
This image is an artist concept of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory OCO.
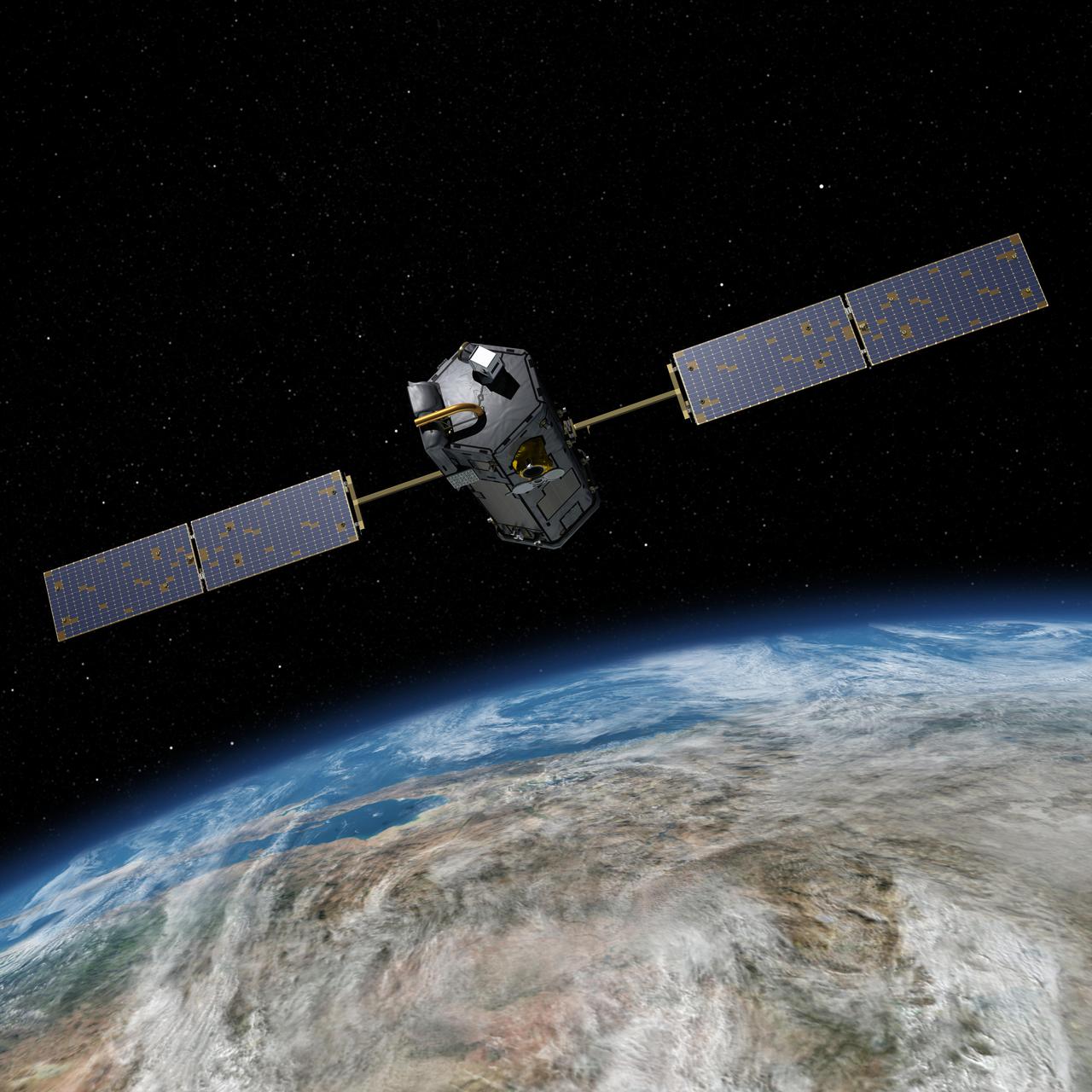

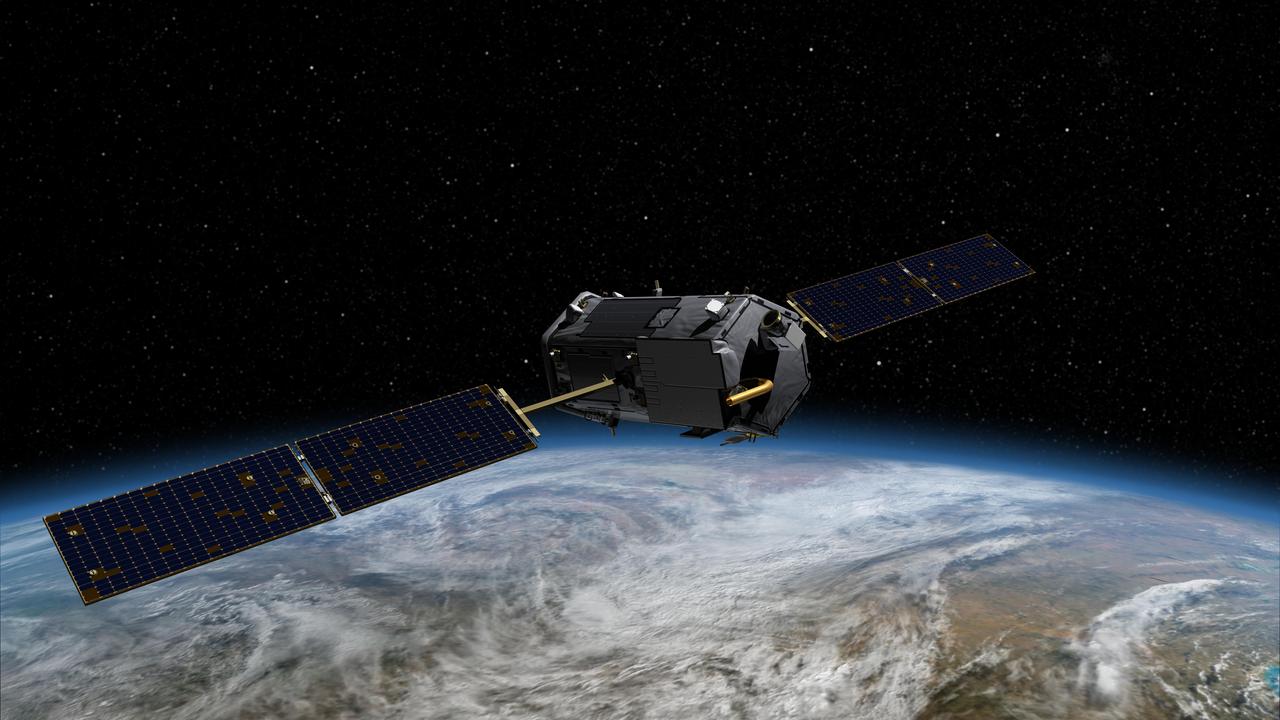
This most recent artist rendering shows NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory OCO-2, one of five new NASA Earth science missions set to launch in 2014, and one of three managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory JPL.
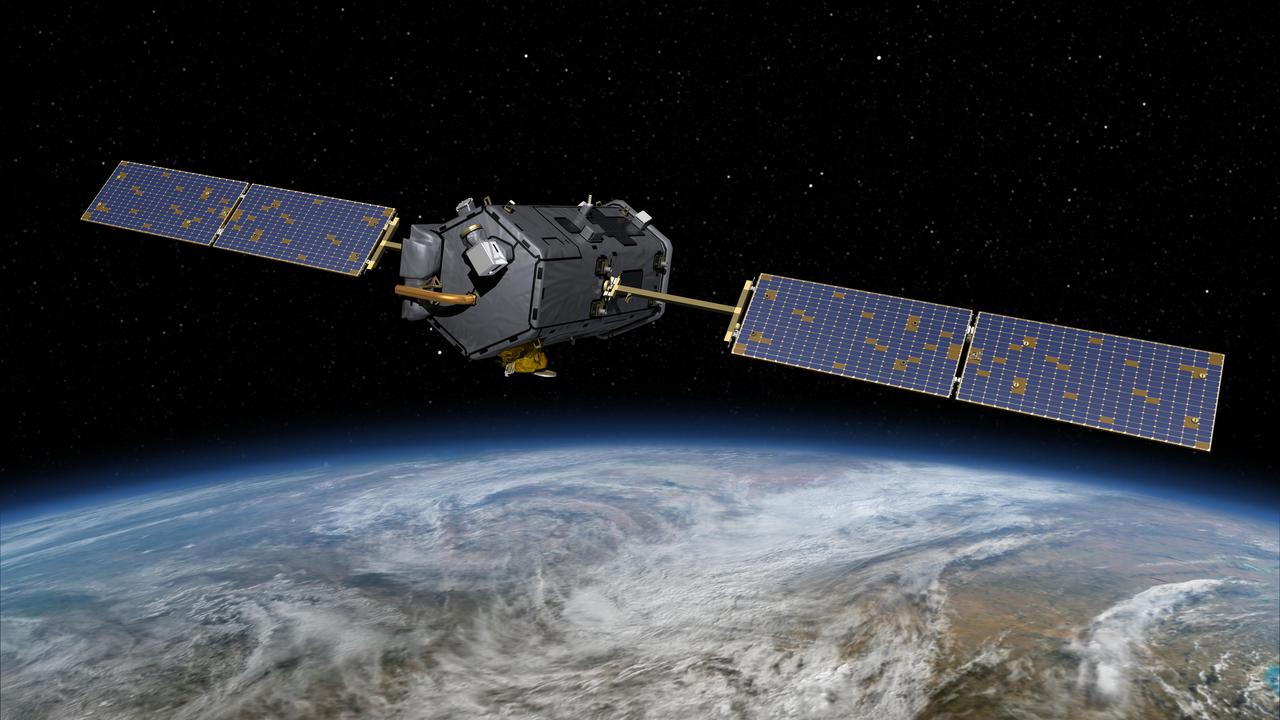

This most recent artist rendering shows NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory OCO-2, one of five new NASA Earth science missions set to launch in 2014, and one of three managed by the Jet Propulsion Laboratory JPL.
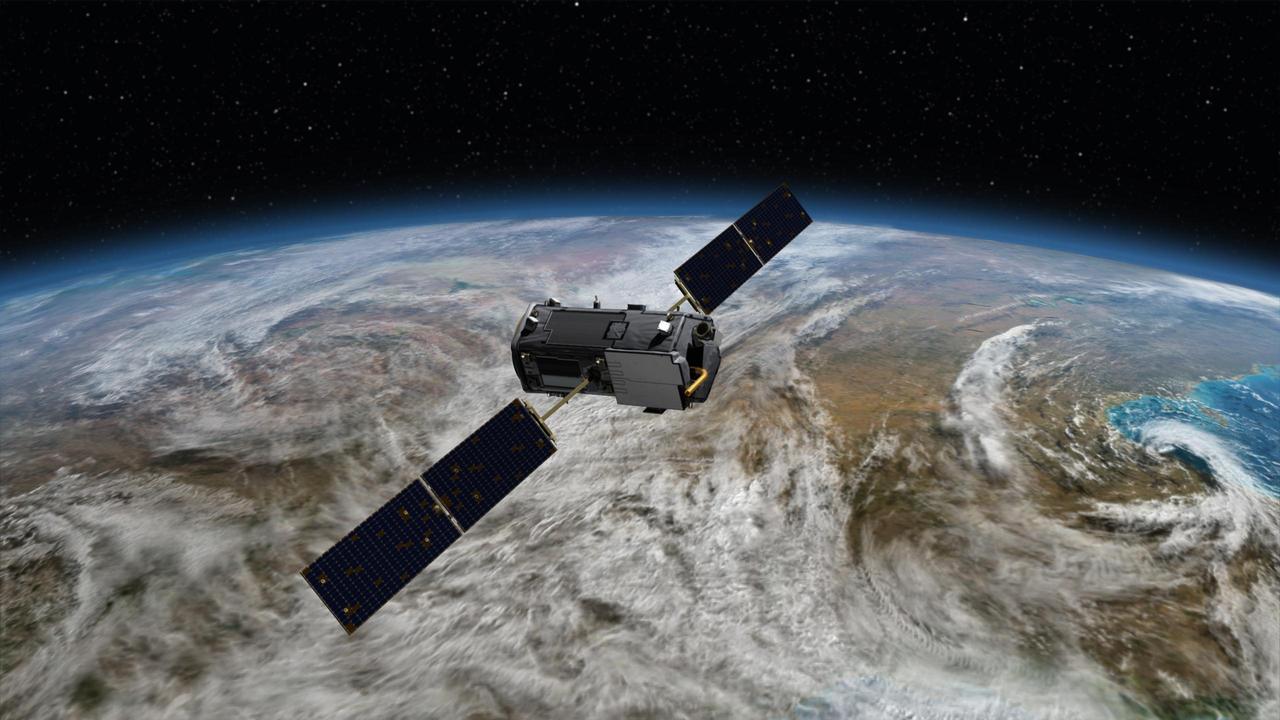

Artist rendering of NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory OCO-2, one of five new NASA Earth science missions set to launch in 2014, and one of three managed by JPL.

Dave Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader, JPL talks during an Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) science briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Ken Jucks, OCO-2 program scientist, NASA Headquarters talks during an Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) science briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Ken Jucks, OCO-2 program scientist, NASA Headquarters talks during an Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) science briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Dave Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader, JPL talks during an Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) science briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist, JPL talks during an Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) science briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
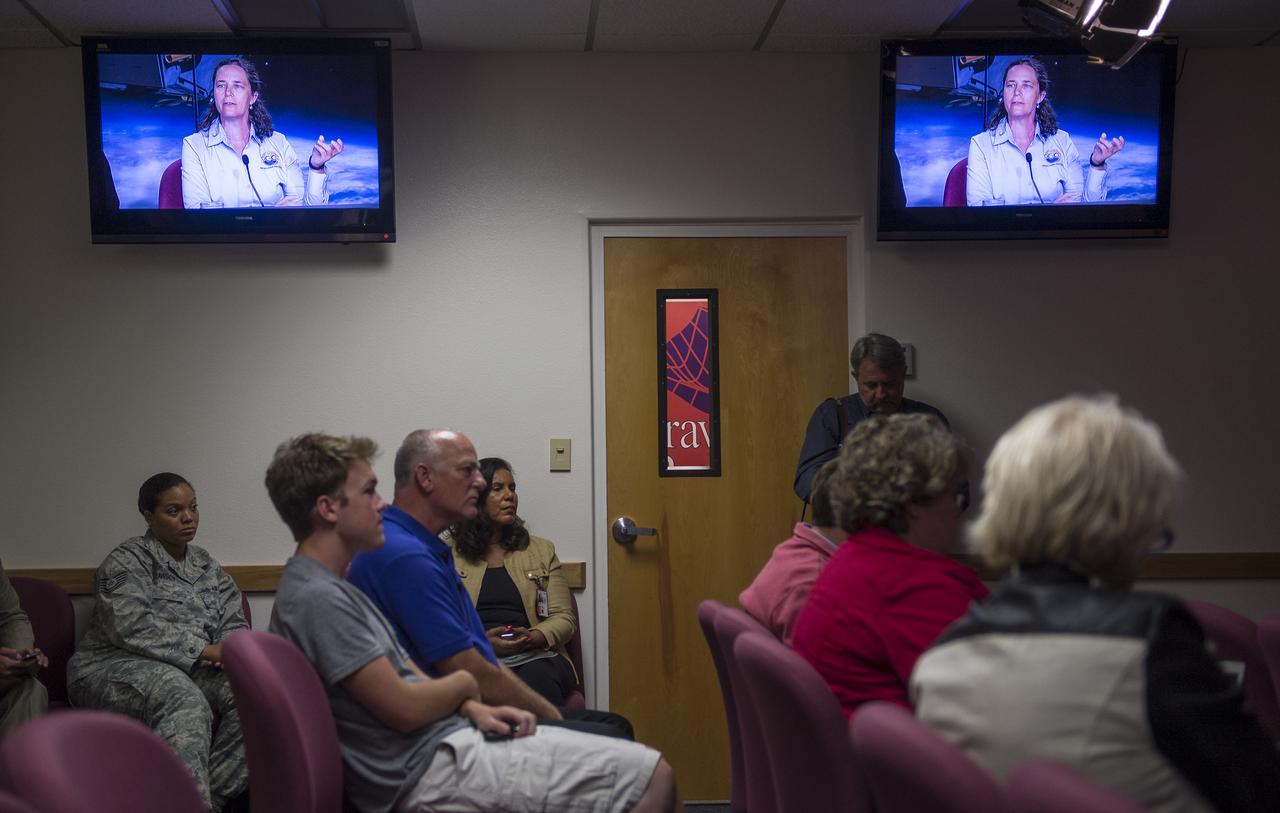

Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist, JPL is seen talking on the monitors during an Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) science briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
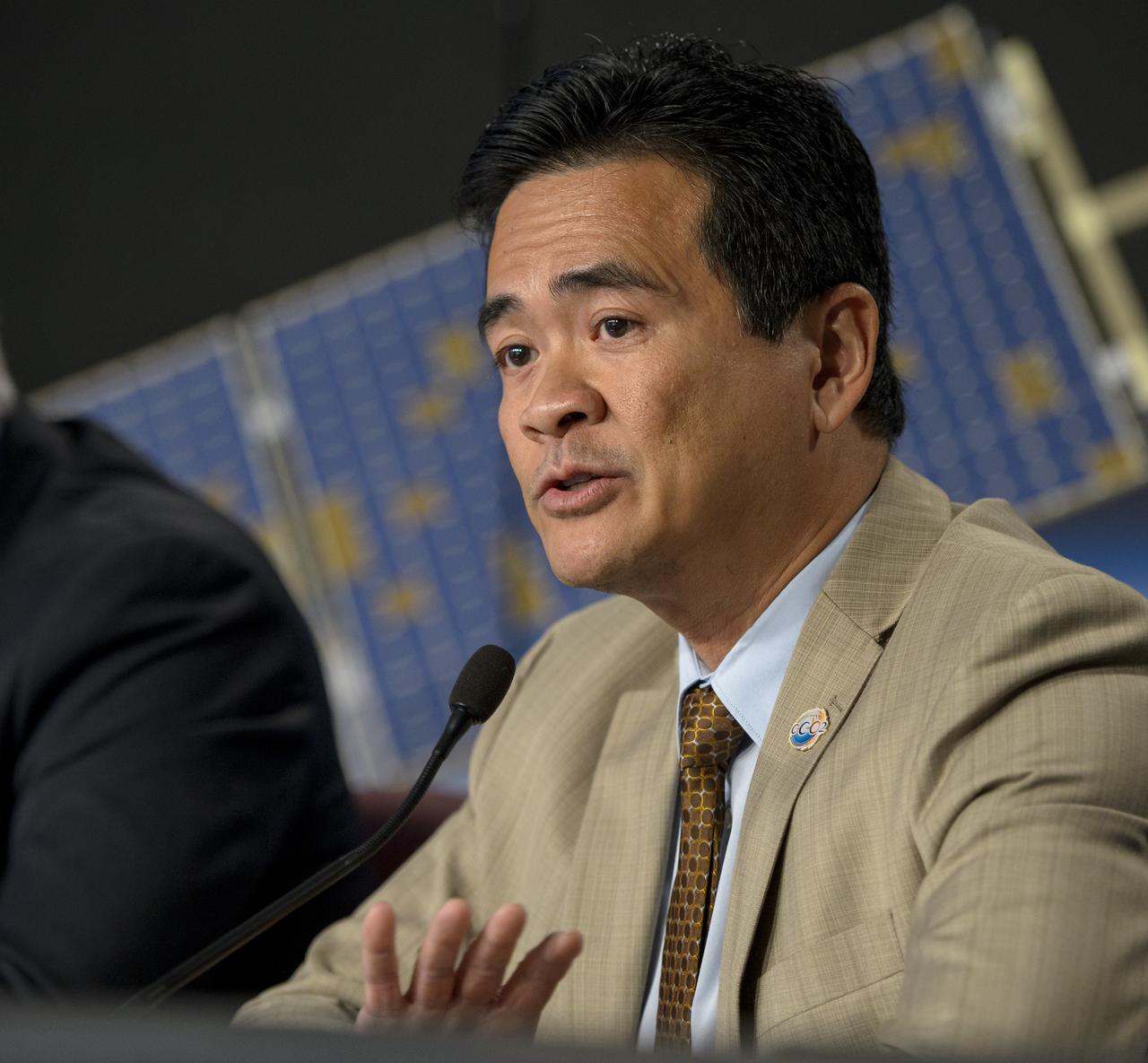

Ralph Basilio, OCO-2 project manager, JPL, discusses the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
Ralph Basilio, OCO-2 project manager with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, left, and Mike Gunson, OCO-2 project scientist at JPL, discuss the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Thursday, June 12, 2014, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Its mission is to measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Ralph Basilio, OCO-2 project manager, JPL, discusses the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
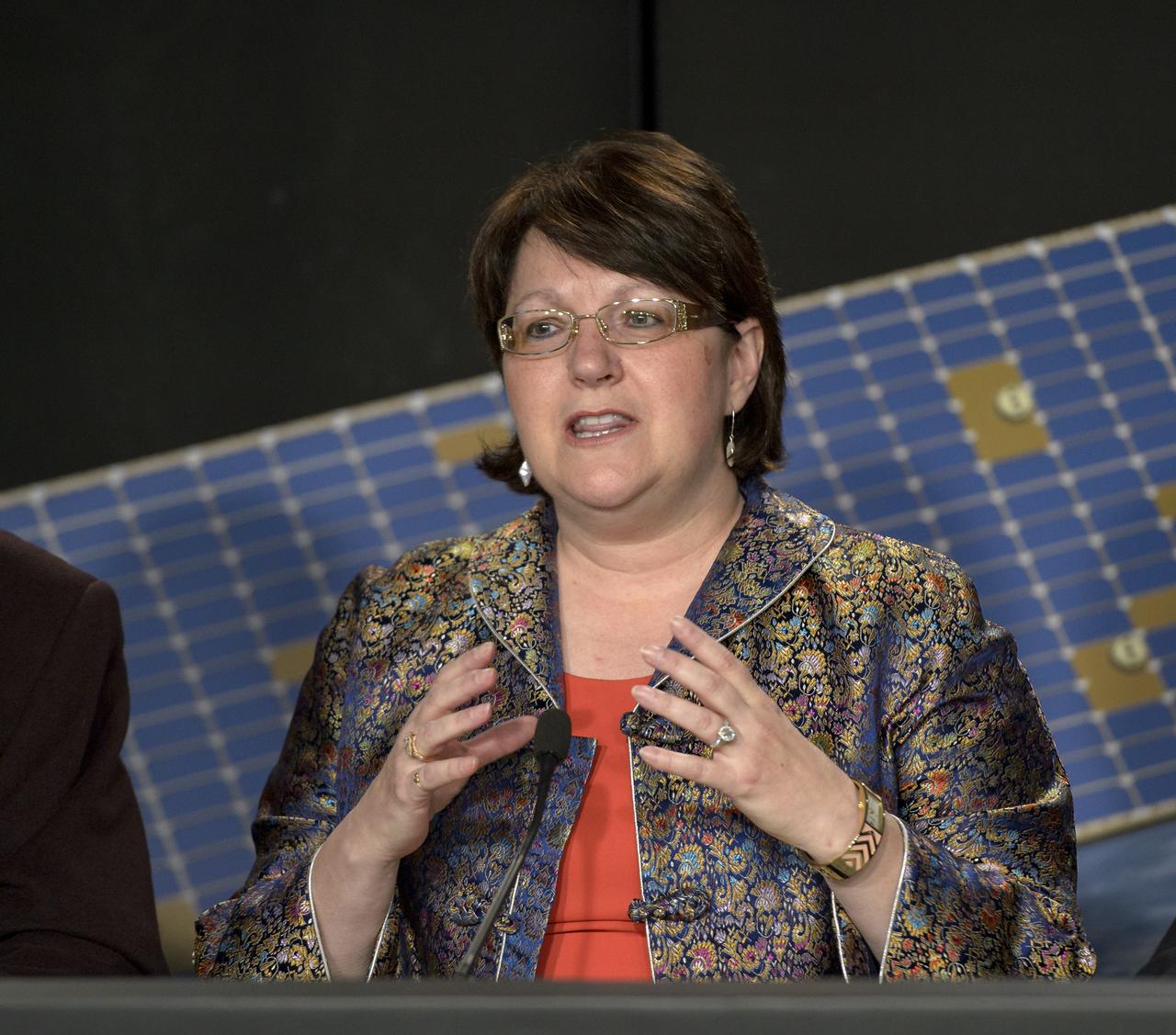

Betsy Edwards, OCO-2 program executive, NASA Headquarters, discusses the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
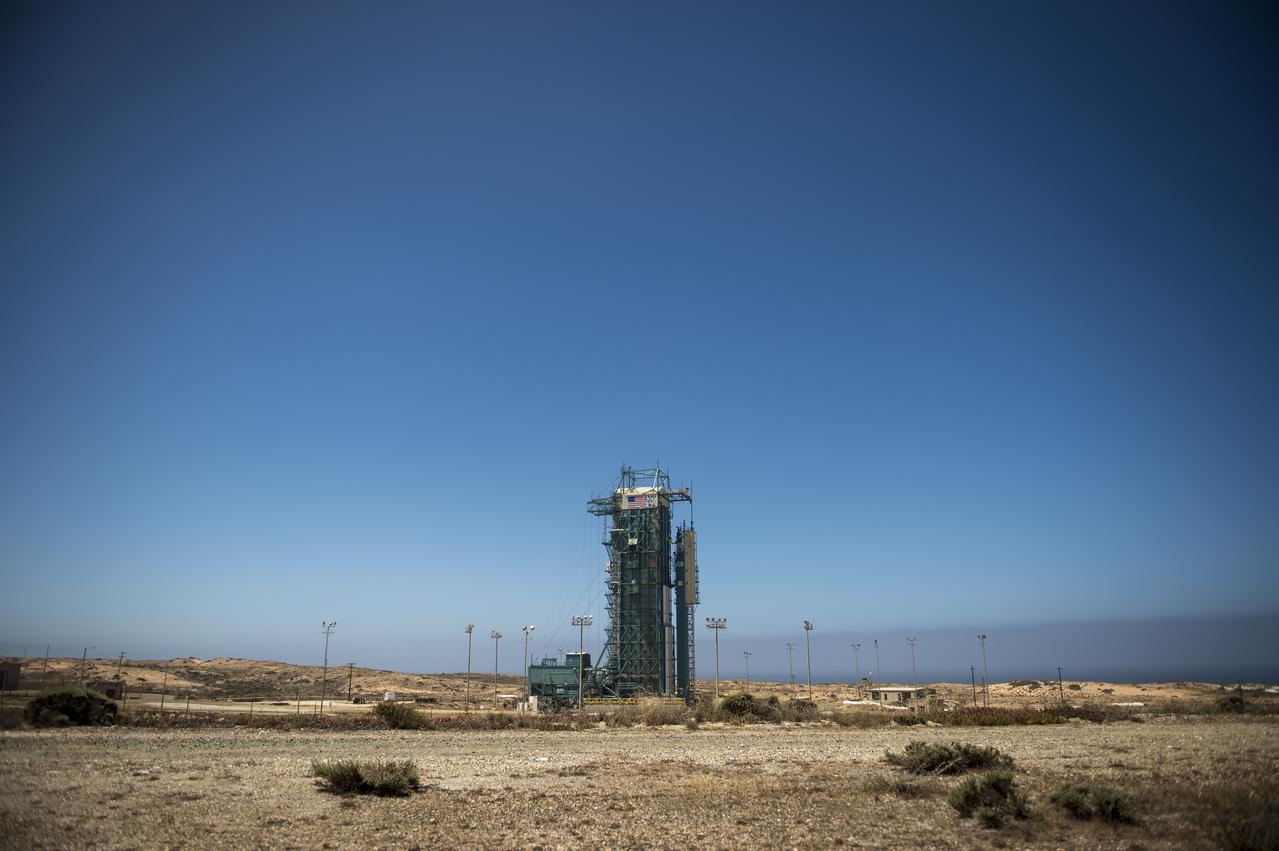

The launch gantry, surrounding the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard, is seen at the Space Launch Complex 2, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
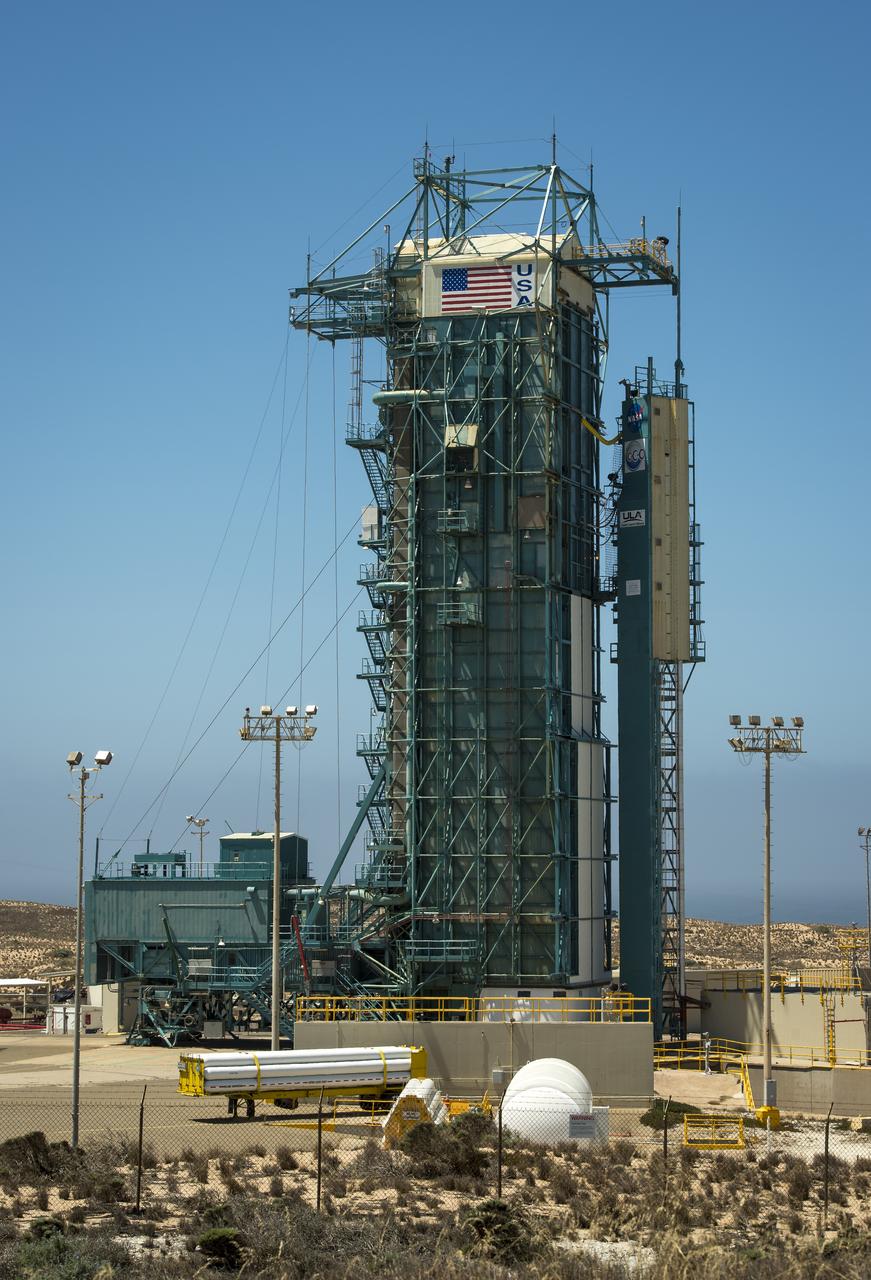

The launch gantry, surrounding the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard, is seen at the Space Launch Complex 2, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
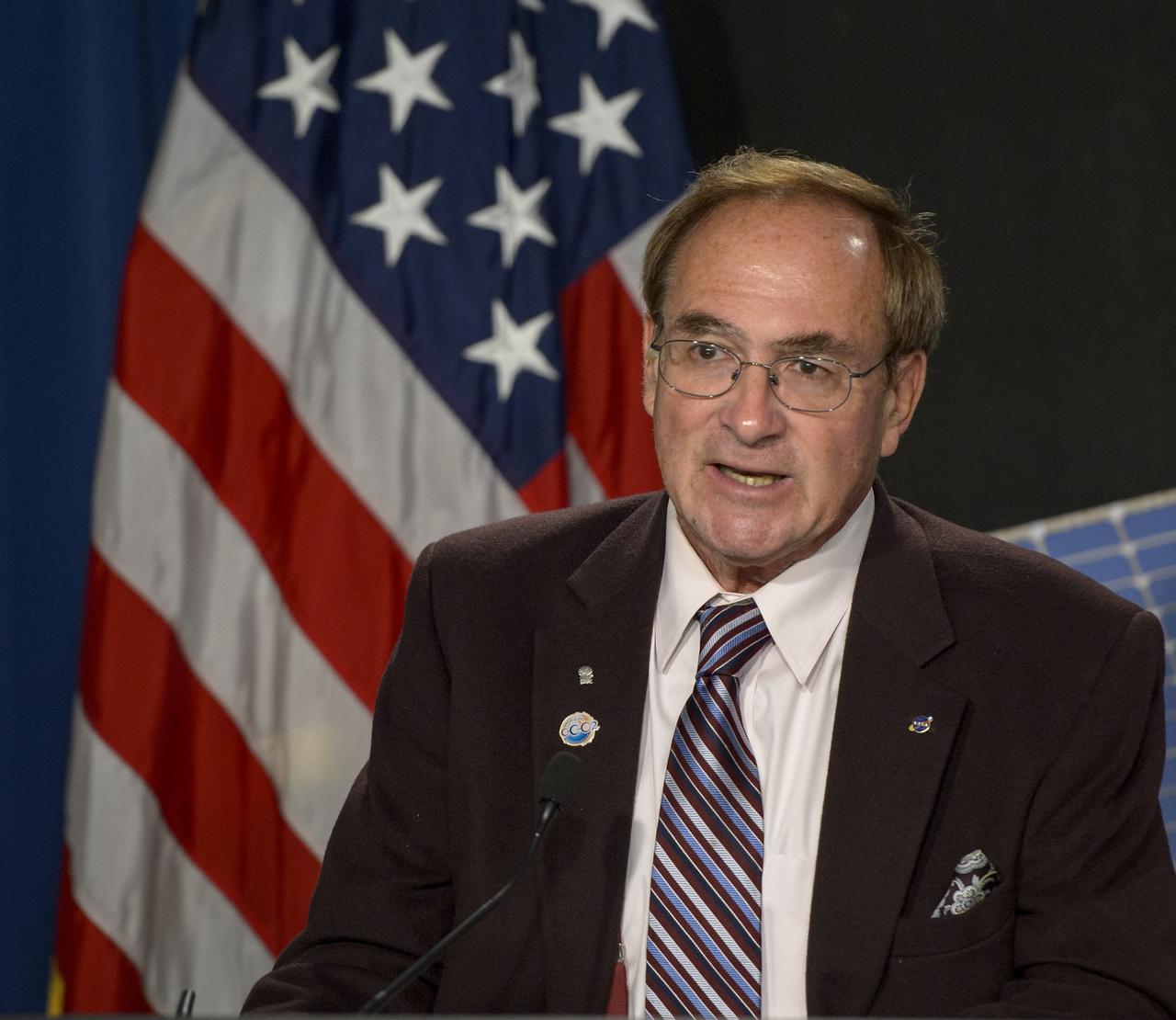

NASA Kennedy Space Center Public Affairs Officer George Diller, moderates a briefing ahead of the planned launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
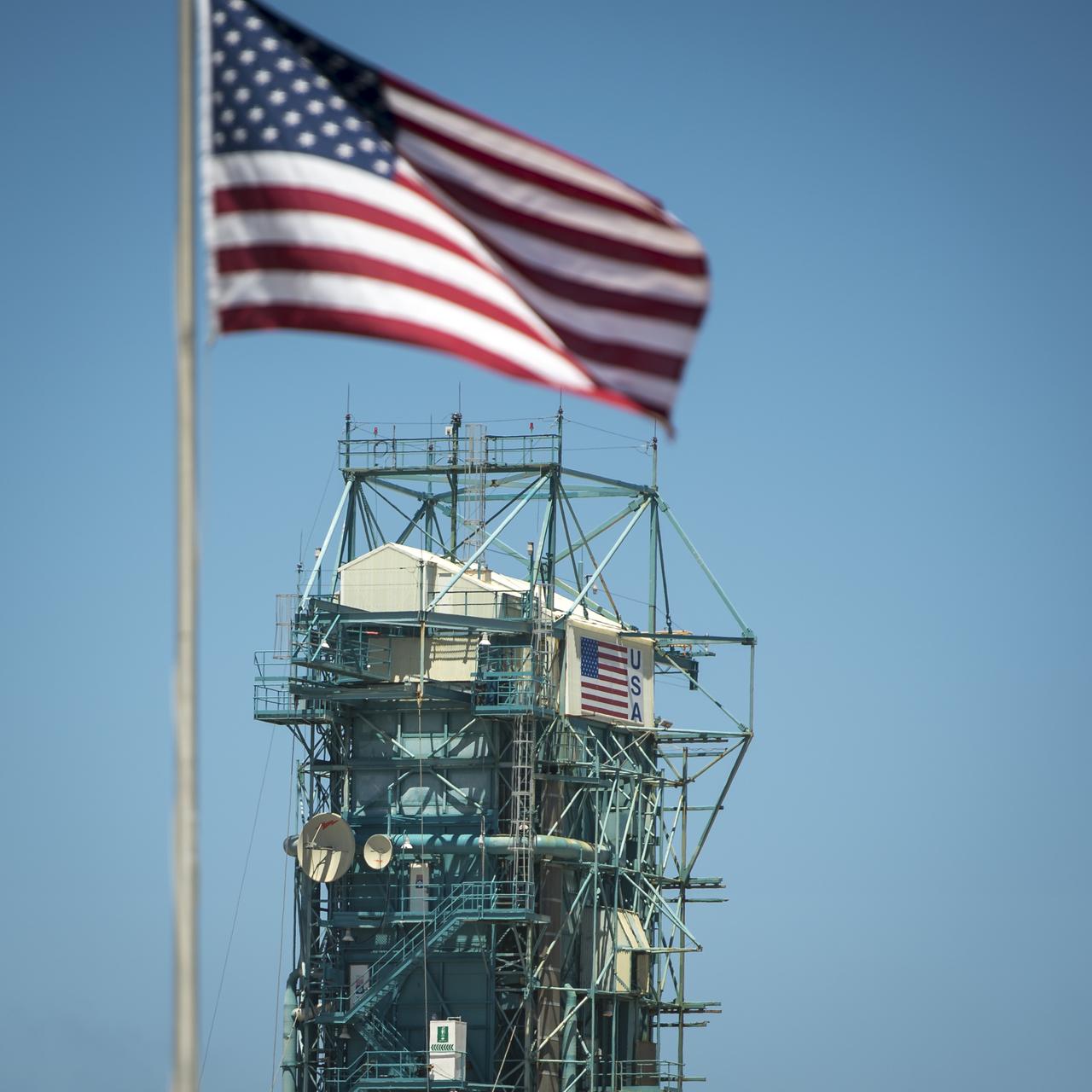

The upper levels of the launch gantry, surrounding the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard, are seen at the Space Launch Complex 2, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
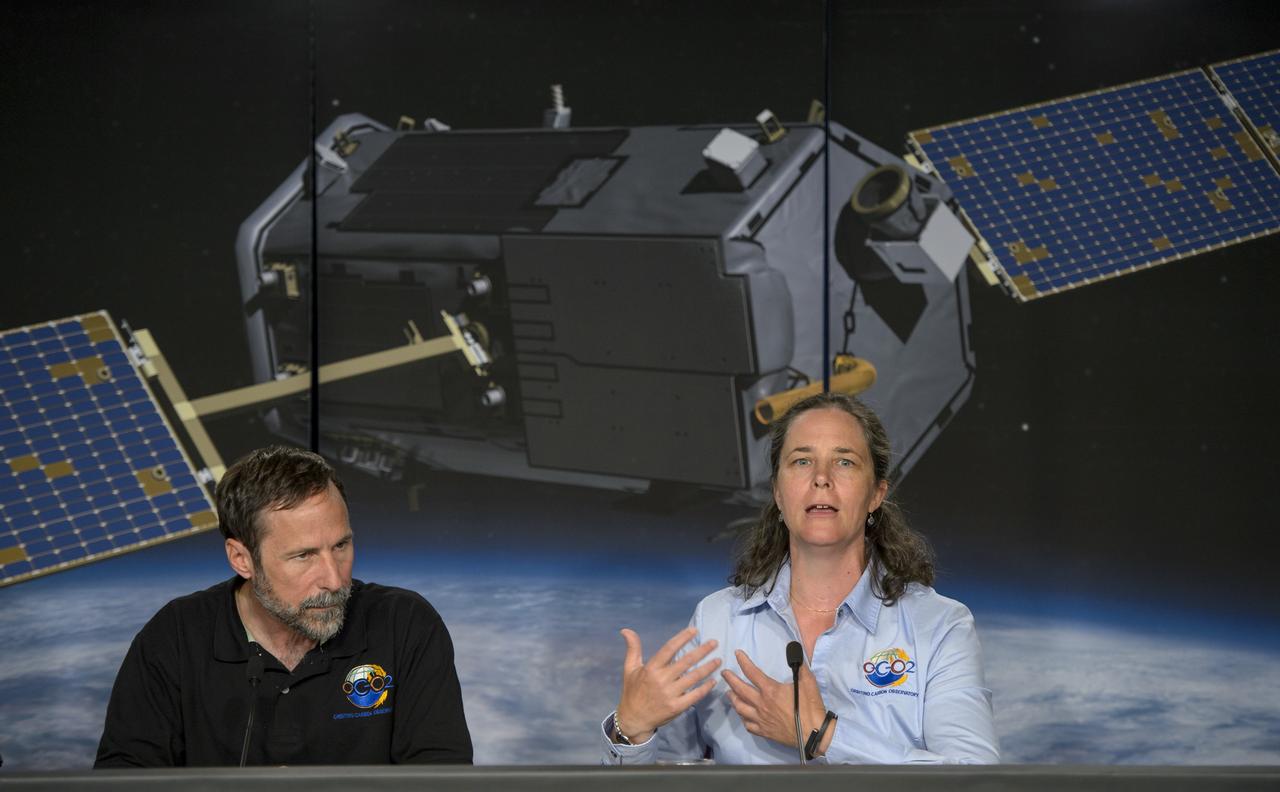

Dave Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader, JPL, left, and Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist, JPL, are seen during a science briefing ahead of the planned launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Mike Gunson, OCO-2 project scientist with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, listens to a question during a press briefing for the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, Thursday, June 12, 2014, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Its mission is to measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Ralph Basilio, OCO-2 project manager with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California discusses the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Thursday, June 12, 2014, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Its mission is to measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
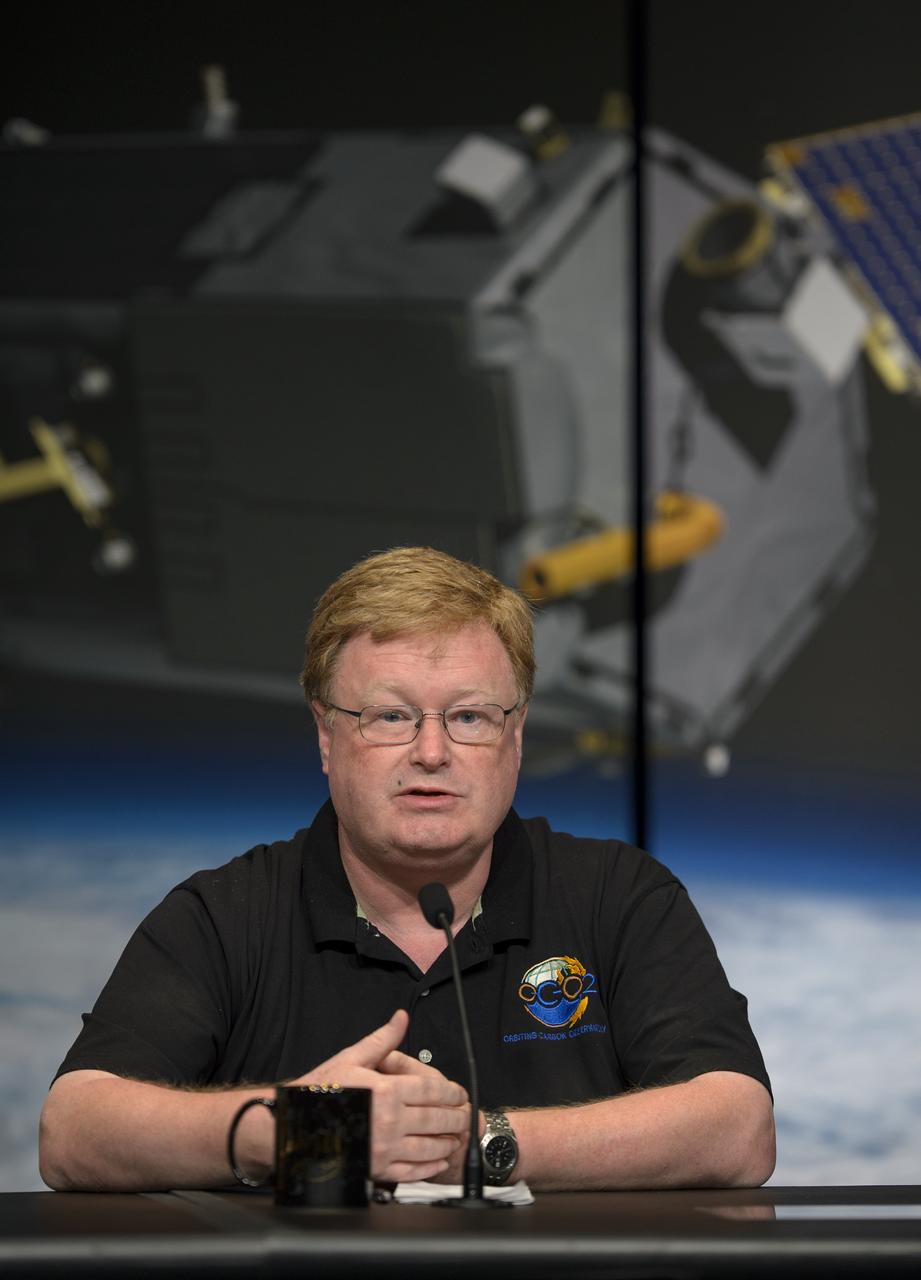

Mike Gunson, OCO-2 project scientist with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, discusses the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Thursday, June 12, 2014, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Its mission is to measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
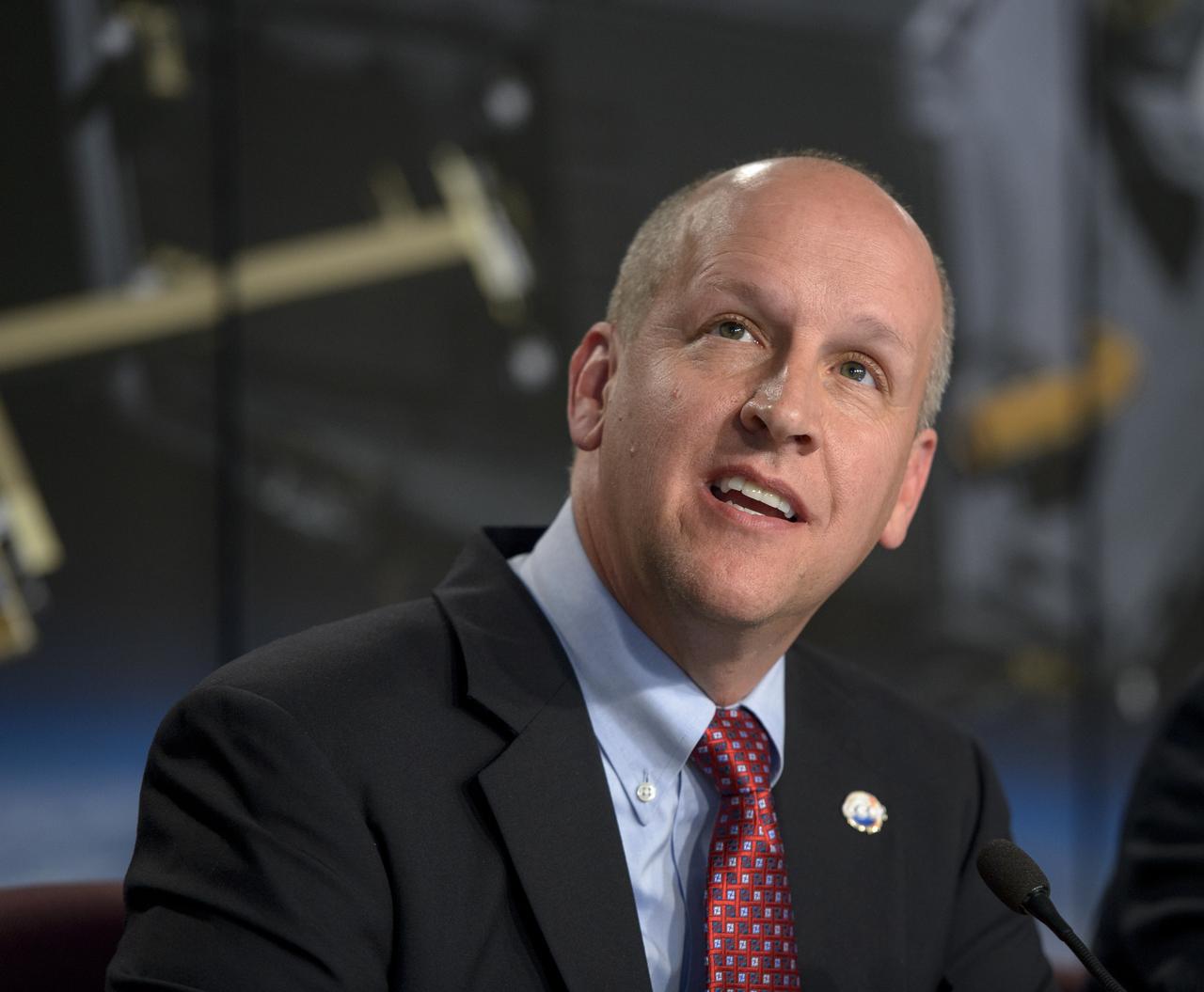

Tim Dunn, NASA launch director, Kennedy Space Center, discusses the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
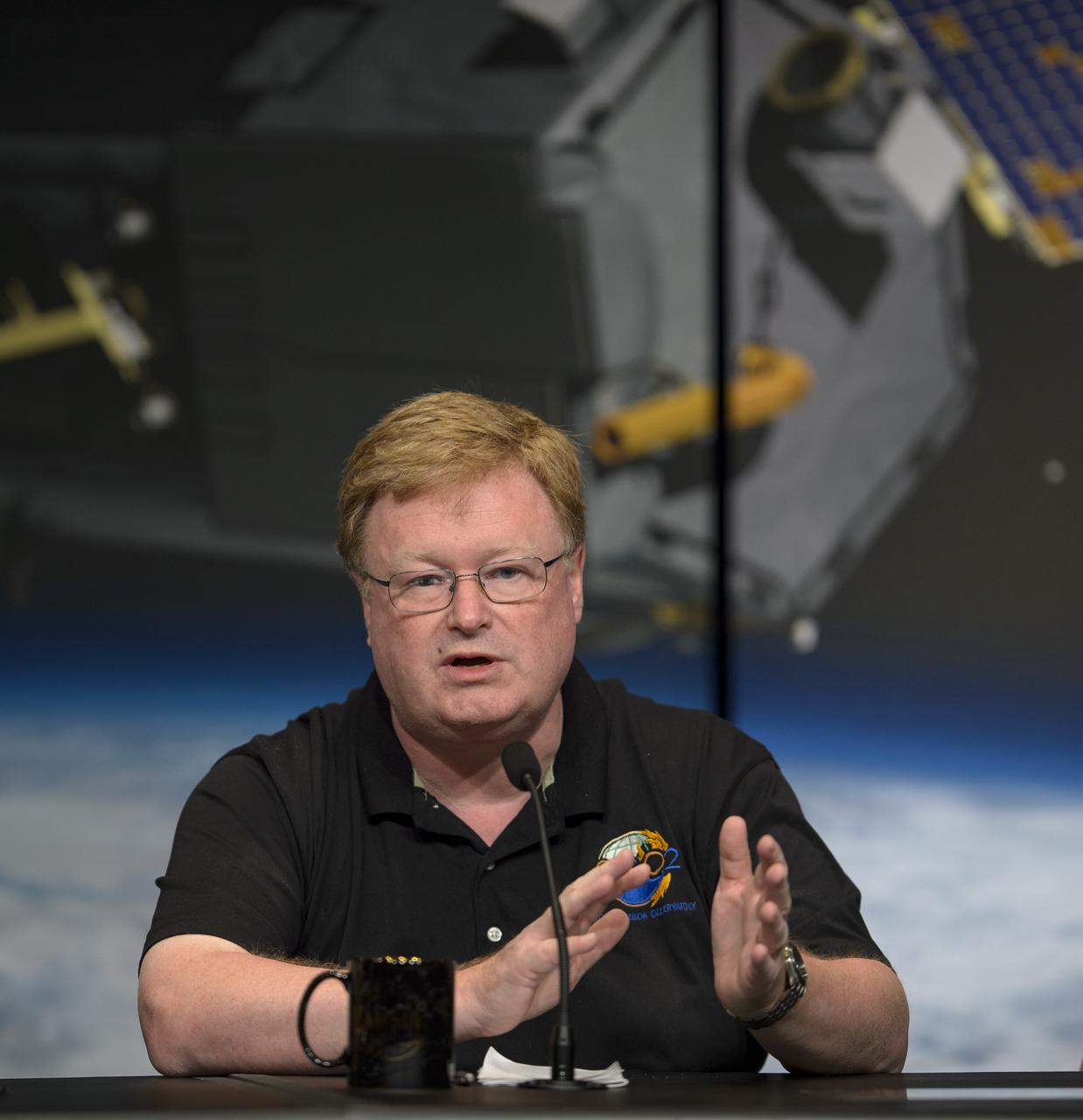

Mike Gunson, OCO-2 project scientist with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, discusses the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Thursday, June 12, 2014, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Its mission is to measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
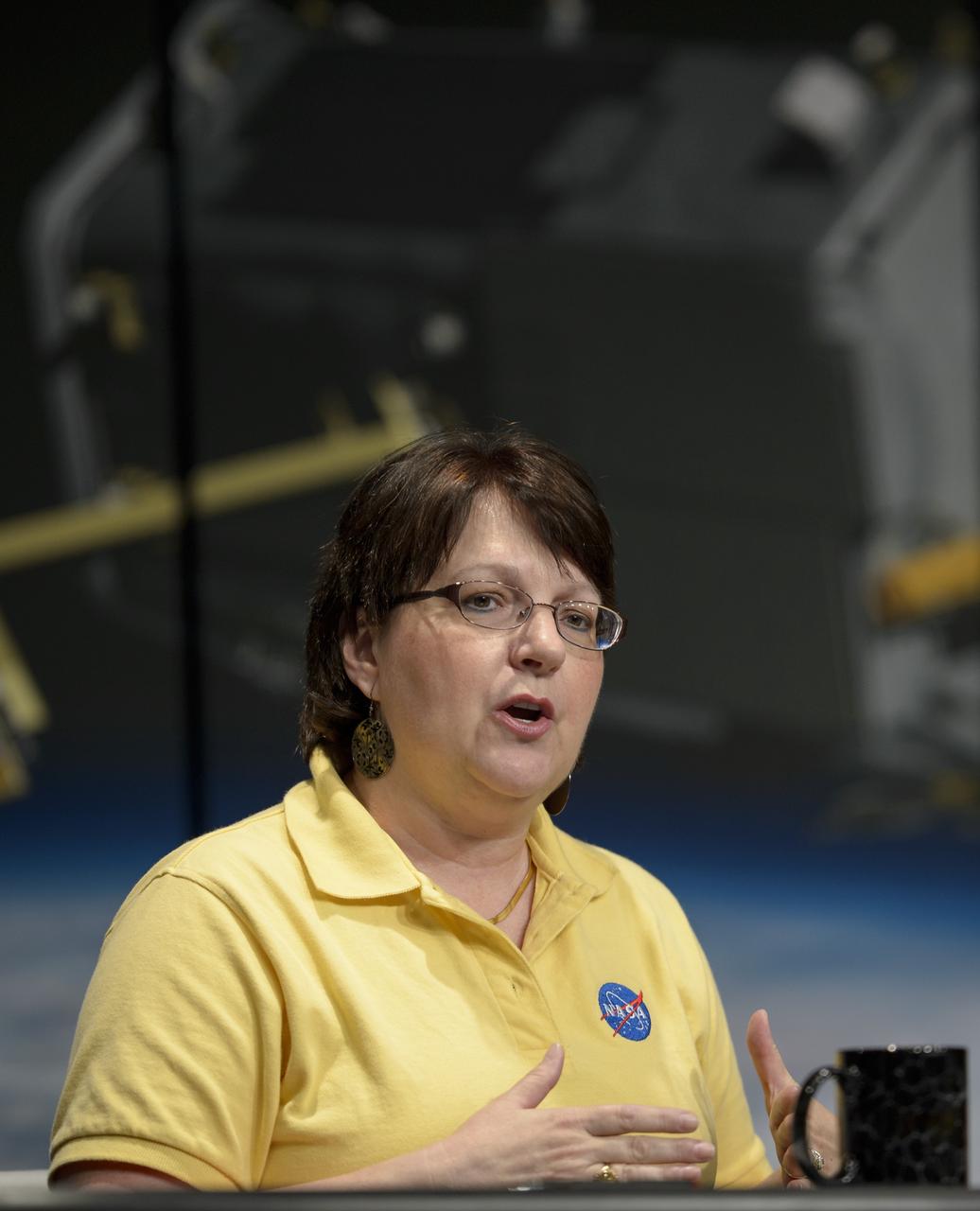

Betsy Edwards, OCO-2 program executive with the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters in Washington discusses the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Thursday, June 12, 2014, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Its mission is to measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
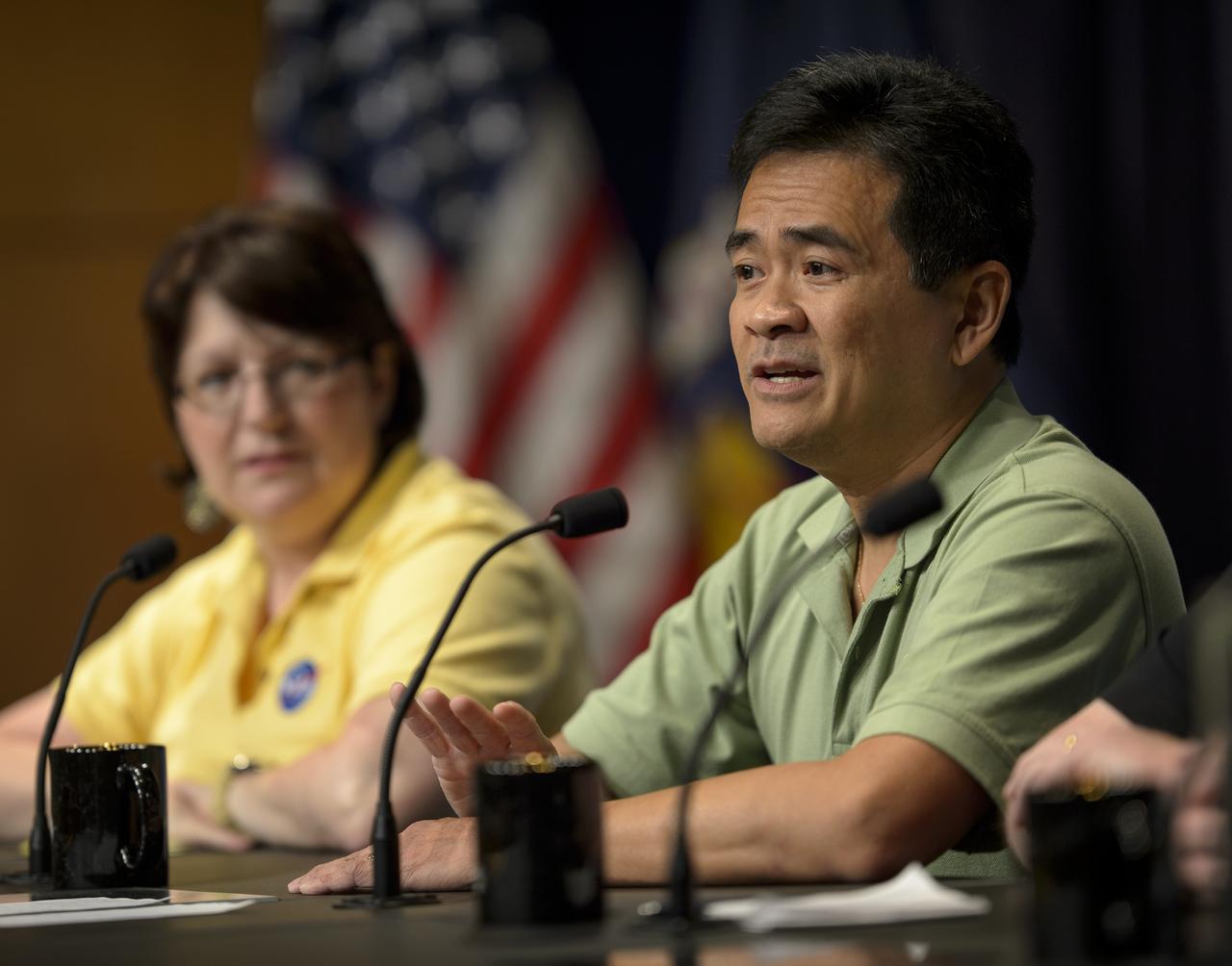

Ralph Basilio, OCO-2 project manager with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California discusses the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Thursday, June 12, 2014, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Its mission is to measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
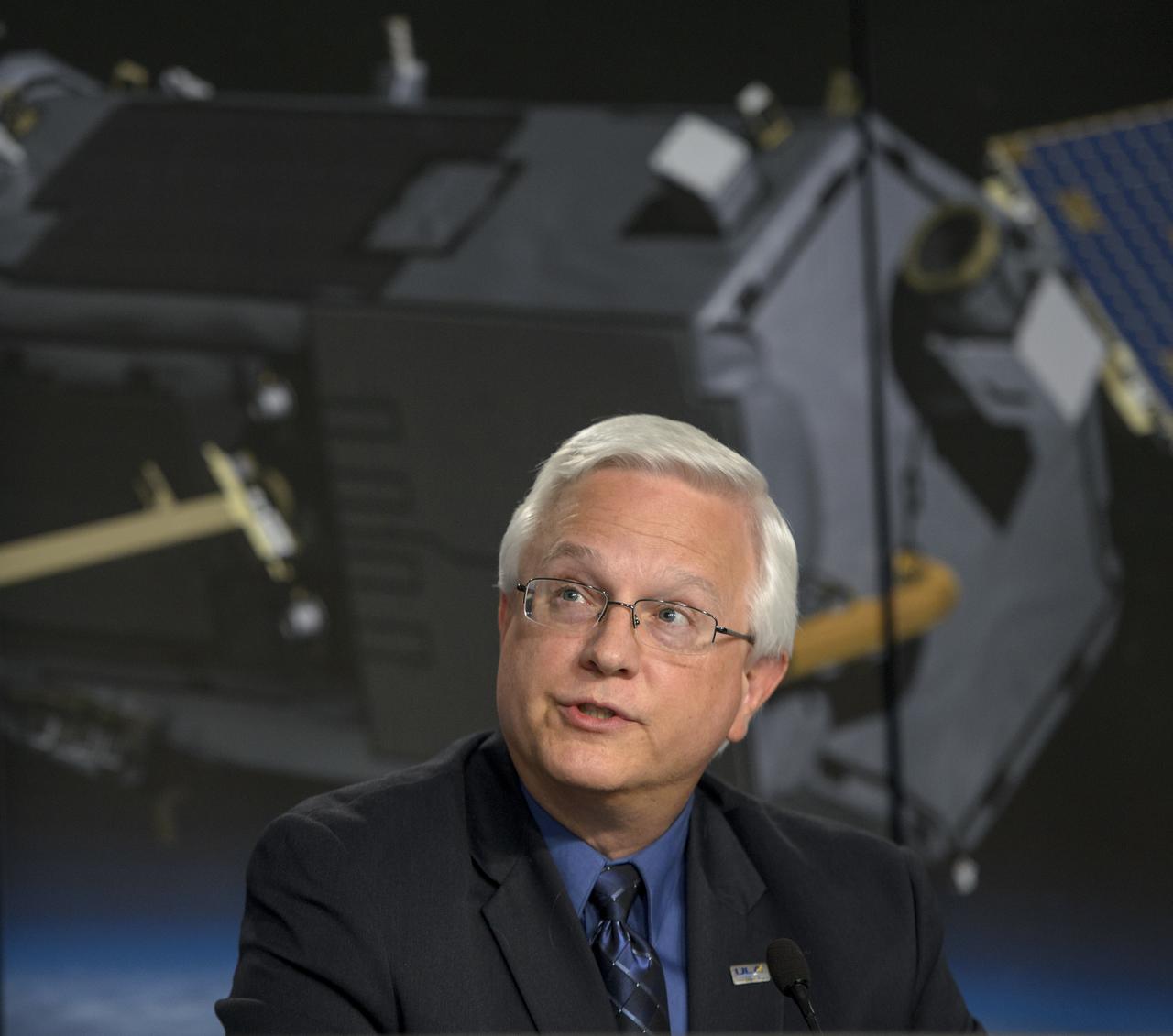

Vern Thorp, United Launch Alliance program manager, NASA missions, discusses the launch of NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) onboard a ULA Delta II rocket, during a press briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
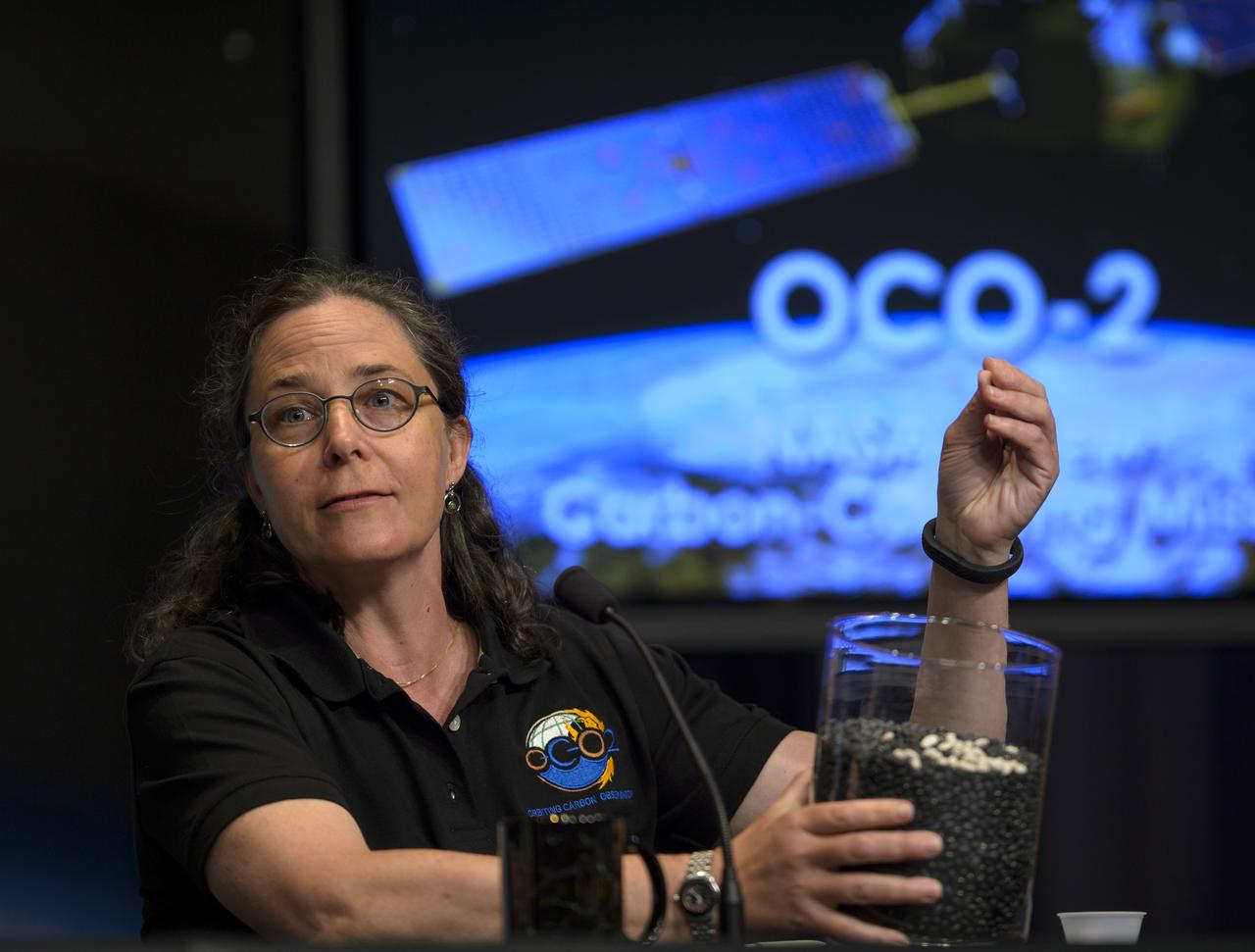

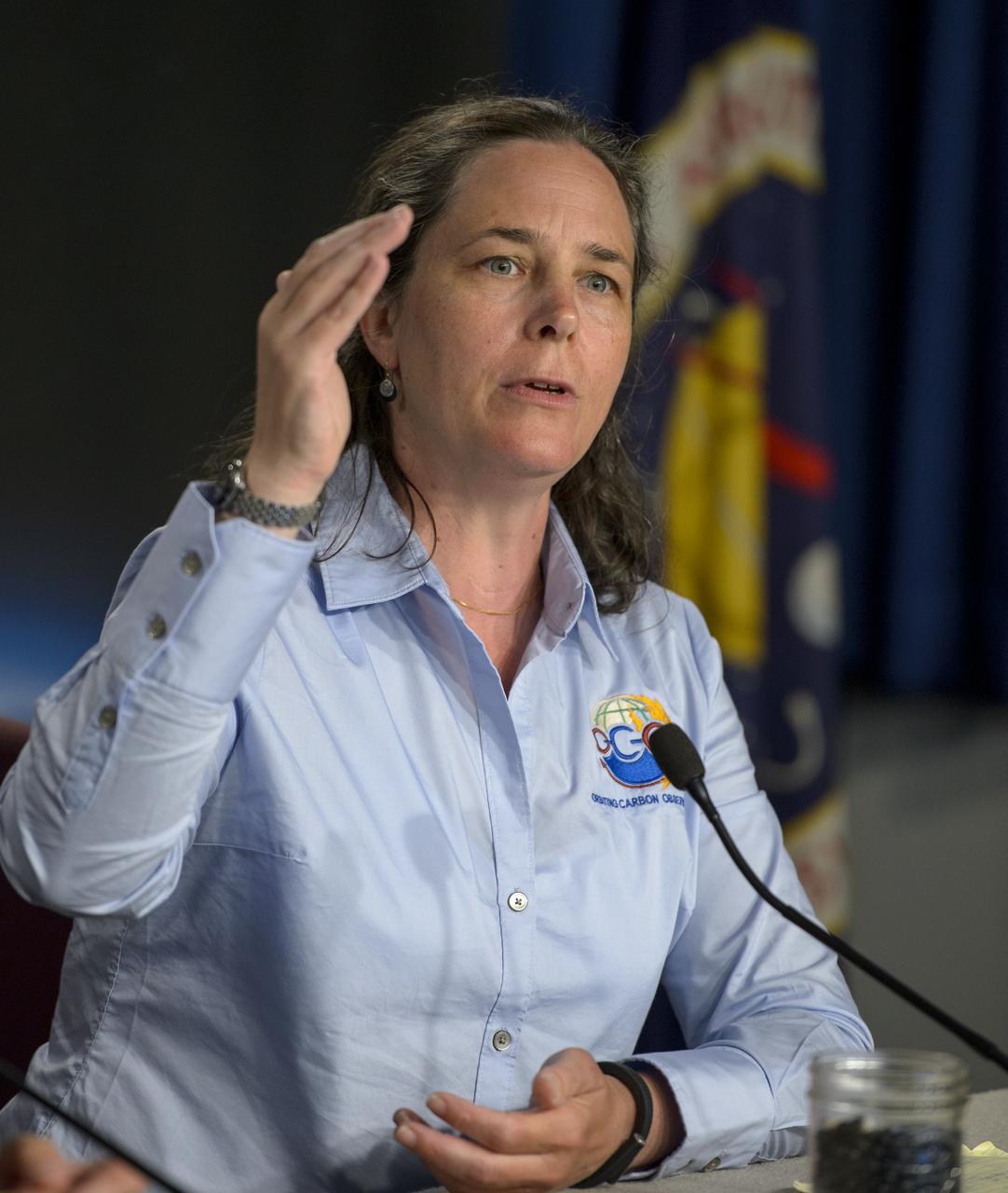
Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, demonstrates with a few white beans in a container of black beans the small differences in carbon dioxide in the atmosphere that the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) will be able to measure, during a press briefing, Thursday, June 12, 2014, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. OCO-2, NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, is set for a July 1, 2014, launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Its mission is to measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Ken Jucks, OCO-2 program scientist, NASA Headquarters, left, Dave Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader, JPL, and Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist, JPL, right, give a science briefing ahead of the planned launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
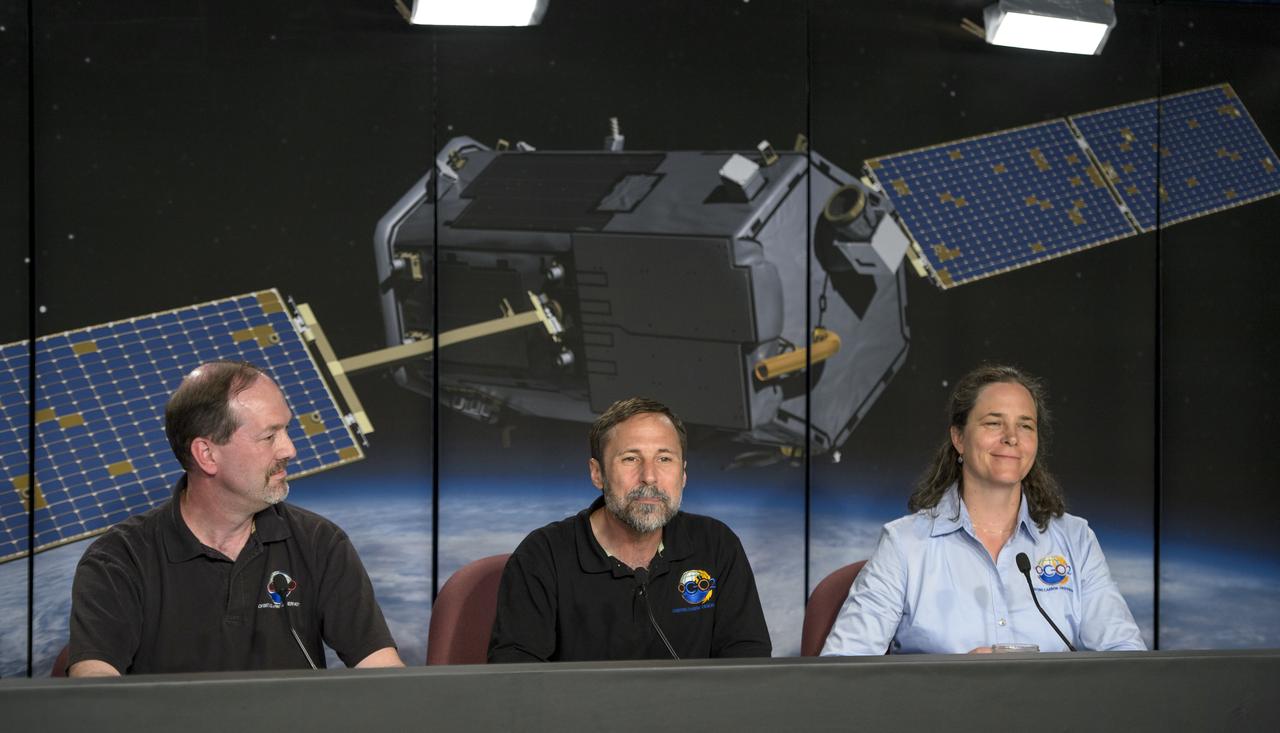

Ken Jucks, OCO-2 program scientist, NASA Headquarters, left, Dave Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader, JPL, and Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist, JPL, right, give a science briefing ahead of the planned launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
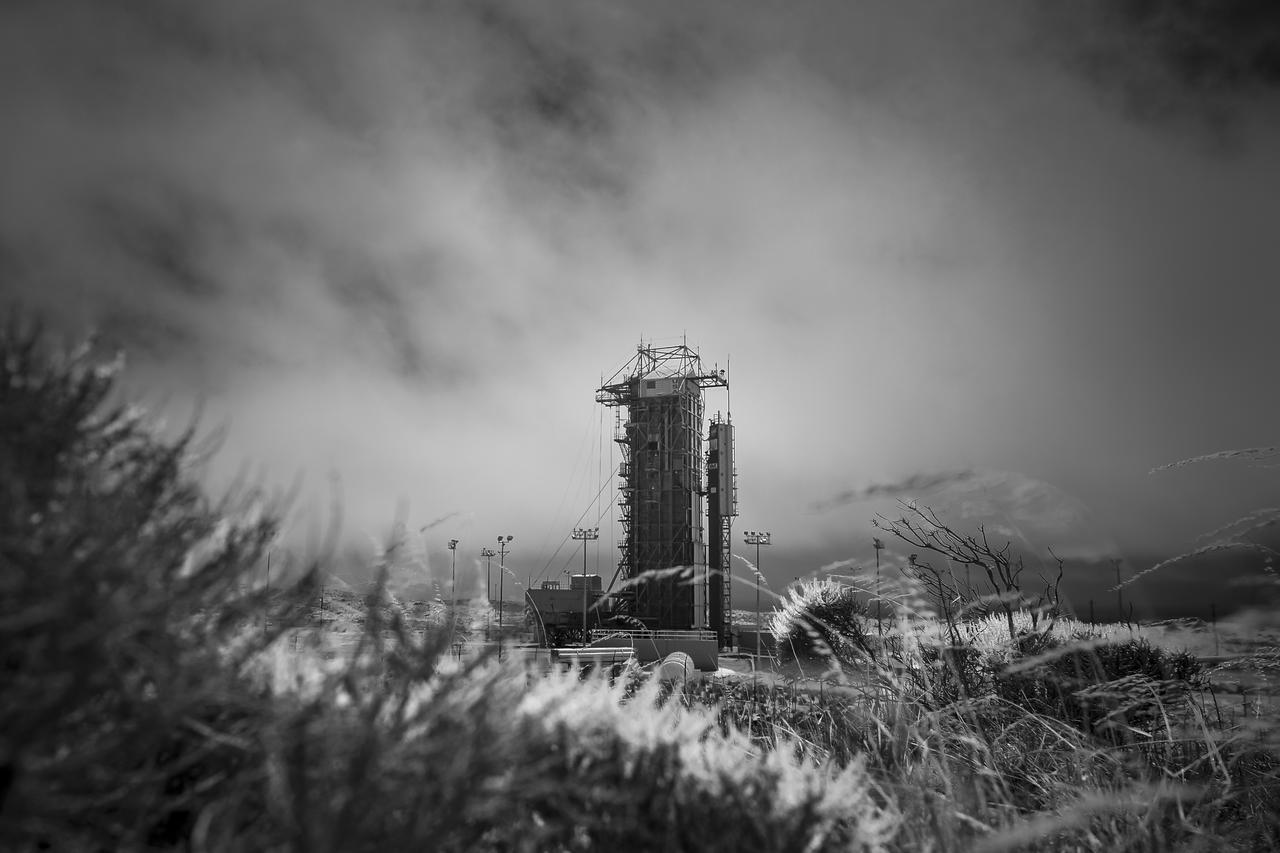

The launch gantry, surrounding the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard, is seen in this black and white infrared view at Space Launch Complex 2, Friday, June 27, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
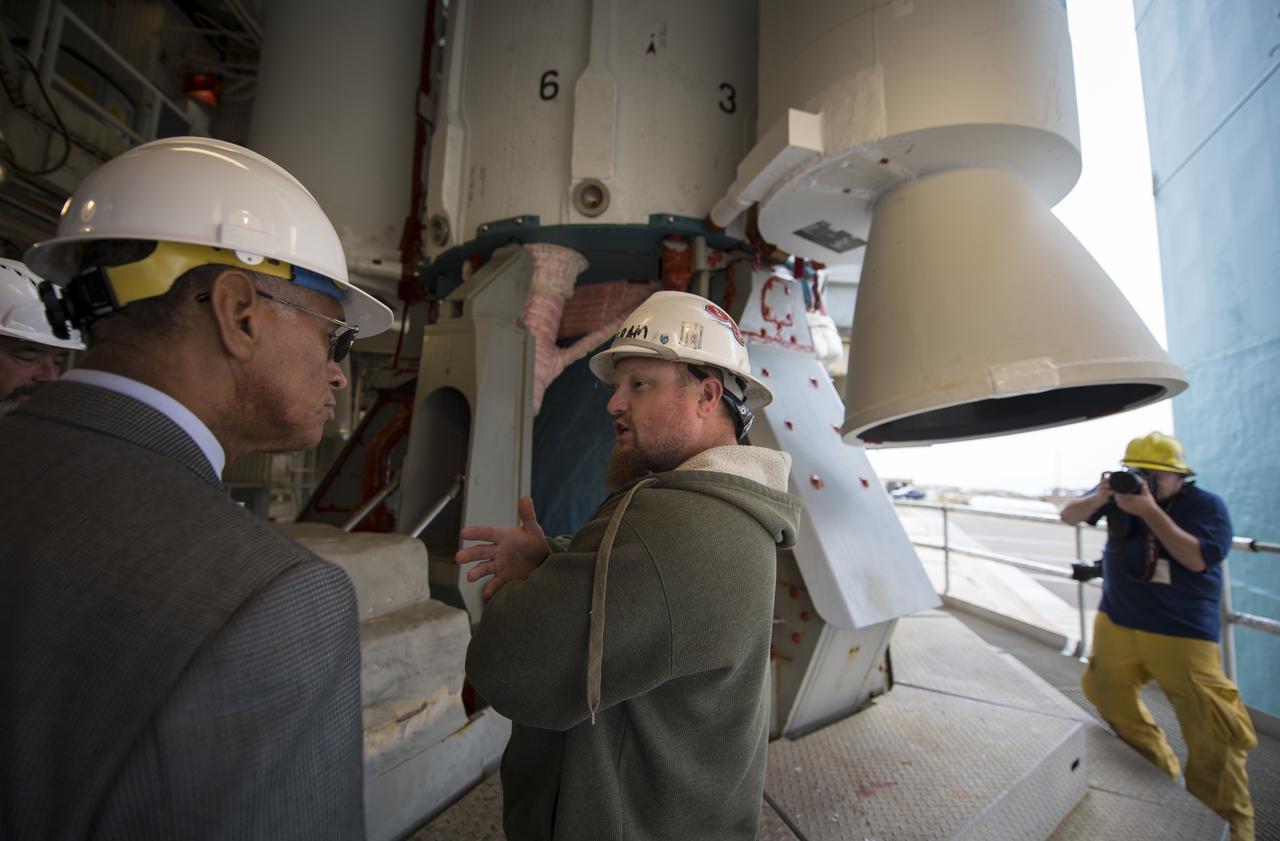

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden, left, talks with an engineer at the base of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard, Monday, June 30, 2014, Space Launch Complex 2, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Headquarters Public Affairs Officer Steve Cole, standing, moderates a Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) briefing with (from left), Betsy Edwards, OCO-2 program executive with the Science Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters, Ralph Basilio, OCO-2 project manager with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena, California, Mike Gunson, OCO-2 project scientist with JPL, and Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist JPL, , Thursday, June 12, 2014, at NASA Headquarters in Washington. OCO-2, NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, is set for a July 1, 2014 launch from Vandenberg Air Force Base in California. Its mission is to measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
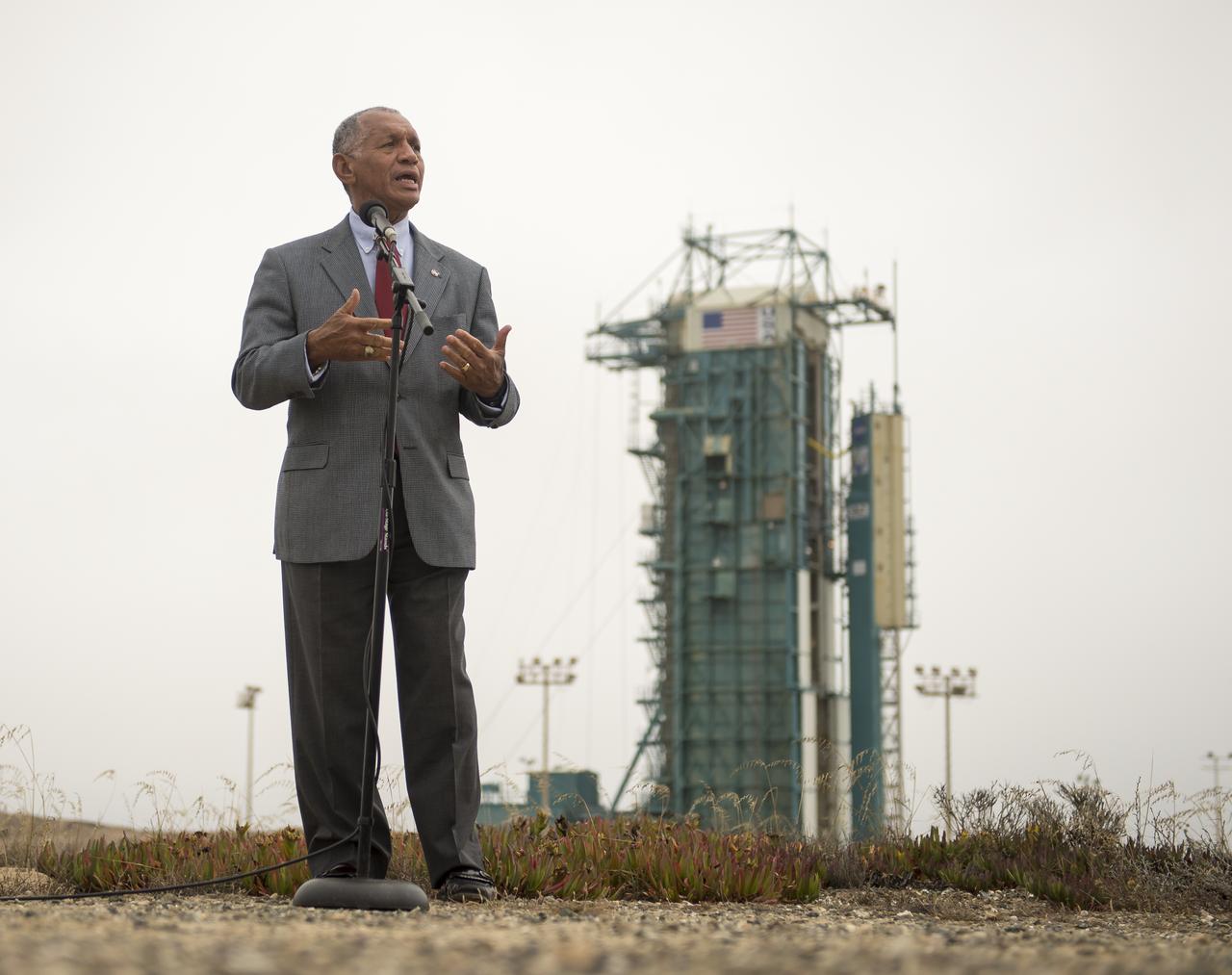

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden answers social media attendees questions from just outside the launch pad where the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard sits ready to launch, Monday, June 30, 2014, Space Launch Complex 2 Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
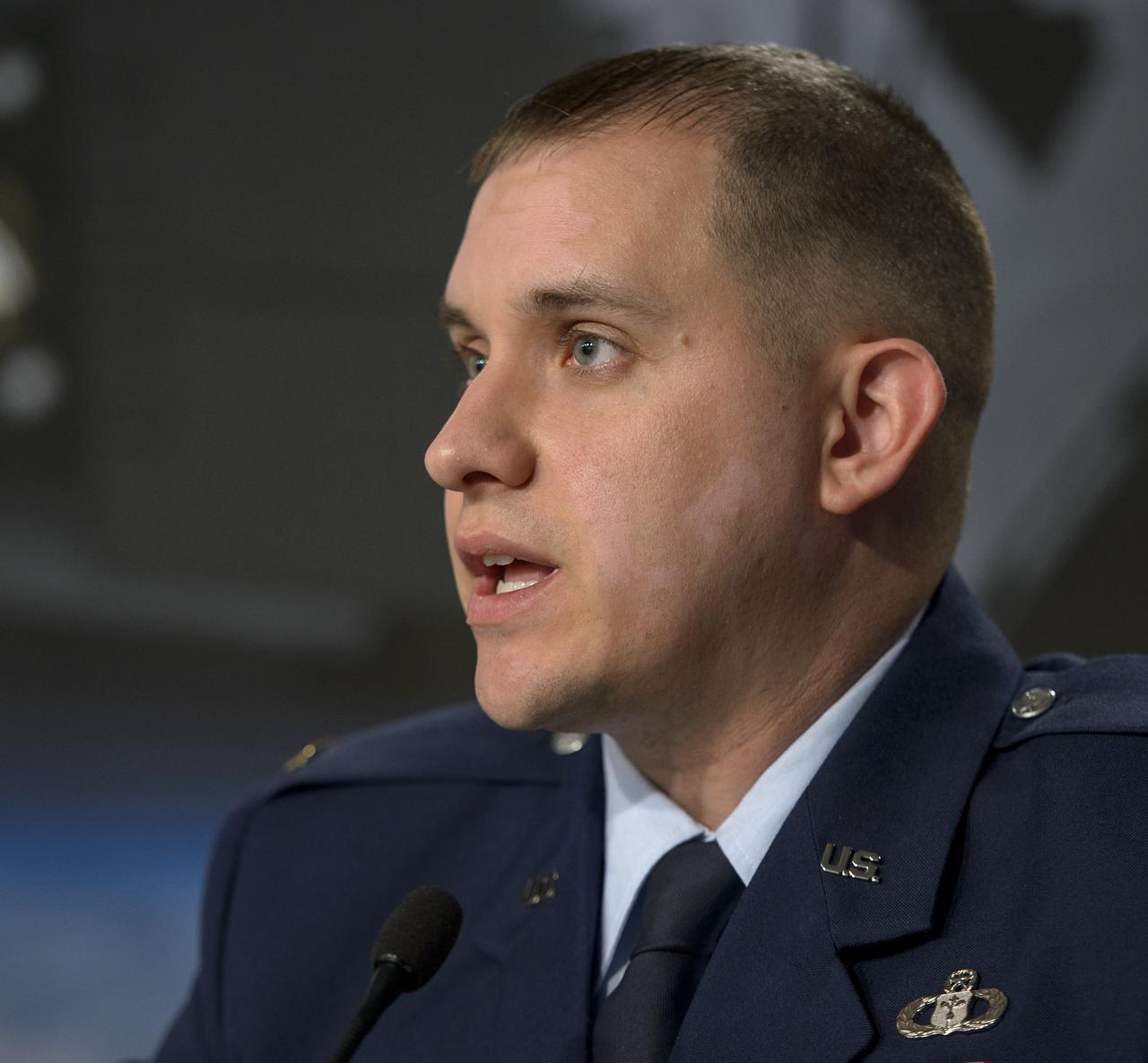

Lt. Joseph Round, launch weather officer, USAF 30th Space Wing Weather Squadron, discusses the weather forecast for launch of NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) onboard a ULA Delta II rocket, during a press briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

From left, NASA Kennedy Space Center Public Affairs Officer George Diller, Ken Jucks, OCO-2 program scientist, NASA Headquarters, Dave Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader, JPL, and Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist, JPL, give a science briefing ahead of the planned launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
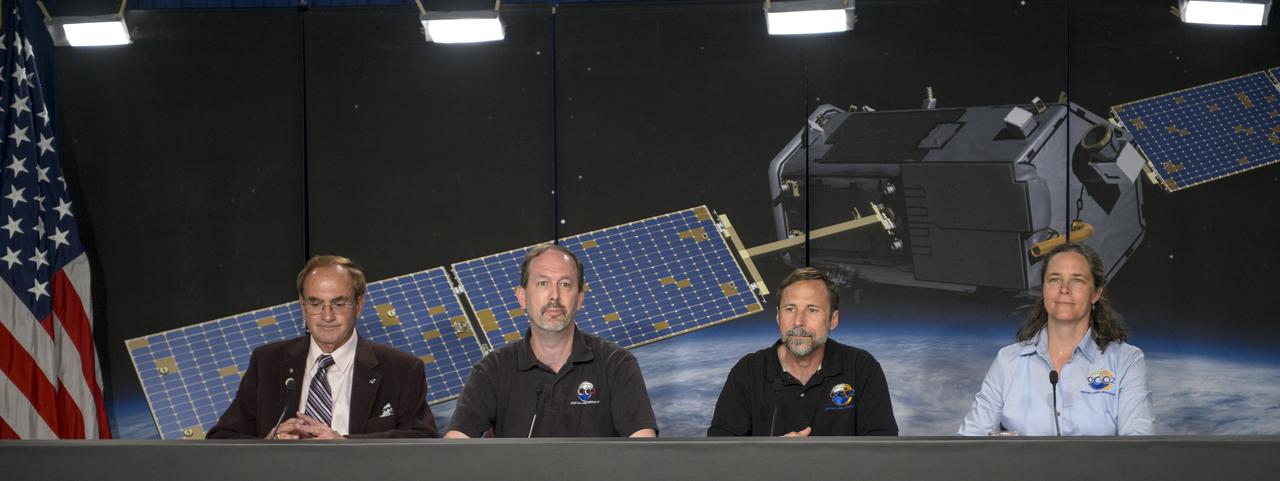

From left, NASA Kennedy Space Center Public Affairs Officer George Diller, Ken Jucks, OCO-2 program scientist, NASA Headquarters, Dave Crisp, OCO-2 science team leader, JPL, and Annmarie Eldering, OCO-2 deputy project scientist, JPL, give a science briefing ahead of the planned launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
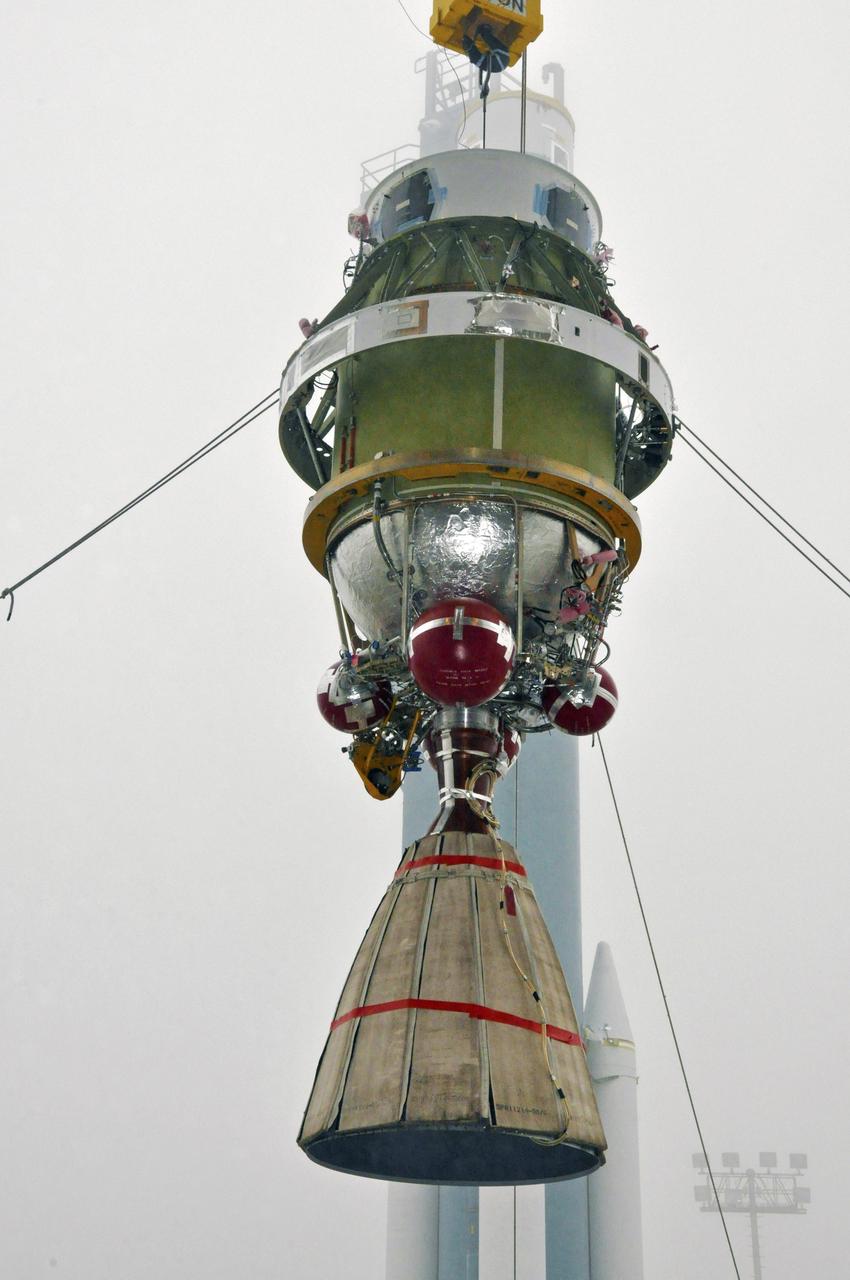

The Delta II second stage for NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is lifted to the top of the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
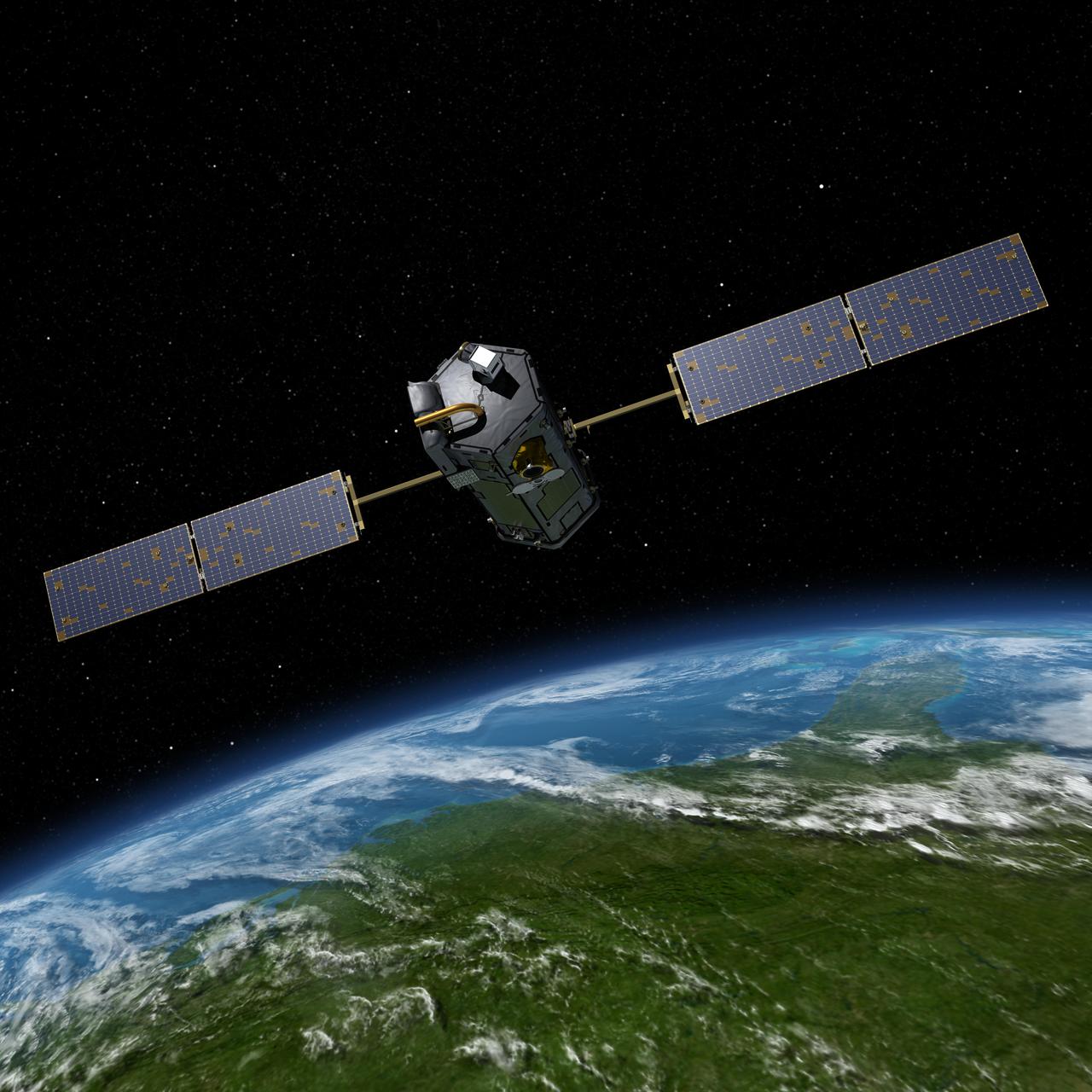

Artist rendering of NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory OCO-2, one of five new NASA Earth science missions set to launch in 2014, and one of three managed by JPL.
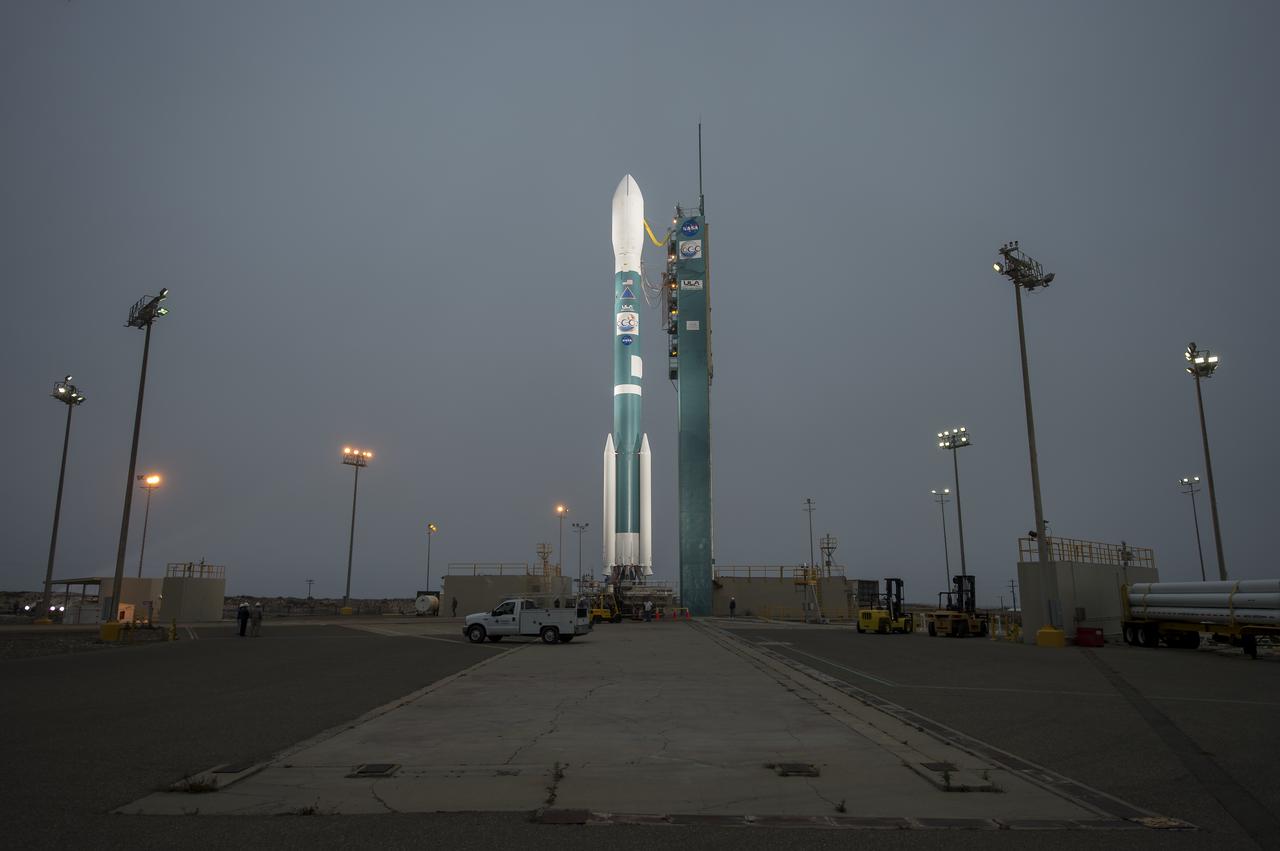

The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard, is seen moments after the launch gantry was moved at the Space Launch Complex 2, Monday, June 30, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
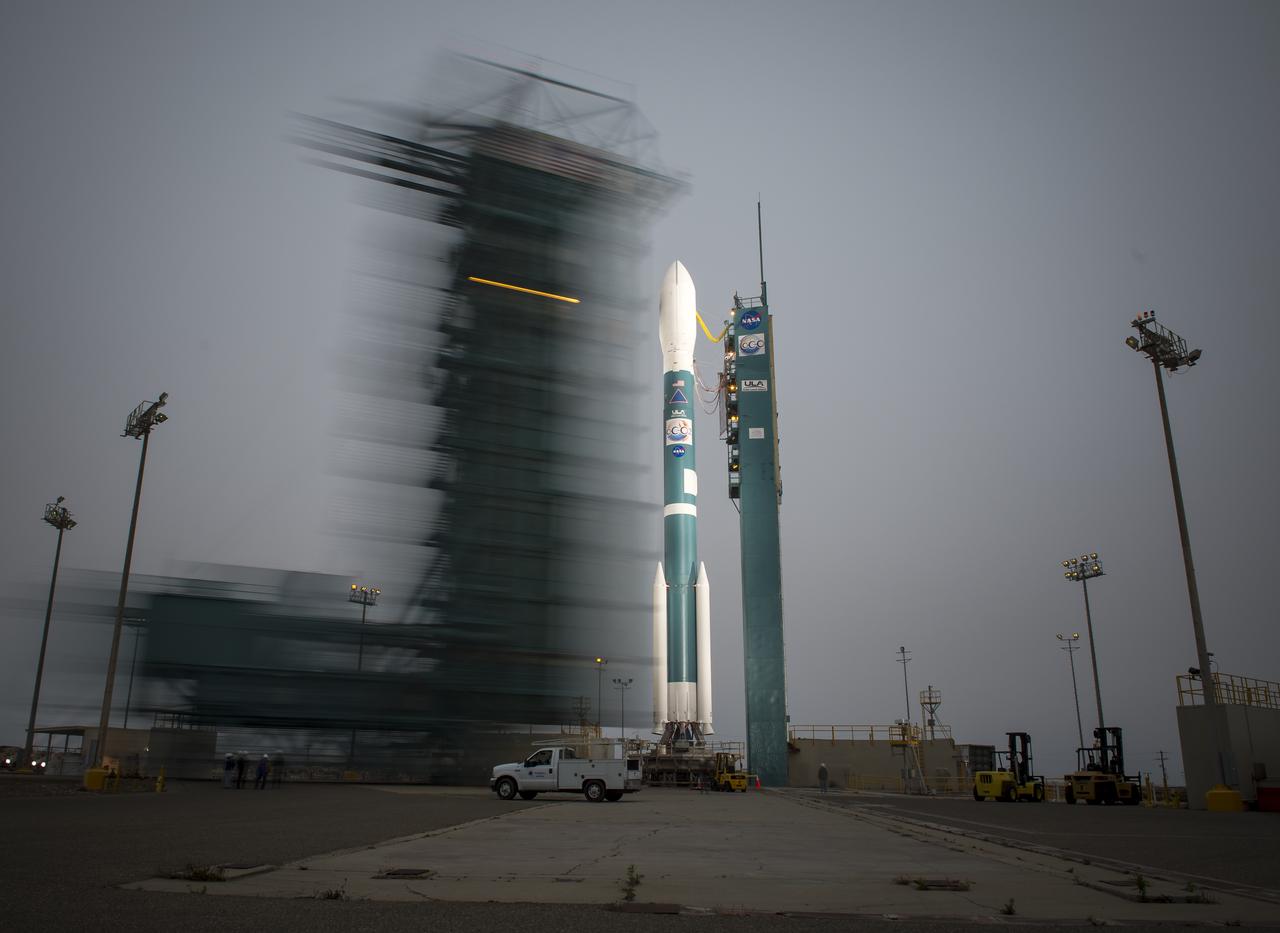

The launch gantry is rolled back to reveal the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard, at the Space Launch Complex 2, Monday, June 30, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
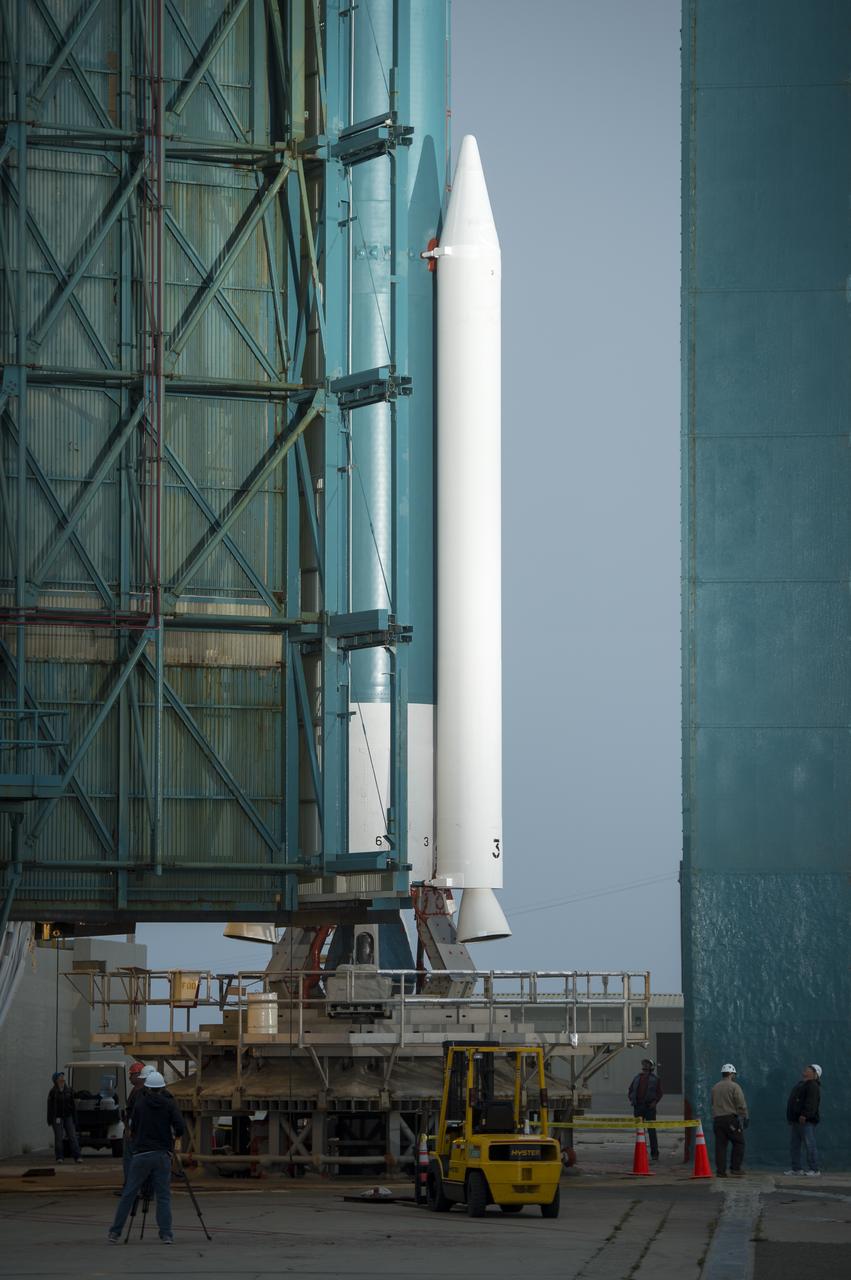

Workers monitor the progress of the rollback of the launch gantry from the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard, at Space Launch Complex 2, Monday, June 30, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
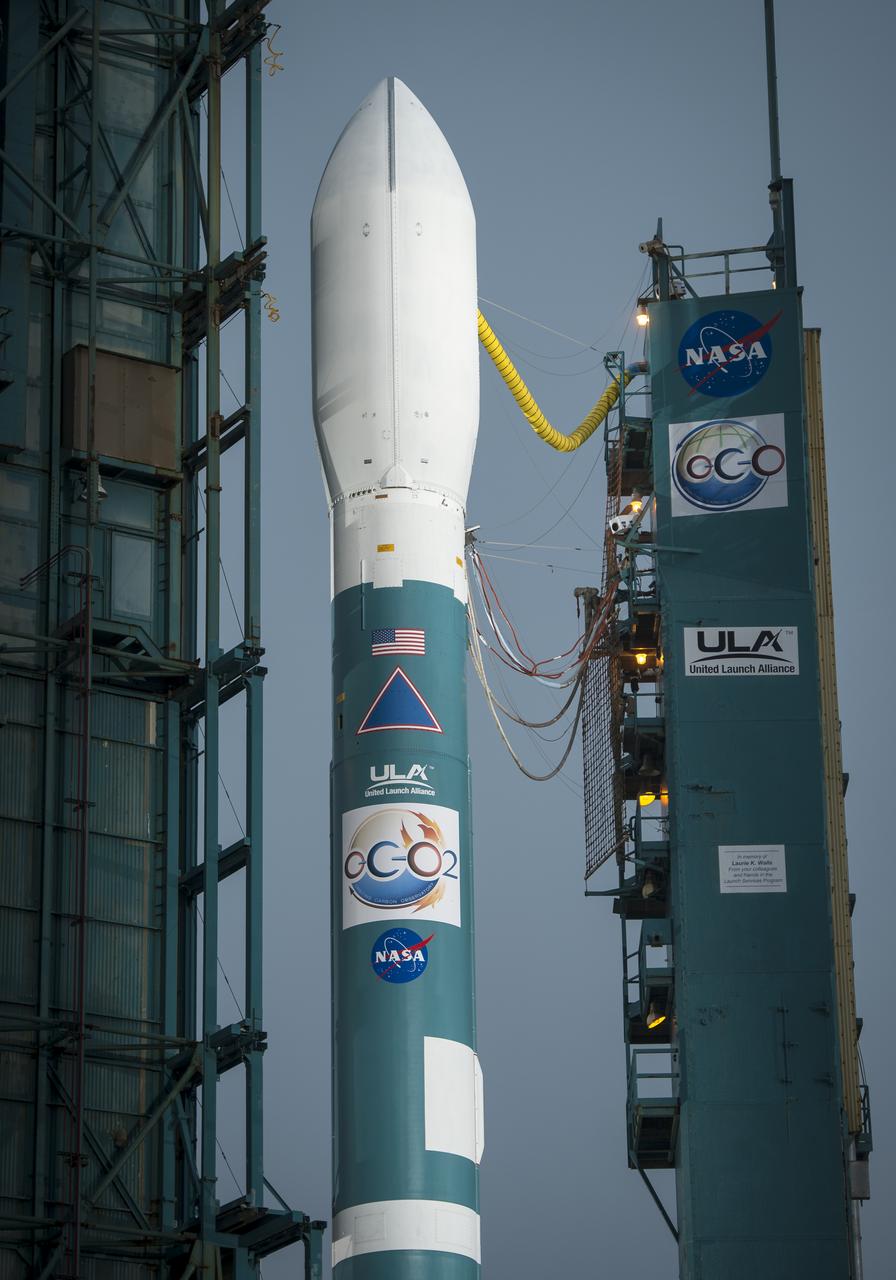

The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard, is seen as the launch gantry is moved at the Space Launch Complex 2, Monday, June 30, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set for a July 1, 2014 launch. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
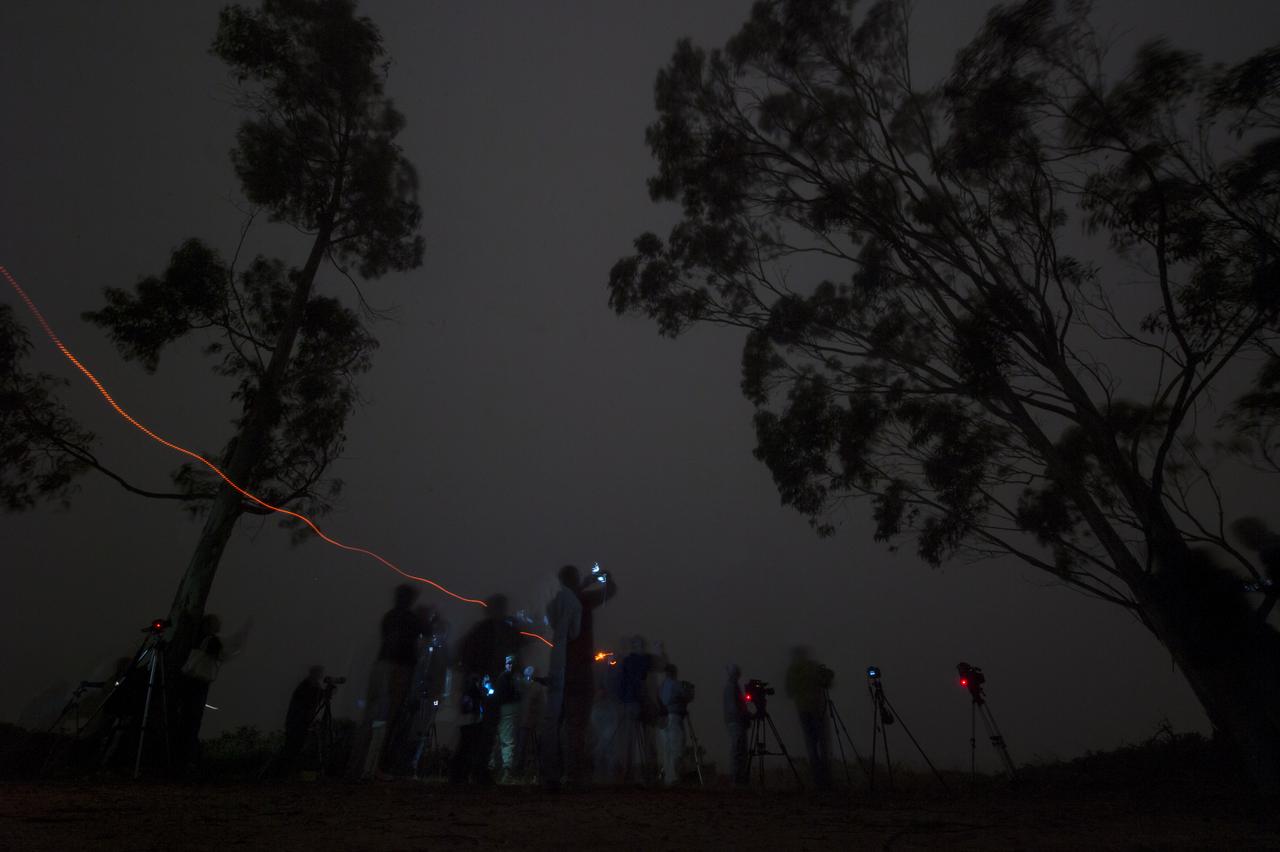

Members of the media are unable to see the launch of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite onboard due to heavy fog at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Wednesday, July 2, 2014. OCO-2 launched at 2:56 a.m. PDT. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
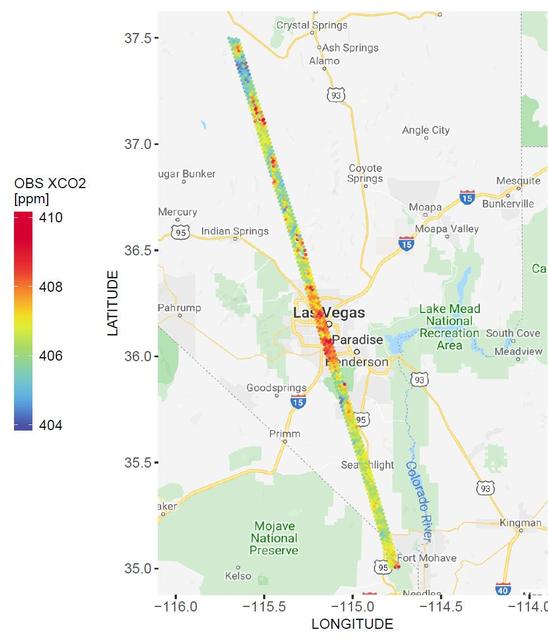
A spatial map of the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) present in columns of the atmosphere below NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) satellite as it flew over Las Vegas on Feb. 8, 2018. Warmer colors over the city center indicate higher amounts of carbon dioxide. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23781
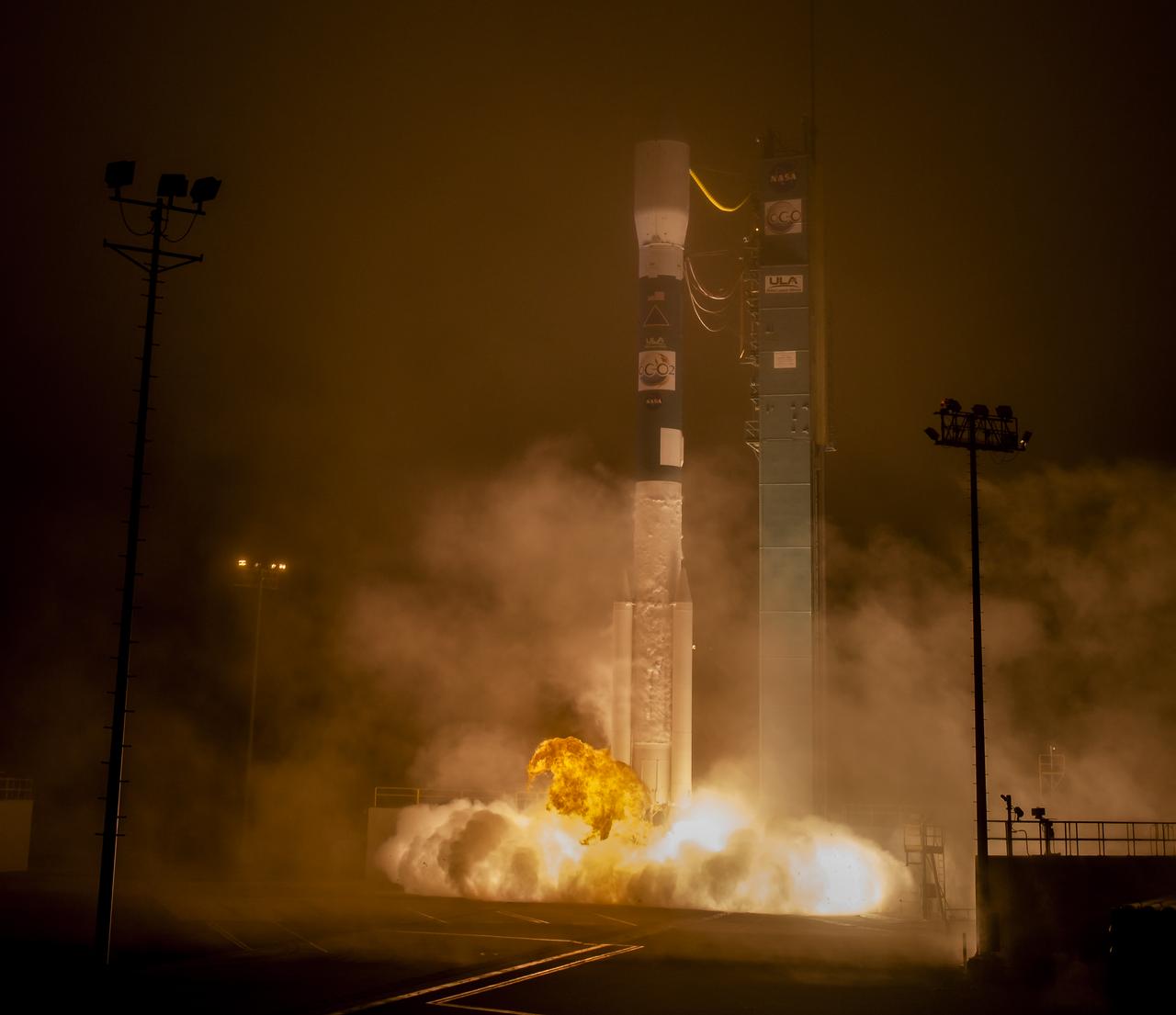

A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket launches with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2)satellite onboard from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Wednesday, July 2, 2014. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
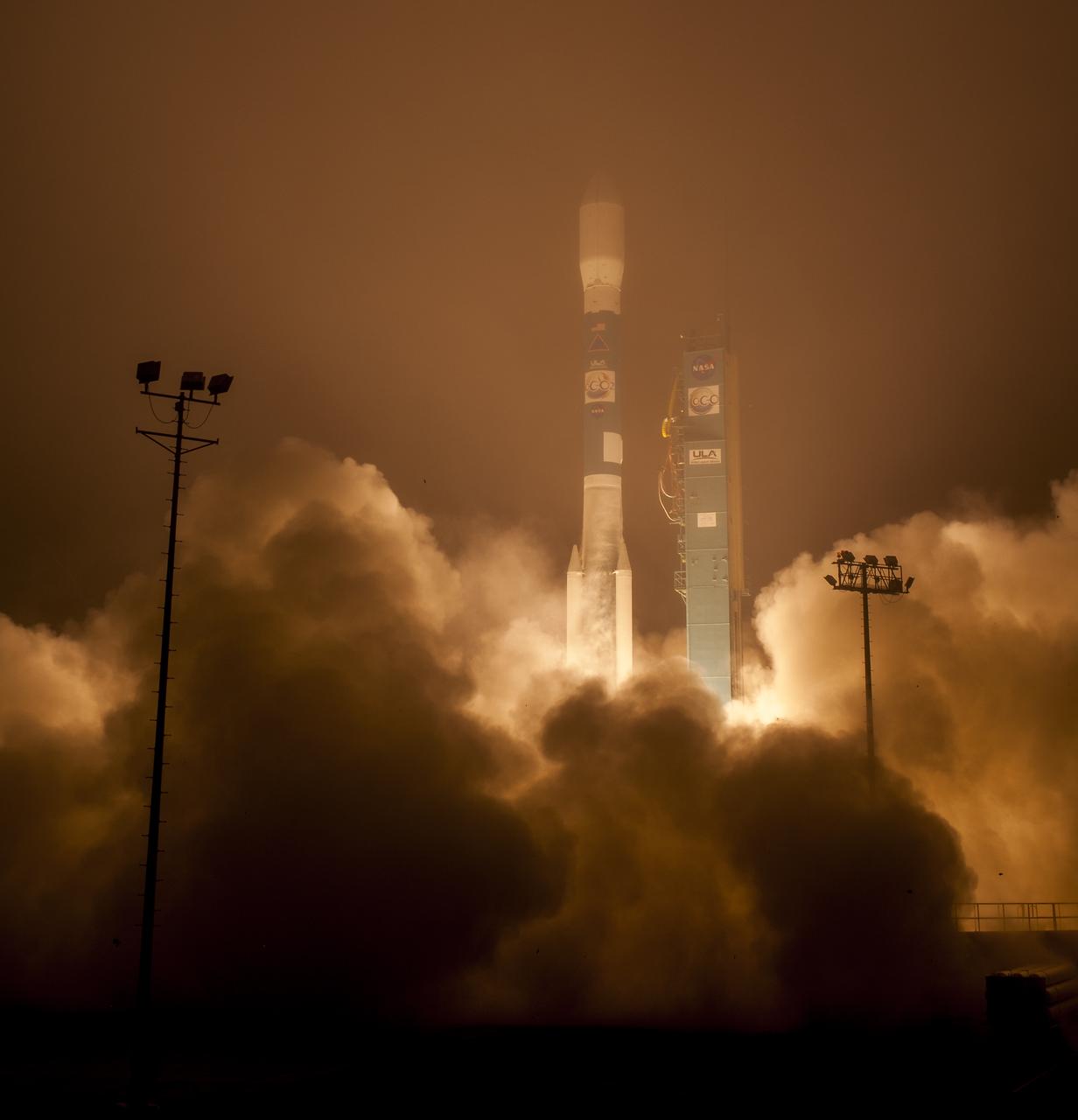

A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket launches with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2)satellite onboard from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Wednesday, July 2, 2014. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
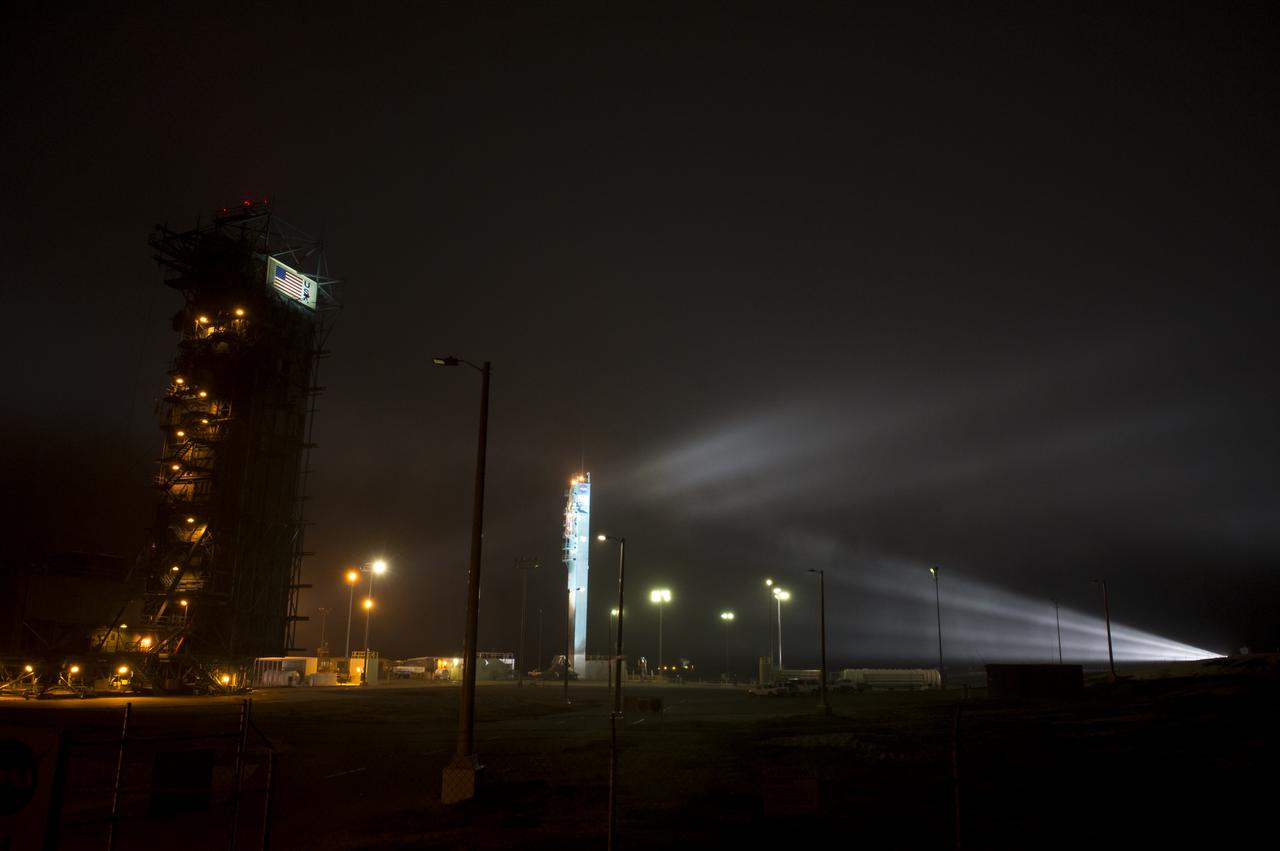

Lights shine on the umbilical tower shortly after a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket launched with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2)satellite onboard from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Wednesday, July 2, 2014. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
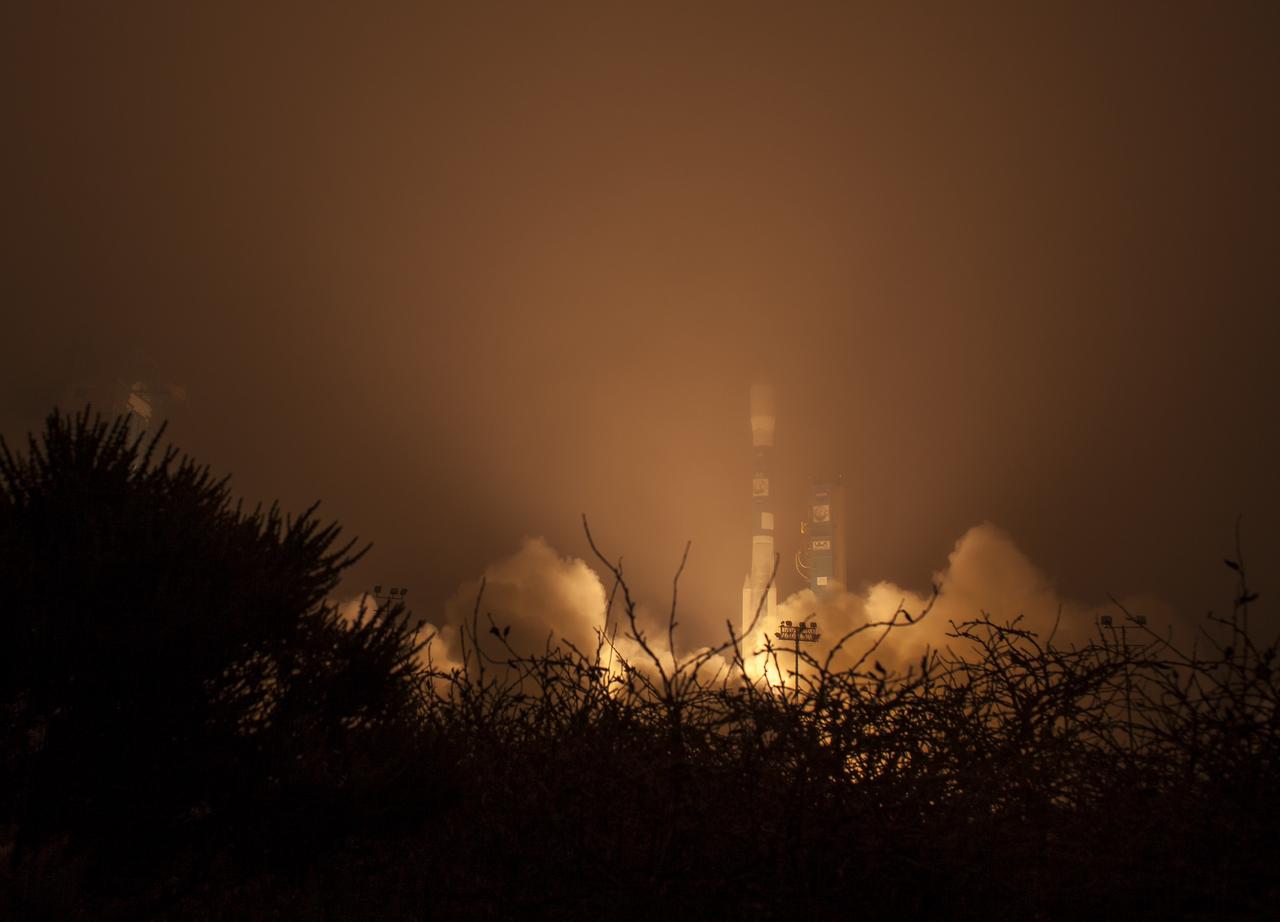

A United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket launches with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2)satellite onboard from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. on Wednesday, July 2, 2014. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
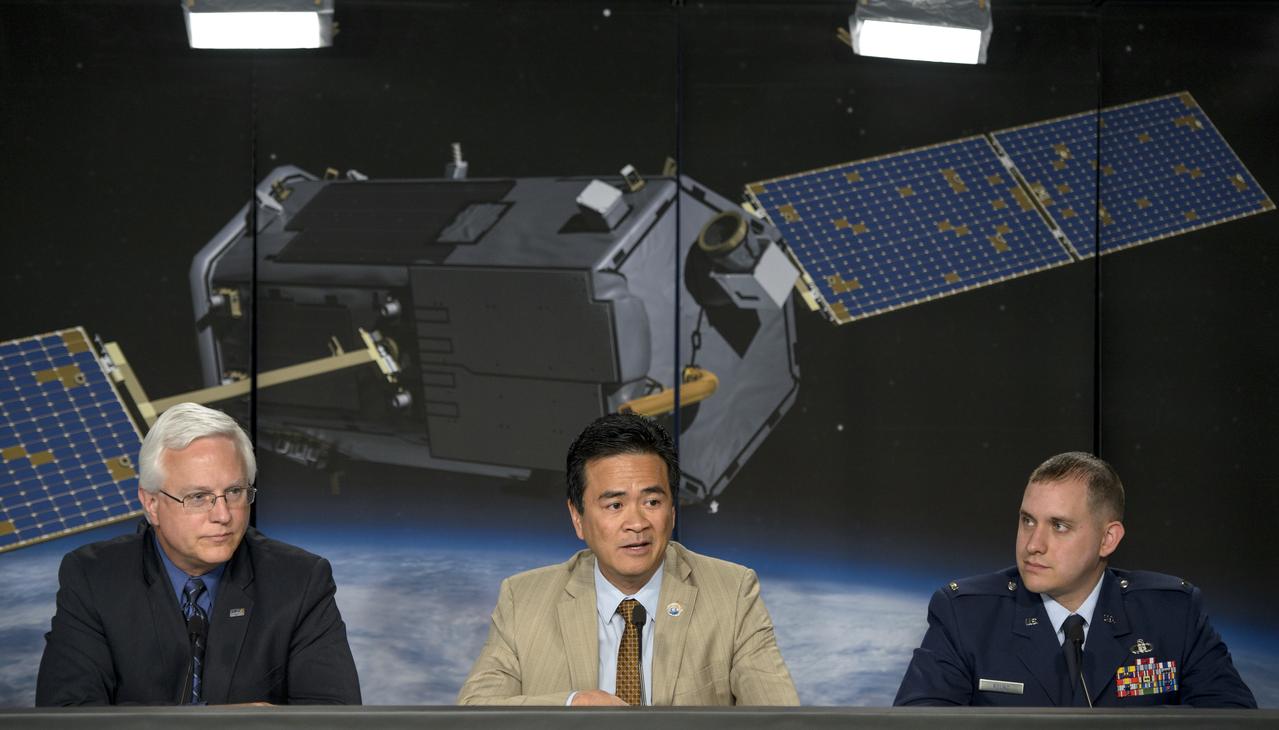

Vern Thorp, United Launch Alliance program manager, NASA missions,, left, Ralph Basilio, OCO-2 project manager, JPL, and Lt. Joseph Round, launch weather officer, USAF 30th Space Wing Weather Squadron, right, discuss the planned launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Sunday, June 29, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 is set to launch on July 1, 2014 at 2:59 a.m. PDT. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
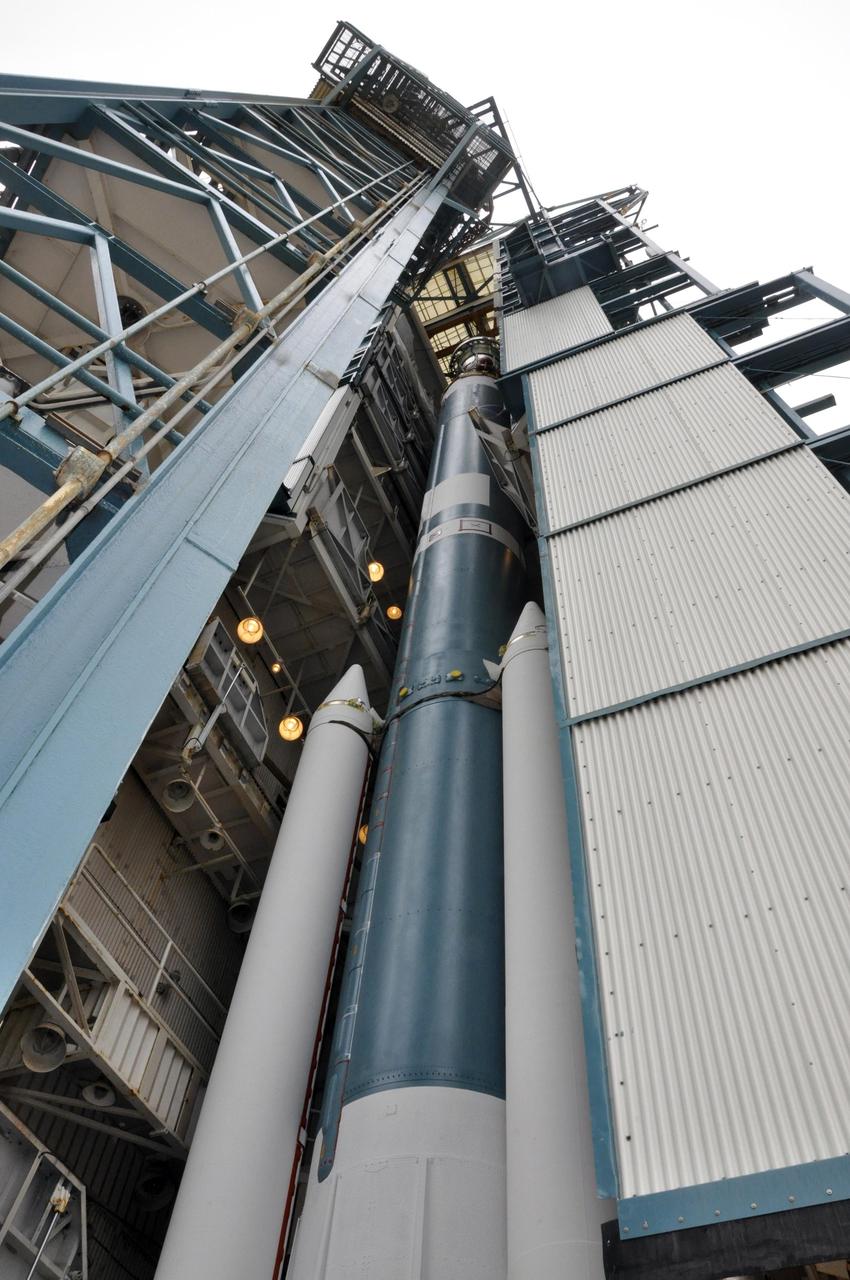

The Delta II second stage for NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, is positioned atop the rocket first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
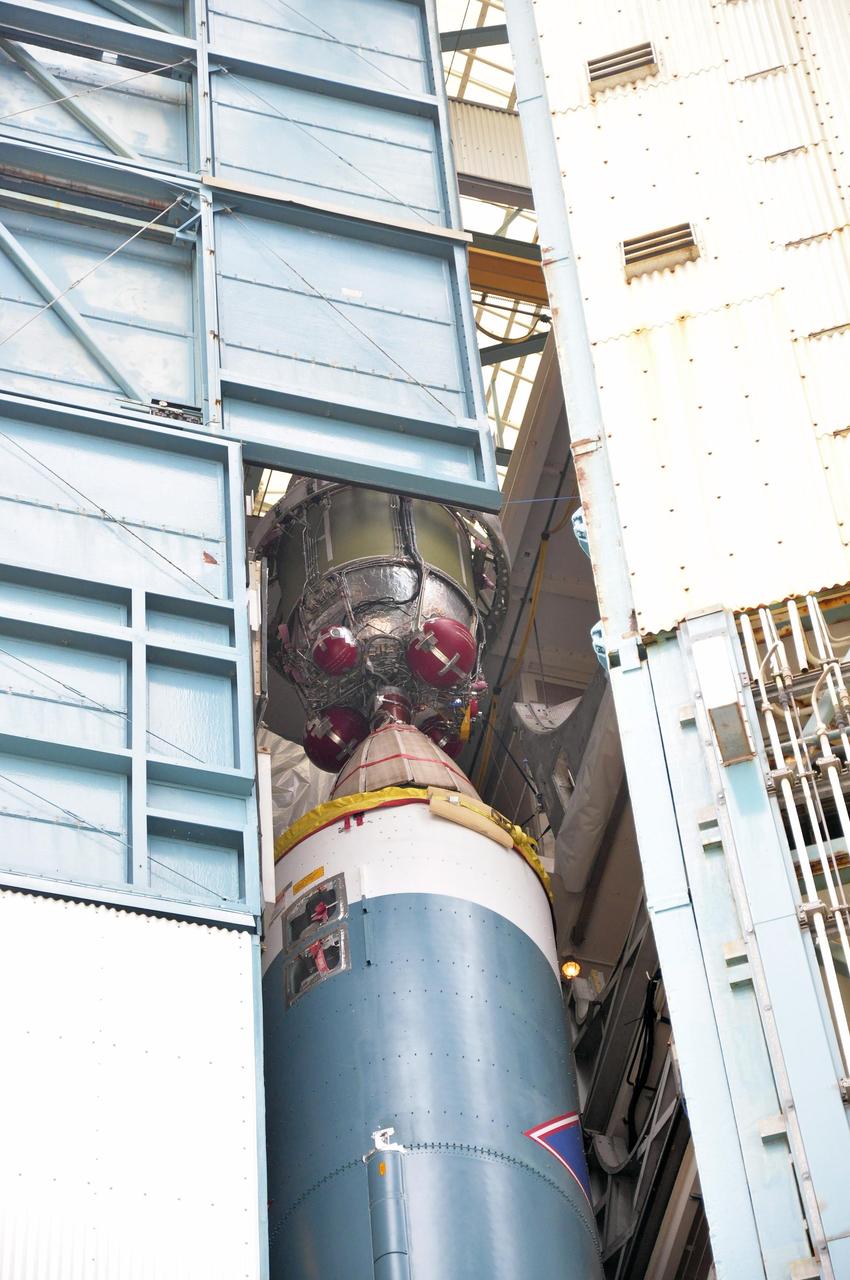

The Delta II second stage for NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, or OCO-2, makes contact with the rocket first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
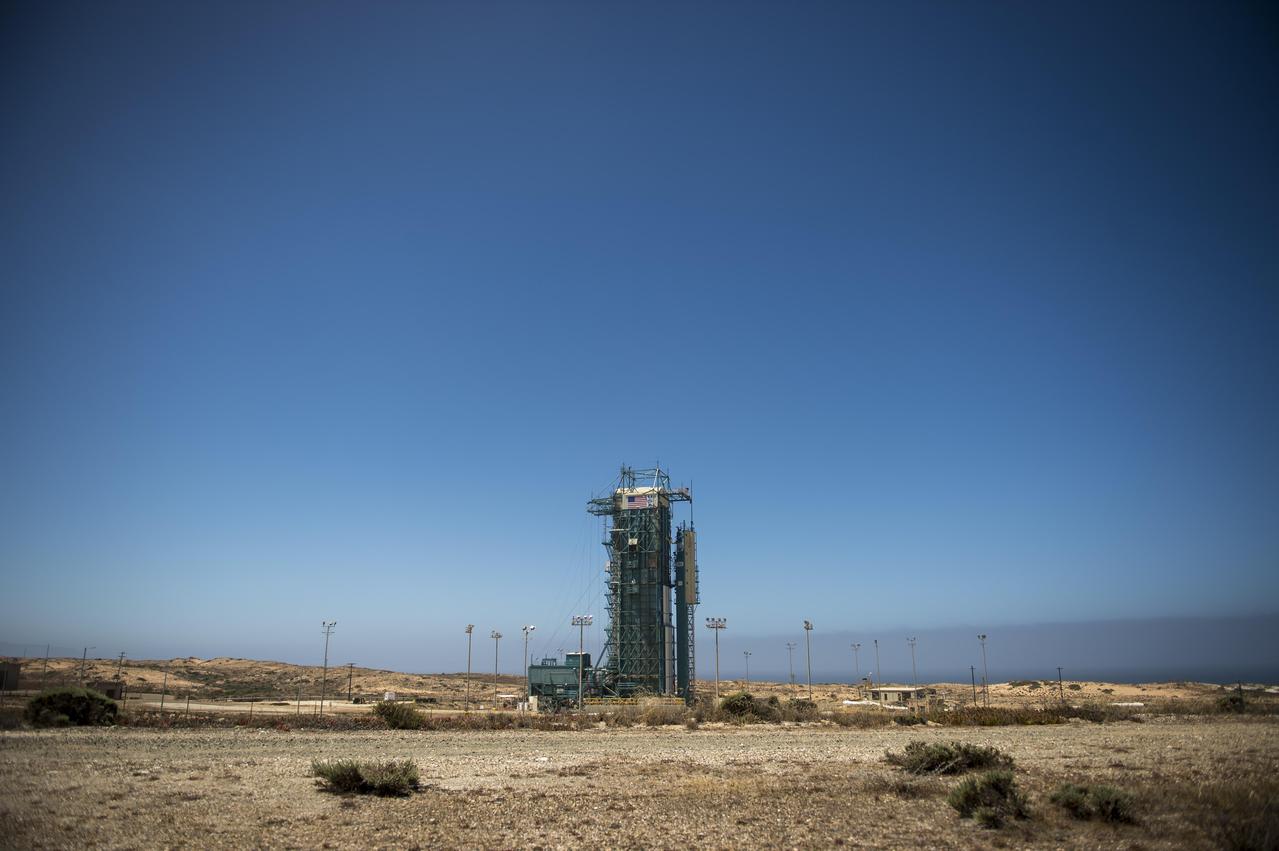

The launch gantry, surrounding the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket with the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 OCO-2 satellite onboard, is seen at Space Launch Complex 2, Sunday, June 29, 2014, Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif.
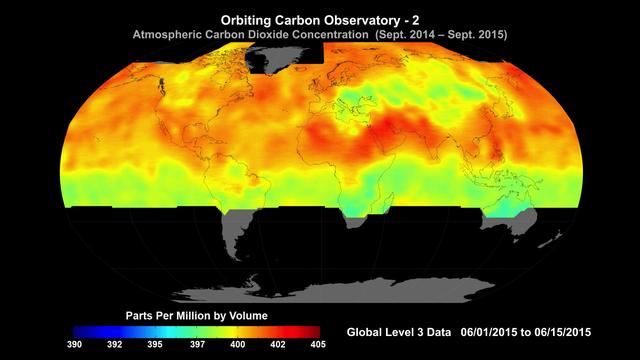
Global average carbon dioxide concentrations as seen by NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 mission, June 1-15, 2015. OCO-2 measures carbon dioxide from the top of Earth's atmosphere to its surface. Higher carbon dioxide concentrations are in red, with lower concentrations in yellows and greens. Scientists poring over data from OCO-2 mission are seeing patterns emerge as they seek answers to questions about atmospheric carbon dioxide. Among the most striking features visible in the first year of OCO-2 data is the increase in carbon dioxide in the northern hemisphere during winter, when trees are not removing carbon dioxide, followed by its decrease in spring, as trees start to grow and remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20039
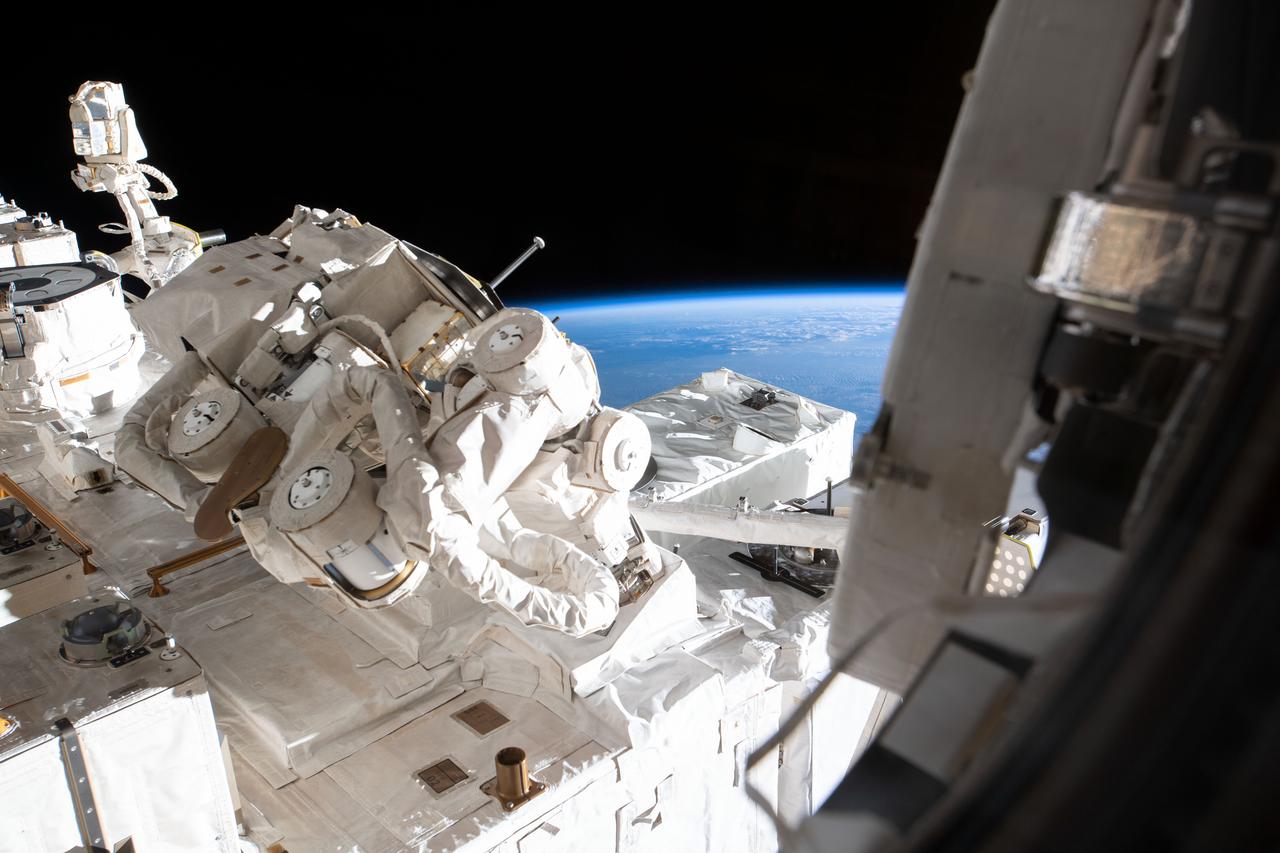

iss059e114054 (6/20/2019) --- View of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) payload on the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Exposed Facility (EF). The OCO-3, to be installed on the Japanese Experiment Module-Exposed Facility (JEM-EF) of the International Space Station (ISS), observes the complex dynamics of the Earth’s atmospheric carbon cycle. The OCO-3 payload is designed to collect the space-based measurements needed to quantify variations in the column-averaged atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) dry-air mole fraction, XCO2, with the precision, resolution, and coverage needed to improve the understanding of surface CO2 sources and sinks (fluxes) on regional scales (?1000 km), and the processes controlling their variability over the seasonal cycle.
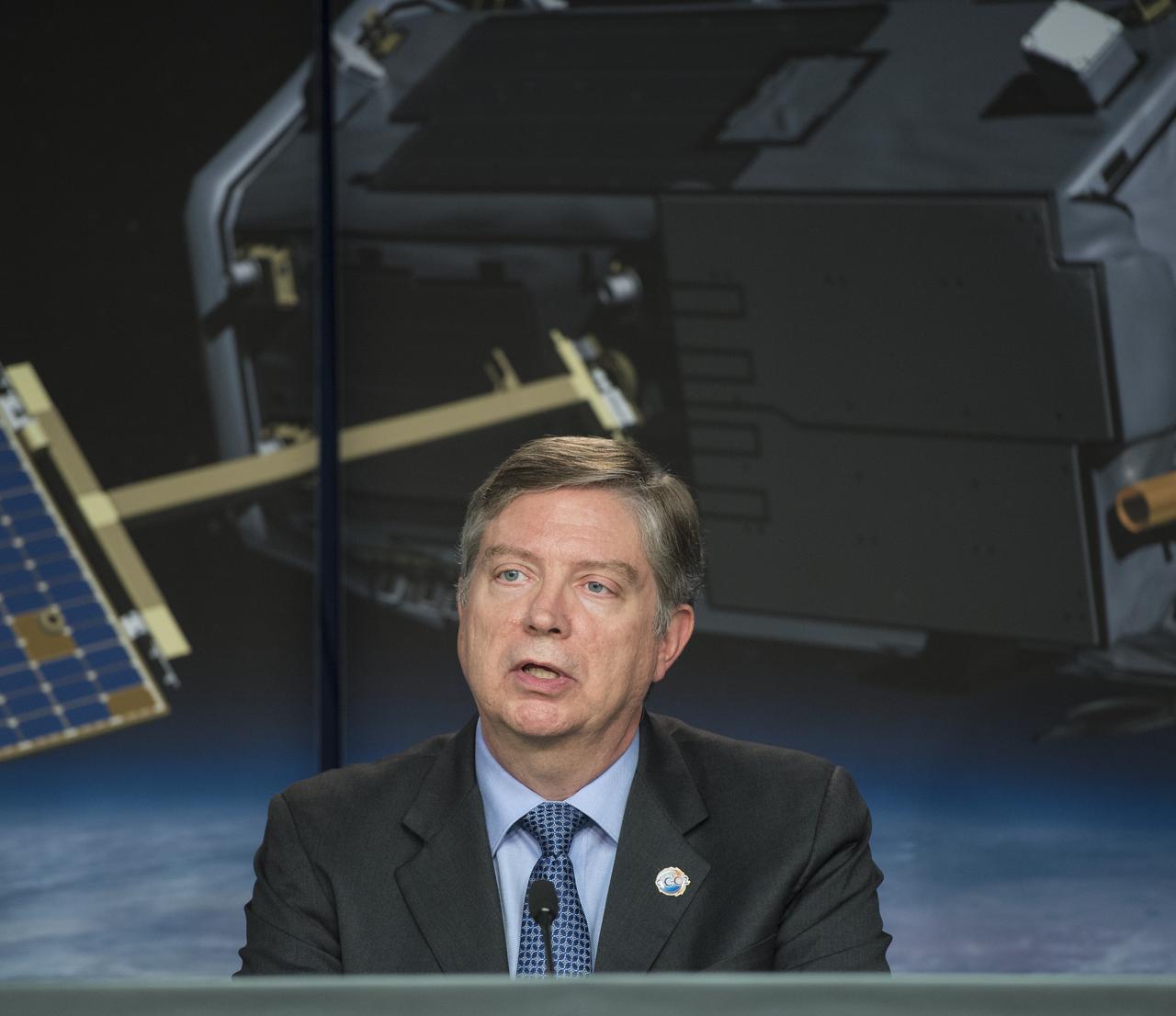
Ralph Basilio, OCO-2 project manager, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, discusses the successful launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Wednesday, July 2, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Mike Miller, senior vice president, Science and Environmental Satellite Programs, Orbital Sciences Space Systems Group, discusses the successful launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Wednesday, July 2, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

Mike Miller, senior vice president, Science and Environmental Satellite Programs, Orbital Sciences Space Systems Group, discusses the successful launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Wednesday, July 2, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
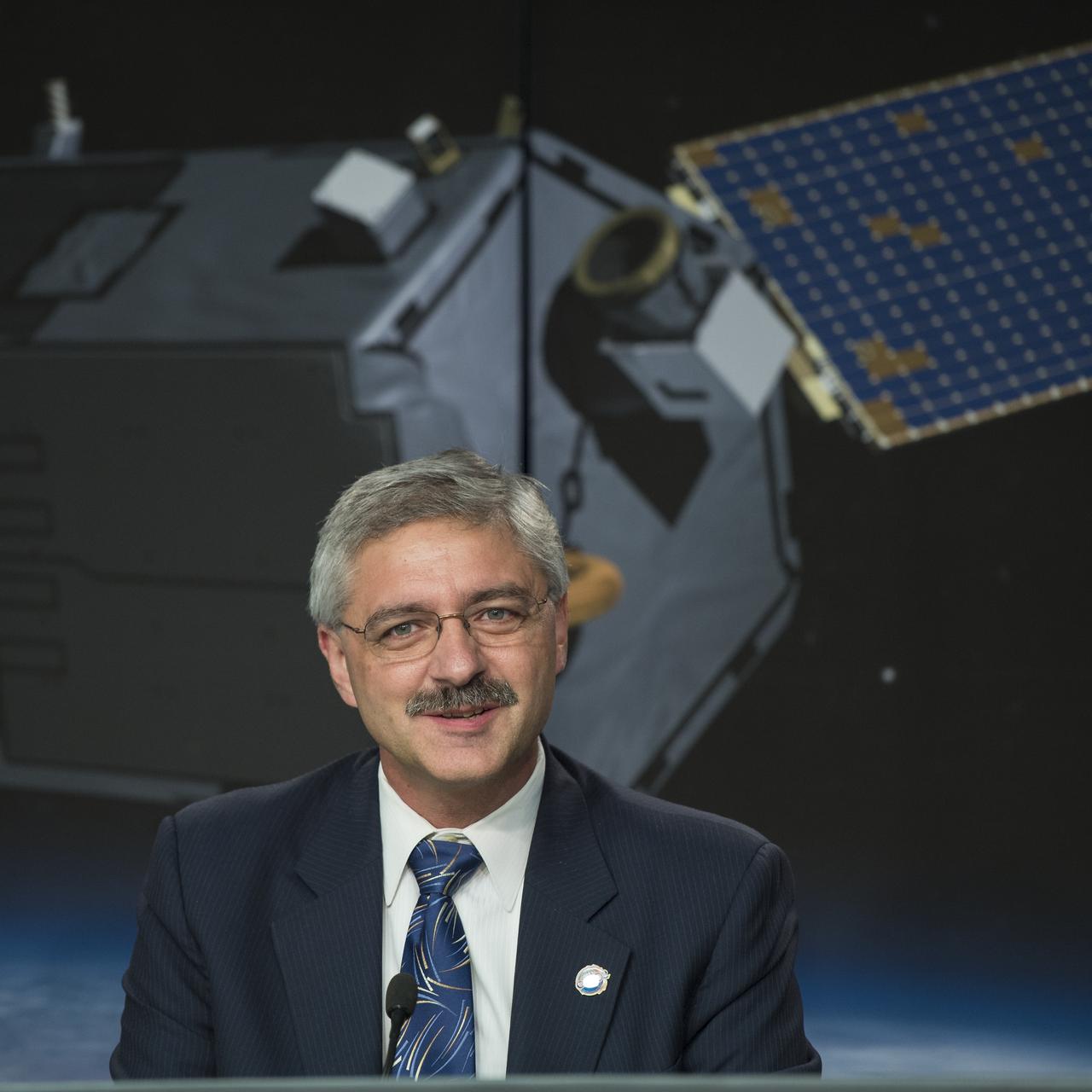

Geoff Yoder, deputy associate administrator for programs, Science Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters, discusses the successful launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Wednesday, July 2, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

NASA Kennedy Space Center Public Affairs Officer George Diller, moderates a post-launch press briefing, following the successful launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, Wednesday, July 2, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
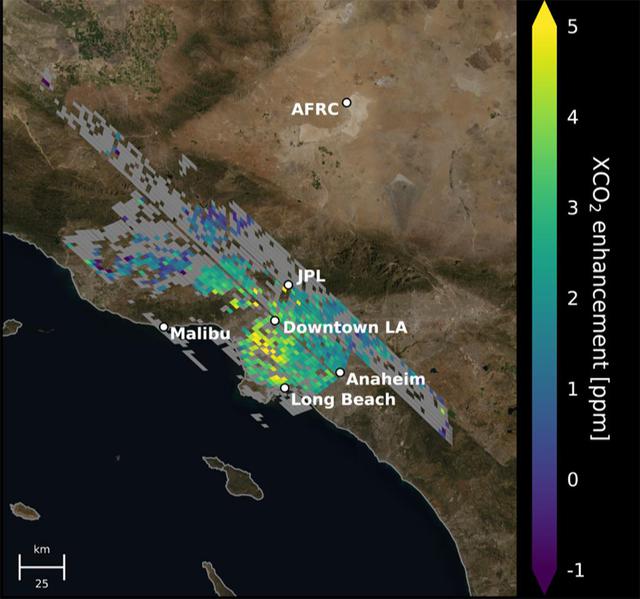
This animation shows the accumulation of five adjoining swaths of data over the Los Angeles metropolitan area that when combined, create a map of carbon dioxide (CO2) concentrations that covers about 50 square miles (80 square kilometers). Researchers have used the data, collected by NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3 (OCO-3) instrument aboard the space station, to create one of the most accurate maps ever made from space of the human influence on CO2 abundances in the L.A. Basin Each pixel is about 1.3 miles (2.2 kilometers); the color indicates how much higher the concentration of CO2 is in that spot than in clean desert air north of the city (measured at NASA's Armstrong Research Center, upper right). The highest CO2 readings, in yellow on the map, are on the west side of downtown L.A. – a densely populated area with congested freeways and CO2-emitting industries. Yellow indicates atmospheric CO2 elevated by five or more molecules out of every million molecules of air, or five parts per million. That's equivalent to the amount that global atmospheric CO2 is rising globally on average every two years Most of the increasing CO2 in the global atmosphere comes from humans burning fossil fuels for energy, and 70% of that comes from cities. Los Angeles has set goals for cutting its carbon emissions. This type of data can help decisionmakers choose the most effective policies to reach those goals and to measure the effectiveness of new regulations. Data from ground level provides critical local measurements, but satellite data is equally necessary because it covers a wider area and also measure CO2 throughout the entire depth of the atmosphere. Animation available at https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24523

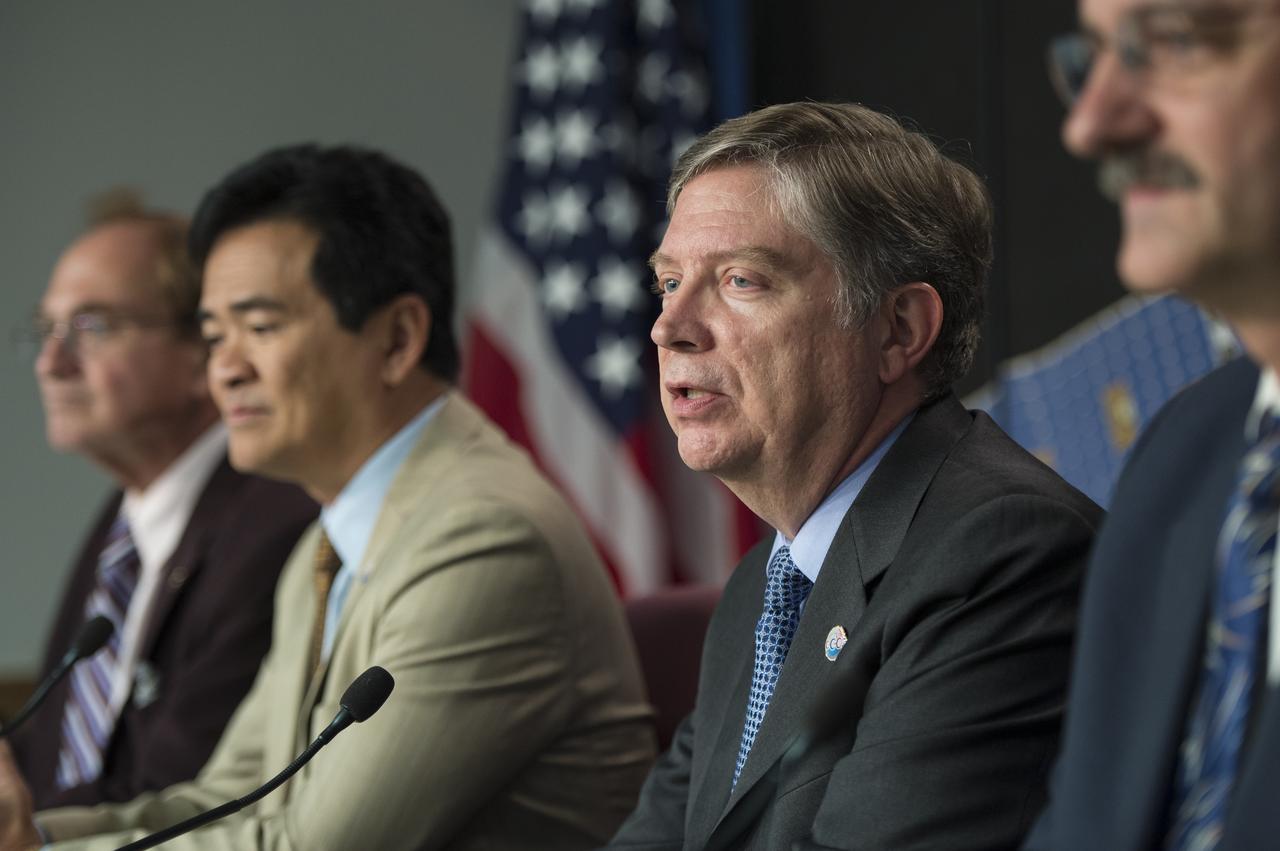
Ralph Basilio, OCO-2 project manager, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, left, Mike Miller, senior vice president, Science and Environmental Satellite Programs, Orbital Sciences Space Systems Group,and Geoff Yoder, deputy associate administrator for programs, Science Mission Directorate, NASA Headquarters, right, discuss the successful launch of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2), NASA’s first spacecraft dedicated to studying carbon dioxide, during a press briefing, Wednesday, July 2, 2014, at the Vandenberg Air Force Base, Calif. OCO-2 will measure the global distribution of carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)

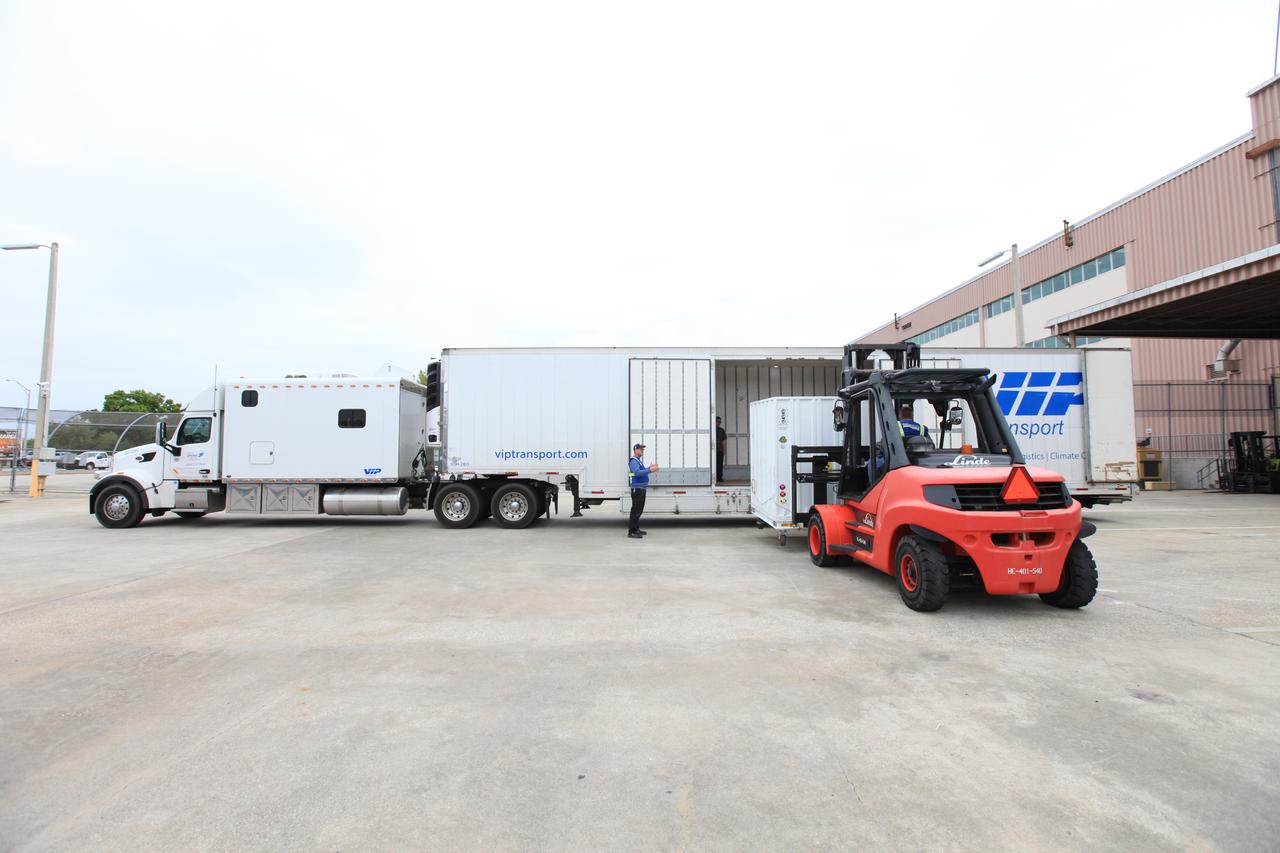
Kevin Mark, Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3 (OCO-3) purge engineer with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, secures a separate fixture of OCO-3, stored apart from its payload container, on the truck transporting it from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.

Kevin Mark, Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3 (OCO-3) purge engineer with NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, fastens a separate fixture of OCO-3, stored apart from its payload container, to a truck for transport from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
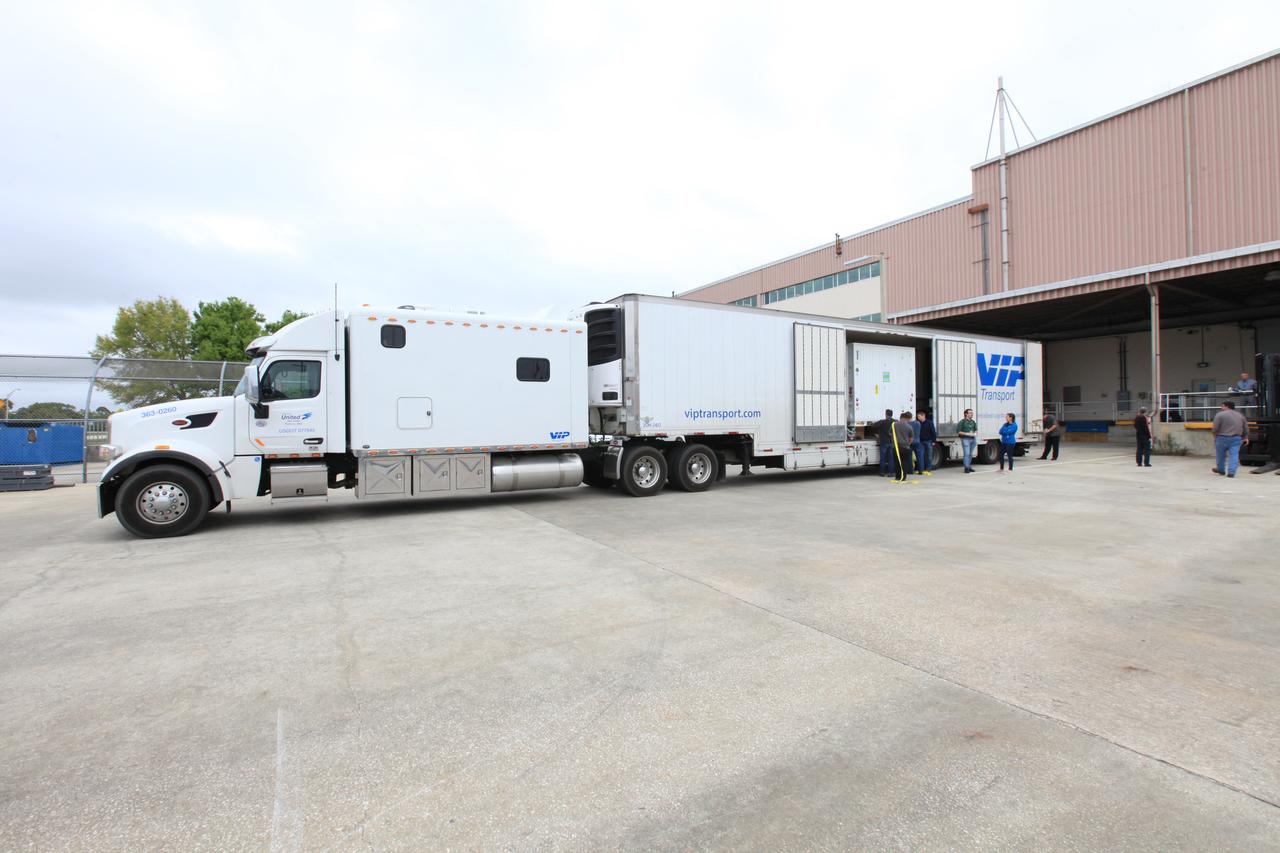

A transportation container carrying NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload is moved to a truck for its transport from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.

NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, sits in a transportation container at the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prior to its move to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
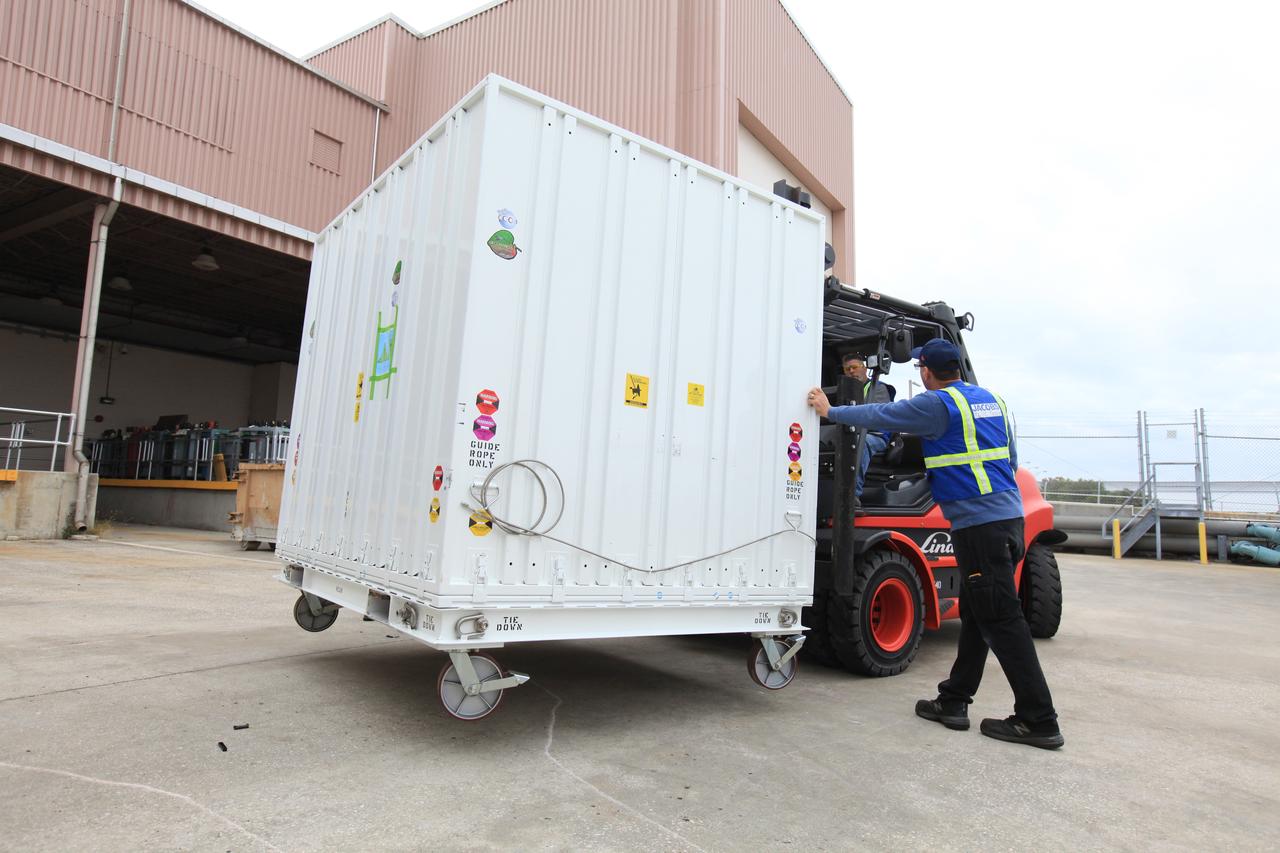

A forklift moves the transportation container carrying NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload to a truck for its move from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.

Workers move NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload container out of the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to board a truck that will transport it to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.

NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload sits in a transportation container at the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida in preparation for its move to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
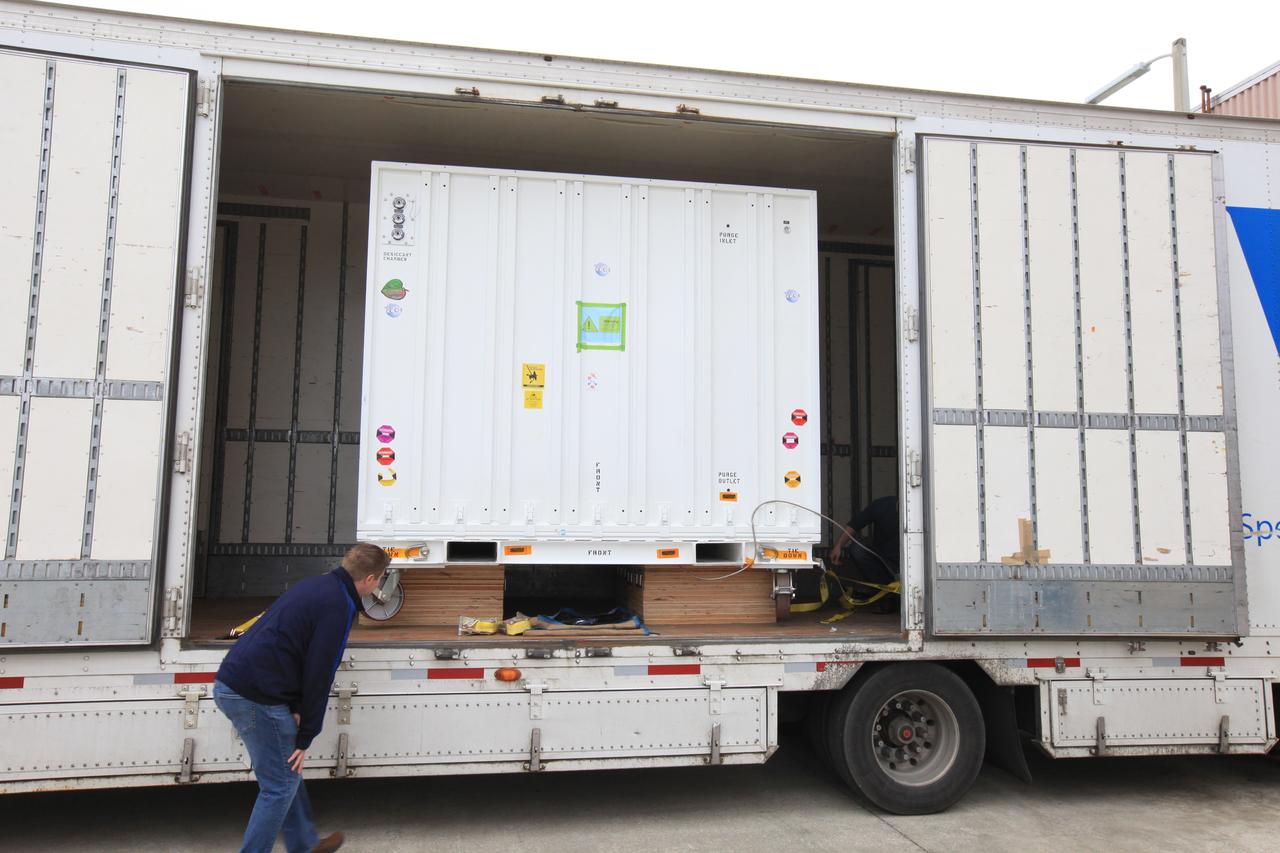

A transportation container carrying NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload is moved to a truck for transport from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
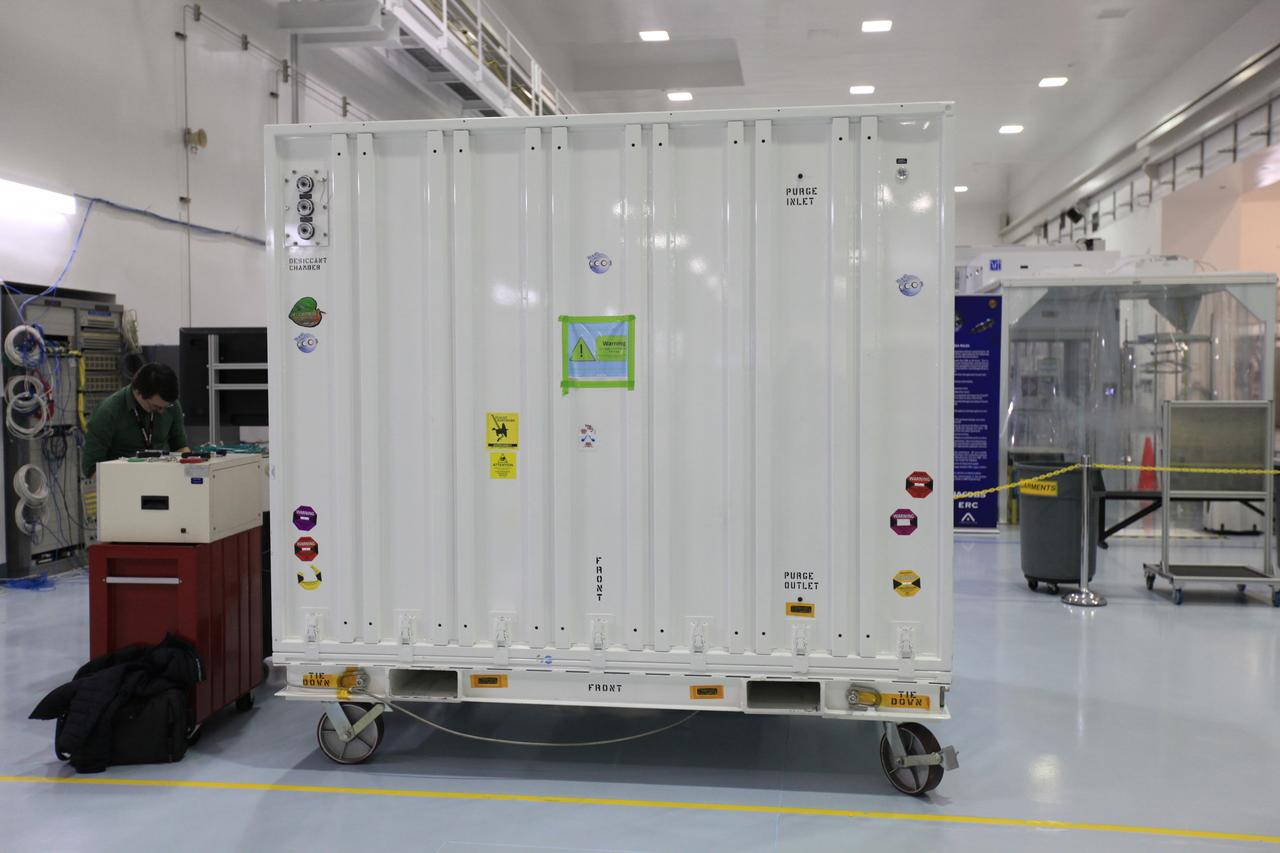

NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, sits in a transportation container at the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida prior to its move to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, which will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
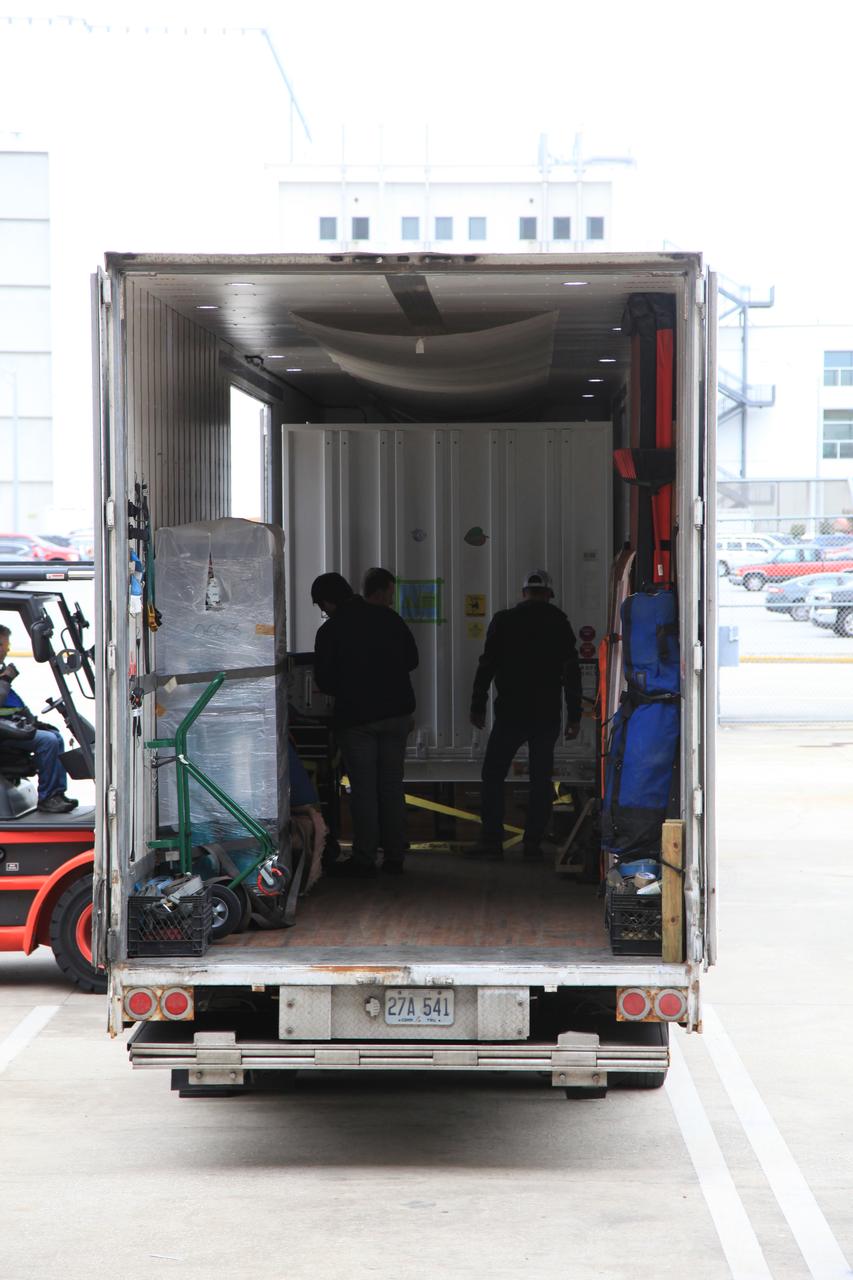

NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload container is moved from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to a truck that will transport it to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.

Workers prepare to move NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload container out of the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida onto a truck that will transport it to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, which will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.

A forklift moves the transportation container carrying NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload to a truck for its move from the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.

Workers prepare to move NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload container out of the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida onto a truck that will transport it to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft, where it will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
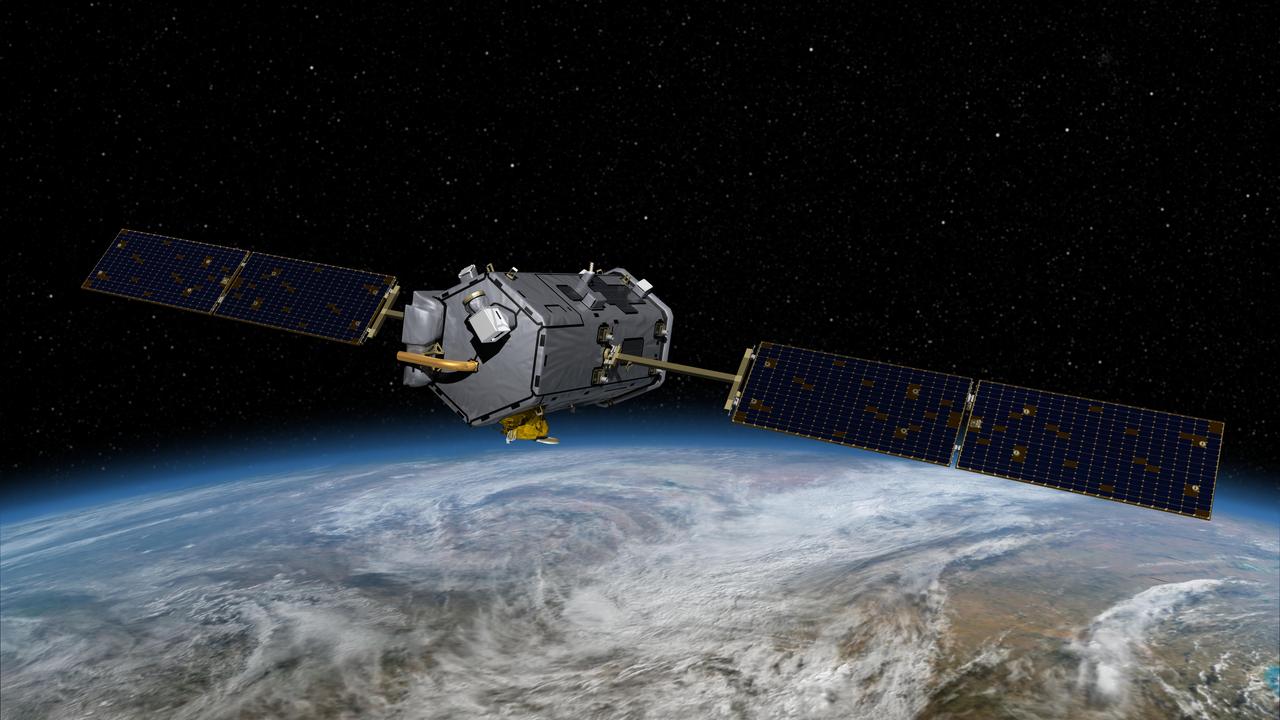

This image is an artist’s concept of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory
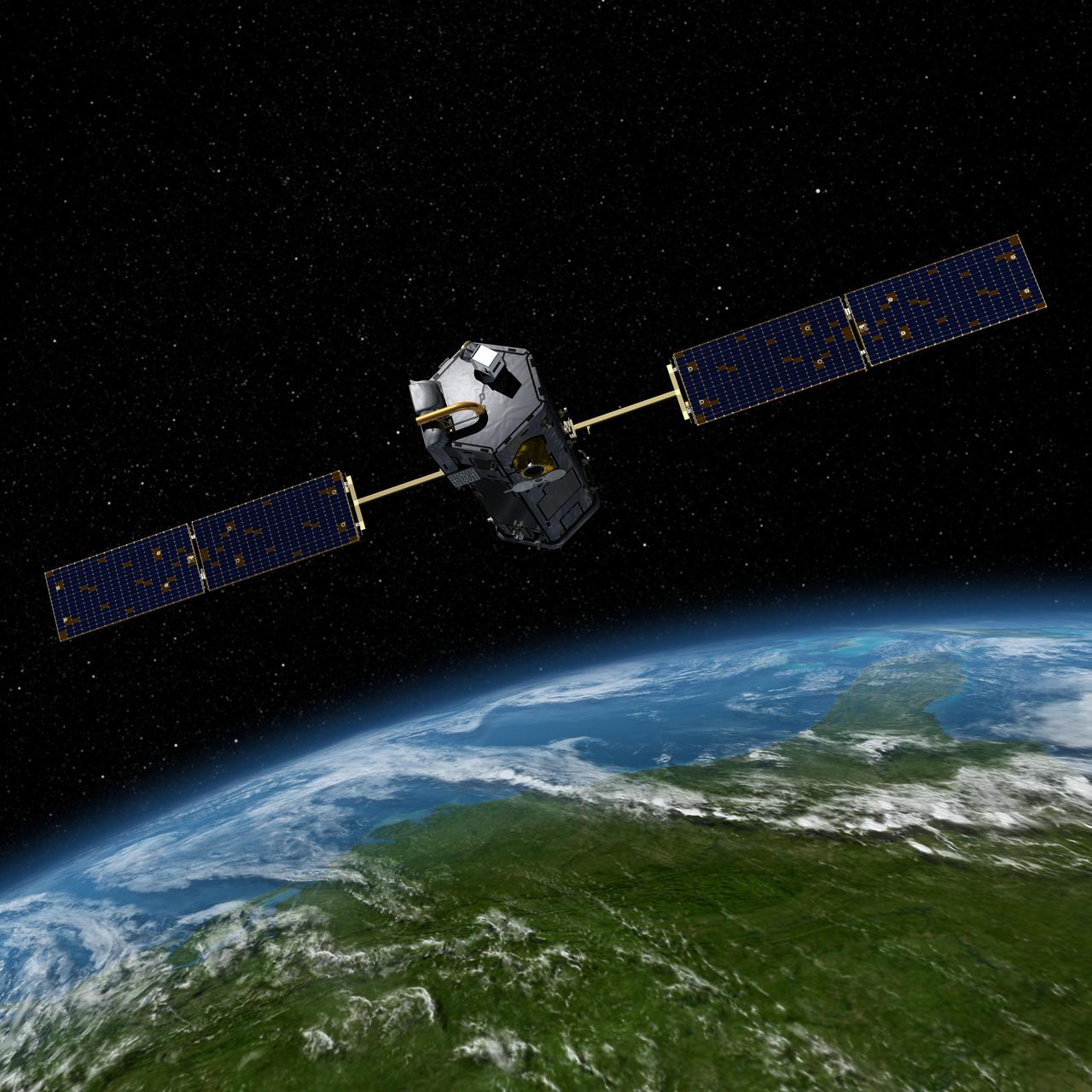

Artist’s concept of the Orbiting Carbon Observatory.
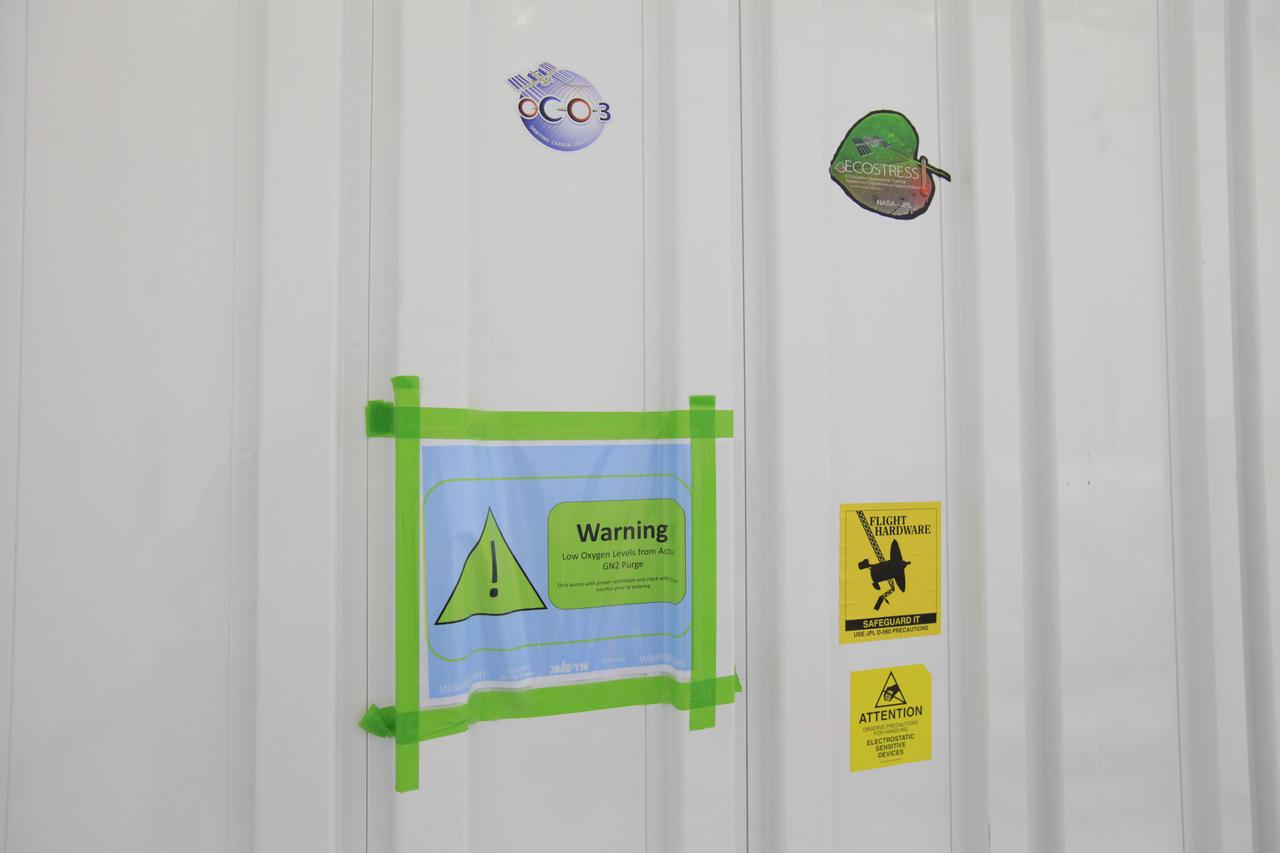

A transportation container carrying NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3, or OCO-3, payload sits at the Space Station Processing Facility high bay at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida bearing a warning sign of low oxygen levels from an active GN2 (gaseous nitrogen that creates a dry atmosphere) purge prior to its move to the SpaceX facility on March 18, 2019. The OCO-3 payload will be stowed in the trunk of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft and will launch aboard a Falcon 9 rocket on the company’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission to the International Space Station. Launch is scheduled for April 25, 2019, from Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Once the payload reaches the station, it will be removed from Dragon and robotically installed on the exterior of the orbiting laboratory’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate.
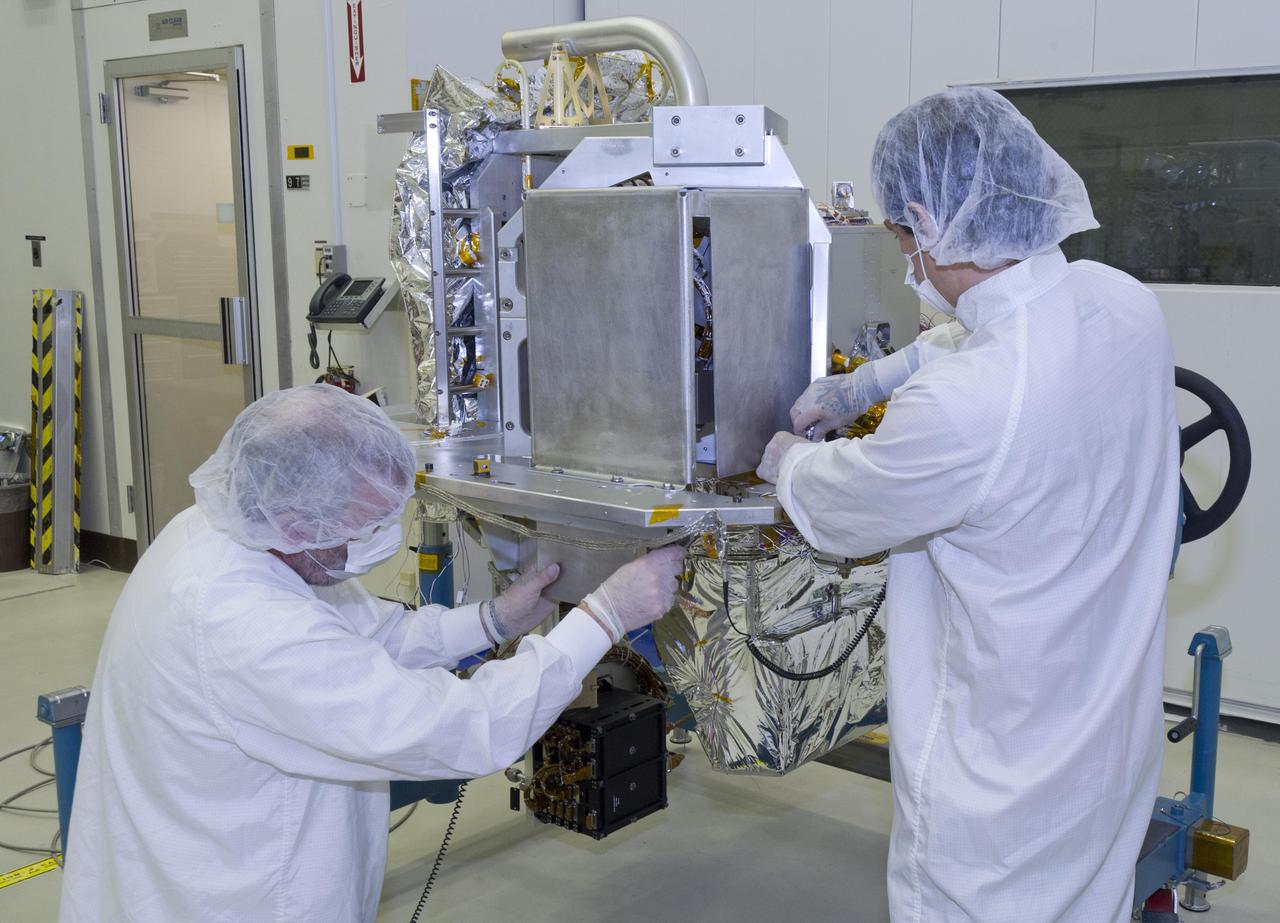

Technicians prep NASA OCO-2 instrument for shipping at Jet Propulsion Lab in Pasadena, Ca.
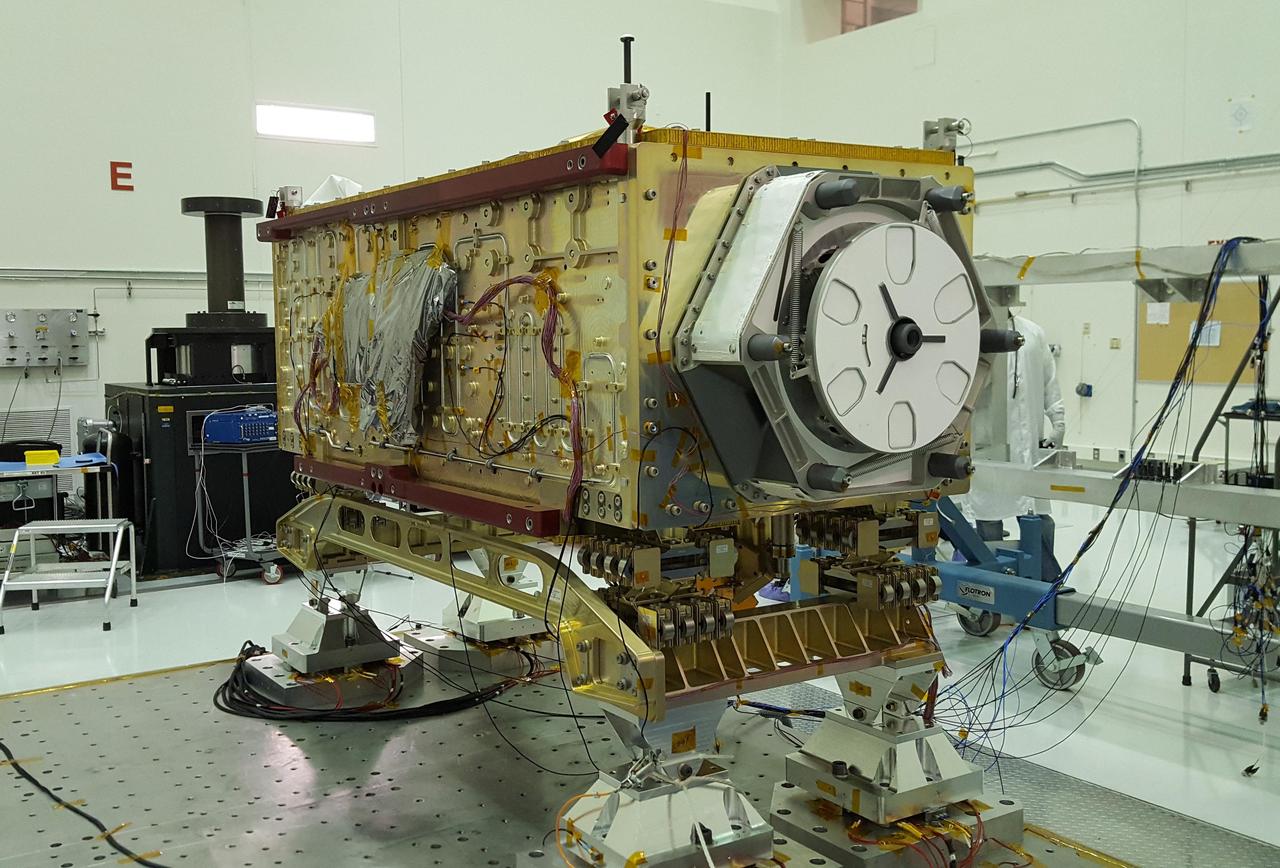

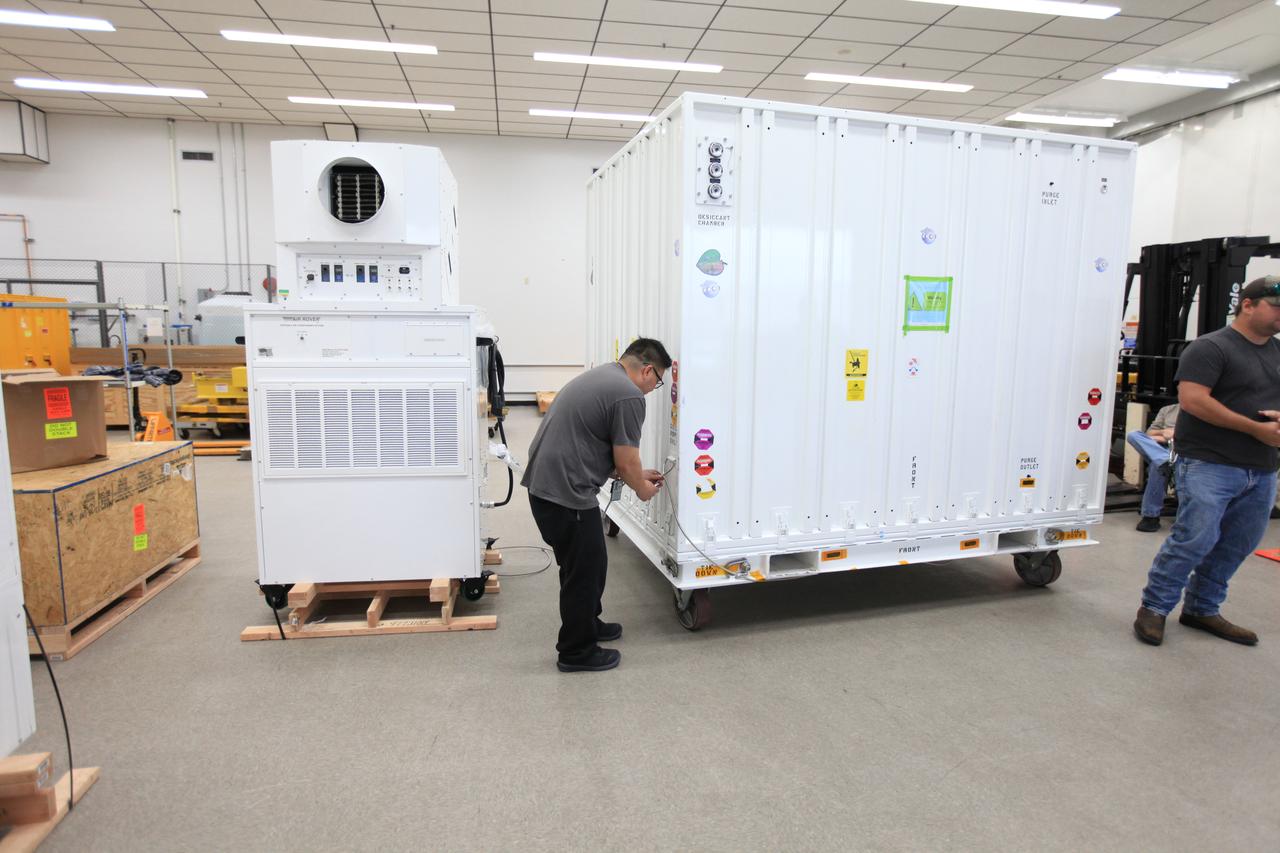
OCO-3 sits on the large vibration table (known as the "shaker") in the Environmental Test Lab at the Jet Propulsion Laboratory. The exposed wires lead to sensors used during dynamics and thermal-vacuum testing. Thermal blankets will be added to the instrument at Kennedy Space Center, where a Space-X Dragon capsule carrying OCO-3 will launch in on a Falcon 9 rocket to the space station on May 1, 2019. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23211

Technicians prep NASA OCO-2 instrument for shipping at Jet Propulsion Lab in Pasadena, Ca. Animation available in More Details.
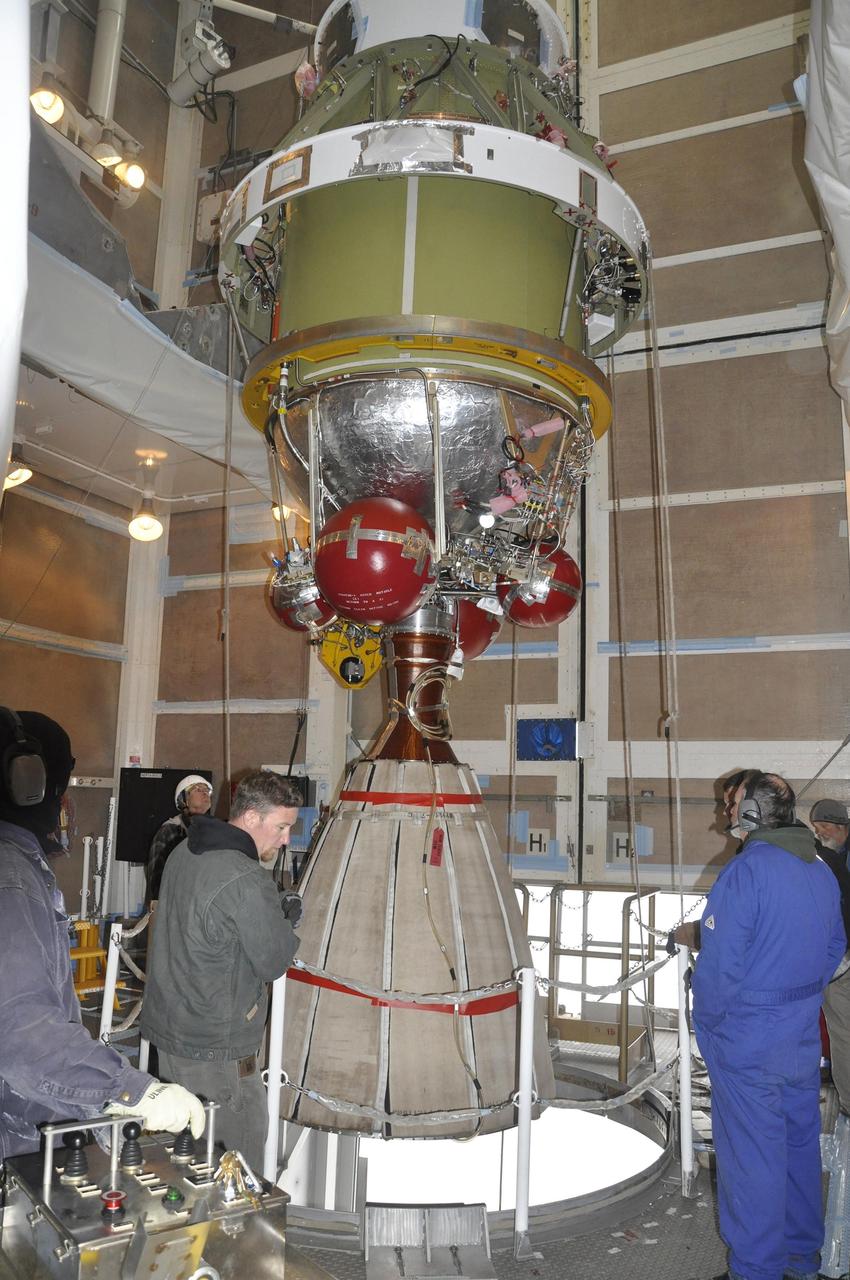

Workers monitor the Delta II second stage for NASA OCO-2, as it is lifted into position for mating with the rocket first stage in the mobile service tower at Space Launch Complex 2 on Vandenberg Air Force Base in California.
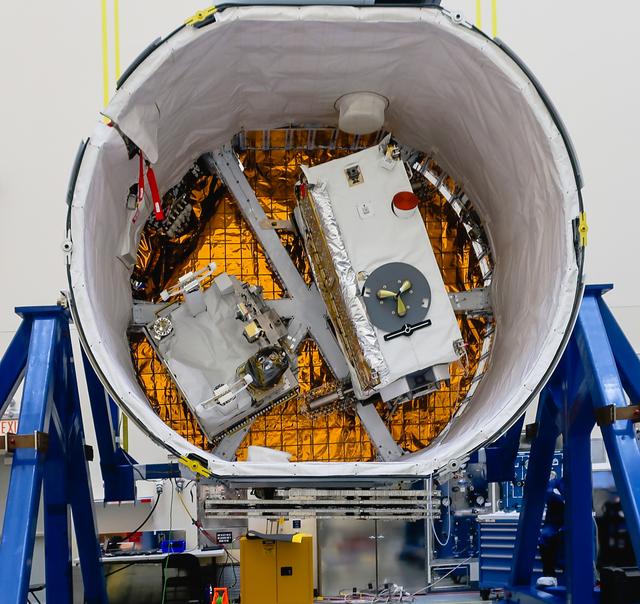

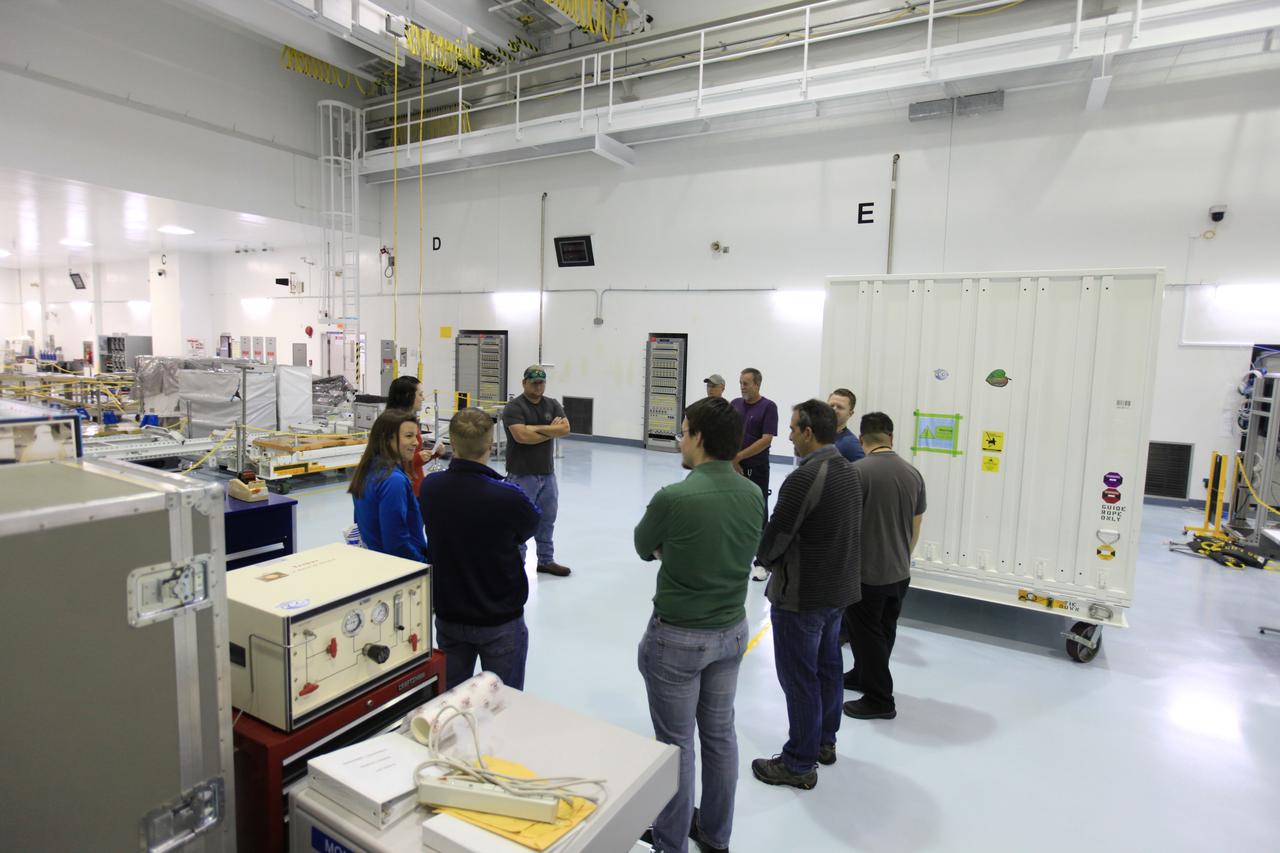
NASA’s Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) and Space Test Program-Houston 6 (STP-H6) are in view installed in the truck of SpaceX’s Dragon spacecraft inside the SpaceX facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 23, 2019. OCO-3 and STP-H6 will be delivered to the International Space Station on SpaceX’s 17th Commercial Resupply Services mission (CRS-17) for NASA. STP-H6 is an x-ray communication investigation that will be used to perform a space-based demonstration of a new technology for generating beams of modulated x-rays. This technology may be useful for providing efficient communication to deep space probes, or communicating with hypersonic vehicles where plasma sheaths prevent traditional radio communications. OCO-3 will be robotically installed on the exterior of the space station’s Japanese Experiment Module Exposed Facility Unit, where it will measure and map carbon dioxide from space to provide further understanding of the relationship between carbon and climate. CRS-17 is scheduled to launch from Space Launch Complex 40 on Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in late April.
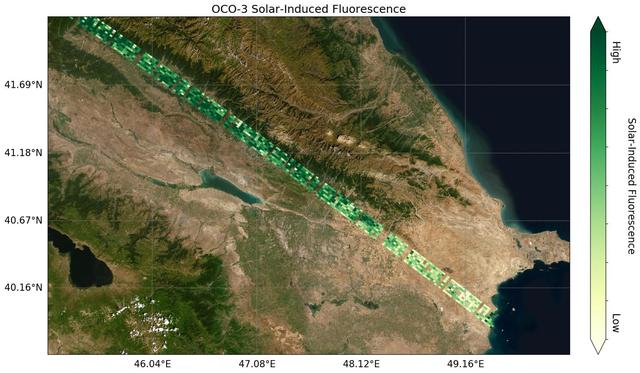
Image shows OCO-3's first preliminary solar-induced fluorescence (SIF) measurements over western Asia. Solar-induced fluorescence is the glow plants emit from photosynthesis — the process of plant growth that includes the capture of carbon from the atmosphere. Areas with lower photosynthesis activity are in shown in light green; areas with higher photosynthesis activity are shown in dark green. As expected, there is significant contrast in plant activity from areas of low vegetation near the Caspian Sea to areas of more dense vegetation like the forests and farms north and east of the Mingachevir Reservoir (near the center of the image). The mission team expects to complete OCO-3's In-orbit checkout phase — the period where they ensure all instruments and components are working and calibrated correctly — in August 2019. They are scheduled to release official CO2 and solar-induced fluorescence data to the science community a year later; however, the data will likely be available sooner given the quality of the measurements that OCO-3 is already making. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23353
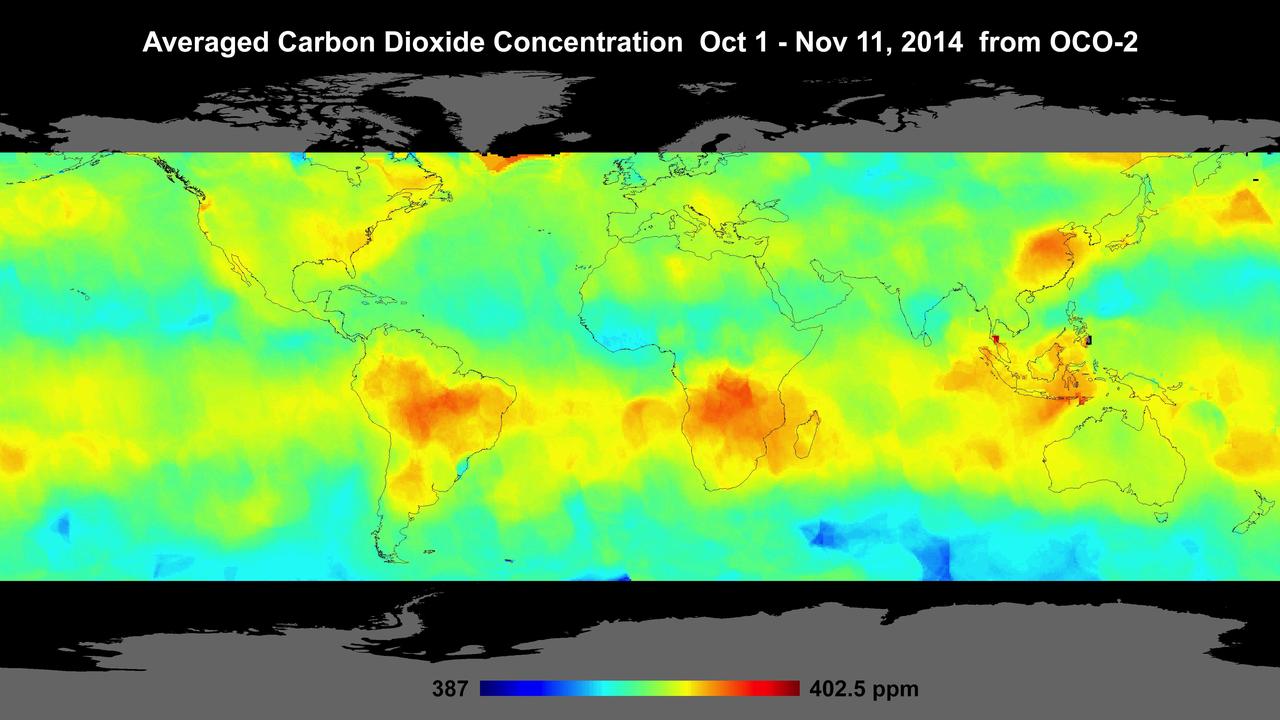
Global atmospheric carbon dioxide concentrations from Oct. 1 through Nov. 11, as recorded by NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2.
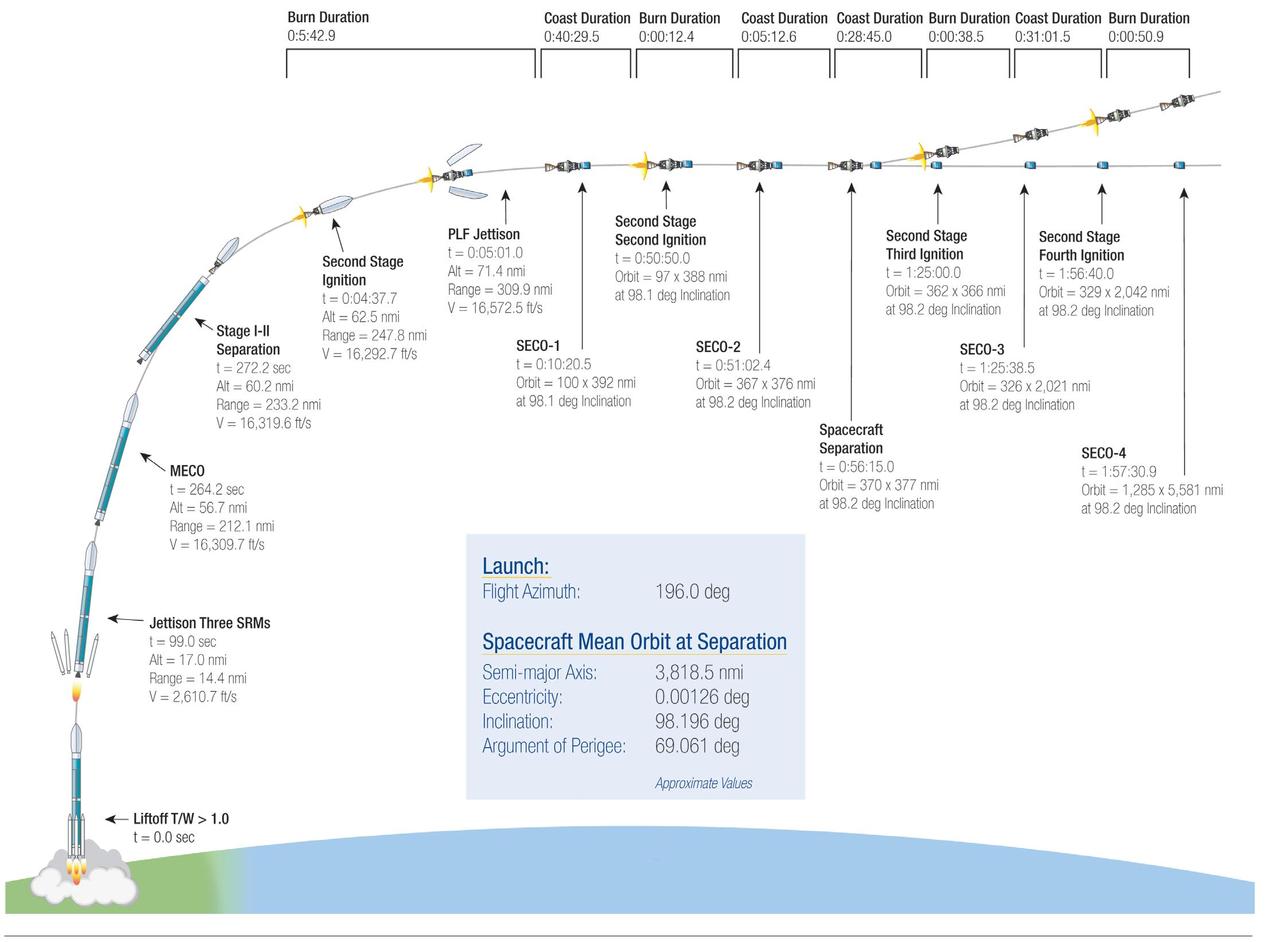
This illustration highlights key events in the launch of NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, beginning with its liftoff from Vandenberg Air Force Base in central California.
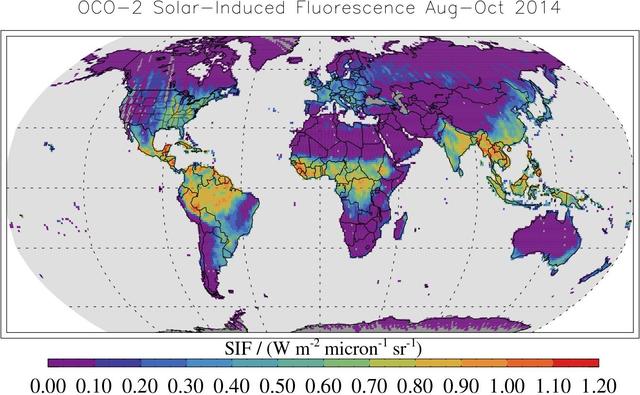
This map shows solar-induced fluorescence, a plant process that occurs during photosynthesis, from Aug. through Oct. 2014 as measured by NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2.
Illustration of NASA's OCO-3 mounted on the underside of the International Space Station. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22837
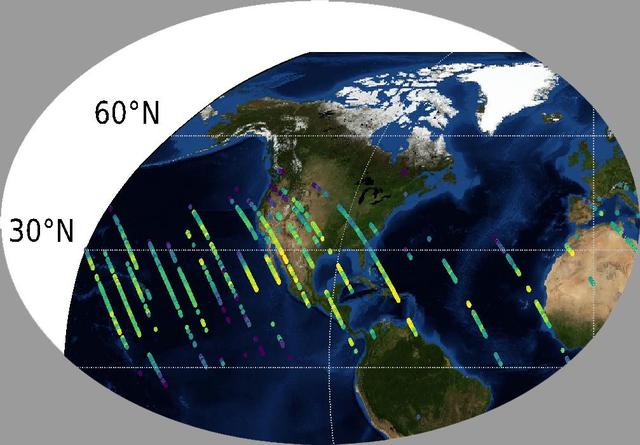
This image shows CO2 over the United States during OCO-3's first few days of science data collection. These initial measurements are consistent with measurements taken by OCO-3's older sibling, OCO-2, over the same area — meaning that even though OCO-3's instrument calibration is not yet complete, it is right on track to continue its (currently still operational) predecessor's data record. The mission team expects to complete OCO-3's in-orbit checkout phase — the period where they ensure all instruments and components are working and calibrated correctly — in August 2019. They are scheduled to release official CO2 and solar-induced fluorescence data to the science community a year later; however, this data will likely be available sooner given the quality of the measurements that OCO-3 is already making. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA23352
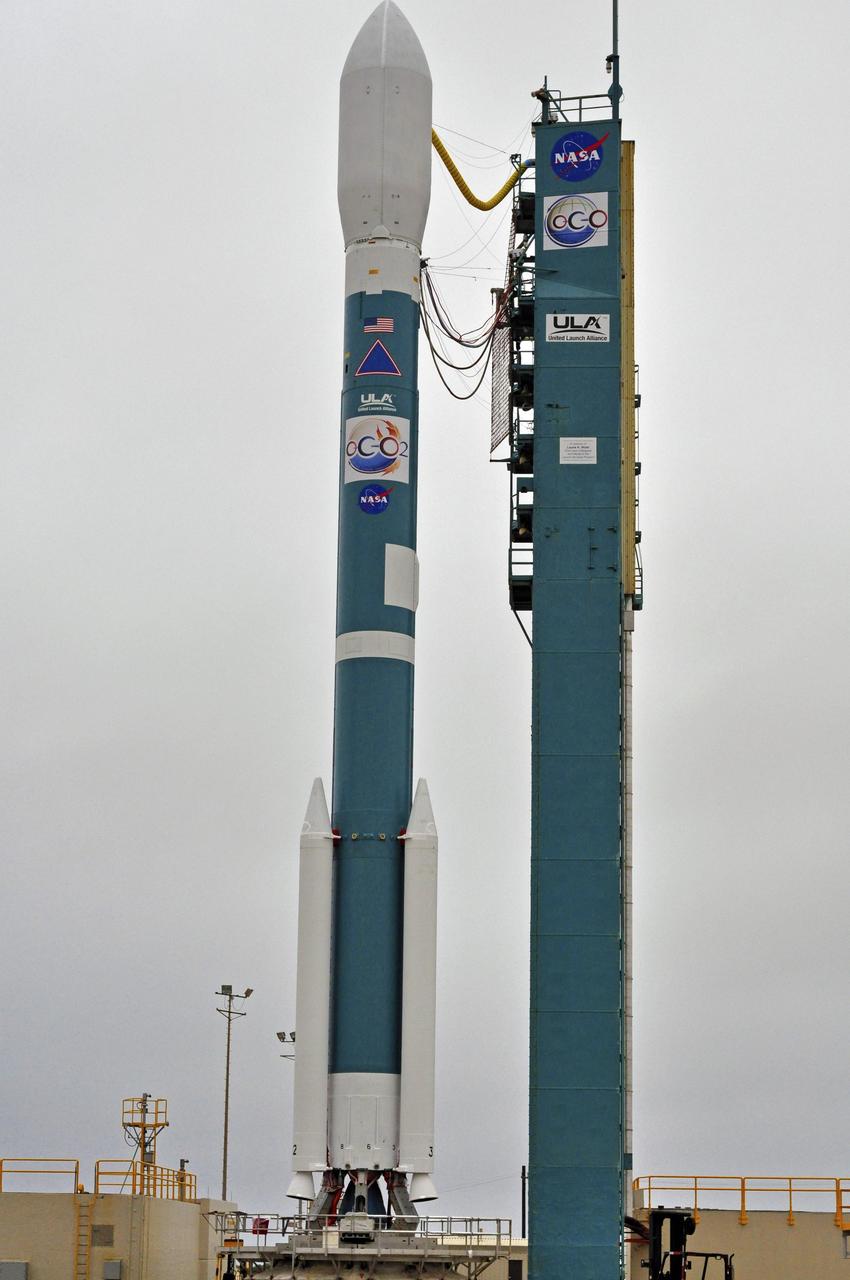

NASA Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, perched atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket, awaits launch at the Vandenberg Air Force Base in central California.
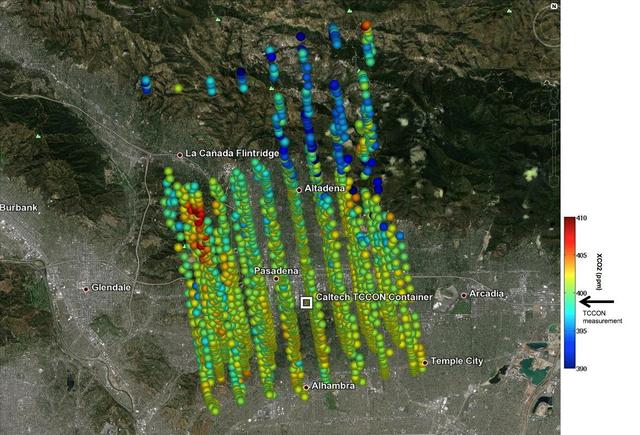
This image shows NASA OCO-2 measurements of carbon dioxide levels over Pasadena and the northern Los Angeles basin on Sept. 5, 2014. Each colored dot represents a single measurement of the greenhouse gas made during an overflight of the area.
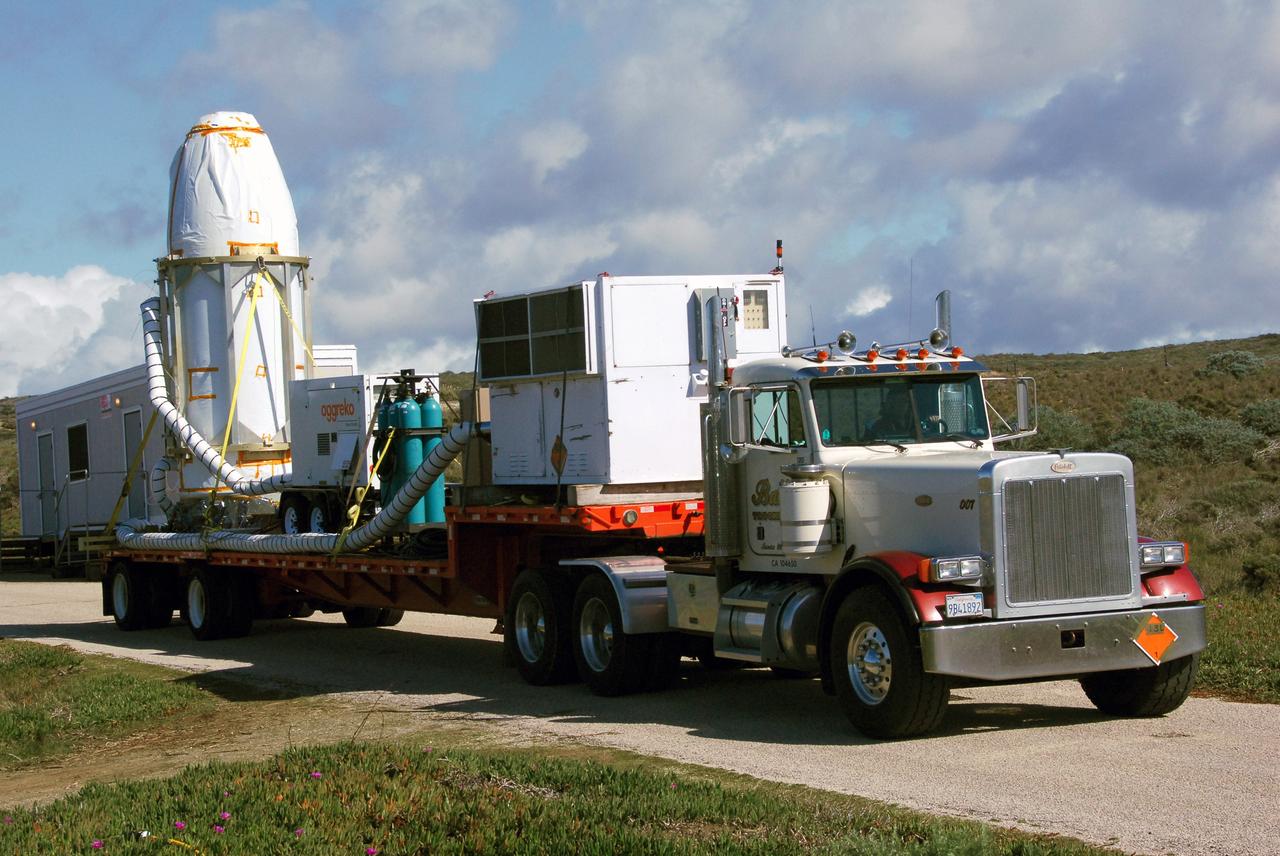

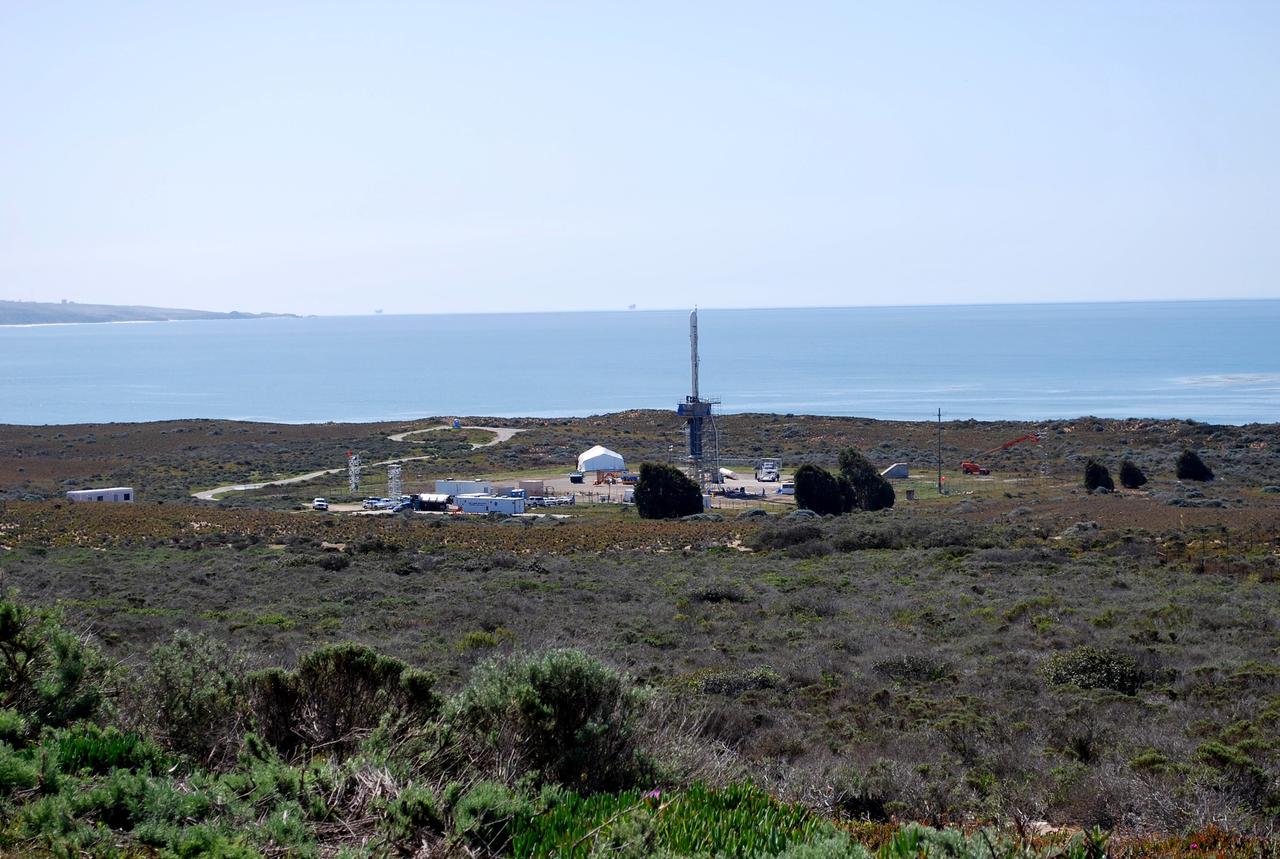
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the transporter holding NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, heads for Launch Complex 576-E. OCO will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. OCO is scheduled to launch Feb. 24 aboard an Orbital Sciences' Taurus XL rocket. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
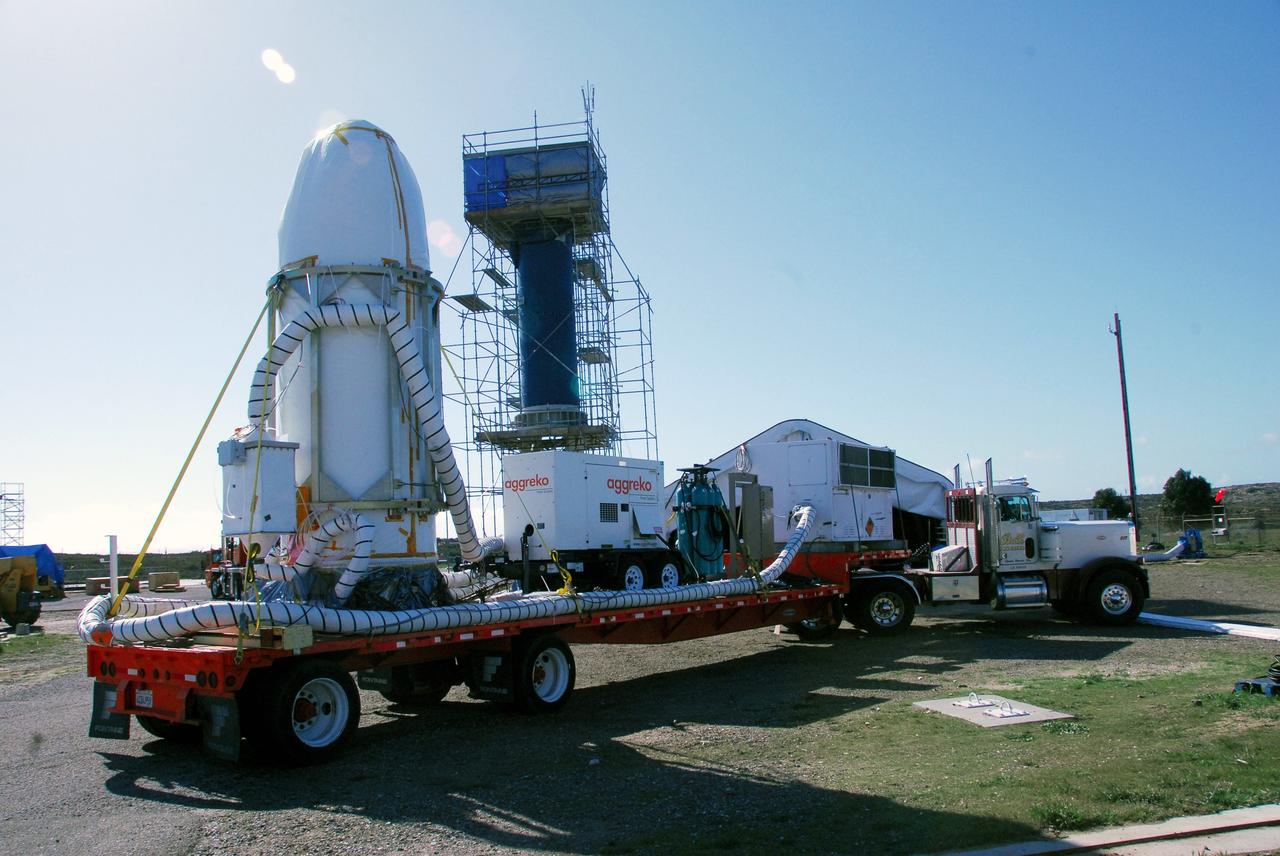

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the transporter holding NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, arrives on Launch Complex 576-E. OCO will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. OCO is scheduled to launch Feb. 24 aboard an Orbital Sciences' Taurus XL rocket. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB
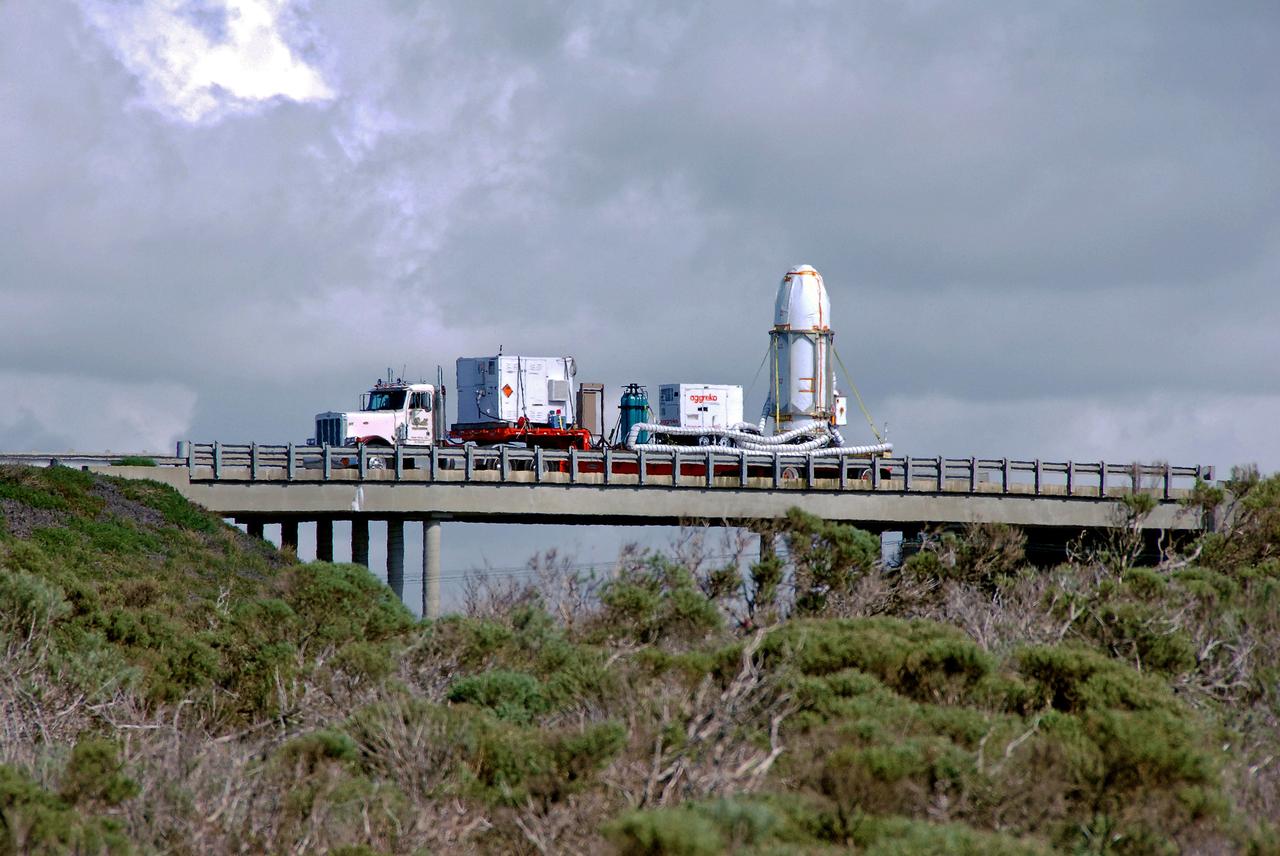

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the transporter holding NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, heads for Launch Complex 576-E. OCO will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. OCO is scheduled to launch Feb. 24 aboard an Orbital Sciences' Taurus XL rocket. Photo credit: NASA/VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – News media representatives converge on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California to cover the launch of NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2. Final preparations for launch of OCO-2 at 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1 aboard a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket are underway on the pad. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://www.nasa.gov/oco2. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

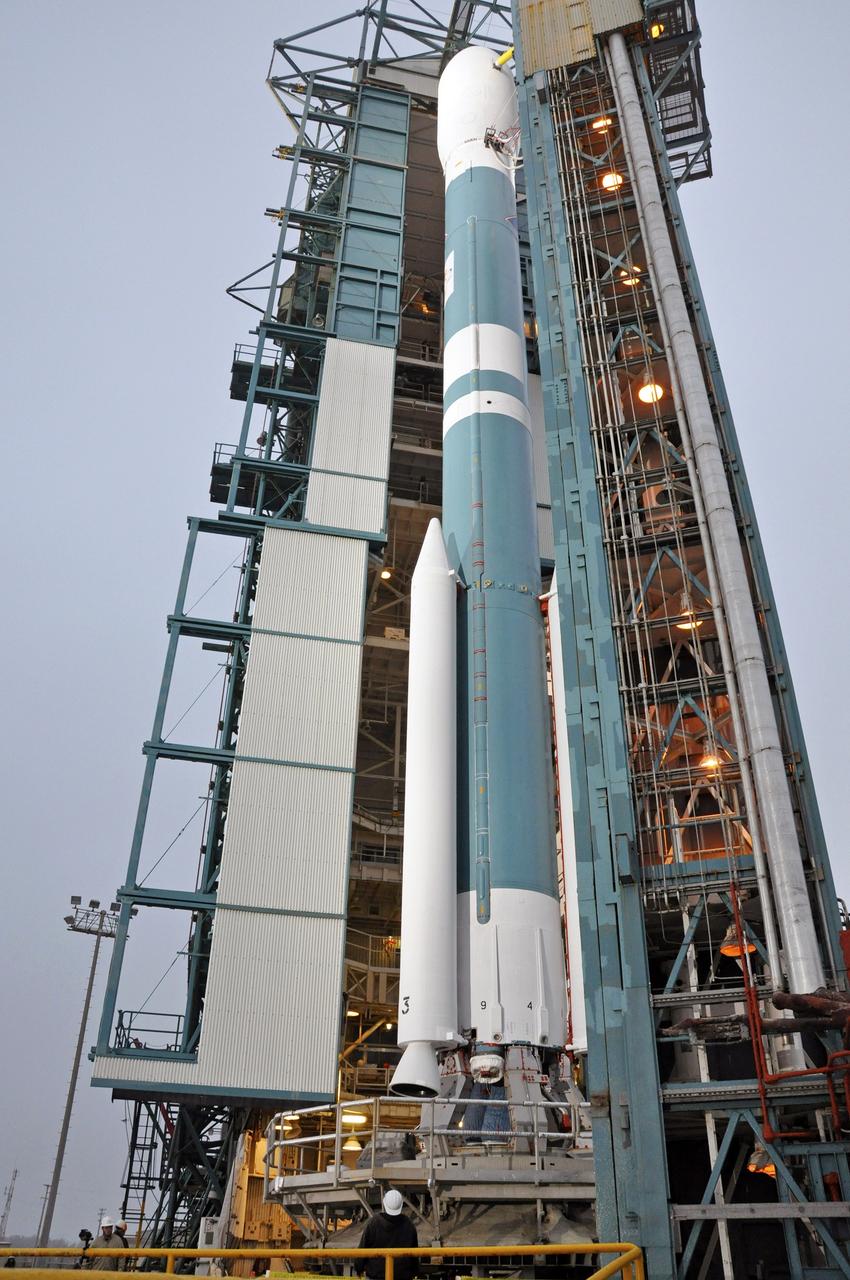
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – Logos affixed to the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket in the mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California identify the major participants in the upcoming launch. The rocket will be carrying NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, to orbit. Launch is scheduled for 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://www.nasa.gov/oco2. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
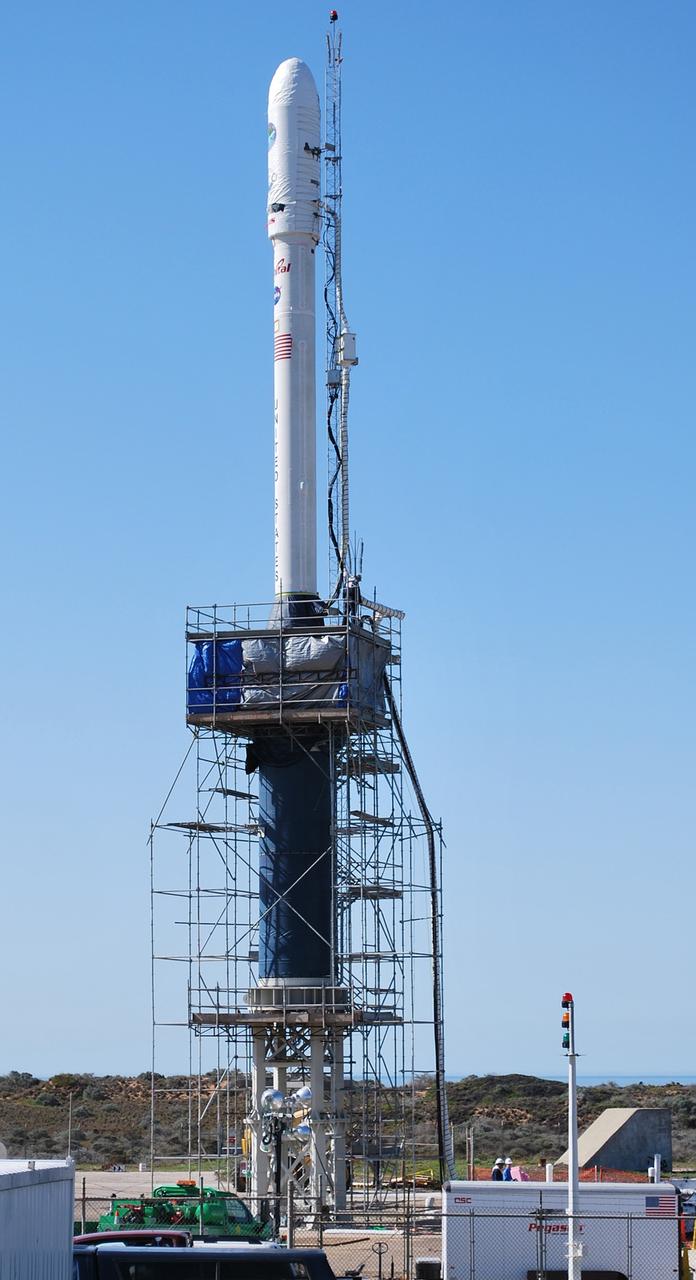

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- On Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, has been erected atop Orbital Sciences' Taurus XL rocket for a Feb. 24 launch. OCO will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- On Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory, or OCO, has been erected atop Orbital Sciences' Taurus XL rocket for a Feb. 24 launch. OCO will collect precise global measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the Earth's atmosphere. Scientists will analyze OCO data to improve our understanding of the natural processes and human activities that regulate the abundance and distribution of this important greenhouse gas. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The mobile service tower on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California rolls away from the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket carrying NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2. Launch is scheduled for 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://www.nasa.gov/oco2. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin
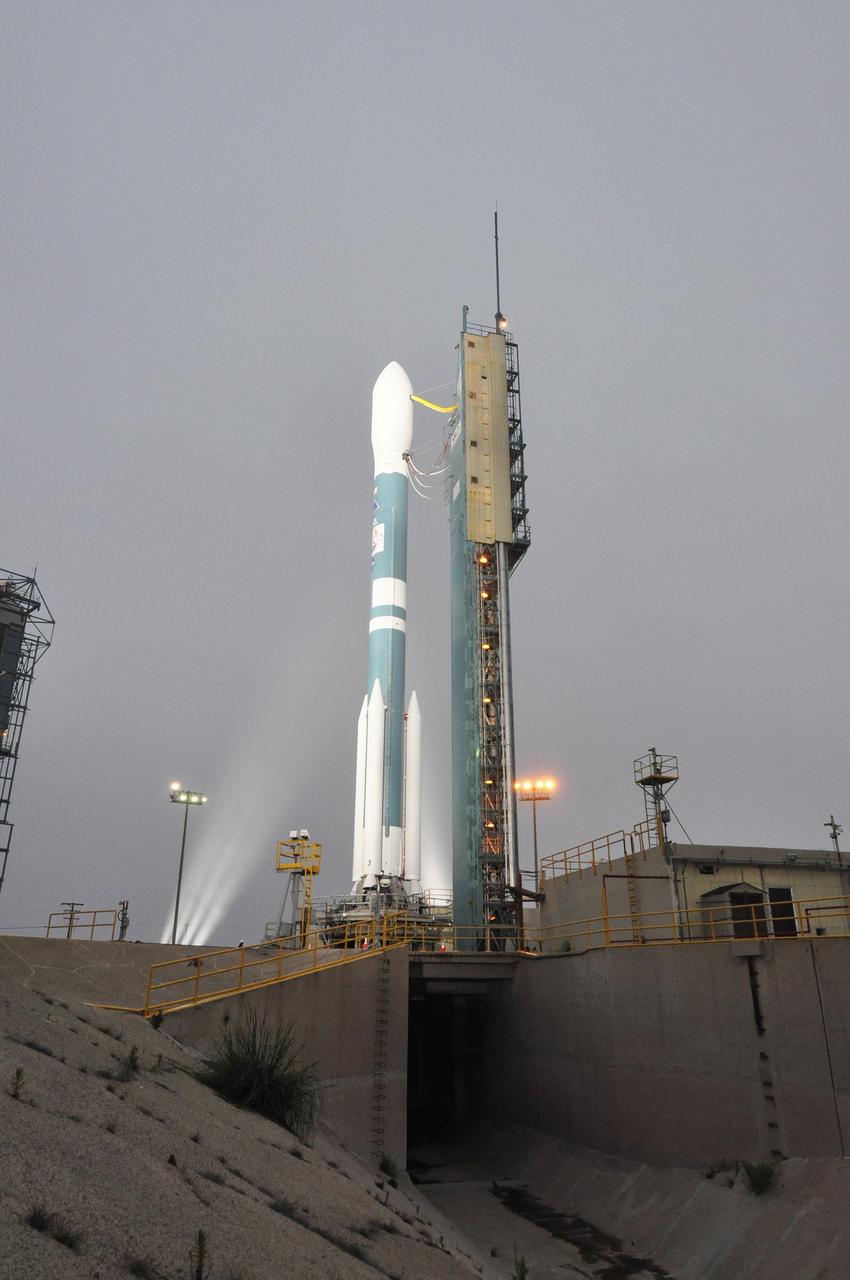

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. – The United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket carrying NASA's Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2, or OCO-2, is ready for launch over the flame trench on Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California following rollback of the mobile service tower. Launch is scheduled for 5:56 a.m. EDT on July 1. OCO-2 is NASA’s first mission dedicated to studying atmospheric carbon dioxide, the leading human-produced greenhouse gas driving changes in Earth’s climate. OCO-2 will provide a new tool for understanding the human and natural sources of carbon dioxide emissions and the natural "sinks" that absorb carbon dioxide and help control its buildup. The observatory will measure the global geographic distribution of these sources and sinks and study their changes over time. To learn more about OCO-2, visit http://www.nasa.gov/oco2. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin