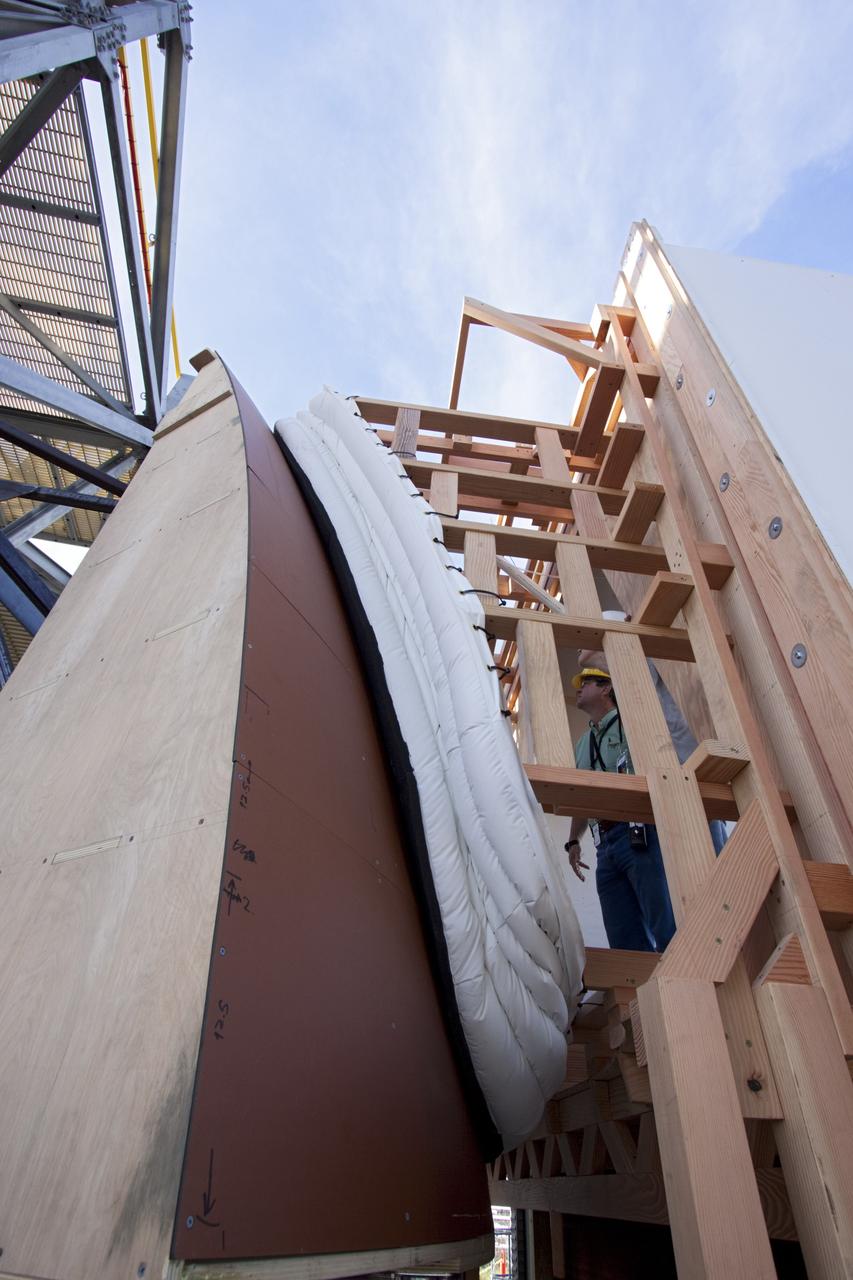

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft crew access arm, or CAA, seal prototype is being checked out at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests will use a mockup of the vehicle Outer Mold Line and CAA white room to test the performance of the seal while simulating vehicle to CAA white room excursions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
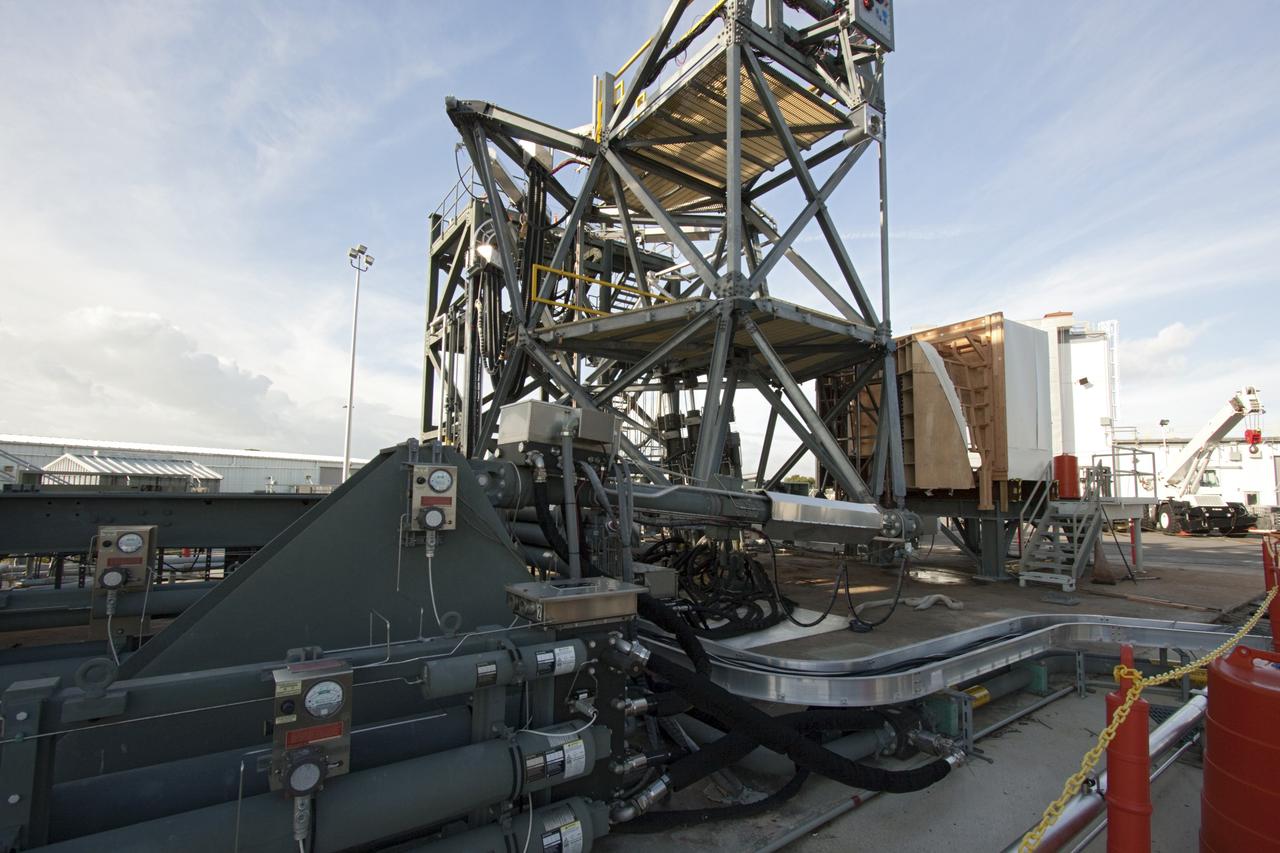

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft crew access arm, or CAA, seal prototype is being checked out at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests will use a mockup of the vehicle Outer Mold Line and CAA white room to test the performance of the seal while simulating vehicle to CAA white room excursions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
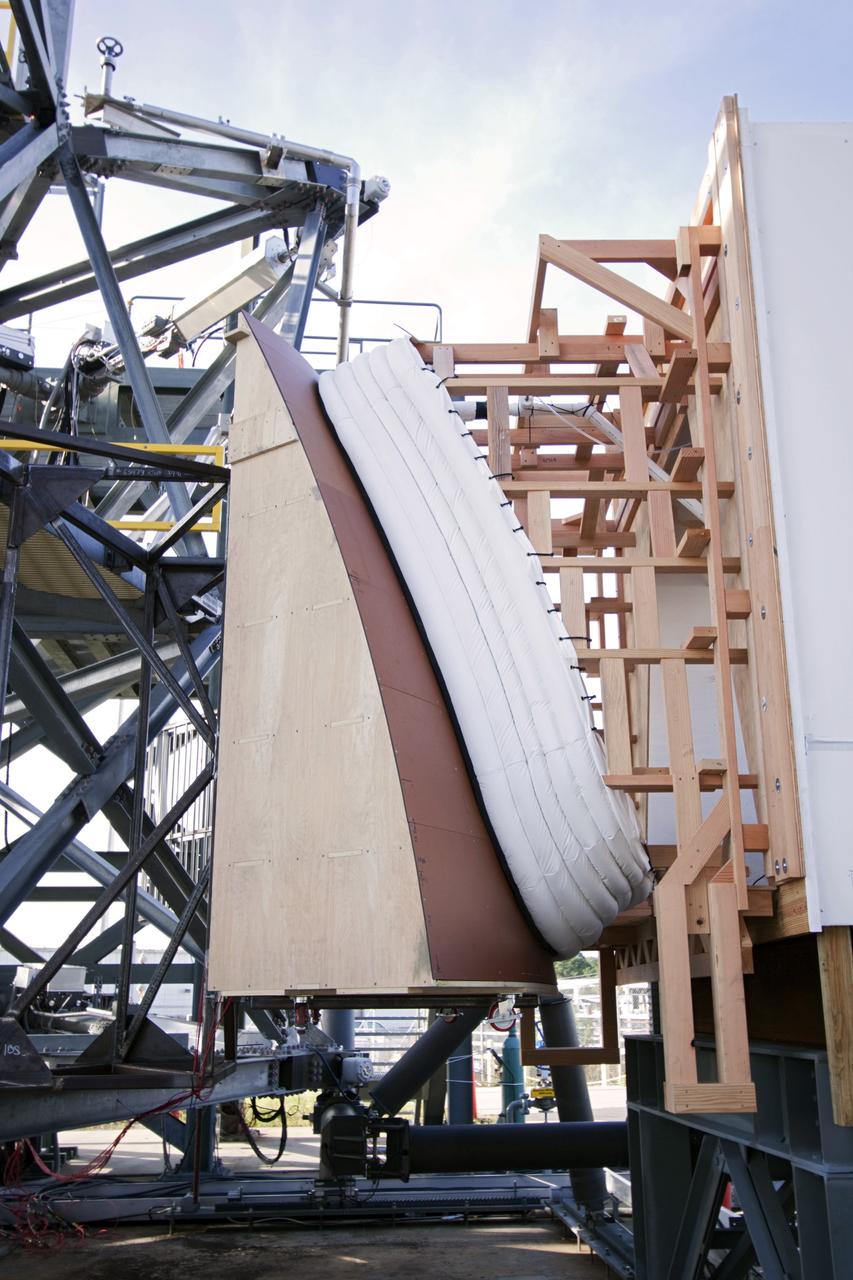

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft crew access arm, or CAA, seal prototype is being checked out at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests will use a mockup of the vehicle Outer Mold Line and CAA white room to test the performance of the seal while simulating vehicle to CAA white room excursions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
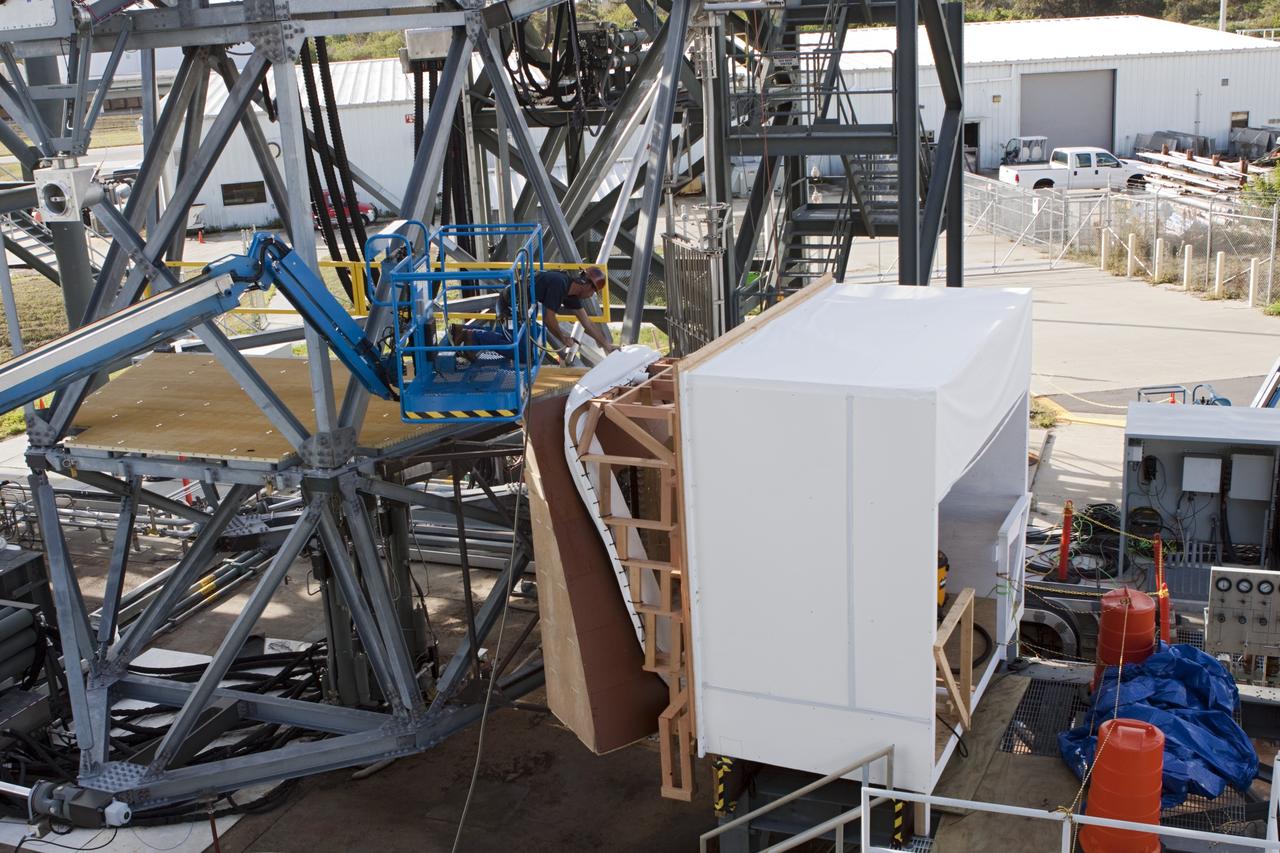

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft crew access arm, or CAA, seal prototype is being checked out at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests will use a mockup of the vehicle Outer Mold Line and CAA white room to test the performance of the seal while simulating vehicle to CAA white room excursions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
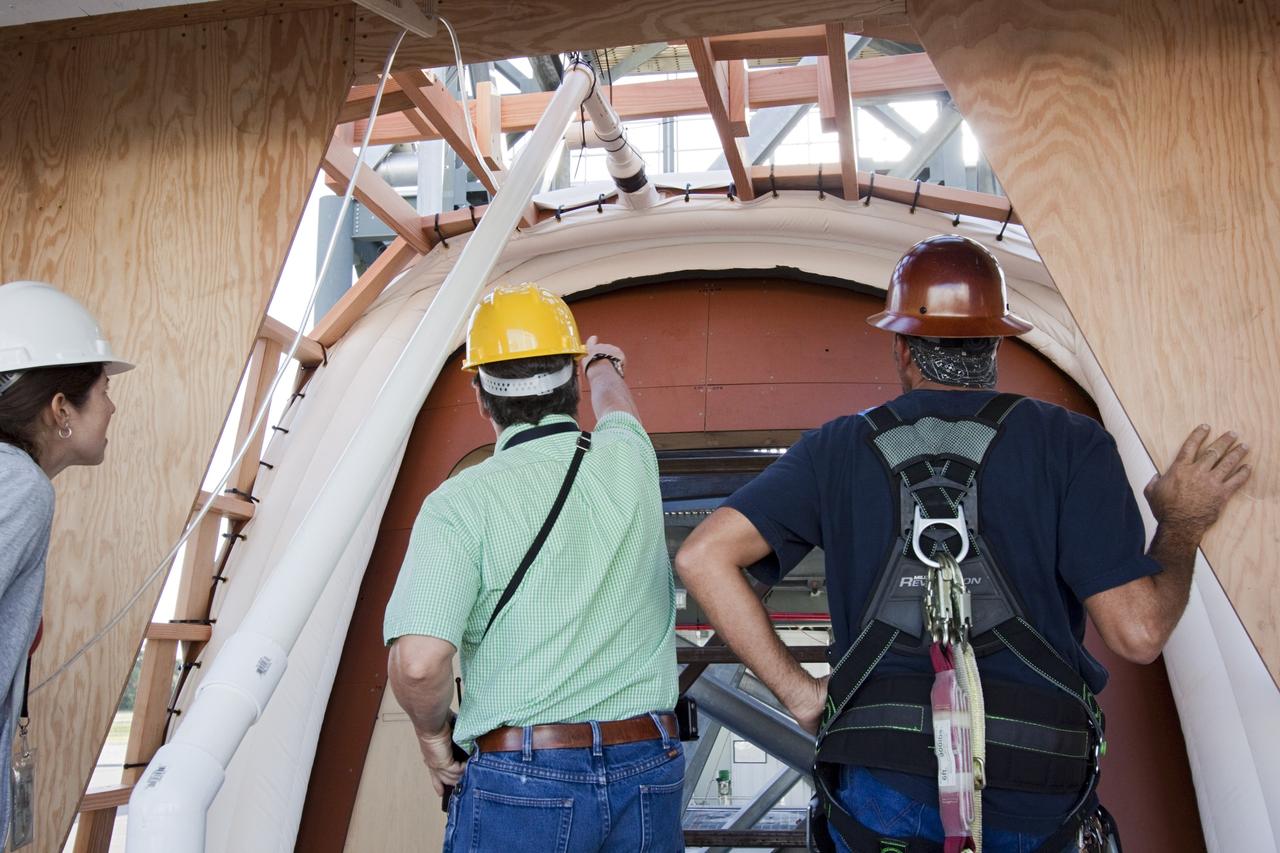

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft crew access arm, or CAA, seal prototype is being checked by technicians and engineers at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASAs Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests will use a mockup of the vehicle Outer Mold Line and CAA white room to assess the performance of the seal while simulating vehicle to CAA white room excursions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
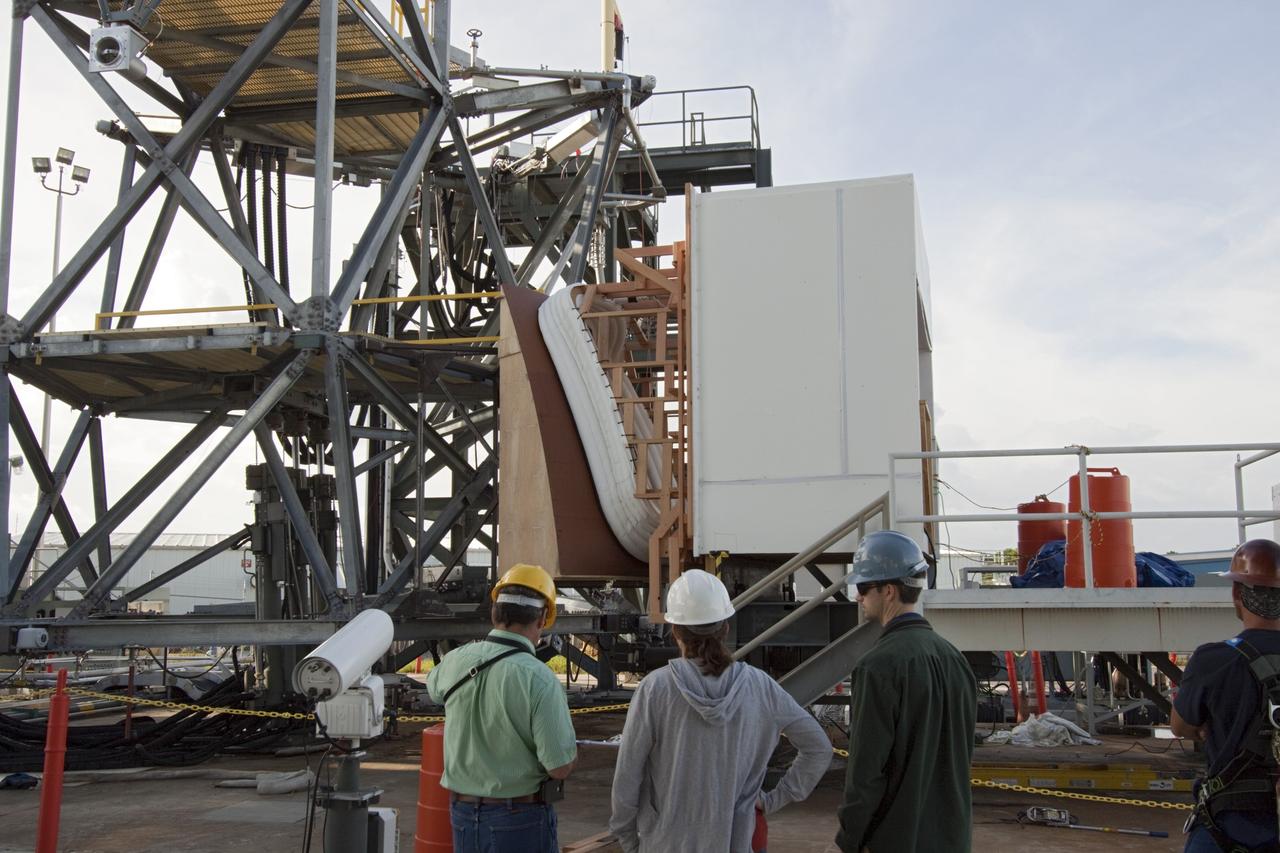

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft crew access arm, or CAA, seal prototype is being checked out at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Monitoring the activity, from the left are Kent Bachelor, Stinger Ghaffarian Technologies lead, Kelli Maloney, NASA lead and Clayton Gvasse, Nelson Engineering lead. The tests will use a mockup of the vehicle Outer Mold Line and CAA white room to test the performance of the seal while simulating vehicle to CAA white room excursions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion spacecraft crew access arm, or CAA, seal prototype is being checked by technicians and engineers at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASAs Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The tests will use a mockup of the vehicle Outer Mold Line and CAA white room to assess the performance of the seal while simulating vehicle to CAA white room excursions. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
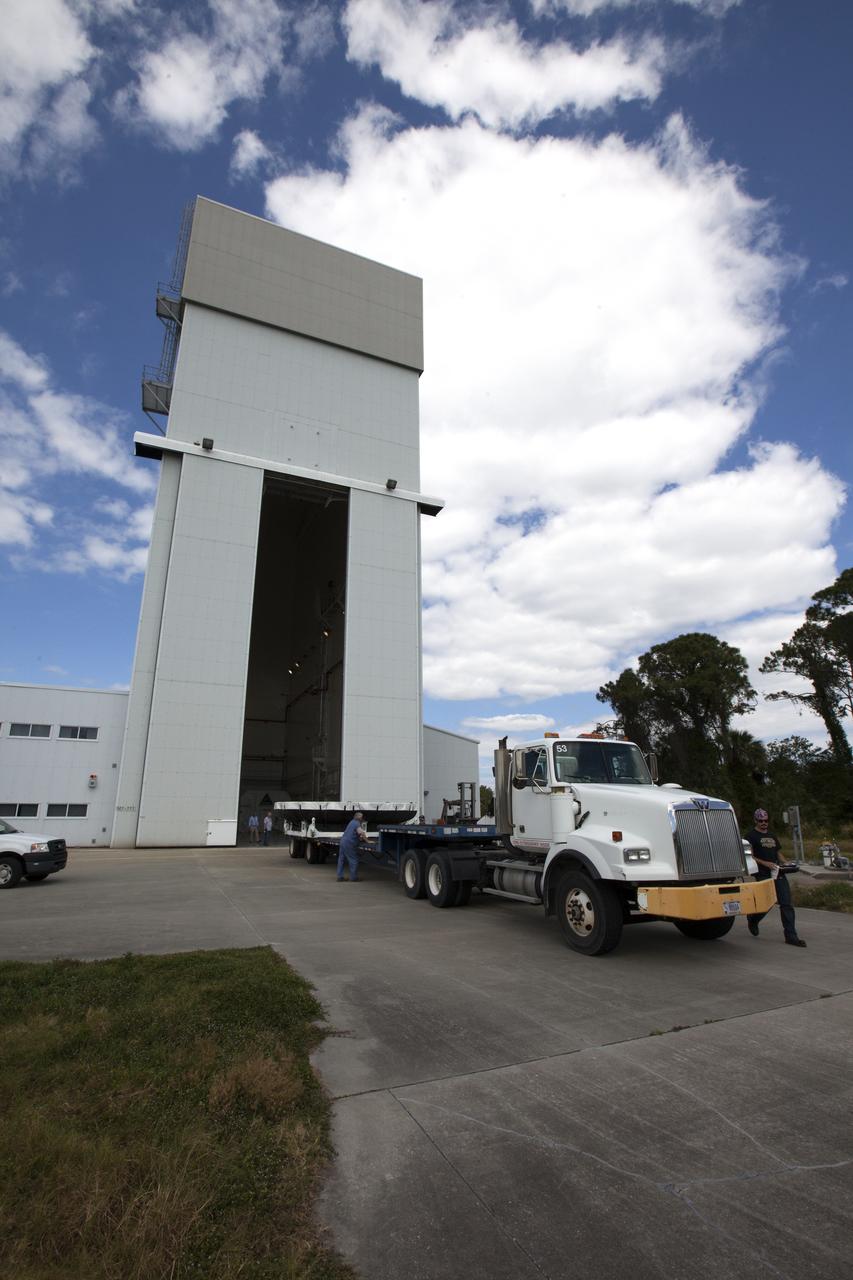

The Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1, secured on a transporter, departs the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
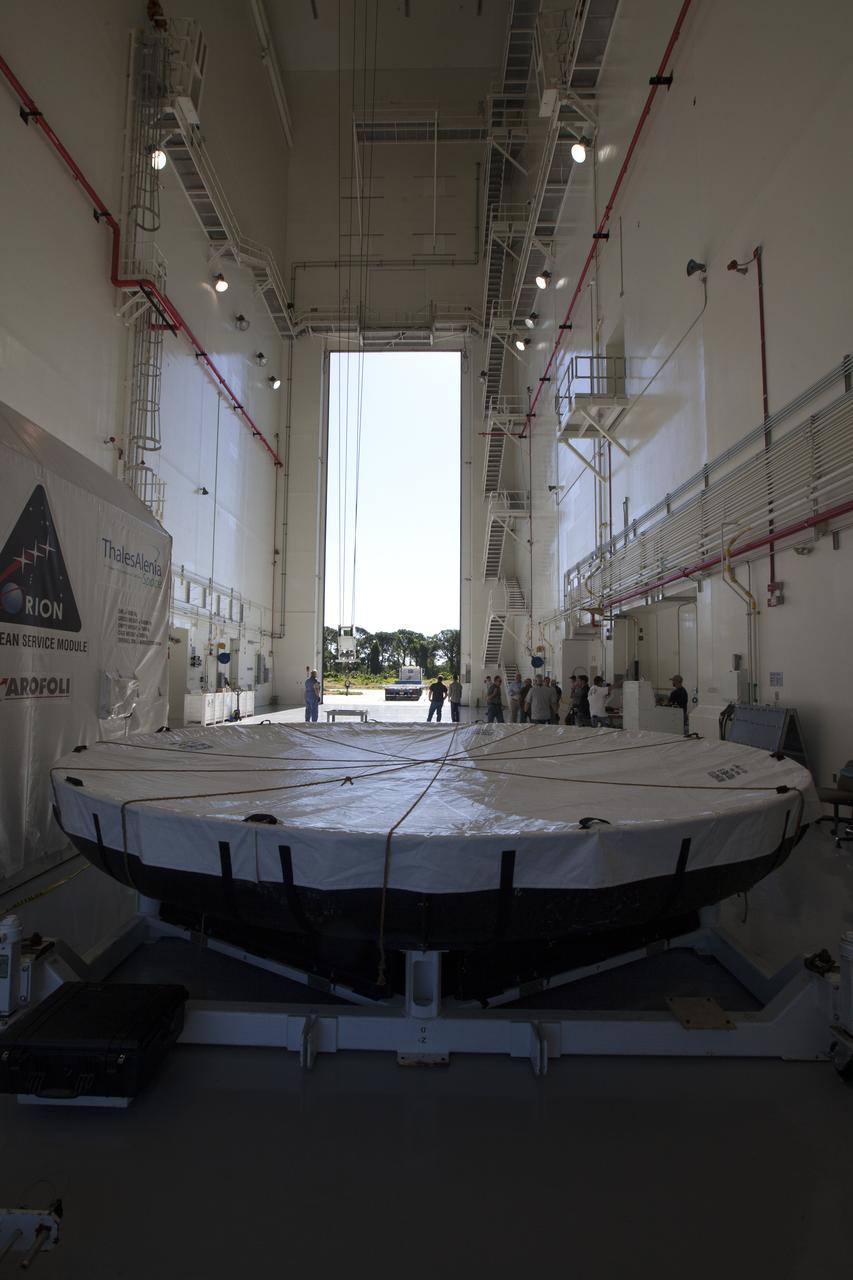

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 is being prepared for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
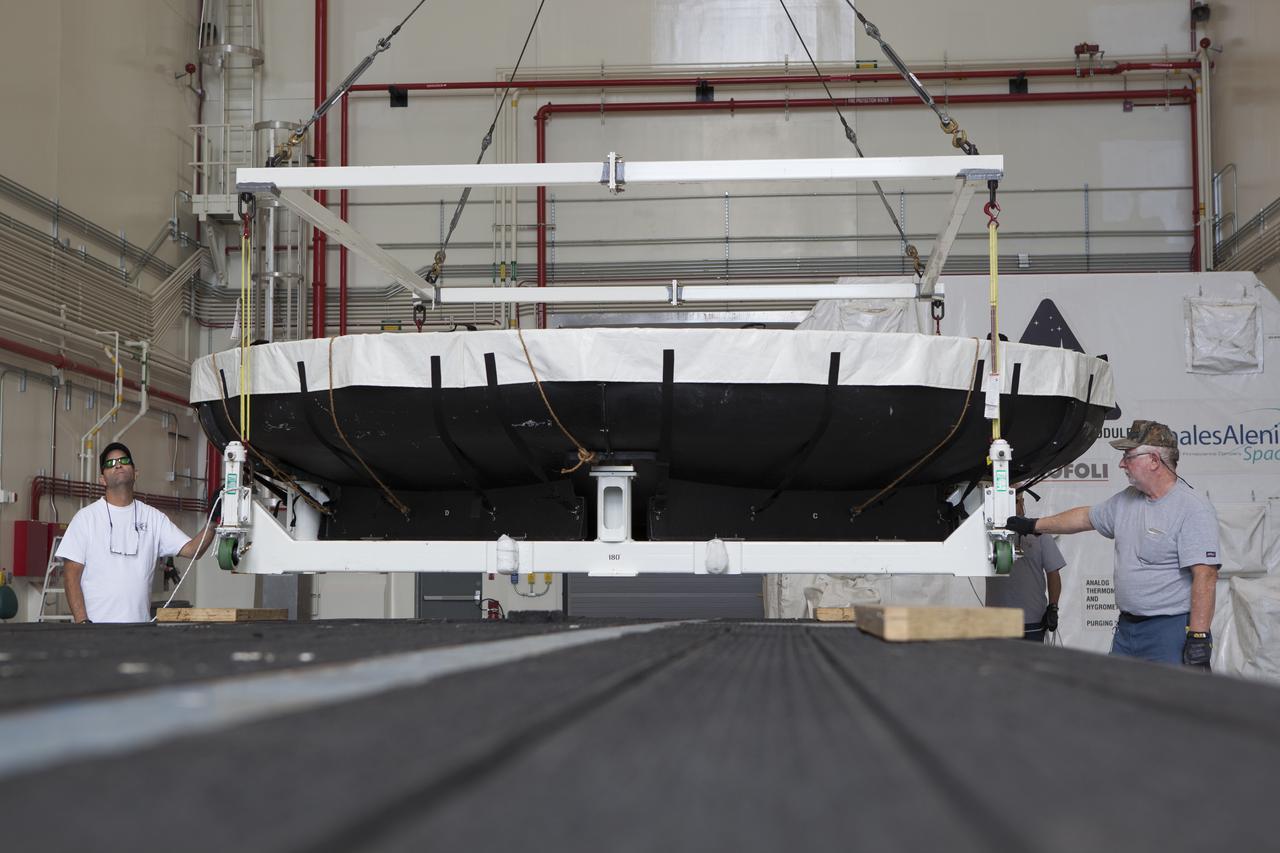

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 is being loaded onto a transporter for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
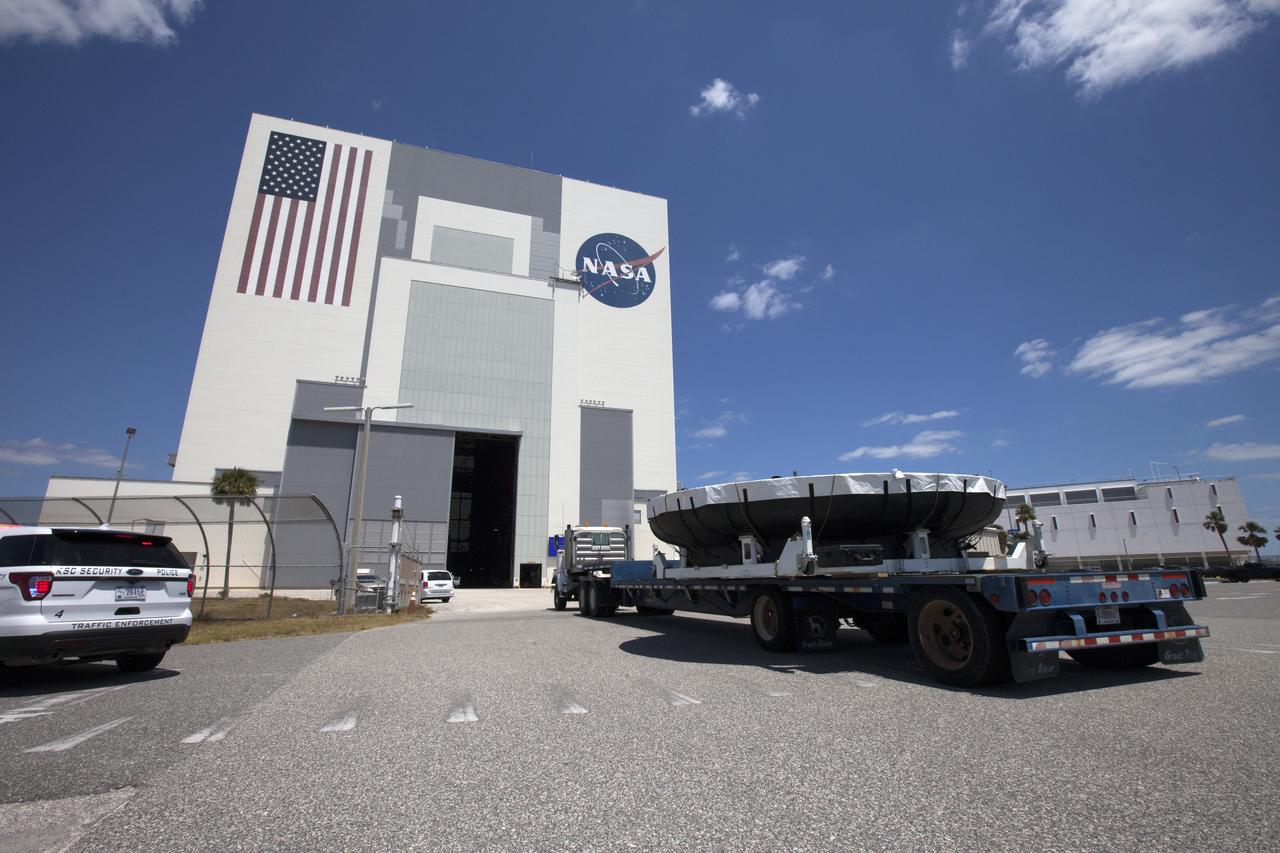

The Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1, secured on a transporter, arrives at the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield was moved from the Launch Abort System Facility. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
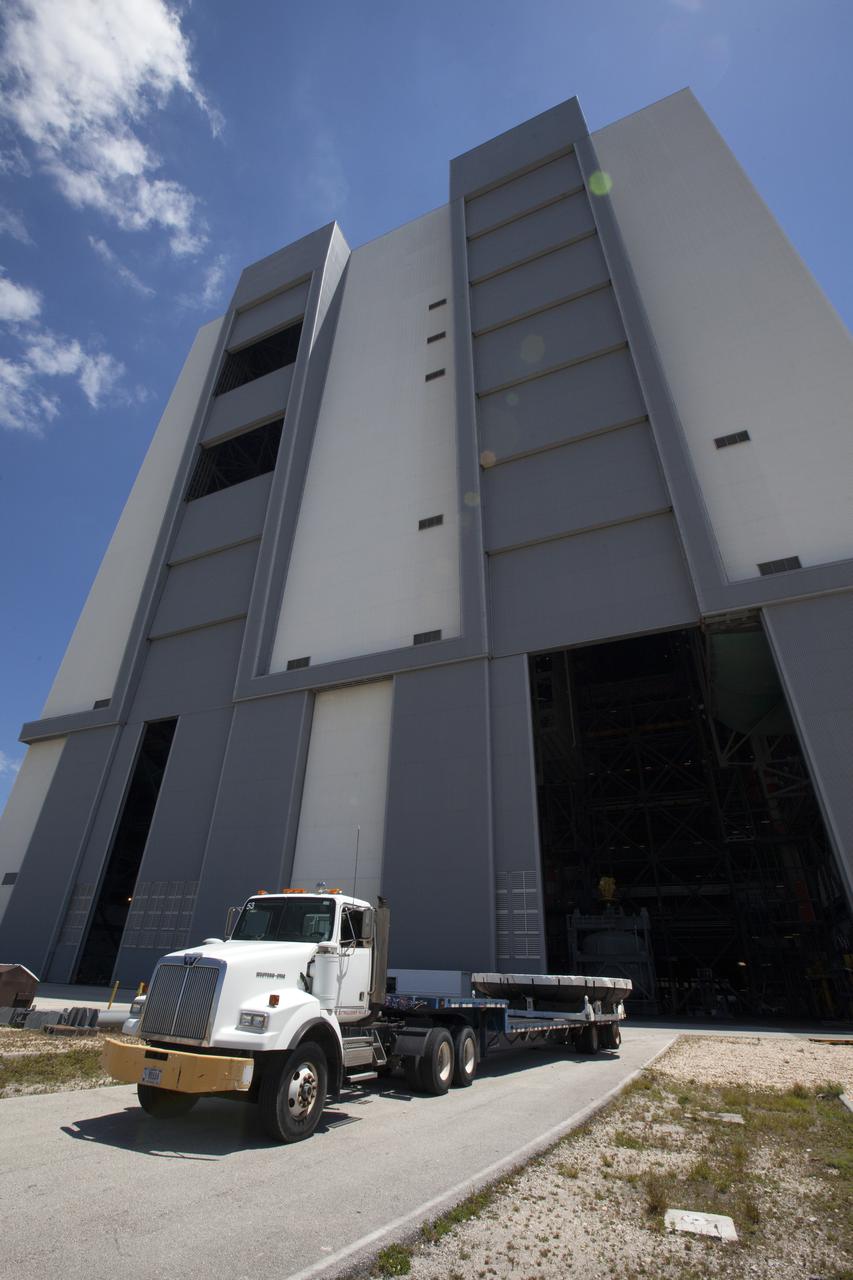

A flatbed truck carrying the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1, prepares to back into High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield was moved from the Launch Abort System Facility. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
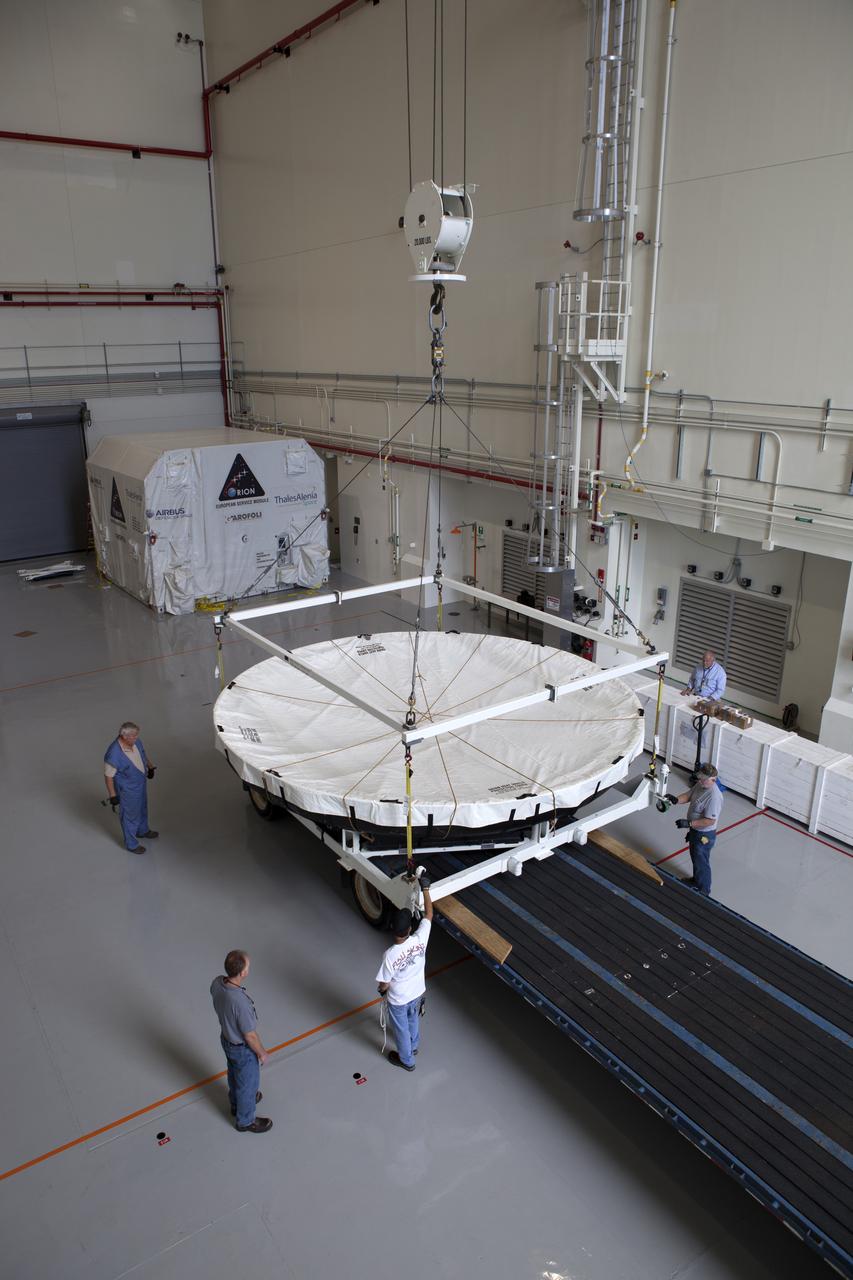

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane lowers the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 onto a transporter for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
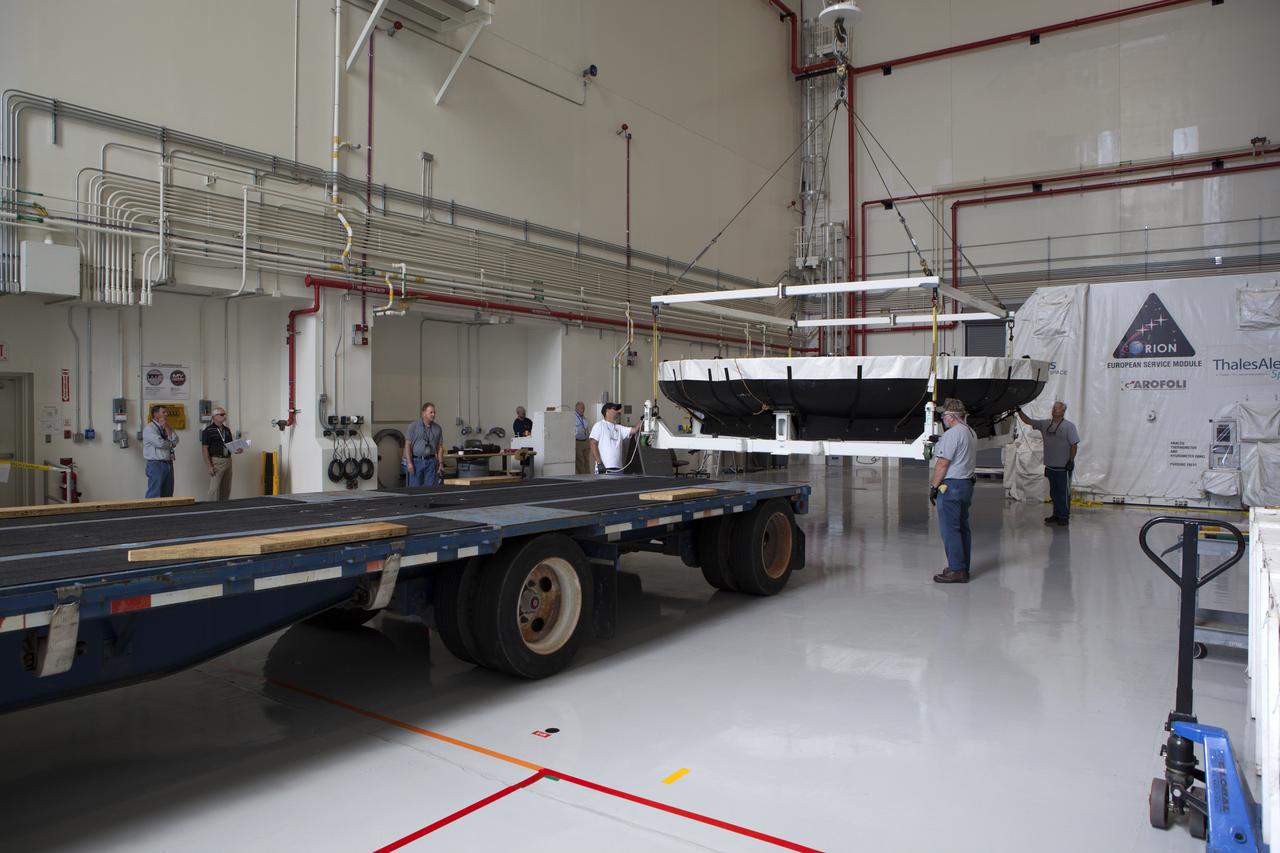

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 is being loaded onto a transporter for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
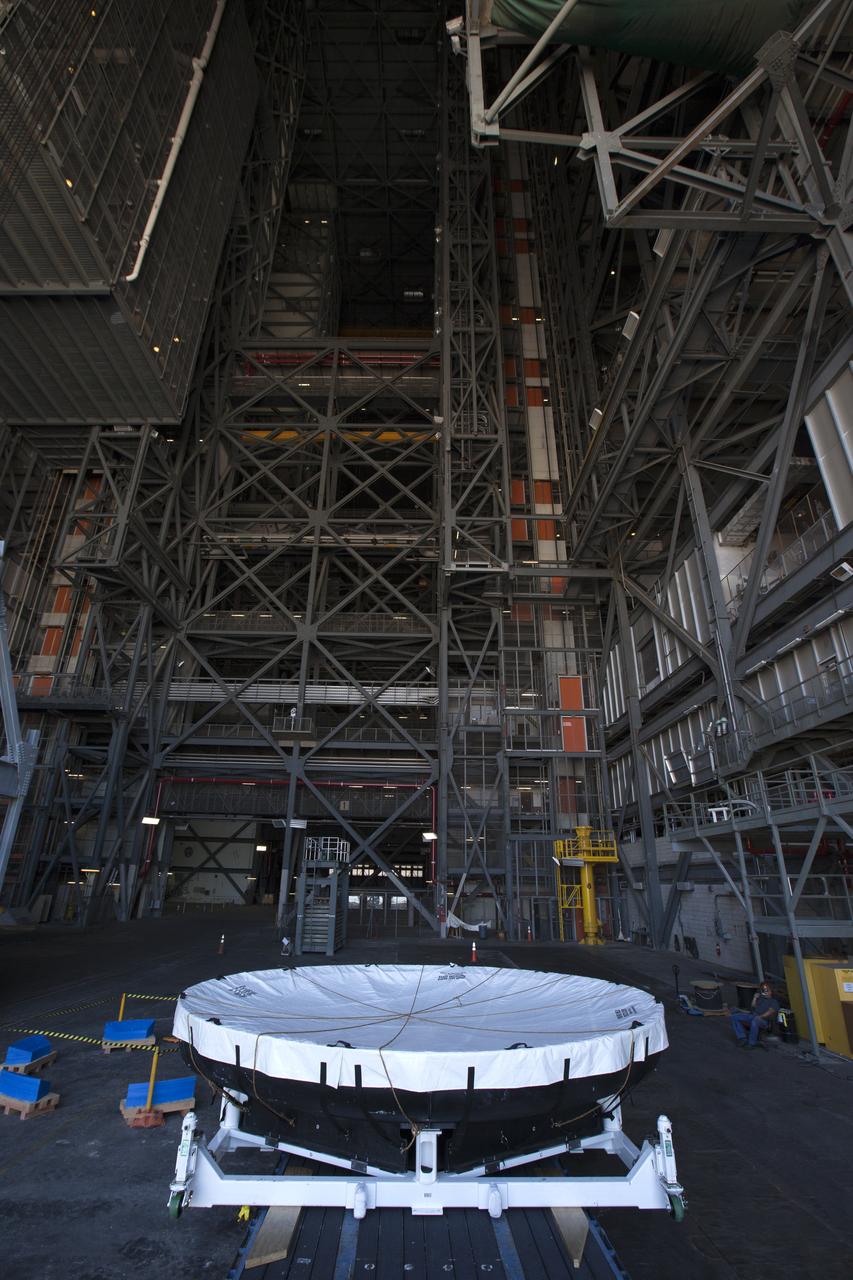

The Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 has arrived in High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield was moved from the Launch Abort System Facility. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
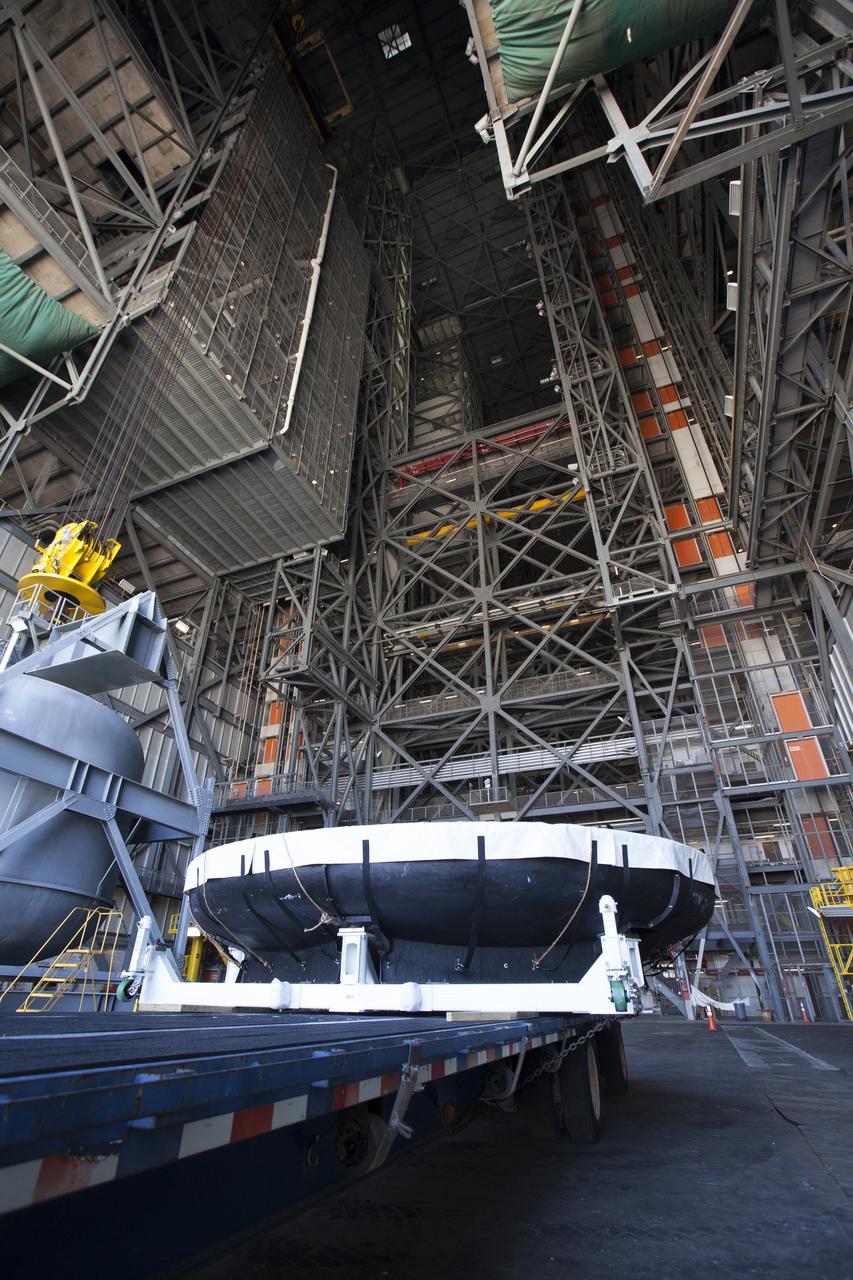

A flatbed truck carrying the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1, backs into High Bay 2 in the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The heat shield was moved from the Launch Abort System Facility. The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
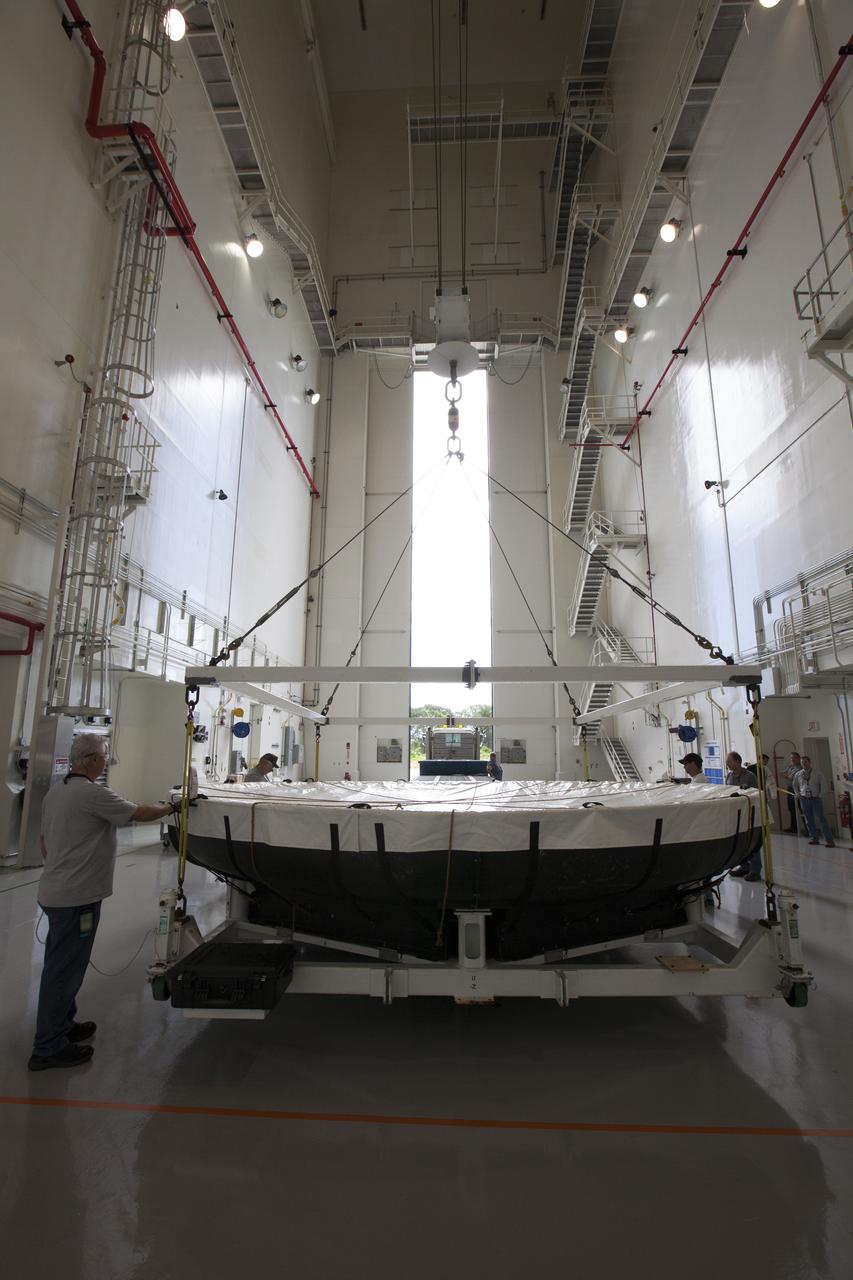

Inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion heat shield from Exploration Flight Test-1 is secured on a transporter and ready for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB). The heat shield is being transferred from the Orion Program to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, Landing and Recovery Operations. In the VAB, the heat shield will be integrated with the Orion ground test article and used for future underway recovery testing.
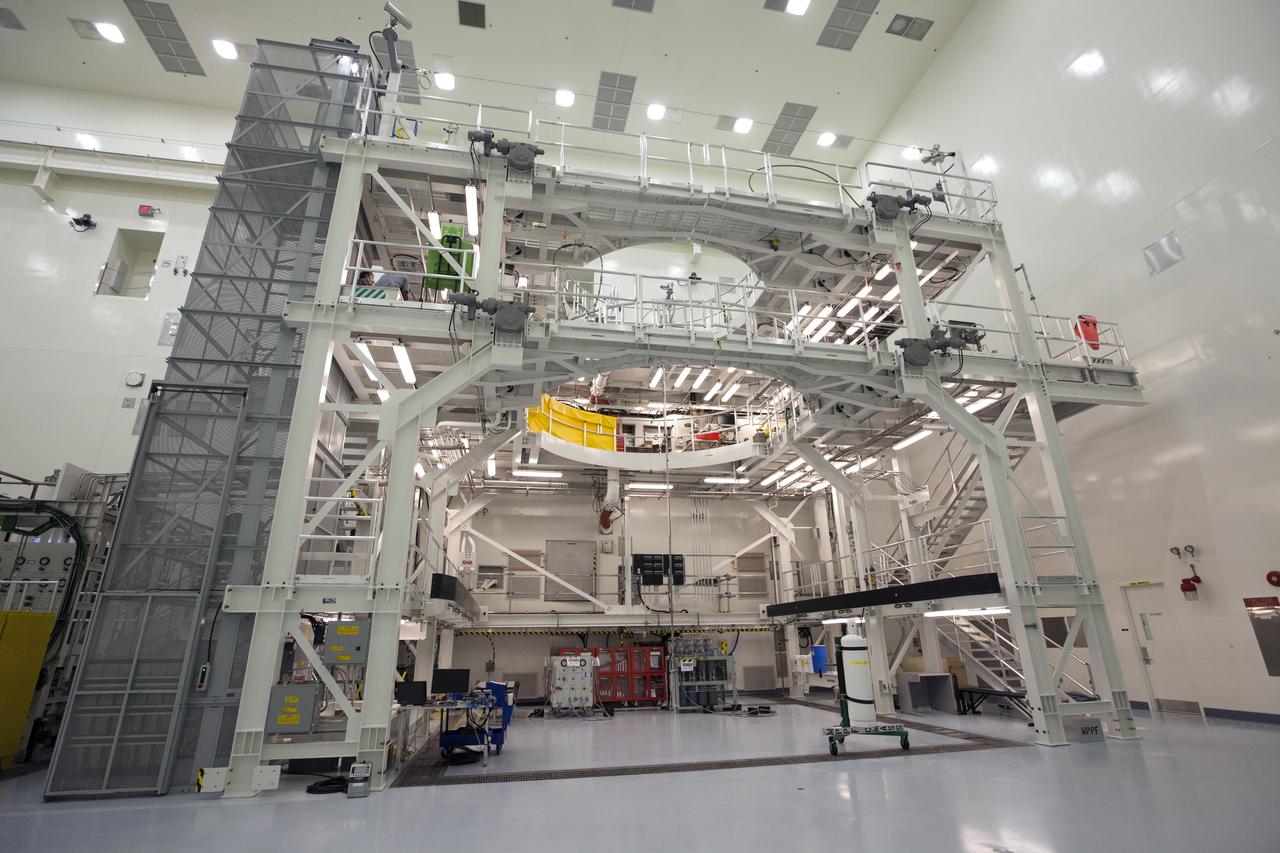

Engineers and technicians completed verification and validation testing of several pneumatic systems inside and outside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view is the service platform for Orion spacecraft processing. The MPPF will be used for offline processing and fueling of the Orion spacecraft and service module stack before launch. Orion also will be de-serviced in the MPPF after a mission. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program (GSDO) is overseeing upgrades to the facility. The Engineering Directorate led the recent pneumatic tests.
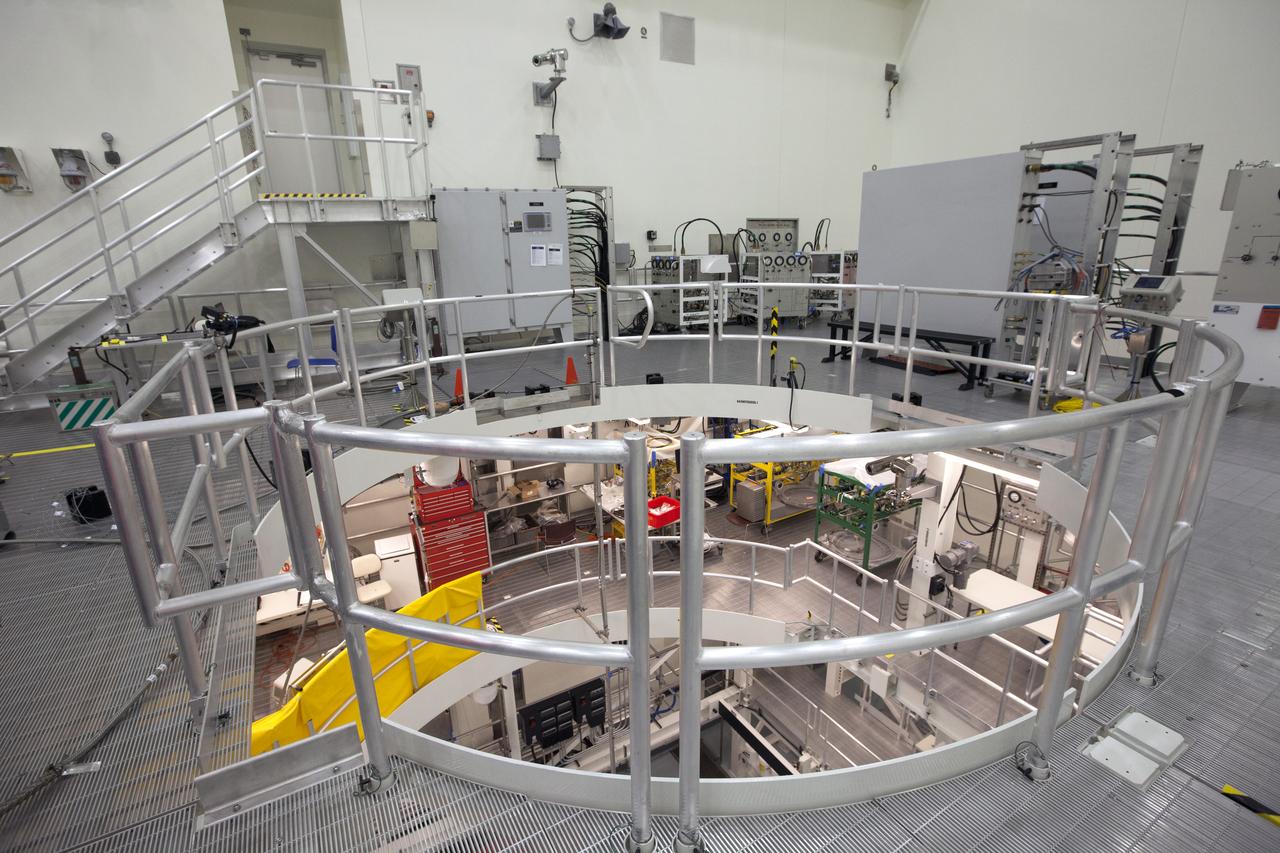

Engineers and technicians completed verification and validation testing of several pneumatic systems inside and outside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view is the top level of the service platform for Orion spacecraft processing. The MPPF will be used for offline processing and fueling of the Orion spacecraft and service module stack before launch. Orion also will be de-serviced in the MPPF after a mission. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program (GSDO) is overseeing upgrades to the facility. The Engineering Directorate led the recent pneumatic tests.
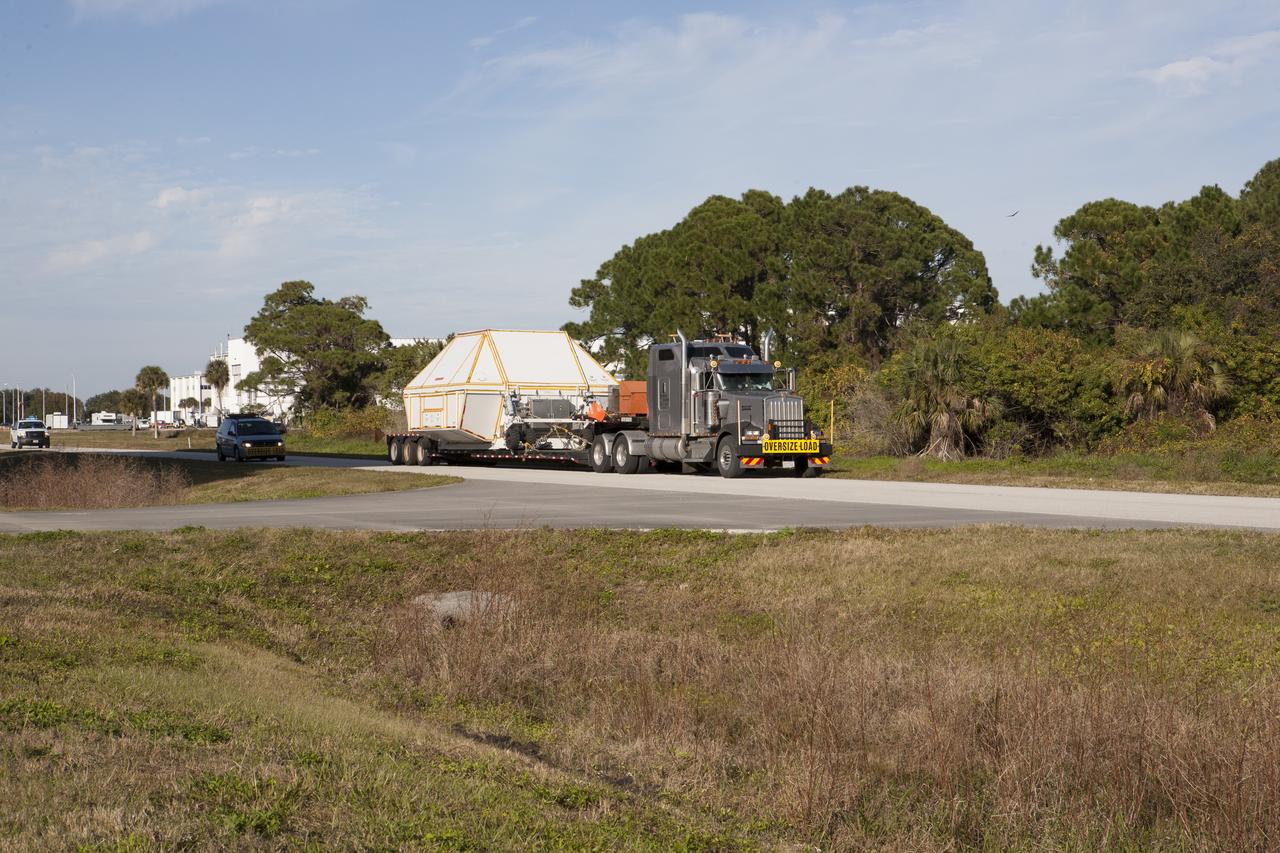

NASA's Orion crew module, enclosed in its crew module transportation fixture and secured on a flatbed truck, leaves the Multi-Operation Support Building and is being transported to the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion was transported 2,700 miles overland from Naval Base San Diego in California. Orion was recovered from the Pacific Ocean after completing a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
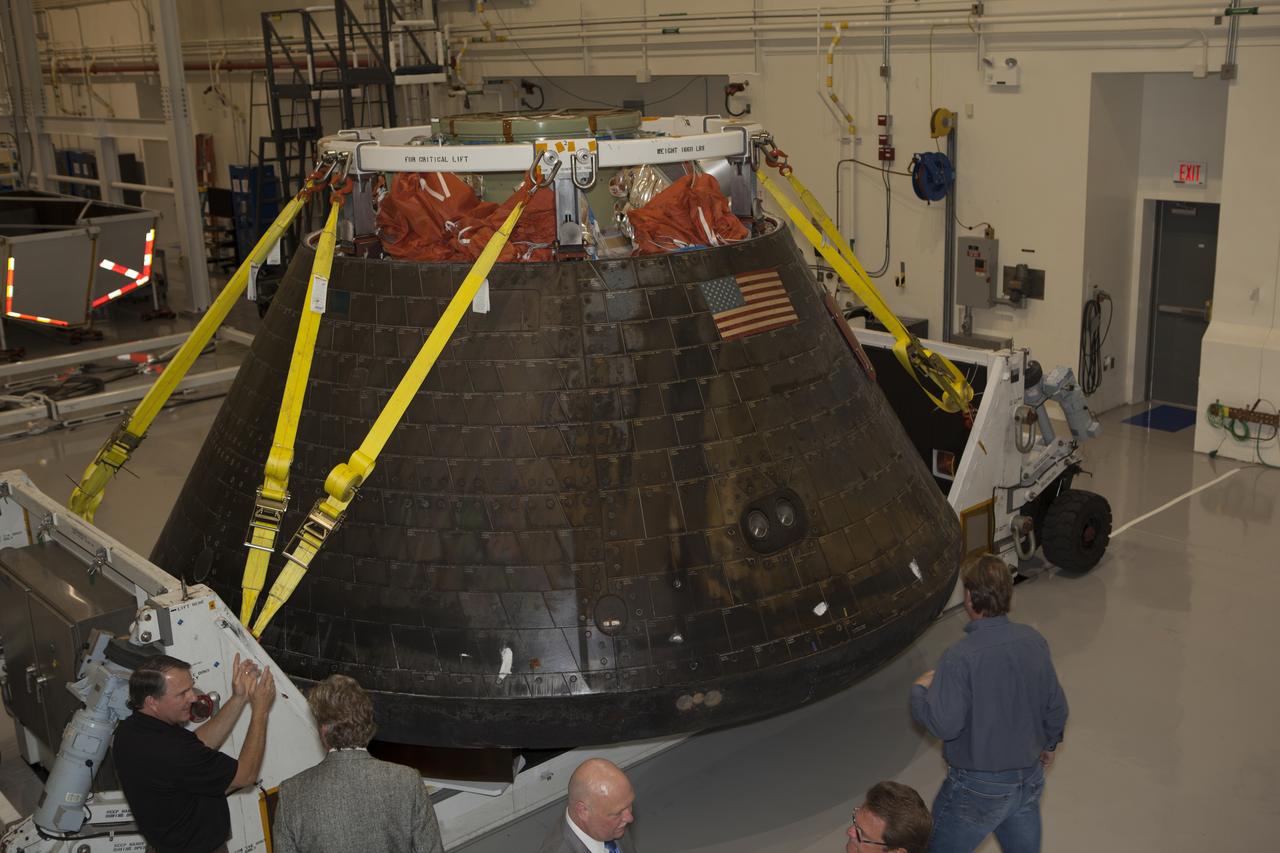

NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.

NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
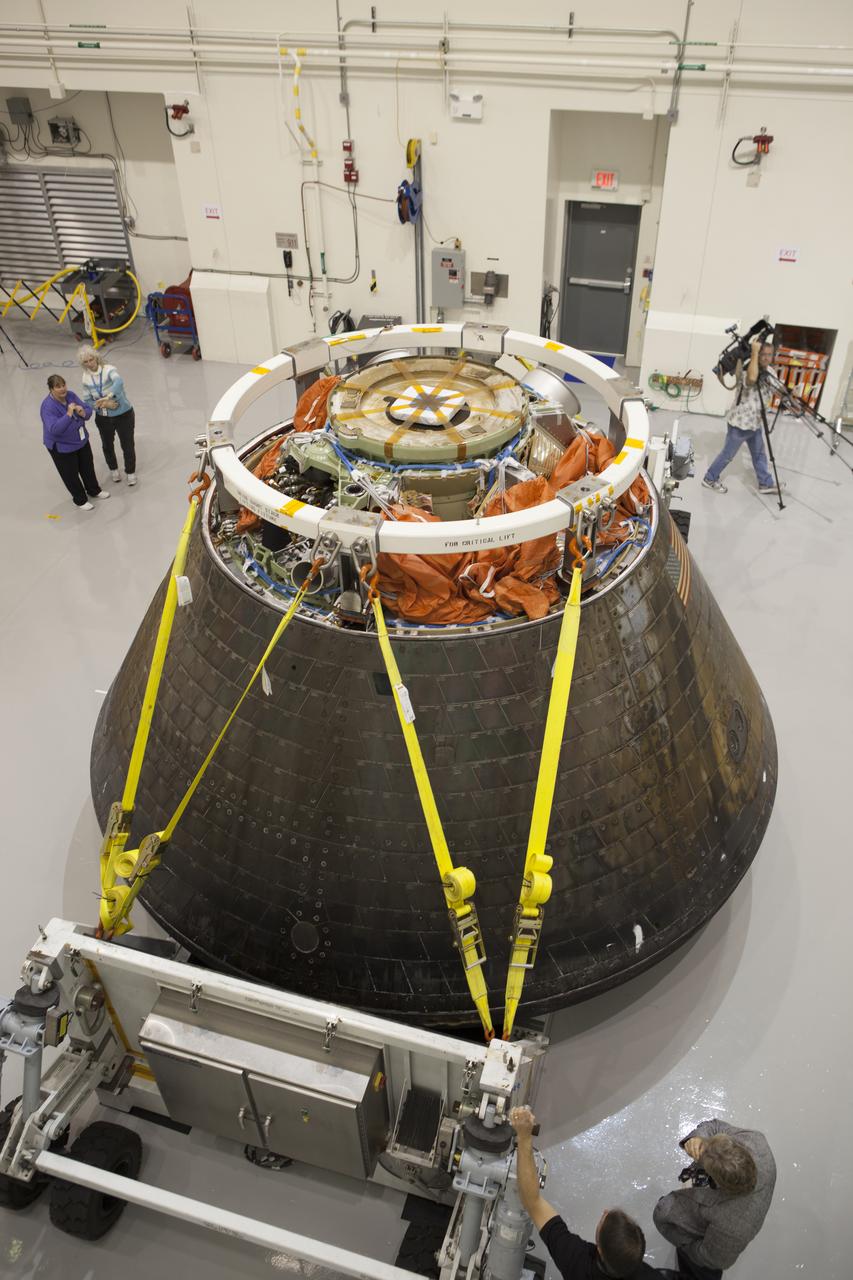

NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.

NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
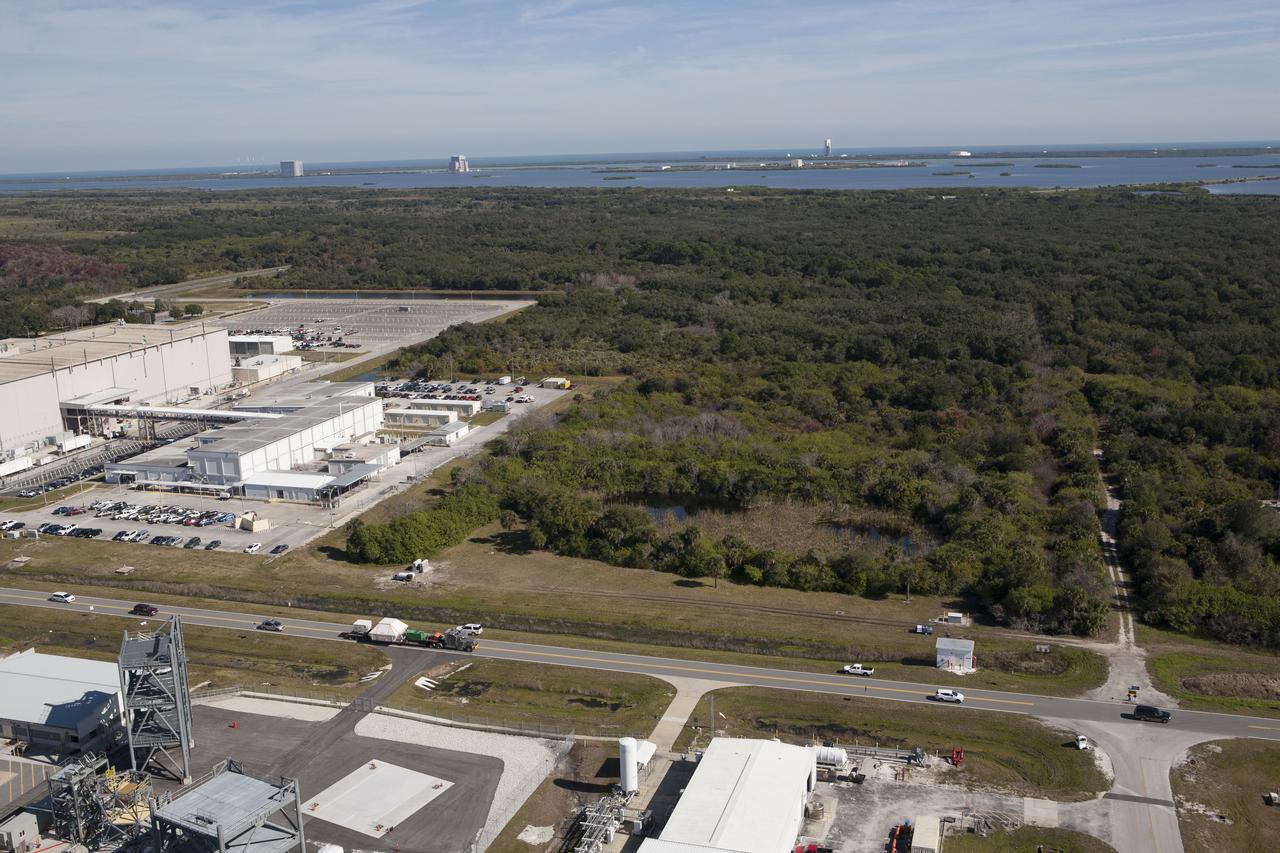

An aerial view reveals the Orion crew module, enclosed in its crew module transportation fixture and secured on a flatbed truck is passing the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on its way to the Multi-Operation Support Building. Orion made the 2,700 mile overland trip from Naval Base San Diego in California. The spacecraft was recovered from the Pacific Ocean after completing a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.

NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the media during the viewing opportunity is Glenn Chin, Orion Production Operations. To his right is Phil Weber, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
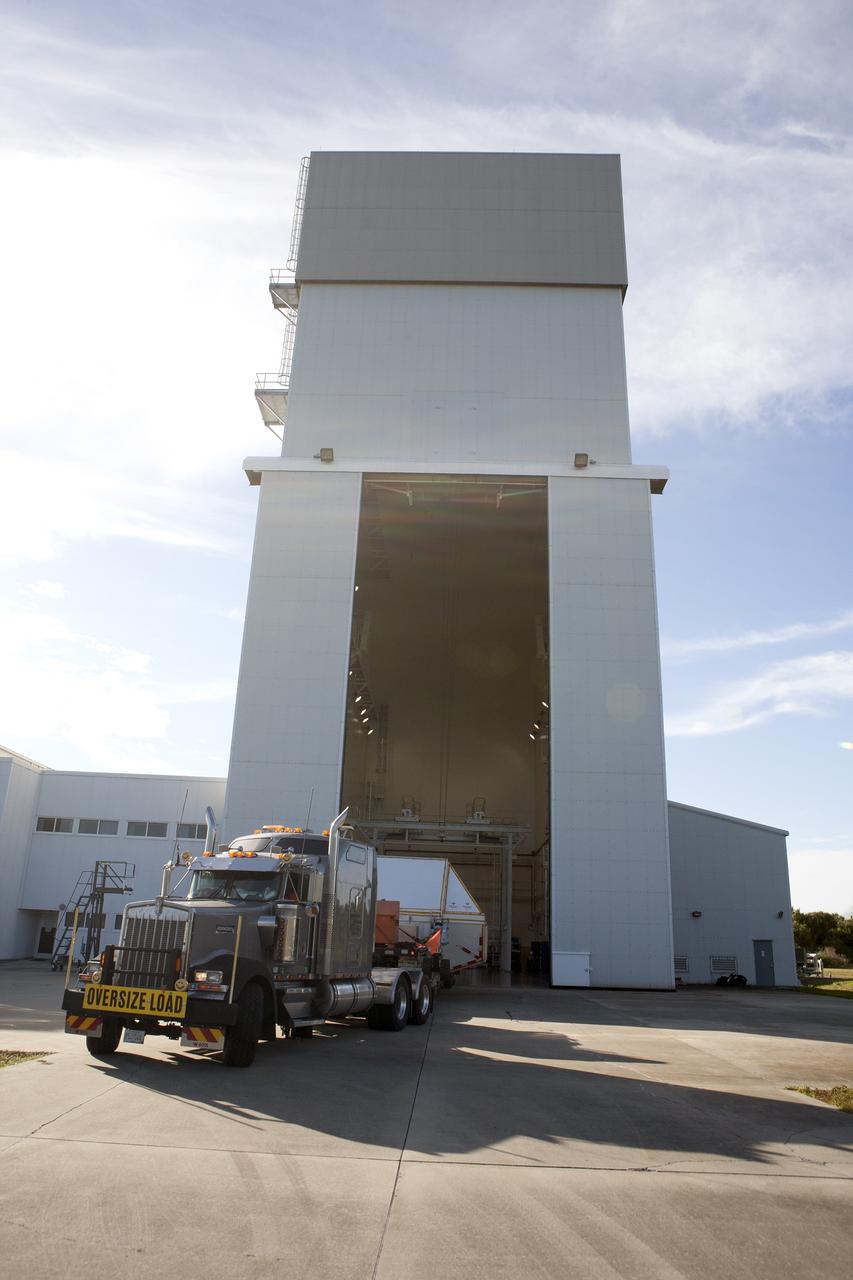

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft was transported 2,700 miles overland from Naval Base San Diego in California, on a flatbed truck secured in its crew module transportation fixture for the trip. During its first flight test, Orion completed a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
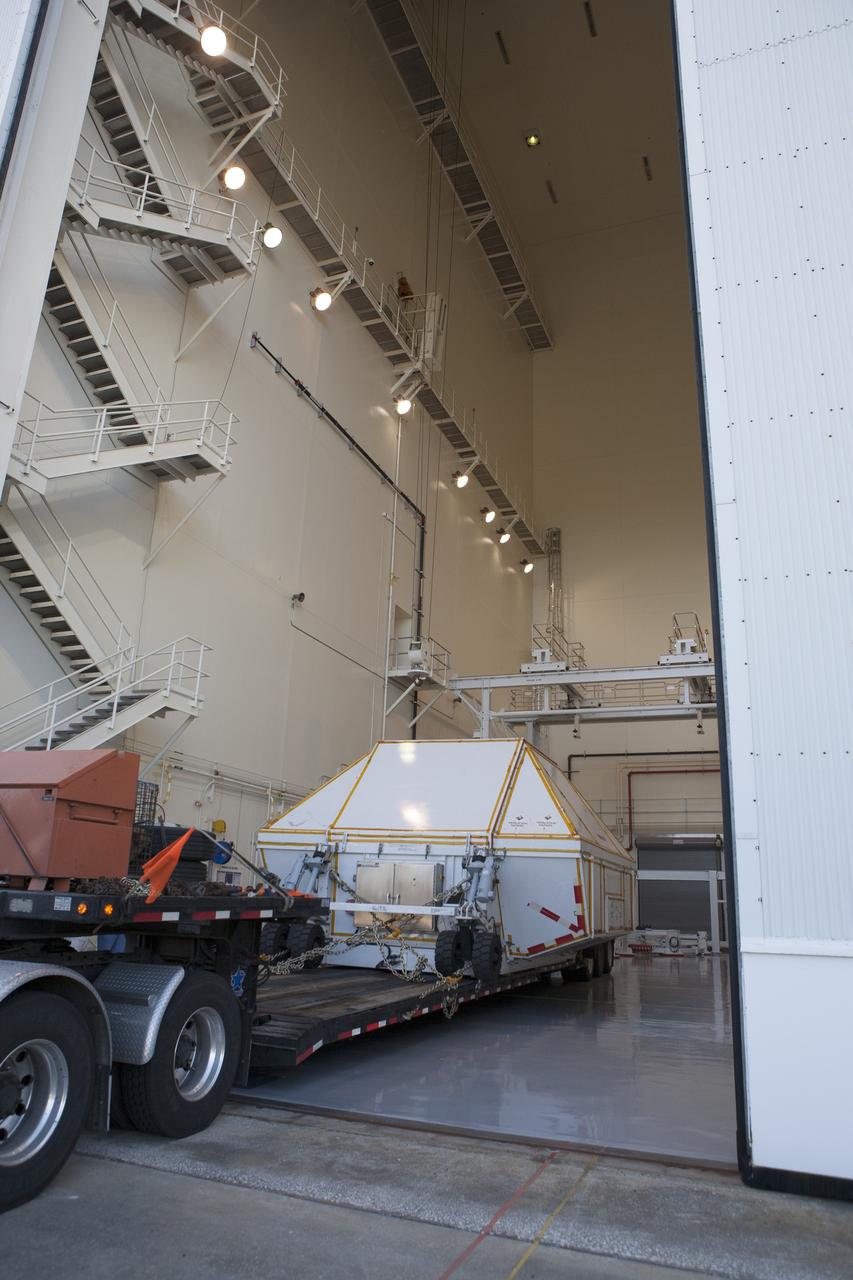

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft was transported 2,700 miles overland from Naval Base San Diego in California, on a flatbed truck secured in its crew module transportation fixture for the trip. During its first flight test, Orion completed a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
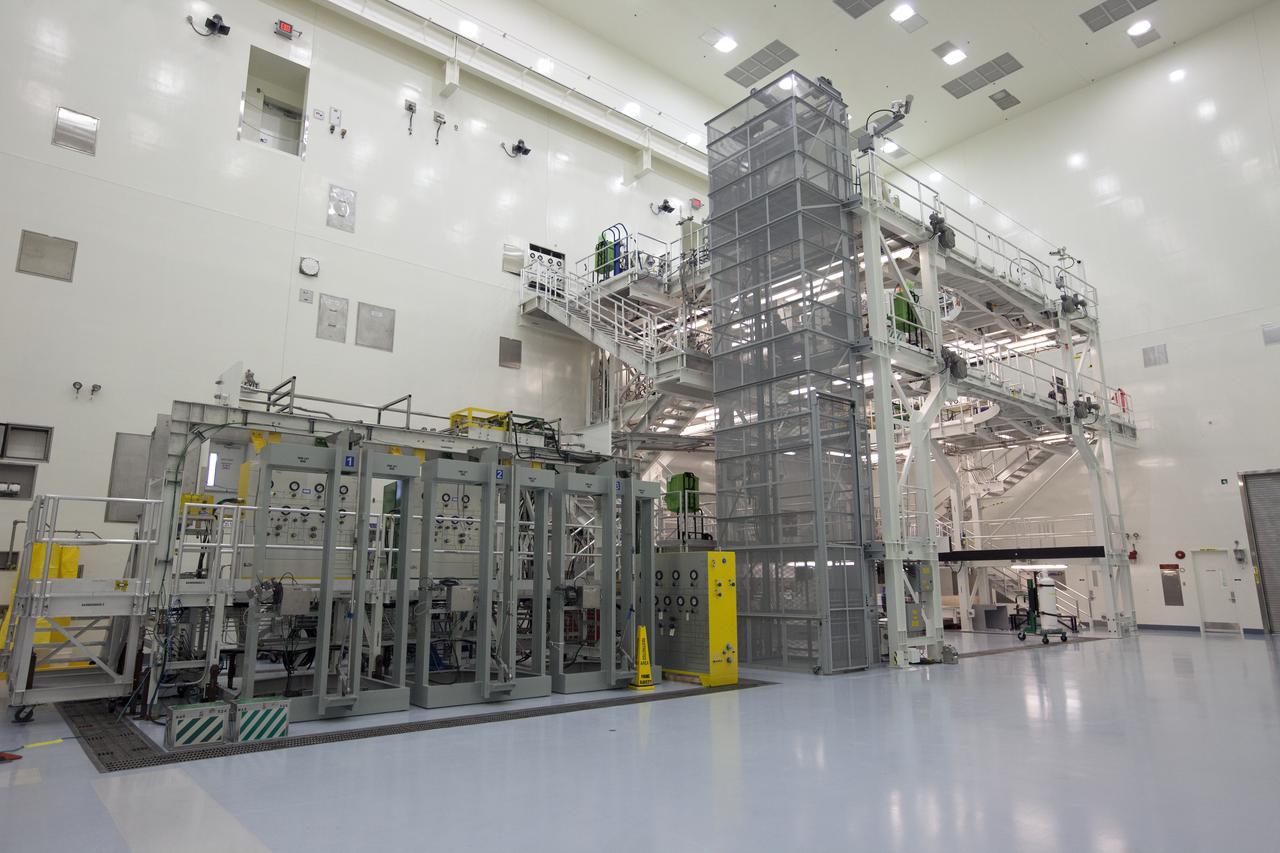

Engineers and technicians completed verification and validation testing of several pneumatic systems inside and outside the Multi-Payload Processing Facility (MPPF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view is the service platform for Orion spacecraft processing. To the left are several pneumatic panels. The MPPF will be used for offline processing and fueling of the Orion spacecraft and service module stack before launch. Orion also will be de-serviced in the MPPF after a mission. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program (GSDO) is overseeing upgrades to the facility. The Engineering Directorate led the recent pneumatic tests.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Modifications continue on the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, or MPPF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the high bay, a new fire suppression system and piping are being installed in the ceiling. Kennedy's Center Operations Directorate is overseeing upgrades to the MPPF for the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program. The extensive upgrades and modernizations will support processing of Orion spacecraft for NASA's exploration missions. The 19,647-square-foot building, originally constructed in 1995, primarily will be used for Orion hypergolic fueling, ammonia servicing and high-pressure gas servicing and checkout before being transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for integration with the Space Launch System. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
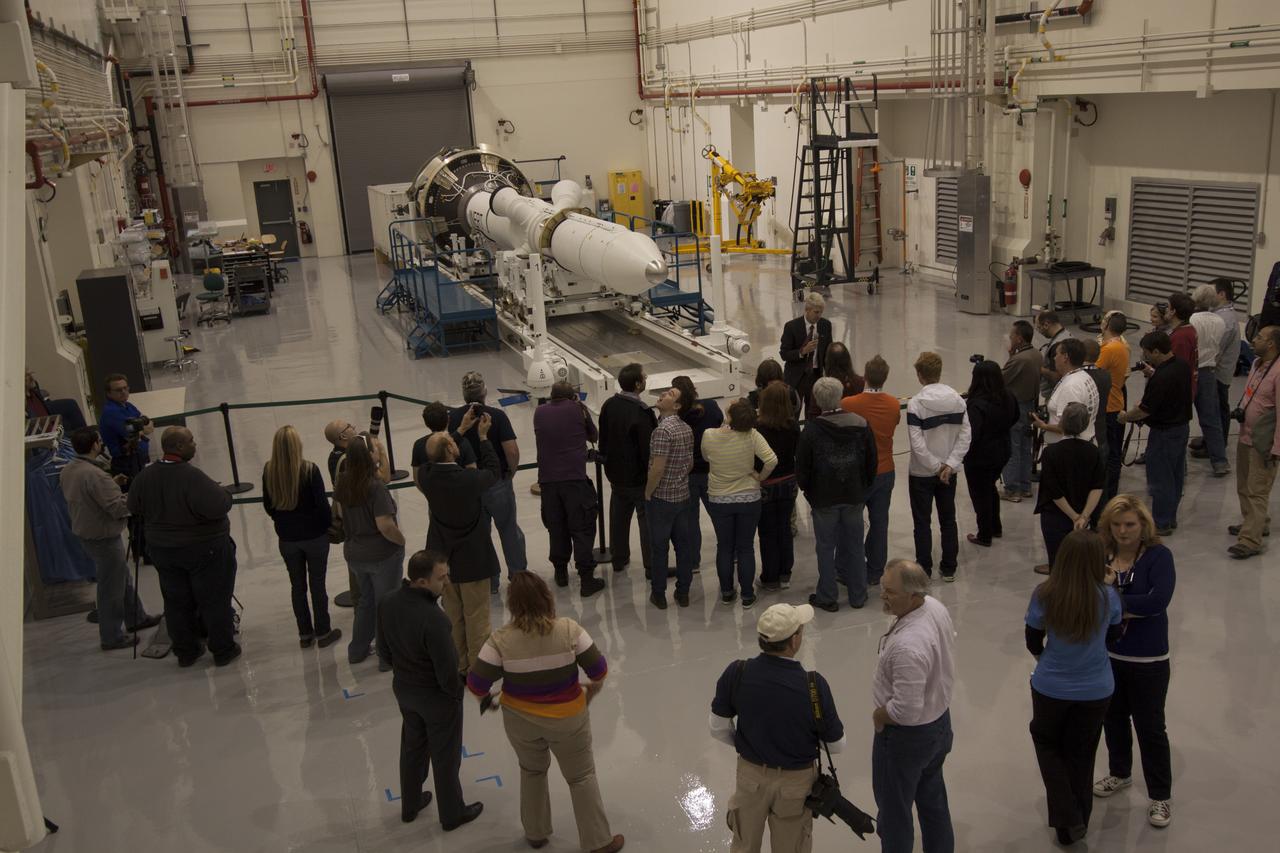

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A group of news media and social media tweeters toured the Launch Abort System Facility and viewed the launch abort system for the Orion spacecraft at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the group is Scott Wilson, manager of Production Operations for the Orion Program. The group also toured the Launch Control Center and Vehicle Assembly Building, legacy facilities that are being upgraded by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program at Kennedy to prepare for processing and launch of NASA's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. NASA is developing the Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft to provide an entirely new capability for human exploration beyond low-Earth orbit, with the flexibility to launch spacecraft for crew and cargo missions, including to an asteroid and Mars. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for fiscal year 2018 on the Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
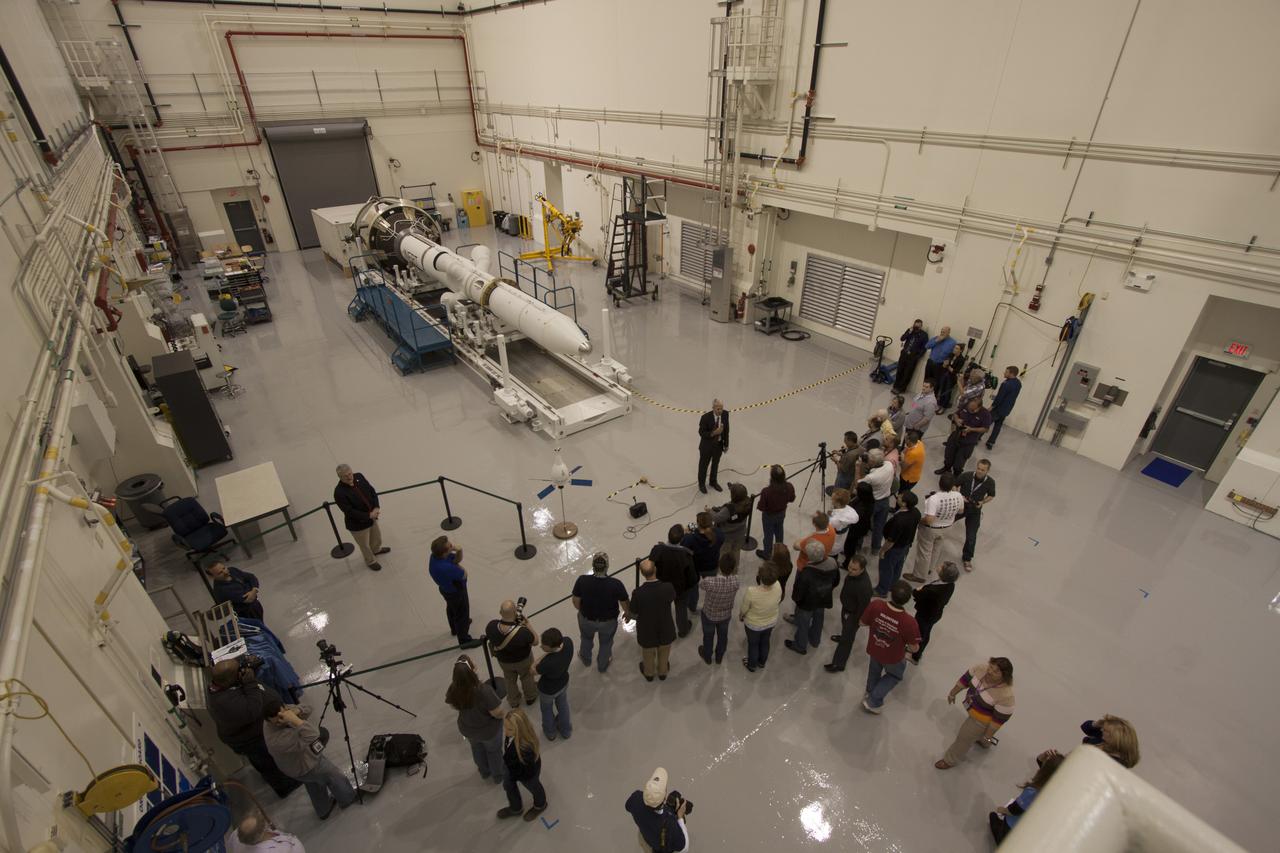

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A group of news media and social media tweeters toured the Launch Abort System Facility and viewed the launch abort system for the Orion spacecraft at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the group is Scott Wilson, manager of Production Operations for the Orion Program. The group also toured the Launch Control Center and Vehicle Assembly Building, legacy facilities that are being upgraded by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program at Kennedy to prepare for processing and launch of NASA's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. NASA is developing the Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft to provide an entirely new capability for human exploration beyond low-Earth orbit, with the flexibility to launch spacecraft for crew and cargo missions, including to an asteroid and Mars. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for fiscal year 2018 on the Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A group of news media and social media tweeters toured the Launch Abort System Facility and viewed the launch abort system for the Orion spacecraft at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the group is Scott Wilson, manager of Production Operations for the Orion Program. The group also toured the Launch Control Center and Vehicle Assembly Building, legacy facilities that are being upgraded by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program at Kennedy to prepare for processing and launch of NASA's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. NASA is developing the Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft to provide an entirely new capability for human exploration beyond low-Earth orbit, with the flexibility to launch spacecraft for crew and cargo missions, including to an asteroid and Mars. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for fiscal year 2018 on the Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
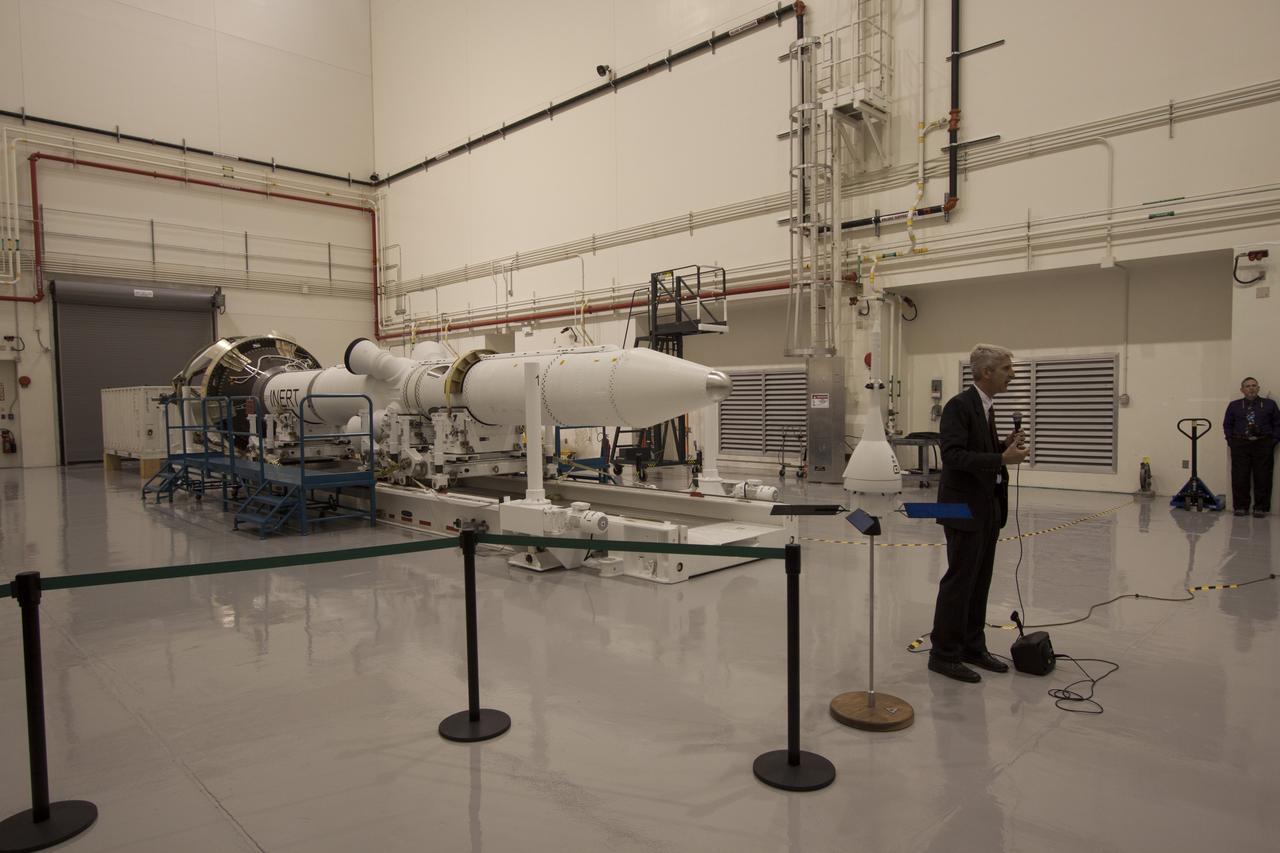

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A group of news media and social media tweeters toured the Launch Abort System Facility and viewed the launch abort system for the Orion spacecraft at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the group is Scott Wilson, manager of Production Operations for the Orion Program. The group also toured the Launch Control Center and Vehicle Assembly Building, legacy facilities that are being upgraded by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program at Kennedy to prepare for processing and launch of NASA's Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft. NASA is developing the Space Launch System and Orion spacecraft to provide an entirely new capability for human exploration beyond low-Earth orbit, with the flexibility to launch spacecraft for crew and cargo missions, including to an asteroid and Mars. Orion’s first unpiloted test flight is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV rocket. A second uncrewed flight test is scheduled for fiscal year 2018 on the Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
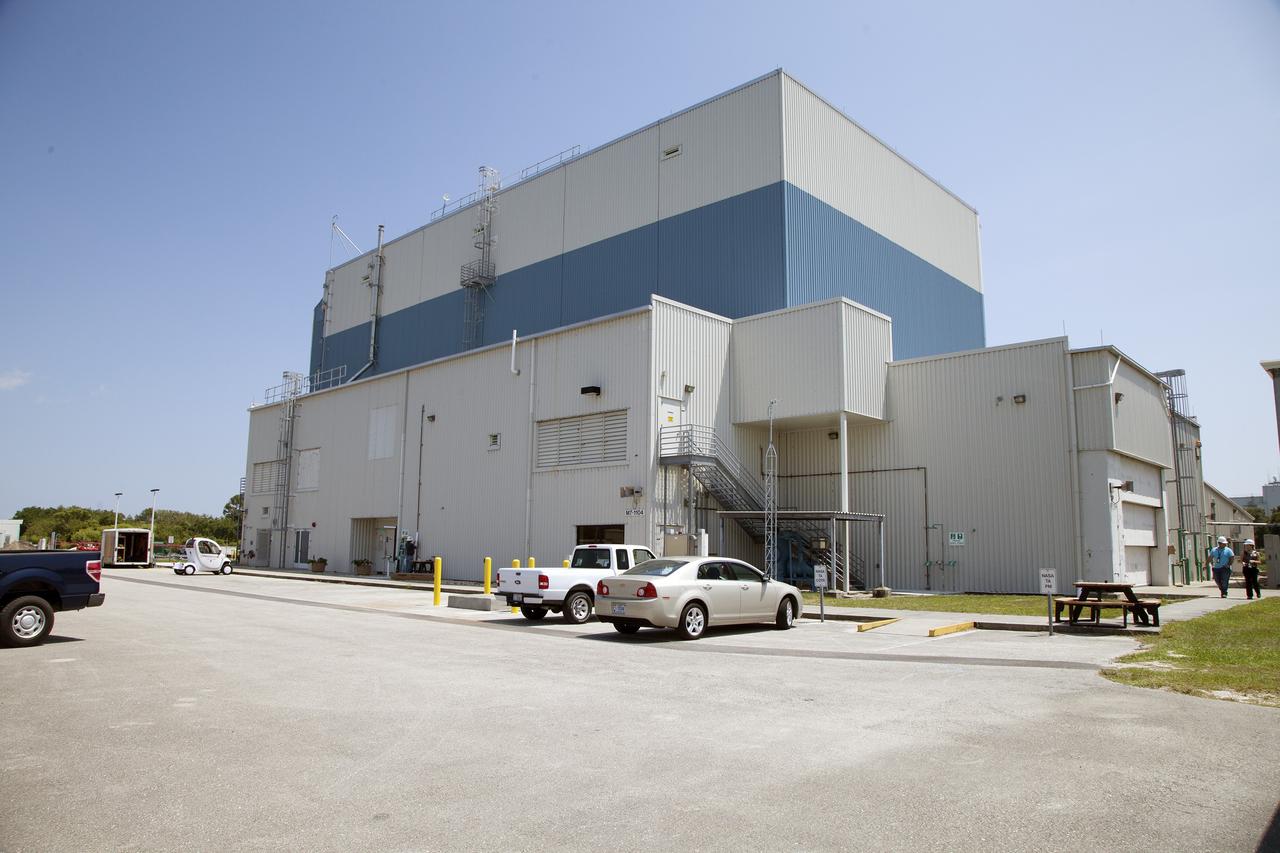

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Modifications continue on the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, or MPPF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A view looking northwest, shows the exterior of the MPPF. Kennedy's Center Operations Directorate is overseeing upgrades to the MPPF for the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program. The extensive upgrades and modernizations will support processing of Orion spacecraft for NASA's exploration missions. The 19,647-square-foot building, originally constructed in 1995, primarily will be used for Orion hypergolic fueling, ammonia servicing and high-pressure gas servicing and checkout before being transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for integration with the Space Launch System. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
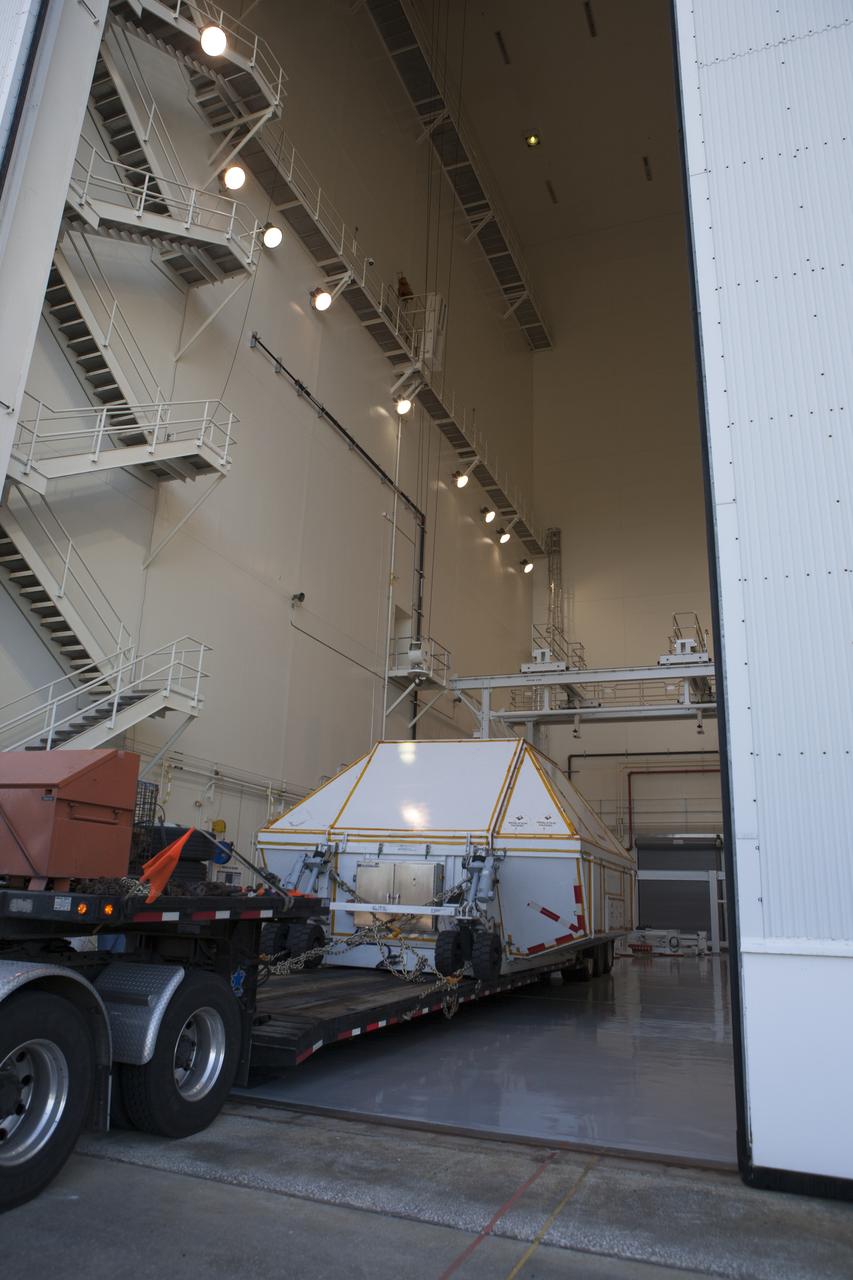

NASA's Orion spacecraft arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft was transported 2,700 miles overland from Naval Base San Diego in California, on a flatbed truck secured in its crew module transportation fixture for the trip. During its first flight test, Orion completed a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
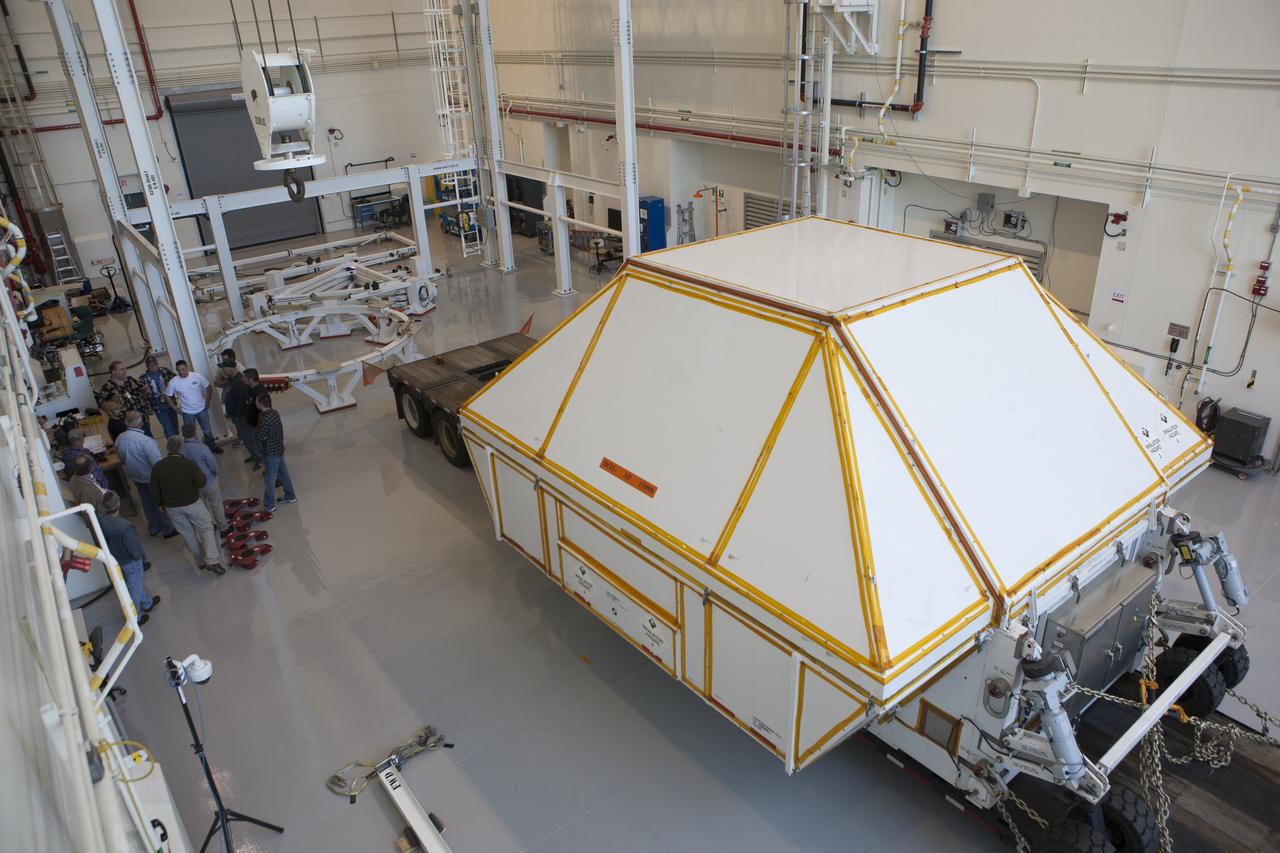

NASA's Orion spacecraft arrives inside the Launch Abort System Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft was transported 2,700 miles overland from Naval Base San Diego in California, on a flatbed truck secured in its crew module transportation fixture for the trip. During its first flight test, Orion completed a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
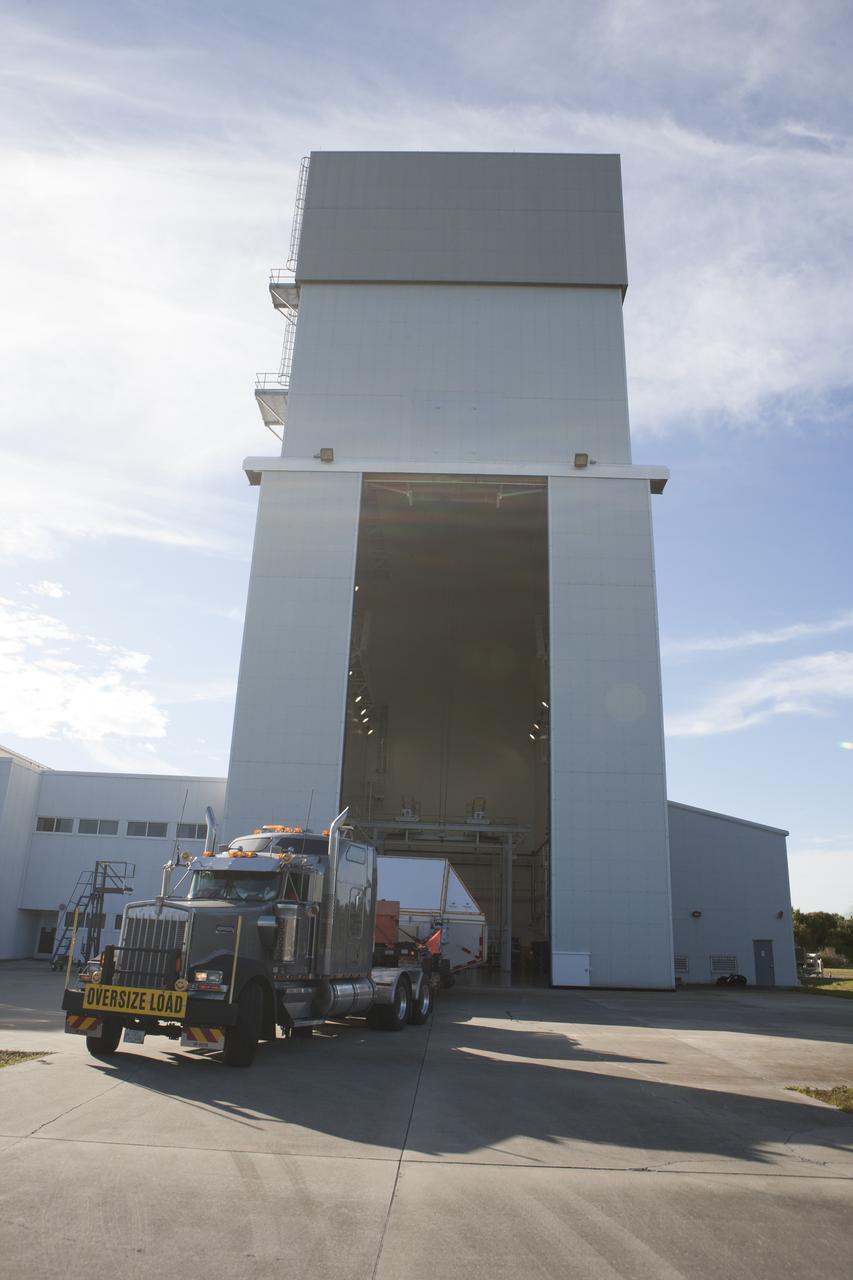

NASA's Orion spacecraft arrives at the Launch Abort System Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft was transported 2,700 miles overland from Naval Base San Diego in California, on a flatbed truck secured in its crew module transportation fixture for the trip. During its first flight test, Orion completed a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
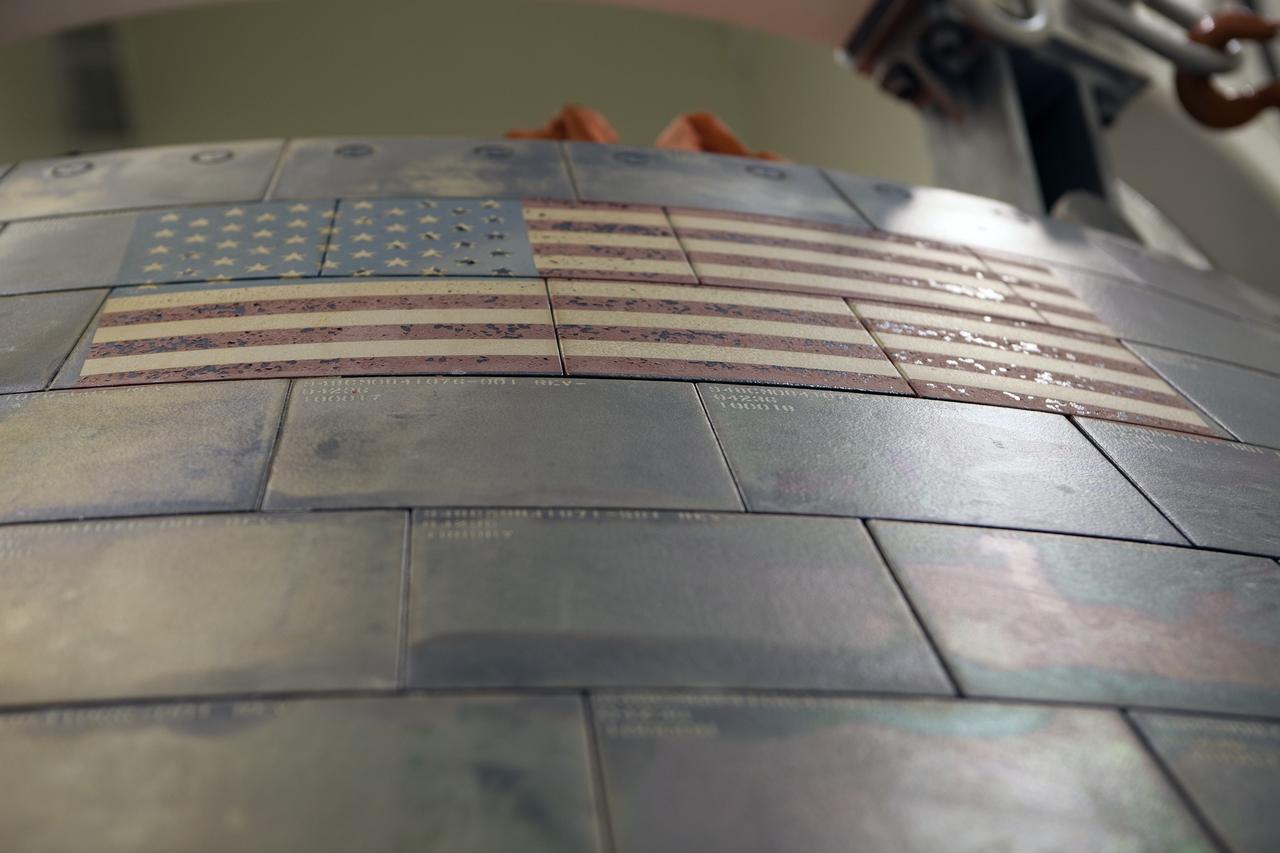
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The U.S. Flag is in view on NASA's Orion spacecraft inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a media event. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
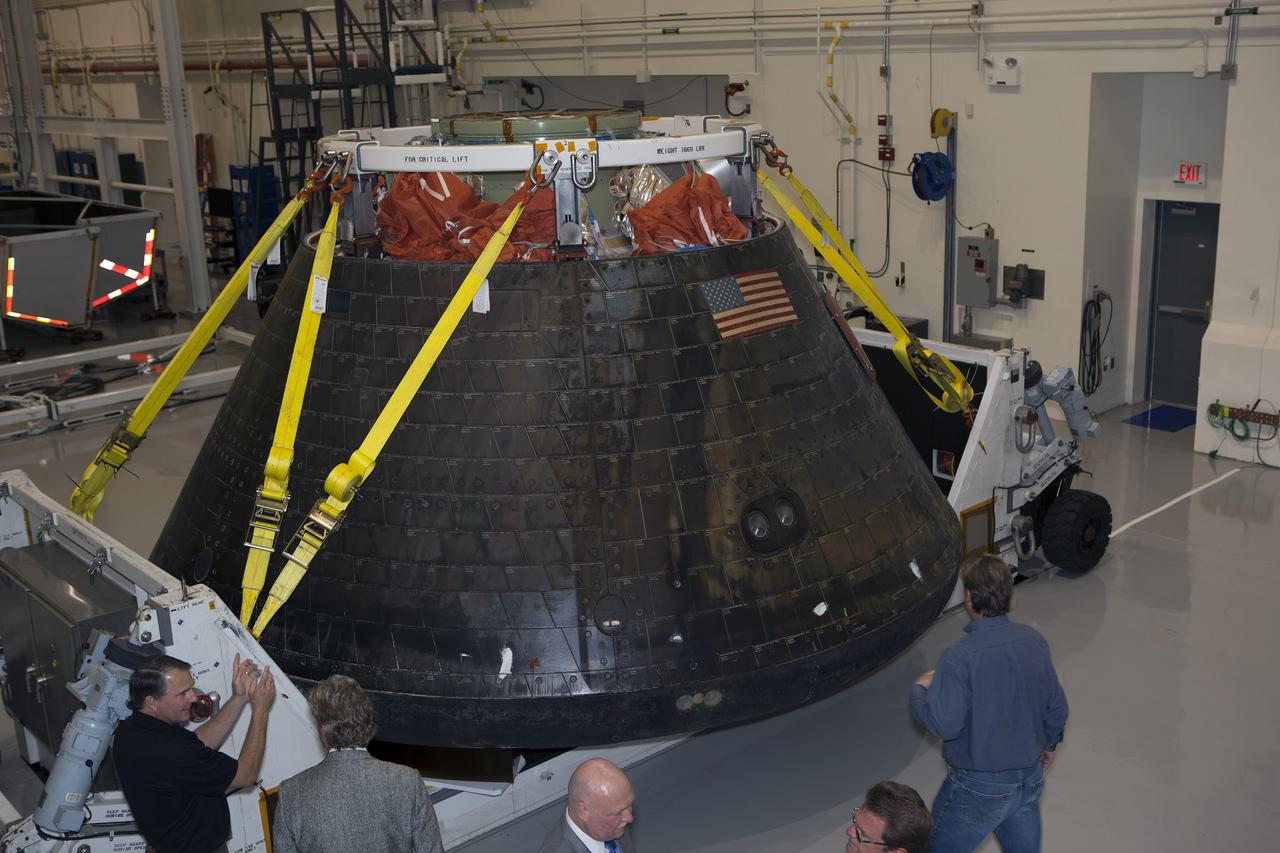

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
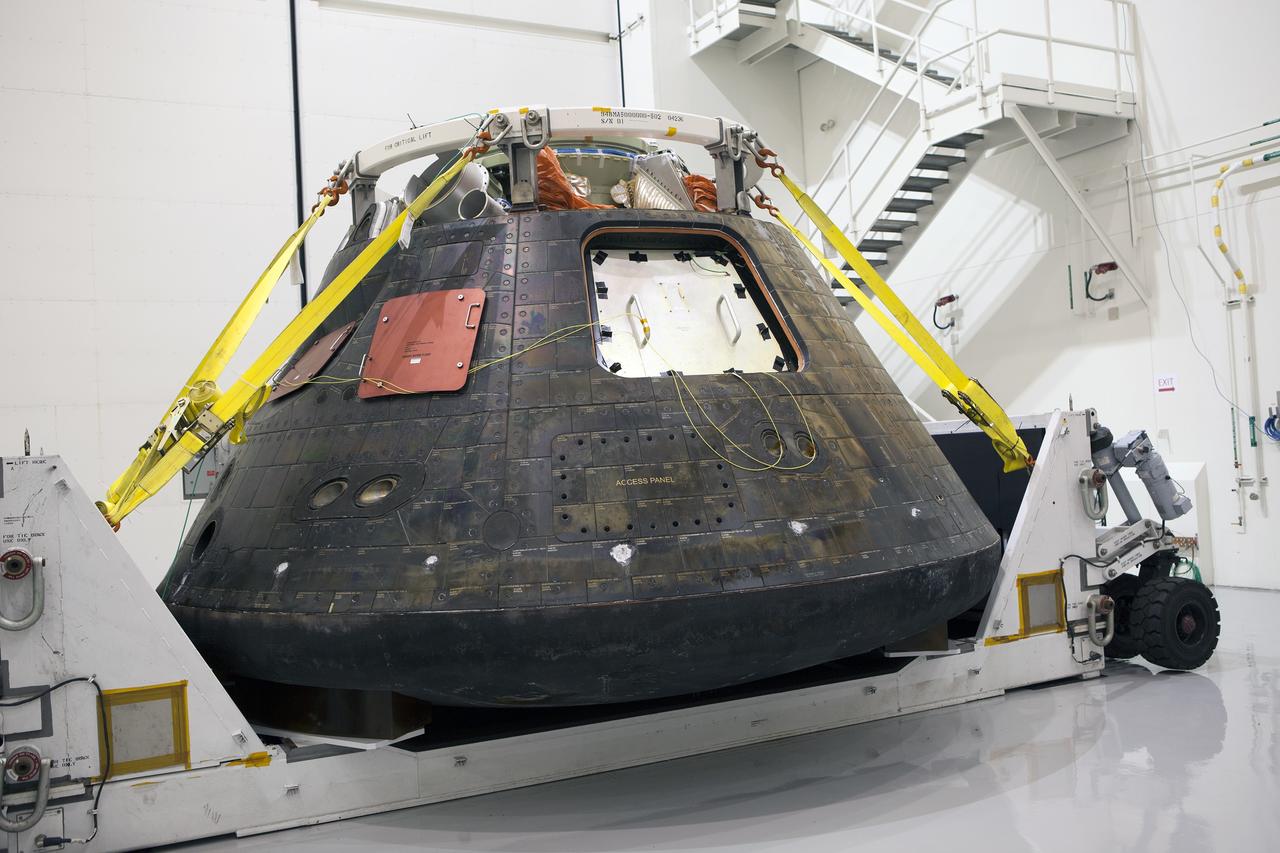

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft has been uncrated and is inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a media event. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion crew module, enclosed in its crew module transportation fixture and secured on a flatbed truck, leaves the Multi-Operation Support Building and is being transported to the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orion was transported 2,700 miles overland from Naval Base San Diego in California. Orion was recovered from the Pacific Ocean after completing a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility (BFF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Jeff Cook, a thermal protection system specialist with Orbital ATK, displays a sample of the painted thermal protection system that is being applied to booster segments. Members of the news media toured the BFF. Orbital ATK is a contractor for NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama, and operates the BFF to prepare aft booster segments and hardware for the SLS rocket boosters. The SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft will launch on Exploration Mission-1 in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is preparing the infrastructure to process and launch spacecraft for deep-space missions and the journey to Mars.
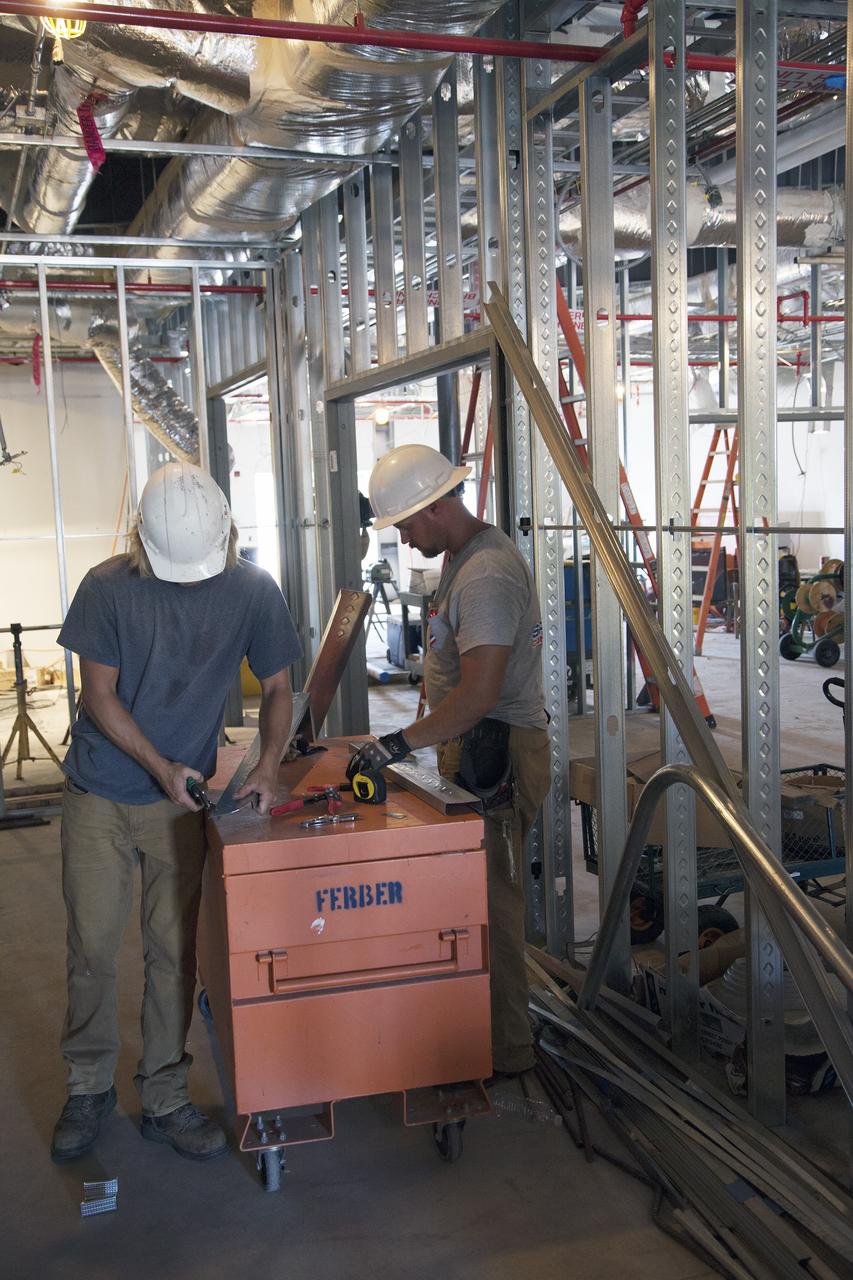

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Modifications continue on the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, or MPPF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the MPPF annex building, construction workers are converting the building to a ground support equipment storage area and work area. The pipes overhead are part of the Environmental Control System. Kennedy's Center Operations Directorate is overseeing upgrades to the MPPF for the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program. The extensive upgrades and modernizations will support processing of Orion spacecraft for NASA's exploration missions. The 19,647-square-foot building, originally constructed in 1995, primarily will be used for Orion hypergolic fueling, ammonia servicing and high-pressure gas servicing and checkout before being transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for integration with the Space Launch System. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
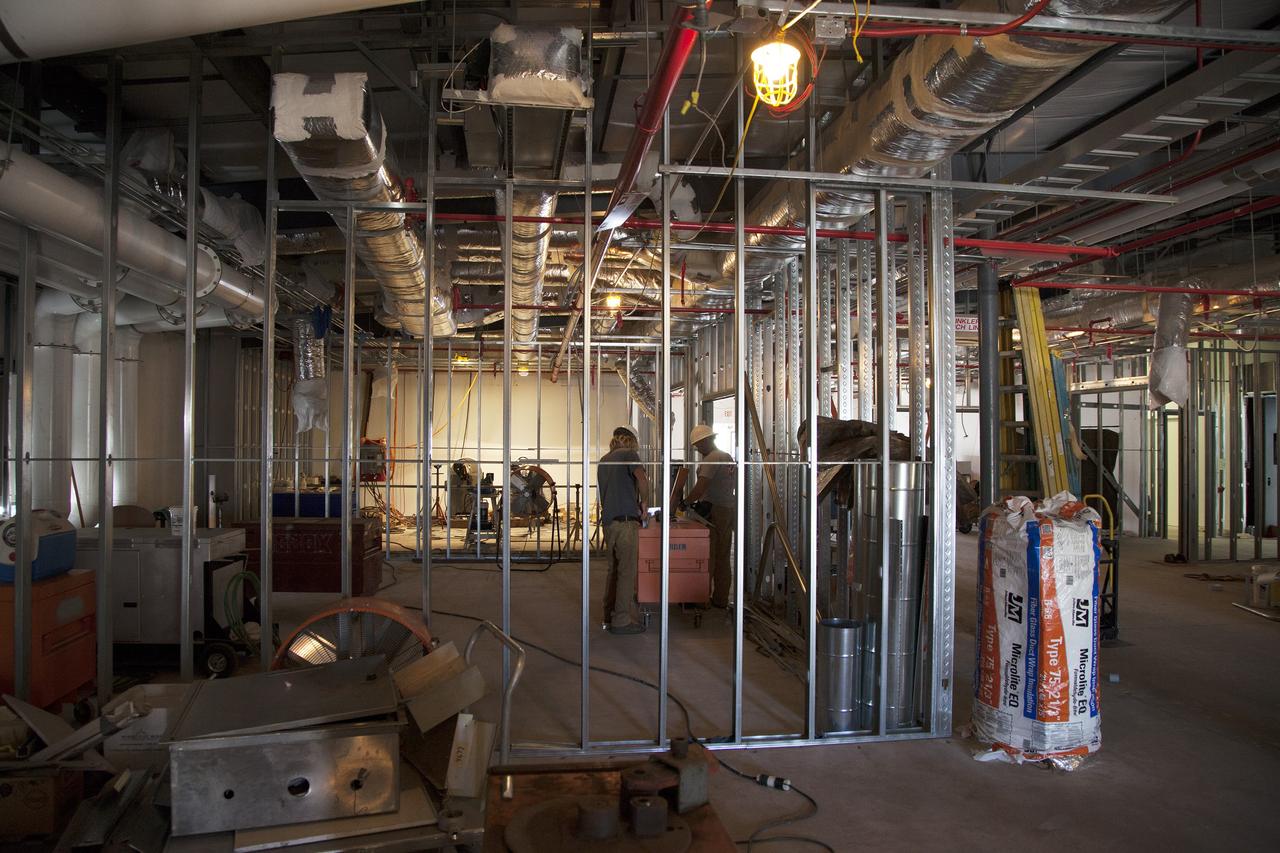

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Modifications continue on the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, or MPPF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the MPPF annex building, construction workers are converting the building to a ground support equipment storage area and work area. The pipes overhead are part of the Environmental Control System. Kennedy's Center Operations Directorate is overseeing upgrades to the MPPF for the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program. The extensive upgrades and modernizations will support processing of Orion spacecraft for NASA's exploration missions. The 19,647-square-foot building, originally constructed in 1995, primarily will be used for Orion hypergolic fueling, ammonia servicing and high-pressure gas servicing and checkout before being transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for integration with the Space Launch System. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
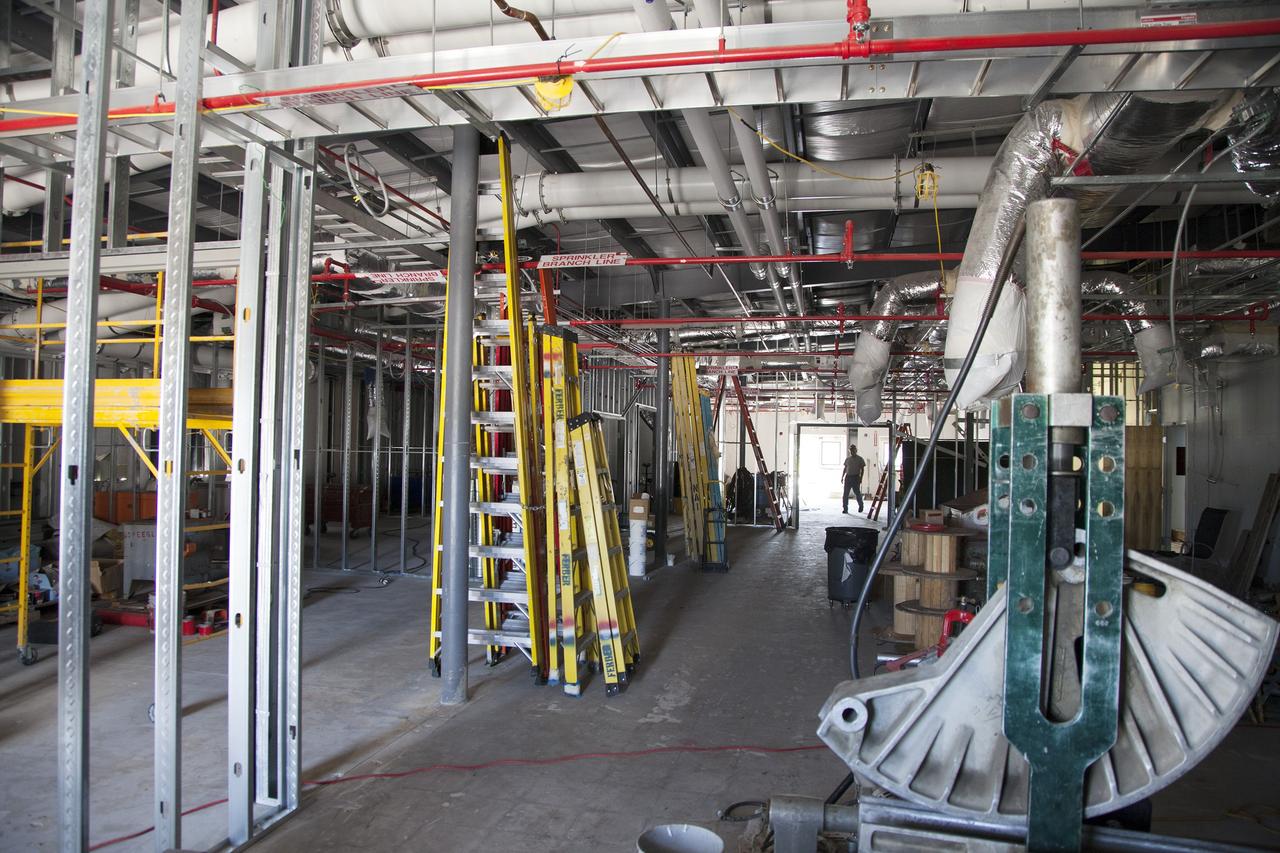

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Modifications continue on the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, or MPPF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the MPPF annex building, construction workers are converting the building to a ground support equipment storage area and work area. The pipes overhead are part of the Environmental Control System. Kennedy's Center Operations Directorate is overseeing upgrades to the MPPF for the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program. The extensive upgrades and modernizations will support processing of Orion spacecraft for NASA's exploration missions. The 19,647-square-foot building, originally constructed in 1995, primarily will be used for Orion hypergolic fueling, ammonia servicing and high-pressure gas servicing and checkout before being transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for integration with the Space Launch System. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

Lockheed Martin Manager Jules Schneider speaks to members of the media during a viewing of NASA's Orion spacecraft at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft's cross-country return, a 2,700 mile road trip from Naval Base San Diego to Kennedy, sets the stage for in-depth analysis of data obtained during Orion's trip to space. It will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared during its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight test, completed on Dec. 5. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
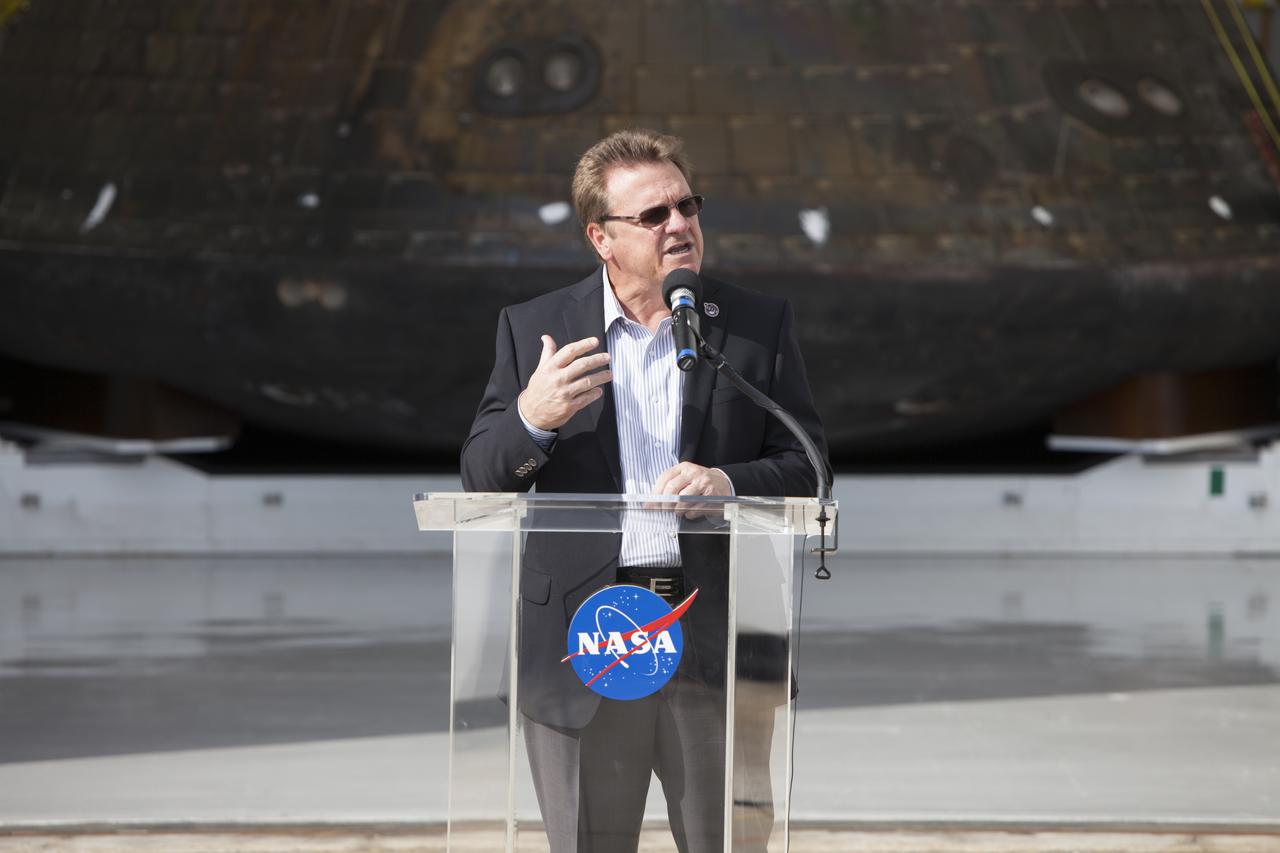

Lockheed Martin Manager Jules Schneider speaks to members of the media during a viewing of NASA's Orion spacecraft at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft's cross-country return, a 2,700 mile road trip from Naval Base San Diego to Kennedy, sets the stage for in-depth analysis of data obtained during Orion's trip to space. It will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared during its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight test, completed on Dec. 5. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.

NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Lou Garcia, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO, speaks to the media during the viewing opportunity. The spacecraft's cross-country return, a 2,700 mile road trip from Naval Base San Diego to Kennedy, sets the stage for in-depth analysis of data obtained during Orion's trip to space. It will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared during its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight test, completed on Dec. 5. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.

NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Kennedy News Chief Mike Curie speaks to the media during the viewing opportunity. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
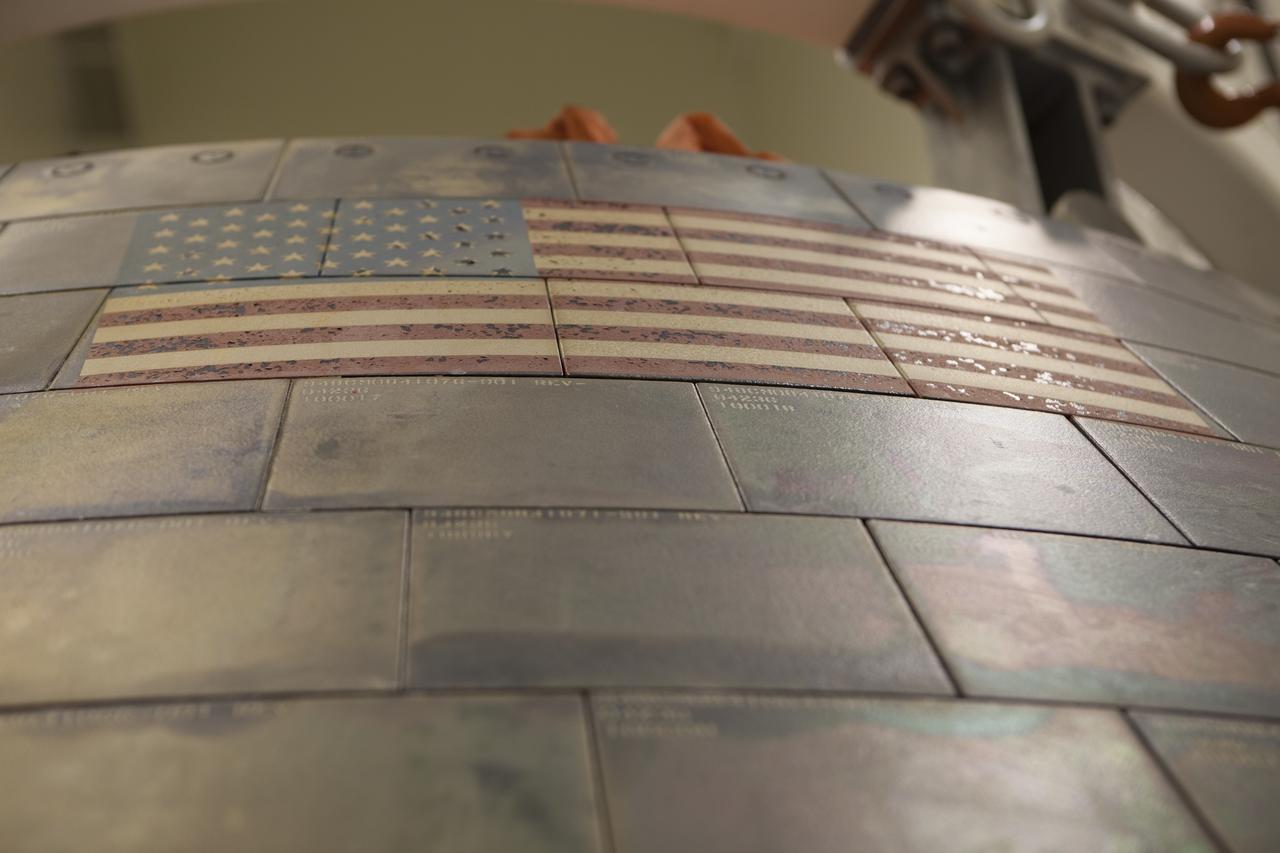
The U.S. Flag is in view on NASA's Orion spacecraft inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a media event. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.

NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Kennedy's News Chief Mike Curie speaks to the media during the viewing opportunity. The spacecraft's cross-country return, a 2,700 mile road trip from Naval Base San Diego to Kennedy, sets the stage for in-depth analysis of data obtained during Orion's trip to space. It will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared during its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight test, completed on Dec. 5. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.

NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Lou Garcia, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO, speaks to the media during the viewing opportunity. The spacecraft's cross-country return, a 2,700 mile road trip from Naval Base San Diego to Kennedy, sets the stage for in-depth analysis of data obtained during Orion's trip to space. It will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared during its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight test, completed on Dec. 5. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
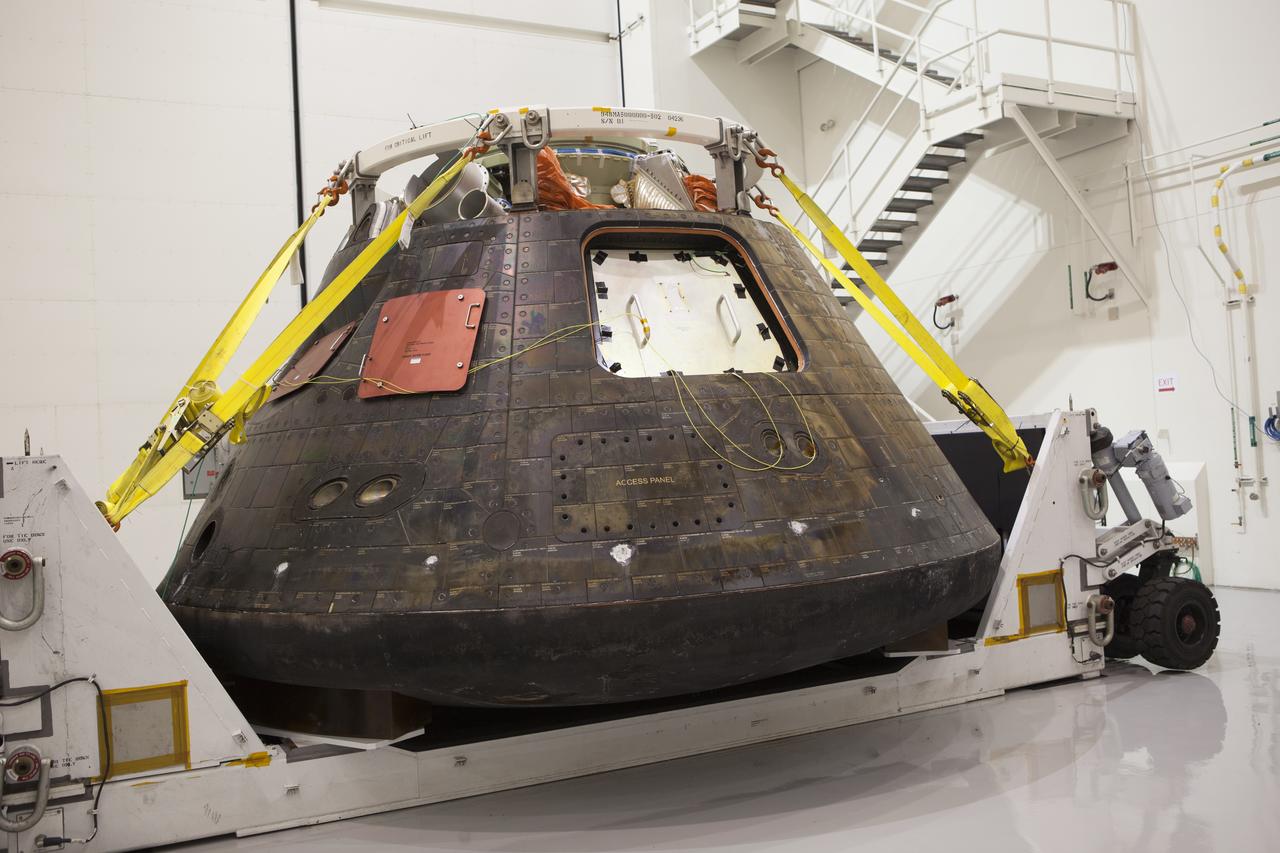

NASA's Orion spacecraft has been uncrated and is inside the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida during a media event. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
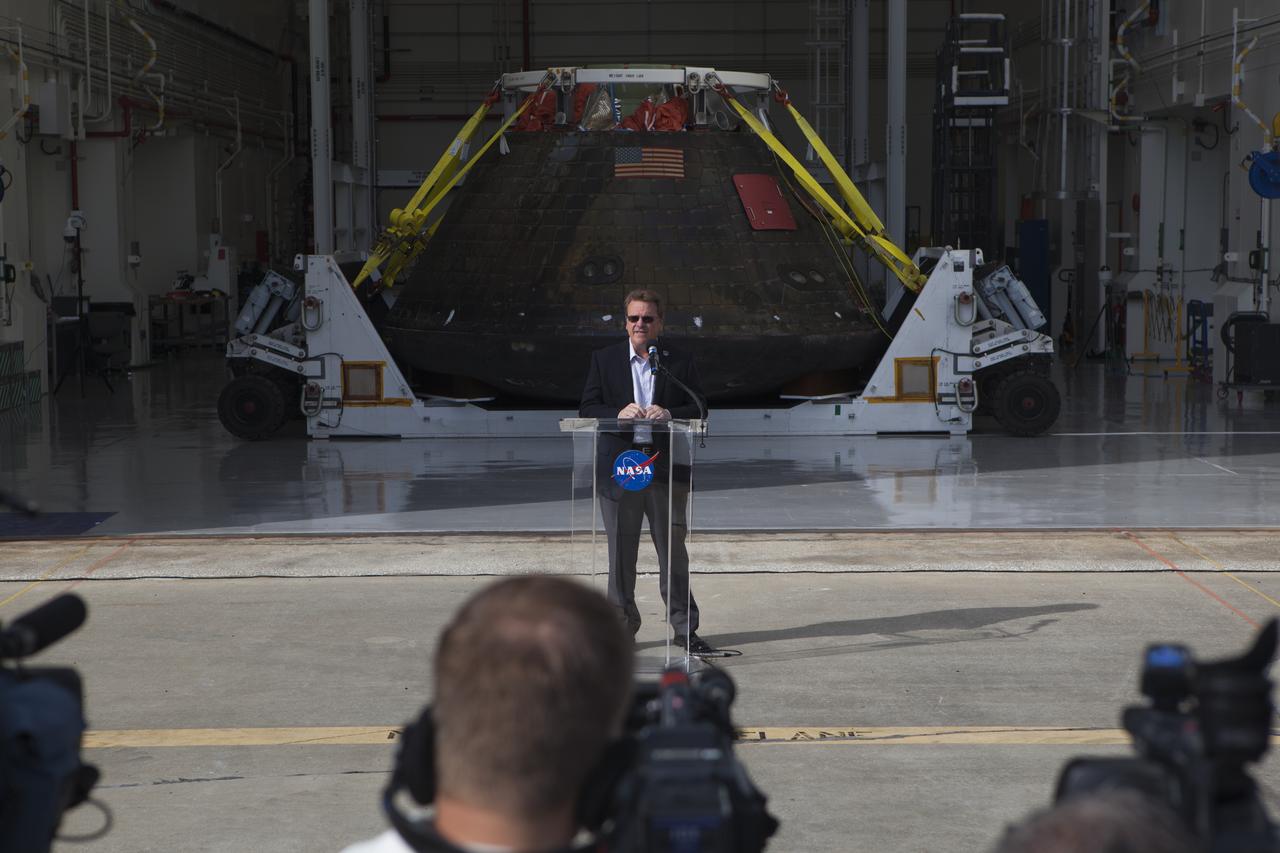

Lockheed Martin Manager Jules Schneider speaks to members of the media during a viewing of NASA's Orion spacecraft at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft's cross-country return, a 2,700 mile road trip from Naval Base San Diego to Kennedy, sets the stage for in-depth analysis of data obtained during Orion's trip to space. It will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared during its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight test, completed on Dec. 5. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.

NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Lou Garcia, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO, speaks to the media during the viewing opportunity. The spacecraft's cross-country return, a 2,700 mile road trip from Naval Base San Diego to Kennedy, sets the stage for in-depth analysis of data obtained during Orion's trip to space. It will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared during its two-orbit, 4.5-hour flight test, completed on Dec. 5. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
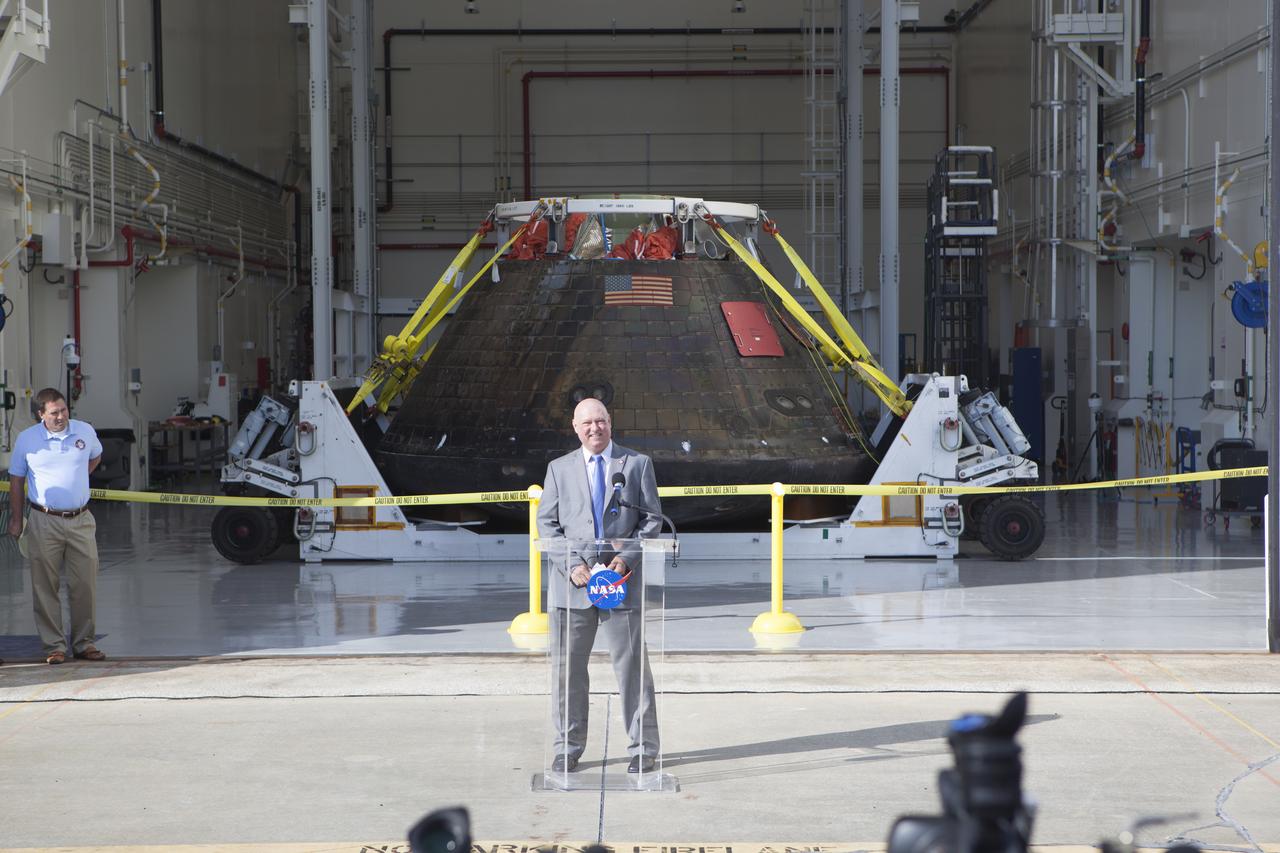

NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Kennedy News Chief Mike Curie speaks to the media during the viewing opportunity. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of data obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
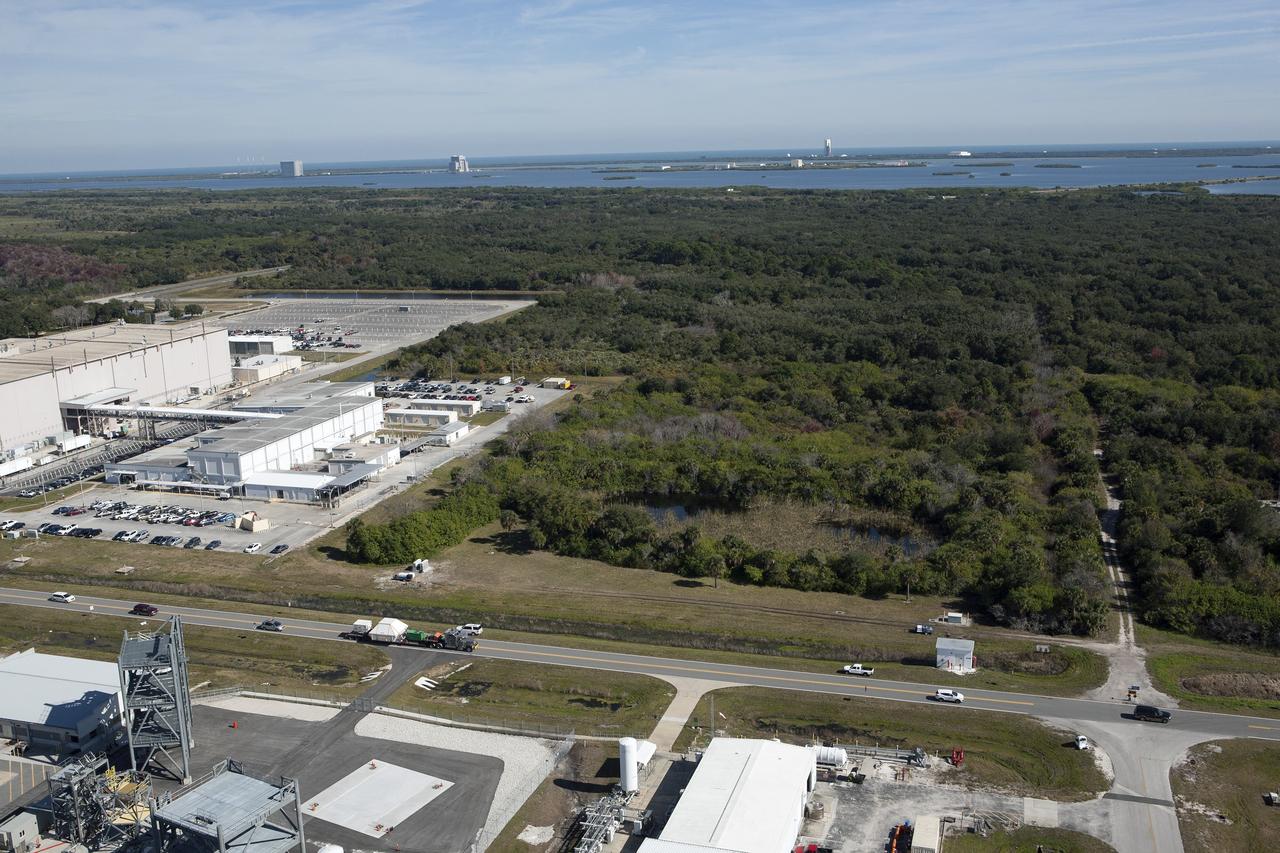

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- An aerial view reveals the Orion crew module, enclosed in its crew module transportation fixture and secured on a flatbed truck is passing the Space Station Processing Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on its way to the Multi-Operation Support Building. Orion made the 2,700 mile overland trip from Naval Base San Diego in California. The spacecraft was recovered from the Pacific Ocean after completing a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
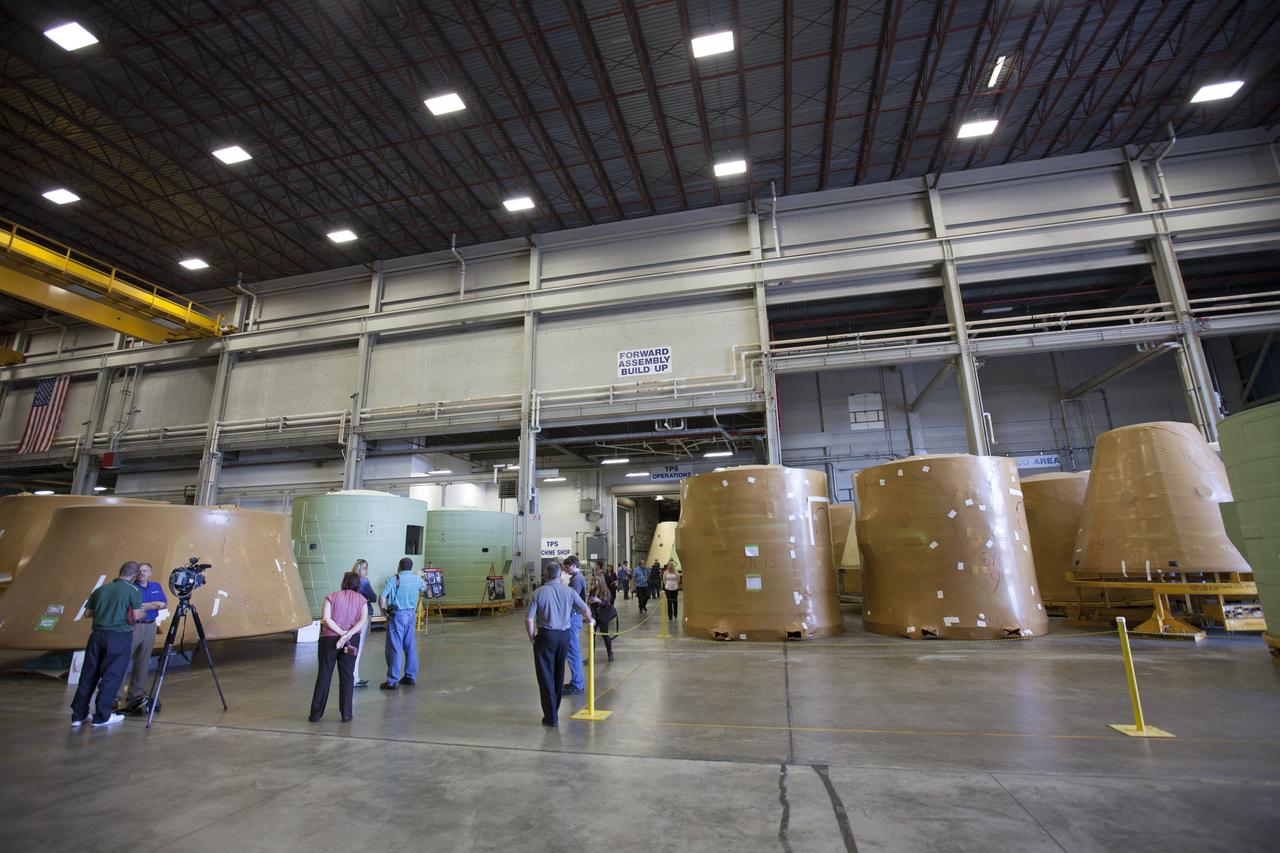

Members of the news media view forward booster segments (painted green) for NASA’s Space Launch System rocket boosters inside the Booster Fabrication Facility (BFF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orbital ATK is a contractor for NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama, and operates the BFF to prepare aft booster segments and hardware for the SLS rocket boosters. The SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft will launch on Exploration Mission-1 in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is preparing the infrastructure to process and launch spacecraft for deep-space missions and the journey to Mars.

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility (BFF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the news media photograph a frustrum that will be stacked atop a forward skirt for one of NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) solid rocket boosters. Orbital ATK is a contractor for NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama, and operates the BFF to prepare aft booster segments and hardware for the SLS solid rocket boosters. The SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft will launch on Exploration Mission-1 in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is preparing the infrastructure to process and launch spacecraft on deep-space missions and the journey to Mars.
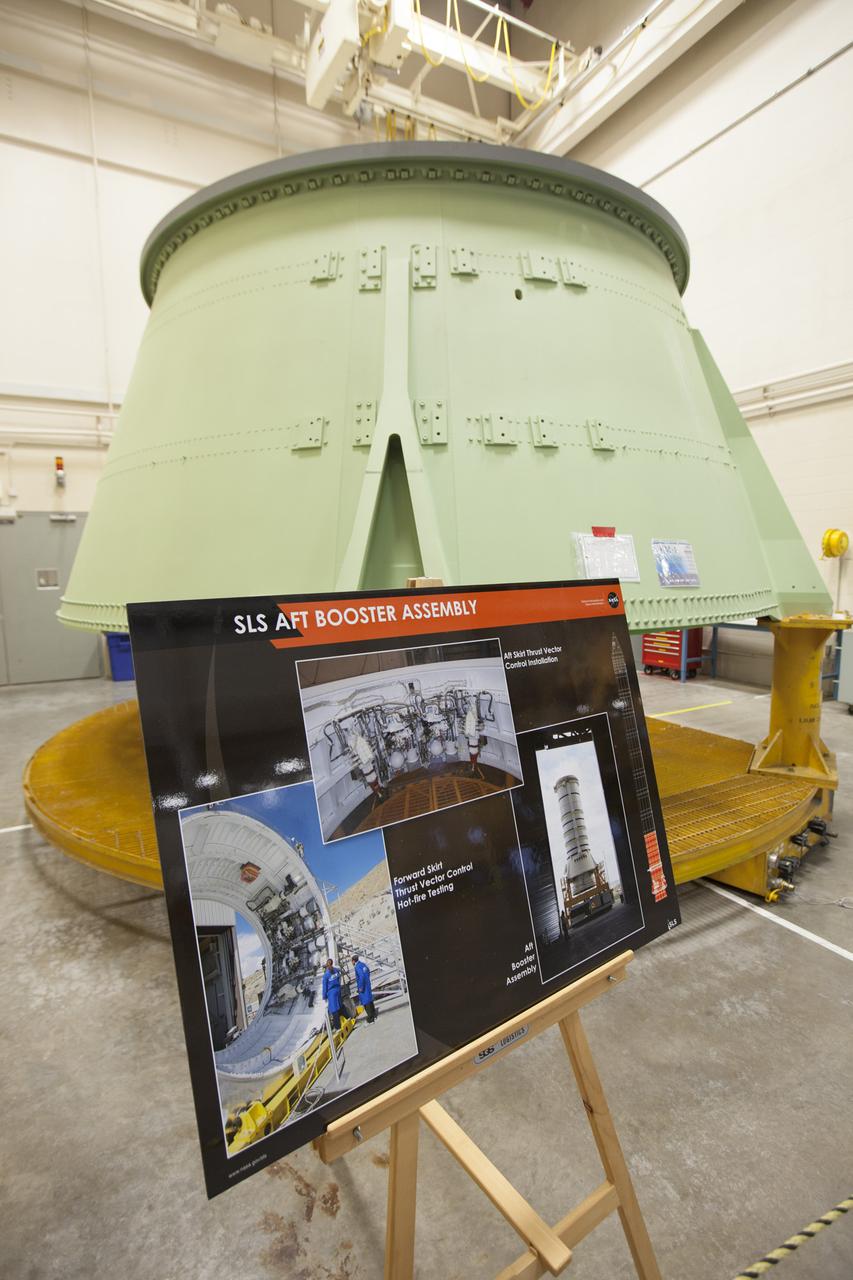

The right-hand aft skirt, one part of the aft booster assembly for NASA’s Space Launch System solid rocket boosters, is in view in a processing cell inside the Booster Fabrication Facility (BFF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orbital ATK is a contractor for NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama, and operates the BFF to prepare aft booster segments and hardware for the SLS rocket boosters. The SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft will launch on Exploration Mission-1 in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is preparing the infrastructure to process and launch spacecraft for deep-space missions and the journey to Mars.

Bethany March, an element integration engineer at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) in Alabama, speaks to members of the news media during a tour of the Booster Fabrication Facility (BFF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Orbital ATK is a contractor for MSFC, and operates the BFF to prepare aft booster segments and hardware for the agency’s Space Launch System (SLS) solid rocket boosters. To her right is Rick Serfozo, Orbital ATK Florida site director. The SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft will launch on Exploration Mission-1 in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is preparing the infrastructure to process and launch spacecraft for deep-space missions and the journey to Mars.

Inside the Booster Fabrication Facility (BFF) at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the news media view a forward skirt that will be used on a solid rocket booster for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) rocket. Orbital ATK is a contractor for NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Alabama, and operates the BFF to prepare aft booster segments and hardware for the SLS solid rocket boosters. Rick Serfozo, Orbital ATK Florida site director, talks to the media. The SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft will launch on Exploration Mission-1 in 2018. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is preparing the infrastructure to process and launch spacecraft for deep-space missions and the journey to Mars.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Distinguished speakers are seated in the front row in Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Checkout Building high bay for an event marking the arrival of NASA's first space-bound Orion capsule in Florida. From left are Dan Dumbacher, NASA deputy associate administrator for Exploration Systems Development, NASA Kennedy Space Center Director Robert Cabana, NASA Deputy Administrator Lori Garver, U.S. Senator Bill Nelson, Mark Geyer, Orion program manager, David Beaman, NASA Space Launch System spacecraft and payload integration manager, Pepper Phillips, program manager for NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations, and John Karas, vice president and general manager of Human Spaceflight for Lockheed Martin Space Systems. Slated for Exploration Flight Test-1, an uncrewed mission planned for 2014, the capsule will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The capsule was shipped to Kennedy from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where the crew module pressure vessel was built. The Orion production team will prepare the module for flight at Kennedy by installing heat-shielding thermal protection systems, avionics and other subsystems. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the media during the viewing opportunity is Jules Schneider, Lockheed Martin Manager. Behind him, from left, are Glenn Chin, Orion Production Operations manager and Phil Weber and Lou Garcia, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the media during the viewing opportunity is Phil Weber, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO. At left is Jules Schneider, Lockheed Martin manager. At right is Glenn Chin, Orion Production Operations, and Lou Garcia, with GSDO. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the media during the viewing opportunity is Glenn Chin, Orion Production Operations. To his right is Phil Weber, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
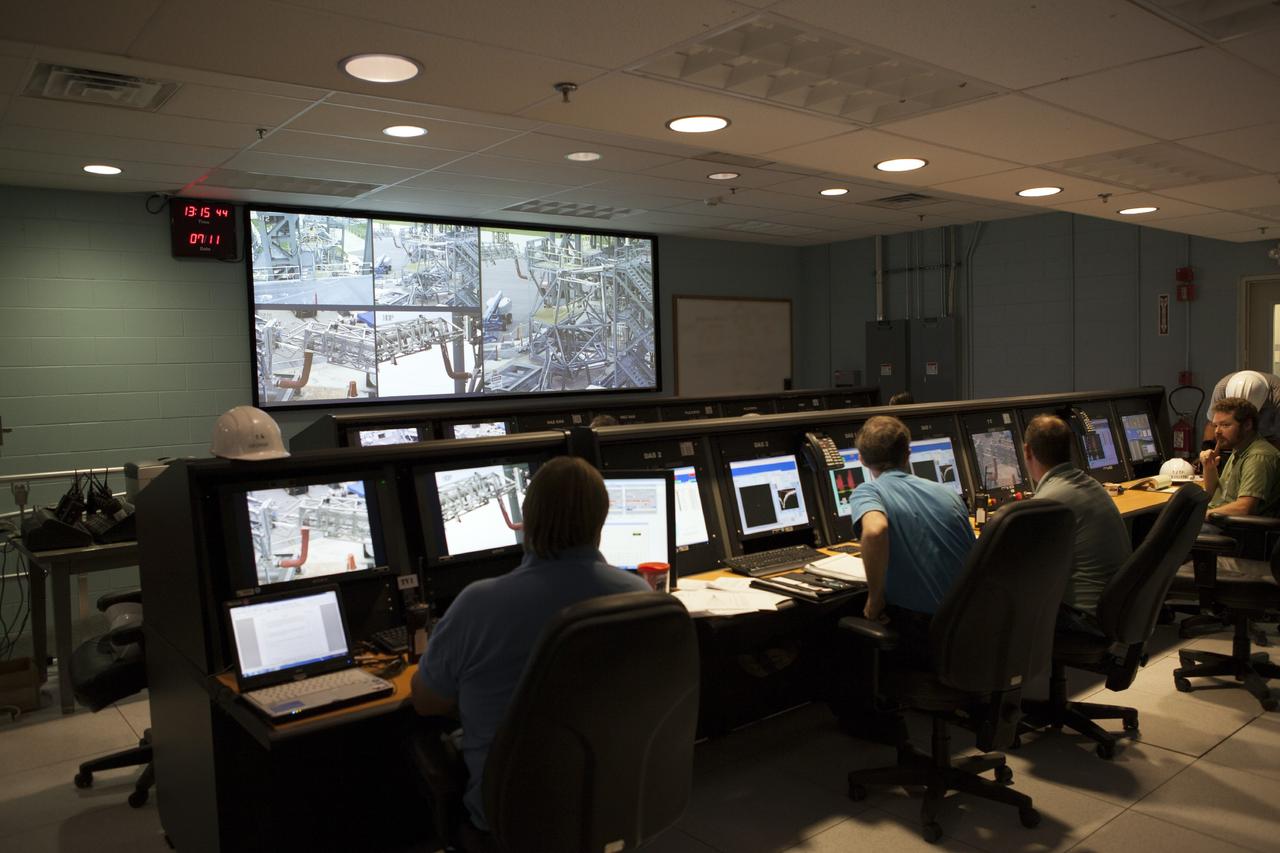

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Engineers in a control center at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida monitor a test on the quick disconnect for a modified instrument unit and liquid hydrogen tilt up umbilical at the Launch Equipment Test Facility. The test is being performed by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program. The umbilical will be partially reutilized for the Orion Service Module Unit. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
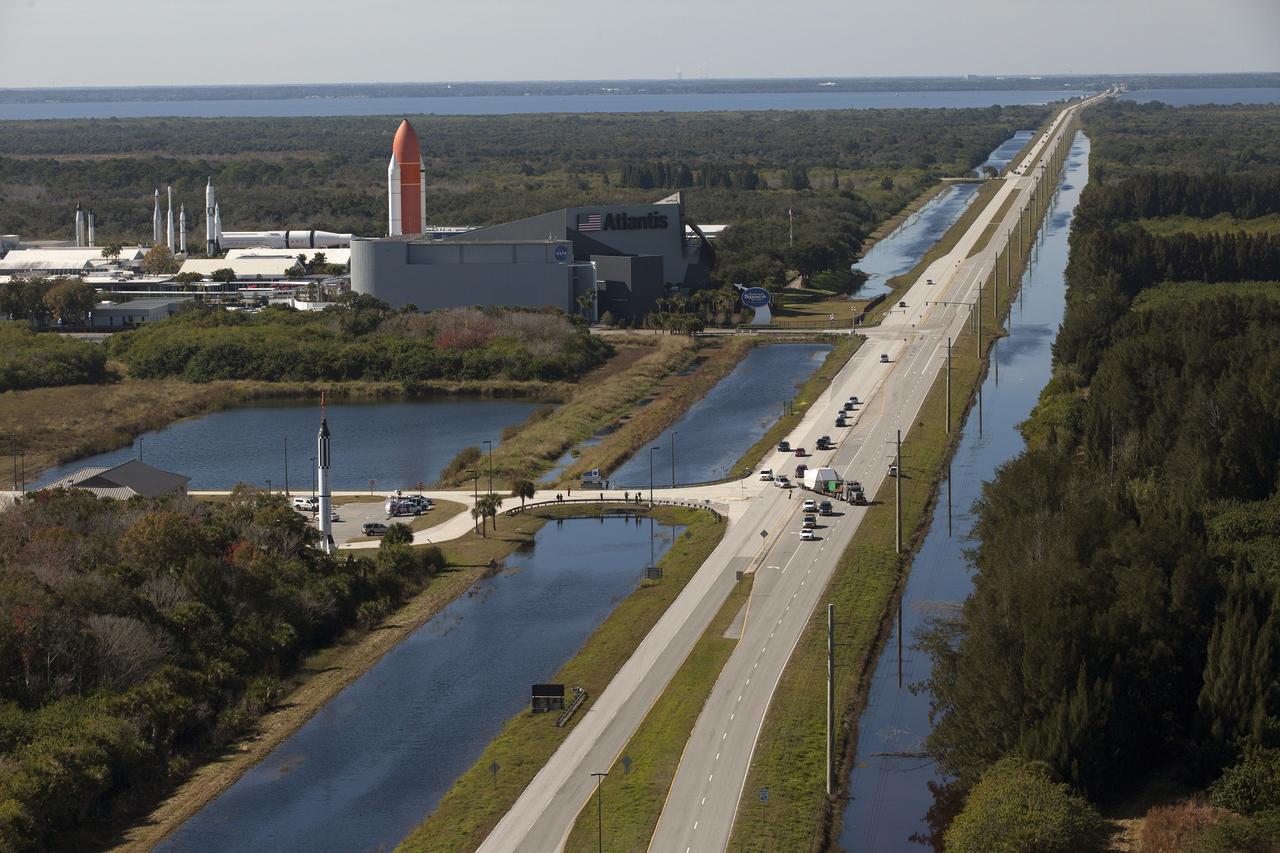

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In this aerial view, NASA's Orion crew module, enclosed in its crew module transportation fixture and secured on a flatbed truck is passing the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex on its way to the entrance gate to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view is the Space Shuttle Atlantis facility. Orion made the 2,700 mile overland trip from Naval Base San Diego in California. Orion was recovered from the Pacific Ocean after completing a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In this aerial view, NASA's Orion crew module, enclosed in its crew module transportation fixture and secured on a flatbed truck is passing the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex on its way to the entrance gate to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view is the Space Shuttle Atlantis facility. Orion made the 2,700 mile overland trip from Naval Base San Diego in California. Orion was recovered from the Pacific Ocean after completing a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

Launch Complex 39B current and past NASA and contractor workers gathered at pad B to mark the 50th anniversary of the launch complex at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Upgrades to the surface of pad B, as well as the systems below and surrounding the pad will support the new processing and launch requirements for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and the Orion spacecraft for deep-space missions, including the journey to Mars. The modifications and improvements to processing and launch facilities will support Kennedy as a multi-user spaceport for government and commercial launches for years to come. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B.
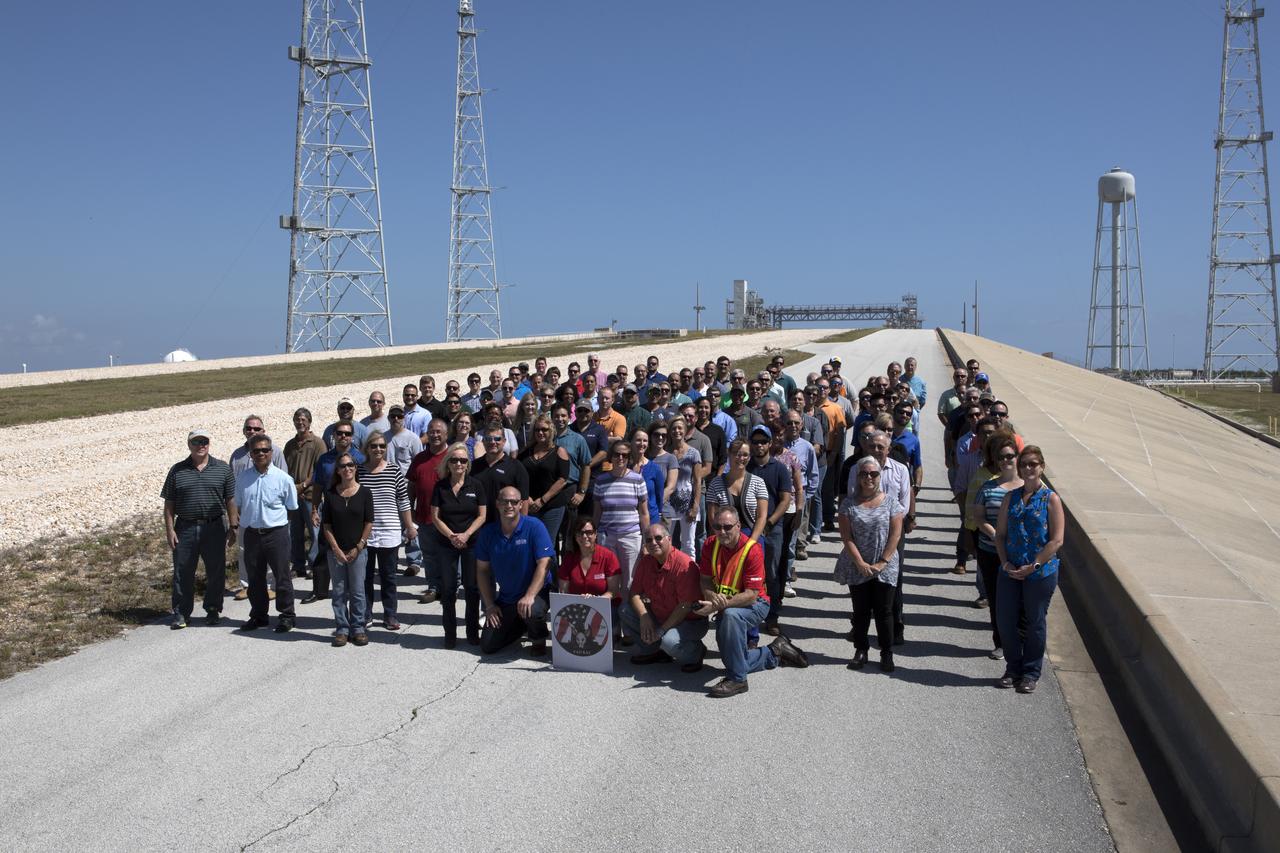

Launch Complex 39B current and past NASA and contractor workers gathered at pad B to mark the 50th anniversary of the launch complex at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Upgrades to the surface of pad B, as well as the systems below and surrounding the pad will support the new processing and launch requirements for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and the Orion spacecraft for deep-space missions, including the journey to Mars. The modifications and improvements to processing and launch facilities will support Kennedy as a multi-user spaceport for government and commercial launches for years to come. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B.
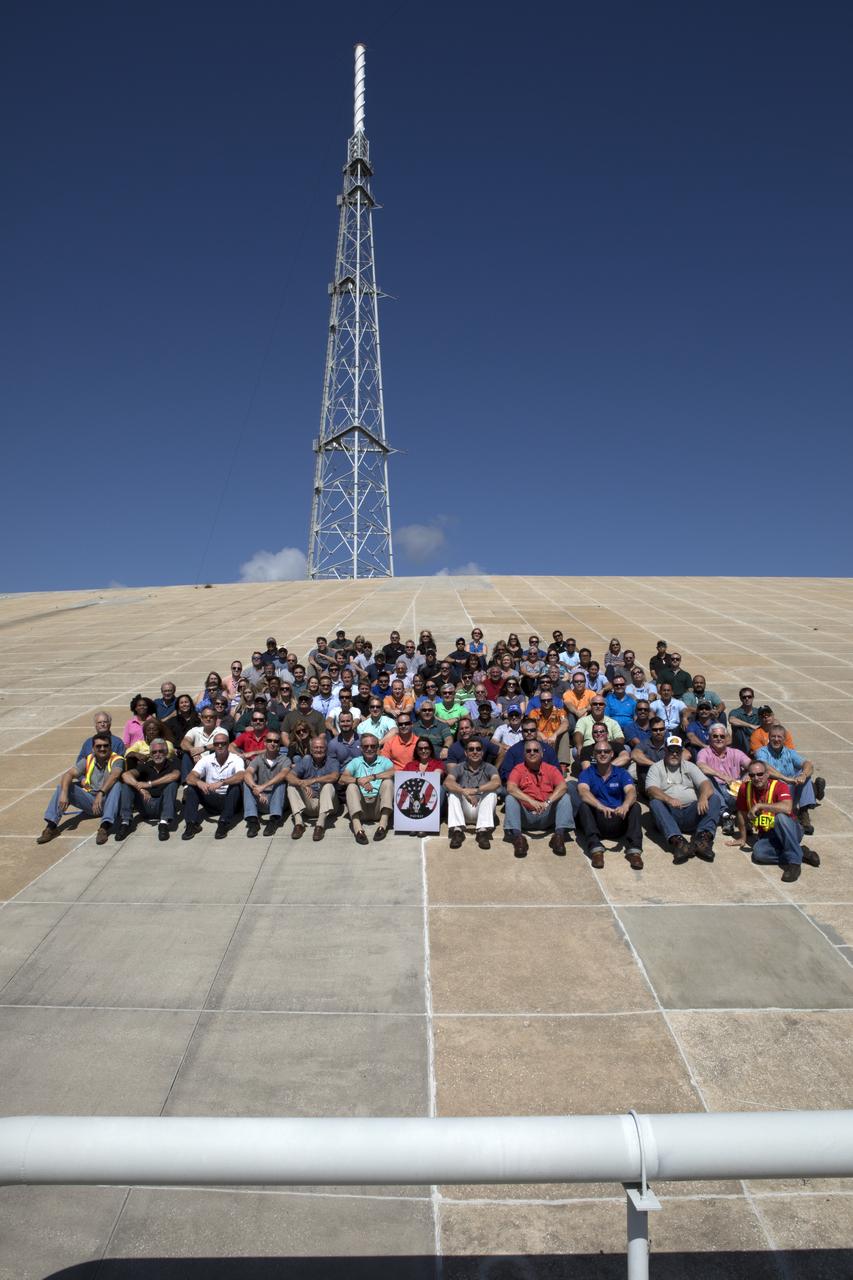

Launch Complex 39B current and past NASA and contractor workers gathered at pad B to mark the 50th anniversary of the launch complex at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Upgrades to the surface of pad B, as well as the systems below and surrounding the pad will support the new processing and launch requirements for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and the Orion spacecraft for deep-space missions, including the journey to Mars. The modifications and improvements to processing and launch facilities will support Kennedy as a multi-user spaceport for government and commercial launches for years to come. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B.
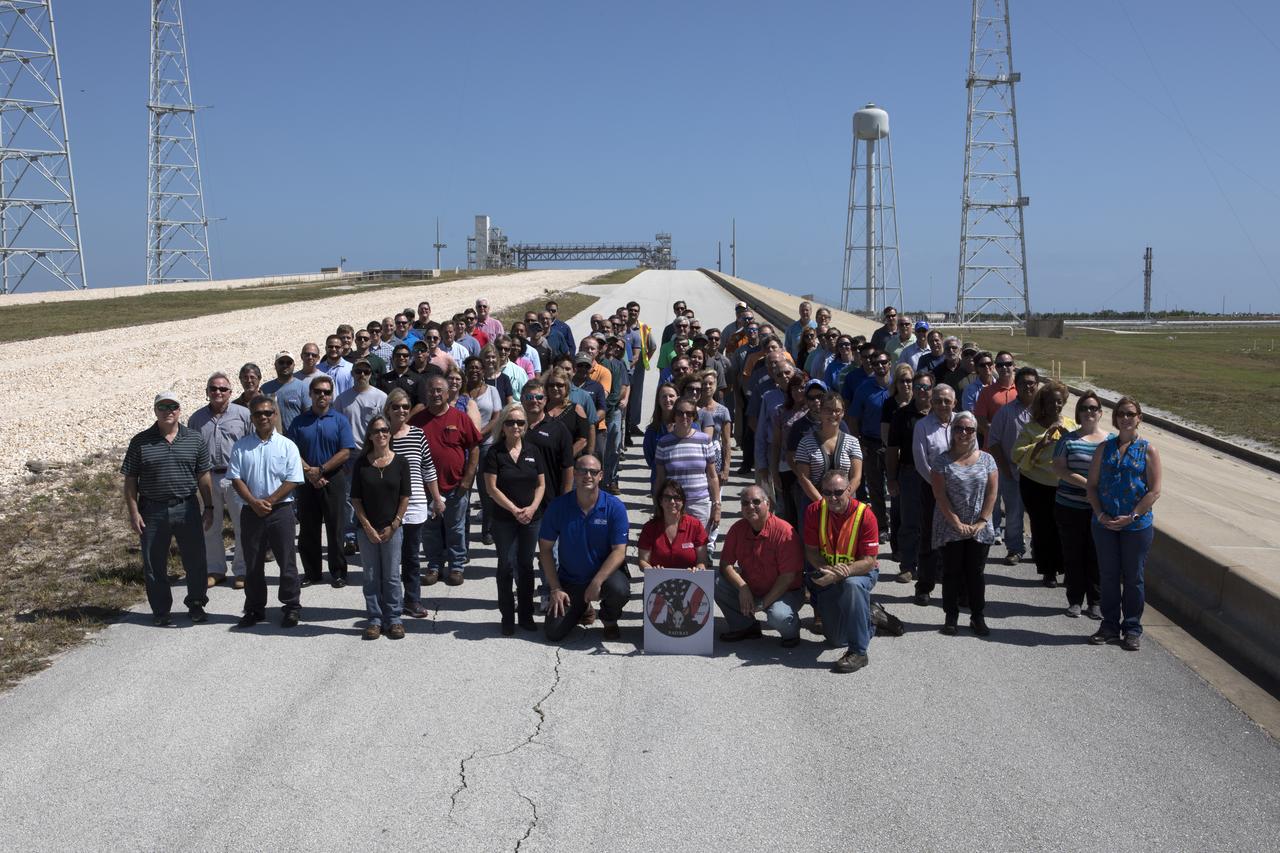

Launch Complex 39B current and past NASA and contractor workers gathered at pad B to mark the 50th anniversary of the launch complex at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Upgrades to the surface of pad B, as well as the systems below and surrounding the pad will support the new processing and launch requirements for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and the Orion spacecraft for deep-space missions, including the journey to Mars. The modifications and improvements to processing and launch facilities will support Kennedy as a multi-user spaceport for government and commercial launches for years to come. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B.
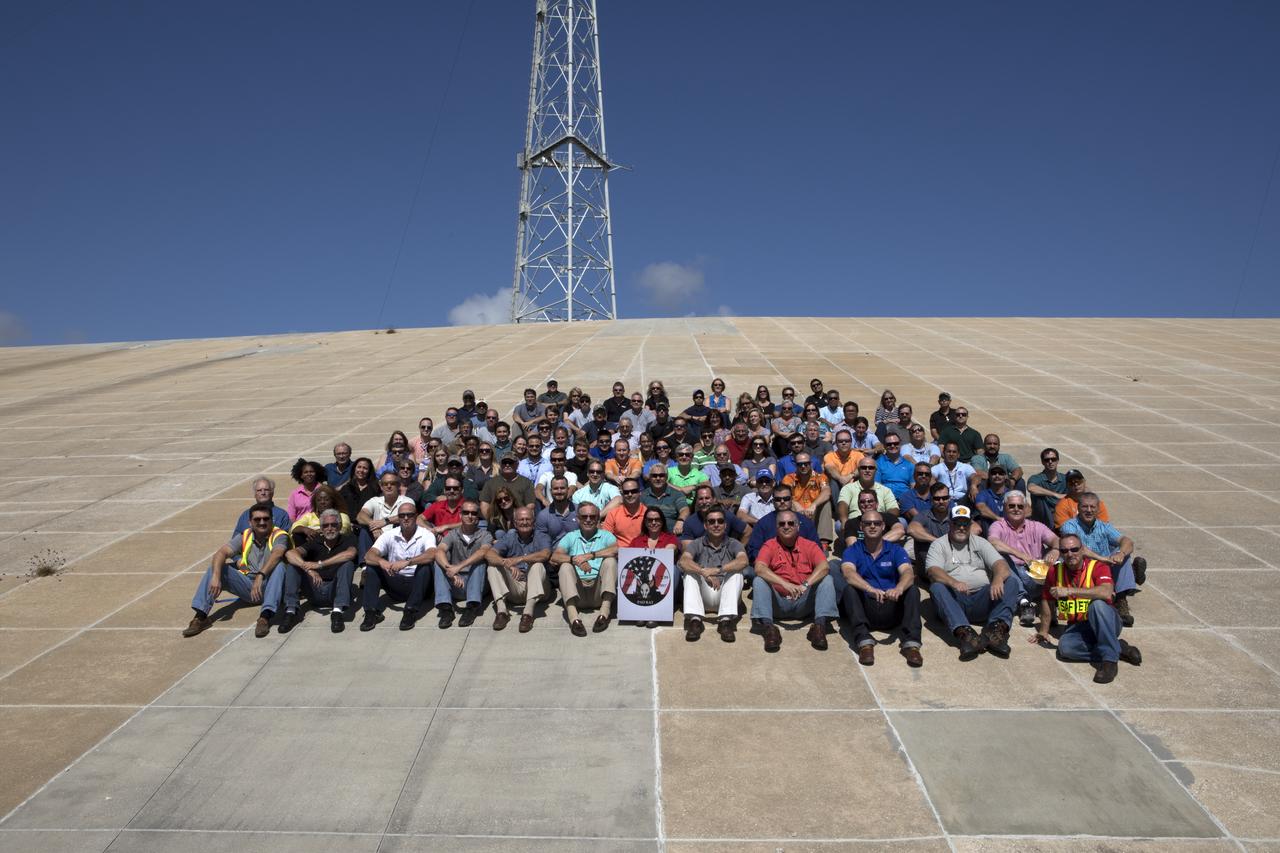

Launch Complex 39B current and past NASA and contractor workers gathered at pad B to mark the 50th anniversary of the launch complex at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Upgrades to the surface of pad B, as well as the systems below and surrounding the pad will support the new processing and launch requirements for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and the Orion spacecraft for deep-space missions, including the journey to Mars. The modifications and improvements to processing and launch facilities will support Kennedy as a multi-user spaceport for government and commercial launches for years to come. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B.
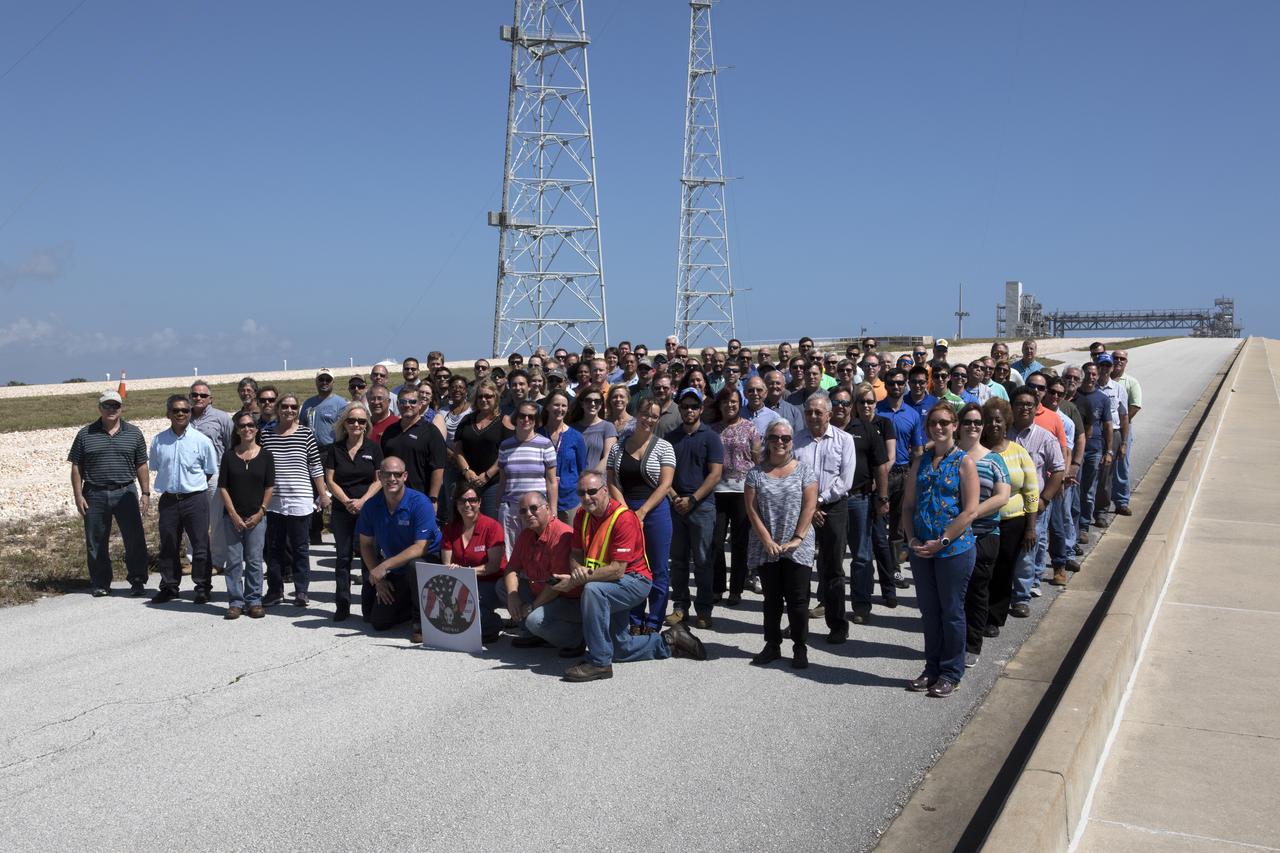

Launch Complex 39B current and past NASA and contractor workers gathered at pad B to mark the 50th anniversary of the launch complex at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Upgrades to the surface of pad B, as well as the systems below and surrounding the pad will support the new processing and launch requirements for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and the Orion spacecraft for deep-space missions, including the journey to Mars. The modifications and improvements to processing and launch facilities will support Kennedy as a multi-user spaceport for government and commercial launches for years to come. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B.
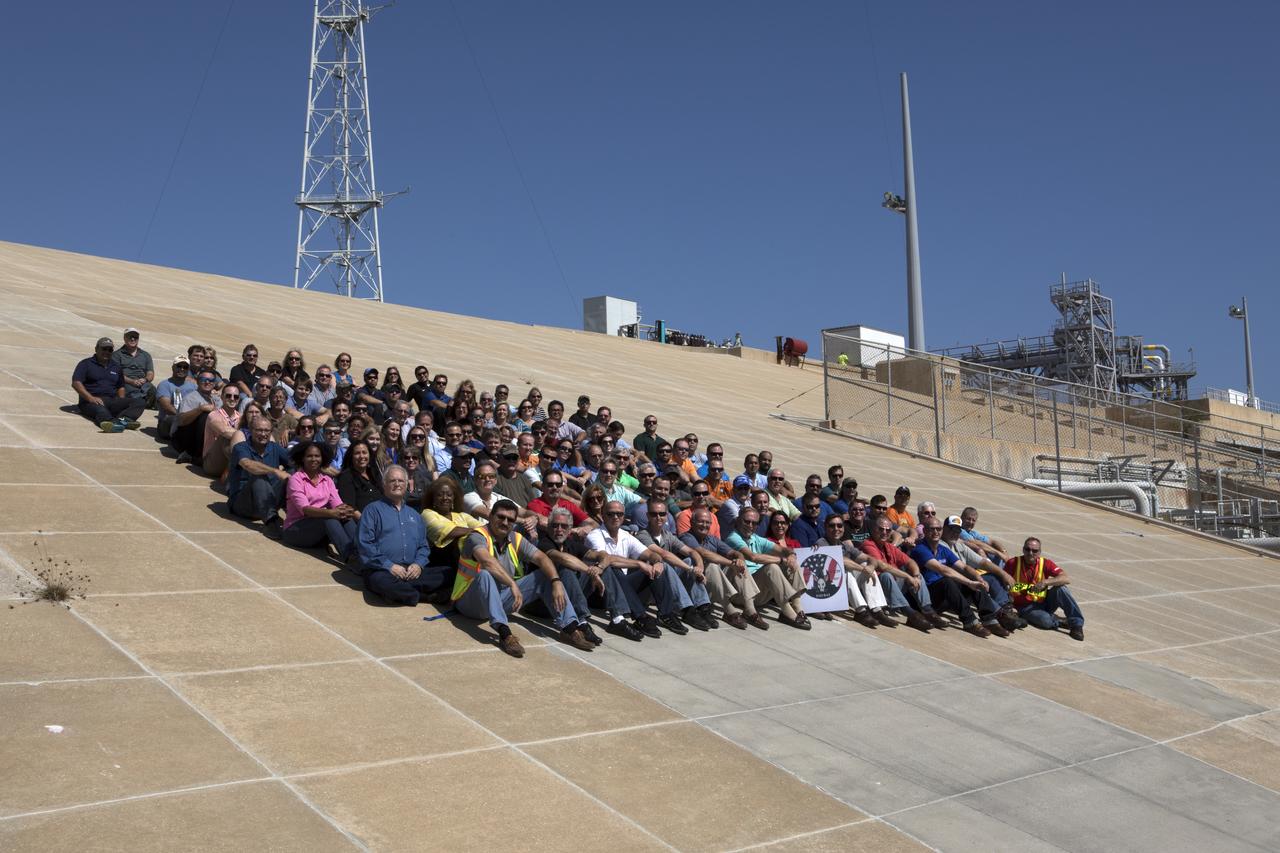

Launch Complex 39B current and past NASA and contractor workers gathered at pad B to mark the 50th anniversary of the launch complex at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Upgrades to the surface of pad B, as well as the systems below and surrounding the pad will support the new processing and launch requirements for NASA's Space Launch System (SLS) and the Orion spacecraft for deep-space missions, including the journey to Mars. The modifications and improvements to processing and launch facilities will support Kennedy as a multi-user spaceport for government and commercial launches for years to come. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program is overseeing upgrades and modifications to Pad 39B.
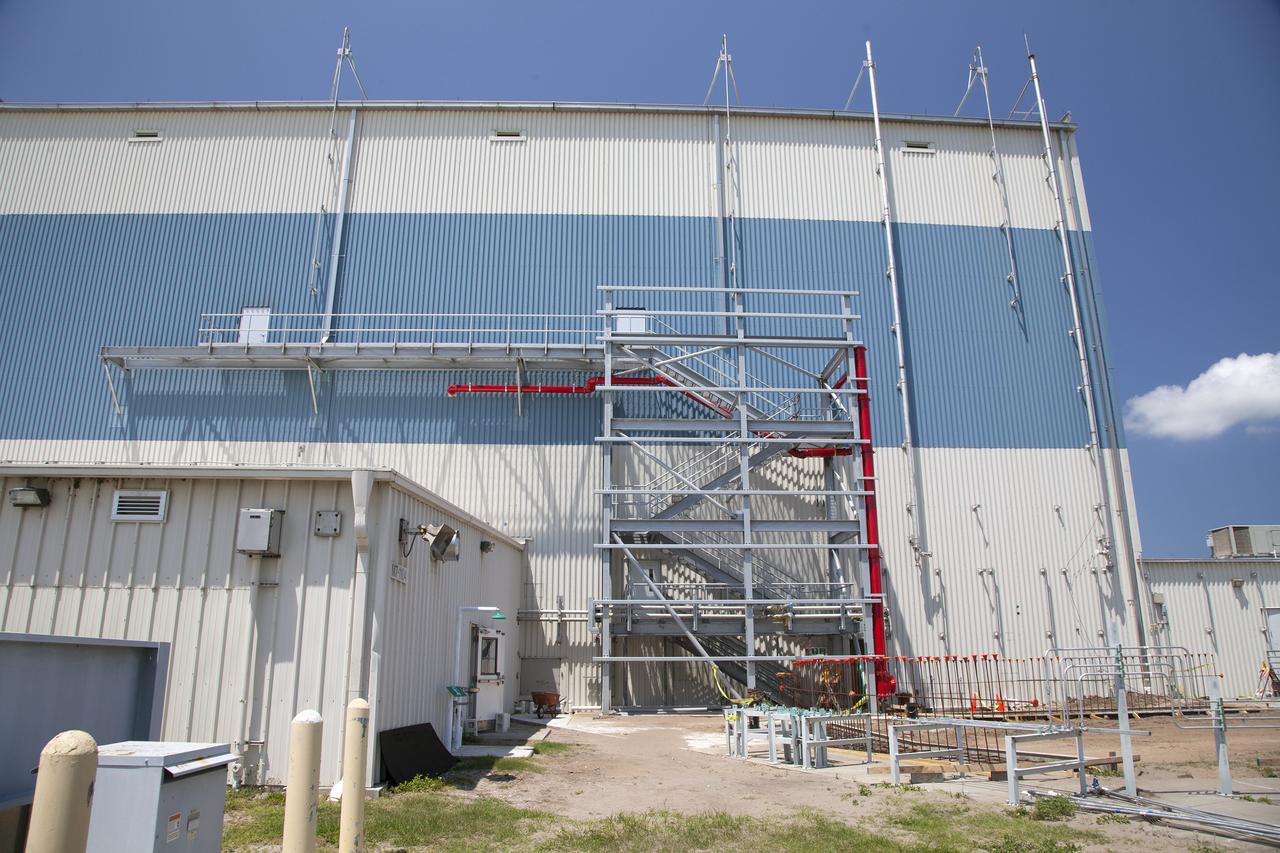

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Modifications continue on the Multi-Payload Processing Facility, or MPPF, at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A new emergency egress stairway has been constructed and a steel structure has been built around it so that walls can be added. The red pipes are the recently-installed fire deluge system. The gray pipes are the hazardous gas venting system. Kennedy's Center Operations Directorate is overseeing upgrades to the MPPF for the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program. The extensive upgrades and modernizations will support processing of Orion spacecraft for NASA's exploration missions. The 19,647-square-foot building, originally constructed in 1995, primarily will be used for Orion hypergolic fueling, ammonia servicing and high-pressure gas servicing and checkout before being transported to the Vehicle Assembly Building for integration with the Space Launch System. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
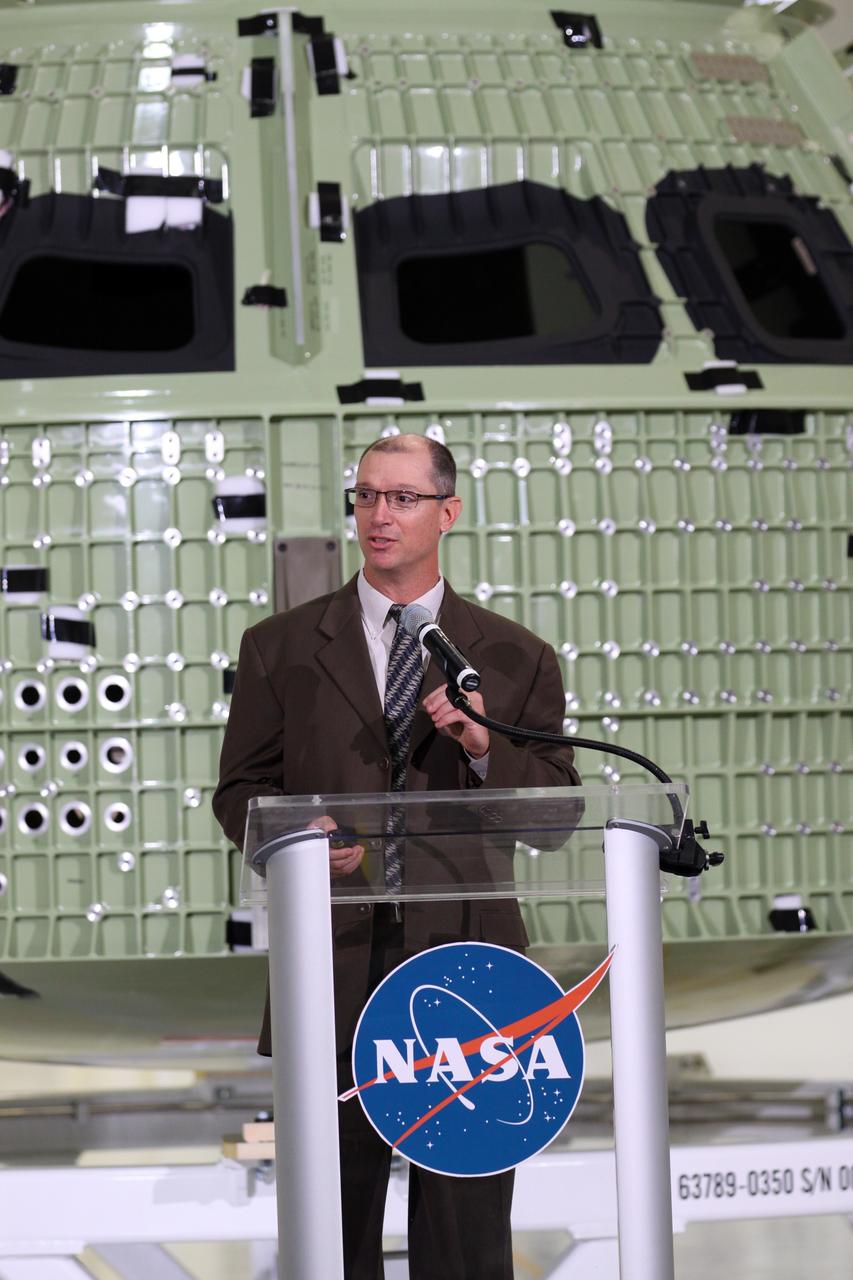

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Pepper Phillips, program manager for NASA's Ground Systems Development and Operations, addresses the audience assembled in Kennedy Space Center's Operations and Checkout Building high bay for an event marking the arrival of NASA's first space-bound Orion capsule in Florida. Slated for Exploration Flight Test-1, an uncrewed mission planned for 2014, the capsule will travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years. The capsule was shipped to Kennedy from NASA's Michoud Assembly Facility in New Orleans where the crew module pressure vessel was built. The Orion production team will prepare the module for flight at Kennedy by installing heat-shielding thermal protection systems, avionics and other subsystems. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the media during the viewing opportunity is Jules Schneider, Lockheed Martin Manager. Behind him, from left, are Glenn Chin, Orion Production Operations manager and Phil Weber and Lou Garcia, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers with detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.

NASA's Orion spacecraft is viewed by members of the media at the Launch Abort System Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Speaking to the media during the viewing opportunity is Phil Weber, with the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program, or GSDO. At left is Jules Schneider, Lockheed Martin manager. At right is Glenn Chin, Orion Production Operations, and Lou Garcia, with GSDO. Orion made the 8-day, 2,700 mile overland trip back to Kennedy from Naval Base San Diego in California. Analysis of date obtained during its two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 will provide engineers detailed information on how the spacecraft fared. GSDO led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
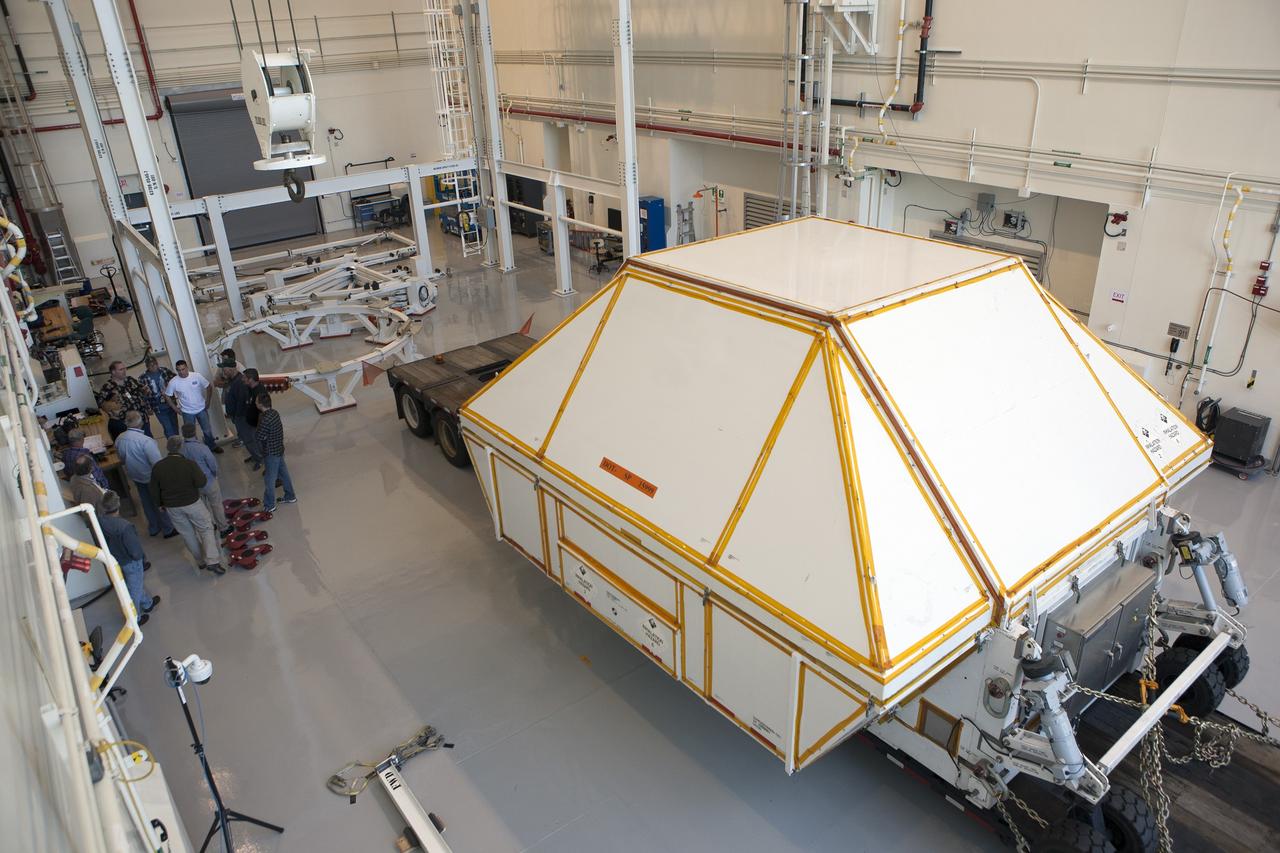

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- NASA's Orion spacecraft arrives inside the Launch Abort System Facility at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft was transported 2,700 miles overland from Naval Base San Diego in California, on a flatbed truck secured in its crew module transportation fixture for the trip. During its first flight test, Orion completed a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
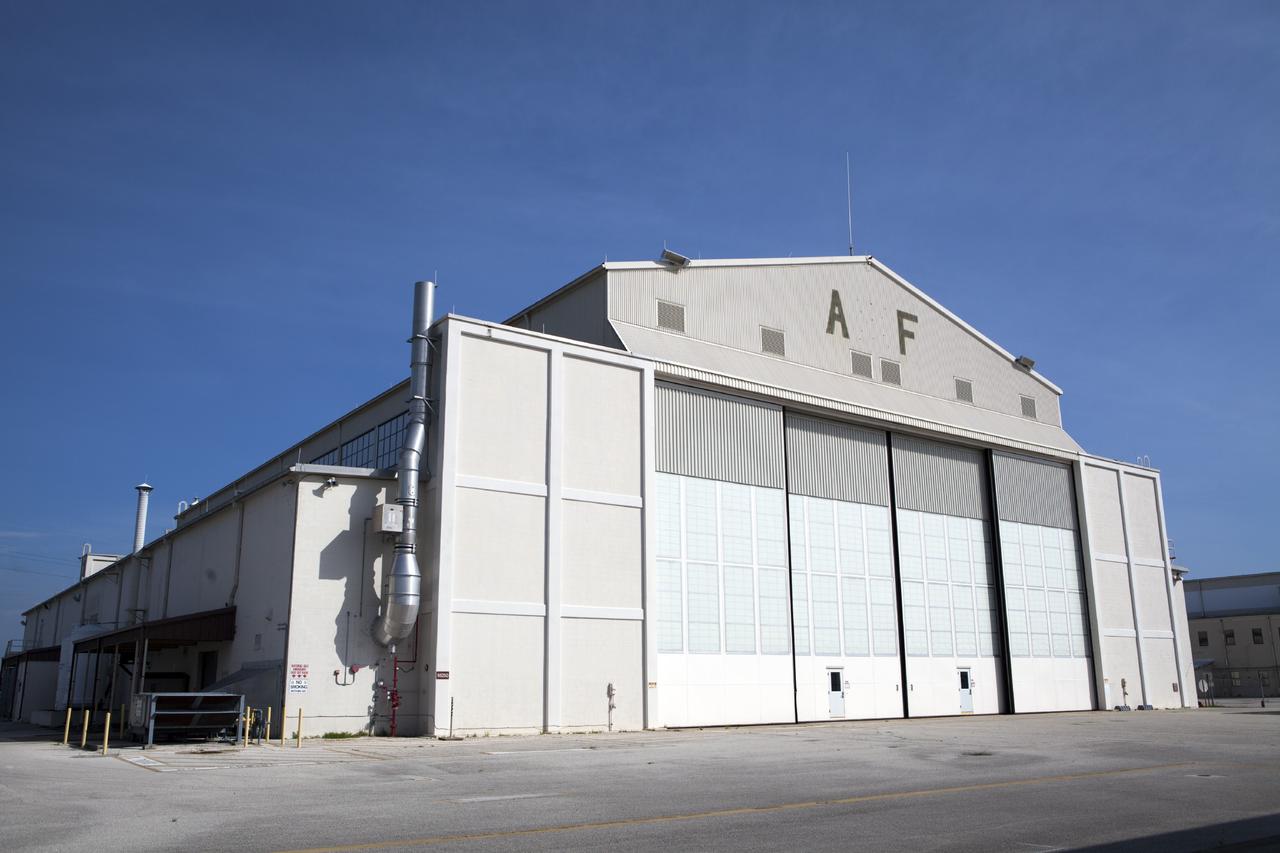

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – An exterior view of Hangar AF at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The facility may be used by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program at Kennedy Space Center for production activities for NASA’s Space Launch System, or SLS. The booster aft and forward skirts and case stiffener attach ring may be processed in the hangar, as well as refurbishment of the frustrum, before they are transferred to the Booster Fabrication Facility for buildup. The SLS rocket will launch the Orion spacecraft on an uncrewed flight test scheduled for 2017. Orion ’s first unpiloted test flight, Exploration Flight Test 1, is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
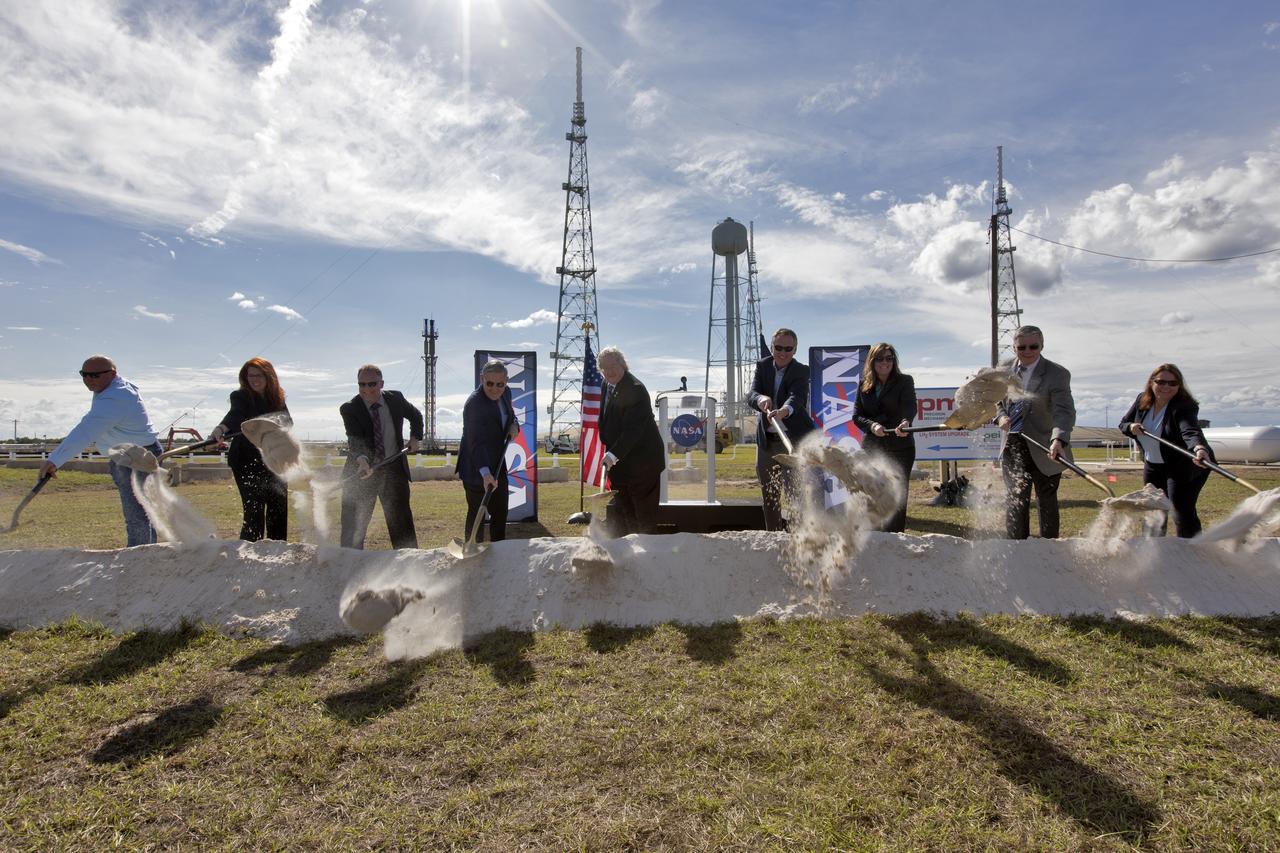

On Dec. 19, 2018, at NASA Kennedy Space Center's Launch Complex 39B, agency and contractor managers break ground for a new liquid hydrogen tank. Participating, from the left, are Todd Gray, president of Precision Mechanical, prime contractor for the project; Charlie Blackwell-Thompson, launch director; Shawn Quinn, director of Engineering; Bob Cabana, center director; Bill Hill, deputy associate administrator for Exploration Systems Development at NASA Headquarters in Washington; Mike Bolger, program manager for Exploration Ground Systems (EGS); Jennifer Kunz, deputy program manager for EGS, Andy Allen, general manager for Jacobs, NASA's Test and Operations Support Contractor; and Regina Spellman, launch pad senior project manager in EGS. The storage facility will hold 1.25 million gallons of the propellant for NASA's Space Launch System rocket designed to boost the agency's Orion spacecraft, sending humans to distant destinations such as the Moon and Mars.

Testing of the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) was completed at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The OSMU was attached to Vehicle Motion Simulator 1 for a series of simulated launch tests to validate it for installation on the mobile launcher. The test team gathered with a special banner during an event to mark the end of testing. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. Kennedy's Engineering Directorate is providing support to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for testing of the OSMU. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018.

Testing of the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) was completed at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The OSMU was attached to Vehicle Motion Simulator 1 for a series of simulated launch tests to validate it for installation on the mobile launcher. One of the test team members signs a banner during an event to mark the end of testing. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. Kennedy's Engineering Directorate is providing support to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for testing of the OSMU. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018.
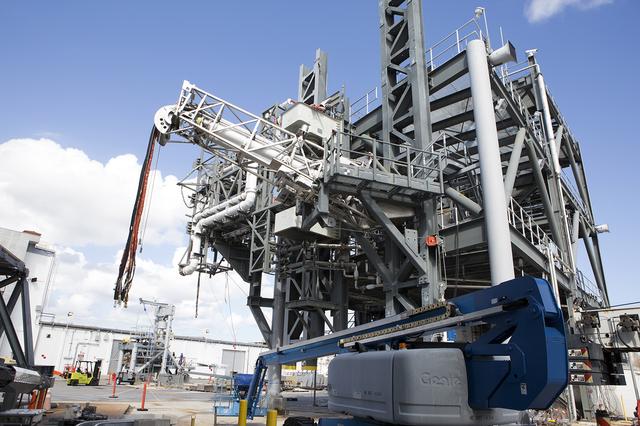

Testing of the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) was completed at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The OSMU was attached to Vehicle Motion Simulator 1 for a series of simulated launch tests to validate it for installation on the mobile launcher. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. Kennedy's Engineering Directorate is providing support to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for testing of the OSMU. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018.

Testing of the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) was completed at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The OSMU was attached to Vehicle Motion Simulator 1 for a series of simulated launch tests to validate it for installation on the mobile launcher. The test team signed a special banner during an event to mark the end of testing. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. Kennedy's Engineering Directorate is providing support to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for testing of the OSMU. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018.
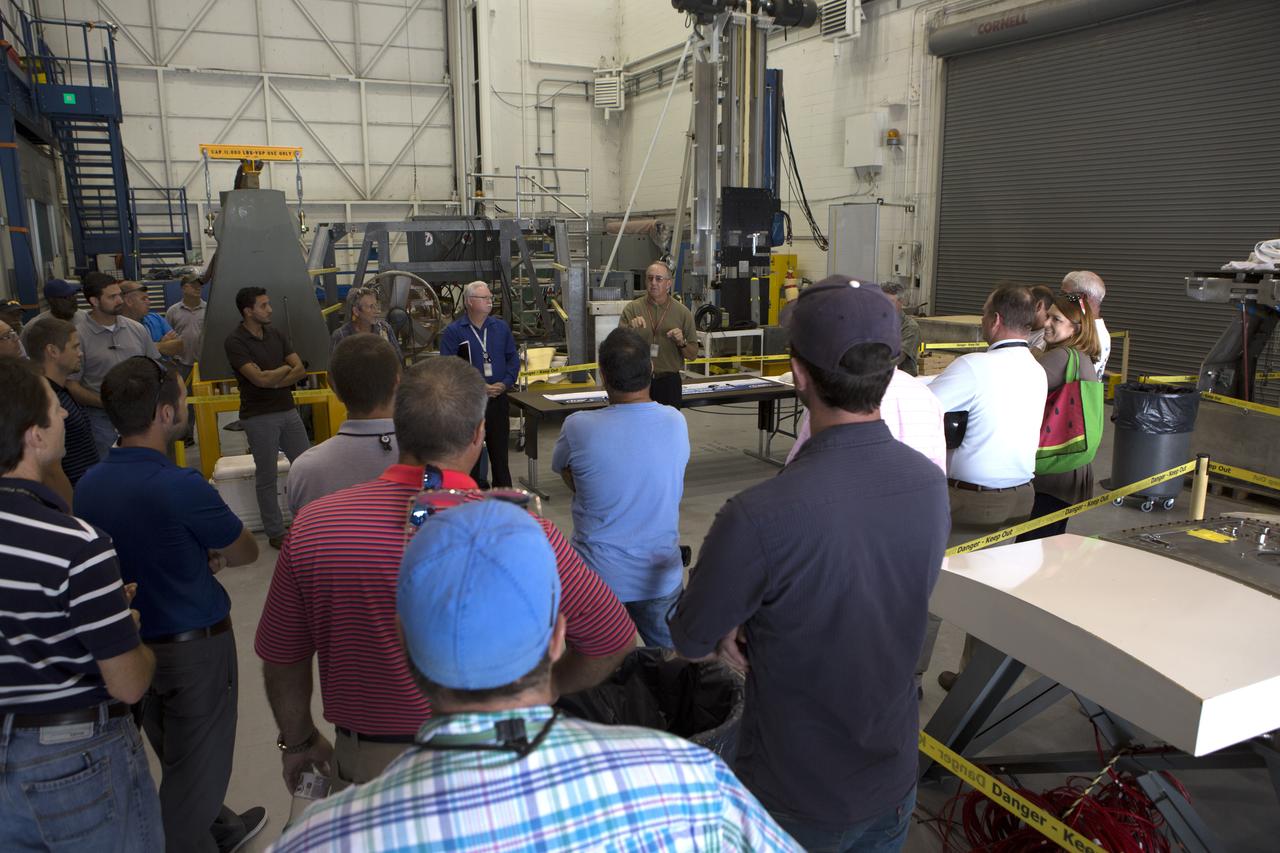

Testing of the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) was completed at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The OSMU was attached to Vehicle Motion Simulator 1 for a series of simulated launch tests to validate it for installation on the mobile launcher. Patrick Simpkins, director of Engineering, speaks to the test team during an event to mark the end of testing. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. Kennedy's Engineering Directorate is providing support to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for testing of the OSMU. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018.
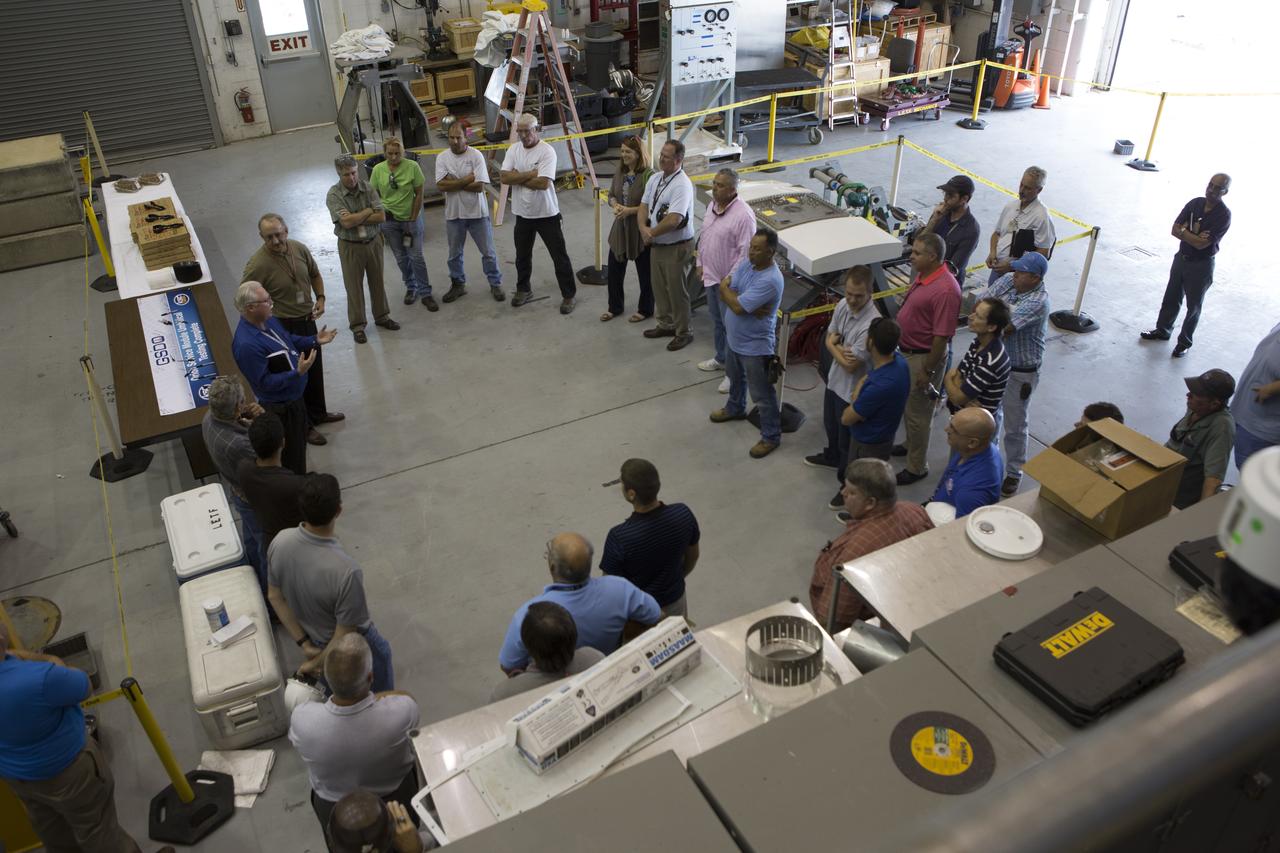

Testing of the Orion Service Module Umbilical (OSMU) was completed at the Launch Equipment Test Facility at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The OSMU was attached to Vehicle Motion Simulator 1 for a series of simulated launch tests to validate it for installation on the mobile launcher. The test team gathered for an event to mark the end of testing. The mobile launcher tower will be equipped with a number of lines, called umbilicals that will connect to the Space Launch System rocket and Orion spacecraft for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1). The OSMU will be located high on the mobile launcher tower and, prior to launch, will transfer liquid coolant for the electronics and air for the Environmental Control System to the Orion service module that houses these critical systems to support the spacecraft. Kennedy's Engineering Directorate is providing support to the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program for testing of the OSMU. EM-1 is scheduled to launch in 2018.
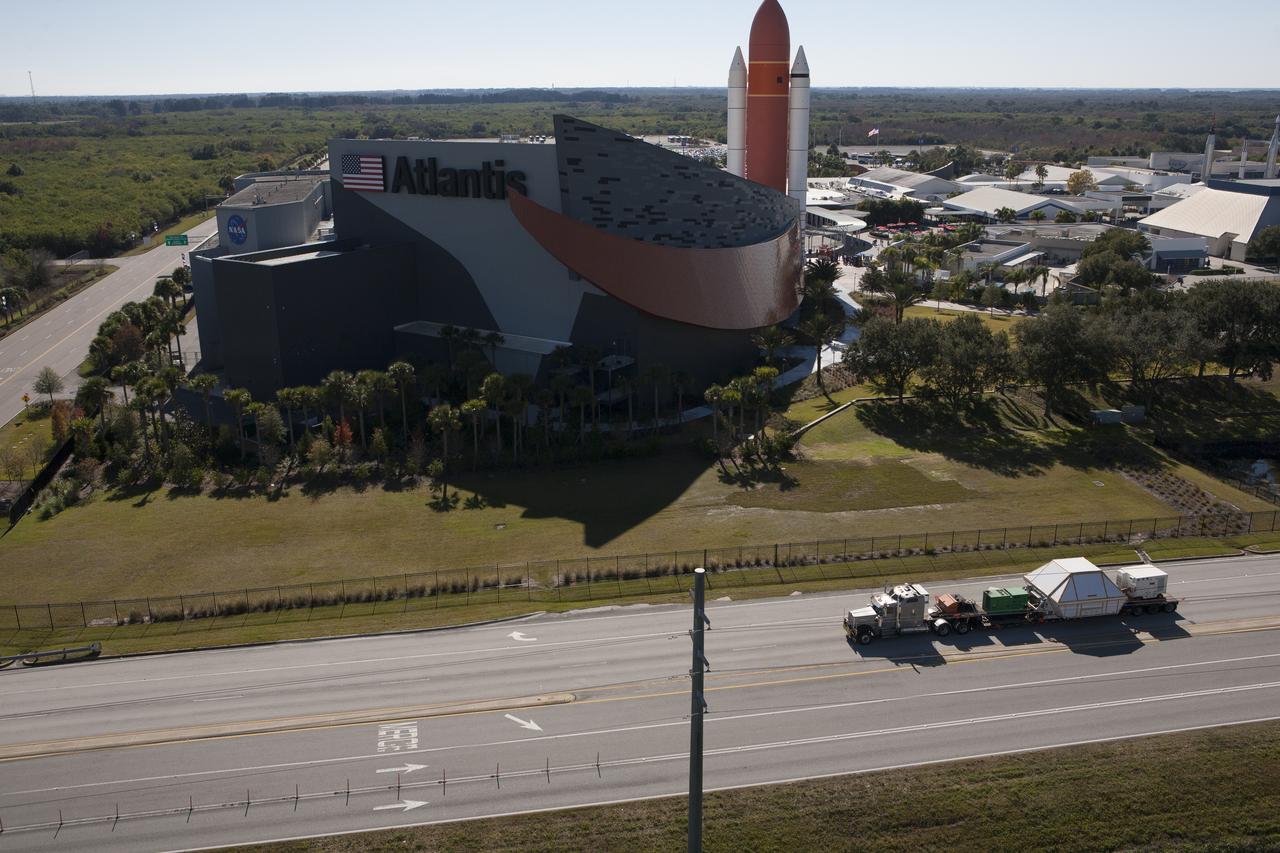

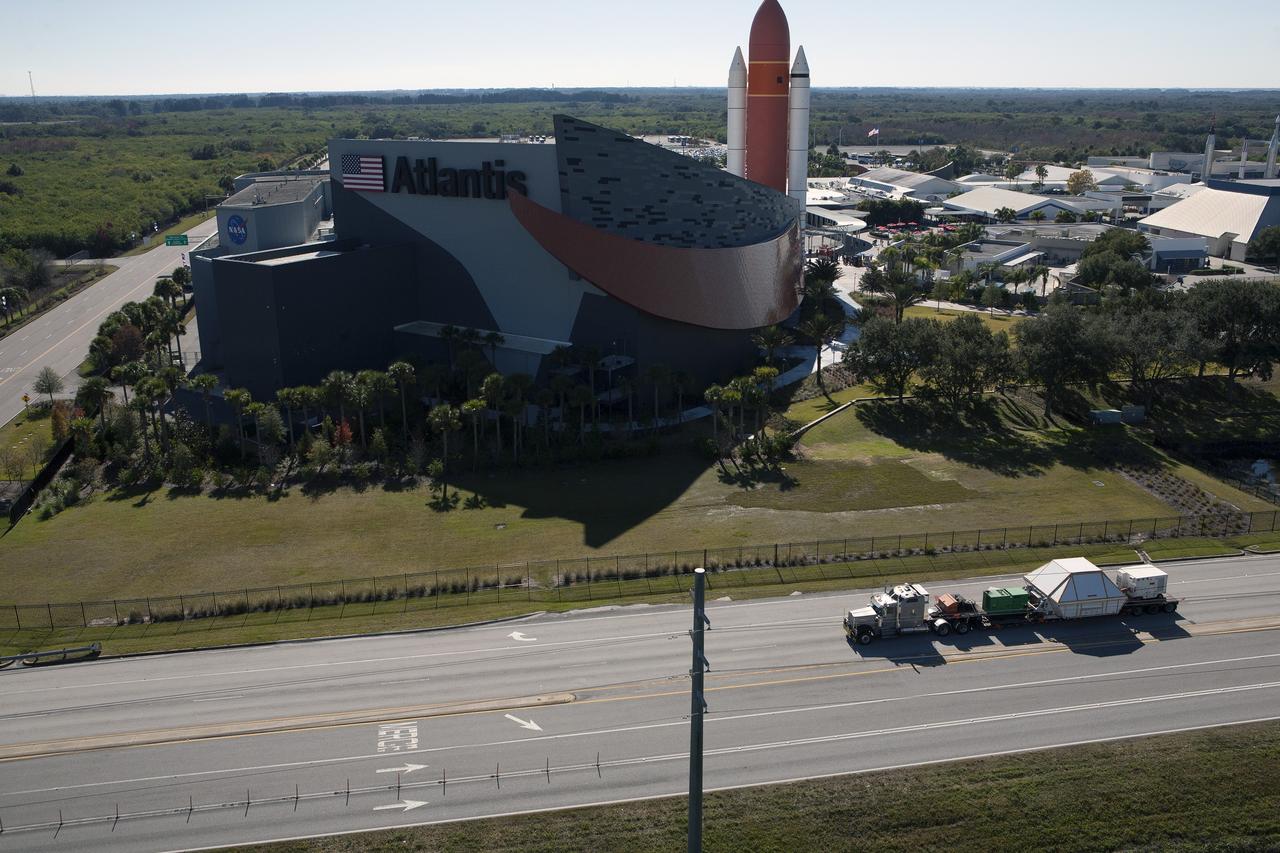
In this aerial view, NASA's Orion crew module, enclosed in its crew module transportation fixture and secured on a flatbed truck is passing the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex on its way to the entrance gate to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view is the Space Shuttle Atlantis facility. Orion made the 2,700 mile overland trip from Naval Base San Diego in California. Orion was recovered from the Pacific Ocean after completing a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
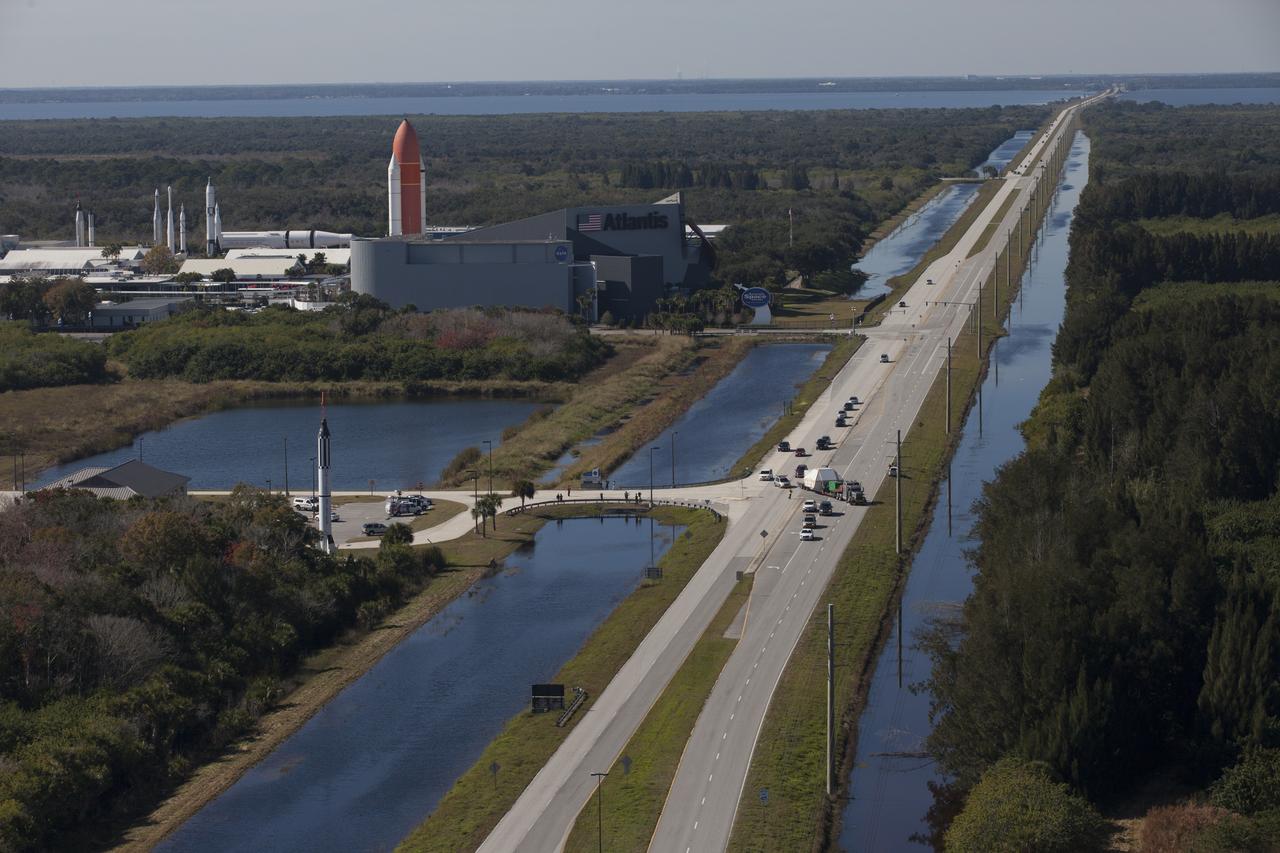

In this aerial view, NASA's Orion crew module, enclosed in its crew module transportation fixture and secured on a flatbed truck is passing the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex on its way to the entrance gate to Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view is the Space Shuttle Atlantis facility. Orion made the 2,700 mile overland trip from Naval Base San Diego in California. Orion was recovered from the Pacific Ocean after completing a two-orbit, four-and-a-half hour mission Dec. 5 to test systems critical to crew safety, including the launch abort system, the heat shield and the parachute system. The Ground Systems Development and Operations Program led the recovery, offload and transportation efforts.
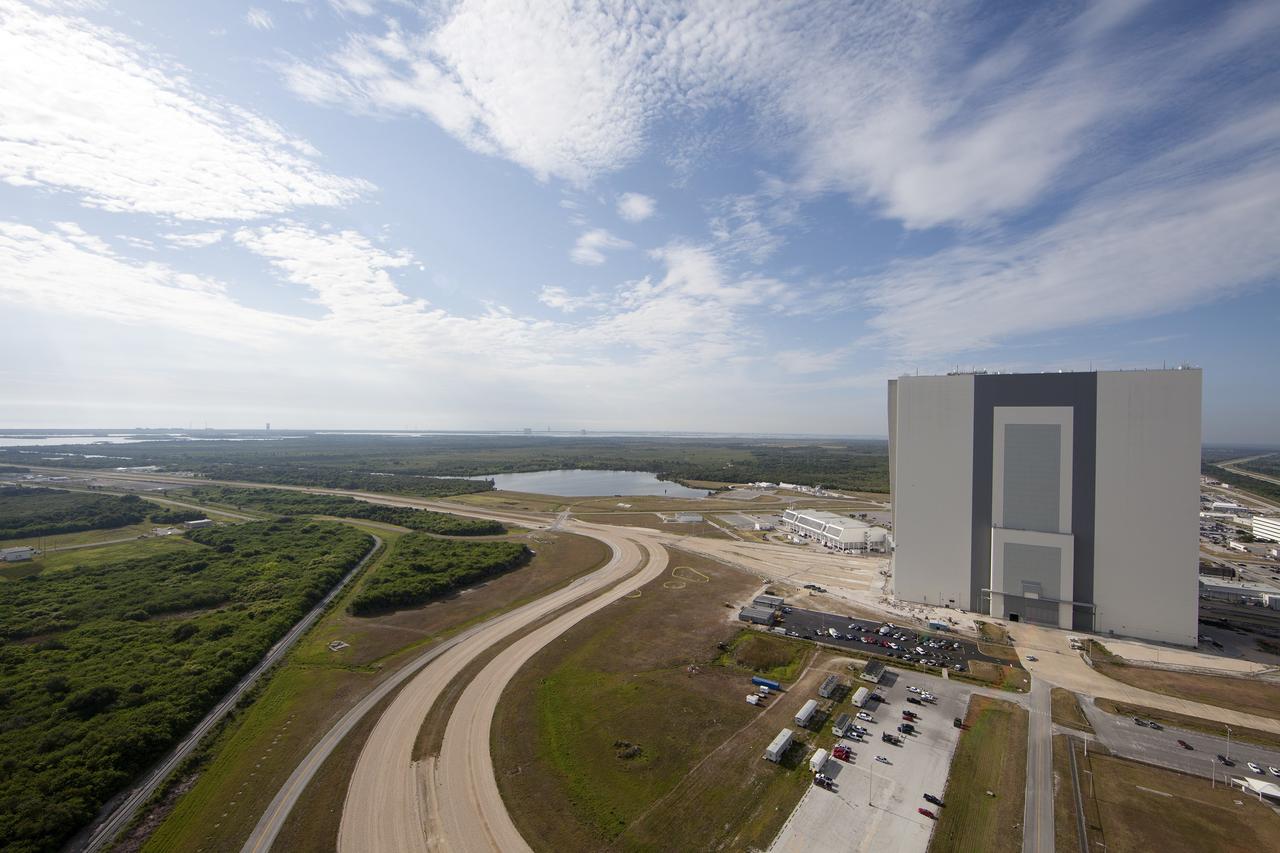

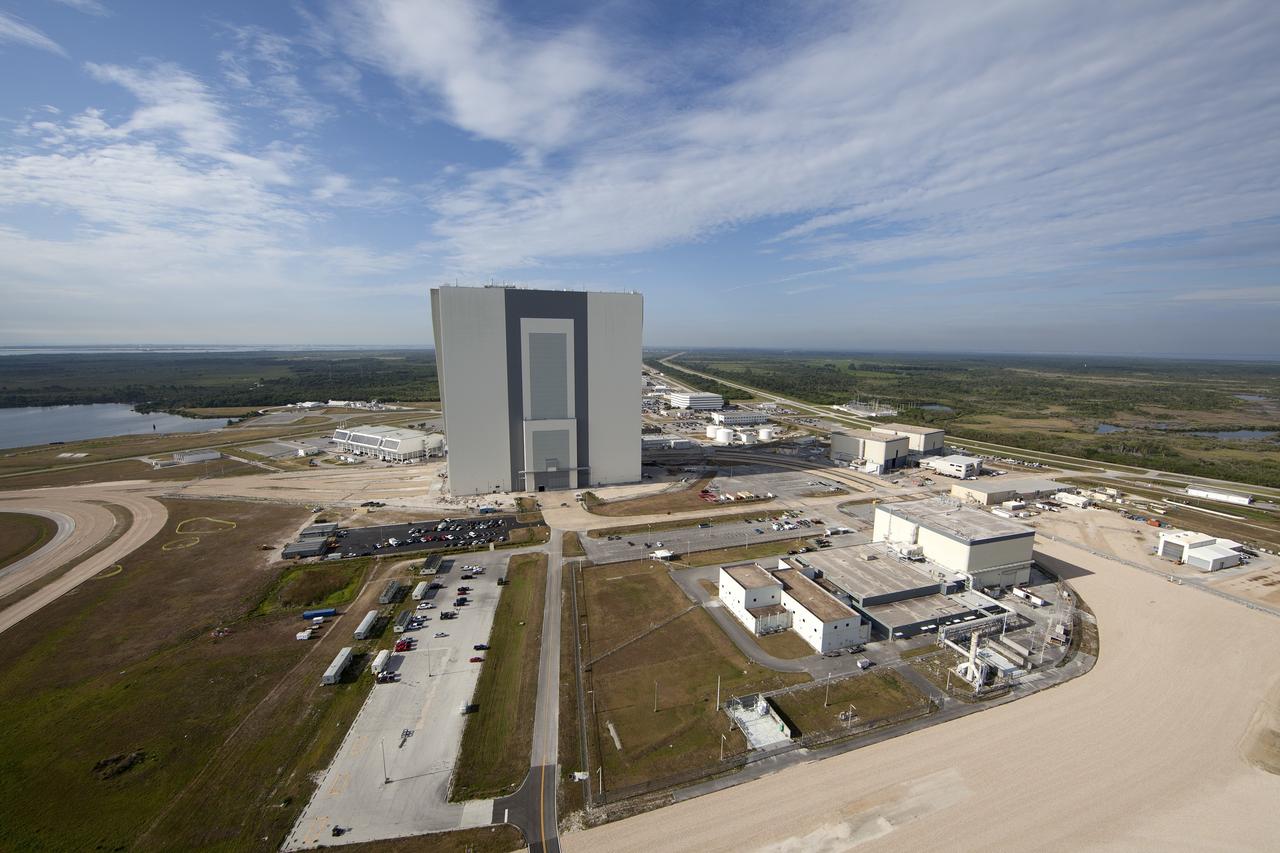
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Modifications continue on the Mobile Launcher, or ML, at the Mobile Launcher Park Site at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view from the top of the ML is the Vehicle Assembly Building, the Launch Control Center at left and various other facilities in the Launch Complex 39 area. The ML is being modified and strengthened to accommodate the weight, size and thrust at launch of NASA's Space Launch System, or SLS, and Orion spacecraft. In 2013, the agency awarded a contract to J.P. Donovan Construction Inc. of Rockledge, Fla., to modify the ML, which is one of the key elements of ground support equipment that is being upgraded by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy. The existing 24-foot exhaust hole is being enlarged and strengthened for the larger, heavier SLS rocket. The ML will carry the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft to Launch Pad 39B for its first mission, Exploration Mission-1, in 2017. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
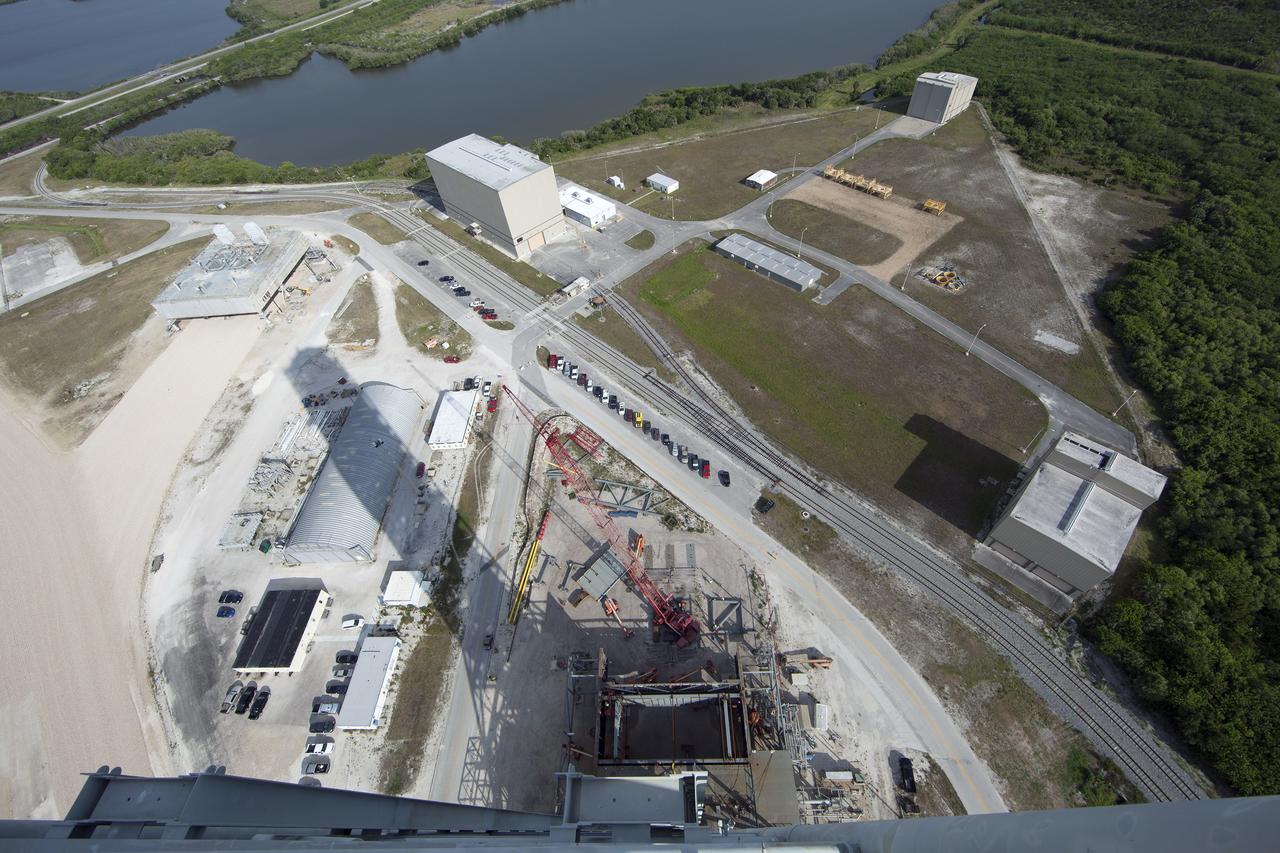

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Modifications continue on the Mobile Launcher, or ML, at the Mobile Launcher Park Site at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In a view looking down from the top of the ML is the base of the ML and various facilities in the Launch Complex 39 area. The ML is being modified and strengthened to accommodate the weight, size and thrust at launch of NASA's Space Launch System, or SLS, and Orion spacecraft. In 2013, the agency awarded a contract to J.P. Donovan Construction Inc. of Rockledge, Fla., to modify the ML, which is one of the key elements of ground support equipment that is being upgraded by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy. The existing 24-foot exhaust hole is being enlarged and strengthened for the larger, heavier SLS rocket. The ML will carry the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft to Launch Pad 39B for its first mission, Exploration Mission-1, in 2017. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Modifications continue on the Mobile Launcher, or ML, at the Mobile Launcher Park Site at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. In view from the top of the ML is the Vehicle Assembly Building, the Launch Control Center at left and various other facilities in the Launch Complex 39 area. The ML is being modified and strengthened to accommodate the weight, size and thrust at launch of NASA's Space Launch System, or SLS, and Orion spacecraft. In 2013, the agency awarded a contract to J.P. Donovan Construction Inc. of Rockledge, Fla., to modify the ML, which is one of the key elements of ground support equipment that is being upgraded by the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program office at Kennedy. The existing 24-foot exhaust hole is being enlarged and strengthened for the larger, heavier SLS rocket. The ML will carry the SLS rocket and Orion spacecraft to Launch Pad 39B for its first mission, Exploration Mission-1, in 2017. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
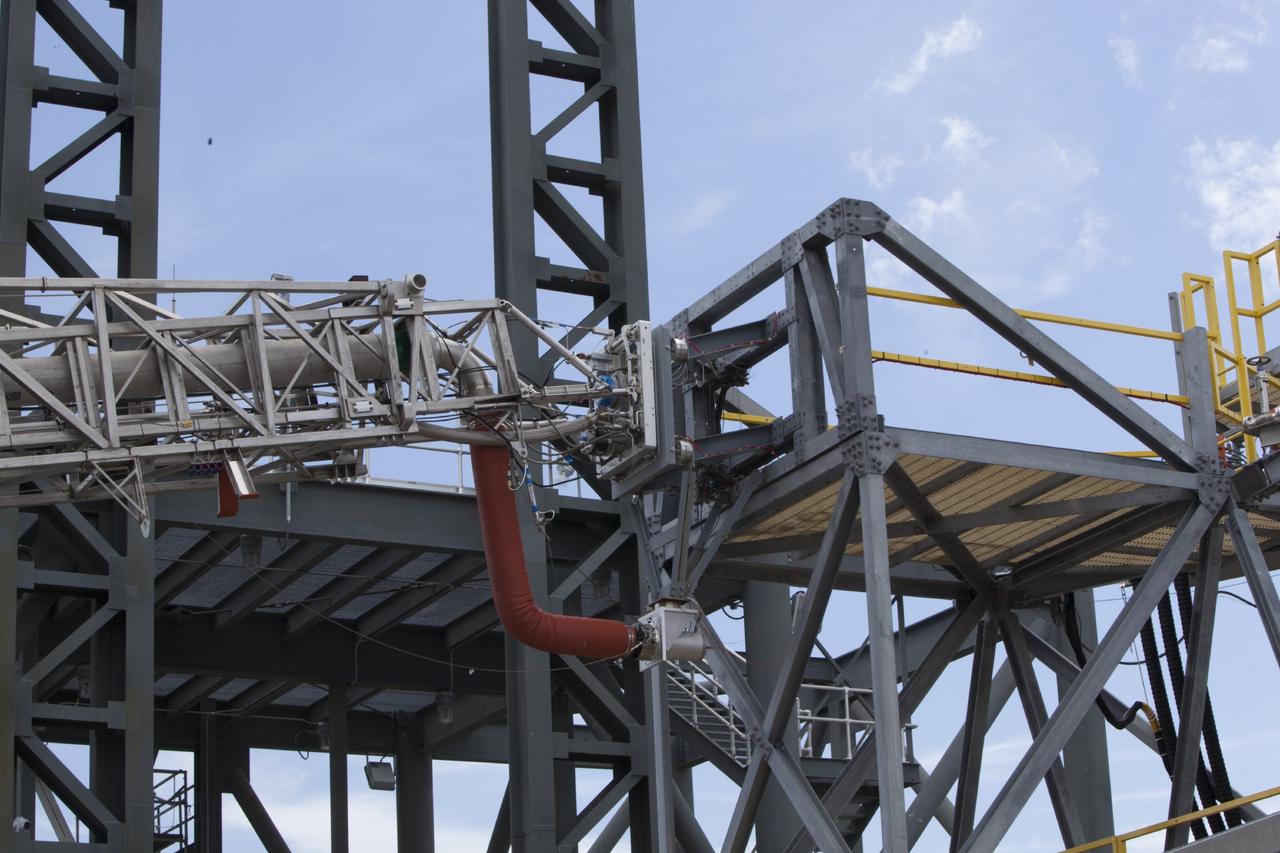

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The quick disconnect for a modified instrument unit and liquid hydrogen tilt up umbilical is being tested at the Launch Equipment Test Facility by engineers in the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The umbilical will be partially reutilized for the Orion Service Module Unit. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
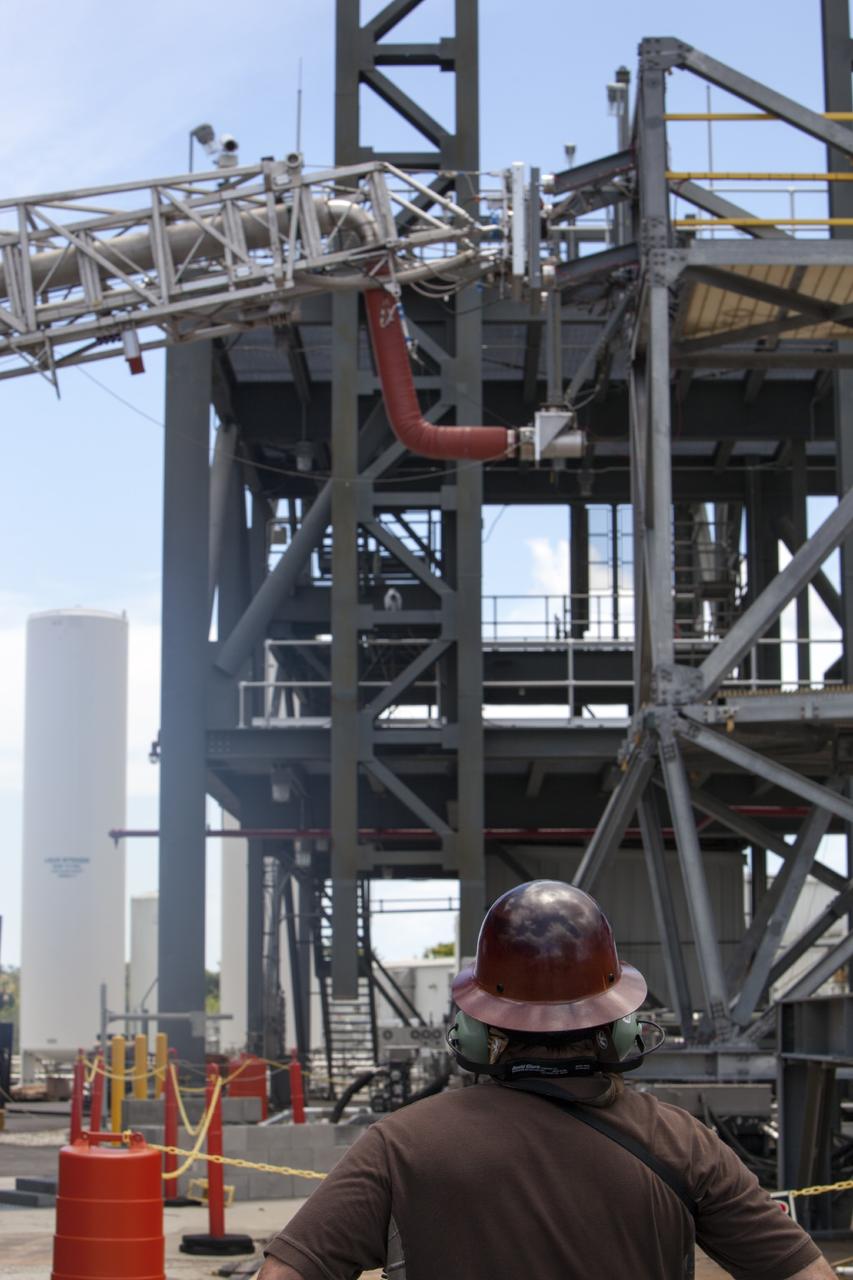

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The quick disconnect for a modified instrument unit and liquid hydrogen tilt up umbilical is being tested at the Launch Equipment Test Facility by engineers in the Ground Systems Development and Operations Program at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The umbilical will be partially reutilized for the Orion Service Module Unit. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry crews to space beyond low Earth orbit. It will provide emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during the space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on a Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis