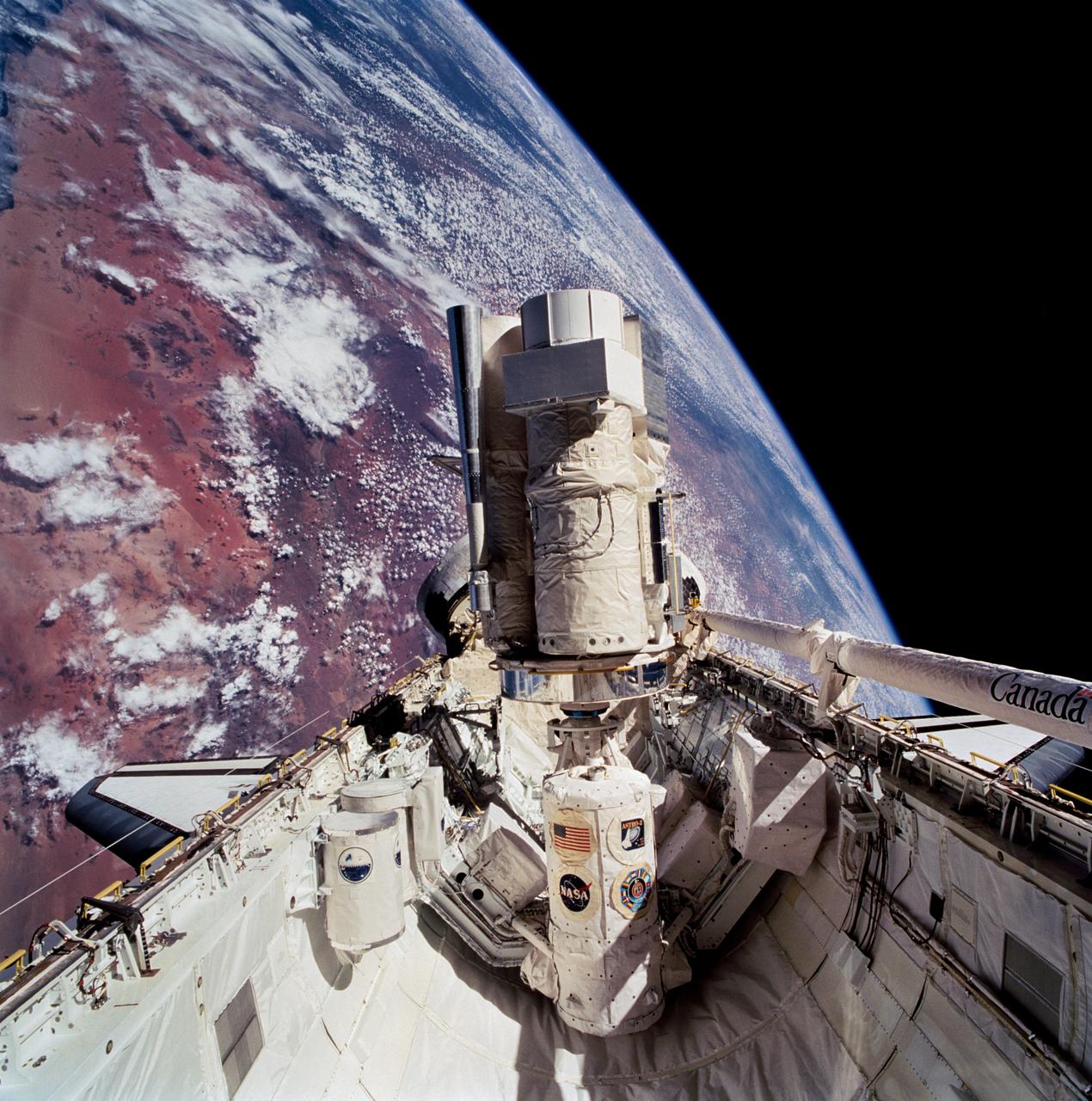

STS067-713-072 (2-18 March 1995) --- This 70mm cargo bay scene, backdropped against a desert area of Namibia, typifies the view that daily greeted the Astro-2 crew members during their almost 17-days aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. Positioned on the Spacelab pallet amidst other hardware, the Astro-2 payload is in its operational mode. Visible here are the Instrument Pointing System (IPS), Hopkins Ultraviolet Telescope (HUT), Star Tracker (ST), Ultraviolet Imaging Telescope (UIT), Wisconsin Ultraviolet Photo-Polarimeter Experiment (WUPPE), and Integrated Radiator System (IRS). At this angle, the Optical Sensor Package (OPS) is not seen. The Igloo, which supports the package of experiments, is in center foreground. Two Get-Away Special (GAS) canisters are in lower left foreground. The Extended Duration Orbiter (EDO) pallet, located aft of the cargo bay, is obscured by the Astro-2 payload. The Endeavour was 190 nautical miles above Earth.
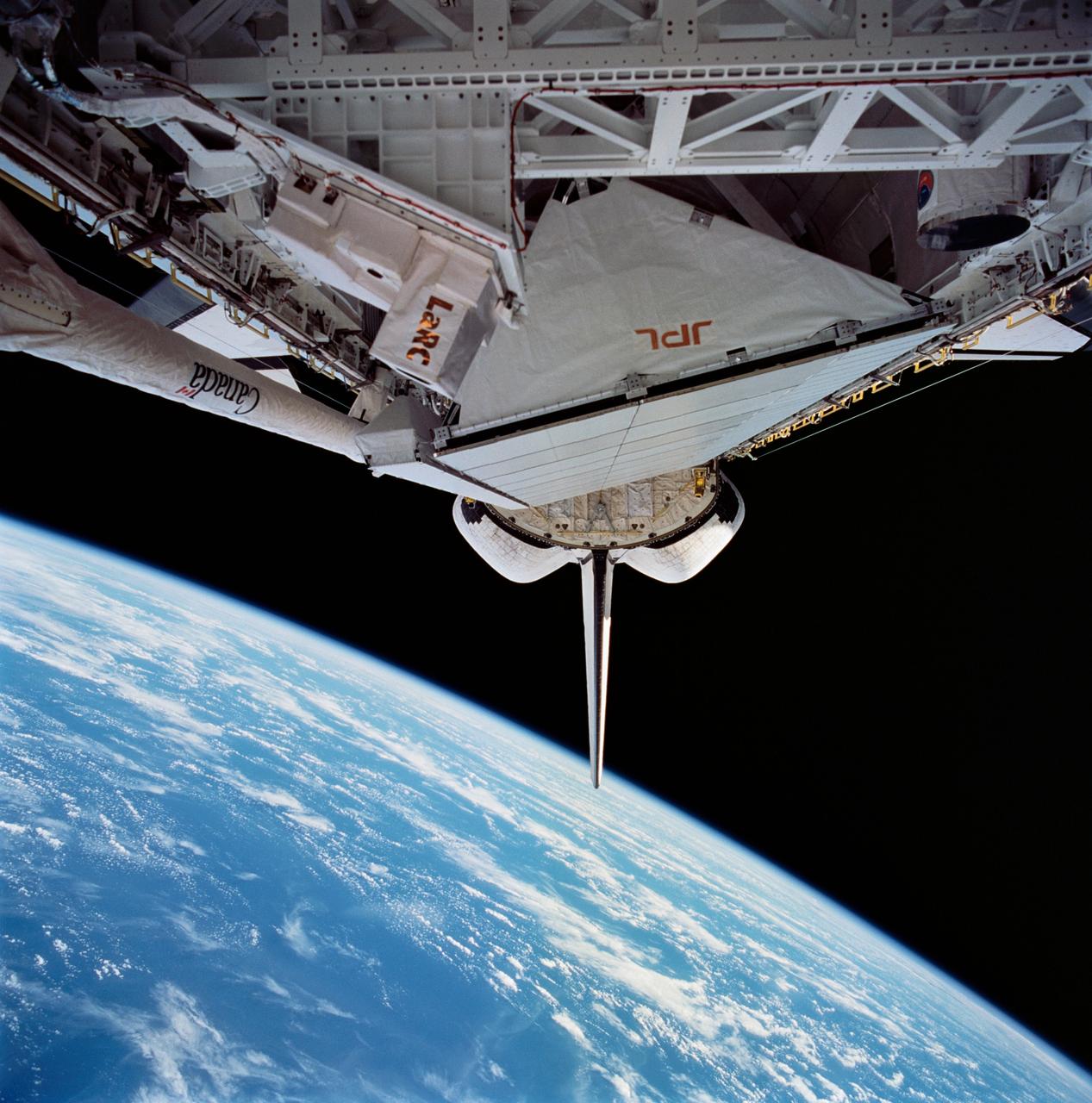

STS59-215-022 (12 April 1994) --- This 70mm frame, photographed through the aft flight deck windows of the Space Shuttle Endeavour, features the Space Radar Laboratory (SRL) payload in the cargo bay. An area of the Pacific Ocean northeast of Hawaii forms the backdrop for the image. Six NASA astronauts spent a week and a half in Earth orbit in support of the SRL mission.
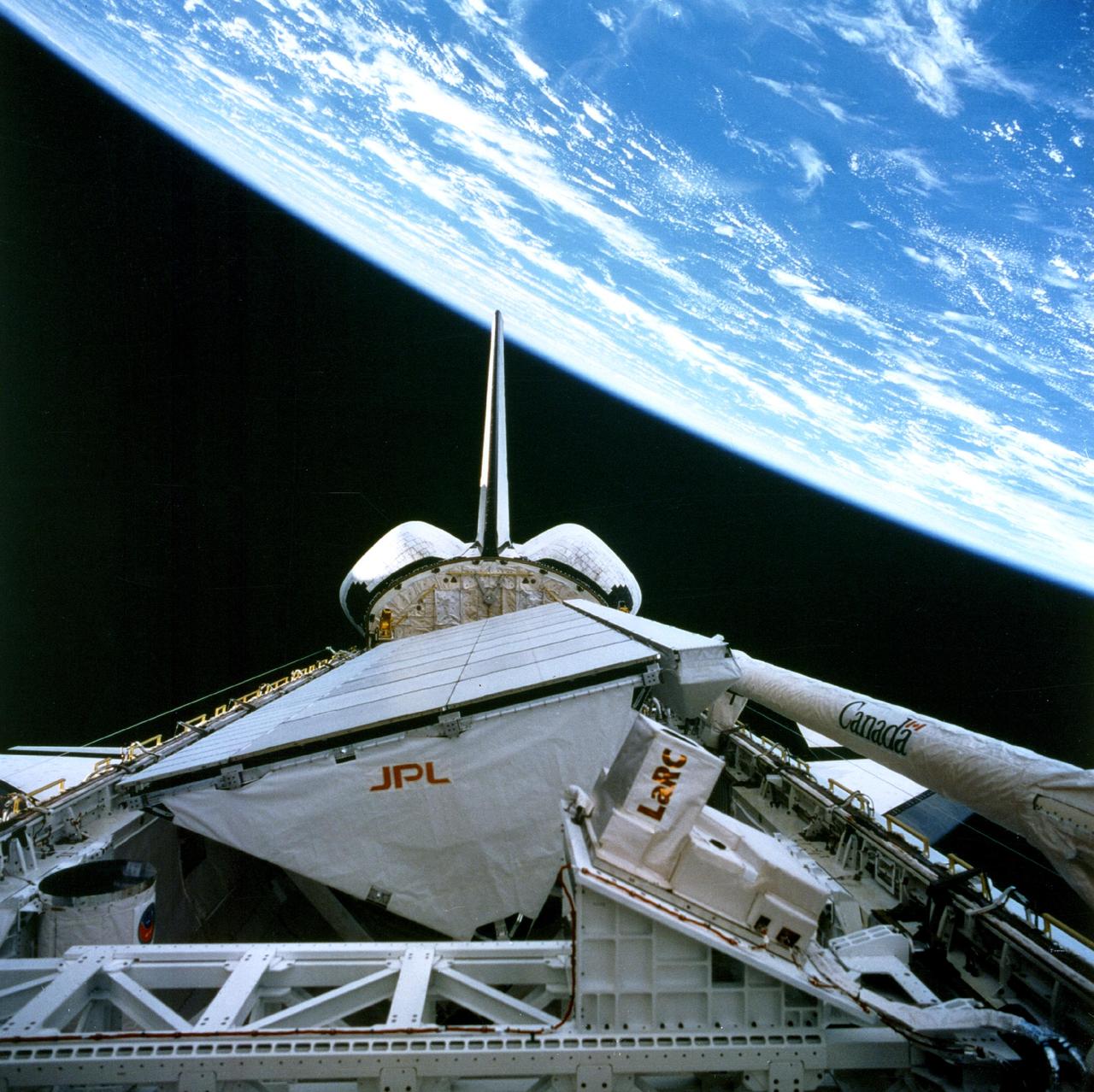

NASA SIR-C/X-SAR is shown here in the payload bay of the orbiting space shuttle Endeavour STS-59, with an area of the Pacific Ocean northeast of Hawaii in the background.
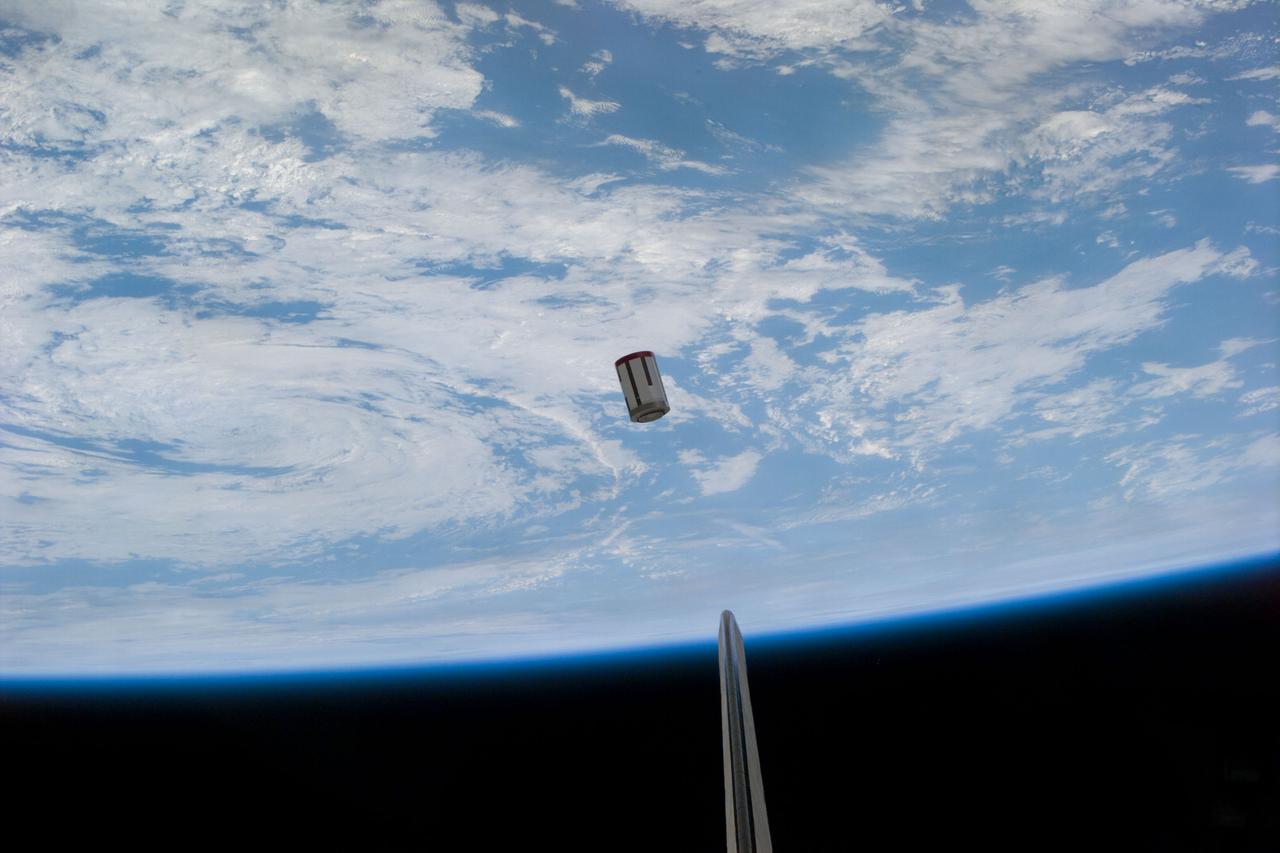

S77-E-5069 (22 May 1996) --- The Satellite Test Unit (STU), part of the Passive Aerodynamically Stabilized Magnetically Damped Satellite (PAMS) is seen moments after its ejection from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Endeavour. The scene was photographed with an Electronic Still Camera (ESC) onboard Endeavour's crew cabin during the deployment. The six-member crew will continue operations (tracking, rendezvousing and station-keeping) with PAMS-STU periodically throughout the remainder of the mission.
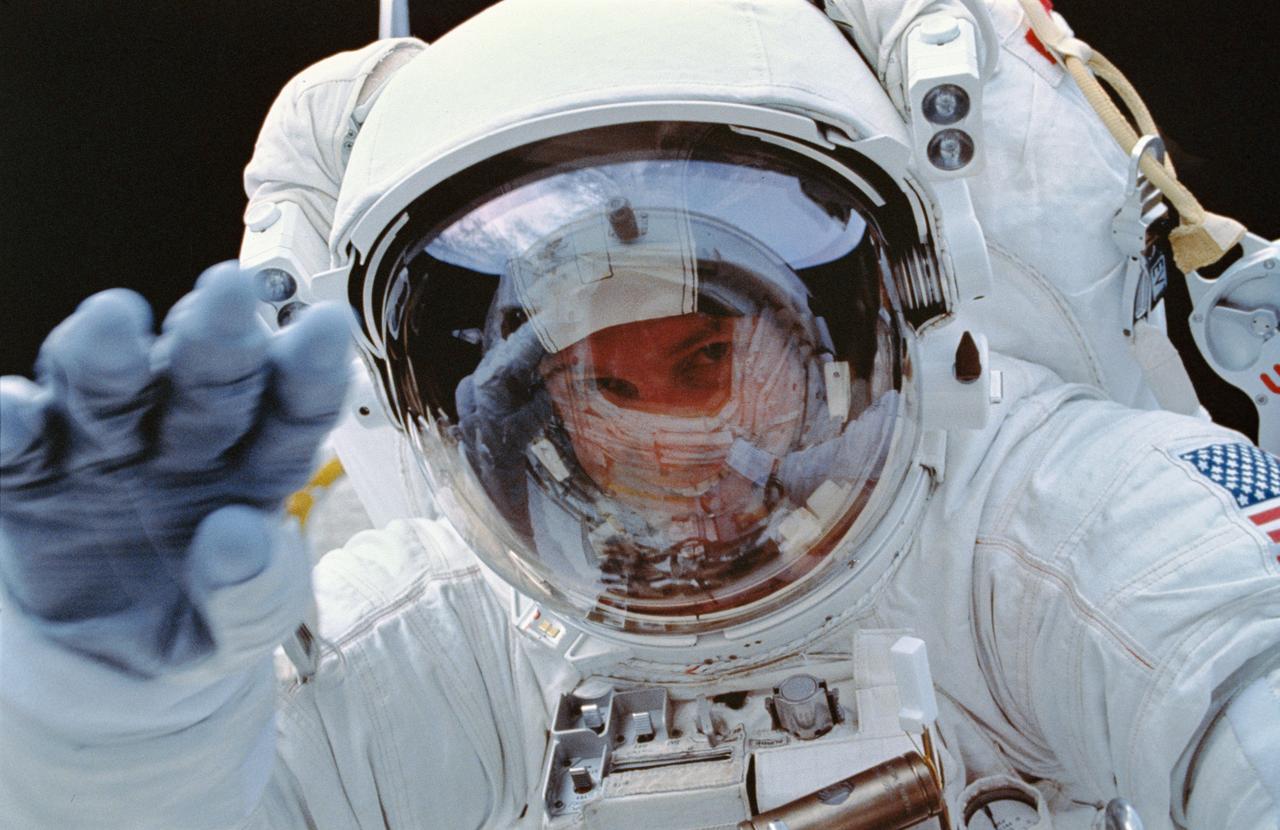

STS054-31-031 (17 Jan 1993) --- Astronaut Gregory J. Harbaugh, mission specialist, waves to fellow crew members on Endeavour's aft flight deck from the payload bay during the four-plus hours extravehicular activity (EVA). Harbaugh was joined on the EVA by astronaut Mario Runco Jr., mission specialist.
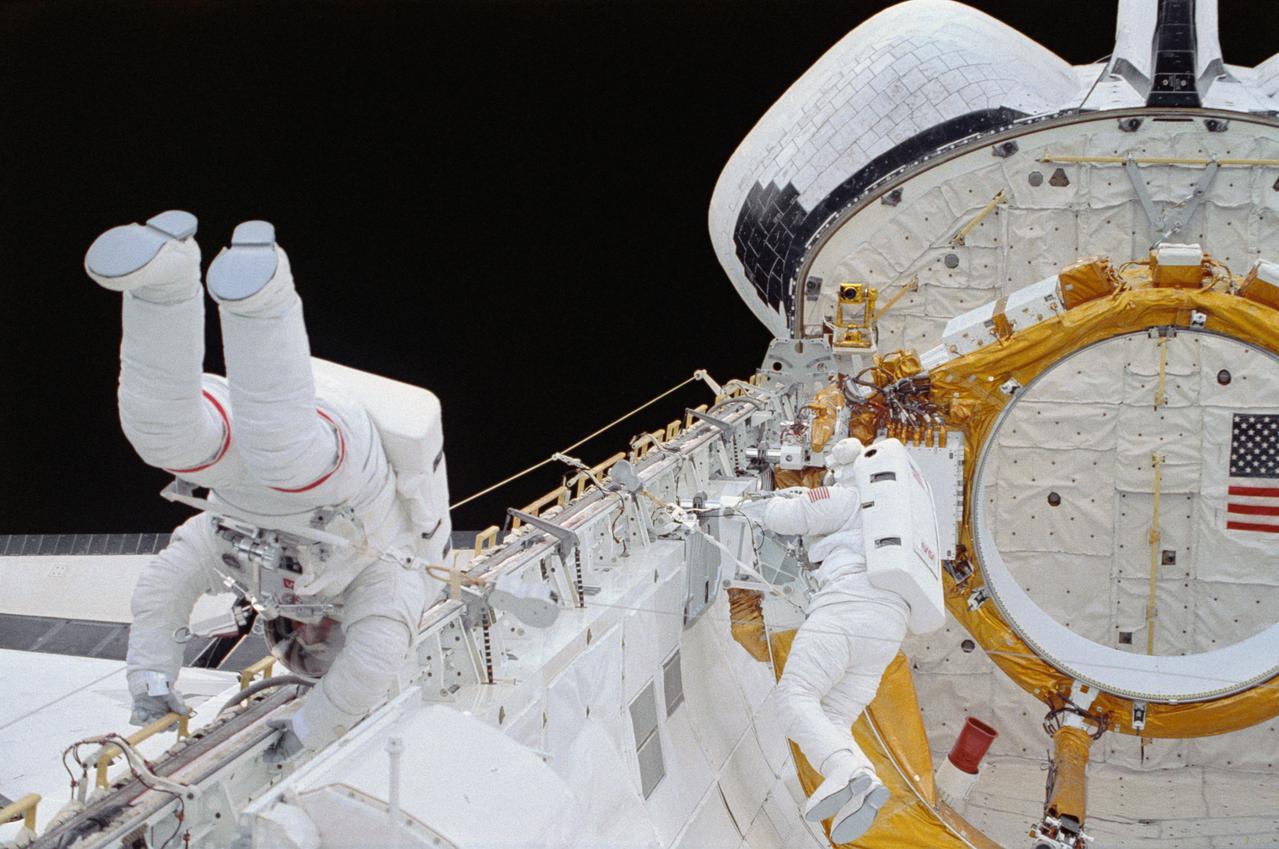

STS054-33-030 (17 Jan. 1993) --- Astronaut Gregory J. Harbaugh (left) translates along the starboard longeron in space shuttle Endeavour's cargo bay while astronaut Mario Runco Jr. prepares to work on a restraint device near the aft cargo bay firewall. The two mission specialists spent four-plus hours on the extravehicular activity (EVA) on Jan. 17, 1993. Others onboard NASA's newest shuttle for the six-day mission were astronauts John H. Casper, mission commander; Donald R. McMonagle, pilot; and Susan J. Helms, mission specialist. The photograph was taken with a 35mm camera. Photo credit: NASA
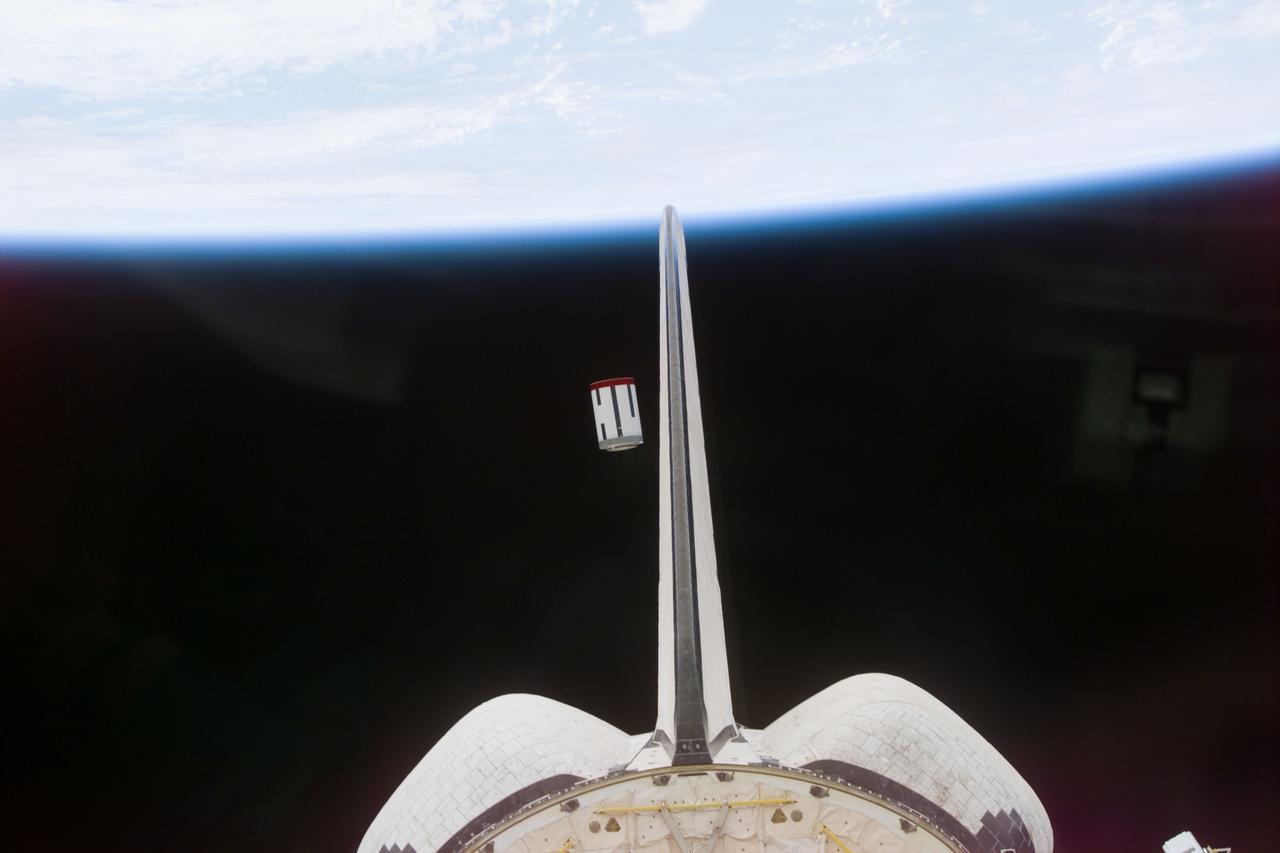

S77-E-5068 (22 May 1996) --- The Satellite Test Unit (STU), part of the Passive Aerodynamically Stabilized Magnetically Damped Satellite (PAMS) is seen moments after its ejection from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Endeavour. The scene was photographed with an Electronic Still Camera (ESC) onboard Endeavour's crew cabin during the deployment. The six-member crew will continue operations (tracking, rendezvousing and station-keeping) with PAMS-STU periodically throughout the remainder of the mission.
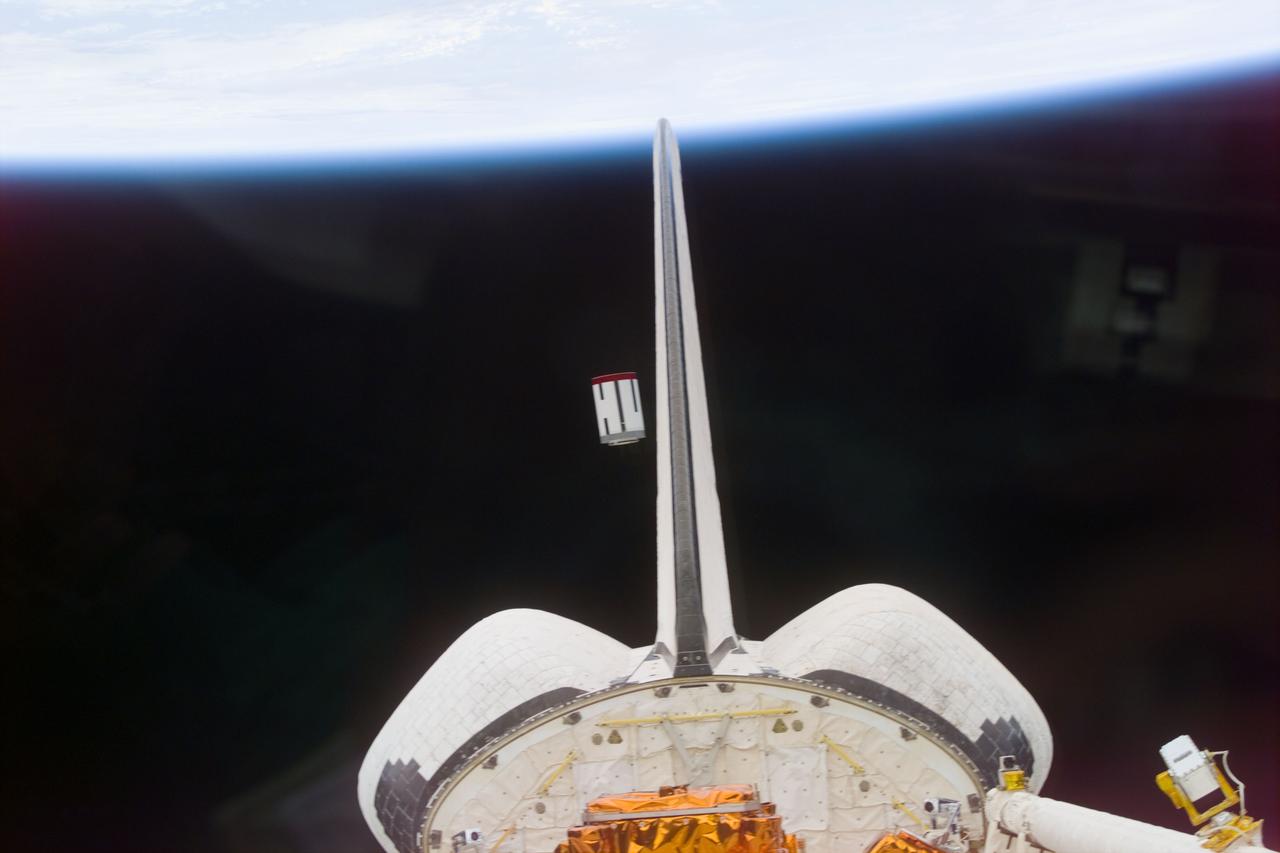

S77-E-5067 (22 May 1996) --- The Satellite Test Unit (STU), part of the Passive Aerodynamically Stabilized Magnetically Damped Satellite (PAMS) is seen moments after its ejection from the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Endeavour. The scene was photographed with an Electronic Still Camera (ESC) onboard Endeavour's crew cabin during the deployment. The six-member crew will continue operations (tracking, rendezvousing and station-keeping) with PAMS-STU periodically throughout the remainder of the mission.
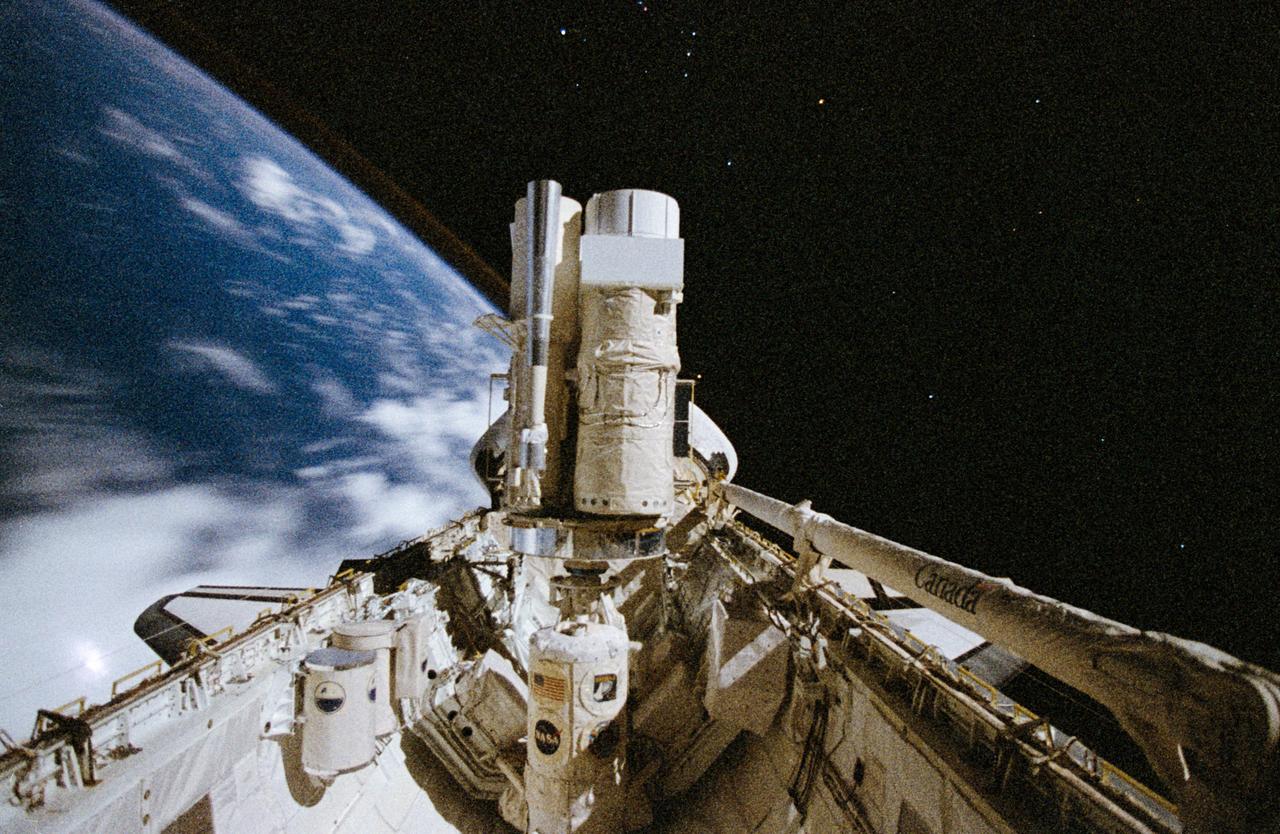

STS067-371-028 (2-18 March 1995) --- This 35mm lunar-illuminated scene of the Astro-2 payload in the Space Shuttle Endeavour's cargo bay was recorded by one of by the seven crew members during one of the many night passes of the almost 17-day mission. The cluster of telescopes and the Instrument Pointing System (IPS) are backdropped against the blue and white Earth and the darkness of space. What is believed to be the Constellation Orion is visible at upper center.
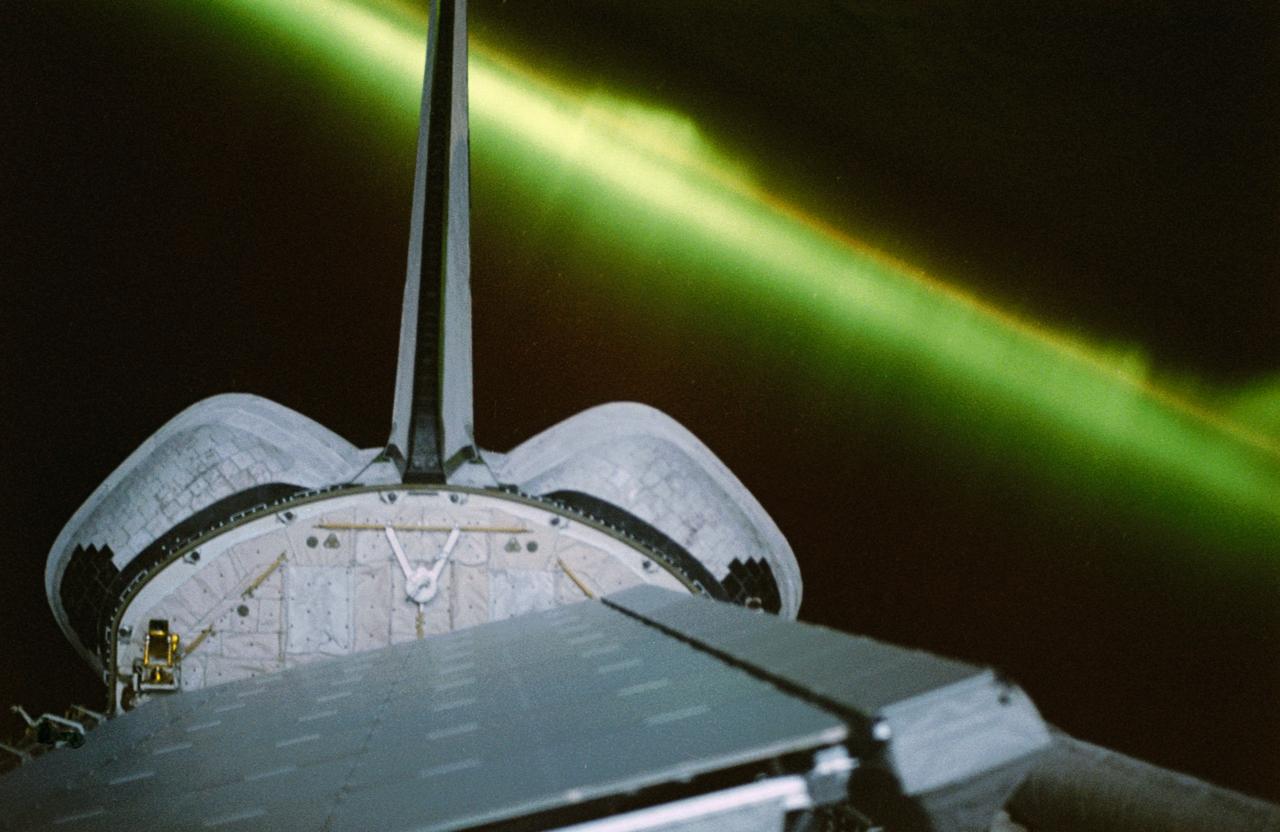

STS059-50-011 (9-20 April 94) --- A greenish appearing aurora forms the backdrop for this 35mm scene of the Earth orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour's aft cargo bay. Featured in the bay are the antennae for the SIR-C/X-SAR imaging radar instruments, illuminated by moonlight. The crew sighted the southern lights (aurora australis) several times during each of the eleven days of the mission.
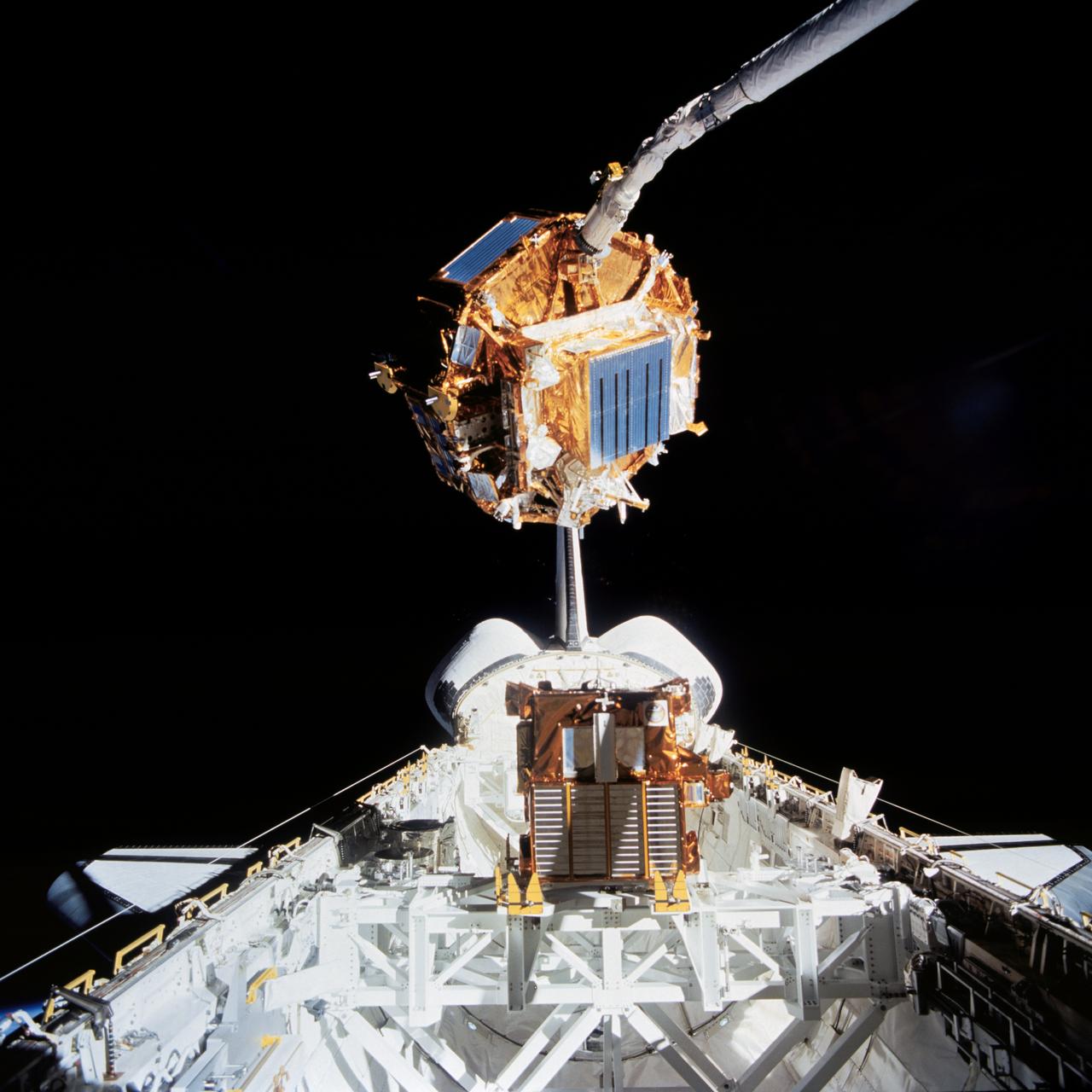

STS072-734-011 (11 Jan. 1996) --- The crewmembers captured this 35mm view of the Japanese Space Flyer Unit (SFU) during its berthing with the Remote Manipulator System (RMS). Yet to be deployed is the Office of Aeronautics and Space Technology (OAST) Flyer satellite, seen at bottom center.
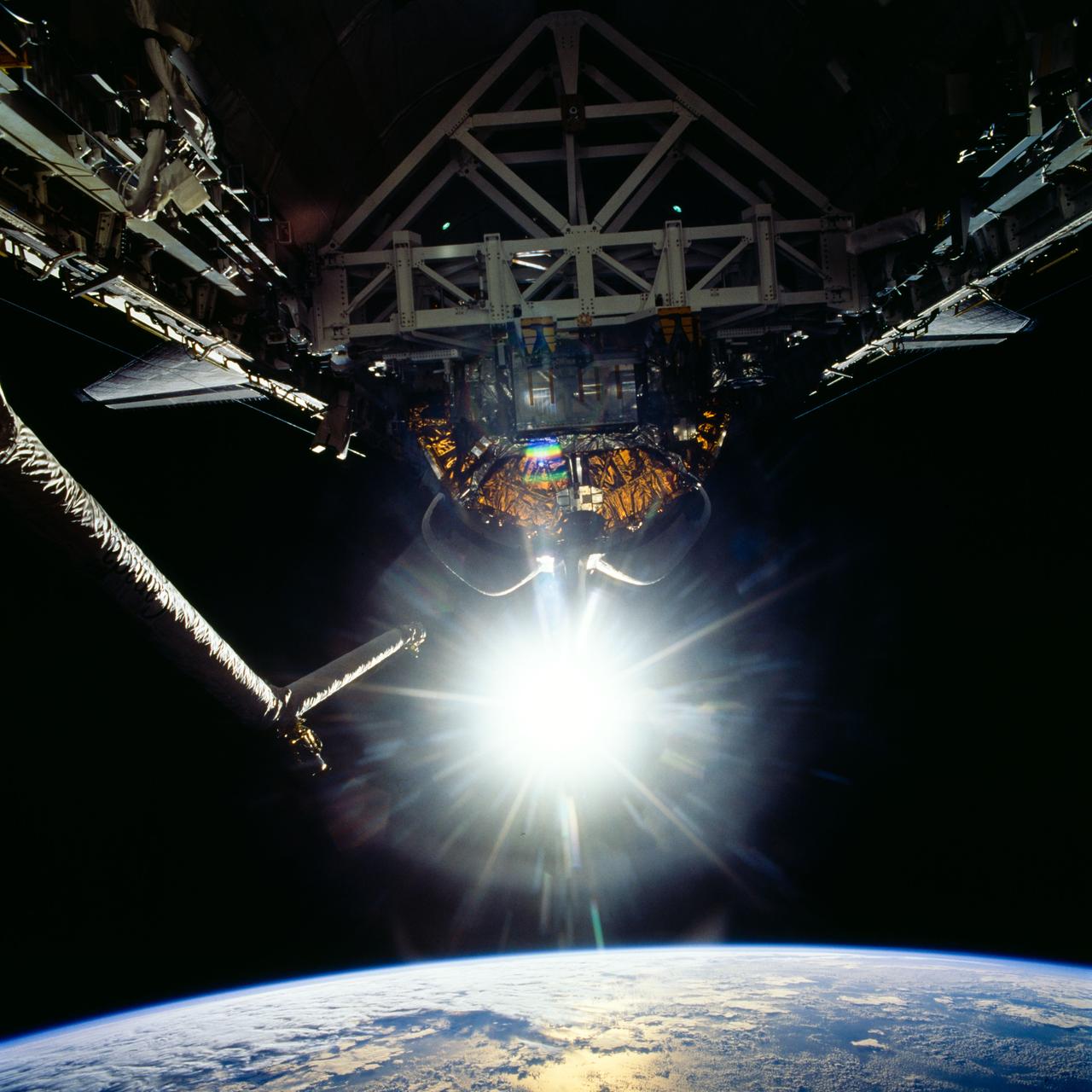

STS072-726-085 (11-20 Jan. 1996) --- The crew members captured this 70mm view of the Space Shuttle Endeavour’s cargo bay, with the reflection of sunglint over Earth’s horizon. The Canadian-built Remote Manipulator System (RMS) arm, with two television cameras affixed, is at frame right. The crew earlier had retrieved the Japanese Space Flyer (SFU) and berthed in the aft cargo bay, along with the Office of Aeronautics and Space Technology (OAST) Flyer satellite.
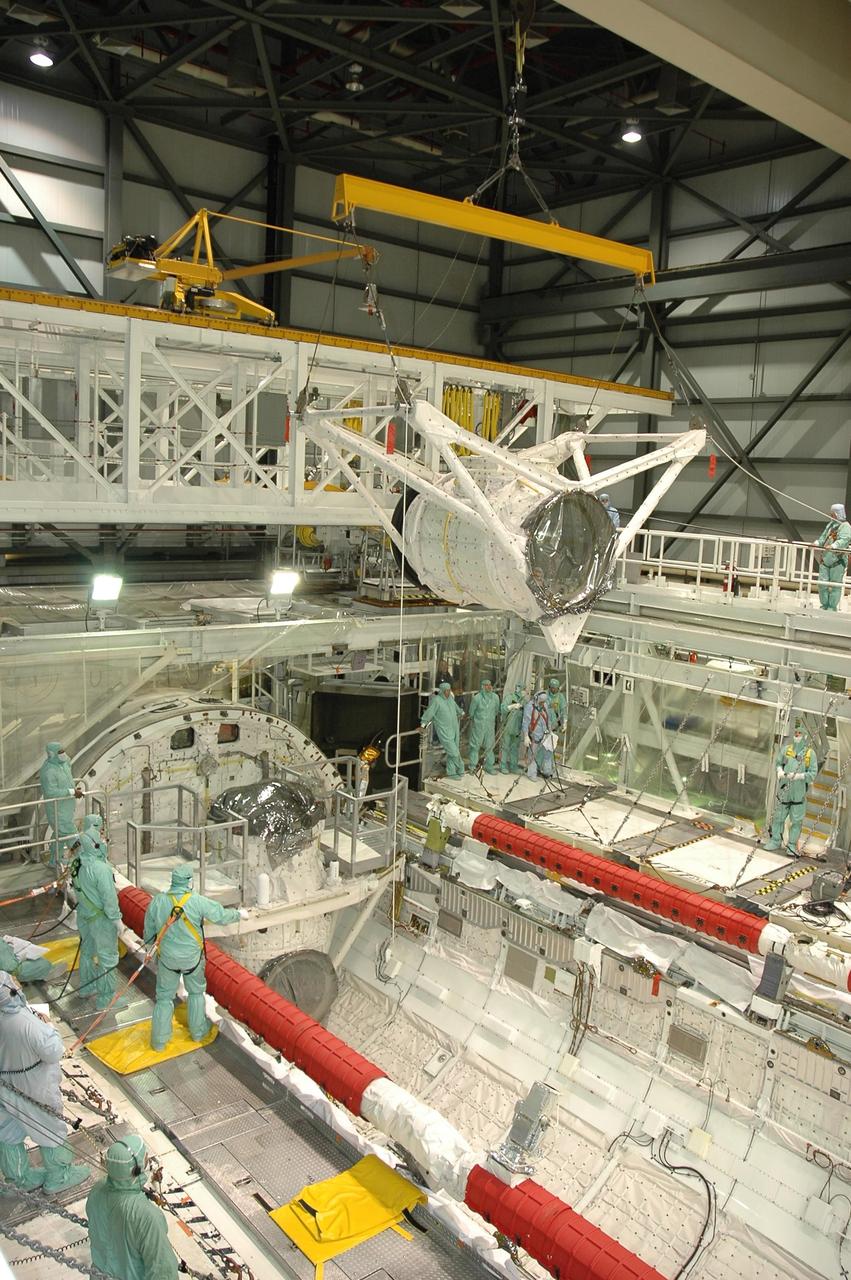

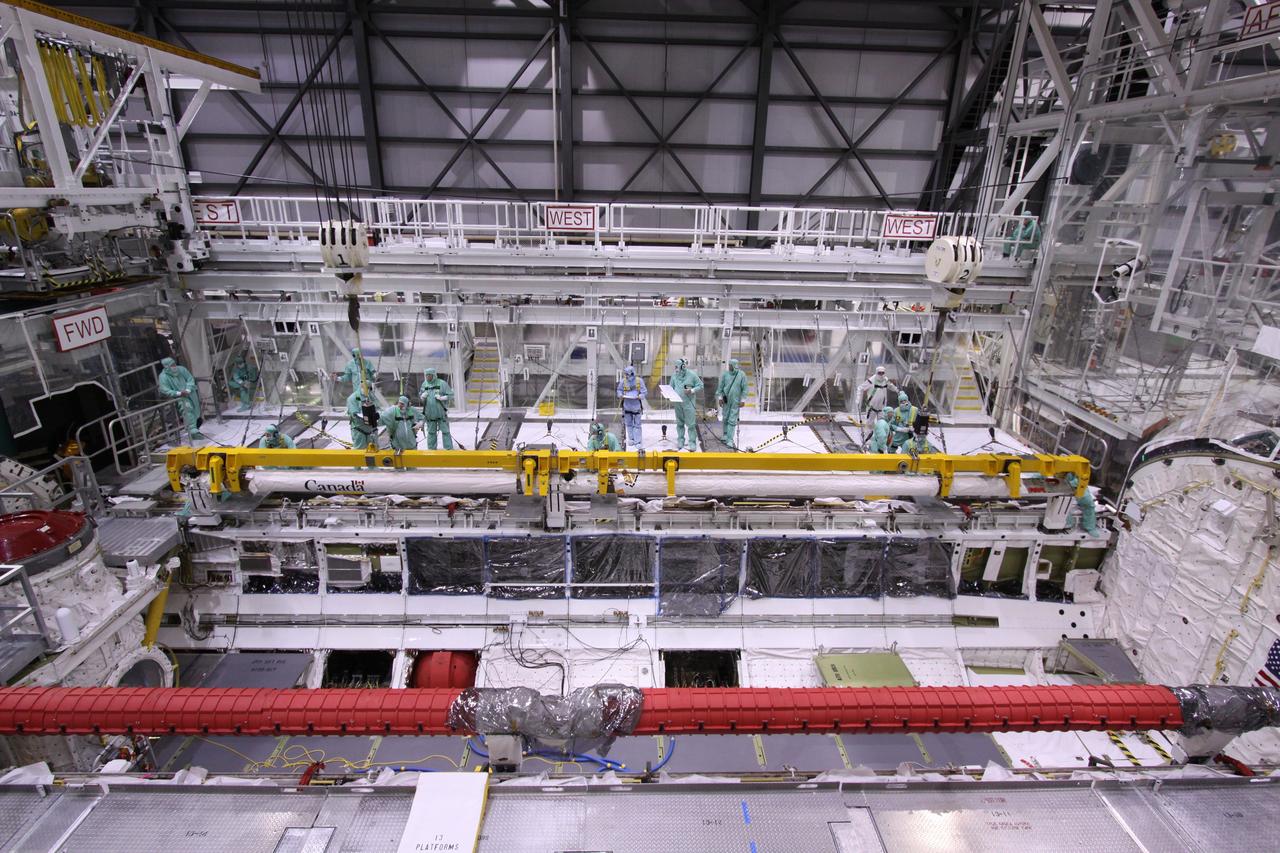
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the crew airlock module is suspended above Endeavour's payload bay. The module will be lowered into the payload bay and installed. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
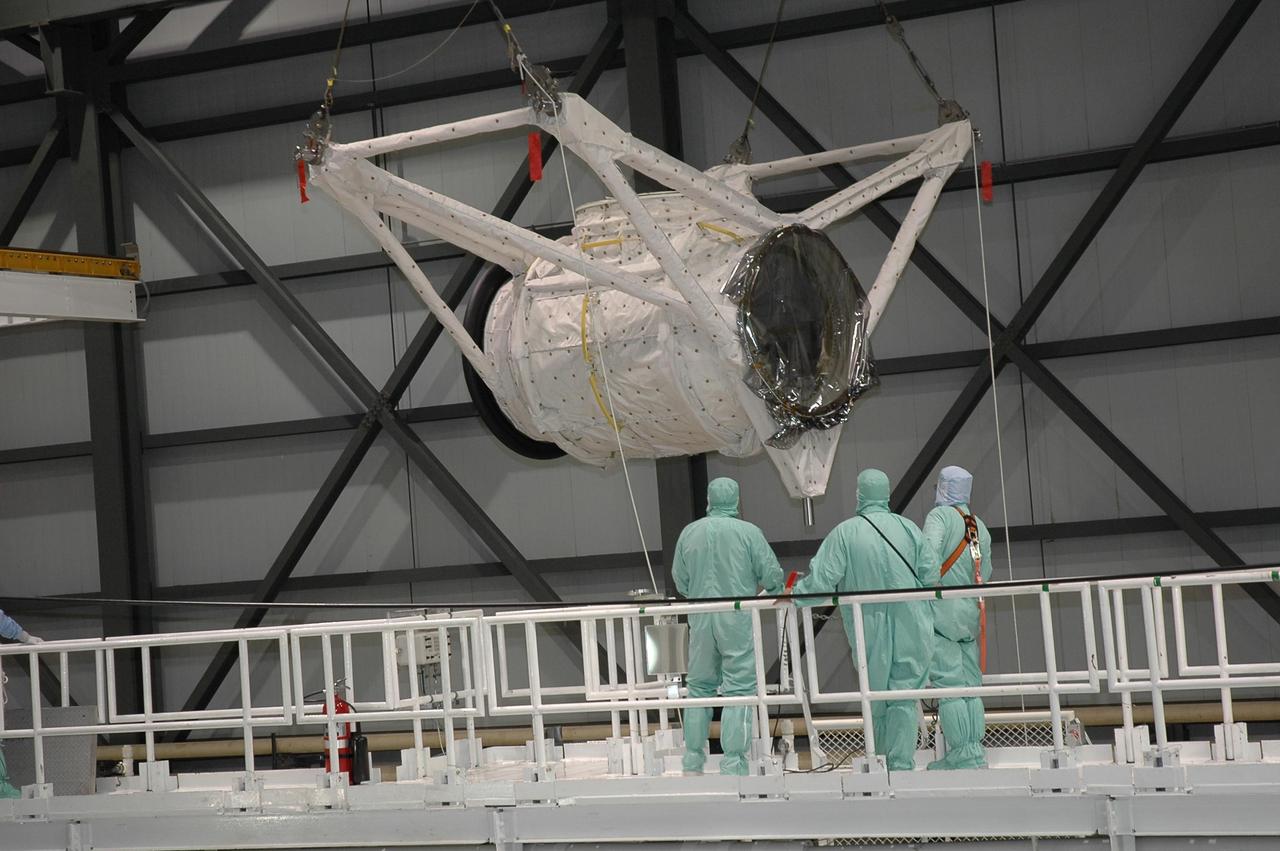

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane moves the crew airlock module toward Endeavour. It will be installed in Endeavour's payload bay. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In NASA Kennedy Space Center's Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, space shuttle Endeavour's Orbiter Boom Sensor System is lowered into position in the shuttle's payload bay. The OBSS is being reinstalled in the payload bay. The OBSS is being reinstalled in the payload bay. The OBSS is a 50-foot boom with a laser and cameras on it that astronauts use to inspect a shuttle's heat shield while in orbit. After returning from the STS-127 mission July 31, 2009, Endeavour now is being processed for the STS-130 mission targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. Endeavour will deliver to the International Space Station the Tranquility pressurized module that will provide room for many of the station's life support systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In NASA Kennedy Space Center's Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, space shuttle Endeavour's Orbiter Boom Sensor System is lowered into position in the shuttle's payload bay. The OBSS is being reinstalled in the payload bay. The OBSS is being reinstalled in the payload bay. The OBSS is a 50-foot boom with a laser and cameras on it that astronauts use to inspect a shuttle's heat shield while in orbit. After returning from the STS-127 mission July 31, 2009, Endeavour now is being processed for the STS-130 mission targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. Endeavour will deliver to the International Space Station the Tranquility pressurized module that will provide room for many of the station's life support systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
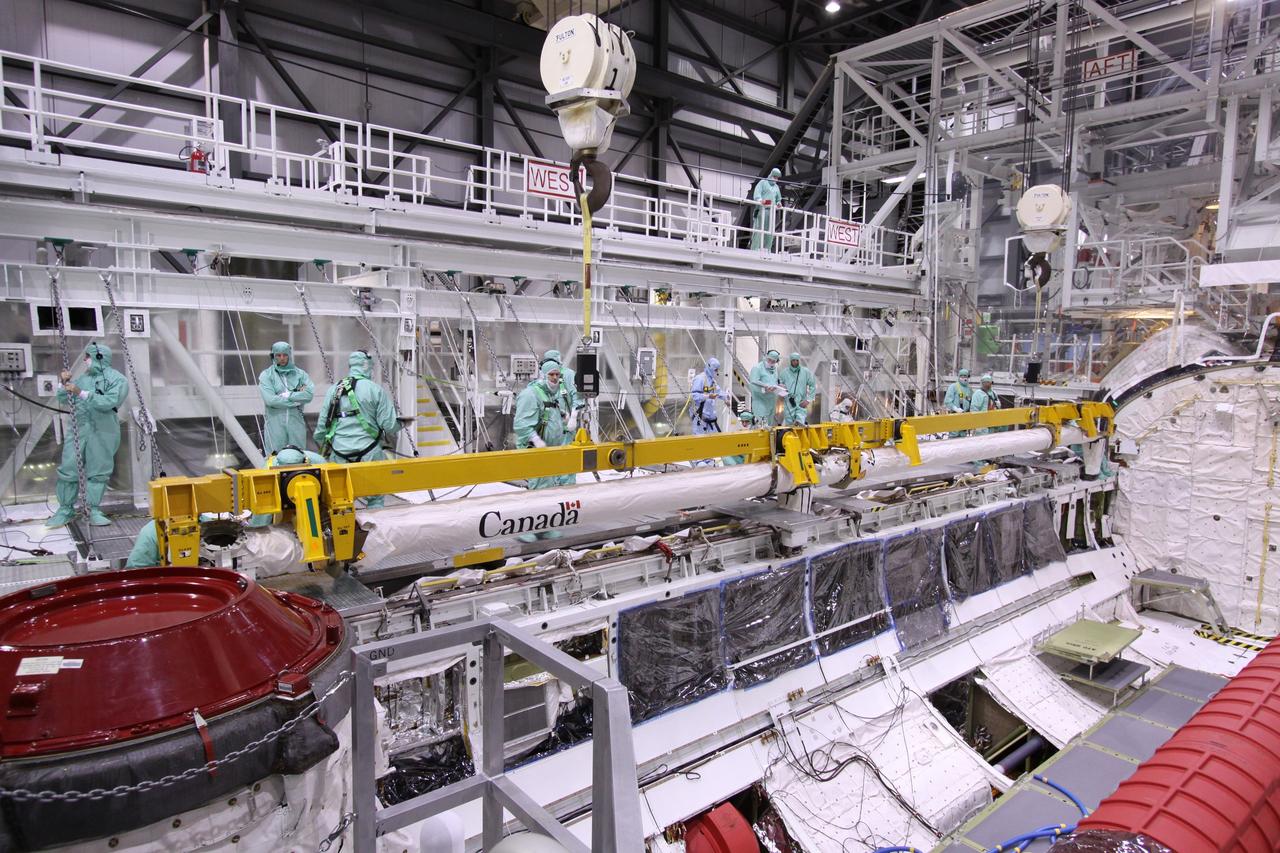

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In NASA Kennedy Space Center's Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, workers check the movement of space shuttle Endeavour's Orbiter Boom Sensor System as it is lowered into the payload bay. The OBSS is being reinstalled in the payload bay. The OBSS is being reinstalled in the payload bay. The OBSS is a 50-foot boom with a laser and cameras on it that astronauts use to inspect a shuttle's heat shield while in orbit. After returning from the STS-127 mission July 31, 2009, Endeavour now is being processed for the STS-130 mission targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. Endeavour will deliver to the International Space Station the Tranquility pressurized module that will provide room for many of the station's life support systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
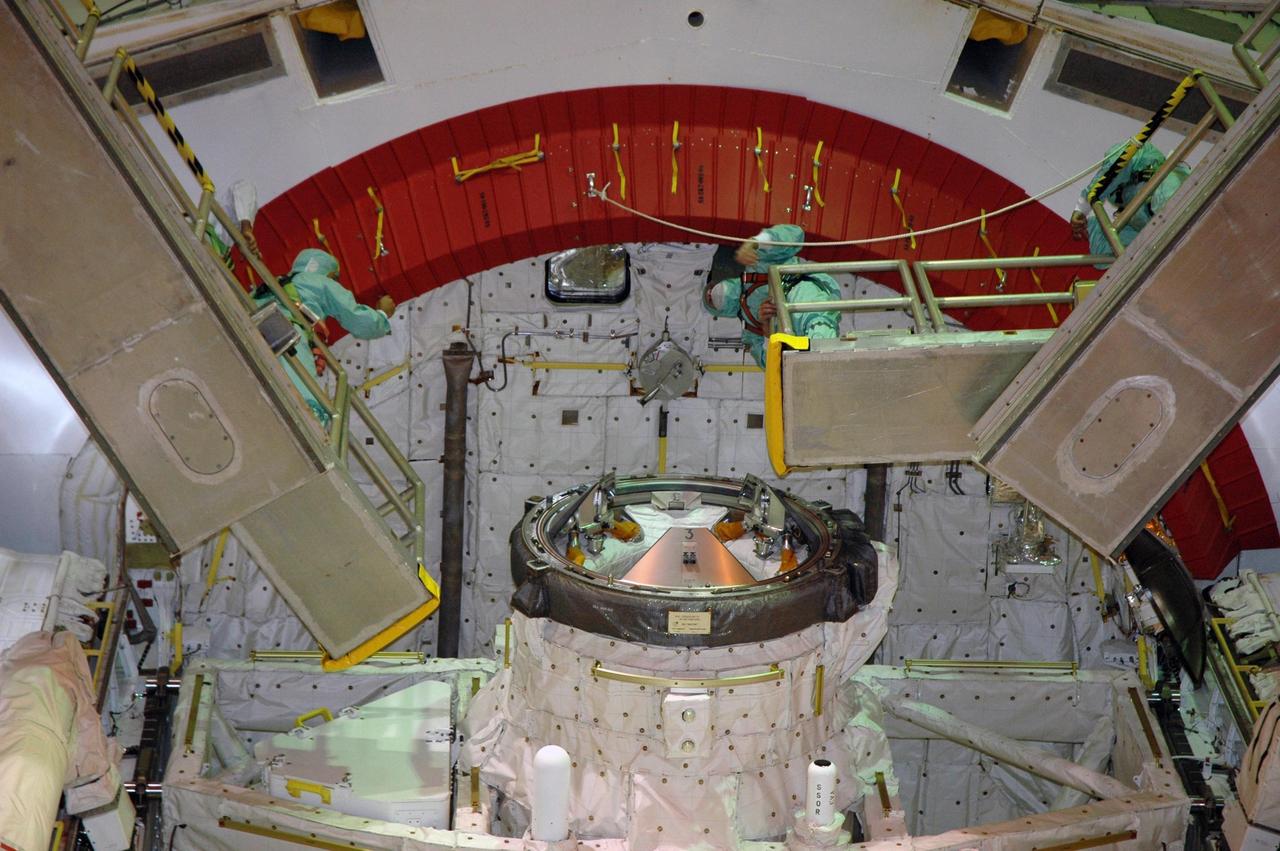

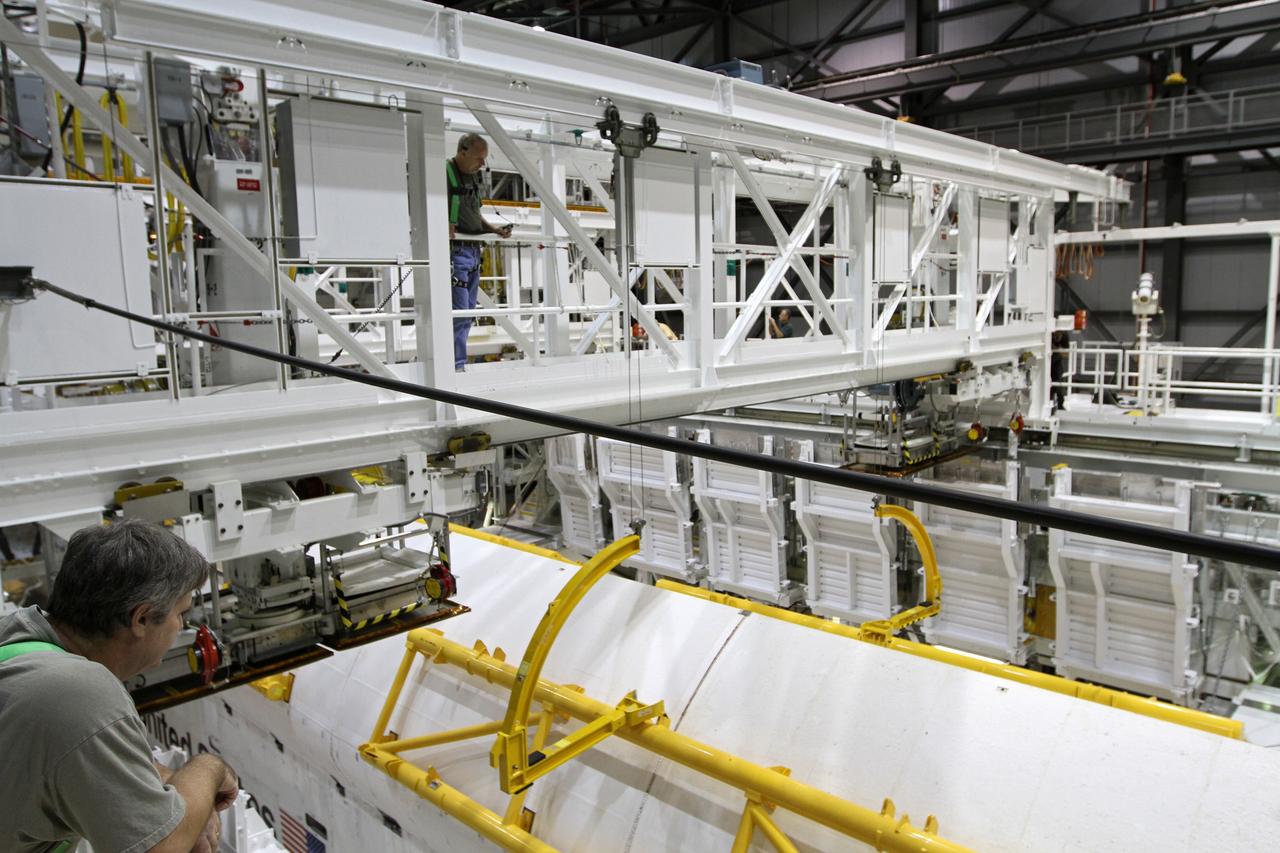
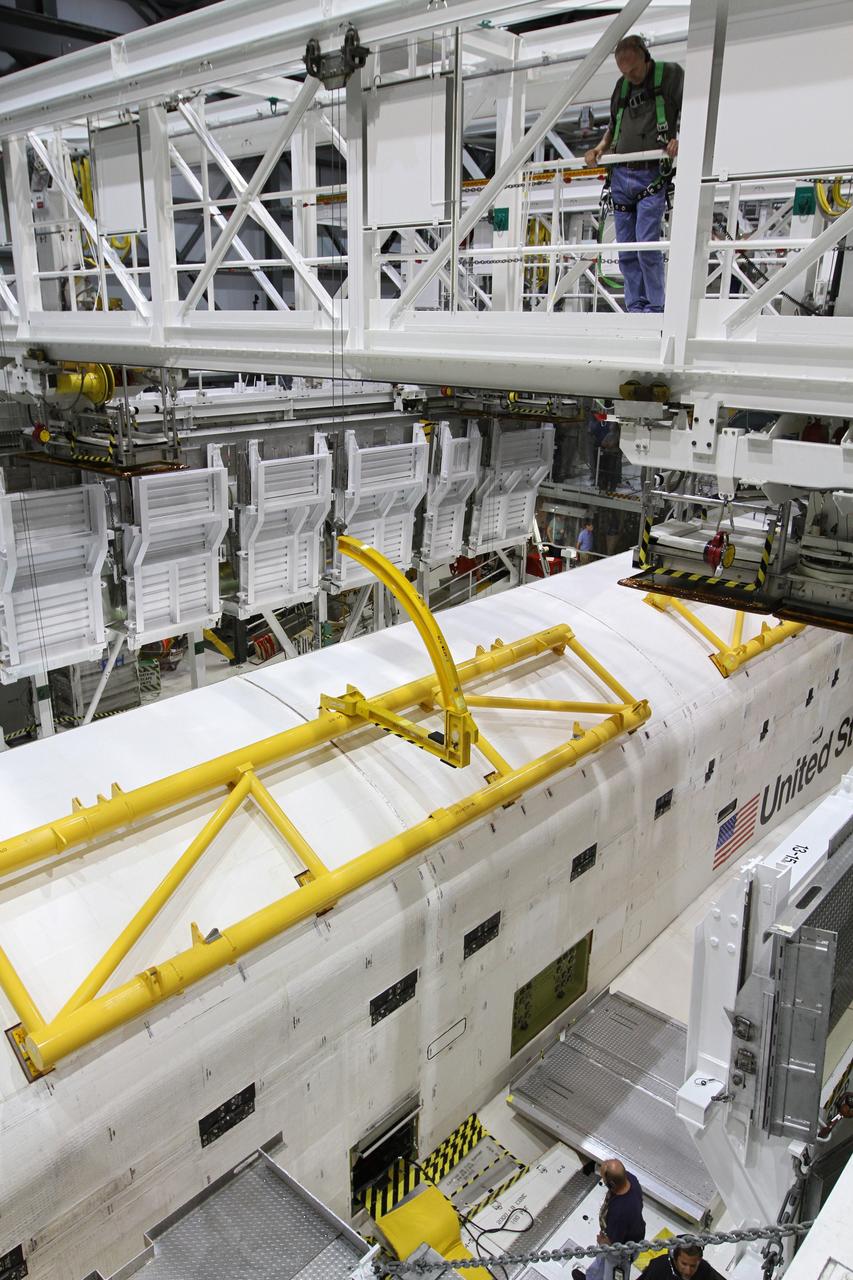
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Looking into the open payload bay doors of Space Shuttle Endeavour, workers conclude closeouts. At center foreground is the orbital docking system. The red ring at top comprises rain gutters to prevent leaks into the bay from rain while the shuttle is on the pad. The payload bay doors were opened to allow for payload closeouts, including camera tests on the shuttle robotic arm and the extension, known as the orbiter boom sensor system. Endeavour is scheduled to launch Aug. 7 on mission STS-118, the 22nd flight to the International Space Station. NASA/Charisse Nahser
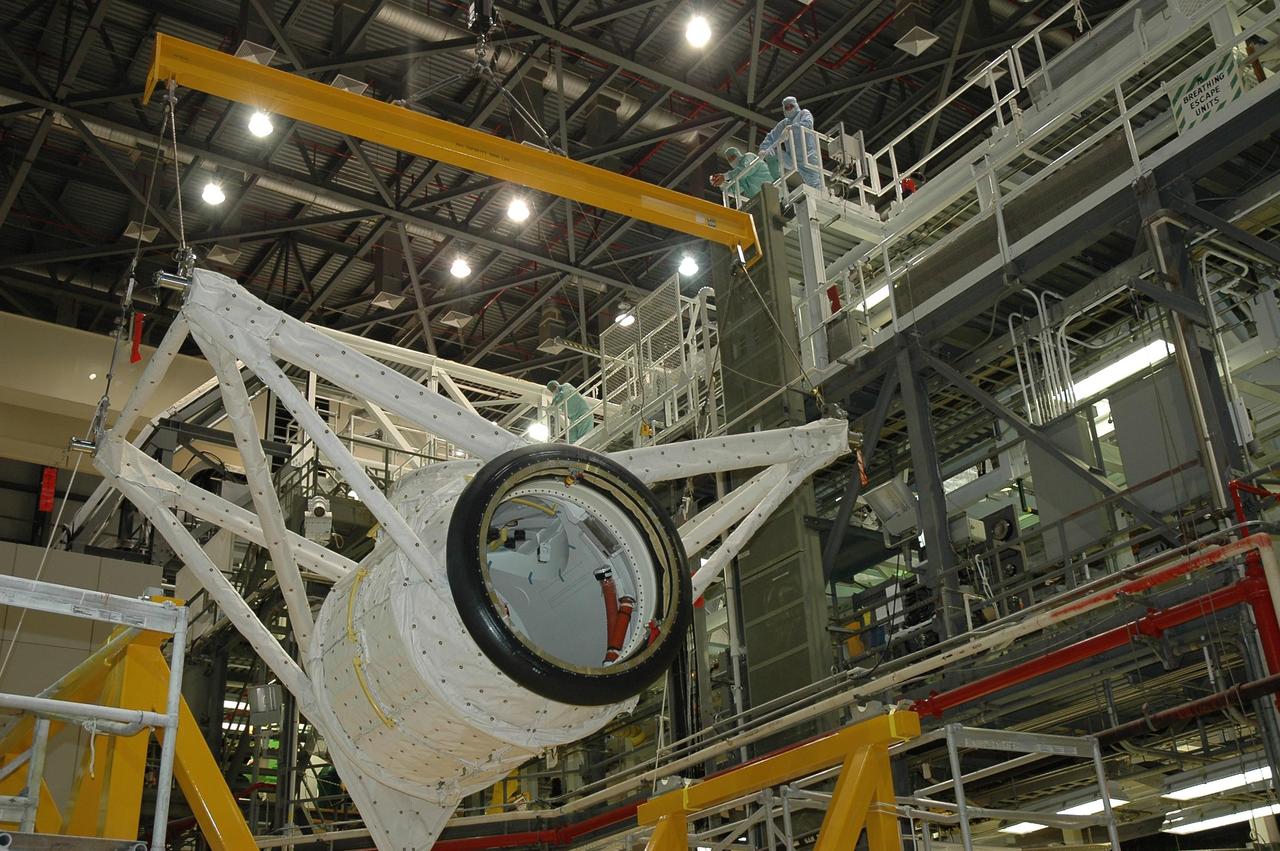

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane moves the crew airlock module across the bay to install it in Endeavour's payload bay. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
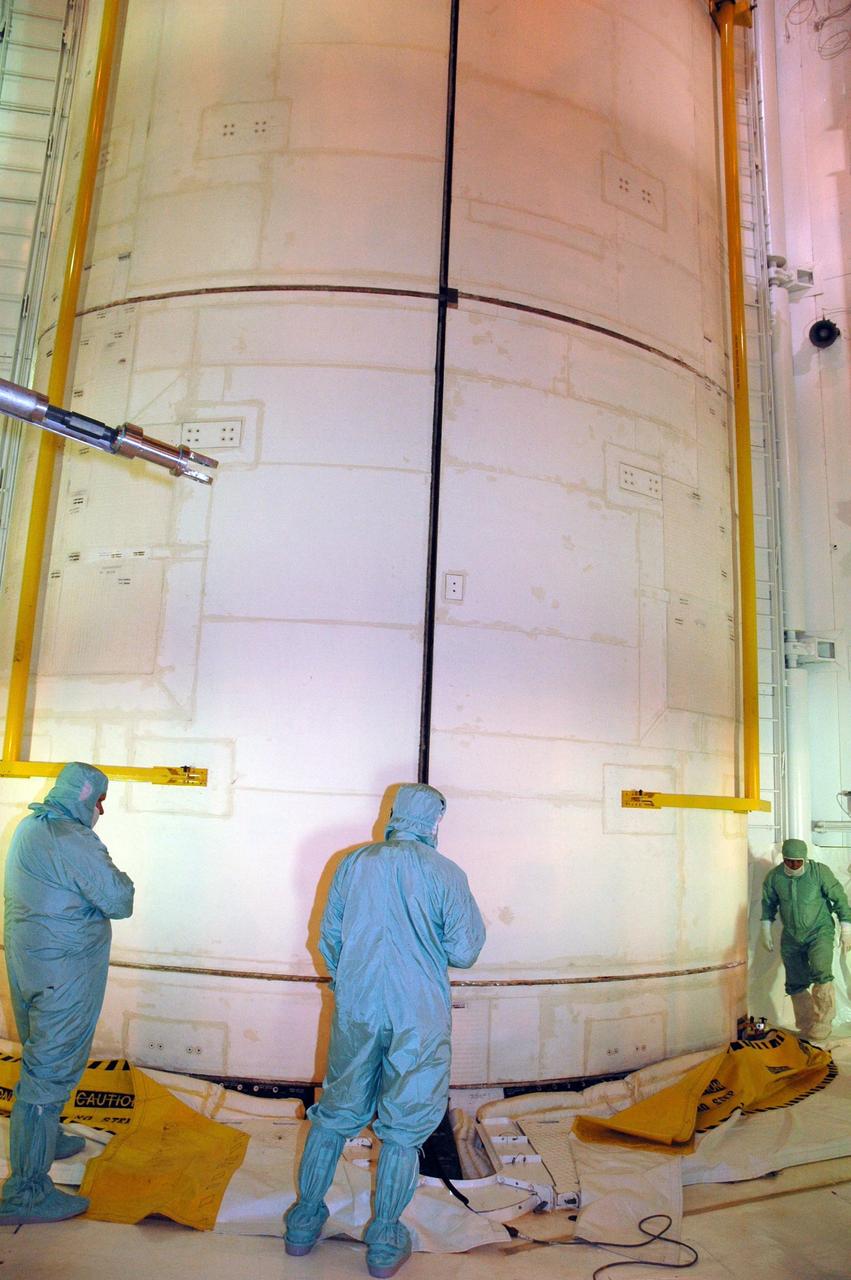

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 39A, workers check the closing of Endeavour's payload bay doors. The payload bay doors were opened to allow for payload closeouts, including camera tests on the shuttle robotic arm and the extension, known as the orbiter boom sensor system. Endeavour is scheduled to launch Aug. 7 on mission STS-118, the 22nd flight to the International Space Station. NASA/Charisse Nahser
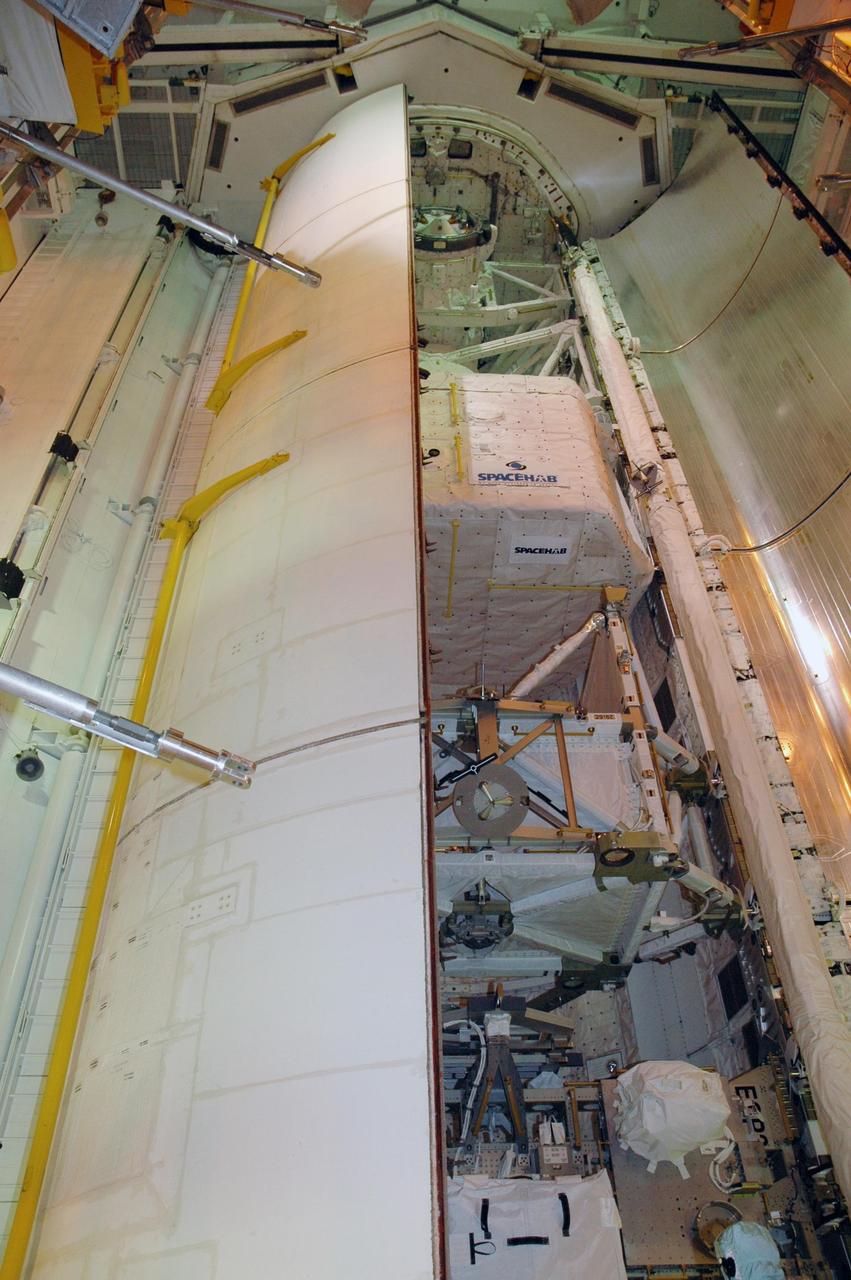

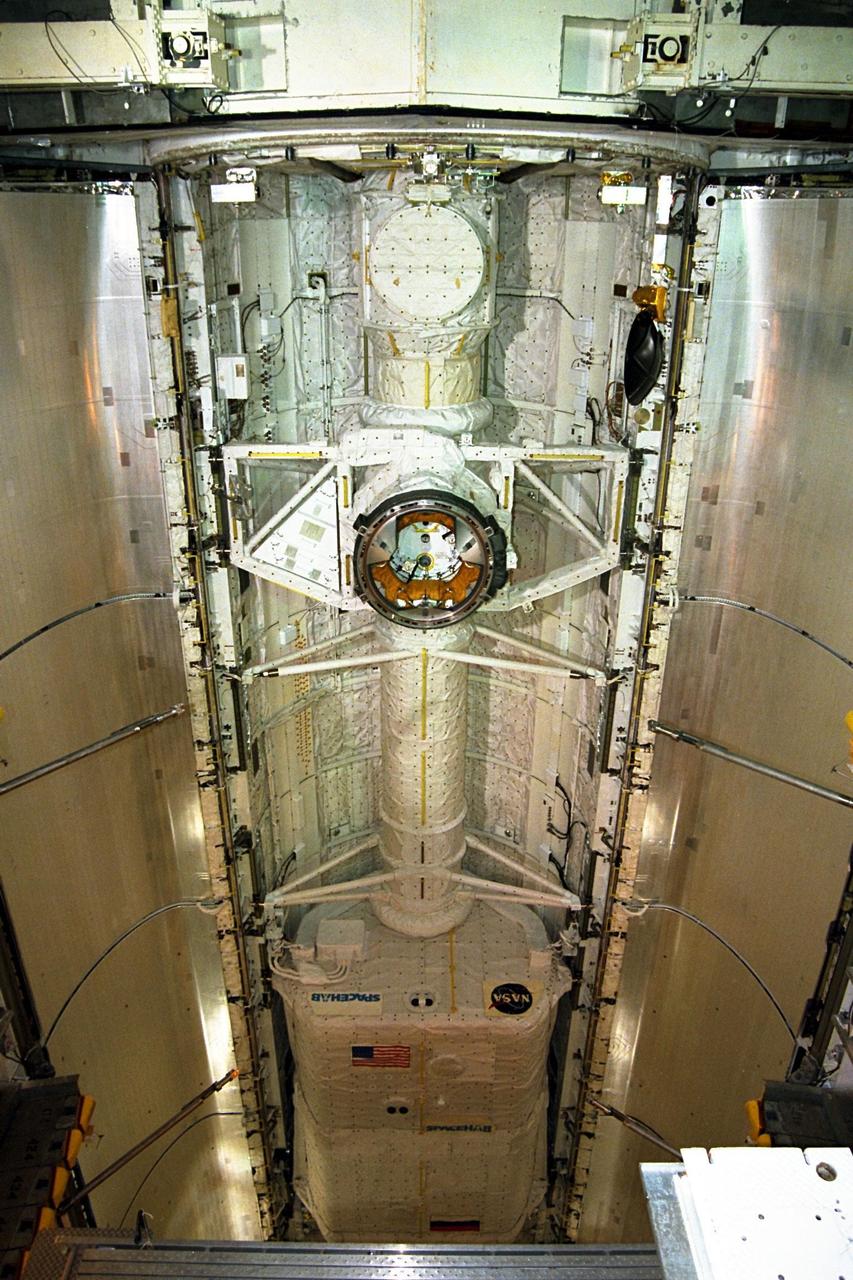
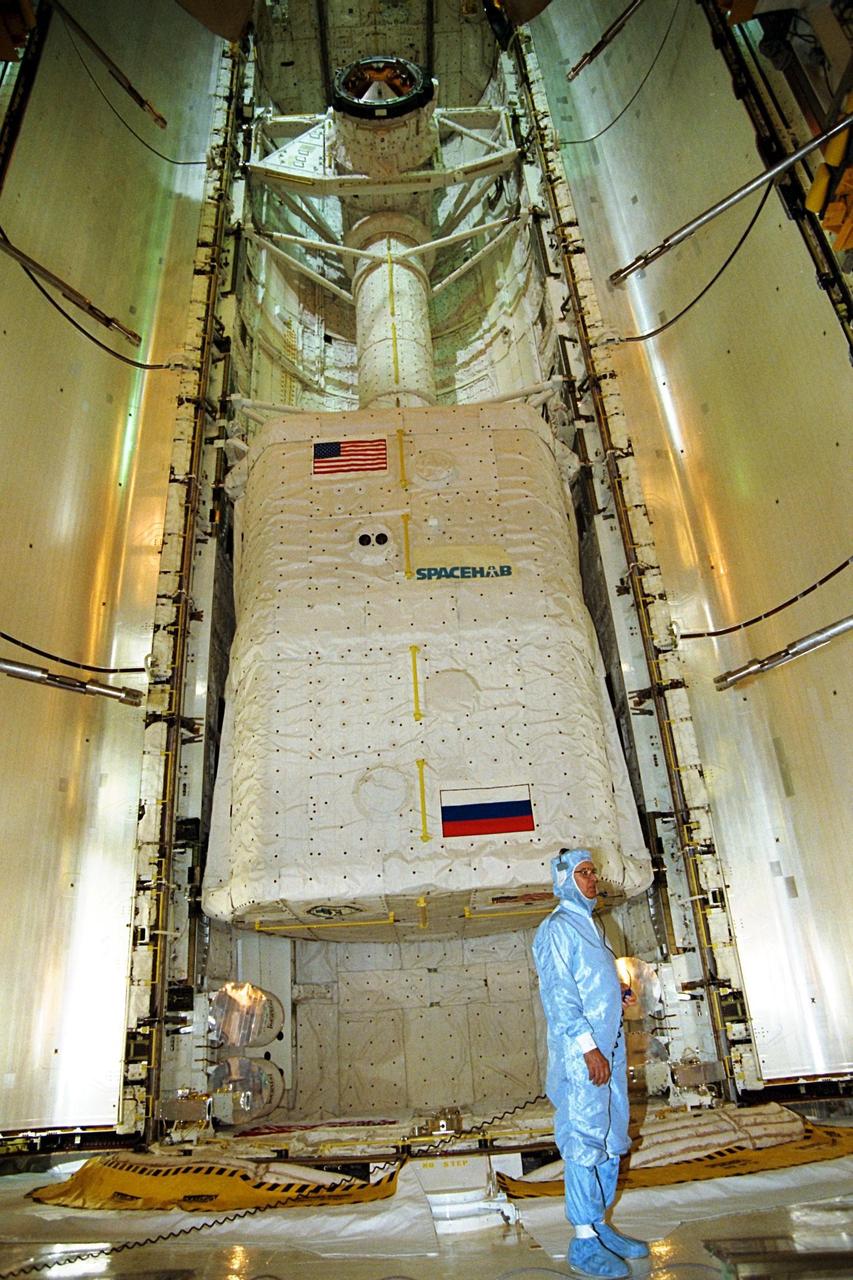
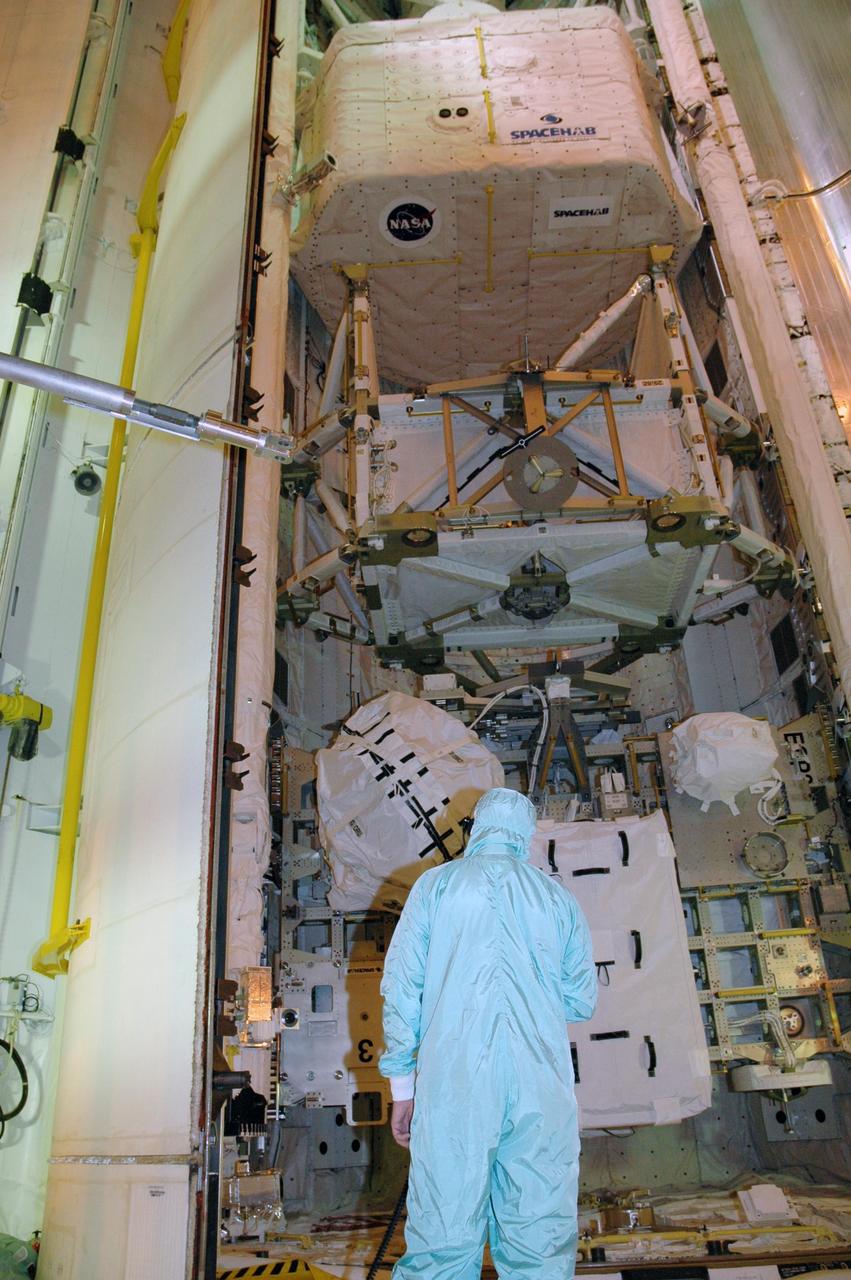
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 39A, one of Endeavour's payload bay doors is closed. Part of the cargo inside can still be seen in the center: the SPACEHAB module and the S5 truss. The payload bay doors were opened to allow for payload closeouts, including camera tests on the shuttle robotic arm and the extension, known as the orbiter boom sensor system. Endeavour is scheduled to launch Aug. 7 on mission STS-118, the 22nd flight to the International Space Station. NASA/Charisse Nahser
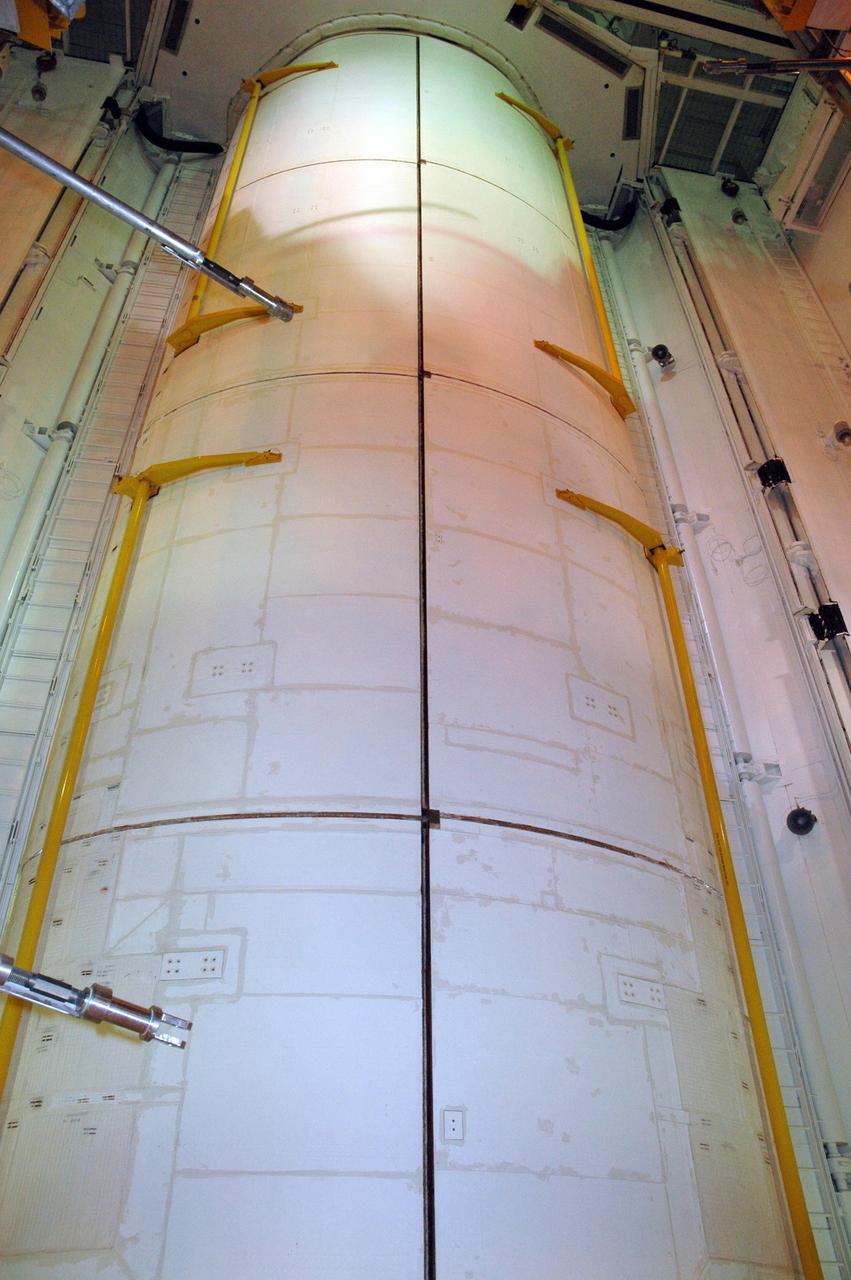

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 39A, Endeavour's payload bay doors are again closed and secure for launch. The payload bay doors were opened to allow for payload closeouts, including camera tests on the shuttle robotic arm and the extension, known as the orbiter boom sensor system. Endeavour is scheduled to launch Aug. 7 on mission STS-118, the 22nd flight to the International Space Station. NASA/Charisse Nahser
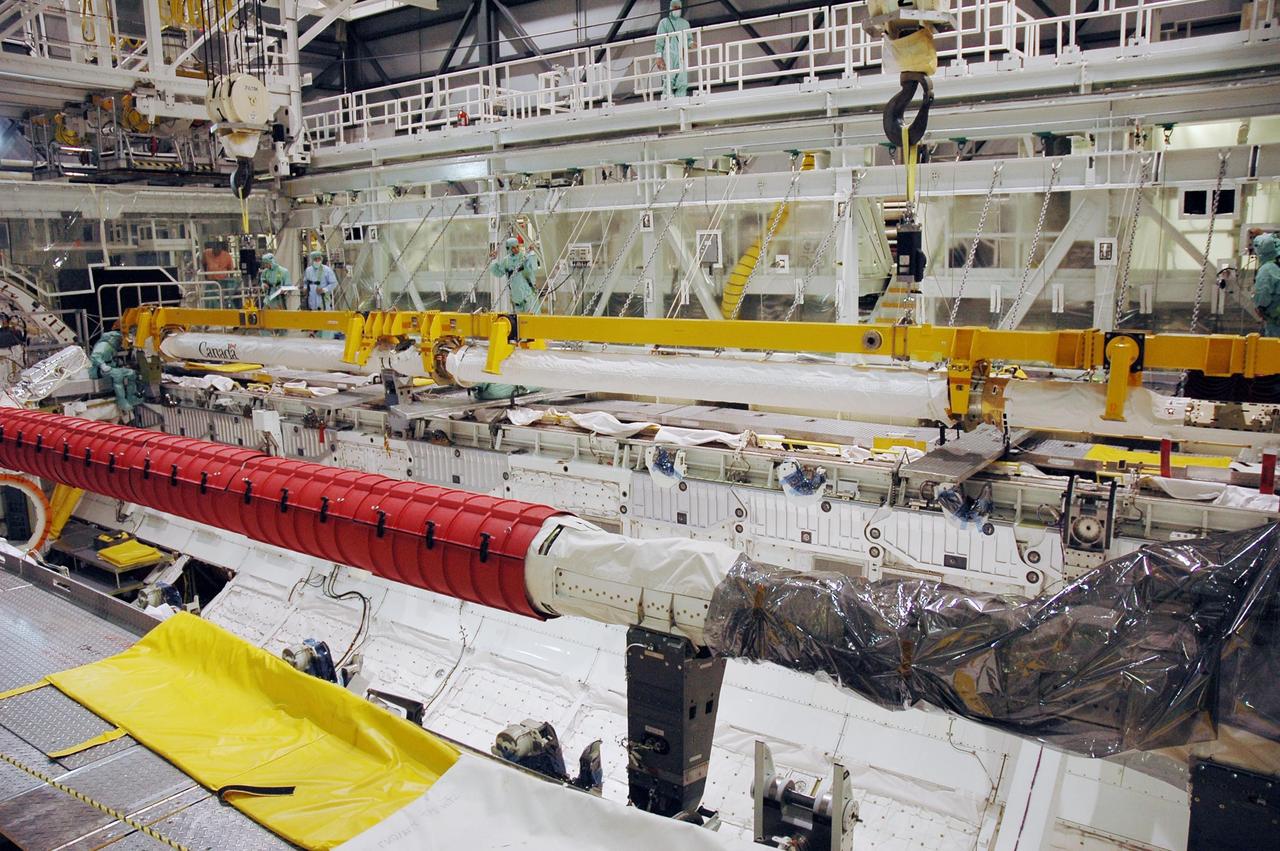

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, workers secure the orbiter boom sensor system in Endeavour's payload bay. The orbiter is scheduled to fly on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station in the summer of 2007. It will deliver the third starboard truss segment, S5. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
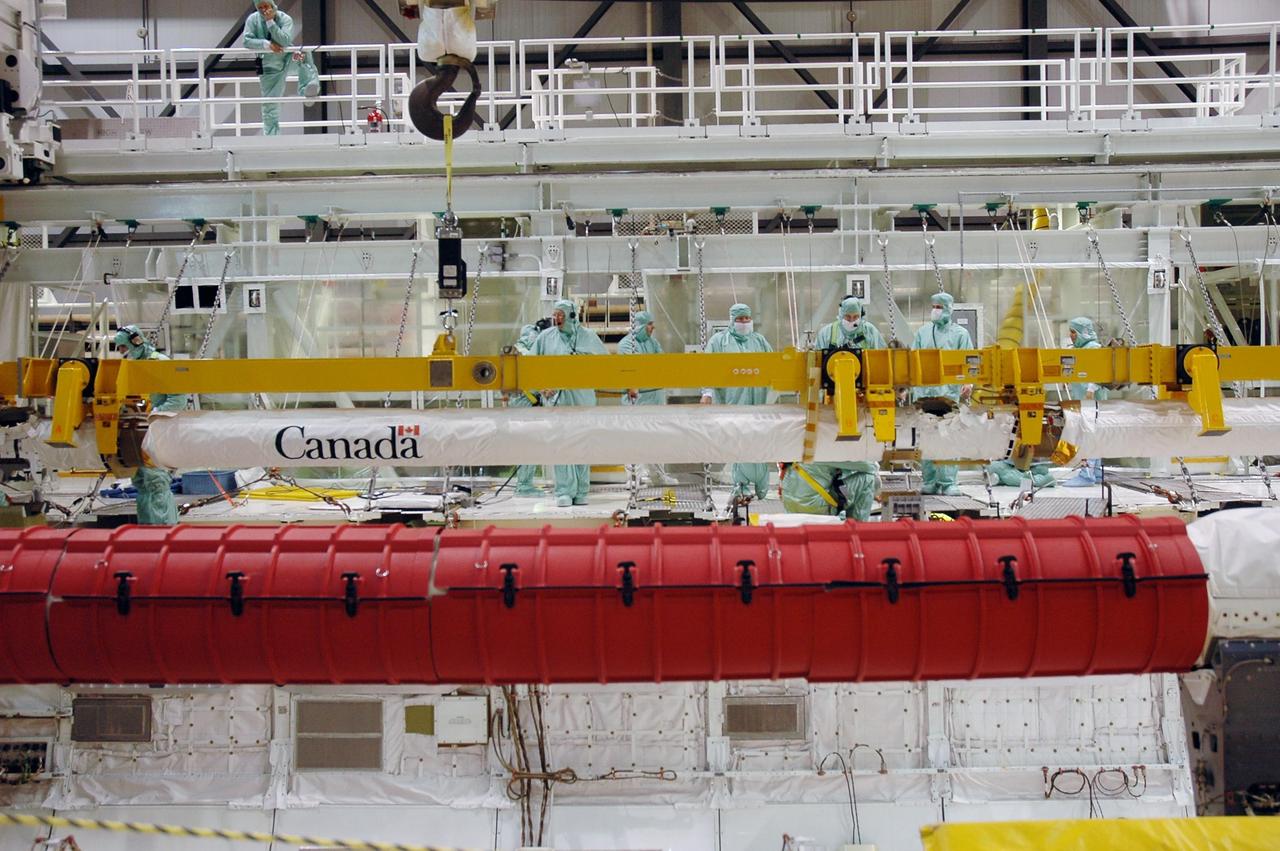

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, the orbiter boom sensor system (in the background) is lowered into the open payload bay of Endeavour. The boom will be installed in the payload bay for launch. The orbiter is scheduled to fly on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station in the summer of 2007. It will deliver the third starboard truss segment, S5. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, the orbiter boom sensor system (in the background) is moved toward the open payload bay of Endeavour. The boom will be installed in the payload bay for launch. The orbiter is scheduled to fly on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station in the summer of 2007. It will deliver the third starboard truss segment, S5. Photo credit: NASA/Troy Cryder
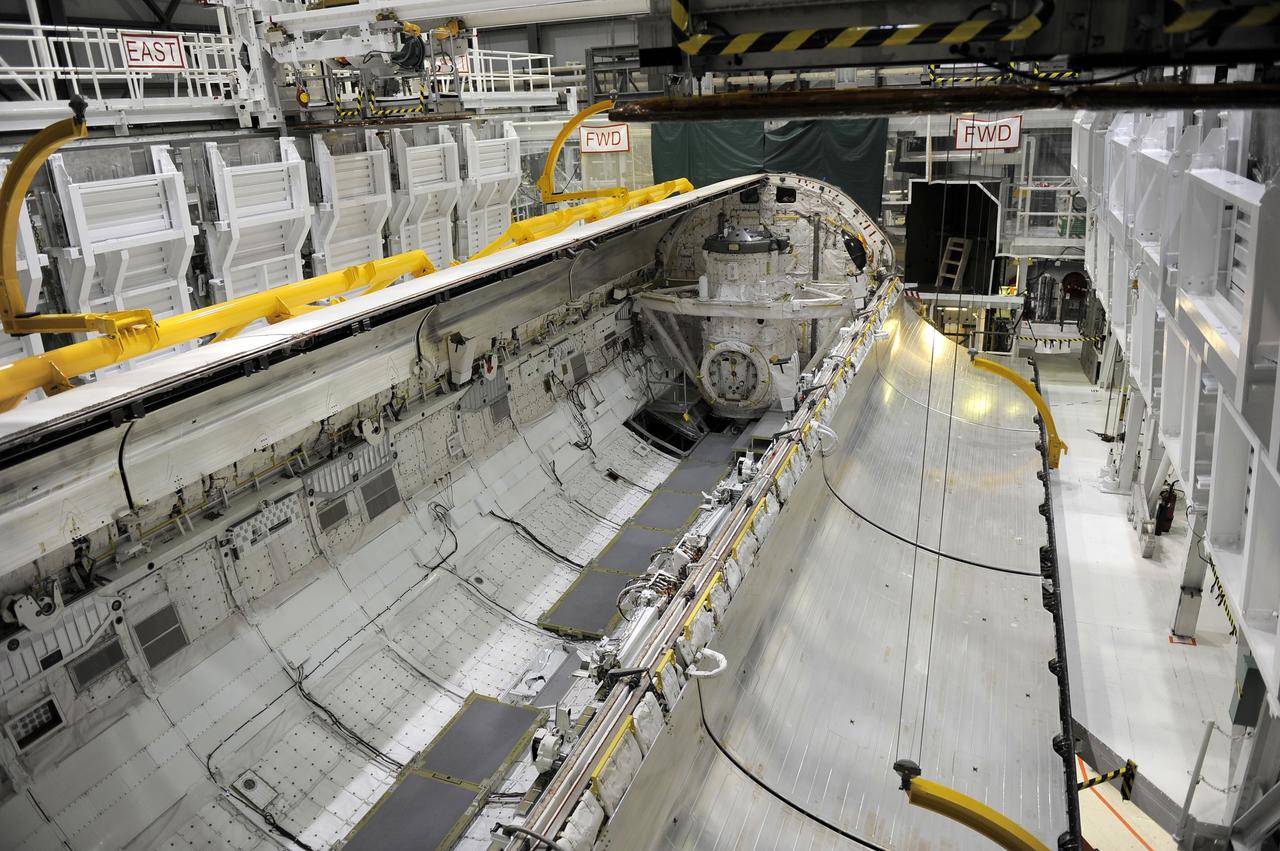

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay doors has been fully opened so that an antenna can be retracted. Space Shuttle Program transition and retirement work continues on Discovery and Endeavour in the orbiter processing facilities, while shuttle Atlantis is in temporary storage in high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour is being prepared for display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –In NASA Kennedy Space Center's Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, a crane lifts space shuttle Endeavour's Orbiter Boom Sensor System out of the payload bay. After returning from the STS-127 mission July 31, 2009, Endeavour now is being processed for the STS-130 mission targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. Endeavour will deliver to the International Space Station the Tranquility pressurized module that will provide room for many of the station's life support systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a technician monitors the progress as one of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay doors is opened so that an antenna can be retracted. Space Shuttle Program transition and retirement work continues on Discovery and Endeavour in the orbiter processing facilities, while shuttle Atlantis is in temporary storage in high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour is being prepared for display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians begin to open space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay doors in order to retract an antenna. Space Shuttle Program transition and retirement work continues on Discovery and Endeavour in the orbiter processing facilities, while shuttle Atlantis is in temporary storage in high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour is being prepared for display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, technicians prepare to open space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay doors in order to retract an antenna. Space Shuttle Program transition and retirement work continues on Discovery and Endeavour in the orbiter processing facilities, while shuttle Atlantis is in temporary storage in high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour is being prepared for display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay doors has been fully opened so that an antenna can be retracted. Space Shuttle Program transition and retirement work continues on Discovery and Endeavour in the orbiter processing facilities, while shuttle Atlantis is in temporary storage in high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour is being prepared for display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay doors has been fully opened so that an antenna can be retracted. Space Shuttle Program transition and retirement work continues on Discovery and Endeavour in the orbiter processing facilities, while shuttle Atlantis is in temporary storage in high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour is being prepared for display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay doors has been fully opened and an antenna has been retracted. Space Shuttle Program transition and retirement work continues on Discovery and Endeavour in the orbiter processing facilities, while shuttle Atlantis is in temporary storage in high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour is being prepared for display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay doors has been fully opened so that an antenna can be retracted. Space Shuttle Program transition and retirement work continues on Discovery and Endeavour in the orbiter processing facilities, while shuttle Atlantis is in temporary storage in high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour is being prepared for display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
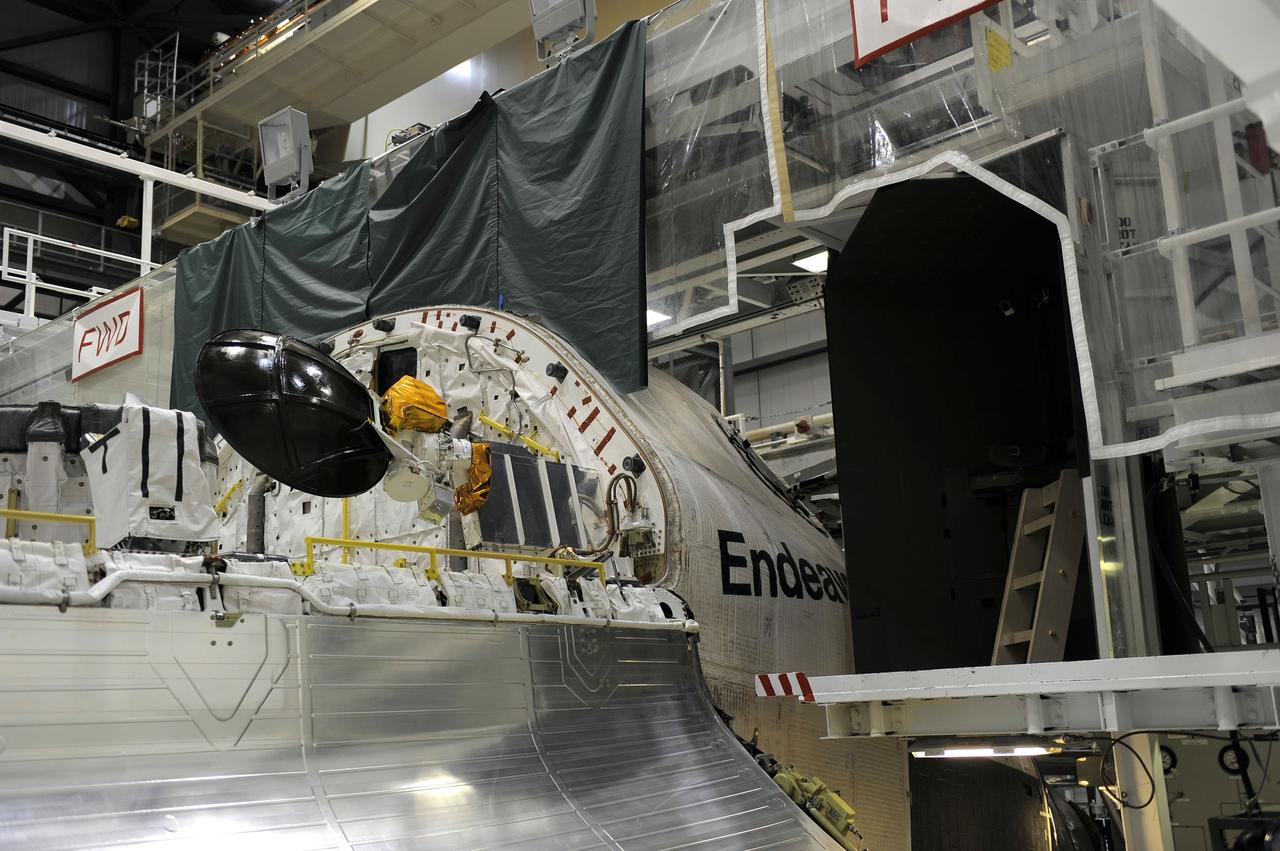

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay doors has been fully opened so that an antenna can be retracted. Space Shuttle Program transition and retirement work continues on Discovery and Endeavour in the orbiter processing facilities, while shuttle Atlantis is in temporary storage in high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour is being prepared for display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
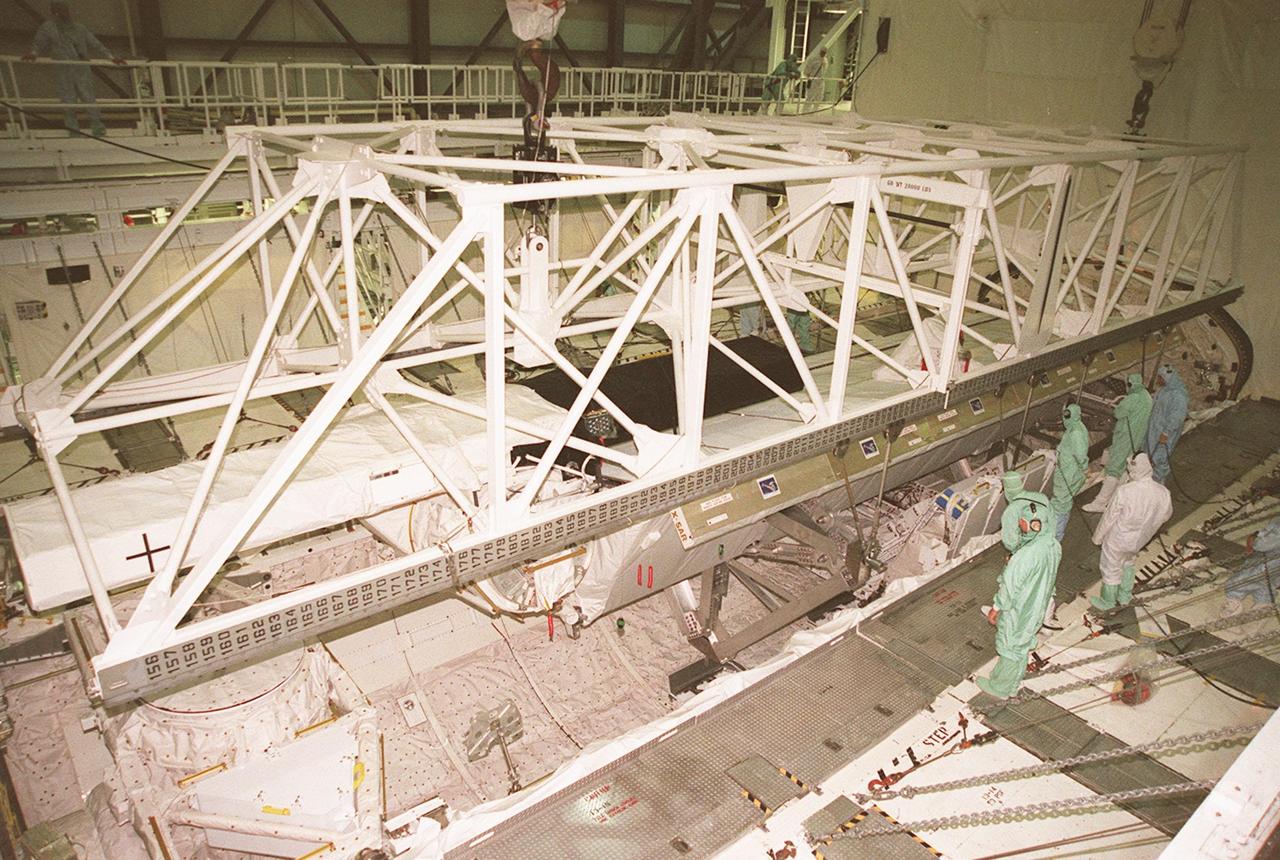

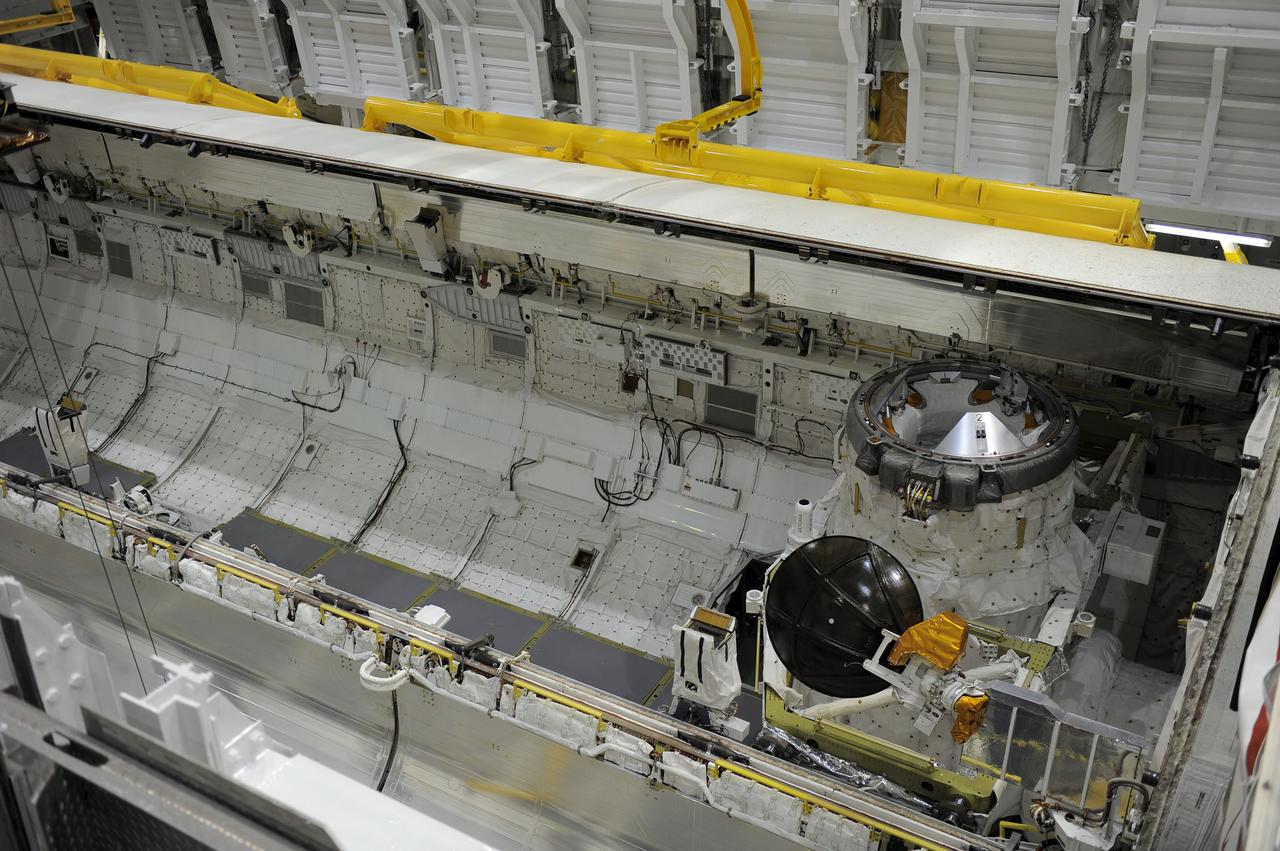
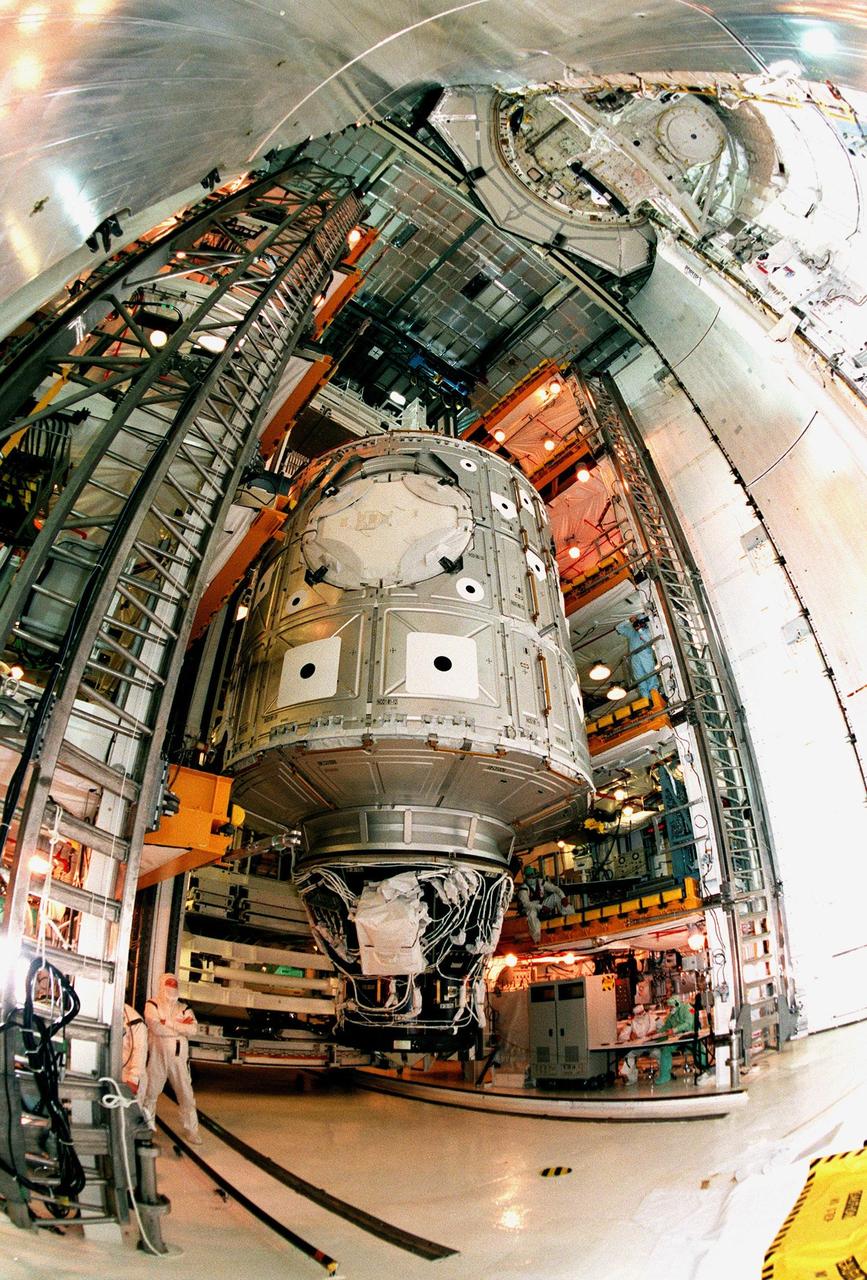
Workers inside orbiter Endeavour's payload bay observe as an overhead crane maneuvers to lift the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) for its transfer out of the orbiter to a payload canister. The payload on mission STS-99, SRTM is being removed to allow technicians access to the orbiter's midbody for planned wiring inspections. Endeavour is in the Orbiter Processing Facility. The entire fleet of orbiters is being inspected for wiring abrasions after the problem was first discovered in Columbia. Shuttle managers are reviewing several manifest options and could establish new target launch dates for the balance of 1999 next week. Shuttle Endeavour currently remains slated for launch in early October
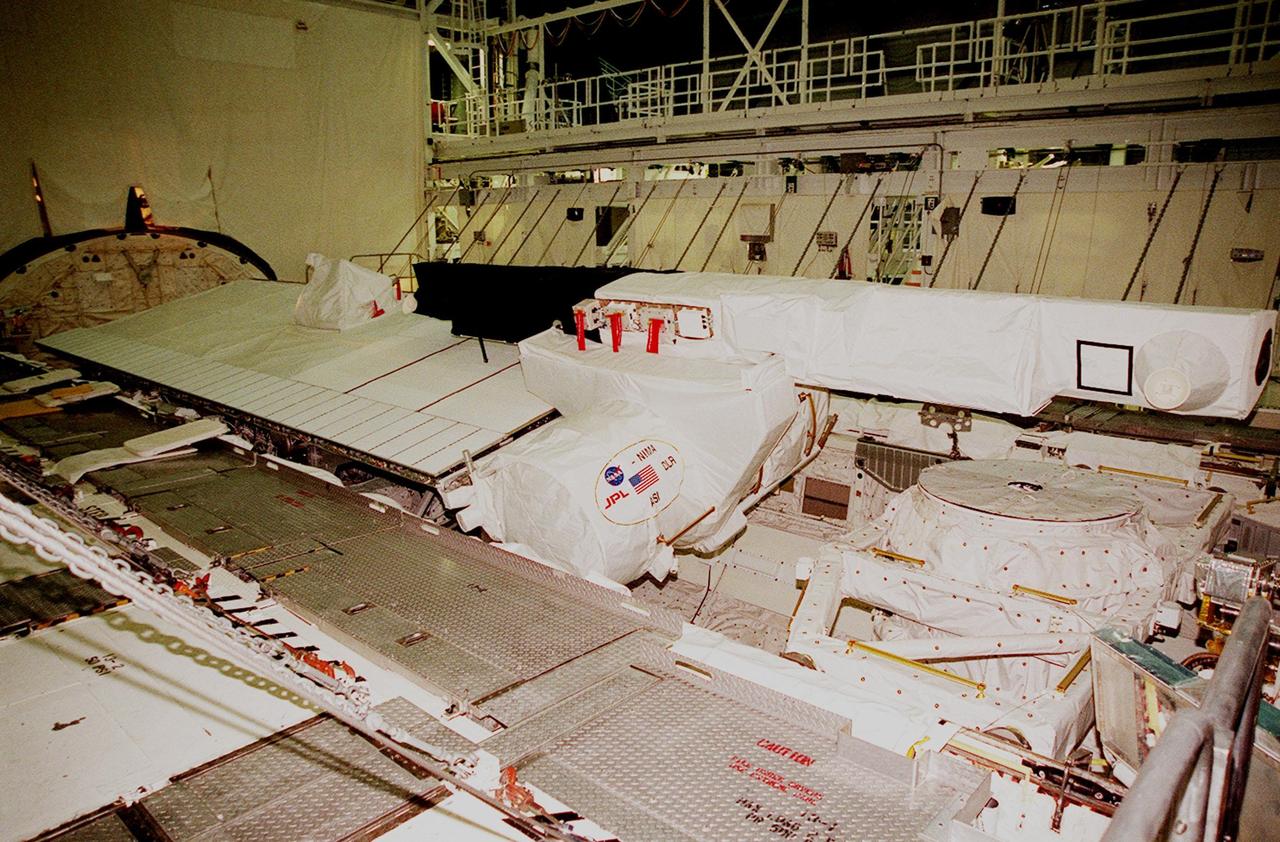

In the center of orbiter Endeavour's payload bay is the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM), being prepared for transfer out of the orbiter to a payload canister. The payload on mission STS-99, SRTM is being removed to allow technicians access to the orbiter's midbody for planned wiring inspections. Endeavour is in the Orbiter Processing Facility. The entire fleet of orbiters is being inspected for wiring abrasions after the problem was first discovered in Columbia. Shuttle managers are reviewing several manifest options and could establish new target launch dates for the balance of 1999 next week. Shuttle Endeavour currently remains slated for launch in early October
Inside orbiter Endeavour's payload bay, a crane lifts the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) clear of the orbiter for transfer to a payload canister. The payload on mission STS-99, SRTM is being removed to allow technicians access to the orbiter's midbody for planned wiring inspections. Endeavour is in the Orbiter Processing Facility. The entire fleet of orbiters is being inspected for wiring abrasions after the problem was first discovered in Columbia. Shuttle managers are reviewing several manifest options and could establish new target launch dates for the balance of 1999 next week. Shuttle Endeavour currently remains slated for launch in early October
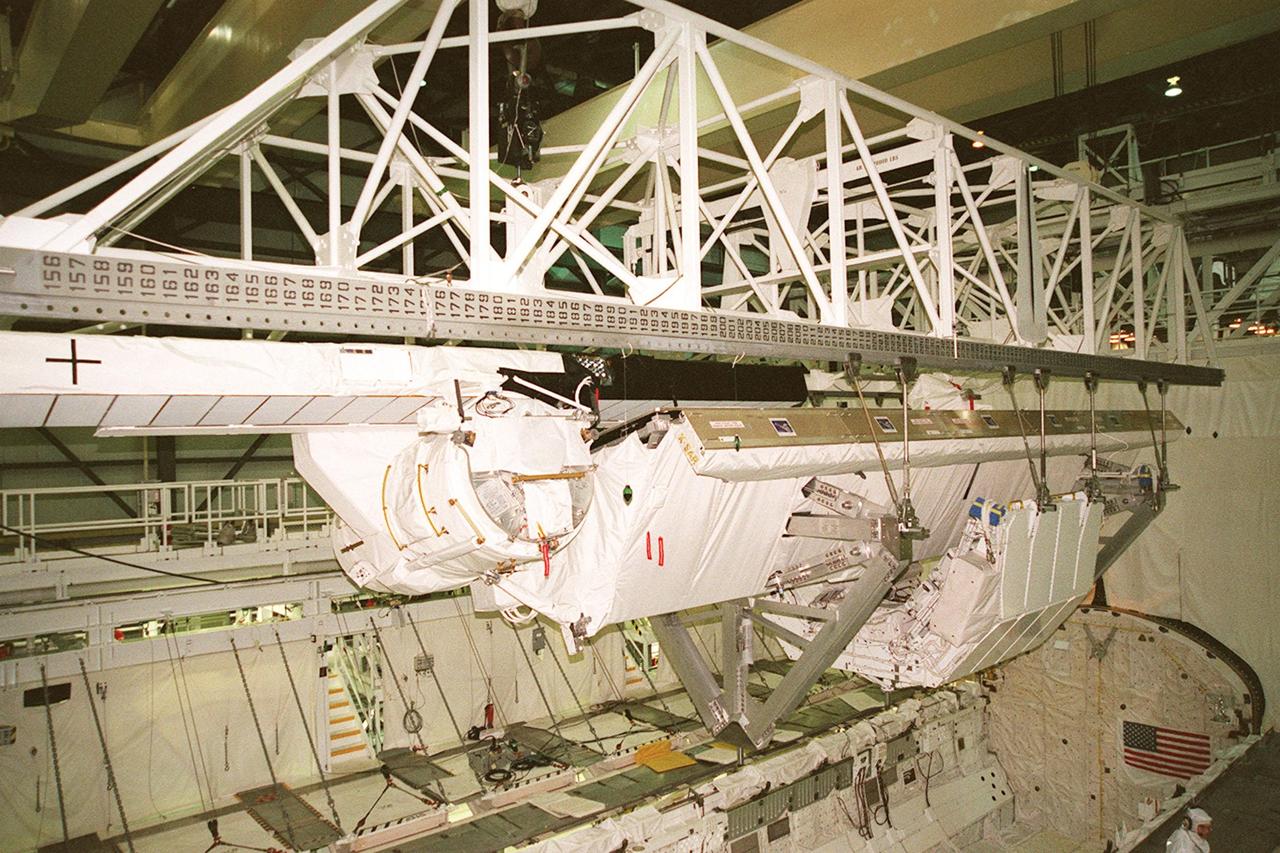

Inside orbiter Endeavour's payload bay, a crane lifts the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) for its transfer out of the orbiter to a payload canister. The payload on mission STS-99, SRTM is being removed to allow technicians access to the orbiter's midbody for planned wiring inspections. Endeavour is in the Orbiter Processing Facility. The entire fleet of orbiters is being inspected for wiring abrasions after the problem was first discovered in Columbia. Shuttle managers are reviewing several manifest options and could establish new target launch dates for the balance of 1999 next week. Shuttle Endeavour currently remains slated for launch in early October
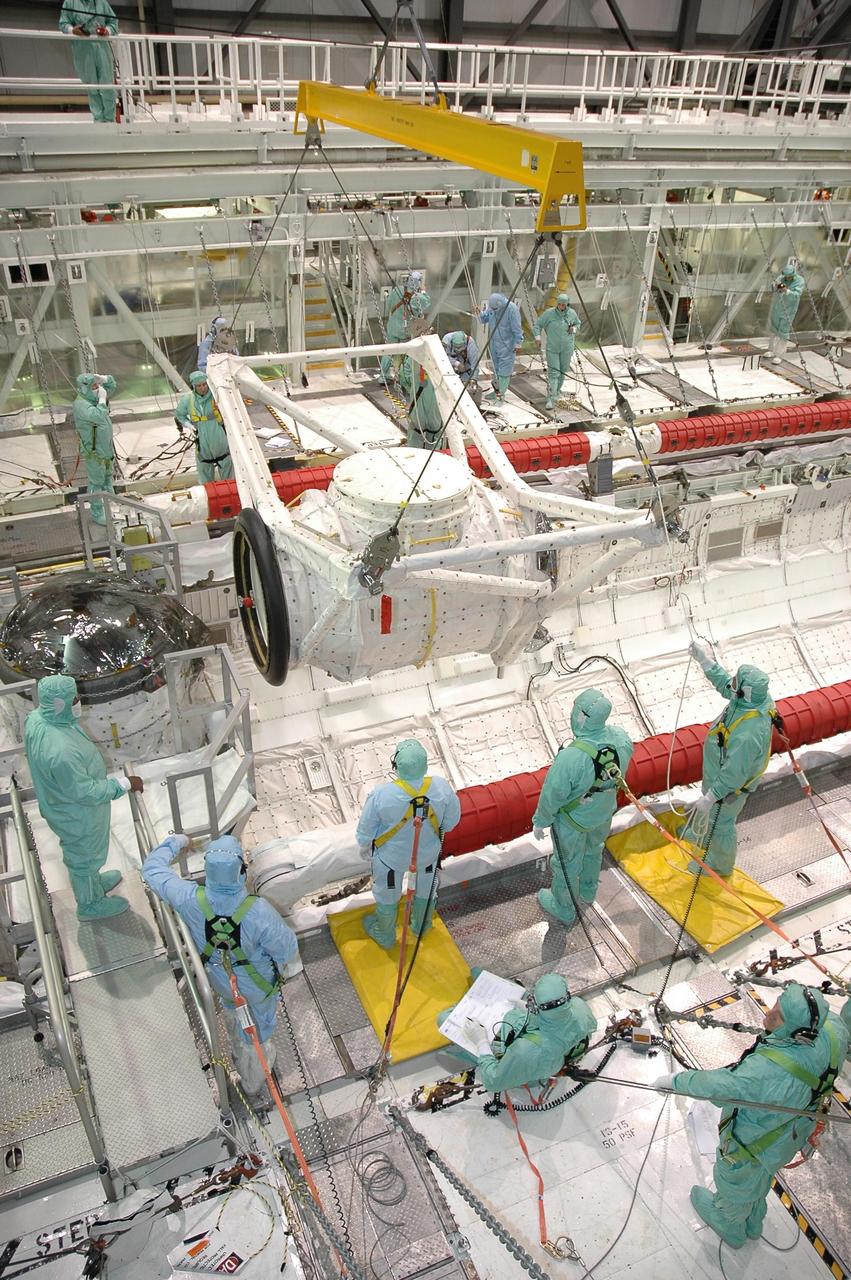
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians control the descent of the crew airlock module into Endeavour's payload bay, where it will be installed. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
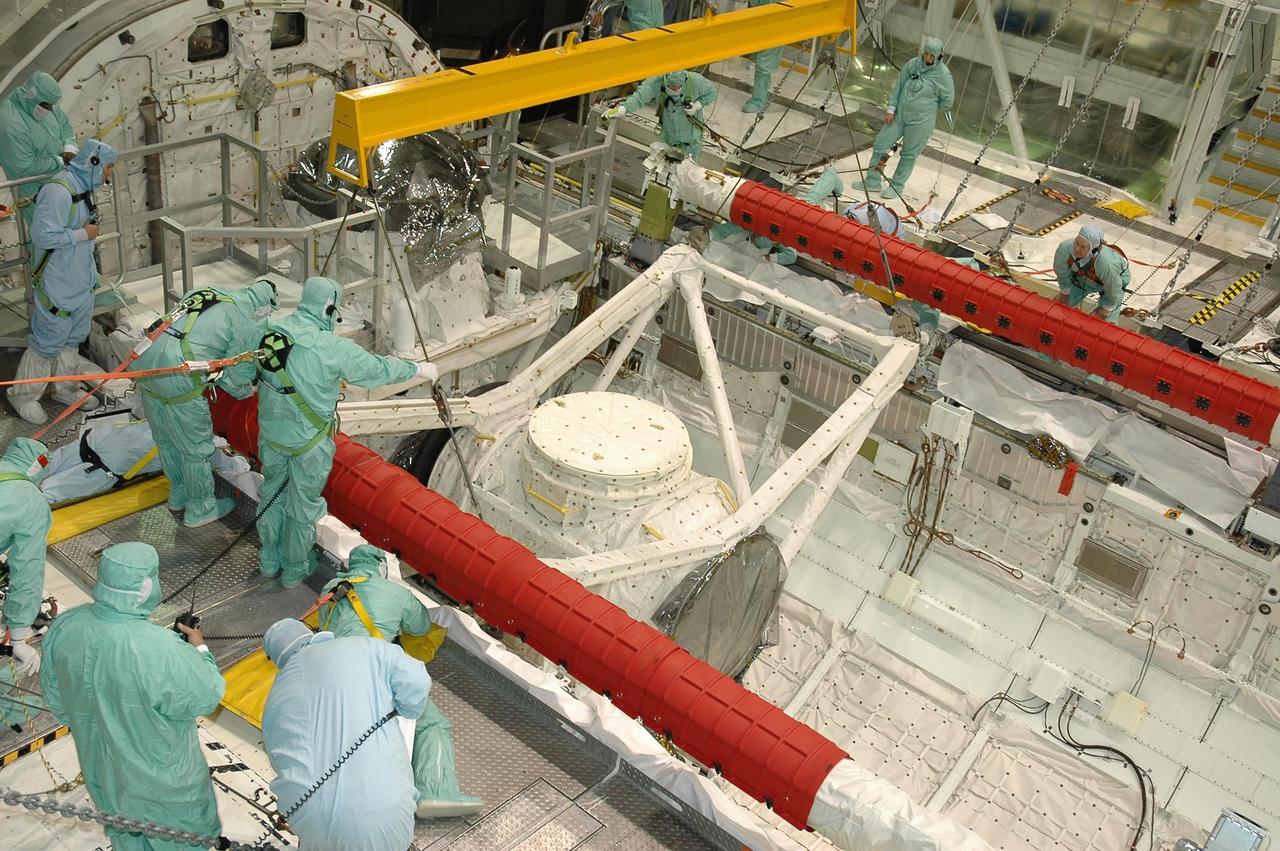
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians direct the placement of the crew airlock module into Endeavour's payload bay, where it will be installed. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
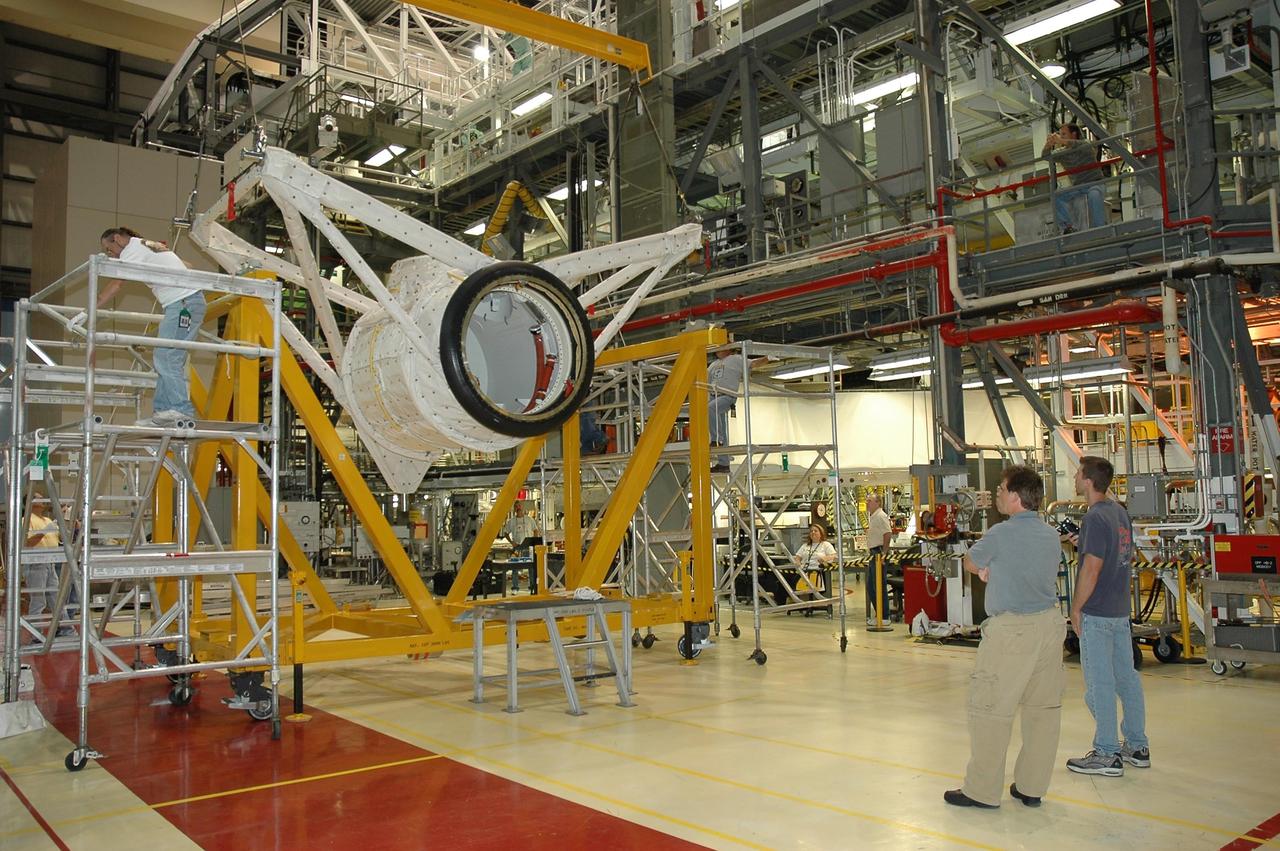

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, an overhead crane lifts the crew airlock module off its stand. The airlock is being moved to install it in Endeavour's payload bay. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
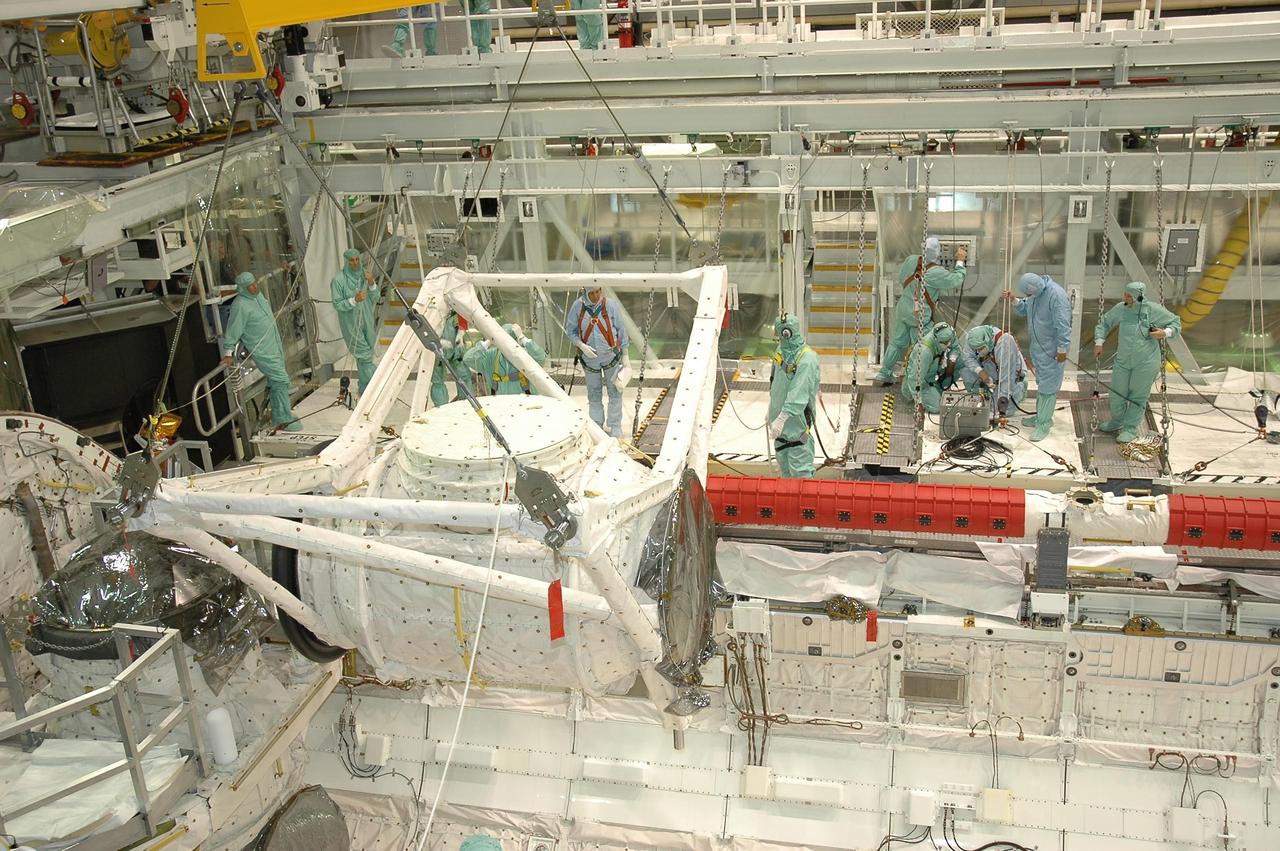

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the crew airlock module is lowered into place in Endeavour's payload bay, where it will be installed. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians direct the placement of the crew airlock module into Endeavour's payload bay, where it will be installed. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Endeavour is targeted for flight on Aug. 9 on mission STS-118 to the International Space Station. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
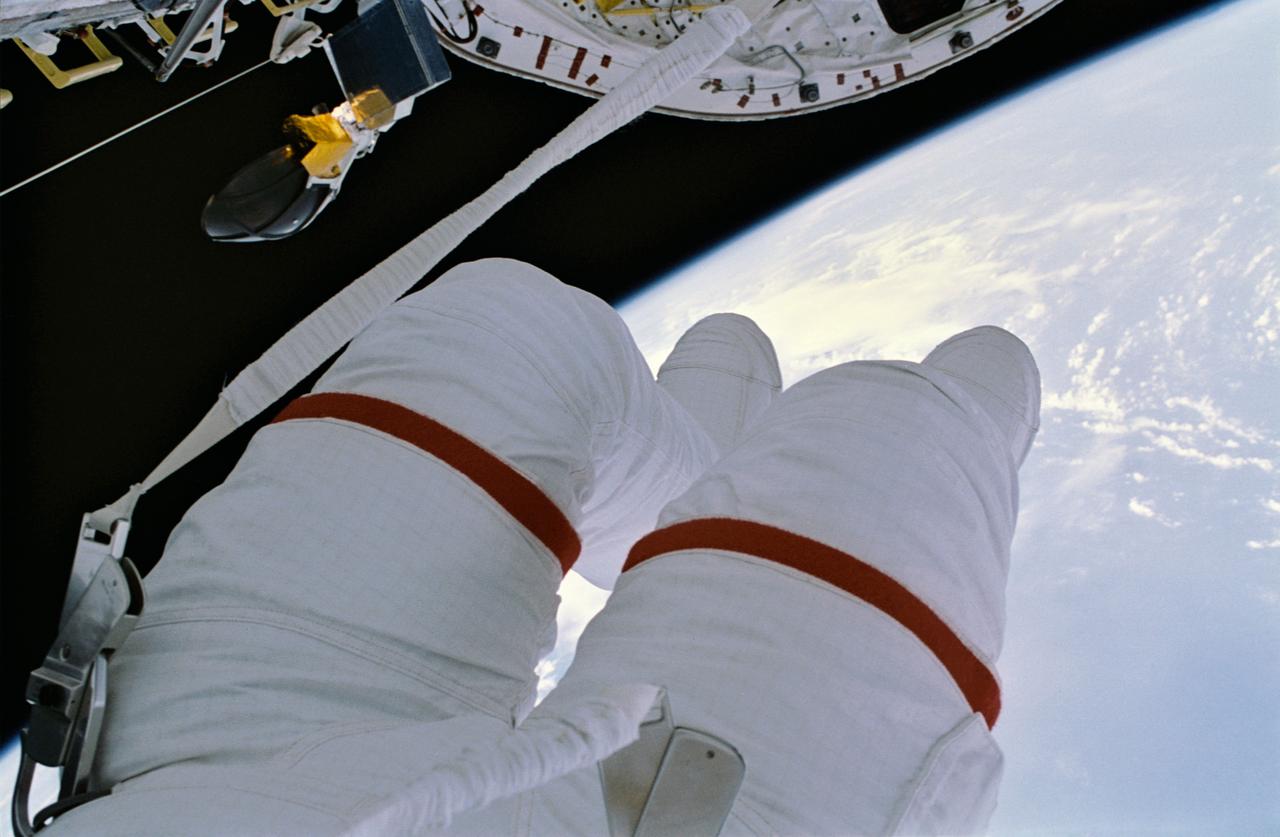

STS054-29-028 (17 Jan 1993) --- Astronaut Gregory J. Harbaugh, mission specialist, used a 35mm camera to photograph his legs and feet during the four-plus hours extravehicular activity (EVA) to depict the vast void below. Harbaugh was joined on the EVA by astronaut Mario Runco Jr., mission specialist.
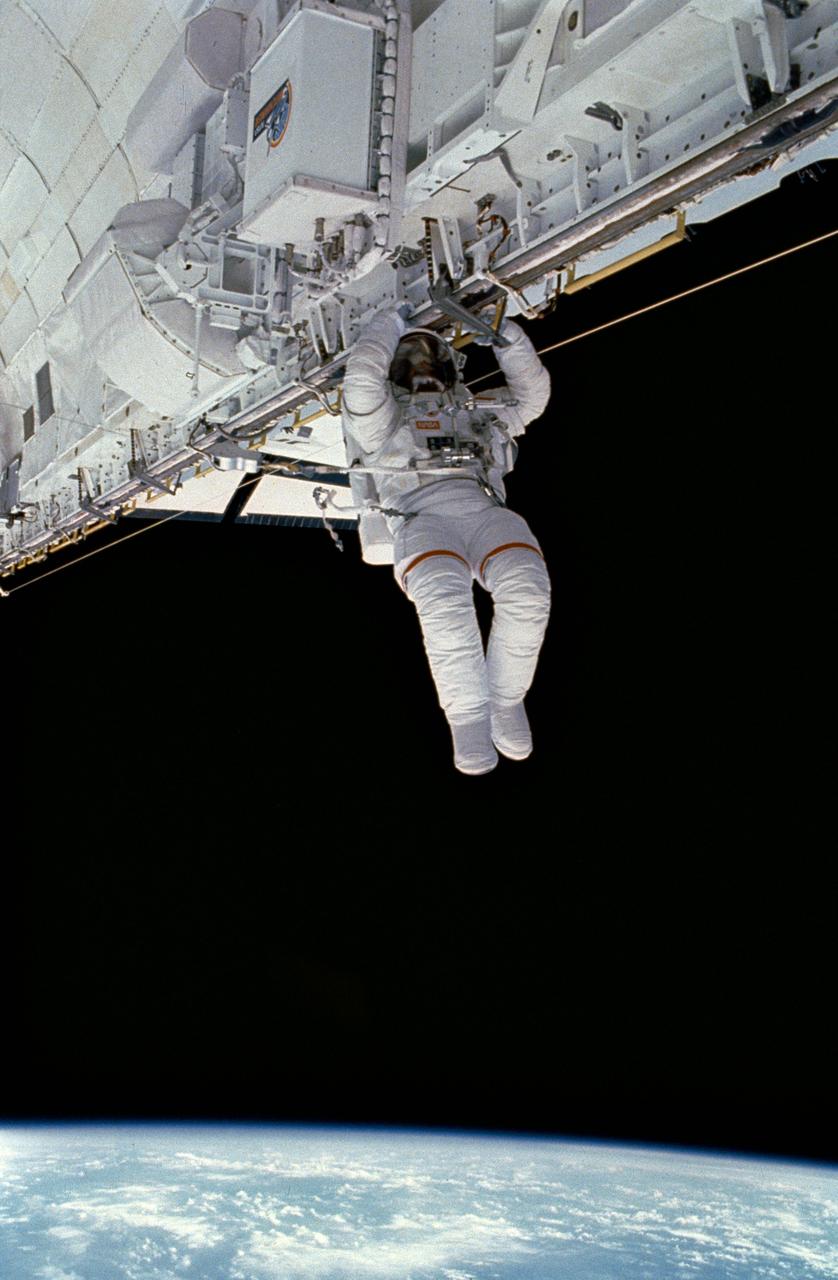

STS054-05-008 (17 Jan 1993) --- Astronaut Gregory J. Harbaugh translates along the starboard longeron of Endeavour's cargo bay. Astronauts Harbaugh and Mario Runco Jr., mission specialists, spent four-plus hours on the extravehicular activity (EVA) on January 17, 1993. Also onboard NASA's newest Shuttle for the six-day mission were astronauts John H. Casper, mission commander; and Donald R. McMonagle, pilot; and Susan J. Helms, mission specialist. The photograph was taken with a 35mm camera.
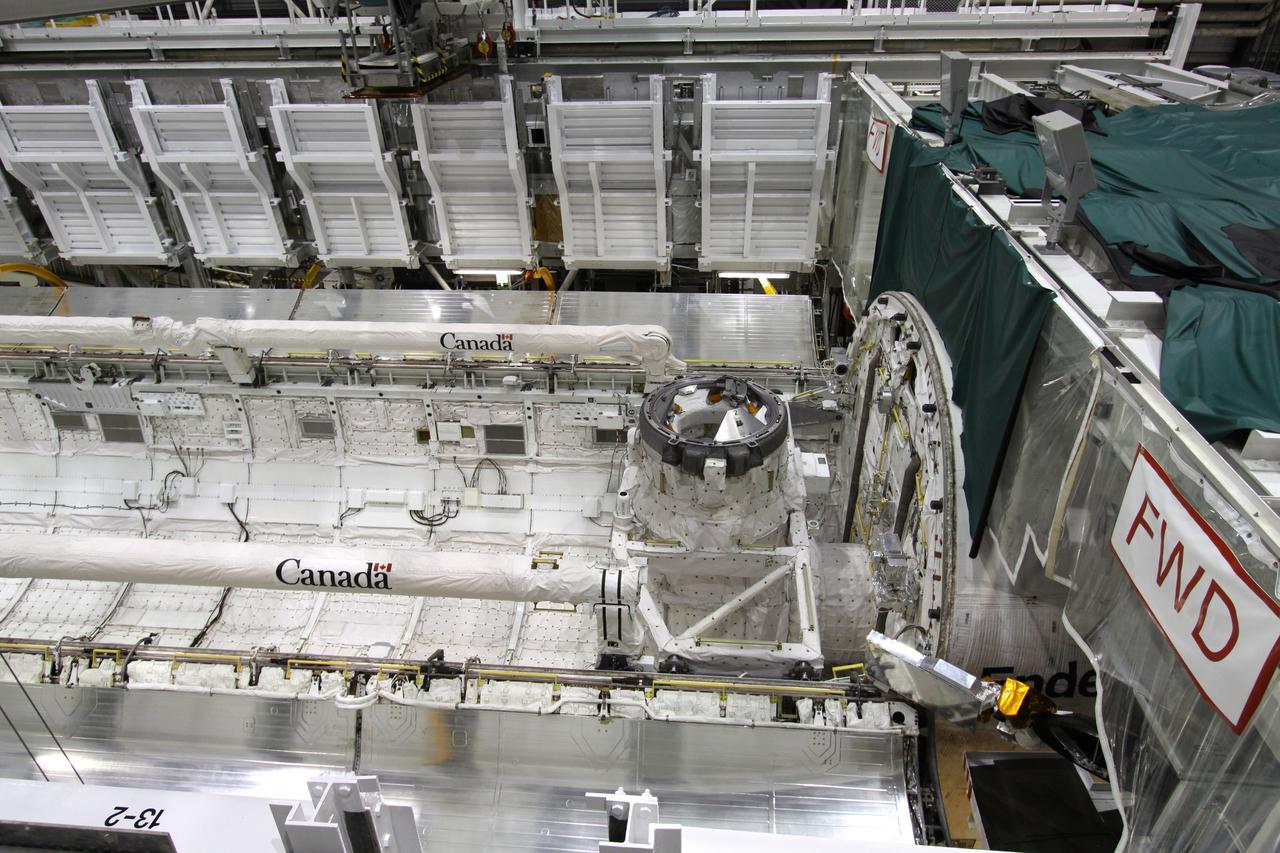
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, processing of space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay is complete and its doors will be closed for the shuttle's move to the Vehicle Assembly Building. The move, or "rollover," is targeted for Dec. 12. The Tranquility module, the payload for Endeavour's STS-130 mission to the International Space Station, will be installed in the payload bay after the shuttle has reached the pad. Endeavour's launch is targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. For information on the STS-130 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts130/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
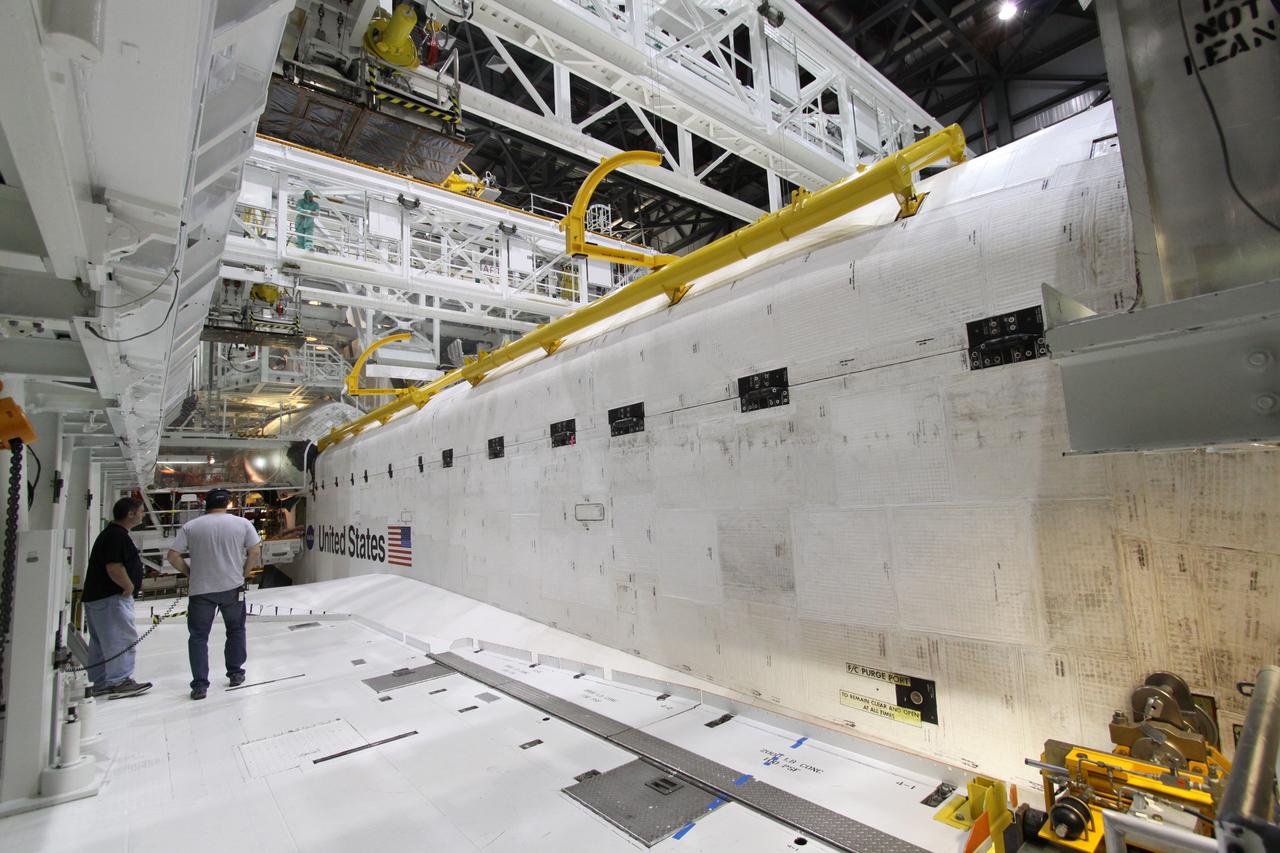

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers secure space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay doors for the shuttle's upcoming move to the Vehicle Assembly Building. The move, or "rollover," is targeted for Dec. 12. The Tranquility module, the payload for Endeavour's STS-130 mission to the International Space Station, will be installed in the payload bay after the shuttle has reached the pad. Endeavour's launch is targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. For information on the STS-130 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts130/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
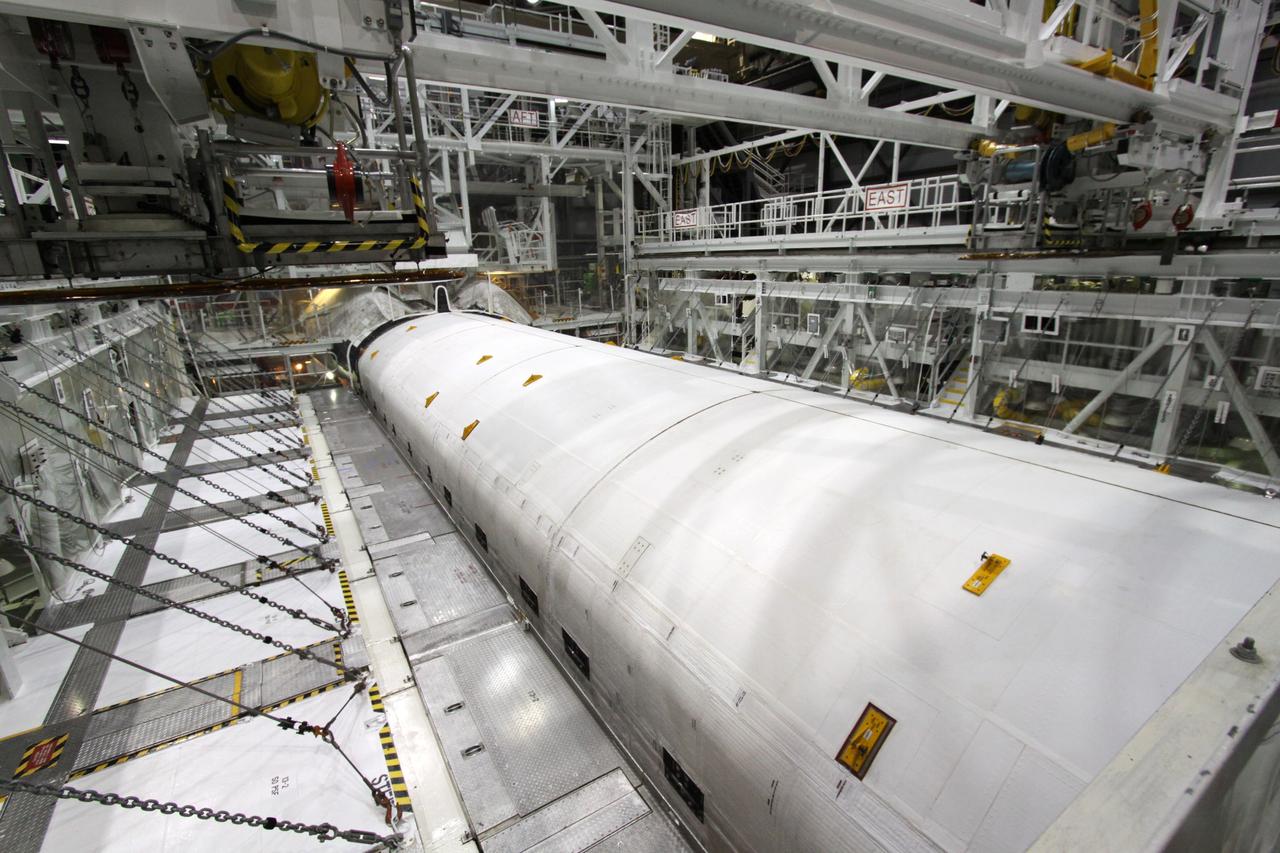

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, processing of space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay is complete, and its doors are closed for the shuttle's move to the Vehicle Assembly Building. The move, or "rollover," is targeted for Dec. 12. The Tranquility module, the payload for Endeavour's STS-130 mission to the International Space Station, will be installed in the payload bay after the shuttle has reached the pad. Endeavour's launch is targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. For information on the STS-130 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts130/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
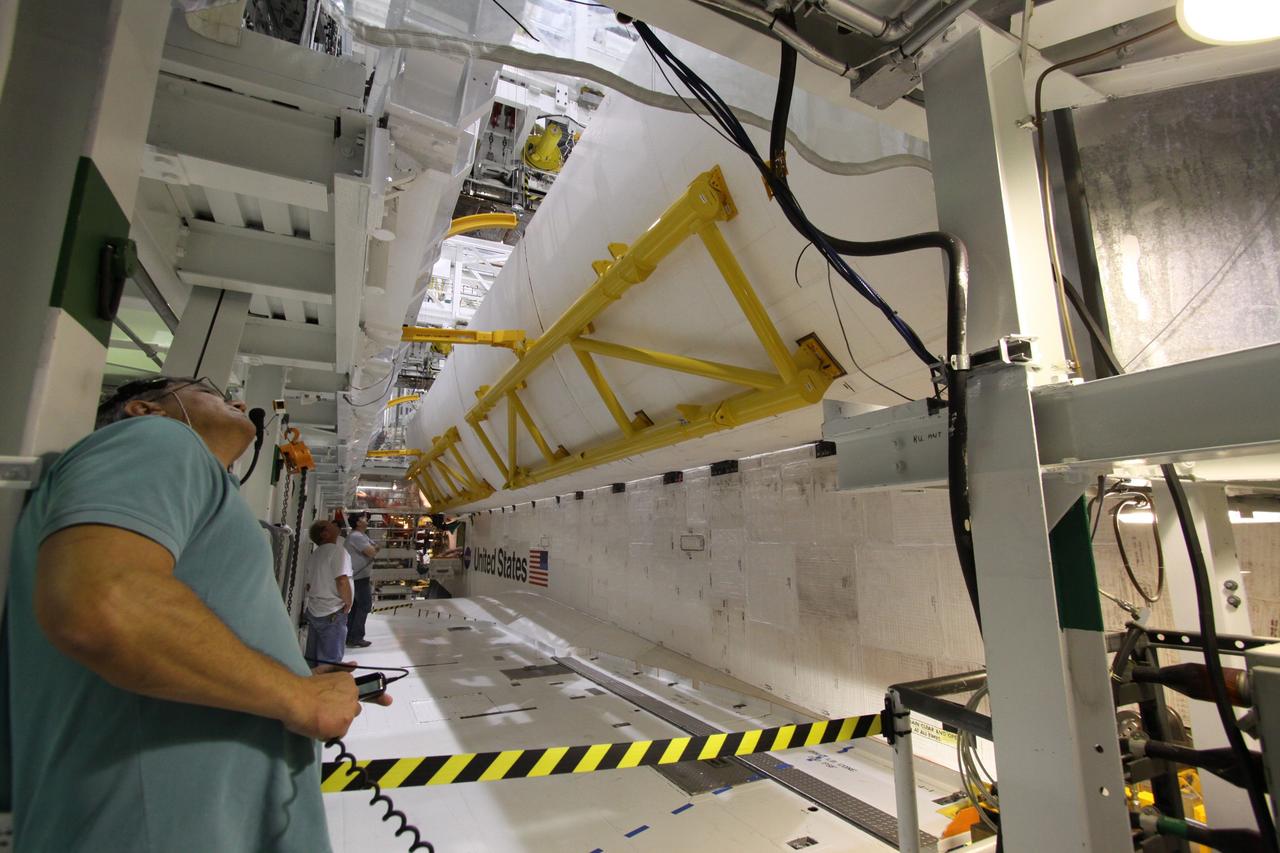

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers begin to close space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay doors for the shuttle's upcoming move to the Vehicle Assembly Building. The move, or "rollover," is targeted for Dec. 12. The Tranquility module, the payload for Endeavour's STS-130 mission to the International Space Station, will be installed in the payload bay after the shuttle has reached the pad. Endeavour's launch is targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. For information on the STS-130 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts130/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
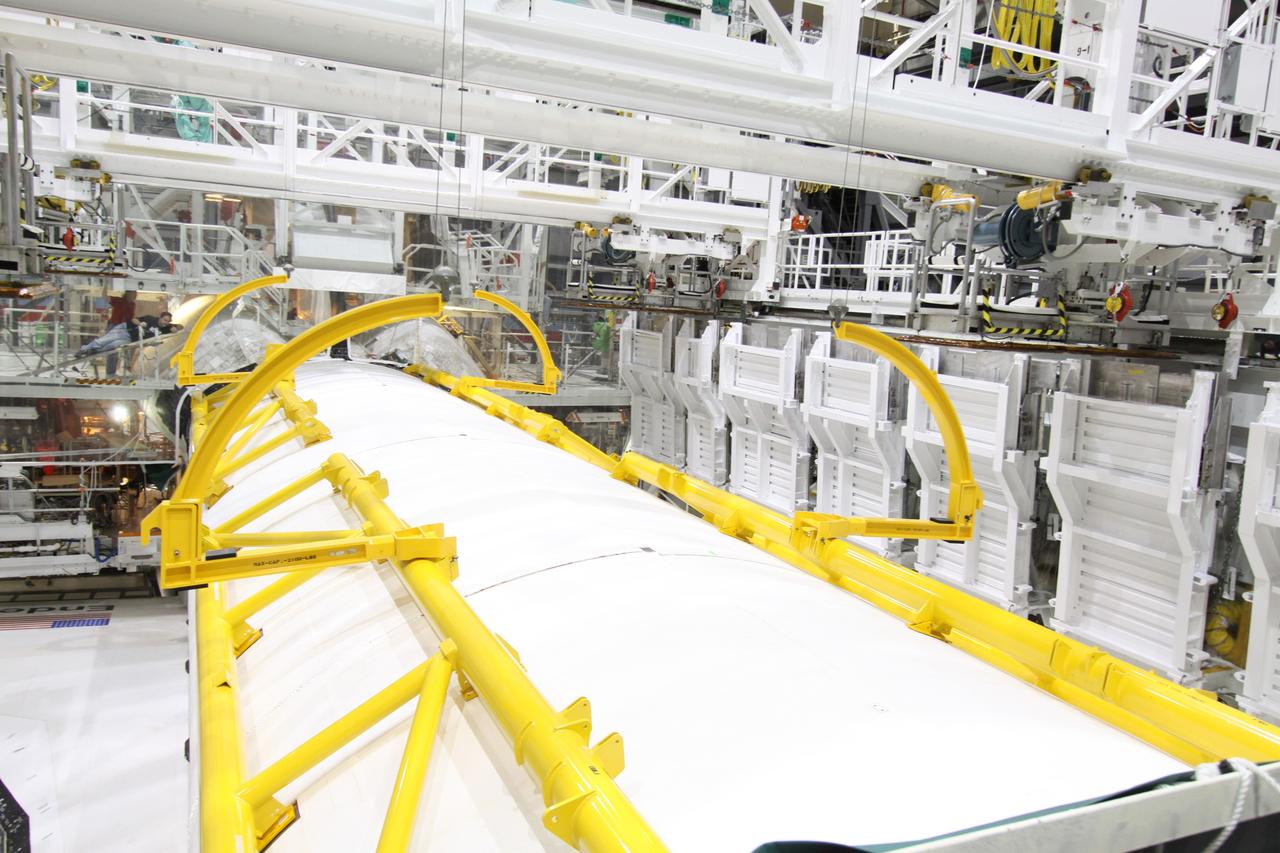

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay doors are closed for the shuttle's move to the Vehicle Assembly Building. The move, or "rollover," is targeted for Dec. 12. The Tranquility module, the payload for Endeavour's STS-130 mission to the International Space Station, will be installed in the payload bay after the shuttle has reached the pad. Endeavour's launch is targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. For information on the STS-130 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts130/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
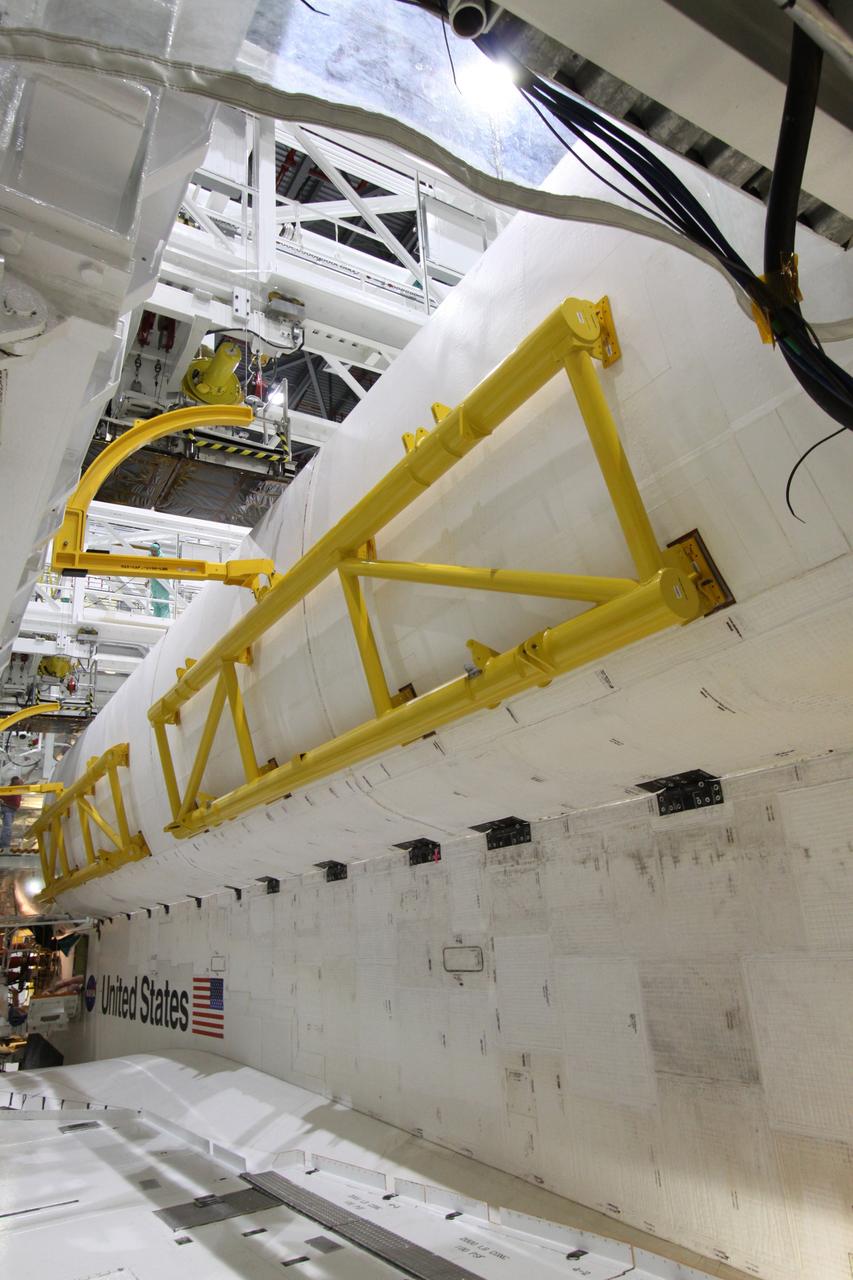

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay doors are being closed for the shuttle's move to the Vehicle Assembly Building. The move, or "rollover," is targeted for Dec. 12. The Tranquility module, the payload for Endeavour's STS-130 mission to the International Space Station, will be installed in the payload bay after the shuttle has reached the pad. Endeavour's launch is targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. For information on the STS-130 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts130/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
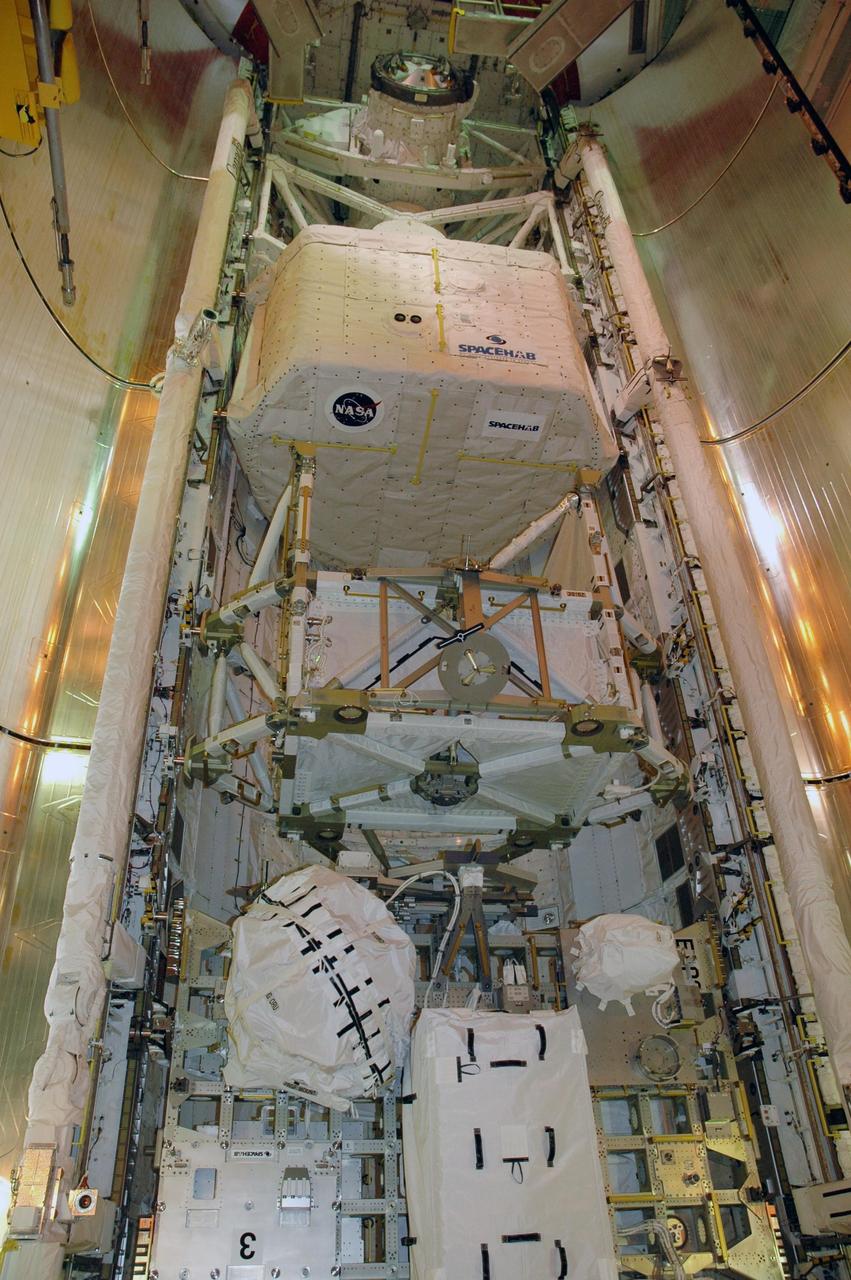

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 39A, Endeavour's payload bay doors are open, revealing the cargo and equipment inside. At the top is the orbiter docking system; below it are the SPACEHAB module, the S5 truss and the external stowage platform 3 holding a control moment gyro at left and other supplies. The payload bay doors were opened to allow for payload closeouts, including camera tests on the shuttle robotic arm and the extension, known as the orbiter boom sensor system. Endeavour is scheduled to launch Aug. 7 on mission STS-118, the 22nd flight to the International Space Station. NASA/Charisse Nahser
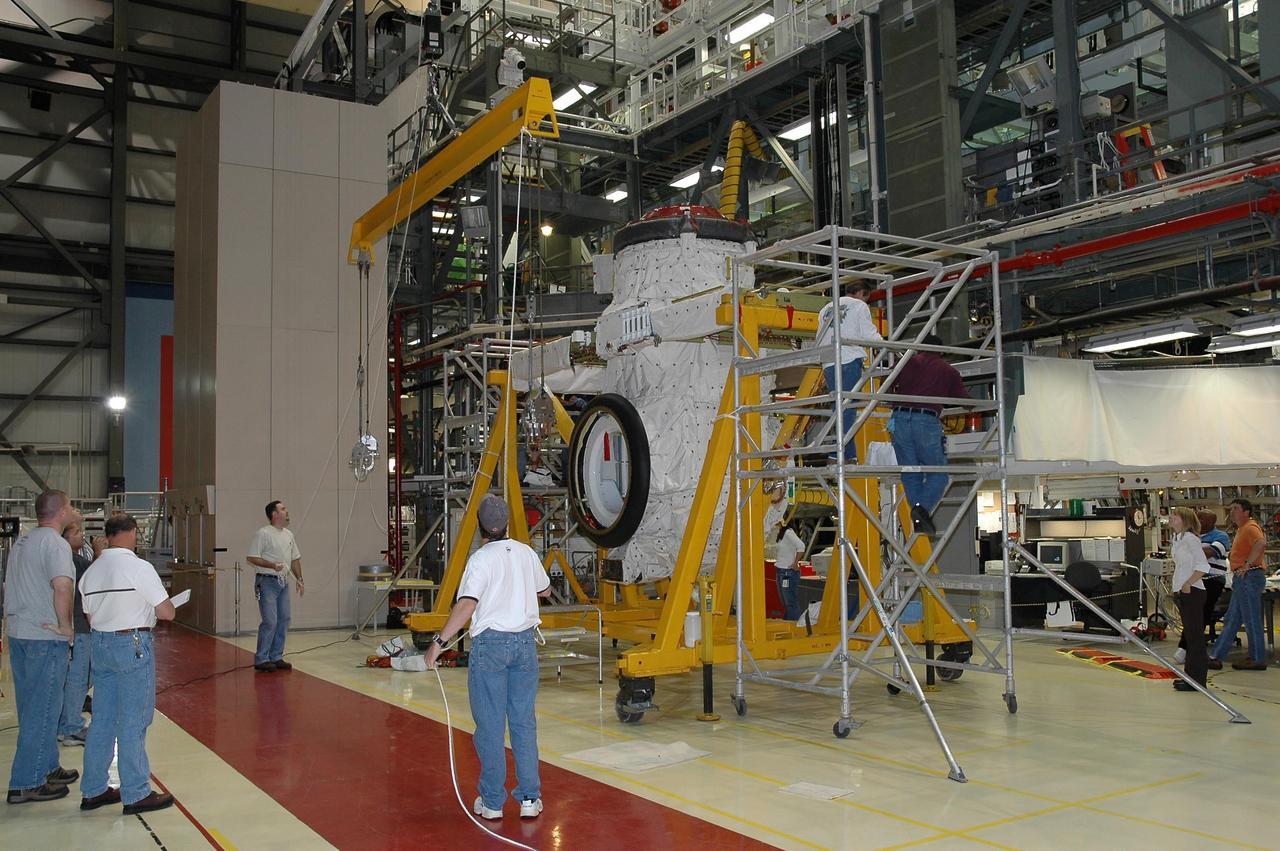

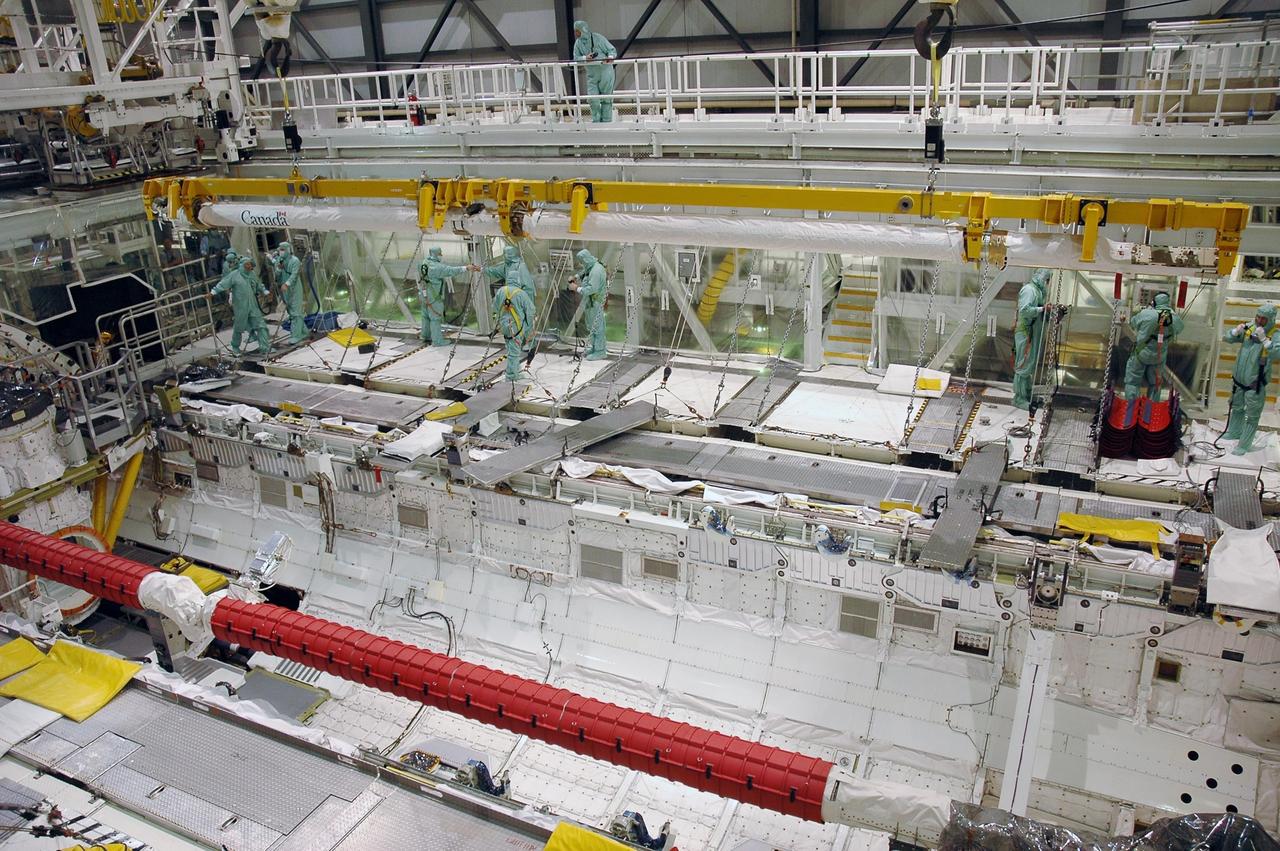
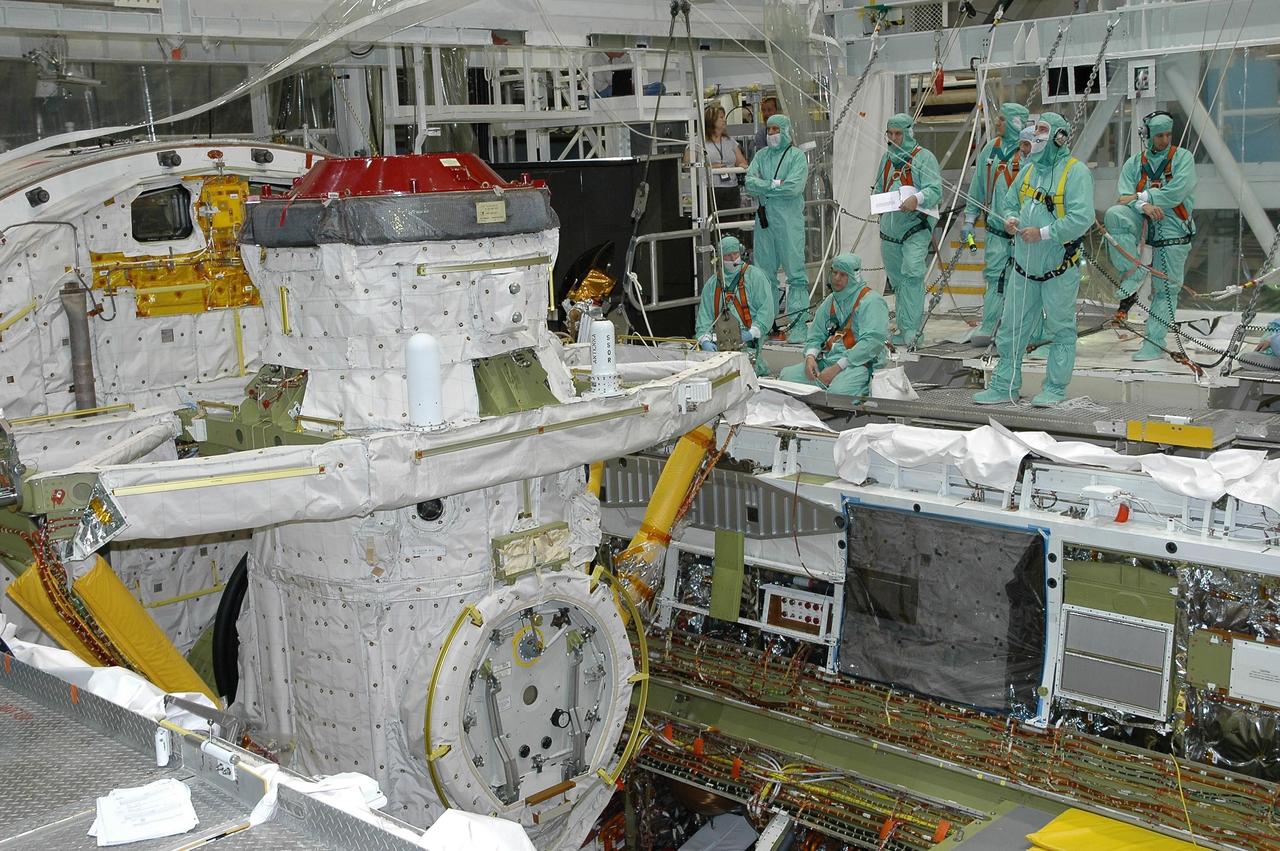
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the airlock is being lifted for installation in Endeavour's payload bay. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
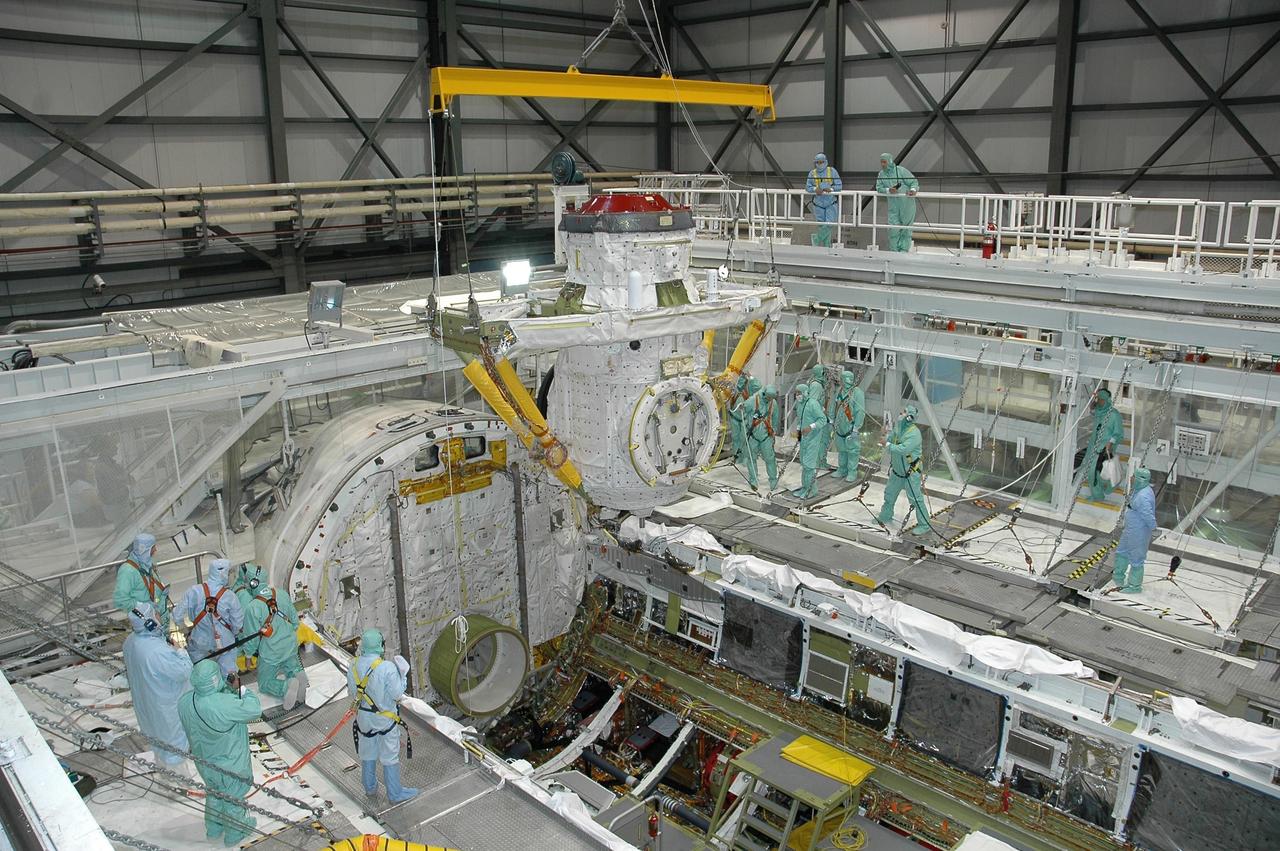

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the airlock is lowered by an overhead crane into Endeavour's payload bay for installation. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
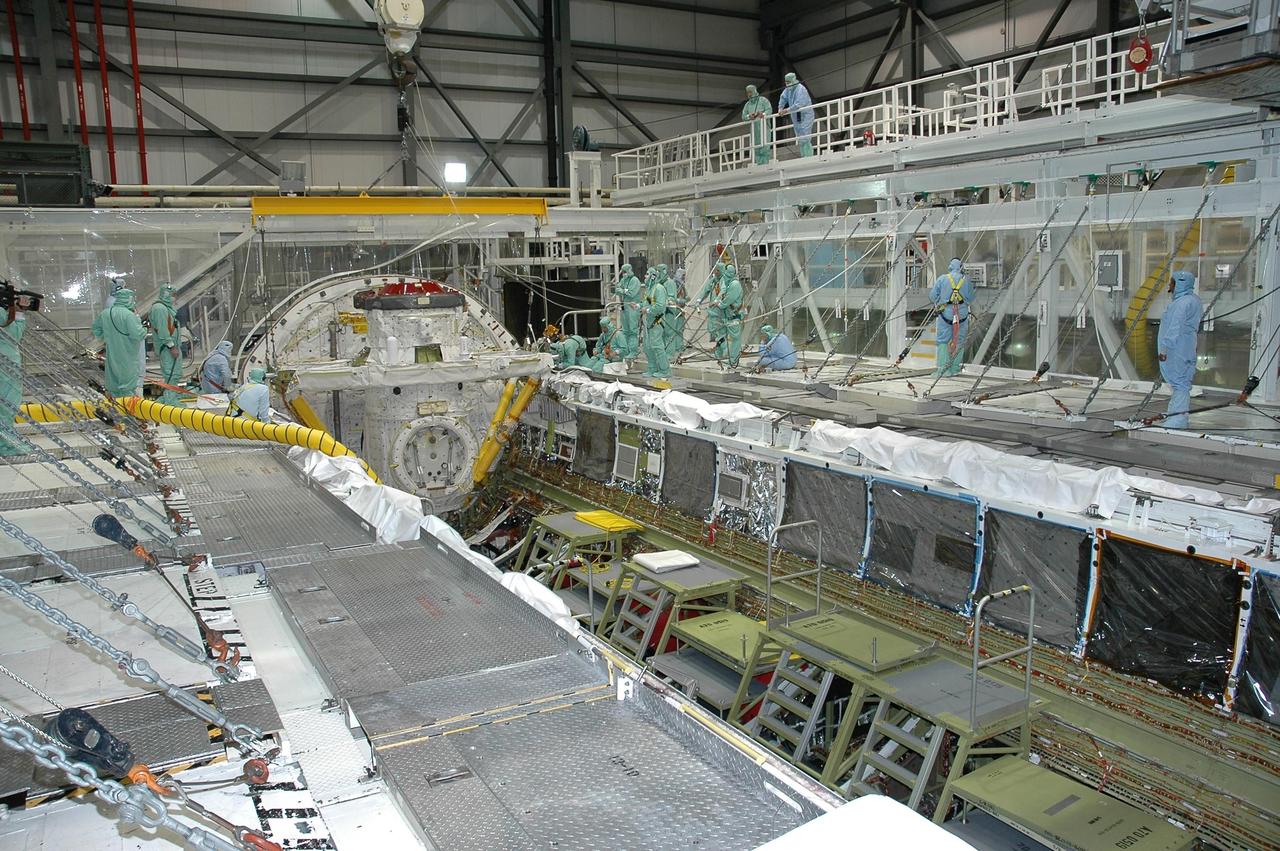

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the airlock has been lowered into place for installation into Endeavour's payload bay. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers stand by as the airlock is lowered into place for installation into Endeavour's payload bay. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
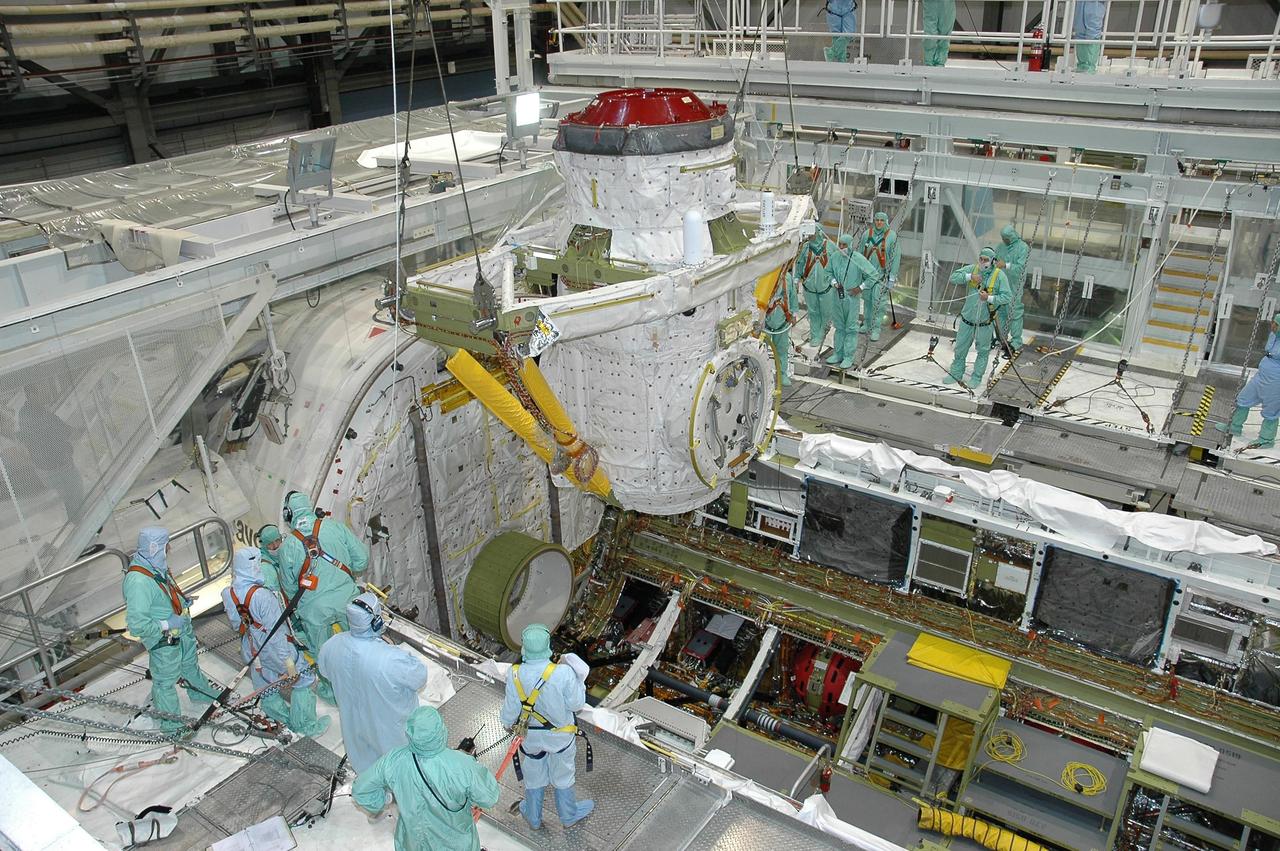
KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. - In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers observe the movement of the airlock as it is lowered into Endeavour's payload bay for installation. The airlock is located in the middeck. The airlock and airlock hatches permit flight crew members to transfer from the middeck crew compartment into the payload bay for extravehicular activities in their space suits without depressurizing the orbiter crew cabin. The airlock is sized to accommodate two fully suited flight crew members simultaneously. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
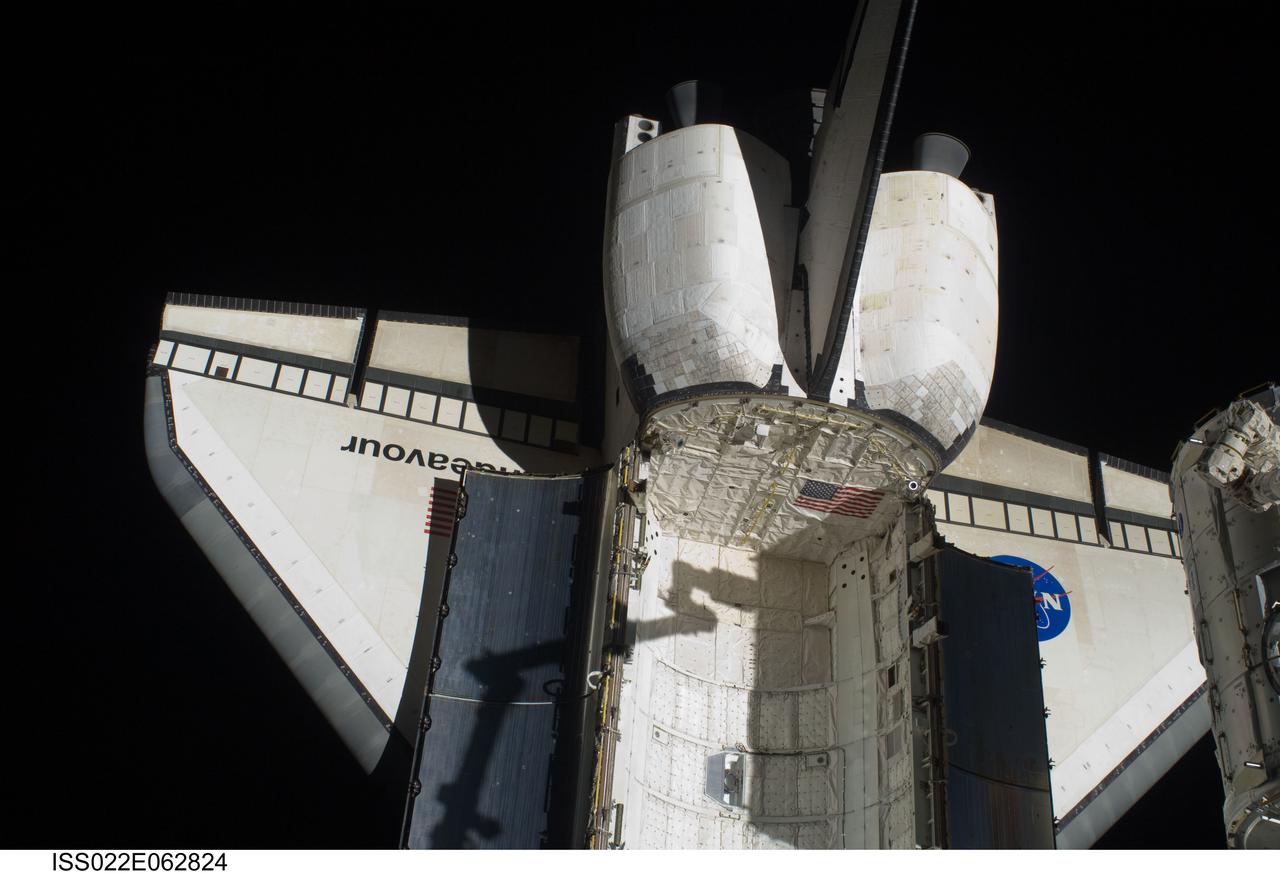

ISS022-E-062824 (11 Feb. 2010) --- Space shuttle Endeavour?s aft payload bay, orbital maneuvering system (OMS) pods, vertical stabilizer and wings are featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 22 crew member during the transfer of the Tranquility node (mostly out of frame at right) from its stowage position in Endeavour's (STS-130) payload bay to position it on the port side of the Unity node of the International Space Station. The shadow of Tranquility in the grasp of the Canadarm2 is visible on the shuttle.

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- In Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the Multi-Purpose Logistics Module Leonardo is placed into the payload canister after being removed from space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. Leonardo carried 32,000 pounds of supplies to the International Space Station on the STS-126 mission in November. Endeavour returned to Kennedy on a piggyback flight from California Dec. 12. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay doors is closed. Endeavour’s payload bay doors will be closed for the final time. The work is part of Transition and Retirement of the remaining space shuttles, Endeavour and Atlantis. Endeavour is being prepared for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Its ferry flight to California is targeted for mid-September. Endeavour was the last space shuttle added to NASA’s orbiter fleet. Over the course of its 19-year career, Endeavour spent 299 days in space during 25 missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
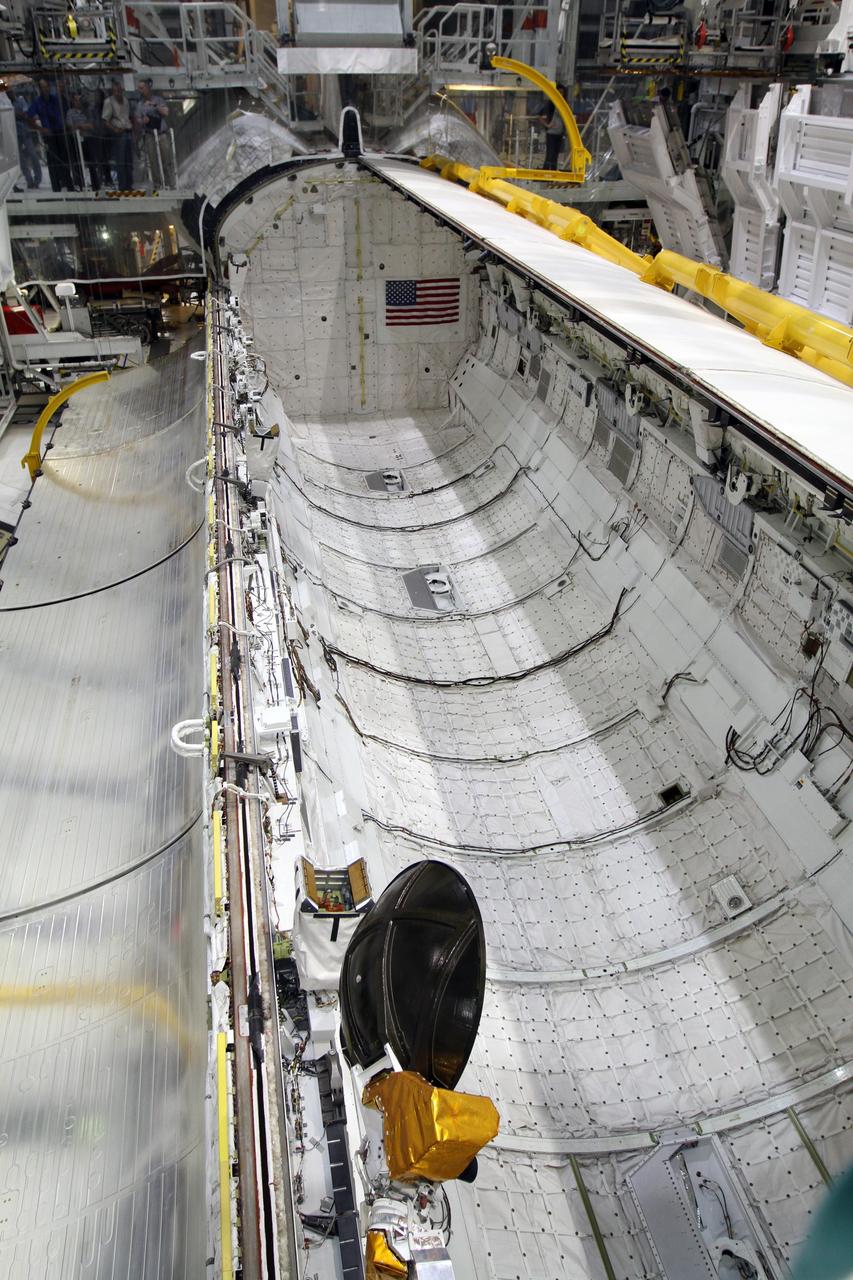

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay doors is closed. Endeavour’s payload bay doors will be closed for the final time. The work is part of Transition and Retirement of the remaining space shuttles, Endeavour and Atlantis. Endeavour is being prepared for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Its ferry flight to California is targeted for mid-September. Endeavour was the last space shuttle added to NASA’s orbiter fleet. Over the course of its 19-year career, Endeavour spent 299 days in space during 25 missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay doors is closed as United Space Alliance technicians monitor the progress of the second door’s closure. Endeavour’s payload bay doors are being closed for the final time. The work is part of Transition and Retirement of the remaining space shuttles, Endeavour and Atlantis. Endeavour is being prepared for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Its ferry flight to California is targeted for mid-September. Endeavour was the last space shuttle added to NASA’s orbiter fleet. Over the course of its 19-year career, Endeavour spent 299 days in space during 25 missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Inside Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay doors is closed as a United Space Alliance technician monitors the progress of the second door’s closure. Endeavour’s payload bay doors are being closed for the final time. The work is part of Transition and Retirement of the remaining space shuttles, Endeavour and Atlantis. Endeavour is being prepared for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Its ferry flight to California is targeted for mid-September. Endeavour was the last space shuttle added to NASA’s orbiter fleet. Over the course of its 19-year career, Endeavour spent 299 days in space during 25 missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/shuttle. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In NASA Kennedy Space Center's Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, workers check the movement of space shuttle Endeavour's Orbiter Boom Sensor System as it is lowered into the payload bay. The OBSS is being reinstalled in the payload bay. The OBSS is a 50-foot boom with a laser and cameras on it that astronauts use to inspect a shuttle's heat shield while in orbit. After returning from the STS-127 mission July 31, 2009, Endeavour now is being processed for the STS-130 mission targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. Endeavour will deliver to the International Space Station the Tranquility pressurized module that will provide room for many of the station's life support systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

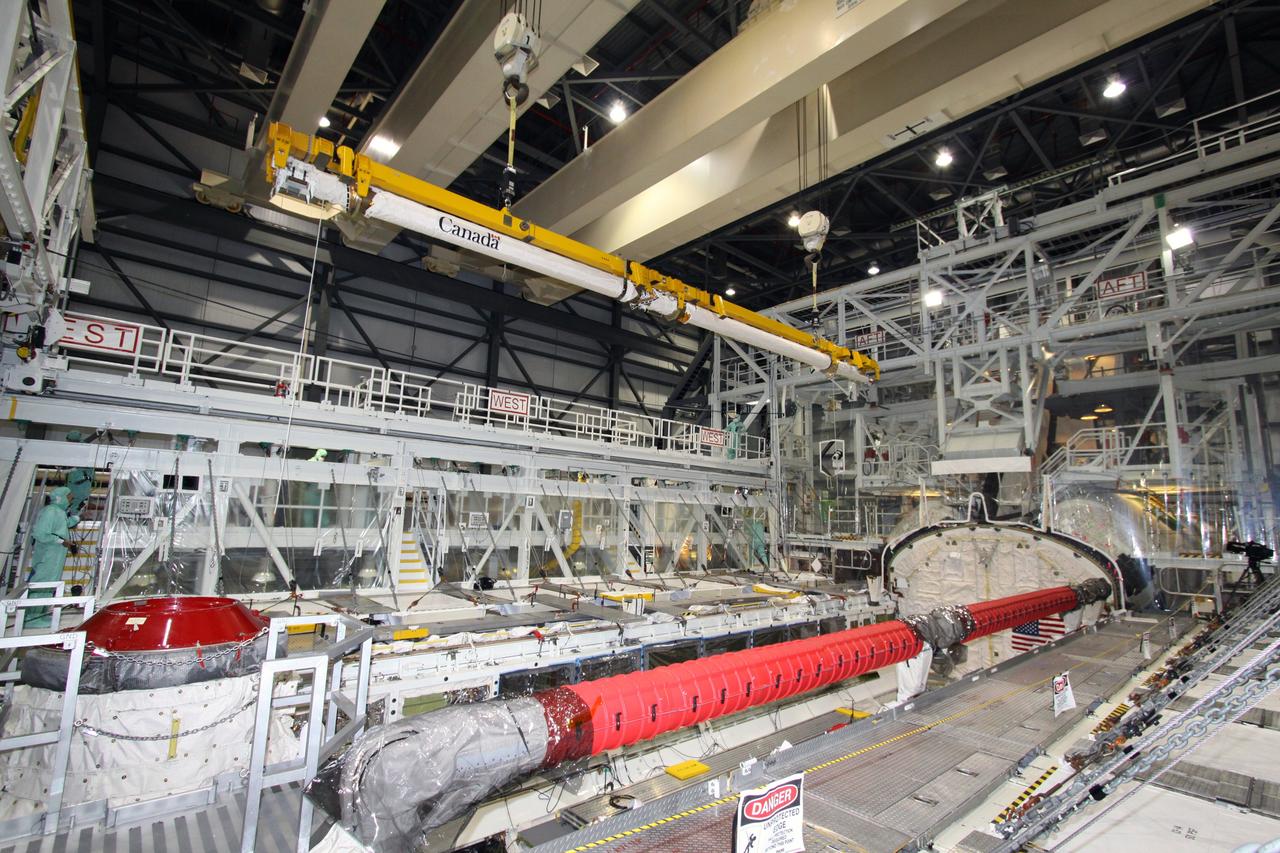
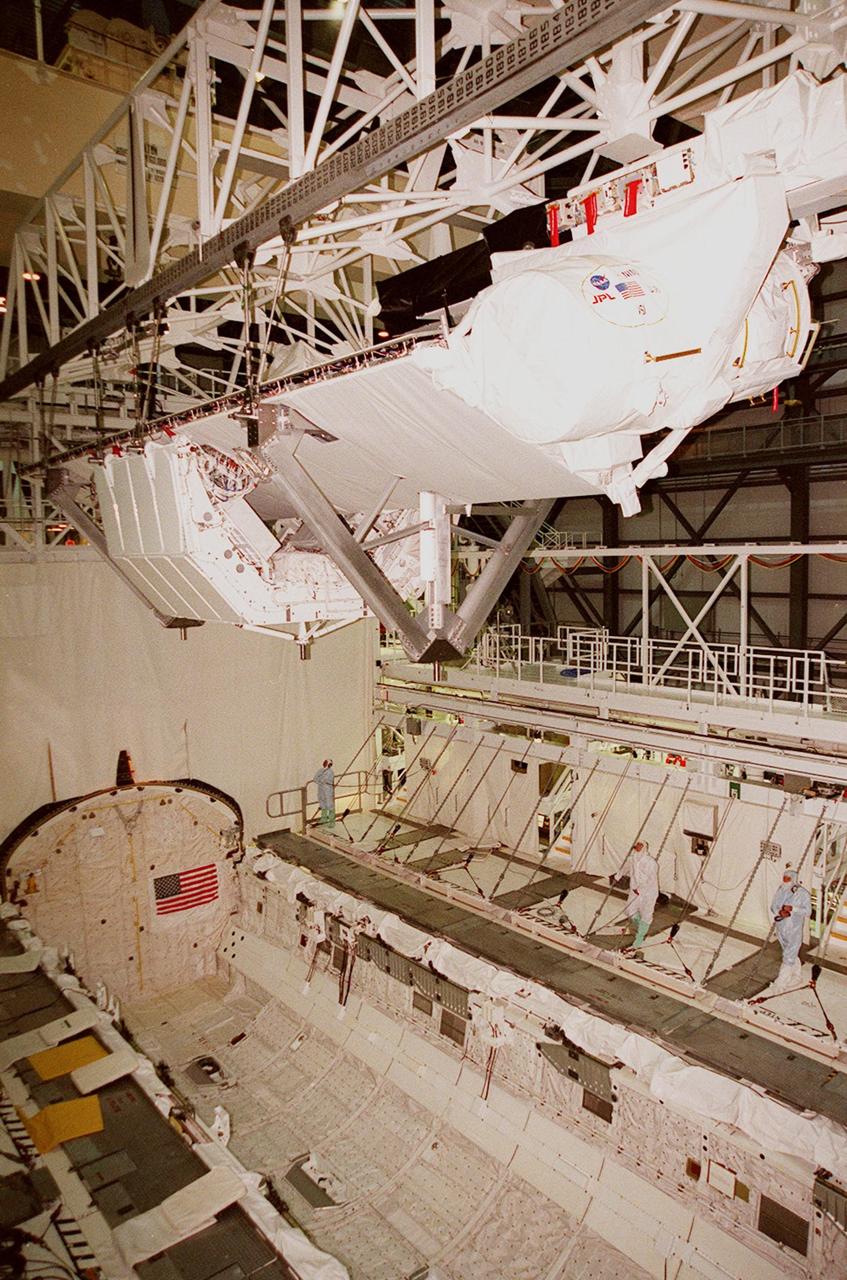
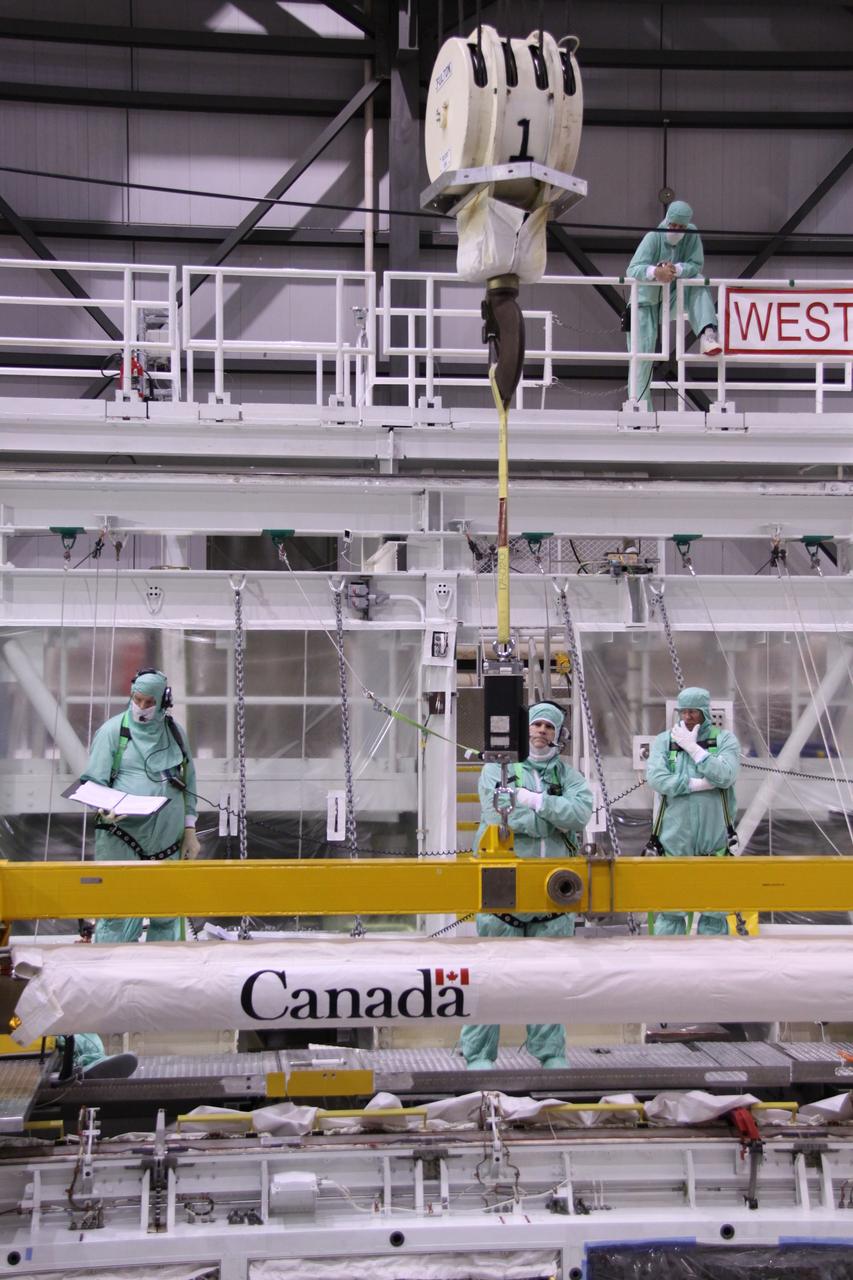
Looking like a painting, this wide-angle view shows the Unity connecting module being moved toward the payload bay of the orbiter Endeavour at Launch Pad 39A. Part of the International Space Station (ISS), Unity is scheduled for launch Dec. 3, 1998, on Mission STS-88. The Unity is a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of ISS. While on orbit, the flight crew will deploy Unity from the payload bay and attach it to the Russian-built Zarya control module which will be in orbit at that time
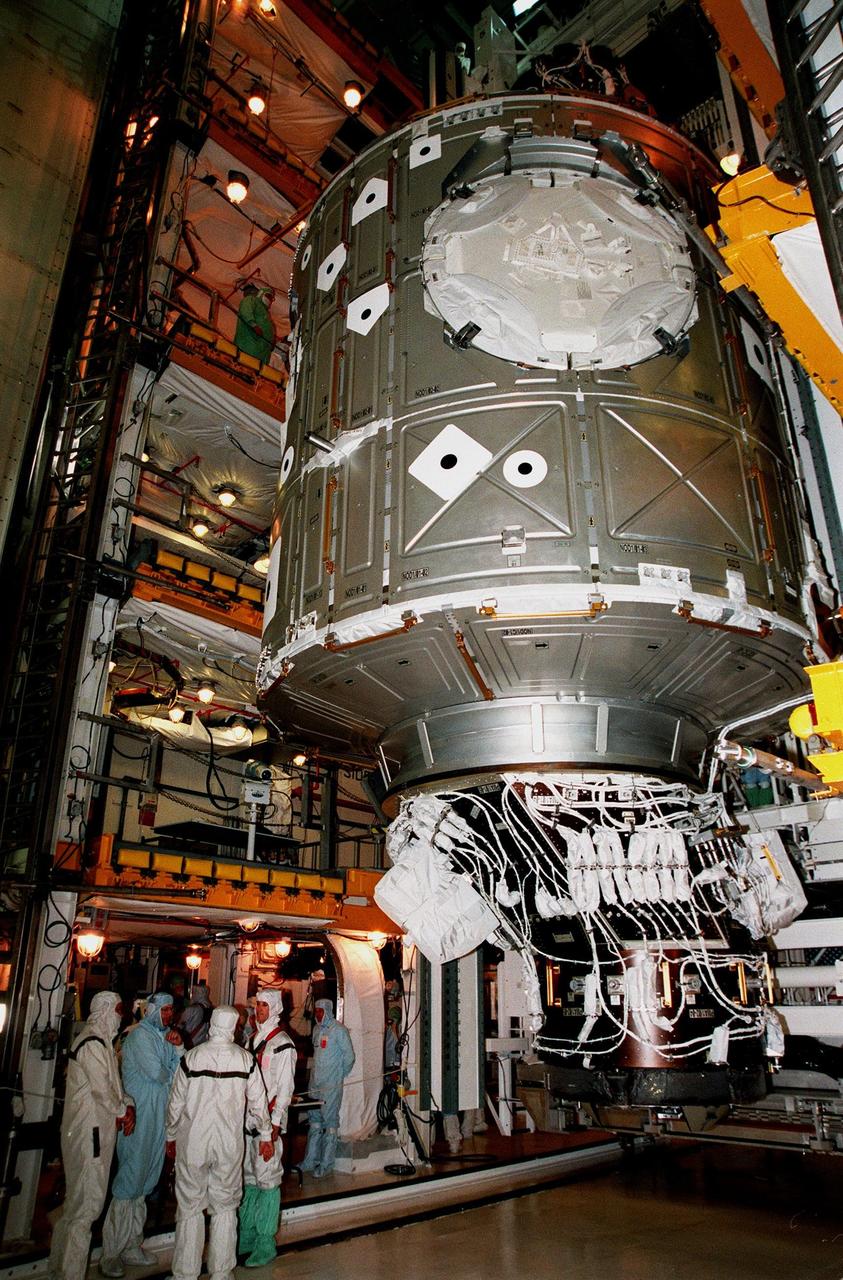
The Unity connecting module is moved toward the payload bay of the orbiter Endeavour at Launch Pad 39A. Part of the International Space Station (ISS), Unity is scheduled for launch Dec. 3, 1998, on Mission STS-88 . The Unity is a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of ISS. While on orbit, the flight crew will deploy Unity from the payload bay and attach it to the Russian-built Zarya control module which will be in orbit at that time
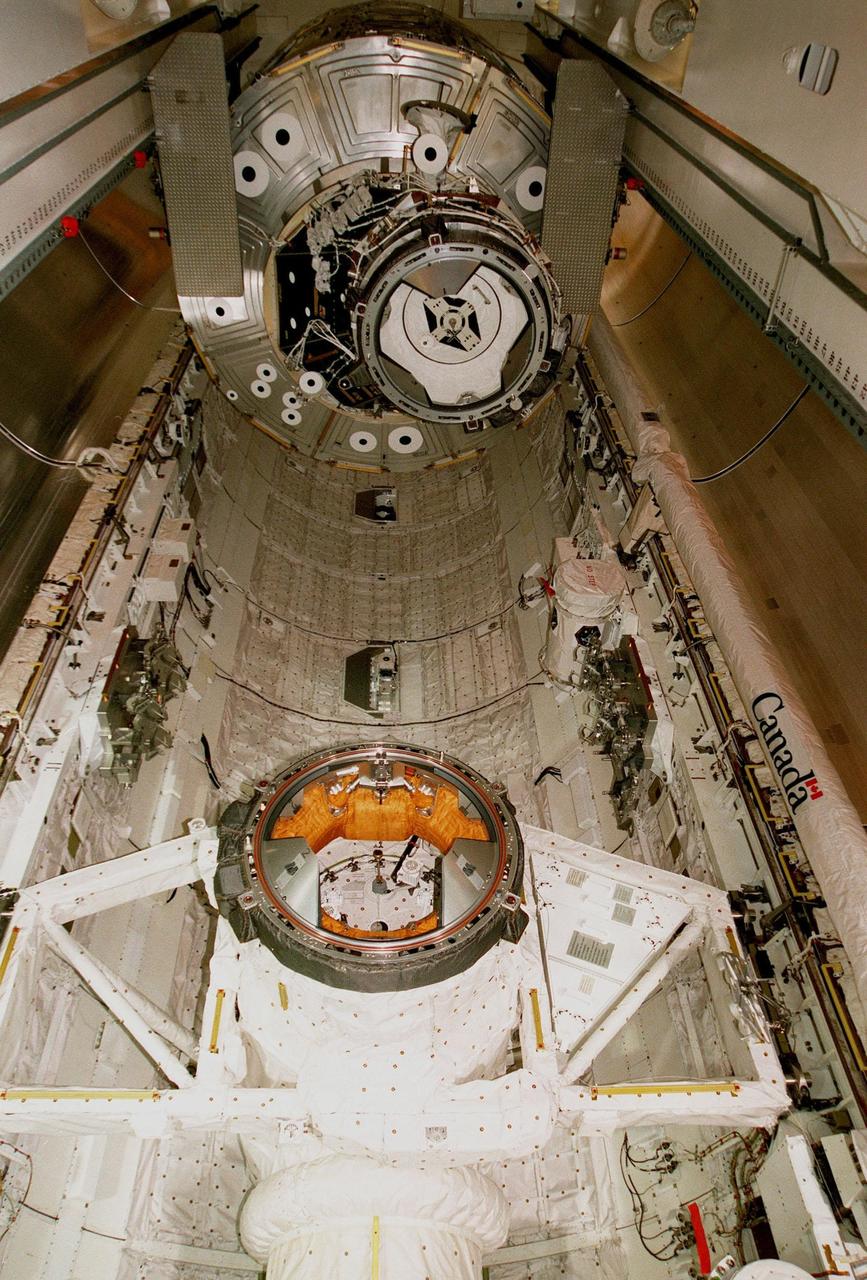

Viewed from below, the Unity connecting module is moved into the payload bay of the orbiter Endeavour at Launch Pad 39A. Part of the International Space Station (ISS), Unity is scheduled for launch Dec. 3, 1998, on Mission STS-88. The Unity is a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of ISS. While on orbit, the flight crew will deploy Unity from the payload bay and attach it to the Russian-built Zarya control module which will be in orbit at that time

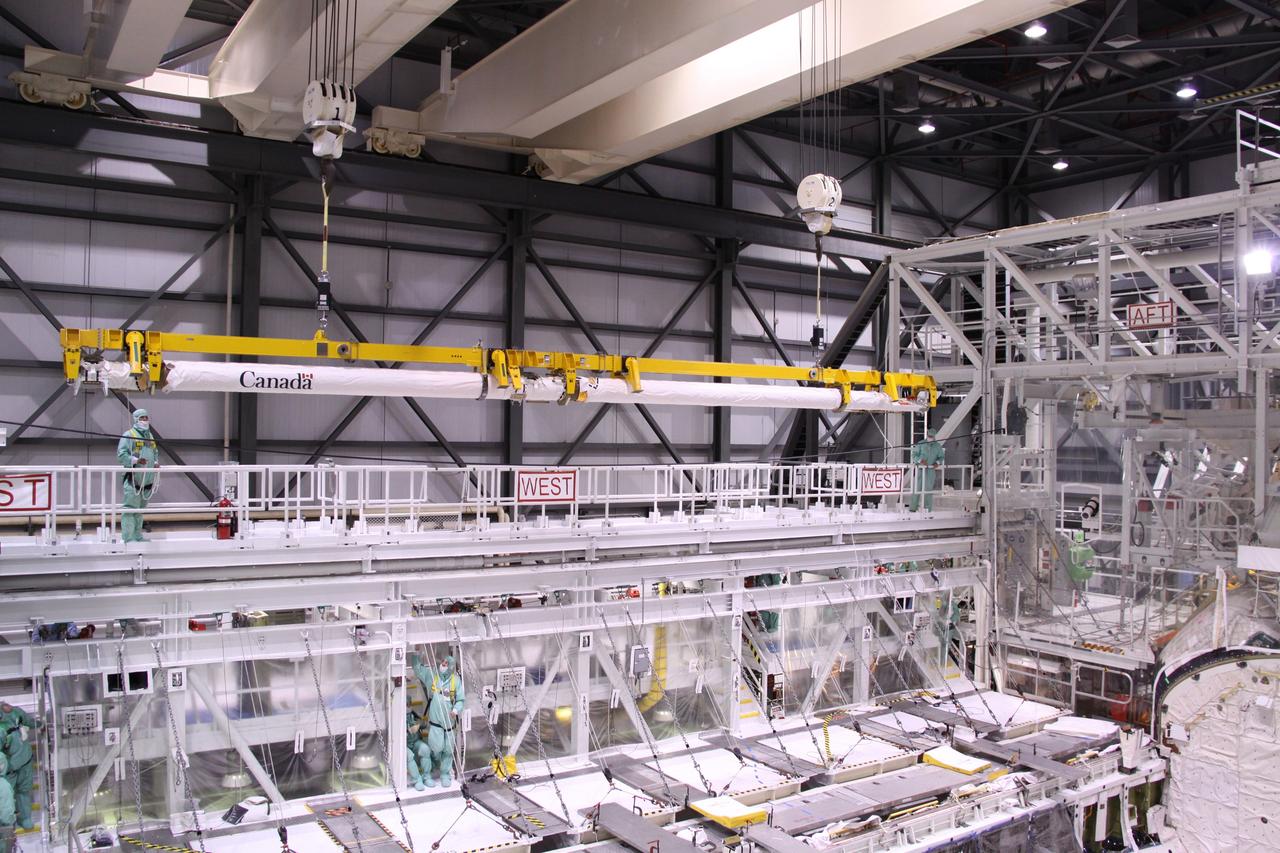
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. –In NASA Kennedy Space Center's Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, a crane lowers space shuttle Endeavour's Orbiter Boom Sensor System toward a mobile stand. The OBSS was removed from Endeavour's payload bay. After returning from the STS-127 mission July 31, 2009, Endeavour now is being processed for the STS-130 mission targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. Endeavour will deliver to the International Space Station the Tranquility pressurized module that will provide room for many of the station's life support systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

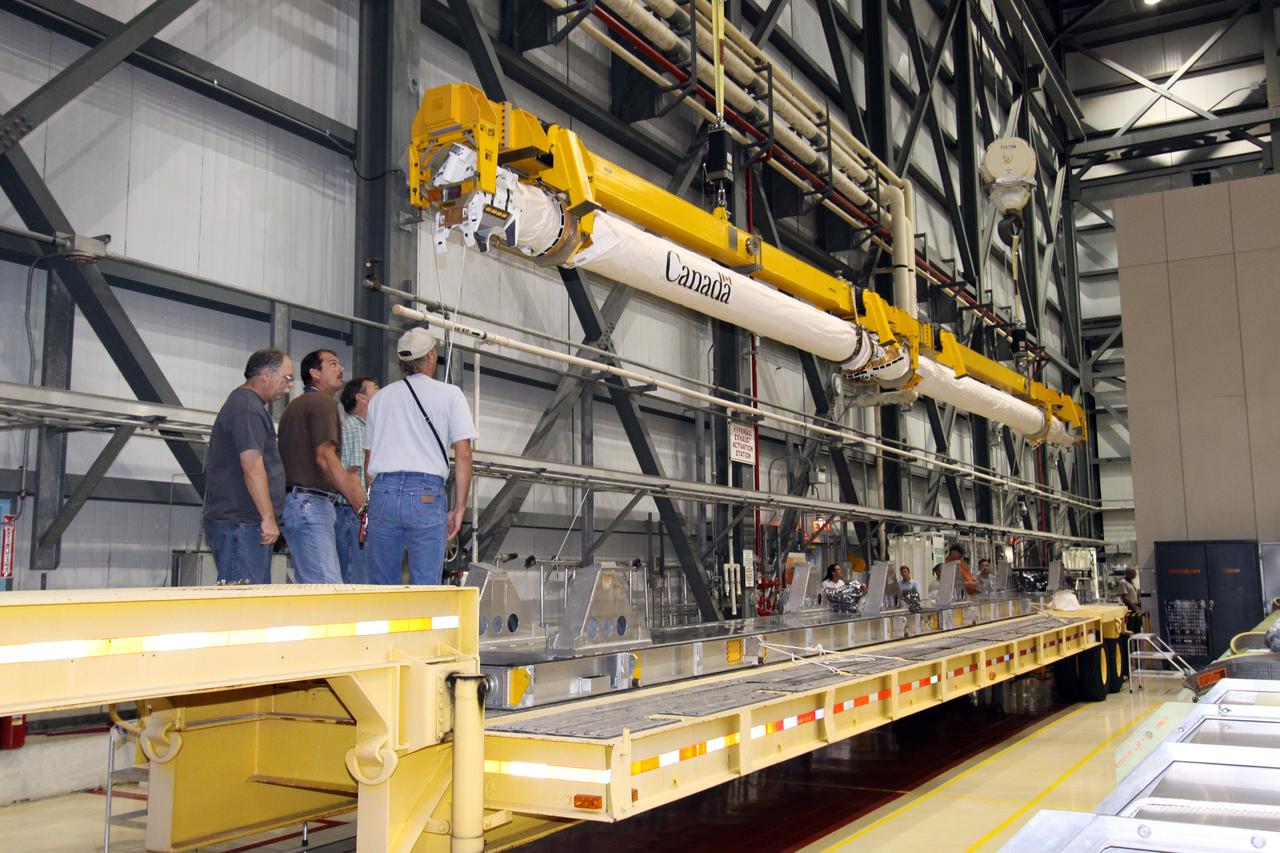
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In NASA Kennedy Space Center's Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, a crane lifts space shuttle Endeavour's Orbiter Boom Sensor System and moves it toward the payload bay for reinstallation. The OBSS is a 50-foot boom with a laser and cameras on it that astronauts use to inspect a shuttle's heat shield while in orbit. After returning from the STS-127 mission July 31, 2009, Endeavour now is being processed for the STS-130 mission targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. Endeavour will deliver to the International Space Station the Tranquility pressurized module that will provide room for many of the station's life support systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
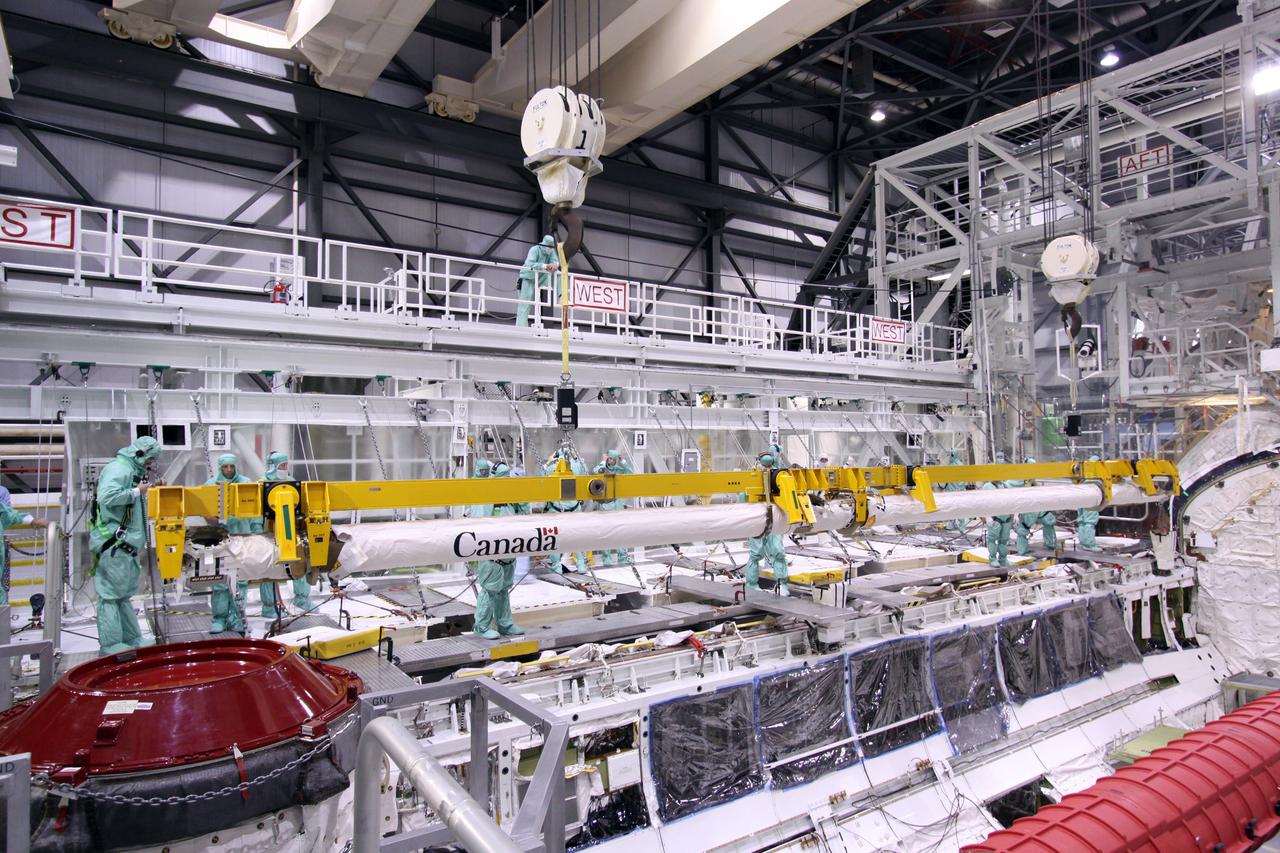
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In NASA Kennedy Space Center's Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, a crane lowers space shuttle Endeavour's Orbiter Boom Sensor System toward the payload bay for reinstallation. The OBSS is a 50-foot boom with a laser and cameras on it that astronauts use to inspect a shuttle's heat shield while in orbit. After returning from the STS-127 mission July 31, 2009, Endeavour now is being processed for the STS-130 mission targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. Endeavour will deliver to the International Space Station the Tranquility pressurized module that will provide room for many of the station's life support systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
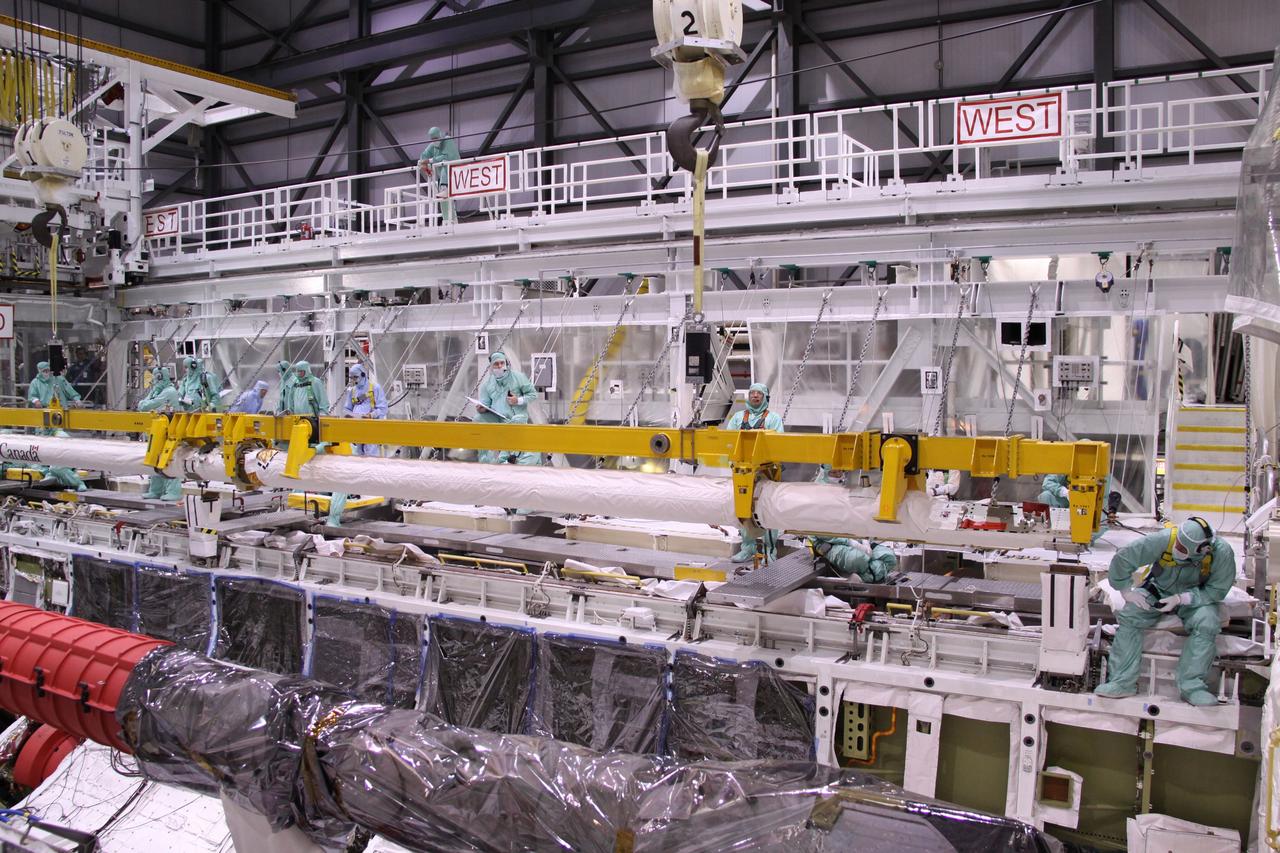

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In NASA Kennedy Space Center's Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2, workers watch the movement of space shuttle Endeavour's Orbiter Boom Sensor System as it is lowered into the payload bay. The OBSS is a 50-foot boom with a laser and cameras on it that astronauts use to inspect a shuttle's heat shield while in orbit. After returning from the STS-127 mission July 31, 2009, Endeavour now is being processed for the STS-130 mission targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. Endeavour will deliver to the International Space Station the Tranquility pressurized module that will provide room for many of the station's life support systems. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

The Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay doors were successfully cycled and closed for flight on Jan. 19 following replacement of a seal on the left door. Endeavour will be carrying the SPACEHAB module in the payload bay of the orbiter. The double module configuration will house experiments to be performed by Endeavour's crew along with logistics equipment to be transferred to the Russian Space Station Mir, where Mission Specialist Andrew Thomas, Ph.D., will succeed David Wolf, M.D. STS-89 will be the eighth docking of the Space Shuttle with Mir. Launch is scheduled for January 22 at 9:48 p.m. EST

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- The Space Shuttle Endeavour's payload bay doors were successfully cycled and closed for flight on Jan. 19 following replacement of a seal on the left door. Endeavour will be carrying the SPACEHAB module in the payload bay of the orbiter. The double module configuration will house experiments to be performed by Endeavour's crew along with logistics equipment to be transferred to the Russian Space Station Mir, where Mission Specialist Andrew Thomas, Ph.D., will succeed David Wolf, M.D. STS-89 will be the eighth docking of the Space Shuttle with Mir. Launch is scheduled for January 22 at 9:48 p.m. EST
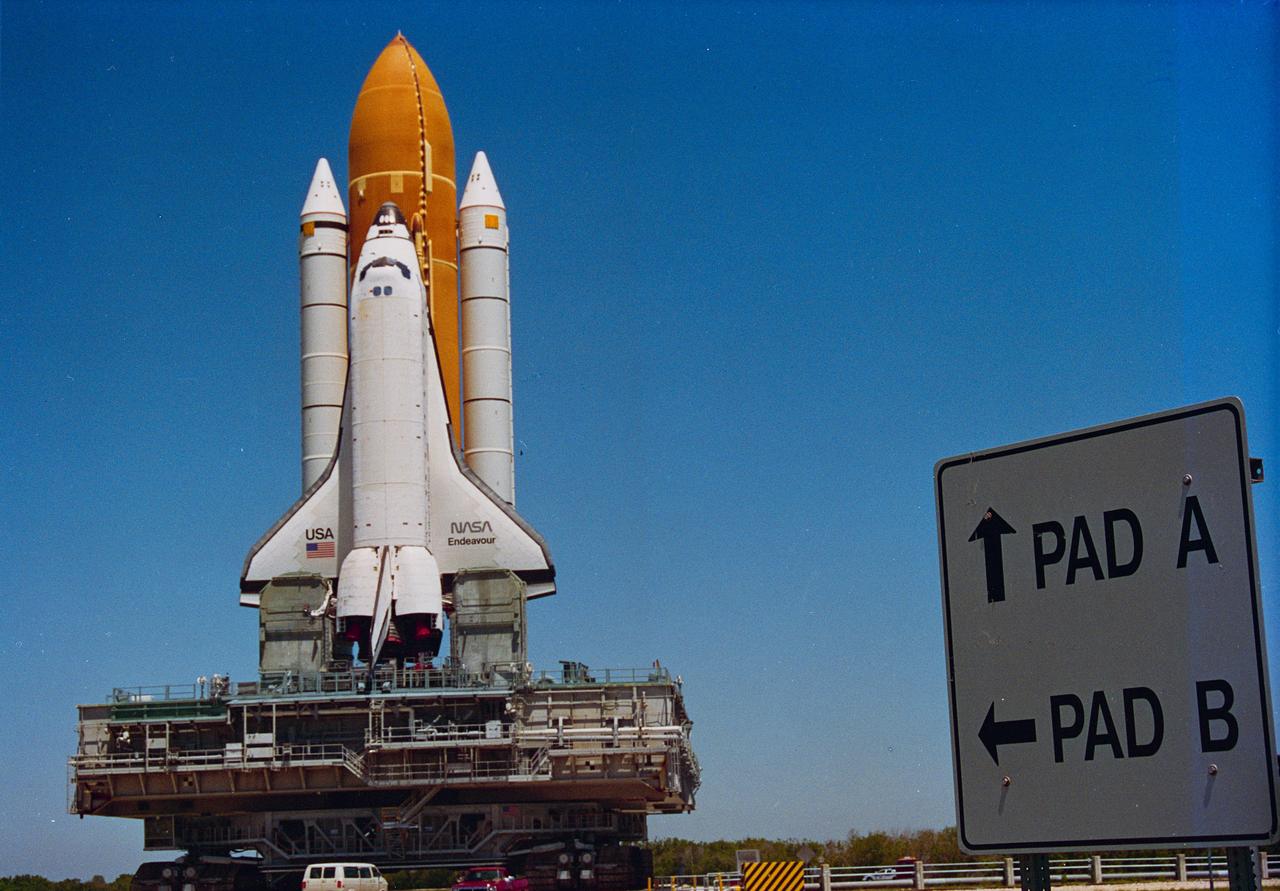
S96-07957 (16 April 1996) --- A road sign points to Launch Pad 39B, the final earthly destination for the Space Shuttle Endeavour and its final stepping stone into space. Endeavour began the slow journey from the Vehicle Assembly Building (VAB) at about 10:00a.m., April 16, 1996, perched atop the Mobile Launcher Platform and carried by the Crawler-Transporter. Upcoming activities at the pad to prepare Endeavour for flight on STS-77 include installation of the payloads in the Orbiter?s payload bay.

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, STS-123 Pilot Dominic Gorie (second from right) checks out the orbiter boom sensor system in Endeavour's payload bay. He and other crew members are at NASA's Kennedy Space Center for a crew equipment interface test, a process of familiarization with payloads, hardware and the space shuttle. The STS-123 mission is targeted for launch on space shuttle Endeavour on Feb. 14. It will be the 25th assembly flight of the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- In the Orbiter Processing Facility, STS-123 Pilot Dominic Gorie (second from right) checks out the orbiter boom sensor system in Endeavour's payload bay. He and other crew members are at NASA's Kennedy Space Center for a crew equipment interface test, a process of familiarization with payloads, hardware and the space shuttle. The STS-123 mission is targeted for launch on space shuttle Endeavour on Feb. 14. It will be the 25th assembly flight of the station. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
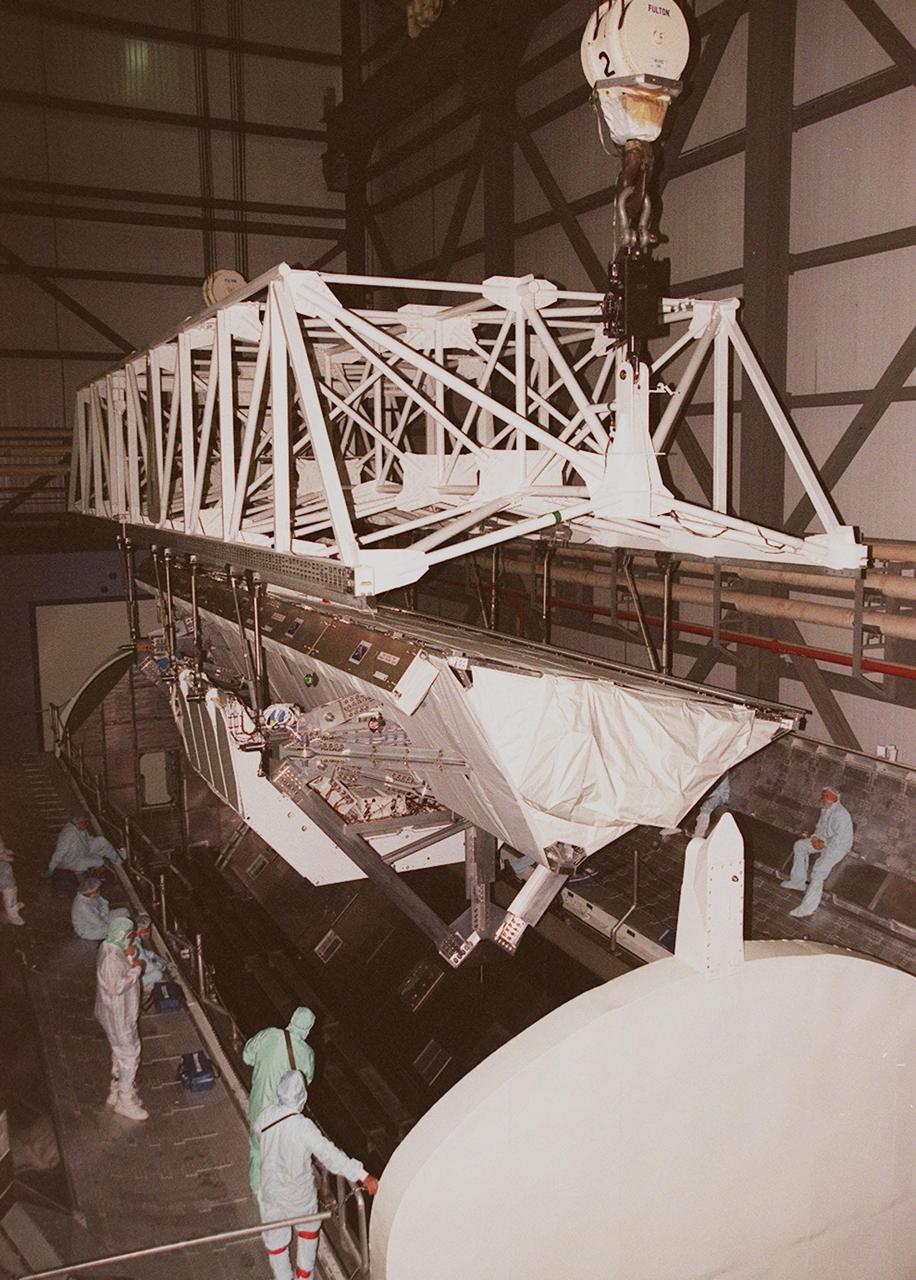

In the Orbiter Processing Facility, workers observe as an overhead crane lowers the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) into a payload canister. The payload on mission STS-99, SRTM was removed from orbiter Endeavour's payload bay to allow technicians access to the orbiter's midbody for planned wiring inspections. The entire fleet of orbiters is being inspected for wiring abrasions after the problem was first discovered in Columbia. Shuttle managers are reviewing several manifest options and could establish new target launch dates for the balance of 1999 next week. Shuttle Endeavour currently remains slated for launch in early October
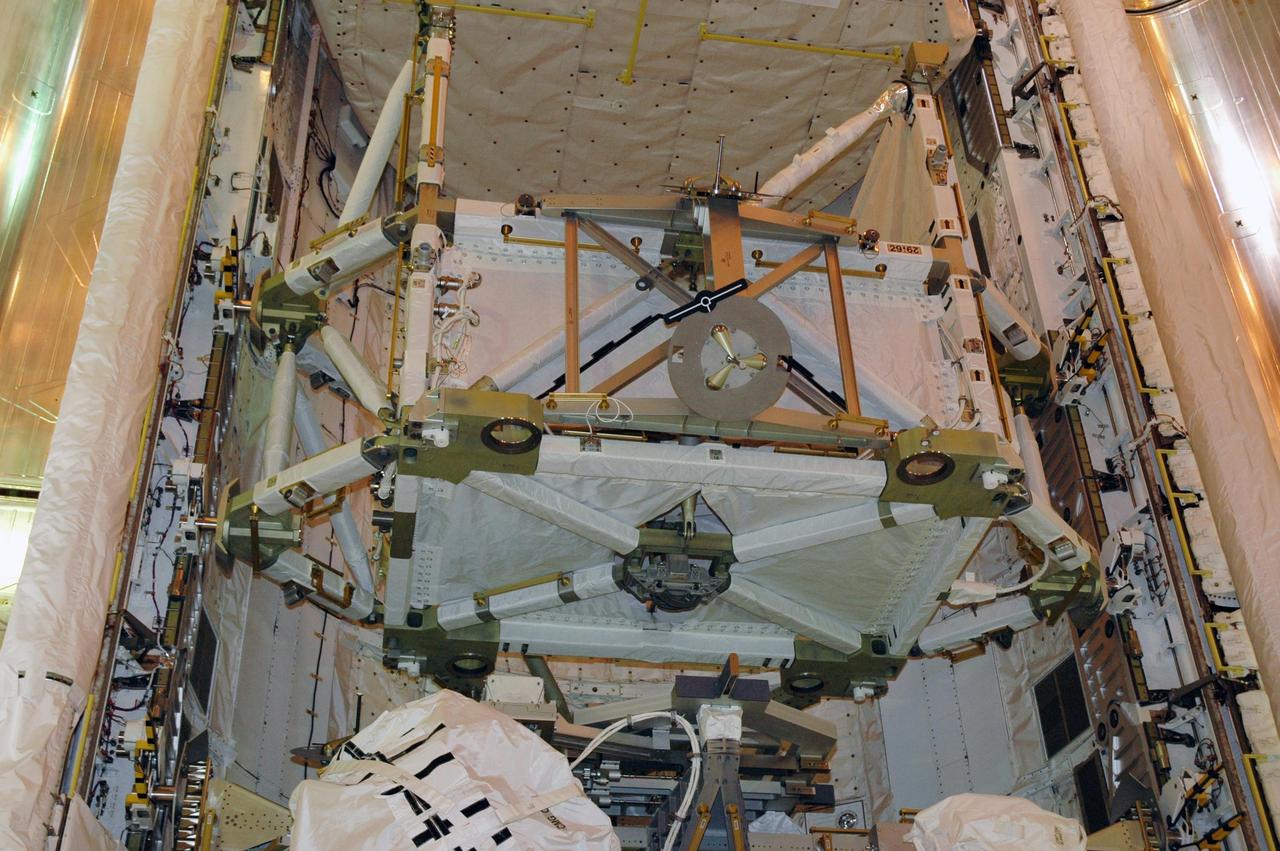

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Looking into the open payload bay doors of Space Shuttle Endeavour, the S5 truss takes the spotlight. Other cargo elements are the SPACEHAB module and the external stowage platform 3. At lower right is the control moment gyro. The payload bay doors were opened to allow for payload closeouts, including camera tests on the shuttle robotic arm and the extension, known as the orbiter boom sensor system. Endeavour is scheduled to launch Aug. 7 on mission STS-118, the 22nd flight to the International Space Station. NASA/Charisse Nahser

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- On Launch Pad 39A, a worker checks the movement of one of Endeavour's payload bay doors as it closes. Seen in the photo are the cargo, from top, the SPACEHAB module, the S5 truss and the external stowage platform 3 with a control moment gyro at left. The payload bay doors were opened to allow for payload closeouts, including camera tests on the shuttle robotic arm and the extension, known as the orbiter boom sensor system. Endeavour is scheduled to launch Aug. 7 on mission STS-118, the 22nd flight to the International Space Station. NASA/Charisse Nahser
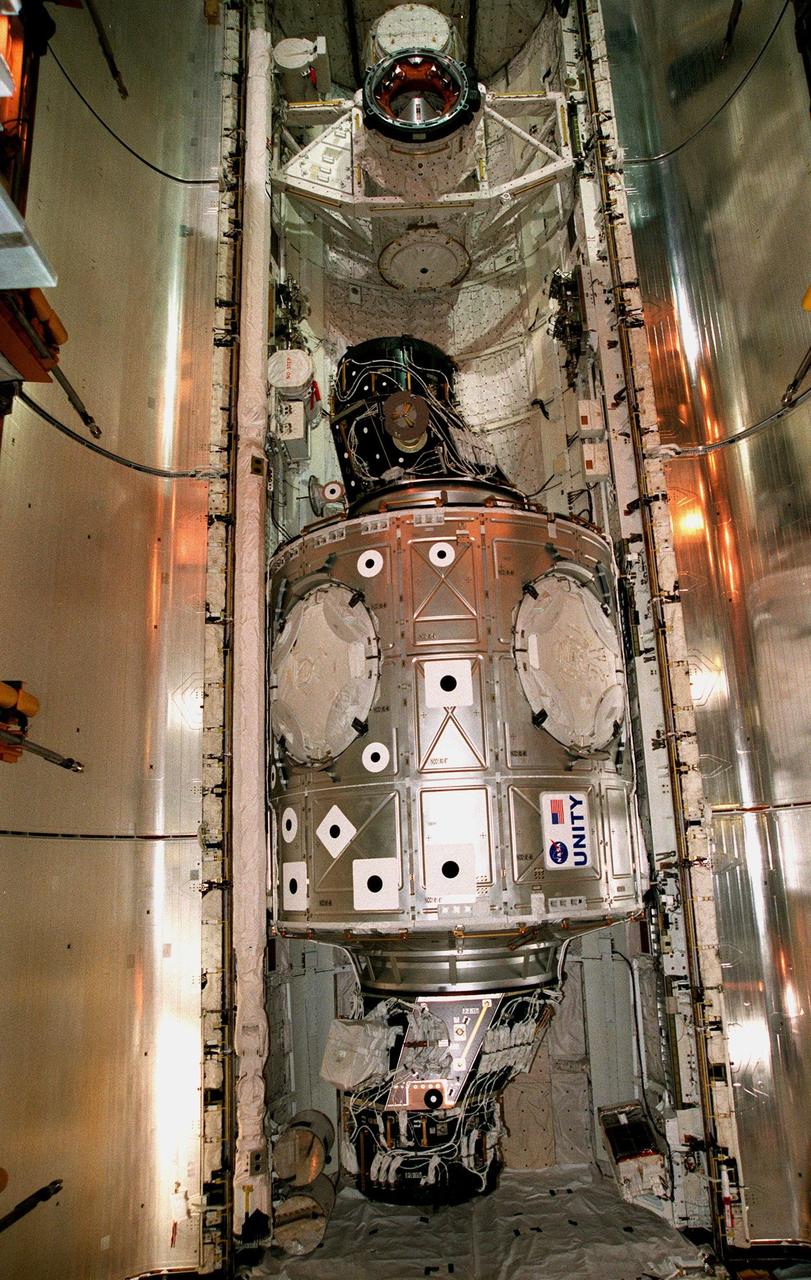
The Unity connecting module rests inside the open payload bay of the orbiter Endeavour at Launch Pad 39A. At the top of bay is the docking mechanism first used with launches to Mir, the Russian space station. Unity is the first U.S. element of the International Space Station (ISS) and is scheduled for launch Dec. 3, 1998, on Mission STS-88. The Unity is a connecting passageway to the living and working areas of ISS. While on orbit, the flight crew will deploy Unity from the payload bay and attach it to the Russian-built Zarya control module which will be in orbit at that time. The mission is expected to last nearly 12 days, landing back at the Kennedy Space Center on Dec. 14
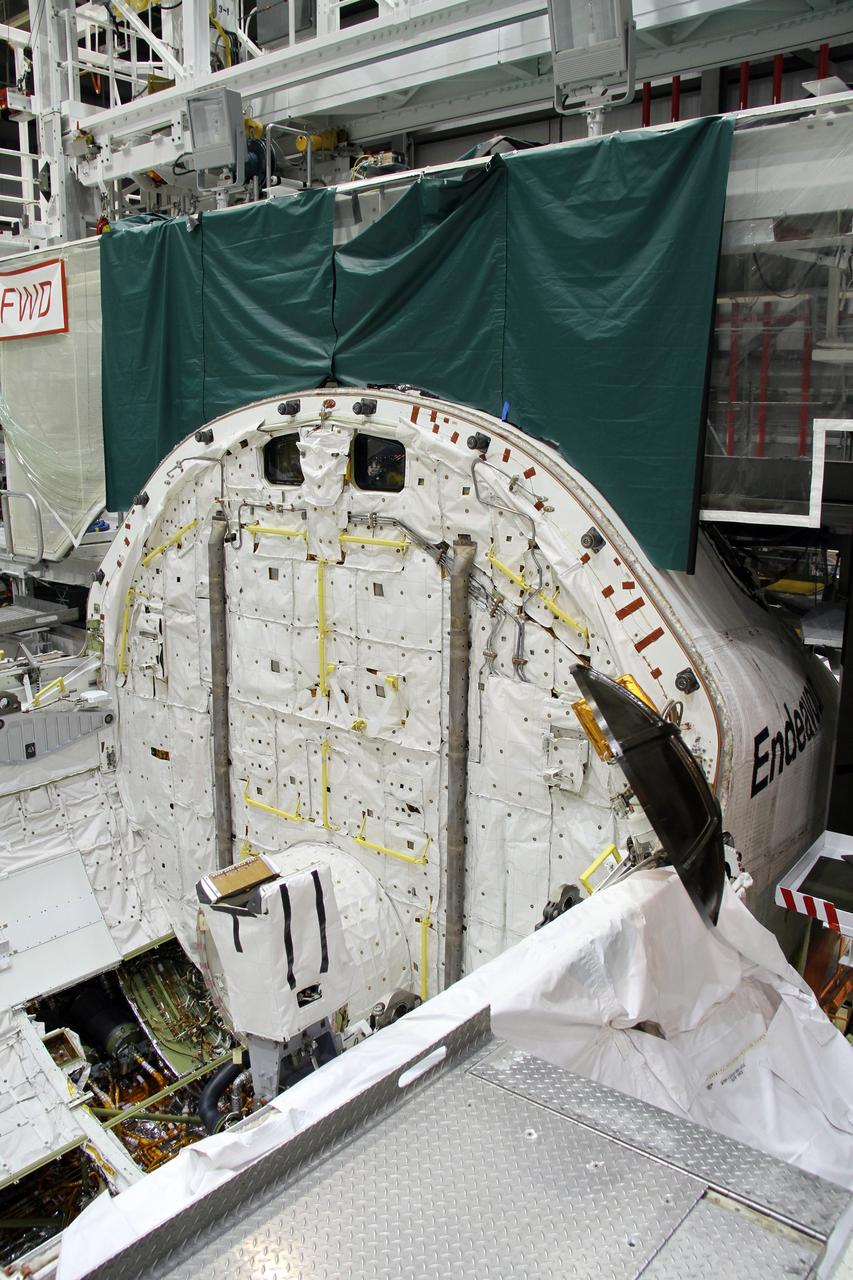

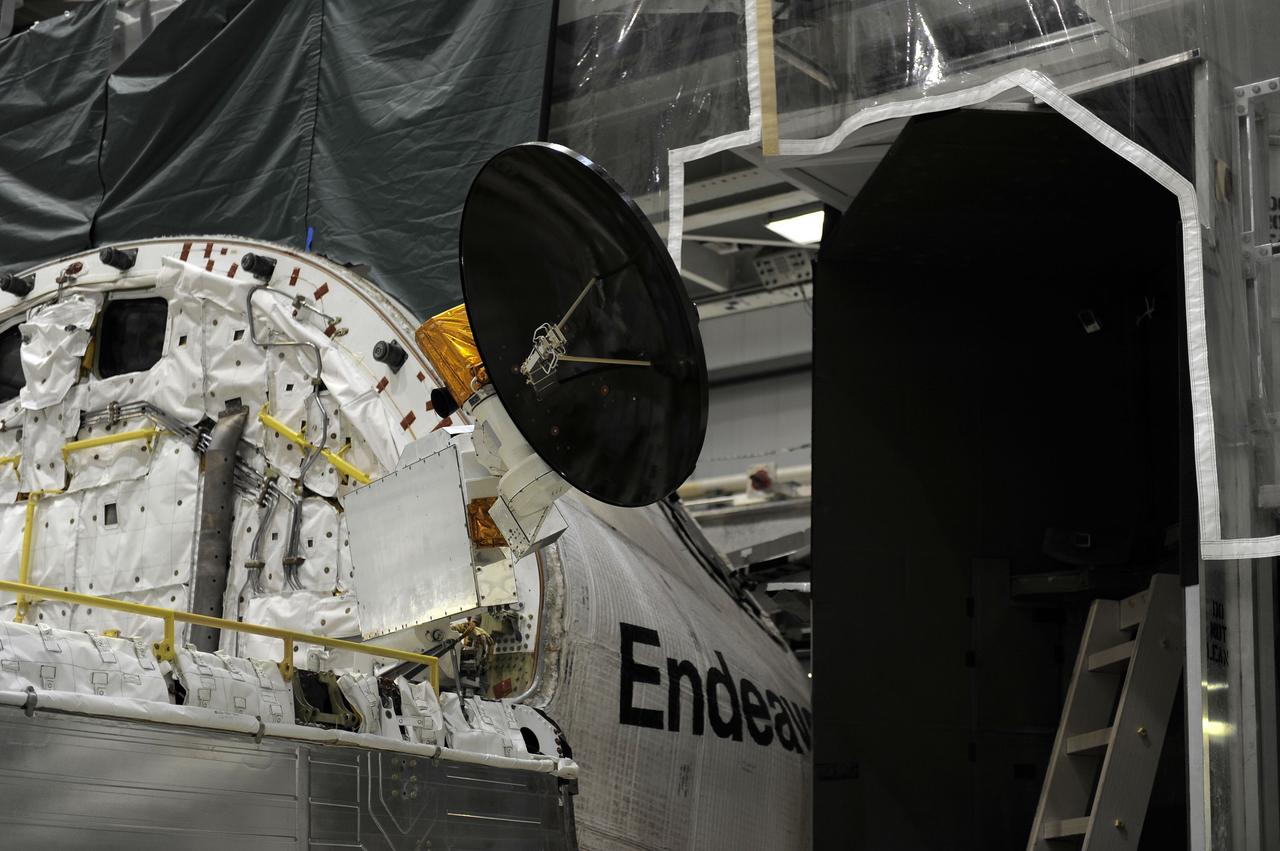
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, stowage of a Ku-band antenna in space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay is under way in preparation for final closure of the shuttle’s payload bay doors. The antenna, which resembles a mini-satellite dish, was used to transmit audio, video and data between the shuttle and ground stations on Earth. Endeavour is being prepared for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Its ferry flight to California is targeted for mid-September. Endeavour was the last space shuttle added to NASA’s orbiter fleet. Over the course of its 19-year career, Endeavour spent 299 days in space during 25 missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
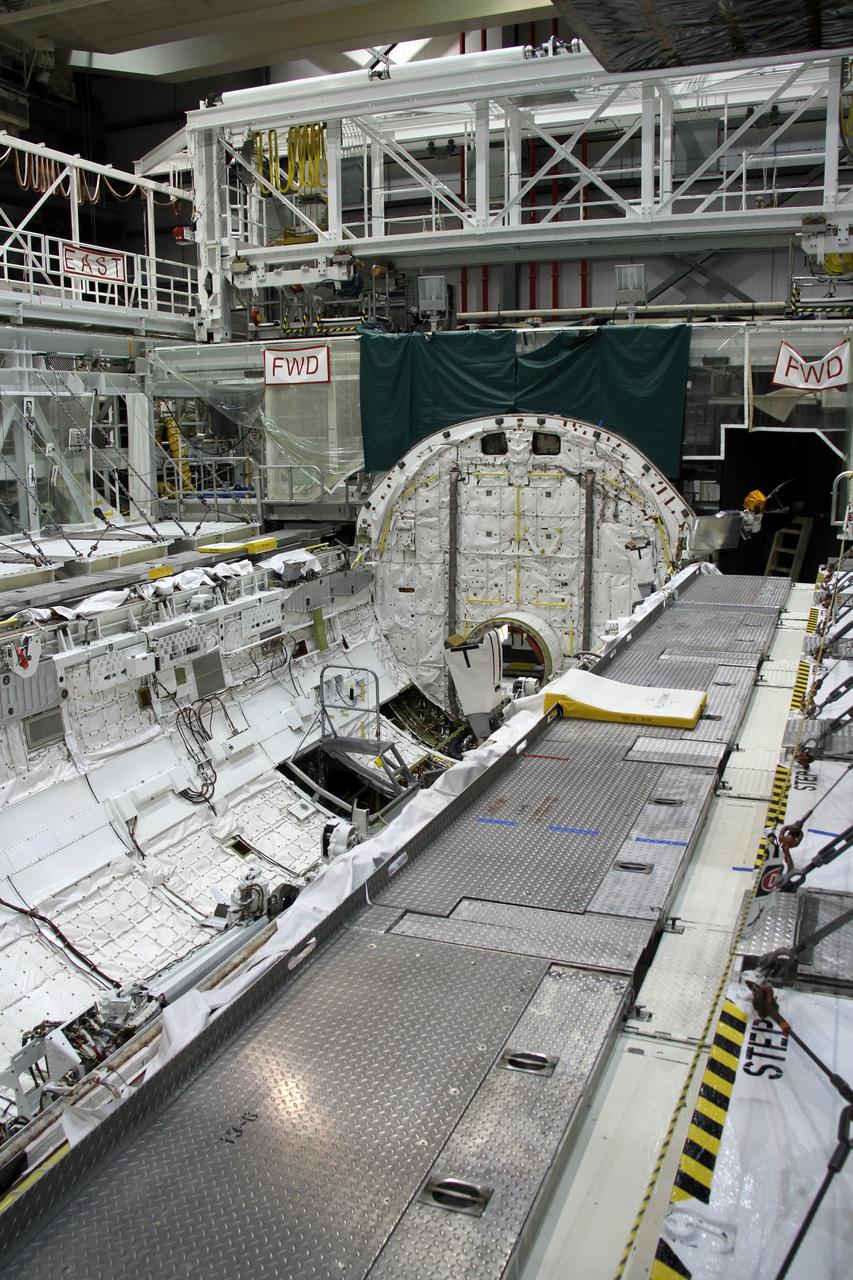
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, stowage of a Ku-band antenna at the forward end of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay is in progress in preparation for final closure of the shuttle’s payload bay doors. The antenna, which resembles a mini-satellite dish, was used to transmit audio, video and data between the shuttle and ground stations on Earth. Endeavour is being prepared for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Its ferry flight to California is targeted for mid-September. Endeavour was the last space shuttle added to NASA’s orbiter fleet. Over the course of its 19-year career, Endeavour spent 299 days in space during 25 missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
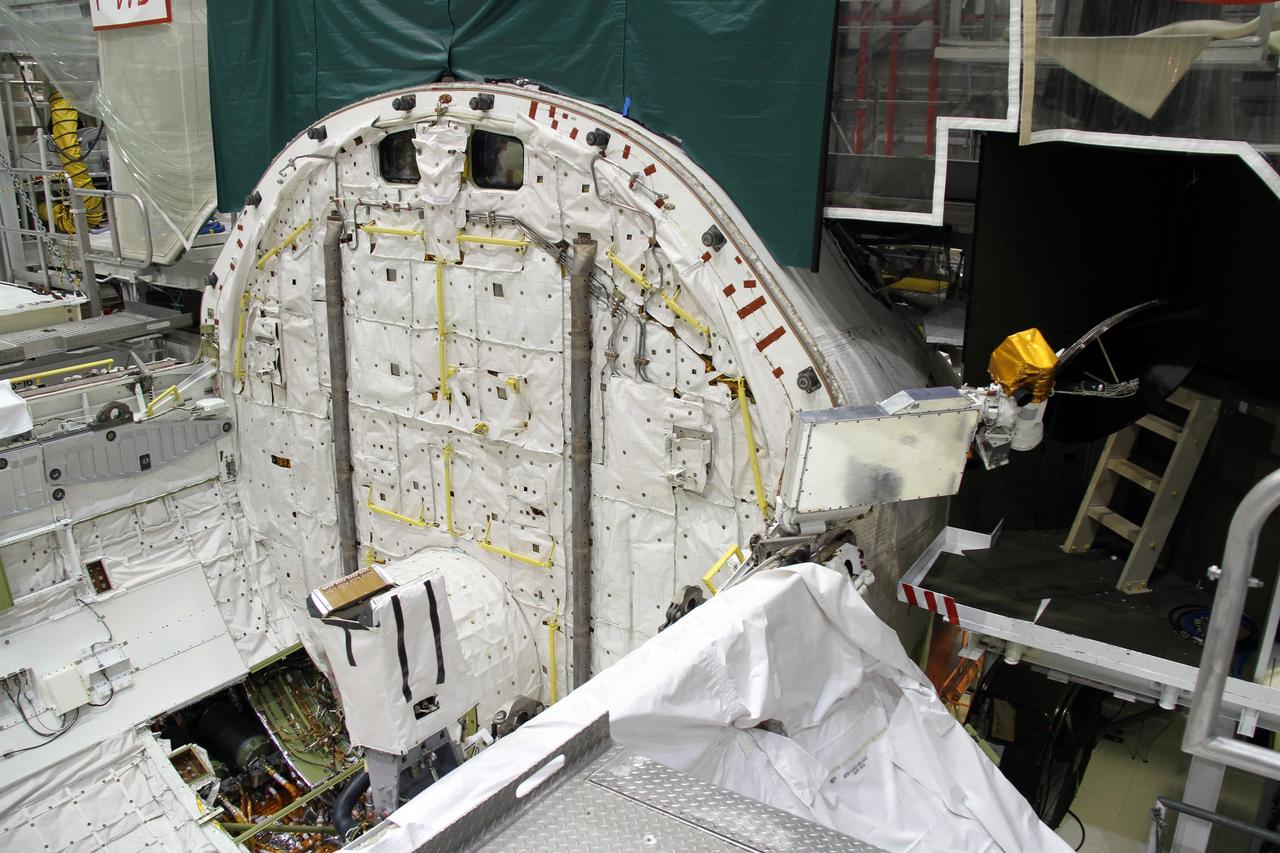

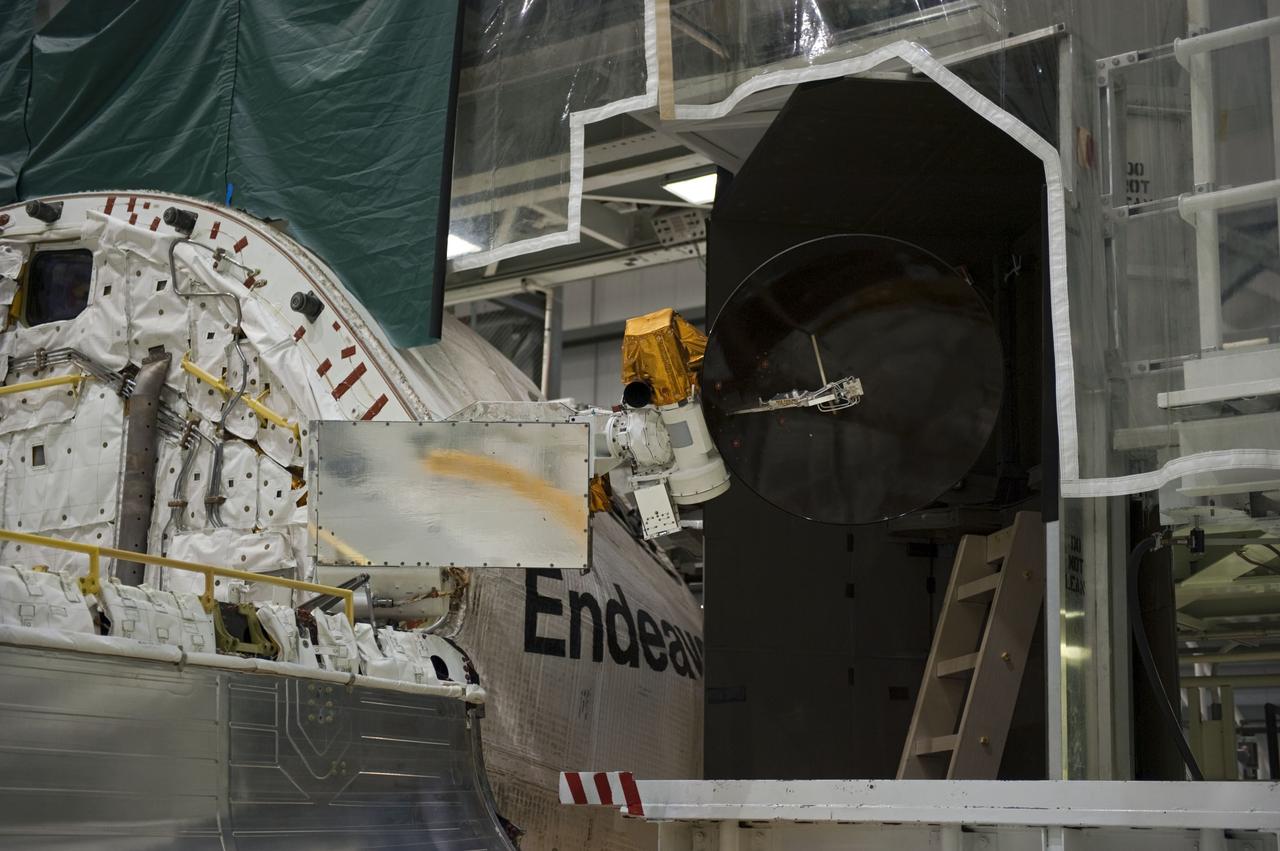
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Ku-band antenna is being stowed in space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay in preparation for final closure of the shuttle’s payload bay doors. The antenna, which resembles a mini-satellite dish, was used to transmit audio, video and data between the shuttle and ground stations on Earth. Endeavour is being prepared for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Its ferry flight to California is targeted for mid-September. Endeavour was the last space shuttle added to NASA’s orbiter fleet. Over the course of its 19-year career, Endeavour spent 299 days in space during 25 missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
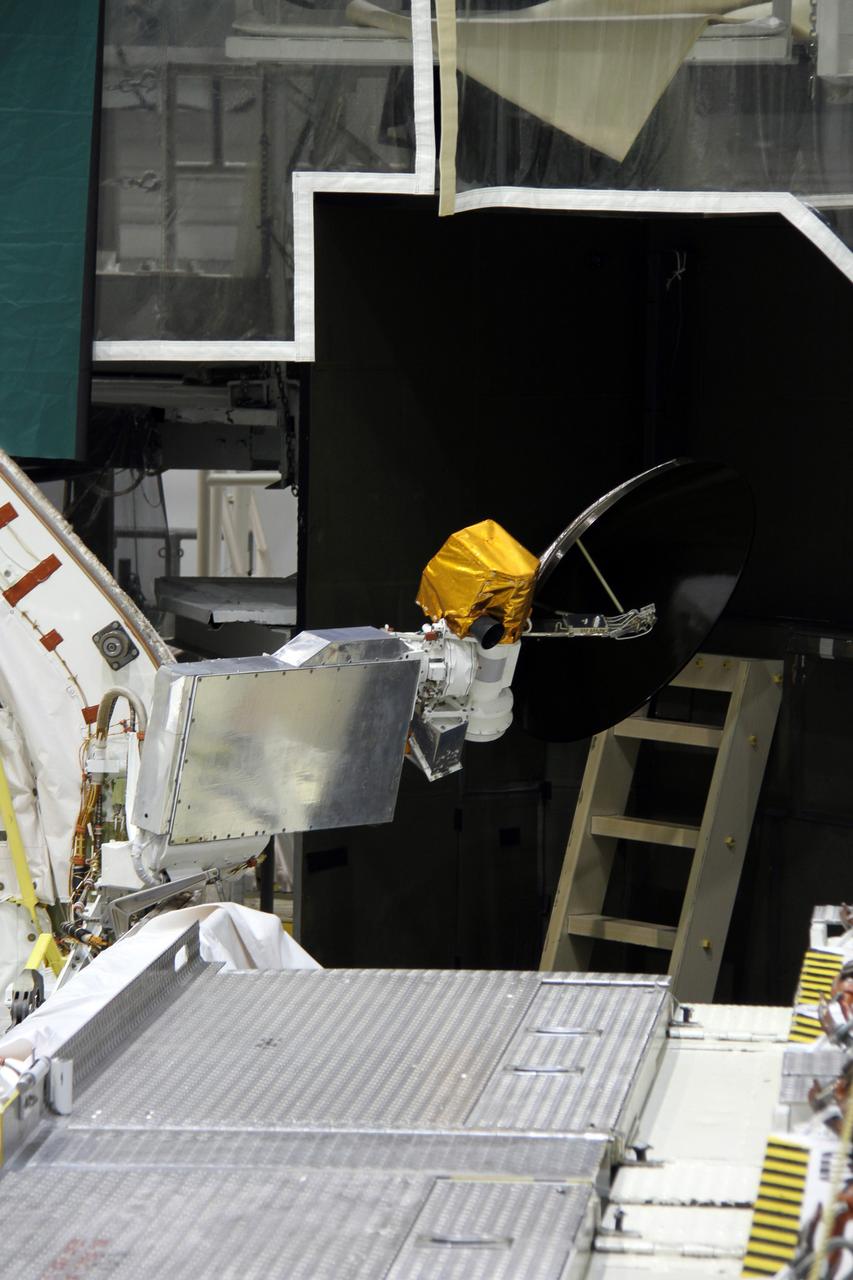

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, operations are under way to stow a Ku-band antenna in space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay in preparation for final closure of the shuttle’s payload bay doors. The antenna, which resembles a mini-satellite dish, was used to transmit audio, video and data between the shuttle and ground stations on Earth. Endeavour is being prepared for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Its ferry flight to California is targeted for mid-September. Endeavour was the last space shuttle added to NASA’s orbiter fleet. Over the course of its 19-year career, Endeavour spent 299 days in space during 25 missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
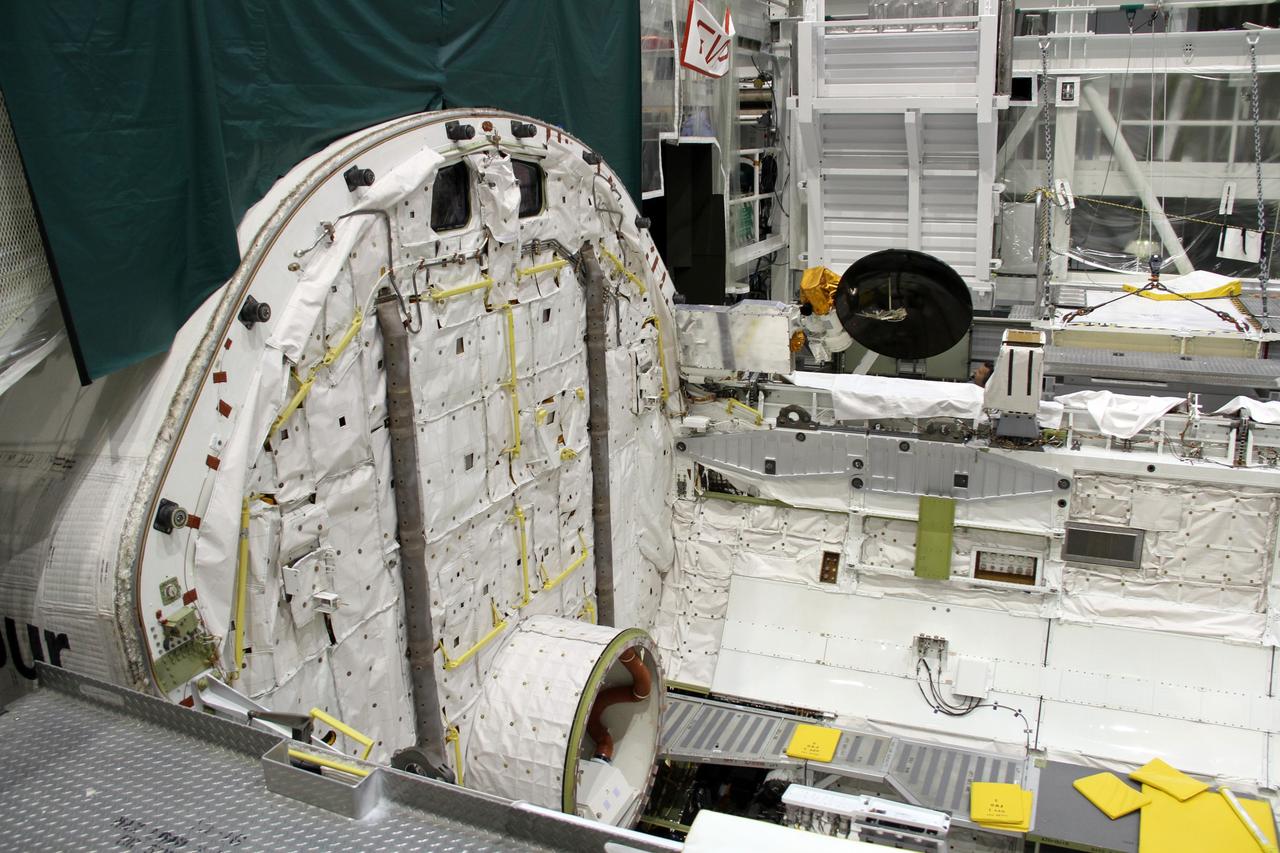
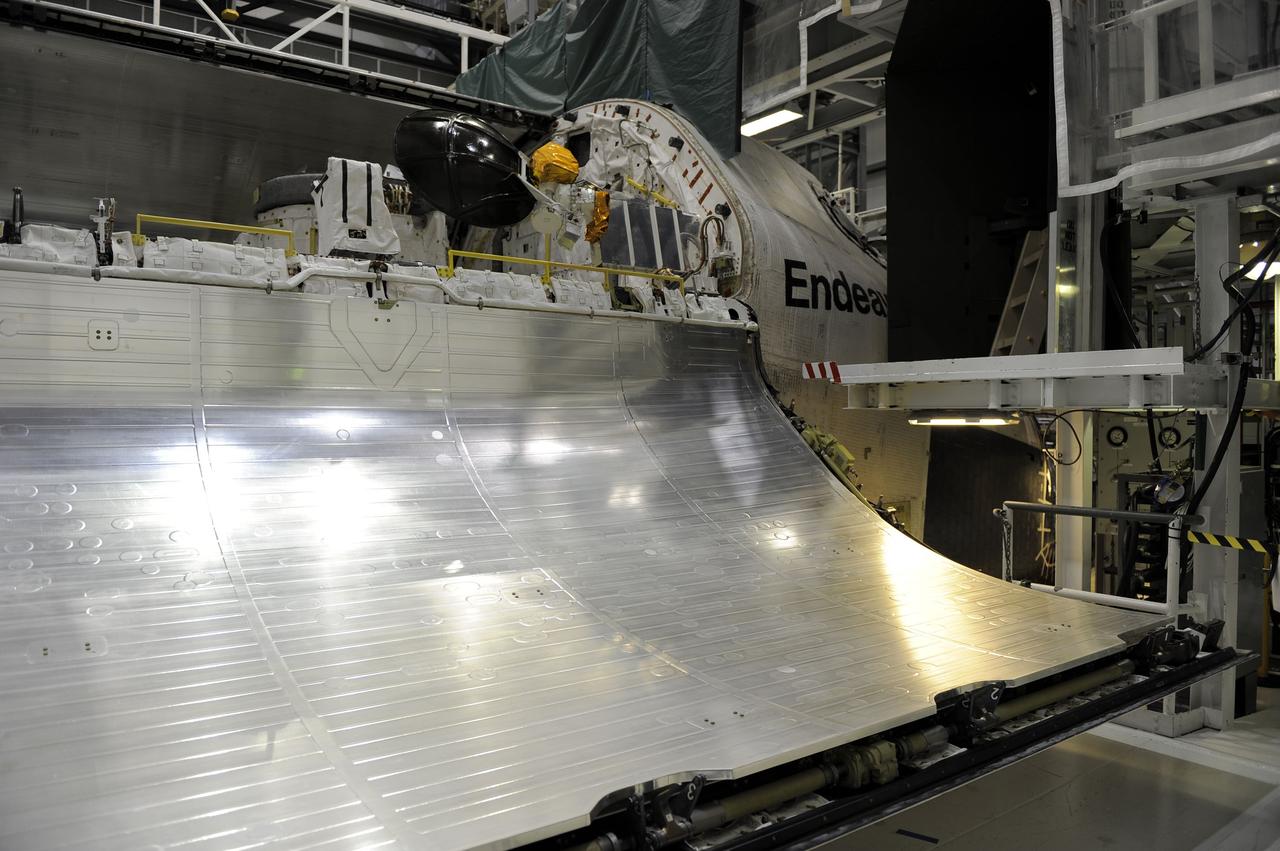
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Ku-band antenna is stowed at the forward end of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay in preparation for final closure of the shuttle’s payload bay doors. The antenna, which resembles a mini-satellite dish, was used to transmit audio, video and data between the shuttle and ground stations on Earth. Endeavour is being prepared for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Its ferry flight to California is targeted for mid-September. Endeavour was the last space shuttle added to NASA’s orbiter fleet. Over the course of its 19-year career, Endeavour spent 299 days in space during 25 missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
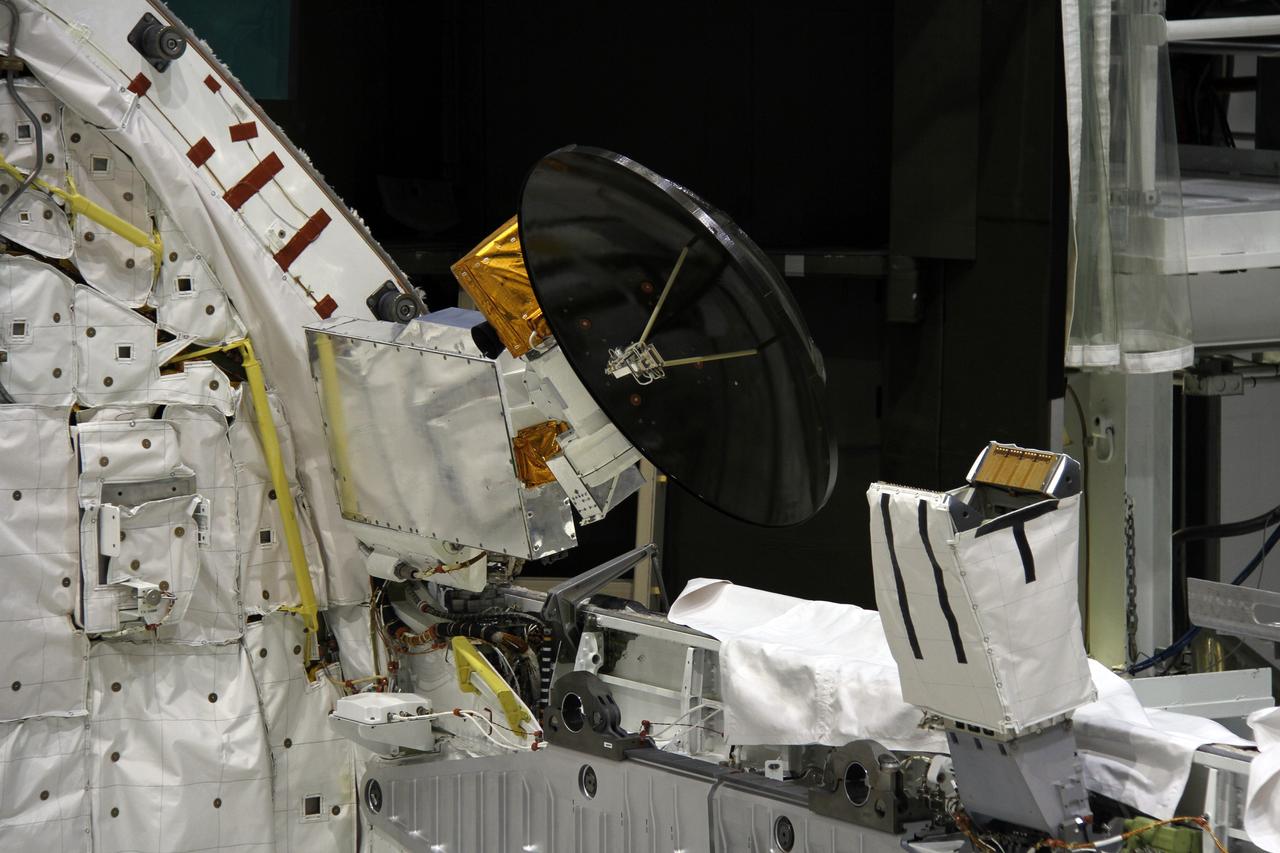
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Ku-band antenna is stowed at the forward end of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay in preparation for final closure of the shuttle’s payload bay doors. The antenna, which resembles a mini-satellite dish, was used to transmit audio, video and data between the shuttle and ground stations on Earth. Endeavour is being prepared for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Its ferry flight to California is targeted for mid-September. Endeavour was the last space shuttle added to NASA’s orbiter fleet. Over the course of its 19-year career, Endeavour spent 299 days in space during 25 missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
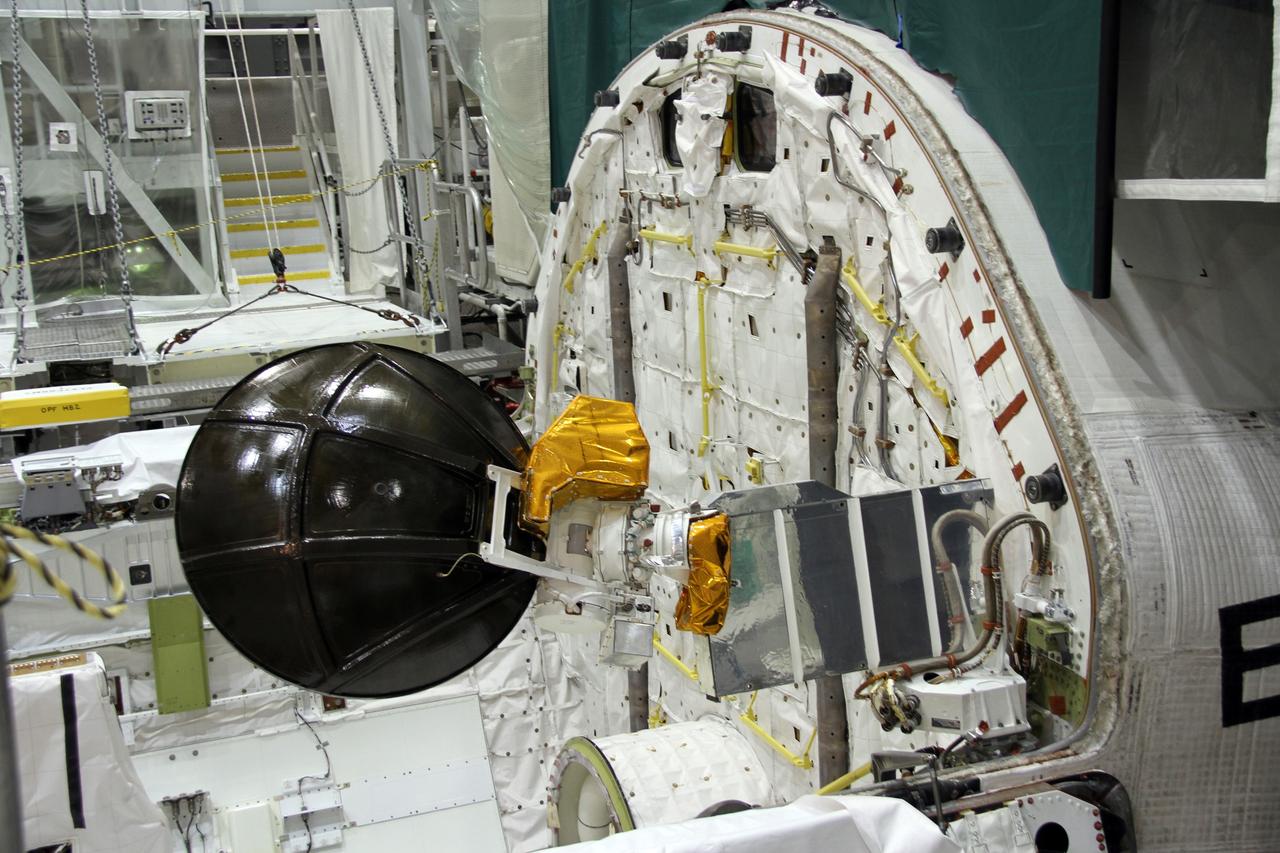

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Ku-band antenna is stowed in space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay in preparation for final closure of the shuttle’s payload bay doors. The antenna, which resembles a mini-satellite dish, was used to transmit audio, video and data between the shuttle and ground stations on Earth. Endeavour is being prepared for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Its ferry flight to California is targeted for mid-September. Endeavour was the last space shuttle added to NASA’s orbiter fleet. Over the course of its 19-year career, Endeavour spent 299 days in space during 25 missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
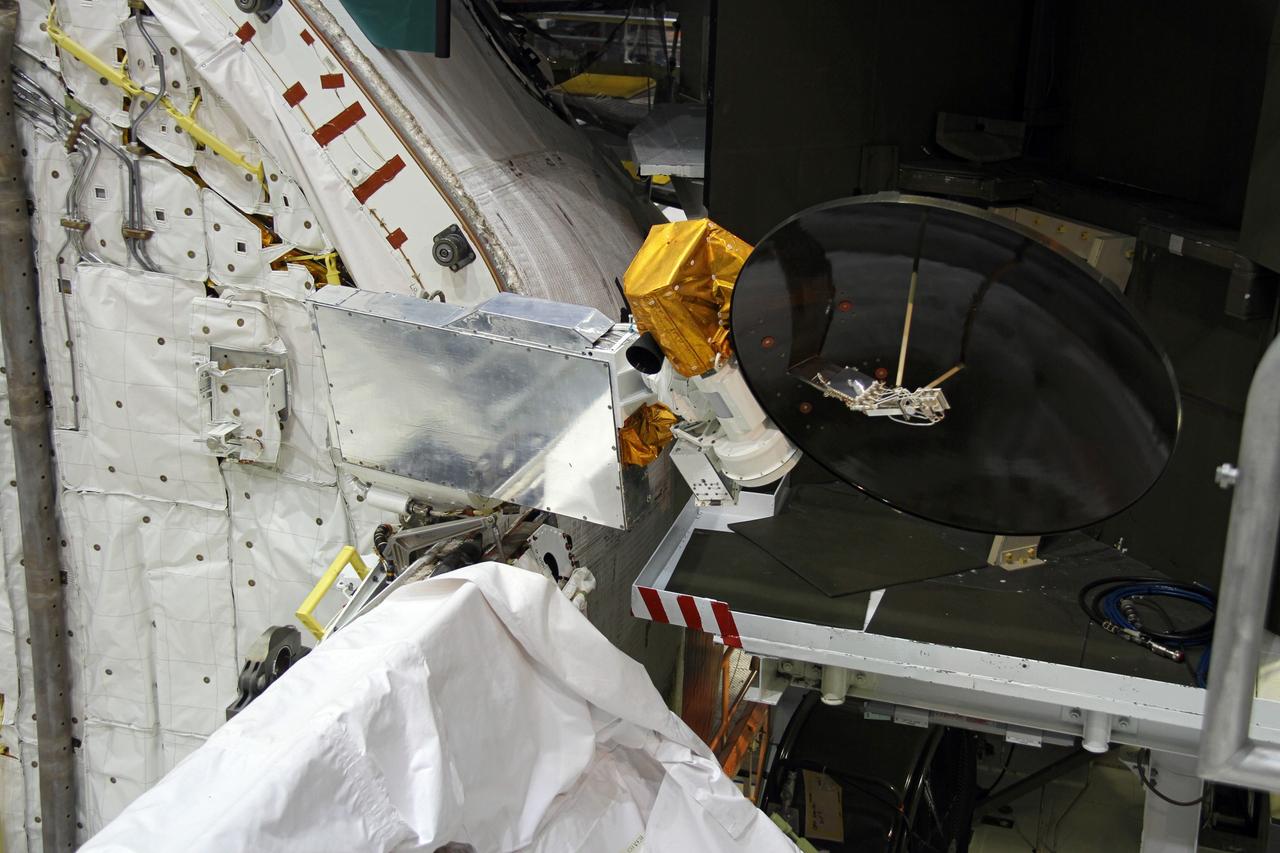

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, a Ku-band antenna is being stowed in space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay in preparation for final closure of the shuttle’s payload bay doors. The antenna, which resembles a mini-satellite dish, was used to transmit audio, video and data between the shuttle and ground stations on Earth. Endeavour is being prepared for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Its ferry flight to California is targeted for mid-September. Endeavour was the last space shuttle added to NASA’s orbiter fleet. Over the course of its 19-year career, Endeavour spent 299 days in space during 25 missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
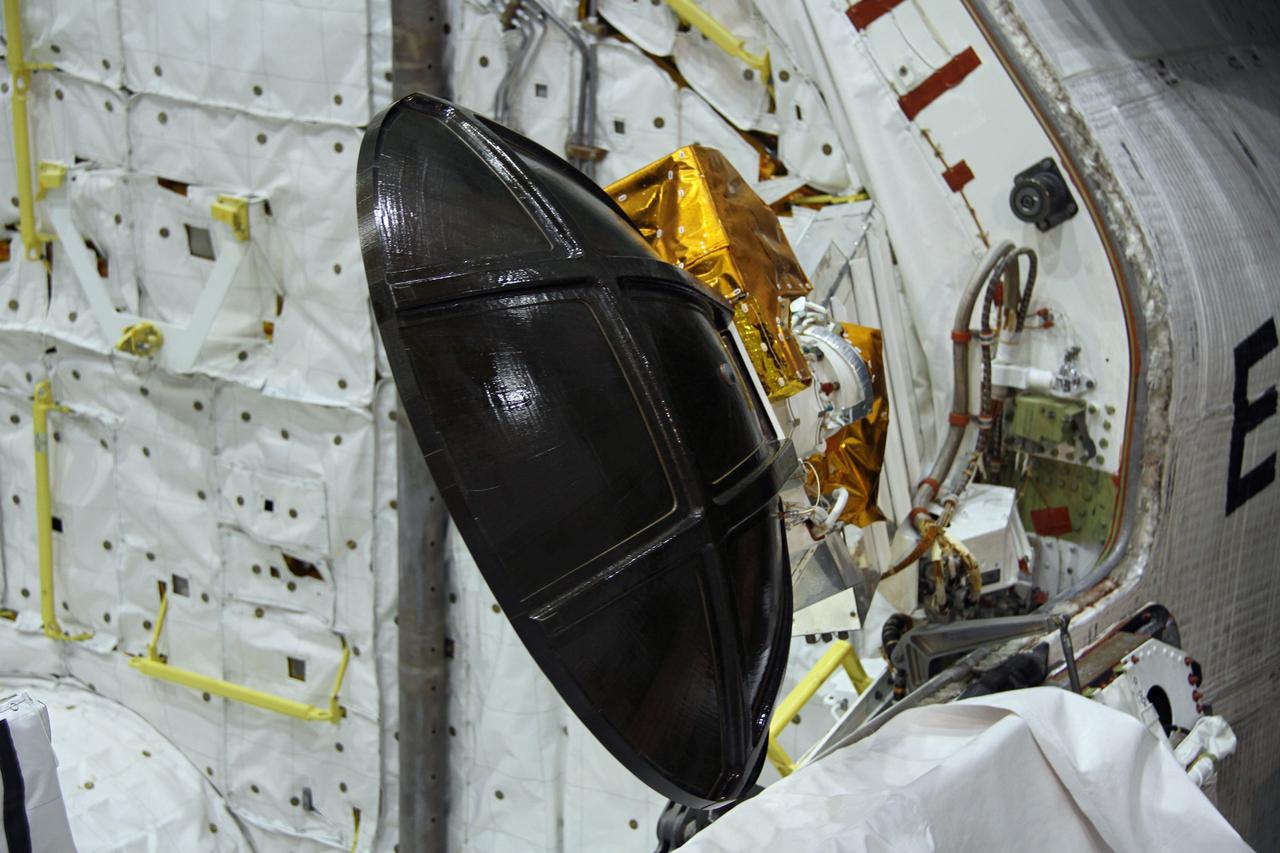

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, stowage of a Ku-band antenna in space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay is under way in preparation for final closure of the shuttle’s payload bay doors. The antenna, which resembles a mini-satellite dish, was used to transmit audio, video and data between the shuttle and ground stations on Earth. Endeavour is being prepared for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Its ferry flight to California is targeted for mid-September. Endeavour was the last space shuttle added to NASA’s orbiter fleet. Over the course of its 19-year career, Endeavour spent 299 days in space during 25 missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
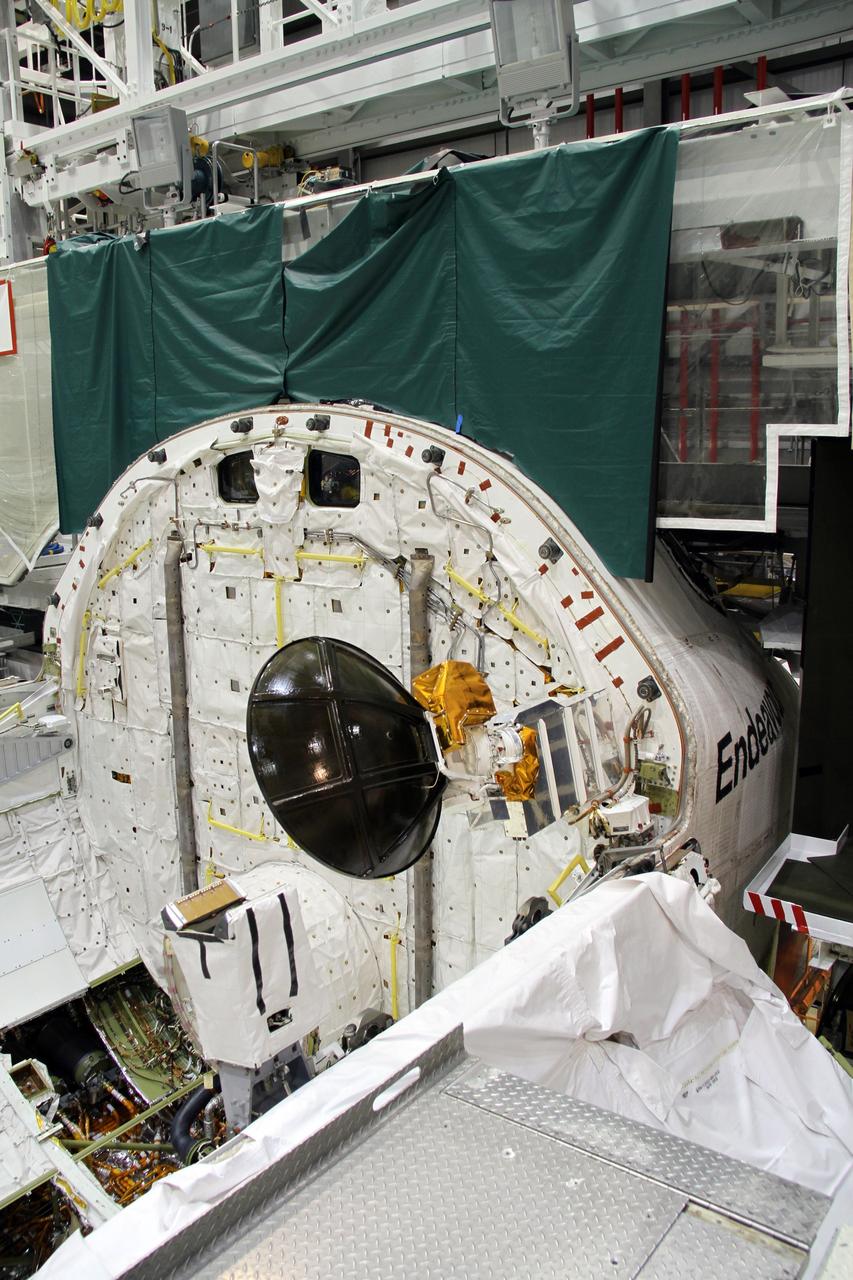

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, stowage of a Ku-band antenna in space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay is under way in preparation for final closure of the shuttle’s payload bay doors. The antenna, which resembles a mini-satellite dish, was used to transmit audio, video and data between the shuttle and ground stations on Earth. Endeavour is being prepared for public display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Its ferry flight to California is targeted for mid-September. Endeavour was the last space shuttle added to NASA’s orbiter fleet. Over the course of its 19-year career, Endeavour spent 299 days in space during 25 missions. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/transition. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
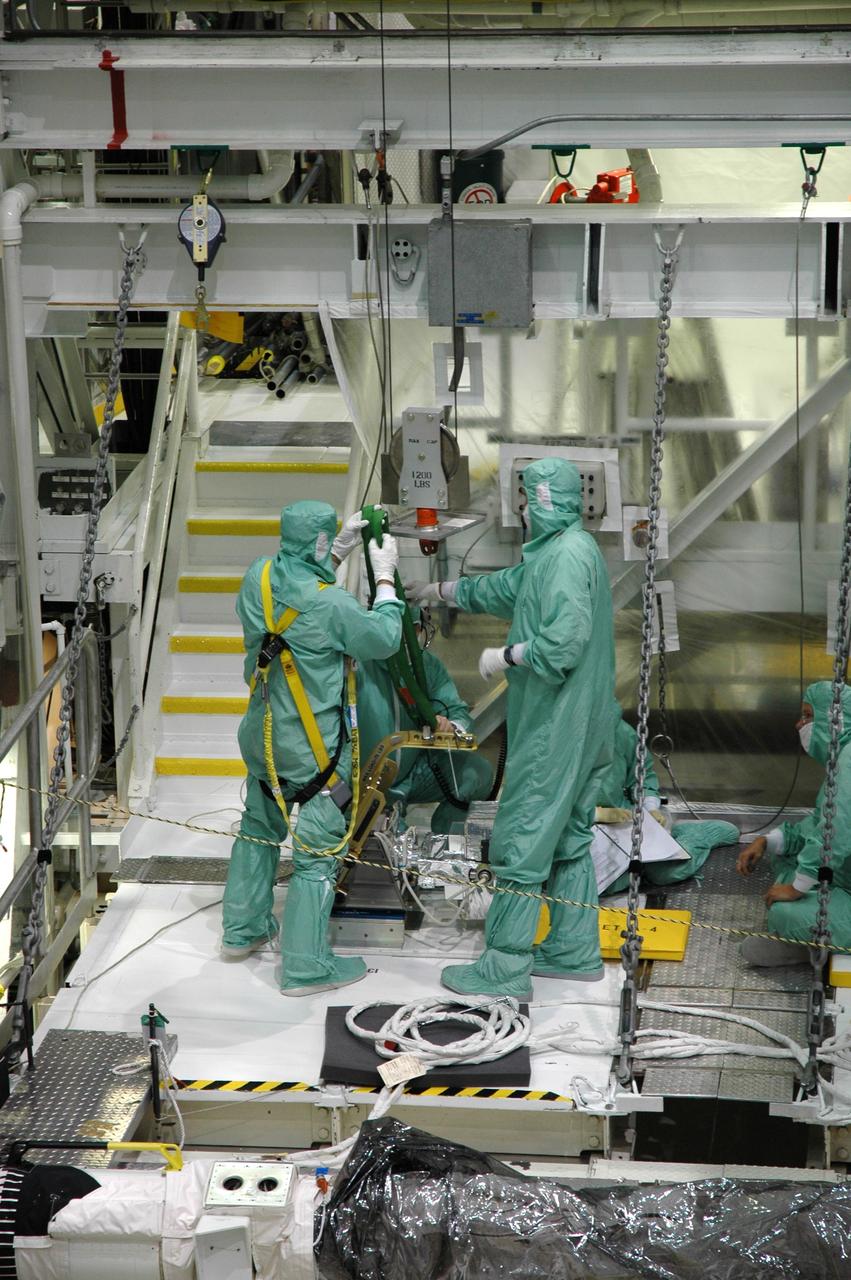

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers prepare to install a camera pack on the orbiter boom sensor system in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The scheduled launch vehicle for the STS-126 missions, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Endeavour is also the backup shuttle, if needed for rescue, for the STS-125 mission in October that will make repairs on NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. For that purpose, it is designated STS-400. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
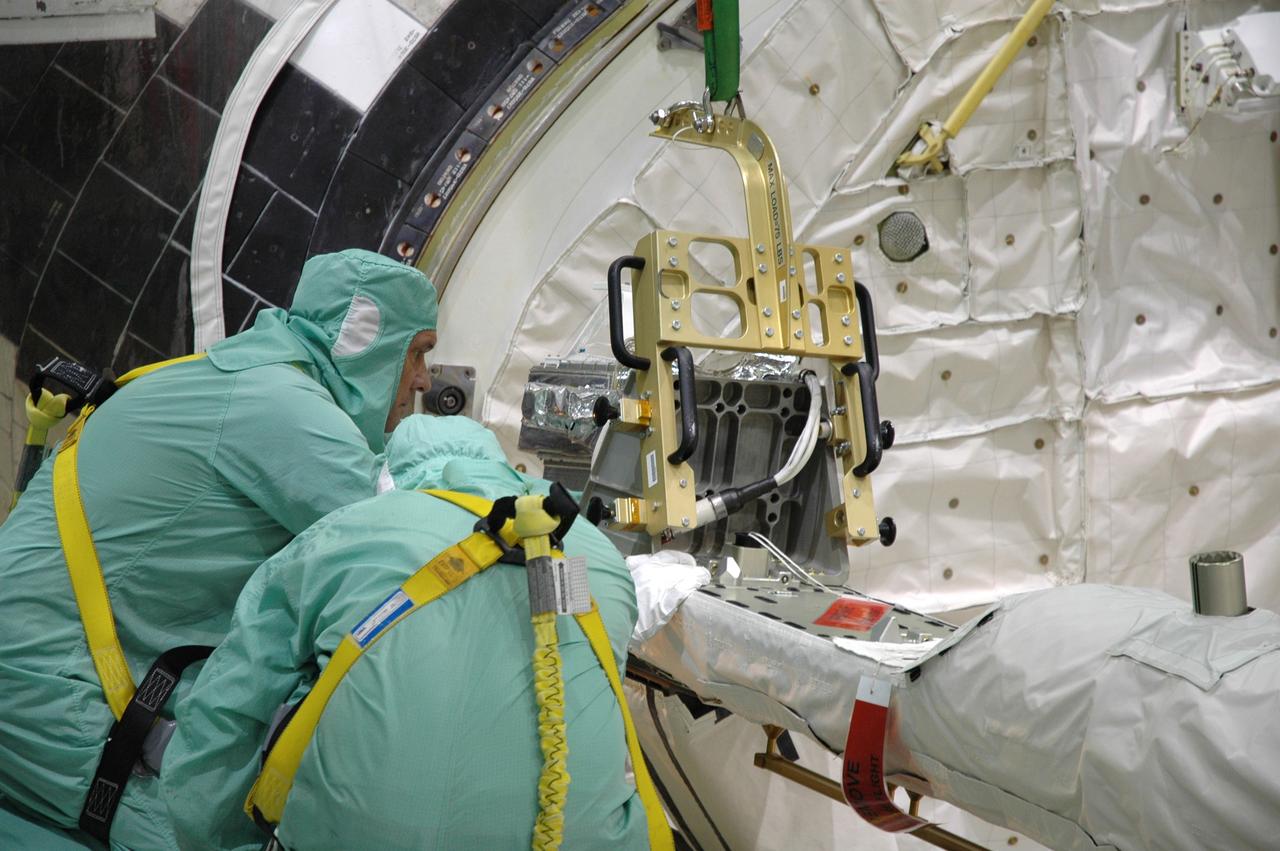

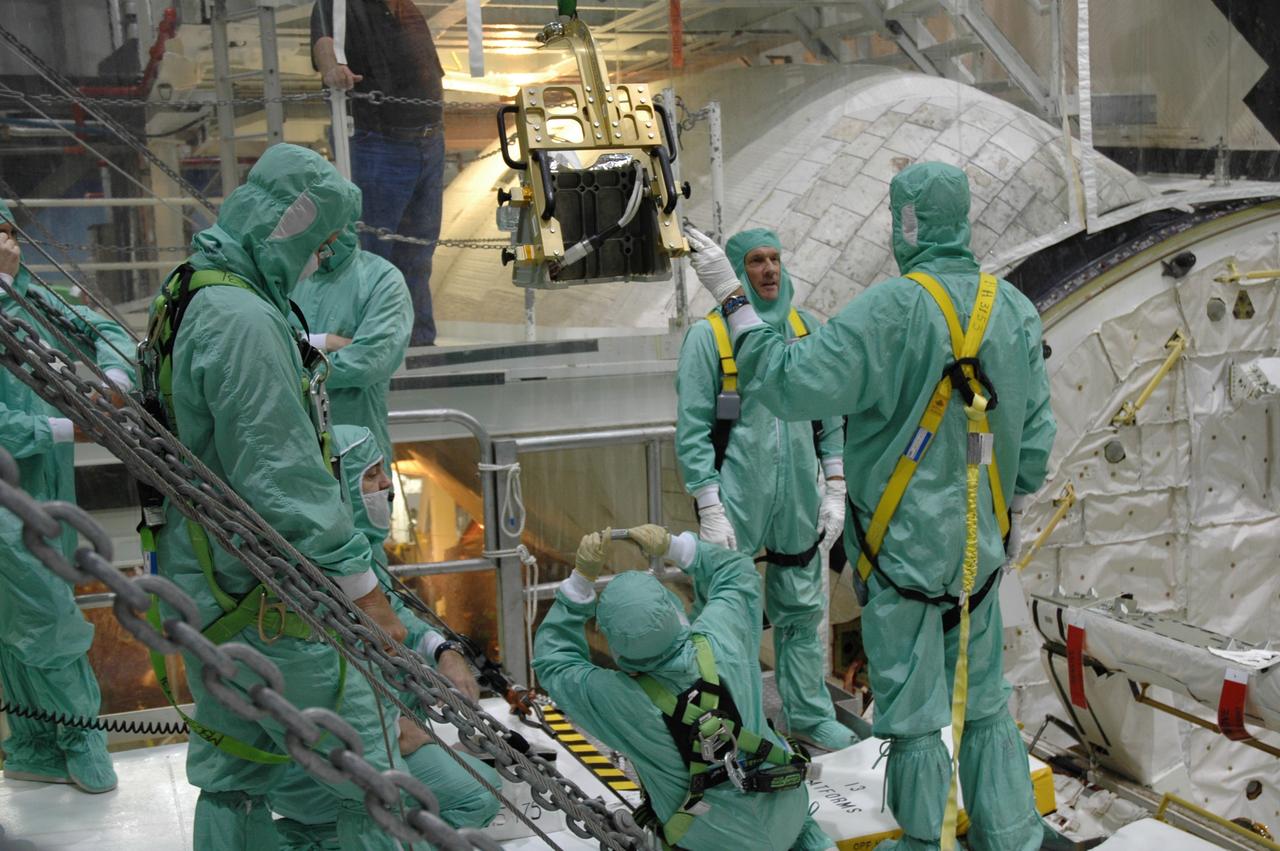
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers install a camera pack on the orbiter boom sensor system in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The scheduled launch vehicle for the STS-126 missions, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Endeavour is also the backup shuttle, if needed for rescue, for the STS-125 mission in October that will make repairs on NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. For that purpose, it is designated STS-400. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
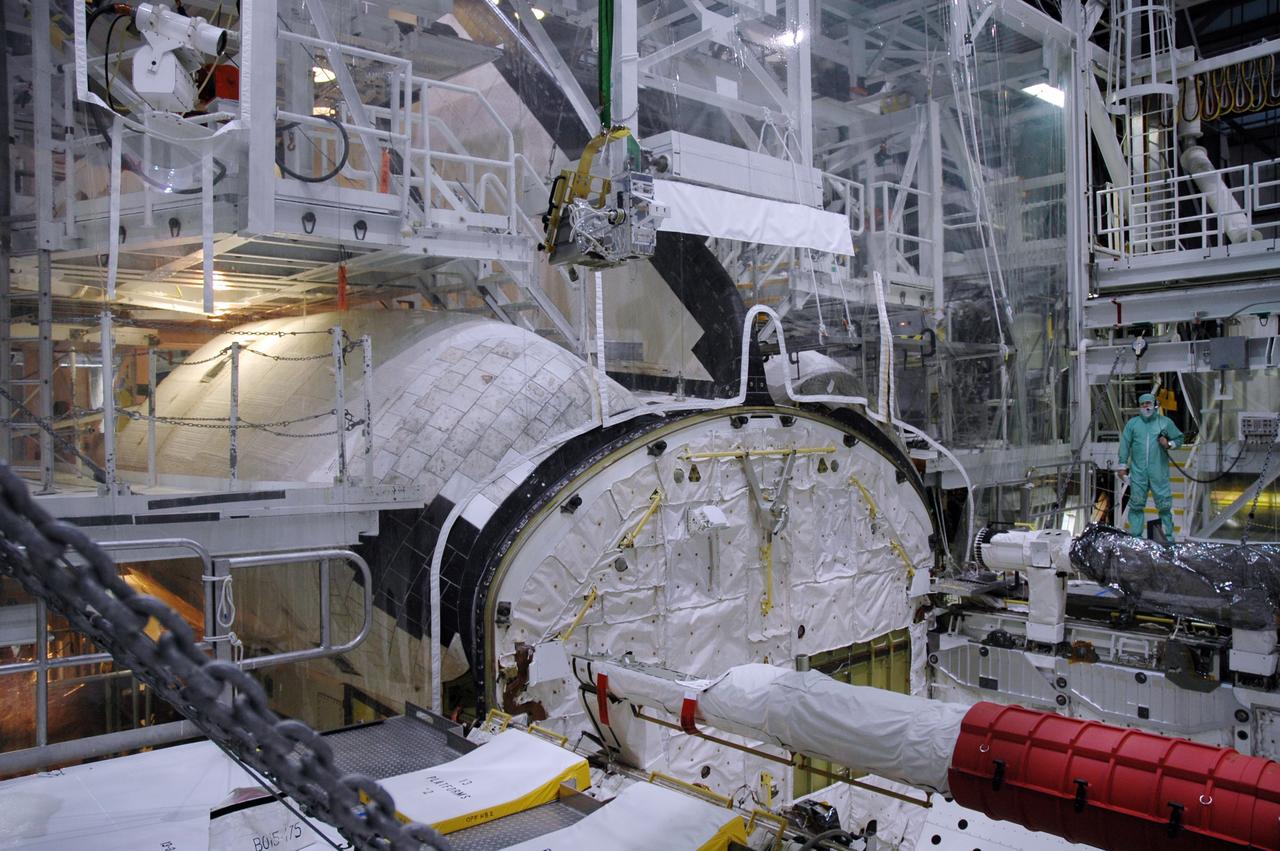
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a camera pack is moved above space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The camera will be installed on the shuttle's orbiter boom sensor system. The scheduled launch vehicle for the STS-126 missions, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Endeavour is also the backup shuttle, if needed for rescue, for the STS-125 mission in October that will make repairs on NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. For that purpose, it is designated STS-400. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers get ready to install a camera pack on the orbiter boom sensor system in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The scheduled launch vehicle for the STS-126 missions, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Endeavour is also the backup shuttle, if needed for rescue, for the STS-125 mission in October that will make repairs on NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. For that purpose, it is designated STS-400. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. - In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, one of space shuttle Endeavour’s payload bay doors has been fully opened so that technicians can retract an antenna. Space Shuttle Program transition and retirement work continues on Discovery and Endeavour in the orbiter processing facilities, while shuttle Atlantis is in temporary storage in high bay 4 of the Vehicle Assembly Building. Endeavour is being prepared for display at the California Science Center in Los Angeles. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
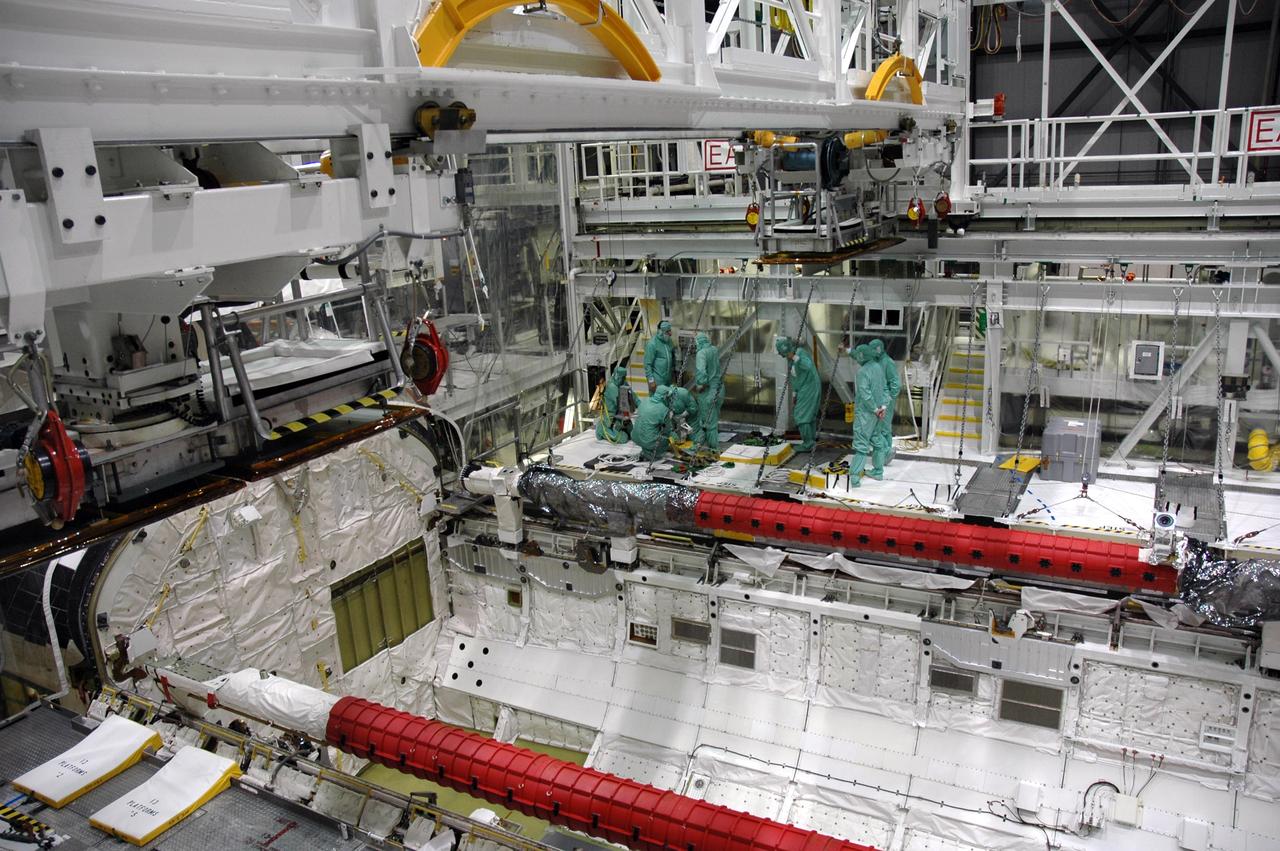
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Orbiter Processing Facility bay 2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, workers prepare to install a camera pack on the orbiter boom sensor system in space shuttle Endeavour's payload bay. The scheduled launch vehicle for the STS-126 missions, Endeavour will deliver a multi-purpose logistics module to the International Space Station. Launch is targeted for Nov. 10. Endeavour is also the backup shuttle, if needed for rescue, for the STS-125 mission in October that will make repairs on NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. For that purpose, it is designated STS-400. Photo credit: NASA/Jim Grossmann
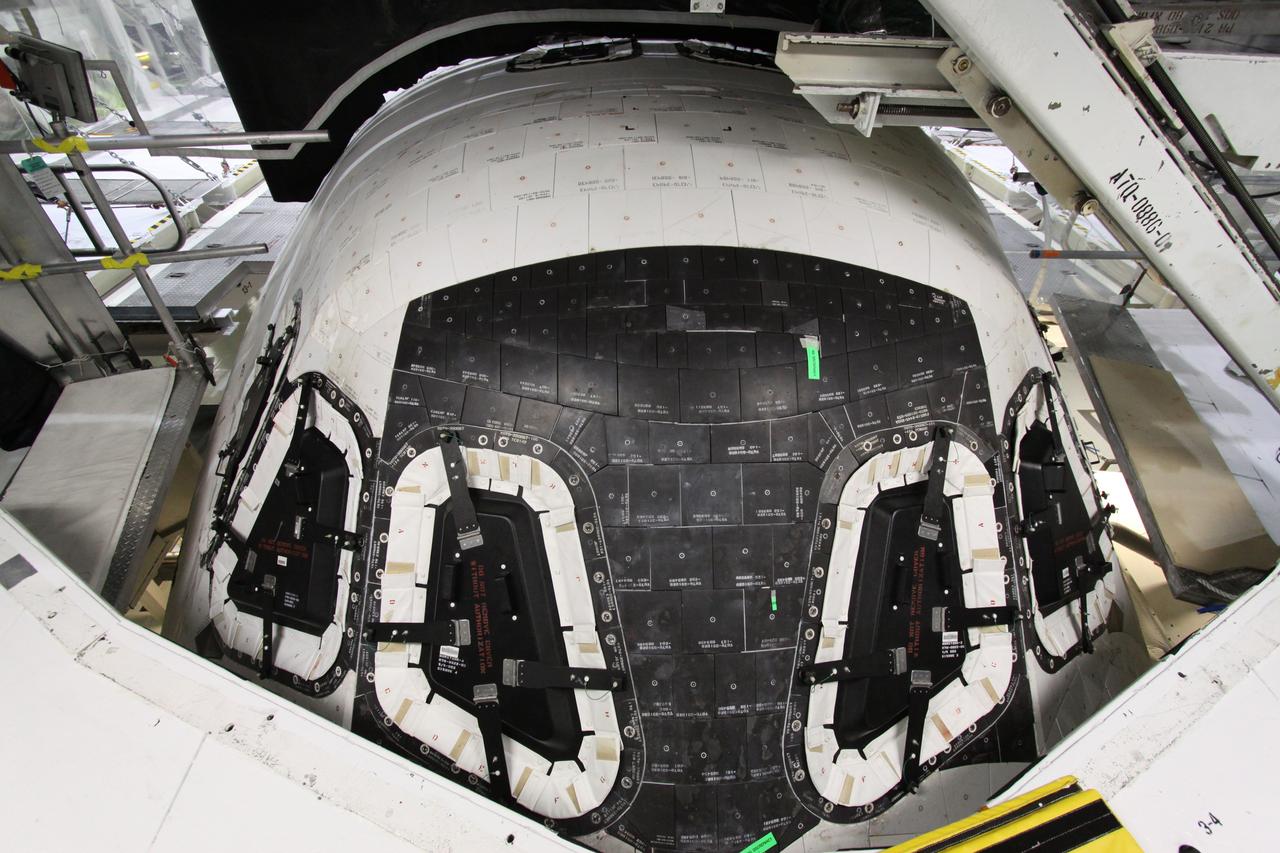

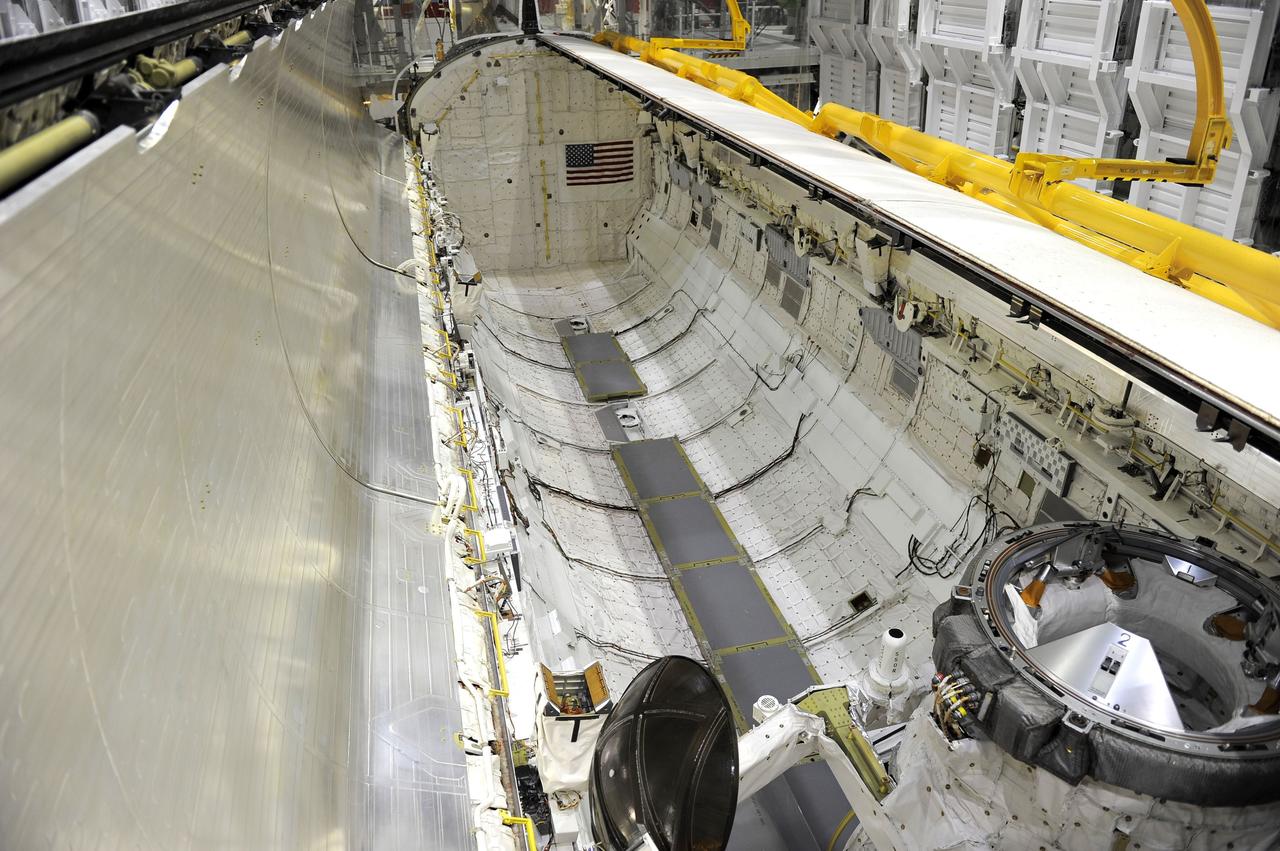
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, processing of space shuttle Endeavour is complete, its payload bay doors are closed, and it is ready for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building. This close-up is of the thermal protection system tiles protecting Endeavour's cockpit. The move, or "rollover," is targeted for Dec. 12. The Tranquility module, the payload for Endeavour's STS-130 mission to the International Space Station, will be installed in the payload bay after the shuttle has reached the pad. Endeavour's launch is targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. For information on the STS-130 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts130/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
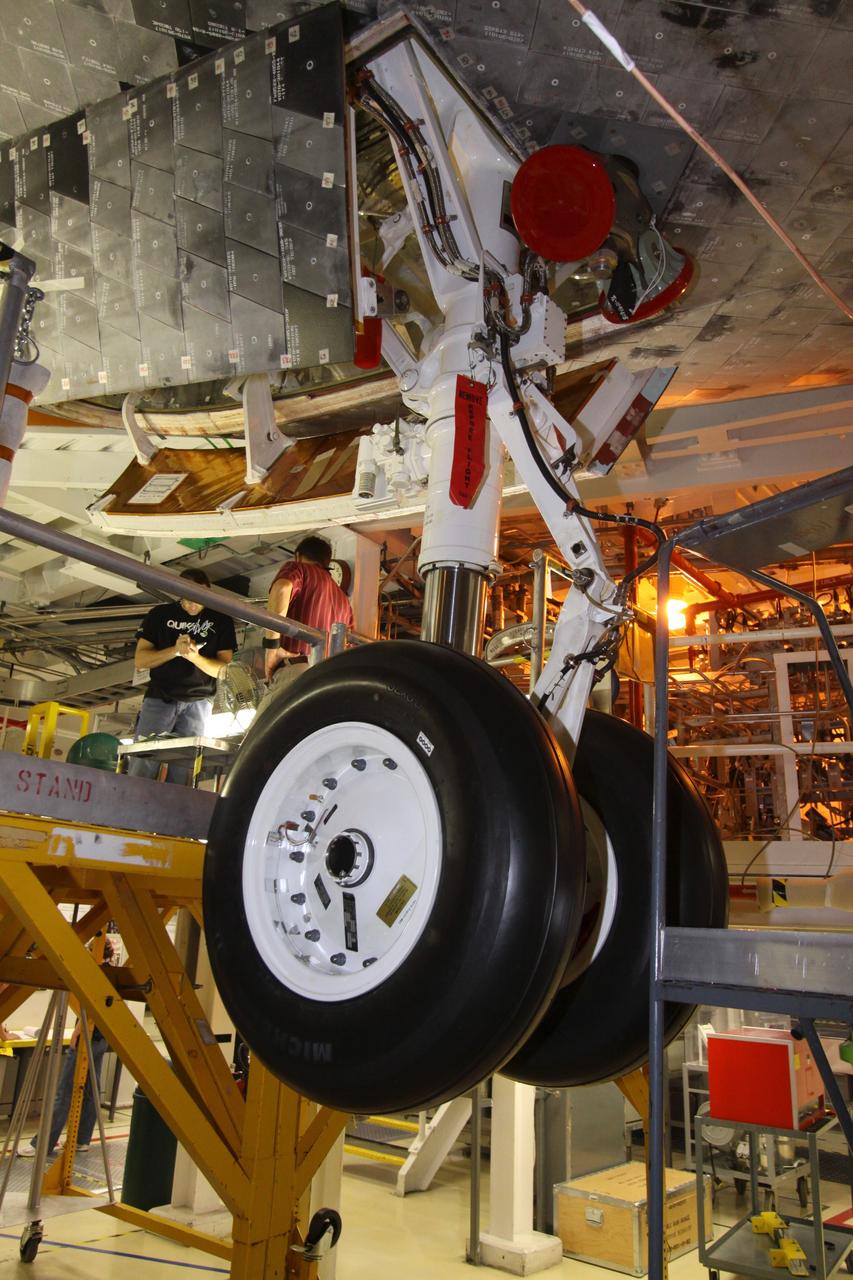

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In Orbiter Processing Facility-2 at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, workers verify that the processing of space shuttle Endeavour is complete, its payload bay doors are closed, and it is ready for its move to the Vehicle Assembly Building. This close-up is of Endeavour's nose-wheel landing gear and tires. The move, or "rollover," is targeted for Dec. 12. The Tranquility module, the payload for Endeavour's STS-130 mission to the International Space Station, will be installed in the payload bay after the shuttle has reached the pad. Endeavour's launch is targeted for Feb. 4, 2010. For information on the STS-130 mission and crew, visit http://www.nasa.gov/mission_pages/shuttle/shuttlemissions/sts130/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
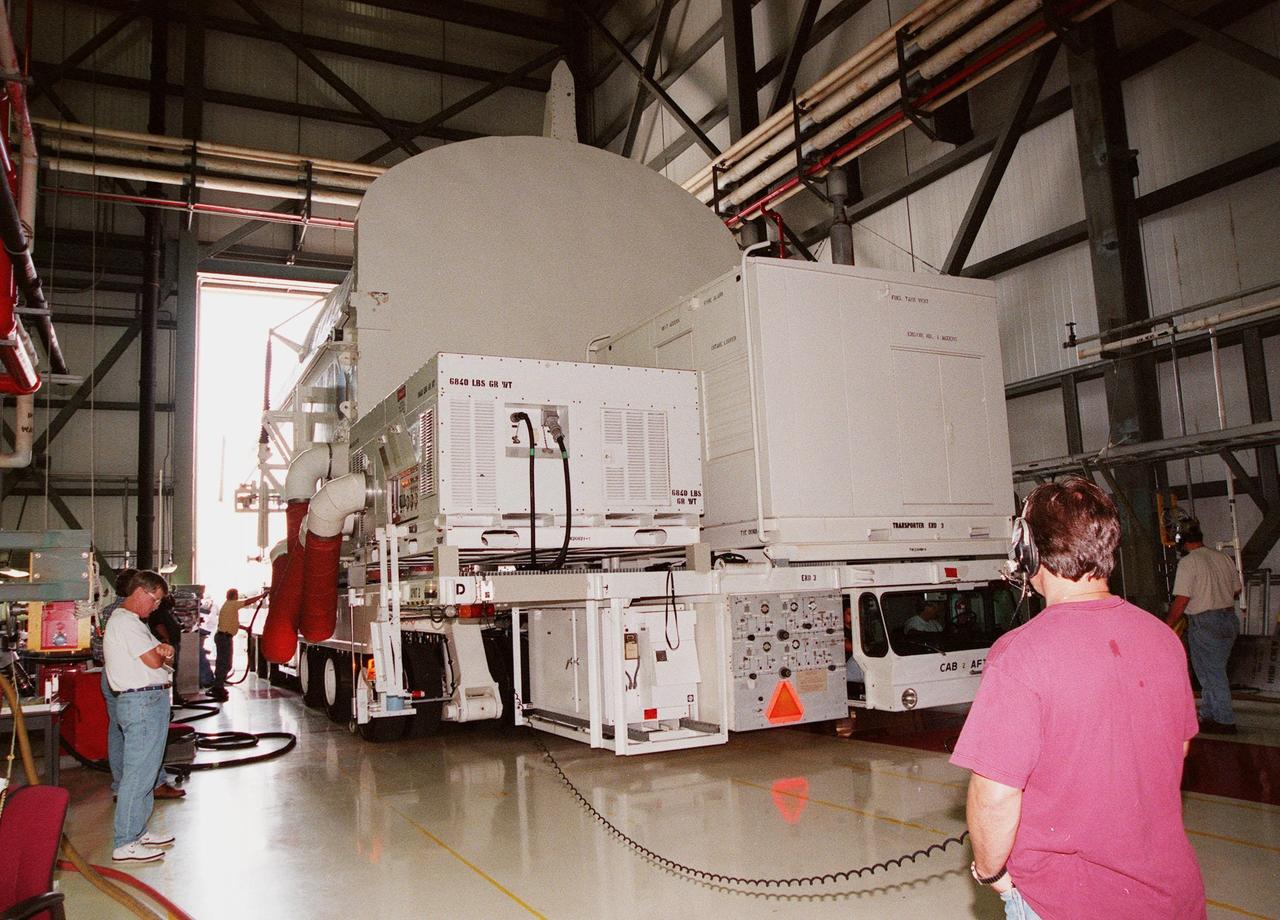

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A payload transporter, carrying a payload canister with the Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM) inside, pulls into Orbiter Processing Facility (OPF) bay 2. The SRTM, the primary payload on STS-99, will soon be installed into the payload bay of the orbiter Endeavour already undergoing processing in bay 2. The SRTM consists of a specially modified radar system that will gather data for the most accurate and complete topographic map of the Earth's surface that has ever been assembled. SRTM will make use of radar interferometry, wherein two radar images are taken from slightly different locations. Differences between these images allow for the calculation of surface elevation. The SRTM hardware includes one radar antenna in the Shuttle payload bay and a second radar antenna attached to the end of a mast extended 60 meters (195 feet) from the shuttle. STS-99 is scheduled to launch Sept. 16 at 8:47 a.m. from Launch Pad 39A