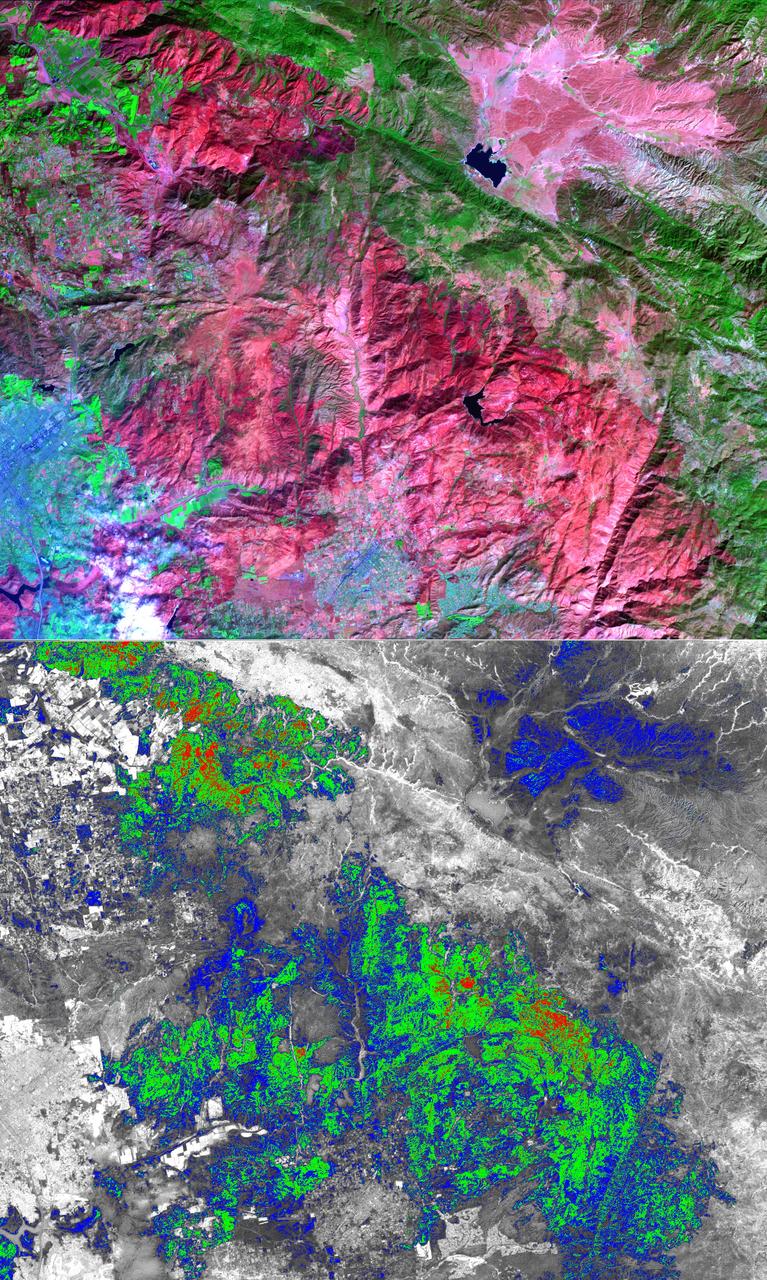
The October 2007 wildfires, including the Witch Wildland fire, plagued southern California and were some of the worst on record. Image from NASA Terra satellite.
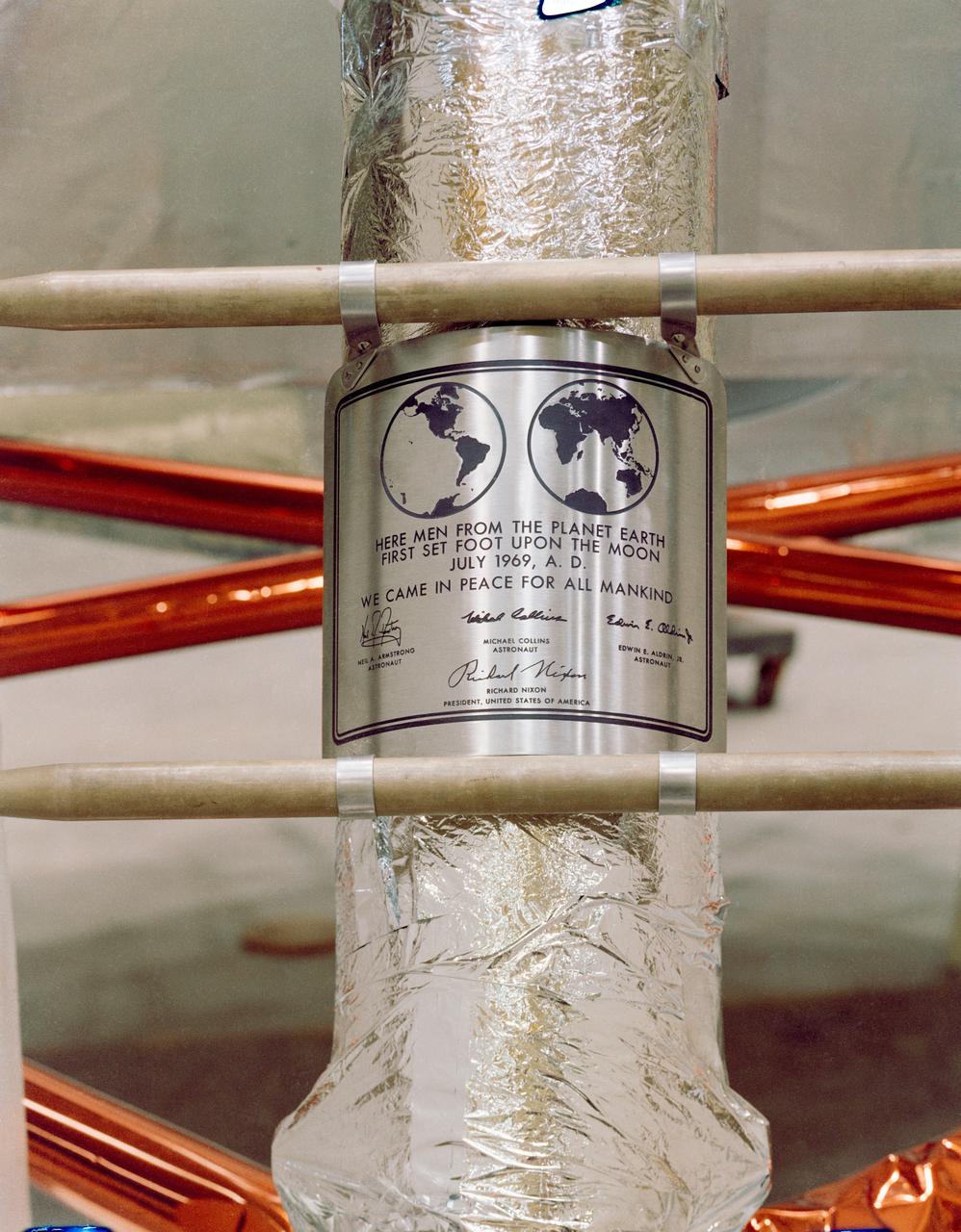

S69-38749 (July 1969) --- Close-up view of the plaque which the Apollo 11 astronauts will leave behind on the moon in commemoration of the historic event. The plaque is made of stainless steel measuring nine by seven and five-eighths inches, and one-sixteenth inch thick. The plaque will be attached to the ladder on the landing gear strut on the descent stage of the Apollo 11 Lunar Module (LM). Covering the plaque during flight will be a thin sheet of stainless steel which will be removed on the lunar surface.
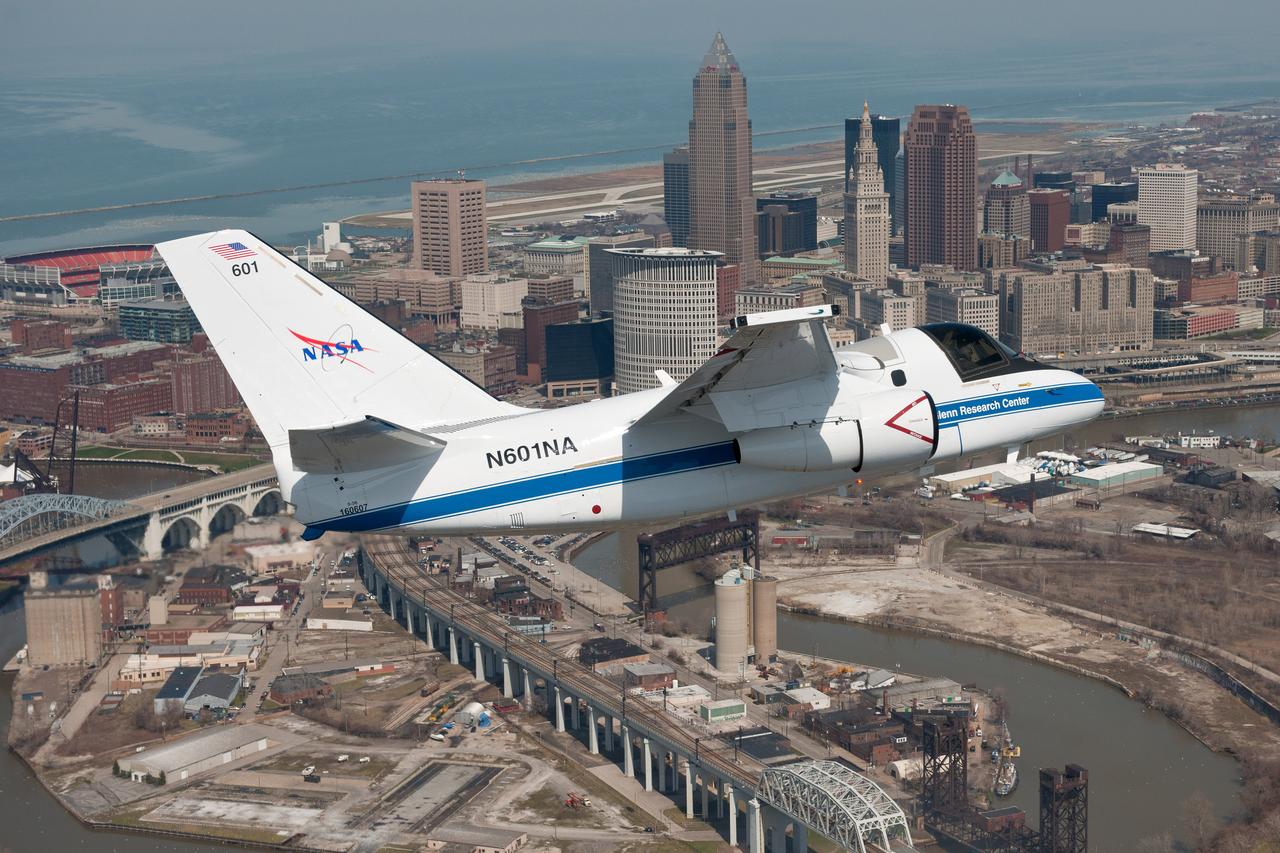

This photo shows NASA Glenn’s S-3 Viking Aircraft flying over downtown Cleveland, Ohio. The S-3 continues to conduct important research including regular flights over Lake Erie and other waterways to image algal blooms that have plagued the area’s waters.

41C-22-885 (8 April 1984) --- The 35mm camera was used to photograph this scene of Astronaut George D. Nelson, STS-41C mission specialist, as he uses the manned maneuvering unit (MMU) to make an excursion to the plagued Solar Maximum, Mission Satellite (SMMS)._Astronaut James D. van Hoften remained in the Challenger's cargo bay during the April 8 extravehicular activity (EVA).
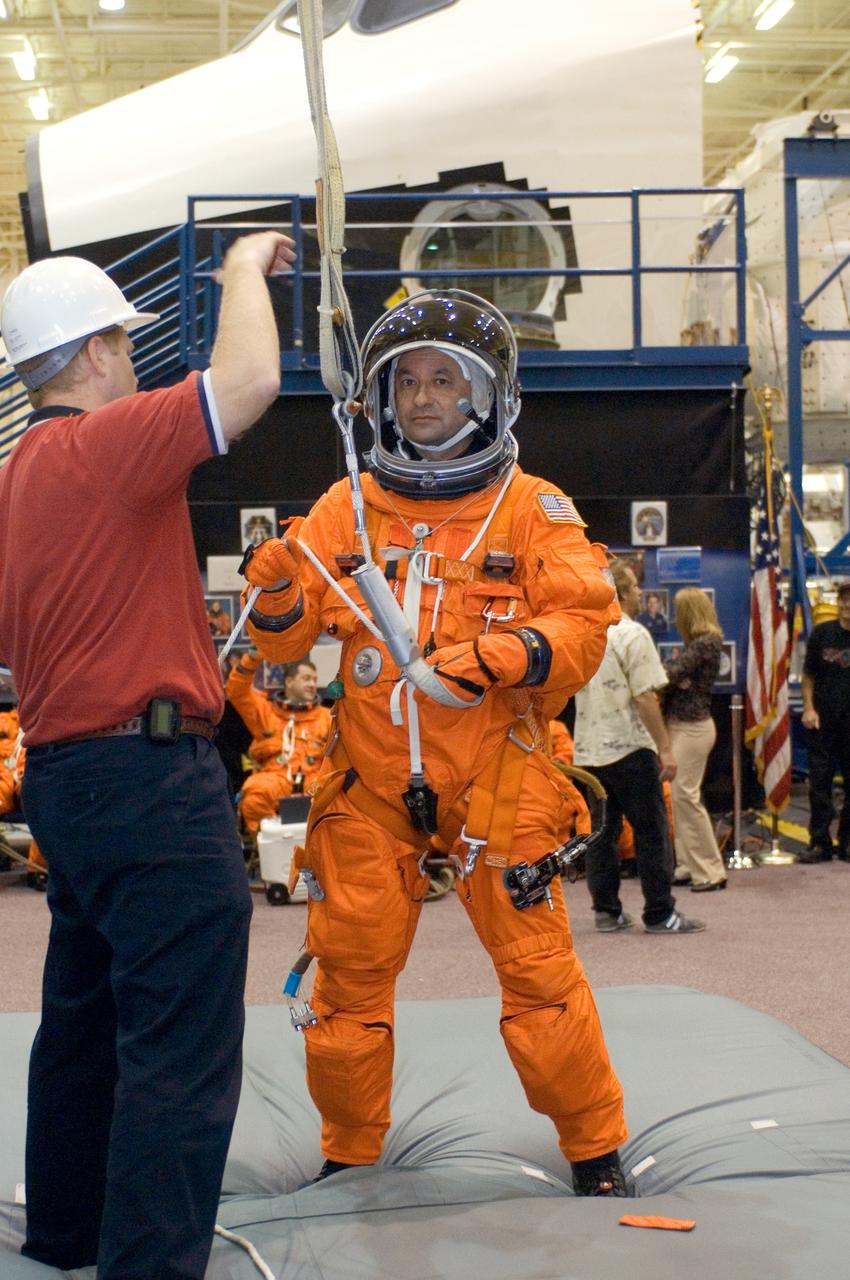

JSC2005-E-32736 (1 Aug. 2005) --- Crew trainer Bob Behrendsen briefs astronaut Mark L. Polansky, STS-116 commander, on the usage of a special pulley device, used to lower oneself from a trouble-plagued shuttle, during a training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center. Polansky is attired in a training version of the shuttle launch and entry suit.
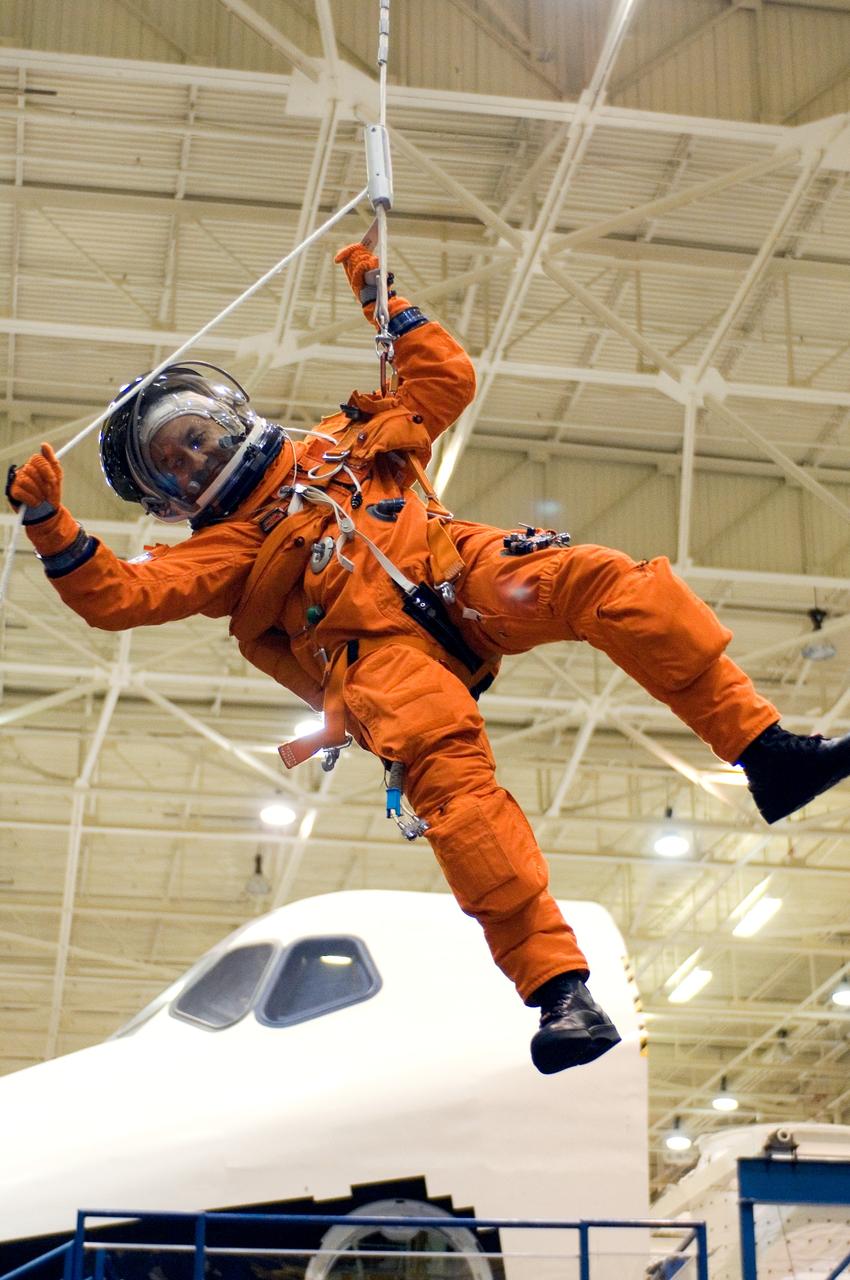

JSC2005-E-32739 (1 Aug. 2005) --- Astronaut Mark L. Polansky, STS-116 commander, uses a special pulley device to lower himself from a simulated trouble-plagued shuttle during a training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center. Polansky is wearing a training version of the shuttle launch and entry suit.
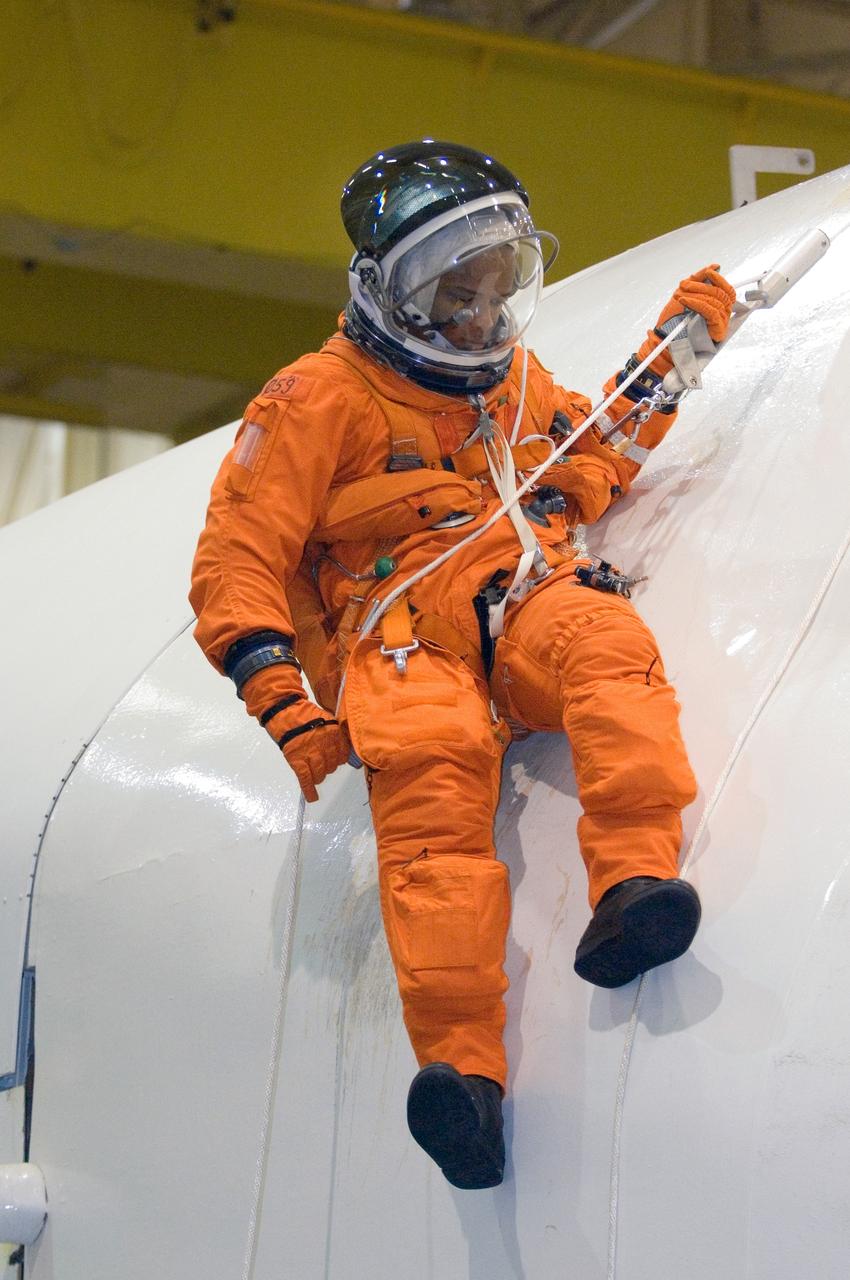

JSC2005-E-32763 (1 Aug. 2005) --- Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, STS-116 mission specialist, uses a special pulley device to escape from a simulated trouble-plagued shuttle during a session of egress training in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at Johnson Space Center. The full fuselage trainer (FFT) is a full-scale mockup of a shuttle. Curbeam is wearing a training version of the shuttle launch and entry suit.
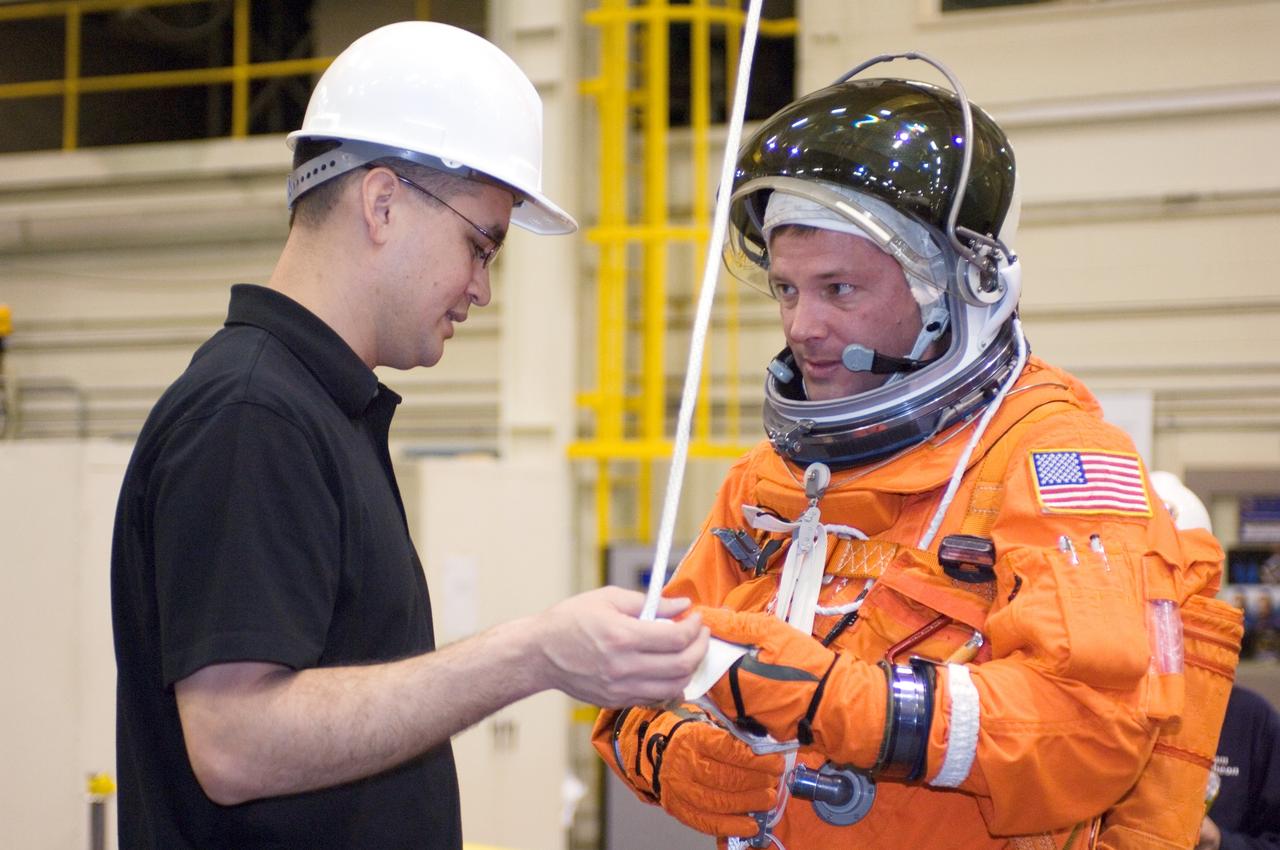

JSC2007-E-18102 (9 April 2007) --- United Space Alliance (USA) crew trainer Adam Flagan (left) briefs astronaut Douglas H. Wheelock, STS-120 mission specialist, on the usage of a special pulley device, used to lower oneself from a trouble-plagued shuttle. The briefing came during an emergency egress training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center. Wheelock is wearing a training version of his shuttle launch and entry suit.
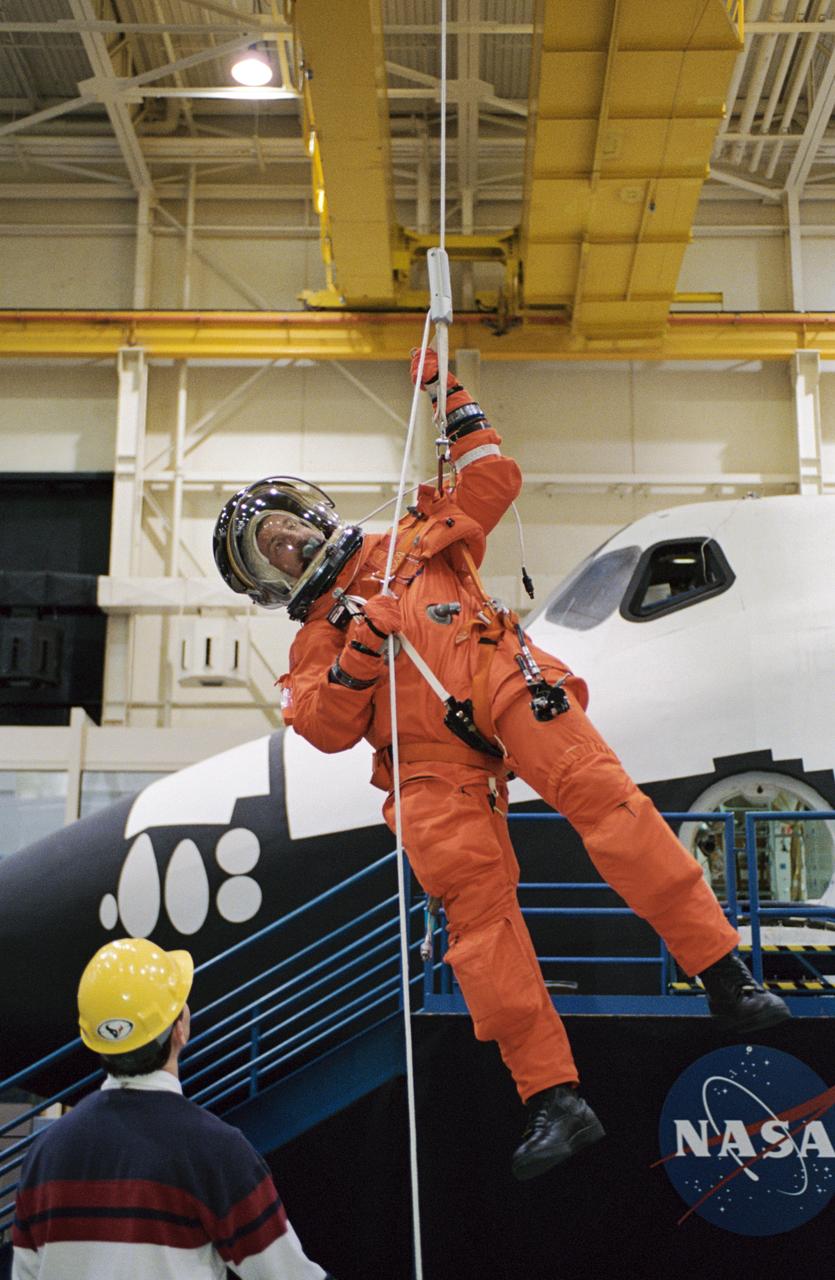

JSC2002-02132 (3 December 2002) --- Astronaut Daniel C. Burbank, STS-115 mission specialist, uses the Sky-genie to lower himself from a simulated trouble-plagued shuttle in an emergency egress training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Burbank is wearing a training version of the shuttle launch and entry suit. United Space Alliance (USA) crew trainer David Pogue assisted Burbank.

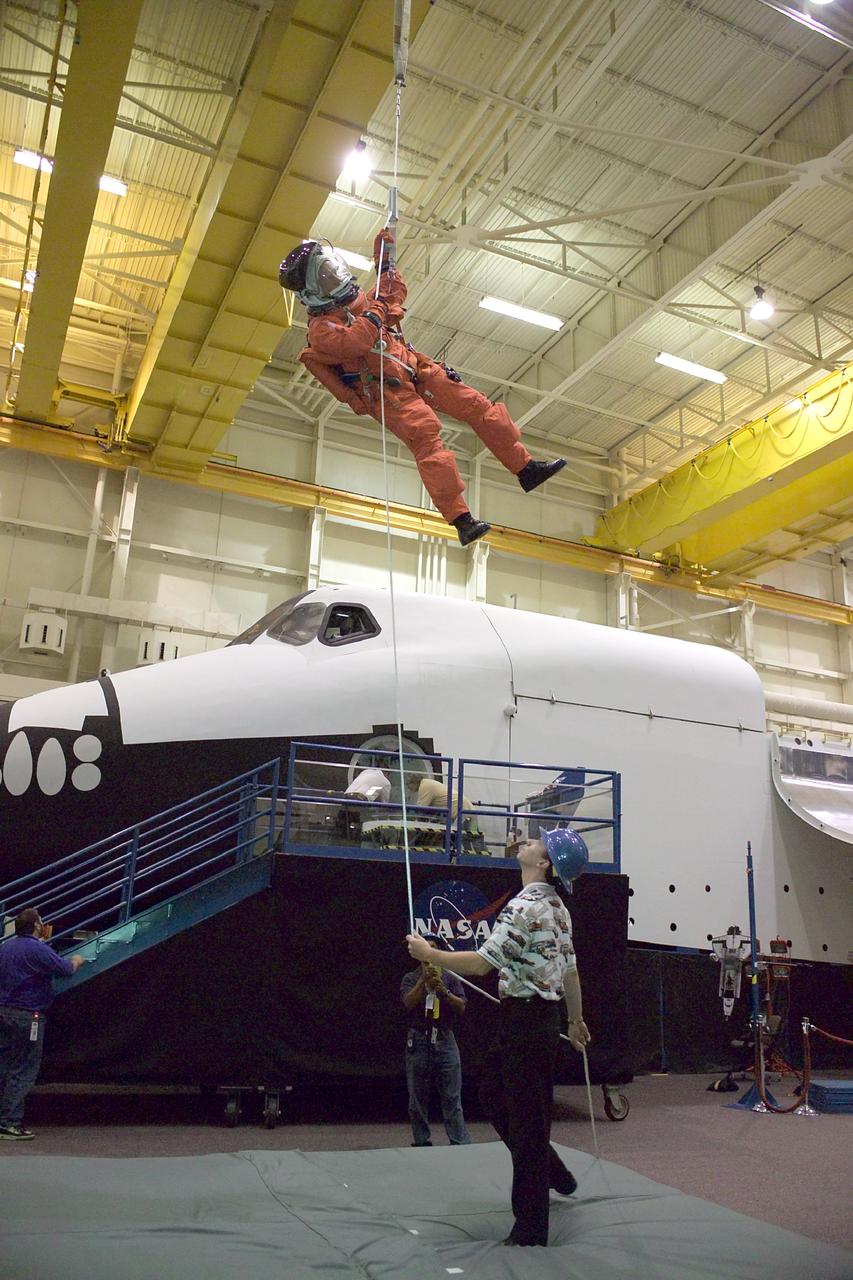
JSC2002-01563 (8 August 2002) --- Astronaut Robert L. Curbeam, Jr., STS-116 mission specialist, uses the Sky-genie to lower himself from a simulated trouble-plagued shuttle in a training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Curbeam is wearing a training version of the shuttle launch and entry suit.

S70-35368 (16 April 1970) --- Overall view showing some of the feverish activity in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) of the Mission Control Center (MCC) during the final 24 hours of the problem-plagued Apollo 13 mission. Here, flight controllers and several NASA/MSC officials confer at the flight director's console. When this picture was made, the Apollo 13 lunar landing had already been canceled, and the Apollo 13 crewmembers were in trans-Earth trajectory attempting to bring their crippled spacecraft back home.

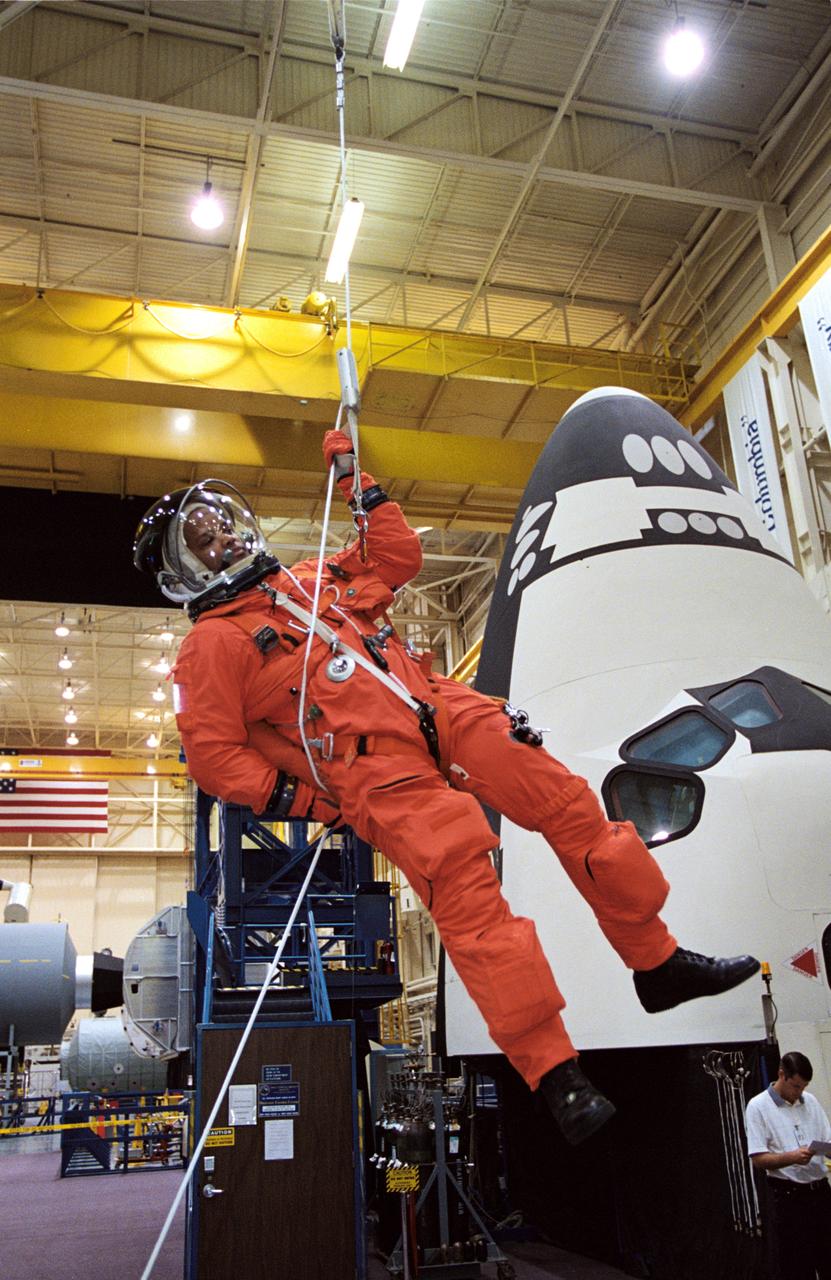
JSC2004-E-37689 (18 August 2004) --- Astronaut Steven W. Lindsey, STS-121 commander, uses a climbing apparatus to lower himself from a simulated trouble-plagued shuttle in an emergency egress training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Lindsey is wearing a training version of the shuttle launch and entry suit. United Space Alliance (USA) crew trainer David Pogue assisted Lindsey.
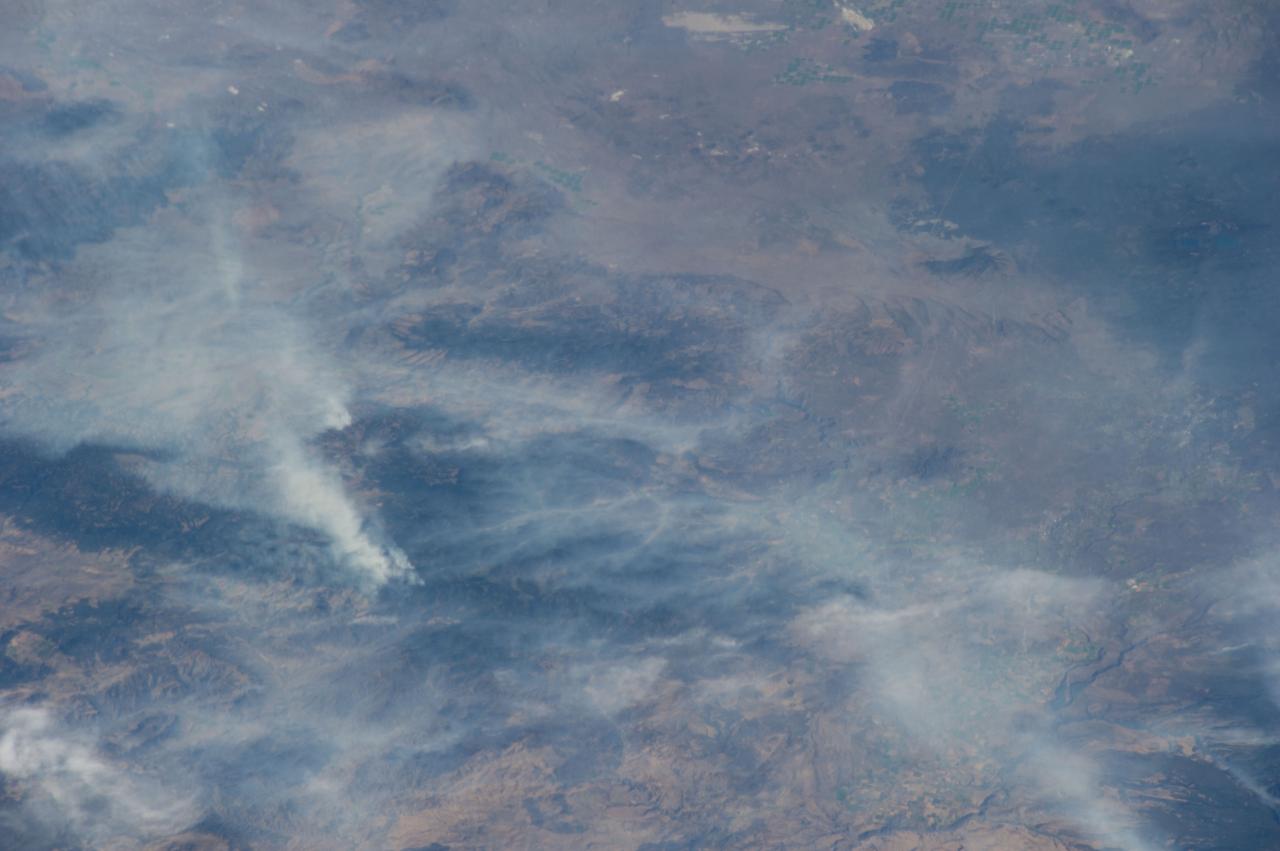

ISS040-E-070424 (19 July 2014) --- One of the Expedition 40 crew members aboard the Earth-orbiting International Space Station recorded this July 19 image of wildfires which are plaguing the Northwest and causing widespread destruction. The orbital outpost was flying 223 nautical miles above Earth at the time of the photo. Lightning has been given as the cause of the Ochoco Complex fires in the Ochoco National Forest in central Oregon. The complex has gotten larger since this photo was taken.
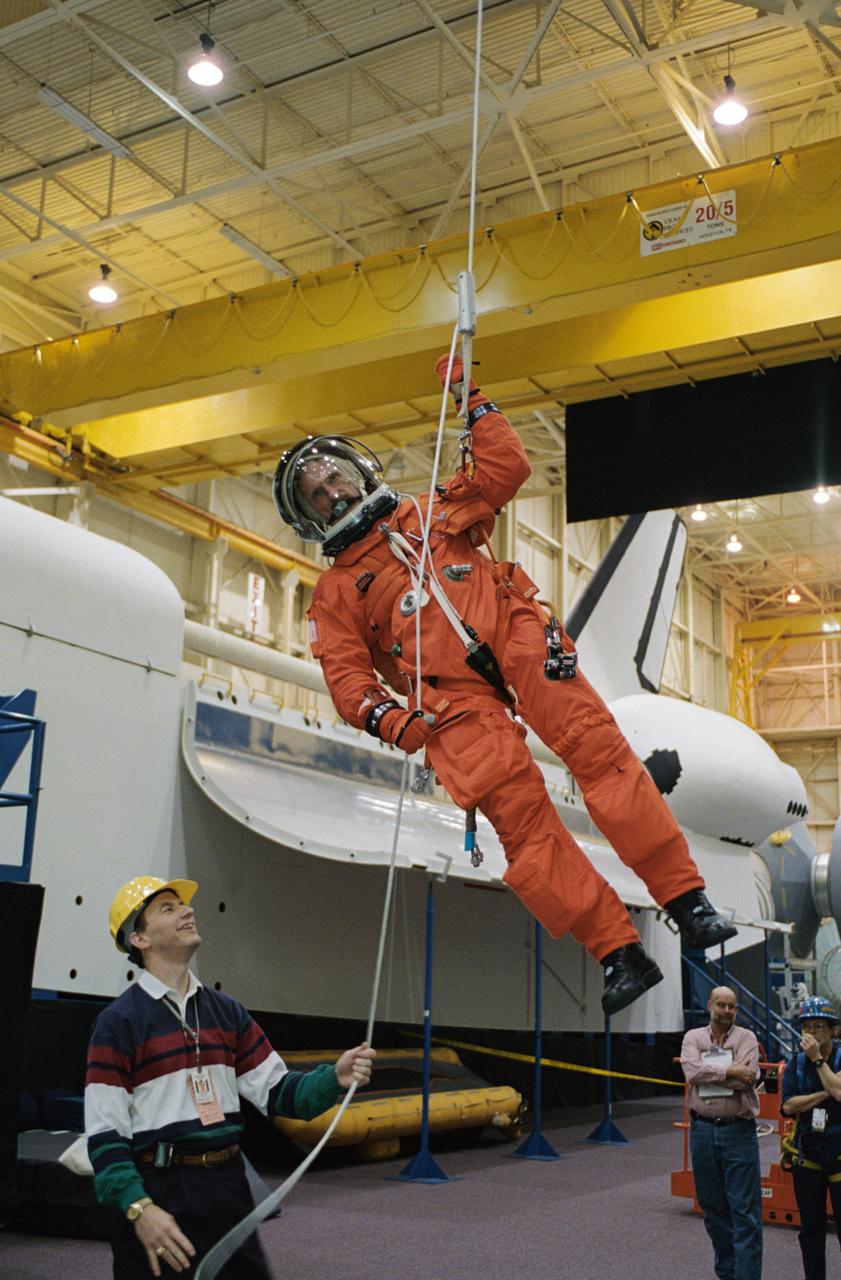

JSC2002-02121 (3 December 2002) --- Astronaut Joseph R. (Joe) Tanner, STS-115 mission specialist, uses the Sky-genie to lower himself from a simulated trouble-plagued shuttle in an emergency egress training session in the Space Vehicle Mockup Facility at the Johnson Space Center (JSC). Tanner is wearing a training version of the shuttle launch and entry suit. United Space Alliance (USA) crew trainer David Pogue assisted Tanner.
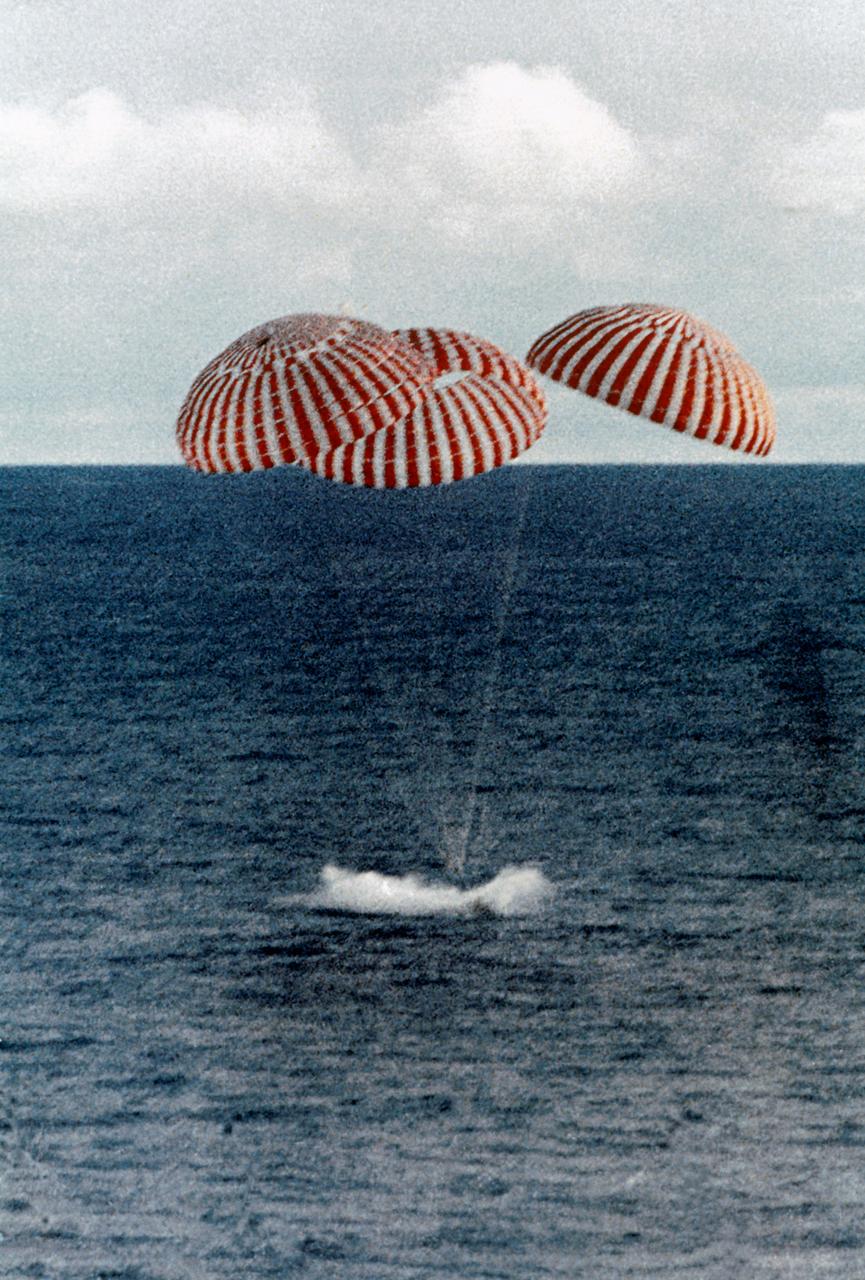

S70-35638 (17 April 1970) --- A perilous space mission comes to a smooth ending with the safe splashdown of the Apollo 13 Command Module (CM) in the South Pacific, only four miles from the prime recovery ship. The spacecraft with astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., John L. Swigert Jr., and Fred W. Haise Jr. aboard, splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST) April 17, 1970, to conclude safely the problem-plagued flight. The crewmen were transported by helicopter from the immediate recovery area to the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery vessel.
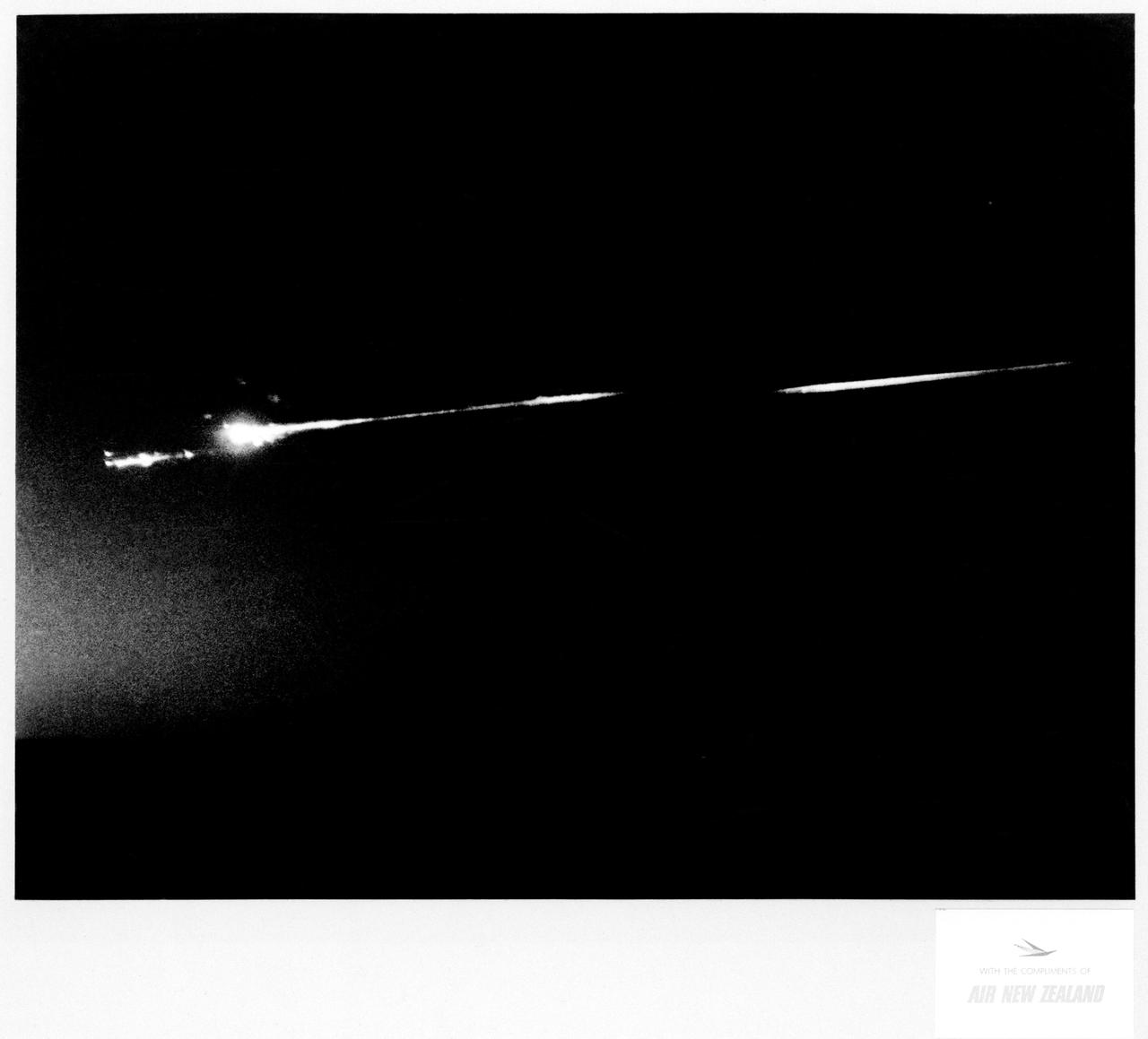

S70-17646 (18 April 1970) --- An unidentified airline passenger snapped these bright objects, believed to be the Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) and Lunar Module (LM) as they entered Earth's atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean on April 18, 1970. The aircraft, an Air New Zealand DC-8 was midway between the Fiji Islands (Nandi Island to be specific) and Auckland, New Zealand, when the photograph was taken. The crew men of the problem plagued Apollo 13 mission jettisoned the LM and SM prior to entering Earth's atmosphere in the Apollo 13 Command Module (CM).

S70-15501 (17 April 1970) --- Astronaut James A. Lovell Jr., Apollo 13 mission commander, reads a newspaper account of the safe recovery of the problem plagued mission. Lovell is on board the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship for Apollo 13, which was on a course headed for Pago Pago. From Pago Pago the astronauts flew to Hickam Air Force Base, Hawaii, where they were presented the Presidential Medal of Freedom by President Richard M. Nixon. Other Apollo 13 crew members were astronauts John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot, and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot.
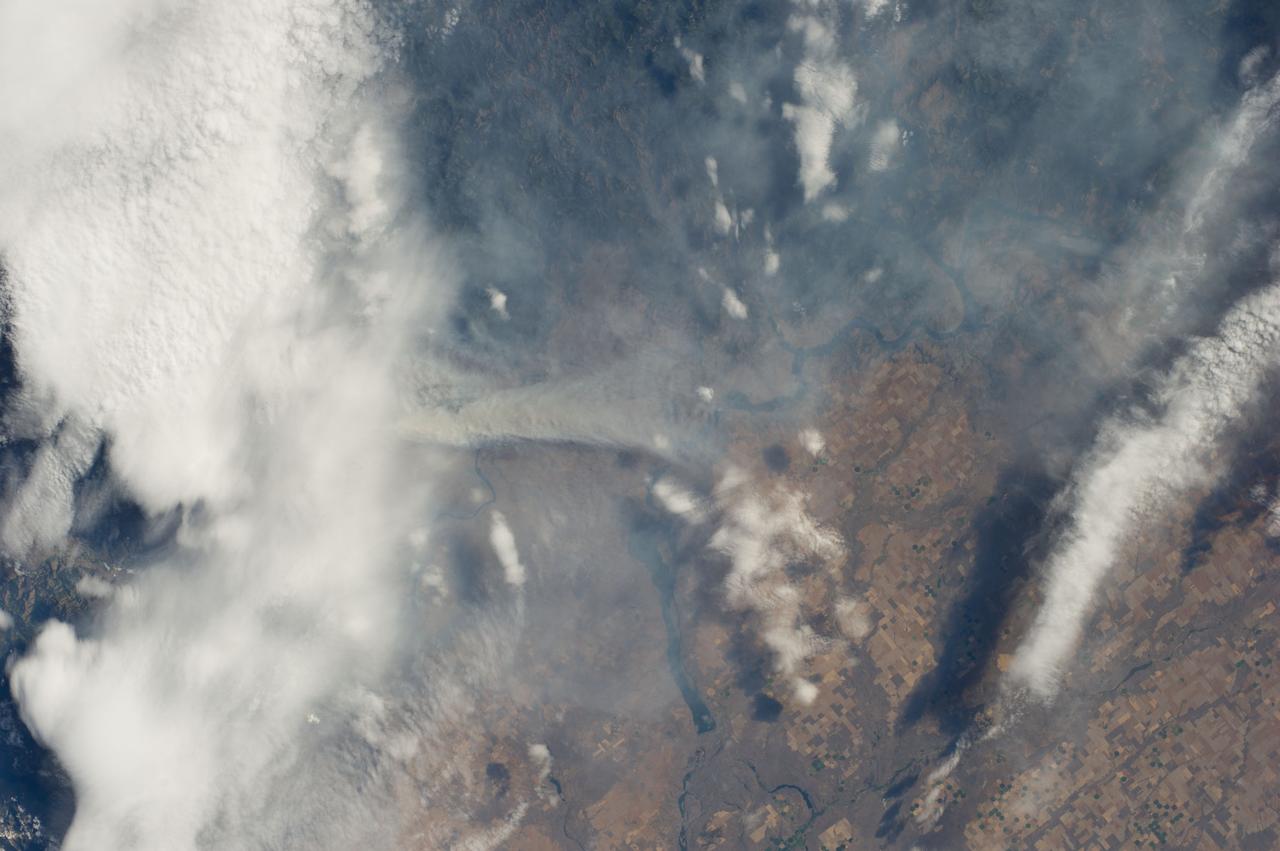

ISS040-E-070439 (19 July 2014) --- One of the Expedition 40 crew members aboard the Earth-orbiting International Space Station recorded this July 19 image of wildfires which are plaguing the Northwest and causing widespread destruction. The orbital outpost was flying 223 nautical miles above a point on Earth located at 48.0 degrees north latitude and 116.9 degrees west longitude when the image was exposed. The state of Washington is especially affected by the fires, many of which have been blamed on lightning. This particular fire was part of the Carlton Complex Fire, located near the city of Brewster in north central Washington. The reservoir visible near the center of the image is Banks Lake.
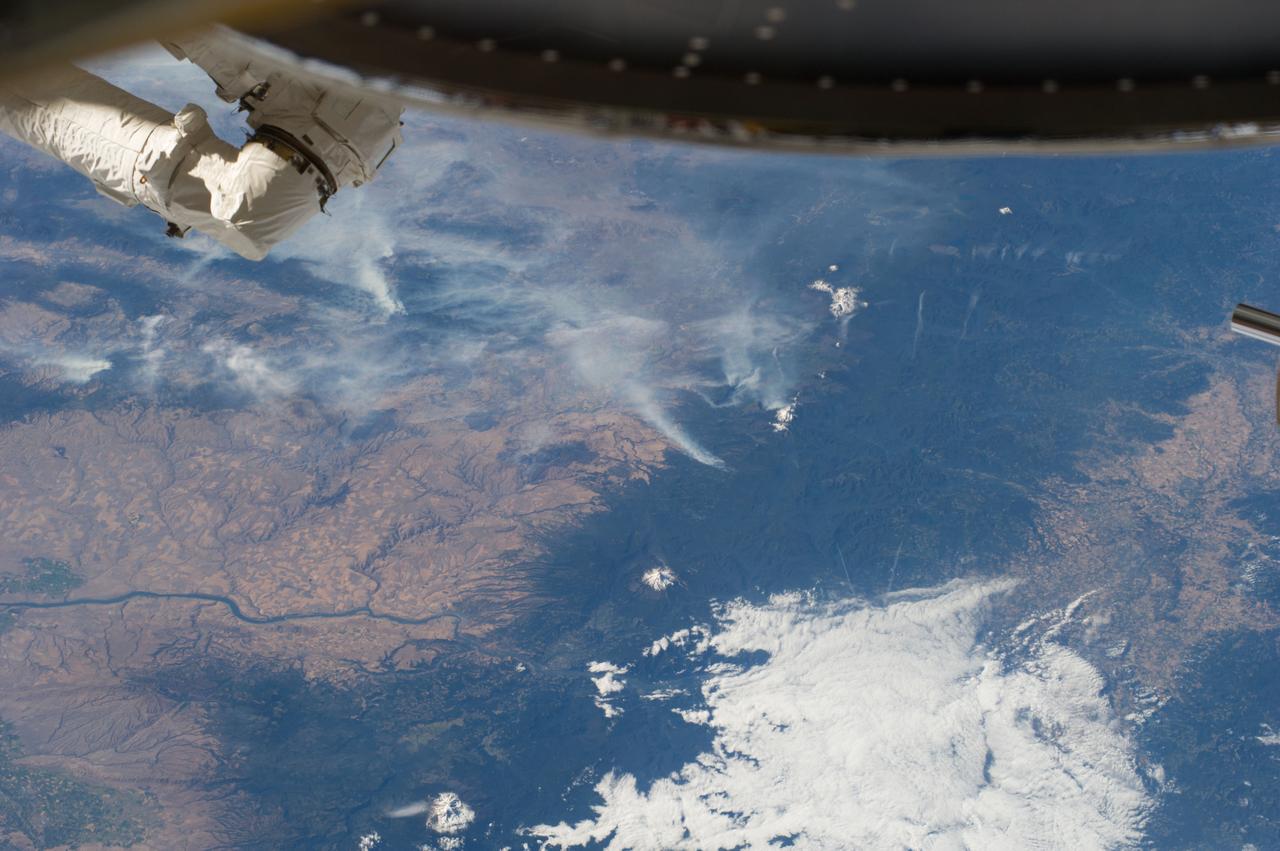

ISS040-E-070412 (19 July 2014) --- One of the Expedition 40 crew members aboard the Earth-orbiting International Space Station recorded this July 19 panorama featuring wildfires which are plaguing the Northwest and causing widespread destruction. (Note: south is at the top of the frame). The orbital outpost was flying 223 nautical miles above Earth at the time of the photo. Parts of Oregon and Washington are included in the scene. Mt. Jefferson, Three Sisters and Mt. St. Helens are all snow-capped and visible in the photo, and the Columbia River can also be delineated.

ISS019-E-007720 (15 April 2009) --- Three Gorges Dam in China is featured in this image photographed by an Expedition 19 crew member on the International Space Station. A new reservoir is filling in central China. The Three Gorges Dam on the Yangtze River - the world?s largest dam ? was completed in 2006, and the river is filling up its valley behind the dam to form a narrow reservoir extending more than 600 kilometers. This image is one of the first images documenting the flooding behind the dam. The main objective for the dam is to supply water for the largest hydroelectric plant in the world and help control the devastating floods that plague the lowlands downstream from the dam.

S70-35747 (20 April 1970) --- The three crew men of the problem plagued Apollo 13 mission are photographed during the first day of their postflight debriefing activity at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Left to right, are astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. The apparent rupture of oxygen tank number two in the Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) and the subsequent damage forced the three astronauts to use the Lunar Module (LM) as a "lifeboat" to return home safely after their moon landing was canceled.
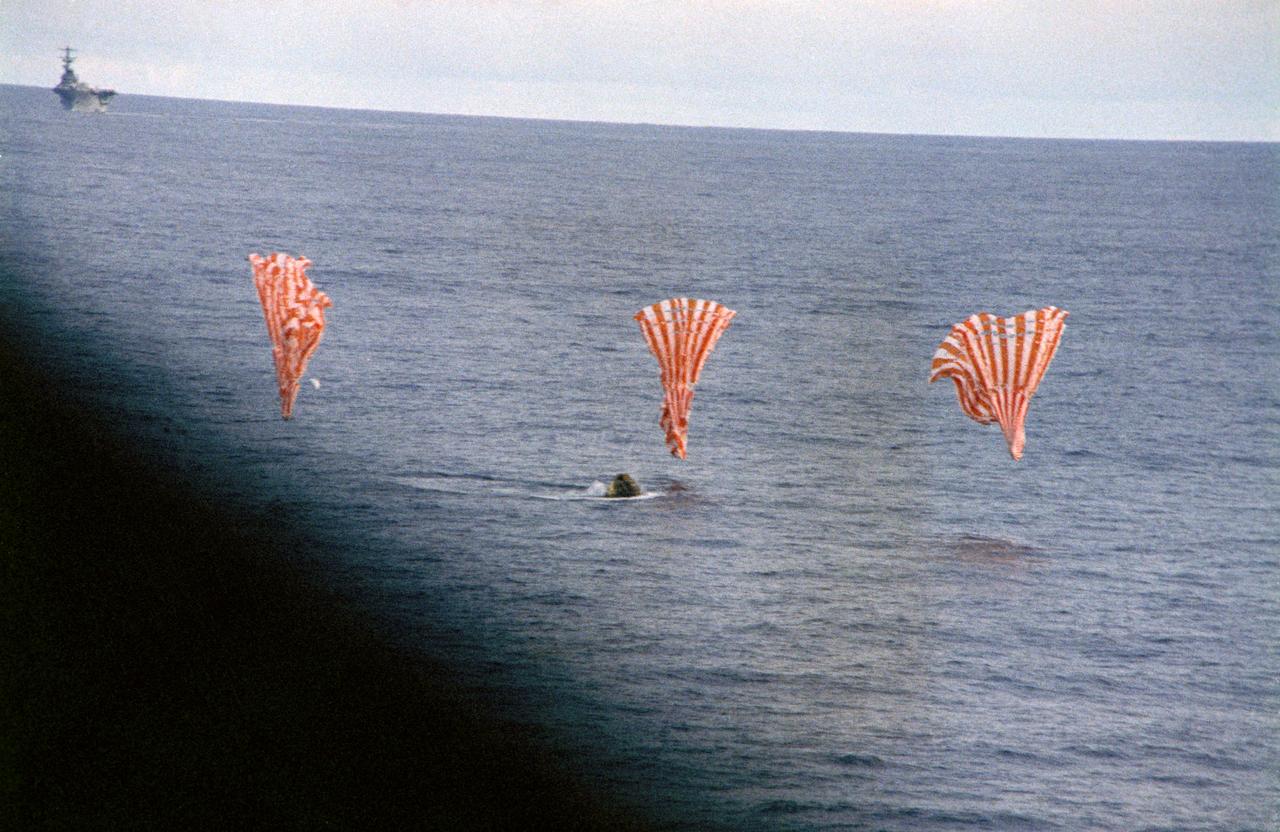

S70-35644 (17 April 1970) --- The Apollo 13 Command Module (CM) splashes down and its three main parachutes collapse, as the week-long problem-plagued Apollo 13 mission comes to a premature, but safe end. The spacecraft, with astronauts James A. Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot, aboard splashed down at 12:07:44 p.m. (CST) April 17, 1970, in the South Pacific Ocean, only about four miles from the USS Iwo Jima, prime recovery ship.
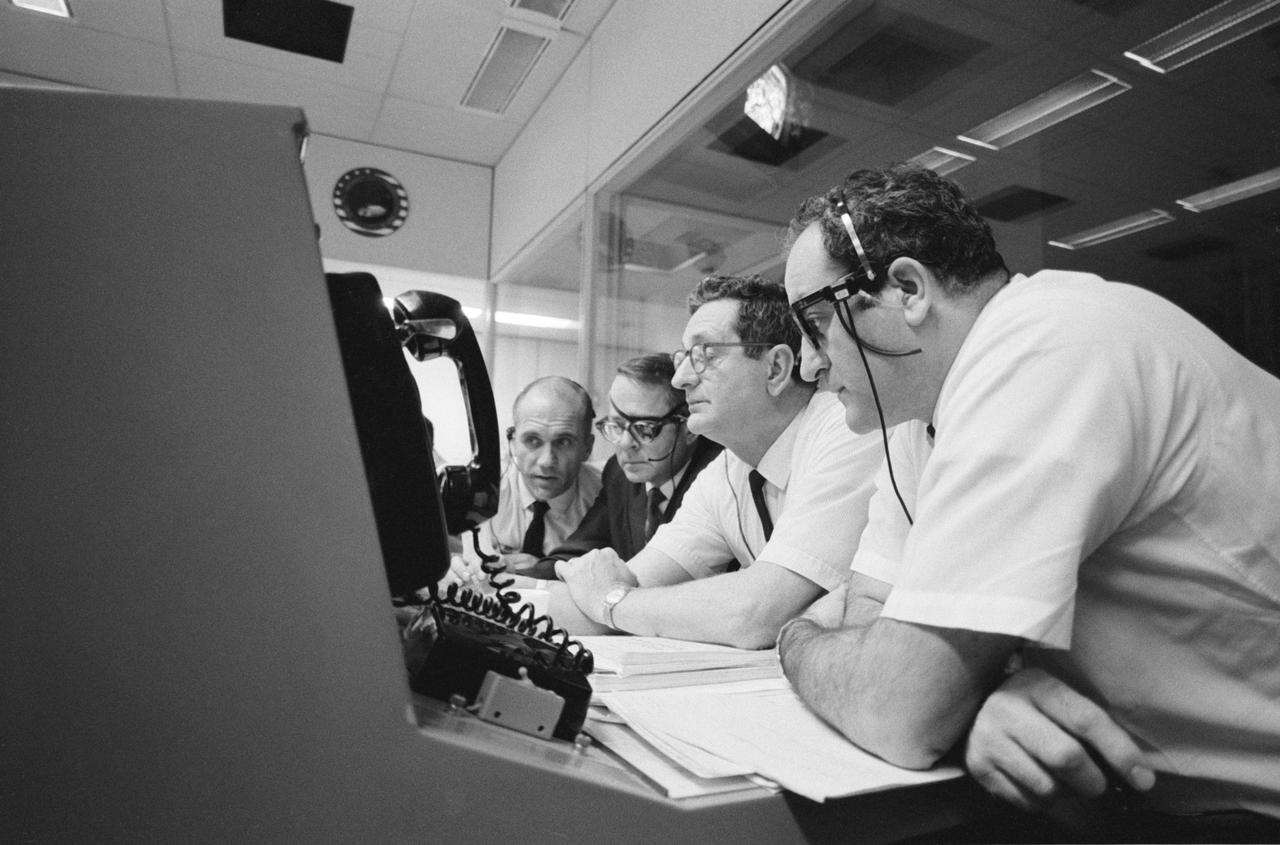

S70-35096 (16 April 1970) --- As the problem-plagued Apollo 13 crewmen entered their final 24 hours in space, several persons important to the mission remained attentive at consoles in the Mission Operations Control Room of the Mission Control Center at Manned Spacecraft Center. Among those monitoring communications and serving in supervisory capacities were these four officials from National Aeronautics and Space Administration Headquarters, Washington, D.C.: (from left) Thomas H. McMullen, Office of Manned Space Flight, who served as Shift 1 mission director; Dale Myers, associate administrator, Manned Space Flight; Chester M. Lee of the Apollo Program Directorate, OMSF, Apollo 13 mission director; and Dr. Rocco A. Petrone, Apollo program director, OMSF.

S70-35014 (15 April 1970) --- A group of flight controllers gathers around the console of Glenn S. Lunney (seated, nearest camera), Shift 4 flight director, in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) of Mission Control Center (MCC), located in Building 30 at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC). Their attention is drawn to a weather map of the proposed landing site in the South Pacific Ocean. Among those looking on is Dr. Christopher C. Kraft, deputy director, MSC, standing in black suit, on right. When this photograph was taken, the Apollo 13 lunar landing mission had been canceled, and the problem-plagued Apollo 13 crew members were in trans-Earth trajectory attempting to bring their crippled spacecraft back home.
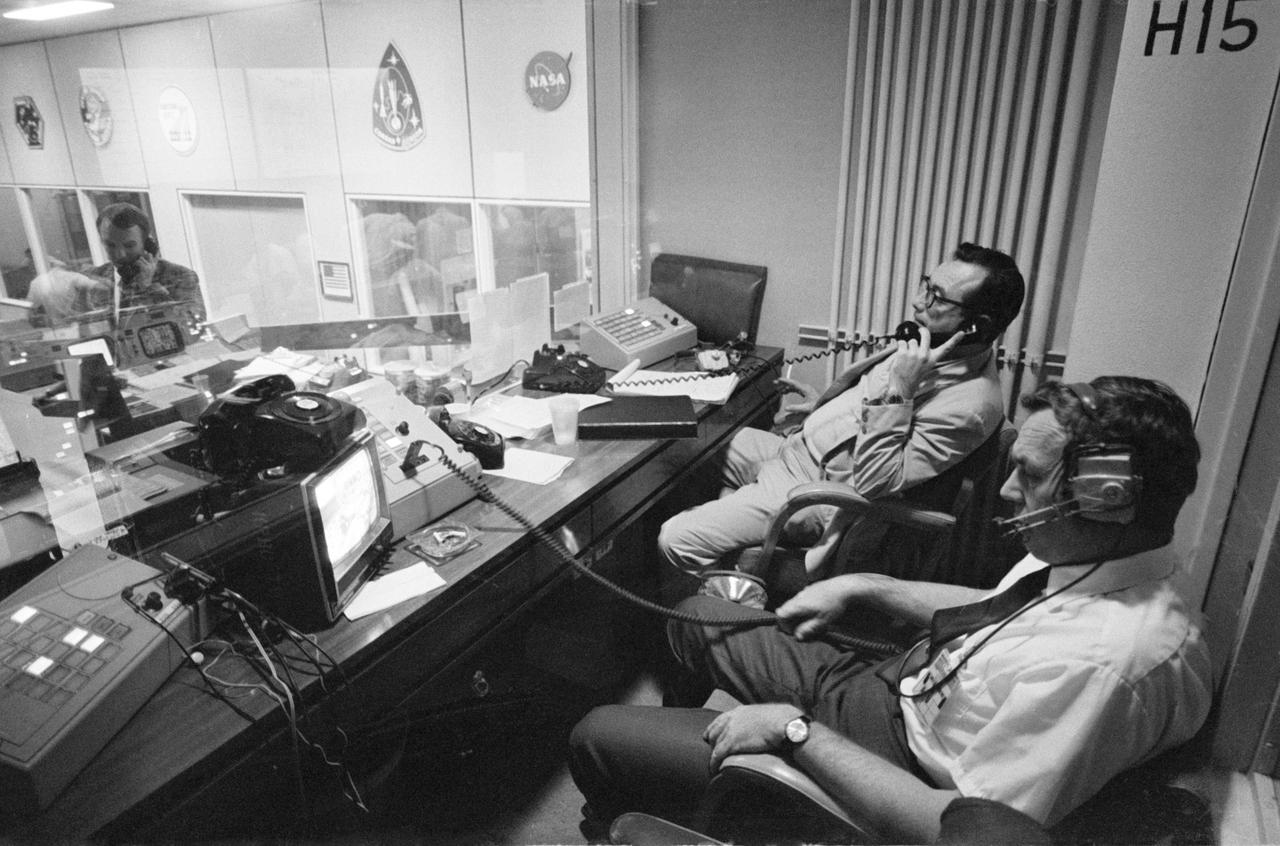

S70-35012 (15 April 1970) --- Two phases of busy activity during critical moments of the Apollo 13 mission are reflected in this view in the Mission Control Center, Building 30, Manned Spacecraft Center. In the foreground, Henry Simmons (left) of Newsweek magazine and John E. Riley, public information specialist, Public Affairs Office, MSC, man their positions in the Press Room. At extreme left of photo, Gerald D. Griffin, Shift 2 flight director, talks on telephone in Mission Operations Control Room. When this photograph was taken, the Apollo 13 lunar landing had been canceled, and the problem-plagued Apollo 13 crewmen were in trans-Earth trajectory attempting to bring their crippled spacecraft back home.
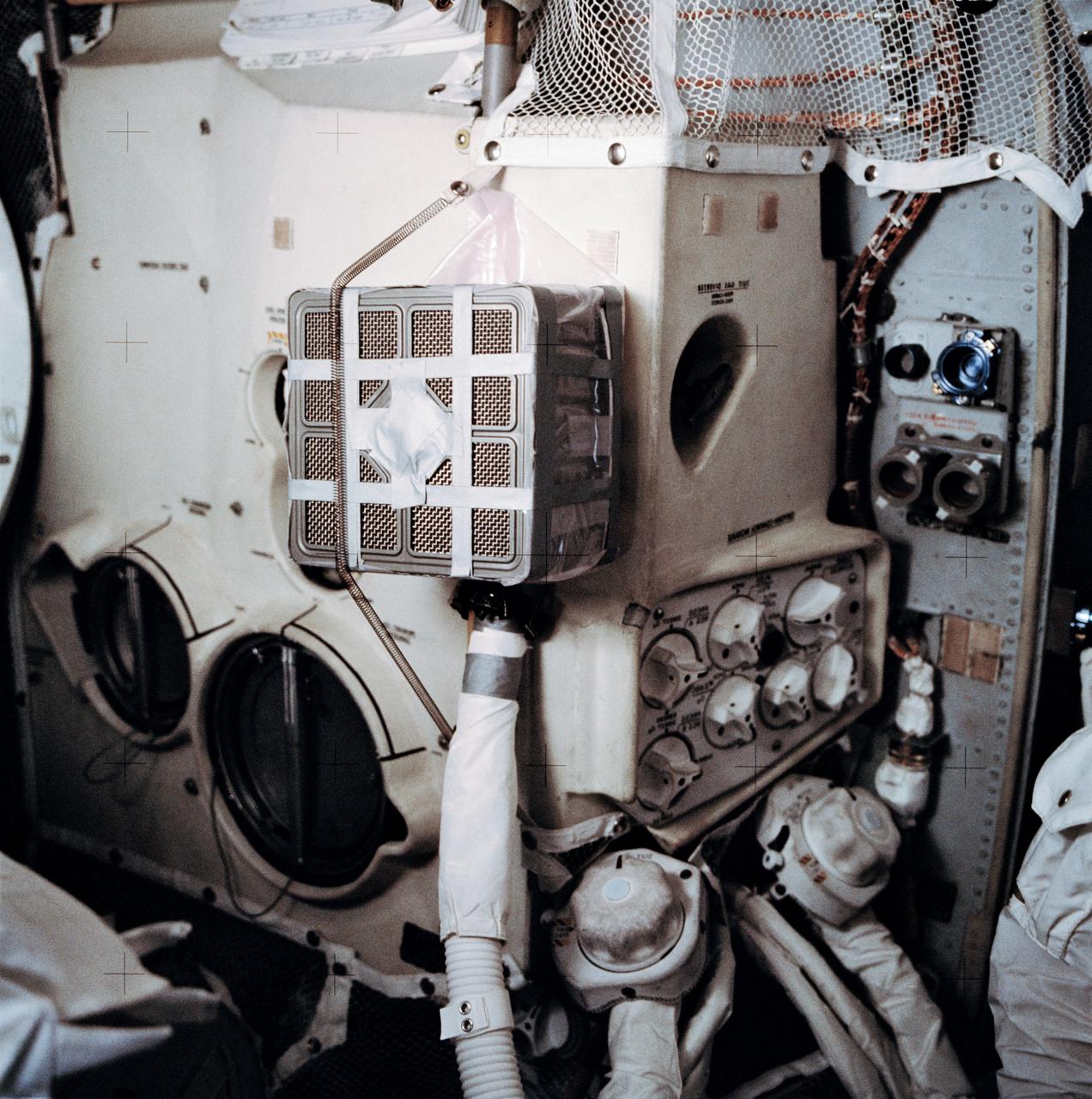
AS13-62-8929 (11-17 April 1970) --- Interior view of the Apollo 13 Lunar Module (LM) showing the "mail box," a jury-rigged arrangement which the Apollo 13 astronauts built to use the Command Module (CM) lithium hydroxide canisters to purge carbon dioxide from the LM. Lithium hydroxide is used to scrub CO2 from the spacecraft's atmosphere. Since there was a limited amount of lithium hydroxide in the LM, this arrangement was rigged up to utilize the canisters from the CM. The "mail box" was designed and tested on the ground at the Manned Spacecraft Center (MSC) before it was suggested to the problem-plagued Apollo 13 crew men. Because of the explosion of one of the oxygen tanks in the Service Module (SM), the three crew men had to use the LM as a "lifeboat".

S70-35748 (20 April 1970) --- Dr. Donald K. Slayton (center foreground), MSC director of flight crew operations, talks with Dr. Wernher von Braun (right), famed rocket expert, at an Apollo 13 postflight debriefing session. The three crewmen of the problem-plagued Apollo 13 mission (left to right) in the background are astronauts James A Lovell Jr., commander; John L. Swigert Jr., command module pilot; and Fred W. Haise Jr., lunar module pilot. The apparent rupture of oxygen tank number two in the Apollo 13 Service Module (SM) and the subsequent damage forced the three astronauts to use the Lunar Module (LM) as a "lifeboat" to return home safely after their moon landing was canceled. Dr. von Braun is the deputy associate administrator for planning of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA).
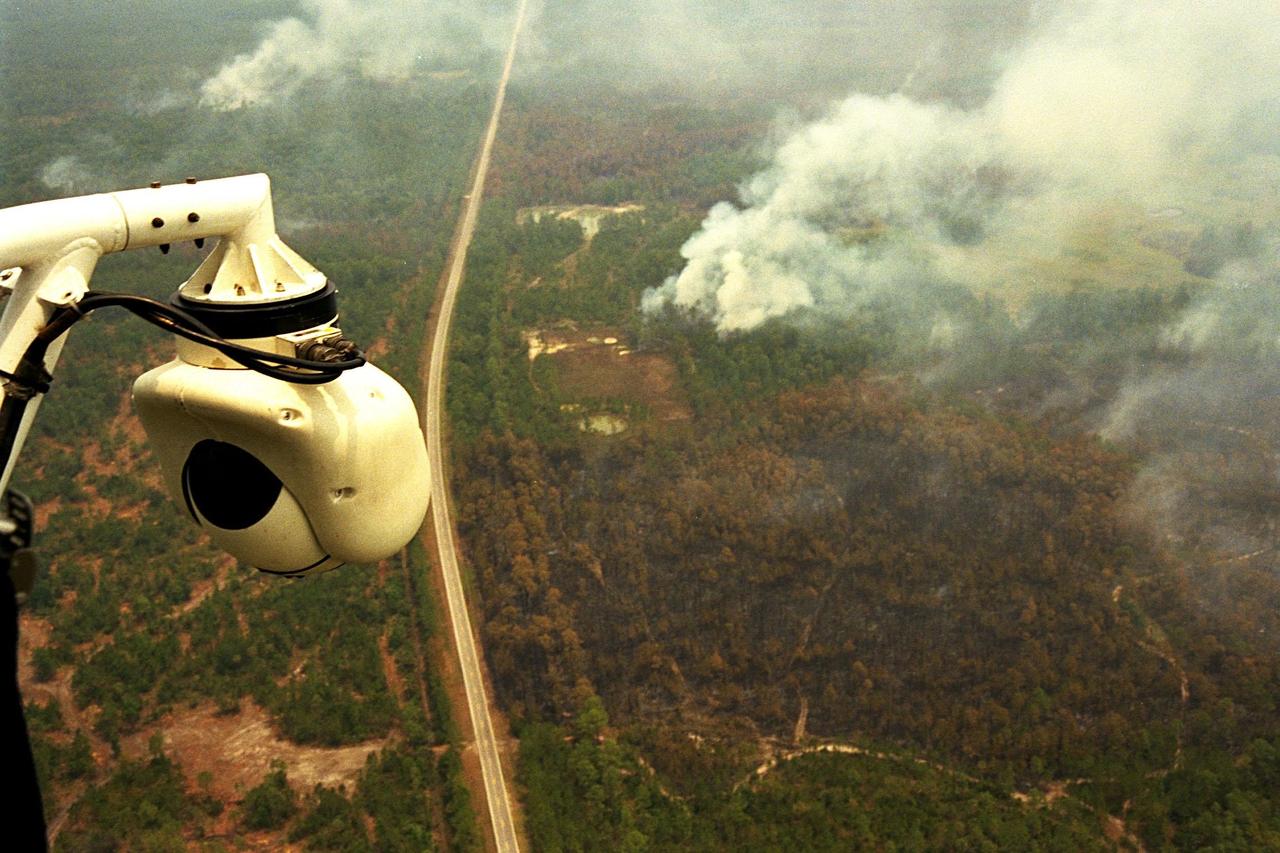

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A beach ball-sized infrared camera, part of the Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR), has been mounted on the right siderail of NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter and is being used to search for fires in Volusia County, Florida. The helicopter has also been outfitted with a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system to support Florida's Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. The FLIR also includes a real-time television monitor and recorder installed inside the helicopter. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. The Kennedy Space Center (KSC) security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter
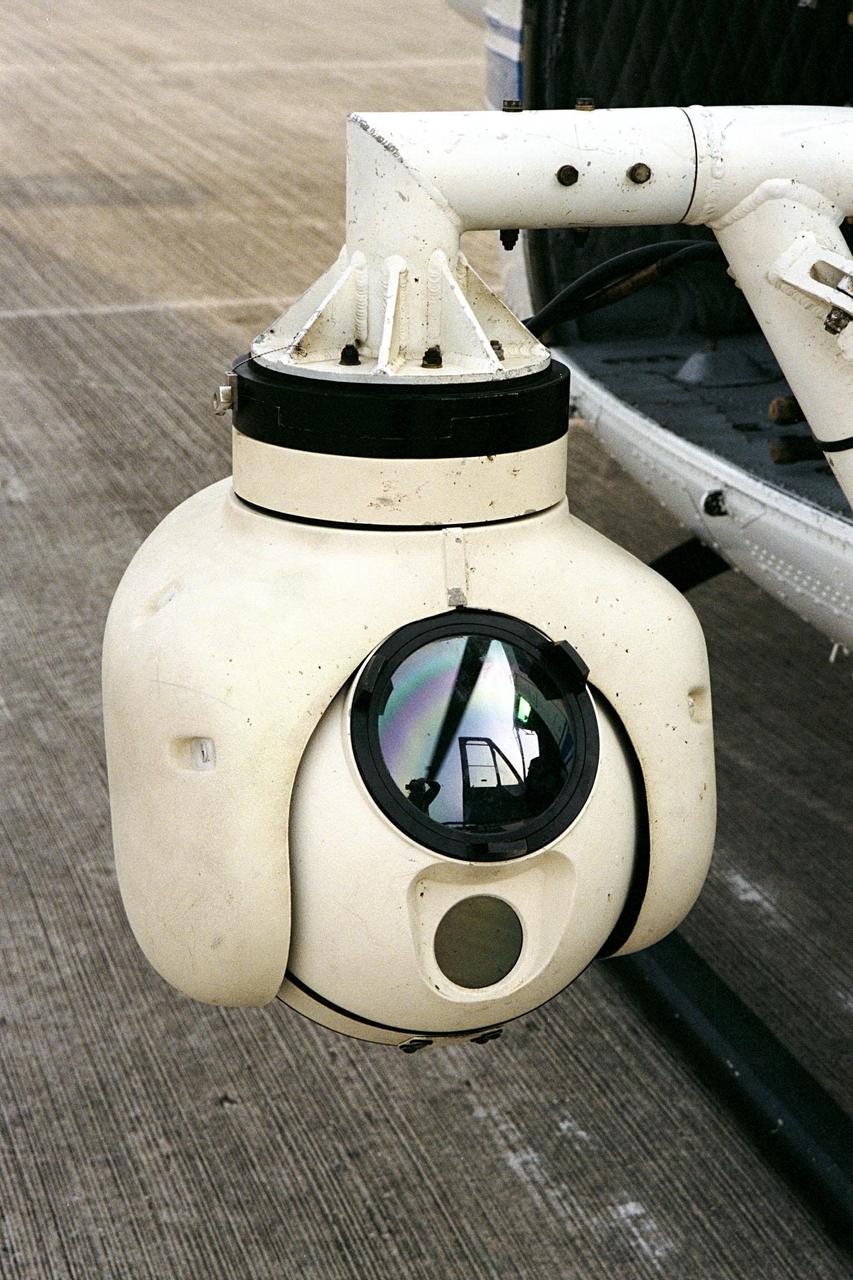

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A beach ball-sized infrared camera, part of the Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR), has been mounted on the right siderail of NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter. The helicopter has also been outfitted with a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system to support Florida's Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. The FLIR also includes a real-time television monitor and recorder installed inside the helicopter. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. The Kennedy Space Center (KSC) security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter
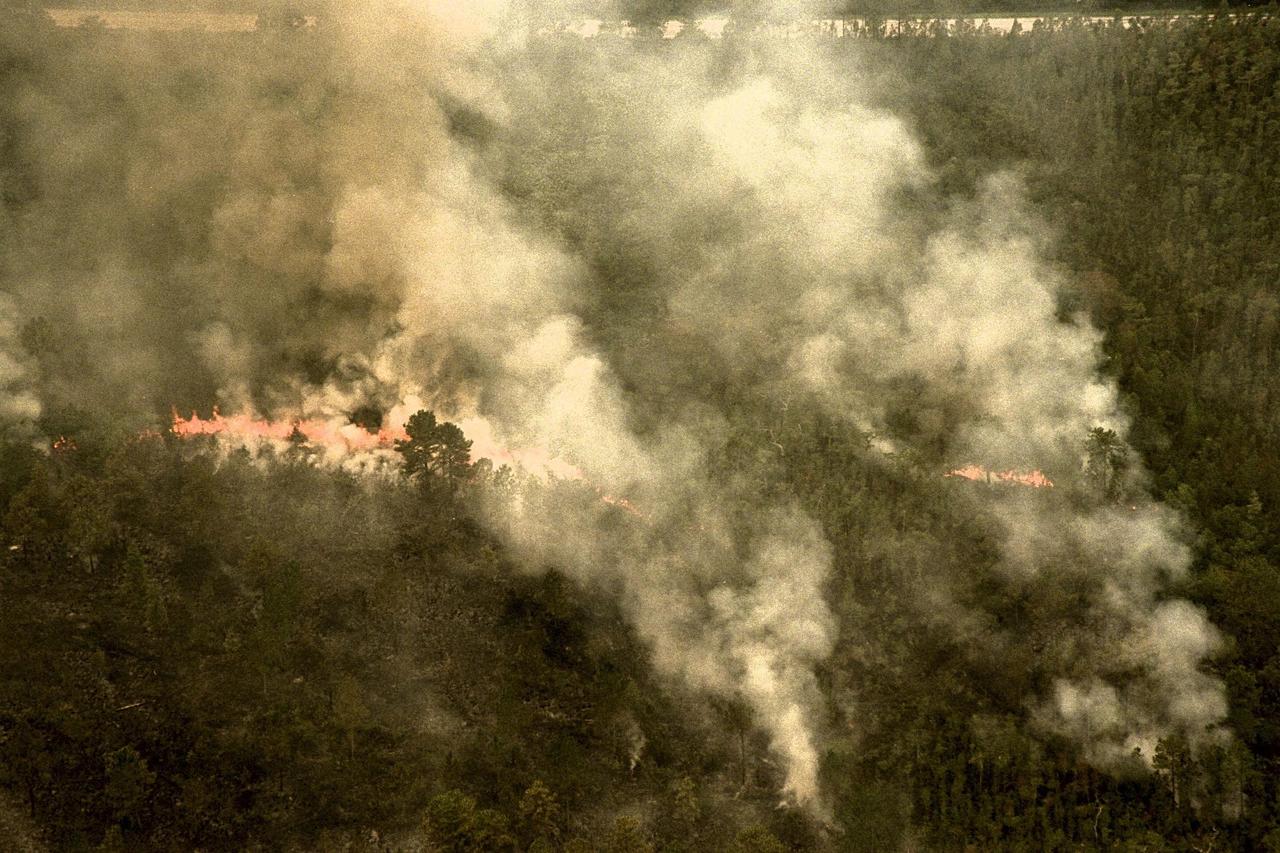

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A forest fire burning in Volusia County, Florida, is clearly visible from NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter. The helicopter has been outfitted with a Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR) and a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system to support Florida's Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. The FLIR includes a beach ball-sized infrared camera that is mounted on the helicopter's right siderail and a real-time television monitor and recorder installed inside. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. The Kennedy Space Center (KSC) security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter
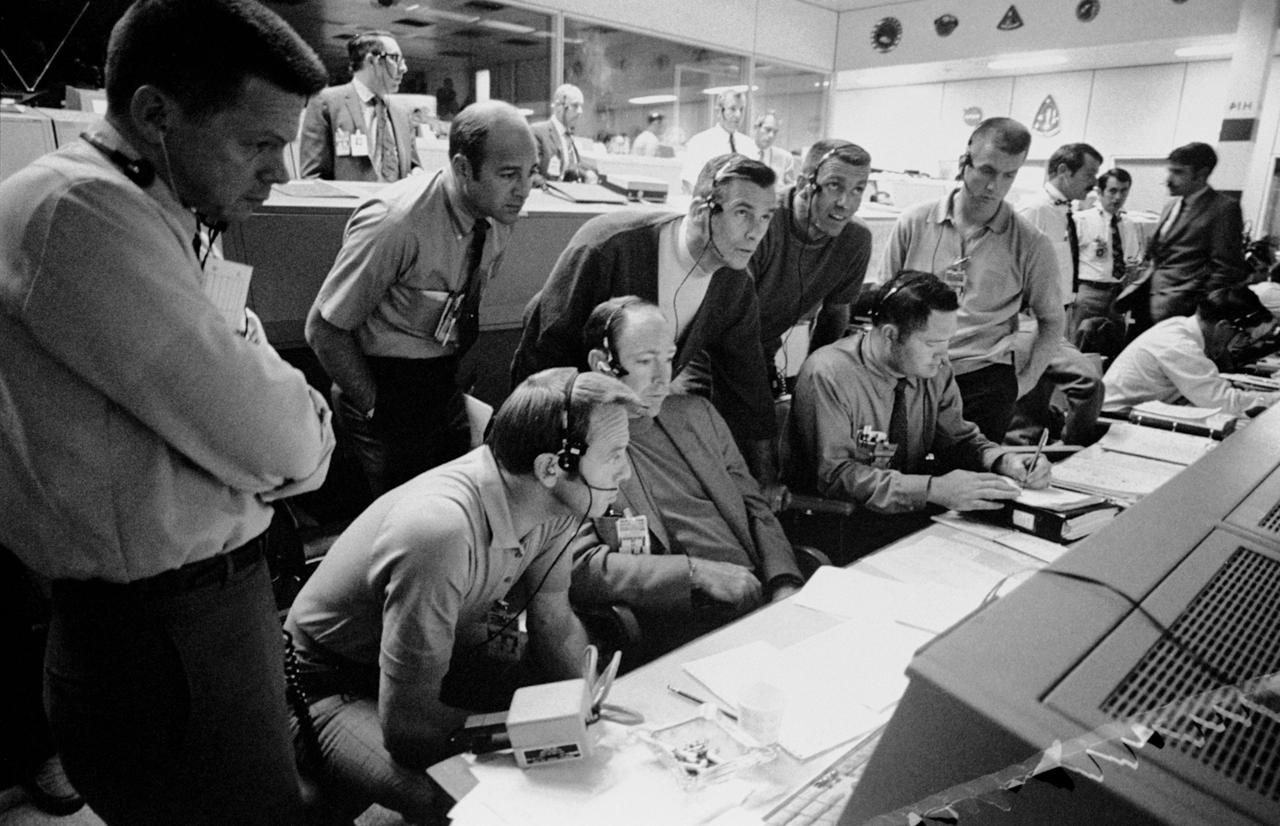

S70-34986 (14 April 1970) --- A group of six astronauts and two flight controllers monitor the console activity in the Mission Operations Control Room (MOCR) of the Mission Control Center (MCC) during the problem-plagued Apollo 13 lunar landing mission. Seated, left to right, are MOCR Guidance Officer Raymond F. Teague; astronaut Edgar D. Mitchell, Apollo 14 prime crew lunar module pilot; and astronaut Alan B. Shepard Jr., Apollo 14 prime crew commander. Standing, left to right, are scientist-astronaut Anthony W. England; astronaut Joe H. Engle, Apollo 14 backup crew lunar module pilot; astronaut Eugene A. Cernan, Apollo 14 backup crew commander; astronaut Ronald E. Evans, Apollo 14 backup crew command module pilot; and M.P. Frank, a flight controller. When this picture was made, the Apollo 13 moon landing had already been canceled, and the Apollo 13 crew men were in trans-Earth trajectory attempting to bring their damaged spacecraft back home.
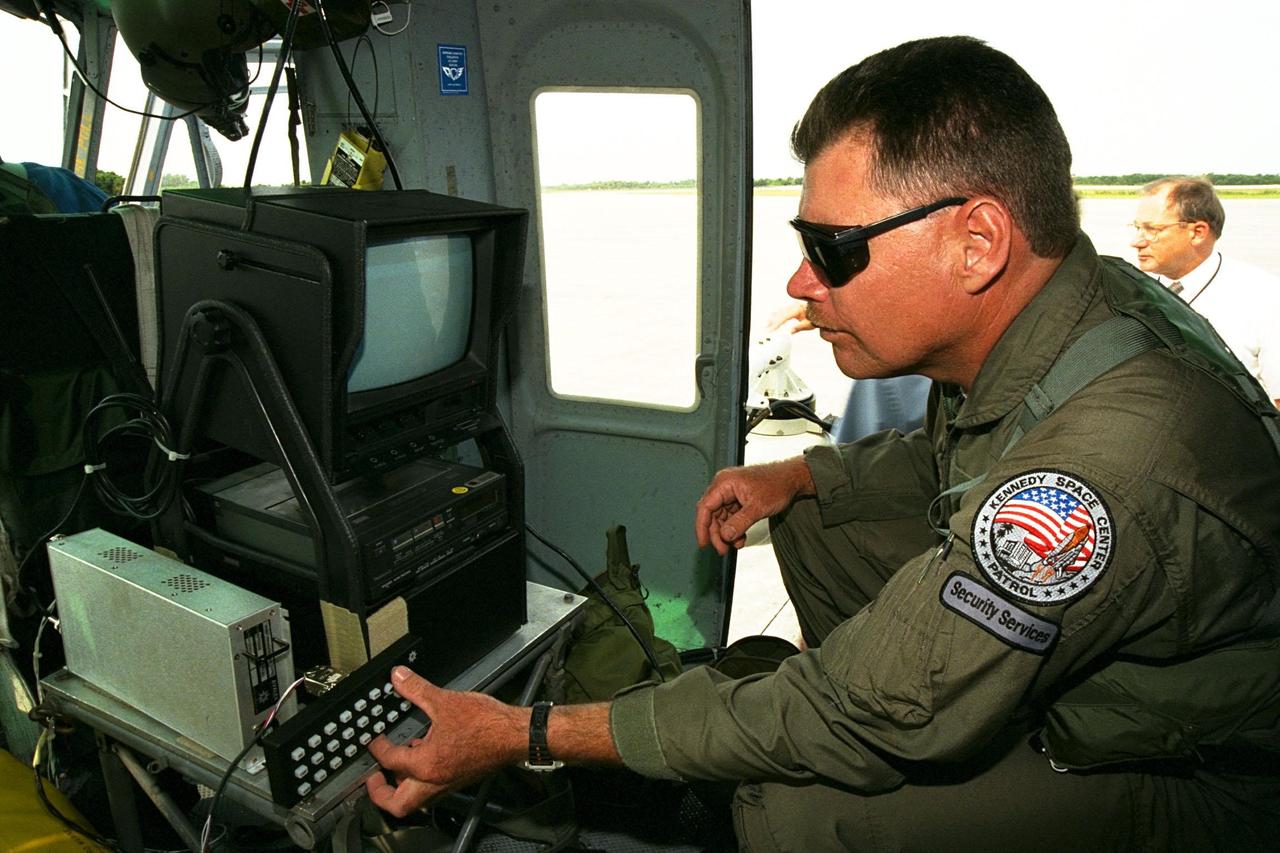

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Sgt. Mark Hines, of Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Security, checks out equipment used to operate the Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR) installed on NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter. The helicopter has also been outfitted with a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system to support Florida's Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. The FLIR includes a beach ball-sized infrared camera that is mounted on the helicopter's right siderail and a real-time television monitor and recorder installed inside. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. KSC's security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter
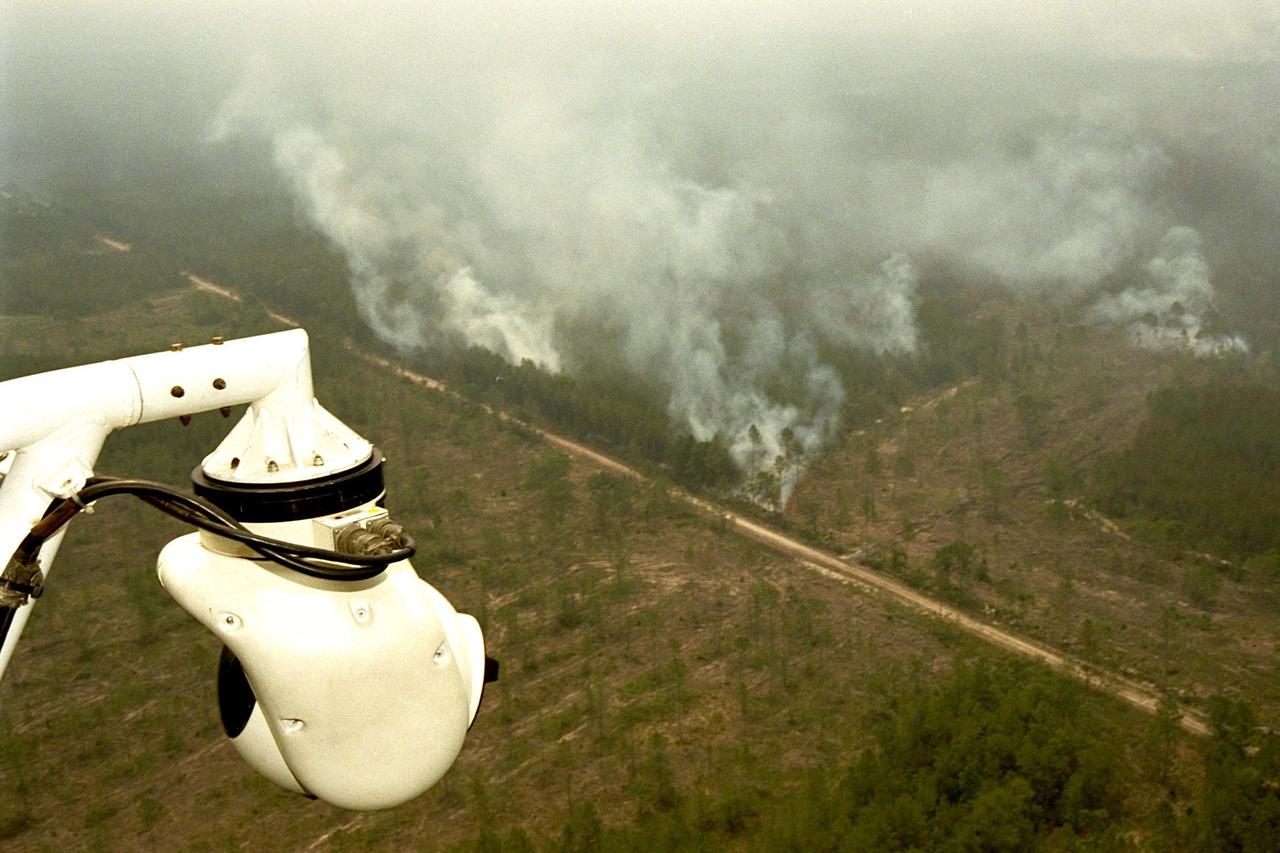

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A beach ball-sized infrared camera, part of the Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR), has been mounted on the right siderail of NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter and is being used to scan a large area of Volusia County, Florida, where a fire burns. The helicopter has also been outfitted with a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system to support Florida's Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. The FLIR also includes a real-time television monitor and recorder installed inside the helicopter. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. The Kennedy Space Center (KSC) security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter
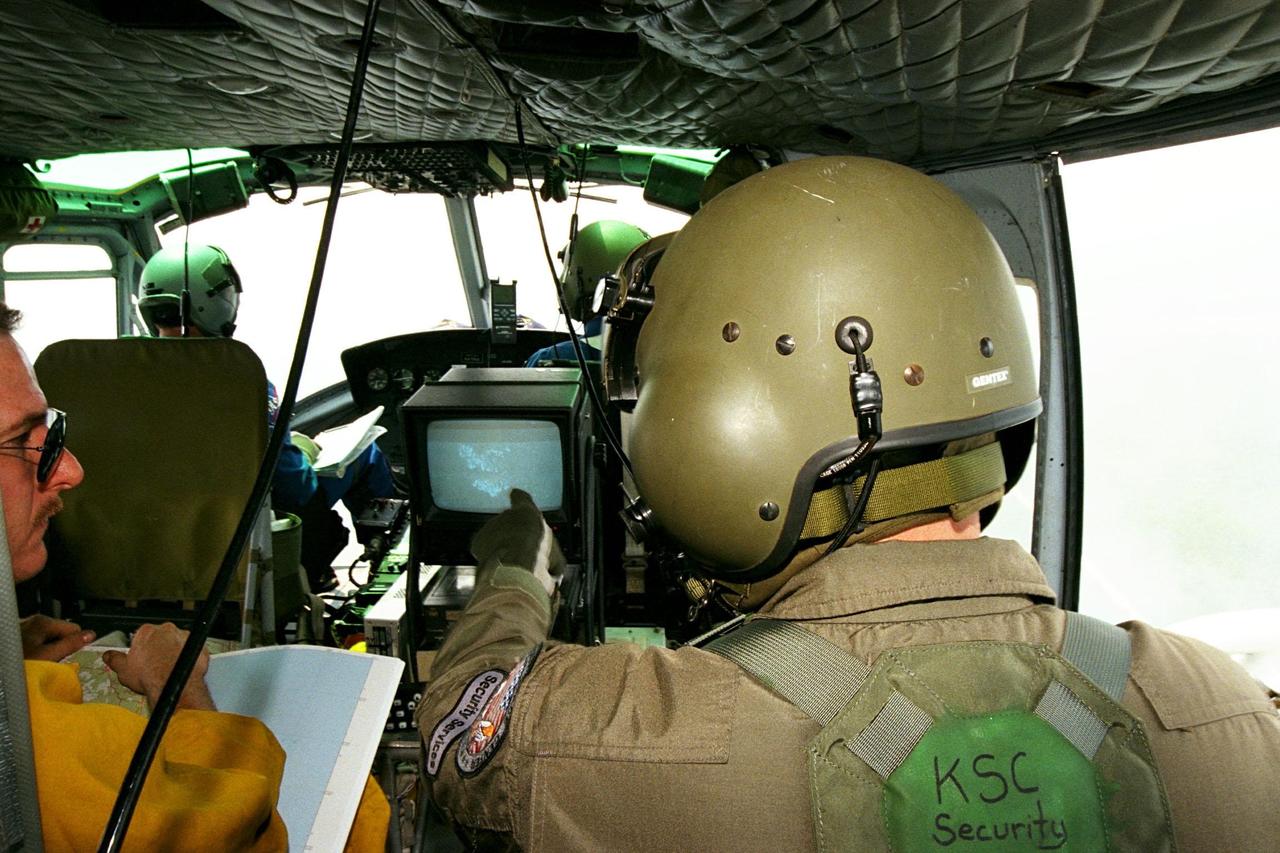

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- Sgt. Mark Hines, of Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Security, points out a view of a fire on the Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR) video screen to Greg Dunn, of Florida's Division of Forestry, as KSC pilots fly NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter over fires burning in Volusia County, Florida. The FLIR includes a beach-ball sized infrared camera that is mounted on the helicopter's right siderail and a real-time TV monitor and recorder installed inside. The helicopter has also been outfitted with a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system to support the Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. KSC's security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter.
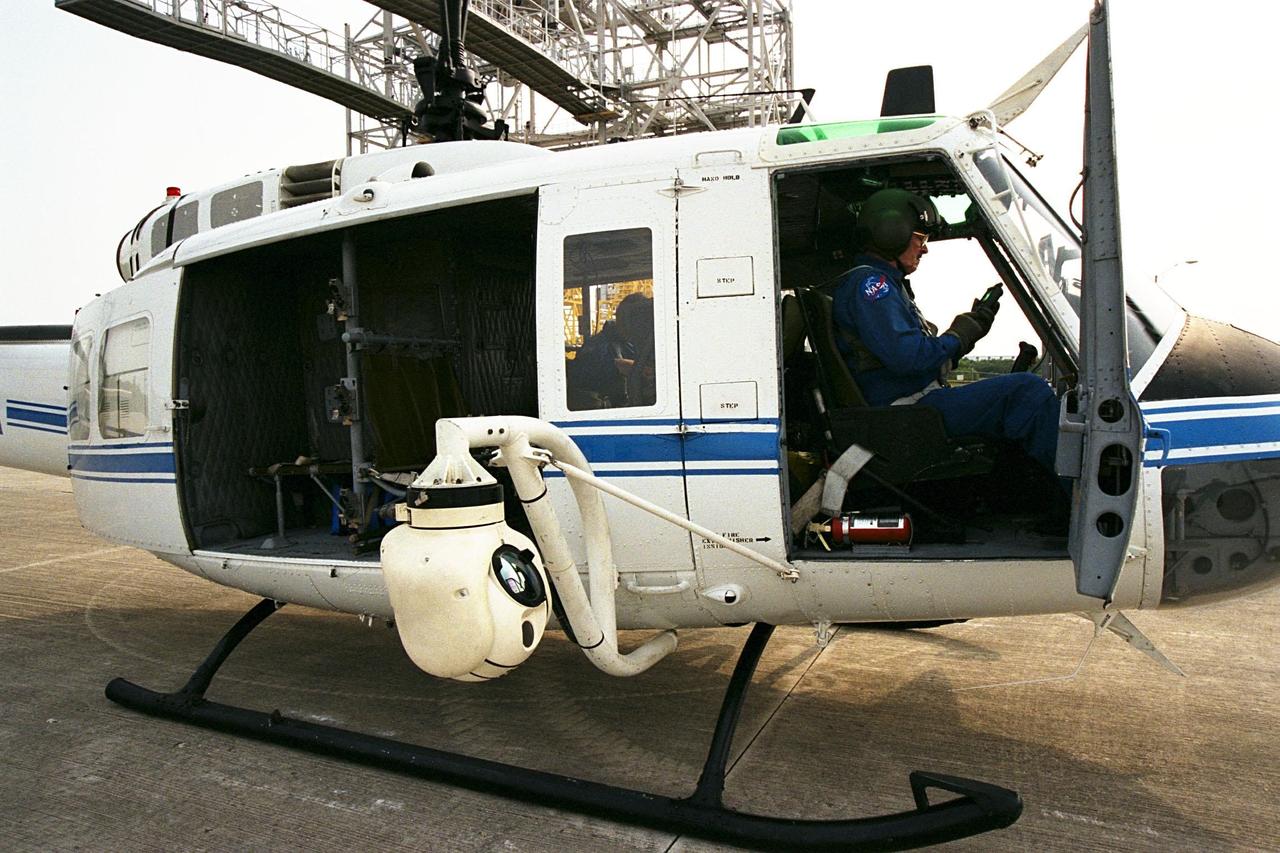

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- A beach ball-sized infrared camera, part of the Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR), has been mounted on the right siderail of NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter. A KSC pilot prepares to fly the helicopter, which has also been outfitted with a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system, to support Florida's Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. The FLIR also includes a real-time television monitor and recorder installed inside the helicopter. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. The Kennedy Space Center (KSC) security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter
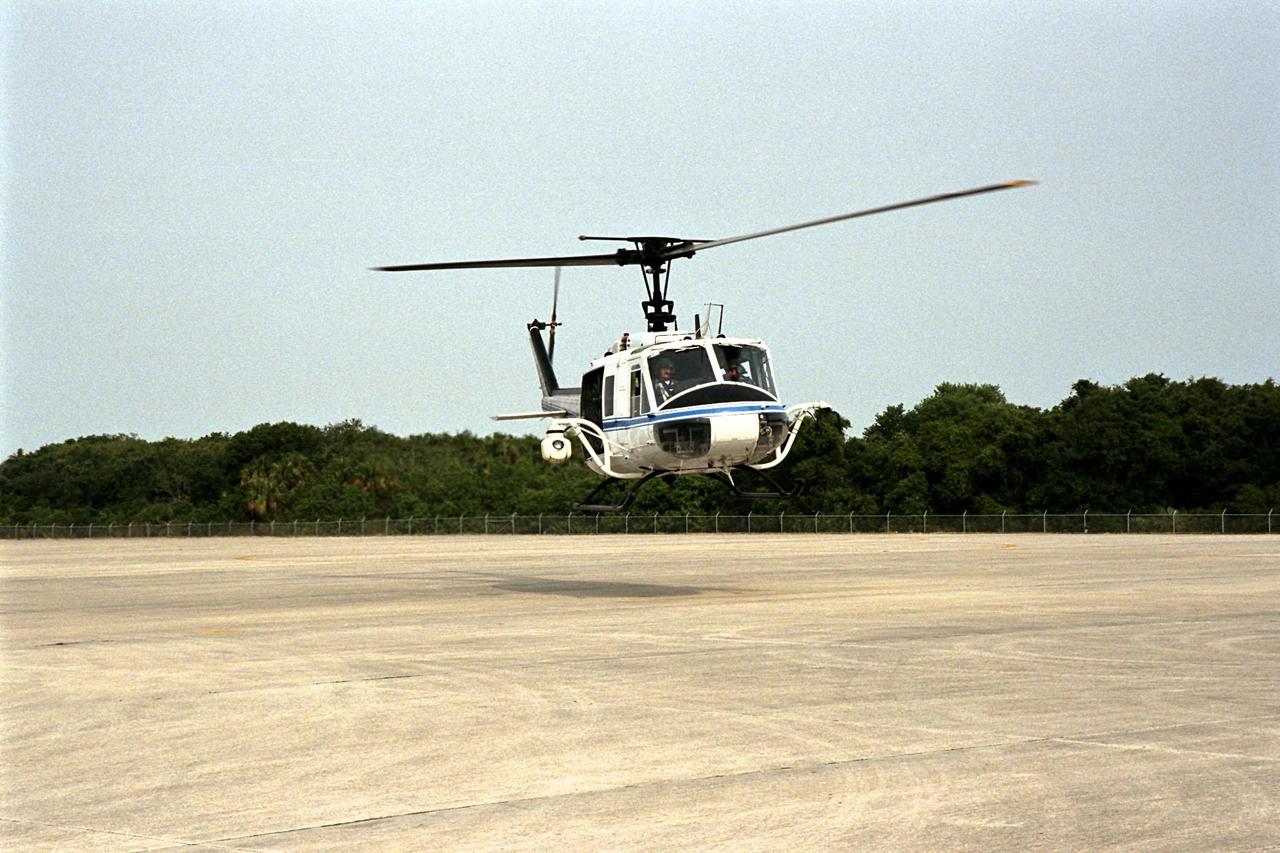

KENNEDY SPACE CENTER, FLA. -- NASA's Huey UH-1 helicopter lands at the Shuttle Landing Facility to pick up Kennedy Space Center (KSC) Security personnel who operate the Forward Looking Infrared Radar (FLIR) installed on board. The helicopter has also been outfitted with a portable global positioning satellite (GPS) system to support Florida's Division of Forestry as they fight the brush fires which have been plaguing the state as a result of extremely dry conditions and lightning storms. The FLIR includes a beach ball-sized infrared camera that is mounted on the helicopter's right siderail and a real-time television monitor and recorder installed inside. While the FLIR collects temperature data and images, the GPS system provides the exact coordinates of the fires being observed and transmits the data to the firefighters on the ground. KSC's security team routinely uses the FLIR equipment prior to Shuttle launch and landing activities to ensure that the area surrounding the launch pad and runway are clear of unauthorized personnel. KSC's Base Operations Contractor, EG&G Florida, operates the NASA-owned helicopter
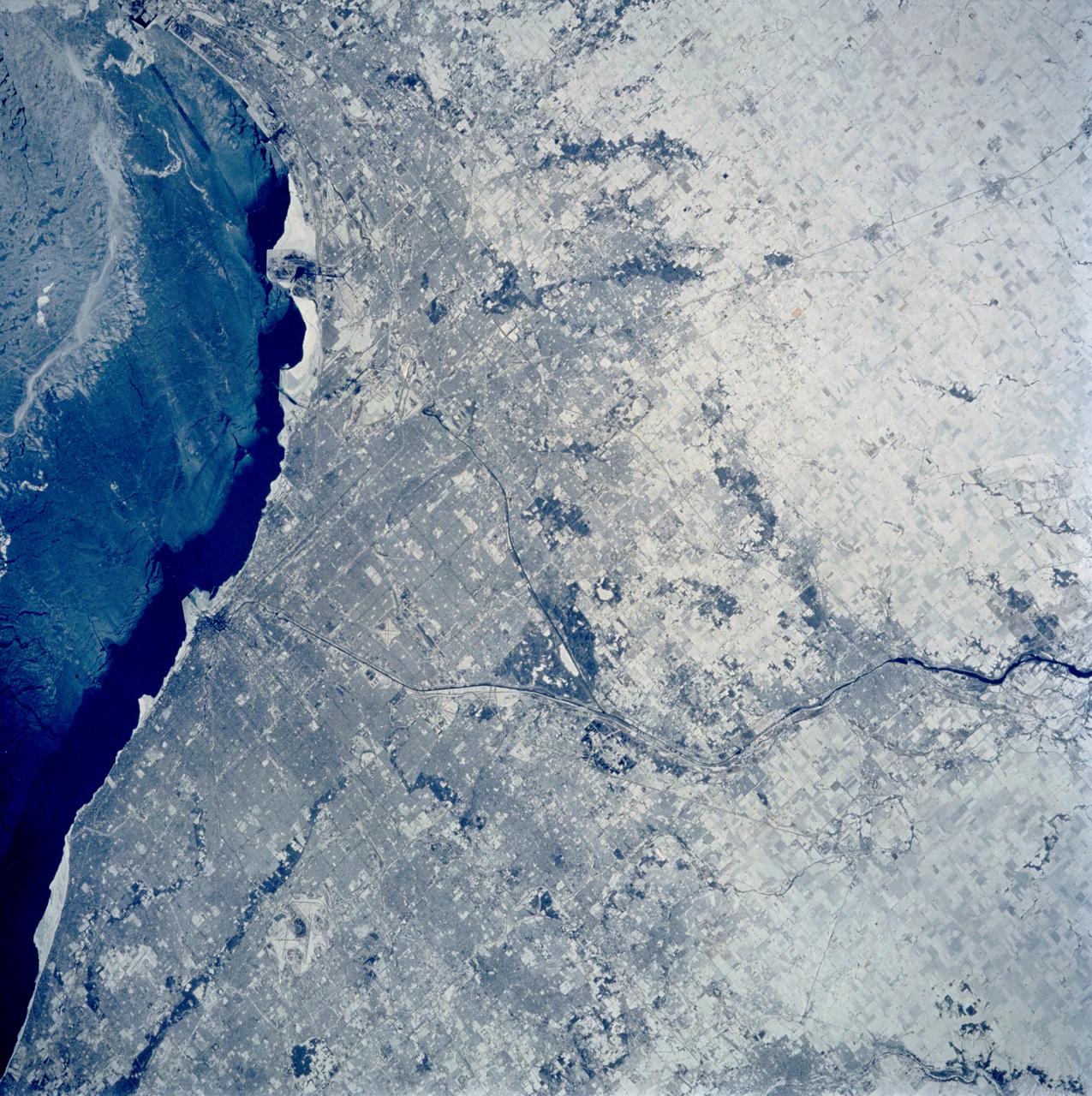

STS060-103-089 (3-11 Feb. 1994) --- The Chicago, Illinois area is in this northeast looking low oblique view obtained in February, 1994. Lake Michigan, a good portion covered with ice due to the very cold winter weather that has plagued this region since early December, 1993, can be seen to the east of the city. The Des Plaines river is visible traversing northeast to southwest through the center of the city. O'Hare International Airport and the Glenview Naval Air Station can be seen to the north of the Des Plaines River. Midway Airport is visible just to the south of the river. Chicago is a port of entry; a major Great Lakes port located at the junction of the St. Lawrence Seaway with the Mississippi River system; the busiest air center in the United States; and an important rail and highway transportation hub. Chicago is known for large grain mills and elevators, iron and steel works, steel fabrication plants, stockyards, meat-packing establishments, and printing and publishing houses. In the early days of settlement, the narrow watershed between Lake Michigan and the Des Plaines River (draining the Mississippi River through the Illinois River), offered an easy portage that led explorers like Father Marquette and Louis Joliet and others to the Great Central Plains. Fort Dearborn, a military post was established in 1803. By 1860, the railroad connected Chicago to the rest of the country and the city became a great mid-continent shipping and receiving center. In 1871, the city built of wood, was almost entirely destroyed by a great fire. After the fire, Chicago was built as a city of steel and stone. During the World's Colombian Exposition held in Chicago in 1893, the city became a leading architectural center. It was here during the Exposition that the skyscraper came into being. Chicago continues to lead the way in this type of architectural structure as is evidenced with the completion of the Sears Tower in 1974.
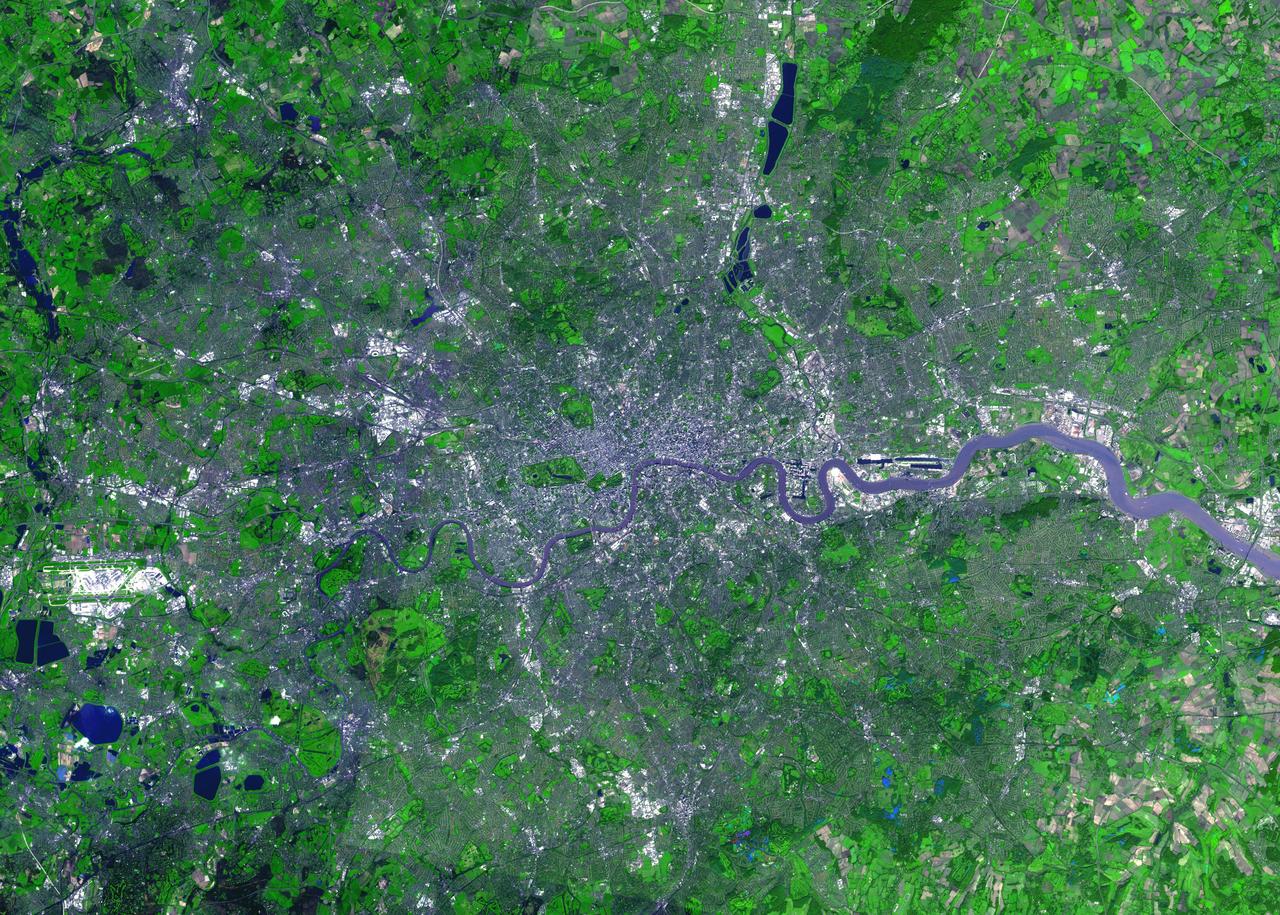

For almost 2,000 years, the River Thames has served as the life force of London, capital of the United Kingdom and one of the world's most famous cities. In AD 43 the Romans established the trading settlement of Londinium at a favorable crossing point on the river. The Romans remained until the 5th century, when the city came under Saxon control. The early 17th century saw enormous growth, but the deadly plague of 1664 and 1665 ravaged the population, and in the following year the Great Fire, which burned for four days, destroyed most of the city. A public transportation system and other city services in the early 19th century eased many of the increasing urban problems of the burgeoning capital of the wealthy British Empire. After coping with the devastating effects of bombing during World War II and the gradual dismantling of the empire, London today thrives as a vital modern metropolis. London is one of 100 cities being studied using ASTER data to map and monitor urban use patterns and growth. This image was acquired on October 12, 2001 by the Advanced Spaceborne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer (ASTER) on NASA's Terra satellite. With its 14 spectral bands from the visible to the thermal infrared wavelength region, and its high spatial resolution of 15 to 90 meters (about 50 to 300 feet), ASTER images Earth to map and monitor the changing surface of our planet. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA04301
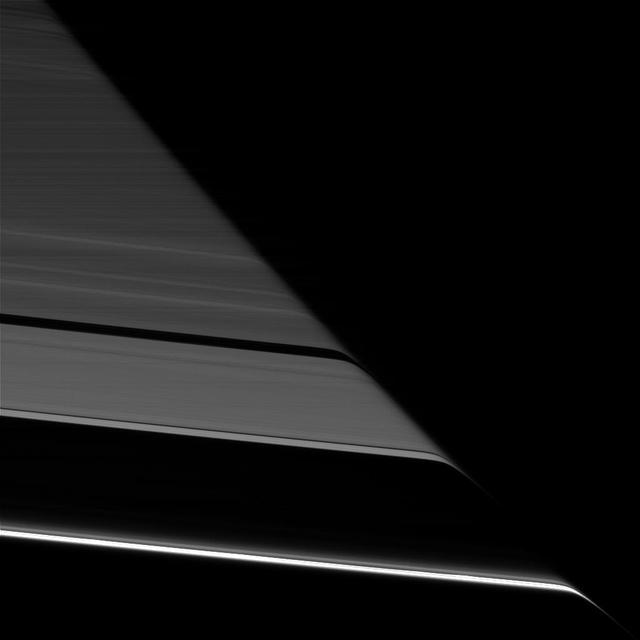

Saturn's rings appear to bend as they pass behind the planet's darkened limb due to refraction by Saturn's upper atmosphere. The effect is the same as that seen in an earlier Cassini view (see PIA20491), except this view looks toward the unlit face of the rings, while the earlier image viewed the rings' sunlit side. The difference in illumination brings out some noticeable differences. The A ring is much darker here, on the rings' unlit face, since its larger particles primarily reflect light back toward the sun (and away from Cassini's cameras in this view). The narrow F ring (at bottom), which was faint in the earlier image, appears brighter than all of the other rings here, thanks to the microscopic dust that is prevalent within that ring. Small dust tends to scatter light forward (meaning close to its original direction of travel), making it appear bright when backlit. (A similar effect has plagued many a driver with a dusty windshield when driving toward the sun.) This view looks toward the unilluminated side of the rings from about 19 degrees below the ring plane. The image was taken in red light with the Cassini spacecraft narrow-angle camera on July 24, 2016. The view was acquired at a distance of approximately 527,000 miles (848,000 kilometers) from Saturn and at a sun-Saturn-spacecraft, or phase, angle of 169 degrees. Image scale is 3 miles (5 kilometers) per pixel. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA20497