
SL3-88-004 (July-September 1973) --- A vertical view of the Salinas River Valley area south of Monterey Bay, California area is seen in this Skylab 3 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch Earth terrain camera) photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The valley is an irrigated agricultural area, and is indicated by the dark-green and light-gray rectangular patterns in the centre of the picture. The city of Salinas is barely visible under the cloud cover at the top (north) end of the valley. The dark mass on the left (west) side of the valley is the Santa Lucia mountain range. The Big Sur area is on the left and partly covered by clouds. The Diablo Range forms the dark mass in the lower right (southeast) corner of the photograph. The town of Hollister is the gray area in the dark-green rectangular farm tracts which occupy the floor of the San Benito Valley in the upper right (northeast) corner of the photograph. The Salinas River flows northwestward toward Monterey Bay. The towns of Soledad, Greenfield and King City appear as gray areas along U.S. 101 in the Salinas Valley. The geology of the area is complex, and has been racked by several earthquakes resulting from movement along the San Andreas and subsidiary faults. Here, the surface expression of the San Andreas Fault can be traced from a point just west of Hollister at the contrast of dark brown and tan to a point about one inch left of the lower right (southeast) corner of the picture. Subsidiary faults are indicated by the curving trend of the rocks along the right side. The photograph will provide detailed information on land use patterns (Dr. R. Colwell, University of California, Berkeley) and fault tectonics (Dr. P. Merifield, Earth Science Res., Inc. and Dr. M. Abdel-Gawad, Rockwell International). Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior’s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA

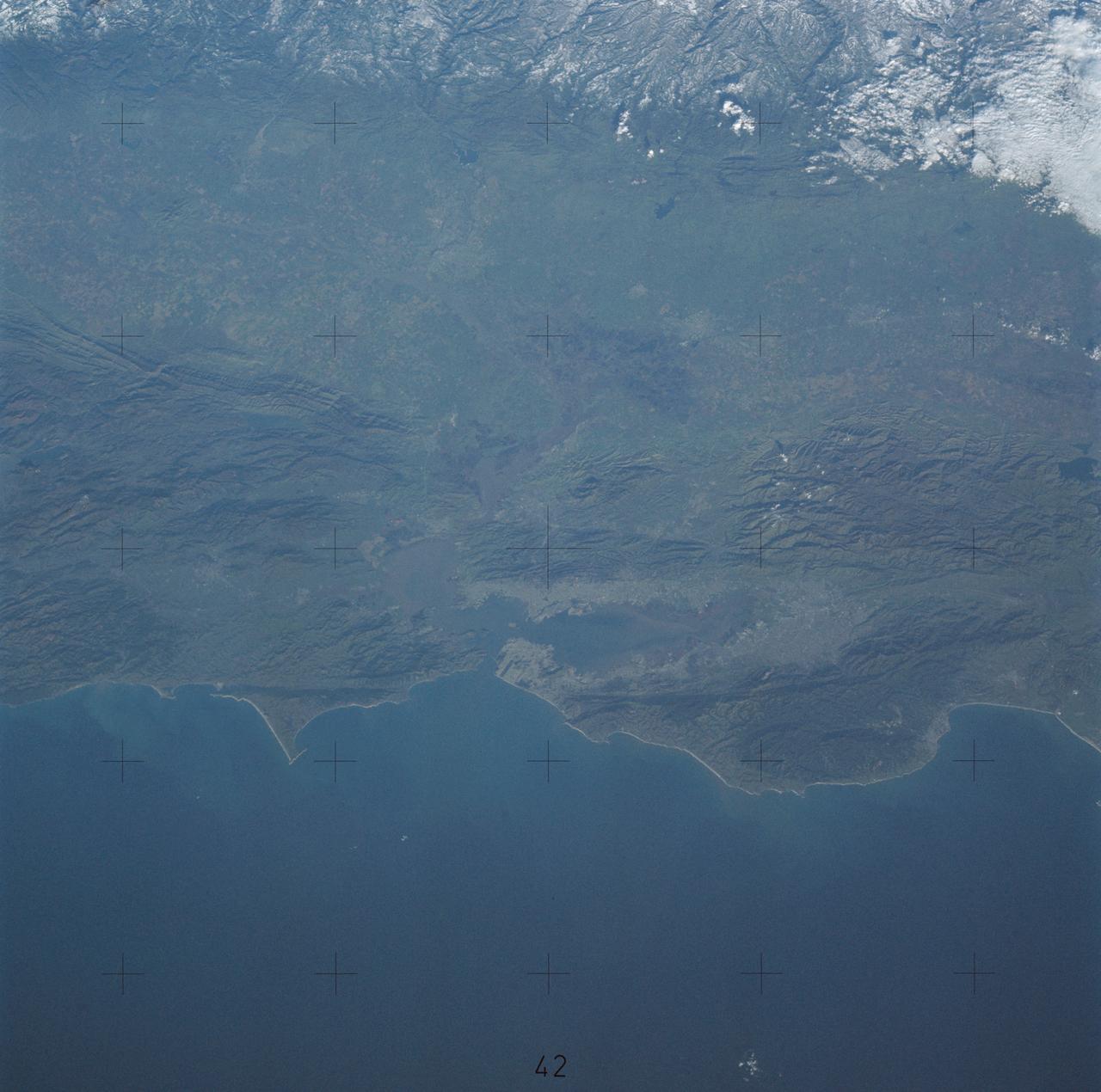
SL3-33-156 (July-September 1973) --- A near vertical view of the Florence, Italy area as photographed from Earth orbit by one of the Itek-furnished S190-A Multispectral Photographic Facility Experiment aboard the Skylab space station. The view extends from the Ligurian Sea, an extension of the Mediterranean Sea, across the Apennine Mountains to the Po River Valley. Florence (Firenze) is near the center of the land mass. The mouth of the Arno River is at the center of the coastline. The city of Leghorn (Livorno) is on the coast just south of the Arno River. This picture was taken with type 2443 infrared color film. The S190-A experiment is part of the Skylab Earth Resources Experiments Package. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Department of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA

SL4-93-153 (February 1974) --- A vertical view of the Birmingham and central Alabama area is seen in this Skylab 4 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch earth terrain camera) infrared photographed taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. Illustrated here is the utility of color infrared film in depicting distribution of living vegetation in the 3,600 square mile Birmingham region. The Birmingham industrial complex, with a population of nearly 850,000, is the light gray area nestled in the valley between the northeast-trending ridges that are prominent topographic features in the southern Appalachian Mountains. The narrow ridges and adjacent valleys reflect folded and faulted sedimentary rocks, indicating the complex geological history of the region. Two major rivers and several reservoirs are easily distinguished in this photograph. Bankhand Lake, formed by a dam on the Black Warrior River, appears as bright blue west of Birmingham. Two lakes are formed by dams on the Goosa River east of Birmingham. Federal and state highways appear as thin white lines and are easily identified. Interstate 65 to Montgomery is the prominent white line extending southward from Birmingham. Power line clearings are visible in the center of the picture along the Goosa River, and can be traced northwestward to northern parts of Birmingham. The predominant deep red color of the picture is due to the reflections from living vegetation. In contrast are the light tan areas that commonly occur as rectangular patterns in the east part of the photograph and represent mature agricultural crops or grazing lands. Analysis of the photographic data from the earth terrain camera will be conducted by Dr. H. Jayroe of the Marshall Space Flight Center in developing analytical techniques. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior's Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA
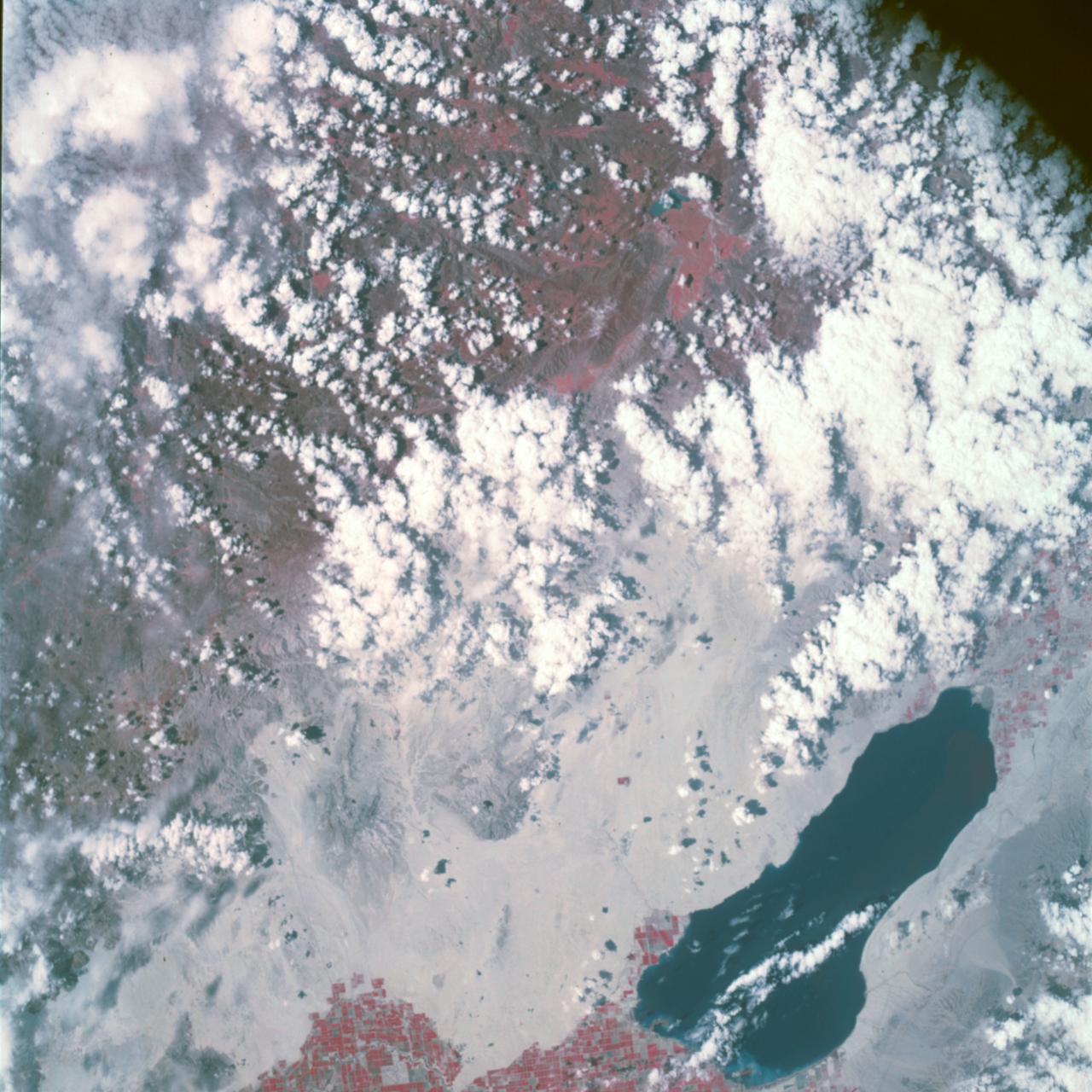
Earth Observation taken by the Apollo 9 crew. View is of Salton Sea and Imperial Valley in California. Latitude was 33.09 N by Longitude 116.14 W, Overlap was 50%, Altitude miles were 103 and cloud cover was 35%. This imagery taken as part of the NASA S0-65 Experiment "Multispectral Terrain Photography". The experiment provides simultaneous satellite photography of the Earth's surface in three distinct spectral bands. The photography consists of four almost spatially identical photographs. The images of ground objects appear in the same coordinate positions on all four photos in the multispectral set within the opto-mechanical tolerances of the Hasselblad cameras in the Apollo 9 spacecraft. Band designation for this frame is A. Film and filter is Ektachrome SO-368,Infrared Color Wratten 15. Mean Wavelength of Sensitivity is green,red and infrared. The Nominal Bandpass is total sensitivity of all dye layers 510-900nm.
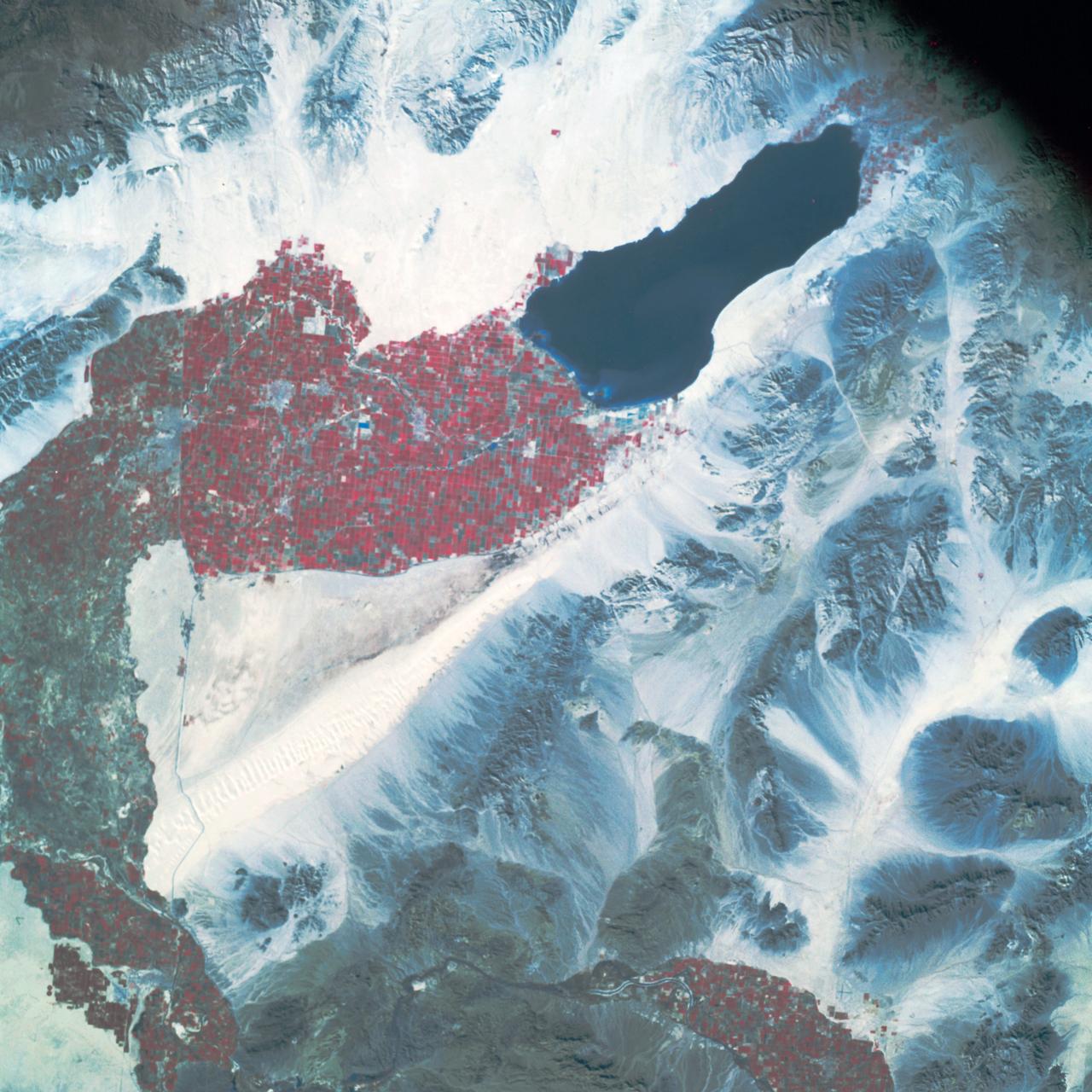

AS09-26A-3799A (12 March 1969) --- Color infrared photograph of the Salton Sea and Imperial Valley area of Southern California as seen from the Apollo 9 spacecraft. This picture was taken as a part of the SO-65 Multispectral Terrain Photography Experiment. On the eastern edge of the picture are the Colorado River and a small portion of Arizona. Yuma, Arizona, is at the bottom right corner. The cities of El Centro, California, and Mexicali, Mexico, are at the bottom center.
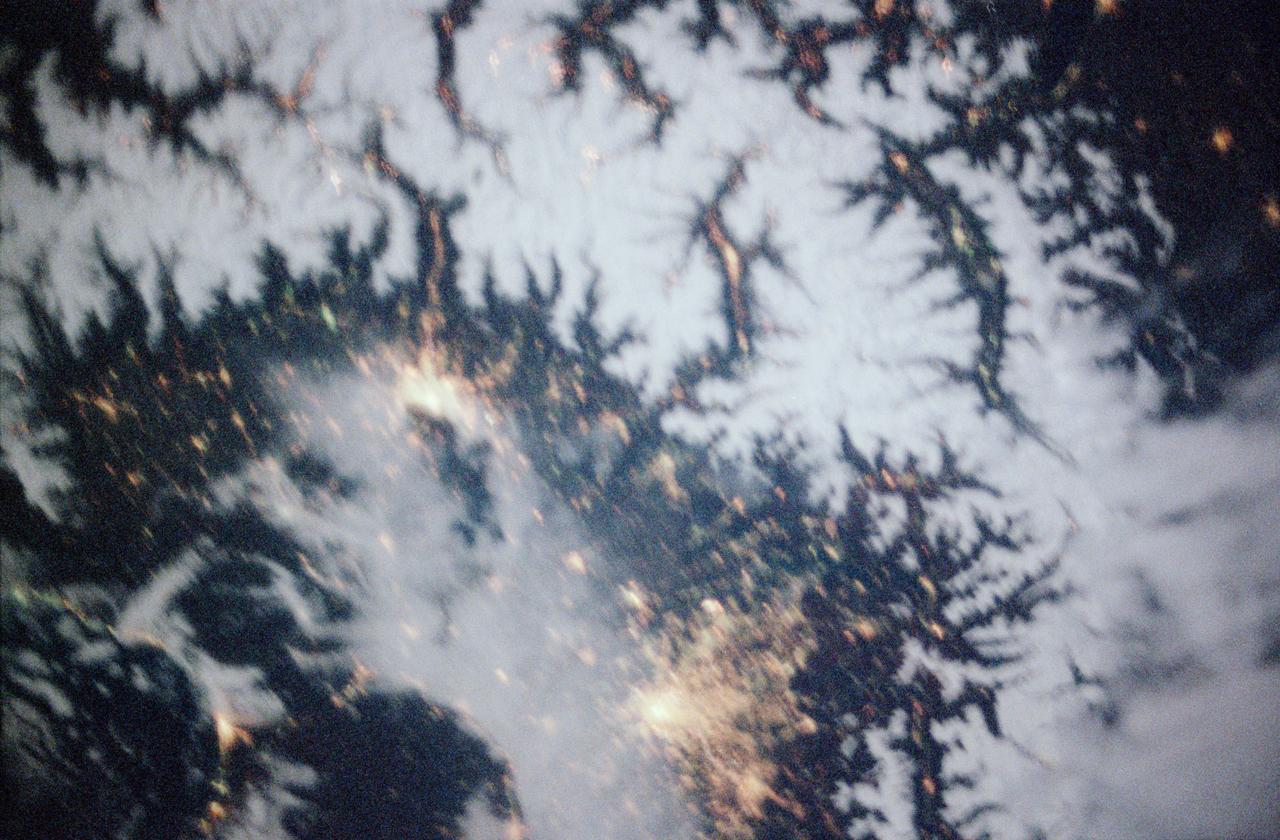

STS097-355-011 (30 Nov. -11 Dec. 2000) --- This vertical scene showing Torino and Milano, Italy, at night, was photographed with a 35mm camera by one of the STS-97 crew members aboard the Earth-orbiting Space Shuttle Endeavour. The night lights of Torino and Milano (two larger illuminated areas) are visible in the view, which covers the western end of the Po River Valley. Torino is the bright spot slightly left of center and Milano is the larger bright spot towards the bottom center of the image. The deeply eroded flanks of the snow-covered Alps Mountains (serrated-looking, light-colored terrain top half of the image) is visible north of the two large cities. Several mountain passes that connect the Po River Valley with France and Switzerland can be identified by the string of lights in the narrow, linear valleys. A translucent-looking cloud (bottom center) somewhat obscures the nighttime landscape south of Torino and Milano. The northwest coast of Italy, including the Italian city of Genova, can be identified in the lower left corner of the image. This photography was taken by astronauts using high speed film and long exposure on a night with a full moon illuminating the surface of the Earth.

This view of southern California as seen from the Apollo 7 spacecraft during its 18th revolution of the earth. Photographed from an altitude of 124 nautical miles. The coast of California can be seen from Point Mugu southward to Oceanside. Santa Catalina can be seen below the off shore clouds. Details of the Los Angeles area are obscured by pollution which extends from Banning westard for 100 miles to beyond Malibu. In the upper portion of the photograph can be seen (left to right) the San Joaquin Valley beyond Bakersfield, the Techachapi Mountains, the Sierra Nevada, Owens Valley, Death Valley and the Mojave Desert.

SL4-138-3843 (1 Jan. 1974) --- A part of northern California centered near San Francisco Bay photographed at 3 p.m. Jan. 2, 1974, from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. This near vertical view encompasses the coastline from Monterey Bay (right) to about 50 miles north of Point Reyes (left) and includes, from bottom to top, San Francisco Bay (center), Sacramento Valley (left center), San Joaquin Valley (right center), and the snow-covered Sierra Nevada. Afternoon shadows sharply delineate a valley which parallels San Francisco Bay, crosses Point Reyes, and lies between the Bay and the Pacific coastline. This valley marks the location of the San Andreas Fault, a major break in the Earth's crust. Forces acting on the crust are causing the land west (bottom) of the fault line to move north relative to land on the east side. The Skylab 4 astronauts photographed major fault zones in South America, New Zealand, Japan and Africa for use in the study of worldwide tectonic system. Agricultural areas in the Sacramento and San Joaquin Valleys are indicated by the tan areas which are easily discerned in contrast to the green-gray background. Photo credit: NASA

SL3-22-0214 (July-September 1973) --- A vertical view of southeastern Washington State as photographed from Earth orbit by one of the six lenses of the Itek-furnished S190-A Multispectral Photographic Facility Experiment aboard the Skylab space station. The Snake River flows into the Columbia River in the most southerly corner of the picture. The Wallula Lake is below the junction of the two rivers. The Yakima Valley is at the southwestern edge of the photograph. The Columbia Basin is in the center of the picture. The Cascade Range extends across the northwest corner of the photograph. This picture was taken with type SO-356 regular color film. The S190-A experiment is part of the Earth Resources Experiments Package. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA
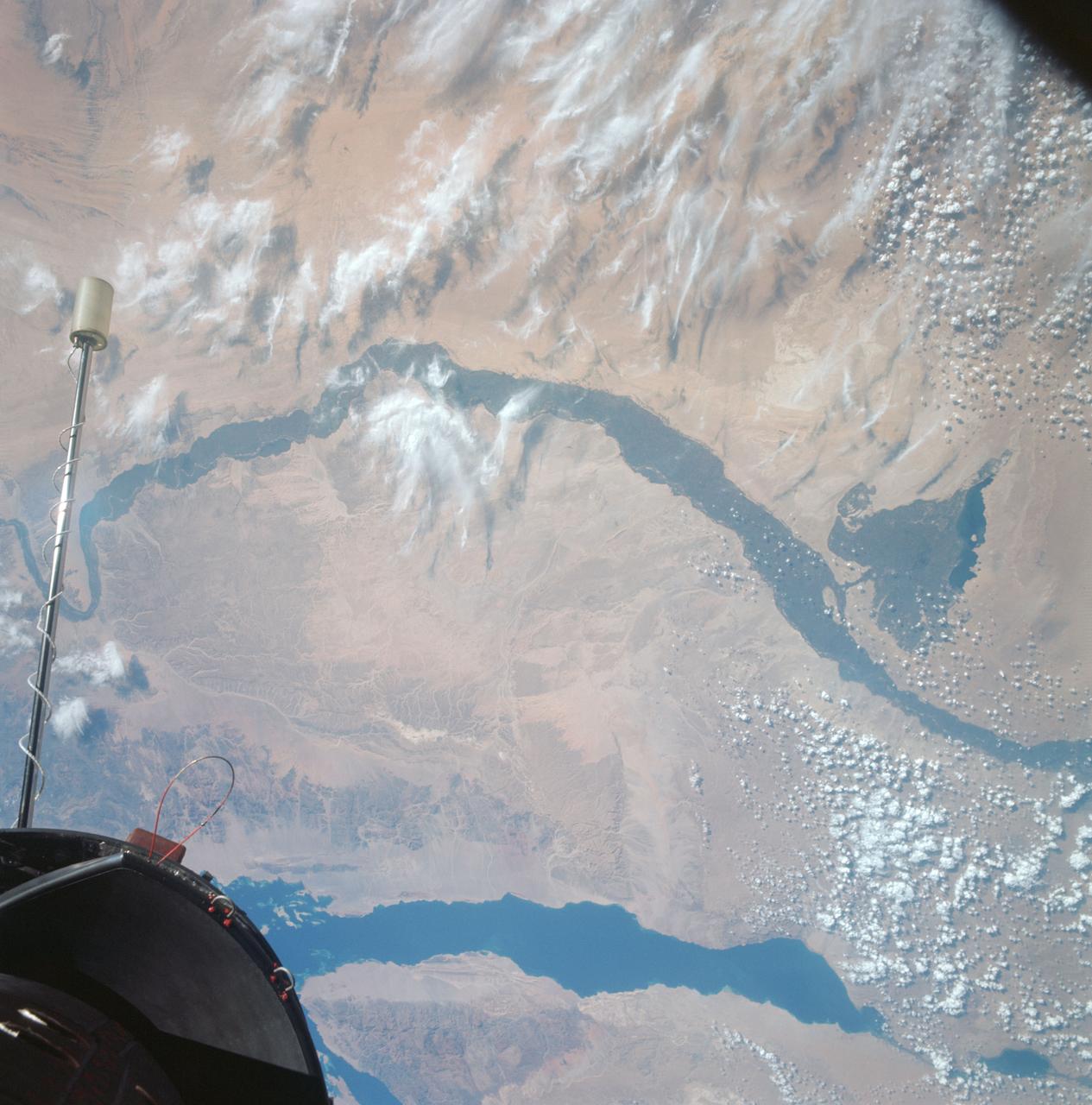

S66-63477 (13 Nov. 1966) --- United Arab Republic (Egypt), the Nile Valley from Luxor to Cairo, El Payium, Gulf of Suez, Sinai as seen from Gemini-12 spacecraft on its 25th revolution of Earth. Photo credit: NASA
![ISS007-E-18078 (26 October 2003) --- The fires in the San Bernardino Mountains, fueled by Santa Ana winds, burned out of control on the morning of Oct. 26, 2003, when these images were taken from the International Space Station at roughly 11 a.m. (PST). Thick yellow smoke blows south, blanketing the valley below. This image and ISS007-E-18082, looking southeast, capture the smoke pall as the ISS approached and passed over the region. Image numbers 18078 and 18082 were taken roughly a minute apart. A small break in the smoke marks Cajon pass. Content was provided by JSC’s Earth Observation Lab. The International Space Station Program {link to http://spaceflight.nasa.gov} supports the laboratory to help crew members take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public, and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth [link to http://eol.jsc.nasa.gov/].](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/iss007e18078/iss007e18078~medium.jpg)
ISS007-E-18078 (26 October 2003) --- The fires in the San Bernardino Mountains, fueled by Santa Ana winds, burned out of control on the morning of Oct. 26, 2003, when these images were taken from the International Space Station at roughly 11 a.m. (PST). Thick yellow smoke blows south, blanketing the valley below. This image and ISS007-E-18082, looking southeast, capture the smoke pall as the ISS approached and passed over the region. Image numbers 18078 and 18082 were taken roughly a minute apart. A small break in the smoke marks Cajon pass. Content was provided by JSC’s Earth Observation Lab. The International Space Station Program {link to http://spaceflight.nasa.gov} supports the laboratory to help crew members take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public, and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth [link to http://eol.jsc.nasa.gov/].
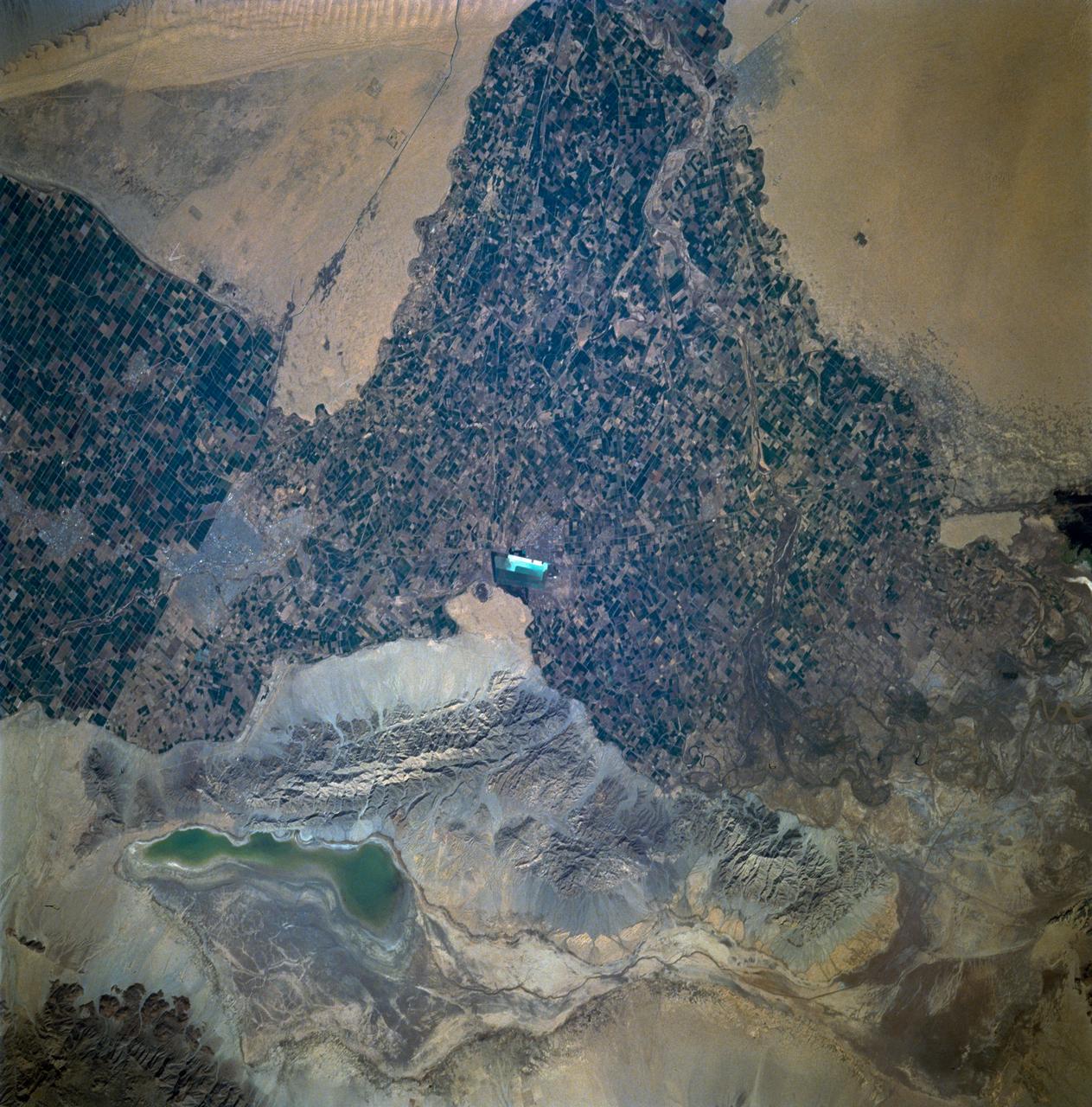

STS060-93-081 (3-11 Feb 1994)--- The Imperial Valley was documented using three films - color visible (seen here), the American infrared film (Kodak Aerochrome 2443), and the Russian panchromatic infrared film (SN-10). Results of this test still await detailed science analysis. However it does appear that good data was acquired of the region, and this data will be complemented by photography acquired by the Mir cosmonauts. In this frame, the U.S.-Mexico border goes from the upper left to the middle right. It is discernible as a vegetation line between Calexico, California and Mexicali, Mexico. The darker vegetation north of that line is due to different agricultural practices, heavier uses of fertilizers and pesticides, and lined (tiled) agricultural fields allowing subterraneean runoff of saline irrigation runoff. South of the line, the more polluted water draining out of the U.S. agricultural areas into the Mexican area has resulted in higher soil salinities and a consequent reduction in agricultural productivity. At the center of the frame, a large settling and desalinization plant has been built to attempt to purify, to some degree, the polluted irrigation waters draining south out of California. The All-American Canal, which brings in water from the Colorado River (off the frame, to the right), is located in the middle right hand portion of the frame. To the upper left is the normally dry Laguna Salada.
![ISS007-E-18082 (26 October 2003) --- The fires in the San Bernardino Mountains, fueled by Santa Ana winds, burned out of control on the morning of Oct. 26, 2003, when these images were taken from the International Space Station at roughly 11 a.m. (PST). Thick yellow smoke blows south, blanketing the valley below. This image and ISS007-E-18078, looking southeast, capture the smoke pall as the ISS approached and passed over the region. Image numbers 18078 and 18082 were taken roughly a minute apart. A small break in the smoke marks Cajon pass. Content was provided by JSC’s Earth Observation Lab. The International Space Station Program {link to http://spaceflight.nasa.gov} supports the laboratory to help crew members take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public, and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth [link to http://eol.jsc.nasa.gov/].](https://images-assets.nasa.gov/image/iss007e18082/iss007e18082~medium.jpg)
ISS007-E-18082 (26 October 2003) --- The fires in the San Bernardino Mountains, fueled by Santa Ana winds, burned out of control on the morning of Oct. 26, 2003, when these images were taken from the International Space Station at roughly 11 a.m. (PST). Thick yellow smoke blows south, blanketing the valley below. This image and ISS007-E-18078, looking southeast, capture the smoke pall as the ISS approached and passed over the region. Image numbers 18078 and 18082 were taken roughly a minute apart. A small break in the smoke marks Cajon pass. Content was provided by JSC’s Earth Observation Lab. The International Space Station Program {link to http://spaceflight.nasa.gov} supports the laboratory to help crew members take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public, and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth [link to http://eol.jsc.nasa.gov/].
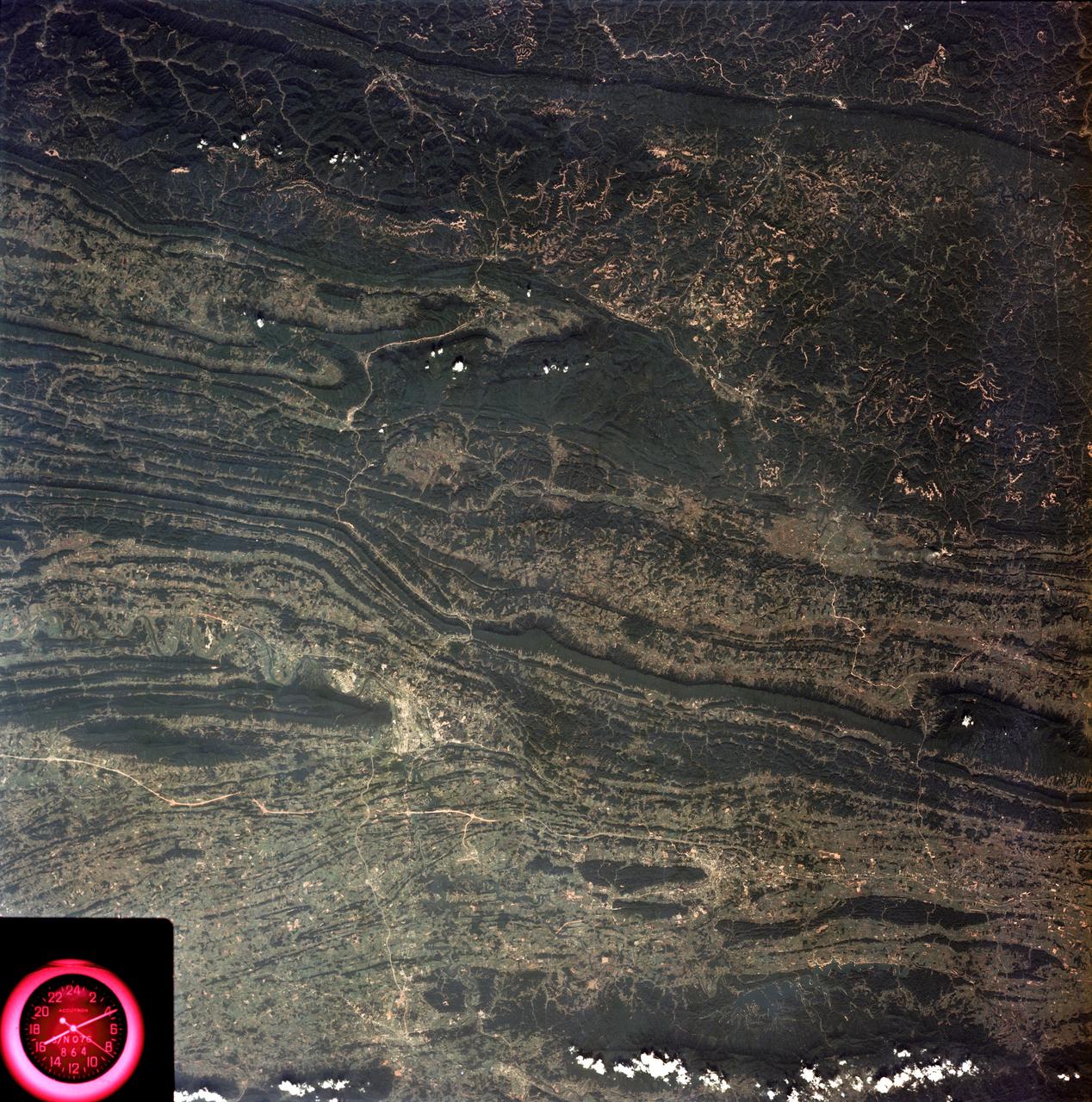
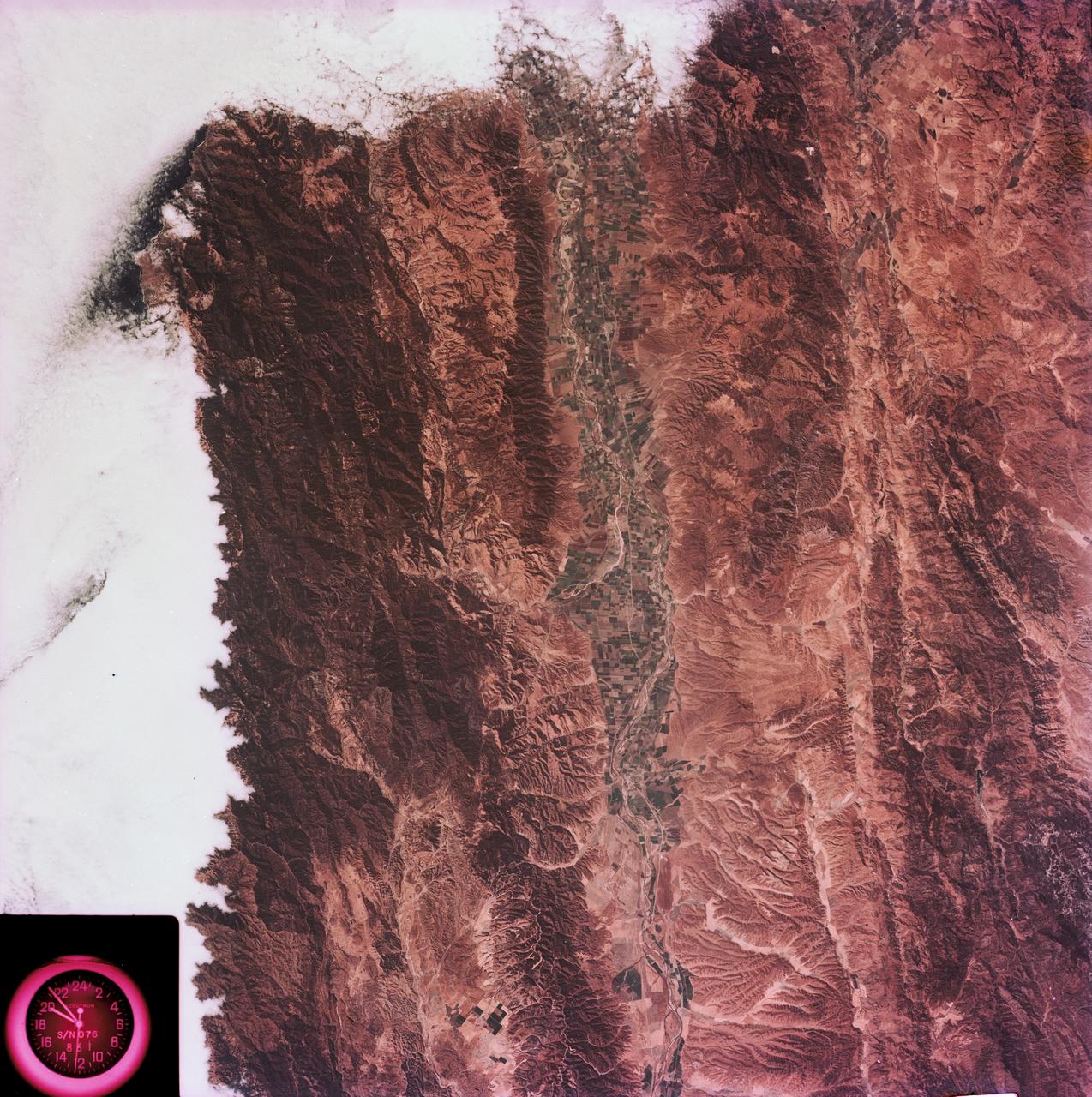
SL3-88-053 (July-September 1973) --- A near vertical view of the Tennessee-Virginia-Kentucky border area is seen in this Skylab 3 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch Earth terrain camera) photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The clock is in the most southerly corner of the picture. Interstate 81 under construction extends northeast-southwest across the bottom portion of the photograph. The larger urban area nearest the center of the picture is Kingsport, Tennessee. On the southern side of I-80 and east of Kingsport is the city of Bristol, Tennessee-Virginia. Johnson City, Tennessee is the urban area near the edge of the picture southeast of Kingsport. The Holston River, a tributary of the Tennessee River, meanders through the Kingsport area. The characteristic ridge and valley features in the Cumberland Plateau of Kentucky, Tennessee and Virginia are clearly visible. Forests (dark green) occur on the ridges and clearly outline the folded and faulted rock formations. The valleys (light) were formed in the softer rocks as a result of erosion. Agricultural areas are indicated by the characteristic rectangular patterns. Coal production is an important industry of this area; and it is mined by surface open pit operations. The irregular light areas in the Kentucky-Virginia border area are the strip mines which follow the contour of the land. Reclamation of the strip mine areas is aided through accurate knowledge of the mine and drainage systems. Dr. Ronald Brooks of the Wolf Research and Development Corporation can use this photograph in study of strip mine areas in the east central U.S. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior’s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. Photo credit: NASA
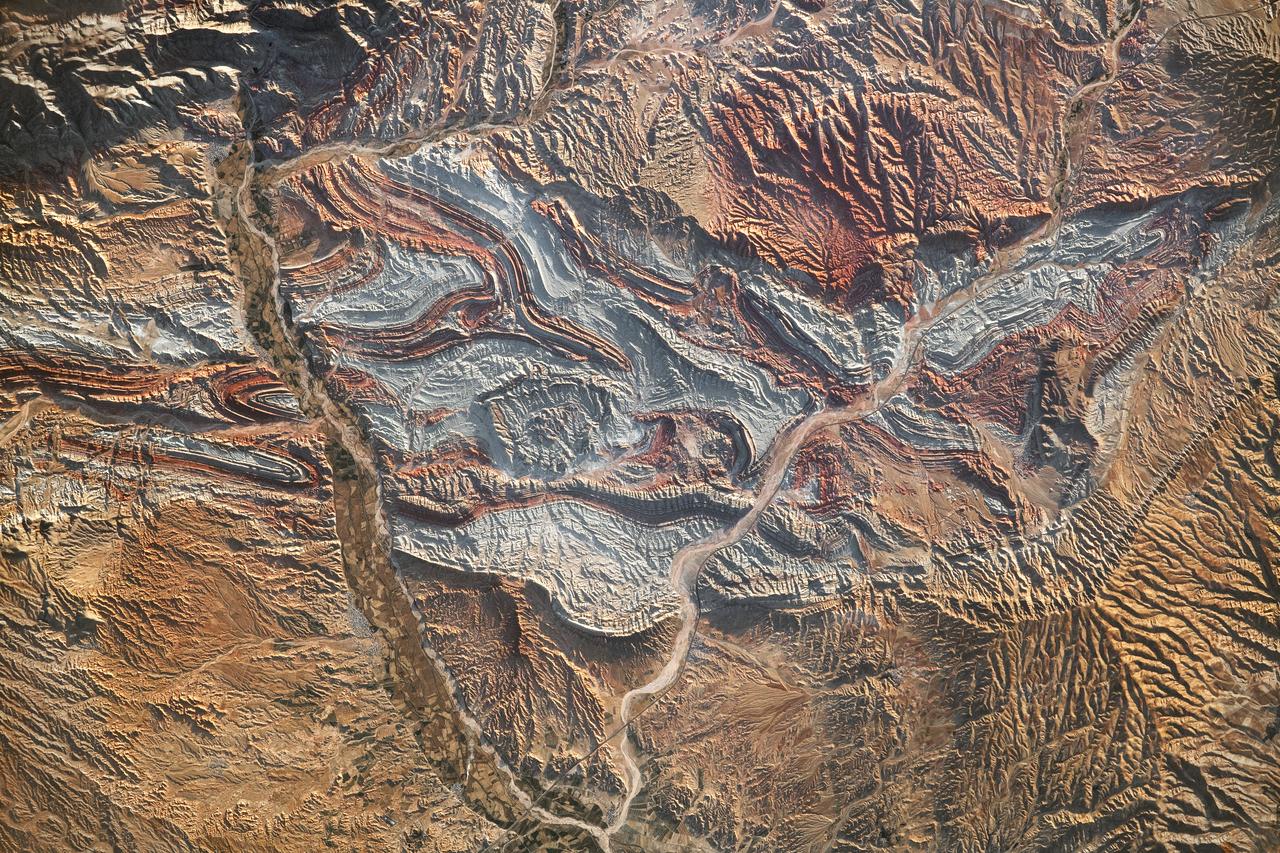

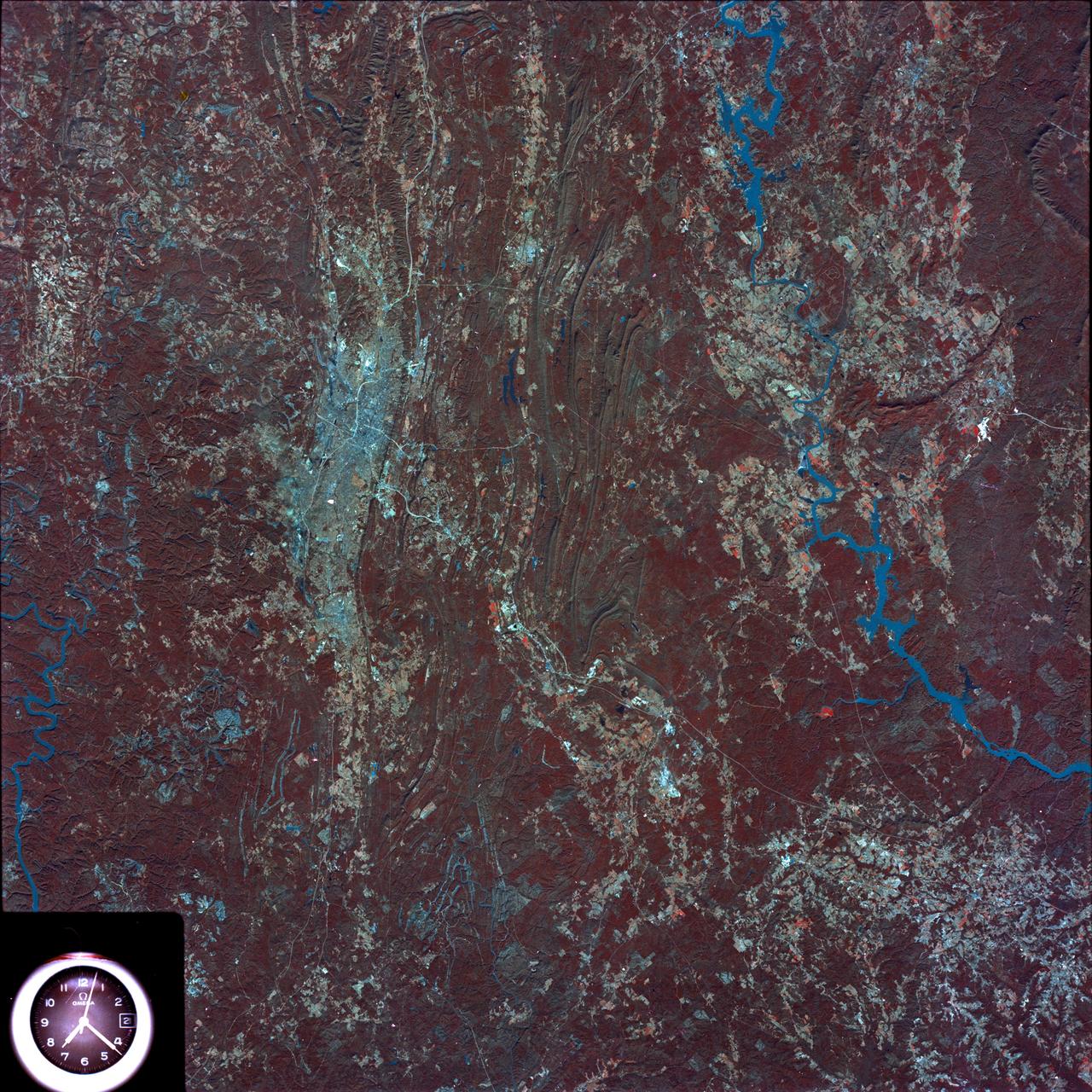
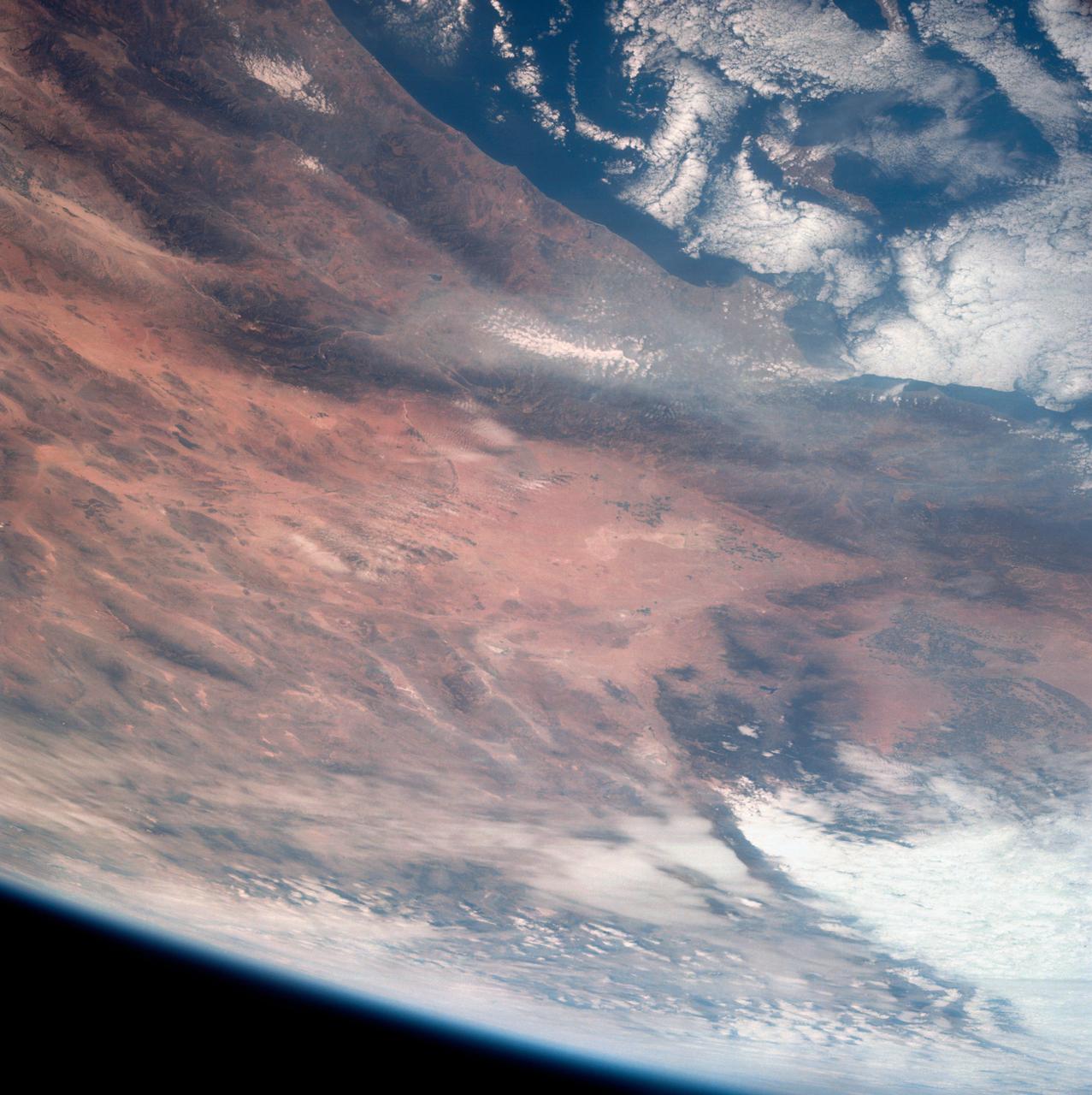
iss069-e-089946_lrg (09/19/2023) --- An astronaut aboard the International Space Station took this photograph of the rugged landscape of the Aladaghlar Mountains in northwestern Iran. Ridges cast shadows in the valleys and other low elevation areas, creating a three-dimensional appearance. Human alterations to the landscape are most evident in riverbeds, where the even topography is easier to build on and navigate. Natural processes over millions of years have folded rock layers of various compositions and colors into the curved patterns seen here. These folds are produced by tectonic forces operating along the convergent plate boundary of the Arabia and Eurasia plates. The convergence of these tectonic plates causes uplift, folding, and deformation of the colorful rock layers, and subsequent erosion exposes them. On the left side of this photo, the Qezel Ozan River, a major river in northern Iran, cuts across the landscape. Agricultural fields are visible along the riverbanks tucked between the mountains. The Qezel Ozan also intersects the Zanjan-Tabriz freeway (Freeway 2), a major thoroughfare built on a dried riverbed connecting the cities of Tehran and Tabriz. Astronaut photograph ISS069-E-89946 was acquired on September 19, 2023, with a Nikon D5 digital camera using a focal length of 400 millimeters. The image was provided by the ISS Crew Earth Observations Facility and the Earth Science and Remote Sensing Unit at Johnson Space Center. The image was taken by a member of the Expedition 69 crew. It has been cropped and enhanced to improve contrast, and lens artifacts have been removed. The International Space Station Program supports the laboratory as part of the ISS National Lab to help astronauts take pictures of Earth that will be of the greatest value to scientists and the public and to make those images freely available on the Internet. Additional images taken by astronauts and cosmonauts can be viewed at the NASA/JSC Gateway to Astronaut Photography of Earth. Caption by Sara Schmidt, GeoControl Systems, JETS II Contract at NASA-JSC and Andrea Wenzel, Jacobs-JETS II Contract at NASA-JSC.

STS047-151-488 (12 - 20 Sept 1992) --- In this large format camera image, the forested Cascade Range appears along the left side; the Pacific Ocean, on the right. The frame was photographed as the Space Shuttle Endeavour flew north to south over Vancouver and Seattle. Many peaks in the Cascades reach altitudes greater than 9,000 feet and remain snowcapped even in mid-summer. The Strait of Juan de Fuca separates the Olympic Peninsula (top right) from Vancouver Island (bottom right). Snowcapped Mt. Olympus (7,965 feet) is one of the wettest places in the continental United States, with rainfall in excess of 120 inches per year. The port cities of Seattle and Tacoma occupy the heavily indented coastline of Puget Sound (top center). They appear as light-colored areas on the left side of the Sound. The angular street pattern of Tacoma is visible at the top of the picture. The international boundary between Canada and the United States of America runs across the middle of the view. The city of Victoria (center) is the light patch on the tip of Vancouver Island. Canada's Fraser River Delta provides flat topography on which the cities of Vancouver, Burnaby, and New Westminster were built. These cities appear as the light-colored area just left of center. The Fraser River can be seen snaking its way out of the mountains at the apex of the delta. Numerous ski resorts dot the slopes of the mountains (bottom left) that rise immediately to the north of Vancouver. In the same area the blue water of Harrison and other, smaller lakes fills some of the valleys that were excavated by glaciers in the "recent" geological past, according to NASA scientists studying the photography. A Linhof camera was used to expose the frame.
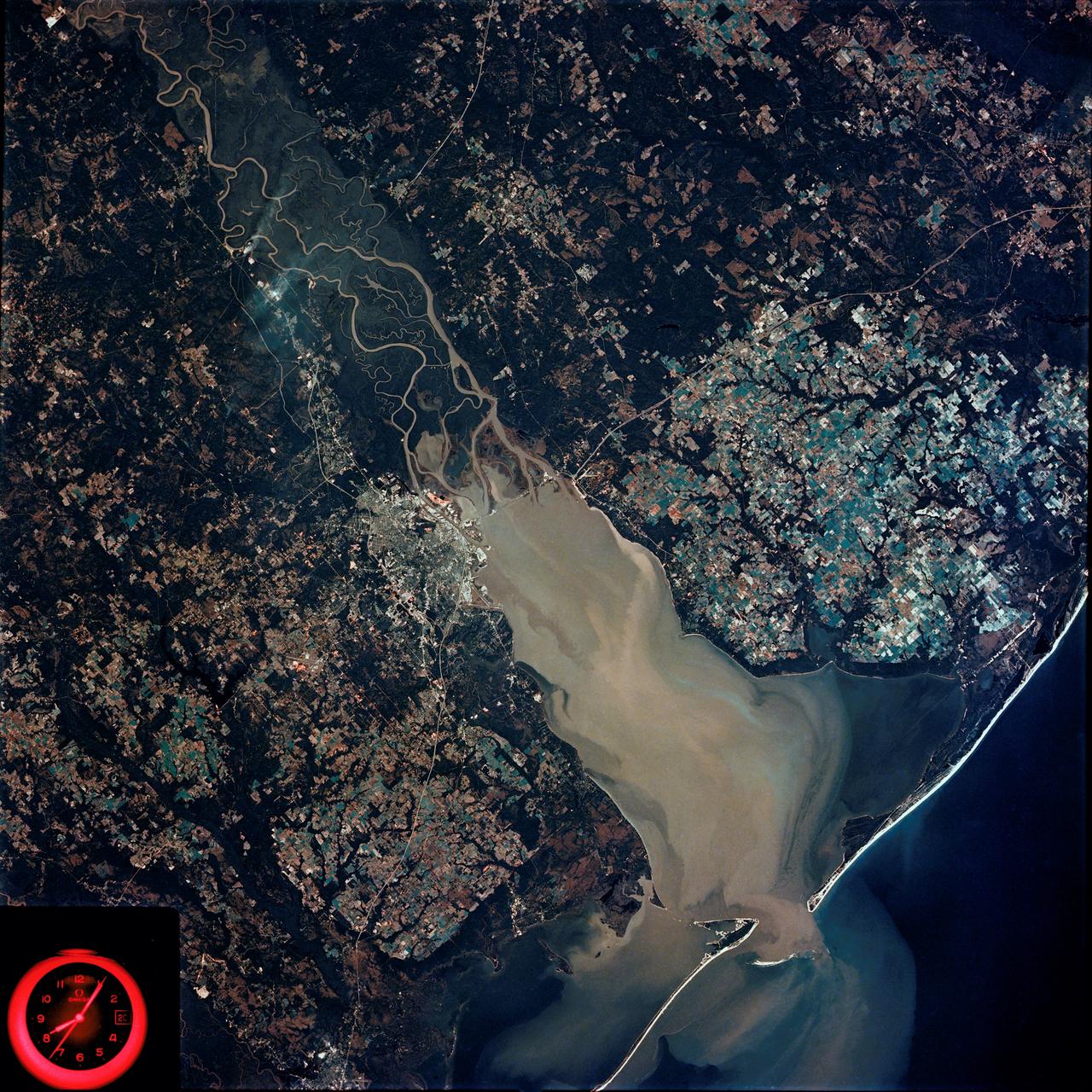

SL4-92-300 (February 1974) --- A near vertical view of the Mobile Bay, Alabama area is seen in this Skylab 4 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch earth terrain camera) photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. North of Mobile the Tombigbee and Alabama Rivers join to form the Mobile River. Detailed configuration of the individual stream channels and boundaries can be defined as the Mobile River flows into Mobile Bay, and thence into the Gulf of Mexico. The Mobile River Valley with its numerous stream channels is a distinct light shade in contrast to the dark green shade of the adjacent areas. The red coloration of Mobile Bay reflects the sediment load carried into the Bay by the rivers. Variations in red color indicate sediment load and the current paths within Mobile Bay. The waterly movement of the along shore currents at the mouth of Mobile Bay is shown by the contrasting light blue of the sediment-laden current and the blue of the Gulf predominately. Agricultural areas east and west of Mobile Bay are characterized by a rectangular pattern in green to white shades. Color variations may reflect the type and growth cycle of crops. Agricultural areas (light gray-greens) are also clearly visible in other parts of the photograph. Interstate 10 extends from near Pascagoula, Mississippi eastward through Mobile to the outskirts of Pensacola, Florida. Analysis of the EREP photographic data will be undertaken by the U.S. Corps of Engineers to determine bay dynamic processes. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior's Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota. 57198 Photo credit: NASA

A comparison of images taken by the Hubble Space Telescope Wide Field/Planetary Camera (HST/WFPC) and the Mars Global Surveyor Orbiter Camera (MGS/MOC) shows the progress of a regional dust storm within the Valles Marineris canyons on Mars. The first HST image (left), taken in mid-May, shows no dust within the canyons. The most recent HST image (center), taken on 27 June in support of the Mars Pathfinder landing activities, shows a dust storm filling part of the canyon system and extending into the chaotic terrains at the eastern end of the canyons. The MGS/MOC image (right), acquired on July 2, shows that bright dust continues to fill the valleys. However, it does not appear to have moved significantly north of the previously observed position, suggesting that the storm remains confined to the canyon region, and does not appear to directly threaten the Pathfinder landing site (small black circle). The HST images shown here have been reduced in scale to match that of the MGS/MOC image. Although the HST is 10 times farther from Mars than MGS, its images are sharper because its resolving power is 15 times better than the MOC, and the light gathering area is almost 50 times greater. However, MGS is presently 45,000 times farther from Mars than it will be when the MOC begins its primary photography mission. At 400 km above the martian surface, the MOC wide angle camera will collect daily images at a resolution of 7.5 km/pixel, compared to HST's best of about 20 km/pixel. The narrow angle camera will observe portions of Mars at better than 1.5 m/pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA00607

S73-35082 (July-Sept. 1973) --- A near vertical view of a portion of west Africa ravaged by drought for the past five years is seen in this Skylab 3 Earth Resources Experiments Package S190-B (five-inch Earth terrain camera) photograph taken from the Skylab space station in Earth orbit. The semi-desert scene is in southeastern Niger about 200 nautical miles east-northeast of the capital city of Niamey. A polygonal-shaped area (dark) in the lower right corner of the picture represents a range-management ranch. The dry stream beds trending diagonally across the photograph locally contain some water or vegetation (green). The beds are sources of water through shallow drilling and contain soils suitable for production of crops. The variety of tans, browns and grays are typical desert colors that represent barren rocks and soil or sand-filled ancient stream valleys. Absence of vegetation is the singular feature of the area. Dr. G. Stuckmann of the Geographic Institute, University of Technology, Mannover, Federal Republic of Germany, will use this photograph in the study of the hydrologic regime of the region through analysis of fossil drainage patterns, geological structures and accumulations of surface water. Federal agencies participating with NASA on the EREP project are the Departments of Agriculture, Commerce, Interior, the Environmental Protection Agency and the Corps of Engineers. All EREP photography is available to the public through the Department of Interior?s Earth Resources Observations Systems Data Center, Sioux Falls, South Dakota, 57198. (Alternate number SL3-86-166) Photo credit: NASA
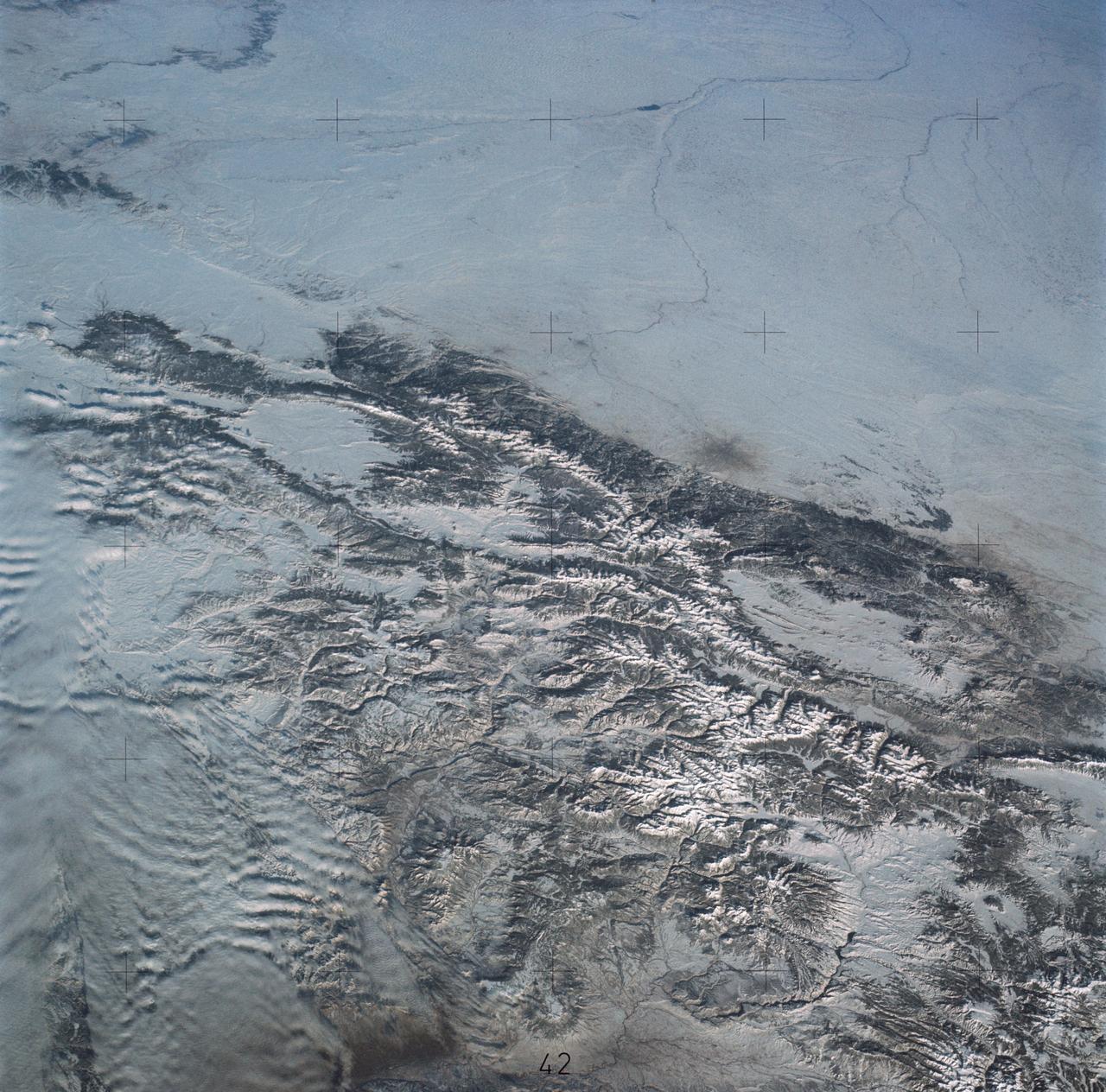

SL4-138-3875 (February 1974) --- A color oblique photograph looking east over the Rocky Mountains and Great Plains. This view covers a portion of the States of Colorado, Wyoming, and Nebraska. A Skylab 4 crewmen took this picture with a hand-held 70mm Hasselblad camera. This entire region, covered with a blanket of snow, depicts much of the structural and topographic features of the Rocky Mountain chain. Man's only apparent change to the snow pattern seen here is the (right center) metropolitan areas of Denver and Colorado Springs, Colorado, which can be observed along the eastern edge of the mountain front. Grand Junction, Colorado on the western slope of the Rocky Mountains is just off the photograph at left center bottom. The major inter-montane valleys of South Park (right center), Middle Park (center), and North Park (left center) are clearly visible and separate the Colorado Rockies Front Range from the high rugged mountains can be discovered such as Pikes Peak near right border (center), Mt. Cunnison region, circular feature accentuated by the Cunnison River (dark) in the right center (bottom) of the photograph. The snow covered peaks of Mts. Harvard, Princeton and Yale form the high region of the Collegiate Range which is the pronounced mountain area in the right center. Snow cover not only enhances mountain features but also the drainage patterns. East of Denver (right corner) the sinuous trace of the South Platte River (center) and its junction with the North Platte River near North Platte, Nebraska. Lake McConaughy in Nebraska is the body of water (black) near the river intersection. The trace of the Republic River in southern Nebraska is visible near the right corner of the photography. Geologic and hydro logic studies using this photograph will be conducted by Dr. Roger Morrison, U.S. Geological Survey. Photo credit: NASA