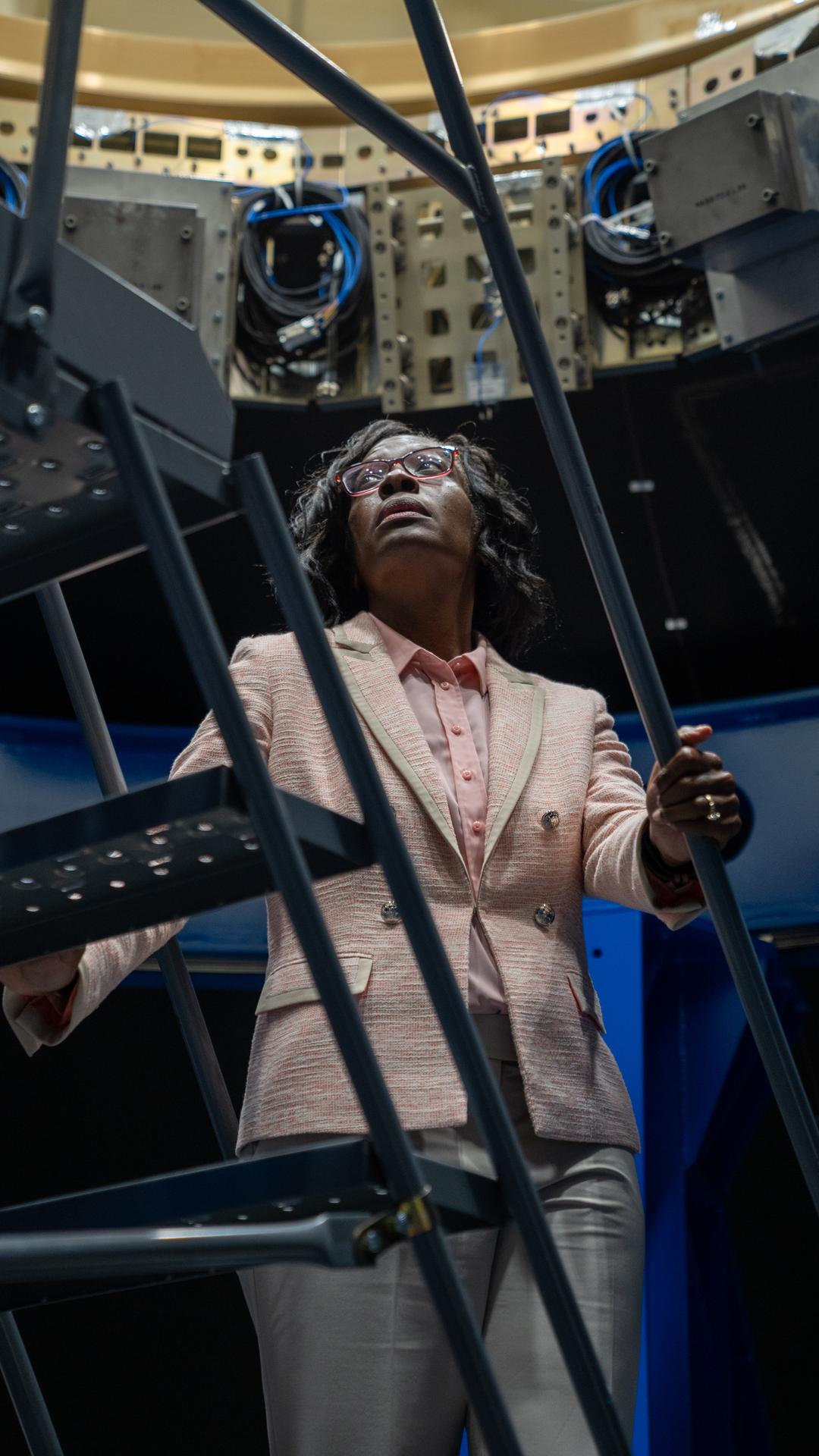

Lakiesha Hawkins, Assistant Deputy Associate Administrator for the Moon to Mars (M2M) Program within the Exploration Systems Development Mission Directorate (ESDMD), takes a peek at the Payload Adapter test article at Marshall Space Flight Center. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program.
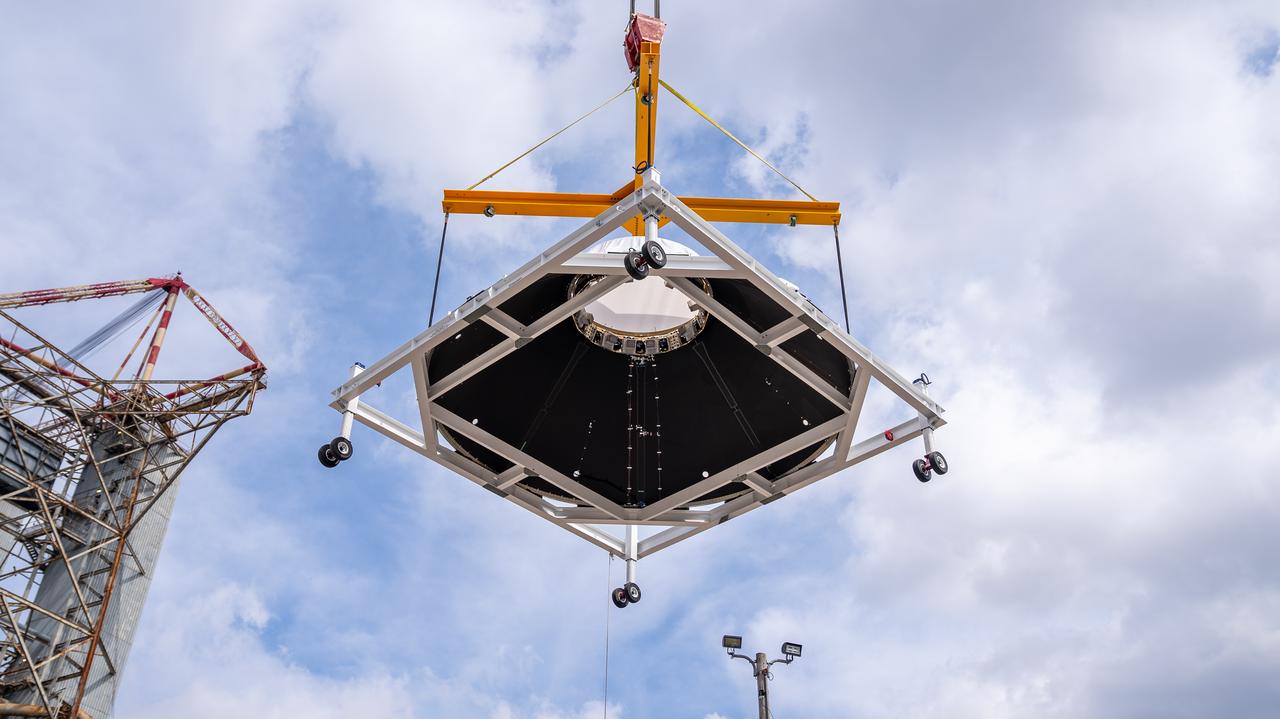

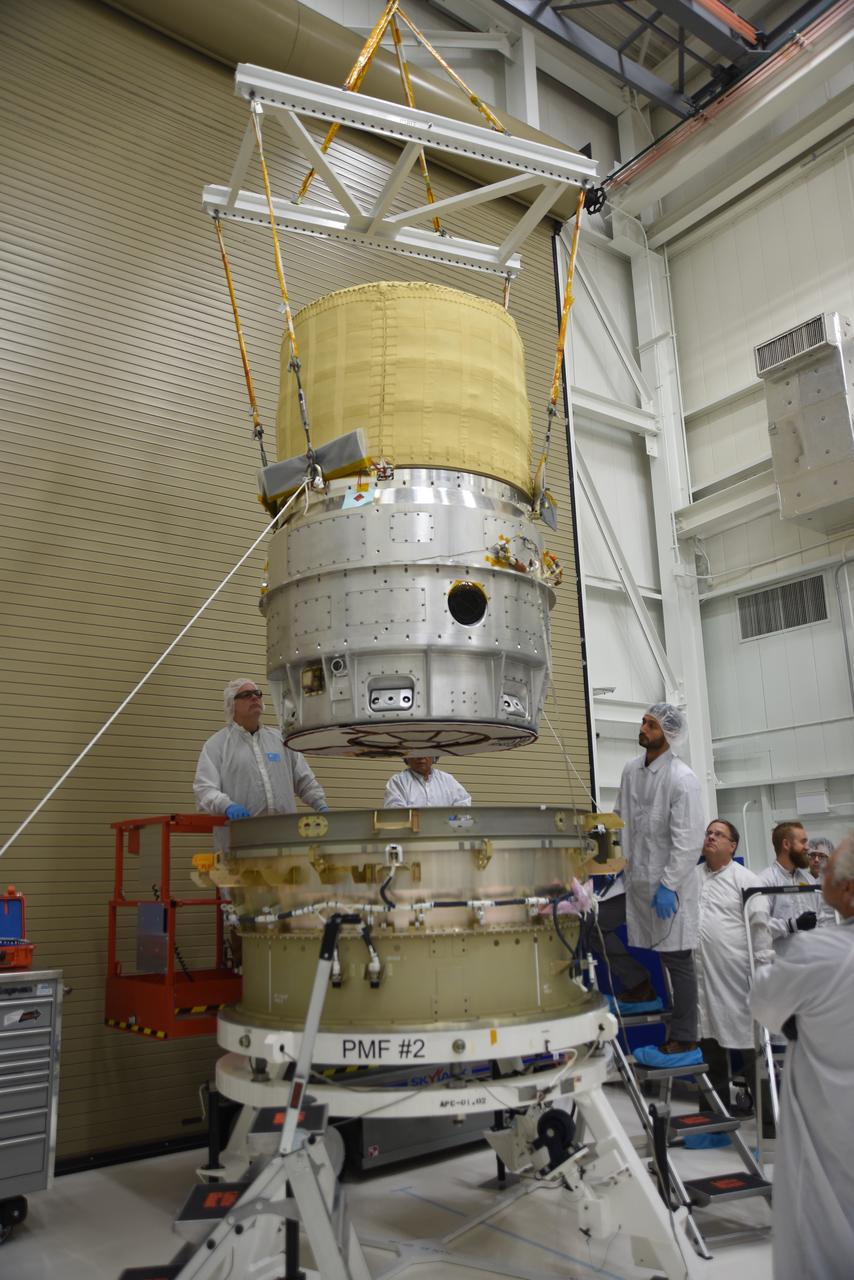
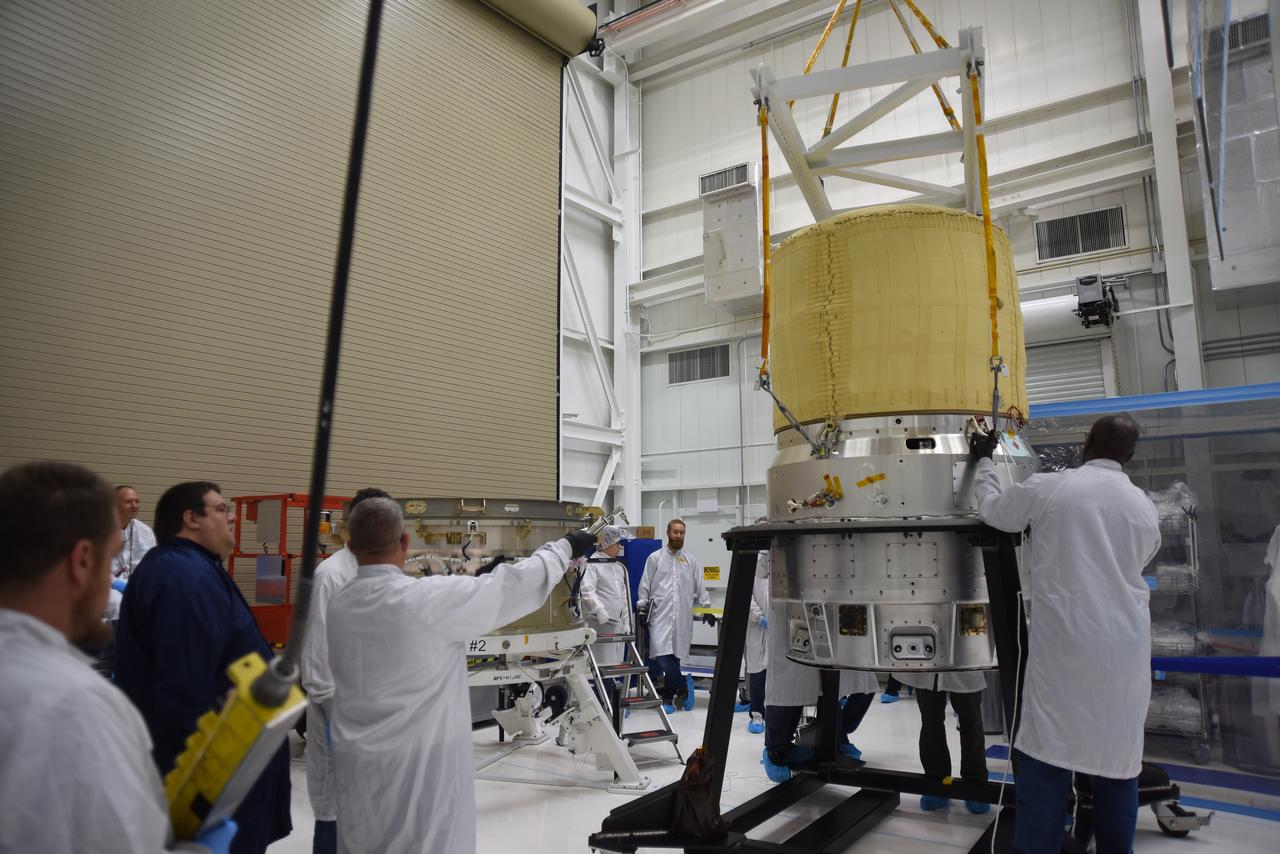
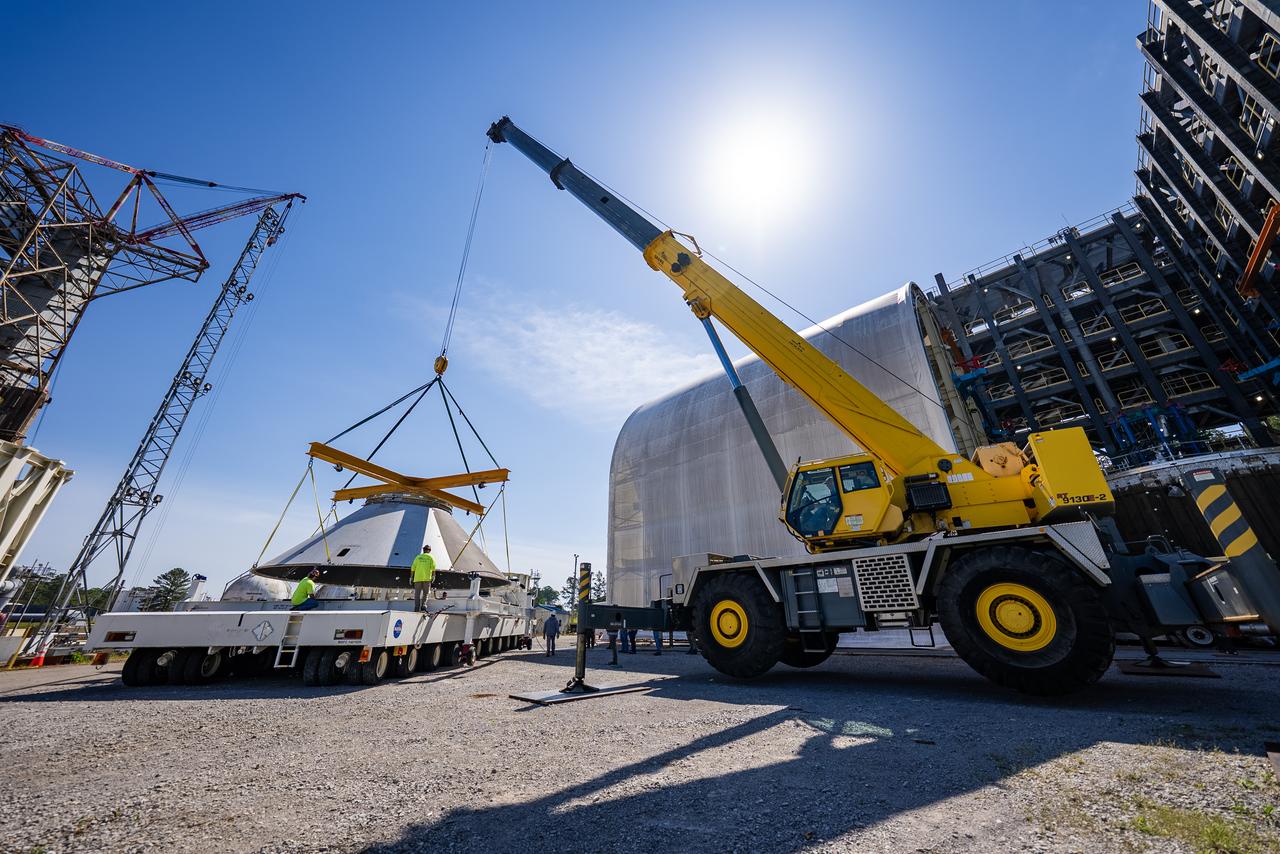
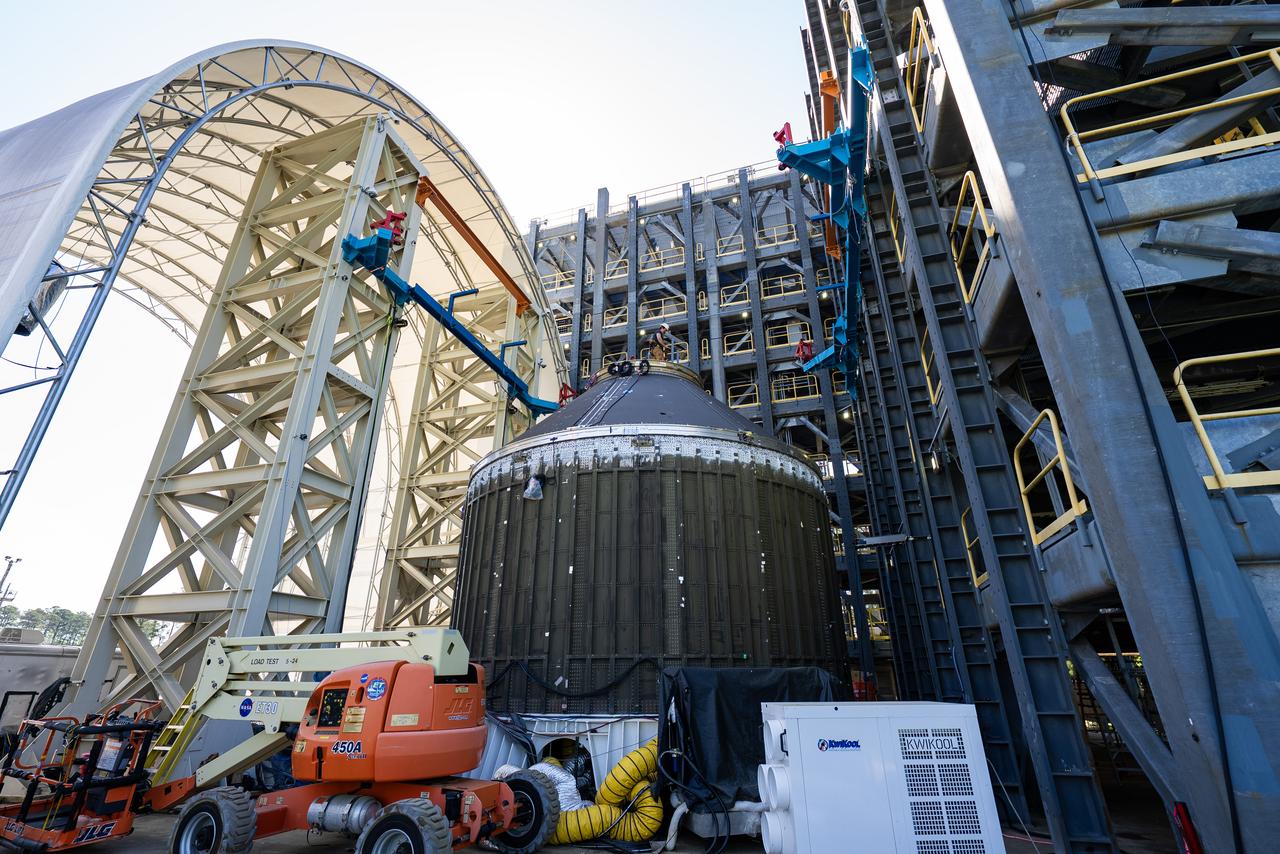
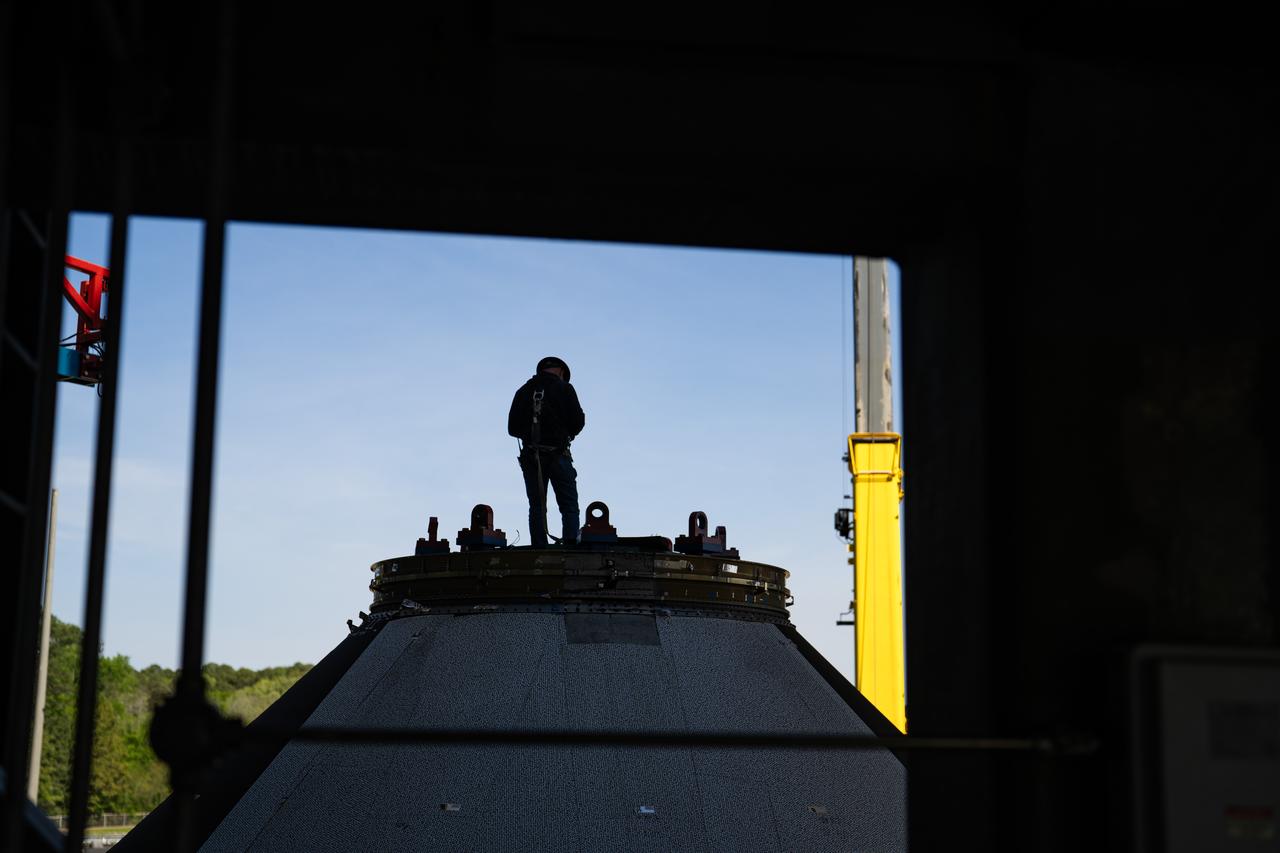
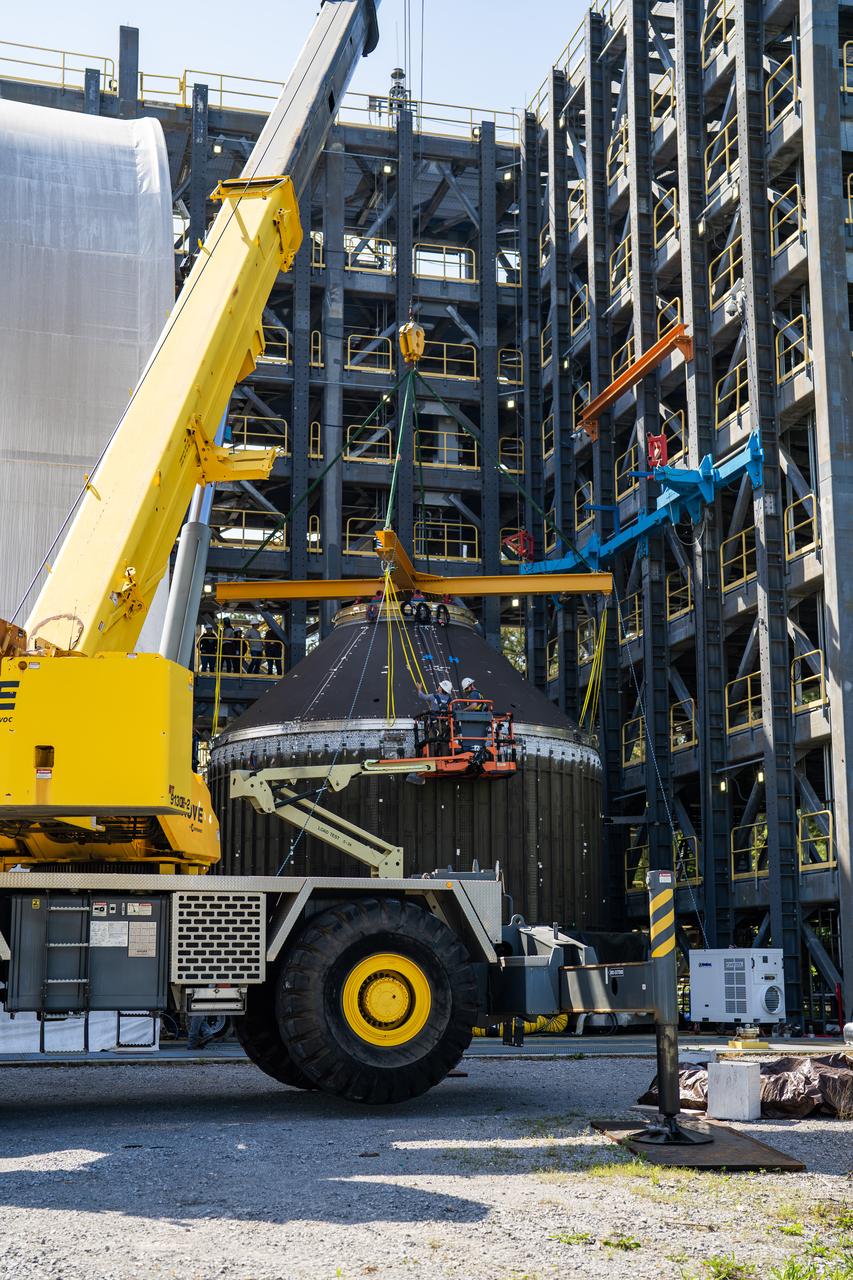
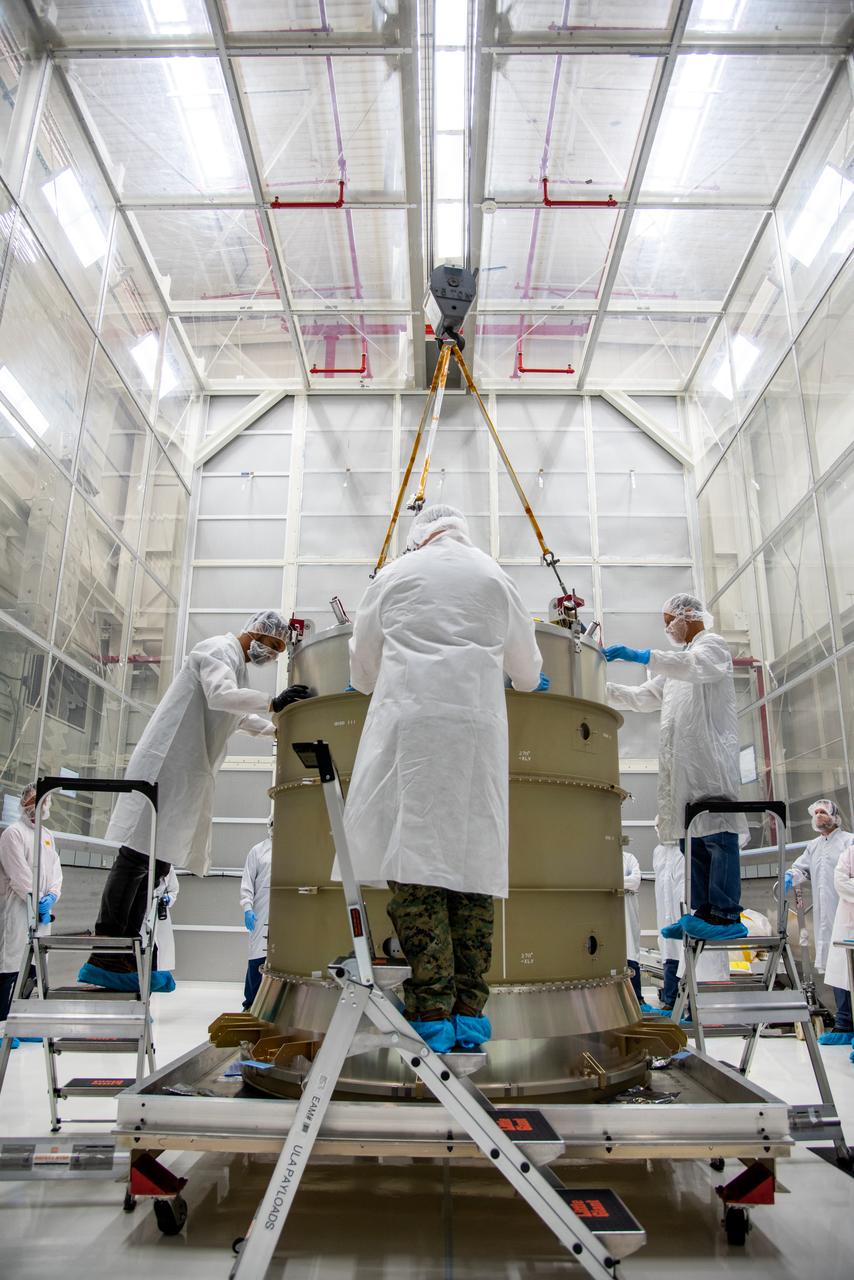
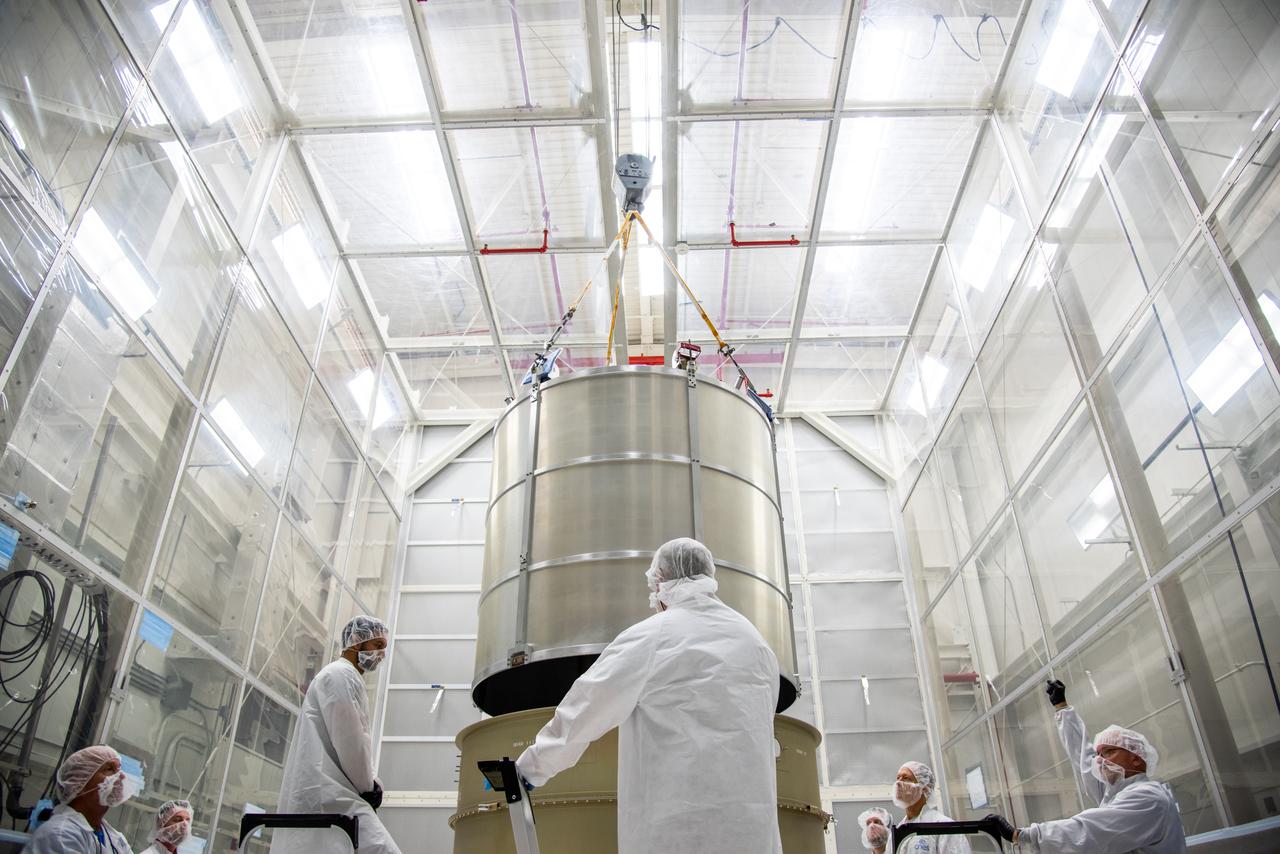
Crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13.
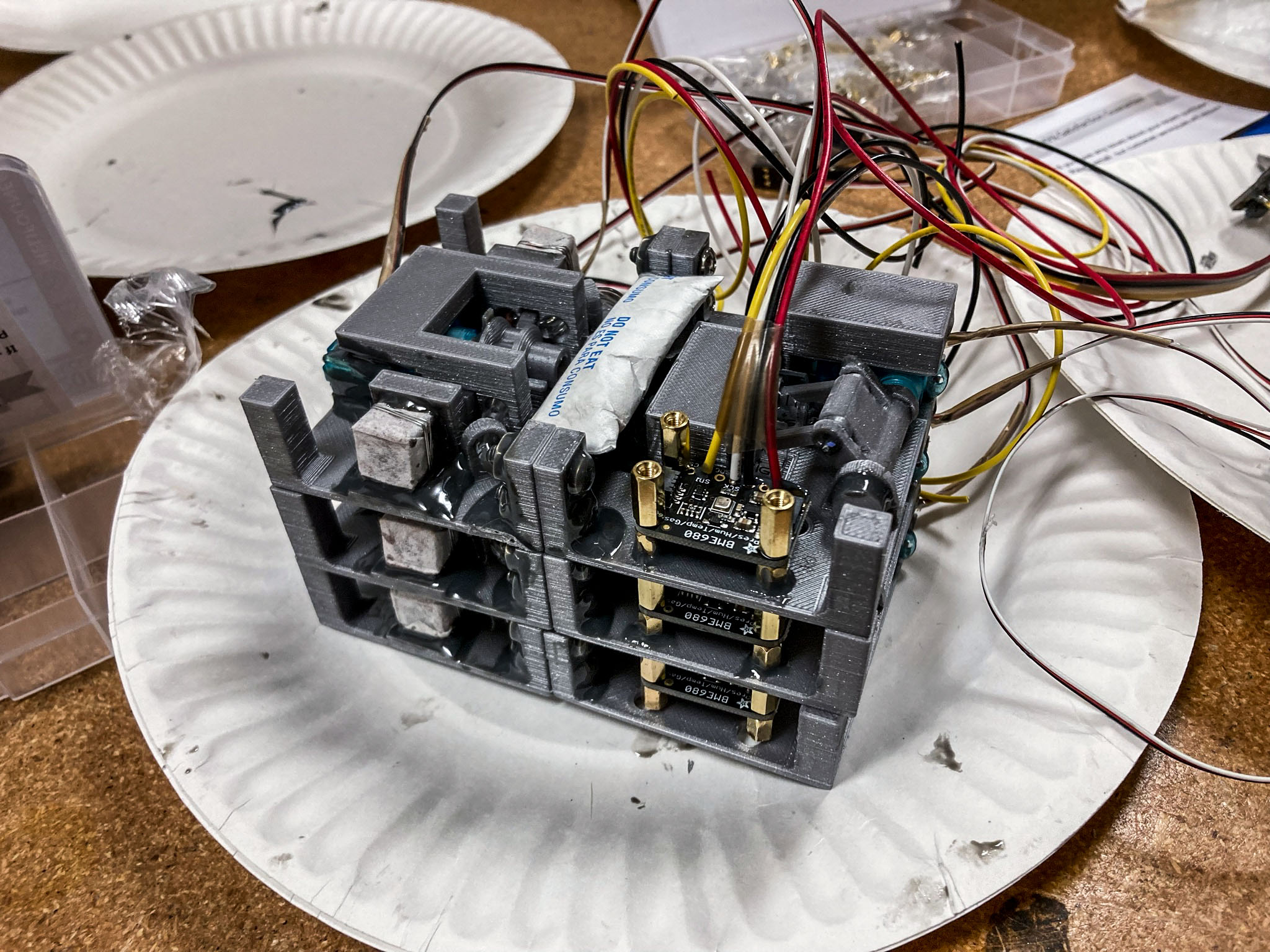
jsc2022e042479 (2/3/2022) --- This image shows three modules of flight hardware for the Biopolymer Research for In-Situ Capabilities investigation, launching aboard SpaceX’s 25th commercial resupply services mission to the International Space Station. The hardware is 3D printed in gray PLA, a desiccant packet is epoxied in the center of the module, and a pressure and humidity sensor is fastened to the left. Each module makes two bricks, for a total of six bricks that will be made in space. This investigation studies how microgravity affects the process of creating biopolymer soil composite (BSC), a concrete alternative that could be made with on-site material such as lunar or Martian dust. Image curtsey of James Wall.
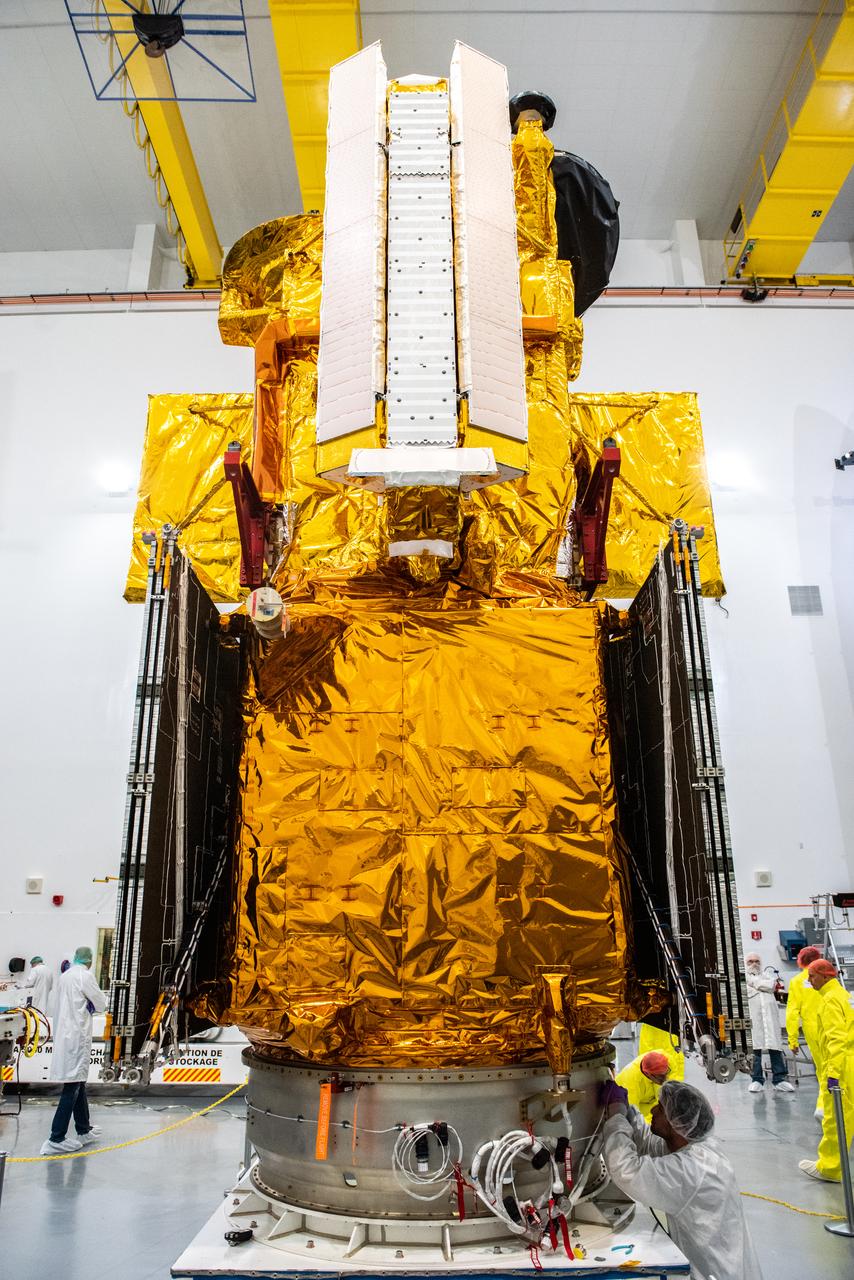

Inside the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, a crane lifts the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite onto the payload adapter on Dec. 5, 2022. A collaboration between NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency, SWOT will be the first satellite to survey nearly all water on Earth’s surface. SWOT is scheduled to lift off aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST.
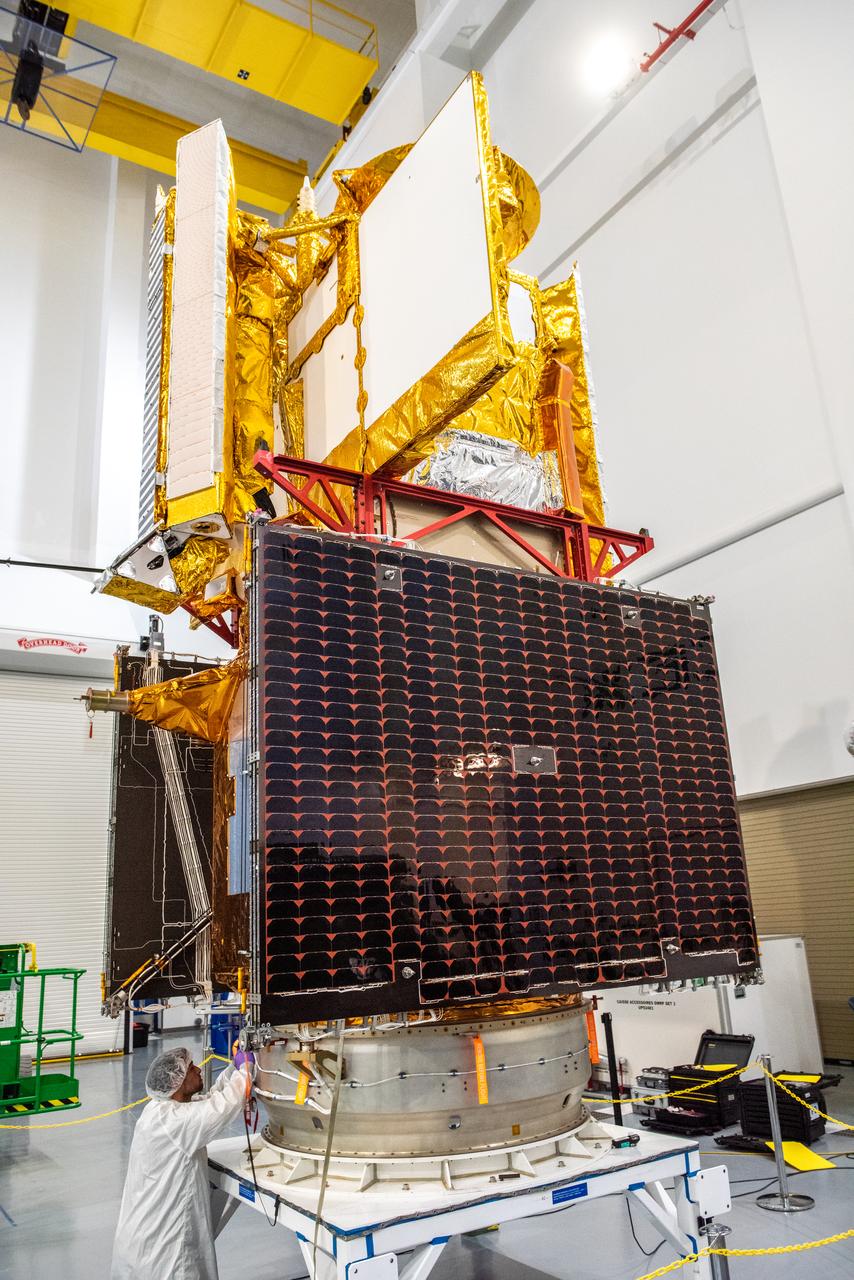

Inside the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, a technician helps secure the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite onto the payload adapter on Dec. 5, 2022. A collaboration between NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency, SWOT will be the first satellite to survey nearly all water on Earth’s surface. SWOT is scheduled to lift off aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST.
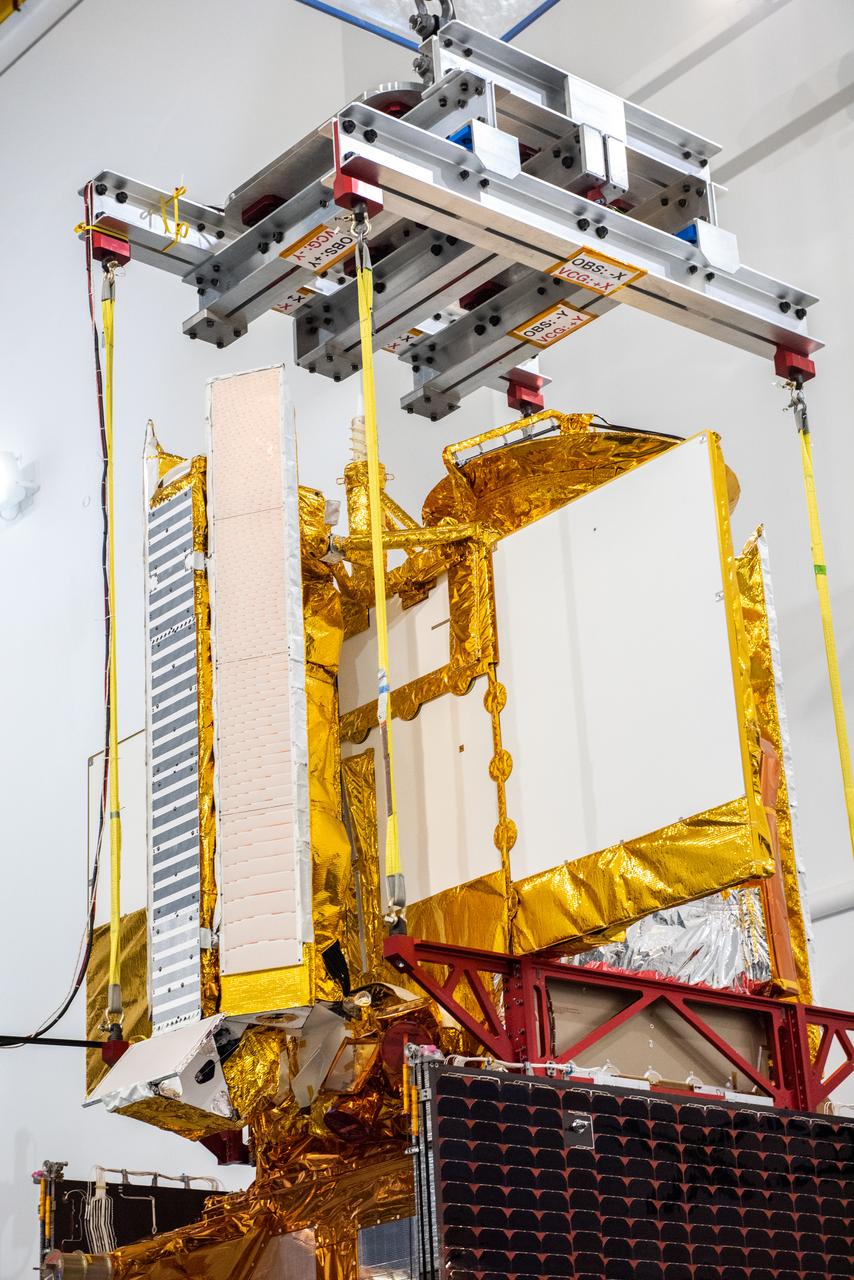

Inside the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, a crane is used to lift the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite for mating to the payload adapter on Dec. 5, 2022. A collaboration between NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency, SWOT will be the first satellite to survey nearly all water on Earth’s surface. SWOT is scheduled to lift off aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST.
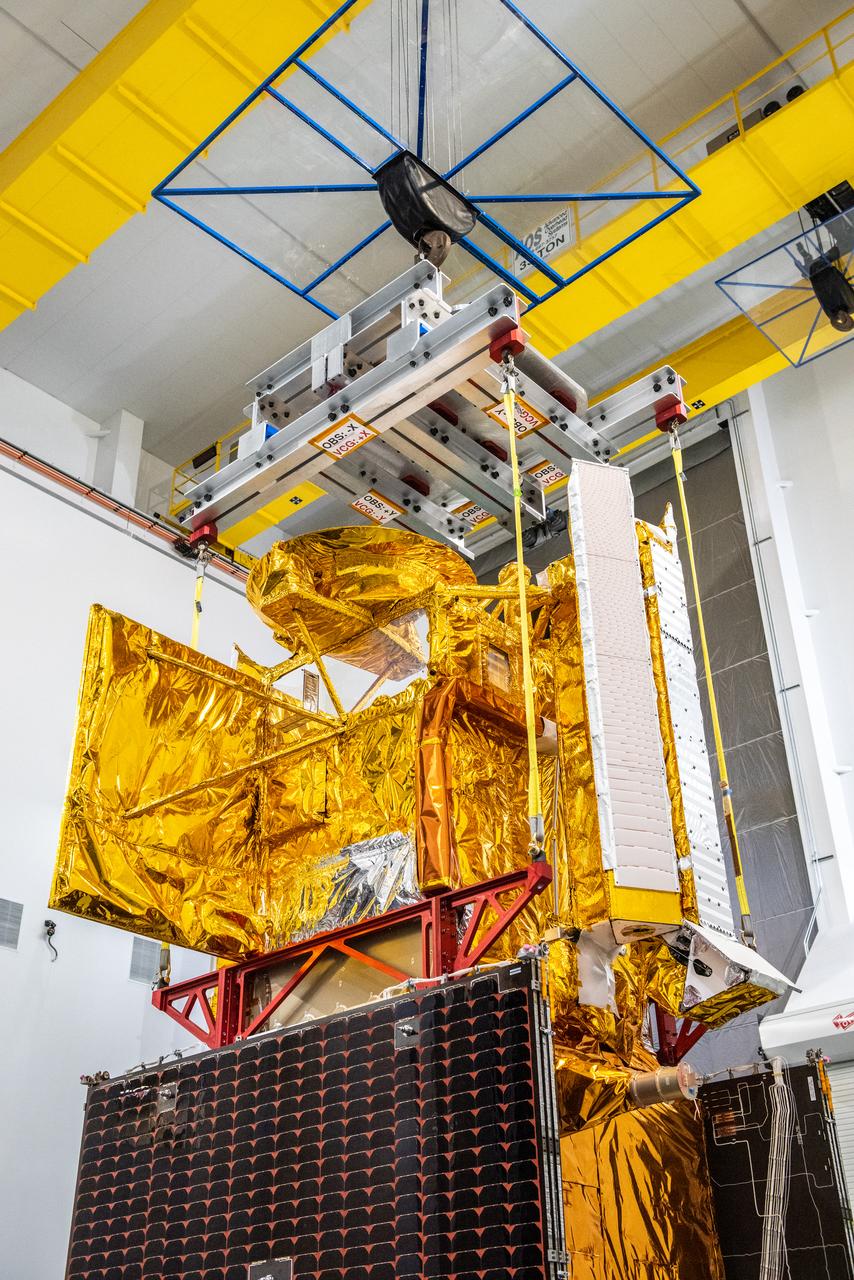

Inside the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, a crane is used to lift the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite for mating to the payload adapter on Dec. 5, 2022. A collaboration between NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency, SWOT will be the first satellite to survey nearly all water on Earth’s surface. SWOT is scheduled to lift off aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST.
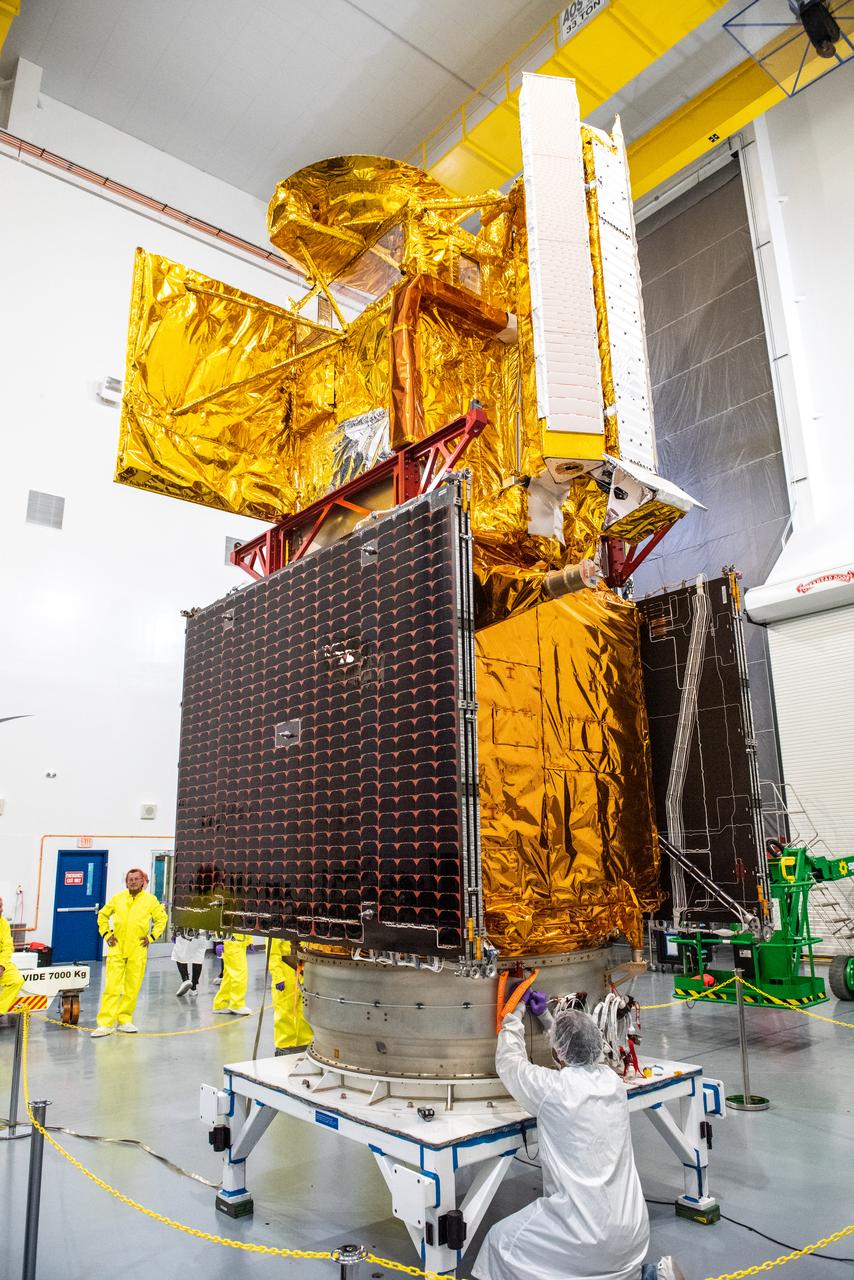

Inside the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, a technician assists as a crane lowers the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite onto the payload adapter on Dec. 5, 2022. A collaboration between NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency, SWOT will be the first satellite to survey nearly all water on Earth’s surface. SWOT is scheduled to lift off aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST.
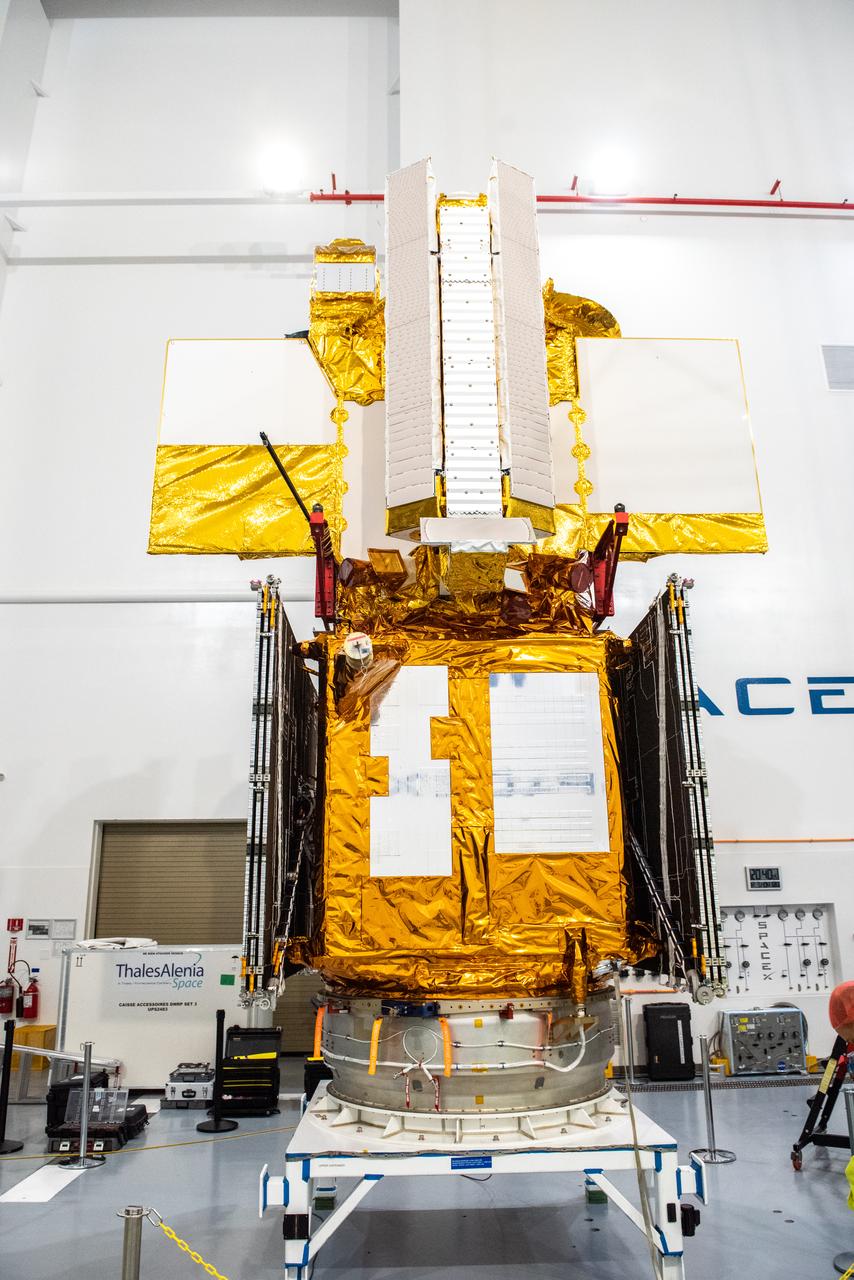

Inside the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, a crane is used to lower the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite for mating to the payload adapter on Dec. 5, 2022. A collaboration between NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency, SWOT will be the first satellite to survey nearly all water on Earth’s surface. SWOT is scheduled to lift off aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST.
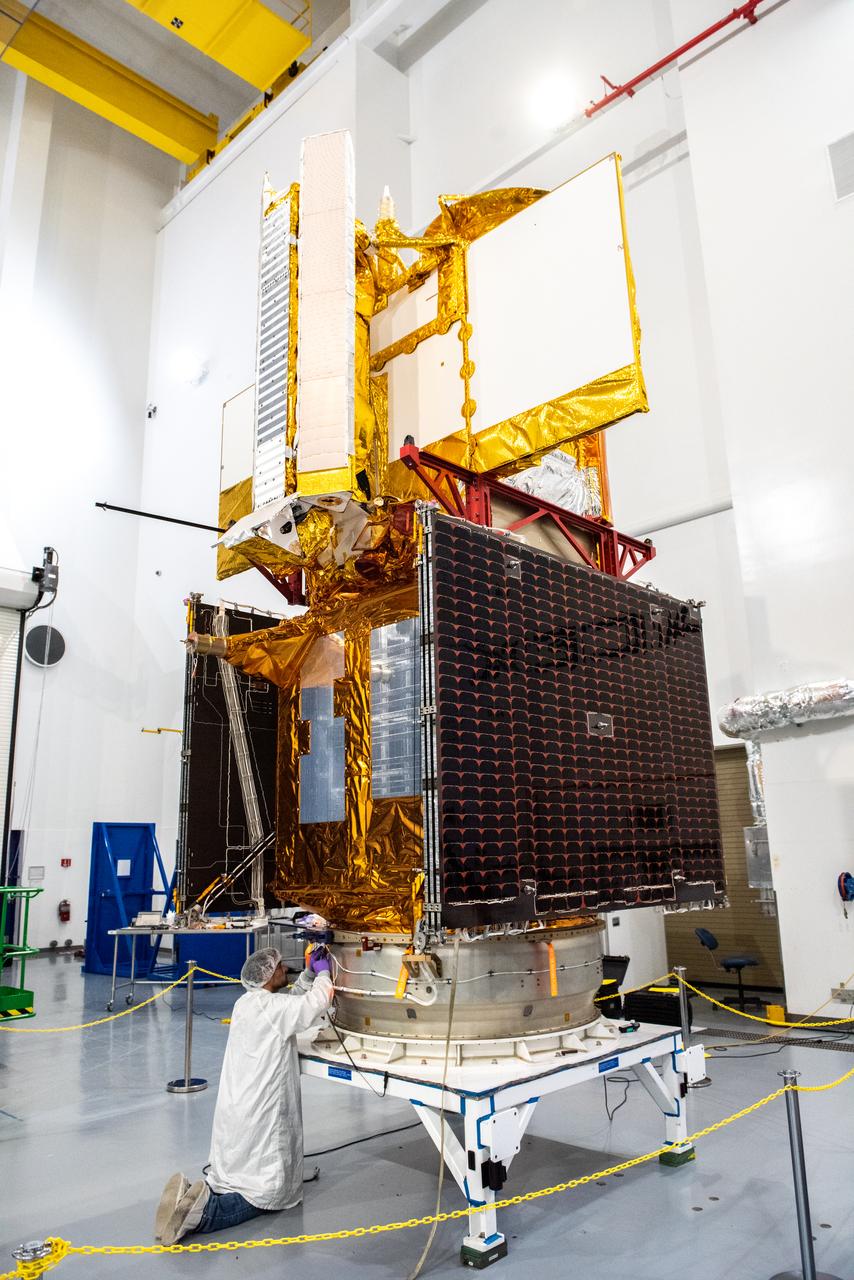

Inside the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, a technician assists as a crane lowers the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite onto the payload adapter on Dec. 5, 2022. A collaboration between NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency, SWOT will be the first satellite to survey nearly all water on Earth’s surface. SWOT is scheduled to lift off aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST.
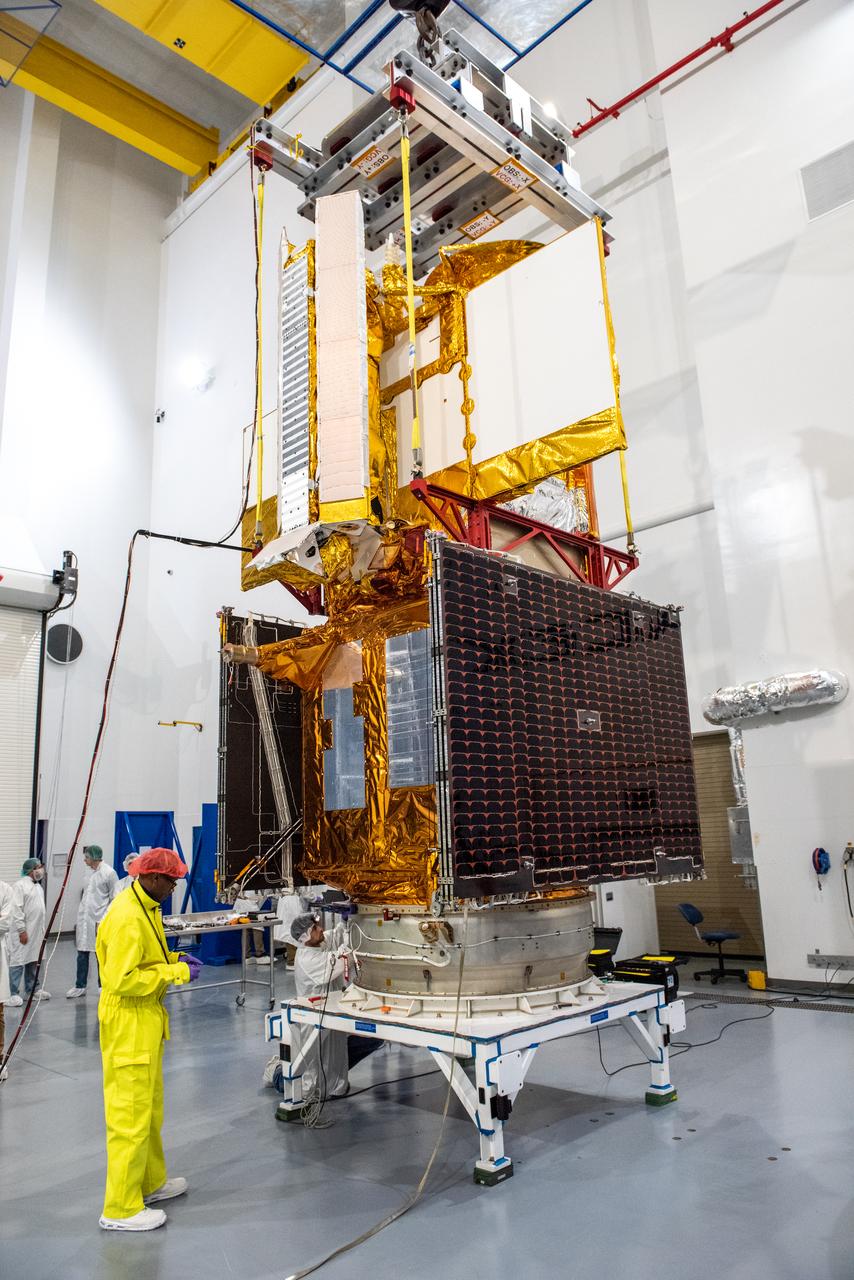

Inside the SpaceX facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California, a technician assists as a crane is used to lift the Surface Water and Ocean Topography (SWOT) satellite for mating to the payload adapter on Dec. 5, 2022. A collaboration between NASA and the French space agency Centre National d’Études Spatiales (CNES), with contributions from the Canadian Space Agency and the UK Space Agency, SWOT will be the first satellite to survey nearly all water on Earth’s surface. SWOT is scheduled to lift off aboard the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Vandenberg on Dec. 15, 2022, at 3:46 a.m. PST.
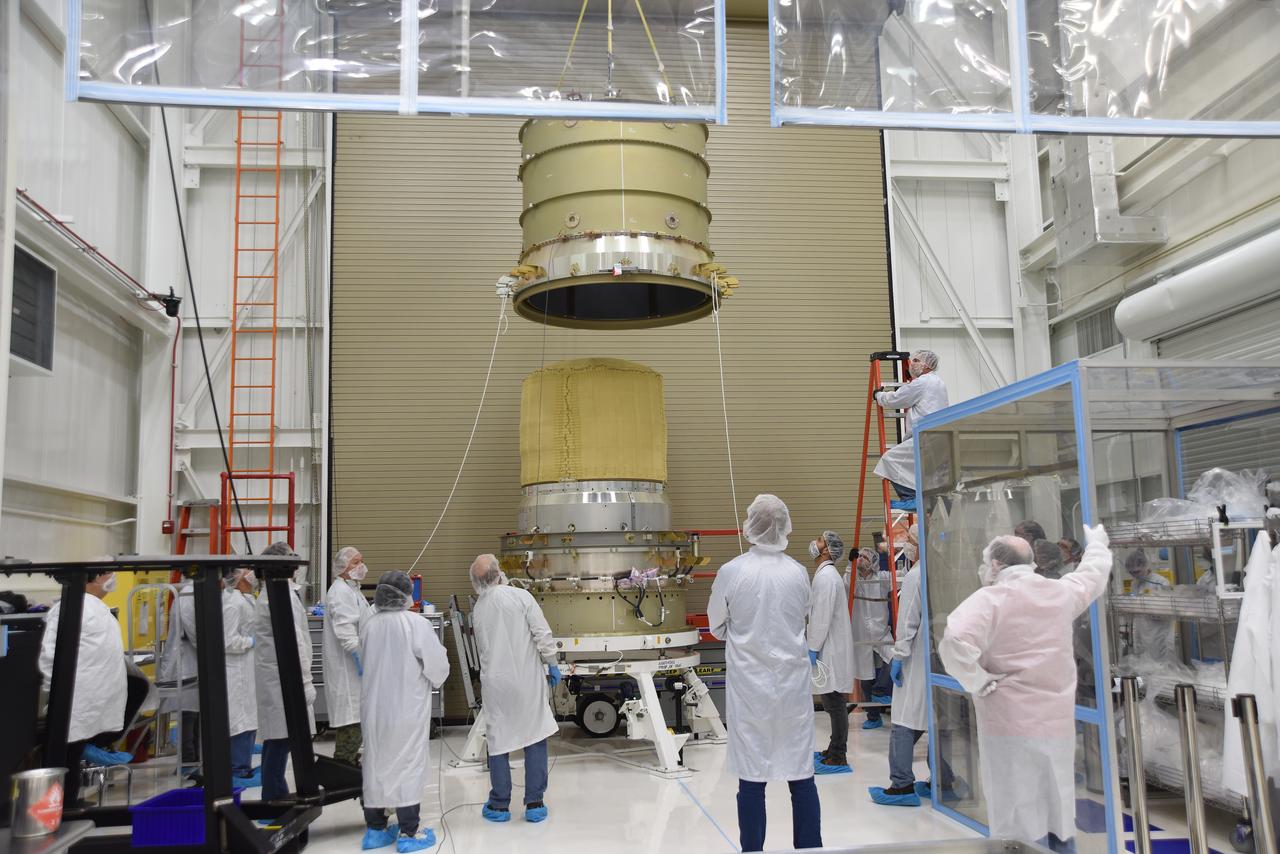

Technicians use a crane to mate the re-entry vehicle payload adapter canister for the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) with the payload adapter separation systems canister as part of launch preparations occurring inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 8, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily.
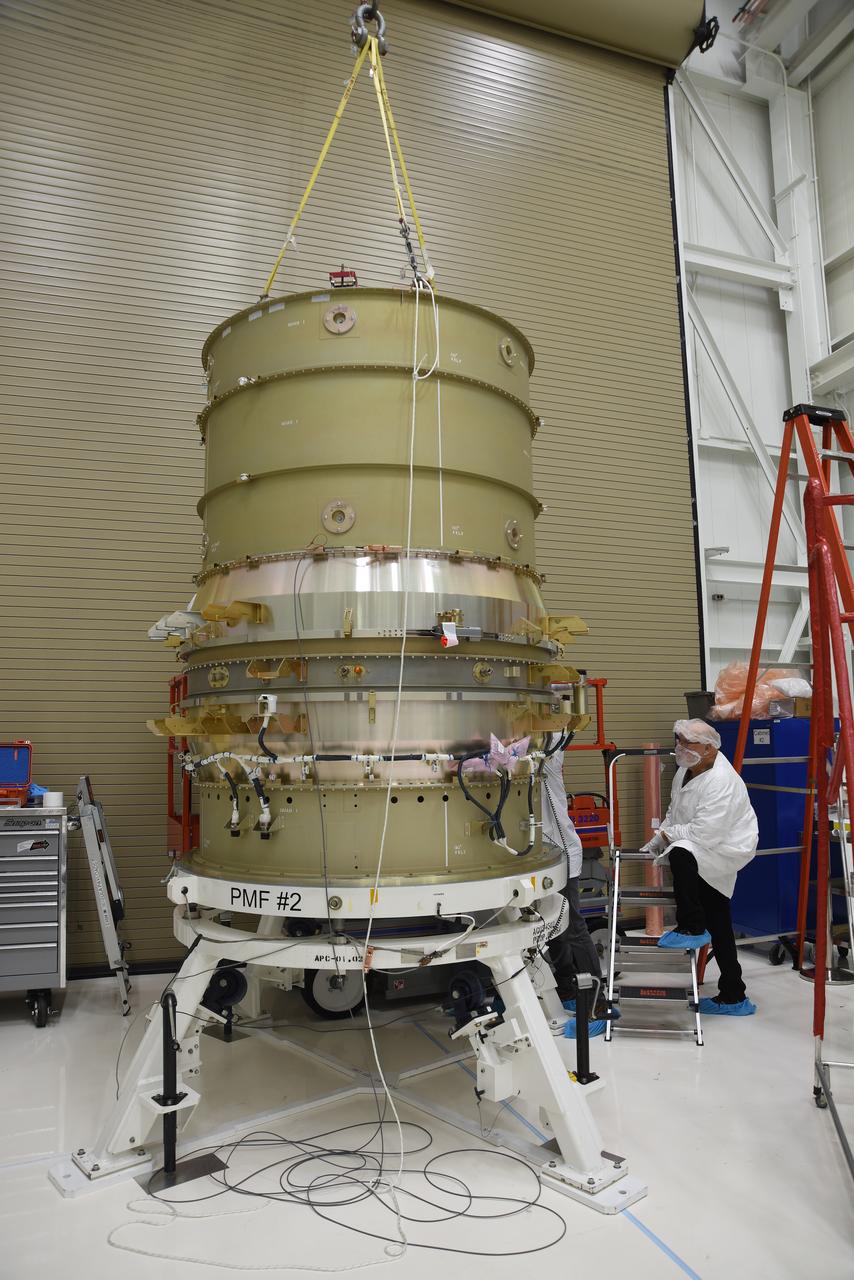

Technicians secure the re-entry vehicle payload adapter canister for the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) onto the payload adapter separation systems canister as part of launch preparations occurring inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 8, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily.
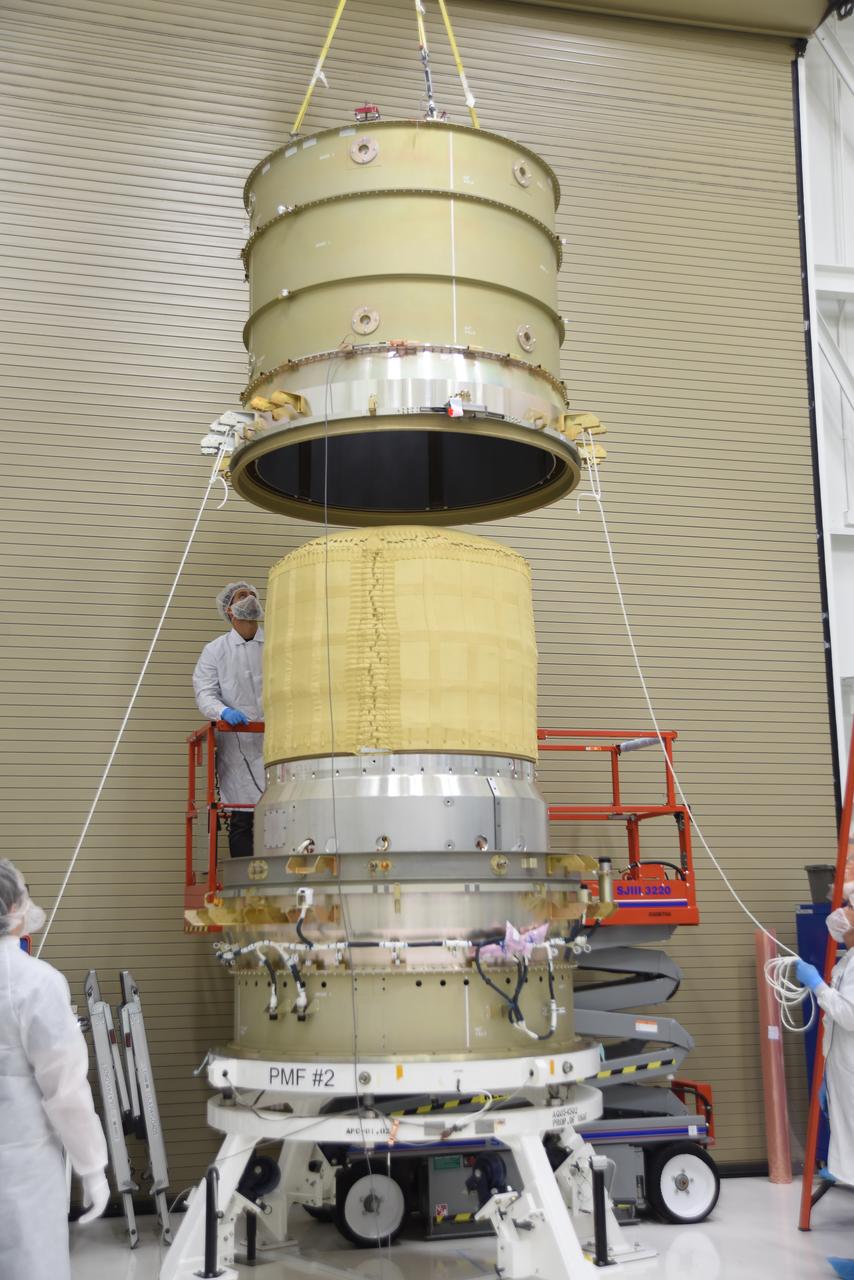

Technicians use a crane to mate the re-entry vehicle payload adapter canister for the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) with the payload adapter separation systems canister as part of launch preparations occurring inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 8, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily.

In a clean room at Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida, technicians and engineers monitor progress as NOAA's Geostationary Operational Environmental Satellite-S, or GOES-S, is mated to its payload attach fitting. It soon will be moved to Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station for mounting atop the Atlas V rocket that will boost the satellite to orbit. GOES-S is the second in a series of four advanced geostationary weather satellites that will significantly improve the detection and observation of environmental phenomena that directly affect public safety, protection of property and the nation's economic health and prosperity. GOES-S is slated to launch March 1, 2018 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket.
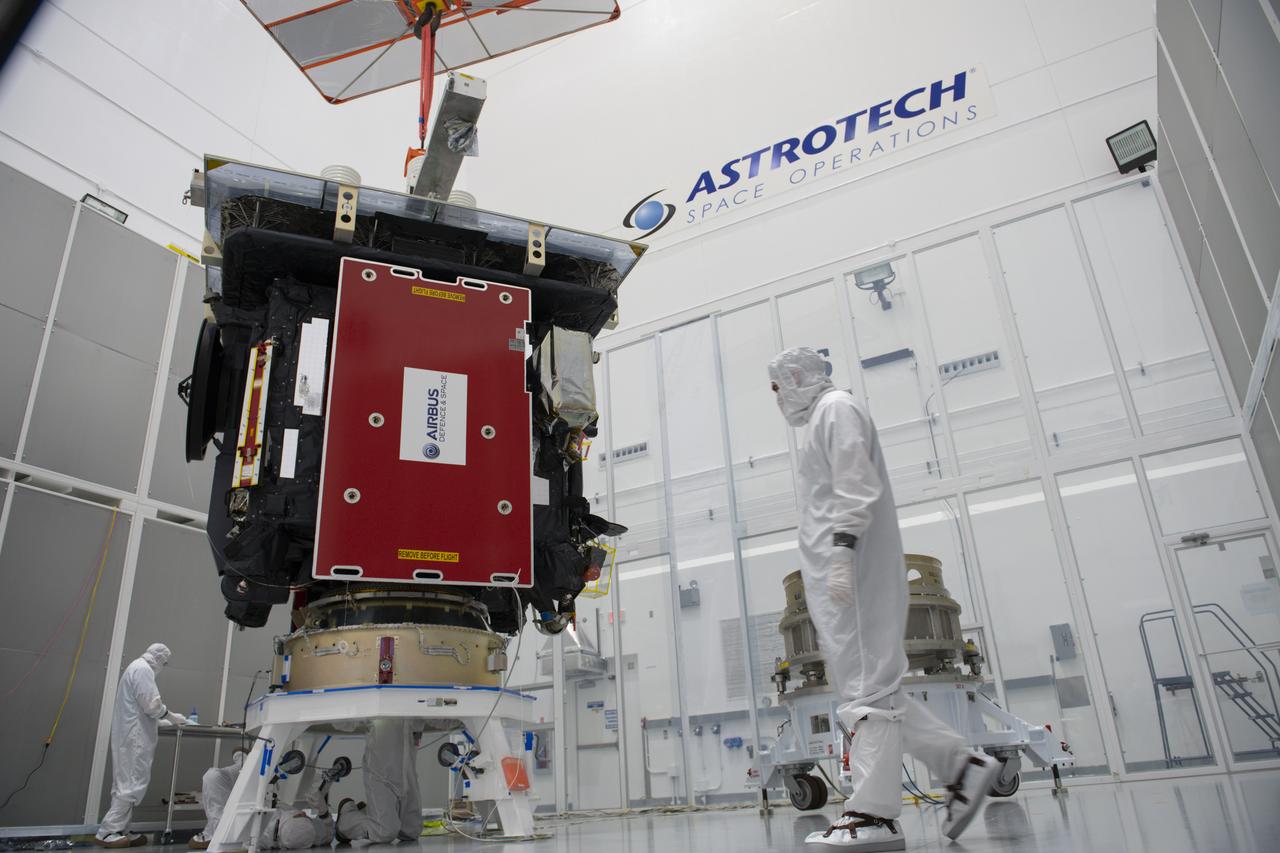

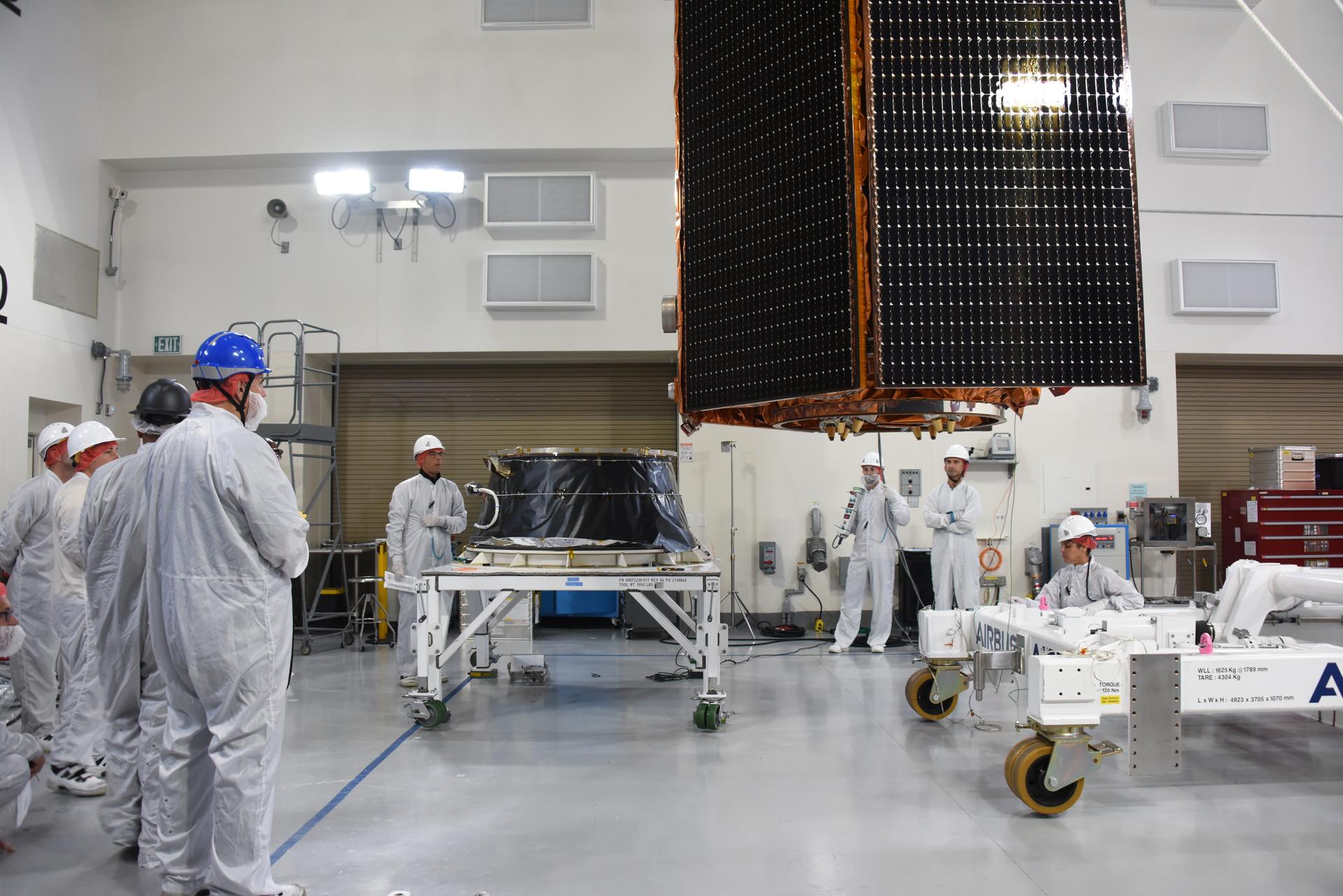
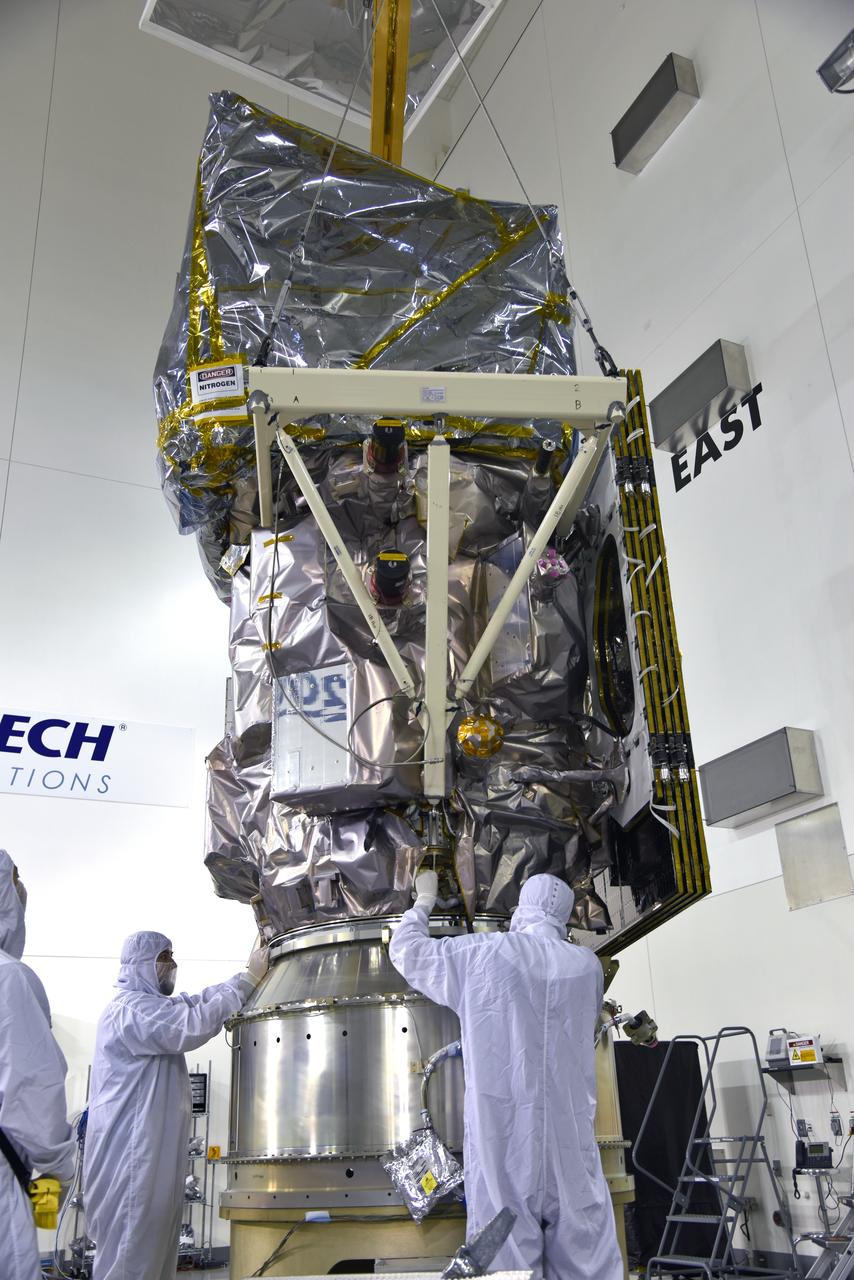
The Solar Orbiter spacecraft is mated to the payload adapter inside Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida on Jan. 16, 2020. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The spacecraft has been developed by Airbus Defence and Space. Solar Orbiter will launch in February 2020 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
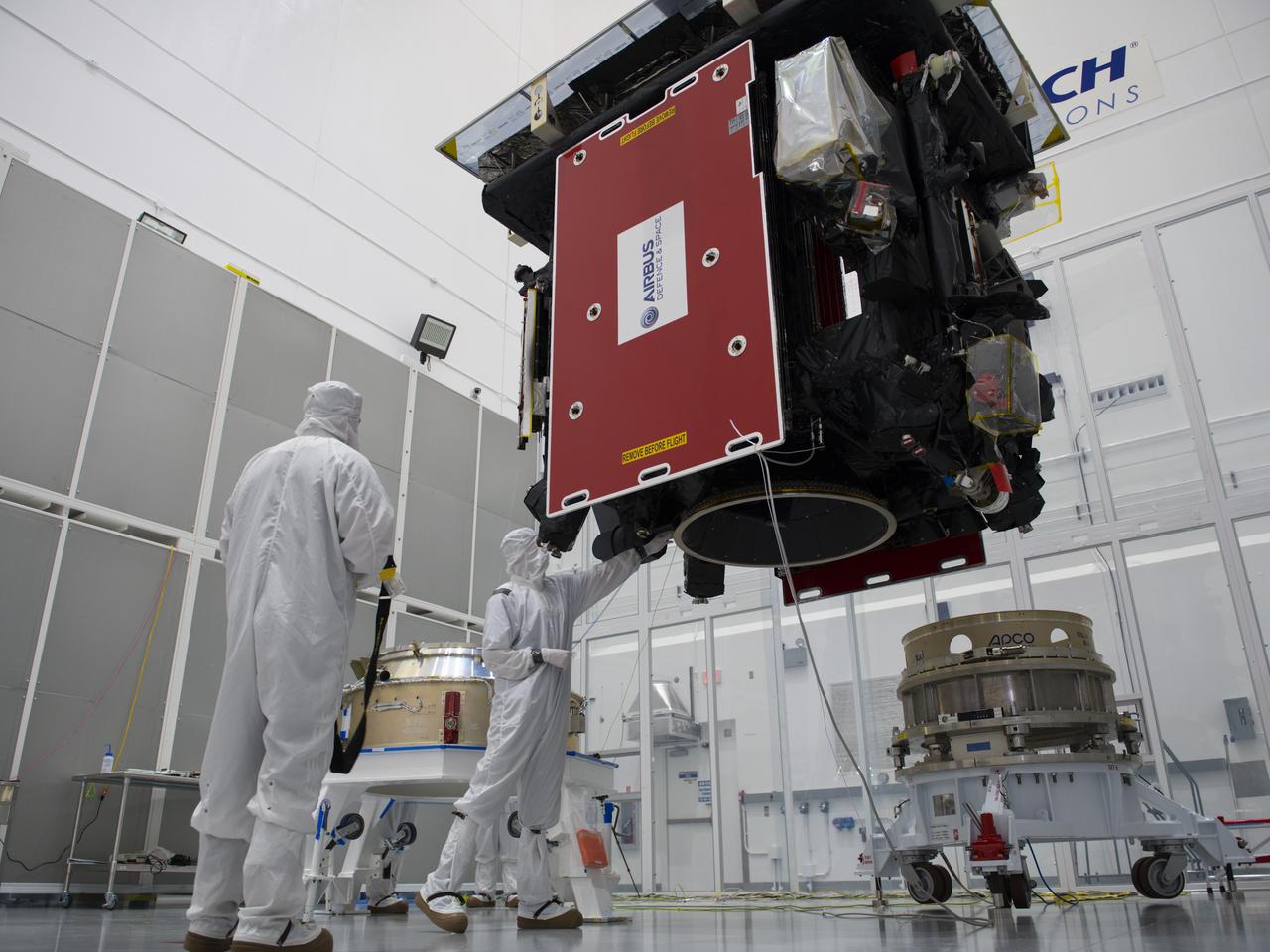

The Solar Orbiter spacecraft is moved by crane from a work stand to the payload adapter inside Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida on Jan. 16, 2020. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The spacecraft has been developed by Airbus Defence and Space. Solar Orbiter will launch in February 2020 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
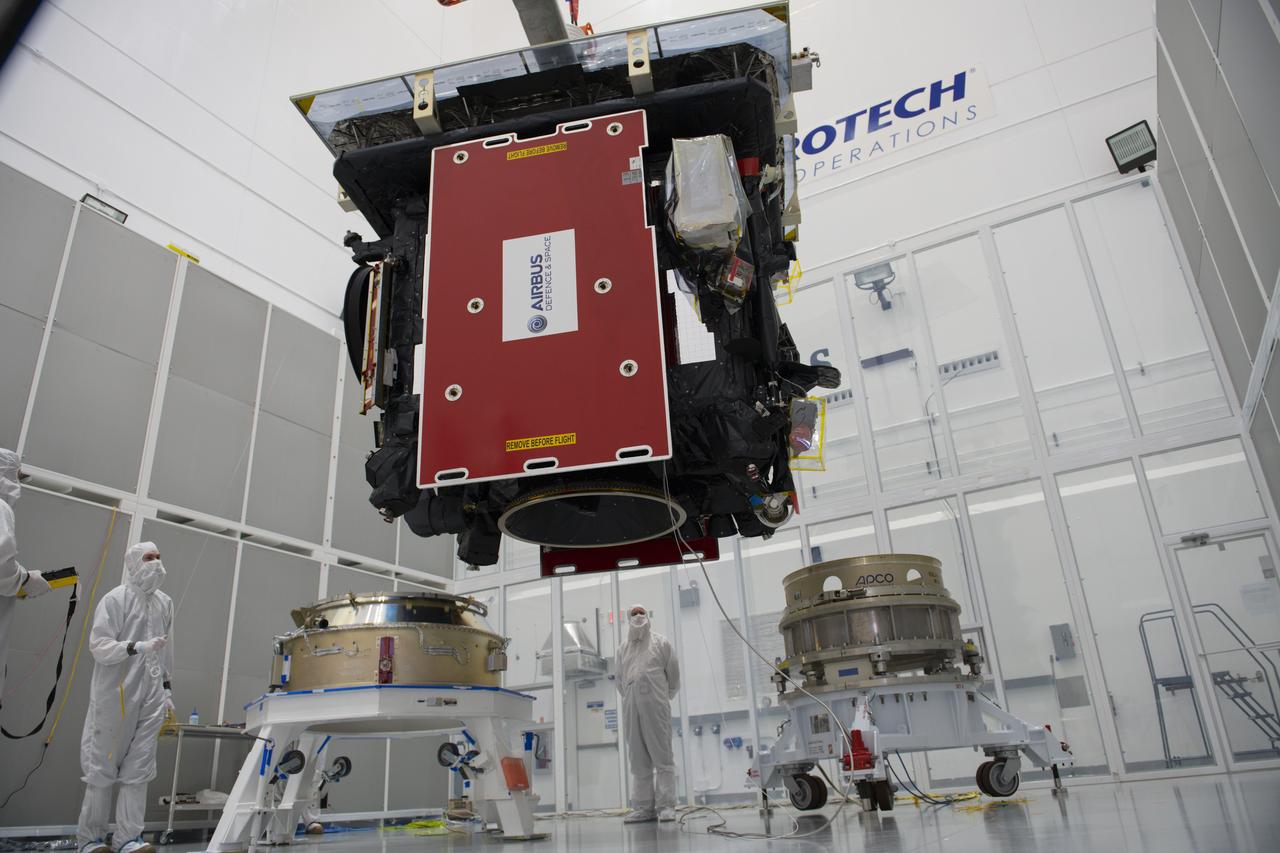

The Solar Orbiter spacecraft is moved by crane from a work stand to the payload adapter inside Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida on Jan. 16, 2020. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The spacecraft has been developed by Airbus Defence and Space. Solar Orbiter will launch in February 2020 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
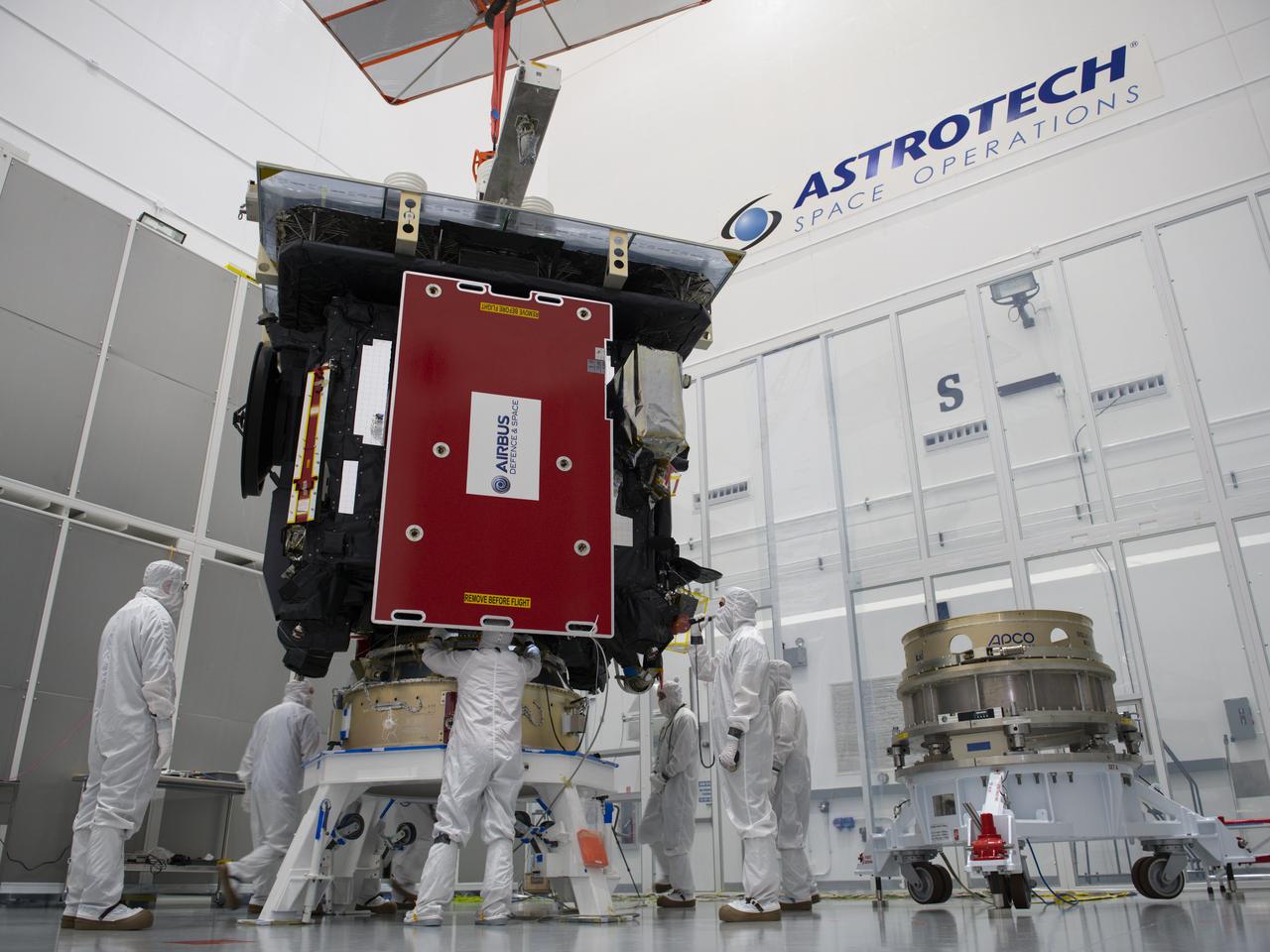

European Space Agency workers assist as a crane lowers the Solar Orbiter spacecraft onto the payload adapter inside the Astrotech Space Operations facility in Titusville, Florida on Jan. 17, 2020. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The spacecraft has been developed by Airbus Defence and Space. Solar Orbiter will launch in February 2020 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
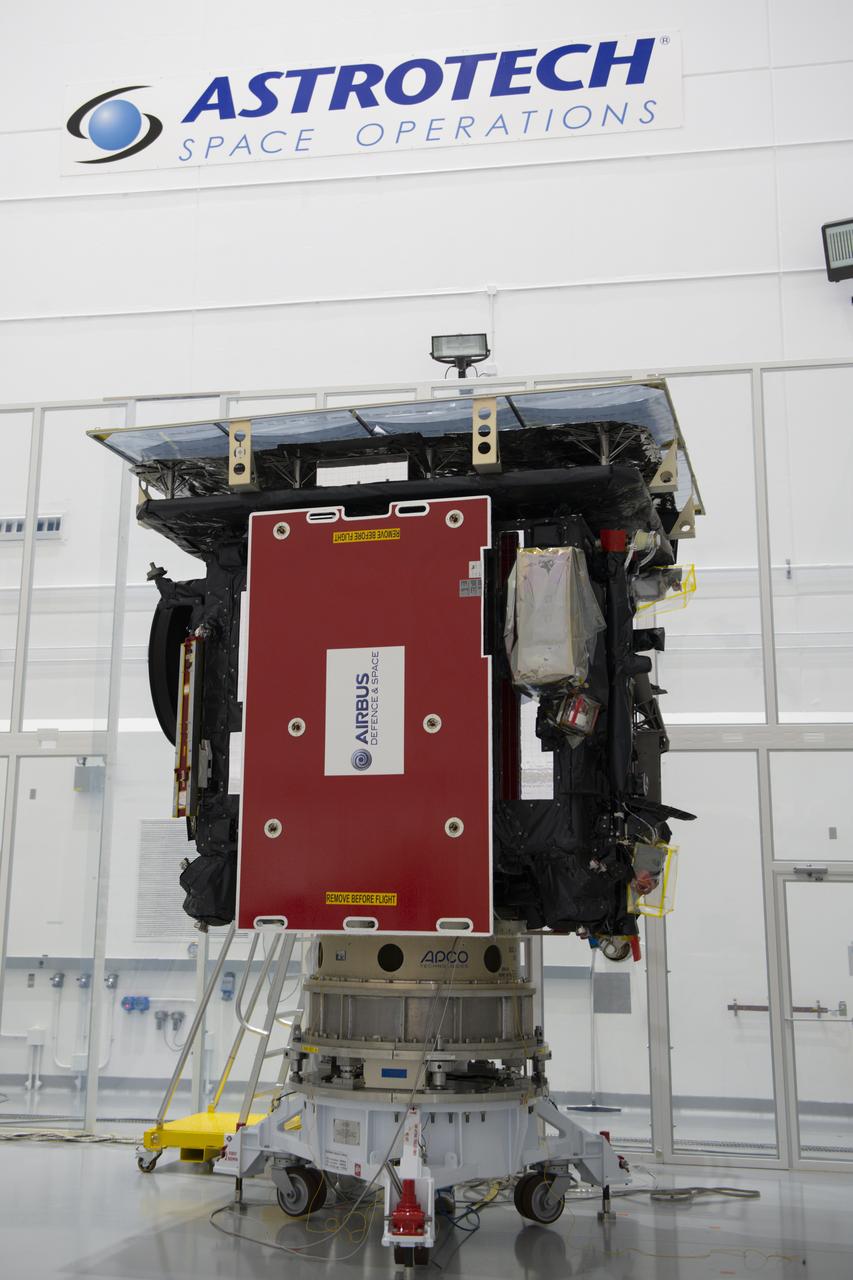

The Solar Orbiter spacecraft is secured on a work stand for processing inside Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida on Jan. 16, 2020. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The spacecraft has been developed by Airbus Defence and Space. Solar Orbiter will launch in February 2020 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
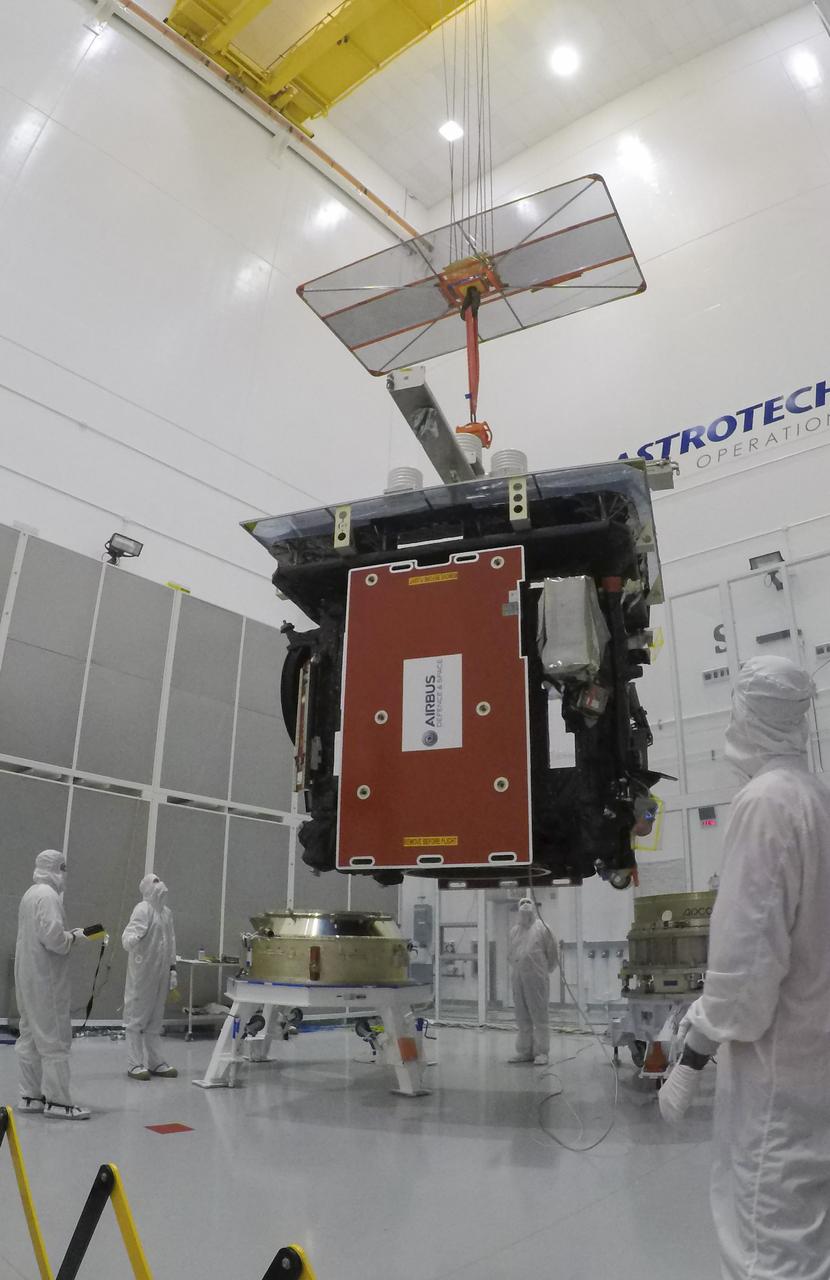

The Solar Orbiter spacecraft is lifted and moved by crane from a work stand for mating to the payload adapter inside Astrotech Space Operations in Titusville, Florida on Jan. 16, 2020. Solar Orbiter is an international cooperative mission between ESA (European Space Agency) and NASA. The mission aims to study the Sun, its outer atmosphere and solar wind. The spacecraft will provide the first images of the Sun’s poles. NASA’s Launch Services Program based at Kennedy is managing the launch. The spacecraft has been developed by Airbus Defence and Space. Solar Orbiter will launch in February 2020 aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Space Launch Complex 41 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
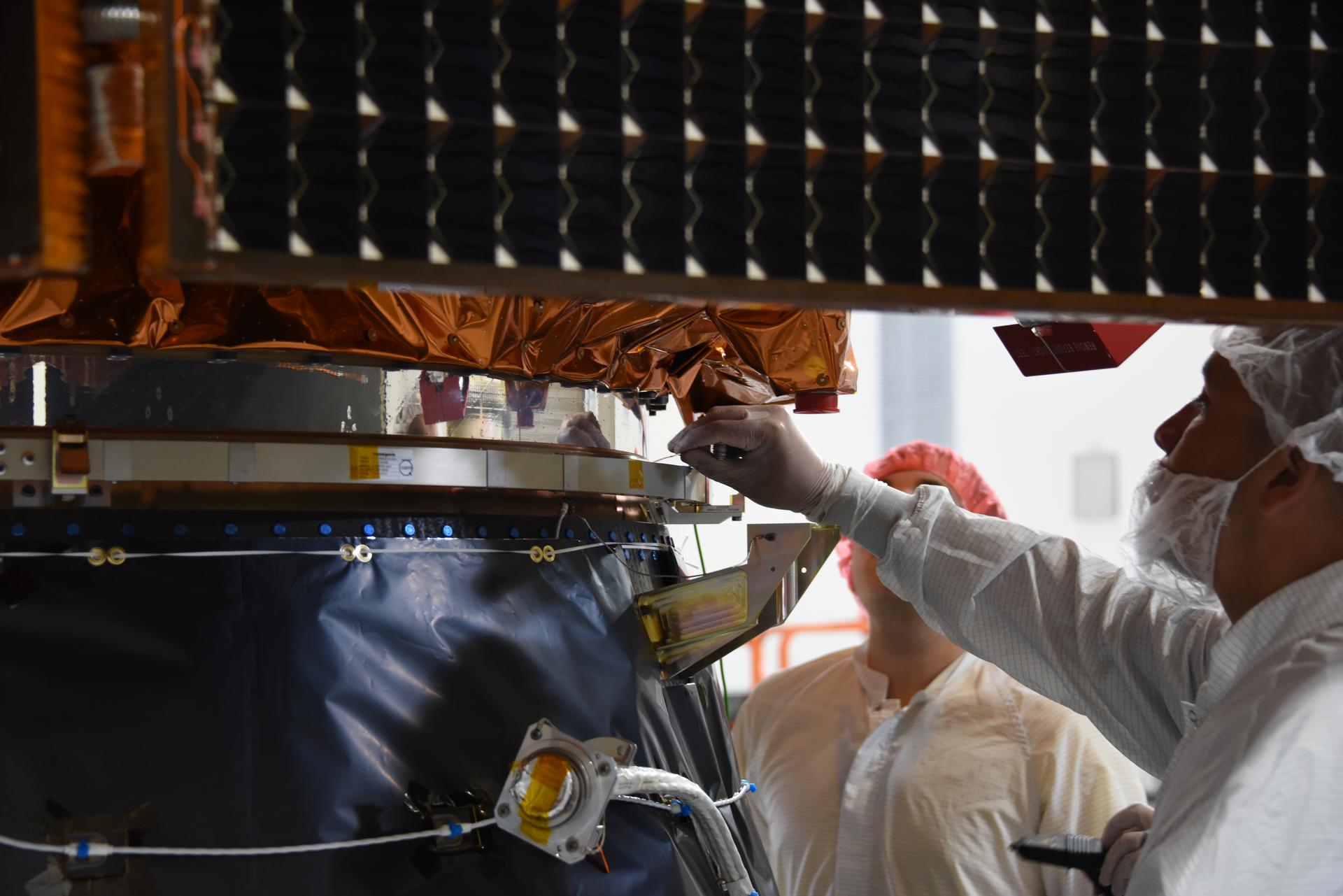

Technicians integrate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft to the payload adapter inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Nov. 4, 2025. The payload adapter is part of the system that connects Sentinel-6B to the second stage of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket that will carry it to orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.

Technicians integrate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft to the payload adapter inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Nov. 4, 2025. The payload adapter is part of the system that connects Sentinel-6B to the second stage of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket that will carry it to orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.

Technicians integrate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft to the payload adapter inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Nov. 4, 2025. The payload adapter is part of the system that connects Sentinel-6B to the second stage of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket that will carry it to orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
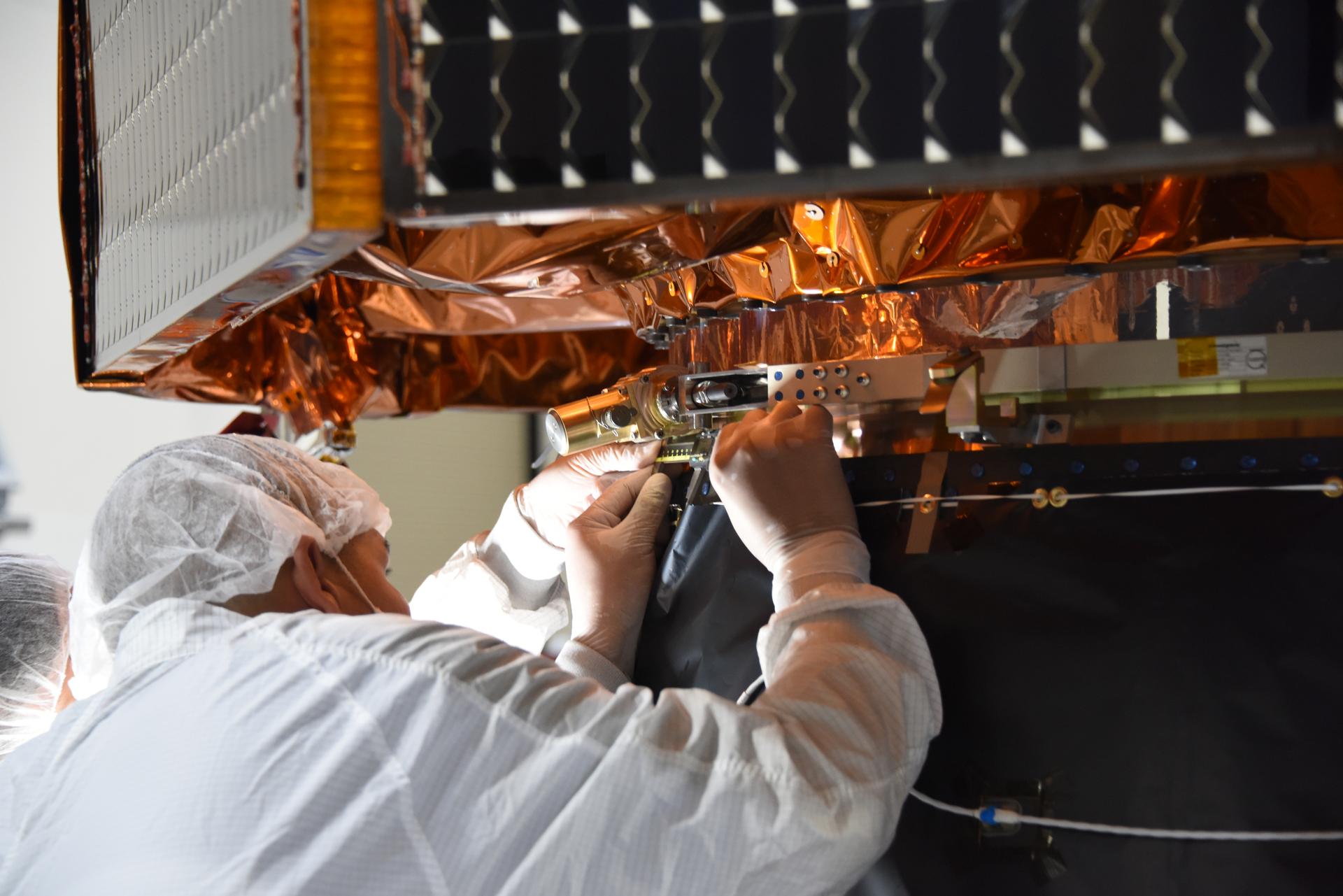

Technicians integrate the Sentinel-6B spacecraft to the payload adapter inside the Astrotech Space Operations payload processing facility at Vandenberg Space Force Base in California on Tuesday, Nov. 4, 2025. The payload adapter is part of the system that connects Sentinel-6B to the second stage of the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket that will carry it to orbit. A collaboration between NASA, ESA (European Space Agency), EUMETSAT (European Organisation for the Exploitation of Meteorological Satellites), and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), Sentinel-6B is designed to measure sea levels down to roughly an inch for about 90% of the world’s oceans. NASA is targeting launch no earlier than Sunday, Nov. 16, on a SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket from Space Launch Complex 4 East at Vandenberg.
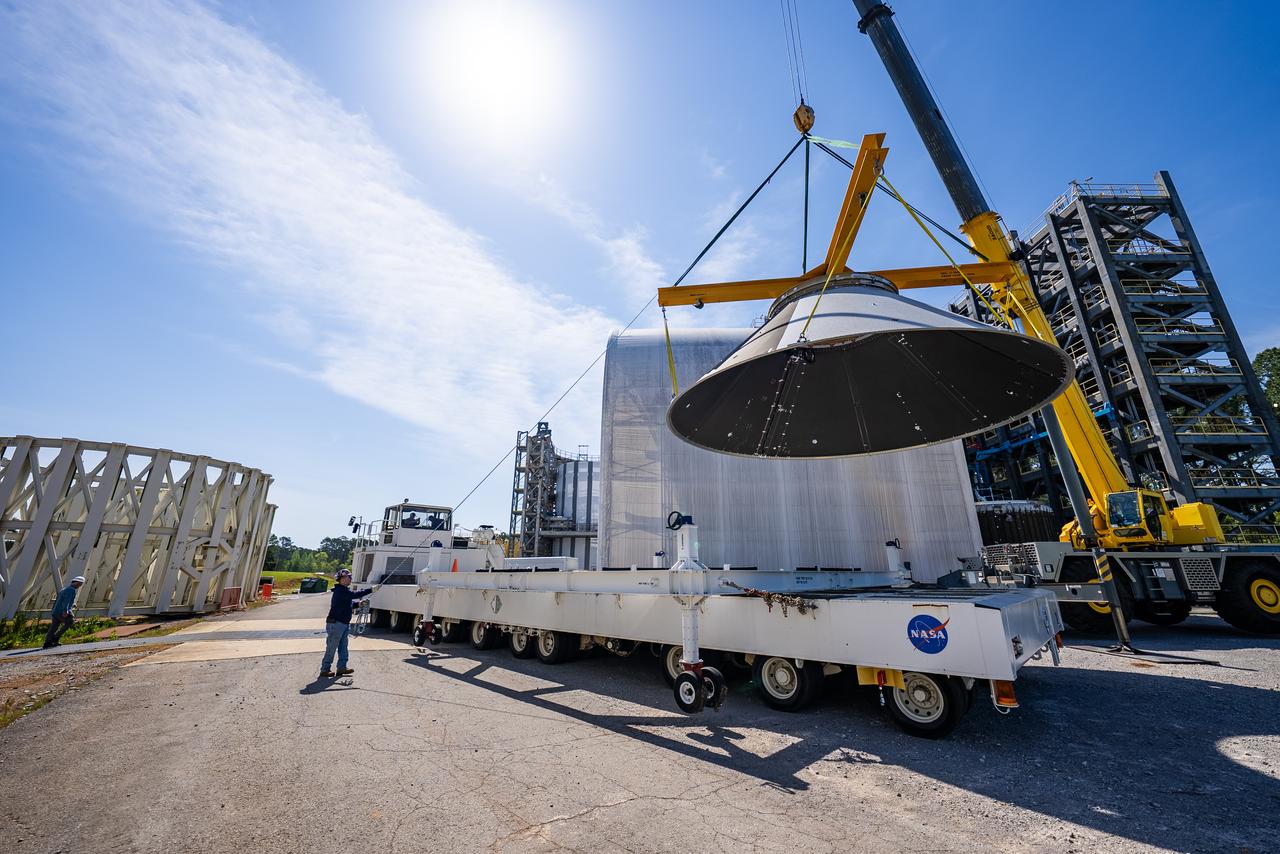

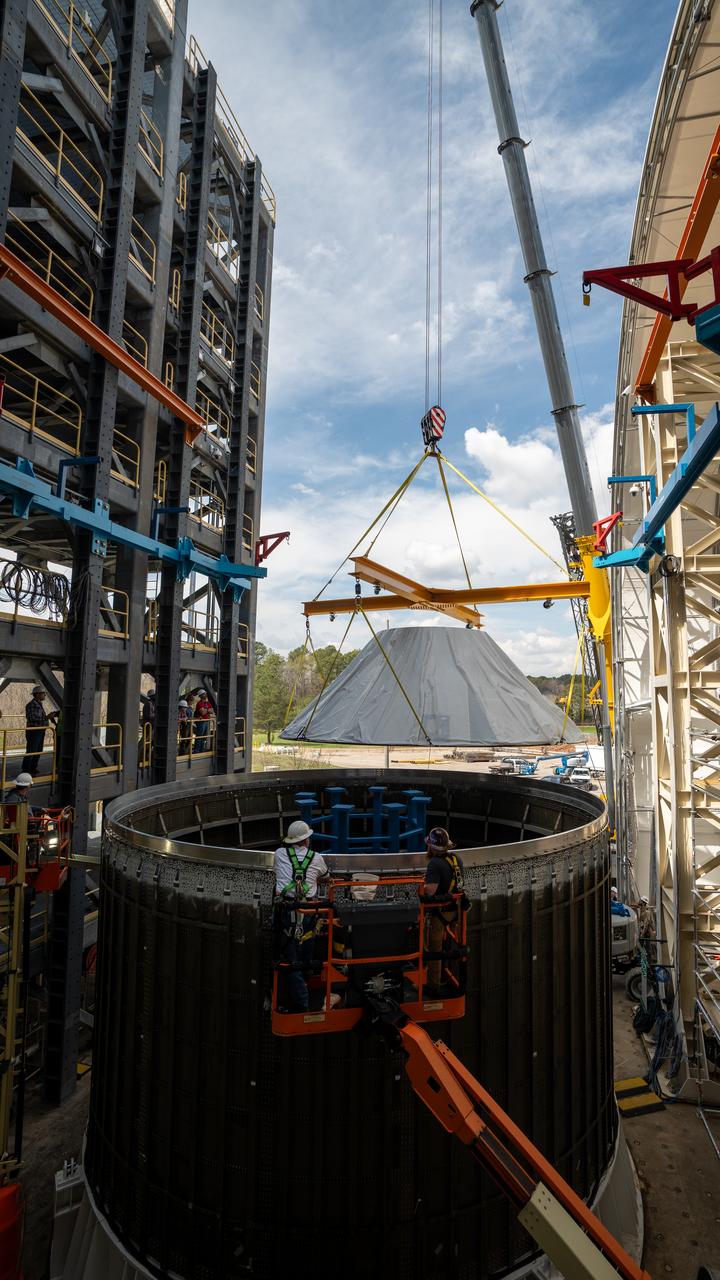
Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.
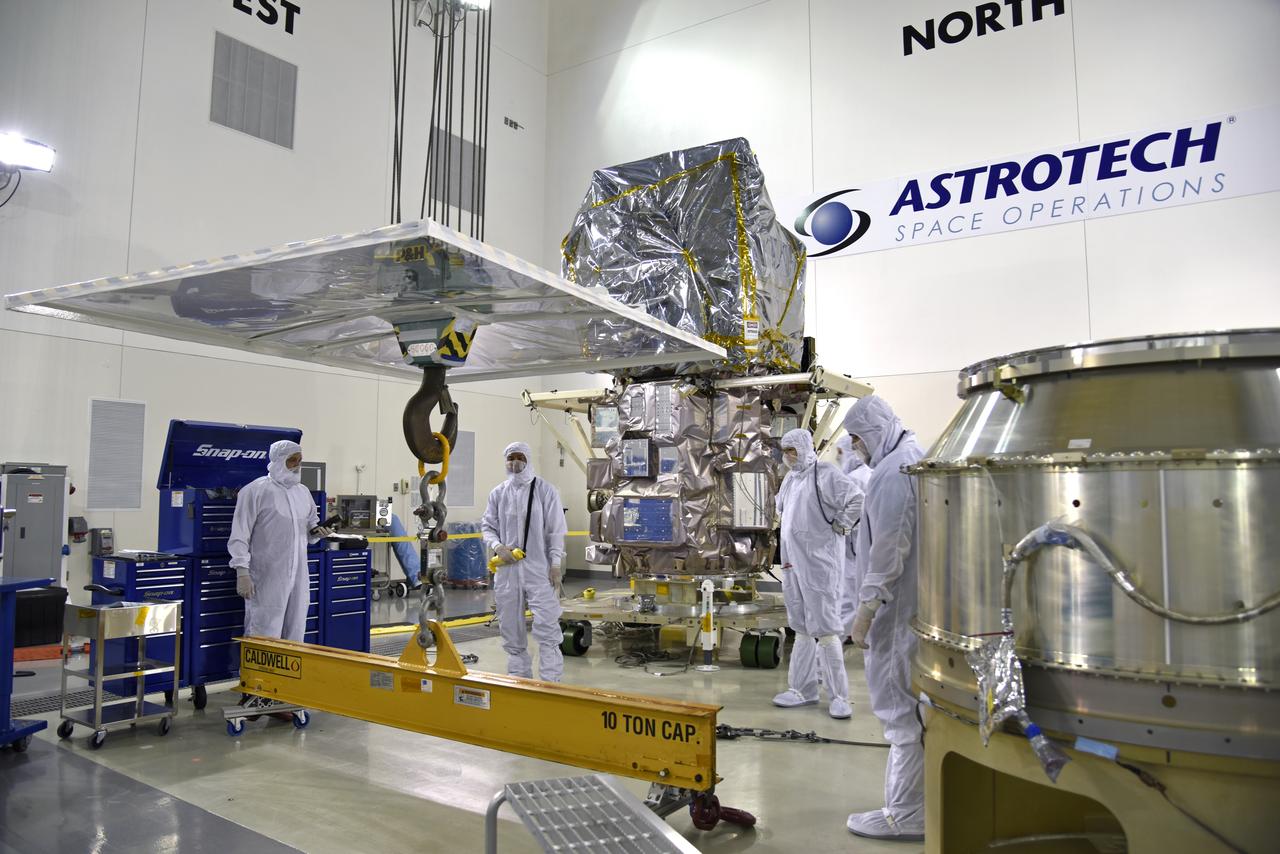

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to attach NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) to the payload adapter, on Aug. 20, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.
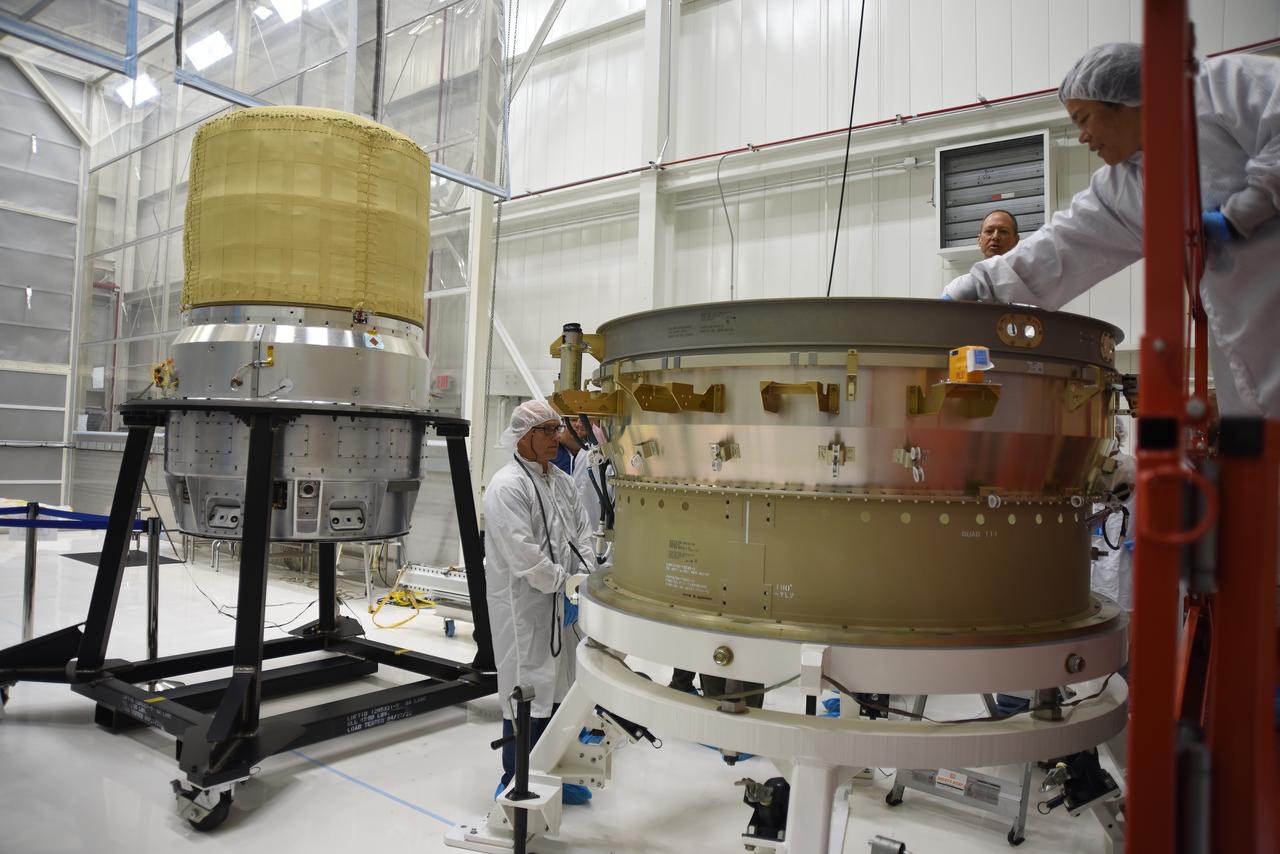

Technicians prepare the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) re-entry payload adapter interface ring for mating to the re-entry vehicle as part of launch preparations occurring inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 7, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily.
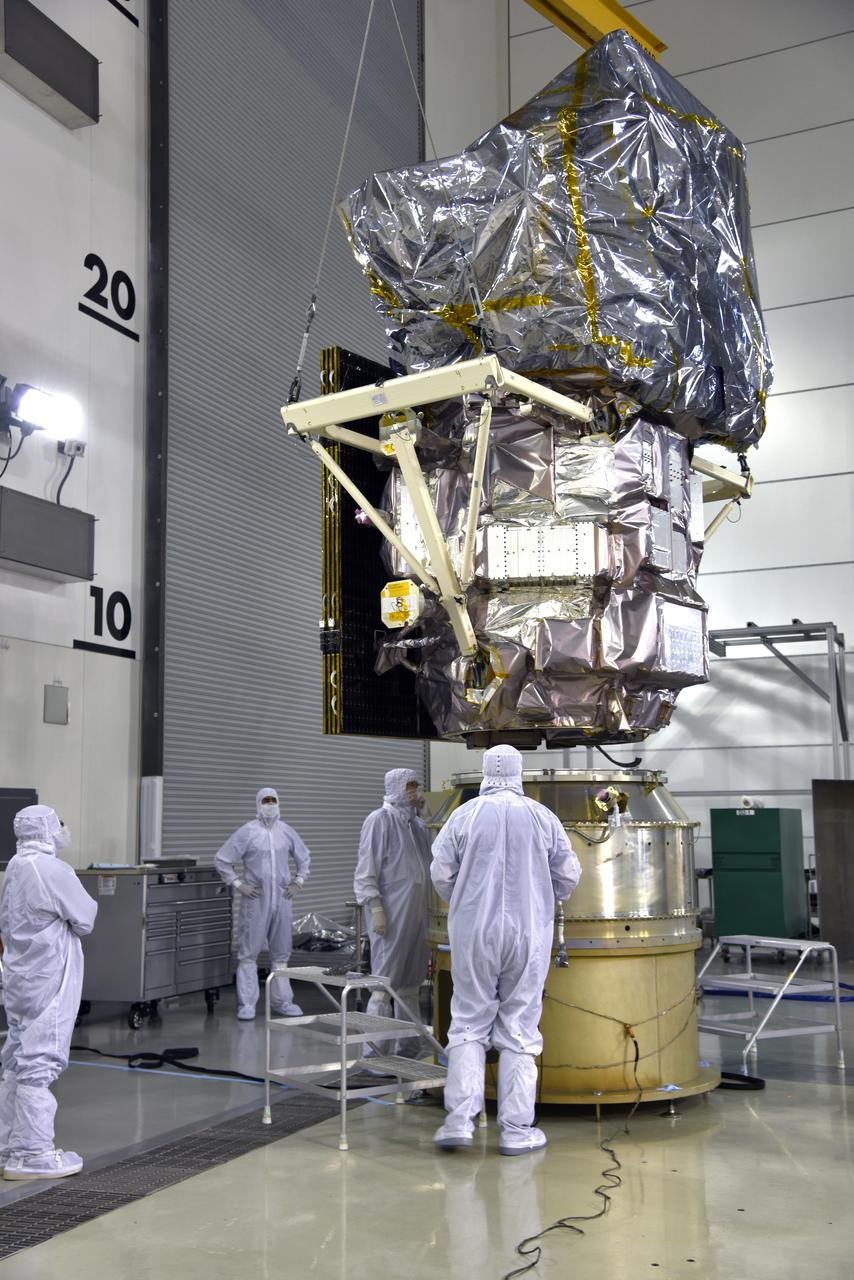

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a crane lifts and moves NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) over the payload adapter on Aug. 30, 2018. The satellite will be attached to the adapter. ICESat-2 is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a technician prepares NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) to be attached to the payload adapter, on Aug. 20, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a crane lifts and moves NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on Aug. 30, 2018. The satellite will be attached to the payload adapter. ICESat-2 is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.

The re-entry vehicle for the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) is now mated to the re-entry vehicle payload adapter interface ring and secured on a work stand as part of launch preparations inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 7, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.

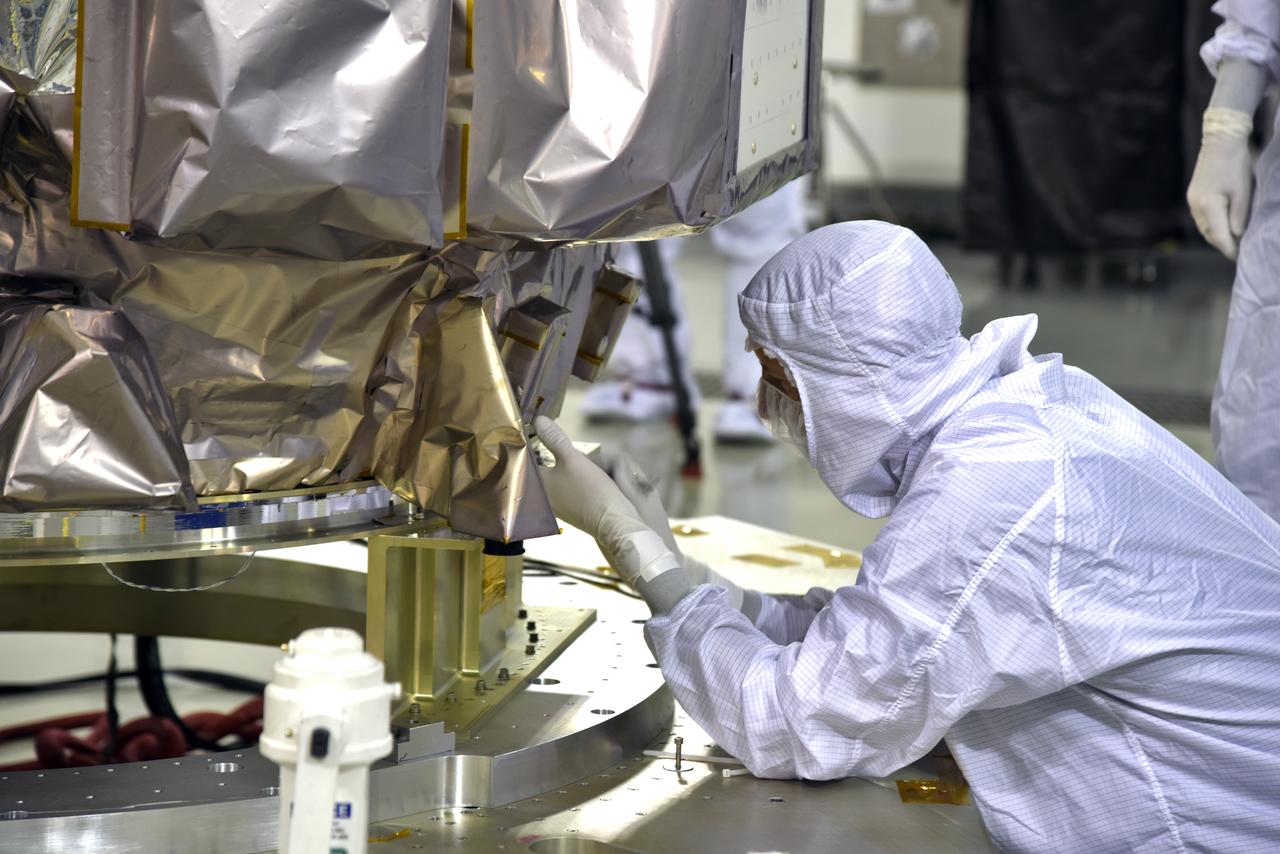
Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians help secure NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) to the payload adapter on Aug. 30, 2018. ICESat-2 is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians prepare to attach NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) to the payload adapter, on Aug. 20, 2018. The satellite is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.

Technicians use a crane to lower the re-entry vehicle for the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) into the re-entry vehicle payload adapter interface ring as part of launch preparations inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 7, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.

Technicians use a crane to lift the re-entry vehicle for the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) for mating to the re-entry vehicle payload adapter interface ring as part of launch preparations inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 7, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. The LOFTID is dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.
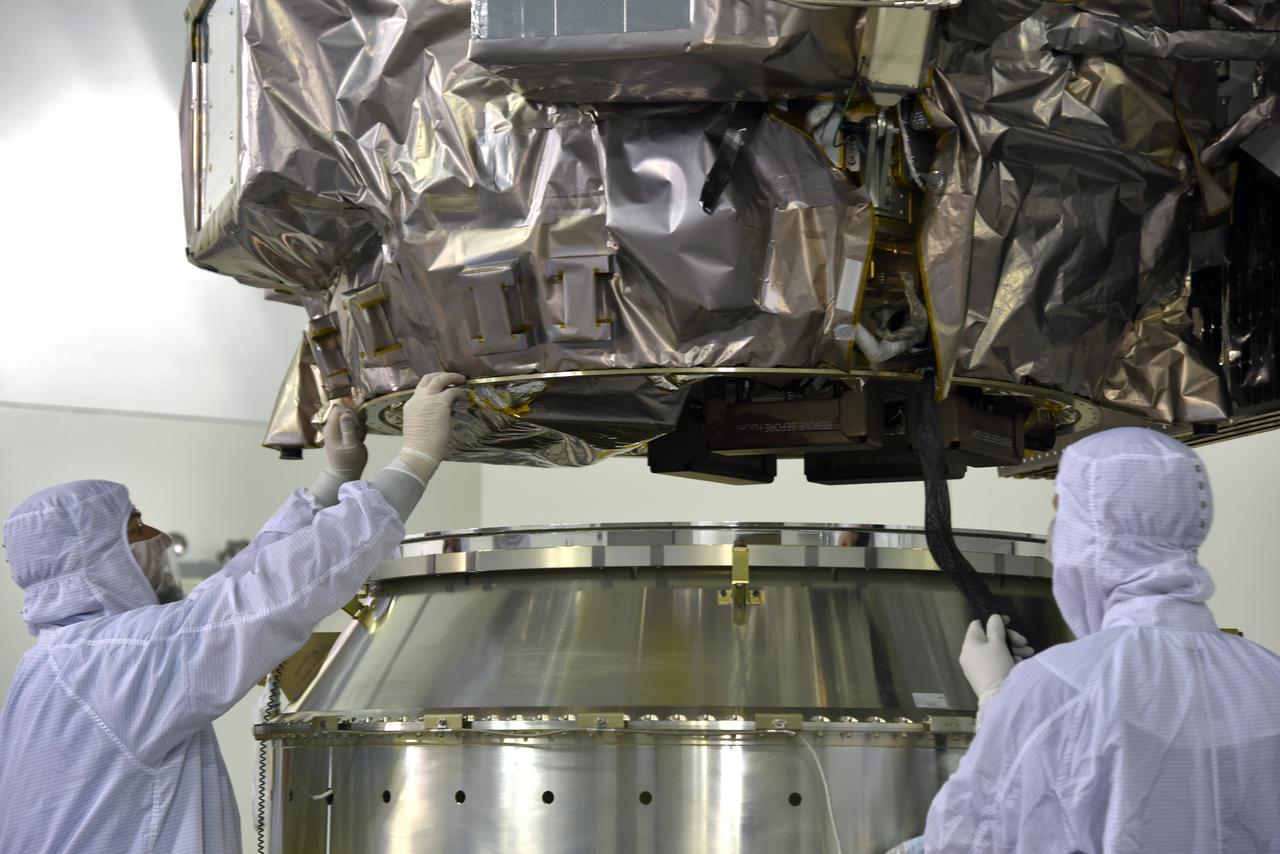

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, technicians assist as a crane lowers NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) onto the payload adapter on Aug. 30, 2018. ICESat-2 is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.

Inside the high bay of the Astrotech Space Operations facility at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California, a crane lifts and moves NASA's Ice, Cloud and land Elevation Satellite-2 (ICESat-2) on Aug. 30, 2018. The satellite will be attached to the payload adapter. ICESat-2 is being prepared for its scheduled launch from Space Launch Complex 2 at Vandenberg on the final United Launch Alliance Delta II rocket. ICESat-2 will measure the height of a changing Earth, one laser pulse at a time, 10,000 laser pulses a second. The satellite will carry the Advanced Topographic Laser Altimeter System (ATLAS). ICESat-2 will help scientists investigate why, and how much our planet's frozen and icy areas, called the cryosphere, are changing in a warming climate.
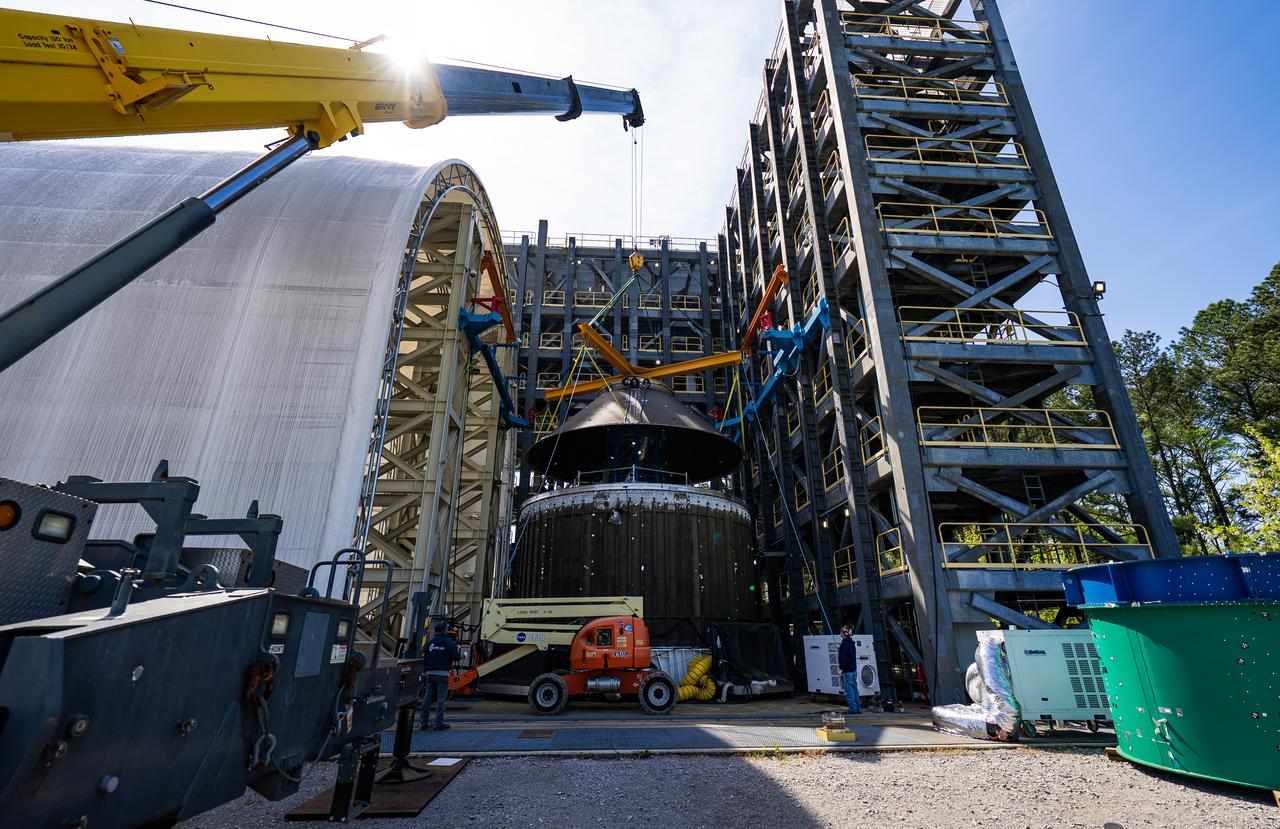

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.
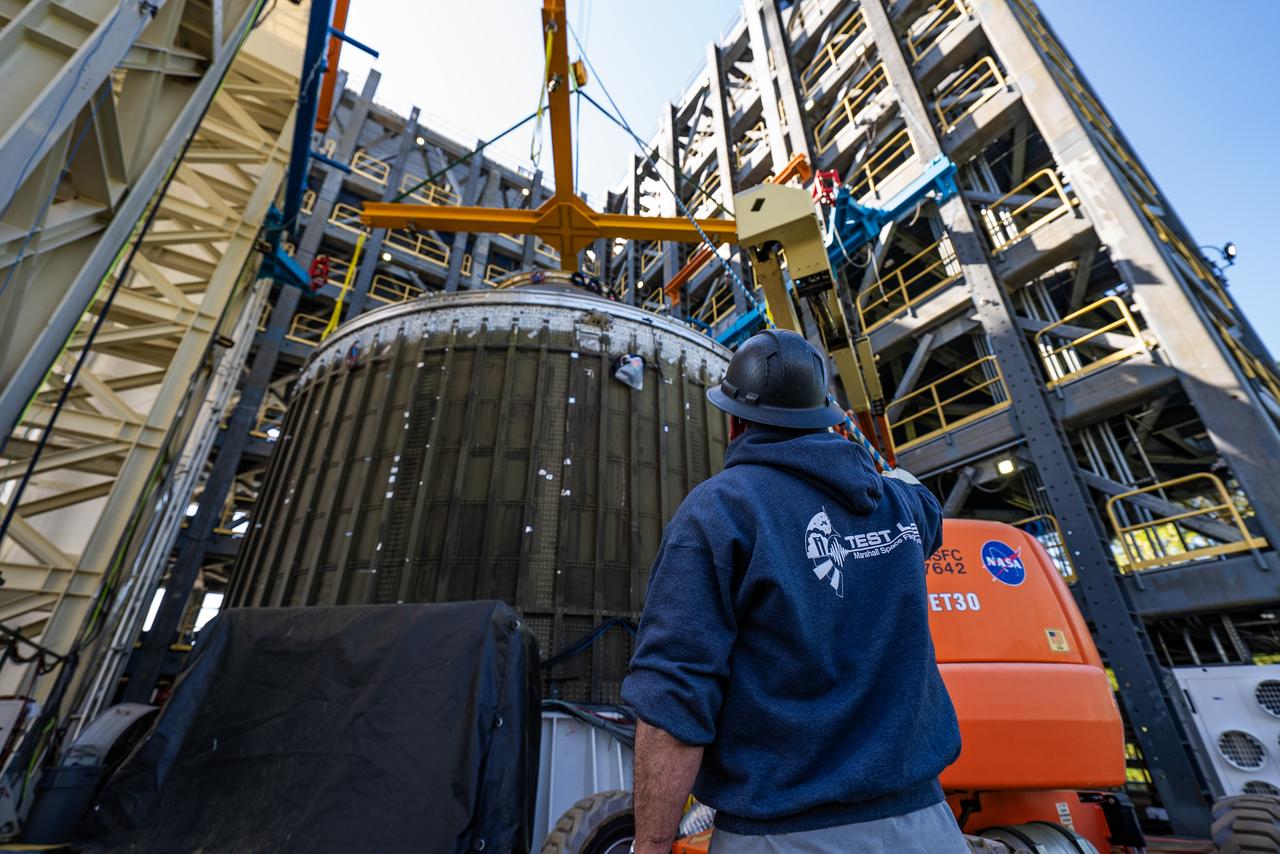

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.

Technicians at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, are seen in these images taken April 17, 2025, moving the payload adapter test article from Building 4697 to Building 4705 for storage. This move marks the end of structural testing for the test article. Next, engineers will complete the qualification article and conduct additional for further testing before building the final flight hardware. Manufactured at Marshall, the test article underwent extensive and rigorous testing to validate the design before engineers finalized the configuration for the flight article. The newly completed composite payload adapter is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter to be used in the upgraded Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket, debuting with Artemis IV.
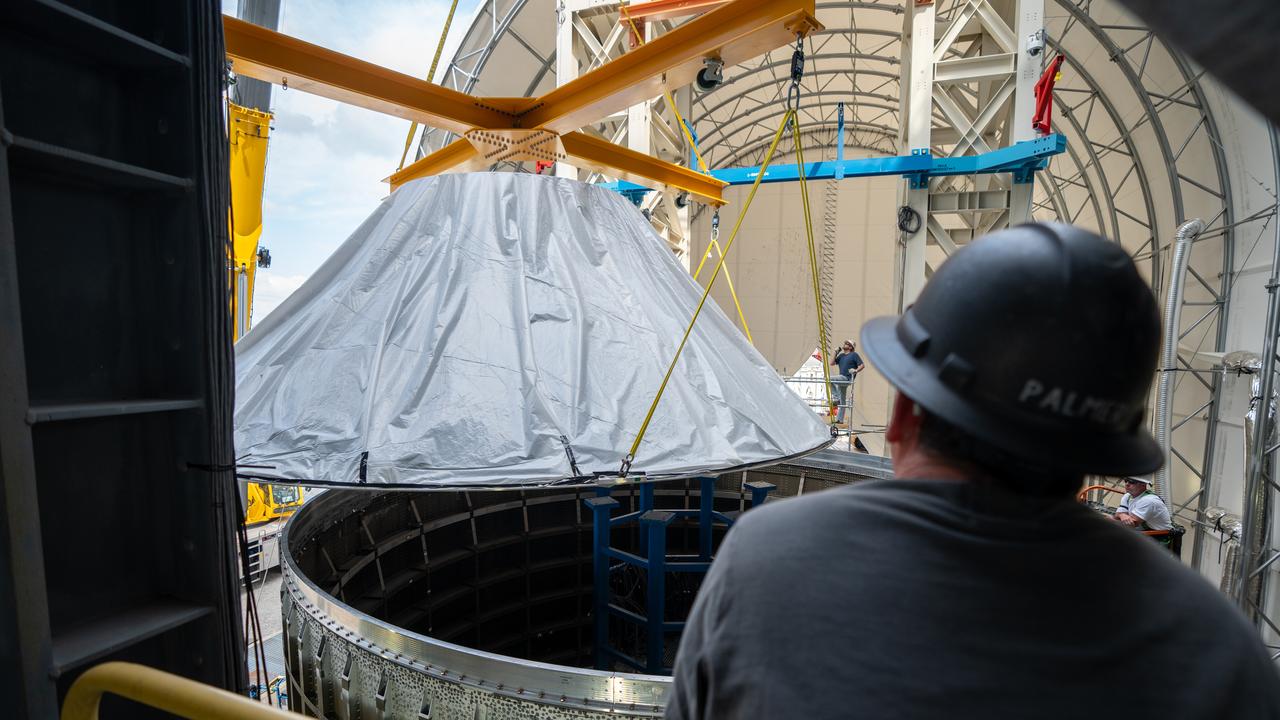

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
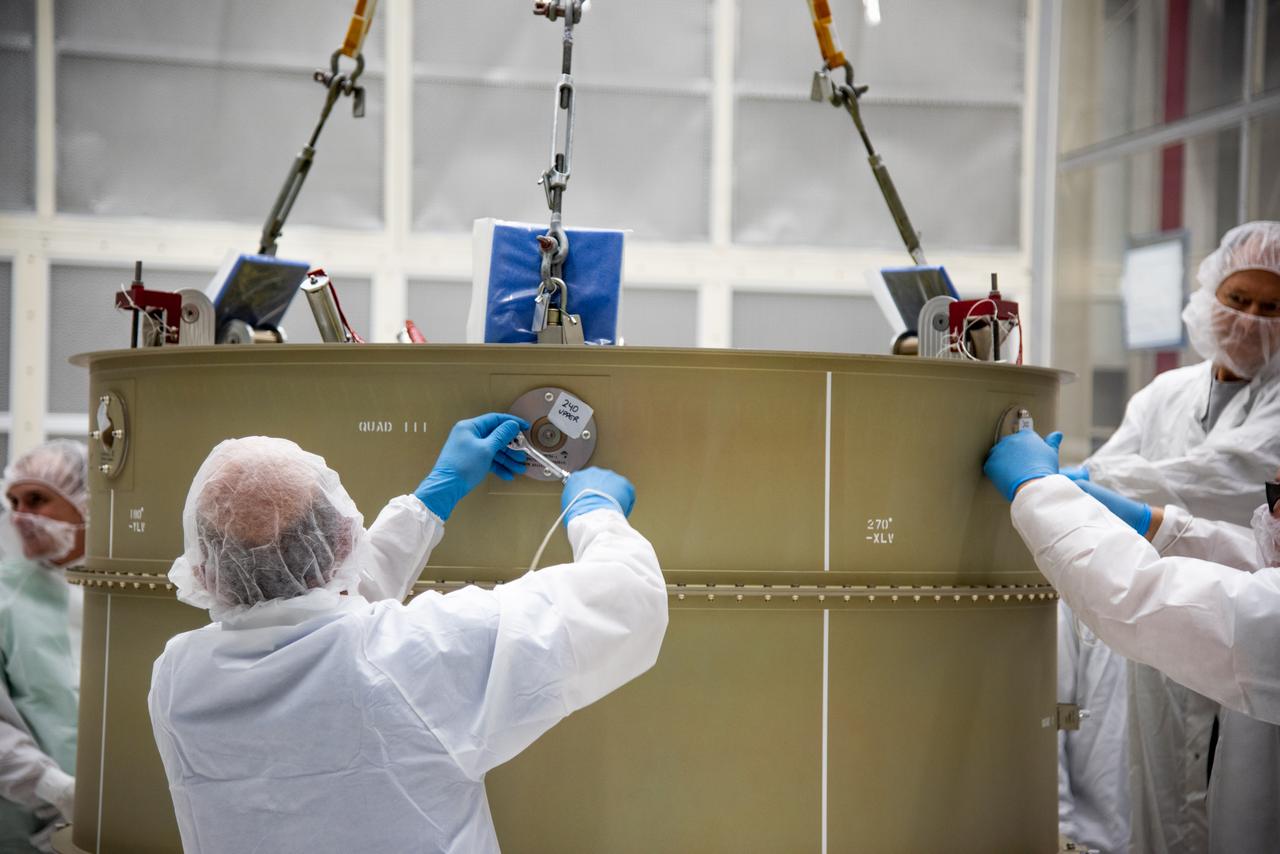

Technicians fasten the payload adapter separation systems canister for the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) to the payload adapter canister as part of launch preparations inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 1, 2022.. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.
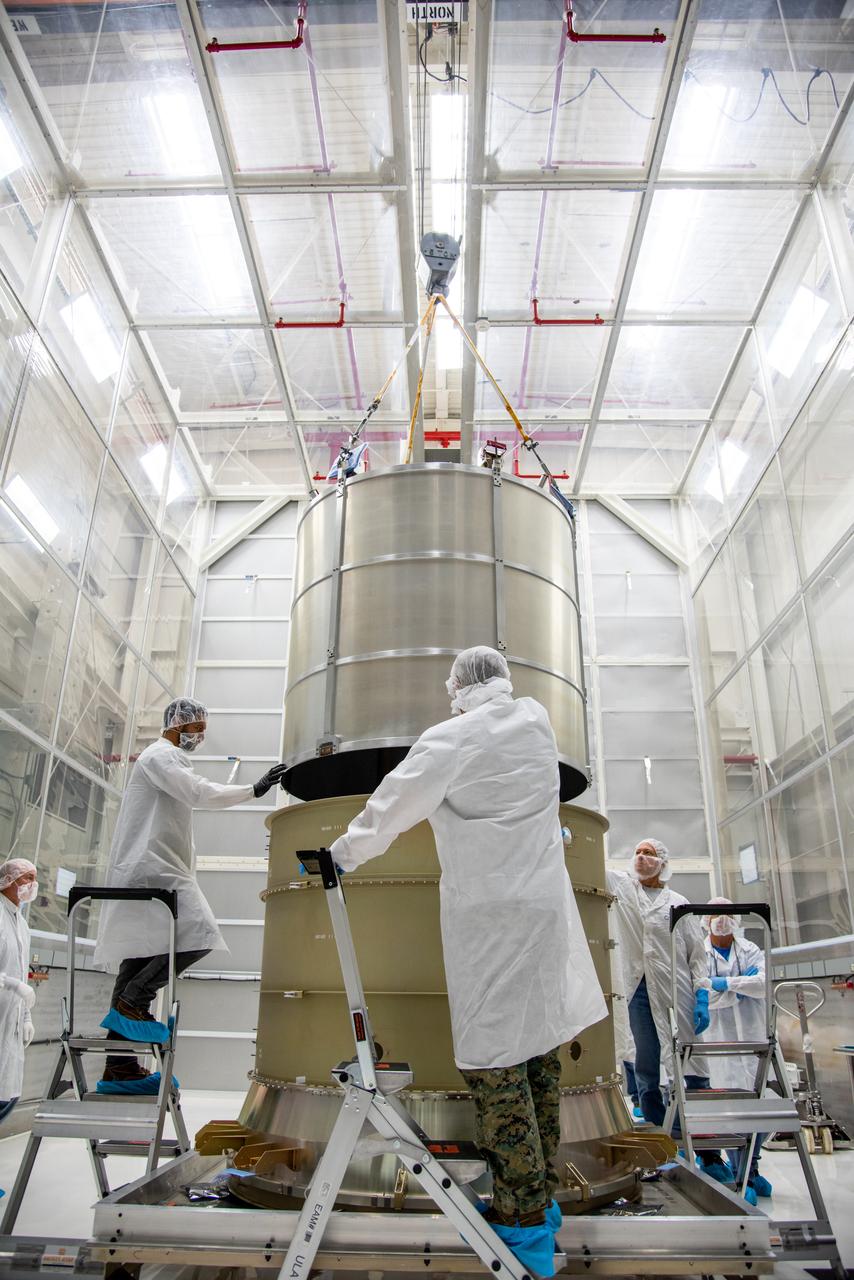

Technicians lower the payload adapter separation systems canister for the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) into the payload adapter canister as part of launch preparations inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 1, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.
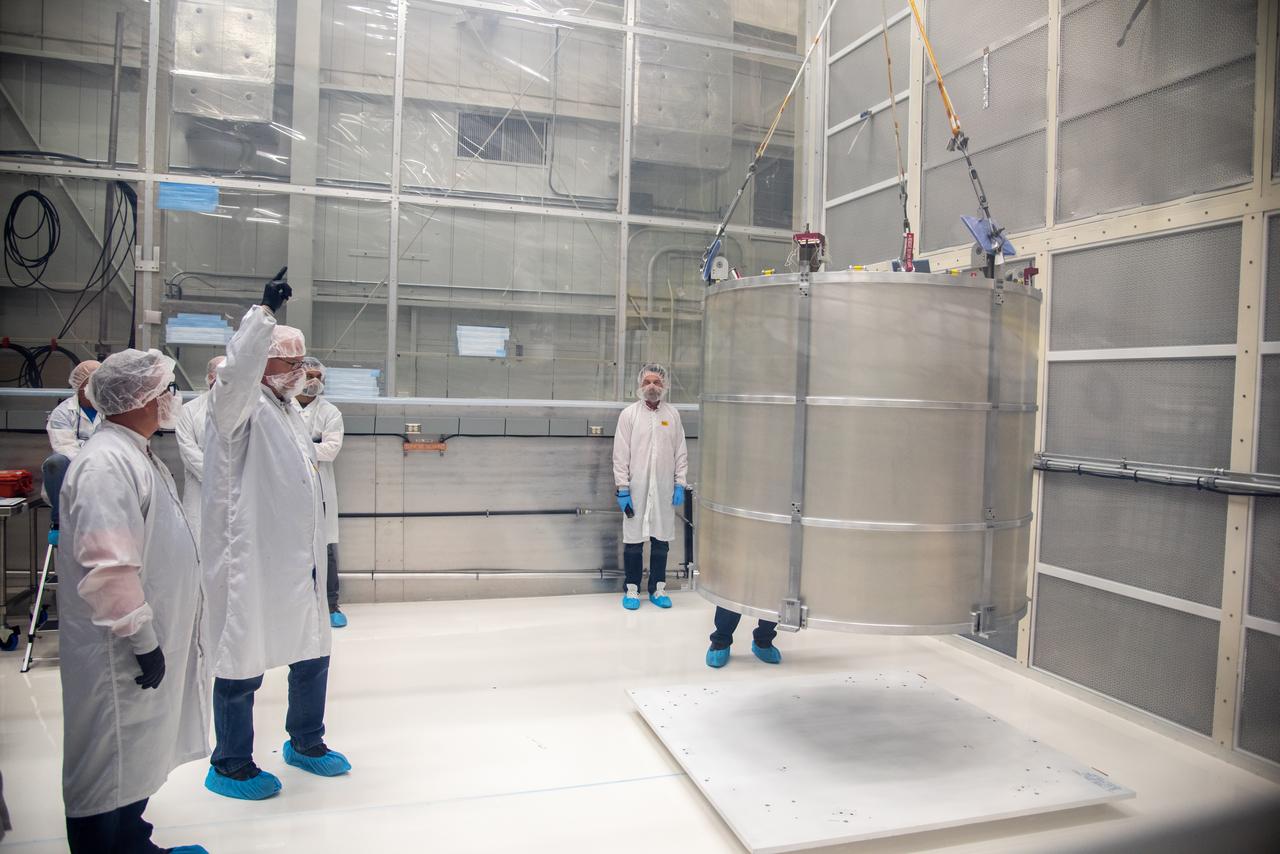

Technicians use a crane to lift the payload adapter separation systems canister for the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) as part of launch preparations inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 1, 2022. The separation system canister loads into the payload adapter canister. The canister will go over the reentry vehicle.. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. The LOFTID is dedicated to the memory of Bernard Kutter. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.

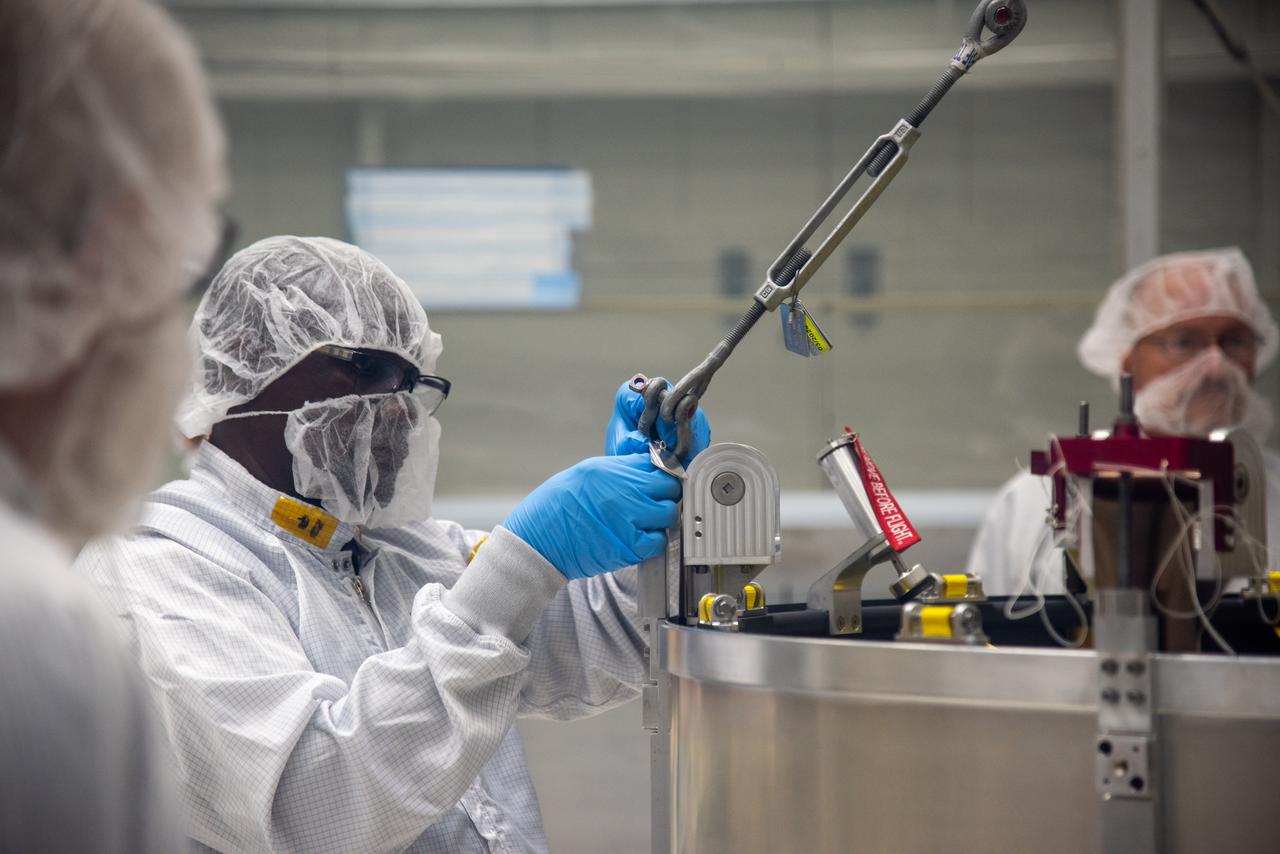
Technicians lower the payload adapter separation systems canister for the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) into the payload adapter canister as part of launch preparations inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 1, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.

Technicians lower the payload adapter separation systems canister for the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) into the payload adapter canister as part of launch preparations inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 1, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily. LOFTID will demonstrate inflatable heat shield technology that could enable a variety of proposed NASA missions to destinations such as Mars, Venus, and Titan, as well as returning heavier payloads from low-Earth orbit.

Technicians prepare to lift the Low-Earth Orbit Flight Test of an Inflatable Decelerator (LOFTID) payload adapter separation systems canister, where it will go inside the payload adapter canister as part of launch preparations occurring inside Building 836 at Vandenberg Space Force Base (VSFB) in California on Sept. 1, 2022. LOFTID is the secondary payload on NASA and the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration’s (NOAA) Joint Polar Satellite System-2 (JPSS-2) satellite mission. JPSS-2 is the third satellite in the Joint Polar Satellite System series. It is scheduled to lift off from VSFB on Nov. 1 from Space Launch Complex-3. JPSS-2, which will be renamed NOAA-21 after reaching orbit, will join a constellation of JPSS satellites that orbit from the North to the South pole, circling Earth 14 times a day and providing a full view of the entire globe twice daily.
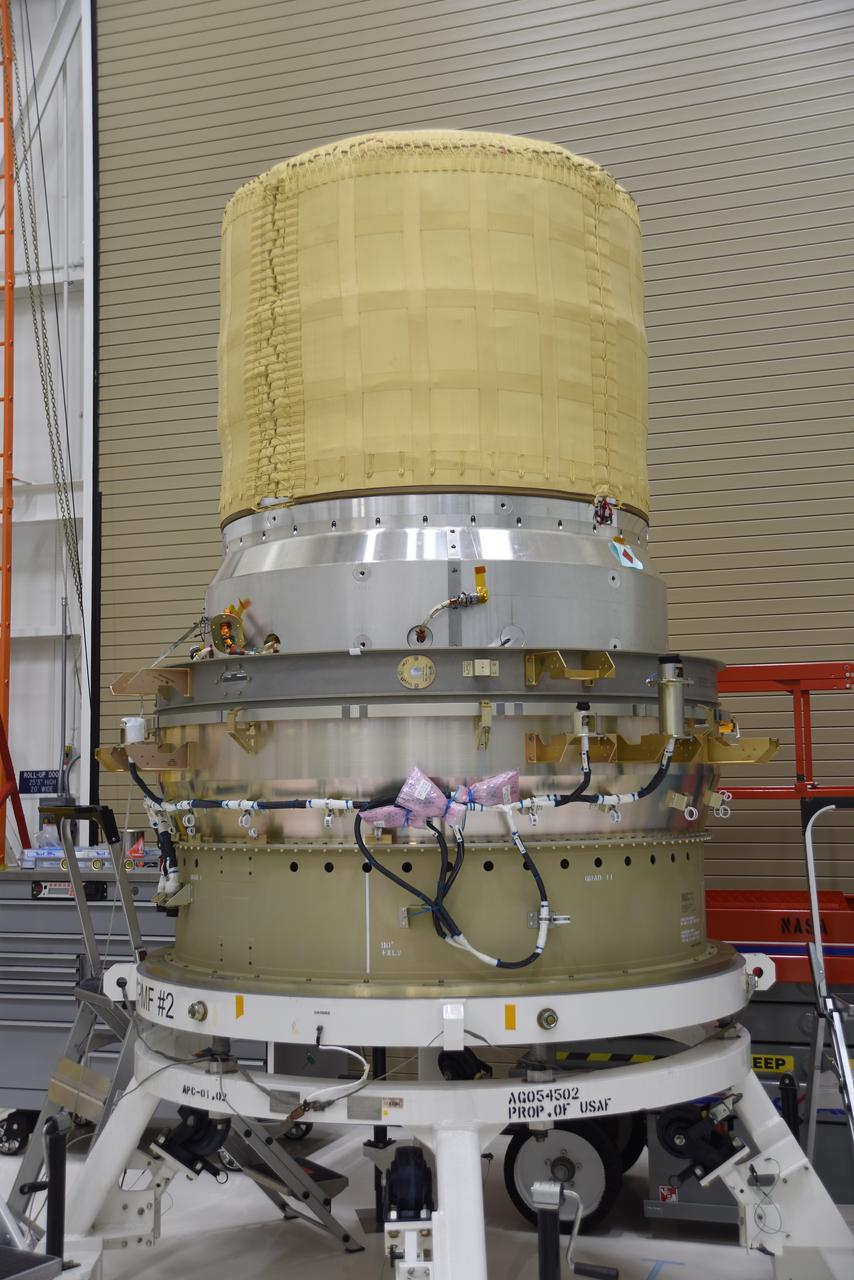
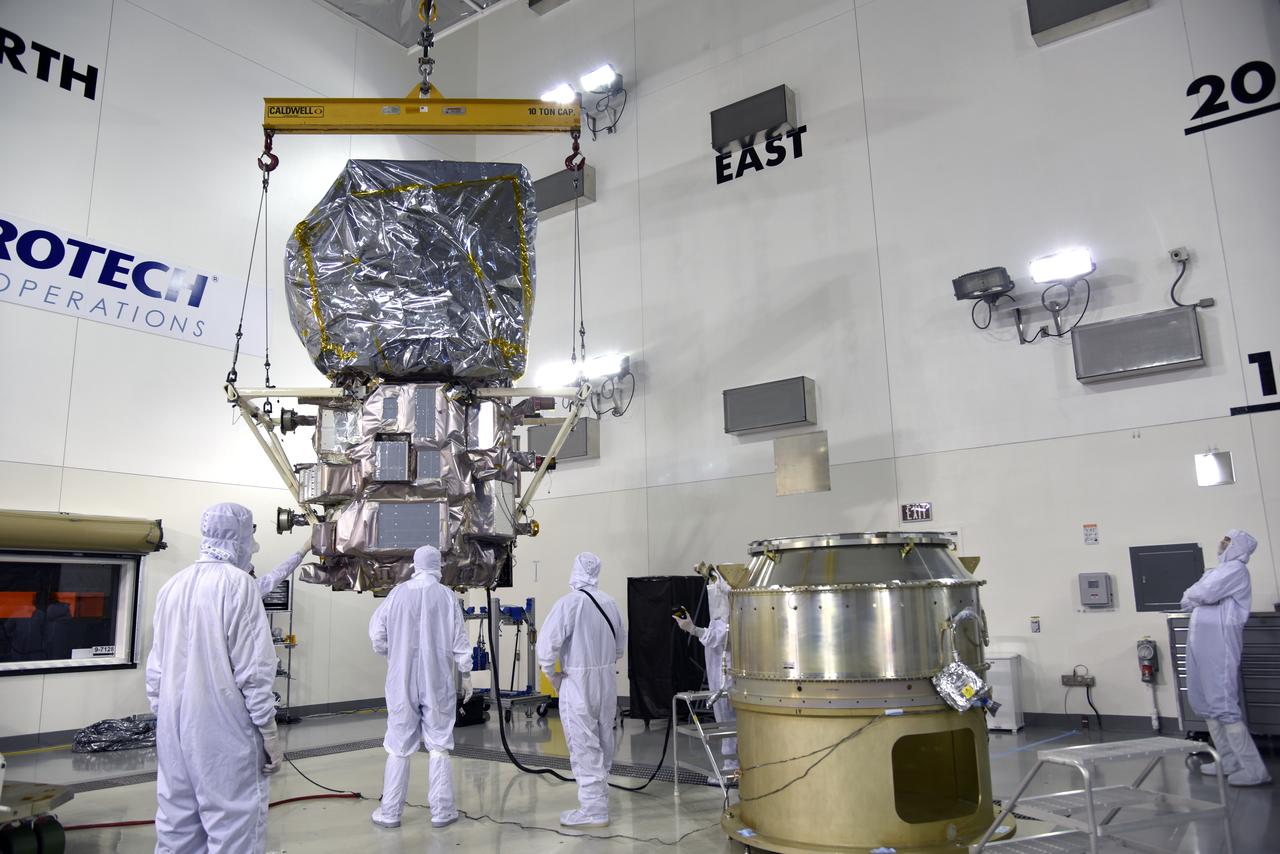
These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
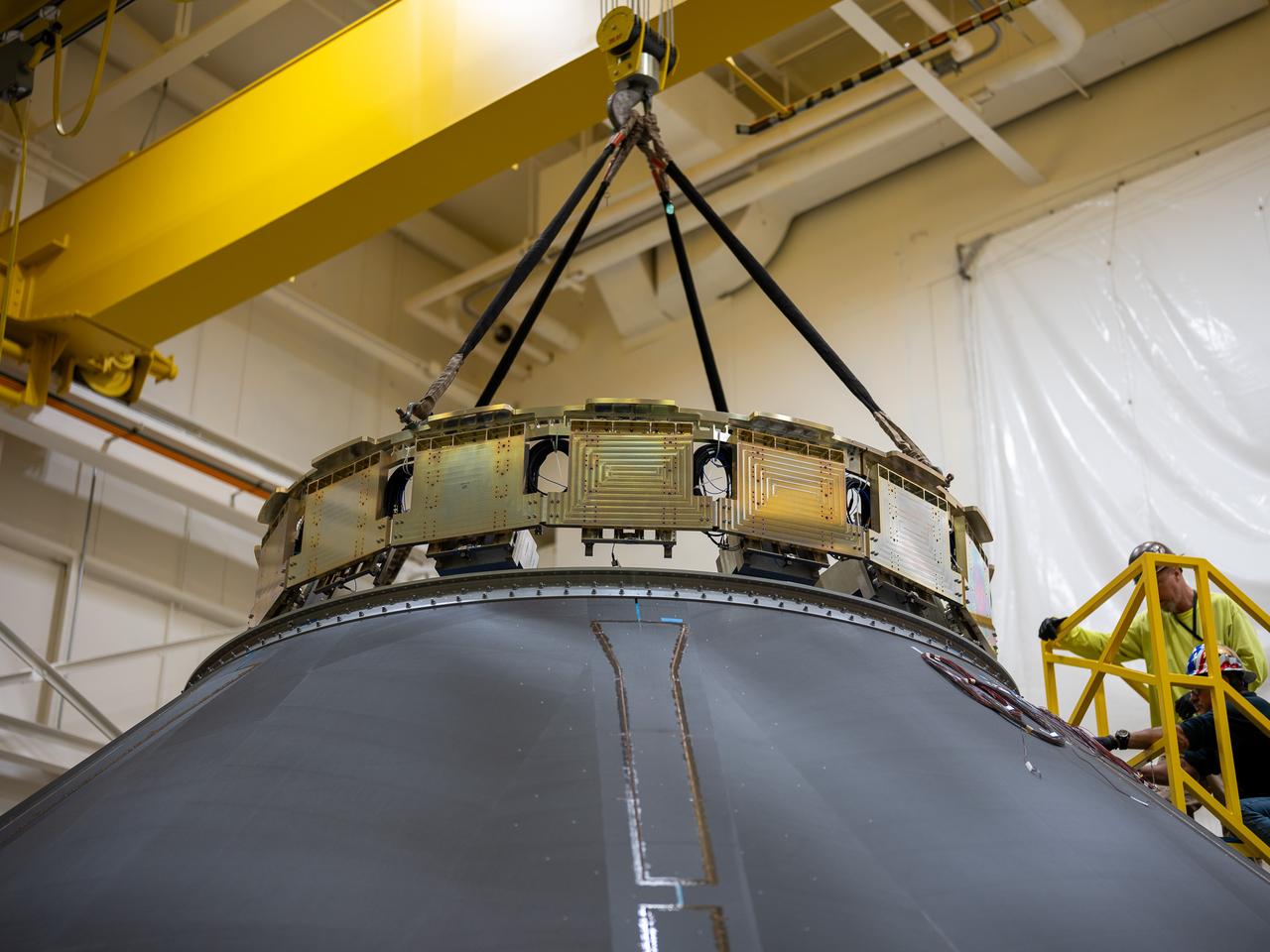

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
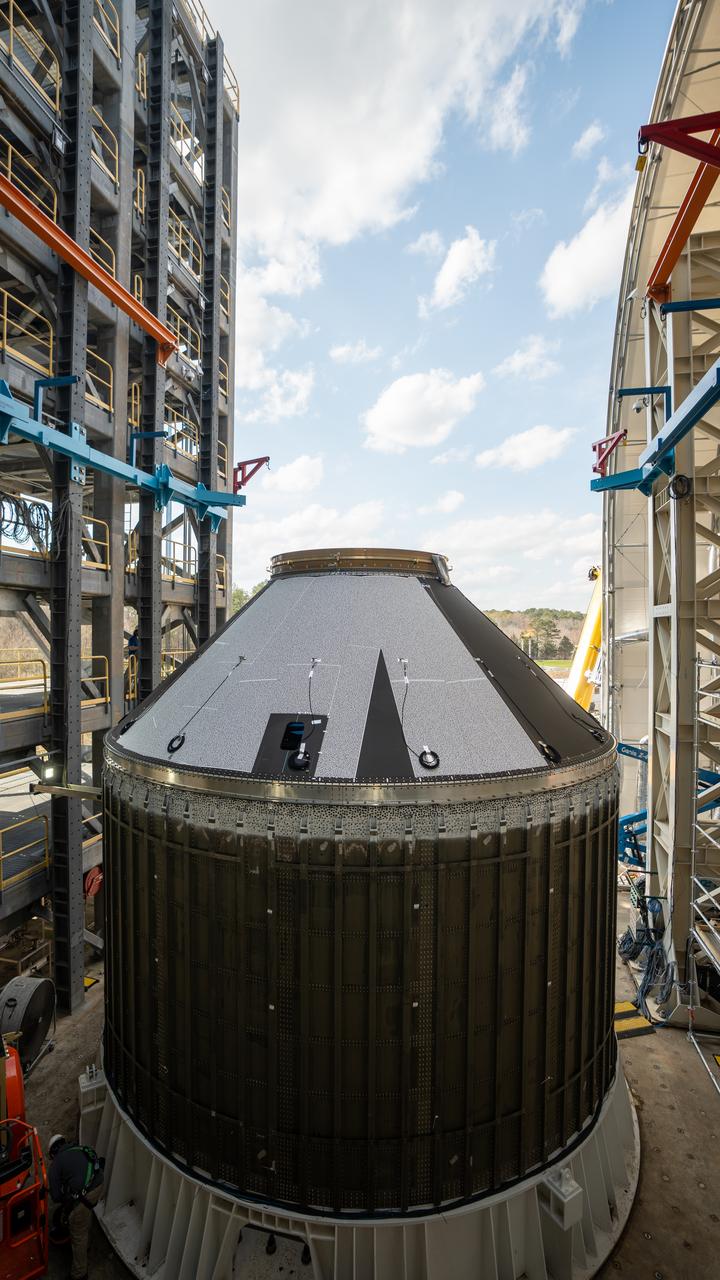

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
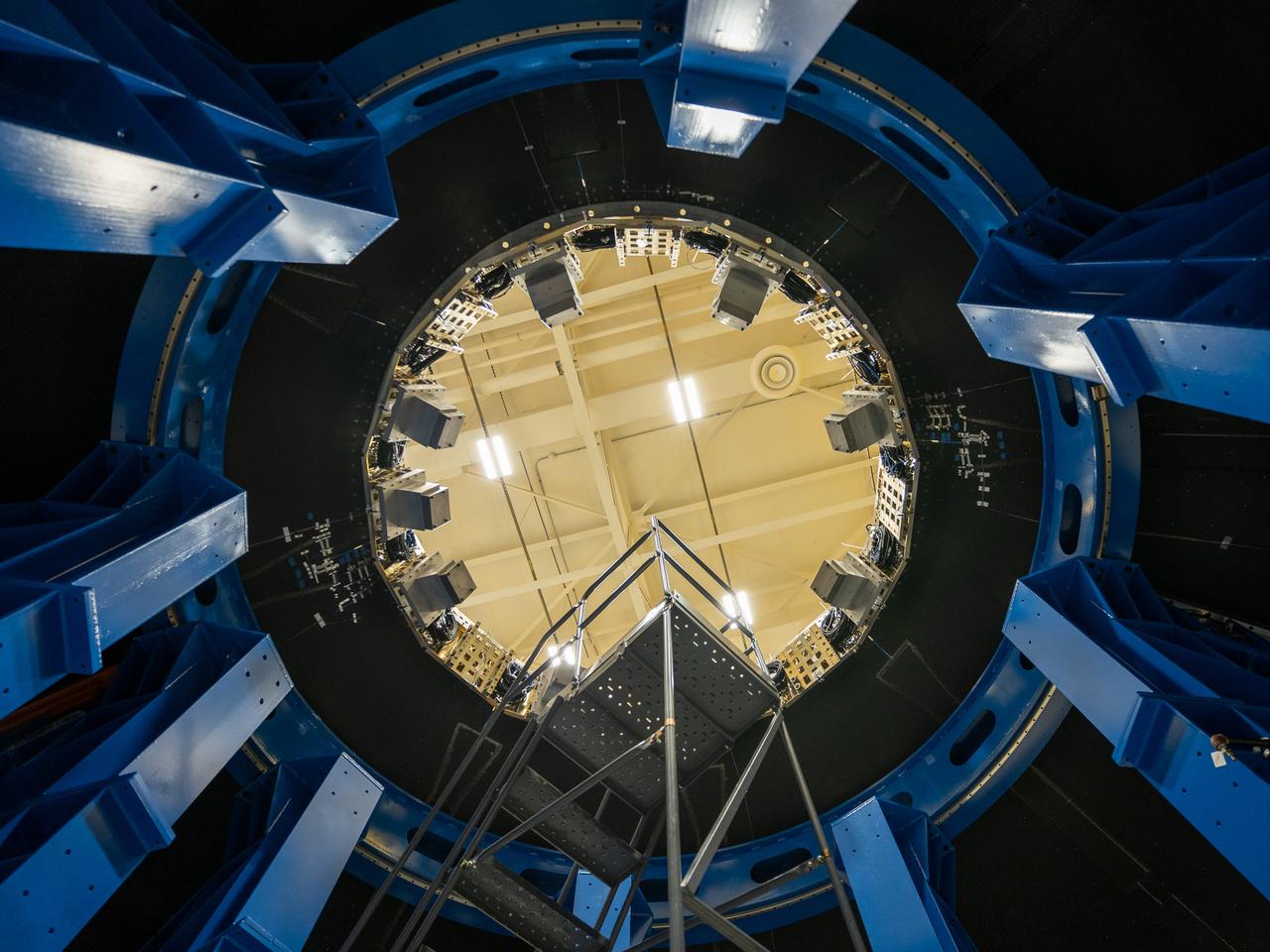

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
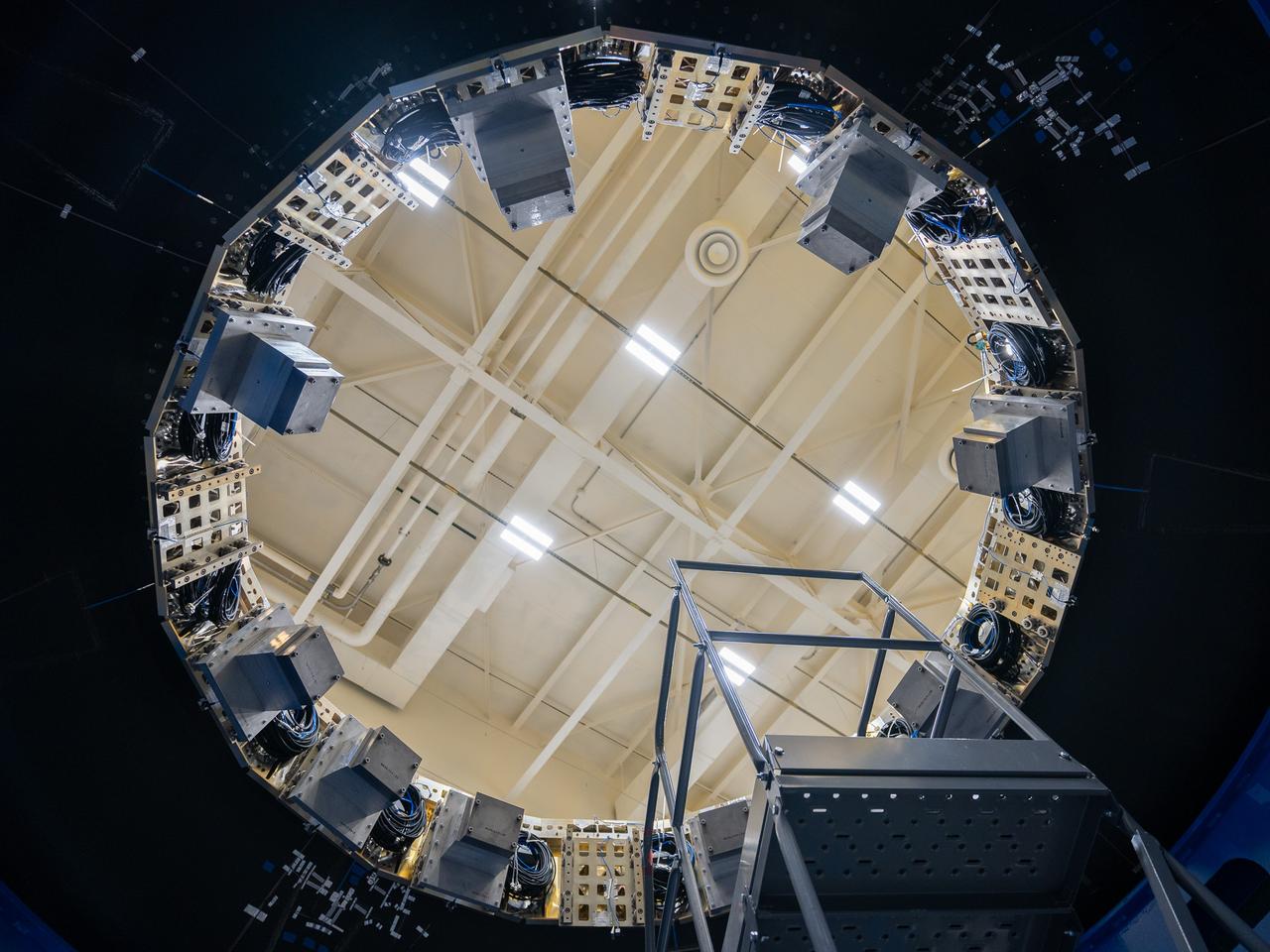

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
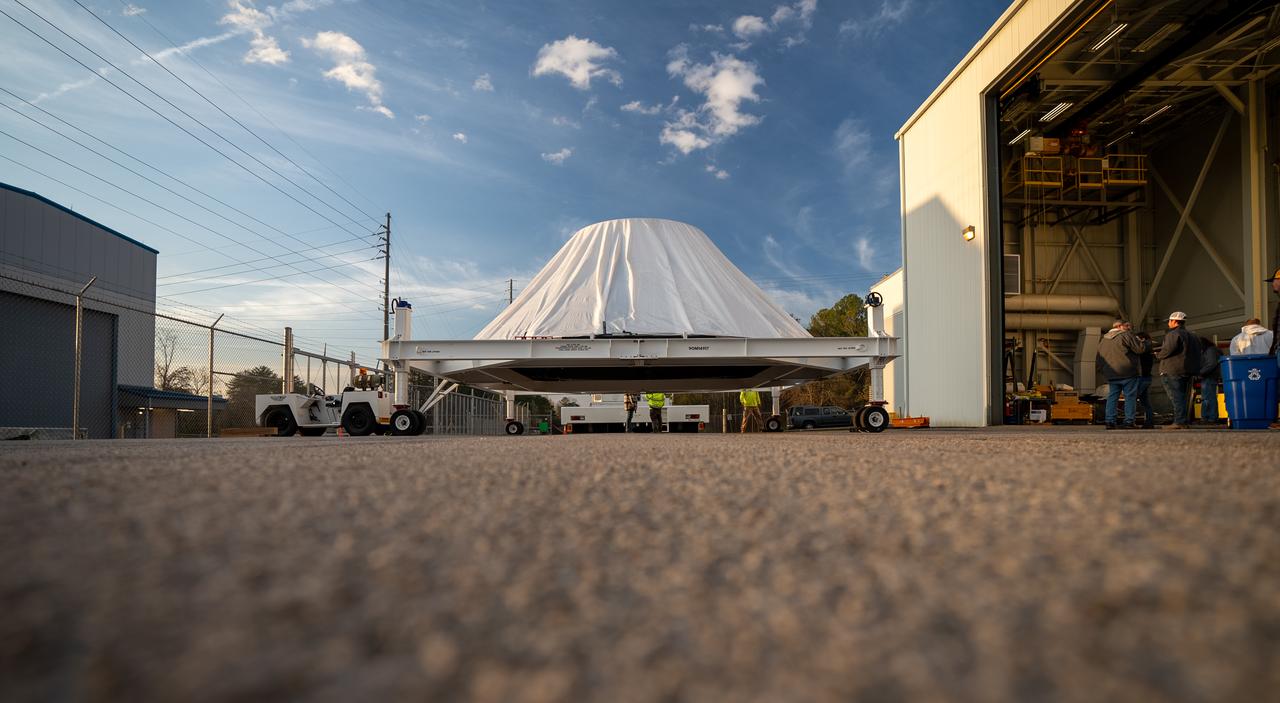

These photos and videos show how crews at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, moved and installed the payload adapter that will be used in the Block 1B configuration of the SLS (Space Launch System) rocket from Building 4708, where it was manufactured, into Structural Test Stand 4697 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center on March 13. Teams at Marshall will begin structural testing the engineering development unit of the payload adapter – an exact replica of the flight version of the hardware – this spring. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
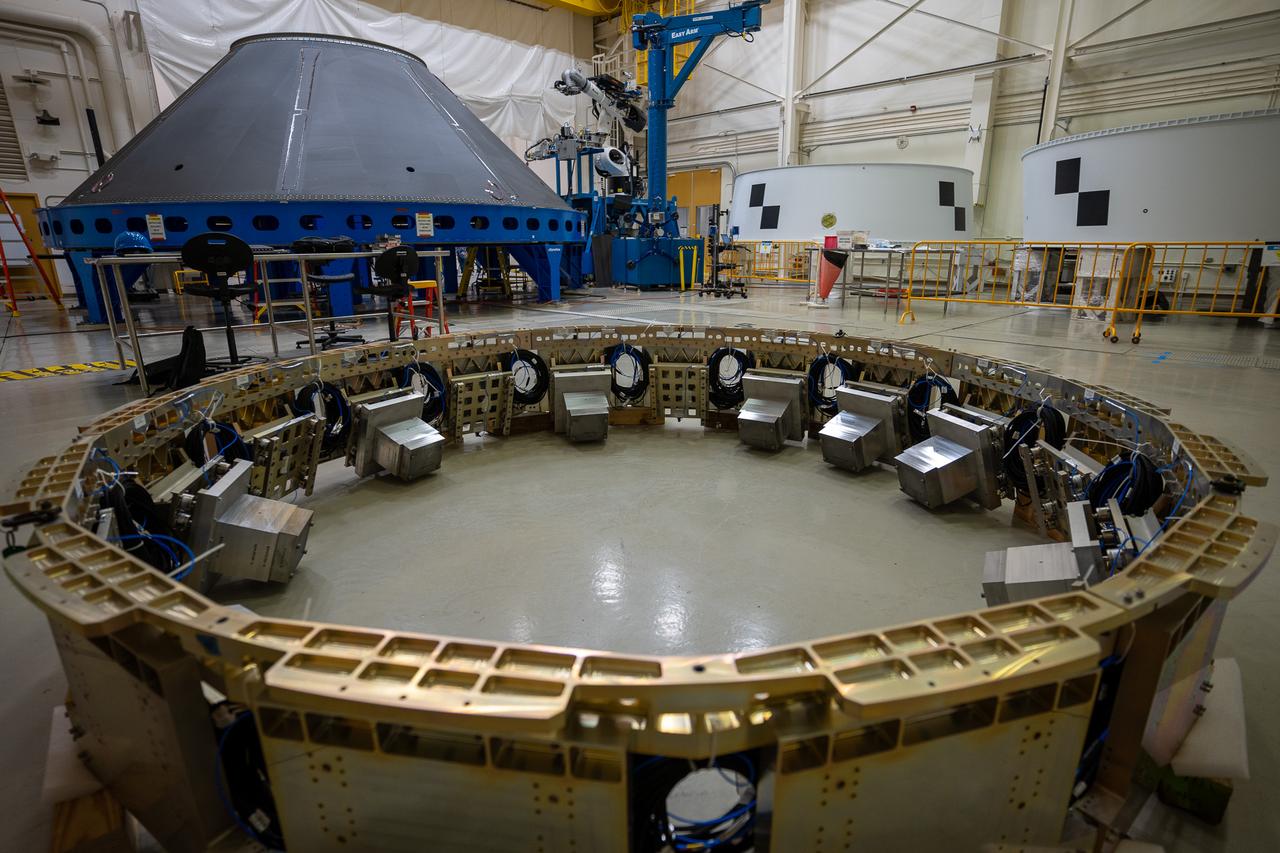

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
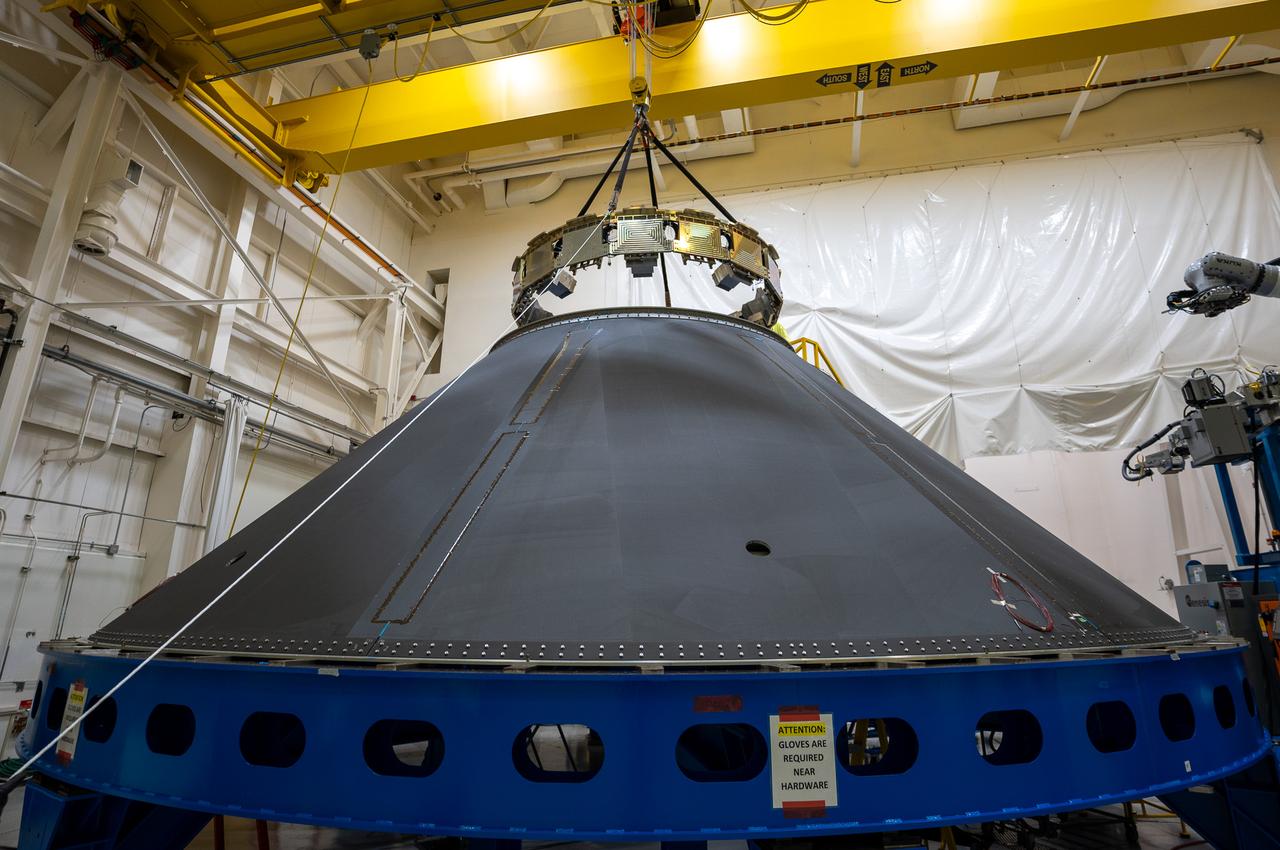

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.
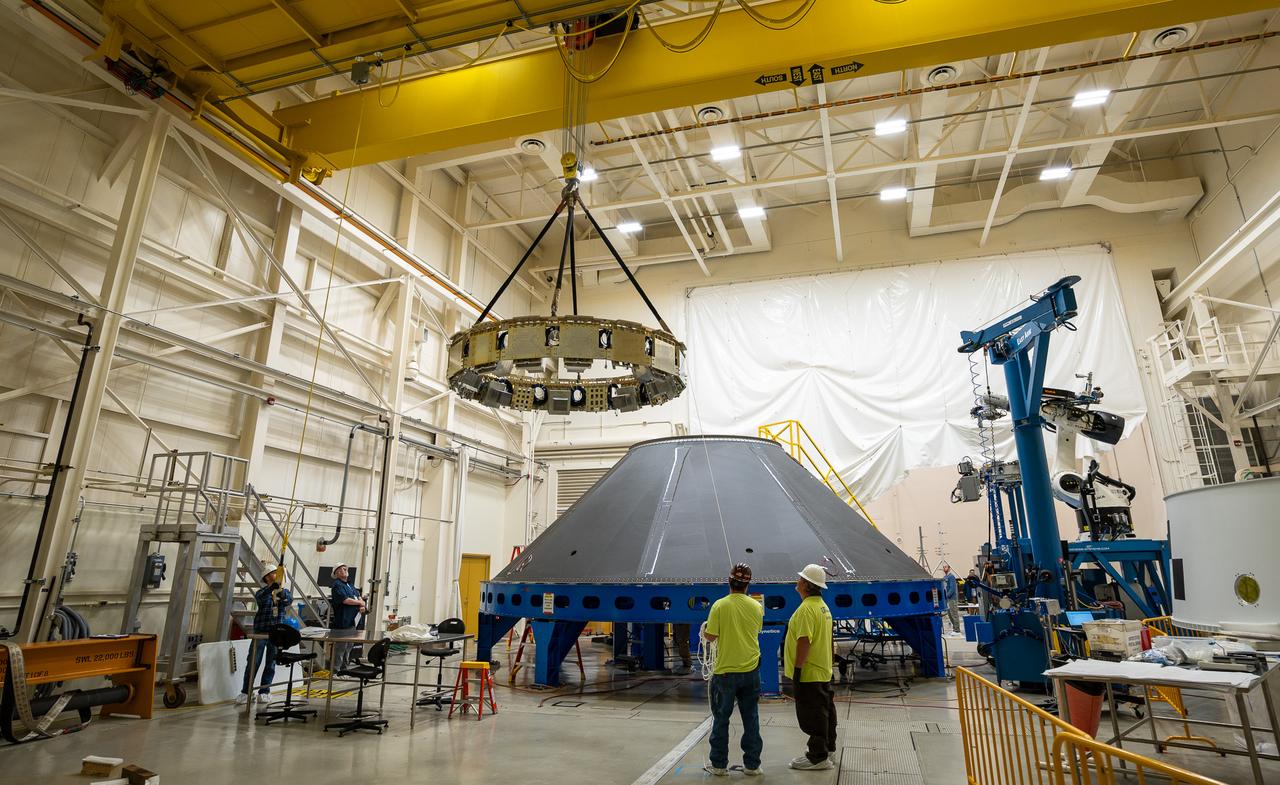

These photos and videos show how NASA manufactured and prepared to transport the payload adapter in February inside Building 4708 at NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. Prior to moving the hardware for testing, teams installed the New Explorations Secondary Transport component, called the NEST, into the top of the engineering development unit. The NEST component will allow the hardware to hold a series of secondary payloads, or small satellites. The cone-shaped payload adapter is about 8.5 feet tall and features two metal rings and eight composite panels. The adapter, which will debut on NASA’s Artemis IV mission, is an evolution from the Orion stage adapter used in the Block 1 configuration of the rocket for the first three Artemis missions. It will be housed inside the universal stage adapter atop the rocket’s more powerful in-space stage, called the exploration upper stage. The payload adapter, like the launch vehicle stage adapter and the Orion stage adapter, is fully manufactured and tested at Marshall, which manages the SLS Program. NASA is working to land the first woman, first person of color, and its first international partner astronaut on the Moon under Artemis. SLS is part of NASA’s backbone for deep space exploration, along with the Orion spacecraft and Gateway in orbit around the Moon and commercial human landing systems, next-generational spacesuits, and rovers on the lunar surface. SLS is the only rocket that can send Orion, astronauts, and supplies to the Moon in a single launch.