
iss047e105727 (5/10/2016) --- Photographic documentation of the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) High Quality Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) Removal. The PCG-Canister Bags were removed from the Cell Biology Experiment Facility (CBEF) and the Protein Crystallization Research Facility (PCRF) before being stowed for return on SpX-8. The JAXA PCG-Demo investigation crystallizes proteins using the counter-diffusion technique and permeation method that minimizes impurities, forming high-quality crystals for use in medical studies and ecological applications.
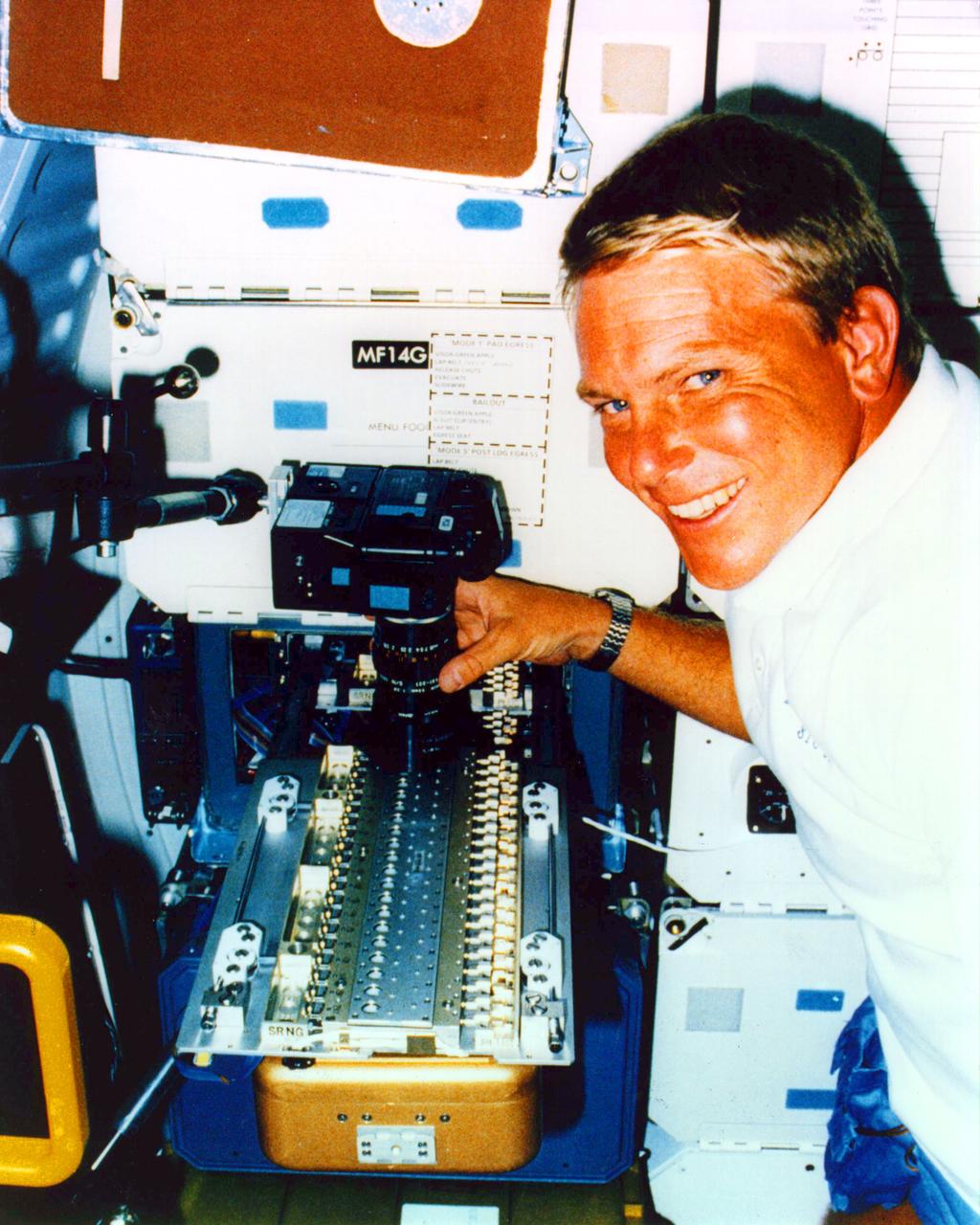
Mission Specialist George (Pinky) D. Nelson uses a 35 mm camera to photograph a protein crystal grown during the STS-26 Protein Crystal Growth (PCG-II-01) experiment. The protein crystal growth (PCG) carrier is shown deployed from the PCG Refrigerator/Incubator Mocule (R/IM) located in the middeck forward locker. The R/IM contained three Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDS) trays (one of which is shown). A total of sixty protein crystal samples were processed during the STS-26 mission.

iss055e010761 (4/5/2018) --- Photographic documentation of CASIS Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -11 hardware during CS-DCB-Unpack2 activity aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators (CASIS PCG 11) produces acetylcholinesterase crystals, a neurotransmitter enzyme. Crystals grown in microgravity are larger, of higher-quality and can be used for a technique called macromolecular neutron crystallography (MNC) to locate hydrogen atoms in the crystal’s structure.

iss055e010753 (4/5/2018) --- Photographic documentation of CASIS Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -11 hardware during CS-DCB-Unpack2 activity aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators (CASIS PCG 11) produces acetylcholinesterase crystals, a neurotransmitter enzyme. Crystals grown in microgravity are larger, of higher-quality and can be used for a technique called macromolecular neutron crystallography (MNC) to locate hydrogen atoms in the crystal’s structure.
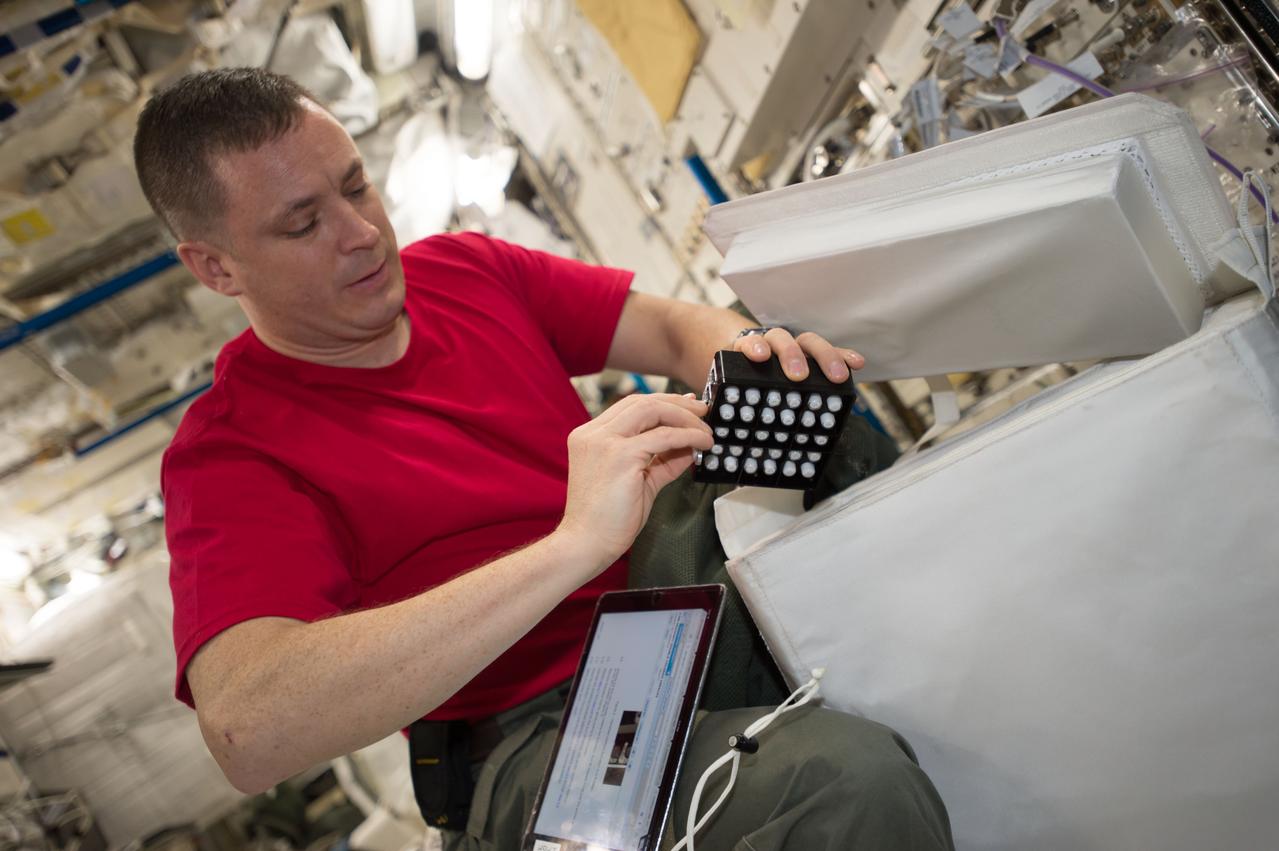

iss052e000508 (June 6, 2017) --- View of astronaut Jack Fischer working with the Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators (CASIS PCG 6) experiment in the Japanese Experiment Module
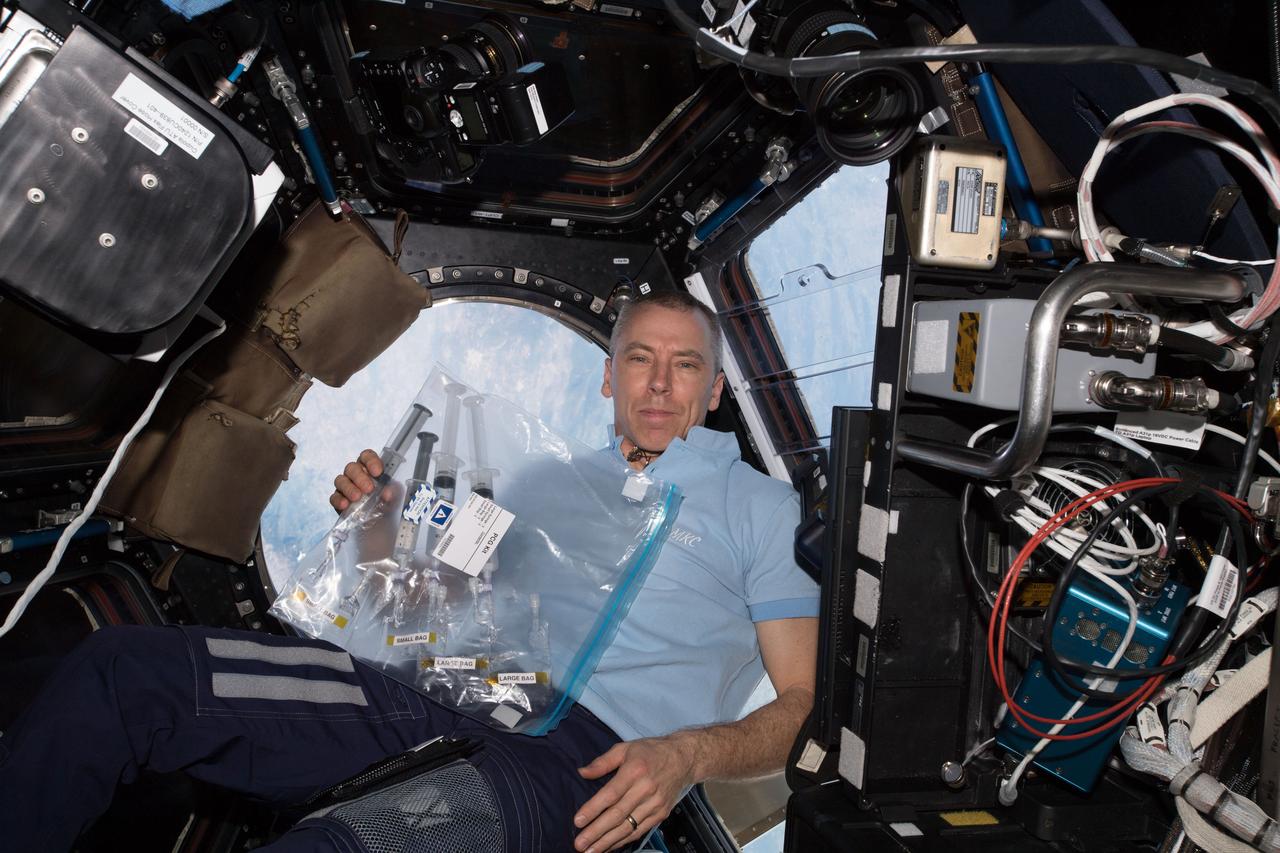

iss055e024523 (Apr. 18, 2018) --- NASA astronaut Andrew Feustel is seen in the Cupola, holding sample bags of crystals grown under experimental conditions controlled by middle and high school students as part of the CASIS PCG-9 investigation
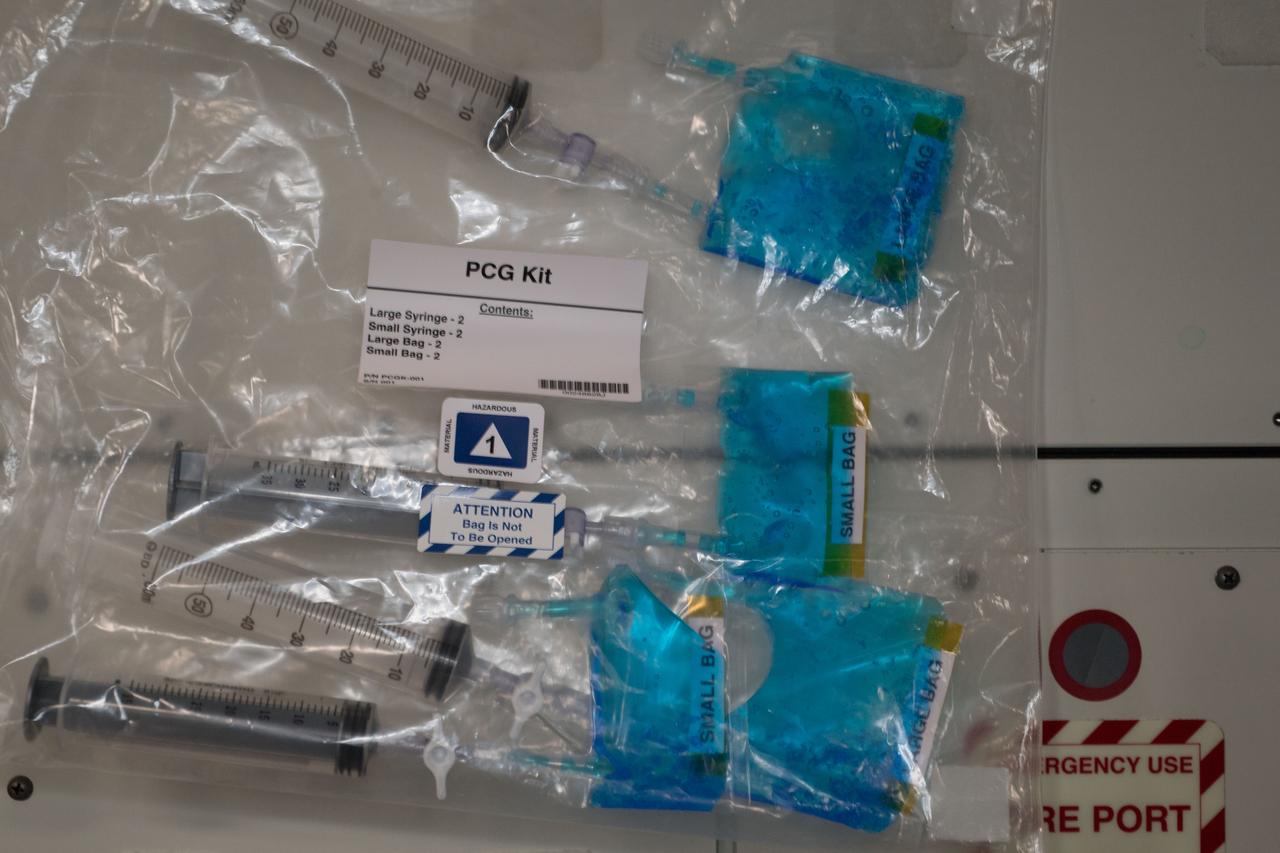
iss055e043705 (Apr. 30, 2018) --- Sample bags of crystals grown under experimental conditions controlled by middle and high school students as part of the CASIS PCG-9 investigation.
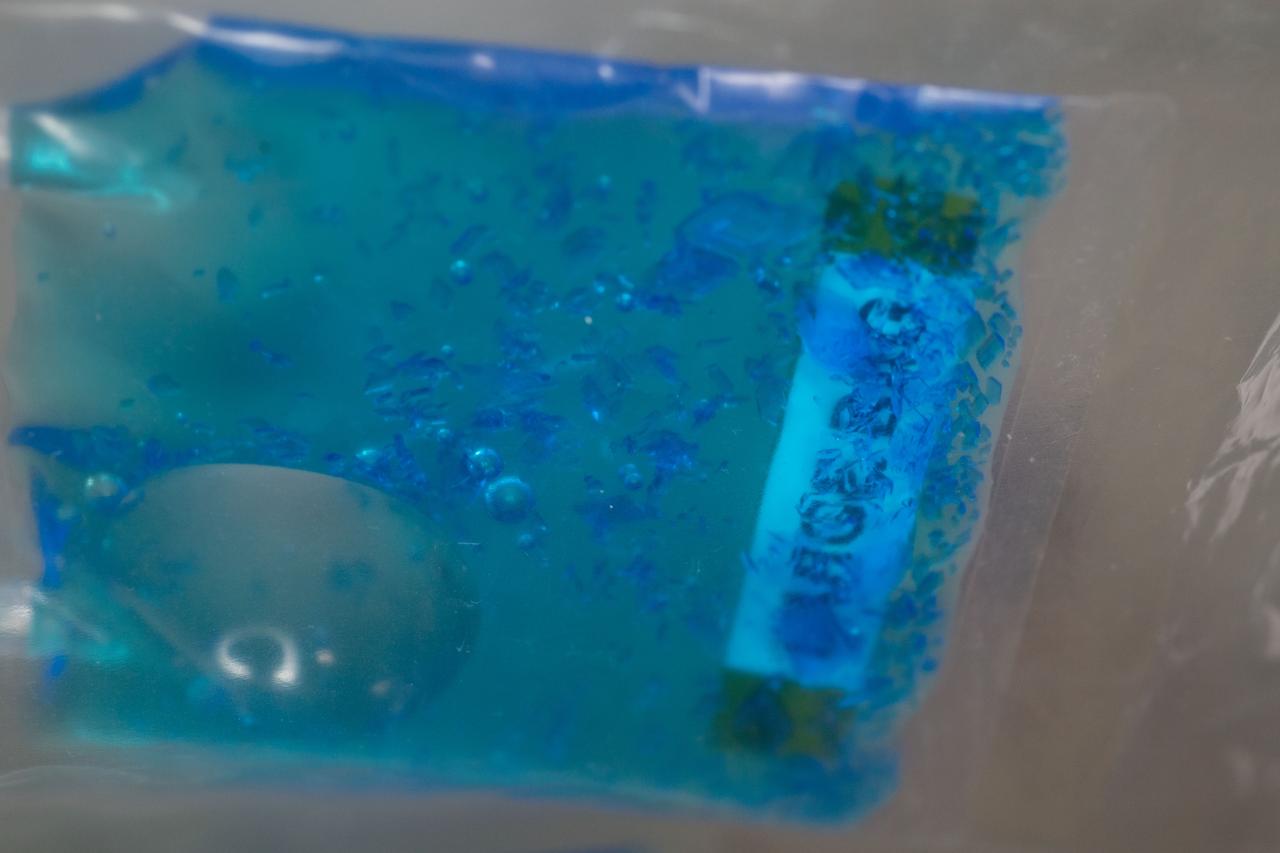

iss055e043707 (Apr. 30, 2018) --- A close look at crystals grown under experimental conditions controlled by middle and high school students as part of the CASIS PCG-9 investigation to examine the effects of microgravity on crystal growth.

iss052e000515 (June 6, 2017) --- View of astronaut Jack Fischer working with the Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators (CASIS PCG 6) experiment in the Japanese Experiment Module.
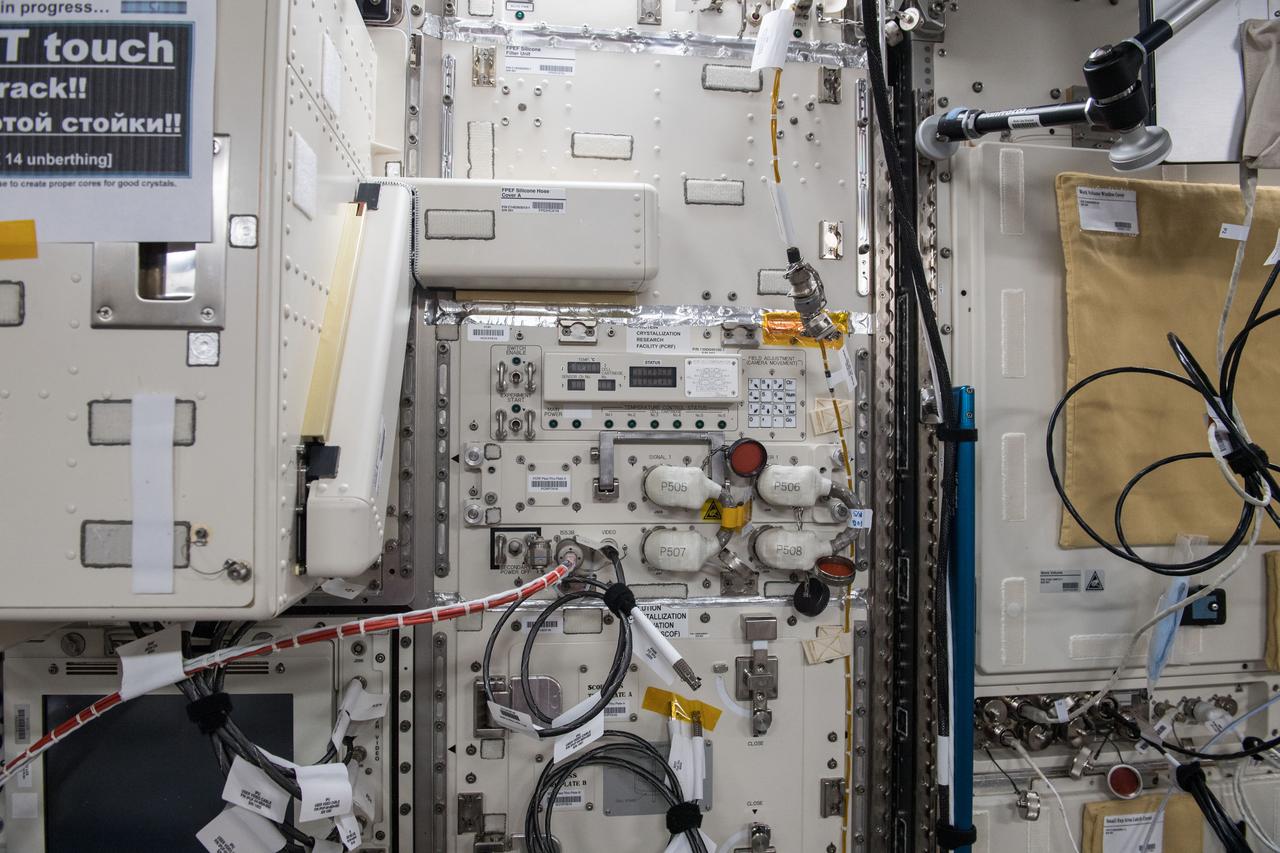

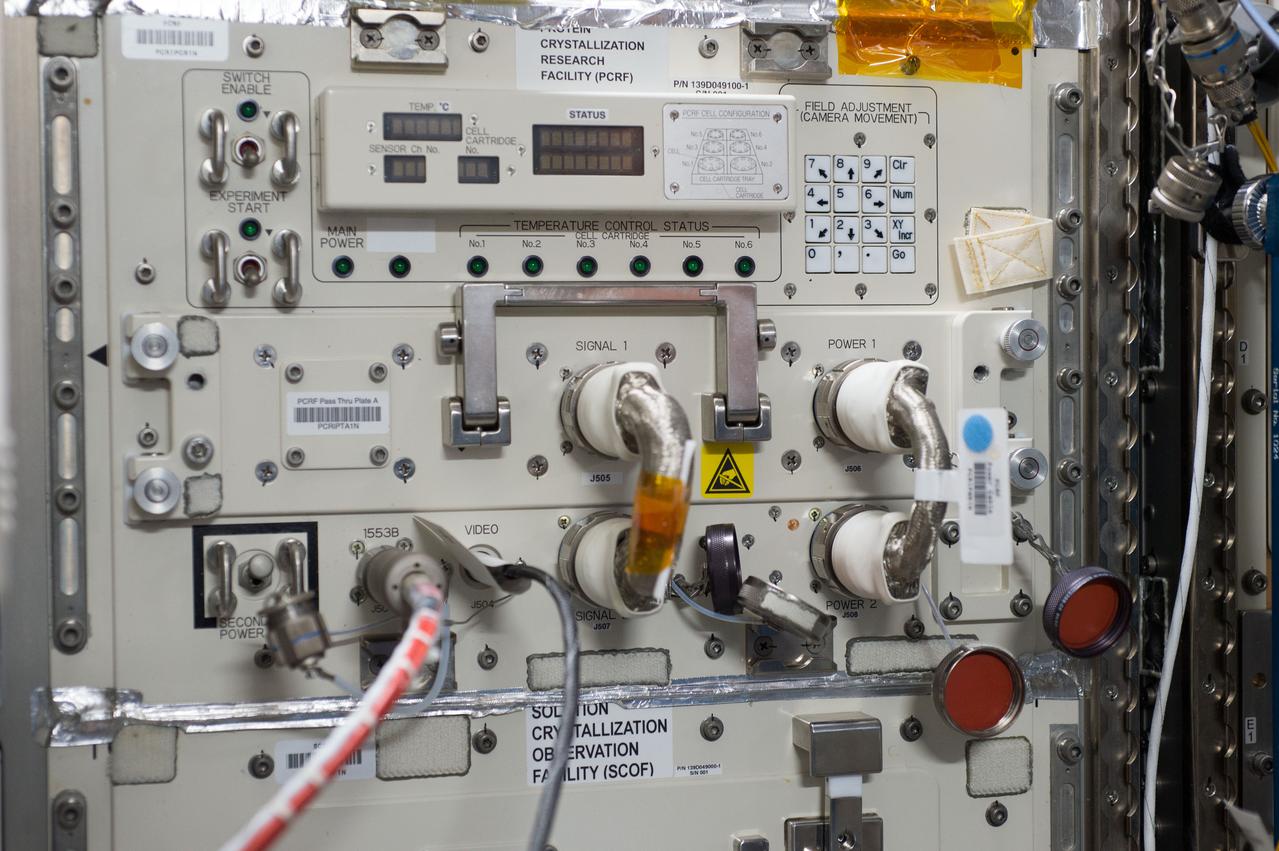
iss055e004890 (3/24/2018) --- Photographic documentation taken during JAXA Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) Installation into the Protein Crystallization Research Facility (PCRF) of the Ryutai Rack.
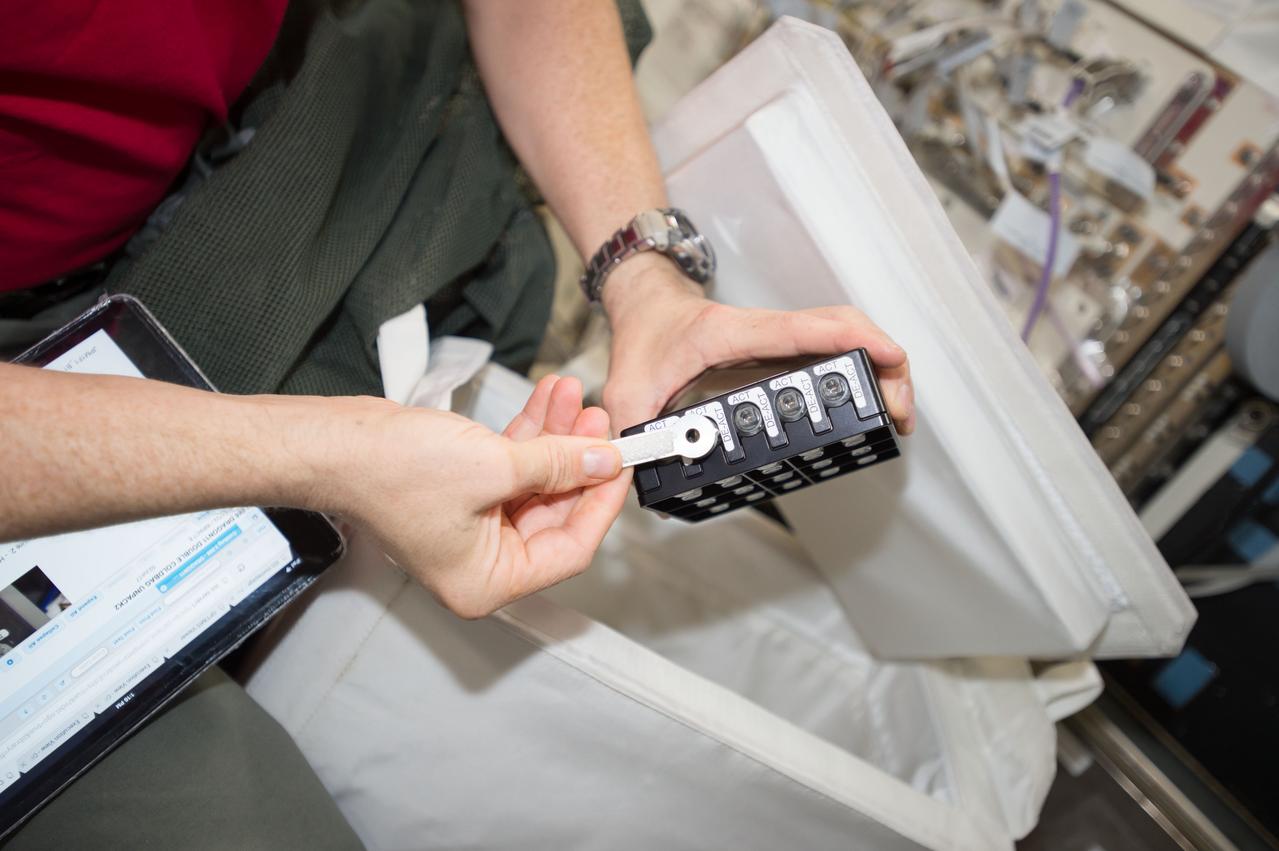

iss052e000503 (June 6, 2017) --- View of astronaut Jack Fischer working with the Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators (CASIS PCG 6) experiment in the Japanese Experiment Module.
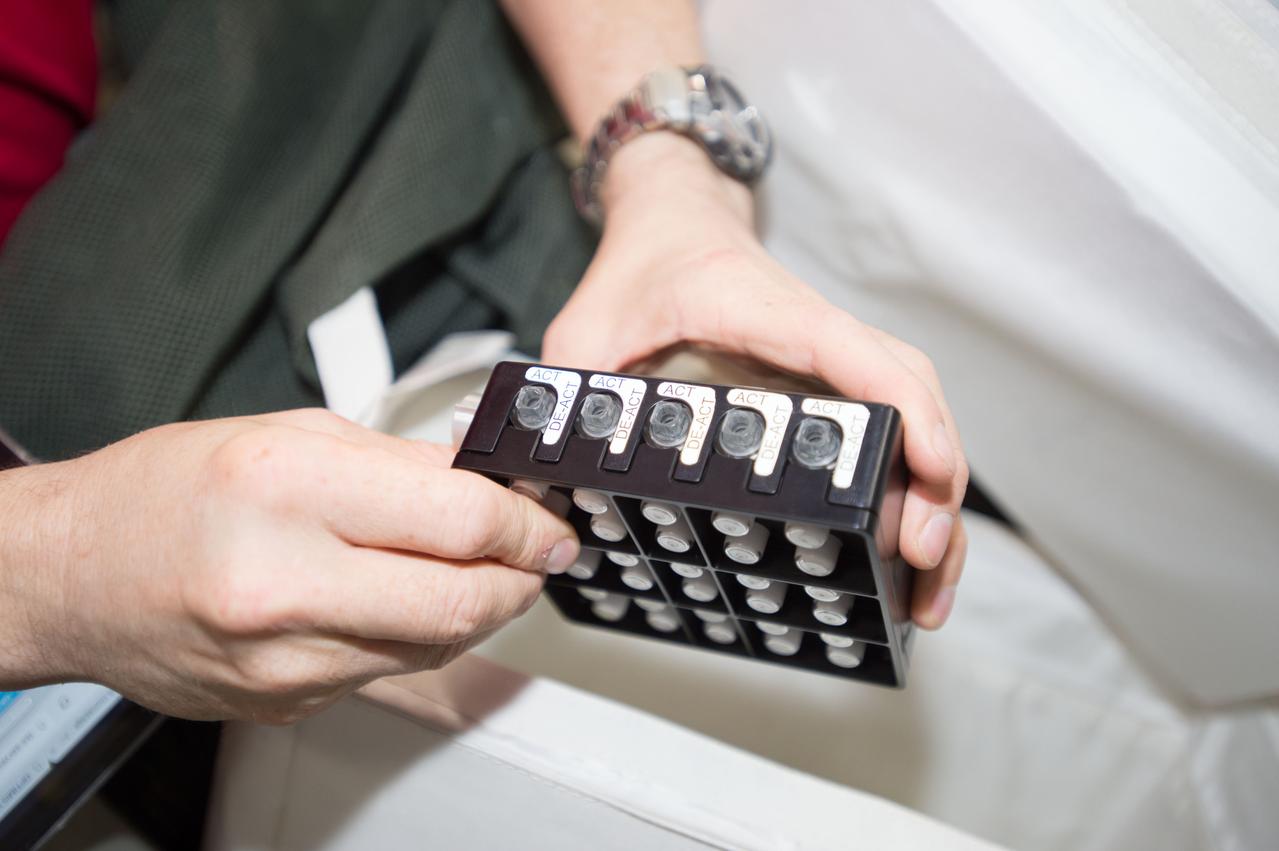

iss052e000504 (June 6, 2017) --- View of astronaut Jack Fischer working with the Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators (CASIS PCG 6) experiment in the Japanese Experiment Module.
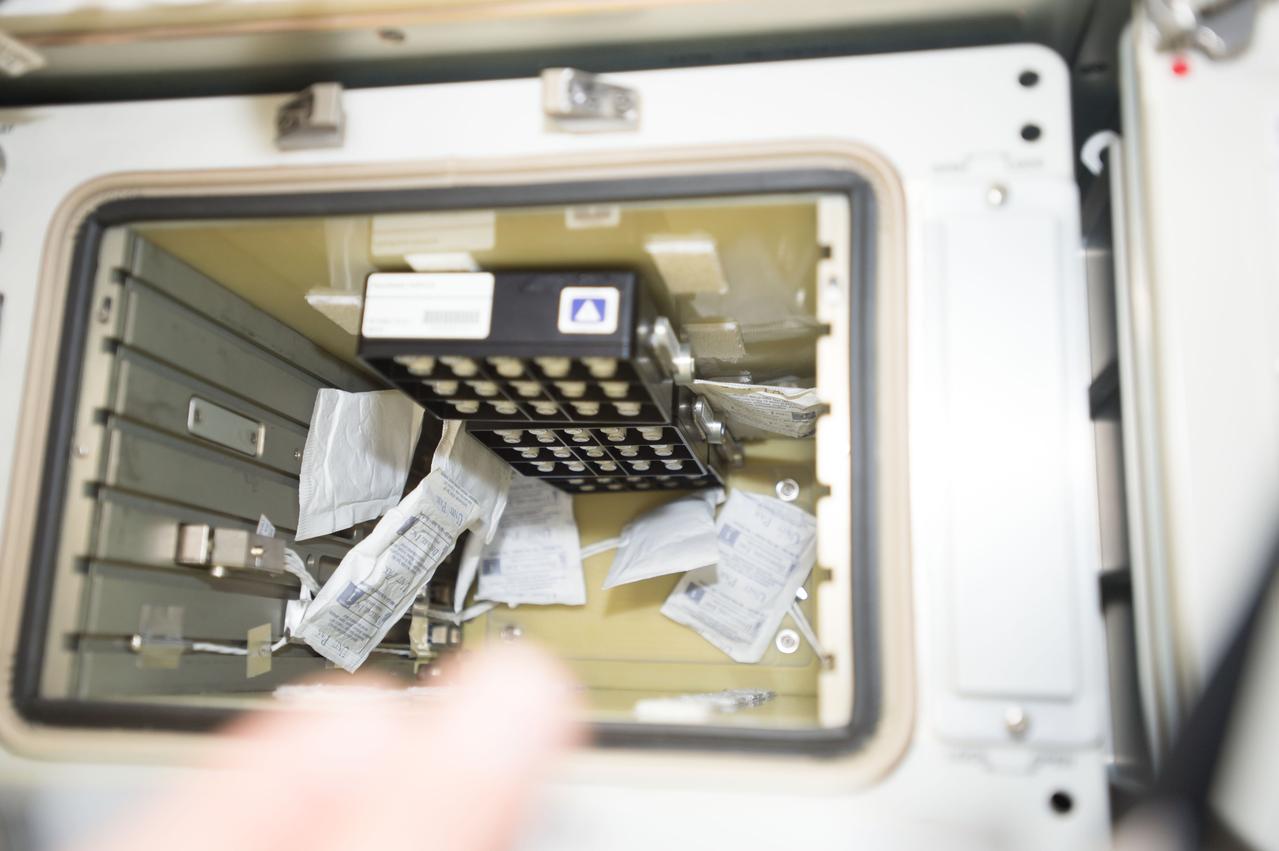

iss052e000516 (6/6/2017) --- View of the Neutron Crystallographic Studies of Human Acetylcholinesterase for the Design of Accelerated Reactivators (CASIS PCG 6) experiment in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM).
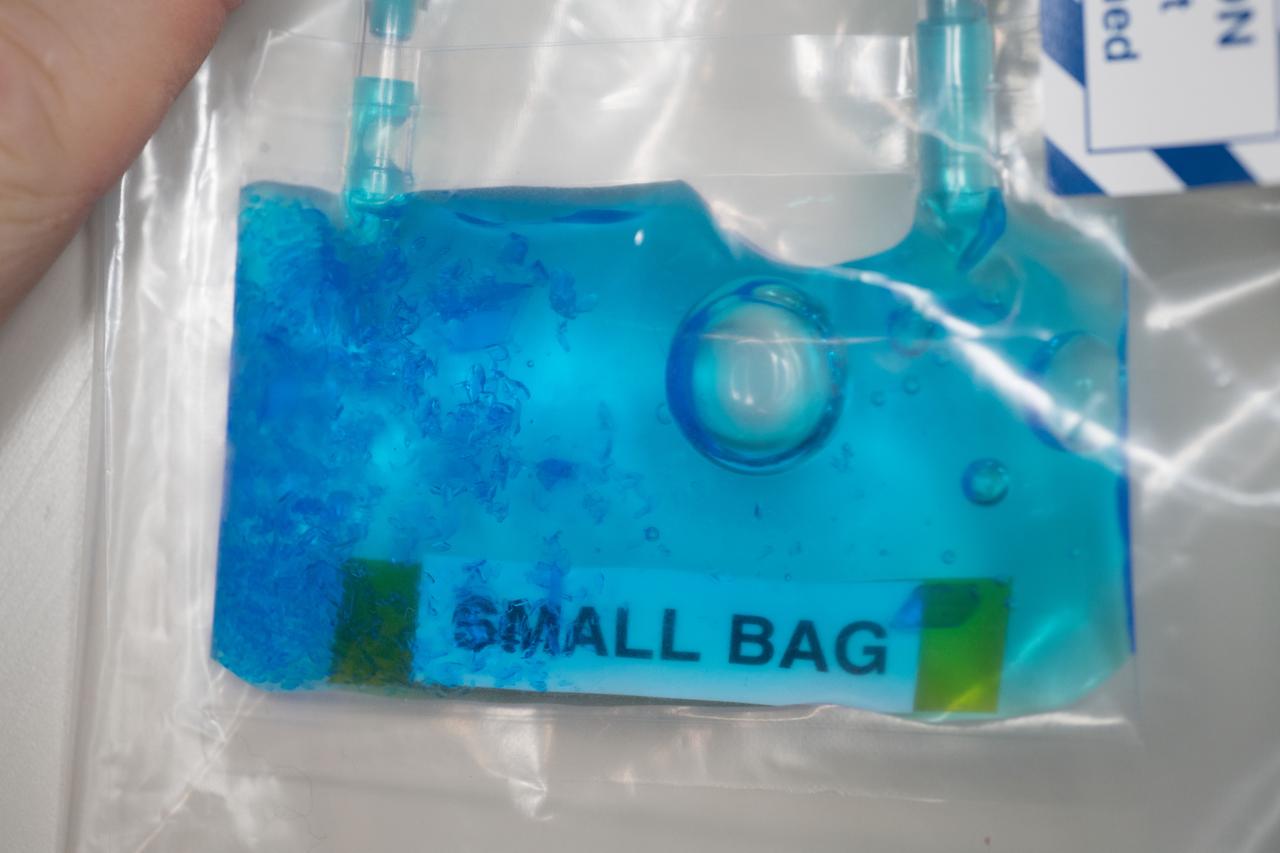
iss055e043718 (Apr. 30, 2018) --- A close look at crystals grown under experimental conditions controlled by middle and high school students as part of the CASIS PCG-9 investigation to examine the effects of microgravity on crystal growth.
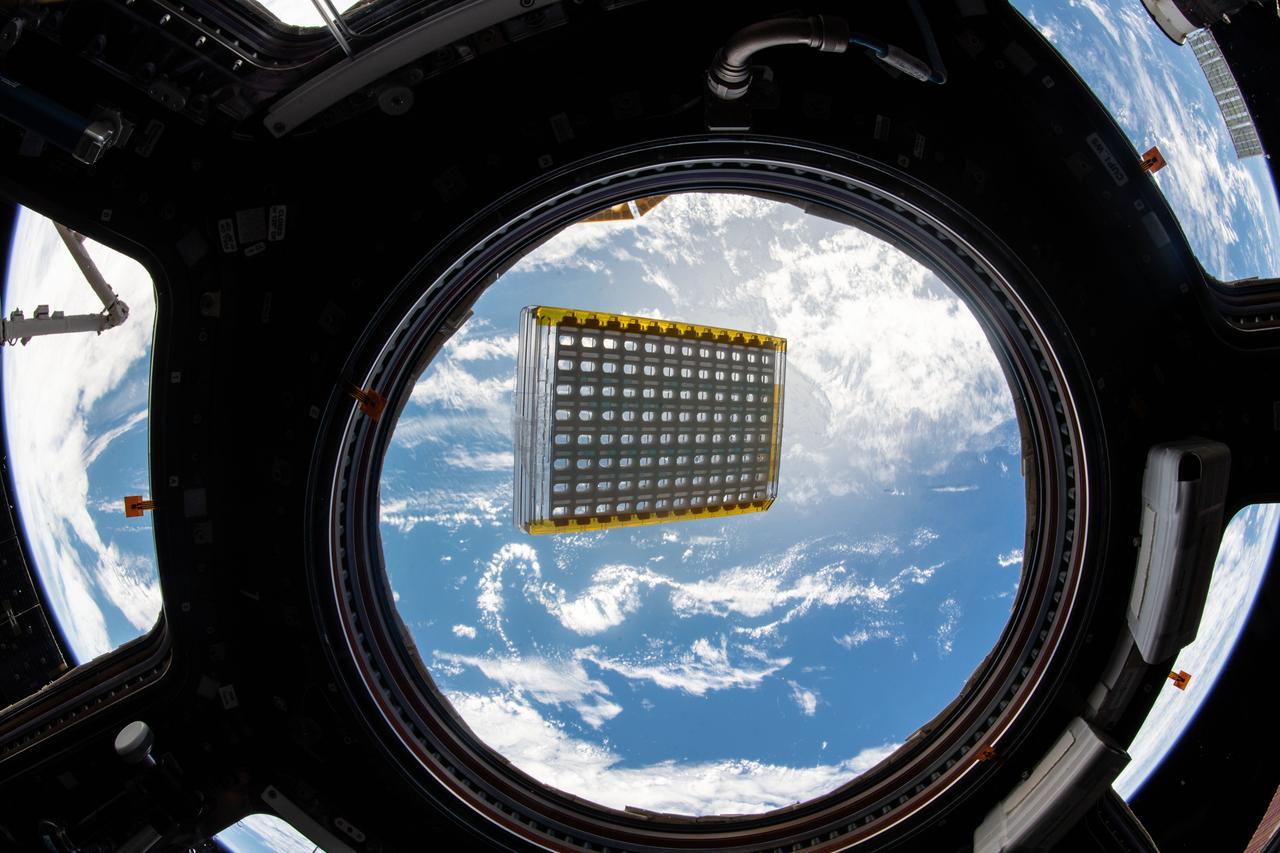
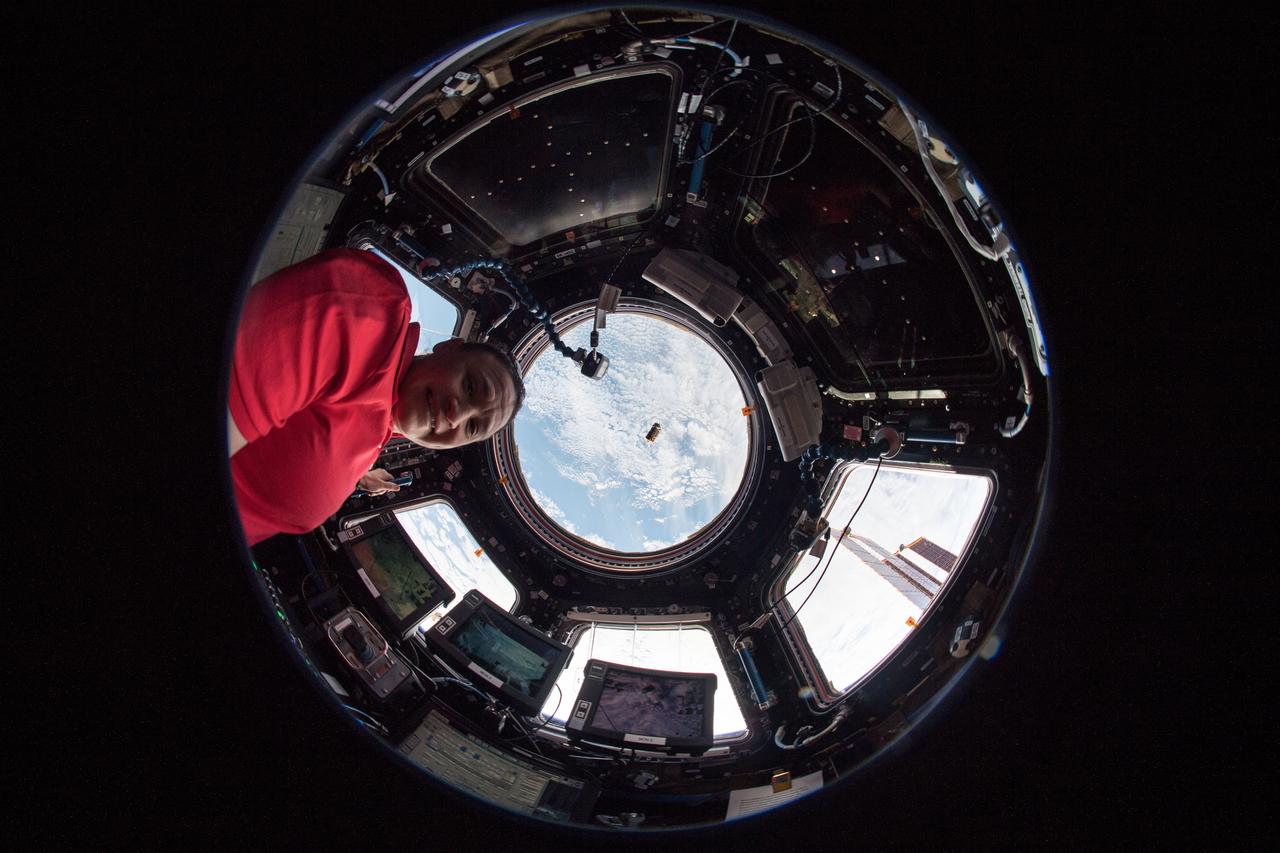
iss058e002064 (1/6/2019) --- CASIS PCG 16 floating in front of Window 7 in the Cupola module. Earth is in the background. Crystallization of LRRK2 Under Microgravity Conditions-2 (CASIS PCG 16) evaluates growth of Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) protein crystals in microgravity. LRRK2 is implicated in Parkinson’s disease, but crystals of the protein grown on Earth are too small and compact to study. Detailed analysis of larger, space-grown crystals can define the protein’s exact shape and morphology and help scientists better understand the disease’s pathology.
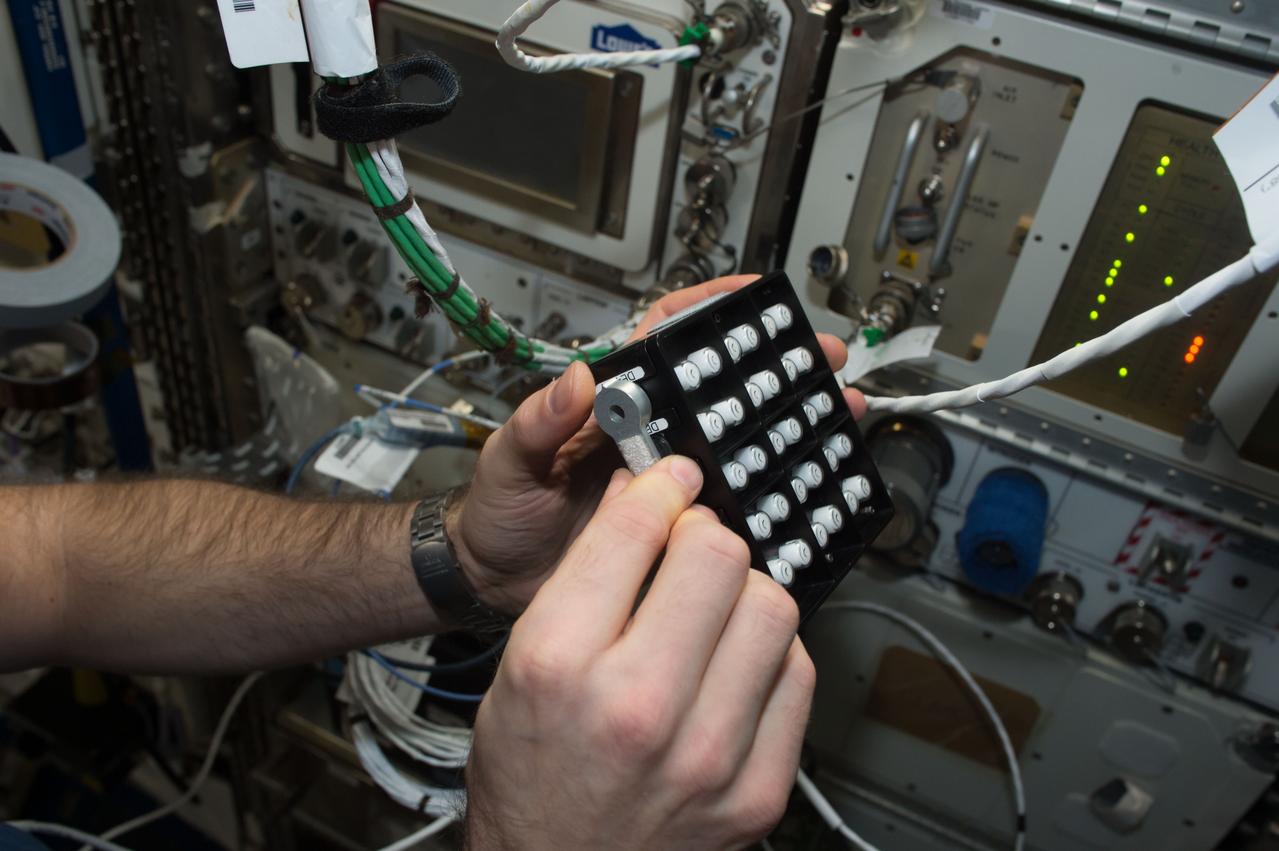

iss050e058807 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.
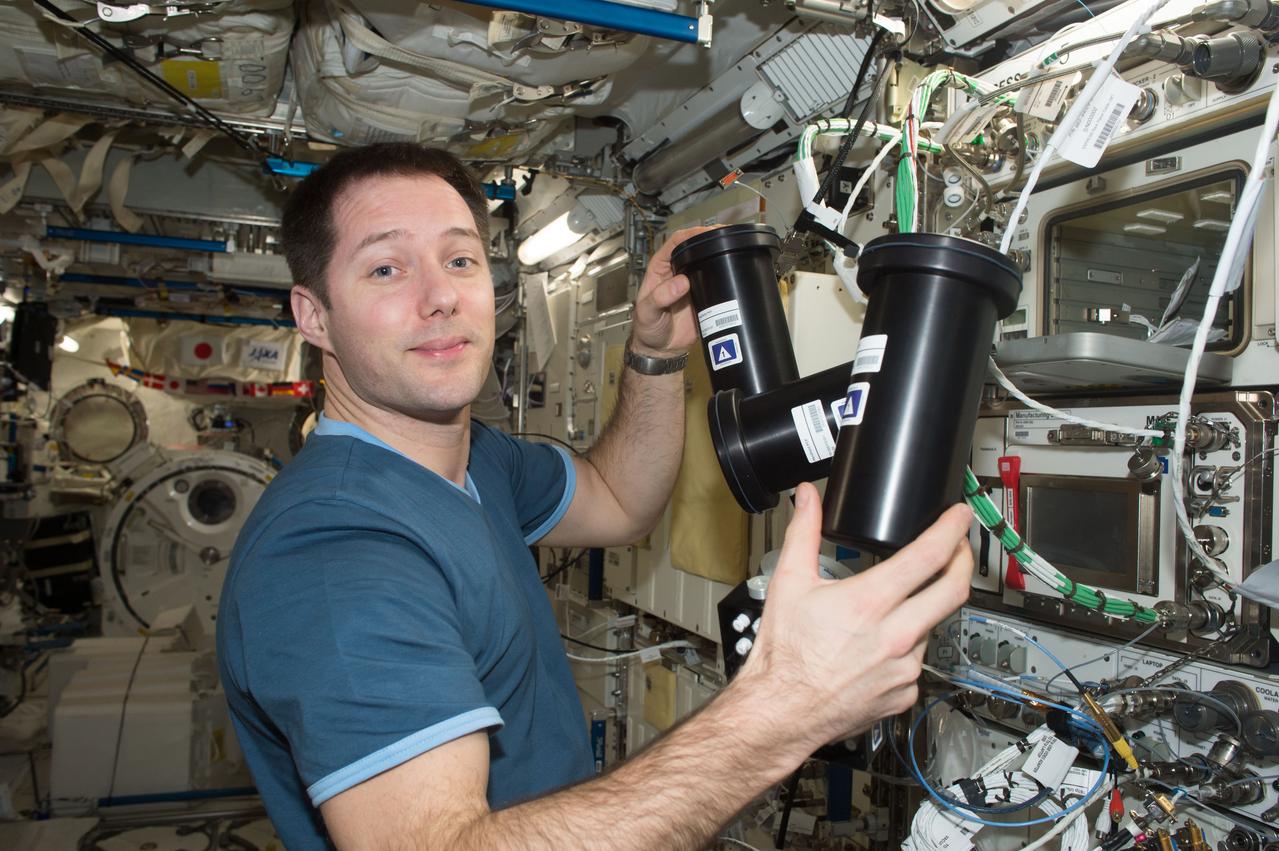

iss050e058812 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.
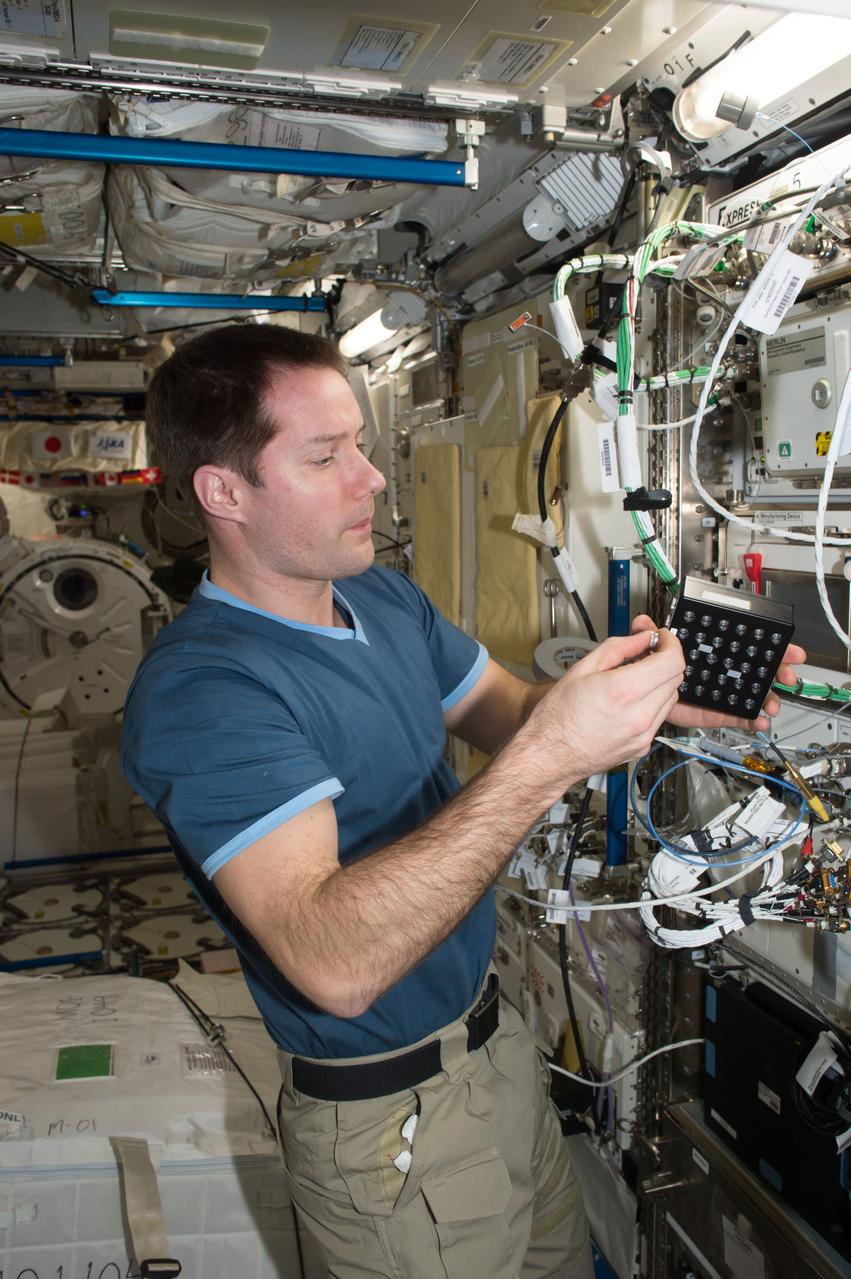

iss050e058802 (3/17/2017) --- A view of European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet, during Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) -5 hardware deactivation and stow, from Microgravity Experiment Research Locker Incubator (MERLIN) on Expedite the Processing of Experiments to the Space Station (EXPRESS) Rack 5. The Microgravity Growth of Crystalline Monoclonal Antibodies for Pharmaceutical Applications (CASIS-PCG-5) investigation crystallizes a monoclonal antibody developed by Merck Research Labs. Microgravity enables the growth of extremely high-quality crystals, which allow scientists to study the proteins’ structure, improve drug delivery, manufacturing, and developing better methods for storing these biological molecules.
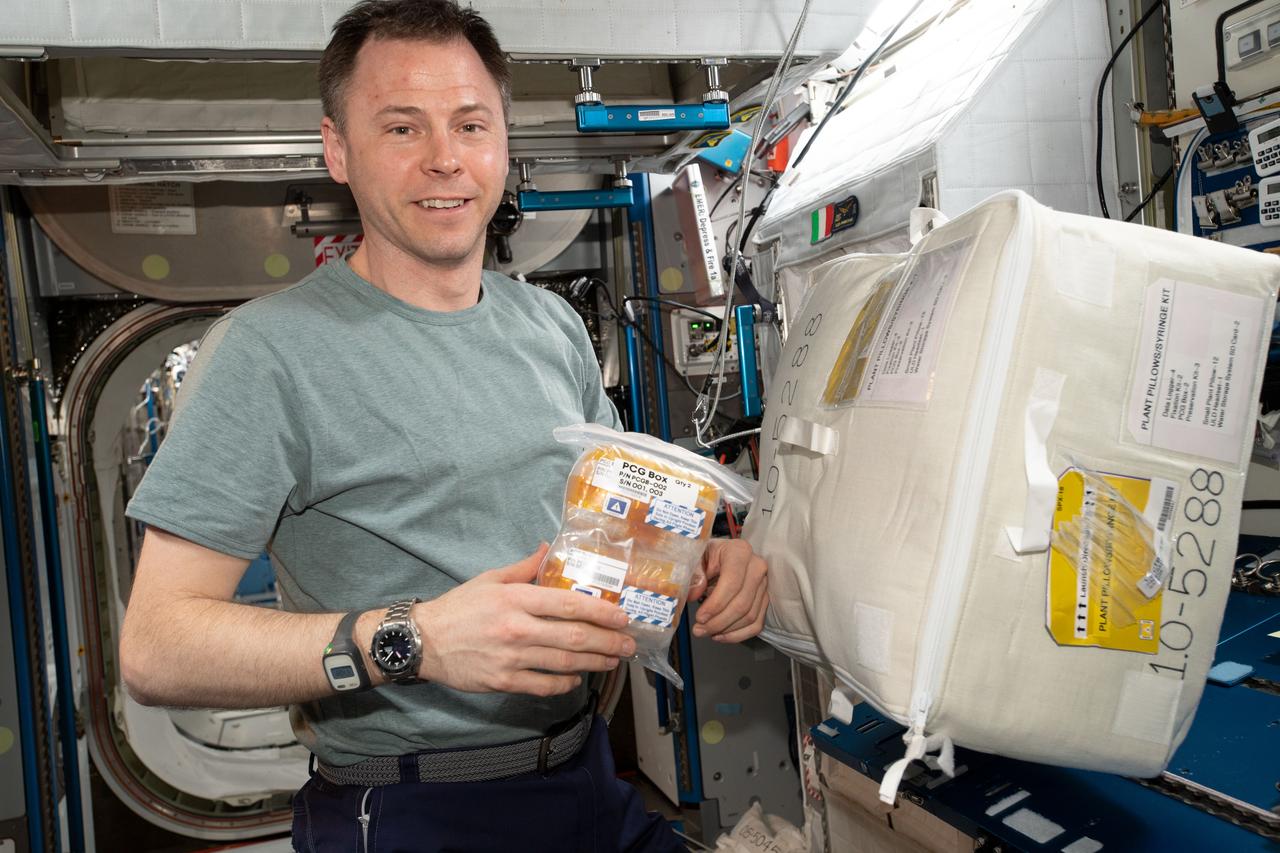

iss060e015014 (7/28/2019) — NASA astronaut Nick Hague is shown holding the CASIS Protein Crystal Growth 15 (CASIS PCG 15) investigation samples aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Microgravity Crystal Growth for Improvement in Neutron Diffraction and the Analysis of Protein Complexes (CASIS PCG 15) seeks a better understanding of enzyme catalysis by examining crystals from two model Pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) dependent enzymes and from a bacteriophage transient deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) repair complex. Analysis of the crystals may reveal catalyst mechanisms and structures and visualize the interaction between the repair proteins. Results could contribute to identification of biomarkers for diagnosis of disease and to development of better antimicrobials.
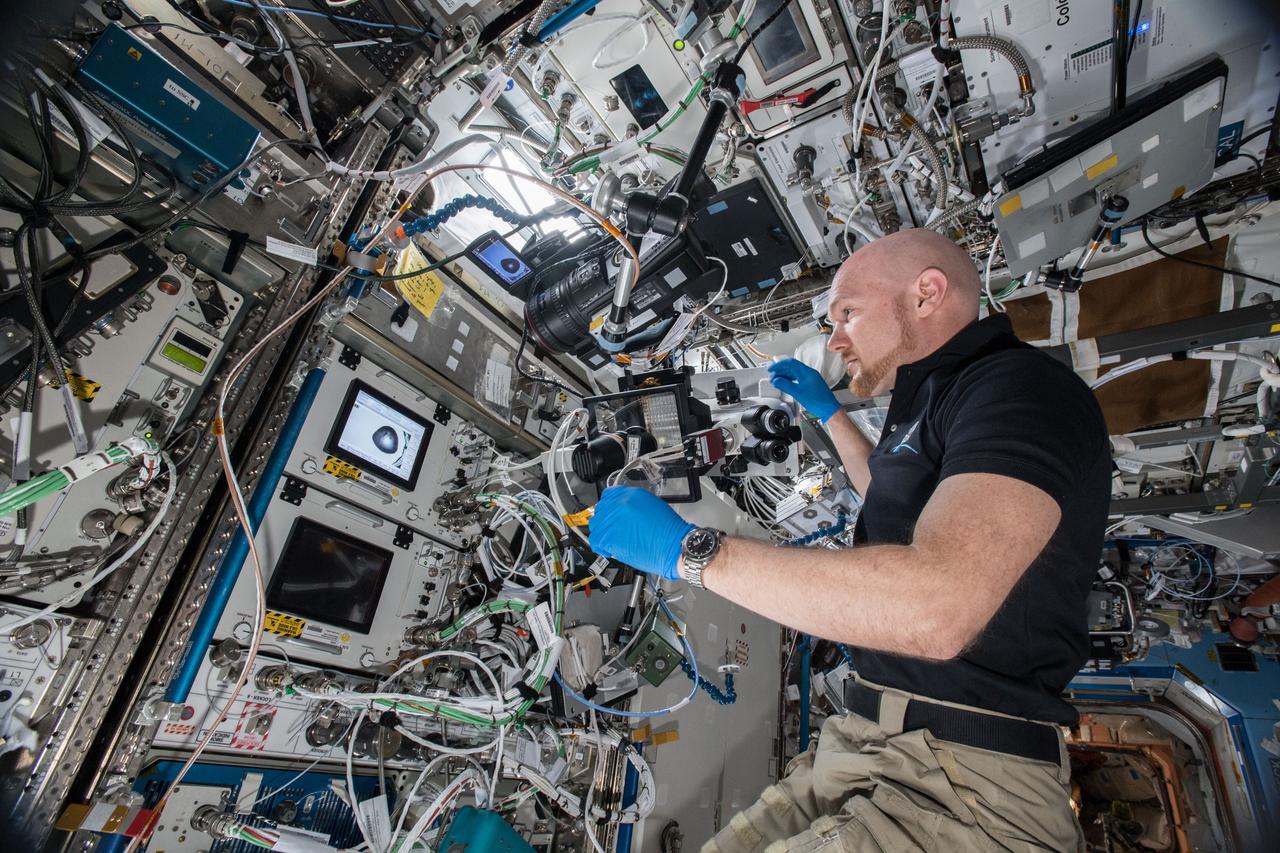

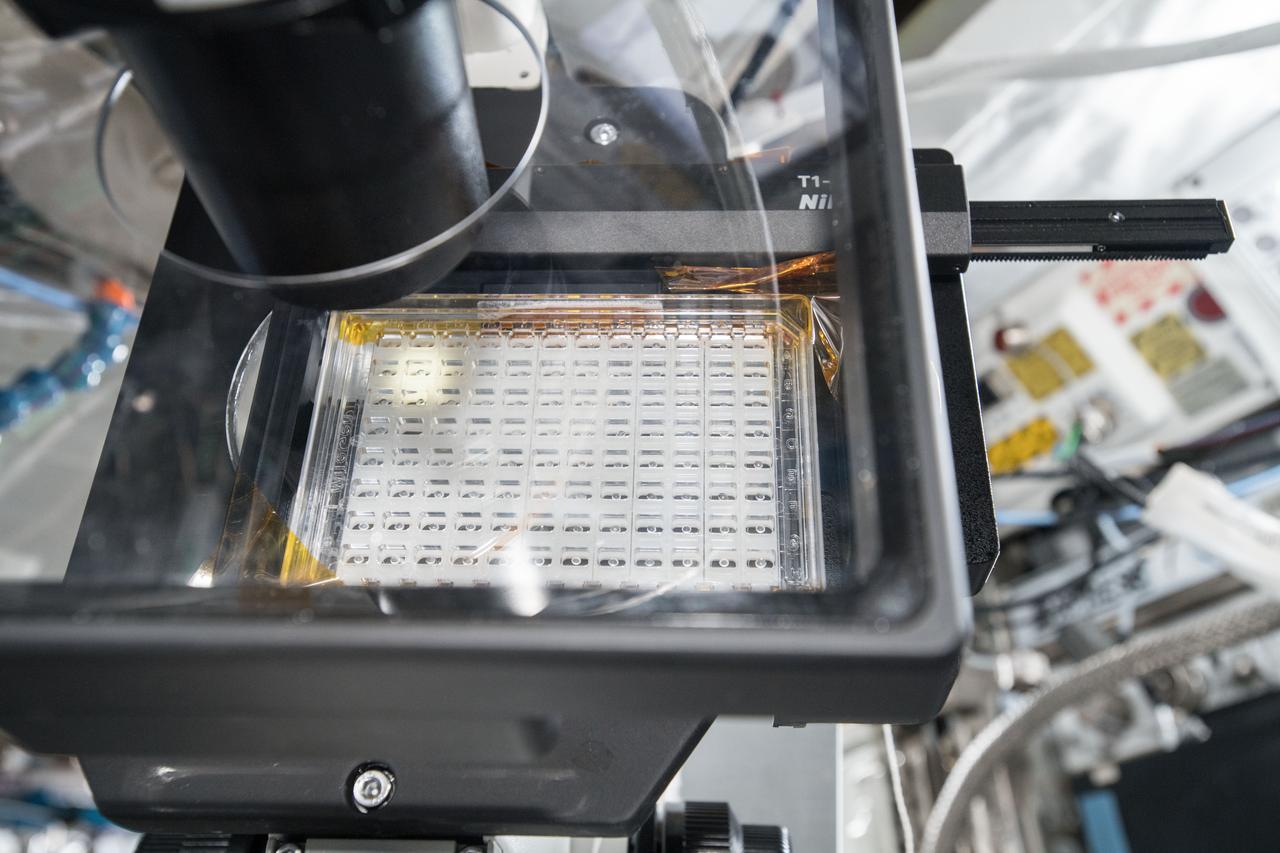
ISS057E106426 - European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Alex Gerst uses a microscope with the Space Automated Bioproduct Laboratory (SABL) Camera attached to document a Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) MicroG Card. The photo was taken in the Destiny U.S. Laboratory aboard the International Space Station (ISS) for the Crystallization of LRRK2 Under Microgravity Conditions-2 (CASIS PCG 16) investigation.
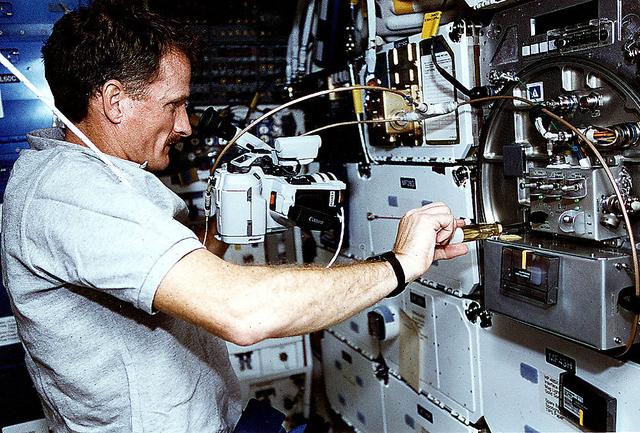

On the Space Shuttle Orbiter Atlantis' middeck, Astronaut Joseph R. Tarner, mission specialist, works at an area amidst several lockers which support the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment during the STS-66 mission. This particular section is called the Crystal Observation System, housed in the Thermal Enclosure System (COS/TES). Together with the Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA), housed in Single Locker Thermal Enclosure (SLTES), the COS/TES represents the continuing research into the structure of proteins and other macromolecules such as viruses.
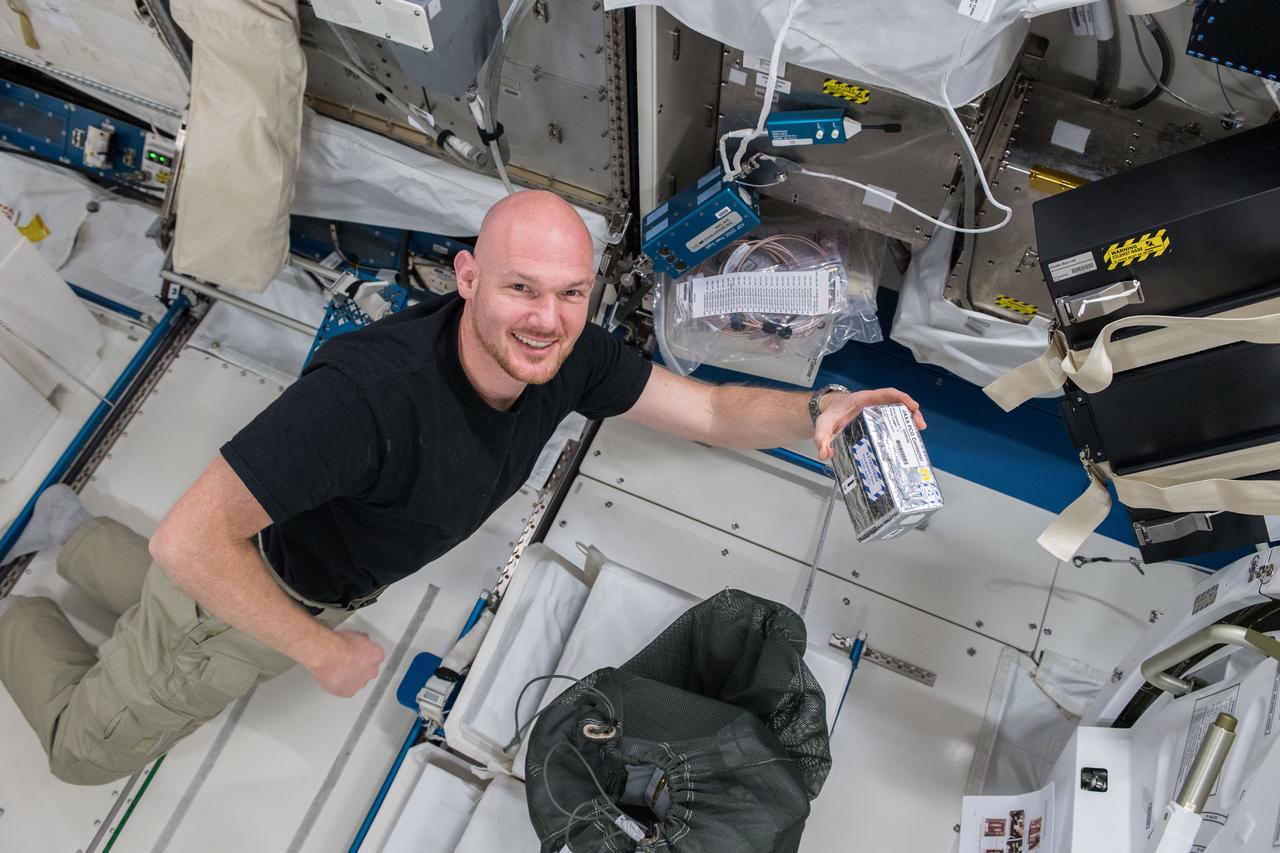

iss056e075928 (7/3/2018) --- Astronaut Alexander Gerst of ESA (European Space Agency), during the JAXA Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) sample retrieval from the Freezer-Refrigerator Of Stirling Cycle 2 (FROST2) and initiation of the crystallization of the samples before inserting them back into the FROST2, where crystallization will continue.
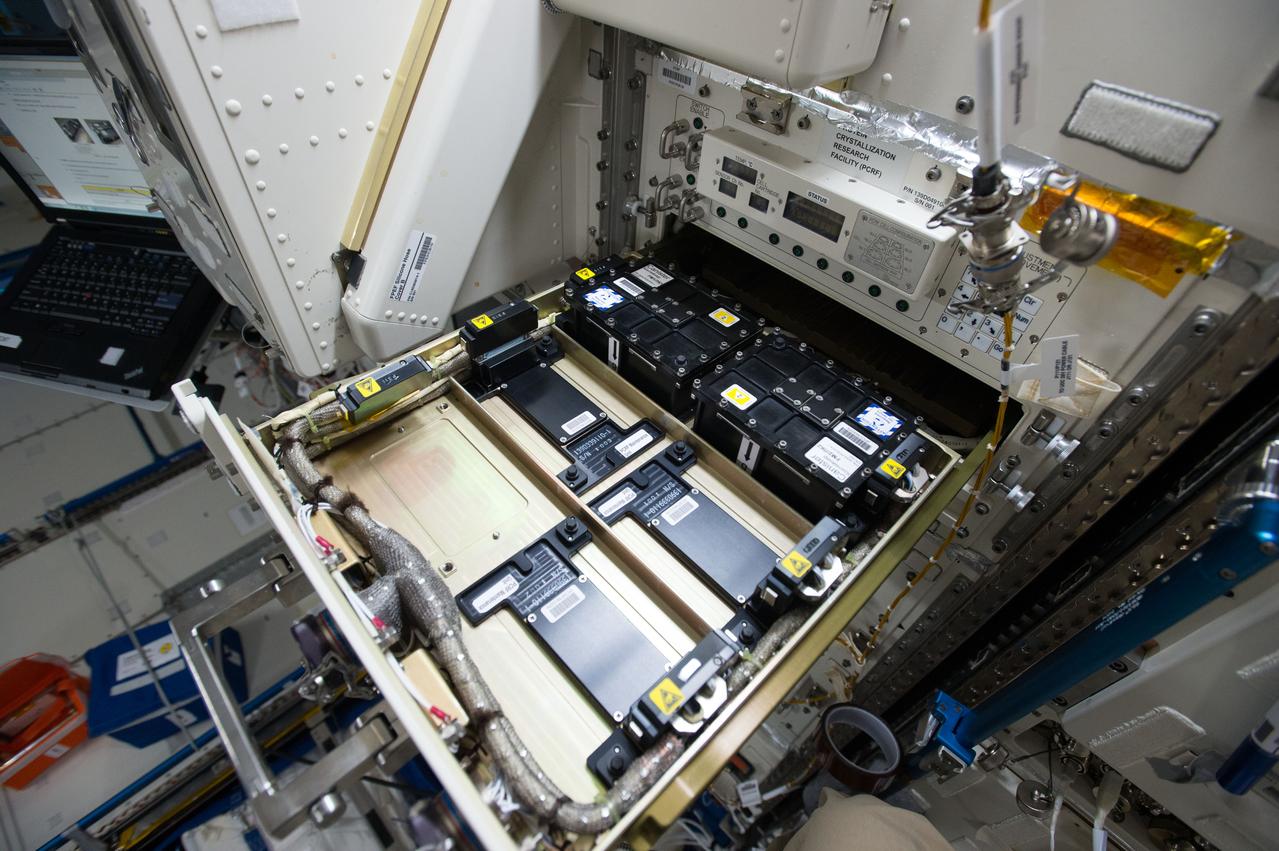

iss049e045287 (10/21/2016) --- Photographic documentation taken during JAXA Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) Installation into the Protein Crystallization Research Facility (PCRF) of the Ryutai Rack.
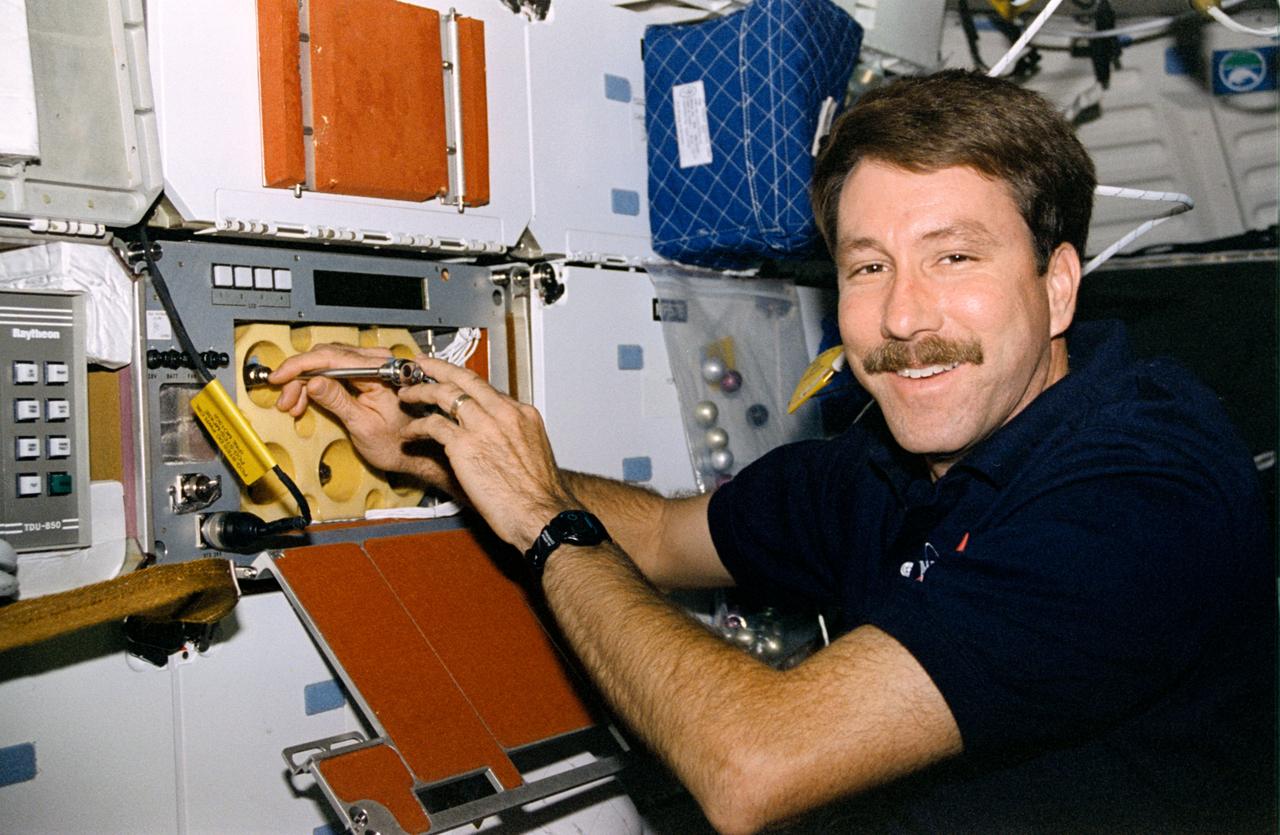

STS085-324-007 (7 - 19 August 1997) --- Astronaut Kent V. Rominger, pilot, uses a tool to deactivate the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment on the mid-deck of the Space Shuttle Discovery near the end of the 12-day STS-85 flight.
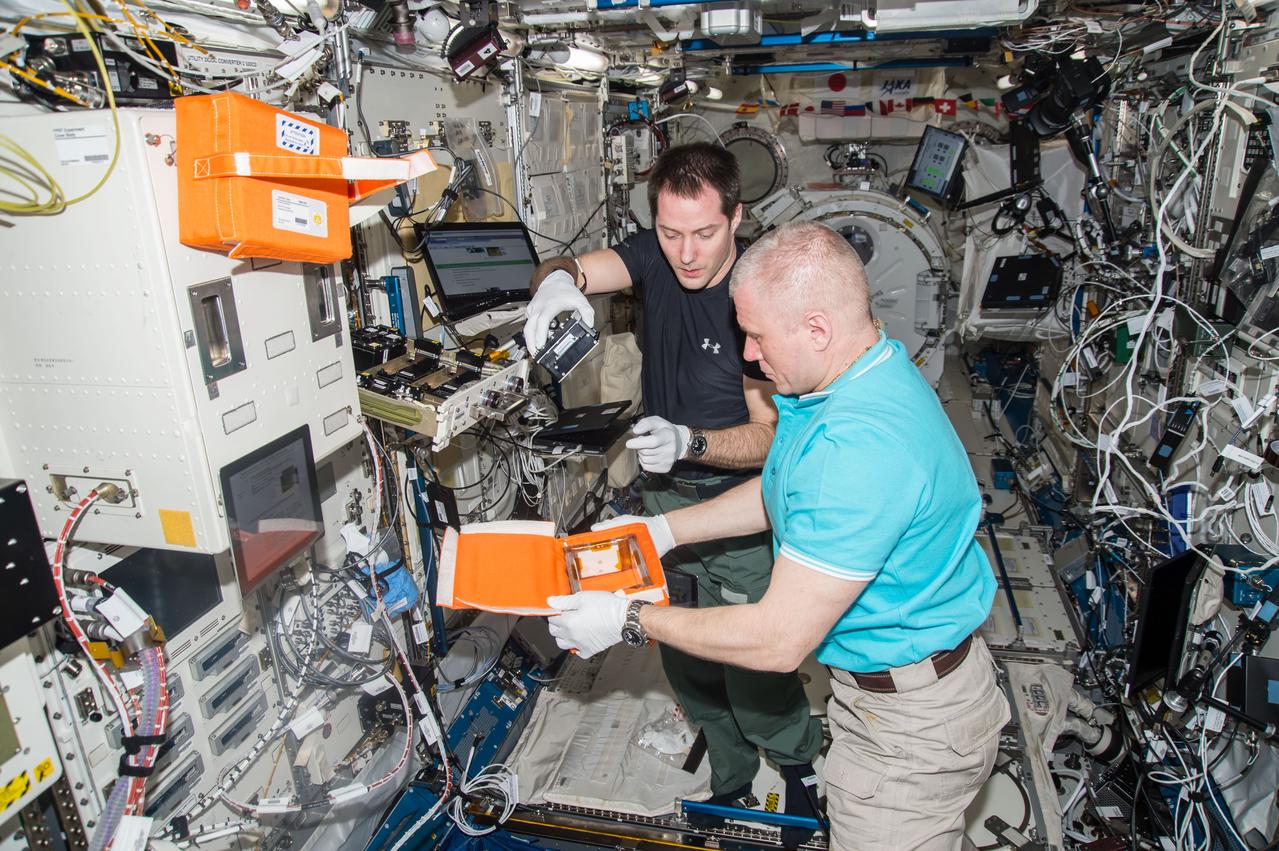

iss051e052364 (6/2/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet works to remove Canisters from the Protein Crystallization Research Facility (PCRF) for handover to cosmonaut Oleg Novitskiy. The image was taken in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Pressurized Module (JPM) during Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) and Kristallizator experiment operations (OPS).
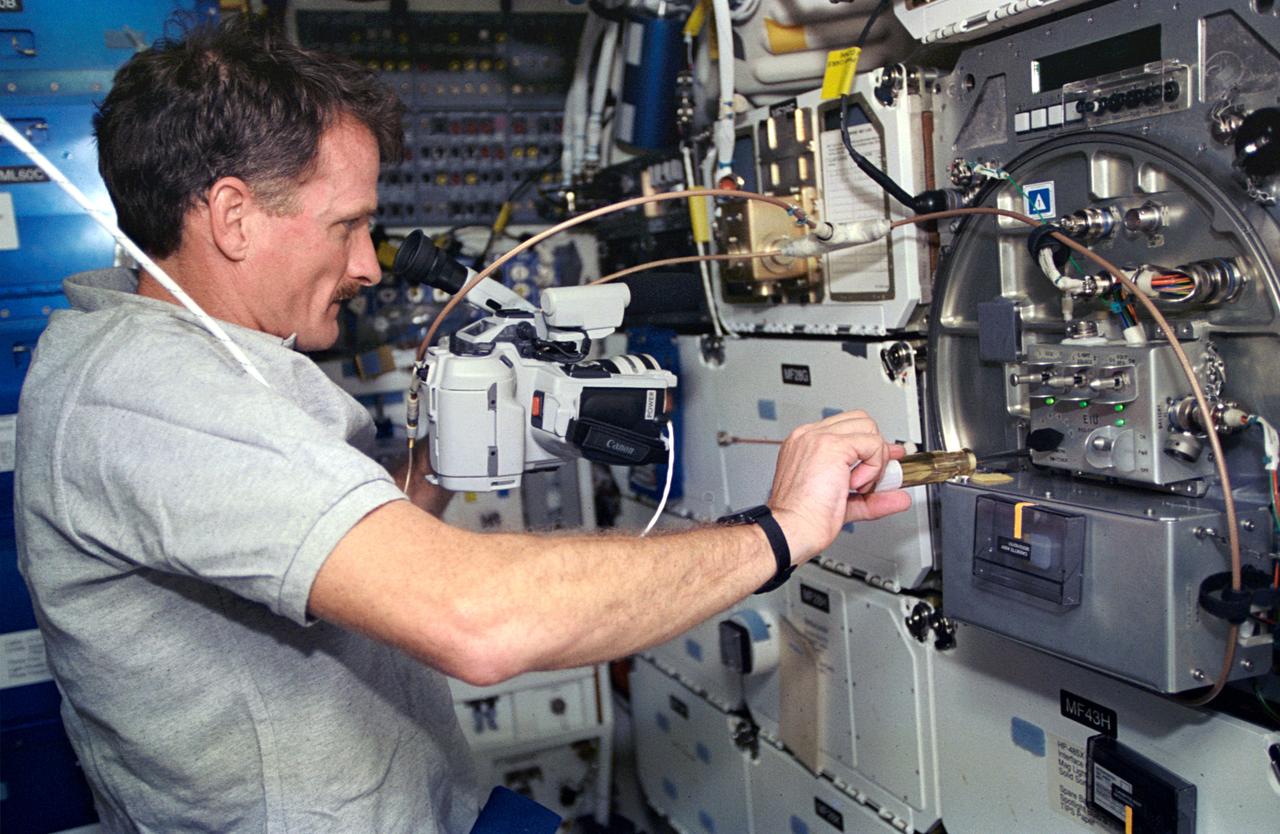

On the Space Shuttle Atlantis' mid-deck, astronaut Joseph R. Tanner, mission specialist, works at area amidst several lockers onboard the Shuttle which support the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment. This particular section is called the Crystal Observation System, housed in the Thermal Enclosure System (COS/TES). Together with the Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA), housed in a Single Locker Thermal Enclosure (SLTES) which is out of frame, the Cos/TES represents the continuing research into the structures of proteins and other macromolecules such as viruses.
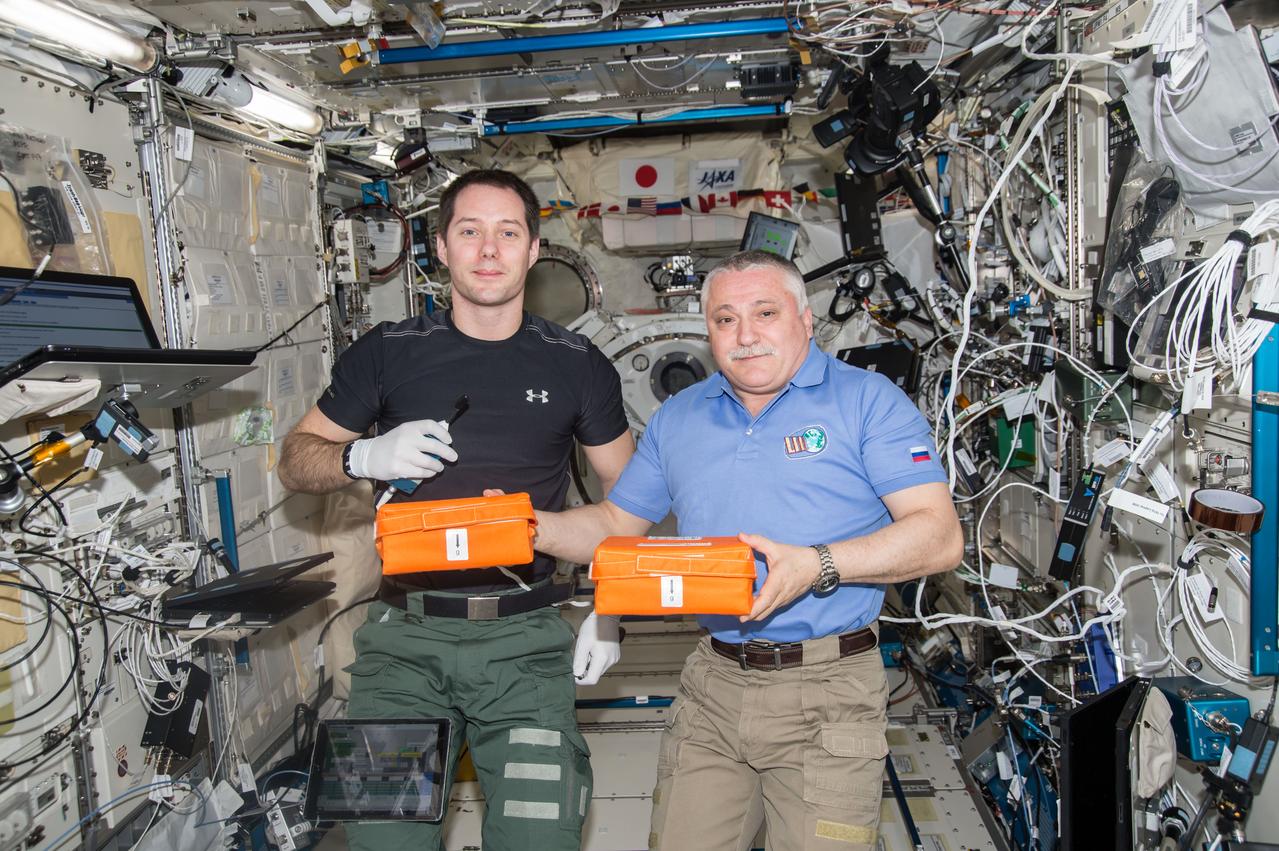

iss051e052377 96/2/2017) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Thomas Pesquet and cosmonaut Fyodor Yurchikhin pose with Canister Bags during handover of Canisters removed from the Protein Crystallization Research Facility (PCRF. The image was taken in the Kibo Japanese Experiment Pressurized Module (JPM) during Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) and Kristallizator experiment operations (OPS).
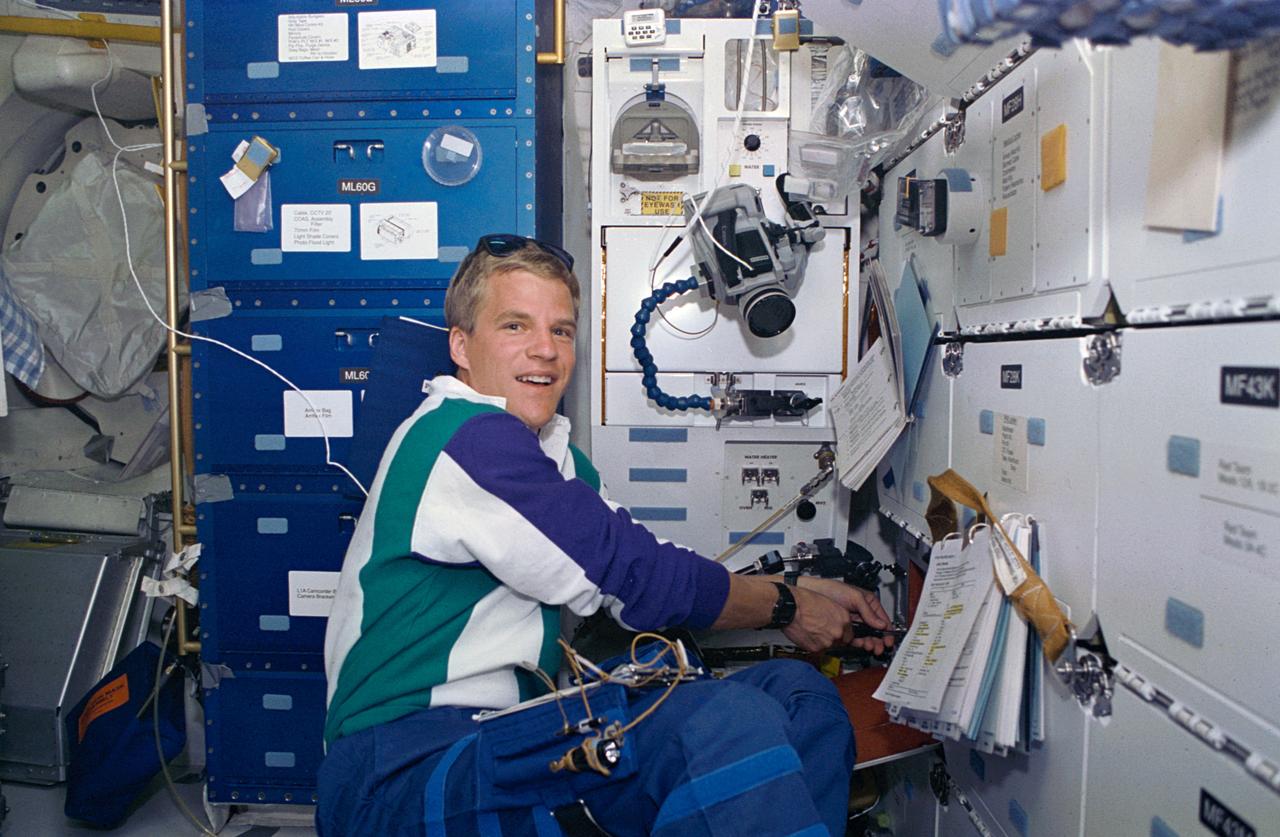

STS066-13-029 (3-14 Nov 1994) --- On the Space Shuttle Atlantis' mid-deck, astronaut Scott E. Parazynski, mission specialist, works at one of two areas onboard the Shuttle which support the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment. This particular section is called the Vapor Diffusion Apparatus (VDA), housed in a Single Locker Thermal Enclosure (STES). Together with the Crystal Observation System, housed in the Thermal Enclosure System (COS/TES) the VDA represents the continuing research into the structures of proteins and other macromolecules such as viruses. In addition to using the microgravity of space to grow high-quality protein crystals for structural analyses, the experiments are expected to help develop technologies and methods to improve the protein crystallization process on Earth as well as in space.
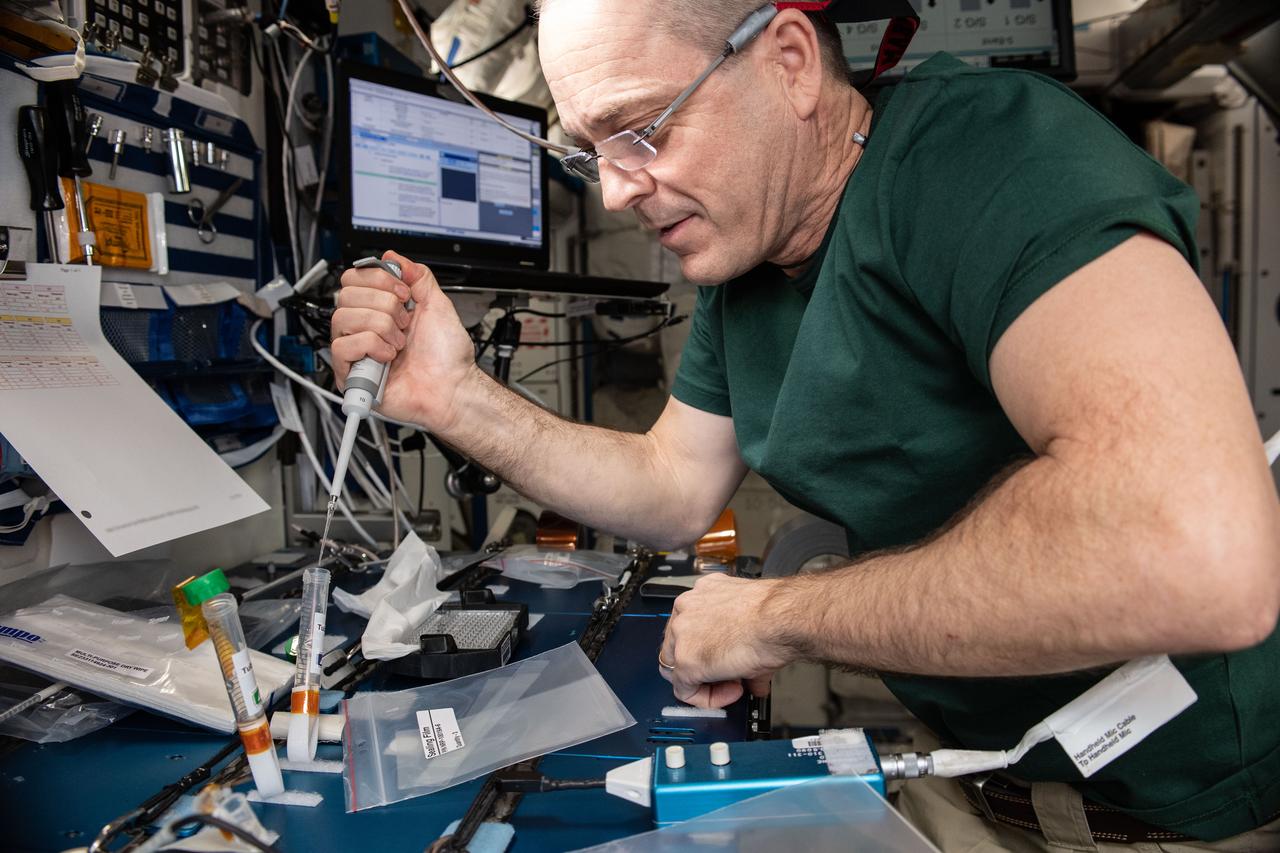

iss056e142862_alt (8/13/2018) --- Astronaut Ricky Arnold prepares samples for the Barrios Protein Crystal Growth (Barrios PCG) experiment in the Maintenance Work Area (MWA) of the International Space Station (ISS). The Barrios PCG experiment defined an approach for optimizing protein crystallization conditions on orbit, eliminating the need to return samples to the ground during the optimization phase, which has the potential for saving substantial time and money on future PCG investigations in microgravity.
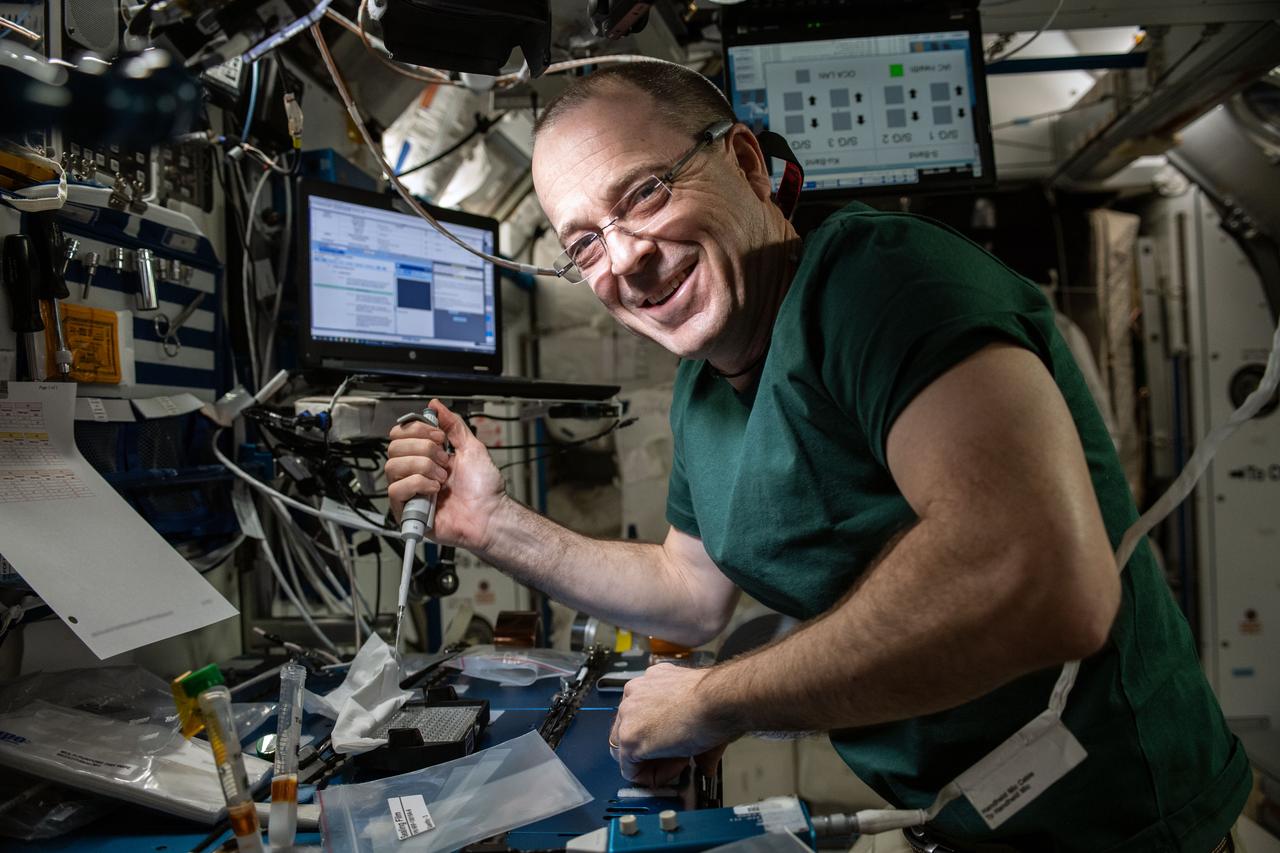

iss056e142865_alt (8/13/2018) --- Astronaut Ricky Arnold prepares samples for the Barrios Protein Crystal Growth (Barrios PCG) experiment in the Maintenance Work Area (MWA) of the International Space Station (ISS). The Barrios PCG experiment defined an approach for optimizing protein crystallization conditions on orbit, eliminating the need to return samples to the ground during the optimization phase, which has the potential for saving substantial time and money on future PCG investigations in microgravity.
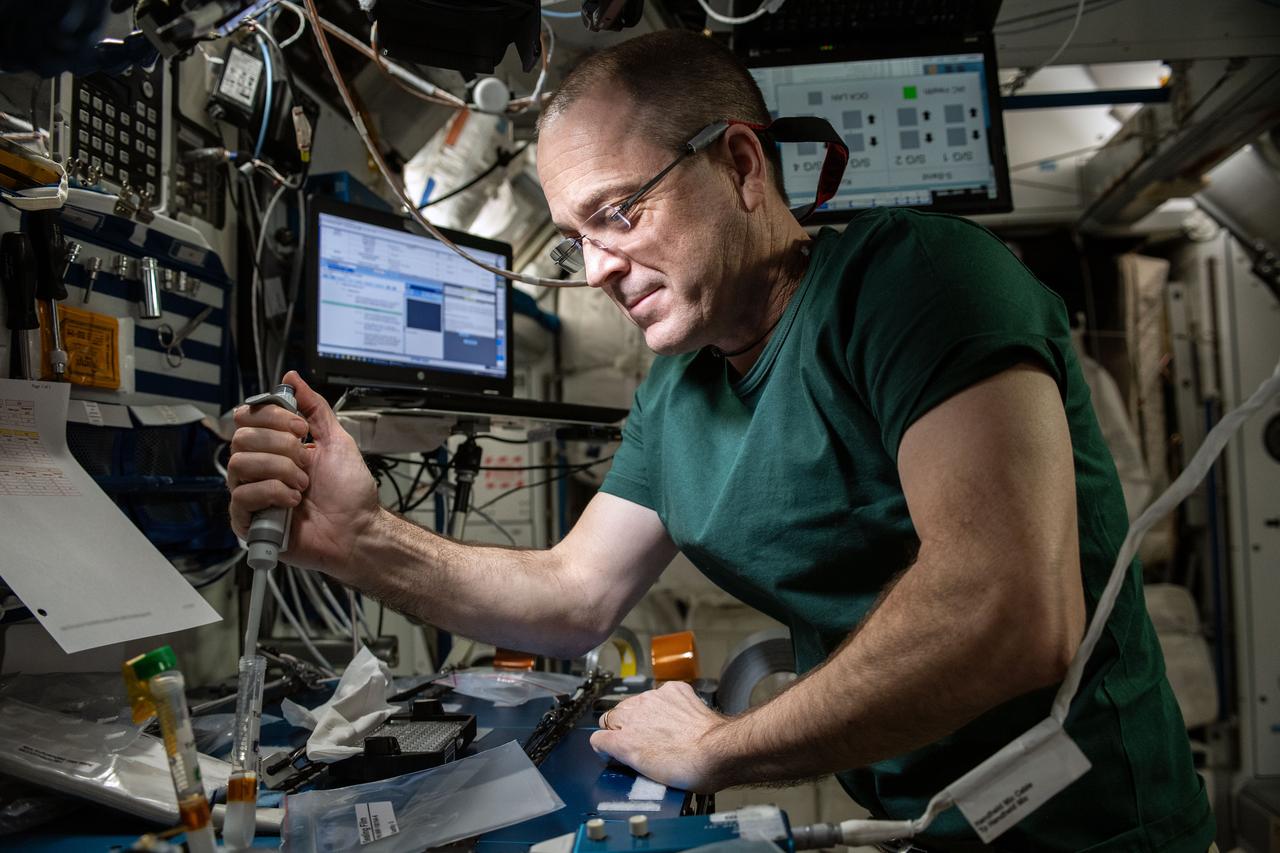

iss056e142871_alt (8/13/2018) --- Astronaut Ricky Arnold prepares samples for the Barrios Protein Crystal Growth (Barrios PCG) experiment in the Maintenance Work Area (MWA) of the International Space Station (ISS). The Barrios PCG experiment defined an approach for optimizing protein crystallization conditions on orbit, eliminating the need to return samples to the ground during the optimization phase, which has the potential for saving substantial time and money on future PCG investigations in microgravity.
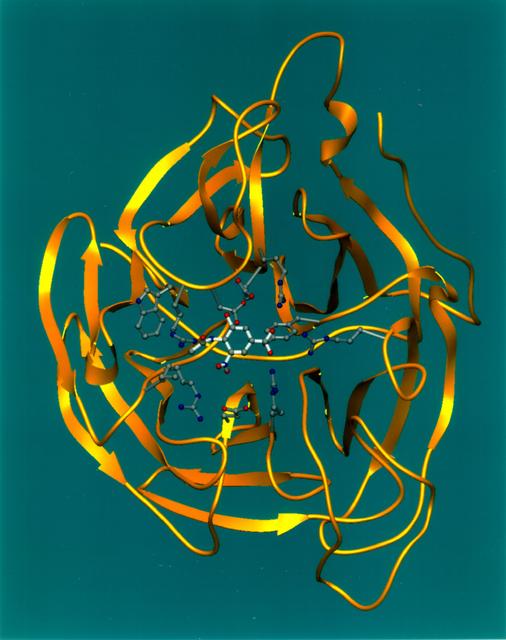
Ribbons is a program developed at UAB used worldwide to graphically depict complicated protein structures in a simplified format. The program uses sophisticated computer systems to understand the implications of protein structures. The Influenza virus remains a major causative agent for a large number of deaths among the elderly and young children and huge economic losses due to illness. Finding a cure will have a general impact both on the basic research of viral pathologists of fast evolving infectious agents and clinical treatment of influenza virus infection. The reproduction process of all strains of influenza are dependent on the same enzyme neuraminidase. Shown here is a segmented representation of the neuraminidase inhibitor compound sitting inside a cave-like contour of the neuraminidase enzyme surface. This cave-like formation present in every neuraminidase enzyme is the active site crucial to the flu's ability to infect. The space-grown crystals of neuraminidase have provided significant new details about the three-dimensional characteristics of this active site thus allowing researchers to design drugs that fit tighter into the site. Principal Investigator: Dr. Larry DeLucas
This is a enzyme, plant chitinase, believed to be a defensive enzyme to discourage invasion of plant tissue by insects.
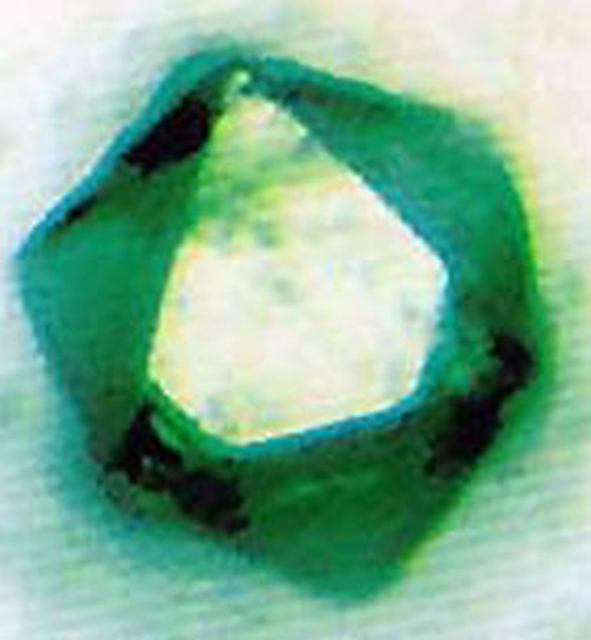

The demetalized form of the major iron storage protein from horse spleen.
Protein isolated from hen egg-white and functions as a bacteriostatic enzyme by degrading bacterial cell walls. First enzyme ever characterized by protein crystallography. It is used as an excellent model system for better understanding parameters involved in microgravity experiments with data from laboratory experiments to study the equilibrium rate of hanging drop experiments in microgravity.
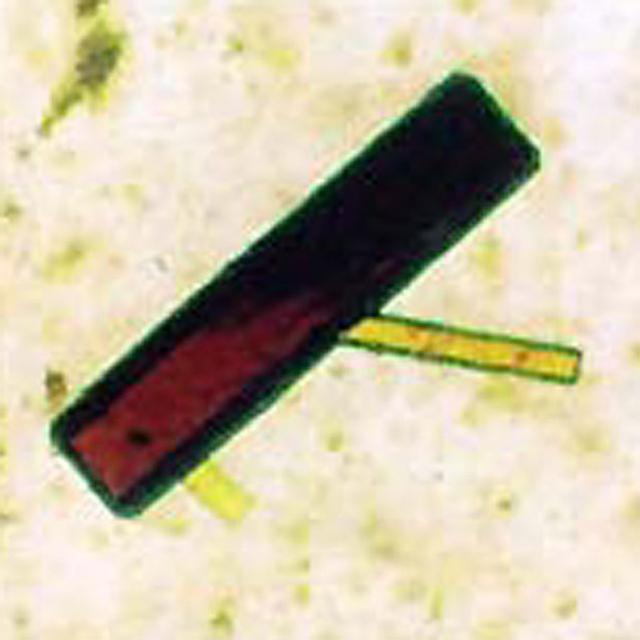

Along with hemoglobin the primary oxygen storage and transport proteins in all higher animals including humans. Important for medical reasons because they are primary blood proteins.
(Rabbit) Converts the major storage form of high energy phosphate (creatine phosphate) to usable energy form (ATP). A major muscle enzyme and implicated in some muscle diseases.
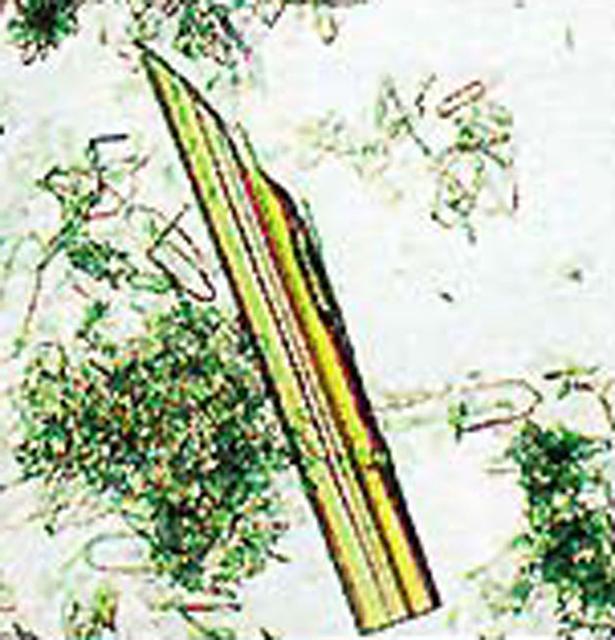

Both (Porcine and bacterial) starch degrading enzymes highly valued by the biotechnology industry. (Porcine) A major target for protein engineering and the study of diabetes, obesity and dental care. (Bacterial) Major industrial and biotechnology interest used in brewing, baking, and food processing. World's number one industrial protein.
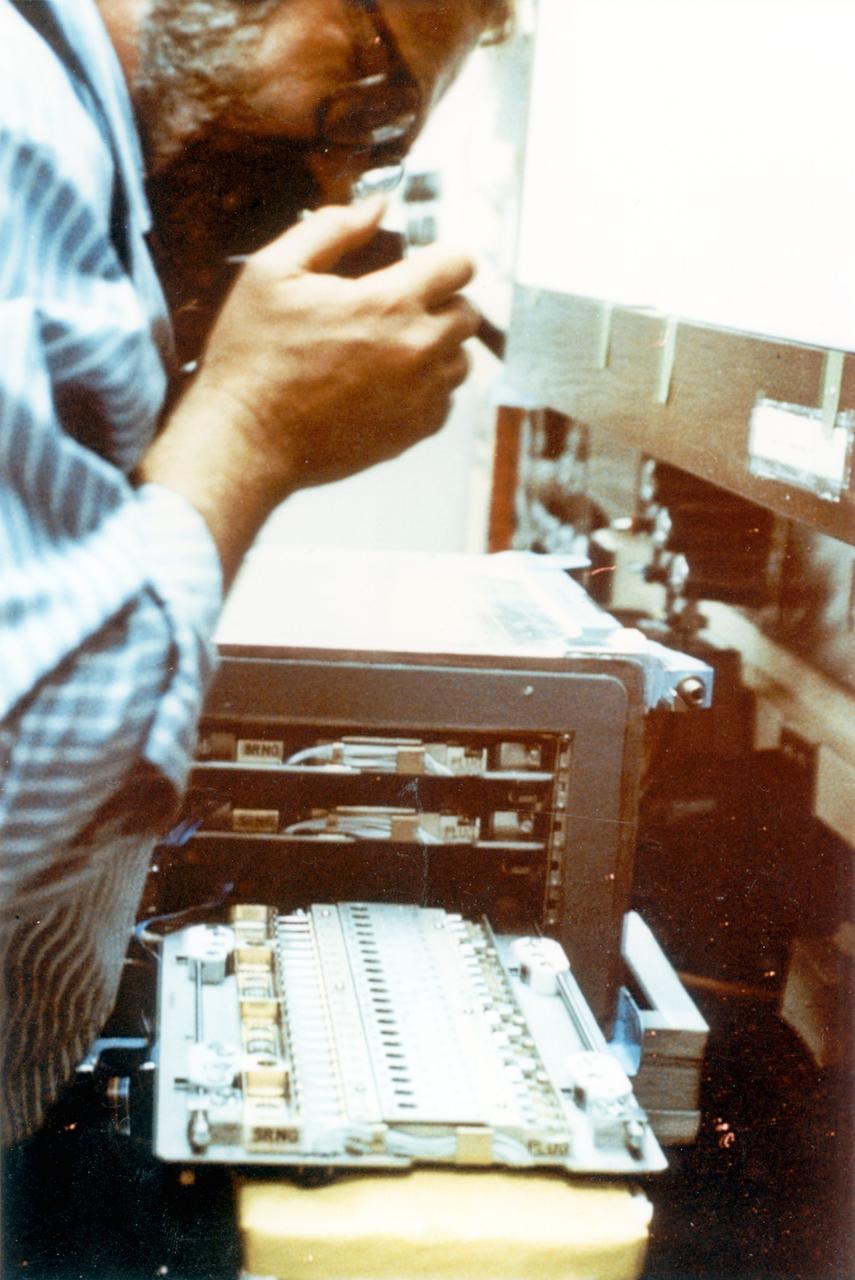

Scientist photographs STS- 26 Post-flight (VDA) Vapor Diffusion Apparatus Tray with (PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Samples.
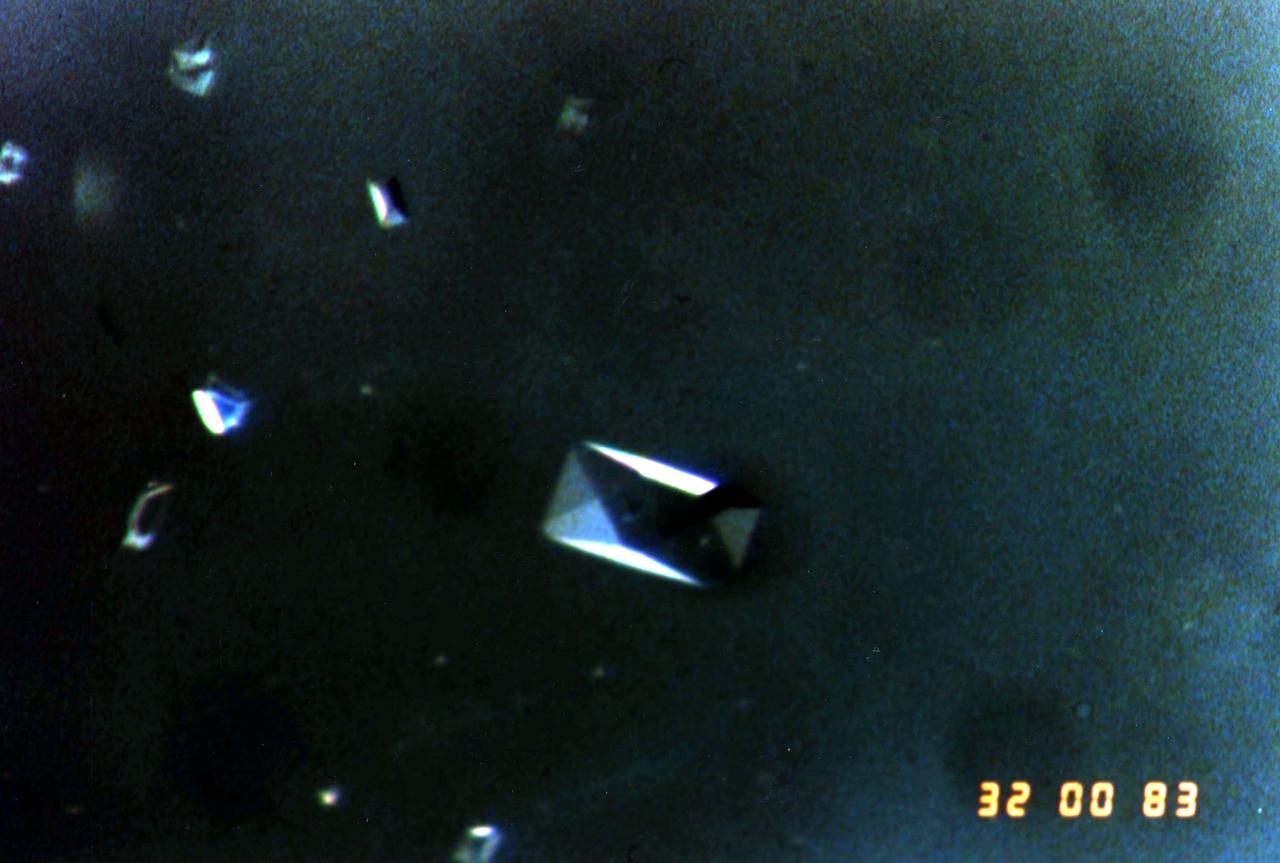
Orbital Documentation of Porcine Elastase grown in (PCG) Protein Crystal Growth (RIM) Refrigerator Incubator Module

Purine Nucleoside Phosphorylase (PNP) is an important target enzyme for the design of anti-cancer and immunosuppressive drugs. Bacterial PNP, which is slightly different from the human enzyme, is used to synthesize chemotherapuautic agents. Knowledge of the three-dimensional structure of the bacterial PNP molecule is useful in efforts to engineer different types of PNP enzymes, that can be used to produce new chemotherapeutic agents. This picture shows a computer model of bacterial PNP, which looks a lot like a display of colorful ribbons. Principal Investigator was Charles Bugg.
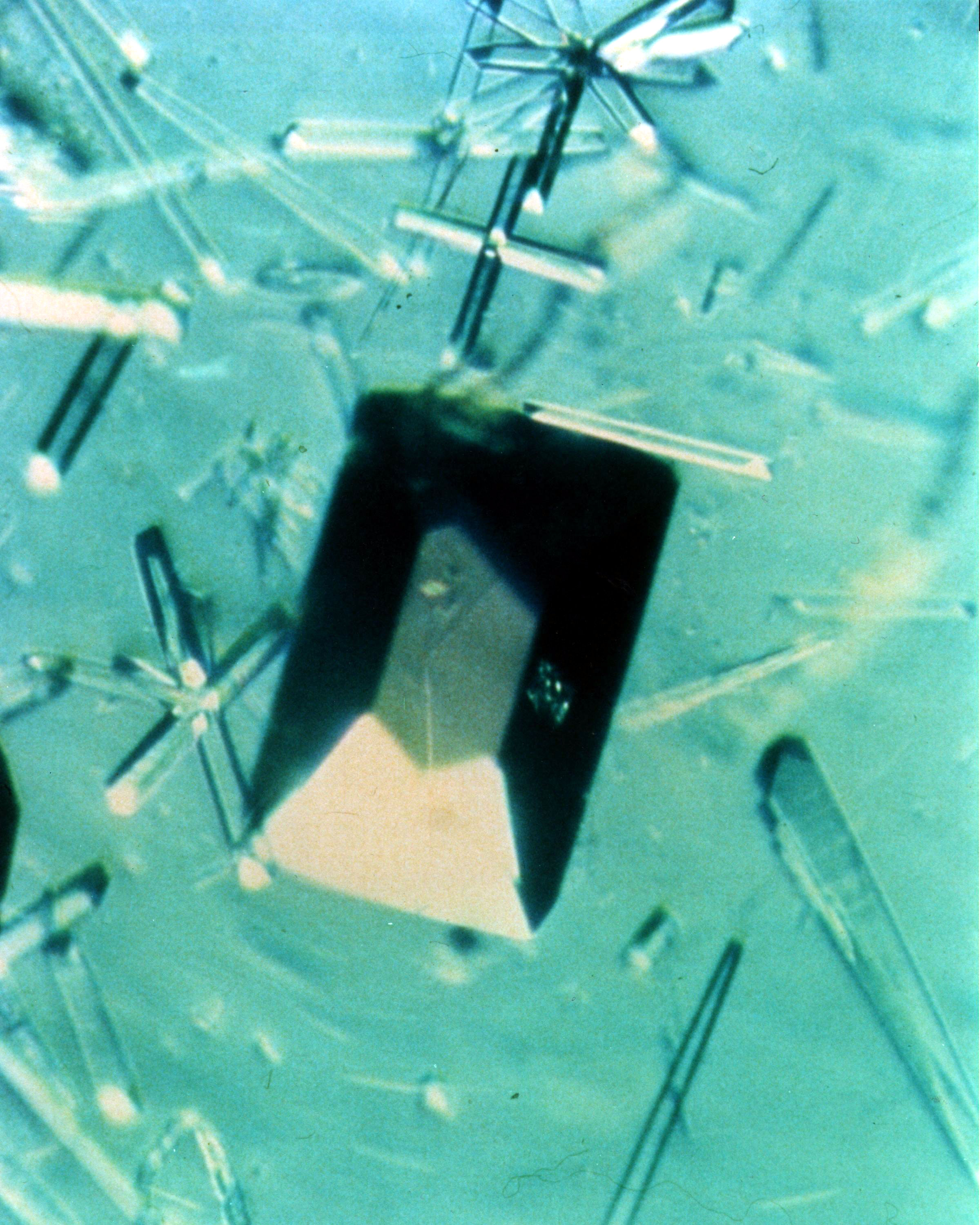
(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth C-reactive Protein. Plays a major role in human immune system response. Principal Investigator on STS-26 was Charles Bugg.
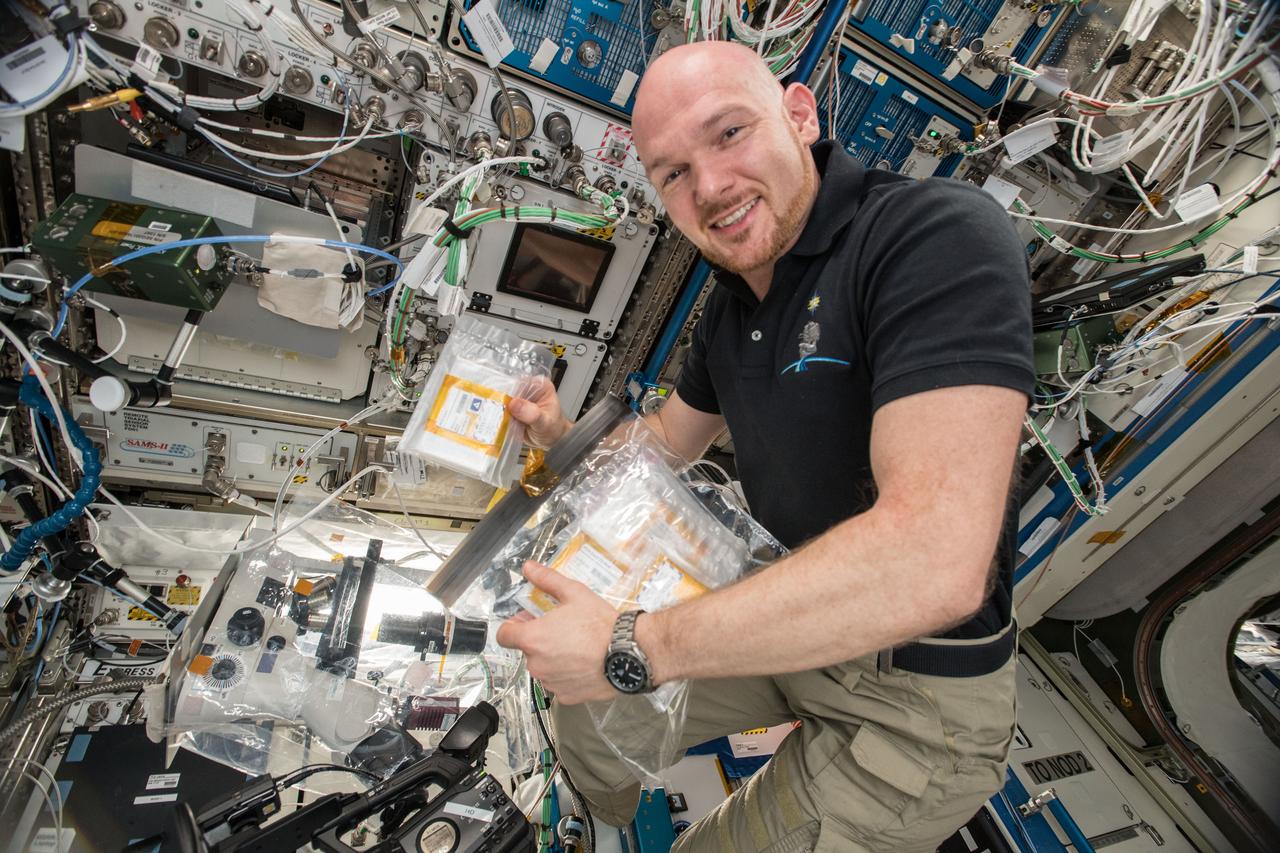

iss057e114766 (12/9/2018) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Alex Gerst is photographed with the Crystallization of RAS in Space (CASIS PCG 17) investigation. CASIS PCG 17grows crystals of KRAS proteins, which have a pivotal role in cell growth and death. Mutations in KRAS proteins are responsible for a third of all cancers and identifying the structure of these proteins is critical to developing therapeutics and treatments. Protein crystals grow larger and more perfectly in microgravity, allowing for detailed laboratory analysis of their structure back on Earth.

iss047e055611 (4/11/2016) --- A view of the JAXA Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) Demo Sample, in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Pressurized Module (JPM) aboard the International space Station (ISS). The objective of JAXA High Quality Protein Crystal Growth Demonstration Experiment (JAXA PCG-Demo) is to grow high quality protein crystals in microgravity.
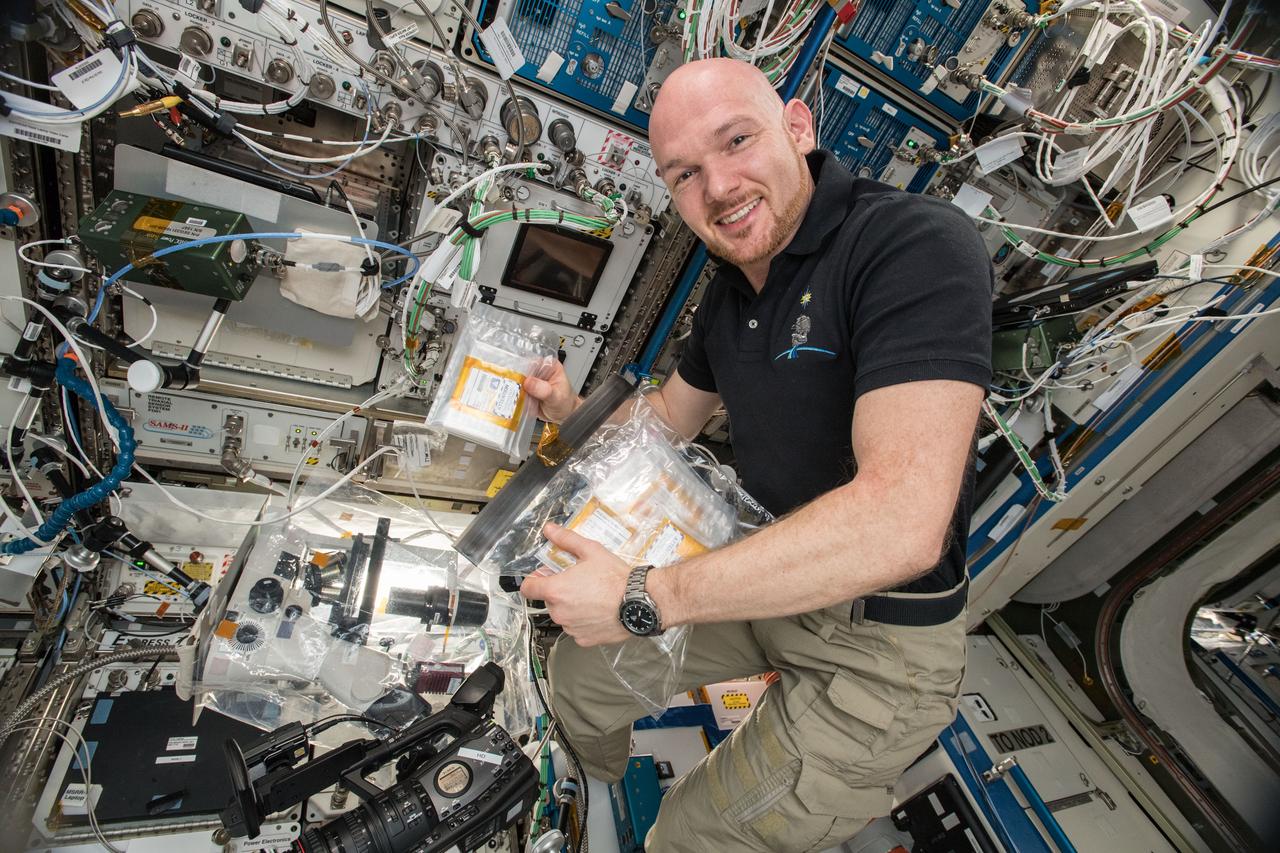

iss057e114765 (12/9/2018) --- European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut Alex Gerst is photographed with the Crystallization of RAS in Space (CASIS PCG 17) investigation. CASIS PCG 17grows crystals of KRAS proteins, which have a pivotal role in cell growth and death. Mutations in KRAS proteins are responsible for a third of all cancers and identifying the structure of these proteins is critical to developing therapeutics and treatments. Protein crystals grow larger and more perfectly in microgravity, allowing for detailed laboratory analysis of their structure back on Earth.
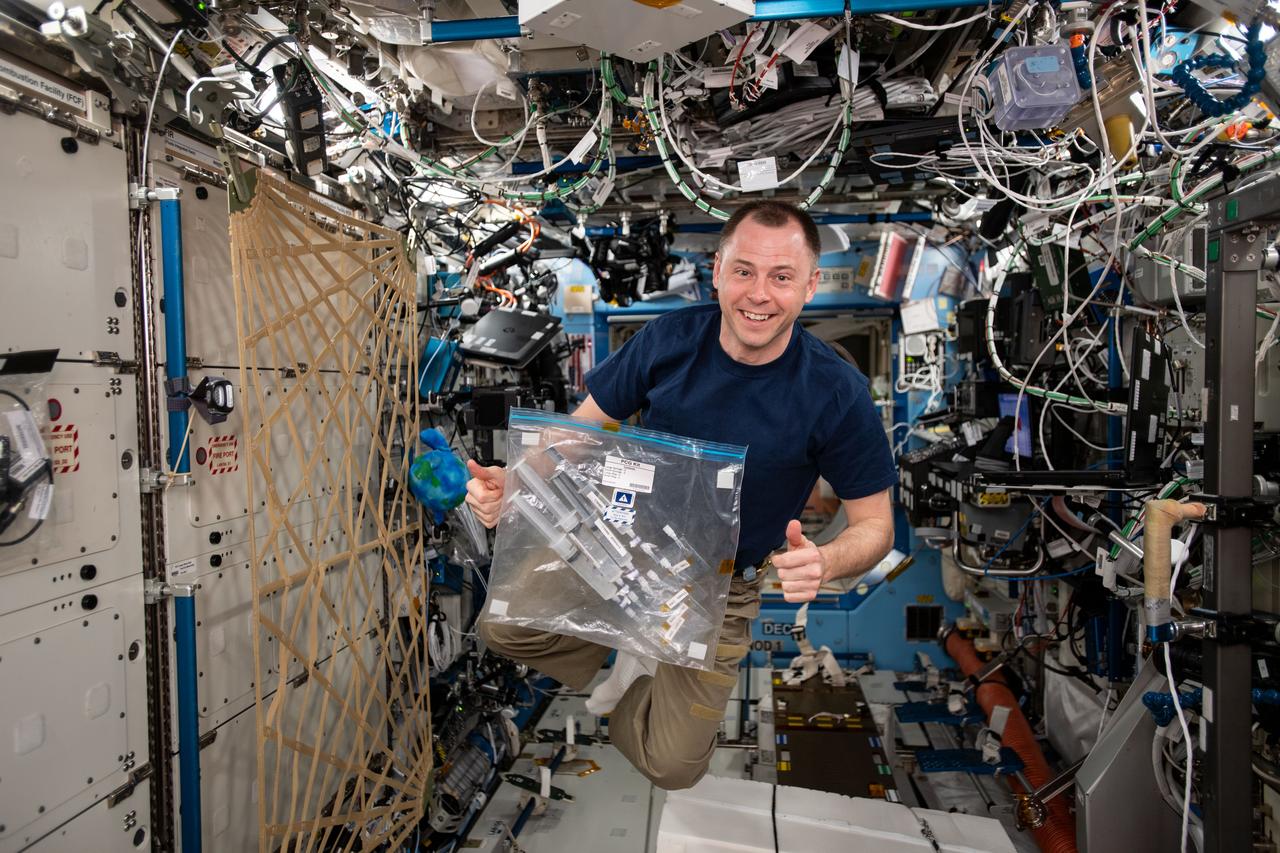

iss059e068212 (5/20/2019) --- NASA astronaut Nick Hague is photographed with the CASIS PCG-14 investigation in the Destiny module of the International Space Station (ISS). The Wisconsin Crystal Growing Contest-Wisconsin Space Crystals (CASIS PCG 14) teaches middle and high school students the unique engineering research and operations of the space program. The investigation allows students to understand the capabilities and constraints of conducting an experiment in microgravity.
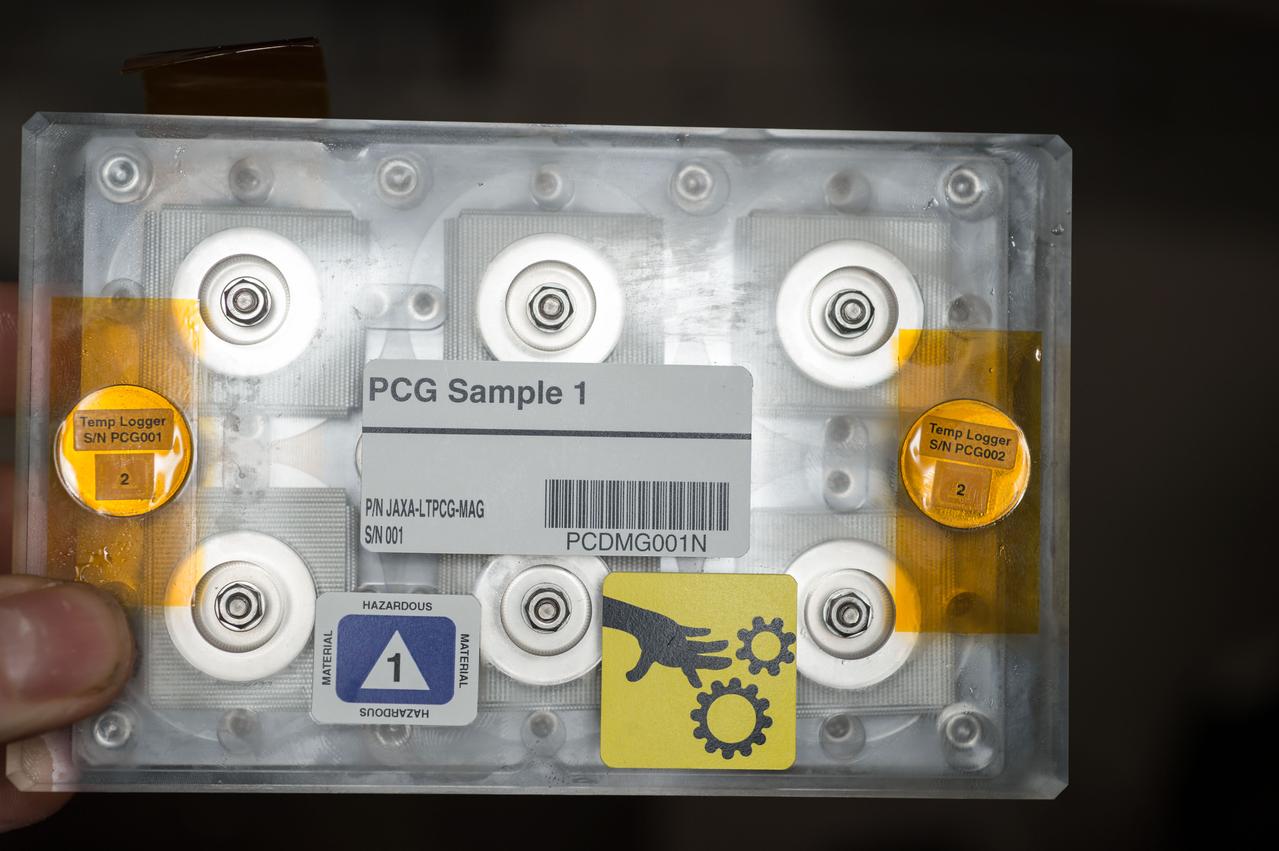

iss047e055613 (4/11/2016) --- A view of the JAXA Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) Demo Sample, in the Japanese Experiment Module (JEM) Pressurized Module (JPM) aboard the International space Station (ISS). The objective of JAXA High Quality Protein Crystal Growth Demonstration Experiment (JAXA PCG-Demo) is to grow high quality protein crystals in microgravity.
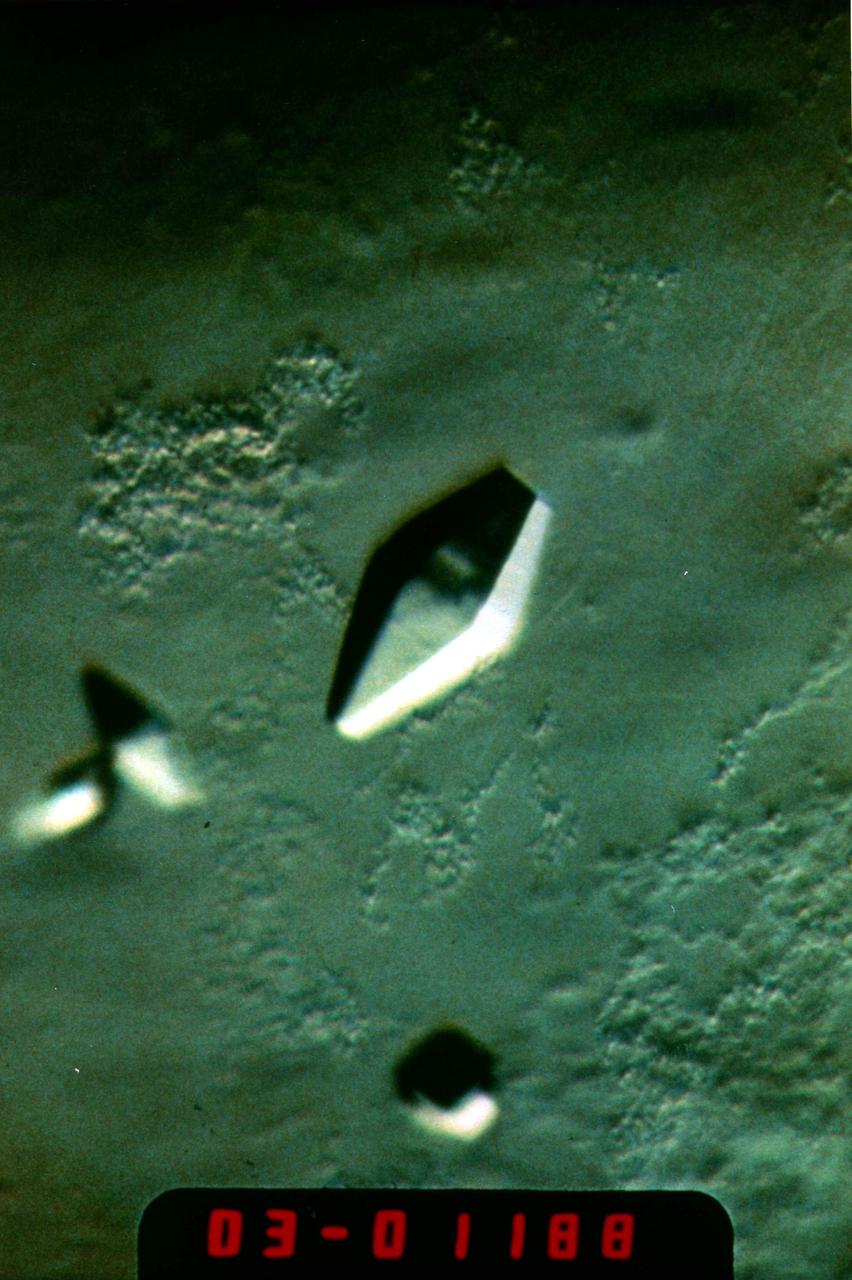
(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Porcine Elastase. This enzyme is associated with the degradation of lung tissue in people suffering from emphysema. It is useful in studying causes of this disease. Principal Investigator on STS-26 was Charles Bugg.
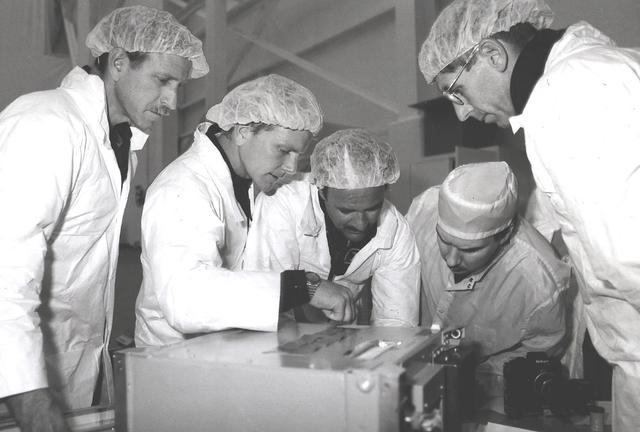

Space Shuttle Discovery (STS-26) astronauts George Nelson, John Lounge, and Richard Covey are pictured training on protein crystal growth (PCG) experiment in Marshall's Building 4708's clean room.
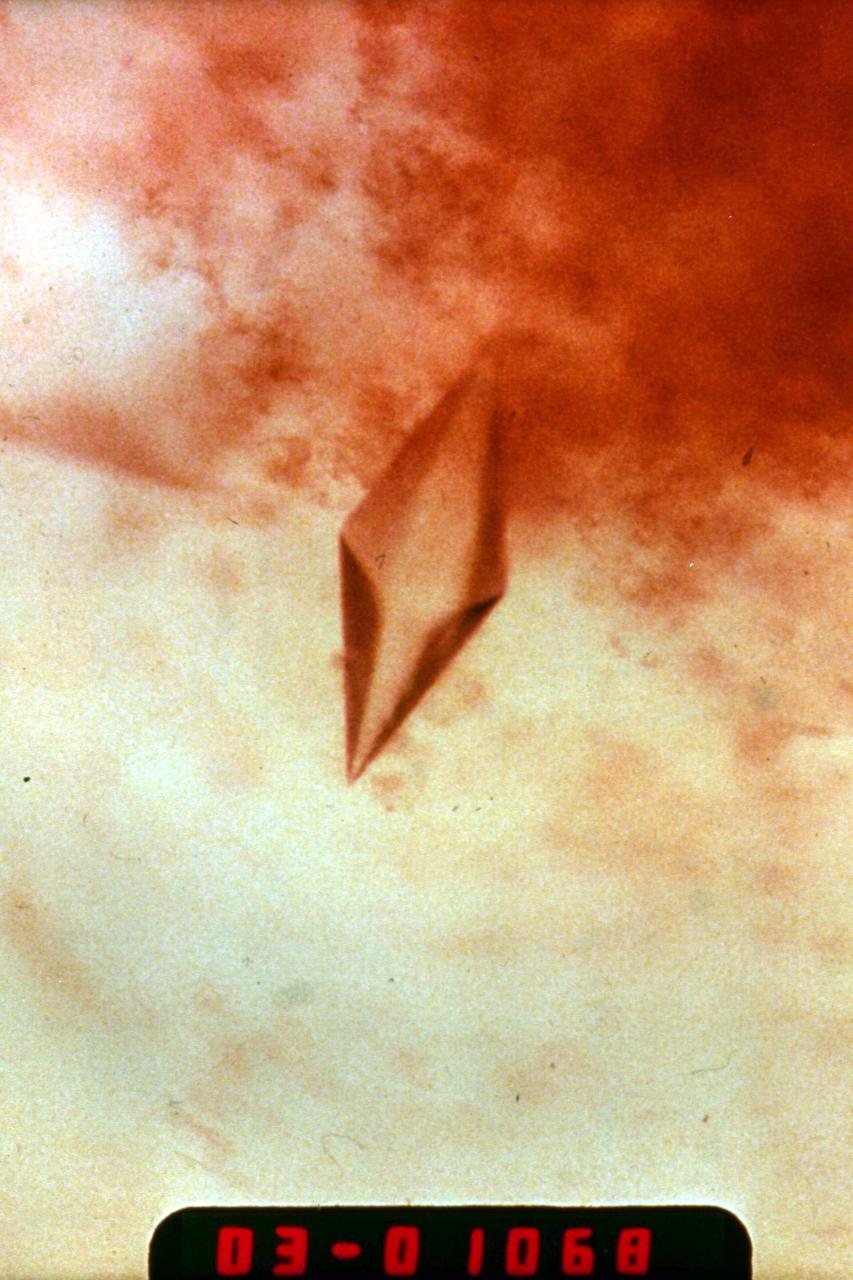
(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Renin. Enzyme produced by the kidneys, plays a major role in the chemical reaction that controls blood pressure. Principal Investigator on STS-26 was Charles Bugg.
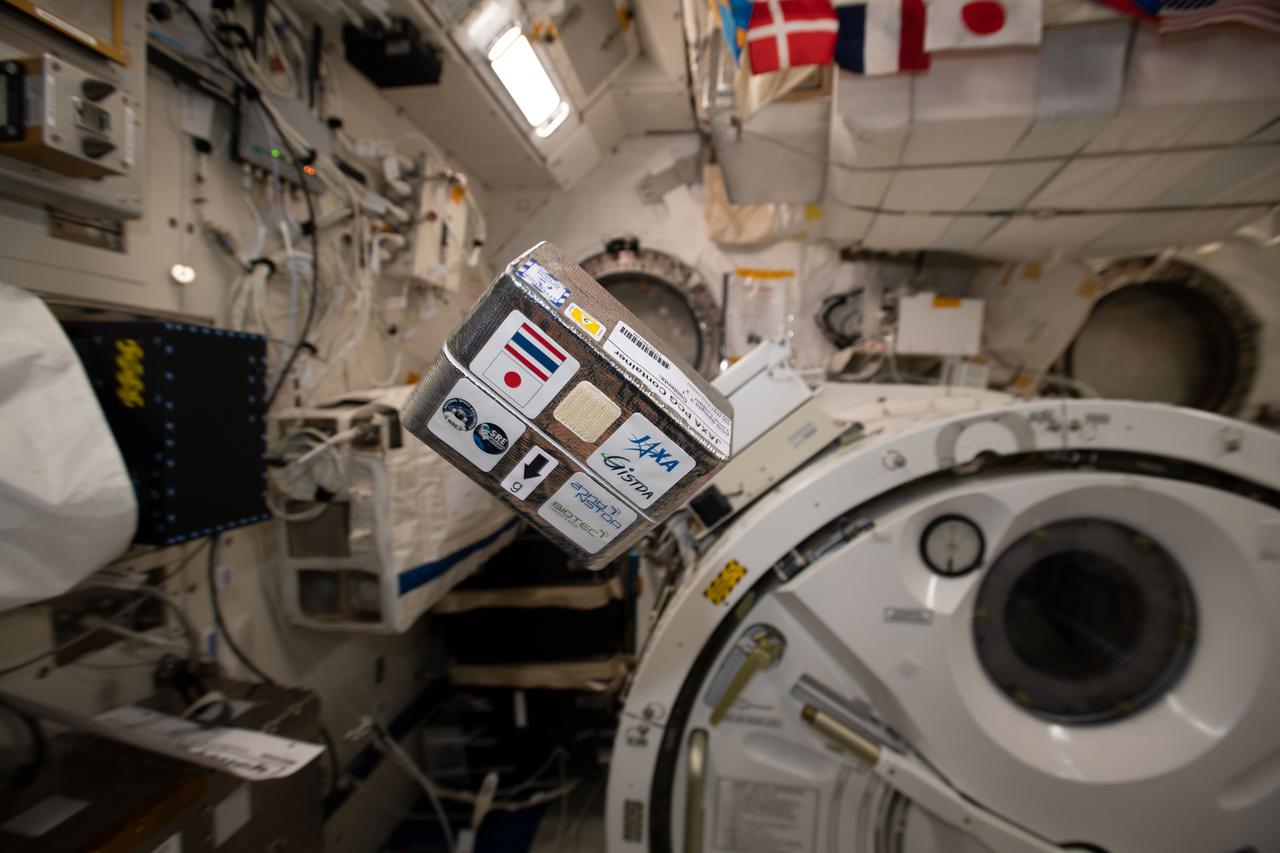

iss060e015700 --- (7/28/2019) - Photo documentation of the the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency Moderate Temperature Protein Crystallization Growth (JAXA Moderate Temp PCG) investigation in the KIBO laboratory aboard the International Space Station (ISS). This research contributes to understanding of how the microgravity environment of space can be used in a productive capacity.
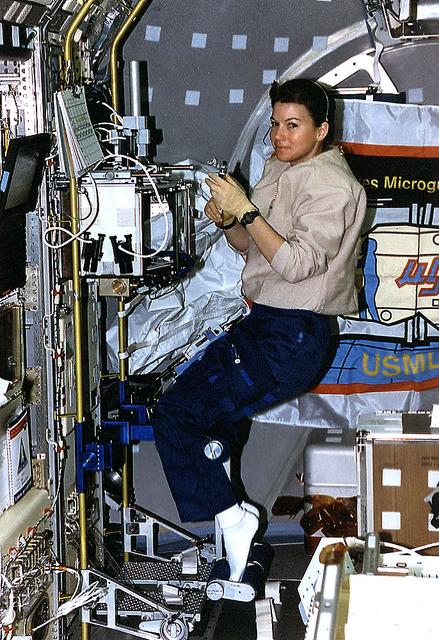

Onboard Space Shuttle Columbia (STS-73) Mission Specialists Catherine Cady Coleman works at the glovebox facility in support of the Protein Crystal Growth Glovebox (PCG-GBX) experiment in the United States Microgravity Laboratory 2 (USML-2) Spacelab science module.
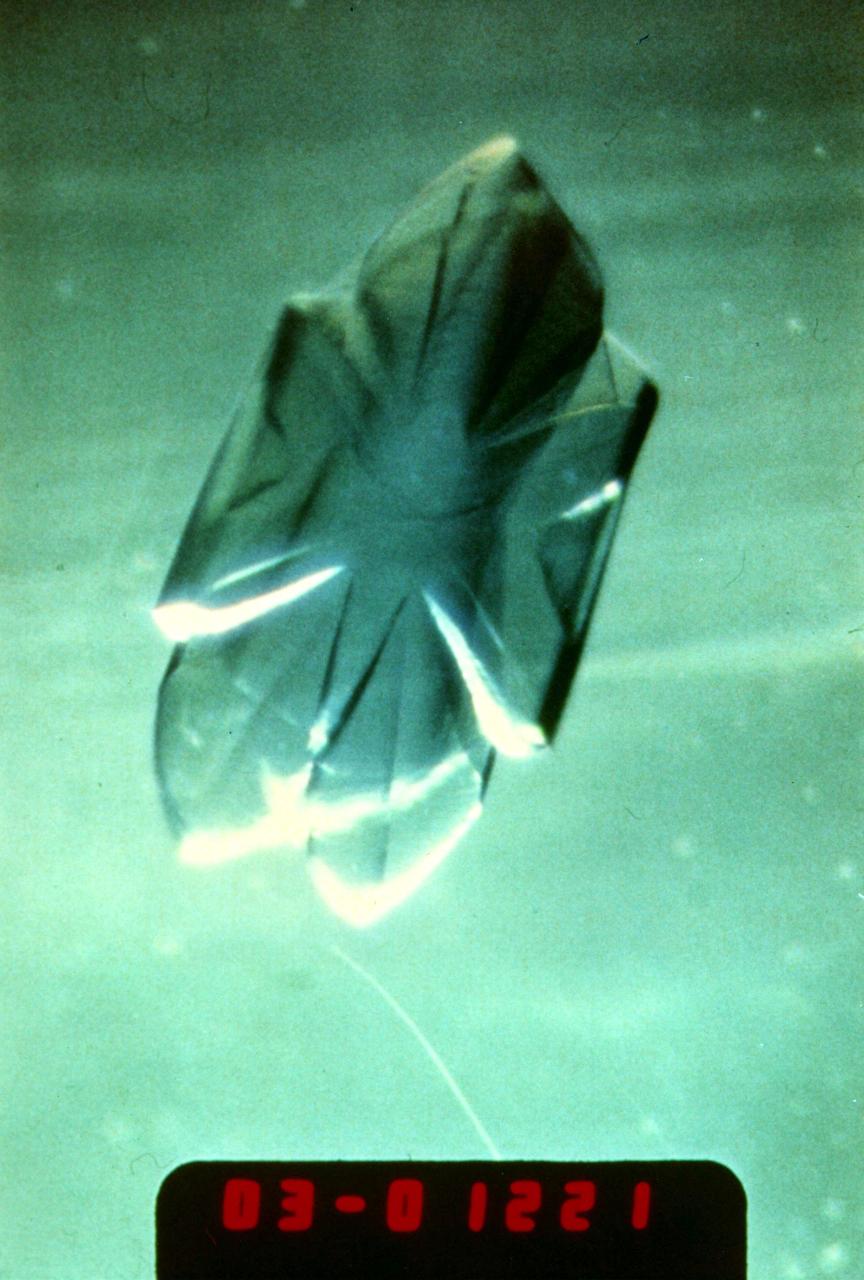

(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Isocitrate Lyase. Target enzyme for fungicides. A better understanding of this enzyme should lead to the discovery of more potent fungicides to treat serious crop diseases such as rice blast. It regulates the flow of metabolic intermediates required for cell growth. Principal Investigator for STS-26 was Charles Bugg.
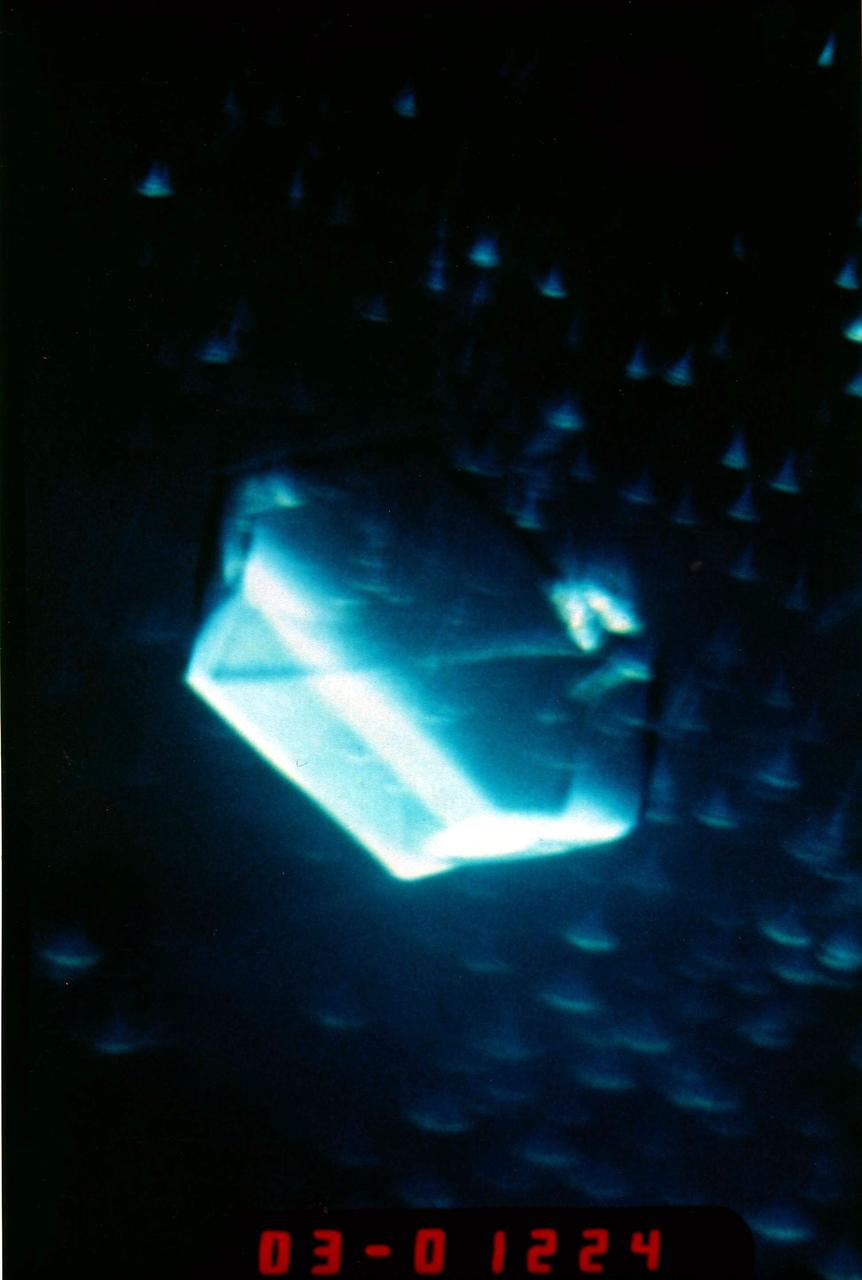

(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Isocitrate Lysase. Target enzyme for fungicides. A better understanding of this enzyme should lead to the discovery of more potent fungicides to treat serious crop diseases such as rice blast. It regulates the flow of metabolic intermediates required for cell growth. Principal Investigator on STS-26 was Charles Bugg.
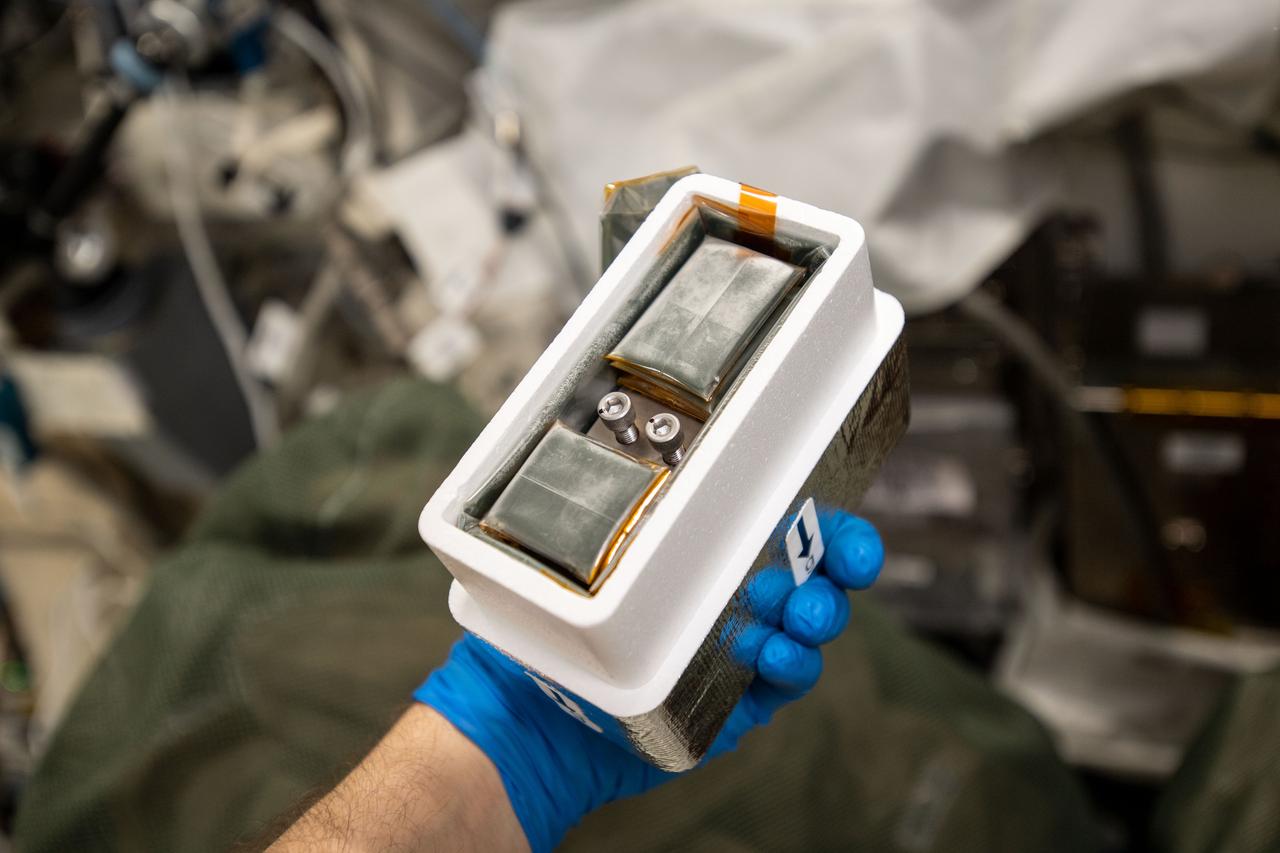

iss059e054476 (5/8/2019) - Photo documentation of the the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency Low Temperature Protein Crystallization Growth (JAXA Moderate Temp PCG) investigation in the KIBO laboratory aboard the International Space Station (ISS). This research contributes to understanding of how the microgravity environment of space can be used in a productive capacity.

iss060e015711 (7/28/2019) - Photo documentation of the the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency Moderate Temperature Protein Crystallization Growth (JAXA Moderate Temp PCG) investigation in the KIBO laboratory aboard the International Space Station (ISS). This research contributes to understanding of how the microgravity environment of space can be used in a productive capacity.
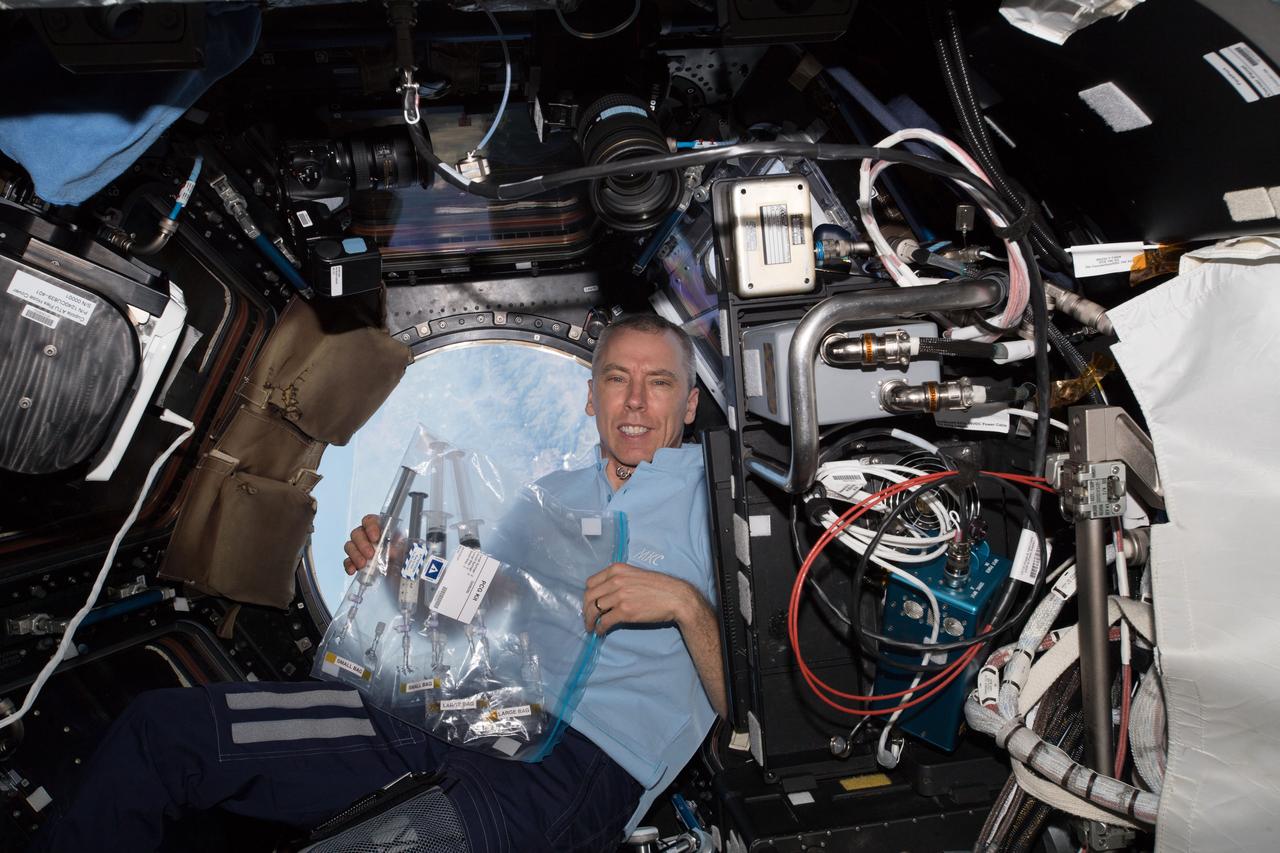

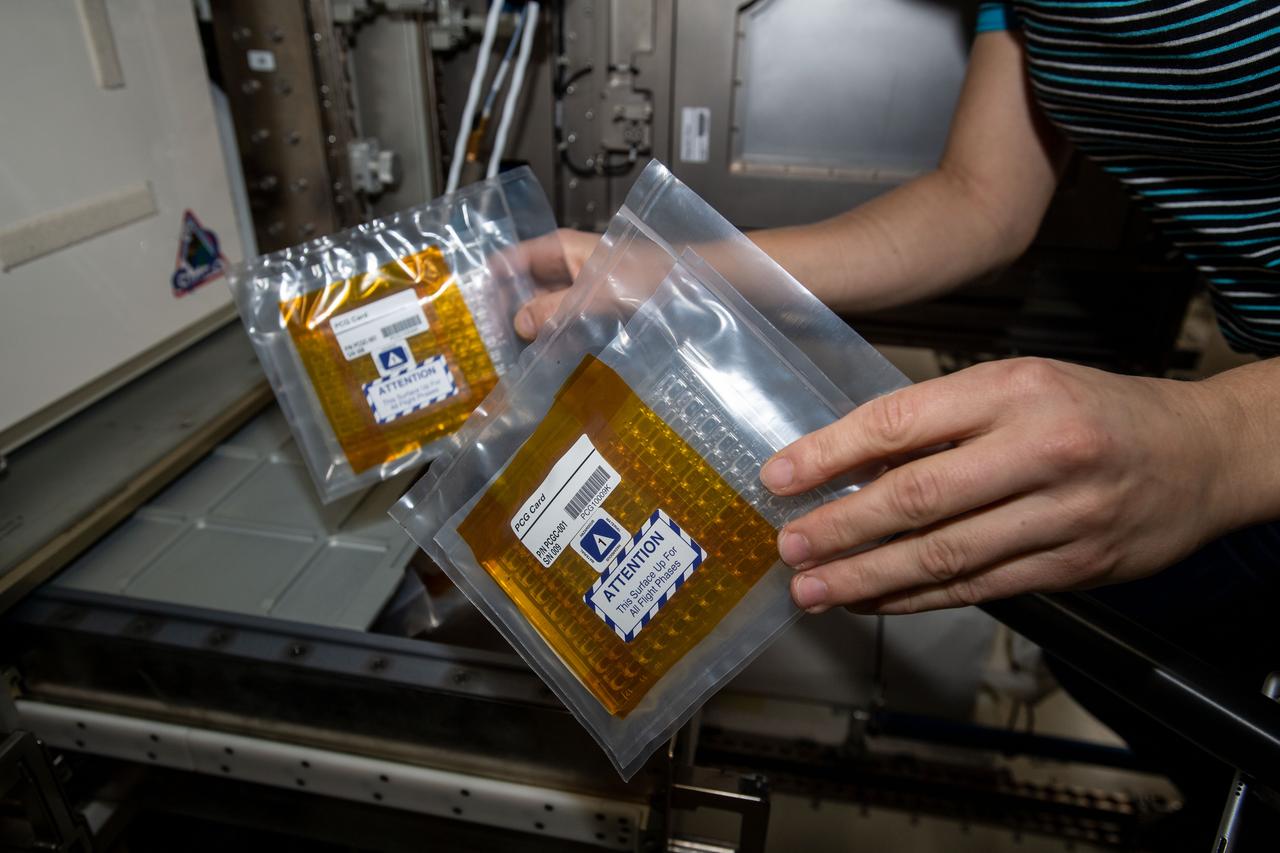
iss055e024521 (April 18, 2018) --- Flight Engineer Drew Feustel holds a bag containing samples that had been collected, documented and inspected for the Protein Crystal Growth-9 experiment. Feustel was in the Cupola as the International Space Station was orbiting over southern Mexico near the Guatemalan border.
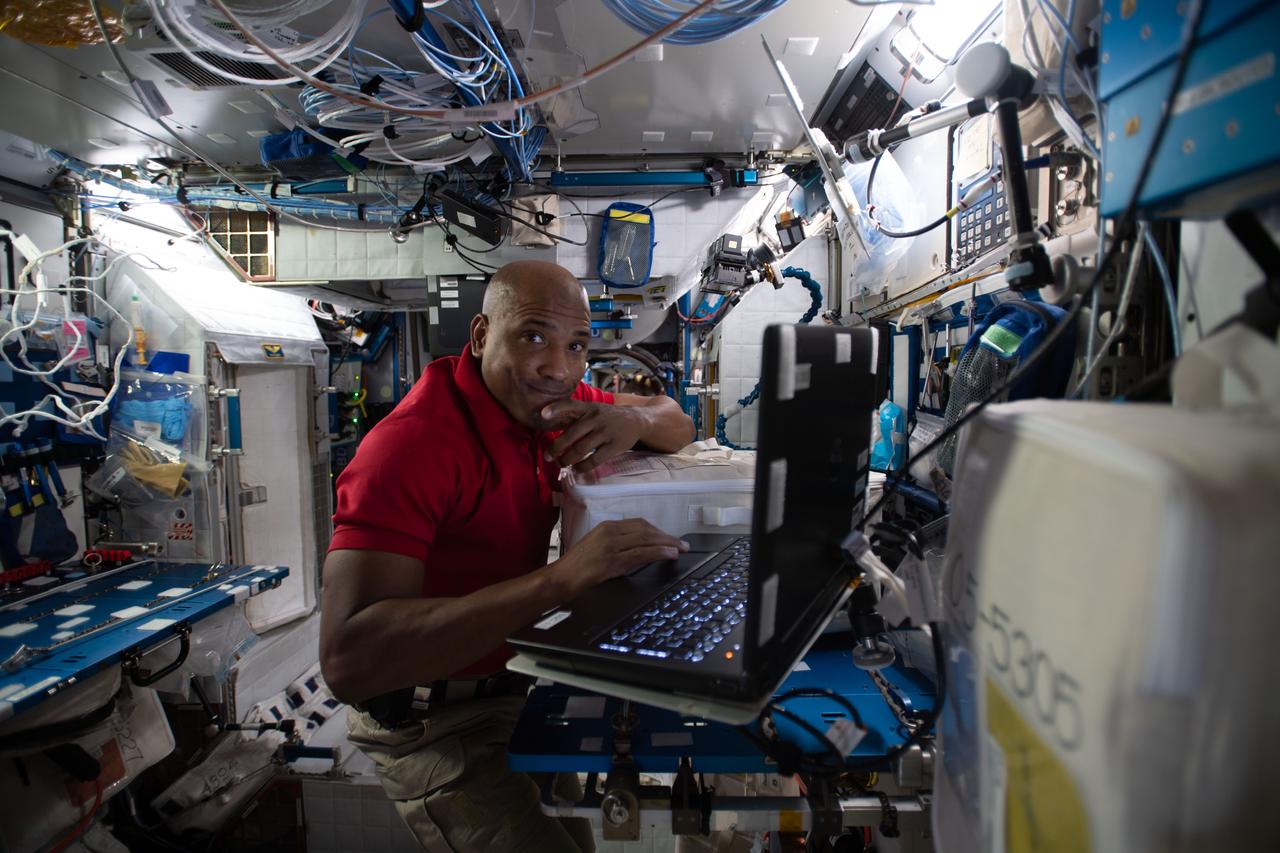

iss064e011646 (Dec. 10, 2020) --- NASA astronaut and Expedition 64 Flight Engineer Victor Glover reviews procedures on a computer for the Monoclonal Antibodies Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment inside the Harmony module. The biomedical study crystallizes therapeutic monoclonal antibodies of higher quality than Earth and could accelerate the development of advanced therapies that target cancer cells.
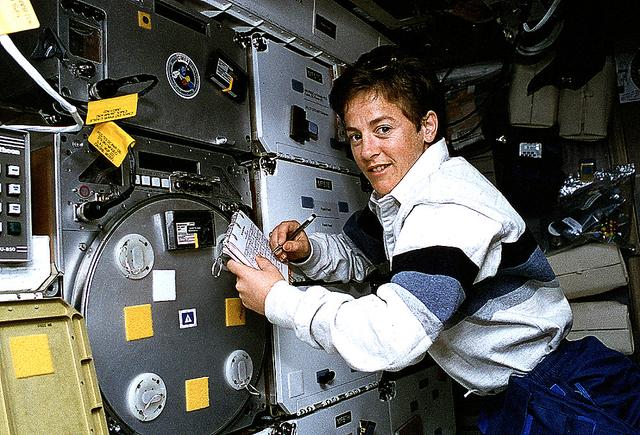

Astronaut Wendy B. Lawrence, flight engineer and mission specialist for STS-67, scribbles notes on the margin of a checklist while monitoring an experiment on the Space Shuttle Endeavour's mid-deck. The experiment is the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG), which takes up locker space near the Commercial Materials Dispersion Apparatus Instruments Technology Associates Experiment (CMIX).

(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Gamma-Interferon. Stimulates the body's immune system and is used clinically in the treatment of cancer. Potential as an anti-tumor agent against solid tumors as well as leukemia's and lymphomas. It has additional utility as an anti-ineffective agent, including antiviral, anti-bacterial, and anti-parasitic activities. Principal Investigator on STS-26 was Charles Bugg.
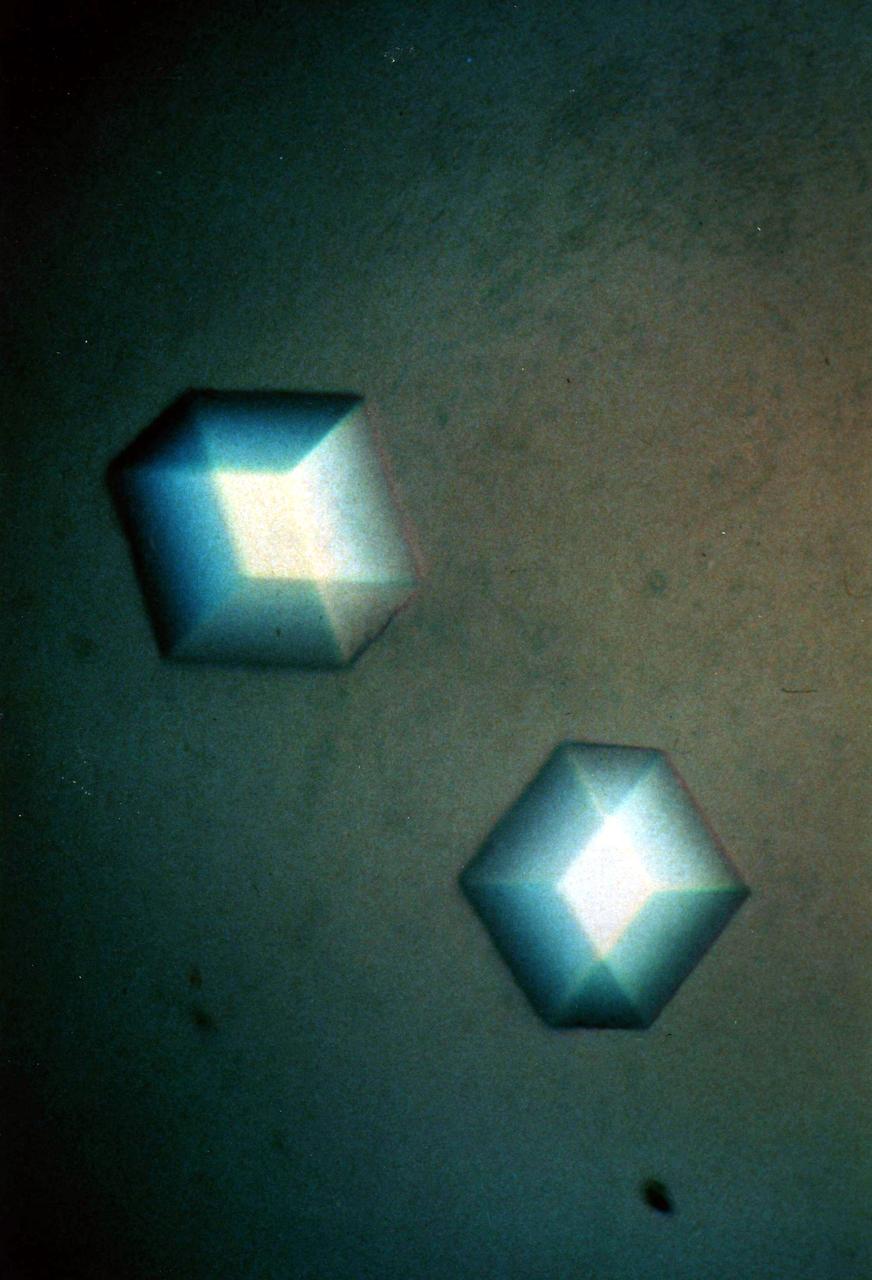
(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Canavalin. The major storage protein of leguminous plants and a major source of dietary protein for humans and domestic animals. It is studied in efforts to enhance nutritional value of proteins through protein engineerings. It is isolated from Jack Bean because of it's potential as a nutritional substance. Principal Investigator on STS-26 was Alex McPherson.
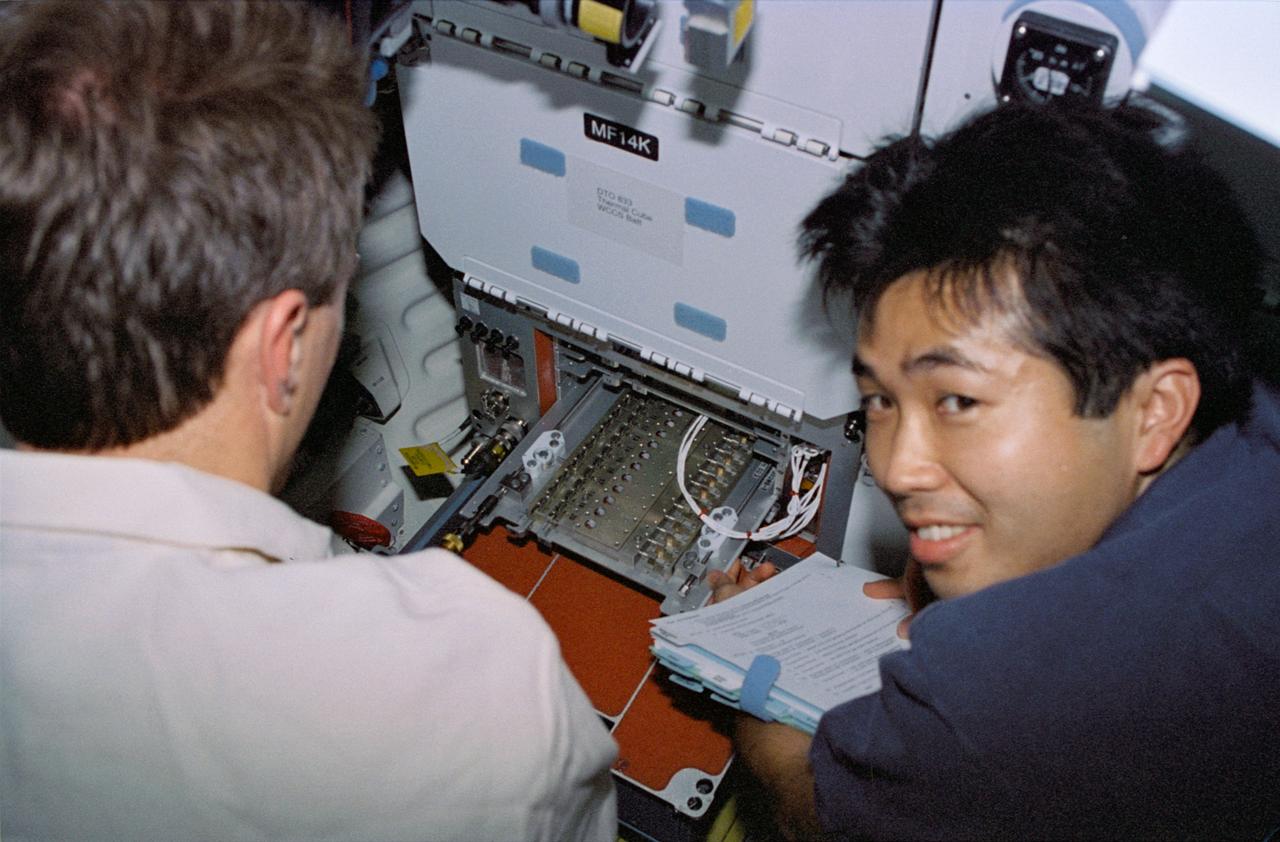
STS072-310-007 (11-20 Jan. 1996) --- Astronauts Brent W. Jett Jr. (left) and Koichi Wakata work with the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiment at the Single Locker Thermal Enclosure System (STES) on the Space Shuttle Endeavour’s mid-deck. Jett, making his first flight in space, served as the crew’s pilot, while Wakata served as a mission specialist. Wakata, also a first time Shuttle crew member, represents Japan’s National Space Development Agency (NASDA).
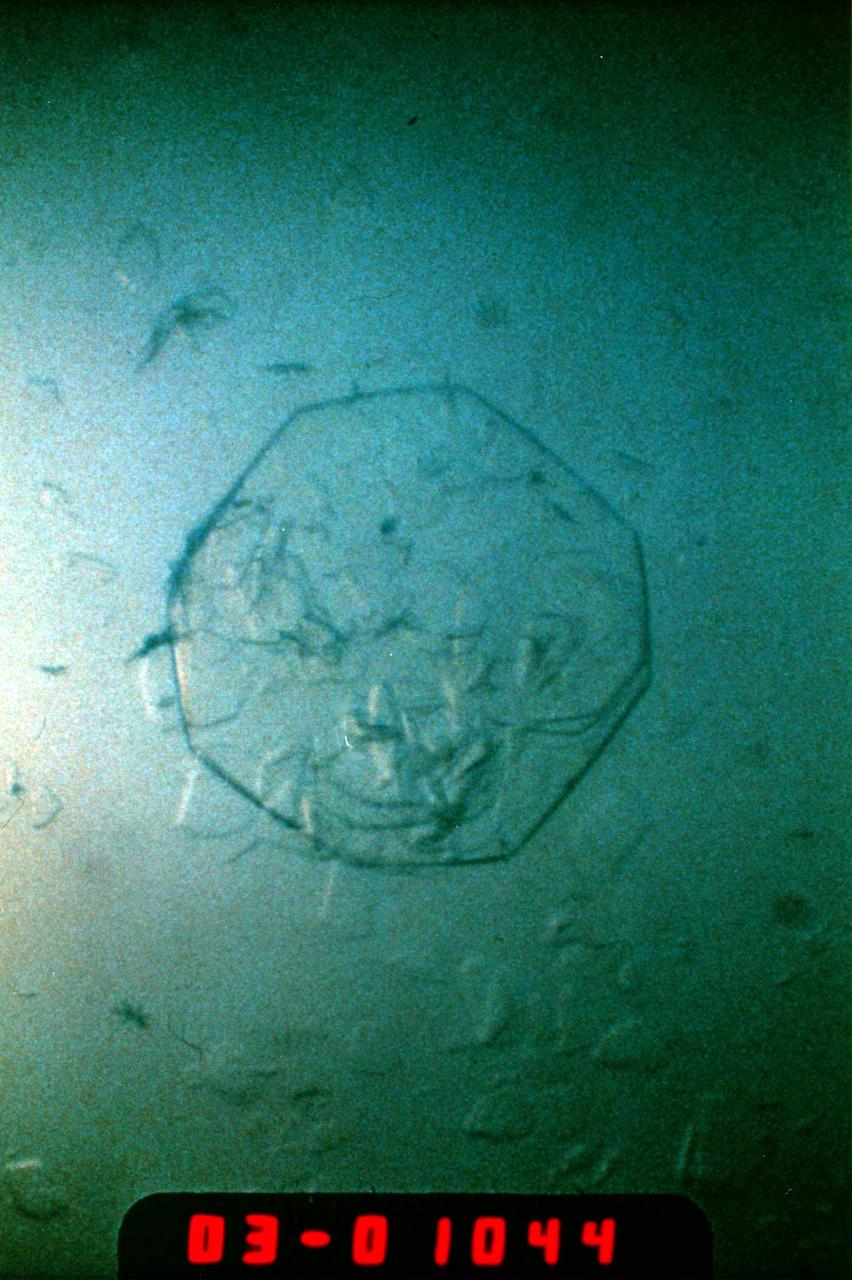
(PCG) Protein Crystal Growth Human Serum Albumin. Contributes to many transport and regulatory processes and has multifunctional binding properties which range from various metals, to fatty acids, hormones, and a wide spectrum of therapeutic drugs. The most abundant protein of the circulatory system. It binds and transports an incredible variety of biological and pharmaceutical ligands throughout the blood stream. Principal Investigator on STS-26 was Larry DeLucas.
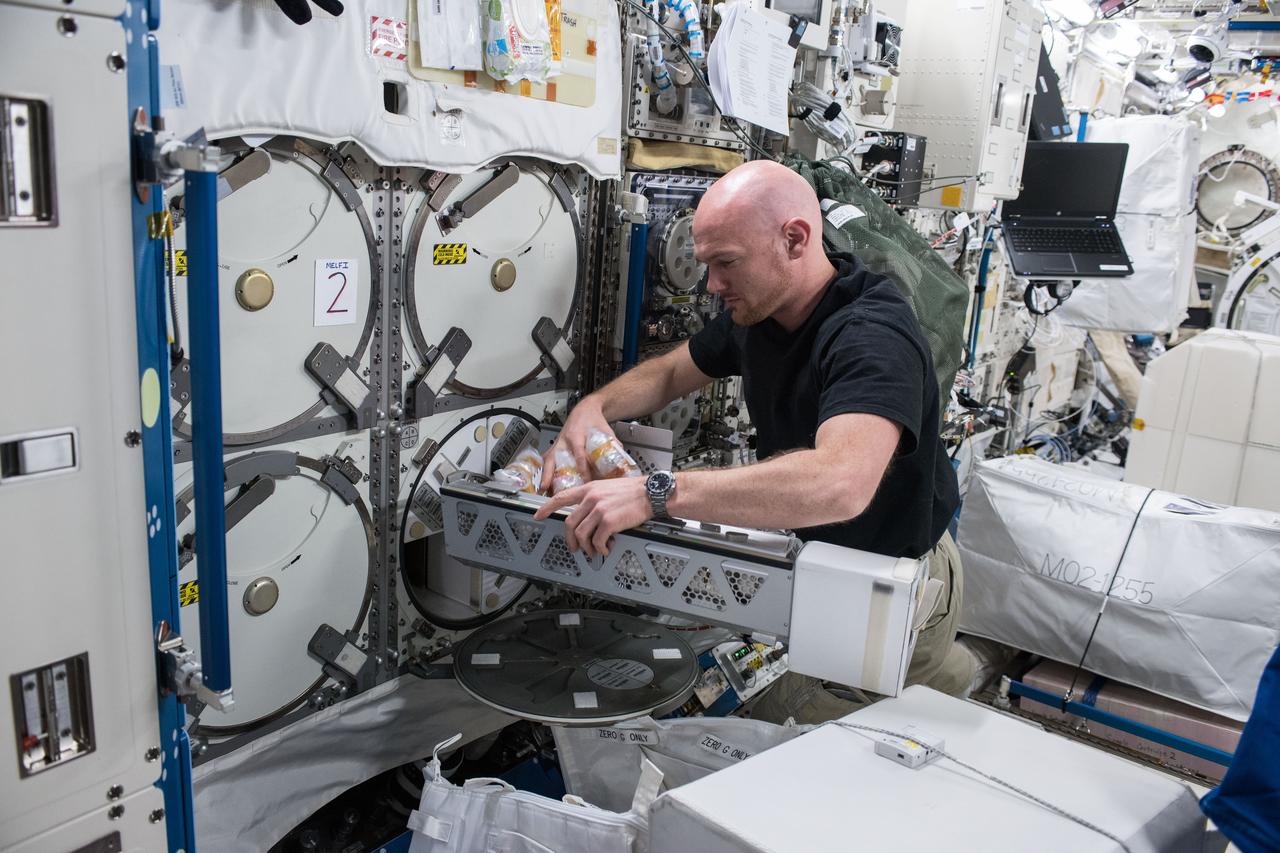

iss056e075950 (July 3, 2018) --- Astronaut Alexander Gerst of ESA (European Space Agency) works inside the Japanese Kibo laboratory module retrieving Protein Crystal Growth samples from a science freezer, also known as the Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI).
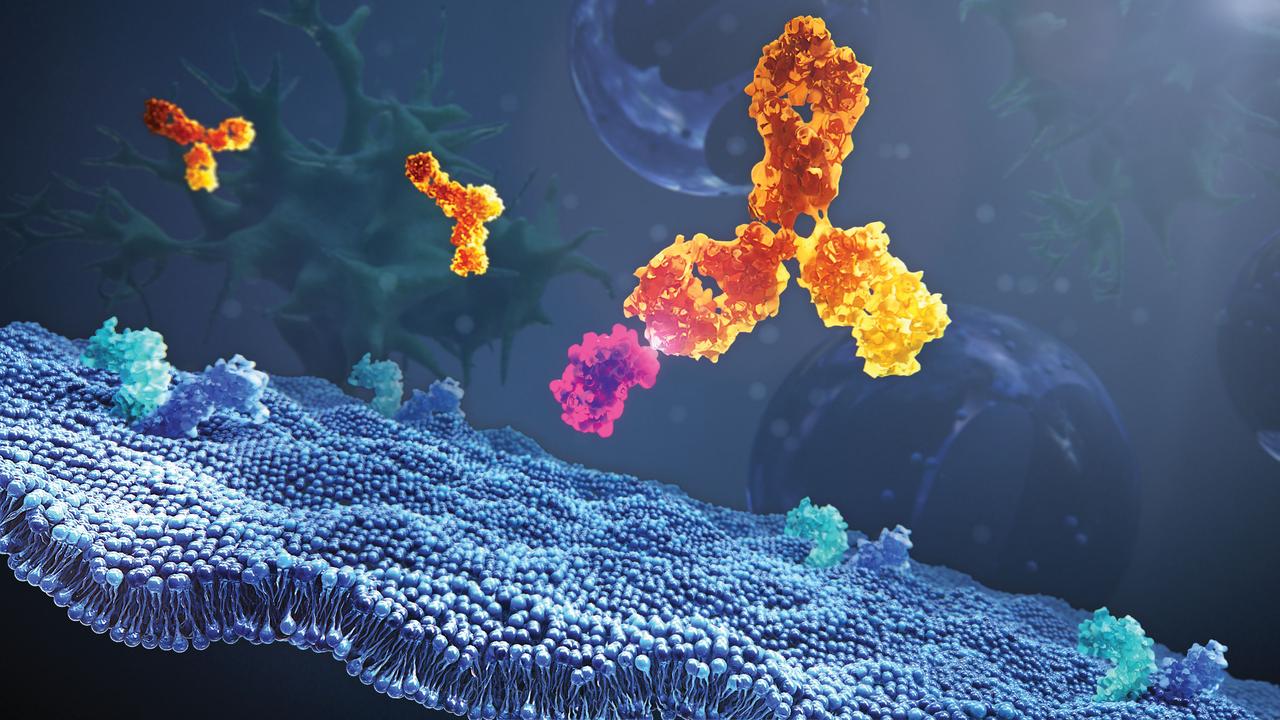
jsc2019e039826 (7/27/2017) --- This preflight image shows a monoclonal antibody binding to a ligand in the inter-cellular space. Monocronal antibodies can fight a wide range of diseases by very selectively binding to their targets, thus leaving healthy tissues and cells intact. Monoclonal Antibody Production and Stability in Microgravity-Formulation Study (CASIS PCG 19) compares the impact of microgravity on antibody formulation stability to stability trends observed on Earth. The study may broaden an understanding of the routes of antibody degradation and, as space travel becomes more common, it may improve knowledge of monoclonal antibody therapeutic stability for treating patients in space environments.
iss057e106419 (Nov. 30, 2018) --- Samples from the Protein Crystal Growth Card are examined using a microscope for an experiment observing protein crystals associated with Parkinson’s disease to potentially improve treatments on Earth. Crystallization of LRRK2 Under Microgravity Conditions-2 (CASIS PCG 16) evaluates growth of Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) protein crystals in microgravity. LRRK2 is implicated in Parkinson’s disease, but crystals of the protein grown on Earth are too small and compact to study. Detailed analysis of larger, space-grown crystals can define the protein’s exact shape and morphology and help scientists better understand the disease’s pathology.
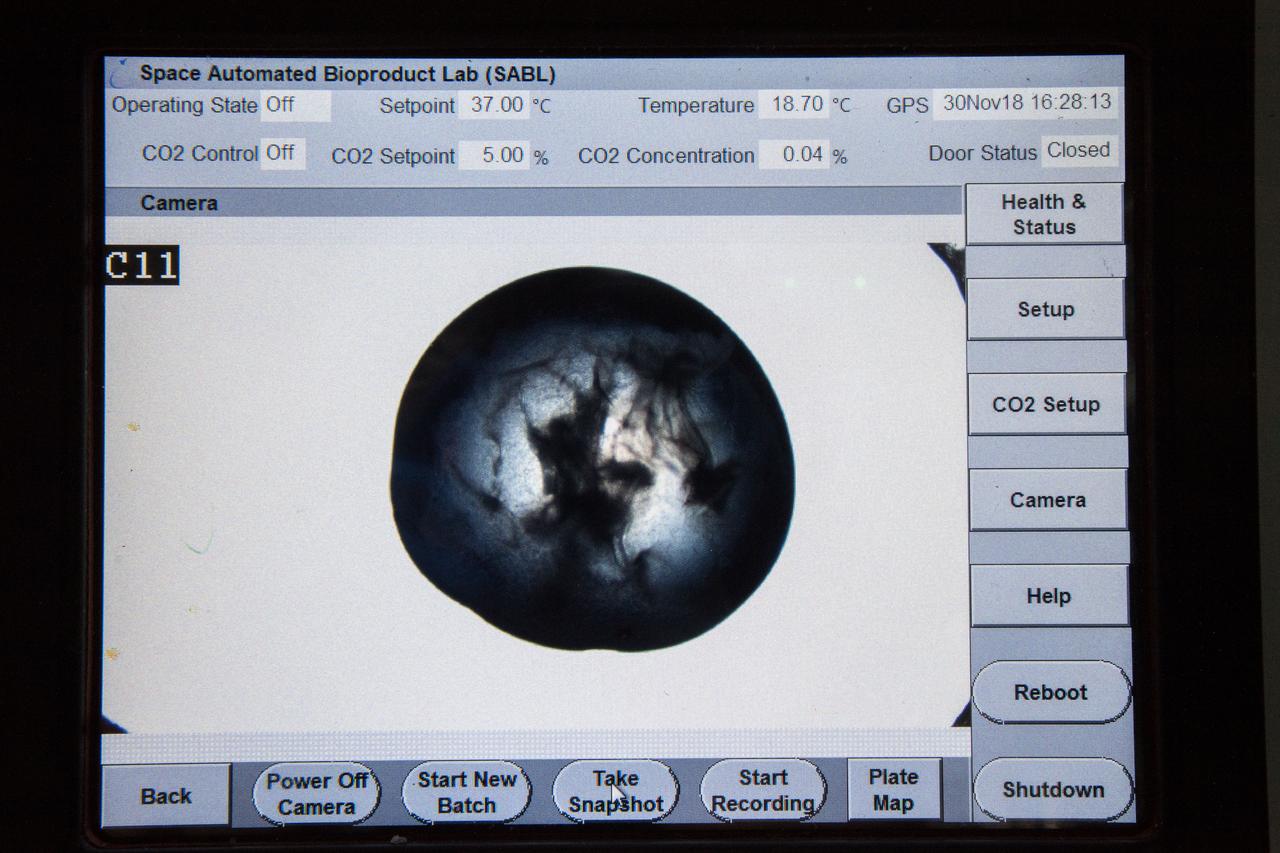
iss057e106417 (Nov. 30, 2018) --- Samples from the Protein Crystal Growth Card are examined using a microscope for an experiment observing protein crystals associated with Parkinson’s disease to potentially improve treatments on Earth. Crystallization of LRRK2 Under Microgravity Conditions-2 (CASIS PCG 16) evaluates growth of Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) protein crystals in microgravity. LRRK2 is implicated in Parkinson’s disease, but crystals of the protein grown on Earth are too small and compact to study. Detailed analysis of larger, space-grown crystals can define the protein’s exact shape and morphology and help scientists better understand the disease’s pathology.
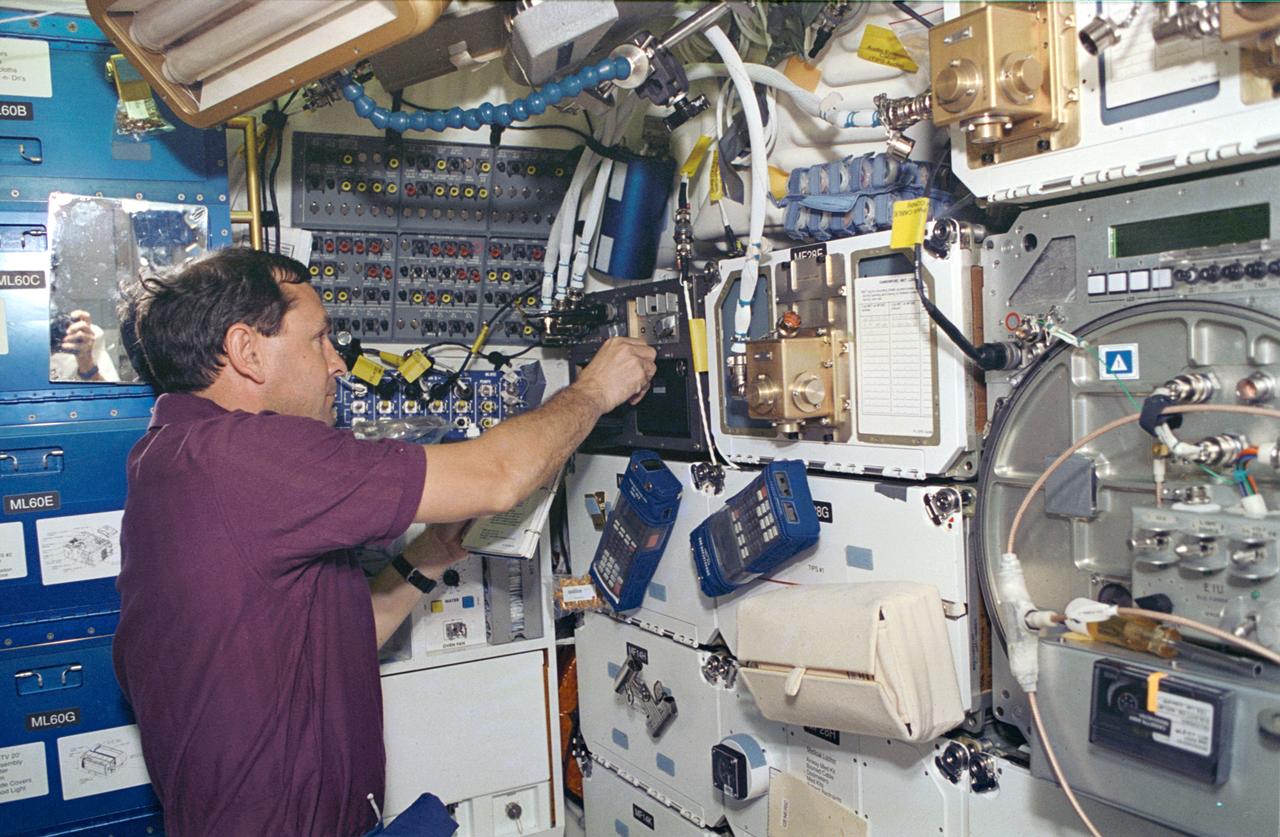

STS066-14-021 (3-14 Nov 1994) --- On the Space Shuttle Atlantis' mid-deck, astronaut Curtis L. Brown, Jr., pilot, works with the Space Acceleration Measurement System (SAMS), which is making its eleventh Shuttle flight. This system supports the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) experiments onboard by collecting and recording data characterizing the microgravity environment in the Shuttle mid-deck. Brown joined four other NASA astronauts and a European Space Agency (ESA) astronaut for 11-days aboard Atlantis in support of the Atmospheric Laboratory for Applications and Science (ATLAS-3) mission.
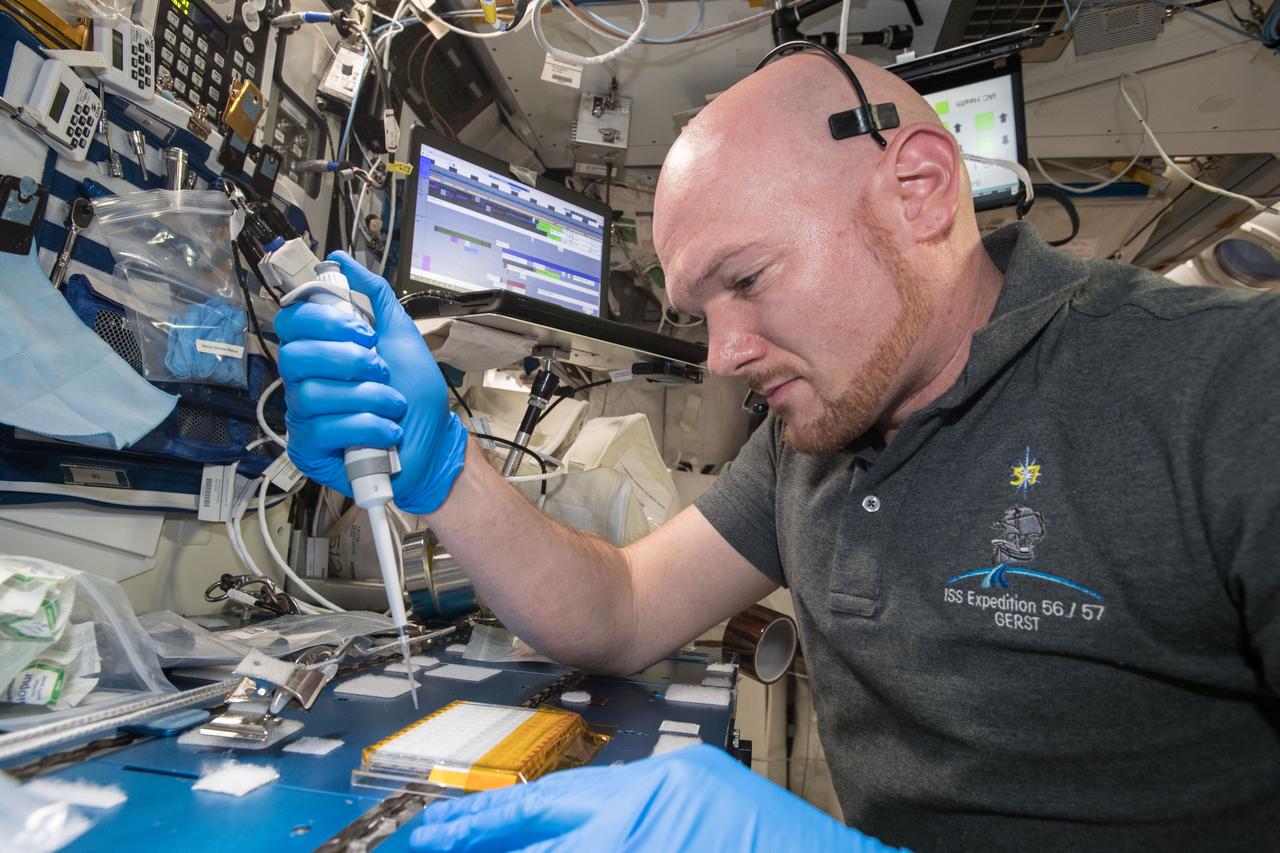

iss057e106231 (Nov. 26, 2018) --- European Space Agency (ESA) asrtonaut Alexander Gerst uses a uses a pipette to transfer a protein solution into the Protein Crystal Growth Card for an experiment observing protein crystals associated with Parkinson’s disease to potentially improve treatments on Earth. Crystallization of LRRK2 Under Microgravity Conditions-2 (CASIS PCG 16) evaluates growth of Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) protein crystals in microgravity. LRRK2 is implicated in Parkinson’s disease, but crystals of the protein grown on Earth are too small and compact to study. Detailed analysis of larger, space-grown crystals can define the protein’s exact shape and morphology and help scientists better understand the disease’s pathology.

iss062e087808 (3/11/2020) --- A view of Protein Crystal Growth-10 experiment hardware inside JAXA's (Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency) Kibo laboratory module aboard the International Space Station (ISS). Microgravity Crystallization of Glycogen Synthase-Glycogenin Protein Complex (CASIS PCG 10) crystallizes human glycogen synthase proteins on the space station. Determining the structure of the human glycogen synthase and full-length glycogenin protein complex could facilitate the development of treatments on Earth for metabolic disorders such as Type 2 diabetes, obesity, rare genetic disorders, and some forms of cancer.

STS050-254-007 (25 June-9 July 1992) --- Lawrence J. DeLucas, payload specialist, handles a Protein Crystal Growth (PCG) sample at the multipurpose glovebox aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Astronaut Bonnie J. Dunbar, payload commander, communicates with ground controllers about the Solid Surface Combustion Experiment (SSCE), one of the United States Microgravity Laboratory 1’s (USML-1) three experiments on Rack 10. Five other crew members joined the pair for a record-setting 14-days of scientific data gathering.

iss056e195892 (Sept. 27, 2018) --- Flight Engineer Serena Auñón-Chancellor of NASA monitors the arrival of the H-II Transfer Vehicle-7 (HTV-7) before it was captured during Expedition 56 by Commander Drew Feustel operating the Canadarm2 robotic arm. The HTV-7 from the Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) delivered six new lithium-ion batteries and adapter plates to upgrade the International Space Station's power systems. The Japanese resupply ship also delivered science experiments and research hardware including a new sample holder for the Electrostatic Levitation Furnace (JAXA-ELF), a protein crystal growth experiment at low temperatures (JAXA LT PCG), an investigation that looks at the effect of microgravity on bone marrow (MARROW), a Life Sciences Glovebox, and additional EXPRESS Racks.
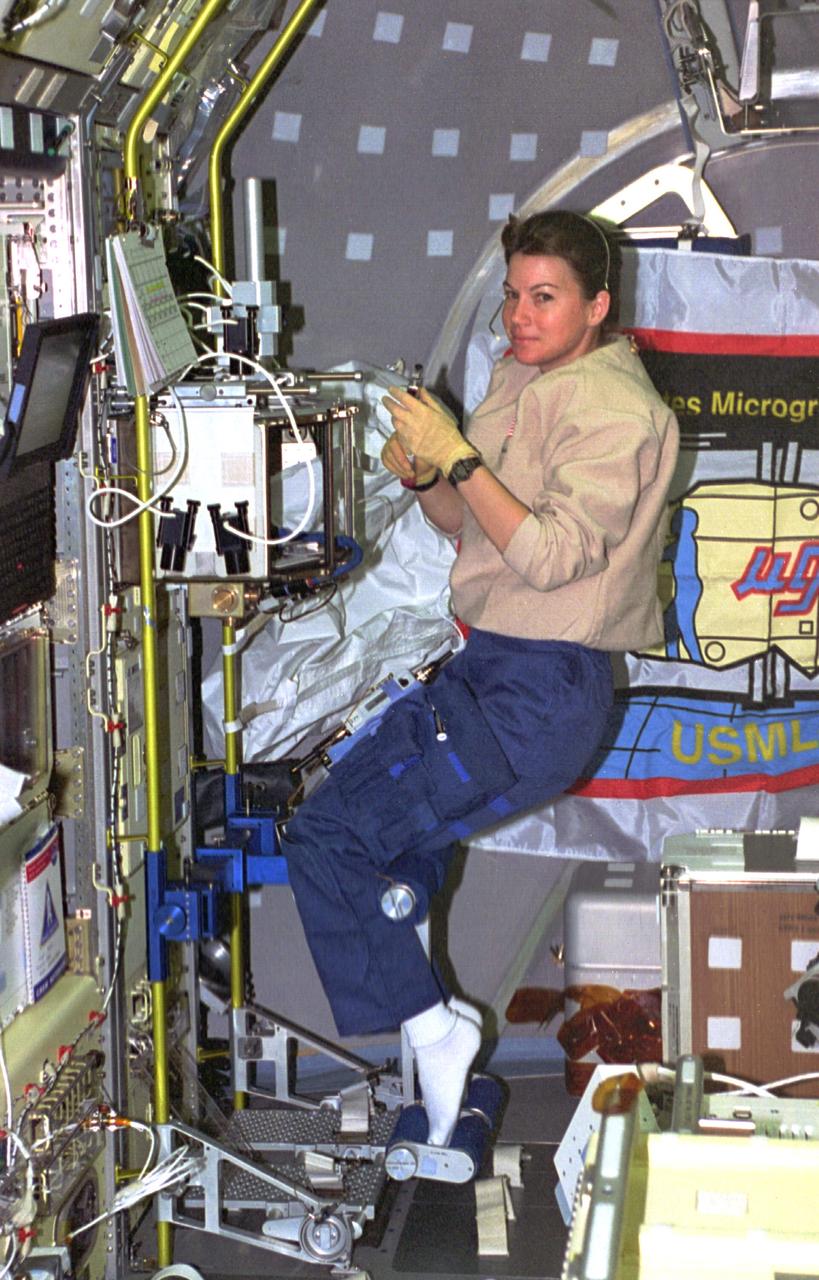

STS073-105-011 (20 October-5 November 1995) --- Astronaut Catherine G. Coleman, STS-73 mission specialist, settles in for a session of work at the glovebox on the starboard side of the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) module. Coleman was joined by four other NASA astronauts and two guest researchers for almost 16 days of research aboard the Space Shuttle Columbia in Earth-orbit.
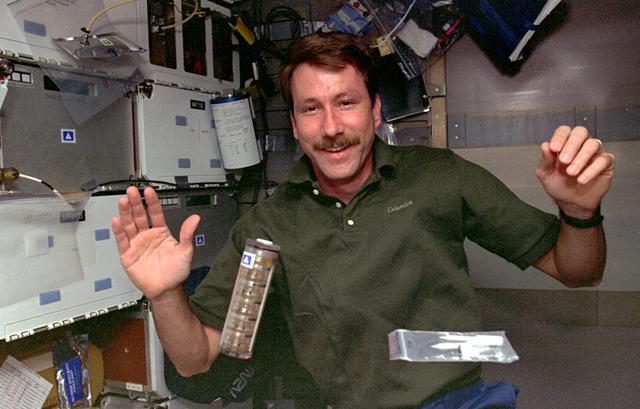

STS073-351-009 (20 October - 5 November 1995) --- Astronaut Kent V. Rominger, STS-73 pilot, retrieves a protein sample on the middeck of the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Columbia. Rominger, along with four other NASA astronauts and two guest researchers, spent 16 full days in space in support of the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission.
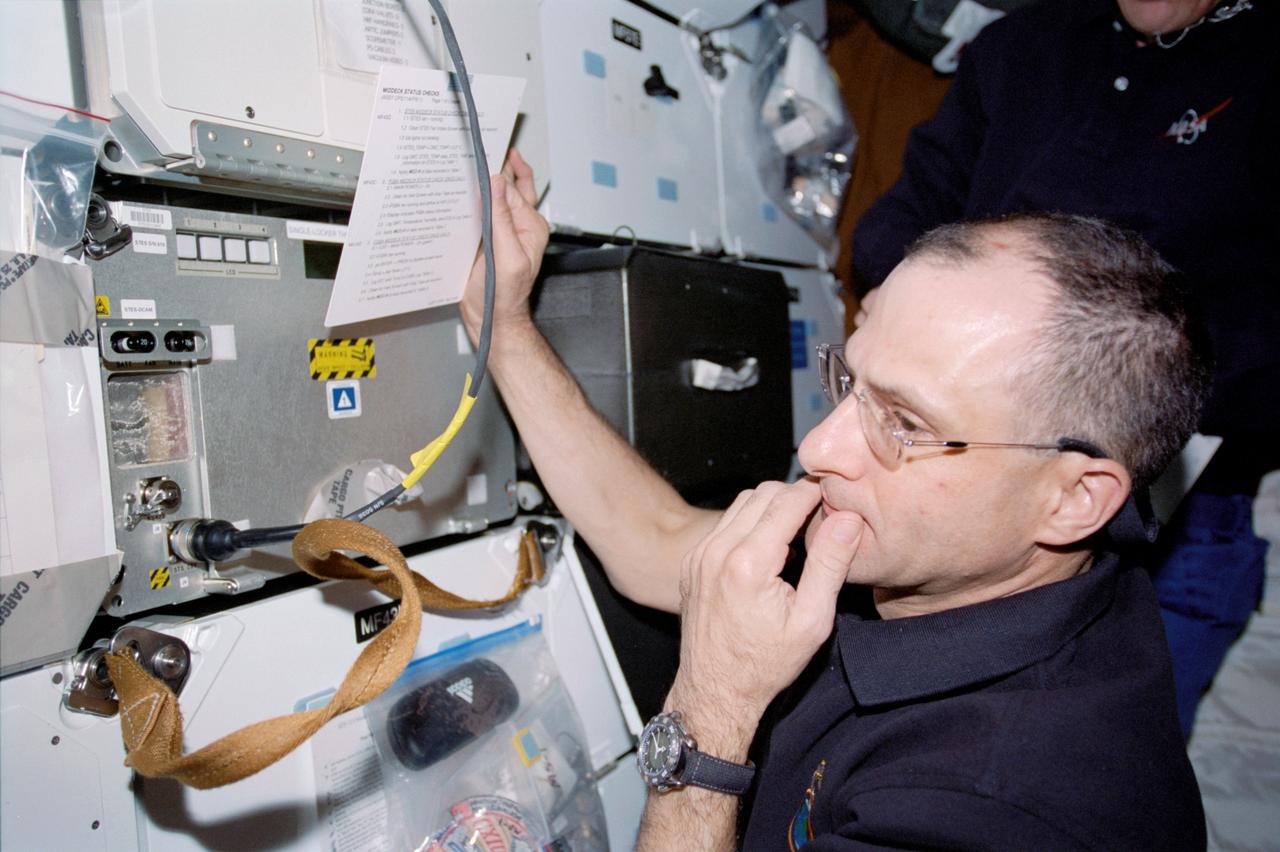

STS113-313-021 (23 November – 7 December 2002) --- Astronaut Donald R. Pettit, Expedition Six NASA ISS science officer, pictured on the middeck of the Space Shuttle Endeavour.
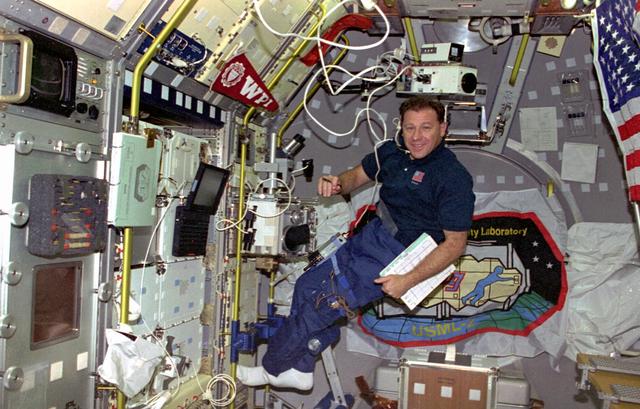

STS073-106-001 (20 October-5 November 1995) --- Payload specialist Albert Sacco Jr. takes direction from a crew mate out of frame onboard the United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) science module in the cargo bay of the Space Shuttle Columbia. Sacco was about to check out an experiment in a glovebox, which represented one of the busier areas during the 16-day USML-2 flight.
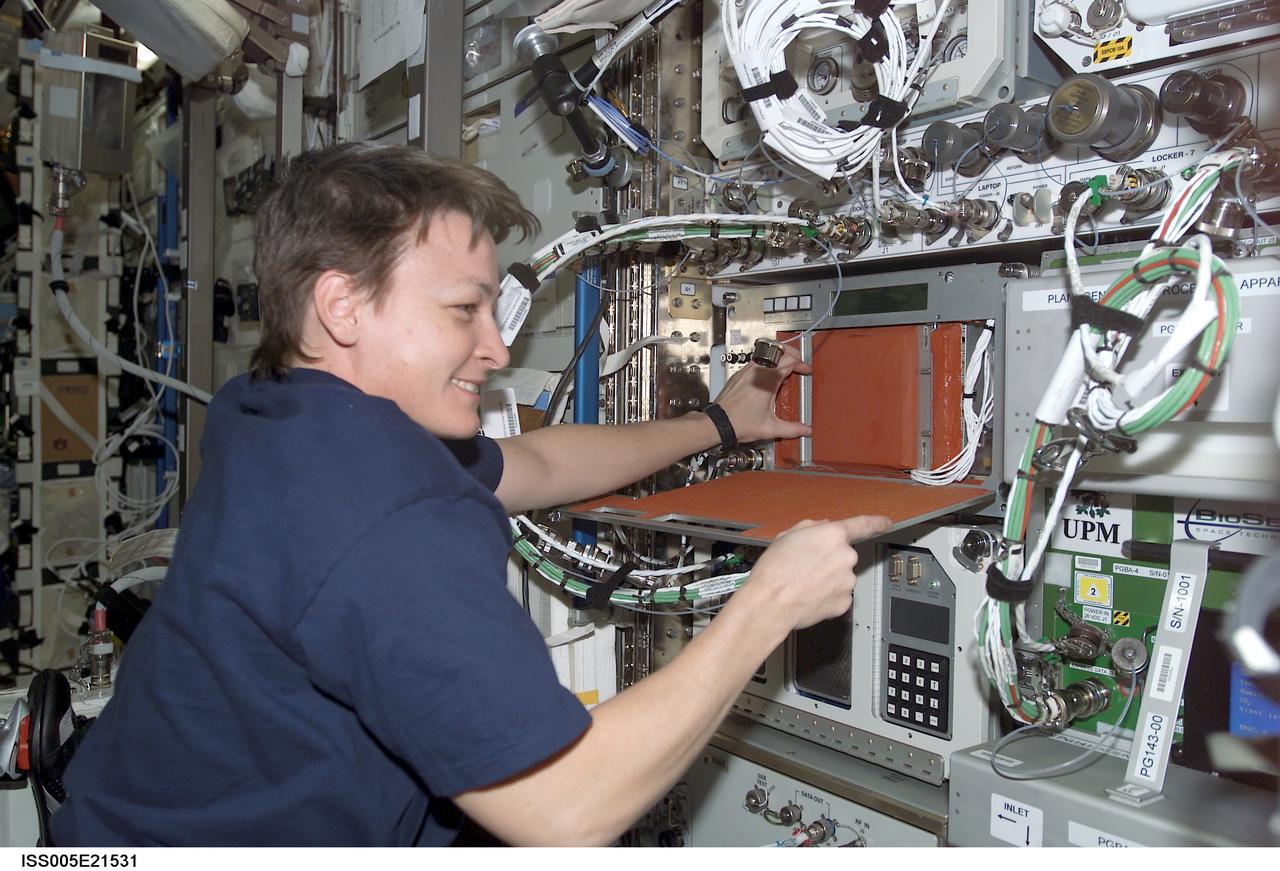

ISS005-E-21531 (24 November 2002) --- Astronaut Peggy A. Whitson, Expedition Five science officer, works with an experiment in the Destiny laboratory as her tenure on board the International Space Station (ISS) winds down.
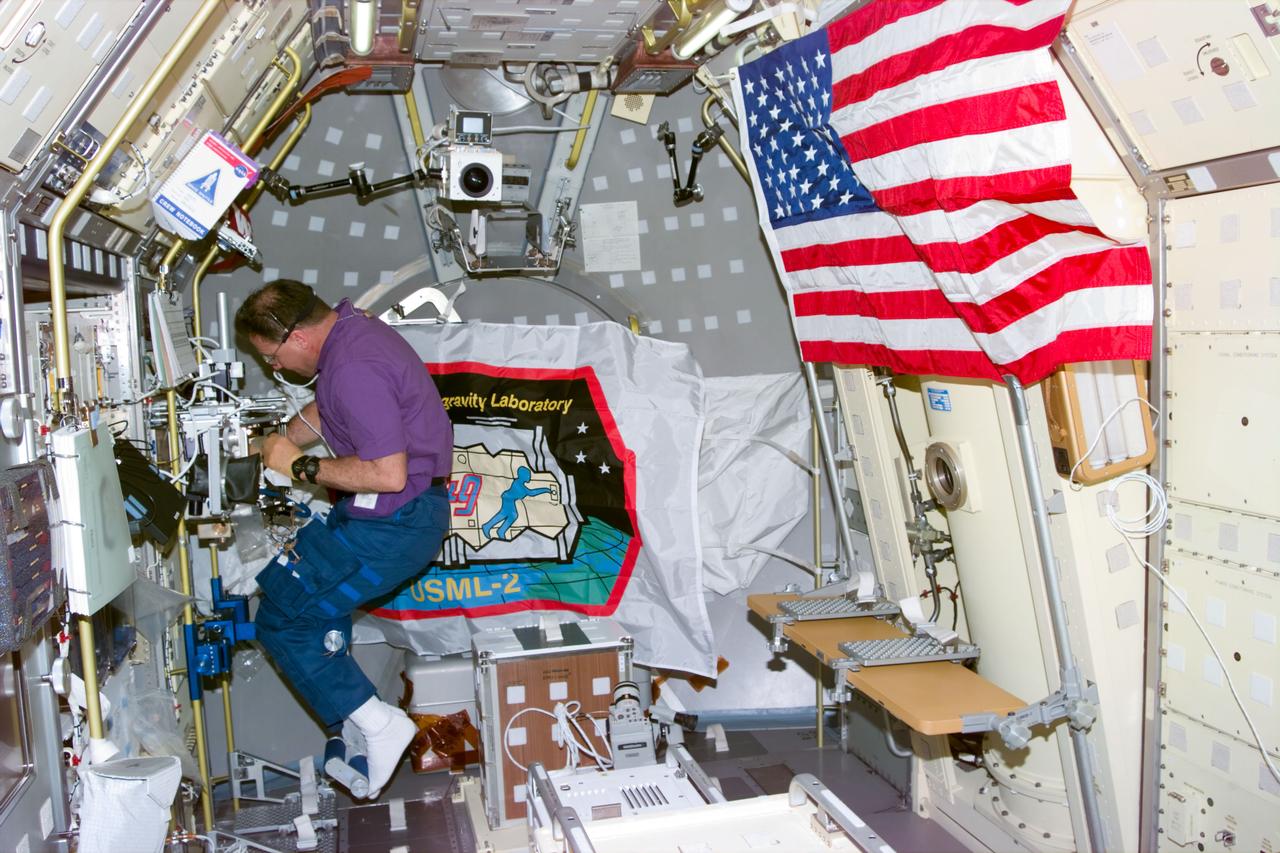

STS073-E-5024 (23 Oct. 1995)--- Albert Sacco Jr., STS-73 payload specialist, works in the Glovebox on the portside of the science module aboard the space shuttle Columbia in Earth orbit. This frame was exposed with the color Electronic Still Camera (ESC) assigned to the scheduled 16-day United States Microgravity Laboratory (USML-2) mission.
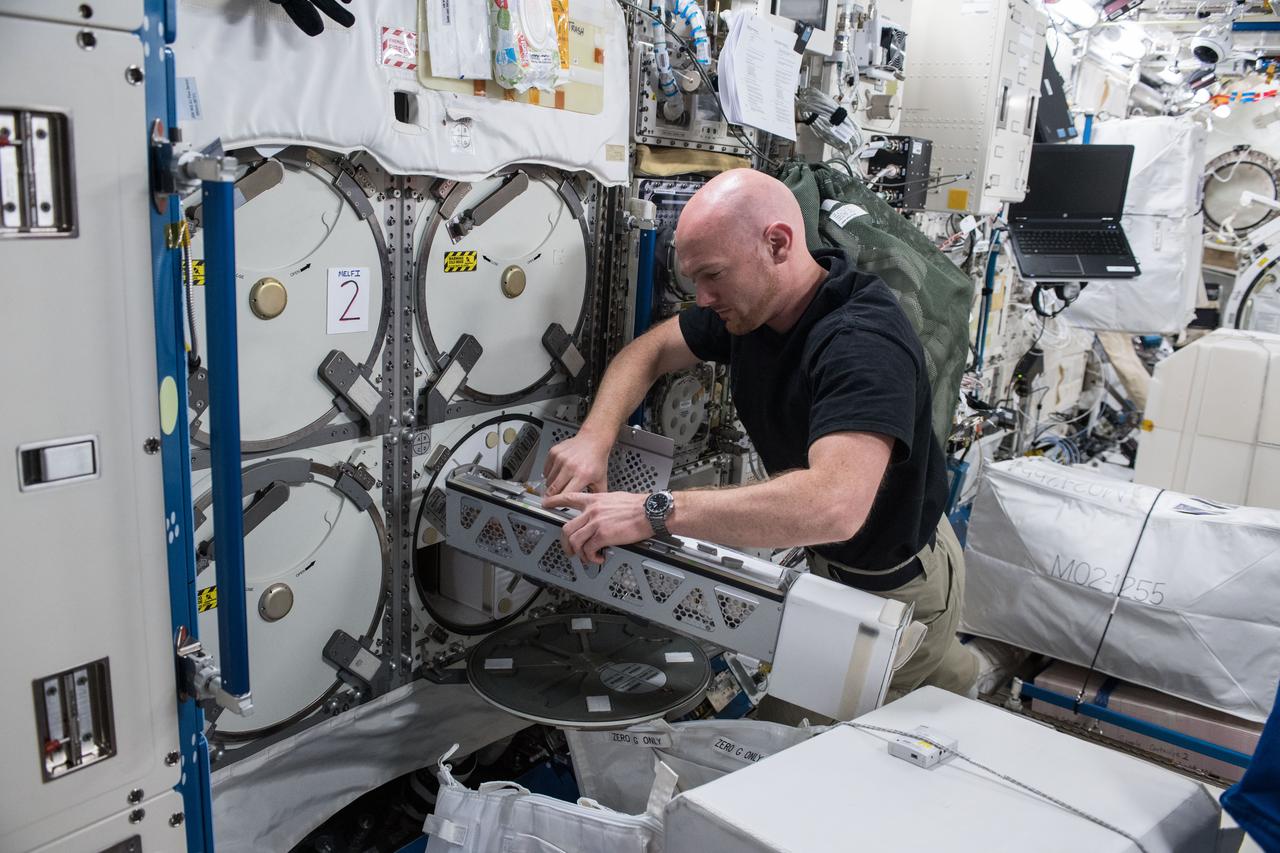

iss056e075951 (July 3, 2018) --- Astronaut Alexander Gerst of ESA (European Space Agency) works inside the Japanese Kibo laboratory module retrieving Protein Crystal Growth samples from a science freezer, also known as the Minus Eighty-Degree Laboratory Freezer for ISS (MELFI).

Aboard the Space Shuttle Atlantis, the STS-37 mission launched April 5, 1991 from launch pad 39B at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida, and landed back on Earth April 11, 1991. The 39th shuttle mission included crew members: Steven R. Nagel, commander; Kenneth D. Cameron, pilot; Jerry L,. Ross, mission specialist 1; Jay Apt, mission specialist 2; and Linda M. Godwin, mission specialist 3. The primary payload for the mission was the Gamma Ray Observatory (GRO). The GRO included the Burst and Transient Experiment (BATSE); the Imaging Compton Telescope (COMPTEL); the Energetic Gamma Ray Experiment Telescope (EGRET); and the Oriented Scintillation Spectrometer Experiment (OSSEE). Secondary payloads included Crew and Equipment Translation Aids (CETA); the Ascent Particle Monitor (APM); the Shuttle Amateur Radio Experiment II (SAREXII), the Protein Crystal Growth (PCG); the Bioserve Instrumentation Technology Associates Materials Dispersion Apparatus (BIMDA); Radiation Monitoring Equipment III (RMEIII); and Air Force Maui Optical Site (AMOS).