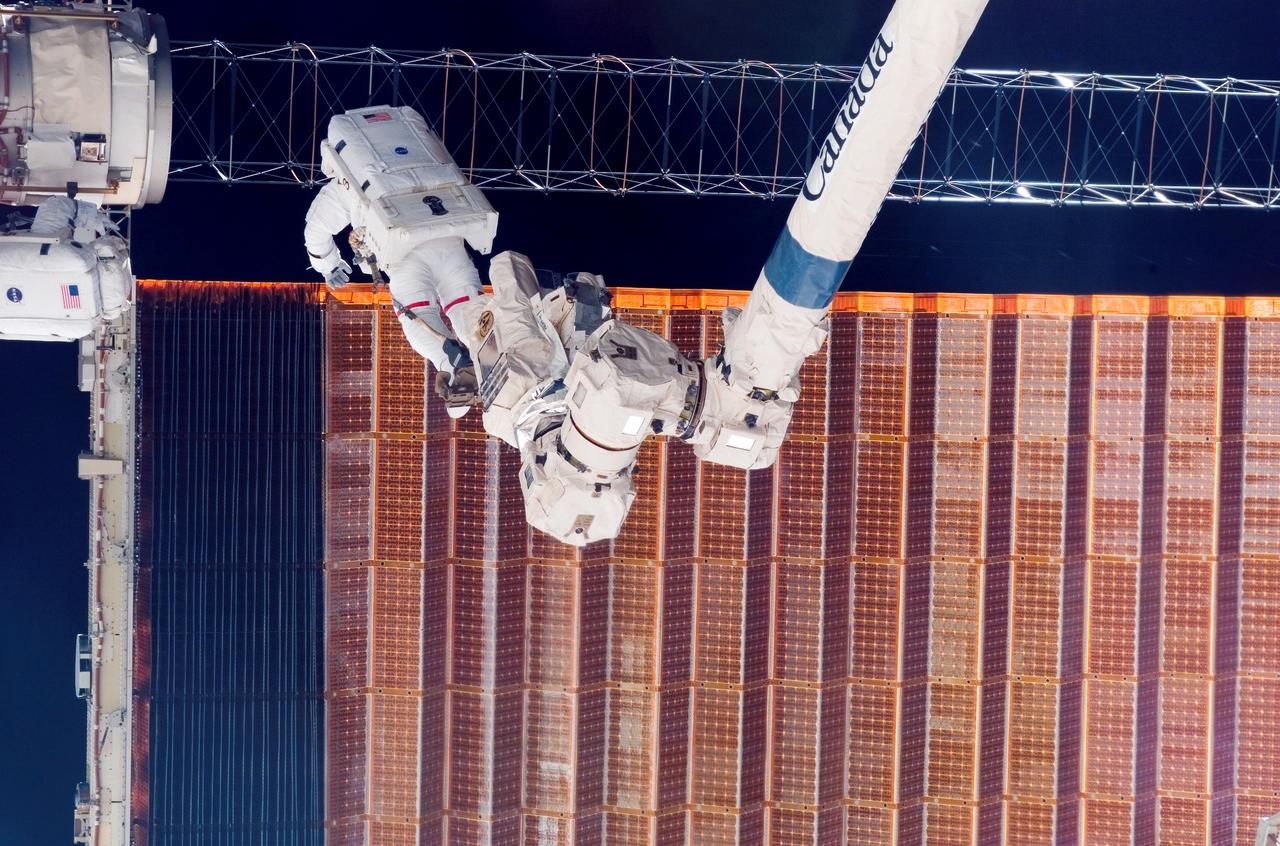

STS-116 astronaut and mission specialist, Robert Curbeam, along with the European Space Agency’s (ESA) Christer Fuglesang (partially out of the frame), are anchored to the International Space Station’s Canadarm2 foot restraints. The two were working on the port overhead solar array wing on the Station’s P6 truss during the mission’s fourth session of Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA). For 6 hours and 38 minutes, the space walkers used specially prepared, tape insulated tools to guide the array wing neatly inside its blanket box.
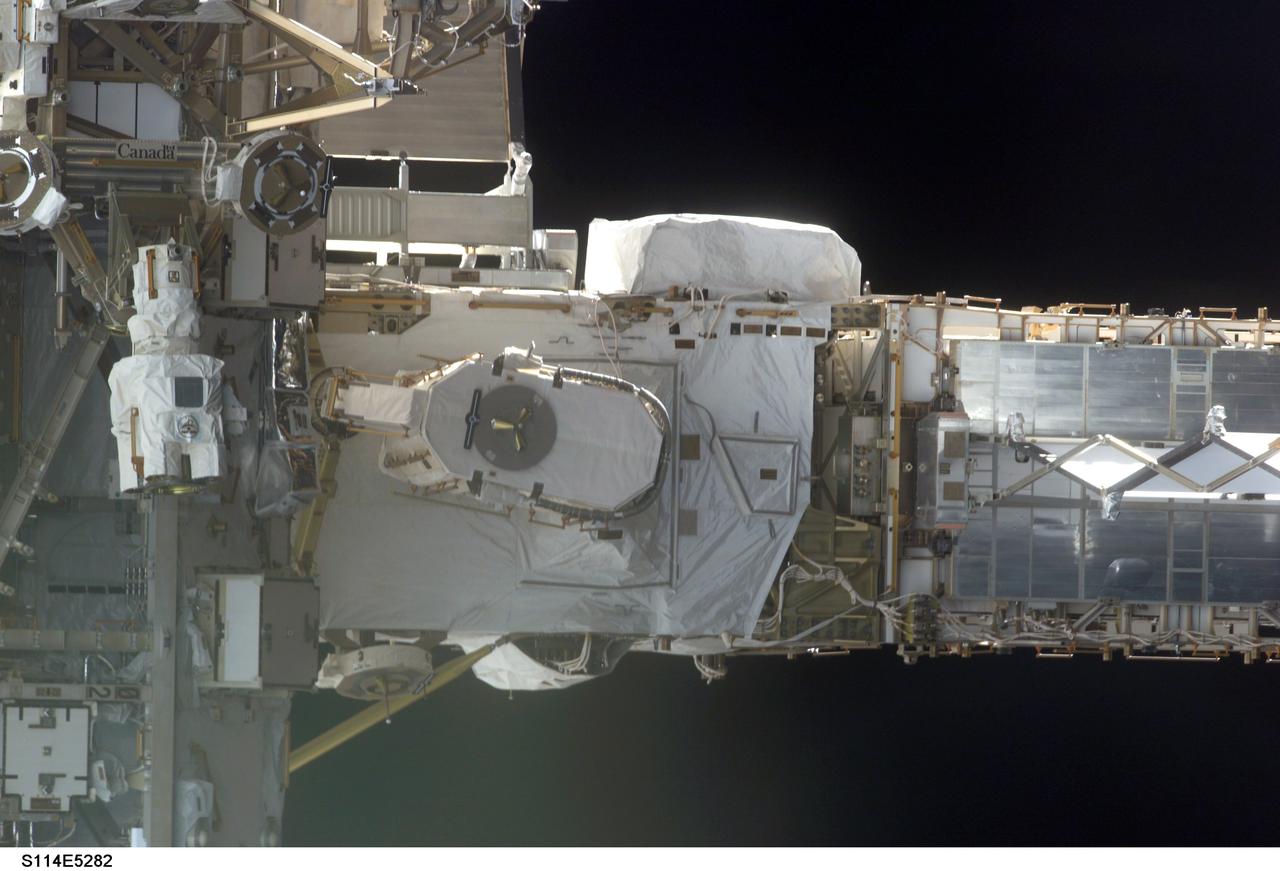

STS114-E-5282 (28 July 2005) --- This frame and STS114-E-5283 actually can be conjoined and rotated 90 degrees to make a single frame, providing an "astronaut's eye view" from Discovery's aft cabin looking toward the recently docked International Space Station. At the left side are the S0 truss and mobile transporter, with the P6 truss on the right side.
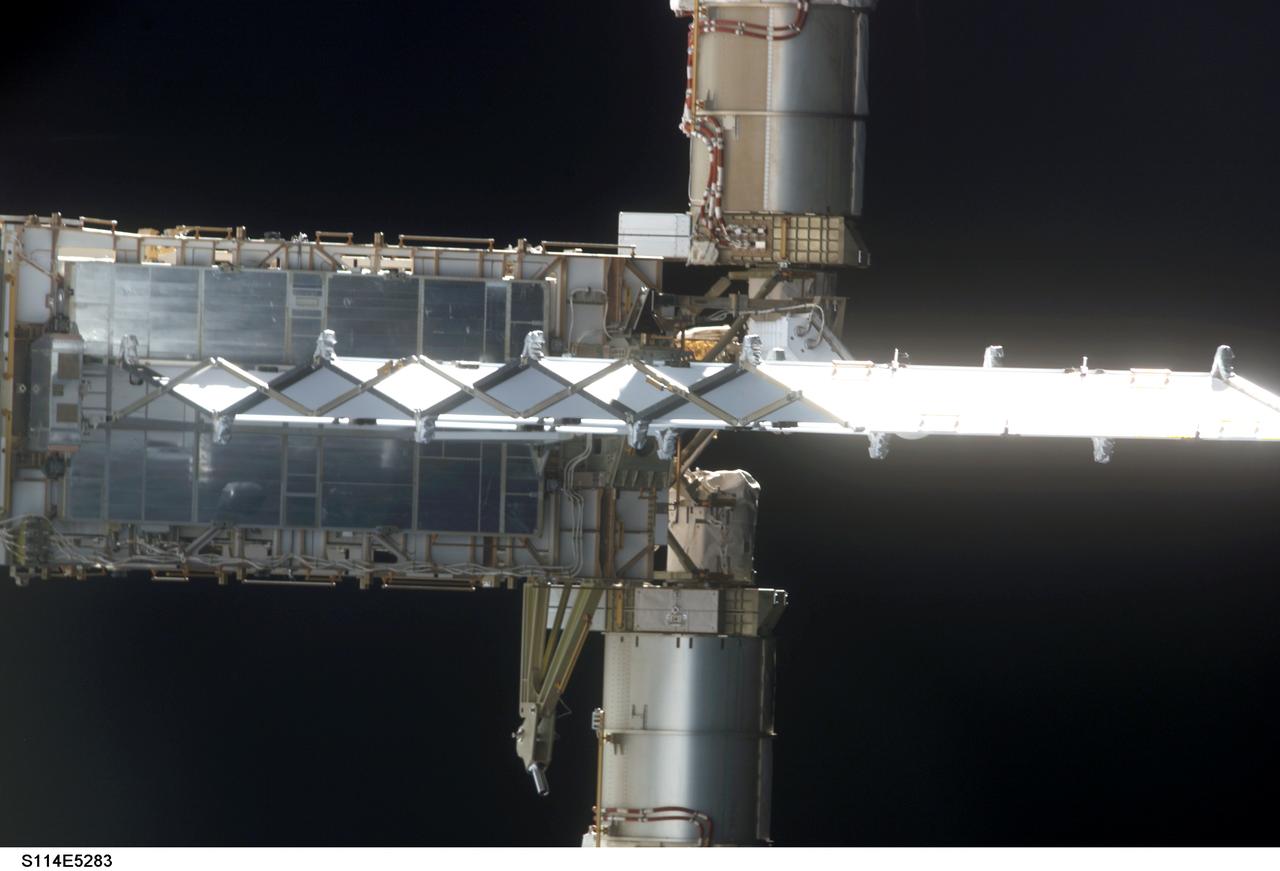

STS114-E-5283 (28 July 2005) --- This frame and STS114-E-5282 actually can be conjoined and rotated 90 degrees to make a single frame, providing an "astronaut's eye view" from Discovery's aft cabin looking toward the recently docked International Space Station. This frame shows the end of the P6 truss and a radiator panel. The two cropped cylinder-shaped objects are actually the base for the large solar array panels (out of frame).
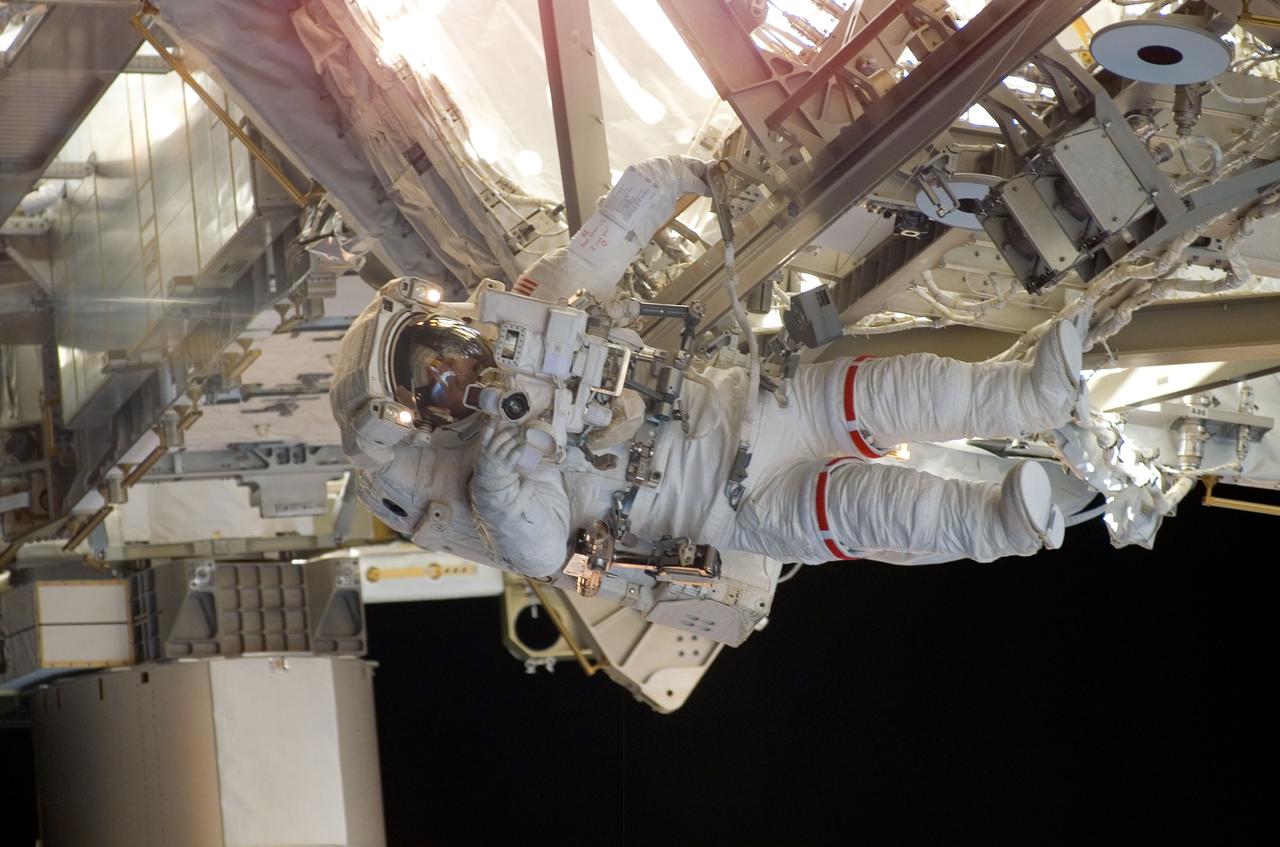

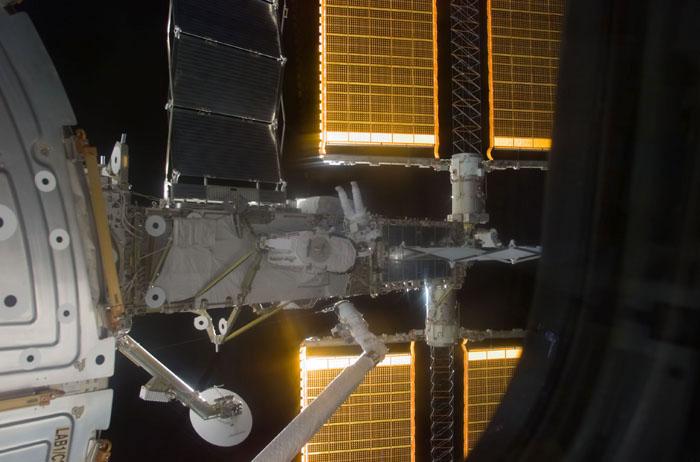
S120-E-007100 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.
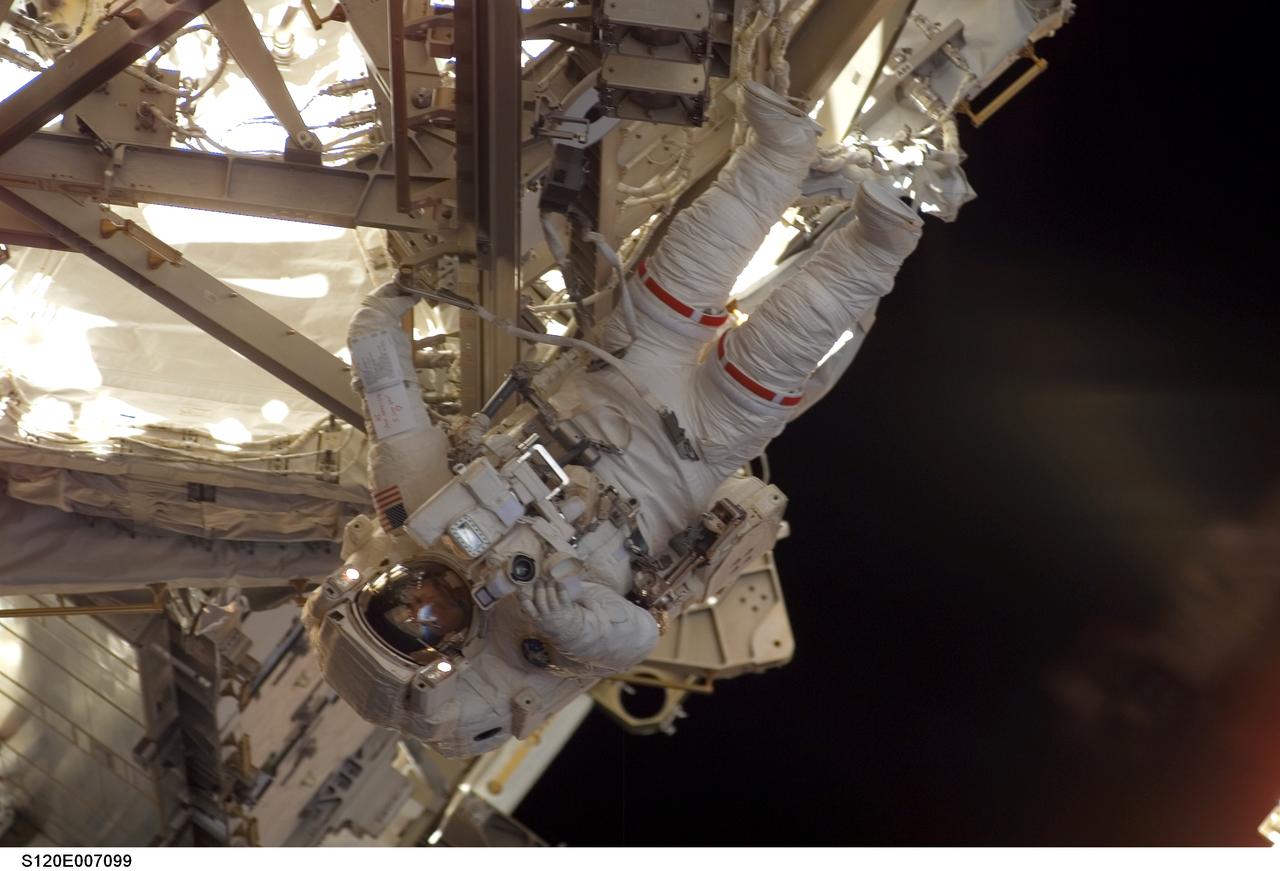

S120-E-007099 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani, Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later.
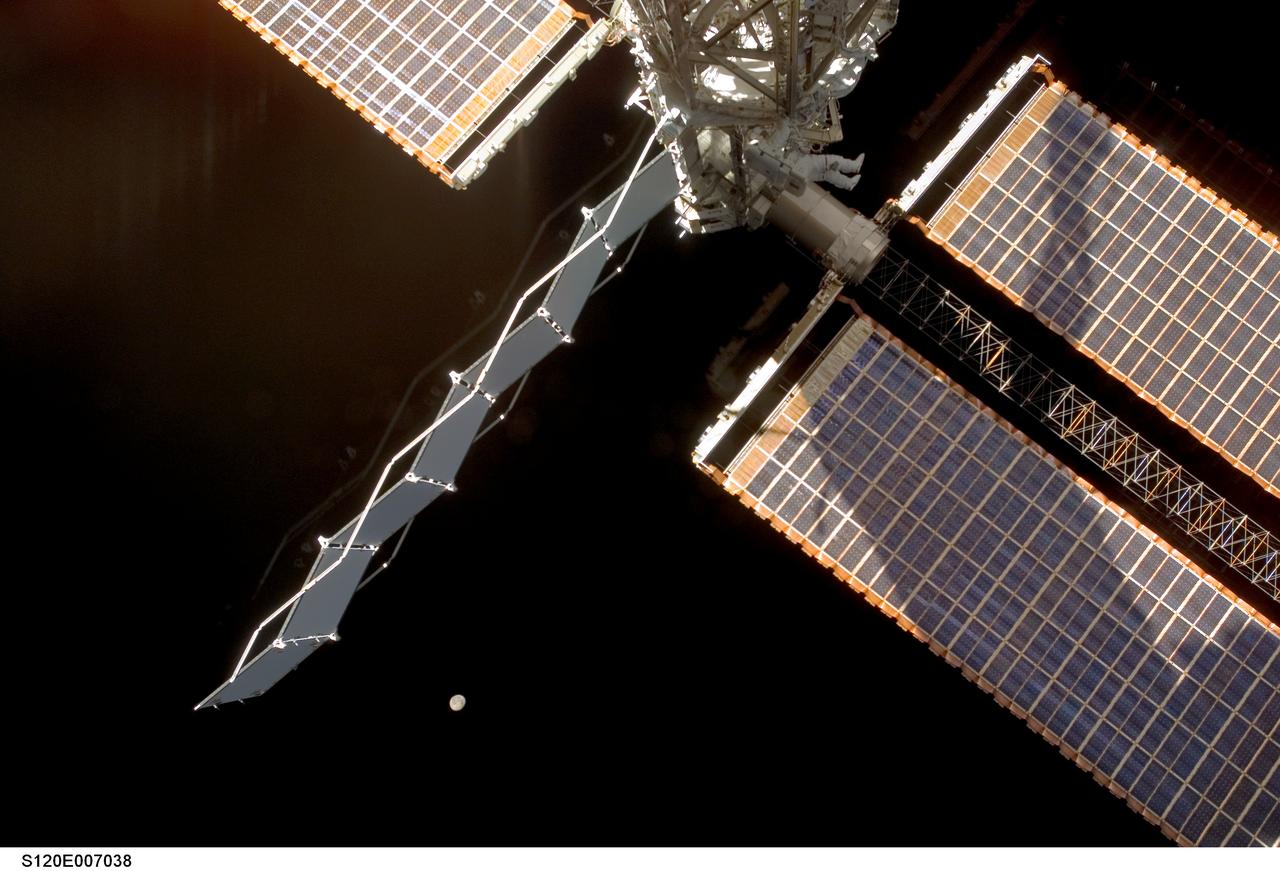

S120-E-007038 (28 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Daniel Tani (top center), Expedition 16 flight engineer, participates in the second of five scheduled sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 33-minute spacewalk Tani and astronaut Scott Parazynski (out of frame), STS-120 mission specialist, worked in tandem to disconnect cables from the P6 truss, allowing it to be removed from the Z1 truss. Tani also visually inspected the station's starboard Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) and gathered samples of "shavings" he found under the joint's multi-layer insulation covers. Also the spacewalkers outfitted the Harmony module, mated the power and data grapple fixture and reconfigured connectors on the starboard 1 (S1) truss that will allow the radiator on S1 to be deployed from the ground later. The moon is visible at lower center.

ISS014-E-13293 (4 Feb. 2007) --- The partially retracted aft radiator of the P6 truss of the International Space Station is featured in this image photographed during the second of three sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) in nine days by astronauts Michael E. Lopez-Alegria (out of frame), Expedition 14 commander and NASA space station science officer; and Sunita L. Williams (out of frame), flight engineer. The Zvezda Service Module and the Zarya module are visible at left. During the spacewalk, Williams and Lopez-Alegria reconfigured the second of two cooling loops for the Destiny laboratory module, secured the aft radiator of the P6 truss after retraction and prepared the obsolete Early Ammonia Servicer (EAS) for removal this summer.

ISS014-E-13296 (4 Feb. 2007) --- The partially retracted aft radiator of the P6 truss of the International Space Station is featured in this image photographed during the second of three sessions of extravehicular activity (EVA) in nine days by astronauts Michael E. Lopez-Alegria (out of frame), Expedition 14 commander and NASA space station science officer; and Sunita L. Williams (out of frame), flight engineer. The Zvezda Service Module and the Zarya module are visible at left. During the spacewalk, Williams and Lopez-Alegria reconfigured the second of two cooling loops for the Destiny laboratory module, secured the aft radiator of the P6 truss after retraction and prepared the obsolete Early Ammonia Servicer (EAS) for removal this summer.
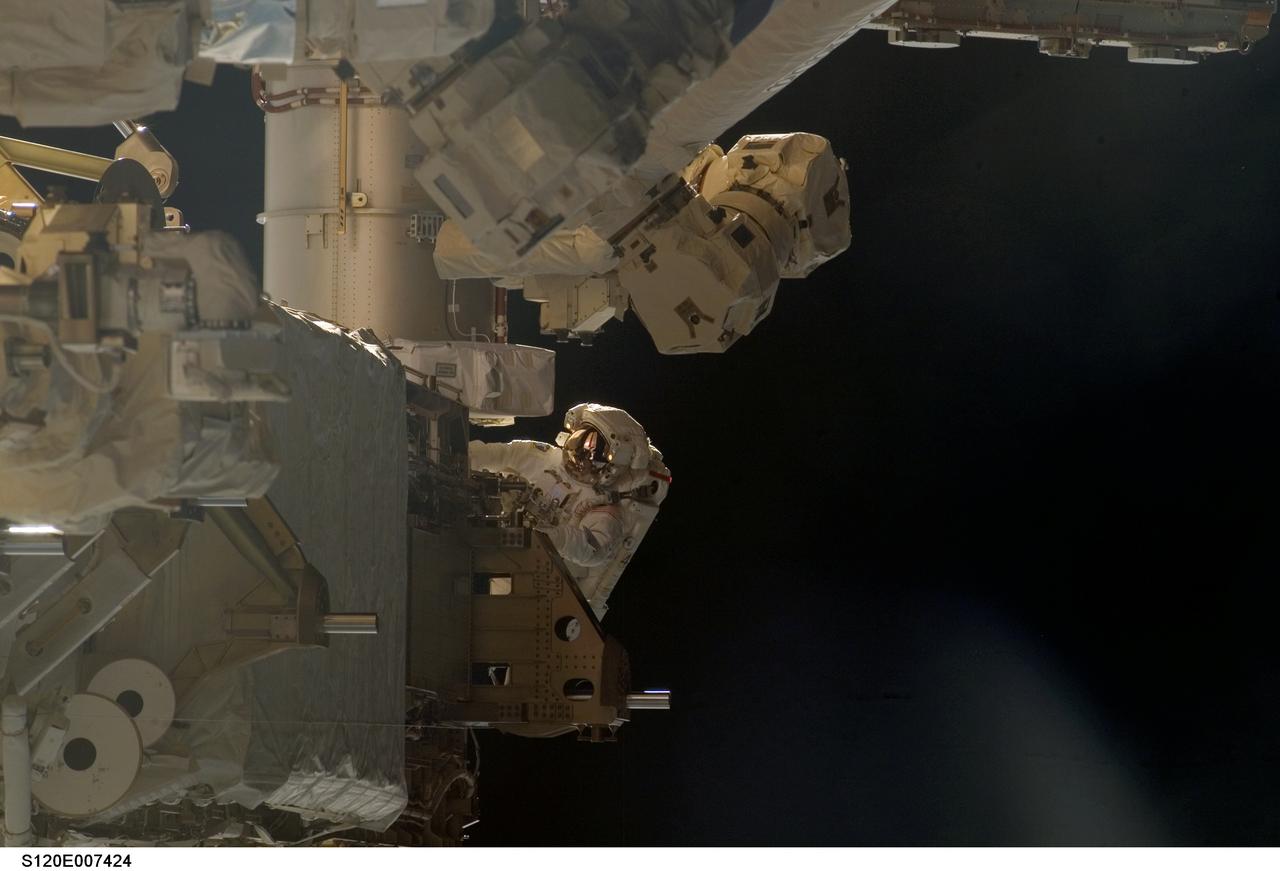

S120-E-007424 (30 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participates in the third scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 7-hour, 8-minute spacewalk Parazynski and astronaut Doug Wheelock (out of frame), mission specialist, installed the P6 truss segment with its set of solar arrays to its permanent home, installed a spare main bus switching unit on a stowage platform, and performed a few get-ahead tasks. Also, Parazynski inspected the port Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) to gather comparison data for the starboard rotary joint.
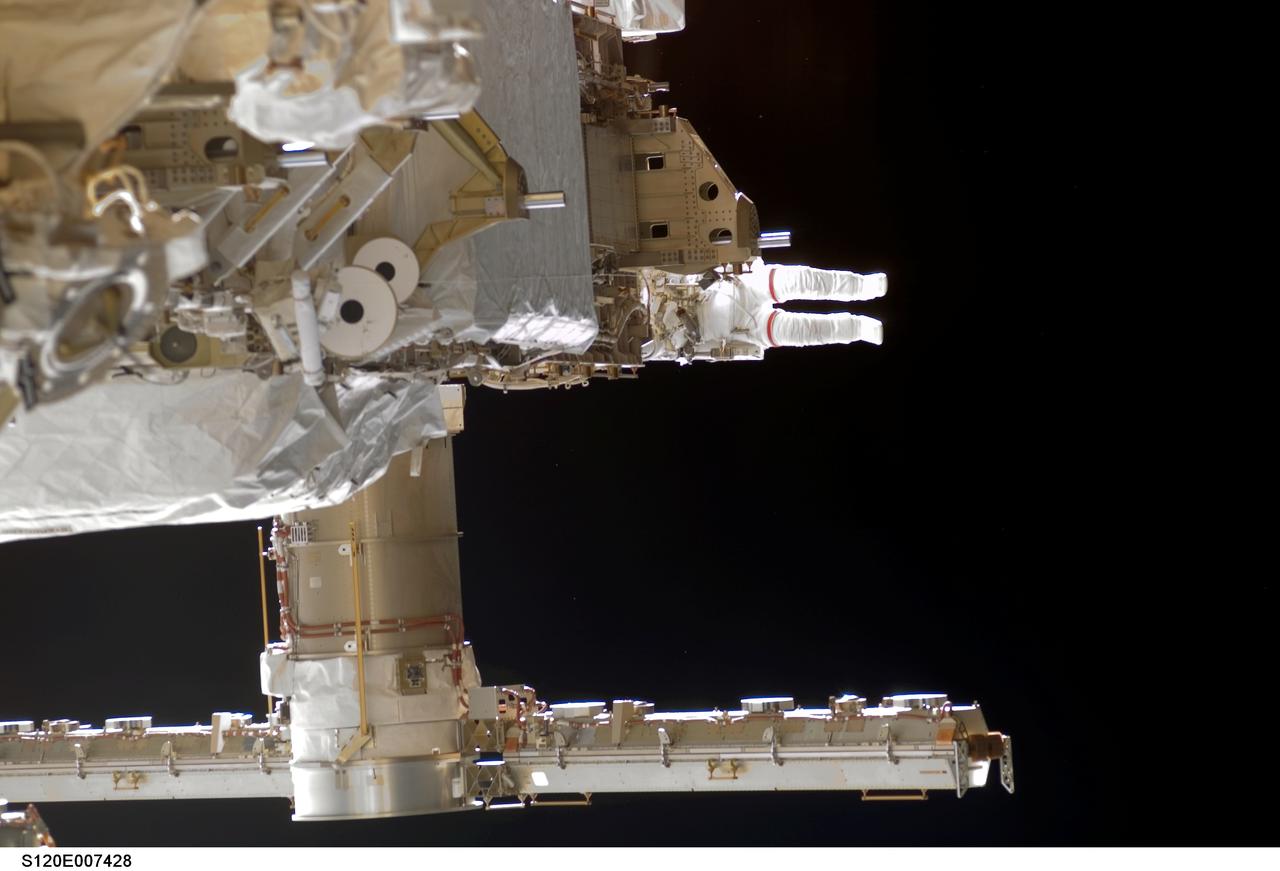
S120-E-007428 (30 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participates in the third scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 7-hour, 8-minute spacewalk Parazynski and astronaut Doug Wheelock (out of frame), mission specialist, installed the P6 truss segment with its set of solar arrays to its permanent home, installed a spare main bus switching unit on a stowage platform, and performed a few get-ahead tasks. Also, Parazynski inspected the port Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) to gather comparison data for the starboard rotary joint.
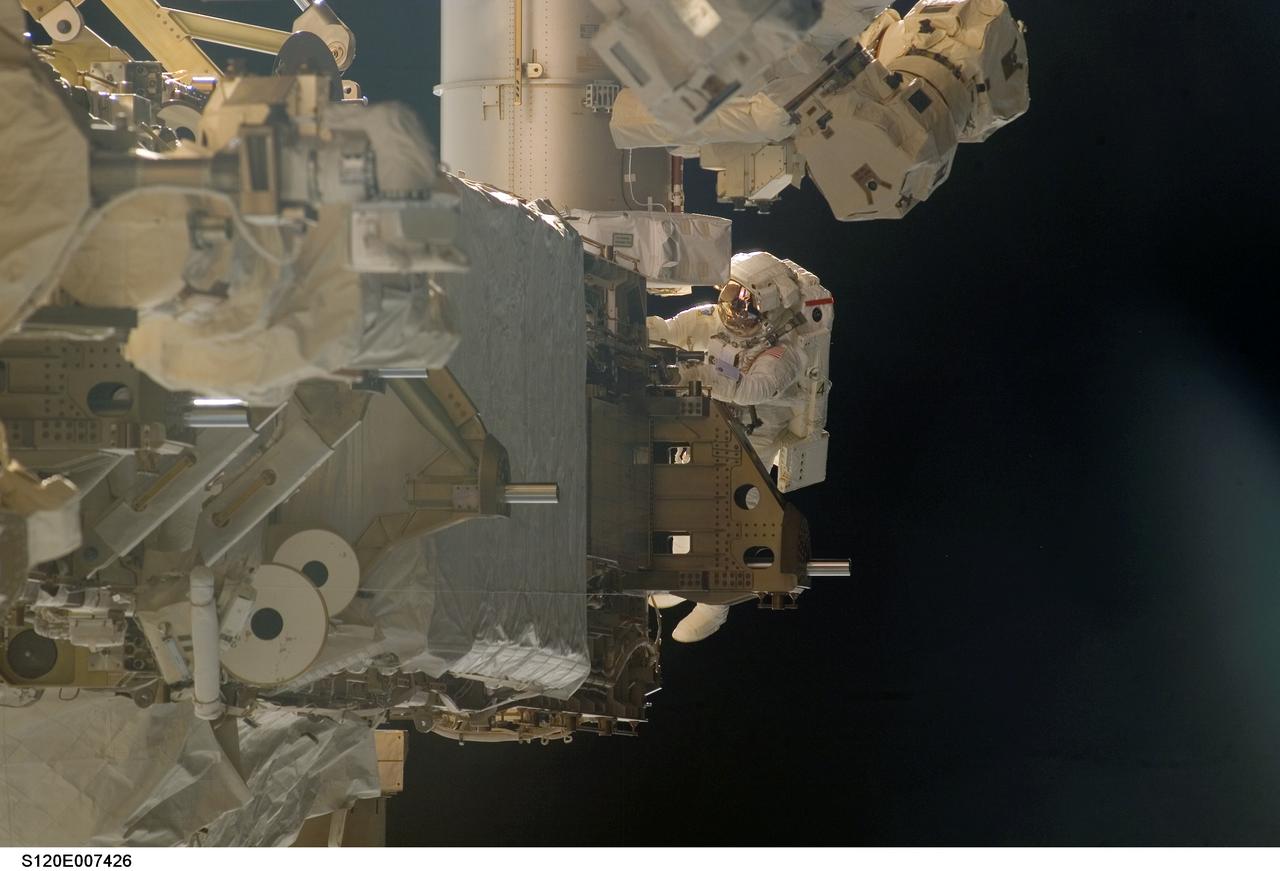

S120-E-007426 (30 Oct. 2007) --- Astronaut Scott Parazynski, STS-120 mission specialist, participates in the third scheduled session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 7-hour, 8-minute spacewalk Parazynski and astronaut Doug Wheelock (out of frame), mission specialist, installed the P6 truss segment with its set of solar arrays to its permanent home, installed a spare main bus switching unit on a stowage platform, and performed a few get-ahead tasks. Also, Parazynski inspected the port Solar Alpha Rotary Joint (SARJ) to gather comparison data for the starboard rotary joint.
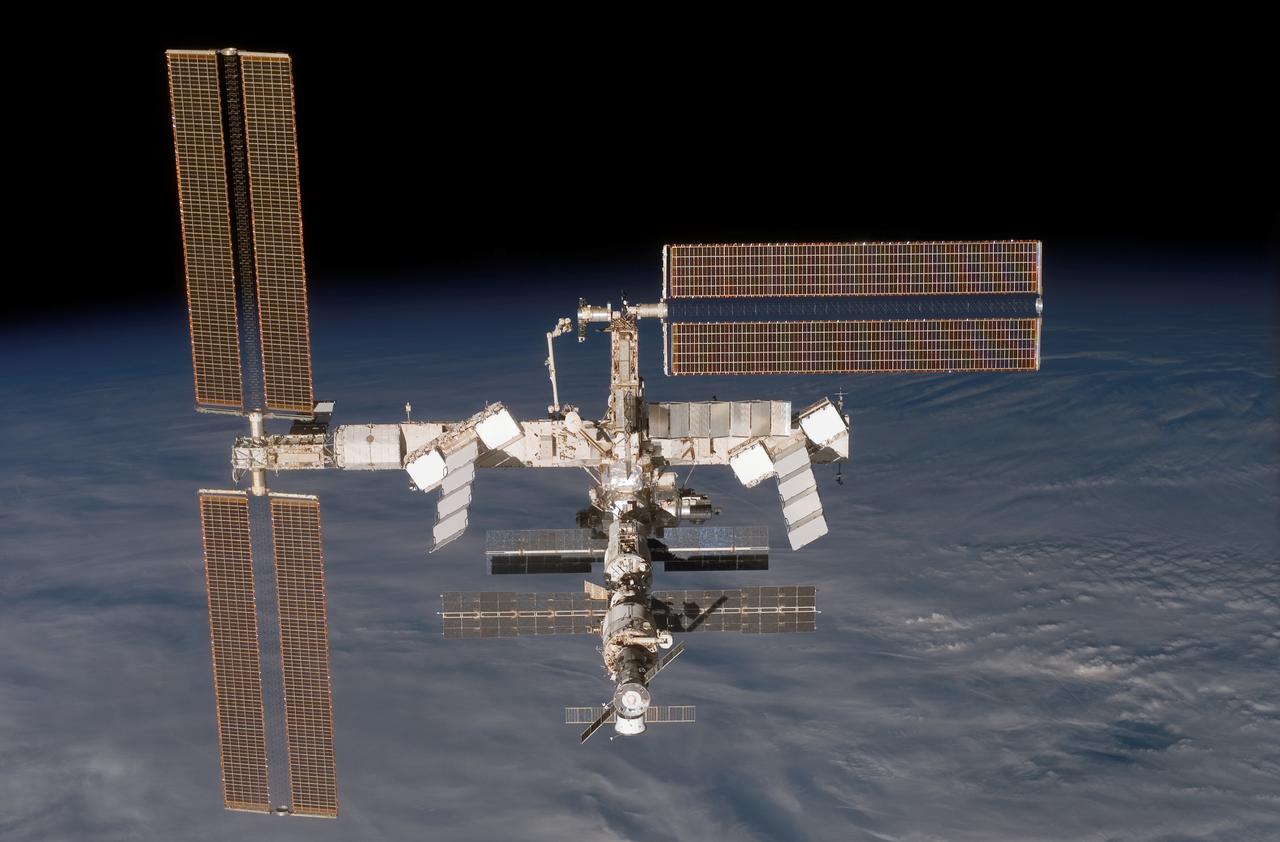

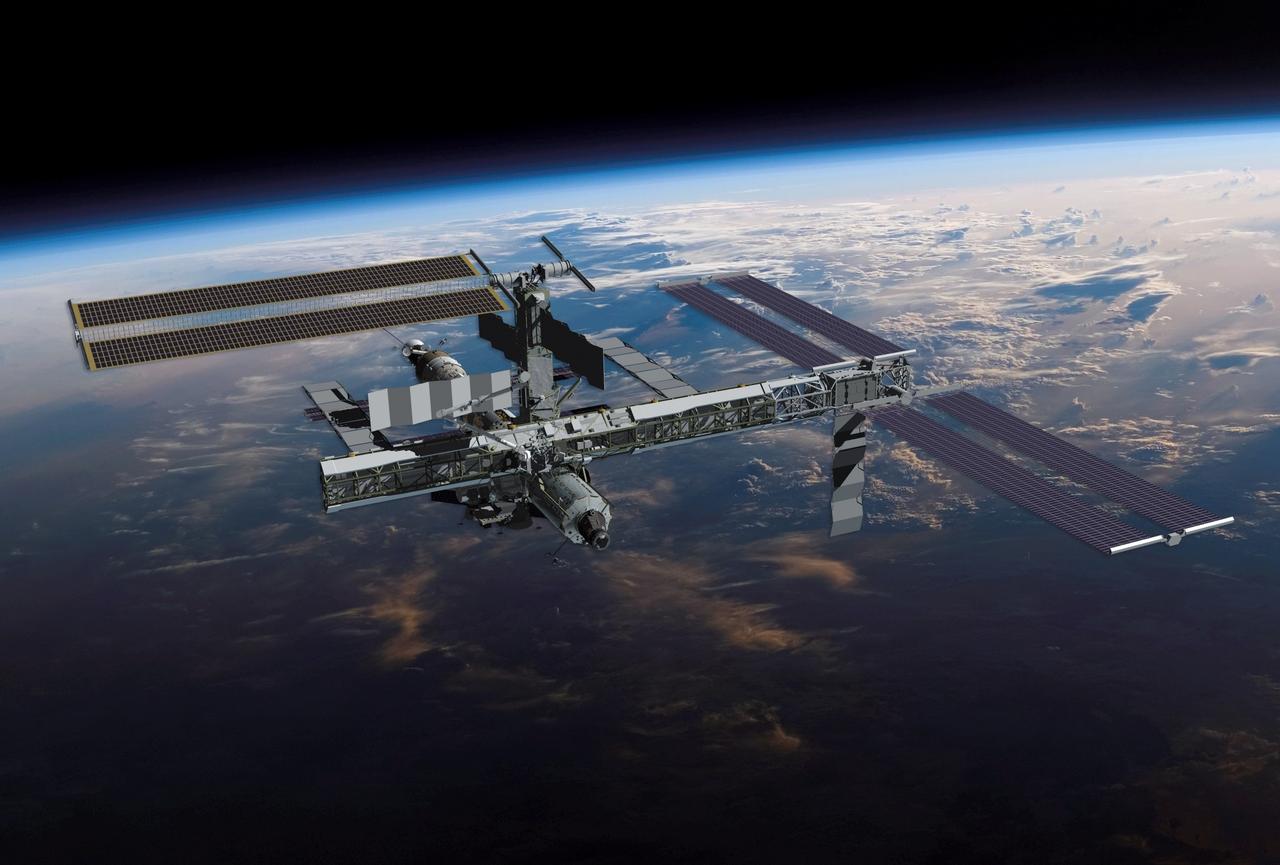
Photographed from the Space Shuttle Discovery upon its separation from the orbital outpost, the International Space Station (ISS) is shown sporting its new additions. A fly-around gave the crew a look at their handiwork, a new P5 spacer truss segment and a fully retracted P6 solar array wing. Earlier, the STS-116 and Expedition 14 crews concluded eight days of cooperative work onboard the shuttle and station where they accomplished the installation of the newest piece of the station and completely rewired the power grid over the course of four space walks. The station is currently the size of a typical three-bedroom house, with a surface area large enough to cover four basketball courts. The image reflects the latest configuration of the ISS as of December 19, 2006.
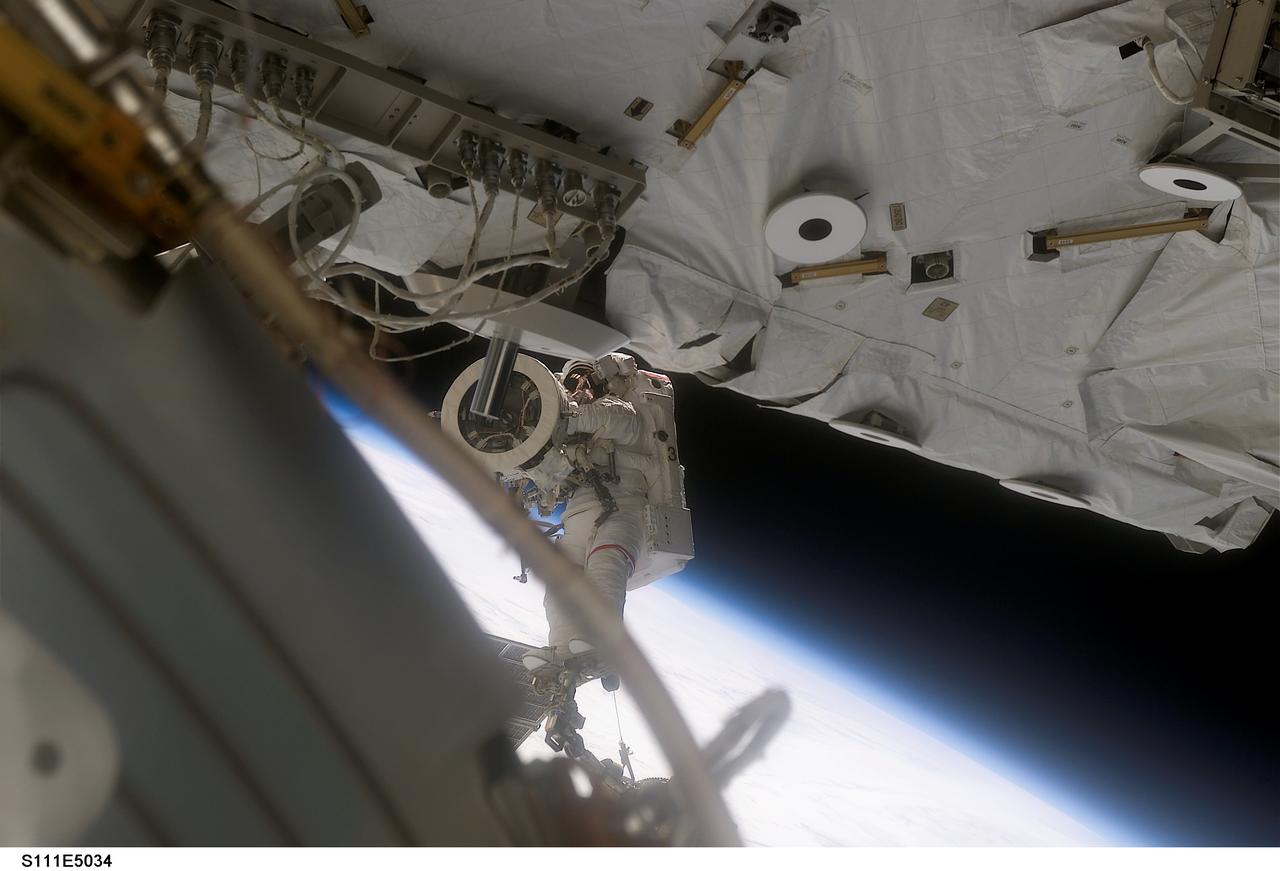

STS111-E-5034 (8 June 2002) --- Astronaut Franklin R. Chang-Diaz works with a grapple fixture during extravehicular activity (EVA) to perform work on the International Space Station (ISS). The first spacewalk of the STS-111 mission began with the installation of a Power and Data Grapple Fixture (PDGF) for the station's robotic arm on the complex's P6 truss. The PDGF will allow the robotic arm to grip the P6 truss for future station assembly operations. Astronauts Chang-Diaz and Philippe Perrin (with French Space Agency, CNES) went on to install the new fixture about halfway up the P6 truss, the vertical structure that currently supports the station's set of large U.S. solar arrays.
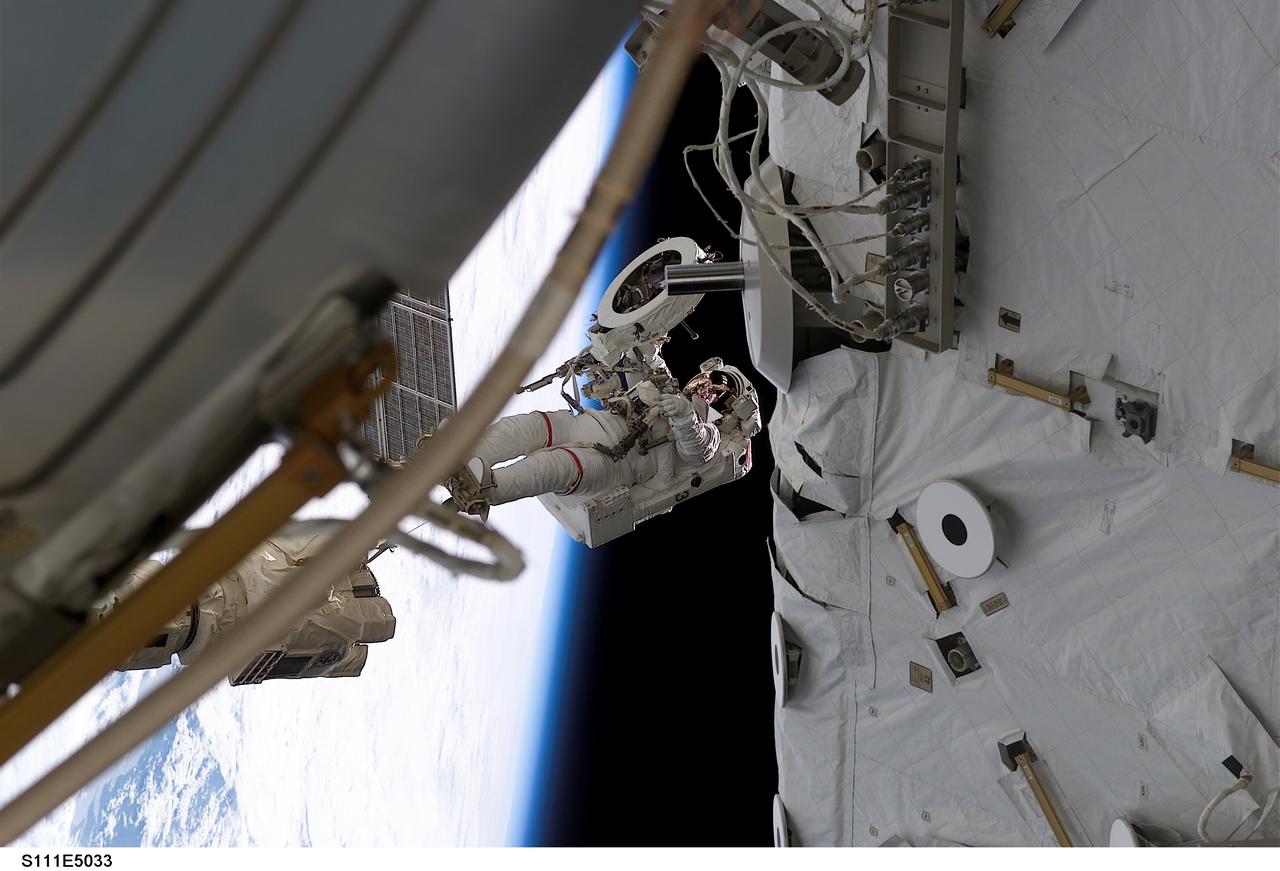

STS111-E-5033 (8 June 2002) --- Astronaut Franklin R. Chang-Diaz works with a grapple fixture during extravehicular activity (EVA) to perform work on the International Space Station (ISS). The first spacewalk of the STS-111 mission began with the installation of a Power and Data Grapple Fixture (PDGF) for the station's robotic arm on the complex's P6 truss. The PDGF will allow the robotic arm to grip the P6 truss for future station assembly operations. Astronauts Chang-Diaz and Philippe Perrin (with French Space Agency, CNES)went on to install the new fixture about halfway up the P6 truss, the vertical structure that currently supports the station's set of large U.S. solar arrays.
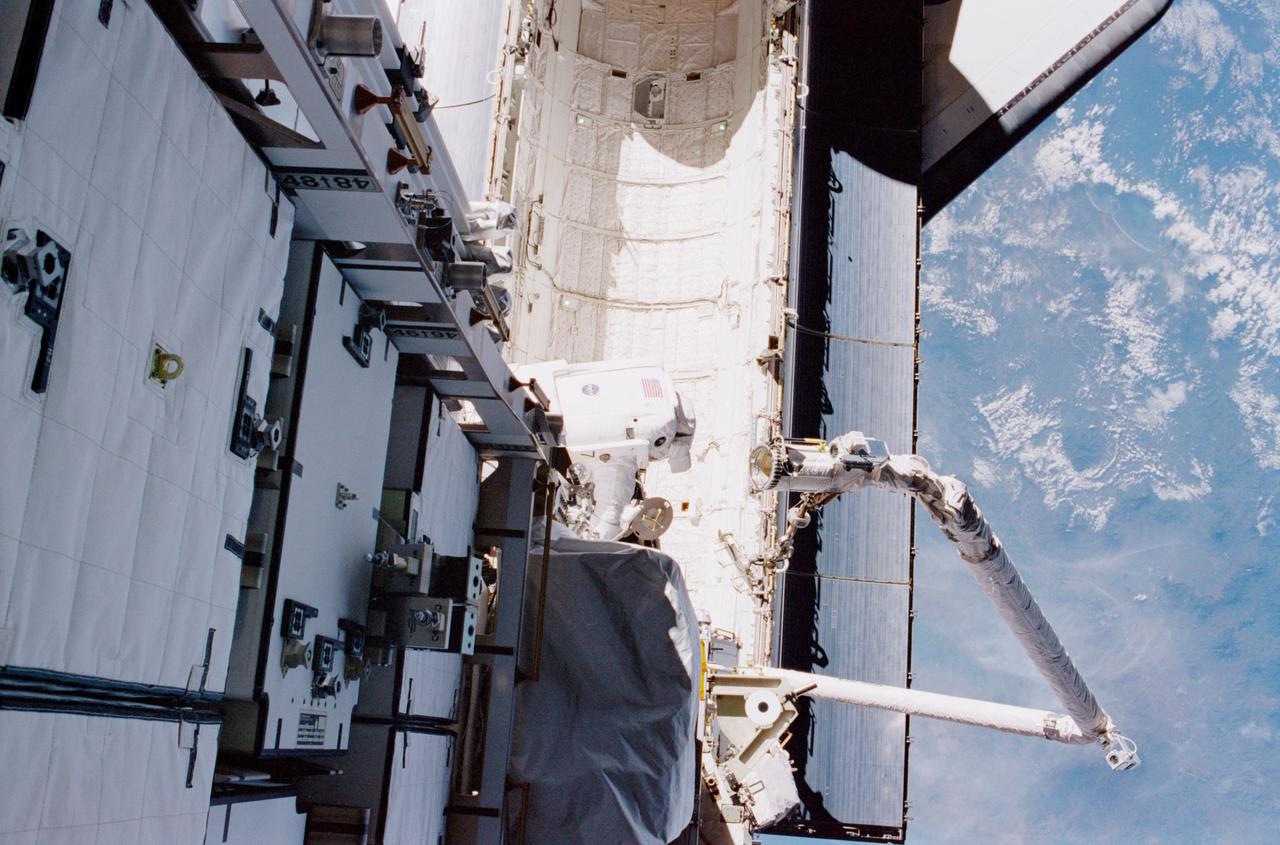

STS097-374-015 (5 December 2000) --- This high angle view shows astronaut Carlos I. Noriega, STS-97 mission specialist, traversing over Endeavour's cargo bay during the flight's first space walk on Dec. 5, 2000. Astronaut Joseph R. Tanner, mission specialist, was near the top of the P6 truss structure when he exposed the 35mm frame. The Canadian-built Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, instrumental in the current operations, can be seen at bottom right.
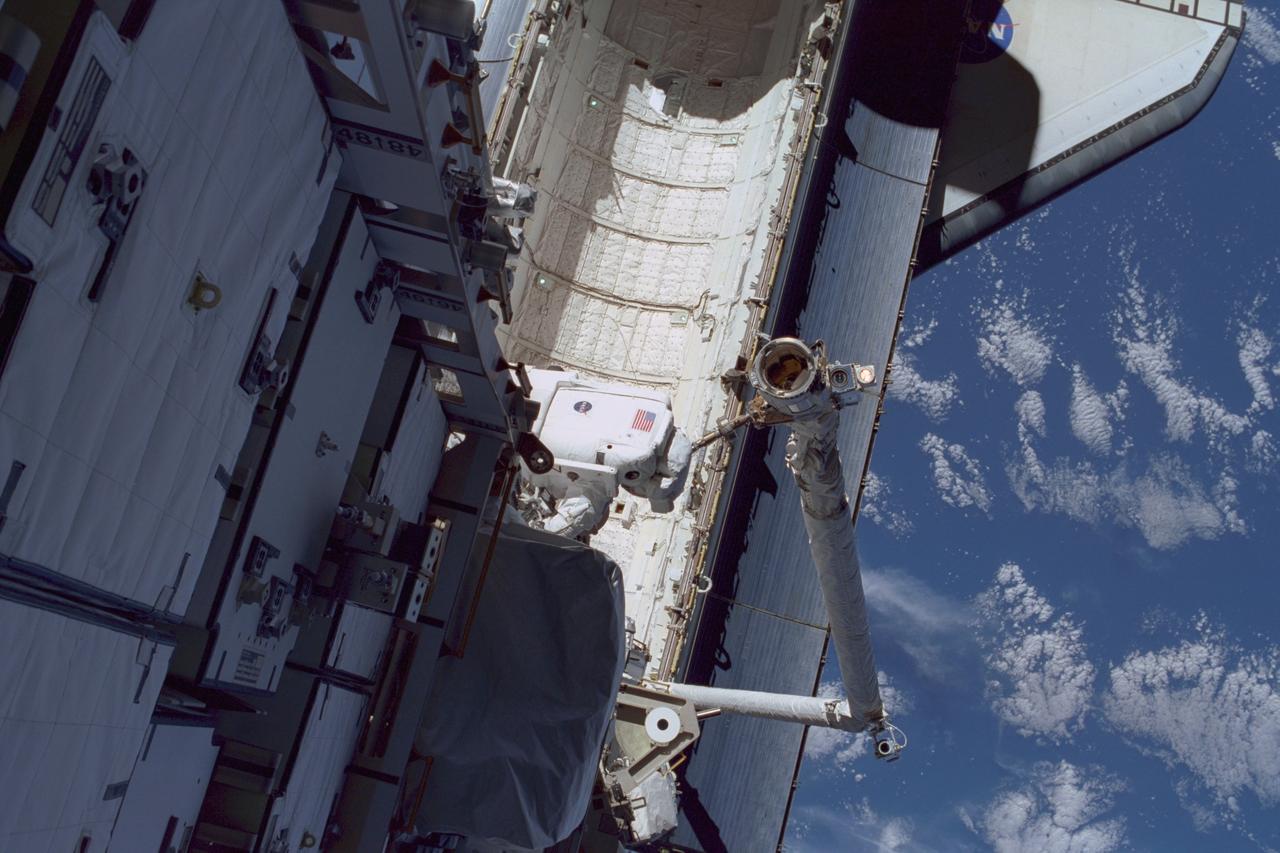

STS097-374-020 (3 December 2000) --- This high angle view shows astronaut Carlos I. Noriega, STS-97 mission specialist, traversing over Endeavour's cargo bay during the flight's first space walk on Dec. 3, 2000. Astronaut Joseph R. Tanner, mission specialist, was near the top of the P6 truss structure when he exposed the 35mm frame. The Canadian-built Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm can be seen at bottom right.
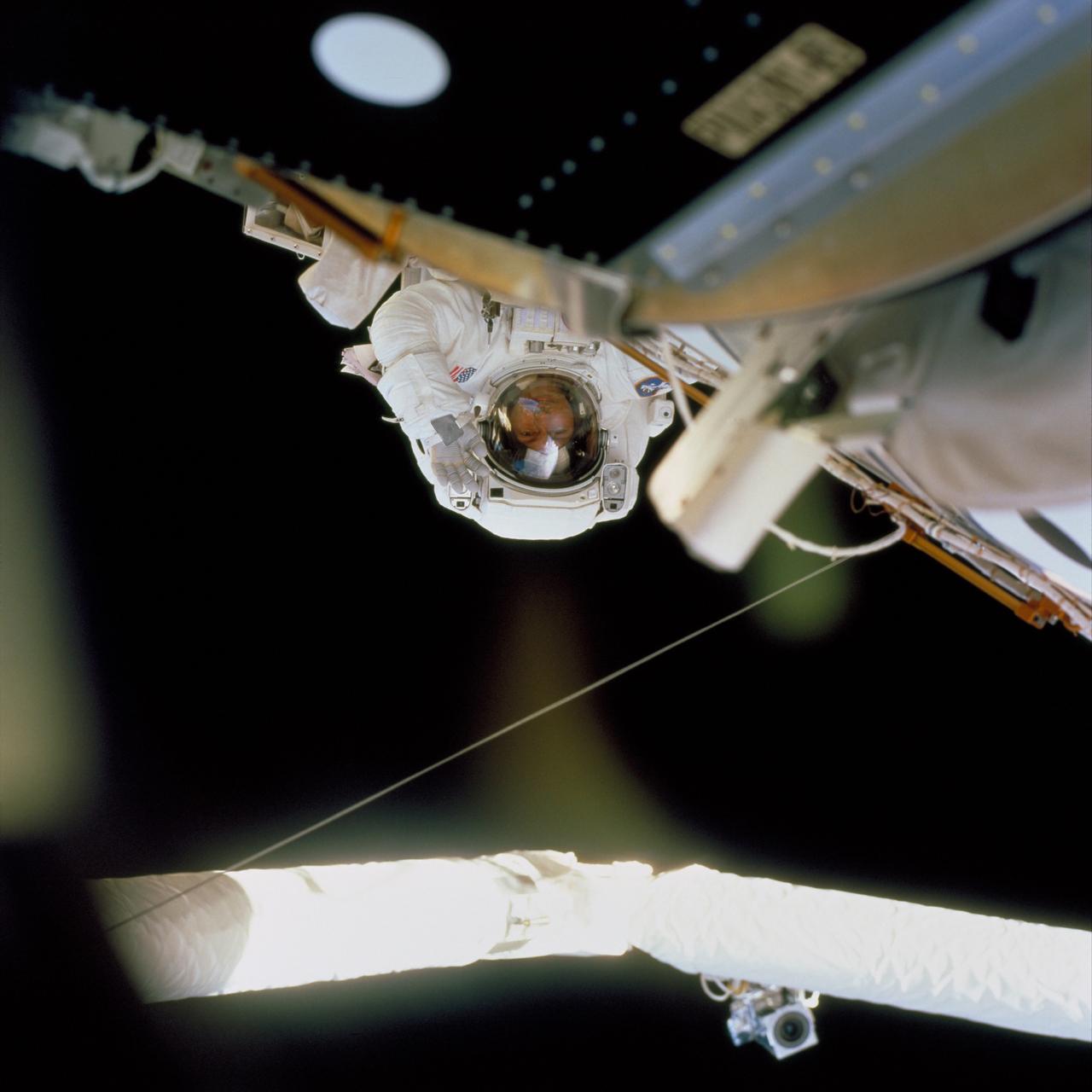
In this image, STS-97 astronaut and mission specialist Carlos I. Noriega waves at a crew member inside Endeavor's cabin during the mission's final session of Extravehicular Activity (EVA). Launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavor on November 30, 2000, the STS-97 mission's primary objective was the delivery, assembly, and activation of the U.S. electrical power system onboard the International Space Station (ISS). The electrical power system, which is built into a 73-meter (240-foot) long solar array structure consists of solar arrays, radiators, batteries, and electronics. The entire 15.4-metric ton (17-ton) package is called the P6 Integrated Truss Segment, and is the heaviest and largest element yet delivered to the station aboard a space shuttle. The electrical system will eventually provide the power necessary for the first ISS crews to live and work in the U.S. segment.
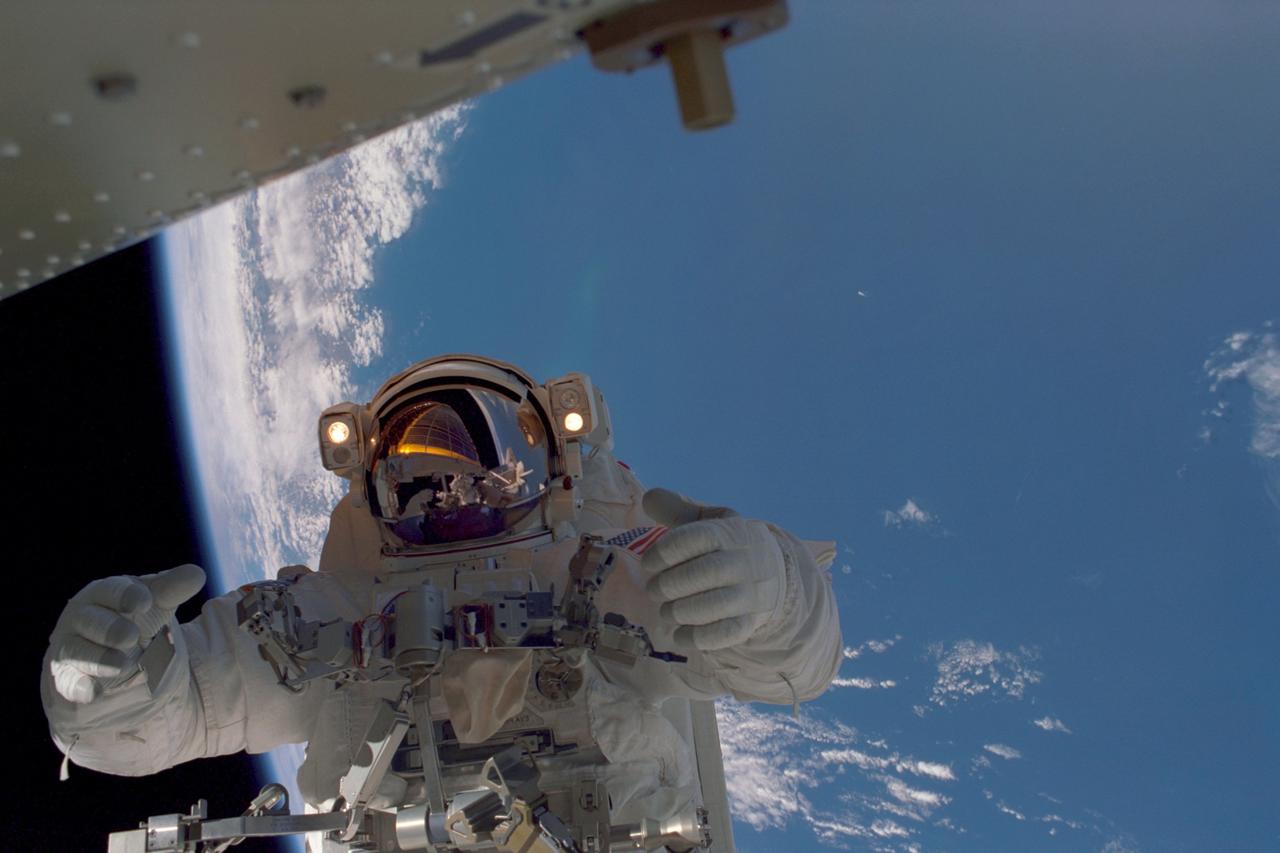

In this image, planet Earth, some 235 statute miles away, forms the back drop for this photo of STS-97 astronaut and mission specialist Joseph R. Tanner, taken during the third of three space walks. The mission's goal was to perform the delivery, assembly, and activation of the U.S. electrical power system onboard the International Space Station (ISS). The electrical power system, which is built into a 73-meter (240-foot) long solar array structure consists of solar arrays, radiators, batteries, and electronics. The entire 15.4-metric ton (17-ton) package is called the P6 Integrated Truss Segment, and is the heaviest and largest element yet delivered to the station aboard a space shuttle. The electrical system will eventually provide the power necessary for the first ISS crews to live and work in the U.S. segment. The STS-97 crew of five launched aboard the Space Shuttle Orbiter Endeavor on November 30, 2000 for an 11 day mission.
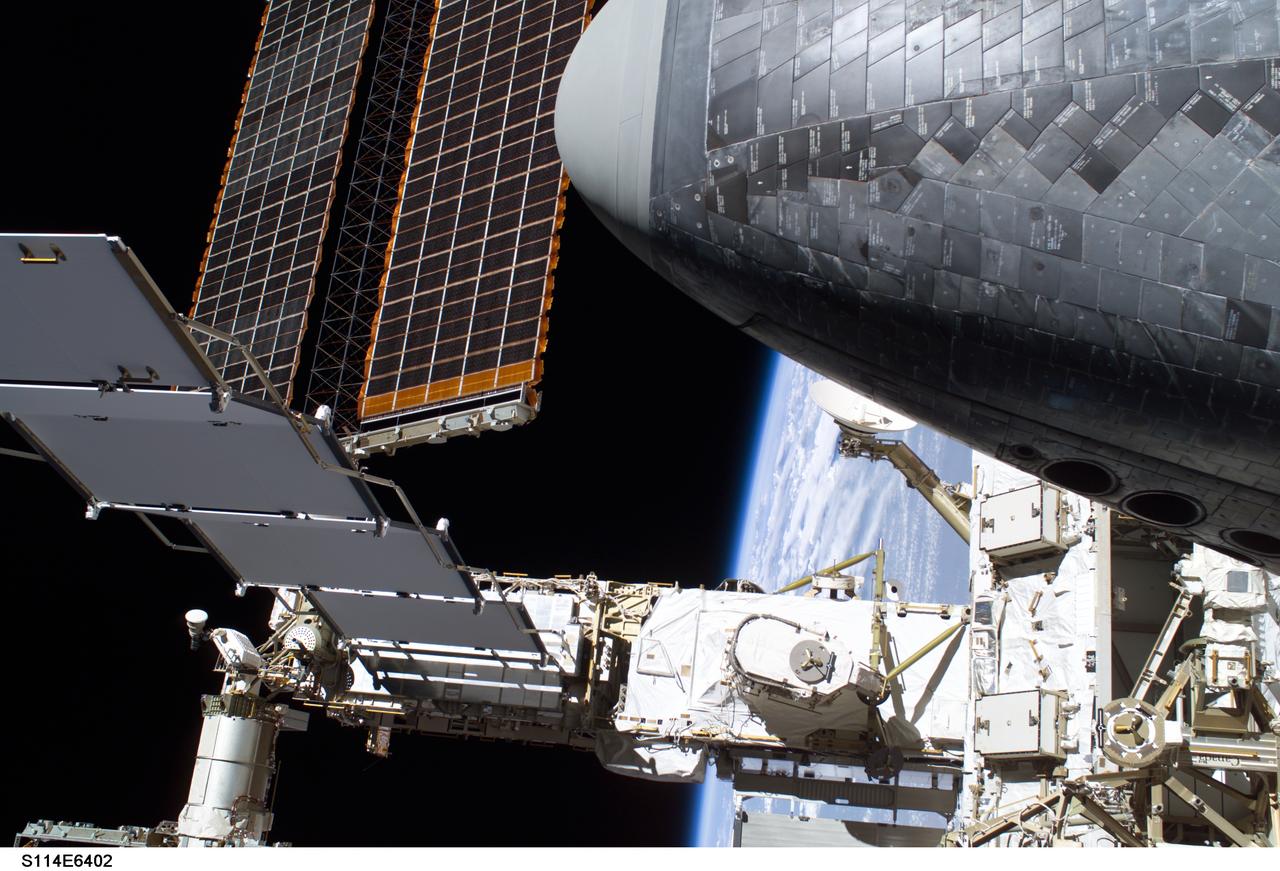

Photograph documenting the P6 Truss Solar Array Wing (SAW), Mast Canisters, Photovoltaic (PV) Radiator and Solar Array Blanket Boxes (SABB) as seen by the STS-114 crew during the third of three Extravehicular Activities (EVAs) of the mission. Part of the orbiter Discovery's nosecone is visible in the upper right of the frame.
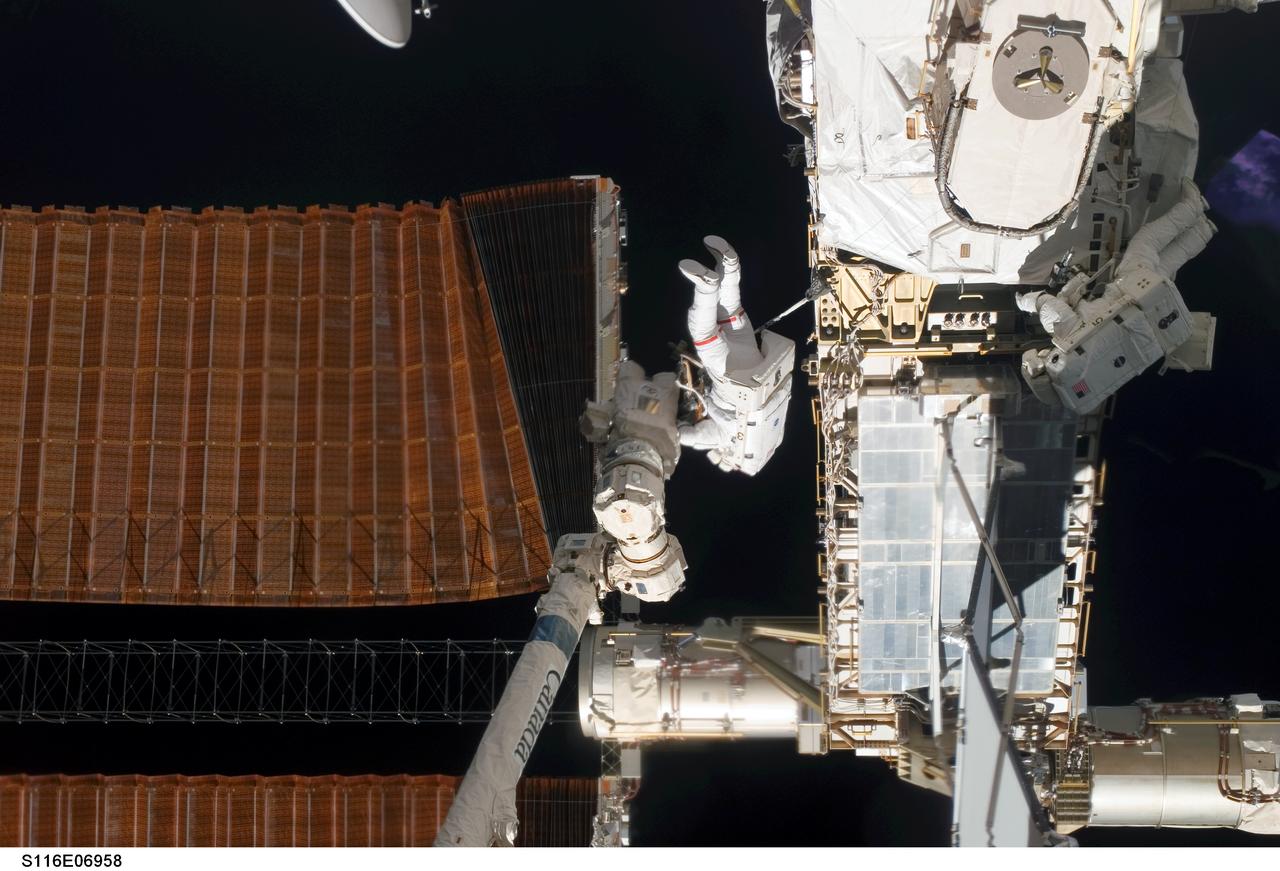

S116-E-06958 (18 Dec. 2006) --- Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam Jr. (center) and European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Christer Fuglesang (right), both STS-116 mission specialists, work with the port overhead solar array wing on the International Space Station's P6 truss during the mission's fourth session of extravehicular activity (EVA). The spacewalkers used specially-prepared, tape-insulated tools, to guide the array wing neatly inside its blanket box during the 6-hour, 38-minute spacewalk.
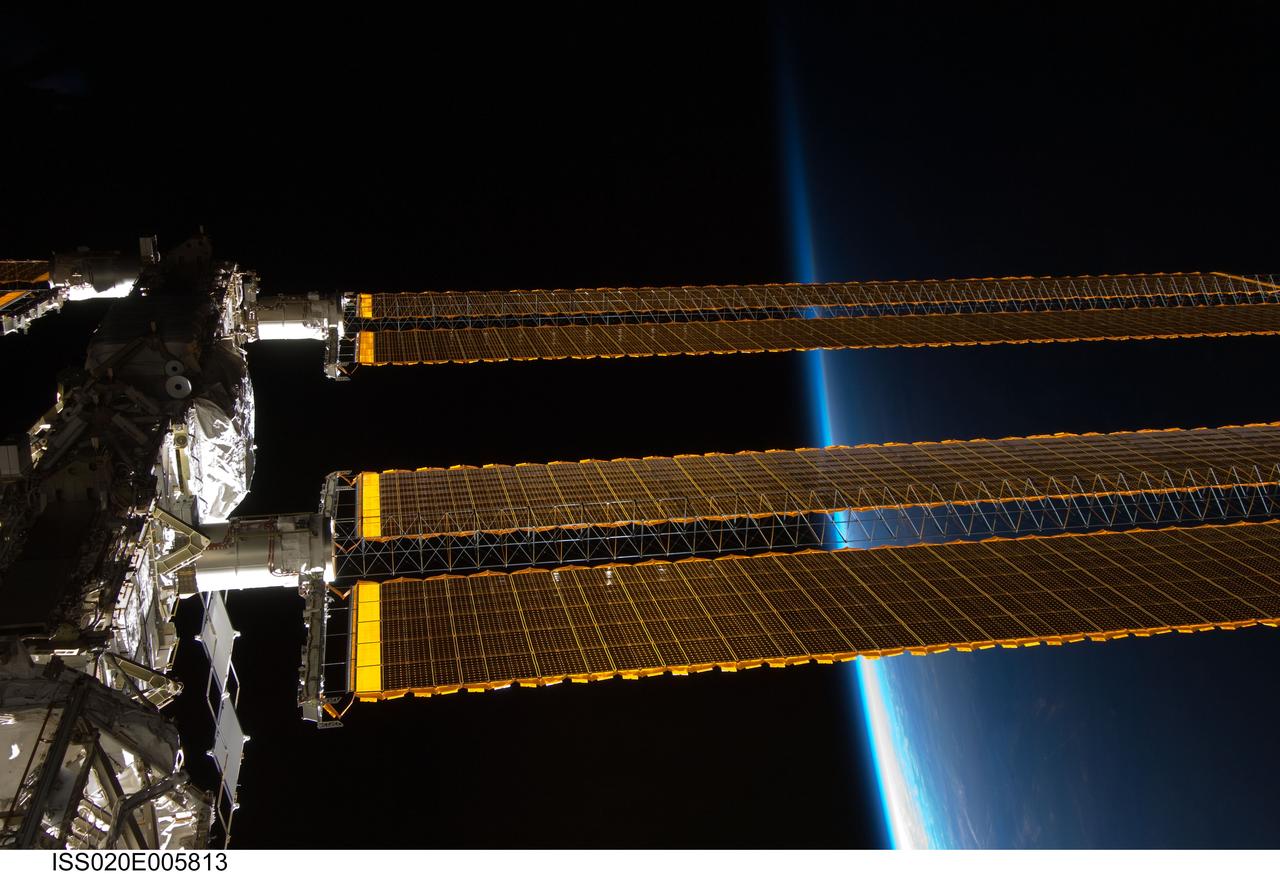

ISS020-E-005813 (31 May 2009) --- Backdropped by Earth's horizon and the blackness of space, a portion of the International Space Station is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 20 crew member aboard the station.
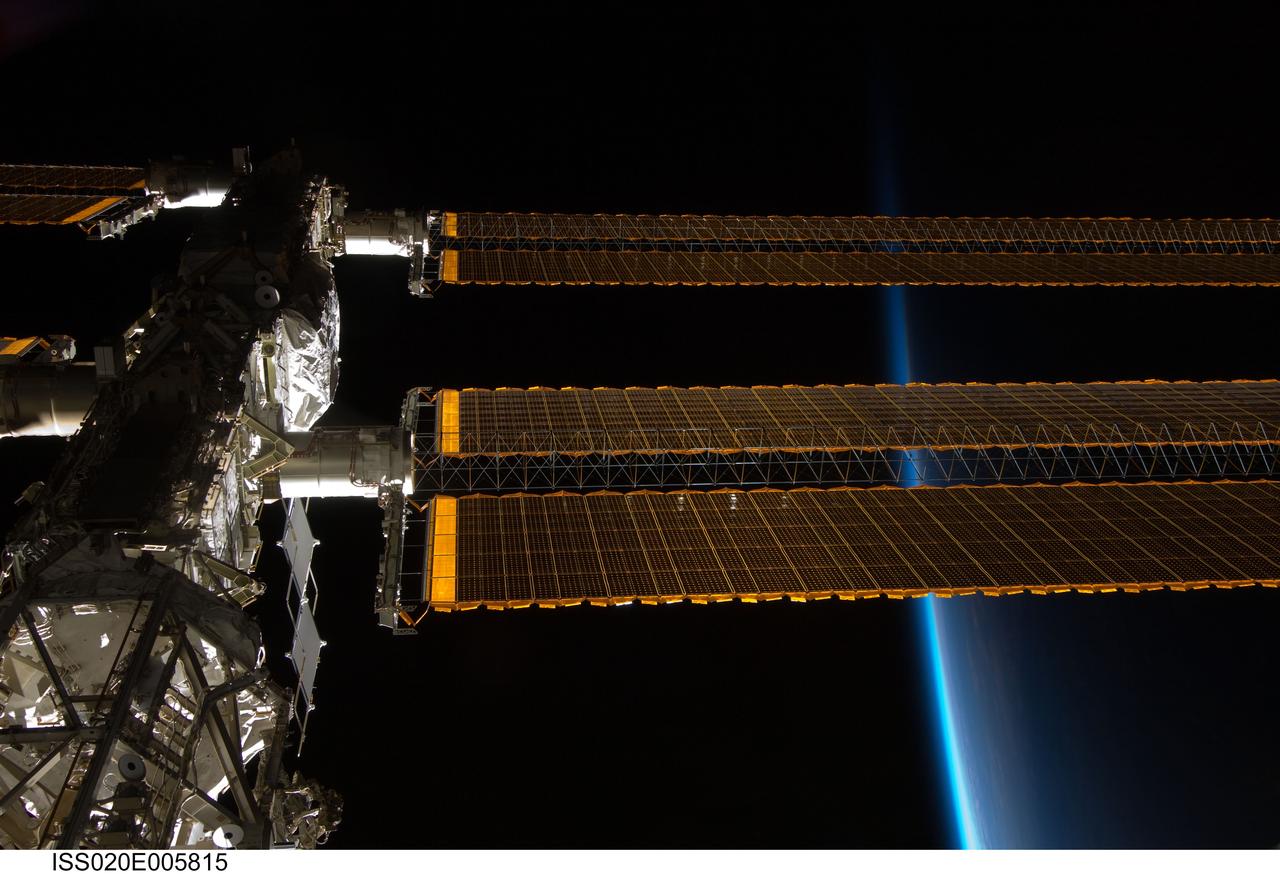

ISS020-E-005815 (31 May 2009) --- Backdropped by the thin line of Earth's atmosphere and the blackness of space, a portion of the International Space Station is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 20 crew member aboard the station.
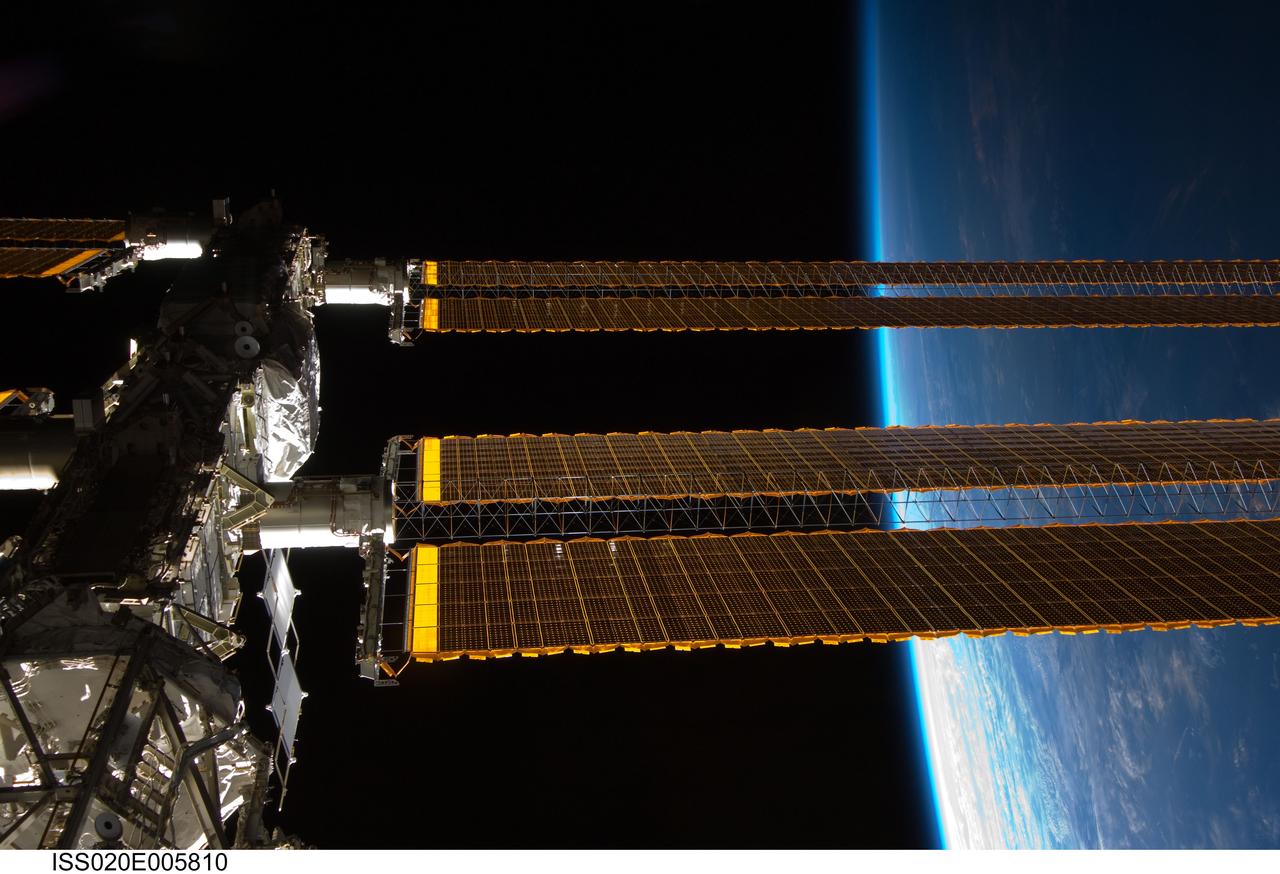

ISS020-E-005810 (31 May 2009) --- Backdropped by Earth's horizon and the blackness of space, a portion of the International Space Station is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 20 crew member aboard the station.
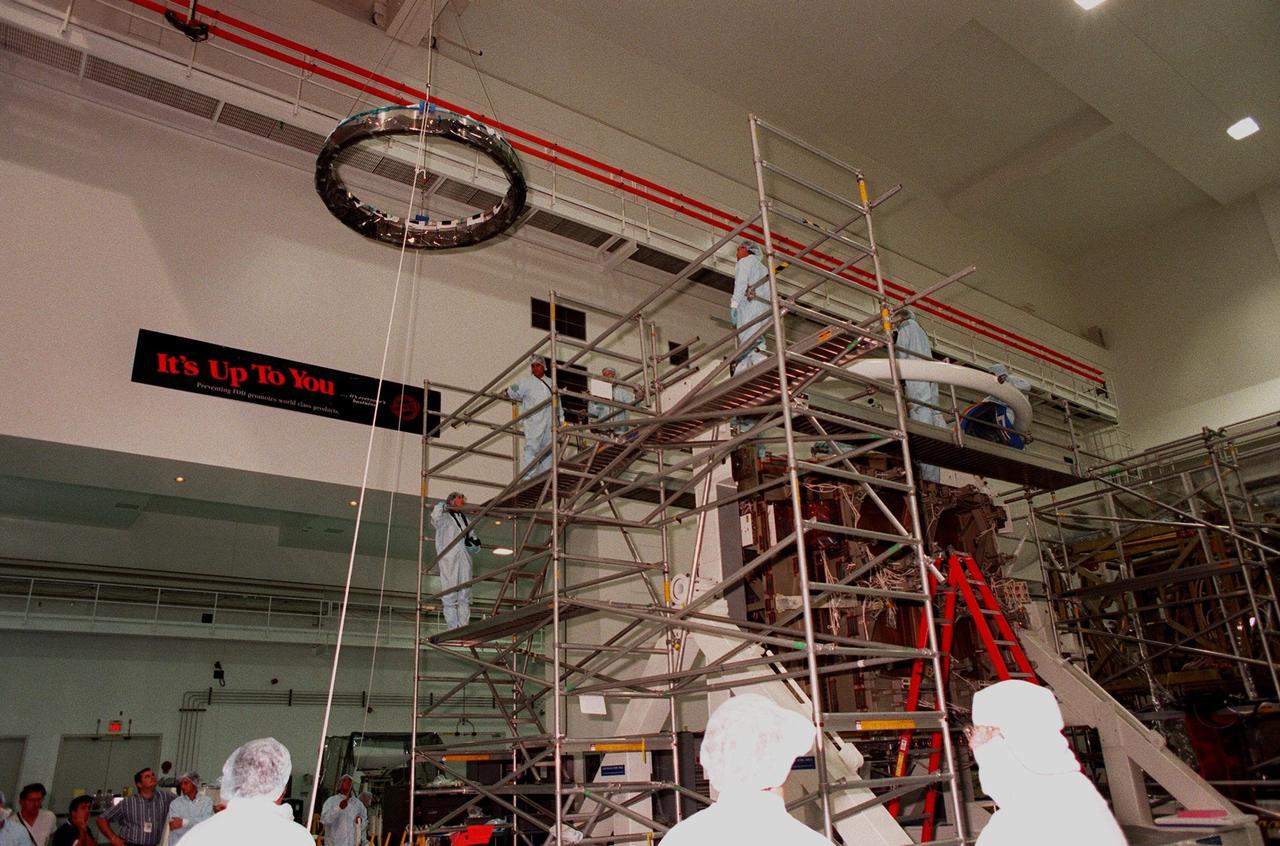

Workers in the Space Station Processing Facility watch the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism (PCBM) lifted high to move it over to the Z1 integrated truss structure at right. It will be mated to the Z1 truss, a component of the International Space Station (ISS). The Z1 truss will be used for the temporary installation of the P6 truss segment to the Unity connecting module. The P6 truss segment contains the solar arrays and batteries which will provide early station power. The truss is scheduled to be launched aboard STS-92 in late 1999
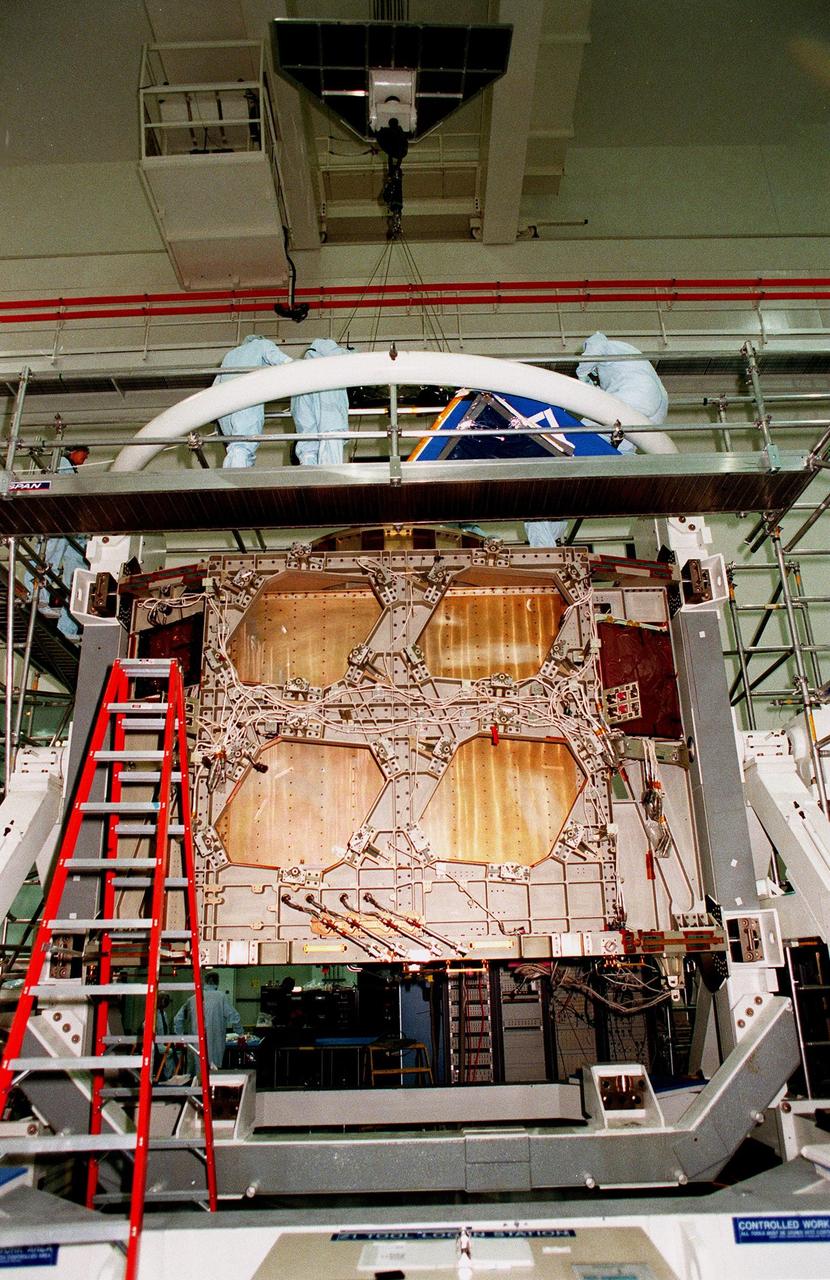

Workers in the Space Station Processing Facility look at the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism (PCBM) that will be attached to the Z1 integrated truss structure, a component of the International Space Station (ISS). The truss will be used for the temporary installation of the P6 truss segment to the Unity connecting module. The P6 truss segment contains the solar arrays and batteries which will provide early station power. The truss is scheduled to be launched aboard STS-92 in late 1999
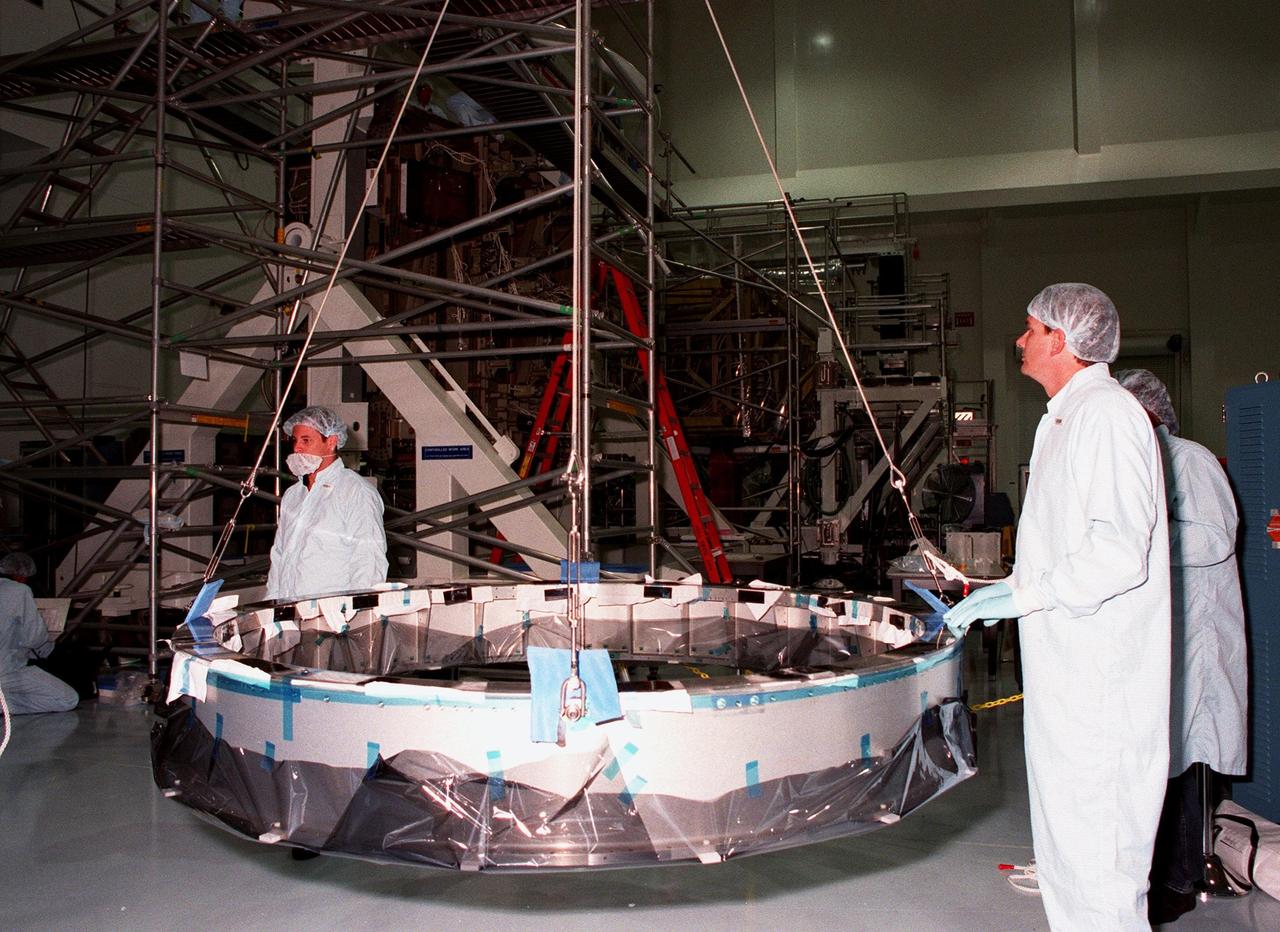

Workers in the Space Station Processing Facility watch as cables and a crane lift the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism (PCBM) before mating it to the Z1 integrated truss structure, a component of the International Space Station (ISS). The Z1 truss will be used for the temporary installation of the P6 truss segment to the Unity connecting module. The P6 truss segment contains the solar arrays and batteries which will provide early station power. The truss is scheduled to be launched aboard STS-92 in late 1999
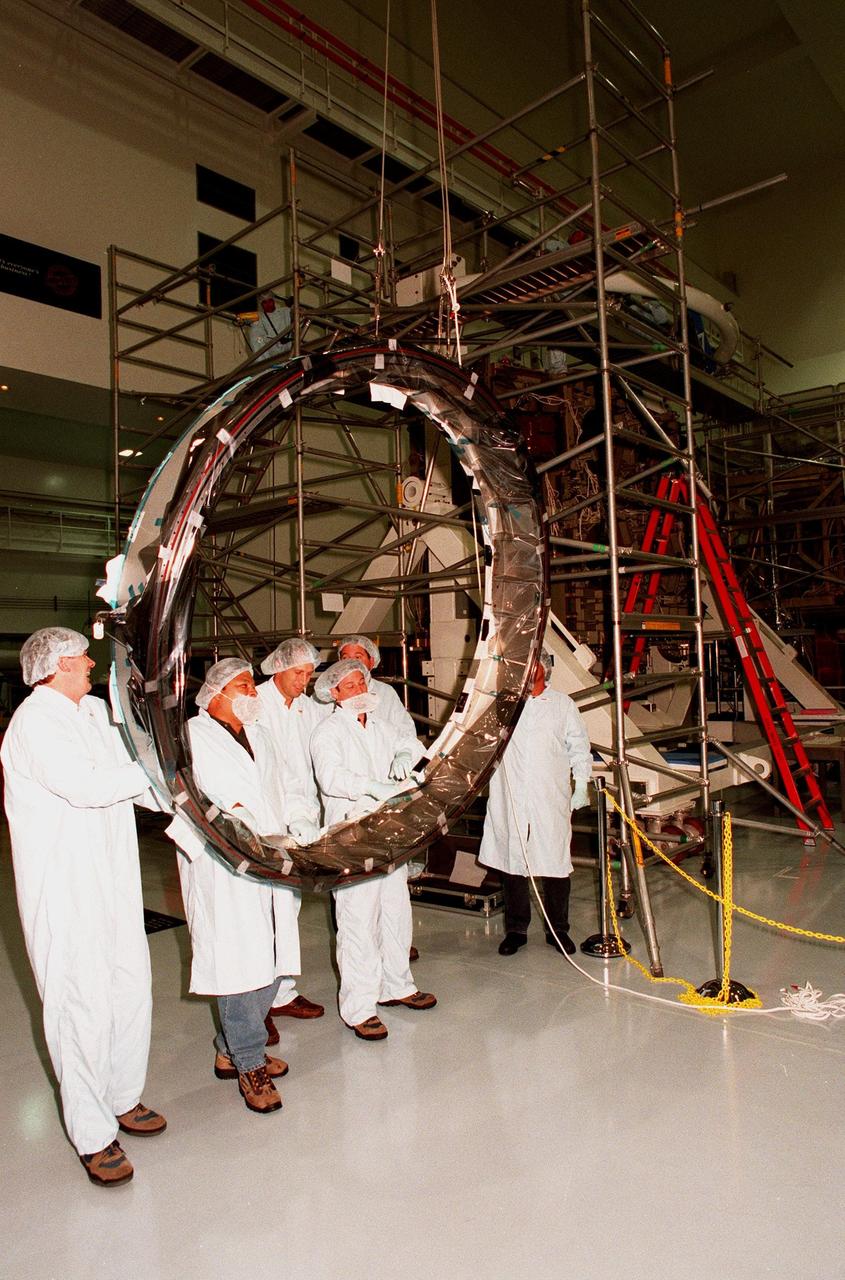

Workers in the Space Station Processing Facility look at the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism (PCBM) that will be attached to the Z1 integrated truss structure, a component of the International Space Station (ISS). The Z1 truss will be used for the temporary installation of the P6 truss segment to the Unity connecting module. The P6 truss segment contains the solar arrays and batteries which will provide early station power. The truss is scheduled to be launched aboard STS-92 in late 1999
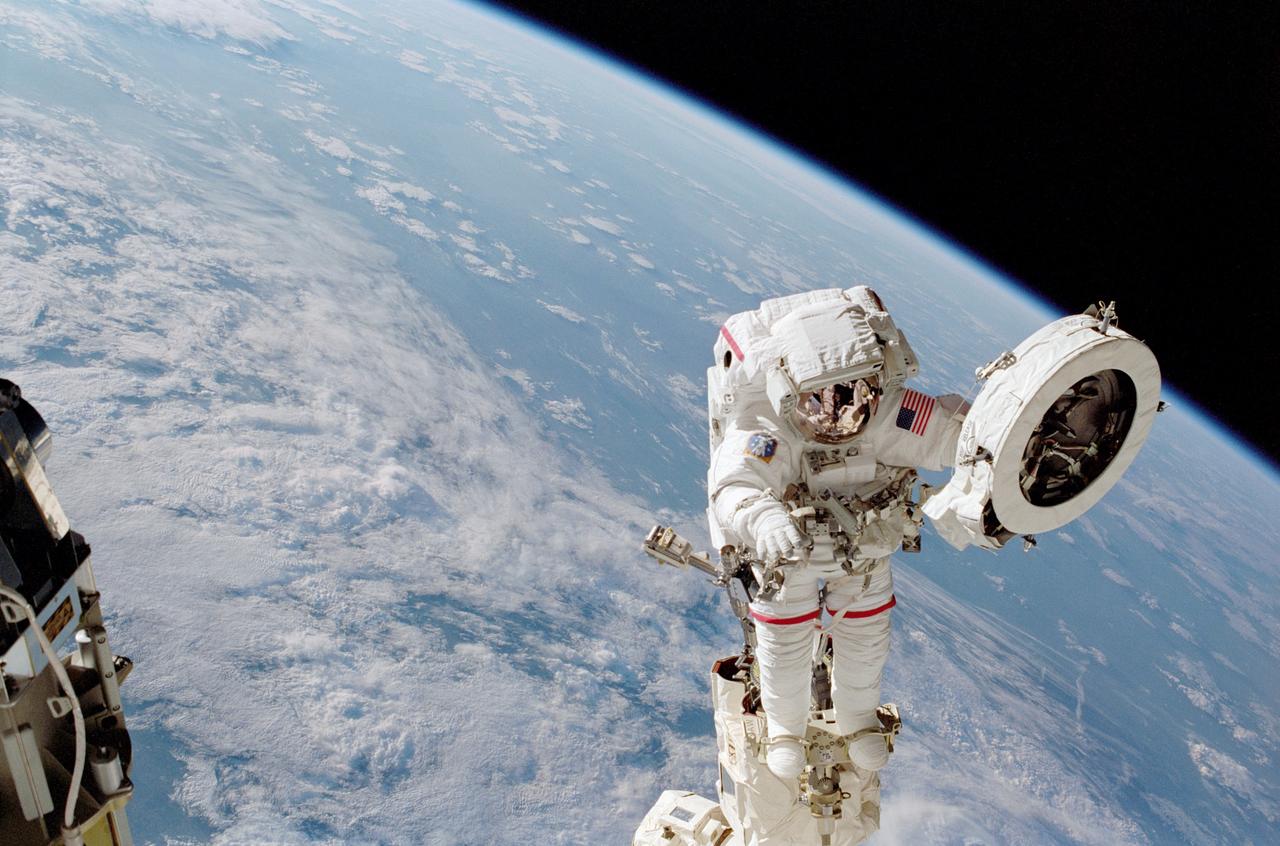

STS111-306-012 (9 June 2002) --- Astronaut Franklin R. Chang-Diaz works with a grapple fixture during extravehicular activity (EVA) to perform work on the International Space Station (ISS). The first spacewalk of the STS-111 mission began with the installation of a Power and Data Grapple Fixture (PDGF) for the station's robotic arm on the complex's P6 truss. The PDGF will allow the robotic arm to grip the P6 truss for future station assembly operations. Astronauts Chang-Diaz and Philippe Perrin (with French Space Agency, CNES) went on to install the new fixture about halfway up the P6 truss, the vertical structure that currently supports the station's set of large U.S. solar arrays.

Still suspended by a crane and cables in the Space Station Processing Facility, yet hidden by the top of the Z1 integrated truss structure, the Passive Common Berthing Mechanism (PCBM) is lowered onto the truss for attachment. Workers at the top of a workstand guide it into place. A component of the International Space Station (ISS), the Z1 truss will be used for the temporary installation of the P6 truss segment to the Unity connecting module. The P6 truss segment contains the solar arrays and batteries which will provide early station power. The truss is scheduled to be launched aboard STS-92 in late 1999
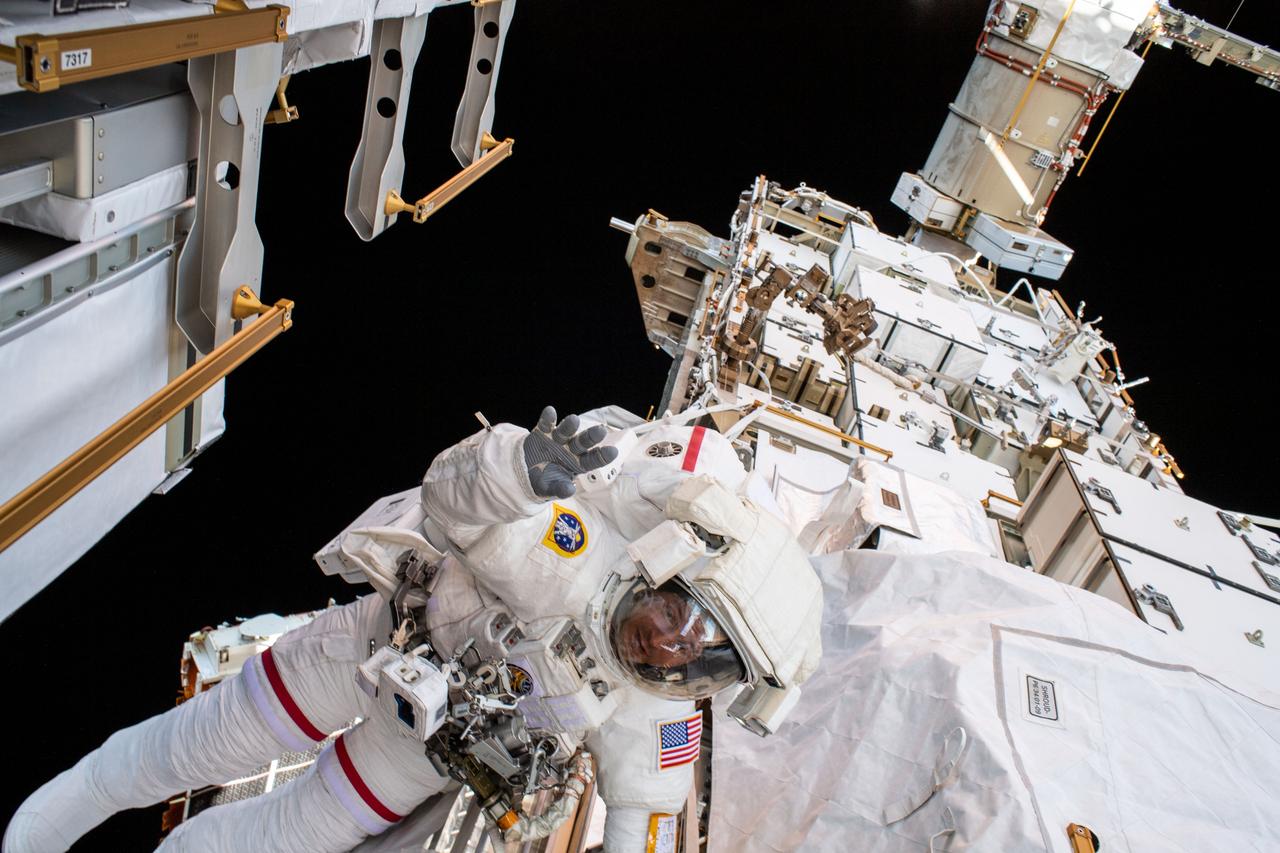

iss061e005520 (Oct. 11, 2019) --- NASA astronaut Andrew Morgan waves to the camera while tethered on the Port 6 (P6) truss segment of the International Space Stations. He and fellow NASA astronaut Christina Koch (out of frame) worked to replace older hydrogen-nickel batteries with newer, more powerful lithium-ion batteries on the P6 truss during the six-hour and 45-minute spacewalk.
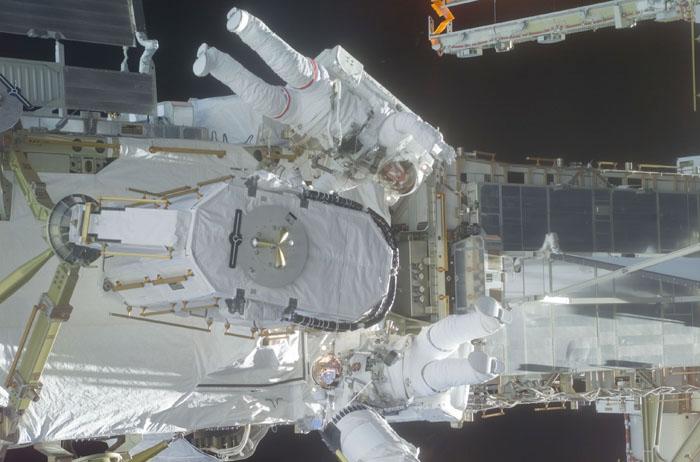

STS105-E-5280 (16 August 2001) --- Astronauts Daniel T. Barry (with red stripes on suit) and Patrick G. Forrester work with the Early Ammonia Servicer (EAS), which they are in the process of installing on a segment of the P6 structure on the International Space Station (ISS). The two mission specialists were participating in the first of two scheduled STS-105 space walks. The image was recorded with a digital still camera.

STS105-E-5265 (16 August 2001) --- Astronauts Daniel T. Barry (left) and Patrick G. Forrester surround the Early Ammonia Servicer (EAS), which they will install on a segment of the P6 structure on the International Space Station (ISS). The two mission specialists were participating in the first of two scheduled STS-105 space walks. The image was recorded with a digital still camera.
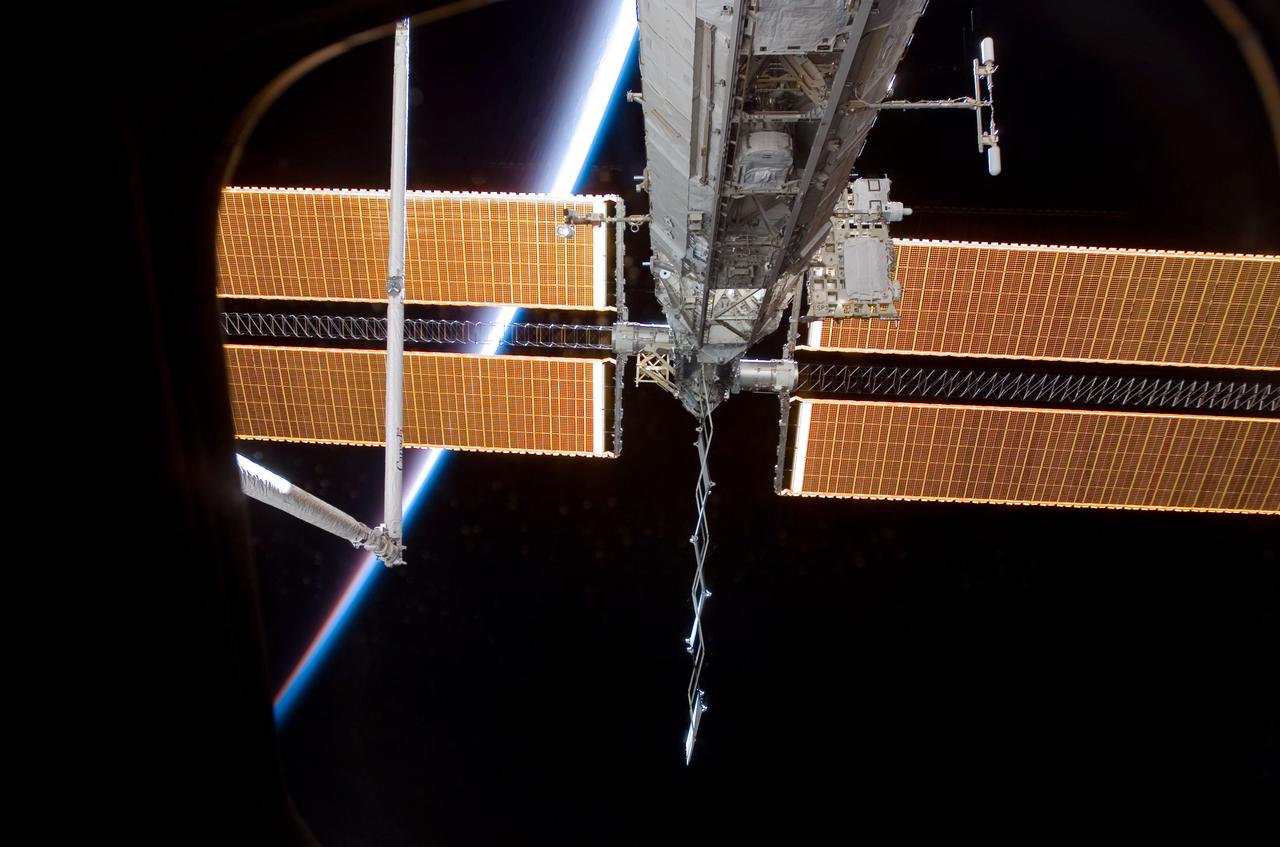

S120-E-006867 (26 Oct. 2007) --- Airglow above Earth's horizon and solar array panels add color to this scene of a portion of the International Space Station as the orbiting complex is docked with the Space Shuttle Discovery while crewmembers aboard the two spacecraft share more than a week's worth of duties to perform important work on the ISS.
STS105-E-5292 (16 August 2001) --- Astronaut Patrick G. Forrester works with the Early Ammonia Servicer (EAS), which he and fellow spacewalker Daniel T. Barry (out of frame) are in the process of installing on a segment of the P6 structure on the International Space Station (ISS). The two mission specialists were participating in the first of two scheduled STS-105 space walks. During the space walk, Discovery's commander Scott J. Horowitz operated the shuttle robot arm, and pilot Frederick W. (Rick) Sturckow choreographed the space walk from the orbiter's flight deck. The image was recorded with a digital still camera.

STS105-E-5277 (16 August 2001) --- Astronauts Daniel T. Barry (with red stripes on suit) and Patrick G. Forrester work with the Early Ammonia Servicer (EAS), which they are in the process of installing on a segment of the P6 structure on the International Space Station (ISS). The two mission specialists were participating in the first of two scheduled STS-105 space walks. The image was recorded with a digital still camera.
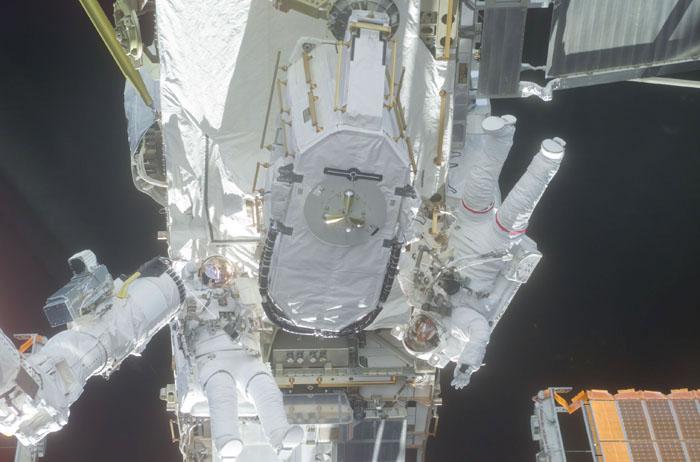

STS105-E-5269 (16 August 2001) --- Astronauts Daniel T. Barry (left) and Patrick G. Forrester work with the Early Ammonia Servicer (EAS), which they are in the process of installing on a segment of the P6 structure on the International Space Station (ISS). The two mission specialists were participating in the first of two scheduled STS-105 space walks. The image was recorded with a digital still camera.
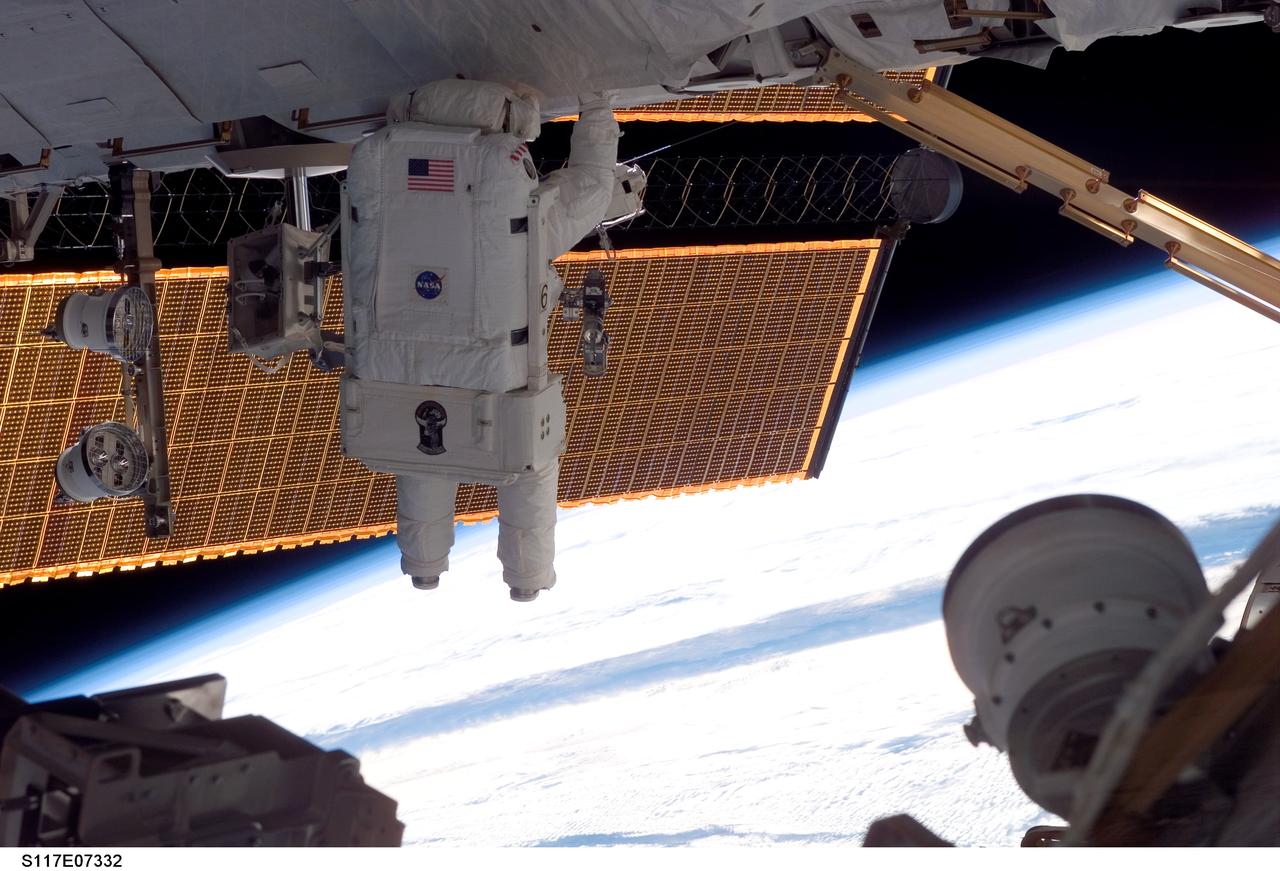

S117-E-07332 (13 June 2007) --- Astronauts Steven Swanson and Patrick Forrester (out of frame), both STS-117 mission specialists, participate in the mission's second planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA), as construction resumes on the International Space Station. Among other tasks, Forrester and Swanson removed all of the launch locks holding the 10-foot-wide solar alpha rotary joint in place and began the solar array retraction.

STS105-E-5254 (16 August 2001) --- Astronauts Daniel T. Barry (near bottom of frame) and Patrick G. Forrester surround the Early Ammonia Servicer (EAS), which they will install on a segment of the P6 structure on the International Space Station (ISS). The two mission specialists were participating in the first of two scheduled STS-105 space walks. The image was recorded with a digital still camera.
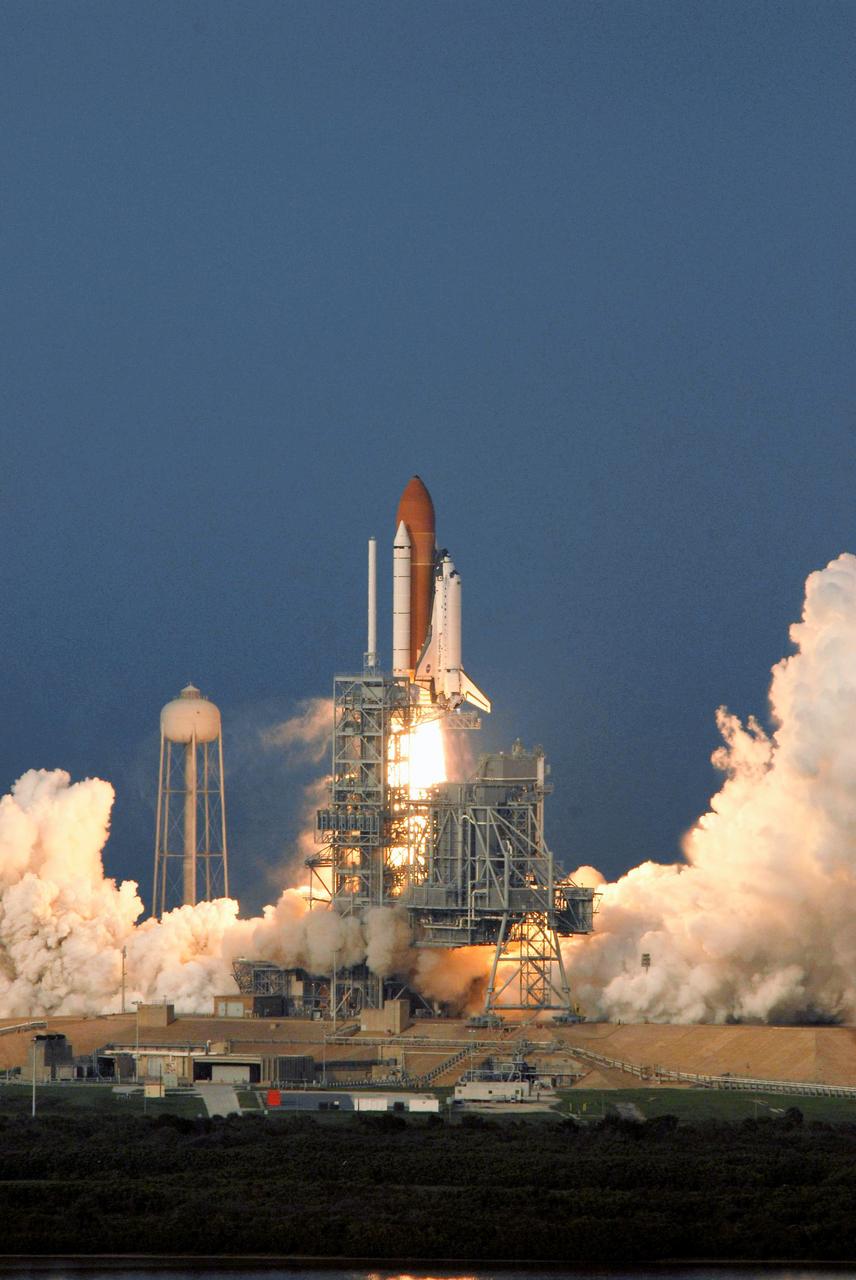

Enroute to the International Space Station (ISS), Space Shuttle Endeavor and its seven member STS-118 crew, blasted off from the launch pad at Kennedy Space Center on August 8, 2007. Construction resumed on the ISS as STS-118 mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the third Starboard 5 (S-5) truss segment, removed a faulty Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG-3), installed a new CMG into the Z1 truss, relocated the S-band Antenna Sub-Assembly from the Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1, retrieved the P6 transponder, and delivered roughly 5,000 pounds of equipment and supplies.
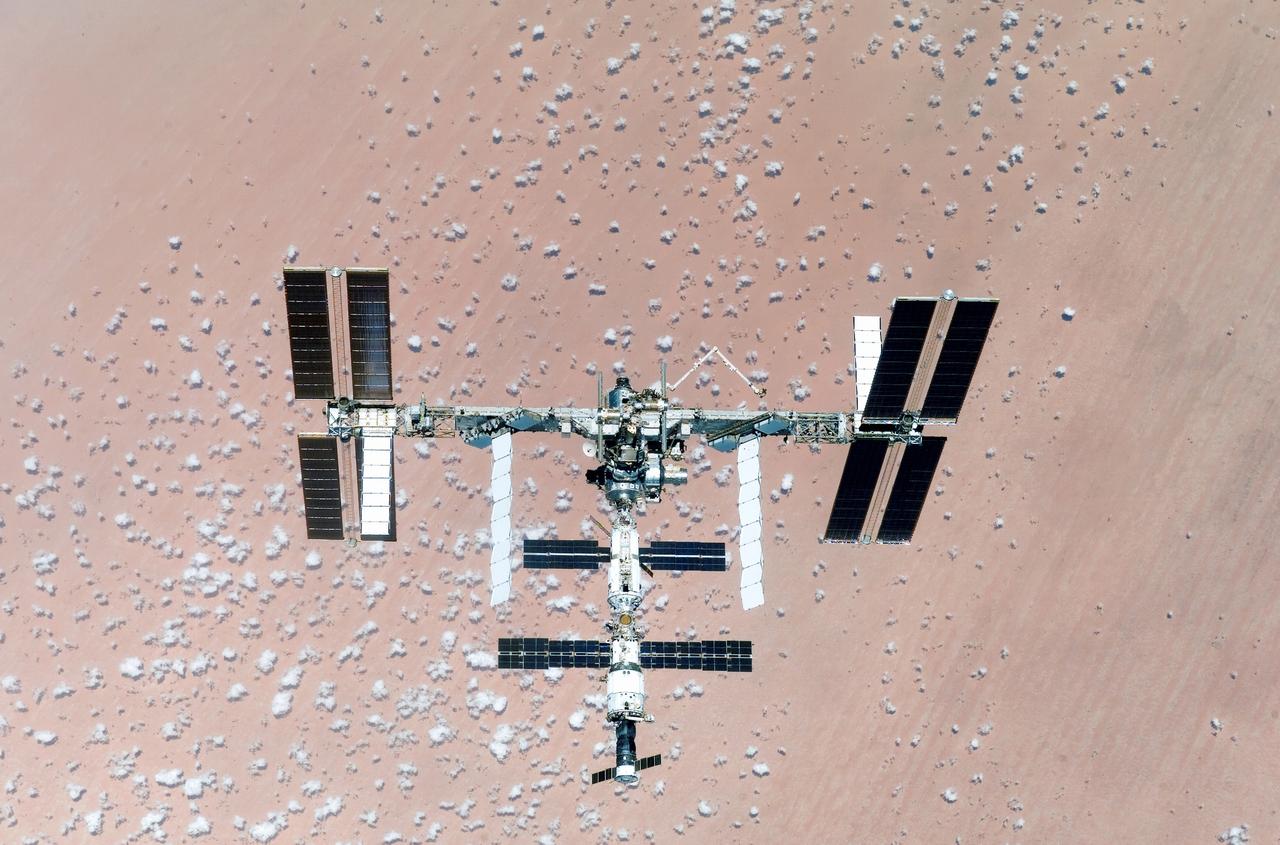

Back dropped by the colorful Earth, the International Space Station (ISS) boasts its newest configuration upon the departure of Space Shuttle Endeavor and STS-118 mission. Days earlier, construction resumed on the ISS as STS-118 mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the Starboard 5 (S-5) truss segment, removed a faulty Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG-3), installed a new CMG into the Z1 truss, relocated the S-band Antenna Sub-Assembly from the Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1, retrieved the P6 transponder, and delivered roughly 5,000 pounds of supplies.
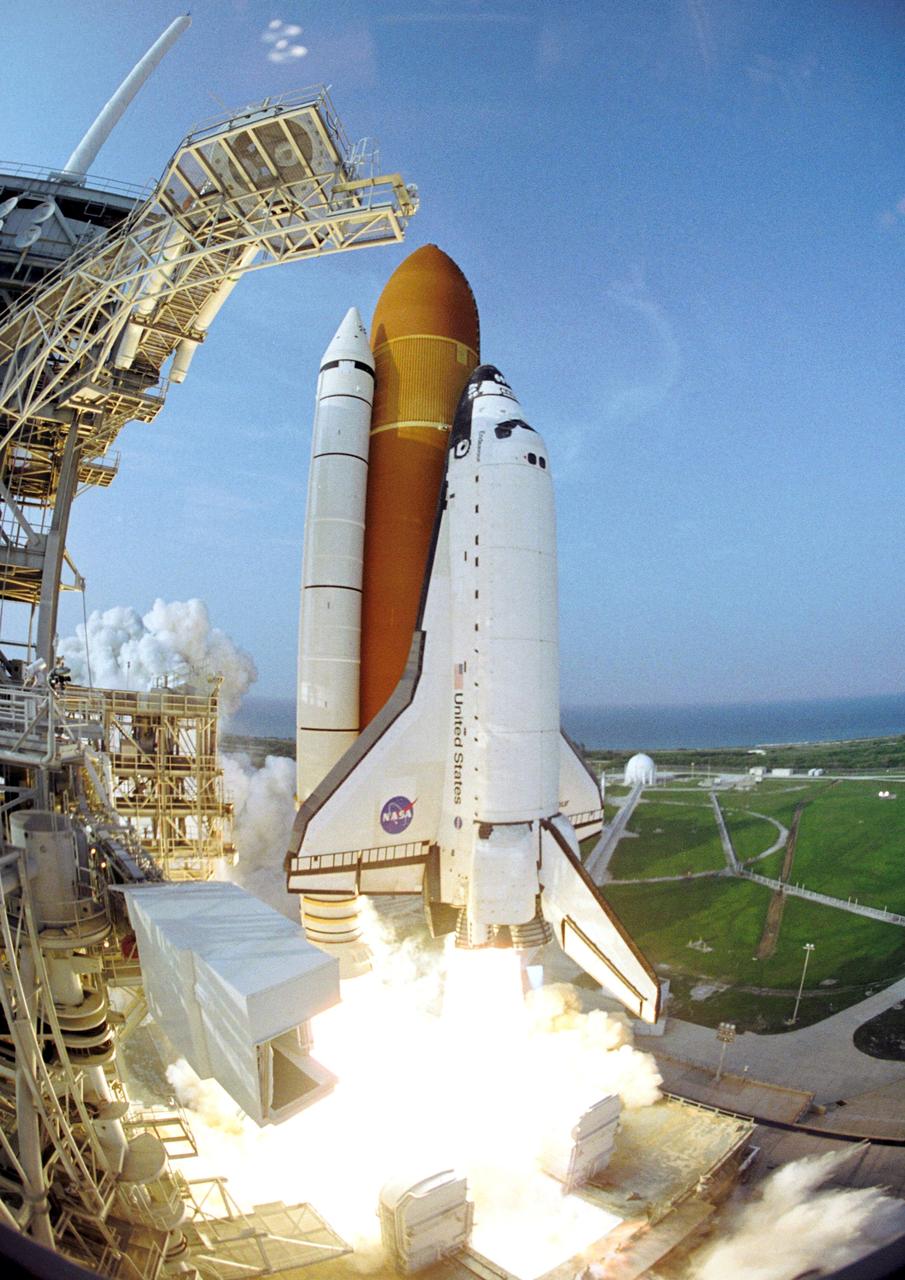

Enroute to the International Space Station (ISS), Space Shuttle Endeavor and its seven member STS-118 crew, blasted off from the launch pad at Kennedy Space Center on August 8, 2007. Construction resumed on the ISS as STS-118 mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the third Starboard 5 (S-5) truss segment, removed a faulty Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG-3), installed a new CMG into the Z1 truss, relocated the S-band Antenna Sub-Assembly from the Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1, retrieved the P6 transponder, and delivered roughly 5,000 pounds of equipment and supplies.
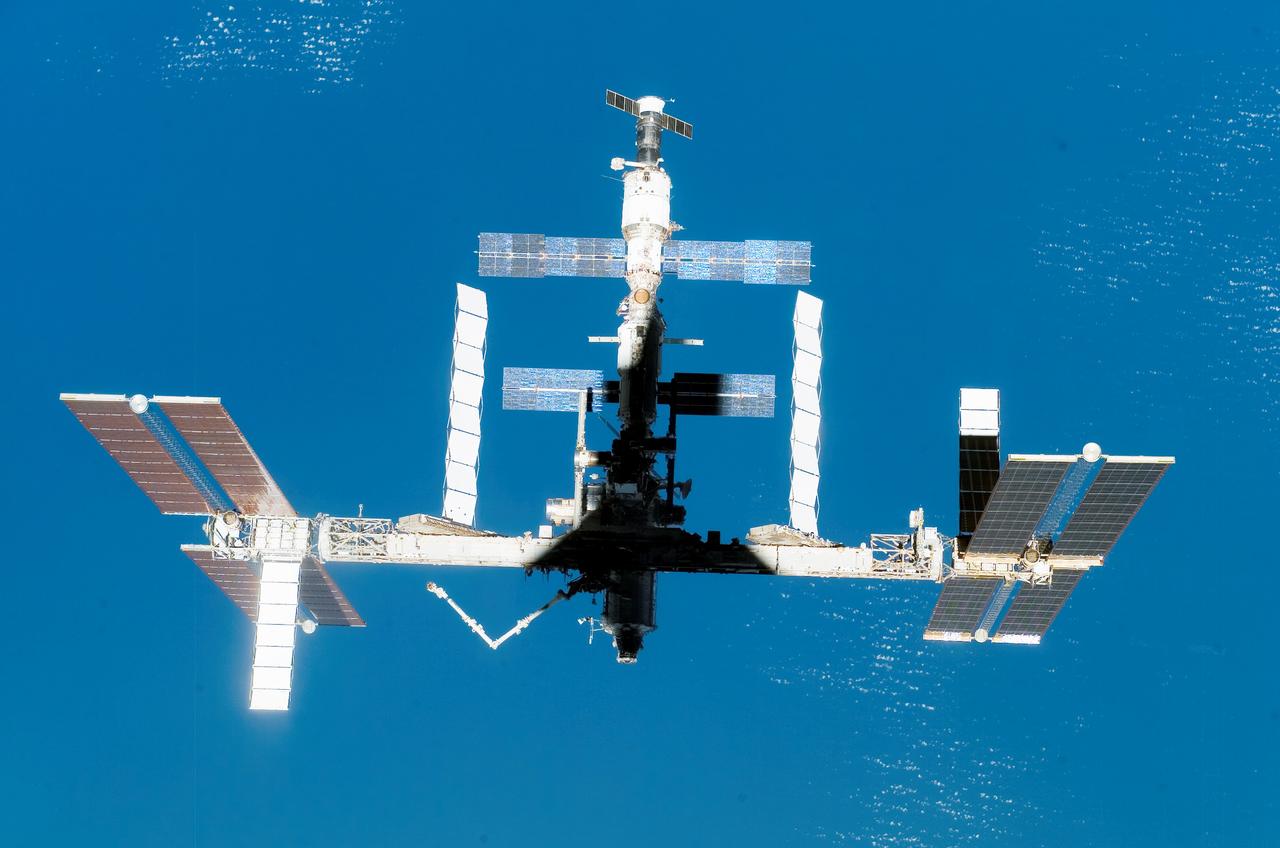

Back dropped by the blue Earth, the International Space Station (ISS) boasts its newest configuration upon the departure of Space Shuttle Endeavor and STS-118 mission. Days earlier, construction resumed on the ISS as STS-118 mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the Starboard 5 (S-5) truss segment, removed a faulty Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG-3), installed a new CMG into the Z1 truss, relocated the S-band Antenna Sub-Assembly from the Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1, retrieved the P6 transponder, and delivered roughly 5,000 pounds of equipment and supplies.
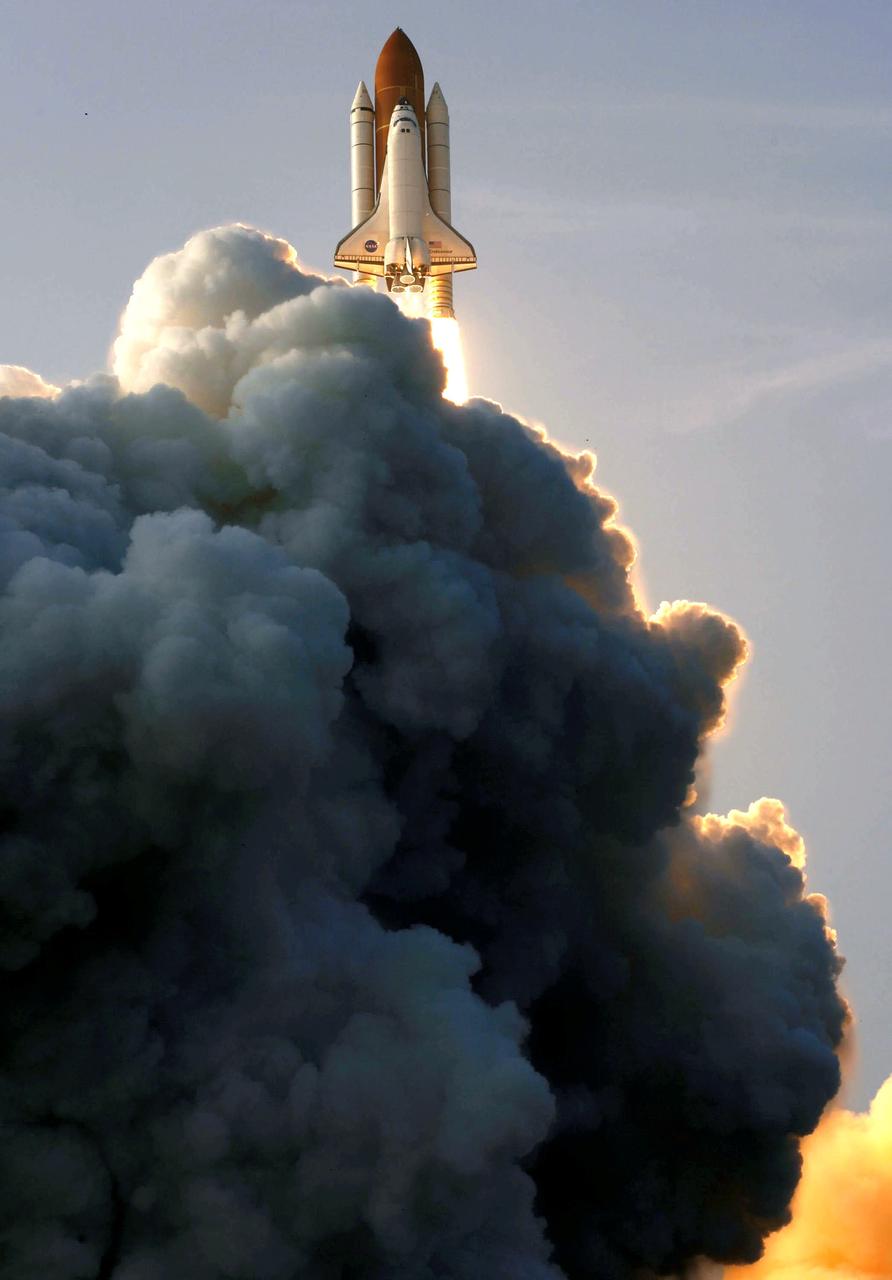

Enroute to the International Space Station (ISS), Space Shuttle Endeavor and its seven member STS-118 crew, blasted off from the launch pad at Kennedy Space Center on August 8, 2007. Construction resumed on the ISS as STS-118 mission specialists and the Expedition 15 crew completed installation of the third Starboard 5 (S-5) truss segment, removed a faulty Control Moment Gyroscope (CMG-3), installed a new CMG into the Z1 truss, relocated the S-band Antenna Sub-Assembly from the Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1, retrieved the P6 transponder, and delivered roughly 5,000 pounds of equipment and supplies.
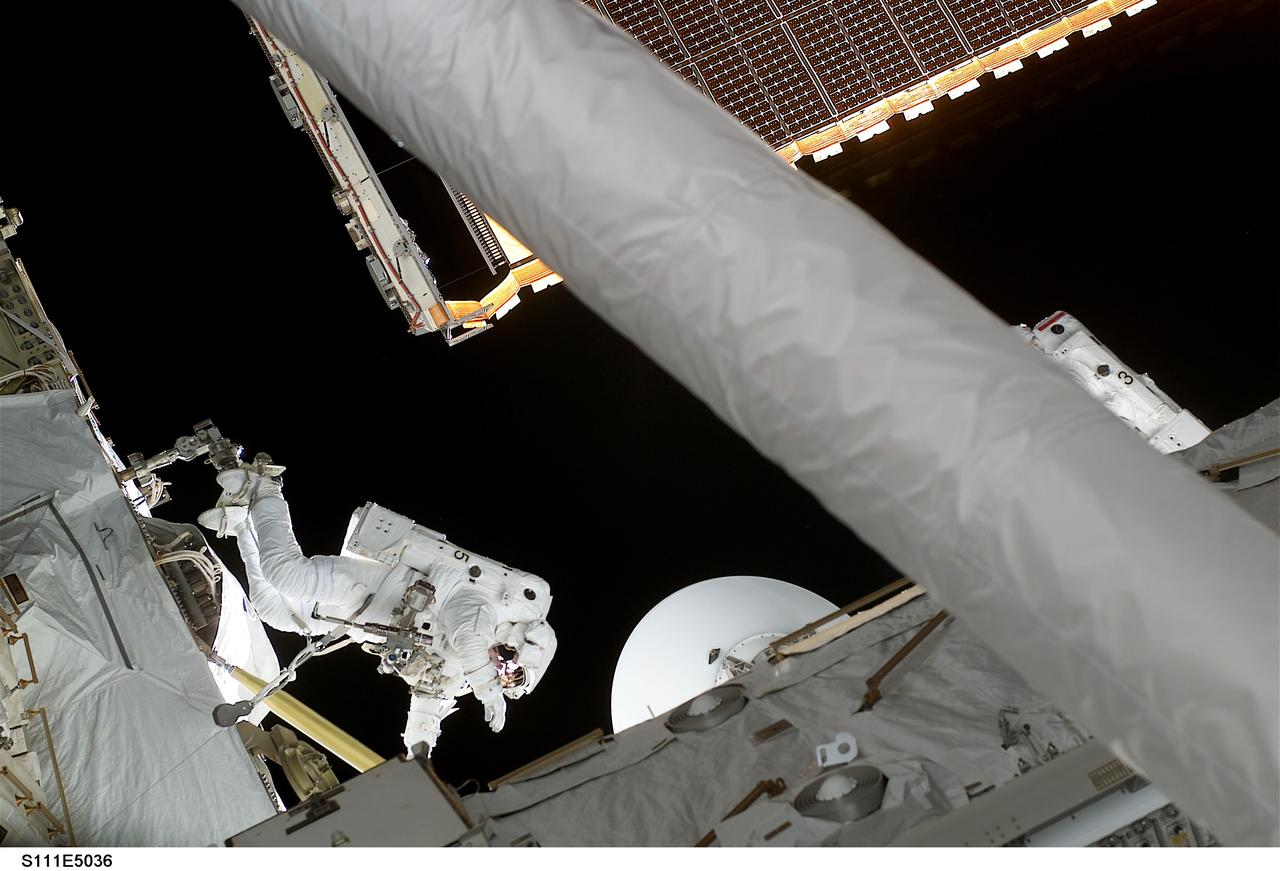

STS111-E-5036 (8 June 2002) --- Astronauts Philippe Perrin (left center) and Franklin R. Chang-Diaz (partially obscured by robot arm) work in chorus during extravehicular activity (EVA) to perform work on the International Space Station (ISS). The first spacewalk of the STS-111 mission began with the installation of a Power and Data Grapple Fixture (PDGF) for the station's robotic arm, known as Canadarm2, on the complex's P6 truss. The PDGF will allow the robotic arm to grip the P6 truss for future station assembly operations. Astronauts Chang-Diaz and Perrin (with French Space Agency, CNES) went on to install the new fixture about halfway up the P6 truss, the vertical structure that currently supports the station's set of large U.S. solar arrays.
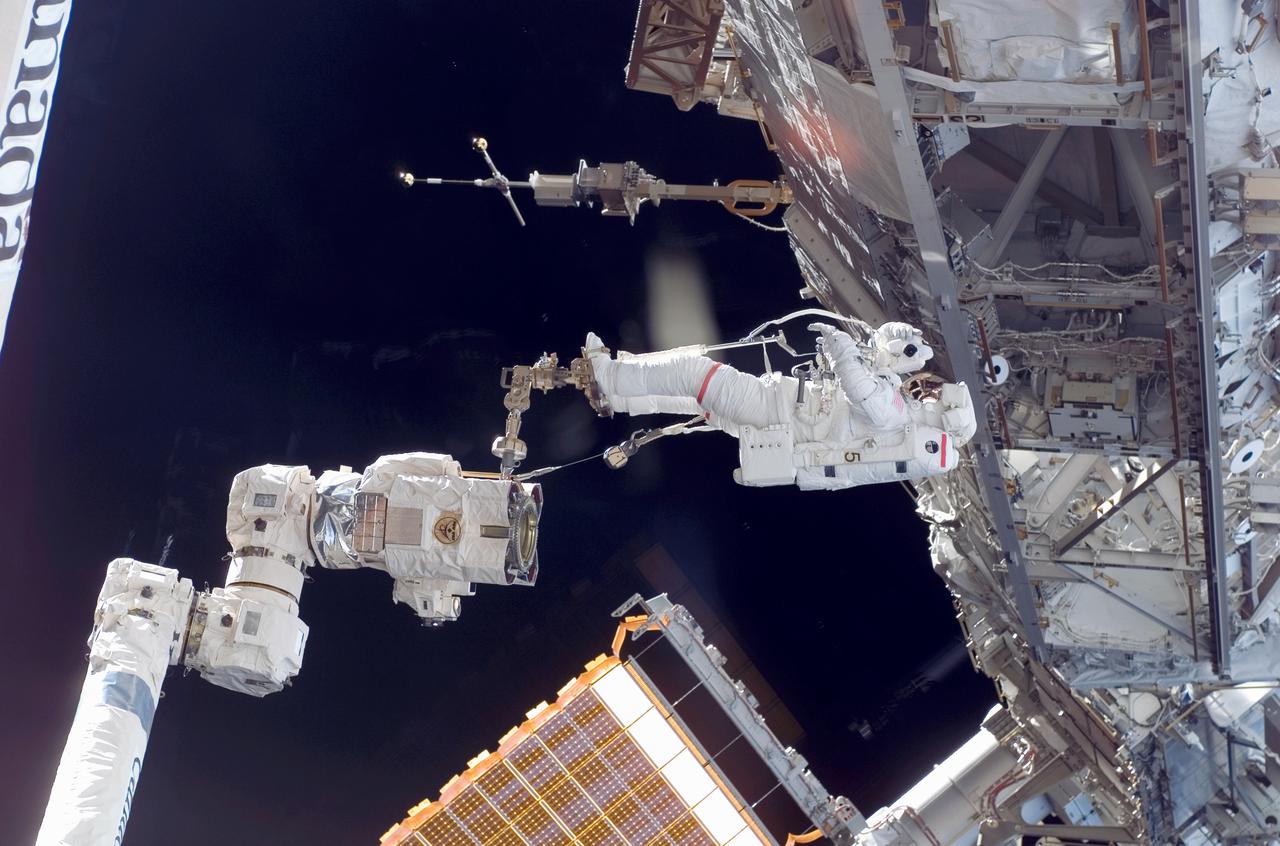

As the construction continued on the International Space Station (ISS), STS-118 astronaut and mission specialist Rick Mastracchio was anchored on the foot restraint of the Canadarm2 as he participated in the third session of Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) for the mission. Assisting Mastracchio was Expedition 15 flight engineer Clay Anderson (out of frame). During the 5 hour, 28 minute space walk, the two relocated the S-band Antenna Sub-Assembly from the Port 6 (P6) truss to the Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
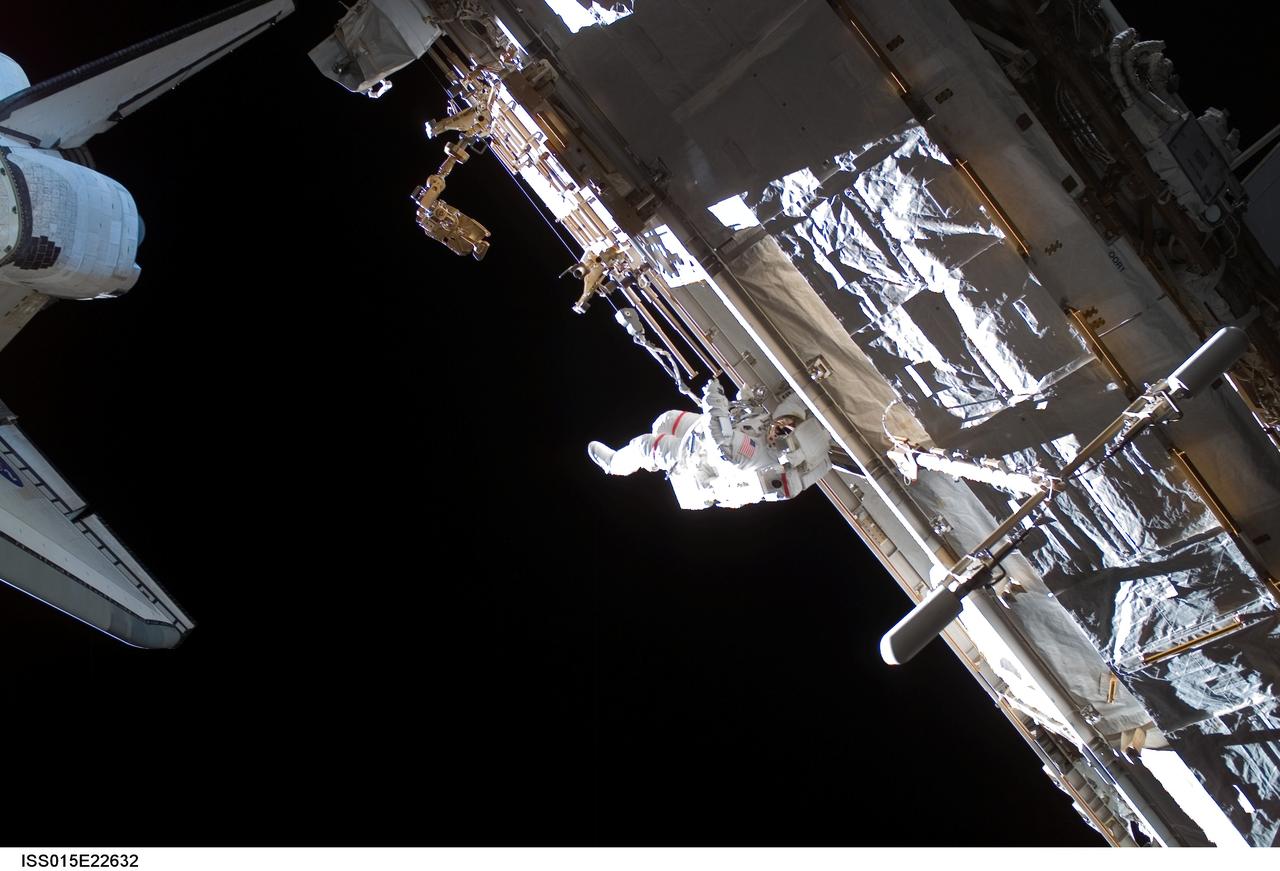

ISS015-E-22632 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
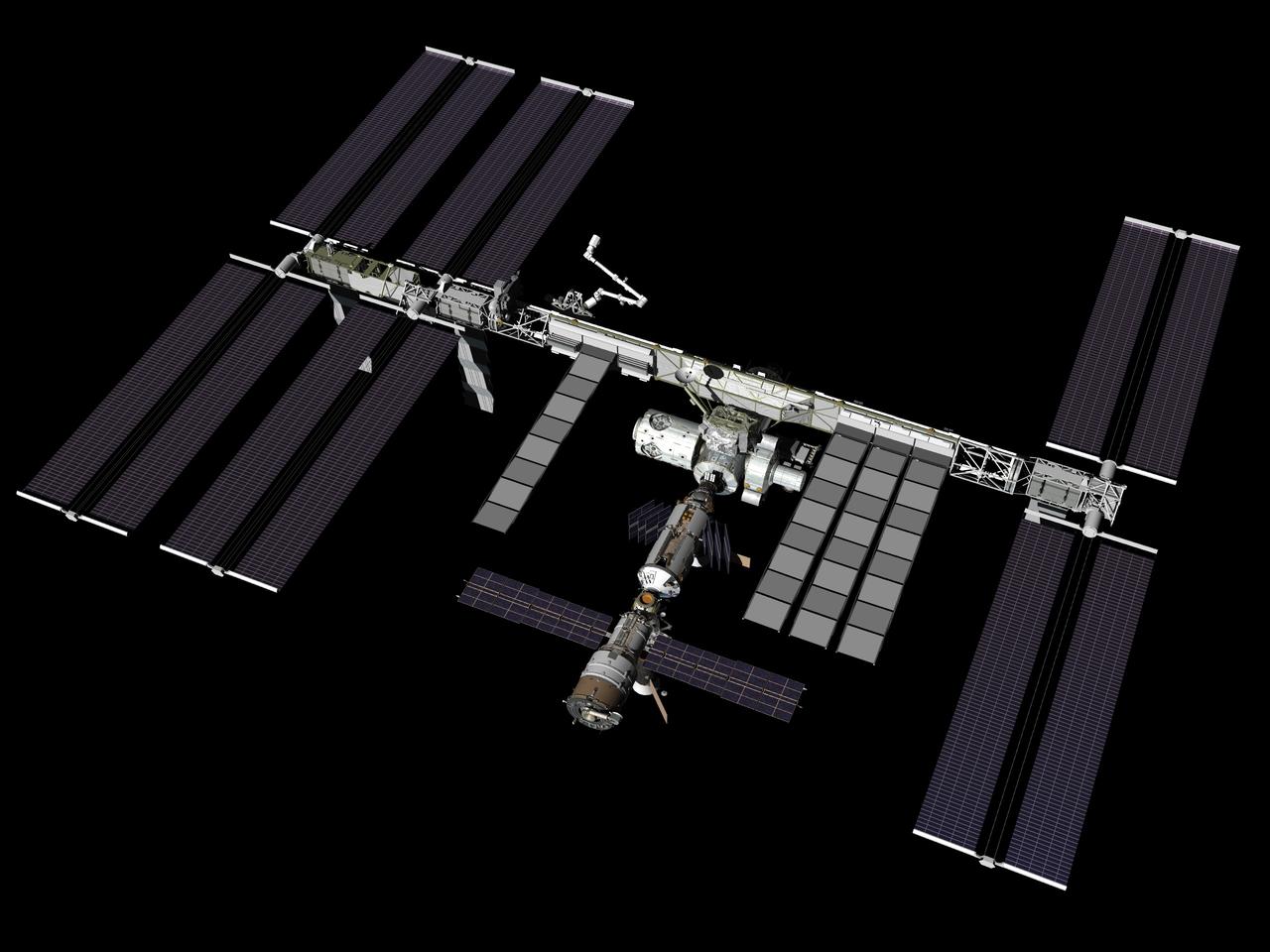

JSC2007-E-093440 (October 2007) --- Computer-generated artist's rendering of the International Space Station as of Oct. 30, 2007 during the STS-120/10A mission. Harmony node is attached to the port side of the Unity node. Starboard TCS radiators are fully deployed. P6 truss segment is relocated to the end of the P5 segment and the P6 solar arrays and radiator are deployed.
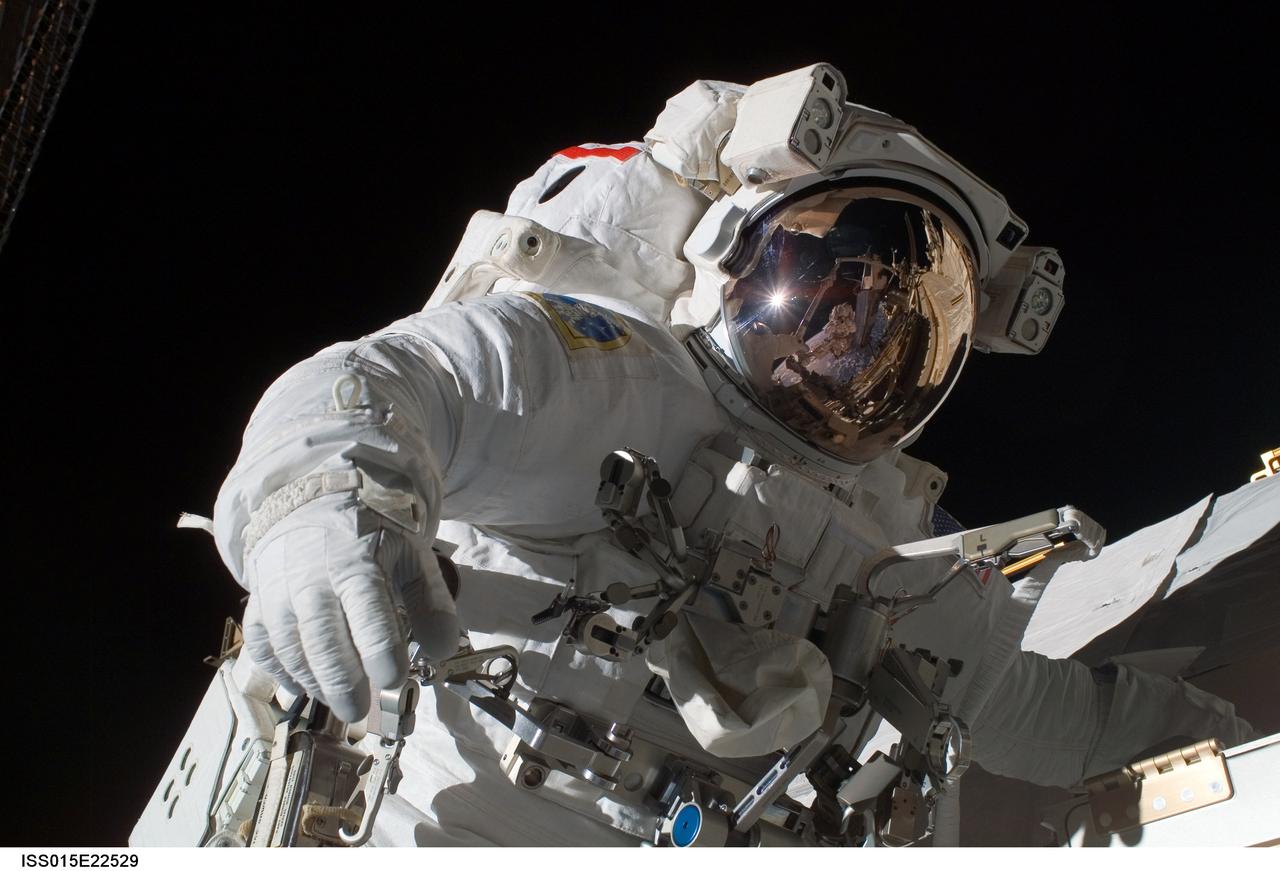

ISS015-E-22529 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
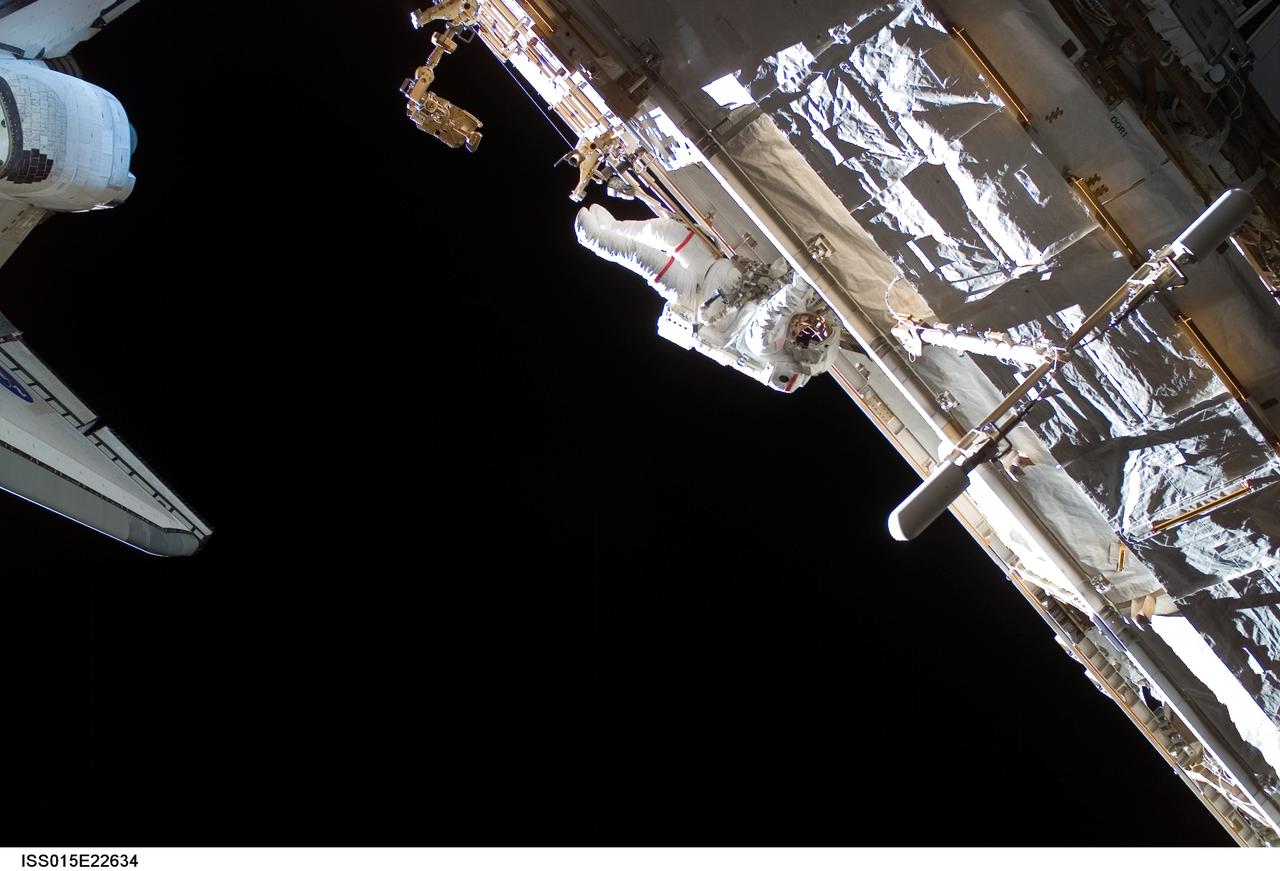

ISS015-E-22634 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
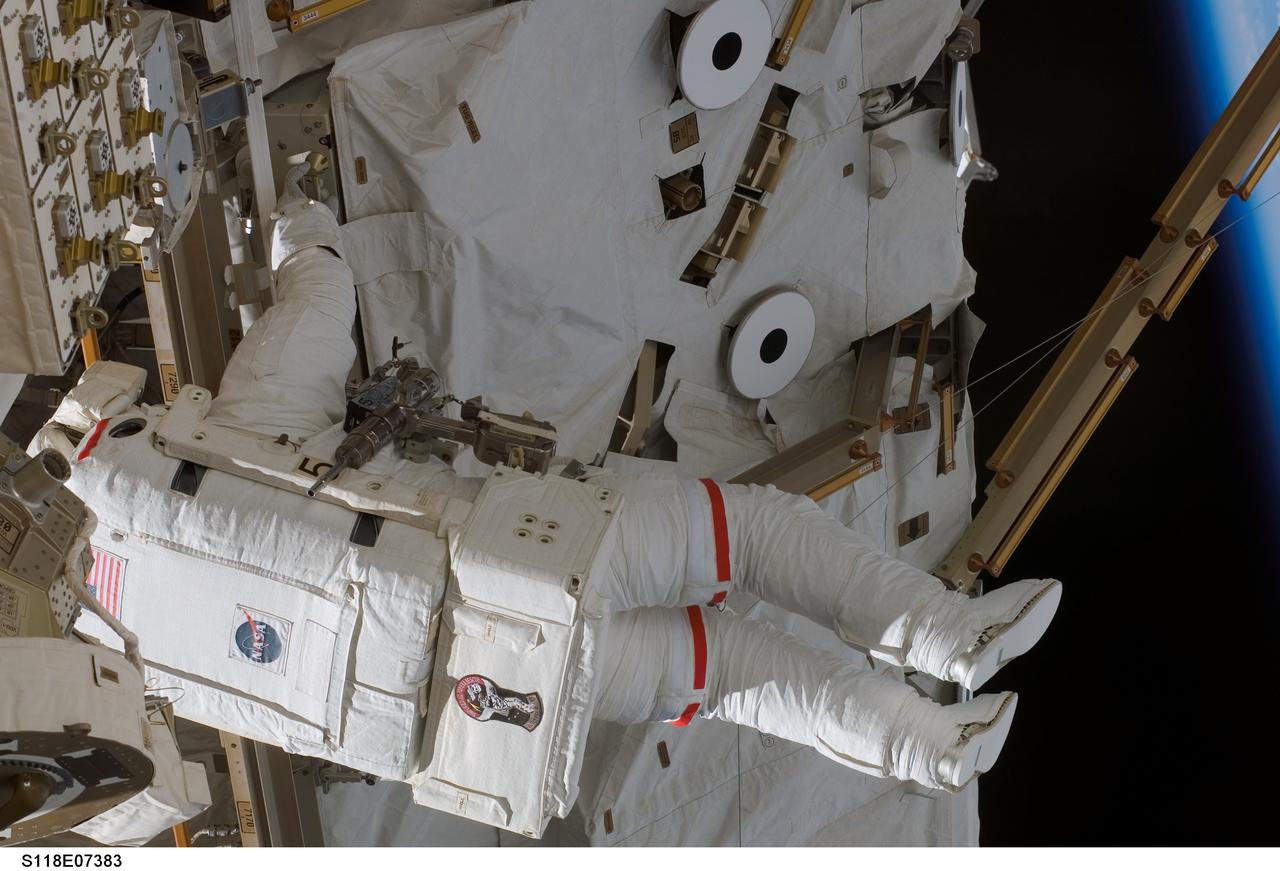

S118-E-07383 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
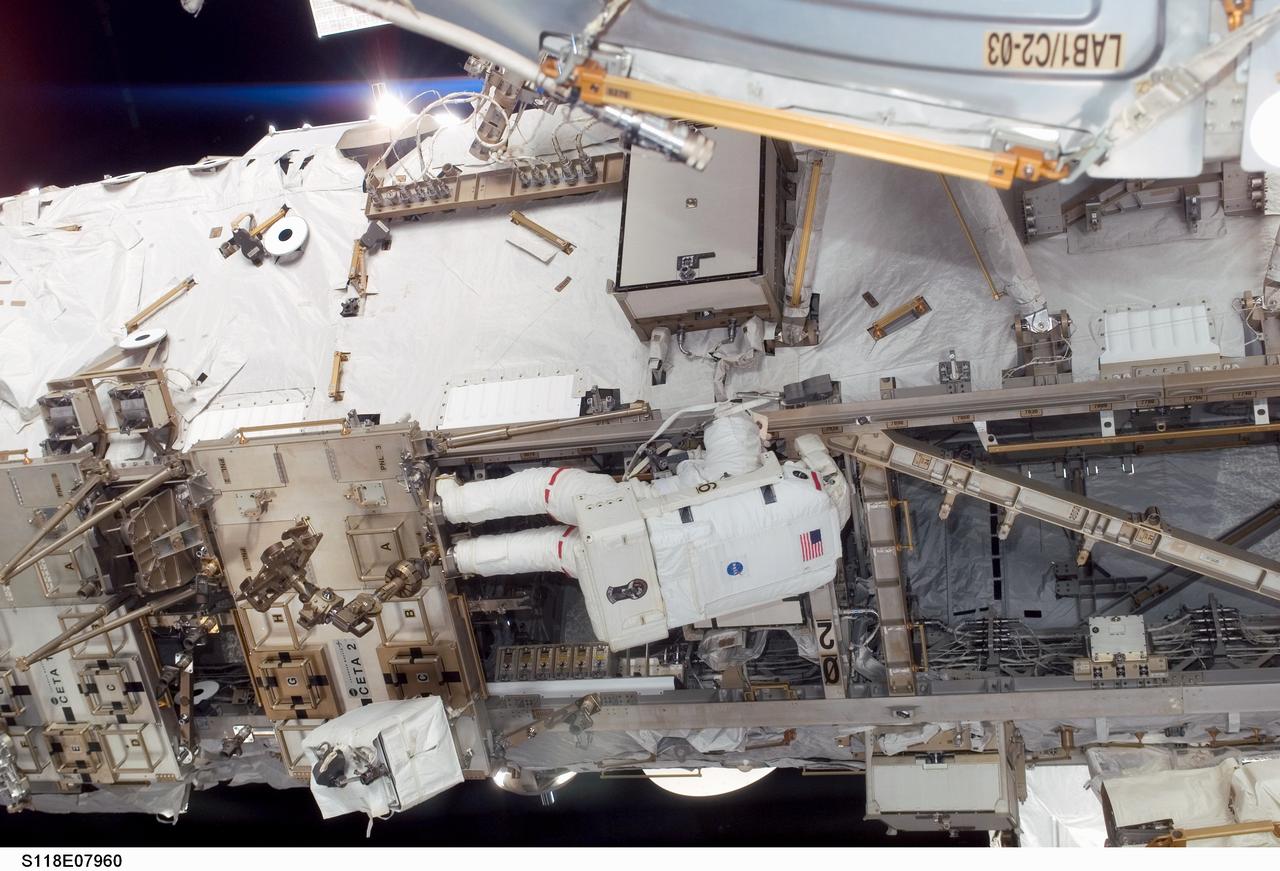

S118-E-07960 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Clay Anderson, Expedition 15 flight engineer, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Anderson and astronaut Rick Mastracchio (out of frame), STS-118 mission specialist, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
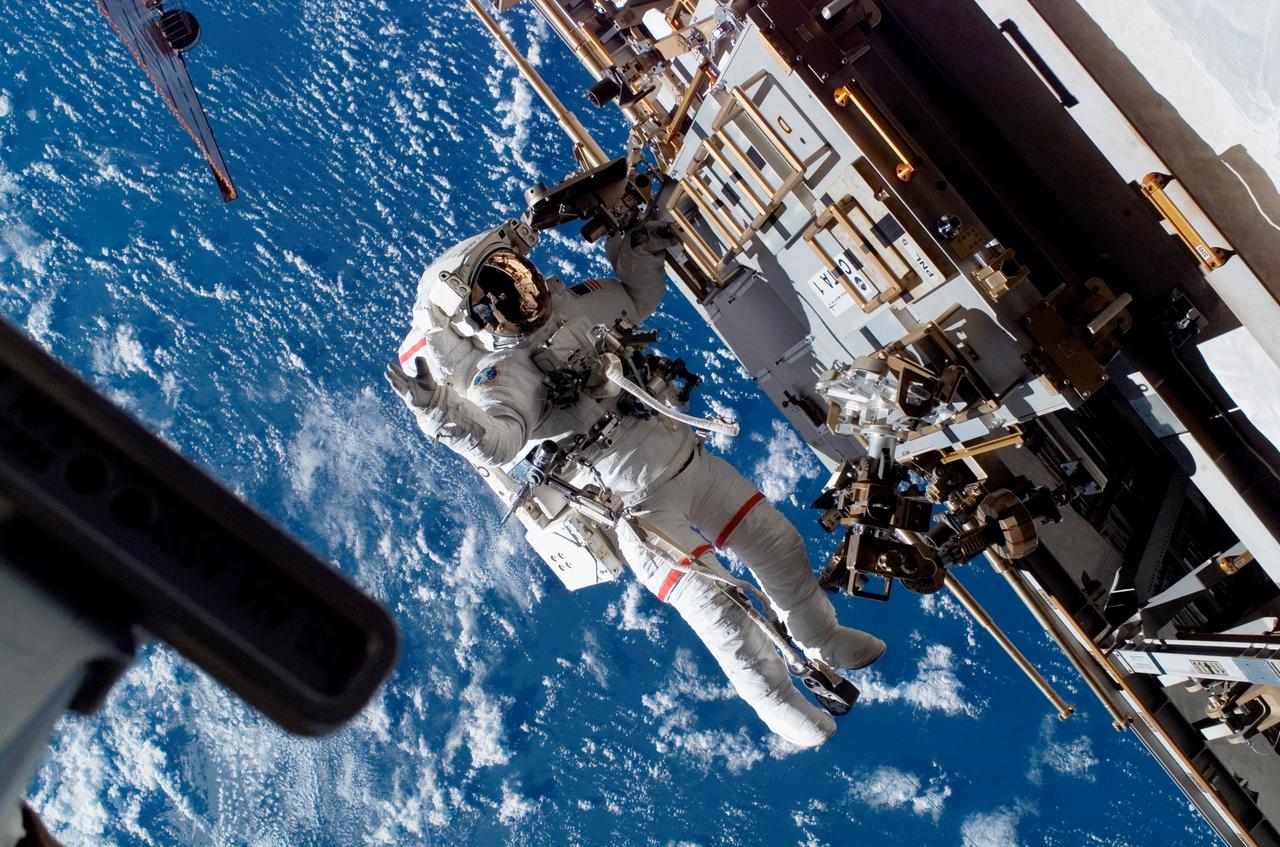

ISS015-E-22539 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
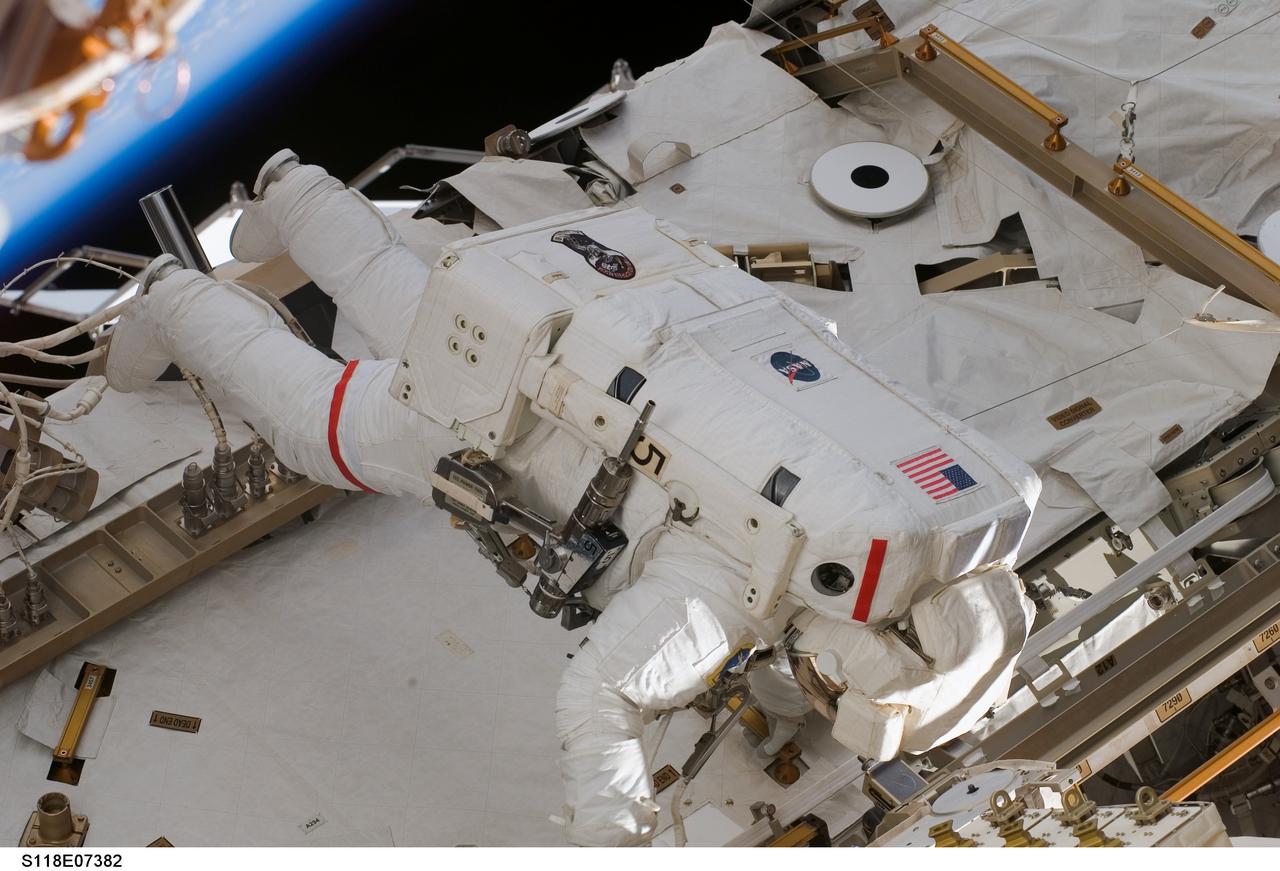

S118-E-07382 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.
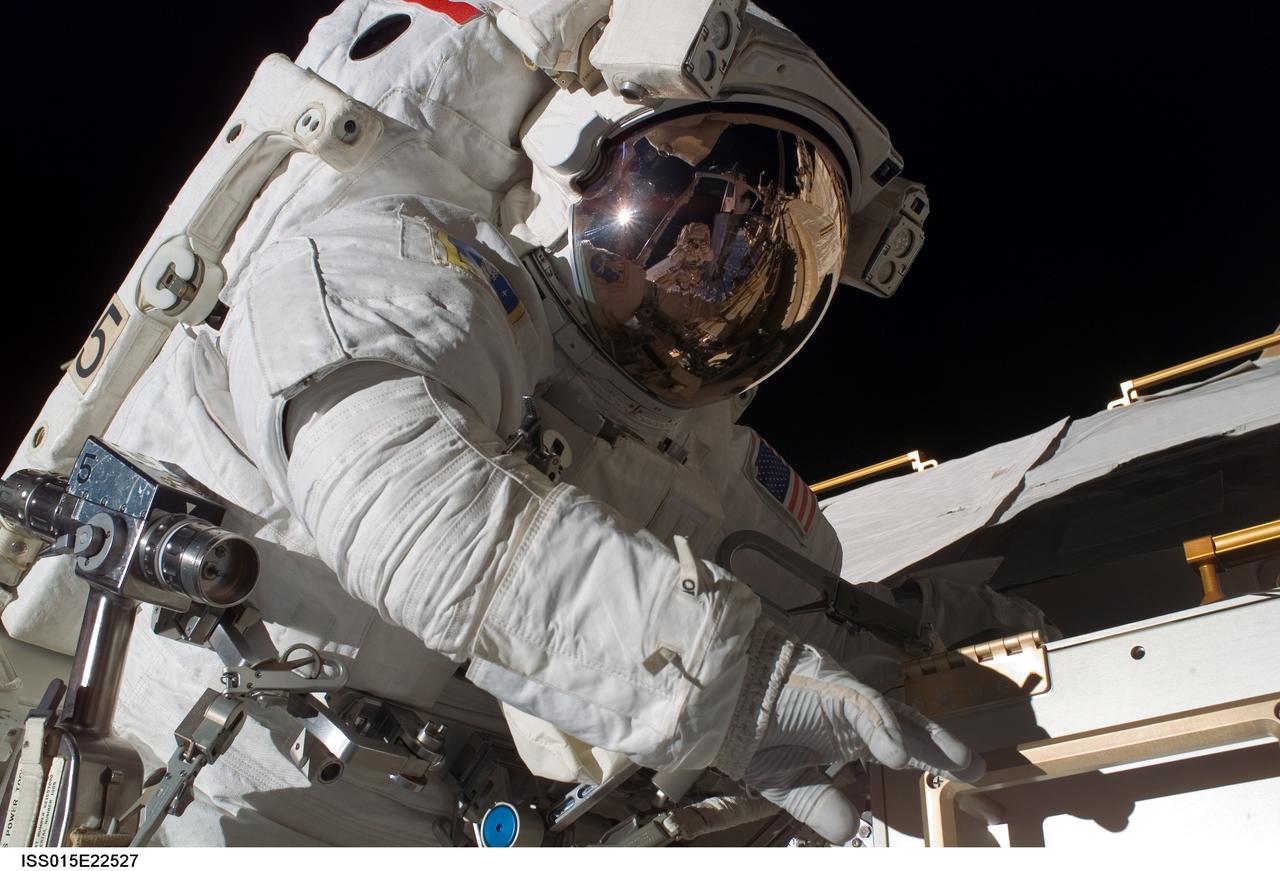

ISS015-E-22527 (15 Aug. 2007) --- Astronaut Rick Mastracchio, STS-118 mission specialist, participates in the mission's third planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA) as construction and maintenance continue on the International Space Station. During the 5-hour, 28-minute spacewalk, Mastracchio and astronaut Clay Anderson (out of frame), Expedition 15 flight engineer, relocated the S-Band Antenna Sub-Assembly from Port 6 (P6) to Port 1 (P1) truss, installed a new transponder on P1 and retrieved the P6 transponder.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-116 Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam is in training at SPACEHAB, Port Canaveral, Fla., along with other crew members Commander Terrence Wilcutt, Pilot William Oelefein and Mission Specialist Christer Fuglesang. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-116 crew look over equipment at SPACEHAB in Port Canaveral, Fla. On the left are Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam and Christer Fuglesang; on the right are Commander Terrence Wilcutt and Pilot William Oefelein. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review.
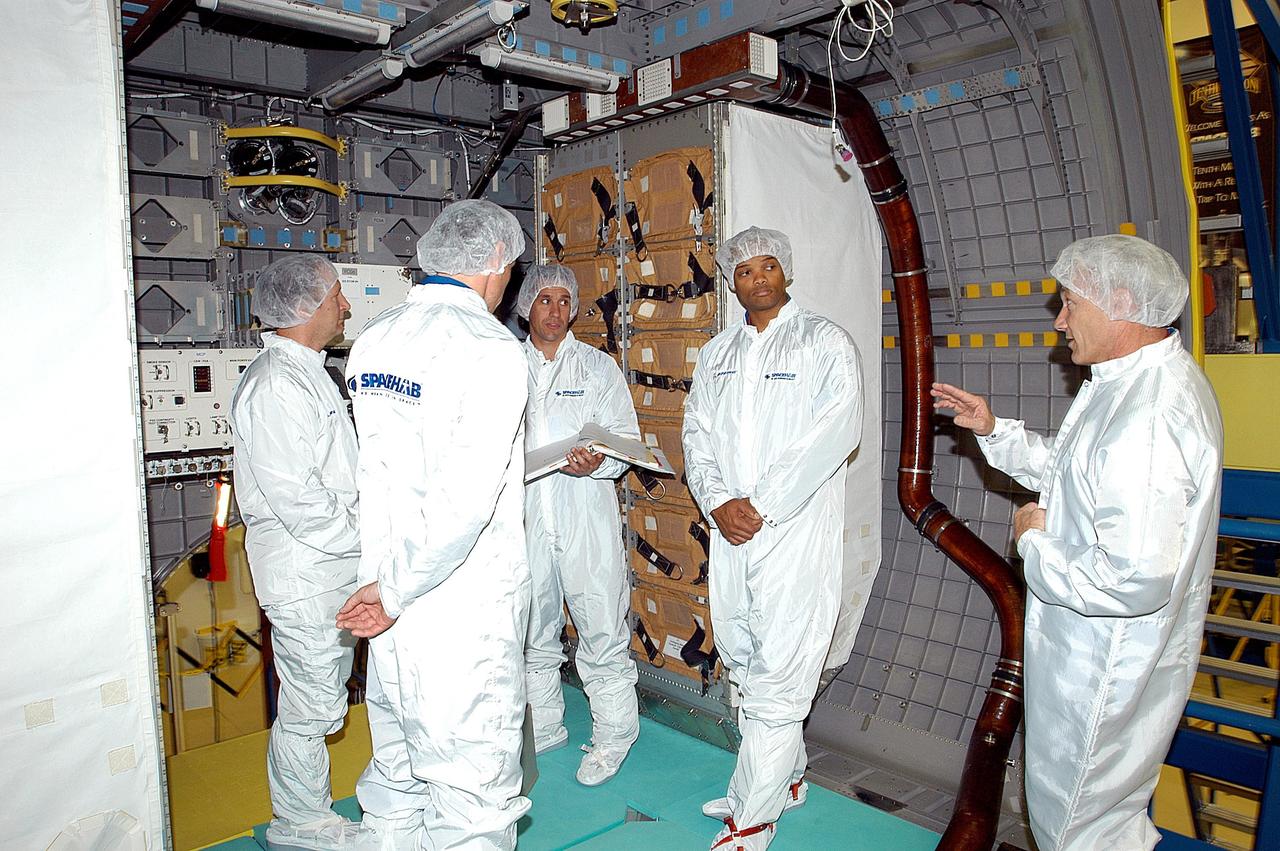

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The STS-116 crew take part in training in the SPACEHAB module. From left are Mission Specialist Christer Fuglesang; a trainer; Pilot Michael Oefelein; Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam; and Commander Terrence Wilcutt. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review
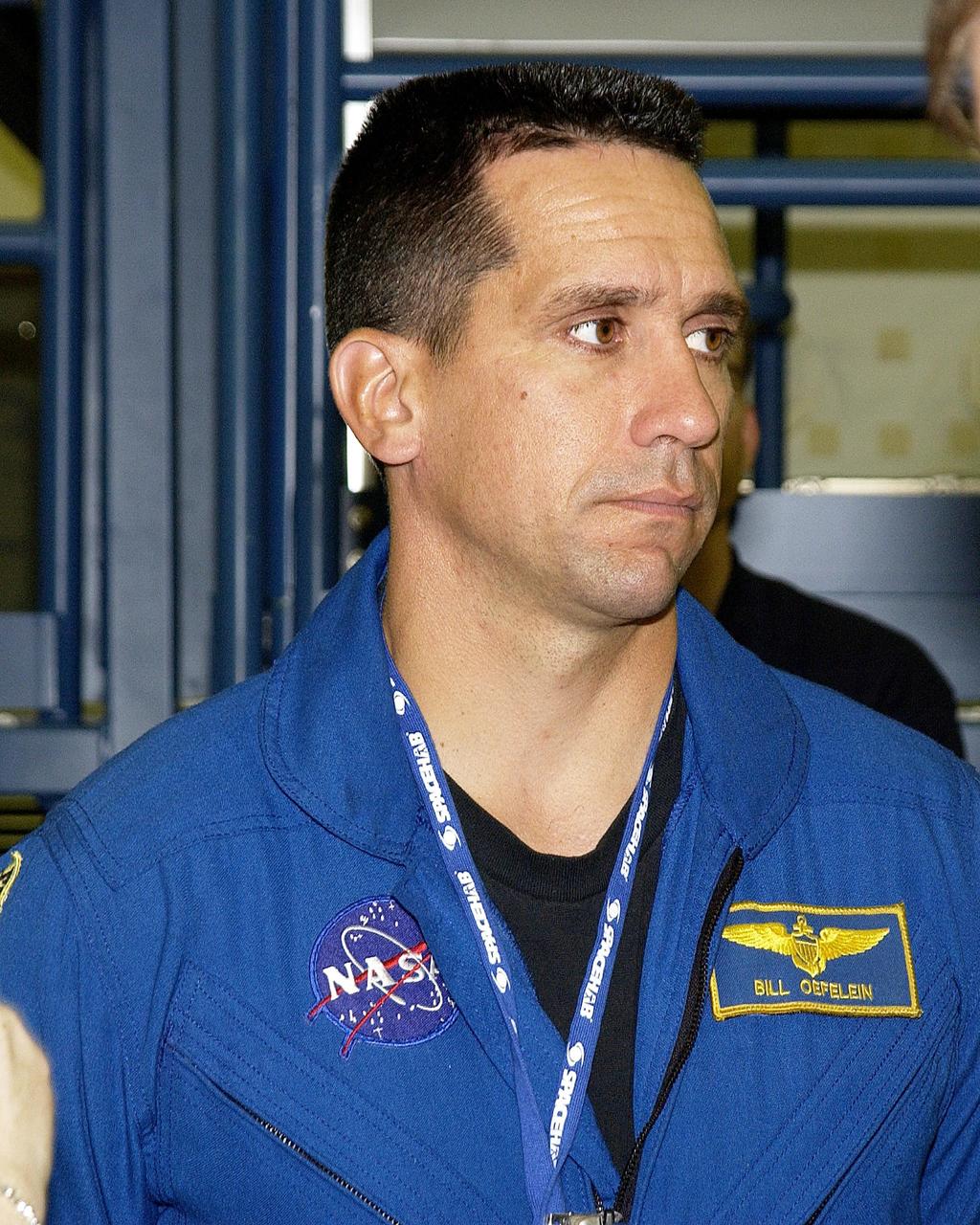

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-116 Pilot William Oelefein is in training at SPACEHAB, Port Canaveral, Fla., along with other crew members Commander Terrence Wilcutt and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam and Christer Fuglesang. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review.
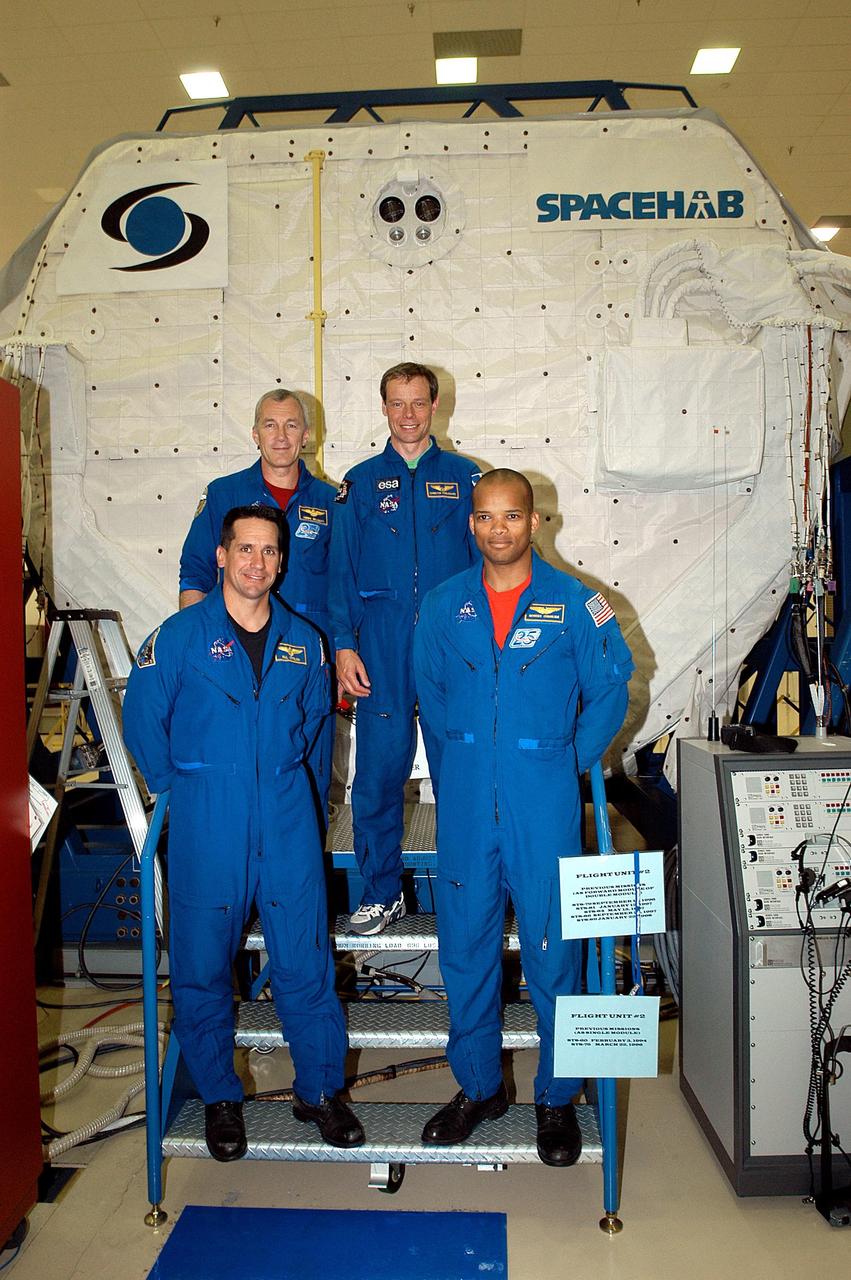

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The STS-116 crew poses outside the SPACEHAB module during training. In the rear are Commander Terrence Wilcutt and Mission Specialist Christer Fuglesang;; in front are Pilot William Oefelein and Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review.
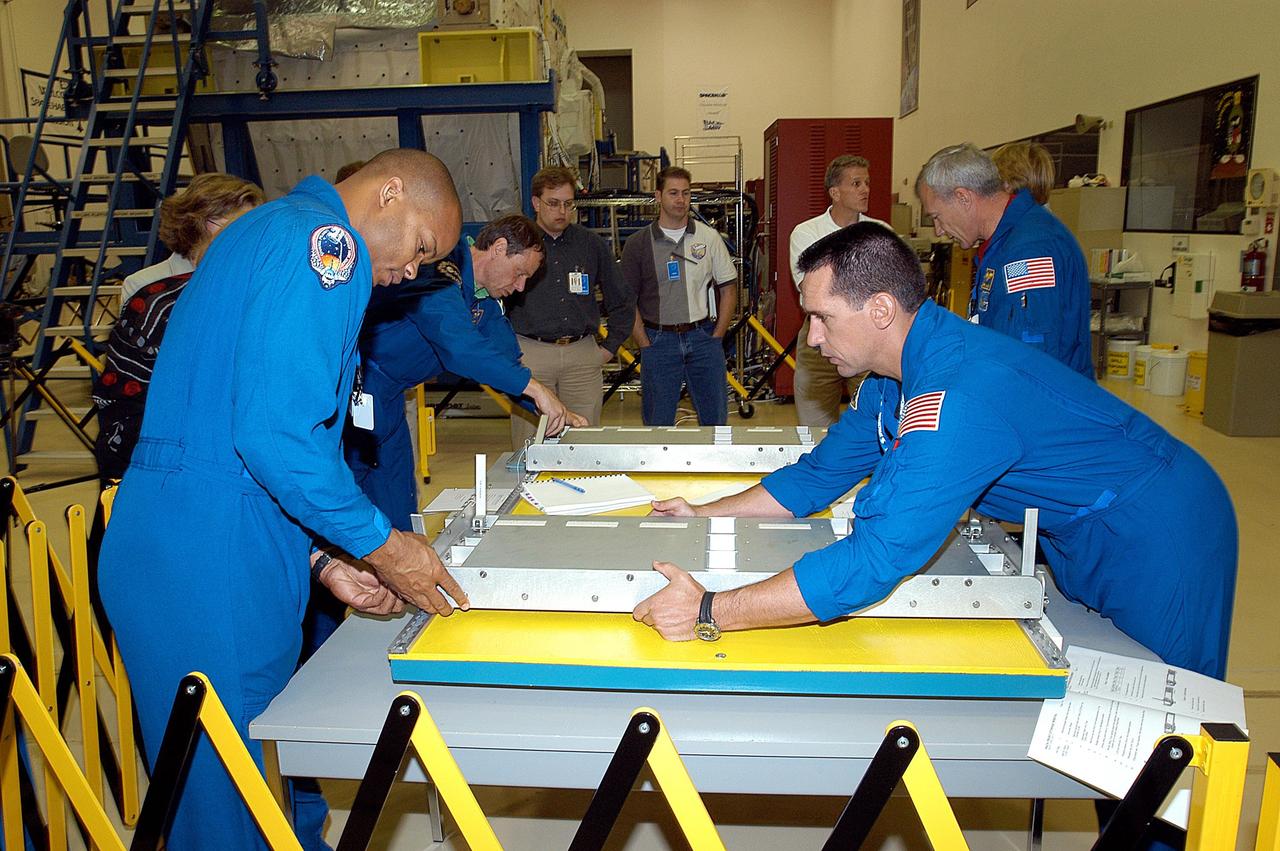

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Members of the STS-116 crew handle equipment at SPACEHAB in Port Canaveral, Fla. On the left are Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam and Christer Fuglesang; on the right are Pilot William Oefelein (front) and Commander Terrence Wilcutt. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The STS-116 crew poses outside the SPACEHAB module during training. In the rear are Commander Terrence Wilcutt and Mission Specialist Christer Fuglesang; in front are Pilot William Oefelein and Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review.
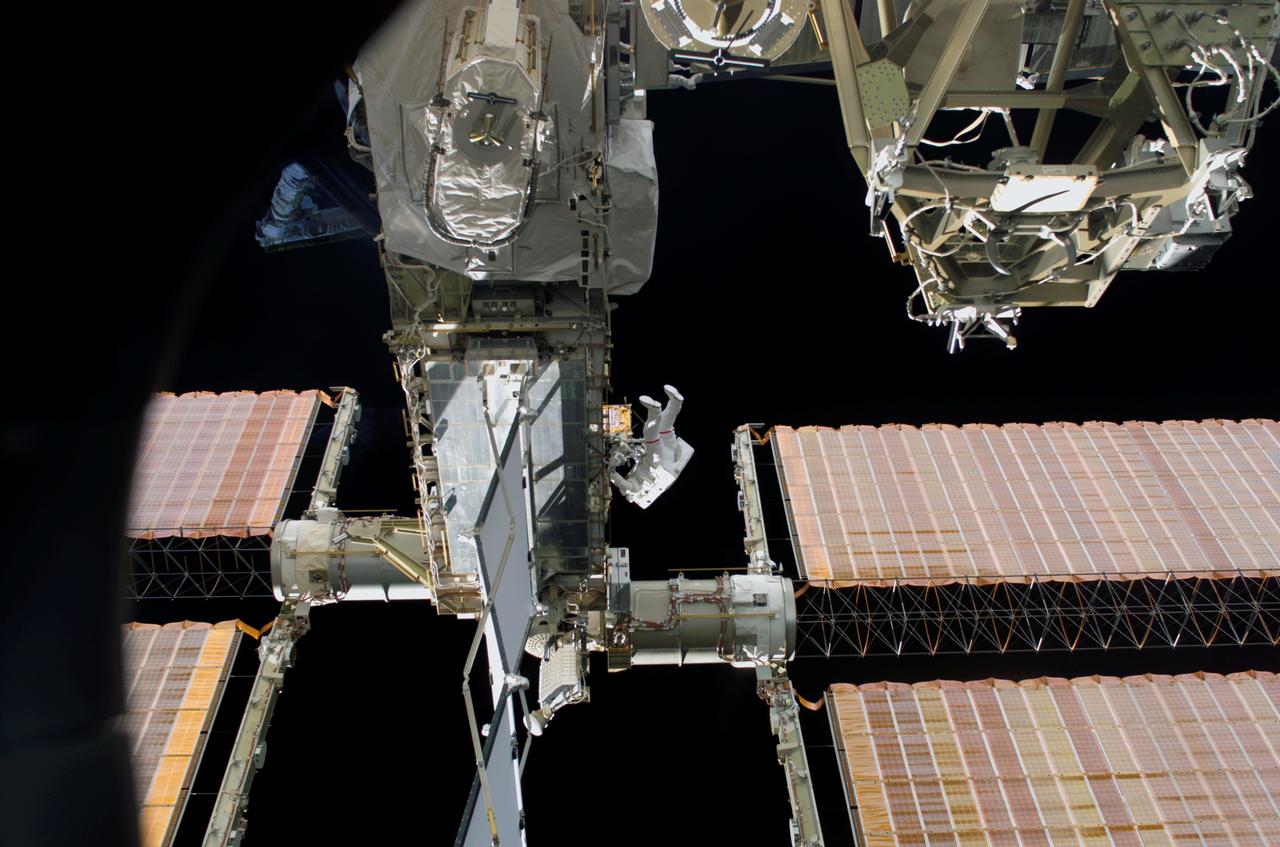
S114-E-6856 (3 August 2005) --- Backdropped by the blackness of space, astronaut Soichi Noguchi, STS-114 mission specialist representing the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA), traverses along the P6 truss near the arrays on the international space station during the mission’s third session of extravehicular activity (EVA).
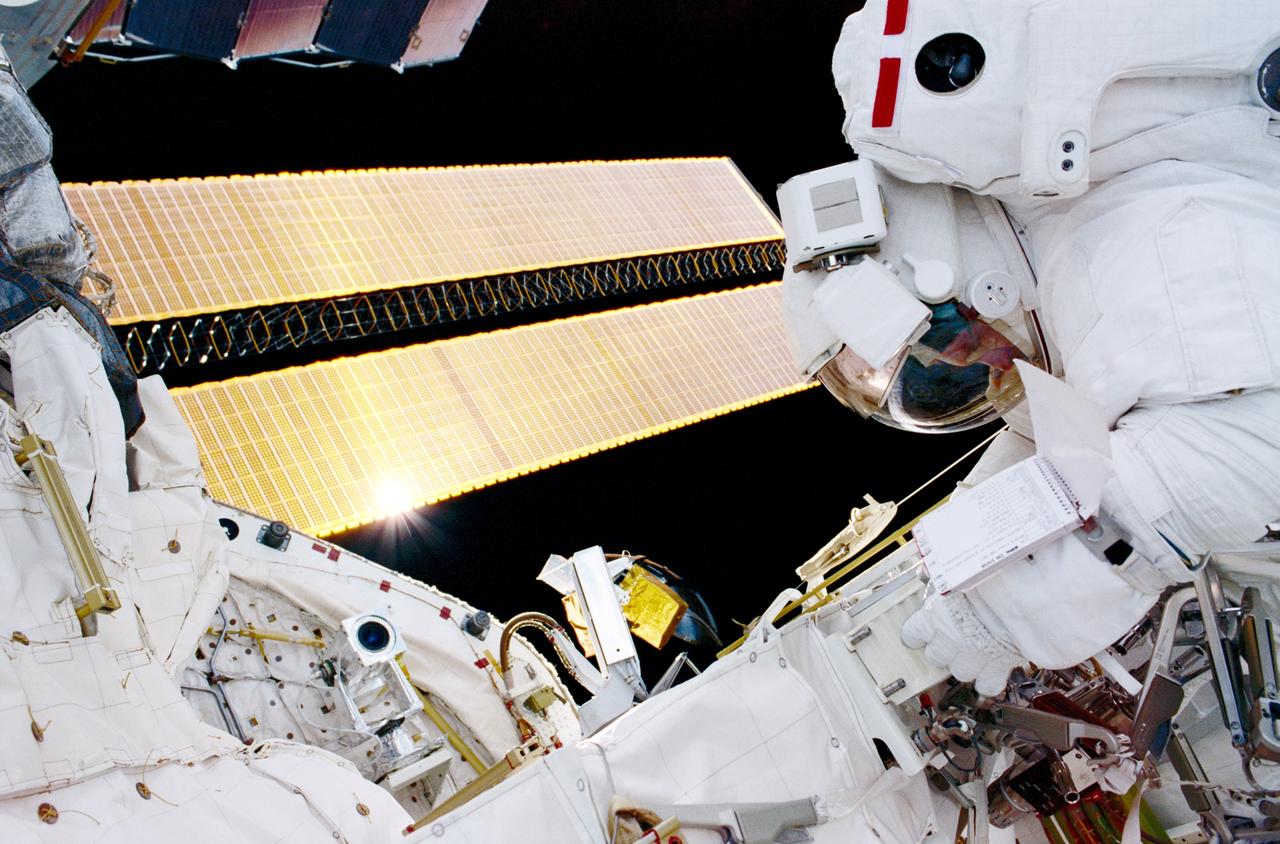

STS102-315-027 (8-21 March 2001)--- Astronaut Andrew S. W. Thomas, mission specialist, is photographed by astronaut Paul W. Richards, mission specialist, while in the cargo bay of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Discovery during the second space walk. Sunglint on the solar array for the P6 Truss is seen in the background.
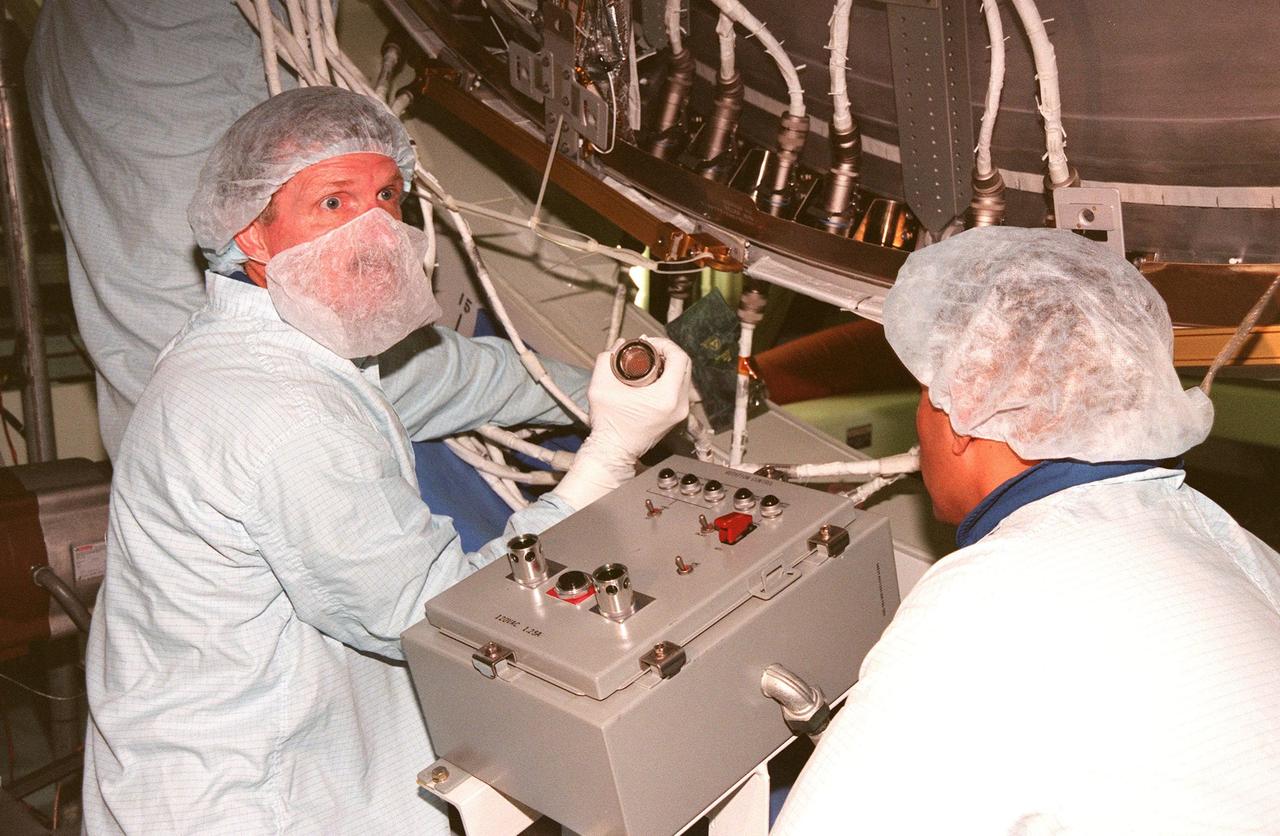

STS-97 Mission Specialists Joseph R. Tanner and Carlos I. Noriega check equipment of the International Space Station inside the Space Station Processing Facility. STS-97, targeted to launch on Aug. 5, 1999, is scheduled to carry integrated truss structure P6, photovoltaic module and radiators

JSC2006-E-47866 (November 2006) --- A computer-generated image of the International Space Station after Discovery's undocking and departure, scheduled for the tenth flight day of STS-116. The image shows the addition of the P5 Integrated Truss Segment and retraction of the P6 solar array.

S127-E-007978 (22 July 2009) Astronauts Christopher Cassidy (left) and Dave Wolf work with the Integrated Cargo Carrier-VLD, as they remove and replace batteries on the P6 truss during STS-127's third session of extravehicular activity.
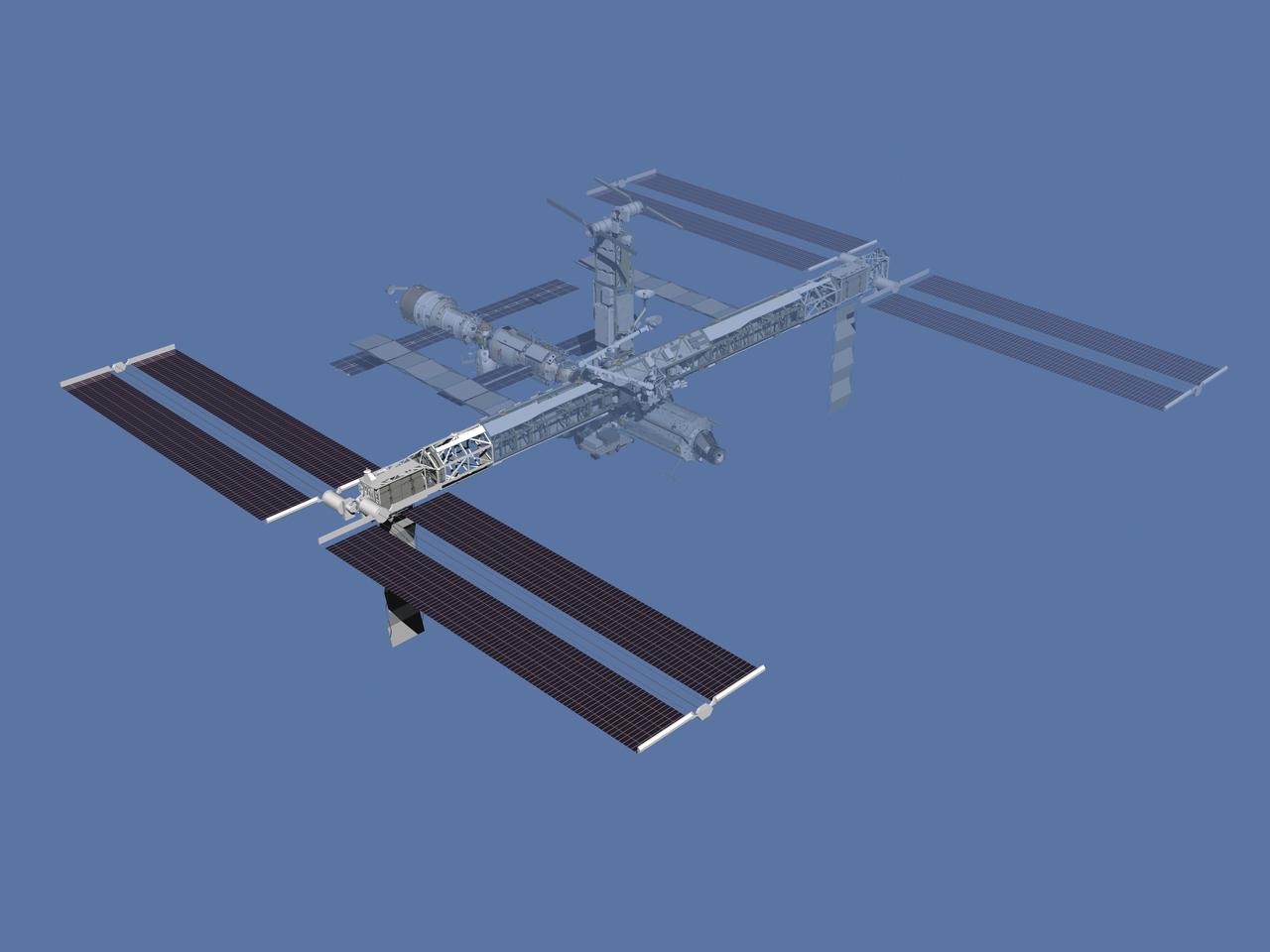
JSC2006-E-43500 (October 2006) --- Computer-generated artist's rendering of the International Space Station after flight STS-117/13A. Second starboard truss segment (S3/S4) is delivered and installed. The third set of solar arrays is deployed. P6 starboard solar array wing and one radiator are retracted.
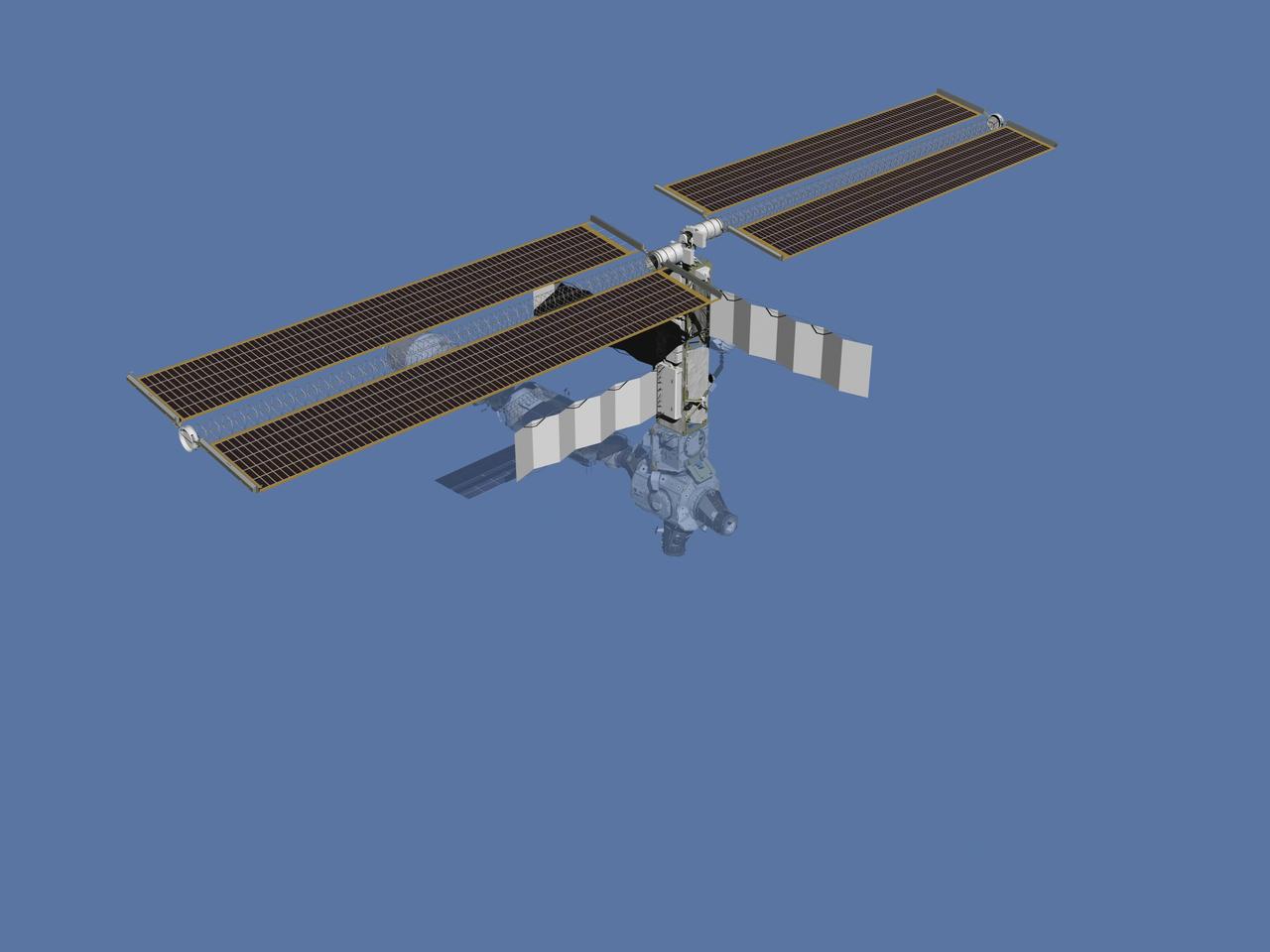

JSC2006-E-43484 (November 2000) --- Computer-generated artist's rendering of the International Space Station after flight STS-97/4A. The STS-97 crew delivered and installed the P6 truss, which support the first U.S. solar arrays.

Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., STS-116 mission specialist, smiles for the camera in the Quest Airlock of the International Space Station (ISS). Curbeam had just completed the mission’s first space walk in which the P6 truss installation was conducted.

JSC2006-E-43499 (October 2006) --- Computer-generated artist's rendering of the International Space Station after flight STS-116/12A.1. Space Shuttle Discovery crew delivers and installs the third port truss segment (P5). P6 port solar array wing and two radiators are retracted.
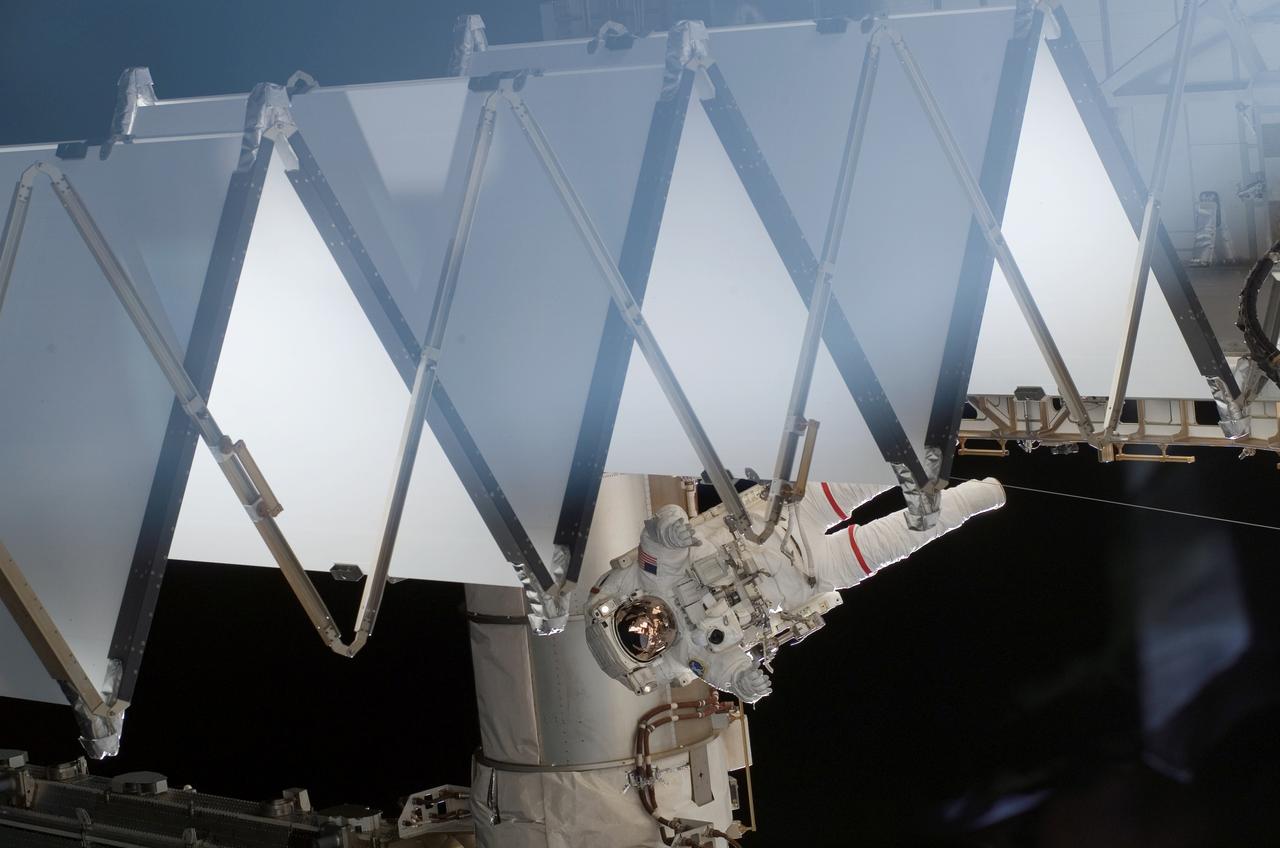
As the construction continued on the International Space Station (ISS), STS-118 Astronaut Rick Mastracchio and Canada Space Agency's Dave Williams (out of frame), participated in the first session of Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) for the mission. During the 6 hour, 17 minute space walk, the two attached the Starboard 5 (S5) segment of truss, retracted the forward heat rejecting radiator from the Port 6 (P6) truss, and performed several get ahead tasks.
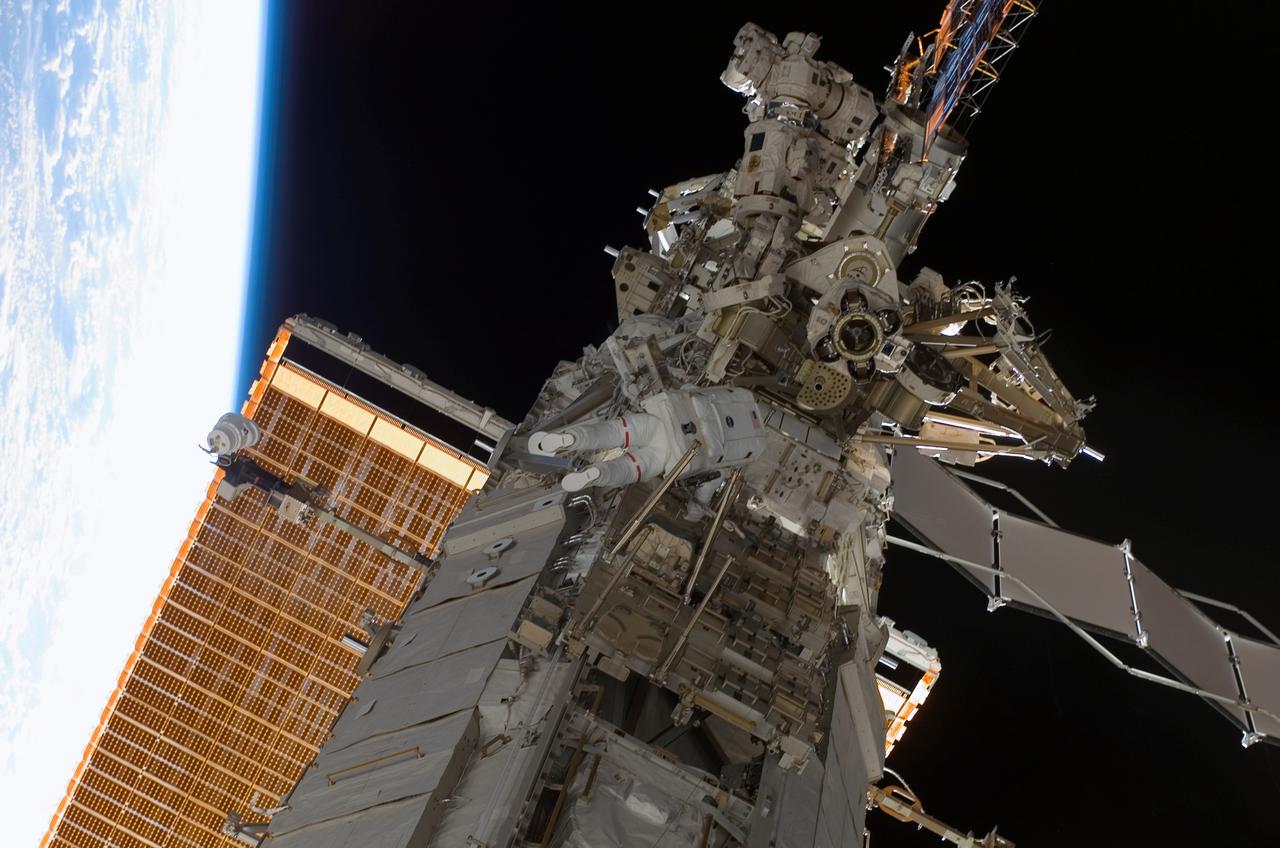

As the construction continued on the International Space Station (ISS), STS-118 Astronaut Rick Mastracchio and Canada Space Agency representative Dave Williams (out of frame), participated in the first session of Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) for the mission. During the 6 hour, 17 minute space walk, the two attached the Starboard 5 (S5) segment of truss, retracted the forward heat rejecting radiator from the Port 6 (P6) truss, and performed several get ahead tasks.
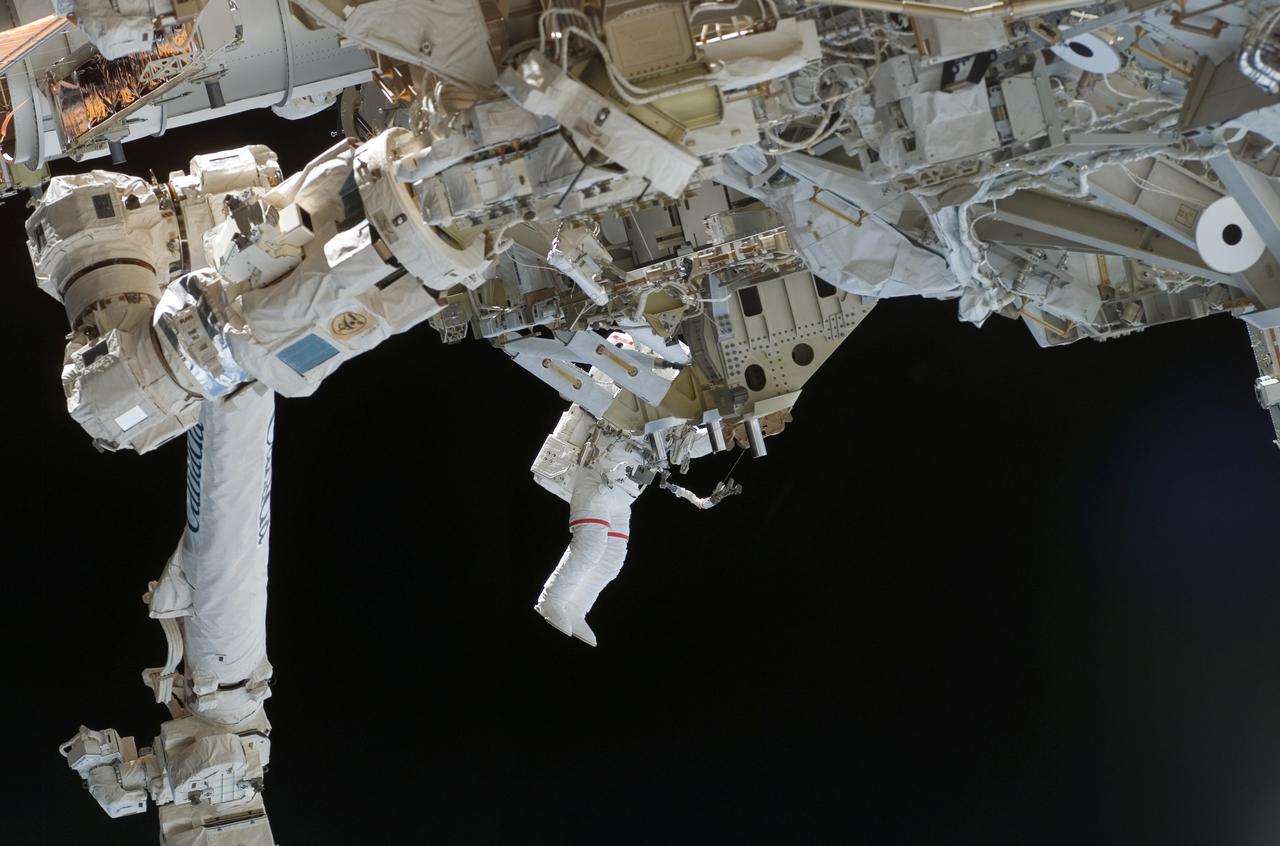

As the construction continued on the International Space Station (ISS), STS-118 Astronaut Rick Mastracchio and Canada Space Agency's Dave Williams (out of frame), participated in the first session of Extra Vehicular Activity (EVA) for the mission. During the 6 hour, 17 minute space walk, the two attached the Starboard 5 (S5) segment of truss, retracted the forward heat rejecting radiator from the Port 6 (P6) truss, and performed several get ahead tasks.
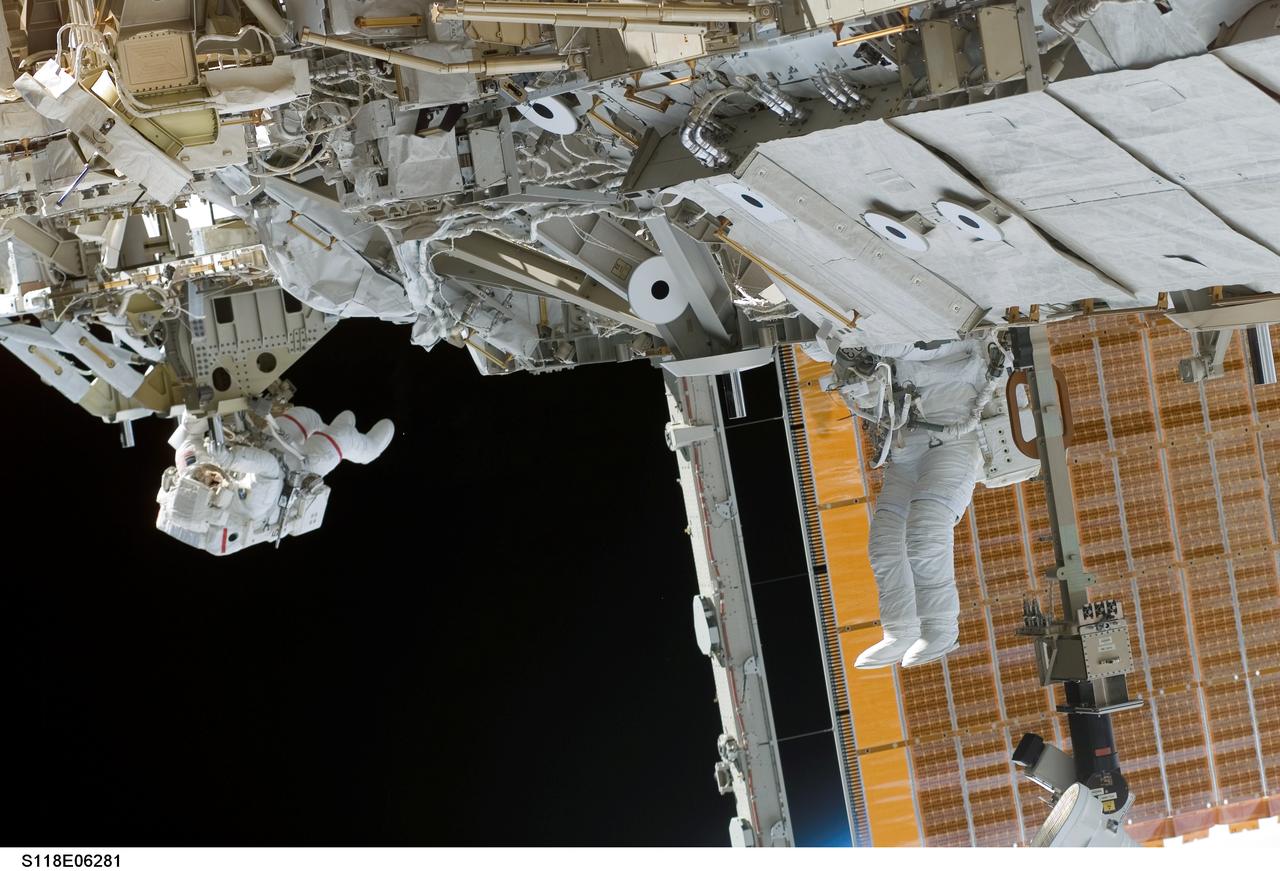

S118-E-06281 (11 Aug. 2007) --- Astronauts Rick Mastracchio (left) and Canadian Space Agency's Dave Williams, both STS-118 mission specialists, participate in the mission's first planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA), as construction continues on the International Space Station. During the 6-hour, 17-minute spacewalk Mastracchio and Williams attached the Starboard 5 (S5) segment of the station's truss, retracted the forward heat-rejecting radiator from the station's Port 6 (P6) truss, and performed several get-ahead tasks.
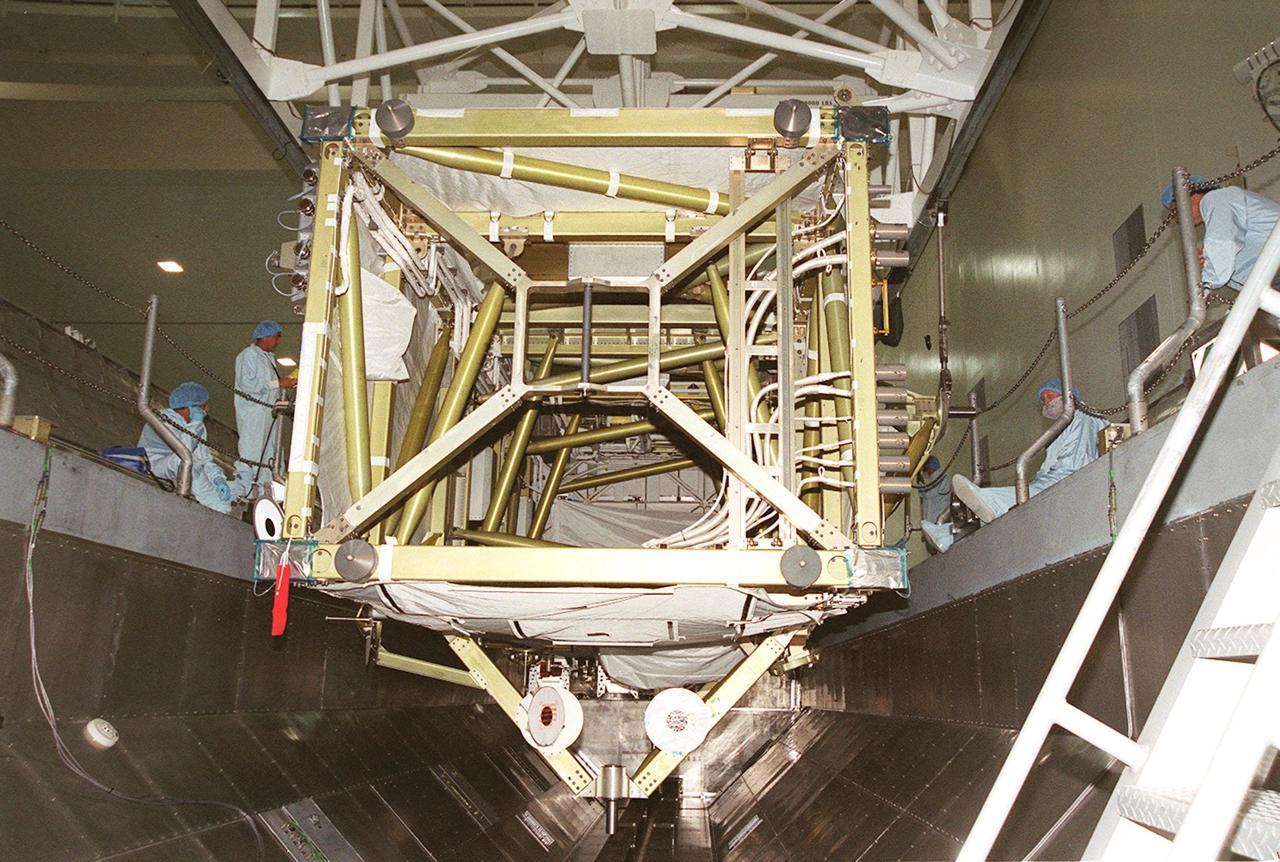

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the P6 integrated truss segment is placed in the payload transport canister while workers watch its progress. After being secured in the canister, the truss will be transported to Launch Pad 39B and the payload changeout room. Then it will be moved into Space Shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay for mission STS-97. The P6 comprises Solar Array Wing-3 and the Integrated Electronic Assembly, to be installed on the Space Station. The Station’s electrical power system will use eight photovoltaic solar arrays, each 112 feet long by 39 feet wide, to convert sunlight to electricity. The solar arrays are mounted on a “blanket” that can be folded like an accordion for delivery. Once in orbit, astronauts will deploy the blankets to their full size. Gimbals will be used to rotate the arrays so that they will face the Sun to provide maximum power to the Space Station. The STS-97 launch is scheduled Nov. 30 at 10:06 p.m. EST
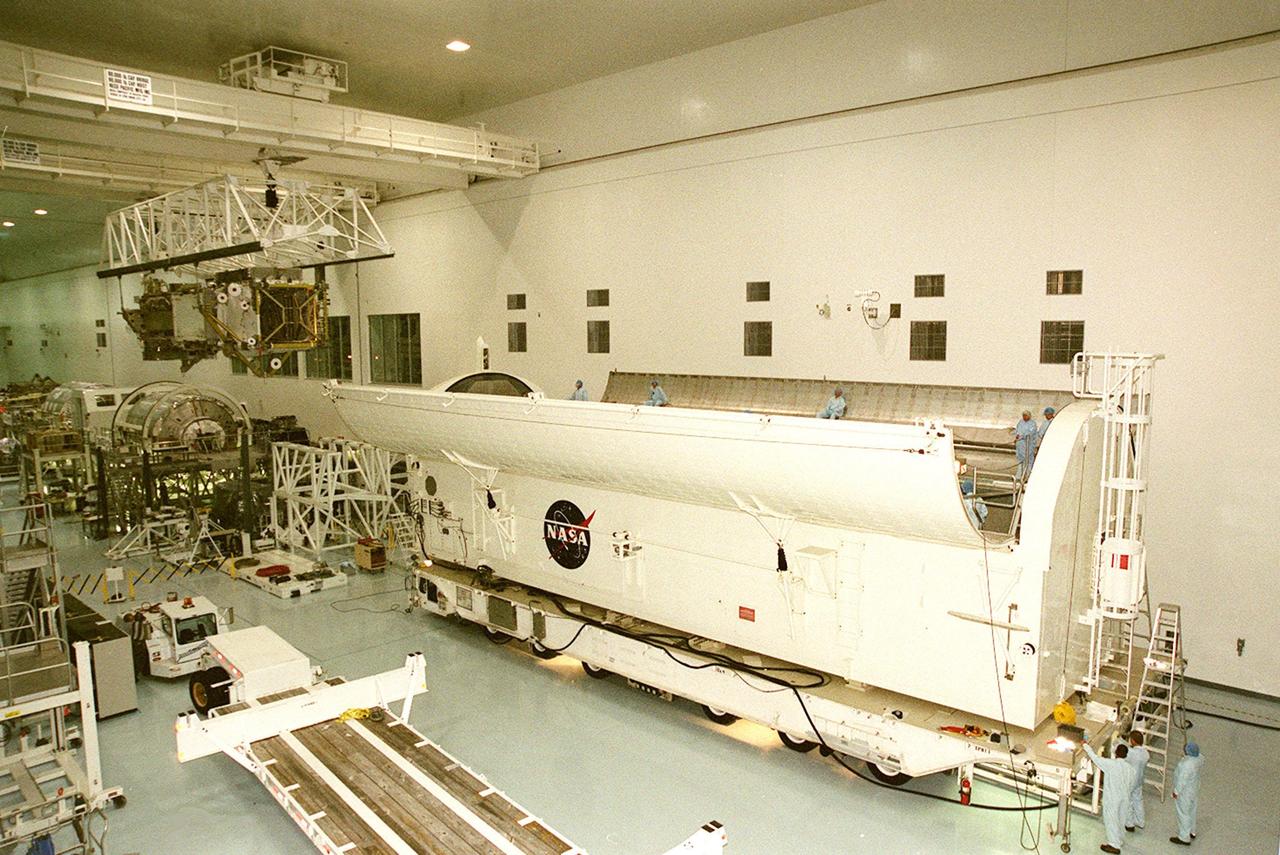

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The payload transport canister (right) and workers wait for the arrival of the P6 integrated truss segment (left) carried by the overhead crane. After being placed in the canister, the truss will be transported to Launch Pad 39B and the payload changeout room. Then it will be moved into Space Shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay for mission STS-97. The P6 comprises Solar Array Wing-3 and the Integrated Electronic Assembly, to be installed on the Space Station. The Station’s electrical power system will use eight photovoltaic solar arrays, each 112 feet long by 39 feet wide, to convert sunlight to electricity. The solar arrays are mounted on a “blanket” that can be folded like an accordion for delivery. Once in orbit, astronauts will deploy the blankets to their full size. Gimbals will be used to rotate the arrays so that they will face the Sun to provide maximum power to the Space Station. The STS-97 launch is scheduled Nov. 30 at 10:06 p.m. EST
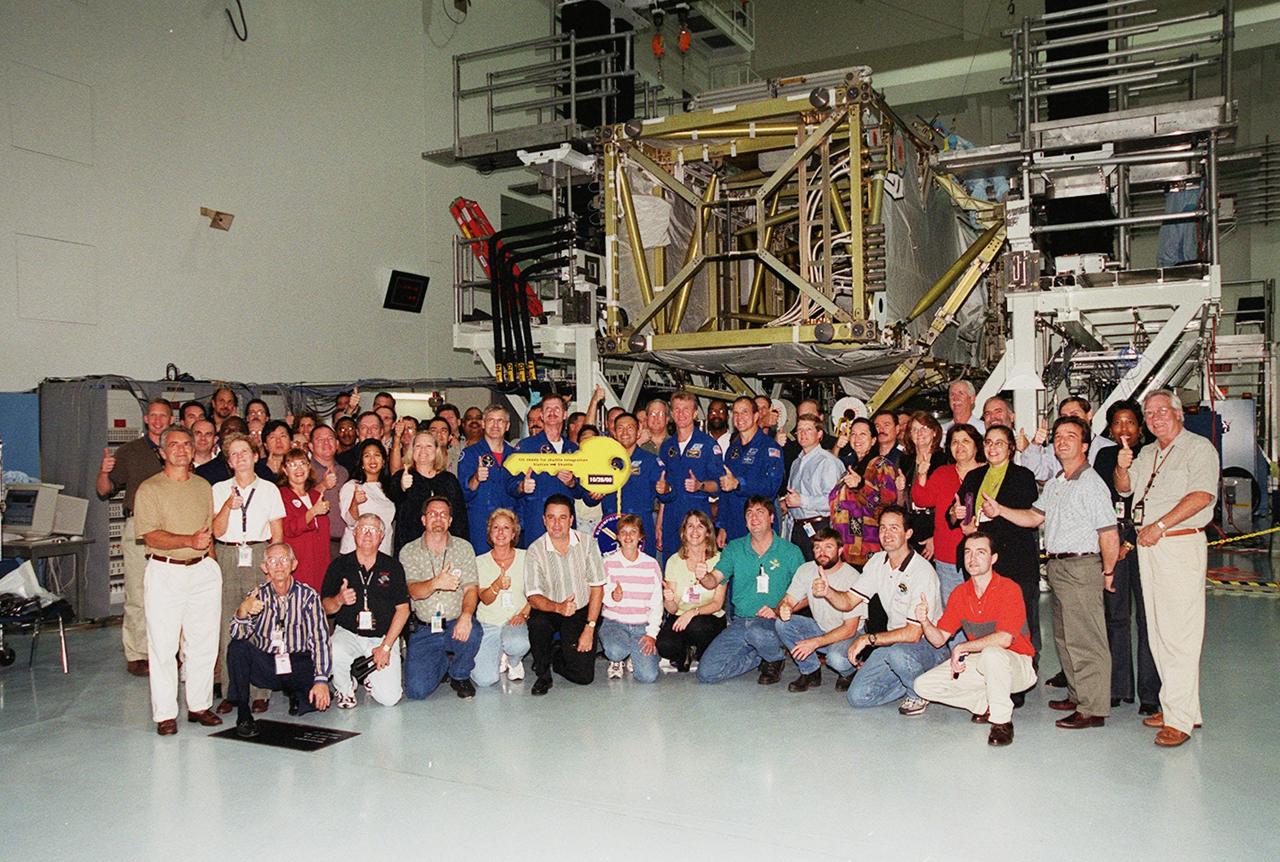

Workers in the Space Station Processing Facility gather with the crew of mission STS-97, who are holding the symbolic key representing the turnover of the P6 Integrated Truss Structure, part of the payload on their mission. During the ceremony the P6 truss segment was transferred from International Space Station ground operations to the NASA shuttle integration team. Commander Brent Jett (second from right) received the key in the ceremony. Standing with him are (left to right) Mission Specialists Marc Garneau, Joe Tanner and Carlos Noriega, at left; and Pilot Mike Bloomfield, at right. Mission STS-97is the sixth construction flight to the International Space Station. Its payload includes a photovoltaic (PV) module, with giant solar arrays that will provide power to the Station. The mission involves two spacewalks to complete the solar array connections. STS-97 is scheduled to launch Nov. 30 at 10:05 p.m. EST
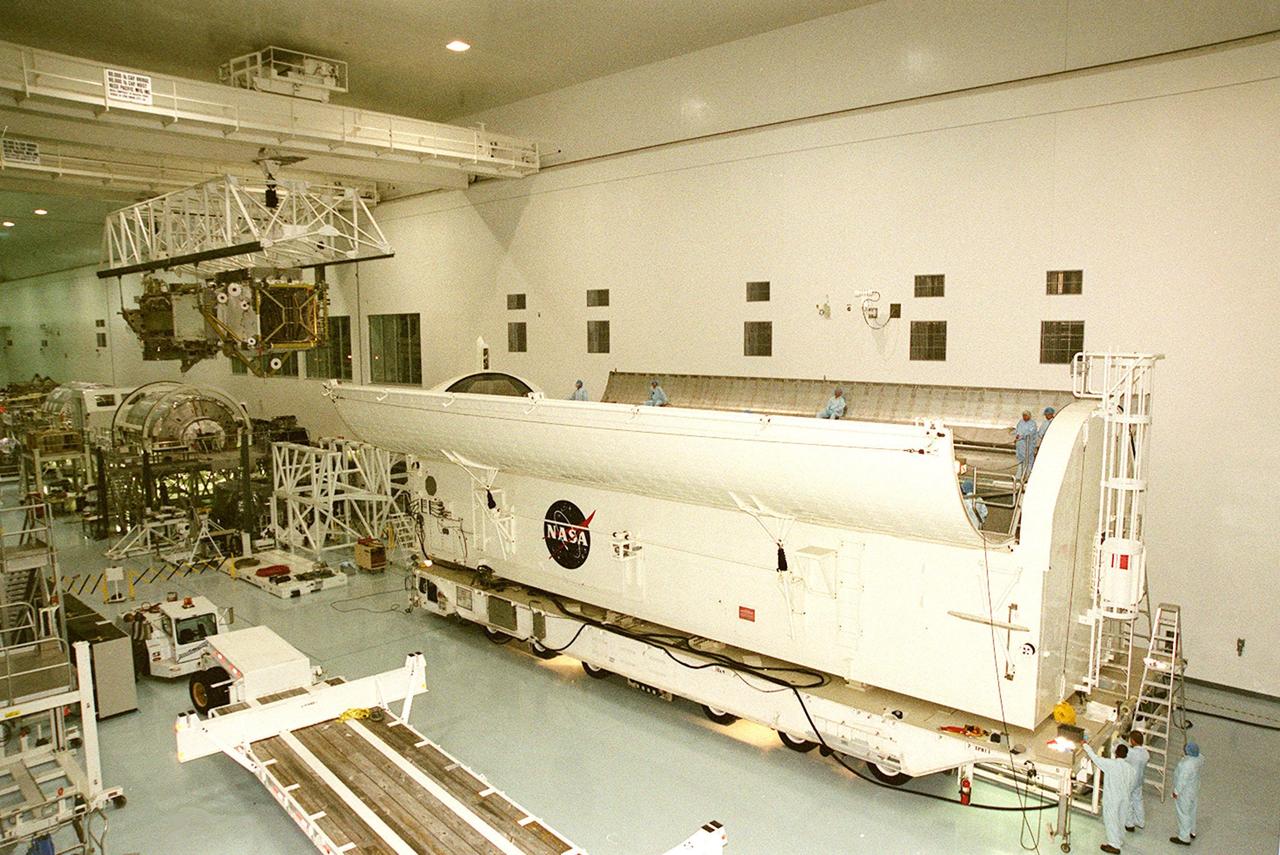

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The payload transport canister (right) and workers wait for the arrival of the P6 integrated truss segment (left) carried by the overhead crane. After being placed in the canister, the truss will be transported to Launch Pad 39B and the payload changeout room. Then it will be moved into Space Shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay for mission STS-97. The P6 comprises Solar Array Wing-3 and the Integrated Electronic Assembly, to be installed on the Space Station. The Station’s electrical power system will use eight photovoltaic solar arrays, each 112 feet long by 39 feet wide, to convert sunlight to electricity. The solar arrays are mounted on a “blanket” that can be folded like an accordion for delivery. Once in orbit, astronauts will deploy the blankets to their full size. Gimbals will be used to rotate the arrays so that they will face the Sun to provide maximum power to the Space Station. The STS-97 launch is scheduled Nov. 30 at 10:06 p.m. EST
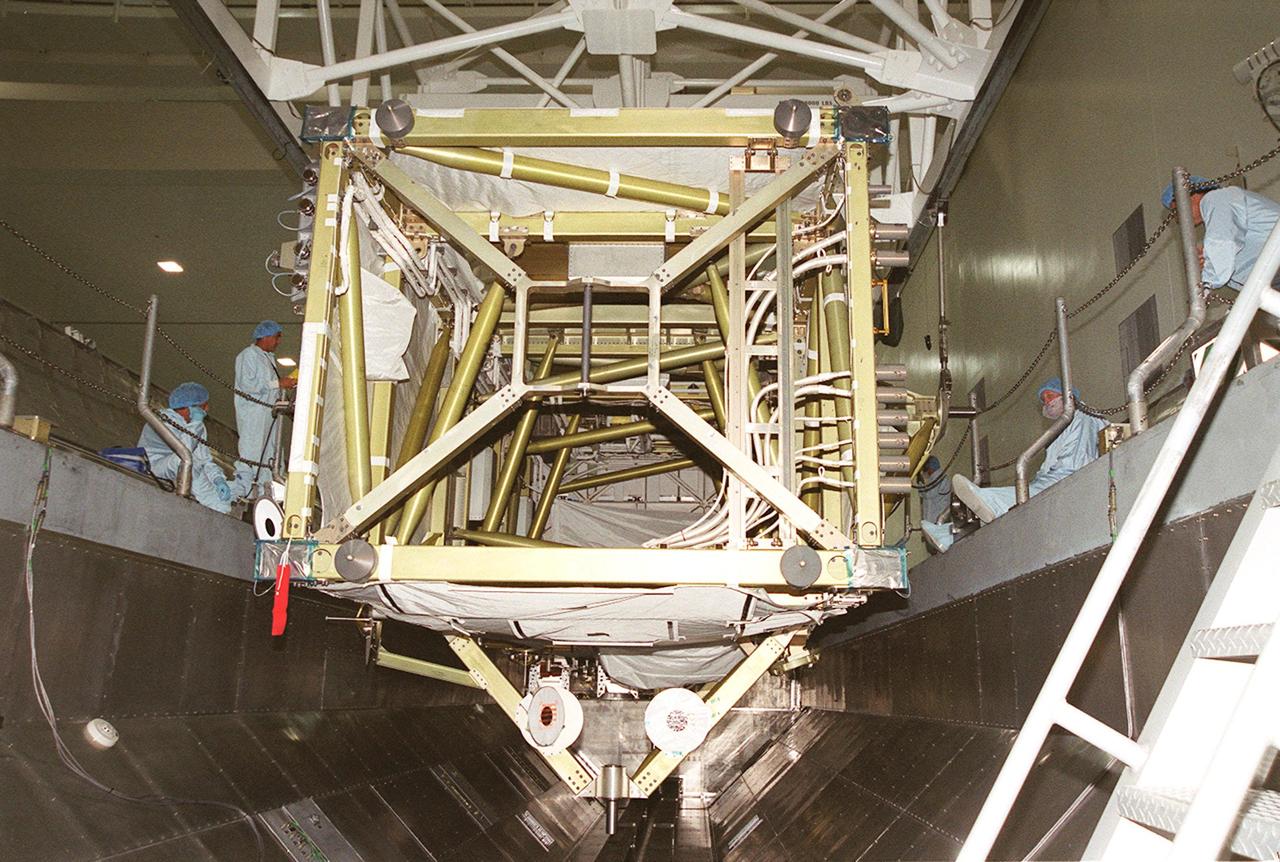

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Space Station Processing Facility, the P6 integrated truss segment is placed in the payload transport canister while workers watch its progress. After being secured in the canister, the truss will be transported to Launch Pad 39B and the payload changeout room. Then it will be moved into Space Shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay for mission STS-97. The P6 comprises Solar Array Wing-3 and the Integrated Electronic Assembly, to be installed on the Space Station. The Station’s electrical power system will use eight photovoltaic solar arrays, each 112 feet long by 39 feet wide, to convert sunlight to electricity. The solar arrays are mounted on a “blanket” that can be folded like an accordion for delivery. Once in orbit, astronauts will deploy the blankets to their full size. Gimbals will be used to rotate the arrays so that they will face the Sun to provide maximum power to the Space Station. The STS-97 launch is scheduled Nov. 30 at 10:06 p.m. EST
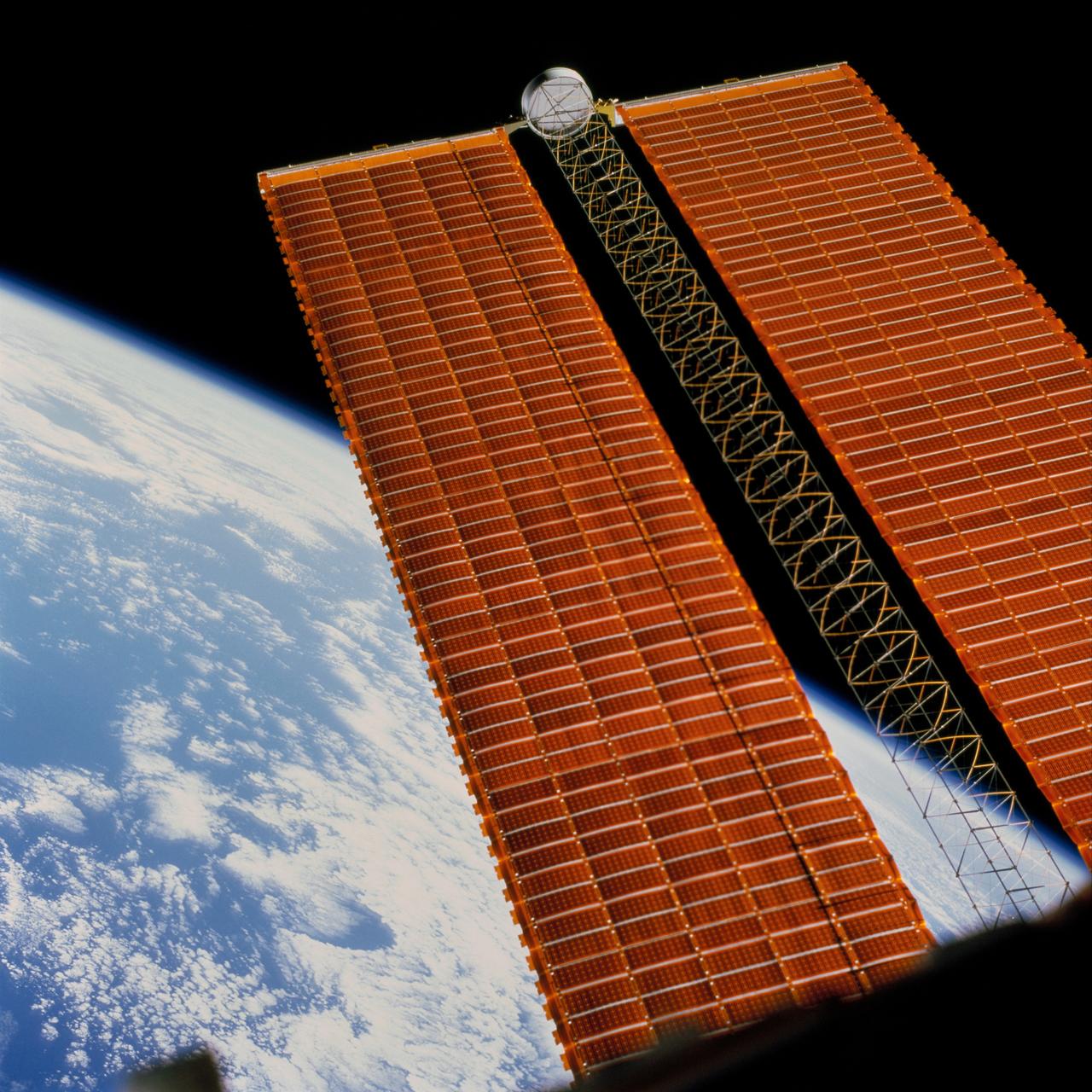
STS097-702-070 (3 December 2000) --- An astronaut inside Endeavour's crew cabin used a handheld 70mm camera to expose this frame of the International Space Station's starboard solar array wing panel, backdropped against an Earth horizon scene.
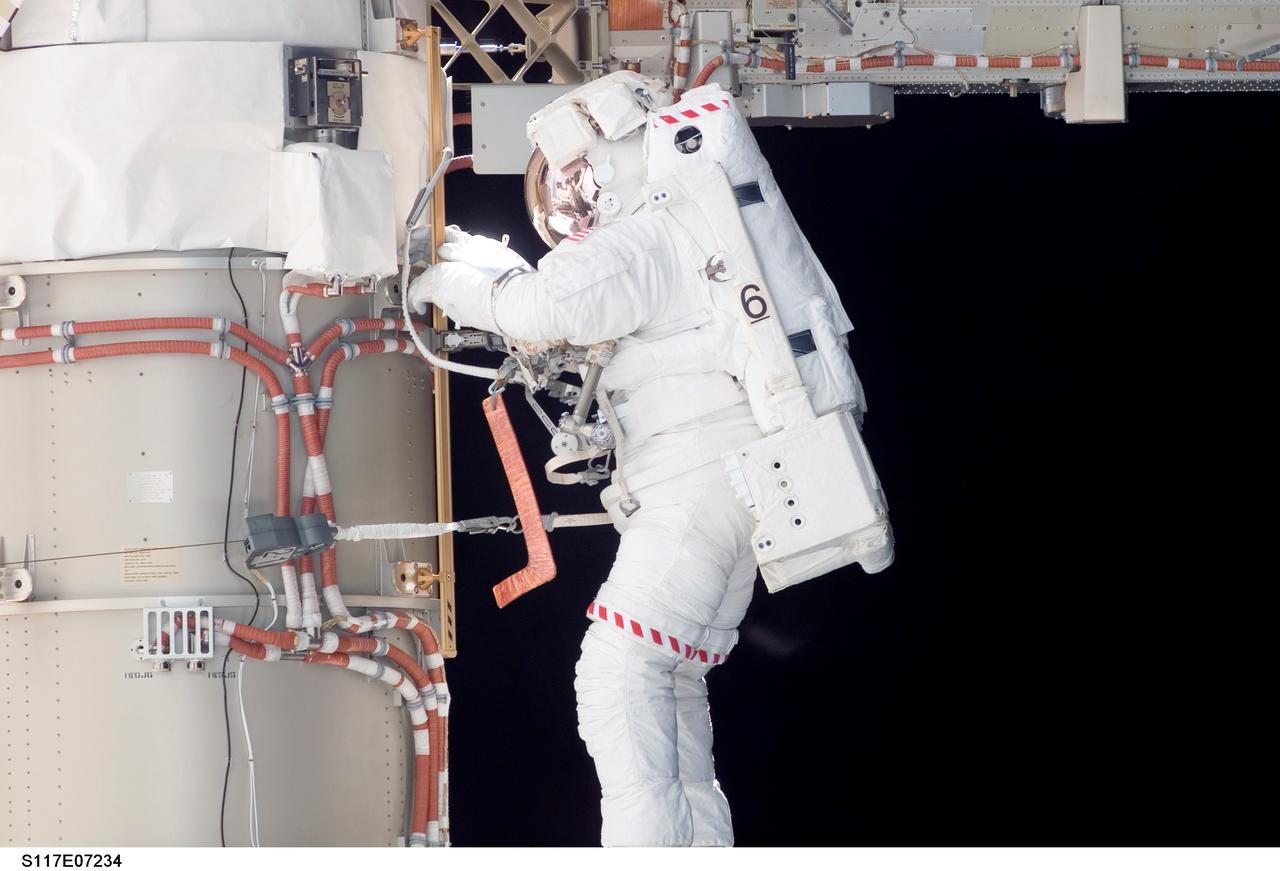

S117-E-07234 (13 June 2007) --- Astronauts Steven Swanson and Patrick Forrester (out of frame), both STS-117 mission specialists, participate in the mission's second planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA), as construction resumes on the International Space Station. Among other tasks, Forrester and Swanson removed all of the launch locks holding the 10-foot-wide solar alpha rotary joint in place and began the solar array retraction. Tethered to his Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuit, a hockey-stick-shaped tool wrapped in insulating tape, is visible in front of Swanson.
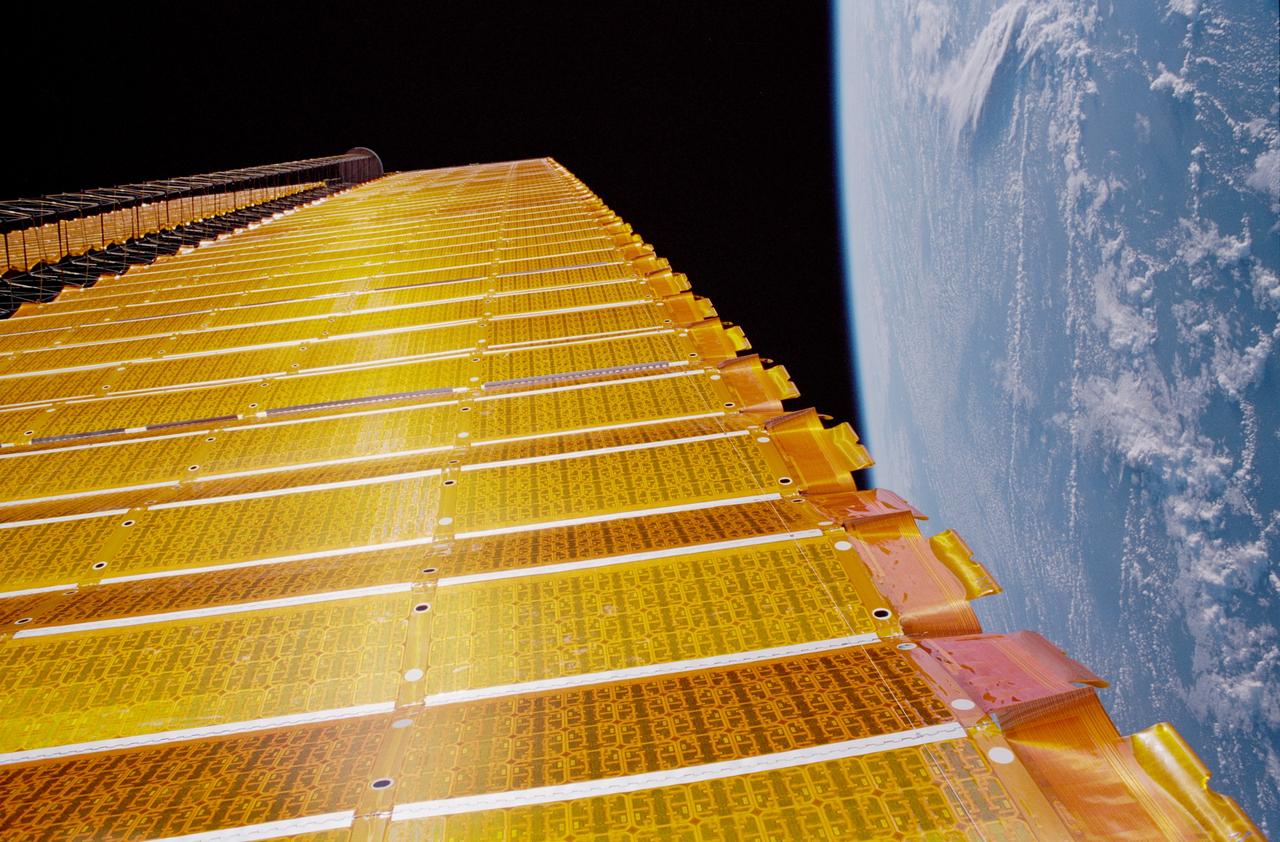

STS097-376-006 (7 Dec 2000) --- A close-up view of the P6 solar array on the International Space Station (ISS), backdropped against the blackness of space and the Earth?s horizon. The P6 solar array is the first of eight sets of solar arrays that at the completion of the space station construction in 2006, will comprise the station?s electrical power system, converting sunlight to electricity.
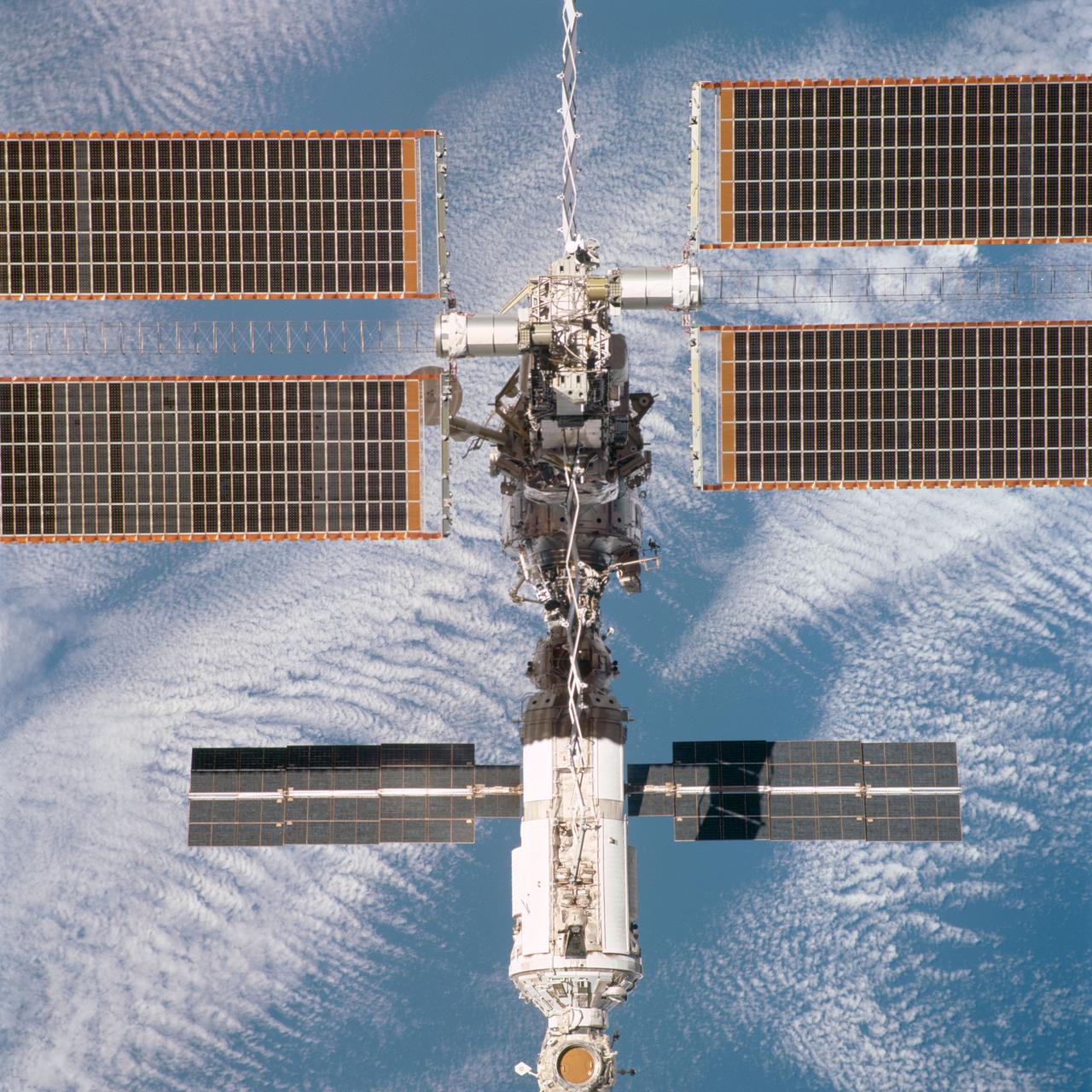

STS097-704-063 (9 December 2000) --- This overhead view is one of a series of 70mm frames exposed of the International Space Station (ISS) following undocking at 1:13 p.m. (CST), December 9, 2000. This series of images, as well as video and digital still imagery taken at the same time, represent the first imagery of the entire station with its new solar array panels deployed. Before separation, the shuttle and space station had been docked to one another for 6 days, 23 hours and 13 minutes. Endeavour moved downward from the space station, then began a tail-first circle at a distance of about 500 feet. The maneuver, with pilot Michael J. Bloomfield at the controls, took about an hour. While Endeavour flew that circle, the two spacecraft, moving at five miles a second, navigated about two-thirds of the way around the Earth. Undocking took place 235 statute miles above the border of Kazakhstan and China. When Endeavour made its final separation burn, the orbiter and the space station were near the northeastern coast of South America.
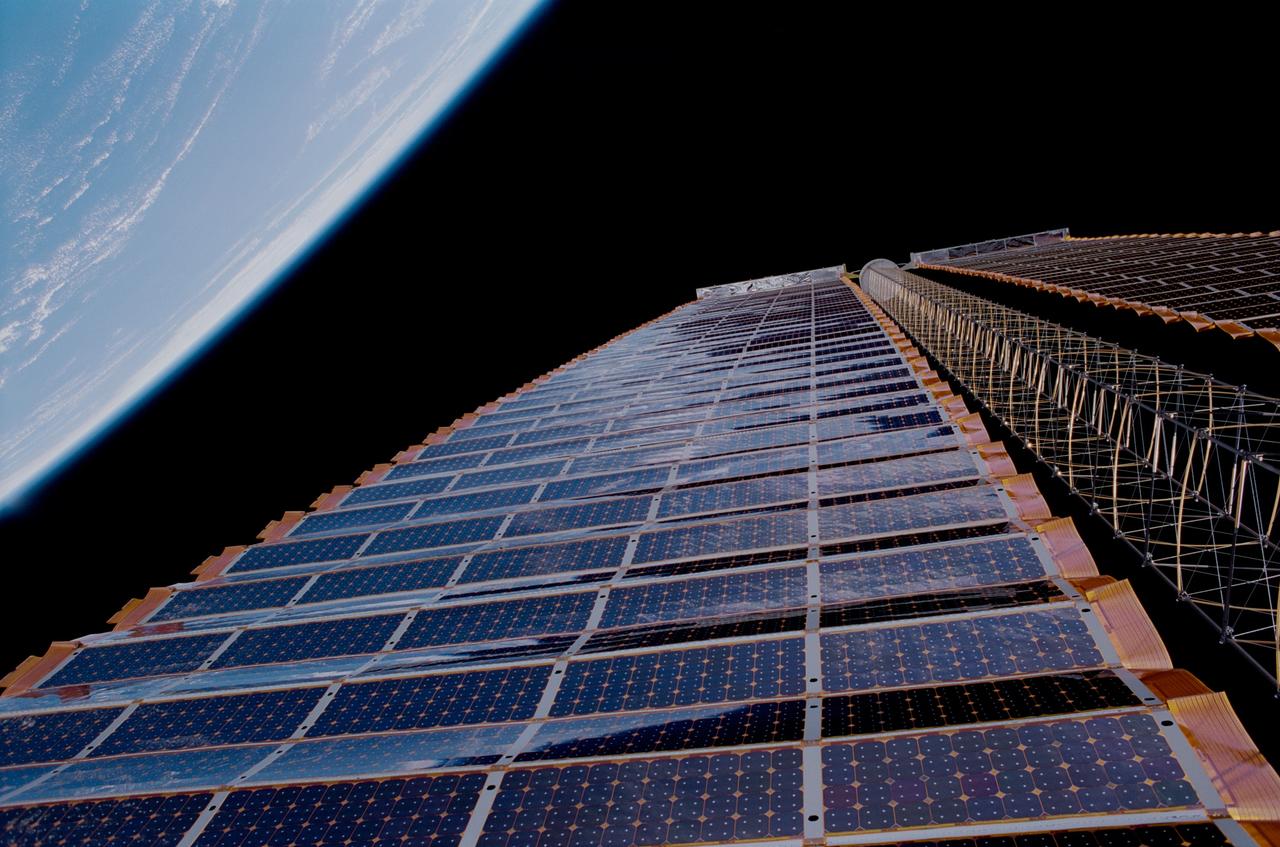

STS097-376-019 (7 December 2000) --- A close-up view of the P6 solar array on the International Space Station (ISS), backdropped against the blackness of space and the Earth’s horizon. The P6 solar array is the first of eight sets of solar arrays that at the completion of the space station construction in 2006, will comprise the station’s electrical power system, converting sunlight to electricity.
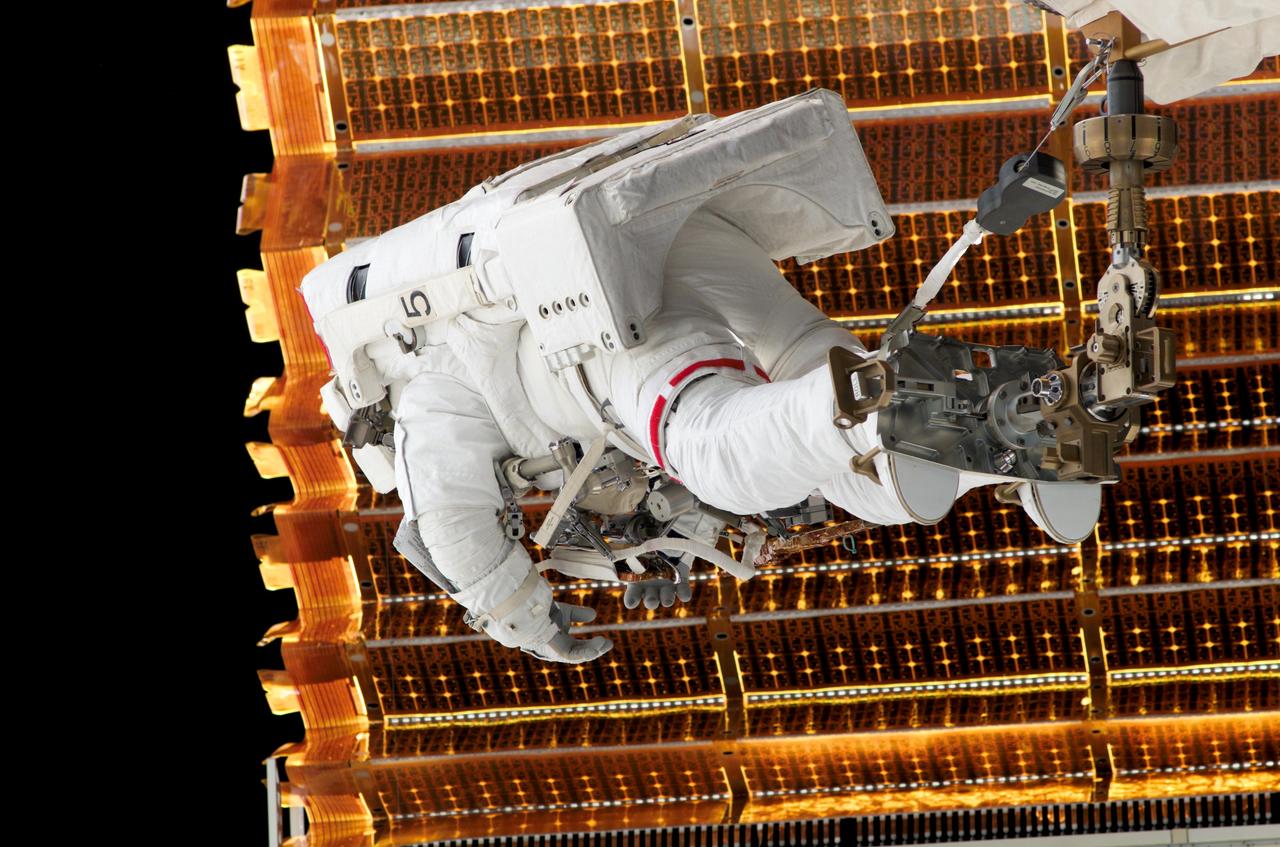

S117-E-07232 (13 June 2007) --- Astronauts Patrick Forrester and Steven Swanson (out of frame), both STS-117 mission specialists, participate in the mission's second planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA), as construction resumes on the International Space Station. Among other tasks, Forrester, seen here perched on the mobile foot restraint connected to the Canadian-built remote manipulator system (RMS), and Swanson removed all of the launch locks holding the 10-foot-wide solar alpha rotary joint in place and began the solar array retraction.
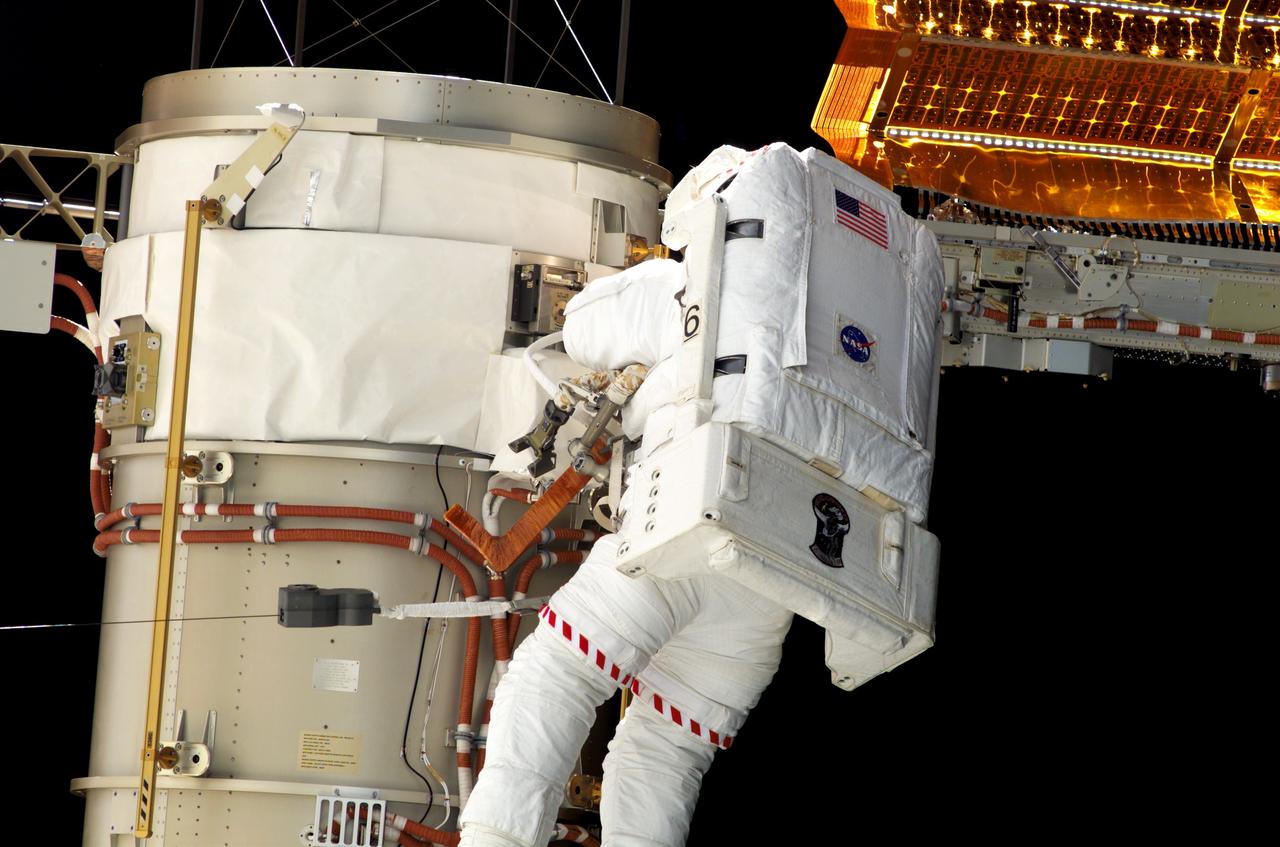

S117-E-07233 (13 June 2007) --- Astronauts Steven Swanson and Patrick Forrester (out of frame), both STS-117 mission specialists, participate in the mission's second planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA), as construction resumes on the International Space Station. Among other tasks, Forrester and Swanson removed all of the launch locks holding the 10-foot-wide solar alpha rotary joint in place and began the solar array retraction. Tethered to his Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) spacesuit, a hockey-stick-shaped tool wrapped in insulating tape, is visible in front of Swanson.
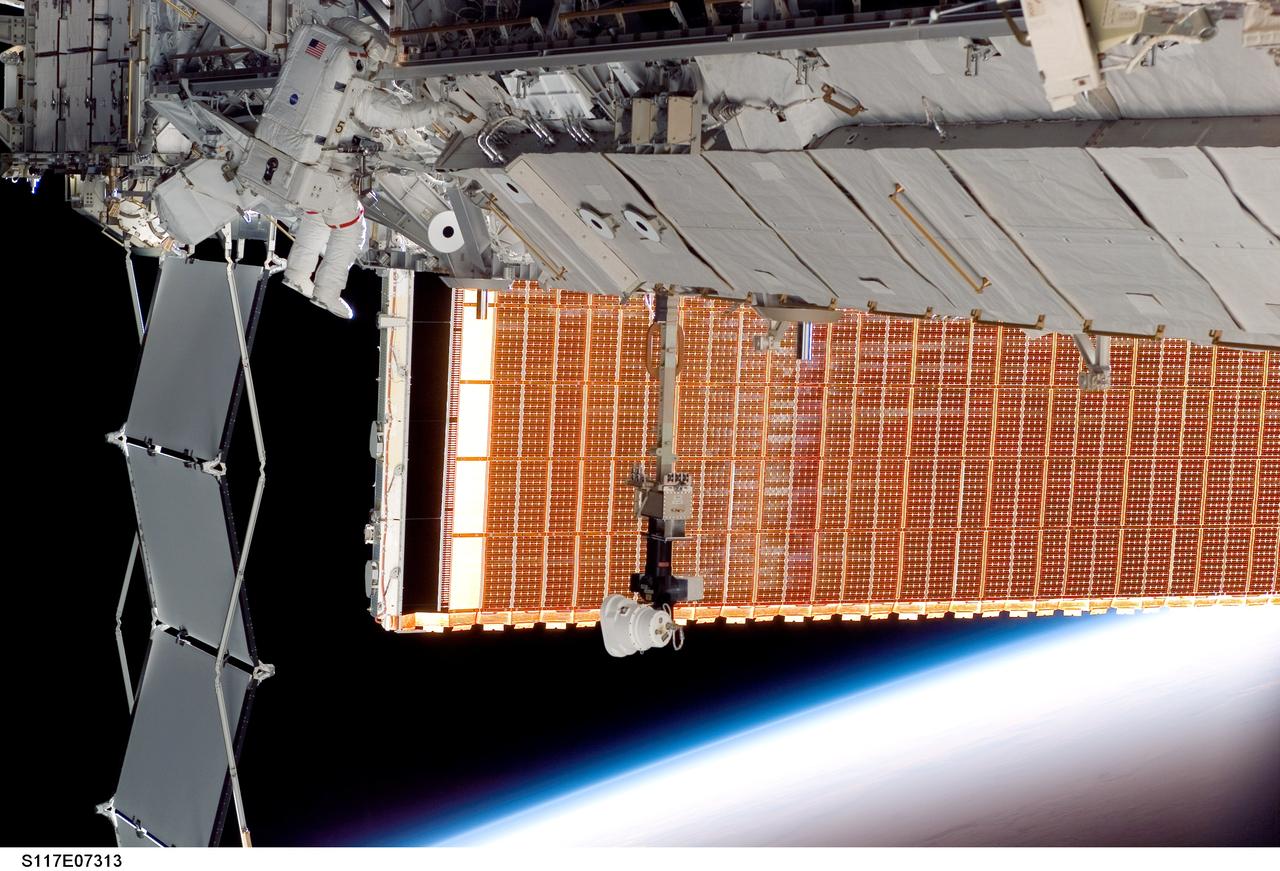

S117-E-07313 (13 June 2007) --- Astronauts Patrick Forrester and Steven Swanson (out of frame), both STS-117 mission specialists, participate in the mission's second planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA), as construction resumes on the International Space Station. Among other tasks, Forrester and Swanson removed all of the launch locks holding the 10-foot-wide solar alpha rotary joint in place and began the solar array retraction.
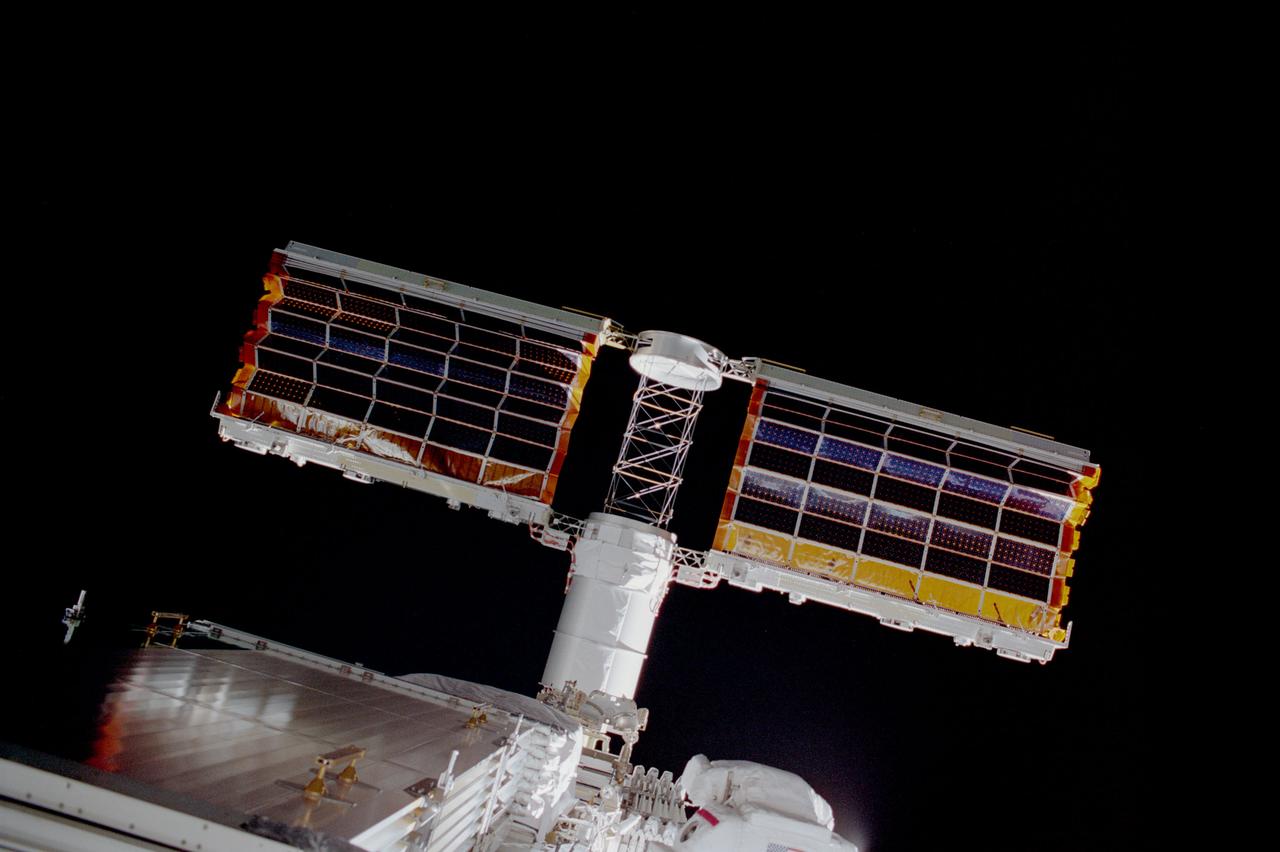

STS097-373-005 (3 December 2000) --- Backdropped against the blackness of space, the deployment of International Space Station (ISS) solar array was photographed with a 35mm camera by astronaut Carlos I. Noriega, mission specialist. Part of the extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) attached to astronaut Joseph R. Tanner, mission specialist, is visible at bottom center. Tanner and Noriega went on to participate together in three separate space walks.
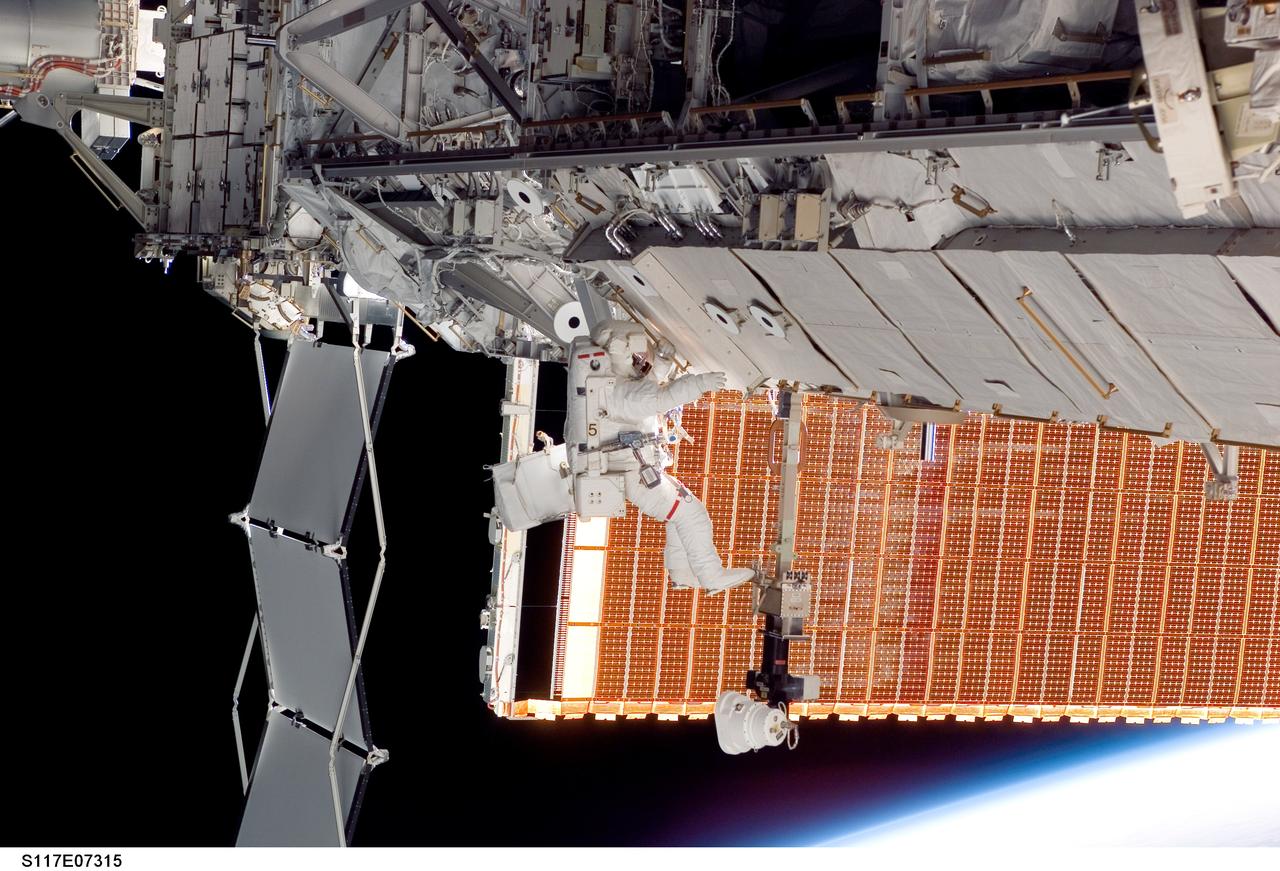

S117-E-07315 (13 June 2007) --- Astronauts Patrick Forrester and Steven Swanson (out of frame), both STS-117 mission specialists, participate in the mission's second planned session of extravehicular activity (EVA), as construction resumes on the International Space Station. Among other tasks, Forrester and Swanson removed all of the launch locks holding the 10-foot-wide solar alpha rotary joint in place and began the solar array retraction.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-116 Mission Specialist Christer Fuglesang, who is with the European Space Agency, is in training at SPACEHAB, Port Canaveral, Fla., along with other crew members Commander Terrence Wilcutt, Pilot William Oefelein and Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At SPACEHAB, Port Canaveral, Fla., STS-116 crew members take part in training for their mission. Seen here are (from left) Mission Specialist Christer Fuglesang, Pilot Michael Oelefein, Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam and Commander Terrence Wilcutt. Fuglesang is with the European Space Agency. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review.
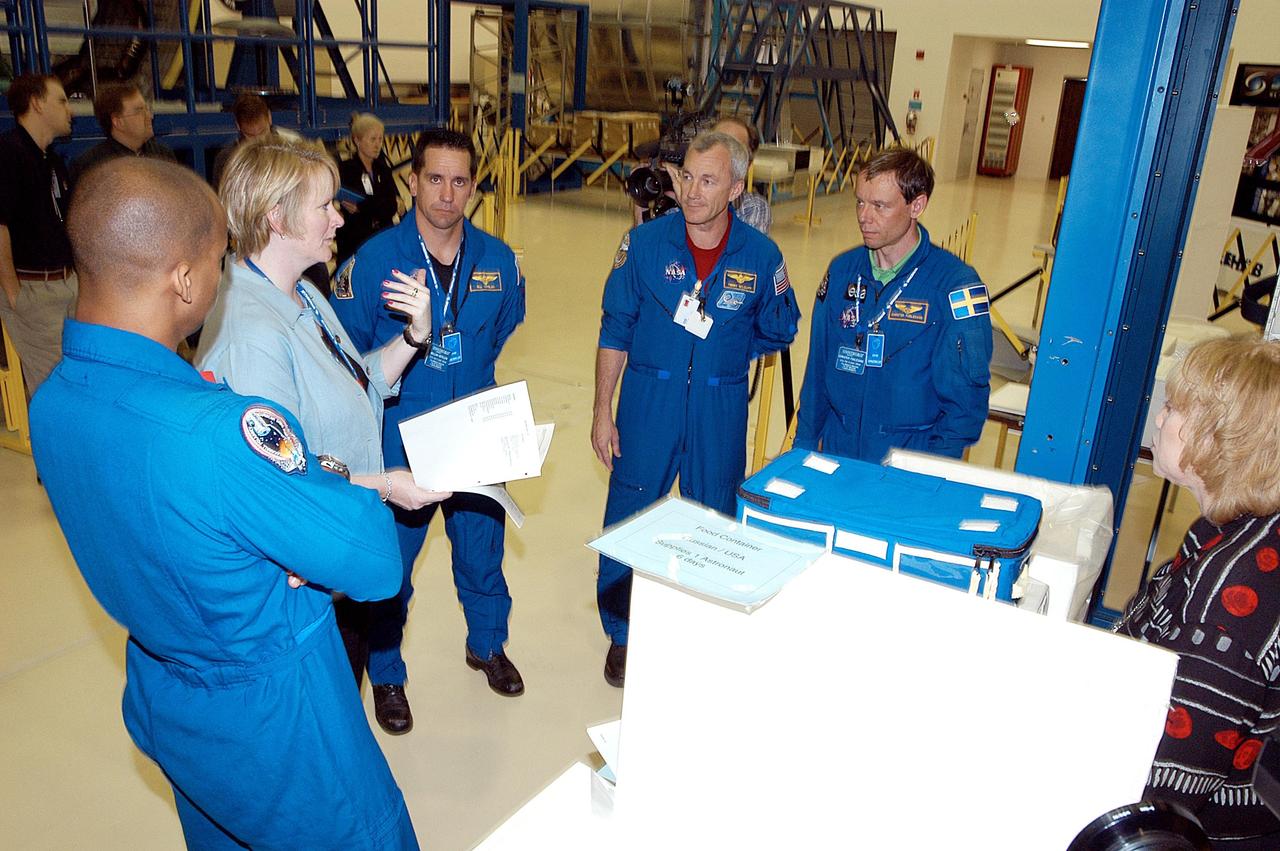

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The STS-116 crew takes part in training at SPACEHAB in Port Canaveral, Fla. From left are Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam, Pilot William Oefelein, Commander Terrence Wilcutt and Mission Specialist Christer Fuglesang. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-116 Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam handles a piece of equipment in the SPACEHAB module. He and other crew members are taking part in equipment familiarization. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays, deliver the Expedition 8 crew to the Station and return the Expedition 7 crew to Earth. The mission is currently targeted for launch in July 2003.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - During a break in training at SPACEHAB, Port Canaveral, Fla., STS-116 Commander Terrence Wilcutt, Mission Specialist Christer Fuglesang and Pilot Michael Oelefein share a laugh. Not seen is Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-116 Mission Specialist Christer Fugelsang, who is with the European Space Agency, listens to instructions in the SPACEHAB module. He and other crew members are taking part in equipment familiarization at SPACEHAB. The objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays, deliver the Expedition 8 crew to the Station and return the Expedition 7 crew to Earth. The mission is currently targeted for launch in July 2003..

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- STS-116 Mission Specialist Christer Fugelsang, who is with the European Space Agency, gets instruction about a piece of equipment in the SPACEHAB module. He and other crew members are taking part in equipment familiarization. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays, deliver the Expedition 8 crew to the Station and return the Expedition 7 crew to Earth. The mission is currently targeted for launch in July 2003.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At SPACEHAB, Port Canaveral, Fla., STS-116 Mission Specialist Christer Fuglesang (left) and Pilot Michael Oelefein share a laugh during a break in training. Fuglesang is with the European Space Agency. Not seen are Commander Terrence Wilcutt and Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - At SPACEHAB, Port Canaveral, Fla., STS-116 crew members take part in training for their mission. Seen here are (from left) Mission Specialist Christer Fuglesang, Pilot Michael Oelefein and Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam. Not seen is Commander Terrence Wilcutt. Fuglesang is with the European Space Agency. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - STS-116 Commander Terrence Wilcutt reaches for a packet placed inside equipment at SPACEHAB, Port Canaveral, Fla. He and other crew members - Pilot William Oefelein and Mission Specialists Robert Curbeam and Christer Fuglesang - are training at the facility. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - The STS-116 crew share thoughts during training at SPACEHAB in Port Canaveral, Fla. From left are Mission Specialist Robert Curbeam, Commander Terrence Wilcutt, Mission Specialist Christer Fuglesang and Pilot William Oefelein. Objective of their mission to the International Space Station is to deliver and attach the third port truss segment, the P5 Truss, deactivate and retract the P6 Truss Channel 4B (port-side) solar array, and reconfigure station power from 2A and 4A solar arrays. A launch date is under review.