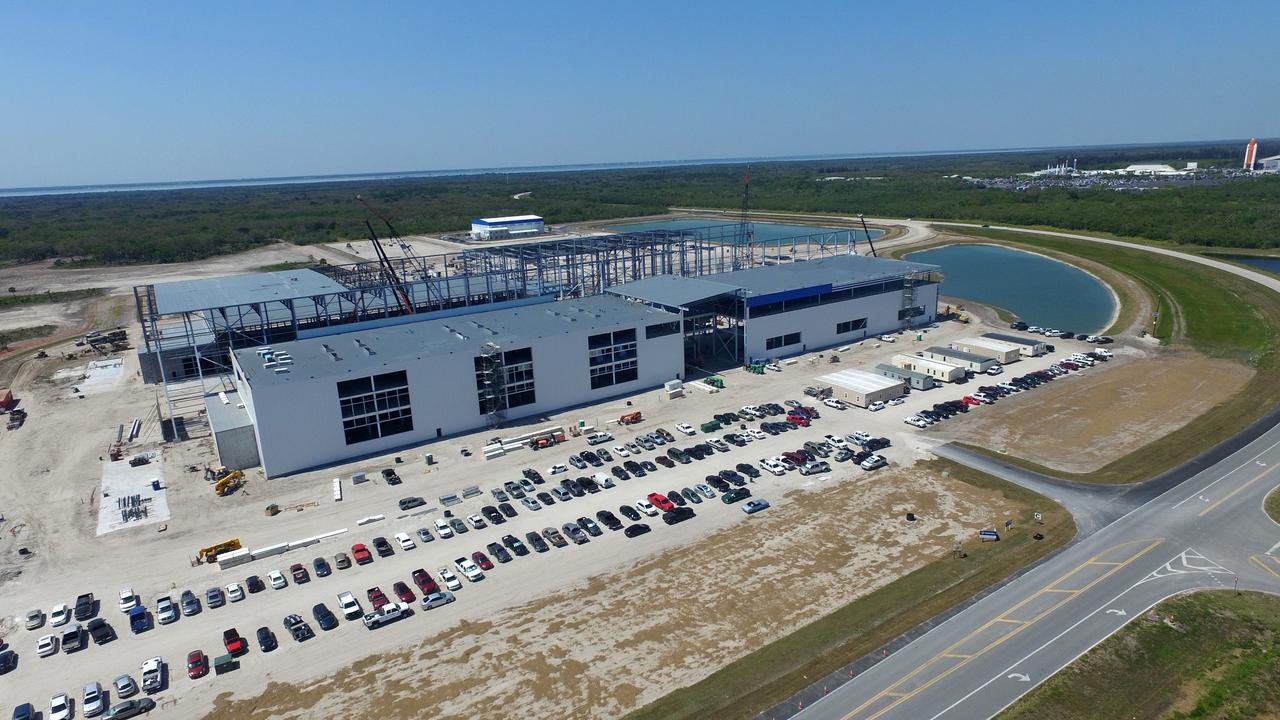

Construction is progressing on Blue Origin's 750,000-square-foot facility being built at Exploration Park on NASA Kennedy Space Center property in Florida. Blue Origin will use the factory to manufacture its two-stage super-heavy-lift New Glenn launch vehicle and launch the vehicles from Space Launch Complex 46 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station.
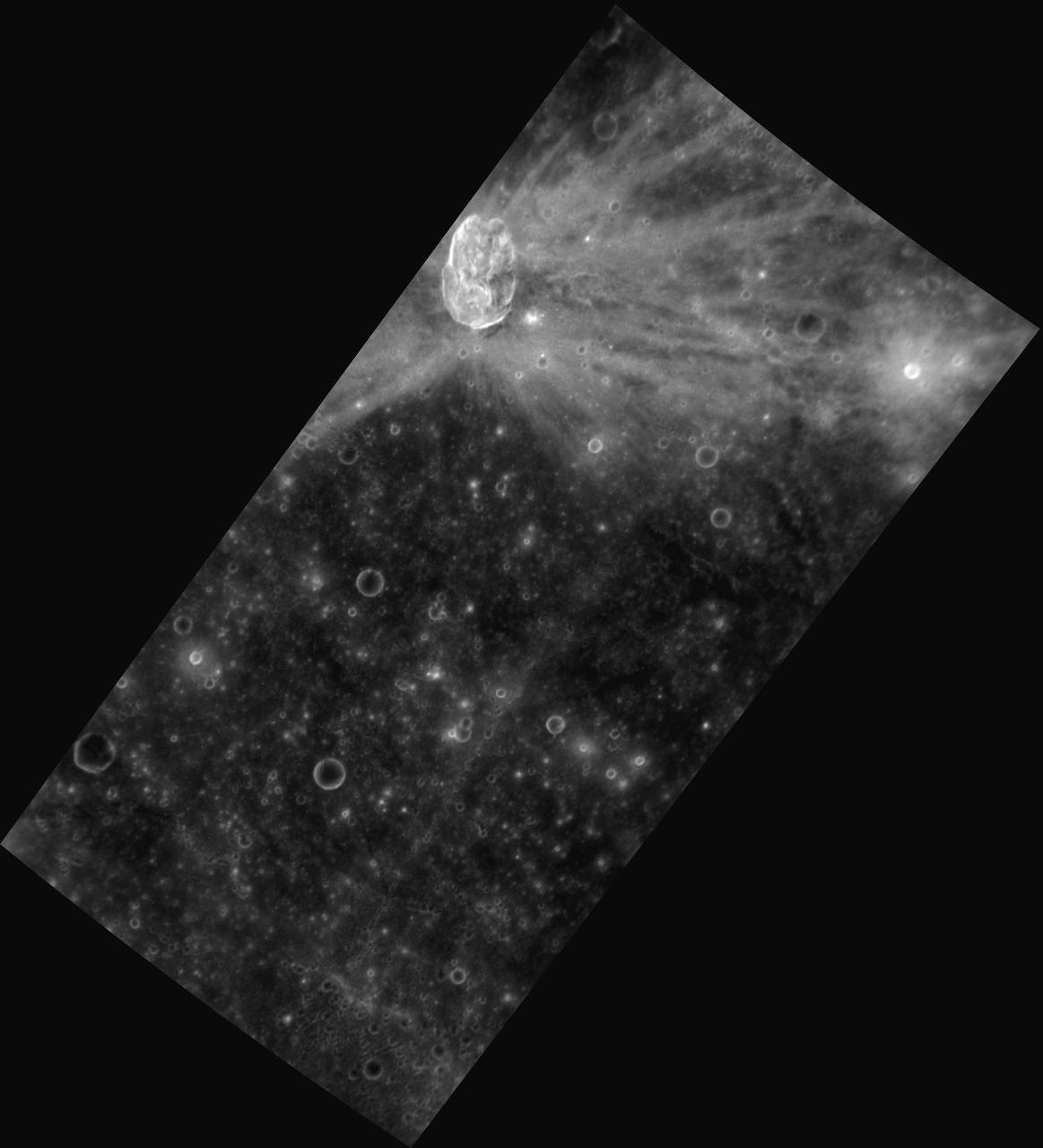
Oblique Origins
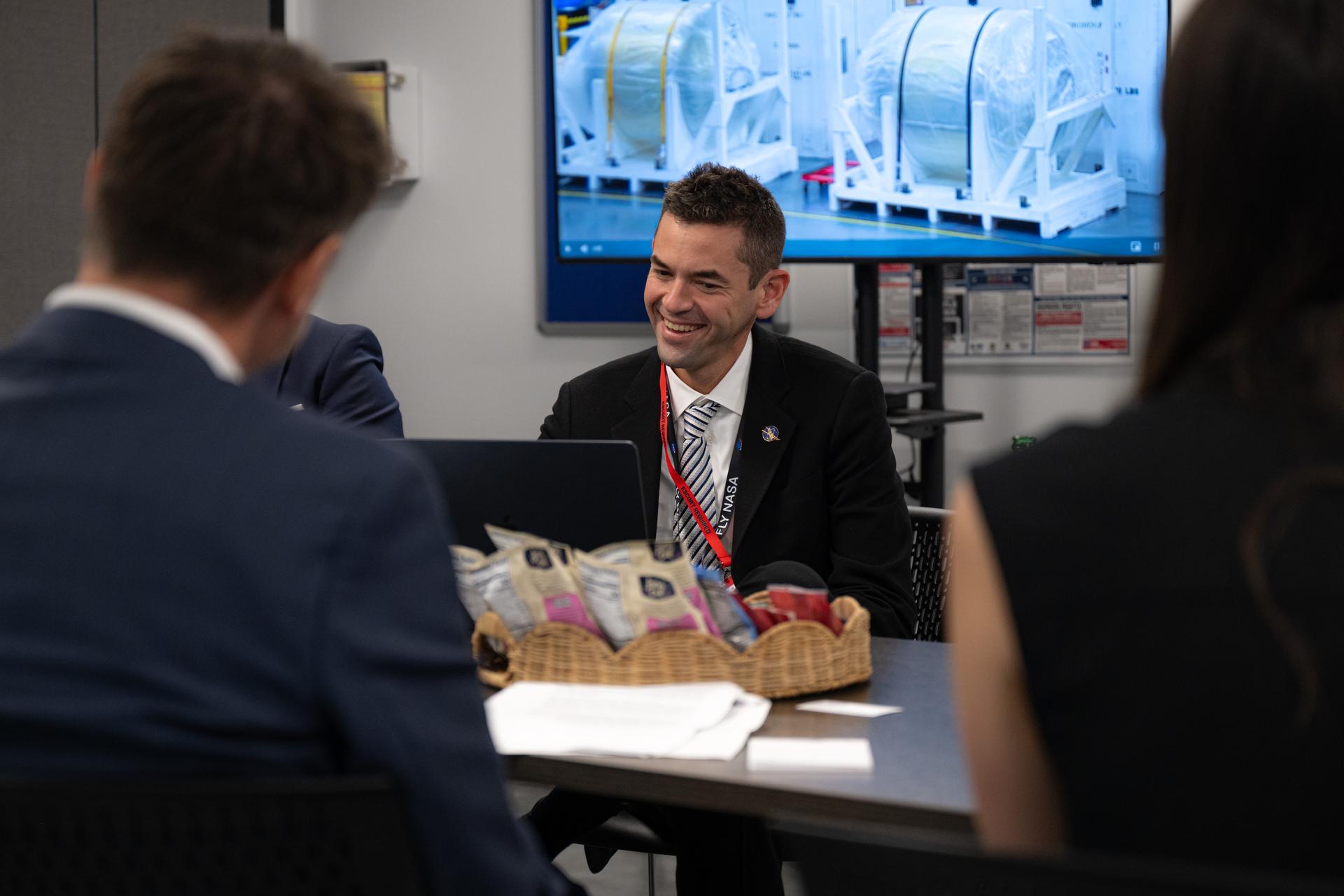

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman meets with Blue Origin leadership, Tuesday, Jan. 13, 2026, at the company’s Lunar Plant 1 facility in Merritt Island, Fla. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
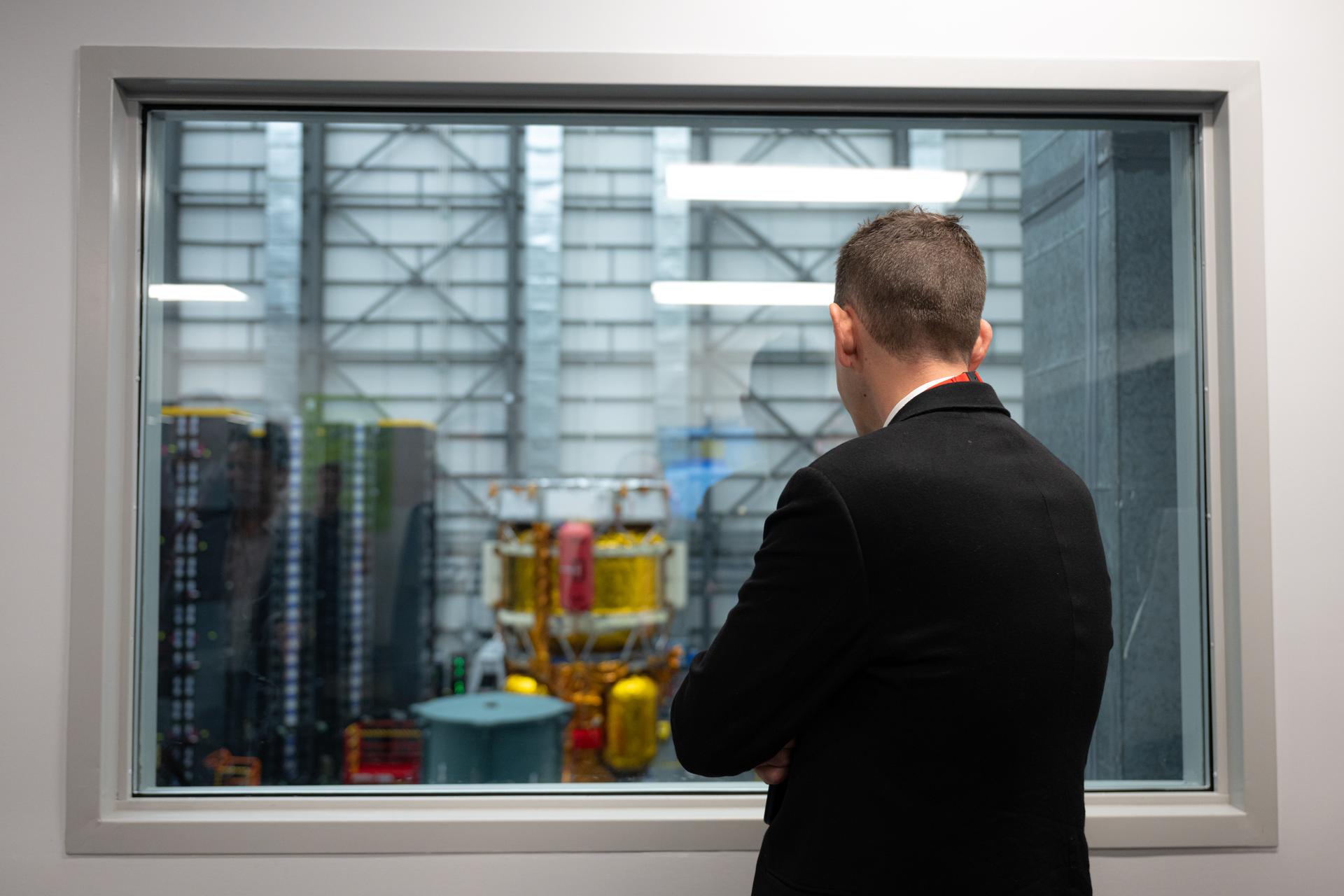

NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman views Blue Origin’s Blue Moon Mark 1 lunar lander, named “Endurance,” Tuesday, Jan. 13, 2026, at the company’s Lunar Plant 1 facility in Merritt Island, Fla., Tuesday. Photo Credit: (NASA/John Kraus)
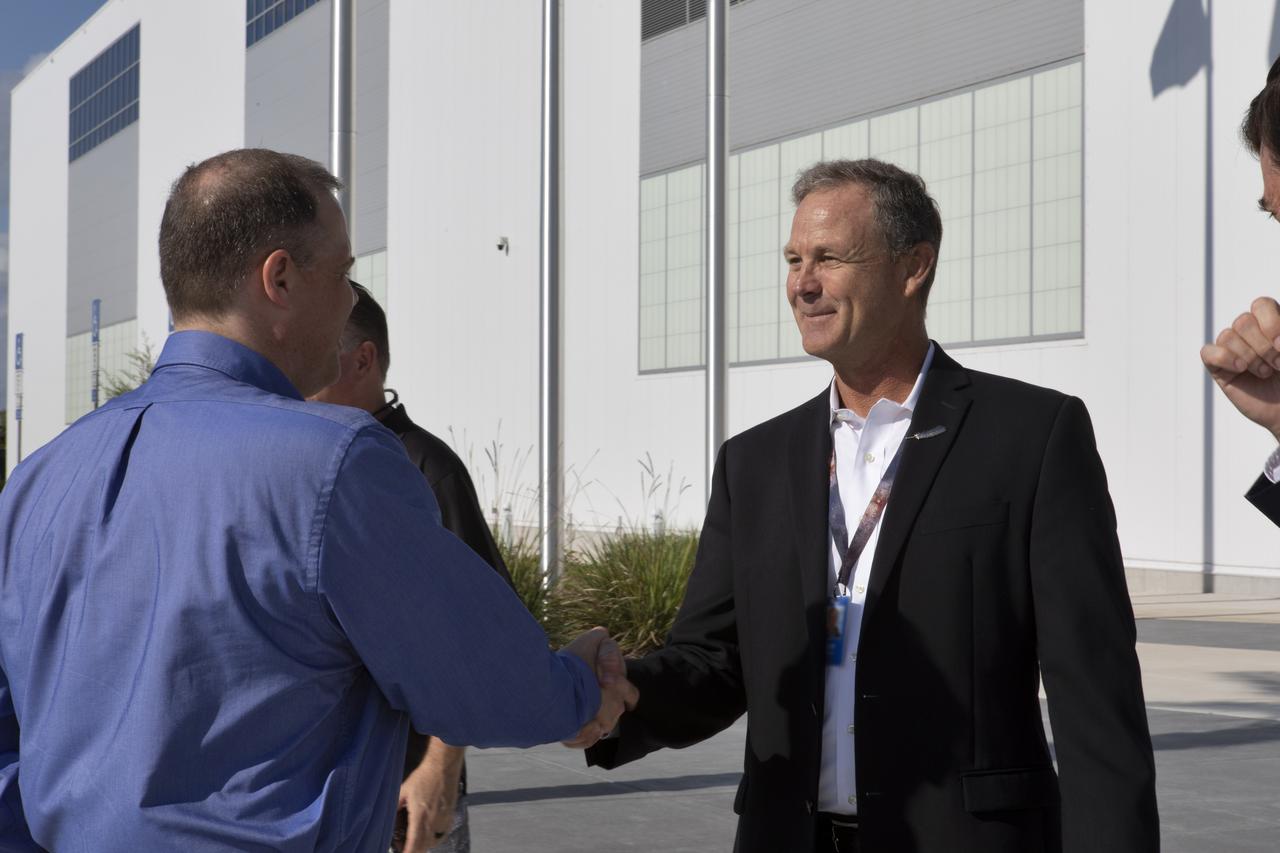

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine shakes hands with Scott Henderson, Blue Origin Orbital Launch director, at the Blue Origin facilities near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 23, 2019. Bridenstine toured the facilities and viewed the New Shepard booster and crew capsule that flew to space and back five times.
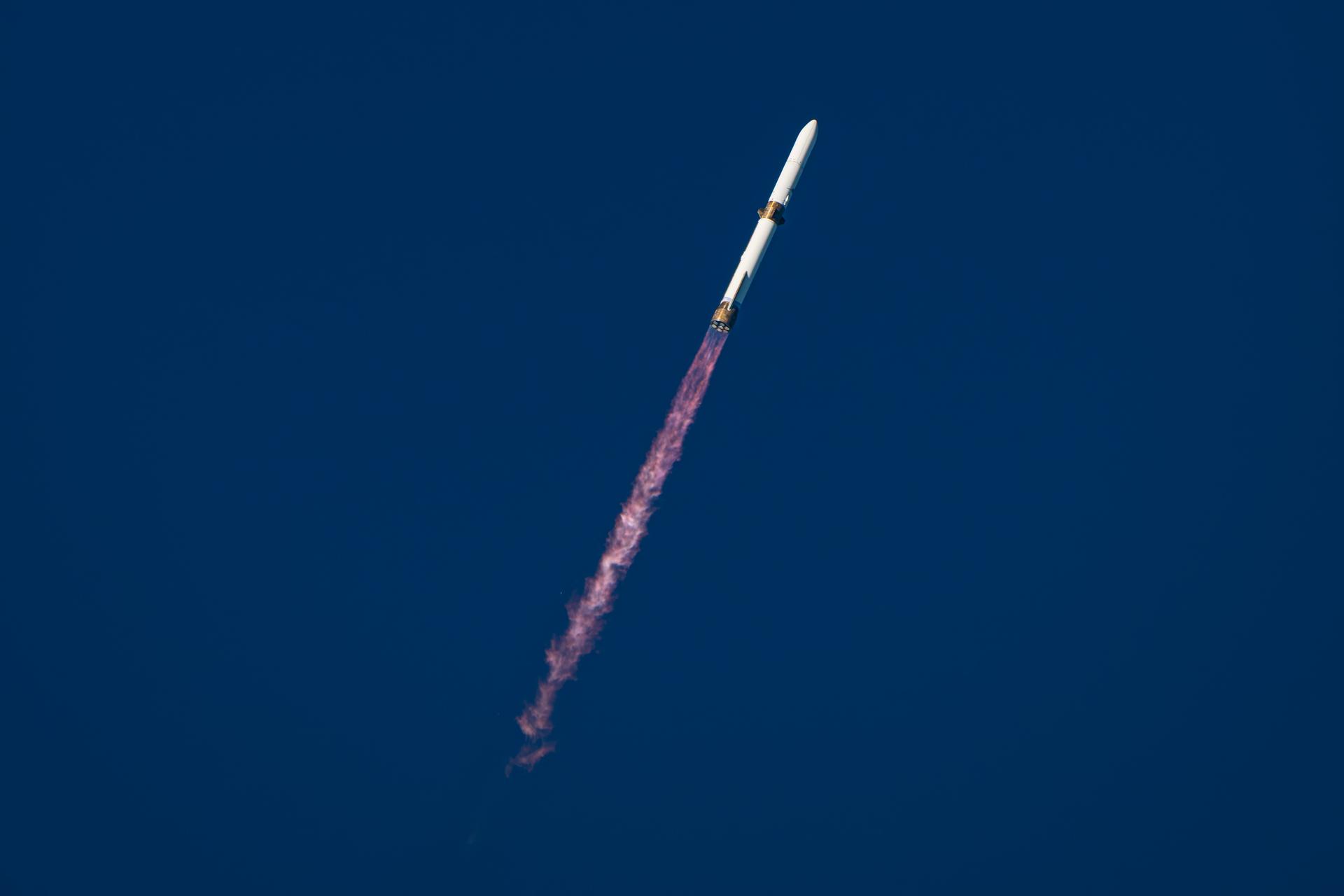

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
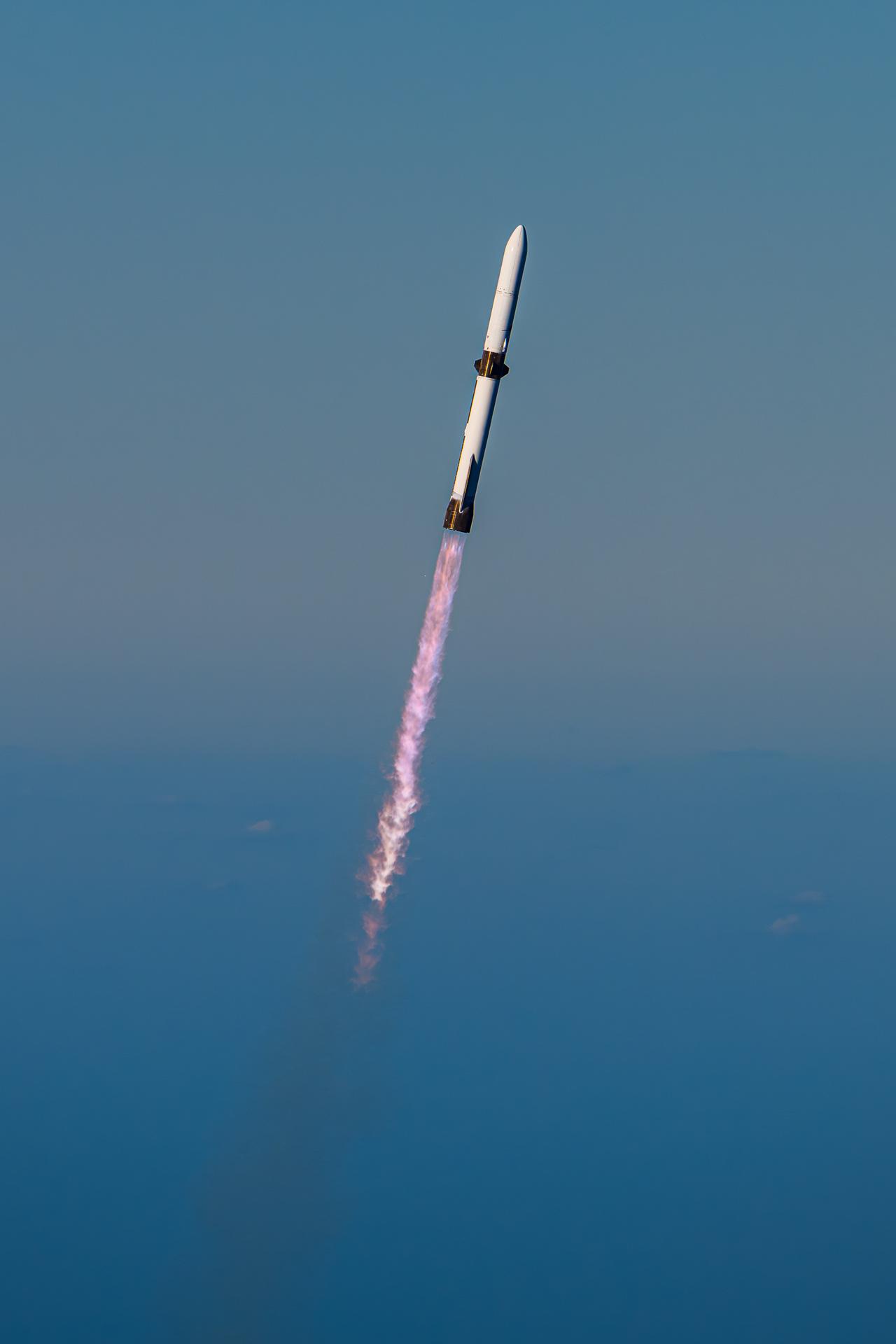

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
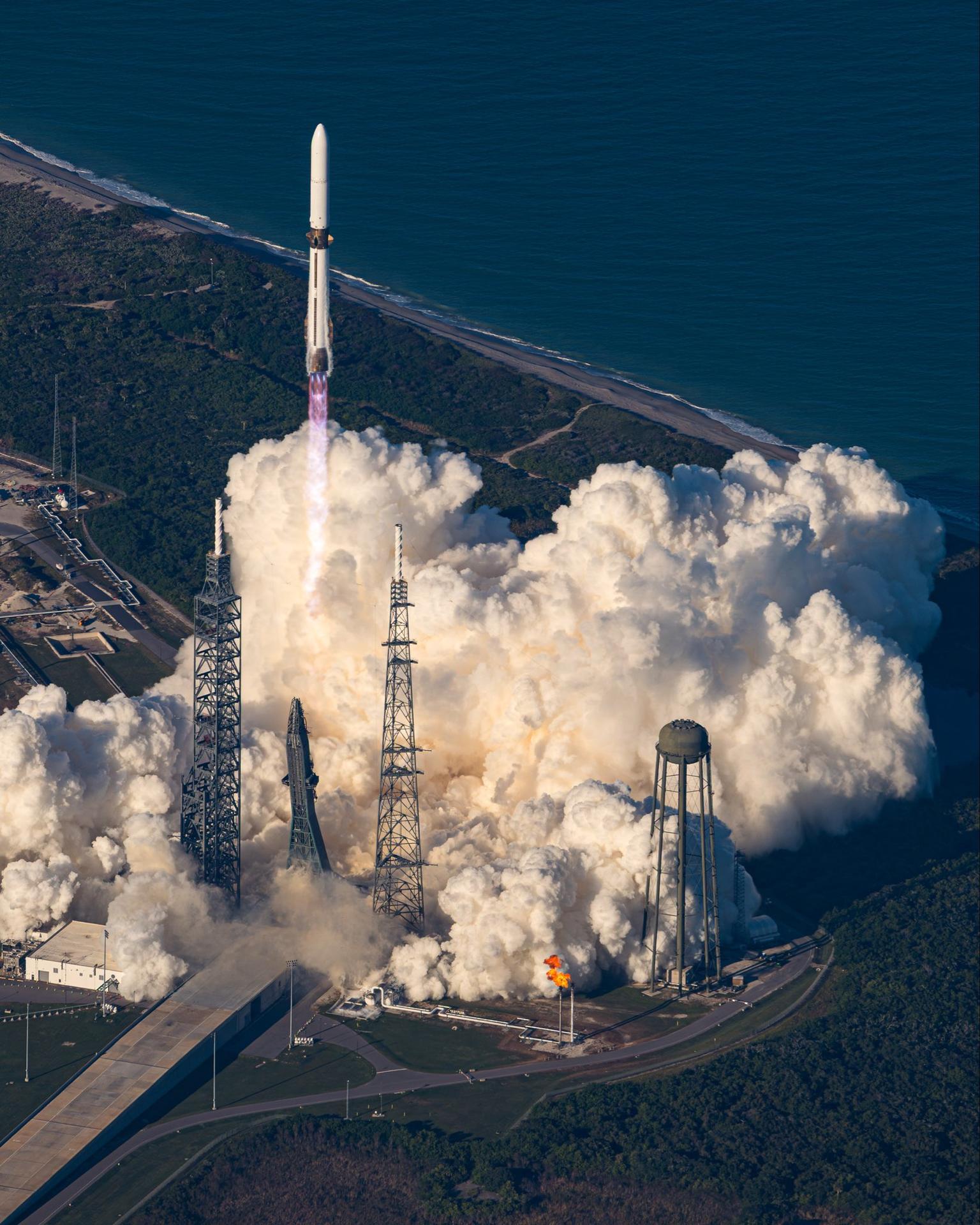

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
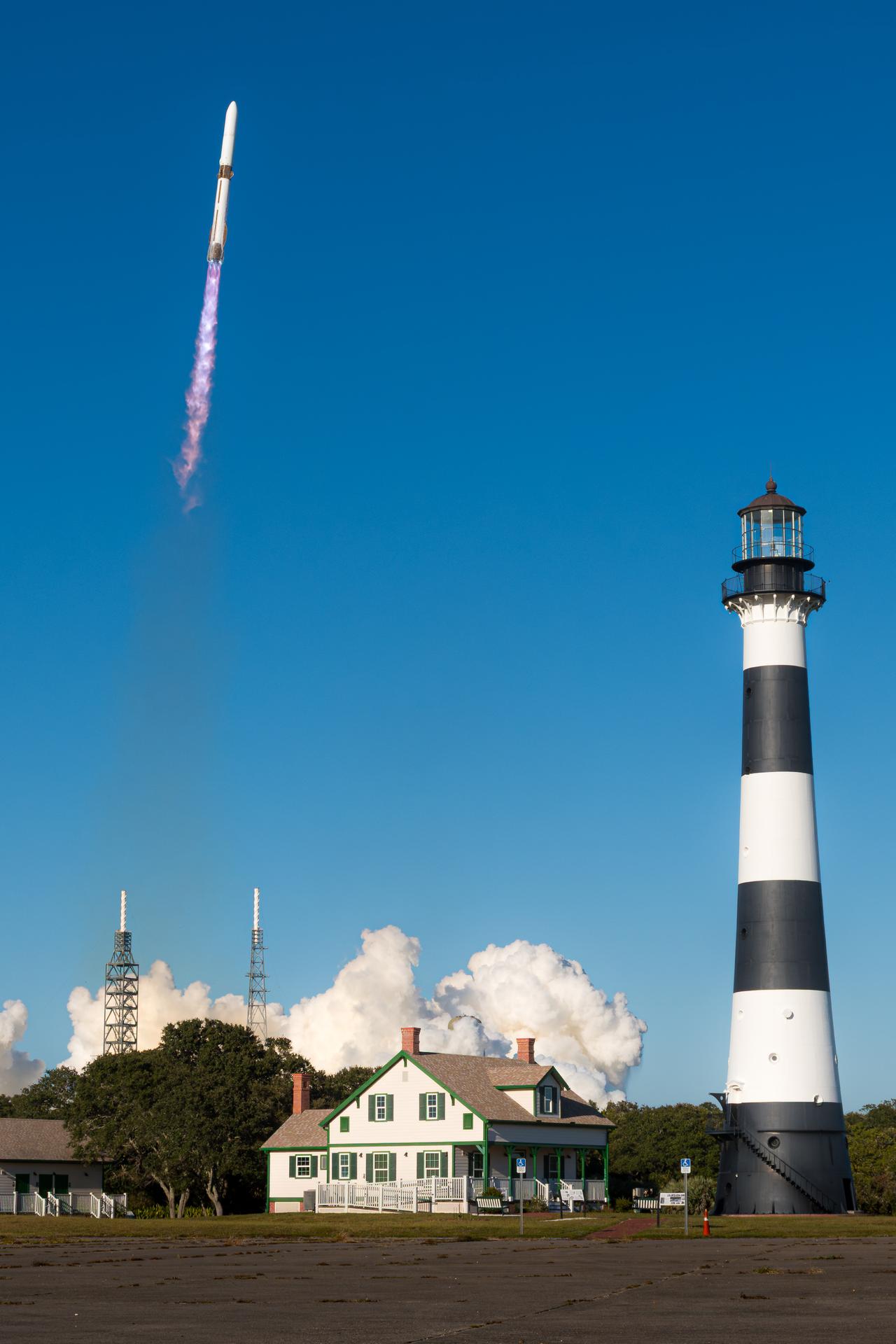

Near Cape Canaveral Lighthouse, Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
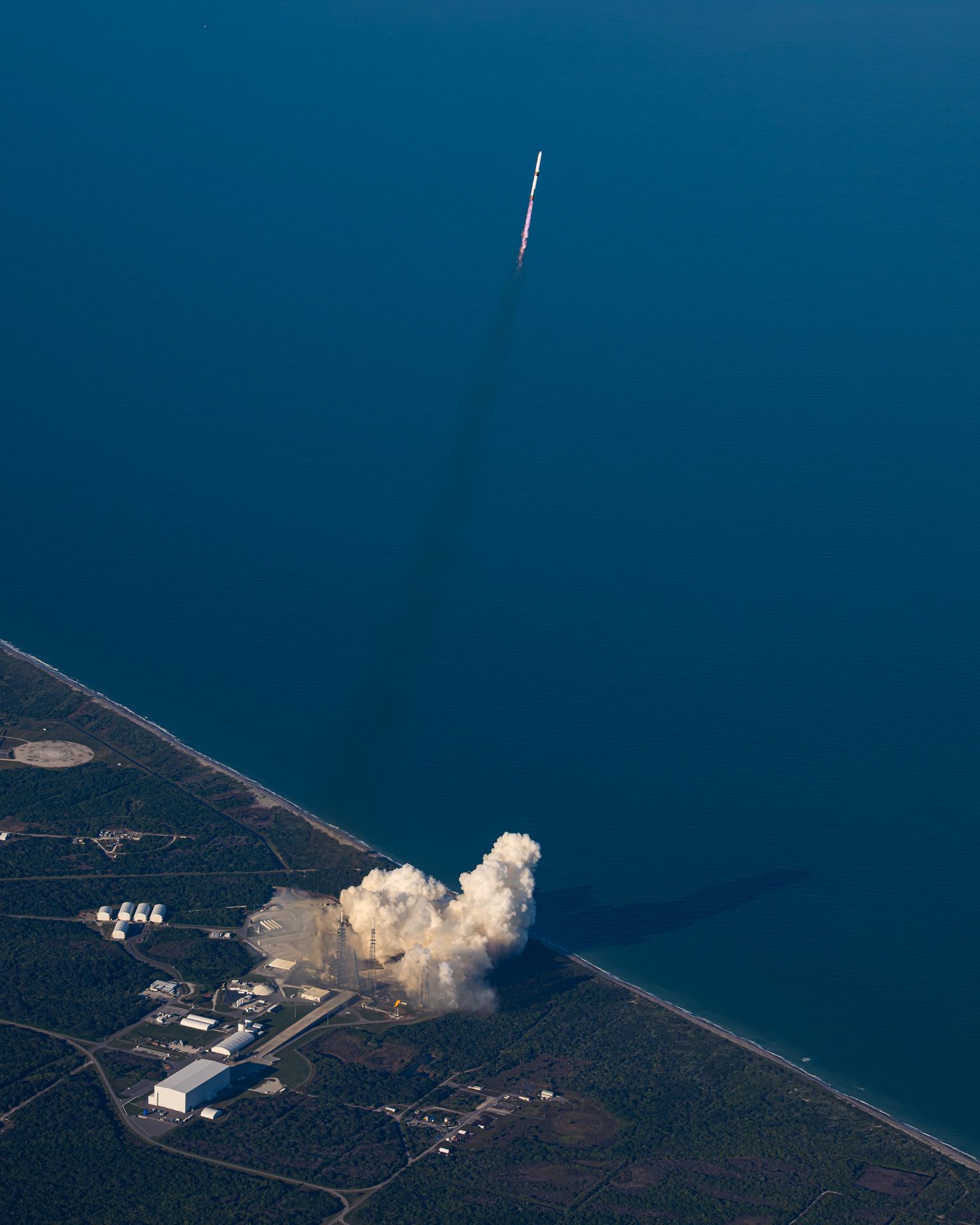

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
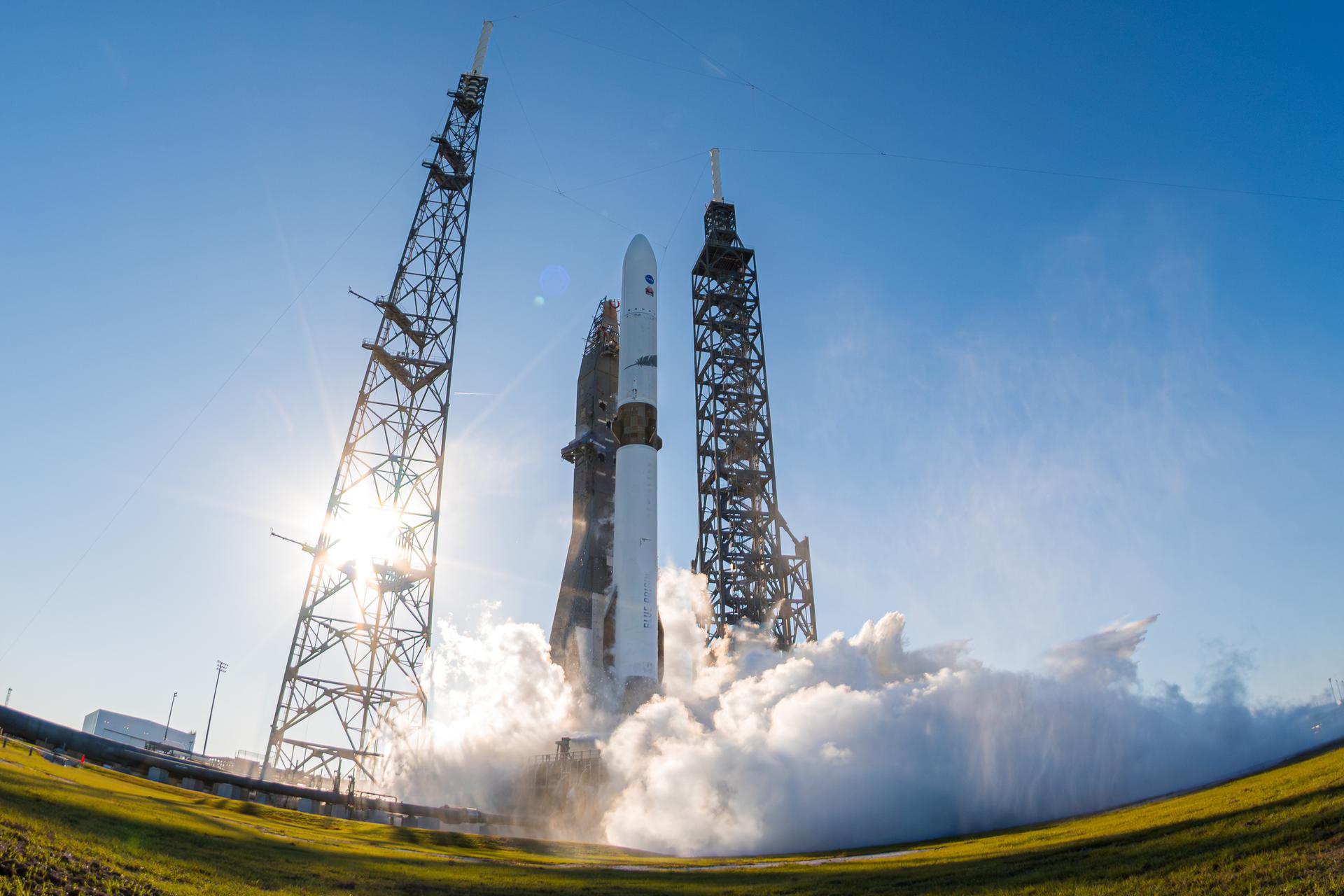

Blue Origin’s New Glenn rocket carrying NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft launches at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.

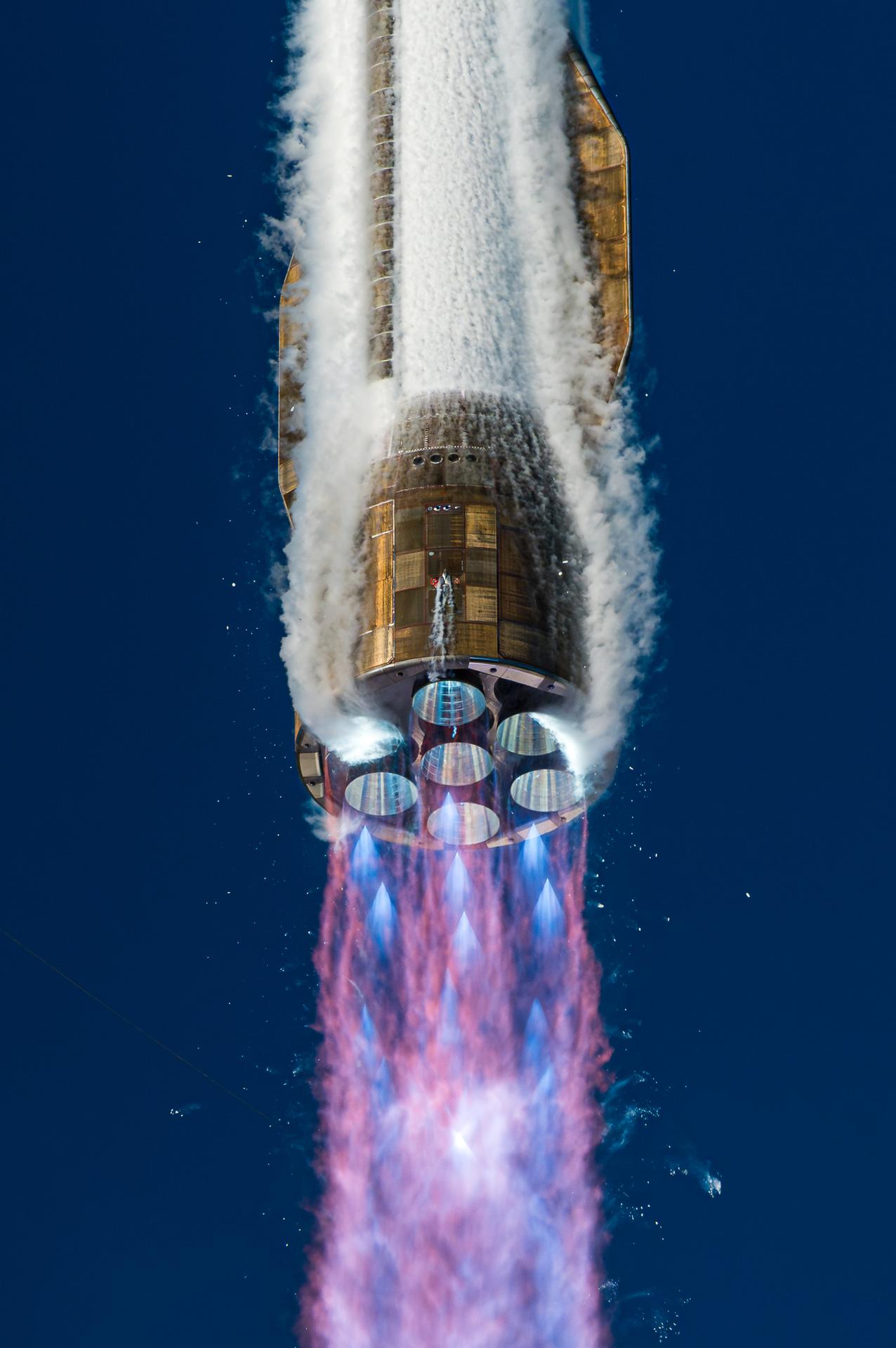
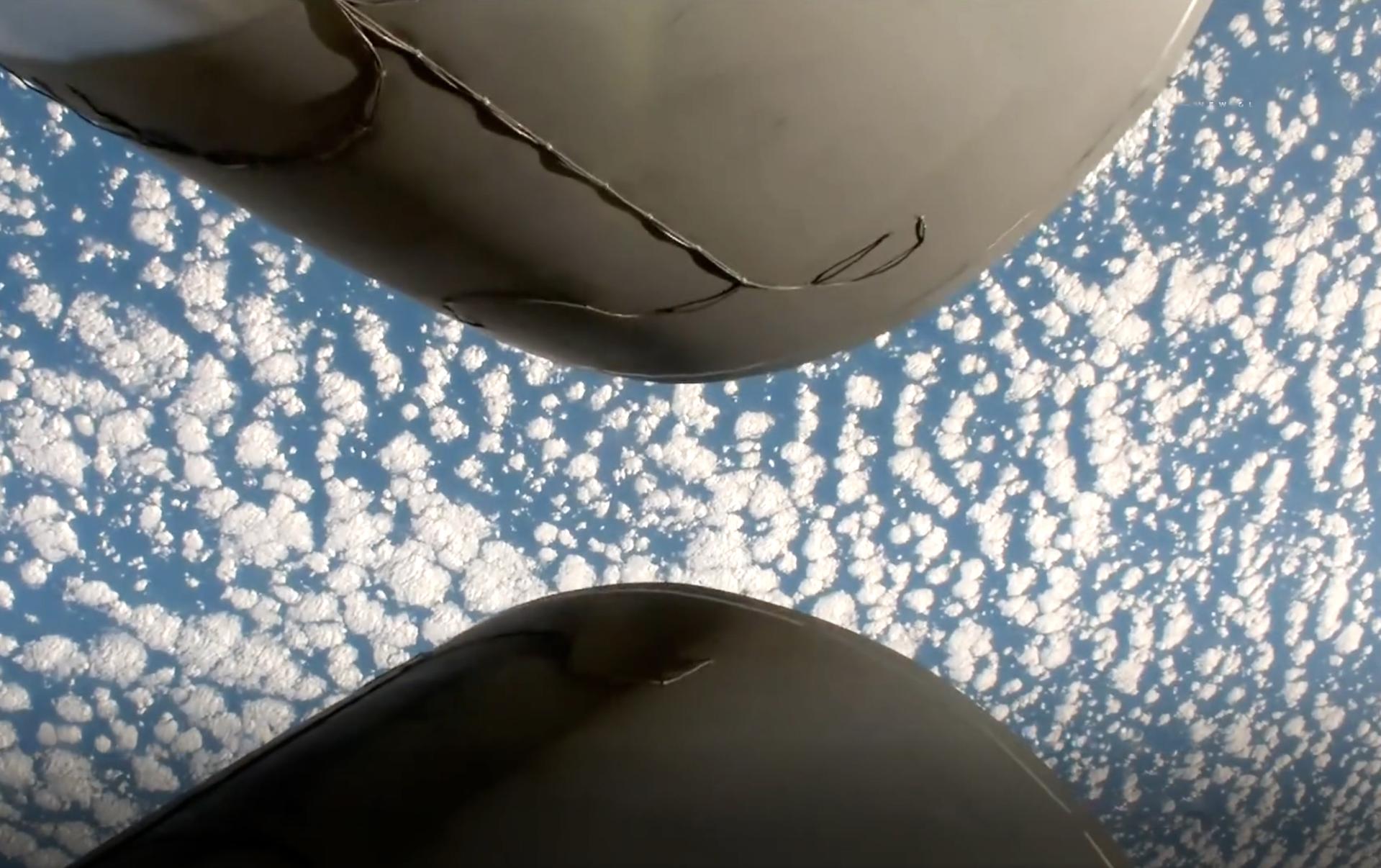
Blue Origin’s New Glenn first stage rocket successfully lands for the first time on a drone ship in the Atlantic Ocean following the launching of NASA’s twin ESCAPADE (Escape and Plasma Acceleration and Dynamics Explorers) spacecraft at 3:55 p.m. EST, Thursday, Nov. 13, 2025, from Launch Complex 36 at Cape Canaveral Space Force Station in Florida. The ESCAPADE mission, built by Rocket Lab, will study how solar wind and plasma interact with Mars’ magnetosphere and how this interaction drives the planet’s atmospheric escape to prepare for future human missions on Mars.
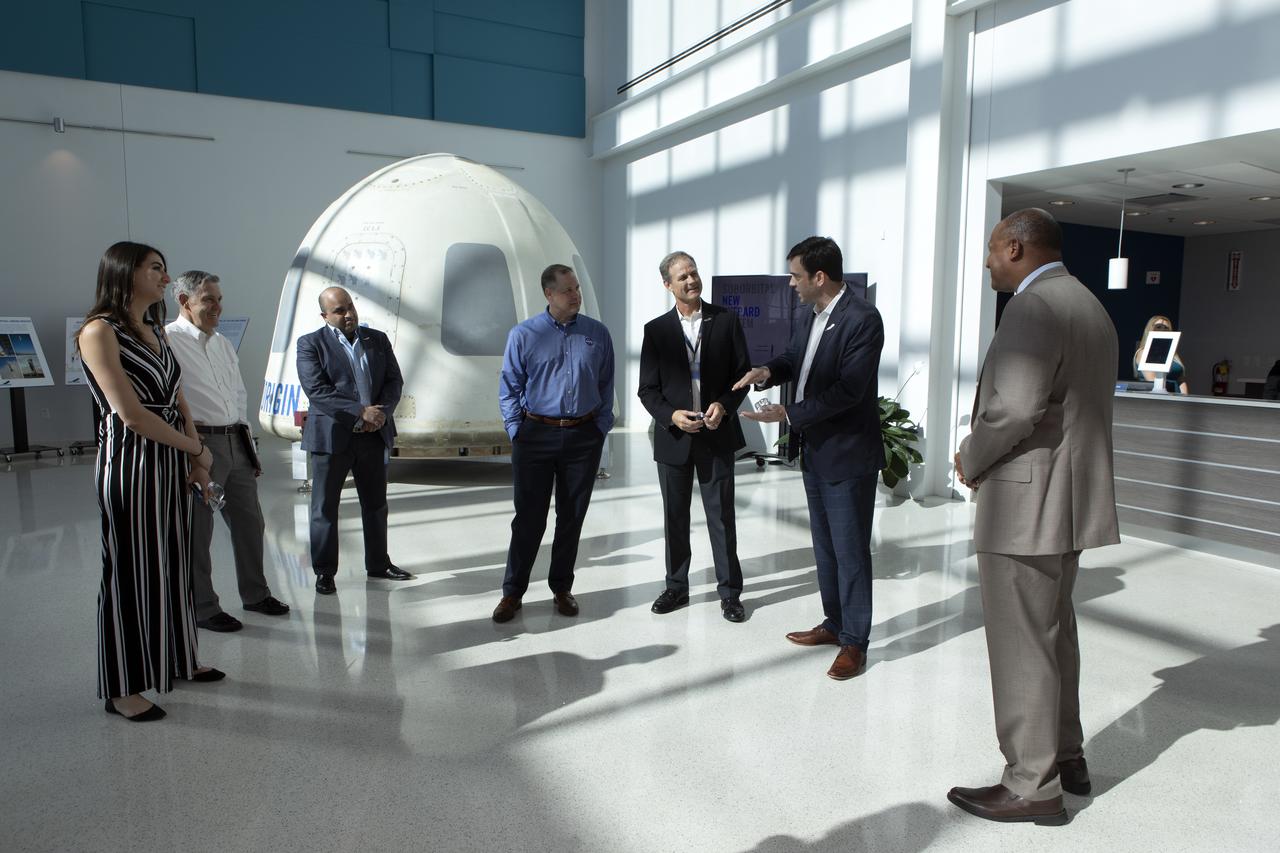

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, fourth from left, tours the Blue Origin facilities near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 23, 2019. Second from left is Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana. They viewed the New Shepard booster and crew capsule that flew to space and back five times.
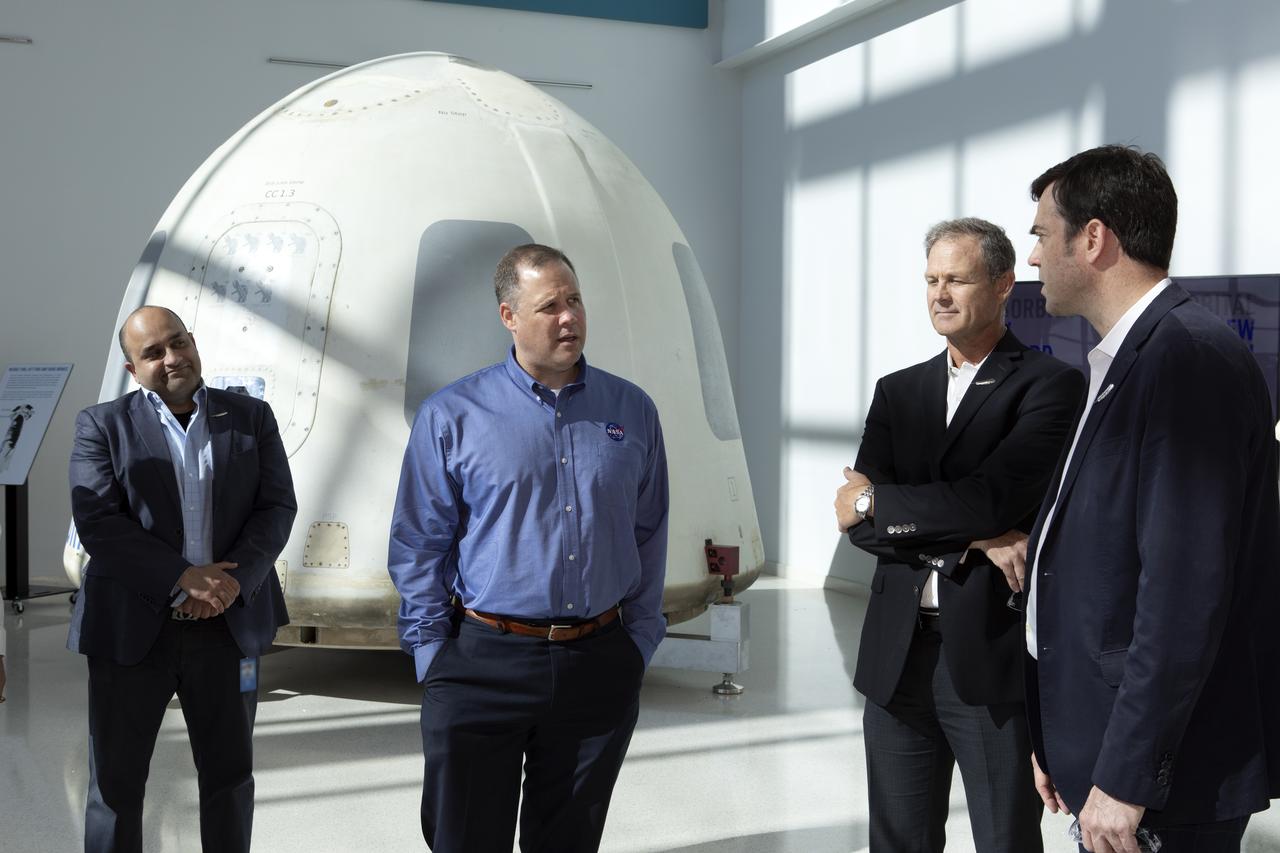

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, second from left, tours the Blue Origin facilities near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 23, 2019. Bridenstine viewed the New Shepard booster and crew capsule that flew to space and back five times.
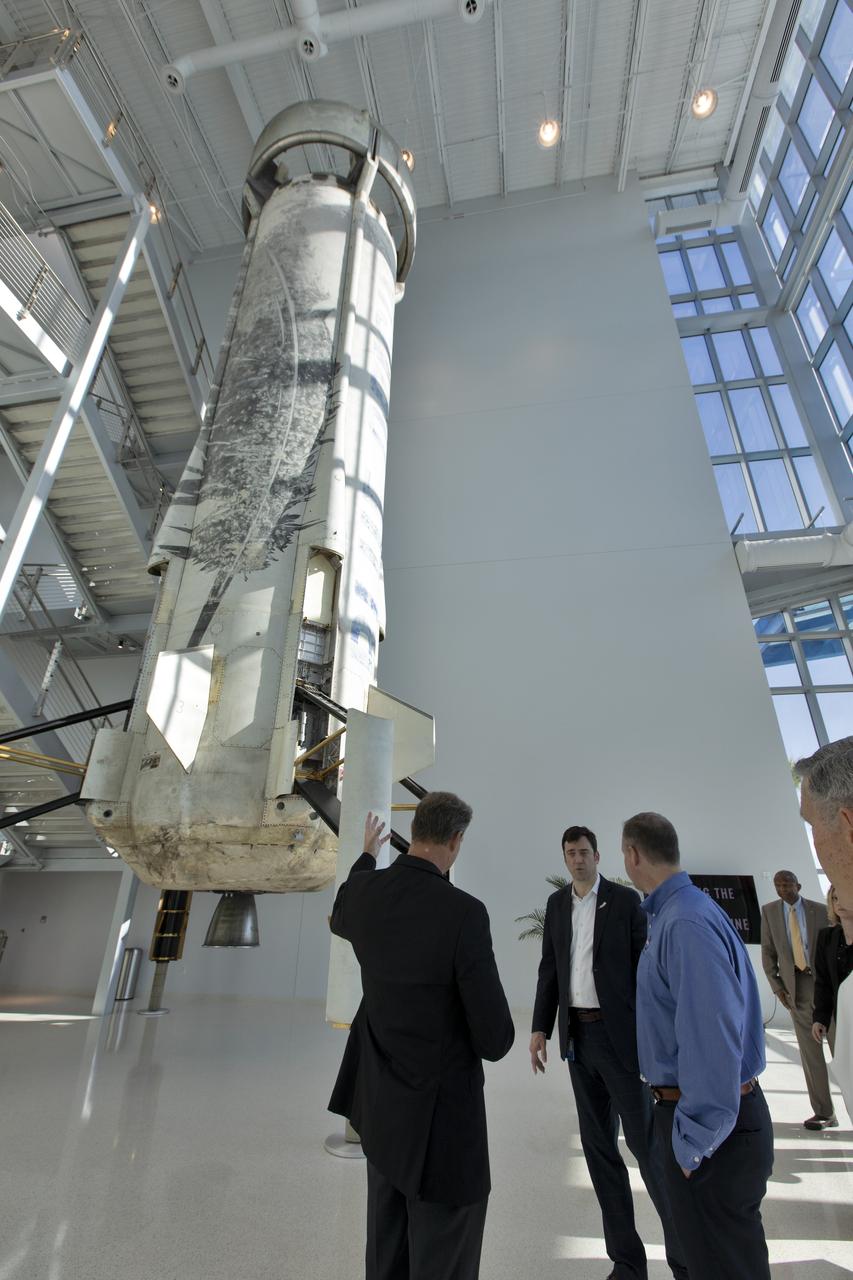

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, second from right in the blue shirt, tours the Blue Origin facilities near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 23, 2019. He viewed the New Shepard booster and crew capsule that flew to space and back five times.
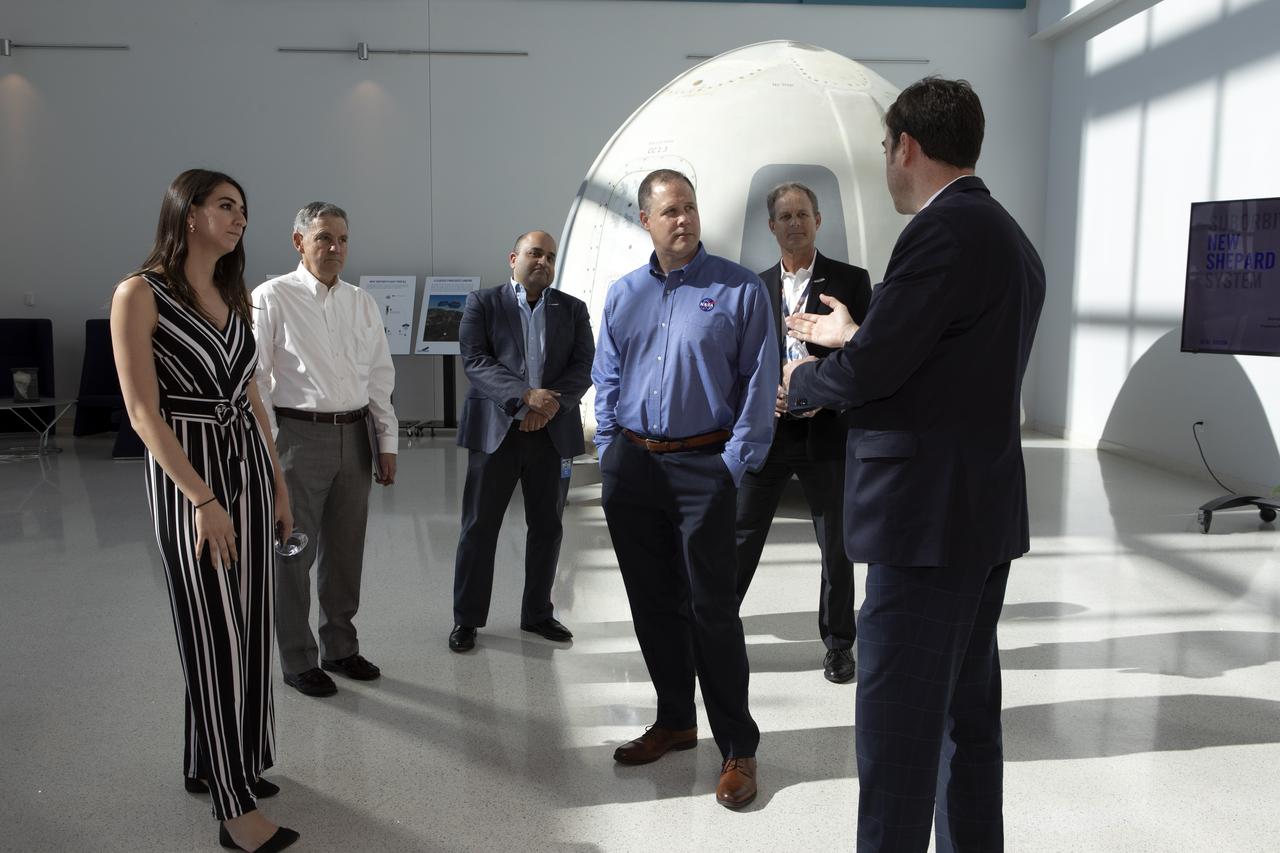

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, second from right, in the blue shirt, tours the Blue Origin facilities near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 23, 2019. Bridenstine viewed the New Shepard booster and crew capsule that flew to space and back five times.
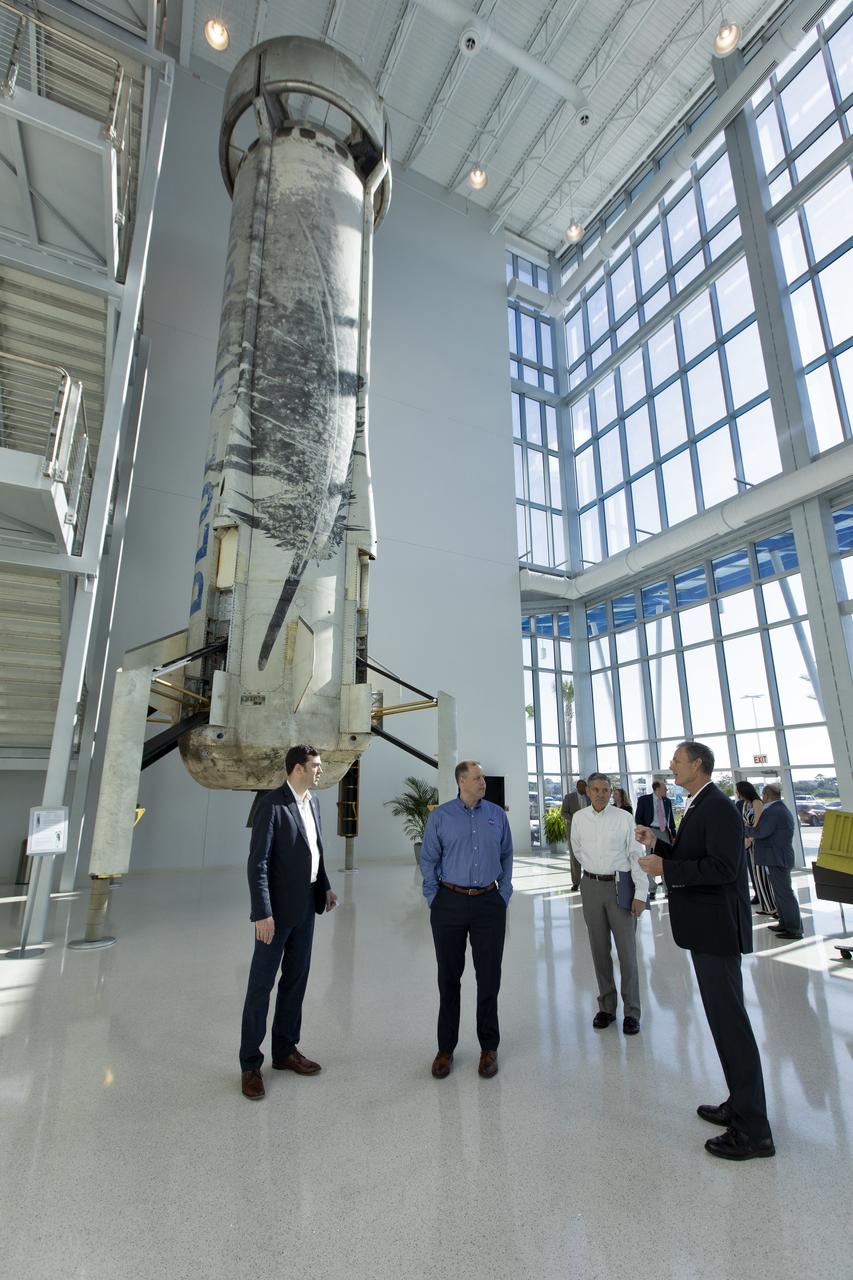

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, second from left, tours the Blue Origin facilities near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 23, 2019. Third from left is Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana. They viewed the New Shepard booster and crew capsule that few to space and back five times.
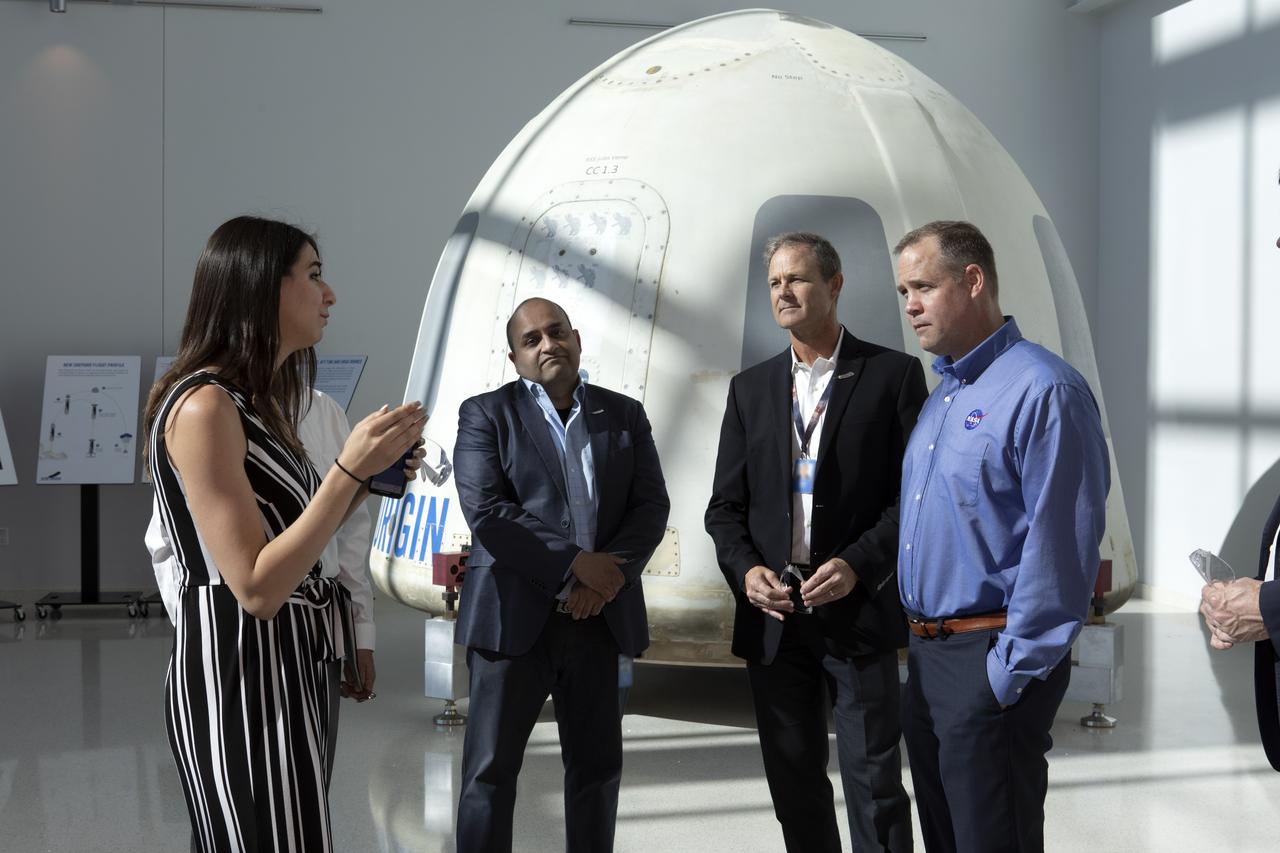

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, far right, tours the Blue Origin facilities near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 23, 2019. Bridenstine viewed the New Shepard booster and crew capsule that flew to space and back five times.
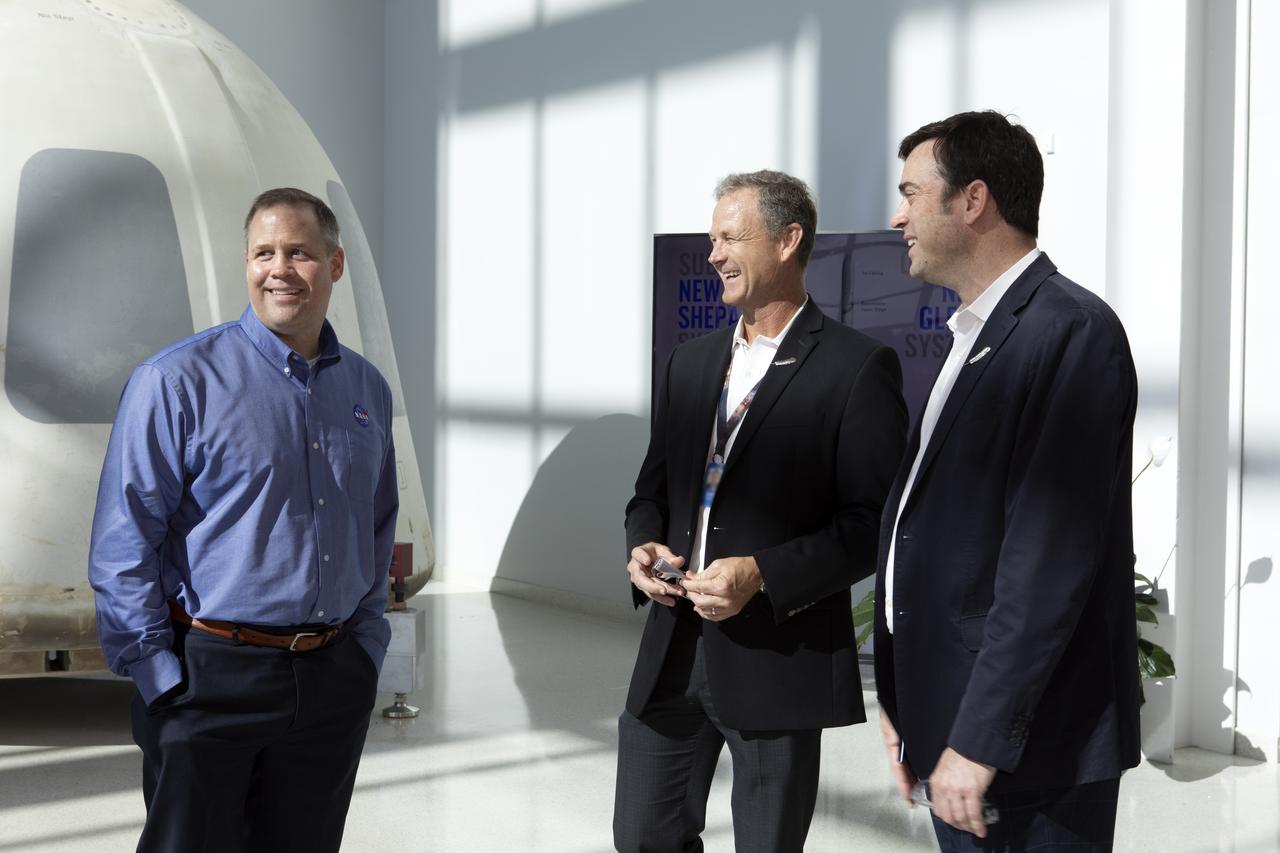

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, at left, tours the Blue Origin facilities near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 23, 2019. Bridenstine viewed the New Shepard booster and crew capsule that flew to space and back five times.
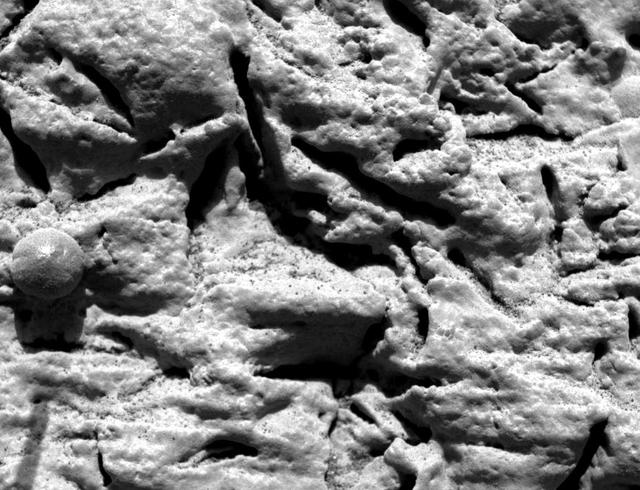

Blueberry Layers Indicate Watery Origins
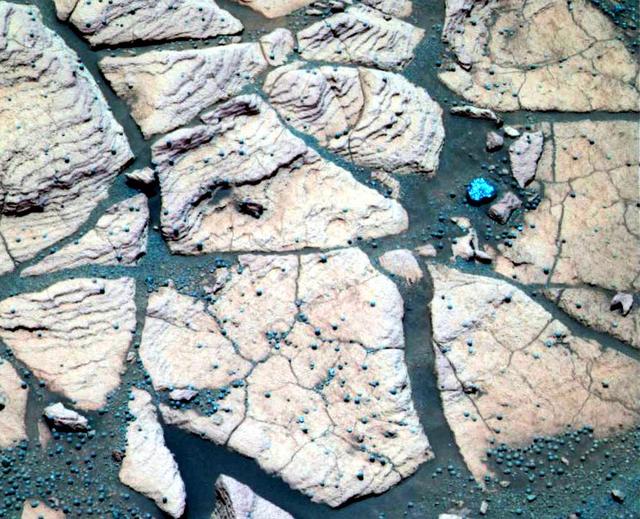

Berries and Rock Share Common Origins

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, third from left, arrives at the Blue Origin facilities near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 23, 2019. Second from right is Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana. The toured the facilities and viewed the New Shepard booster and crew capsule that flew to space and back five times.

NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, second from left, arrives at the Blue Origin facilities near the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on May 23, 2019. Second from right is Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana. They toured the facilities and viewed the New Shepard booster and crew capsule that flew to space and back five times.

While most hills and mountains on Earth originate from tectonic motions or volcanism, Earth also has some examples of hills that originated from impacts of large meteorites, the predominant origin for hills and mountains on the Moon.
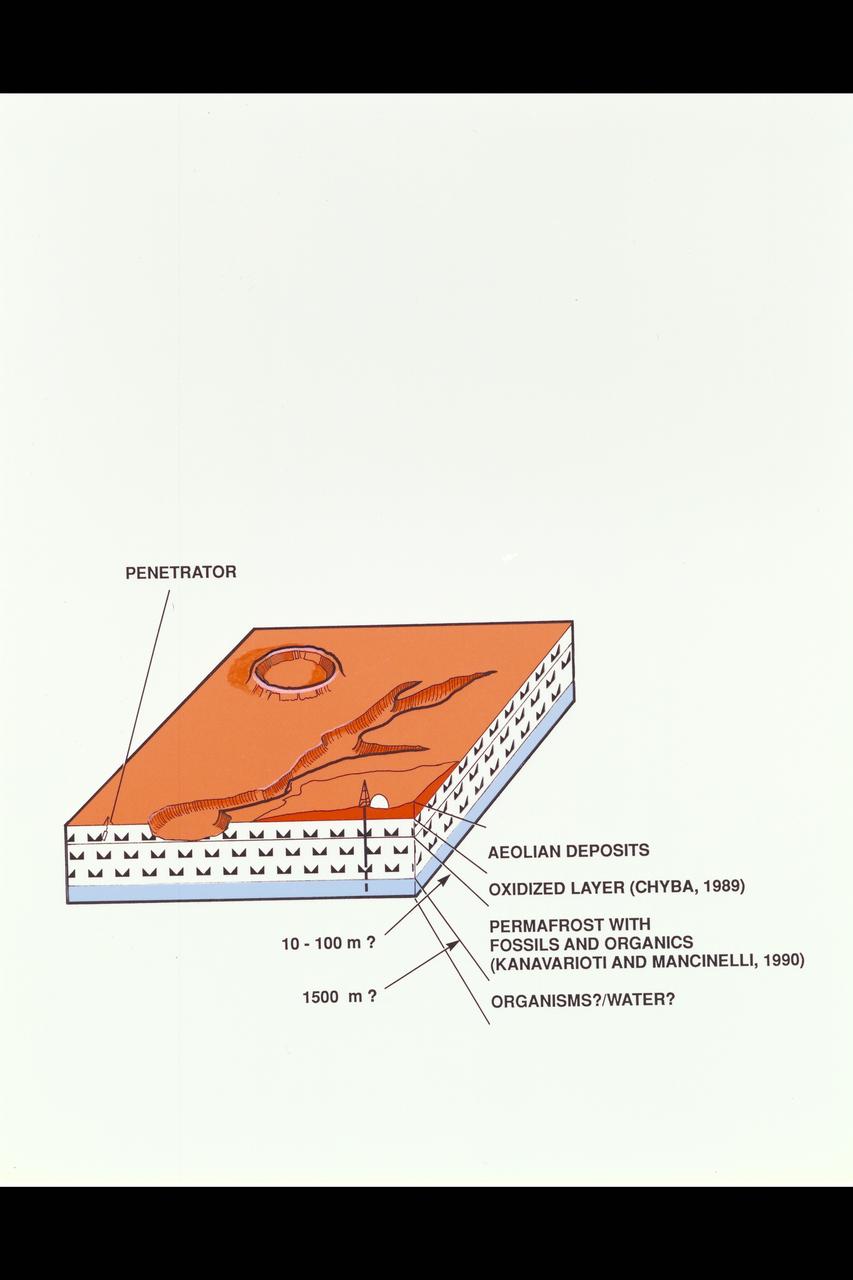
Illustration Origin of Life, Chemical Evolution on Mars: Mars Evolution Layers
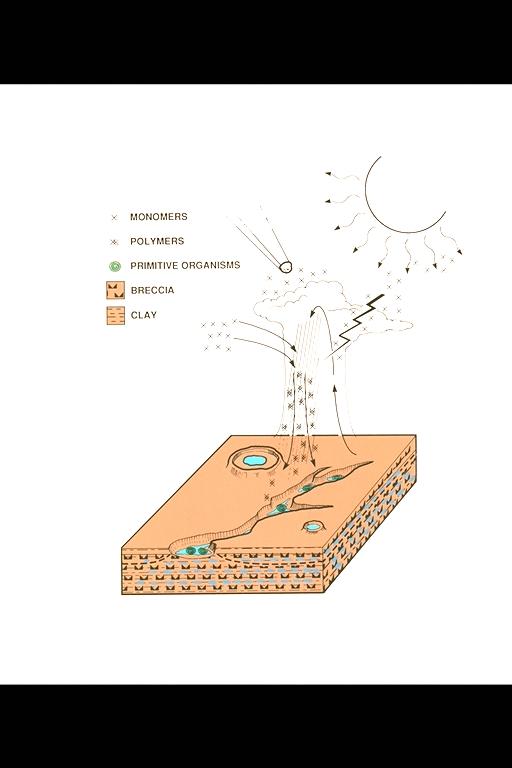
Illustration Origin of Life: Oberbeck, Marshall and Schwartz Theory for Chemical Evolution
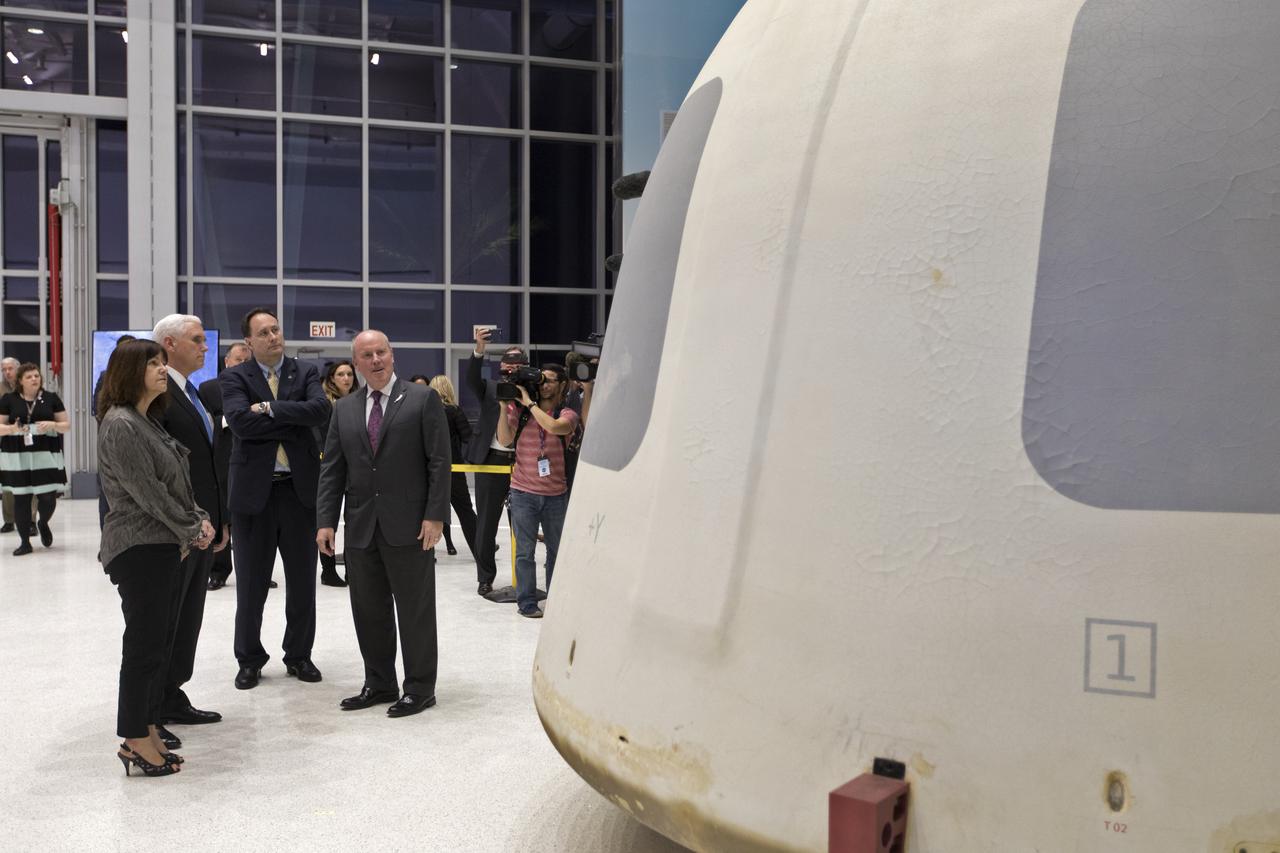

Vice President Mike Pence, second from left, tours the Blue Origin Manufacturing Facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Feb. 20, 2018. At far left is the vice president's wife, Karen Pence. To the right of Vice President Pence are acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot and Blue Origin CEO Robert Smith. Pence viewed the flown New Shepard Booster and Crew Capsule. The Crew Capsule, in view, flew seven times, including a pad abort test and an escape test at maximum dynamic pressure. During his visit, Pence will chair a meeting of the National Space Council on Feb. 21, 2018 in the high bay of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.
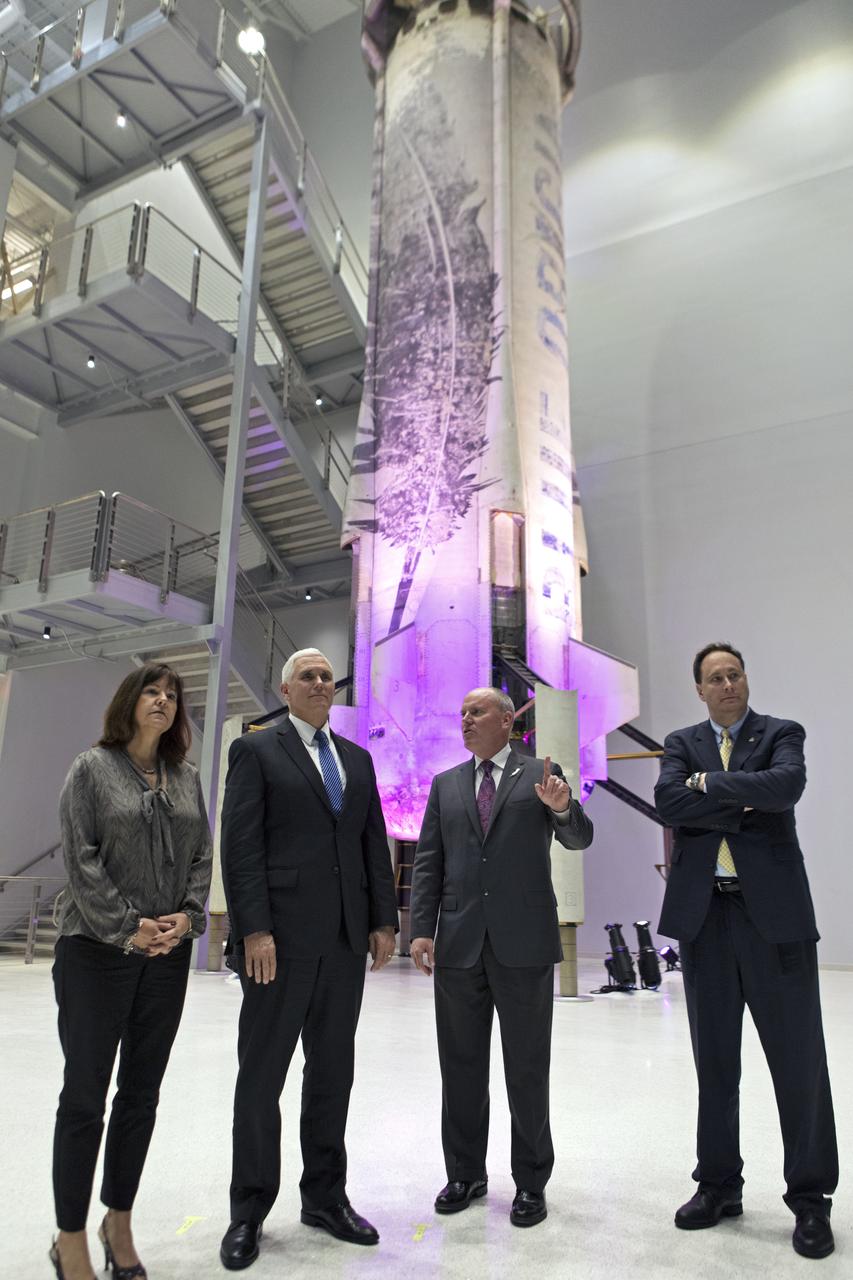

Vice President Mike Pence, second from left, tours the Blue Origin Manufacturing Facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Feb. 20, 2018. From left, are Karen Pence, Blue Origin CEO Robert Smith, and acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot. Vice President Pence viewed the flown New Shepard Booster and Crew Capsule. The booster was the first launch vehicle with a successful vertical takeoff and vertical landing to demonstrate reusability. During his visit, Pence will chair a meeting of the National Space Council on Feb. 21, 2018 in the high bay of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.
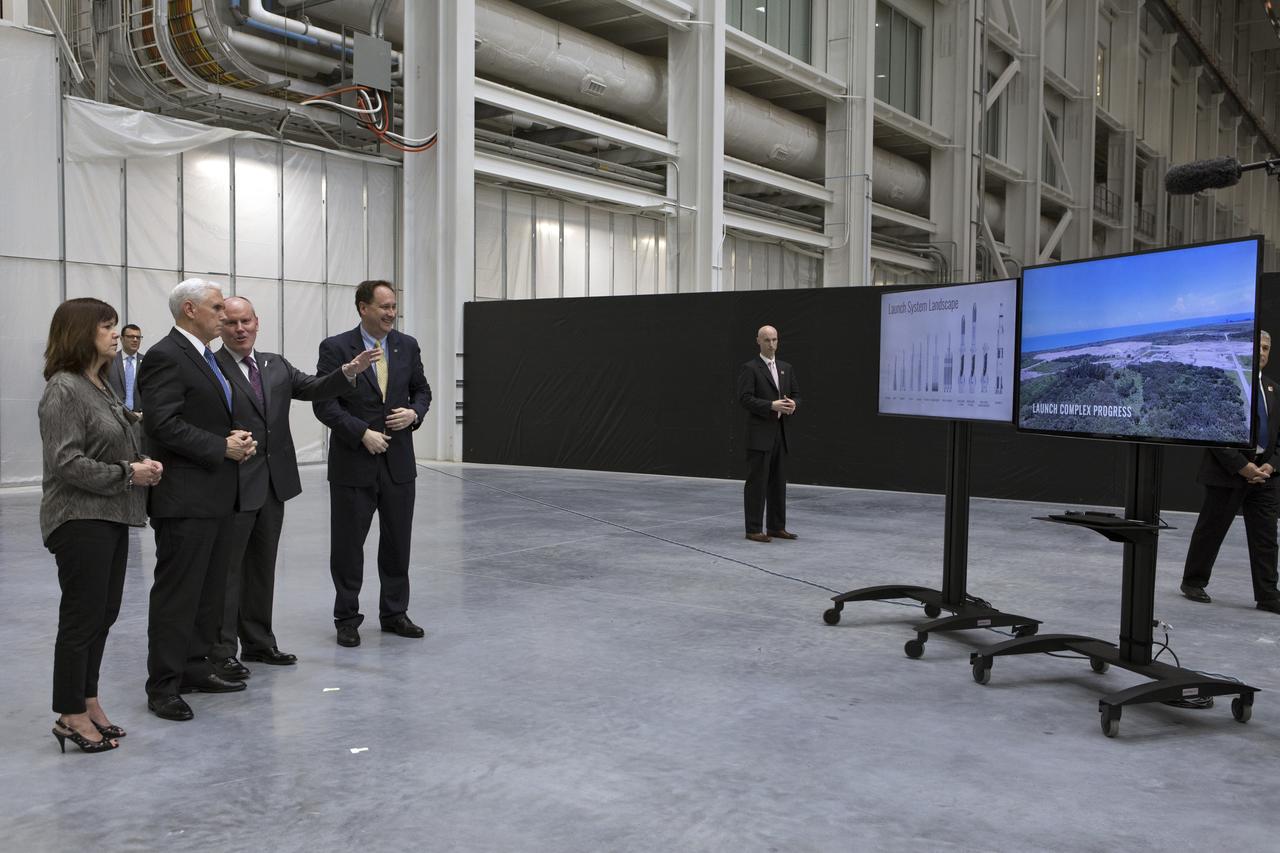

Vice President Mike Pence, second from left, tours the Blue Origin Manufacturing Facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Feb. 20, 2018. At left is the vice president's wife, Karen Pence. To his right are Blue Origin CEO Robert Smith, and acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot. Vice President Pence viewed the flown New Shepard Booster and Crew Capsule. The booster was the first launch vehicle with a successful vertical takeoff and vertical landing to demonstrate reusability. During his visit, Pence will chair a meeting of the National Space Council on Feb. 21, 2018 in the high bay of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.
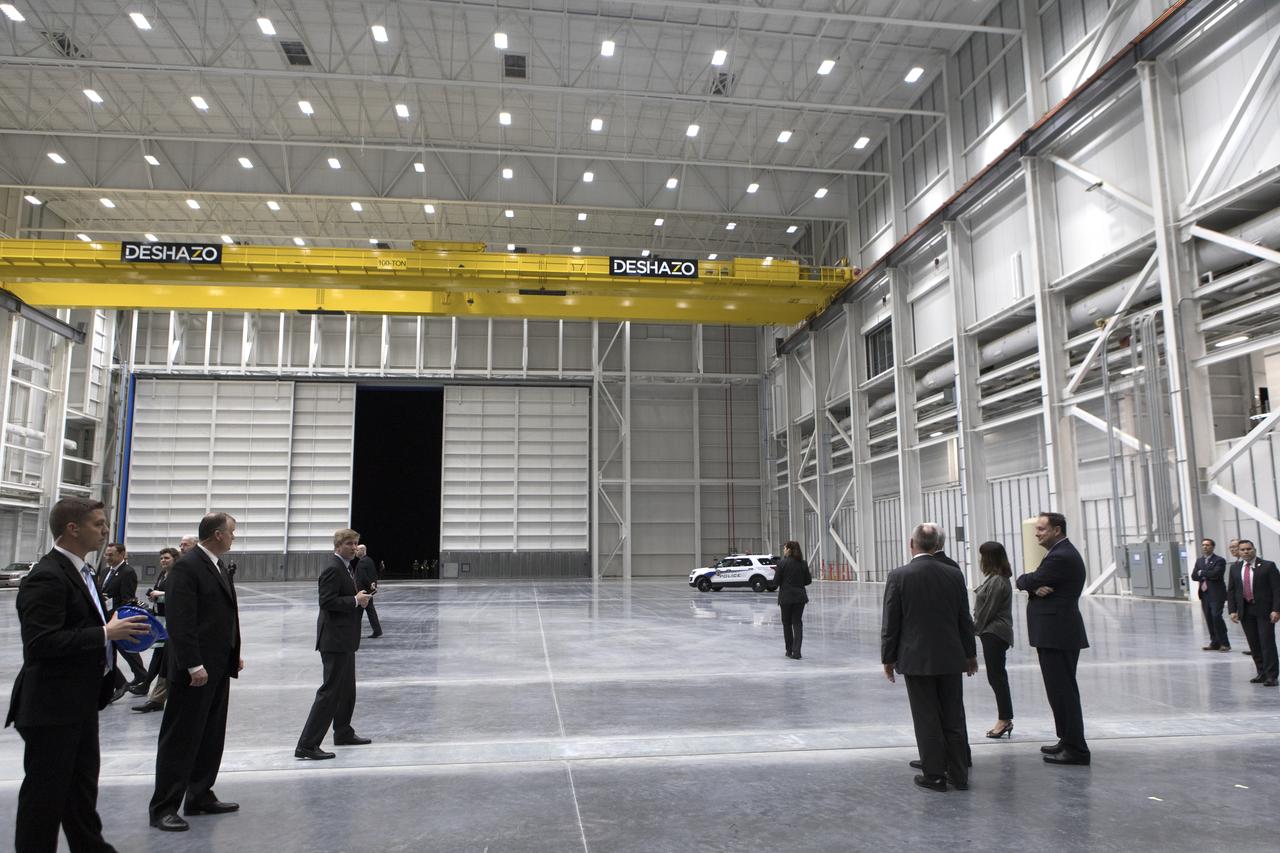

Vice President Mike Pence, hidden at right, tours the Blue Origin Manufacturing Facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Feb. 20, 2018. At far right is the vice president's wife, Karen Pence. Behind her at right are Blue Origin CEO Robert Smith, and acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot. Vice President Pence viewed the flown New Shepard Booster and Crew Capsule. The booster was the first launch vehicle with a successful vertical takeoff and vertical landing to demonstrate reusability. During his visit, Pence will chair a meeting of the National Space Council on Feb. 21, 2018 in the high bay of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.
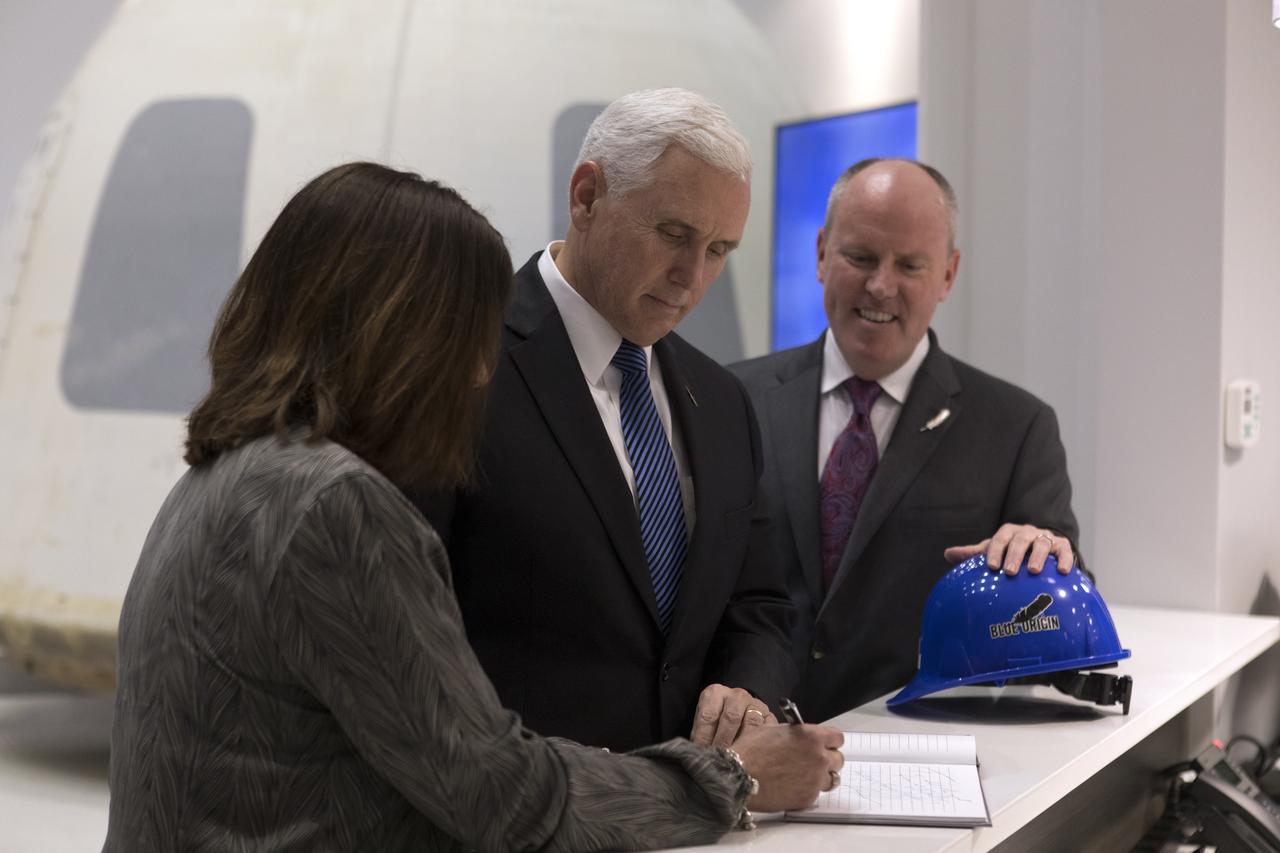

Vice President Mike Pence, center, and his wife, Karen Pence, sign a guest book during a tour of the Blue Origin Manufacturing Facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Feb. 20, 2018. At right is Blue Origin CEO Robert Smith. Vice President Pence viewed the flown New Shepard Booster and Crew Capsule. The booster was the first launch vehicle with a successful vertical takeoff and vertical landing to demonstrate reusability. During his visit, Pence will chair a meeting of the National Space Council on Feb. 21, 2018 in the high bay of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.
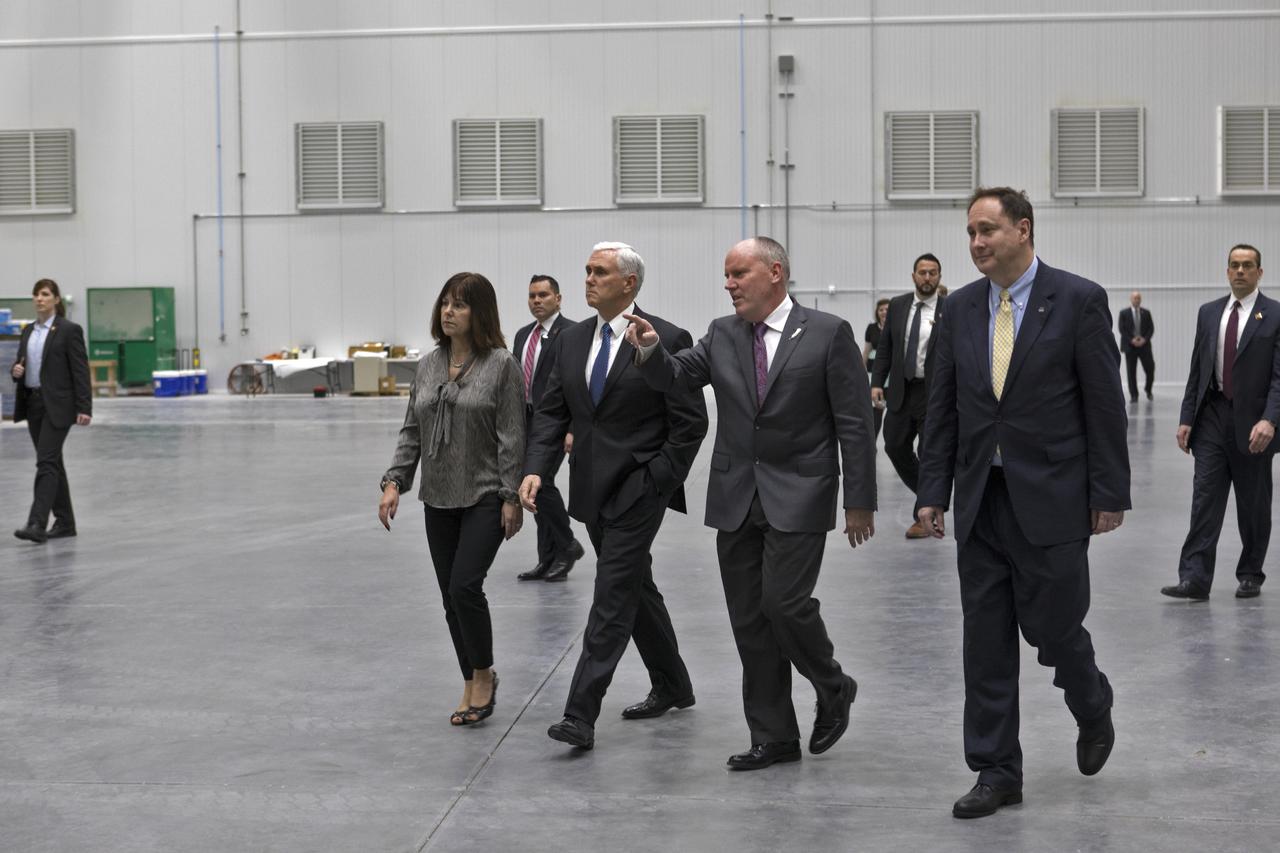

Vice President Mike Pence, second from left, tours the Blue Origin Manufacturing Facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Feb. 20, 2018. At left is the vice president's wife, Karen Pence. To his right are Blue Origin CEO Robert Smith, and acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot. Vice President Pence viewed the flown New Shepard Booster and Crew Capsule. The booster was the first launch vehicle with a successful vertical takeoff and vertical landing to demonstrate reusability. During his visit, Pence will chair a meeting of the National Space Council on Feb. 21, 2018 in the high bay of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.

Vice President Mike Pence, second from left, tours the Blue Origin Manufacturing Facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Feb. 20, 2018. To his left is his wife, Karen Pence. To his right are Blue Origin CEO Robert Smith, and acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot. Vice President Pence viewed the flown New Shepard Booster and Crew Capsule. The booster was the first launch vehicle with a successful vertical takeoff and vertical landing to demonstrate reusability. During his visit, Pence will chair a meeting of the National Space Council on Feb. 21, 2018 in the high bay of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.
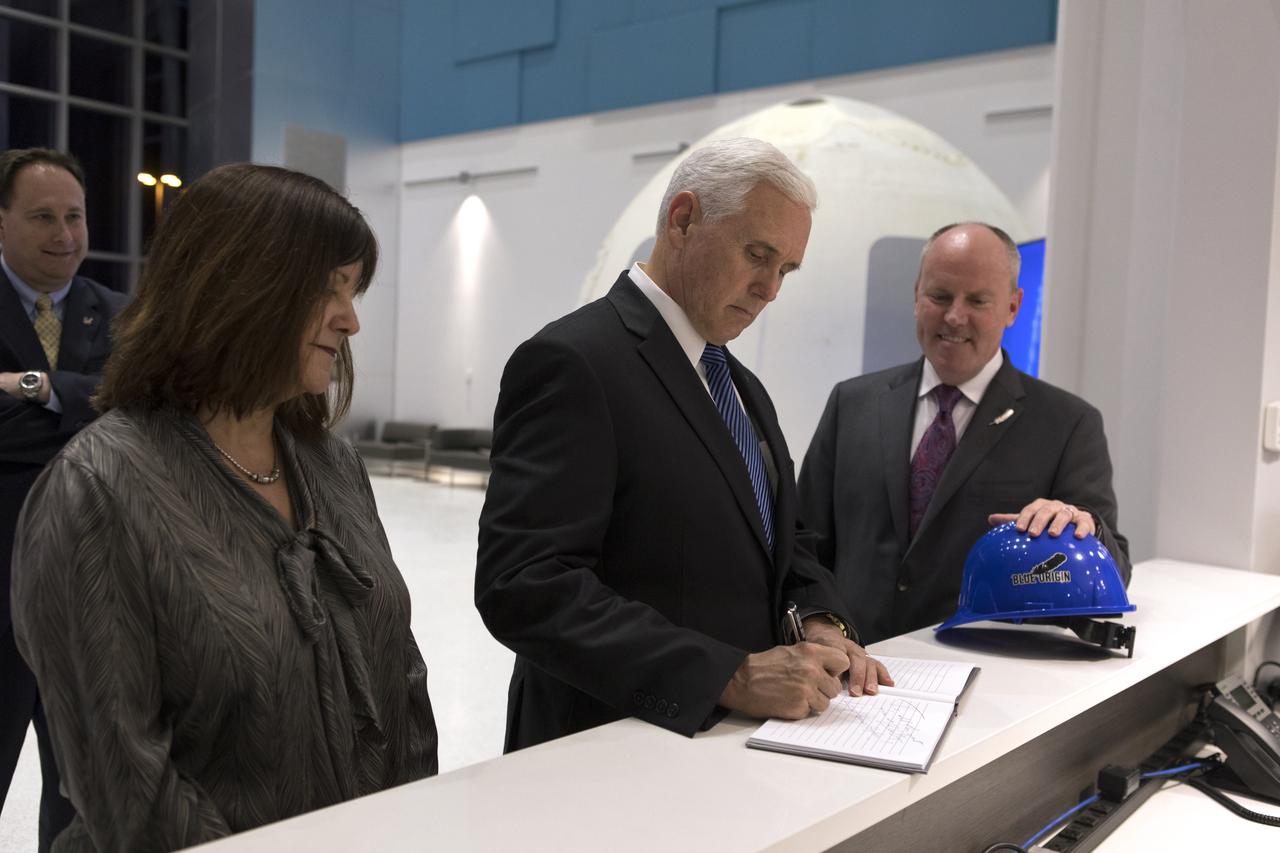

Vice President Mike Pence, center, signs a guest book during his tour of the Blue Origin Manufacturing Facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Feb. 20, 2018. At left is the vice president's wife, Karen Pence. To his right is Blue Origin CEO Robert Smith. Behind them is acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot. Vice President Pence viewed the flown New Shepard Booster and Crew Capsule. The booster was the first launch vehicle with a successful vertical takeoff and vertical landing to demonstrate reusability. During his visit, Pence will chair a meeting of the National Space Council on Feb. 21, 2018 in the high bay of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.

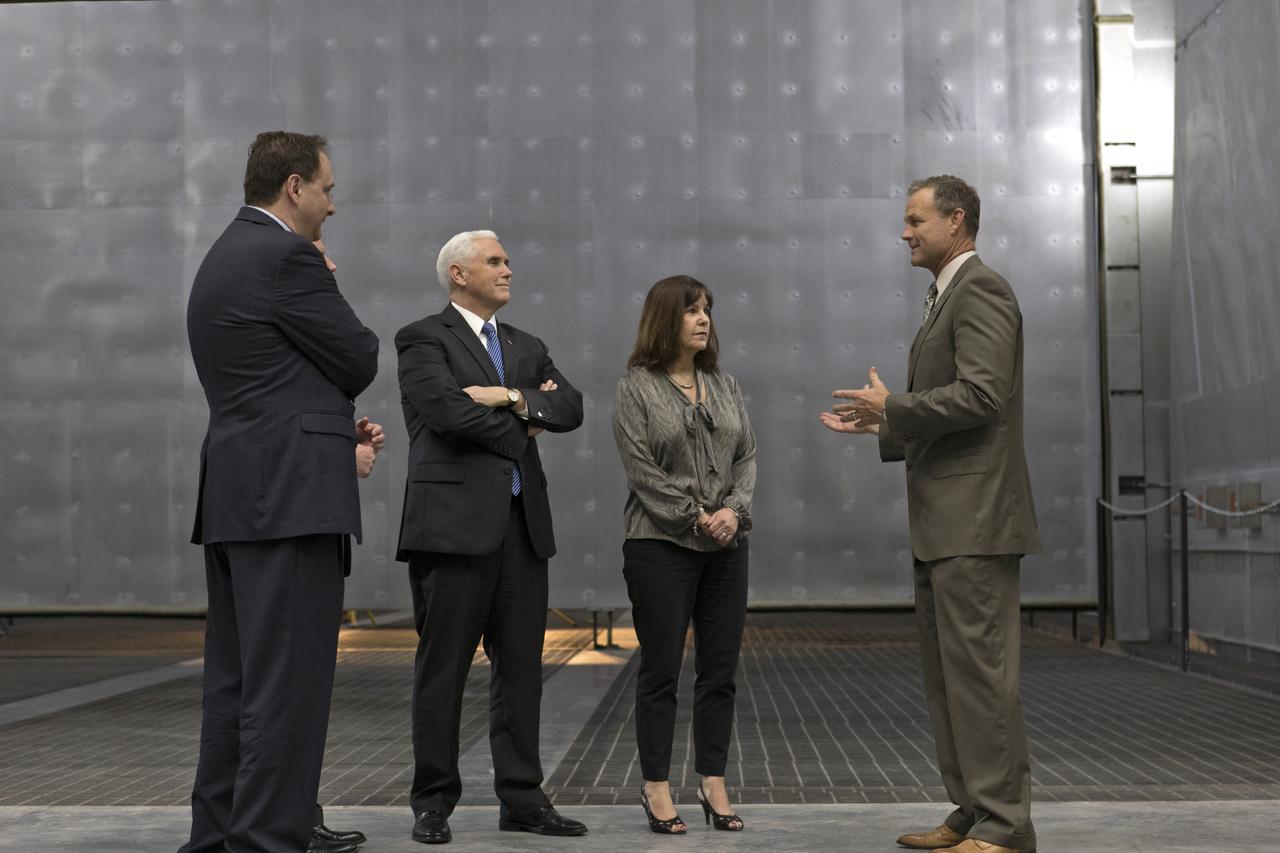
Vice President Mike Pence, second from left, tours the Blue Origin Manufacturing Facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Feb. 20, 2018. At left is the vice president's wife, Karen Pence. To his right are Blue Origin CEO Robert Smith, and acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot. Vice President Pence viewed the flown New Shepard Booster and Crew Capsule. The booster was the first launch vehicle with a successful vertical takeoff and vertical landing to demonstrate reusability. During his visit, Pence will chair a meeting of the National Space Council on Feb. 21, 2018 in the high bay of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.

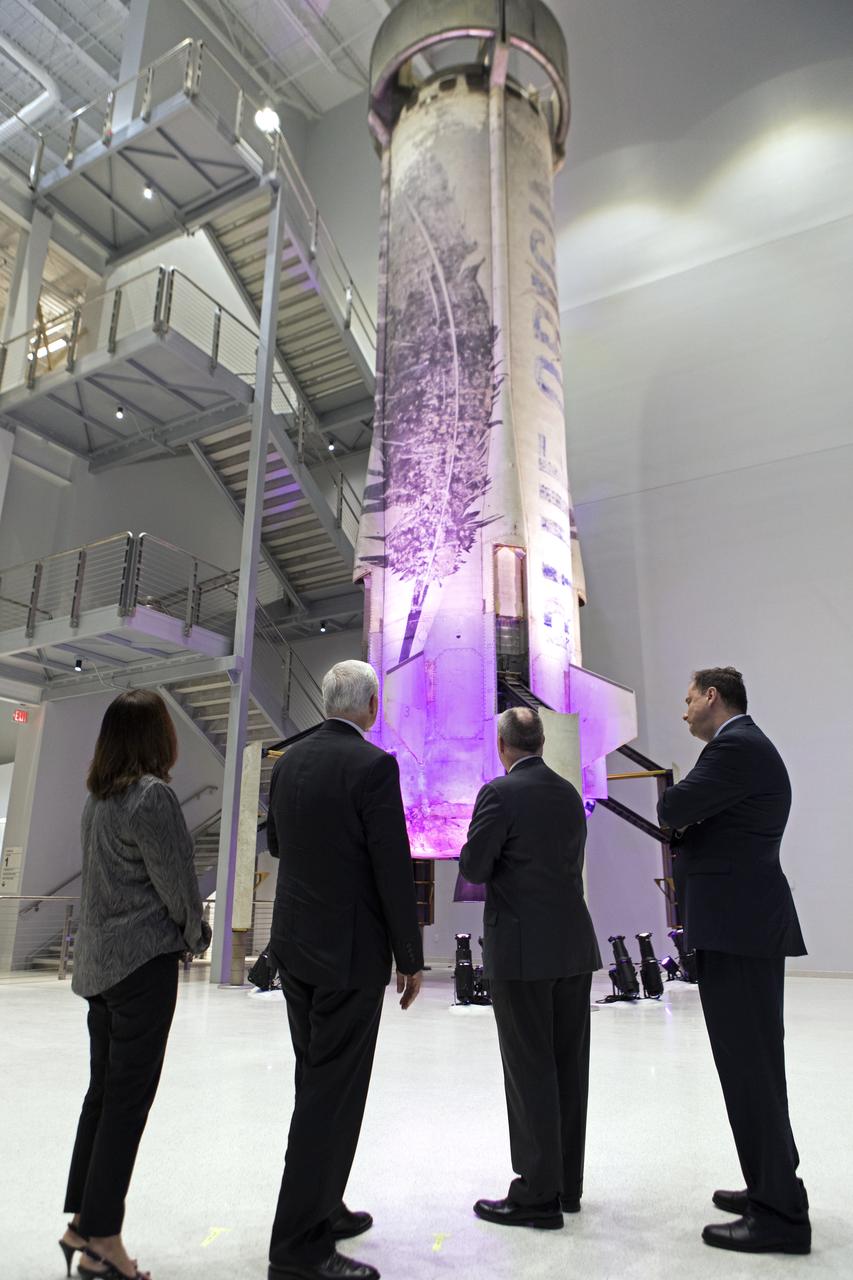
Vice President Mike Pence, second from left, tours the Blue Origin Manufacturing Facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Feb. 20, 2018. To his left is acting NASA Administrator Robert Lightfoot. At right is the vice president's wife, Karen Pence. At far right is Scott Henderson, Blue Origin director of Test and Flight Operations. Vice President Pence viewed the flown New Shepard Booster and Crew Capsule. The booster was the first launch vehicle with a successful vertical takeoff and vertical landing to demonstrate reusability. During his visit, Pence will chair a meeting of the National Space Council on Feb. 21, 2018 in the high bay of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.
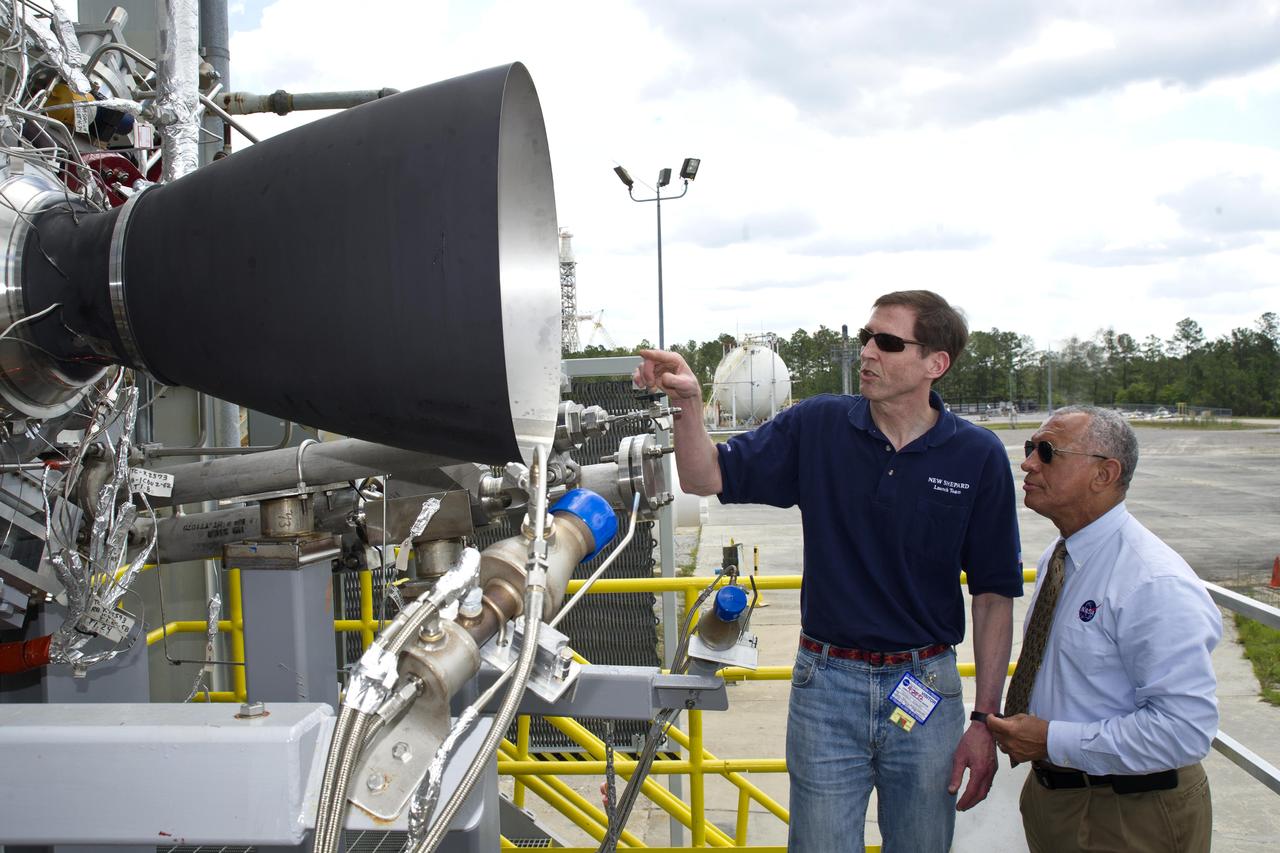

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden (r) discusses the upcoming testing of Blue Origin's BE-3 engine thrust chamber assembly with Steve Knowles, Blue Origin project manager, at the E-1 Test Stand during an April 20, 2012, visit to Stennis Space Center. Blue Origin is one of NASA's partners developing innovative systems to reach low-Earth orbit.
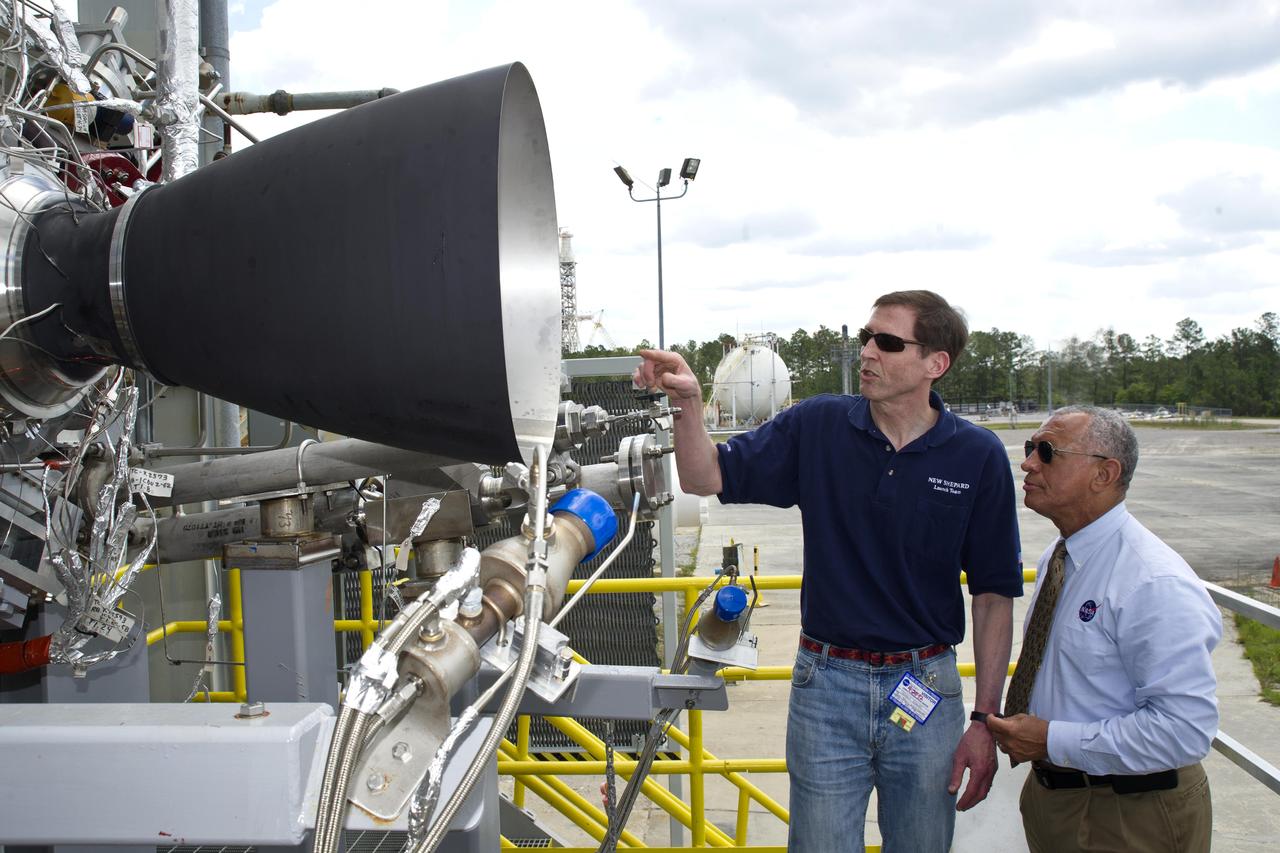

NASA Administrator Charles Bolden (r) discusses the upcoming testing of Blue Origin's BE-3 engine thrust chamber assembly with Steve Knowles, Blue Origin project manager, at the E-1 Test Stand during an April 20, 2012, visit to Stennis Space Center. Blue Origin is one of NASA's partners developing innovative systems to reach low-Earth orbit.
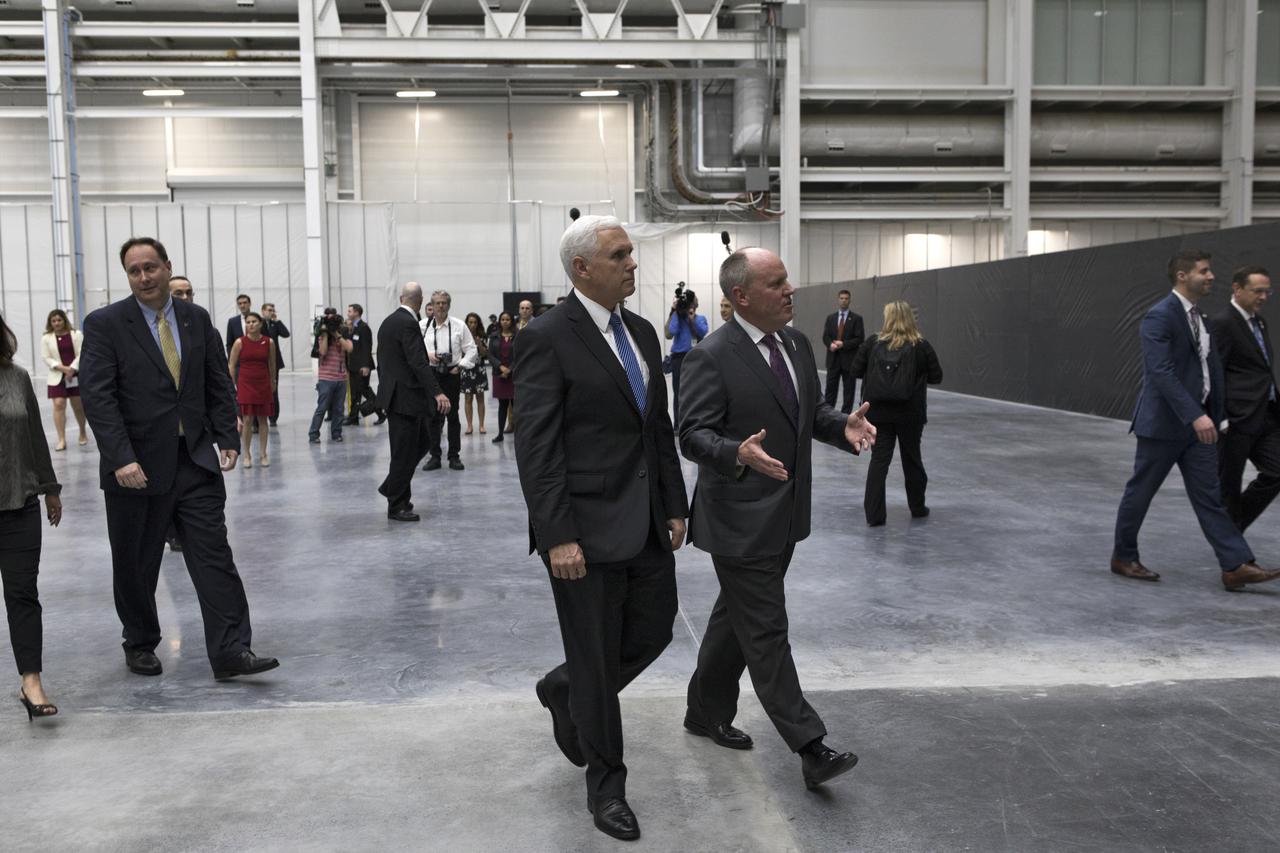

Vice President Mike Pence, at left, tours the Blue Origin Manufacturing Facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Feb. 20, 2018, with the company's CEO Robert Smith. Vice President Pence viewed the flown New Shepard Booster and Crew Capsule. The booster was the first launch vehicle with a successful vertical takeoff and vertical landing to demonstrate reusability. During his visit, Pence will chair a meeting of the National Space Council on Feb. 21, 2018 in the high bay of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.
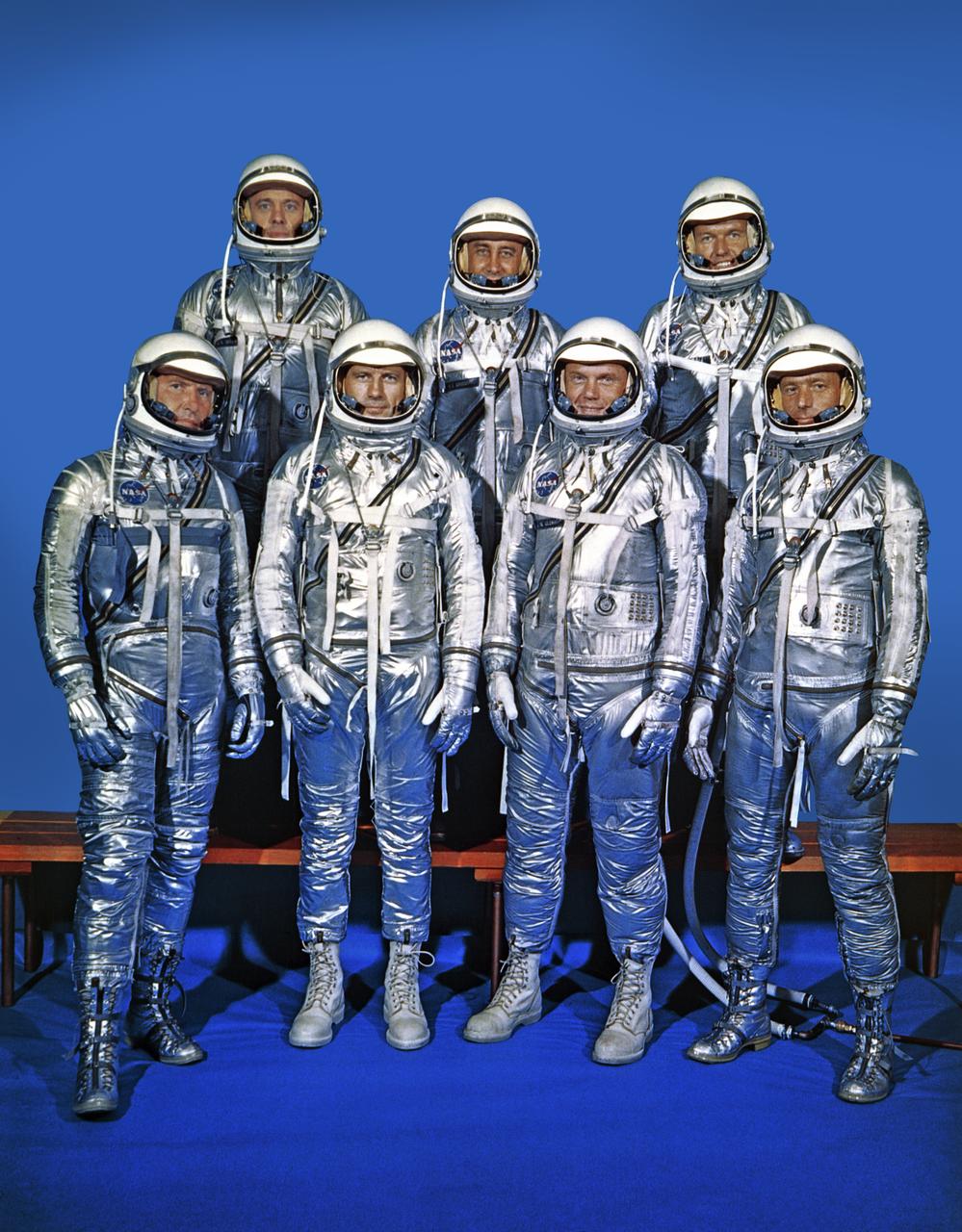

Press release information, September 13, 1968: "FIRST ASTRONAUT TEAM: Project Mercury Astronauts, whose selection was announced on April 9, 1959, only six months after the National Aeronautics and Space Administration was formally established on Oct. 1, 1958, Included: Front row, left to right, Walter M. Schirra, Jr., Donald K. Slayton, John H. Glenn, Jr., and M. Scott Carpenter; back row, Alan B. Shepard, Jr., Virgil I. "Gus" Grissom and L. Gordon Cooper. (1962), *89-361 Also in B&W. This copy of original negative was edited without shadows in the background. Photo taken at NASA Langley Research Center by Life Magazine photographer and negative copied for other centers.
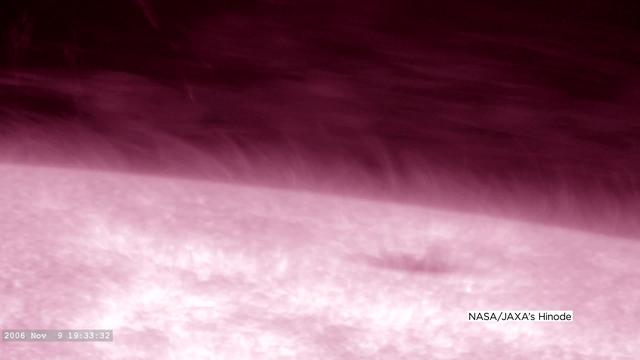
At any given moment, as many as 10 million wild jets of solar material burst from the sun’s surface. They erupt as fast as 60 miles per second, and can reach lengths of 6,000 miles before collapsing. These are spicules, and despite their grass-like abundance, scientists didn’t understand how they form. Now, for the first time, a computer simulation — so detailed it took a full year to run — shows how spicules form, helping scientists understand how spicules can break free of the sun’s surface and surge upward so quickly. Watch here and more at: <a href="https://go.nasa.gov/2t3toMx" rel="nofollow">go.nasa.gov/2t3toMx</a> Credits: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center/Joy Ng, producer <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASAGoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagrid.me/nasagoddard/?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
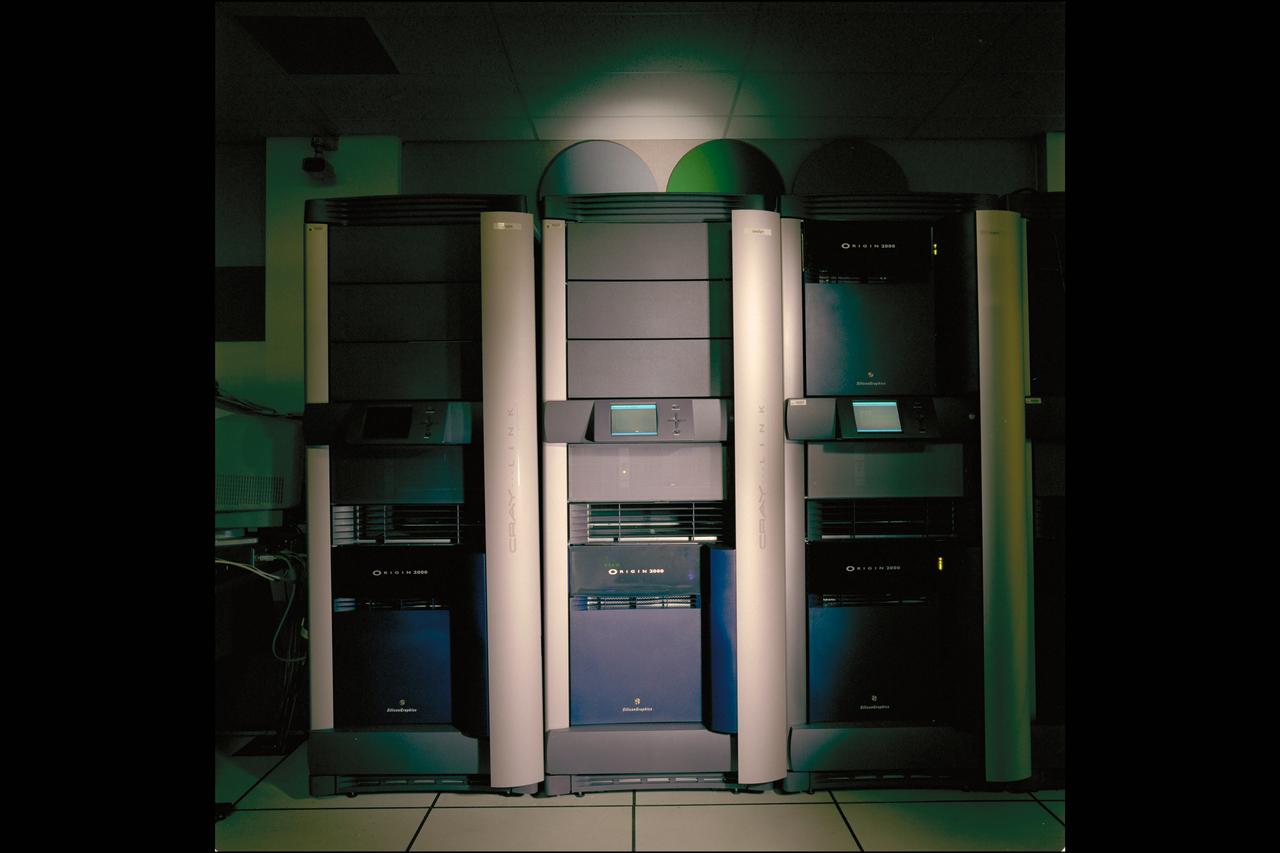

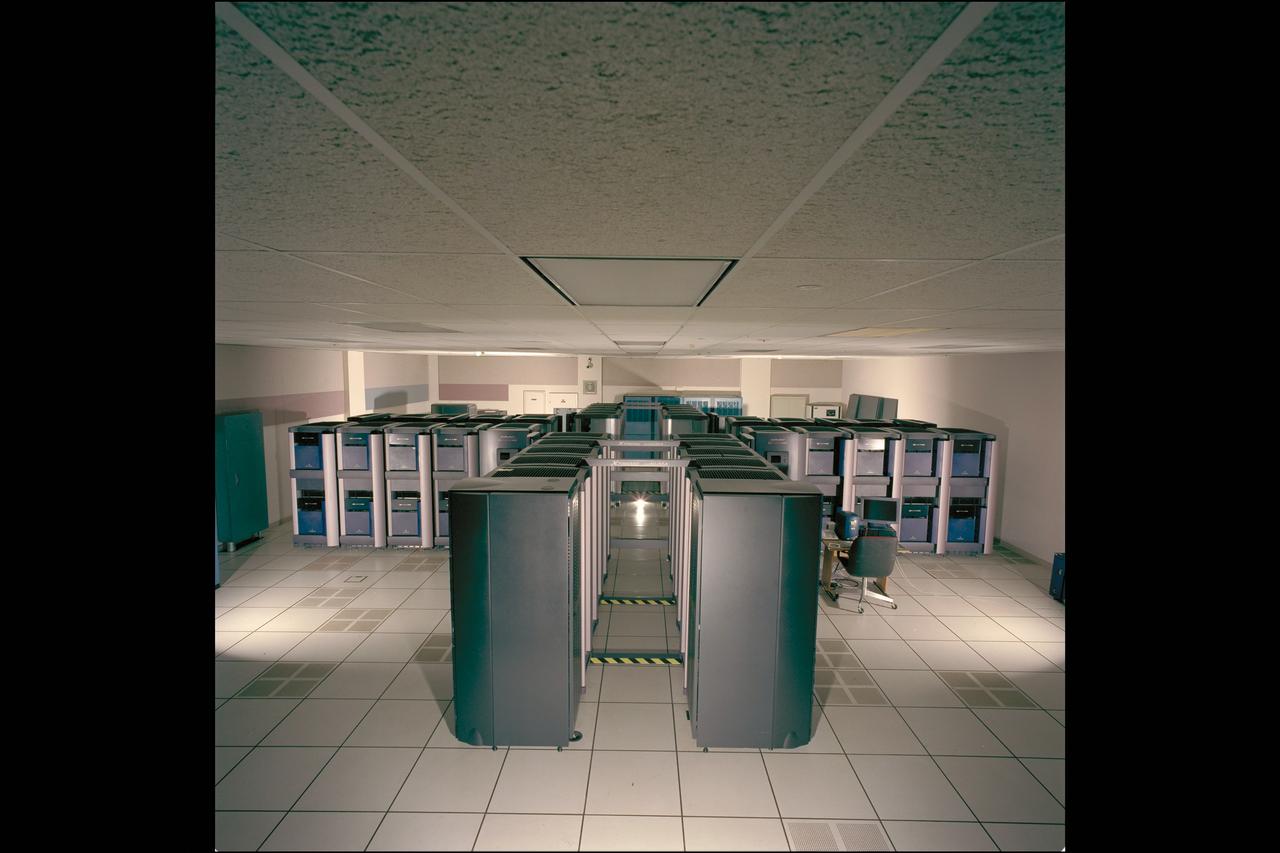
NAS Origin 2000 Computer System - 8 processors 'EVELYN' station
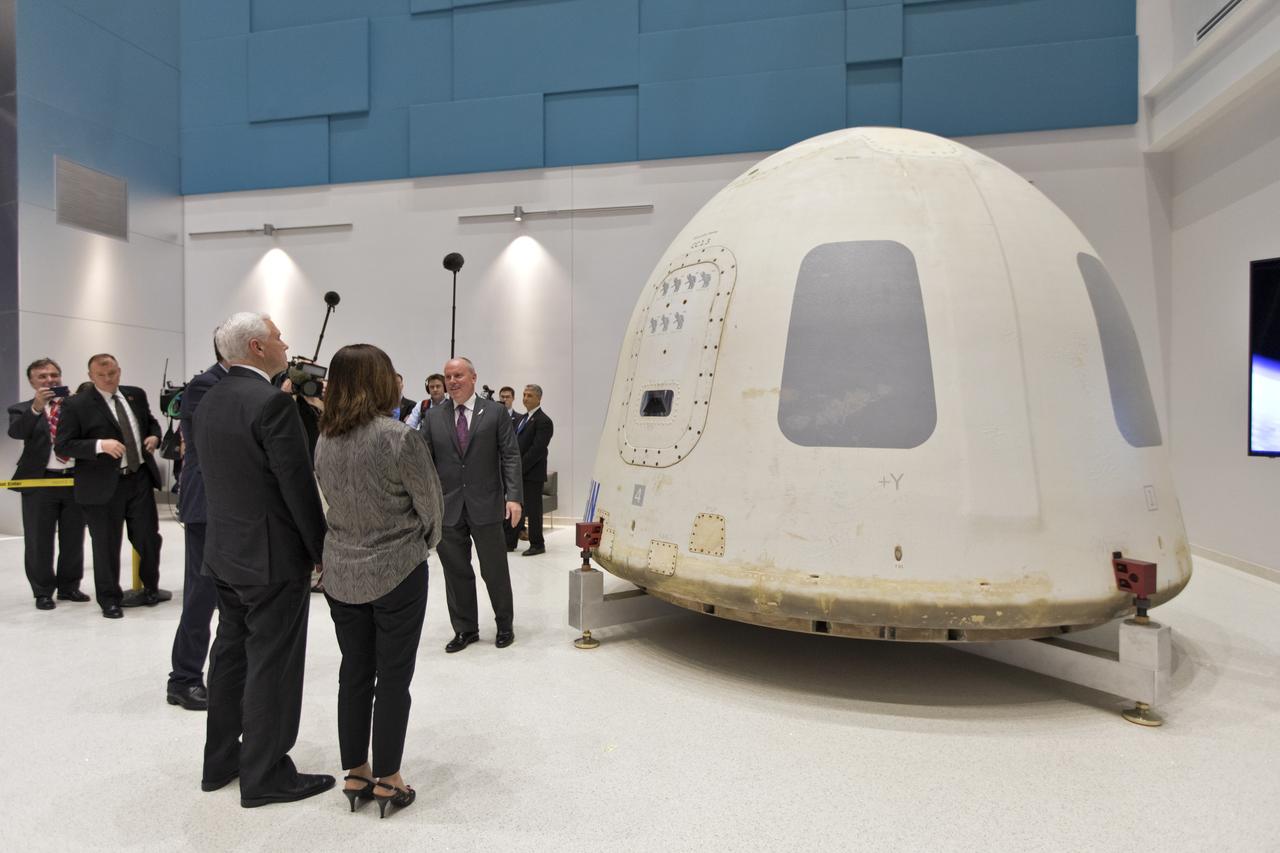

Vice President Mike Pence, second from right, and his wife, Karen Pence, tour the Blue Origin Manufacturing Facility near NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, on Feb. 20, 2018. Vice President Pence viewed the flown New Shepard Booster and Crew Capsule. The Crew Capsule, in view, flew seven times, including a pad abort test and an escape test at maximum dynamic pressure. During his visit, Pence will chair a meeting of the National Space Council on Feb. 21, 2018 in the high bay of NASA Kennedy Space Center's Space Station Processing Facility. The council's role is to advise the president regarding national space policy and strategy, and review the nation's long-range goals for space activities.
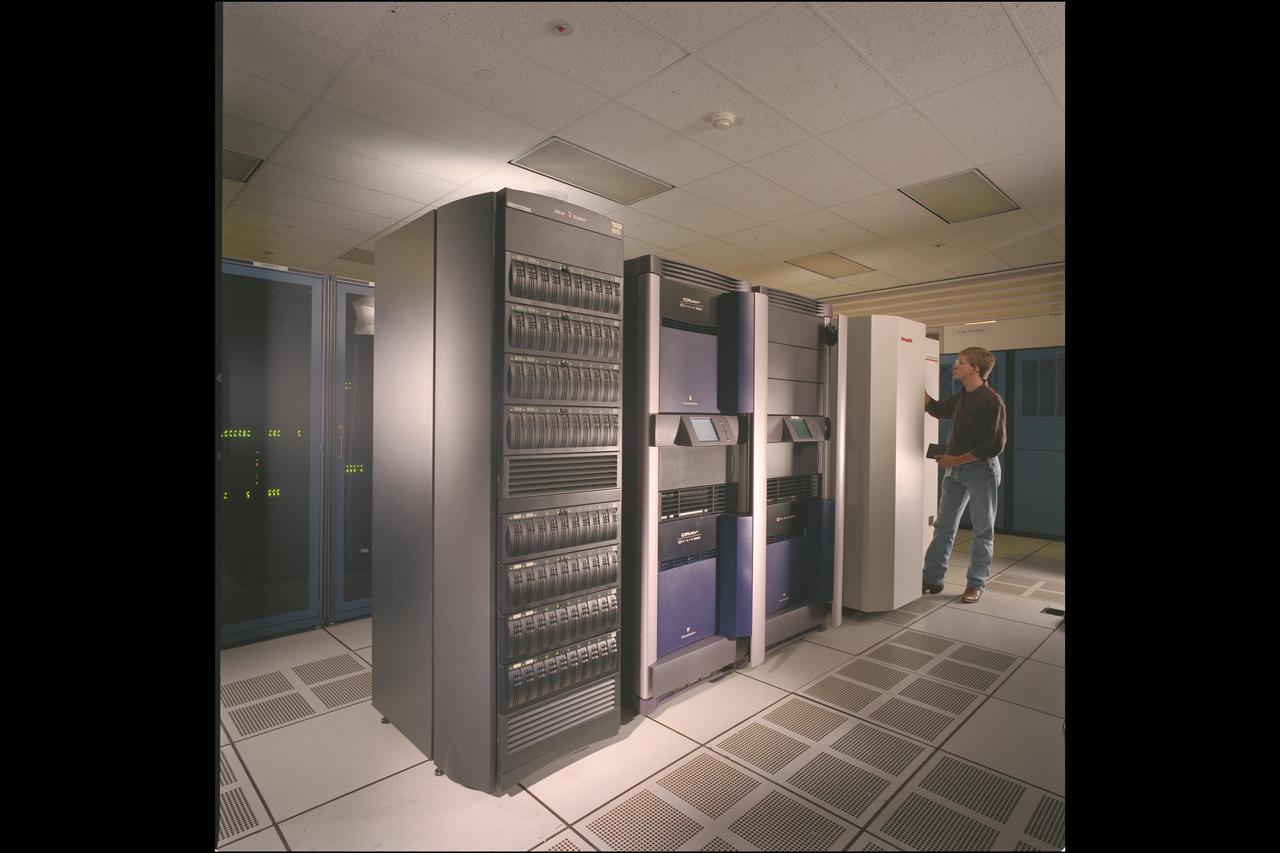

NAS Origin 2000 Computer System - Data Assimilation Office (DAO) storage (Gatun, Raid and Silo) with James Jones
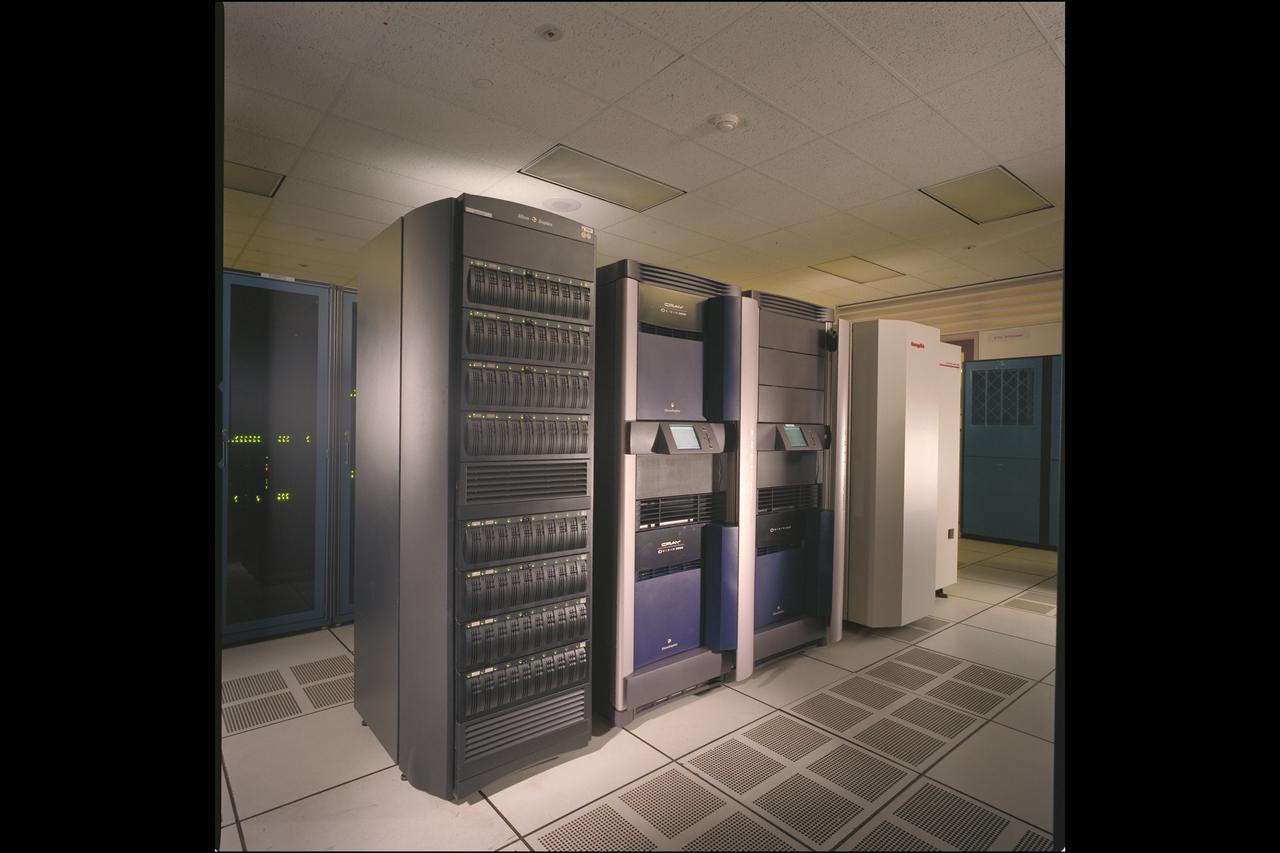

NAS Origin 2000 Computer System - Data Assimilation Office (DAO) storage (Gatun, Raid and Silo)

NAS Origin 2000 Computer System - 512 Processors ('LOMAX') station with Karl Schilke and Rita Williams
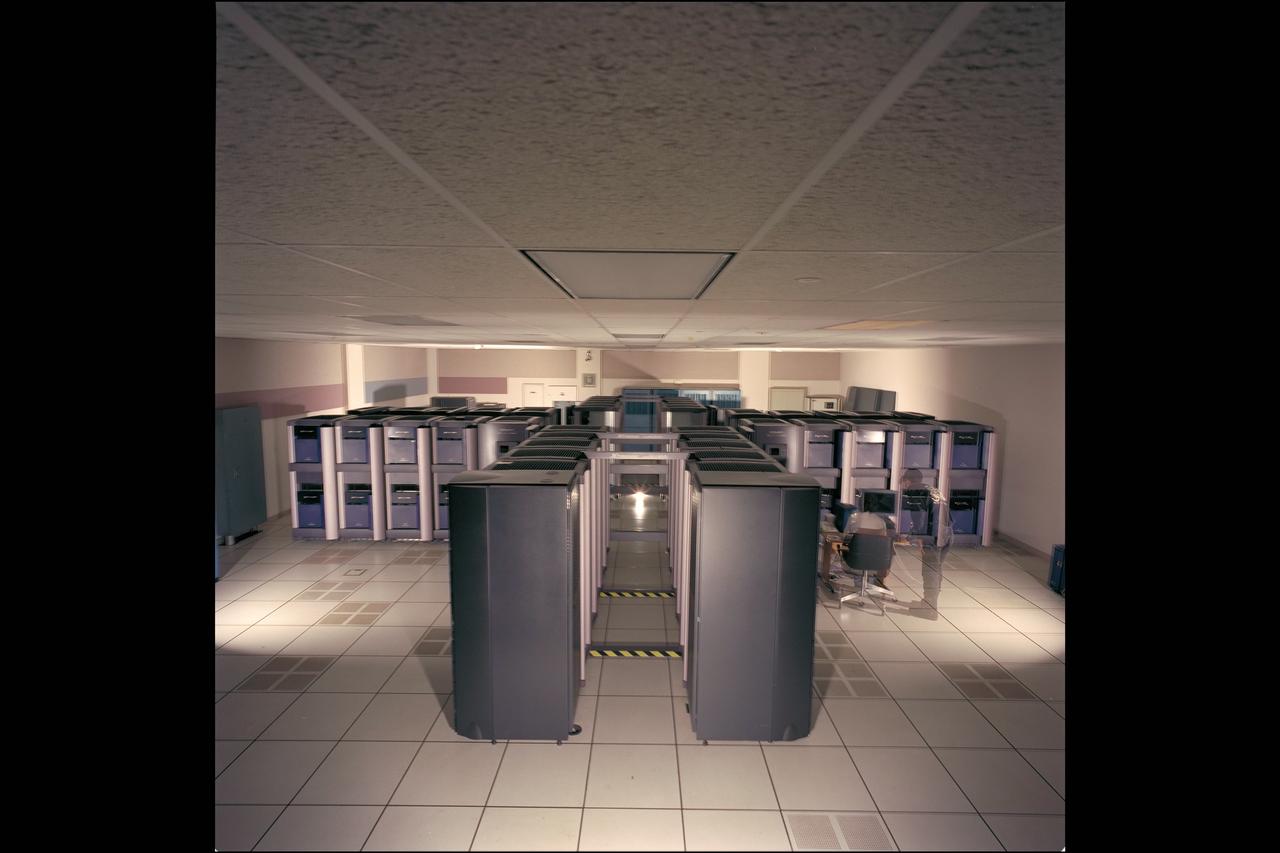

NAS Origin 2000 Computer System - 512 Processors ('LOMAX') station with Karl Schilke and Rita Williams
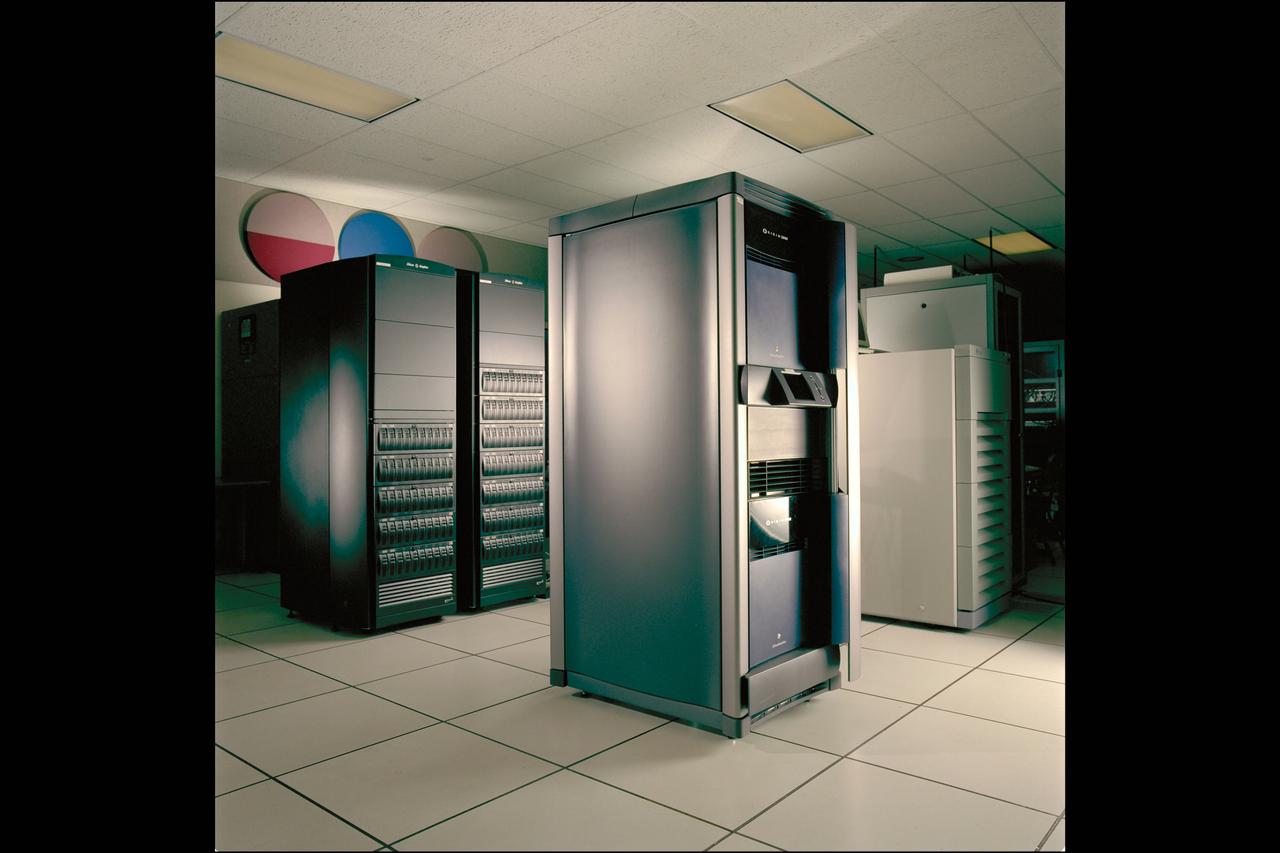

NAS Origin 2000 Computer System - 'LOU and RAID' Array New Mass Storage System AC99-0195-

NAS Origin 2000 Computer System - 512 Processors ('LOMAX') station with Karl Schilke and Rita Williams
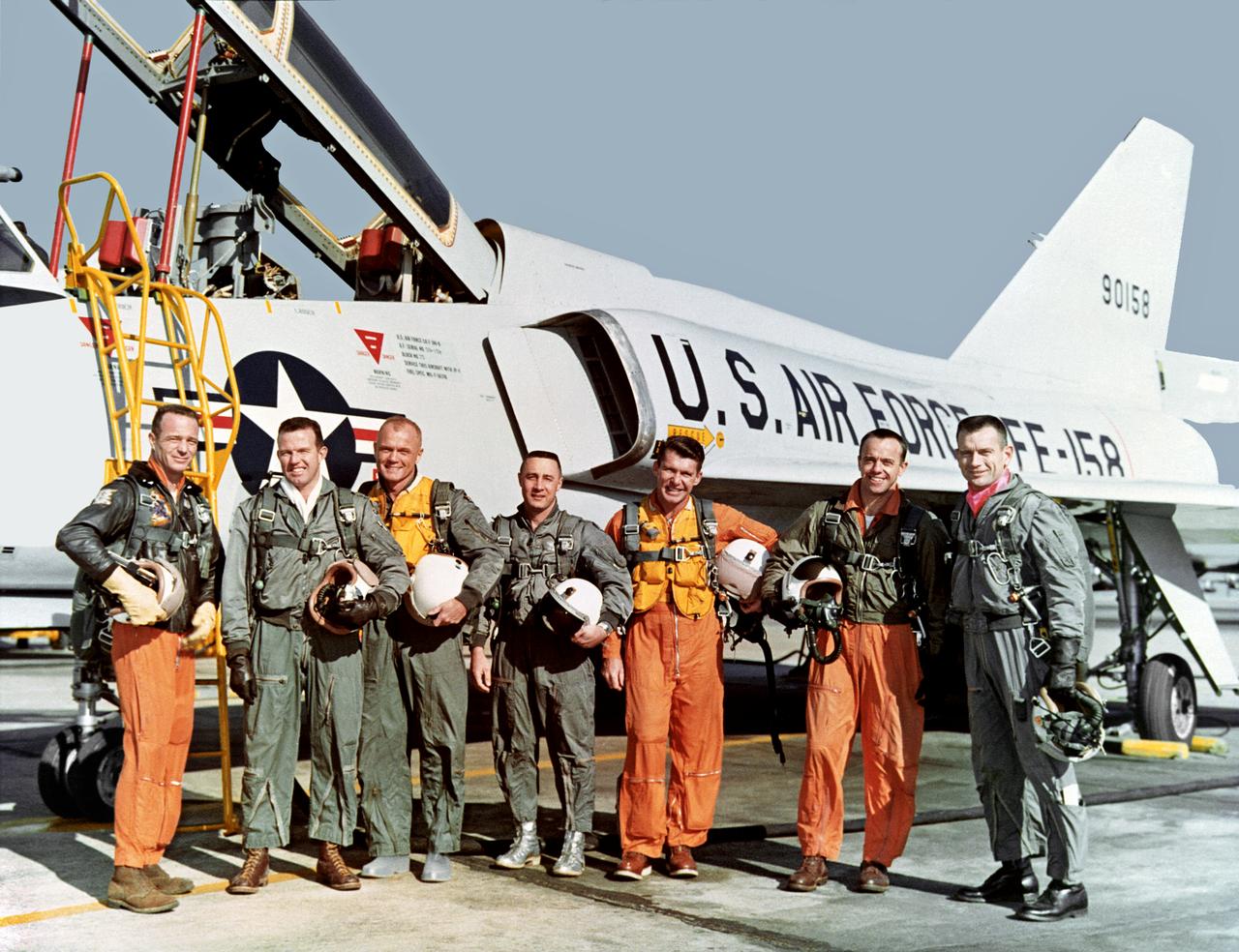

The original seven Mercury astronauts during training at NASA Langley Research Center Project Mercury. The original seven astronauts trained at NASA Langley Research Center. Chosen from among hundreds of applicants, the seven men were all test pilots. Standing in front of the U.S. Air Force Convair F-106B aircraft, the astronauts are, from left, Lt. M. Scott Carpenter, Capt. Gordon Cooper, Col. John H. Glenn Jr., Capt. Virgil "Gus" Grissom, Lt. Comdr. Walter Schirra, Lt. Comdr. Alan B. Shepard Jr. and Capt. Donald K. "Deke" Slayton. While familiarizing the astronauts with the Mercury set-up, Langley employees helped them to specialize in the technical areas crucial to the overall success of Project Mercury. Langley people also guided and monitored the astronauts activities through the many spaceflight simulators and other training devices built at the Center expressly for the manned space program. In less than three years, Project Mercury proved that men could be sent into space and returned safely to Earth, setting the stage for the longer duration Gemini flights and the Apollo lunar landings. This photograph was originally taken on 01/20/1961 and is published in Spaceflight Revolution NASA Langley Research Center from Sputnik to Apollo, NASA SP-4308, by James R. Hansen, 1995, page 40.
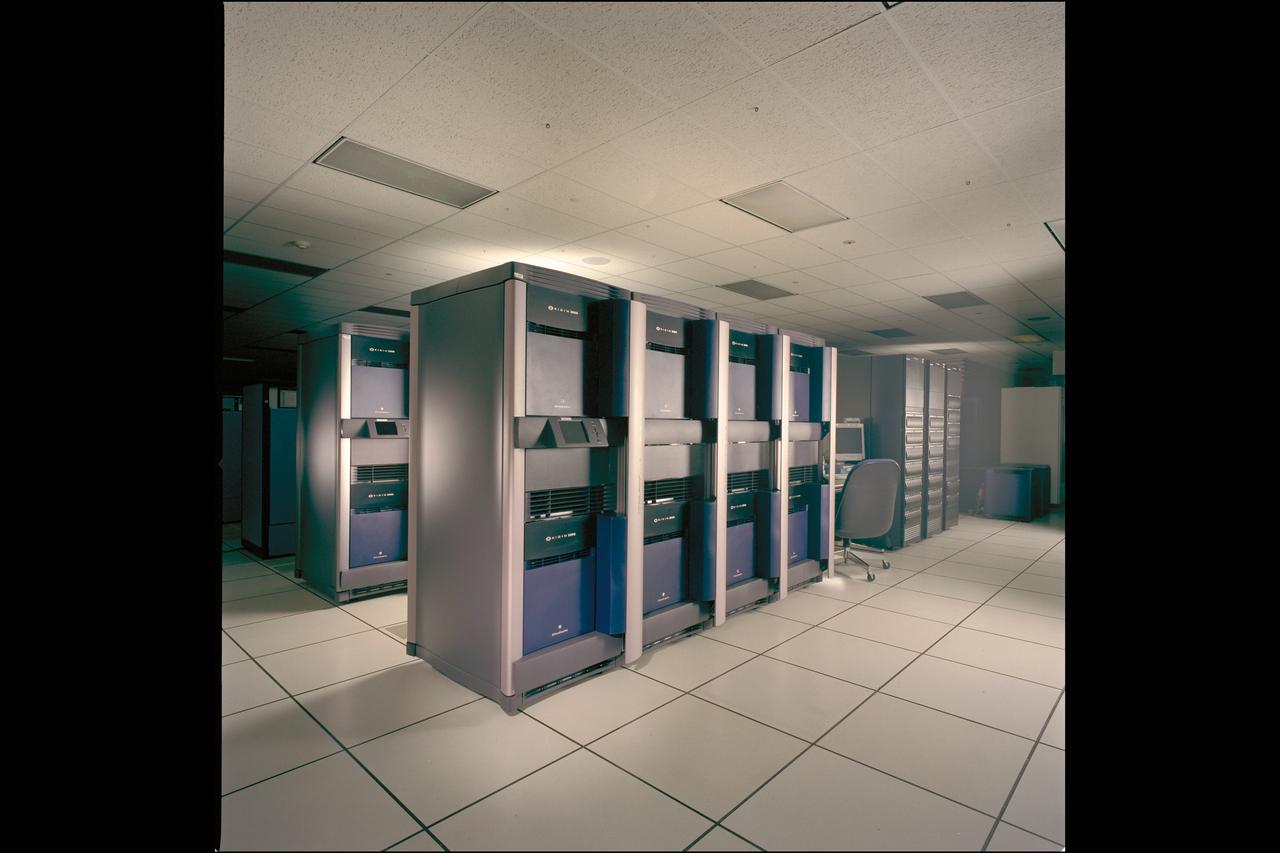

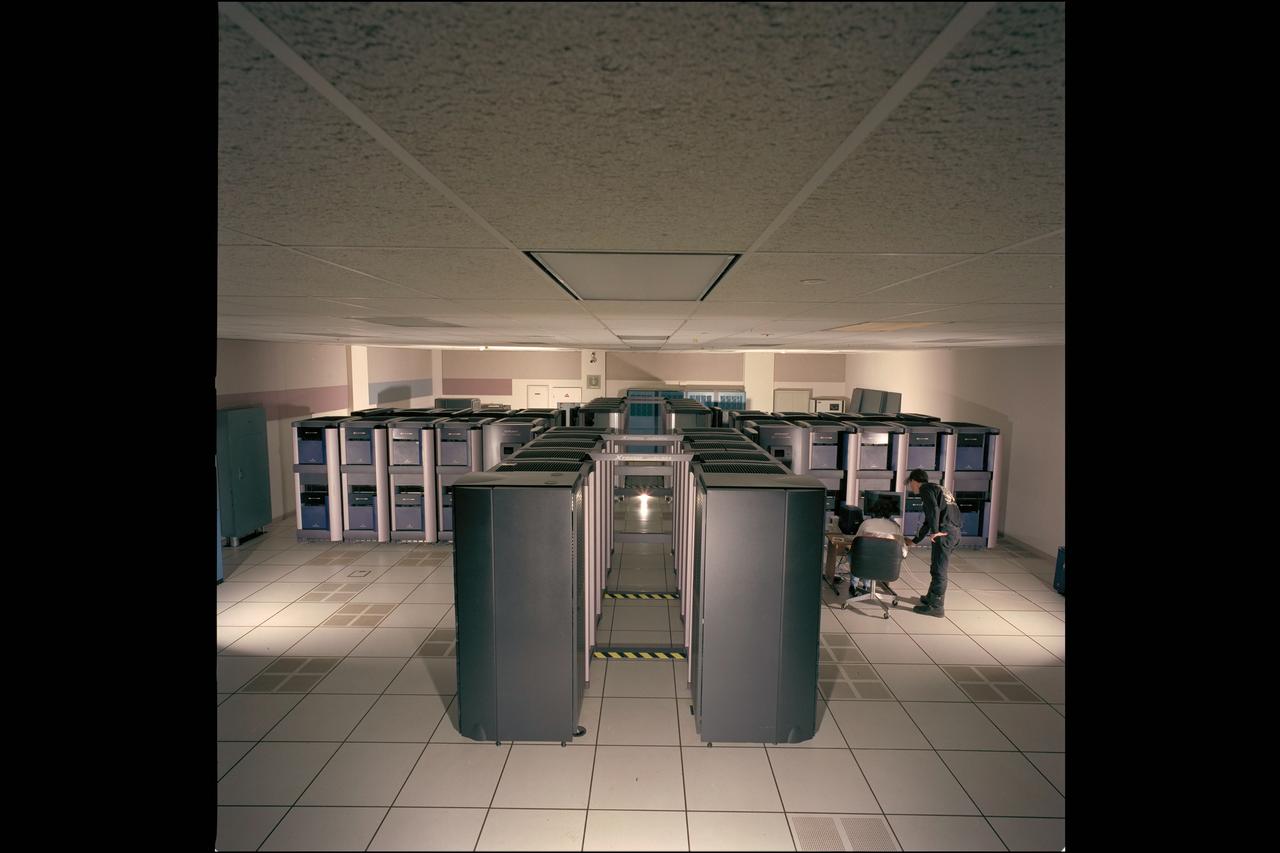
NAS Origin 2000 Computer System - Data Assimilation Office (DAO) cluster (nicknamed Sunrise, Jim PFO, Jim PF1 and Raids)

Jason Hopper of NASA (front row), Jody Ladner of Lockheed Martin (back row, left) and Chris Mulkey of NASA prepare to test the Blue Origin BE-3 engine thrust chamber in the E-1 Test Stand Control Center at John C. Stennis Space Center on Nov. 8. The test was one of 27 conducted in Stennis' E Test Complex the week of Nov. 5.
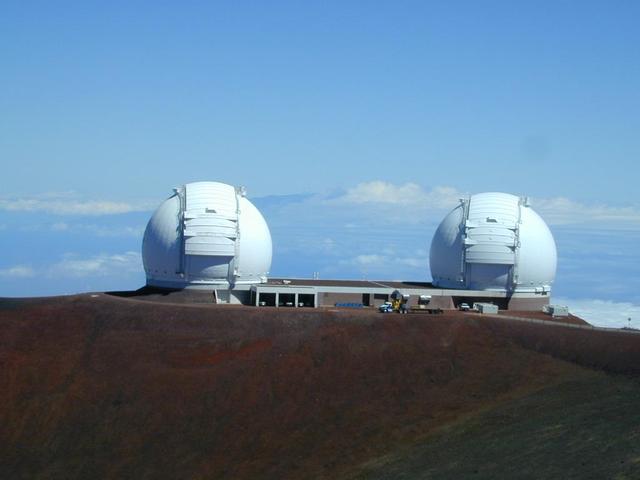

At the summit of Mauna Kea, Hawaii, NASA astronomers have linked the two 10-meter 33-foot telescopes at the W. M. Keck Observatory. The linked telescopes, together are called the Keck Interferometer, the world most powerful optical telescope system.
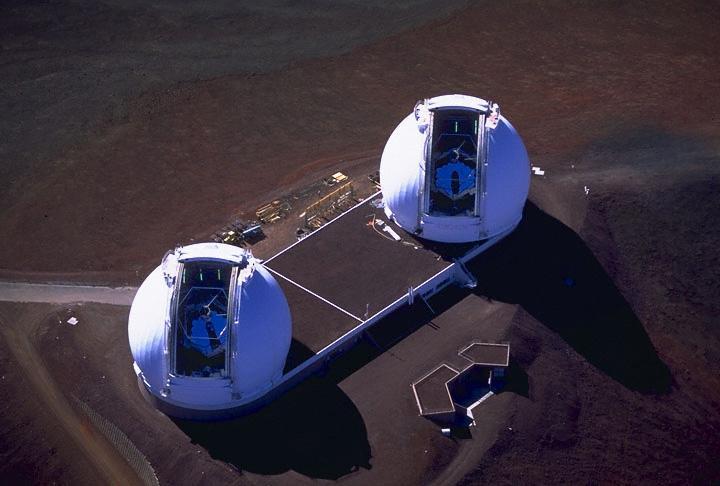

At the summit of Mauna Kea, Hawaii, NASA astronomers have linked the two 10-meter 33-foot telescopes at the W. M. Keck Observatory. The linked telescopes, together are called the Keck Interferometer, the world most powerful optical telescope system.
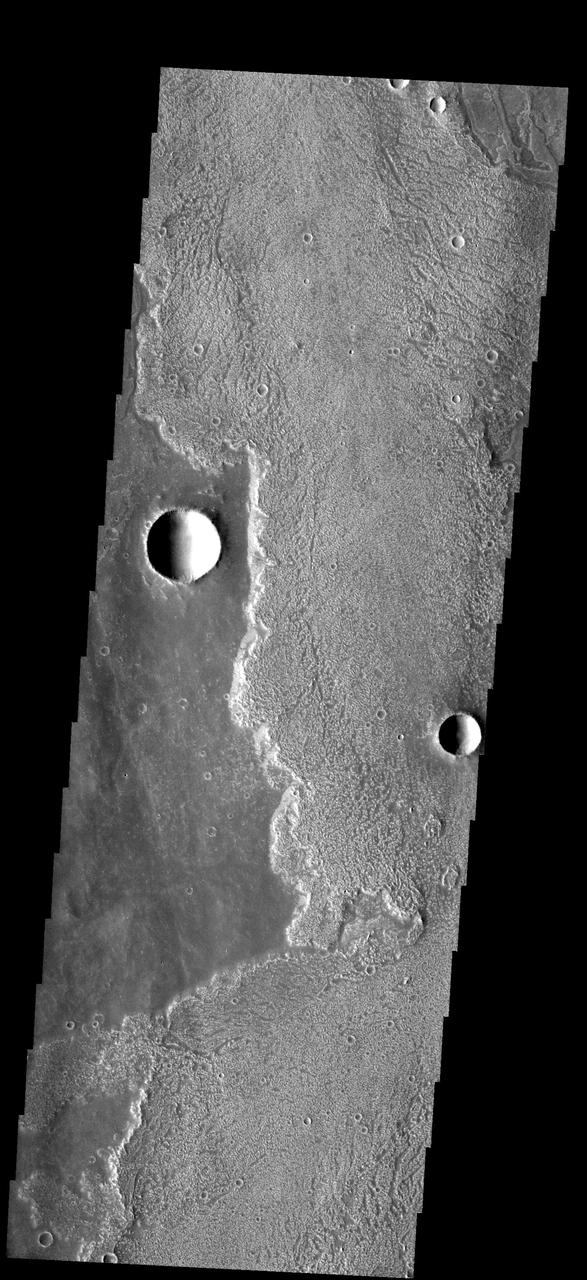
These rough surfaced lava flows originated at Arsia Mons
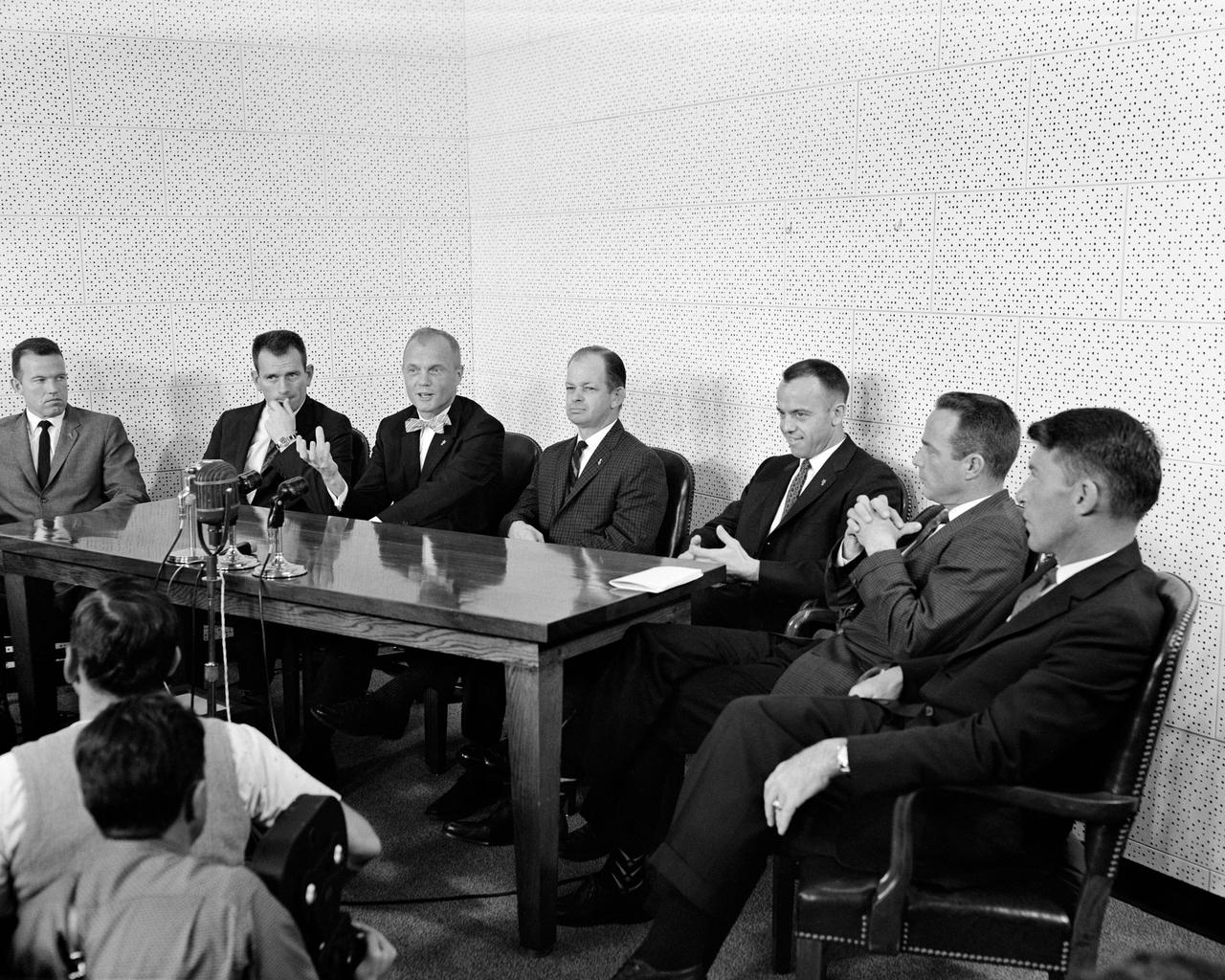

S61-00246 (25 July 1961) --- Photo of the original Mercury astronauts with Col. John A. (Shorty) Powers seated around a table talking to the news media. From left to right are: L. Gordon Cooper, Donald K. Slayton, John H. Glenn Jr., Col. Powers, Alan B. Shepard Jr., M. Scott Carpenter and Walter M. Schirra Jr. Virgil I. Grissom is out of the frame. Photo credit: NASA

Astronaut Alan B. Shepard, one of the original seven astronauts for Mercury Project selected by NASA on April 27, 1959. The Freedom 7 spacecraft boosted by Mercury-Redstone vehicle for the MR-3 mission made the first marned suborbital flight and Astronaut Shepard became the first American in space.
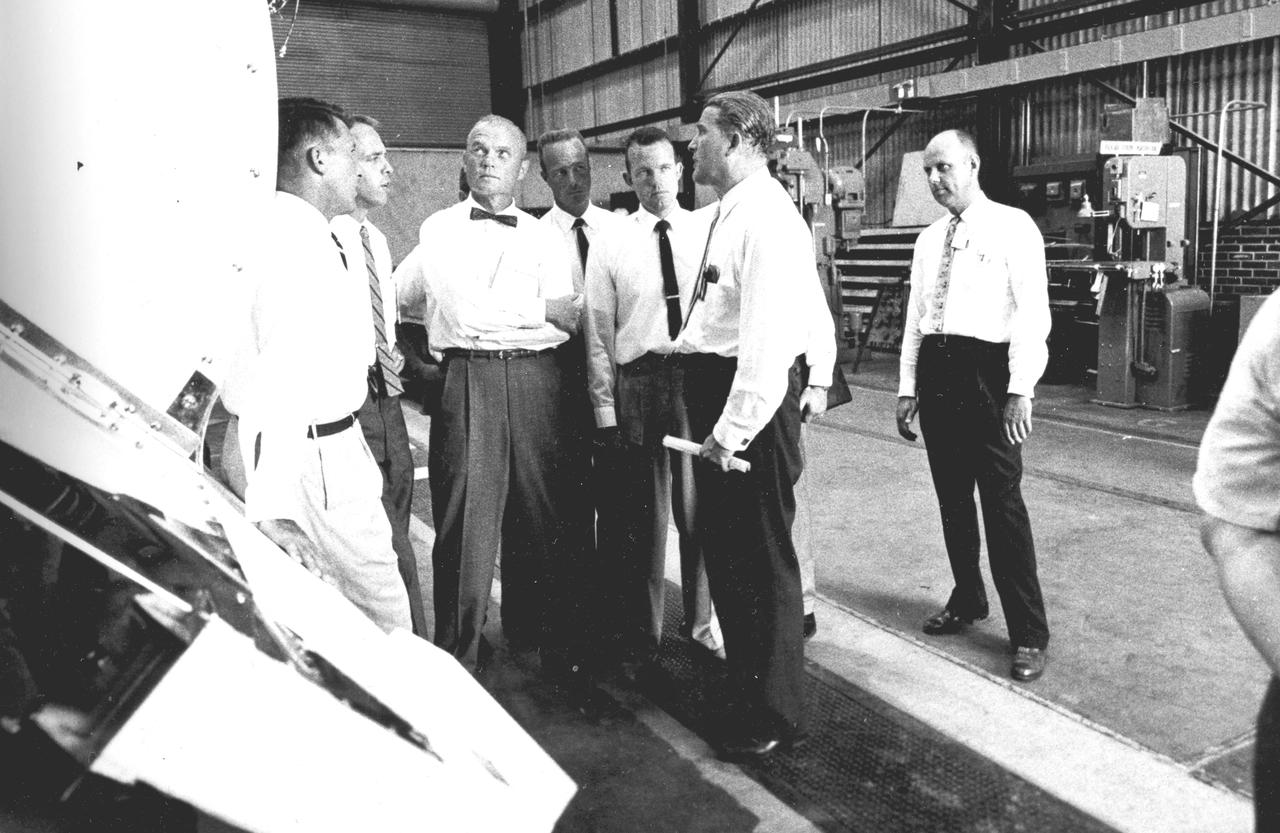

Five of the seven original astronauts are seen with Dr. von Braun inspecting the Mercury-Redstone hardware in the Fabrication Laboratory of Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) in 1959. Left to right: Astronauts Walter Schirra, Alan Shepard, John Glenn, Scott Carpenter, Gordon Cooper, and Dr. von Braun.
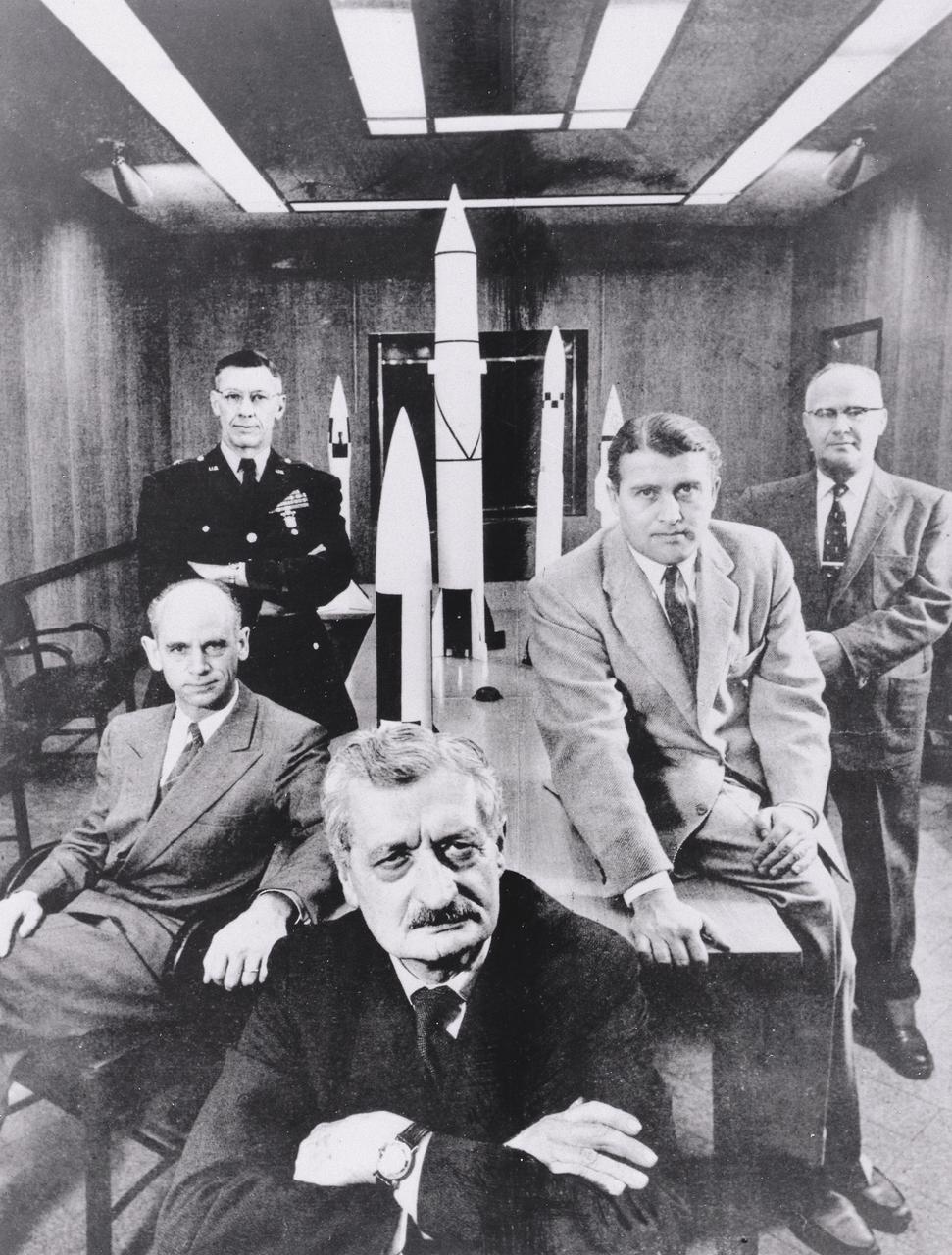
Five pioneers pose with scale models of their missiles they created in the 1950s. From left to right: Dr. Ernst Stuhlinger, a member of the original German rocket team who directed the Research Projects Office, Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA); Major General Holger Toftoy, who consolidated U.S. missile and rocketry development; Professor Herman Oberth, a rocket pioneer and Dr. von Braun's mentor; Dr. Wernher von Braun, Director, Development Operation Division, ABMA; and Dr. Robert Lusser, who served as assistant director for Reliability Engineering for ABMA. This photographis was taken February 1, 1956 by Hank Walker and appeared in February 27, 1956 issue of Life magazine.
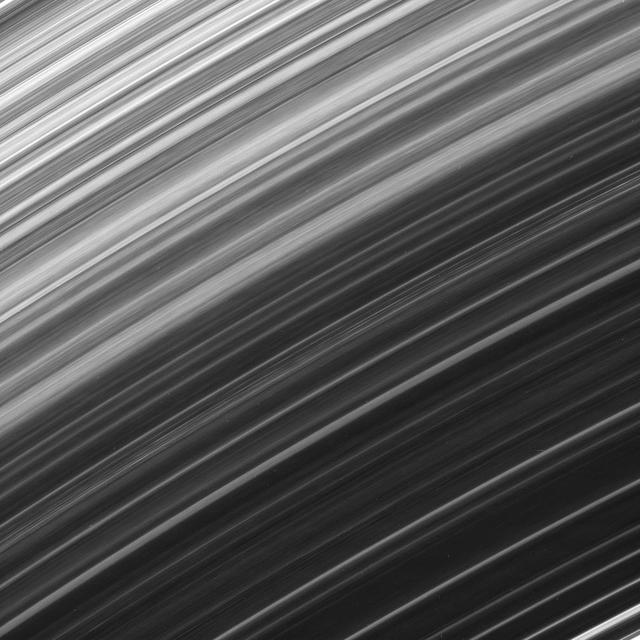

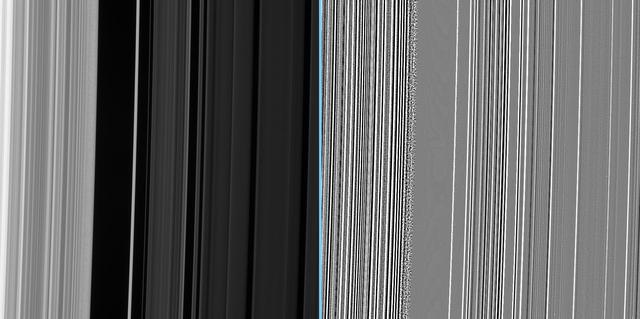
The Cassini spacecraft continues to observe brightness variations along the orbital direction within Saturn B ring
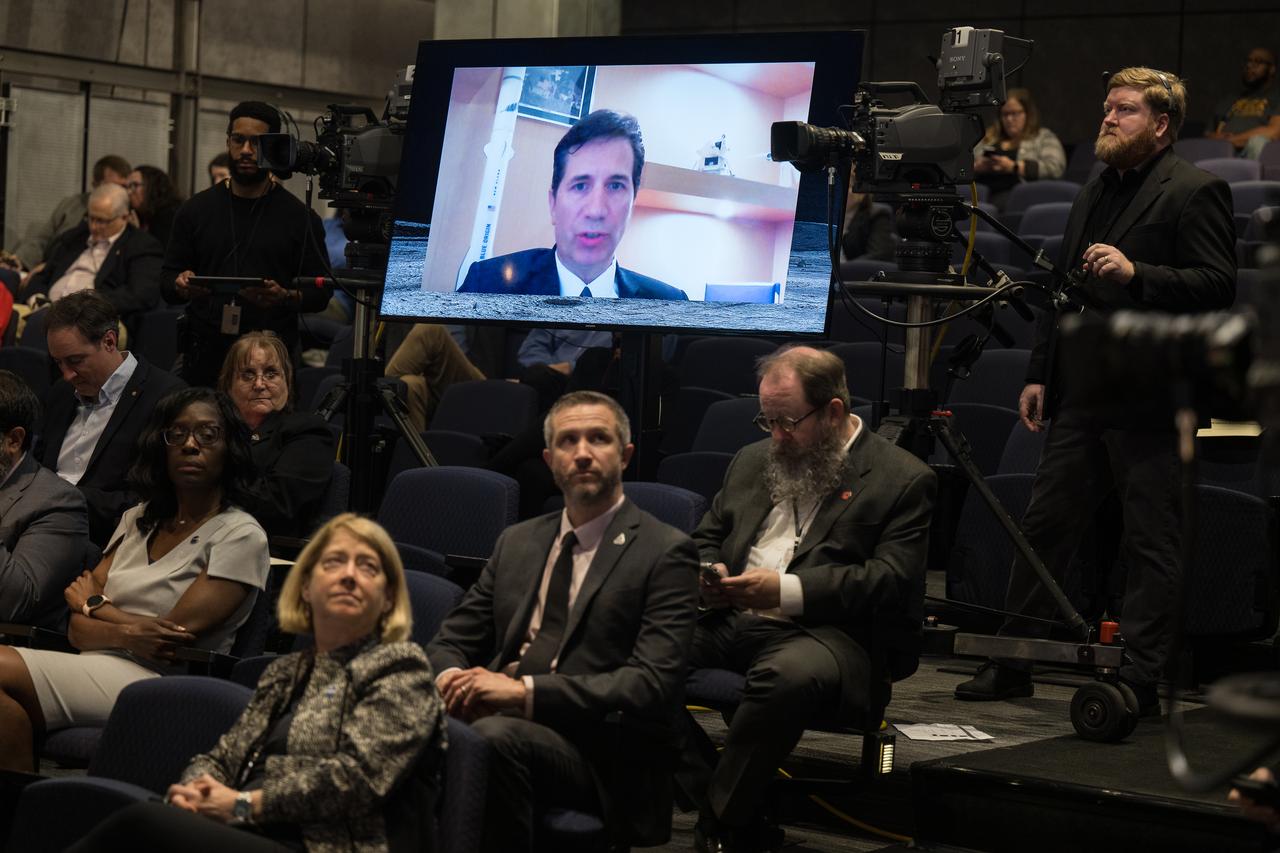

Blue Origin Human Landing System Program Manager, John Couluris, is seen on the monitor answering a question during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

The original seven astronauts for the Mercury Project pose in front of an Air Force Jet. From left to right: Scott Carpenter, L. Gordon Cooper, John H. Glenn, Virgil I. Gus Grissom, Walter M. Wally Schirra, Alan B. Shepard, and Donald K. Deke Slayton.

Astronaut L. Gordon Cooper, Jr., one of the original seven astronauts for Mercury Project selected by NASA on April 27, 1959. The MA-9 mission, boosted by the Mercury-Atlas launch vehicle, was the last flight of the Mercury Project. The Faith 7 spacecraft orbited the Earth 22 times in 1-1/2 days.

Astronaut Virgil I. "Gus" Grissom, one of the original seven astronauts for Mercury Project selected by NASA on April 27, 1959. The MR-4 mission, boosted by the Mercury-Redstone vehicle, made the second marned suborbital flight. The capsule, Liberty Bell 7, sank into the sea after the splashdown.

Astronaut Walter M. "Wally" Schirra, one of the original seven astronauts for Mercury Project selected by NASA on April 27, 1959. The MA-8 (Mercury-Atlas) mission with Sigma 7 spacecraft was the third marned orbital flight by the United States, and made the six orbits in 9-1/4 hours.

Aerial view of the 8- by 6-Foot Supersonic Wind Tunnel in its original configuration at the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) Lewis Flight Propulsion Laboratory. The 8- by 6 was the laboratory’s first large supersonic wind tunnel. It was also the NACA’s most powerful supersonic tunnel, and its first facility capable of running an engine at supersonic speeds. The 8- by 6-foot tunnel has been used to study inlets and exit nozzles, fuel injectors, flameholders, exit nozzles, and controls on ramjet and turbojet propulsion systems. The 8- by 6 was originally an open-throat and non-return tunnel. This meant that the supersonic air flow was blown through the test section and out the other end into the atmosphere. In this photograph, the three drive motors in the structure at the left supplied power to the seven-stage axial-flow compressor in the light-colored structure. The air flow passed through flexible walls which were bent to create the desired speed. The test article was located in the 8- by 6-foot stainless steel test section located inside the steel pressure chamber at the center of this photograph. The tunnel dimensions were then gradually increased to slow the air flow before it exited into the atmosphere. The large two-story building in front of the tunnel was used as office space for the researchers.

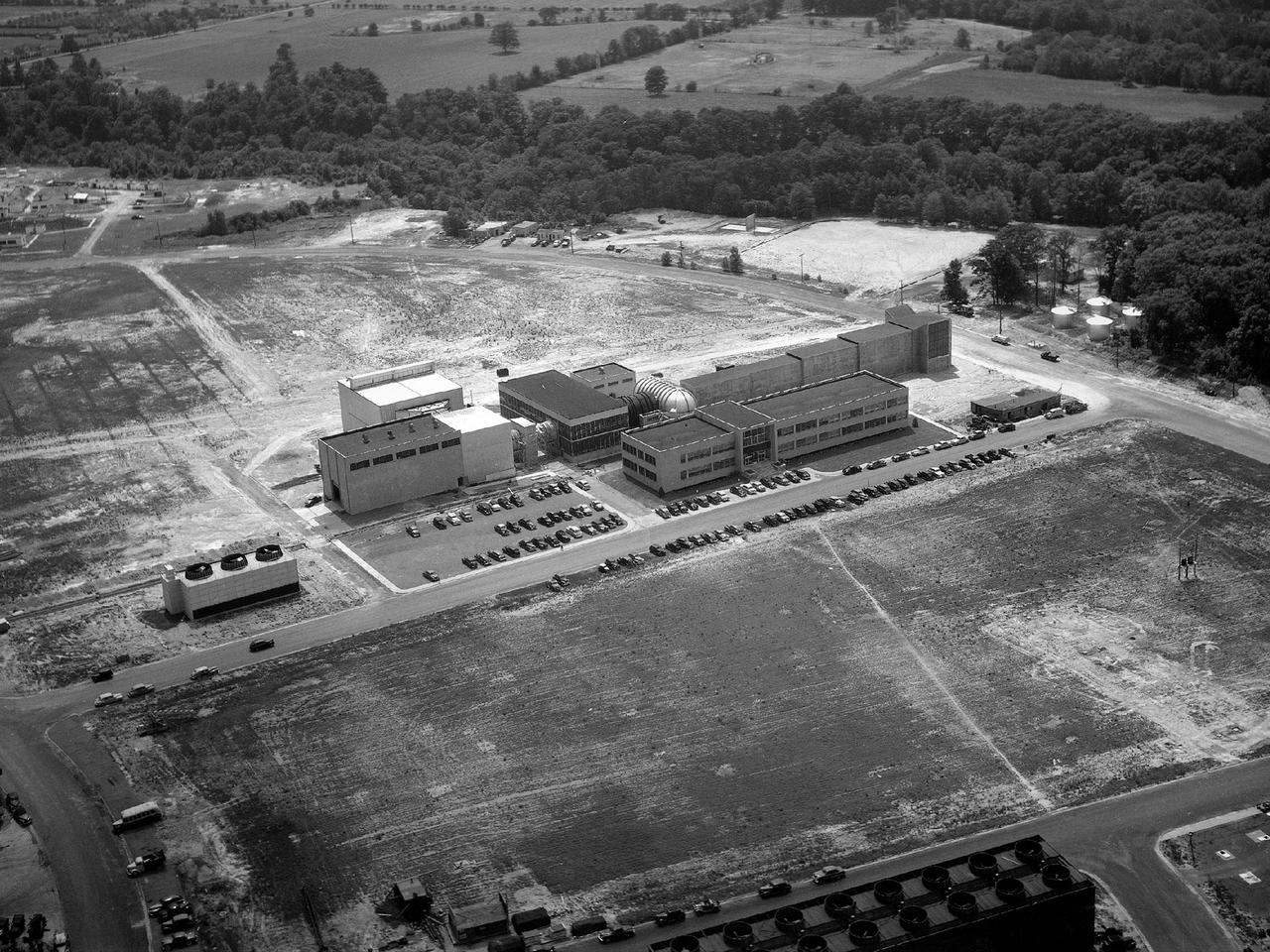
S62-00631 (March 1962) --- Area photograph of Site 1, Manned Spacecraft Center, at Clear Lake, prior to start of construction.
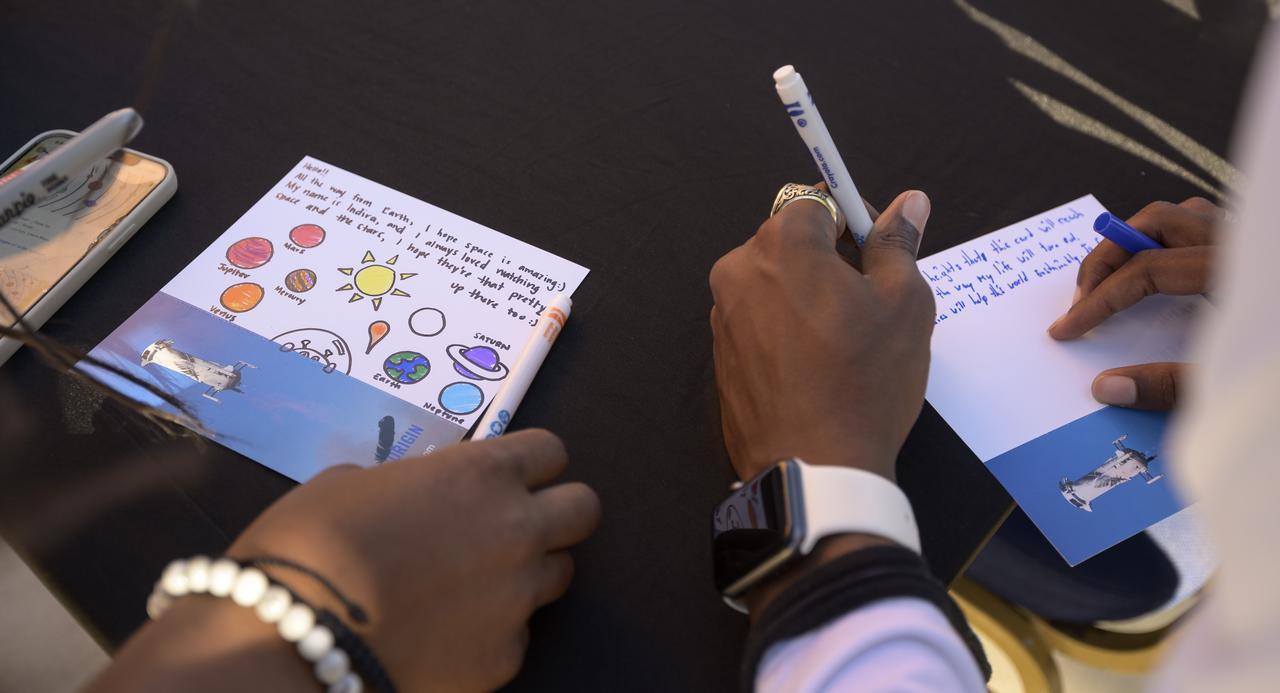

Children in attendance for the screening the NASA produced documentary “The Color of Space” draw on postcards that will be sent to space by Club for the Future on a Blue Origin New Shepard rocket at Howard University’s Cramton Auditorium in Washington, Saturday, June 18, 2022. Premiering on Juneteenth, the federal holiday commemorating the end of slavery in the United States, “The Color of Space” is an inspirational documentary that tells the stories of NASA’s Black astronauts determined to reach the stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
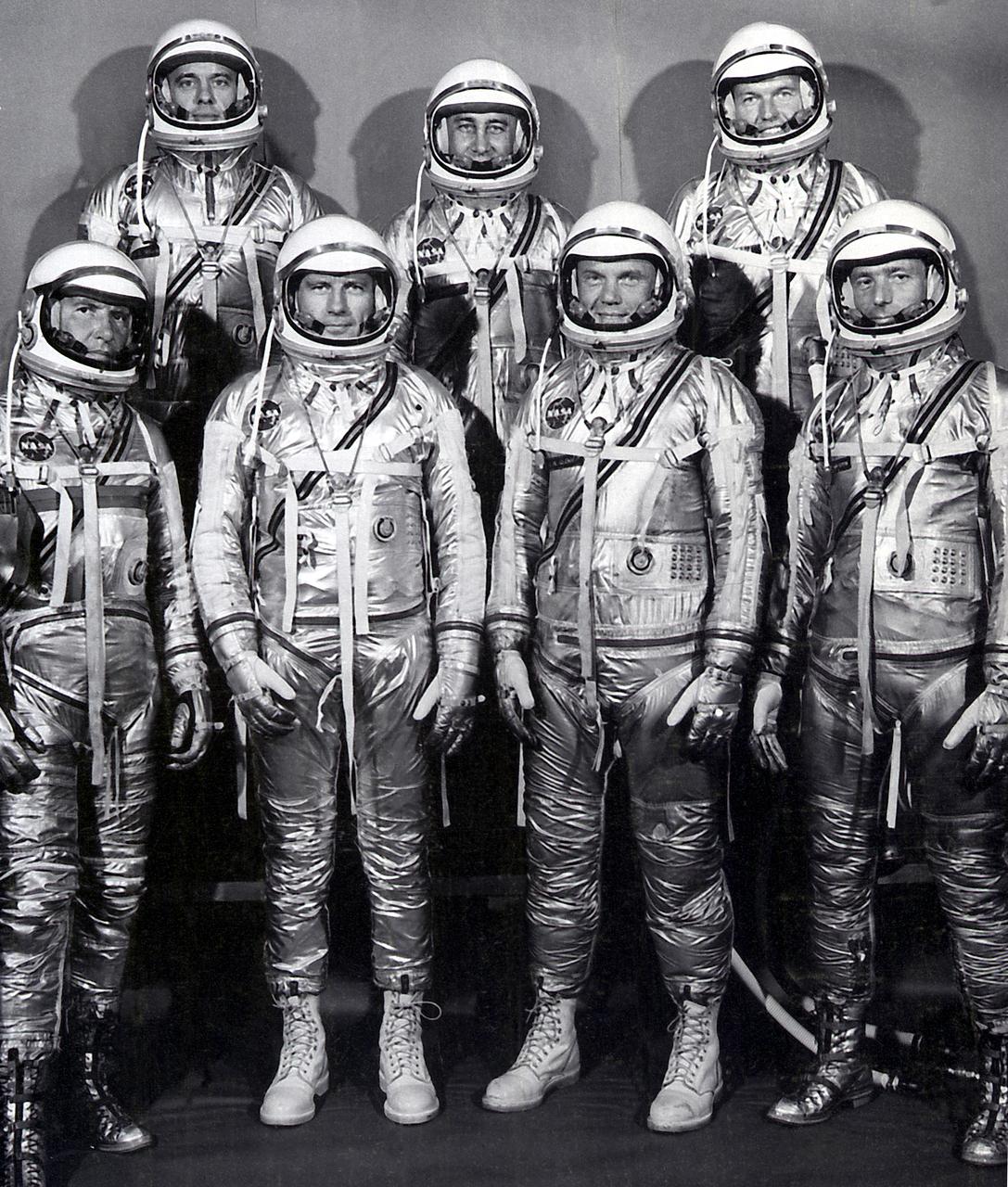

The group portrait of the original seven astronauts for the Mercury Project. NASA selected its first seven astronauts on April 27, 1959. Left to right at front: Walter M. Wally Schirra, Donald K. Deke Slayton, John H. Glenn, Jr., and Scott Carpenter. Left to right at rear: Alan B. Shepard, Virgil I. Gus Grissom, and L. Gordon Cooper, Jr.
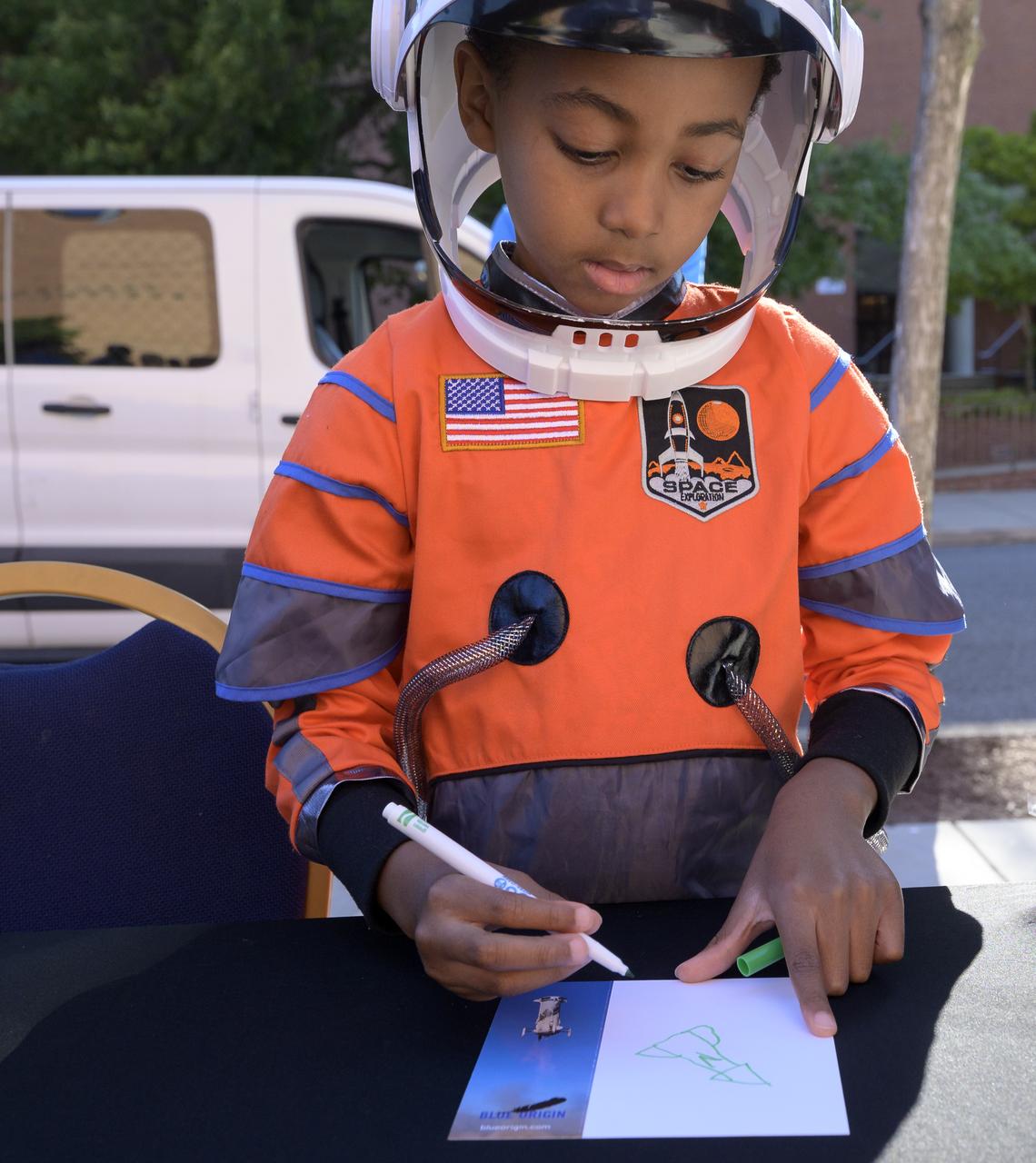

6-year old Armani Bonds draws on a postcard that will be sent to space by Club for the Future on a Blue Origin New Shepard rocket prior to he and his family screening the NASA produced documentary “The Color of Space” at Howard University’s Cramton Auditorium in Washington, Saturday, June 18, 2022. Premiering on Juneteenth, the federal holiday commemorating the end of slavery in the United States, “The Color of Space” is an inspirational documentary that tells the stories of NASA’s Black astronauts determined to reach the stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
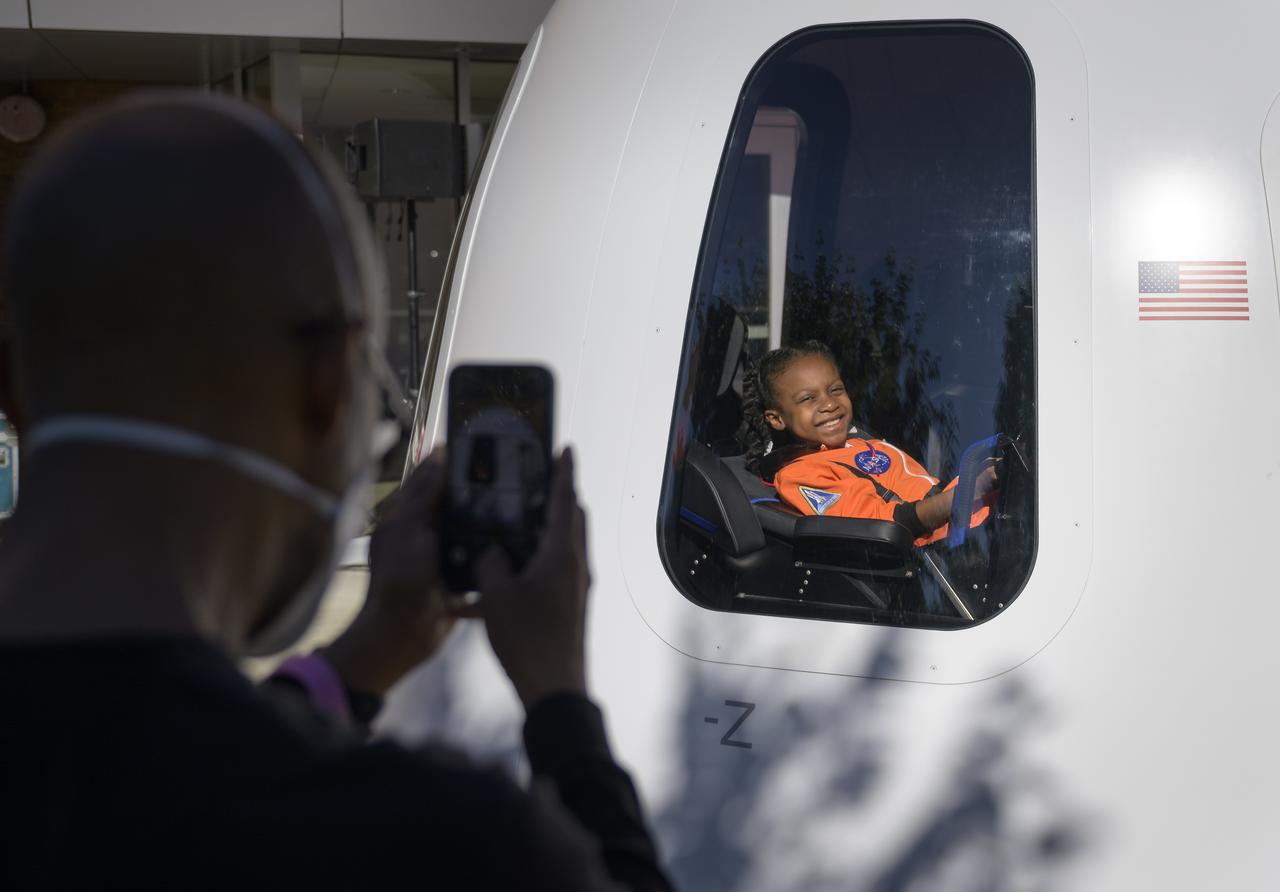

9-year old Amara Bowman smiles as her father photographs her inside a Blue Origin New Shepard capsule mockup prior to the screening of the NASA produced documentary “The Color of Space” at Howard University’s Cramton Auditorium in Washington, Saturday, June 18, 2022. Premiering on Juneteenth, the federal holiday commemorating the end of slavery in the United States, “The Color of Space” is an inspirational documentary that tells the stories of NASA’s Black astronauts determined to reach the stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
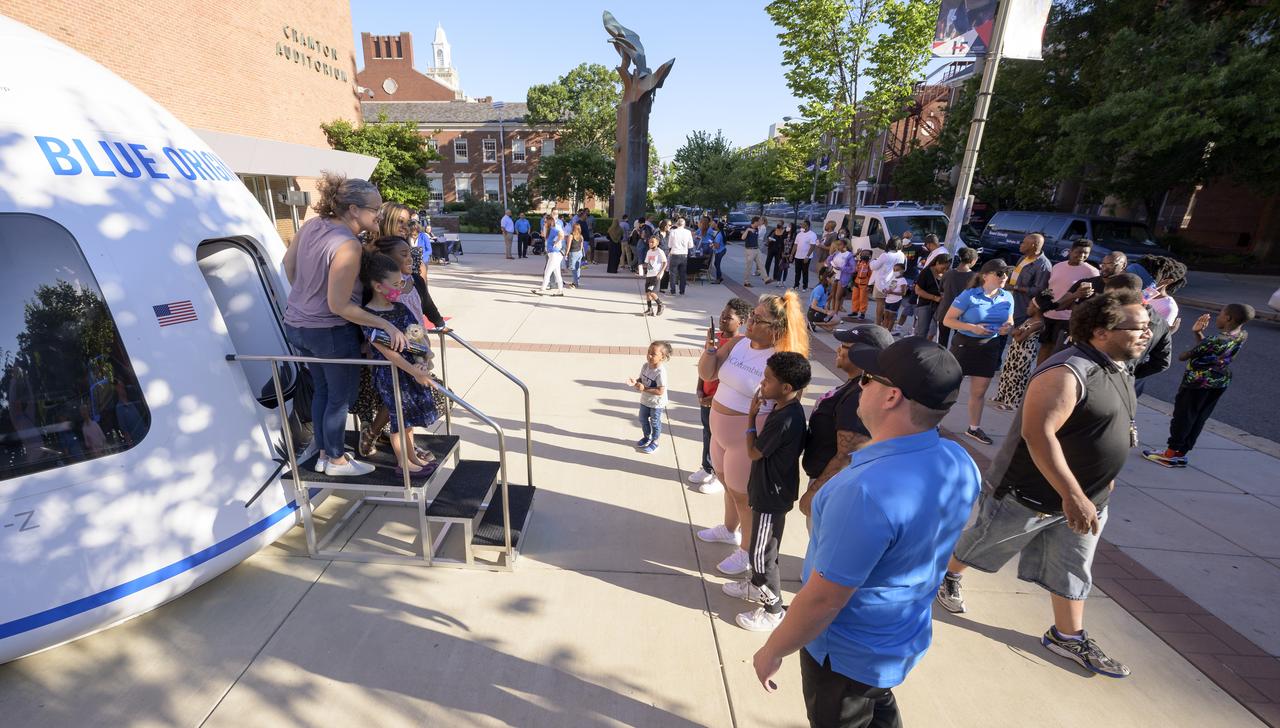

Attendees line up to go inside a Blue Origin New Shepard capsule mockup prior to the screening of the NASA produced documentary “The Color of Space” at Howard University’s Cramton Auditorium in Washington, Saturday, June 18, 2022. Premiering on Juneteenth, the federal holiday commemorating the end of slavery in the United States, “The Color of Space” is an inspirational documentary that tells the stories of NASA’s Black astronauts determined to reach the stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
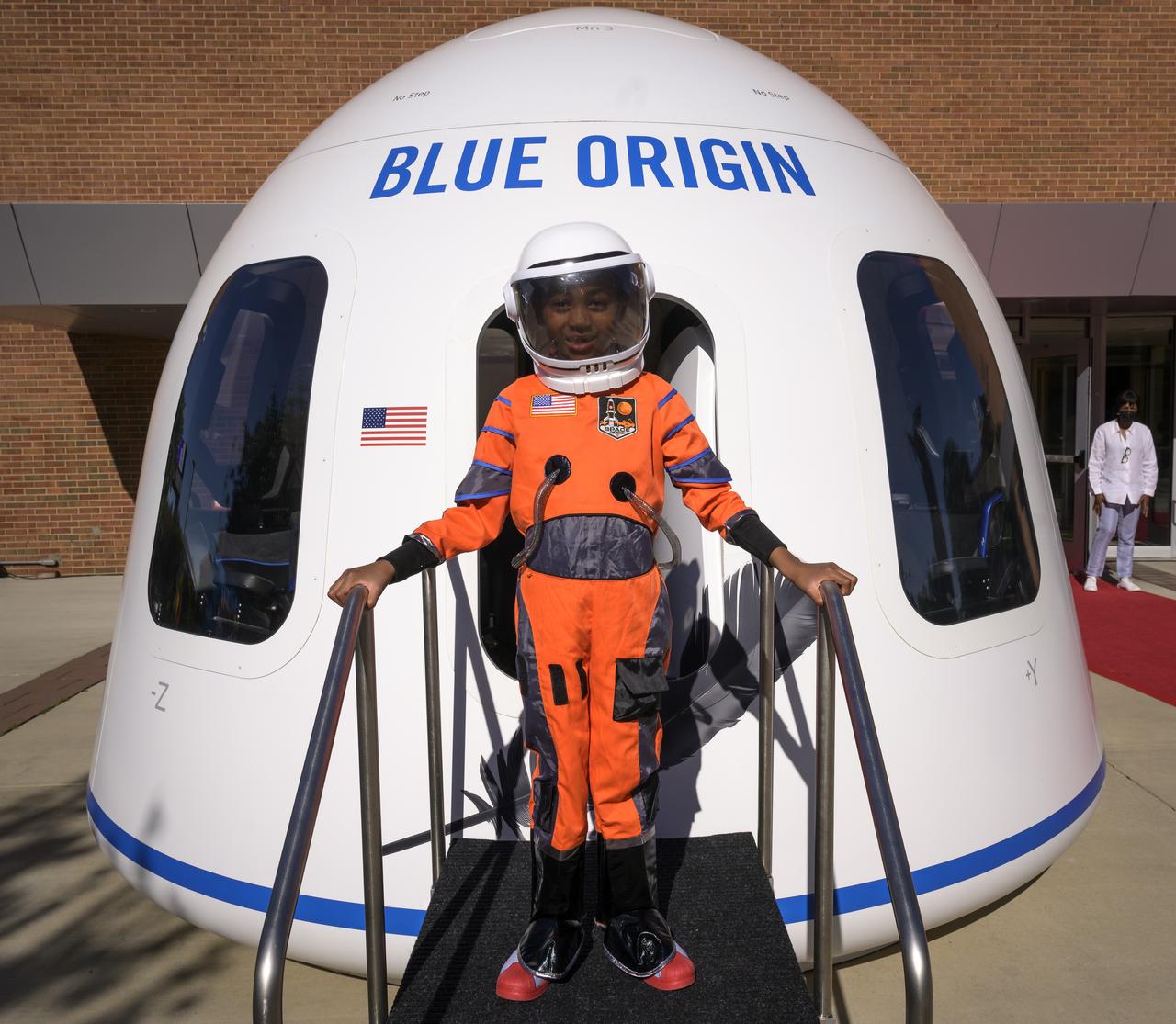

6-year old Armani Bonds poses for a photograph as he exits a Blue Origin New Shepard capsule mockup prior to the screening of the NASA produced documentary “The Color of Space” at Howard University’s Cramton Auditorium in Washington, Saturday, June 18, 2022. Premiering on Juneteenth, the federal holiday commemorating the end of slavery in the United States, “The Color of Space” is an inspirational documentary that tells the stories of NASA’s Black astronauts determined to reach the stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
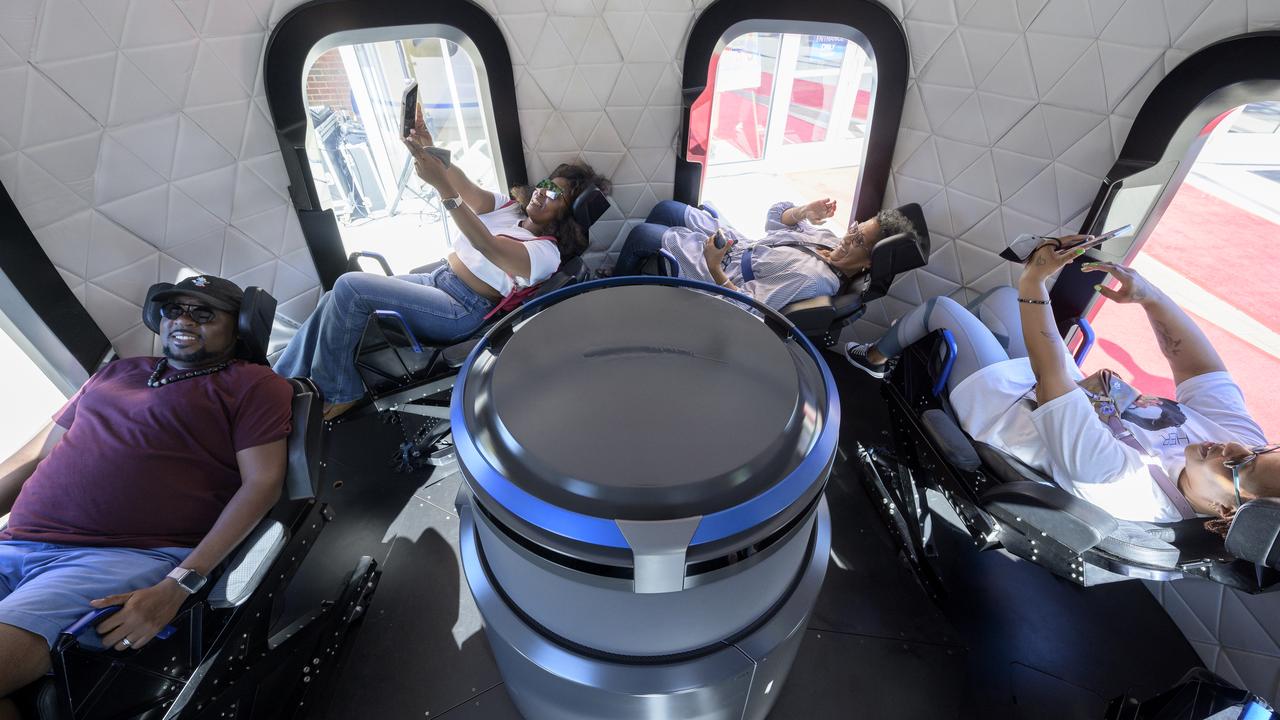

Attendees experience the inside of a Blue Origin New Shepard capsule mockup prior to the screening of the NASA produced documentary “The Color of Space” at Howard University’s Cramton Auditorium in Washington, Saturday, June 18, 2022. Premiering on Juneteenth, the federal holiday commemorating the end of slavery in the United States, “The Color of Space” is an inspirational documentary that tells the stories of NASA’s Black astronauts determined to reach the stars. Photo Credit: (NASA/Bill Ingalls)
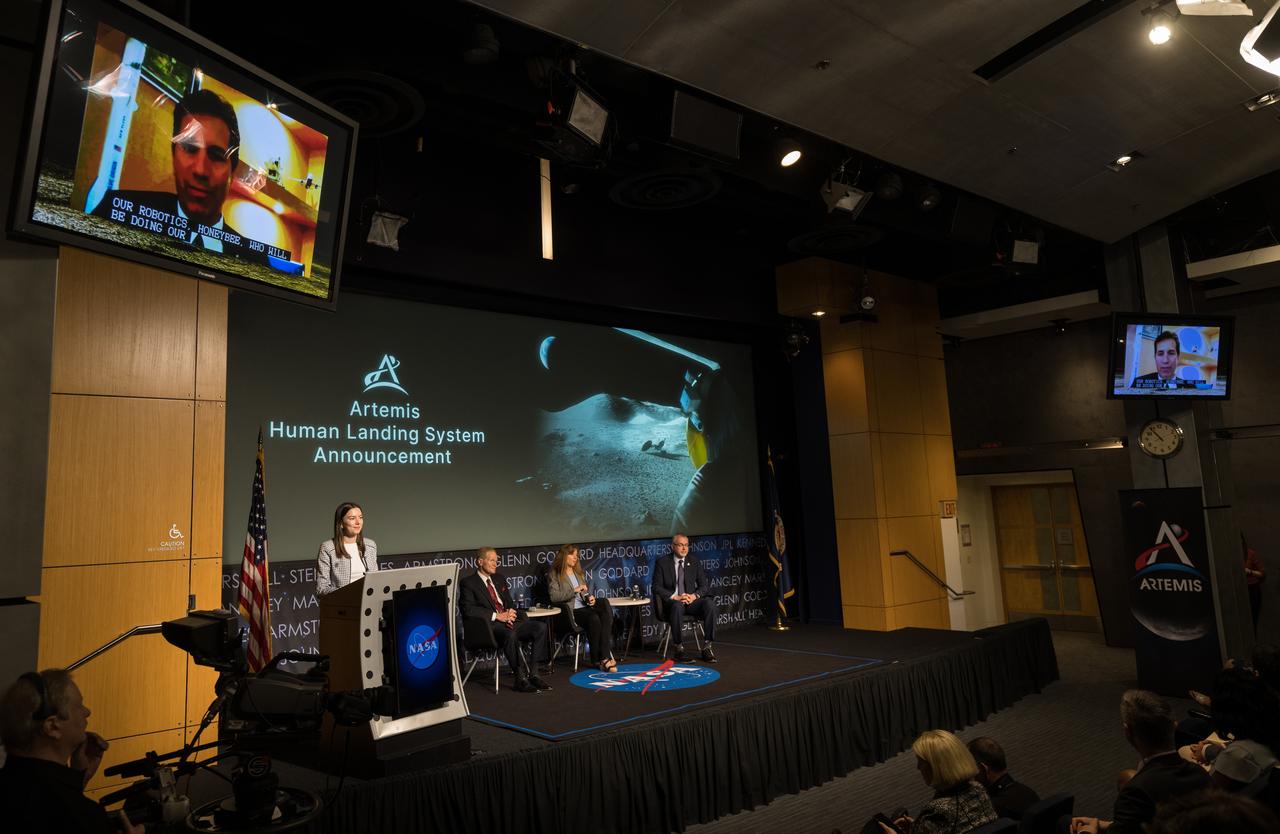

Blue Origin Human Landing System Program Manager, John Couluris, gives remarks during an event announcing Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)
An extreme enhancement of the original image, presented at right, reveals the grainy region with greater clarity
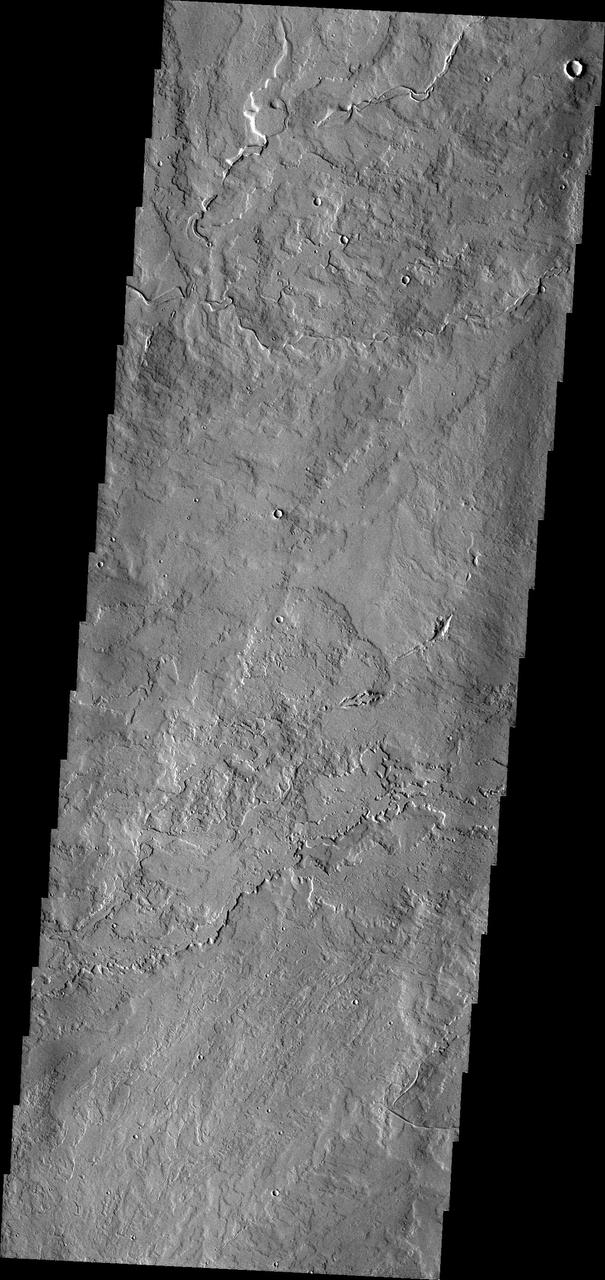

The lava flows in this image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft originated at Pavonis Mons.
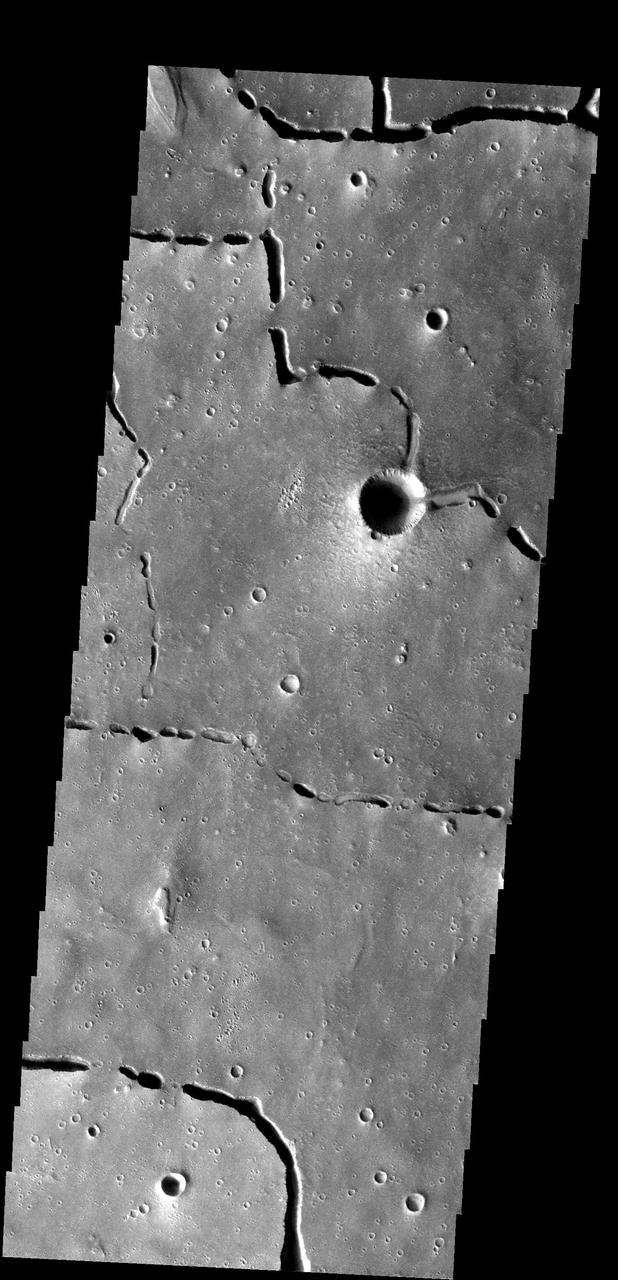

The collapse features in this images are related to lava tubes that likely originated at Elysium volcanic complex
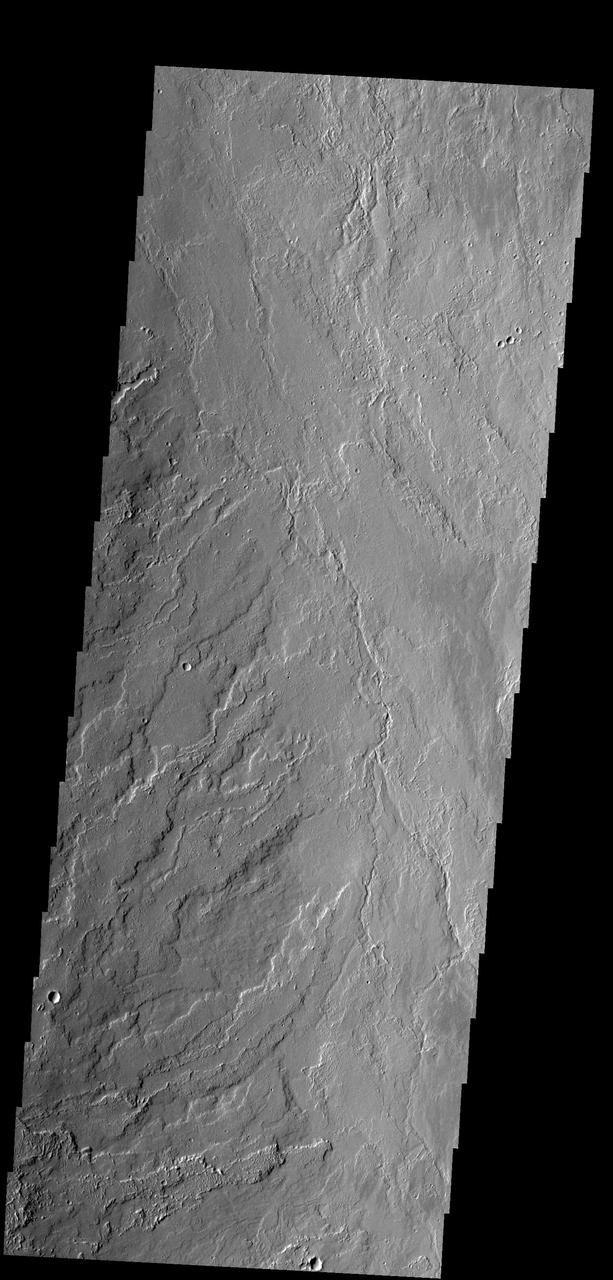

This image shows lava flows that originated at Olympus Mons as seen by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft.
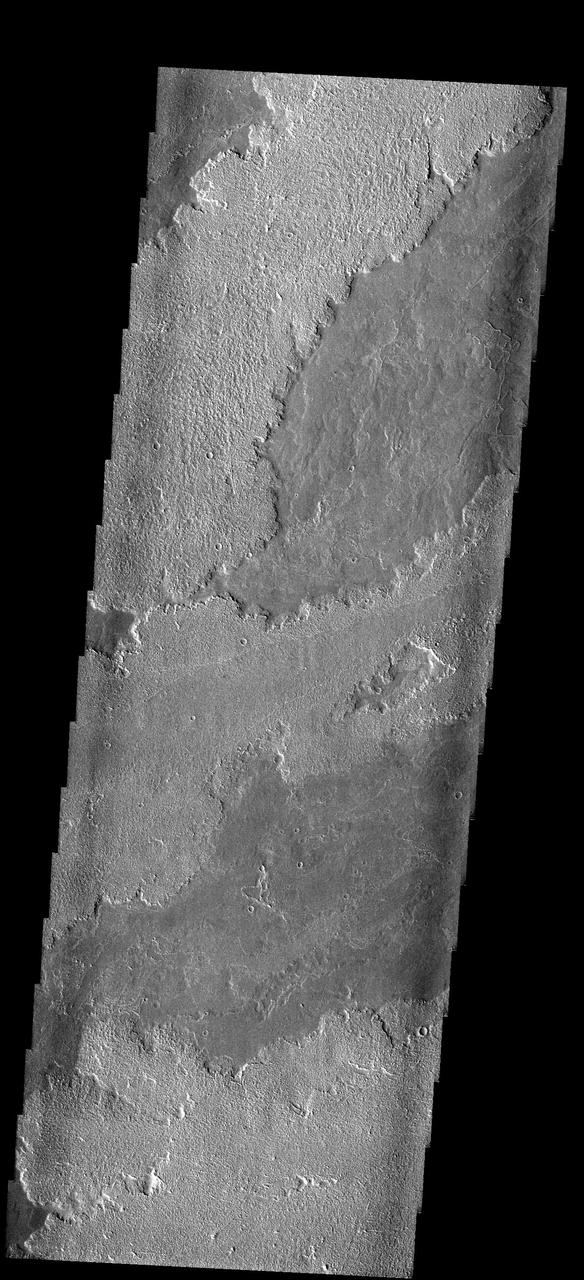
These lava flows originated at Arsia Mons. This image is from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft.

Scientists believe a large number of the meteorites that are found on Earth originate from the protoplanet Vesta. This image is from NASA Dawn spacecraft.
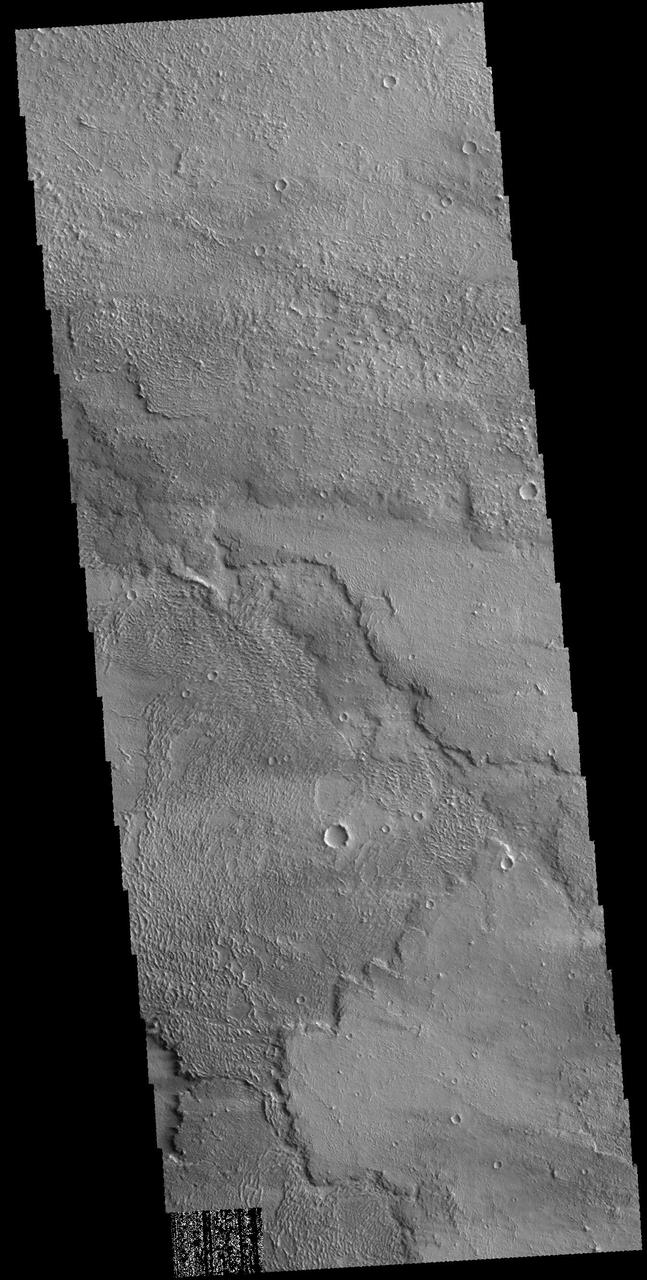

This image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows part of the lava flows that originated from Arsia Mons.
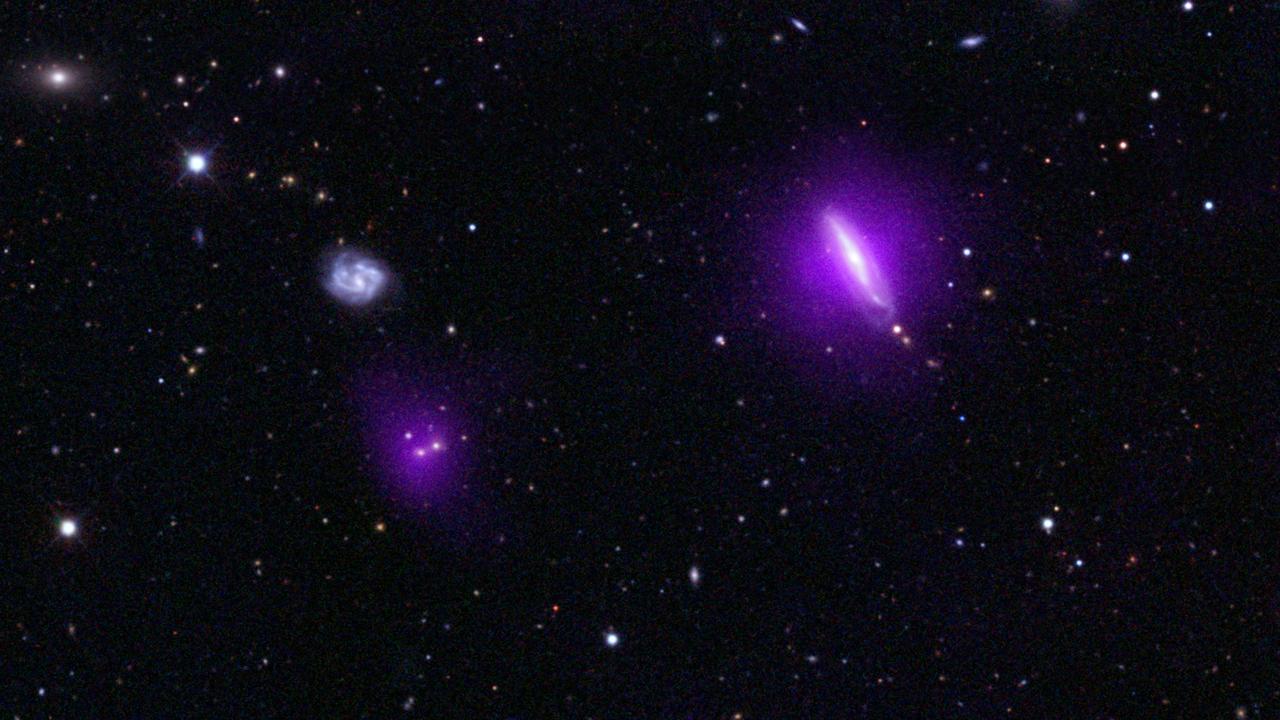

NASA NuSTAR serendipitous discovery in this field lies to the left of a galaxy, called IC751, at which the telescope originally intended to look.
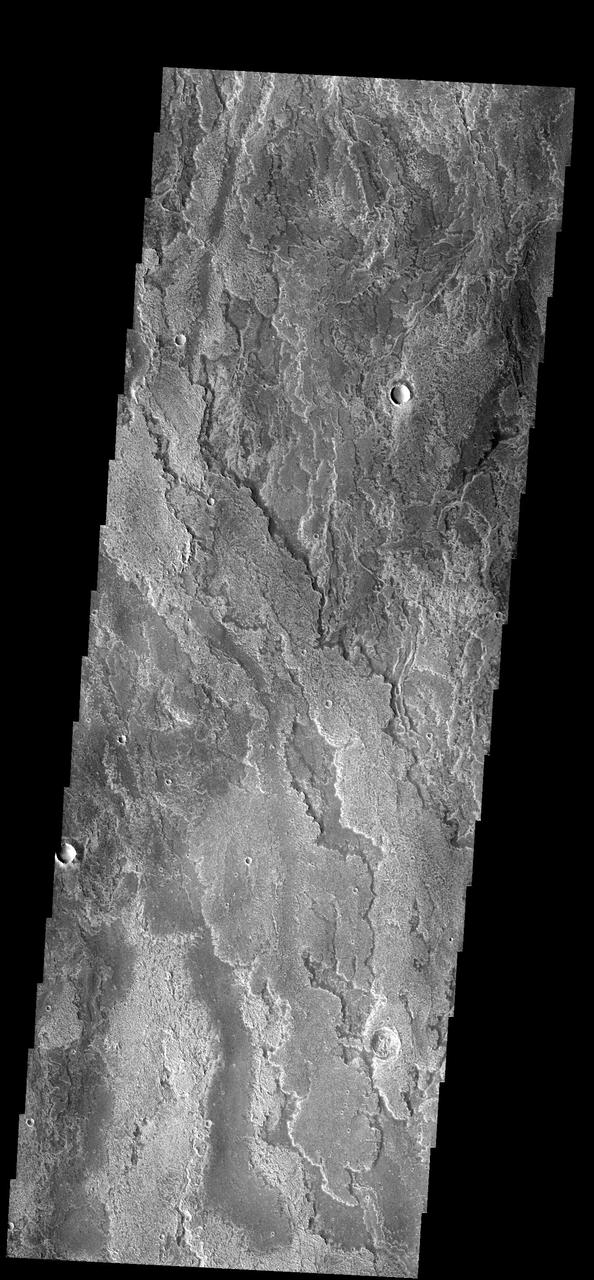
These layered volcanic flows originated from Arsia Mons as seen by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft.
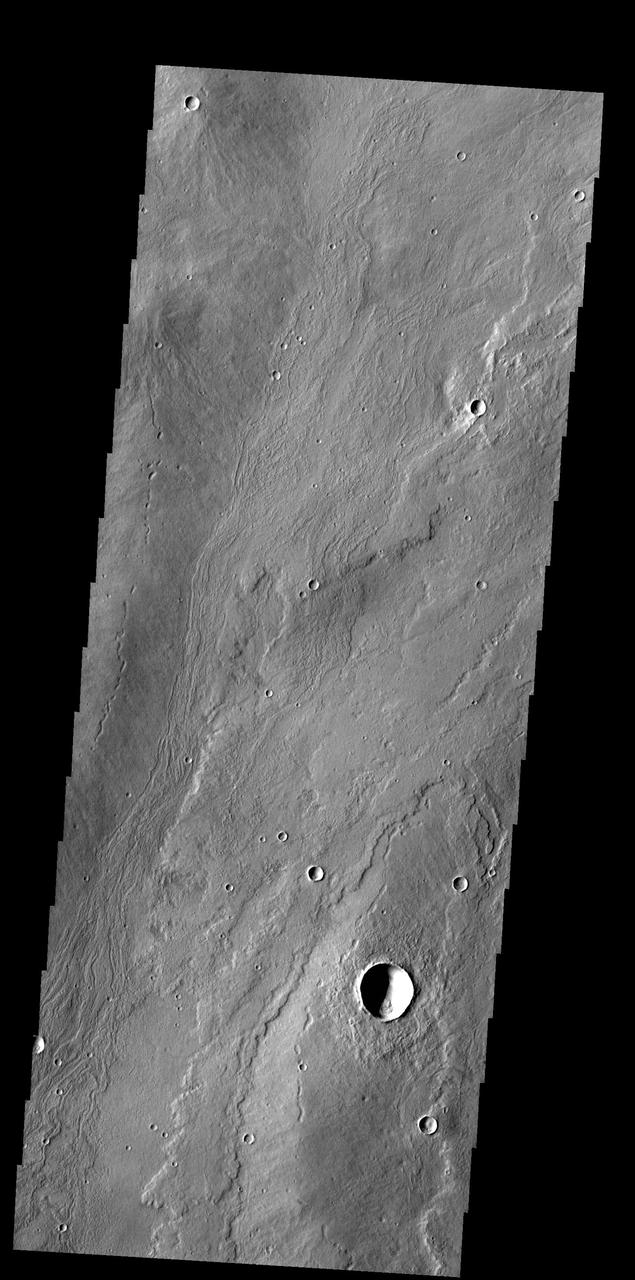

The flows in this image captured by NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft originated at Alba Mons.
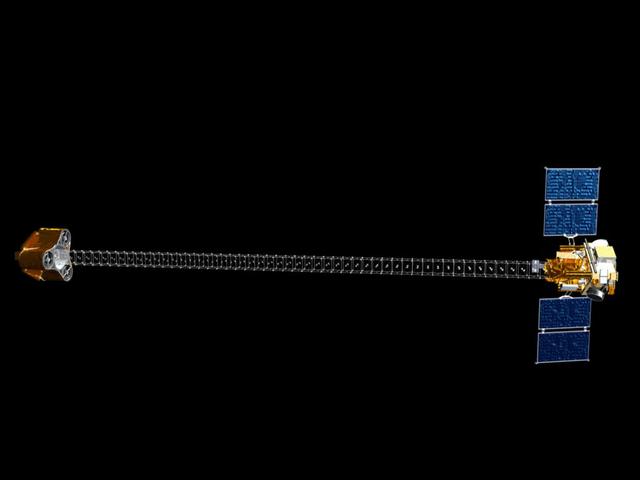

Artist concept of NASA Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array, managed by JPL. It will expand our understanding of the origins and destinies of stars and galaxies.

The volcanic flows in this image from NASA Mars Odyssey spacecraft are part of Daedalia Planum. The flows originated at Arsia Mons.
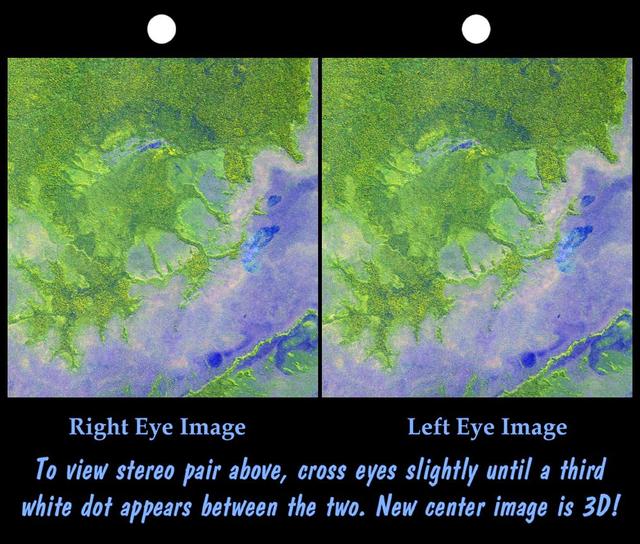
An 8-kilometer 5-mile wide crater of possible impact origin is shown in this stereoscopic view of an isolated part of the Bolivian Amazon.

This image from NASA Mars Odyssey spacecraft shows some of the extensive lava flows that originate at Arsia Mons.
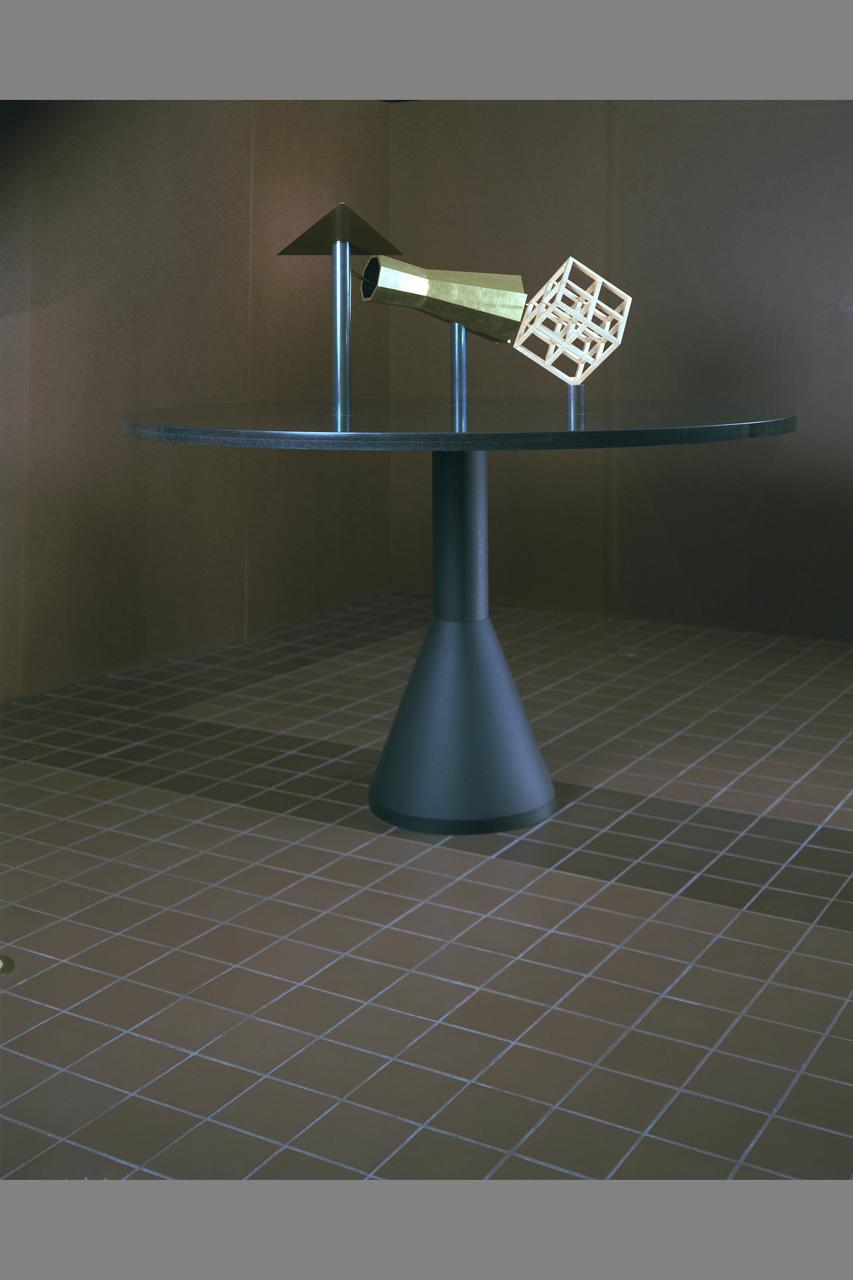

NAS (Numerical Aerodynamic Simulaiton) theme sculpture model: - Ames Triad of Aeronautical Research Exhibit in lobby of building N-258. The sculpture was commissioned from Peter Gutkin by Ames for the dedication of N-258.

NASA Administrator Bill Nelson announces Blue Origin as the company selected to develop a sustainable human landing system for the Artemis V Moon mission, Friday, May 19, 2023 at the Mary W. Jackson NASA Headquarters building in Washington. The human landing system will take astronauts to and from Gateway in lunar orbit to the surface and back to the lunar space station as part of NASA’s return to the Moon for science, exploration, and inspiration. Photo Credit: (NASA/Aubrey Gemignani)

S62-00632 (March 1962) --- Area photograph of Site 1, Manned Spacecraft Center, at Clear Lake, prior to start of construction.
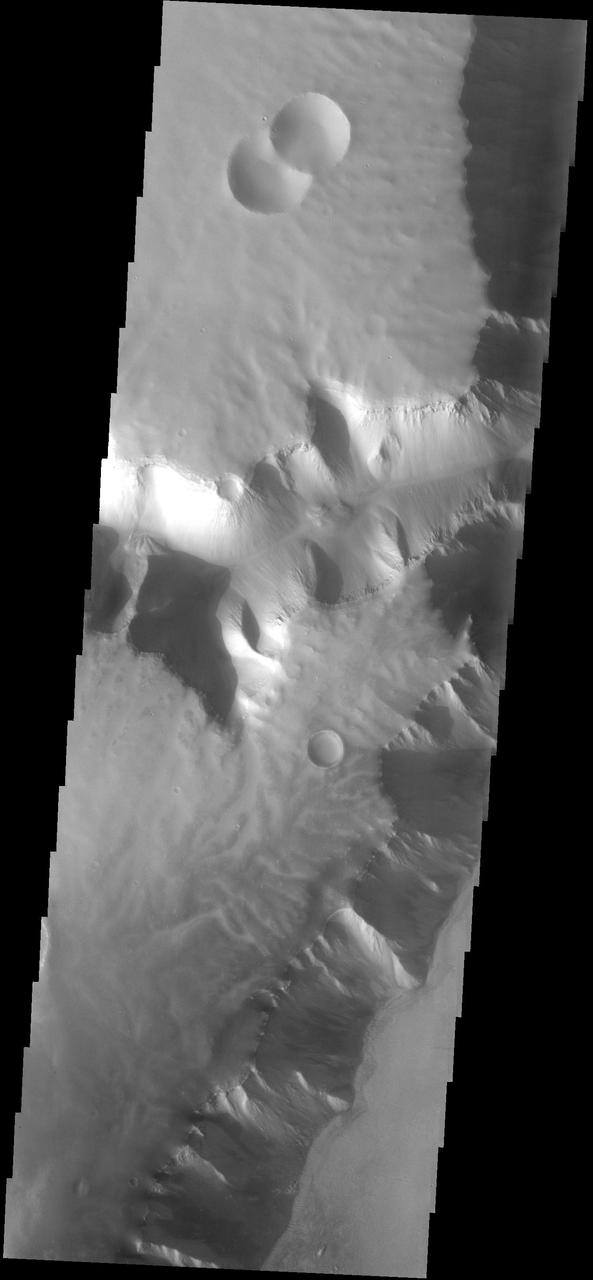

This plateau borders Echus Chasma. The surface of the plateau has been dissected by shallow channels of unknown origin. This image is from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft.
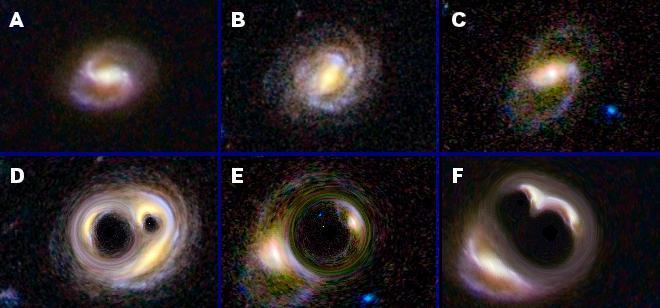
Warping occurs naturally in nature in a phenomenon called strong gravitational lensing as shown in this image simulated from original images from NASA Hubble Space Telescope.
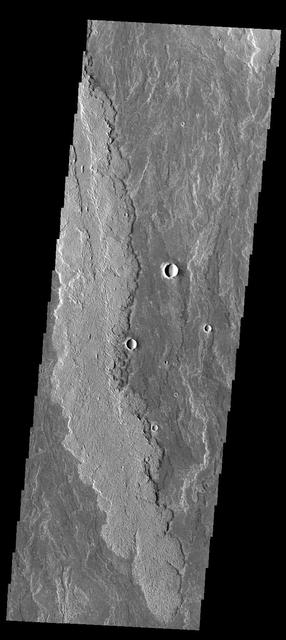
The lava flows in image from NASA 2001 Mars Odyssey spacecraft are part of the vast flow field originating from Arsia Mons.

The volcanic flows in this image captured by NASA Mars Odyssey spacecraft are part of Daedalia Planum, an extensive flow field originating from Arsia Mons.
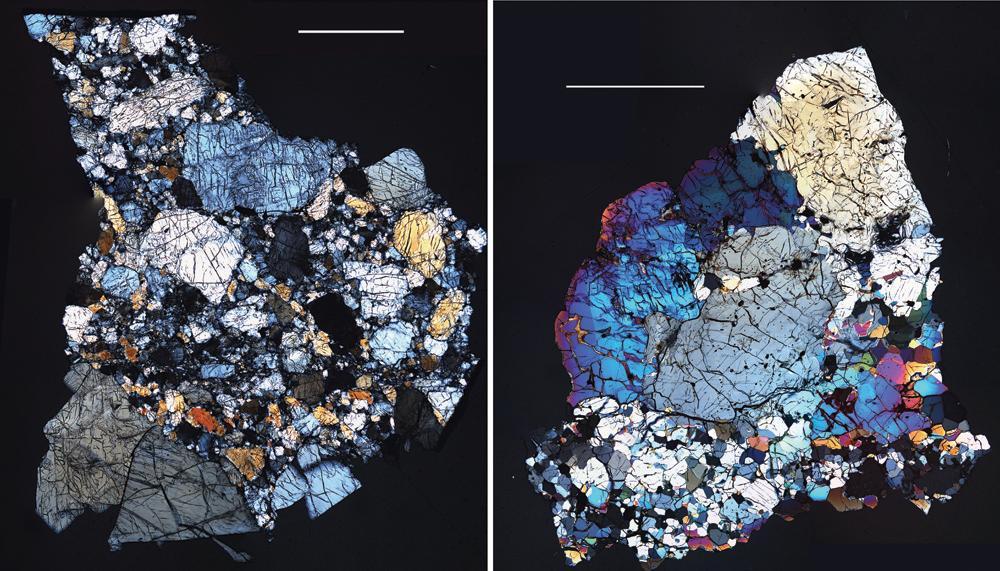
These images are of HED howardite, eucrite and diogenite meteorites are a large group of meteorites believed to originate from asteroid Vesta, a hypothesis that is consistent with current Dawn observations.