would place, rendezvous, dock, and retrieve orbital payloads.
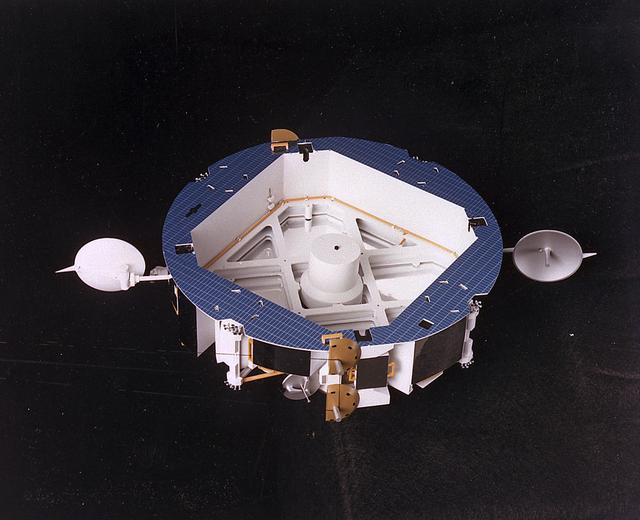
In this 1986 artist's concept, the Orbital Maneuvering Vehicle (OMV), is shown without its main propulsion module. Essentially two propulsion vehicles in one, the OMV could be powered by a main propulsion module , or, in its short range vehicle configuration shown here, use its own hydrazine and cold gas thrusters. As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center plarners, the OMV would be a remotely-controlled free-flying space tug which would place, rendezvous, dock, and retrieve orbital payloads.
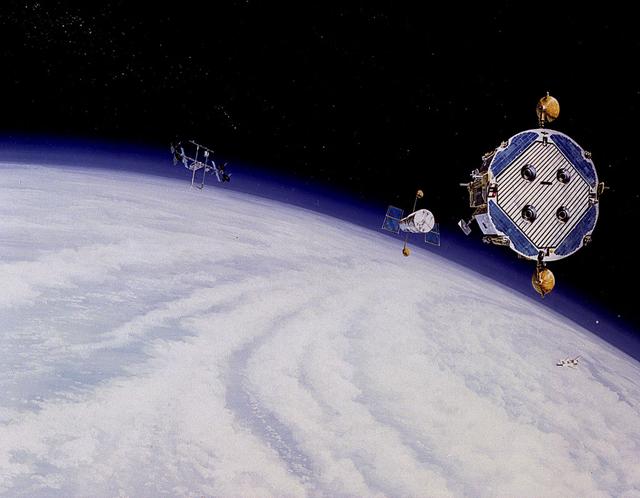

In this 1986 artist's concept, the Orbital Maneuvering Vehicle (OMV), at right, prepares to reboost the Hubble Space Telescope after being deployed from an early Space Station configuration (left). As envisioned by Marshall Space Flight Center plarners, the OMV would be a remotely-controlled free-flying space tug which would place, rendezvous, dock, and retrieve orbital payloads.
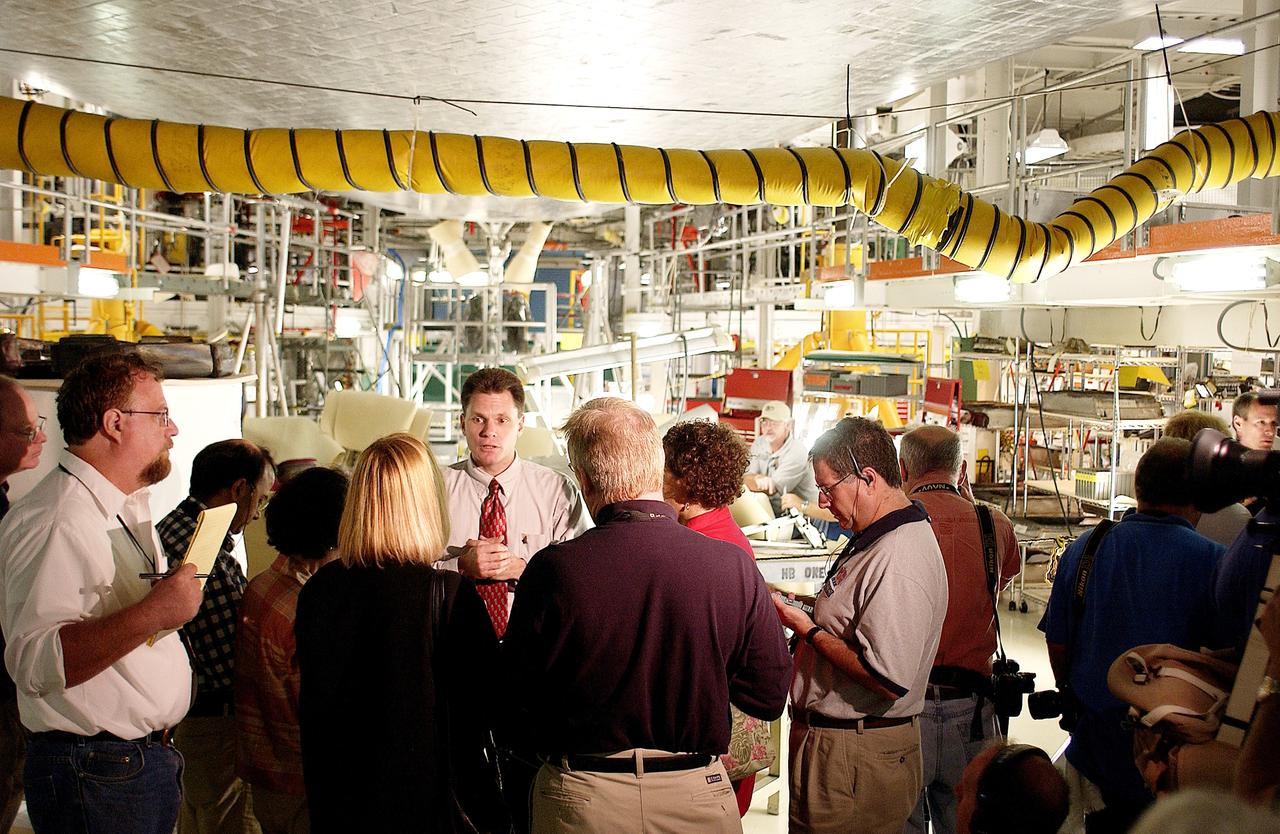

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Vehicle Manager Scott Thurston (facing camera) talks to the media in the Orbiter Processing Facility. The media was invited to see the orbiter Atlantis as it is being prepared for Return to Flight. Both local and national reporters representing print and TV networks were able to see work in progress on Atlantis, including the reinstallation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panels on the orbiter’s wing leading edge; wiring inspections; and checks of the engines in the Orbital Maneuvering System.
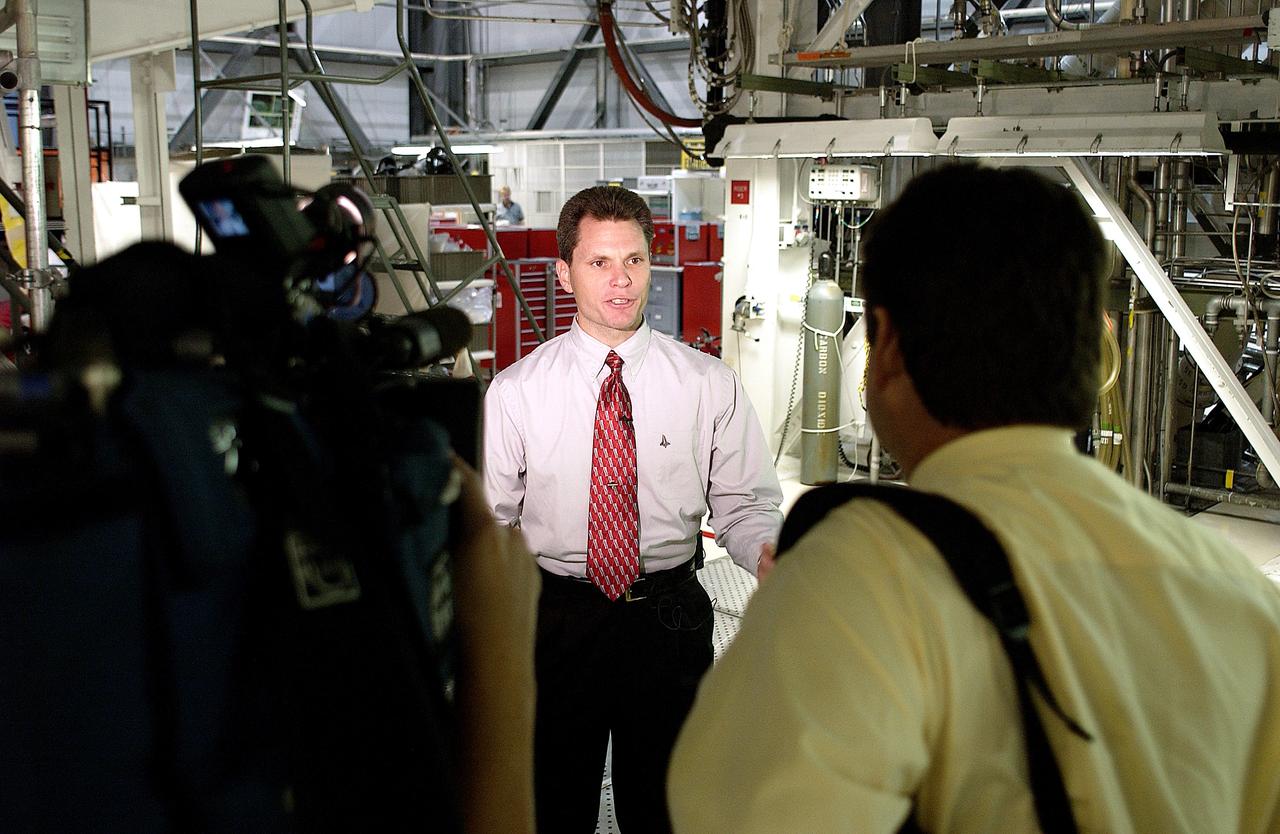

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Vehicle Manager Scott Thurston talks to the media in the Orbiter Processing Facility. The media was invited to see the orbiter Atlantis as it is being prepared for Return to Flight. Both local and national reporters representing print and TV networks were able to see work in progress on Atlantis, including the reinstallation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panels on the orbiter’s wing leading edge; wiring inspections; and checks of the engines in the Orbital Maneuvering System.
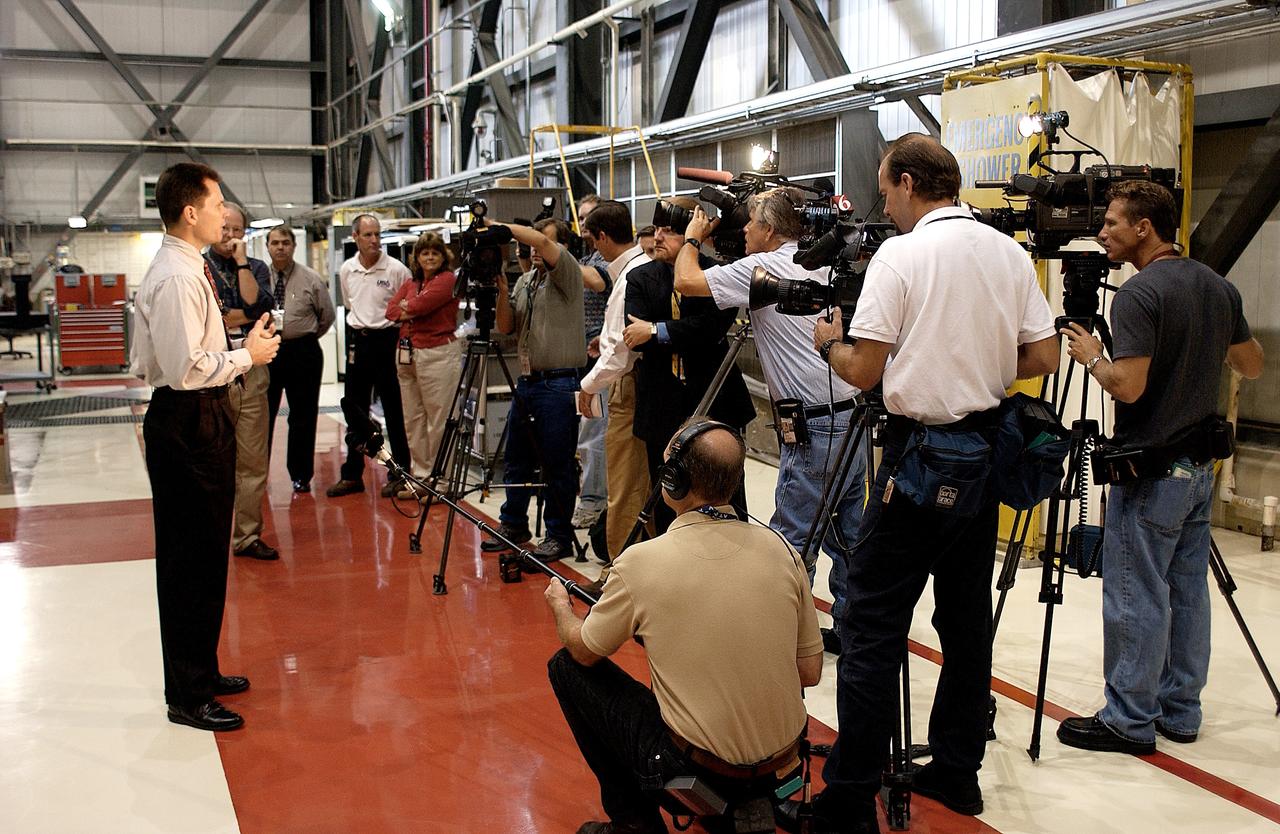

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Vehicle Manager Scott Thurston (left) talks to a phalanx of media in the Orbiter Processing Facility. The media was invited to see the orbiter Atlantis as it is being prepared for Return to Flight. Both local and national reporters representing print and TV networks were able to see work in progress on Atlantis, including the reinstallation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panels on the orbiter’s wing leading edge; wiring inspections; and checks of the engines in the Orbital Maneuvering System.
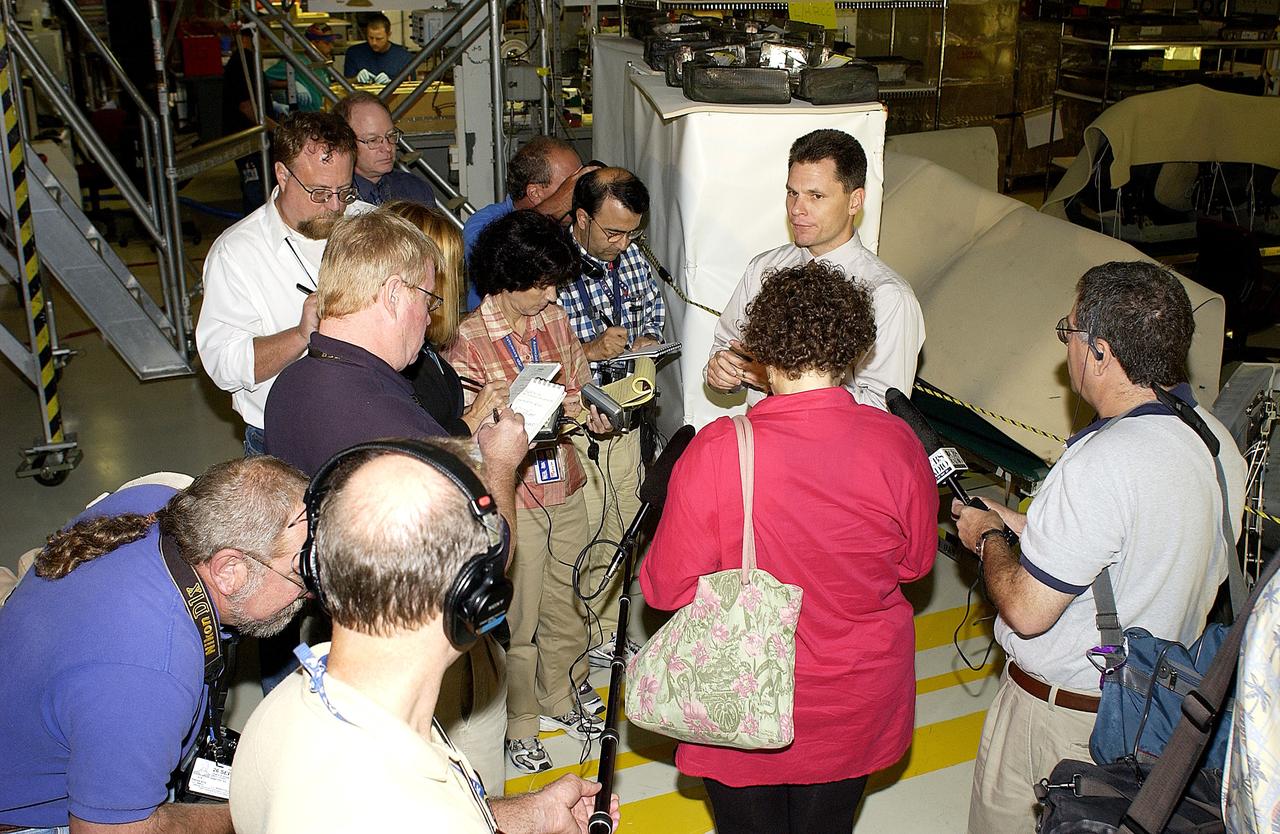

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Vehicle Manager Scott Thurston (facing camera) talks to the media in the Orbiter Processing Facility. The media was invited to see the orbiter Atlantis as it is being prepared for Return to Flight. Both local and national reporters representing print and TV networks were able to see work in progress on Atlantis, including the reinstallation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panels on the orbiter’s wing leading edge; wiring inspections; and checks of the engines in the Orbital Maneuvering System.
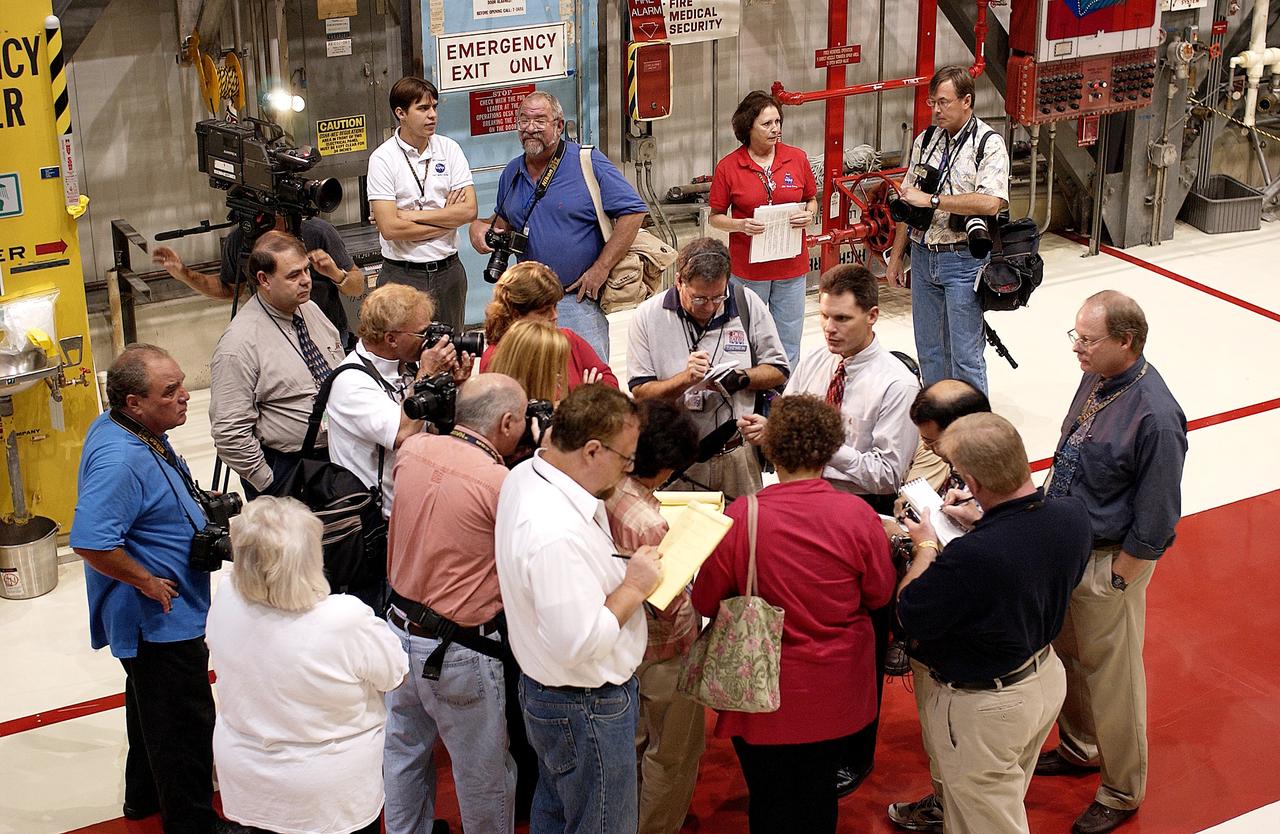

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The media gather around NASA Vehicle Manager Scott Thurston (white shirt, right) who talks about some of the work being done on the orbiter Atlantis as it is being prepared for Return to Flight in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Both local and national reporters representing print and TV networks were able to see work in progress on Atlantis, including the reinstallation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panels on the orbiter’s wing leading edge; wiring inspections; and checks of the engines in the Orbital Maneuvering System.
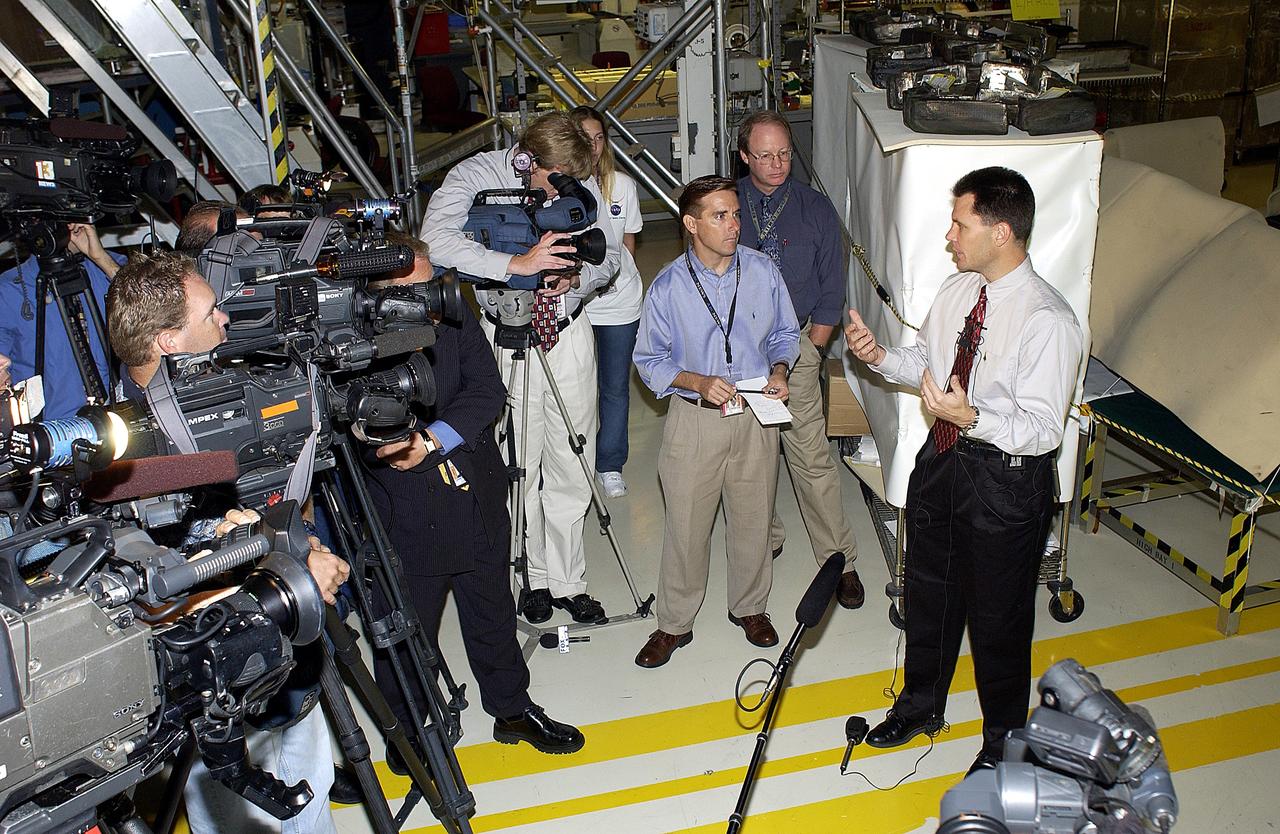

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Vehicle Manager Scott Thurston (right) talks to the media in the Orbiter Processing Facility. The media was invited to see the orbiter Atlantis as it is being prepared for Return to Flight. Both local and national reporters representing print and TV networks were able to see work in progress on Atlantis, including the reinstallation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panels on the orbiter’s wing leading edge; wiring inspections; and checks of the engines in the Orbital Maneuvering System. will be available to discuss the work and answer questions.
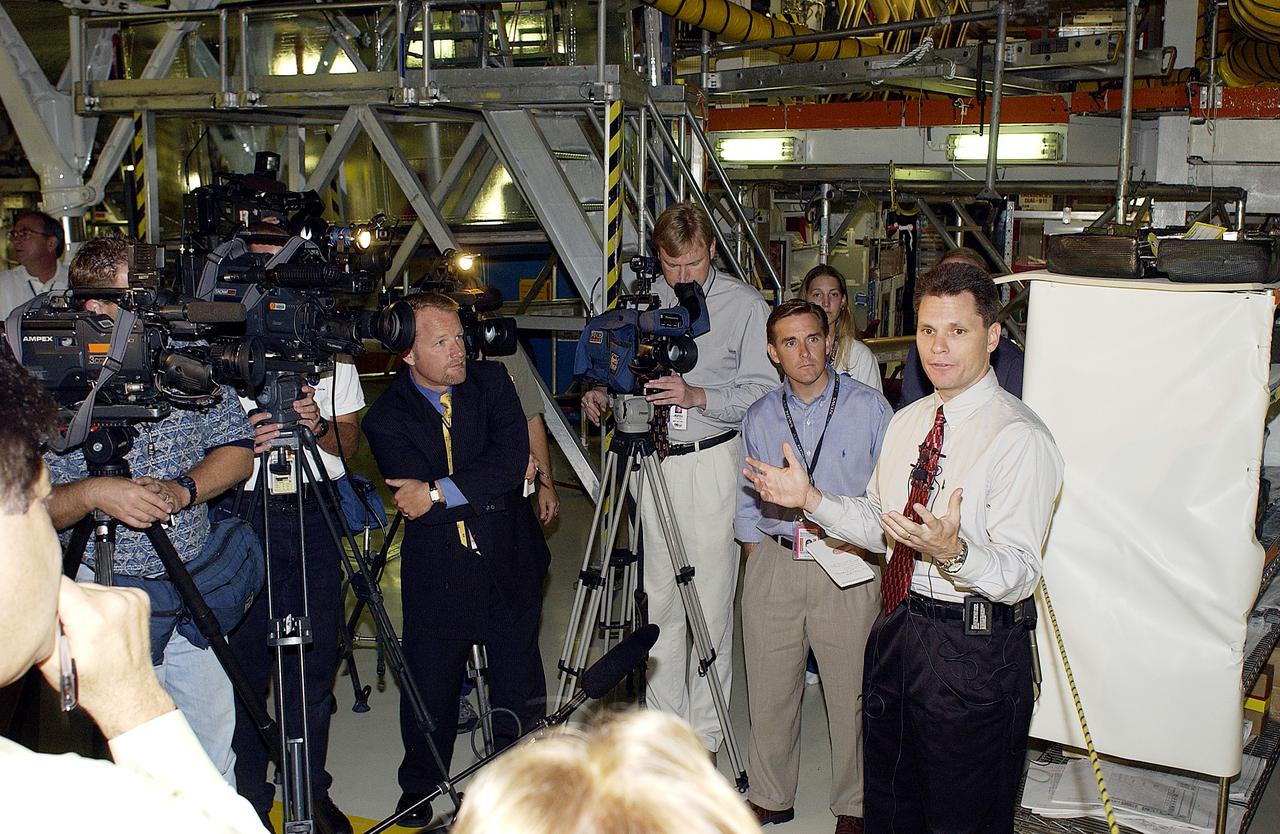

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Vehicle Manager Scott Thurston (right) talks to the media in the Orbiter Processing Facility . The media was invited to see the orbiter Atlantis as it is being prepared for Return to Flight. Both local and national reporters representing print and TV networks were able to see work in progress on Atlantis, including the reinstallation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panels on the orbiter’s wing leading edge; wiring inspections; and checks of the engines in the Orbital Maneuvering System.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Vehicle Manager Scott Thurston talks to the media in the Orbiter Processing Facility. The media was invited to see the orbiter Atlantis as it is being prepared for Return to Flight. Both local and national reporters representing print and TV networks were able to see work in progress on Atlantis, including the reinstallation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panels on the orbiter’s wing leading edge; wiring inspections; and checks of the engines in the Orbital Maneuvering System.
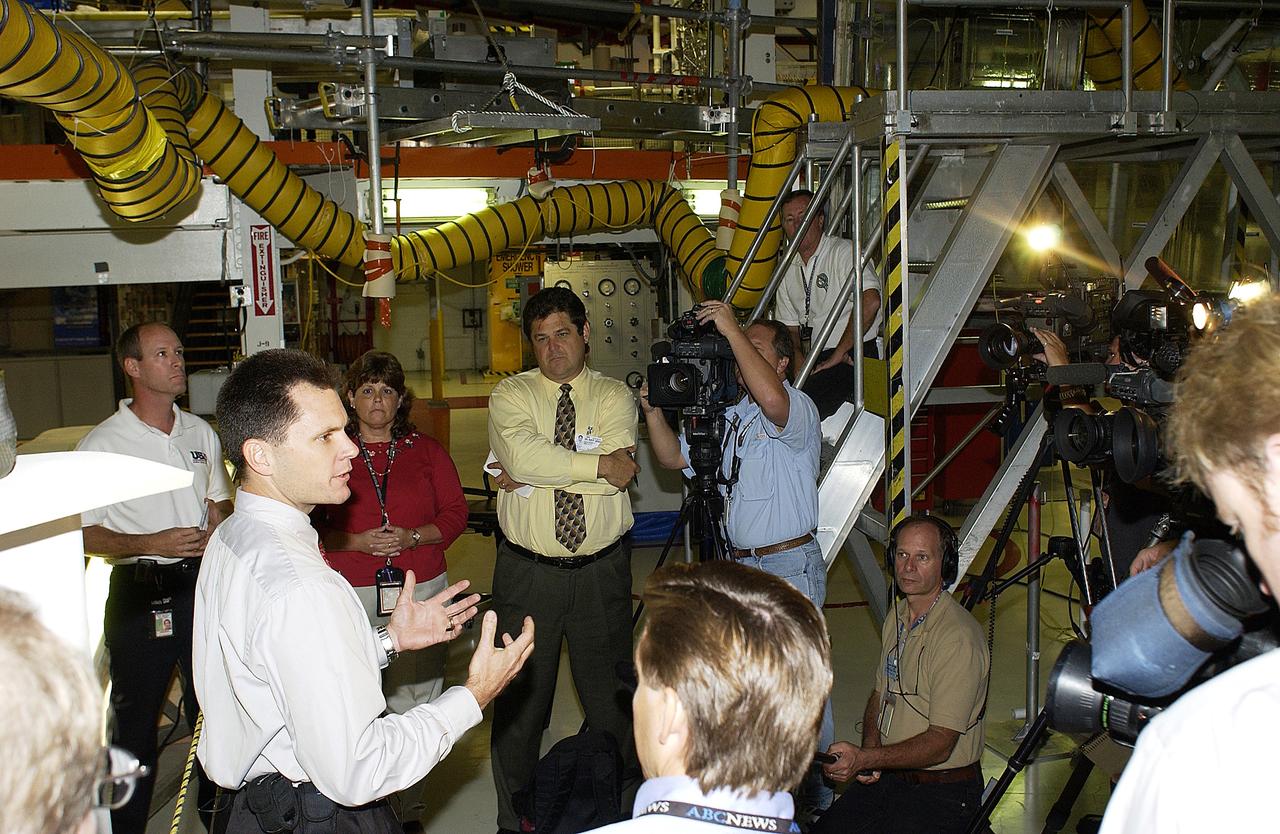

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - NASA Vehicle Manager Scott Thurston (hands extended) talks to the media in the Orbiter Processing Facility. The media was invited to see the orbiter Atlantis as it is being prepared for Return to Flight. Both local and national reporters representing print and TV networks were able to see work in progress on Atlantis, including the reinstallation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panels on the orbiter’s wing leading edge; wiring inspections; and checks of the engines in the Orbital Maneuvering System.
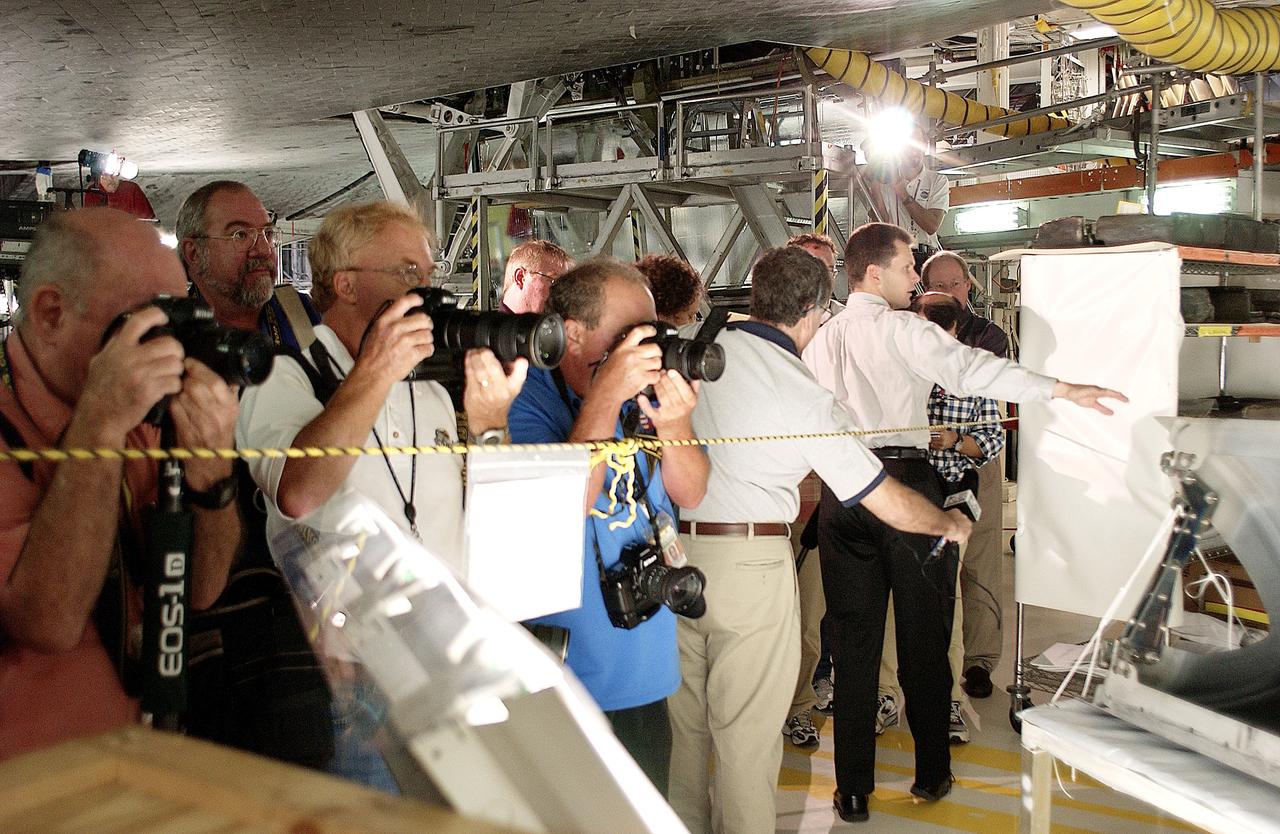

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, while a few photographers (left) set up for photos, NASA Vehicle Manager Scott Thurston (right, with arm extended) talks about the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panel at right. The media was invited to see the orbiter Atlantis as it is being prepared for Return to Flight. Both local and national reporters representing print and TV networks were able to see work in progress on Atlantis, including the reinstallation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panels on the orbiter’s wing leading edge; wiring inspections; and checks of the engines in the Orbital Maneuvering System.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, while a few photographers (left) set up for photos of a Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panel at far right, NASA Vehicle Manager Scott Thurston (right) talks to other media. The media was invited to see the orbiter Atlantis as it is being prepared for Return to Flight. Both local and national reporters representing print and TV networks were able to see work in progress on Atlantis, including the reinstallation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panels on the orbiter’s wing leading edge; wiring inspections; and checks of the engines in the Orbital Maneuvering System.
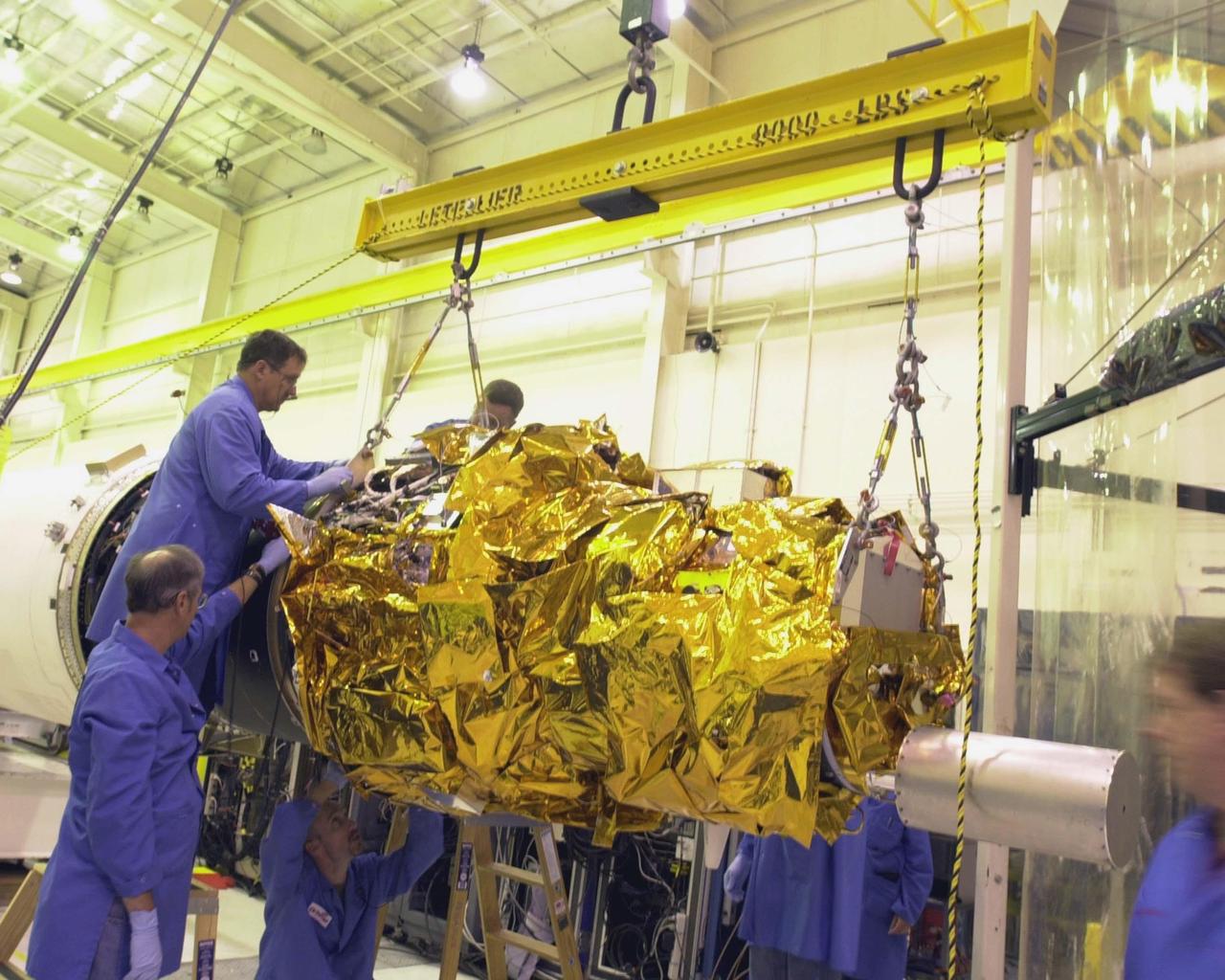

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers maneuver the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and mated upper stage toward the second stage behind them in preparation or launch aboard the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle. Pegasus will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation, DART was designed as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers maneuver the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and mated upper stage toward the second stage at right in preparation or launch aboard the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle. Pegasus will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation, DART was designed as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
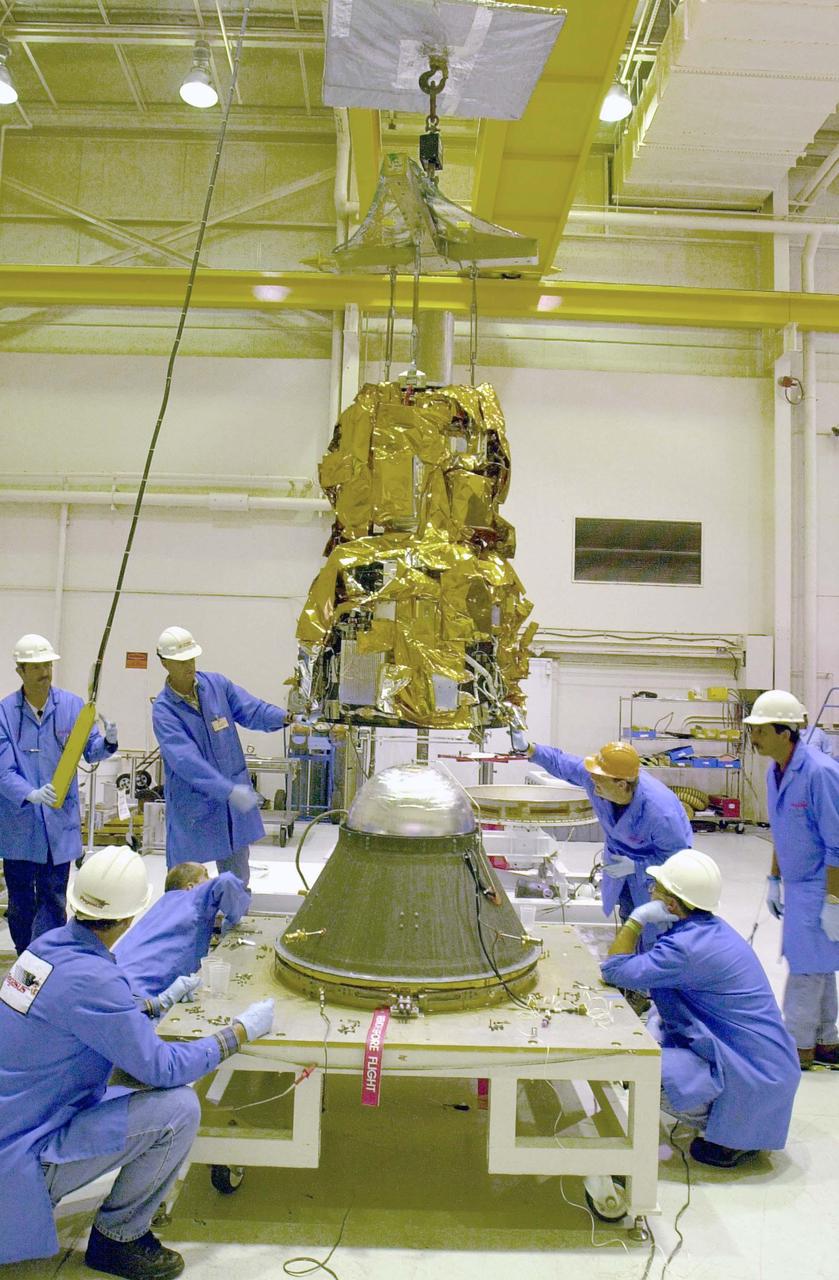

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers maneuver the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft, suspended by a crane, over the upper stage in preparation for launch on the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation, DART was designed as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
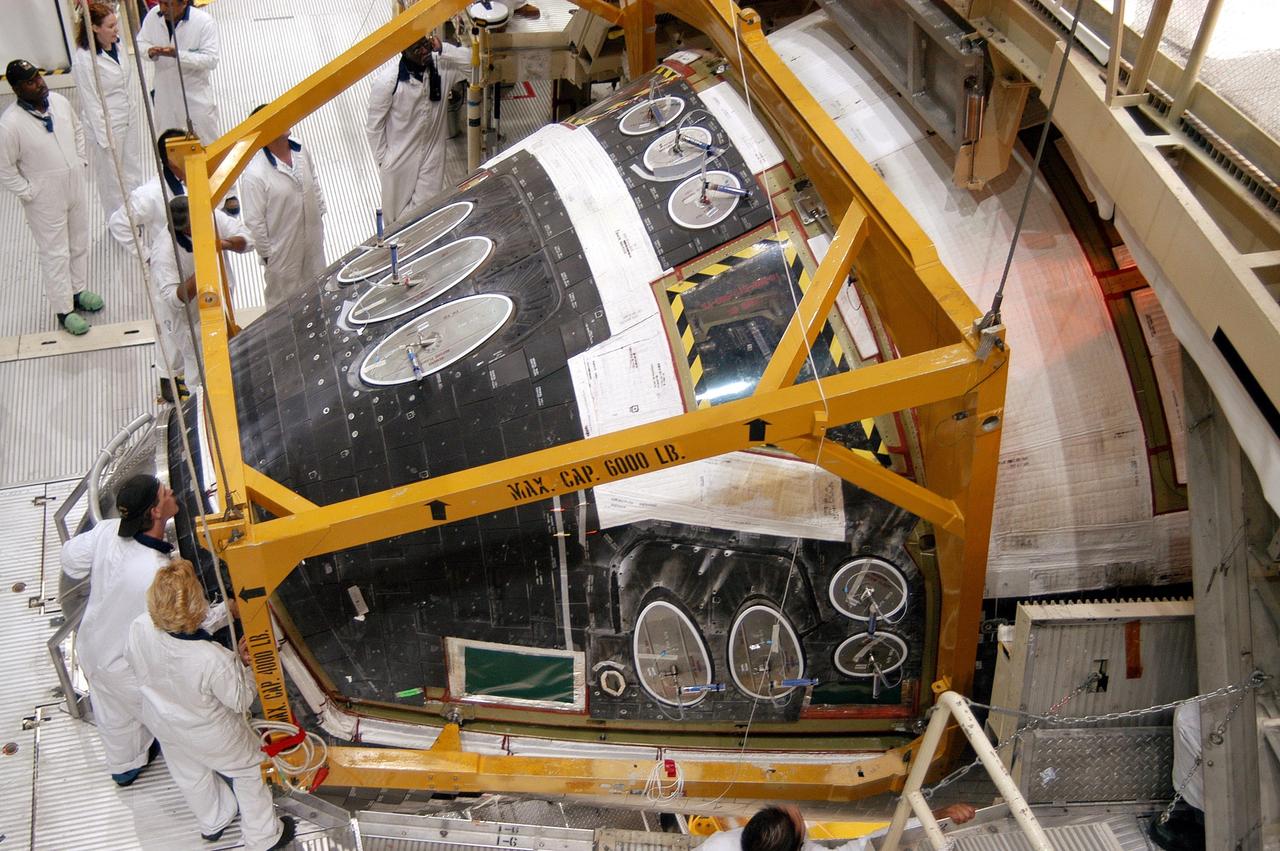

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility watch closely as Discovery’s Forward Reaction Control System (FRCS) is lowered into position in the orbiter’s forward fuselage nose area. The FRCS provides the thrust for attitude (rotational) maneuvers (pitch, yaw and roll) and for small velocity changes along the orbiter axis (translation maneuvers). Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility watch closely as Discovery’s Forward Reaction Control System (FRCS) is lowered into position in the orbiter’s forward fuselage nose area. The FRCS provides the thrust for attitude (rotational) maneuvers (pitch, yaw and roll) and for small velocity changes along the orbiter axis (translation maneuvers). Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.
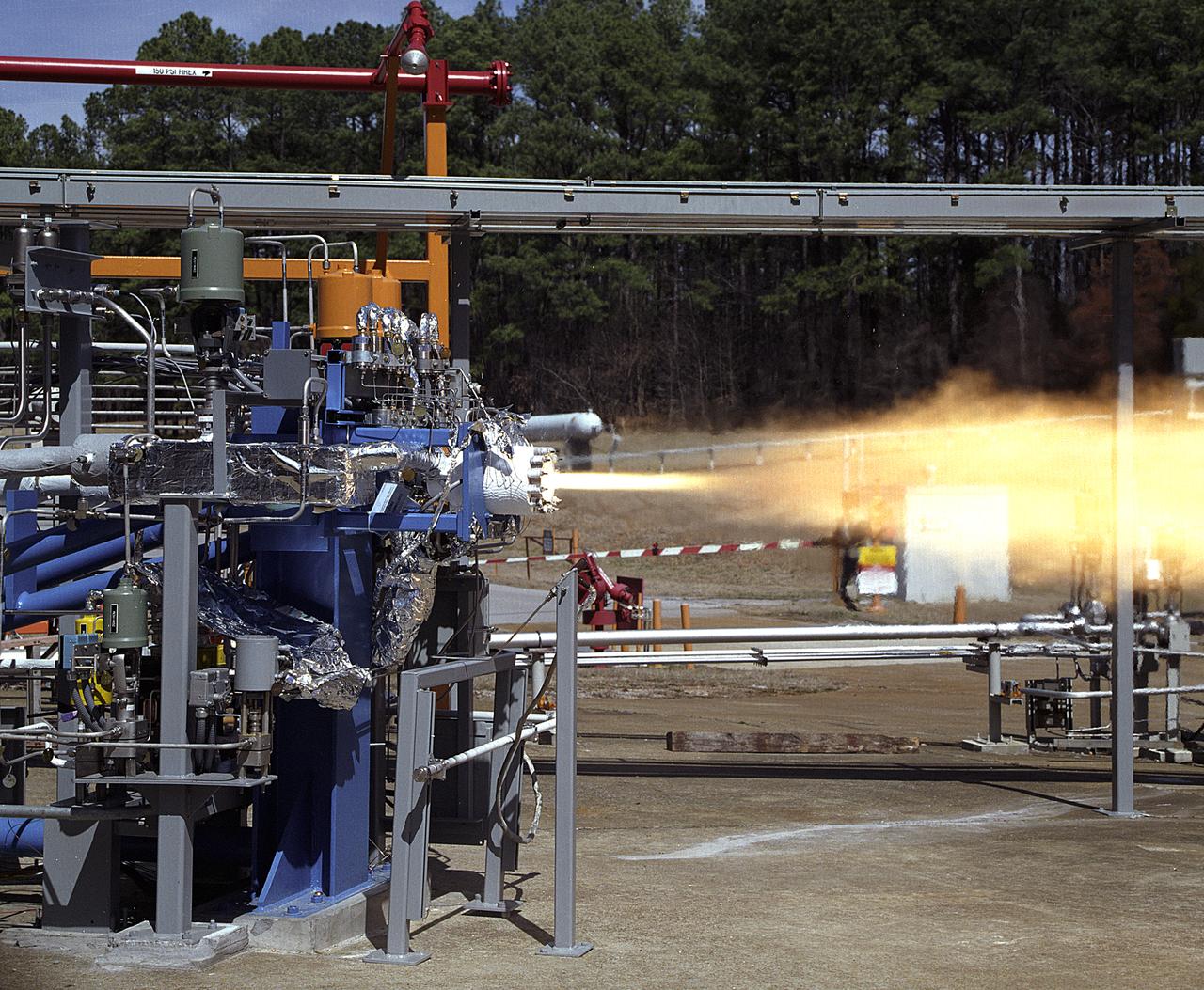
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Huntsville, Alabama, has begun a series of engine tests on the Reaction Control Engine developed by TRW Space and Electronics for NASA's Space Launch Initiative (SLI). SLI is a technology development effort aimed at improving the safety, reliability, and cost effectiveness of space travel for reusable launch vehicles. The engine in this photo, the first engine tested at MSFC that includes SLI technology, was tested for two seconds at a chamber pressure of 185 pounds per square inch absolute (psia). Propellants used were liquid oxygen as an oxidizer and liquid hydrogen as fuel. Designed to maneuver vehicles in orbit, the engine is used as an auxiliary propulsion system for docking, reentry, fine-pointing, and orbit transfer while the vehicle is in orbit. The Reaction Control Engine has two unique features. It uses nontoxic chemicals as propellants, which creates a safer environment with less maintenance and quicker turnaround time between missions, and it operates in dual thrust modes, combining two engine functions into one engine. The engine operates at both 25 and 1,000 pounds of force, reducing overall propulsion weight and allowing vehicles to easily maneuver in space. The force of low level thrust allows the vehicle to fine-point maneuver and dock, while the force of the high level thrust is used for reentry, orbital transfer, and course positioning.
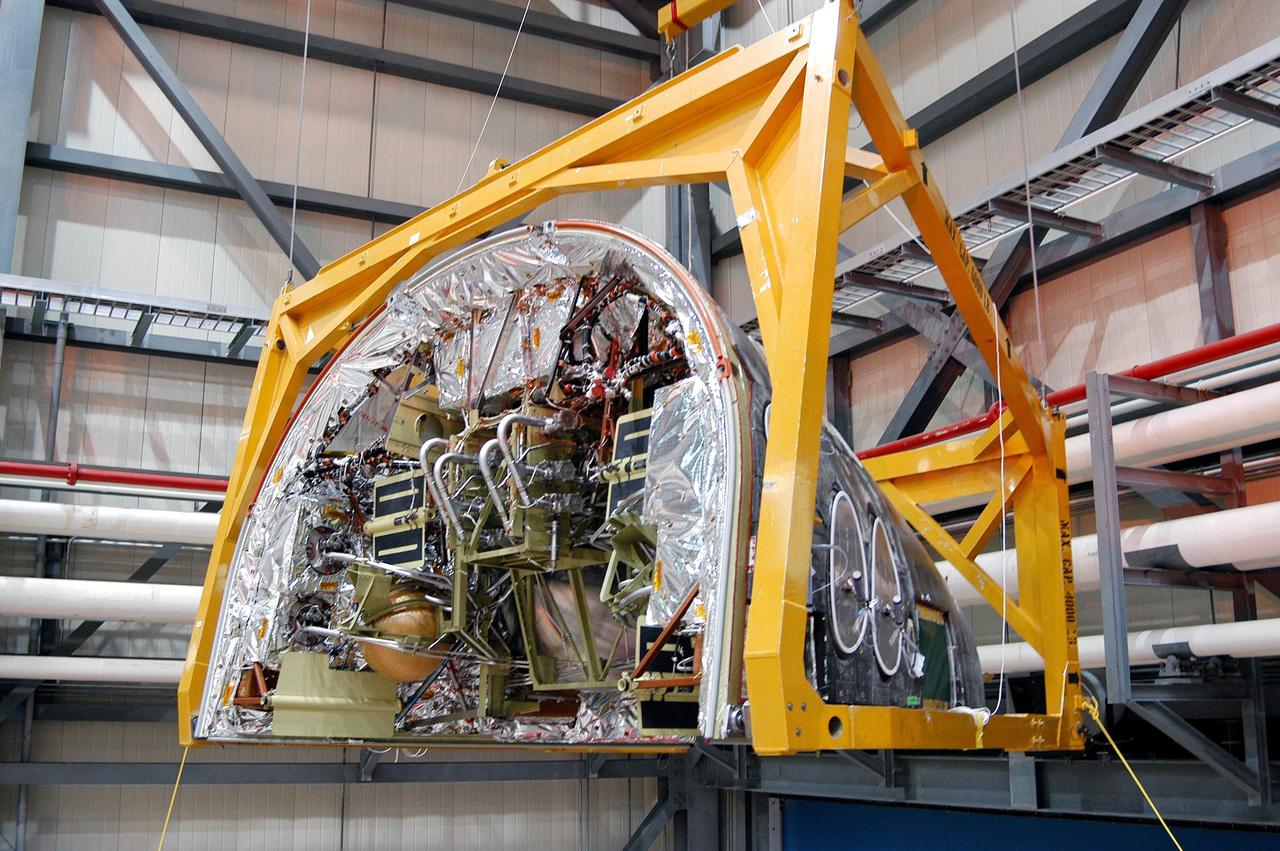

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the Forward Reaction Control System (FRCS) is lifted by an overhead crane for installation in Discovery. Located in the forward fuselage nose area, the FRCS provides the thrust for attitude (rotational) maneuvers (pitch, yaw and roll) and for small velocity changes along the orbiter axis (translation maneuvers). Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.
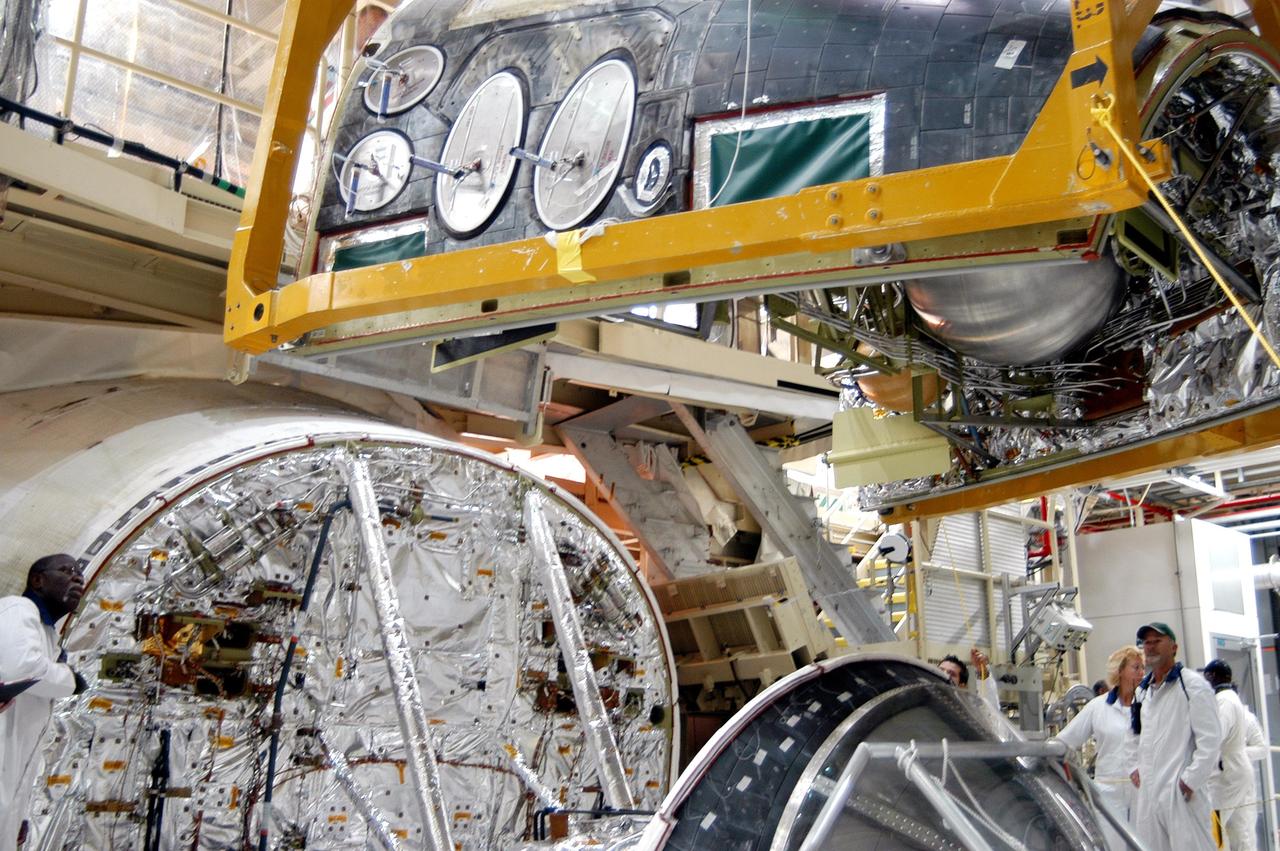
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In the Orbiter Processing Facility, the Forward Reaction Control System (FRCS) is lowered toward Discovery’s forward fuselage nose area where it will be installed. The FRCS provides the thrust for attitude (rotational) maneuvers (pitch, yaw and roll) and for small velocity changes along the orbiter axis (translation maneuvers). Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.
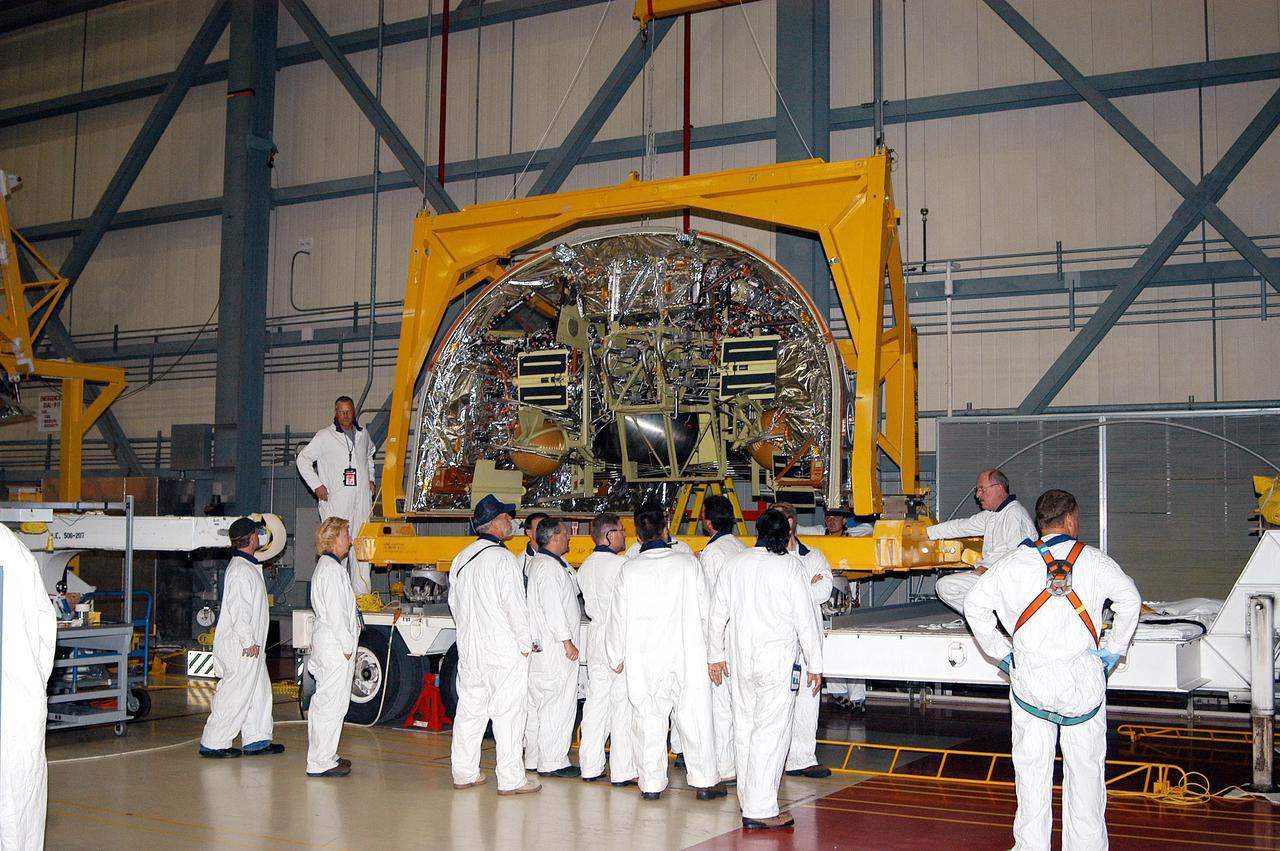

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers in the Orbiter Processing Facility stand by as a crane lifts the Forward Reaction Control System (FRCS) for installation in Discovery. Located in the forward fuselage nose area, the FRCS provides the thrust for attitude (rotational) maneuvers (pitch, yaw and roll) and for small velocity changes along the orbiter axis (translation maneuvers). Discovery is designated as the Return to Flight vehicle for mission STS-114, no earlier than March 2005.
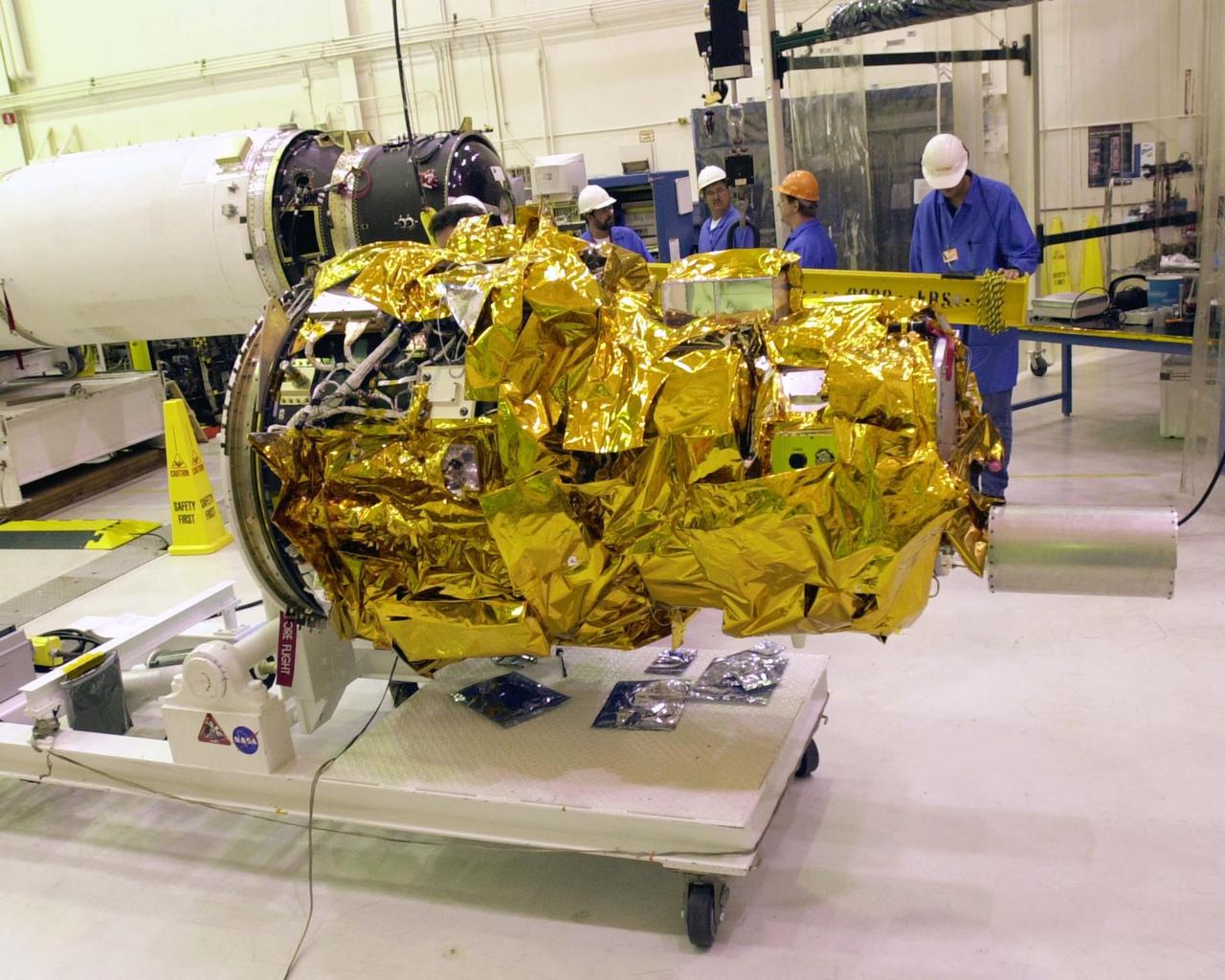

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft (foreground) is ready to be mated to second and third stages in preparation for the launch aboard the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle. Pegasus will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation, DART was designed as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers begin mating the second and third stages of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle that will launch the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA's Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
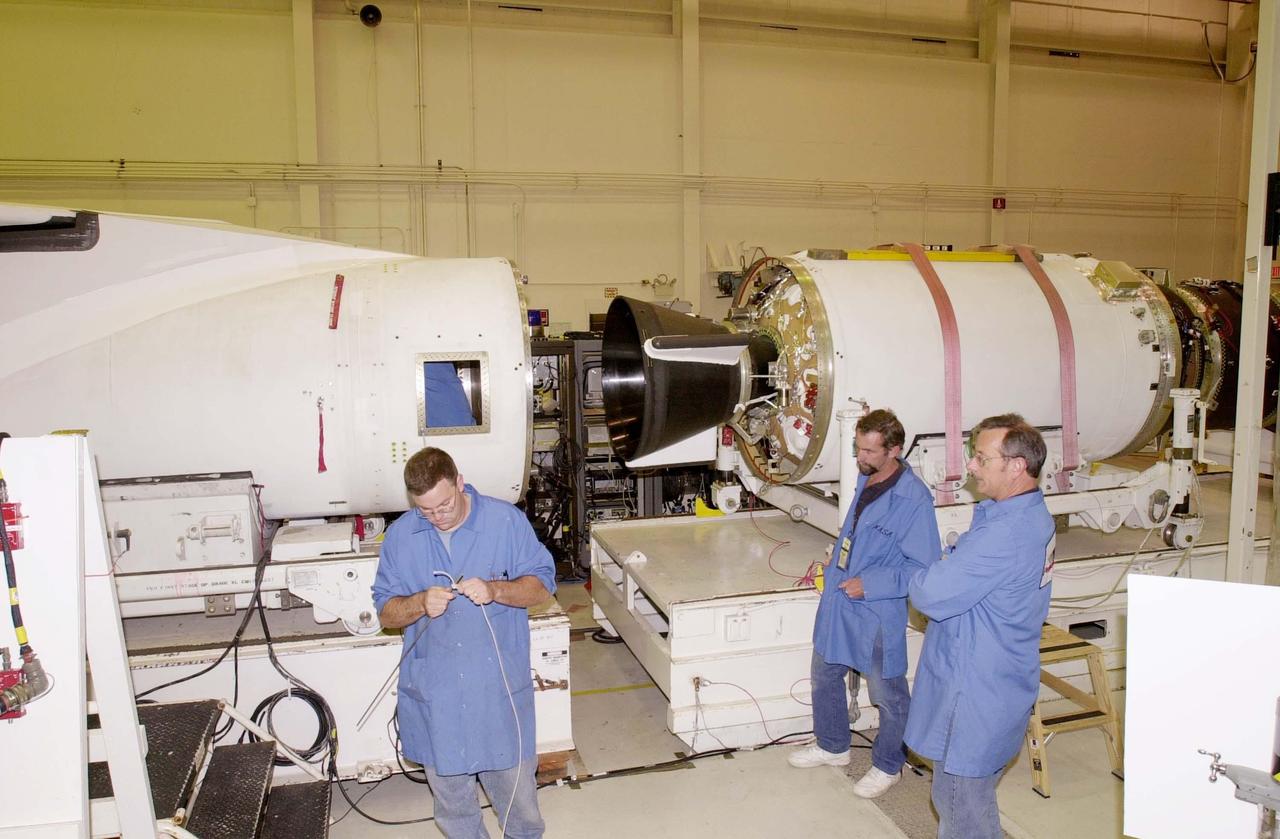

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers prepare to mate the second and third stages of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle that will launch the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA's Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
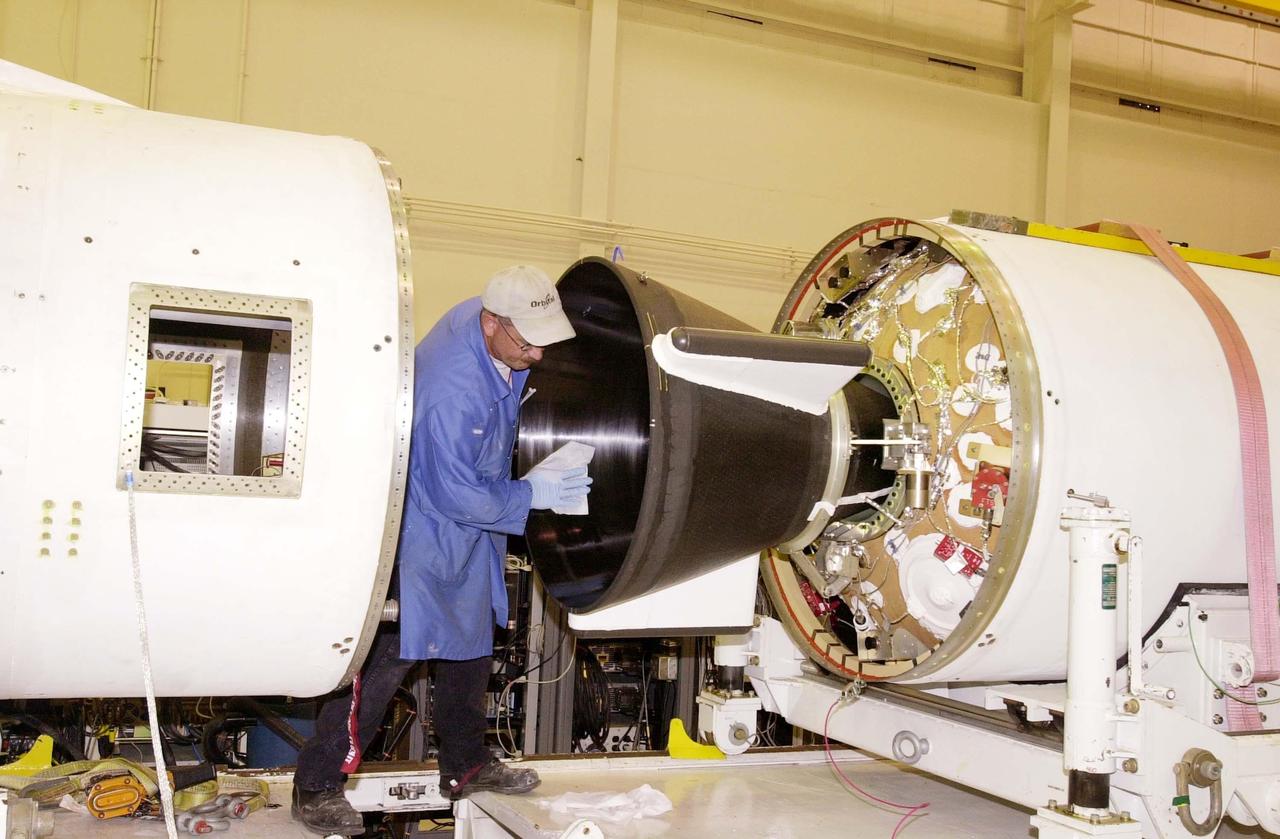
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a worker prepares the second and third stages of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle for mating. The Pegasus XL will launch the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
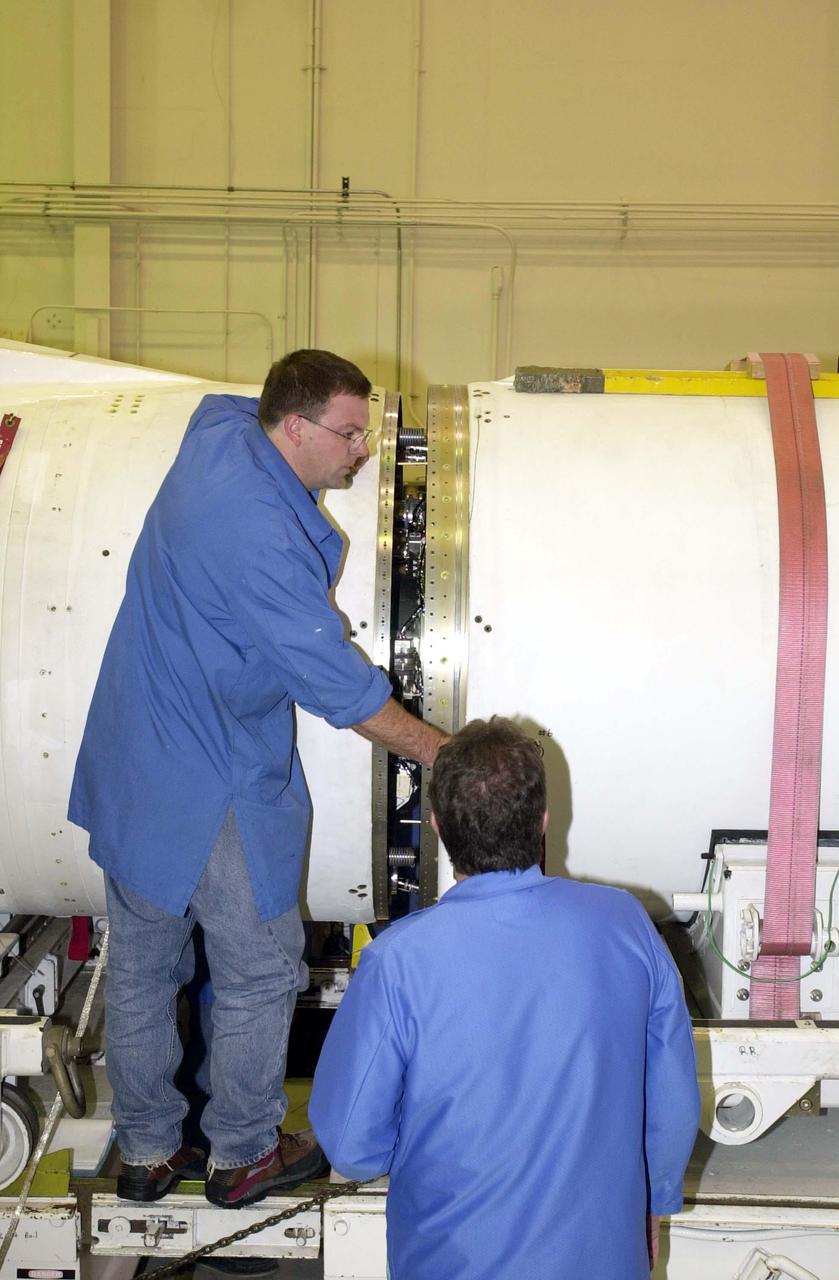

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers begin closing the gap between the second and third stages of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle that will launch the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA's Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
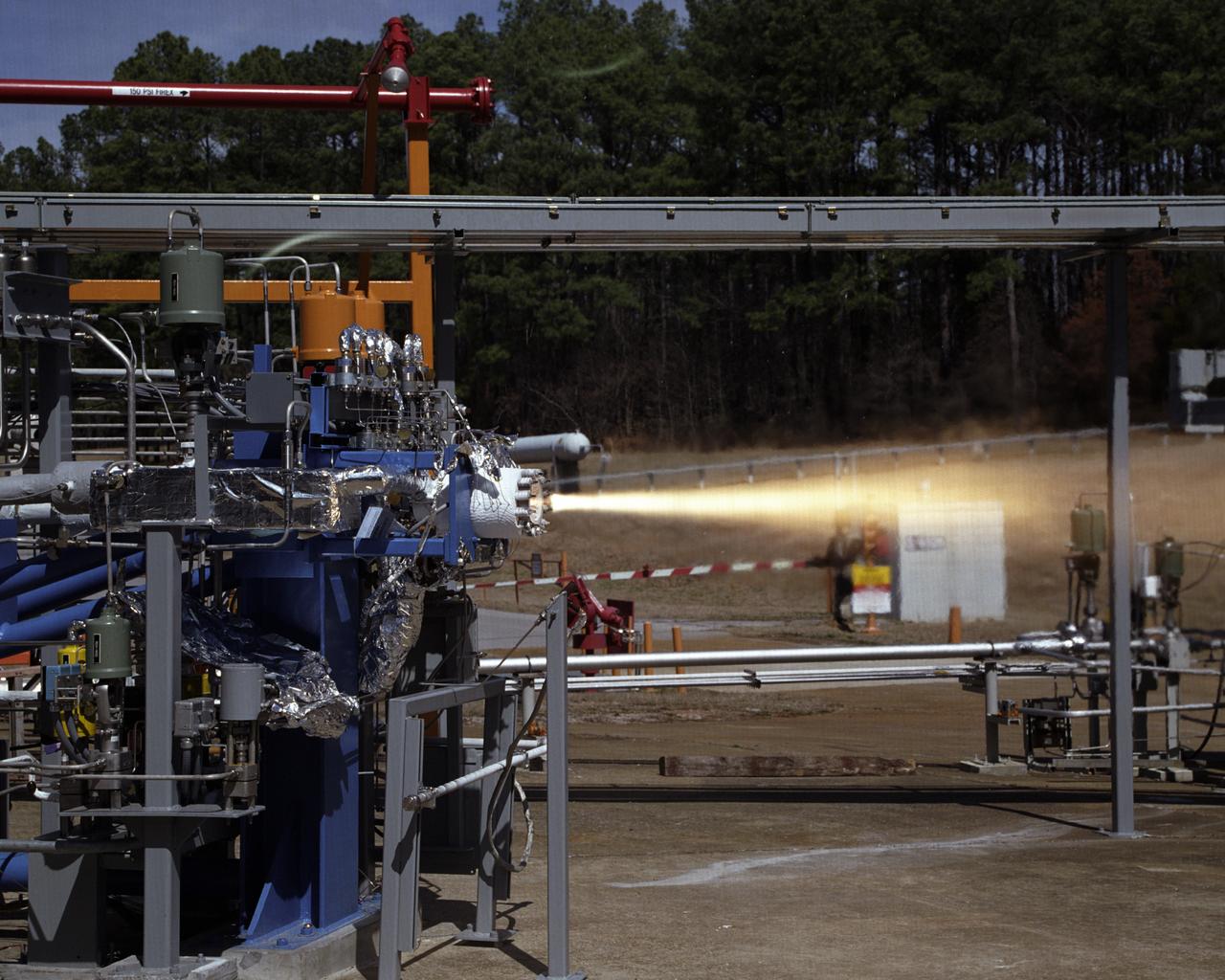

Engineers at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) have begun a series of engine tests on a new breed of space propulsion: a Reaction Control Engine developed for the Space Launch Initiative (SLI). The engine, developed by TRW Space and Electronics of Redondo Beach, California, is an auxiliary propulsion engine designed to maneuver vehicles in orbit. It is used for docking, reentry, attitude control, and fine-pointing while the vehicle is in orbit. The engine uses nontoxic chemicals as propellants, a feature that creates a safer environment for ground operators, lowers cost, and increases efficiency with less maintenance and quicker turnaround time between missions. Testing includes 30 hot-firings. This photograph shows the first engine test performed at MSFC that includes SLI technology. Another unique feature of the Reaction Control Engine is that it operates at dual thrust modes, combining two engine functions into one engine. The engine operates at both 25 and 1,000 pounds of force, reducing overall propulsion weight and allowing vehicles to easily maneuver in space. The low-level thrust of 25 pounds of force allows the vehicle to fine-point maneuver and dock while the high-level thrust of 1,000 pounds of force is used for reentry, orbit transfer, and coarse positioning. SLI is a NASA-wide research and development program, managed by the MSFC, designed to improve safety, reliability, and cost effectiveness of space travel for second generation reusable launch vehicles.
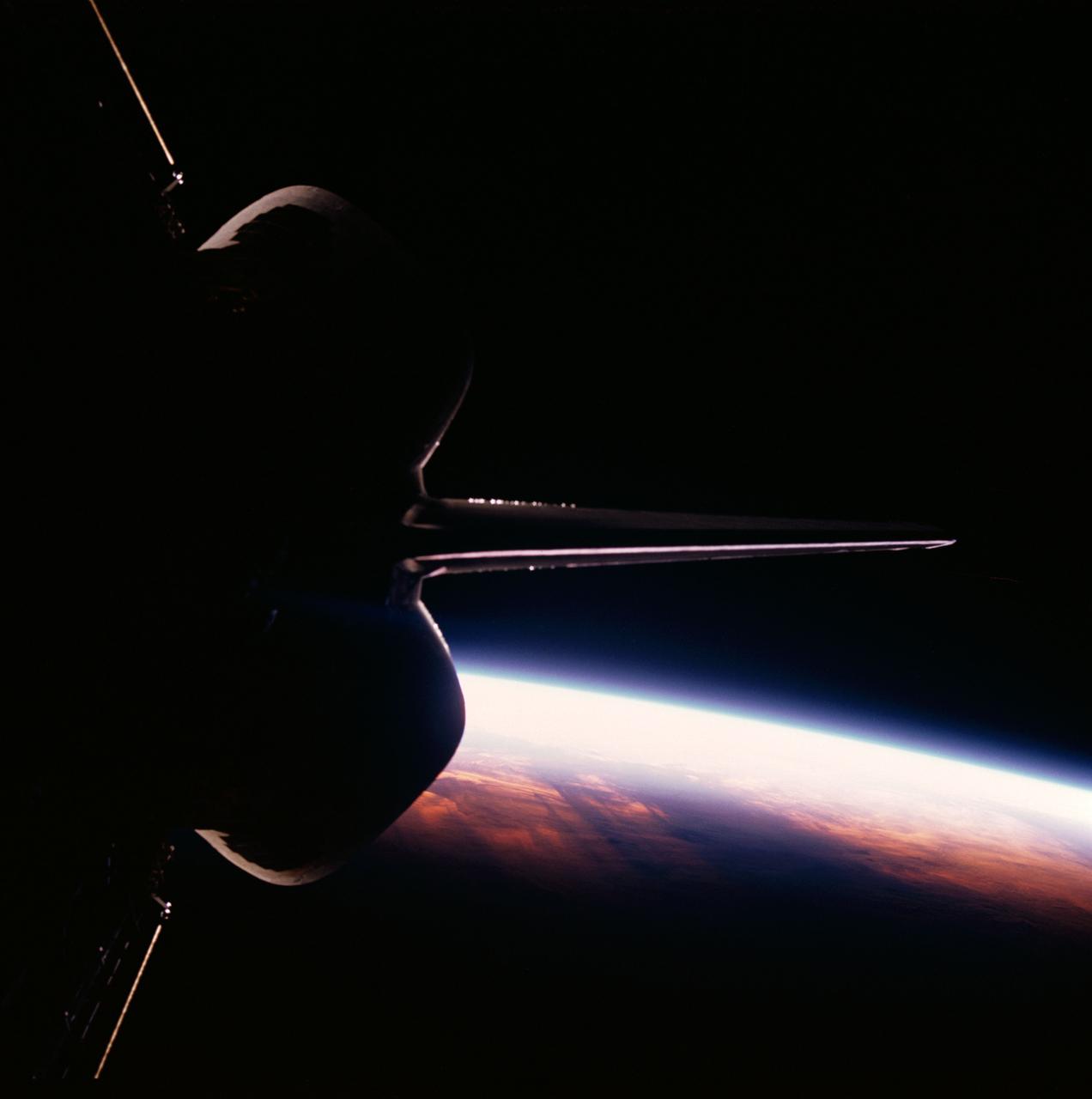

Discovery's, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103's, vertical stabilizer and orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods are backdropped against the contrasted blackness of space illuminated by a colorful Earth / sunrise panorama. View was taken through the aft flight deck viewing windows during STS-26.
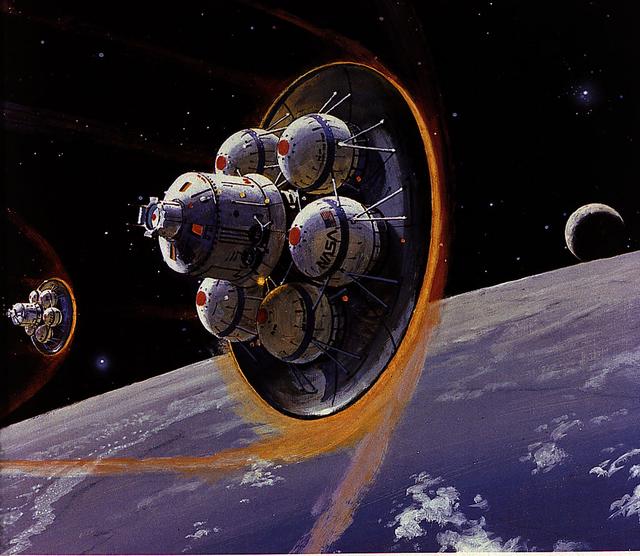
In June 1989 the Marshall Space Flight Center initiated studies of Space Transfer Vehicle (STV) concepts. A successor to the Orbital Transfer Vehicle (OTV) concept, the STV would be a high-performance space vehicle capable of transferring automated payloads from a Space Station to geosynchronous orbits, the Moon, or planets. Illustrated in this artist's concept are two STV's undergoing aerobraking maneuvers as they approach a Space Station.
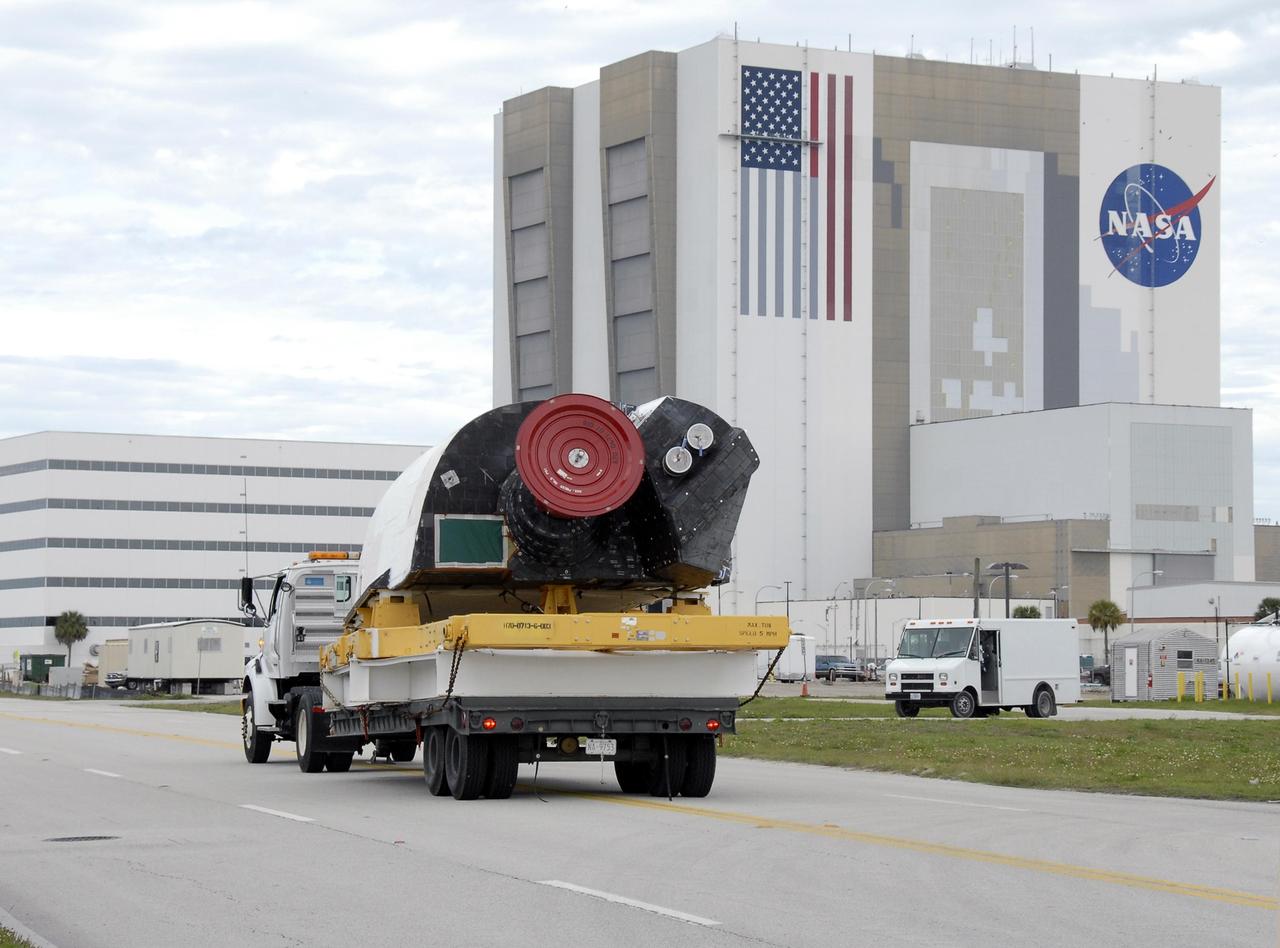

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The right-hand orbital maneuvering system pod is driven past the Vehicle Assembly Building on its way to Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 for installation on the orbiter Endeavour. The orbital maneuvering system/reaction control system left- and right-hand pods are attached to the upper aft fuselage left and right sides. Each pod is fabricated primarily of graphite epoxy composite and aluminum. Each pod is 21.8 feet long and 11.37 feet wide at its aft end and 8.41 feet wide at its forward end, with a surface area of approximately 435 square feet. The orbiter is being prepared for its first launch in just over four years. The vehicle has undergone an extensive modification period, including the addition of all of the return-to-flight safety upgrades added to both Discovery and Atlantis. Endeavour is targeted for launch of mission STS-118 on June 28. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
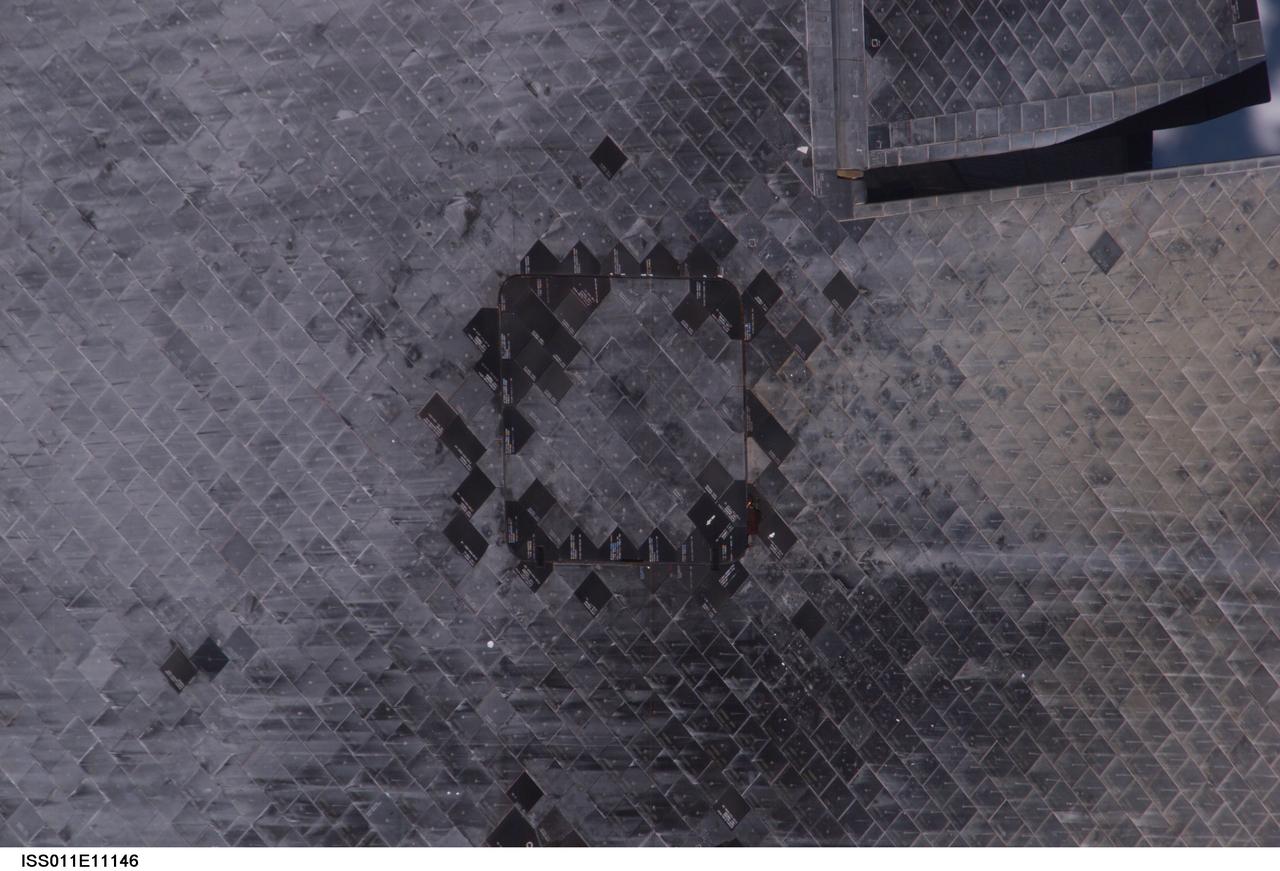

ISS011-E-11146 (28 July 2005) --- View of the Space Shuttle Discovery's underside (near Orbital Maneuvering System pod), photographed as part of the survey sequence performed by the Expedition 11 crew during the STS-114 R-Bar Pitch Maneuver on Flight Day 3. This picture was used by Steve M. Poulos, Jr. Manager, Space Shuttle Vehicle Engineering Office, as one of his visual aids in a July 28, 2005 press conference in the Teague Auditorium at the Johnson Space Center.
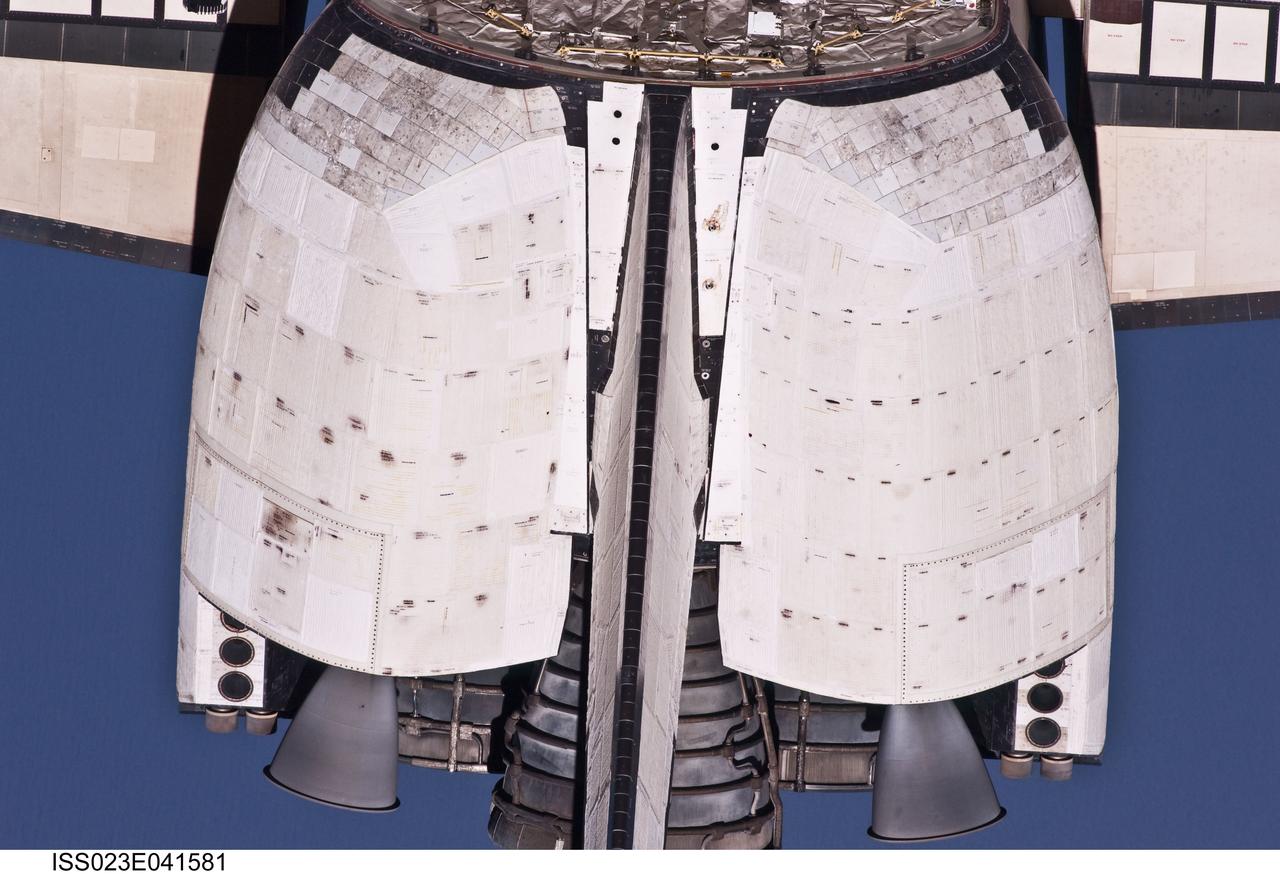
ISS023-E-041581 (16 May 2010) --- This close-up view of the vertical stabilizer and orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods of the space shuttle Atlantis was provided by an Expedition 23 crew member during a survey of the approaching STS-132 vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Atlantis performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
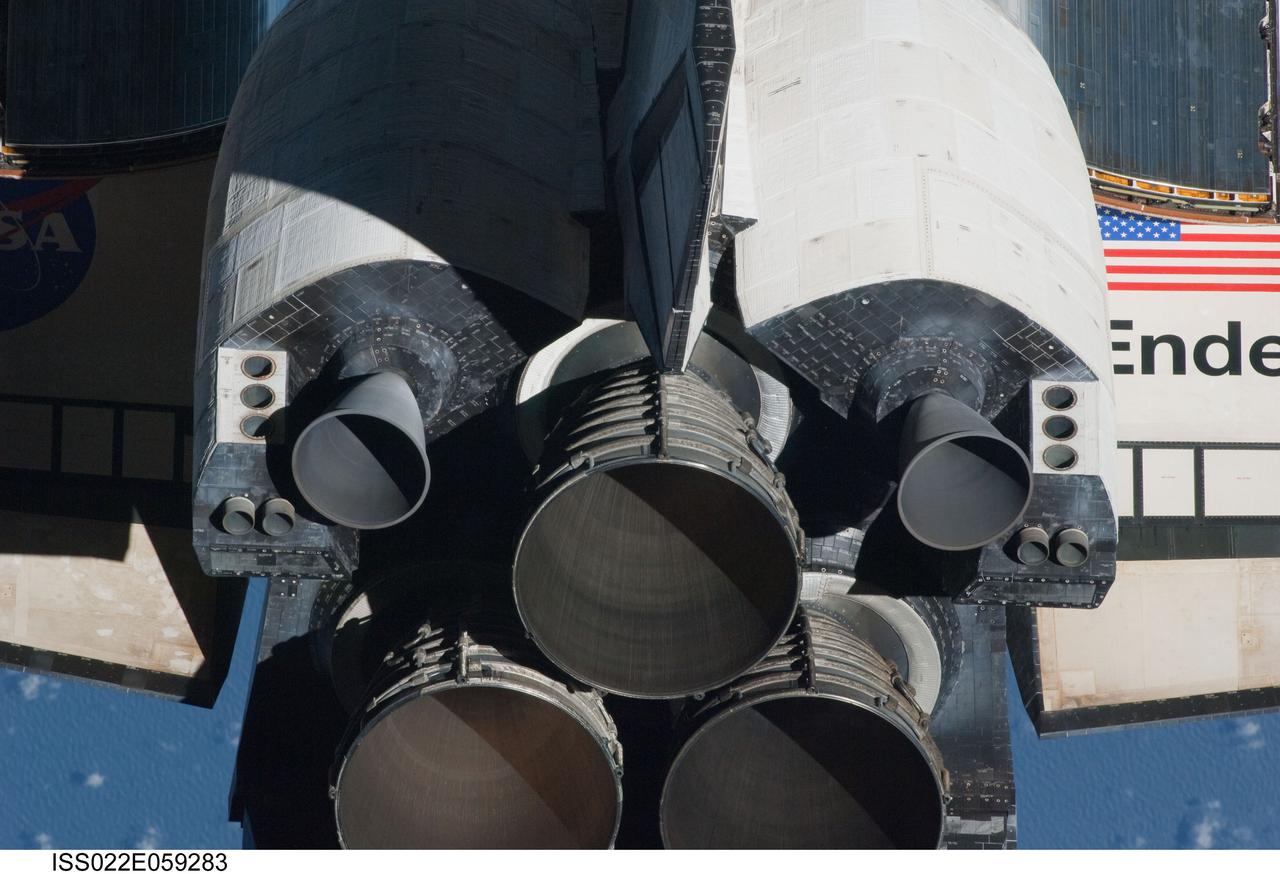

ISS022-E-059283 (9 Feb. 2010) --- This view of the aft portion of the space shuttle Endeavour, including the three main engines and orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods, was provided by an Expedition 22 crew member during a survey of the approaching vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Endeavour performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
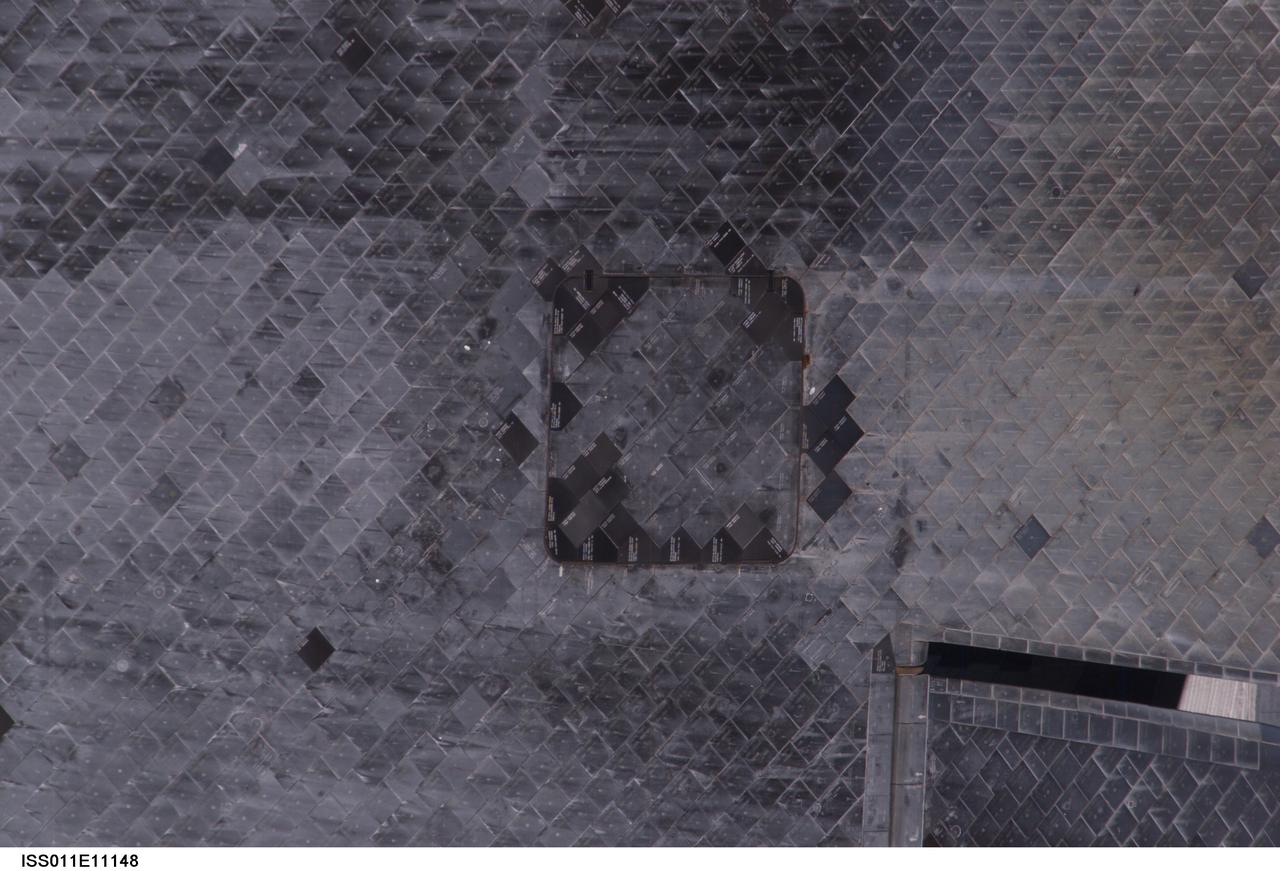

ISS011-E-11148 (28 July 2005) --- View of the Space Shuttle Discovery's underside (near the Orbital Maneuvering System pod), photographed as part of the survey sequence performed by the Expedition 11 crew during the STS-114 R-Bar Pitch Maneuver on Flight Day 3. This picture was used by Steve M. Poulos, Jr. Manager, Space Shuttle Vehicle Engineering Office, as one of his visual aids in a July 28, 2005 press conference in the Teague Auditorium at the Johnson Space Center.
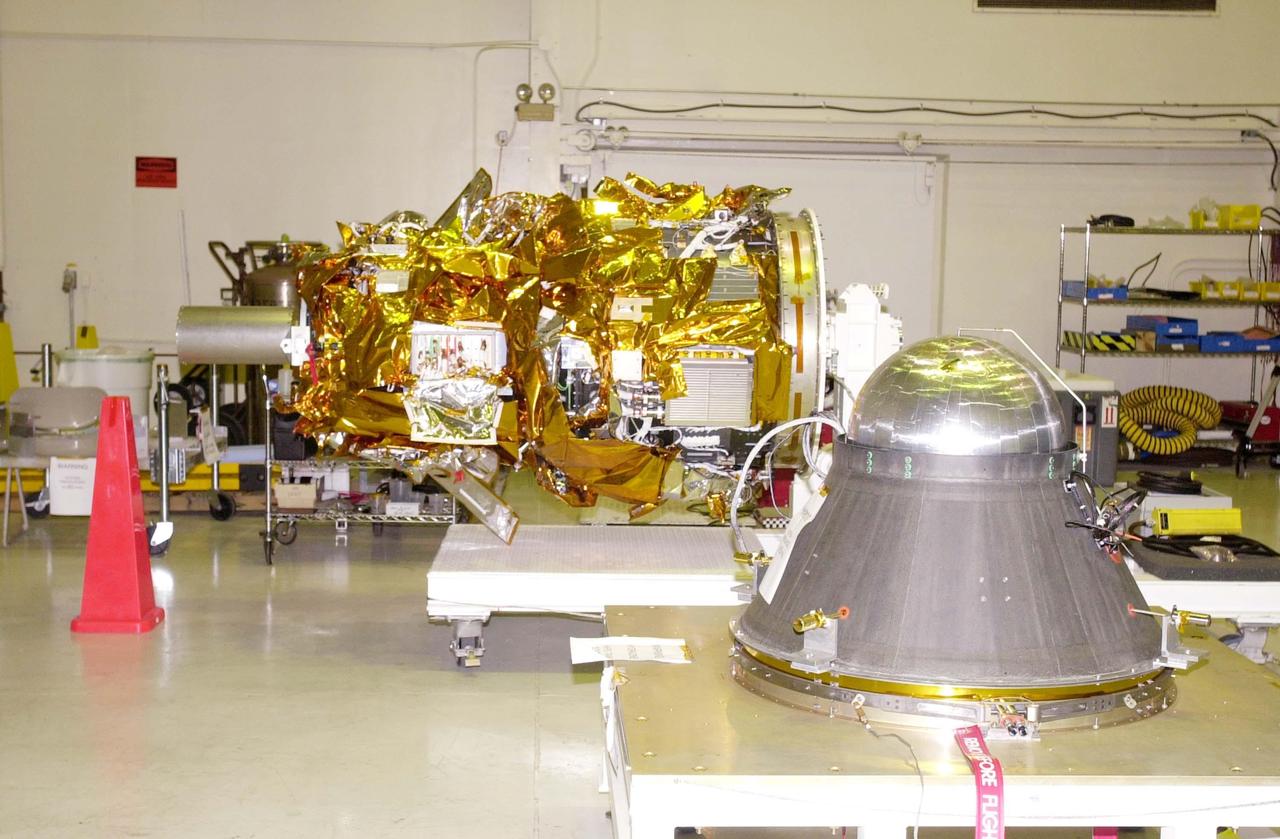

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft (in background) has been rotated from vertical to horizontal and is ready for mating with the upper stage (foreground). DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
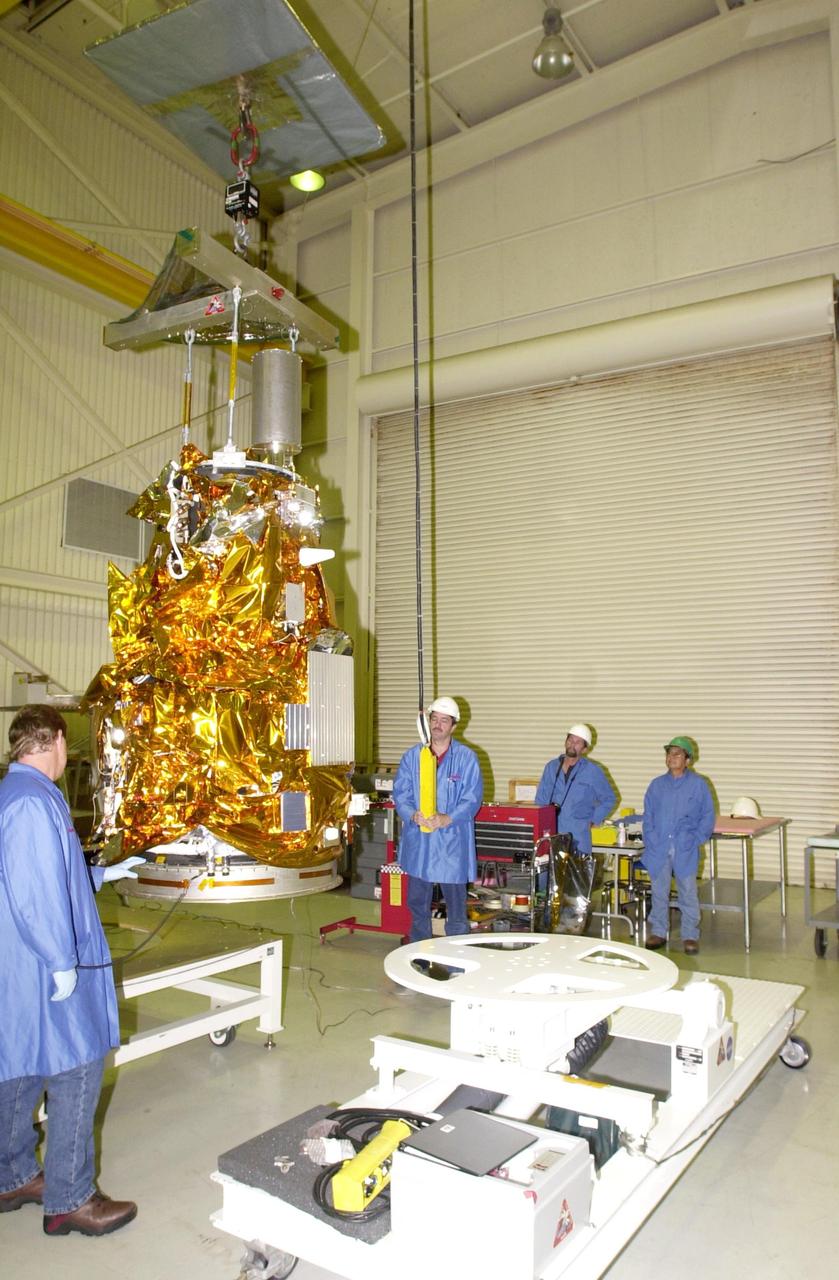

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers stand by while an overhead crane moves the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft onto the mobile stand at right. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft (right) is ready for mating with the upper stage (foreground) in preparation for launch on the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
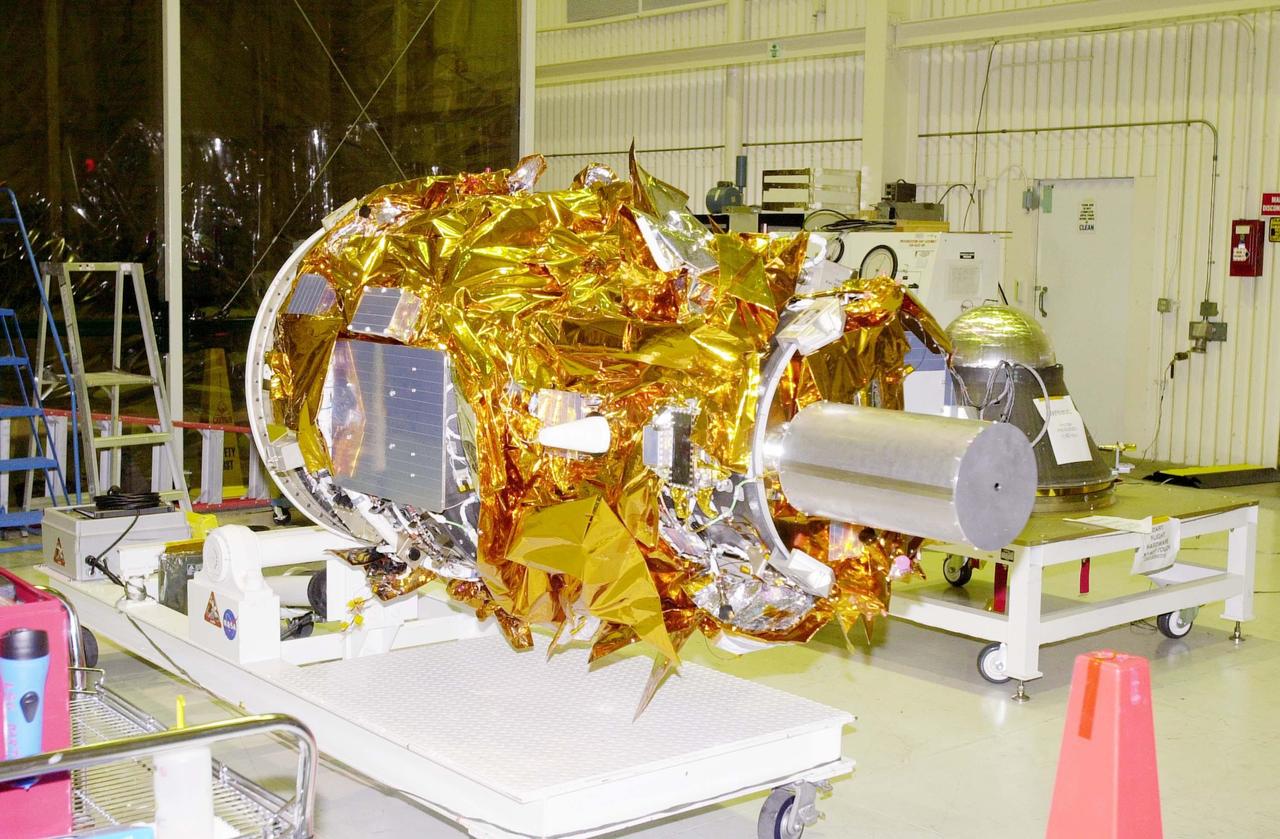

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft is ready for mating with the upper stage of the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL behind it (right). DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
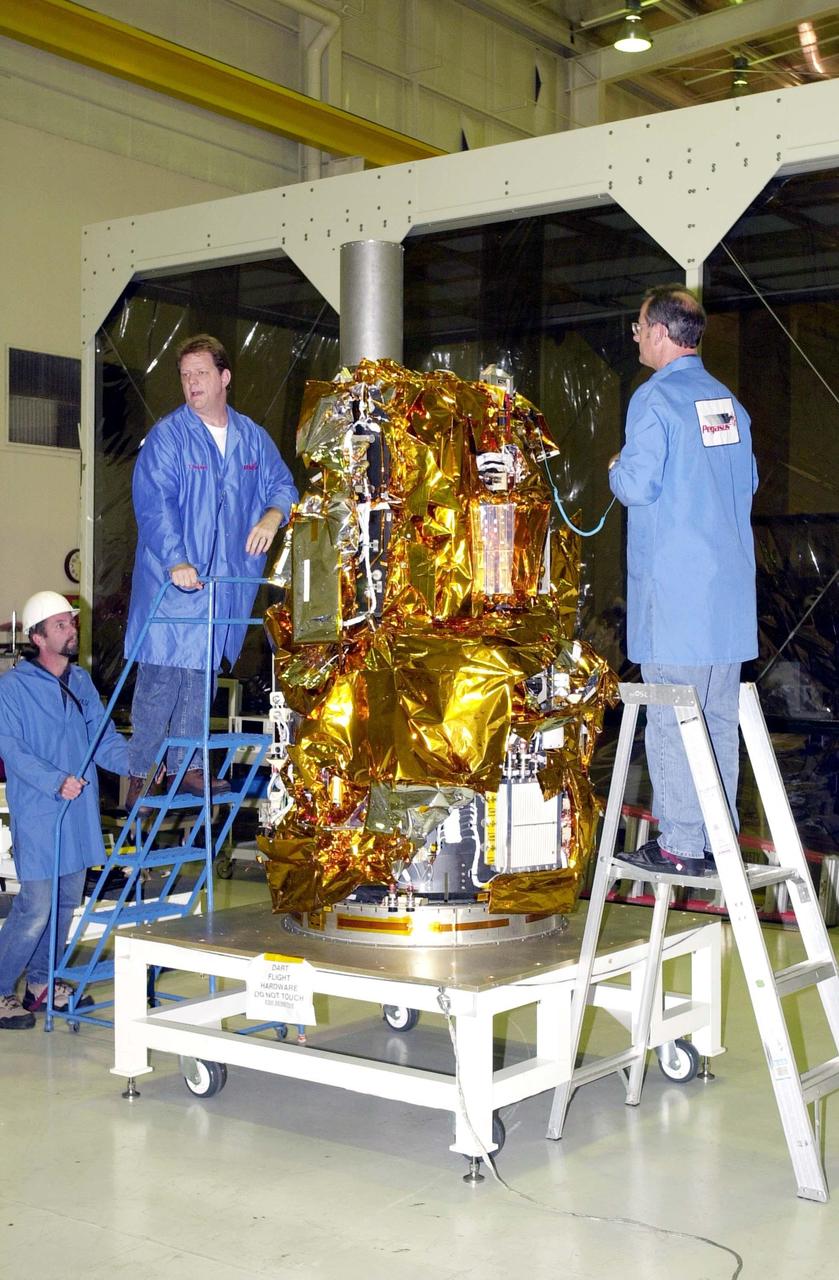

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers prepare the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft for launch. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
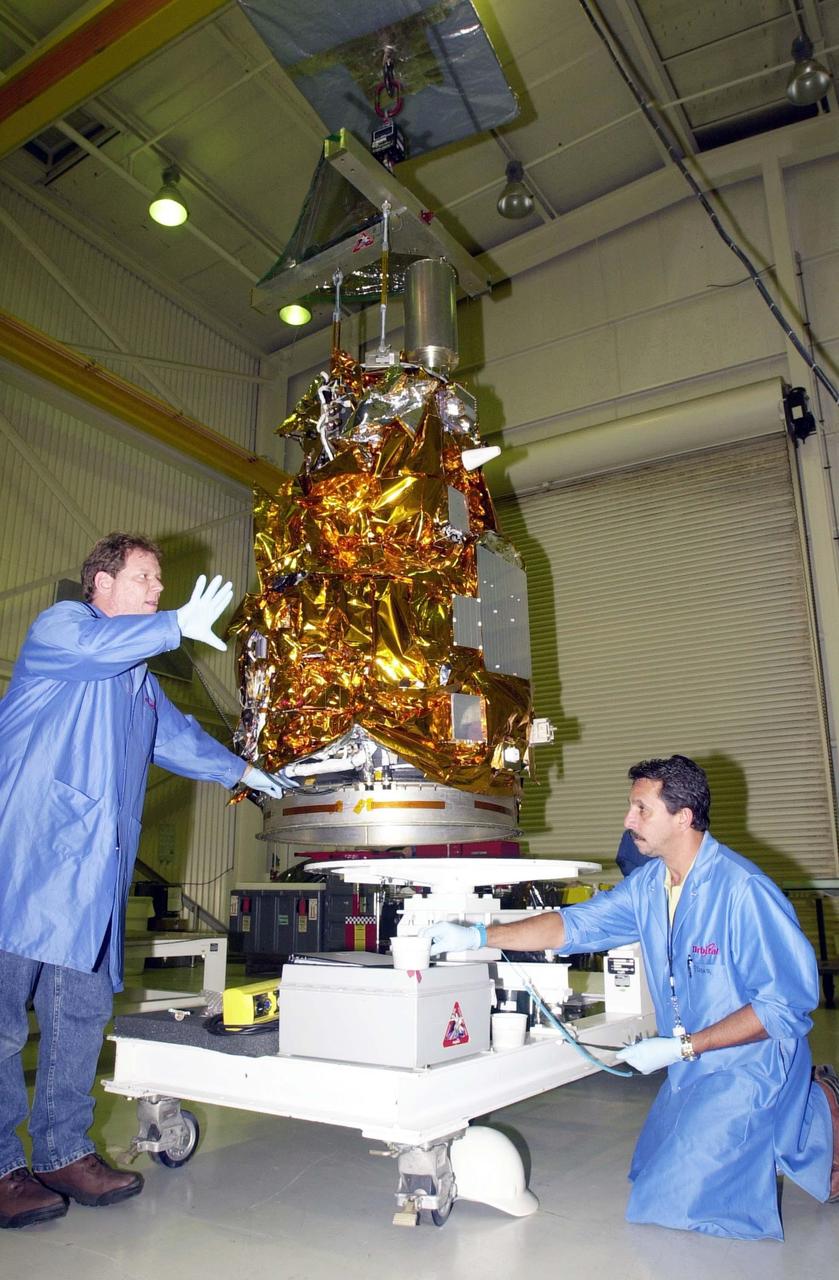

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, workers help guide the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft onto the mobile stand below. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft (right) is ready for mating with the upper stage (behind it) in preparation for launch on the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. DART weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA’s Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station.
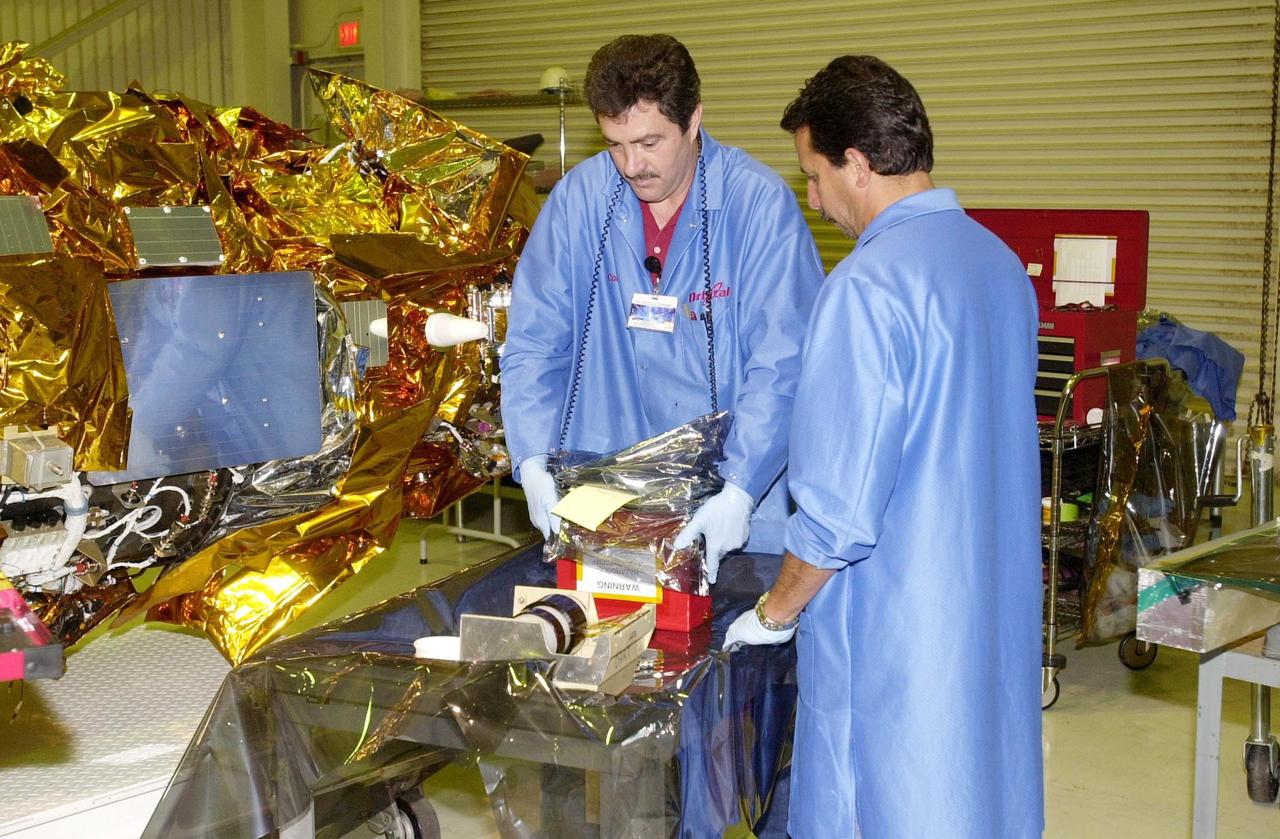

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Corky Philyaw (left) and Edgar Suarez (right) prepare the flight battery for installation on the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft (far left). DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. It is designed to demonstrate technologies required for a spacecraft to locate and rendezvous, or maneuver close to, other craft in space. Results from the DART mission will aid in the development of NASA's Crew Exploration Vehicle and will also assist in vehicle development for crew transfer and crew rescue capability to and from the International Space Station. DART will be launched from an Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL rocket no earlier than Oct. 26.

The media gather around NASA Vehicle Manager Scott Thurston (white shirt, center) who talks about some of the work being done on the orbiter Atlantis as it is being prepared for Return to Flight in the Orbiter Processing Facility. Both local and national reporters representing print and TV networks were able to see work in progress on Atlantis, including the reinstallation of the Reinforced Carbon-Carbon panels on the orbiter’s wing leading edge; wiring inspections; and checks of the engines in the Orbital Maneuvering System.
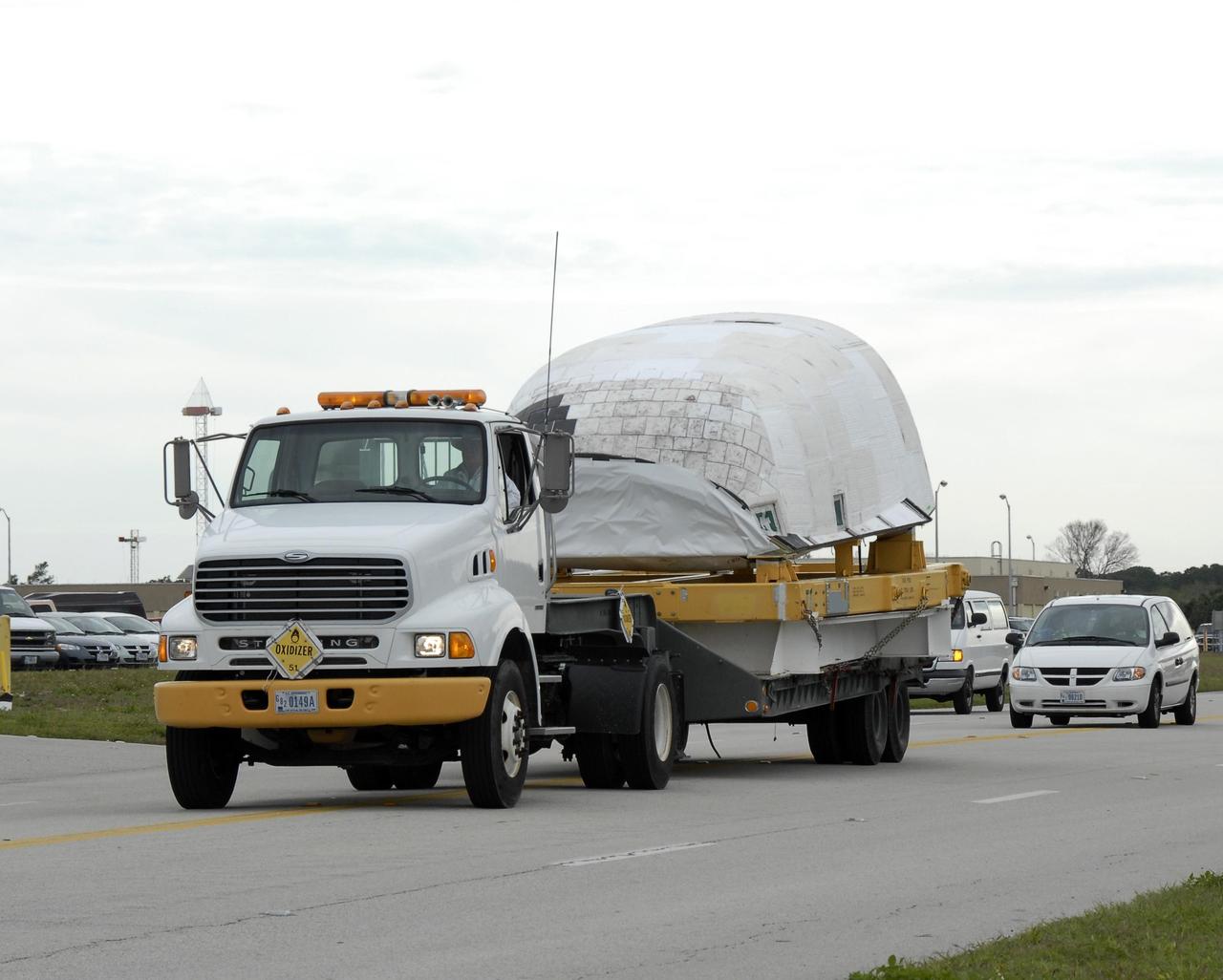

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The right-hand orbital maneuvering system pod is being delivered to Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 for installation on the orbiter Endeavour. The orbital maneuvering system/reaction control system left- and right-hand pods are attached to the upper aft fuselage left and right sides. Each pod is fabricated primarily of graphite epoxy composite and aluminum. Each pod is 21.8 feet long and 11.37 feet wide at its aft end and 8.41 feet wide at its forward end, with a surface area of approximately 435 square feet. The orbiter is being prepared for its first launch in just over four years. The vehicle has undergone an extensive modification period, including the addition of all of the return-to-flight safety upgrades added to both Discovery and Atlantis. Endeavour is targeted for launch of mission STS-118 on June 28. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
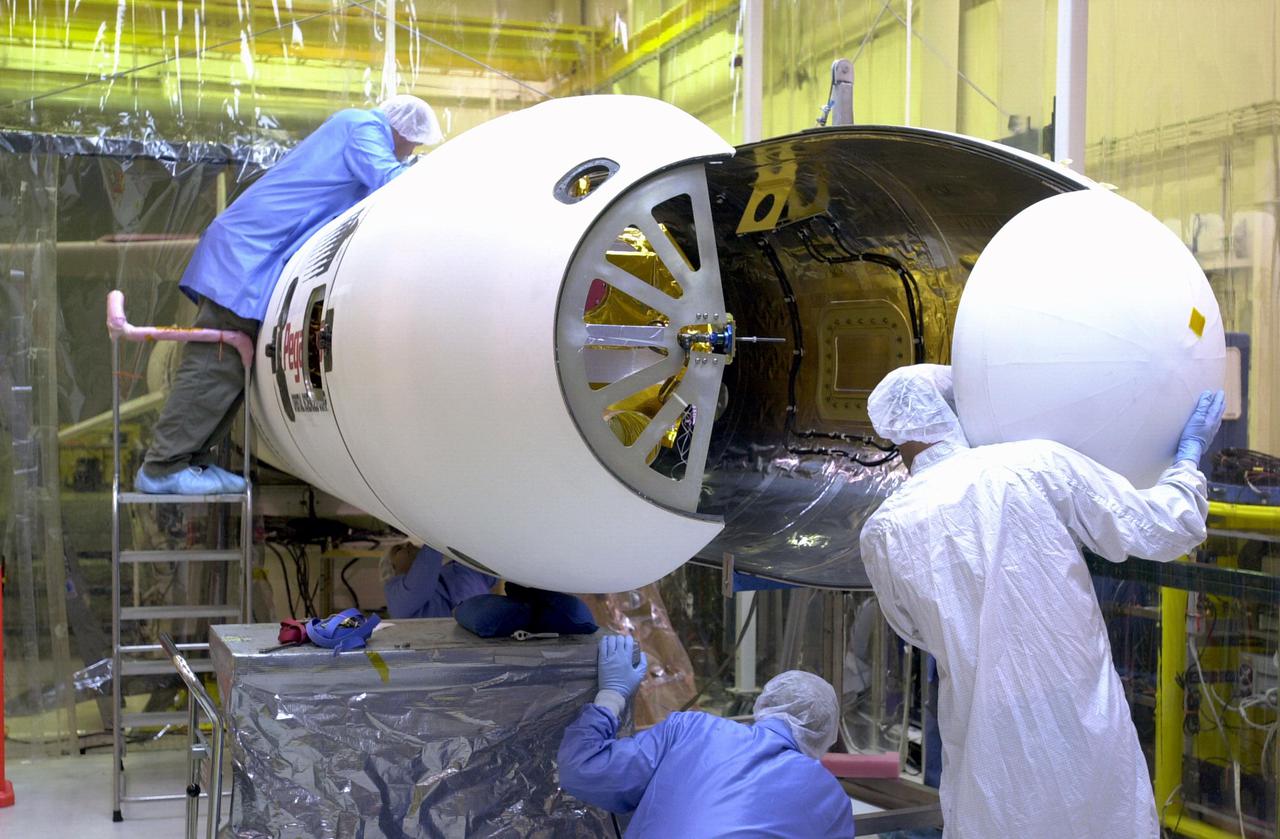

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Orbital Sciences Corporation technicians at Vandenberg AFB in California maneuver the second fairing half into place around the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft in preparation for launch. The fairing will encapsulate DART and protect it while on the launch pad and during ascent. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
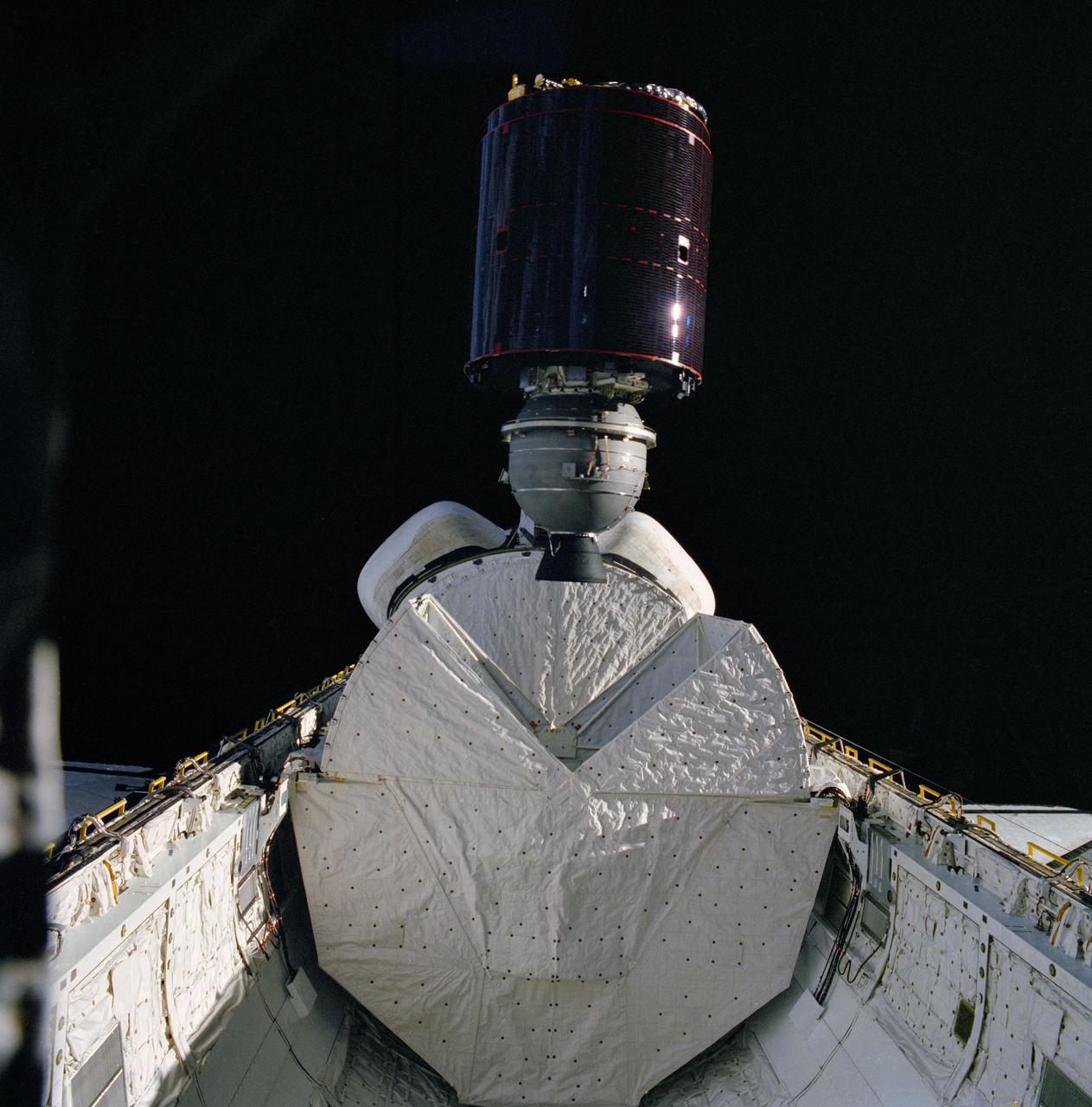

S82-39793 (11 Nov. 1982) --- The Satellite Business Systems (SBS-3) spacecraft springs from its protective ?cradle? in the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting space shuttle Columbia and head toward a series of maneuvers that will eventually place it in a geosynchronous orbit. This moment marks a milestone for the Space Transportation System (STS) program, as the placement of the communications satellites represents the first deployment of a commercial satellite from an orbiting space vehicle. Part of Columbia?s wings can be seen on both the port and starboard sides. Also both orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods are seen at center. The vertical stabilizer is obscured by the satellite. The closed protective cradle device shielding Telesat Canada?s ANIK C-3 spacecraft is seen between the other shield and the OMS pod. ANIK is to be launched on the mission?s second day. This photograph was exposed through the aft windows of the flight deck. Photo credit: NASA
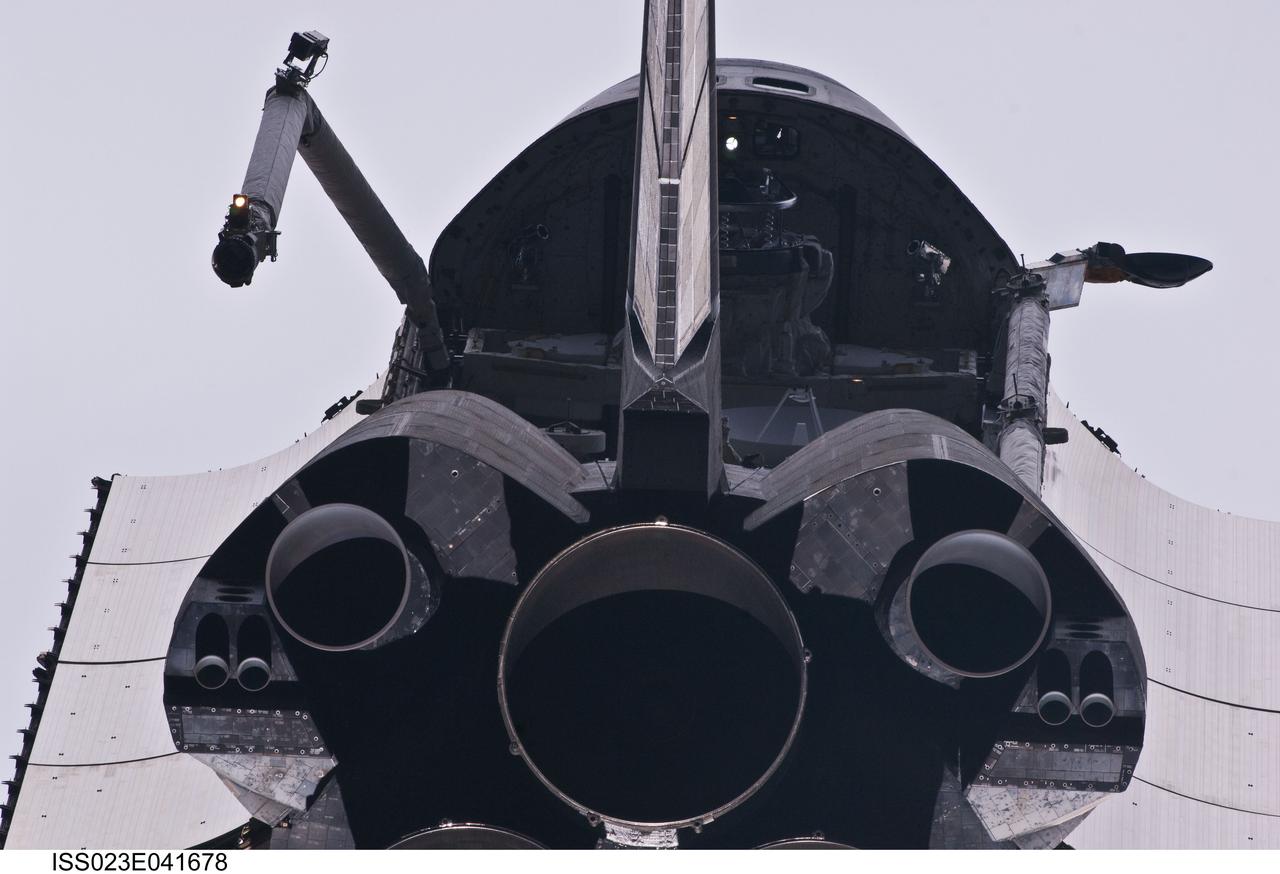

ISS023-E-041678 (16 May 2010) --- This view of the aft portion of the space shuttle Atlantis, including main engines, part of the cargo bay, vertical stabilizer and orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods was provided by an Expedition 23 crew member during a survey of the approaching STS-132 vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Atlantis performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
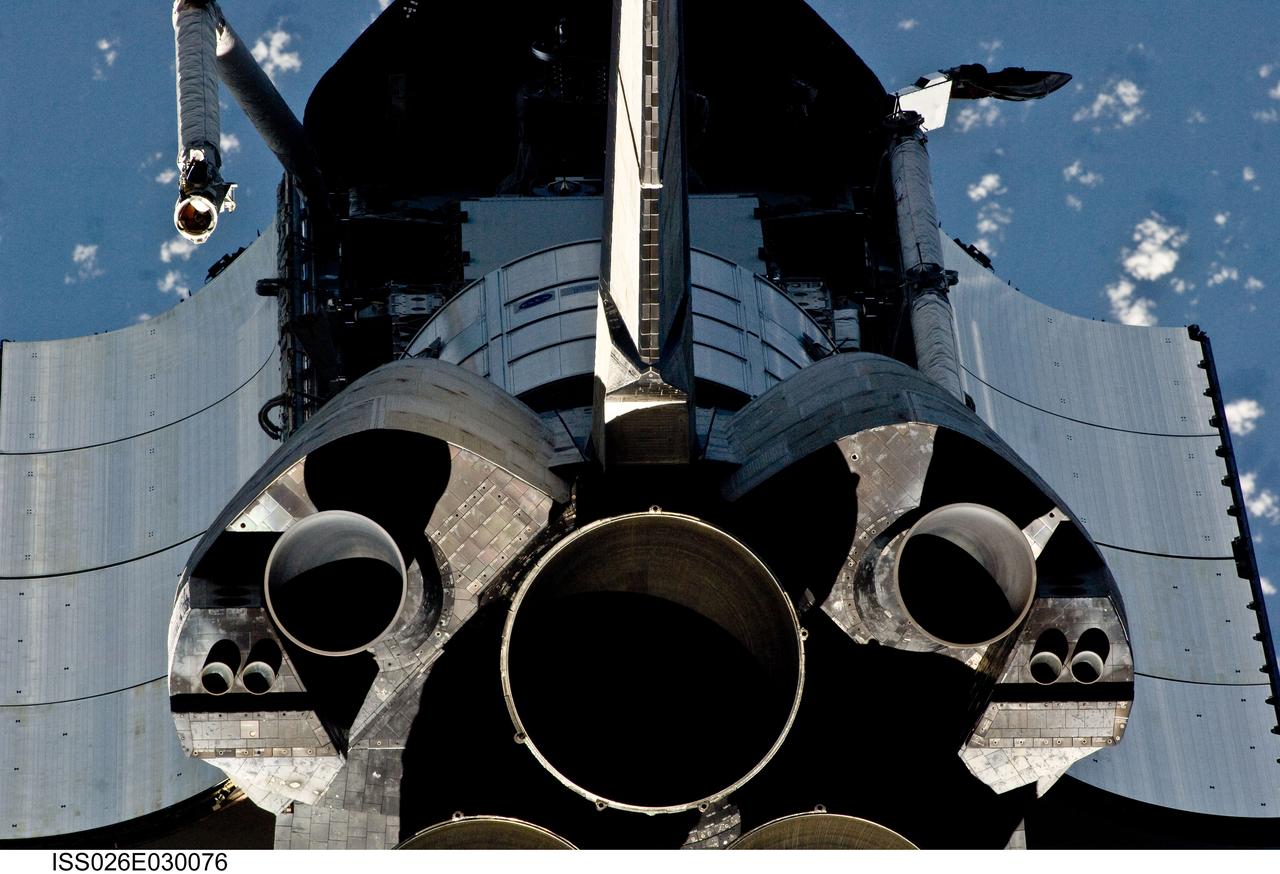

ISS026-E-030076 (26 Feb. 2011) --- This view of the aft portion of the space shuttle Discovery, including main engines, part of the cargo bay, vertical stabilizer and orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods was provided by an Expedition 26 crew member during a survey of the approaching STS-133 vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Discovery performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
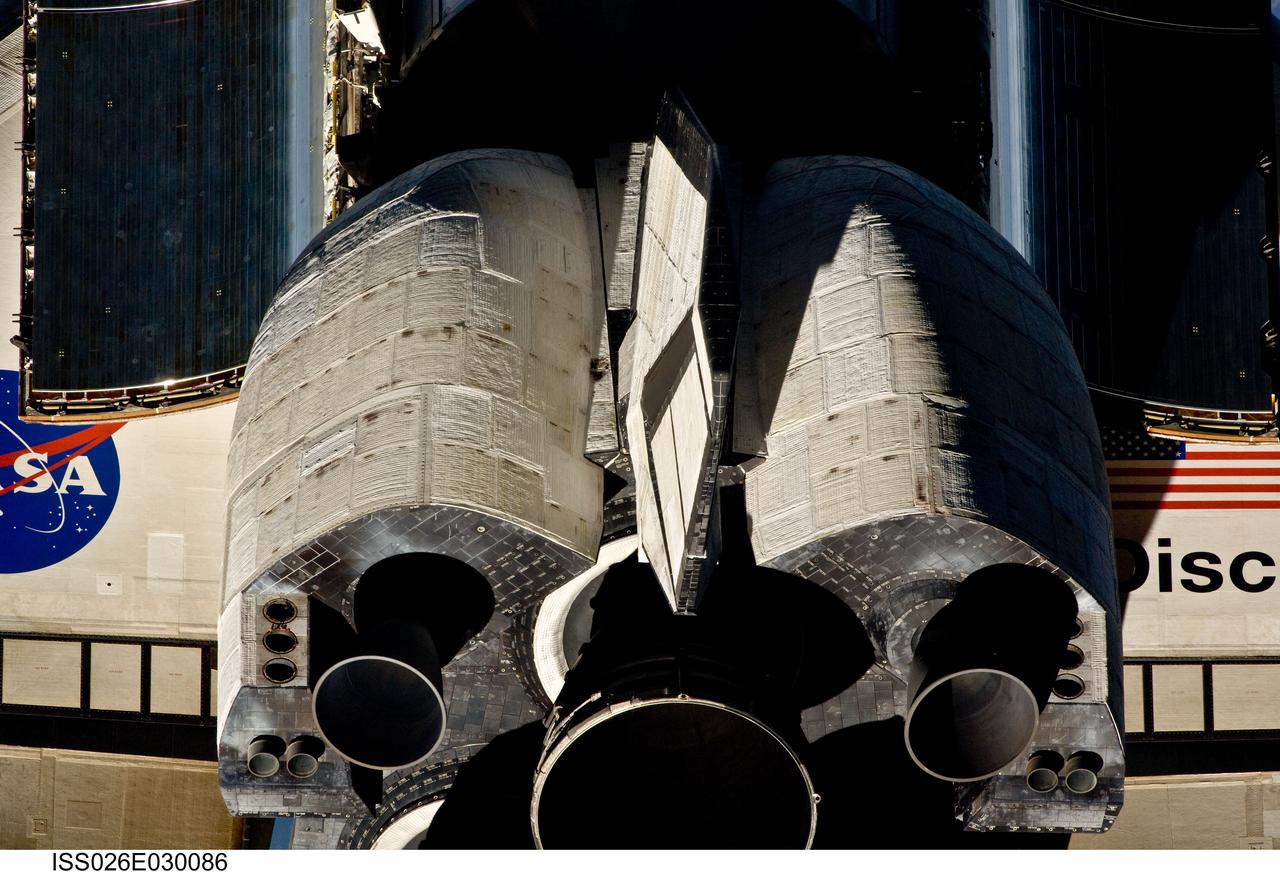

ISS026-E-030086 (26 Feb. 2011) --- This view of the aft portion of the space shuttle Discovery, including the three main engines and orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods, was provided by an Expedition 26 crew member during a survey of the approaching STS-133 vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Discovery performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
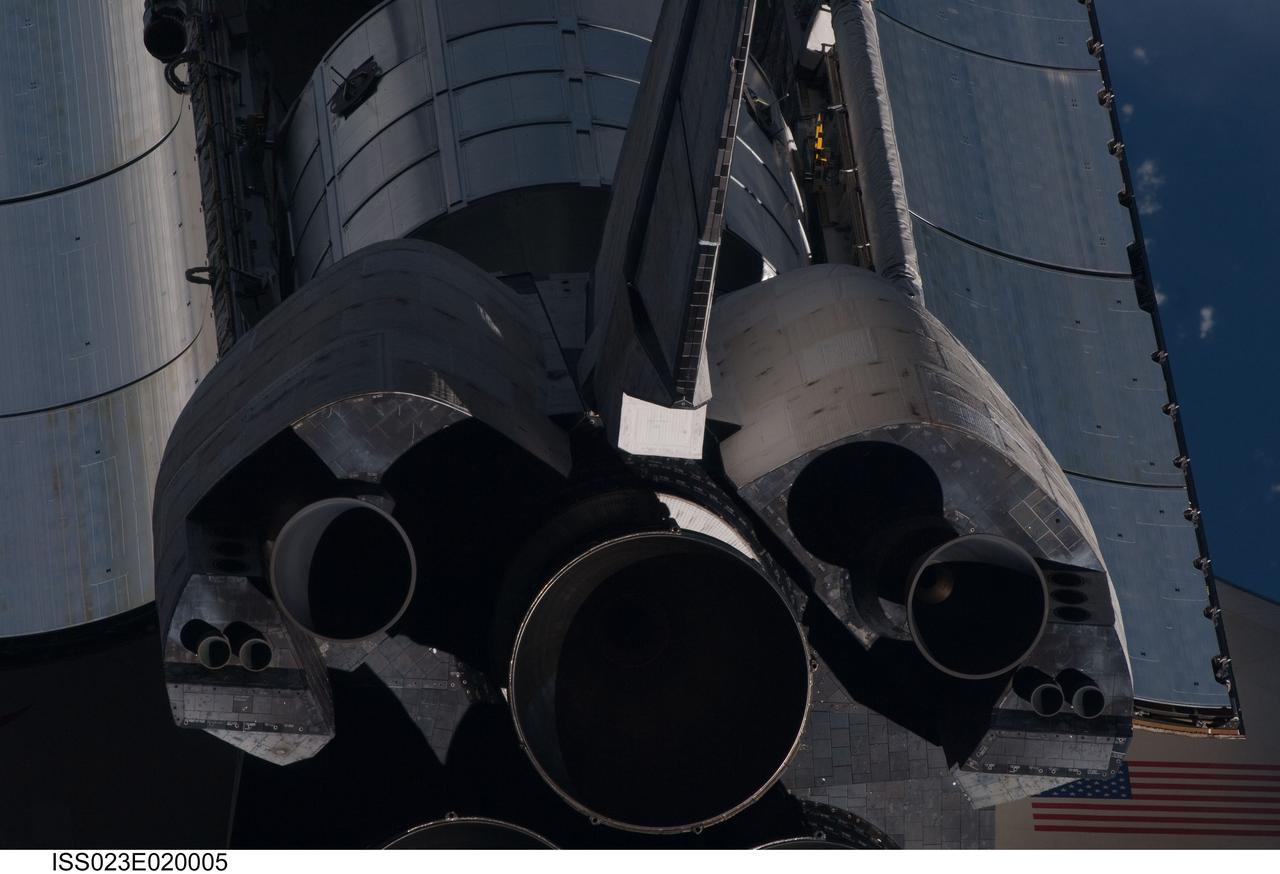

ISS023-E-020005 (7 April 2010) --- This view of the aft portion of the space shuttle Discovery, including the three main engines, part of the cargo bay, vertical stabilizer and orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods, was provided by an Expedition 23 crew member during a survey of the approaching vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, the STS-131 Discovery crew performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters). The multi-purpose logistics module Leonardo is visible in the cargo bay.
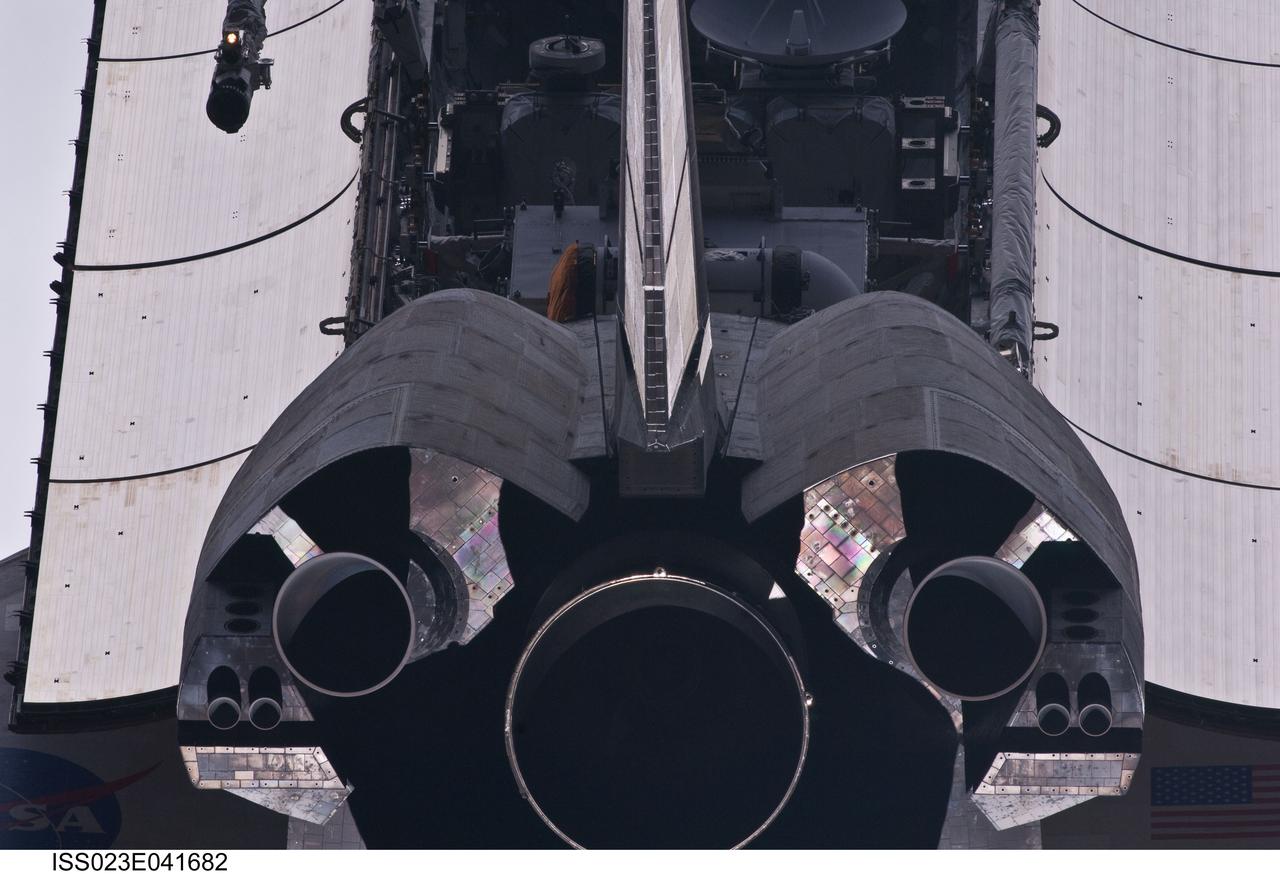

ISS023-E-041682 (16 May 2010) --- This view of the aft portion of the space shuttle Atlantis, including main engines, part of the cargo bay, vertical stabilizer and orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods was provided by an Expedition 23 crew member during a survey of the approaching STS-132 vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Atlantis performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
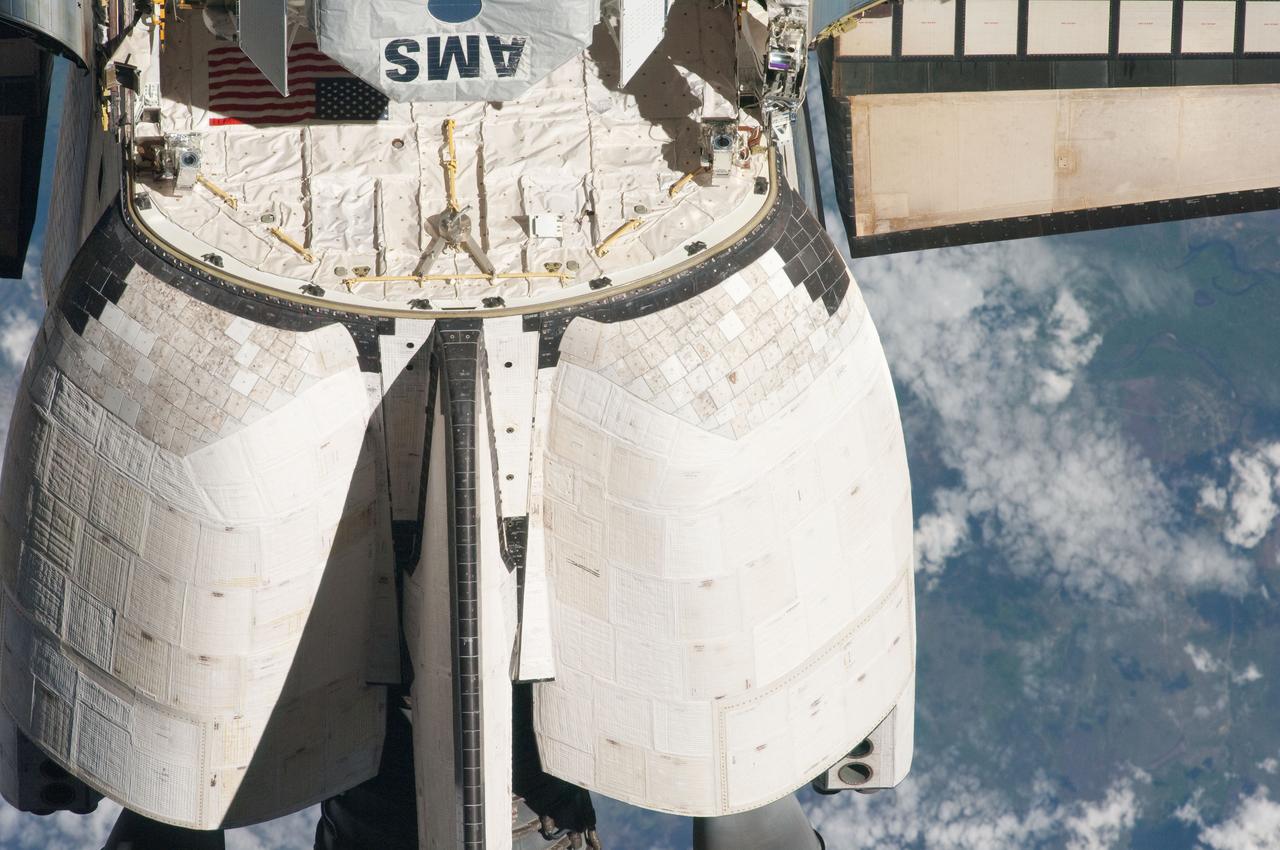

ISS027-E-032241 (18 May 2011) --- This view of the aft portion of the space shuttle Endeavour, including the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer-2 (AMS) in the payload bay, was provided by an Expedition 27 crew member during a survey of the approaching STS-134 vehicle prior to docking with the International Space Station. As part of the survey and part of every mission's activities, Endeavour performed a back-flip for the rendezvous pitch maneuver (RPM). The image was photographed with a digital still camera, using a 400mm lens at a distance of about 600 feet (180 meters).
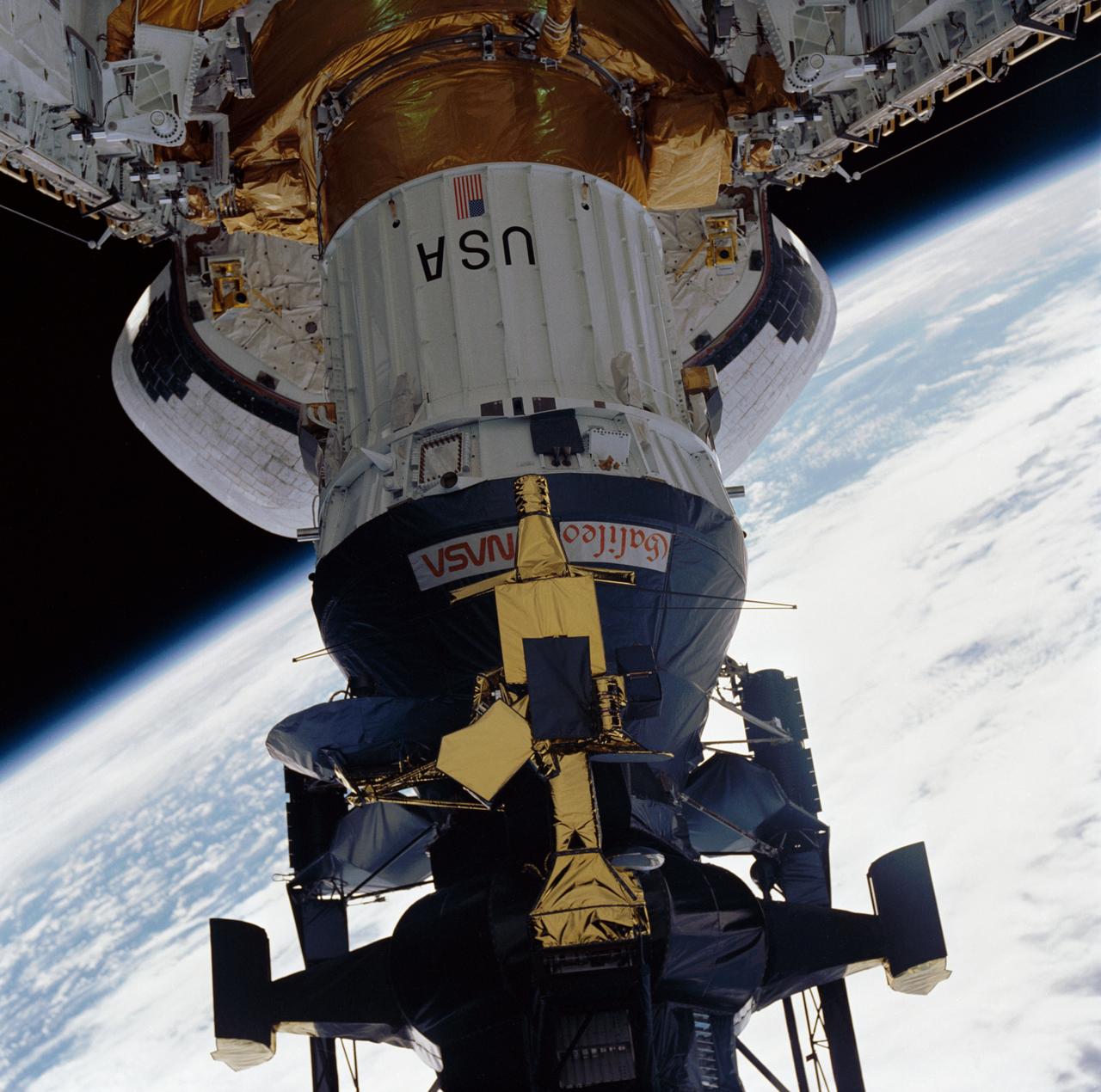

During STS-34 mission, the Galileo spacecraft mounted atop the inertial upper stage (IUS) is tilted to a 58-degree deployment position by the airborne support equipment (ASE) aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA) table in Atlantis', Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 104's, payload bay (PLB). Visible in the foreground is the ASE forward cradle and the umbilical boom which has fallen away from the IUS. OV-104's orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and the Earth's limb appear in the background.
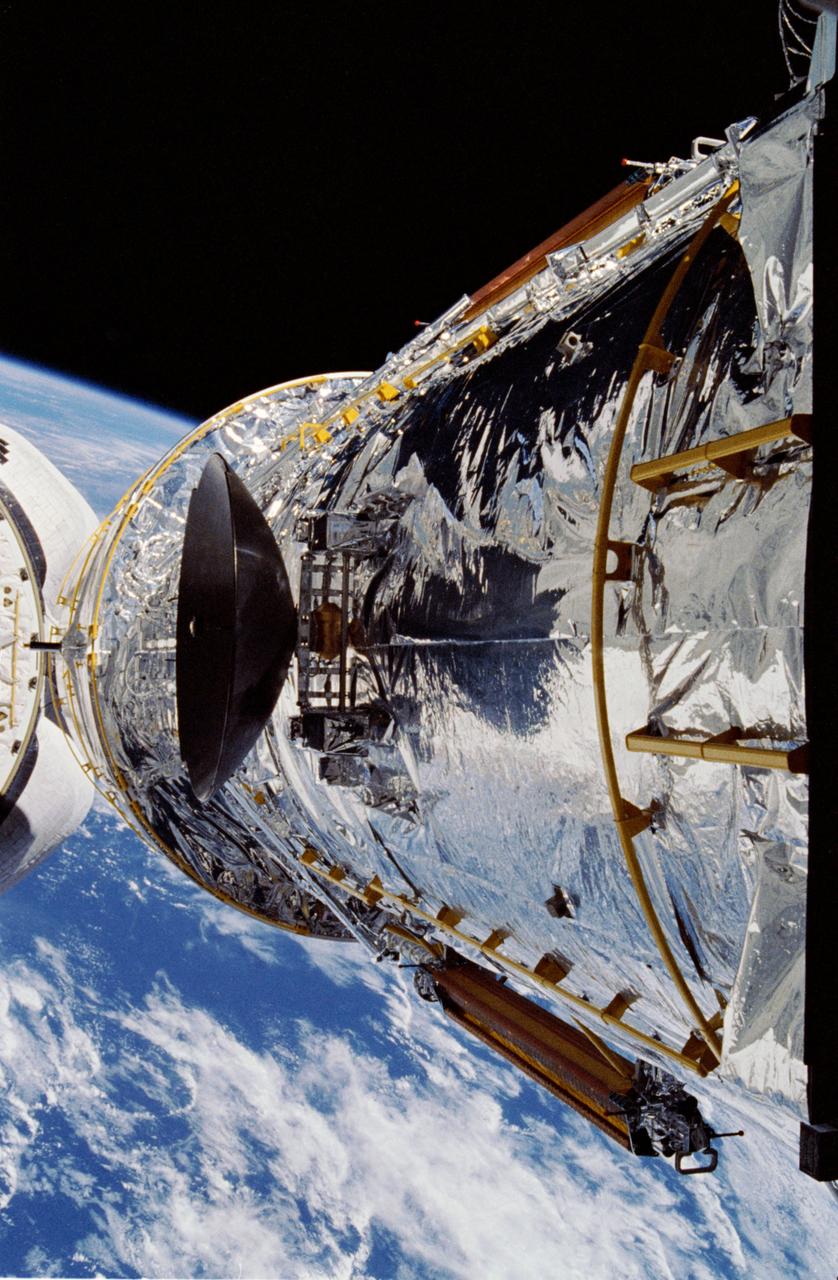
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) is raised above the payload bay (PLB) in low hover position during STS-31 checkout and pre-deployment procedures aboard Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103. Stowed along the HST Support System Module (SSM) are the high gain antenna (HGA) (center) and the two solar arrays (one either side). In the background are the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and the Earth's surface.
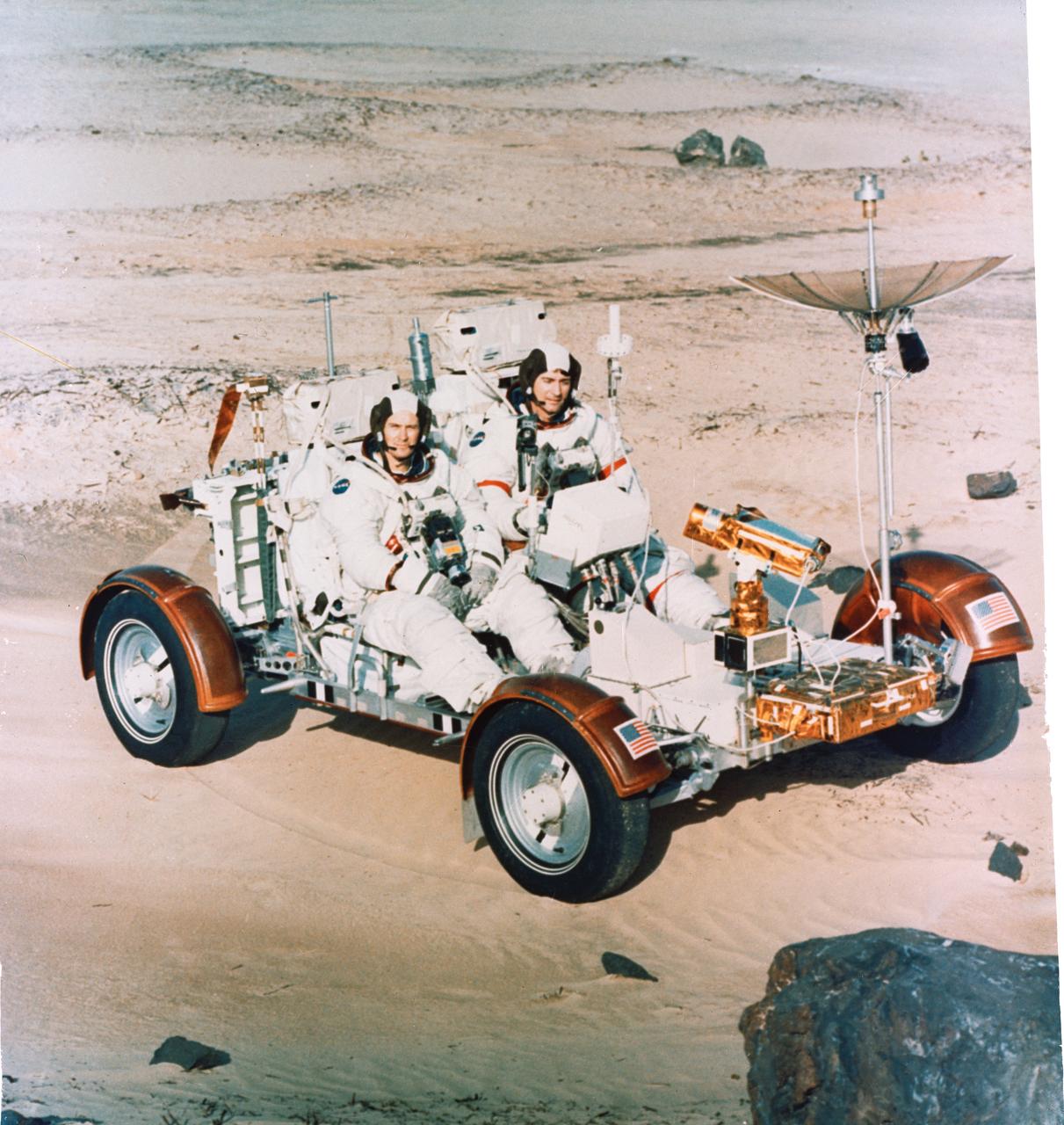

S72-30695 (22 Dec. 1971) --- Astronauts John W. Young, right, Apollo 16 commander, and Charles M. Duke Jr., lunar module pilot, maneuver a training version of the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) about a field at Kennedy Space Center (KSC) simulated to represent the lunar surface. The LRV is planned to transport the two crew men around the Descartes area on the lunar surface while astronaut Thomas K. Mattingly II, command module pilot, orbits the moon in the Command and Service Modules (CSM).
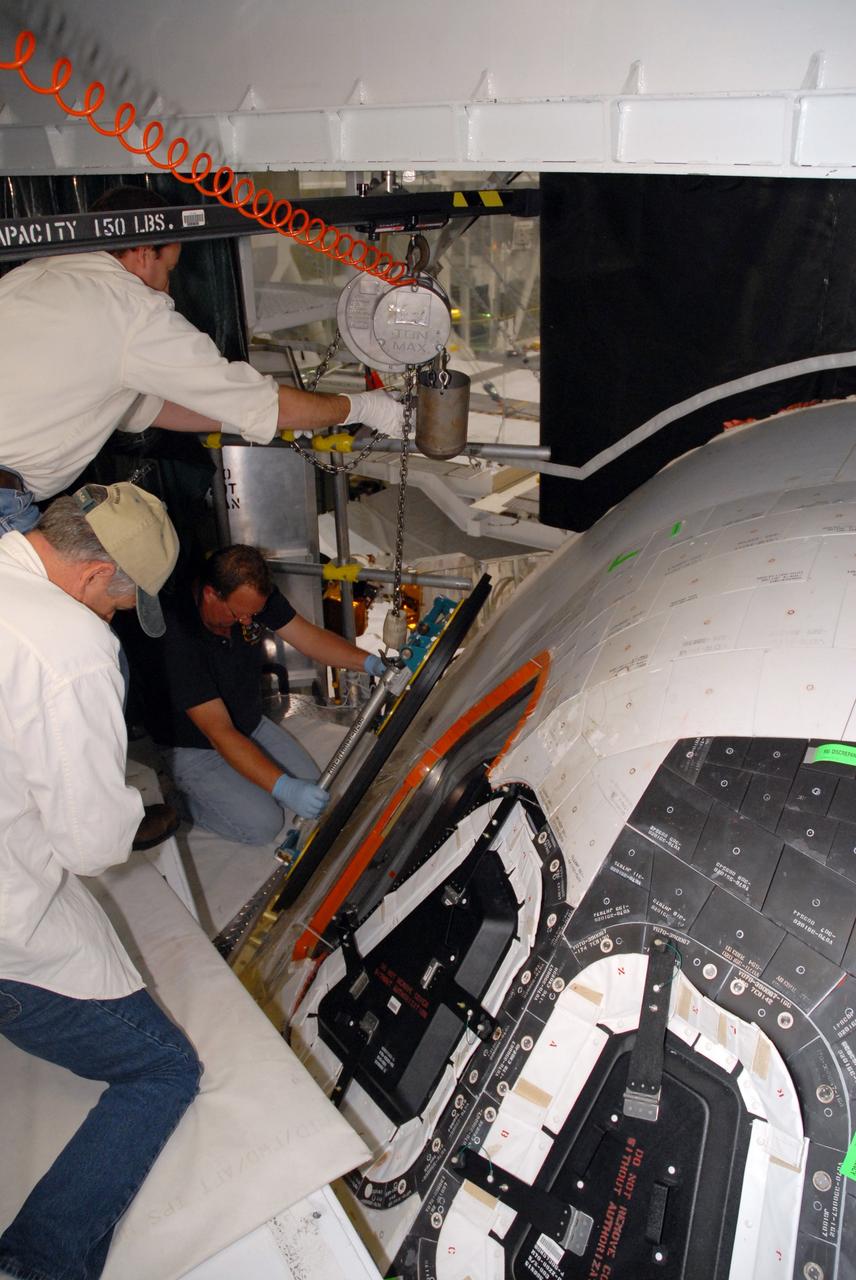

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers maneuver the new window replacing window six on space shuttle Endeavour. Endeavour is the designated launch vehicle for the STS-127 mission. The Japanese Experiment Module's Experiment Logistics Module-Exposed Section, or ELM-ES, is part of the payload on the mission, targeted for launch on May 15. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
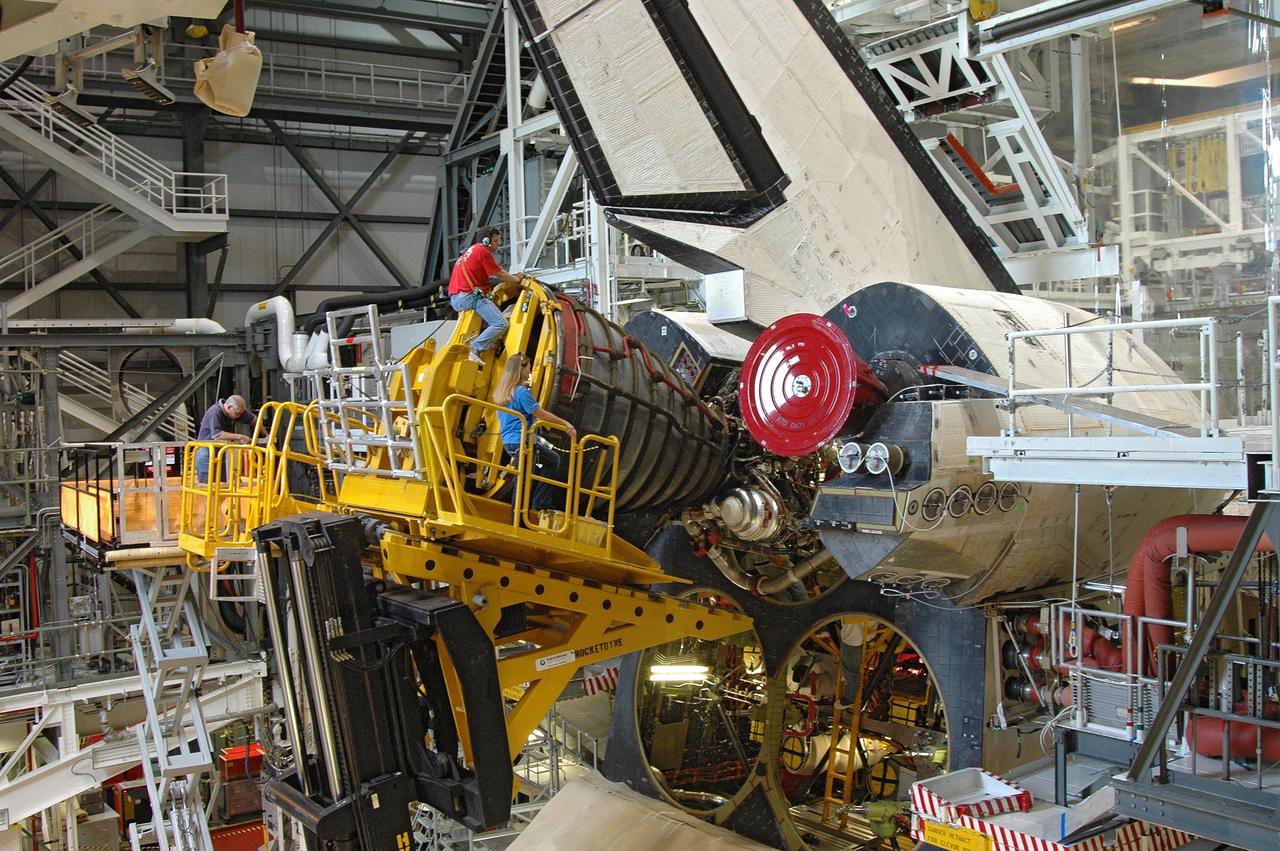

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, technicians work the engine installer to maneuver main engine 1 into place on space shuttle Endeavour. The scheduled launch vehicle for the STS-126 mission, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Endeavour is also the backup shuttle, if needed for rescue, for the STS-125 mission in October that will make repairs on the Hubble Space Telescope. For that purpose, it is designated STS-400. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
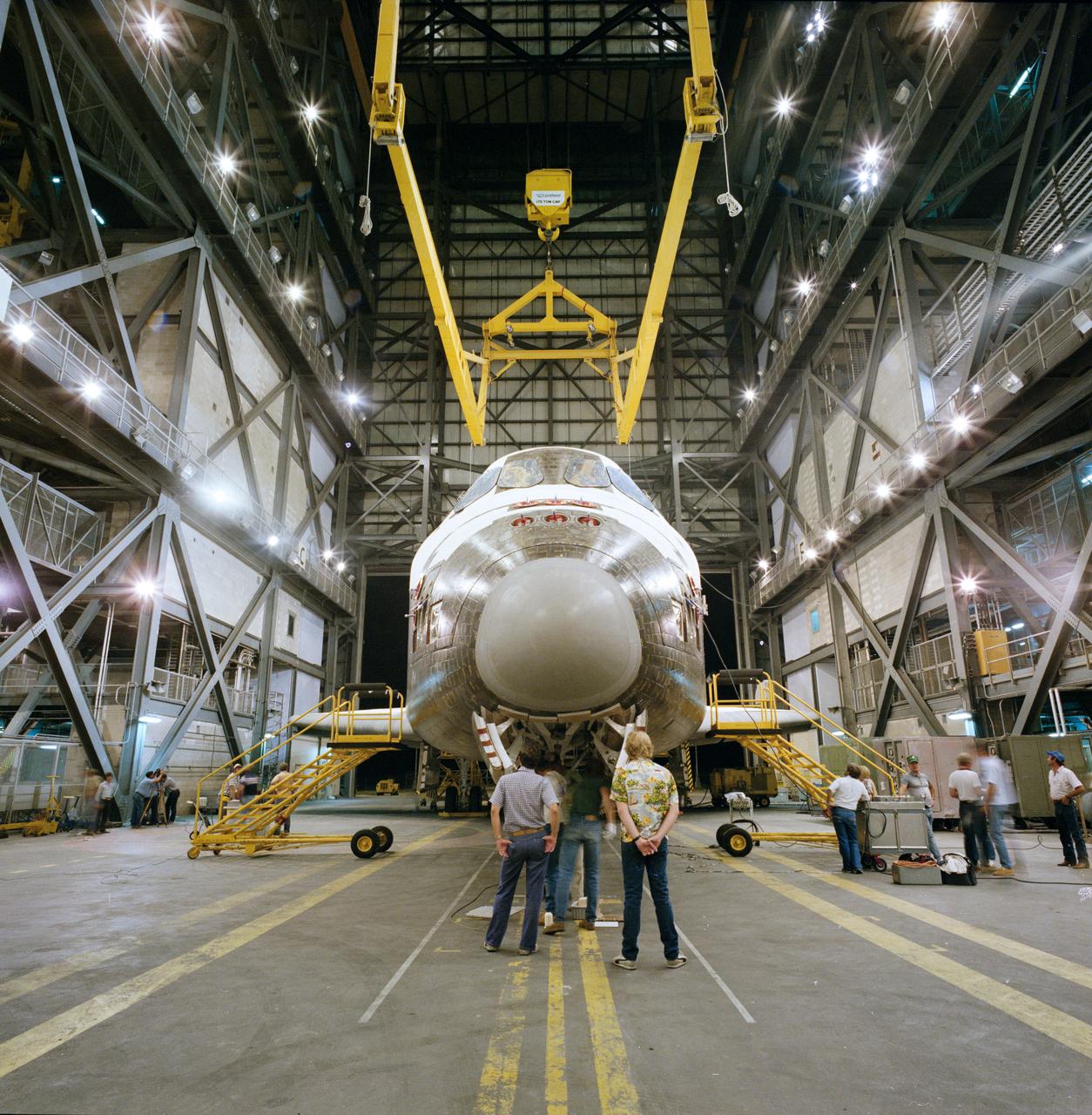

S84-35097 (May 1984) --- The Space Shuttle Orbiter 103 is about to be hoisted into a tail-toward-ground mode for mating to its two solid rocket boosters (SRB) and an external tank (ET) (awaiting the maneuver high out of frame) in the Kennedy Space Center's (KSC) huge vehicle assembly building (VAB). After its arrival here from the manufacturer in Palmdale, California, Discovery underwent extensive pre-launch preparations in the nearby processing facility (OPF).

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility bay No. 1, the technician on the engine installer moves a shuttle main engine into the opening in space shuttle Atlantis. A pitch-and-yaw system helps maneuver the engine into place. Main engine No. 1 has already been installed. Atlantis is the designated vehicle for the STS-125 mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope. Launch is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
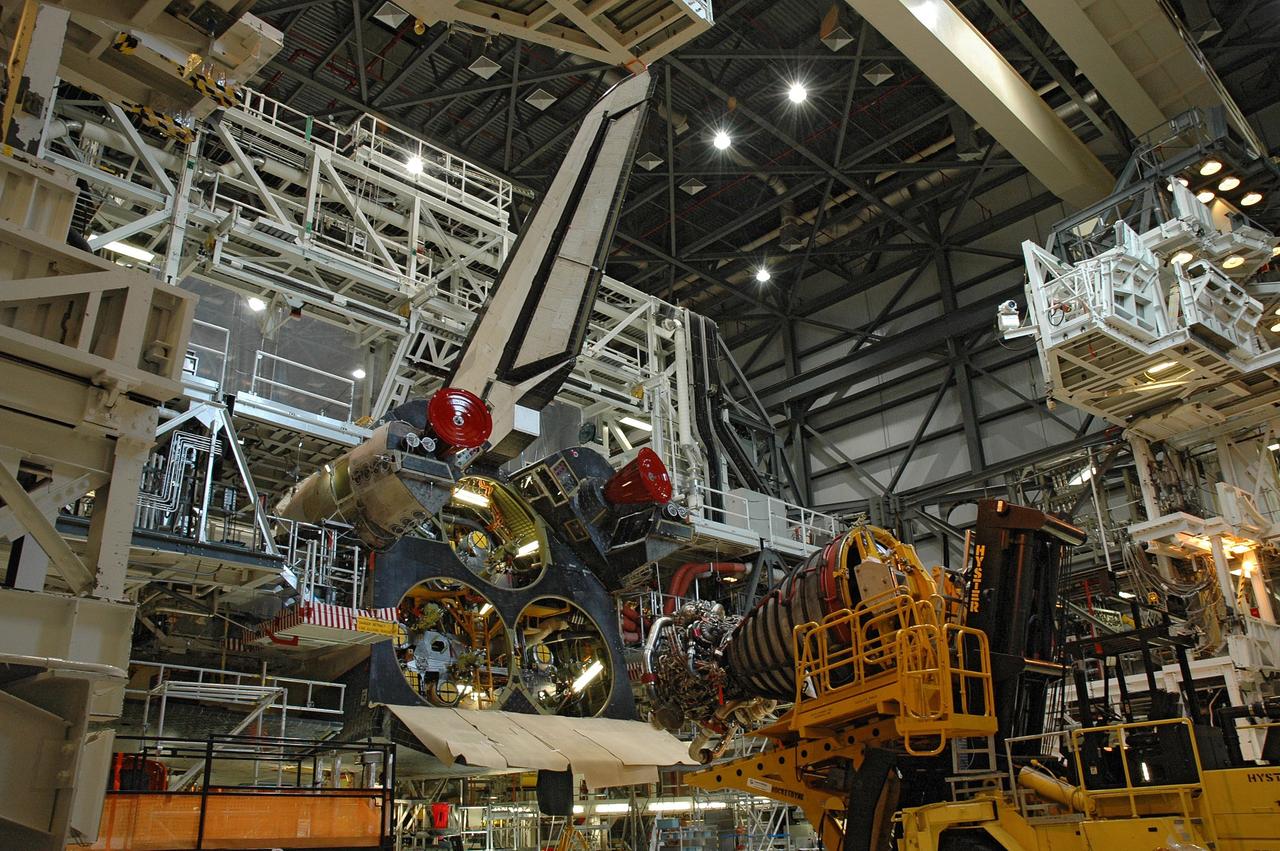

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, technicians on the Hyster forklift maneuver main engine 1 for installation on space shuttle Endeavour. The scheduled launch vehicle for the STS-126 mission, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Endeavour is also the backup shuttle, if needed for rescue, for the STS-125 mission in October that will make repairs on the Hubble Space Telescope. For that purpose, it is designated STS-400. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
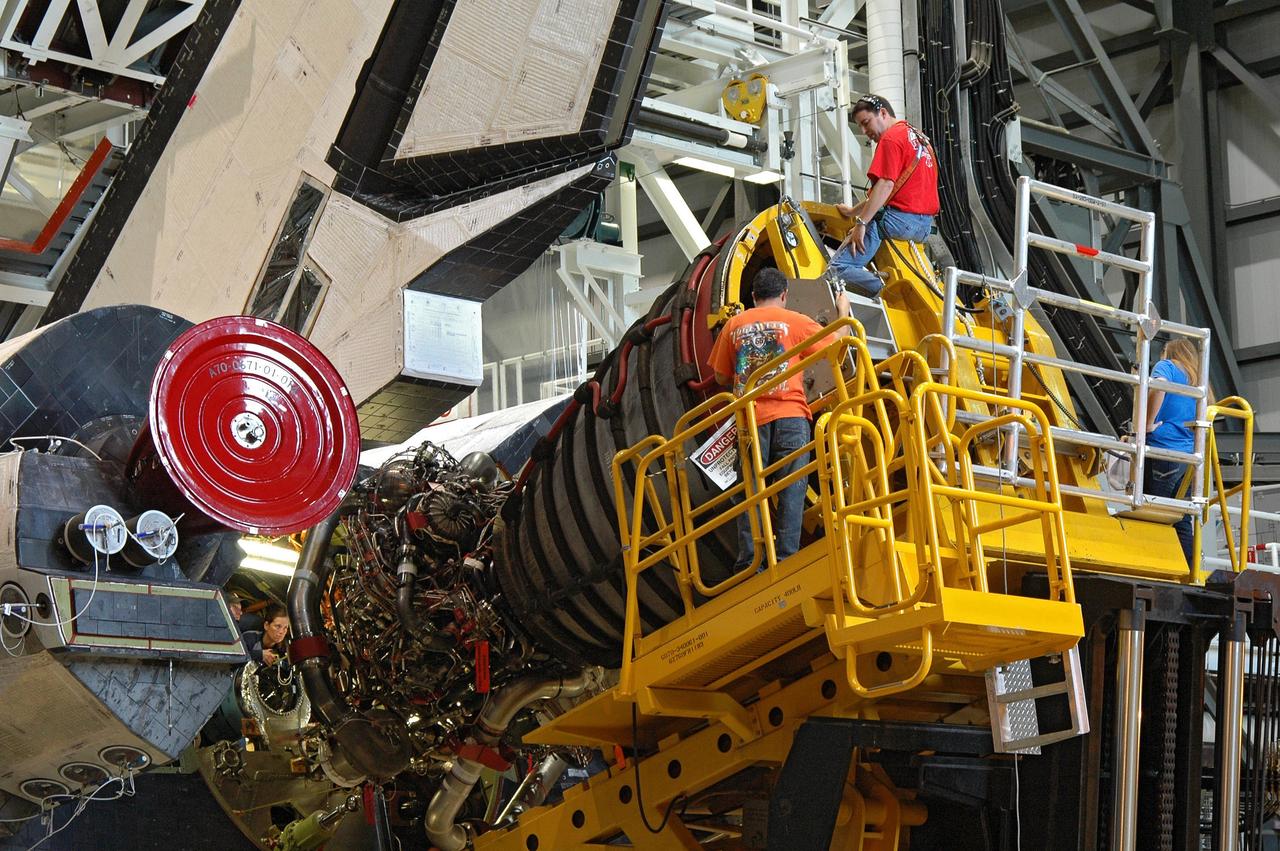

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, technicians on the Hyster forklift maneuver main engine 1 for installation on space shuttle Endeavour. The scheduled launch vehicle for the STS-126 mission, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Endeavour is also the backup shuttle, if needed for rescue, for the STS-125 mission in October that will make repairs on the Hubble Space Telescope. For that purpose, it is designated STS-400. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
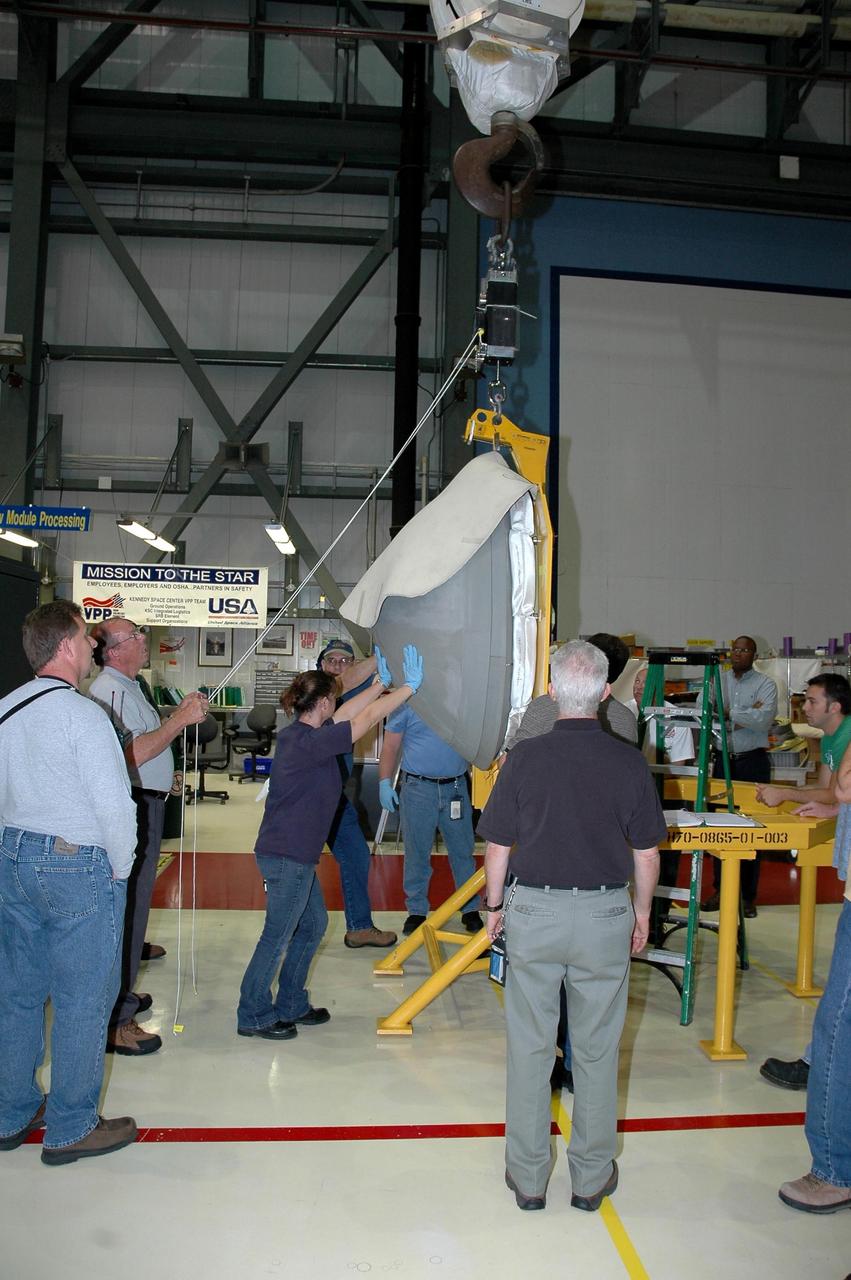

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers maneuver the reinforced carbon-carbon nose cap as it is hoisted into the air. The nose cap will be installed on Endeavour. The nose cap is insulated with thermal protection system blankets made of a woven ceramic fabric. The special blankets help insulate the vehicle's nose cap and protect it from the extreme temperatures it will face during a mission. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
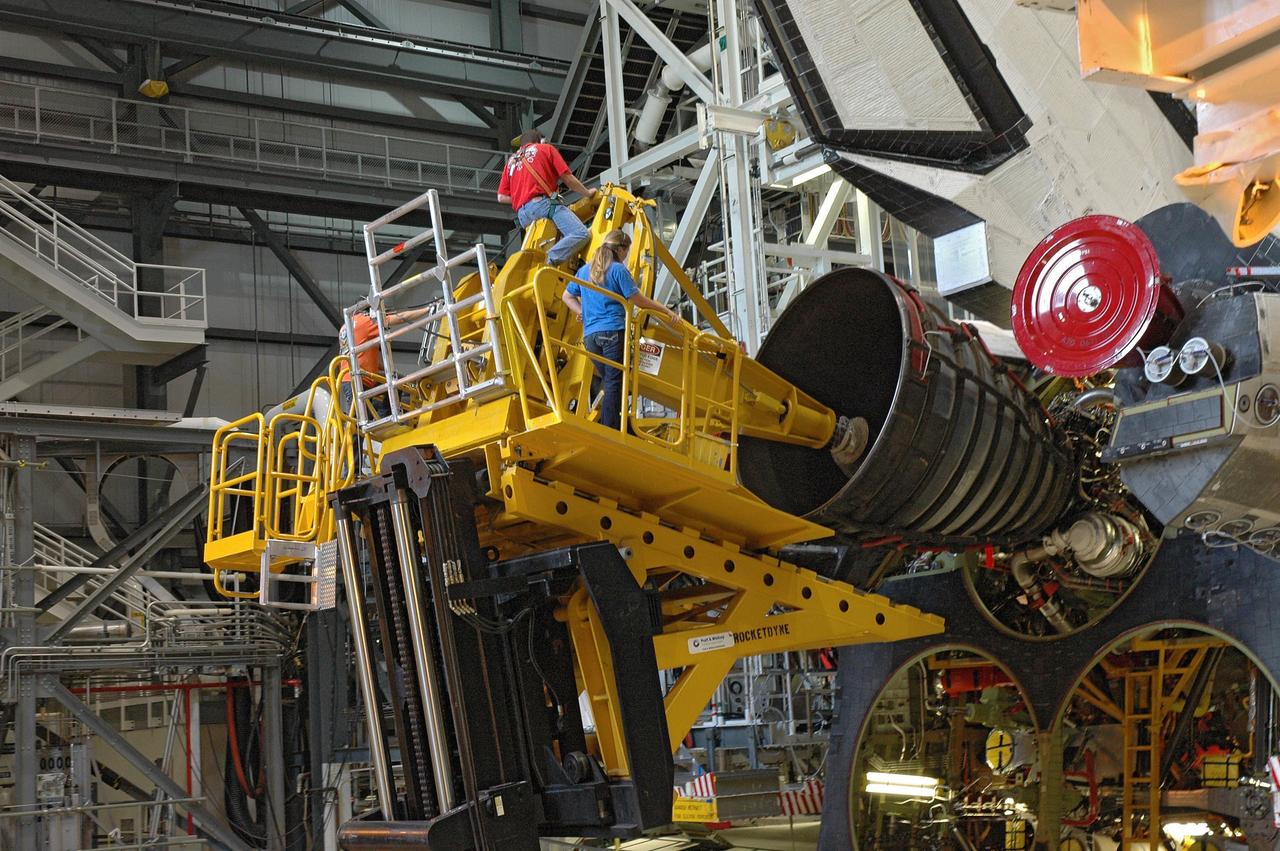

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, technicians work the engine installer to maneuver main engine 1 into place on space shuttle Endeavour. The scheduled launch vehicle for the STS-126 mission, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Endeavour is also the backup shuttle, if needed for rescue, for the STS-125 mission in October that will make repairs on the Hubble Space Telescope. For that purpose, it is designated STS-400. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
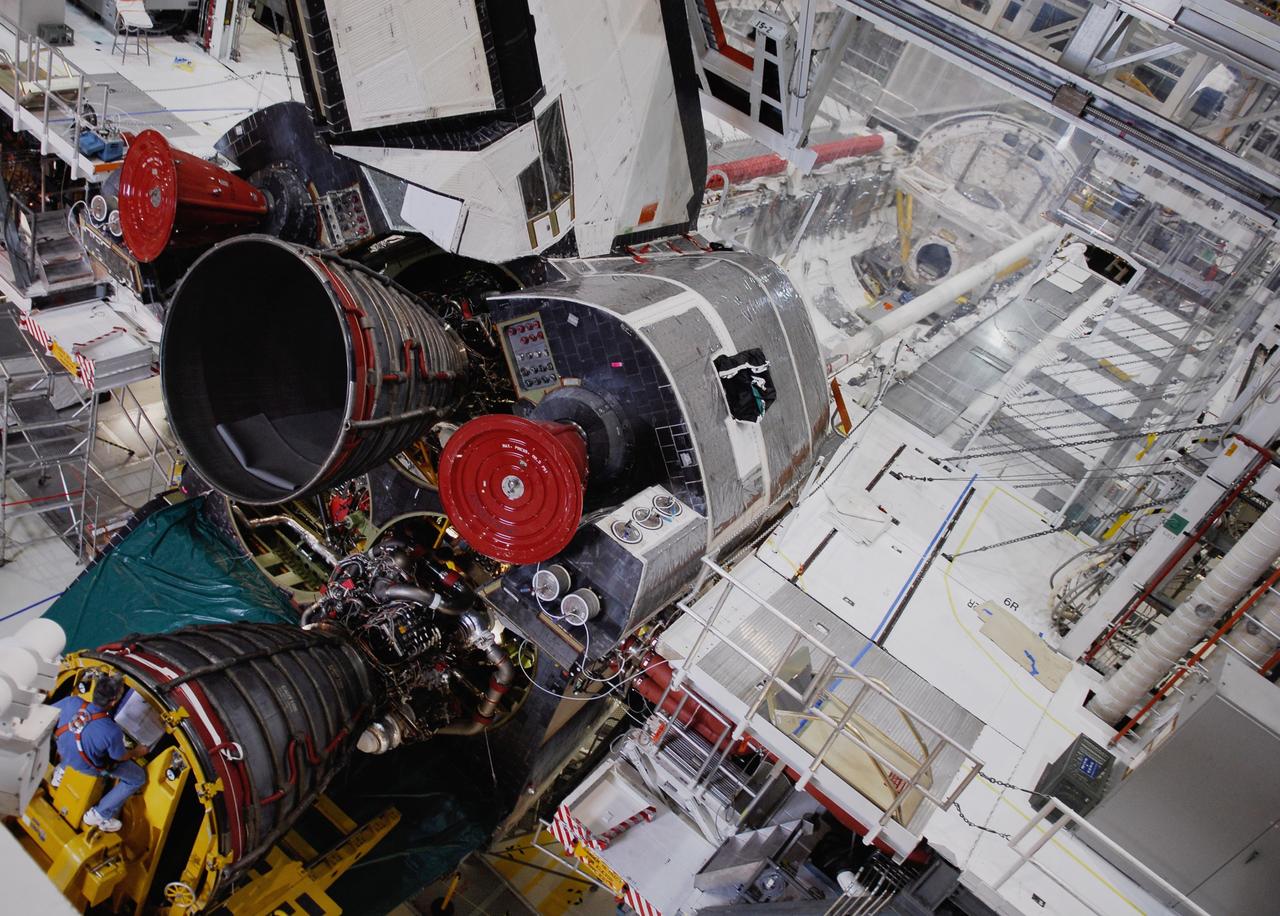
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility bay No. 1, the technician on the engine installer moves a shuttle main engine toward the opening in space shuttle Atlantis. A pitch-and-yaw system helps maneuver the engine into place. Main engine No. 1 has already been installed. Atlantis is the designated vehicle for the STS-125 mission to service the Hubble Space Telescope. Launch is targeted for Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
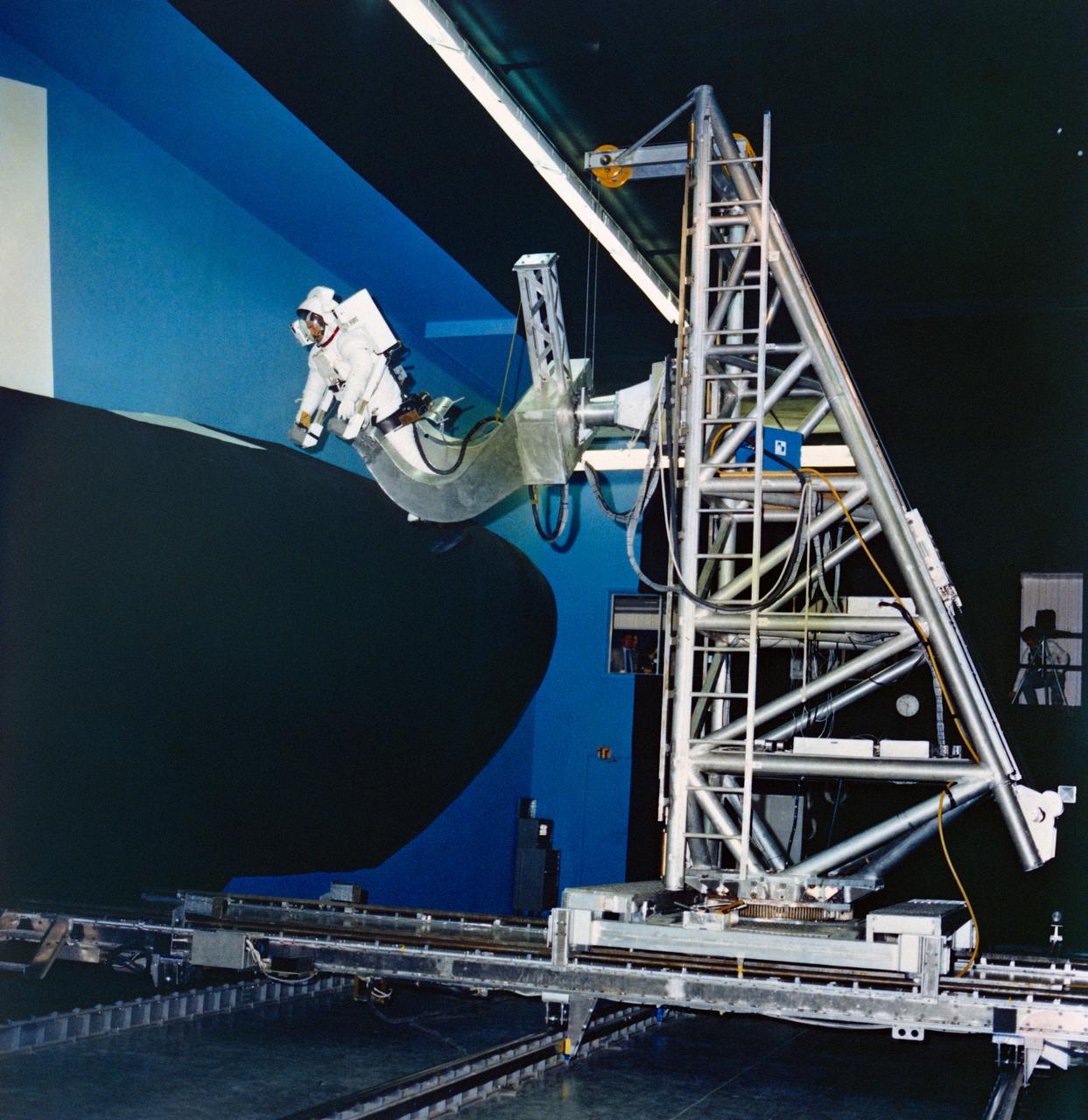

S80-36889 (24 July 1980) --- Astronaut Bruce McCandless II uses a simulator at Martin Marietta?s space center near Denver to develop flight techniques for a backpack propulsion unit that will be used on Space Shuttle flights. The manned maneuvering unit (MMU) training simulator allows astronauts to "fly missions" against a full scale mockup of a portion of the orbiter vehicle. Controls of the simulator are like those of the actual MMU. Manipulating them allows the astronaut to move in three straight-line directions and in pitch, yaw and roll. One possible application of the MMU is for an extravehicular activity chore to repair damaged tiles on the vehicle. McCandless is wearing an extravehicular mobility unit (EMU).
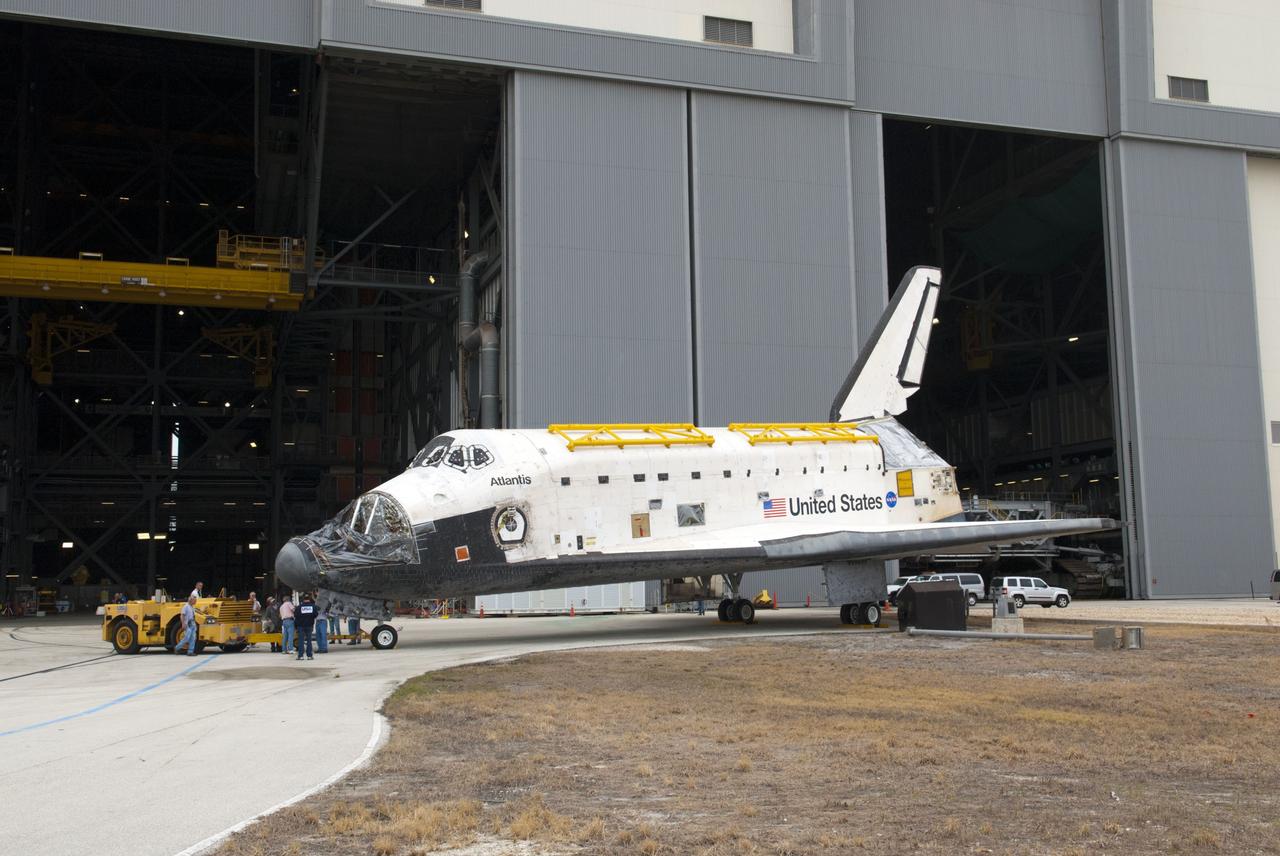

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis is being towed from the Vehicle Assembly Building over to Orbiter Processing Facility-1. Atlantis’ forward reaction control system, orbiter maneuvering system pods and three space shuttle main engines have been removed. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the three space shuttles. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex and is scheduled to rollover to the complex in November. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
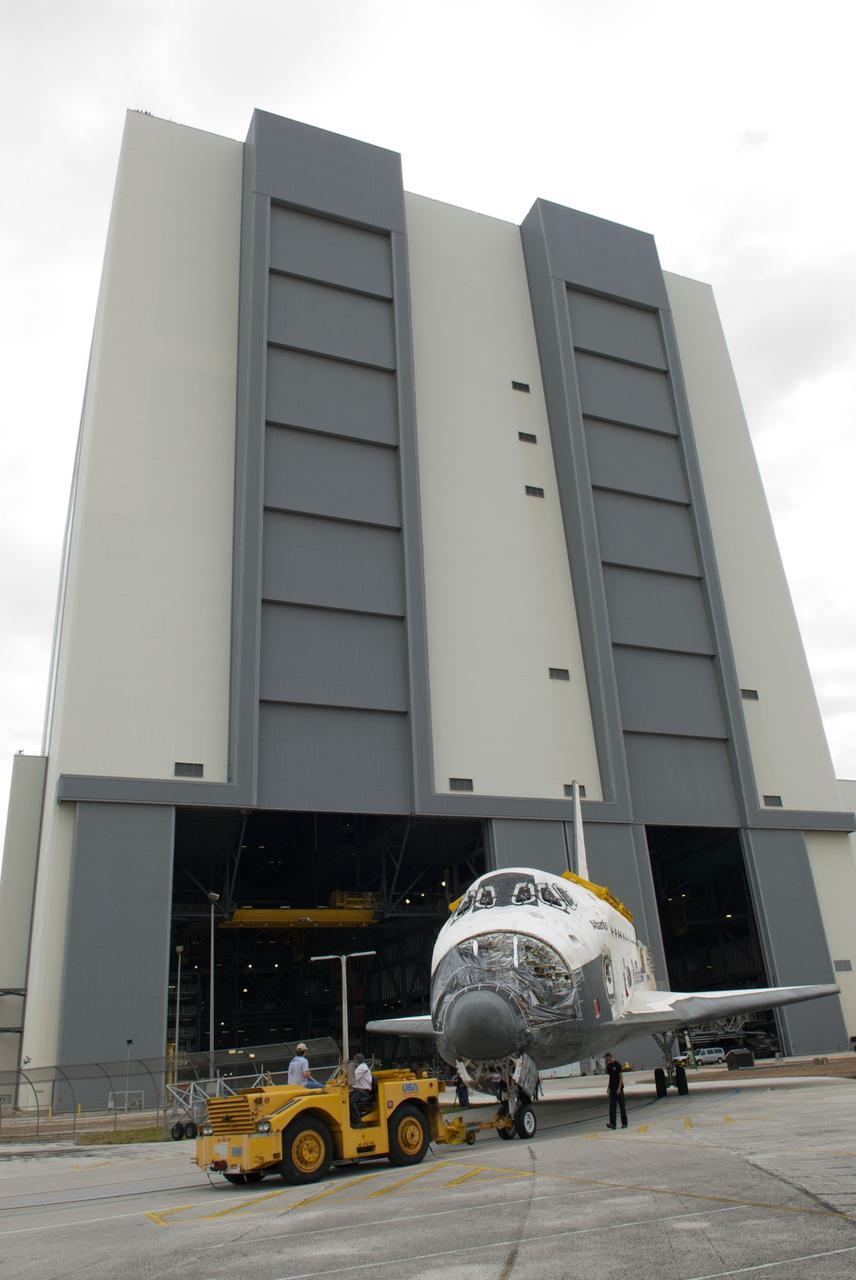

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis is towed out of the Vehicle Assembly Building and over to Orbiter Processing Facility-1. Atlantis’ forward reaction control system, orbiter maneuvering system pods and three space shuttle main engines have been removed. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the three space shuttles. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex and is scheduled to rollover to the complex in November. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
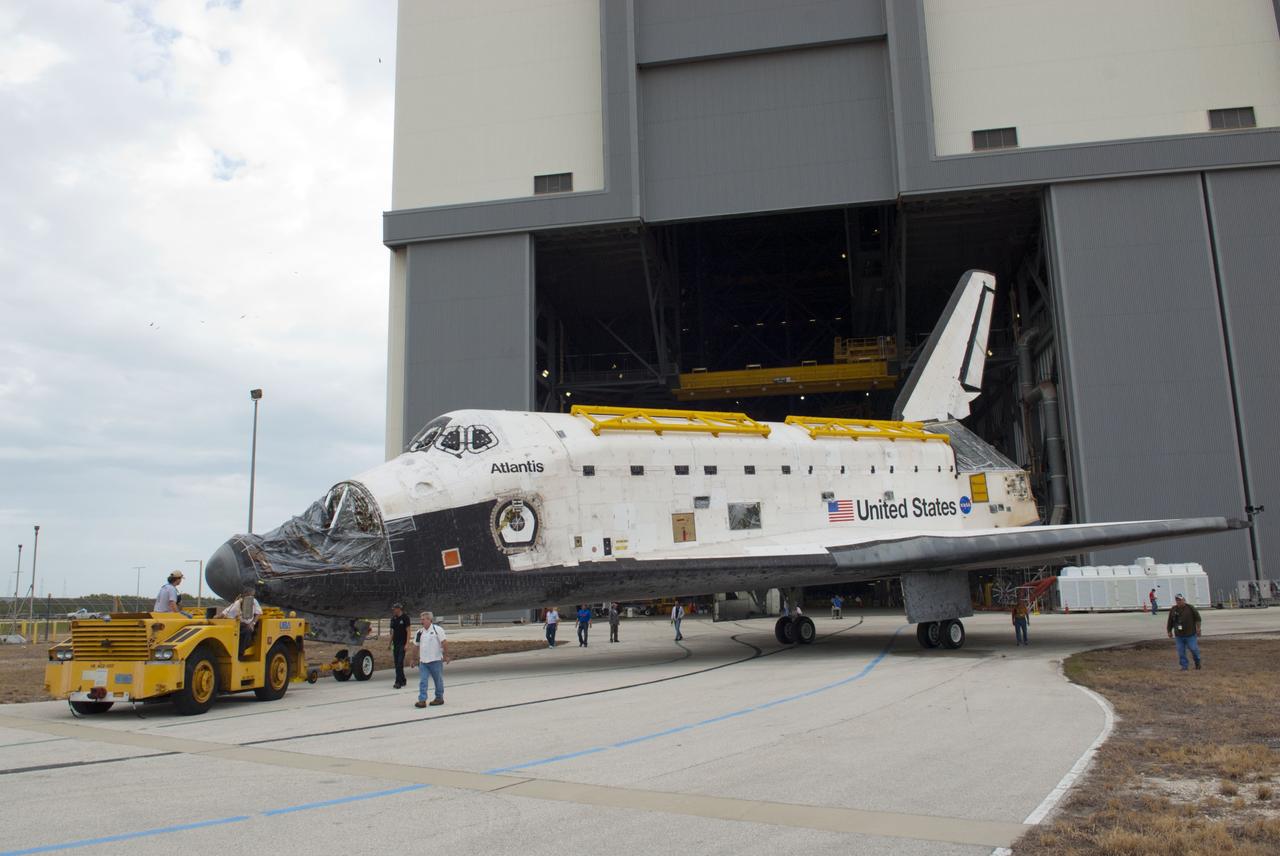

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers walk alongside as space shuttle Atlantis is towed out of the Vehicle Assembly Building and over to Orbiter Processing Facility-1. Atlantis’ forward reaction control system, orbiter maneuvering system pods and three space shuttle main engines have been removed. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the three space shuttles. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex and is scheduled to rollover to the complex in November. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
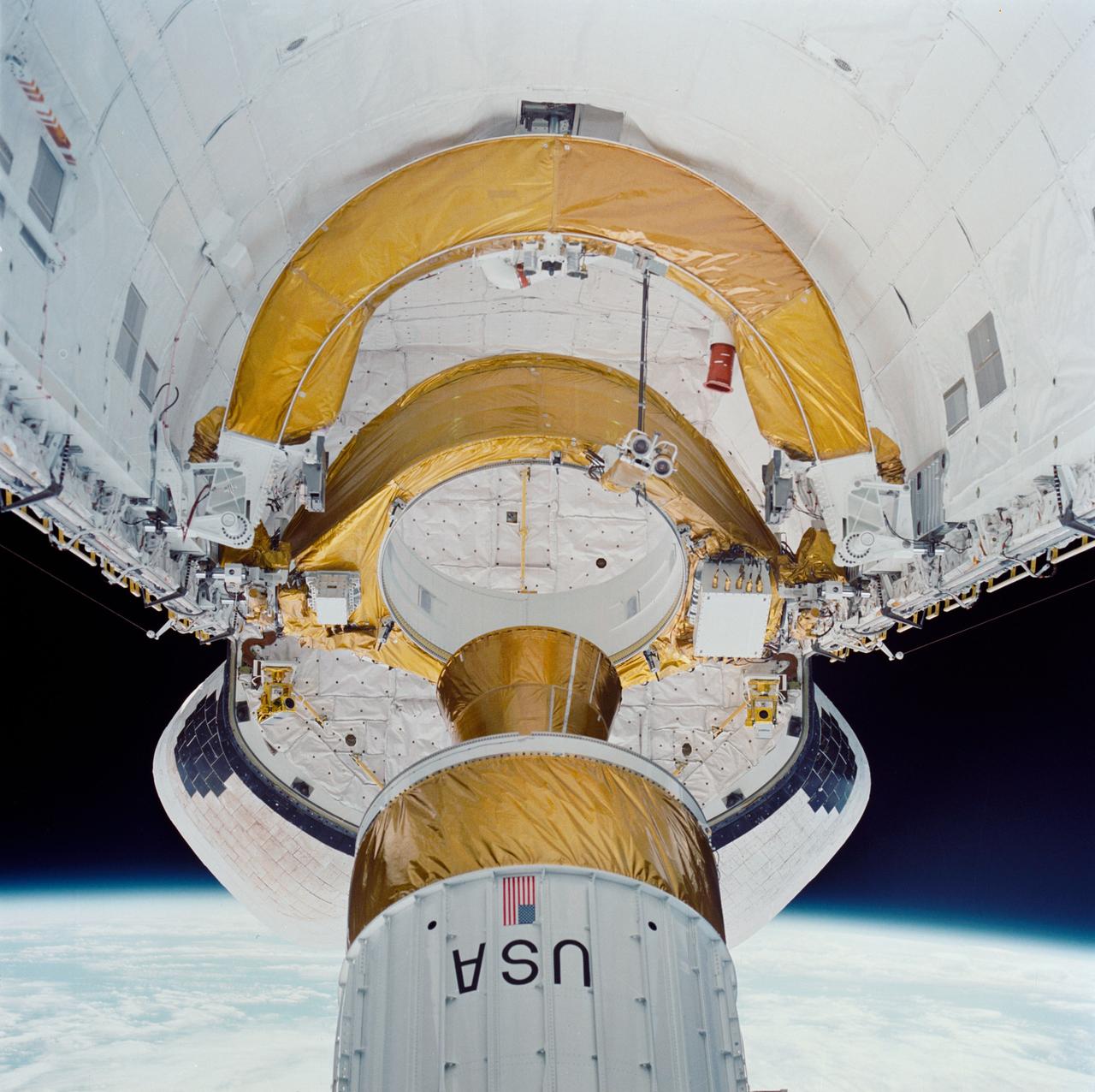

During STS-26, inertial upper stage (IUS) with the tracking and data relay satellite C (TDRS-C) drifts above Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, payload bay (PLB) after being positioned in deployment attitude (an angle of 50 degrees) by the airborne support equipment (ASE). IUS vacates the ASE aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA) table in the PLB while the disconnected ASE umbilical boom floats above ASE forward cradle. IUS first stage rocket motor and nozzle and the interstage are visible as the IUS is deployed. In the background are the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and the Earth's limb.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Lights inside the Vehicle Assembly Building cast an orange glow on Space Shuttle Discovery as waits on top of the Mobile Launcher Platform for rollout to Launch Pad 39B. Rollout is expected to begin about 12:01 a.m. June 15 for the 4-mile, 6-hour trip to the pad. On either side of Discovery’s tail and orbital maneuvering system pods are the Tail Masts that support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Space Shuttle Discovery's Return to Flight mission STS-114 is scheduled for liftoff in a window extending from July 13 to July 31.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis is being towed from the Vehicle Assembly Building over to Orbiter Processing Facility-1. Atlantis’ forward reaction control system, orbiter maneuvering system pods and three space shuttle main engines have been removed. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the three space shuttles. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex and is scheduled to rollover to the complex in November. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
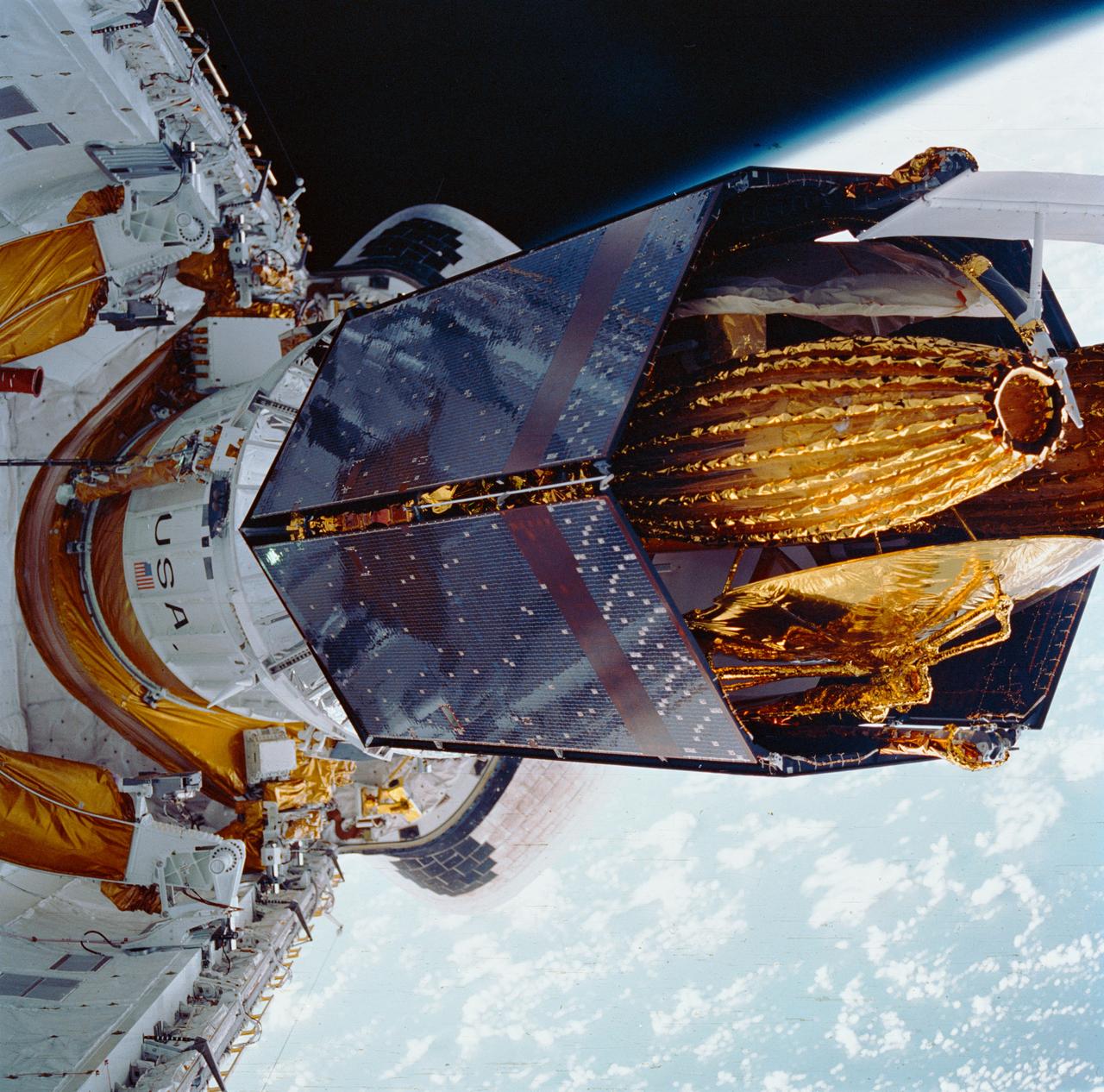

During STS-26, inertial upper stage (IUS) with tracking and data relay satellite C (TDRS-C) located in the payload bay (PLB) of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is positioned into its proper deployment attitude (an angle of 50 degrees) by the airborne support equipment (ASE). In the foreground, the ASE forward cradle is visible. The IUS is mounted in the ASE aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA) table. TDRS-C components in stowed configuration include solar array panels, TDRS single access #1 and #2, TDRS SGL, and S-Band omni antenna. In the background are the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods, the Earth's cloud-covered surface, and the Earth's limb.
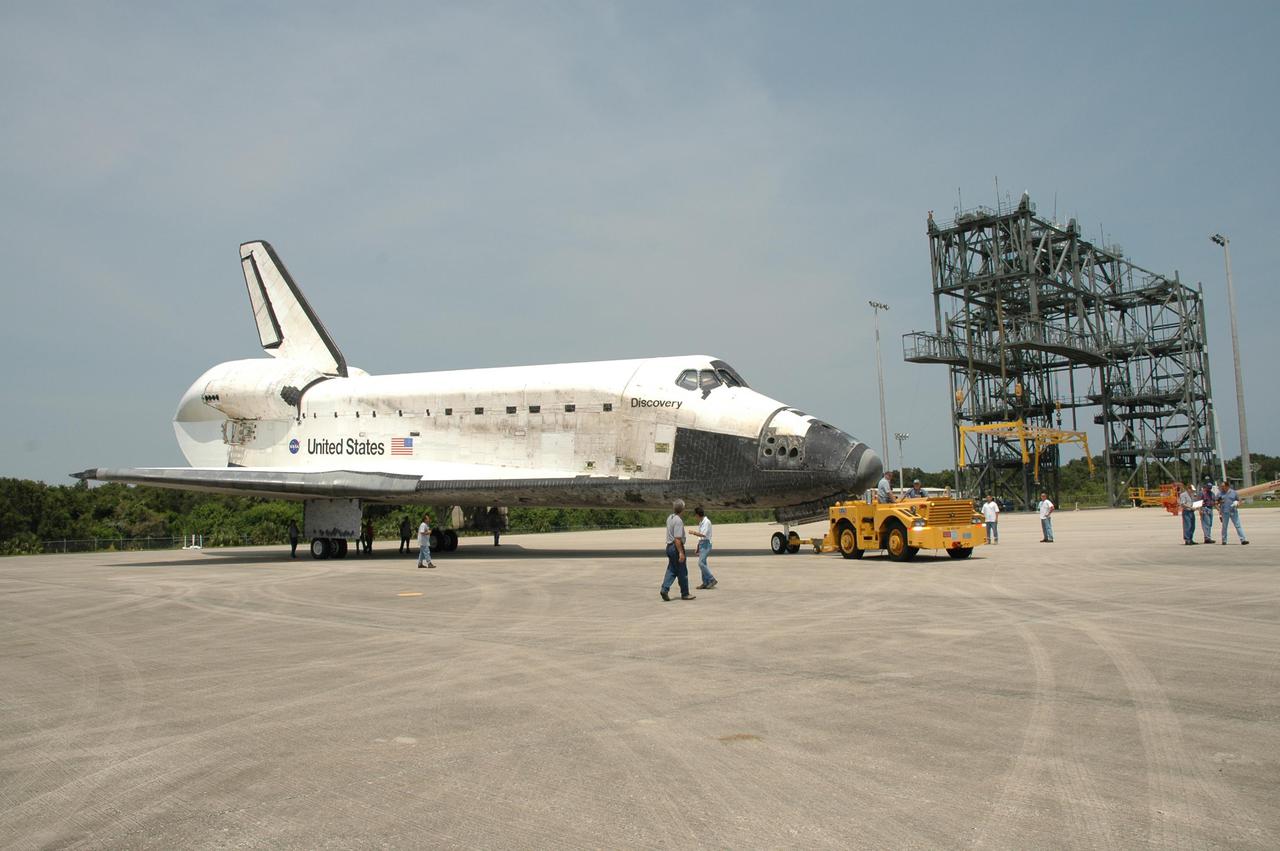

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - A tow vehicle maneuvers Discovery on NASA Kennedy Space Center’s Shuttle Landing Facility into a position for towing. Discovery was returned to NASA Kennedy Space Center on a ferry flight atop the Shuttle Carrier Aircraft (SCA) from Edwards Air Force Base in California, arriving Aug. 21. Discovery will be towed to the Orbiter Processing Facility where the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Raffaello still inside will be removed from the payload bay and transferred to the Space Station Processing Facility. The orbiter will then begin processing for the second Return to Flight mission, STS-121, scheduled for launch no earlier than March 2006.
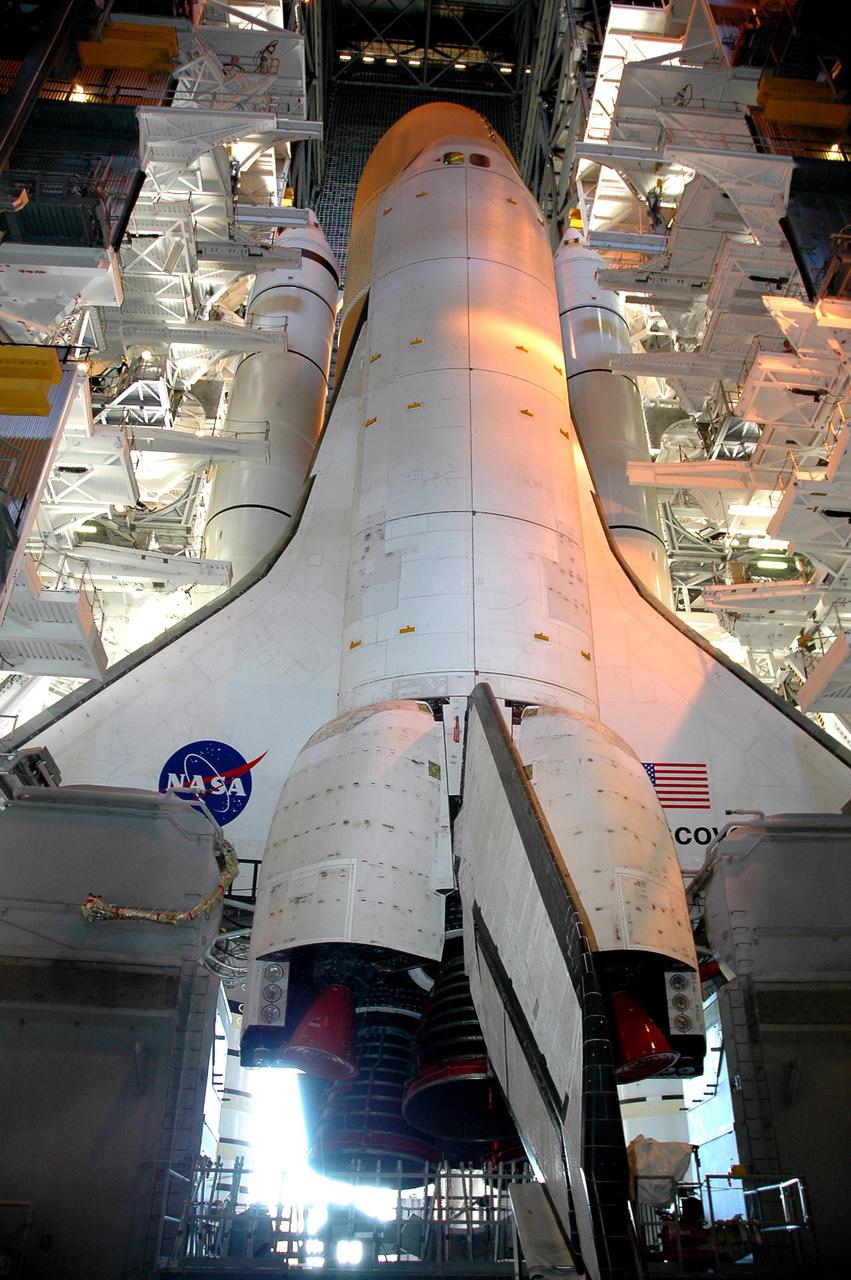

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Framed in lights both inside and from outside, Space Shuttle Discovery waits on top of the Mobile Launcher Platform in the Vehicle Assembly Building for rollout to Launch Pad 39B. Rollout is expected to begin about 12:01 a.m. June 15 for the 4-mile, 6-hour trip to the pad. On either side of Discovery’s tail and orbital maneuvering system pods are the Tail Masts that support the fluid, gas and electrical requirements of the orbiter’s liquid oxygen and liquid hydrogen aft T-0 umbilicals. Space Shuttle Discovery's Return to Flight mission STS-114 is scheduled for liftoff in a window extending from July 13 to July 31.
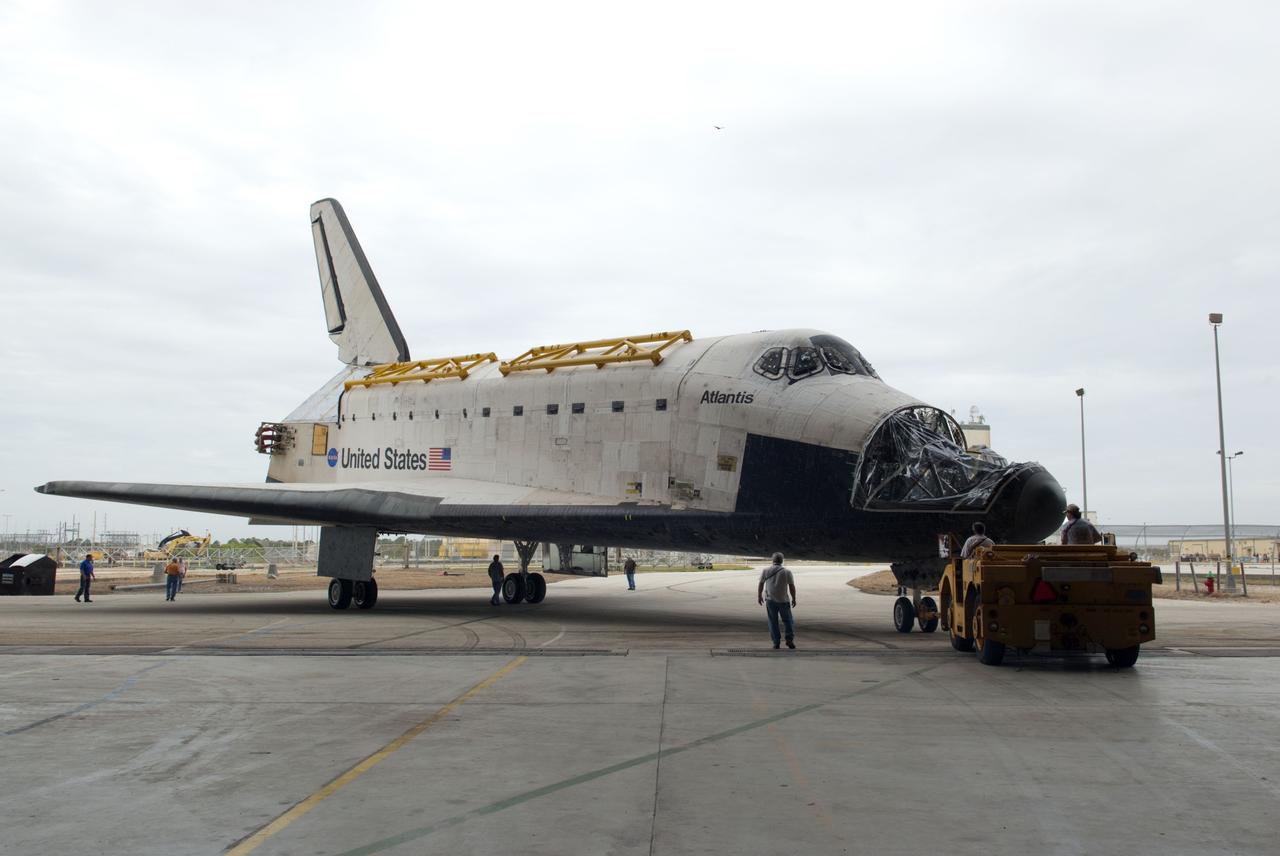

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Atlantis is being towed from the Vehicle Assembly Building over to Orbiter Processing Facility-1. Atlantis’ forward reaction control system, orbiter maneuvering system pods and three space shuttle main engines have been removed. The work is part of the Space Shuttle Program’s transition and retirement processing of the three space shuttles. Atlantis is being prepared for display at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex and is scheduled to rollover to the complex in November. Photo credit: NASA/Tim Jacobs
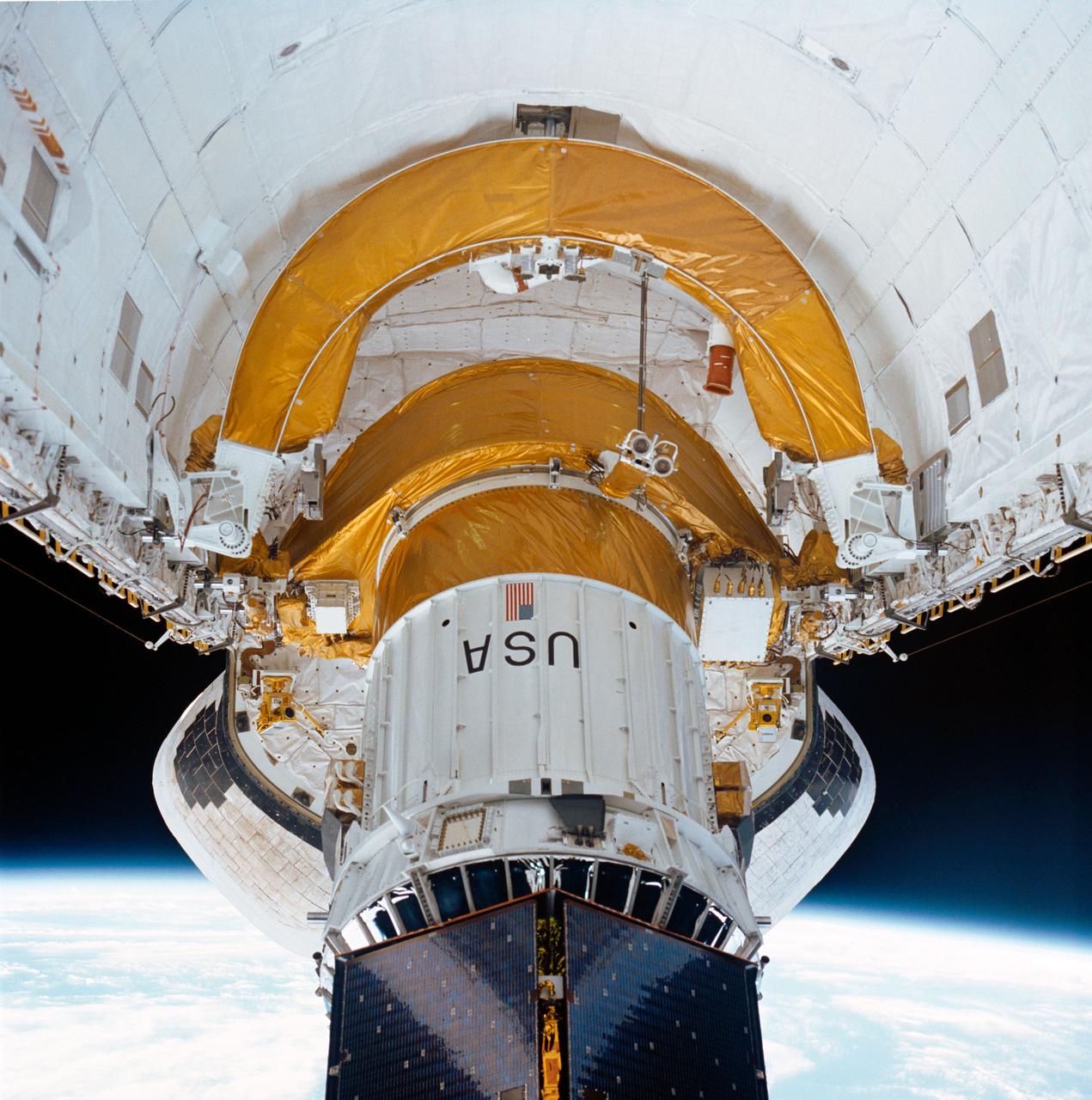

During STS-26, inertial upper stage (IUS) with the tracking and data relay satellite C (TDRS-C) located in the payload bay (PLB) of Discovery, Orbiter Vehicle (OV) 103, is raised into deployment attitude (an angle of 50 degrees) by the airborne support equipment (ASE). ASE aft frame tilt actuator (AFTA) table supports the IUS as it is positioned in the PLB and the ASE umbilical boom drifts away from IUS toward ASE forward cradle. TDRS-C solar array panels (in stowed configuration) are visible on top of the IUS. In the background are the orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods and the Earth's limb.
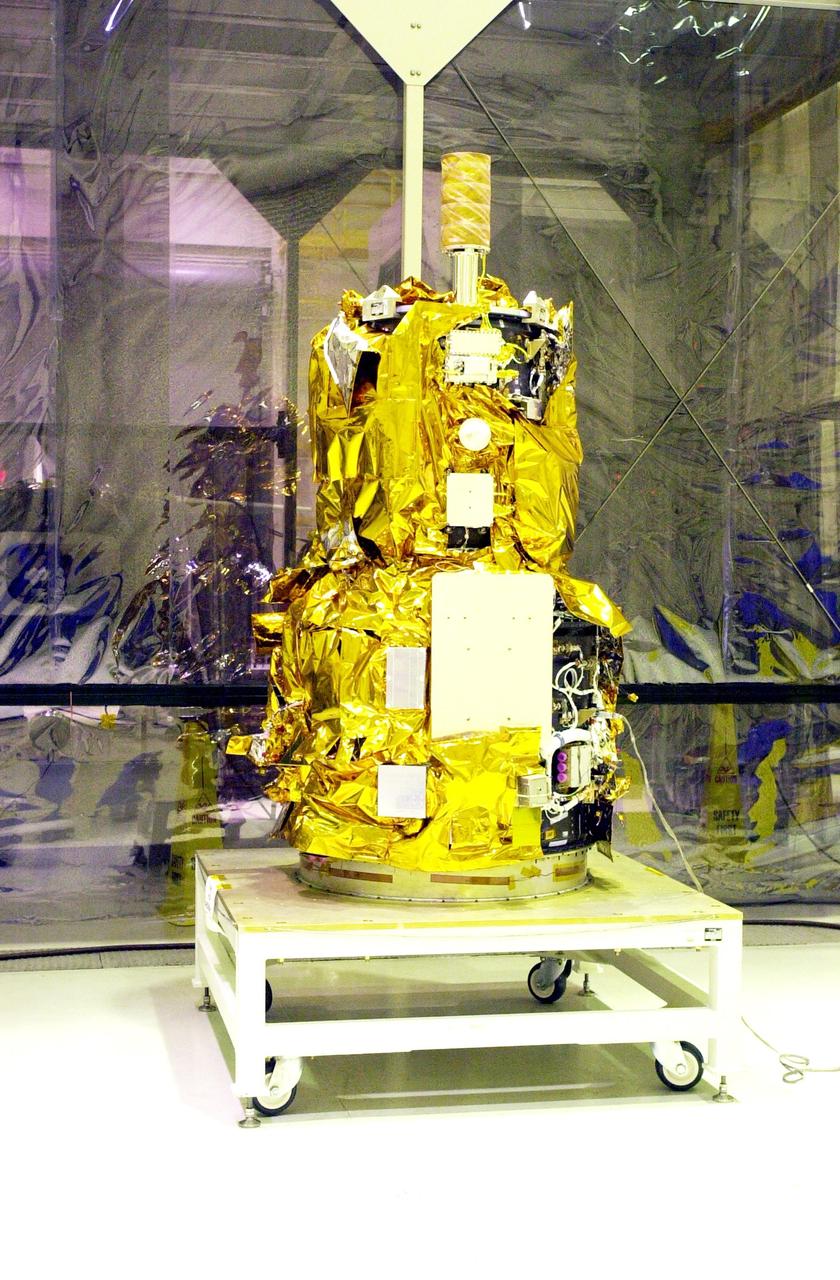

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft is on a work stand waiting for processing activities. The spacecraft was developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. DART will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.
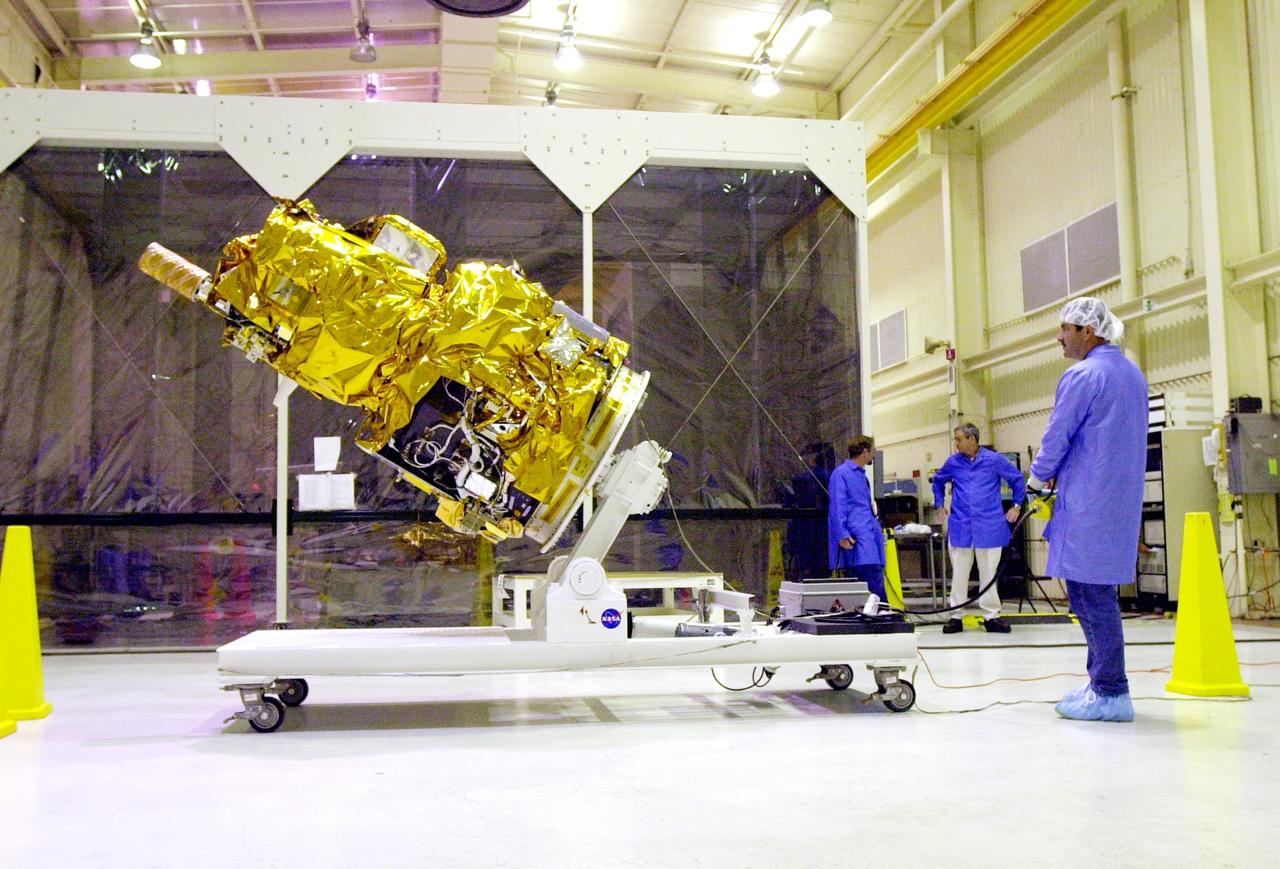

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft is raised to a vertical position. It will be lifted onto a test stand for launch processing activities. The spacecraft was developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. DART will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.
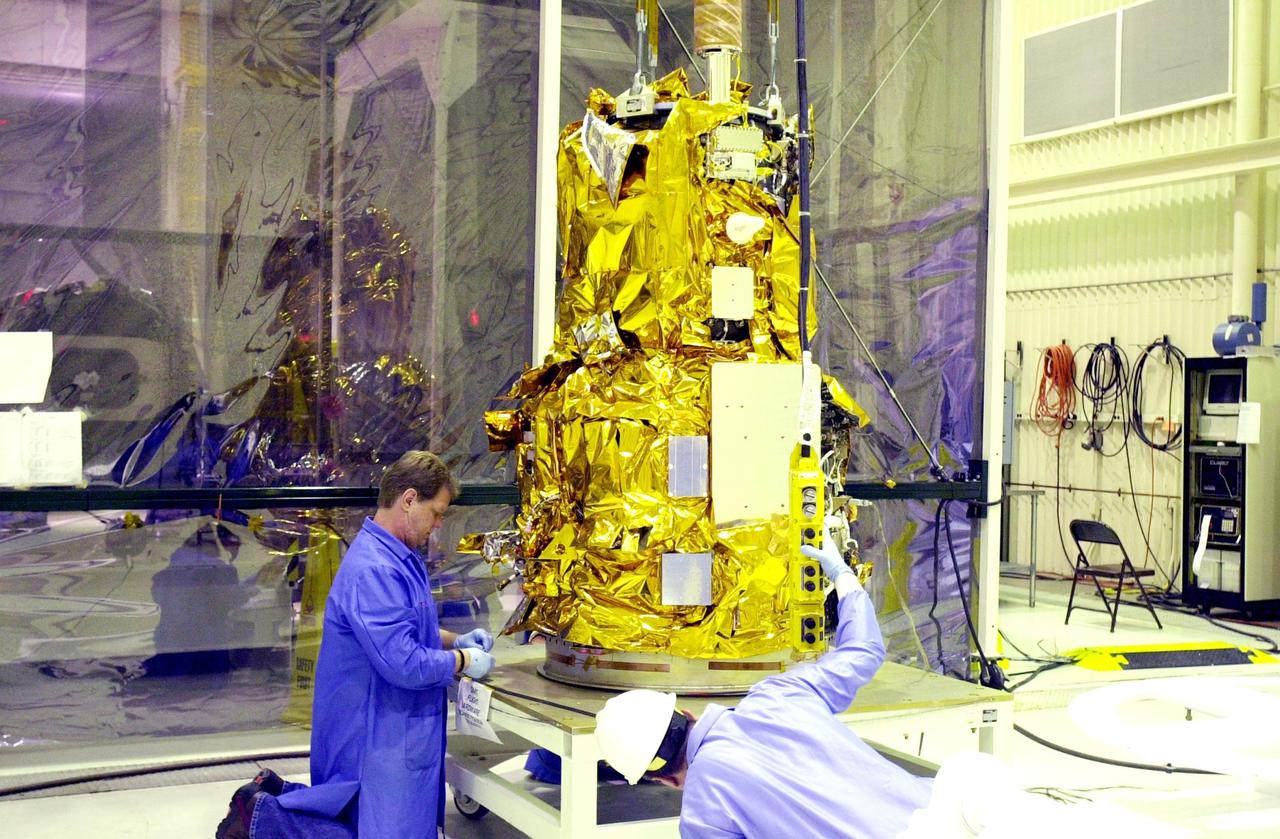

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft is placed on a work stand for processing activities. The spacecraft was developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. DART will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft is raised to a vertical position. It will be lifted onto a test stand for launch processing activities. The spacecraft was developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. DART will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences Corporation technicians get ready to attach the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and Orbital Sciences Pegasus launch vehicle, mated earlier, to the Stargazer L-1011 aircraft above. The Pegasus XL will launch DART at approximately 40,000 feet above the Pacific Ocean into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
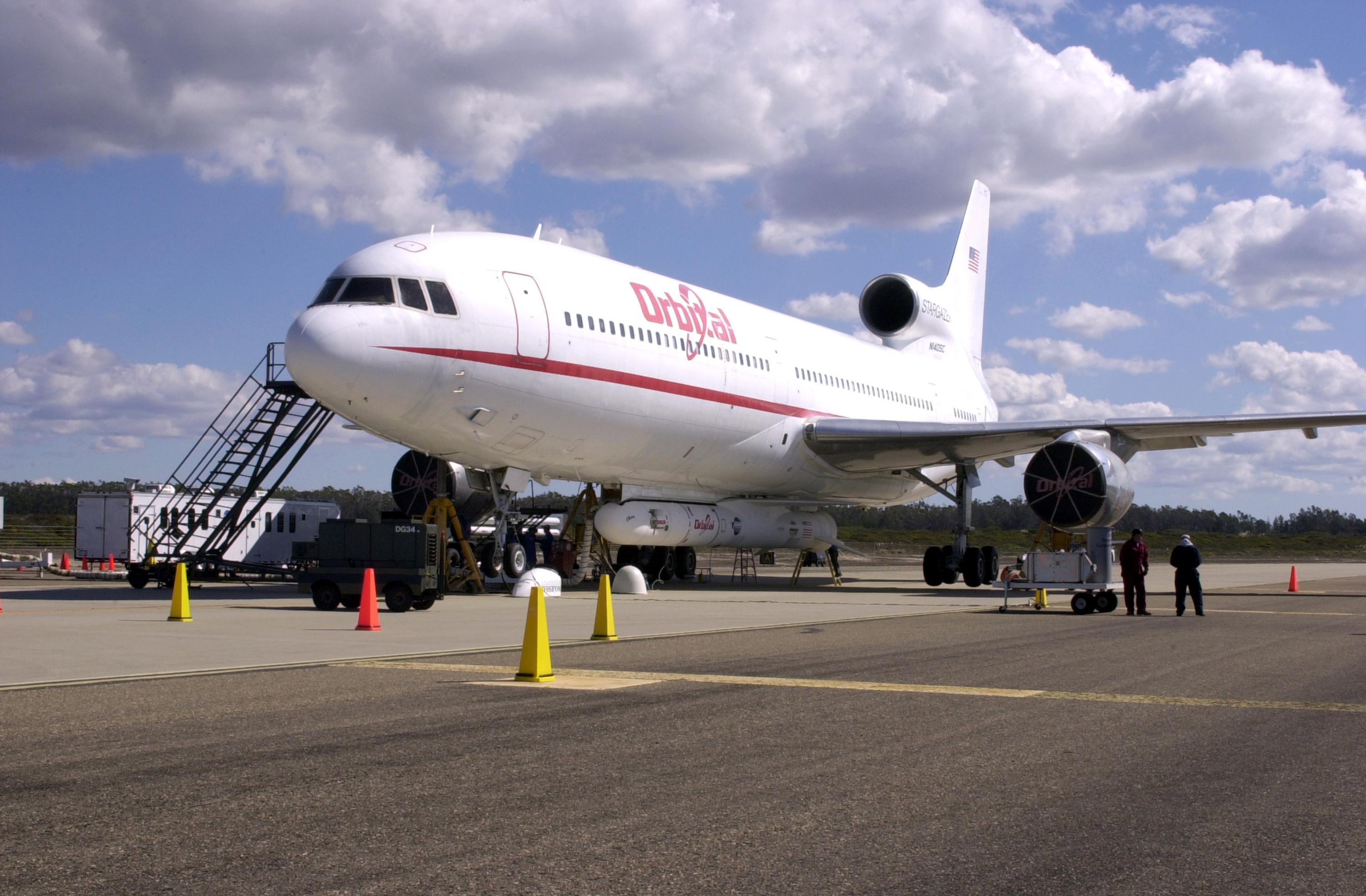

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences Corporation’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft is ready for flight with the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and Orbital Sciences Pegasus launch vehicle attached underneath. The Pegasus XL will launch DART at approximately 40,000 feet above the Pacific Ocean into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) is encapsulated and ready to be moved to the runway where it will be attached to the Orbital Sciences Corporation Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
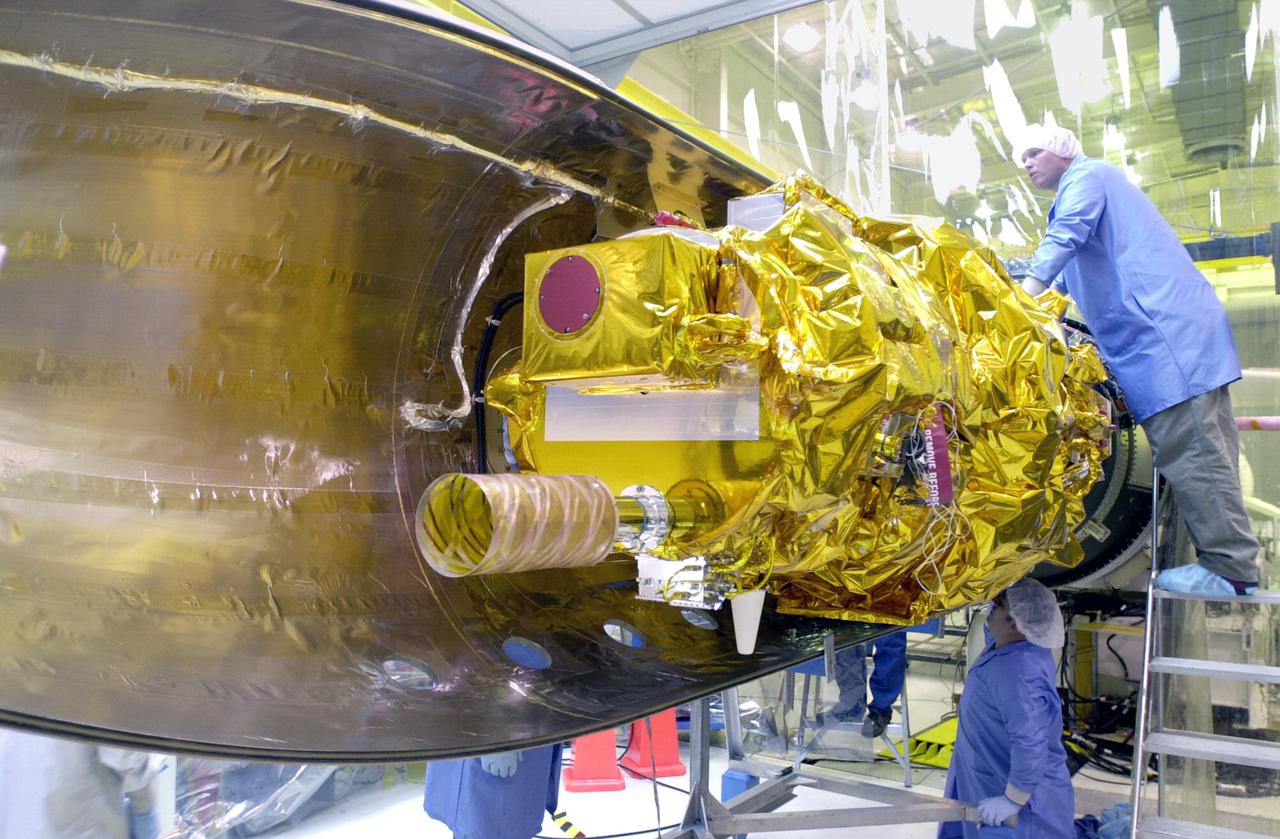

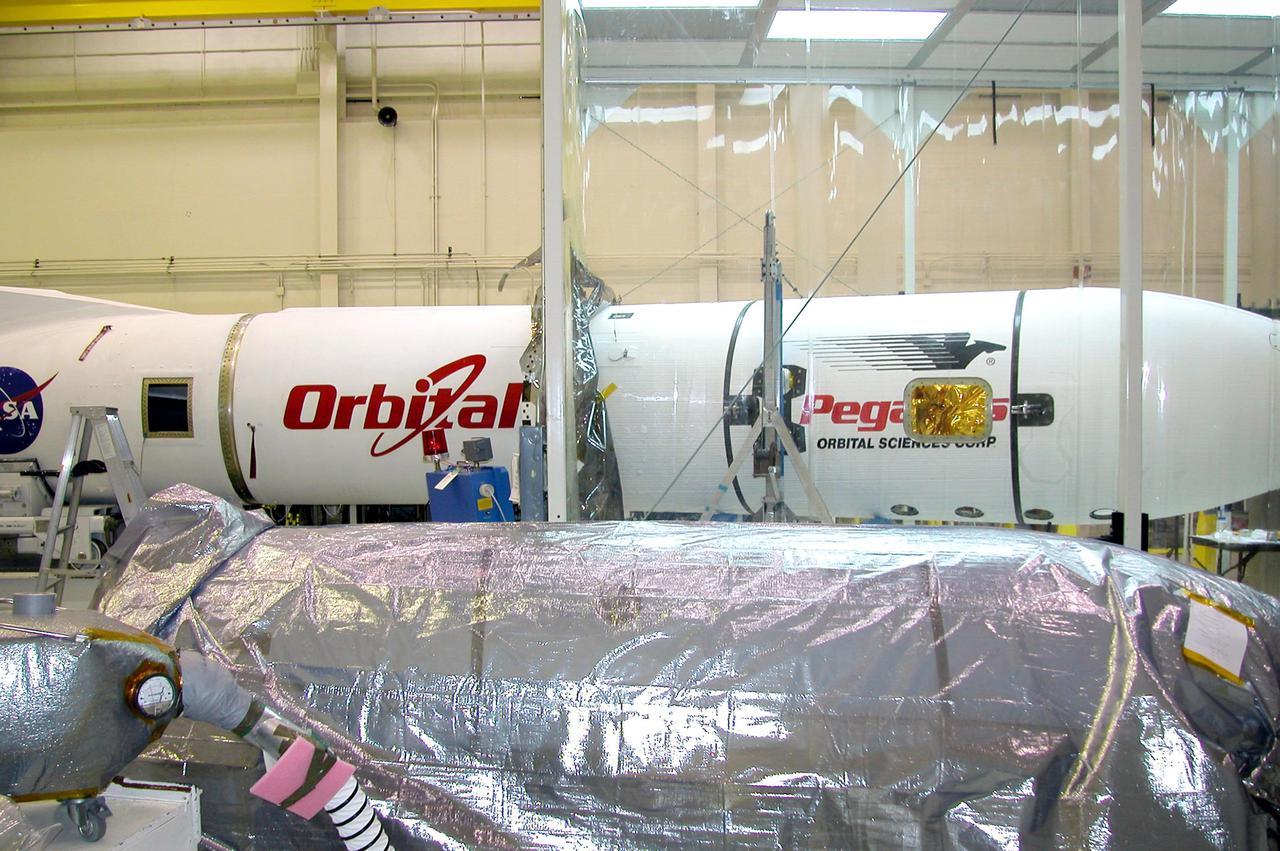
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In preparation for launch, Orbital Sciences Corporation technicians at Vandenberg AFB in California check the placement of the first fairing half around the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. The fairing will encapsulate DART and protect it while on the launch pad and during ascent. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
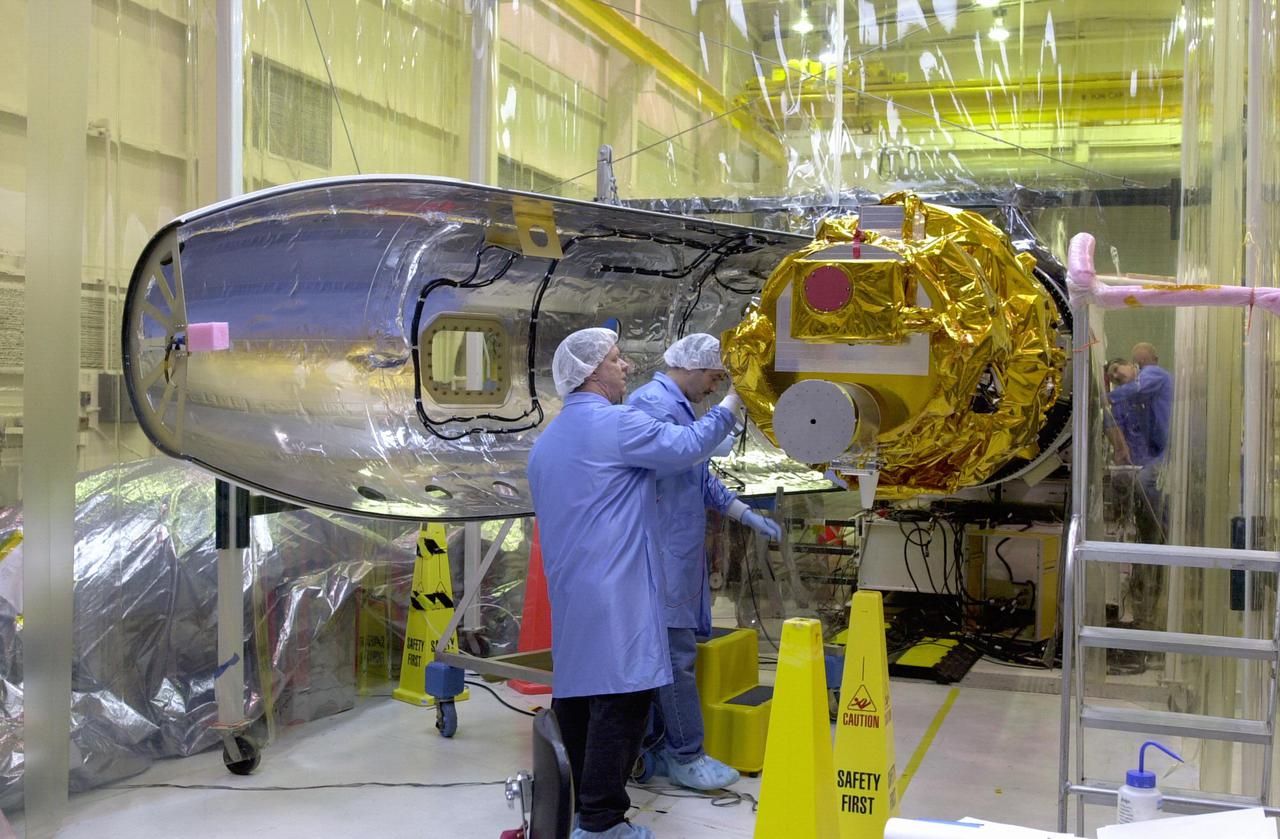

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In preparation for launch, Orbital Sciences Corporation technicians at Vandenberg AFB in California get ready to place the first fairing half around the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft. The fairing will encapsulate DART and protect it while on the launch pad and during ascent. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) is mated to the belly of the Orbital Sciences Corporation Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences Corporation technicians complete attachment of the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and Orbital Sciences Pegasus launch vehicle, to the Stargazer L-1011 aircraft above. The Pegasus XL will launch DART at approximately 40,000 feet above the Pacific Ocean into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
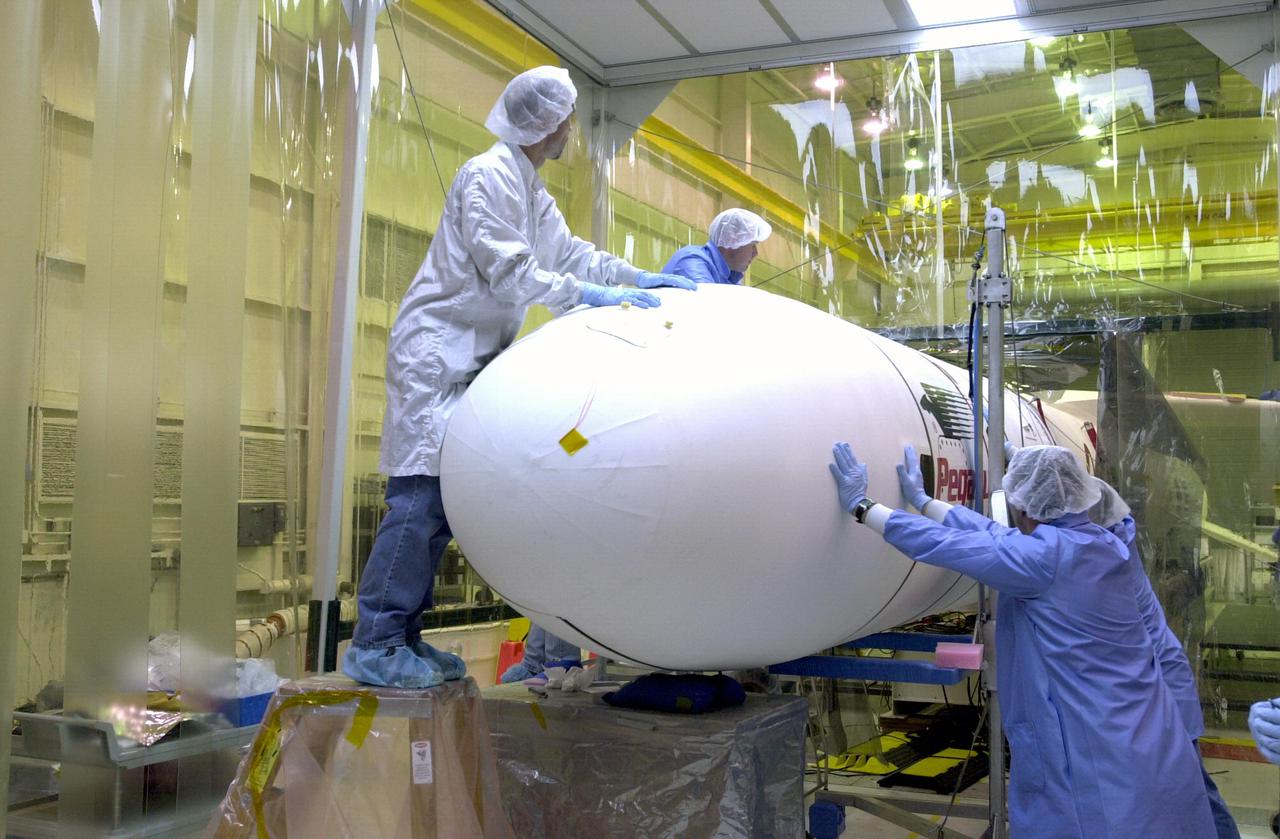

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Orbital Sciences Corporation technicians at Vandenberg AFB in California finish installation of the fairing around the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft in preparation for launch. The fairing will encapsulate DART and protect it while on the launch pad and during ascent. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) is mated to the belly of the Orbital Sciences Corporation Stargazer L-1011 aircraft. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
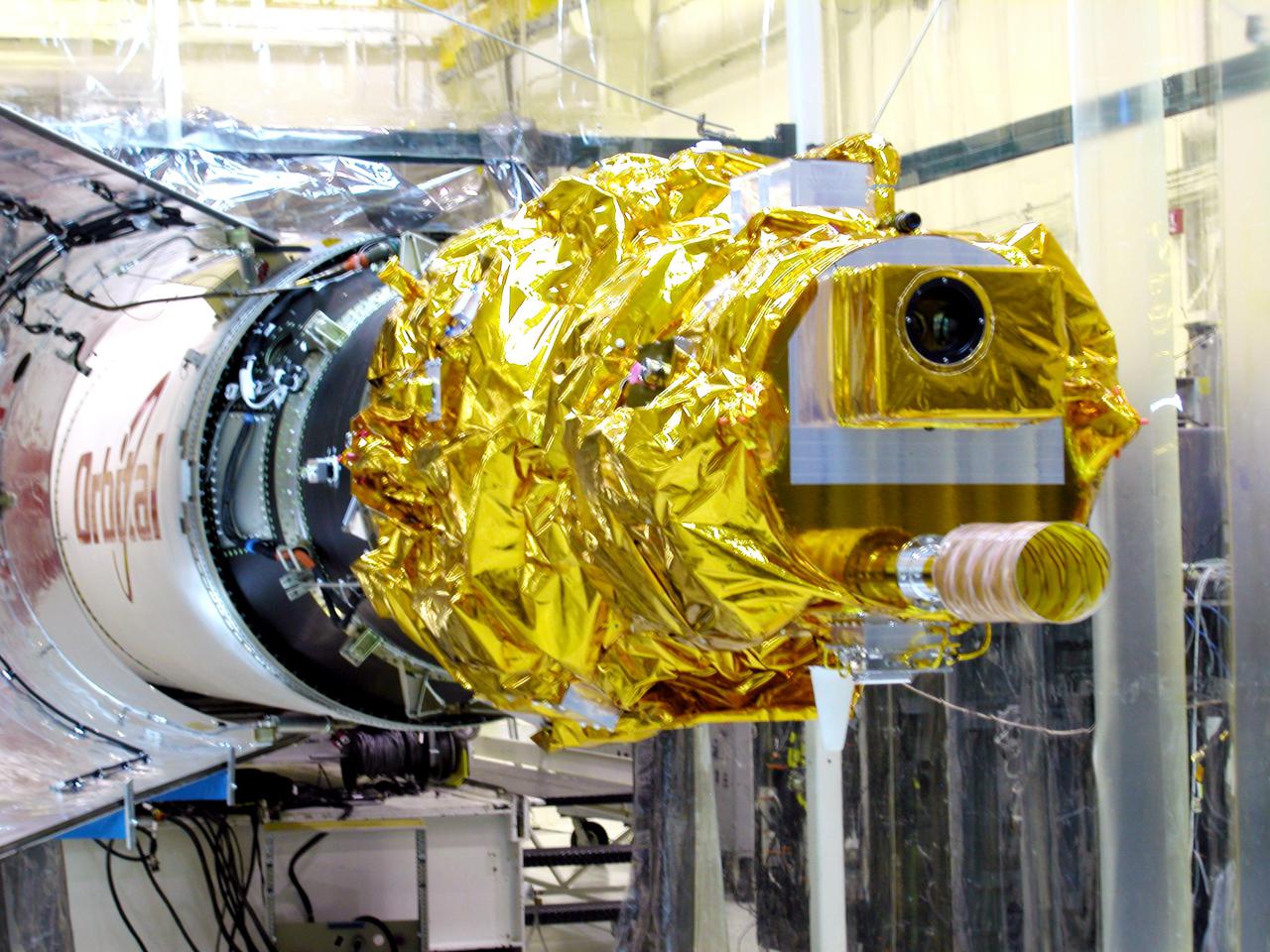
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) waits for fairing installation. The fairing will encapsulate DART and protect it while on the launch pad and during ascent. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. From beneath the belly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft, the Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
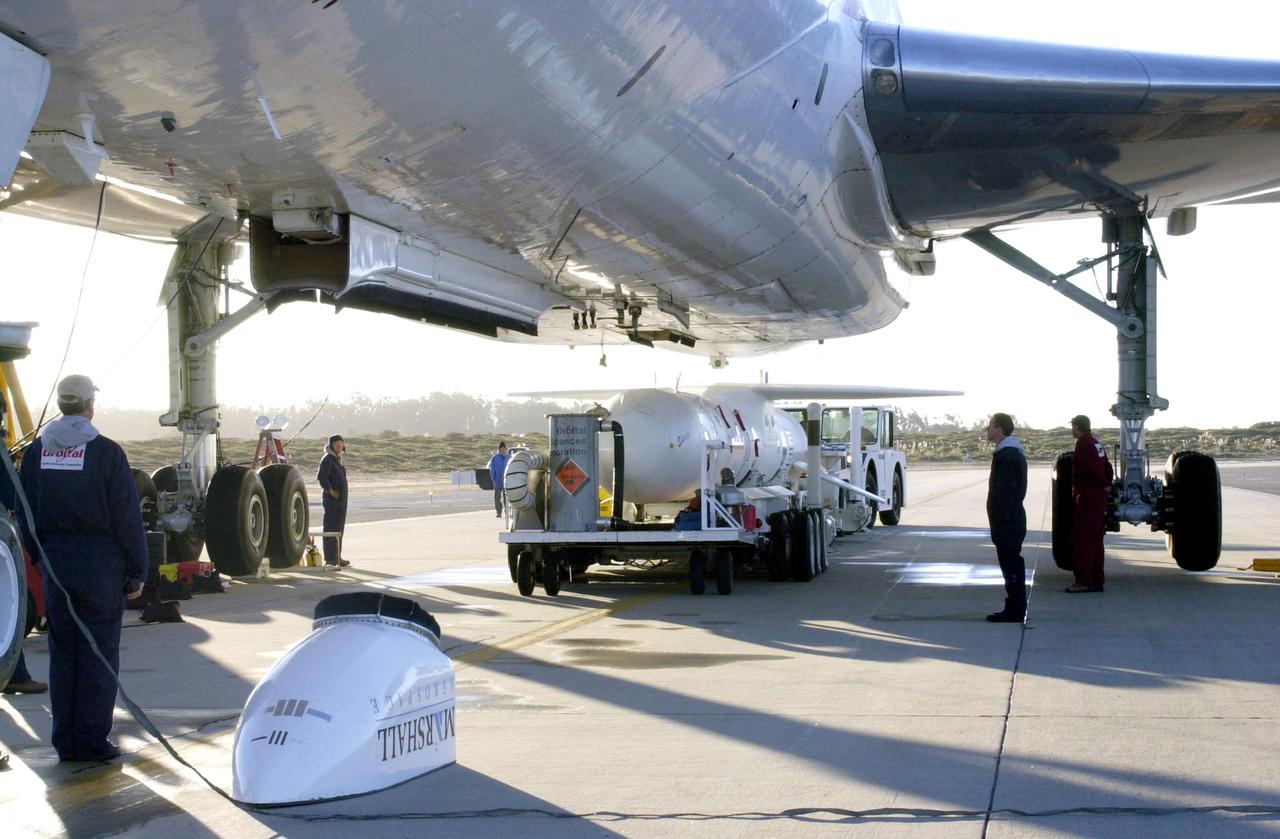

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and Orbital Sciences Pegasus launch vehicle, mated earlier, arrive at the Vandenberg Air Force Base runway for mating to the belly of the Stargazer L-1011 aircraft (foreground). The Pegasus XL will launch DART at approximately 40,000 feet above the Pacific Ocean into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.
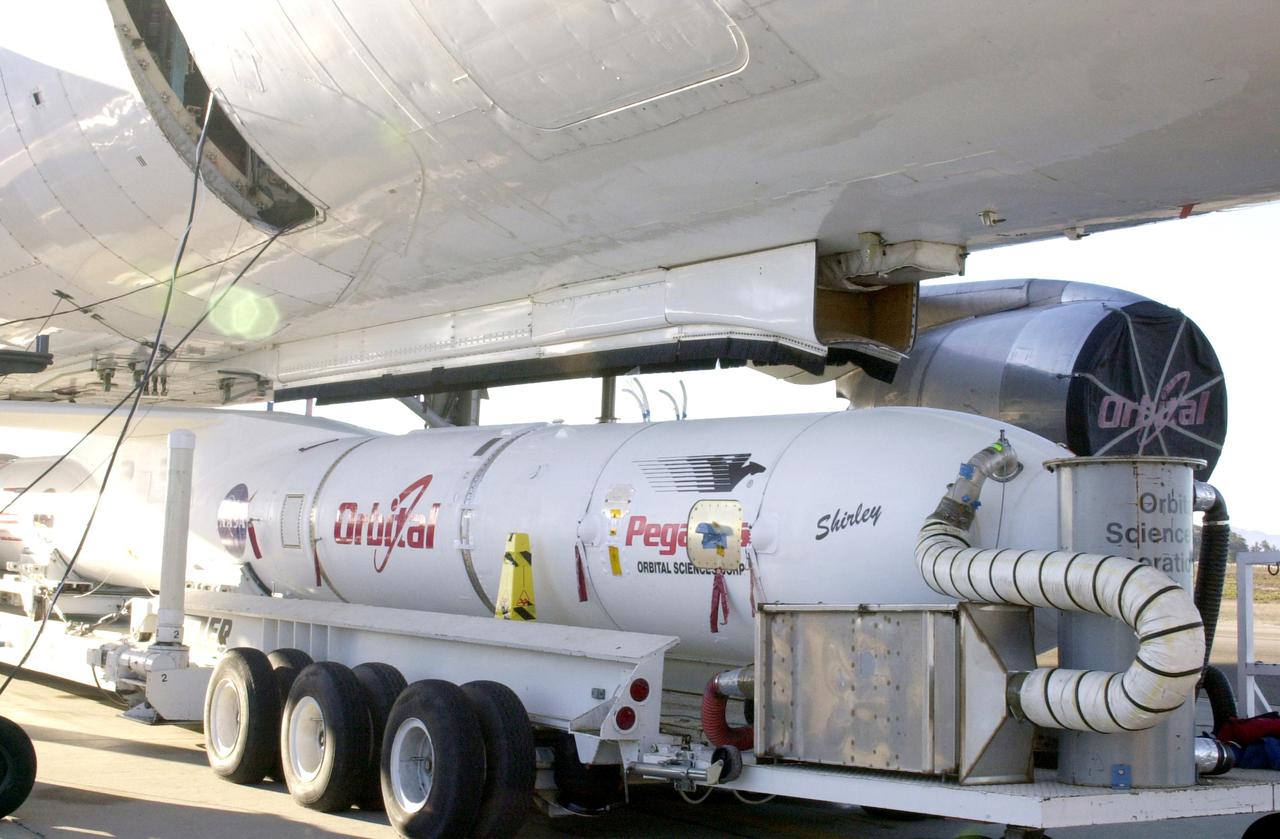

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft and Orbital Sciences Pegasus launch vehicle, mated earlier, are being attached to the Stargazer L-1011 aircraft above. The Pegasus XL will launch DART at approximately 40,000 feet above the Pacific Ocean into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - After postponement of the launch, the Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft is covered with protective material. DART is mated to Orbital Sciences Corporation’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, which will release its cargo over the Pacific Ocean at 40,000 feet. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART satellite provides a key step in establishing autonomous rendezvous capabilities for the U.S. Space Program. While previous rendezvous and docking efforts have been piloted by astronauts, the unmanned DART satellite will have computers and cameras to perform its rendezvous functions.

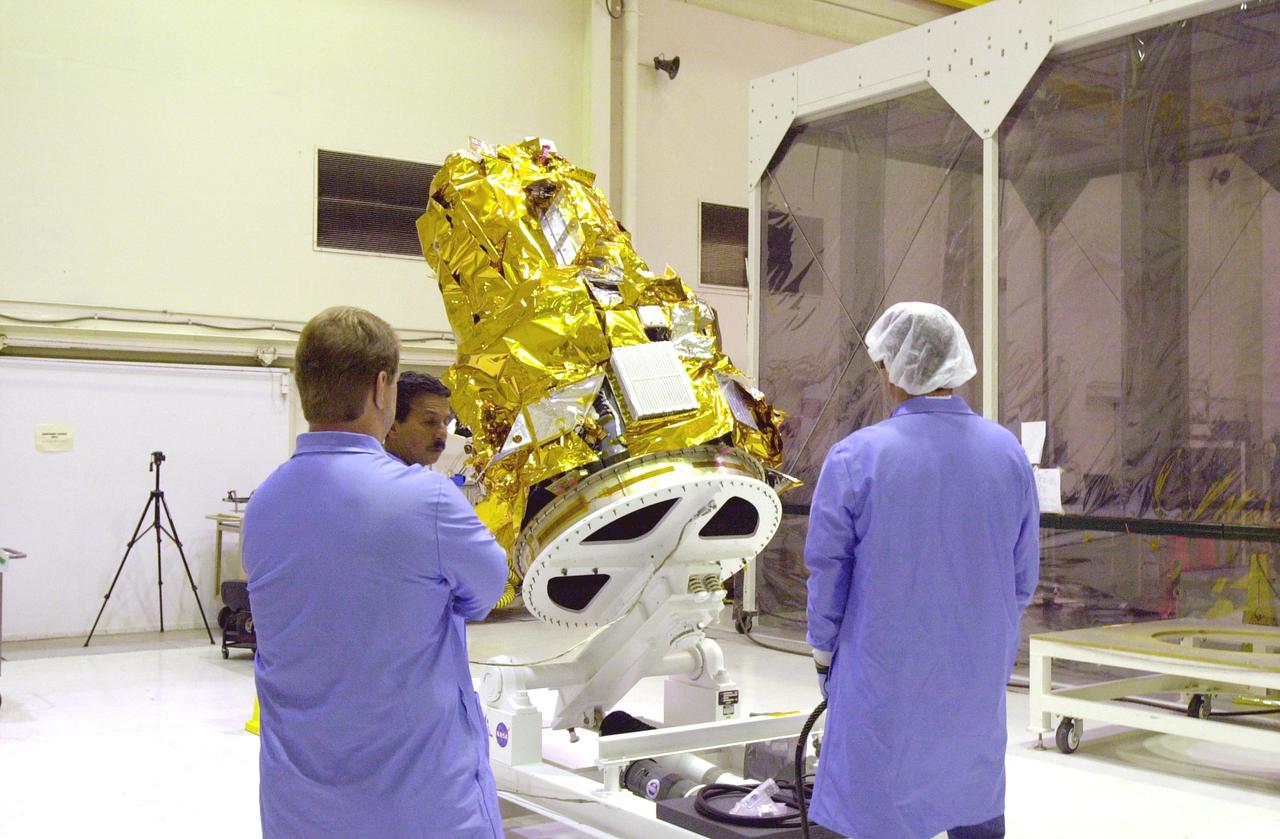
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, Orbital Sciences technicians check the bottom of the DART (Demonstration for Autonomous Rendezvous Technology) flight demonstrator as it is raised off its platform. The spacecraft was developed to prove technologies for locating and maneuvering near an orbiting satellite. Future applications of technologies developed by the DART project will benefit the nation in future space-vehicle systems development requiring in-space assembly, services or other autonomous rendezvous operations. Designed and developed for NASA by Orbital Sciences Corporation in Dulles, Va., the DART spacecraft will be launched on a Pegasus launch vehicle. At about 40,000 feet over the Pacific Ocean, the Pegasus will be released from Orbital’s Stargazer L-1011 aircraft, fire its rocket motors and boost DART into a polar orbit approximately 472 miles by 479 miles. Once in orbit, DART will rendezvous with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Site Communications satellite, also built by Orbital Sciences. DART will then perform several close proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by onboard sensors. DART is scheduled for launch no earlier than Oct. 18.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - Workers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California finish attaching the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft to the underbelly of the Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft for launch Nov. 9. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.
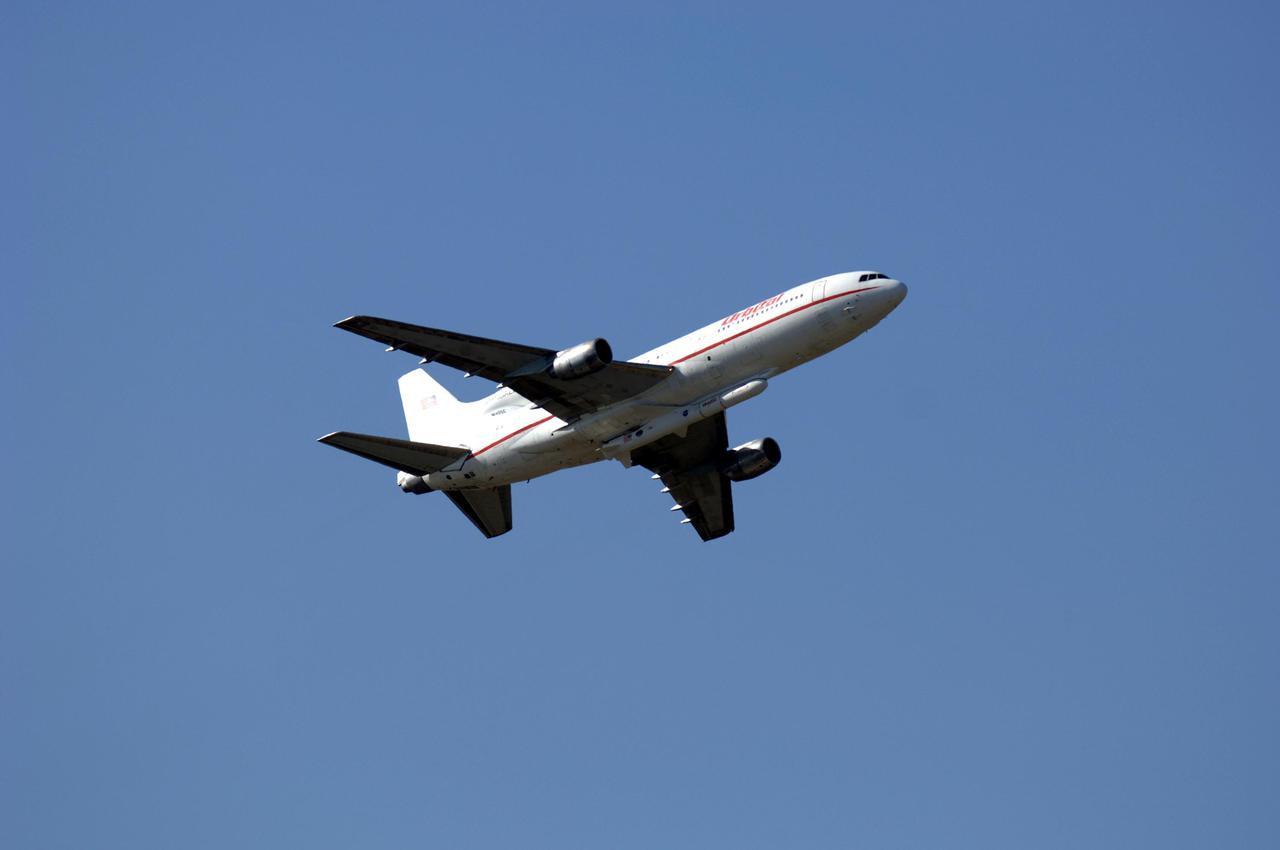

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, FLA. - The Orbital Sciences L-1011 aircraft soars through the sky to launch the Orbital Sciences Pegasus XL launch vehicle and Demonstration of Autonomous Rendezvous Technology (DART) spacecraft attached to its underbelly. DART was designed and built for NASA by Orbital Sciences as an advanced flight demonstrator to locate and maneuver near an orbiting satellite. The DART spacecraft weighs about 800 pounds and is nearly 6 feet long and 3 feet in diameter. The Pegasus XL vehicle will launch DART into a circular polar orbit of approximately 475 miles. Once in orbit, DART will make contact with a target satellite, the Multiple Paths, Beyond-Line-of-Sight Communications (MUBLCOM), also built by Orbital Sciences and launched in 1999. DART will then perform several close-proximity operations, such as moving toward and away from the satellite using navigation data provided by on-board sensors. The entire mission will last only 24 hours and will be accomplished without human intervention. The DART flight computer will determine its own path to accomplish its mission objectives.