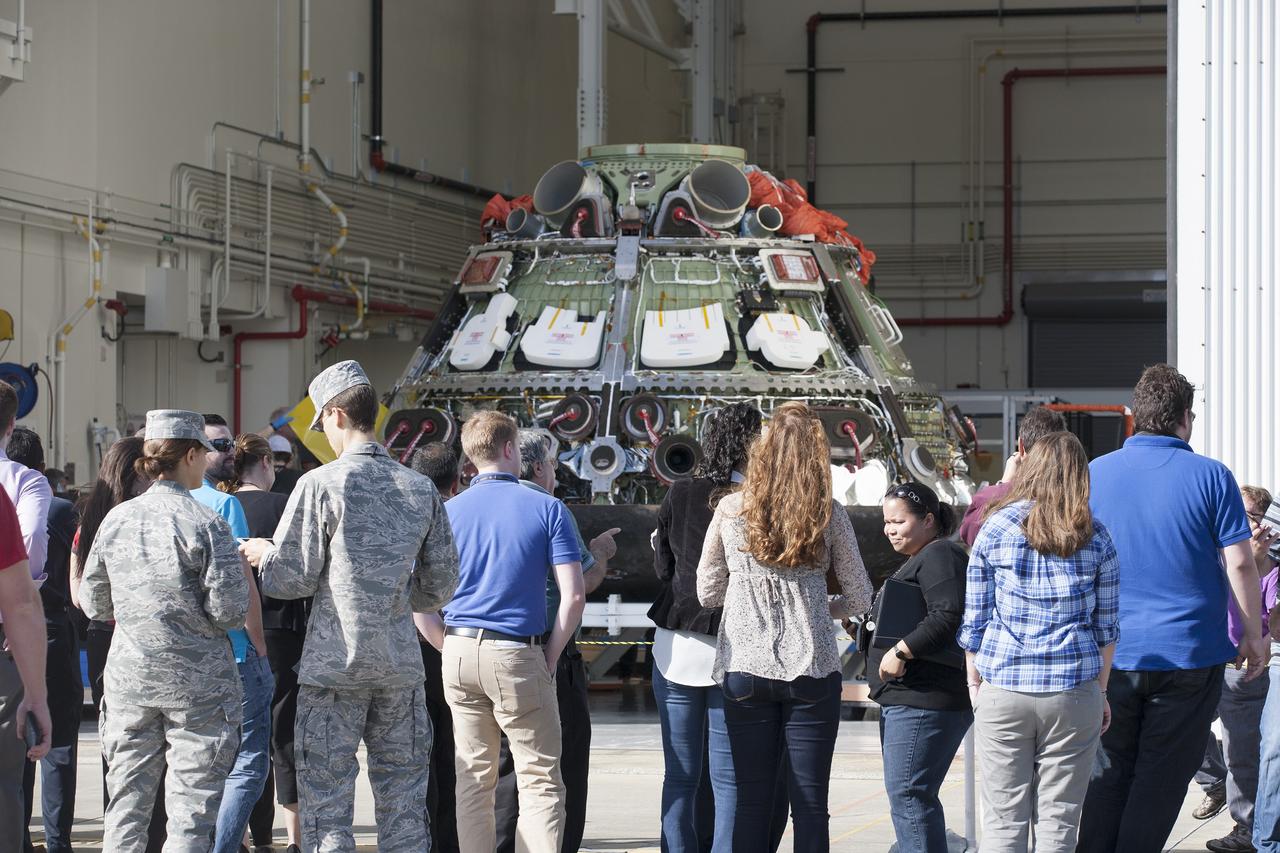

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers take photographs of NASA's Orion spacecraft during a viewing at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion's back shell panels have been removed. The spacecraft completed the first flight test in December, was retrieved from the Pacific Ocean, and transported 2,700 miles overland to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of data obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. Orion will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for deservicing. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
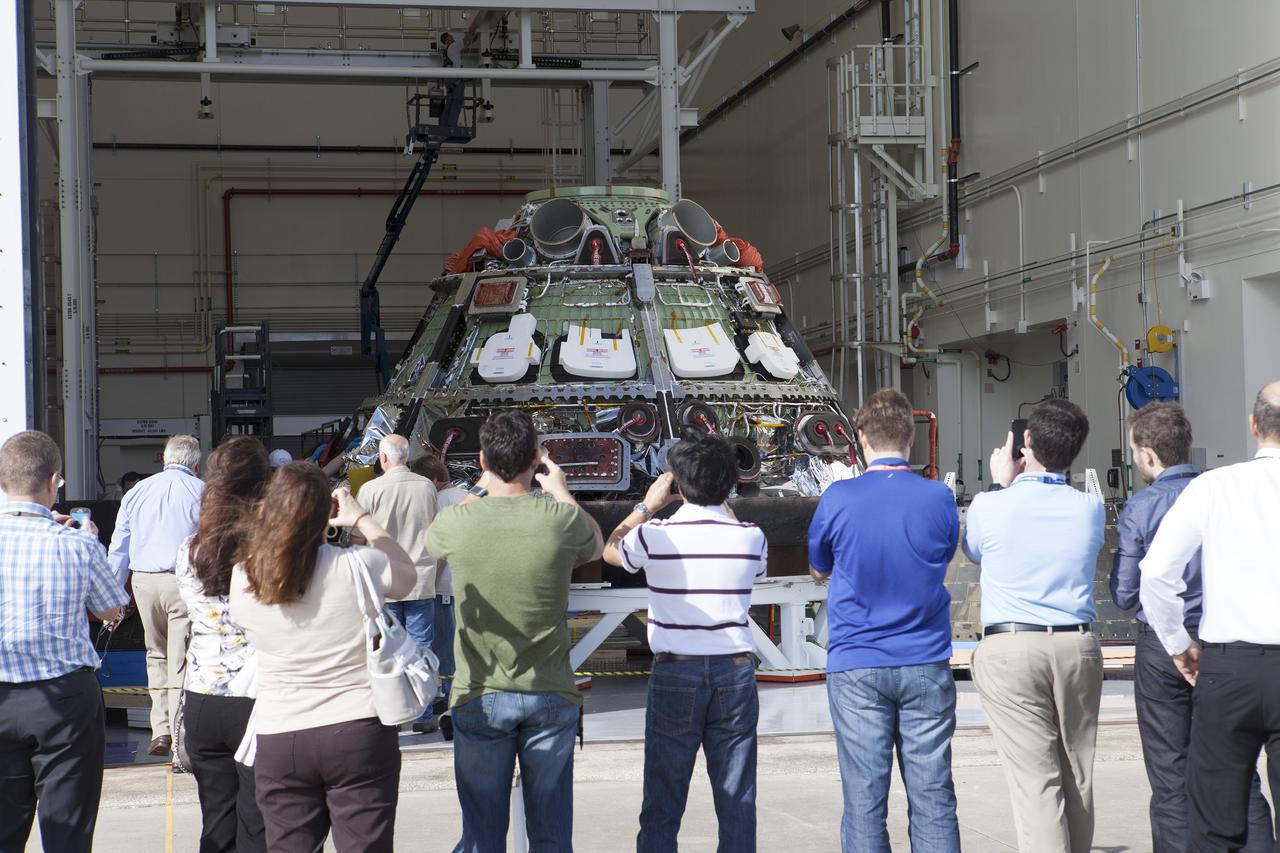

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers take photographs of NASA's Orion spacecraft during a viewing at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion's back shell panels have been removed. The spacecraft completed the first flight test in December, was retrieved from the Pacific Ocean, and transported 2,700 miles overland to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of data obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. Orion will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for deservicing. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers take photographs of NASA's Orion spacecraft during a viewing at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion's back shell panels have been removed. The spacecraft completed the first flight test in December, was retrieved from the Pacific Ocean, and transported 2,700 miles overland to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of data obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. Orion will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for deservicing. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers take photographs of NASA's Orion spacecraft during a viewing at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion's back shell panels have been removed. The spacecraft completed the first flight test in December, was retrieved from the Pacific Ocean, and transported 2,700 miles overland to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of data obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. Orion will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for deservicing. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
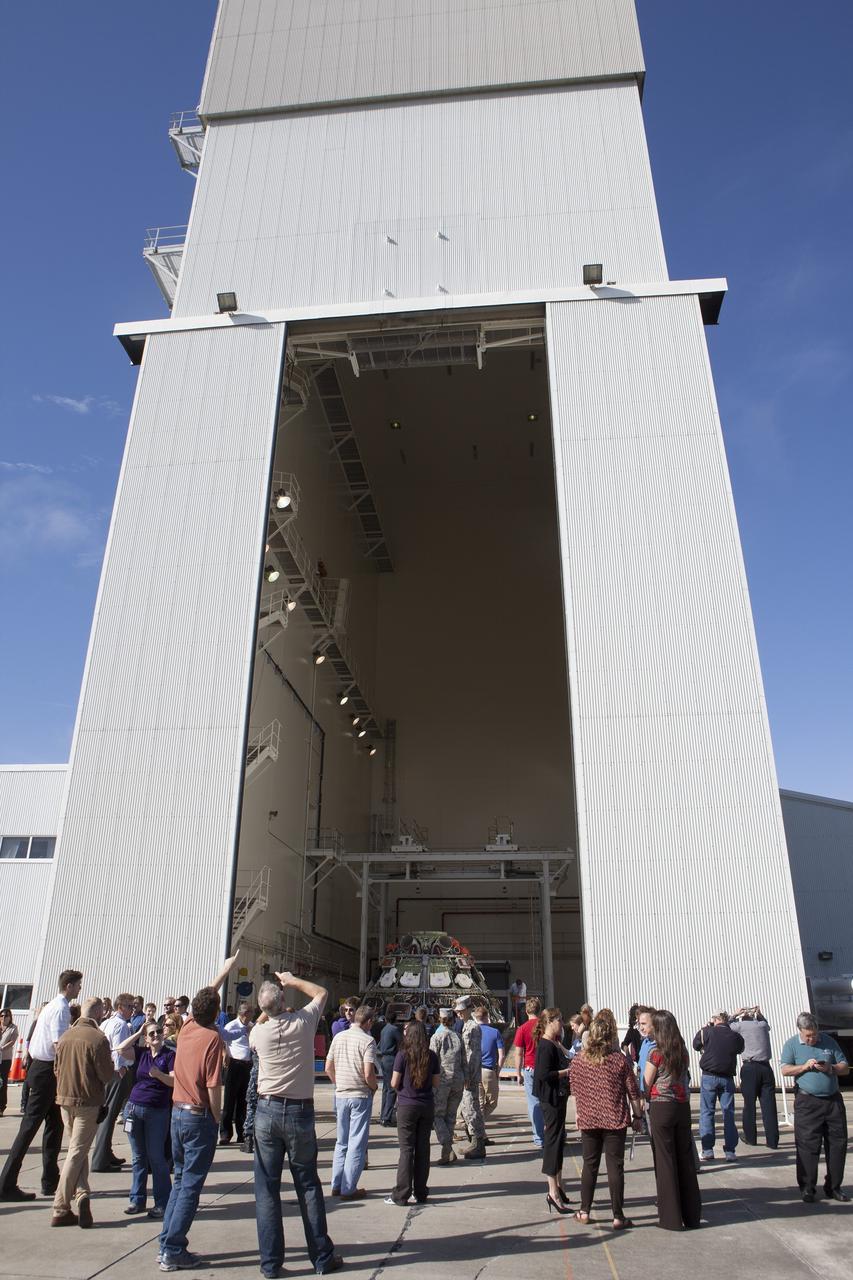

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Workers take photographs of NASA's Orion spacecraft during a viewing at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion's back shell panels have been removed. The spacecraft completed the first flight test in December, was retrieved from the Pacific Ocean, and transported 2,700 miles overland to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of data obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. Orion will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for deservicing. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
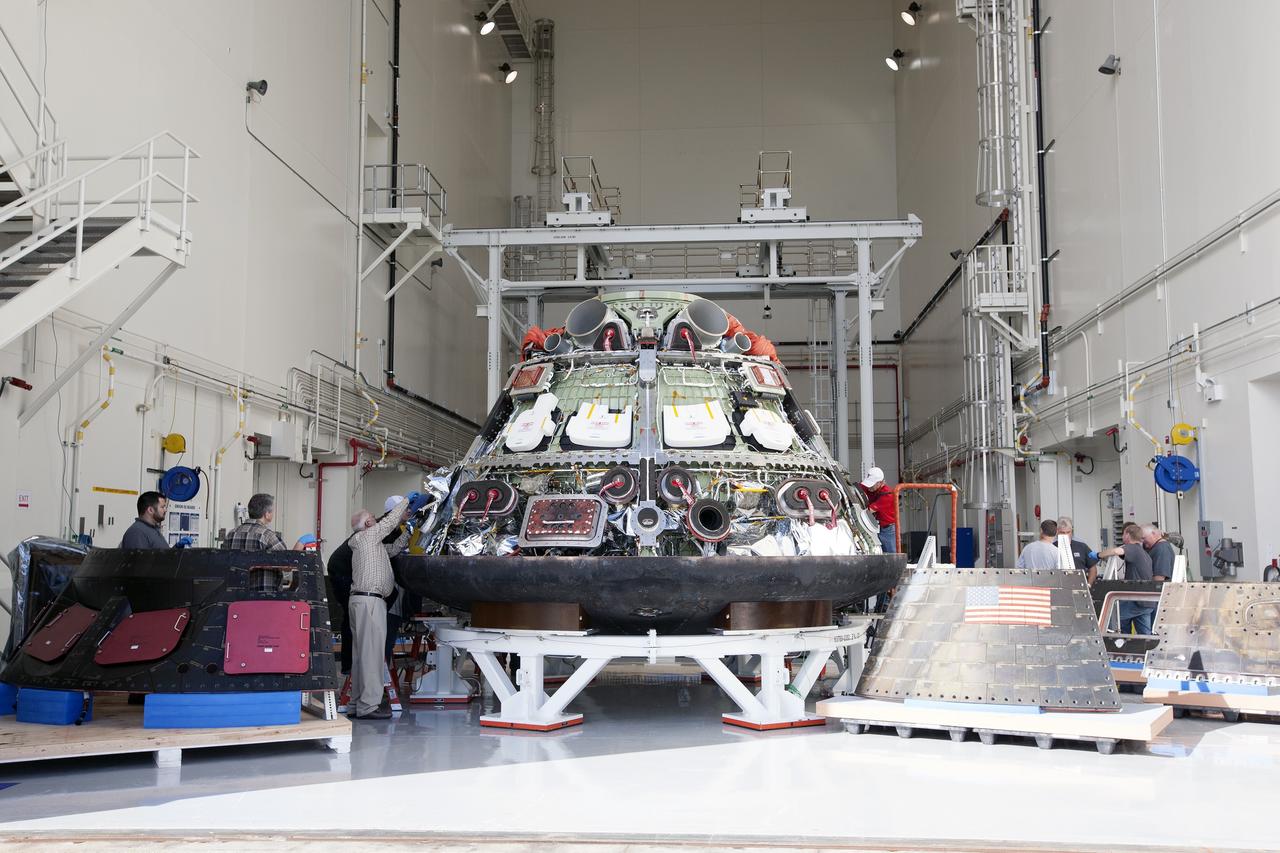

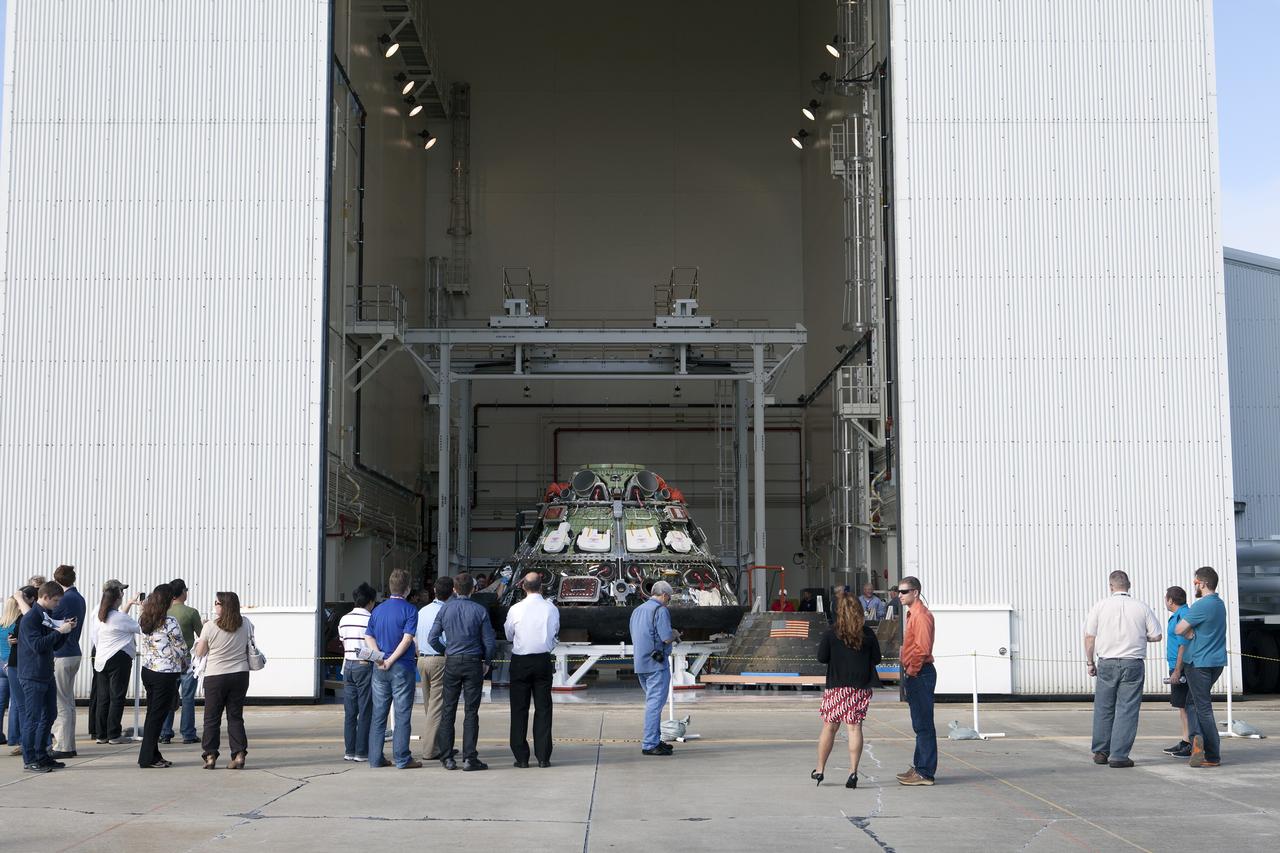
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is positioned inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida in preparation for a viewing by Kennedy workers. Orion's back shell panels have been removed. The spacecraft completed the first flight test in December, was retrieved from the Pacific Ocean, and transported 2,700 miles overland to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of data obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. Orion will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for deservicing. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

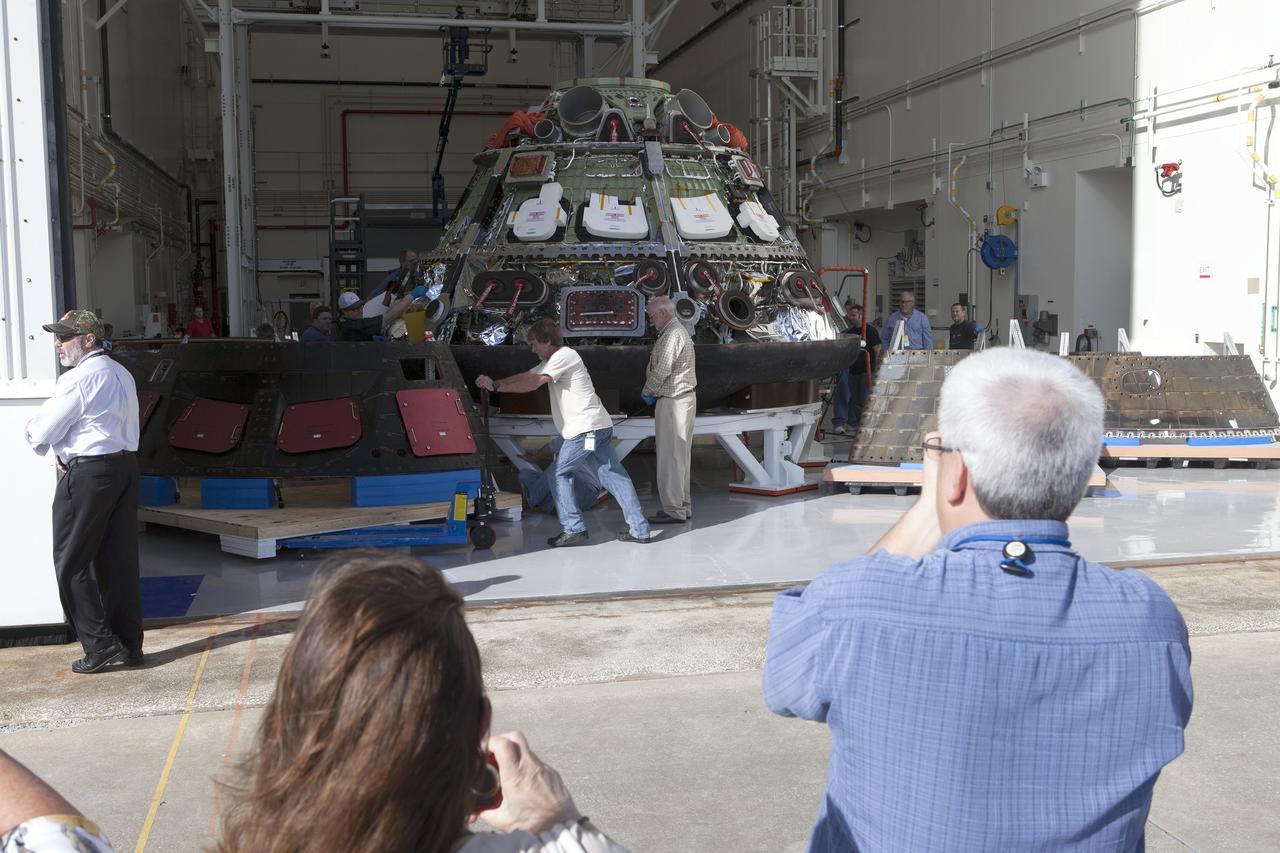
The Orion launch abort system for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is assembled in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 20, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The Orion launch abort system for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is assembled in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 20, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The Orion launch abort system for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is assembled in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 20, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The Orion launch abort system for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is assembled in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on March 20, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system is completed in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on June 9, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
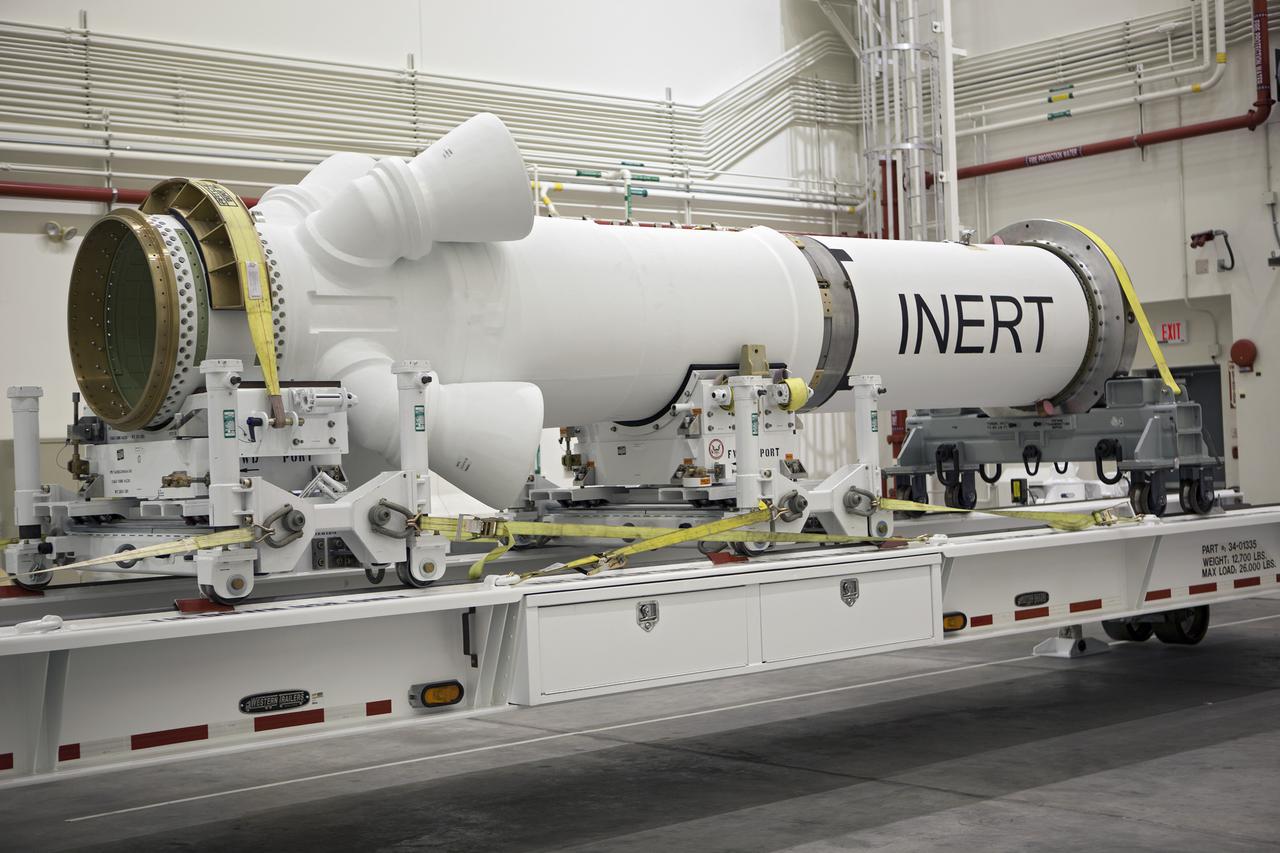
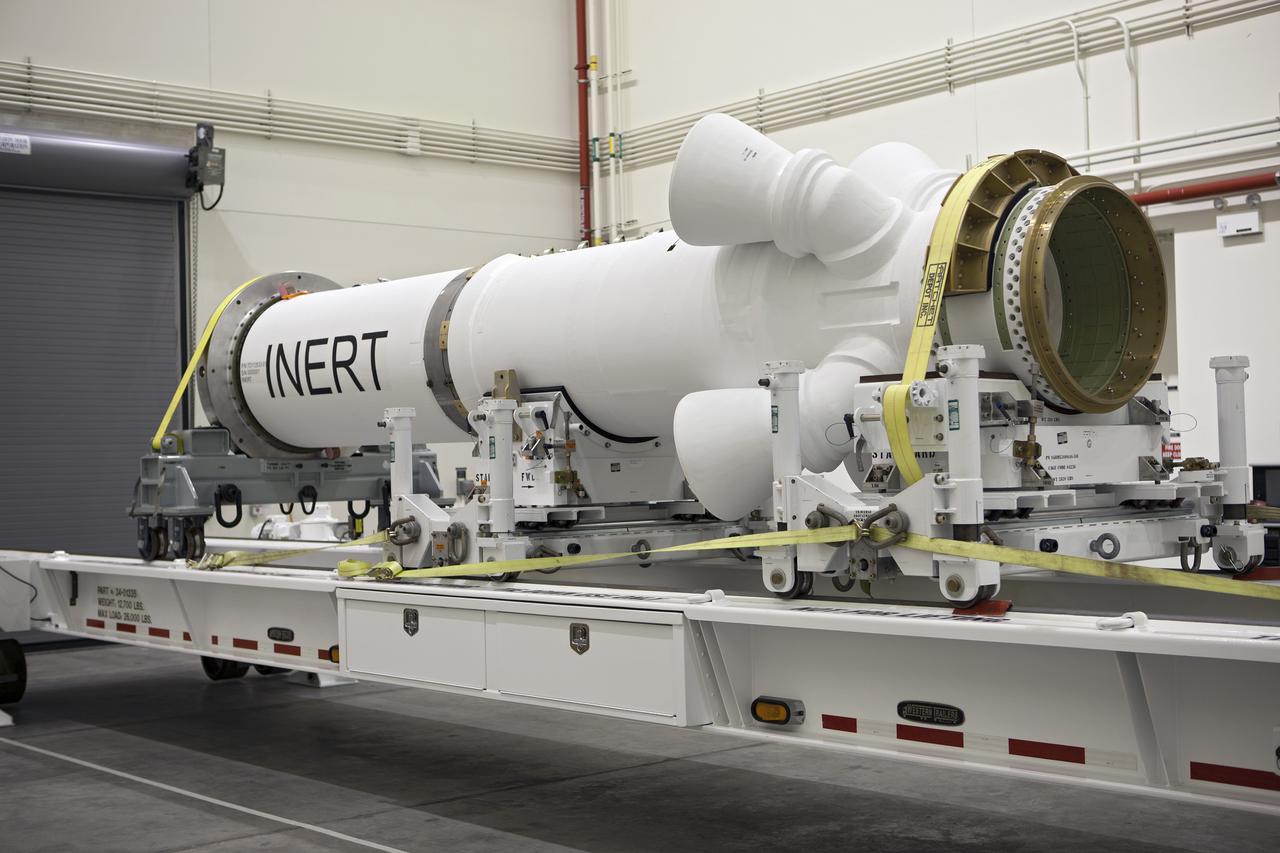
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the media viewed the Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, launch abort motor inside the Launch Abort System Facility. ATK’s abort motor is one of the components of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which will be used for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1. The system is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. The test flight abort motor is configured with inert propellant. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis

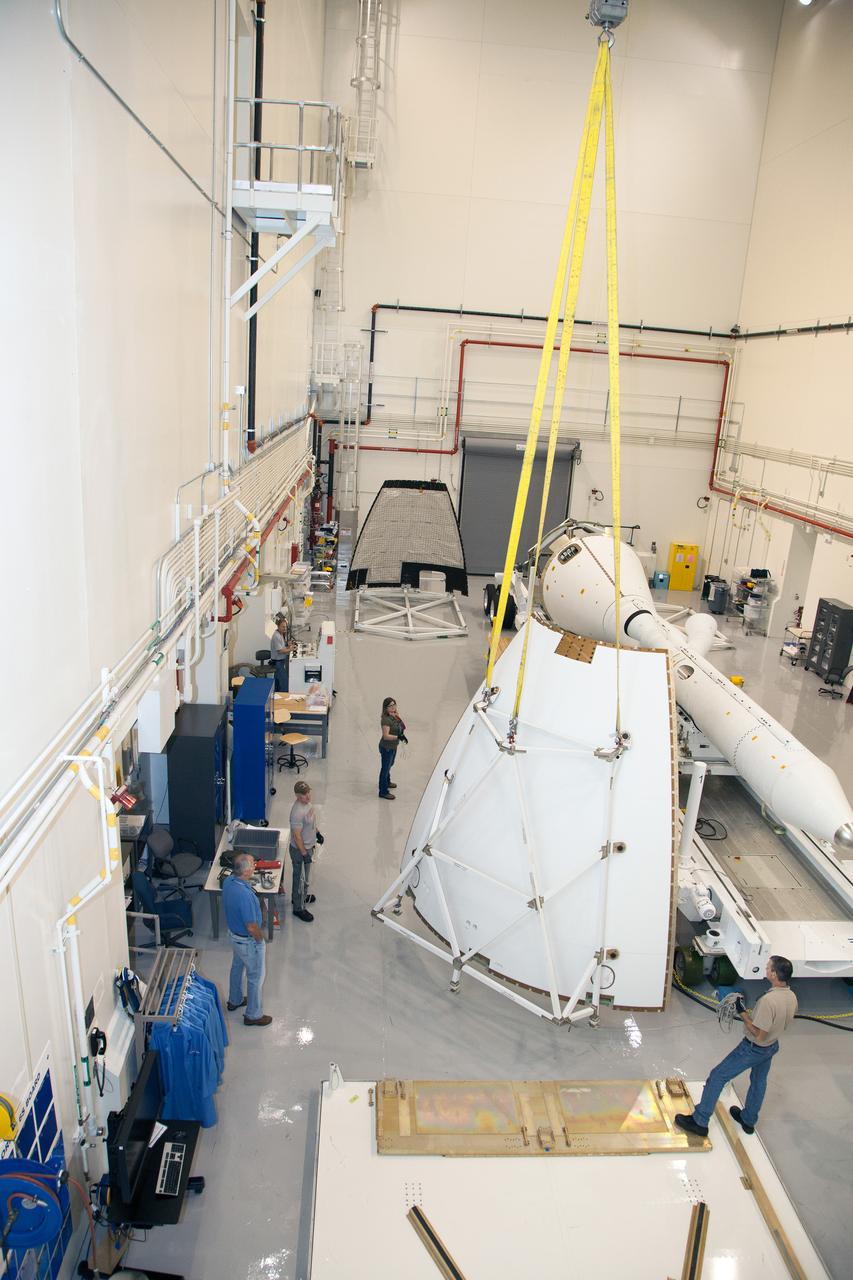
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is moved inside the Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft was moved from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, where it was fueled ahead of its December flight test. In the LASF, the Launch Abort System will be installed around the Orion spacecraft. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
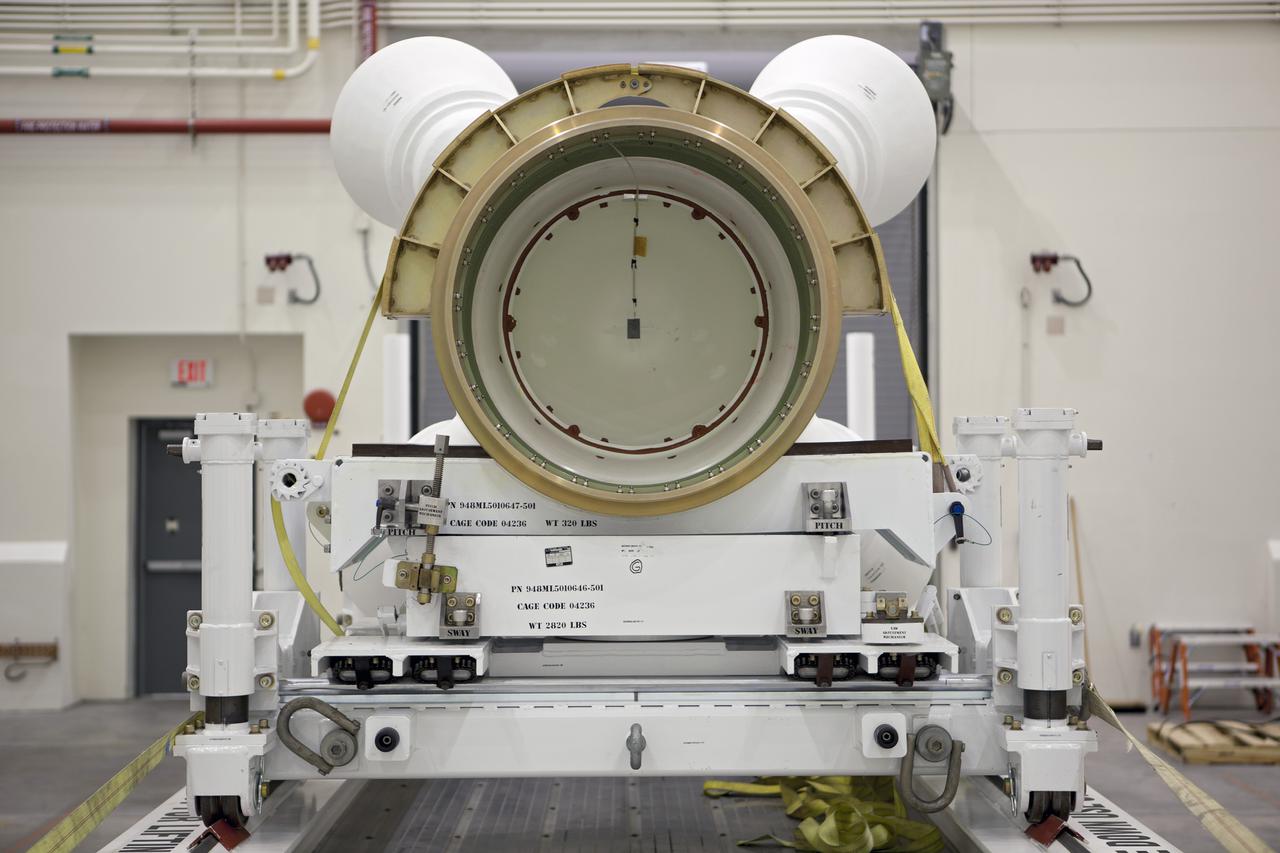

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the media viewed the Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, launch abort motor inside the Launch Abort System Facility. ATK’s abort motor is one of the components of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which will be used for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1. The system is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. The test flight abort motor is configured with inert propellant. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the media viewed the Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, launch abort motor inside the Launch Abort System Facility. ATK’s abort motor is one of the components of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which will be used for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1. The system is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. The test flight abort motor is configured with inert propellant. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis
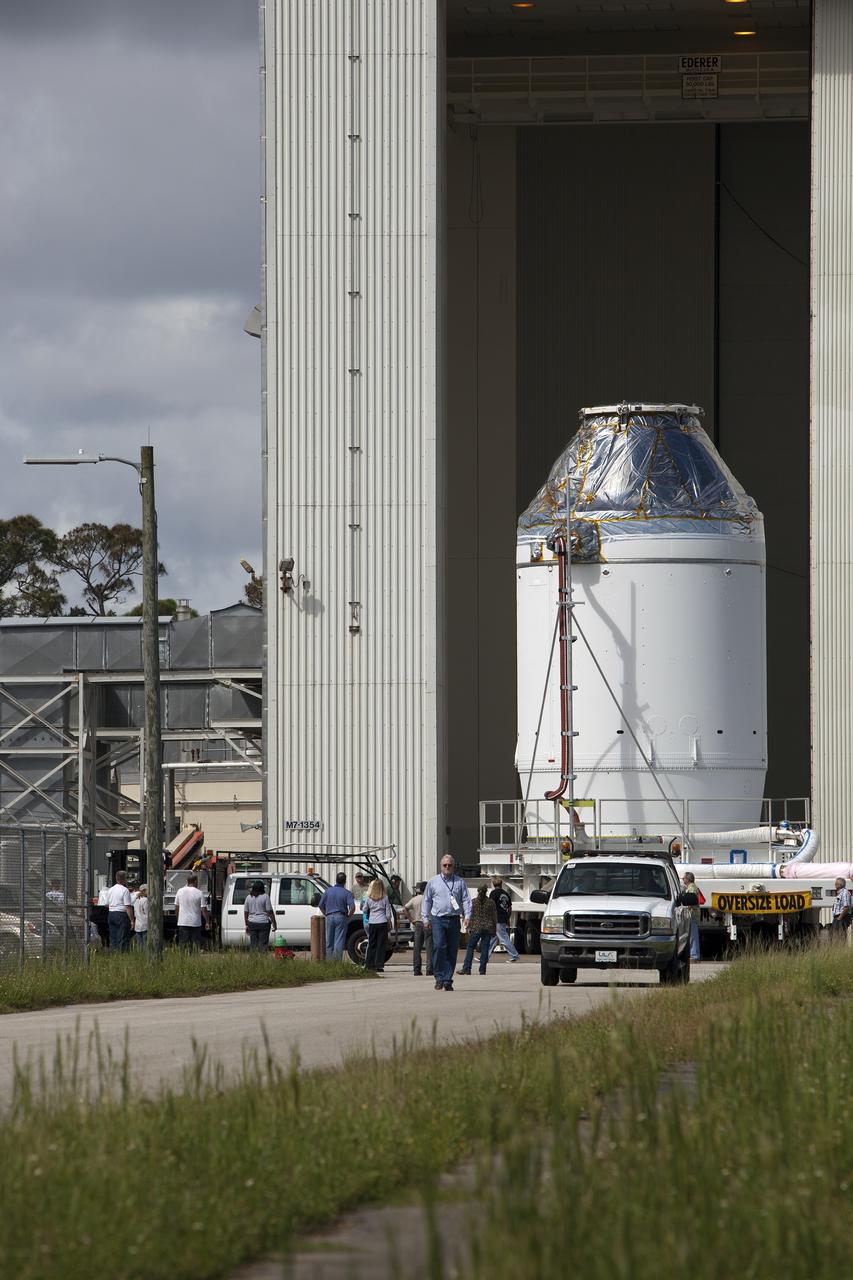

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, begins its move from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, or PHSF, to the Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was fueled in the PHSF. Inside the LASF, the Launch Abort System will be installed around the Orion spacecraft ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

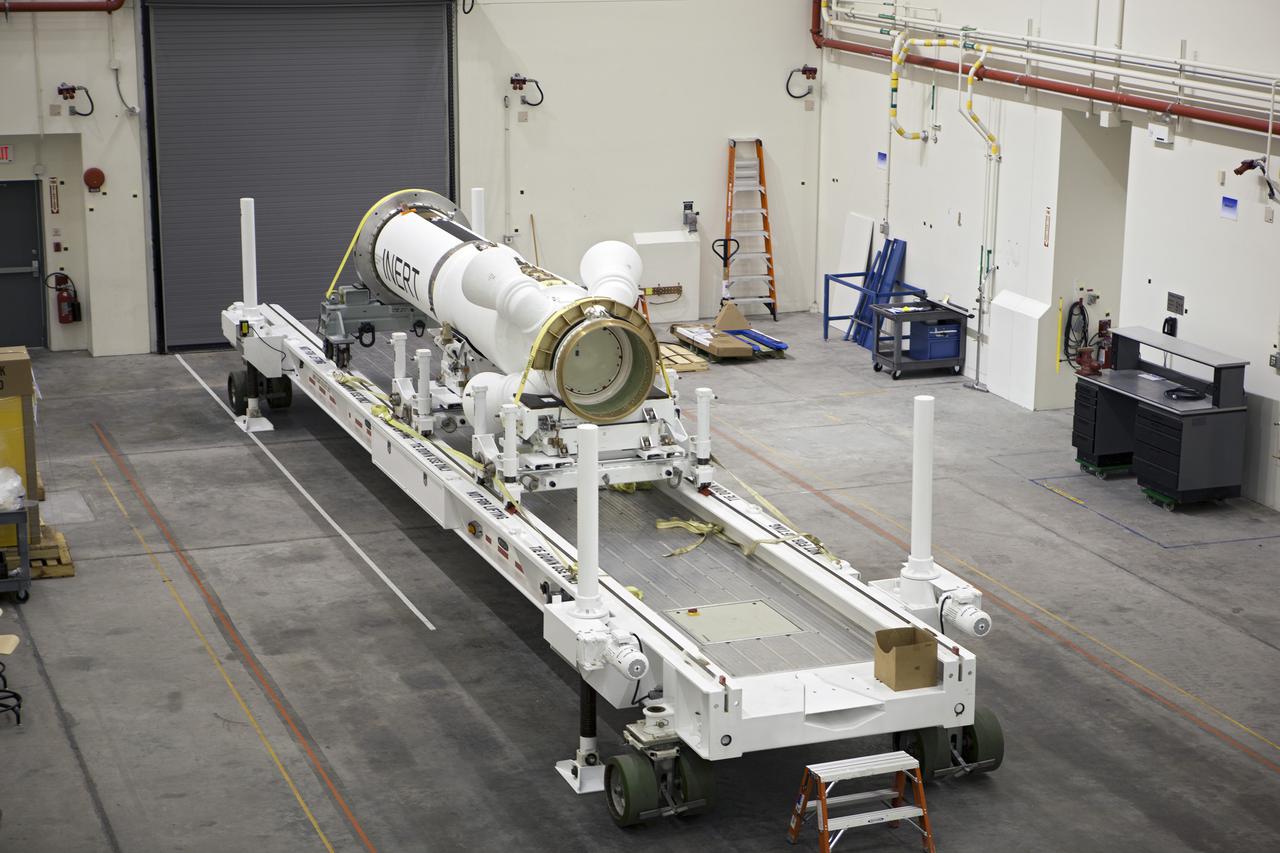
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare the launch abort motor for connection to the attitude control motor. Both are segments of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
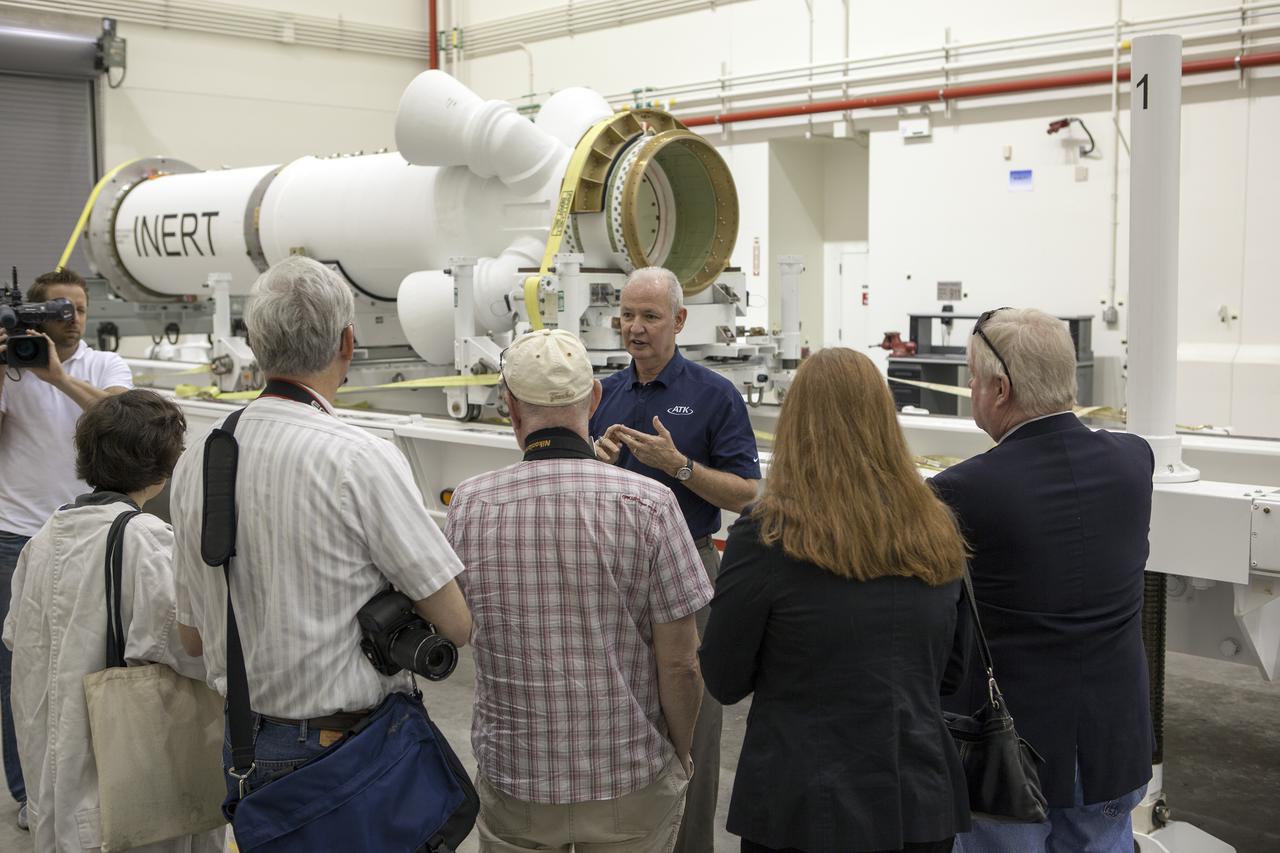

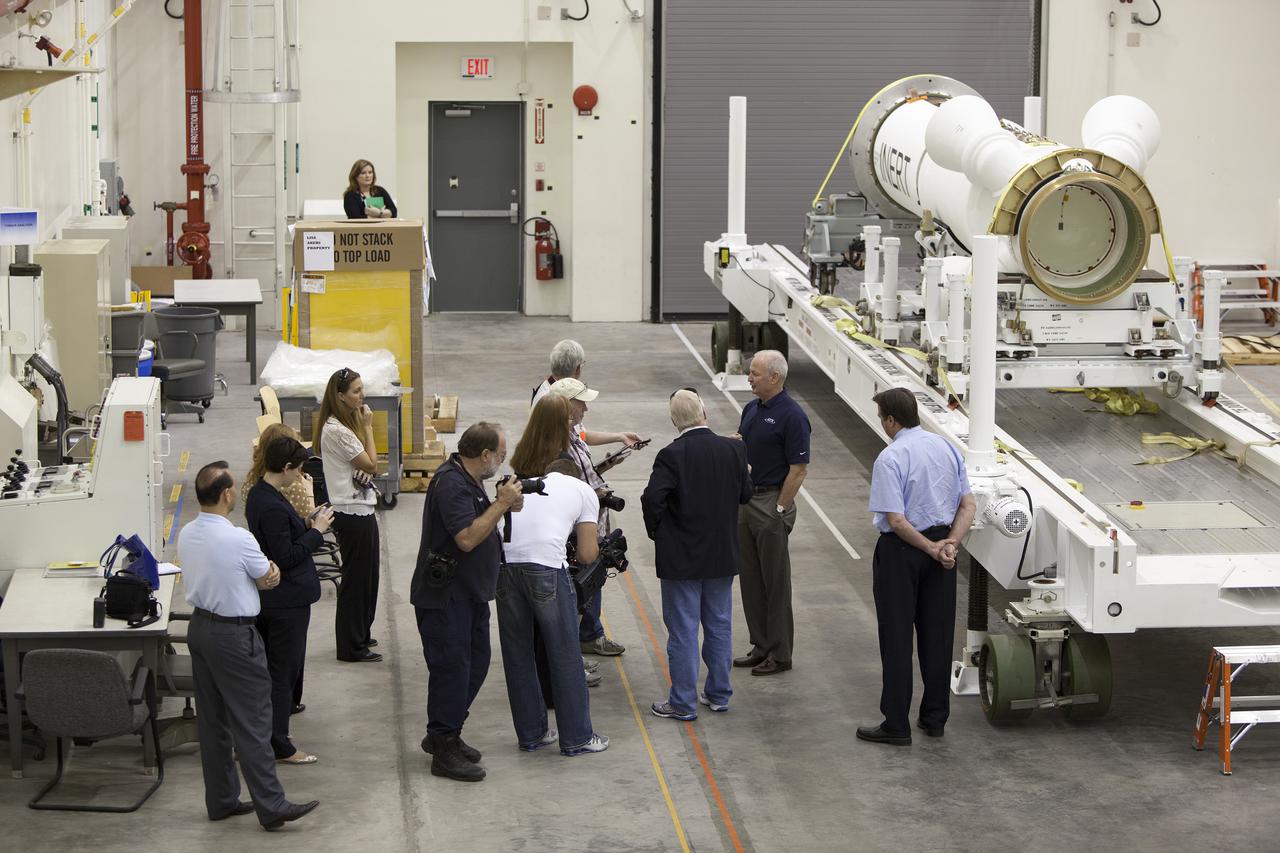
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Brian Duffy, the vice president and Johnson Space Center manager for Exploration Systems with ATK Aerospace Systems, talks with members of the media during a viewing of ATK’s launch abort motor inside the Launch Abort System Facility. The abort motor is one of the components of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which will be used for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1. The system is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. The test flight abort motor is configured with inert propellant. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis
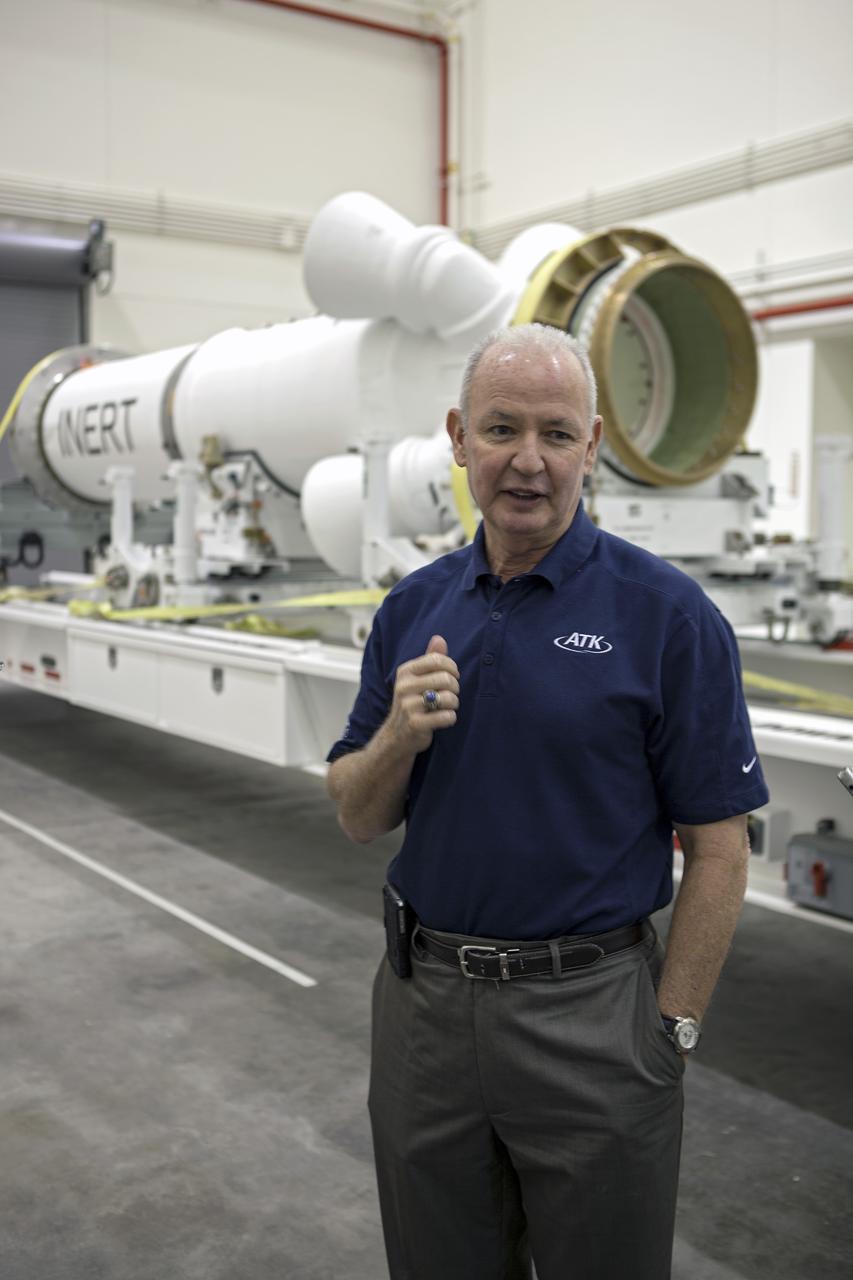

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Brian Duffy, the vice president and Johnson Space Center manager for Exploration Systems with ATK Aerospace Systems, talks with members of the media during a viewing of ATK’s launch abort motor inside the Launch Abort System Facility. The abort motor is one of the components of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which will be used for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1. The system is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. The test flight abort motor is configured with inert propellant. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, begins its move from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, or PHSF, to the Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was fueled in the PHSF. Inside the LASF, the Launch Abort System will be installed around the Orion spacecraft ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician prepares the launch abort motor for connection to the attitude control motor. Both are segments of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Brian Duffy, the vice president and Johnson Space Center manager for Exploration Systems with ATK Aerospace Systems, talks with members of the media during a viewing of ATK’s launch abort motor inside the Launch Abort System Facility. The abort motor is one of the components of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which will be used for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1. The system is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. The test flight abort motor is configured with inert propellant. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis

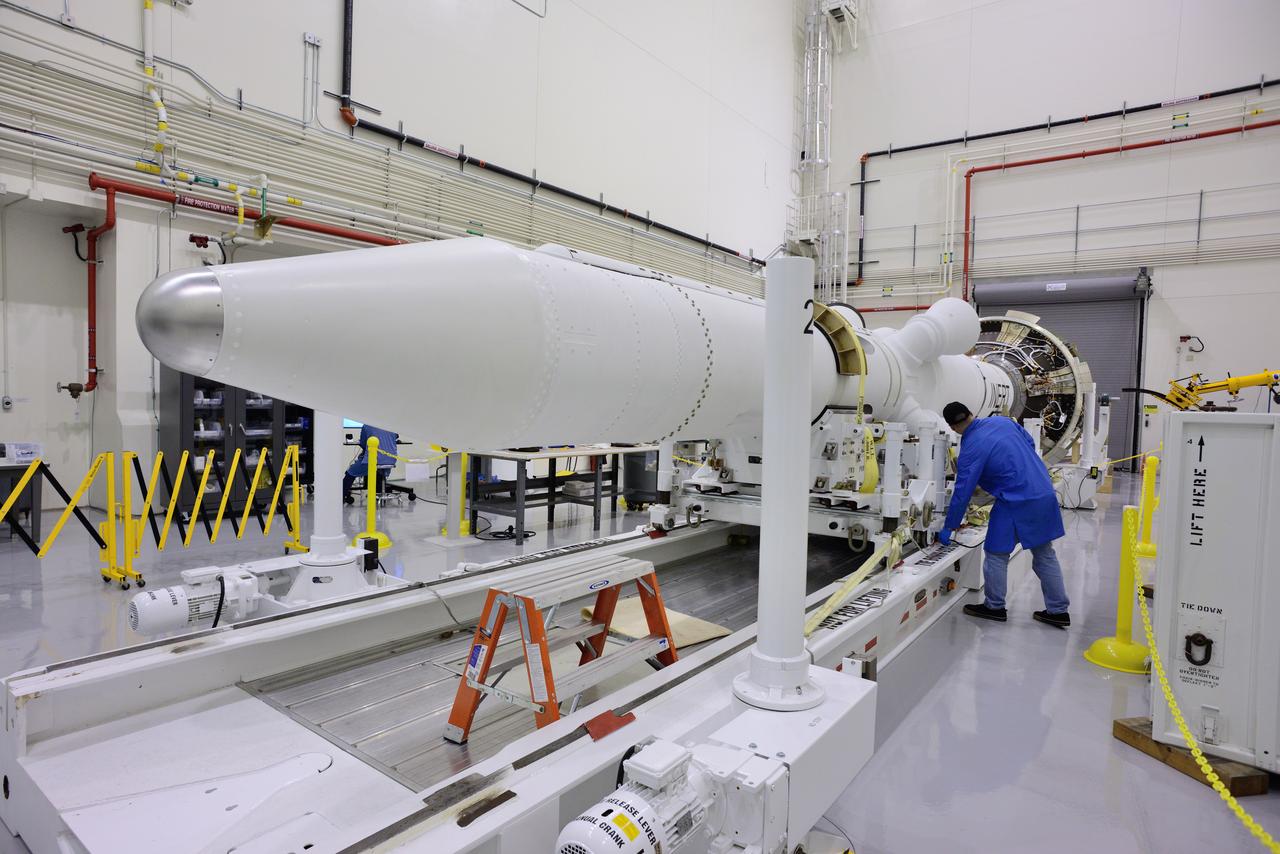
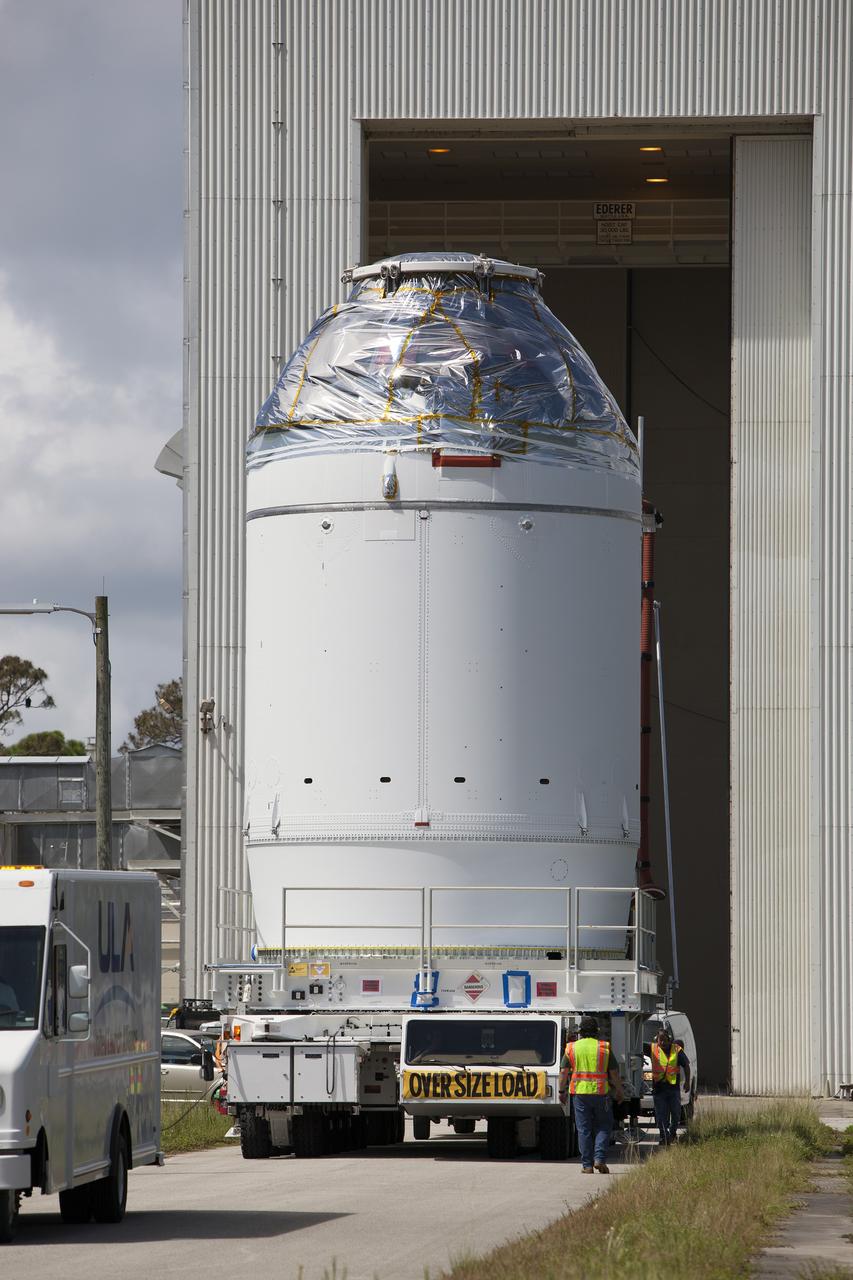
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a truck arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility with the jettison motor from Aerojet in Redmond, Wash. The motor is part of the Launch Abort System, or LAS, for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, of the agency’s Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle. The motor will jettison the LAS away from the Orion crew capsule during the flight test’s early ascent phase. Orion’s Launch Abort System is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis
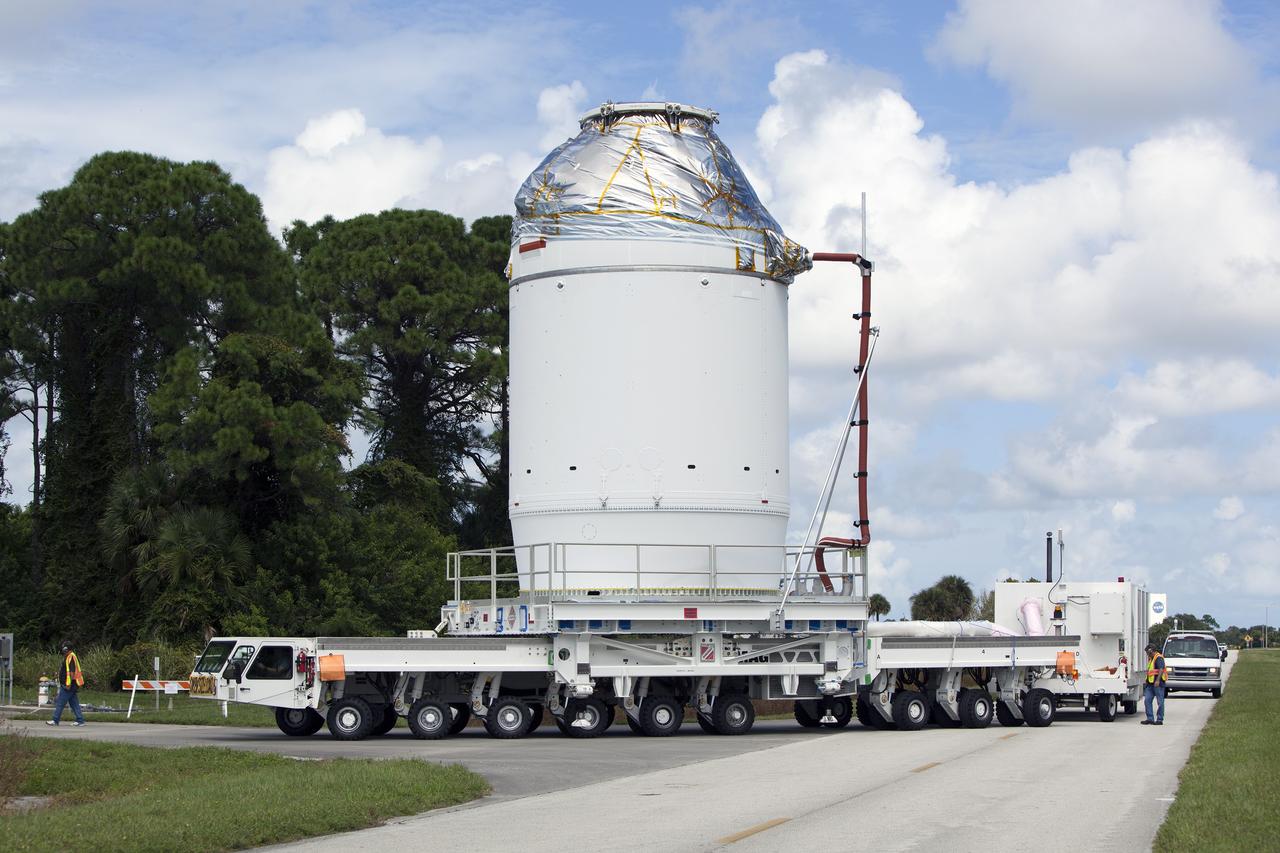

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is on its way from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, or PHSF, to the Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was fueled in the PHSF. Inside the LASF, the Launch Abort System will be installed around the Orion spacecraft ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a truck arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility with the jettison motor from Aerojet in Redmond, Wash. The motor is part of the Launch Abort System, or LAS, for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, of the agency’s Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle. The motor will jettison the LAS away from the Orion crew capsule during the flight test’s early ascent phase. Orion’s Launch Abort System is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the media viewed the Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, launch abort motor inside the Launch Abort System Facility. ATK’s abort motor is one of the components of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which will be used for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1. The system is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. The test flight abort motor is configured with inert propellant. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the launch abort motor has been prepared for connection to the attitude control motor. Both are segments of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
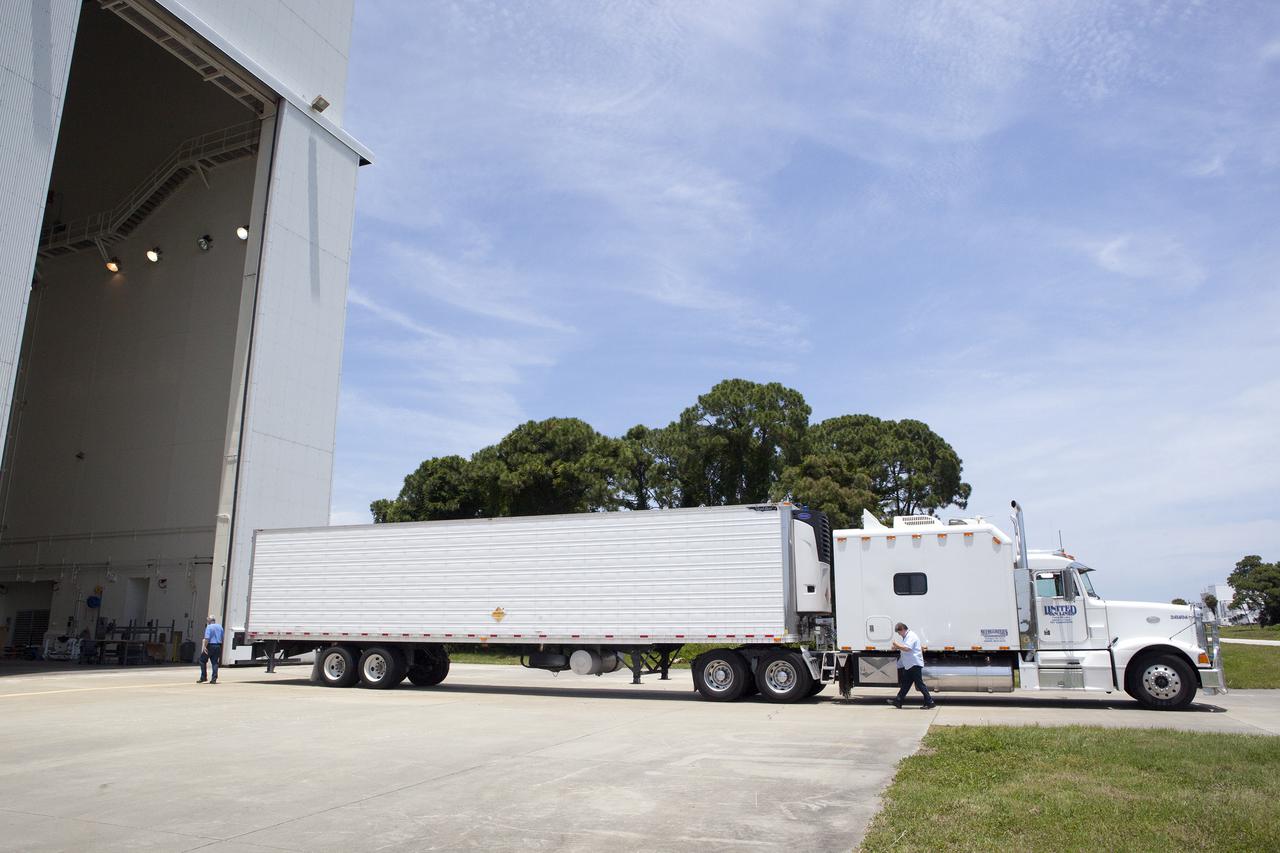

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a truck arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility with the jettison motor from Aerojet in Redmond, Wash. The motor is part of the Launch Abort System, or LAS, for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, of the agency’s Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle. The motor will jettison the LAS away from the Orion crew capsule during the flight test’s early ascent phase. Orion’s Launch Abort System is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Brian Duffy, the vice president and Johnson Space Center manager for Exploration Systems with ATK Aerospace Systems, talks with members of the media during a viewing of ATK’s launch abort motor inside the Launch Abort System Facility. The abort motor is one of the components of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which will be used for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1. The system is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. The test flight abort motor is configured with inert propellant. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is on its way from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, or PHSF, to the Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was fueled in the PHSF. Inside the LASF, the Launch Abort System will be installed around the Orion spacecraft ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a truck arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility with the jettison motor from Aerojet in Redmond, Wash. The motor is part of the Launch Abort System, or LAS, for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, of the agency’s Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle. The motor will jettison the LAS away from the Orion crew capsule during the flight test’s early ascent phase. Orion’s Launch Abort System is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis
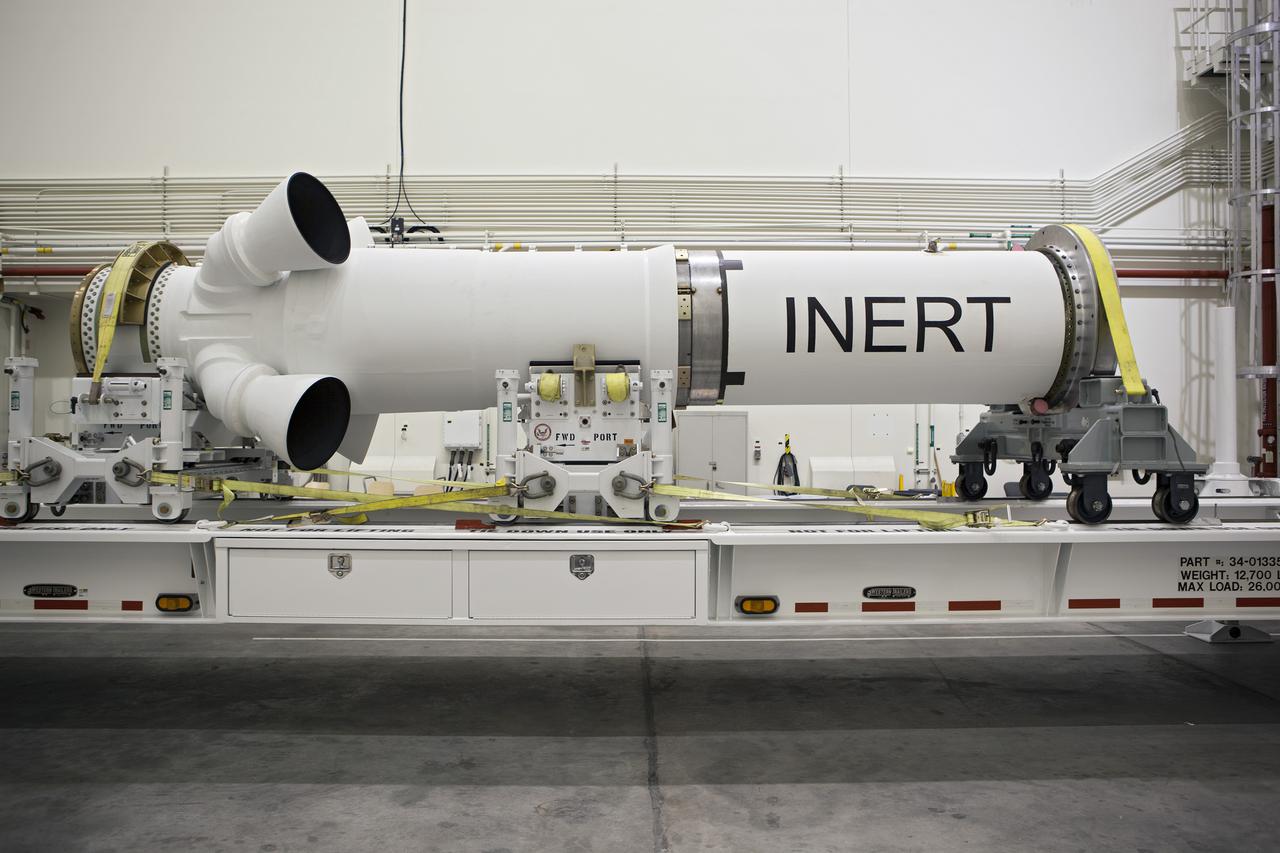
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the media viewed the Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, launch abort motor inside the Launch Abort System Facility. ATK’s abort motor is one of the components of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which will be used for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1. The system is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. The test flight abort motor is configured with inert propellant. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Dimitri Gerondidakis
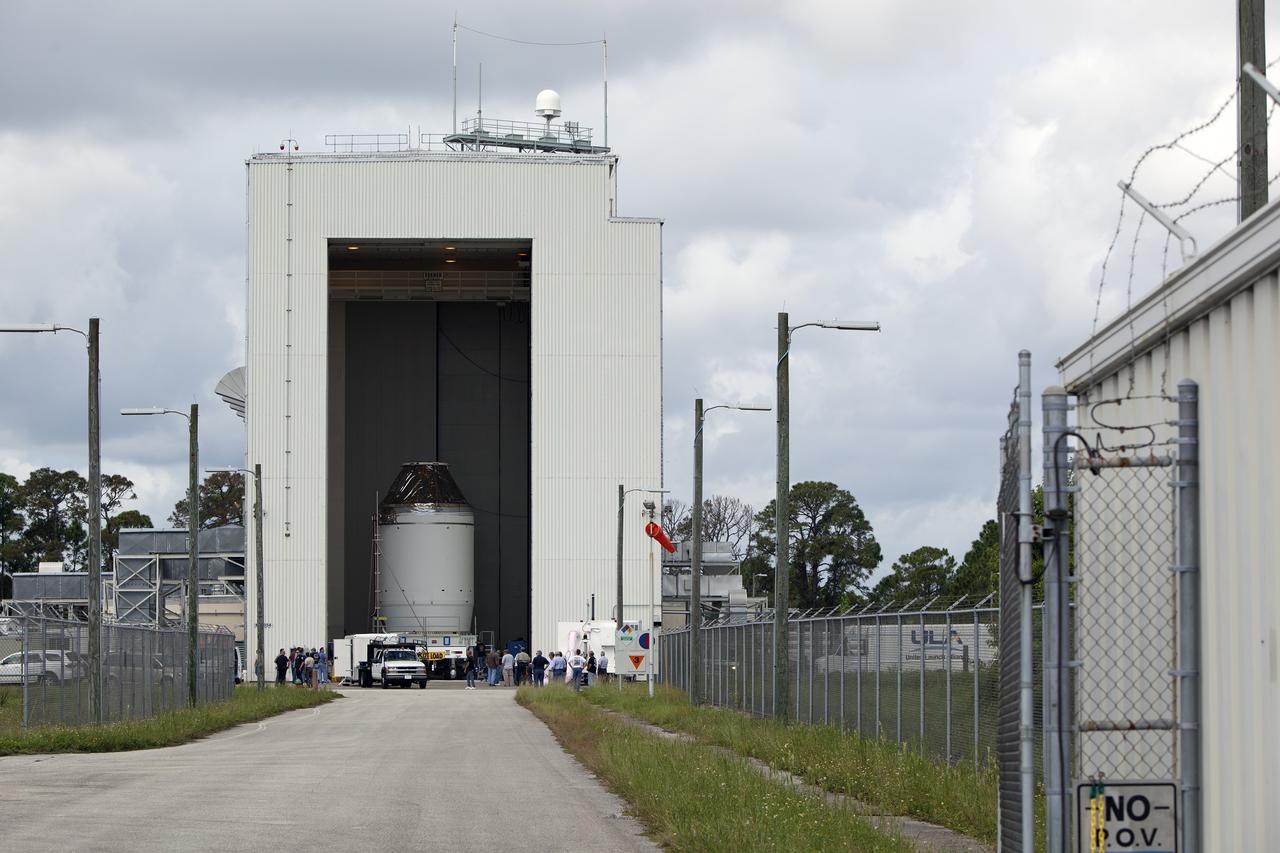

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is prepared for its move out of the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, or PHSF, to the Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was fueled in the PHSF. Inside the LASF, the Launch Abort System will be installed around the Orion spacecraft ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
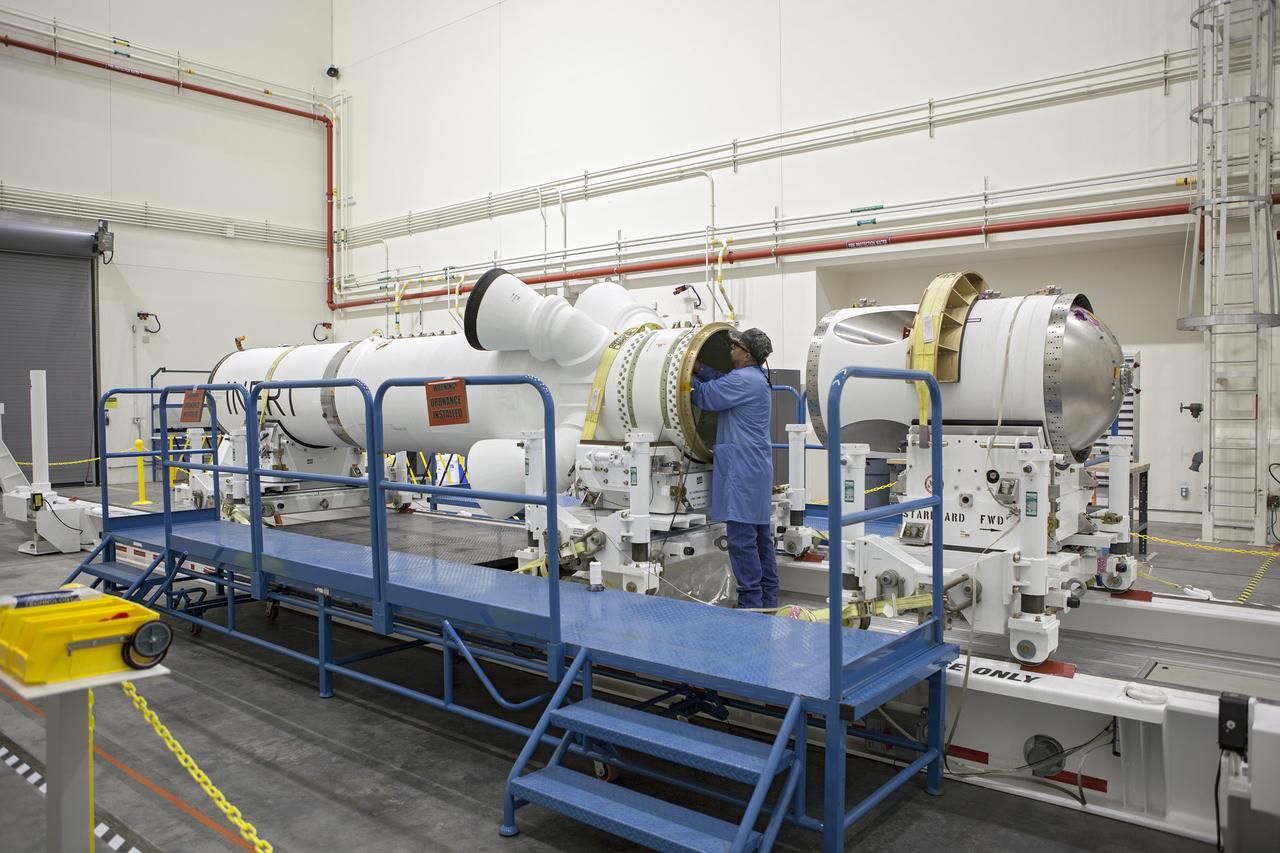

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician prepares the launch abort motor for connection to the attitude control motor. Both are segments of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
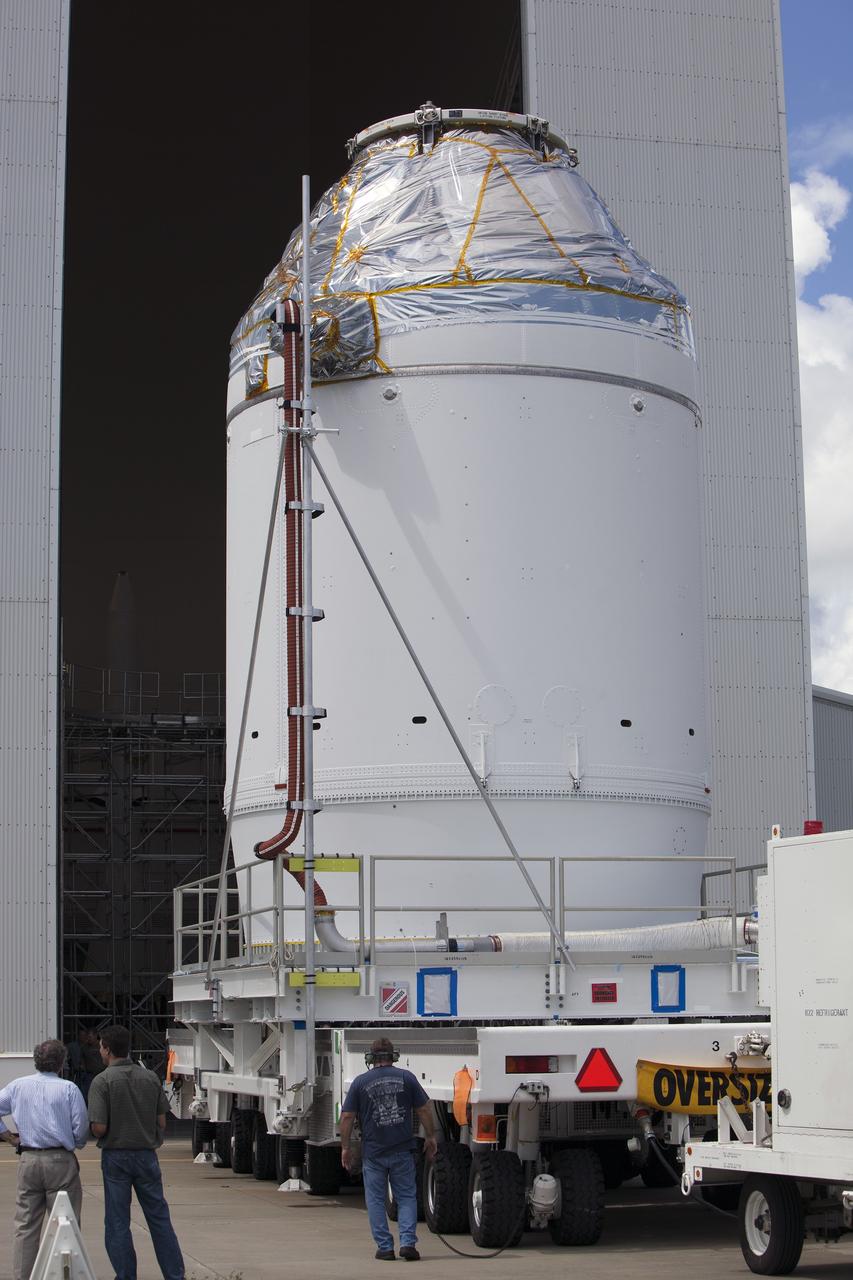

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft was moved from the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility, where it was fueled ahead of its December flight test. In the LASF, the Launch Abort System will be installed around the Orion spacecraft. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
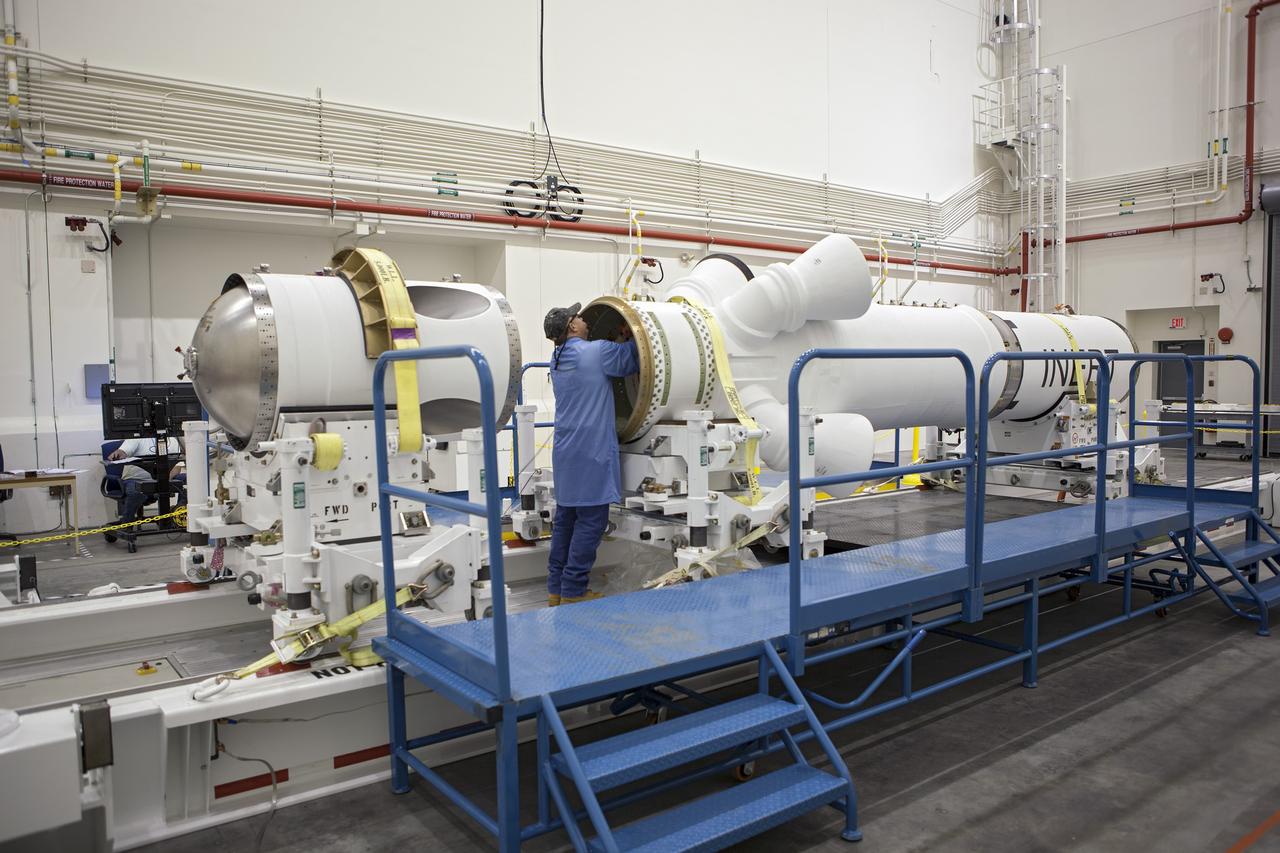

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician prepares the launch abort motor for connection to the attitude control motor. Both are segments of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
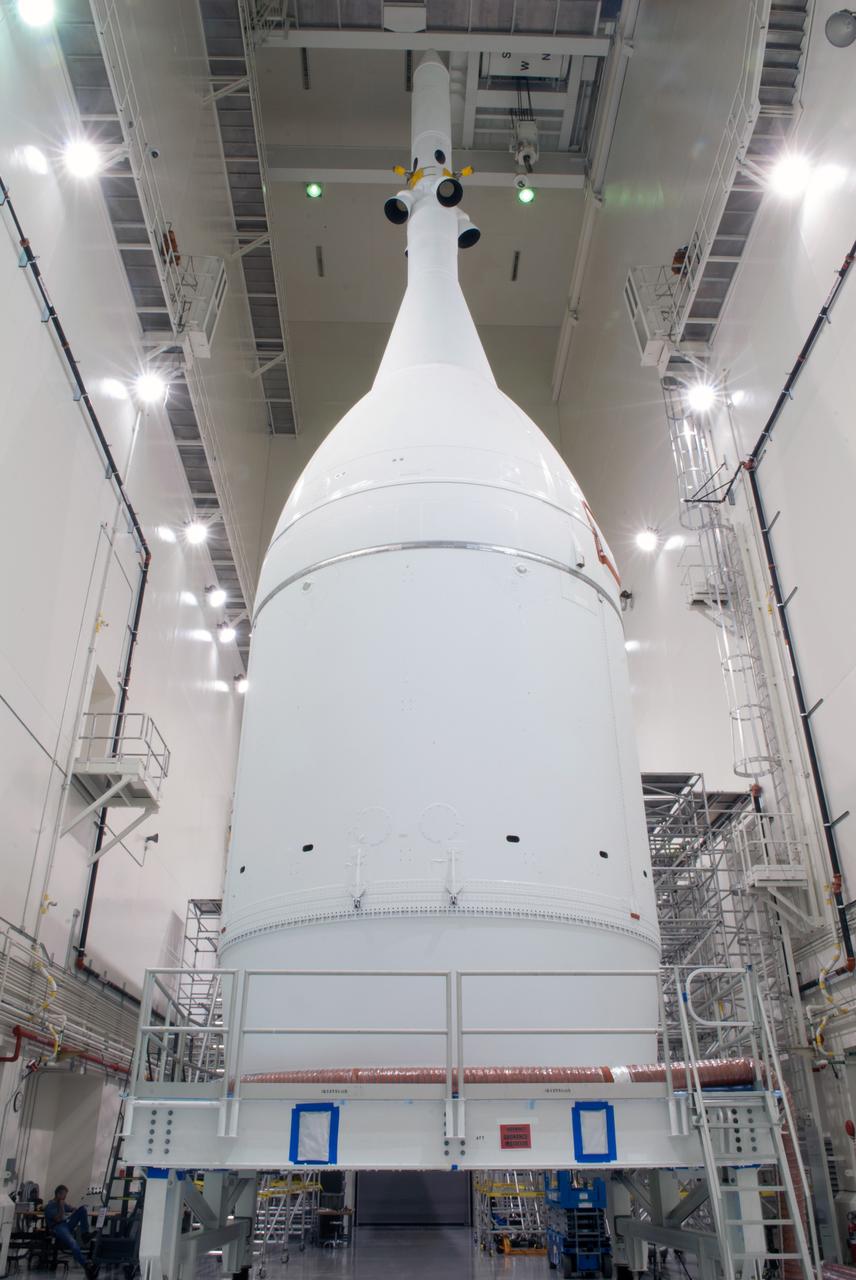

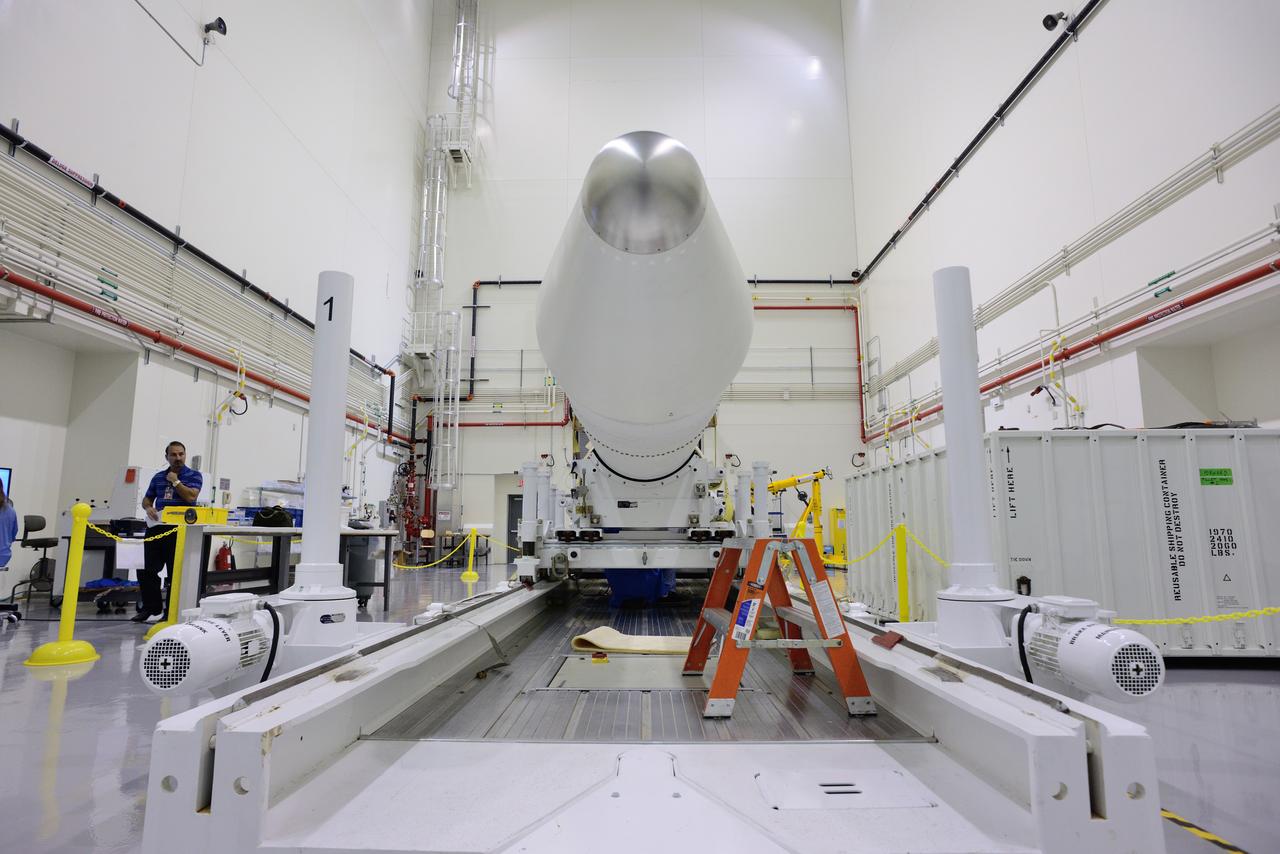
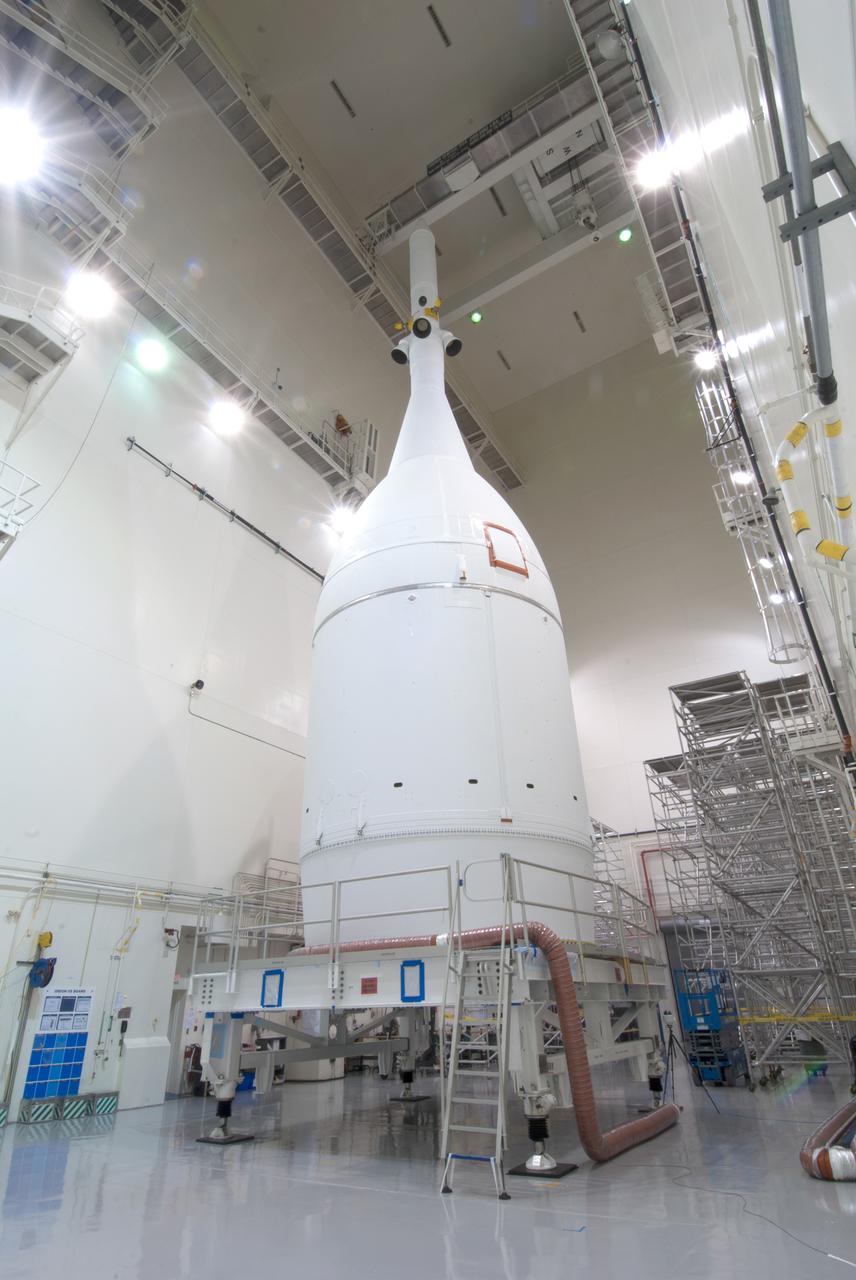
The Orion for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is complete and ready for flight inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 4, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

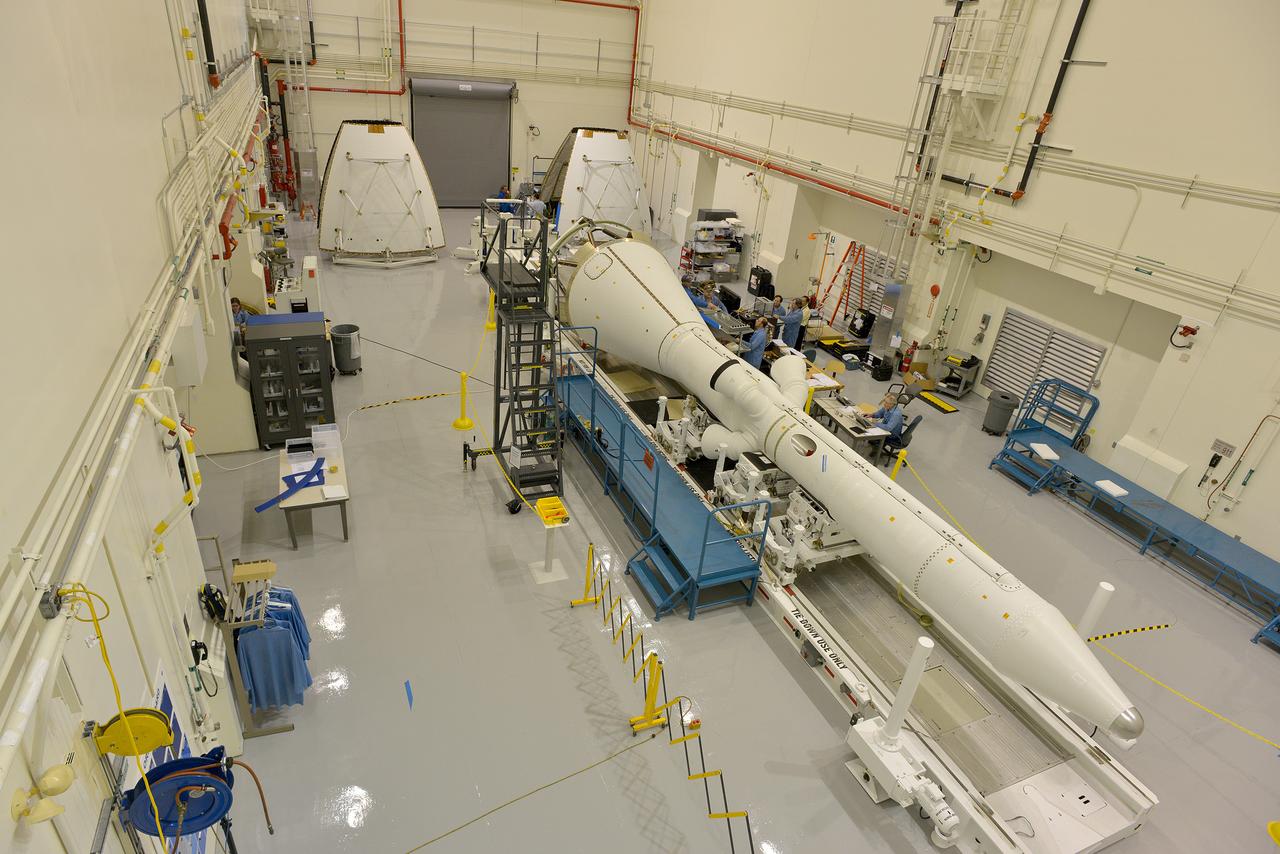
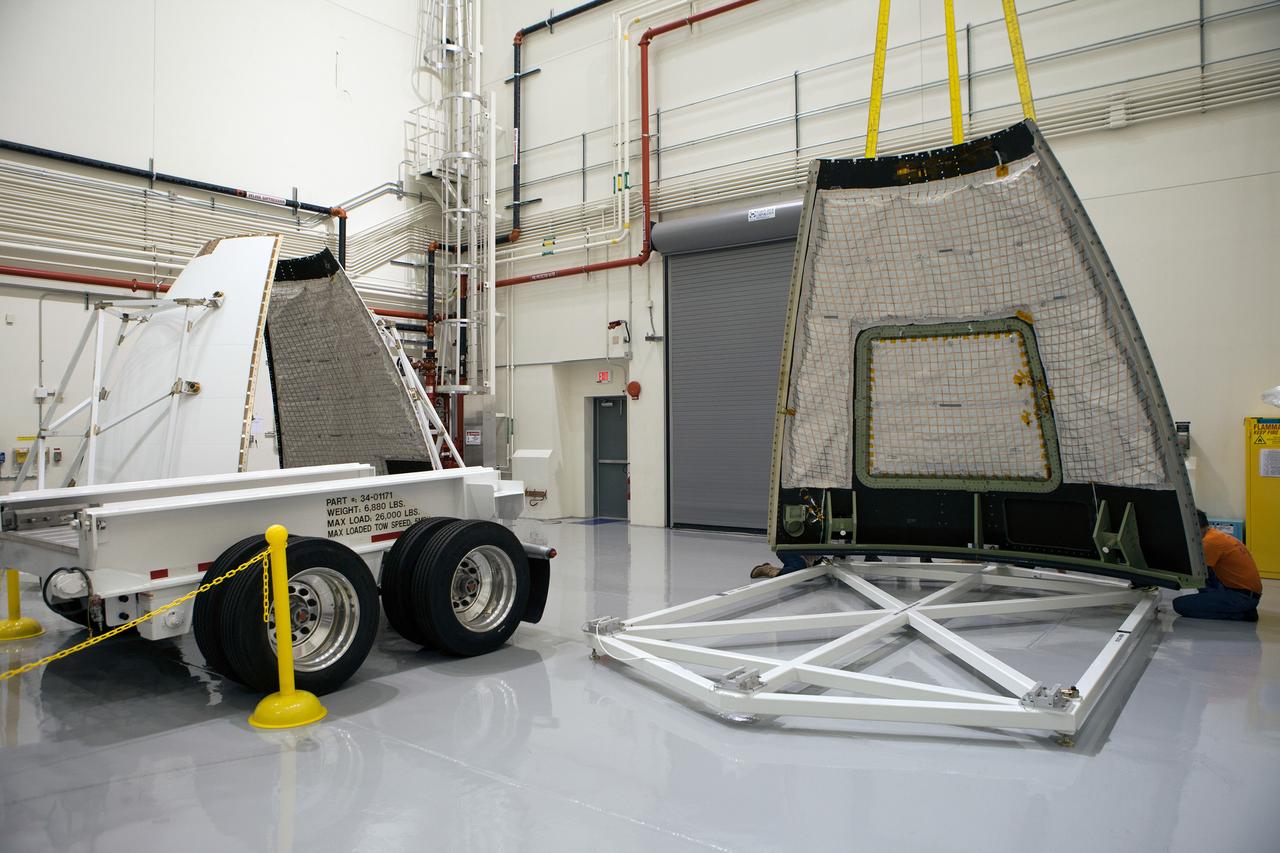
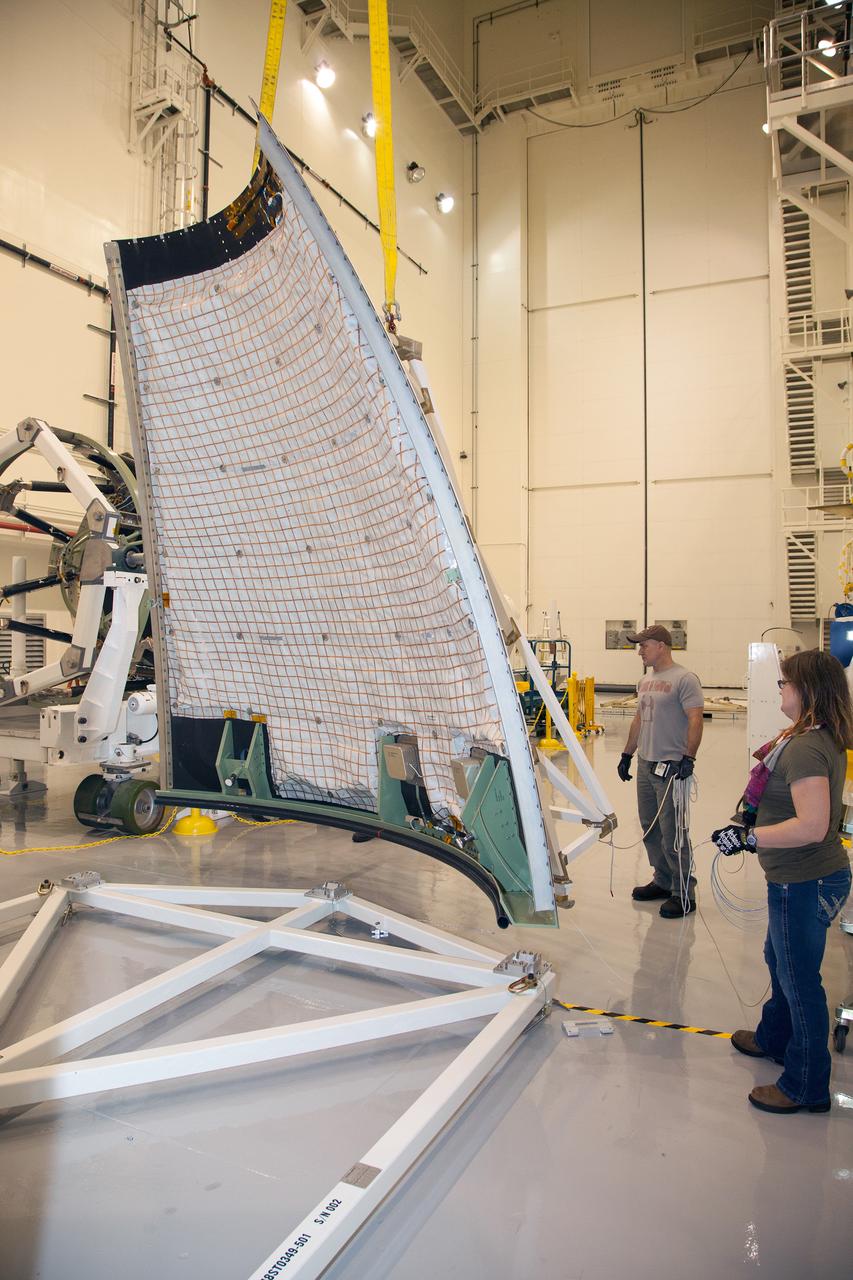
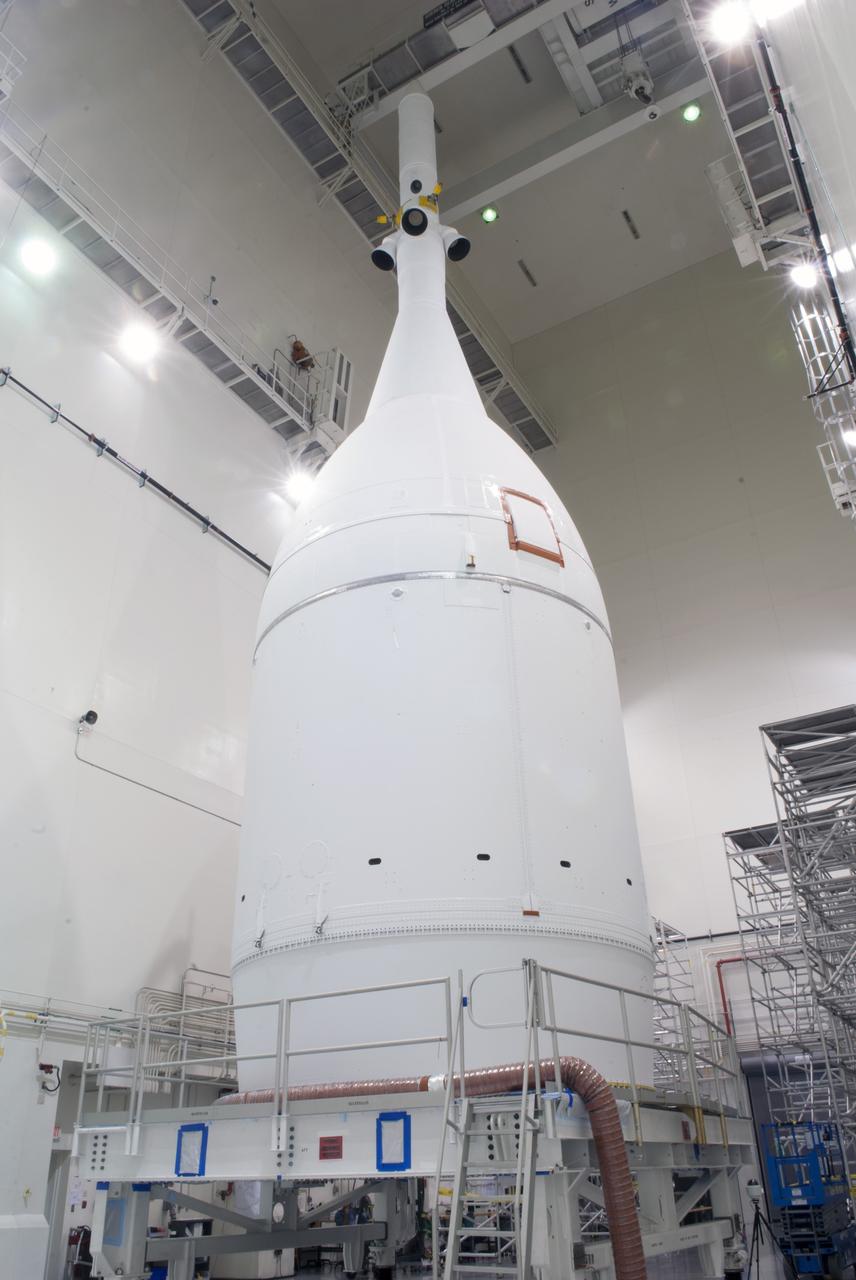
The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
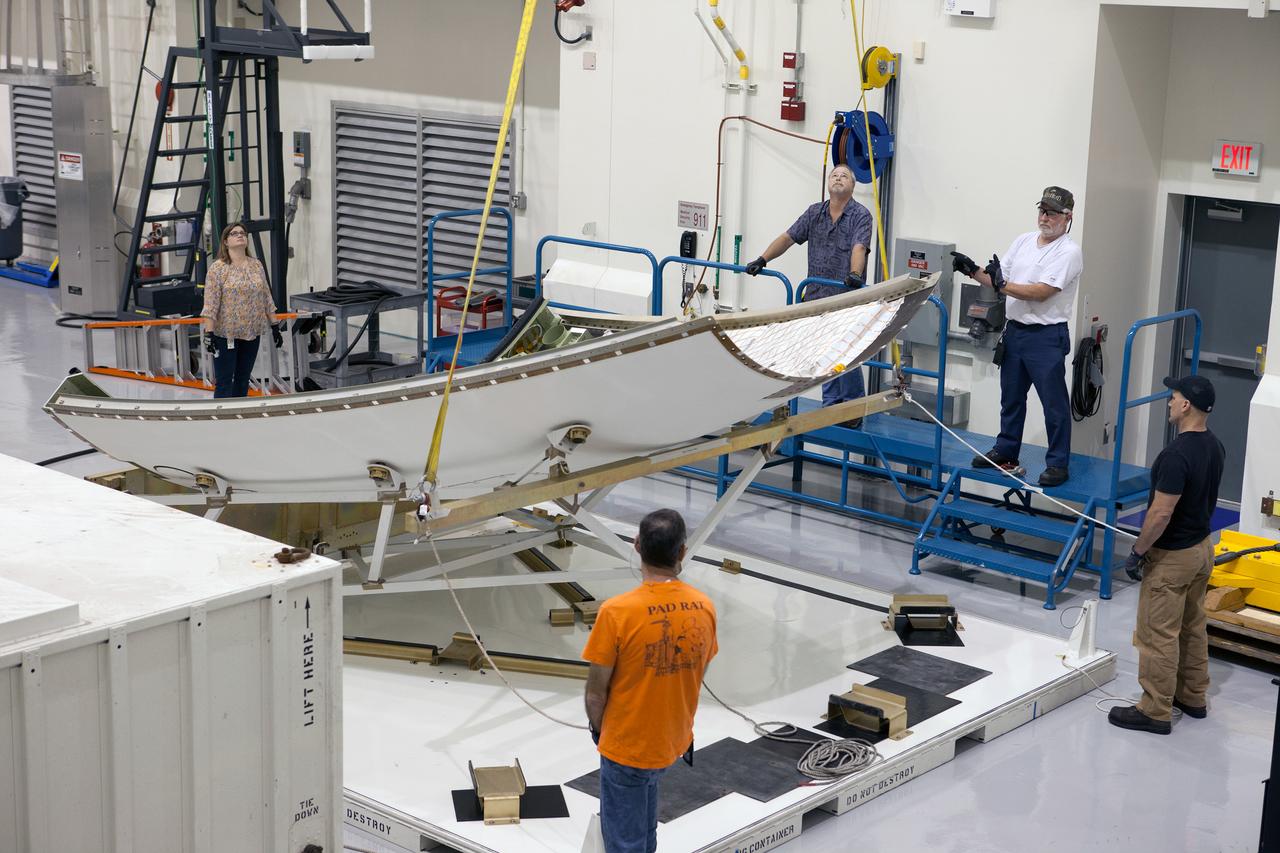

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

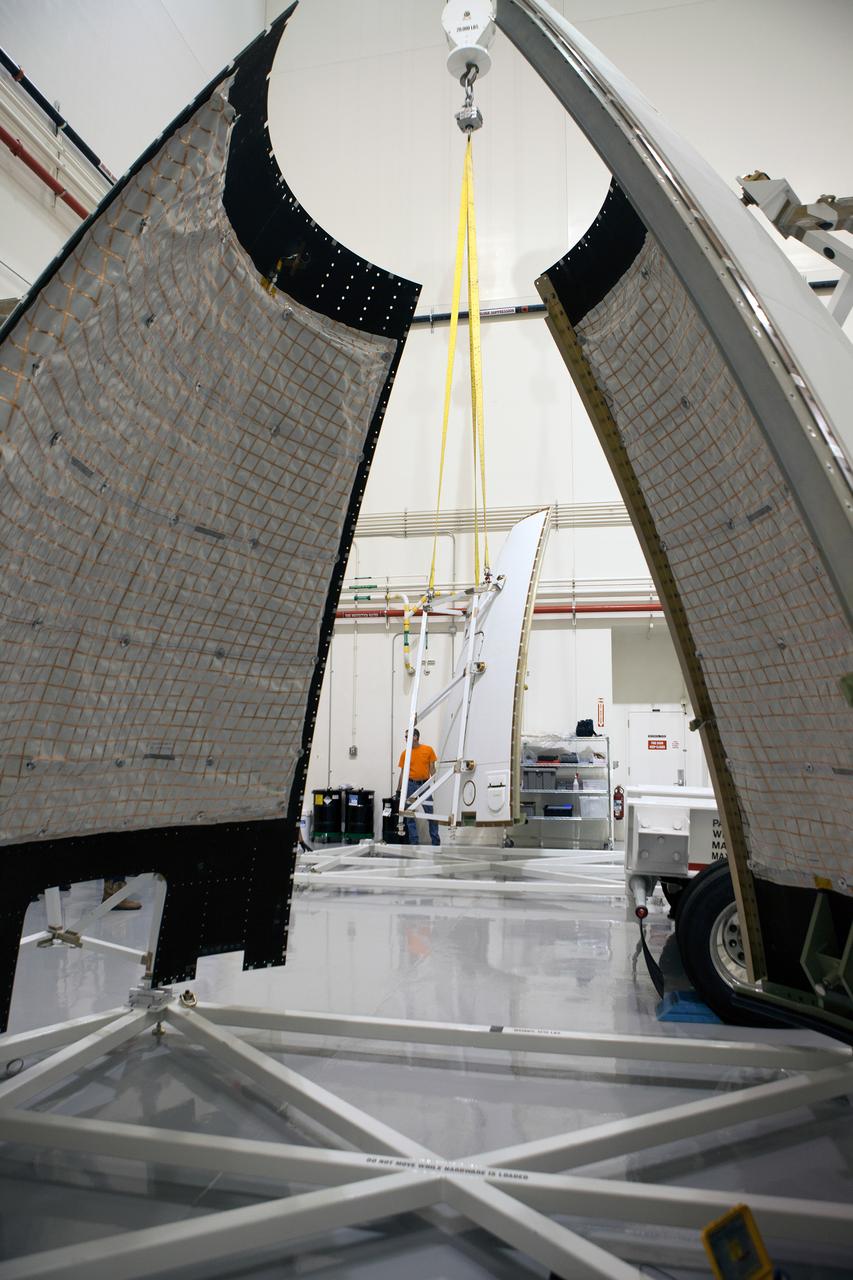
The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
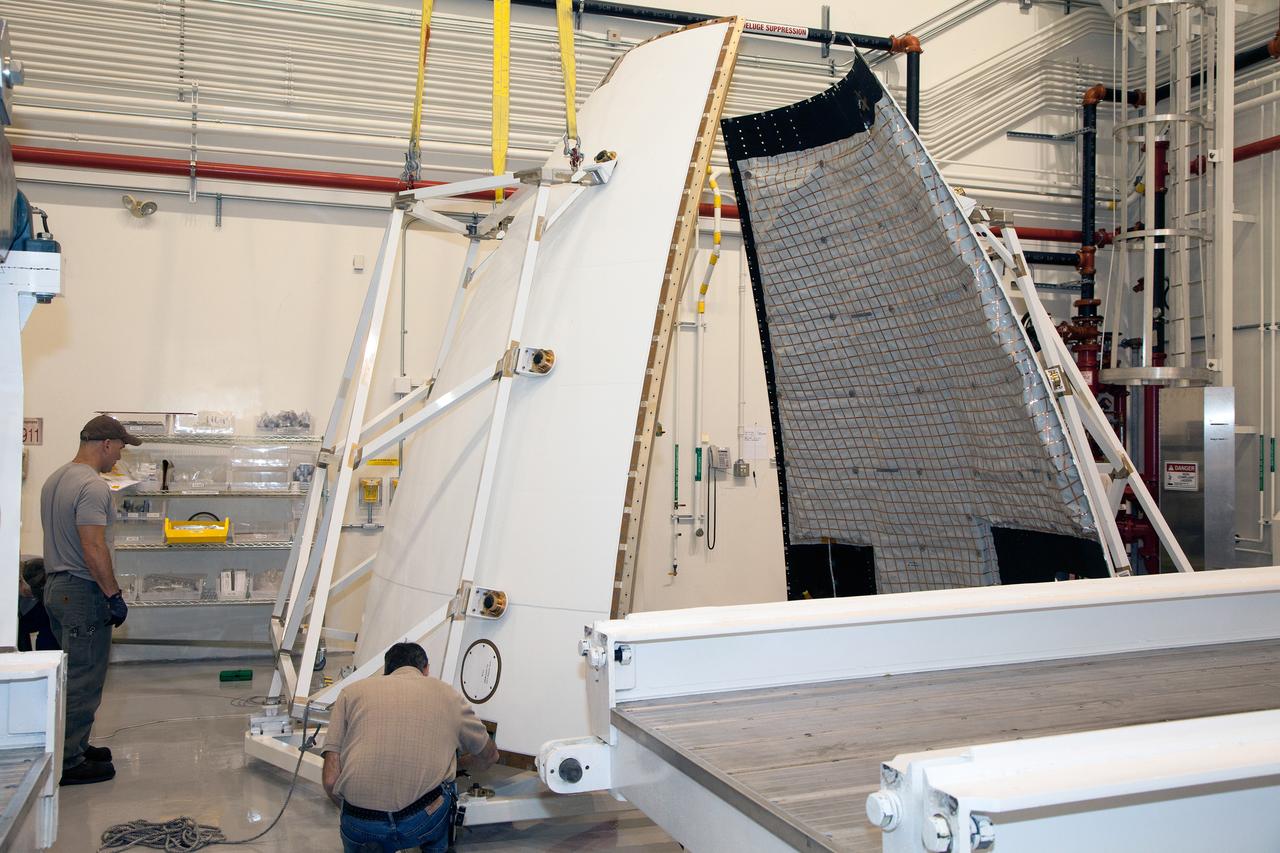

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
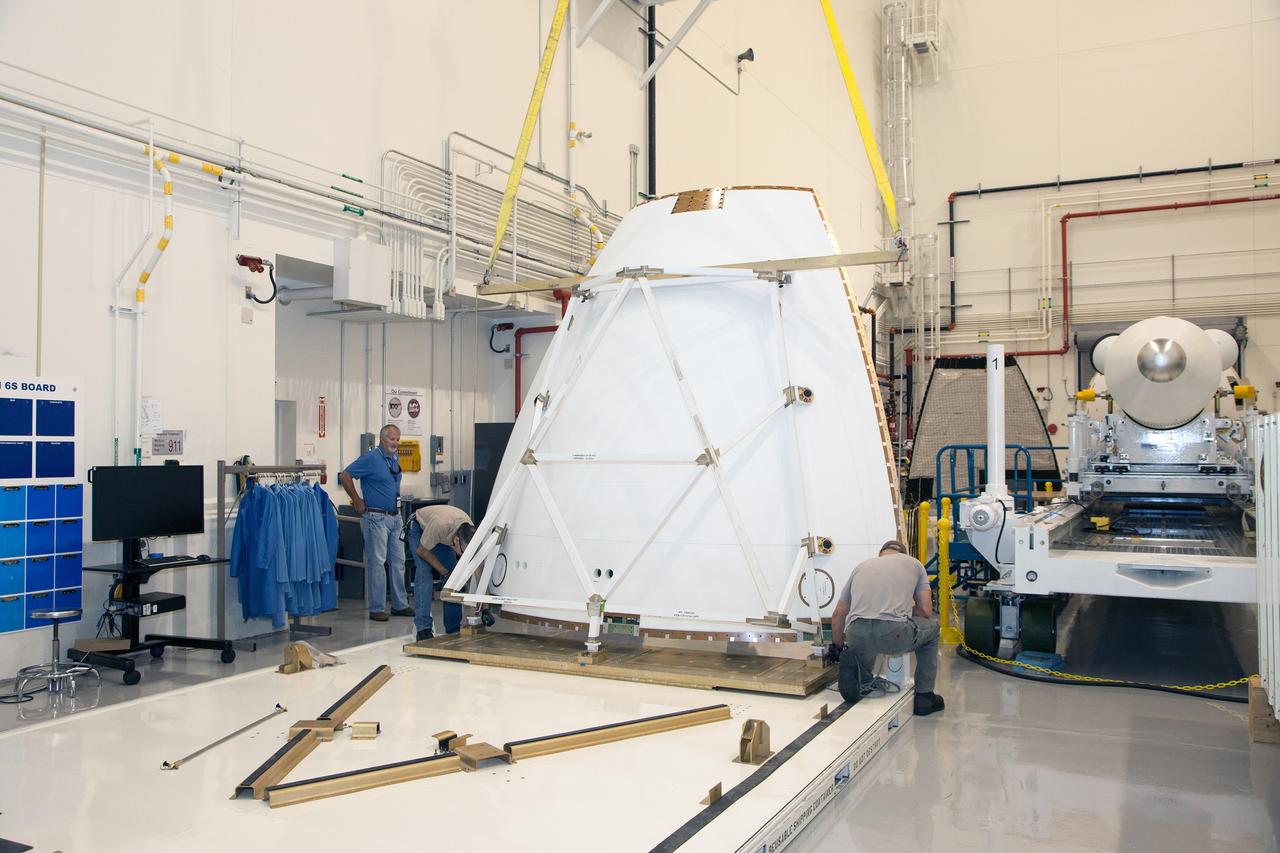

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
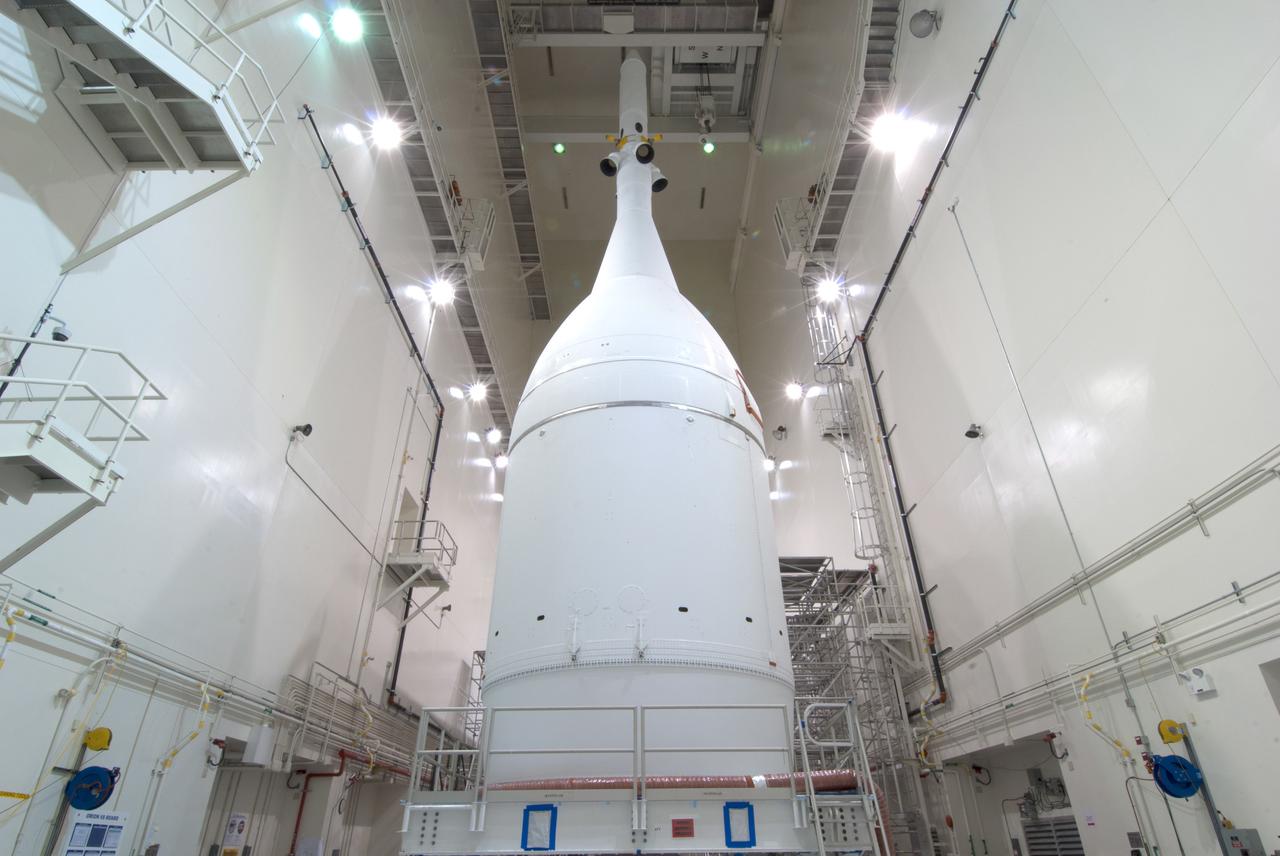

The Orion for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is complete and ready for flight inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 4, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The Orion for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is complete and ready for flight inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 4, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
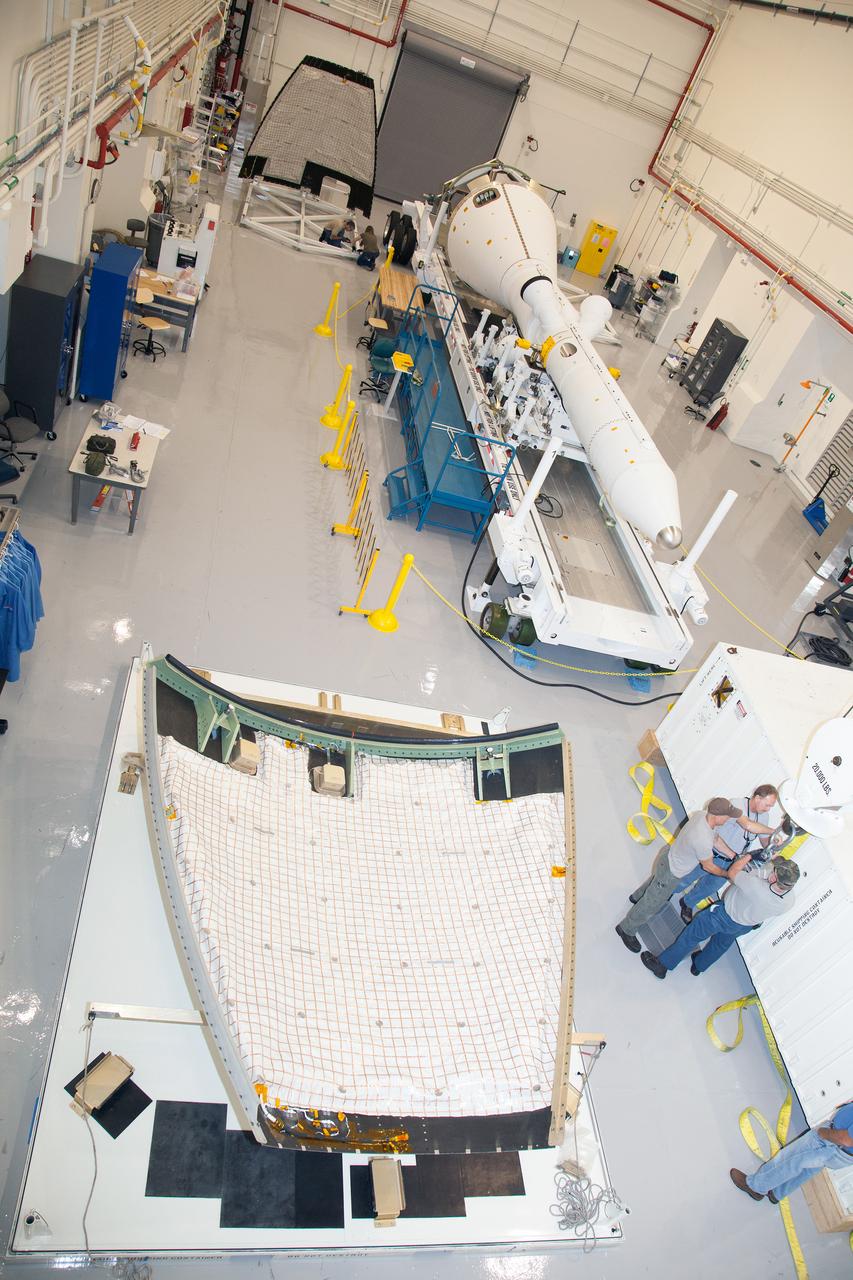
The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
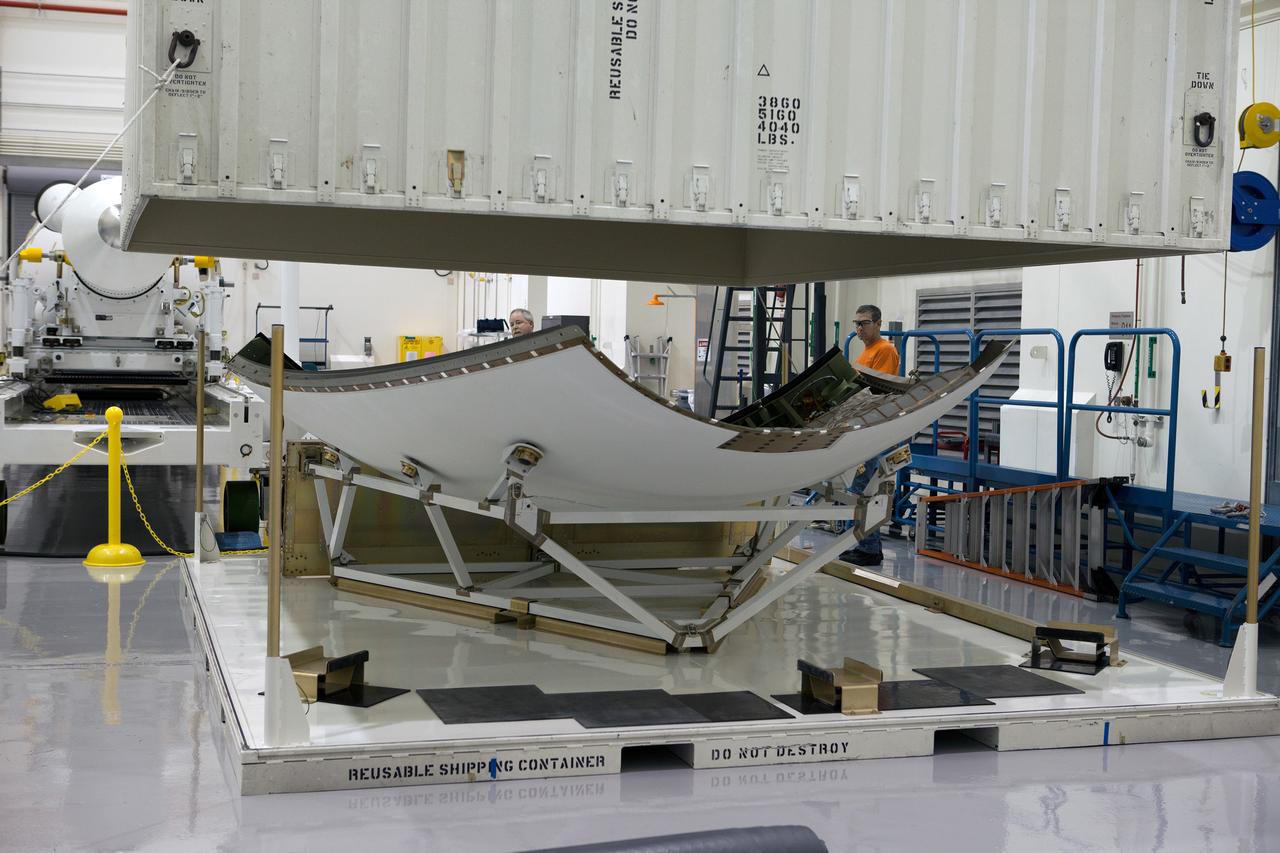

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
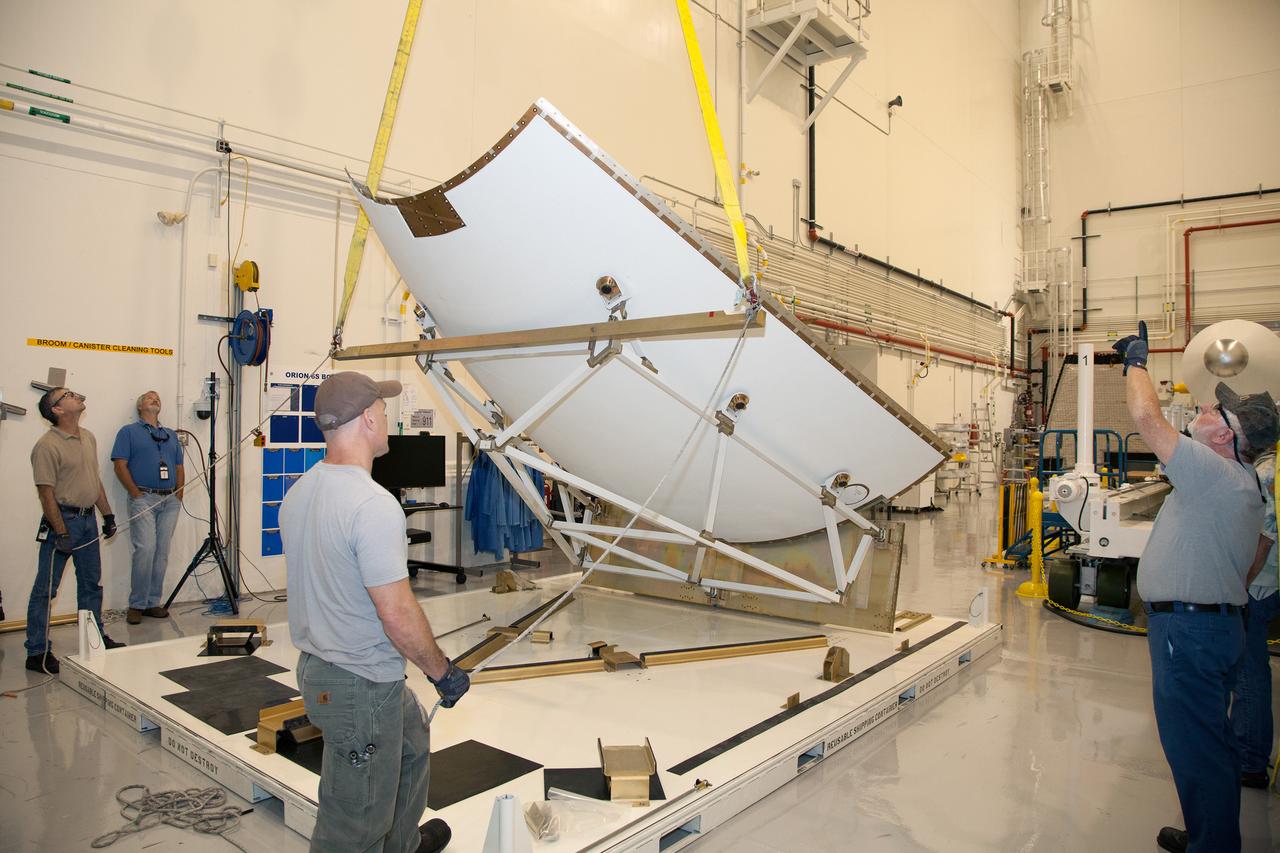

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
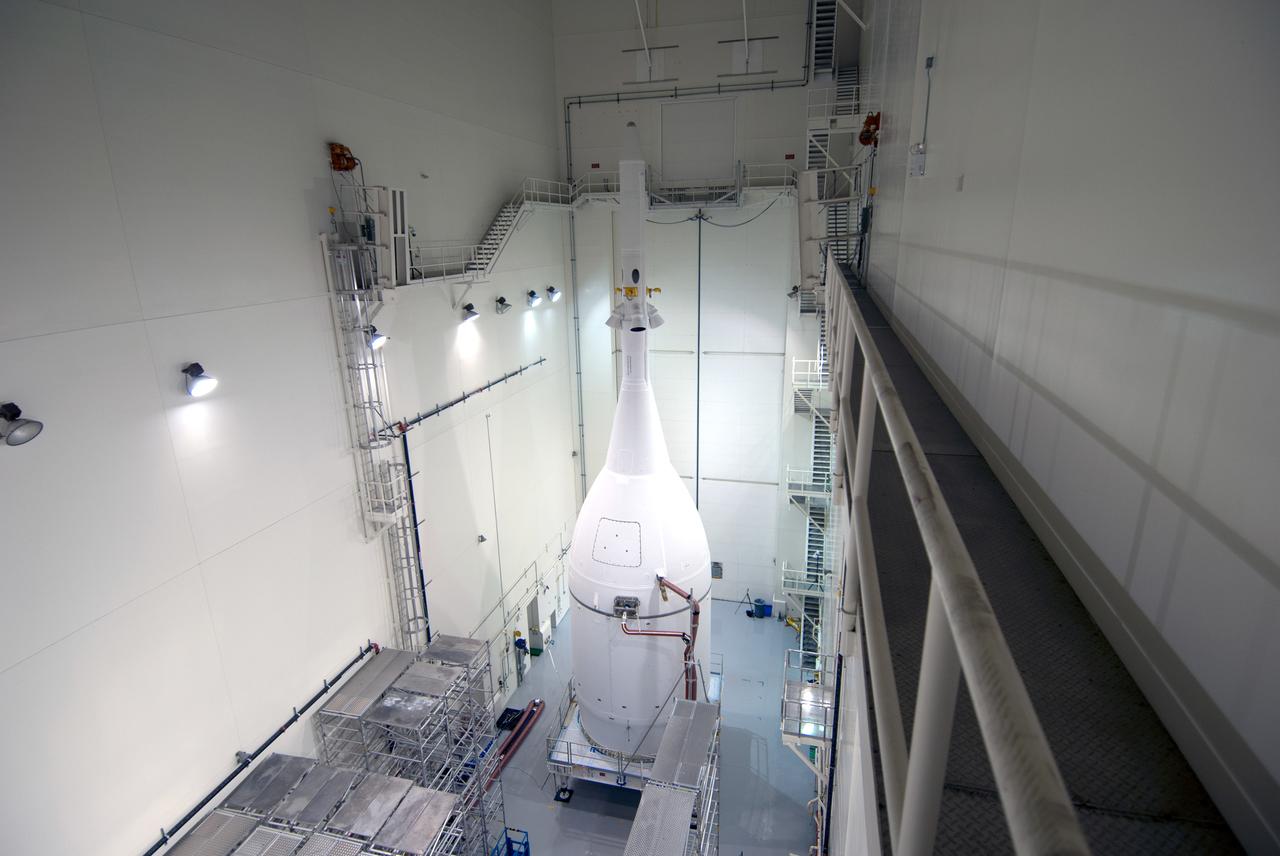

The Orion for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is complete and ready for flight inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 4, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
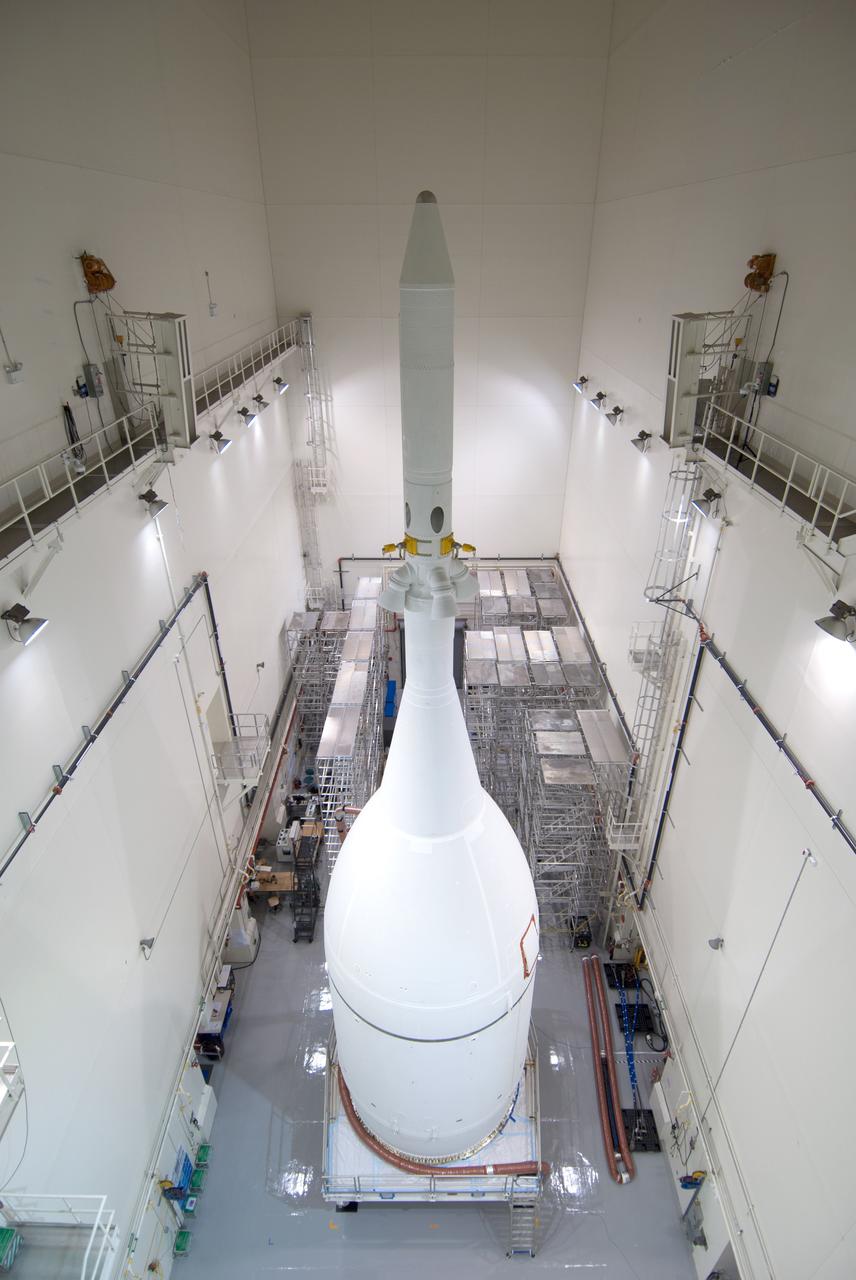

The Orion for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is complete and ready for flight inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 4, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
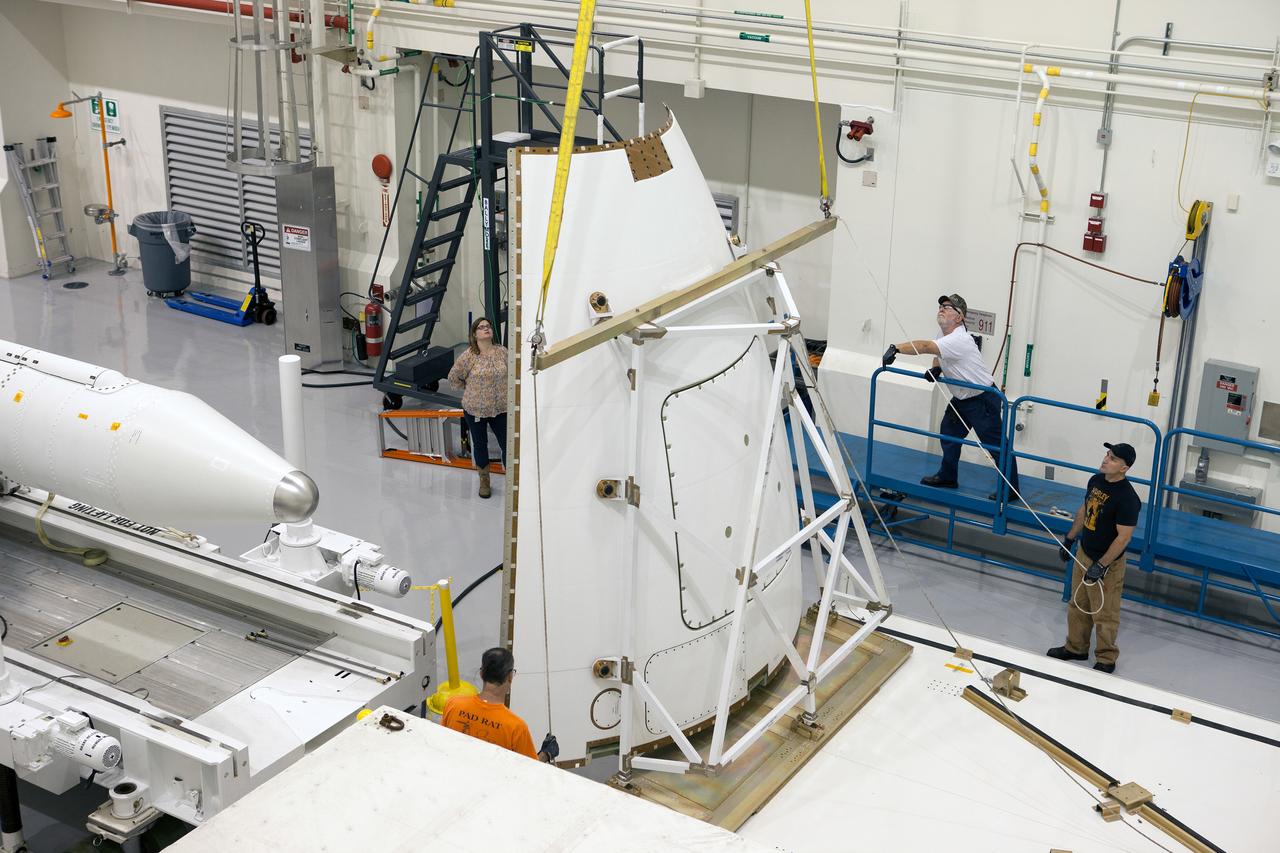

The launch abort system ogive panels are prepared for installation onto the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) launch abort system in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on April 16, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
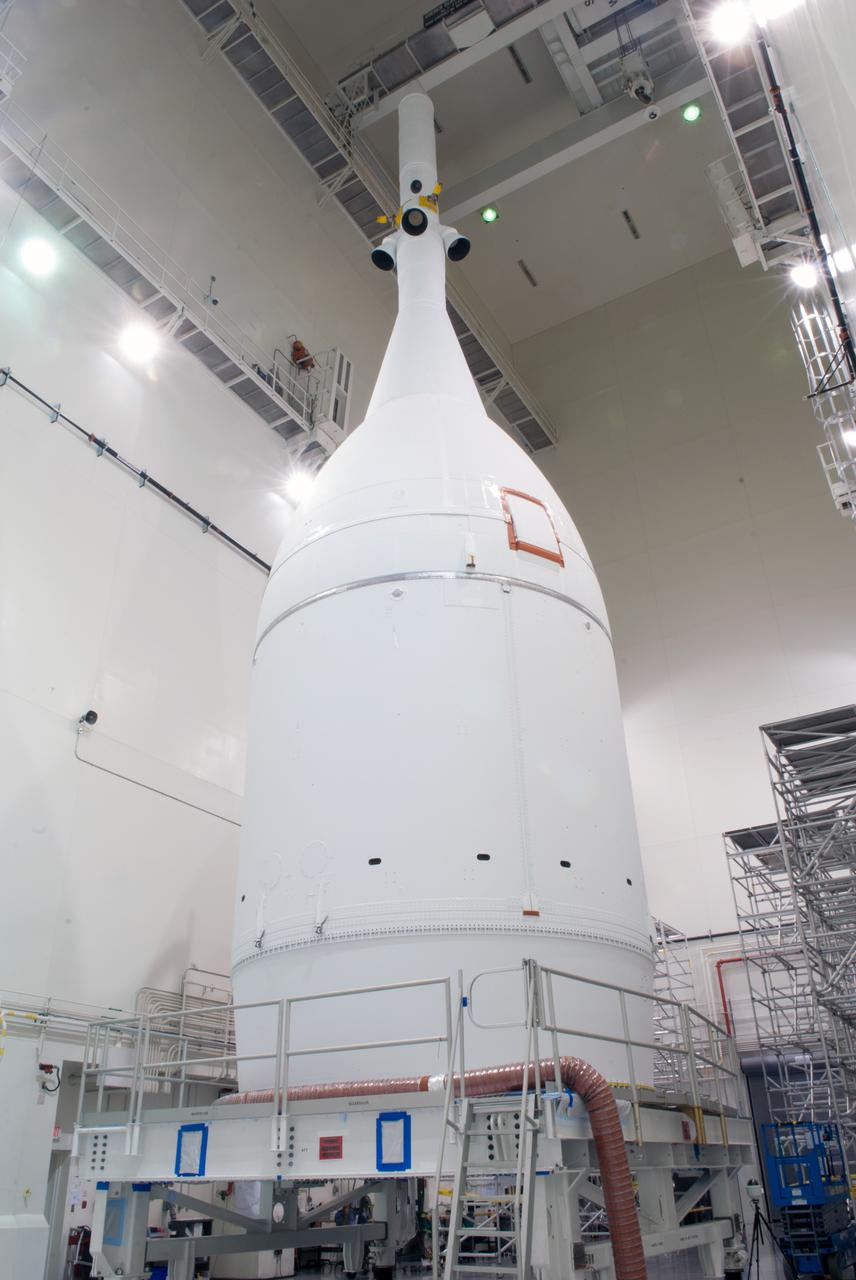

The Orion for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is complete and ready for flight inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 4, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.
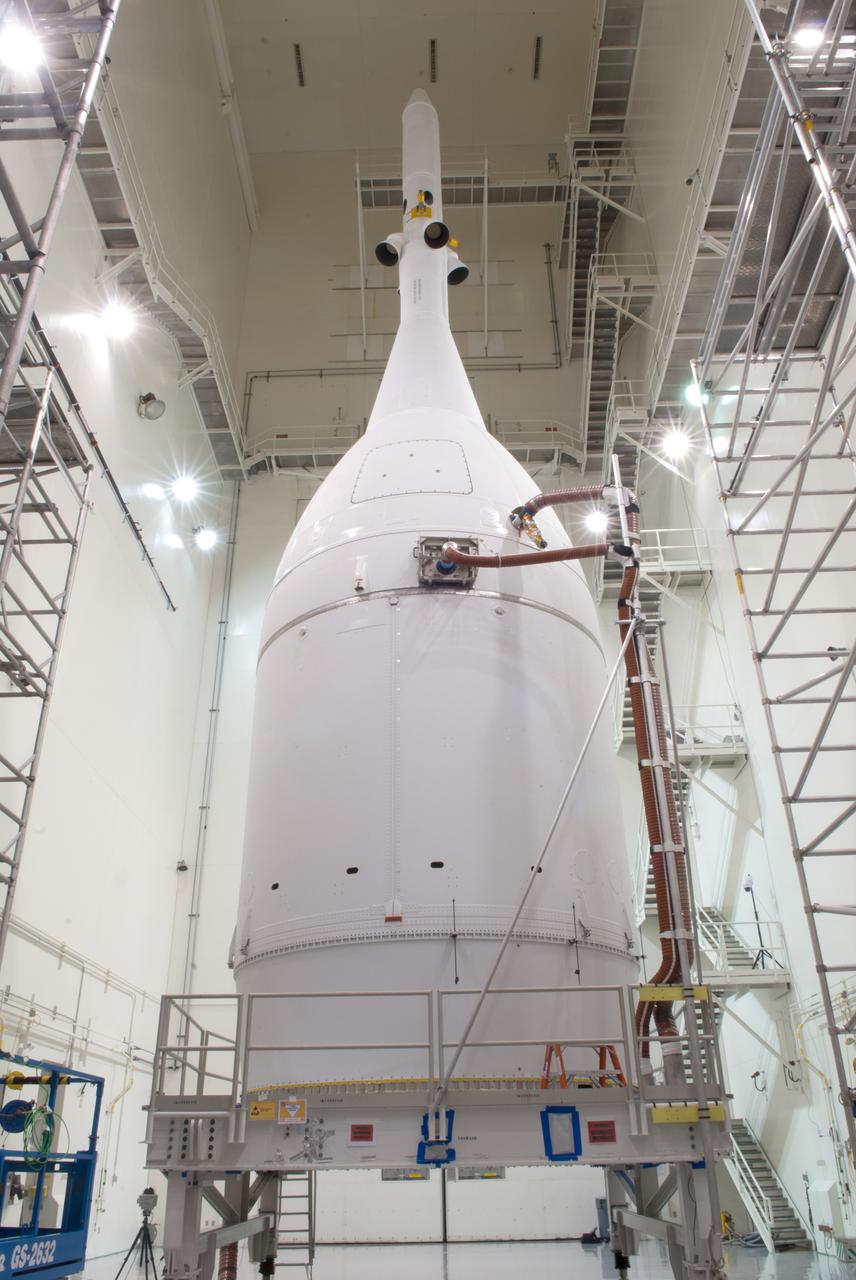

The Orion for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is complete and ready for flight inside the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 4, 2014. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.

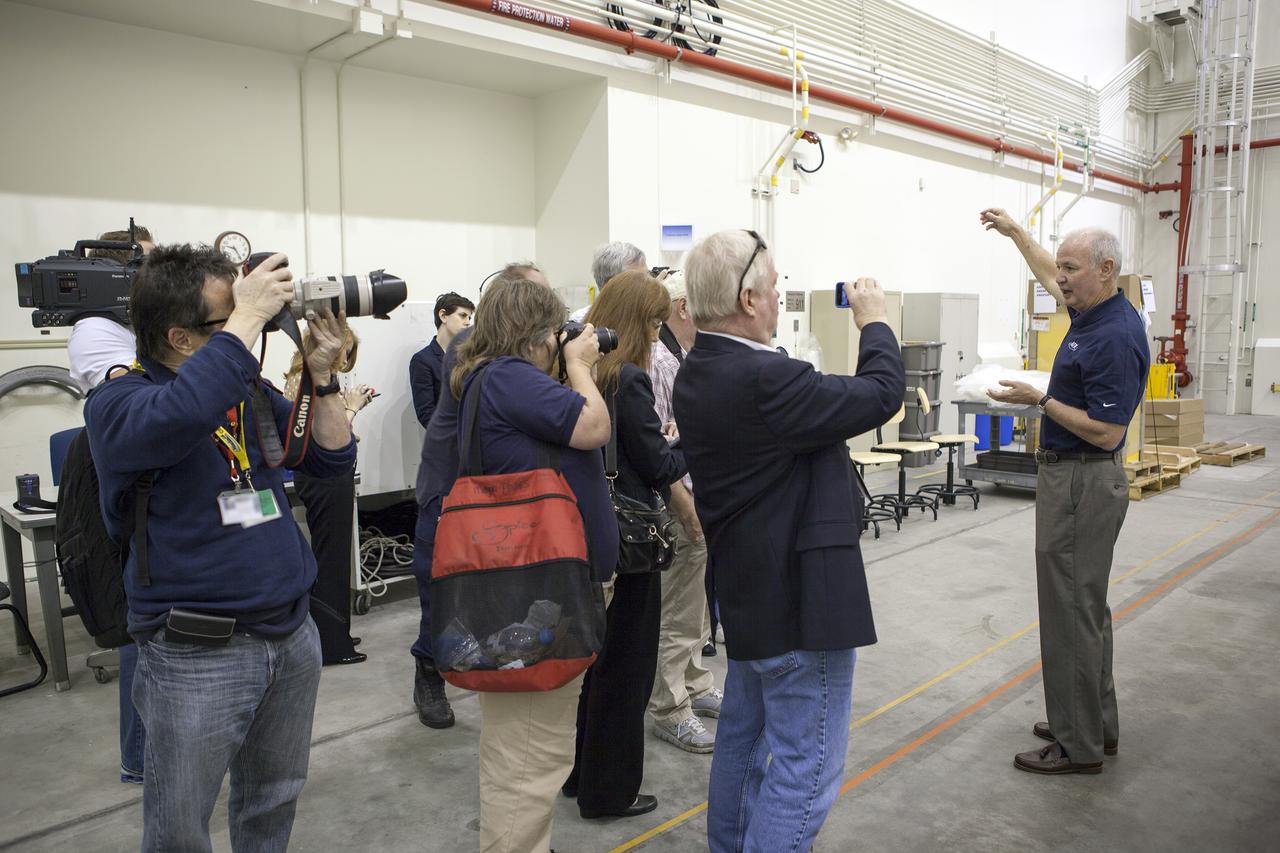
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Kennedy's News Chief Mike Curie speaks to the media during the viewing opportunity. The spacecraft's cross-country return, a 2,700 mile road trip from Naval Base San Diego to Kennedy, sets the stage for in-depth analysis of data obtained during Orion's trip to space. It will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared during its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight test, completed on Dec. 5. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft sits inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ogive panels have been installed around the launch abort system. The panels will smooth the airflow over the conical spacecraft to limit sound and vibration, which will make for a much smoother ride for the astronauts who will ride inside Orion in the future. The spacecraft is being readied for its move to Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for its flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Jim Grossman

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
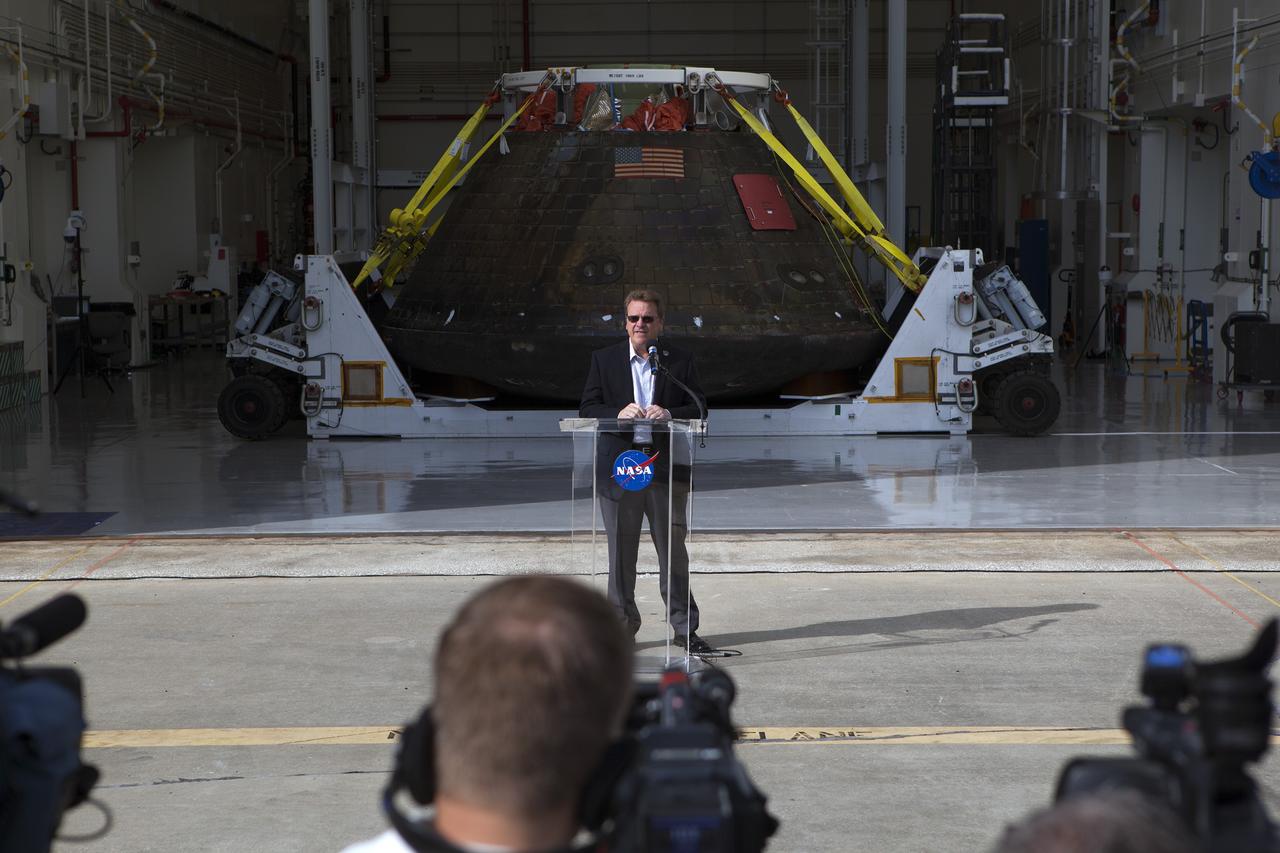

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin Manager Jules Schneider speaks to members of the media during a viewing of NASA's Orion spacecraft at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft's cross-country return, a 2,700 mile road trip from Naval Base San Diego to Kennedy, sets the stage for in-depth analysis of data obtained during Orion's trip to space. It will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared during its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight test, completed on Dec. 5. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
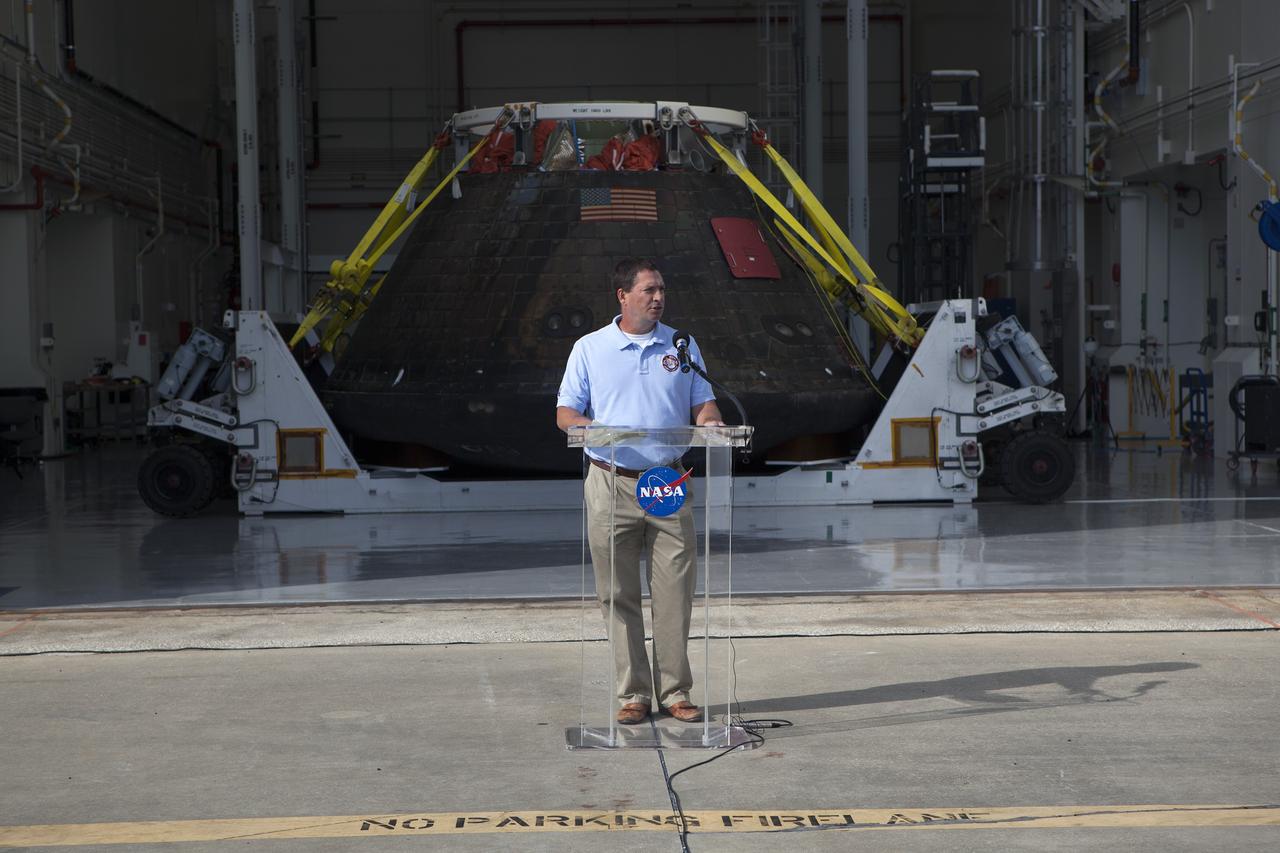

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Lou Garcia, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO, speaks to the media during the viewing opportunity. The spacecraft's cross-country return, a 2,700 mile road trip from Naval Base San Diego to Kennedy, sets the stage for in-depth analysis of data obtained during Orion's trip to space. It will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared during its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight test, completed on Dec. 5. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft sits inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ogive panels have been installed around the launch abort system. The panels will smooth the airflow over the conical spacecraft to limit sound and vibration, which will make for a much smoother ride for the astronauts who will ride inside Orion in the future. The spacecraft is being readied for its move to Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for its flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Jim Grossman
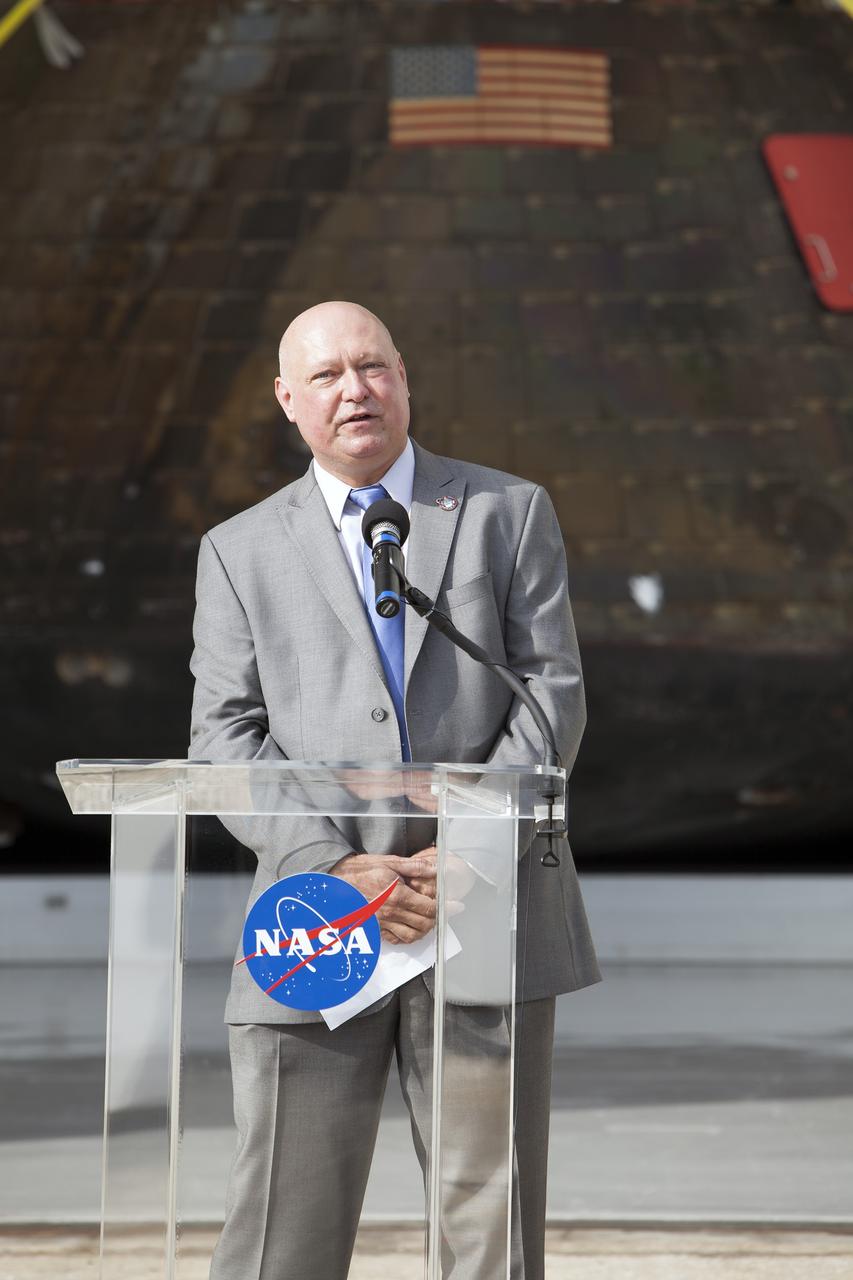

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Kennedy News Chief Mike Curie speaks to the media during the viewing opportunity. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
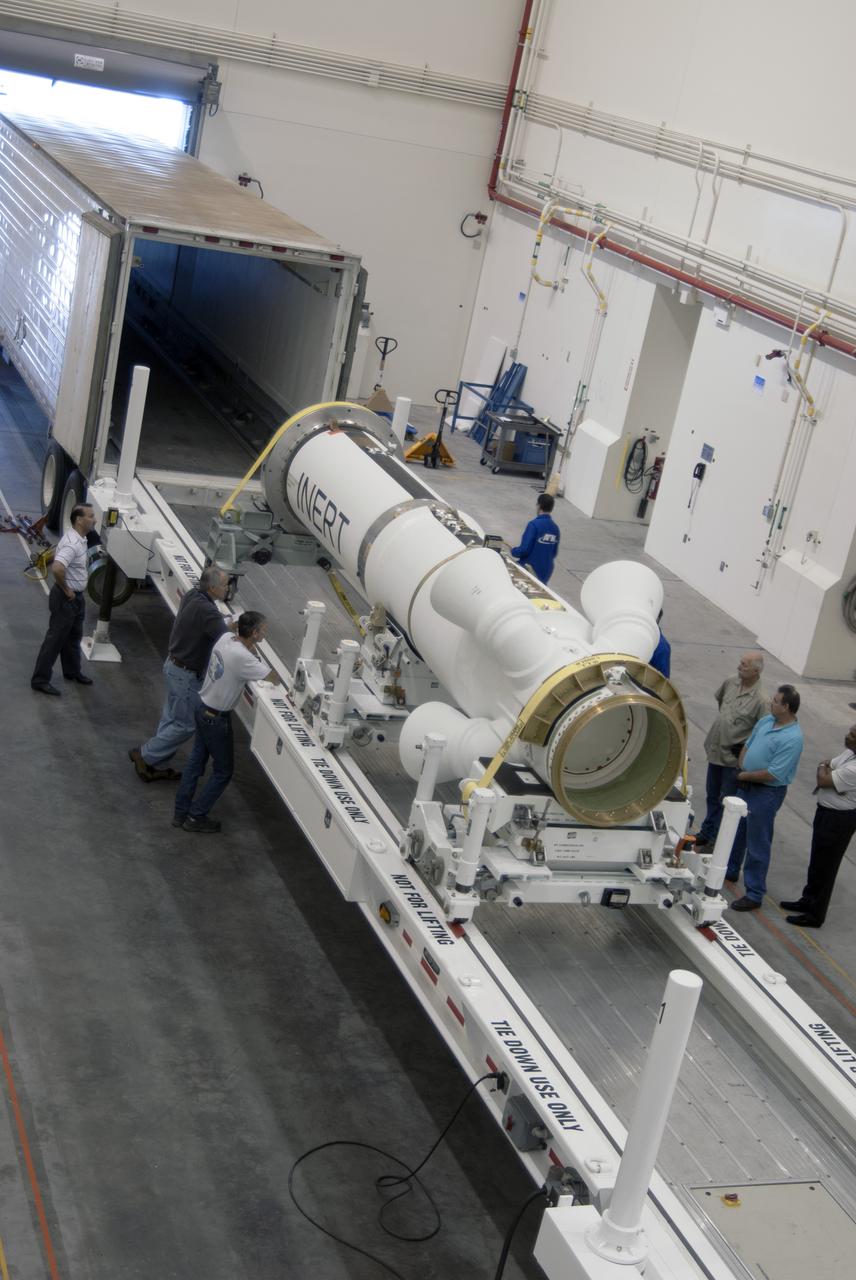

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians have removed the Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, launch abort motor from a truck. The test flight launch abort motor is for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, of the agency’s Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle. It is part of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. The motor is configured with inert propellant. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Charisse Nahser
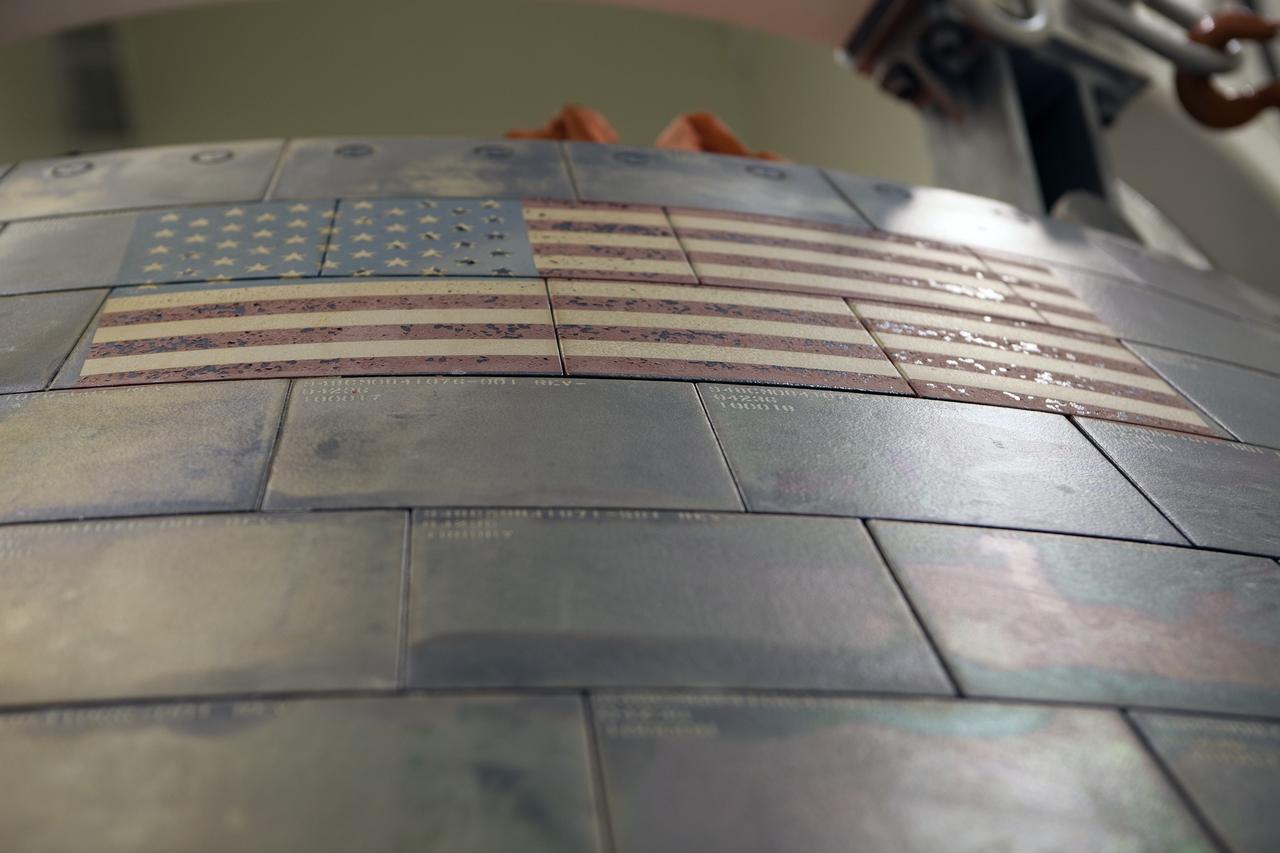
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The U.S. Flag is in view on NASA's Orion spacecraft inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a media event. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the media during the viewing opportunity is Jules Schneider, Lockheed Martin Manager. Behind him, from left, are Glenn Chin, Orion Production Operations manager and Phil Weber and Lou Garcia, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
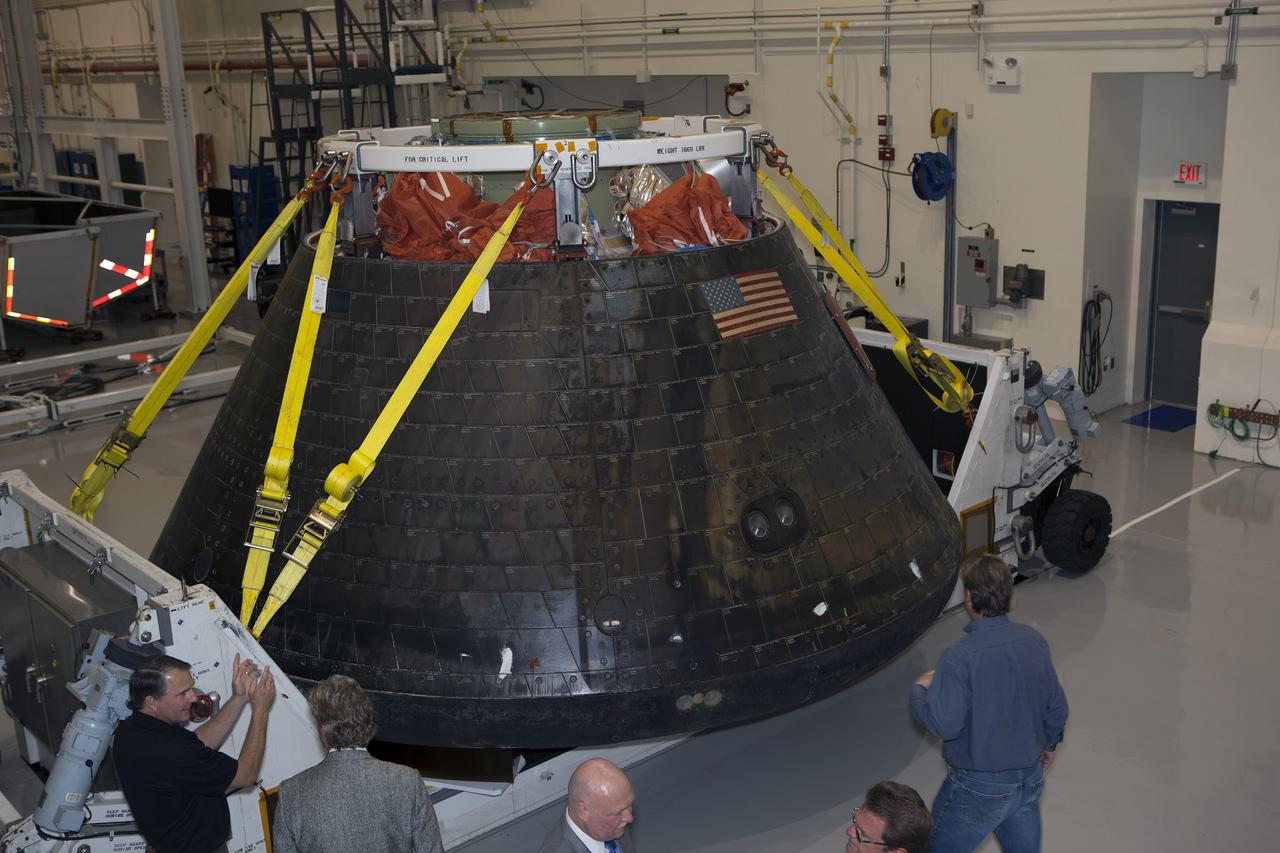

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the media during the viewing opportunity is Phil Weber, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO. At left is Jules Schneider, Lockheed Martin manager. At right is Glenn Chin, Orion Production Operations, and Lou Garcia, with GSDO. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the media during the viewing opportunity is Glenn Chin, Orion Production Operations. To his right is Phil Weber, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
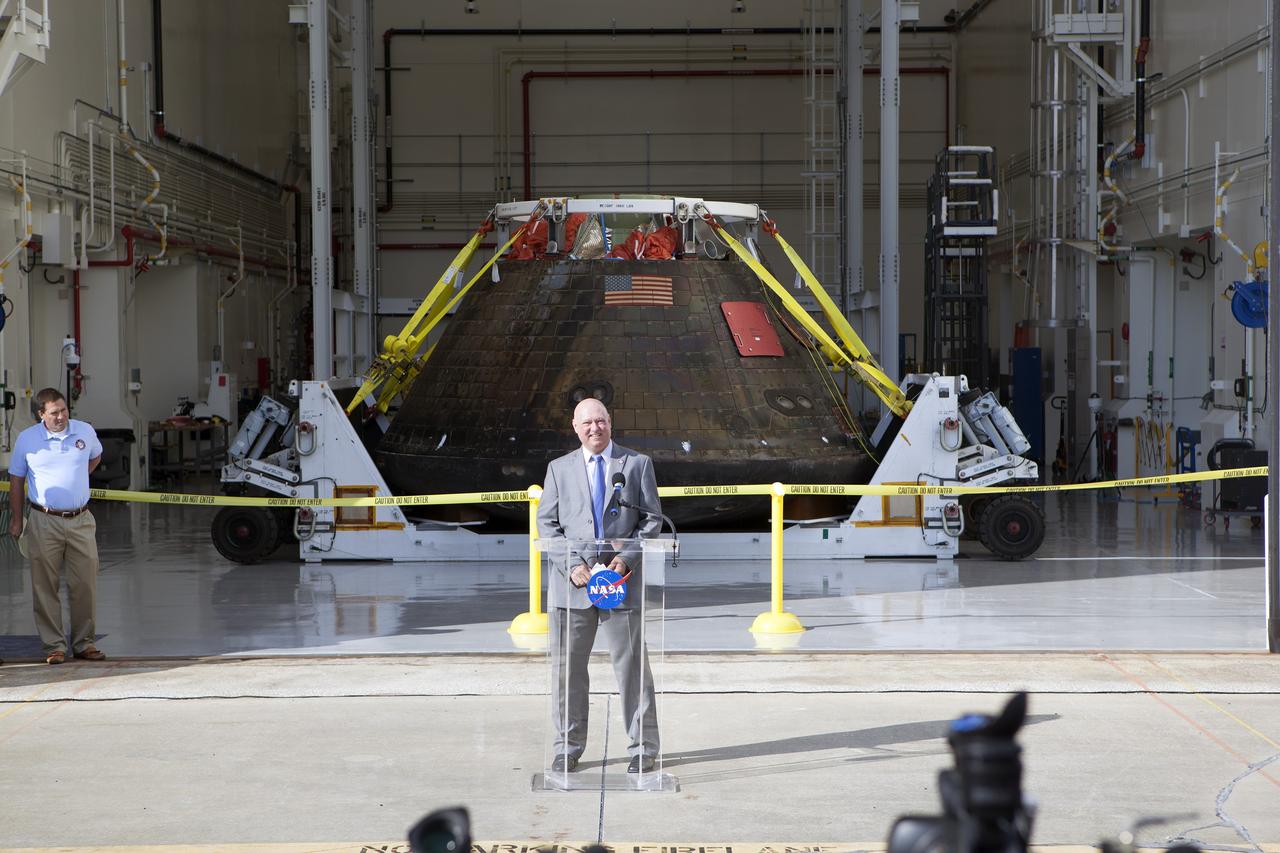

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Kennedy News Chief Mike Curie speaks to the media during the viewing opportunity. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of data obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
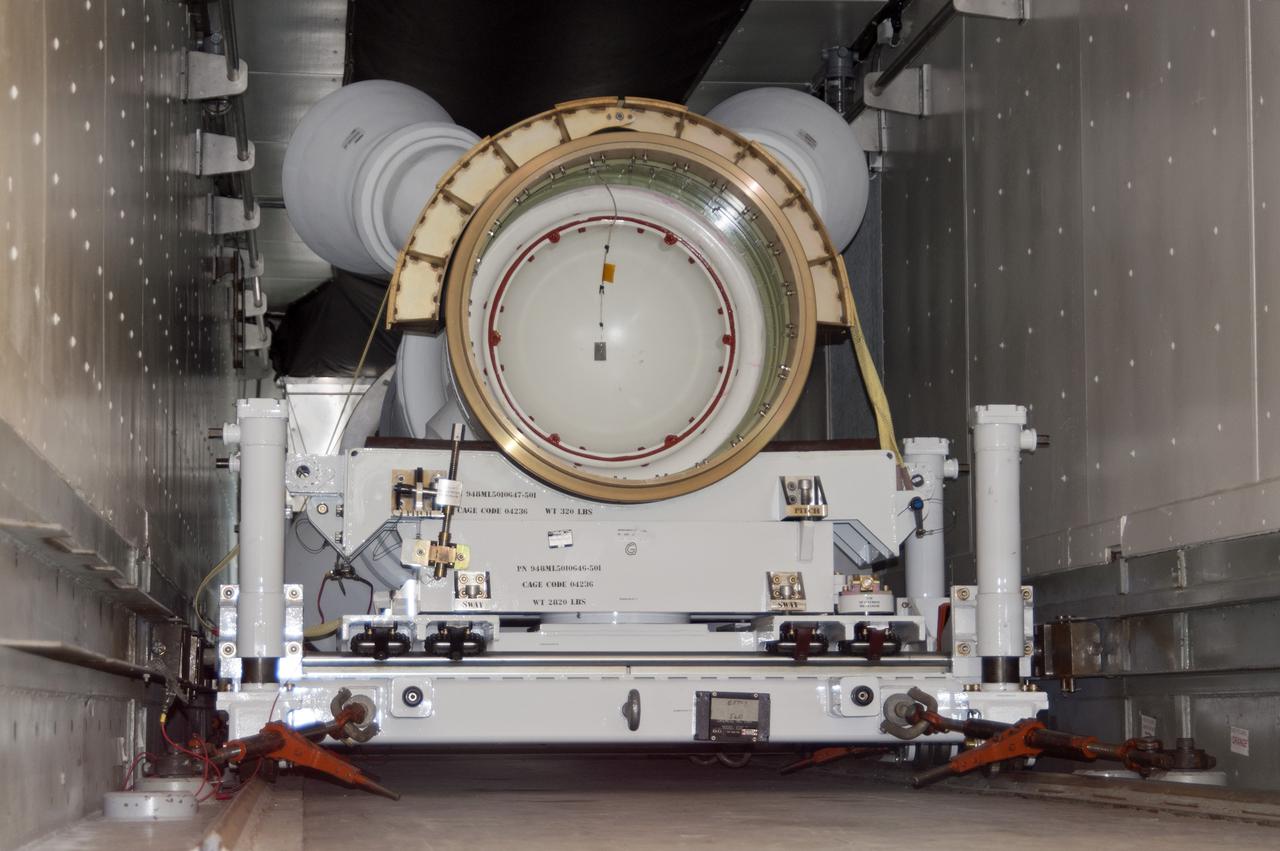

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, launch abort motor arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, of the agency’s Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle. ATK’s abort motor is part of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. The test flight abort motor is configured with inert propellant. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Charisse Nahser
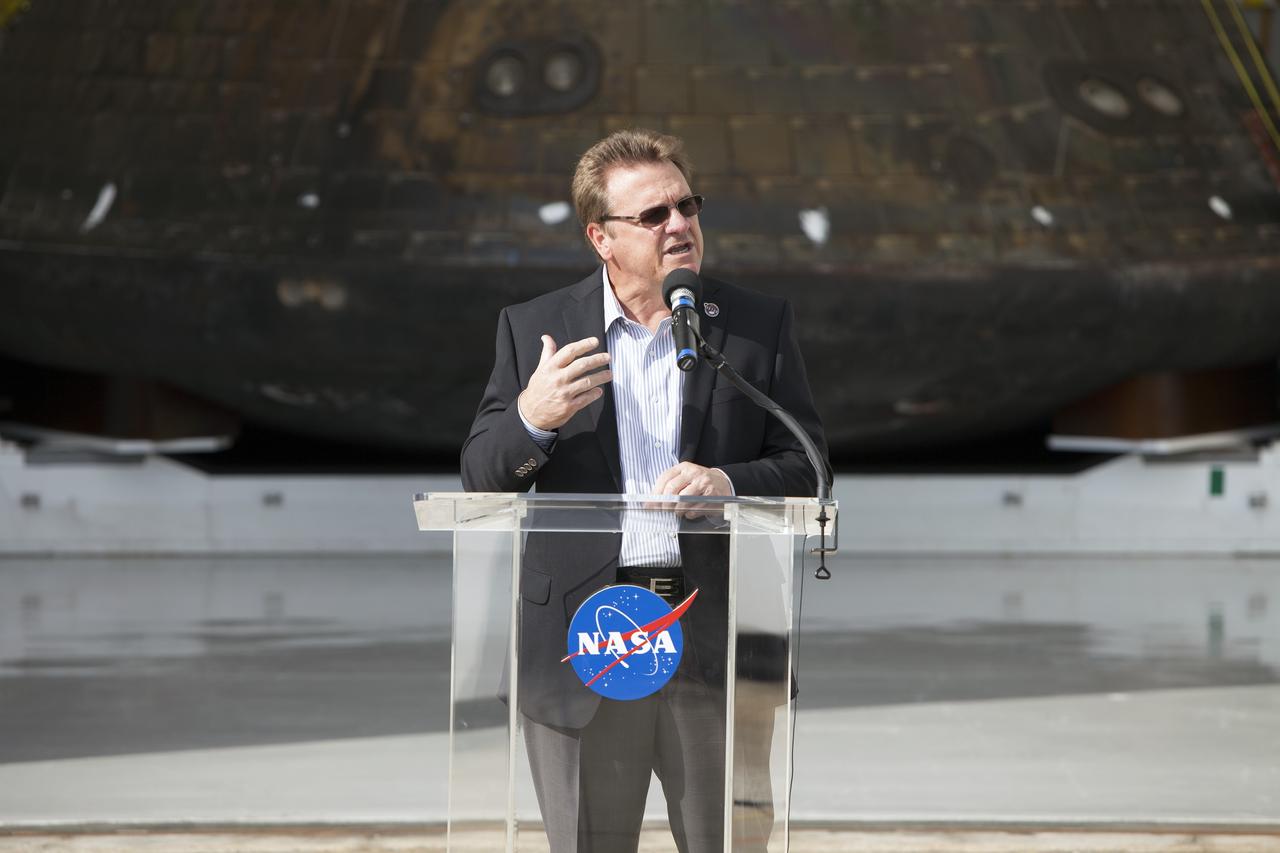

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin Manager Jules Schneider speaks to members of the media during a viewing of NASA's Orion spacecraft at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft's cross-country return, a 2,700 mile road trip from Naval Base San Diego to Kennedy, sets the stage for in-depth analysis of data obtained during Orion's trip to space. It will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared during its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight test, completed on Dec. 5. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
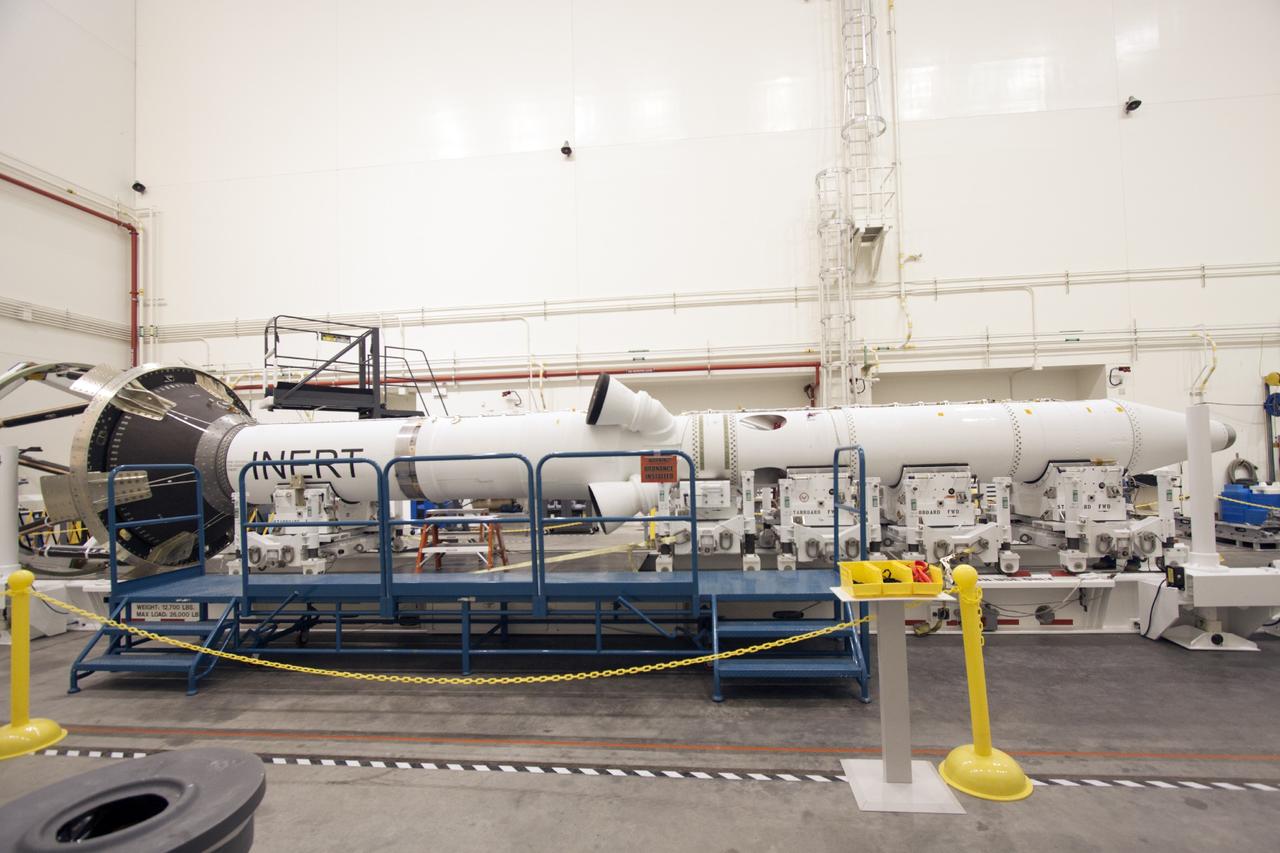

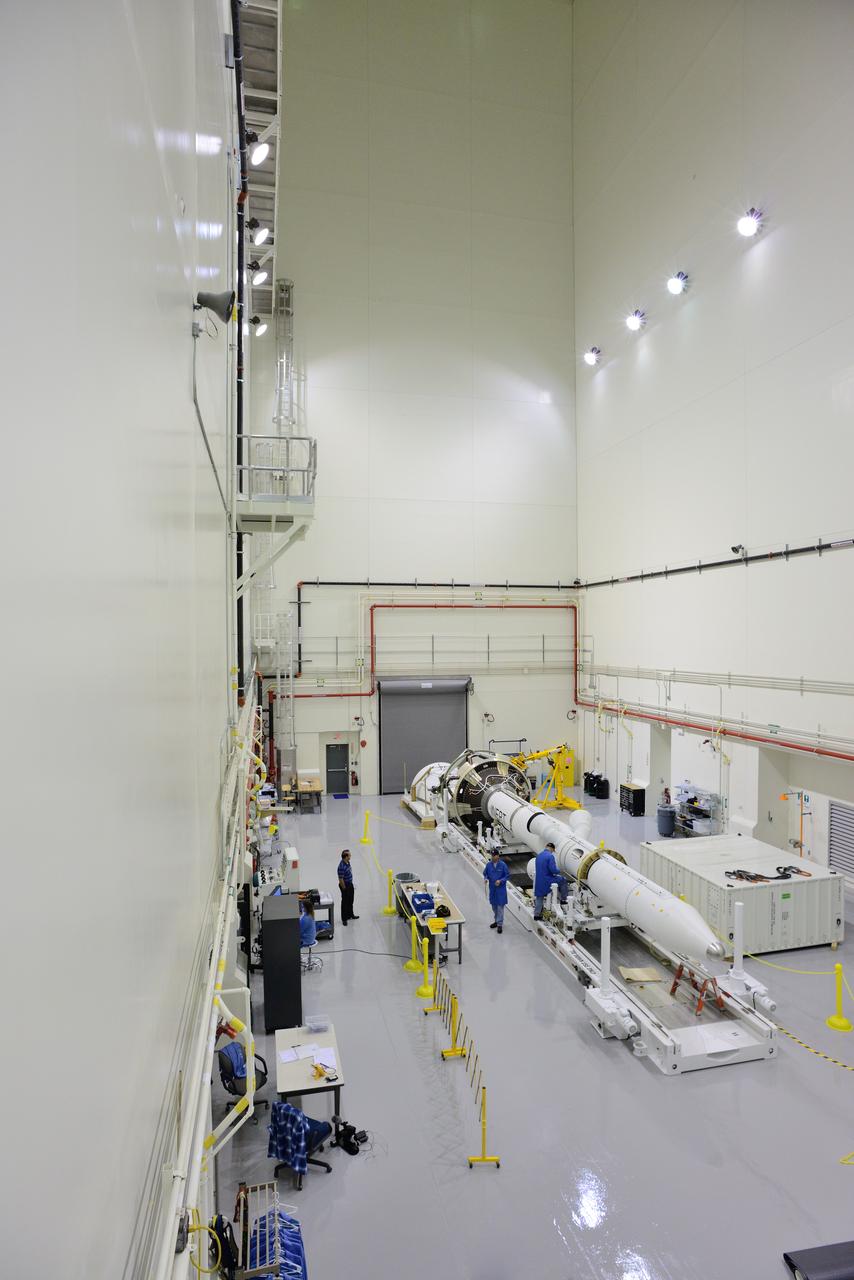
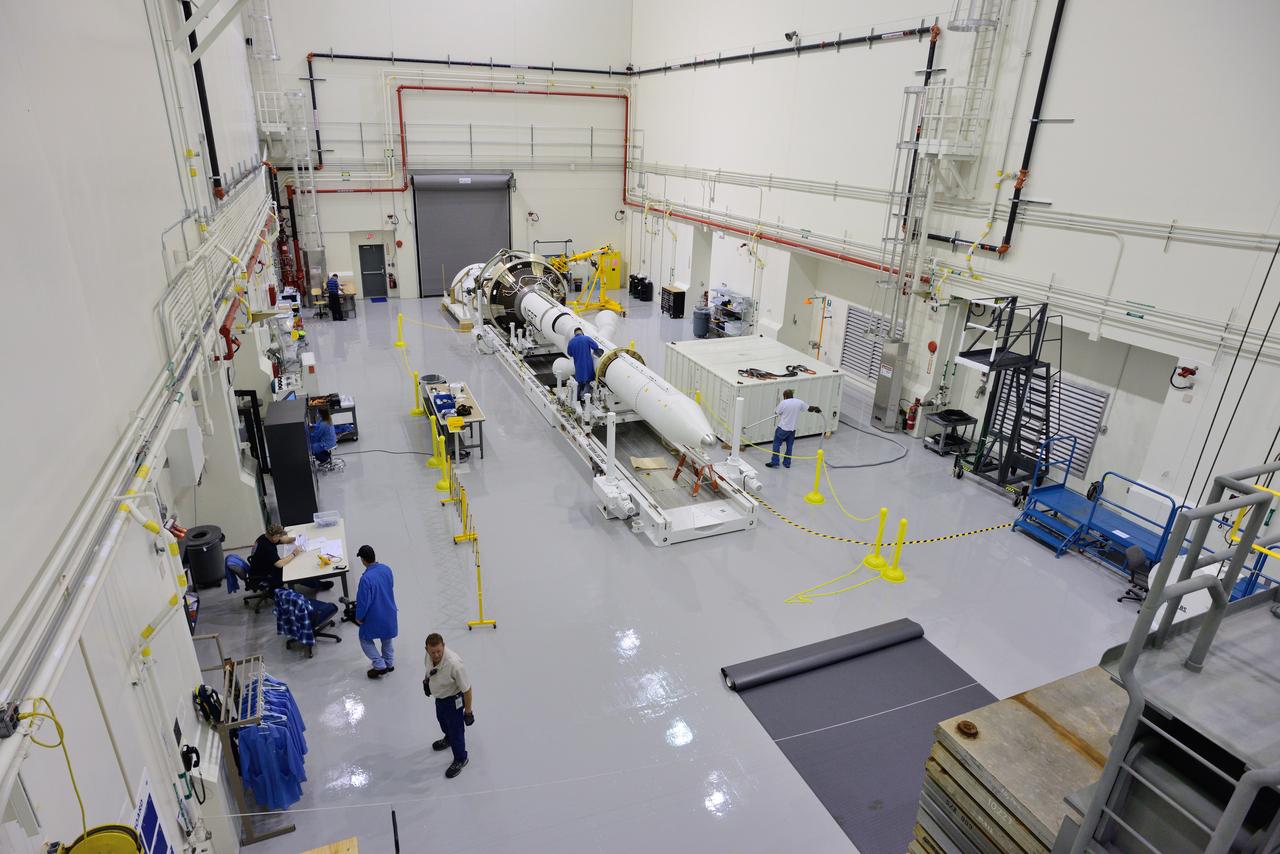
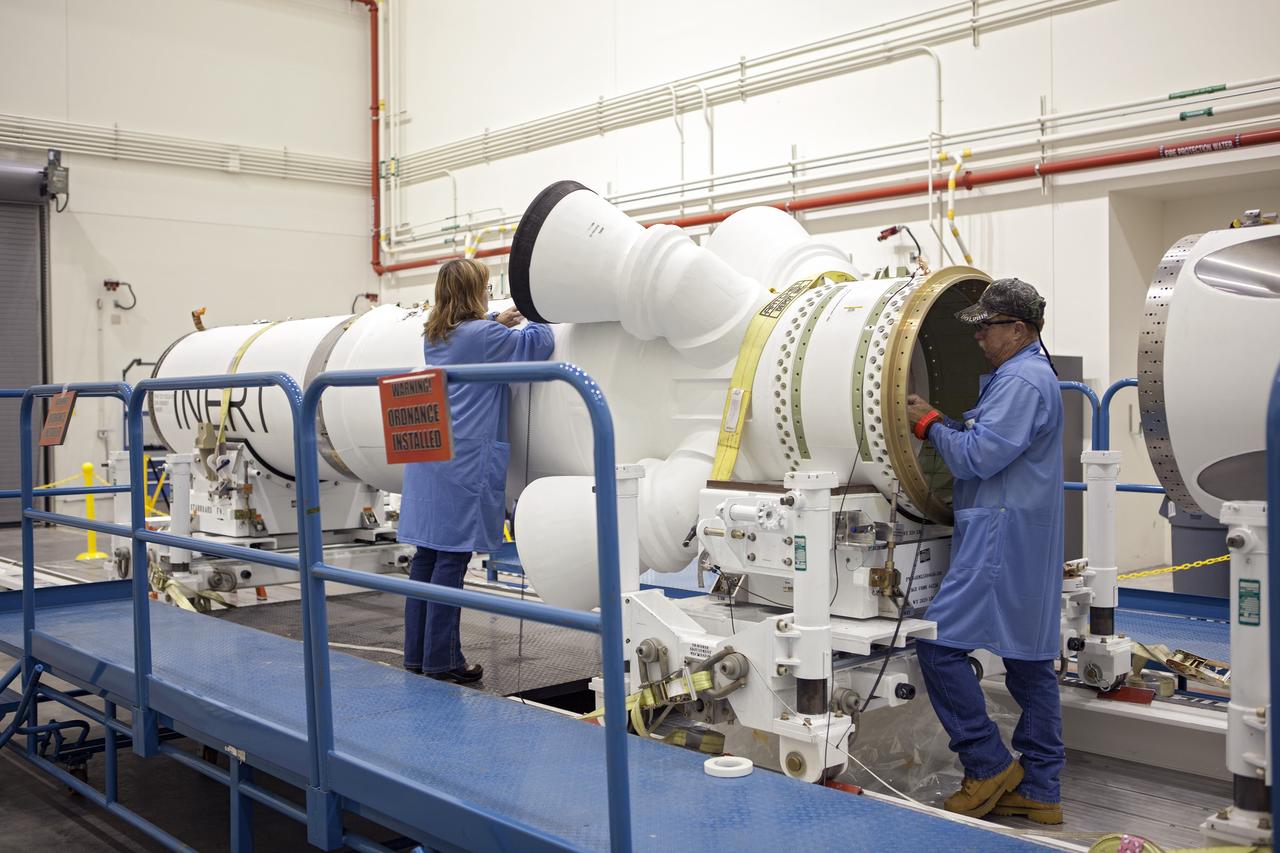
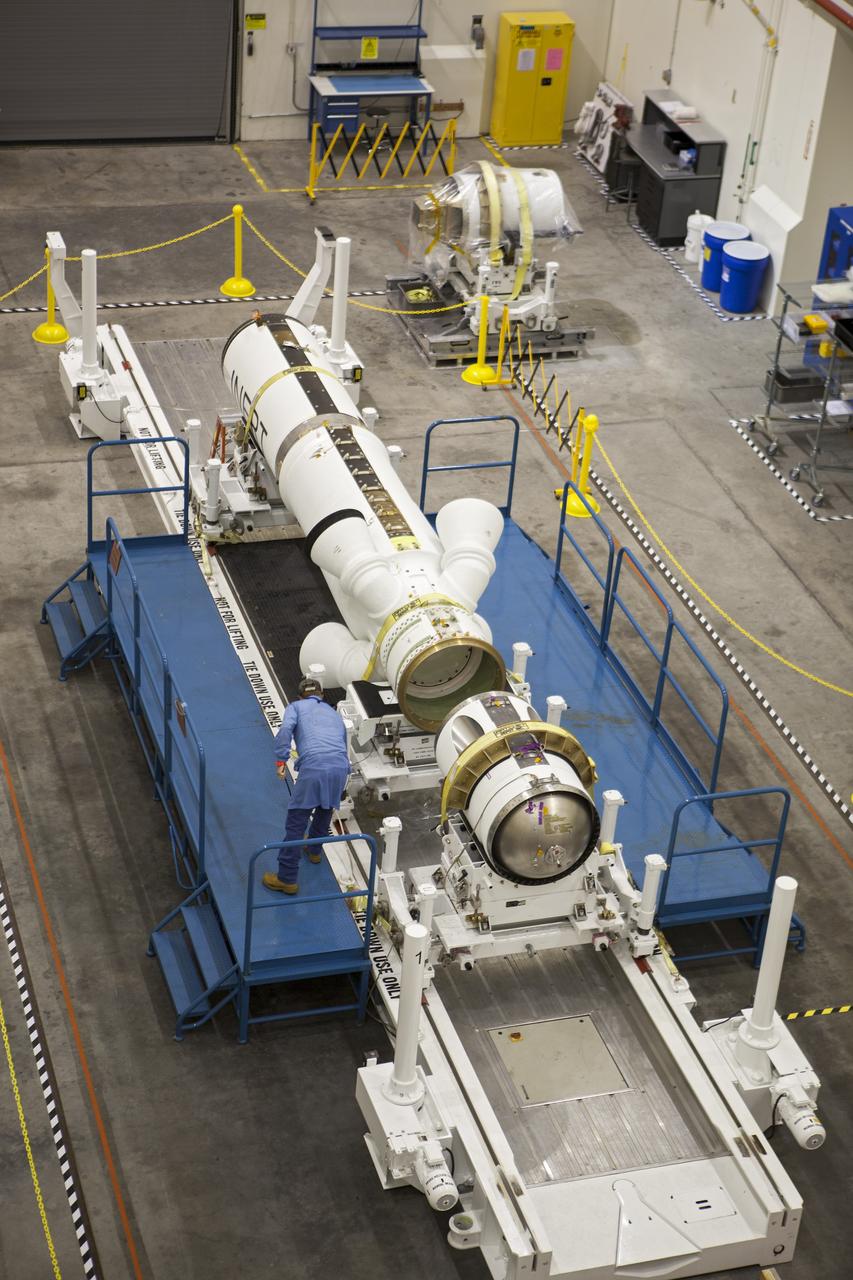
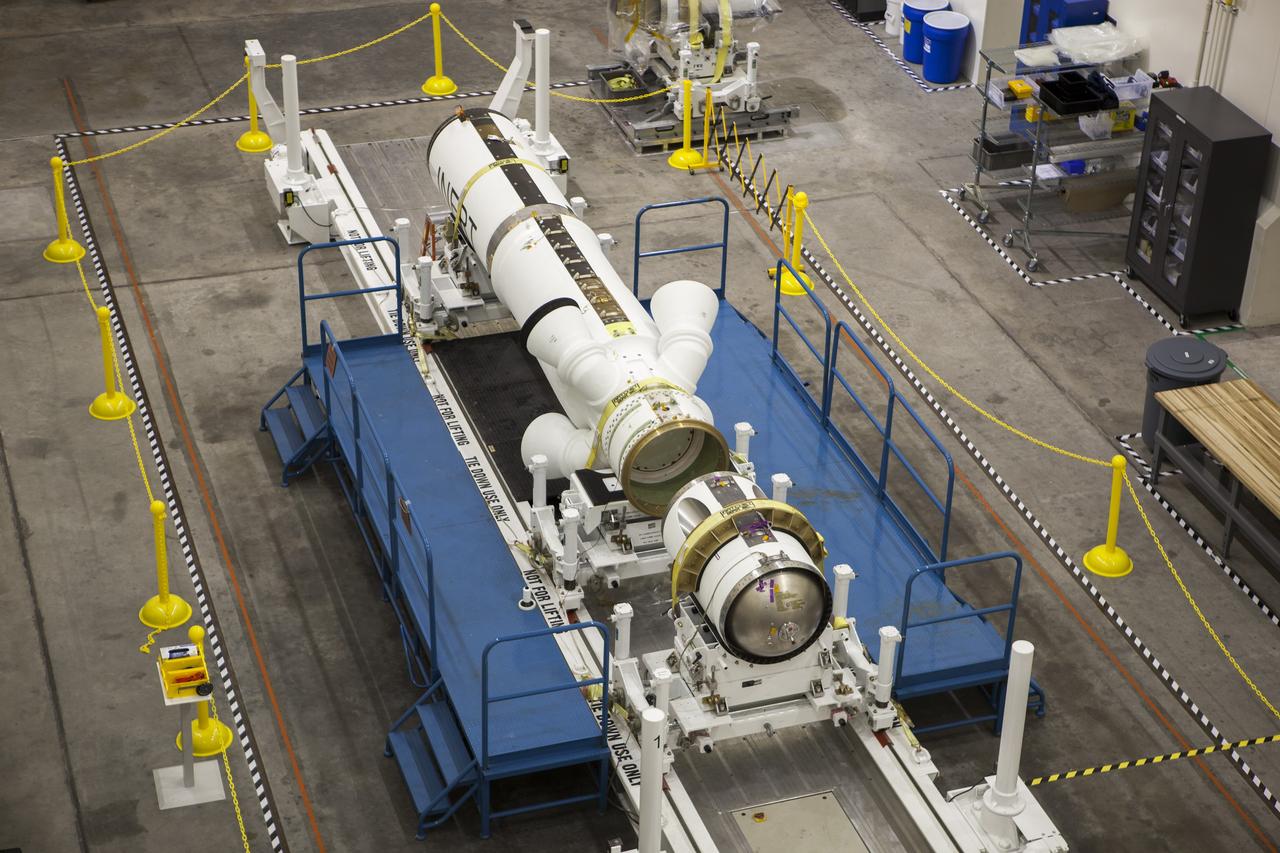
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the launch abort system, or LAS, components are horizontally stacked as processing continues for the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 mission. Components of the LAS are the launch abort motor, the attitude control motor, the jettison motor and the fairing. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The LAS is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
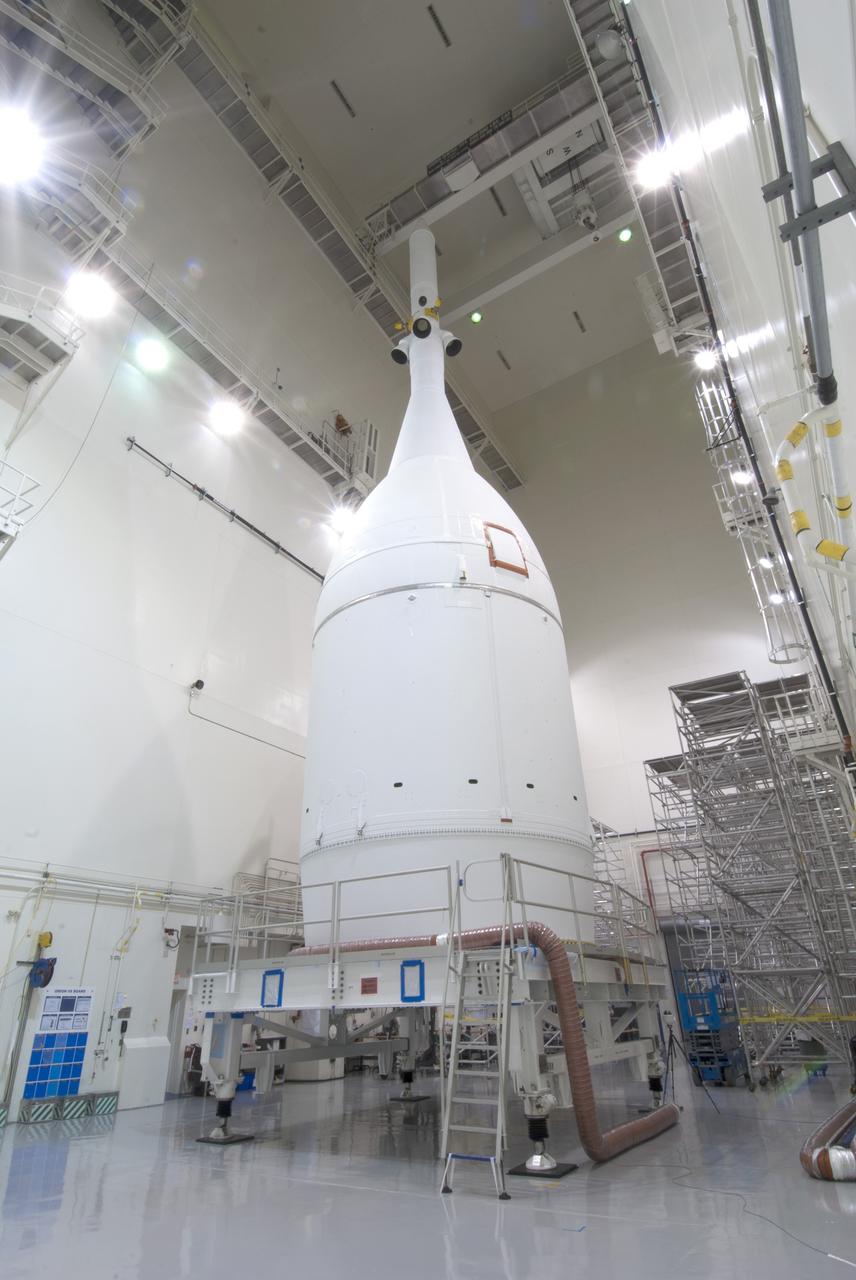

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft sits inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ogive panels have been installed around the launch abort system. The panels will smooth the airflow over the conical spacecraft to limit sound and vibration, which will make for a much smoother ride for the astronauts who will ride inside Orion in the future. The spacecraft is being readied for its move to Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for its flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Jim Grossman
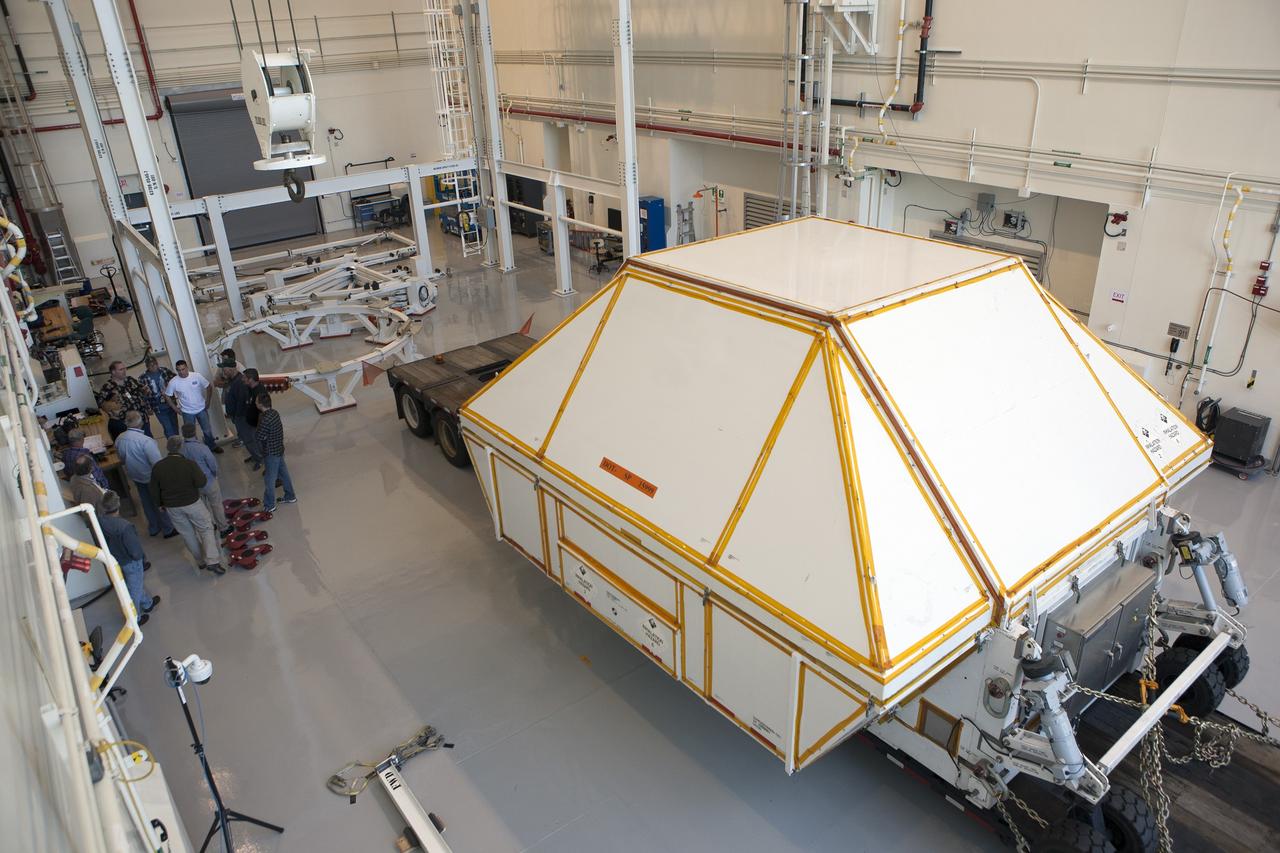

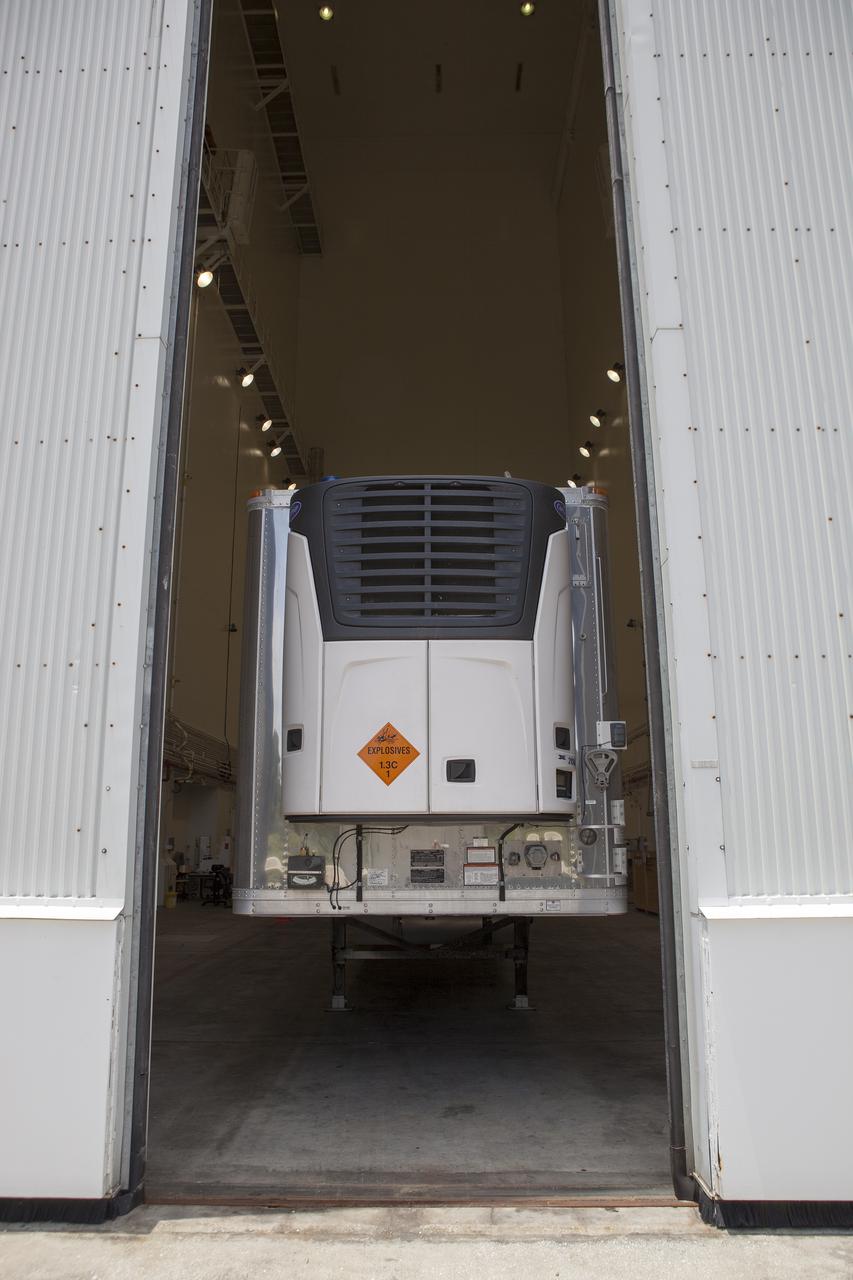
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft arrives inside the Launch Abort System Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft was transported 2,700 miles overland from Naval Base San Diego in California, on a flatbed truck secured in its crew module transportation fixture for the trip. During its first flight test, Orion completed a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Lou Garcia, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO, speaks to the media during the viewing opportunity. The spacecraft's cross-country return, a 2,700 mile road trip from Naval Base San Diego to Kennedy, sets the stage for in-depth analysis of data obtained during Orion's trip to space. It will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared during its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight test, completed on Dec. 5. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
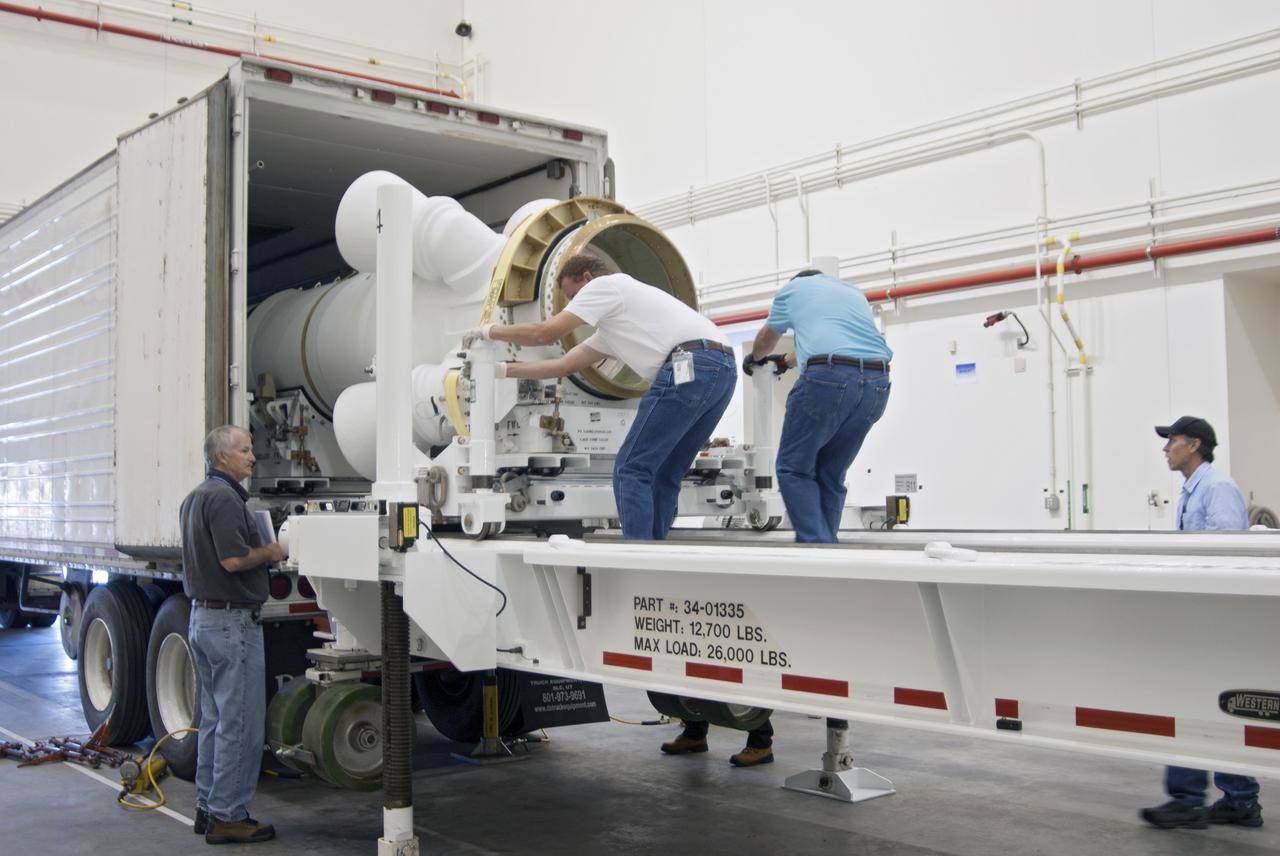

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians help remove the Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, launch abort motor from a truck after arrival at the Launch Abort System Facility. The test flight abort motor is for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, of the agency’s Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle. It is part of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. The motor is configured with inert propellant. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Charisse Nahser
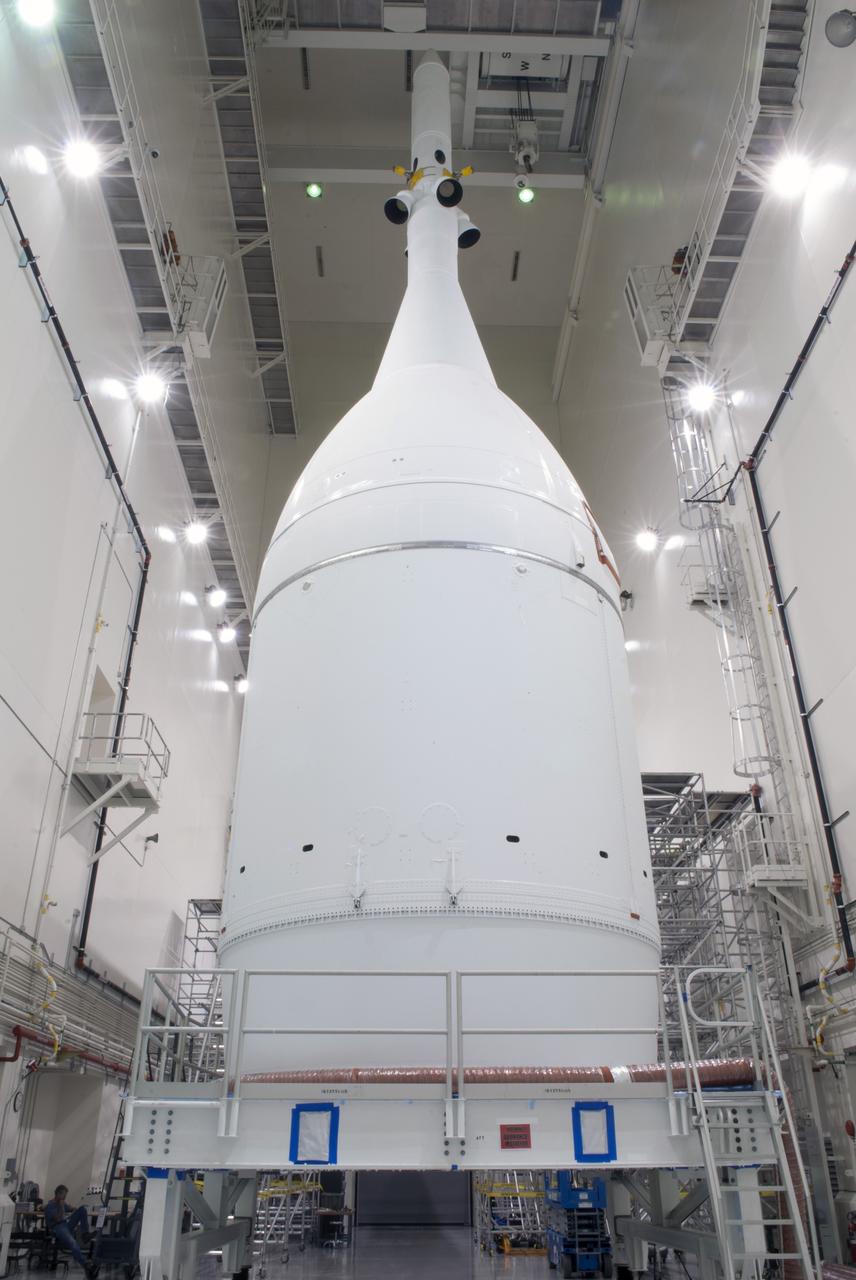

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft sits inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ogive panels have been installed around the launch abort system. The panels will smooth the airflow over the conical spacecraft to limit sound and vibration, which will make for a much smoother ride for the astronauts who will ride inside Orion in the future. The spacecraft is being readied for its move to Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for its flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Jim Grossman

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Lockheed Martin Manager Jules Schneider speaks to members of the media during a viewing of NASA's Orion spacecraft at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft's cross-country return, a 2,700 mile road trip from Naval Base San Diego to Kennedy, sets the stage for in-depth analysis of data obtained during Orion's trip to space. It will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared during its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight test, completed on Dec. 5. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
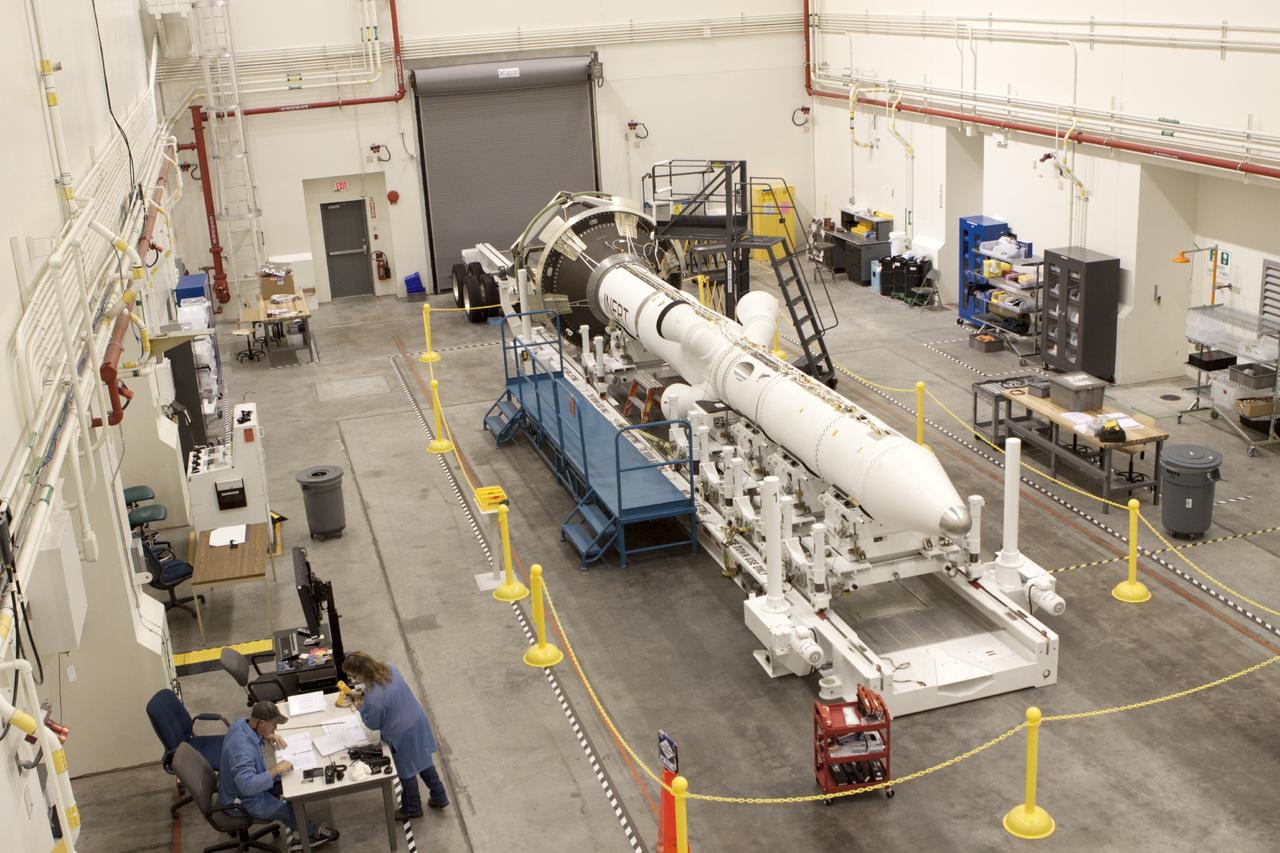

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to work on the launch abort system, or LAS, for the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 mission. Horizontally stacked together are the components of the LAS, the launch abort motor, the attitude control motor, the jettison motor and the fairing. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The LAS is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
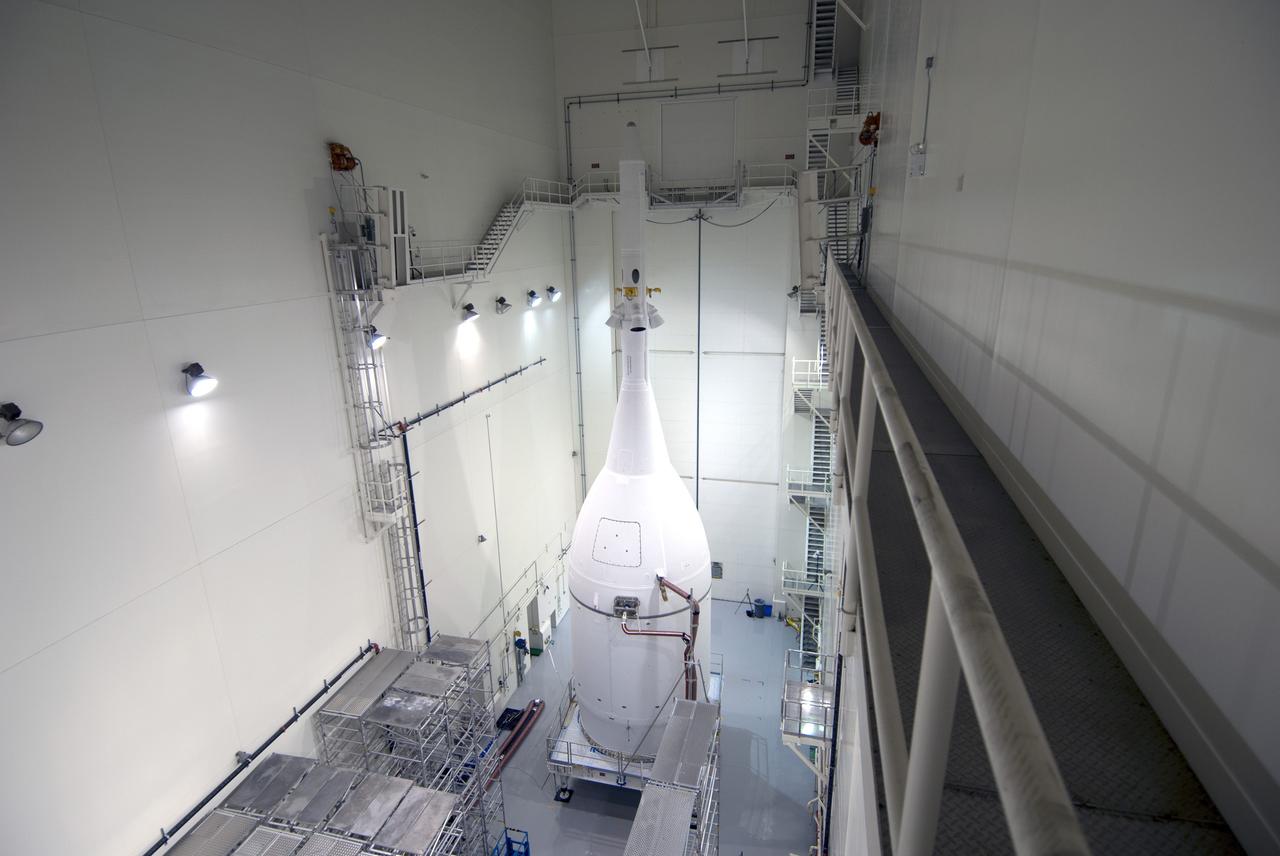

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft sits inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ogive panels have been installed around the launch abort system. The panels will smooth the airflow over the conical spacecraft to limit sound and vibration, which will make for a much smoother ride for the astronauts who will ride inside Orion in the future. The spacecraft is being readied for its move to Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for its flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Jim Grossman
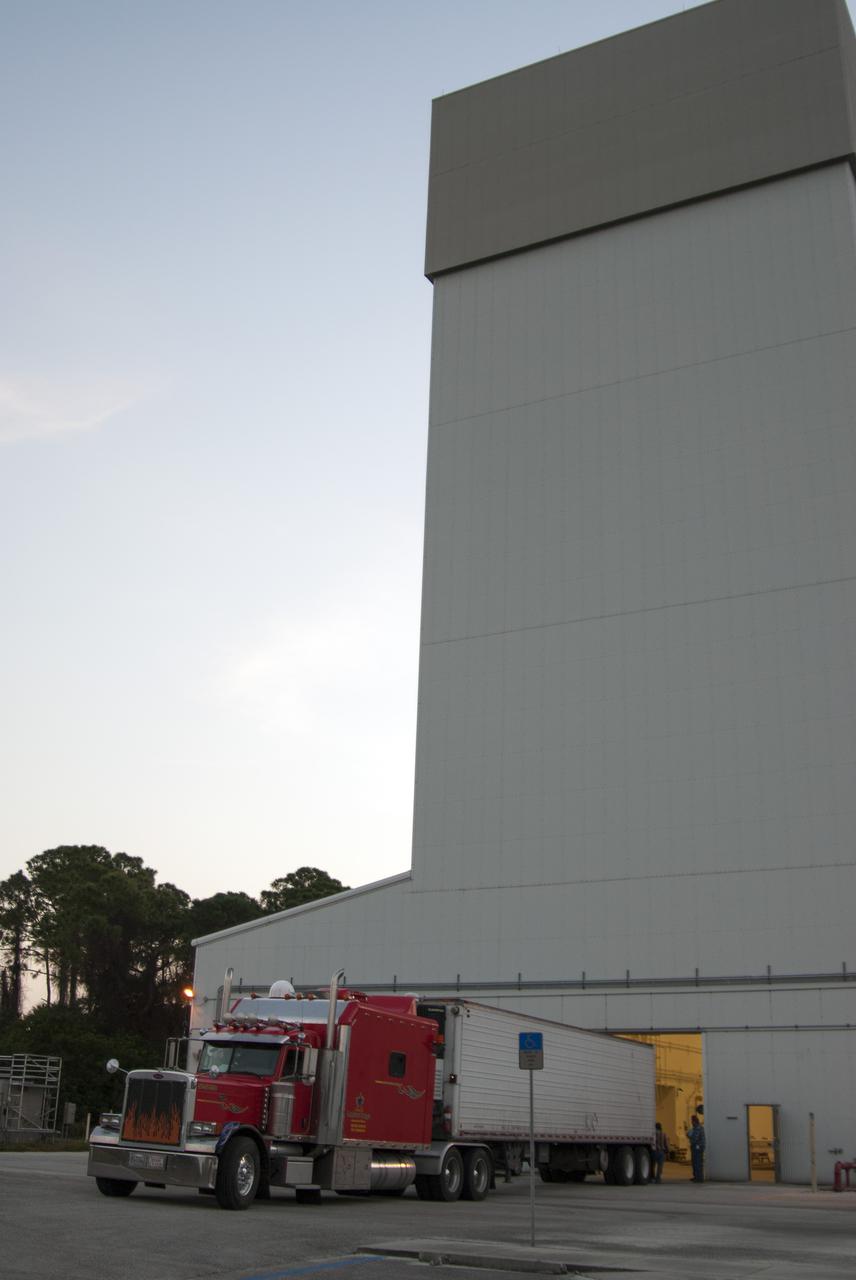

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a truck arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility with a launch abort motor from Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, of the agency’s Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle. ATK’s abort motor is part of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. The test flight abort motor is configured with inert propellant. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Charisse Nahser

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Lou Garcia, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO, speaks to the media during the viewing opportunity. The spacecraft's cross-country return, a 2,700 mile road trip from Naval Base San Diego to Kennedy, sets the stage for in-depth analysis of data obtained during Orion's trip to space. It will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared during its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight test, completed on Dec. 5. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
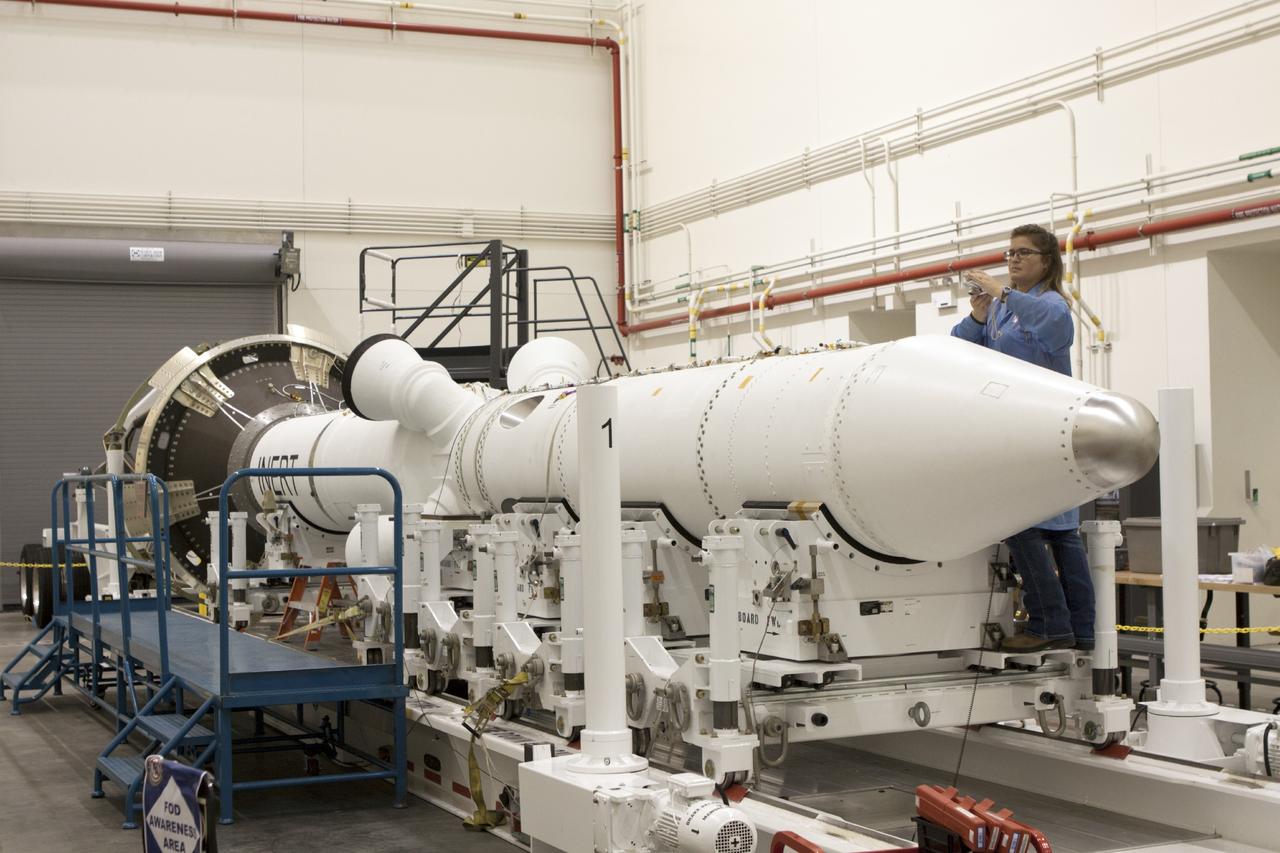

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician works on the launch abort system, or LAS, for the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 mission. Horizontally stacked together are the components of the LAS, the launch abort motor, the attitude control motor, the jettison motor and the fairing. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The LAS is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
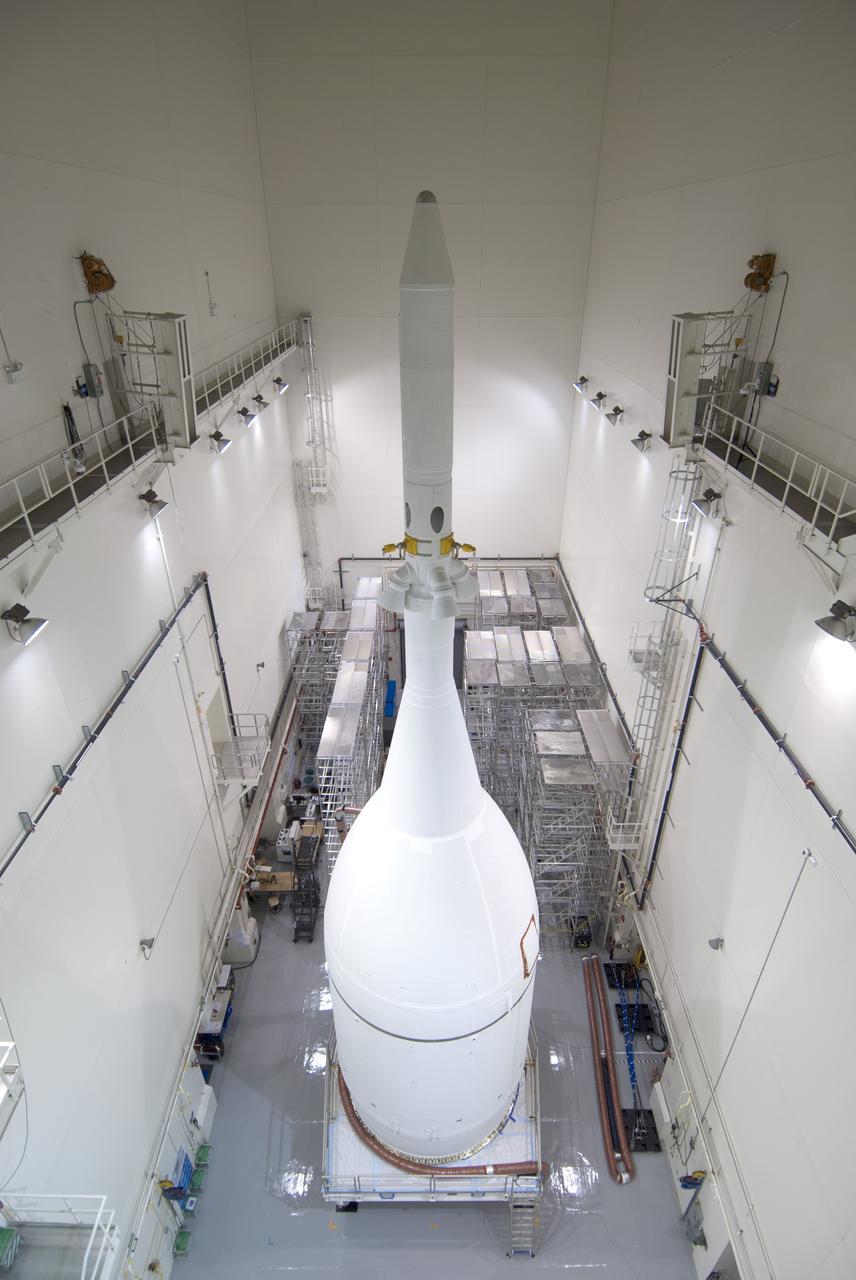

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft sits inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ogive panels have been installed around the launch abort system. The panels will smooth the airflow over the conical spacecraft to limit sound and vibration, which will make for a much smoother ride for the astronauts who will ride inside Orion in the future. The spacecraft is being readied for its move to Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for its flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Jim Grossman
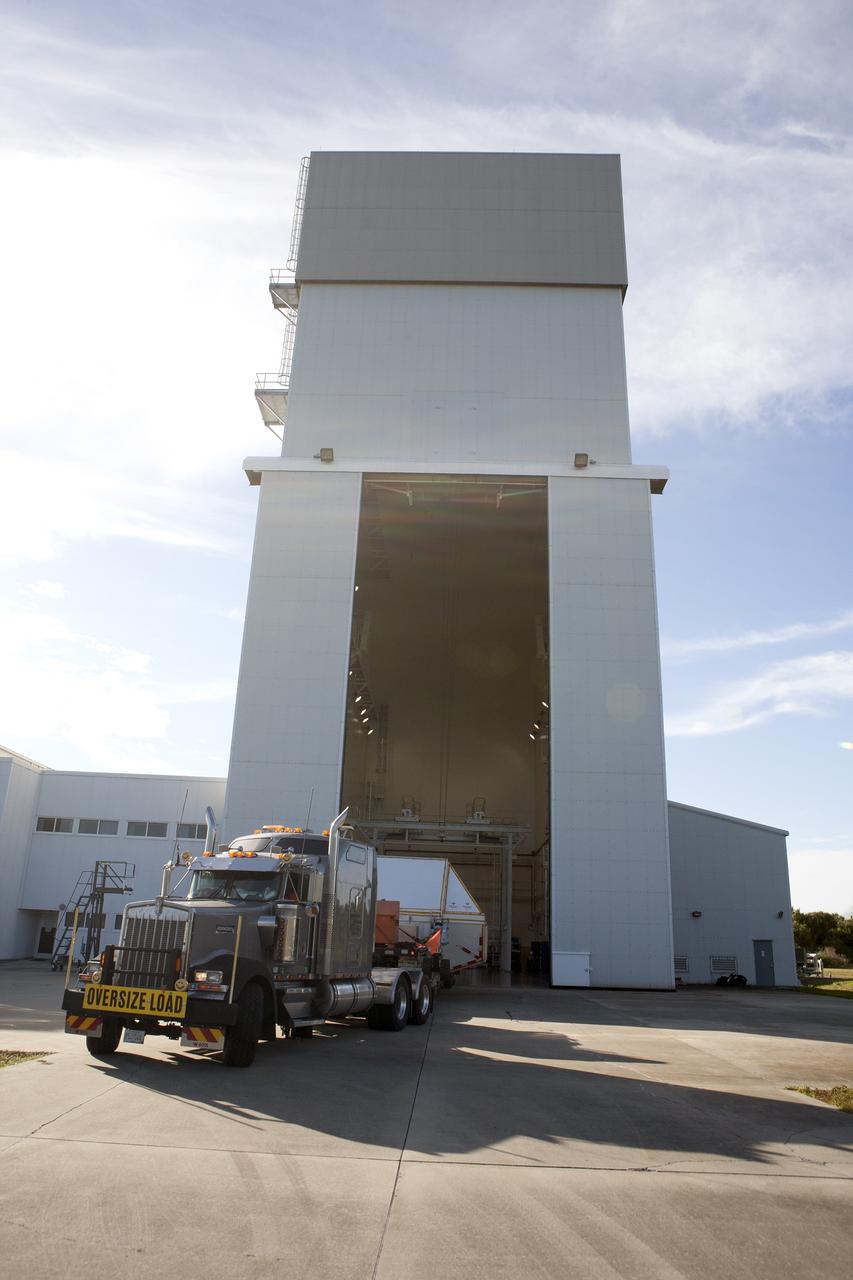

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft was transported 2,700 miles overland from Naval Base San Diego in California, on a flatbed truck secured in its crew module transportation fixture for the trip. During its first flight test, Orion completed a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
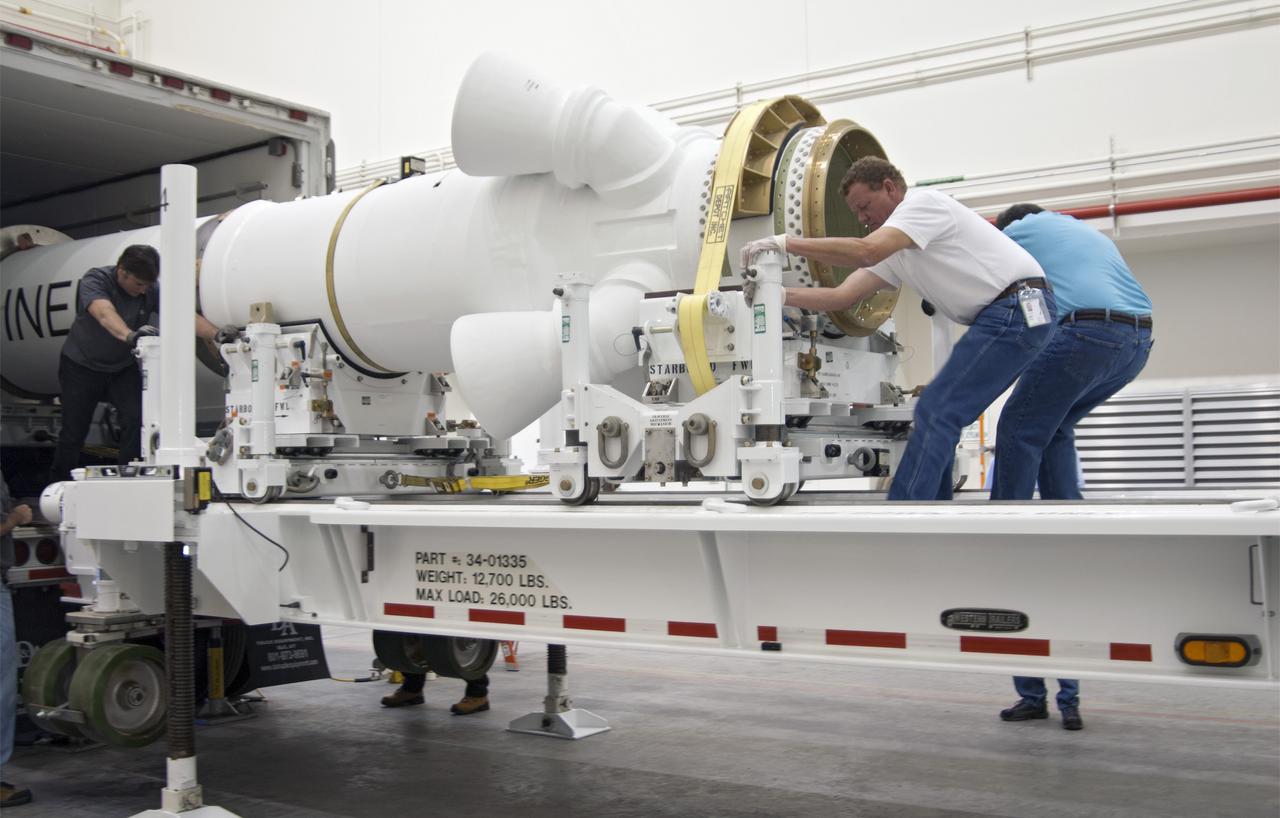

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – At NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians help remove the Alliant Techsystems, or ATK, launch abort motor from a truck after arrival at the Launch Abort System Facility. The test flight abort motor is for Exploration Flight Test 1, or EFT-1, of the agency’s Orion Multi-Purpose Crew Vehicle. It is part of Orion’s Launch Abort System, which is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. The motor is configured with inert propellant. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http:__www.nasa.gov_orion. Photo credit: NASA_Charisse Nahser
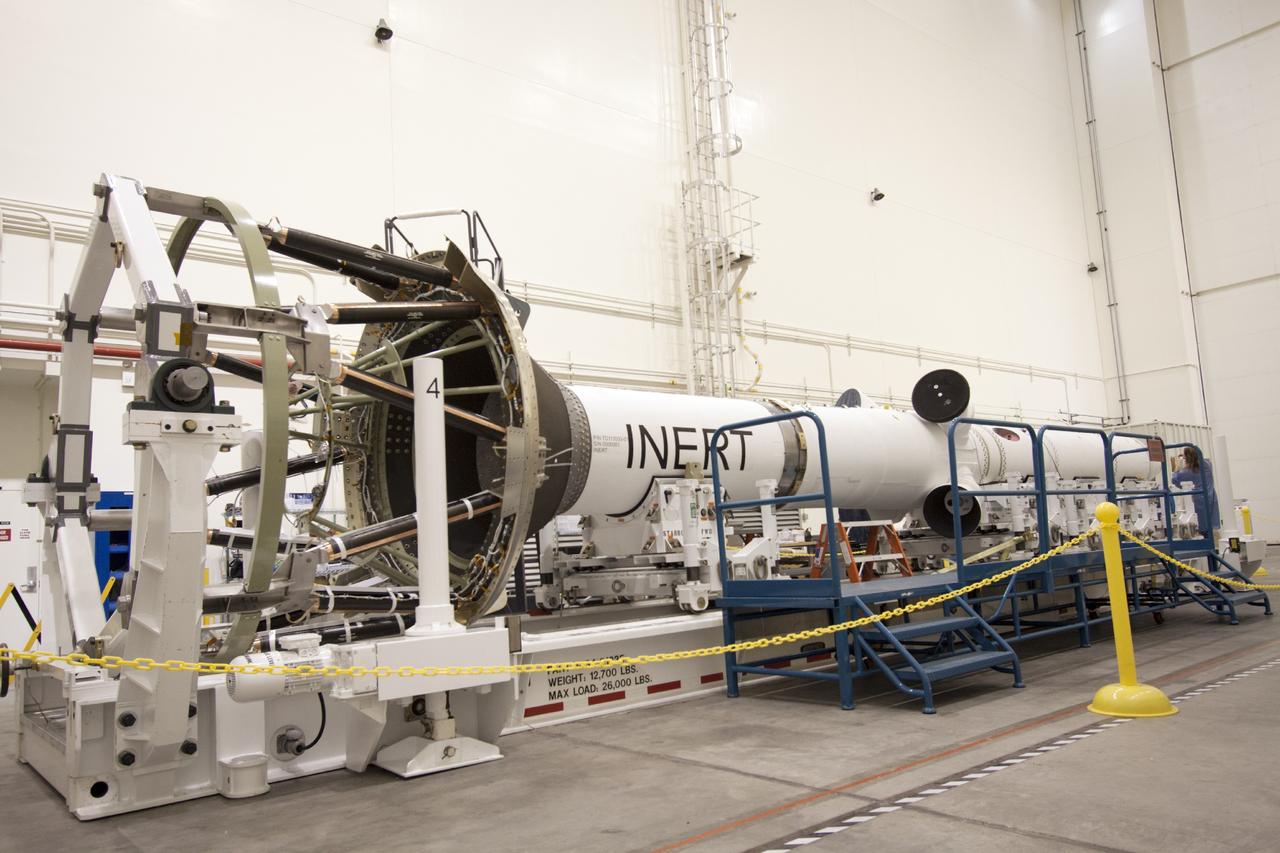

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the launch abort system, or LAS, components are horizontally stacked as processing continues for the Orion Exploration Flight Test-1 mission. Components of the LAS are the launch abort motor, the attitude control motor, the jettison motor and the fairing. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The LAS is designed to safely pull the Orion crew module away from the launch vehicle in the event of an emergency on the launch pad or during the initial ascent of NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS, rocket. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for 2017 on the SLS rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
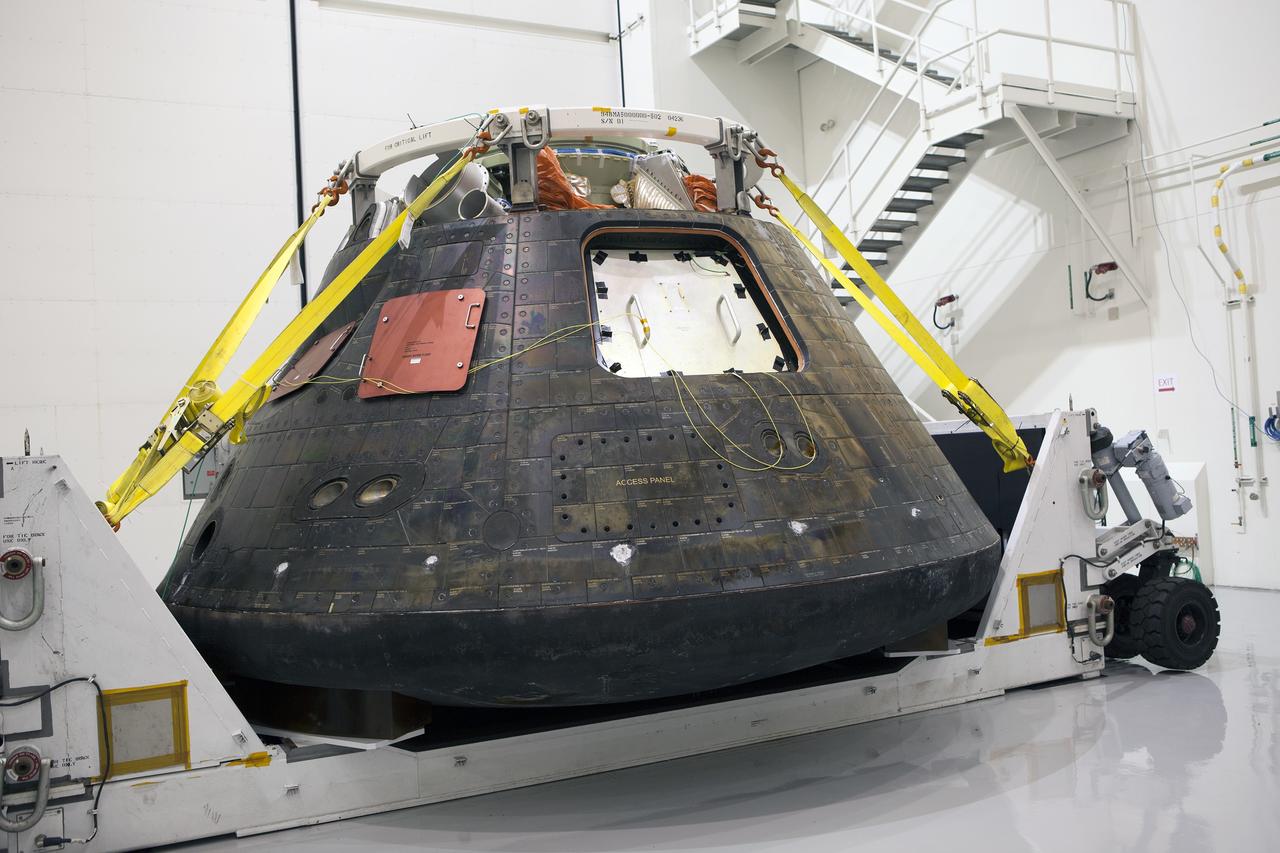

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft has been uncrated and is inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a media event. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
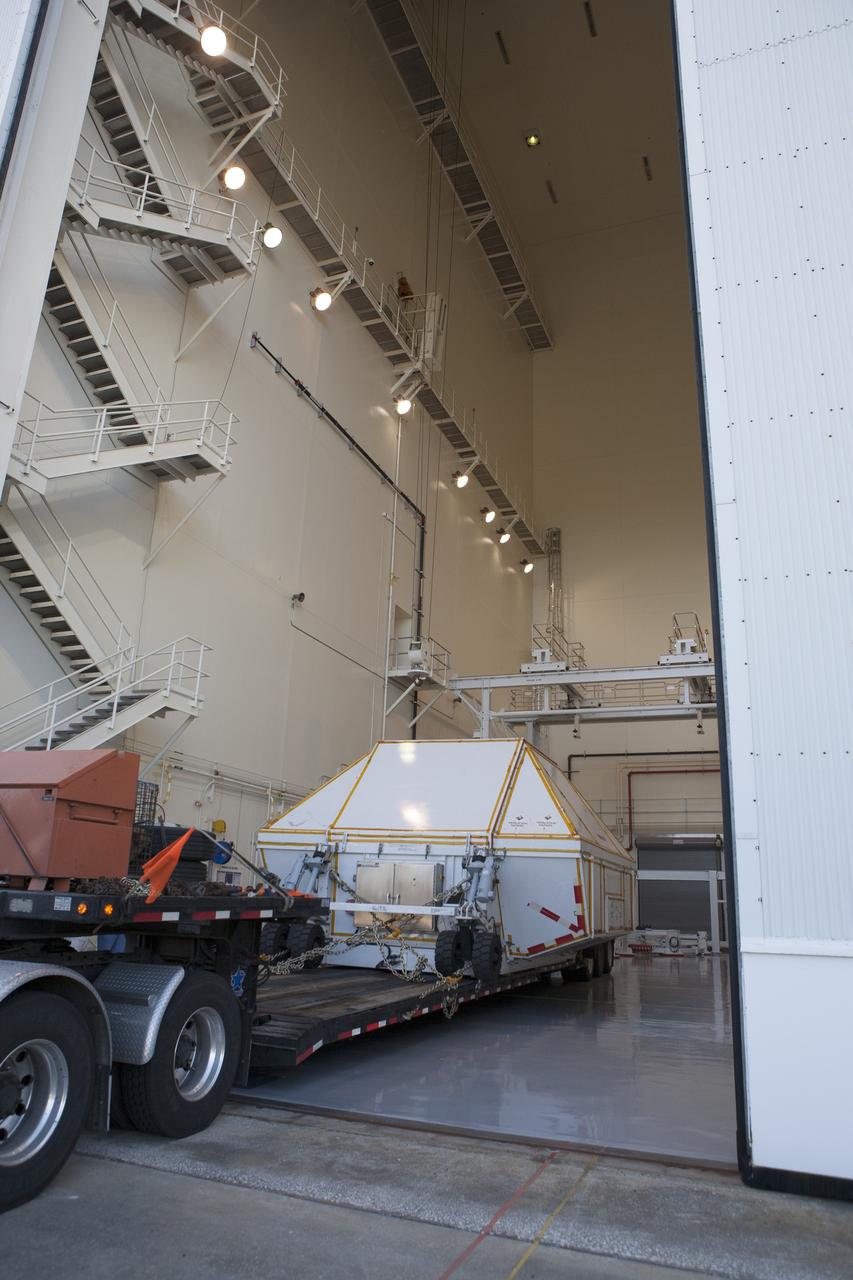

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft was transported 2,700 miles overland from Naval Base San Diego in California, on a flatbed truck secured in its crew module transportation fixture for the trip. During its first flight test, Orion completed a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft sits inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The Ogive panels have been installed around the launch abort system. The panels will smooth the airflow over the conical spacecraft to limit sound and vibration, which will make for a much smoother ride for the astronauts who will ride inside Orion in the future. The spacecraft is being readied for its move to Space Launch Complex 37 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for its flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted flight test of Orion is scheduled to launch in December 2014 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket, and in 2018 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Jim Grossman
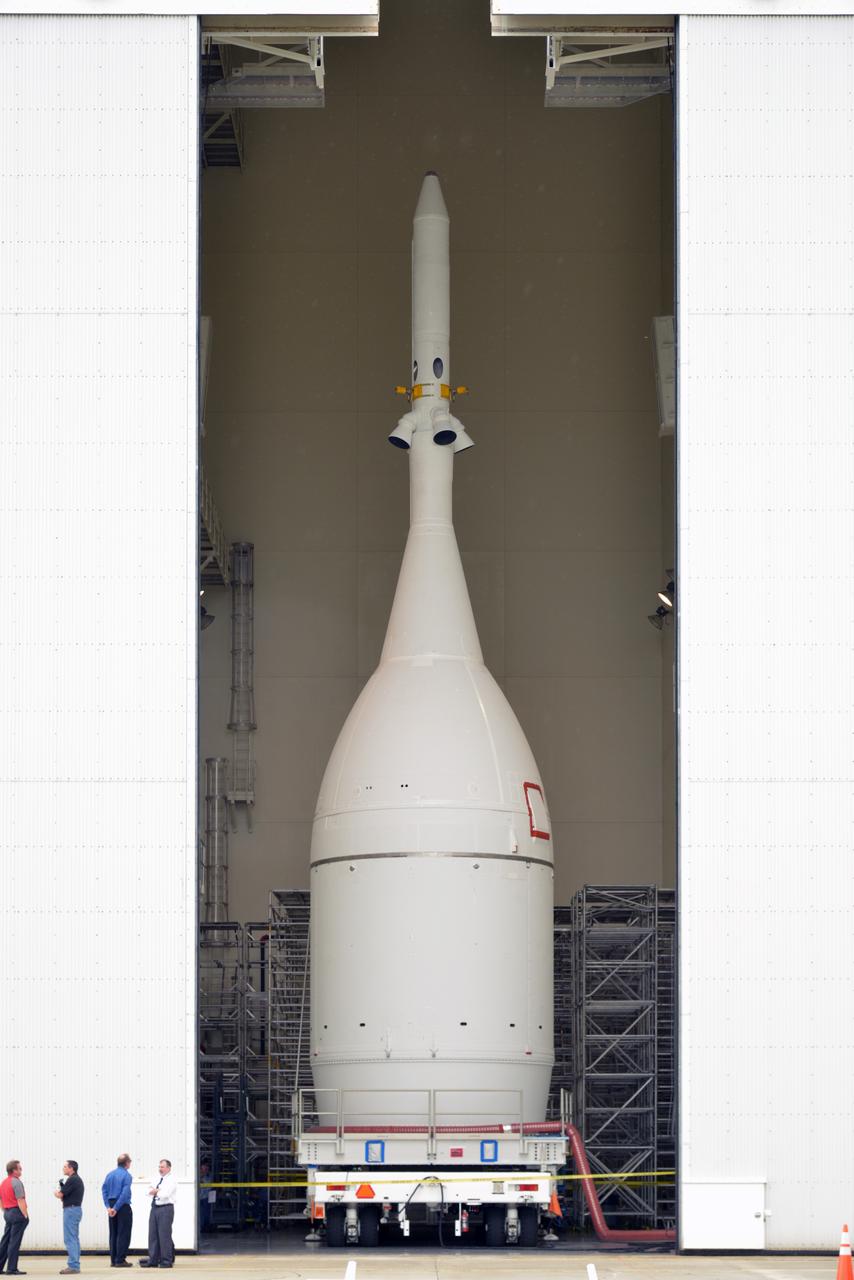

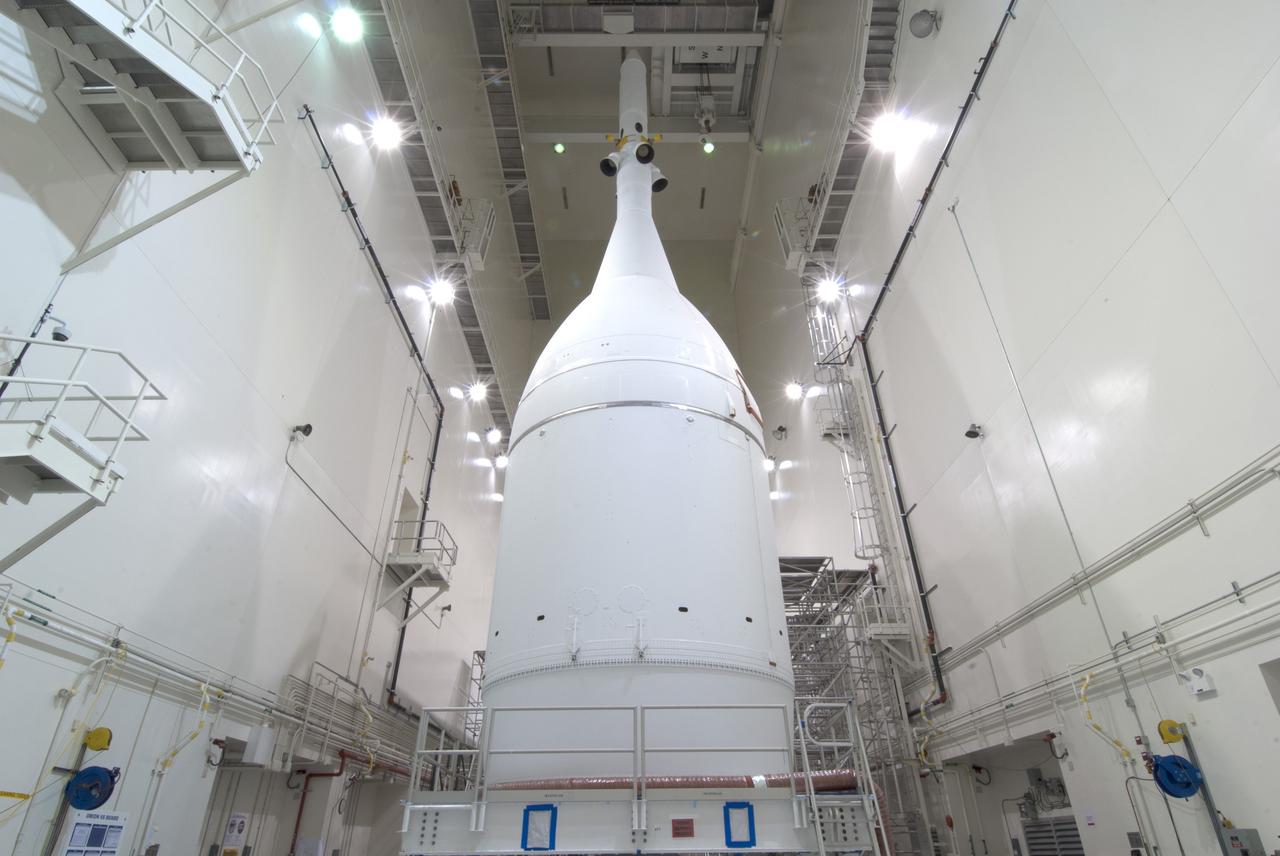
The Orion for Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1) is stacked and ready to roll to the pad in the Launch Abort System Facility (LASF) at Kennedy Space Center on Nov. 10, 2014. The Orion stack, consisting of the launch abort system, the crew module, and the service module measures over 80 feet tall. Part of Batch image transfer from Flickr.