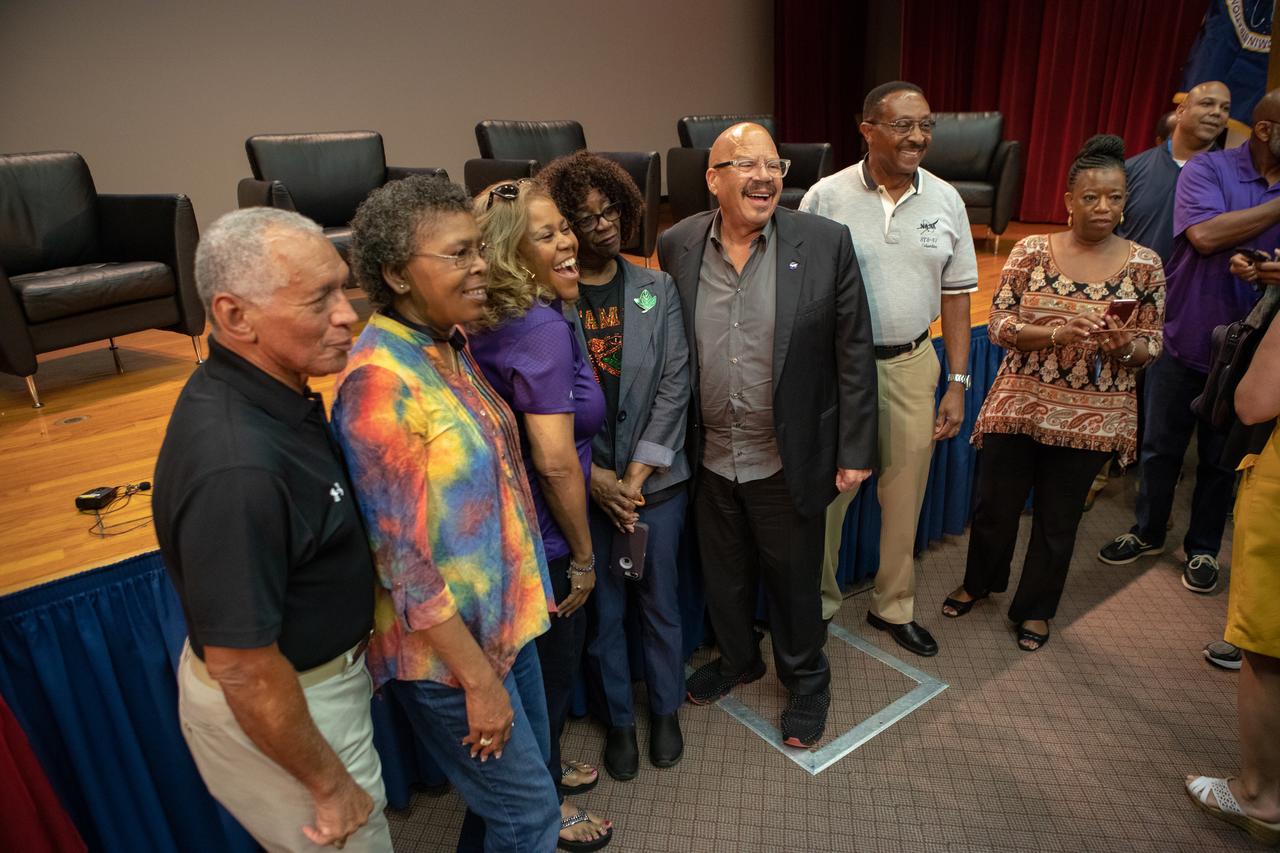

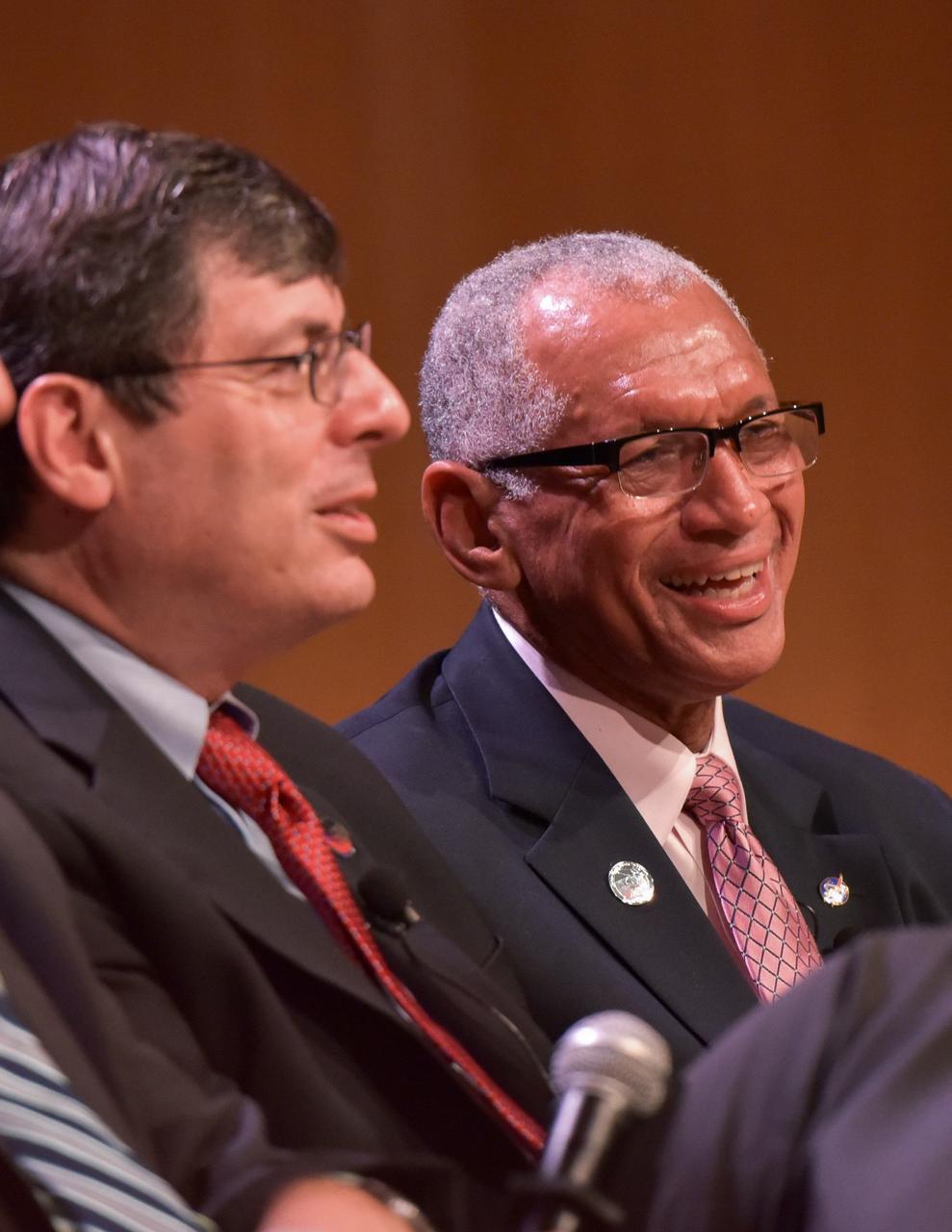
Following a panel discussion at the Kennedy Space Center on Aug. 28, 2019, Kennedy employees pose for a photo with former NASA administrator and panel participant Charlie Bolden, national radio host and panel host Tom Joyner, co-host Sybil Wilkes and former astronaut Winston Scott. The discussion focused on the agency’s Moon to Mars plans and was open for all Kennedy employees to attend. Additional panel participants included Kennedy Chief Technologist Barbara Brown and Exploration Ground Systems Associate Manager, Technical, Kim Carter.

A panel discussion regarding NASA’s Moon to Mars plans takes place at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2019. Seated from left, are Tom Joyner, national radio host and panel host; Charlie Bolden, former NASA administrator and astronaut; Kim Carter, Exploration Ground Systems associate manager, technical; Barbara Brown, Kennedy chief technologist; former astronaut Winston Scott; and panel co-host Sybil Wilkes.
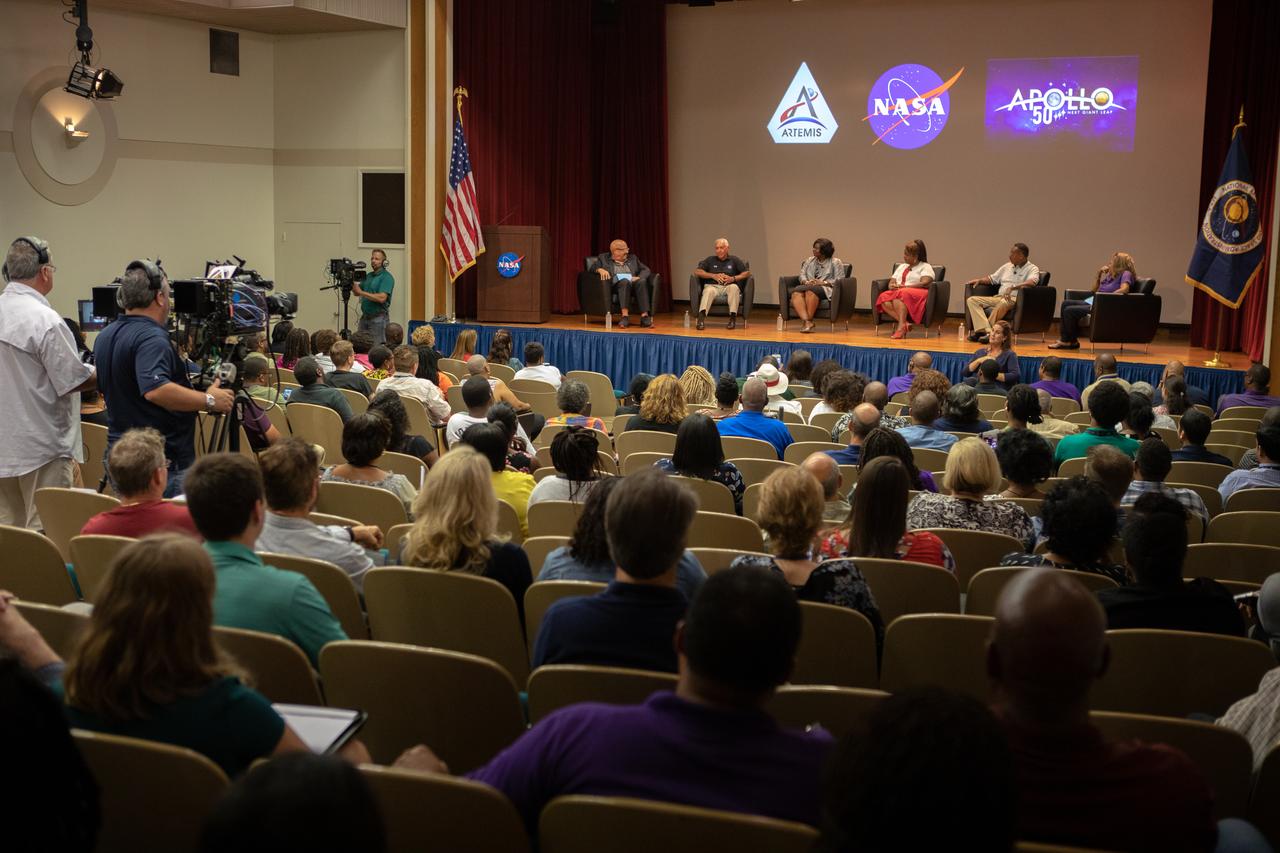

A panel discussion regarding NASA’s Moon to Mars plans takes place at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2019. Seated from left, are Tom Joyner, national radio host and panel host; Charlie Bolden, former NASA administrator and astronaut; Kim Carter, Exploration Ground Systems associate manager, technical; Barbara Brown, Kennedy chief technologist; former astronaut Winston Scott; and panel co-host Sybil Wilkes.

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
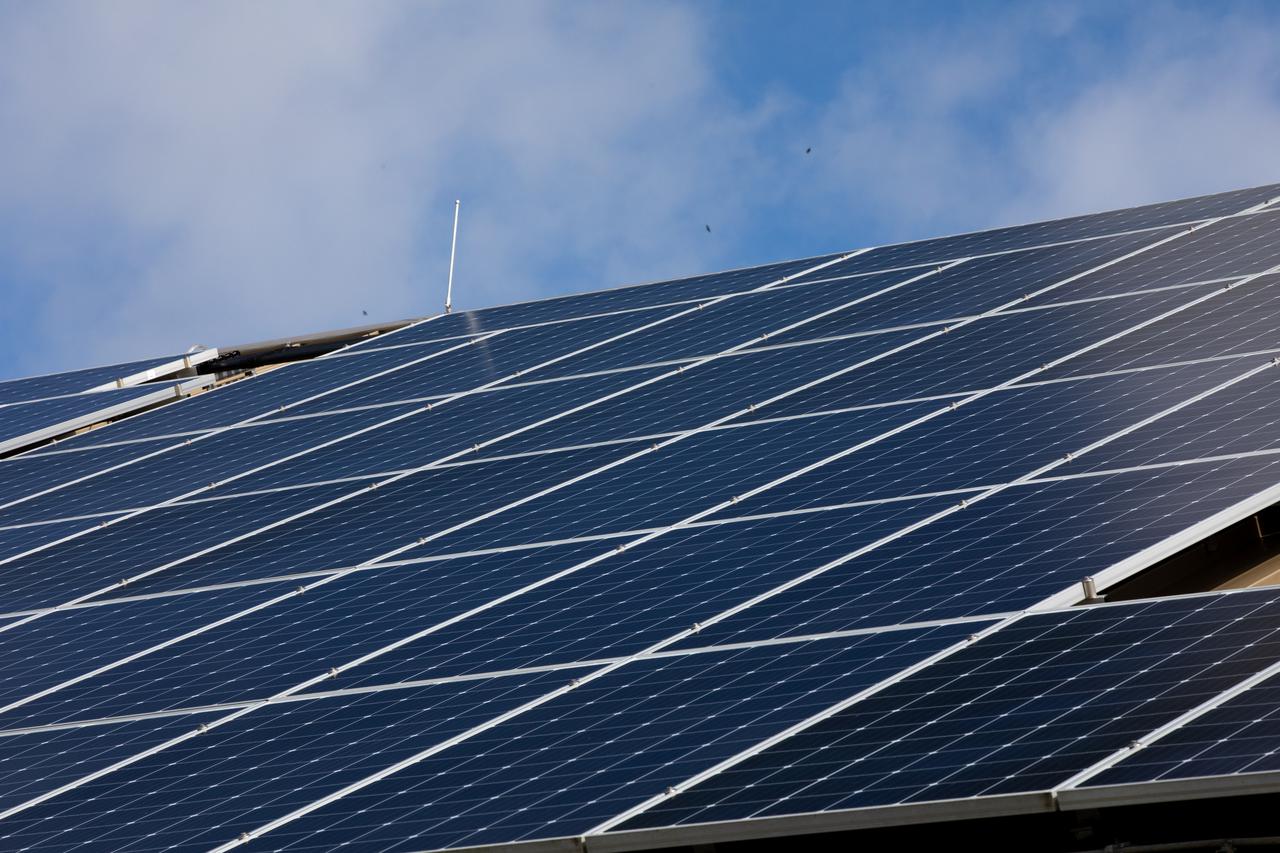

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
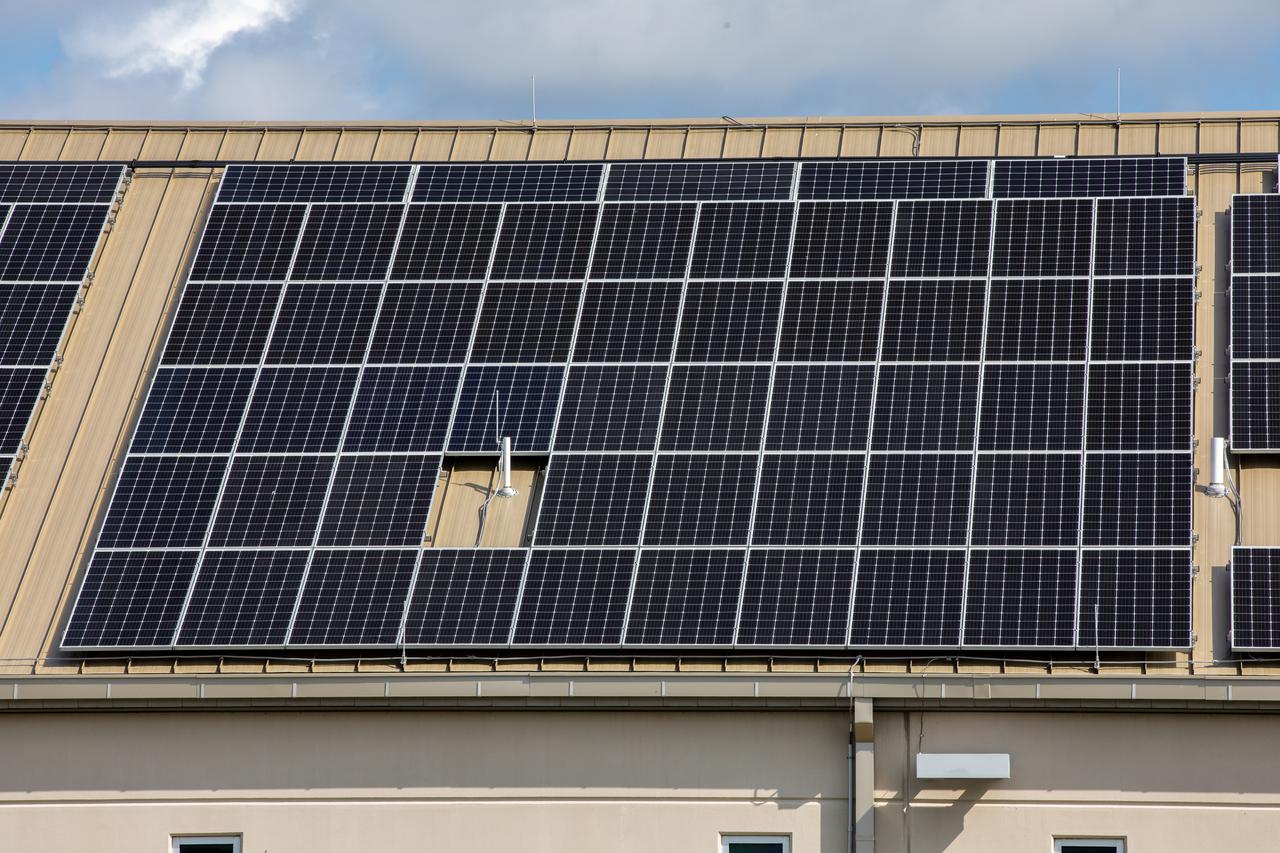

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
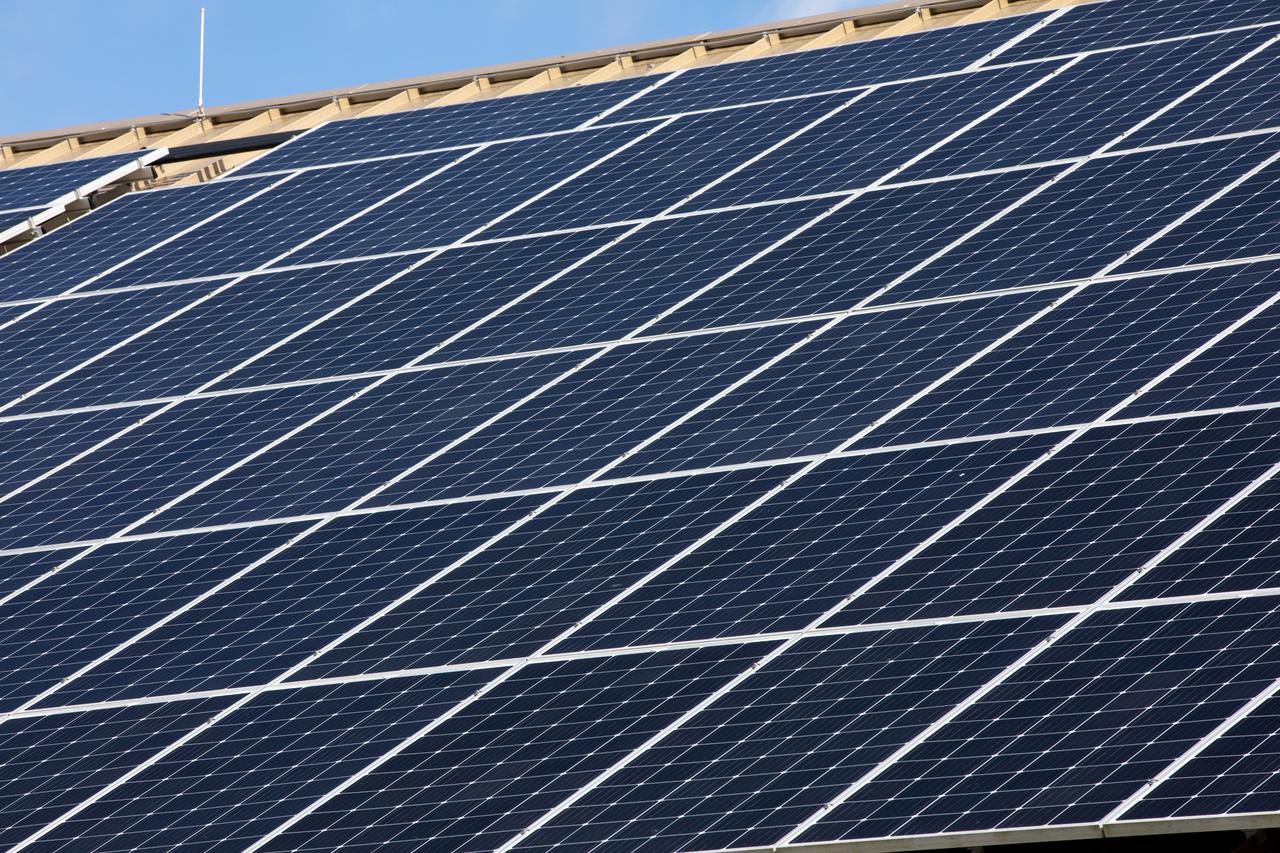

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
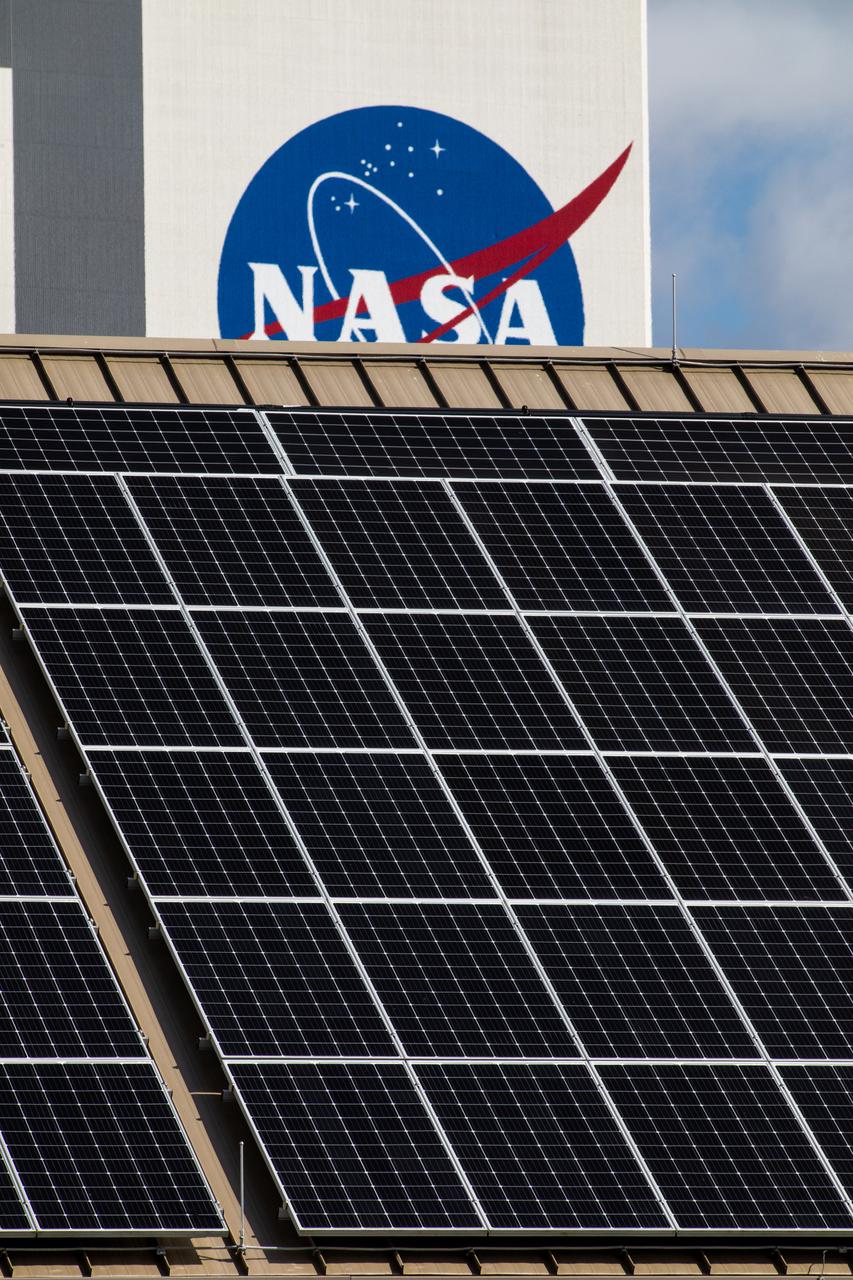

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
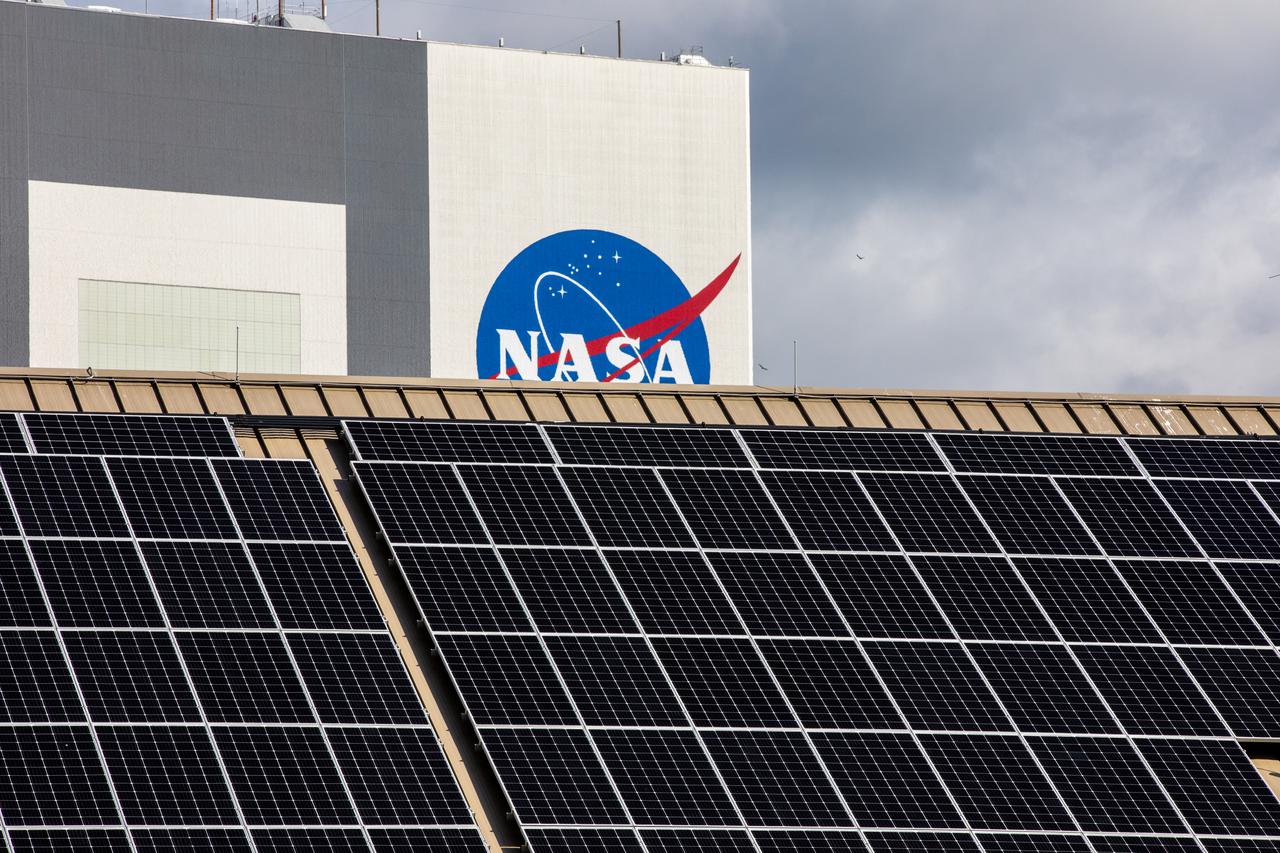

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
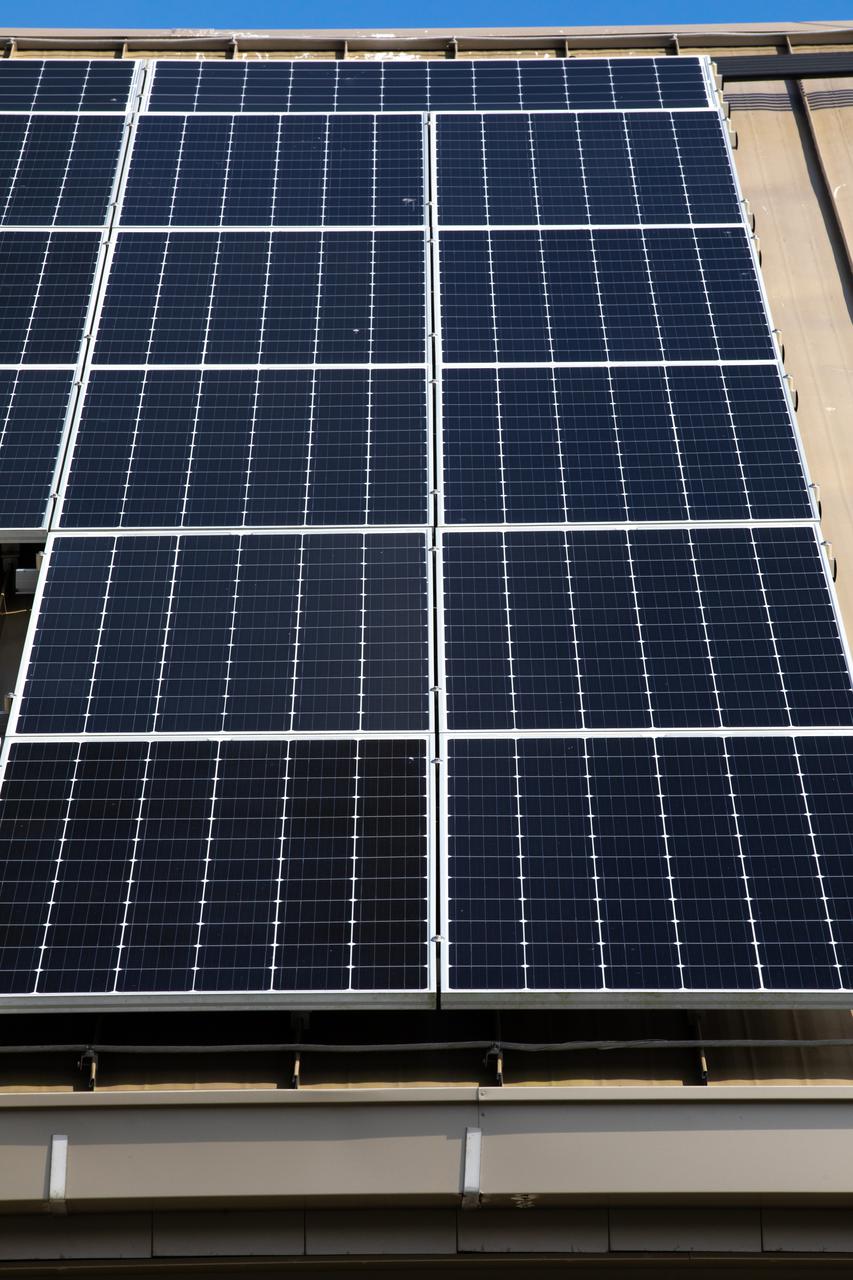

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
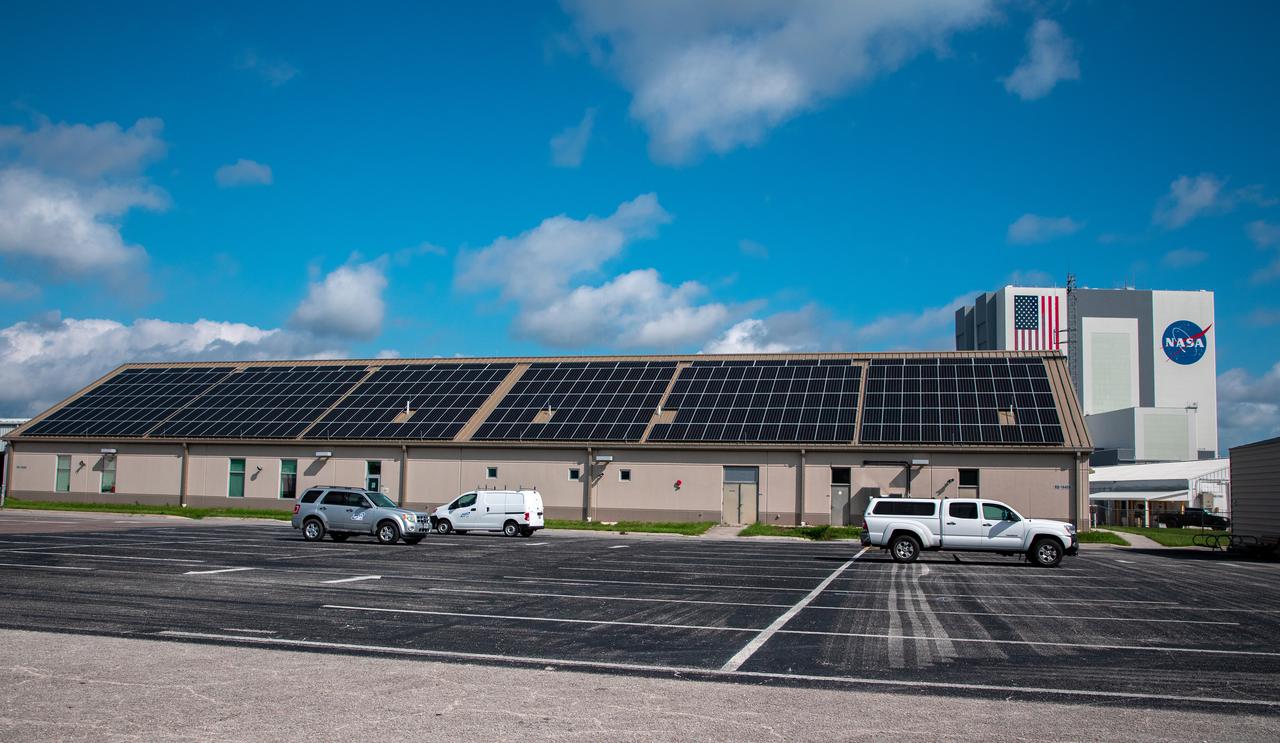

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
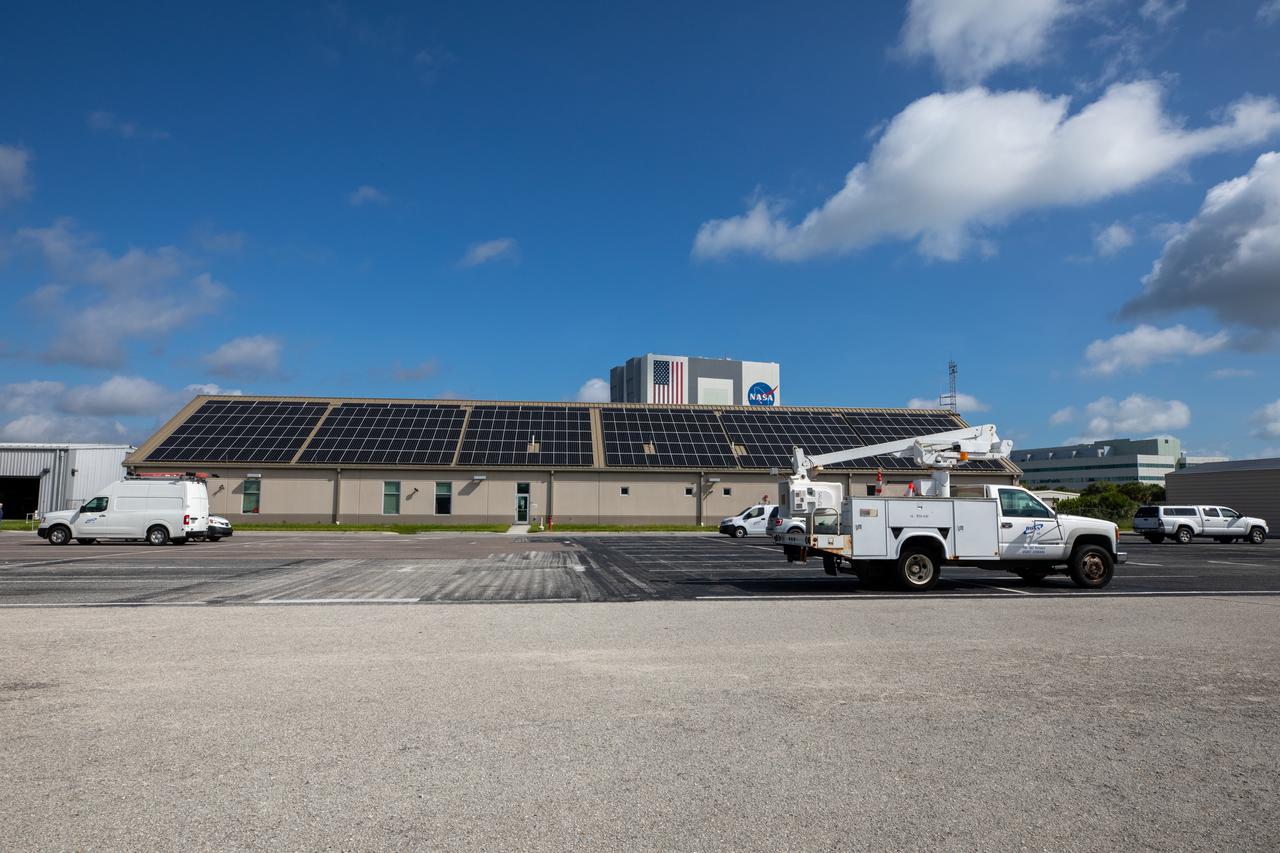

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
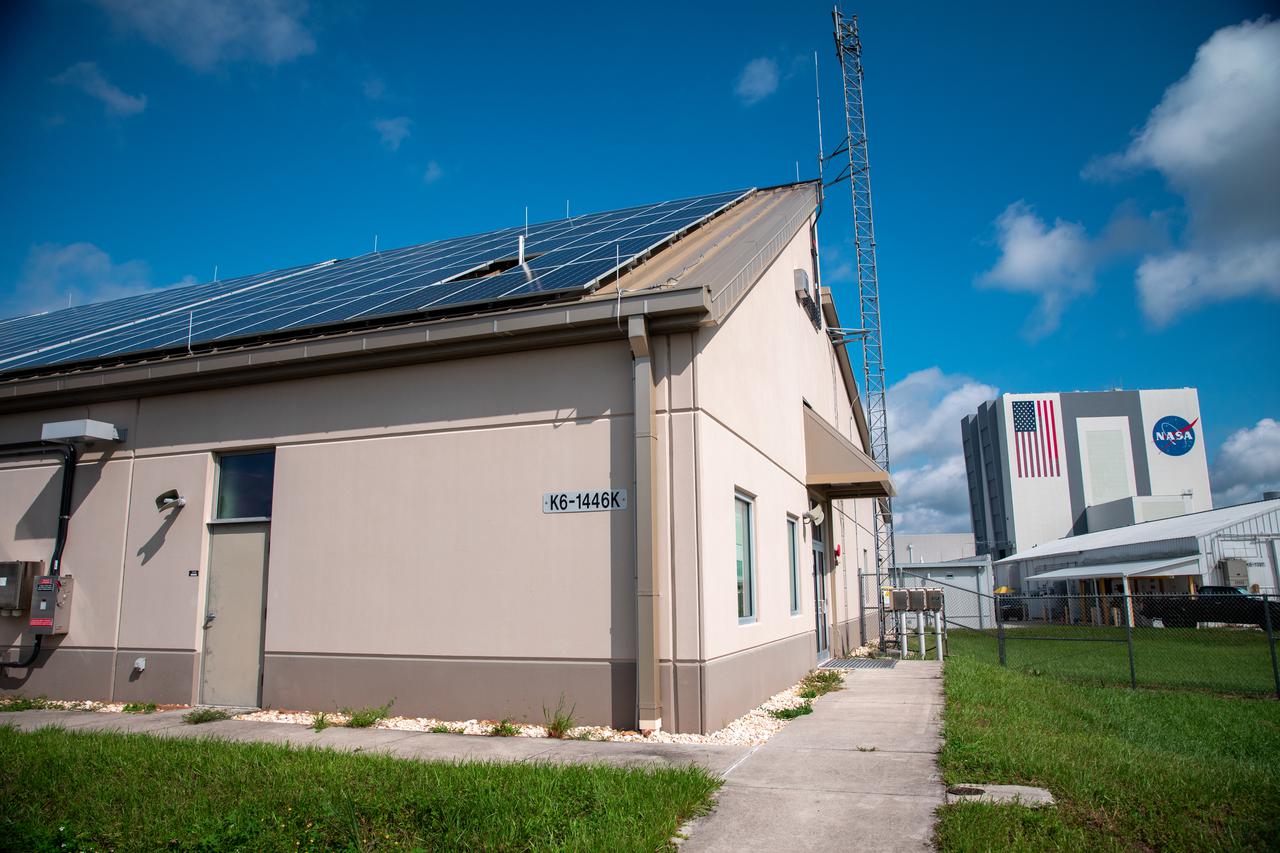

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
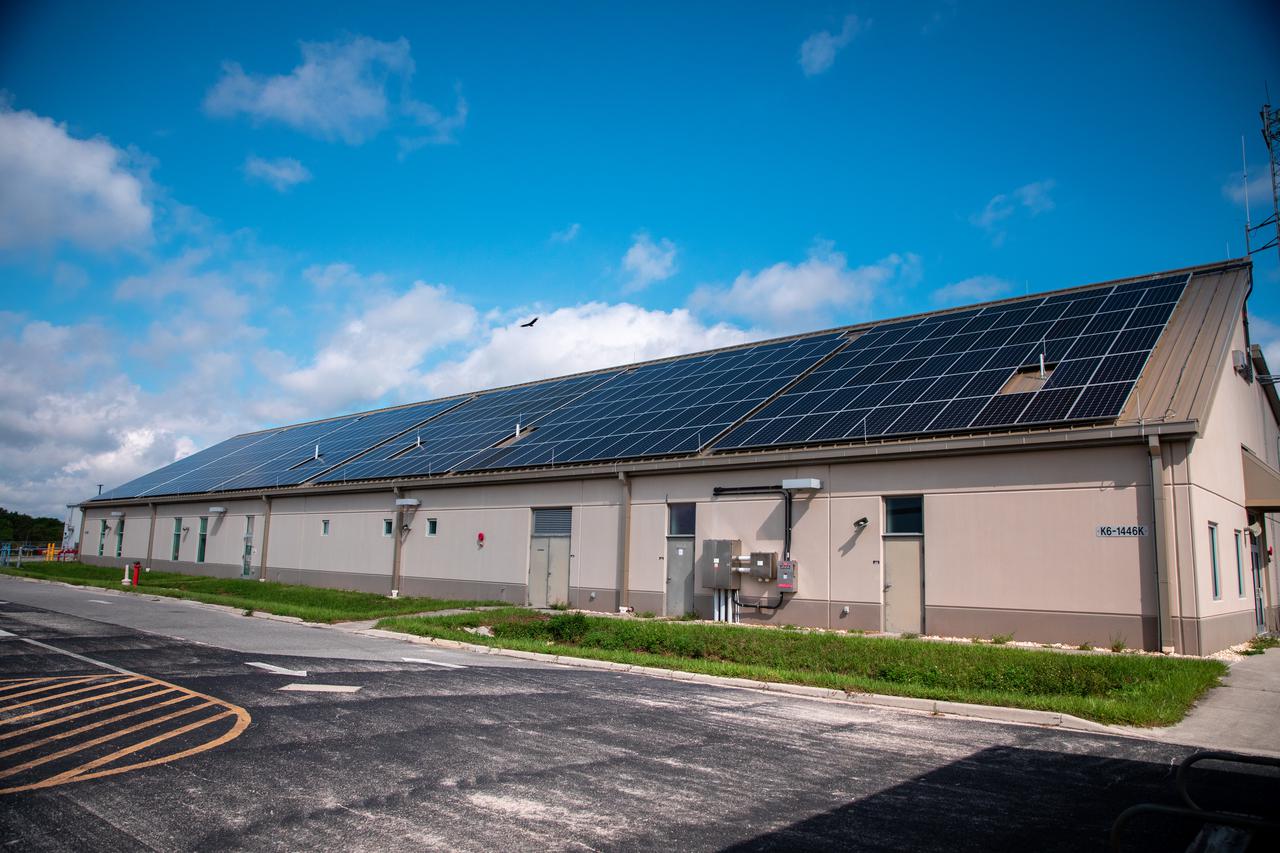

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
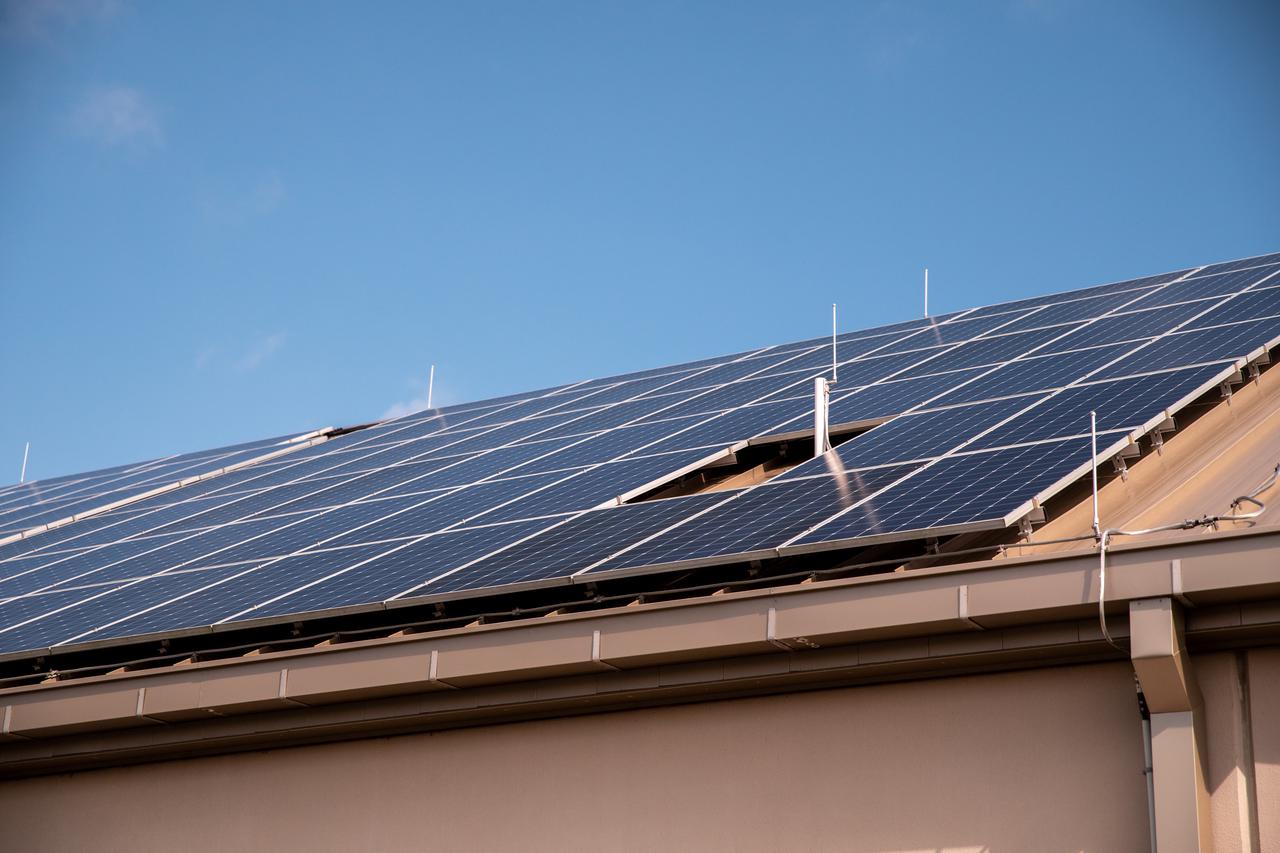

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
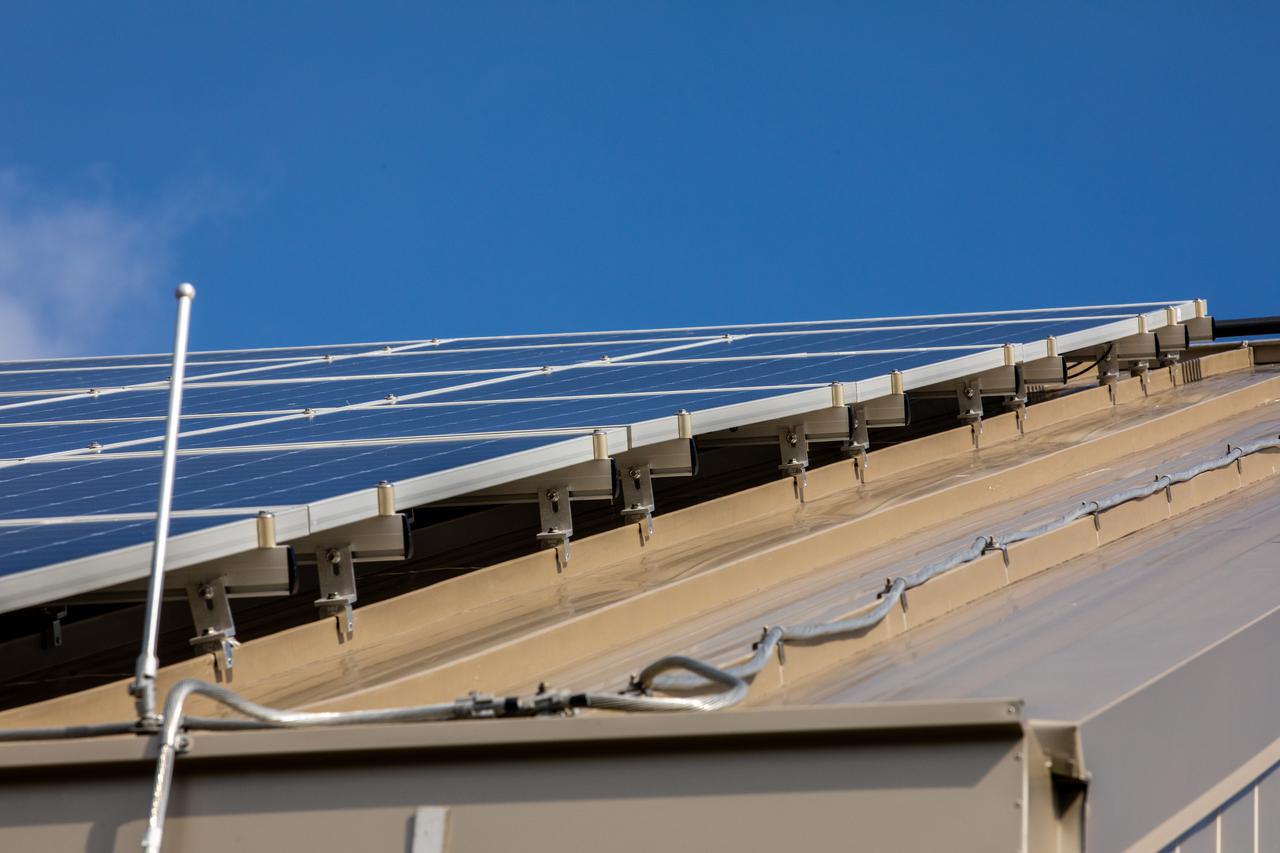

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
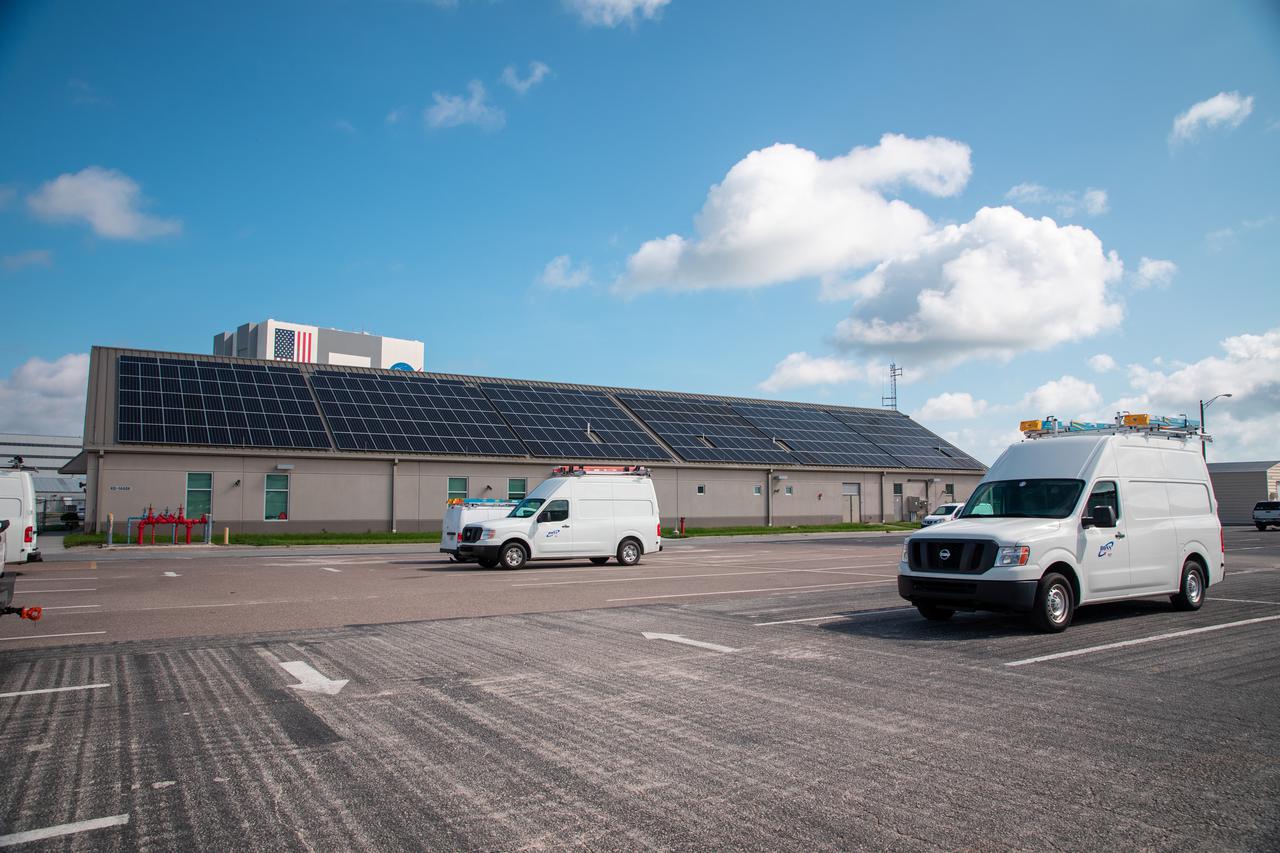

The Electrical Maintenance Facility (EMF) at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida has solar panels capable of producing 125 kilowatts. Installation of the panels began in August 2019 and by February 2020, the panels were up and running, generating enough power to supply the facility. The addition of the solar panels has turned the EMF into a "net positive" facility, meaning it now produces more energy than it consumes.
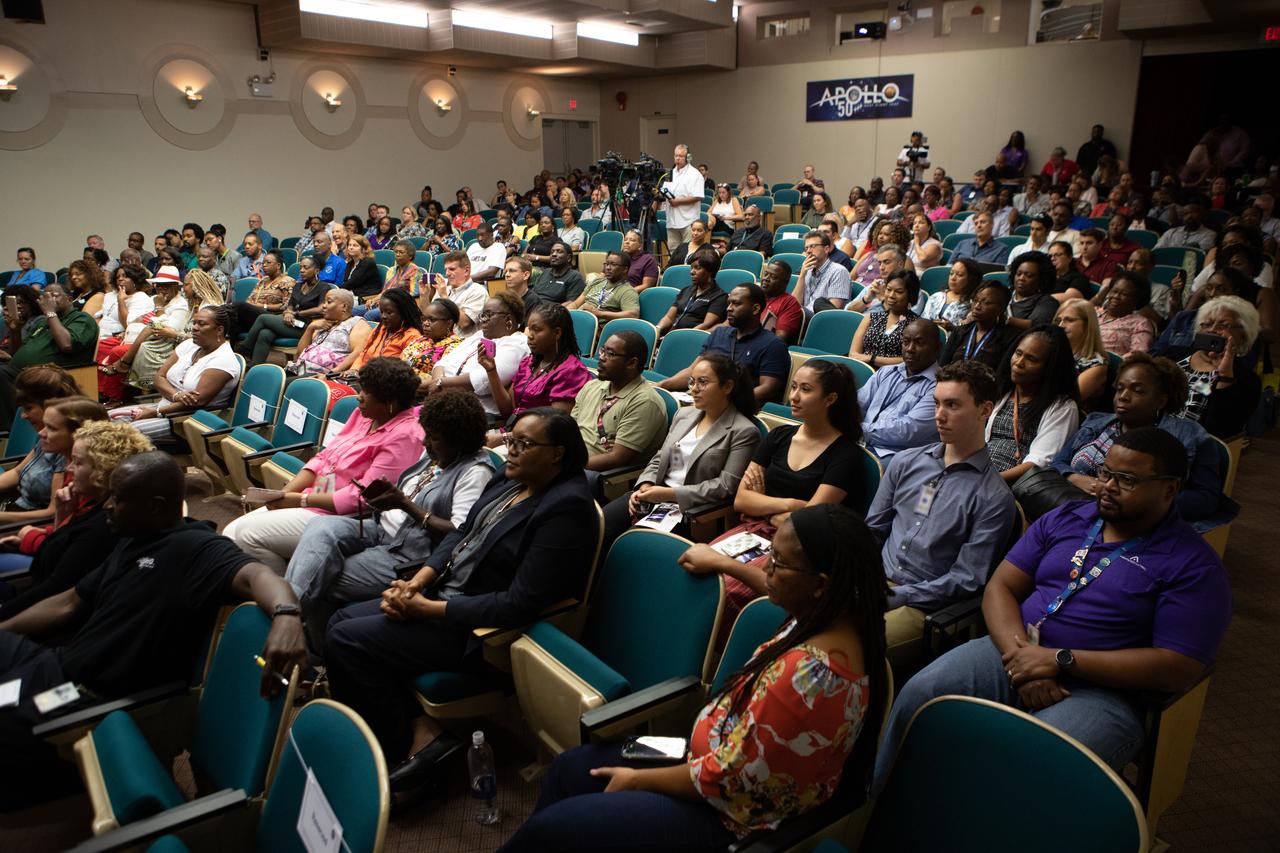

Kennedy Space Center employees attend a panel discussion, hosted by national radio host Tom Joyner, about NASA’s Moon to Mars plans on Aug. 28, 2019. Taking place at the Florida spaceport, panel participants included former NASA administrator and astronaut Charlie Bolden, former astronaut Winston Scott, Kennedy Chief Technologist Barbara Brown and Exploration Ground Systems Associate Manager, Technical, Kim Carter.
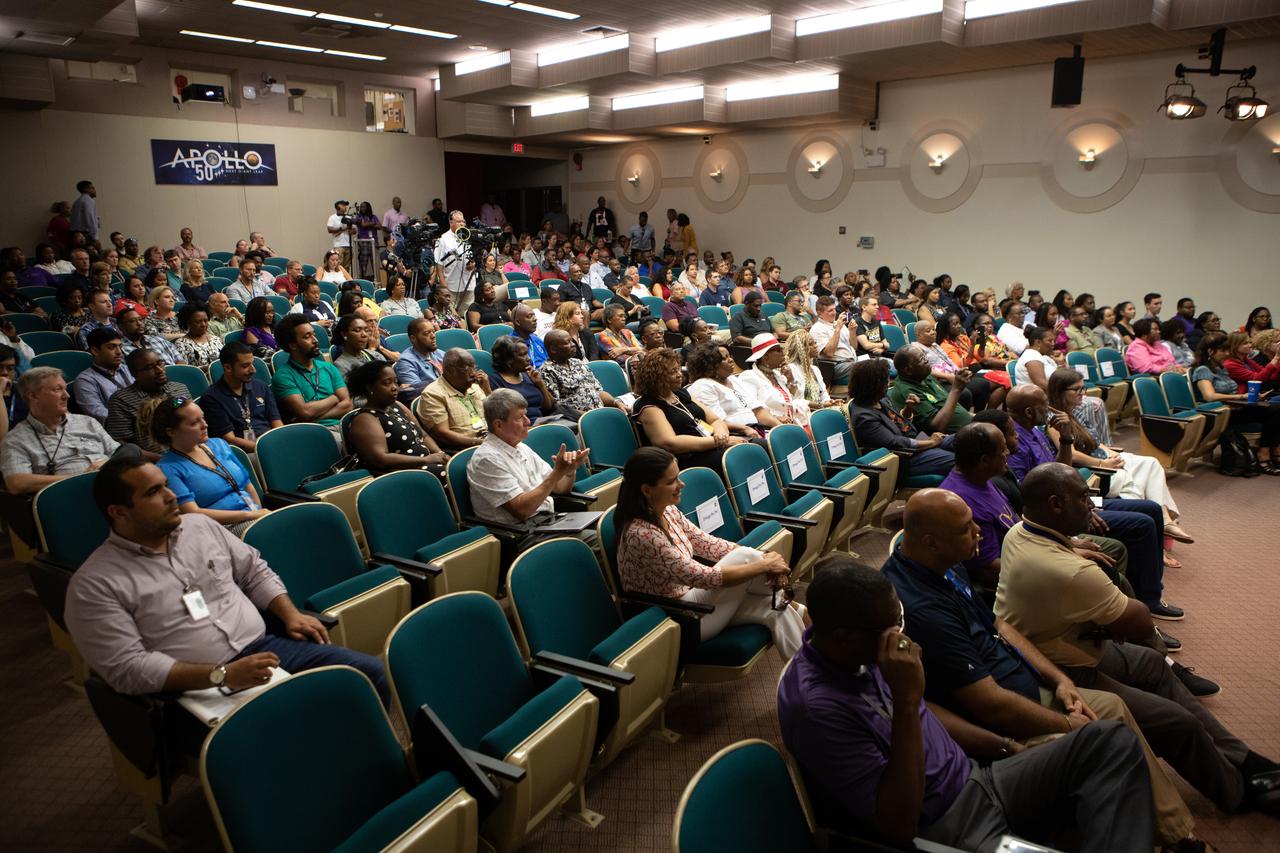

Kennedy Space Center employees attend a panel discussion, hosted by national radio host Tom Joyner, about NASA’s Moon to Mars plans on Aug. 28, 2019. Taking place at the Florida spaceport, panel participants included former NASA administrator and astronaut Charlie Bolden, former astronaut Winston Scott, Kennedy Chief Technologist Barbara Brown and Exploration Ground Systems Associate Manager, Technical, Kim Carter.
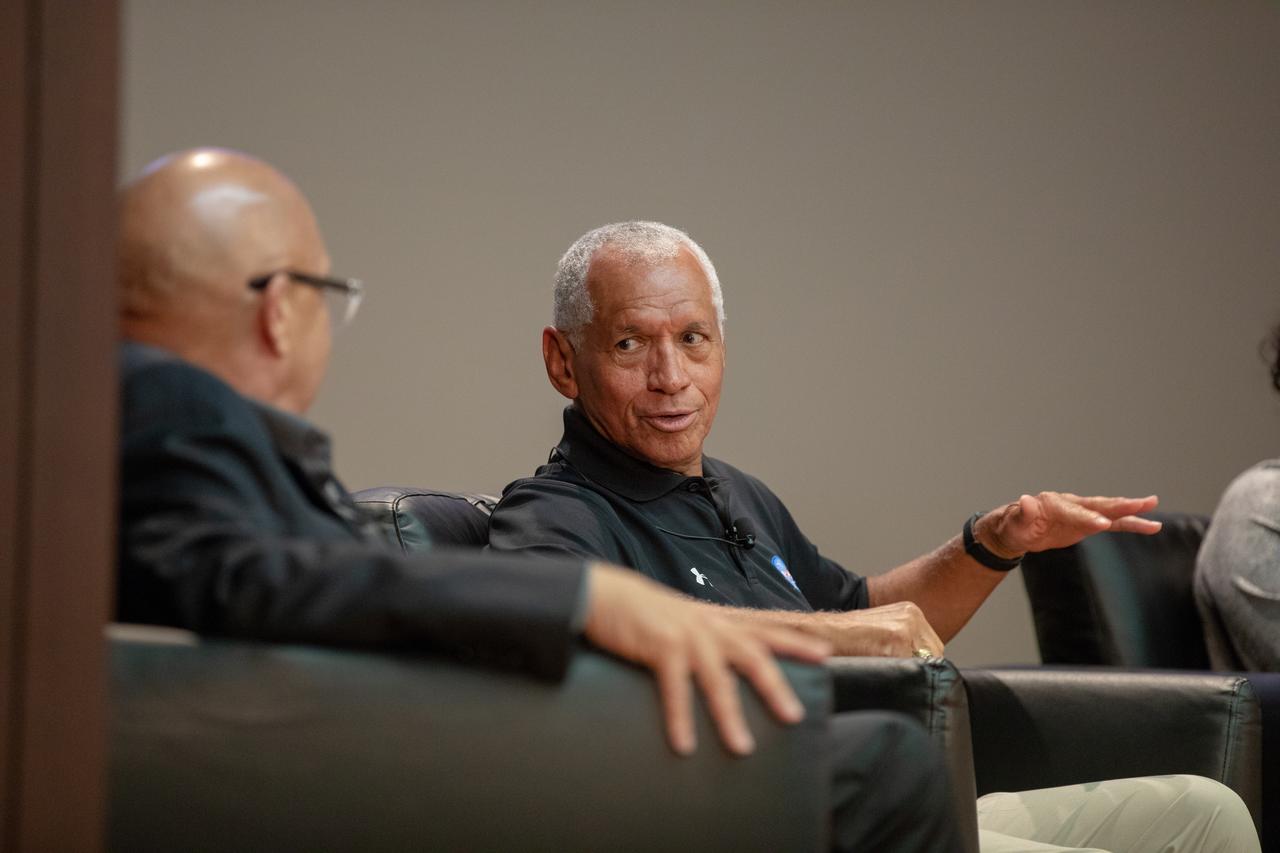

Former NASA administrator and astronaut Charlie Bolden, left, talks to national radio host and panel host Tom Joyner during a panel discussion at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2019. The discussion focused on the agency’s Moon to Mars plans and was open for all Kennedy employees to attend. Additional participants included former astronaut Winston Scott, Kennedy Chief Technologist Barbara Brown and Exploration Ground Systems Associate Manager, Technical, Kim Carter.
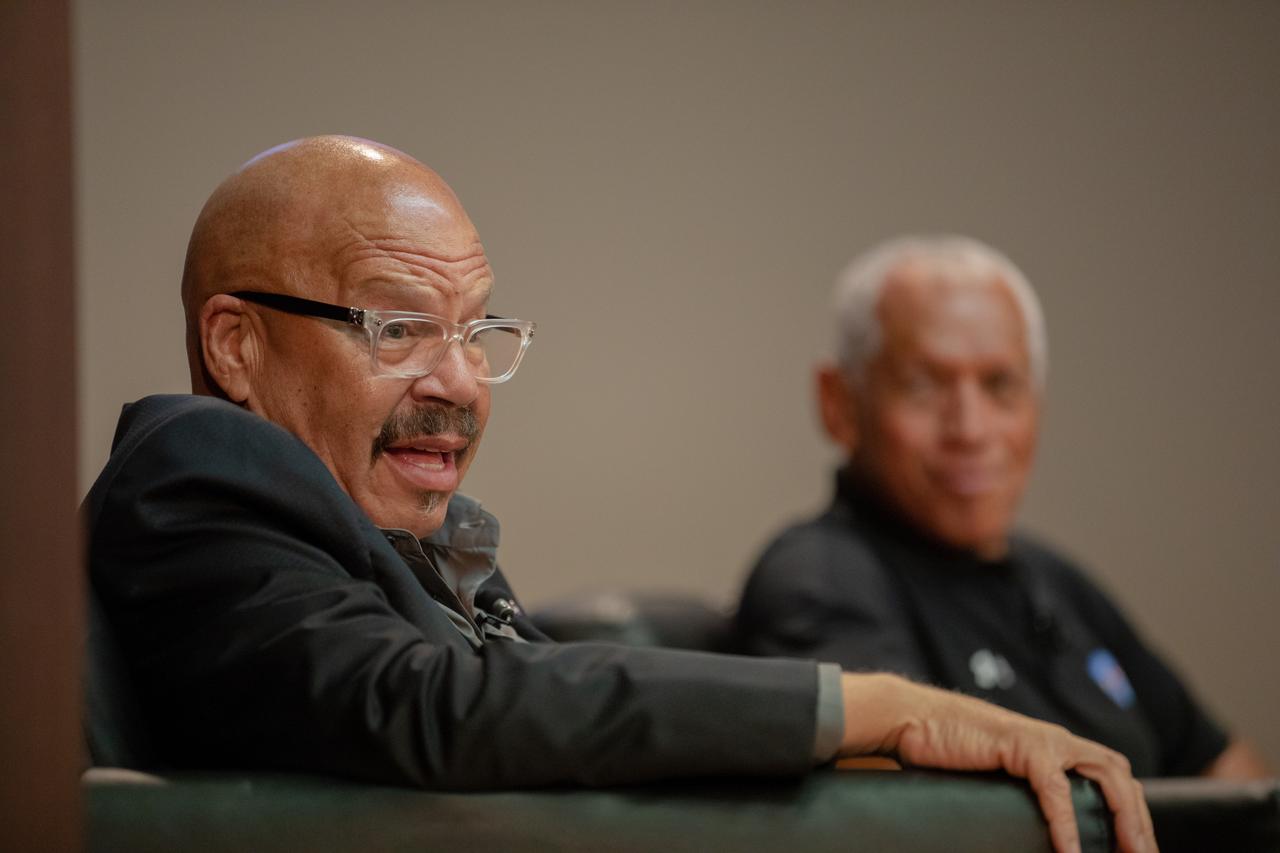

National radio host Tom Joyner hosts a panel discussion at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2019, about the agency’s Moon to Mars plans. The discussion was open for all Kennedy employees to attend. In the background, panel participant and former NASA administrator Charlie Bolden can be seen. Additional participants included Kennedy Chief Technologist Barbara Brown and Exploration Ground Systems Associate Manager, Technical, Kim Carter.
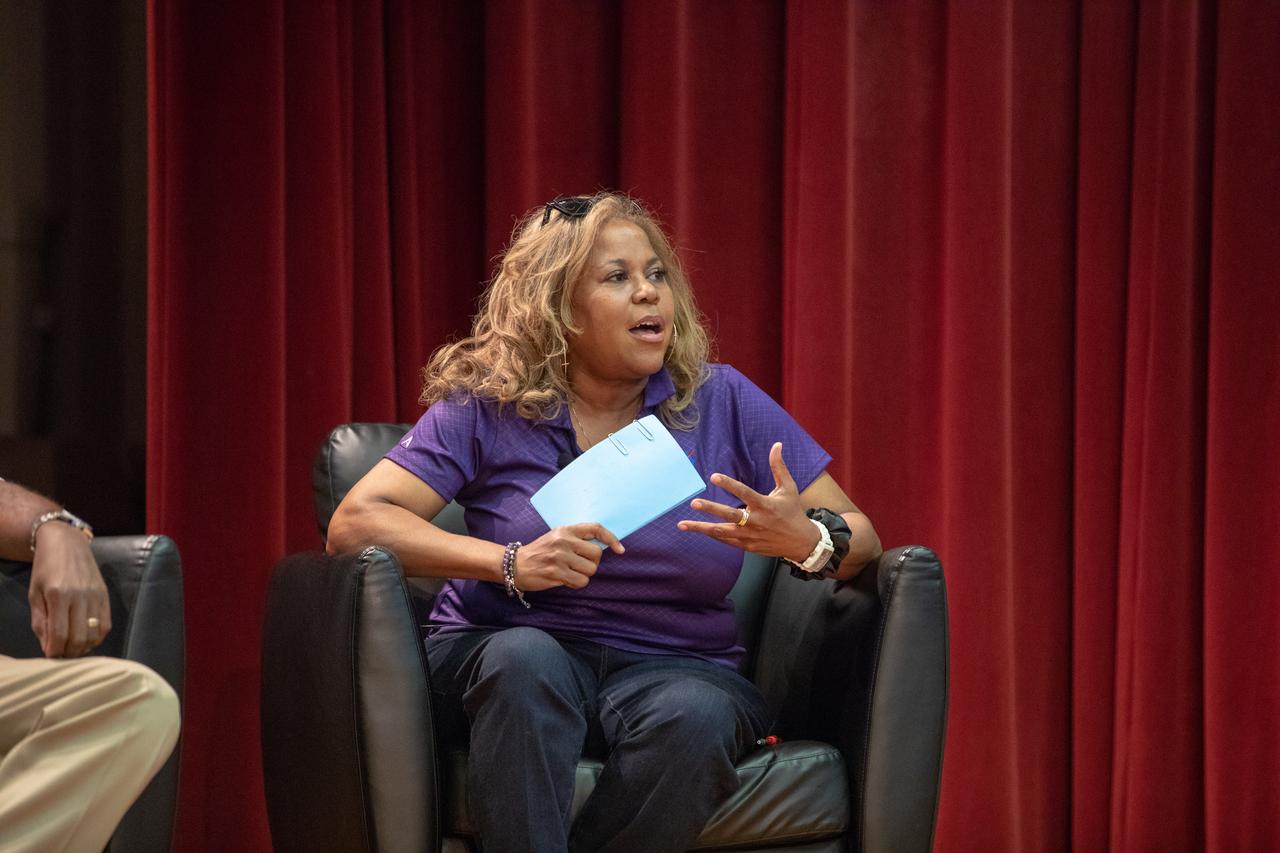

Sybil Wilkes co-hosts a panel discussion at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2019, focusing on NASA’s Moon to Mars plans. Hosted by national radio host Tom Joyner, the discussion was open for all Kennedy employees to attend. Panel participants included former NASA administrator and astronaut Charlie Bolden, former astronaut Winston Scott, Kennedy Chief Technologist Barbara Brown and Exploration Ground Systems Associate Manager, Technical, Kim Carter.
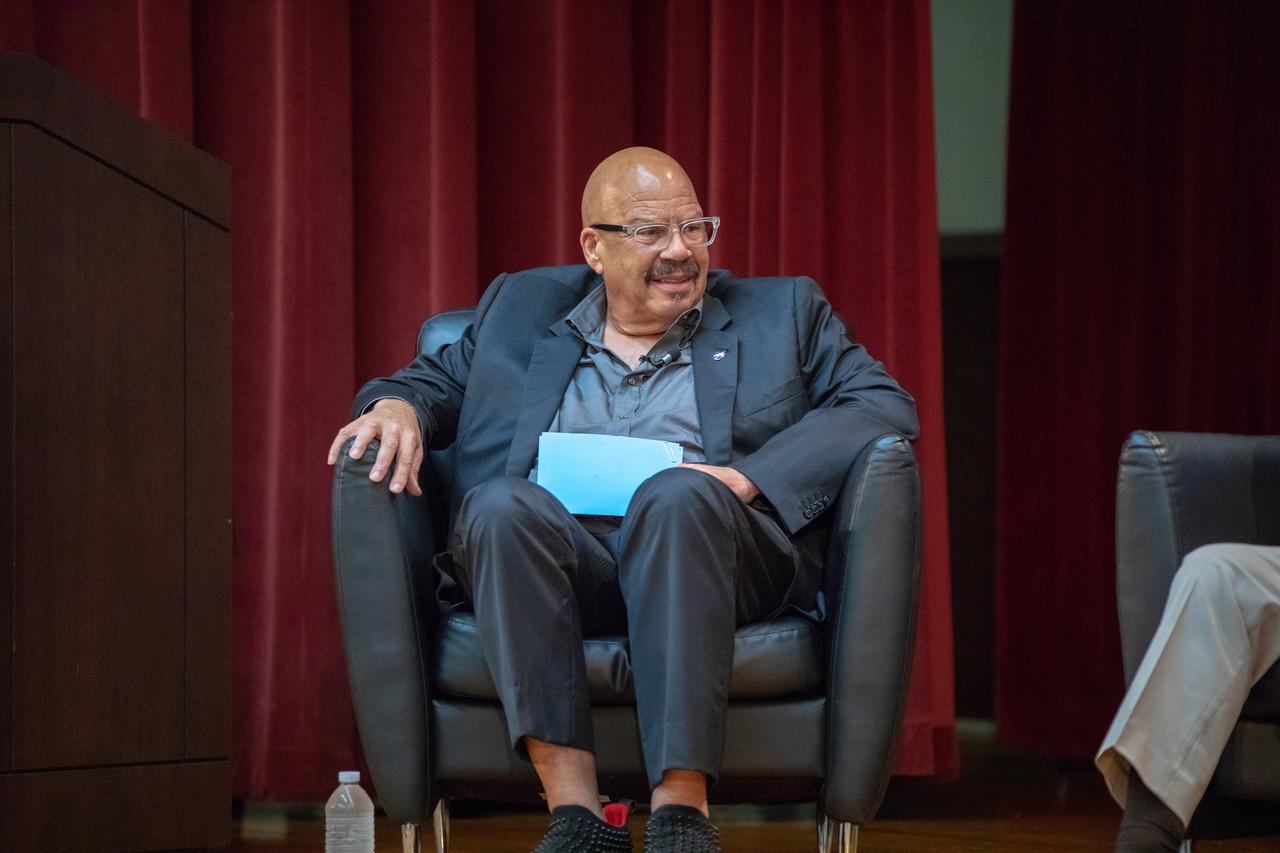

National radio host Tom Joyner hosts a panel discussion at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2019, about the agency’s Moon to Mars plans. The discussion was open for all Kennedy employees to attend. The panel included former NASA administrator and astronaut Charlie Bolden, former astronaut Winston Scott, Kennedy Chief Technologist Barbara Brown and Exploration Ground Systems Associate Manager, Technical, Kim Carter.
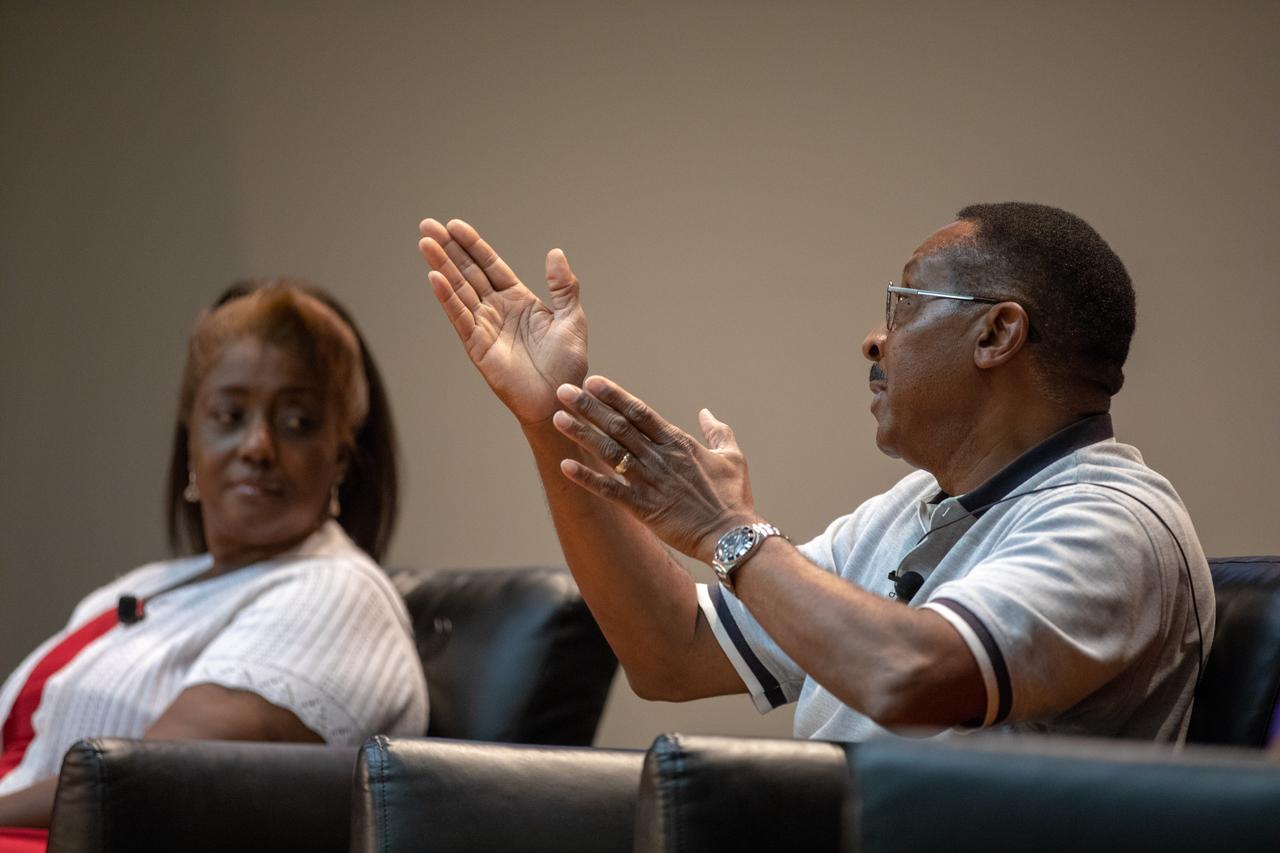

Former NASA astronaut Winston Scott, right, participates in a panel discussion on Aug. 28, 2019, focusing on the agency’s Moon to Mars plans. Hosted at Kennedy Space Center in Florida by national radio host Tom Joyner, the discussion was open for all Kennedy employees to attend. In the background, panel participant and Kennedy Chief Technologist Barbara Brown can be seen. Additional participants included former NASA administrator Charlie Bolden and Exploration Ground Systems Associate Manager, Technical, Kim Carter.
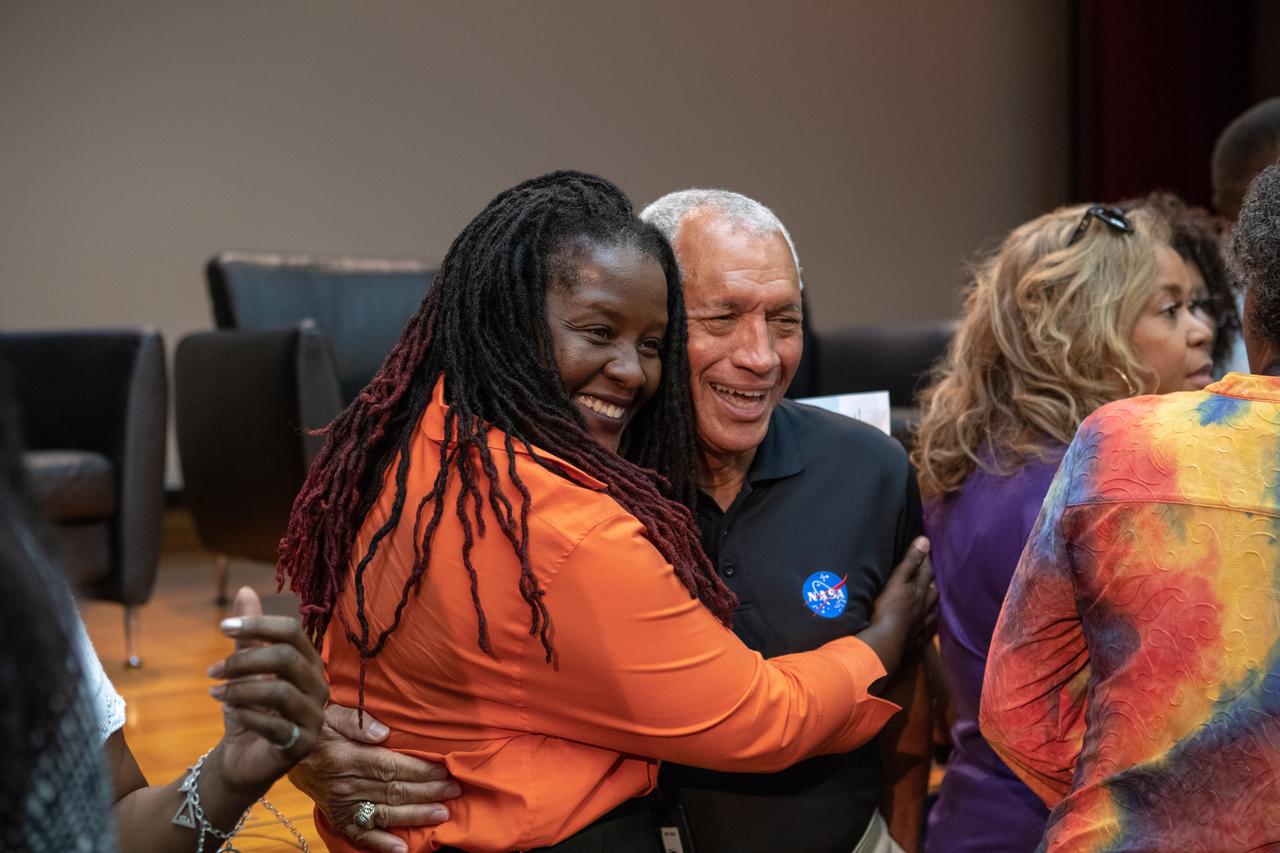
A Kennedy Space Center employee hugs former NASA administrator Charlie Bolden following a panel discussion on Aug. 28, 2019. Hosted at the Florida spaceport by national radio host Tom Joyner, the discussion focused on the agency’s Moon to Mars plans and was open for all Kennedy employees to attend. Additional panel participants included former astronaut Winston Scott, Kennedy Chief Technologist Barbara Brown and Exploration Ground Systems Associate Manager, Technical, Kim Carter.
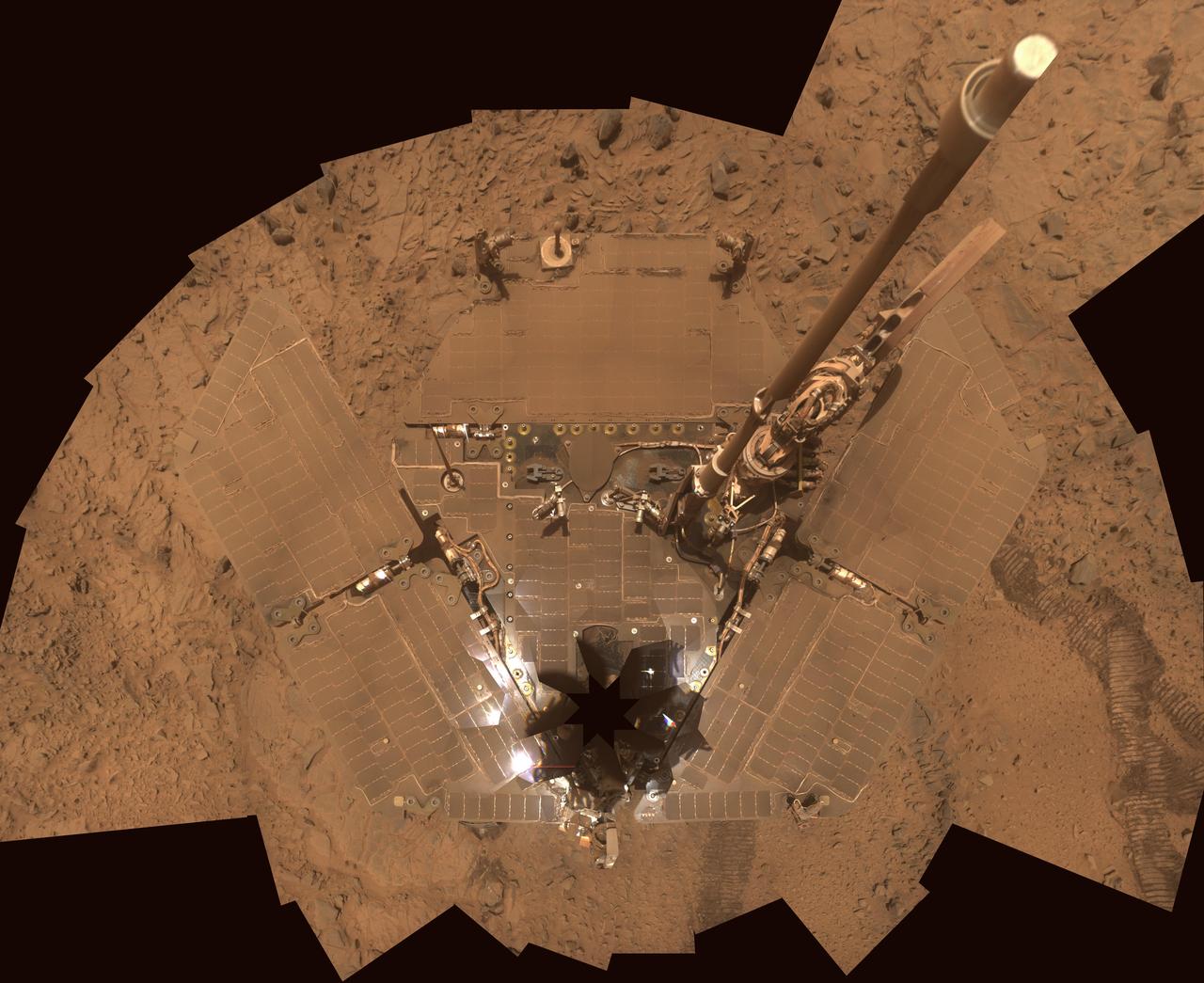

Dusty Solar Panels on Spirit
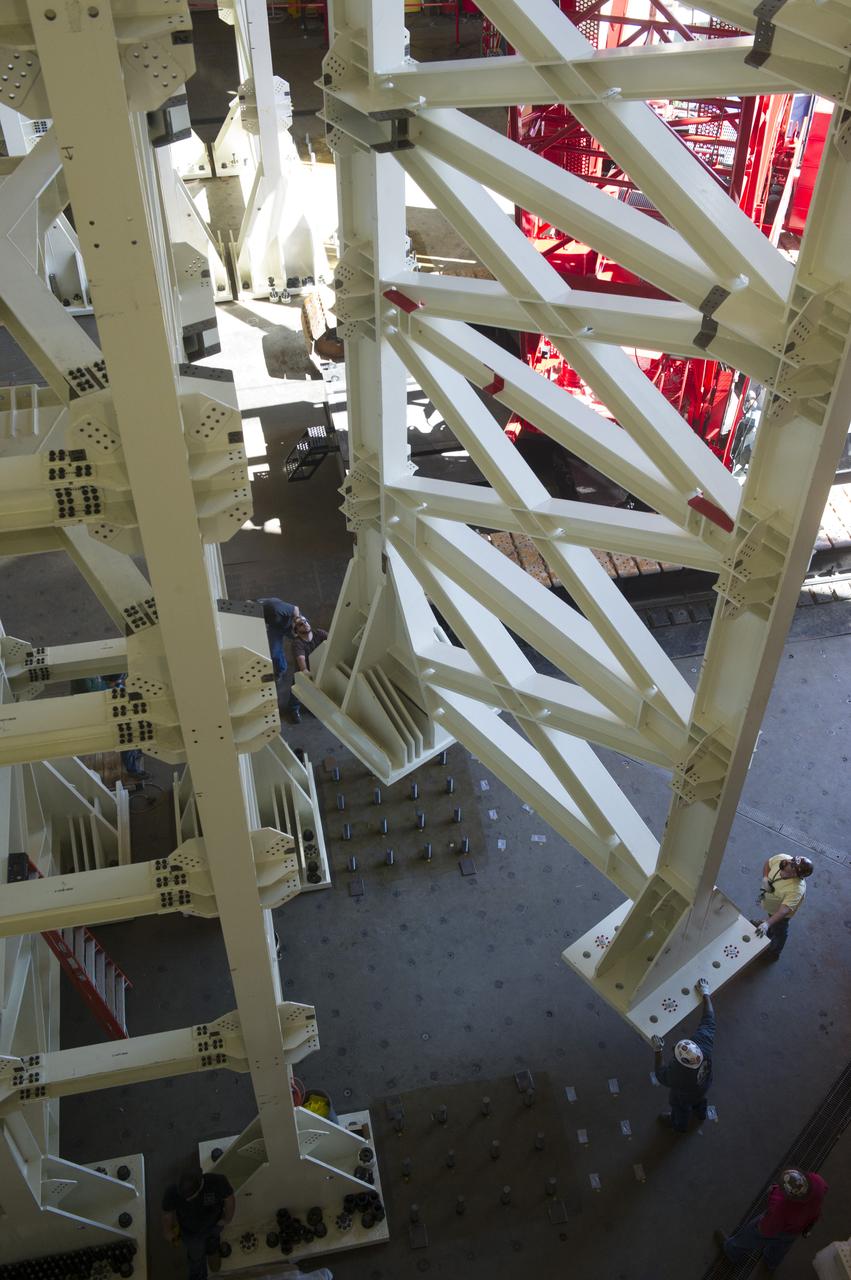
ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
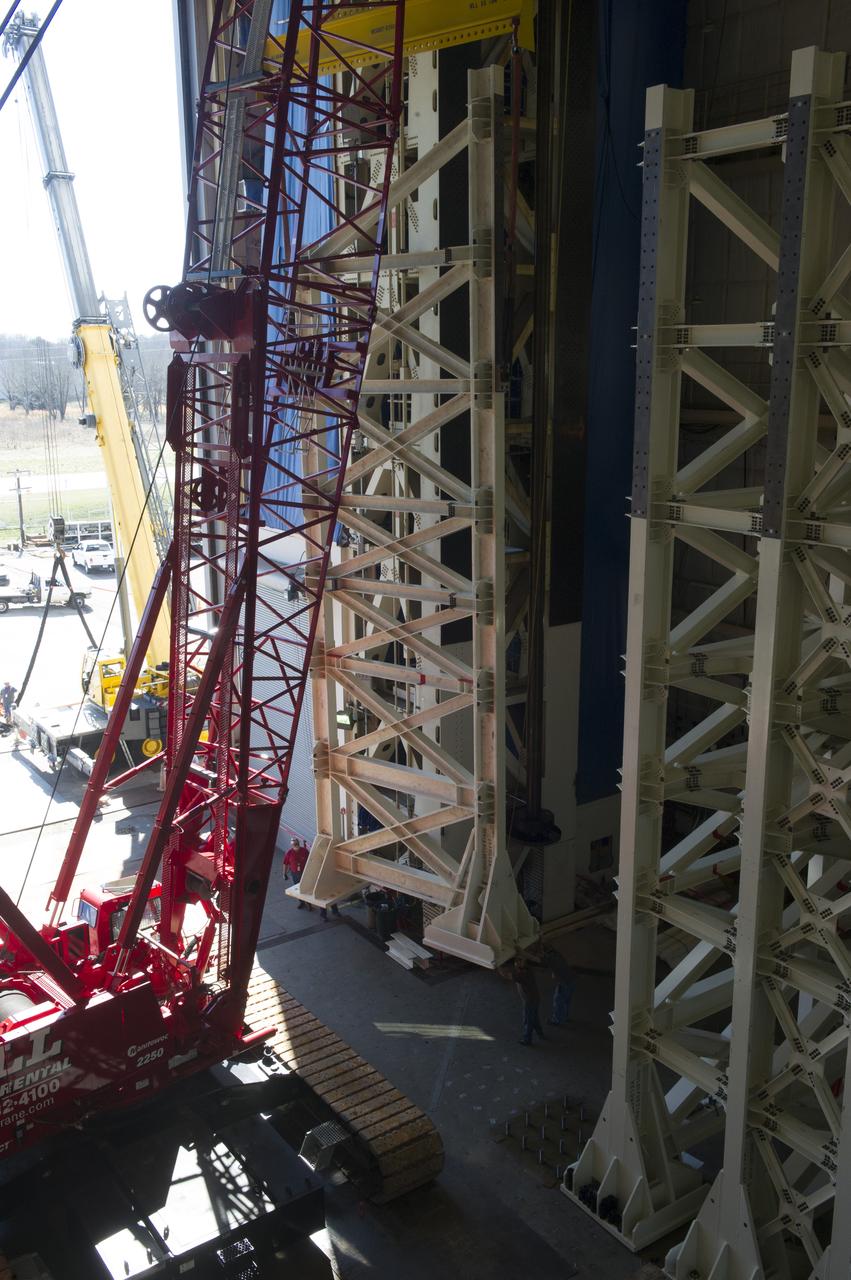

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
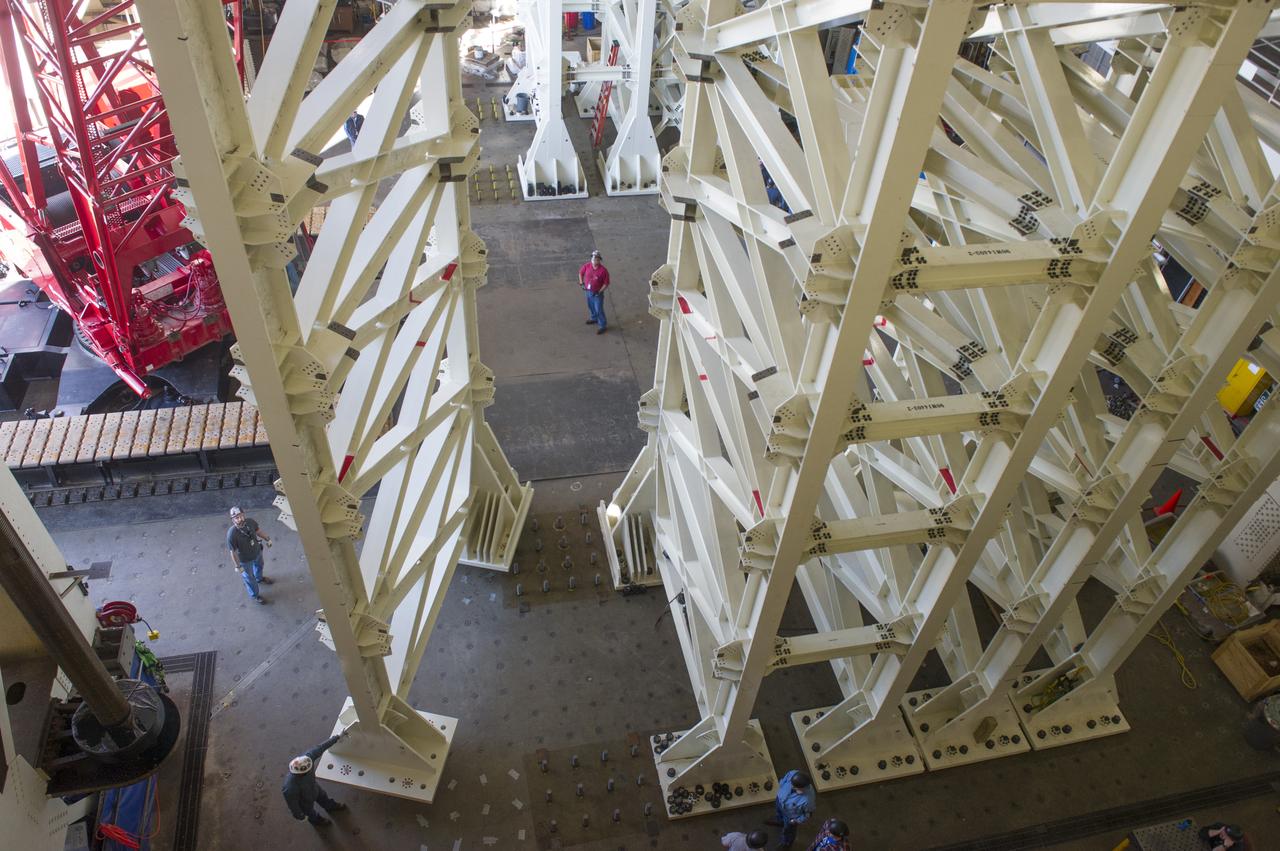

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
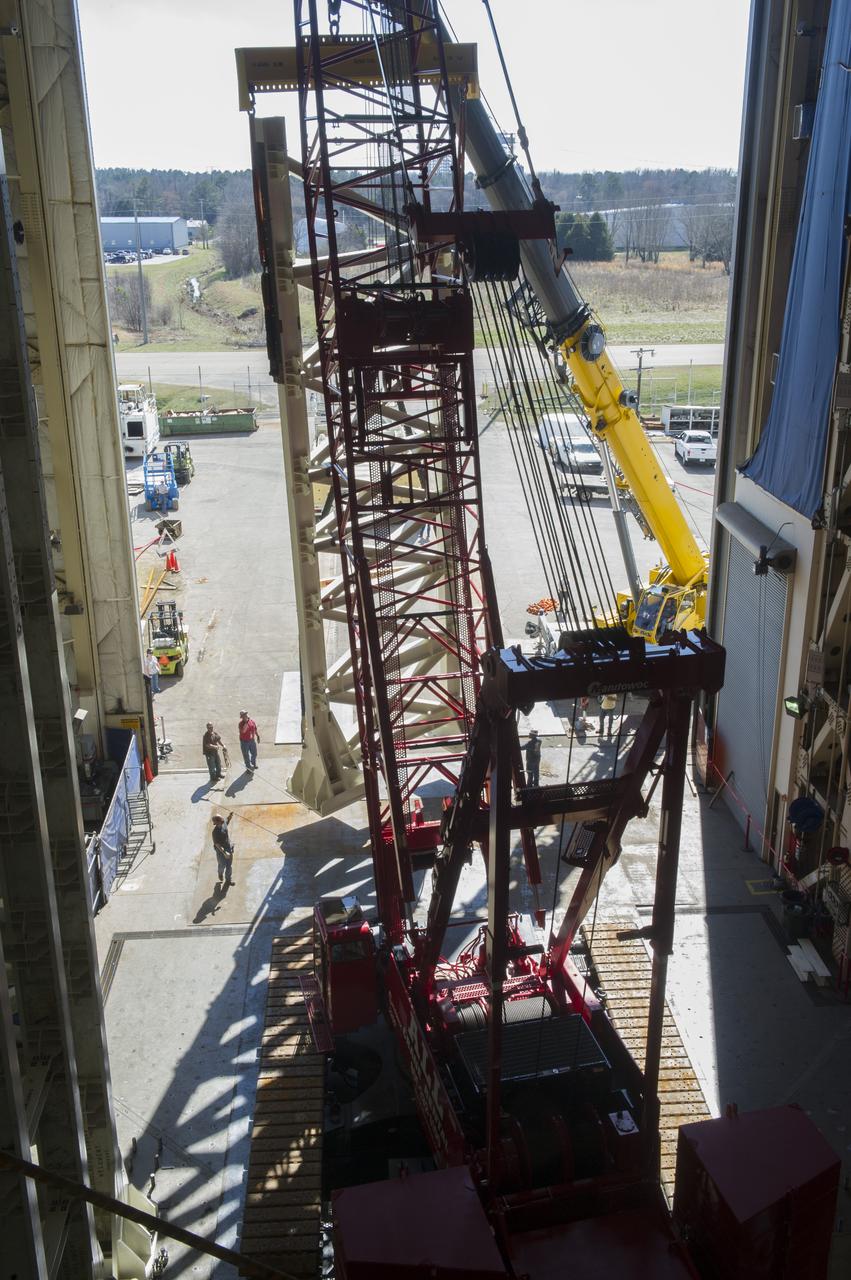

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
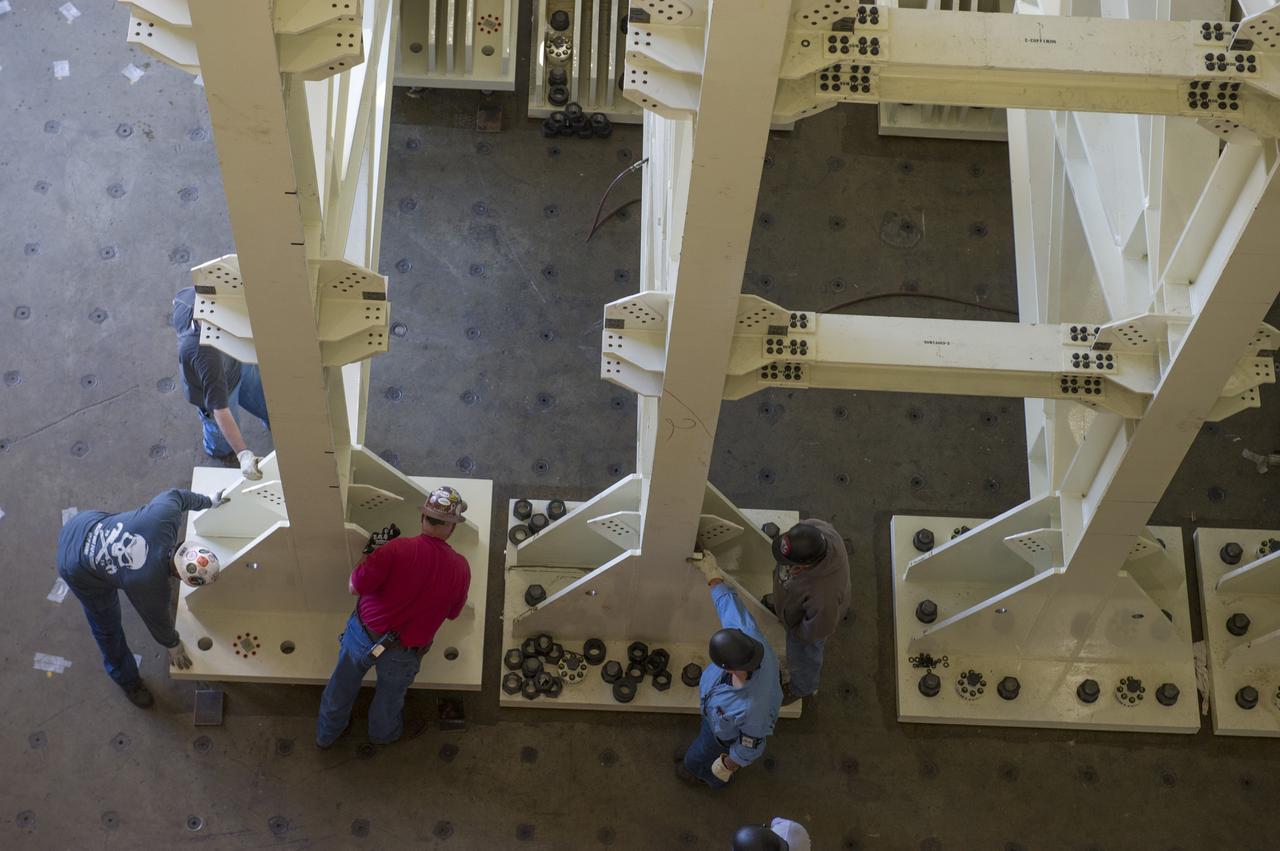

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
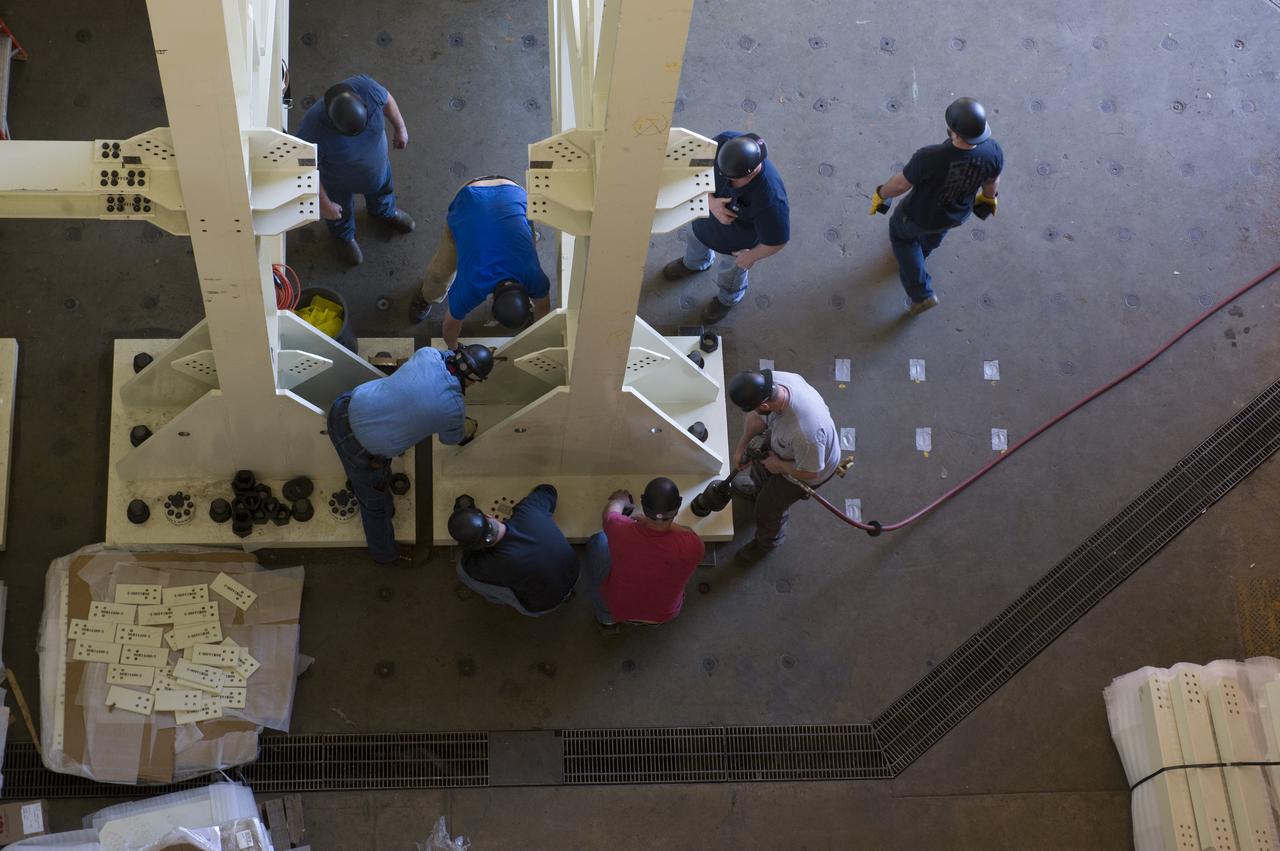

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
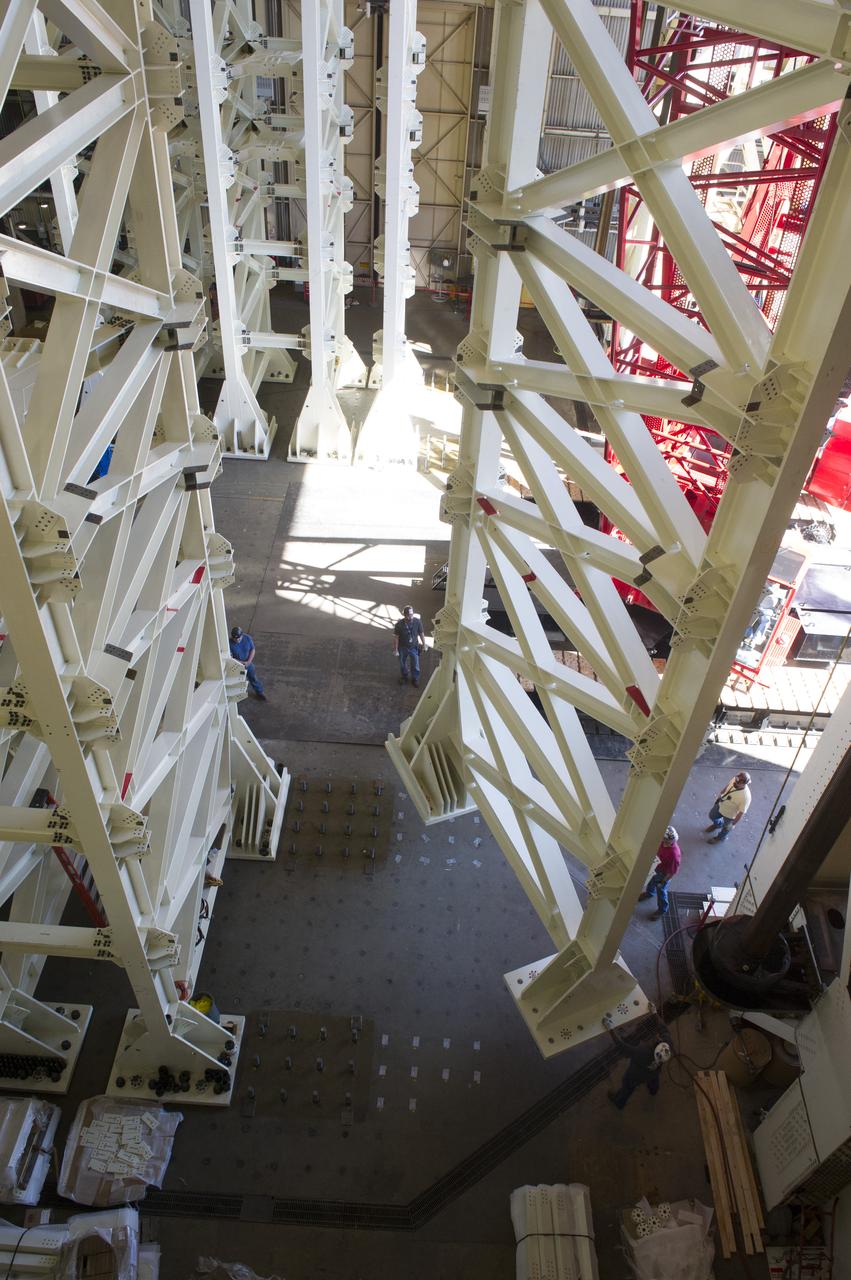

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
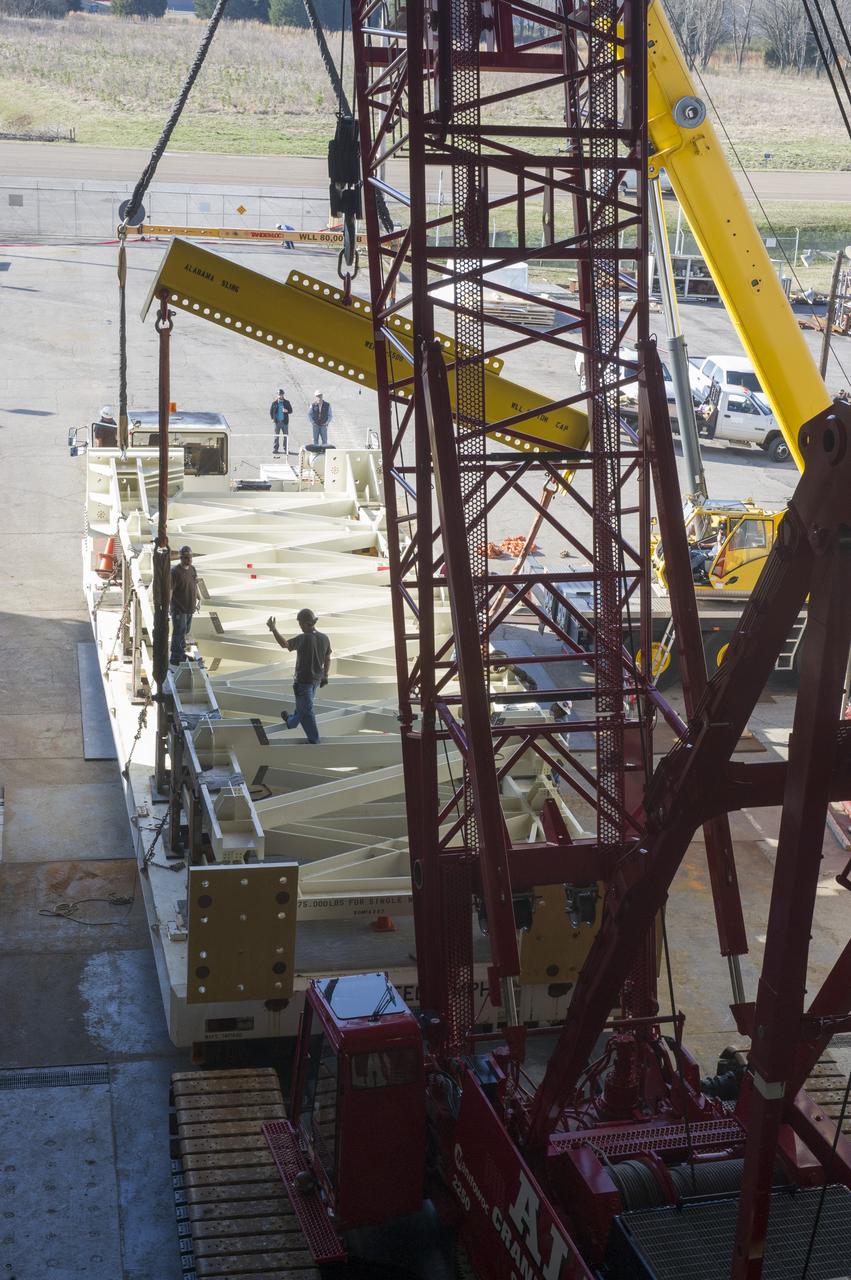

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
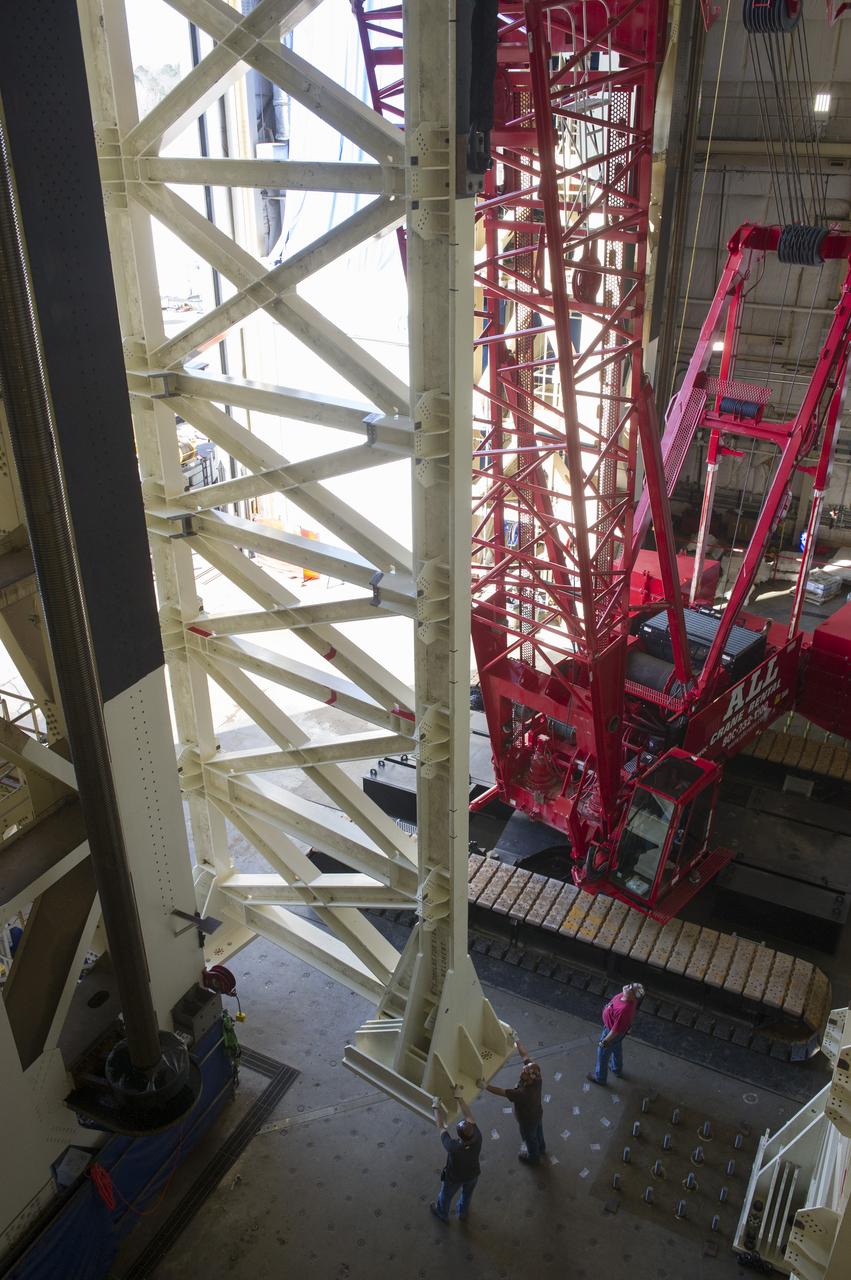

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619
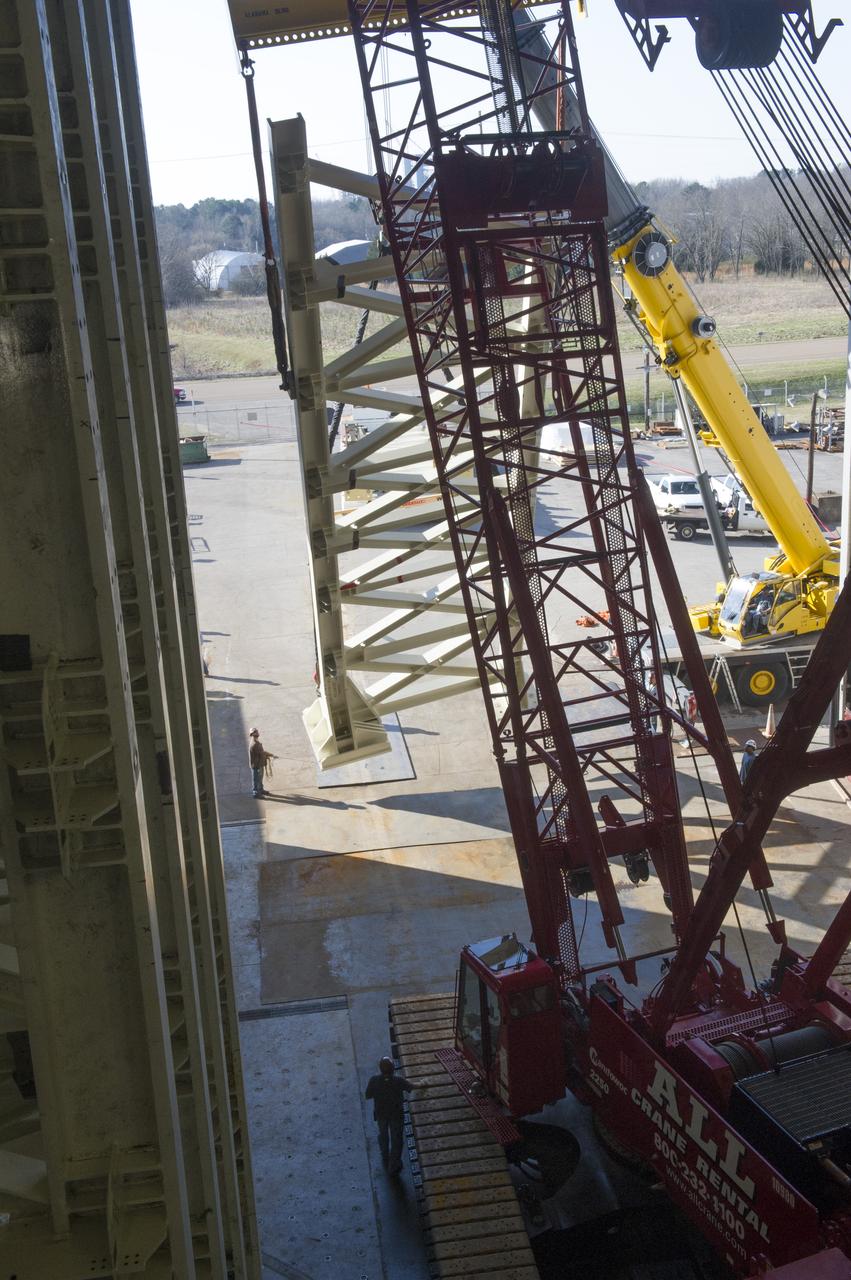

ERECTION OF TWO SLS INTERTANK, (IT), SPECIAL TEST EQUIPMENT, (STE), TOWER PANELS IN BLDG 4619

Kim Carter, Exploration Ground Systems associate manager, technical, participates in a panel discussion at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2019. Hosted by national radio host Tom Joyner, the discussion focused on the agency’s Moon to Mars plans and was open for all Kennedy employees to attend. Additional participants included former NASA administrator and astronaut Charlie Bolden, former astronaut Winston Scott and Kennedy Chief Technologist Barbara Brown.
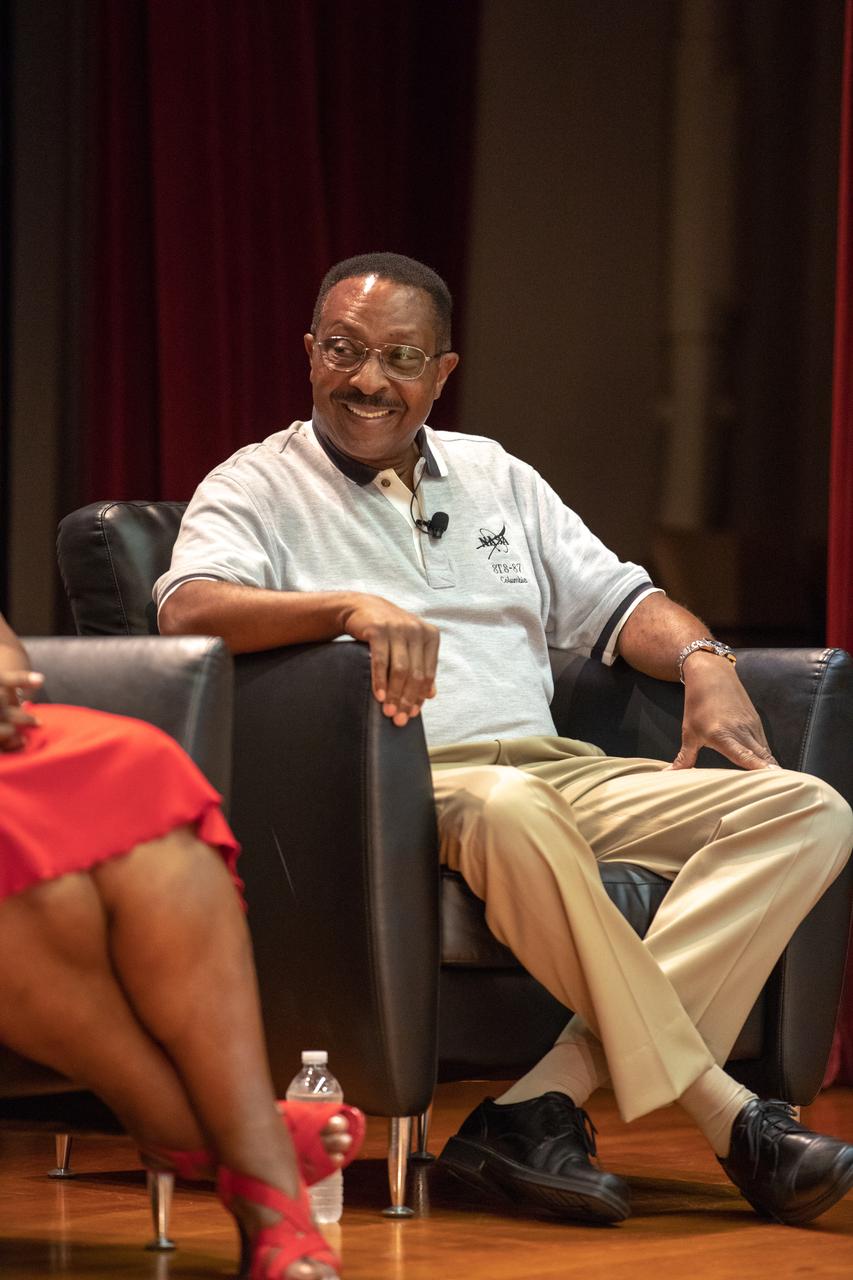

Former NASA astronaut Winston Scott participates in a panel discussion at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2019. Hosted by national radio host Tom Joyner, the discussion focused on the agency’s Moon to Mars plans and was open for all Kennedy employees to attend. Additional participants included former NASA administrator and astronaut Charlie Bolden, Kennedy Chief Technologist Barbara Brown and Exploration Ground Systems Associate Manager, Technical, Kim Carter.

Kim Carter, Exploration Ground Systems associate manager, technical, participates in a panel discussion at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2019. Hosted by national radio host Tom Joyner, the discussion focused on the agency’s Moon to Mars plans and was open for all Kennedy employees to attend. Additional participants included former NASA administrator and astronaut Charlie Bolden, former astronaut Winston Scott and Kennedy Chief Technologist Barbara Brown.
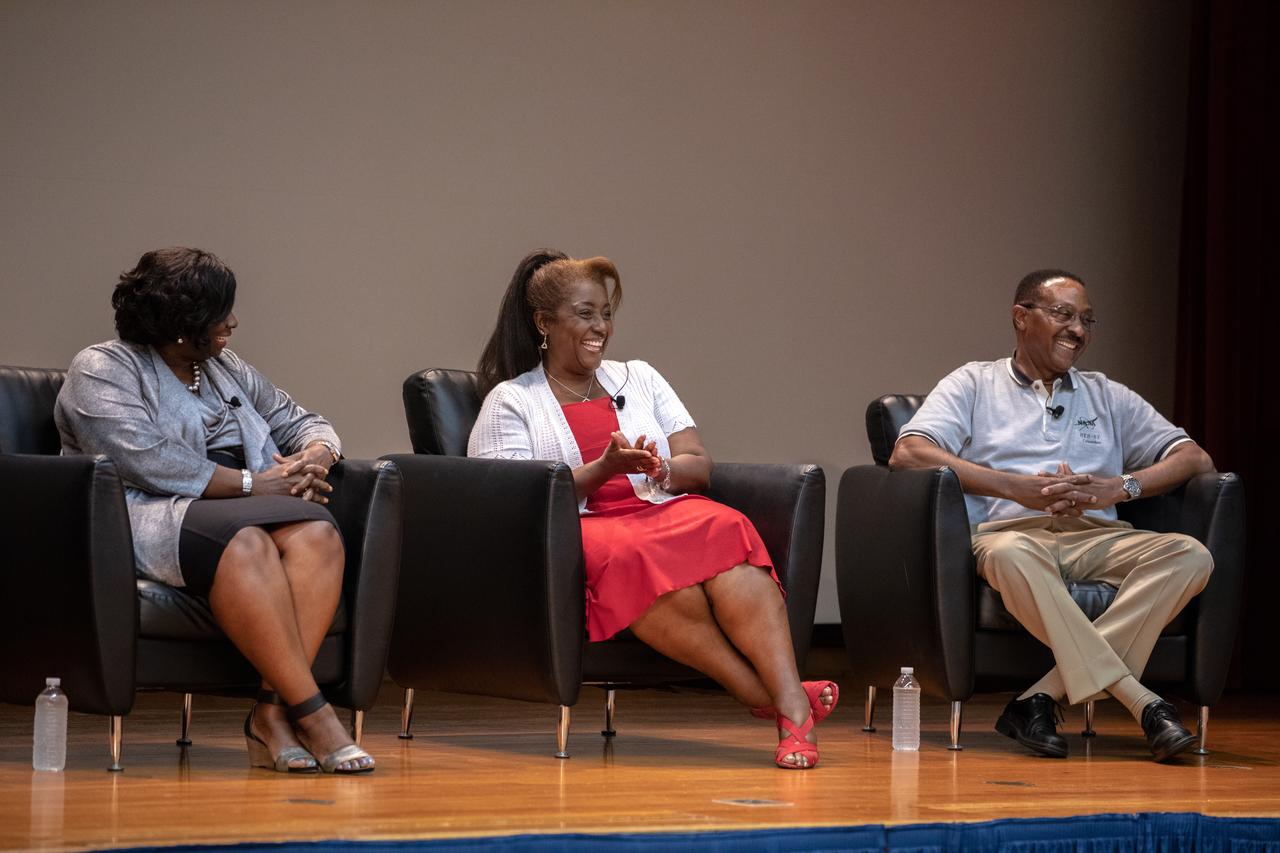

From left, Exploration Ground Systems Associate Manager, Technical, Kim Carter; NASA Kennedy Space Center Chief Technologist Barbara Brown; and former astronaut Winston Scott participate in a panel discussion on Aug. 28, 2019. Hosted at the Florida spaceport by national radio host Tom Joyner, the discussion focused on the agency’s Moon to Mars plans and was open to all Kennedy employees to attend. An additional participant included former NASA administrator and astronaut Charlie Bolden.
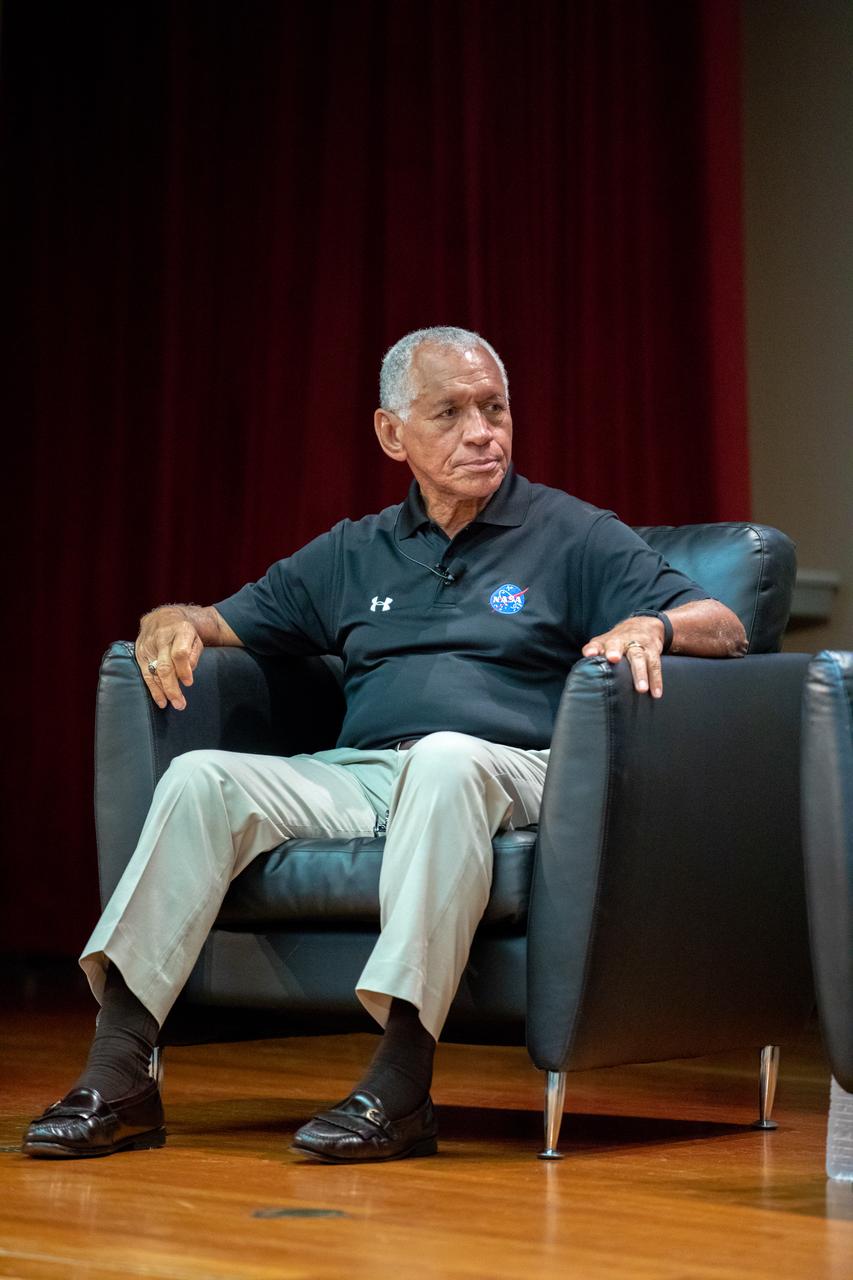

Former NASA administrator and astronaut Charlie Bolden participates in a panel discussion at Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 28, 2019. Hosted by national radio host Tom Joyner, the discussion focused on the agency’s Moon to Mars plans and was open for all Kennedy employees to attend. Additional participants included former astronaut Winston Scott, Kennedy Chief Technologist Barbara Brown and Exploration Ground Systems Associate Manager, Technical, Kim Carter.
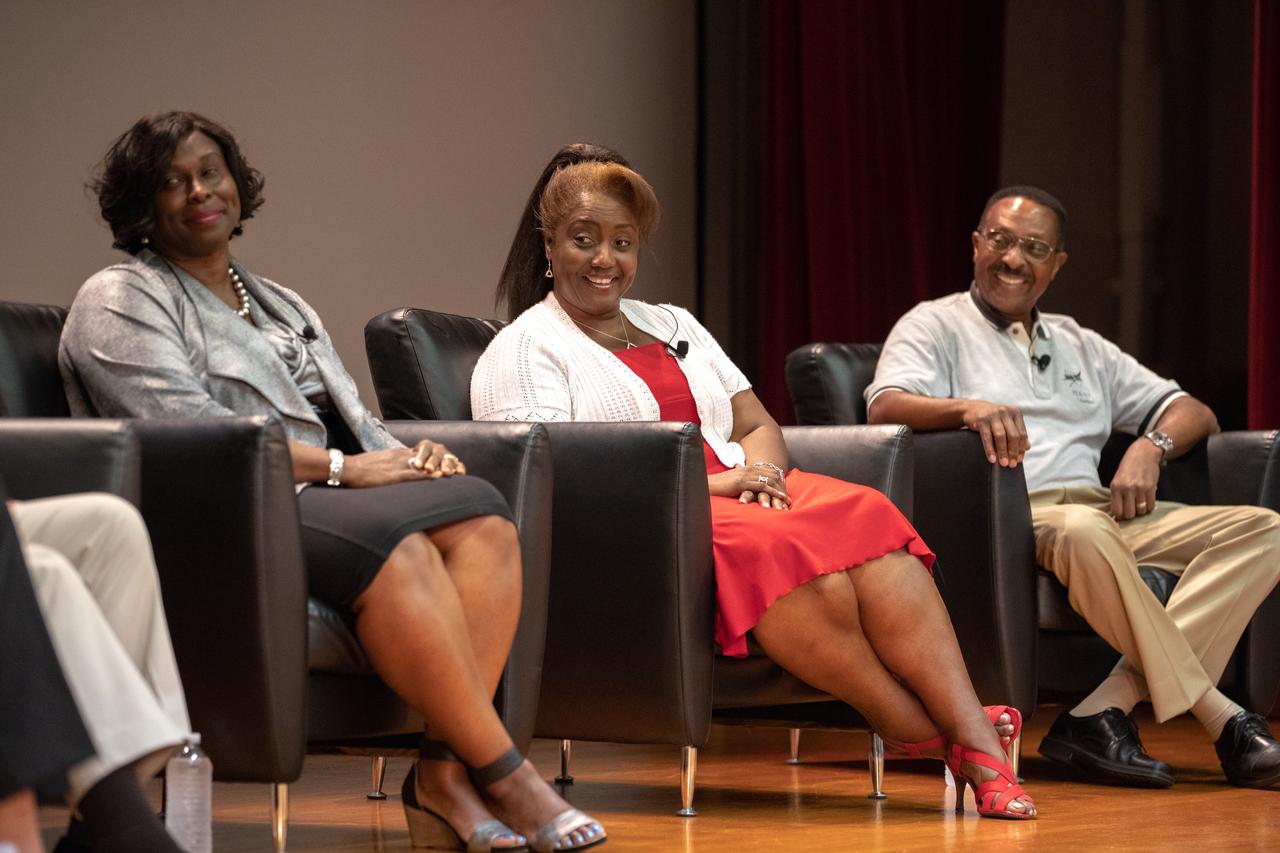

From left, Exploration Ground Systems Associate Manager, Technical, Kim Carter; NASA Kennedy Space Center Chief Technologist Barbara Brown; and former astronaut Winston Scott participate in a panel discussion on Aug. 28, 2019. Hosted by national radio host Tom Joyner at the Florida spaceport, the discussion focused on the agency’s Moon to Mars plans and was open to all Kennedy employees to attend. An additional participant included former NASA administrator and astronaut Charlie Bolden.
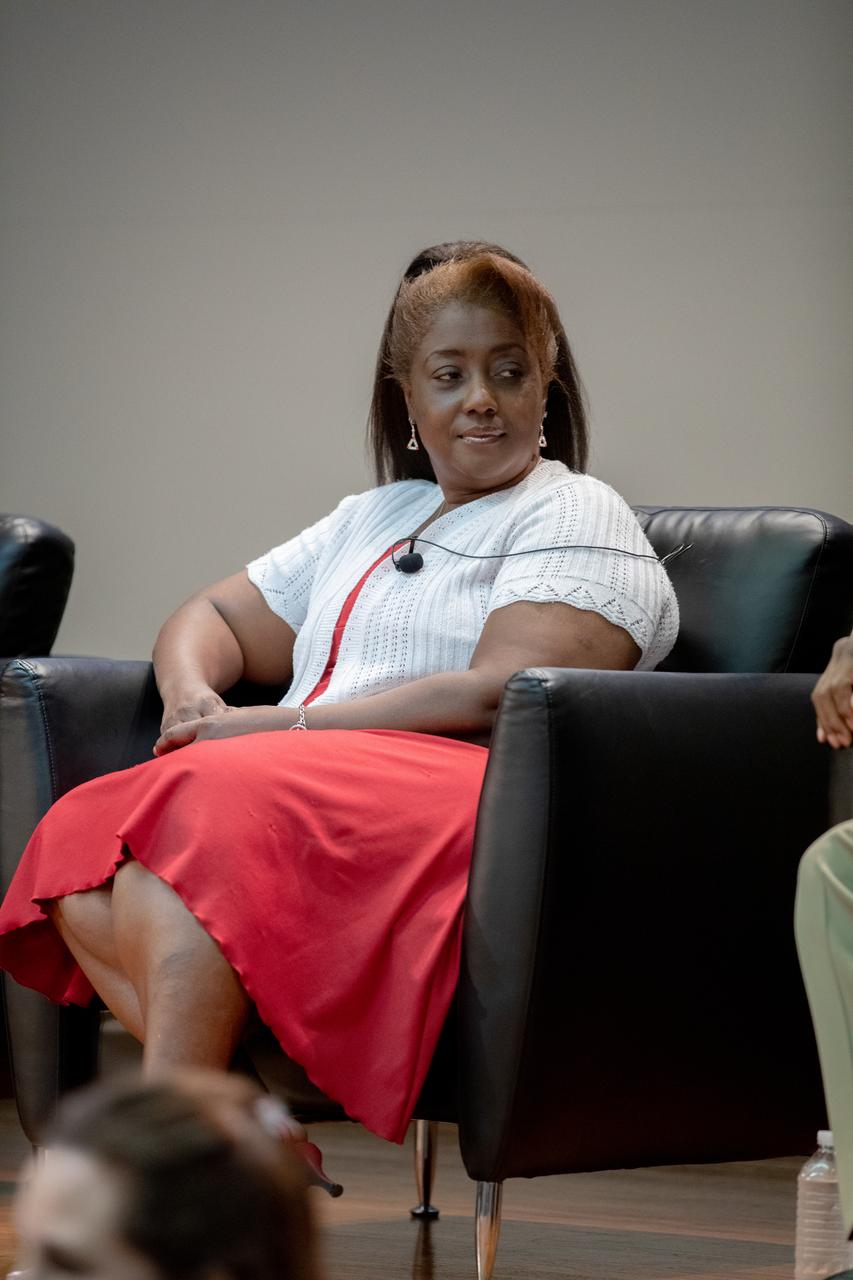

Barbara Brown, NASA Kennedy Space Center’s chief technologist, participates in a panel discussion at the Florida spaceport on Aug. 28, 2019. Hosted by National radio host Tom Joyner, the discussion focused on the agency’s Moon to Mars plans and was open for all Kennedy employees to attend. Additional participants included former NASA administrator and astronaut Charlie Bolden, former astronaut Winston Scott and Exploration Ground Systems Associate Manager, Technical, Kim Carter.
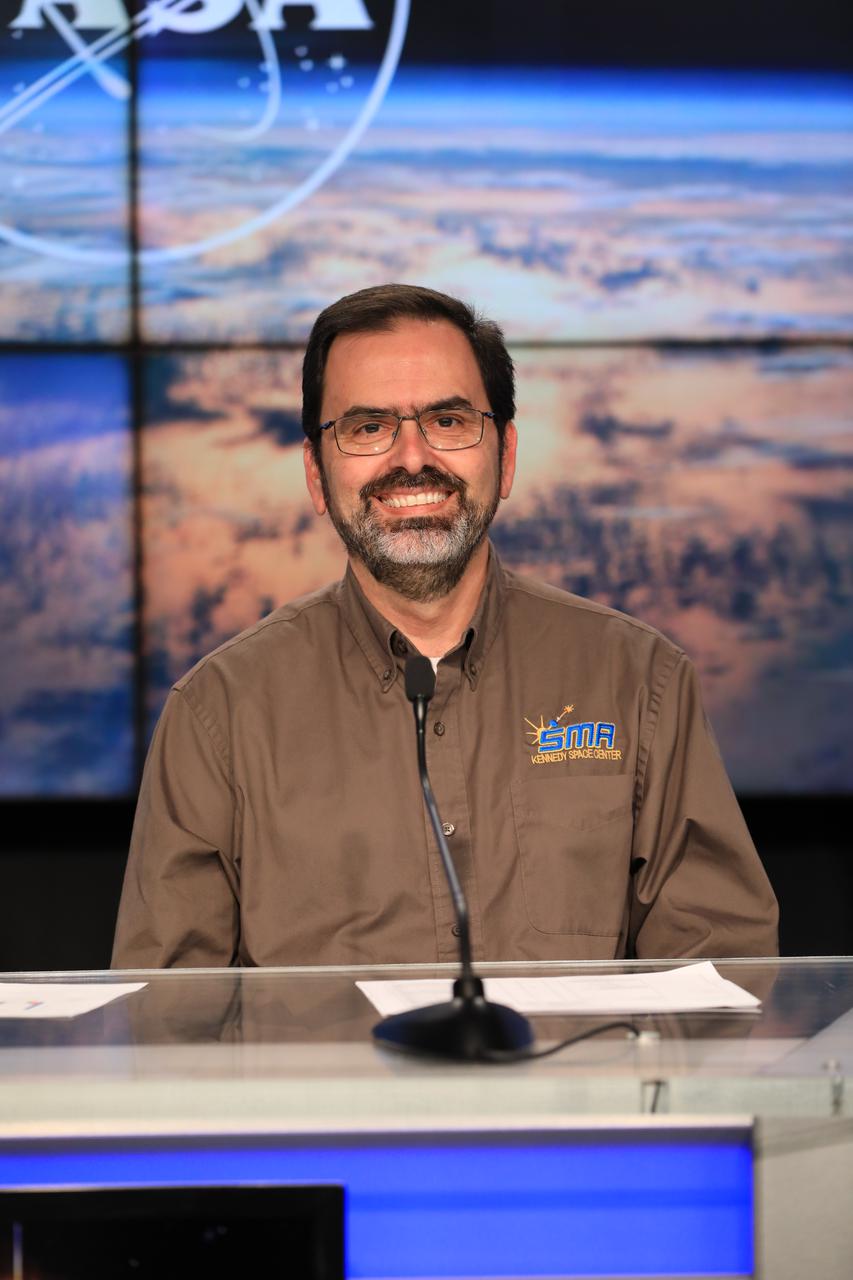

Director of Safety and Mission Assurance Ronnie Rodriguez participates in the Safety Starts With You Leadership Panel on Jan. 25, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panel discussion featured senior leaders from the spaceport addressing ways employees can focus on safely completing mission objectives in the new year. Other panelists included Kennedy Space Center Director Janet Petro, Director of Spaceport Integration and Services Nancy Bray, and Exploration Ground Systems Chief of Staff Sasha Sims.
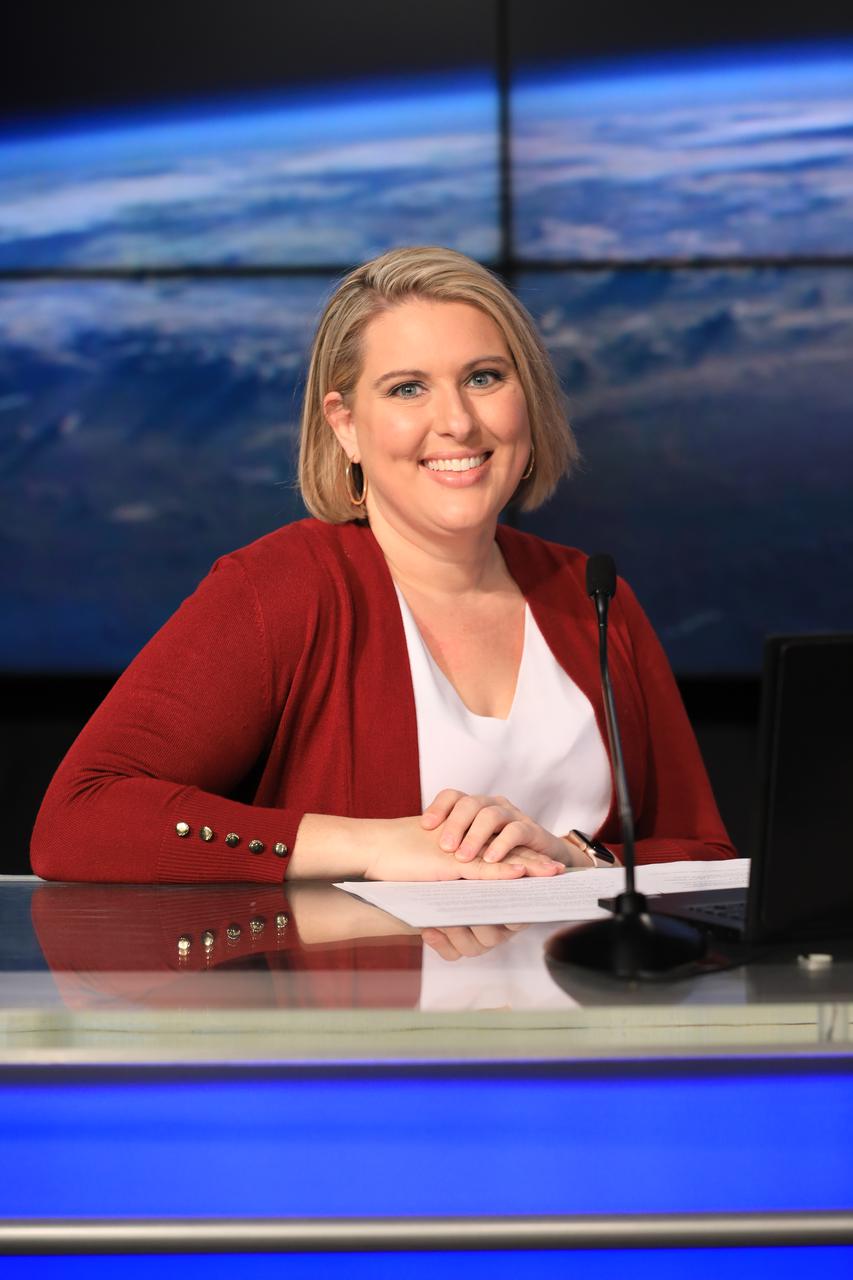

Leah Martin, NASA Communications, moderates the Safety Starts With You Leadership Panel on Jan. 25, 2022, at Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panel discussion featured senior leaders from the spaceport addressing ways employees can focus on safely completing mission objectives in the new year. Panelists included Kennedy Space Center Director Janet Petro, Director of Safety and Mission Assurance Ronnie Rodriguez, Director of Spaceport Integration and Services Nancy Bray, and Exploration Ground Systems Chief of Staff Sasha Sims.
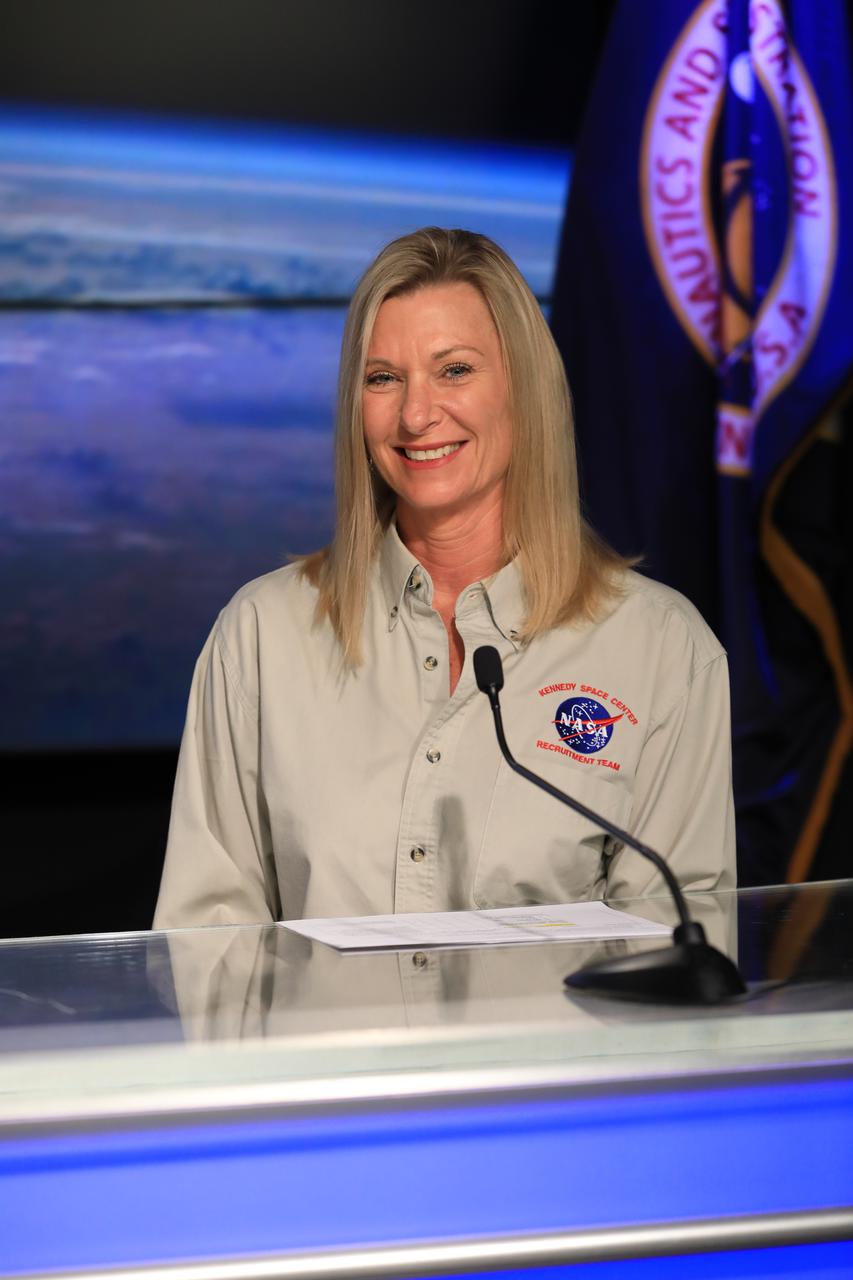

Director of Spaceport Integration and Services Nancy Bray participates in the Safety Starts With You Leadership Panel on Jan. 25, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panel discussion featured senior leaders from the spaceport addressing ways employees can focus on safely completing mission objectives in the new year. Other panelists included Kennedy Space Center Director Janet Petro, Director of KSC Safety and Mission Assurance Ronnie Rodriguez, and Exploration Ground Systems Chief of Staff Sasha Sims.
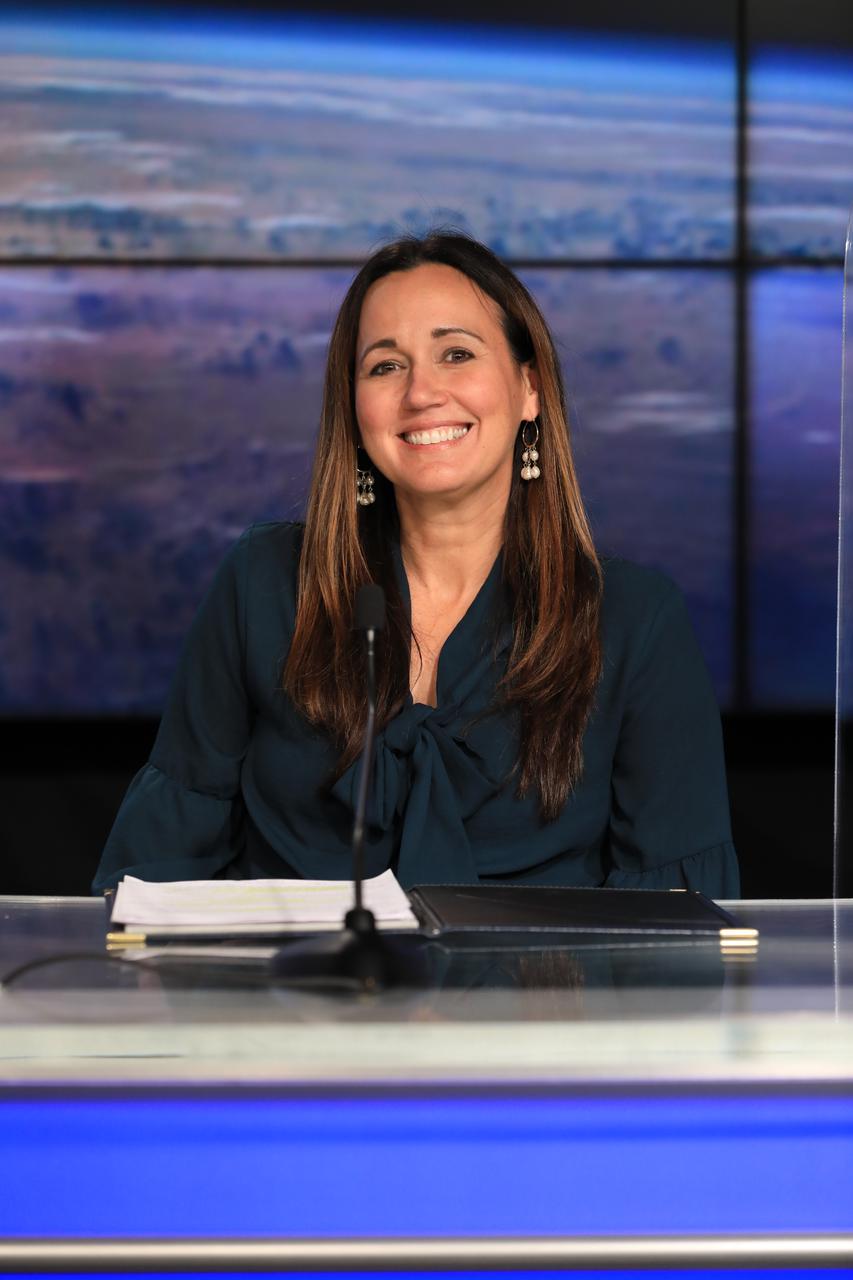

Exploration Ground Systems Chief of Staff Sasha Sims participates in the Safety Starts With You Leadership Panel on Jan. 25, 2022, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The panel discussion featured senior leaders from the spaceport addressing ways employees can focus on safely completing mission objectives in the new year. Other panelists included Kennedy Space Center Director Janet Petro, Director of Safety and Mission Assurance Ronnie Rodriguez, and Director of Spaceport Integration and Services Nancy Bray.
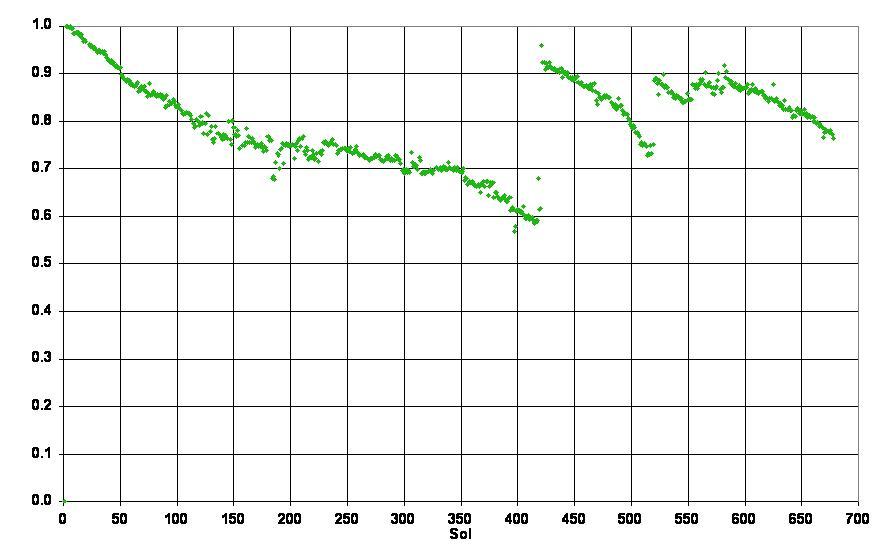
Solar-Panel Dust Accumulation and Cleanings
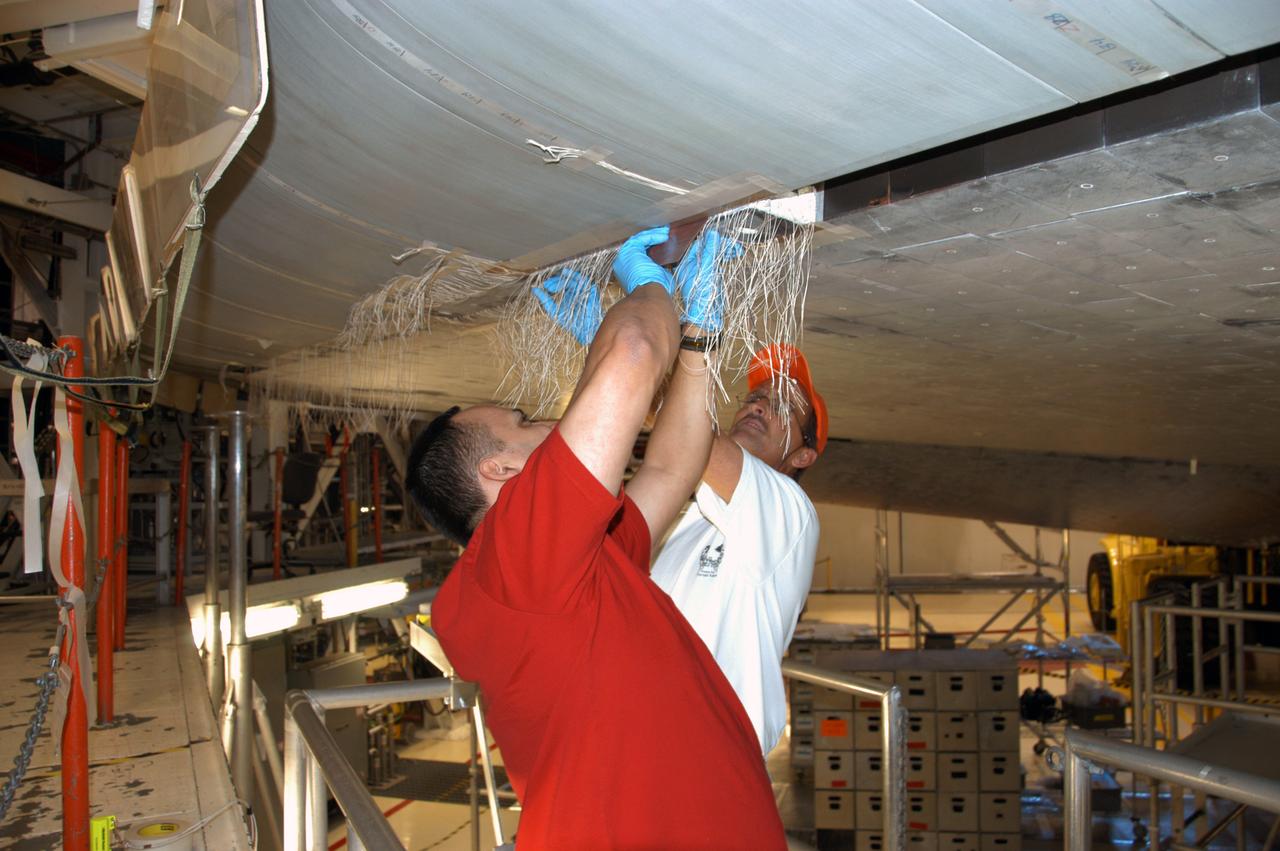

In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, technicians Jesus Rodrigues (left) and James Johnson install a leading edge subsystem carrier panel on the right wing of Endeavour. The orbiter is scheduled for mission STS-118, targeted for launch on June 28. The mission will be the 22nd flight to the International Space Station, carrying another starboard array, S5, for installation.
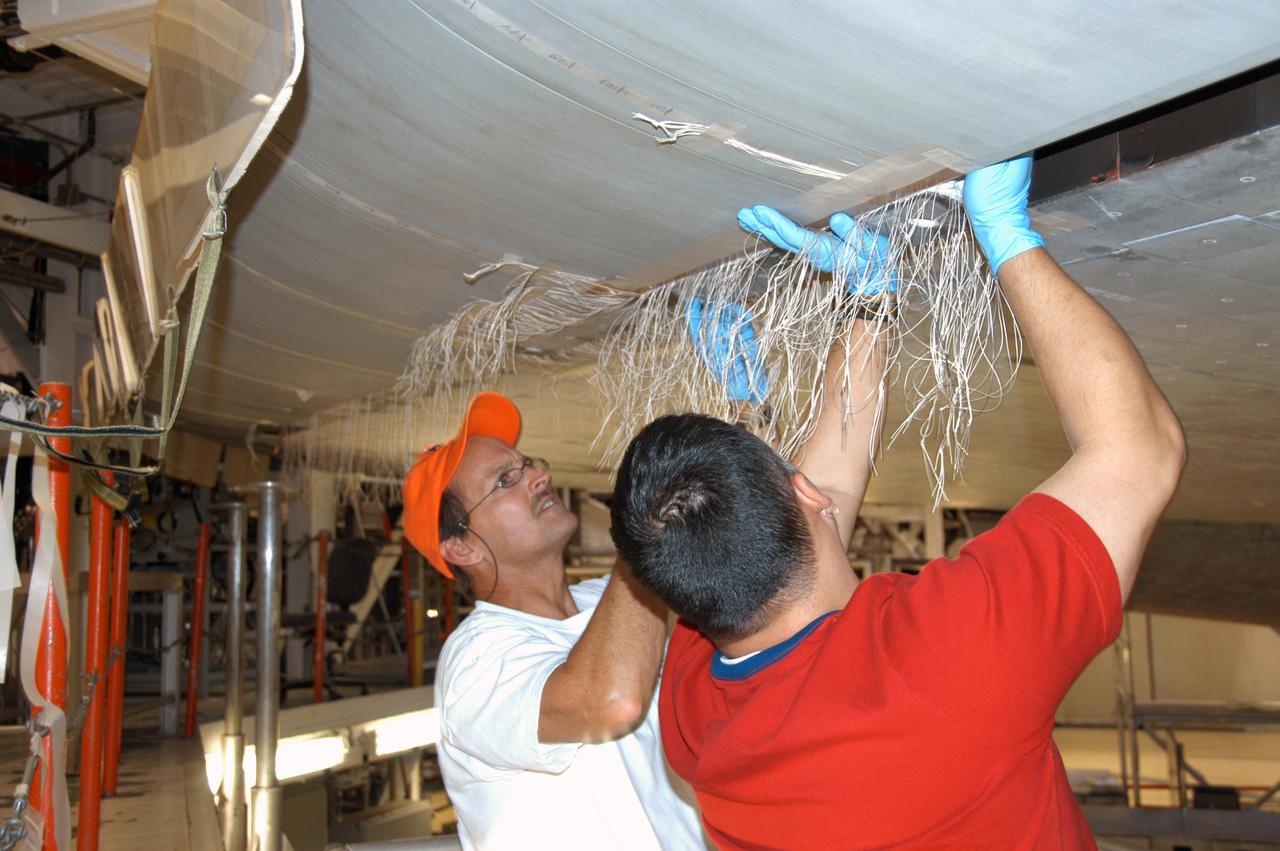

In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, technicians James Johnson (left) and Jesus Rodrigues install a leading edge subsystem carrier panel on the right wing of Endeavour. The orbiter is scheduled for mission STS-118, targeted for launch on June 28. The mission will be the 22nd flight to the International Space Station, carrying another starboard array, S5, for installation.
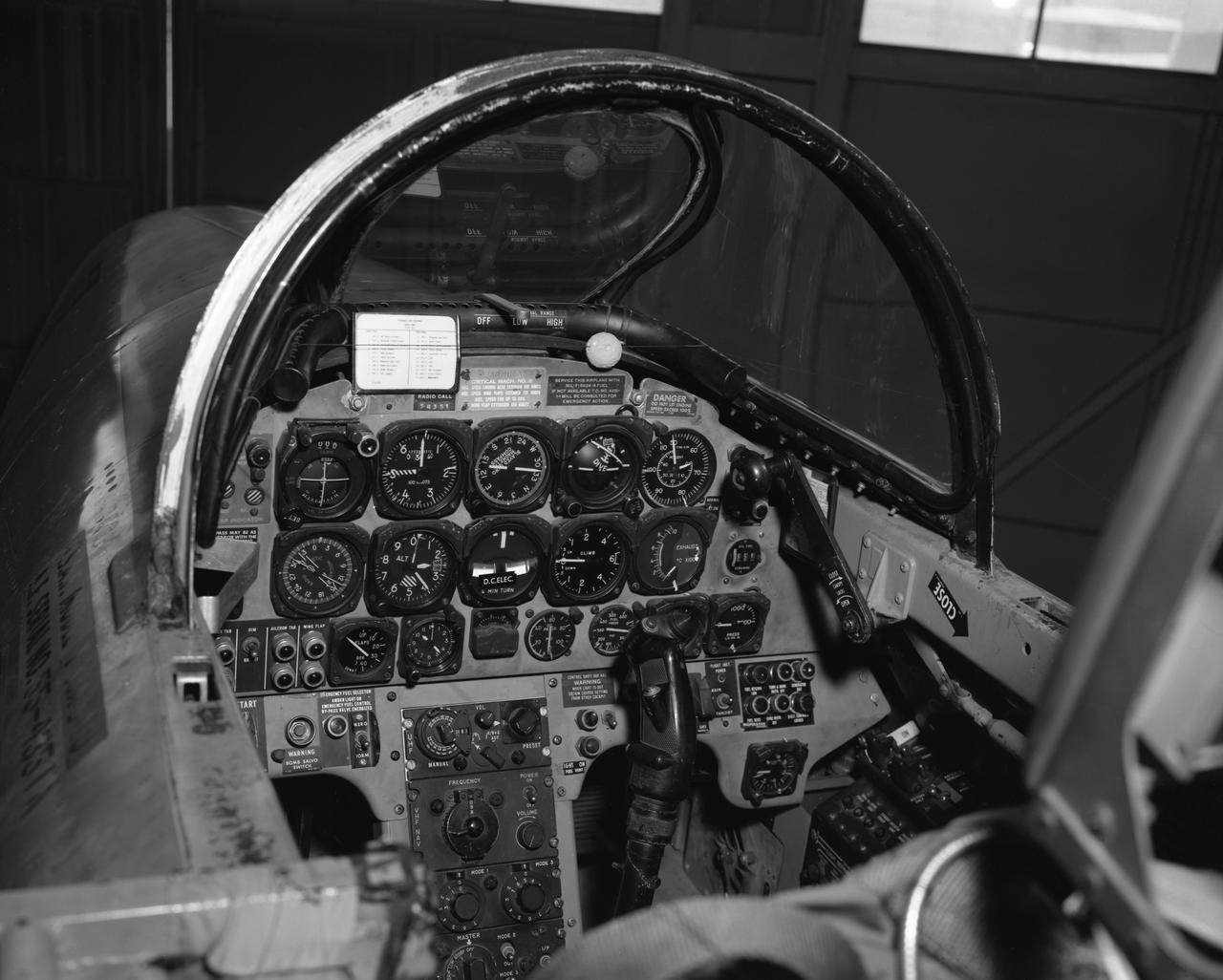

T-33 #351 Cockpit control panel. Feb. 13, 1964

James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) Town Hall - Panel question and answer -
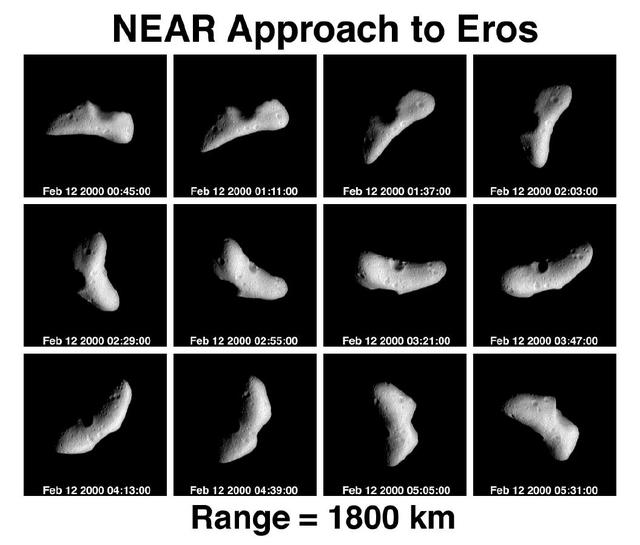
NEAR Approach to Eros - 12 Panel Rotation Sequence

Solar Panel Buffeted by Wind at Phoenix Site

Very Dusty Solar Panel on Spirit, Sol 1811
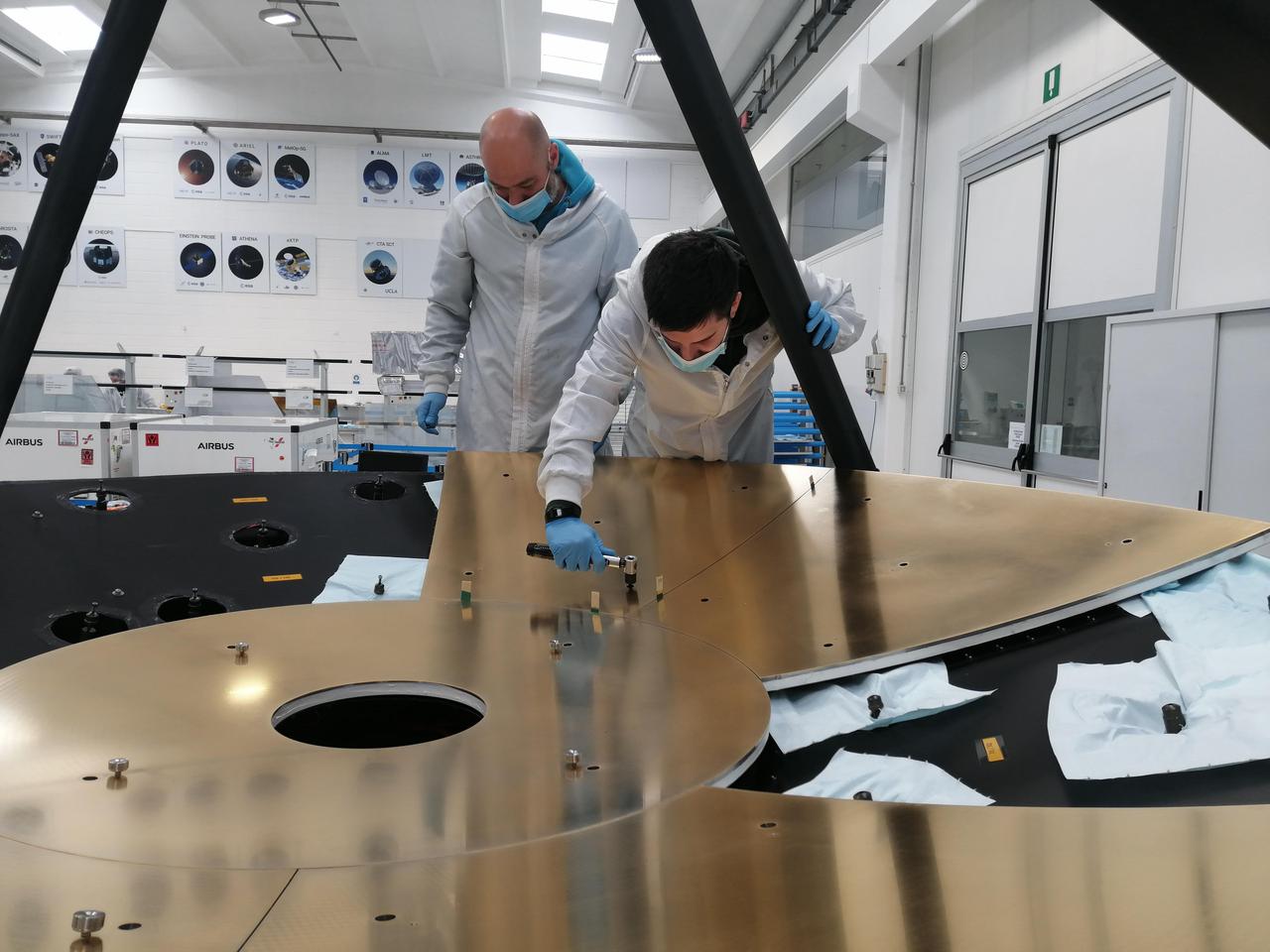

The mirror on NASA's Astrophysics Stratospheric Telescope for High Spectral Resolution Observations at Submillimeter-wavelengths mission, or ASTHROS, is composed of nine panels, coated in nickel and gold. Here, engineers attach panels to the mirror's support structure. The panels must be aligned to within 0.0001 inches (2.5 micrometers), or a fraction of the width of a human hair. Manufacturing multiple panels requires less time and expense than making the mirror as a single piece. NASA contracted Media Lario, an optics company in Bosisio Parini, Italy, to design and produce ASTHROS' full telescope unit, including the primary mirror, a secondary mirror, and supporting structure (called the cradle). The mirror is shown here at Media Lario. The mission's main science goal is to study stellar feedback, the process by which living stars disperse and reshape clouds of gas and dust that may eventually form new stars. Feedback regulates star formation in many galaxies, and too much can halt star formation entirely. ASTHROS will look at several star-forming regions in our galaxy where feedback takes place, and at distant galaxies containing millions of stars to see how feedback plays out at large scales and in different environments. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25167
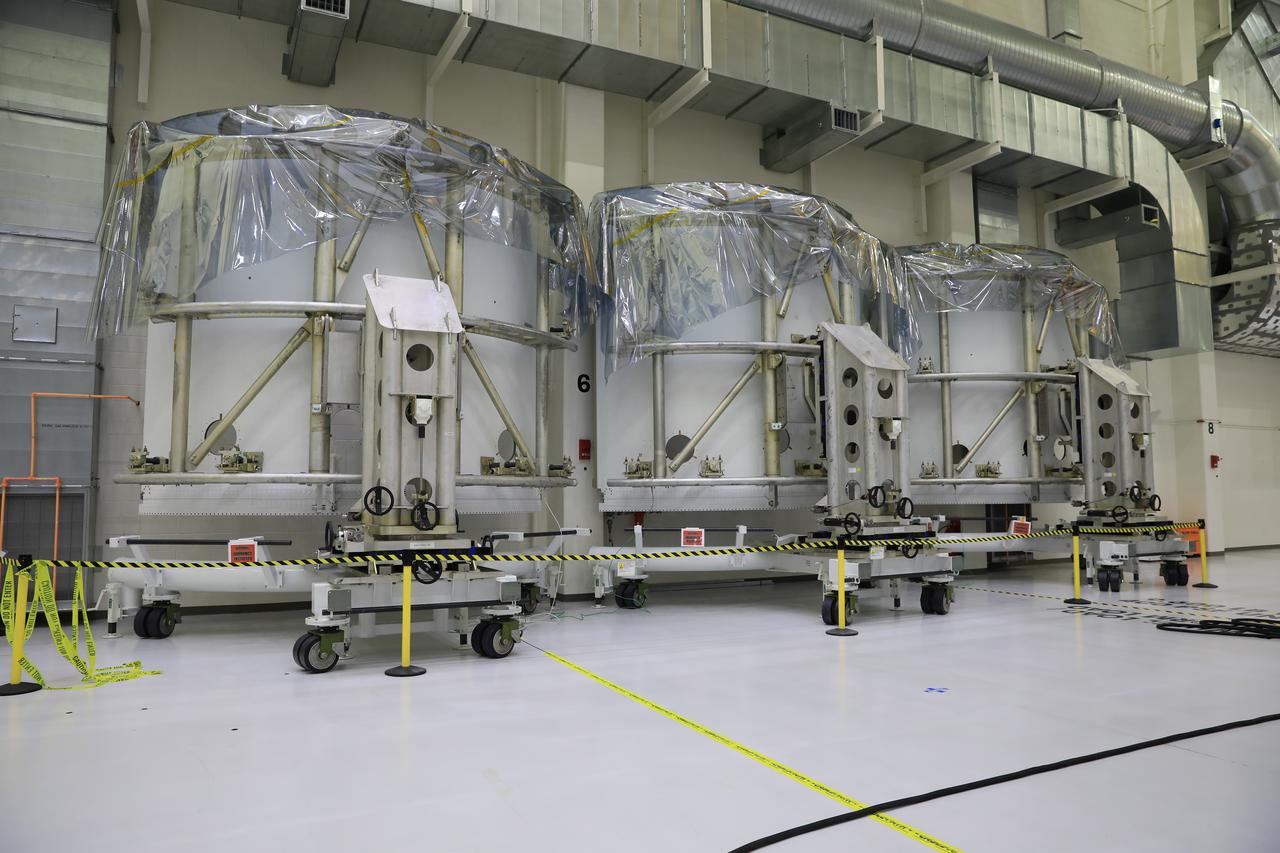

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
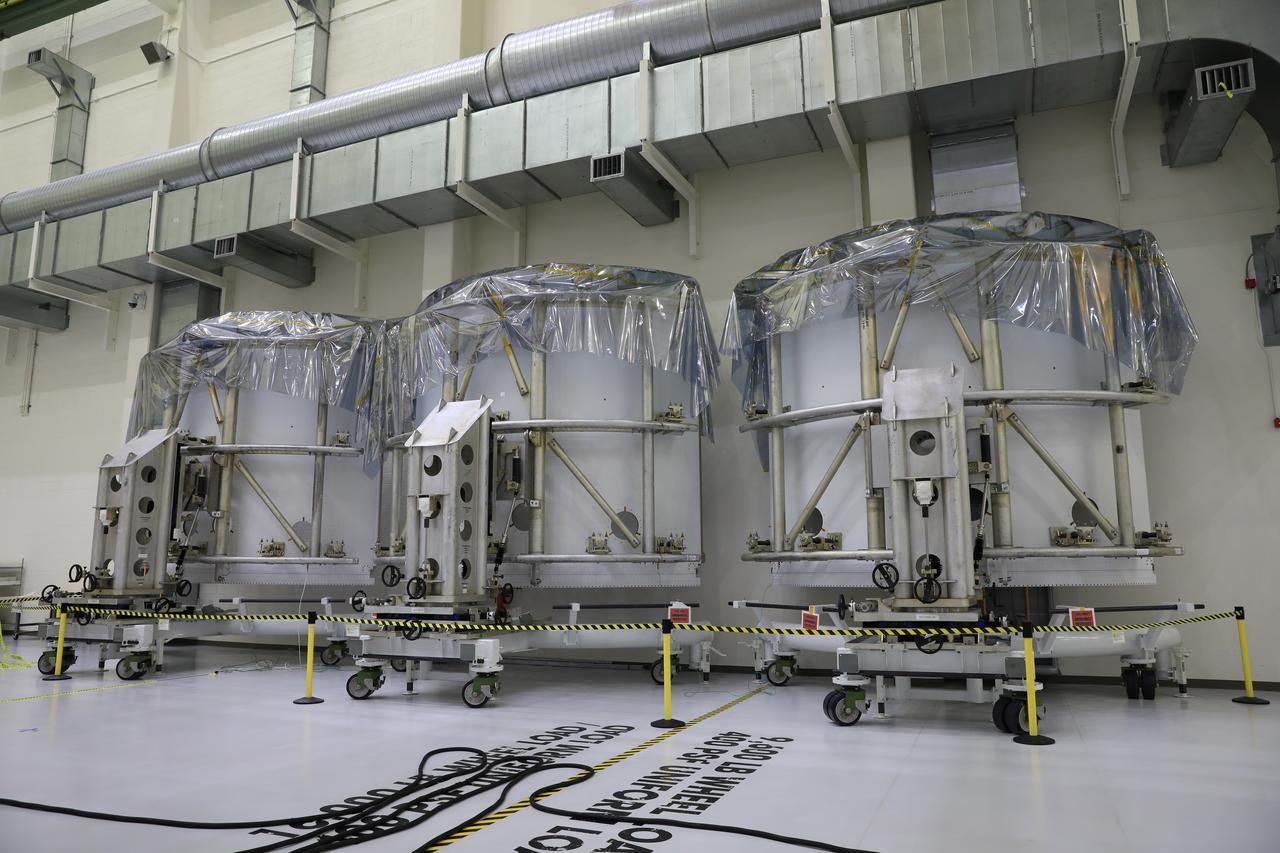

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
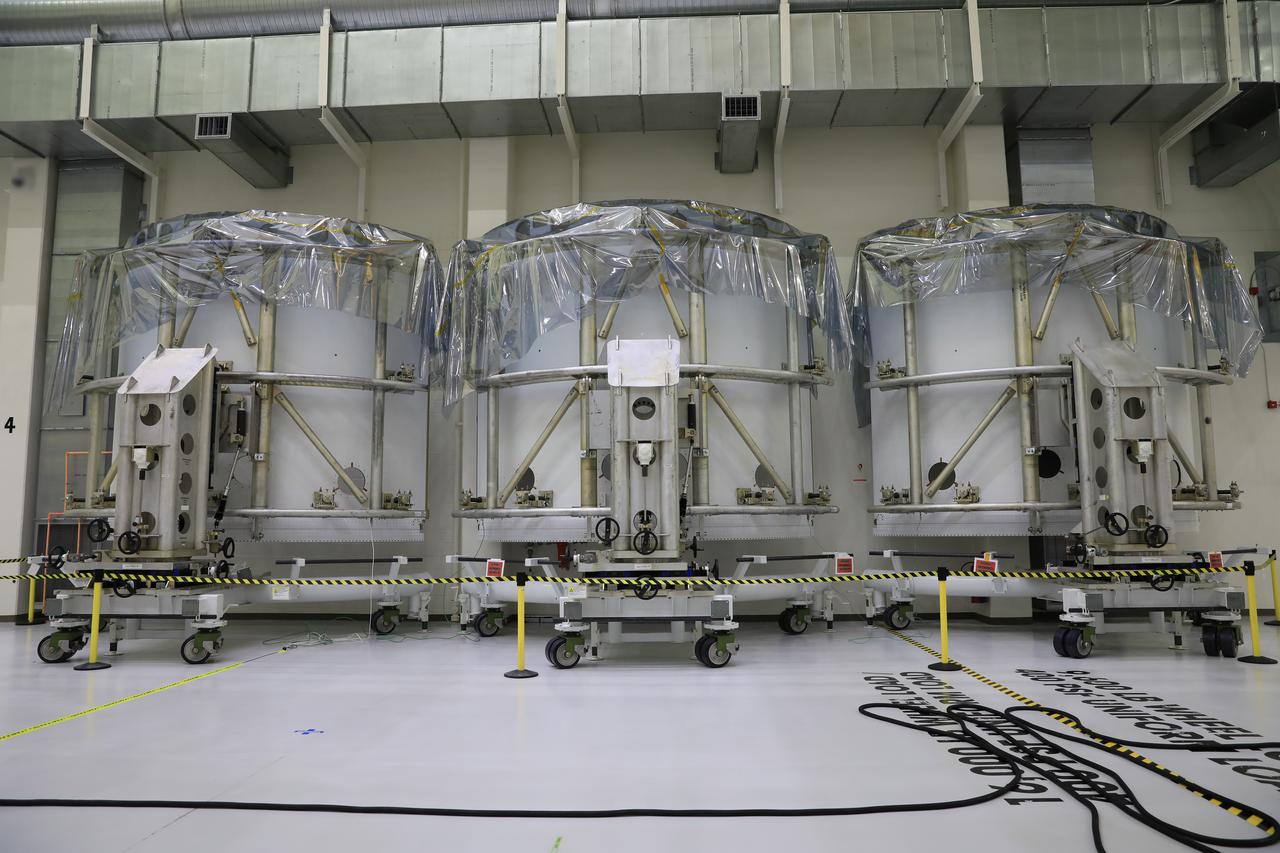

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
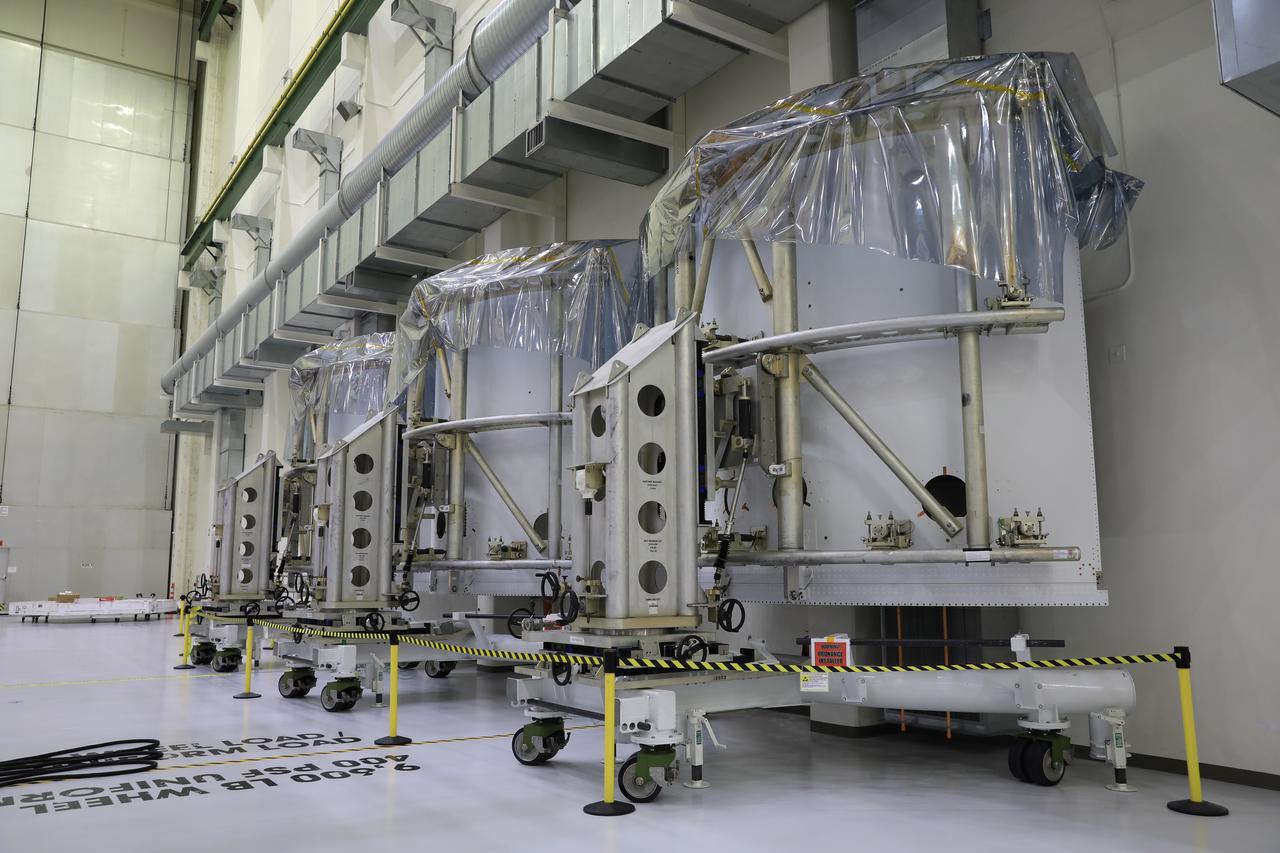

Pictured inside the Neil Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Aug. 6, 2020, are the three Spacecraft Adapter Jettison fairing panels that will protect Orion's service module from the environment around it, whether it's heat, wind or acoustics during the ascent. Unlike conventional rocket fairings, Orion's are designed to support half of the weight of the crew module and launch abort system during launch and ascent, which will maximize the size and capability of the spacecraft that can be delivered to orbit. Orion will fly on the agency’s Artemis I mission – the first in a series of increasingly complex missions to the Moon that will ultimately lead to the exploration of Mars.
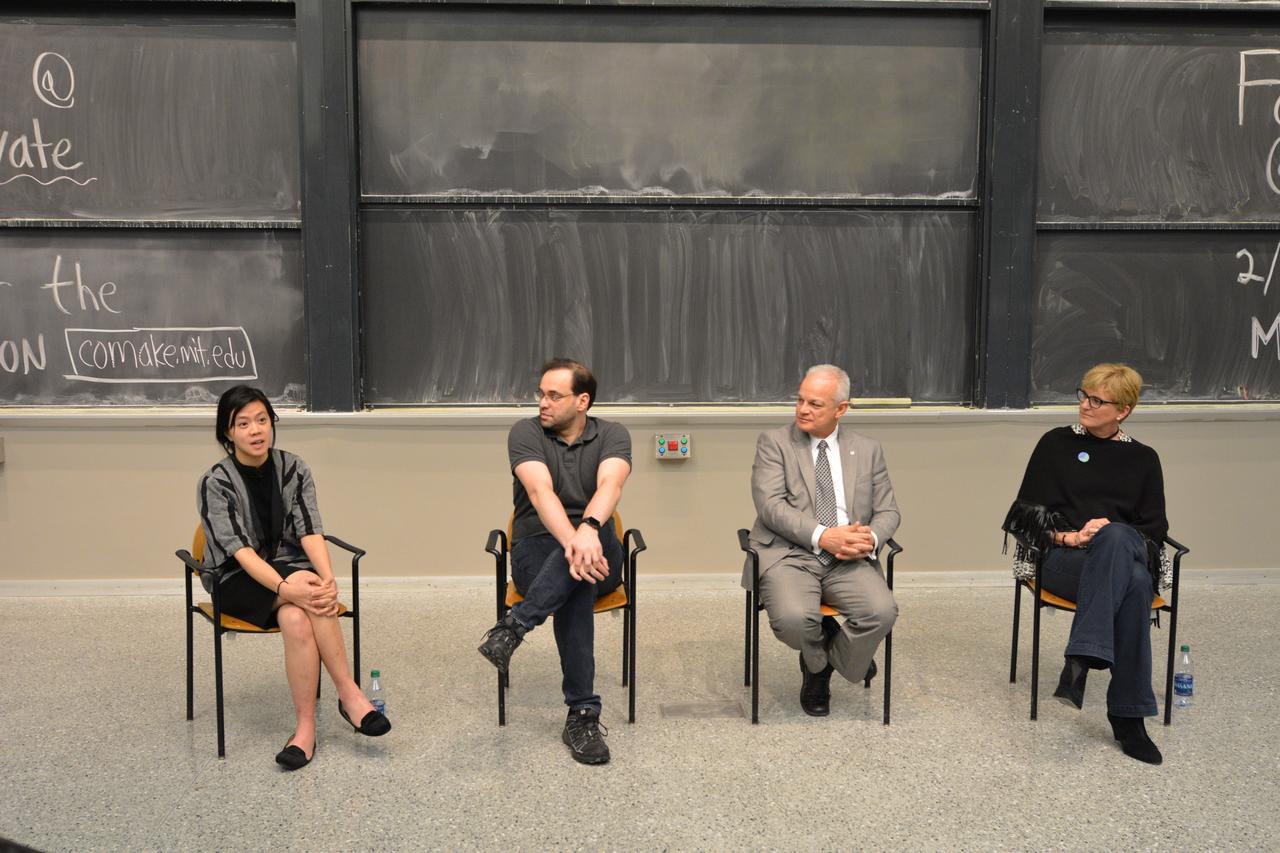

During MIT's "Better MIT Innovation Week 2018," a group of experts discussed innovation as a critical component to and professional accomplishment. From left: Rebecca Chui, founder, RootsStudio; Reinaldo Normand, entrepreneur in residence, MIT; Douglas Terrier, NASA chief technologist; Linda Foster, chief technologist, Lockheed Martin. (Photo: Damian Barabonkov/MIT Technique)
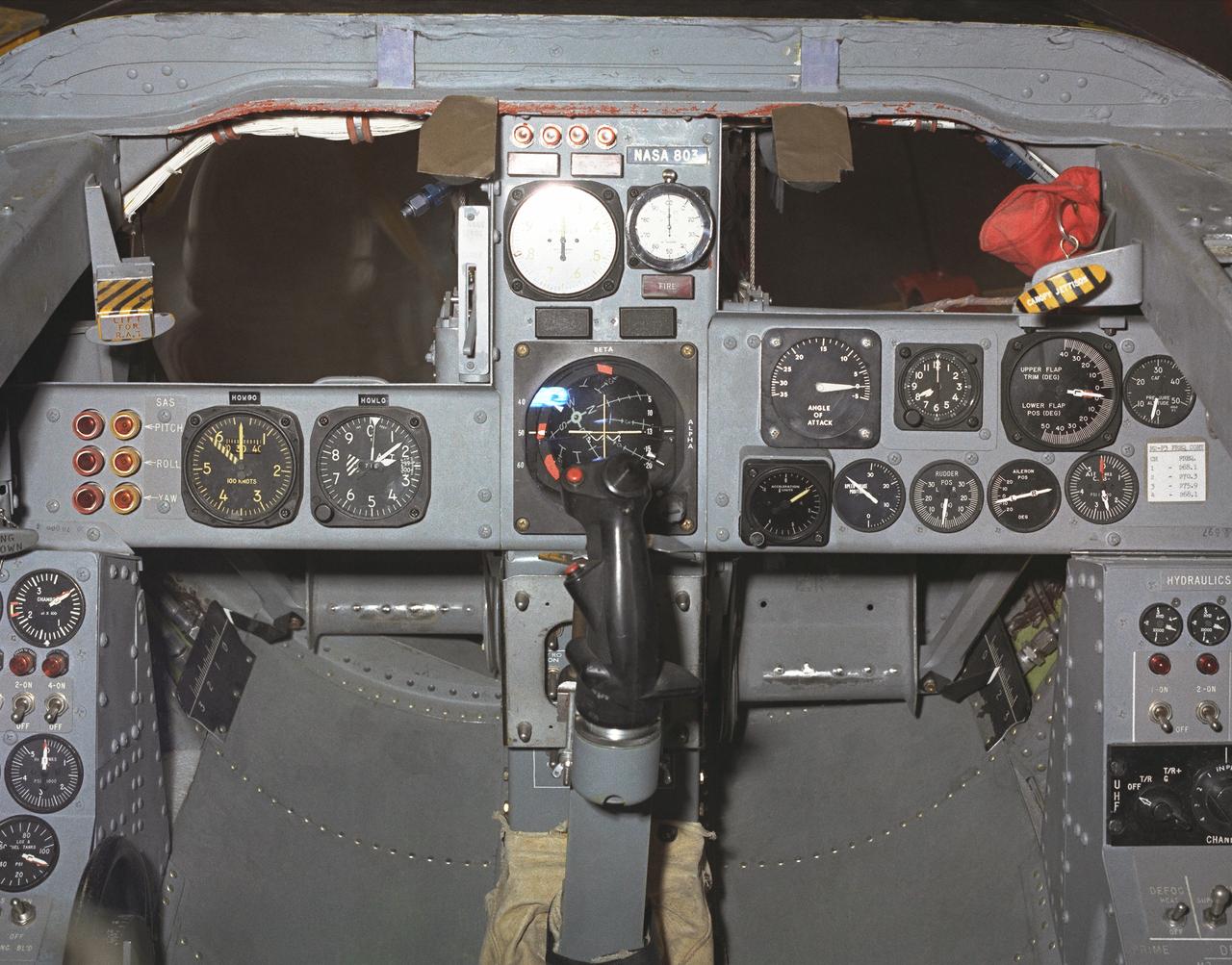

This photo shows the cockpit instrument panel of the M2-F3 Lifting Body.
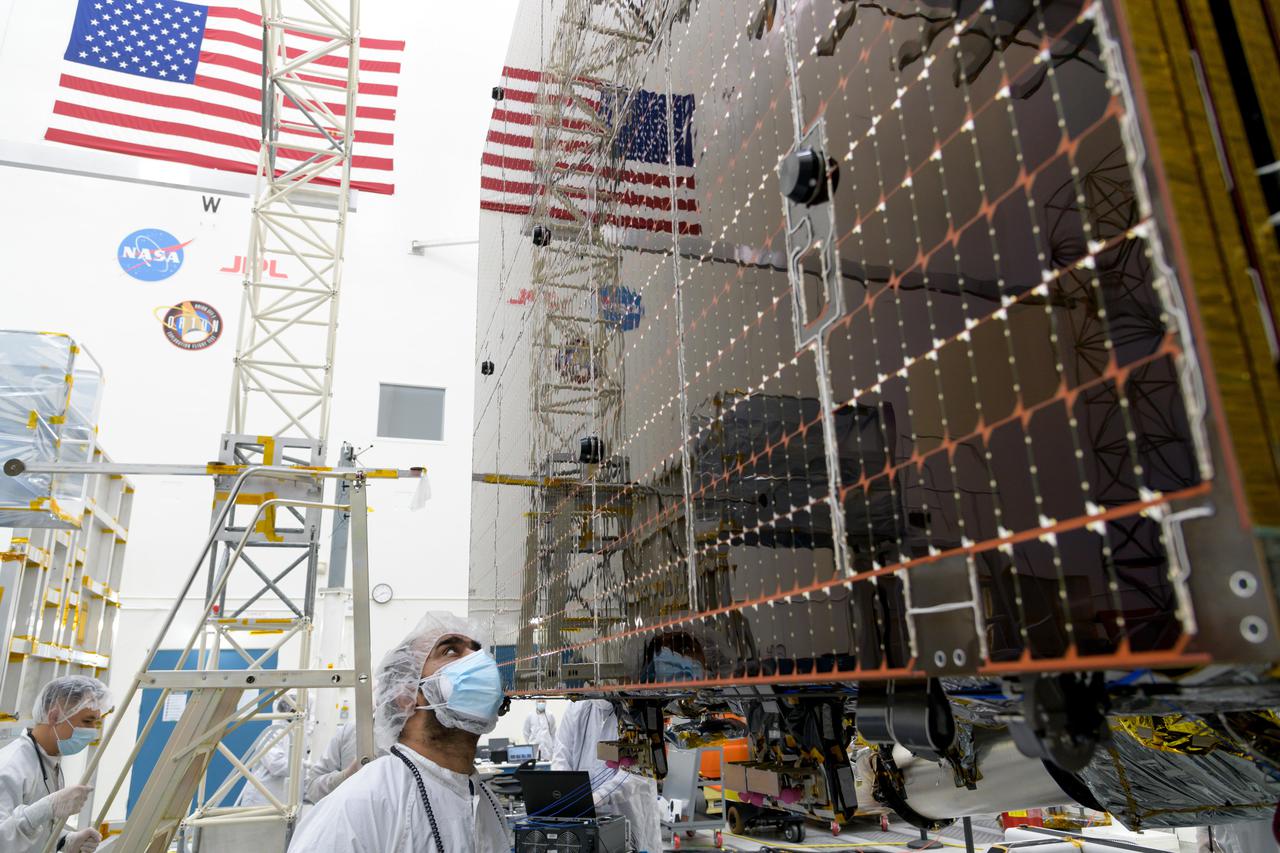

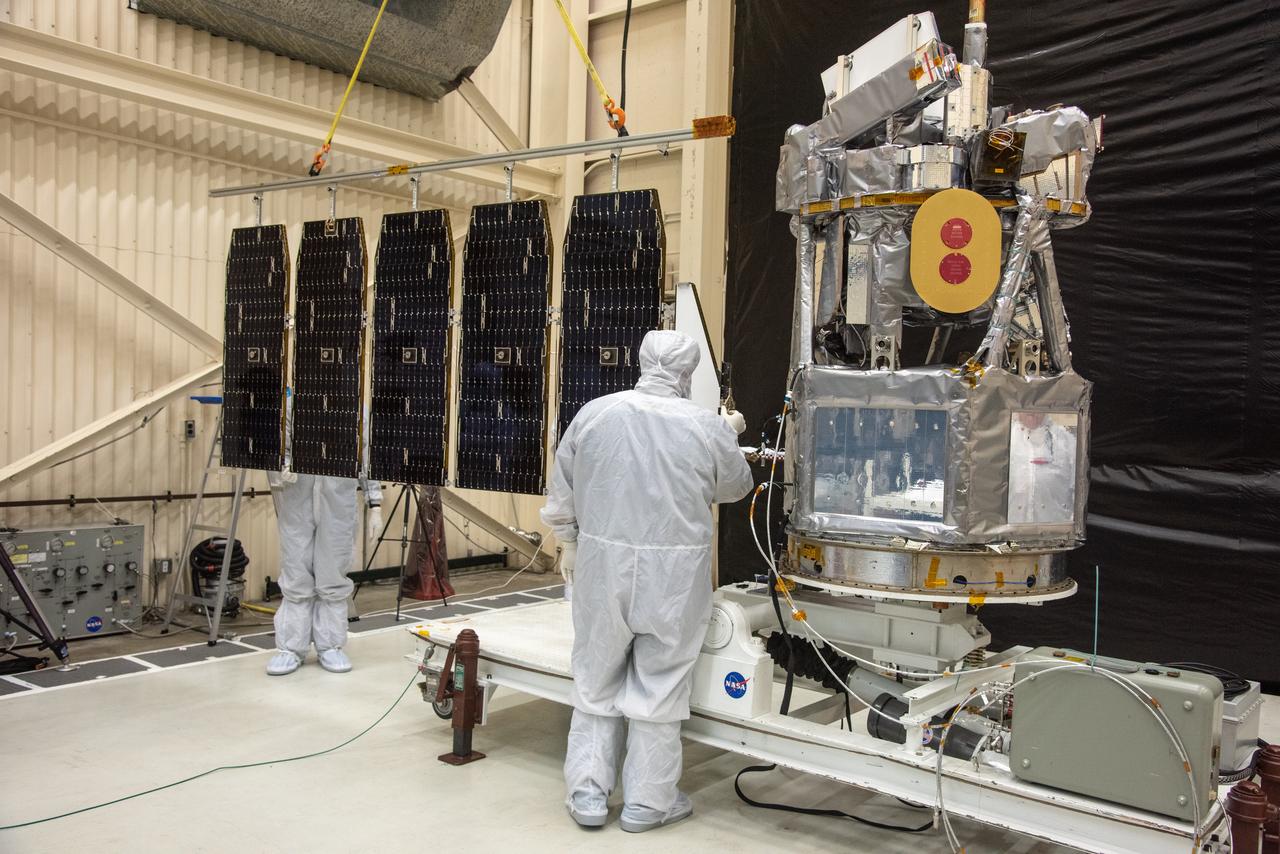
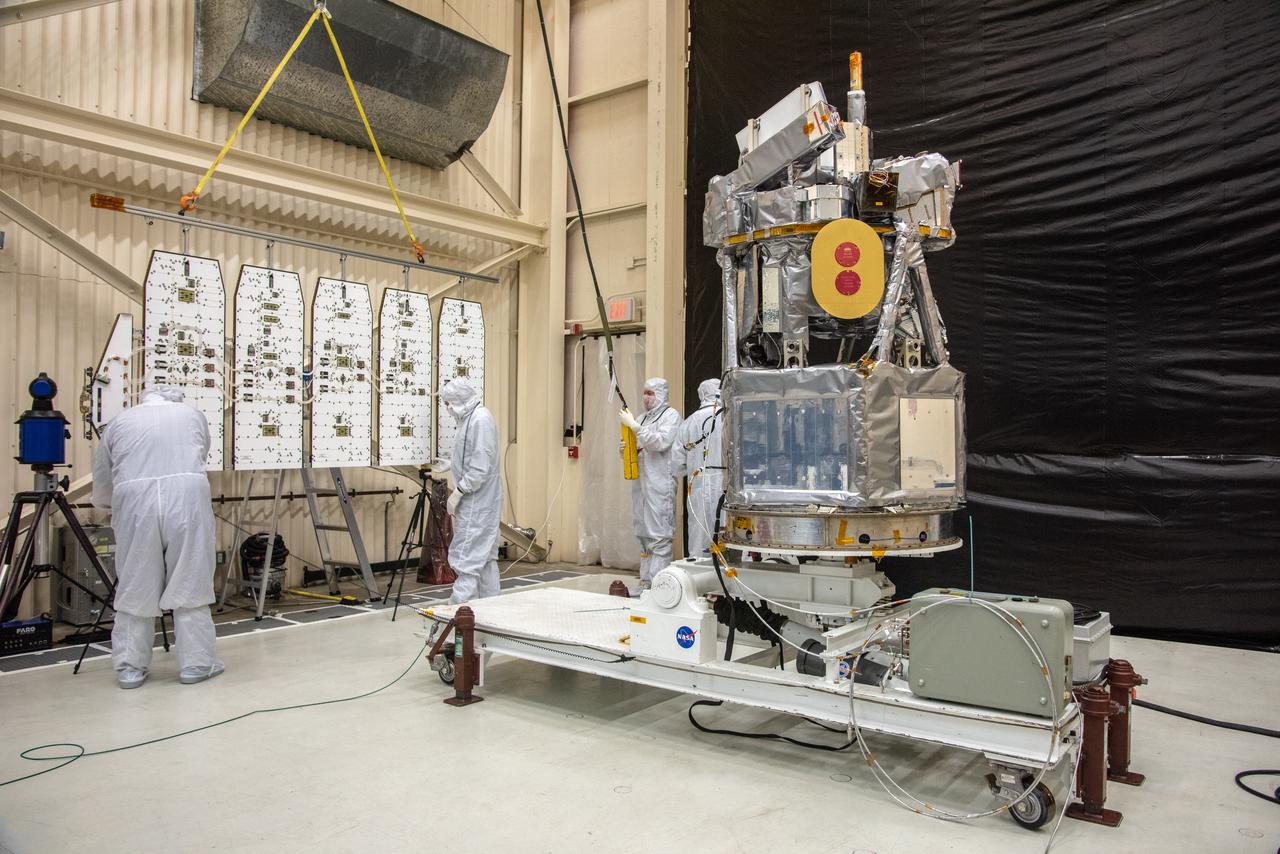
An engineer at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California examines a panel on Psyche's stowed solar arrays prior to a deployment test in the Lab's High Bay 2 clean room in February 2022. The twin arrays are together about 800 square feet (75 square meters) – the largest ever deployed at JPL. Part of a solar electric propulsion system provided by Maxar Technologies, they will power the spacecraft on its 1.5 billion-mile (2.4 billion-kilometer) journey to the large, metal-rich asteroid Psyche. Only the three center panels on each five-panel, cross-shaped array can be deployed at JPL due to the limitations of the gravity-offload fixture and the opposing direction of rotation of the cross panels. Deployment of the two cross panels was previously performed at Maxar with different equipment. After further spacecraft testing is completed at JPL, the arrays will be removed and returned to Maxar in order to repeat the cross-panel deployments, make any final repairs to the solar cells, and test overall performance. The arrays then get shipped from Maxar to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, where they will be reintegrated onto the spacecraft in preparation for launch in August 2022. About an hour after launch, Psyche will deploy the arrays sequentially, first unfolding the three lengthwise center panels, then the two cross panels on one wing before repeating the process with the other wing. Each array takes about 7 ½ minutes to unfurl and latch into place. Each array is 37.1 feet (11.3 meters) long and 24 feet (7.3 meters) wide when fully deployed. With arrays deployed on either side of the chassis, the spacecraft is about the size of a singles tennis court: 81 feet long (24.7 meters) and 24 feet (7.3 meters) wide. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25133
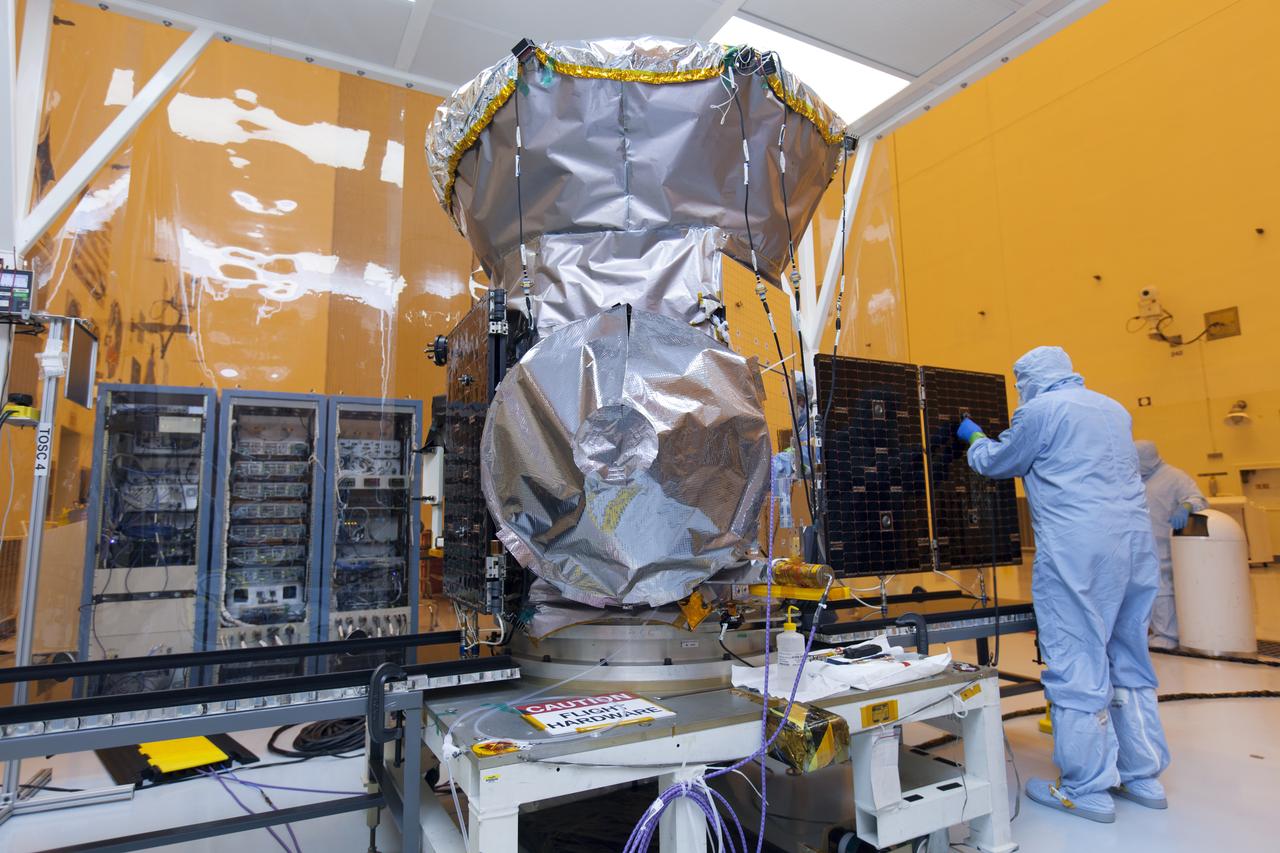

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the first of two solar panels is being deployed on the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. TESS is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
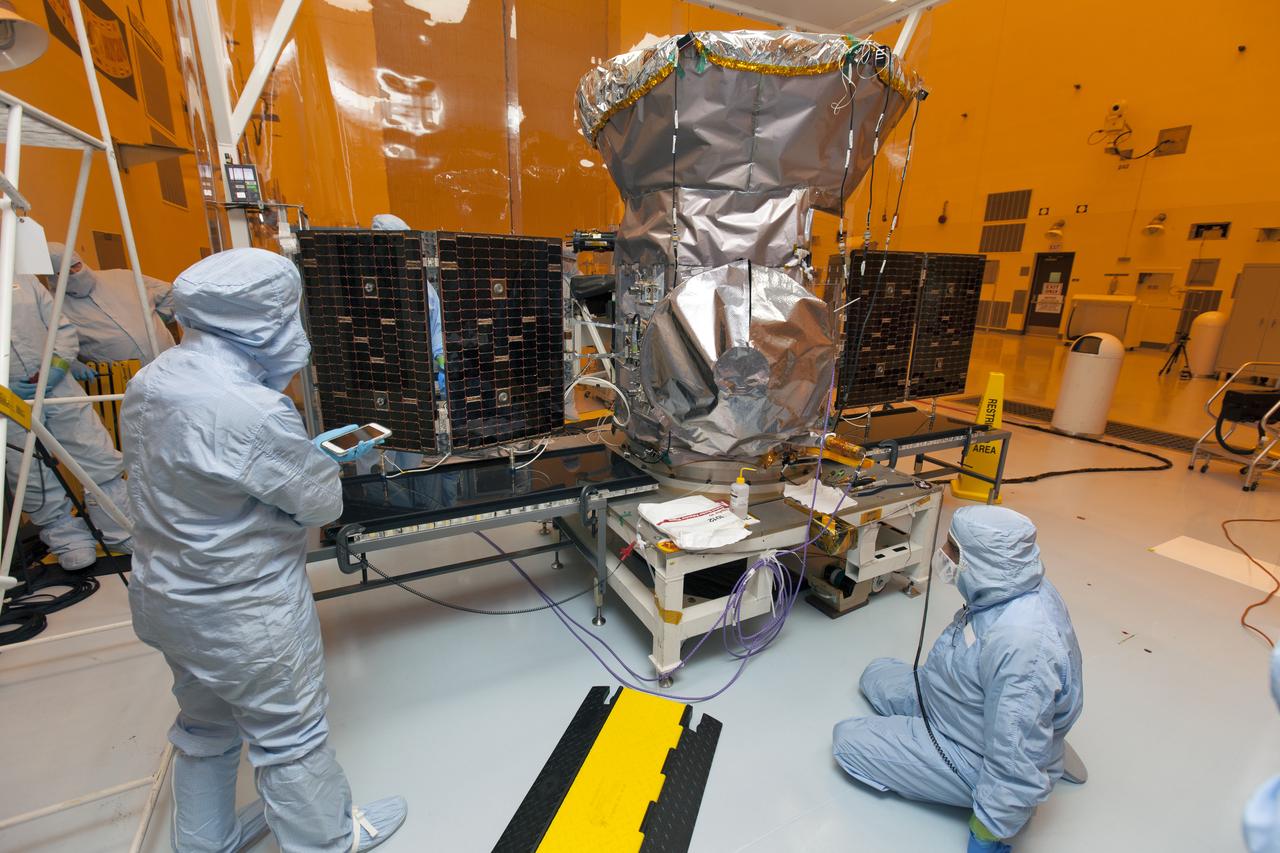

Technicians dressed in clean room suits monitor the progress as both solar panels are deployed on NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the PHSF, the satellite is being processed and prepared for its flight. TESS is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
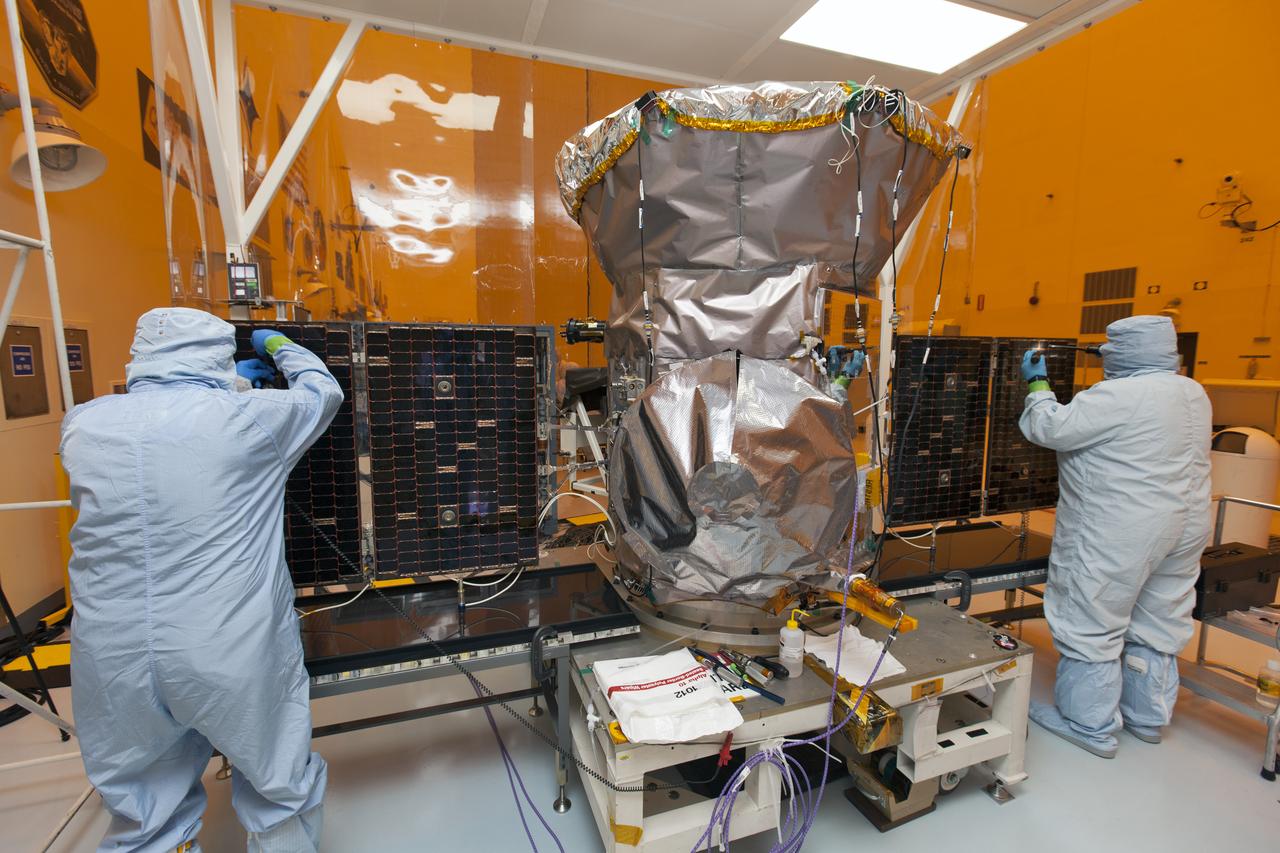

Technicians dressed in clean room suits check the solar panels, which have been deployed, on NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the PHSF, the satellite is being processed and prepared for its flight. TESS is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.

Technicians dressed in clean room suits monitor the progress as both solar panels are deployed on NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility (PHSF) at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Inside the PHSF, the satellite is being processed and prepared for its flight. TESS is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
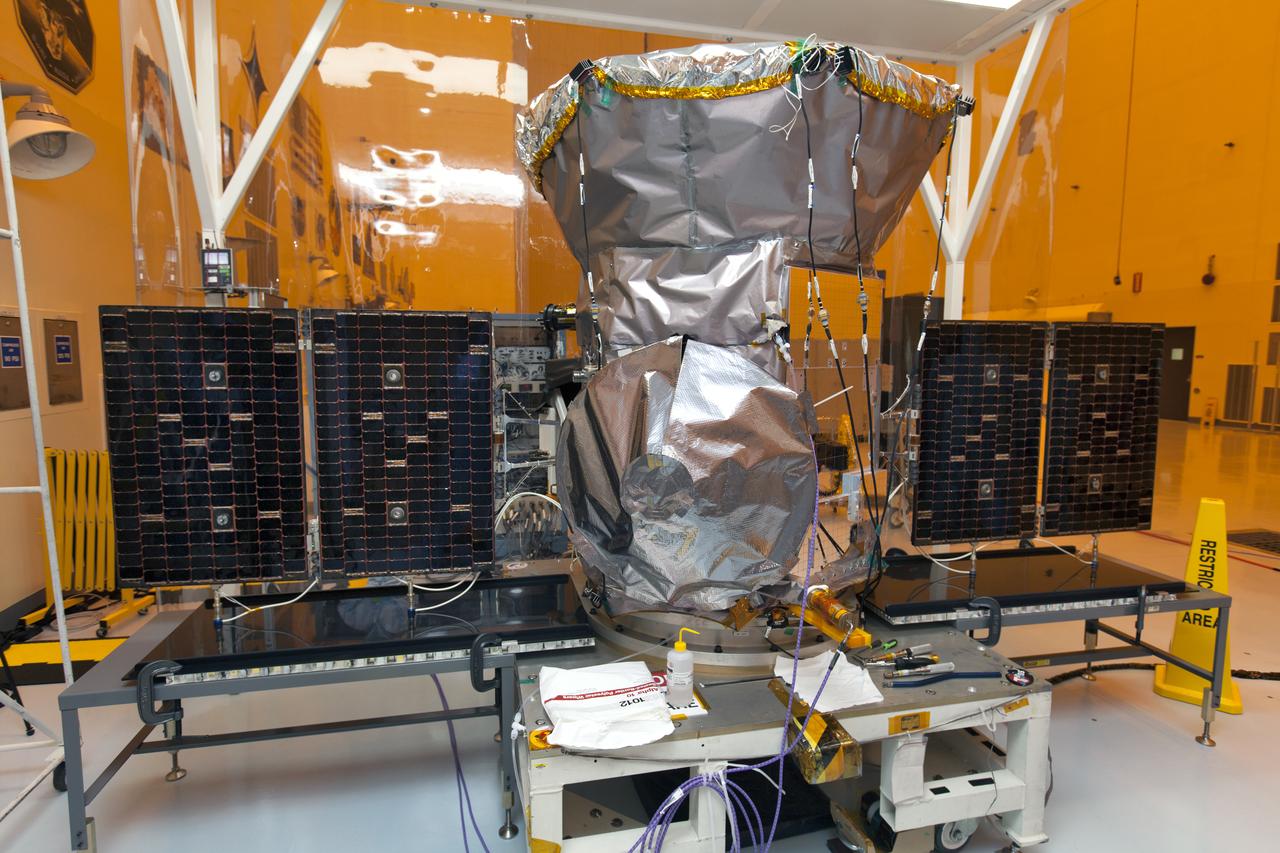

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, both solar panels are deployed on the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. TESS is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
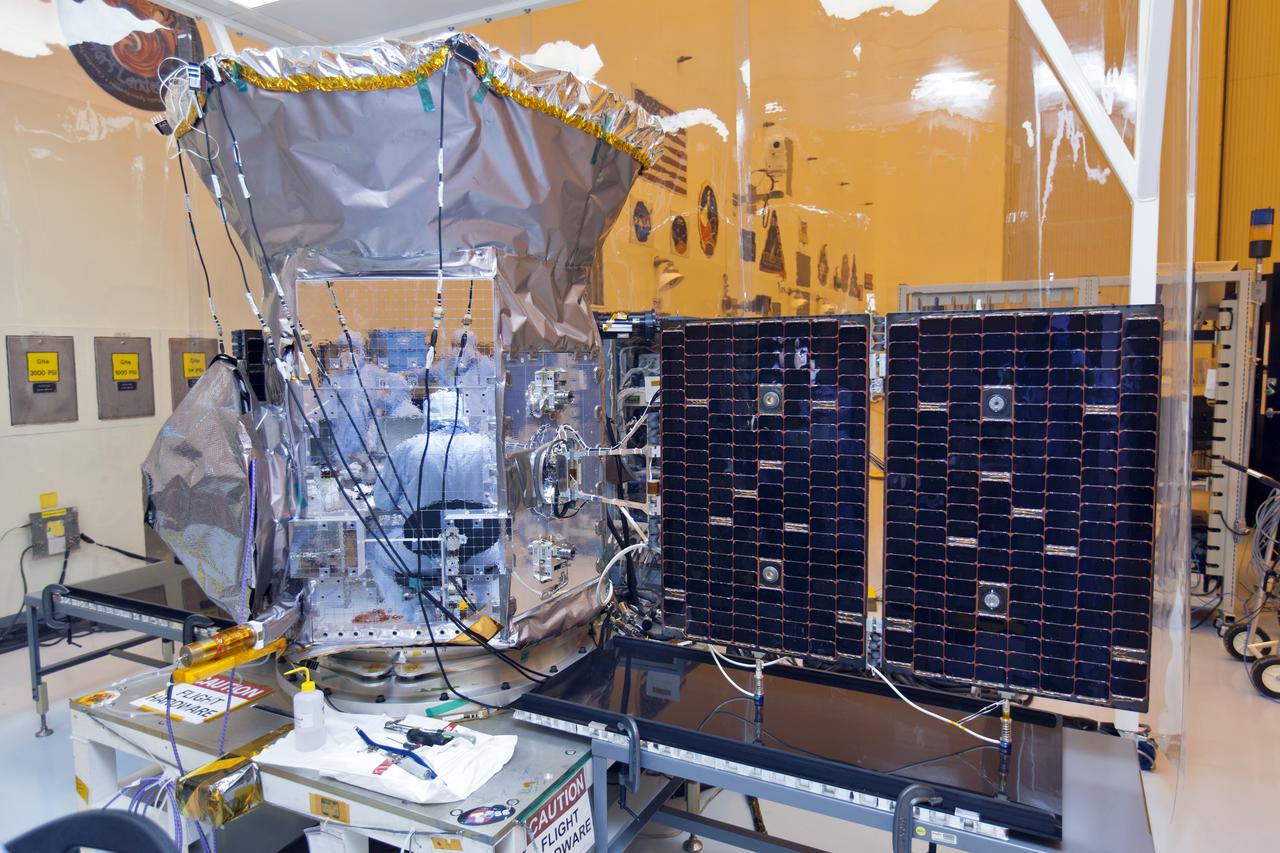

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the first of two solar panels is being deployed on the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. TESS is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
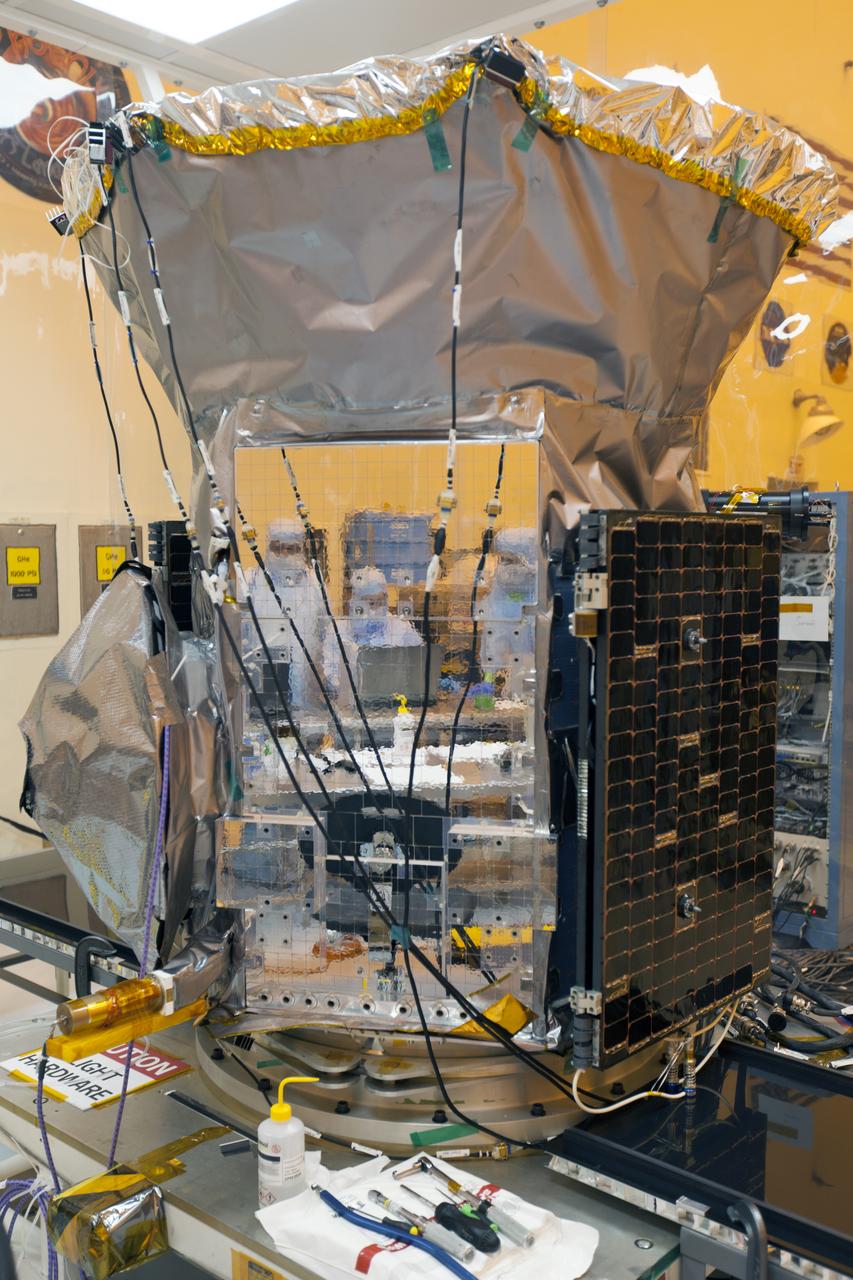

Preparations are underway for solar panel deployment on NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS) inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the agency's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. TESS is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The satellite is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
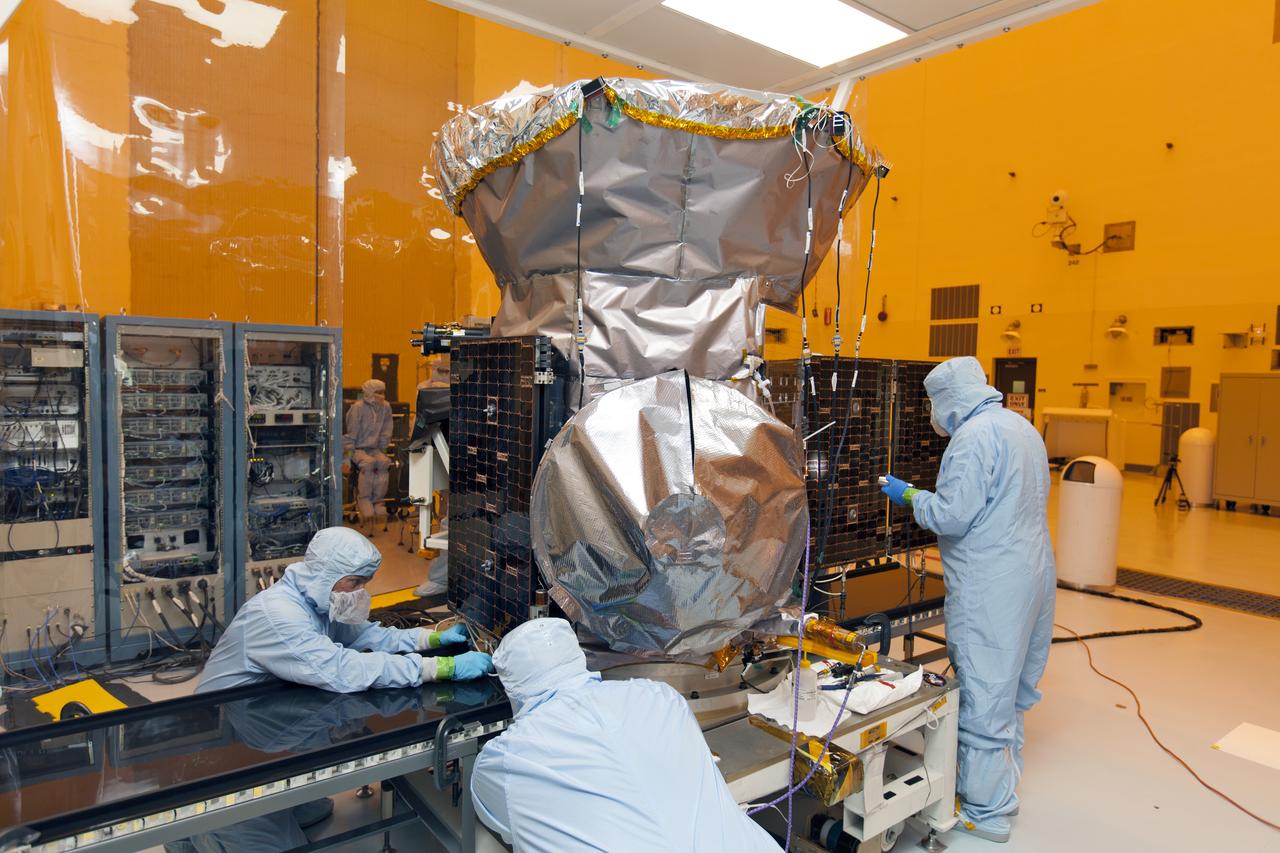

Inside the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at the NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of the solar panels is being deployed on the agency's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS). Technicians are preparing to deploy the second solar array. The satellite is scheduled to launch atop a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 40 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. TESS is the next step in NASA's search for planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets. TESS is a NASA Astrophysics Explorer mission led and operated by MIT in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and managed by NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. Dr. George Ricker of MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Space Research serves as principal investigator for the mission. Additional partners include Orbital ATK, NASA’s Ames Research Center, the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and the Space Telescope Science Institute. More than a dozen universities, research institutes and observatories worldwide are participants in the mission. NASA’s Launch Services Program is responsible for launch management.
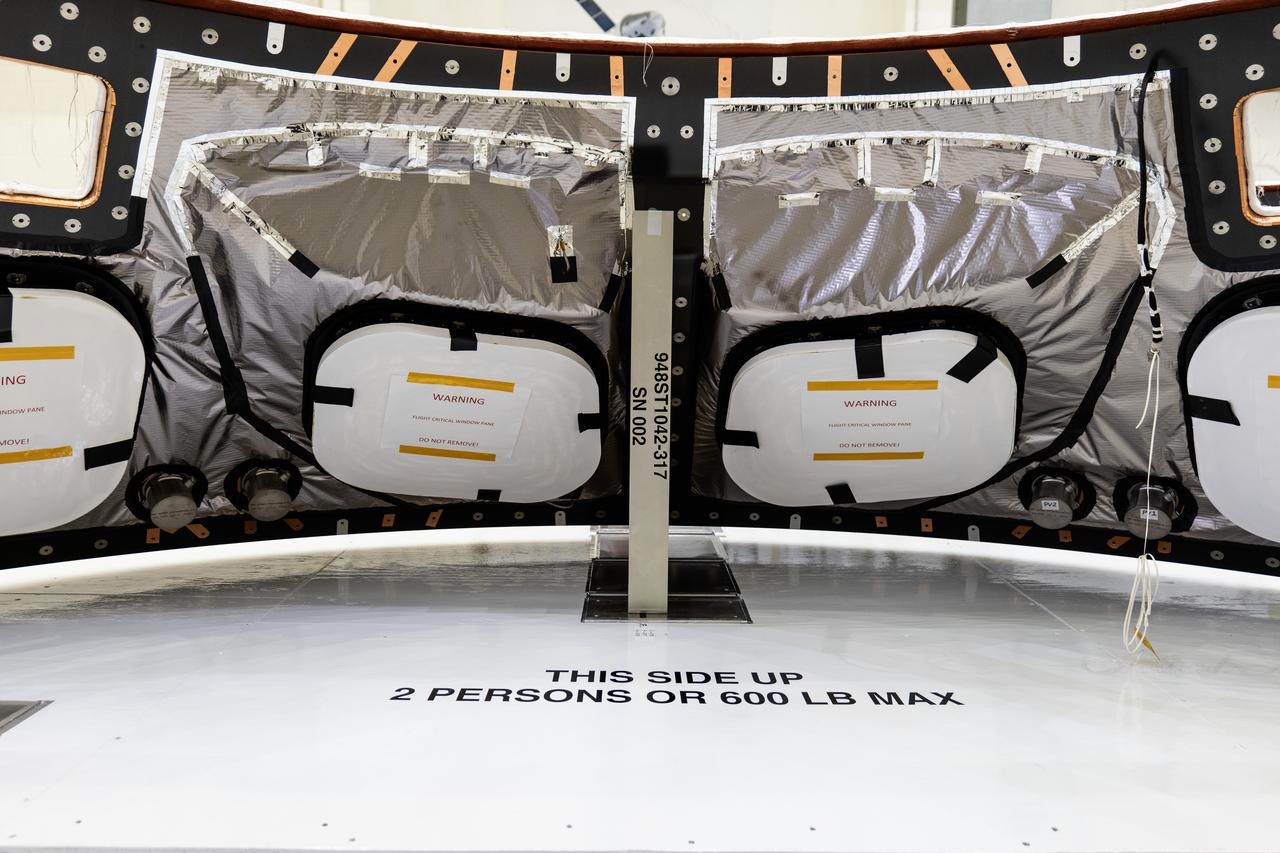

Back shell panels are visible on the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis II mission inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Dec. 15, 2024. The back shell panels serve as the outer layer of the spacecraft and will protect it against the extreme temperatures of re-entry from deep space.
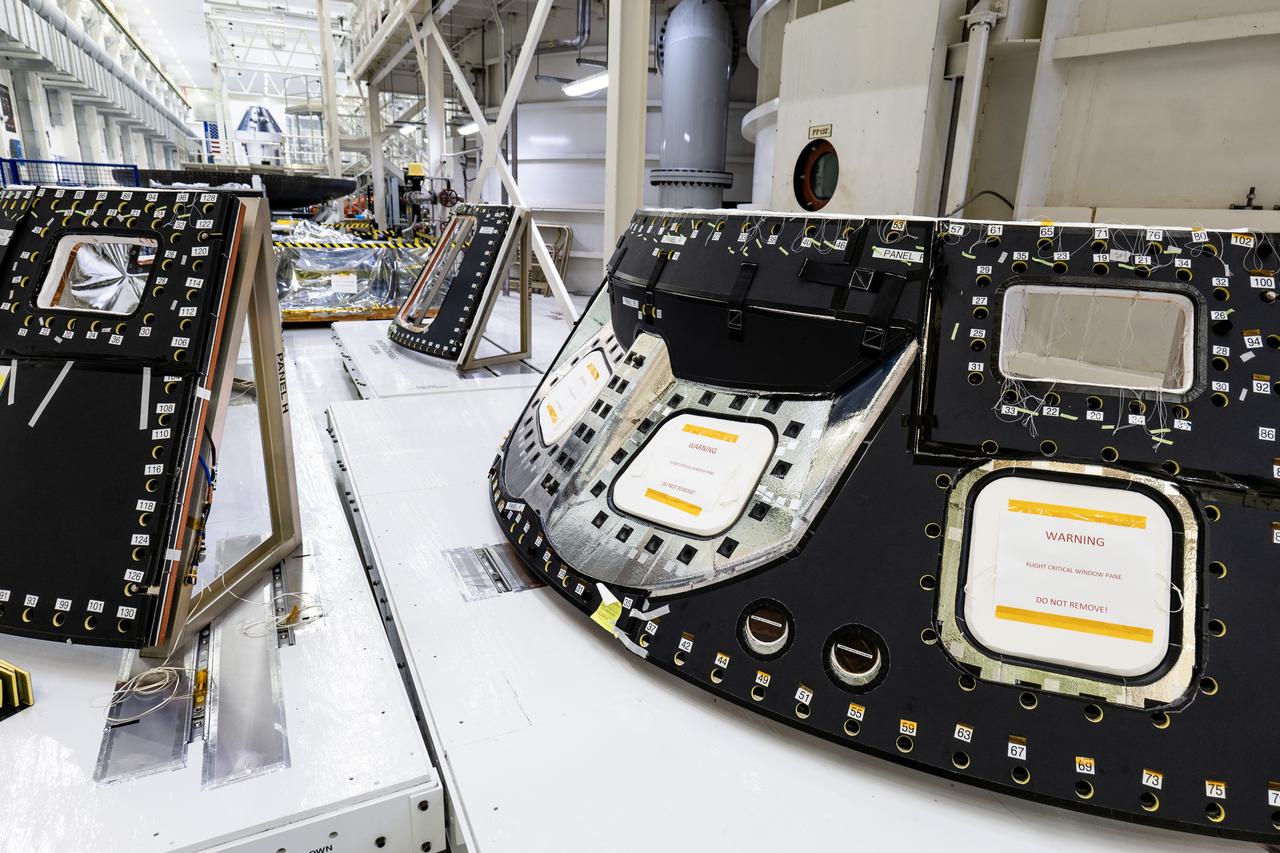

Visible in the foreground are back shell panels on the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis II mission inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Dec. 15, 2024. The back shell panels serve as the outer layer of the spacecraft and will protect it against the extreme temperatures of re-entry from deep space. In the background are the heat shield for Orion’s Artemis IV mission secured on a work stand, as well as the Orion spacecraft for NASA’s Artemis II mission.
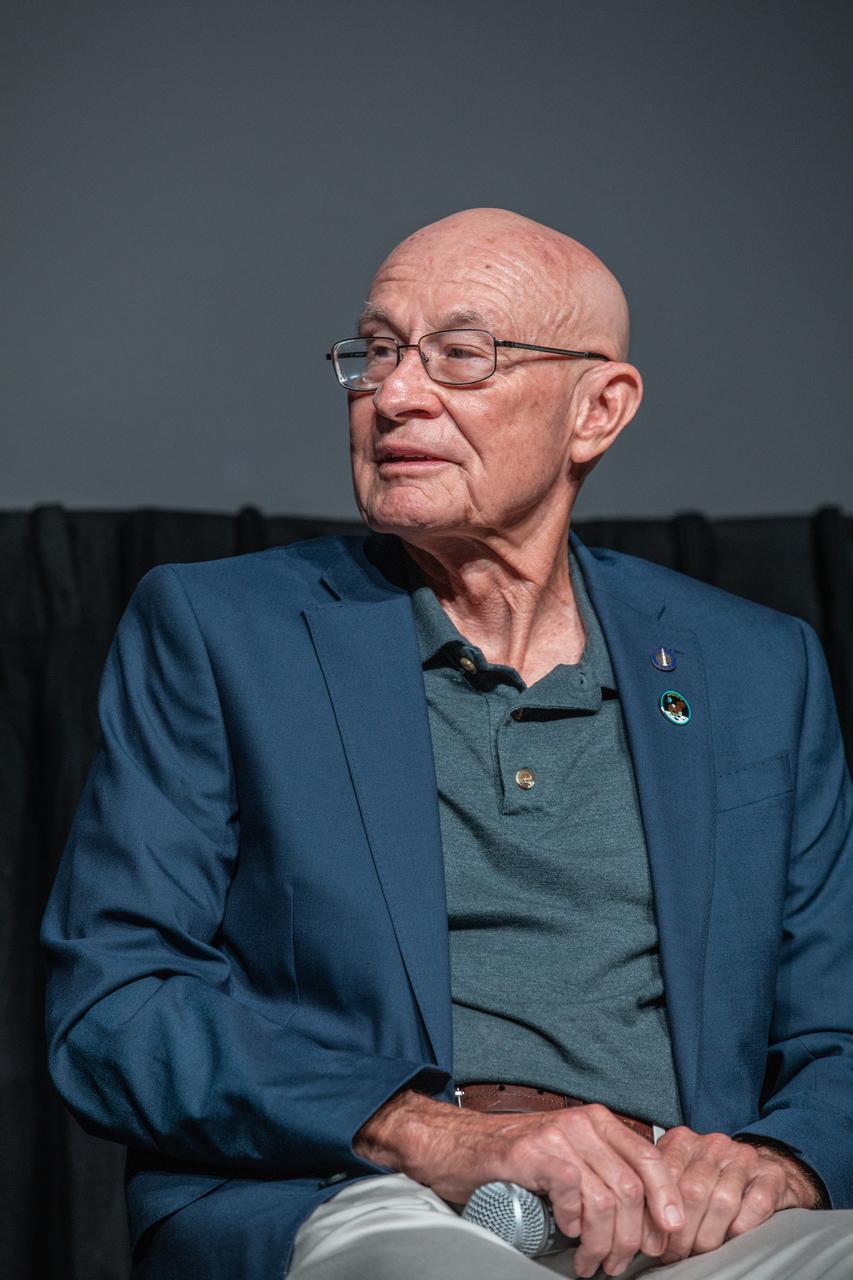

Bob Sieck, Apollo-era launch team member and former space shuttle launch director, particpates in the “Apollo Heroes Panel Discussion” in the IMAX Theater at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on July 16, 2019. The panel discussion is one of several events at the visitor complex to honor the 50th anniversary of NASA’s Saturn V/Apollo 11 launch and landing on the Moon.
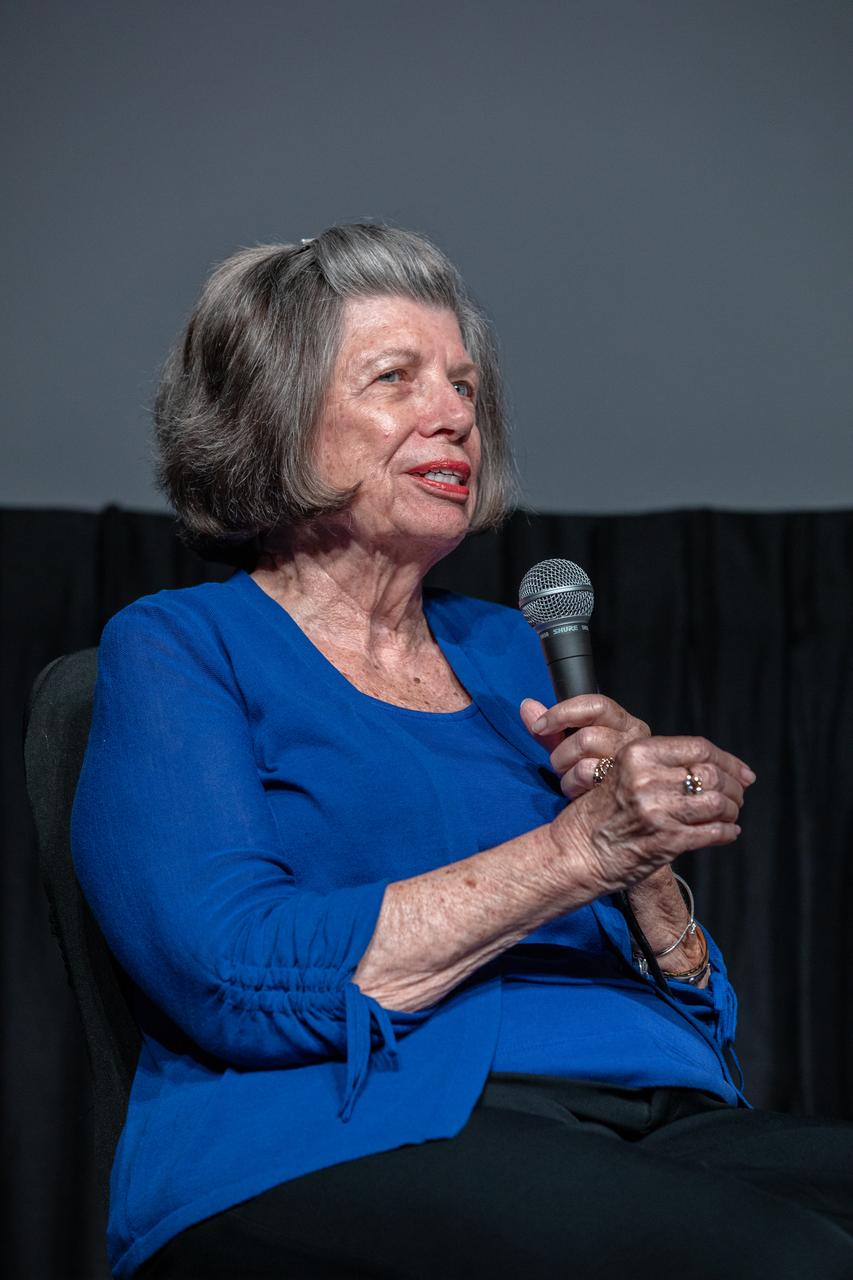

JoAnn Morgan, retired from NASA and the only woman on console in the Launch Control Center during Apollo 11 launch countdown activities, answers questions during the “Apollo Heroes Panel Discussion” in the IMAX Theater at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on July 16, 2019. The panel discussion is one of several events at the visitor complex to honor the 50th anniversary of NASA’s Saturn V/Apollo 11 launch and landing on the Moon.
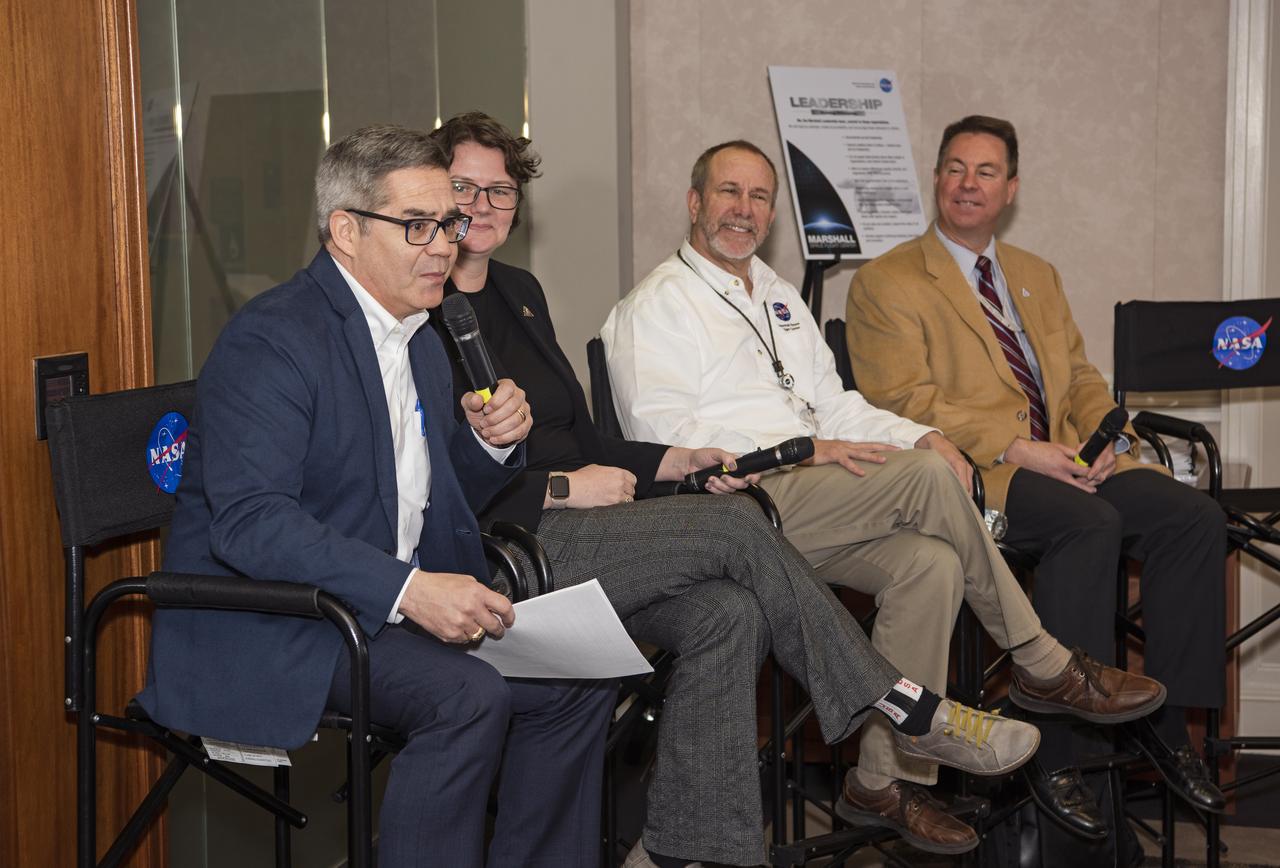

Sam Ortega, left, manager of the Partnerships Office at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center, moderates an Artemis Program panel featuring, second from left, Renee Weber, Marshall chief scientist; David Beaman, manager of Marshall’s Systems Engineering & Integration Office; and Don Krupp, associate program manager for the Human Landing System Program, during Universities of the Tennessee Valley Corridor activities Feb. 27 at Marshall. Leadership staff from eight universities and 10 junior colleges in Alabama, Tennessee and Kentucky also heard presentations on Office of STEM Engagement opportunities, partnership opportunities, Marshall’s Technology Transfer Office, the NASA software catalog and Marshall’s Advanced Concepts Office. The group toured several Marshall facilities to learn more about center capabilities.
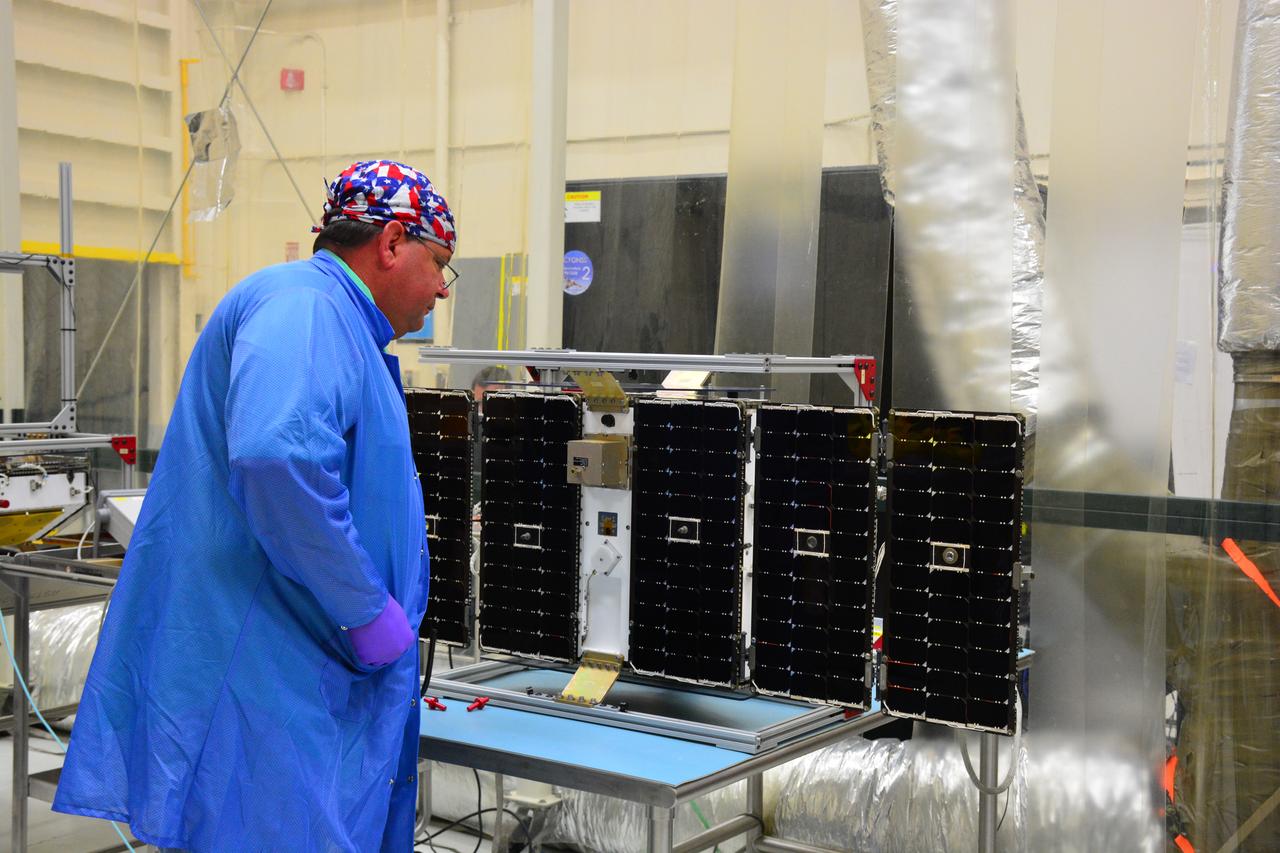

Inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, solar panels for one of eight NASA's Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) spacecraft has been deployed for illumination testing. Processing activities will prepare the spacecraft for launch aboard an Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket. When preparations are completed at Vandenberg, the rocket will be transported to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft within its payload fairing. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.
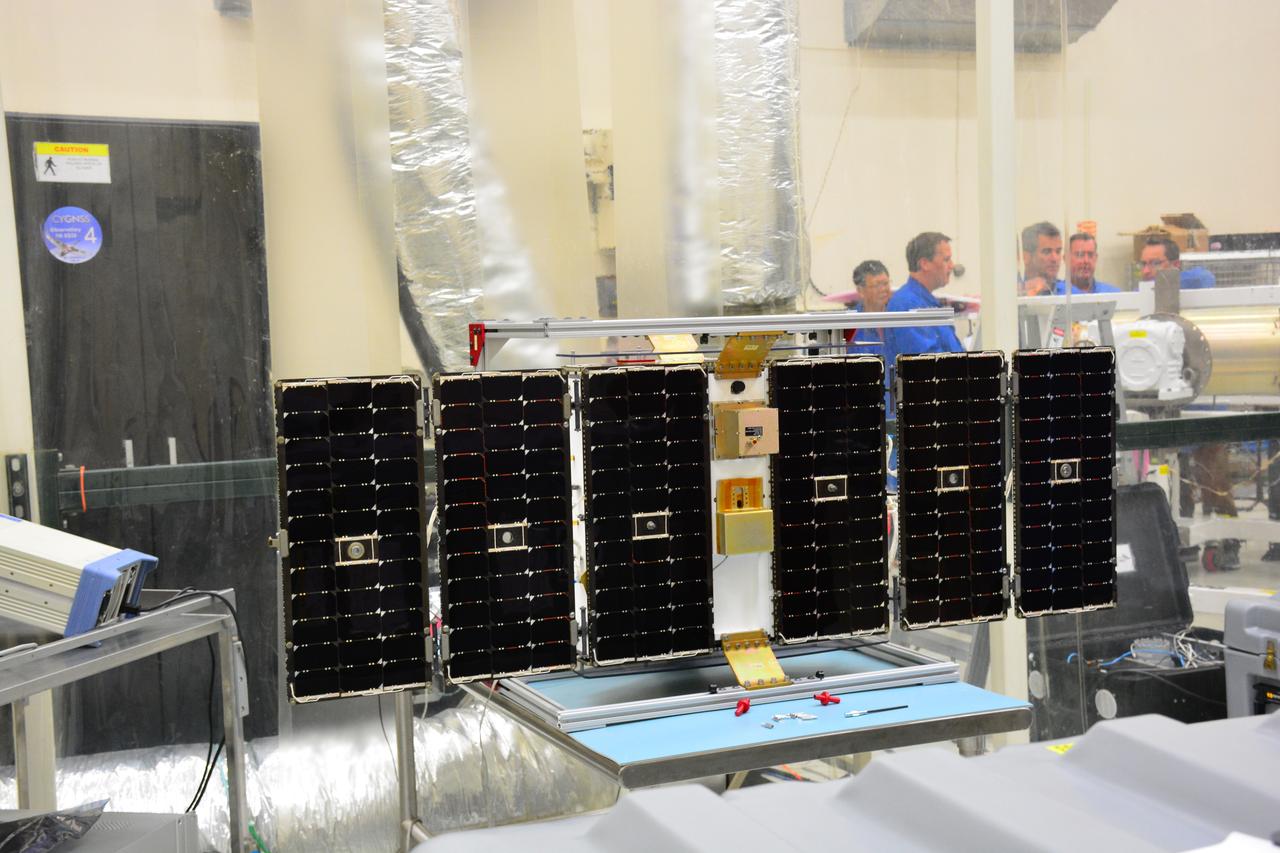

Inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, solar panels for one of eight NASA's Cyclone Global Navigation Satellite System (CYGNSS) spacecraft has been deployed for illumination testing. Processing activities will prepare the spacecraft for launch aboard an Orbital ATK Pegasus XL rocket. When preparations are completed at Vandenberg, the rocket will be transported to NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida attached to the Orbital ATK L-1011 carrier aircraft within its payload fairing. CYGNSS will launch on the Pegasus XL rocket from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. CYGNSS will make frequent and accurate measurements of ocean surface winds throughout the life cycle of tropical storms and hurricanes. The data that CYGNSS provides will enable scientists to probe key air-sea interaction processes that take place near the core of storms, which are rapidly changing and play a critical role in the beginning and intensification of hurricanes.

Spirit Solar Panel on Sol 1813, Still Very Dusty
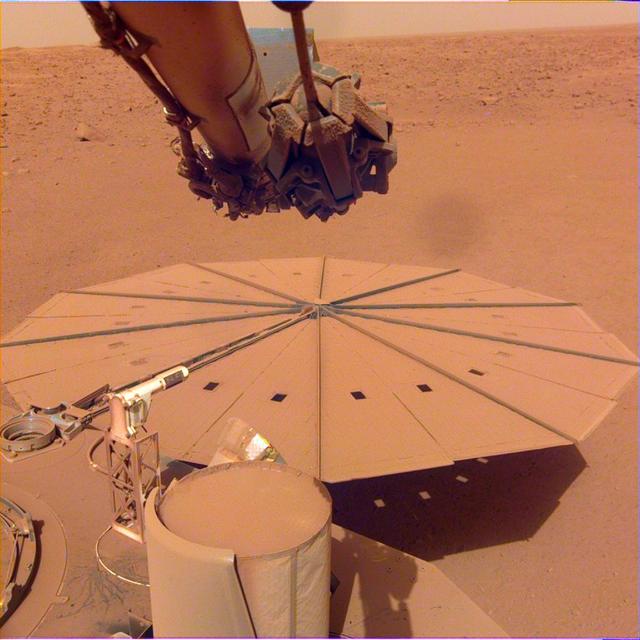
NASA's InSight Mars lander captured this image of one of its dust-covered solar panels on April 24, 2022, the 1,211th Martian day, or sol, of the mission. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25286
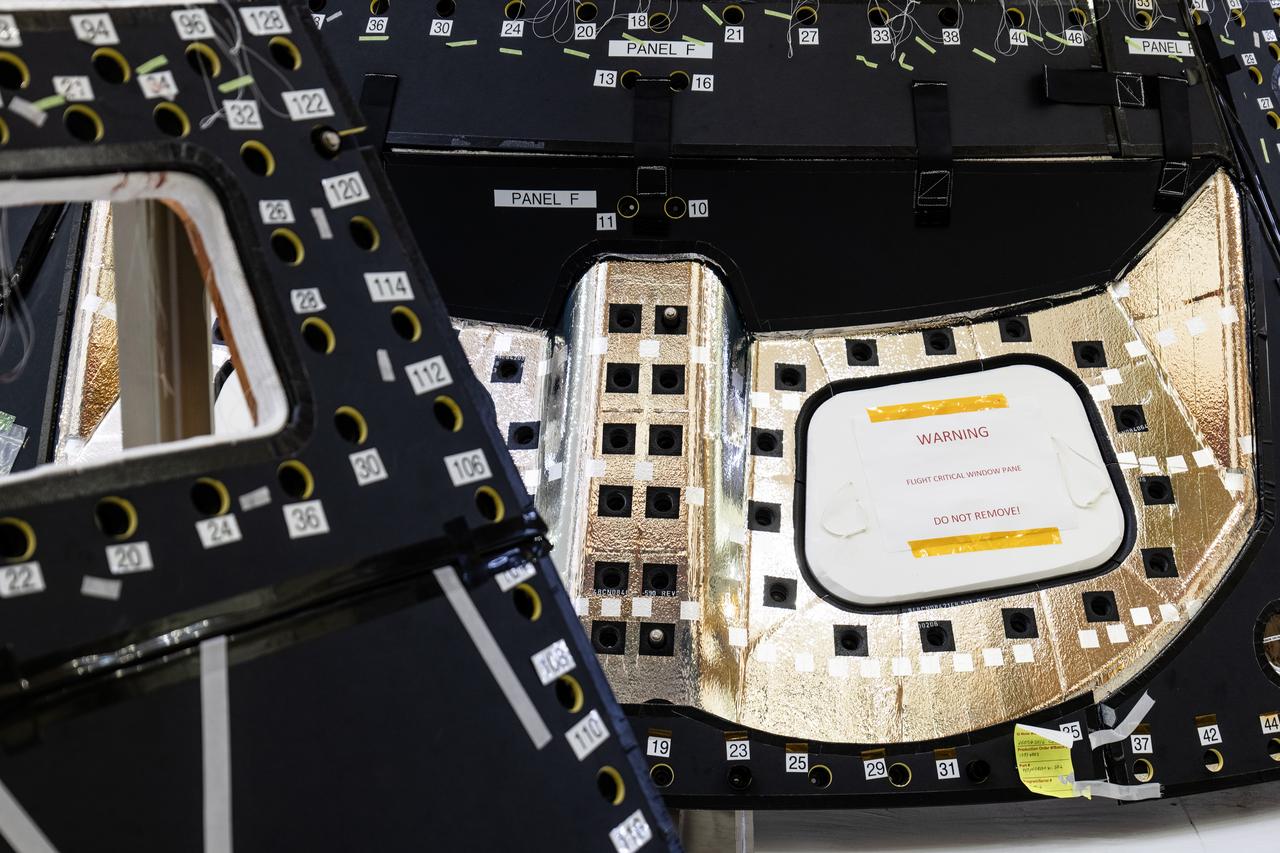

Back shell panels are visible on the Orion spacecraft for the Artemis IV mission inside the Neil A. Armstrong Operations and Checkout Building high bay at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida on Monday, Dec. 15, 2024. The back shell panels serve as the outer layer of the spacecraft and will protect it against the extreme temperatures of re-entry from deep space.
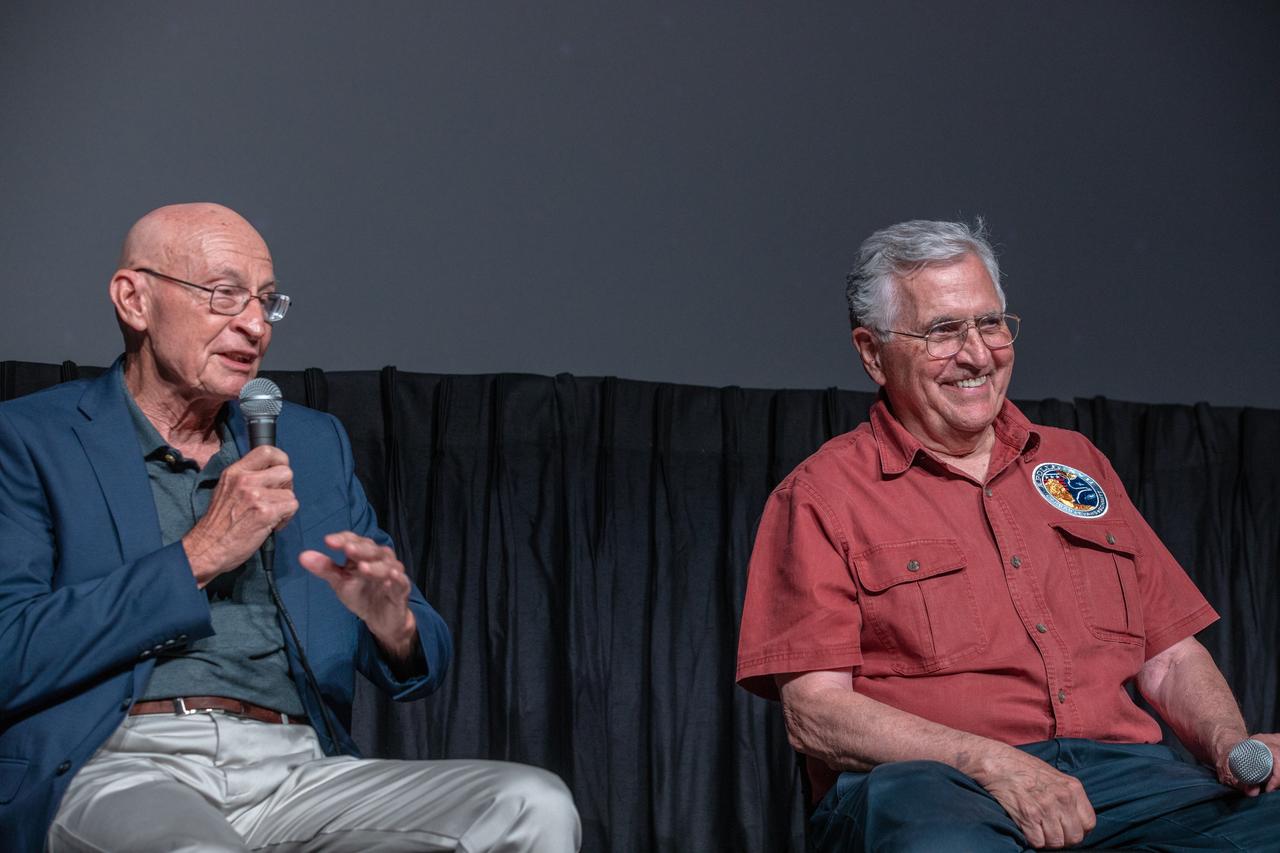

Bob Sieck, left, Apollo-era launch team member and former space shuttle launch director, and Harrison Schmitt, Apollo 17 astronaut and moonwalker, answer questions during the “Apollo Heroes Panel Discussion” in the IMAX Theater at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex in Florida on July 16, 2019. The panel discussion is one of several events at the visitor complex to honor the 50th anniversary of NASA’s Saturn V/Apollo 11 launch and landing on the Moon.
The complete TEMPEST-D spacecraft shown with the solar panels deployed. RainCube, CubeRRT and TEMPEST-D are currently integrated aboard Orbital ATKs Cygnus spacecraft and are awaiting launch on an Antares rocket. After the CubeSats have arrived at the station, they will be deployed into low-Earth orbit and will begin their missions to test these new technologies useful for predicting weather, ensuring data quality, and helping researchers better understand storms. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22458
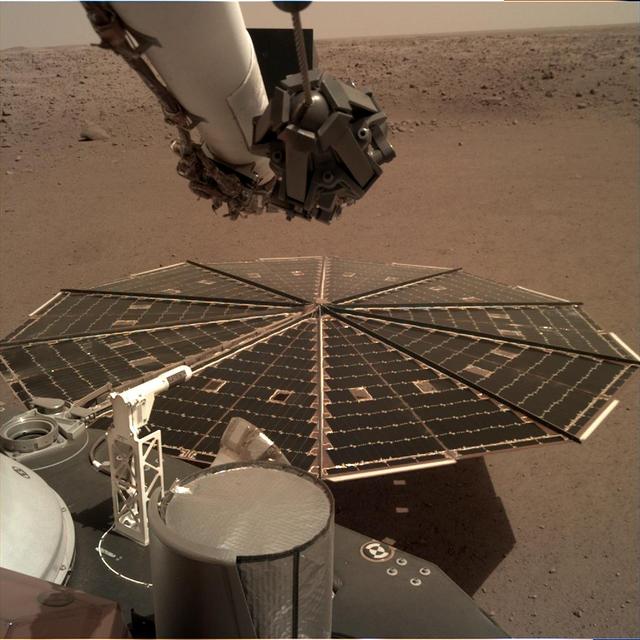

One of InSight's 7-foot (2.2 meter) wide solar panels was imaged by the lander's Instrument Deployment Camera, which is fixed to the elbow of its robotic arm. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA22736

Technicians prepare to install the solar array for NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 28, 2019. ICON launched on a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
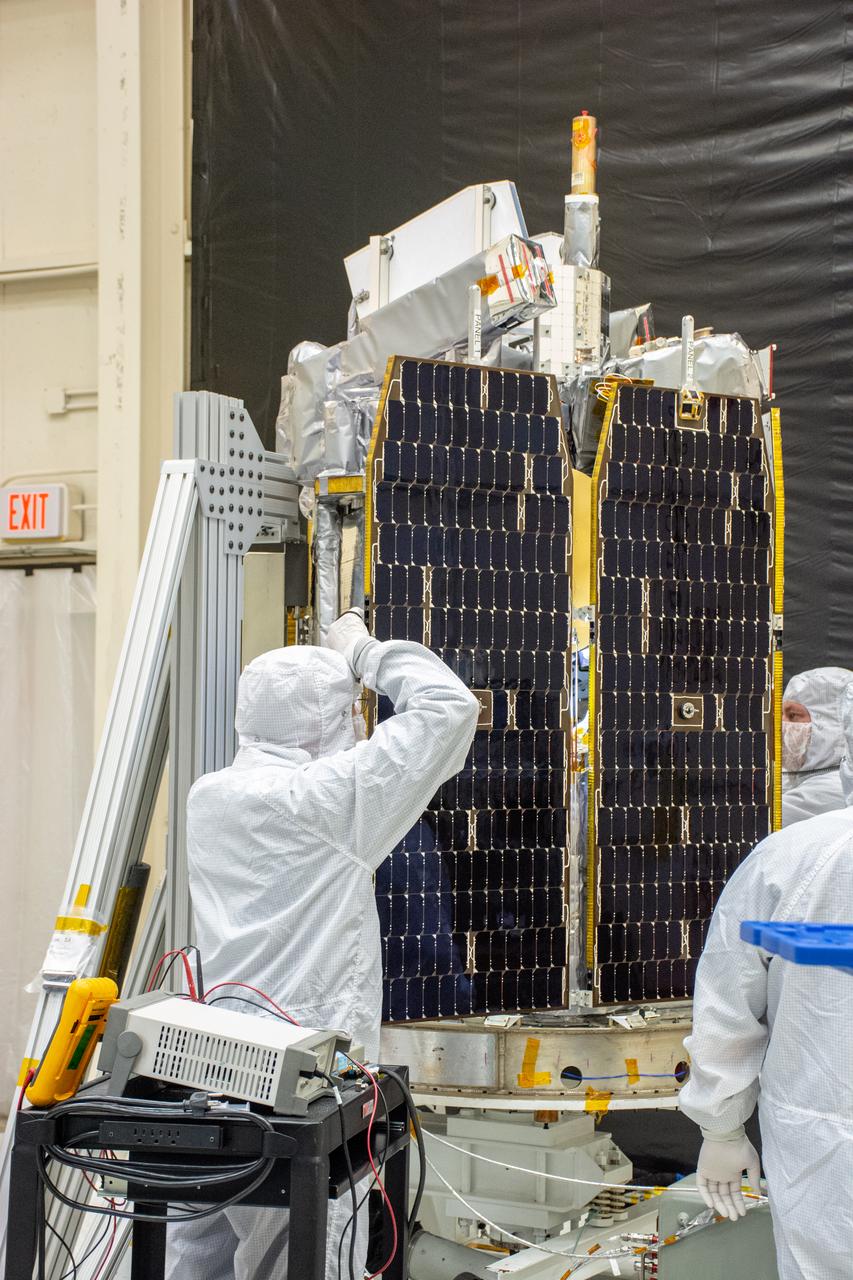

Technicians install the solar array for NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 28, 2019. ICON launched on a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.

NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) is ready for solar array installation inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 28, 2019. ICON launched on a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.

Technicians install the solar array for NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 28, 2019. ICON launched on a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.

Technicians prepare to install the solar array for NASA's Ionospheric Connection Explorer (ICON) inside Building 1555 at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California on Aug. 28, 2019. ICON launched on a Northrop Grumman Pegasus XL rocket, attached beneath the company's L-1011 Stargazer aircraft, on Oct. 10, 2019, after takeoff from the Skid Strip at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. ICON will study the frontier of space - the dynamic zone high in Earth's atmosphere where terrestrial weather from below meets space weather above. The explorer will help determine the physics of Earth's space environment and pave the way for mitigating its effects on our technology, communications systems and society.
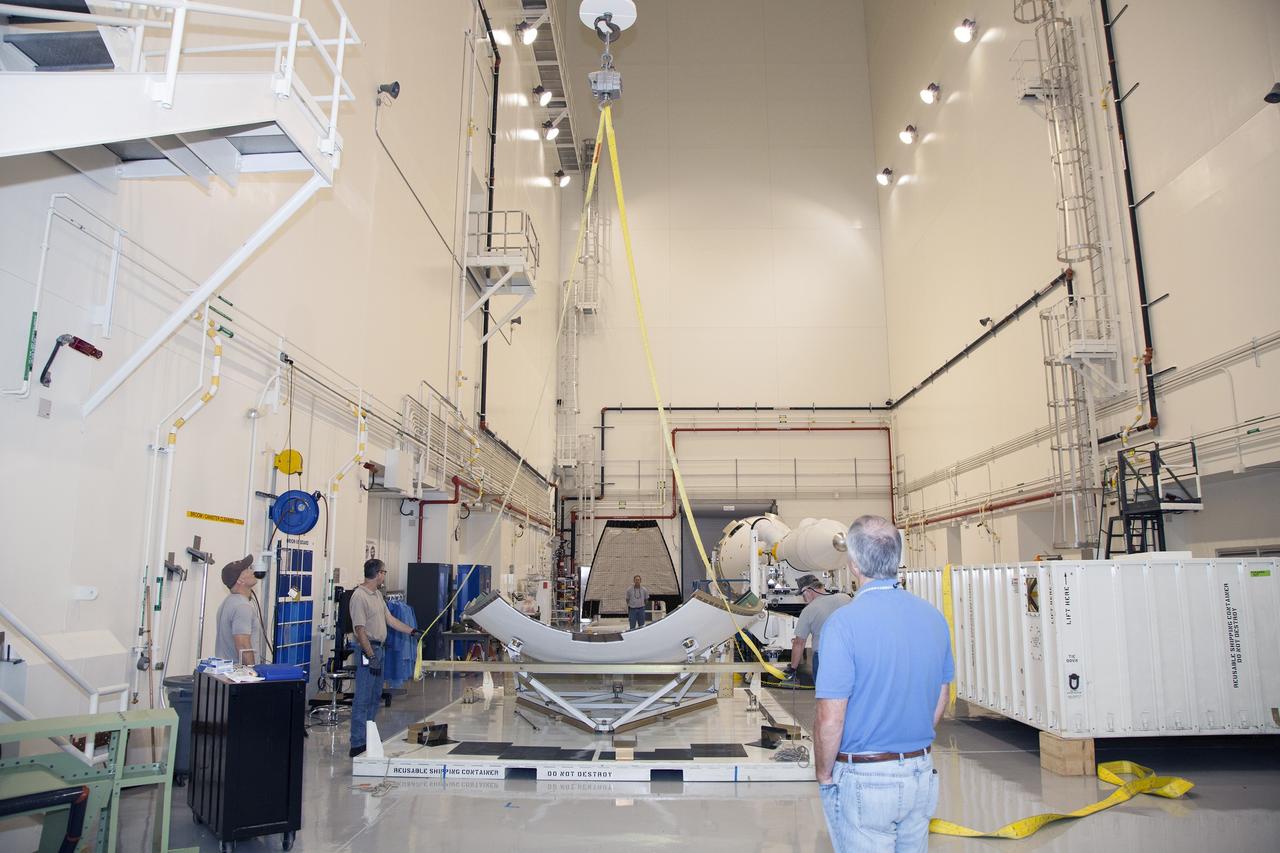

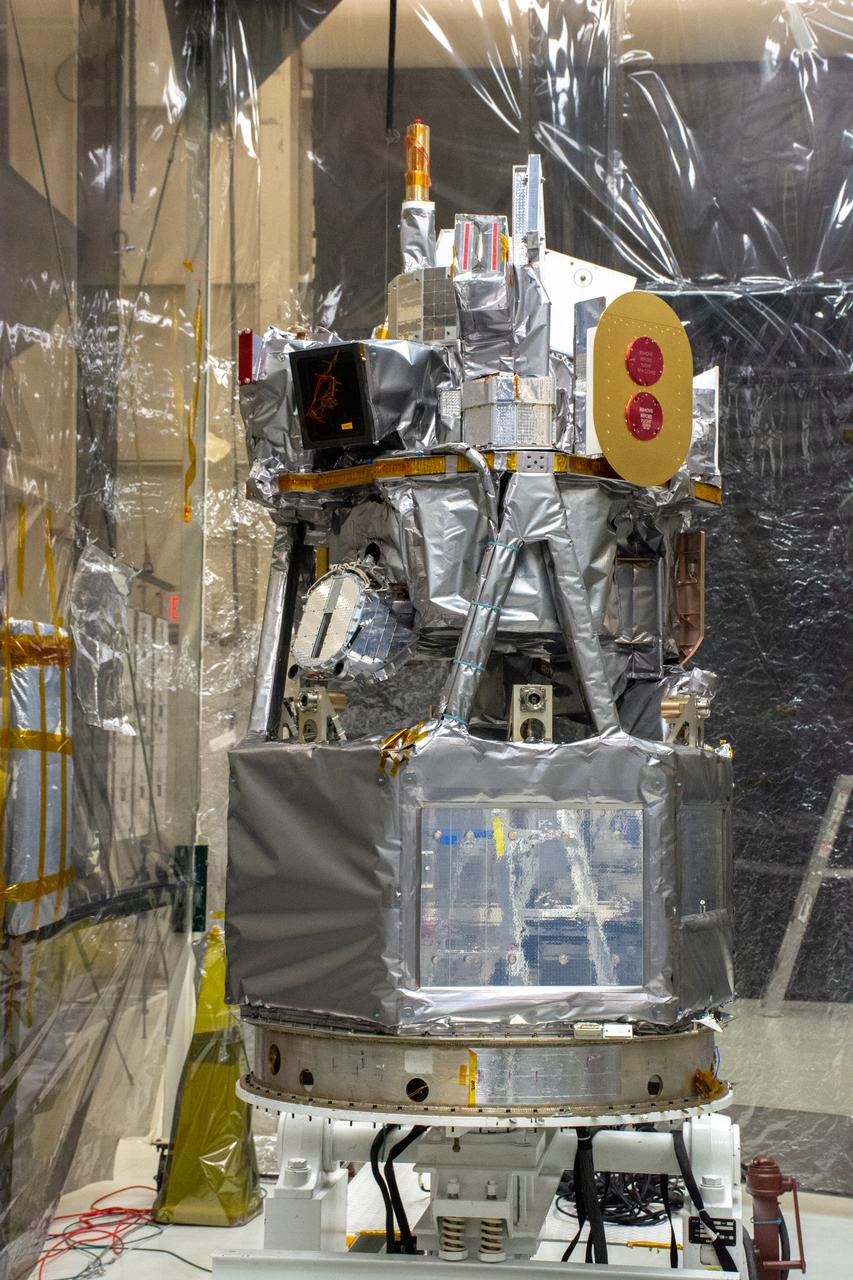
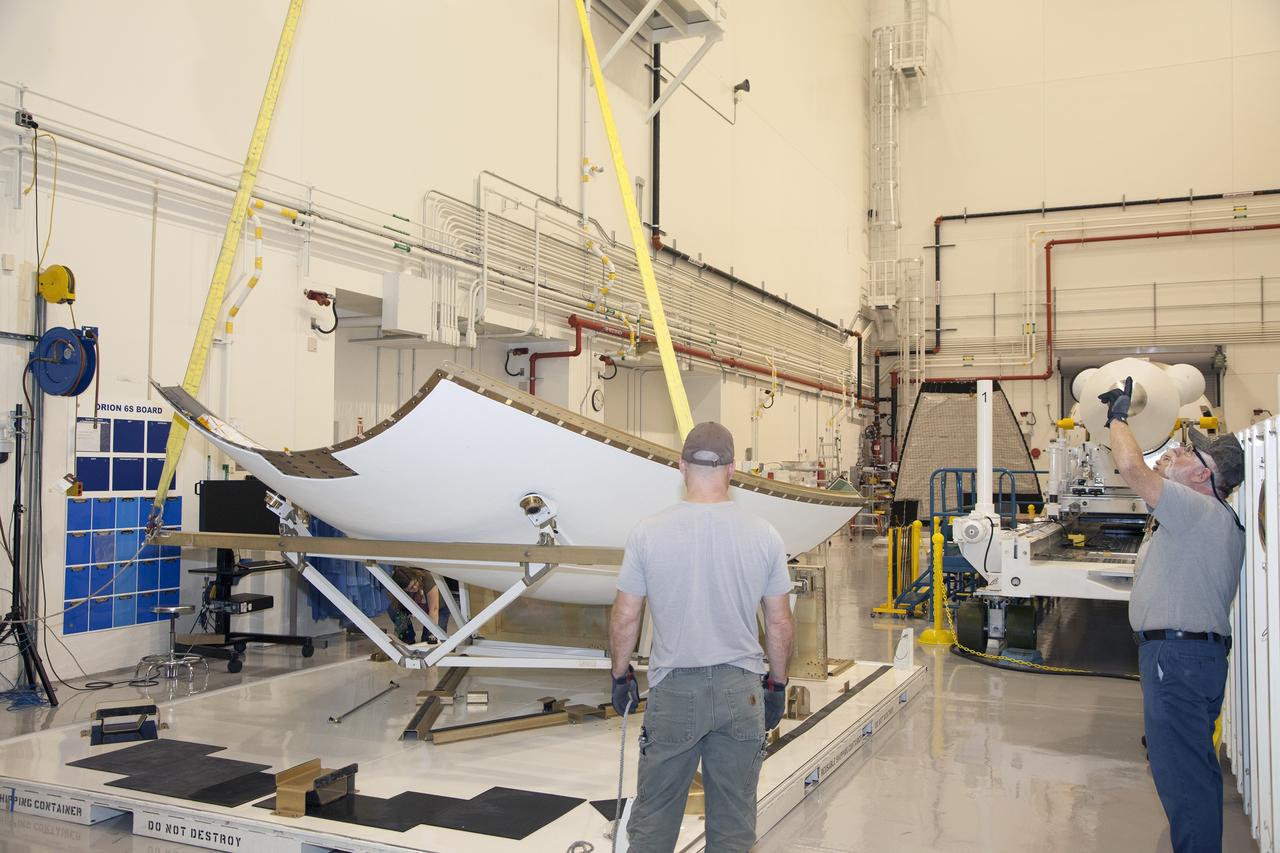
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The first set of two Ogive panels for the Orion Launch Abort System was uncrated inside the Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. One of the panels has been secured on a stand at the far end of the facility. Technicians assist as a crane is attached to the second panel for lifting and moving to the storage stand. During processing, the panels will be secured around the Orion crew module and attached to the Launch Abort System. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Dan Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The first set of two Ogive panels for the Orion Launch Abort System was uncrated inside the Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. One of the panels has been secured on a stand at the far end of the facility. Technicians assist as a crane is attached to the second panel for lifting and moving to the storage stand. During processing, the panels will be secured around the Orion crew module and attached to the Launch Abort System. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Dan Casper
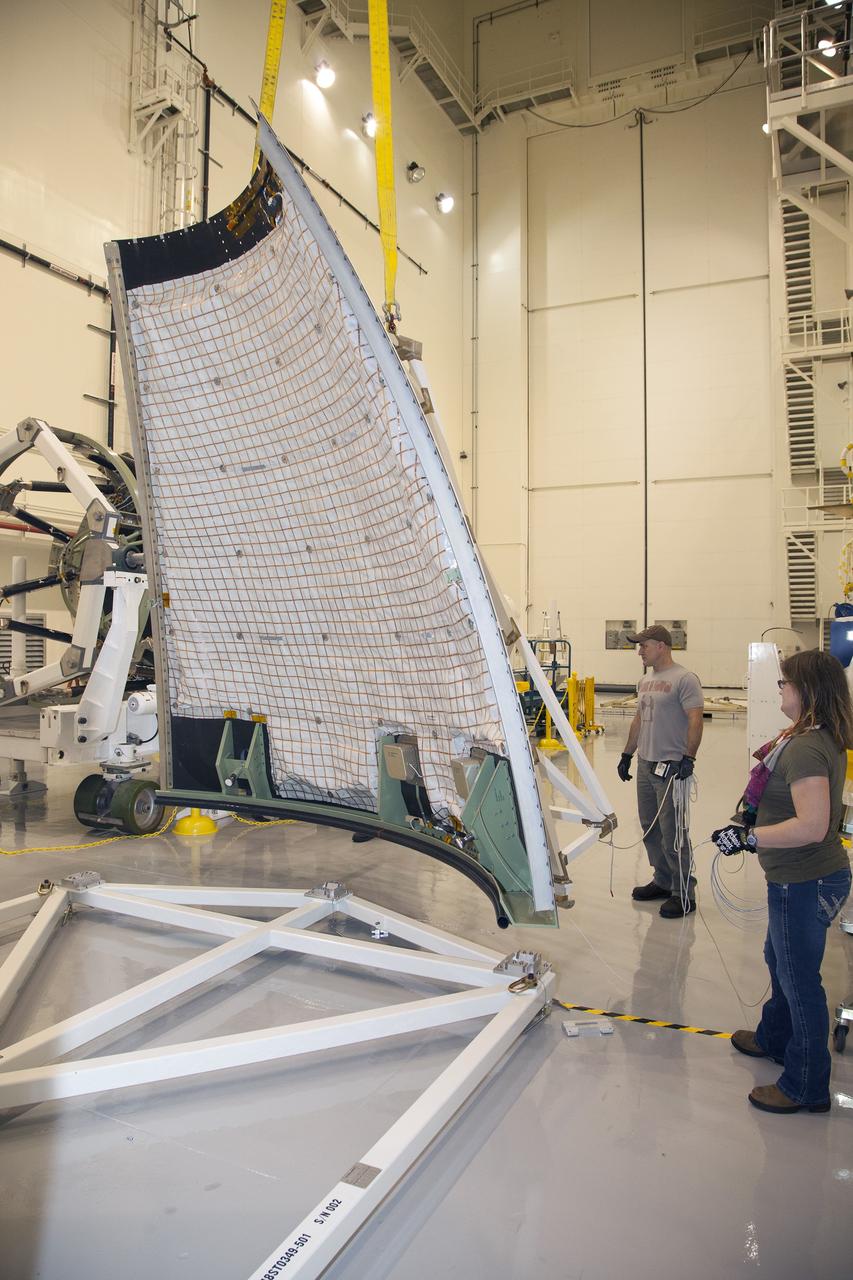

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The first set of two Ogive panels for the Orion Launch Abort System was uncrated inside the Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The second panel is being lifted by crane and technicians are monitoring the progress as it is being moved to join the first panel on the storage stand. During processing, the panels will be secured around the Orion crew module and attached to the Launch Abort System. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Dan Casper

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The first set of two Ogive panels for the Orion Launch Abort System was uncrated inside the Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. One of the panels has been secured on a stand at the far end of the facility while technicians prepare to lift the second panel to move it to the storage stand. During processing, the panels will be secured around the Orion crew module and attached to the Launch Abort System. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Dan Casper
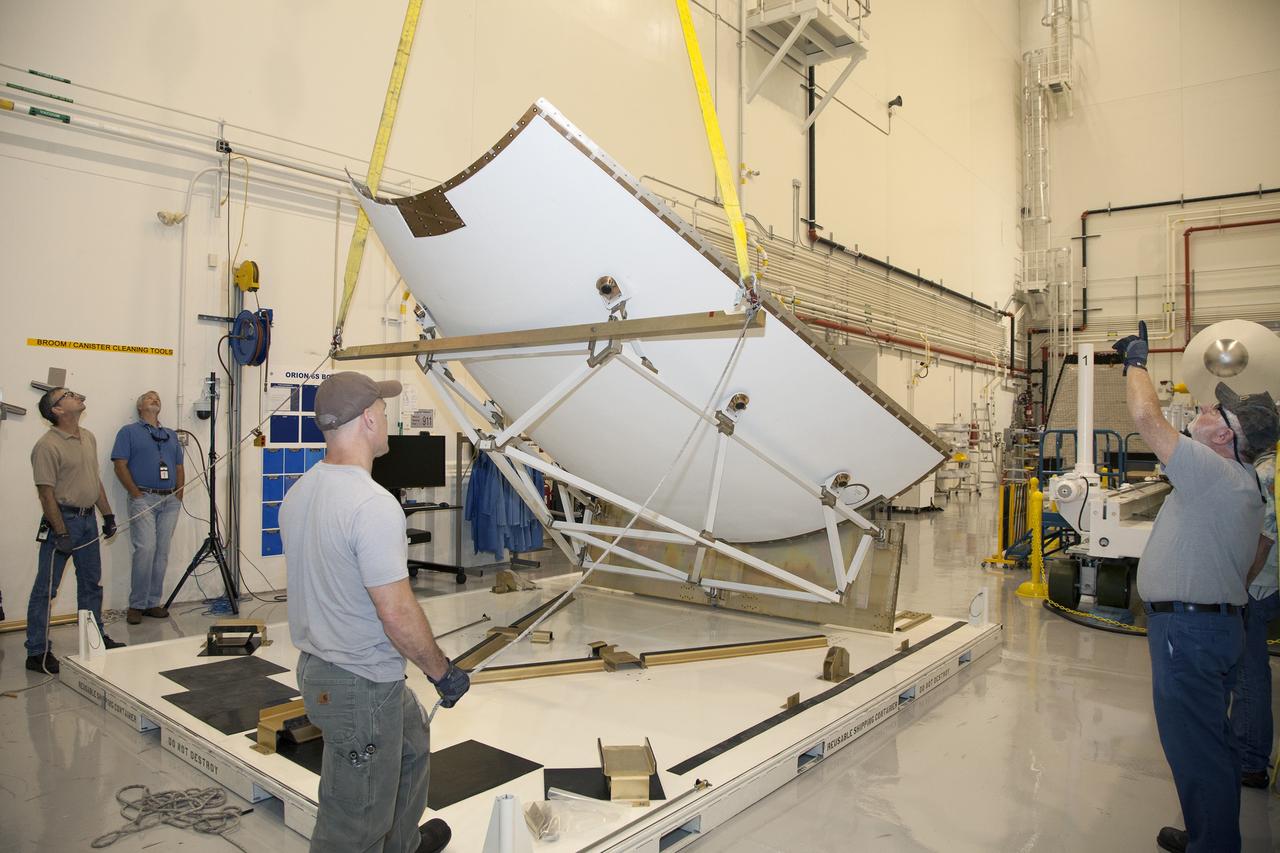

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The first set of two Ogive panels for the Orion Launch Abort System was uncrated inside the Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. One of the panels has been secured on a stand at the far end of the facility. Technicians monitor the progress as a crane lifts the second panel to move it to the storage stand. During processing, the panels will be secured around the Orion crew module and attached to the Launch Abort System. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Dan Casper
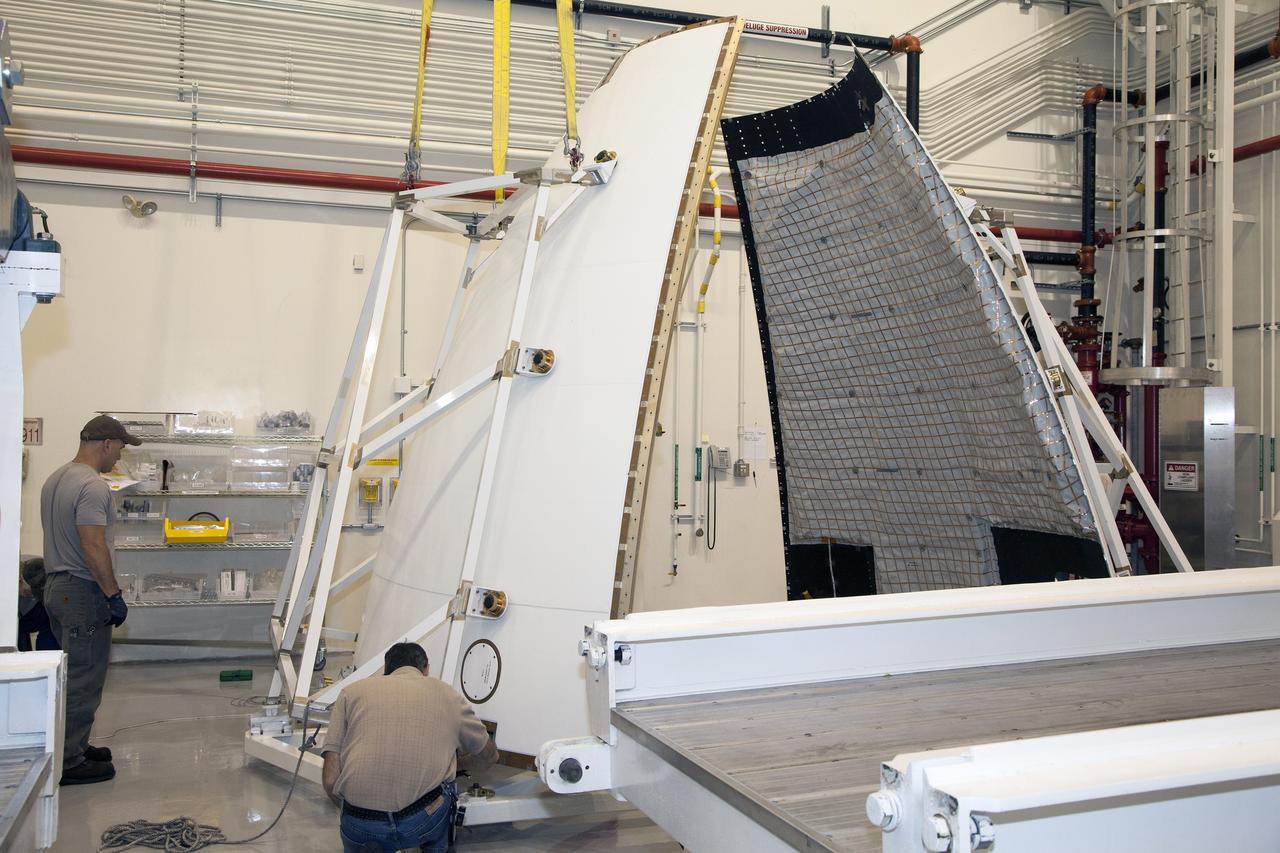

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The first set of two Ogive panels for the Orion Launch Abort System was uncrated inside the Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The first panel is secured on a storage stand while the second panel is being lowered by crane onto the storage stand. During processing, the panels will be secured around the Orion crew module and attached to the Launch Abort System. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Dan Casper
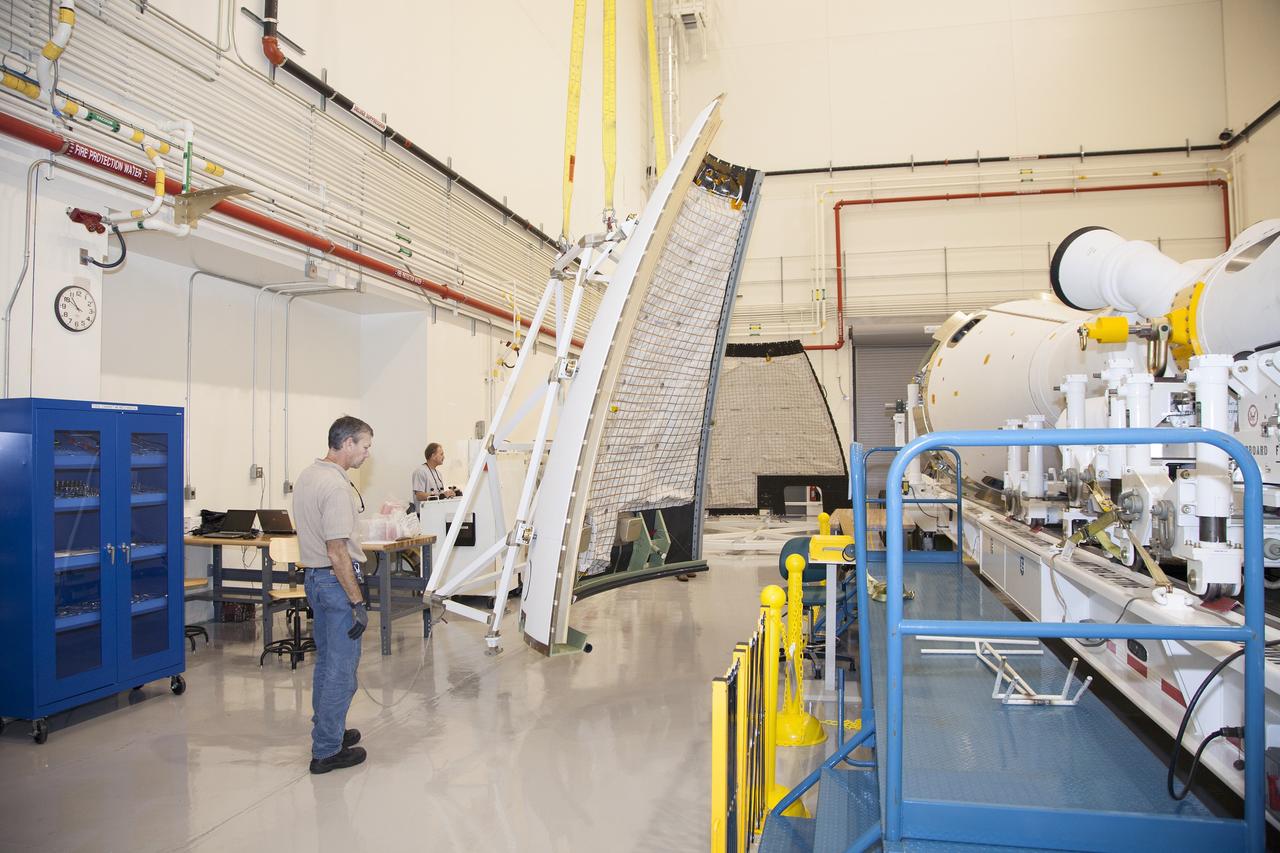

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - The first set of two Ogive panels for the Orion Launch Abort System was uncrated inside the Launch Abort System Facility, or LASF, at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. One of the panels is secured on a storage stand at the other end of the facility. Technicians monitor the progress as the second panel is being moved to join the first panel on the storage stand. To the right is the Launch Abort system secured on a work stand. During processing, the panels will be secured around the Orion crew module and attached to the Launch Abort System. Orion is the exploration spacecraft designed to carry astronauts to destinations not yet explored by humans, including an asteroid and Mars. It will have emergency abort capability, sustain the crew during space travel and provide safe re-entry from deep space return velocities. The first unpiloted test flight of Orion is scheduled to launch in 2014 atop a Delta IV rocket and in 2017 on NASA’s Space Launch System rocket. For more information, visit www.nasa.gov/orion. Photo credit: Dan Casper
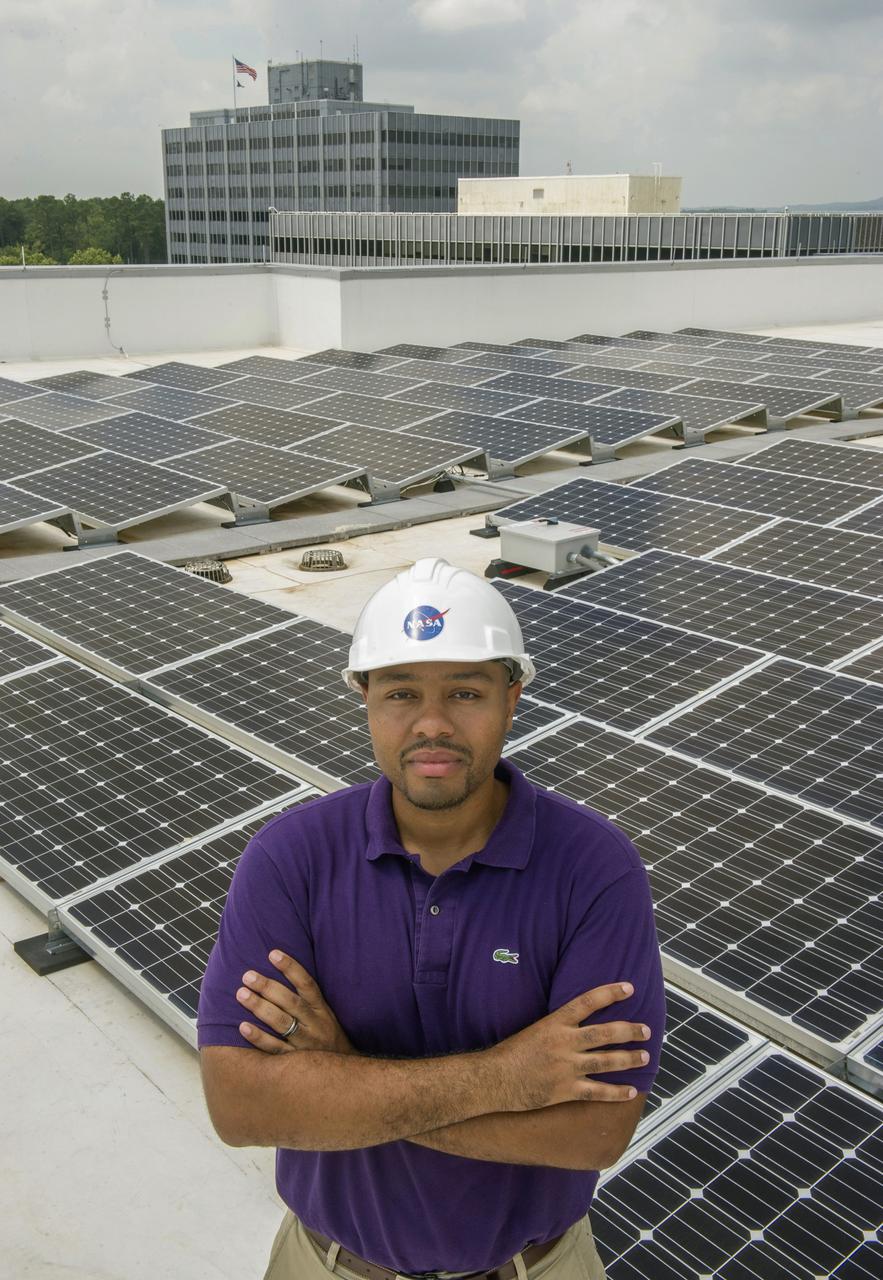

BYRON L. WILLIAMS, FACILITIES MECHANICAL ENGINEER, STANDING ON THE ROOF OF BUILDING 4220 IN FRONT OF THE SOLAR ENERGY PANELS.
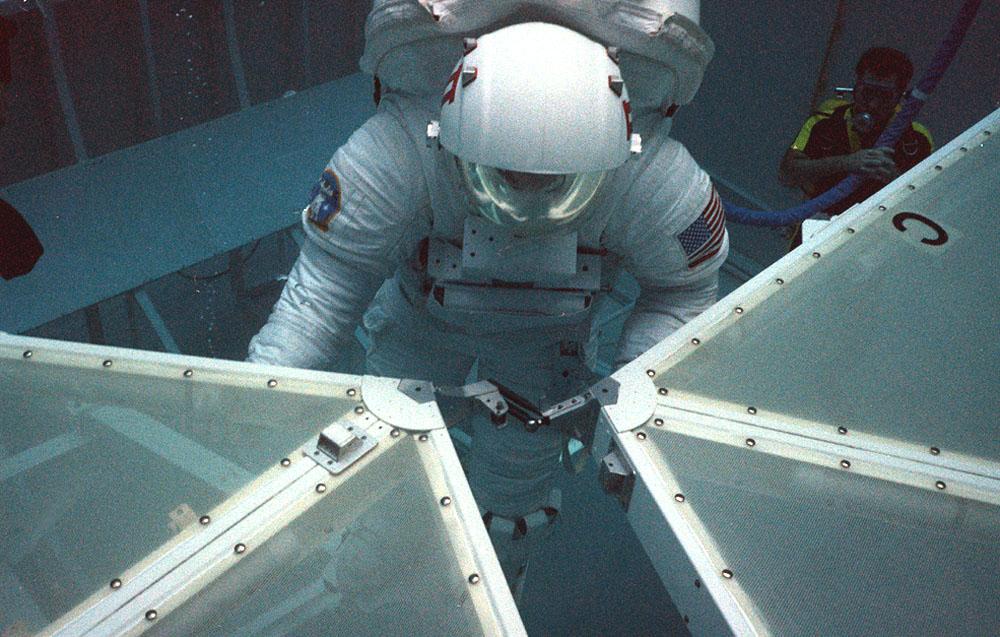

Marshall scientist practices assembling the solar panel array for the space station during the Collector Panel Assembly Test (COPAT) at Marshall's Neutral Buoyancy Simulator (NBS).
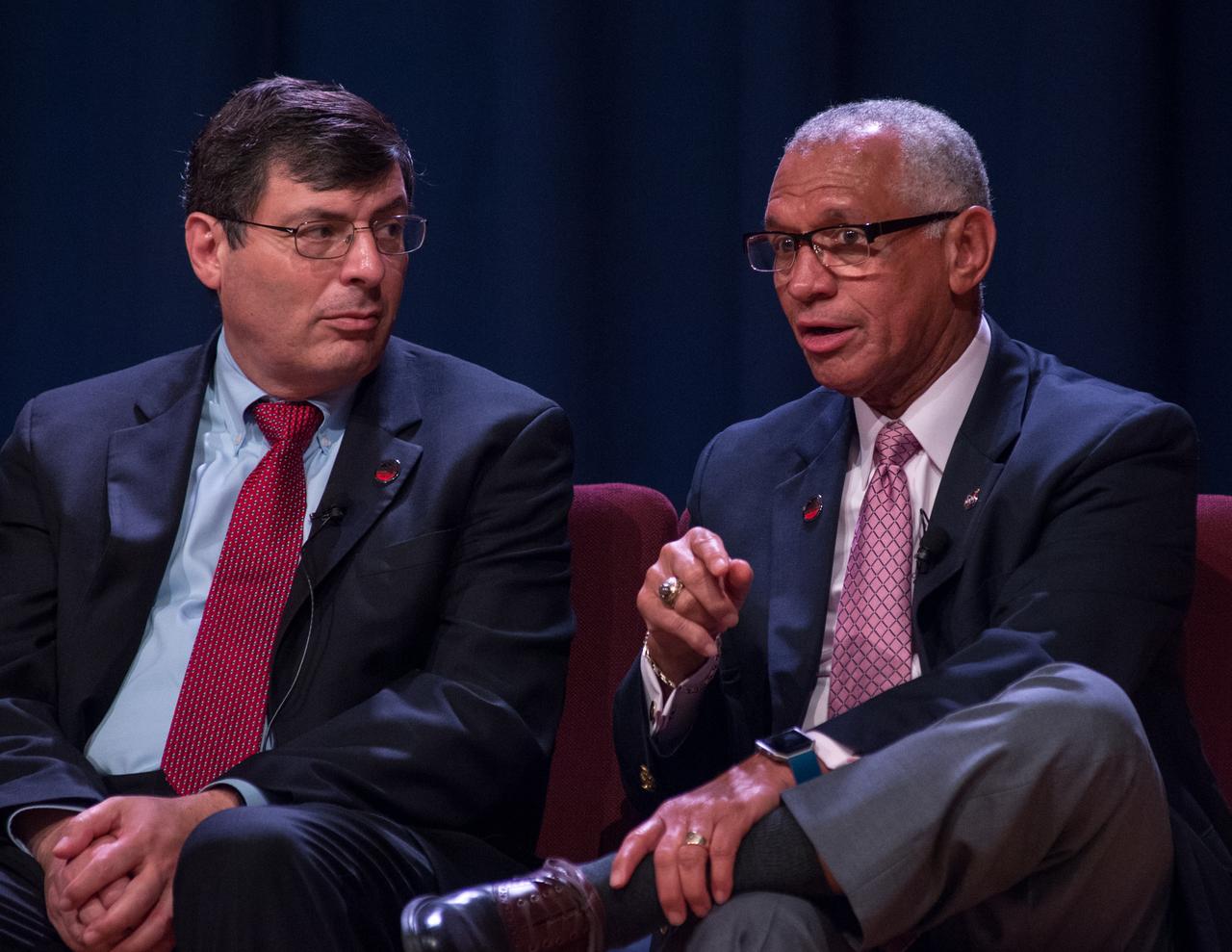

James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) Town Hall - Panel question and answer - Bill Ochs; Dr. John Mather; Dr. Eric Smith; Thomas Zurbuchen; Center Director Chris Scolese; NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden.
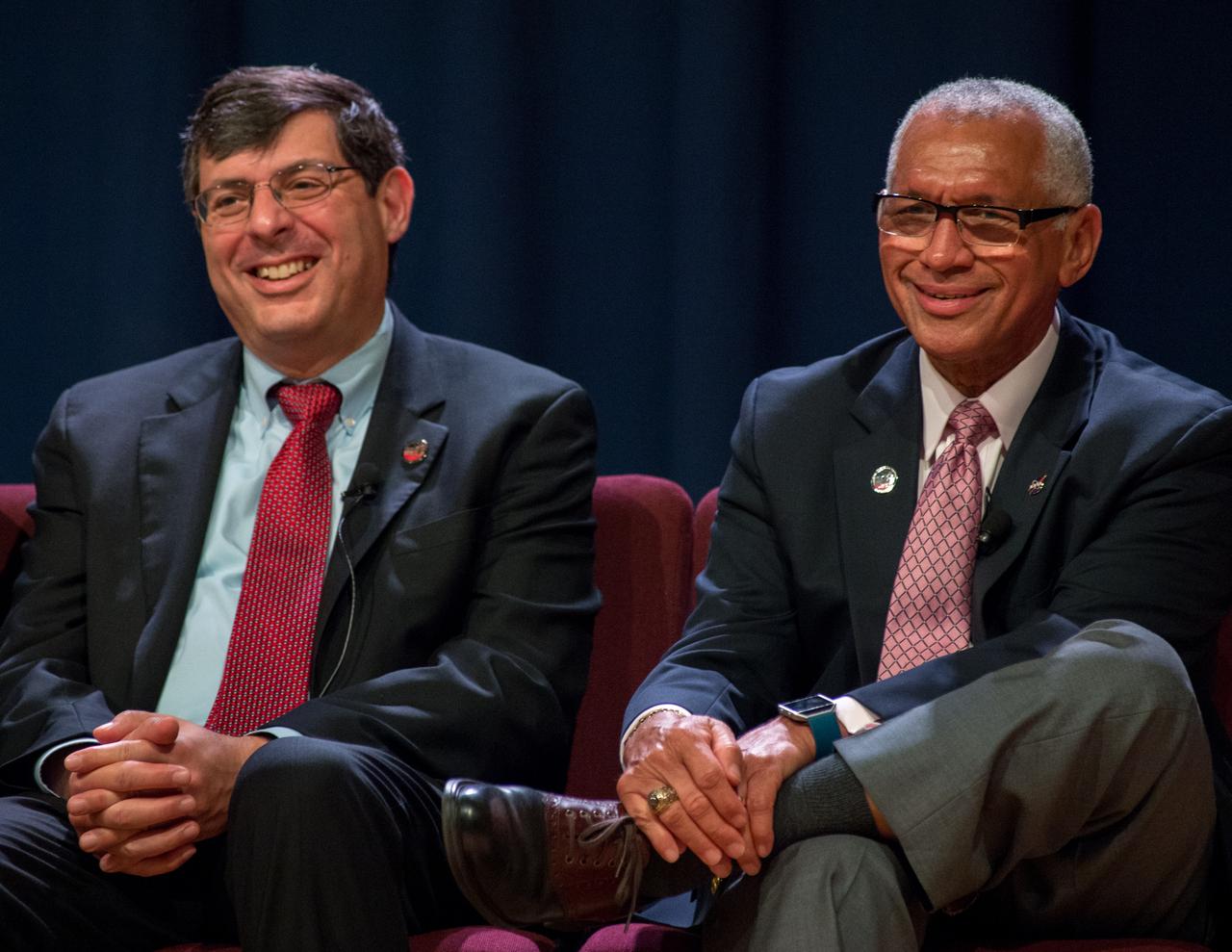

James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) Town Hall - Panel question and answer - Bill Ochs; Dr. John Mather; Dr. Eric Smith; Thomas Zurbuchen; Center Director Chris Scolese; NASA Administrator Charlie Bolden.