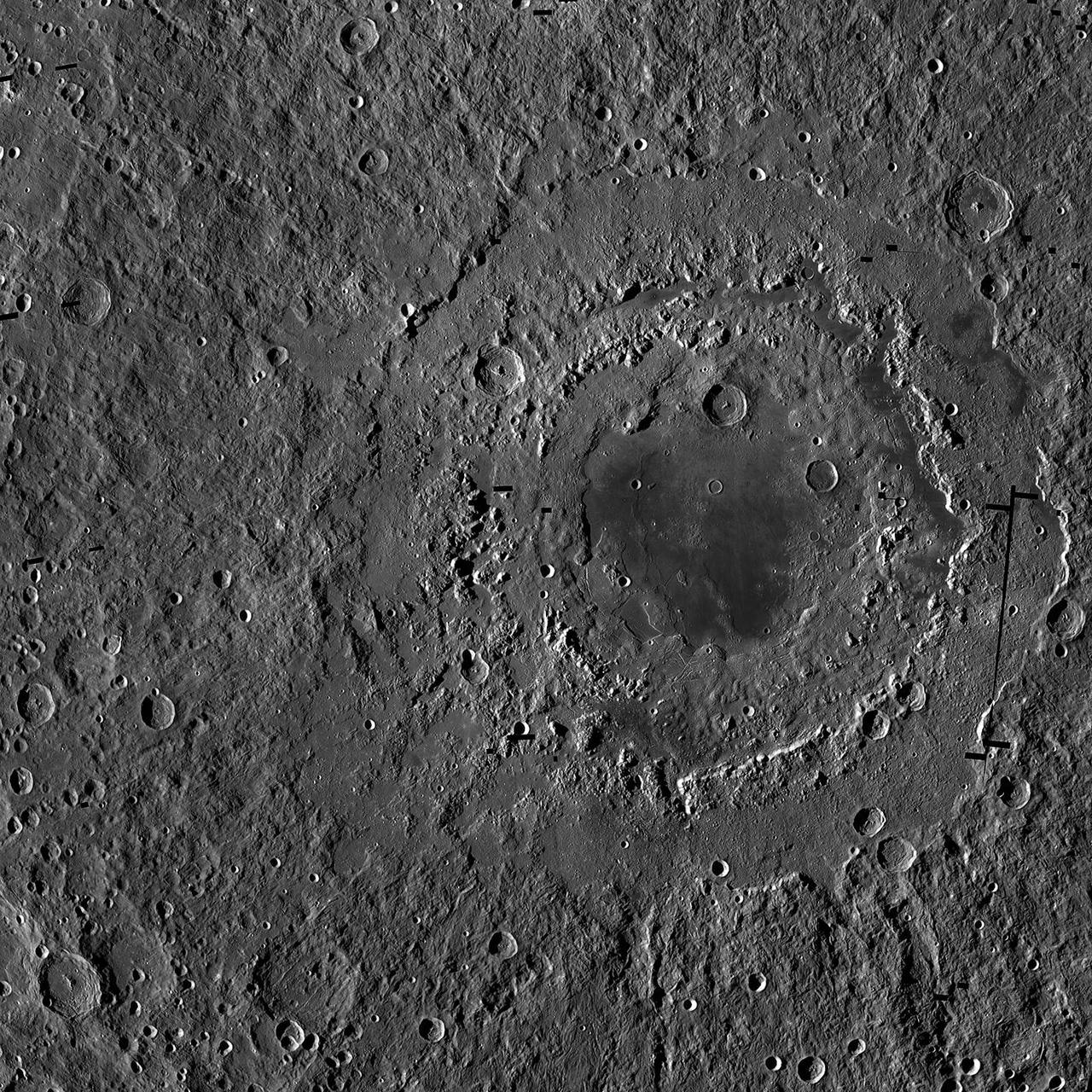

Orientale Basin
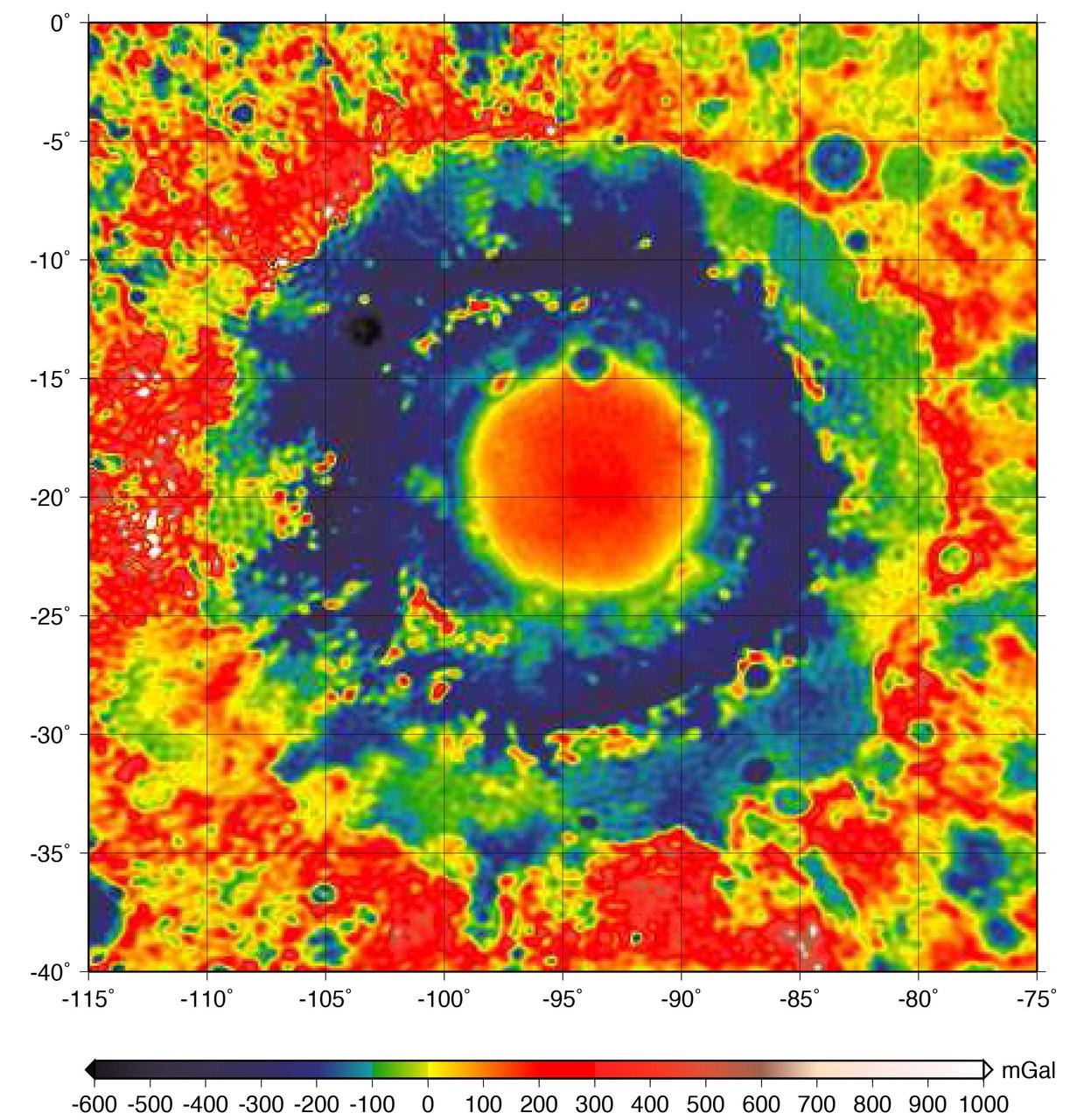
This color-coded map shows the strength of surface gravity around Orientale basin on Earth's moon, derived from data obtained by NASA's GRAIL mission. The GRAIL mission produced a very high-resolution map of gravity over the surface of the entire moon. This plot is zoomed in on the part of that map that features Orientale basin, where the two GRAIL spacecraft flew extremely low near the end of their mission. Their close proximity to the basin made the probes' measurements particularly sensitive to the gravitational acceleration there (due to the inverse squared law). The color scale plots the gravitational acceleration in units of "gals," where 1 gal is one centimeter per second squared, or about 1/1000th of the gravitational acceleration at Earth's surface. (The unit was devised in honor of the astronomer Galileo). Labels on the x and y axes represent latitude and longitude. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21050
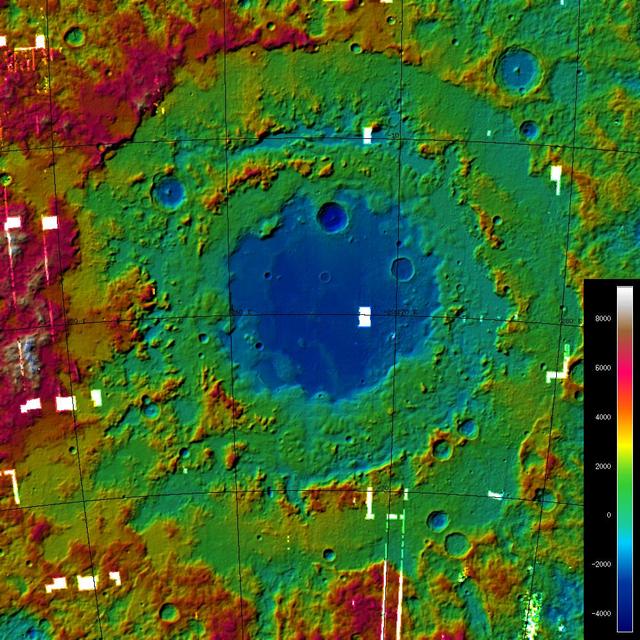

This image is a Digital Terrain Model of the large Orientale Basin, located on the western hemisphere of the Moon.
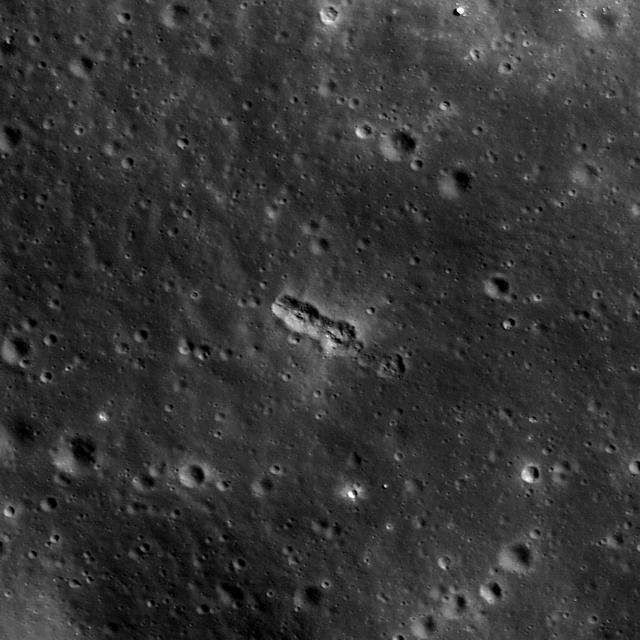

This image taken by NASA Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter shows a small secondary crater chain near the southwestern margin of Mare Orientale, within the Inner Rook Mountains. The ~125-meter-long chain lies within the Orientale multi-ring basin.
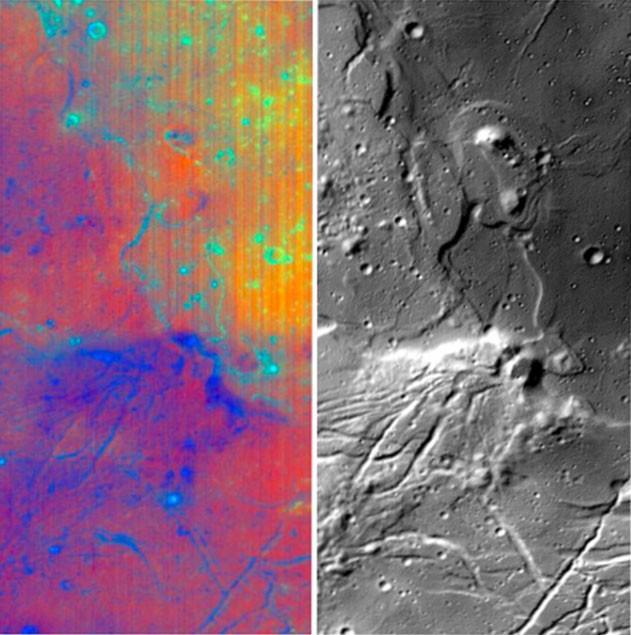
Different wavelengths of light provide new information about the Orientale Basin region of the moon in a composite image taken by NASA Moon Mineralogy Mapper, a guest instrument aboard the Indian Space Research Organization Chandrayaan-1 spacecraft.
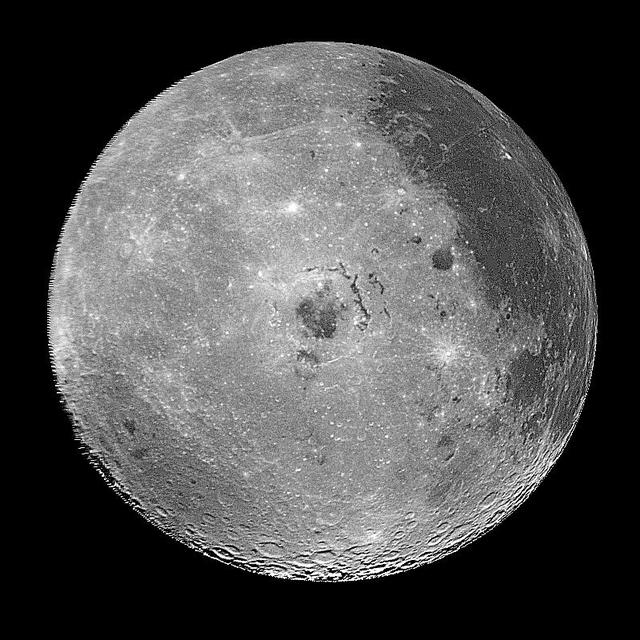

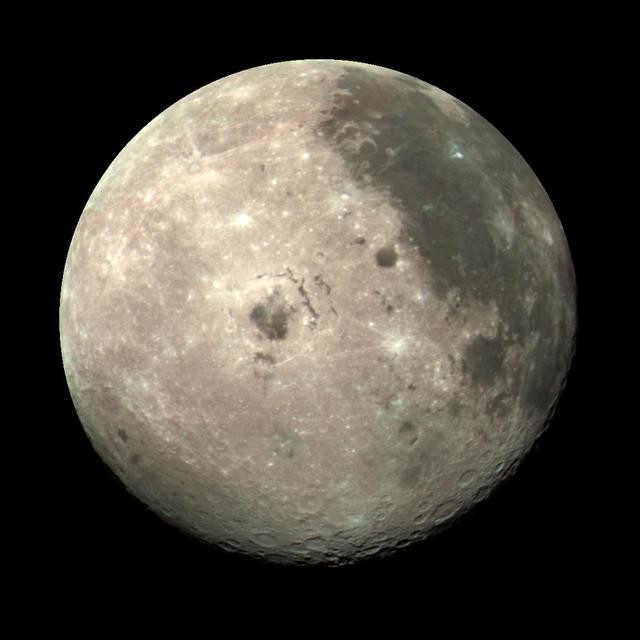
This image of the western hemisphere of the Moon was taken through a green filter by NASA's Galileo spacecraft at 9:35 a.m. PST Dec. 9 at a range of about 350,000 miles. In the center is the Orientale Basin. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00120
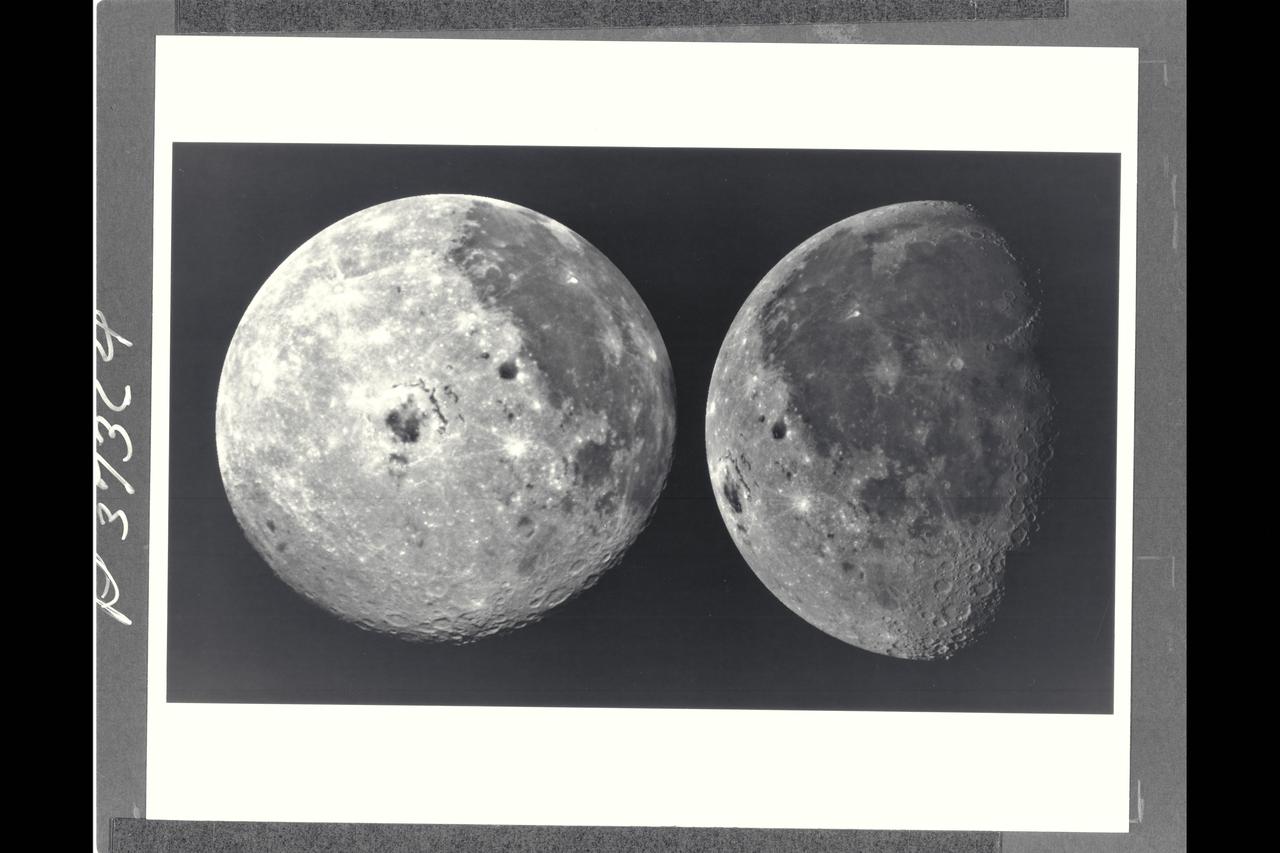

Range : 220,000 mi. (left)/350,000 mi. (right) These pictures of the Moon were taken by the Galileo spacecraft. Image on the right shows the dark Oceanus Procellarum in the upper center, with Mare Imbrium above it and the smaller circular Mare Humorum below. The Orientale Basin, with a small mare in its center, is on the lower left near the limb or edge. Between stretches the cratered highland terrain, with scattered bright young craters on highlands and maria alike. The left image shows the globe of the Moon rotated, putting Mare Imbrium on the eastern limb and moving the Orientale Basin almost to the center. The extent of the cratered highlands on tghe far side is very apparent., At lower left, near the limb, is the South-Pole-Aitken basin, similar to Orientale but very much older and some 1,200 miles in diameter. This feature was previously known as a large depression in the southern far side; this image shows its Orientale-like structure and darkness relative to surrounding highlands.

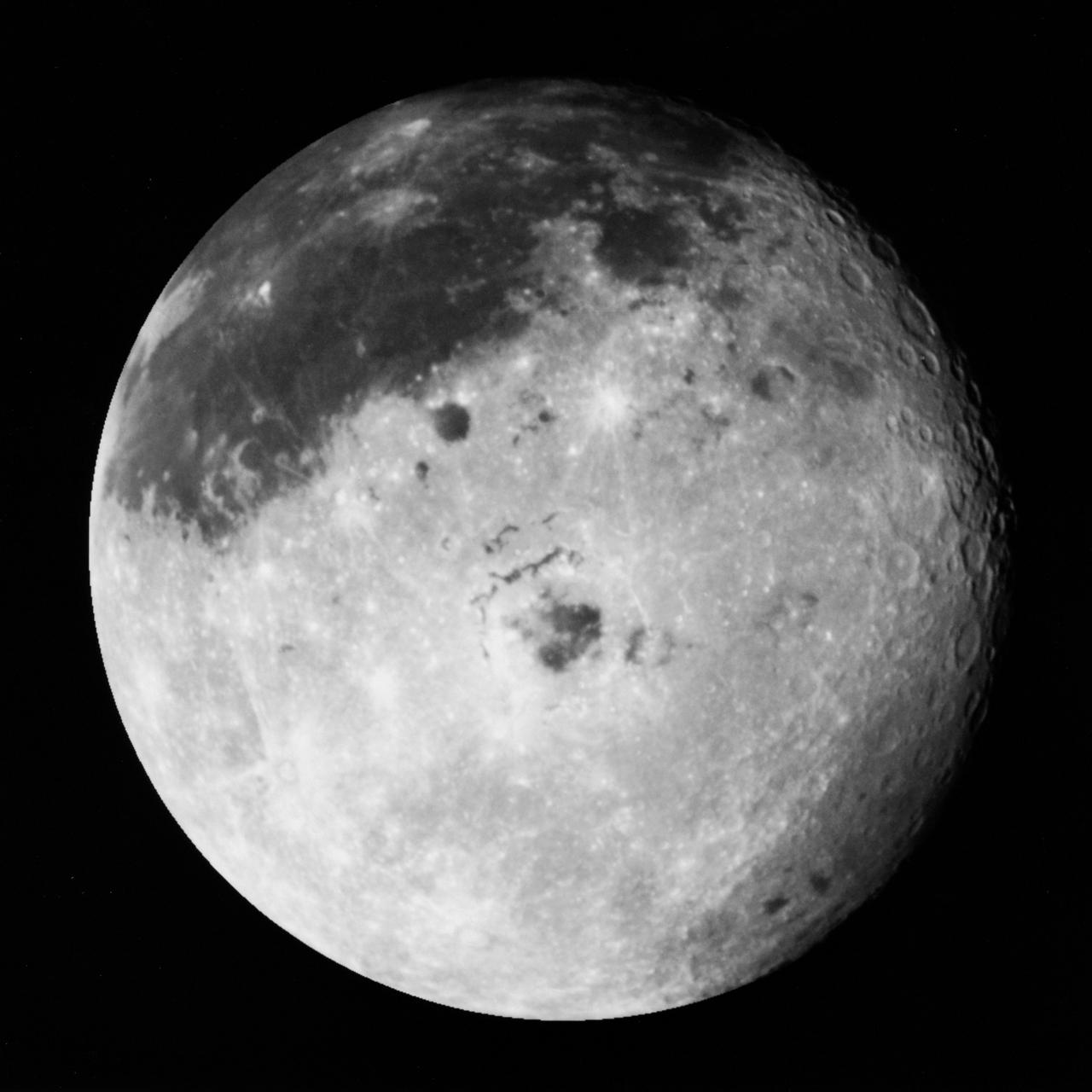
This color image of the Moon was taken by NASA's Galileo spacecraft at 9:35 a.m. PST Dec. 9, 1990, at a range of about 350,000 miles. The concentric, circular Orientale basin, is near the center; the nearside is to the right, the far side to the left. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00113

S90-55753 (9 Dec. 1990) --- This color image of the Moon was taken by the Galileo spacecraft at 9:25 a.m. (PST) December 9, 1990, at a range of about 350,000 miles. The color composite uses monochrome images taken through violet, red, and near infrared filters. The concentric, circular Orientale Basin, 600 miles across, is near the center; the near side is to the right, the far side to the left. At the upper right is the large, dark Oceanus Procellarum; below it is the smaller Mare Humorum. These, like the small dark Mare Orientale in the center of the basin, formed over 3 billion years ago as basaltic lava flows. At the lower left, among the southern cratered highlands of the far side, is the South-Pole-Aitken Basin, similar to Orientale but twice as great in diameter and much older and more degraded by crating and weathering. The cratered highlights of the near and far sides and the Maria are covered with scattered bright, young ray-craters.

Galileo spacecraft image of the Moon recorded at 9:35 am Pacific Standard Time (PST), 12-09-90, after completing its first Earth Gravity Assist. Western hemisphere of the Moon was taken through a green filter at a range of about 350,000 miles. In the center is Orientale Basin, 600 miles in diameter, formed about 3.8 billion years ago by the impact of an asteroid-size body. Orientale's dark center is a small mare. To the right is the lunar near side with the great, dark Oceanus Procellarum above the small, circular, dark Mare Humorum below. Maria are broad plains formed mostly over 3 billion years ago as vast basaltic lava flows. To the left is the lunar far side with fewer maria, but, at lower left South-Pole-Aitken basin, about 1200 miles in diameter, which resembles Orientale but is much older and more weathered and battered by cratering. The intervening cratered highlands of both sides, as well as the maria, are dotted with bright young craters. This image was "reprojected" so as to center the Orientale Basin, and was filtered to enhance the visibility of small features. The digital image processing was done by DLR, the German Aerospace Research Establishment near Munich, an international collaborator in the Galileo mission. Photo was provided by Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) with alternate number P-37327, 12-19-90.

Range : 350,000 miles This image of the western hemisphere of the Moon was taken through a green filter by Galileo at 9:35 am PST. In the center is the Orientale Basin, 600 miles in diameter, formed about 3.8 billion years ago by the impact of an streroid-size body. Orientale's dark center is a small mare. To the right is the lunar near side with the great, dark Oceanus Procellarum above and the small, circular, dark Mare Humorum Below. Maria are broad plains formed mostly over 3 billion years ago as vast bassaltic lava flows. To the left is the lunar far side with fewer maria, but, at lower left, the South-Pole-Aitken basin, about 1200 miles in diameter, which resemble Orientale but is much older and more weathered and battered by cratering. The intervening cratered highlands of both sides, as well as the maria, are dotted with bright, young craters. This image was 'reprojected' so as to center visibility of small features.
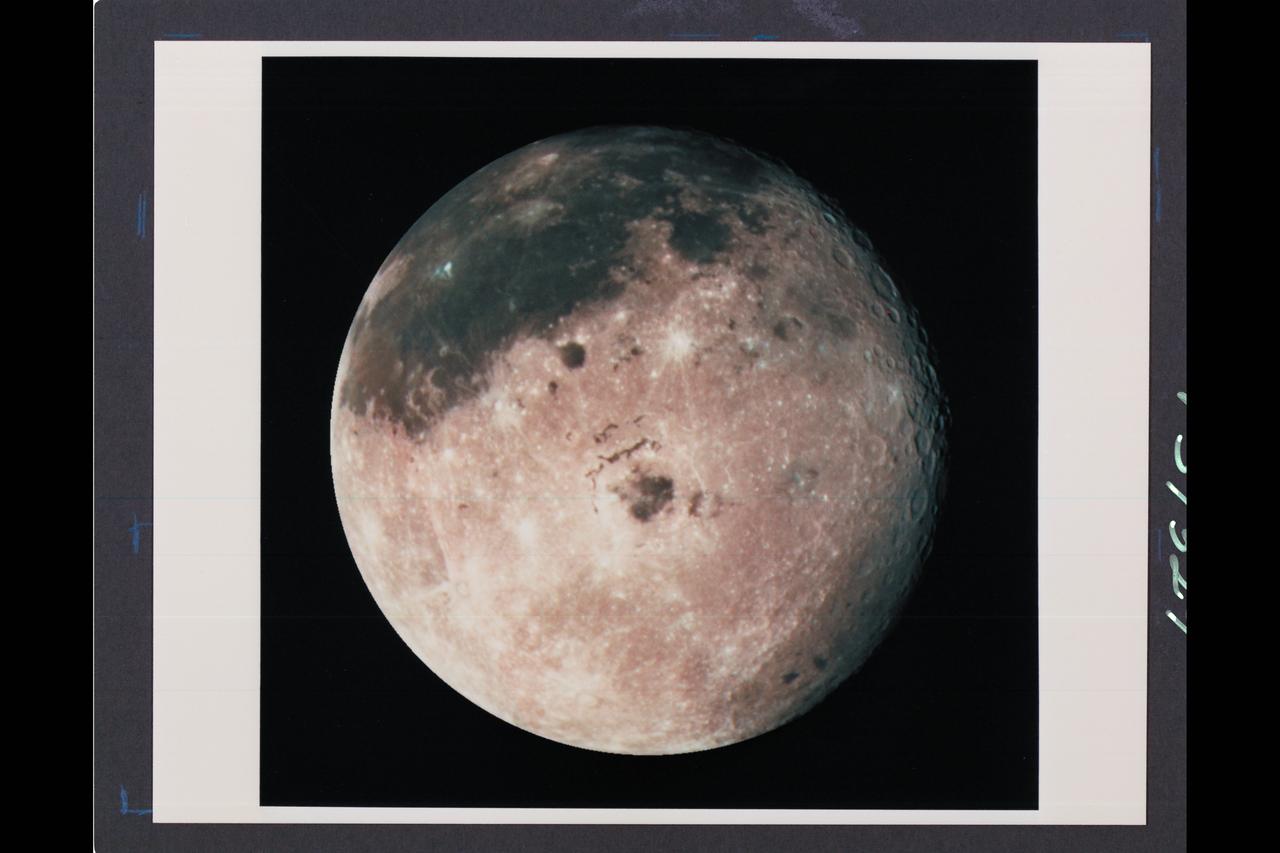

Range : 350,000 miles (JPL Ref: P-37329) This image of the western hemisphere of the Moon was taken through a green filter by Galileo at 9:35 am PST. In the center is the Orientale Basin, 600 miles in diameter, formed about 3.8 billion years ago by the impact of an streroid-size body. Orientale's dark center is a small mare. To the right is the lunar near side with the great, dark Oceanus Procellarum above and the small, circular, dark Mare Humorum Below. Maria are broad plains formed mostly over 3 billion years ago as vast bassaltic lava flows. To the left is the lunar far side with fewer maria, but, at lower left, the South-Pole-Aitken basin, about 1200 miles in diameter, which resemble Orientale but is much older and more weathered and battered by cratering. The intervening cratered highlands of both sides, as well as the maria, are dotted with bright, young craters. This image was 'reprojected' so as to center visibility of small features.

These pictures of the Moon were taken by NASA Galileo spacecraft at right photo Dec.8, 1990 from a distance of almost 220,000 miles, and at left photo Dec. 9, 1990 at a range of more than 350,000 miles. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00077

NASA image release March 11, 2011 Caption: The lunar farside as never seen before! LROC WAC orthographic projection centered at 180° longitude, 0° latitude. Credit: NASA/Goddard/Arizona State University. Because the moon is tidally locked (meaning the same side always faces Earth), it was not until 1959 that the farside was first imaged by the Soviet Luna 3 spacecraft (hence the Russian names for prominent farside features, such as Mare Moscoviense). And what a surprise - unlike the widespread maria on the nearside, basaltic volcanism was restricted to a relatively few, smaller regions on the farside, and the battered highlands crust dominated. A different world from what we saw from Earth. Of course, the cause of the farside/nearside asymmetry is an interesting scientific question. Past studies have shown that the crust on the farside is thicker, likely making it more difficult for magmas to erupt on the surface, limiting the amount of farside mare basalts. Why is the farside crust thicker? That is still up for debate, and in fact several presentations at this week's Lunar and Planetary Science Conference attempt to answer this question. The Clementine mission obtained beautiful mosaics with the sun high in the sky (low phase angles), but did not have the opportunity to observe the farside at sun angles favorable for seeing surface topography. This WAC mosaic provides the most complete look at the morphology of the farside to date, and will provide a valuable resource for the scientific community. And it's simply a spectacular sight! The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC) Wide Angle Camera (WAC) is a push-frame camera that captures seven color bands (321, 360, 415, 566, 604, 643, and 689 nm) with a 57-km swath (105-km swath in monochrome mode) from a 50 km orbit. One of the primary objectives of LROC is to provide a global 100 m/pixel monochrome (643 nm) base map with incidence angles between 55°-70° at the equator, lighting that is favorable for morphological interpretations. Each month, the WAC provides nearly complete coverage of the Moon under unique lighting. As an added bonus, the orbit-to-orbit image overlap provides stereo coverage. Reducing all these stereo images into a global topographic map is a big job, and is being led by LROC Team Members from the German Aerospace Center (Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt; DLR). Several preliminary WAC topographic products have appeared in LROC featured images over the past year (Orientale basin, Sinus Iridum). For a sneak preview of the WAC global DEM with the WAC global mosaic, view a rotating composite moon (70 MB video from ASU's LROC website). The WAC topographic dataset will be completed and released later this year. The global mosaic released today is comprised of over 15,000 WAC images acquired between November 2009 and February 2011. The non-polar images were map projected onto the GLD100 shape model (WAC derived 100 m/pixel DTM), while polar images were map projected on the LOLA shape model. In addition, the LOLA derived crossover corrected ephemeris, and an improved camera pointing, provide accurate positioning (better than 100 m) of each WAC image. As part of the March 2011 PDS release, the LROC team posted the global map in ten regional tiles. Eight of the tiles are equirectangular projections that encompass 60° latitude by 90° longitude. In addition, two polar stereographic projections are available for each pole from ±60° to the pole. These reduced data records (RDR) products will be available for download on March 15, 2011. As the mission progresses, and our knowledge of the lunar photometric function increases, improved and new mosaics will be released! Work your way around the moon with these six orthographic projections constructed from WAC mosaics. The nearside view linked below is different from that released on 21 February. To read more con't here: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/LRO/news/lro-farside.html" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/LRO/news/lro-farside.html</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Join us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b>