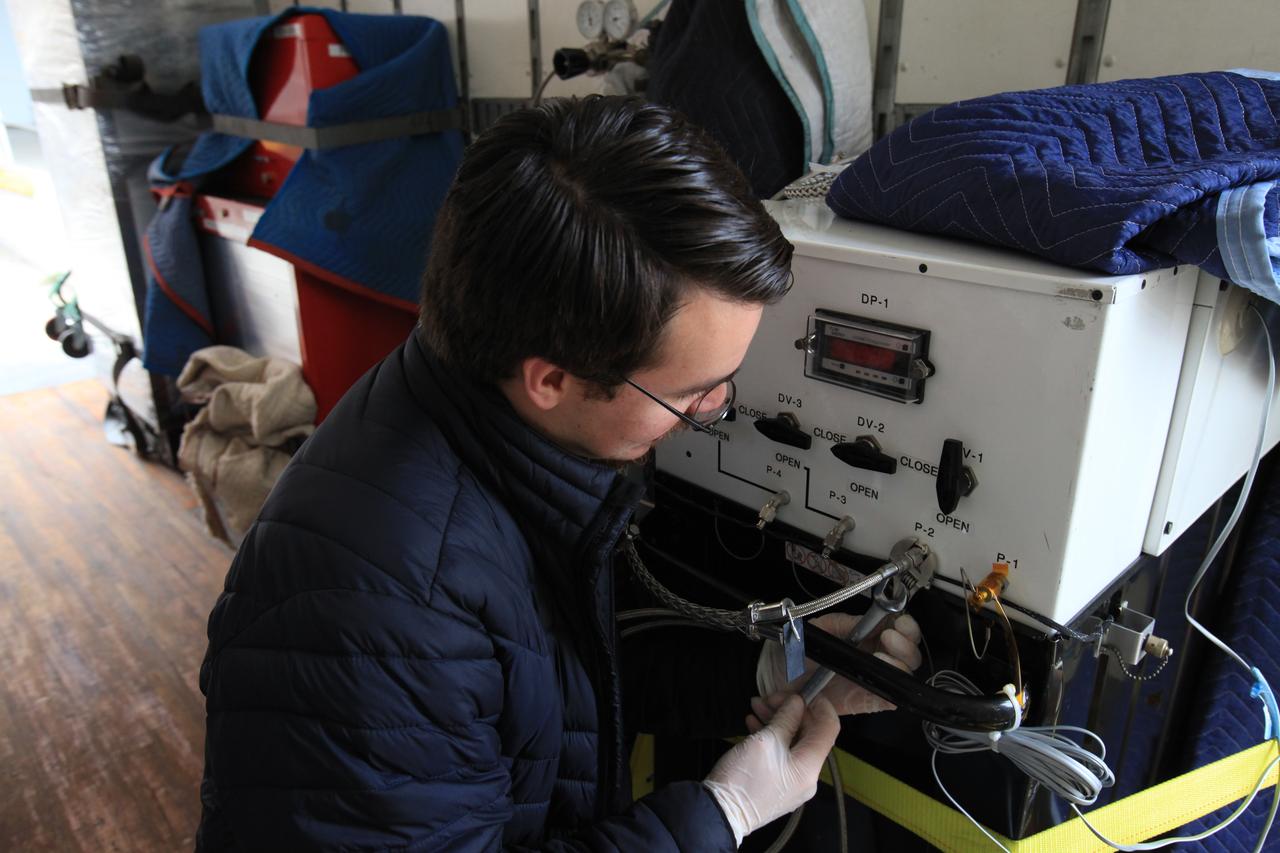

Kevin Mark, Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3 (OCO-3) purge engineer with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, secures a separate fixture of OCO-3, stored apart from its payload container, on the truck transporting it from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
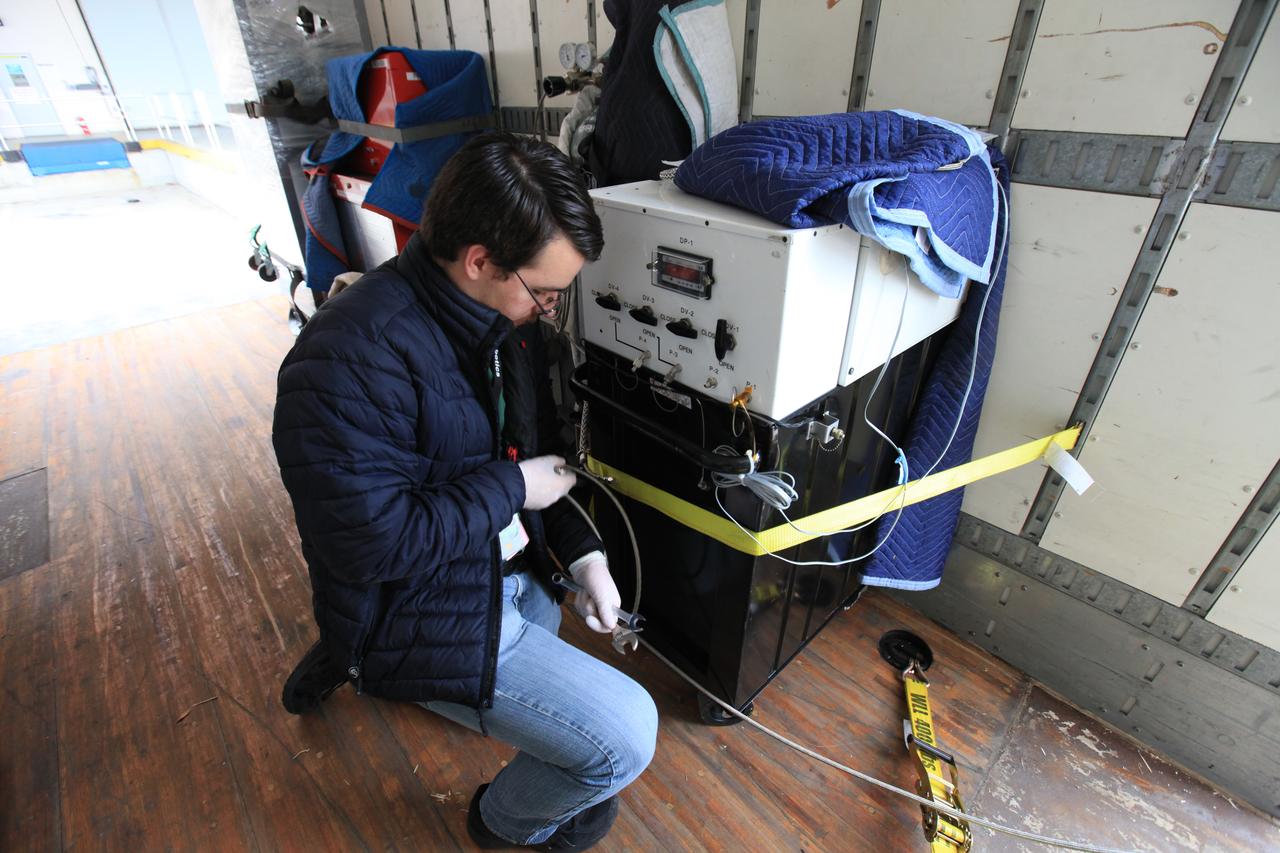

Kevin Mark, Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3 (OCO-3) purge engineer with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, fastens a separate fixture of OCO-3, stored apart from its payload container, to a truck for transport from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
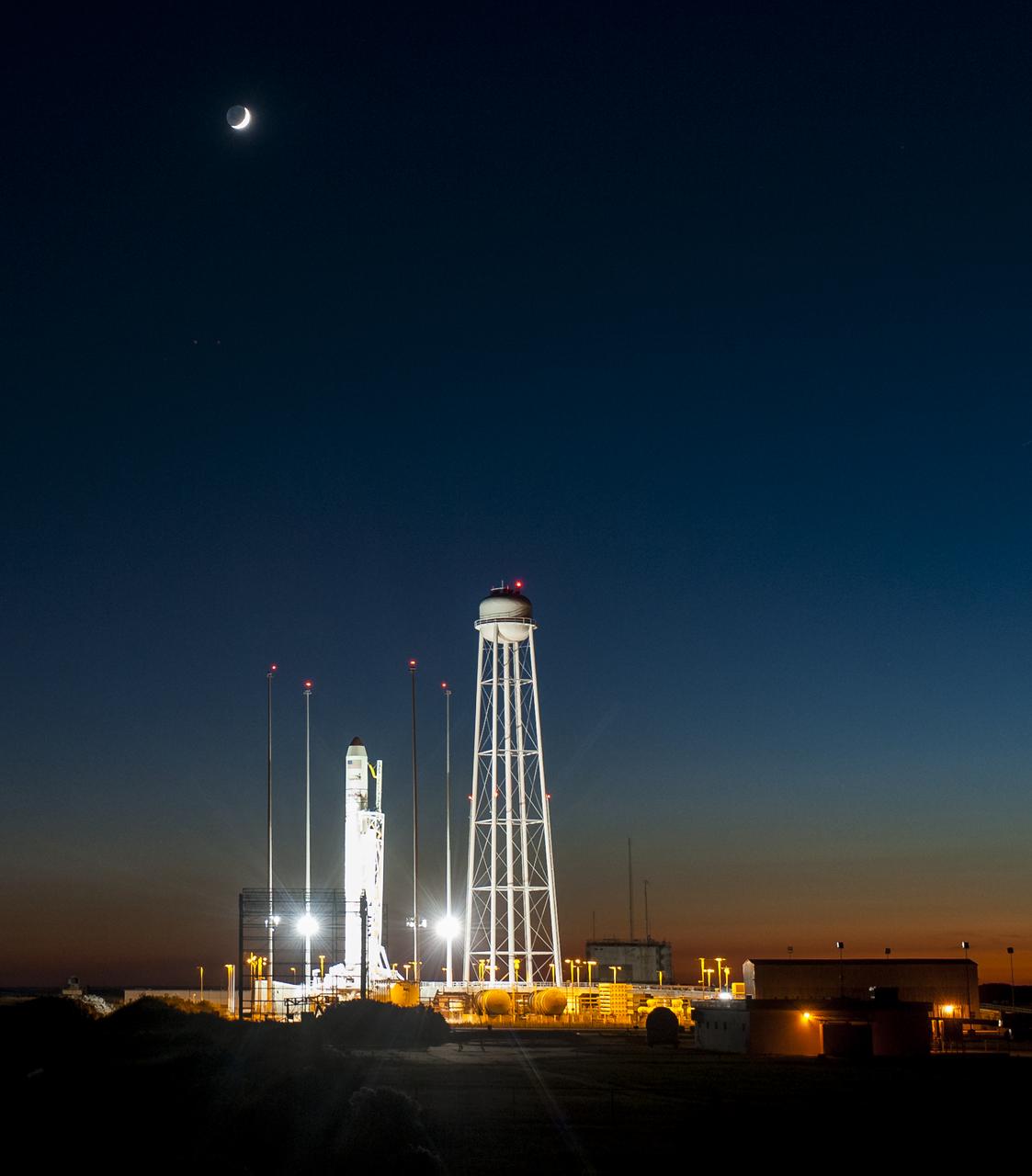

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket, with the Cygnus spacecraft onboard, is seen on launch Pad-0A after the launch attempt was scrubbed because of a boat down range in the trajectory Antares would have flown had it lifted off, Monday, Oct. 27, 2014, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The Antares will launch with the Cygnus spacecraft filled with over 5,000 pounds of supplies for the International Space Station, including science experiments, experiment hardware, spare parts, and crew provisions. The Orbital-3 mission is Orbital Sciences' third contracted cargo delivery flight to the space station for NASA. The next launch attempt will be made on Tuesday, Oct. 28 at 6:22 p.m. EDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)
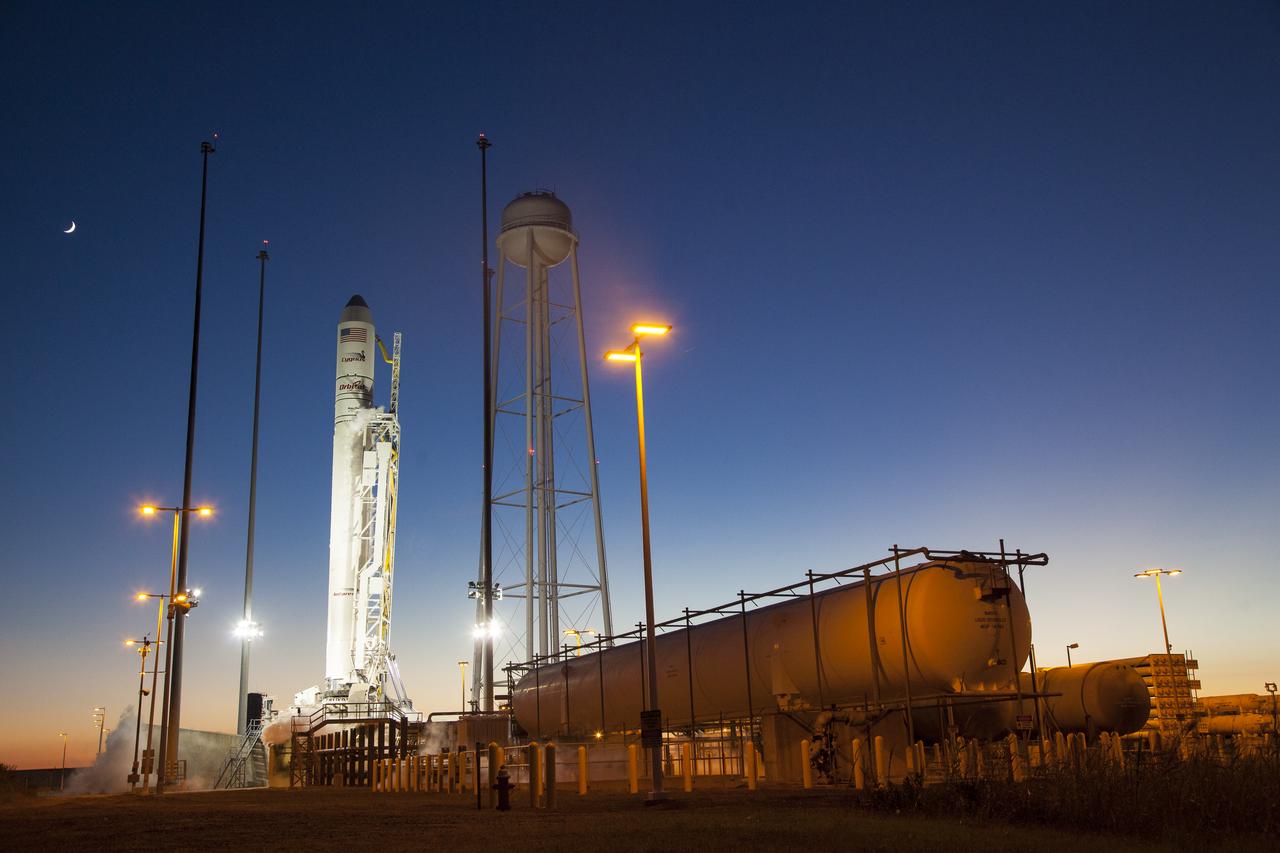

The Orbital Sciences Corporation Antares rocket, with the Cygnus spacecraft onboard, is seen on launch Pad-0A after the launch attempt was scrubbed because of a boat down range in the trajectory Antares would have flown had it lifted off, Monday, Oct. 27, 2014, at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. The Antares will launch with the Cygnus spacecraft filled with over 5,000 pounds of supplies for the International Space Station, including science experiments, experiment hardware, spare parts, and crew provisions. The Orbital-3 mission is Orbital Sciences' third contracted cargo delivery flight to the space station for NASA. The next launch attempt will be made on Tuesday, Oct. 28 at 6:22 p.m. EDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Joel Kowsky)

A transportation container carrying NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload is moved to a truck for its transport from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.

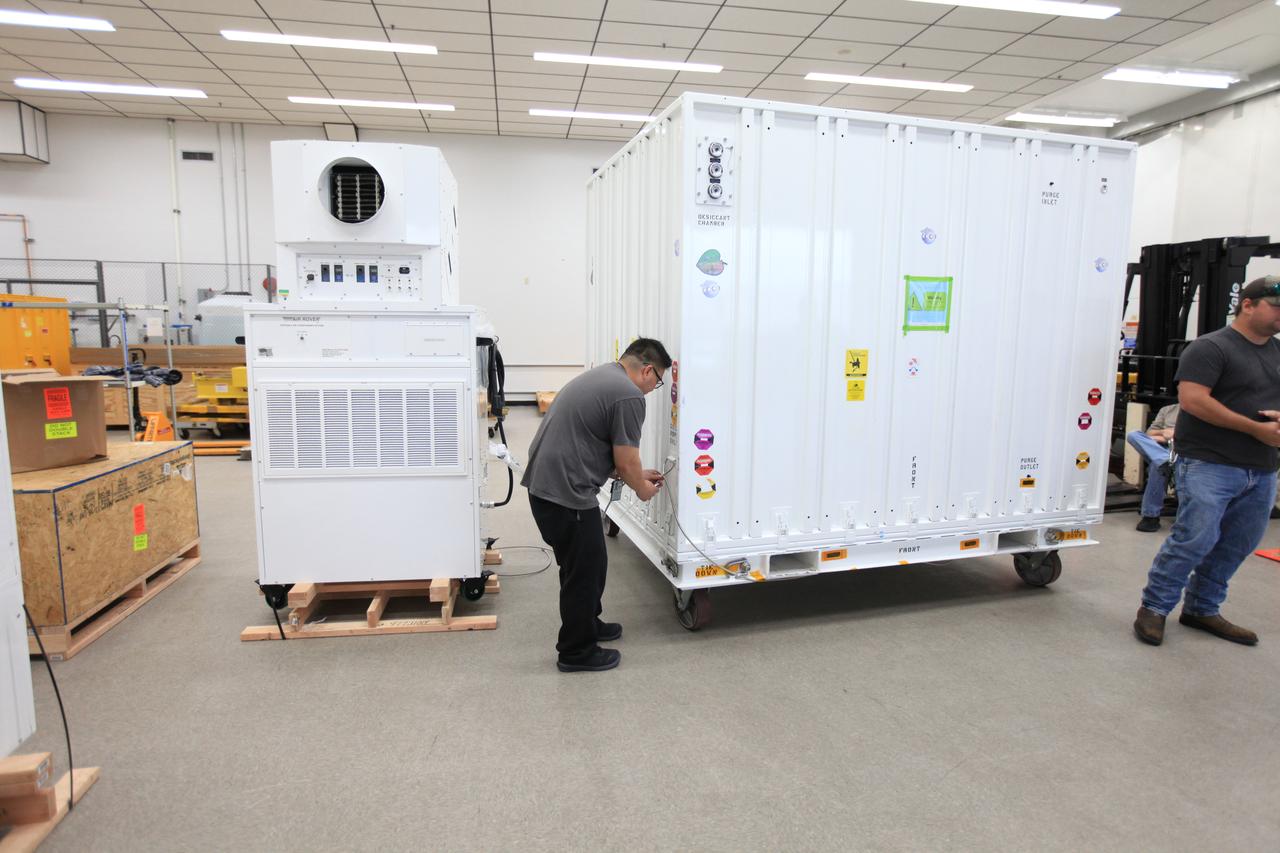
NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, sits in a transportation container at the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prior to its move to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
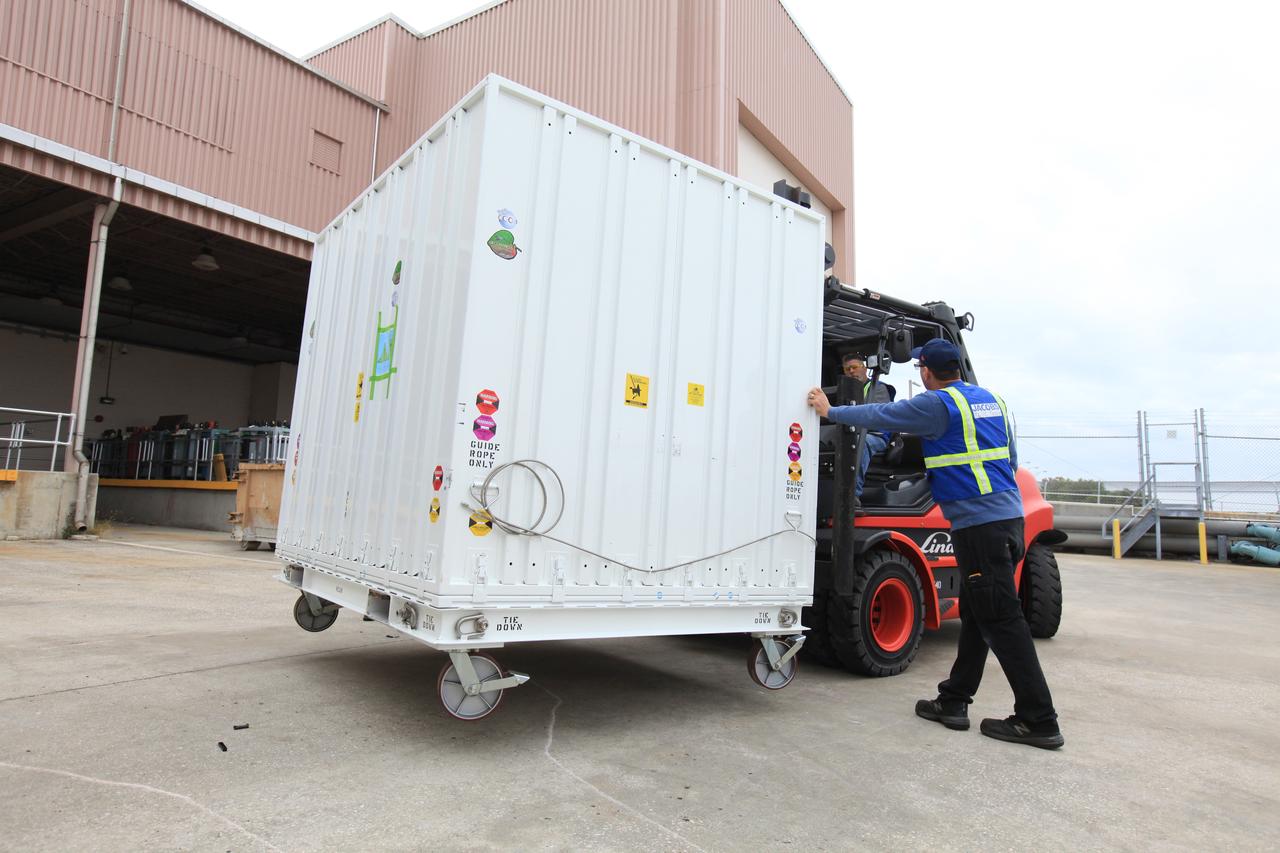

A forklift moves the transportation container carrying NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload to a truck for its move from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.

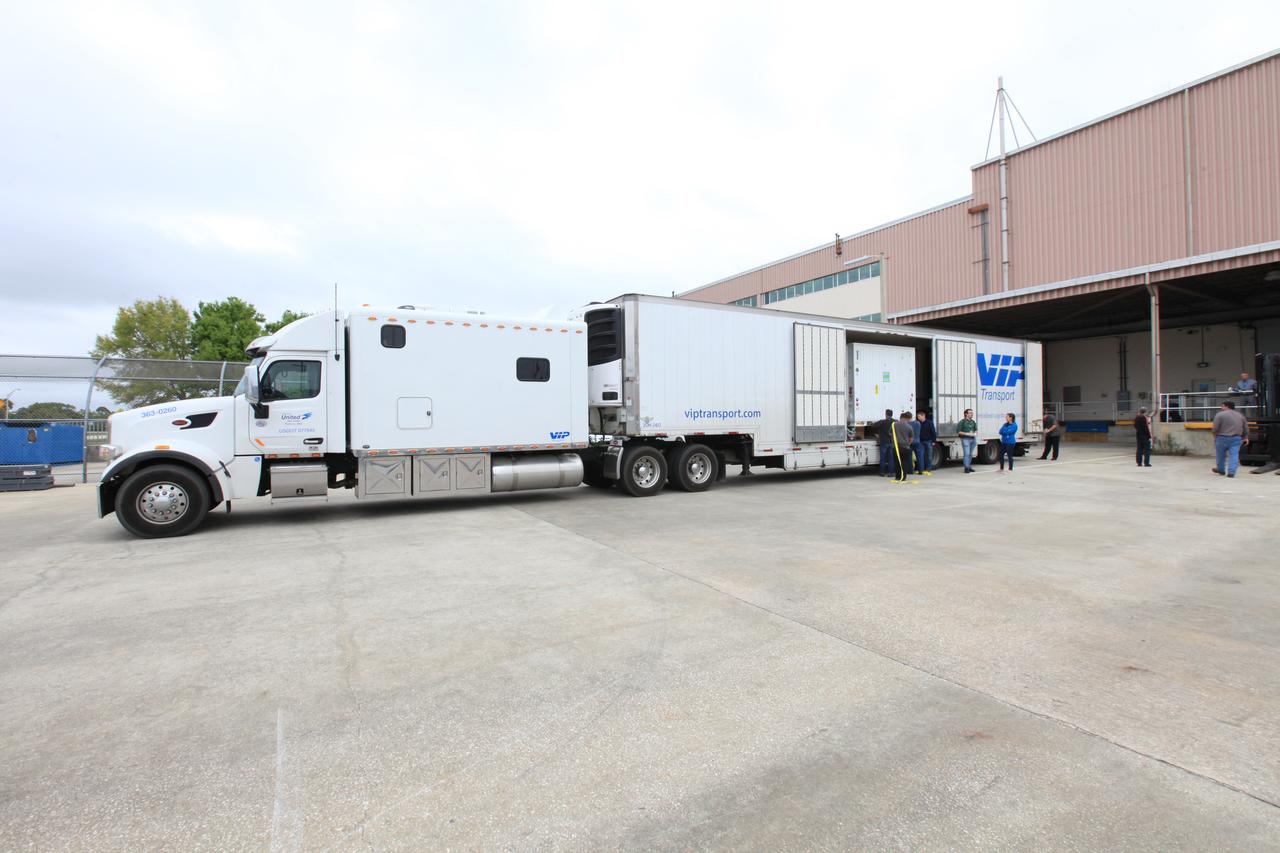
Workers move NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload container out of the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to board a truck that will transport it to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.

NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload sits in a transportation container at the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in preparation for its move to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
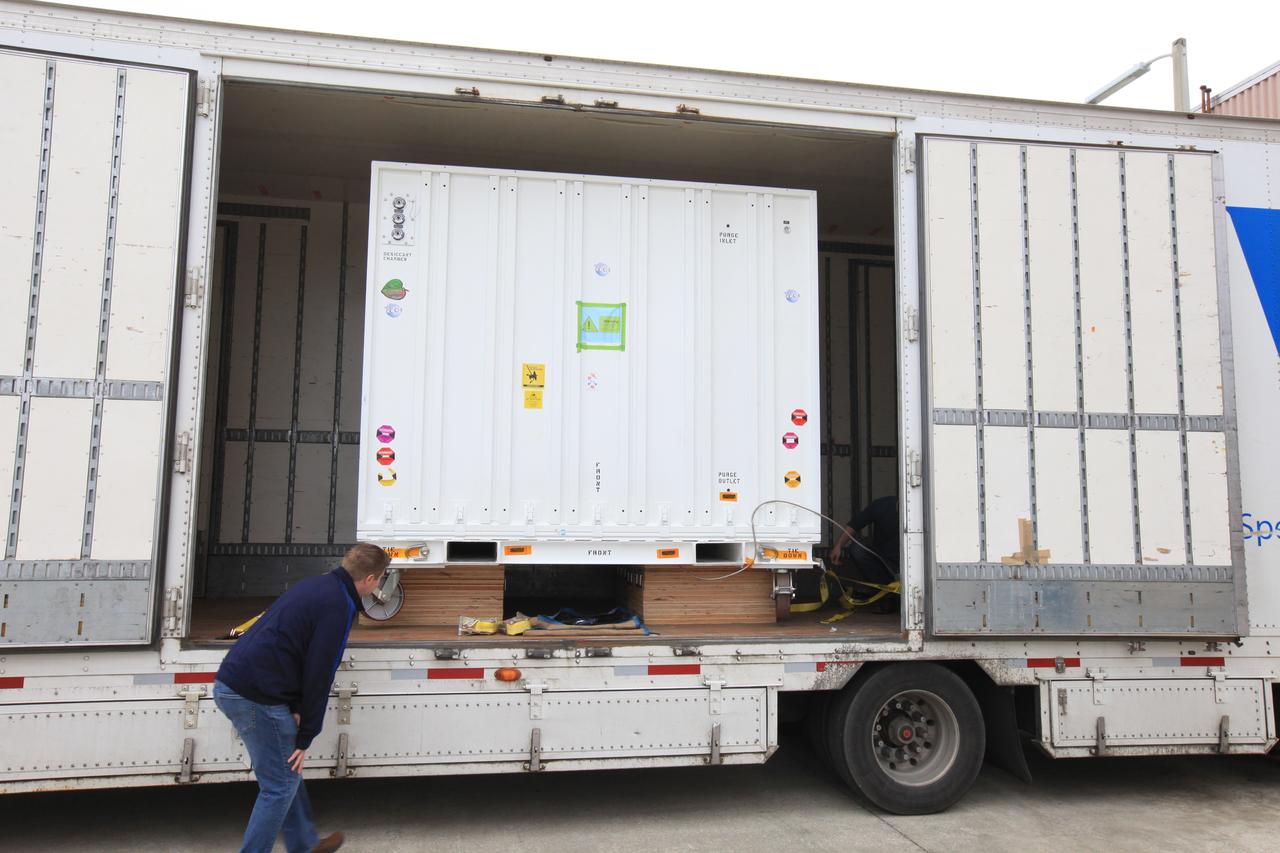

A transportation container carrying NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload is moved to a truck for transport from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
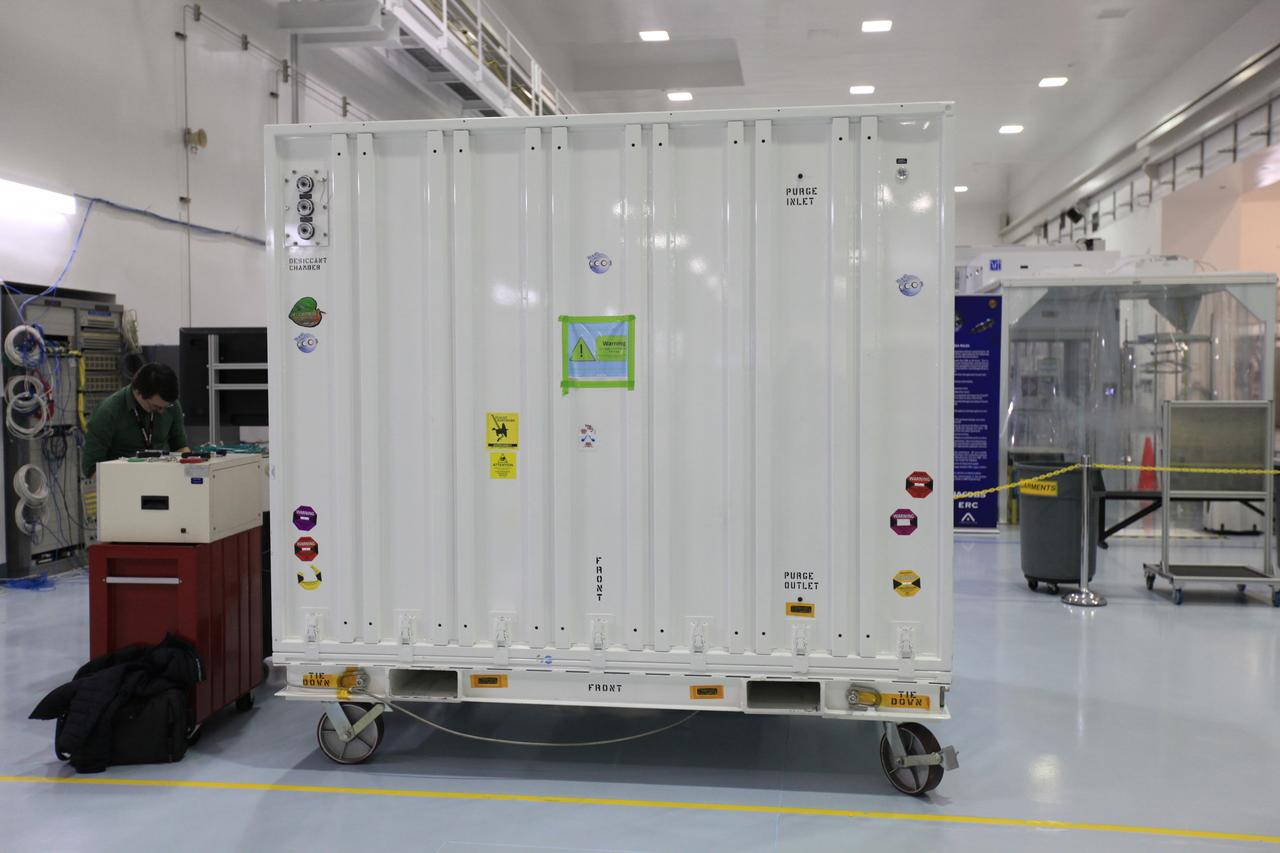

NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, sits in a transportation container at the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prior to its move to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, which will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
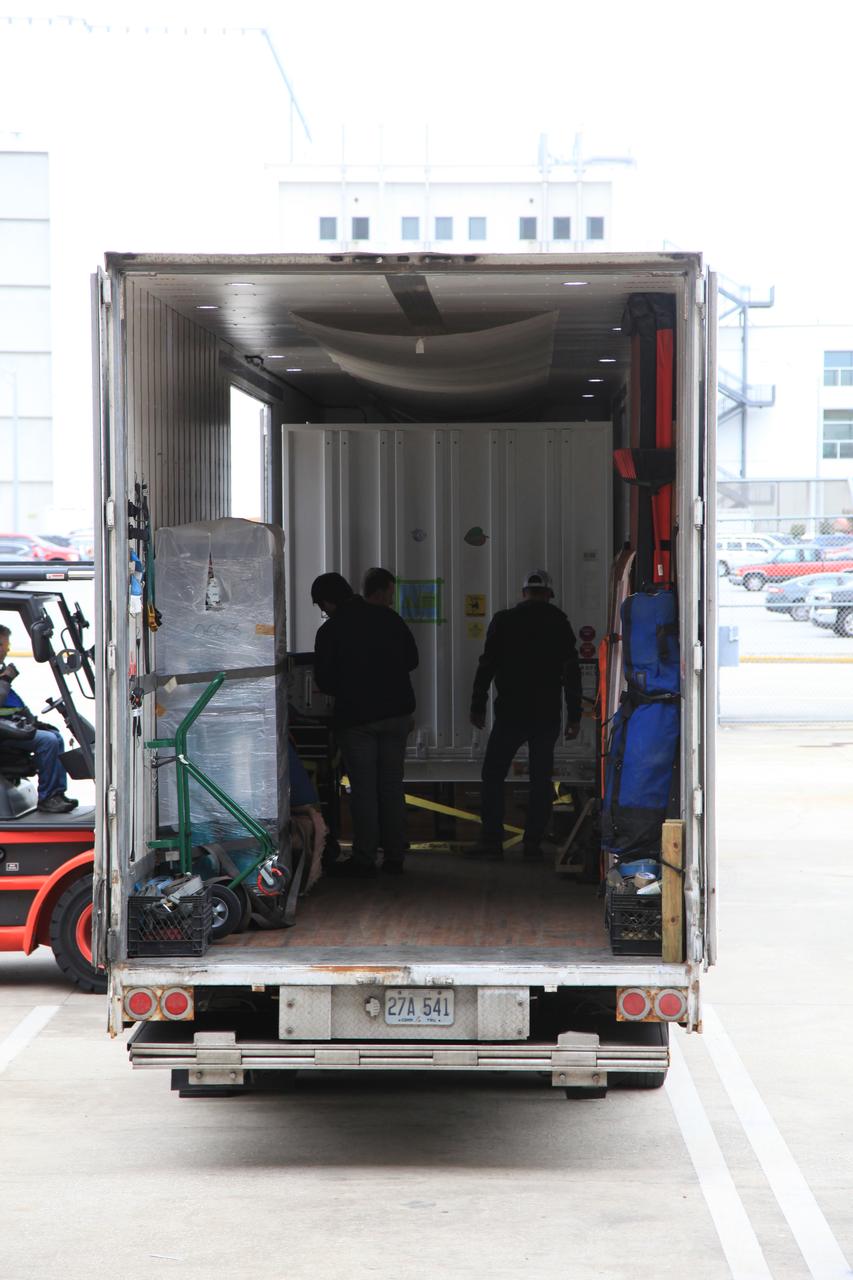

NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload container is moved from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to a truck that will transport it to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
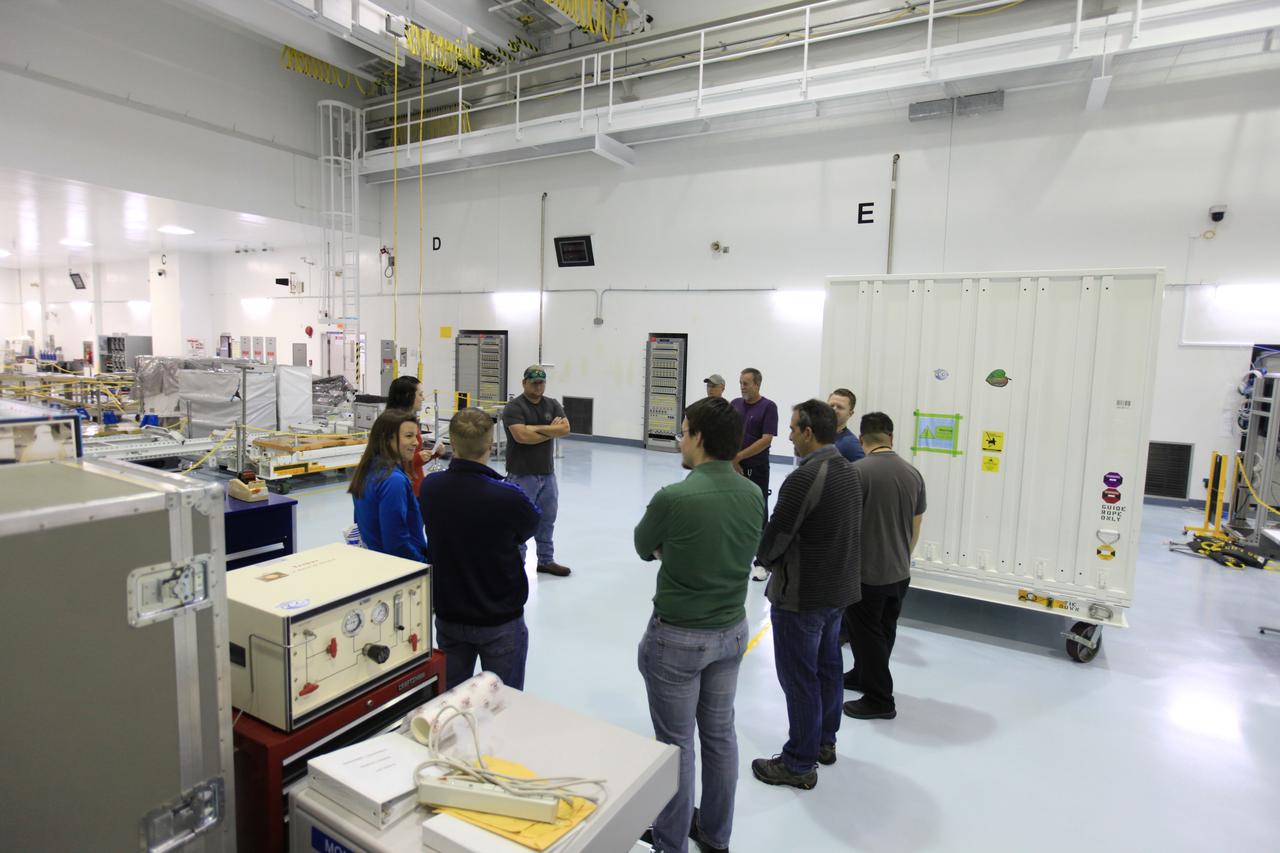

Workers prepare to move NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload container out of the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida onto a truck that will transport it to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, which will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
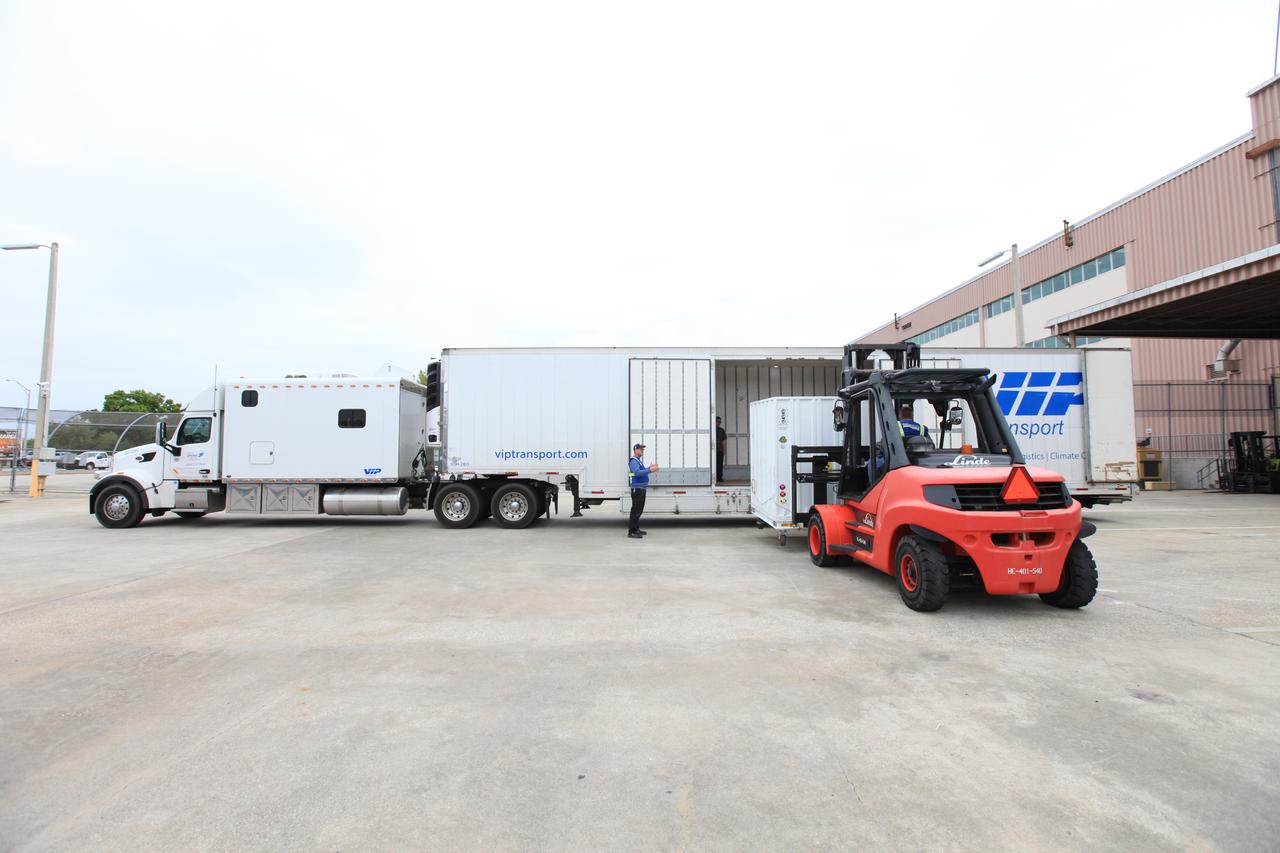

A forklift moves the transportation container carrying NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload to a truck for its move from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.

Workers prepare to move NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload container out of the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida onto a truck that will transport it to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
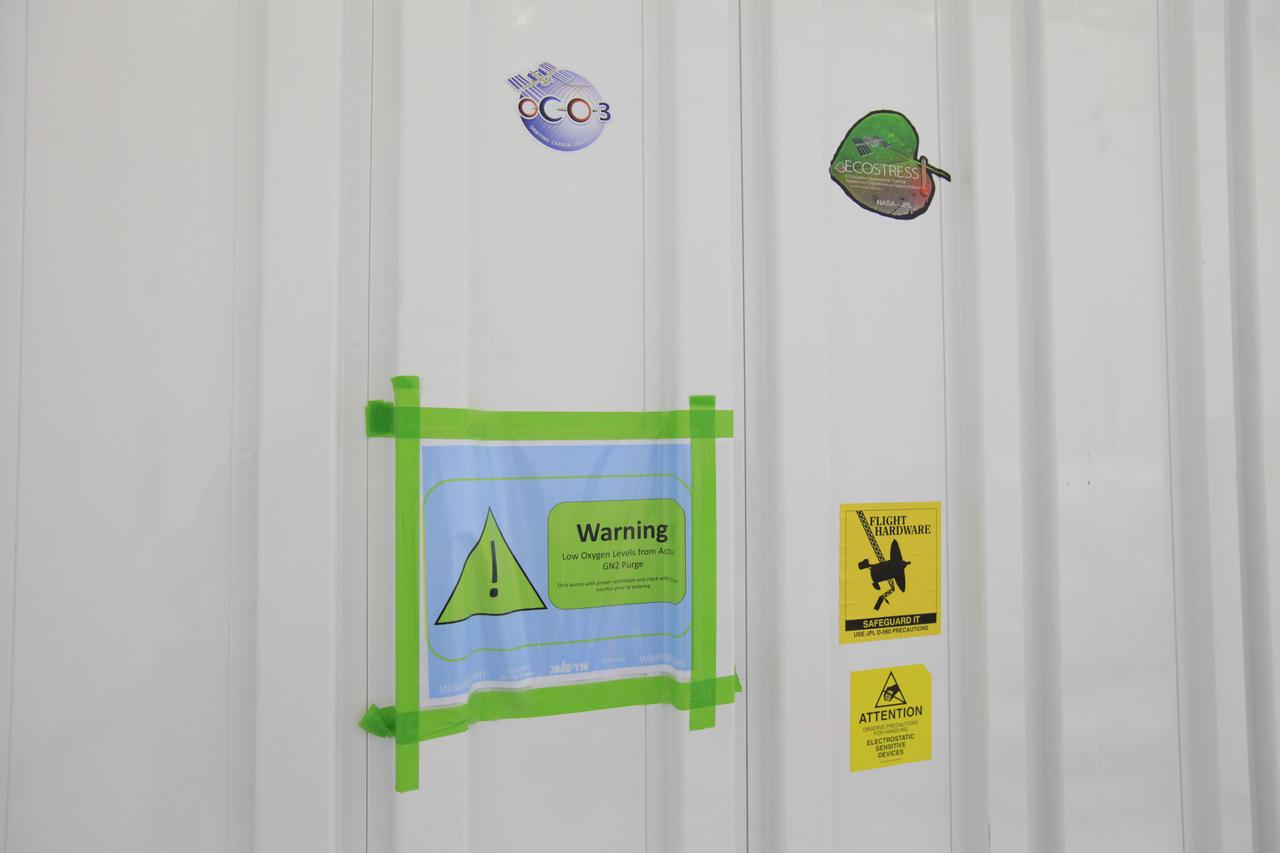

A transportation container carrying NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload sits at the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida bearing a warning sign of low oxygen levels from an active GN2 (gaseous nitrogen that creates a dry atmosphere) purge prior to its move to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft and will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
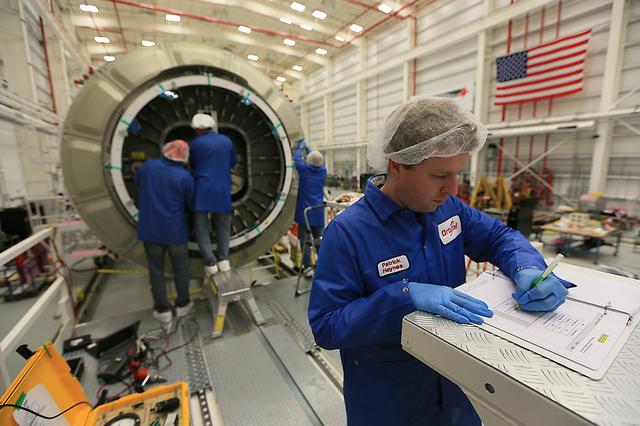

Orbital Sciences Corp. completed final cargo load of the Cygnus cargo spacecraft Oct. 23, 2014, in preparation for launch to the International Space Station, scheduled for 6:45 p.m. EDT, Monday, Oct. 27, from Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport Pad 0A at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility. The spacecraft is mated to the company's Antares rocket with roll-out to the launch pad scheduled for Friday, Oct. 24. This mission is the third of eight Orbital flights NASA contracted with the company to resupply the space station, and the fourth trip by a Cygnus spacecraft to the ISS. Cygnus will transport some 5,000 pounds of supplies and experiments to the orbiting laboratory. More at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/orbital" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/orbital</a> Credit: NASA's Wallops Flight Facility/Patrick Black <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
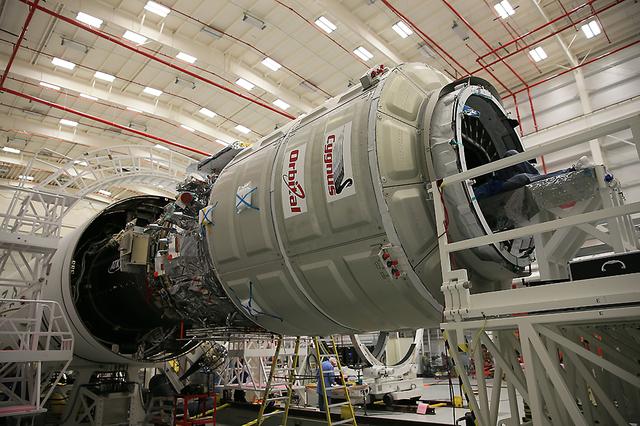

Orbital Sciences Corp. completed final cargo load of the Cygnus cargo spacecraft Oct. 23, 2014, in preparation for launch to the International Space Station, scheduled for 6:45 p.m. EDT, Monday, Oct. 27, from Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport Pad 0A at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility. The spacecraft is mated to the company's Antares rocket with roll-out to the launch pad scheduled for Friday, Oct. 24. This mission is the third of eight Orbital flights NASA contracted with the company to resupply the space station, and the fourth trip by a Cygnus spacecraft to the ISS. Cygnus will transport some 5,000 pounds of supplies and experiments to the orbiting laboratory. More at <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/orbital" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/orbital</a> Credit: NASA's Wallops Flight Facility/Patrick Black <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3
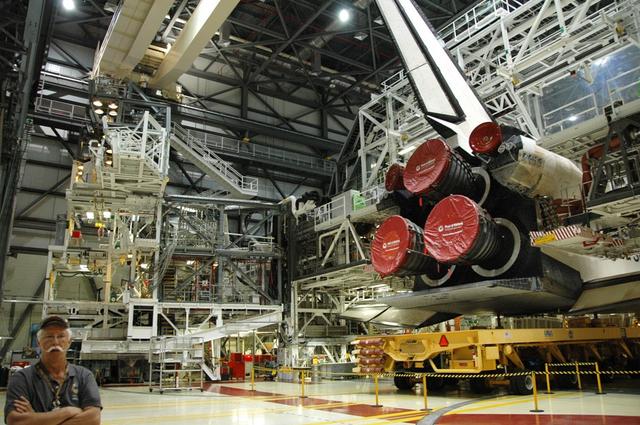

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3
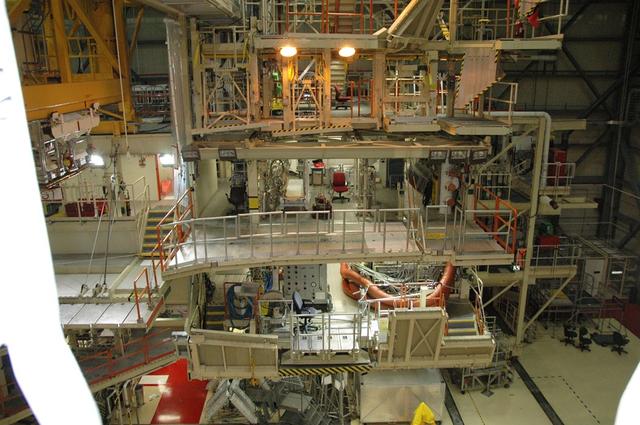

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Exterior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3
Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Exterior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Exterior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3
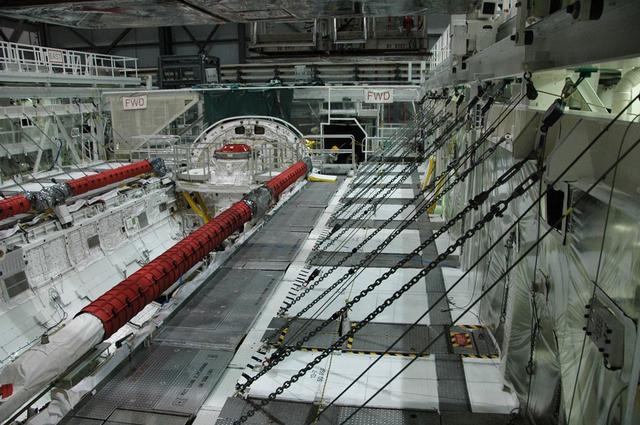

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3
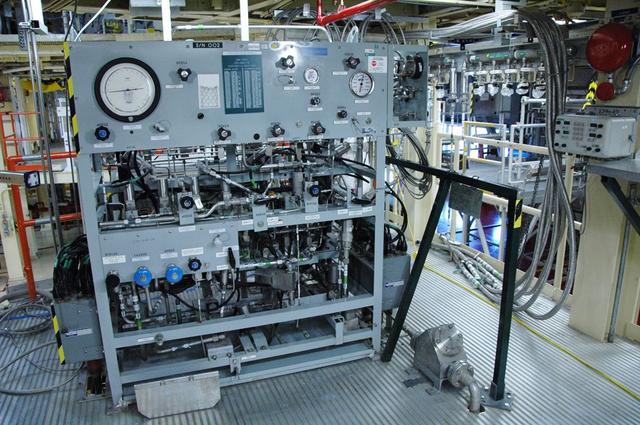

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Exterior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3

Interior View of Orbiter Processing Facility 3