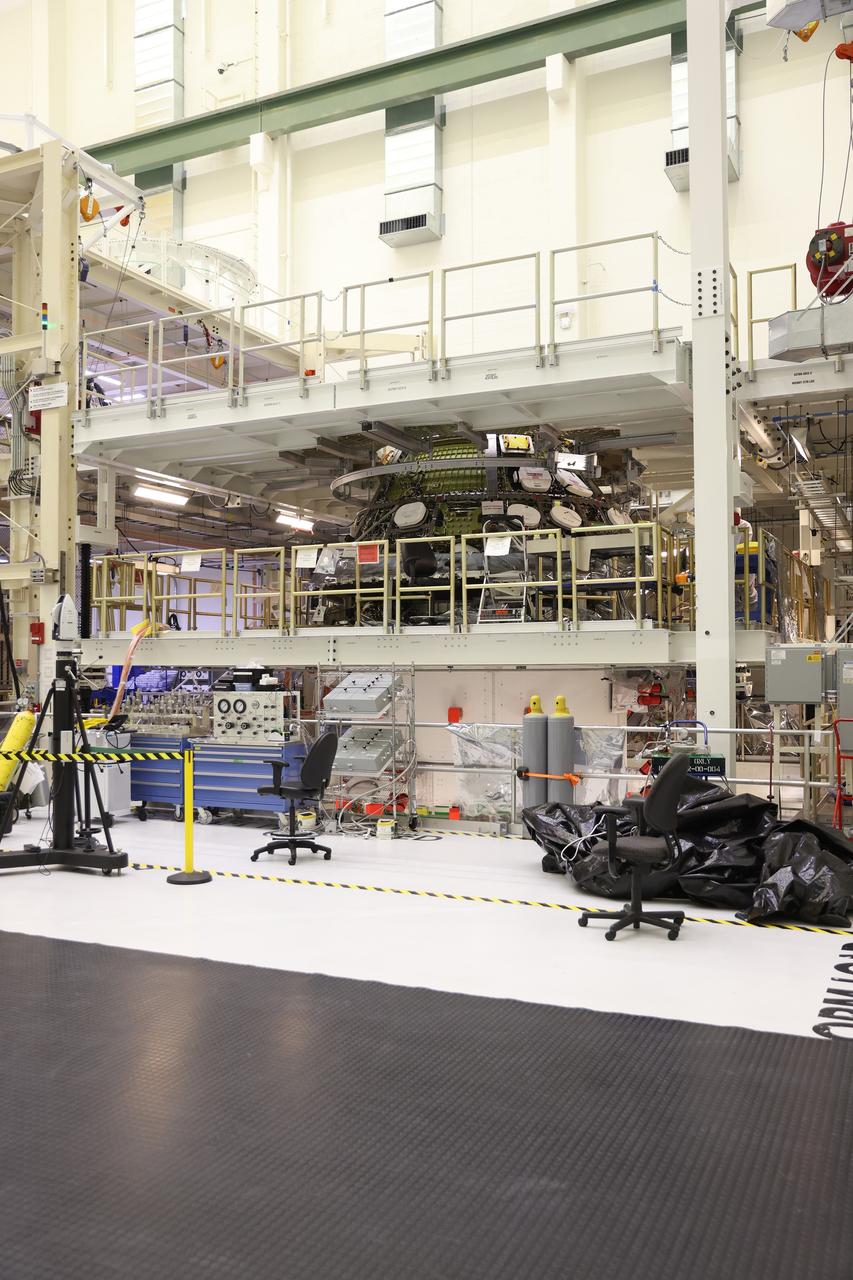

Engineers connect the Orion crew and service modules for the Artemis II mission on Oct. 19, 2023, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. With the crew and service modules integrated, the team will power up the combined crew and service module for the first time. After power on tests are complete, Orion will begin altitude chamber testing, which will put the spacecraft through conditions as close as possible to the environment it will experience in the vacuum of deep space. The crew and service modules are the two major components of Orion that will fly NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, and Christina Koch, along with CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen on a mission around the Moon and bring them home safely.

Engineers connect the Orion crew and service modules for the Artemis II mission on Oct. 19, 2023, inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. With the crew and service modules integrated, the team will power up the combined crew and service module for the first time. After power on tests are complete, Orion will begin altitude chamber testing, which will put the spacecraft through conditions as close as possible to the environment it will experience in the vacuum of deep space. The crew and service modules are the two major components of Orion that will fly NASA astronauts Reid Wiseman, Victor Glover, and Christina Koch, along with CSA (Canadian Space Agency) astronaut Jeremy Hansen on a mission around the Moon and bring them home safely.
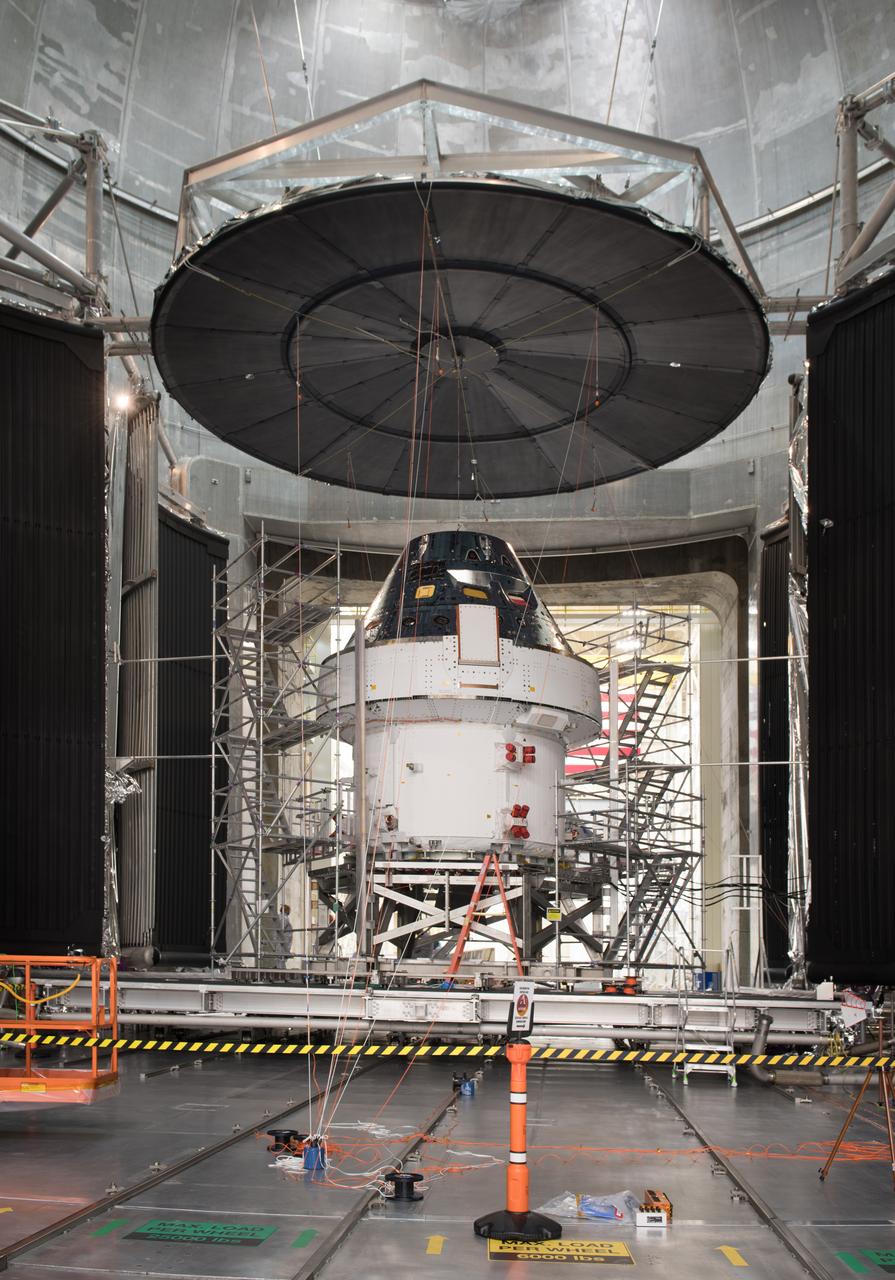

The Orion Spacecraft Crew and Service Module is being prepared for Electromagnetic Interference. EMI testing as part of testing to be certified for launch for the first Artemis mission
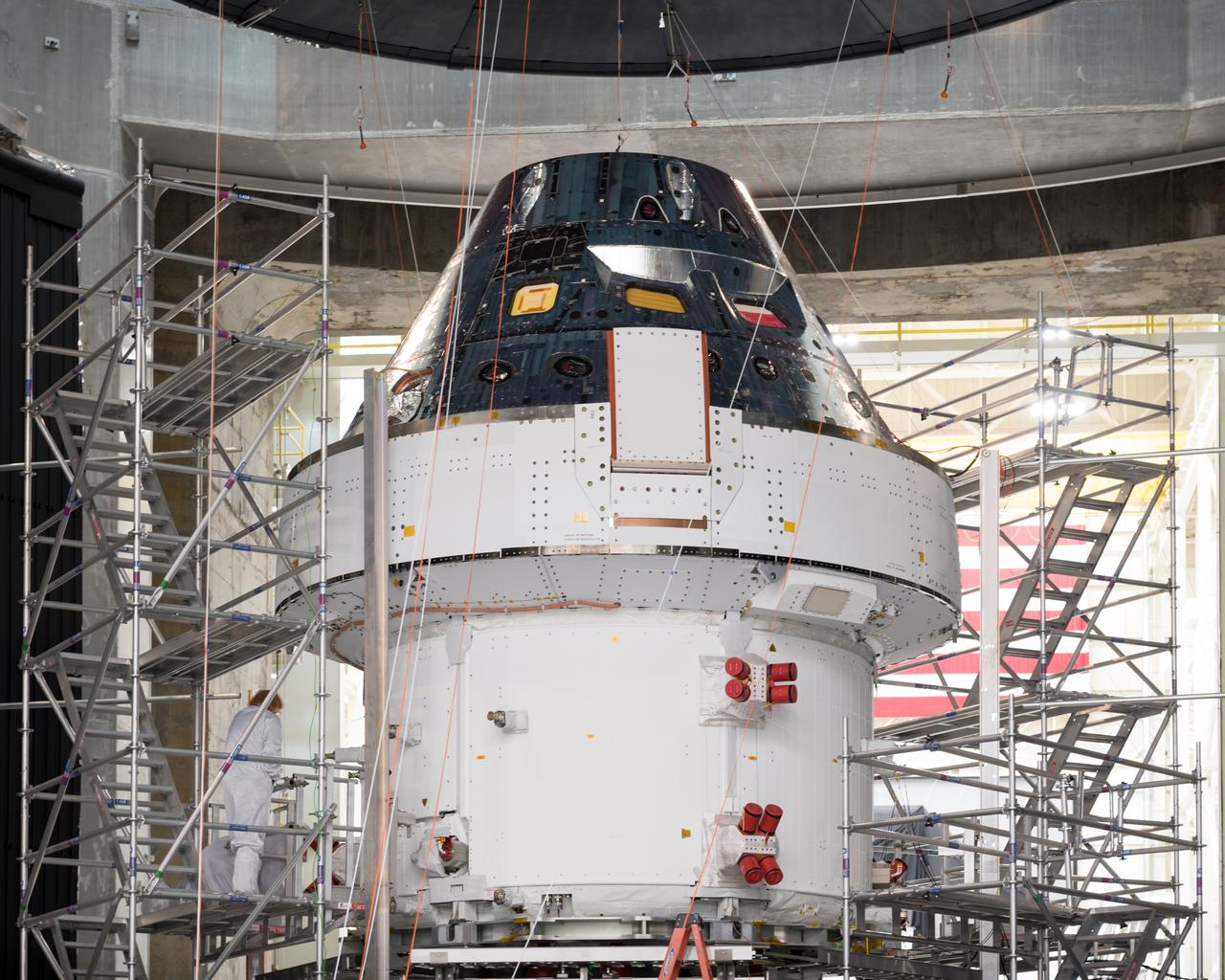

The Orion Spacecraft Crew and Service Module is being prepared for Electromagnetic Interference. EMI testing as part of testing to be certified for launch for the first Artemis mission
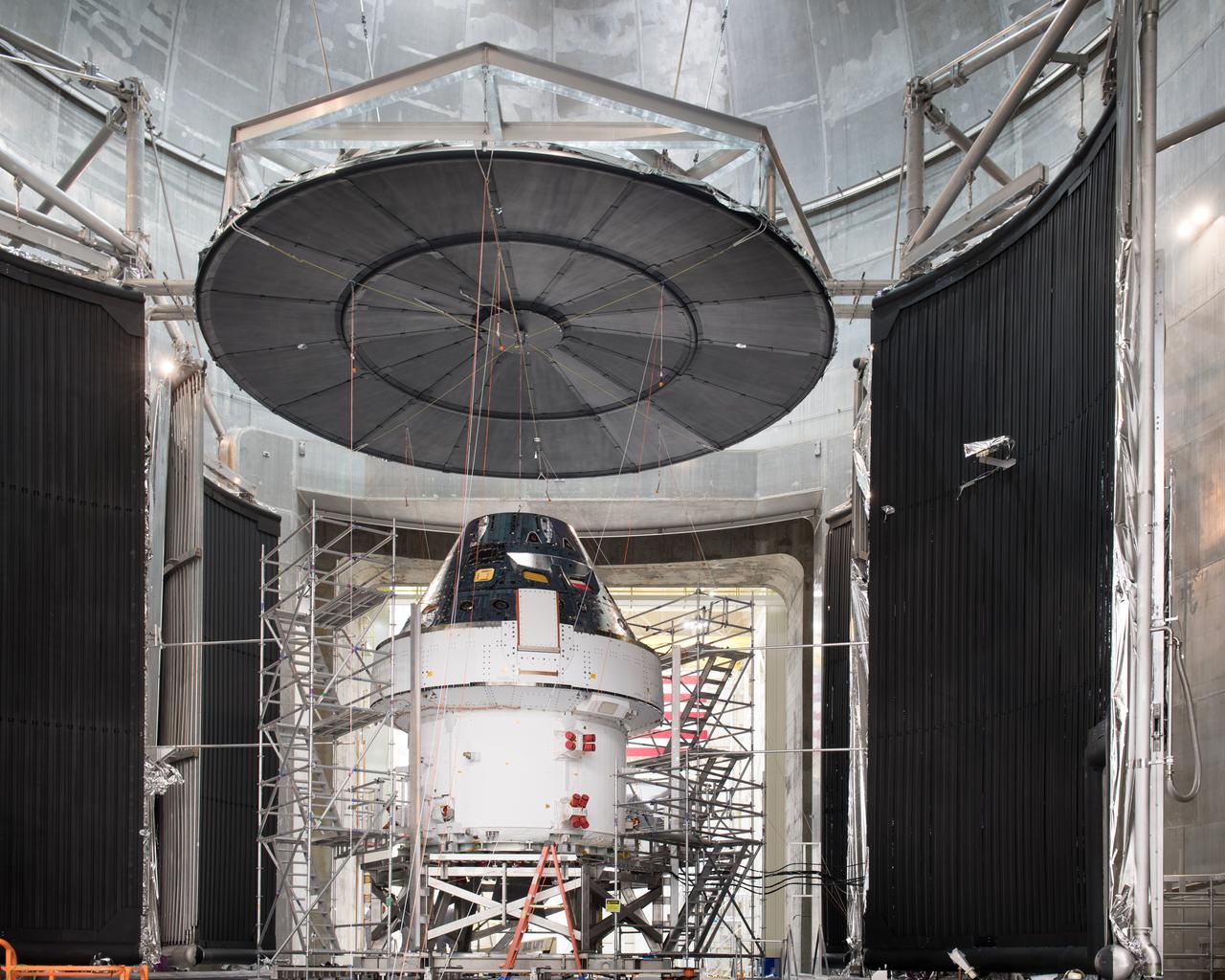

The Orion Spacecraft Crew and Service Module is being prepared for Electromagnetic Interference. EMI testing as part of testing to be certified for launch for the first Artemis mission
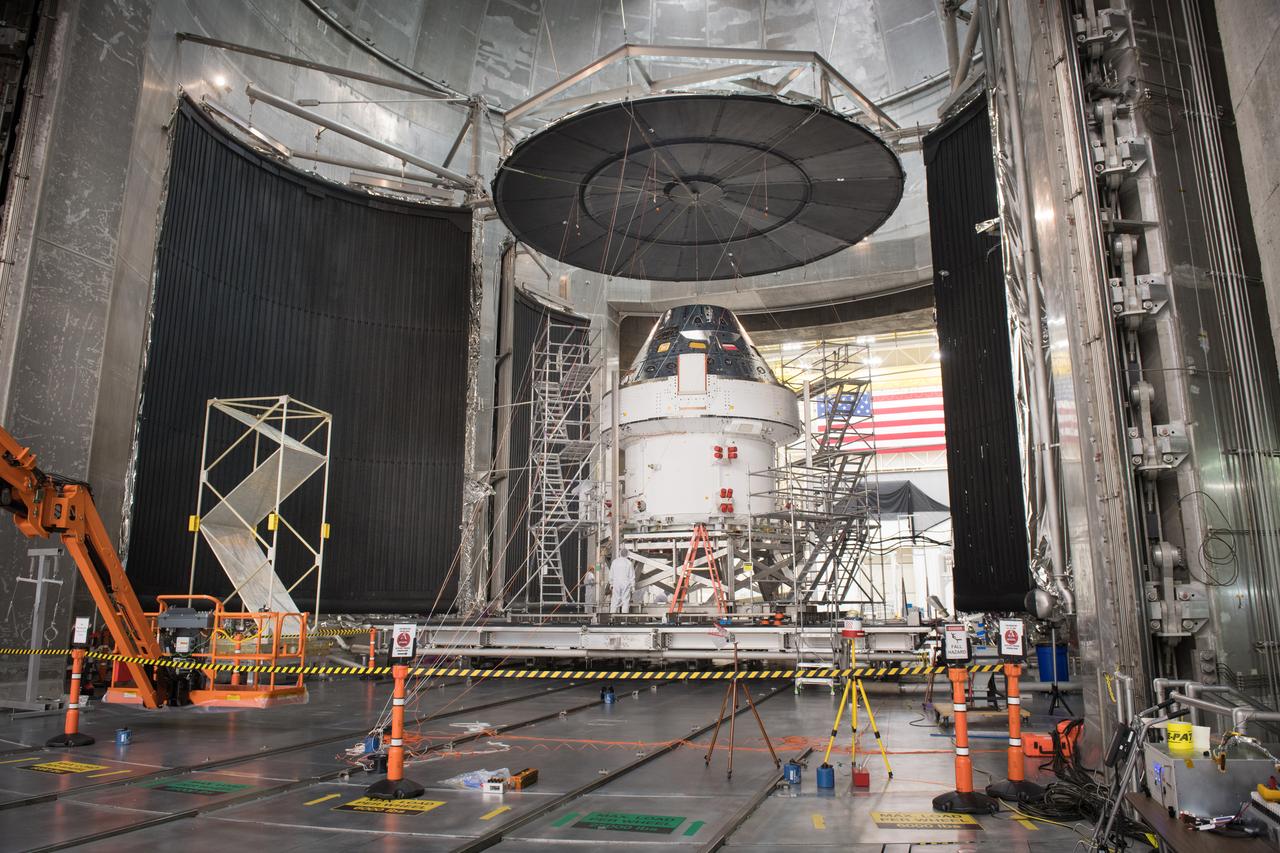
The Orion Spacecraft Crew and Service Module is being prepared for Electromagnetic Interference. EMI testing as part of testing to be certified for launch for the first Artemis mission
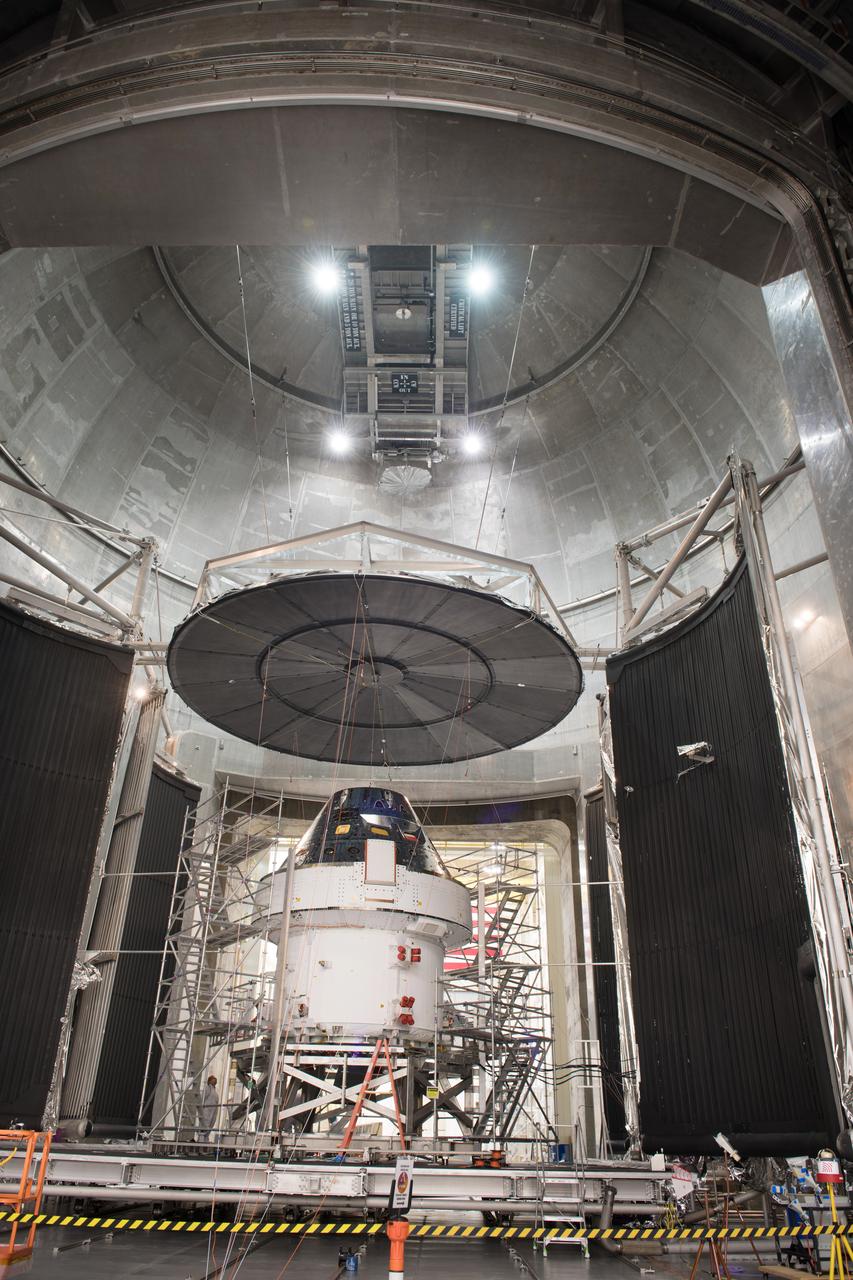

The Orion Spacecraft Crew and Service Module is being prepared for Electromagnetic Interference. EMI testing as part of testing to be certified for launch for the first Artemis mission
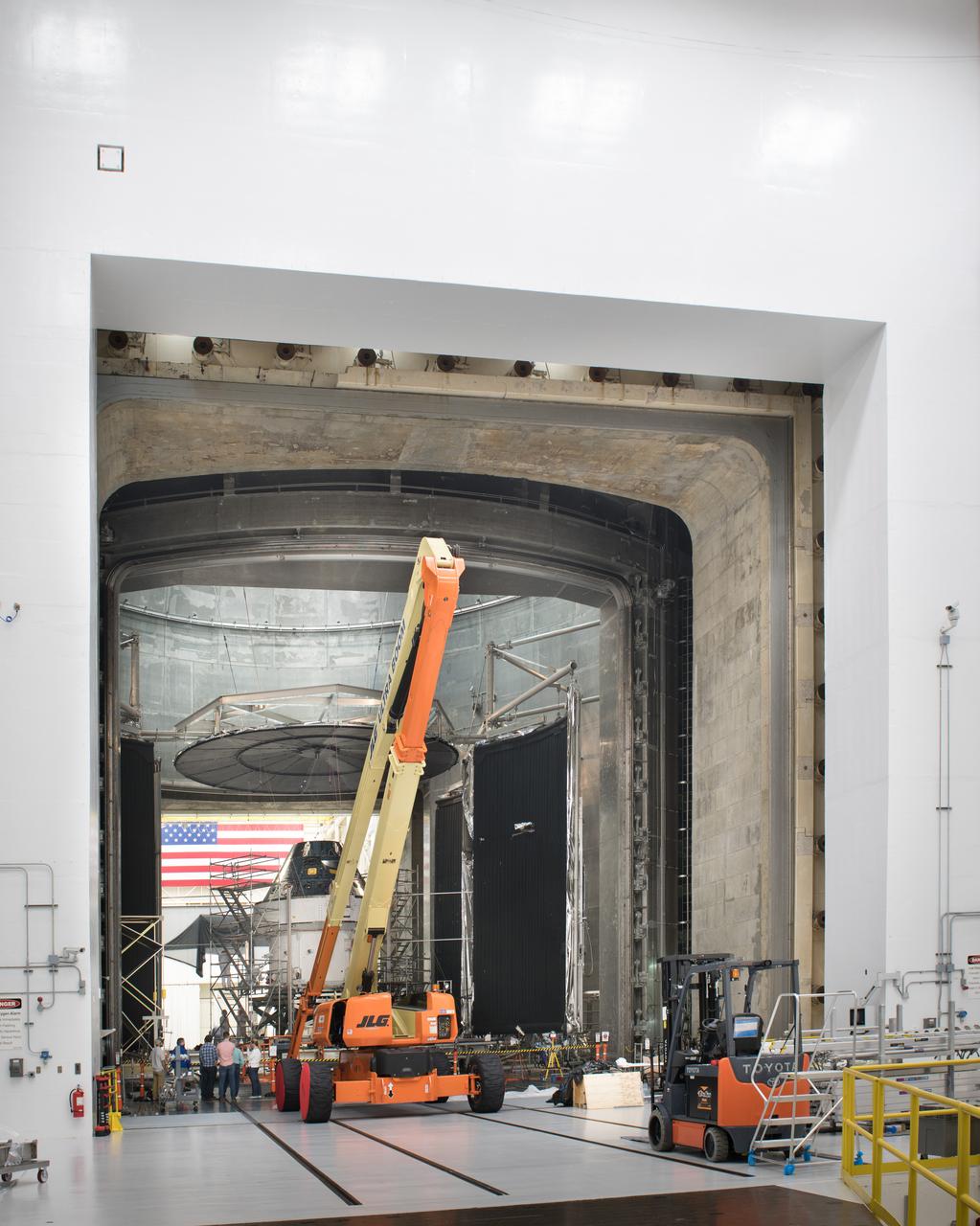

The Orion Spacecraft Crew and Service Module is being prepared for Electromagnetic Interference. EMI testing as part of testing to be certified for launch for the first Artemis mission
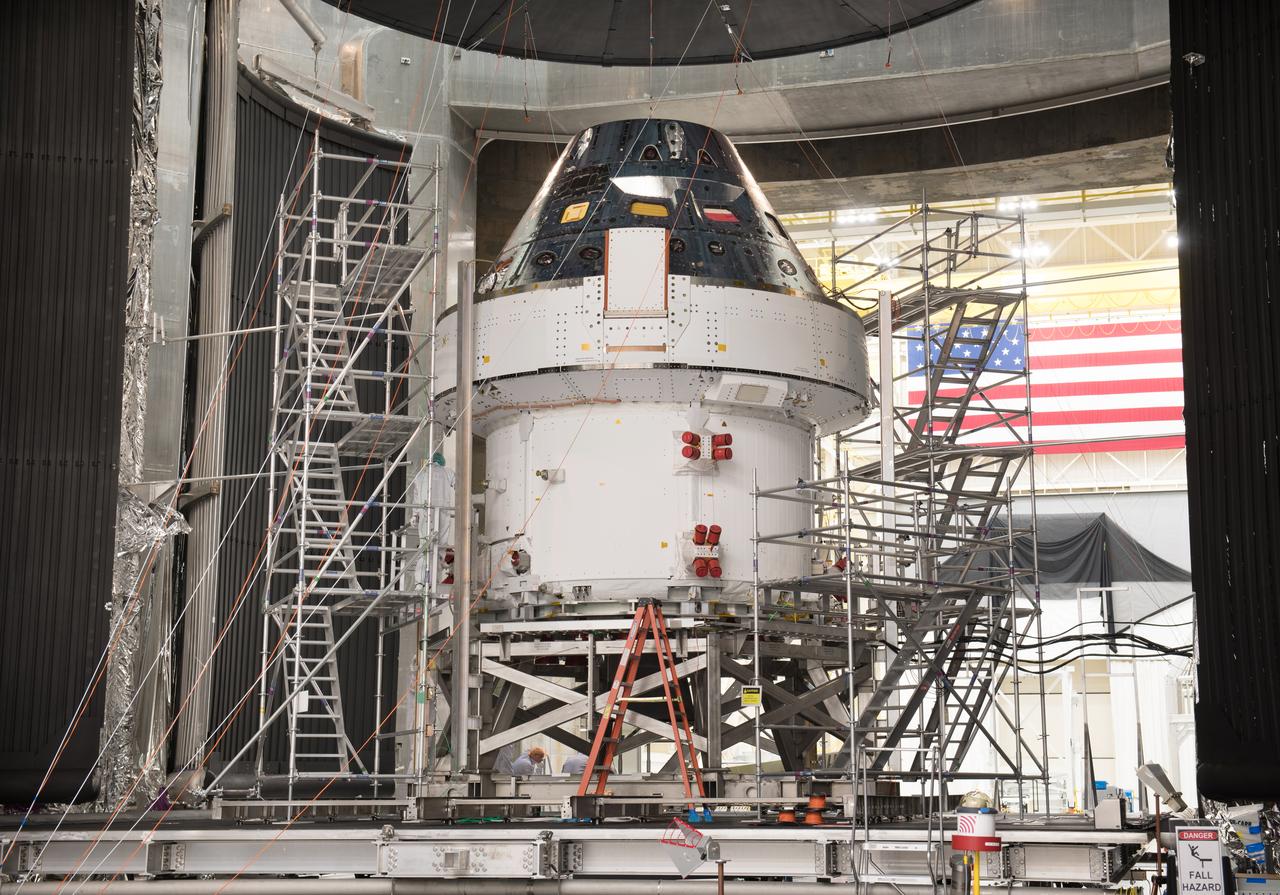

The Orion Spacecraft Crew and Service Module is being prepared for Electromagnetic Interference. EMI testing as part of testing to be certified for launch for the first Artemis mission
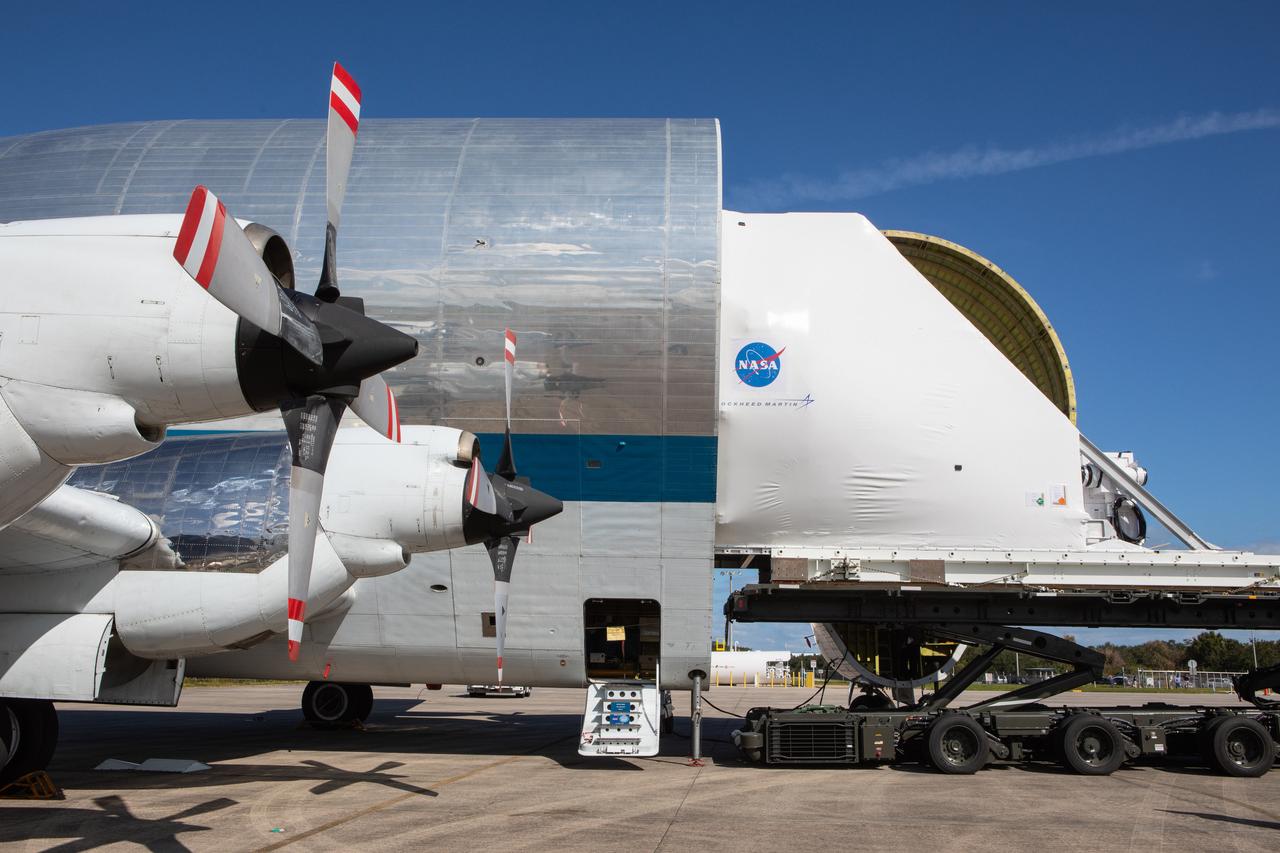

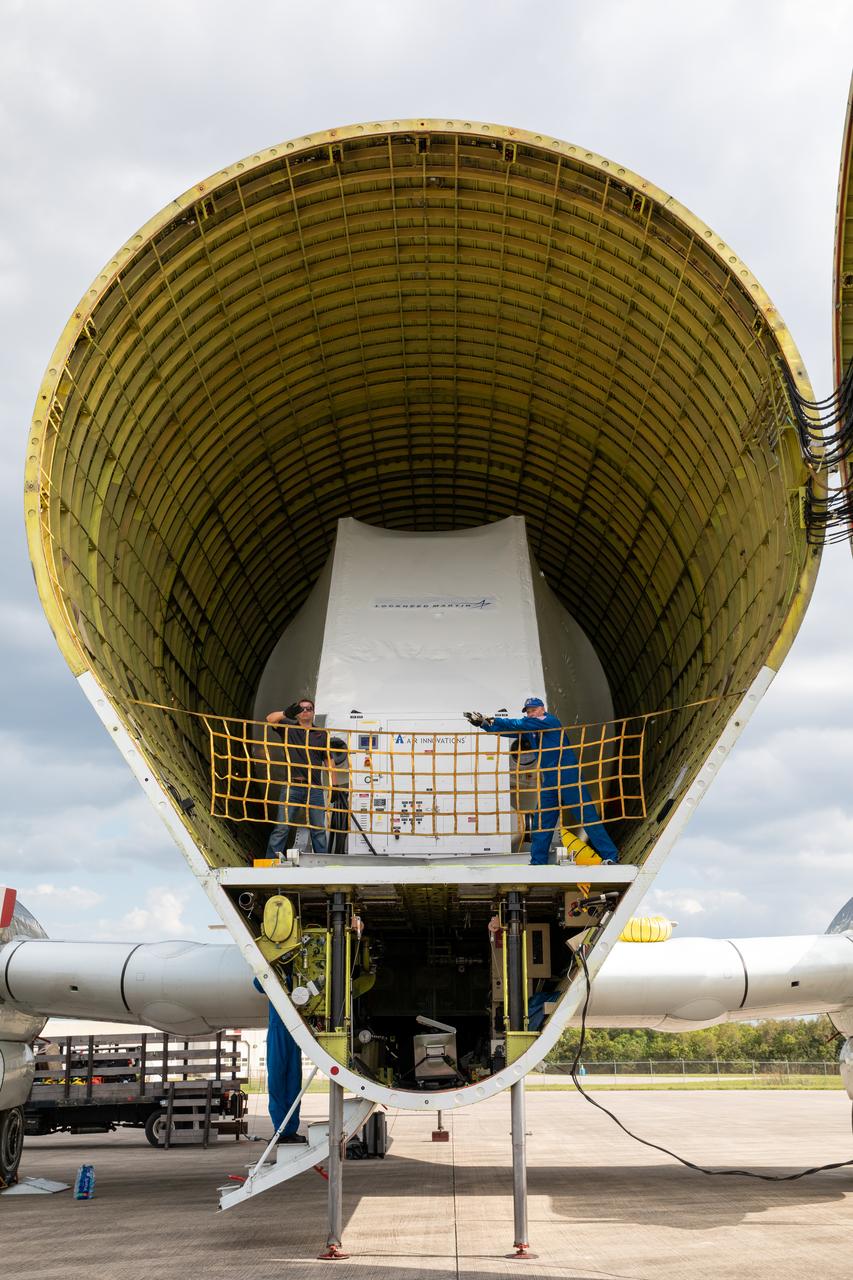
NASA’s Orion spacecraft is loaded into the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019. The spacecraft’s crew and service modules are flying to NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, for full thermal vacuum testing. In this unique facility, the crew and service modules will be put through extensive testing to ensure they can survive the rigors of launch, space travel, re-entry and splashdown. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Artemis I.
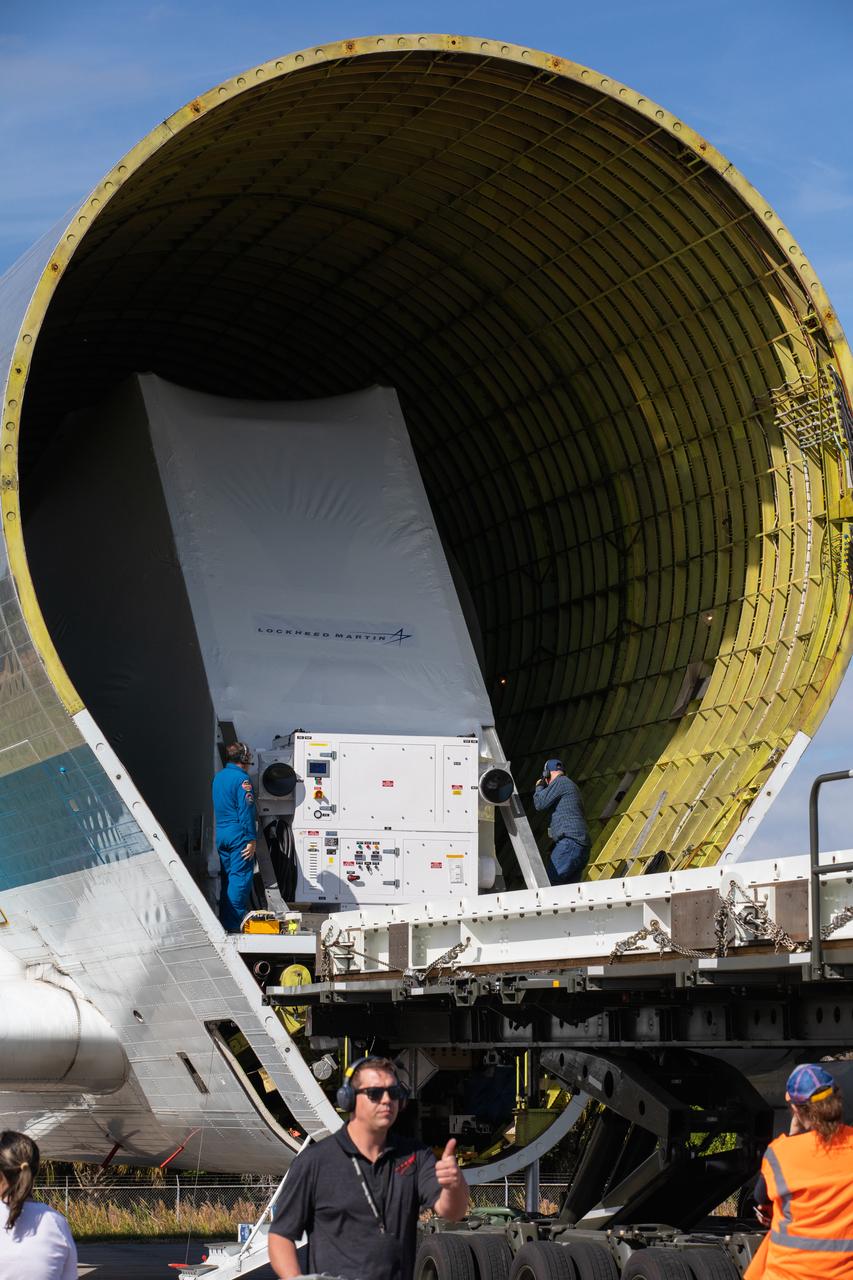

NASA’s Orion spacecraft is loaded into the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019. The spacecraft’s crew and service modules are flying to NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, for full thermal vacuum testing. In this unique facility, the crew and service modules will be put through extensive testing to ensure they can survive the rigors of launch, space travel, re-entry and splashdown. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Artemis I.
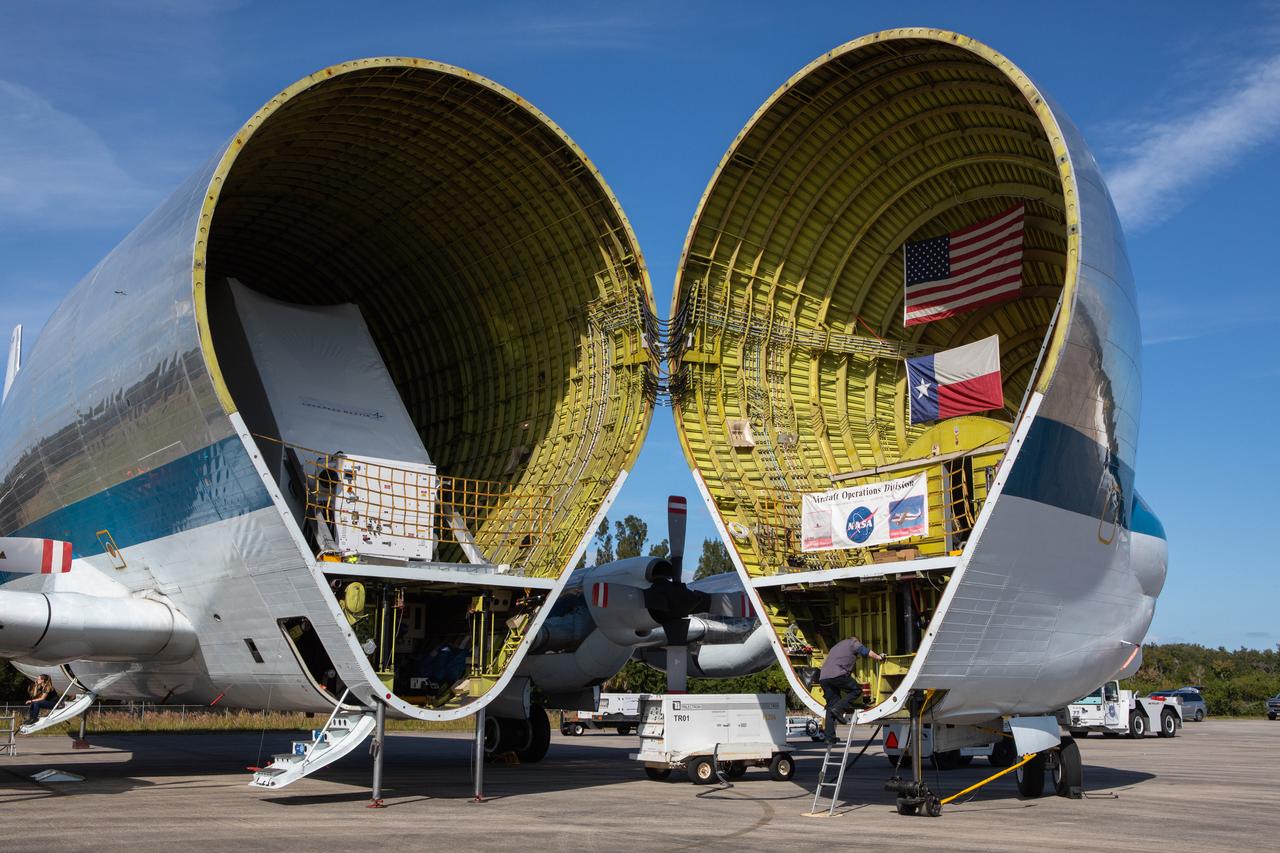

NASA’s Orion spacecraft is loaded into the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019. The spacecraft’s crew and service modules are flying to NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, for full thermal vacuum testing. In this unique facility, the crew and service modules will be put through extensive testing to ensure they can survive the rigors of launch, space travel, re-entry and splashdown. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Artemis I.
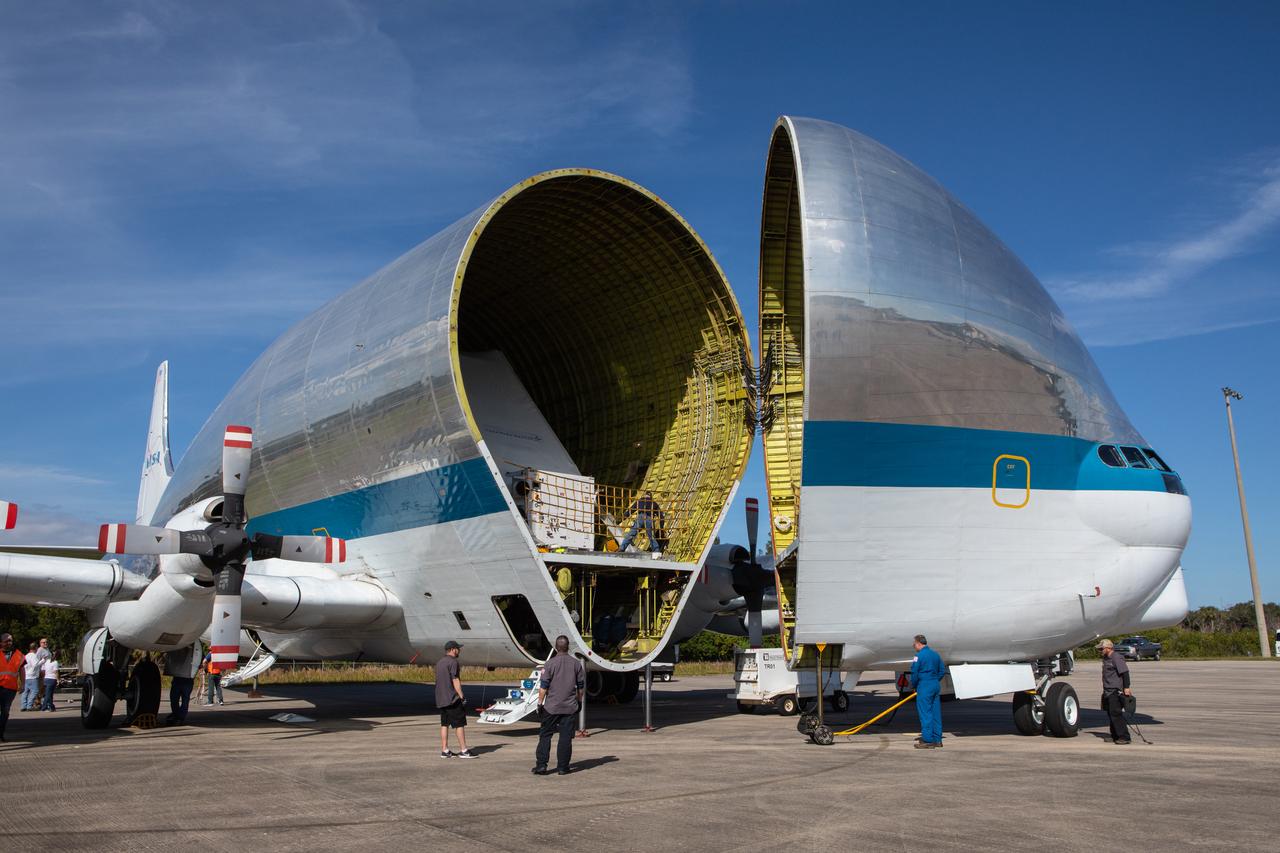

NASA’s Orion spacecraft is loaded into the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019. The spacecraft’s crew and service modules are flying to NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, for full thermal vacuum testing. In this unique facility, the crew and service modules will be put through extensive testing to ensure they can survive the rigors of launch, space travel, re-entry and splashdown. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Artemis I.

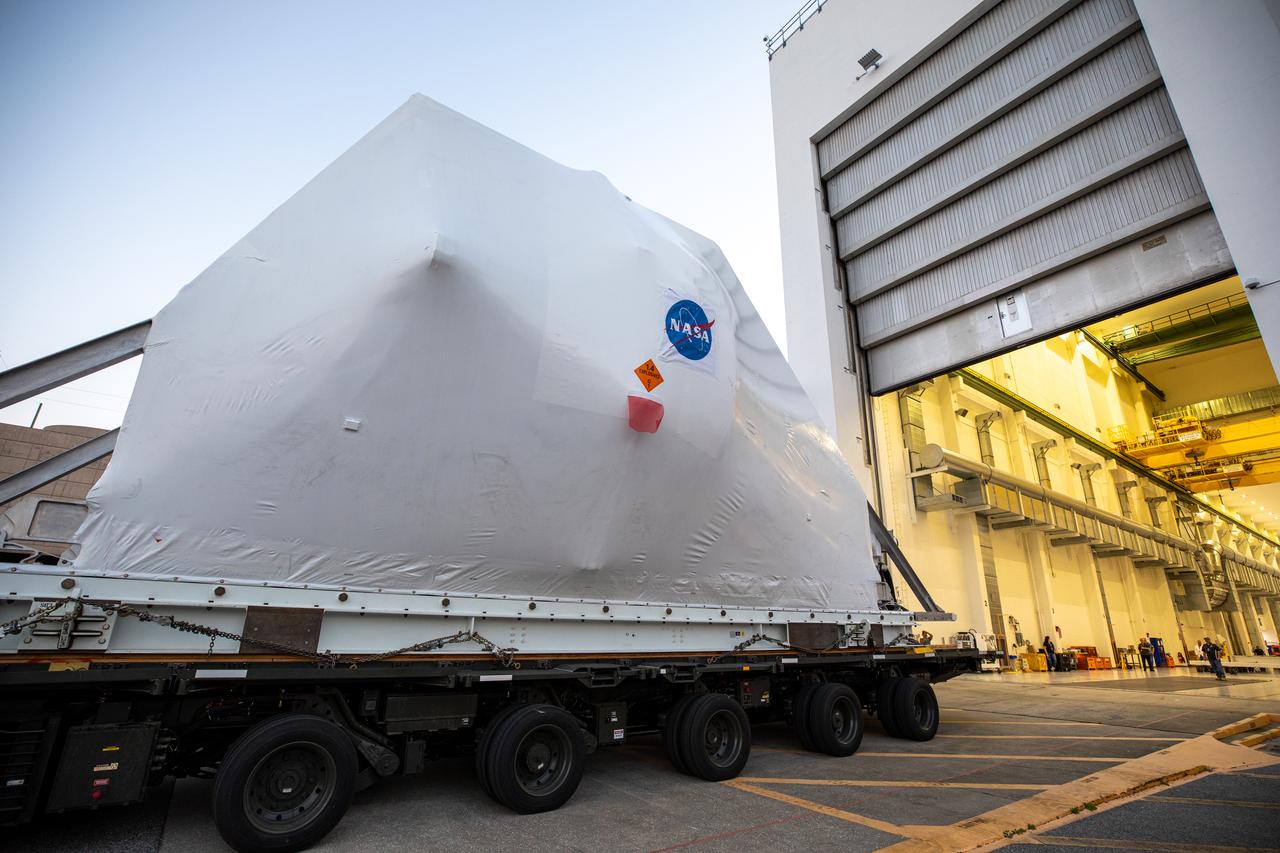
NASA’s Orion spacecraft, wrapped up for shipping, is moved into position for loading into the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019. The spacecraft’s crew and service modules are flying to NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, for full thermal vacuum testing. In this unique facility, the crew and service modules will be put through extensive testing to ensure they can survive the rigors of launch, space travel, re-entry and splashdown. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Artemis I.
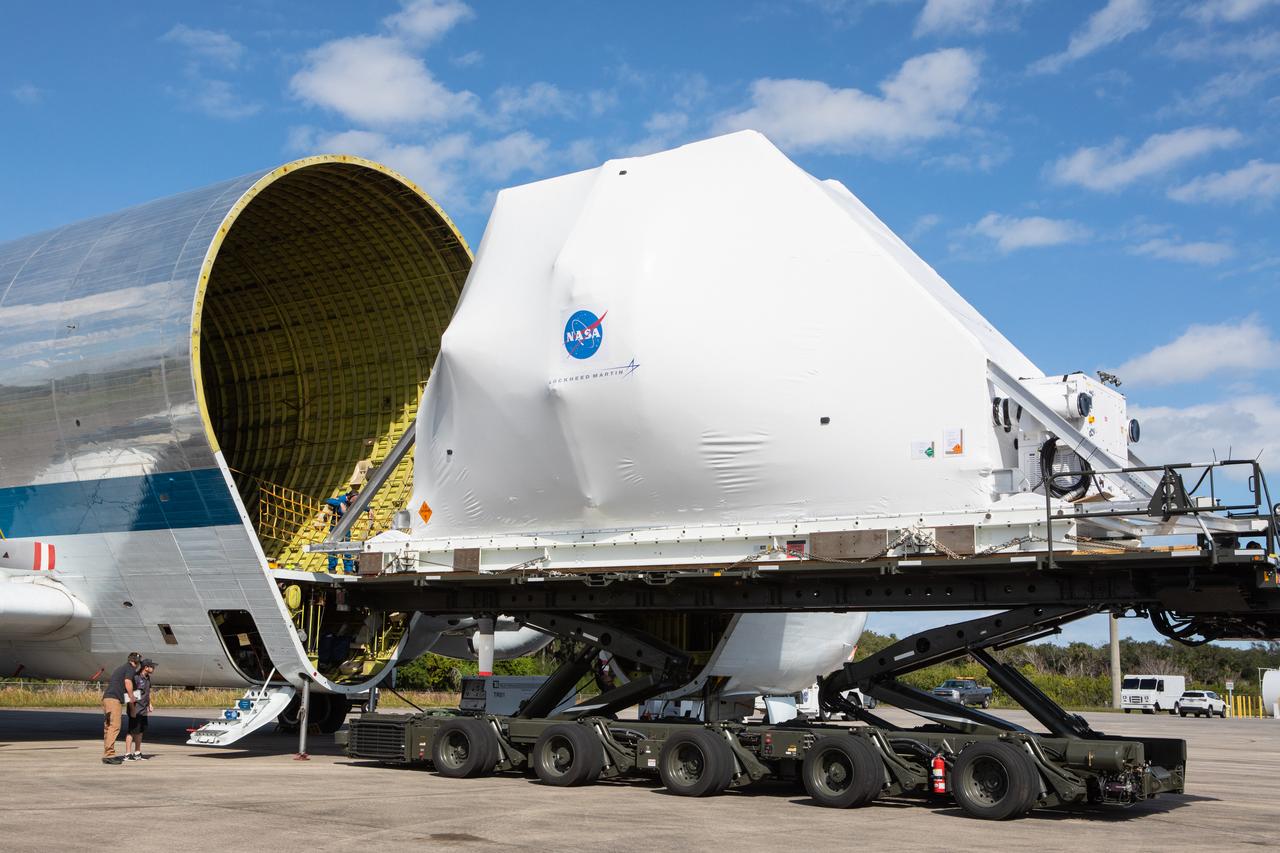

NASA’s Orion spacecraft, wrapped up for shipping, is carefully aligned for loading into the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019. The spacecraft’s crew and service modules are flying to NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, for full thermal vacuum testing. In this unique facility, the crew and service modules will be put through extensive testing to ensure they can survive the rigors of launch, space travel, re-entry and splashdown. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Artemis I.
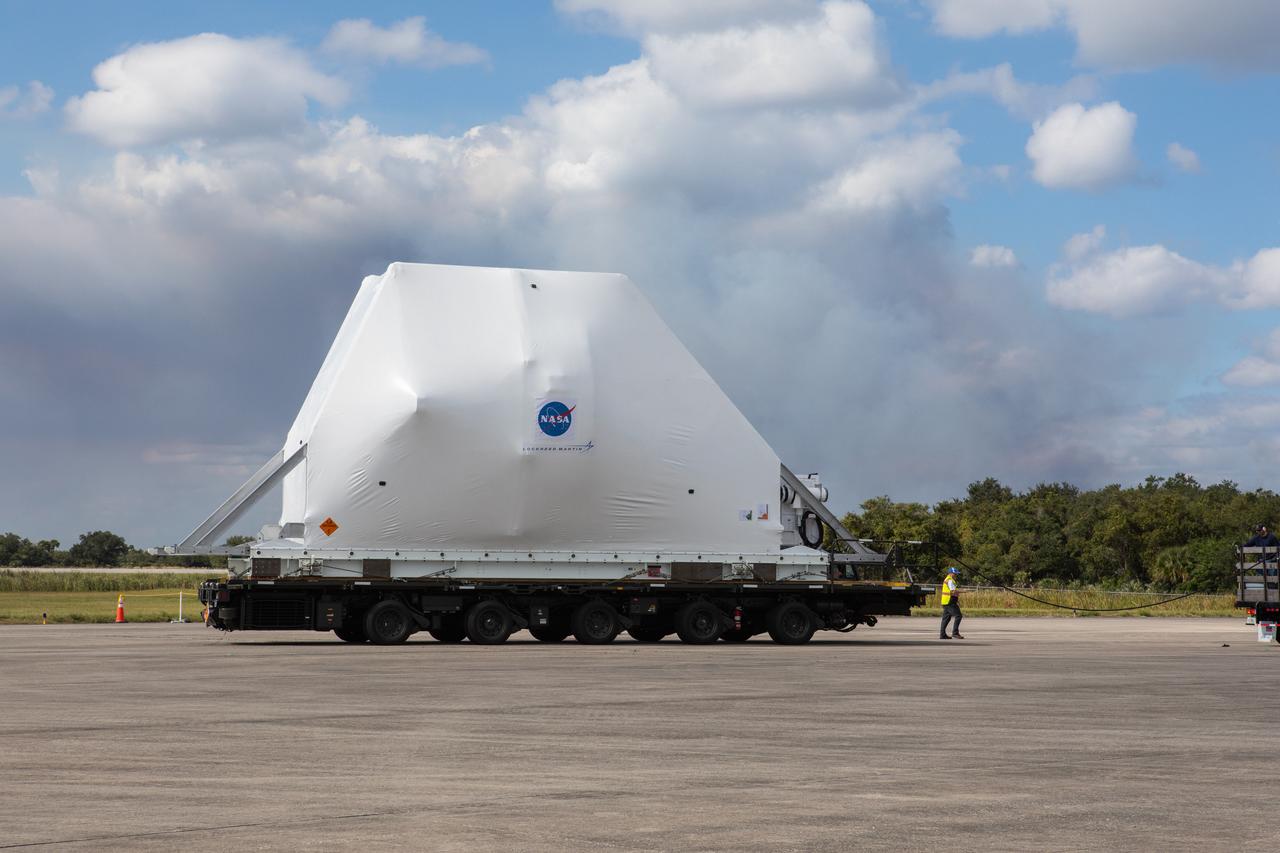

NASA’s Orion spacecraft, wrapped up for shipping, arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch and Landing Facility runway for loading into the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft on Nov. 21, 2019. The spacecraft’s crew and service modules are flying from the Florida spaceport to NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, for full thermal vacuum testing. In this unique facility, the crew and service modules will be put through extensive testing to ensure they can survive the rigors of launch, space travel, re-entry and splashdown. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Artemis I.
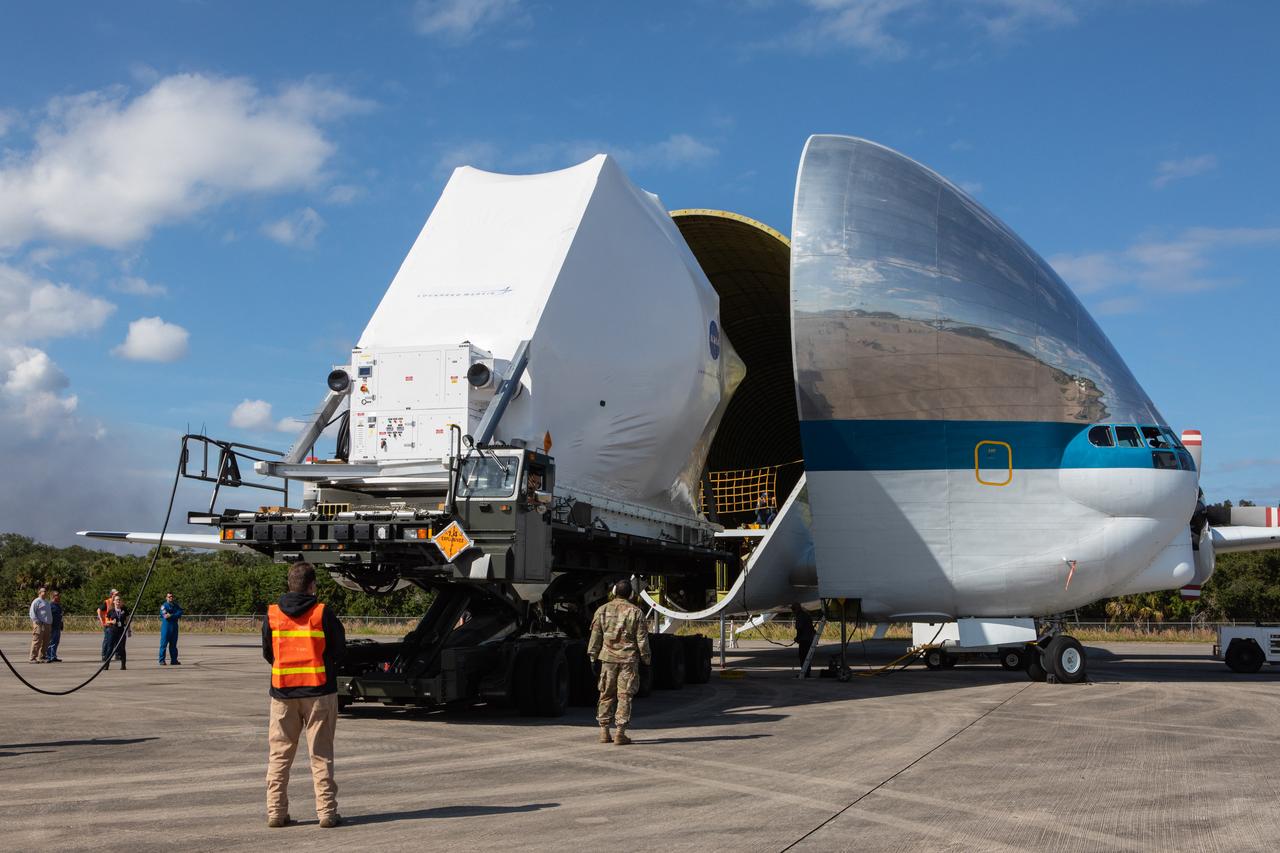

NASA’s Orion spacecraft, wrapped up for shipping, is moved into position for loading into the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019. The spacecraft’s crew and service modules are flying to NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, for full thermal vacuum testing. In this unique facility, the crew and service modules will be put through extensive testing to ensure they can survive the rigors of launch, space travel, re-entry and splashdown. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Artemis I.

NASA’s Orion spacecraft, wrapped up for shipping, arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch and Landing Facility runway for loading into the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft on Nov. 21, 2019. The spacecraft’s crew and service modules are flying from the Florida spaceport to NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, for full thermal vacuum testing. In this unique facility, the crew and service modules will be put through extensive testing to ensure they can survive the rigors of launch, space travel, re-entry and splashdown. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Artemis I.
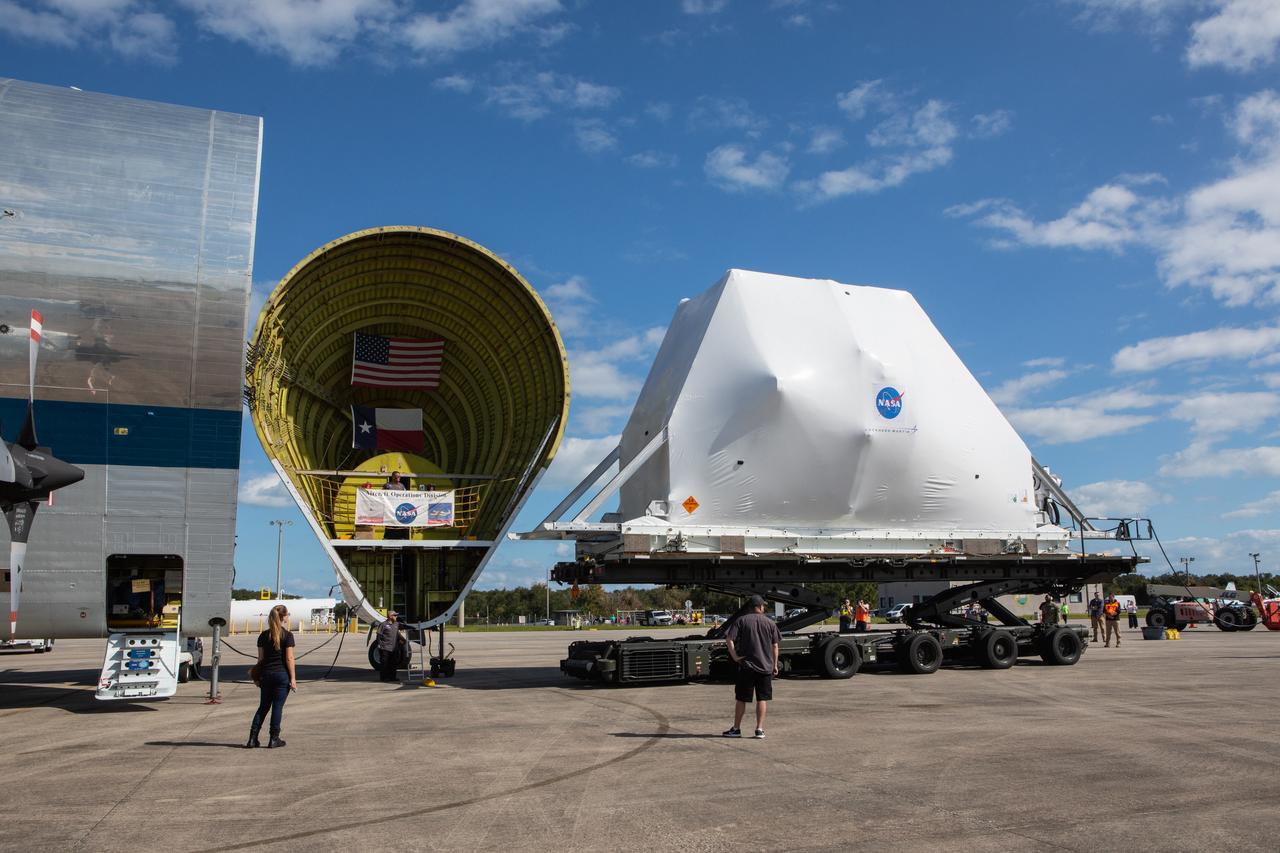

NASA’s Orion spacecraft, wrapped up for shipping, arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch and Landing Facility runway for loading into the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft on Nov. 21, 2019. The spacecraft’s crew and service modules are flying from the Florida spaceport to NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, for full thermal vacuum testing. In this unique facility, the crew and service modules will be put through extensive testing to ensure they can survive the rigors of launch, space travel, re-entry and splashdown. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Artemis I.
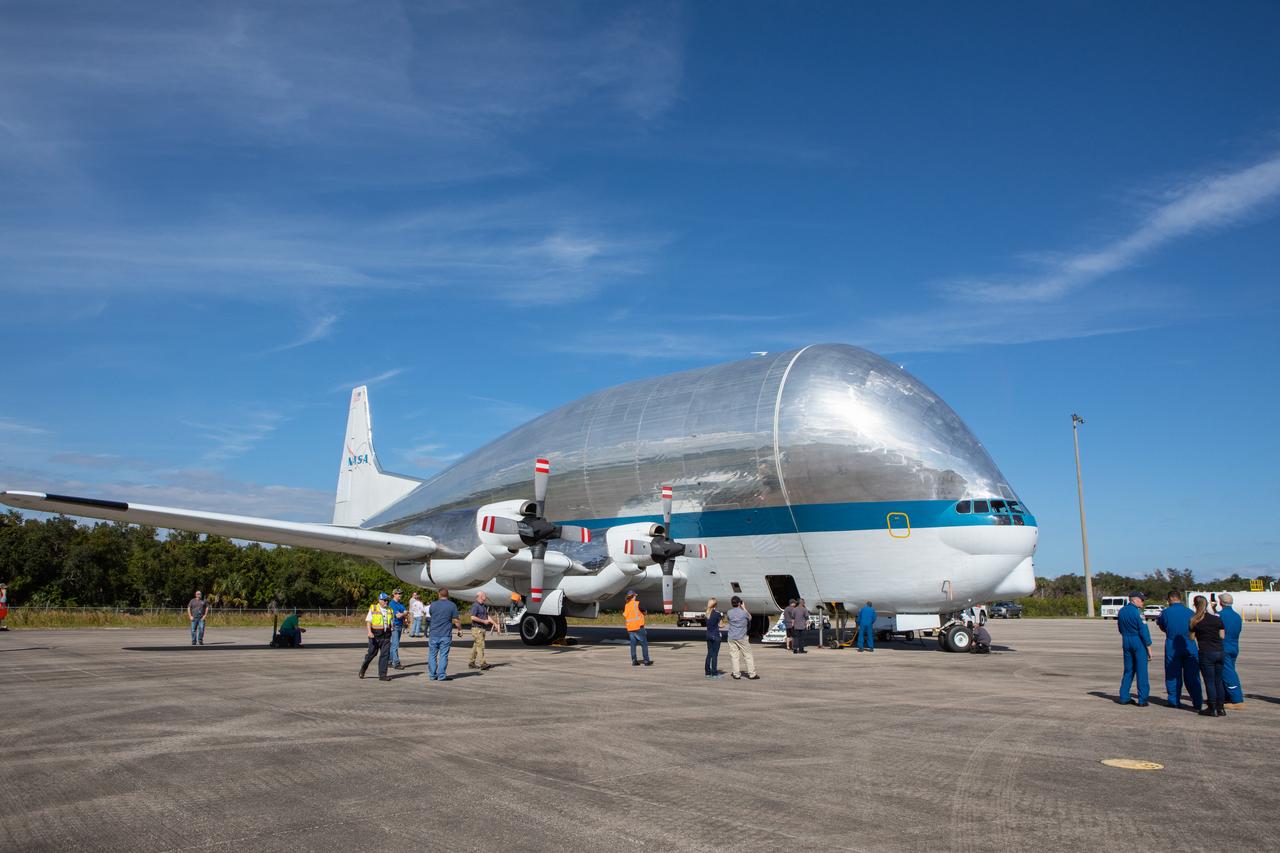

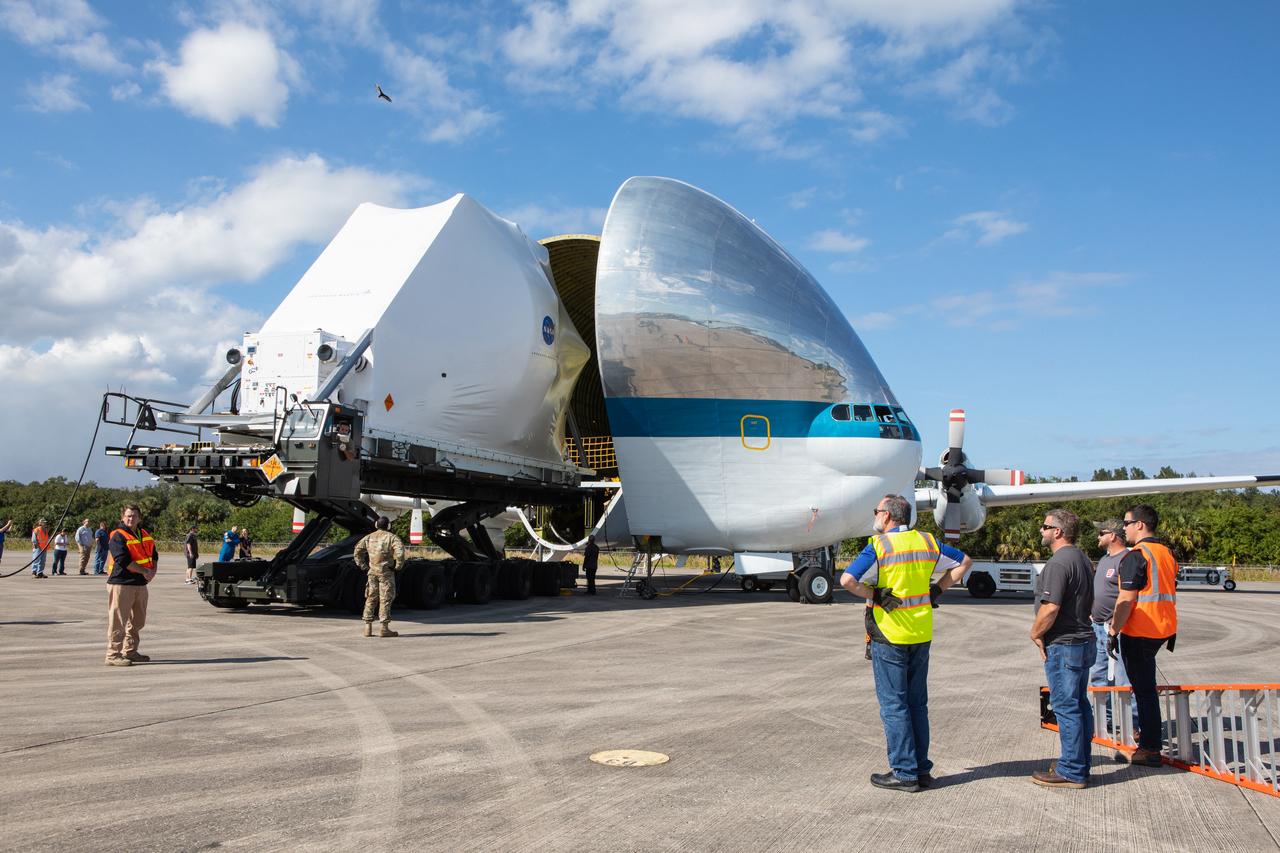
NASA’s Orion spacecraft has been loaded into the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019. The spacecraft’s crew and service modules are flying to NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, for full thermal vacuum testing. In this unique facility, the crew and service modules will be put through extensive testing to ensure they can survive the rigors of launch, space travel, re-entry and splashdown. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Artemis I.
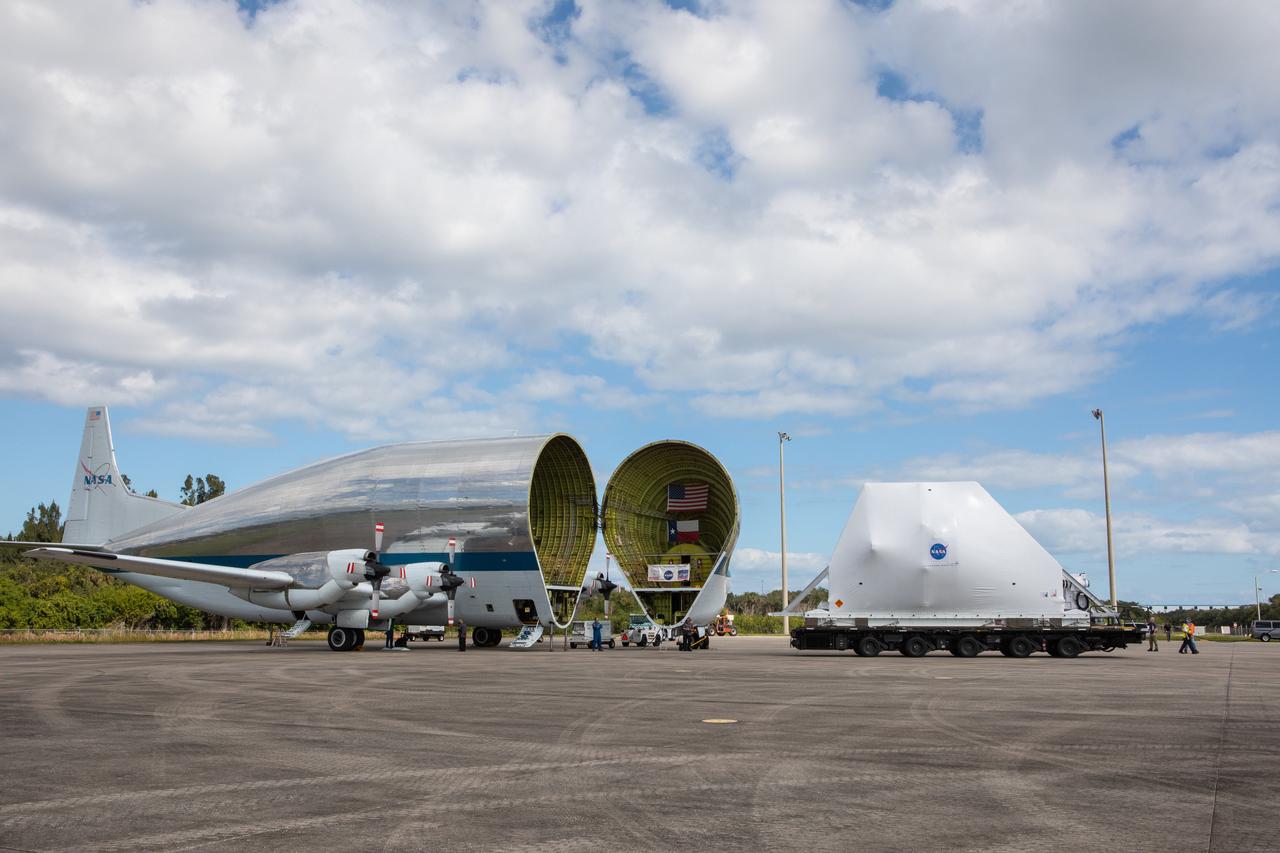

NASA’s Orion spacecraft, wrapped up for shipping, arrives at Kennedy Space Center’s Launch and Landing Facility runway for loading into the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft on Nov. 21, 2019. The spacecraft’s crew and service modules are flying from the Florida spaceport to NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, for full thermal vacuum testing. In this unique facility, the crew and service modules will be put through extensive testing to ensure they can survive the rigors of launch, space travel, re-entry and splashdown. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Artemis I.

NASA’s Orion spacecraft, wrapped up for shipping, is moved into position for loading into the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Nov. 21, 2019. The spacecraft’s crew and service modules are flying to NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Sandusky, Ohio, for full thermal vacuum testing. In this unique facility, the crew and service modules will be put through extensive testing to ensure they can survive the rigors of launch, space travel, re-entry and splashdown. The Orion spacecraft will launch atop the agency's Space Launch System rocket on Artemis I.

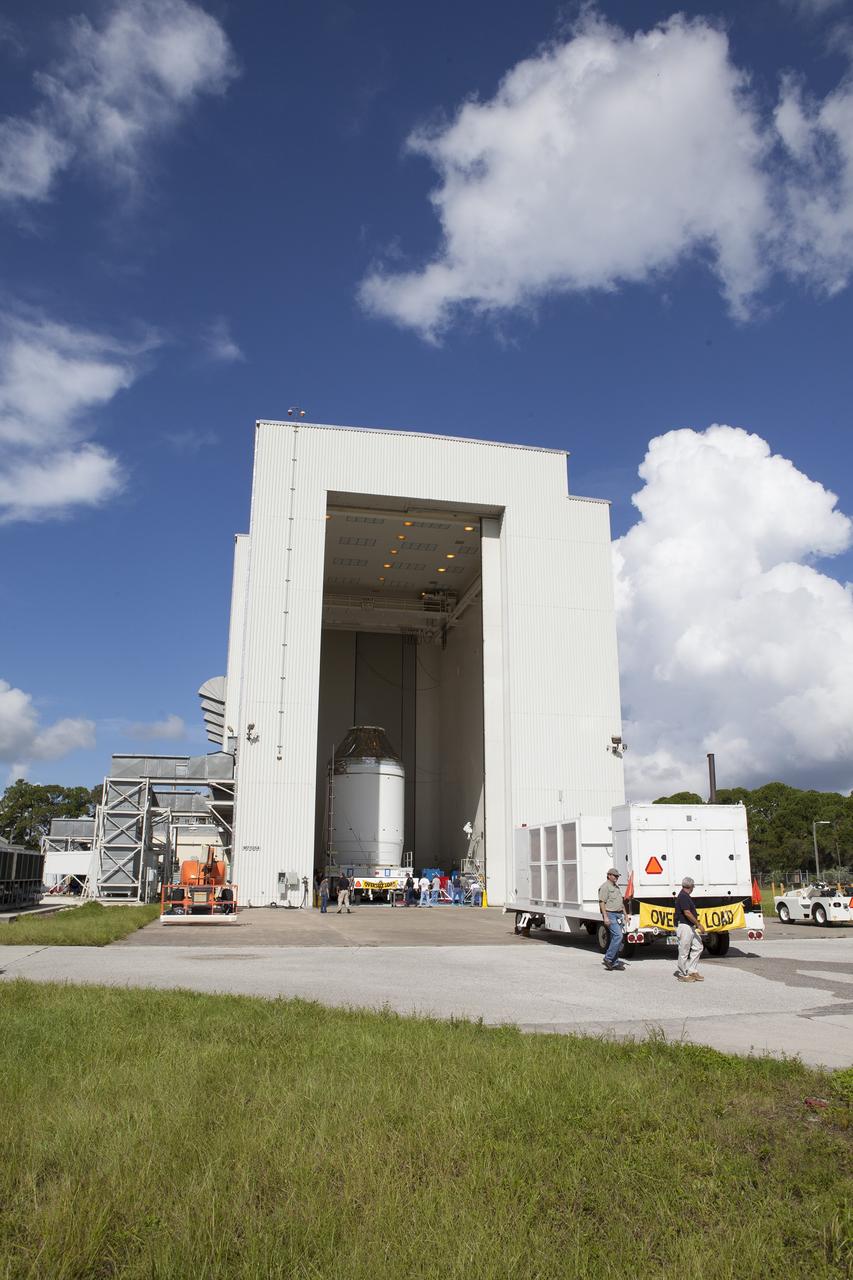
NASA’s Orion spacecraft, protected in its shipping container, is removed from the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center on March 25, 2020, for transportation to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. After testing at NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio verified it can handle the extreme conditions of a deep-space environment, the spacecraft has returned to the Florida spaceport for final testing and assembly. Following this, it will be integrated with the Space Launch System rocket for Artemis I – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
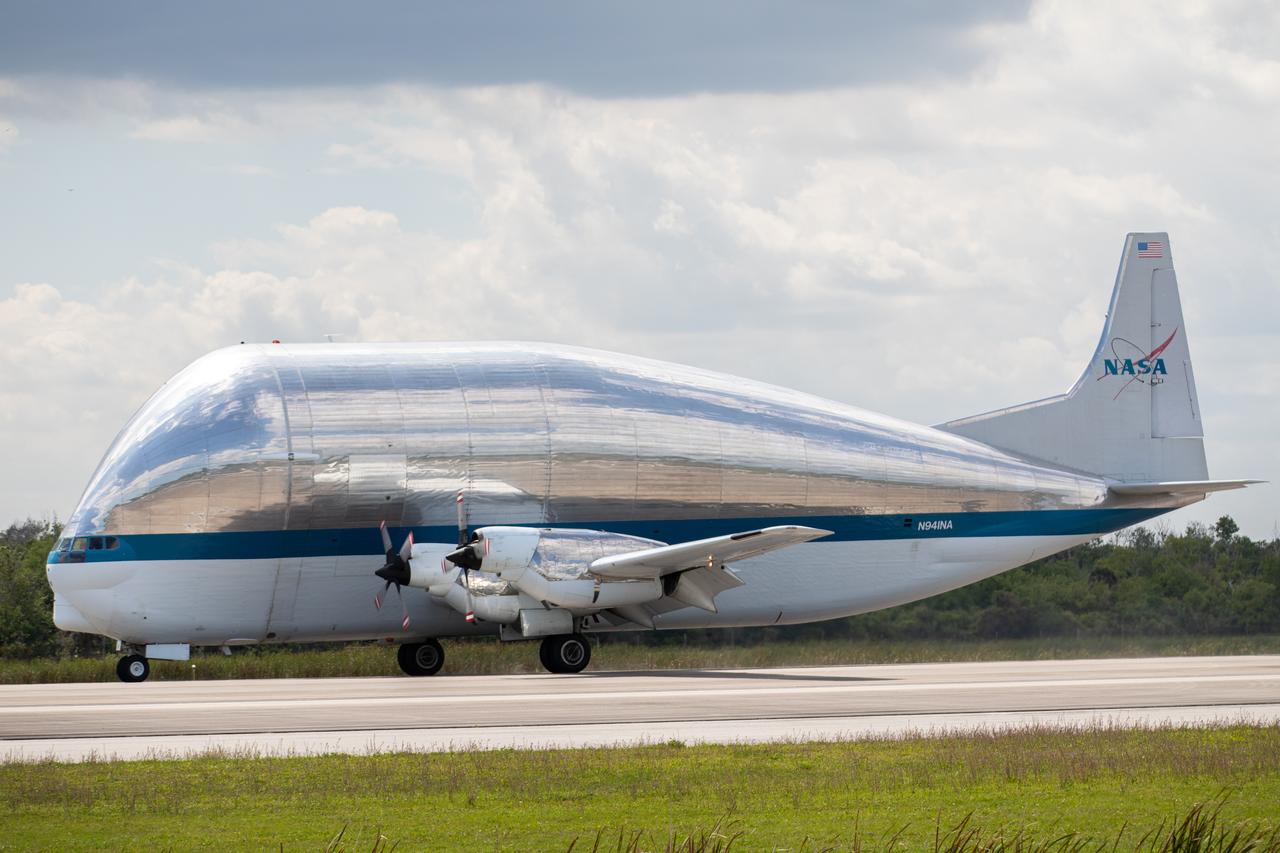

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion spacecraft, lands at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 25, 2020. Orion has returned to Kennedy after testing at the agency’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio verified the spacecraft can handle the extreme conditions of a deep-space environment. The spacecraft will now undergo final testing and assembly prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System rocket. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
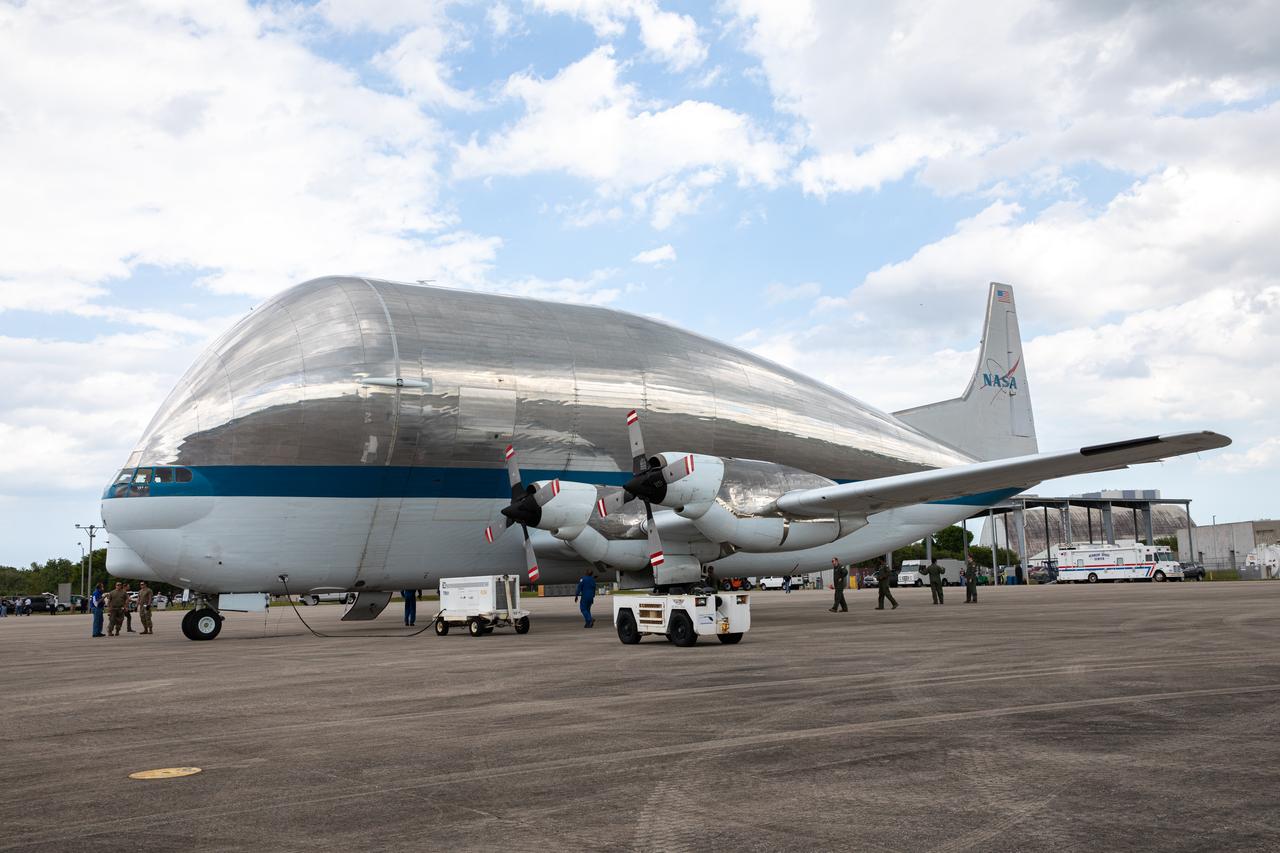

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion spacecraft, lands at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 25, 2020. Orion has returned to Kennedy after testing at the agency’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio verified the spacecraft can handle the extreme conditions of a deep-space environment. The spacecraft will now undergo final testing and assembly prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System rocket. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
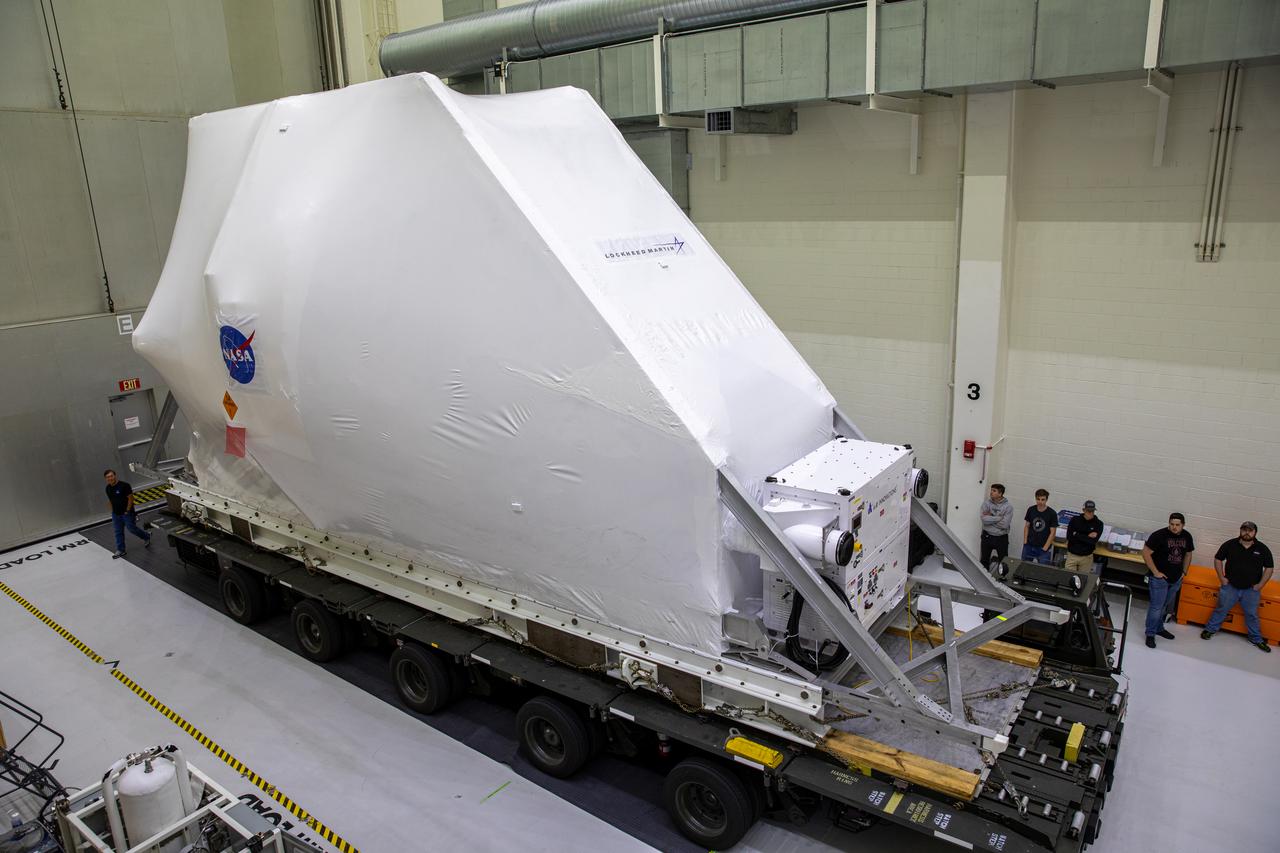

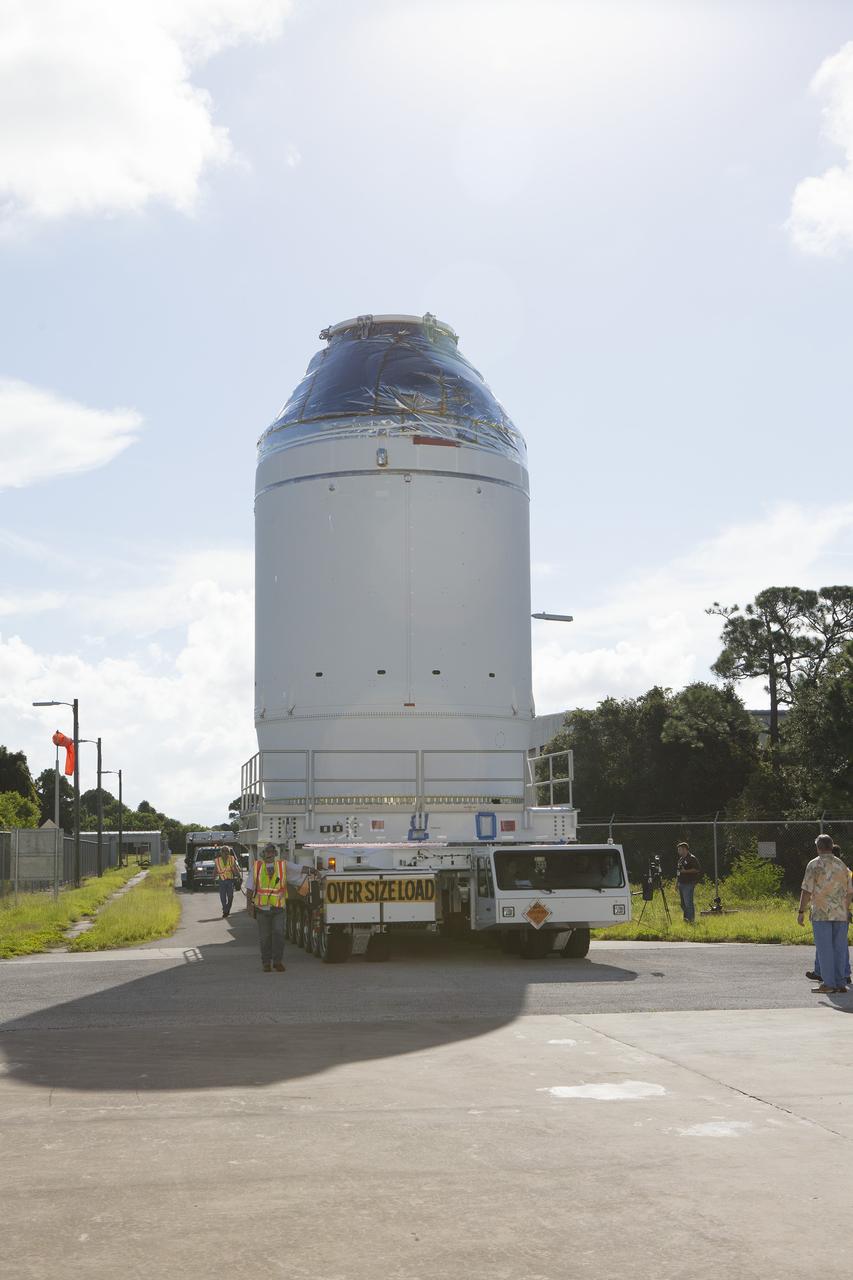
The Orion spacecraft, secured atop a transporter in its shipping container, arrives at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 25, 2020, for final testing and assembly. The spacecraft was transported to Kennedy in NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft from the agency’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio, where it underwent two phase of environmental testing. Following these final preparations, Orion will be integrated with the Space Launch System rocket for the Artemis I launch – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
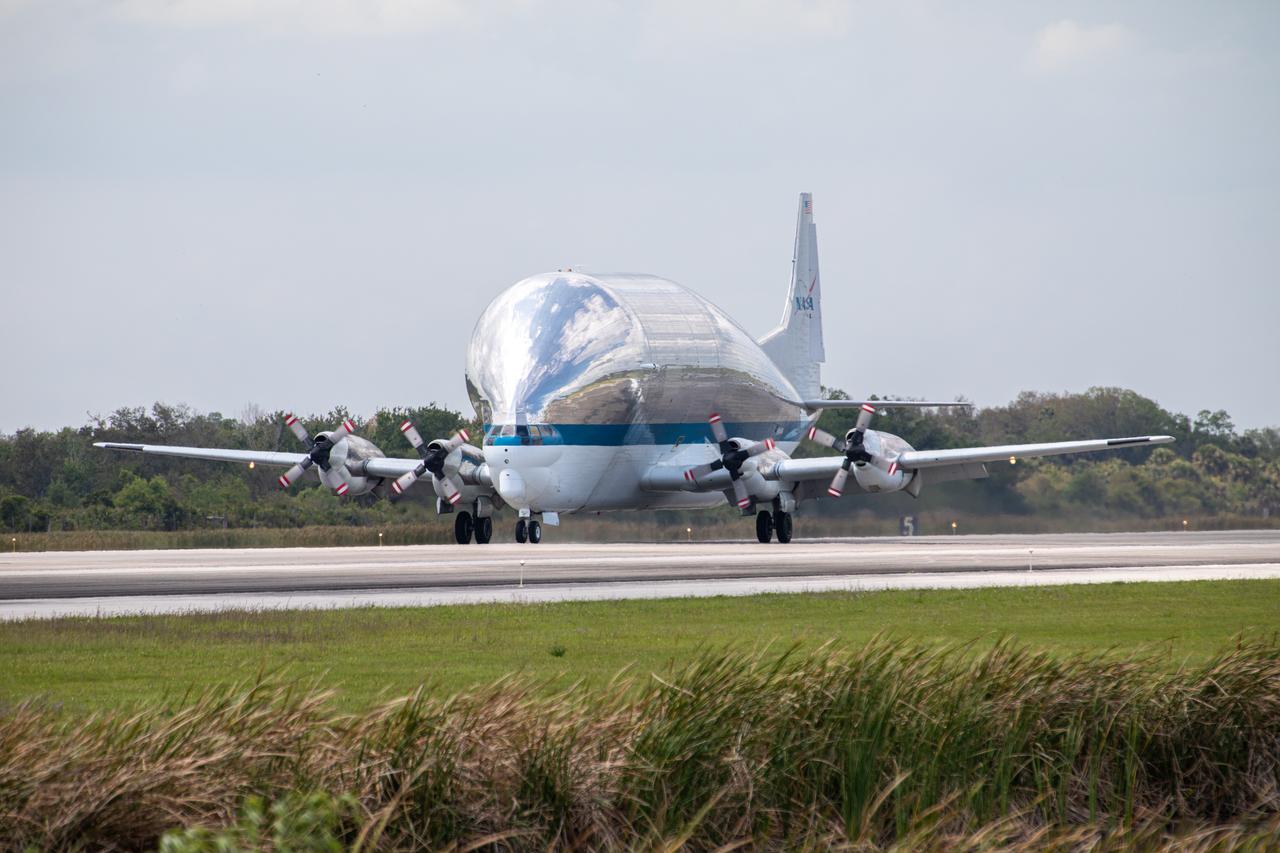

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion spacecraft, lands at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 25, 2020. Orion has returned to Kennedy after testing at the agency’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio verified the spacecraft can handle the extreme conditions of a deep-space environment. The spacecraft will now undergo final testing and assembly prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System rocket. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
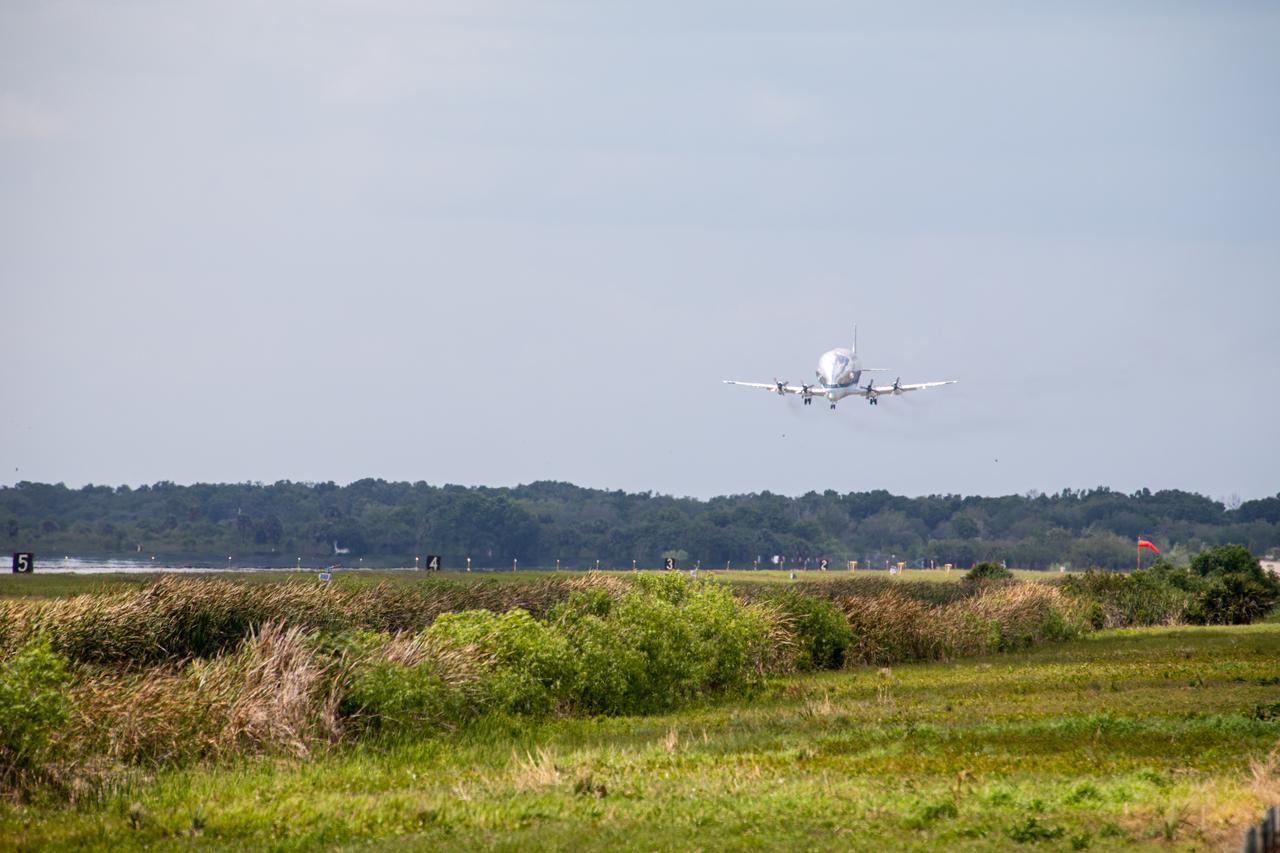

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion spacecraft, lands at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 25, 2020. Orion has returned to Kennedy after testing at the agency’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio verified the spacecraft can handle the extreme conditions of a deep-space environment. The spacecraft will now undergo final testing and assembly prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System rocket. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
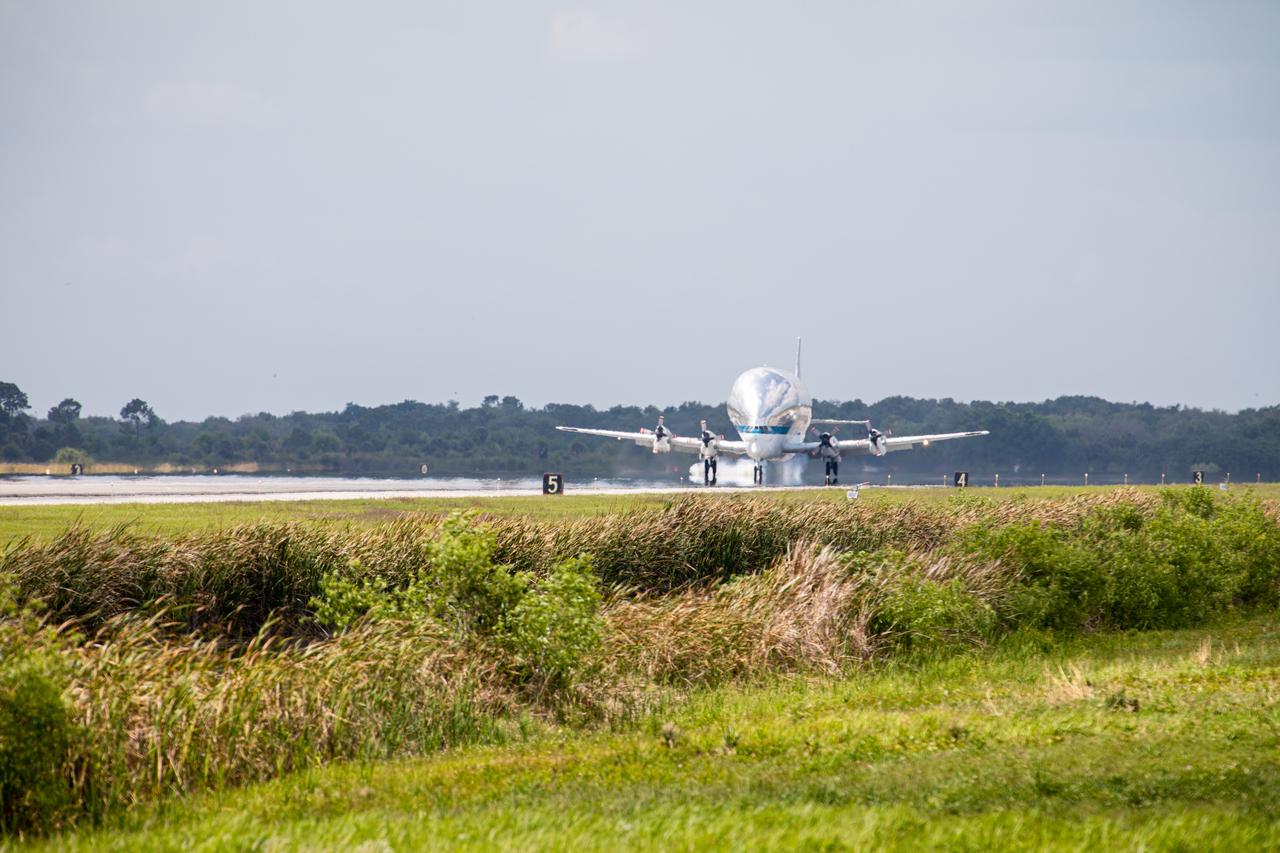

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion spacecraft, touches down at the Launch and Landing Facility at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 25, 2020. The container holding Orion can be seen in the open aircraft. The spacecraft was transported from NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio, where it underwent two phases of testing to demonstrate it can handle the extreme conditions of a deep-space environment. The container will be offloaded and secured onto a transporter for its move to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building for final testing and assembly. Following this, Orion will be integrated with the Space Launch System rocket for Artemis I – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
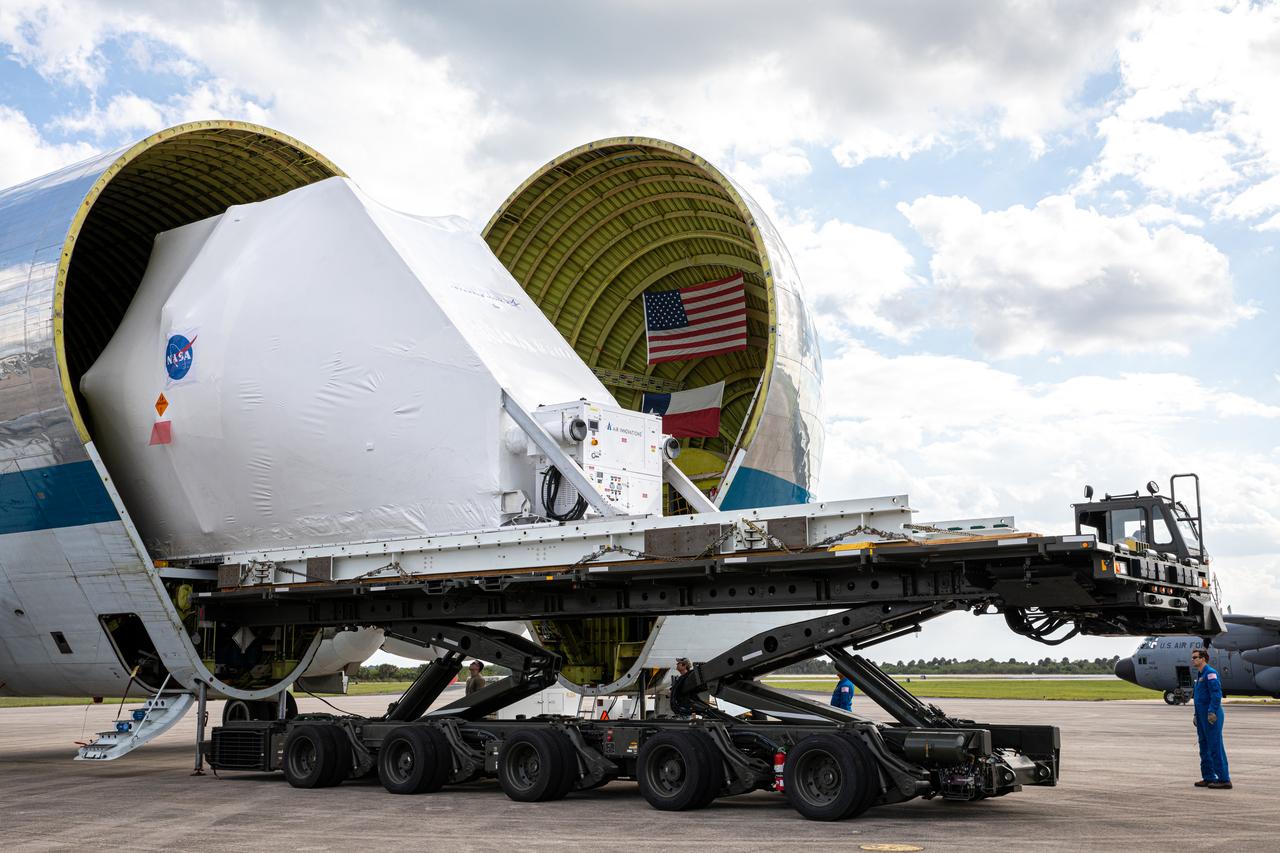

NASA’s Orion spacecraft, protected in its shipping container, is removed from the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center on March 25, 2020, for transportation to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. After testing at NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio verified it can handle the extreme conditions of a deep-space environment, the spacecraft has returned to the Florida spaceport for final testing and assembly. Following this, it will be integrated with the Space Launch System rocket for Artemis I – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
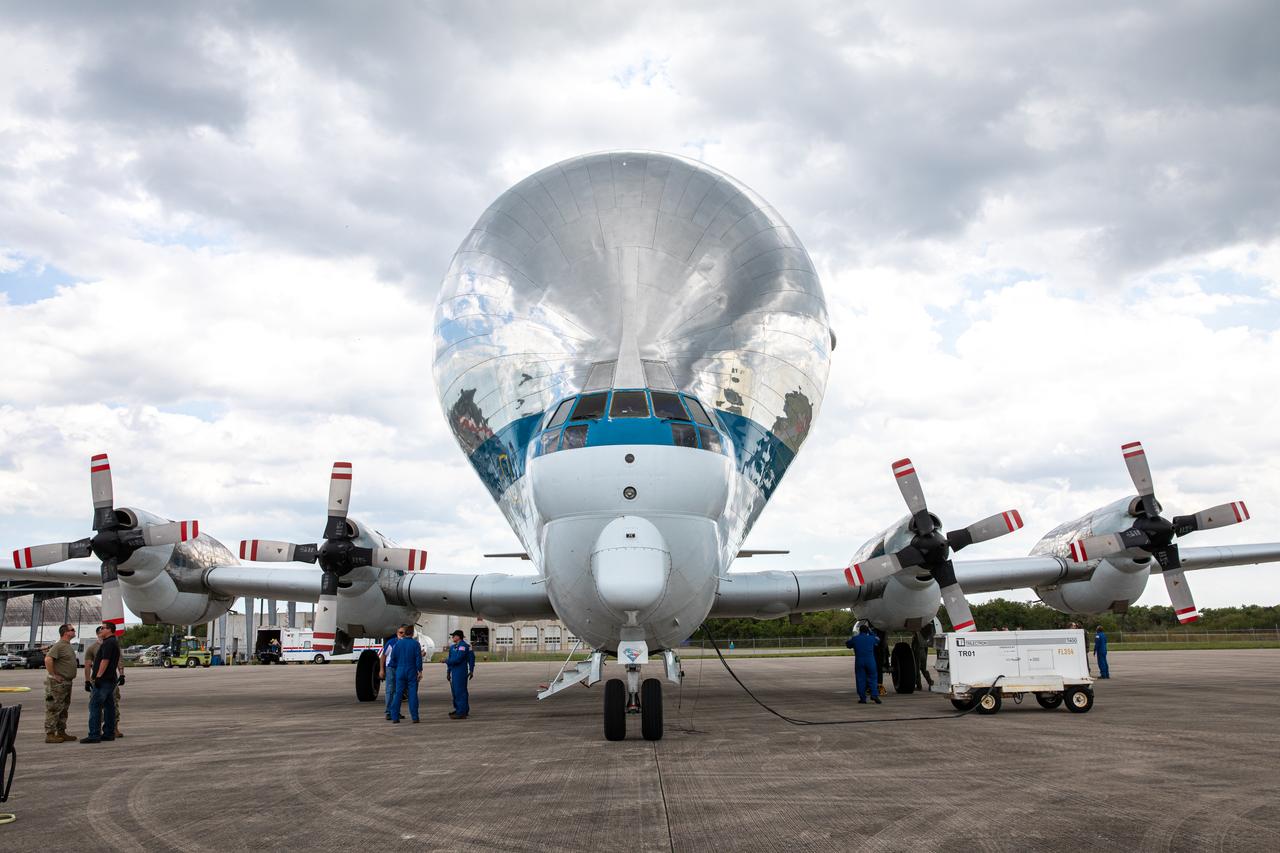

NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft, carrying the Orion spacecraft, lands at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 25, 2020. Orion has returned to Kennedy after testing at the agency’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio verified the spacecraft can handle the extreme conditions of a deep-space environment. The spacecraft will now undergo final testing and assembly prior to being integrated with the Space Launch System rocket. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
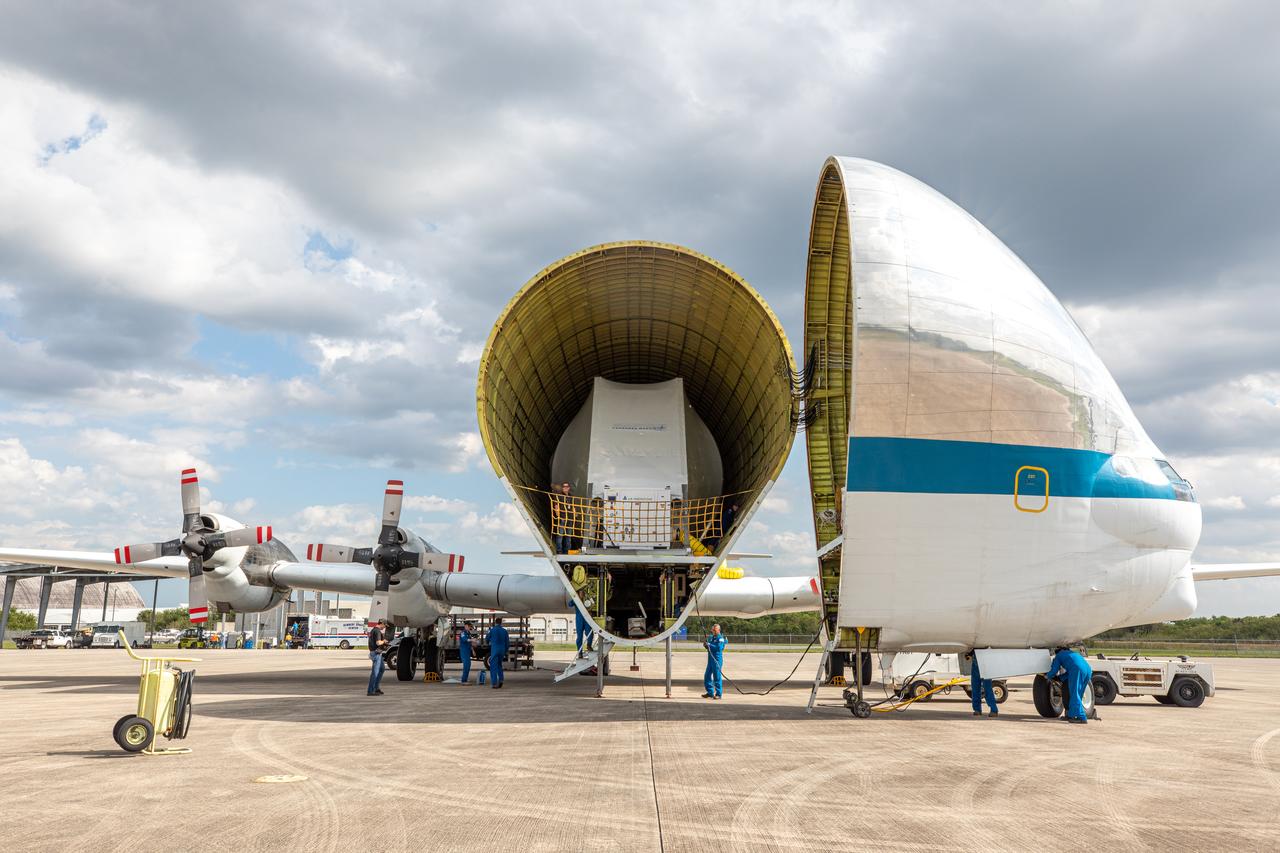

NASA’s Orion spacecraft, protected in its shipping container, is removed from the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft at the Launch and Landing Facility runway at Kennedy Space Center on March 25, 2020, for transportation to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building. After testing at NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio verified it can handle the extreme conditions of a deep-space environment, the spacecraft has returned to the Florida spaceport for final testing and assembly. Following this, it will be integrated with the Space Launch System rocket for Artemis I – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

The Orion spacecraft, secured atop a transporter in its shipping container, arrives at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 25, 2020, for final testing and assembly. The spacecraft was transported to Kennedy in NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft from the agency’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio, where it underwent two phase of environmental testing. Following these final preparations, Orion will be integrated with the Space Launch System rocket for the Artemis I launch – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
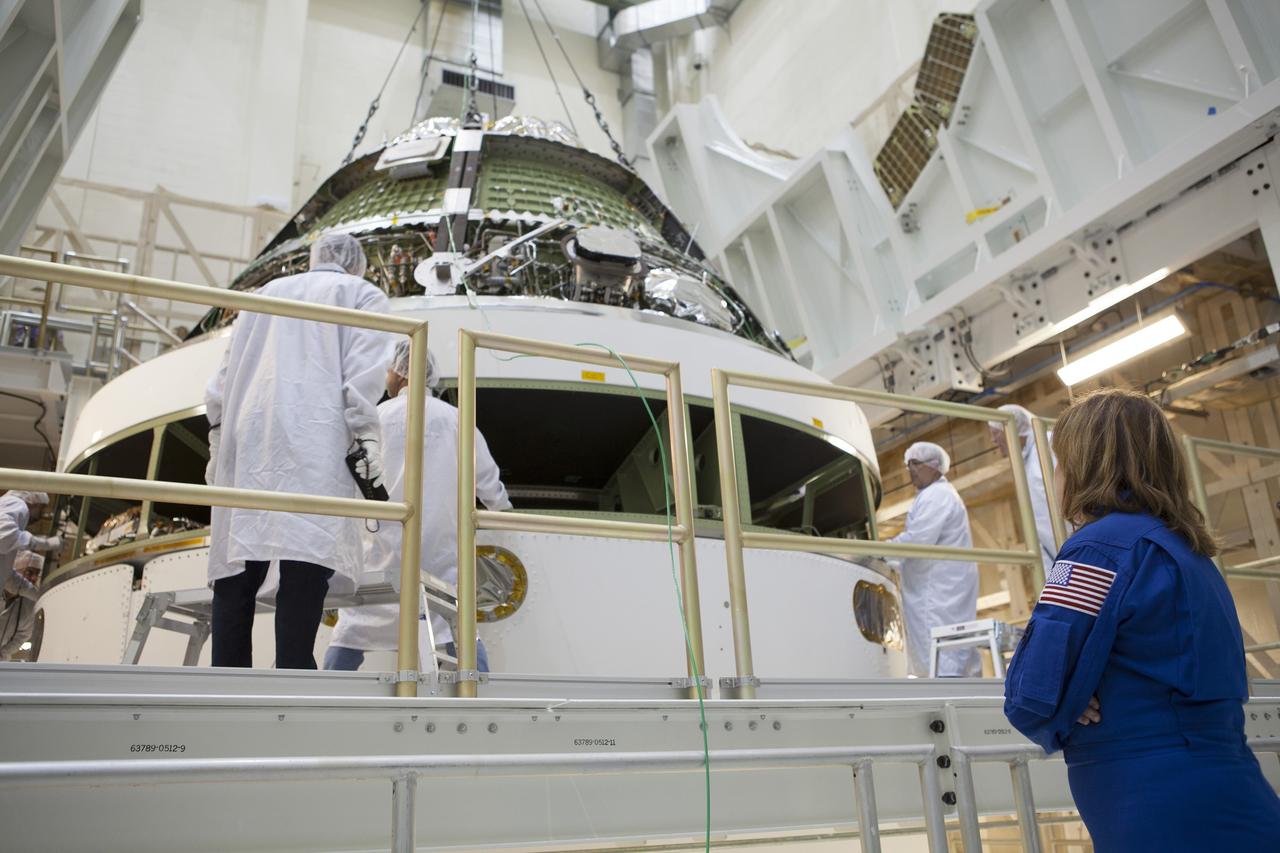

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians monitor the progress as a crane lowers the Orion crew module for stacking on the service module. The modules will be mated and then put through their final system tests before they are transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for fueling. In the foreground, observing the processing, is NASA astronaut Anna Fisher. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion's first flight test is scheduled to launch in December atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Lockheed Martin technicians monitor the progress as a crane lowers the Orion crew module for stacking on the service module. The modules will be mated and then put through their final system tests before they are transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility for fueling. In the foreground, observing the processing, is NASA astronaut Anna Fisher. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. Orion's first flight test is scheduled to launch in December atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, has been moved into the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is being transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
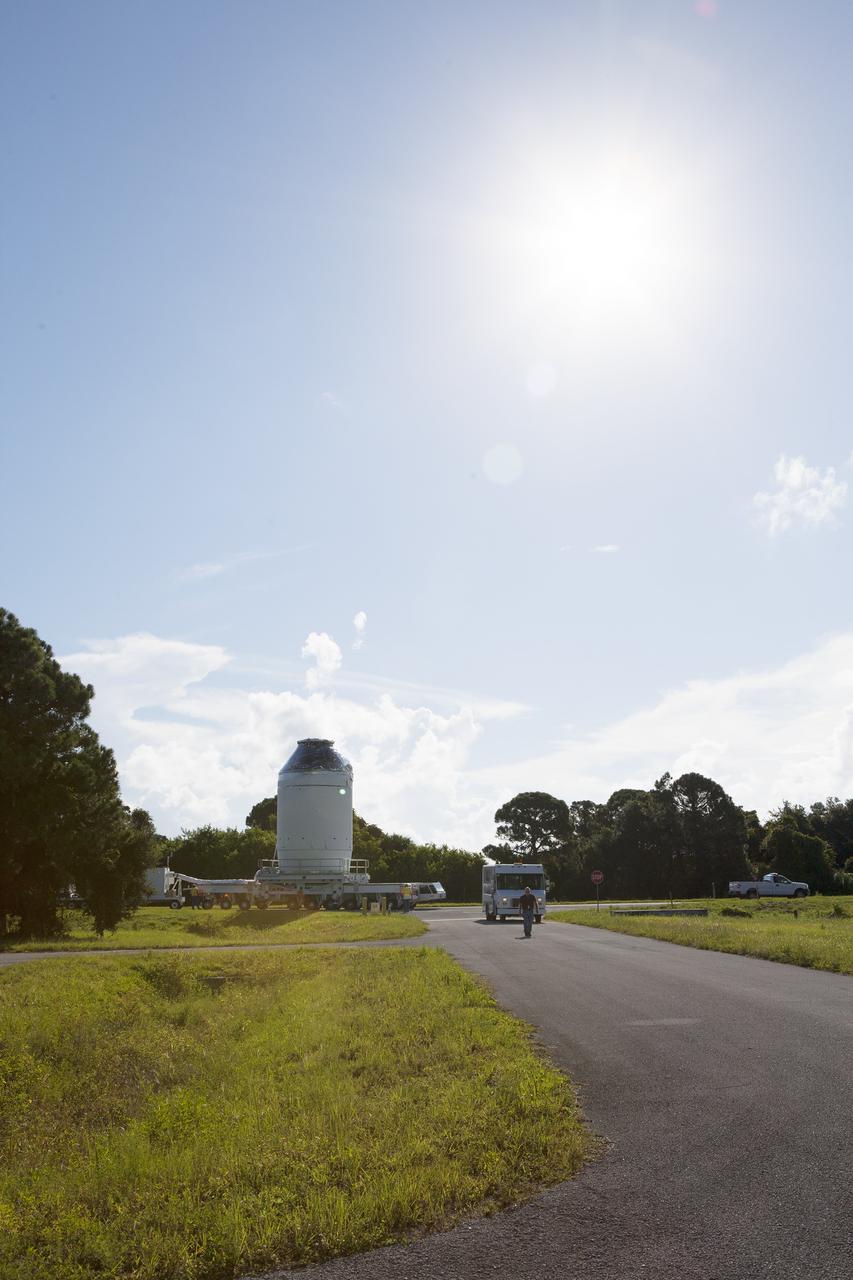

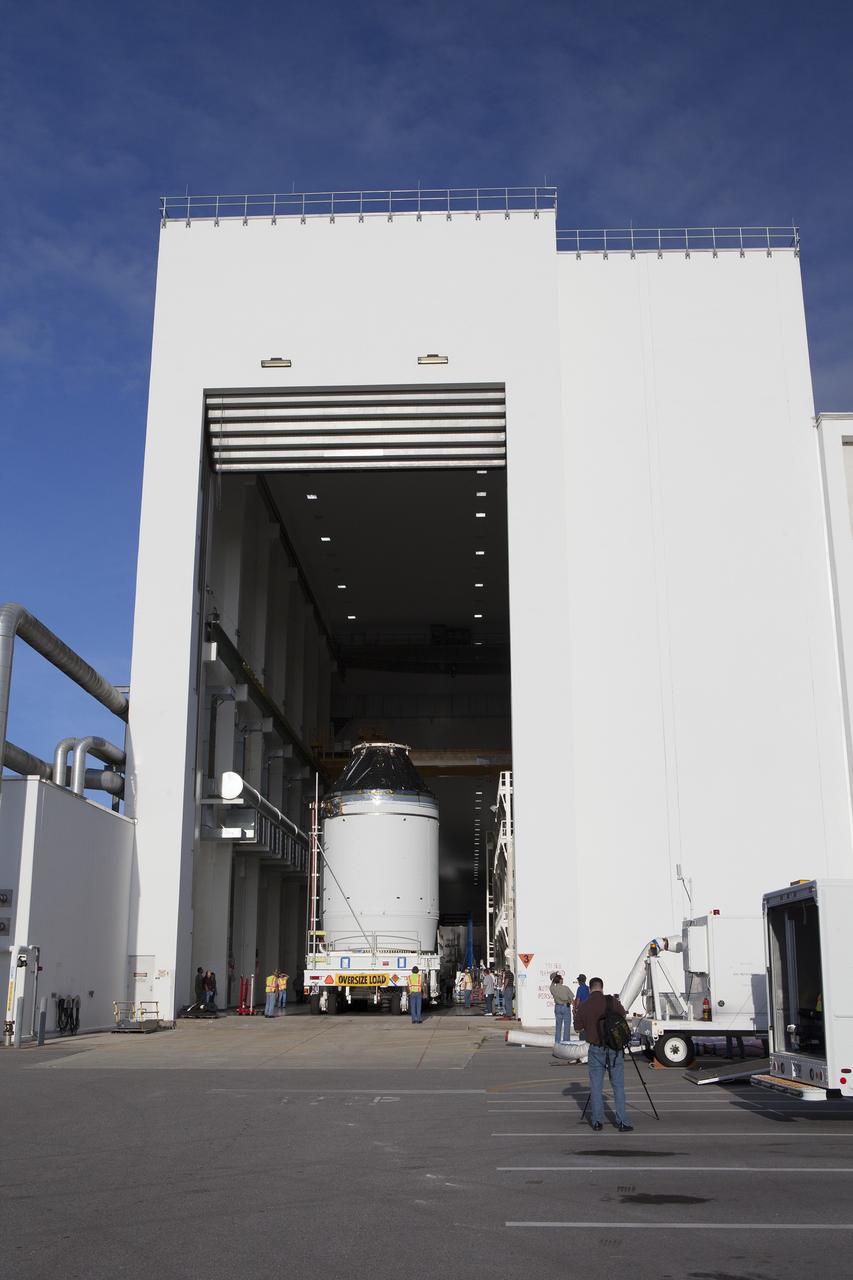
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is being transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is transported into the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
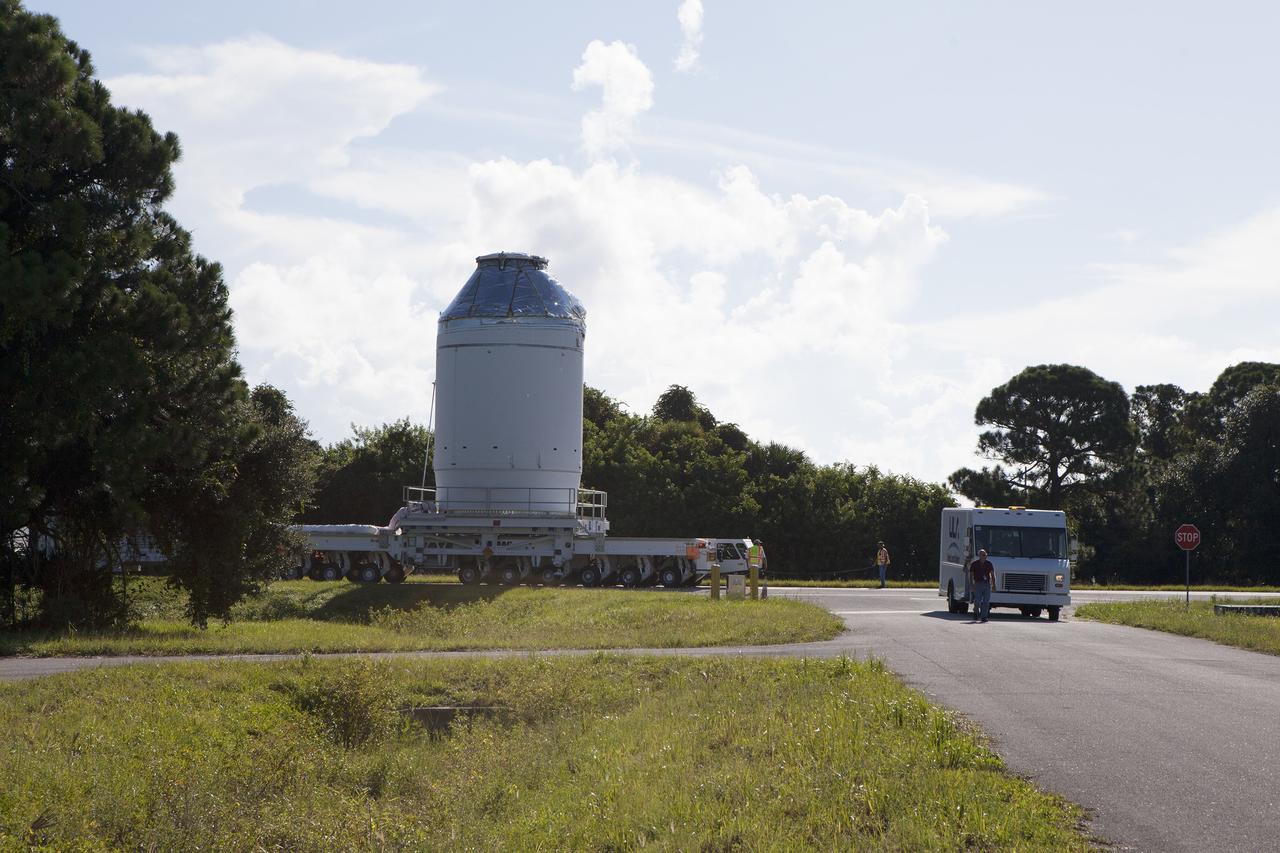

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is being transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

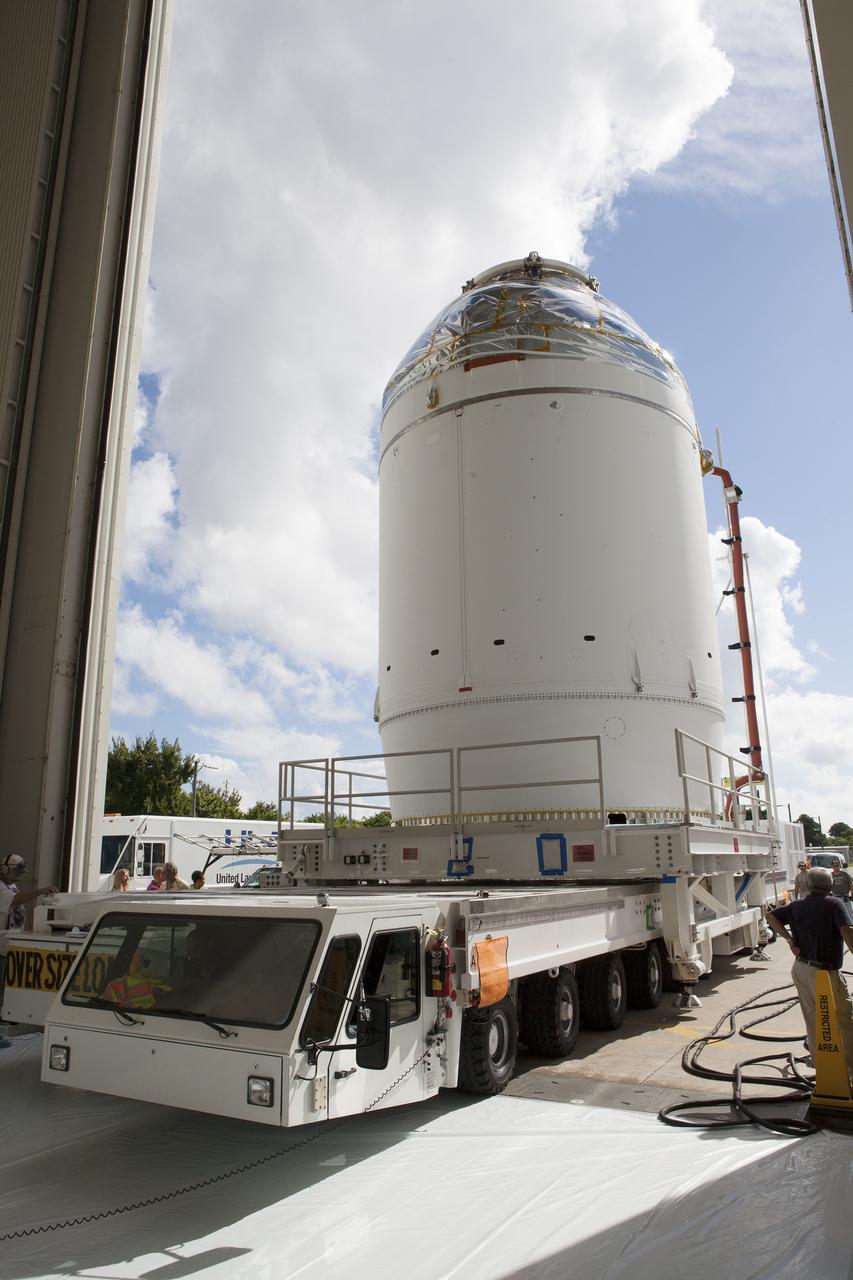
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is moved slowly out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay door at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
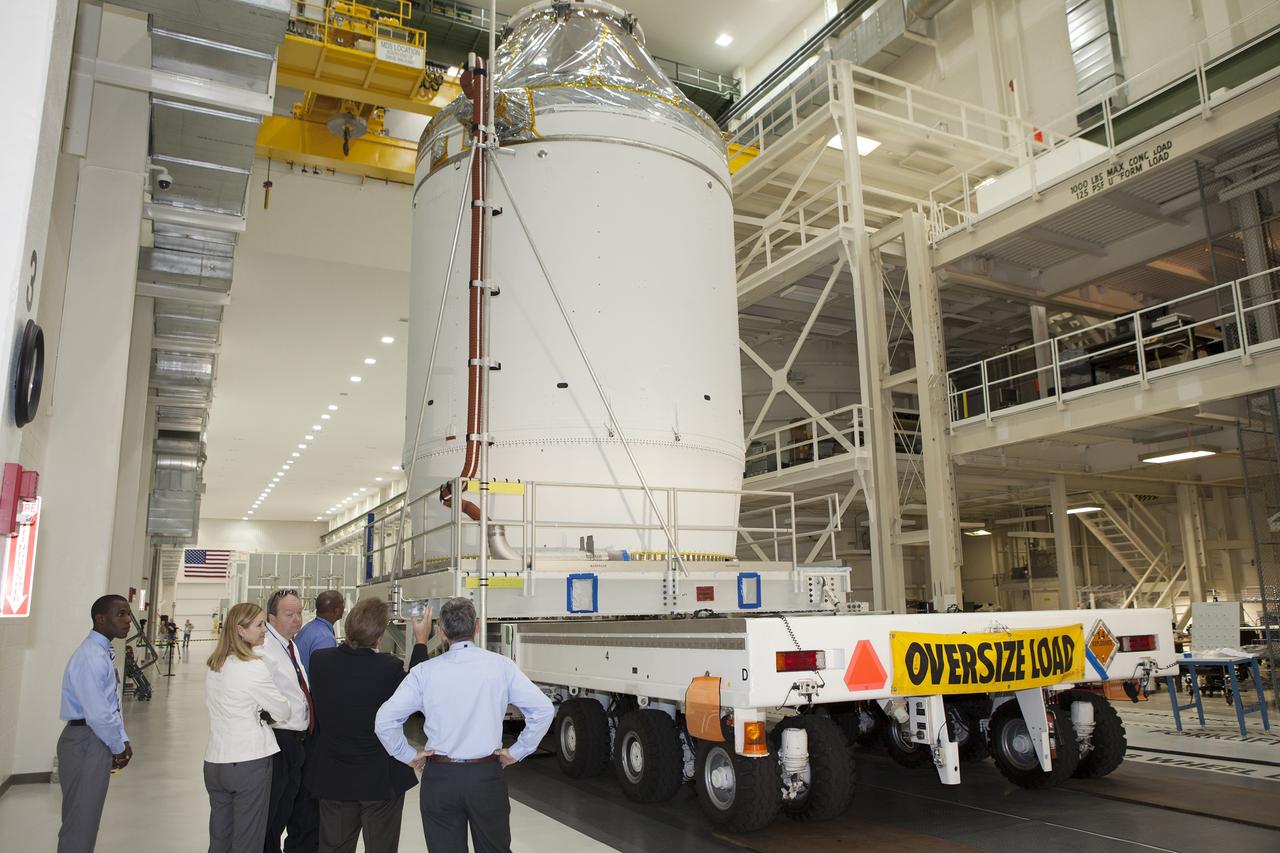

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is being prepared for its move out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
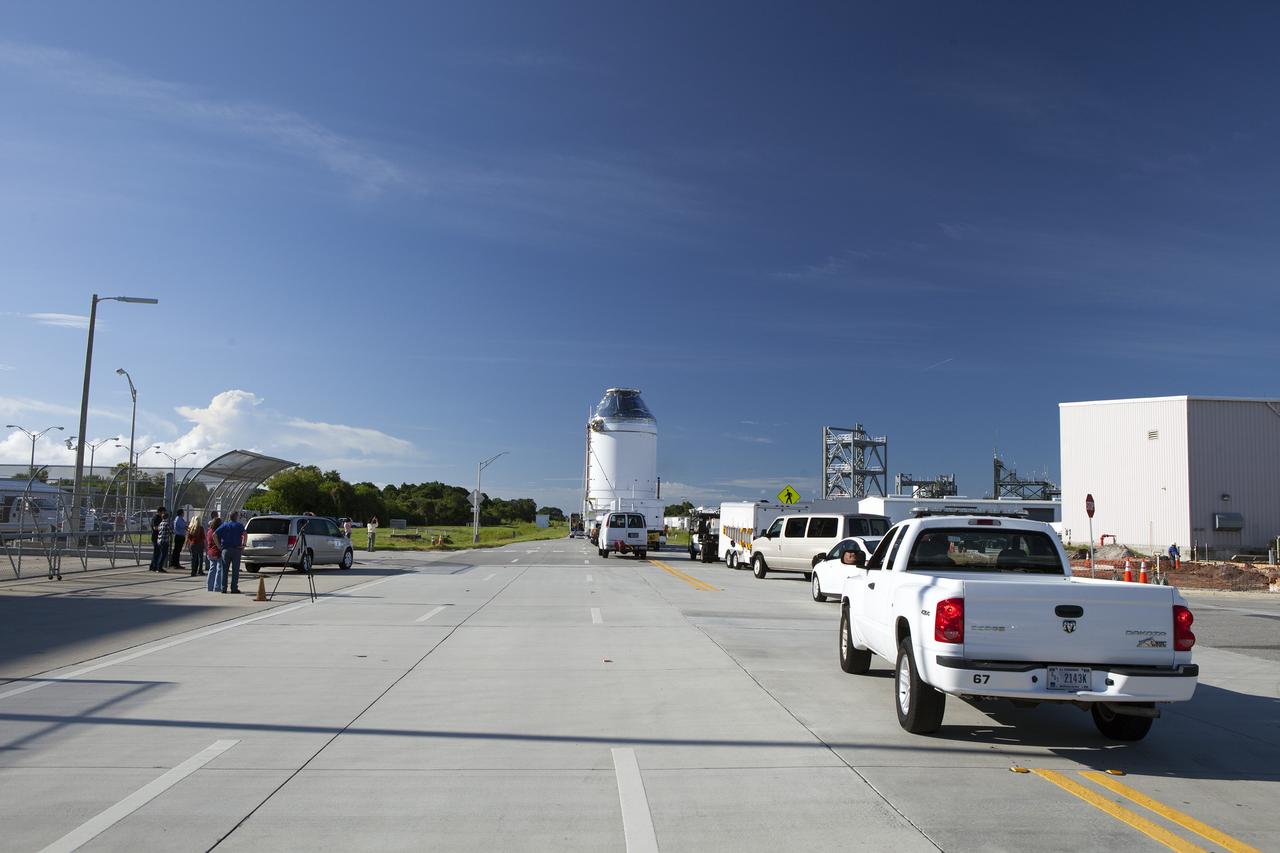

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, has moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 is being transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
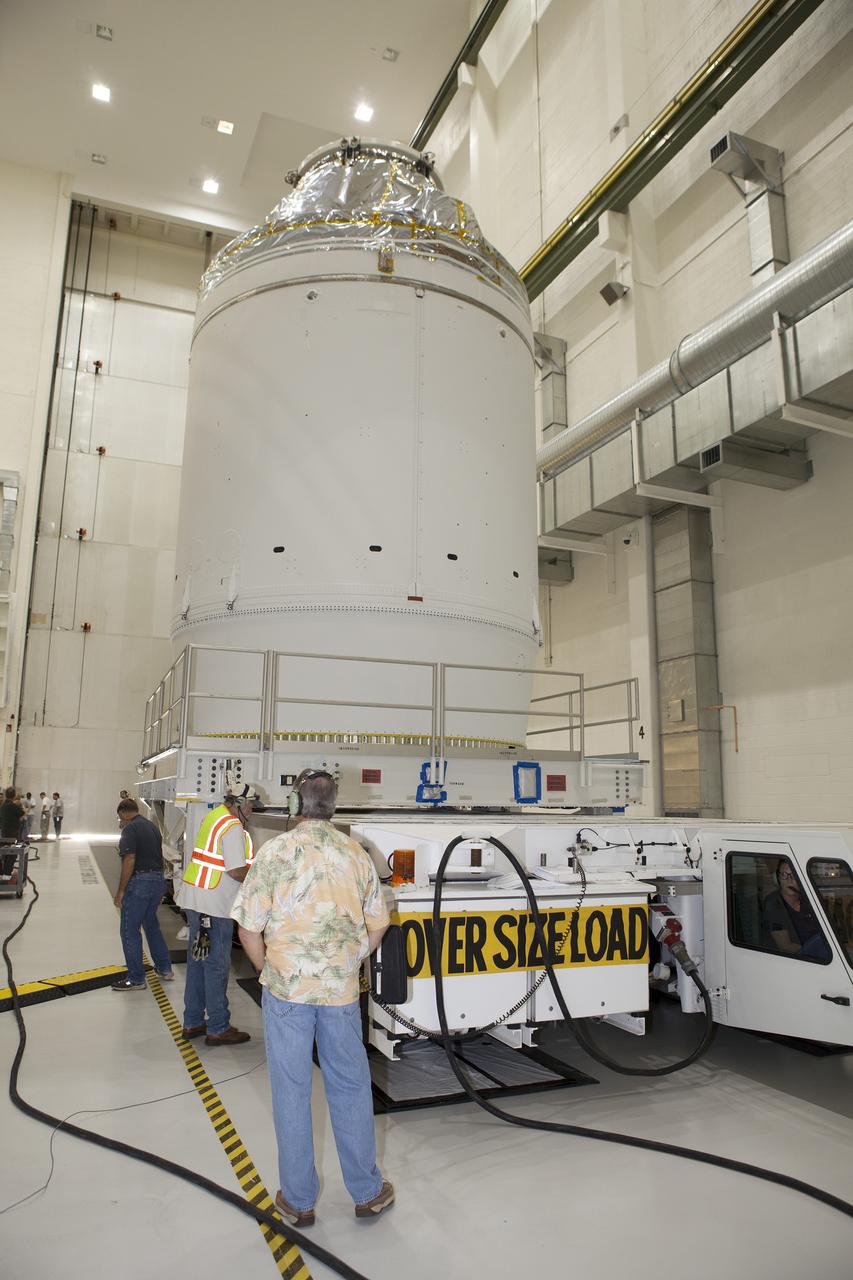

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is being prepared for its move out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
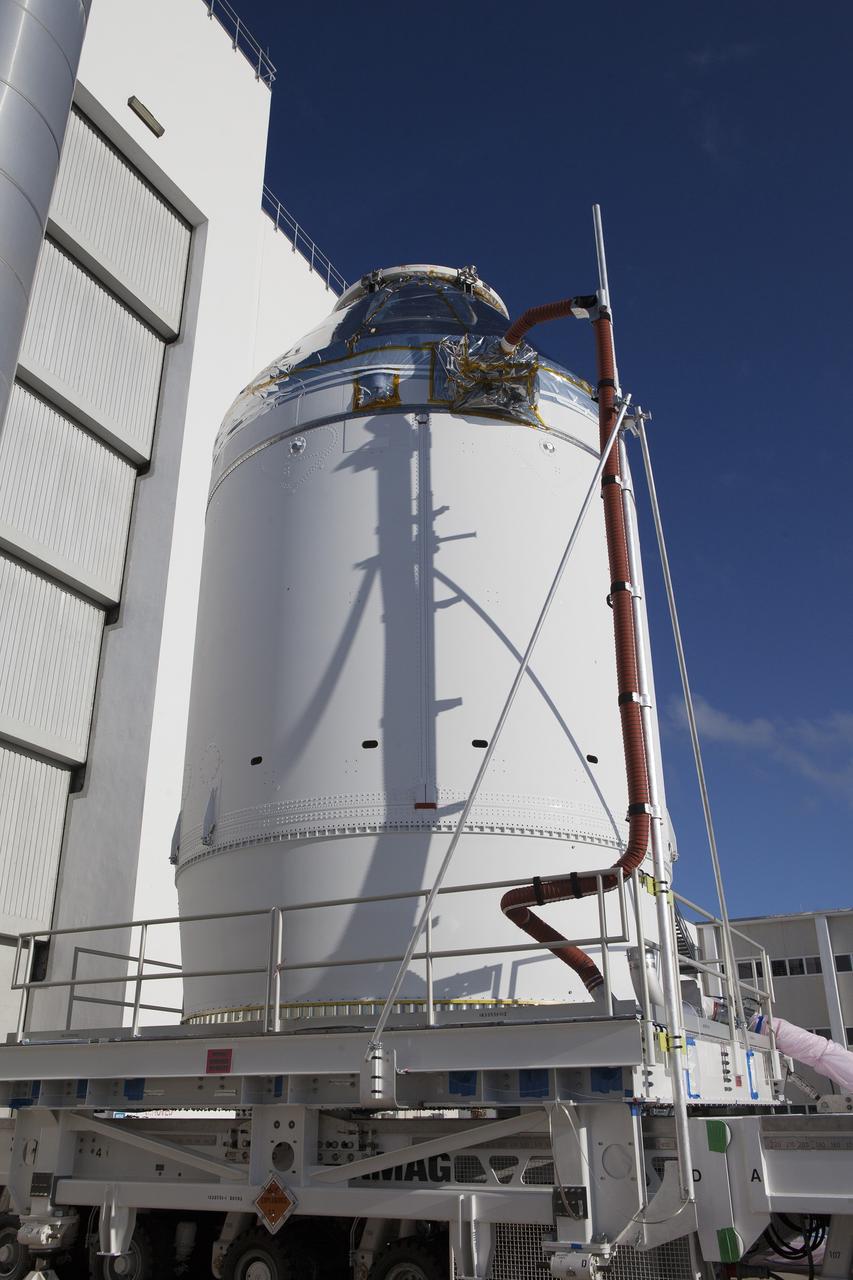

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, has moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
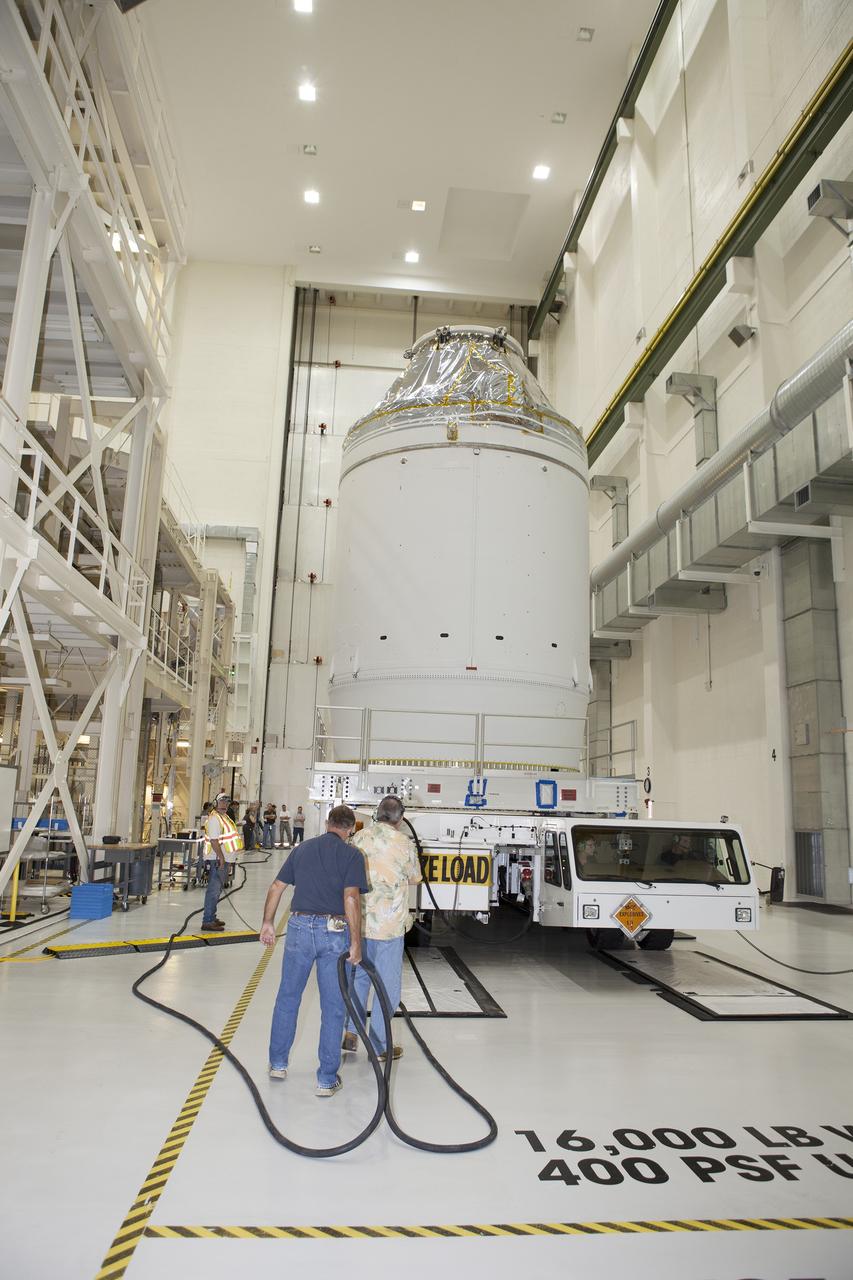

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is being prepared for its move out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
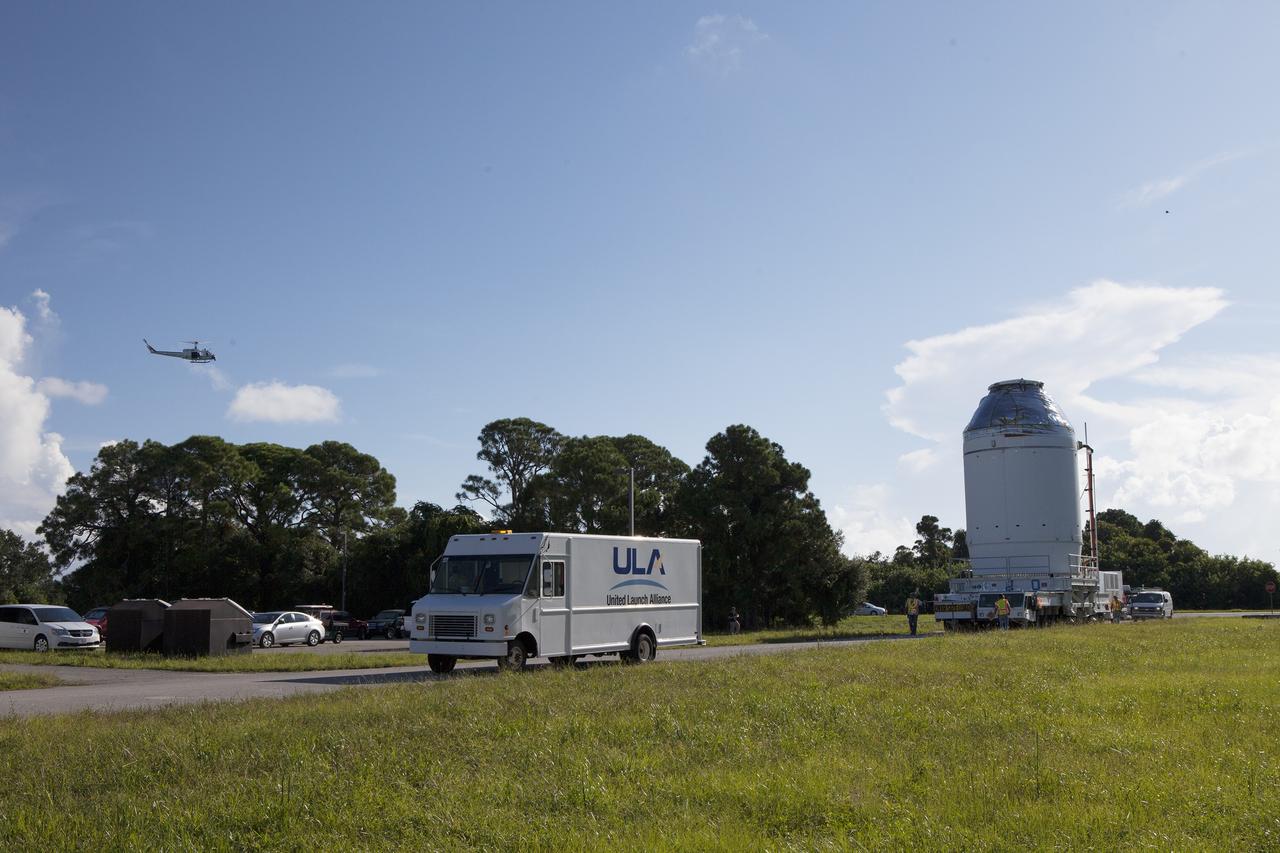

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A NASA helicopter flies overhead as the Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
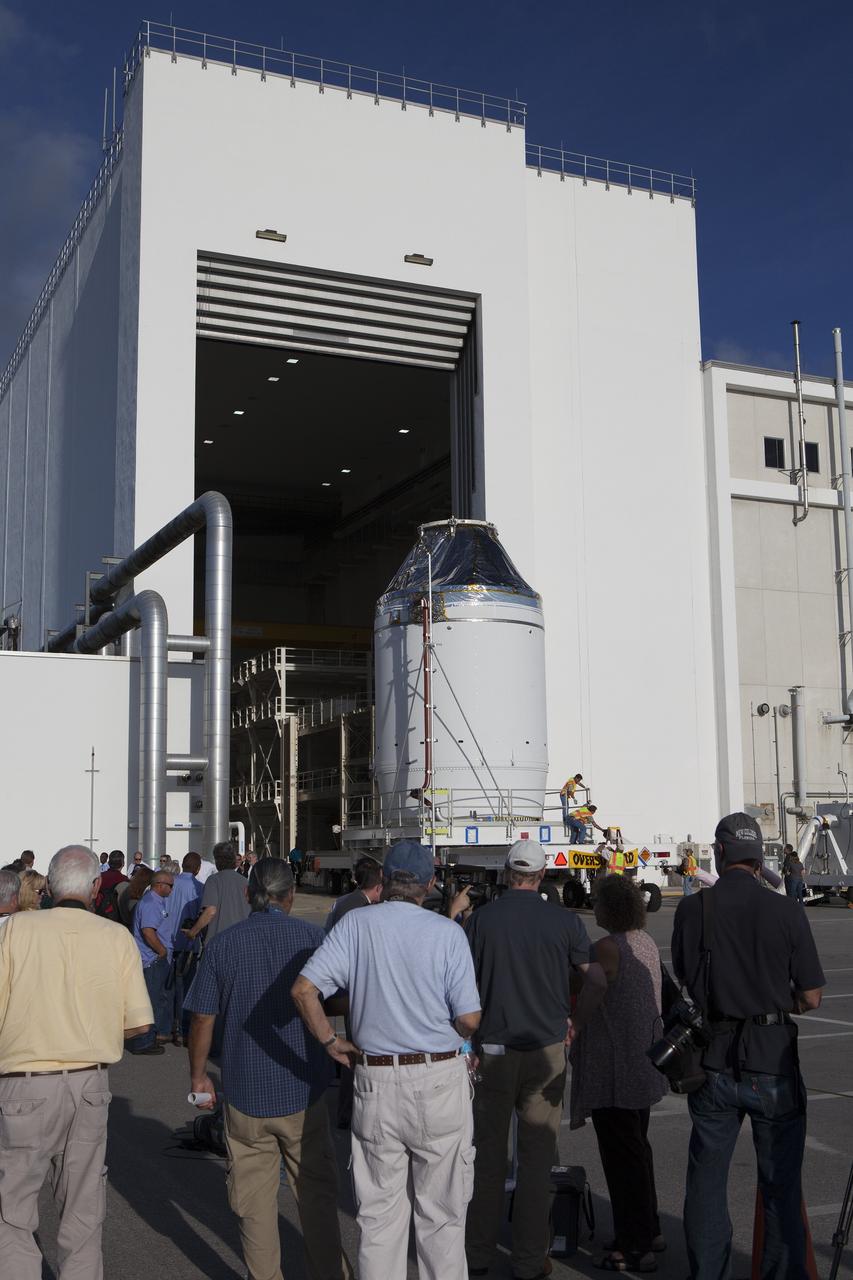

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Reporters and photographers watch as the Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, moves out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, has moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
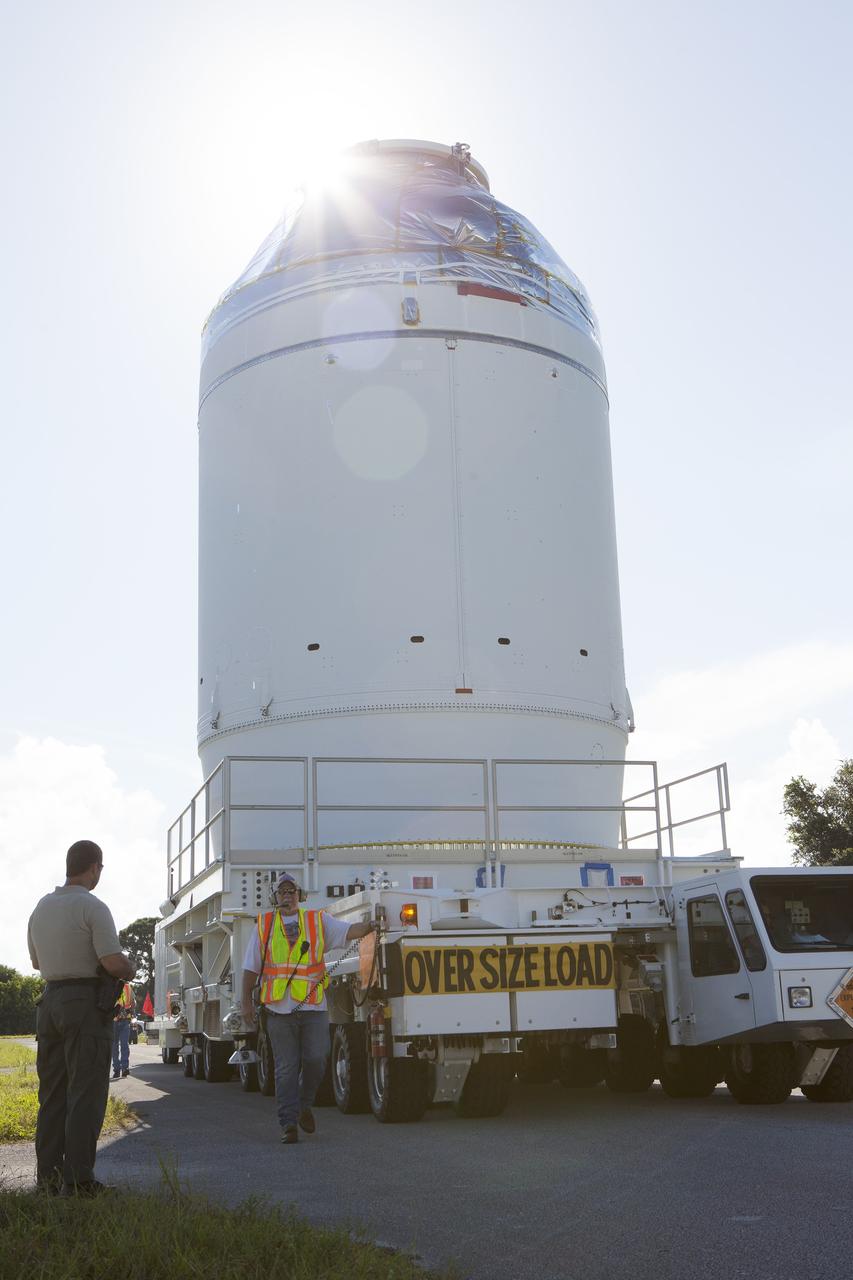

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is being transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
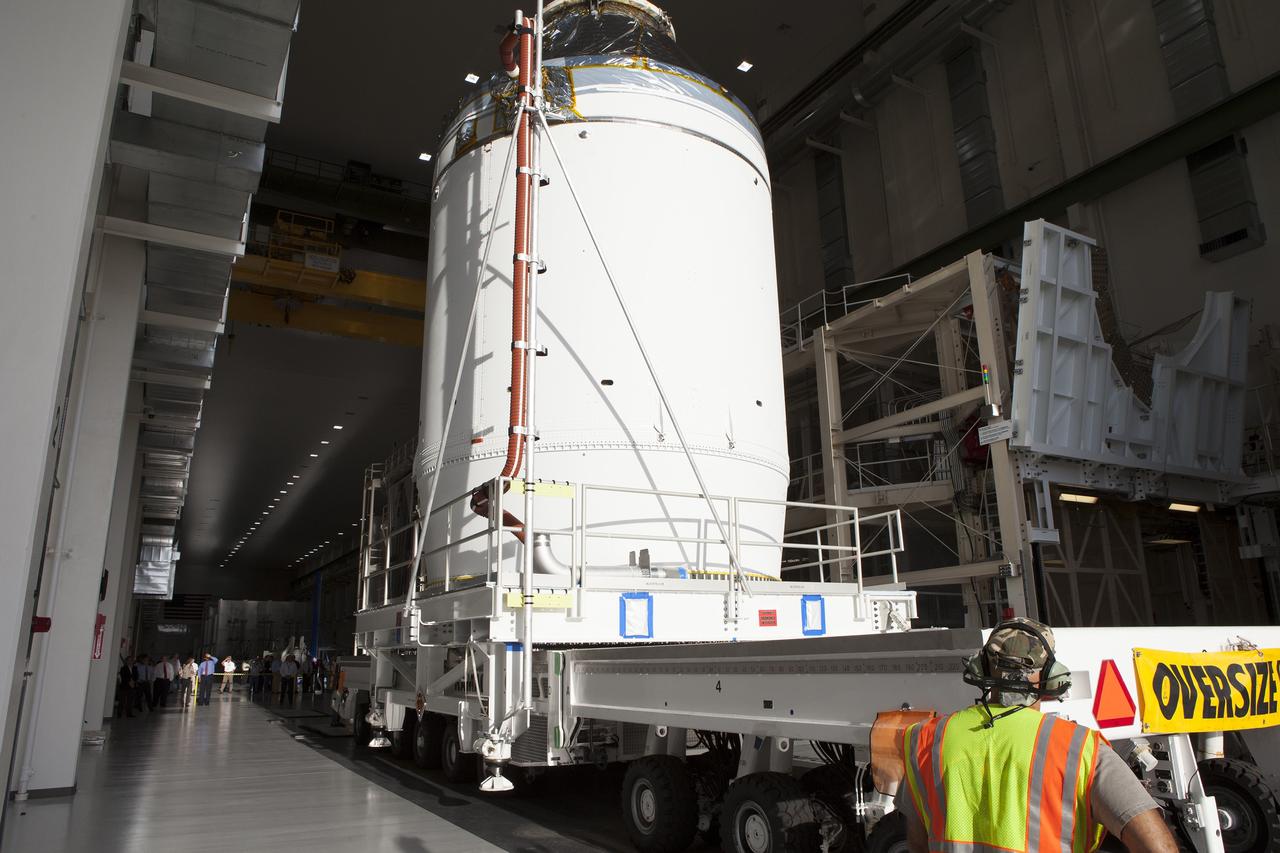

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is moved slowly out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay door at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
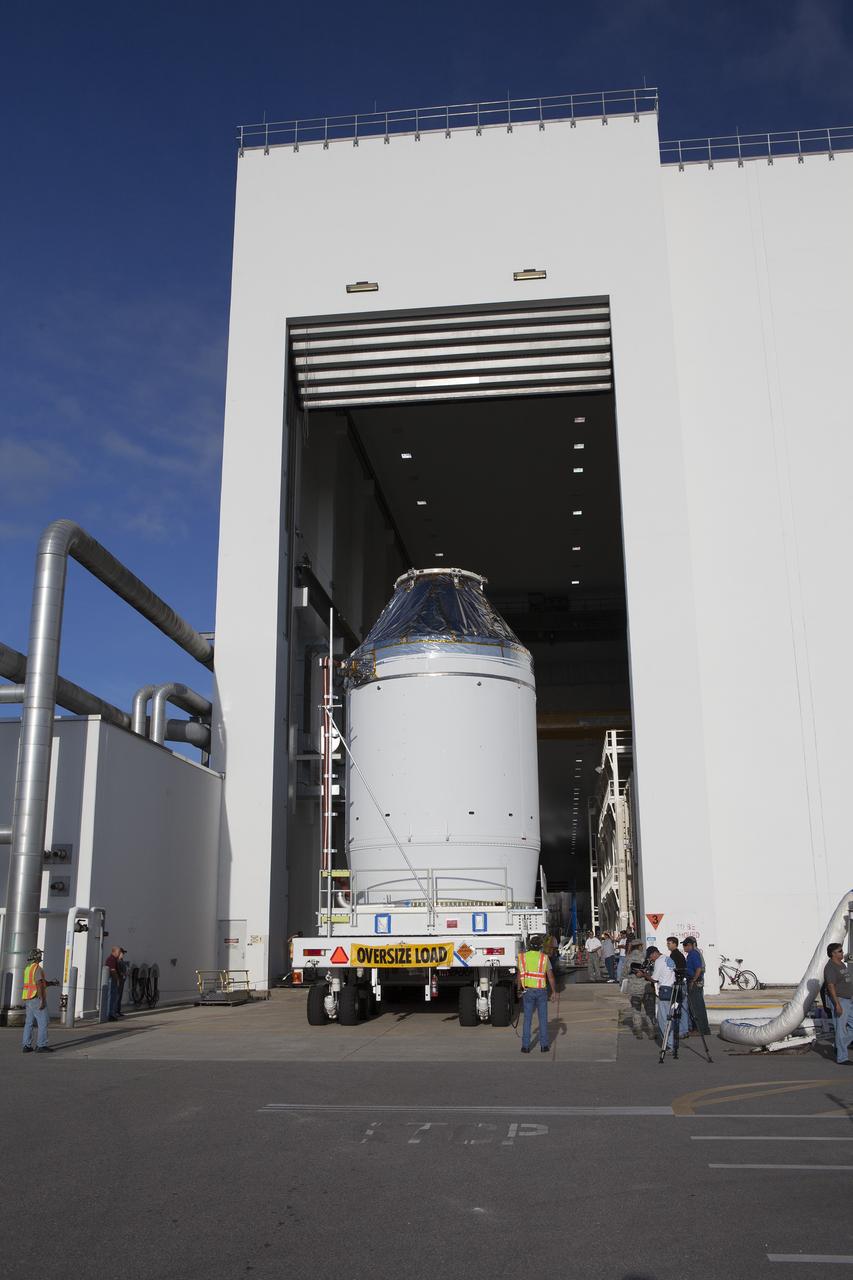

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is slowly transported through the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay door at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
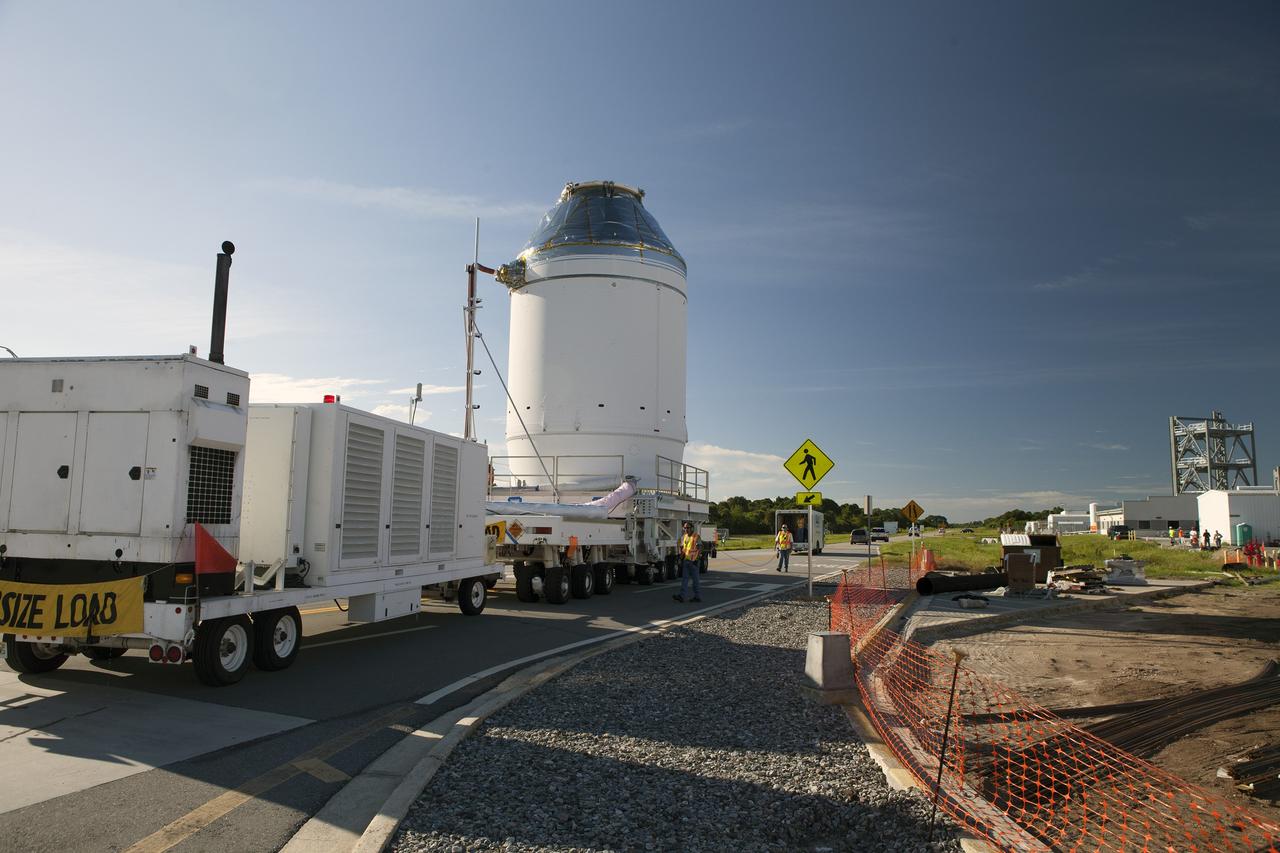

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, has moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 is being transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
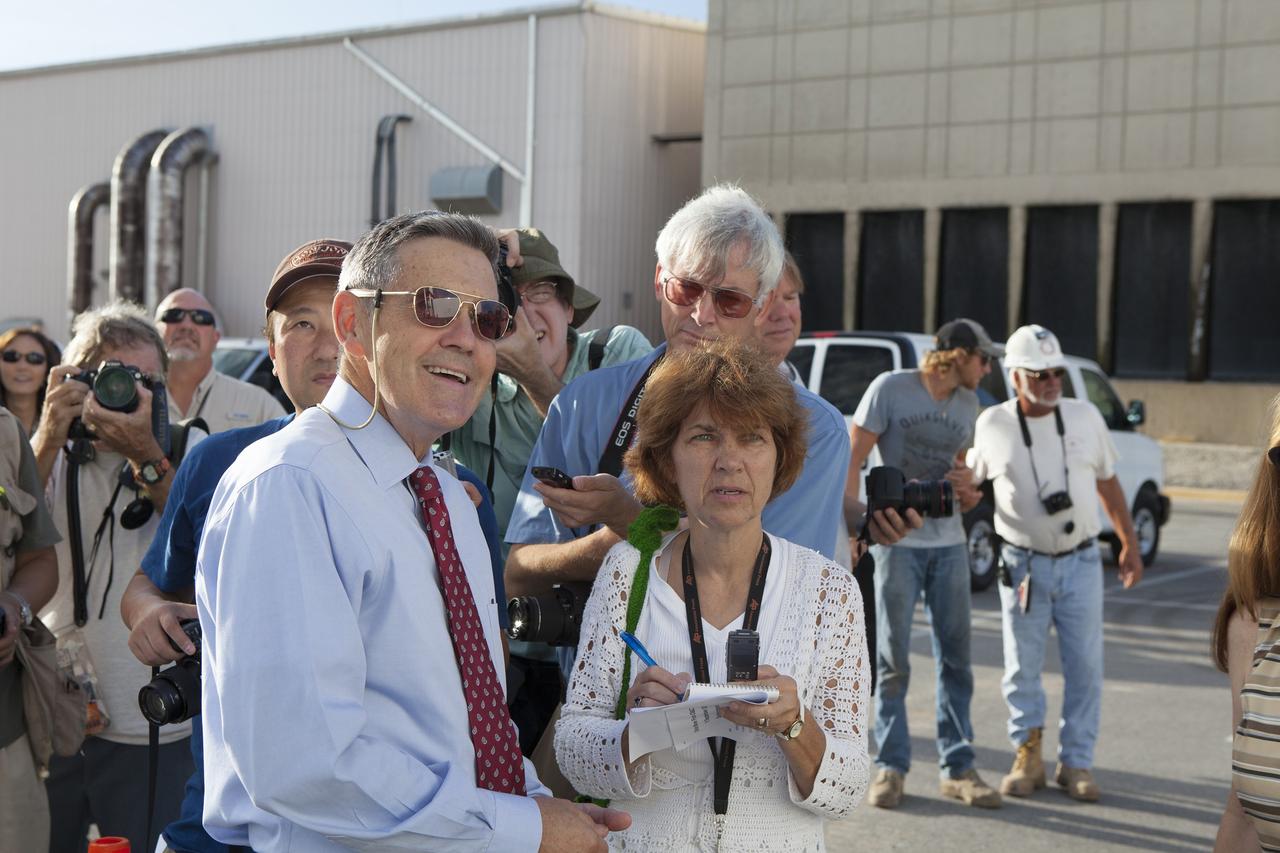

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, at left, watches with reporters and photographers as the Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, moves out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
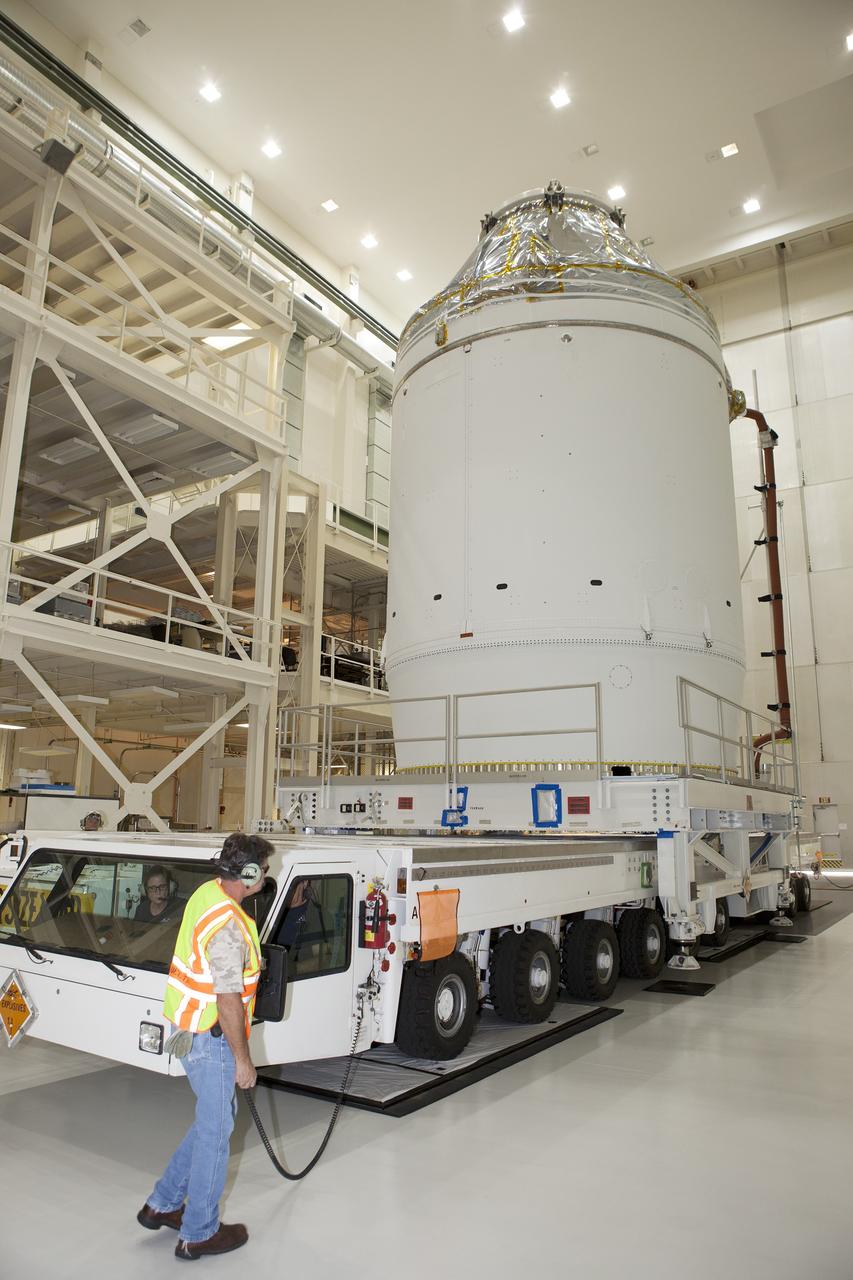

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is being prepared for its move out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The high bay door opens as the Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is moved slowly out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
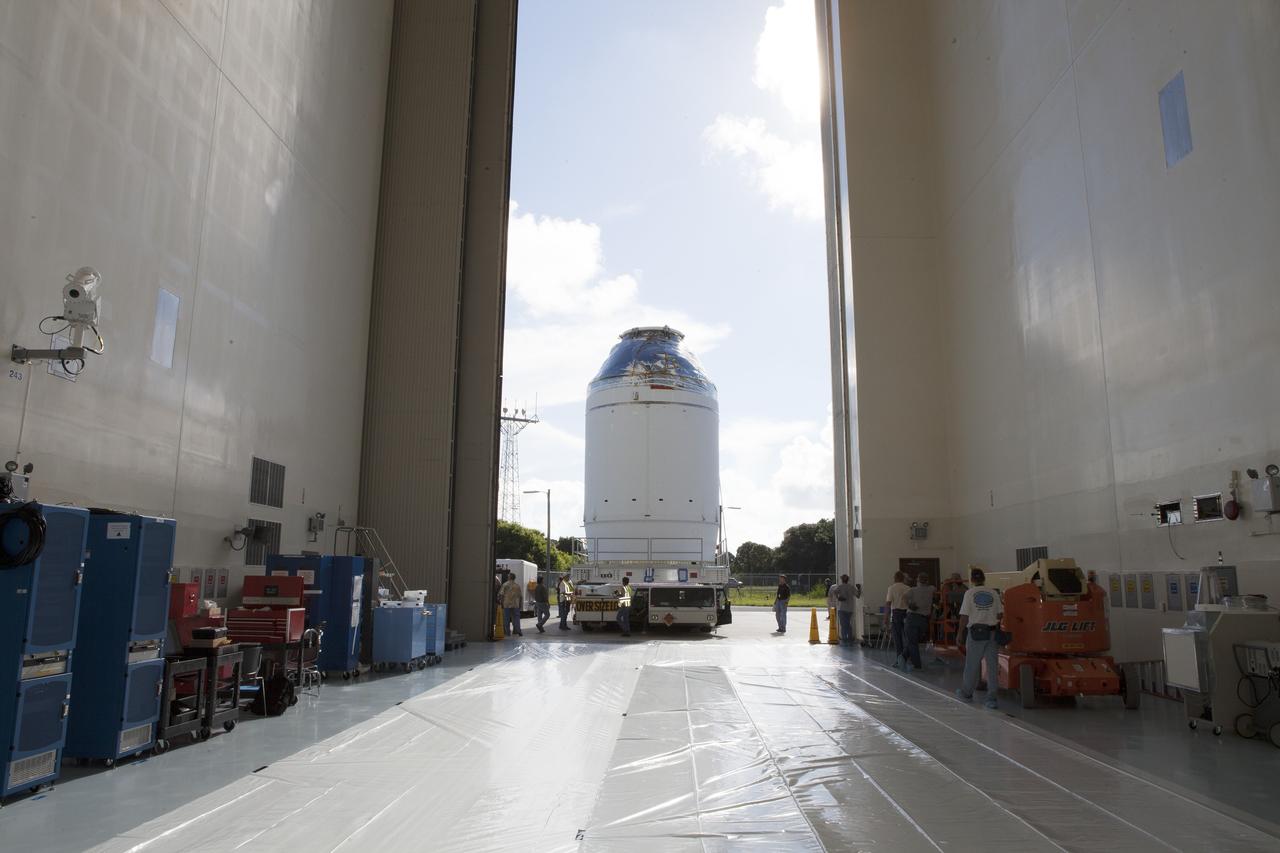

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is transported into the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
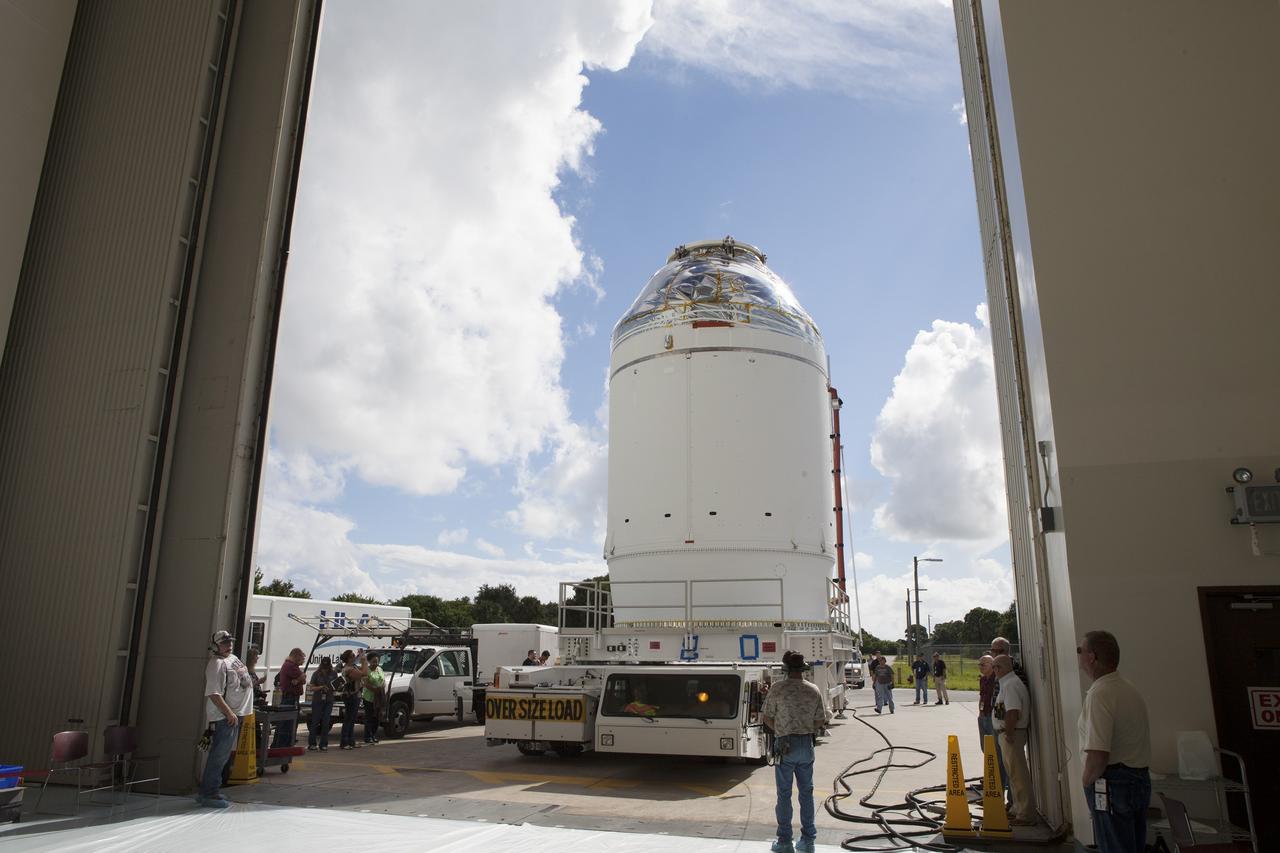

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is transported into the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
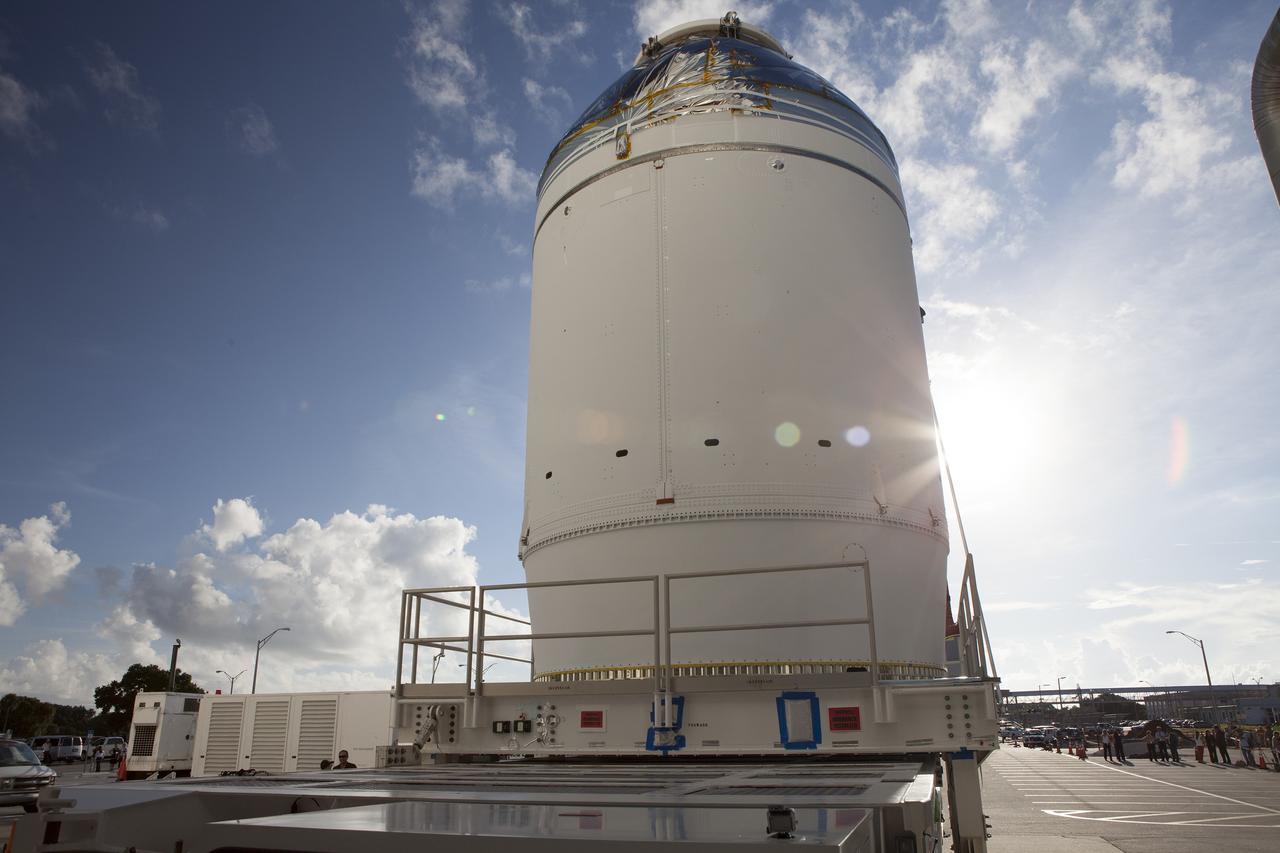

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, has moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
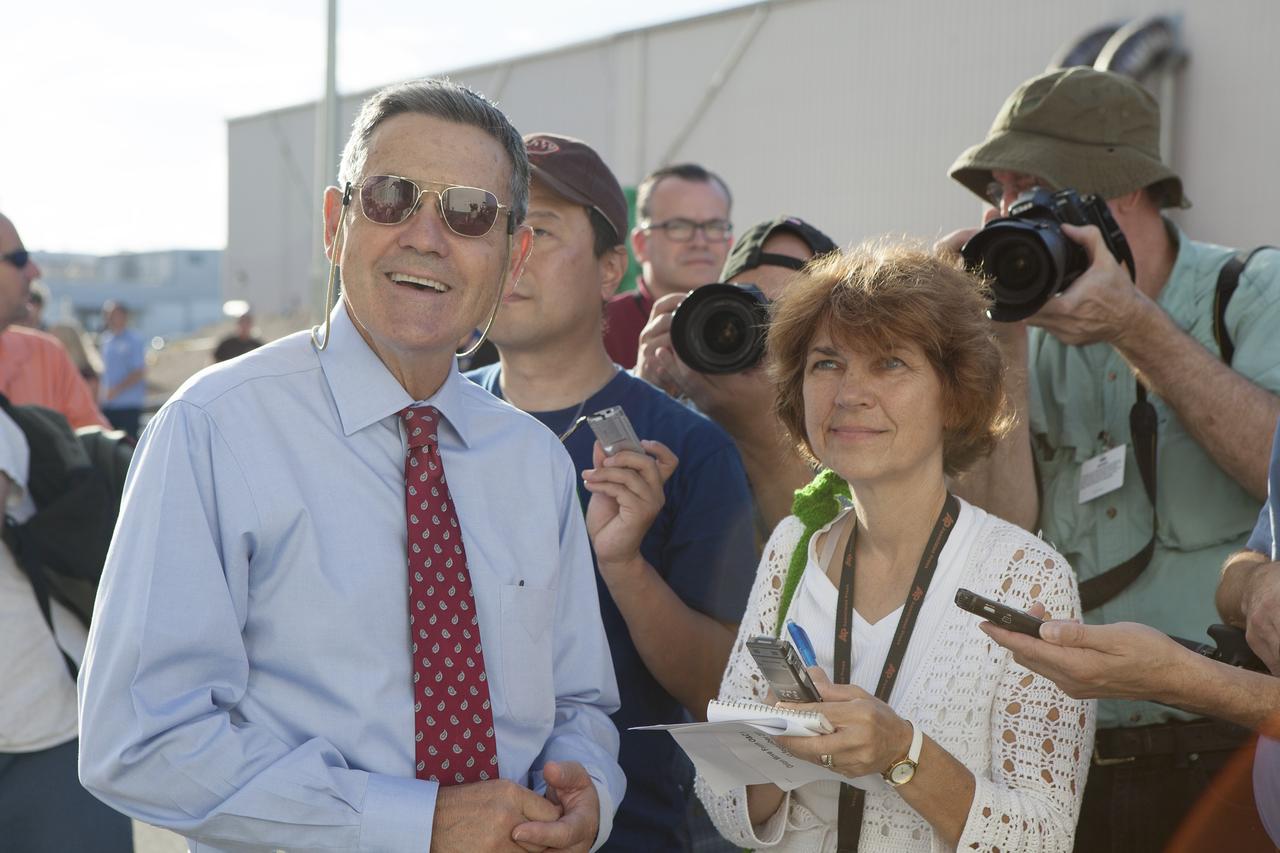

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana, at left, watches with reporters and photographers as the Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, moves out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is being transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
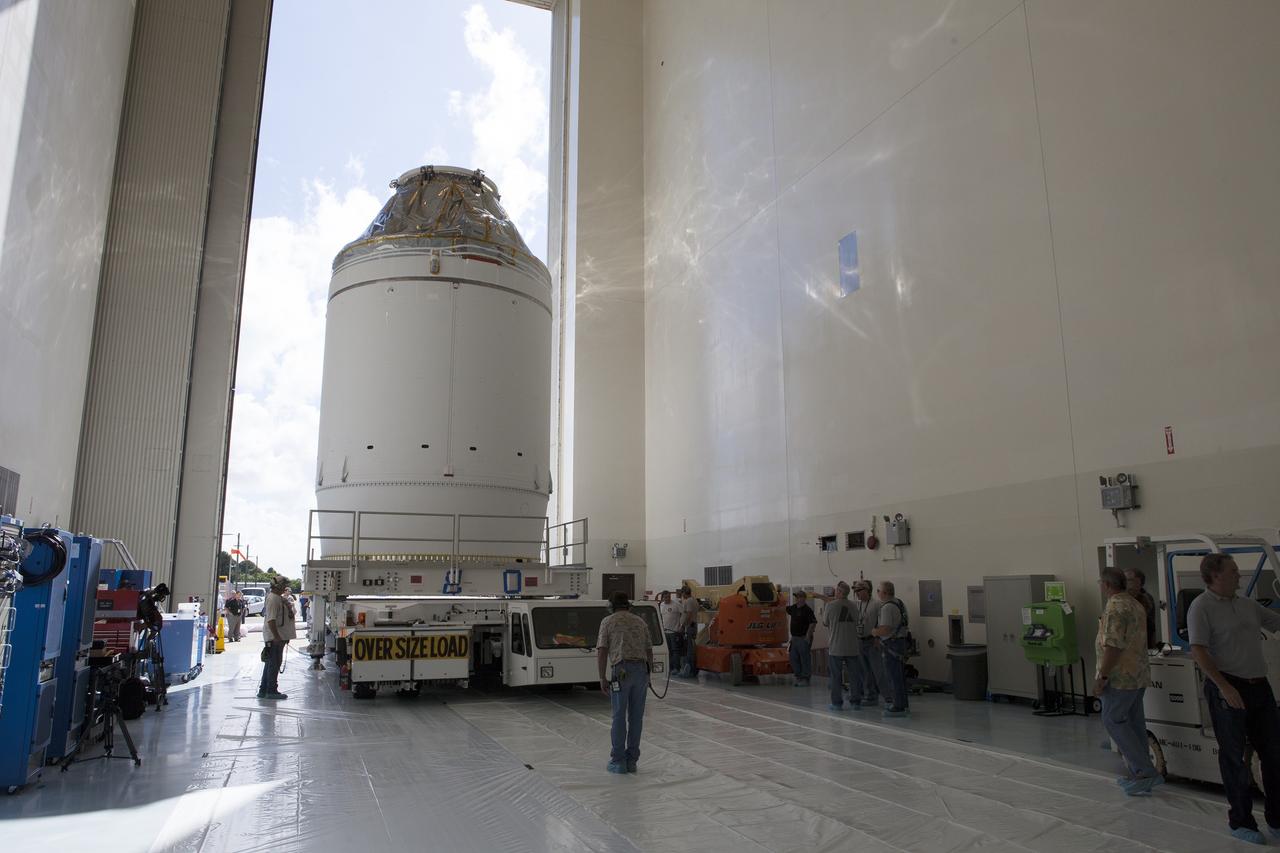

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is transported into the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
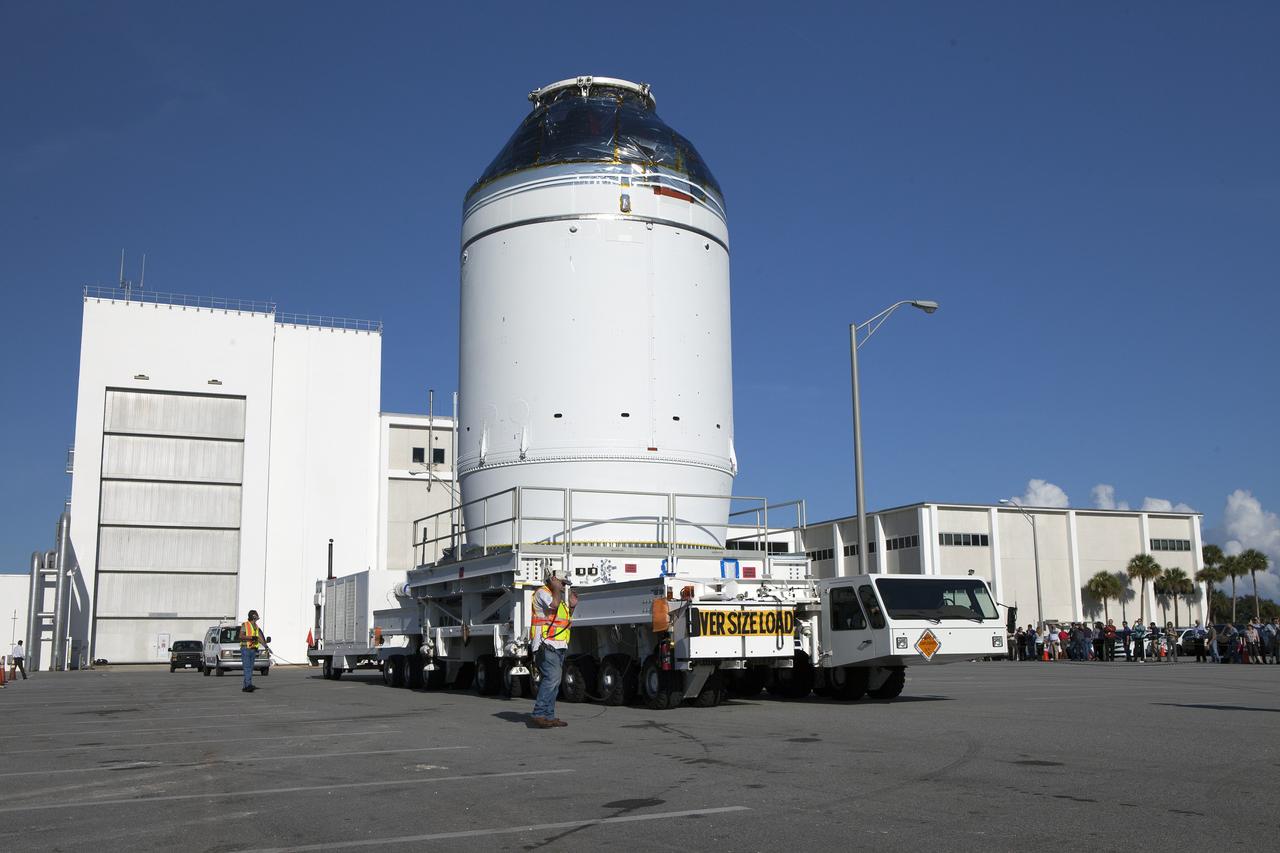

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, has moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
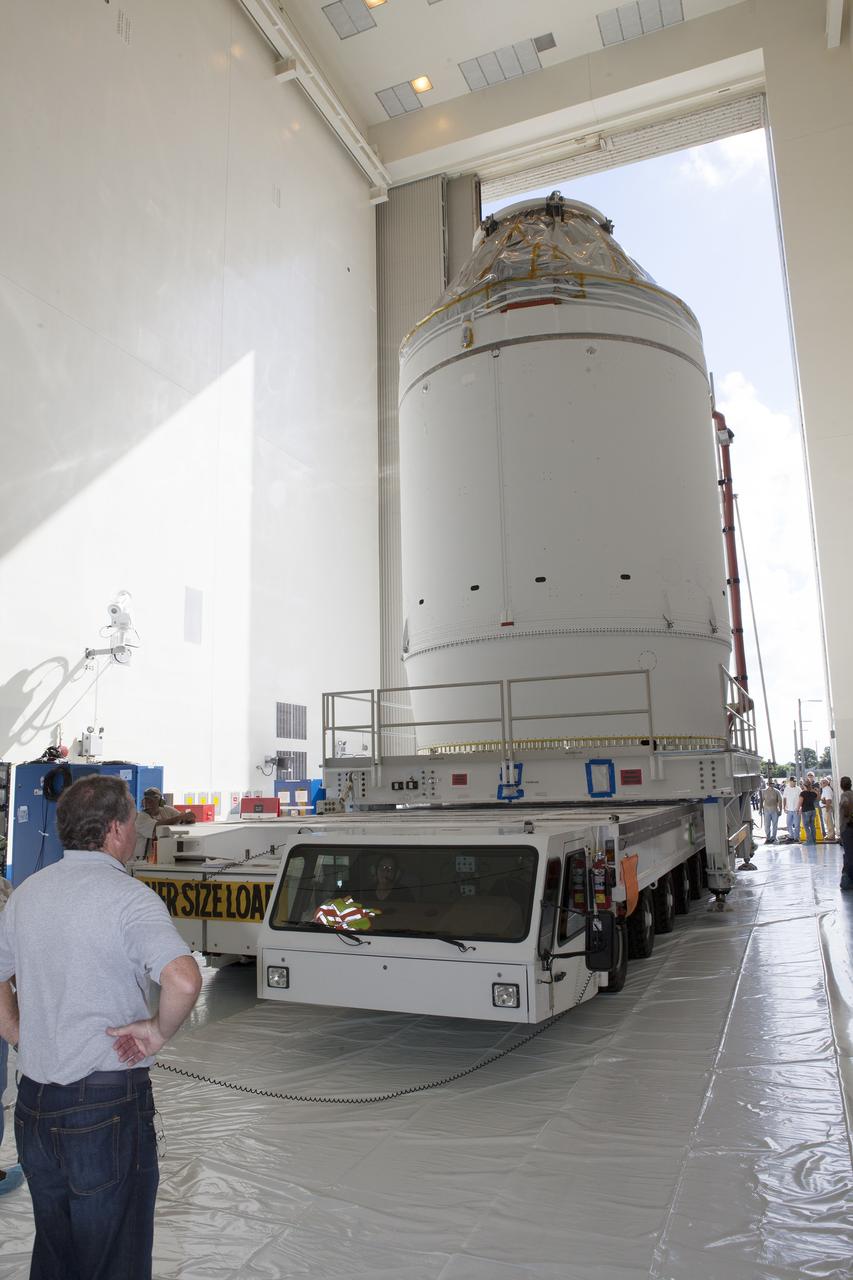

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is transported into the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
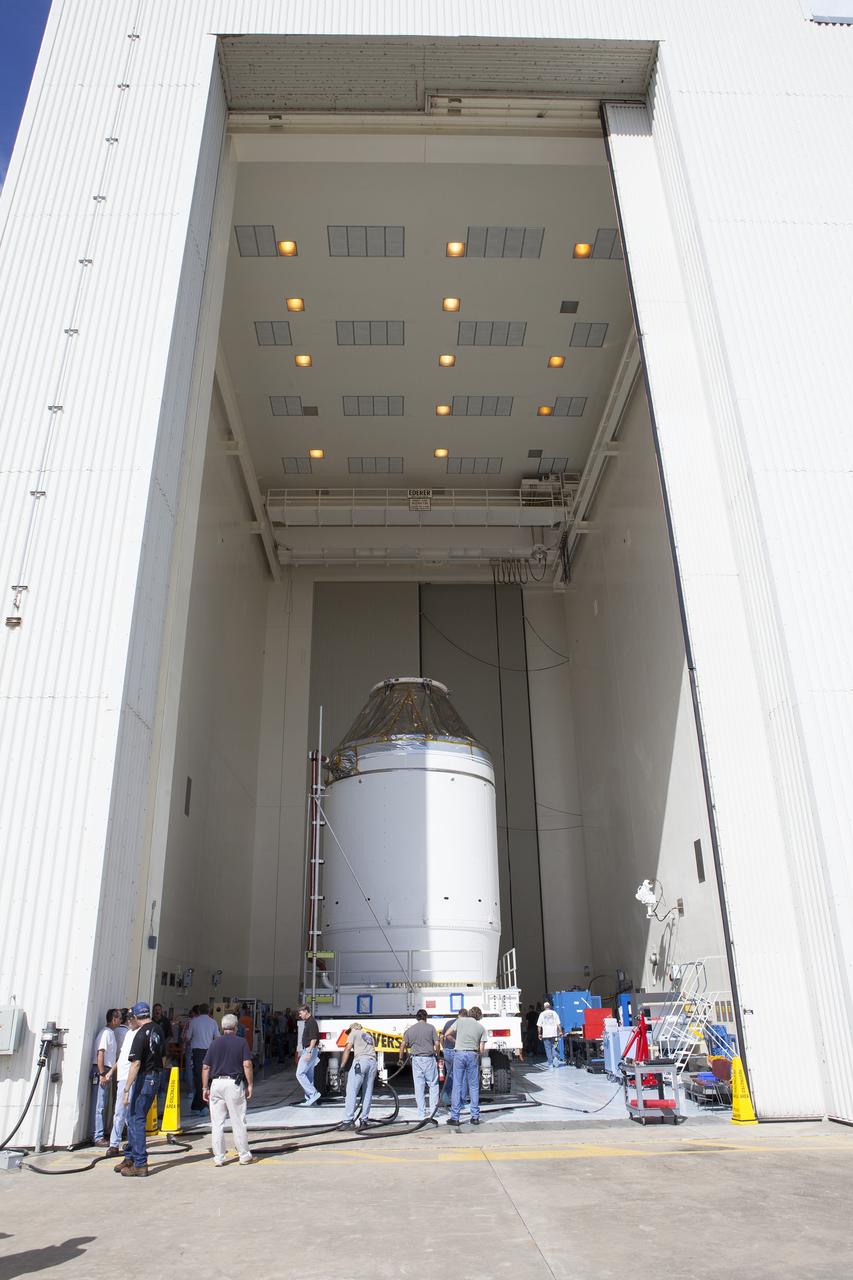

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Technicians assist as the Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is moved into the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
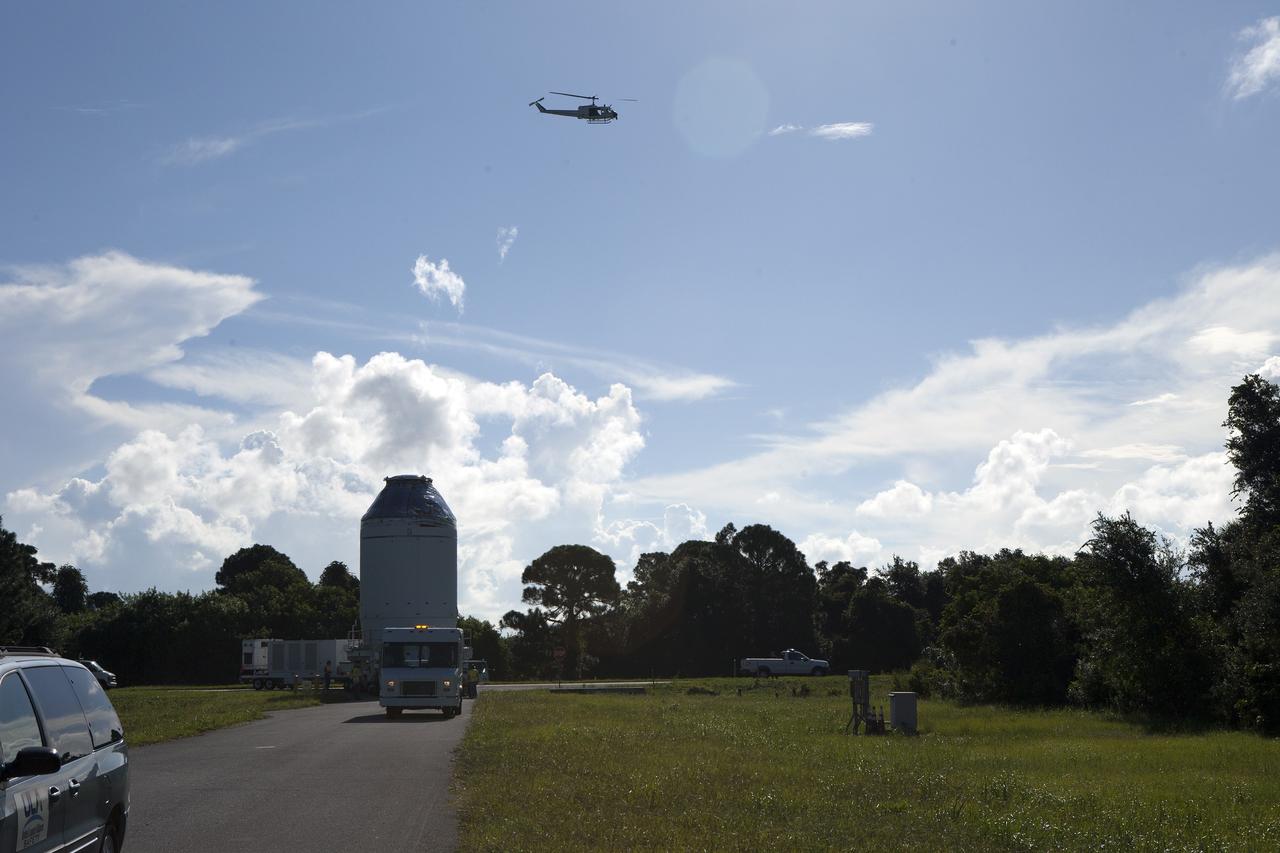

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A NASA helicopter flies overhead as the Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
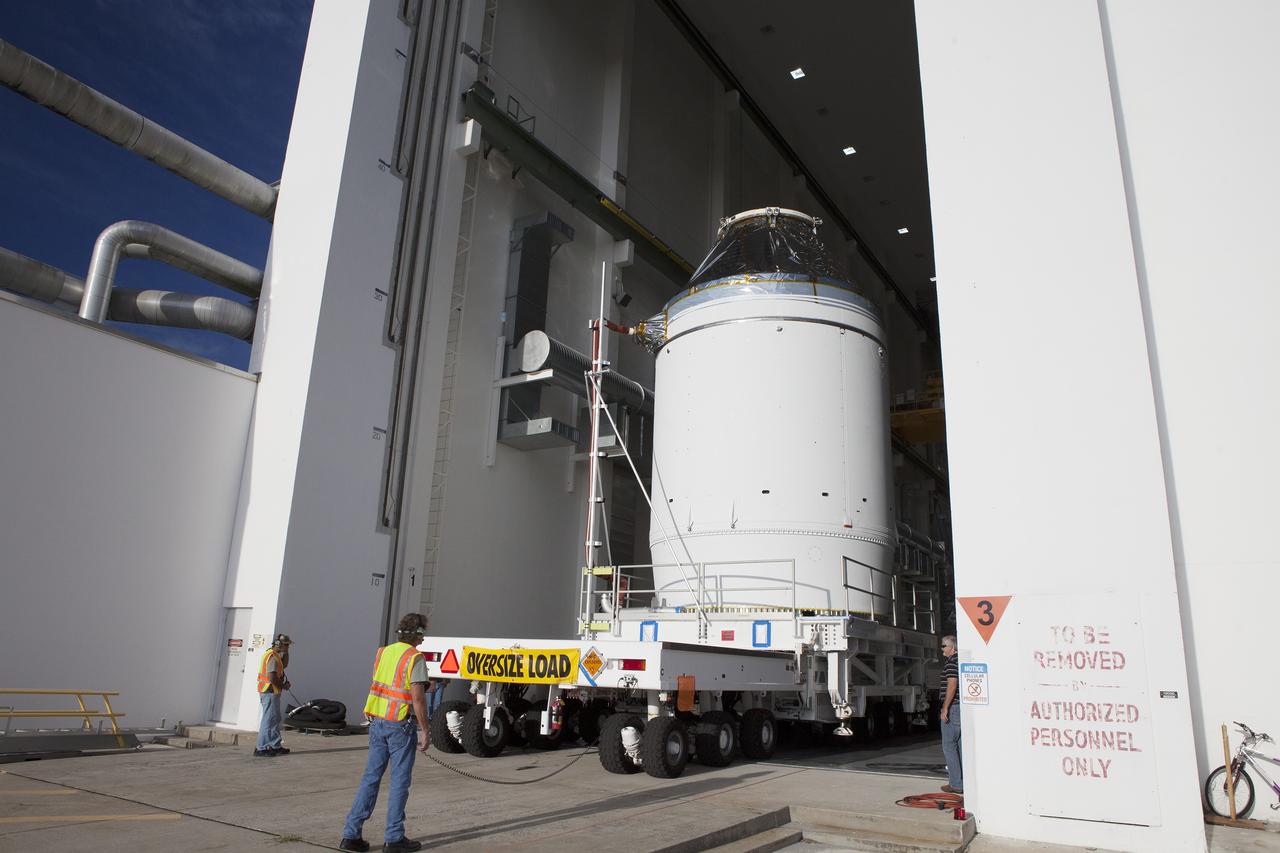

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is moved slowly out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay door at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
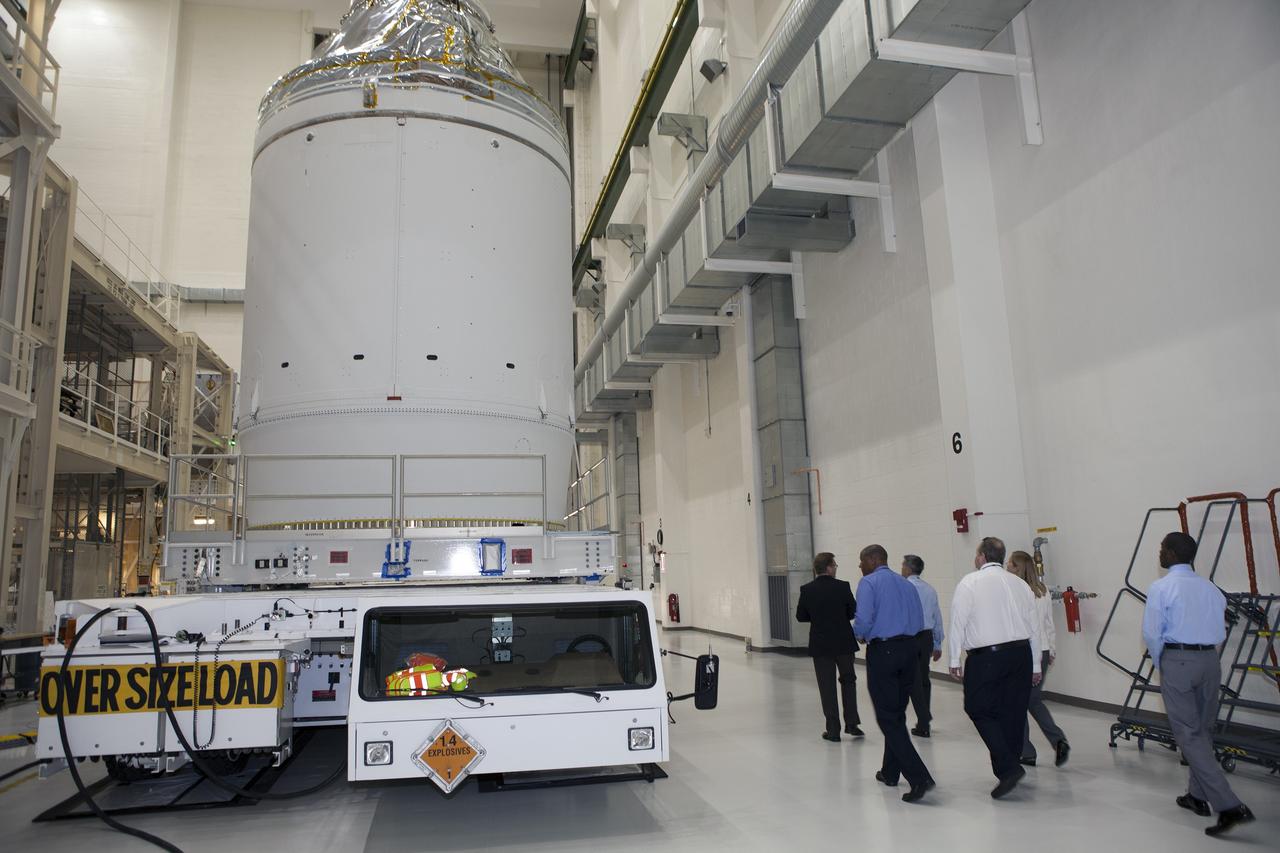

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is being prepared for its move out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
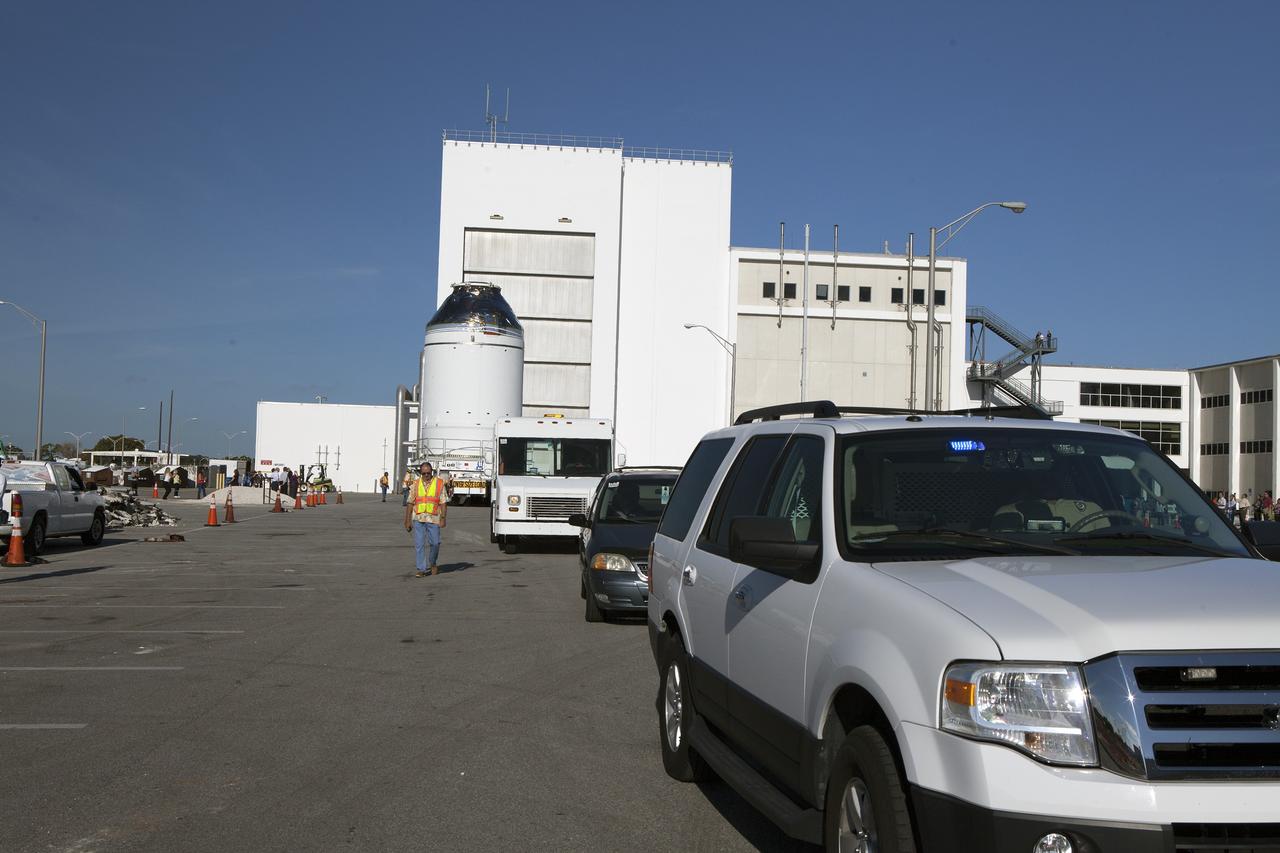

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, has moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. A convoy leads the way as the spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 begins its trek to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is being prepared for its move out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At far left is Kennedy Center Director Bob Cabana. To Cabana's left is Kennedy Deputy Director Janet Petro, and at far right is Kennedy Associate Director Kelvin Manning. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
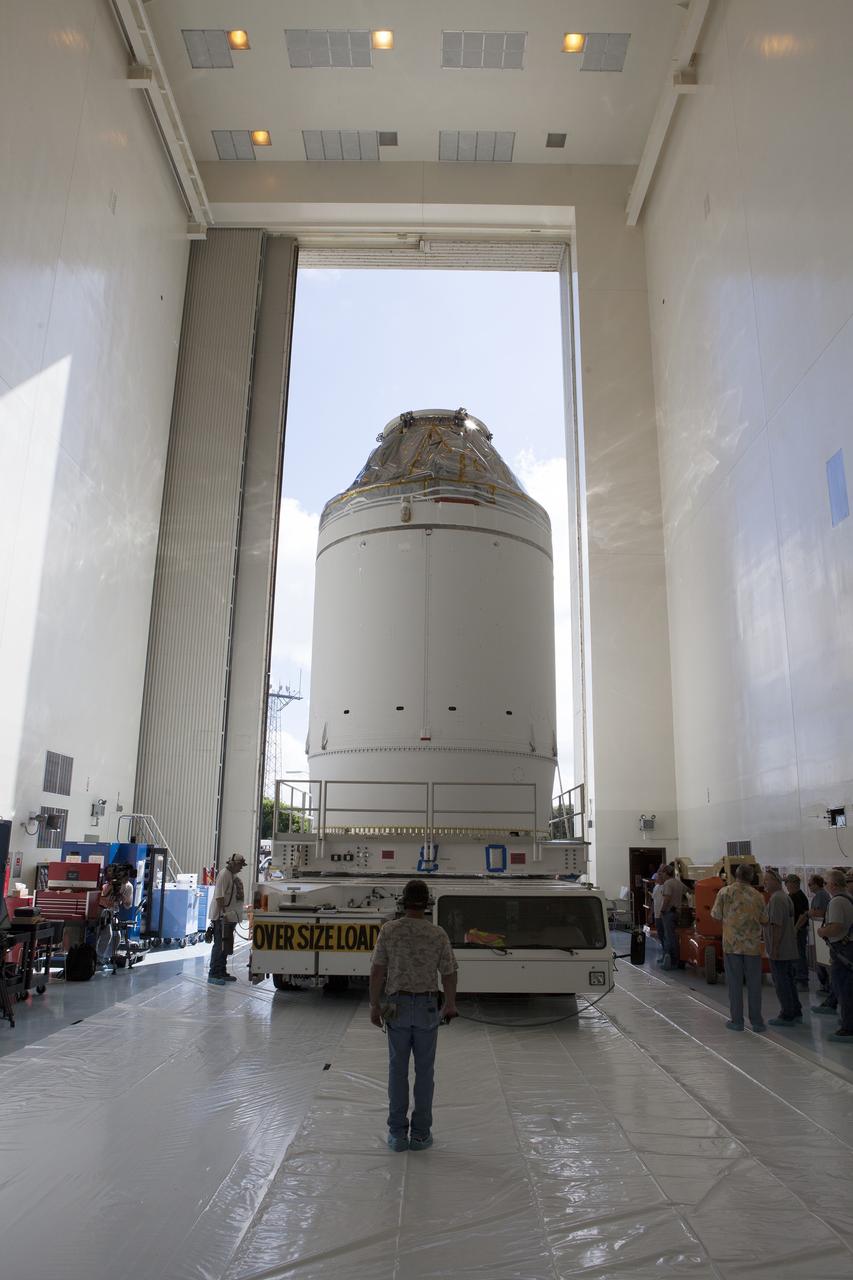

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is transported into the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
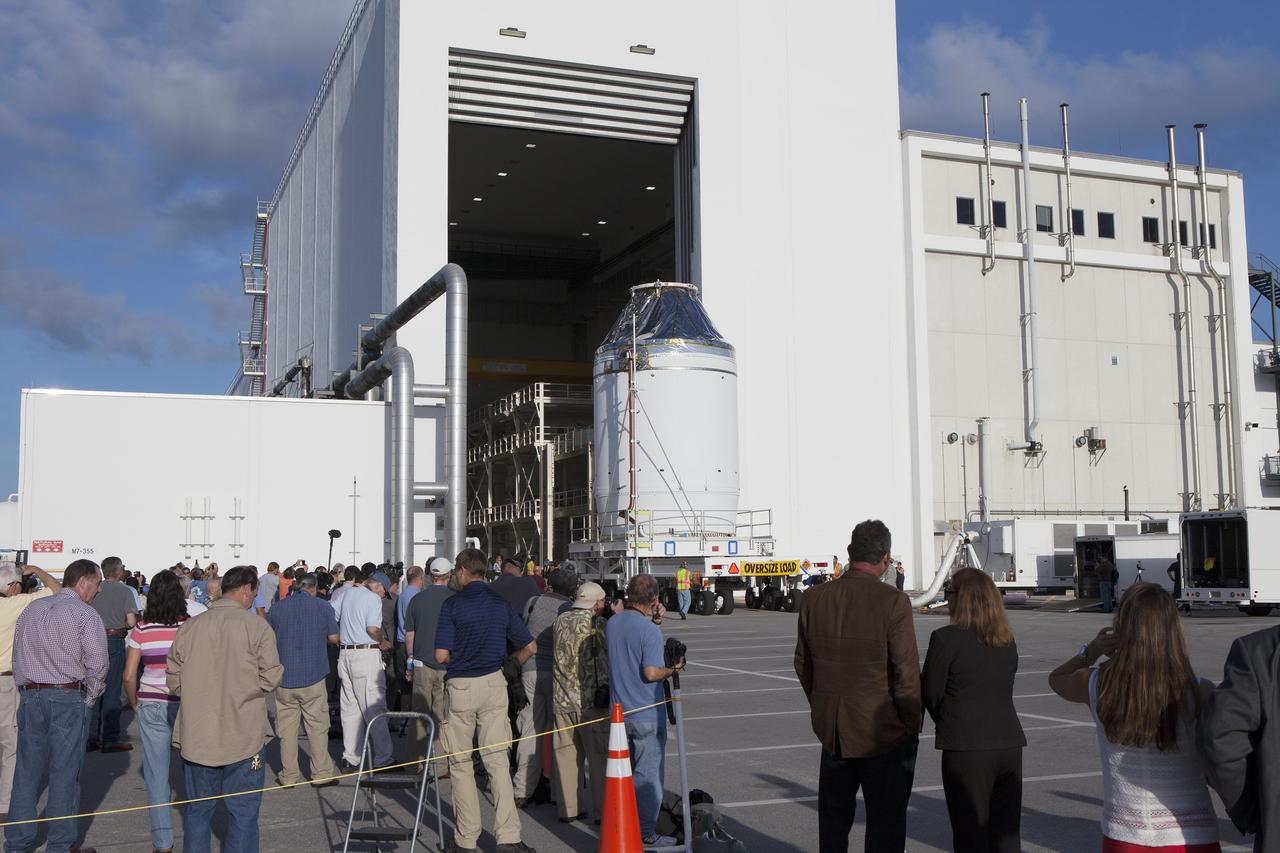

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Reporters and photographers watch as the Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, moves out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
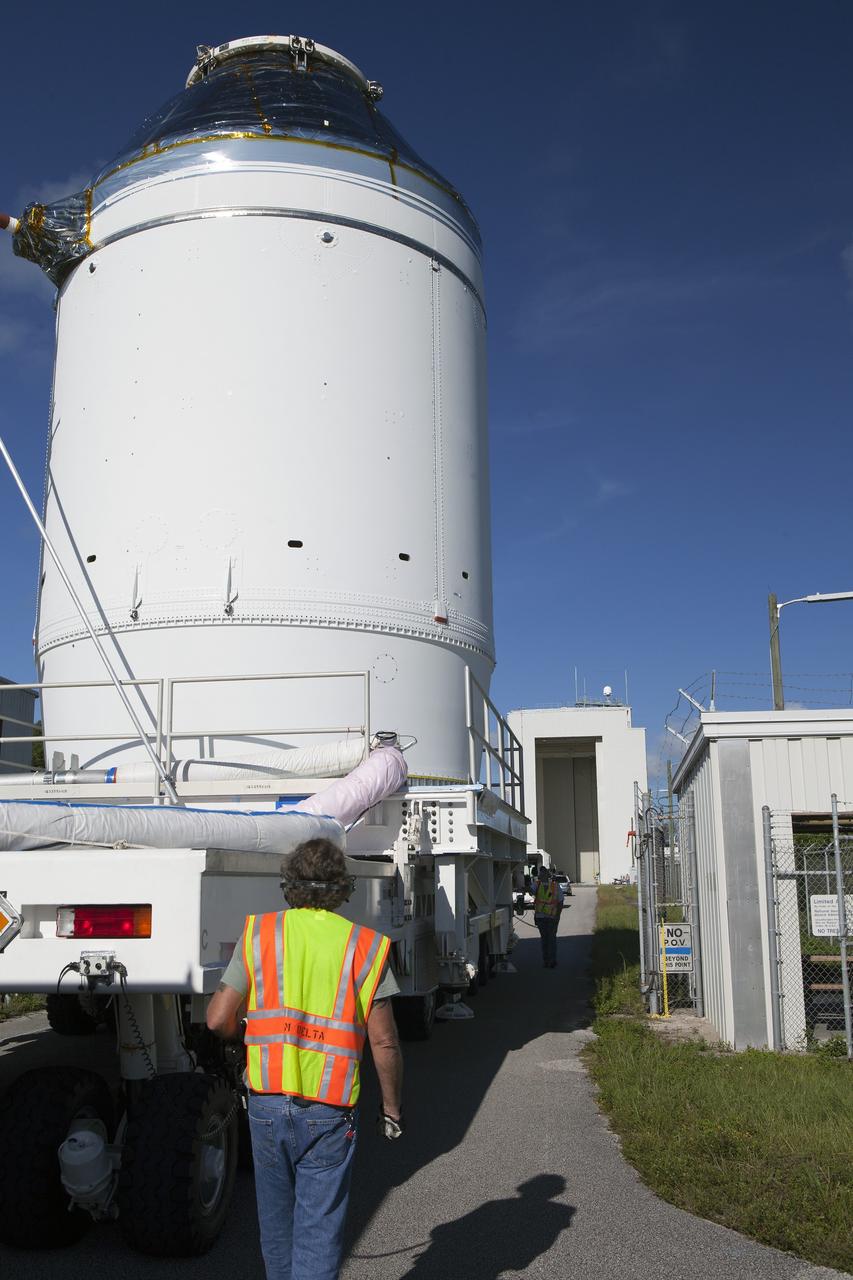

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is being transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
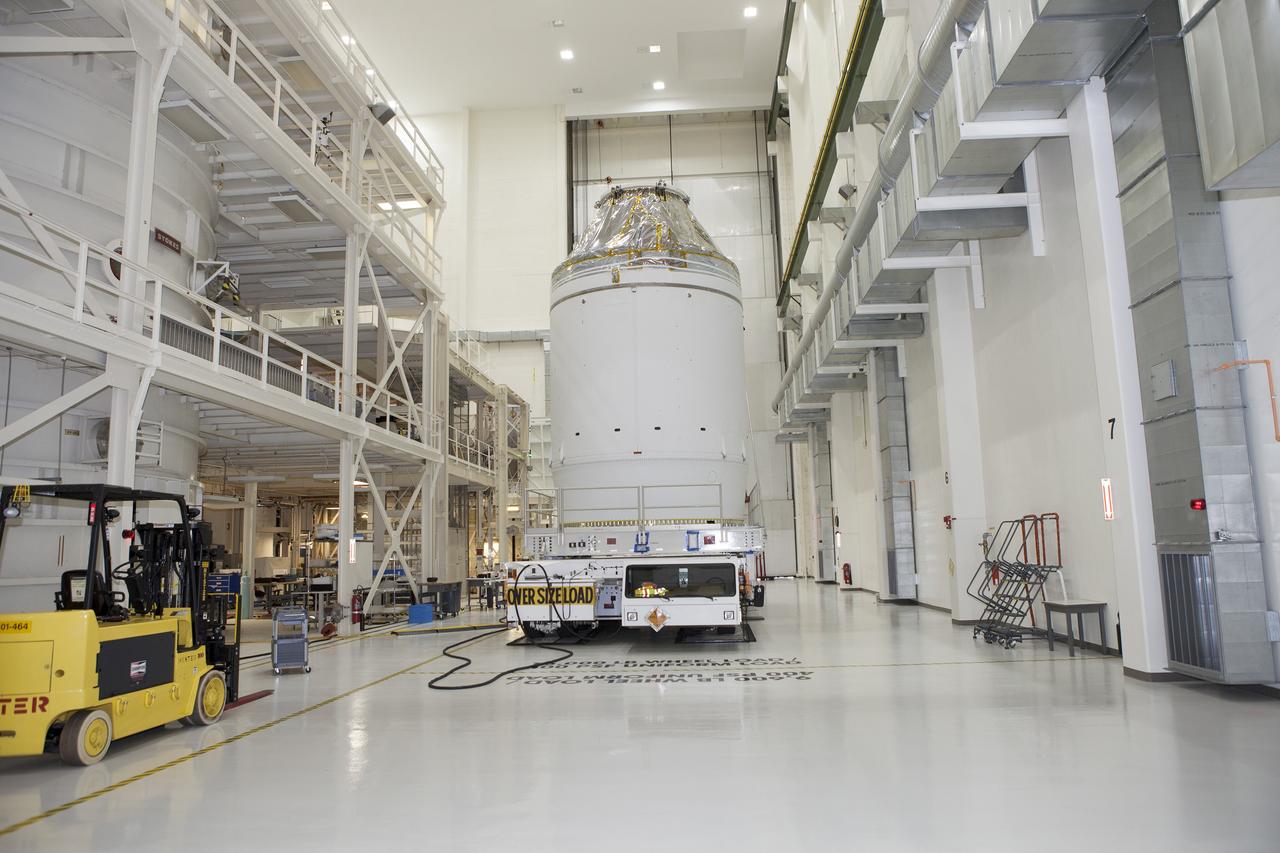

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is being prepared for its move out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
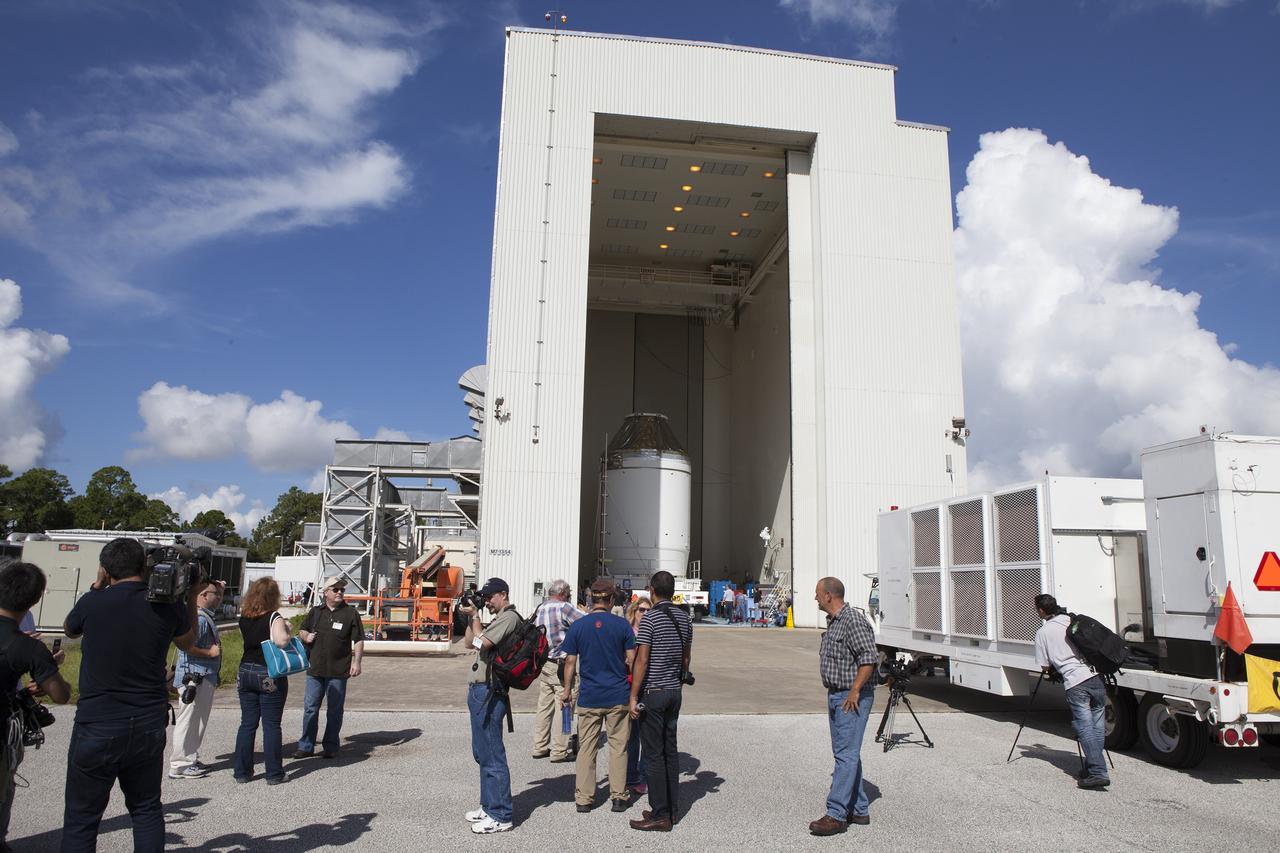

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Reporters and photographers watch as the Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is transported into the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
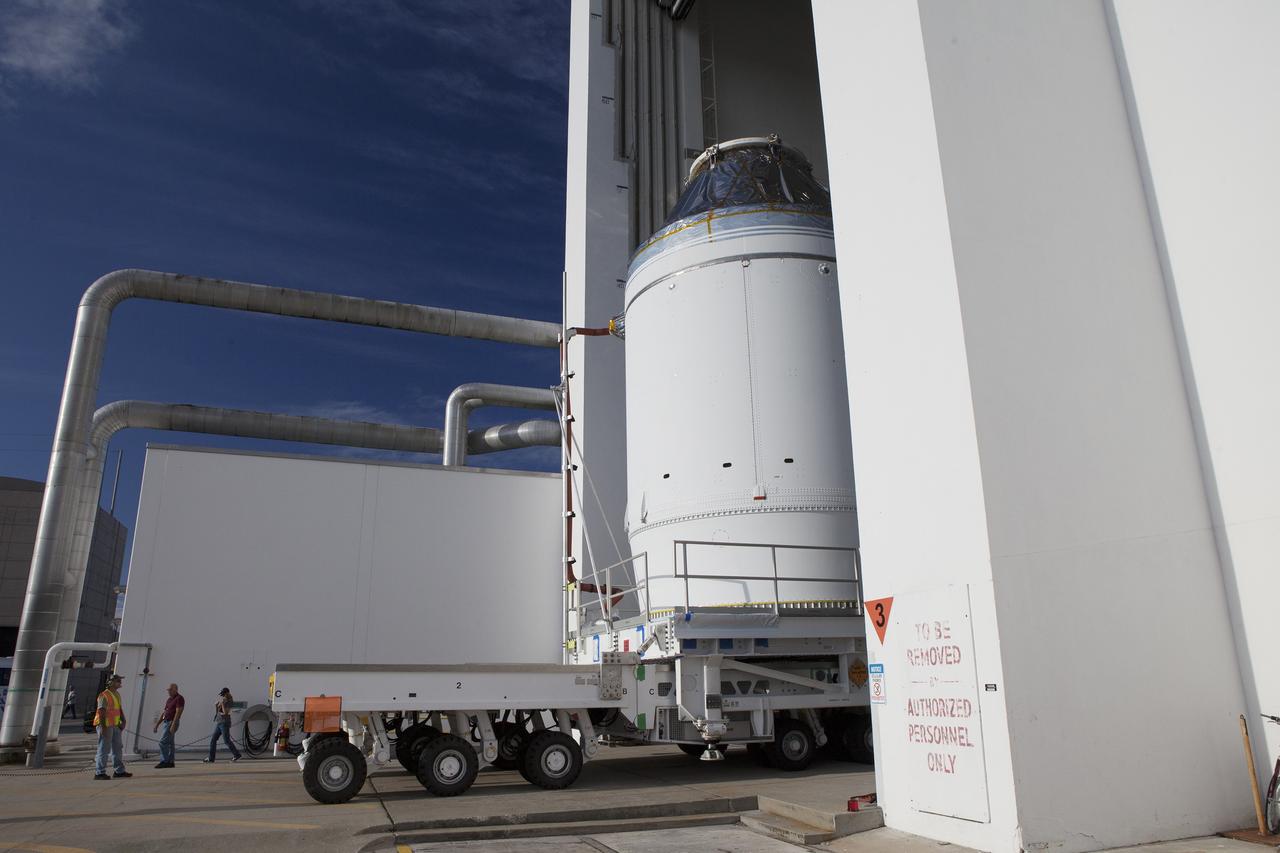

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is slowly transported through the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay door at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
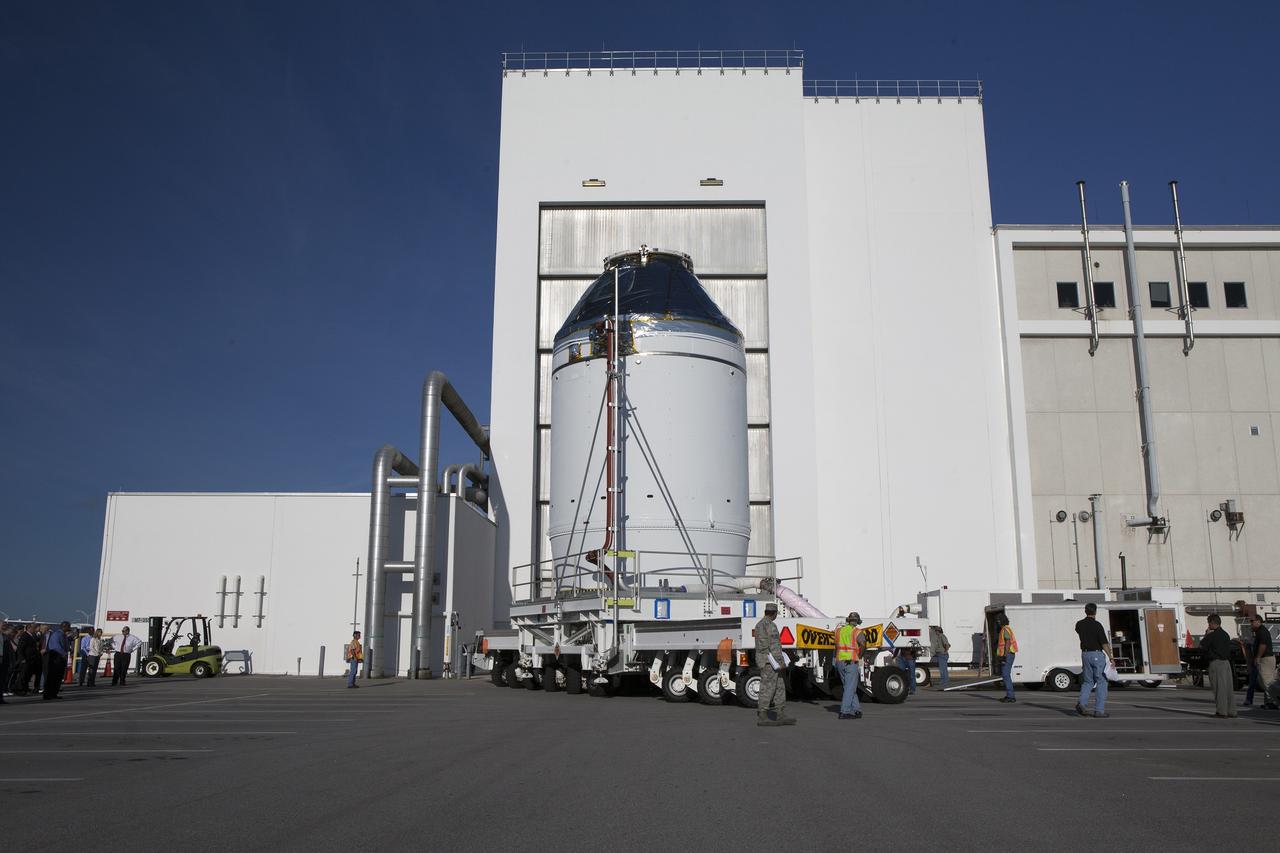

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, has moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
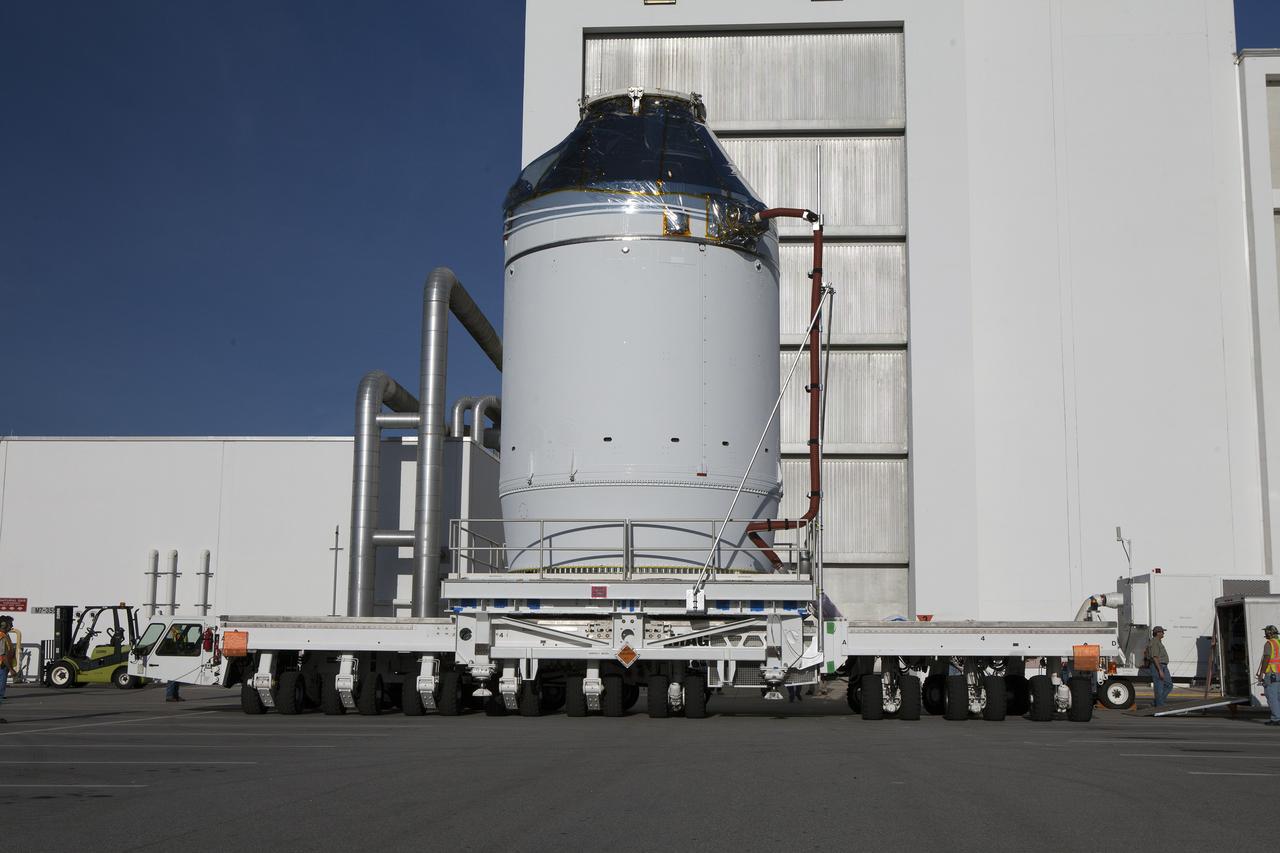

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, has moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 will be transported to the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight test. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
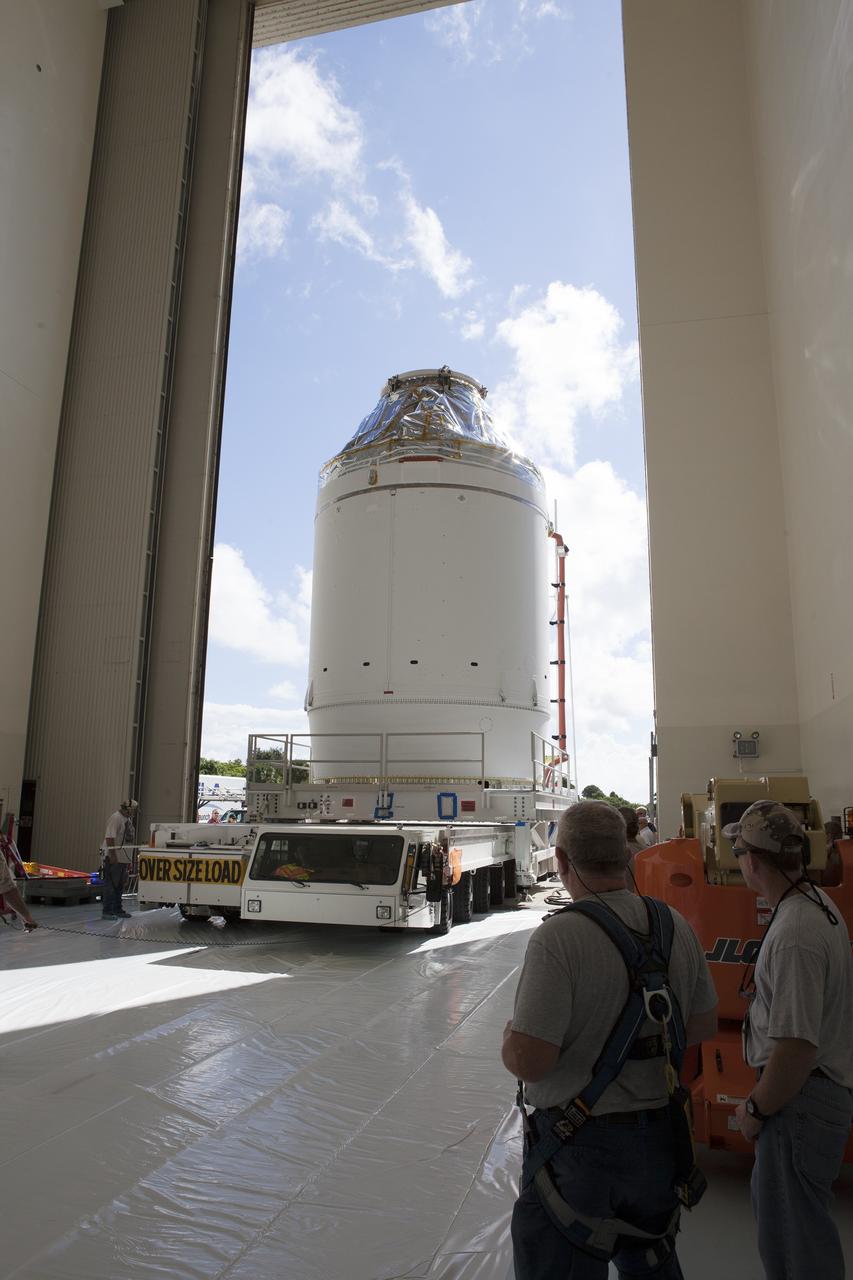

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The Orion crew module, stacked atop its service module, is transported into the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where it will be fueled ahead of its December flight. The spacecraft for Exploration Flight Test-1 was moved out of the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch atop a United Launch Alliance Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Daniel Casper
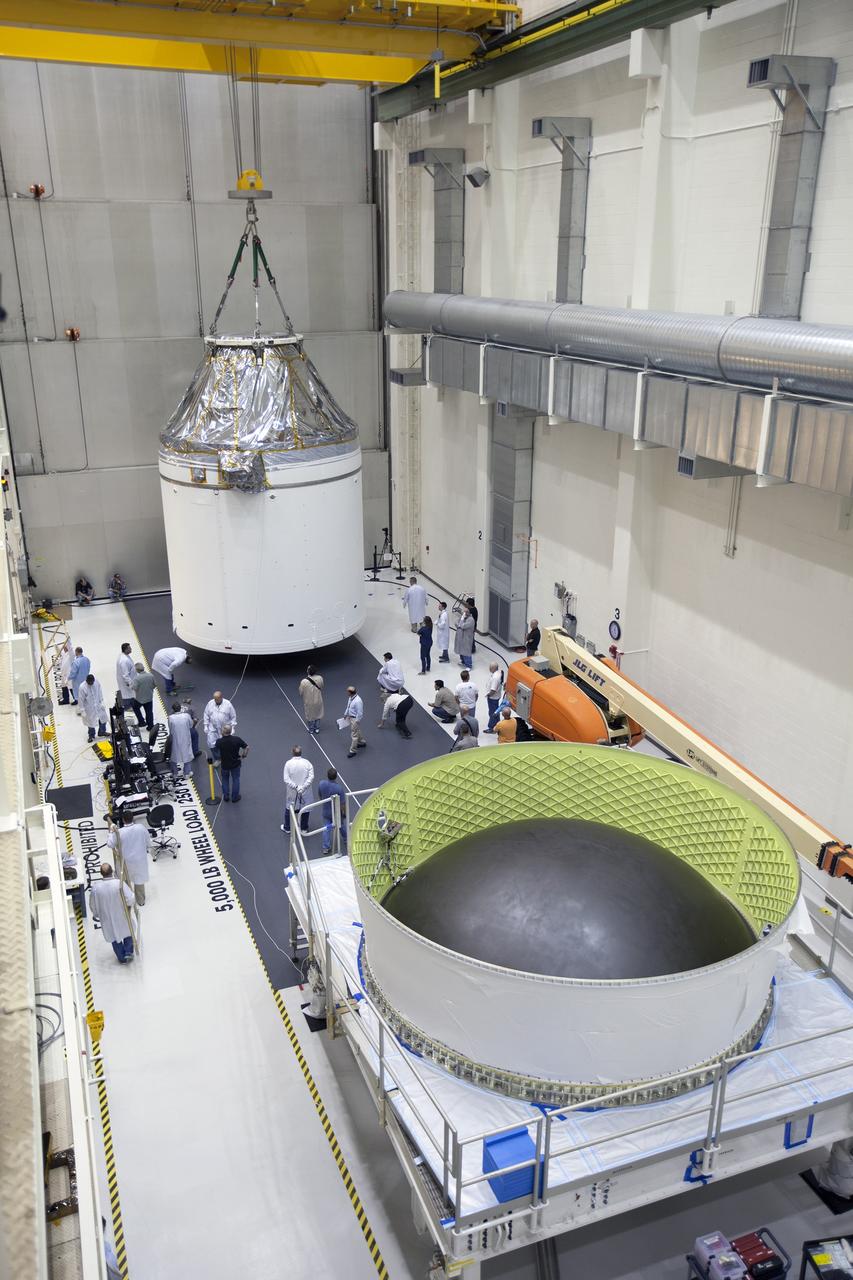

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 was lifted by crane out of the test cell and is being moved along the center aisle. Orion will be transferred to a mating device. A protective covering surrounds the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
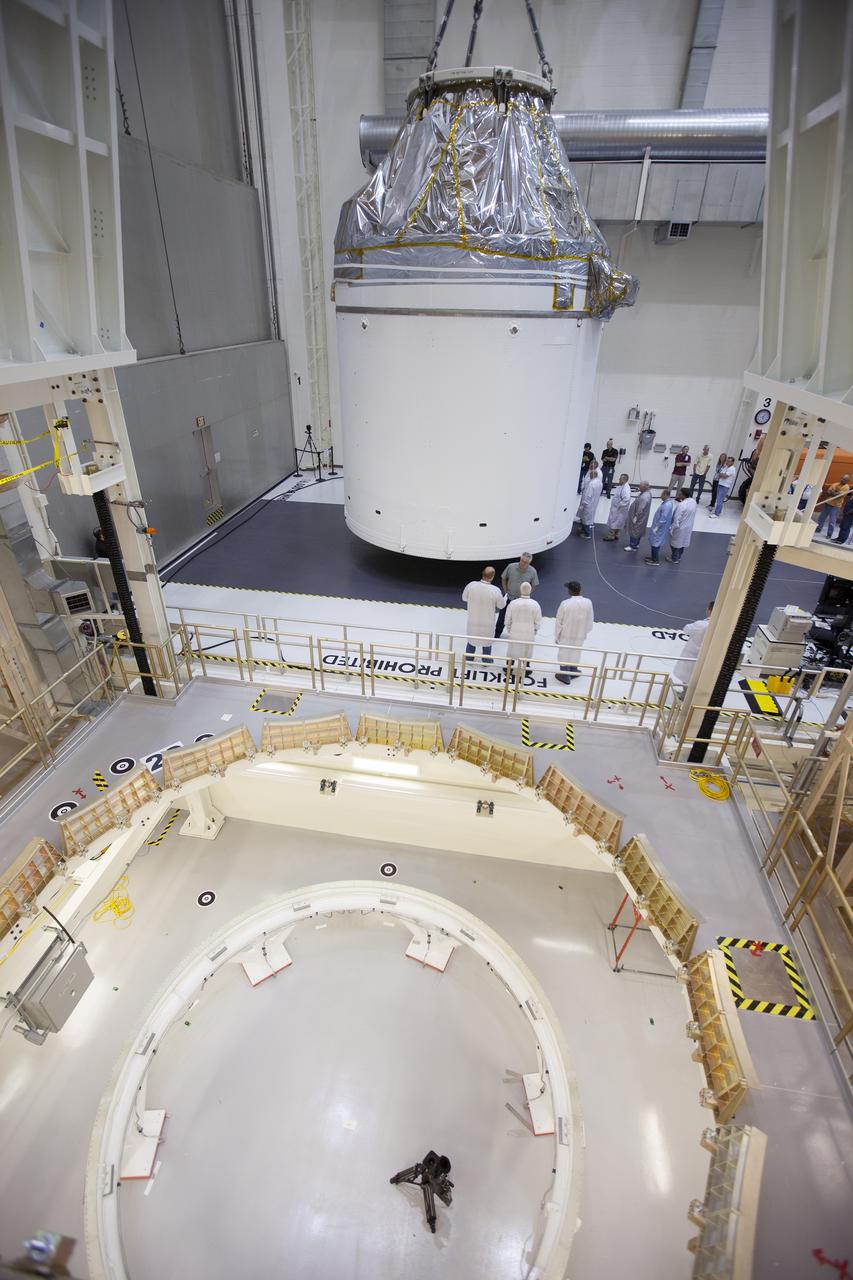

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 was lifted by crane out of the test cell and is being moved along the center aisle. Orion will be transferred to a mating device. A protective covering surrounds the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
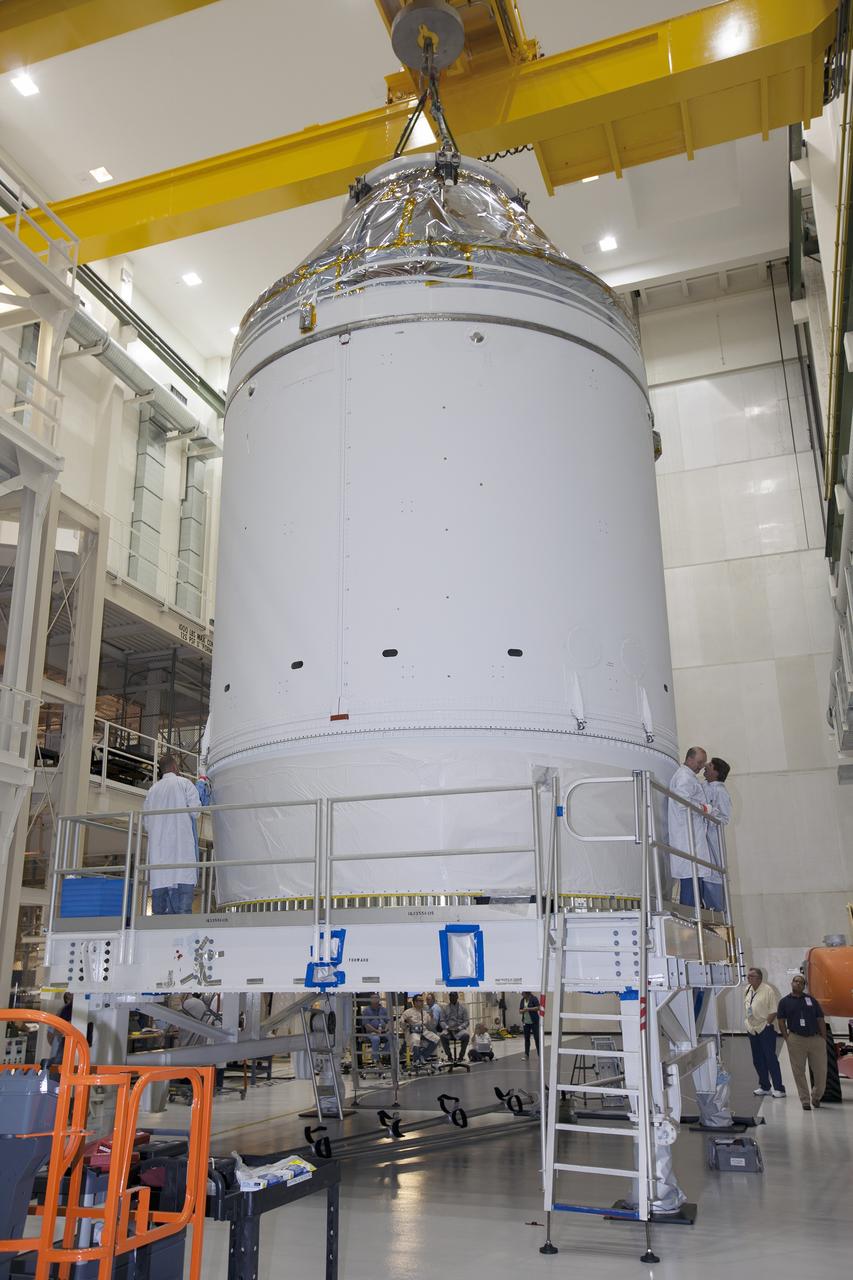

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 was lifted by crane out of the test cell. The stack has been lowered onto the mating device on a stand. A protective covering surrounds the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
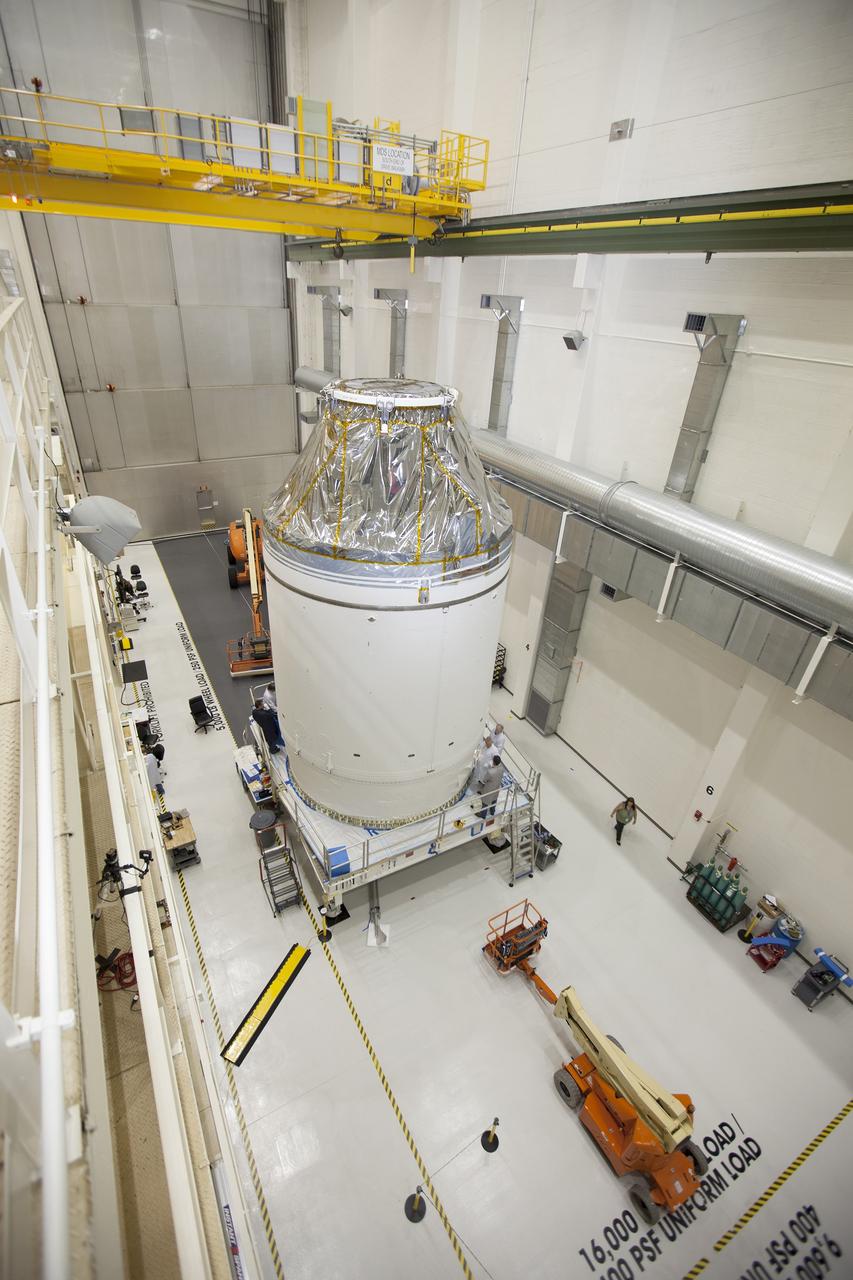

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 was lifted by crane out of the test cell. The stack has been lowered onto the mating device on a stand. Technicians are attaching the stack to the mating device. A protective covering surrounds the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
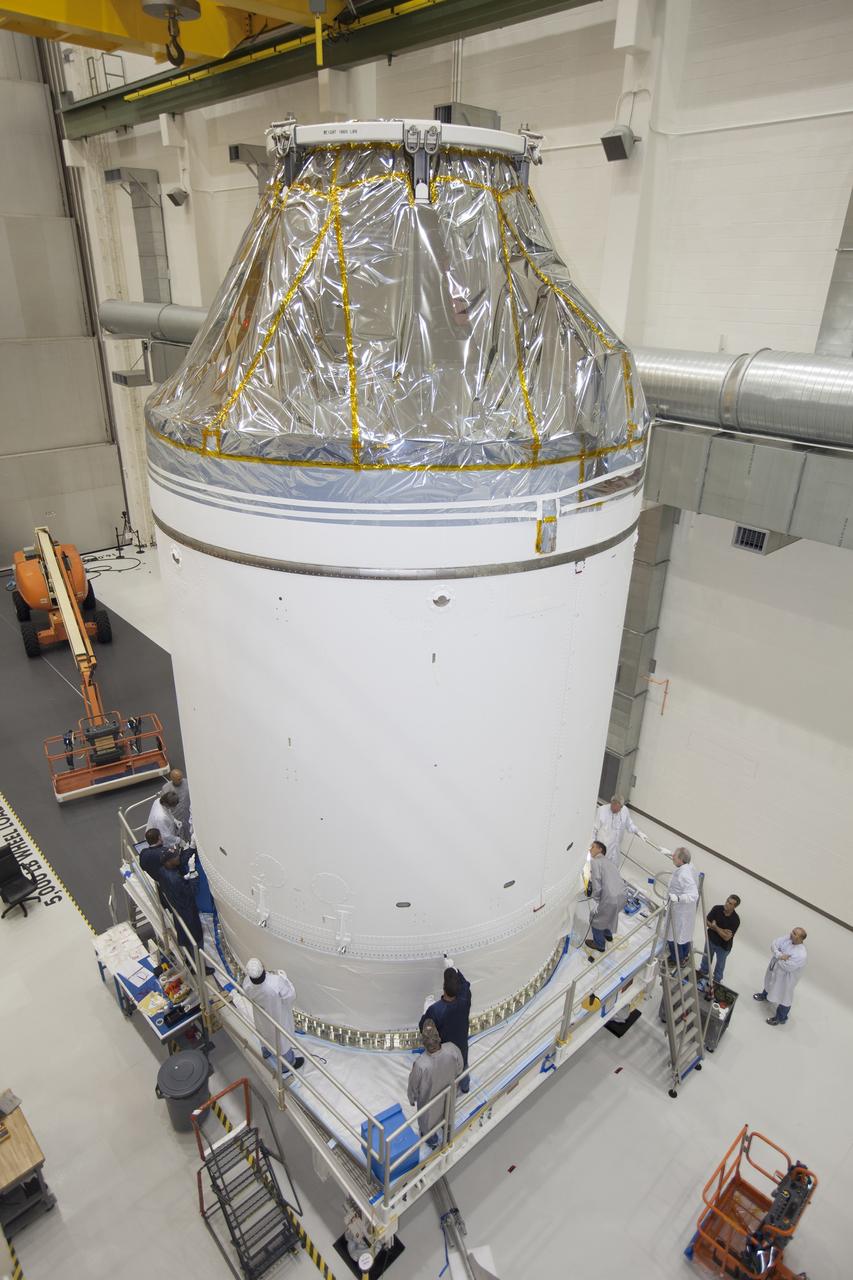

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 was lifted by crane out of the test cell. The stack has been lowered onto the mating device on a stand. Technicians are attaching the stack to the mating device. A protective covering surrounds the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
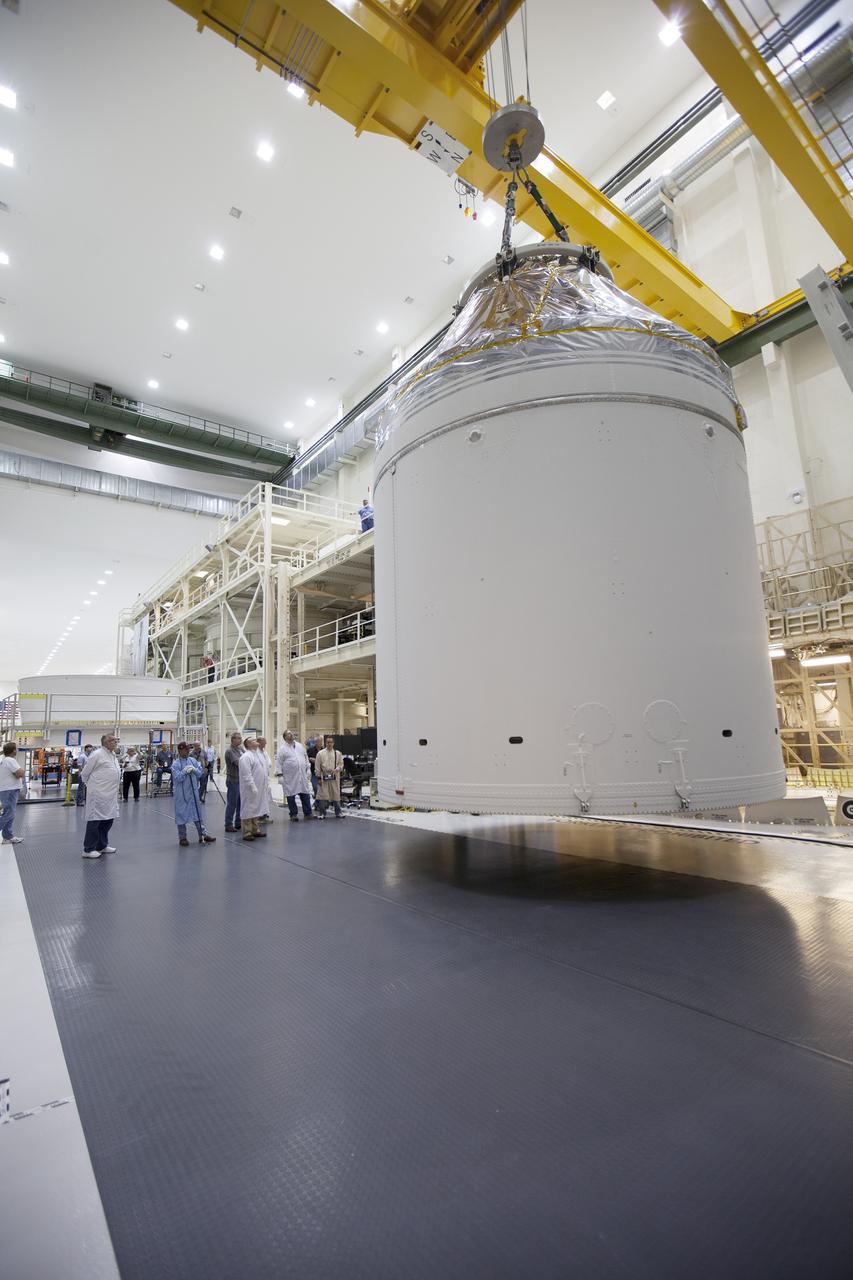

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane has lifted the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 out of the test cell and is being transferred to a mating device. A protective covering surrounds the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
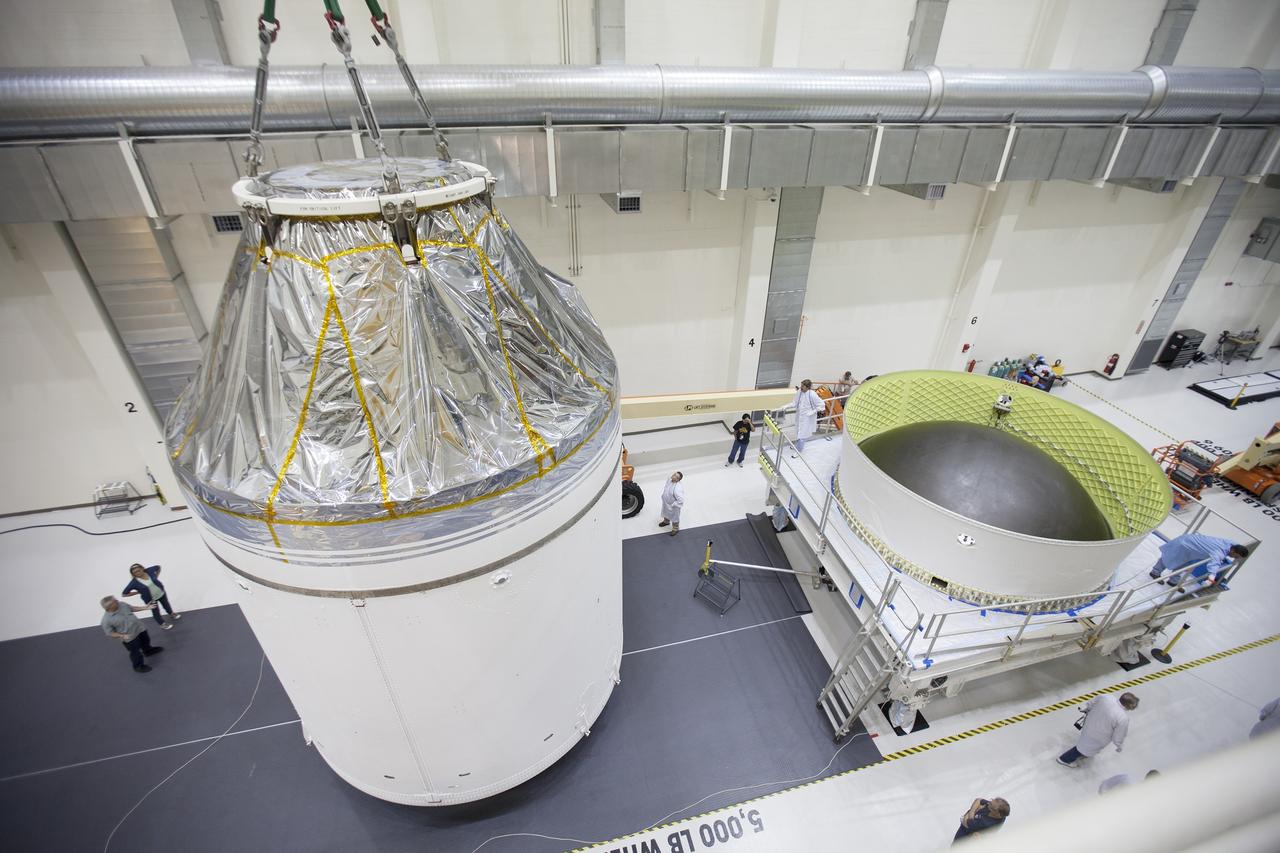

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 was lifted by crane out of the test cell and is being moved along the center aisle toward the mating device. A protective covering surrounds the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
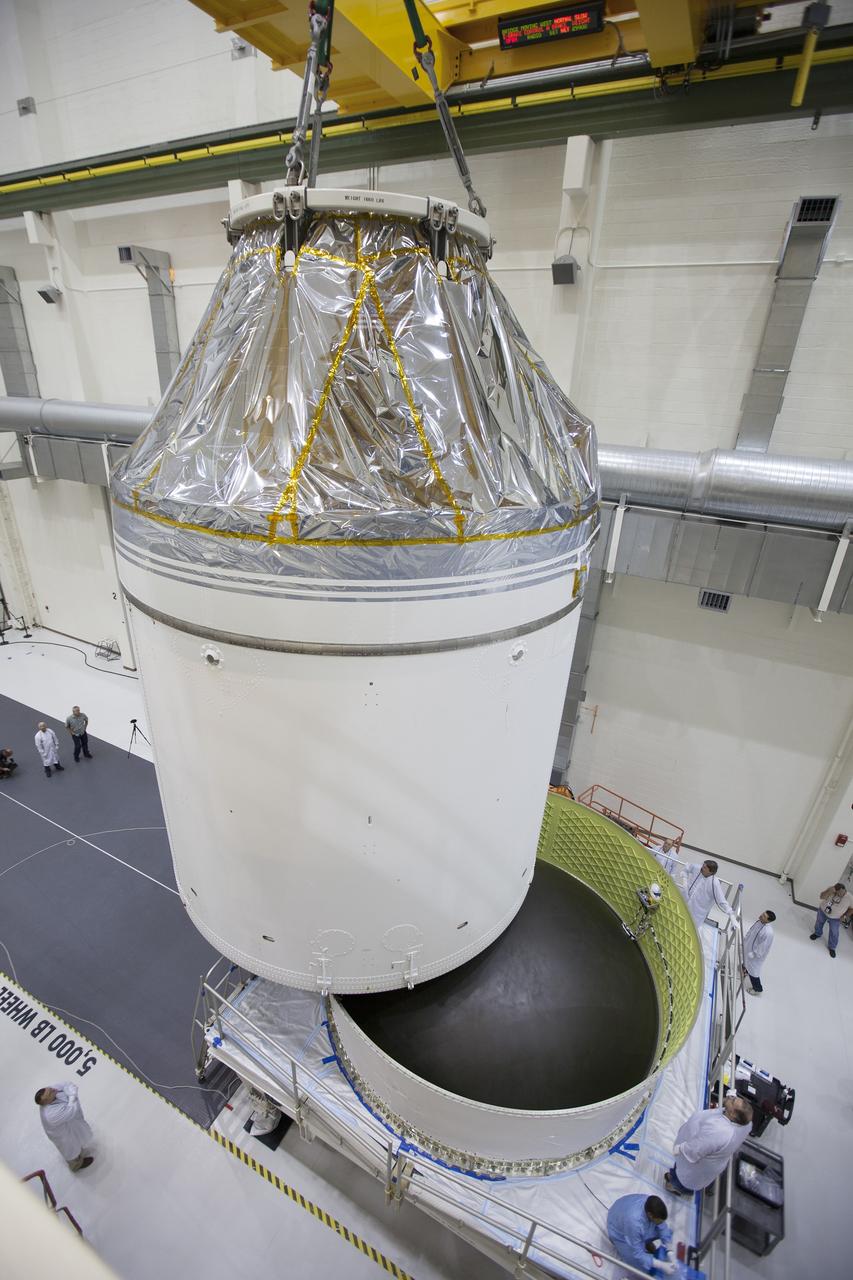

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 was lifted by crane out of the test cell and is being lowered onto a mating device. A protective covering surrounds the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
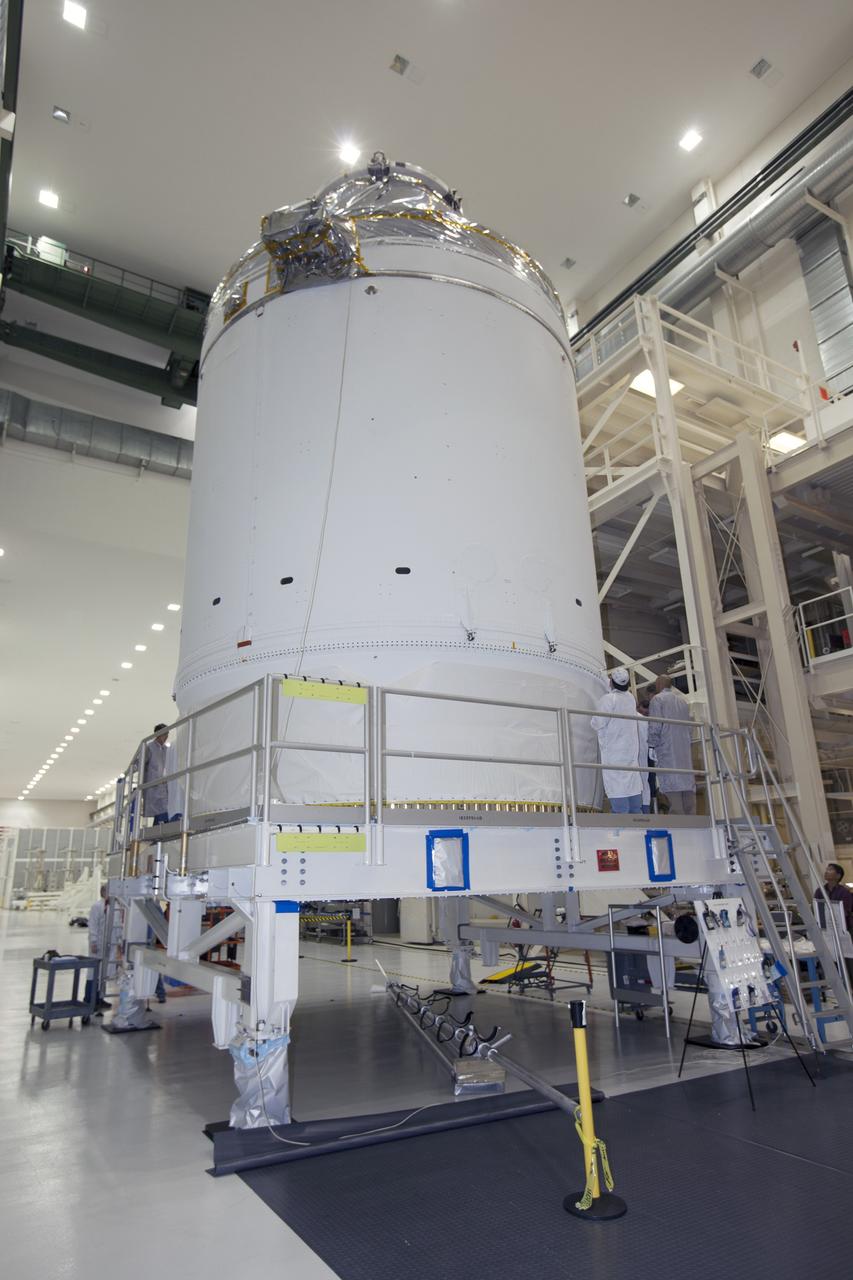

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 was lifted by crane out of the test cell. The stack has been lowered onto the mating device. Technicians are attaching the stack to the mating device. A protective covering surrounds the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
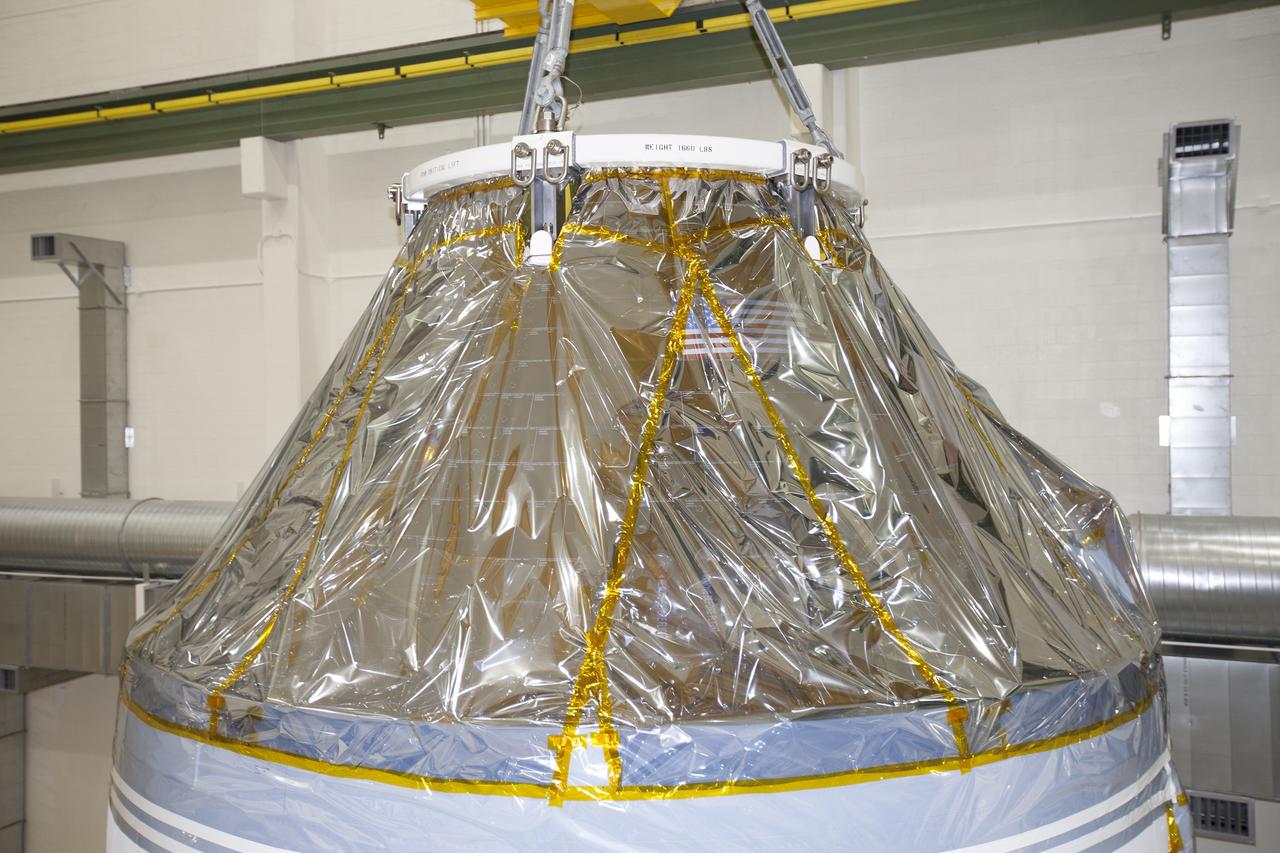

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 was lifted by crane out of the test cell and is being lowered onto a mating device A protective covering surrounds the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 was lifted by crane out of the test cell. Technicians in clean room suits monitor the progress as the crane slowly lowers the stack onto a mating device. A protective covering surrounds the crew module. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
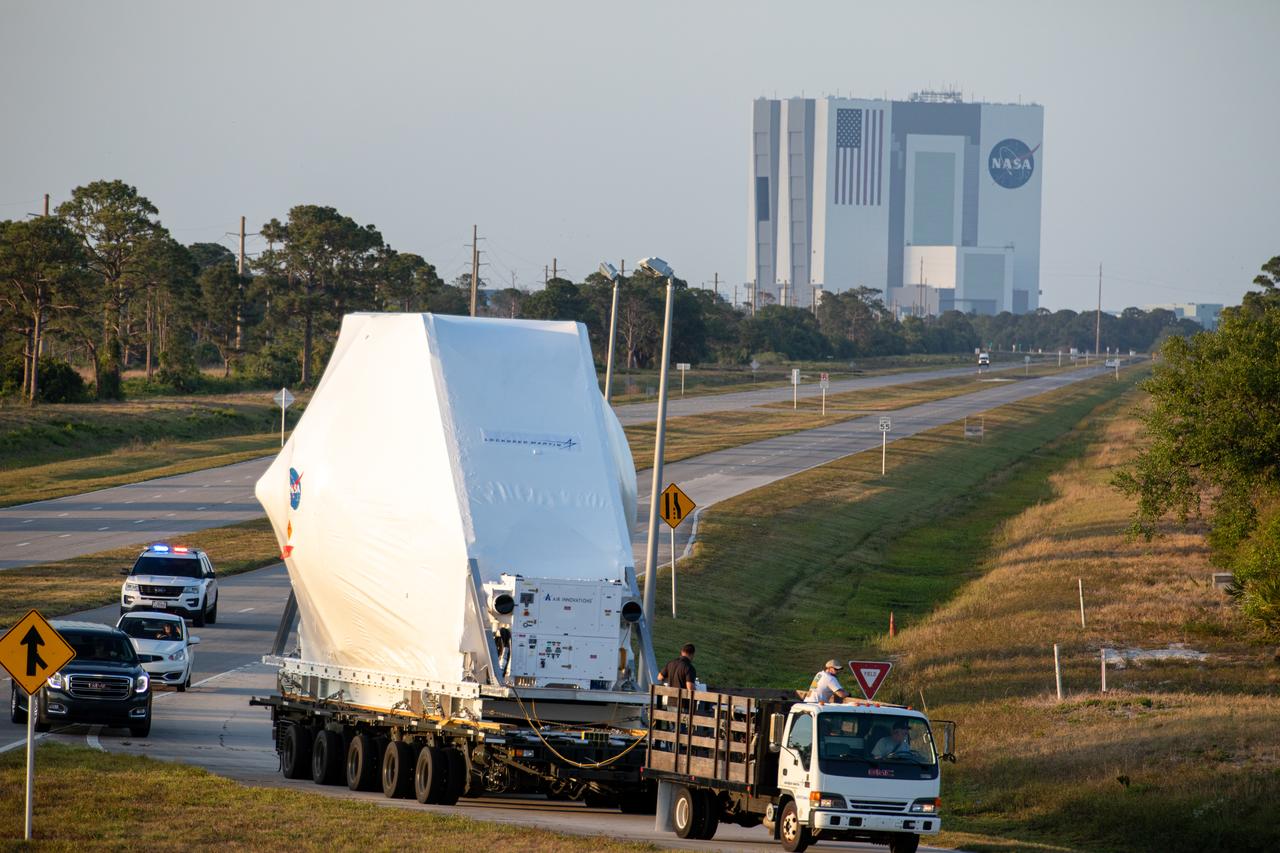

NASA’s Orion spacecraft, protected in its shipping container, is loaded onto a transporter at the Launch and Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center for its move to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on March 25, 2020. After testing at NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio verified it can handle the extreme conditions of a deep-space environment, the spacecraft – carried by the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft – has returned to the Florida spaceport for final testing and assembly. Following this, Orion will be integrated with the Space Launch System rocket for Artemis I – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
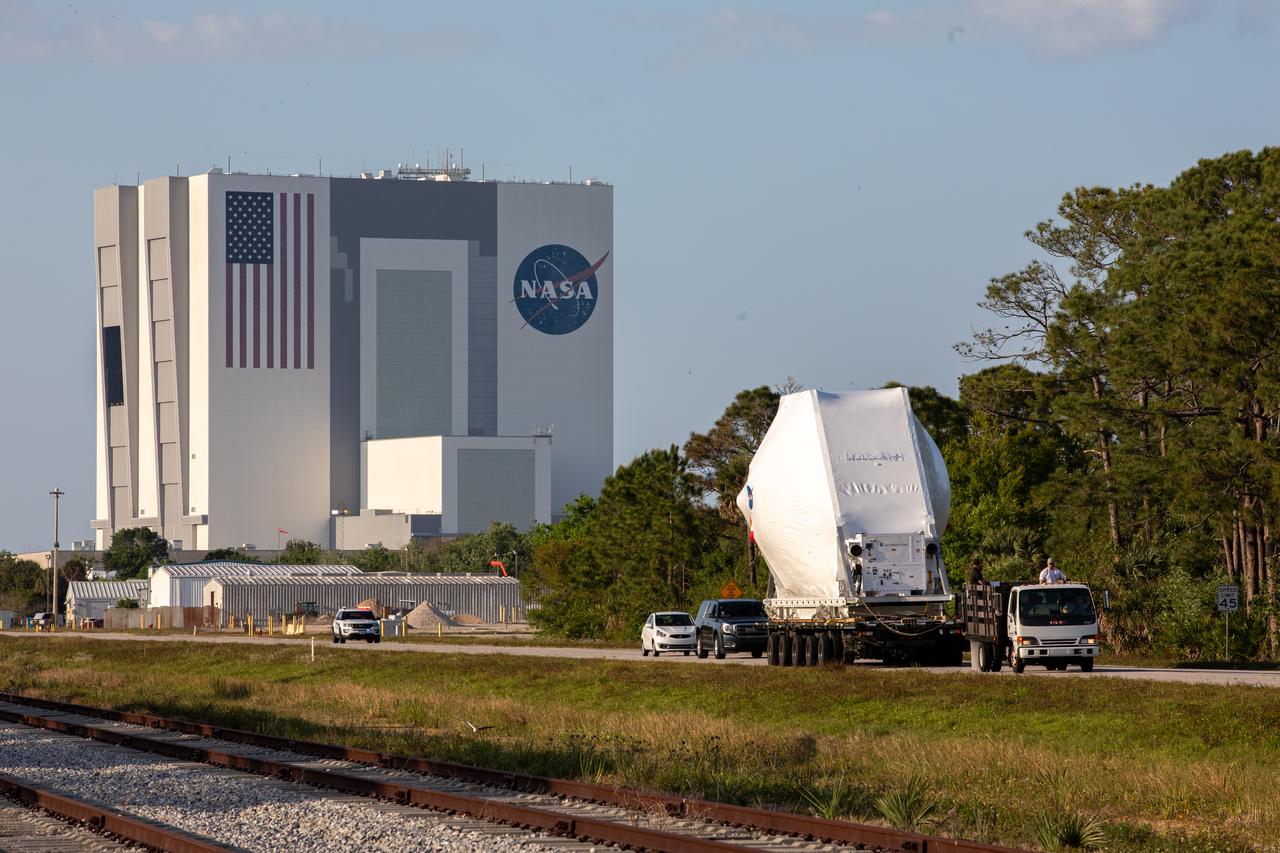

NASA’s Orion spacecraft, protected in its shipping container, is loaded onto a transporter at the Launch and Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center for its move to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on March 25, 2020. After testing at NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio verified it can handle the extreme conditions of a deep-space environment, the spacecraft – carried by the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft – has returned to the Florida spaceport for final testing and assembly. Following this, Orion will be integrated with the Space Launch System rocket for Artemis I – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
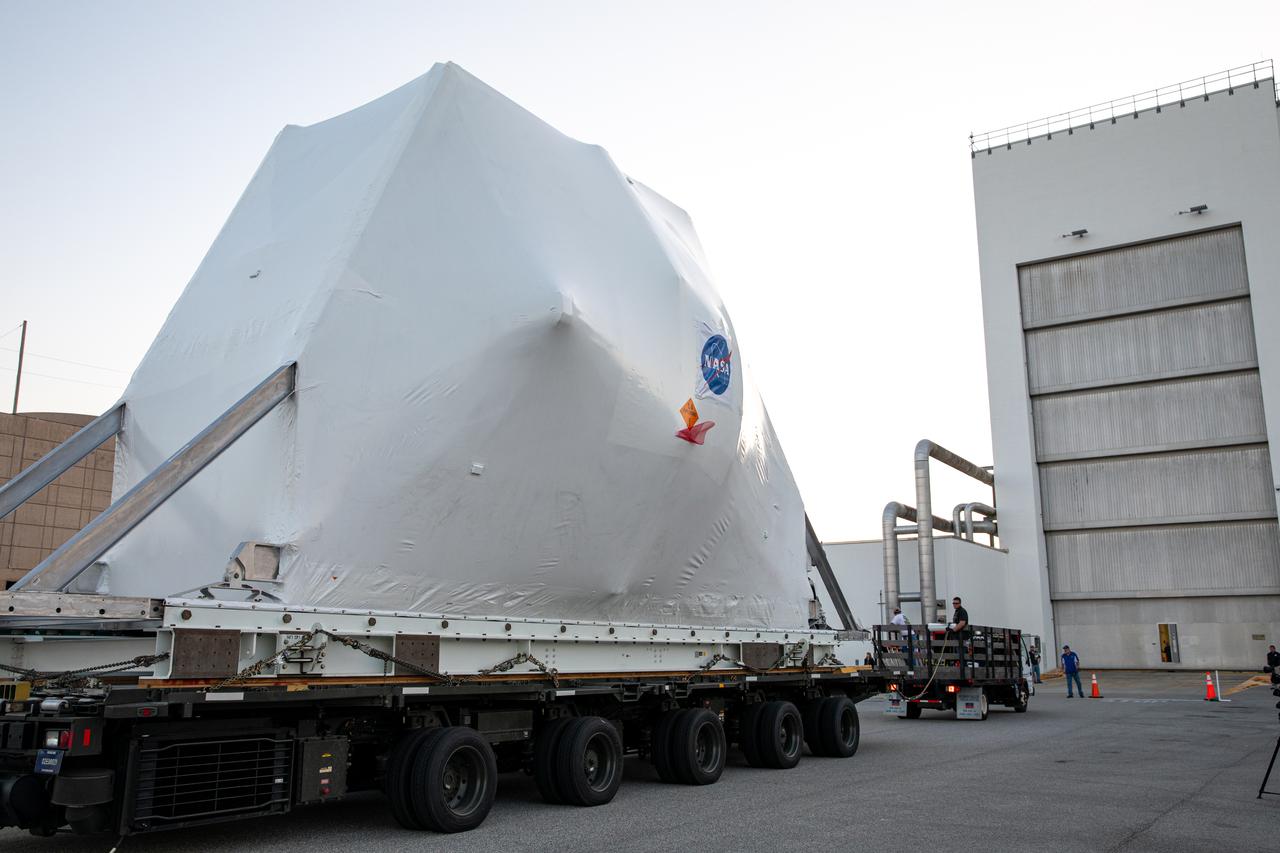

The Orion spacecraft, secured atop a transporter in its shipping container, arrives at the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on March 25, 2020, for final testing and assembly. The spacecraft was transported to Kennedy in NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft from the agency’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio, where it underwent two phase of environmental testing. Following these final preparations, Orion will be integrated with the Space Launch System rocket for the Artemis I launch – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
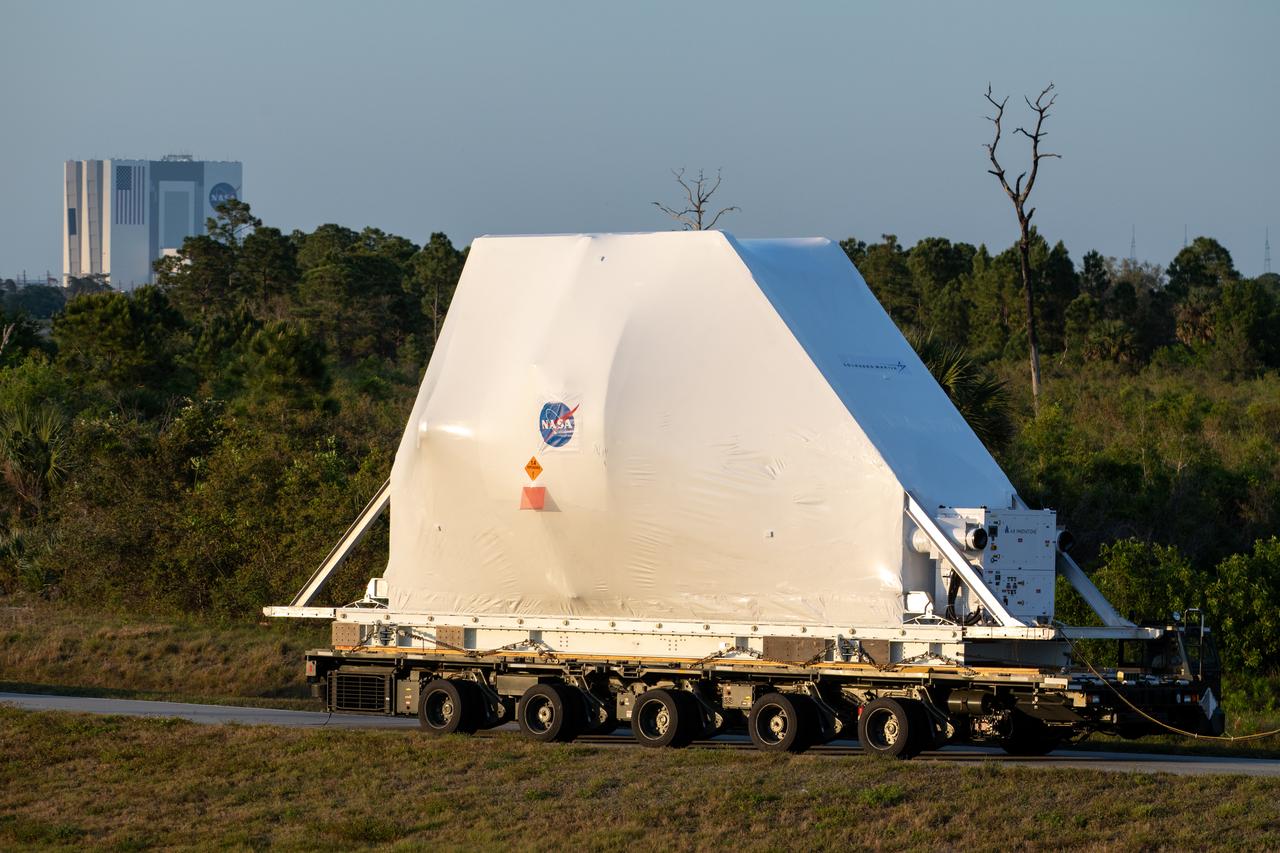

NASA’s Orion spacecraft, protected in its shipping container, is loaded onto a transporter at the Launch and Landing Facility at Kennedy Space Center for its move to the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building on March 25, 2020. After testing at NASA’s Plum Brook Station in Ohio verified it can handle the extreme conditions of a deep-space environment, the spacecraft – carried by the agency’s Super Guppy aircraft – has returned to the Florida spaceport for final testing and assembly. Following this, Orion will be integrated with the Space Launch System rocket for Artemis I – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 was lifted by crane out of the test cell and is being moved along the center aisle. Orion will be transferred to a mating device. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
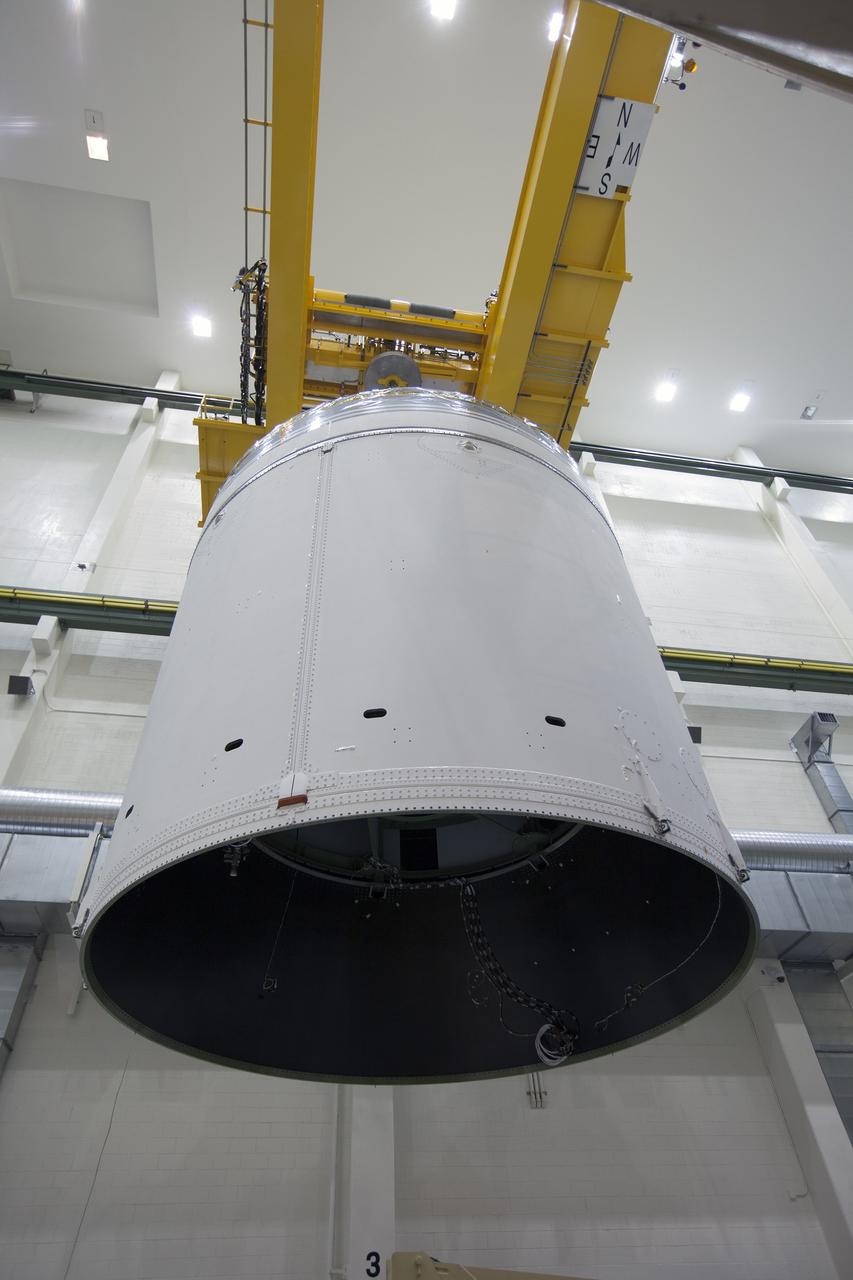

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 was lifted by crane out of the test cell and is being moved along the center aisle. Orion will be transferred to a mating device. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
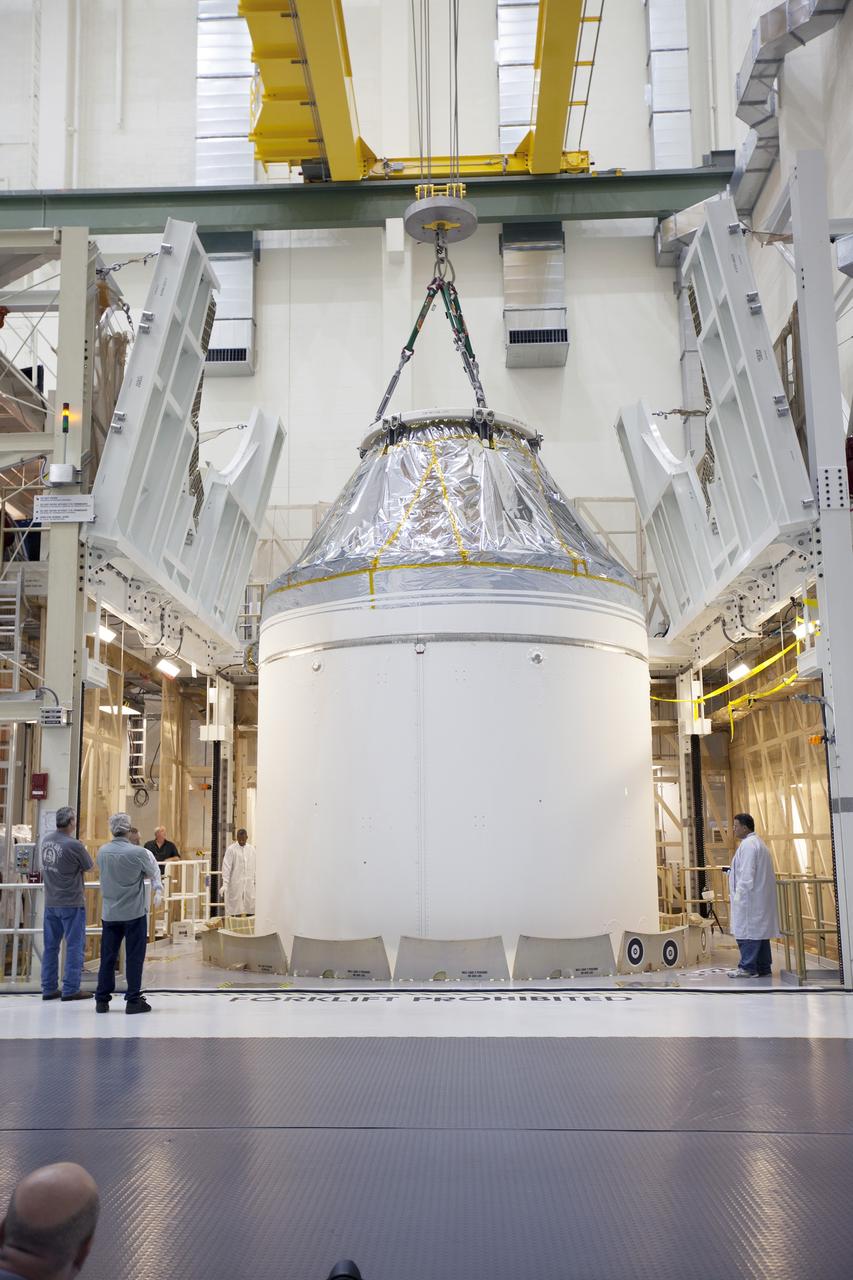

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a crane slowly lifts the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 out of the test cell. Orion will be transferred to a mating device. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1 was lifted by crane out of the test cell and is being moved along the center aisle. Orion will be transferred to a mating device. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
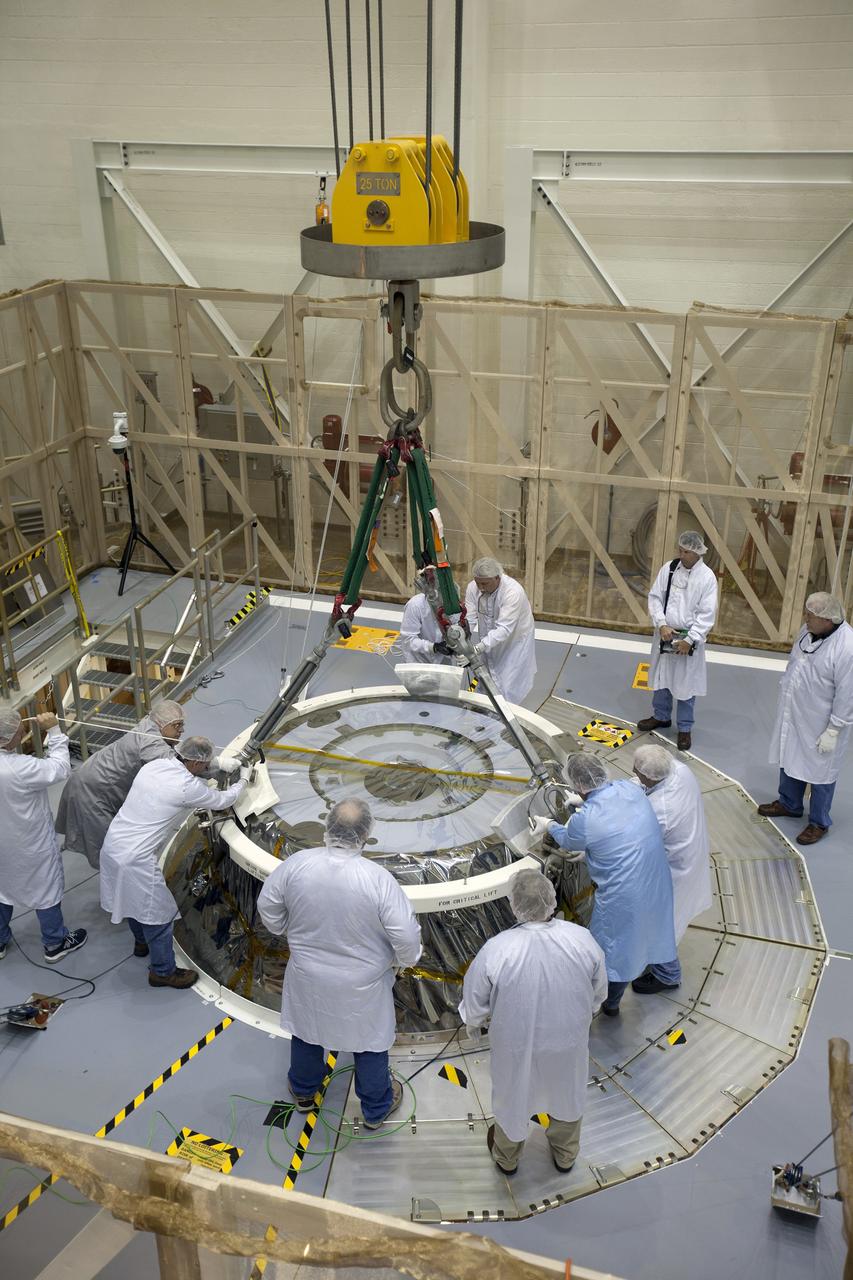

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians dressed in clean room suits attach a crane to the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1. Orion will be lifted out of the test cell and transferred to a mating device. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
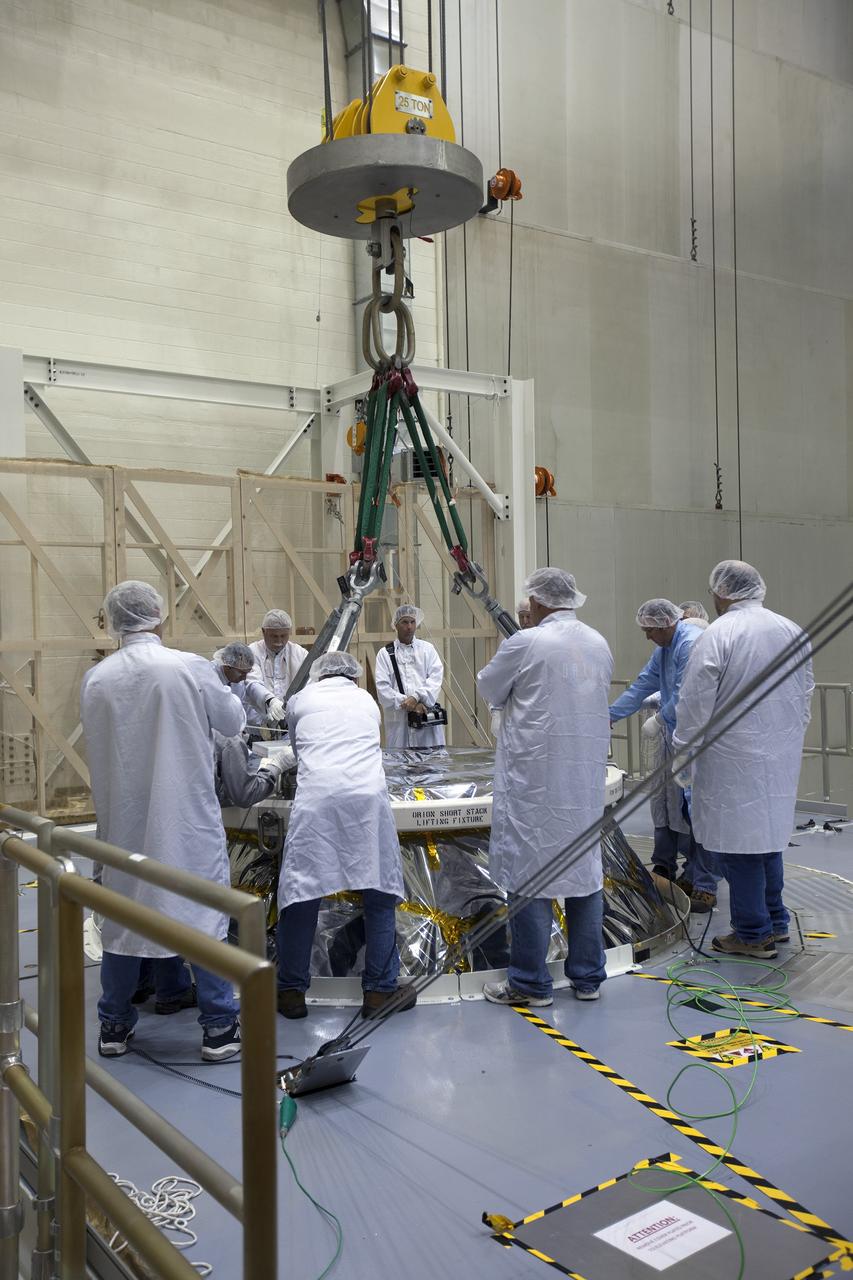

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians dressed in clean room suits attach a crane to the Orion crew and service module stack for Exploration Flight Test-1. Orion will be lifted out of the test cell and transferred to a mating device. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of the Orion is scheduled to launch later this year atop a Delta IV Heavy rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida to an altitude of 3,600 miles above the Earth's surface. The two-orbit, four-hour flight test will help engineers evaluate the systems critical to crew safety including the heat shield, parachute system and launch abort system. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky