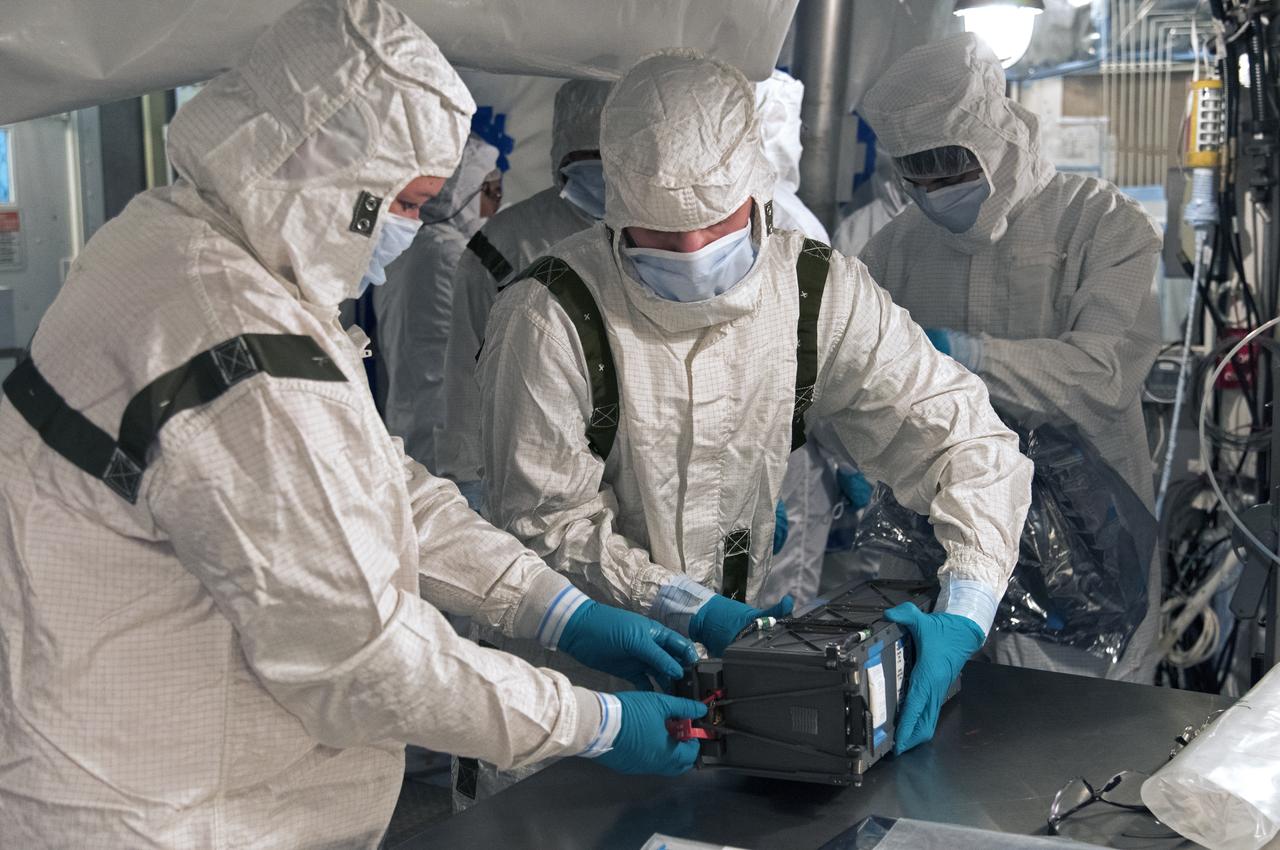

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container for installation on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container is installed on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare to install a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container is installed on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
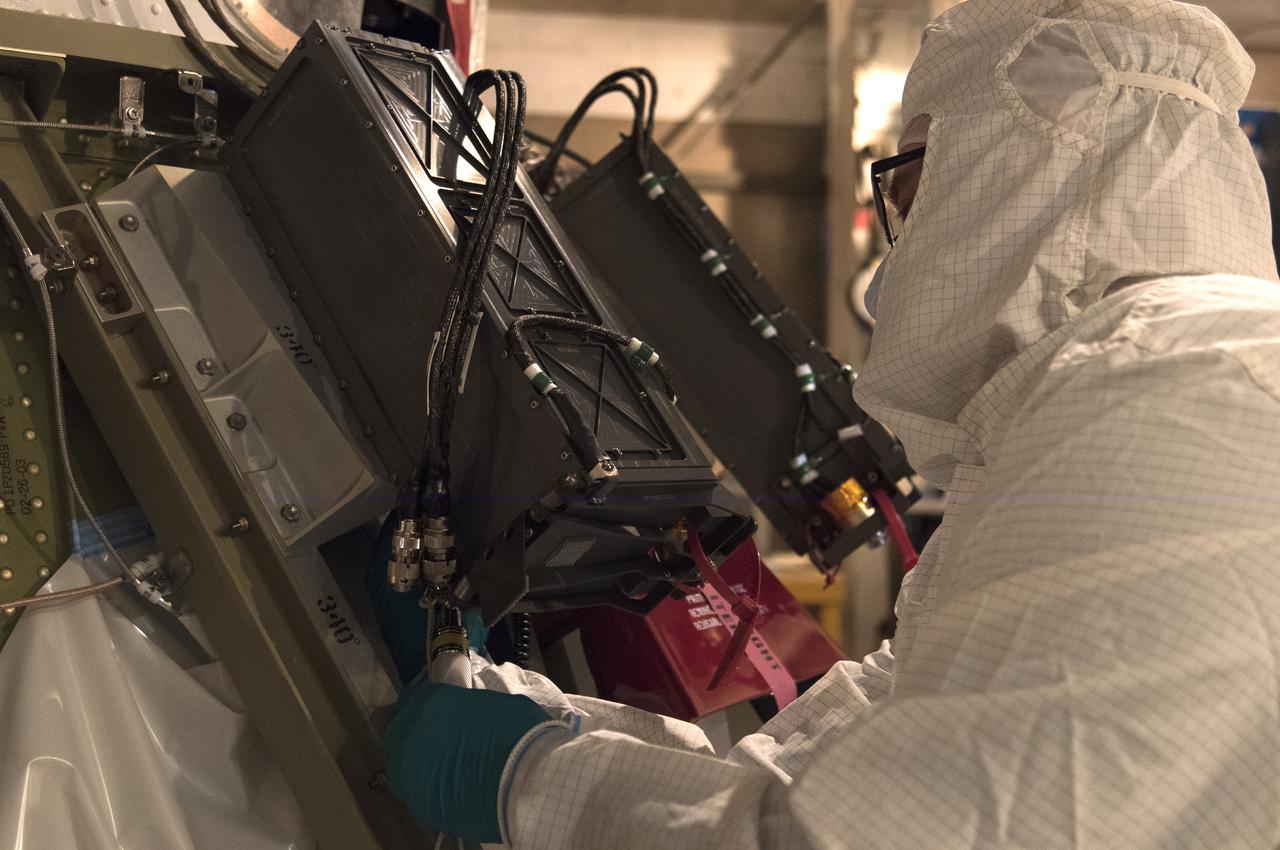

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container is installed on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container for installation on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.

At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians and engineers prepare a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container for installation on the Joint Polar Satellite System-1, or JPSS-1, spacecraft. P-PODS are auxiliary payloads launched aboard NASA expendable launch vehicles carrying up to three small CubeSats. The small cube-shaped satellites are part of NASA’s Educational Launch of Nanosatellite, or ELaNa, missions. The small payloads are designed and built by students from high school-level classes up to college and university students. JPSS is the first in a series of four next-generation environmental satellites in a collaborative program between the NOAA and NASA. Liftoff from Vandenberg's Space Launch Compex-2 atop a United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket is scheduled for 1:47 a.m. PST (4:47 a.m. EST), on Nov. 14, 2017.
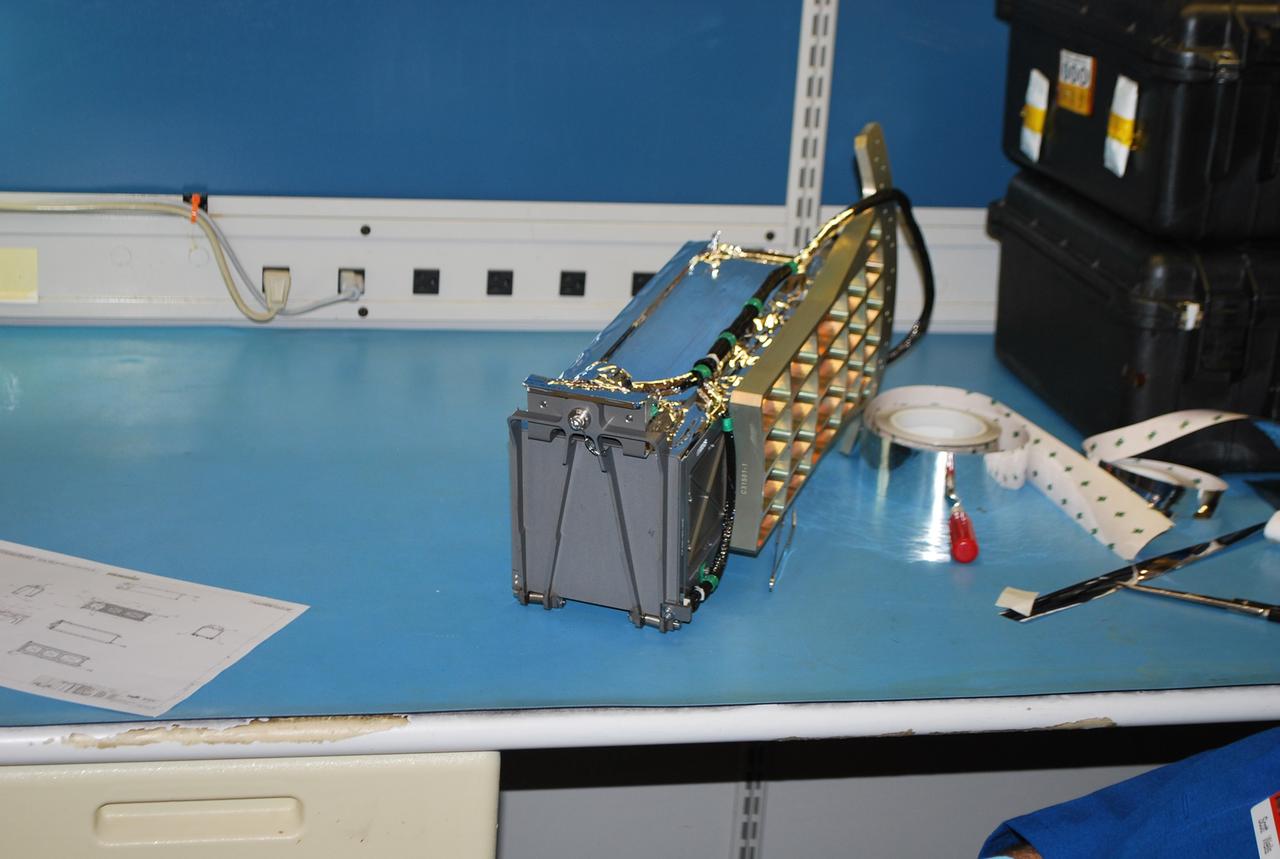

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container is imaged here with the bracket interface installed. The bracket is a connection interface between the P-POD and the Taurus rocket. The P-POD will hold three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin,VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container is imaged here with the bracket interface installed. The bracket is a connection interface between the P-POD and the Taurus rocket. The P-POD will hold three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
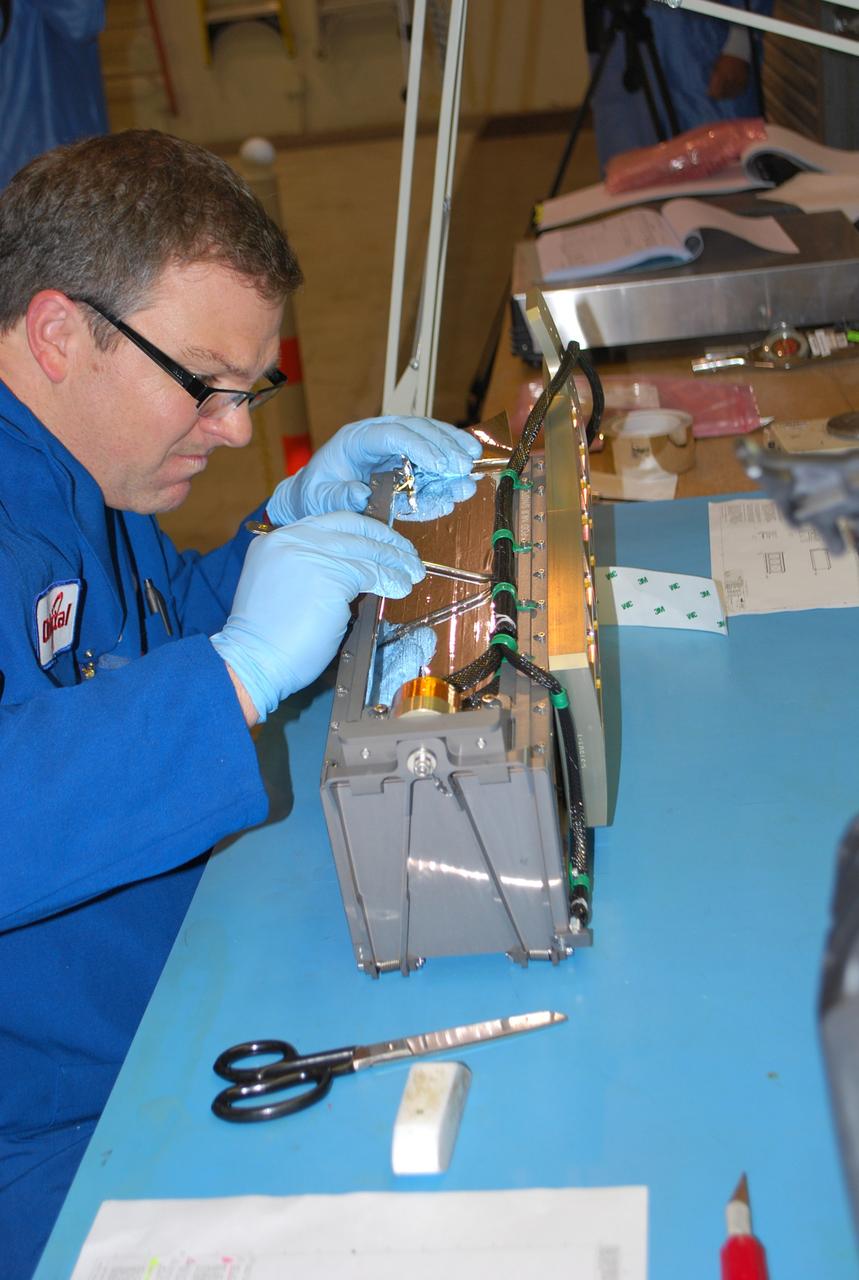

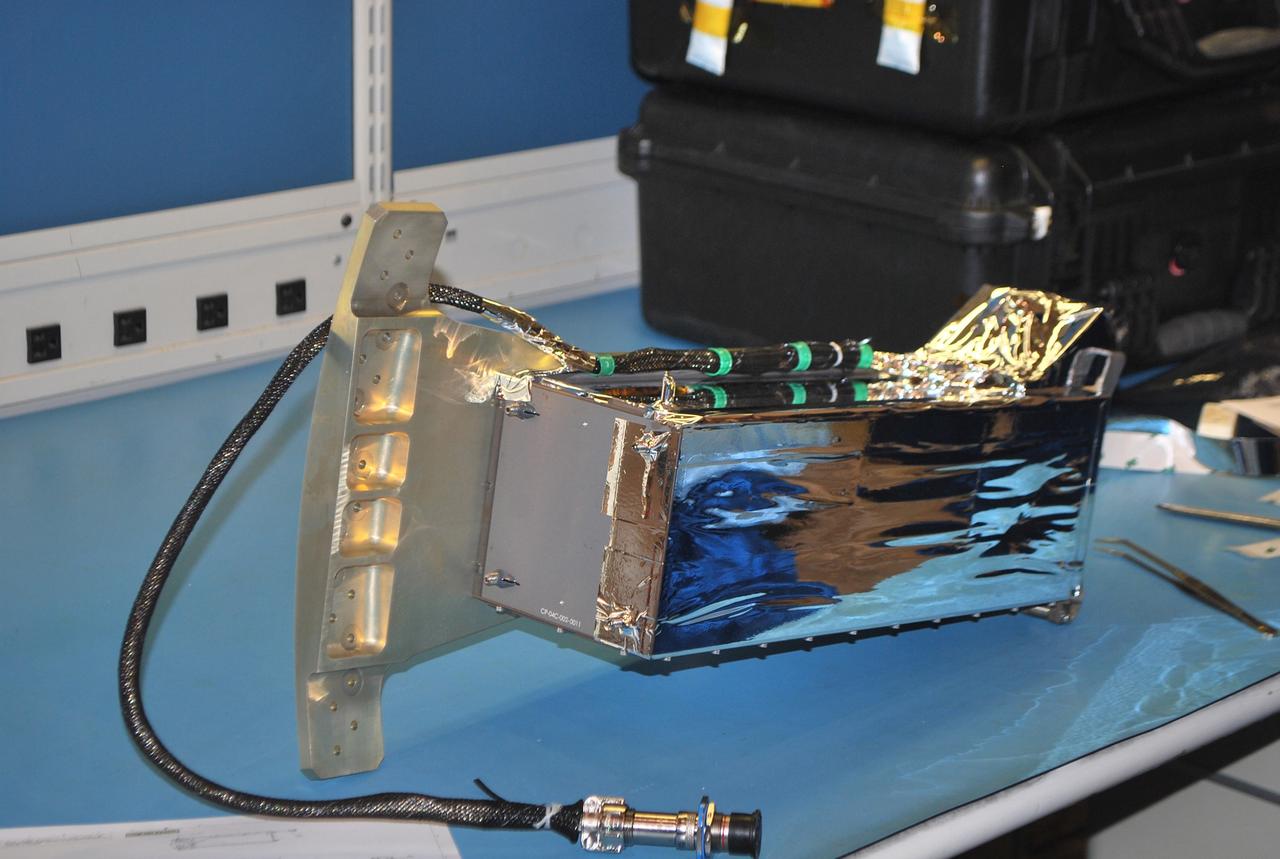
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician installs a bracket on a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container. The bracket is a connection interface between the P-POD and the Taurus rocket. The P-POD will hold three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician applies a sheet of thermal insulation on a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container. The P-POD will hold three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
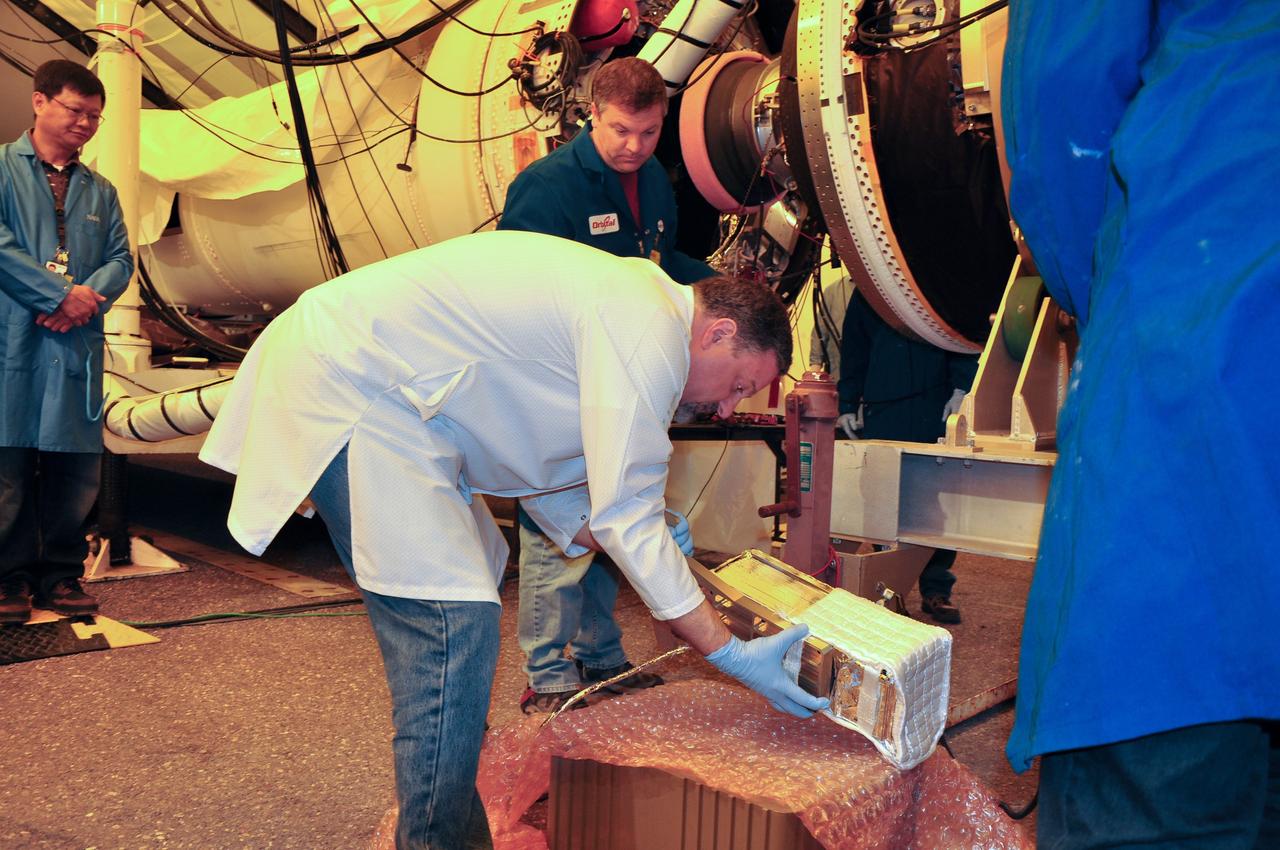

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician lifts the Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, assembly by the Anodized gold aluminum bracket interface. The bracket is the connection point between the P-POD and the aft end of the Taurus rocket's third stage. The P-POD holds three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry Glory into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
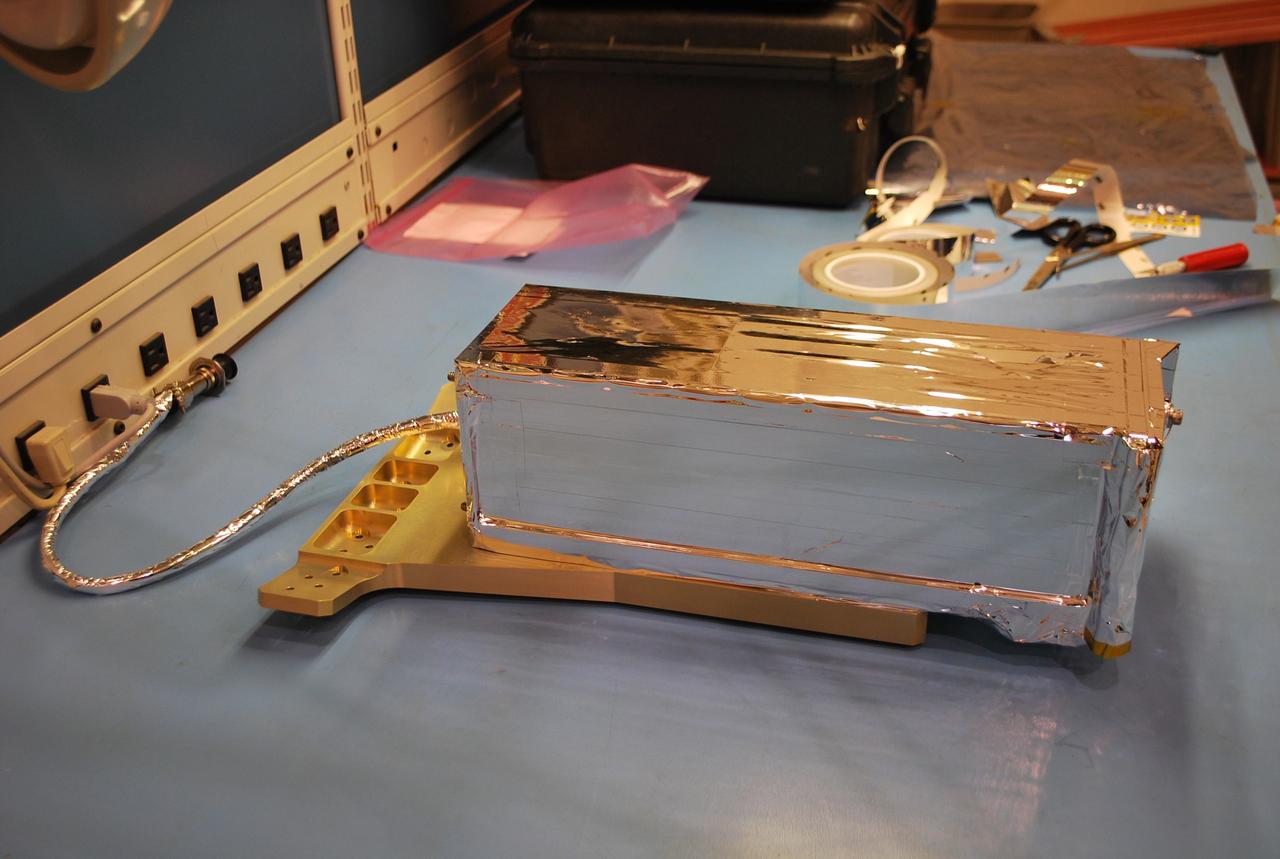
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container is imaged here after a sheet of thermal insulation has been applied and the bracket interface installed. The bracket will serve as a connection interface between the P-POD and the Taurus rocket. The P-POD will hold three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
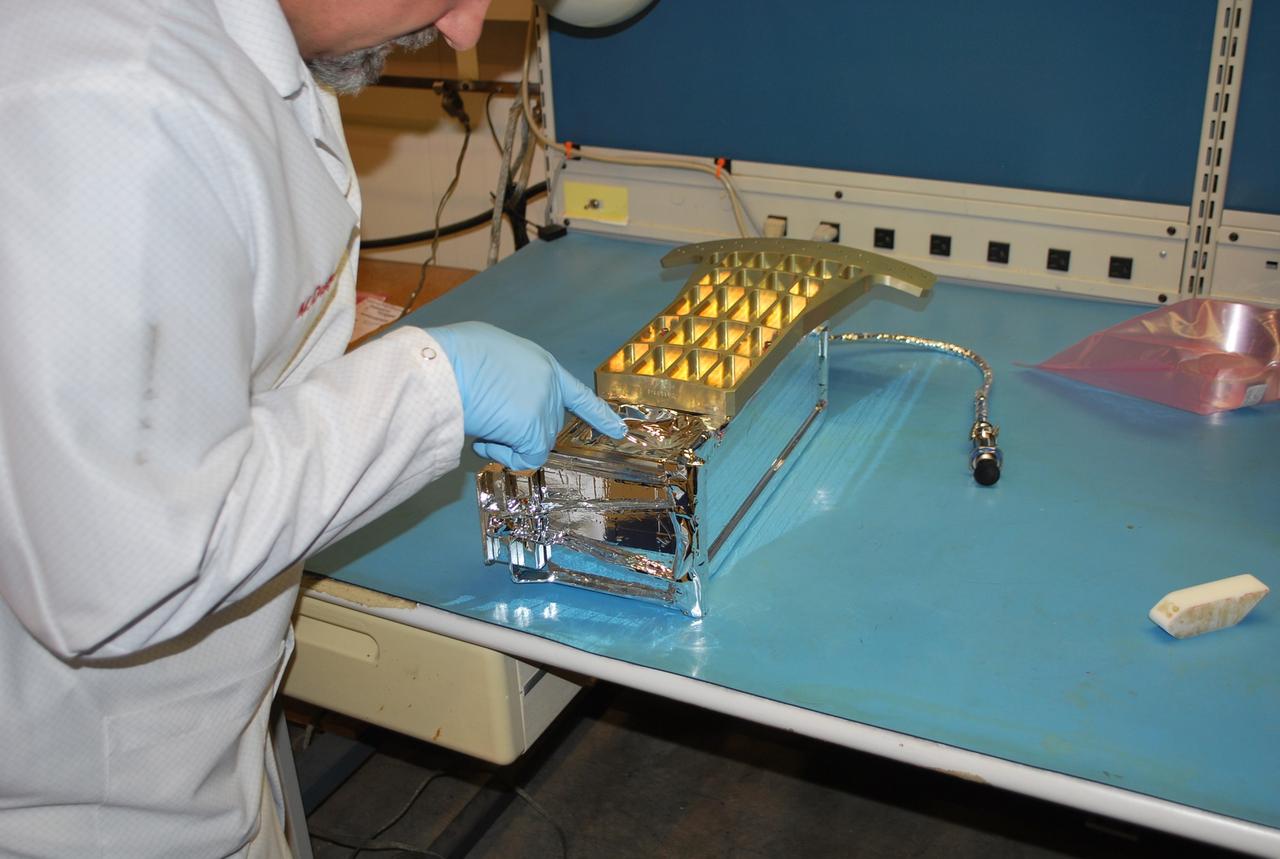

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician is pointing to a vent hole in the Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer , or P-POD, assembly after a sheet of silver reflective tape to protect it from the sun had been applied and the bracket interface installed. The bracket will serve as a connection interface between the P-POD and the aft end of the Taurus rocket's third stage. The P-POD will hold three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
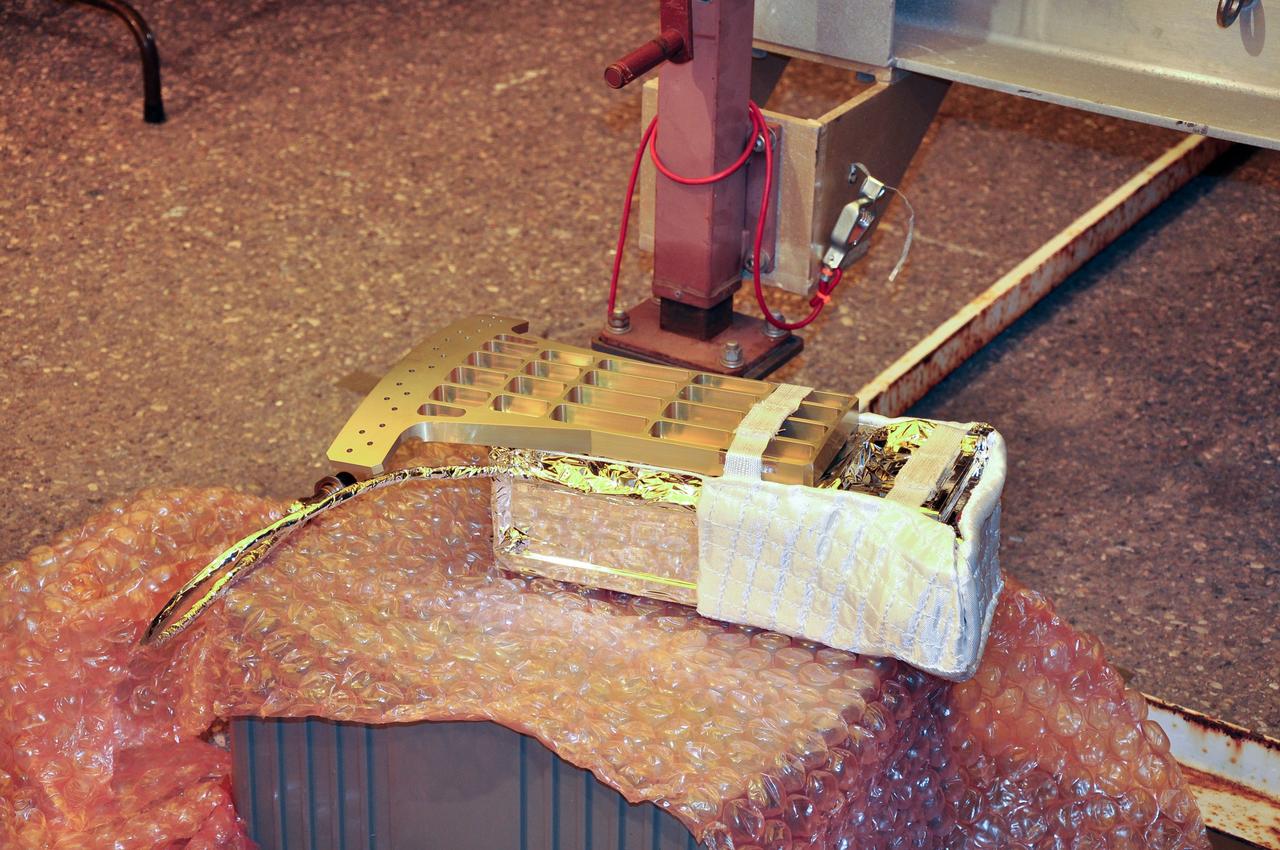

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, assembly is imaged wrapped in its thermal insulation blanket and sheeting and the attached Anodized gold aluminum bracket interface. The bracket is the connection point between the P-POD and the aft end of the Taurus rocket's third stage. The P-POD holds three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry Glory into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
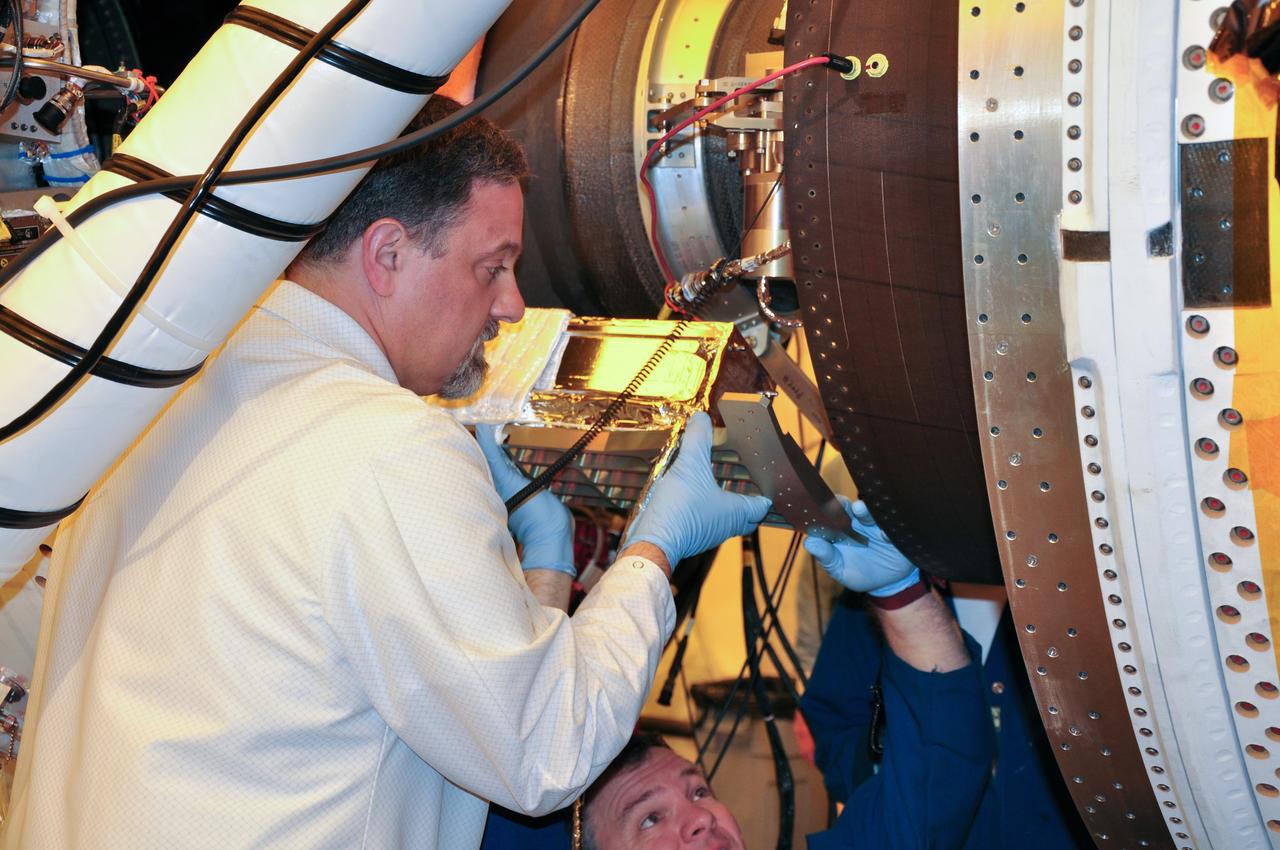

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians install the Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, assembly to the aft end of the Taurus rocket's third stage. The P-POD holds three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry Glory into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
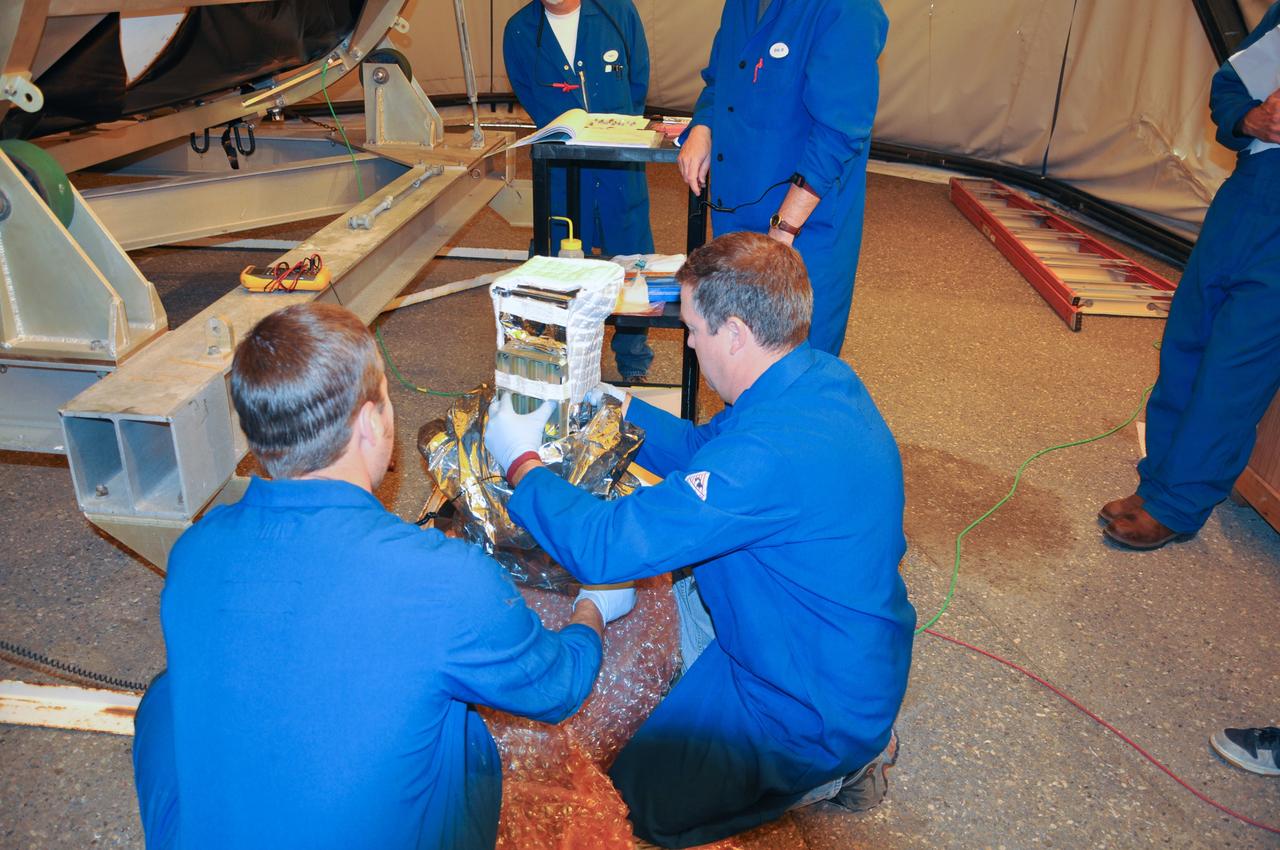

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians unwrap the Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, assembly before installation to the aft end of the Taurus rocket's third stage. The P-POD holds three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry Glory into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
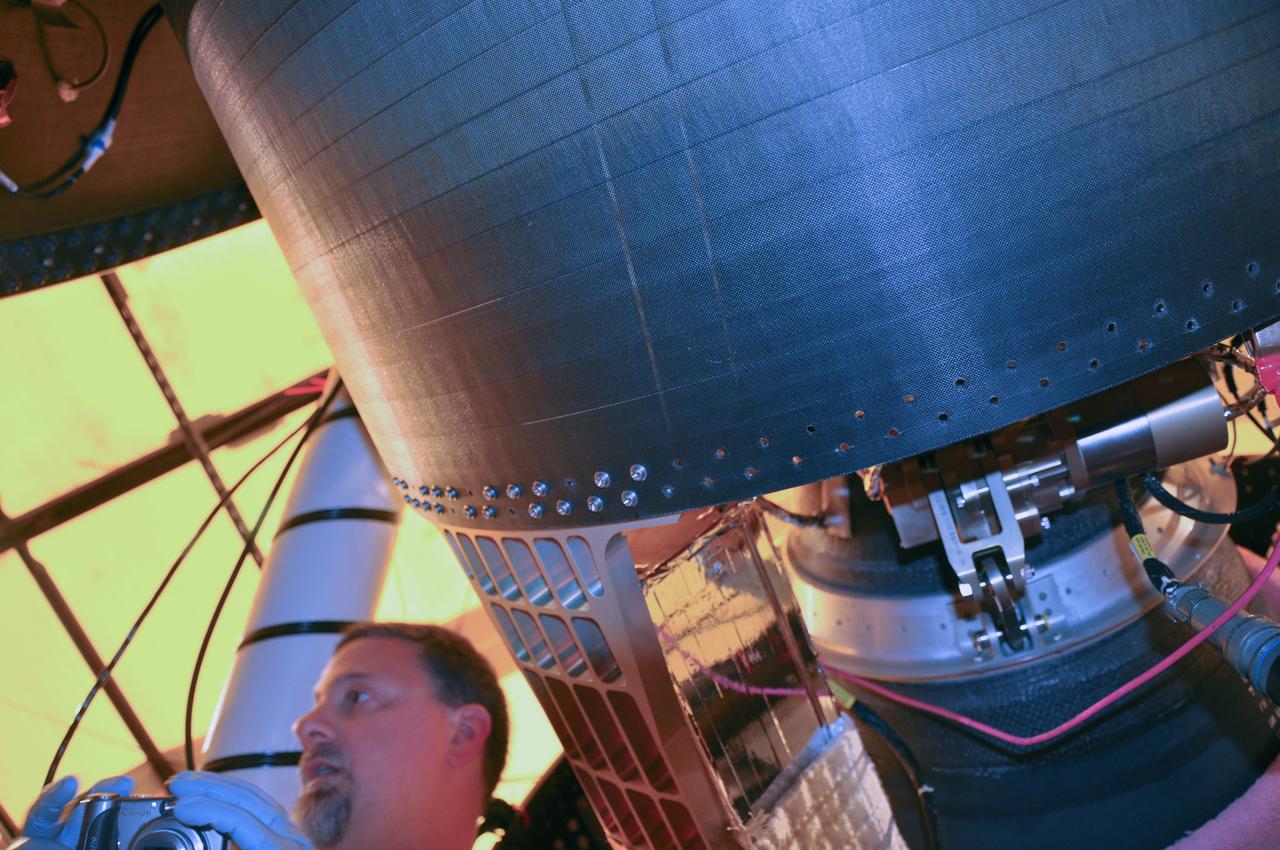
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, assembly has been installed to the aft end of the Taurus rocket's third stage using the Anodized gold aluminum bracket interface. The P-POD holds three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry Glory into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
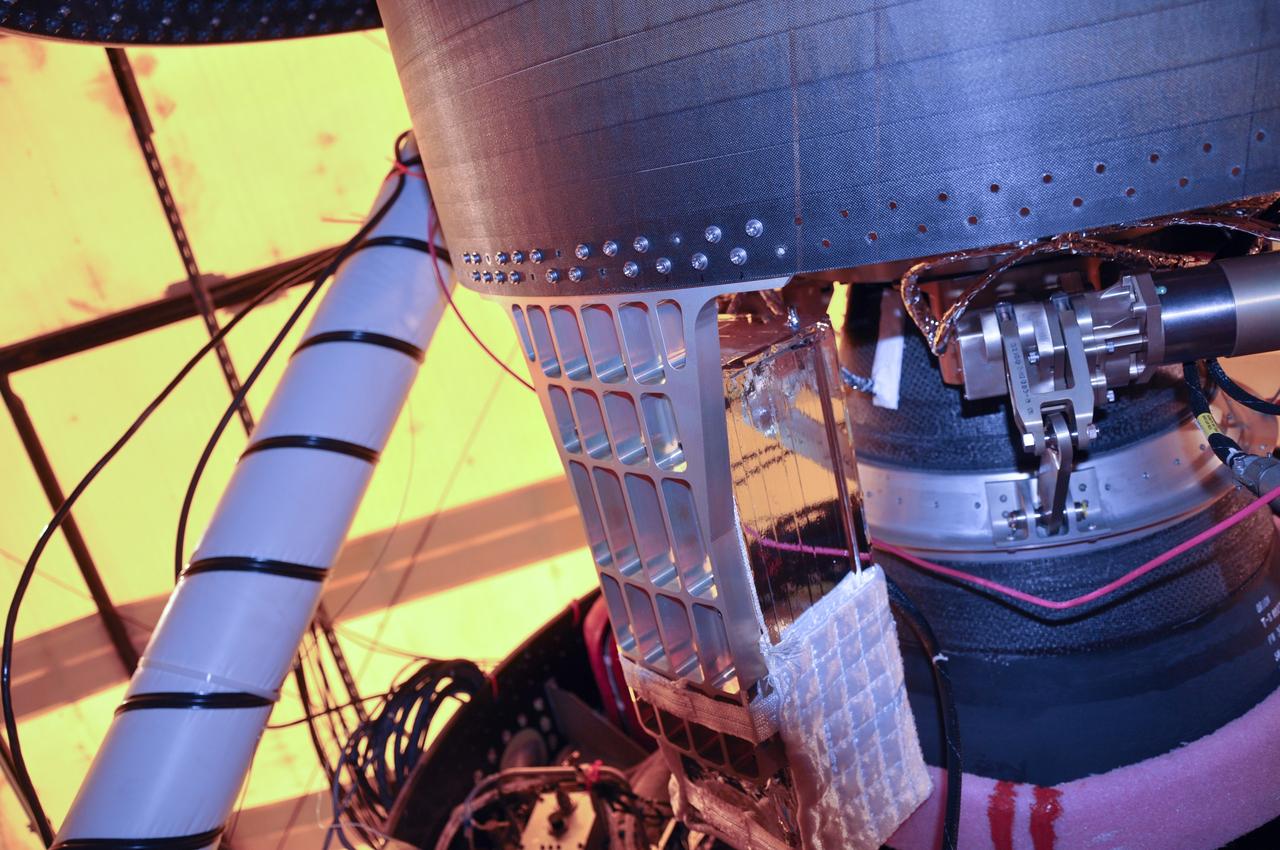

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, assembly has been installed to the aft end of the Taurus rocket's third stage using the Anodized gold aluminum bracket interface. The P-POD holds three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry Glory into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
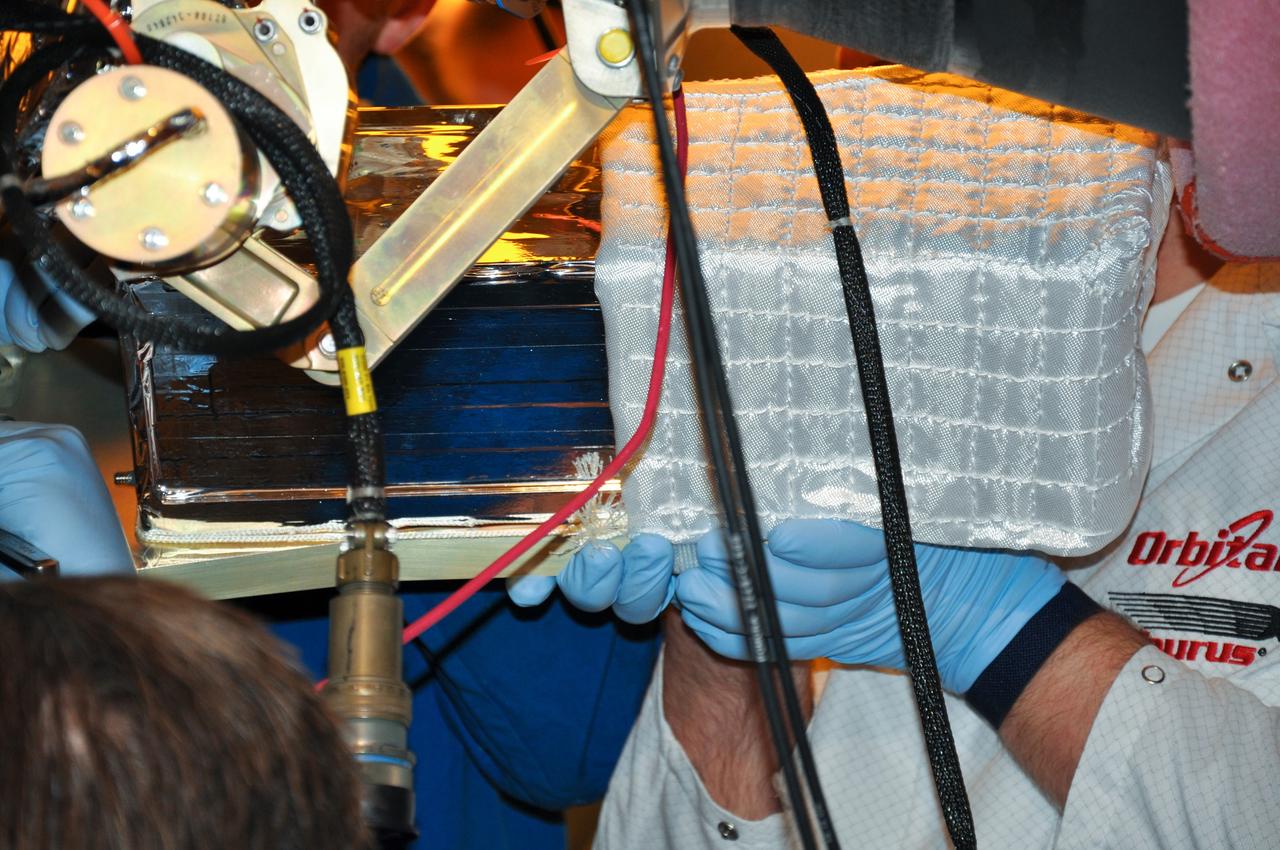

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians install the Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, assembly to the aft end of the Taurus rocket's third stage. The P-POD holds three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry Glory into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
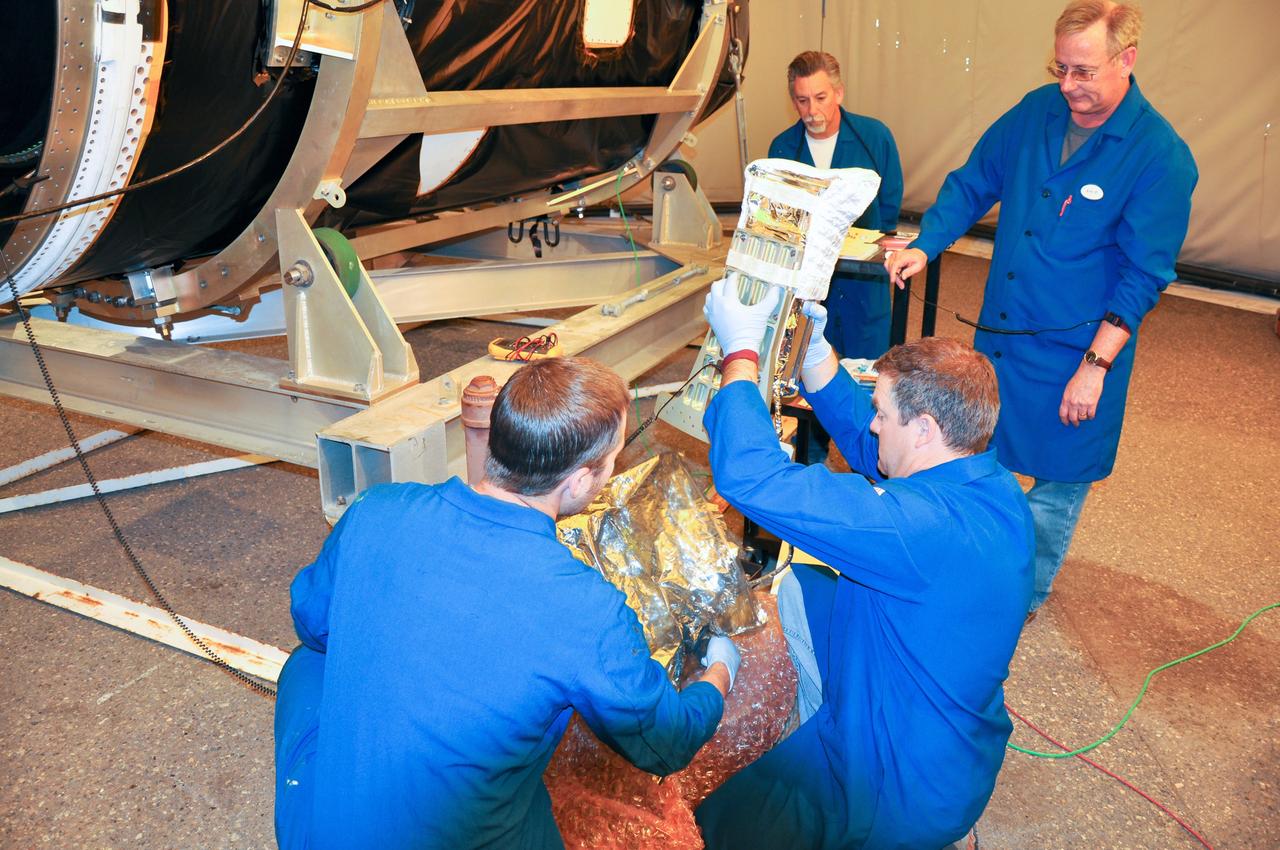

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians carefully lift the Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, assembly out of its wrappings prior to installation to the aft end of the Taurus rocket's third stage. The P-POD holds three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry Glory into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
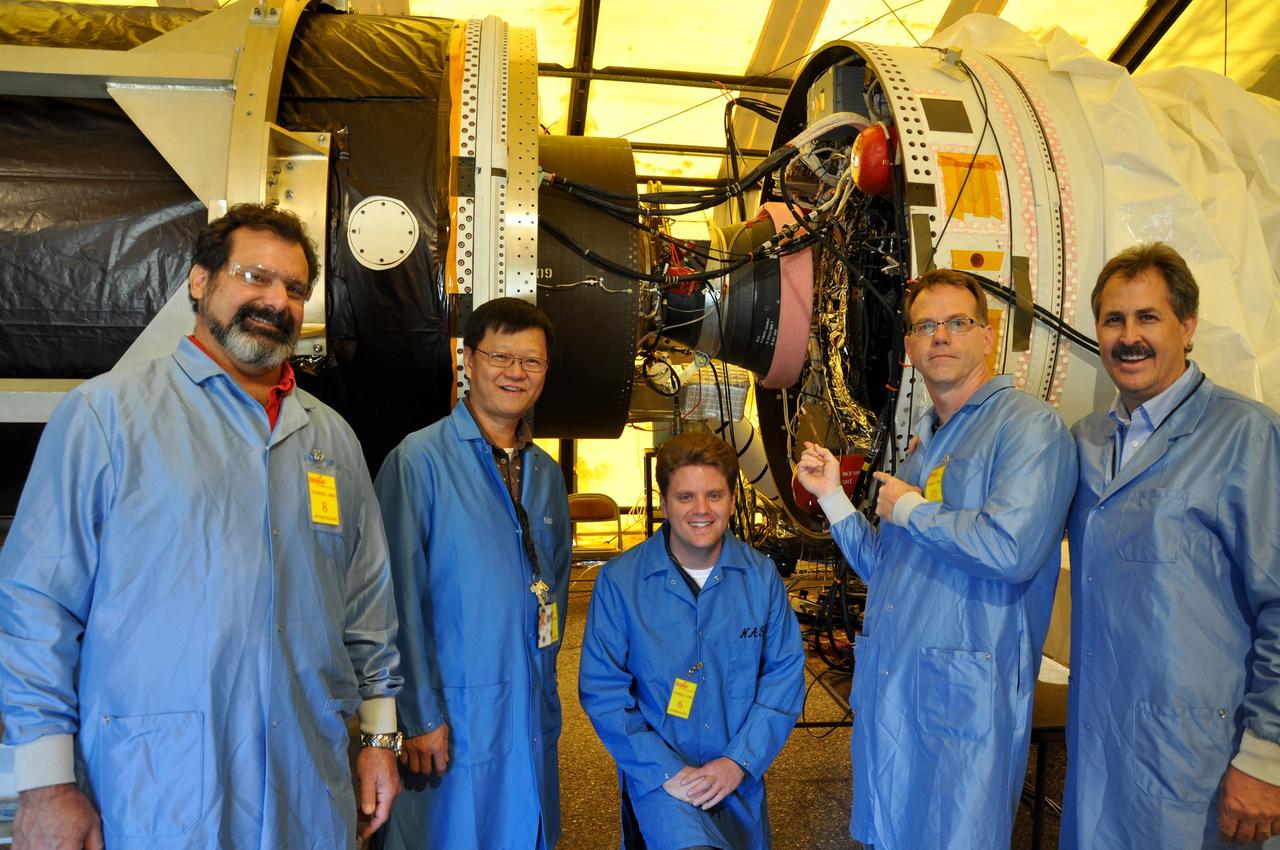

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the engineering team that installed the Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, assembly to the Taurus rocket's third stage pose for a photo opportunity. From left to right are Kevin Harrington, Cuong Nguyen, Ryan Nugent, Richard Nielsen and Larry Fineberg. The P-POD holds three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry Glory into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
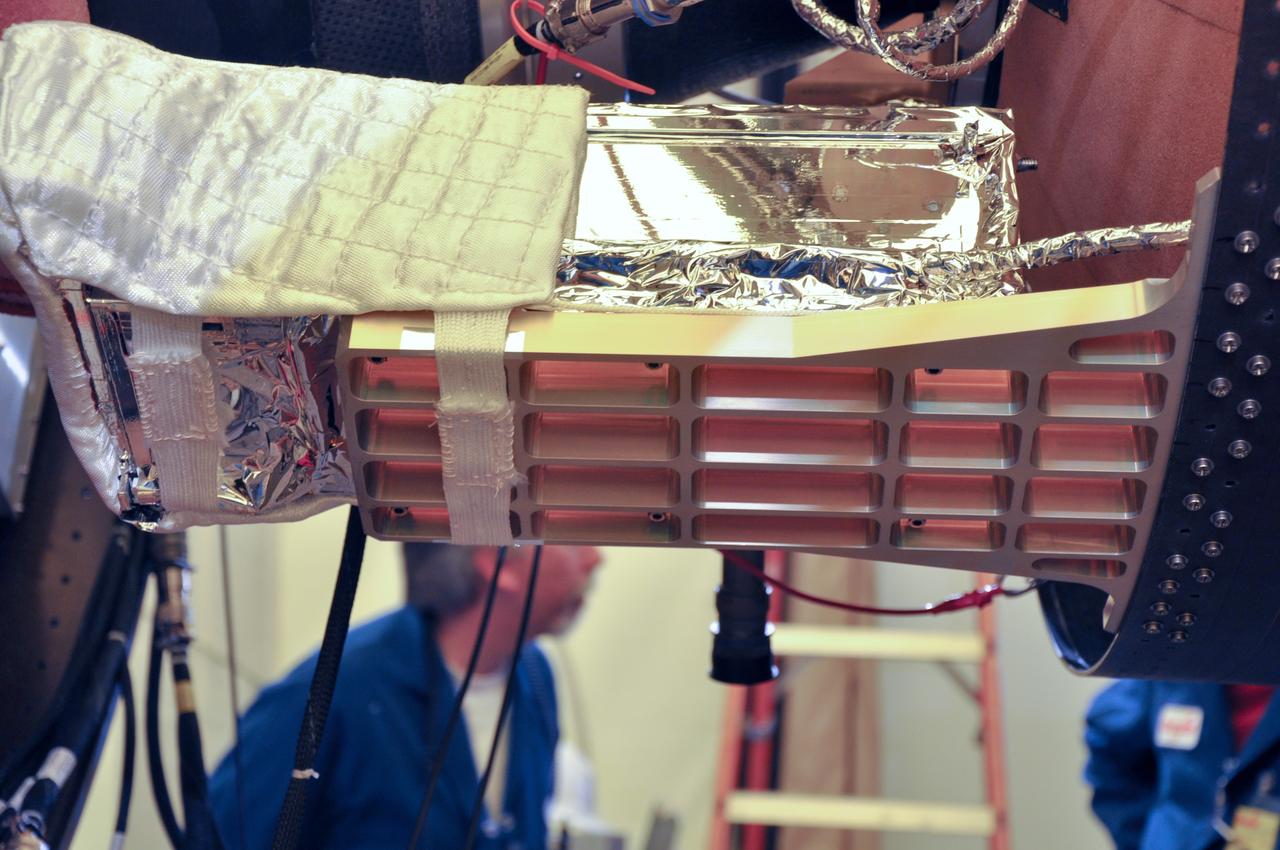
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, assembly has been installed to the aft end of the Taurus rocket's third stage using the Anodized gold aluminum bracket interface. The P-POD holds three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry Glory into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
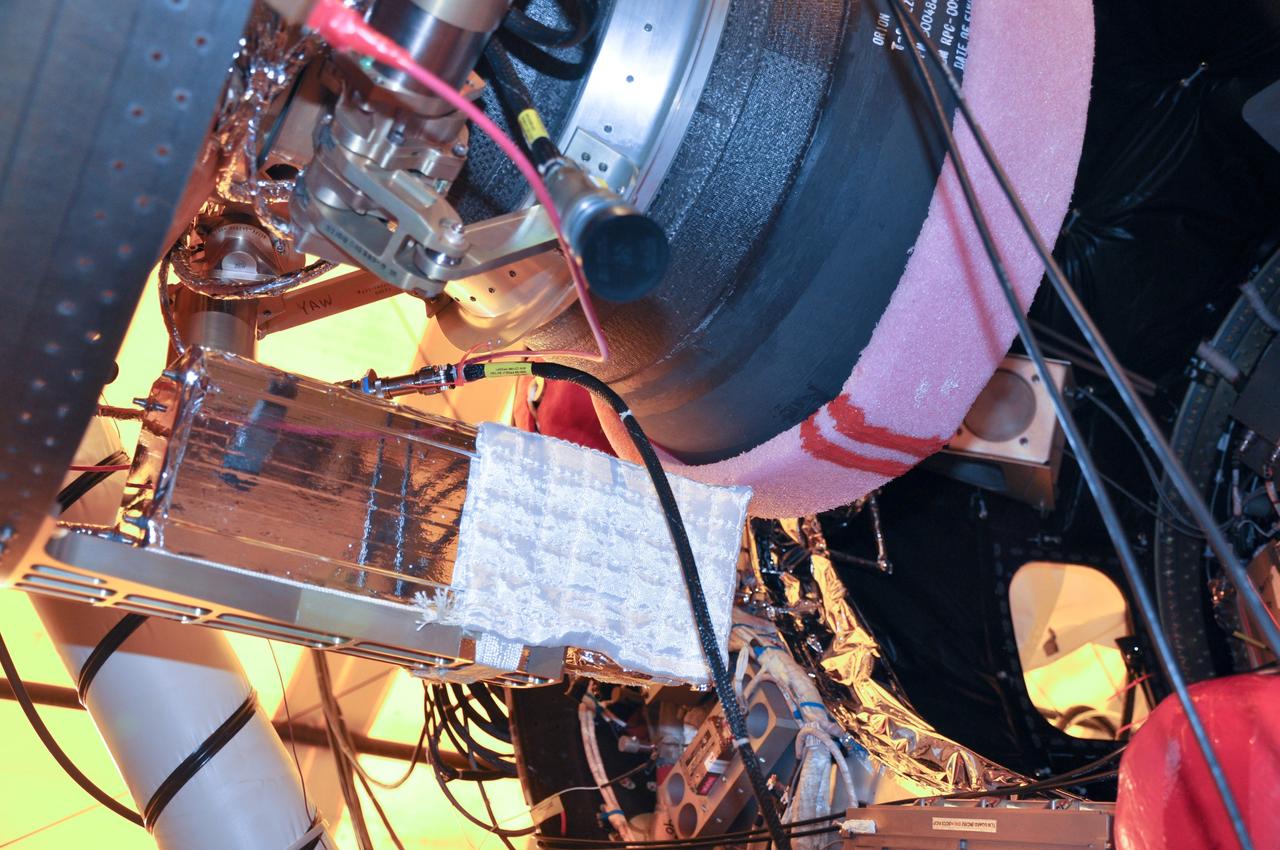
VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Space Launch Complex 576-E at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, the Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, assembly has been installed to the aft end of the Taurus rocket's third stage using the Anodized gold aluminum bracket interface. The P-POD holds three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry Glory into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
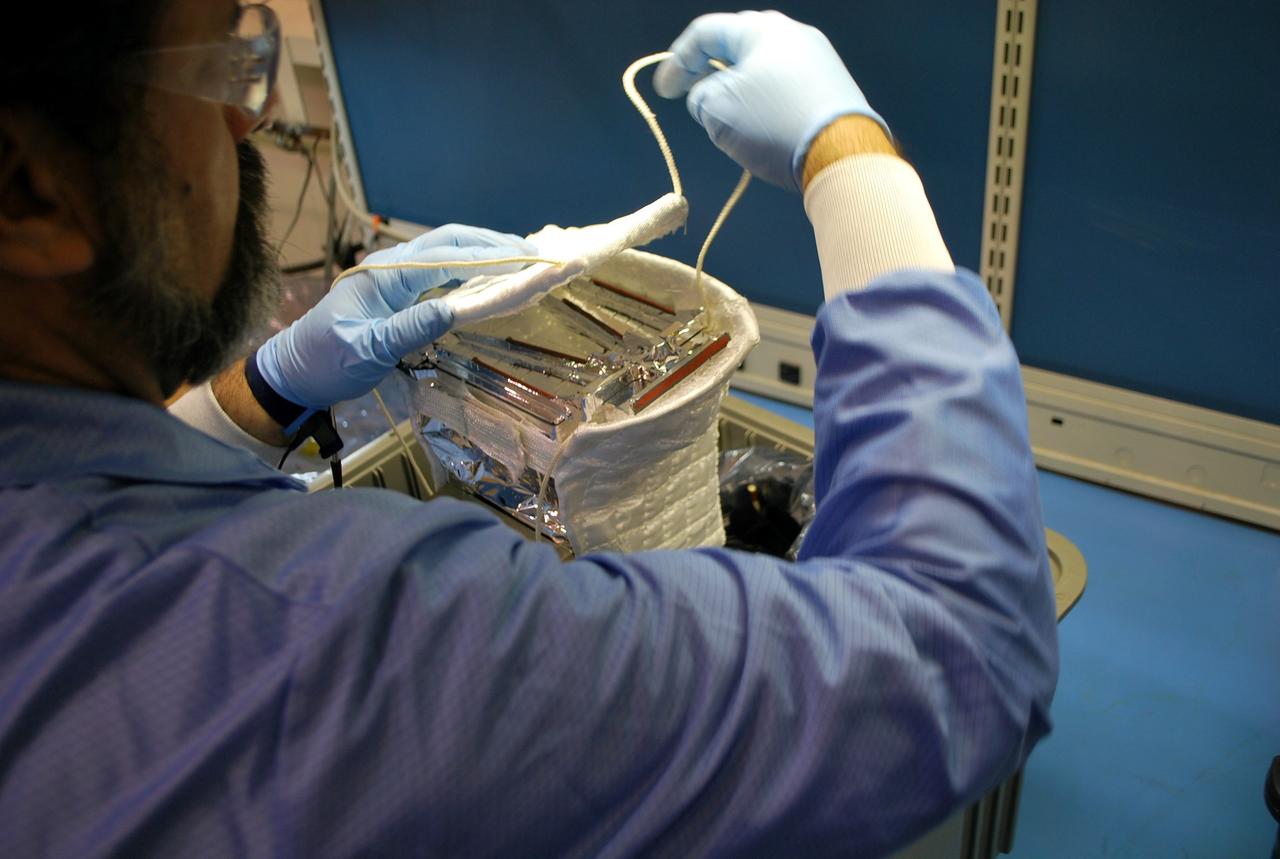

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician wraps the Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, container in a protective insulation blanket. The P-POD will hold three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
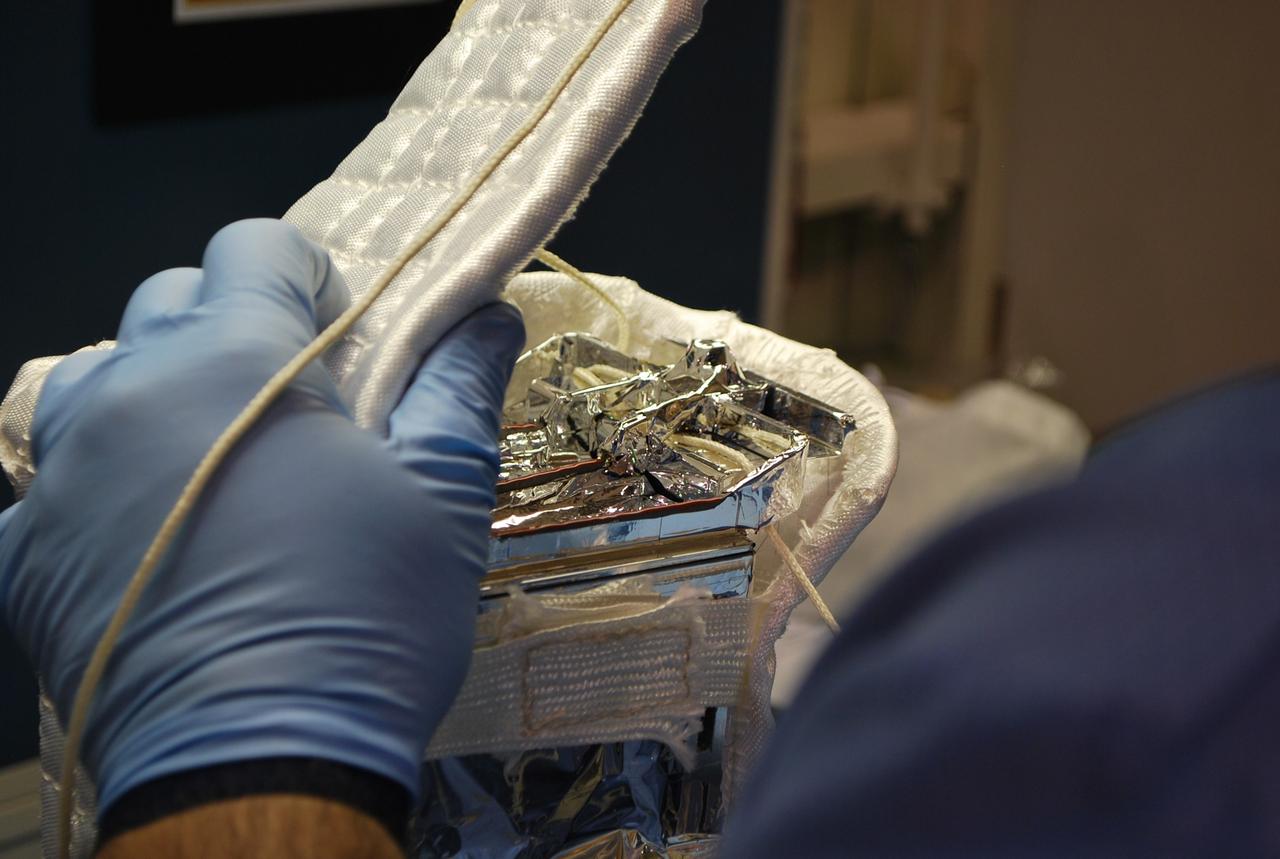

VANDENBERG AIR FORCE BASE, Calif. -- At Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician completes the wrapping of the Poly Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, assembly in a protective insulation blanket. The P-POD will hold three CubeSats or tiny satellites, designed and created by university and college students that will be carried on the Taurus rocket along with the Glory spacecraft. The Orbital Sciences Corp. Taurus XL rocket will carry NASA's Glory spacecraft into low Earth orbit. Once Glory reaches orbit, it will collect data on the properties of aerosols and black carbon. It also will help scientists understand how the sun's irradiance affects Earth's climate. Launch is scheduled for 5:09 a.m. EST Feb. 23. For information, visit www.nasa.gov/glory. Photo credit: NASA/Randy Beaudoin, VAFB
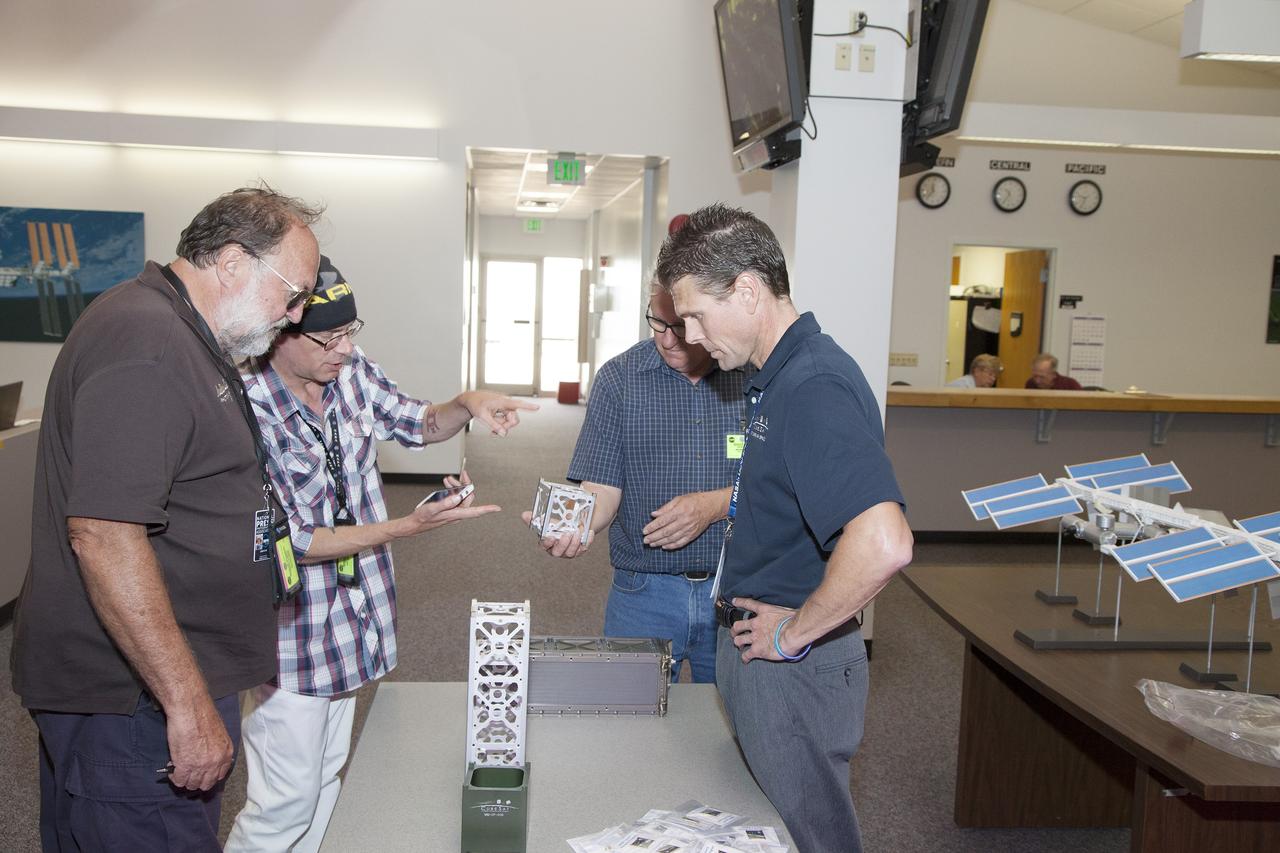

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Scott Higginbotham, right, mission manager for ELaNa V, discusses the concepts behind the design and deployment of the CubeSats flying on the ELaNa V mission with media representatives in the NASA Newsroom at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, using models of the Poly-Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, and various CubeSat canisters. NASA selected five small research satellites, or CubeSats, for the ELaNa V mission launching on SpaceX-3. Four P-PODs aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will ferry them to space. The CubeSats were designed by three universities and the agency's Ames Research Center in California. Launch is scheduled at about 4:58 p.m. EDT April 14. The SpaceX-3 mission, carrying almost 2.5 tons of supplies, technology and science experiments, is the third of 12 flights under NASA's Commercial Resupply Services contract to resupply the orbiting laboratory. For more information about NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
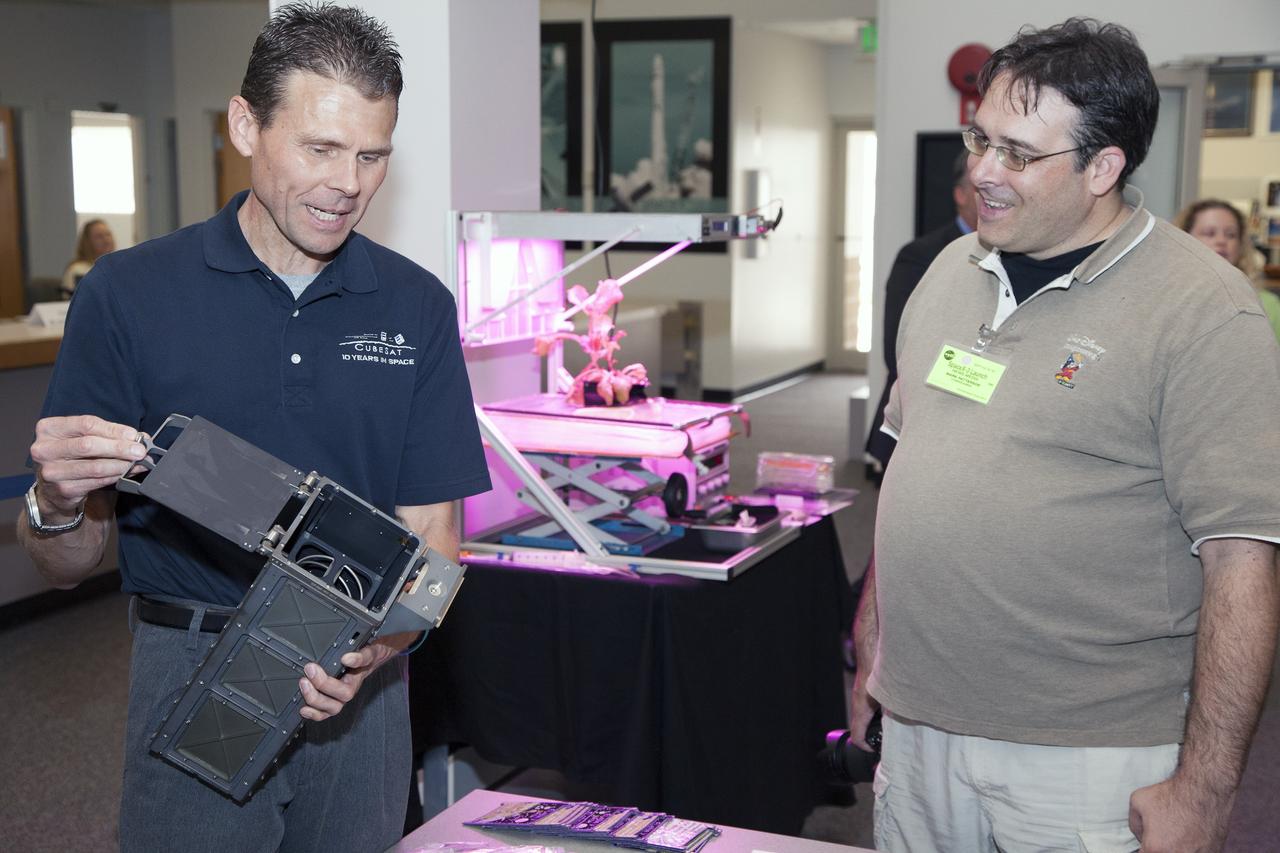

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Scott Higginbotham, left, mission manager for ELaNa V, demonstrates the concepts behind the design and deployment of the CubeSats flying on the ELaNa V mission with a media representative in the NASA Newsroom at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, using a model of the Poly-Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD. NASA selected five small research satellites, or CubeSats, for the ELaNa V mission launching on SpaceX-3. Four P-PODs aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will ferry them to space. The CubeSats were designed by three universities and the agency's Ames Research Center in California. Launch is scheduled at about 4:58 p.m. EDT April 14. The SpaceX-3 mission, carrying almost 2.5 tons of supplies, technology and science experiments, is the third of 12 flights under NASA's Commercial Resupply Services contract to resupply the orbiting laboratory. For more information about NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
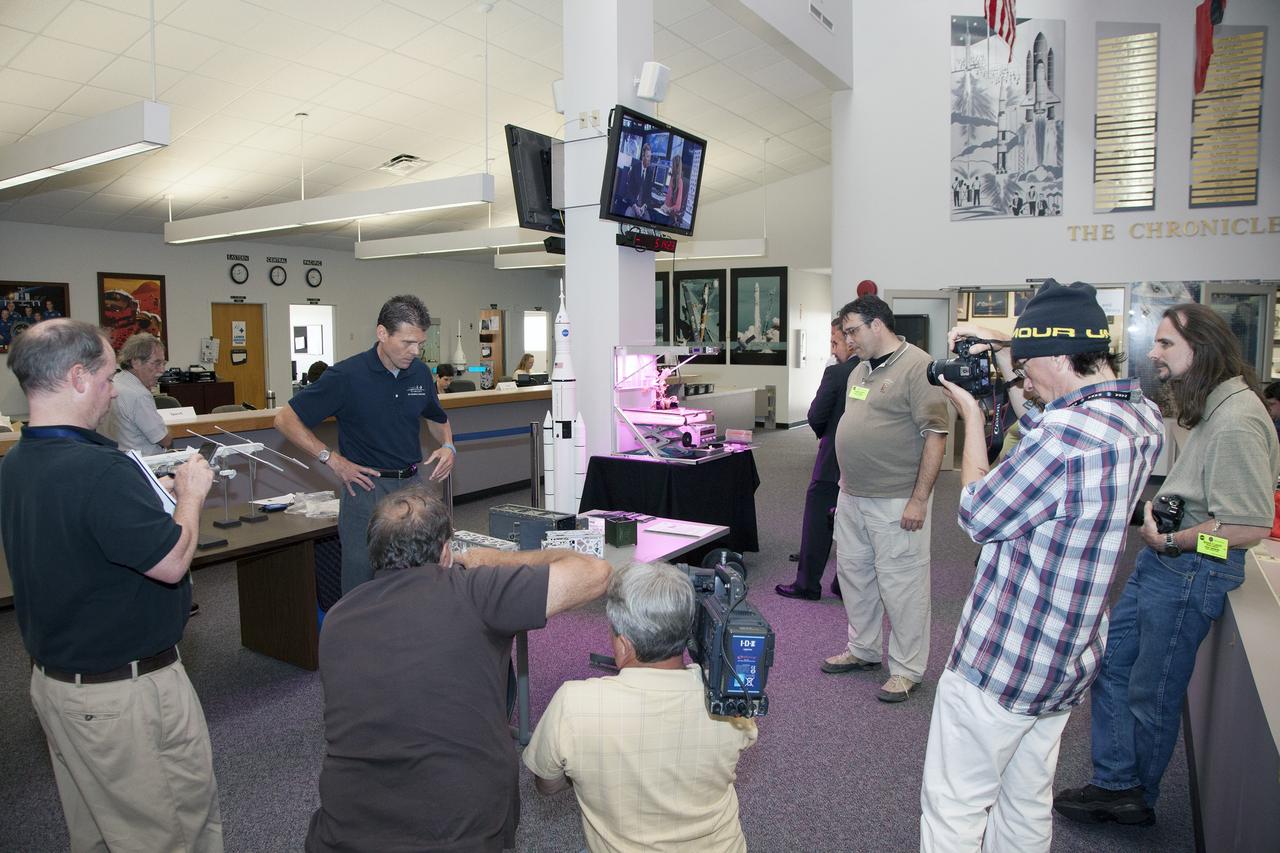

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Scott Higginbotham, center, mission manager for ELaNa V, discusses the concepts behind the design and deployment of the CubeSats flying on the ELaNa V mission with media representatives in the NASA Newsroom at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, using models of the Poly-Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, and various CubeSat canisters. NASA selected five small research satellites, or CubeSats, for the ELaNa V mission launching on SpaceX-3. Four P-PODs aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will ferry them to space. The CubeSats were designed by three universities and the agency's Ames Research Center in California. Launch is scheduled at about 4:58 p.m. EDT April 14. The SpaceX-3 mission, carrying almost 2.5 tons of supplies, technology and science experiments, is the third of 12 flights under NASA's Commercial Resupply Services contract to resupply the orbiting laboratory. For more information about NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
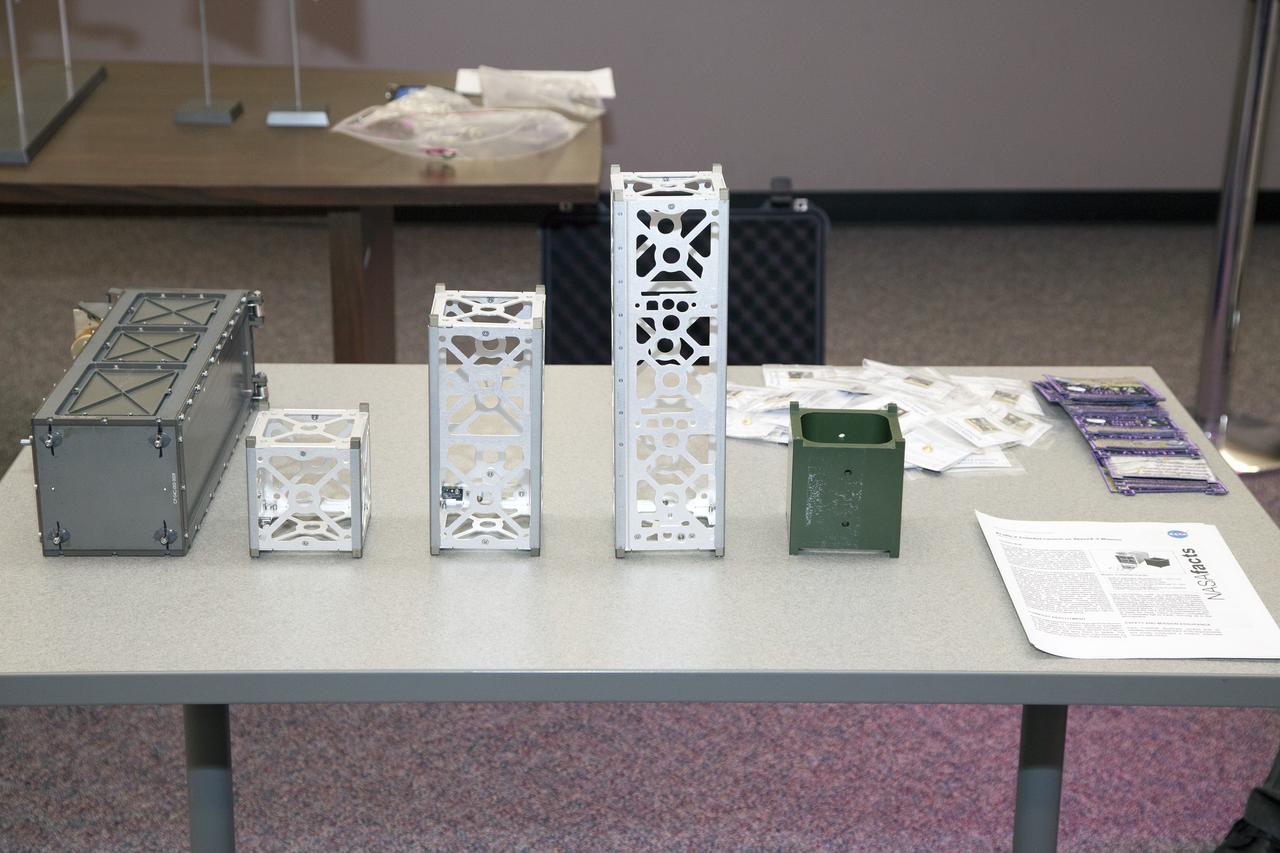

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Models of the hardware used to support the CubeSats flying on the ELaNa V mission are displayed in the NASA Newsroom at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. At left is a model of the Poly-Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, next to models of the various CubeSat canisters. NASA selected five small research satellites, or CubeSats, for the ELaNa V mission launching on SpaceX-3. Four P-PODs aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will ferry them to space. The CubeSats were designed by three universities and the agency's Ames Research Center in California. Launch is scheduled at about 4:58 p.m. EDT April 14. The SpaceX-3 mission, carrying almost 2.5 tons of supplies, technology and science experiments, is the third of 12 flights under NASA's Commercial Resupply Services contract to resupply the orbiting laboratory. For more information about NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
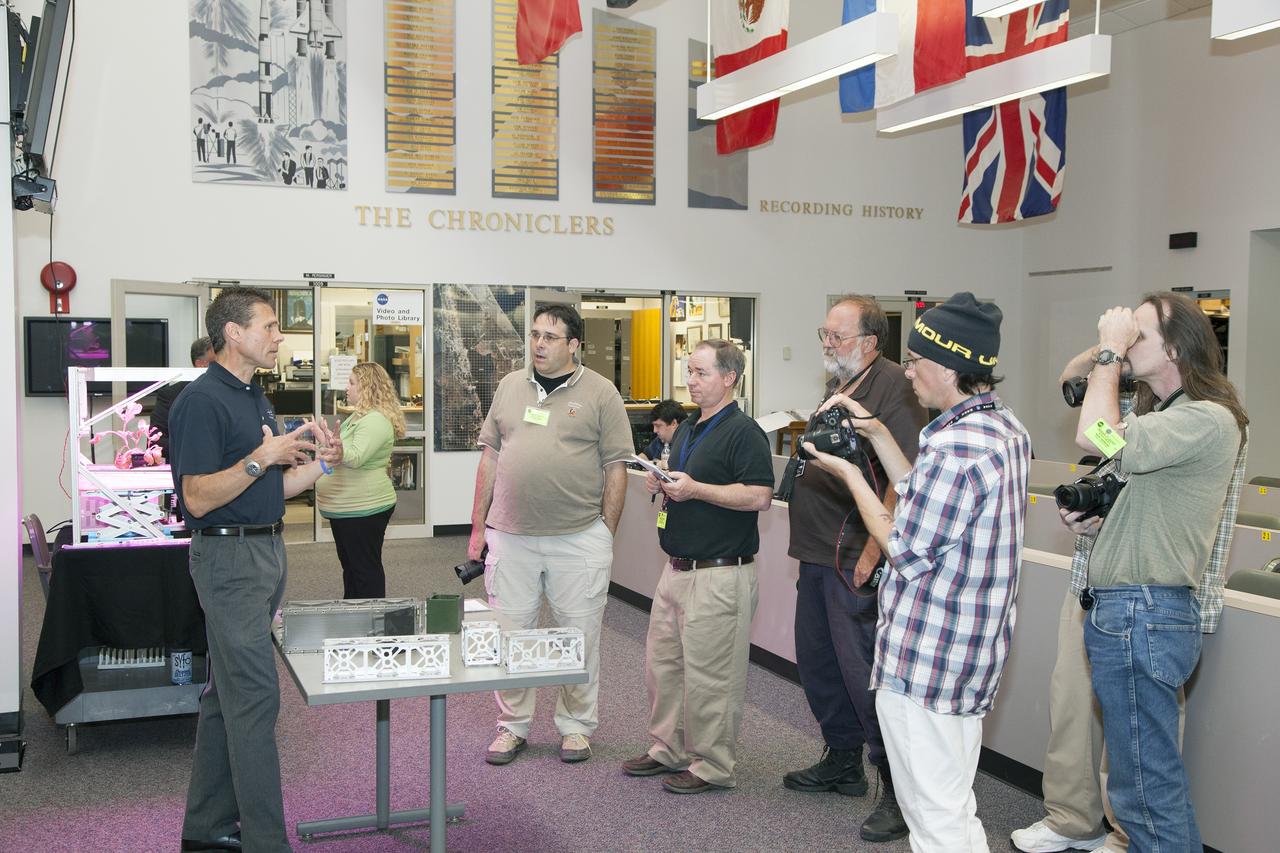

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - Scott Higginbotham, left, mission manager for ELaNa V, discusses the concepts behind the design and deployment of the CubeSats flying on the ELaNa V mission with media representatives in the NASA Newsroom at Kennedy Space Center in Florida, using models of the Poly-Picosatellite Orbital Deployer, or P-POD, and various CubeSat canisters. NASA selected five small research satellites, or CubeSats, for the ELaNa V mission launching on SpaceX-3. Four P-PODs aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket will ferry them to space. The CubeSats were designed by three universities and the agency's Ames Research Center in California. Launch is scheduled at about 4:58 p.m. EDT April 14. The SpaceX-3 mission, carrying almost 2.5 tons of supplies, technology and science experiments, is the third of 12 flights under NASA's Commercial Resupply Services contract to resupply the orbiting laboratory. For more information about NASA's CubeSat Launch Initiative, visit http://go.nasa.gov/CubeSat_initiative. Photo credit: NASA/Glenn Benson
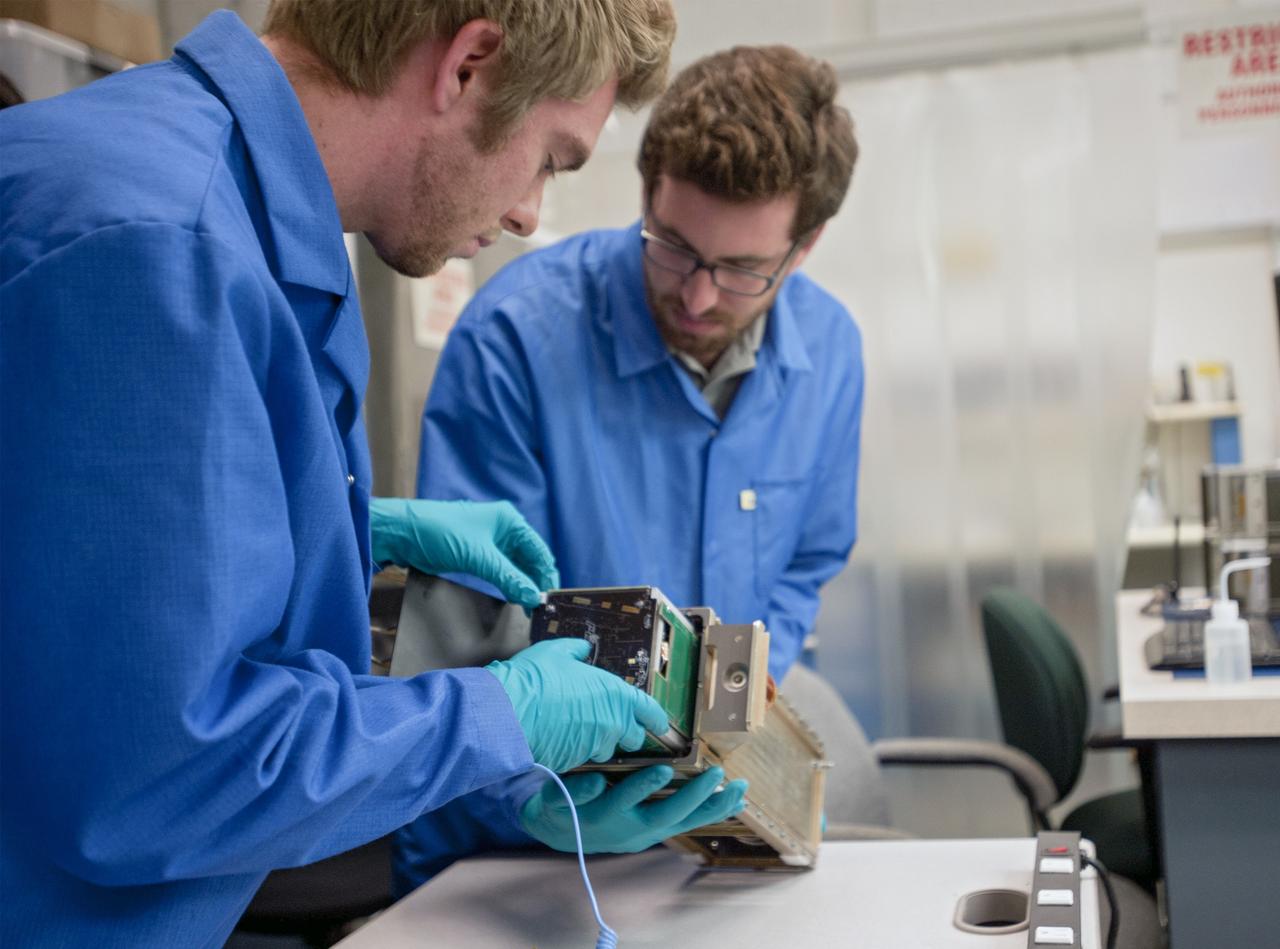

KSC-2013-2721 – SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. –Members of the student launch team load a payload into a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Dispensor, or P-Pod nanolauncher/carrier in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cube sections, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the satellite will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Also, a new launcher/carrier of a lightweight design also is being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
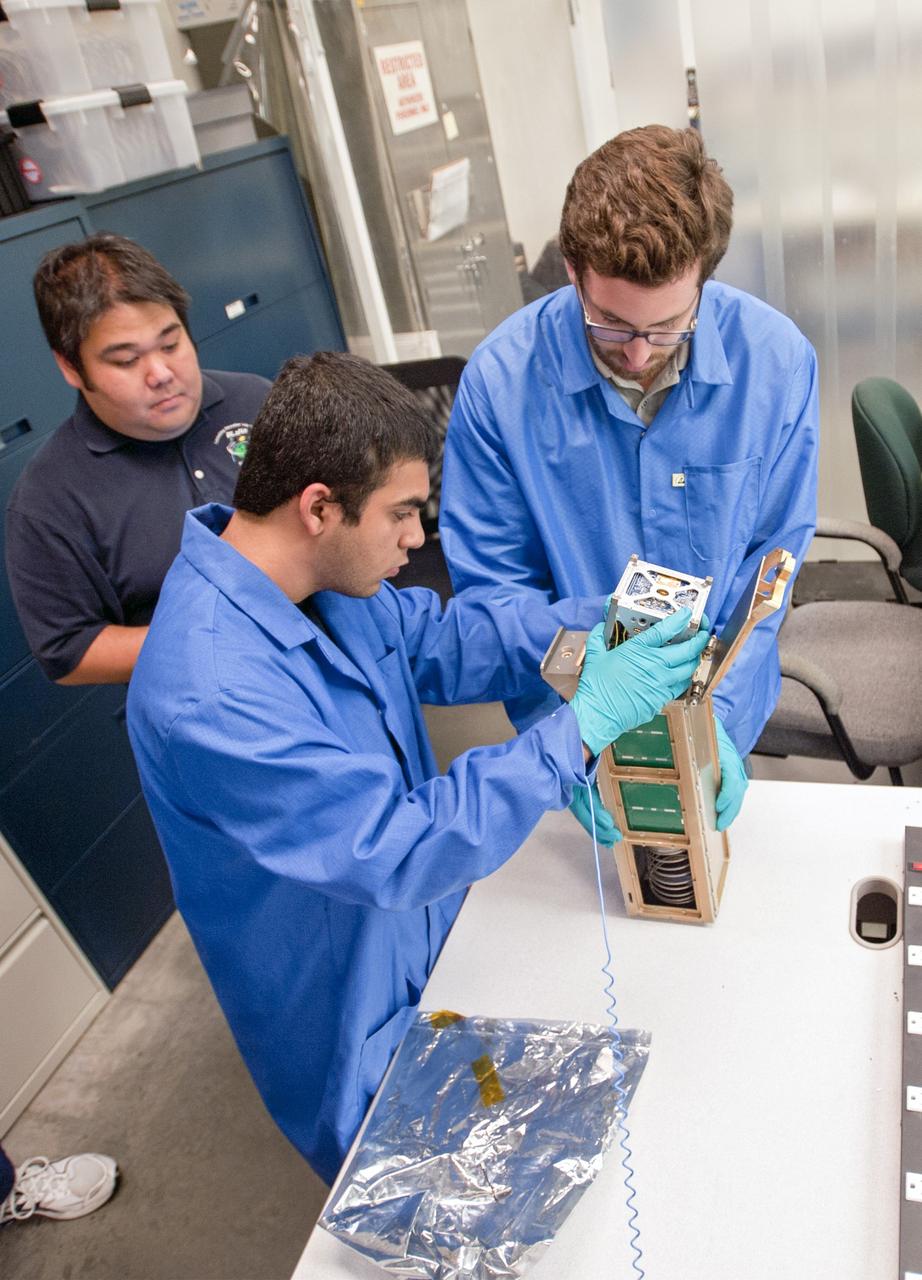

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – Roland Coelho, third from left, CalPoly program lead, and members of the student launch team load a payload into a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Dispensor, or P-Pod nanolauncher/carrier in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cube sections, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the satellite will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Also, a new launcher/carrier of a lightweight design also is being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
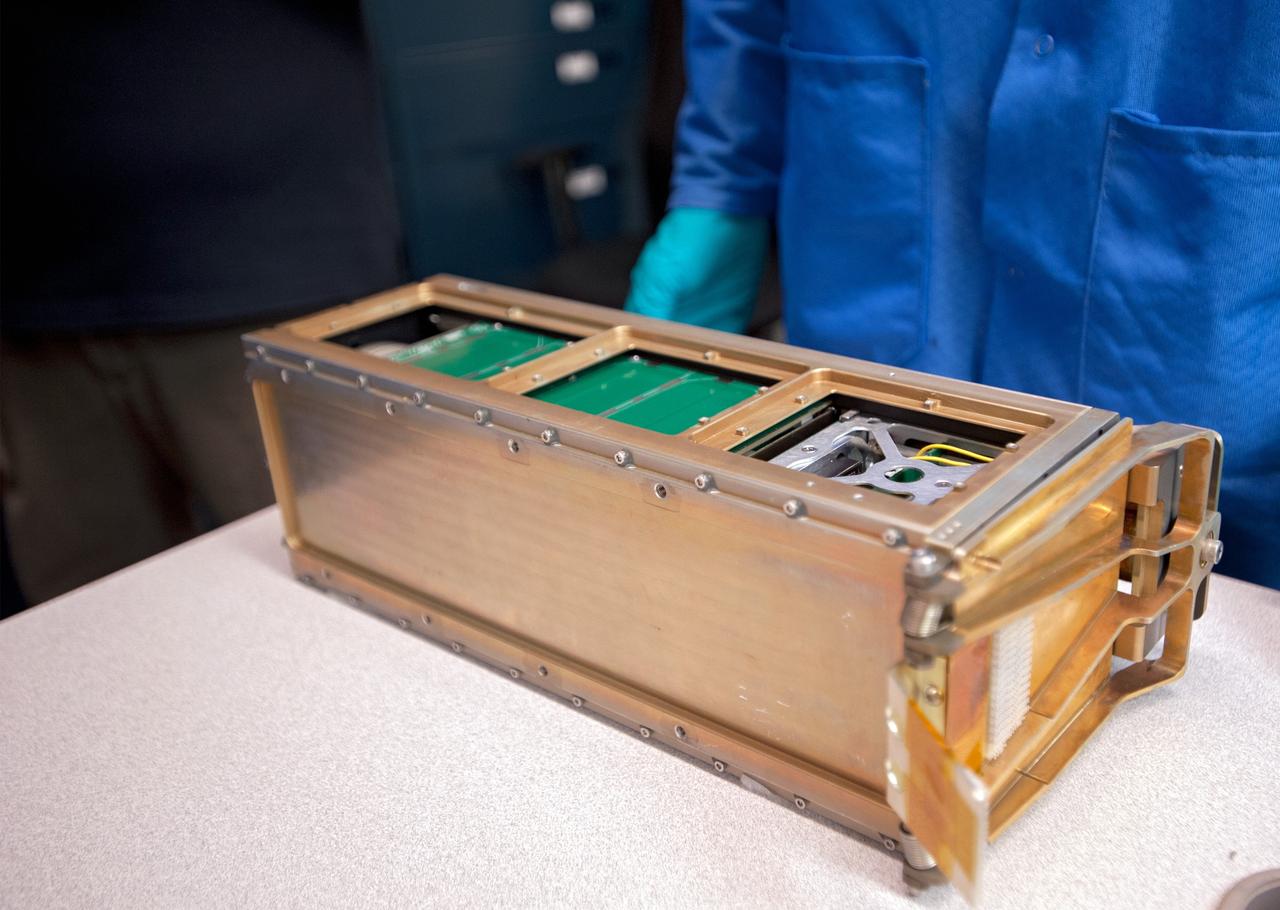

SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. – A Poly Picosatellite Orbital Dispensor, or P-Pod nanolauncher/carrier in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cube sections, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the satellite will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples
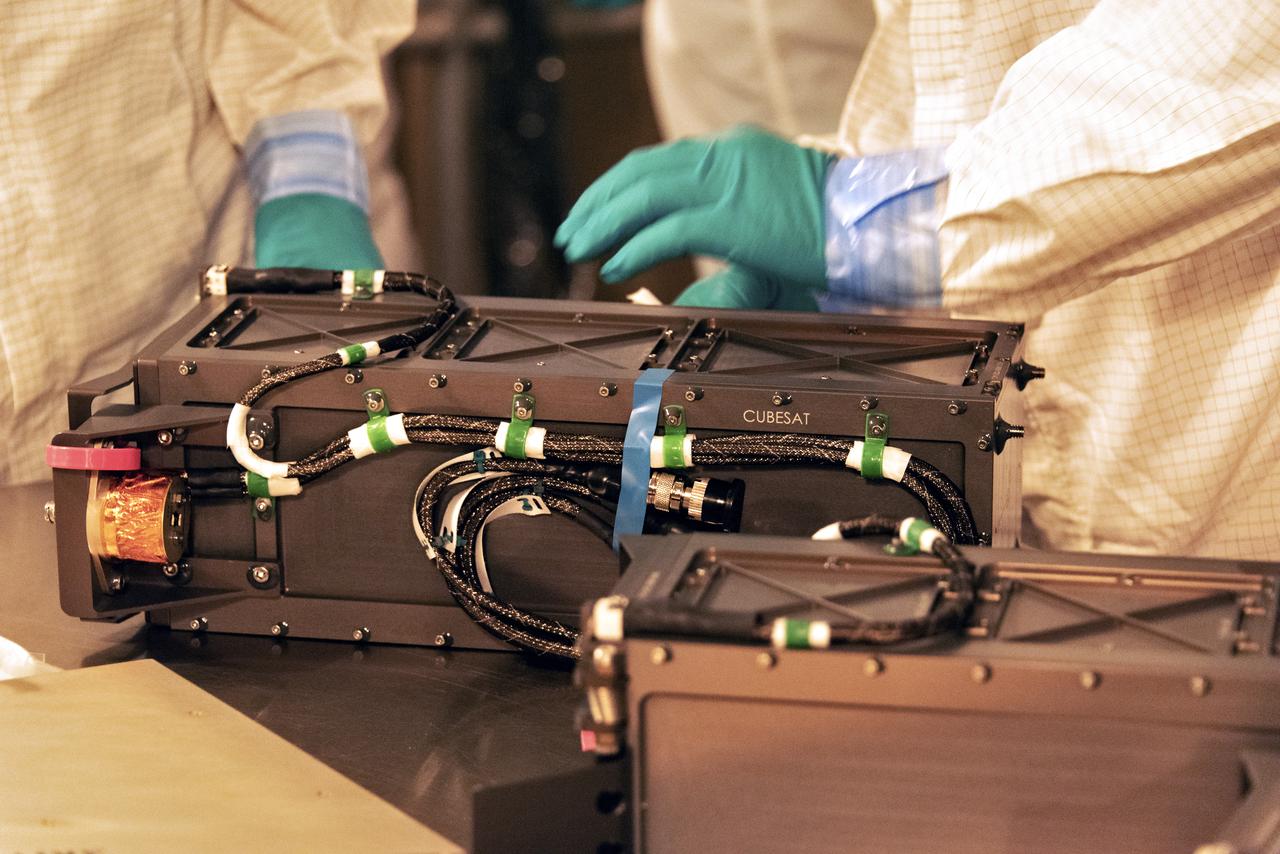

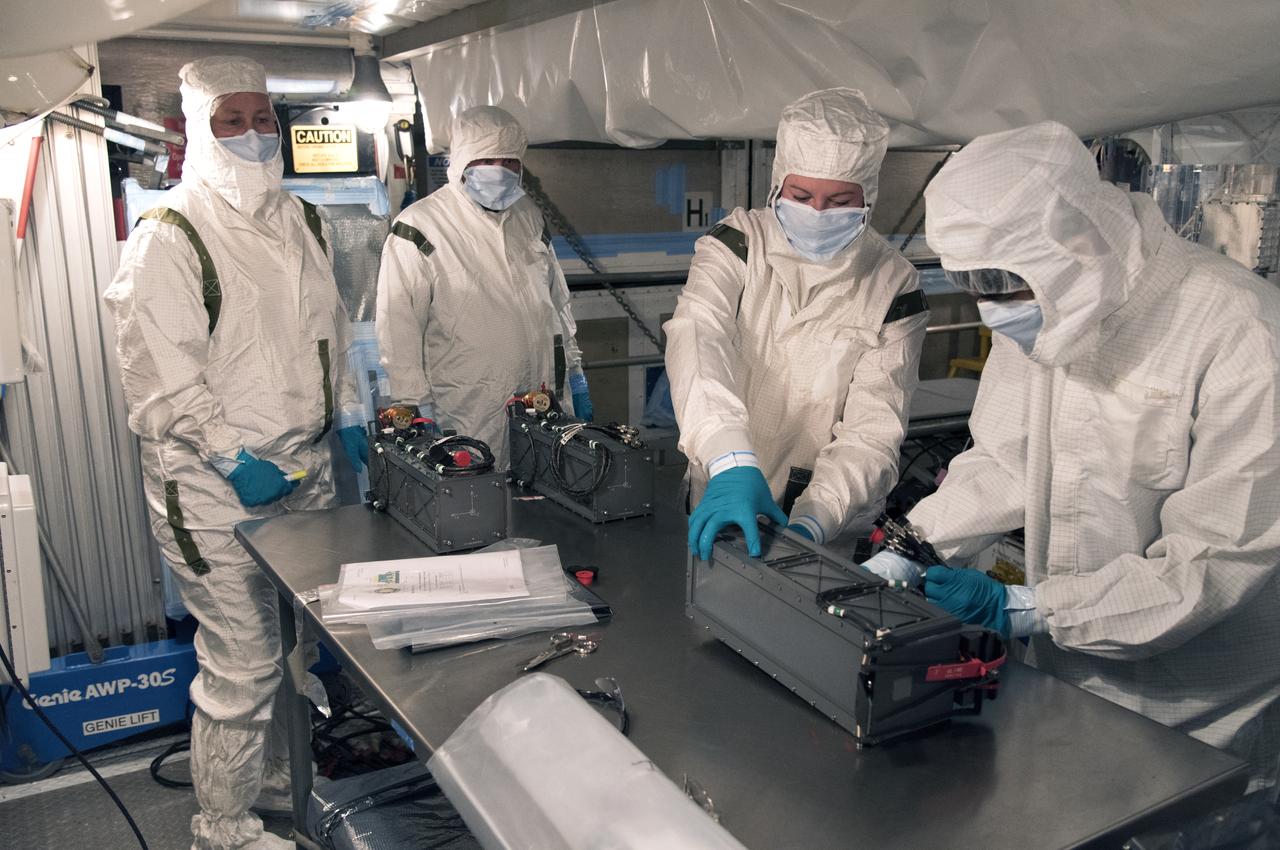
At Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare three poly picosatellite orbital deployers, or P-POD containers, with tiny satellites, called CubeSats inside, for installation on the direct mate adapter of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket, on Aug. 31, 2018. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) is ready for launch aboard the final Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.
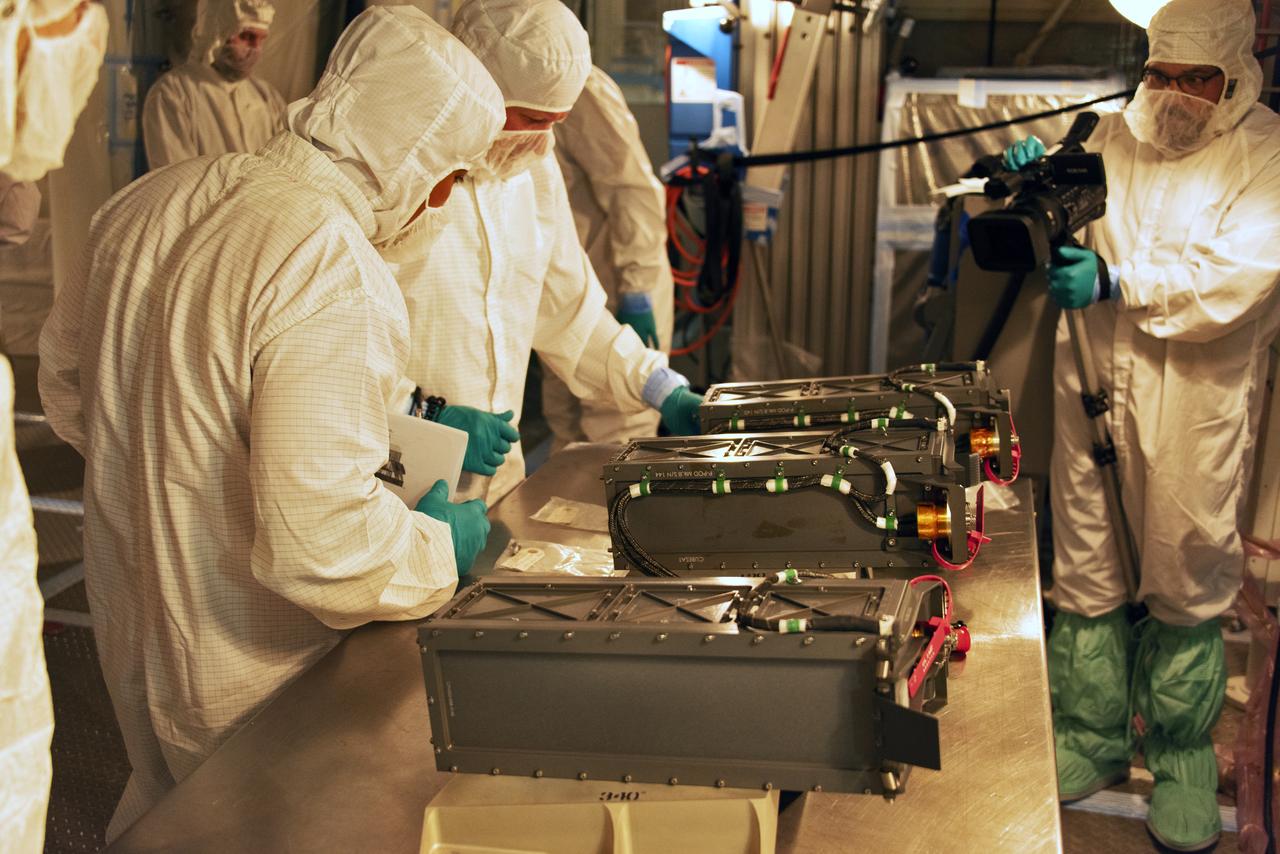

At Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare three poly picosatellite orbital deployers, or P-POD containers, with tiny satellites, called CubeSats inside, for installation on the direct mate adapter of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket, on Aug. 31, 2018. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) is ready for launch aboard the final Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.
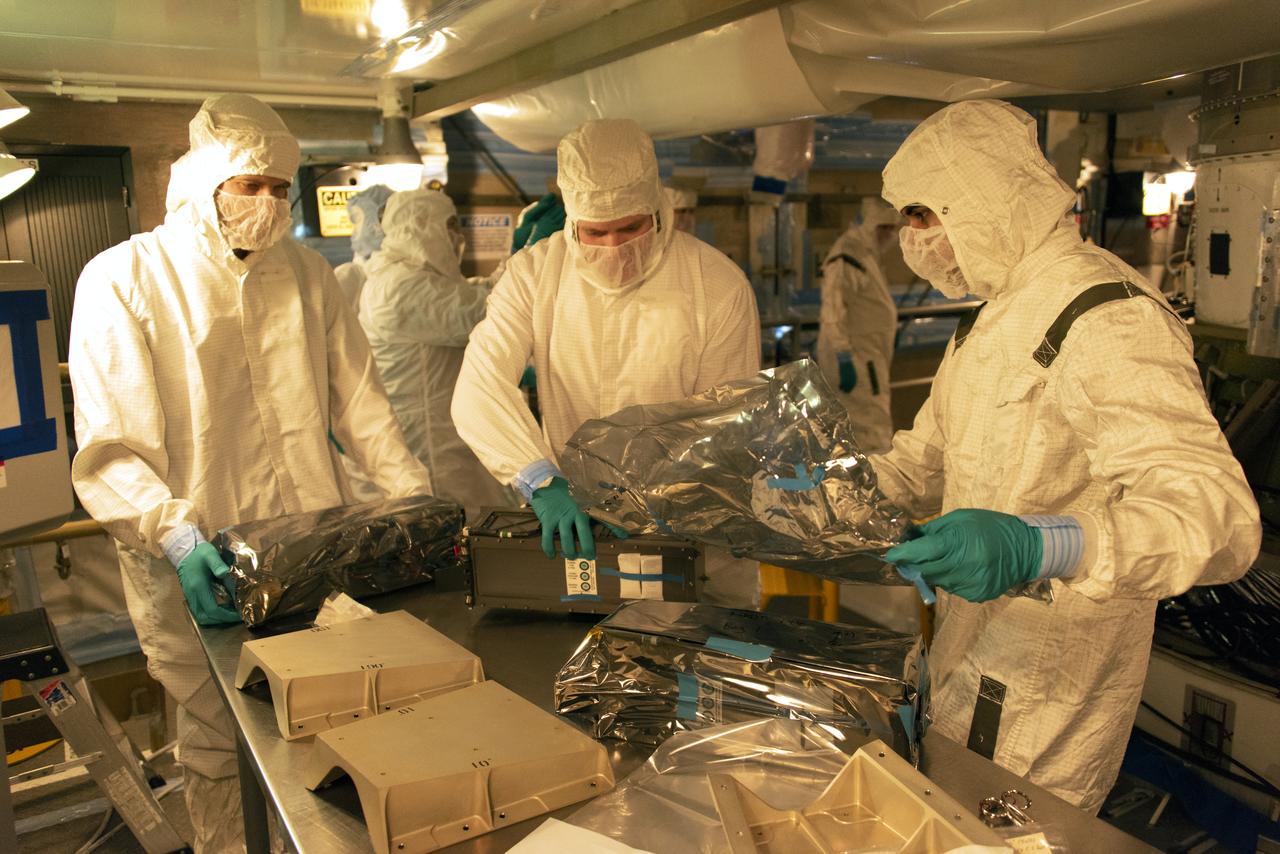

At Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare three poly picosatellite orbital deployers, or P-POD containers, with tiny satellites, called CubeSats inside, for installation on the direct mate adapter of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket, on Aug. 31, 2018. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) is ready for launch aboard the final Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.
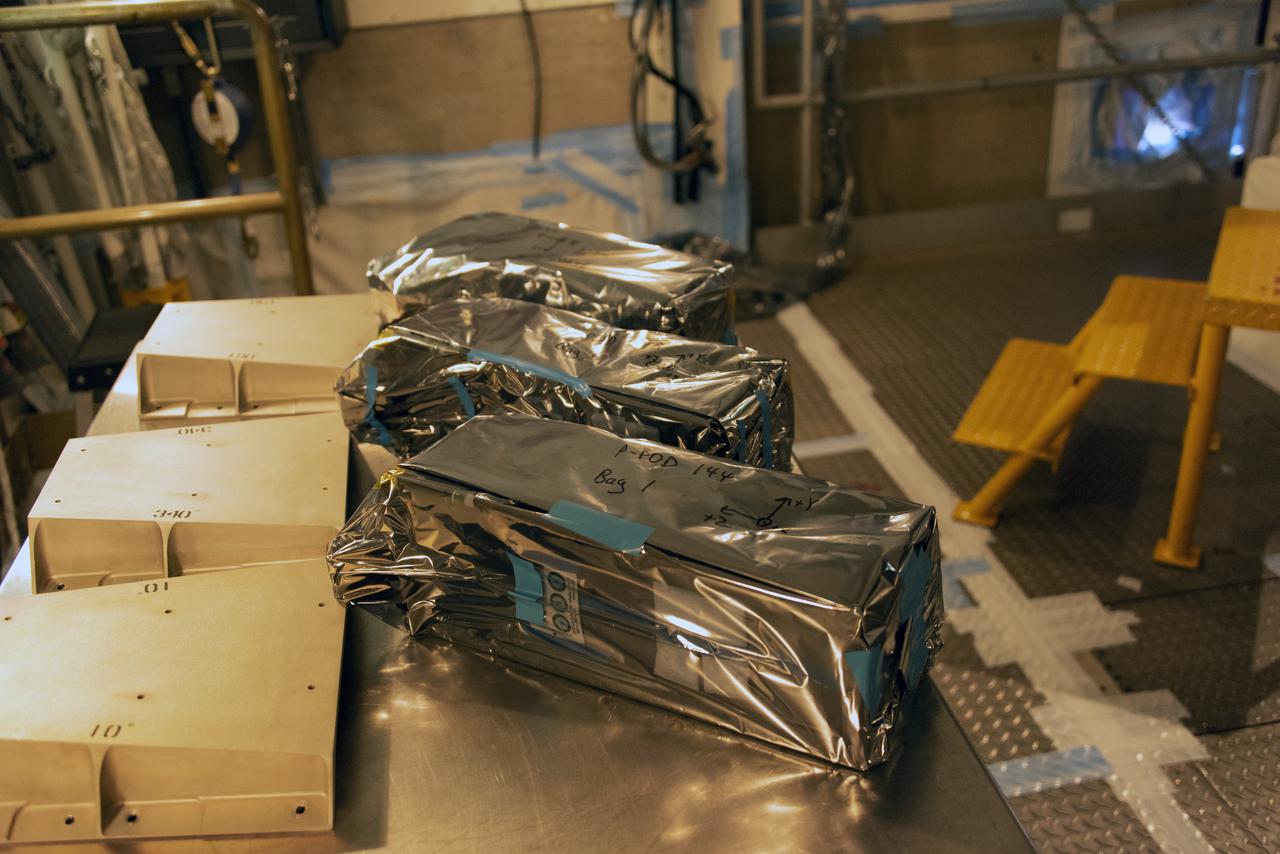

At Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, three poly picosatellite orbital deployers, or P-POD containers, with tiny satellites, called CubeSats inside, are being prepared for installation on the direct mate adapter of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket, on Aug. 31, 2018. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) is ready for launch aboard the final Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.
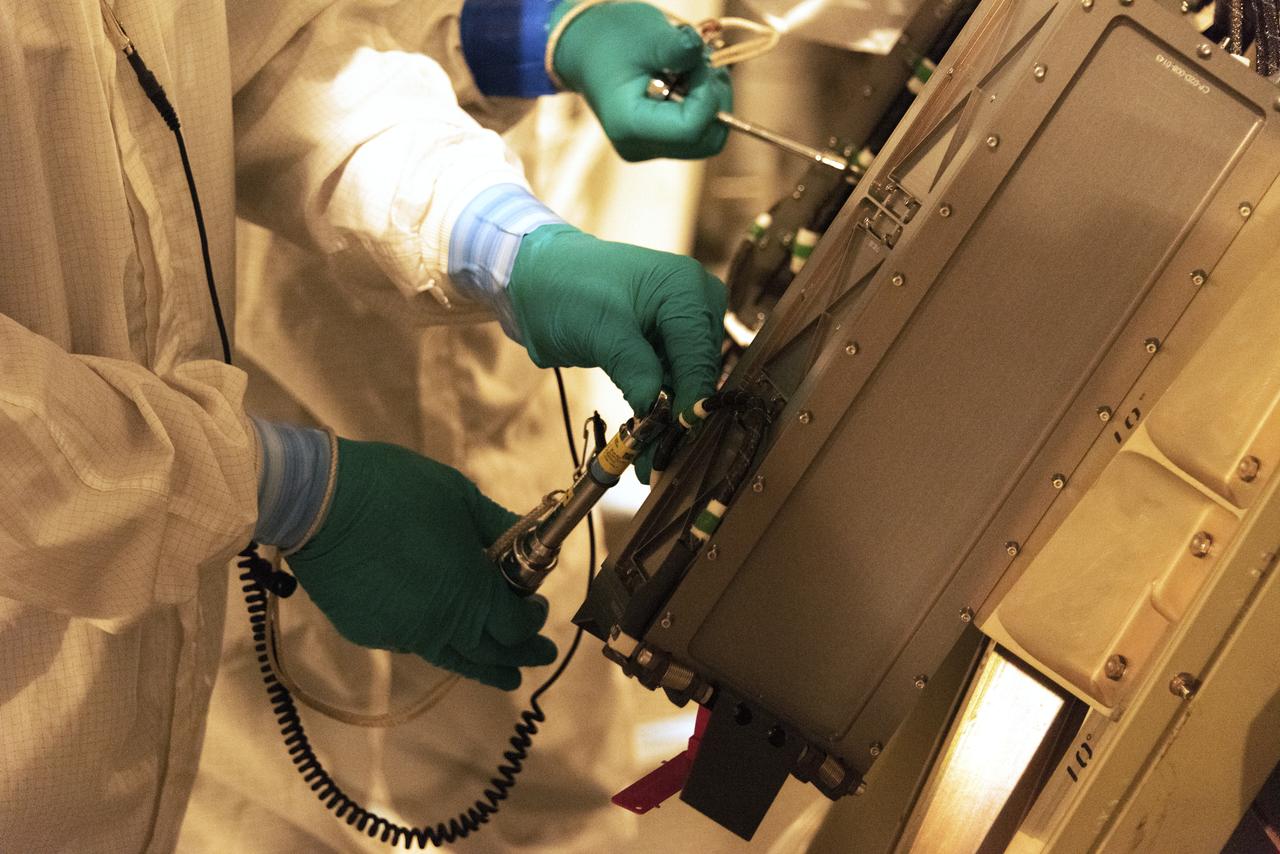

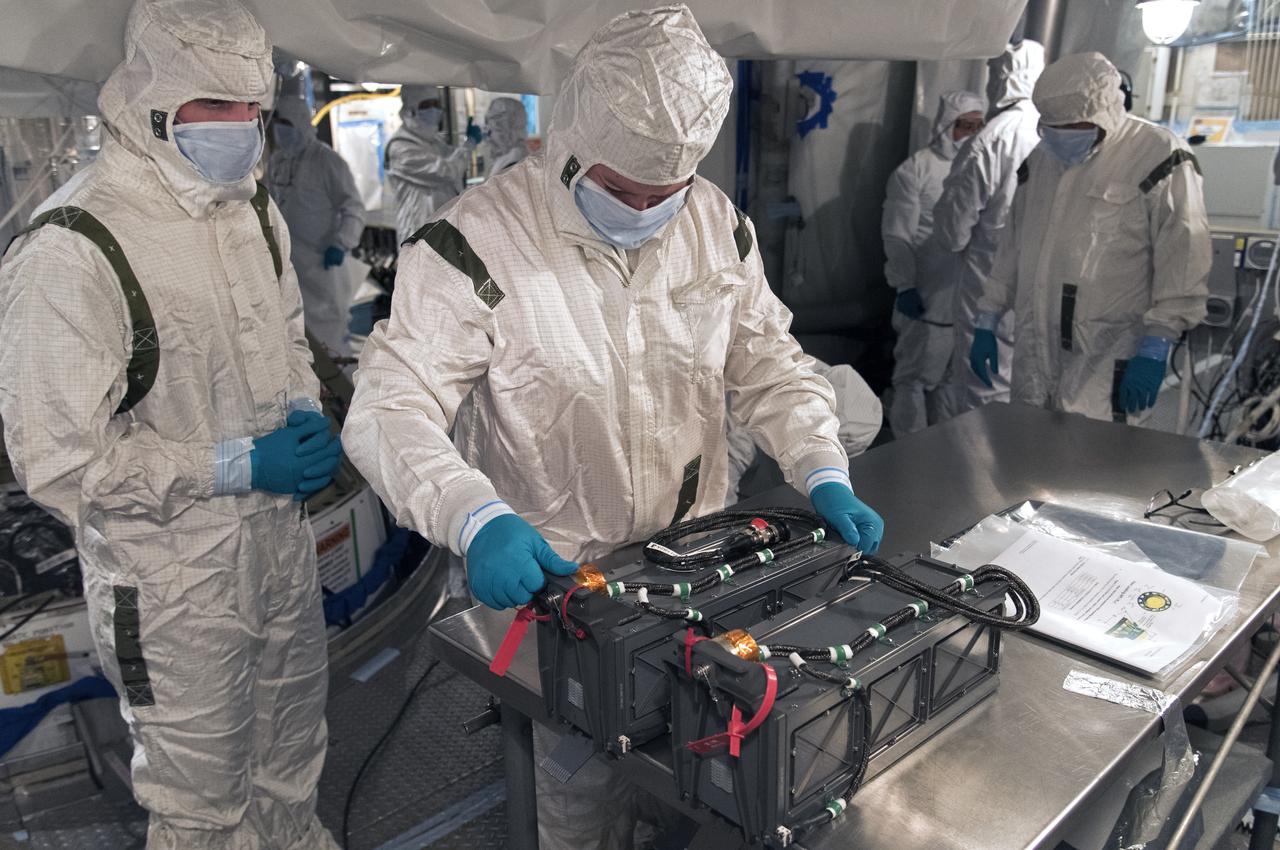
At Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians install a poly picosatellite orbital deployer, or P-POD container, with tiny satellites called CubeSats inside, onto the direct mate adapter of the United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket, on Aug. 31, 2018. NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) is ready for launch aboard the final Delta II rocket. Launch is scheduled for Sept. 15, 2018. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.
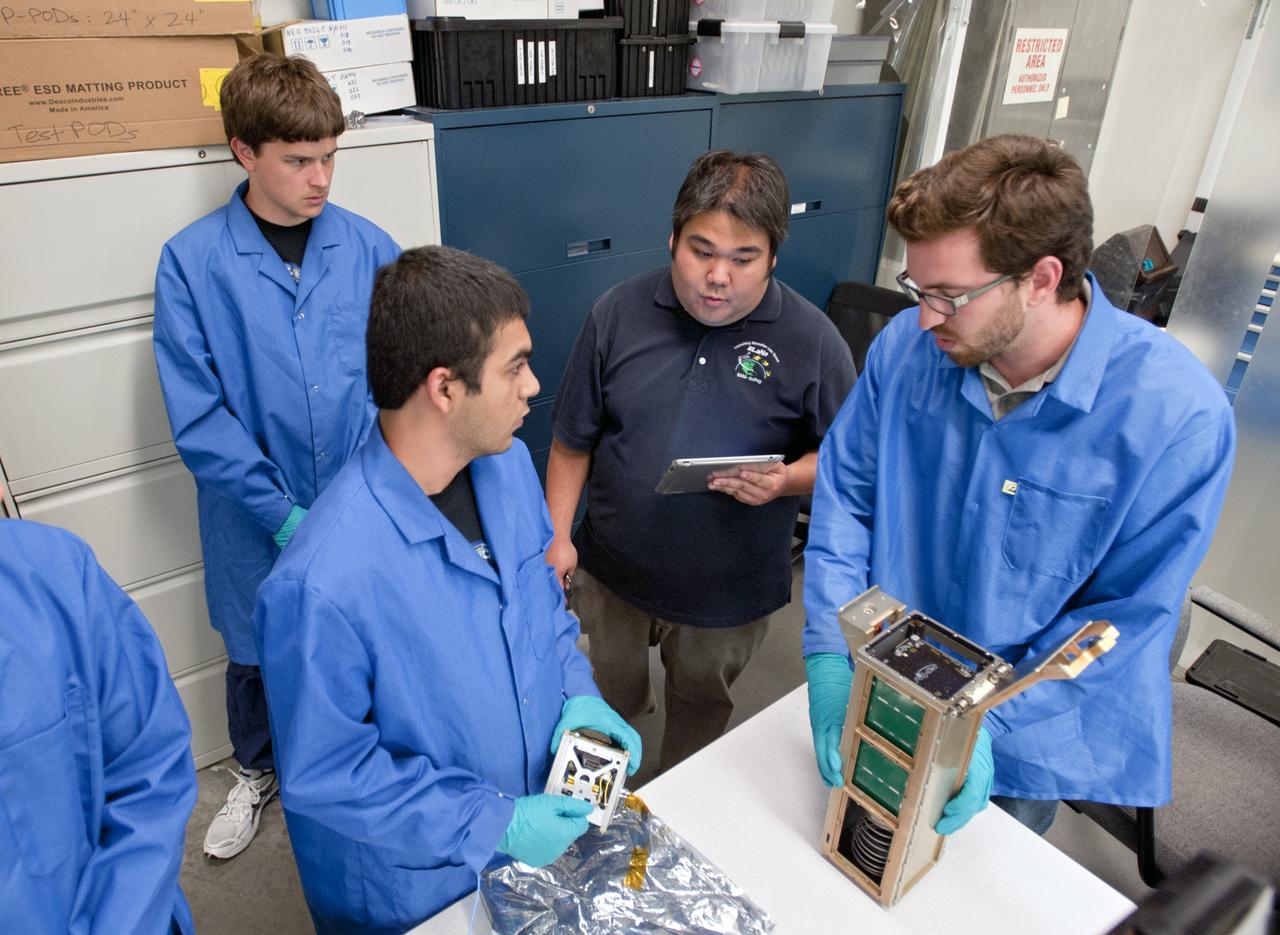

KSC-2013-2721 – SAN LUIS OBISPO, Calif. –Roland Coelho, third from left, CalPoly program lead, and members of the student launch team load a payload into a Poly Picosatellite Orbital Dispensor, or P-Pod nanolauncher/carrier in the CubeSat lab facility at California Polytechnic Institute, or CalPoly. The payload, which includes sensors and equipment carefully packaged into 4-inch cube sections, will ride in the body of a Garvey Spacecraft Corporation's Prospector P-18D rocket during a June 15 launch on a high-altitude, suborbital flight. Known as a CubeSat, the satellite will record shock, vibrations and heat inside the rocket. It will not be released during the test flight, but the results will be used to prove or strengthen their designs before they are carried into orbit in 2014 on a much larger rocket. Also, a new launcher/carrier of a lightweight design also is being tested for use on future missions to deploy the small spacecraft. The flight also is being watched closely as a model for trying out new or off-the-shelf technologies quickly before putting them in the pipeline for use on NASA's largest launchers. Built by several different organizations, including a university, a NASA field center and a high school, the spacecraft are four-inch cubes designed to fly on their own eventually, but will remain firmly attached to the rocket during the upcoming mission. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/smallsats/elana/cubesatlaunchpreview.html Photo credit: VAFB/Kathi Peoples