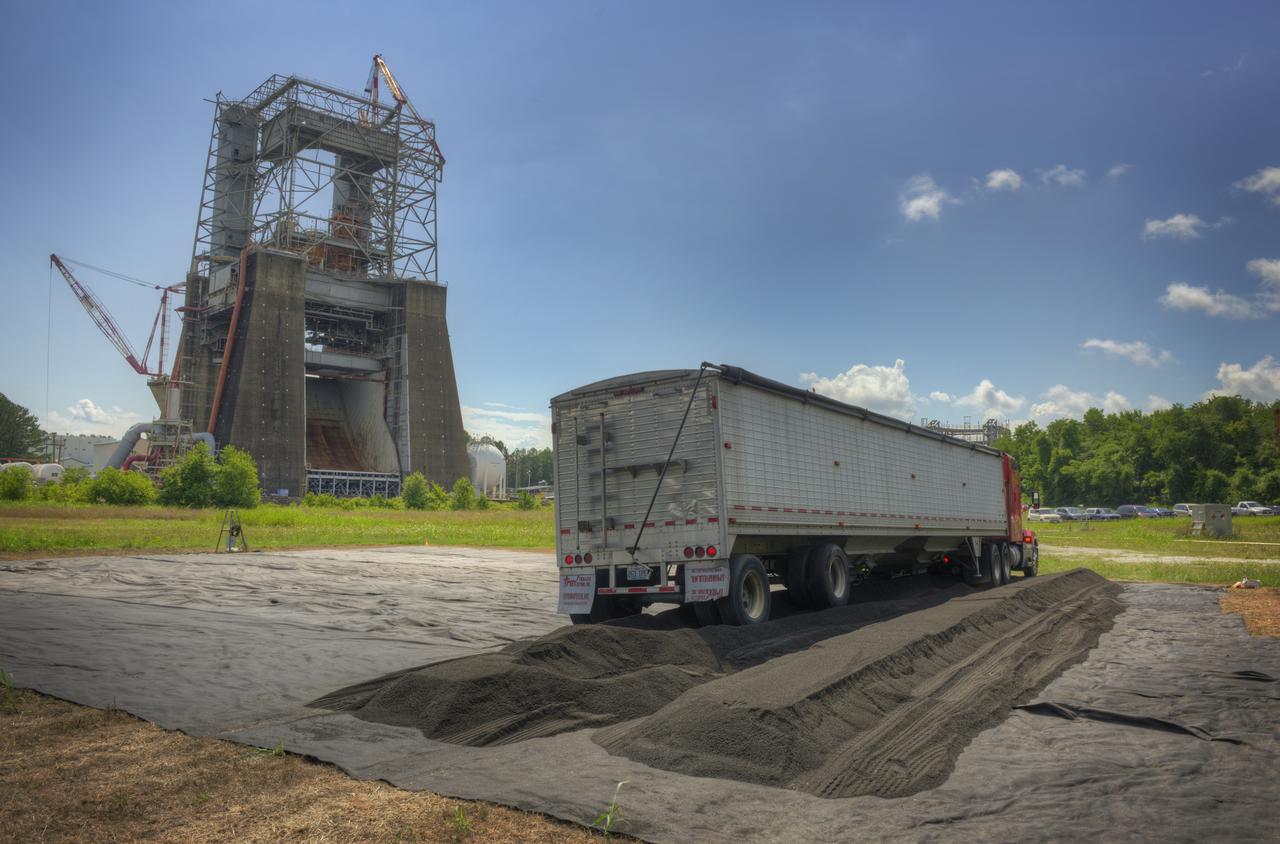

SOIL UNLOAD FOR THE SIMULATED PLANETARY BODY FIELD IN THE WEST TEST AREA. AREA TO BE USED FOR TESTING OF THE MIGHTY EAGLE LANDER
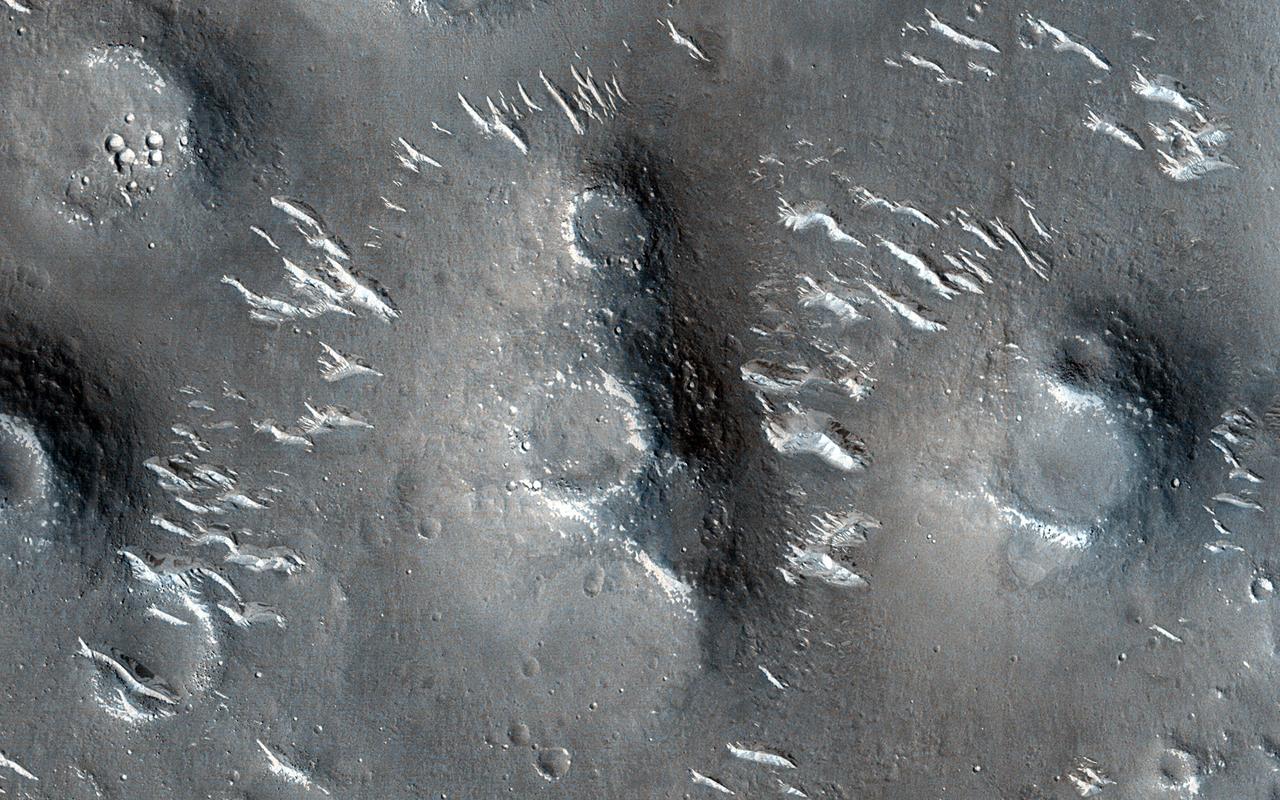

Utopia Planitia, a vast plain in the Northern Hemisphere of Mars, has an interesting and complex history. One of the intriguing features is a field of mounds showing circular depressions at their summits. The fact that many of these "craters" are on top of mounds argues against them being craters created by impacts, as is common on Mars and other planetary bodies across the solar system. There are many processes that can form such landforms, most notably hot lava. However, mud ejected from beneath the surface (through different geologic mechanisms) could also be a possibility. Being able to better understand how these features formed (aided by HiRISE stereo images) is crucial to our understanding of the geologic history of the region. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA25898
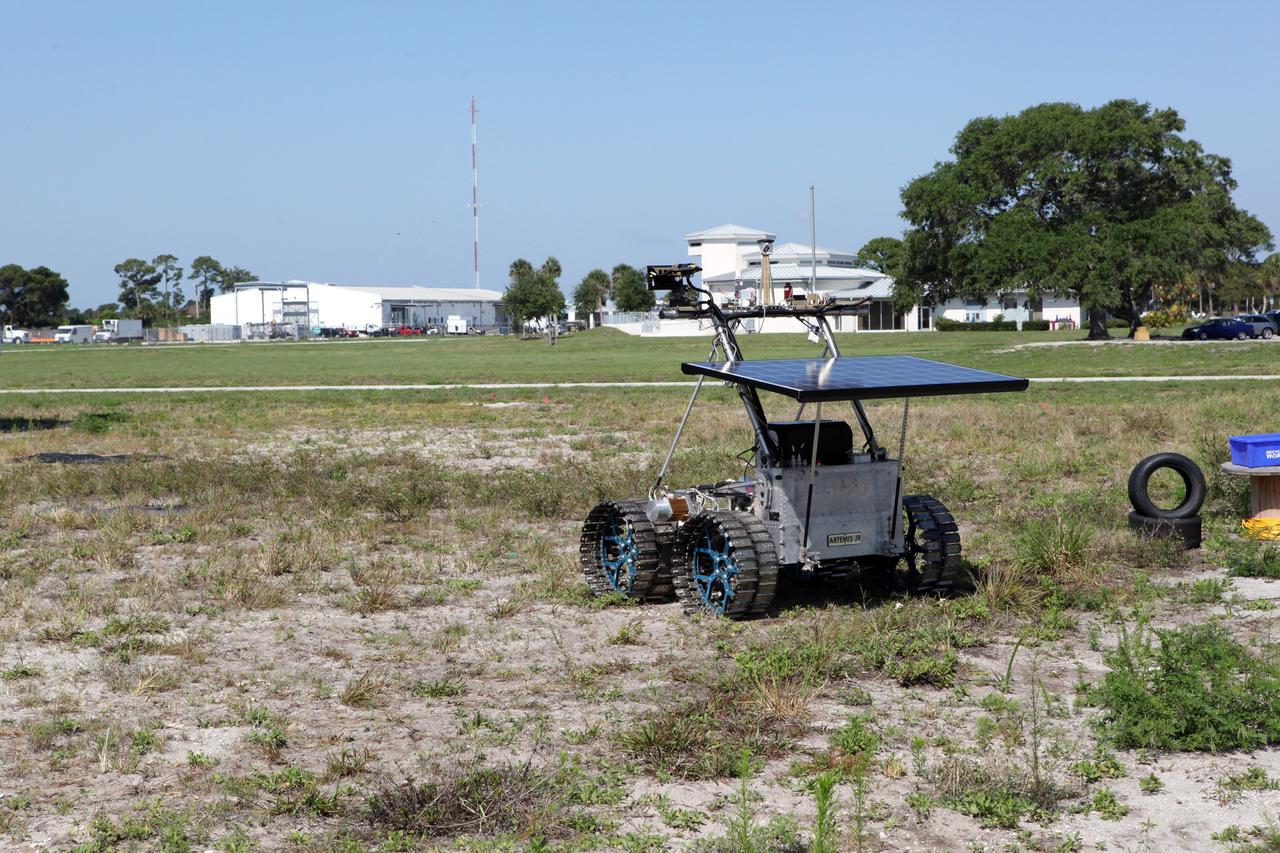

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project takes a spin around the field next to the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
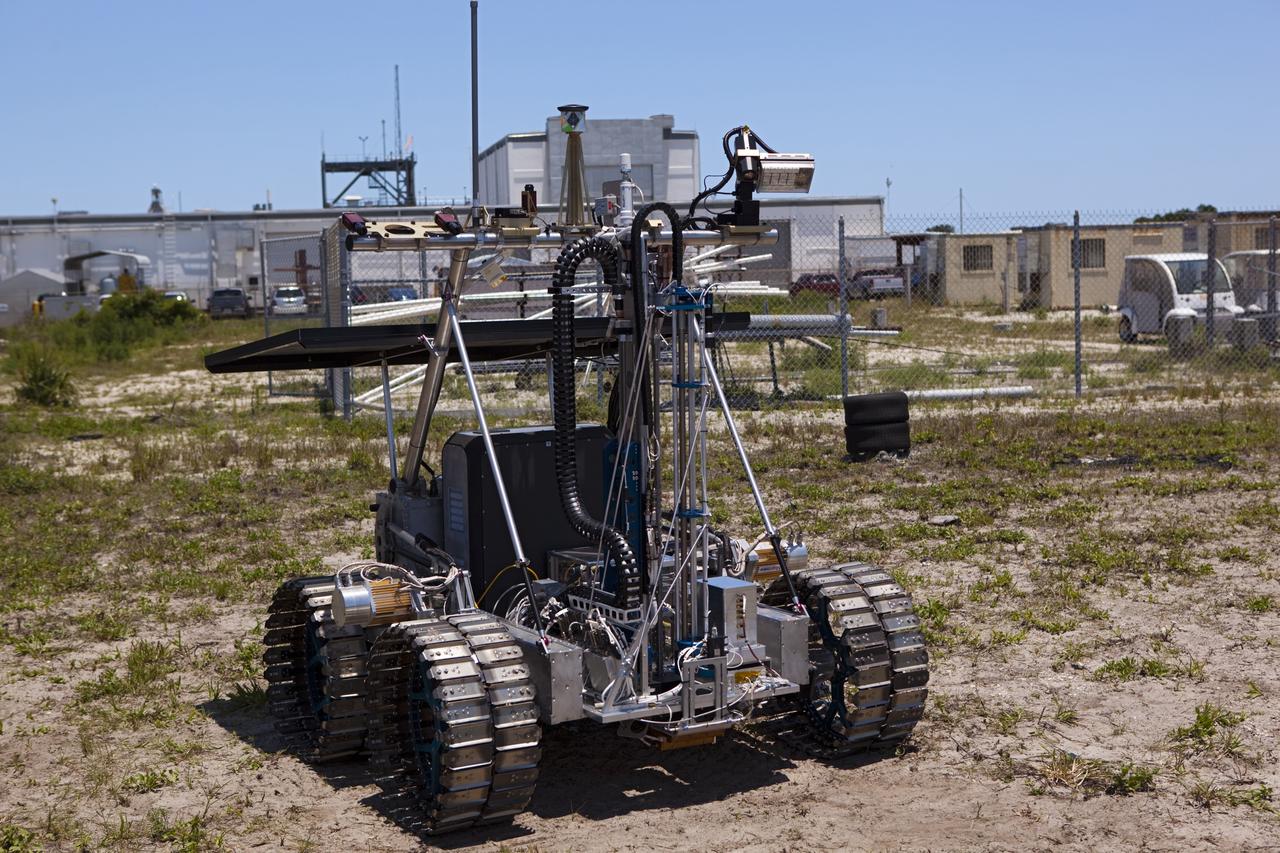

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A demonstration of the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project is conducted in a field beside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rover and its drill are provided by the Canadian Space Agency and work in concert with NASA science instruments to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

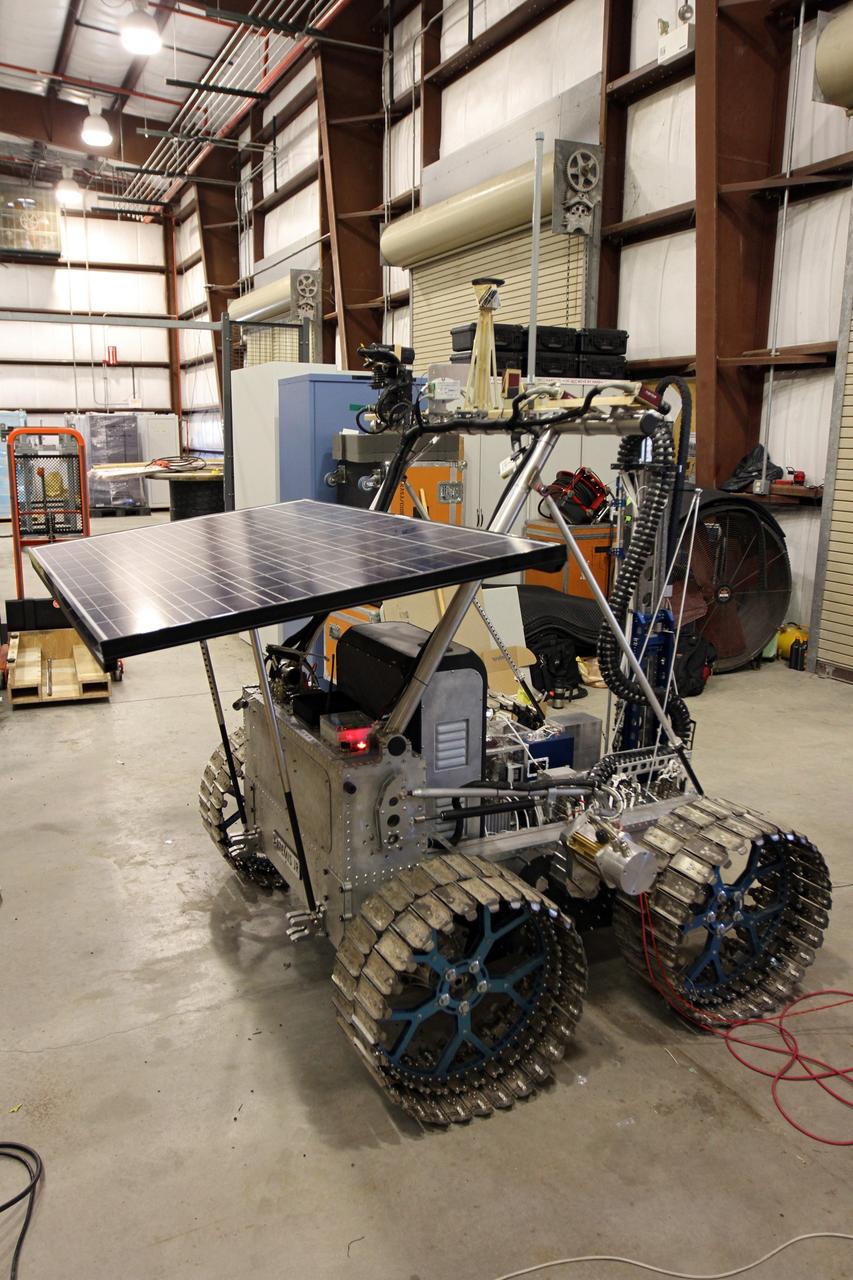
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The solar array on the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project soaks up the sunlight as it takes a test drive around the field next to the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project takes a test drive around the field next to the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
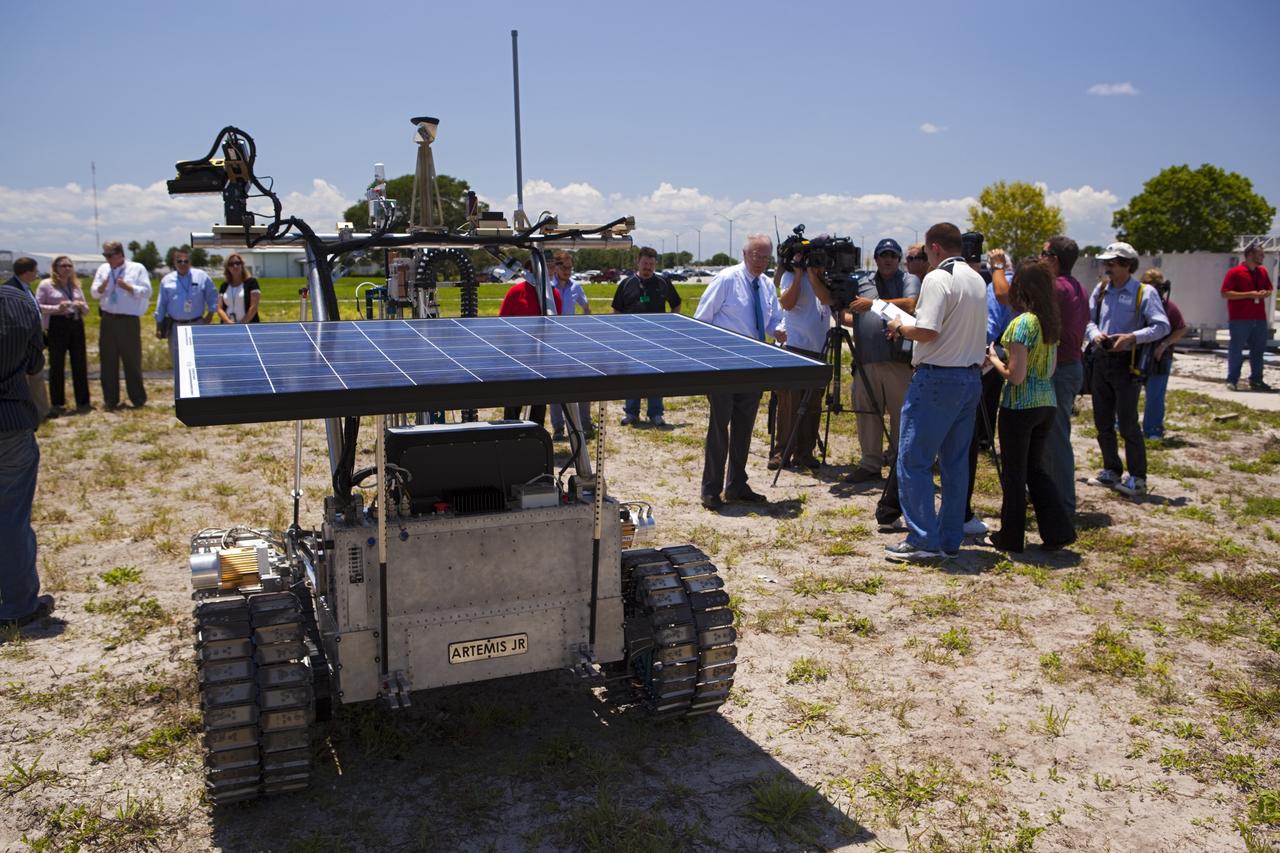

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The solar array on the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project soaks up the sunlight during a rover demonstration for media representatives in a field beside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rover and its drill are provided by the Canadian Space Agency and work in concert with NASA science instruments to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
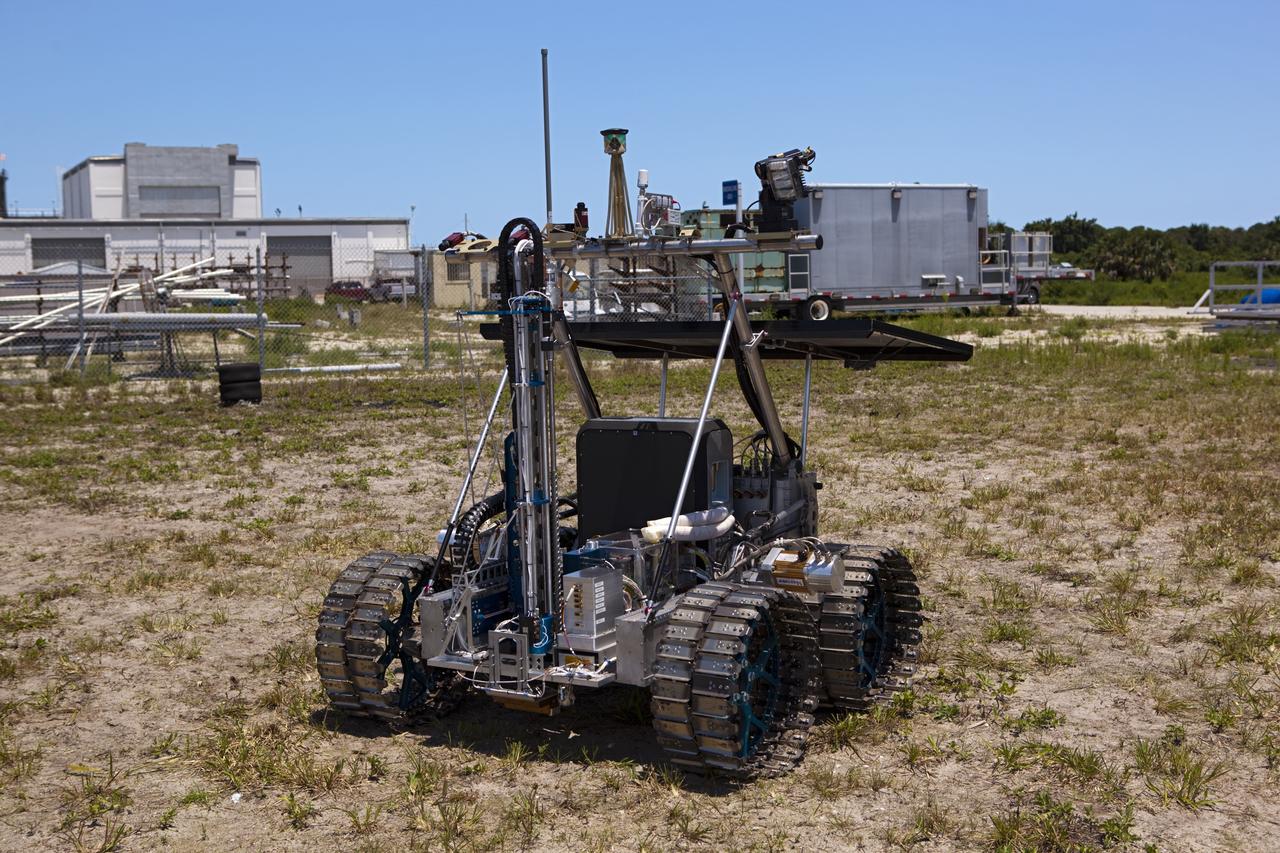

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A demonstration of the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project is conducted in a field beside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rover and its drill are provided by the Canadian Space Agency and work in concert with NASA science instruments to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
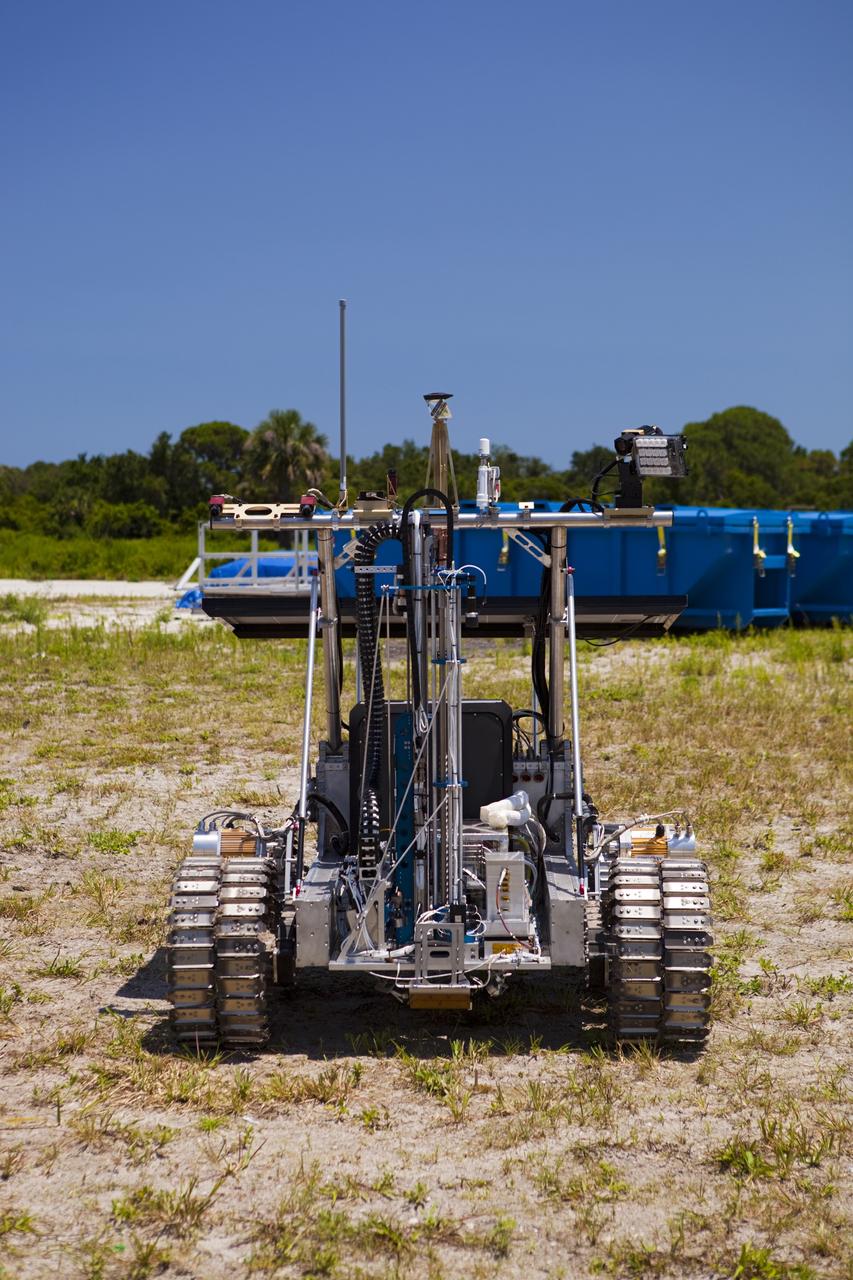

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – A demonstration of the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project is conducted in a field beside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rover and its drill are provided by the Canadian Space Agency and work in concert with NASA science instruments to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
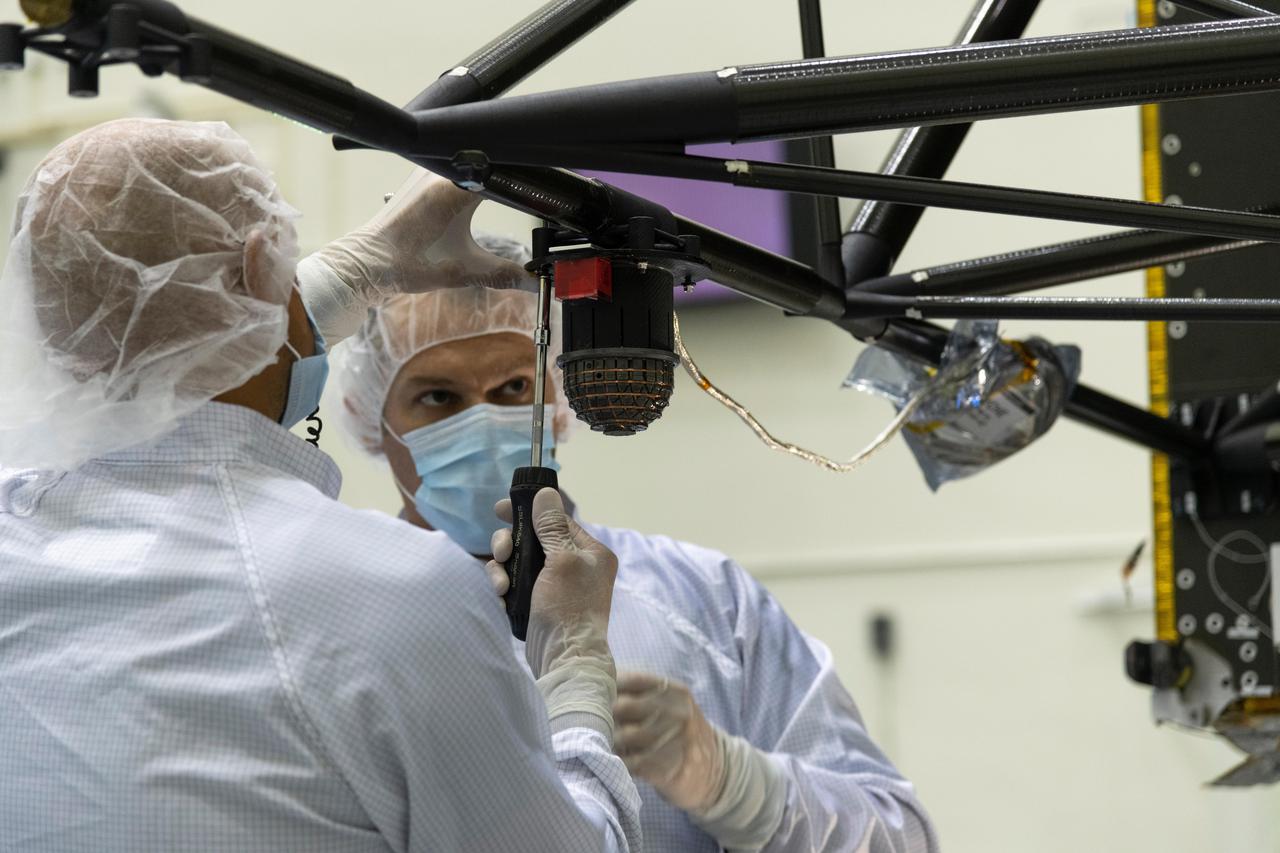

Engineers at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California integrate the magnetometer instrument into the agency's Psyche spacecraft on June 28, 2021. Psyche, set to launch in August 2022, will investigate a metal-rich asteroid of the same name, which lies in the main asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Scientists believe the asteroid could be part or all of the iron-rich interior of an early planetary building block that was stripped of its outer rocky shell as it repeatedly collided with other large bodies during the early formation of the solar system. Scientists know that the asteroid doesn't generate a magnetic field the way Earth does; but if Psyche had a magnetic field in the past, that magnetic field could still be recorded in Psyche's material today. With sensors mounted onto a 6-foot (2-meter) boom, the magnetometer can determine if Psyche is still magnetized. If so, that would confirm that the asteroid is part of the core of a planetesimal, the building block of an early planet. This photo shows one of the magnetometer's sensors. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24893
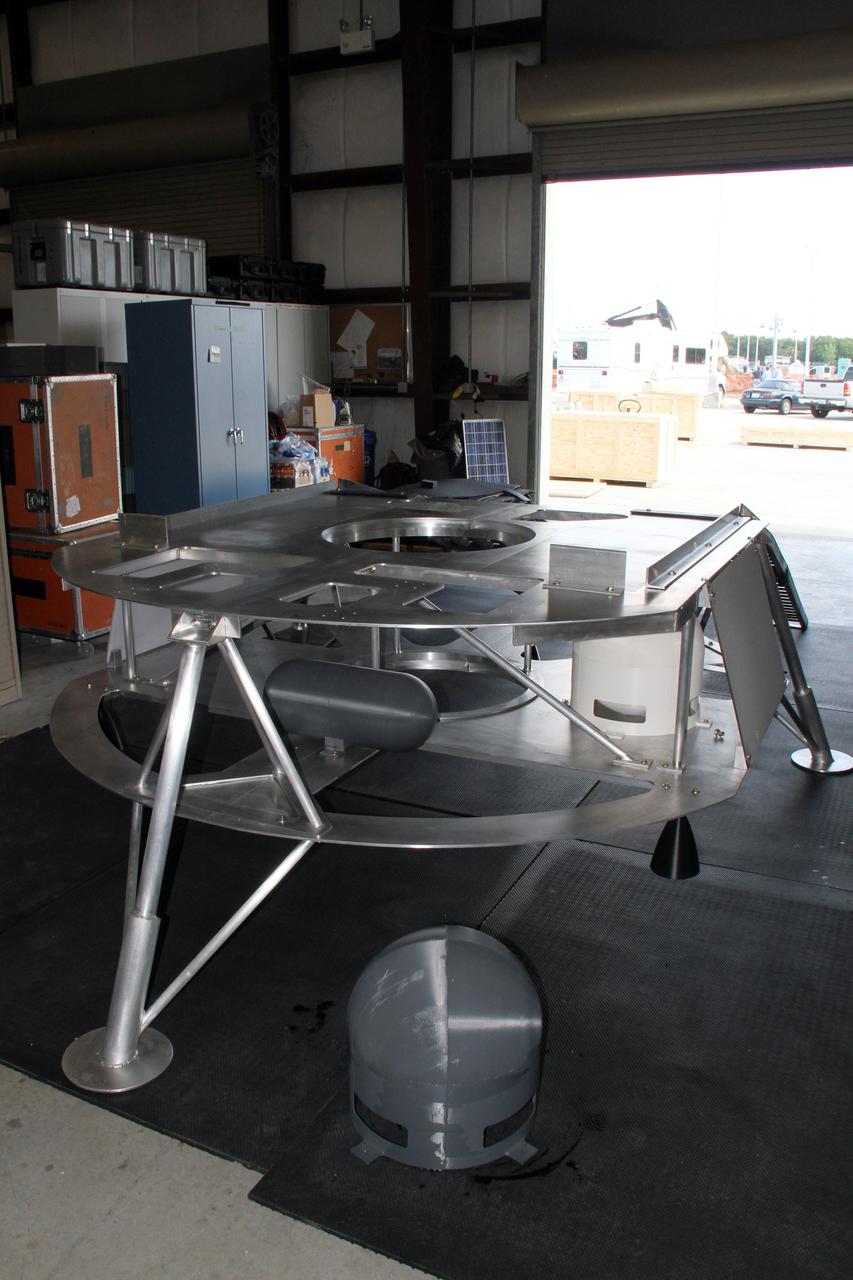

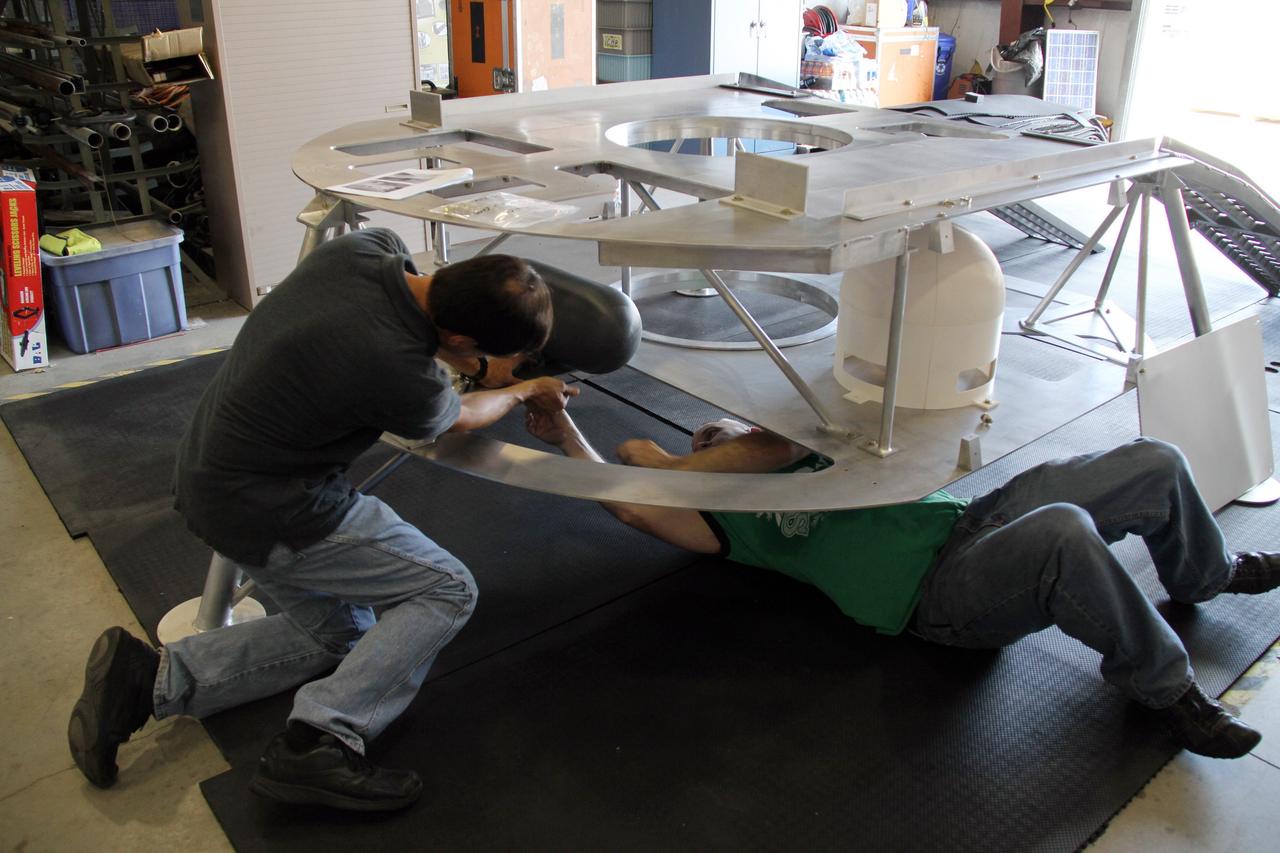
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Assembly of the prototype lander for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project is complete in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will be conducting field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
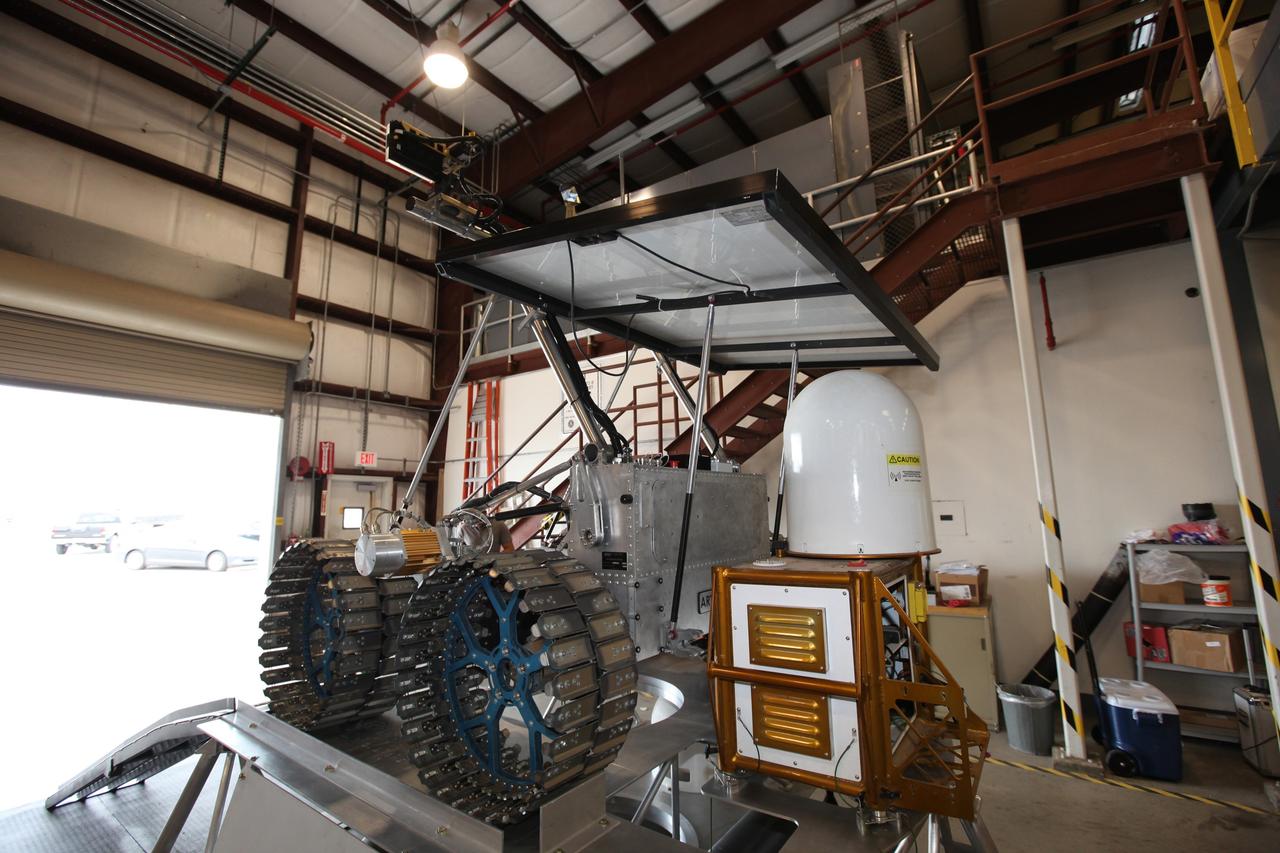

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project rests atop the prototype lander, prepared for further processing in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
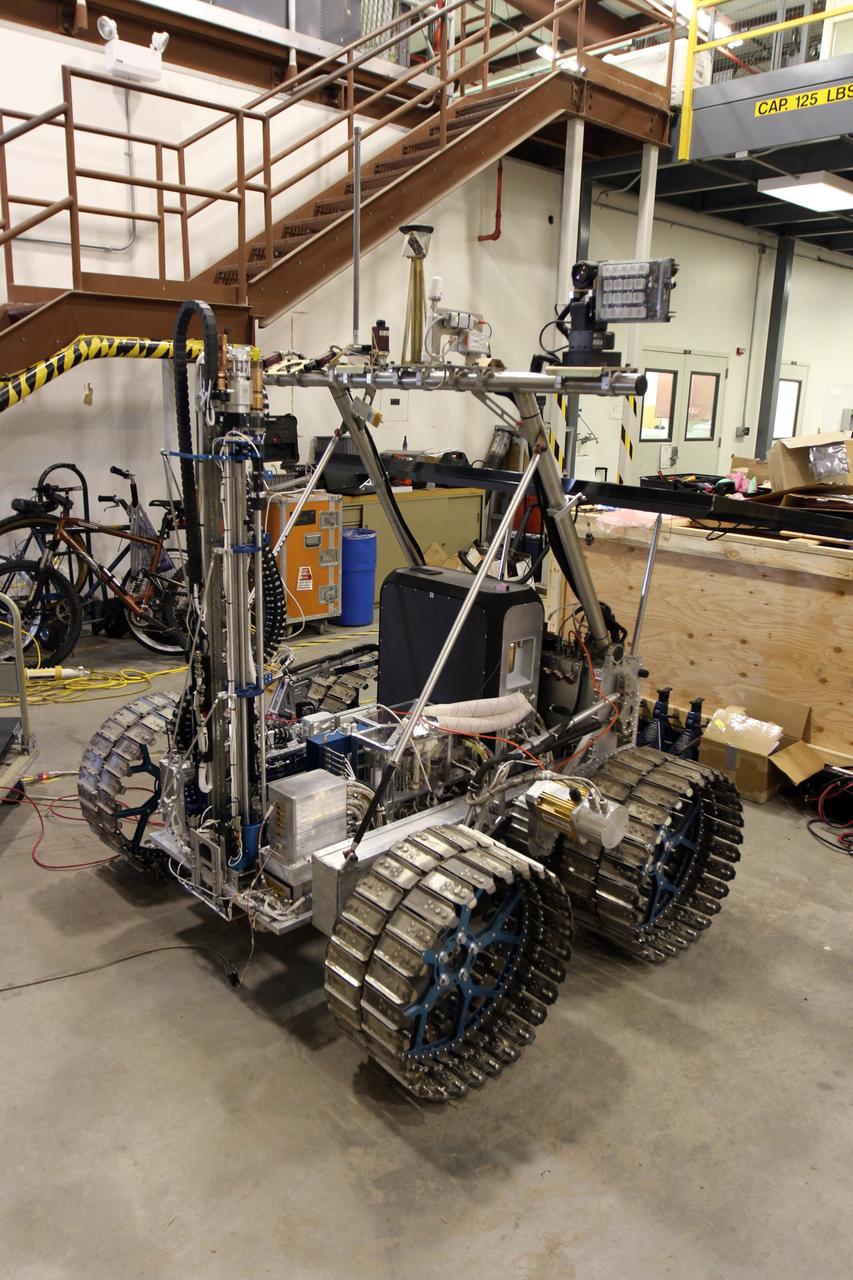

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The NASA payload is installed on the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cylindrical structure at left is the drill. The drill and rover were provided to NASA by the Canadian Space Agency. The NASA payload is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
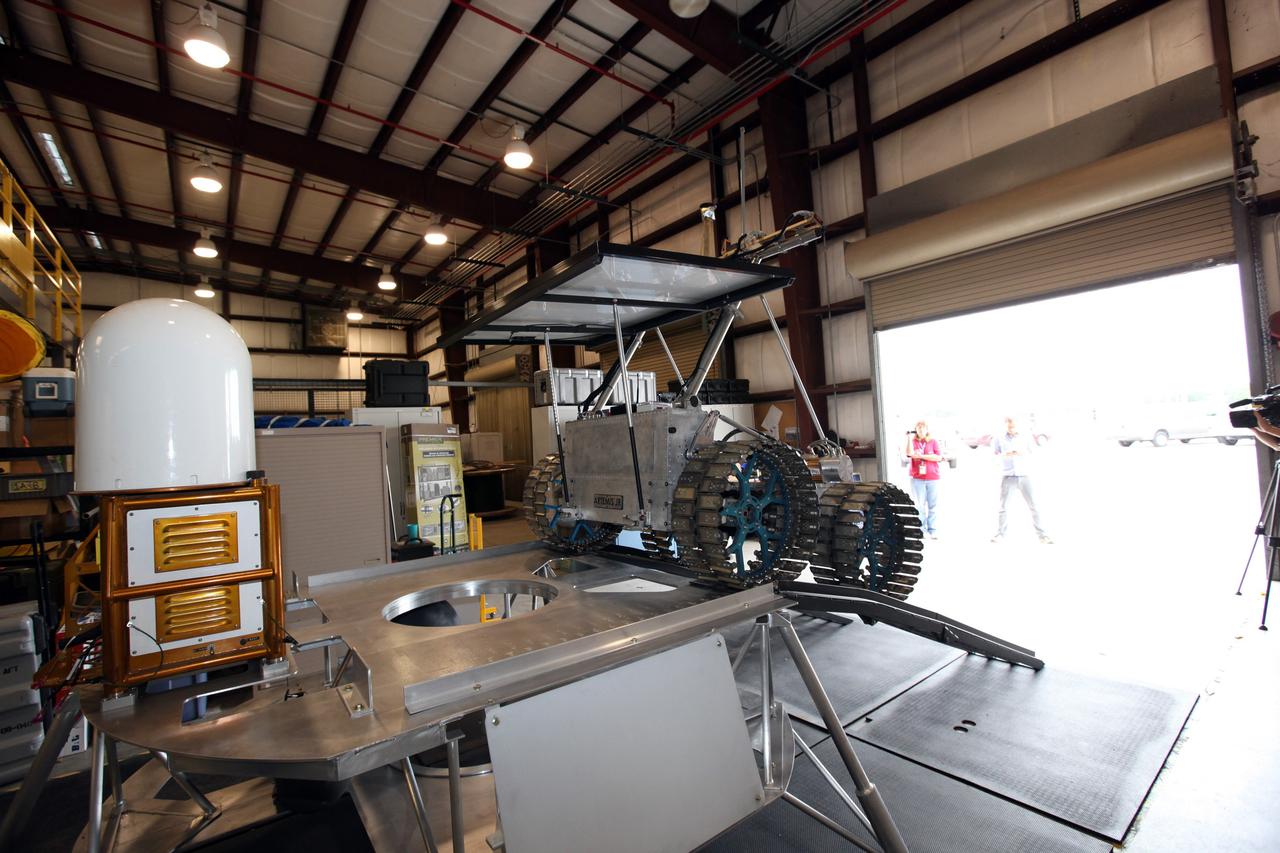

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project dismounts from the RESOLVE lander during a dry run using ramps attached to the prototype lander. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
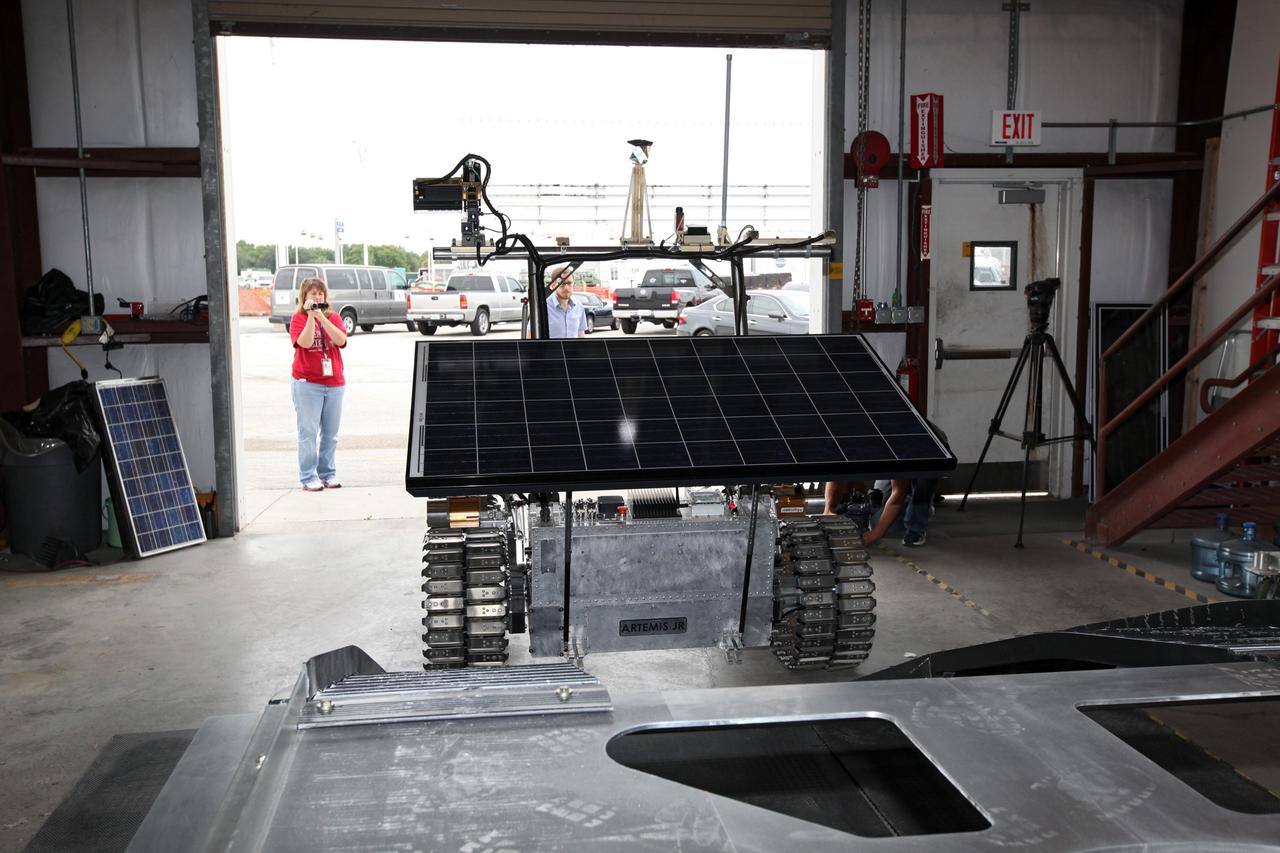

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project dismounts from the RESOLVE lander during a dry run using ramps attached to the prototype lander. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
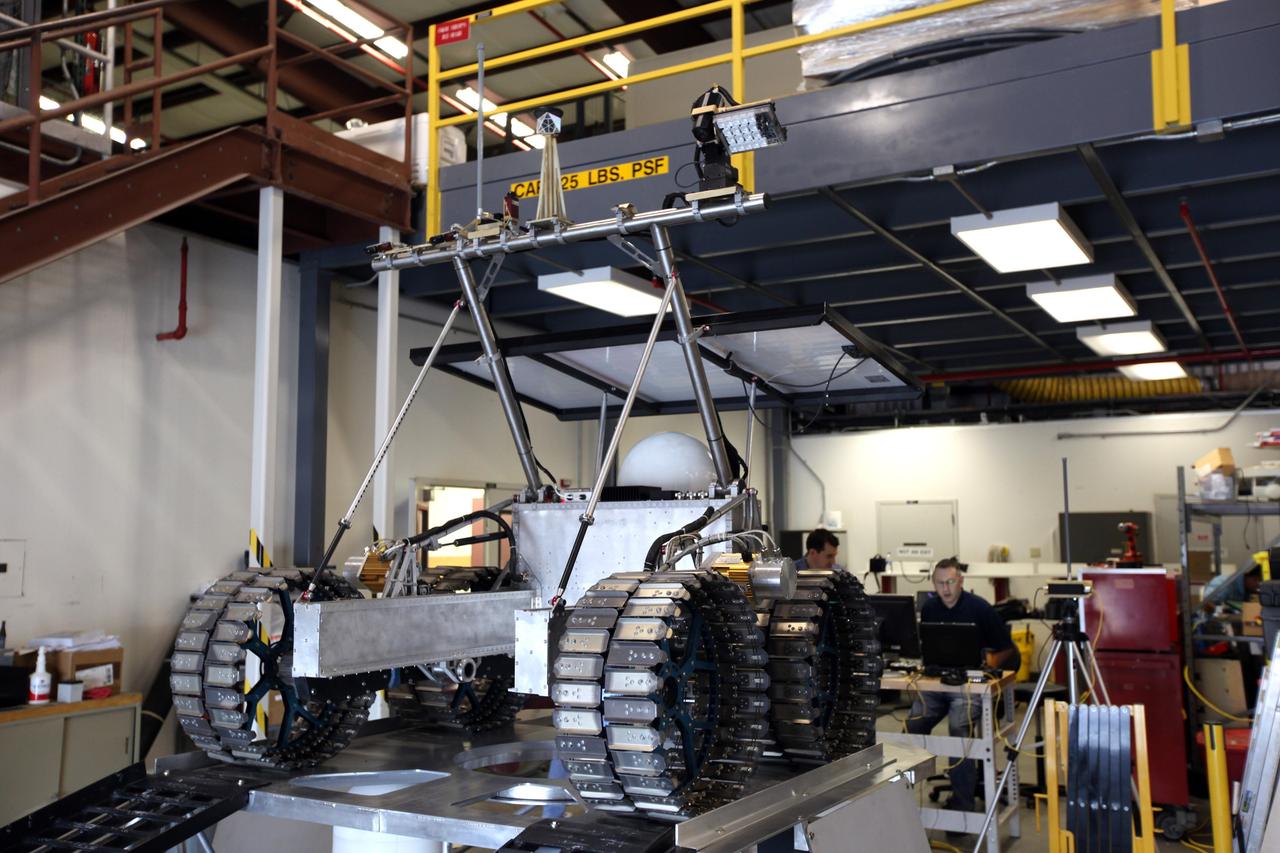

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project is unpacked in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida and in place on top of the prototype lander. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
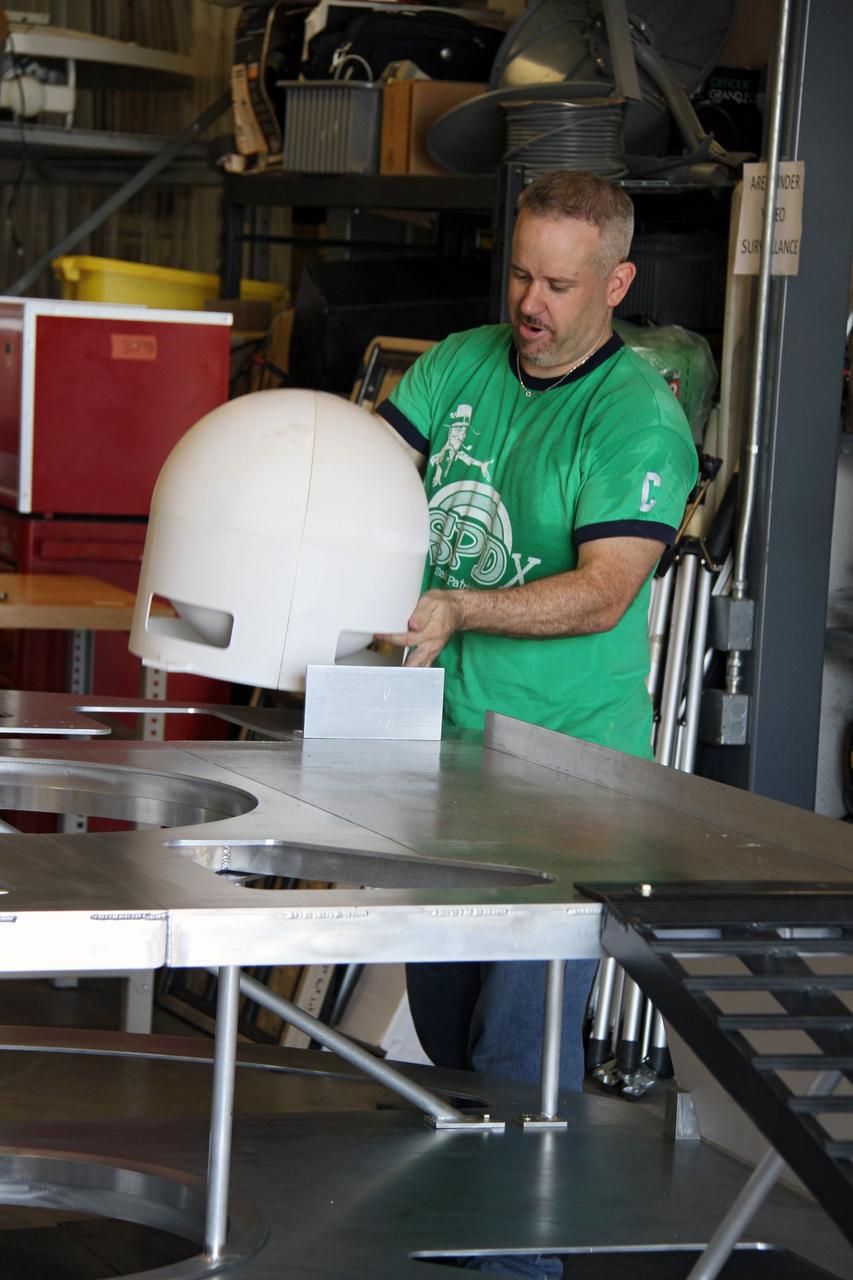

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA systems engineer Jim Smith assembles the prototype lander for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will be conducting field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
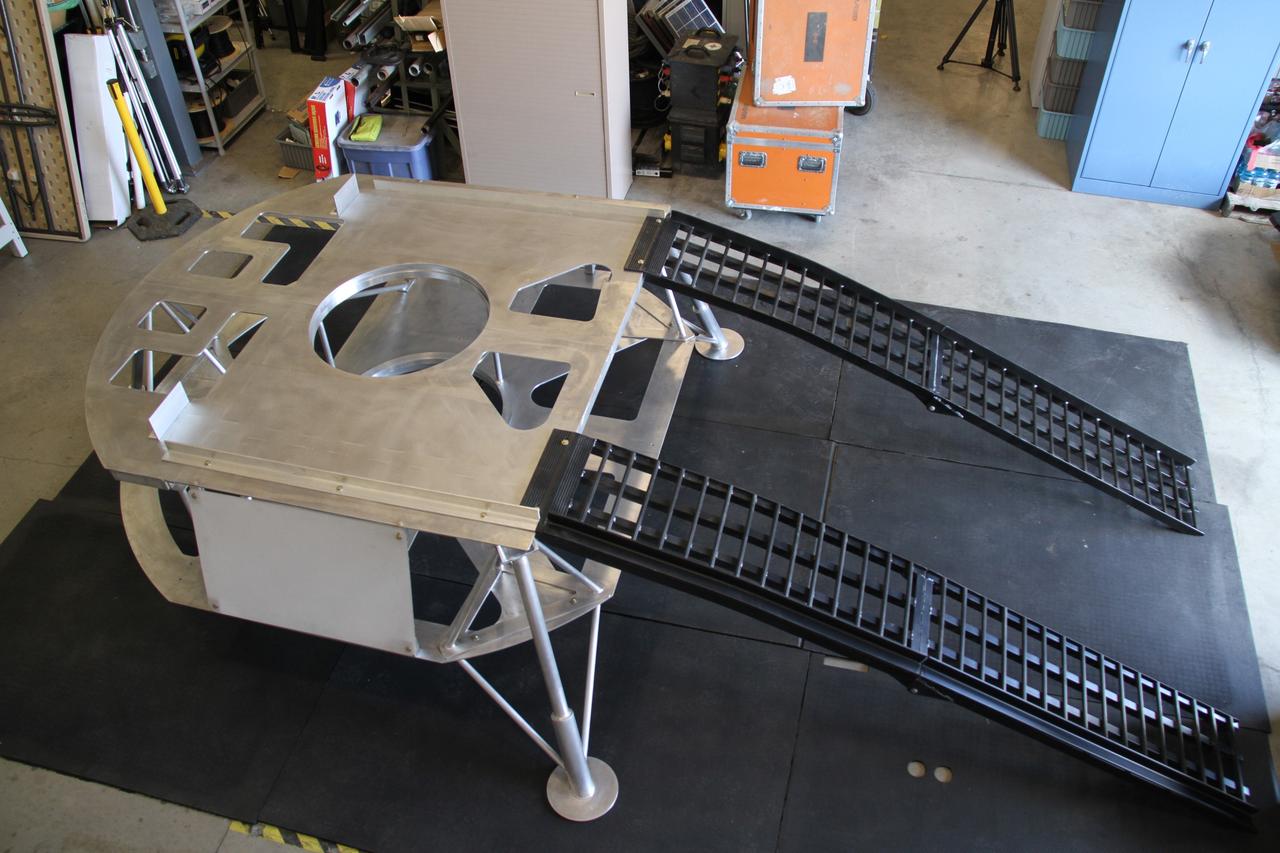

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The prototype lander for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project is prepared for further assembly in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ramps provide RESOLVE’s rover an avenue to mount or dismount the lander. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will be conducting field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The NASA payload is installed on the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cylindrical structure at left is the drill. The drill and rover were provided to NASA by the Canadian Space Agency. The NASA payload is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The prototype lander for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project is assembled and ready for testing in a facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will be conducting field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Engineers complete the assembly of the prototype lander for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will be conducting field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The NASA payload is installed on the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cylindrical structure at right is the drill the tabletop surface at left is the rover’s solar array. The drill and rover were provided to NASA by the Canadian Space Agency. The NASA payload is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida, the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project has dismounted the RESOLVE lander during a dry run using the ramps attached to the prototype lander. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
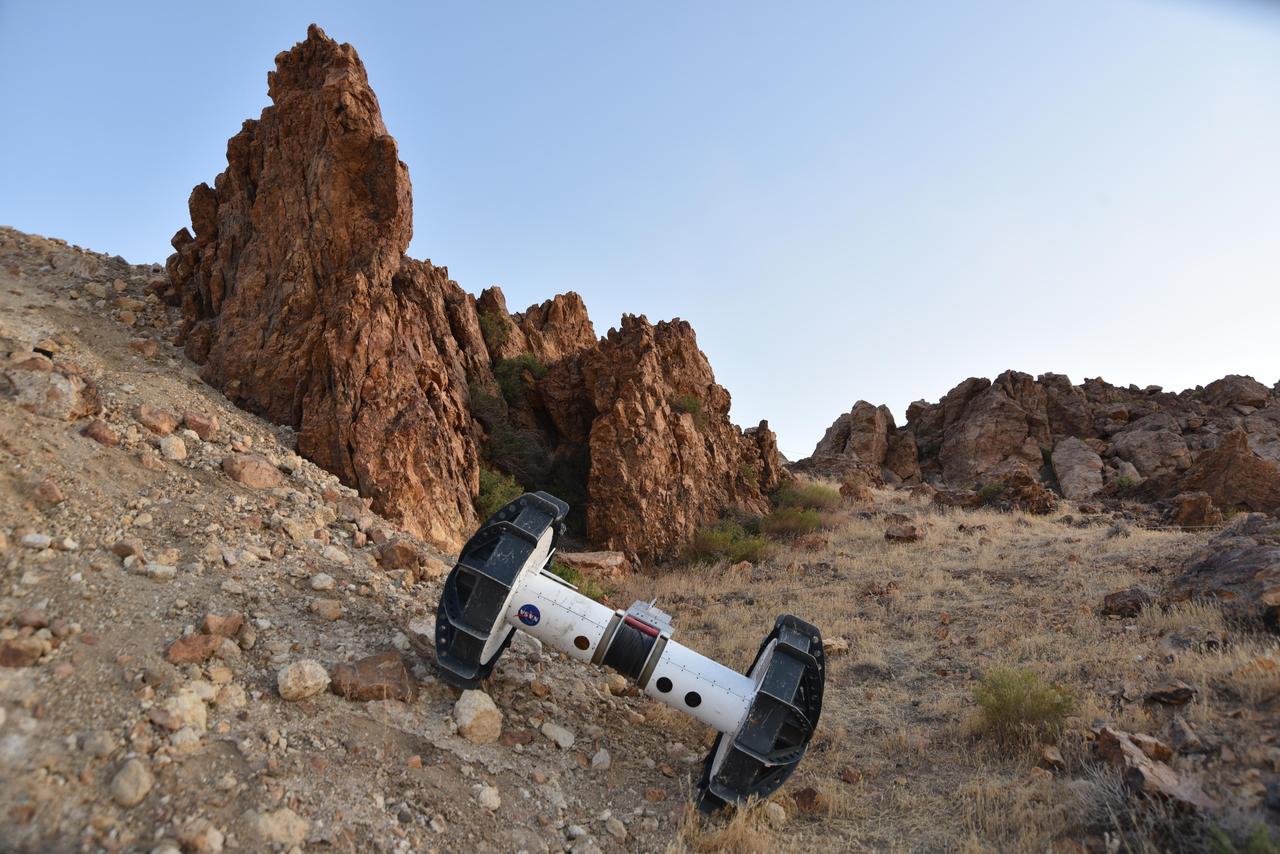

In this photograph, a tethered Axel robot — part of the four-wheeled DuAxel rover — navigates a steep slope during a field test in the Mojave Desert. The tether, which connects to the rover's other half, serves as a climbing rope of sorts while also providing power and a means of communication. This flexibility was built with crater walls, pits, scarps, vents, and other extreme terrain in mind. That's because on Earth, some of the best locations to study geology can be found in rocky outcrops and cliff faces, where many layers of the past are neatly exposed. They're hard enough to reach here, let alone on the Moon, Mars, and other celestial bodies. The DuAxel project is a technology demonstration being developed by roboticists at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California to see how this unconventional rover might fill a niche in planetary exploration. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA24110
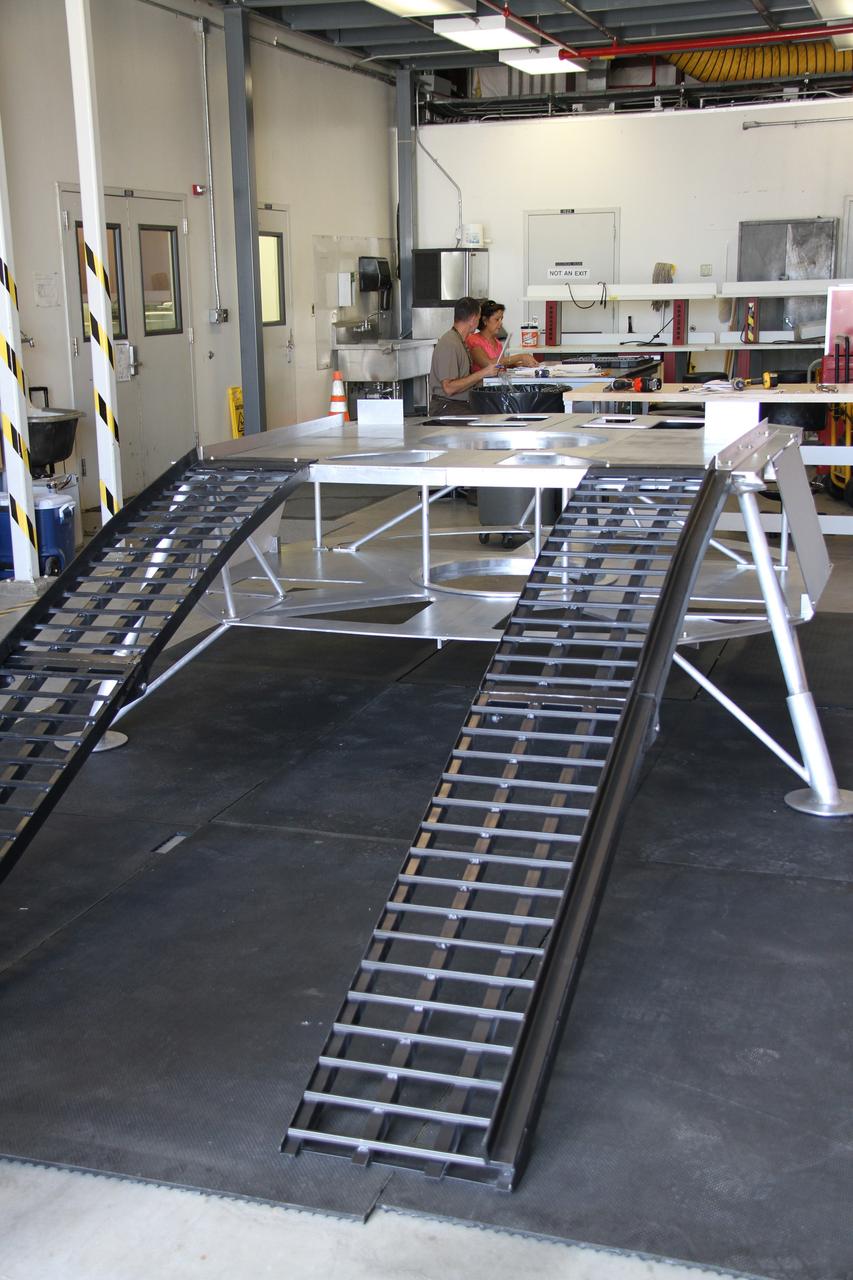

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The prototype lander for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project is unpacked in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The ramps provide RESOLVE’s rover an avenue to mount or dismount the lander. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will be conducting field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
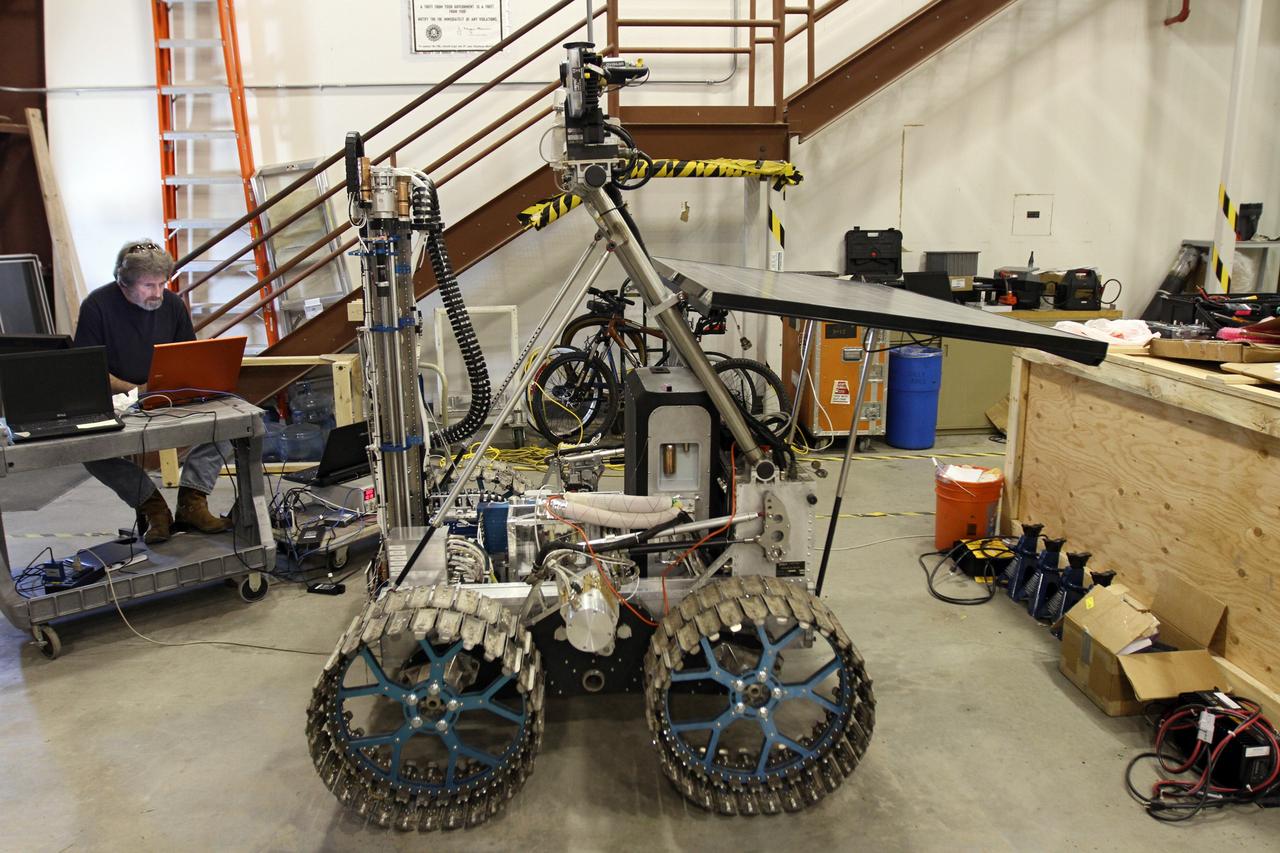

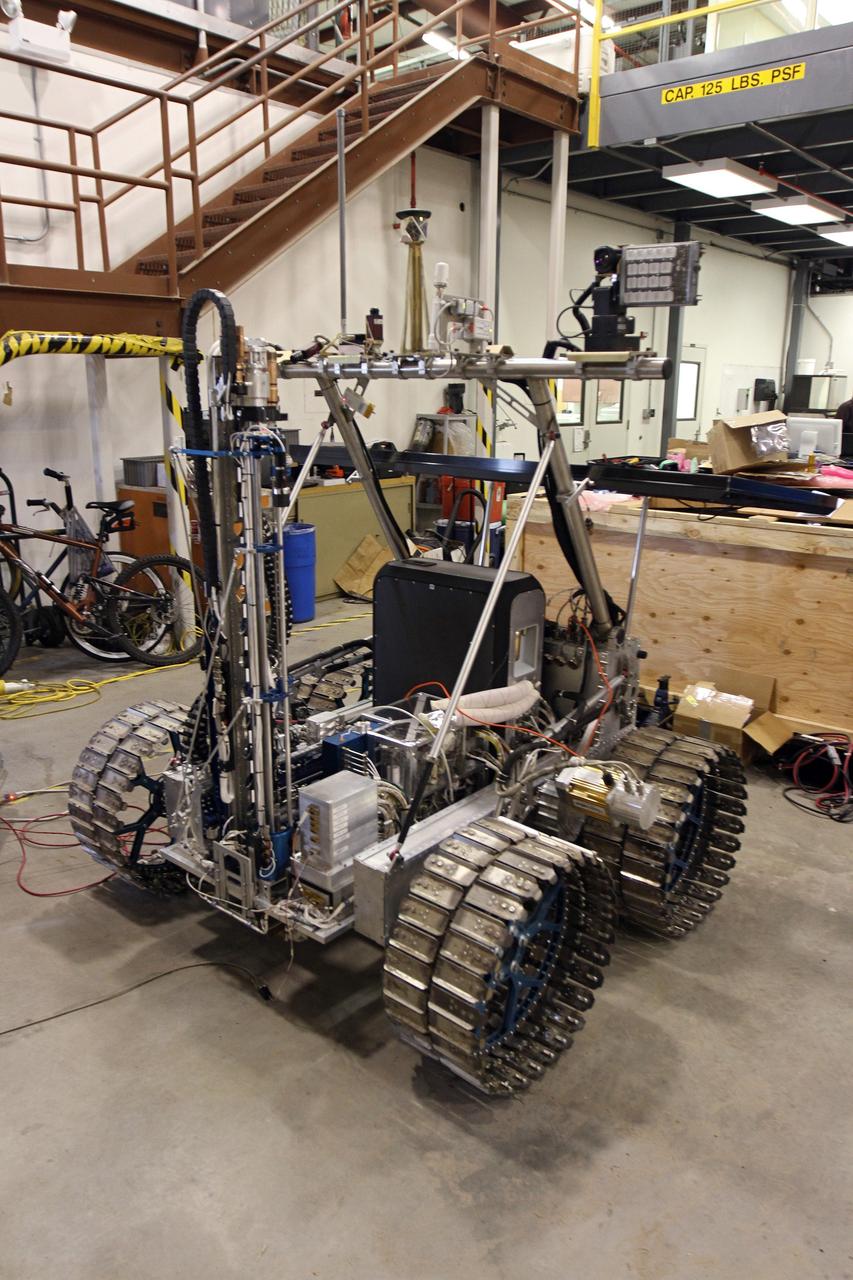
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – The NASA payload is installed on the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The cylindrical structure at left is the drill the tabletop surface at right is the rover’s solar array. The drill and rover were provided to NASA by the Canadian Space Agency. The NASA payload is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Cory Huston
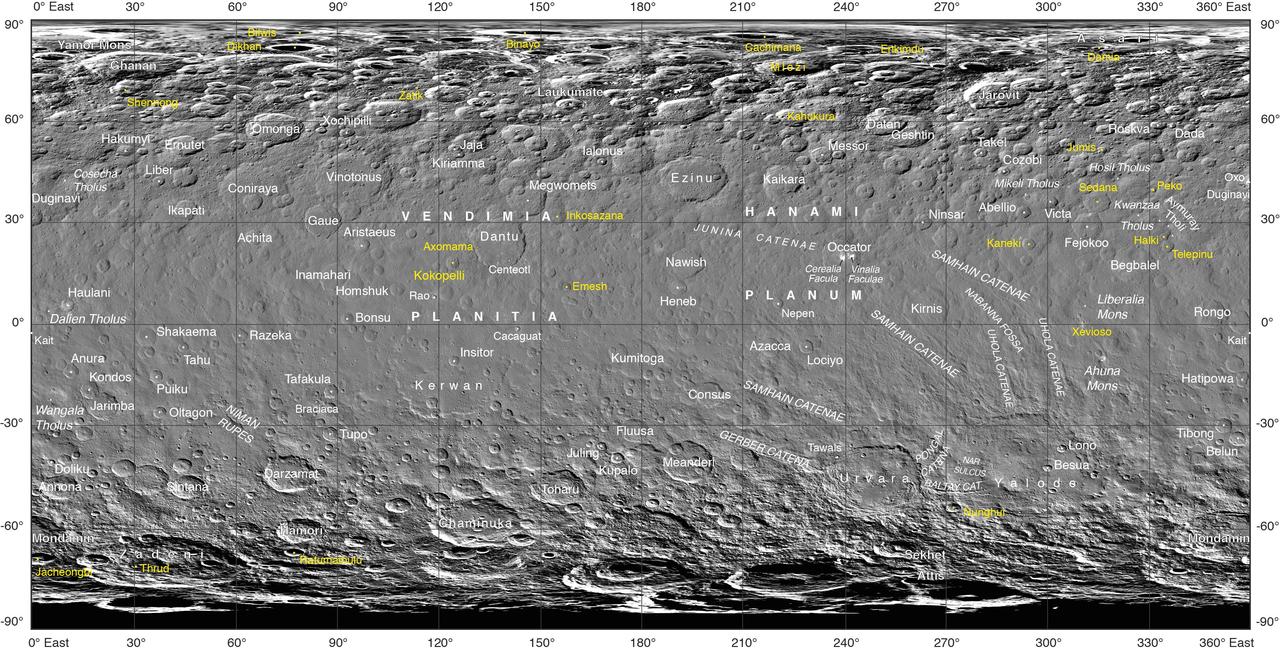
Often, the names of features on planetary bodies are connected through a specific theme -- for example, many features on the Moon have been named after famous scientists. NASA's Dawn mission, together with the International Astronomical Union, established that craters on Ceres would be named for agricultural deities from all over the world, and other features would be named for agricultural festivals. Ceres itself was named after the Roman goddess of corn and harvests by its discoverer, Giuseppe Piazzi, who spotted it with his telescope in 1801. Since March 2015, Dawn has been orbiting Ceres and sending back many intriguing images and other data about its features. Using suggestions from the Dawn team, the IAU recently approved 25 new Ceres feature names tied to theme of agricultural deities, marked in yellow on the map. Emesh Crater, for example, is named for the Sumerian god of vegetation and agriculture. Jumi is the Latvian god of fertility of the field. The newly named surface features vary in size. Thrud, for example, is a crater with a diameter of 4.8 miles (7.8 kilometers) within the larger crater Zadeni, while Mlezi has a diameter of 28 miles (42 kilometers). For more information, the characteristics of these and other features on Ceres can be found in the IAU's Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. https://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21755
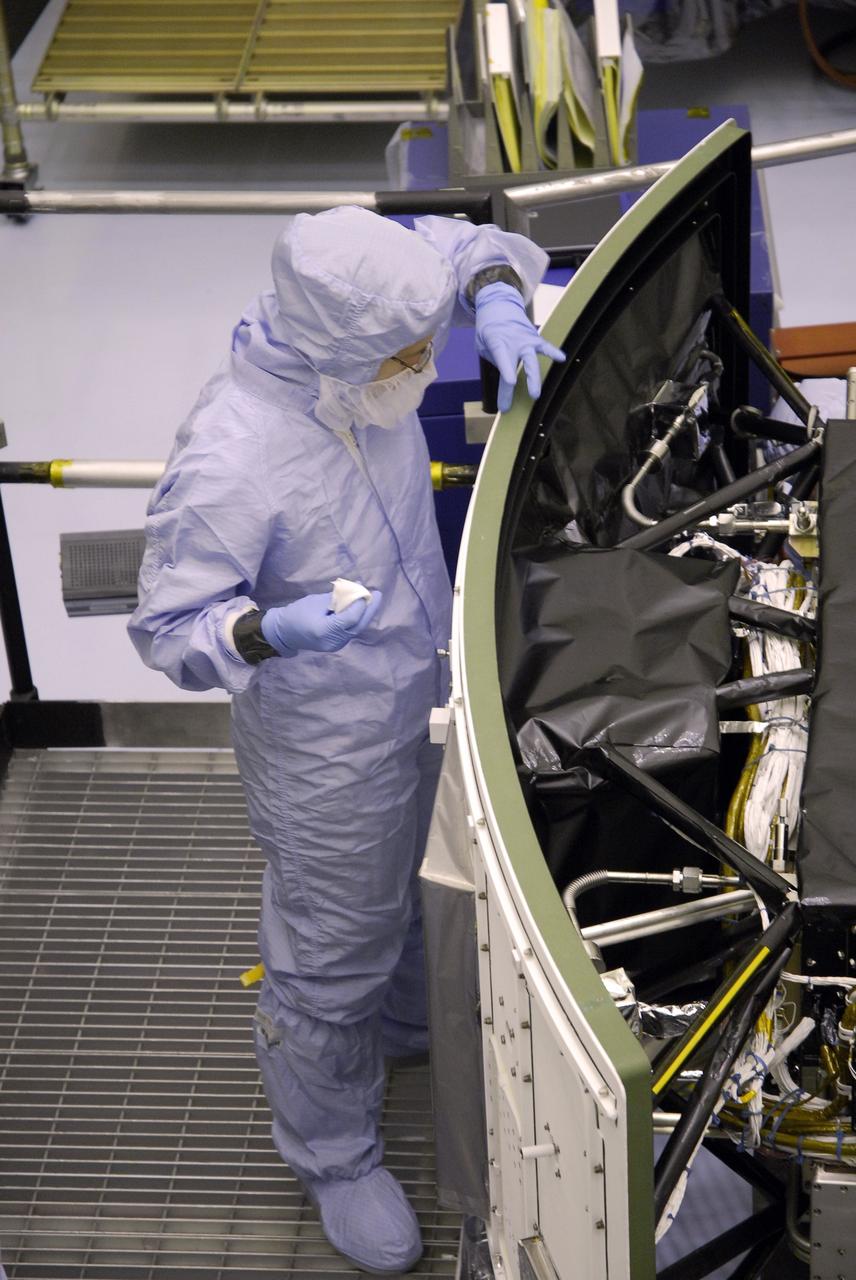

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician cleans the edge of the radiator on the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3,that will be installed on NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The radiator is the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space. It will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
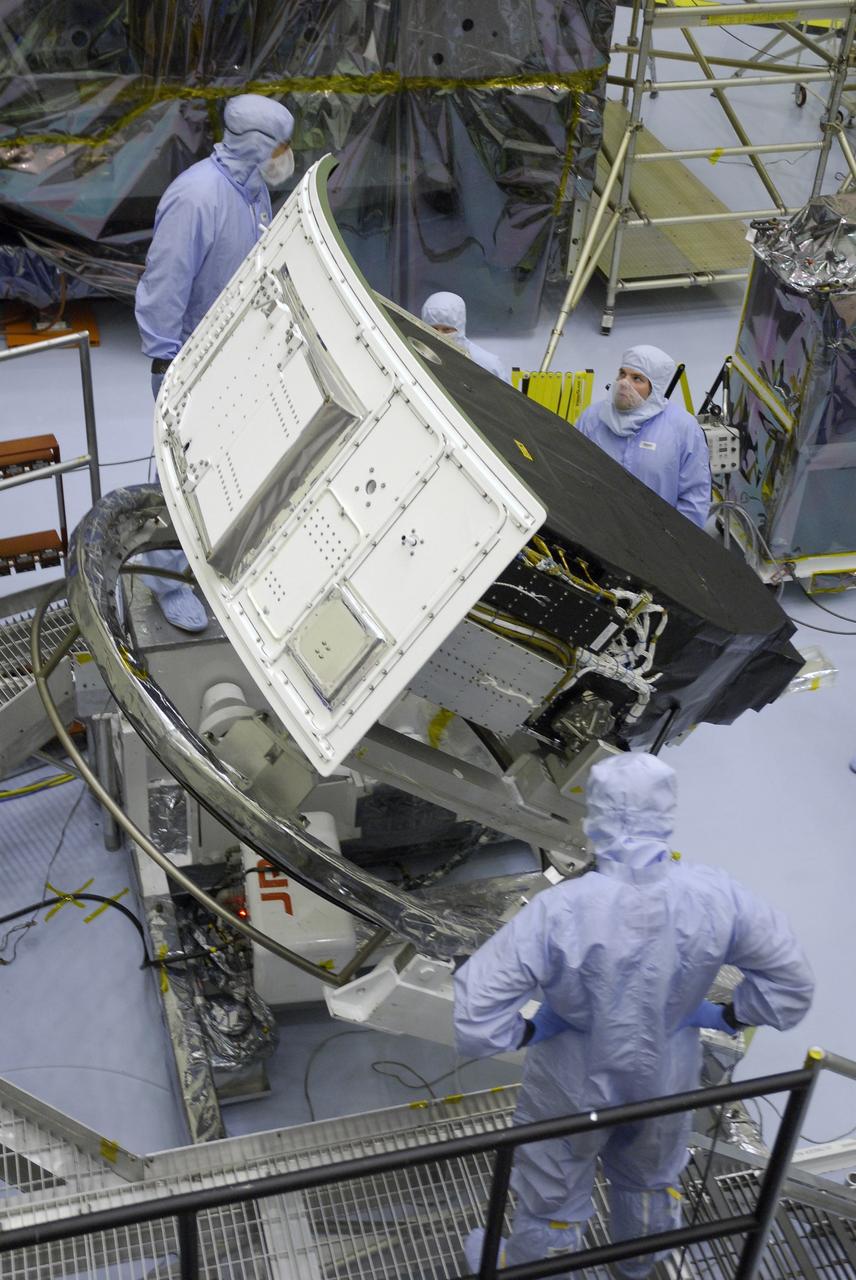

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians stand by as the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, is rotated. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The curved edge shown at left is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
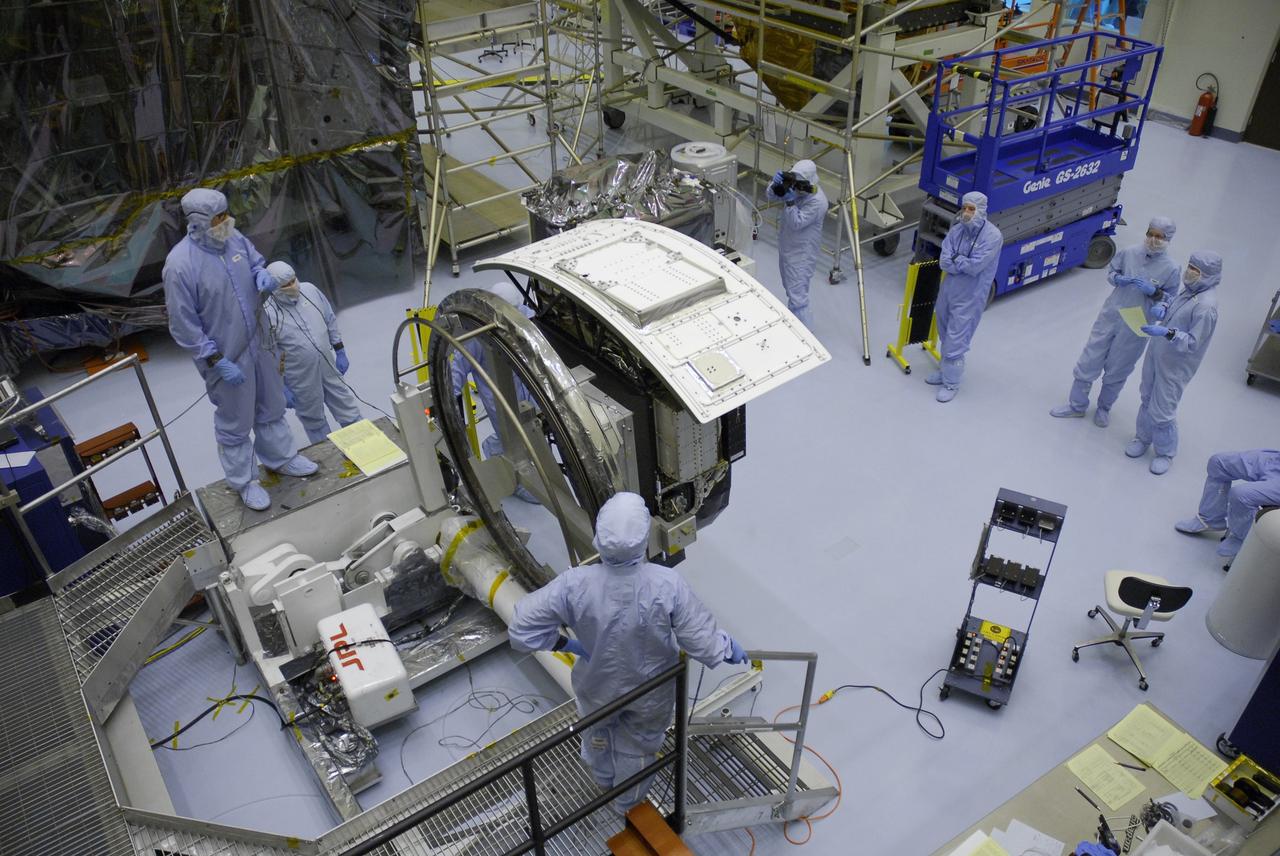

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, has been rotated. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The curved edge shown at top is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
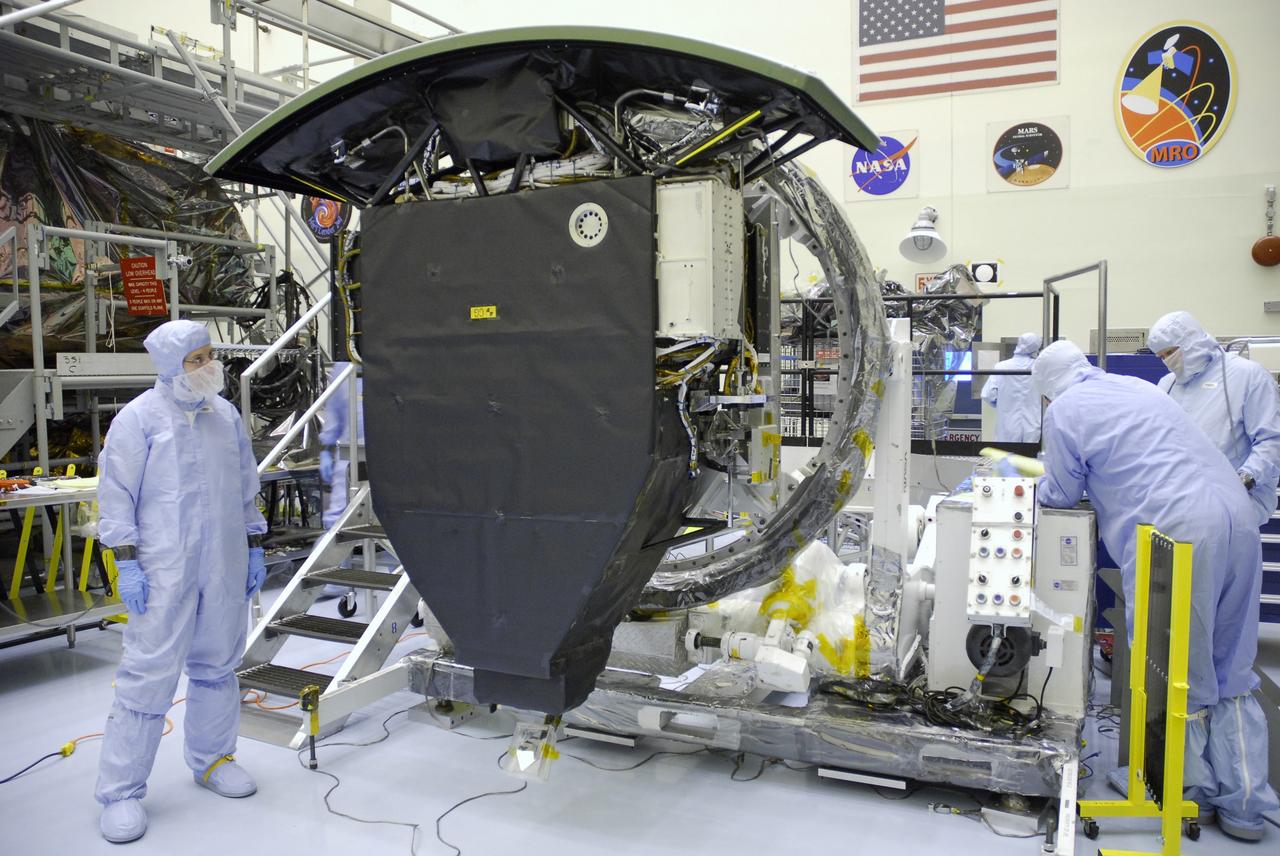

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians observe as the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, is rotated to vertical. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The curved edge shown at top is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
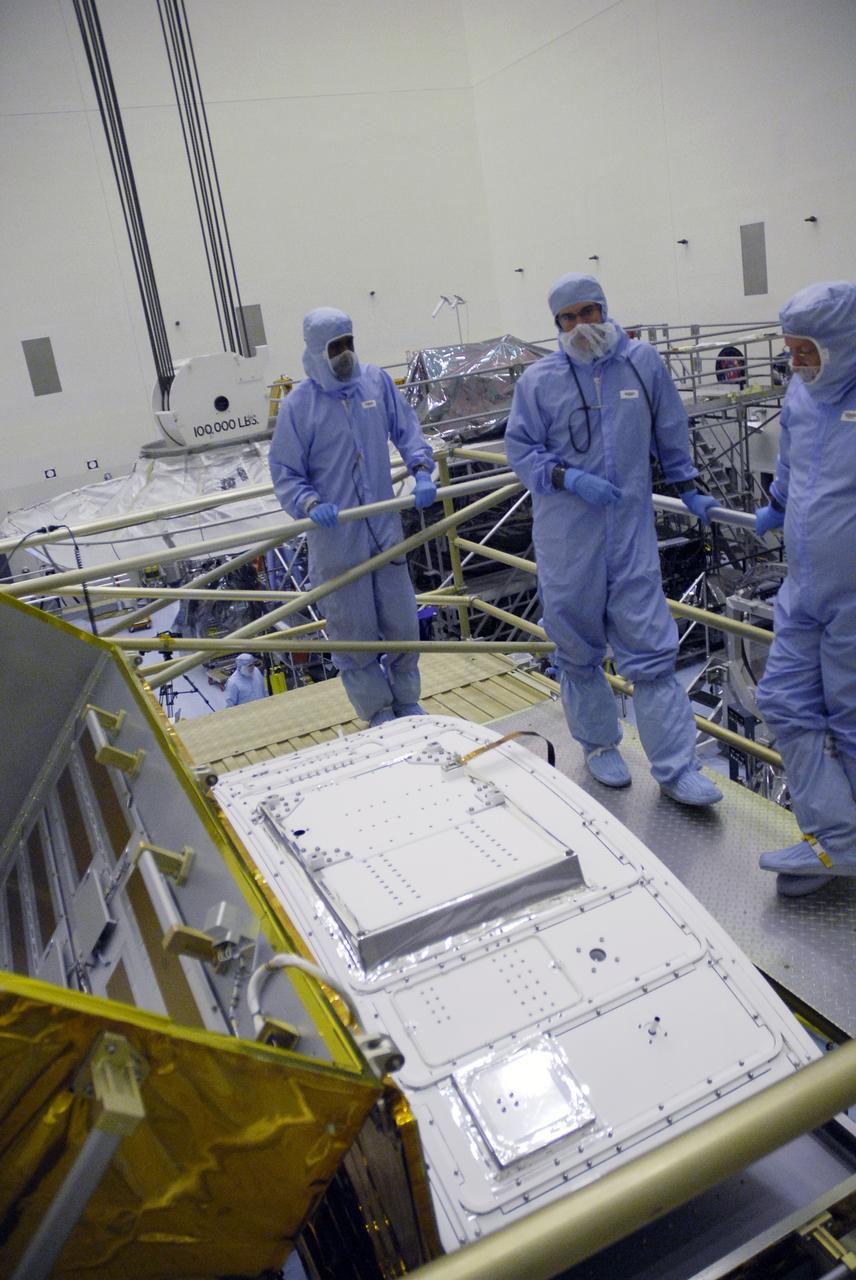

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians wait for the rotation of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, in order to attach a crane. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The part shown here is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Media representatives discuss the design and operation of the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project with NASA In Situ Resource Utilization Project Manager William Larson, facing the rover, in a field beside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rover and its drill are provided by the Canadian Space Agency and work in concert with NASA science instruments to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
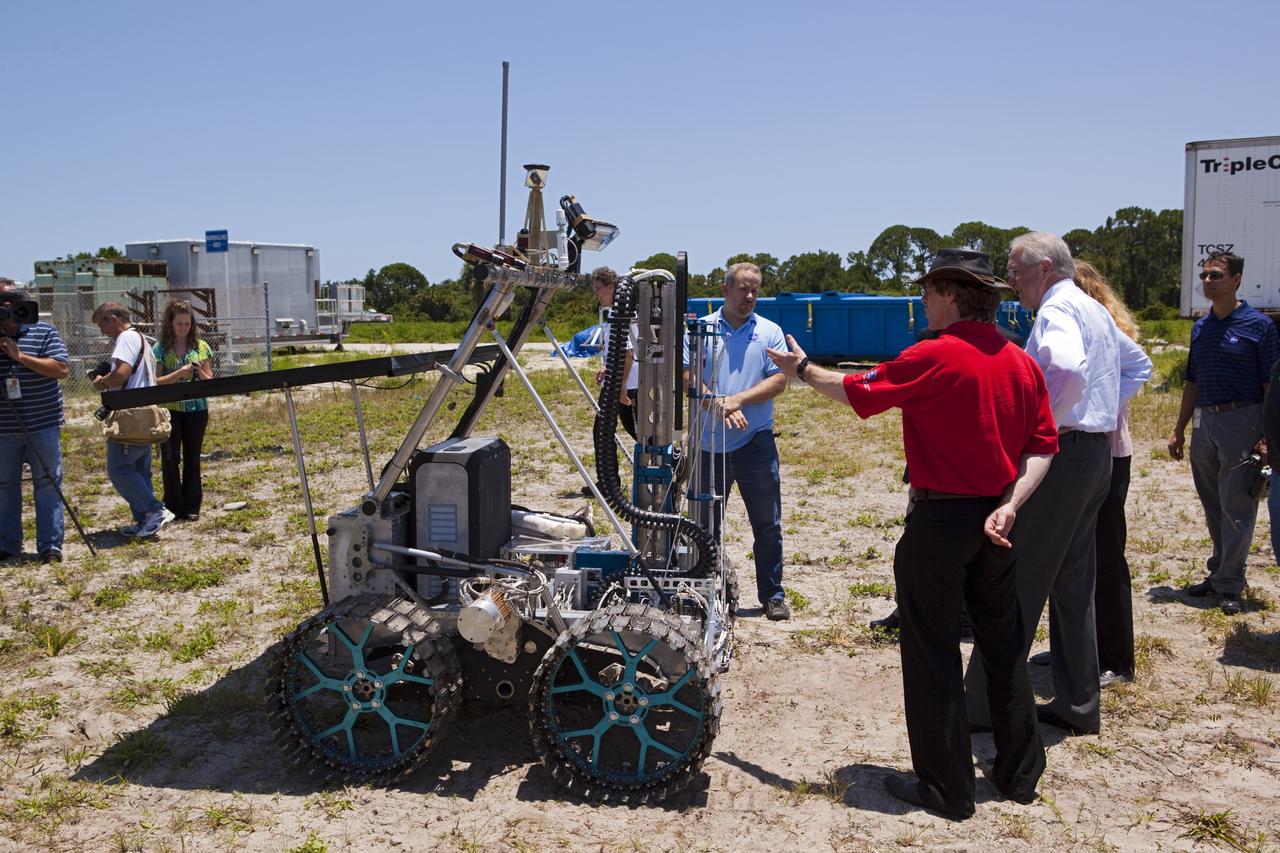

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Daniel Lefebvre, an engineer with the Canadian Space Agency, points out some of the features of the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project to media representatives on hand for a demonstration of the rover in a field beside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rover and its drill are provided by the Canadian Space Agency and work in concert with NASA science instruments to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
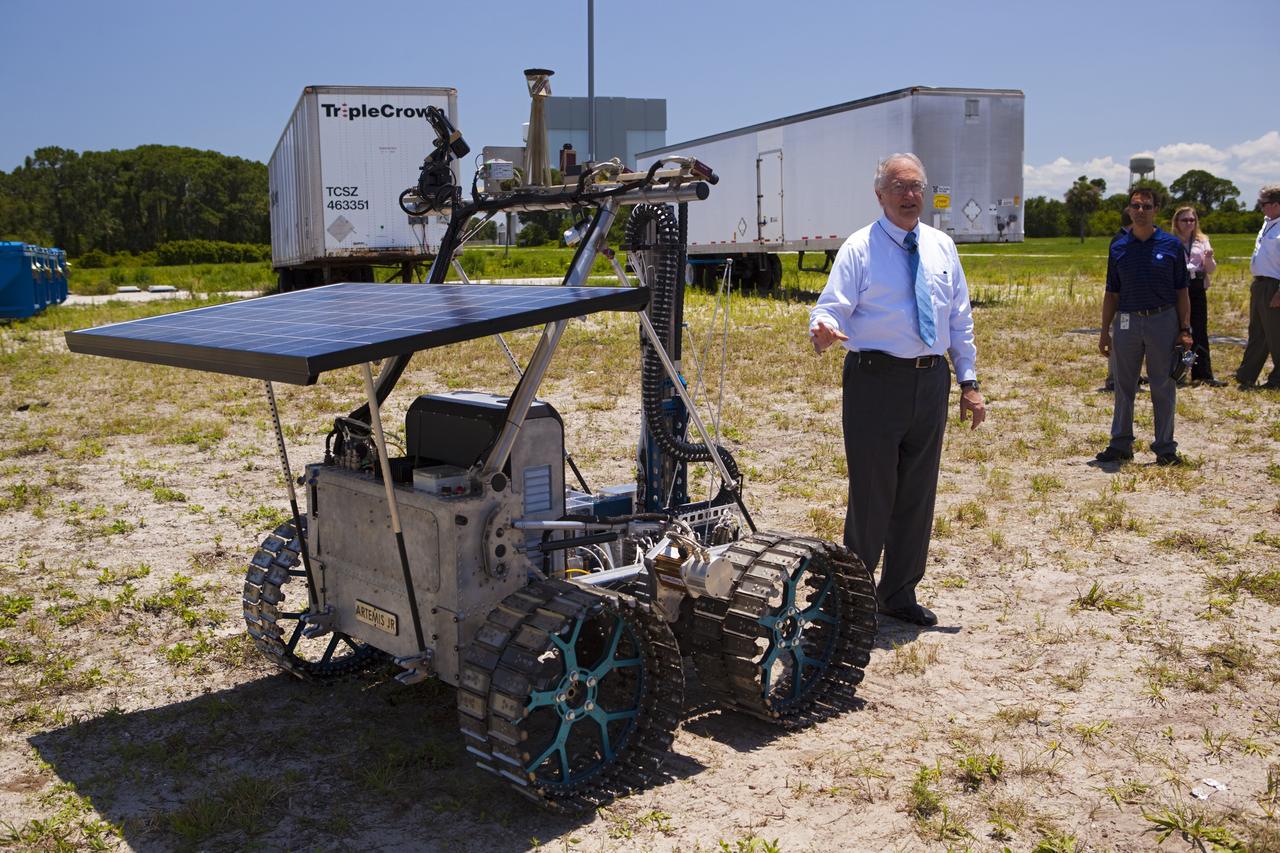

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA In Situ Resource Utilization Project Manager William Larson discusses the design and operation of the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project with media representatives during a rover demonstration for media representatives in a field beside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rover and its drill are provided by the Canadian Space Agency and work in concert with NASA science instruments to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians wait for the rotation of the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, in order to attach a crane. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The curved edge shown at left is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
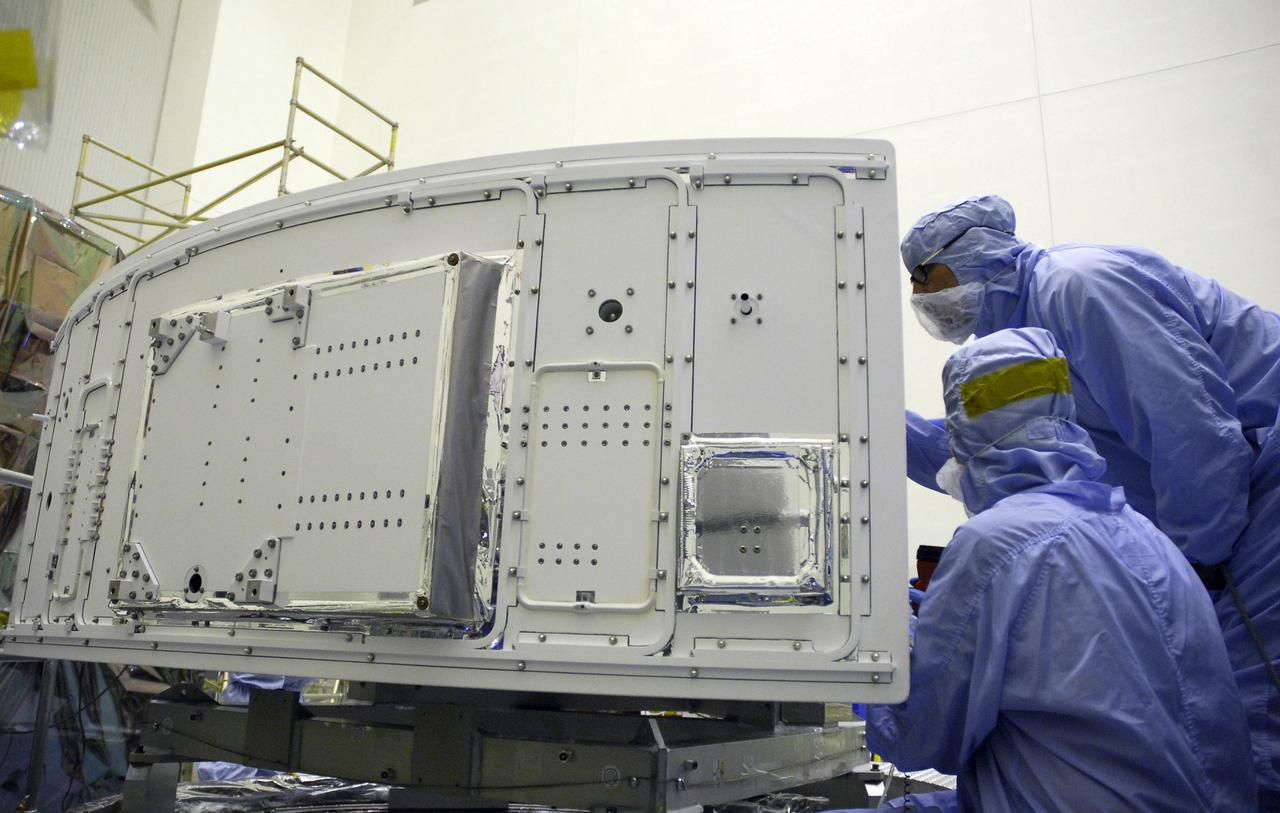

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technicians clean the radiator on the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3,that will be installed on NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The radiator is the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space. It will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
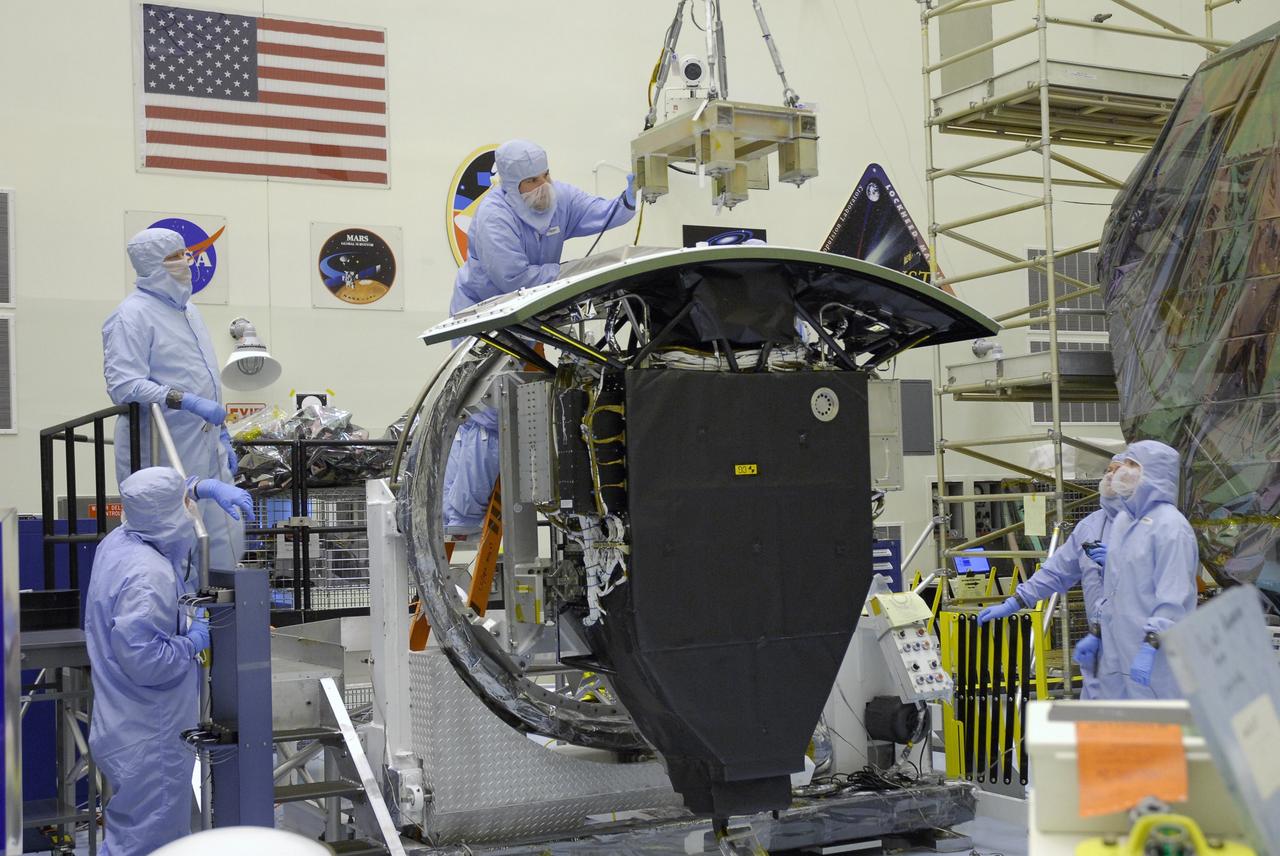

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, a technician guides a crane for attachment to the radiator on the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The radiator is the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
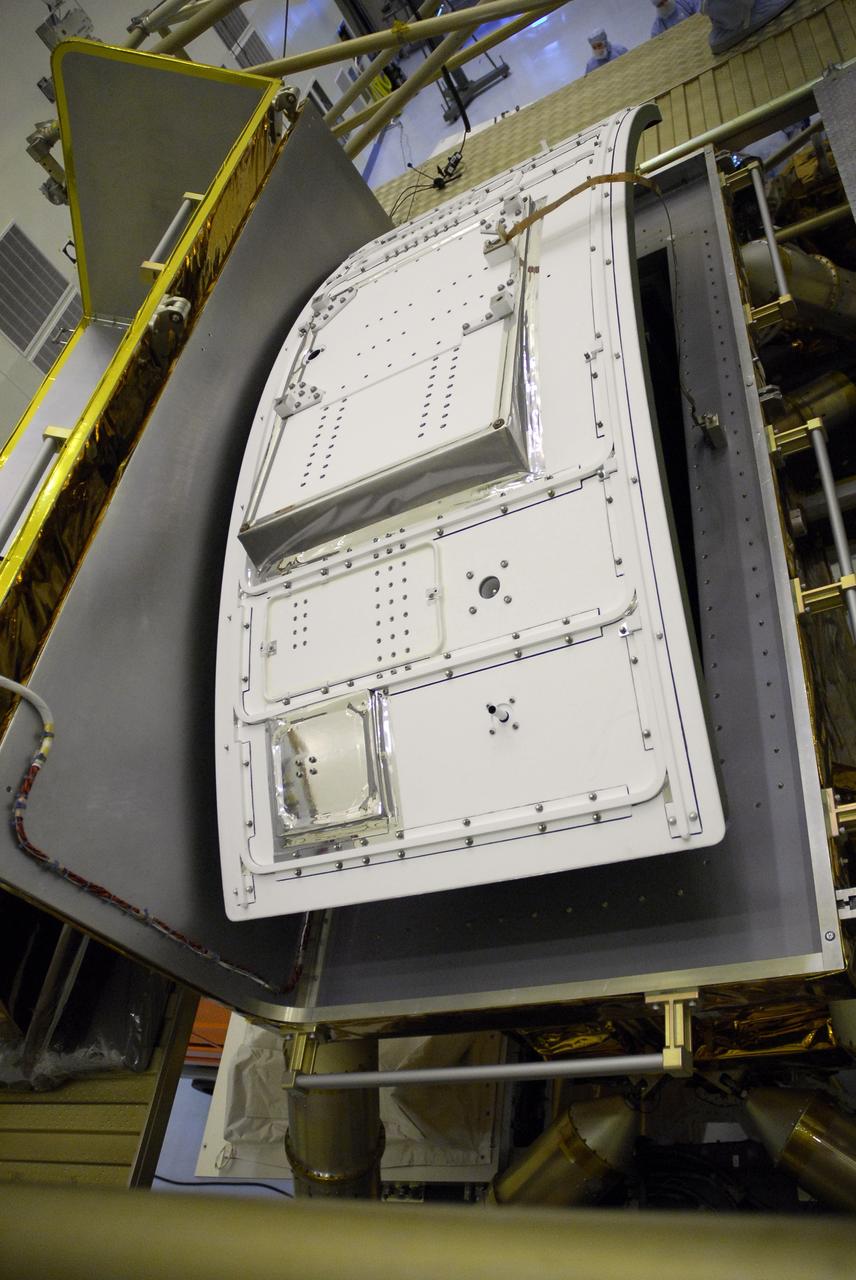
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, waits to be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The part shown here is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – After rotation of the Wide Field Camera 3 (background left), or WFC3, in the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians check the data. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The curved edge shown at top is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
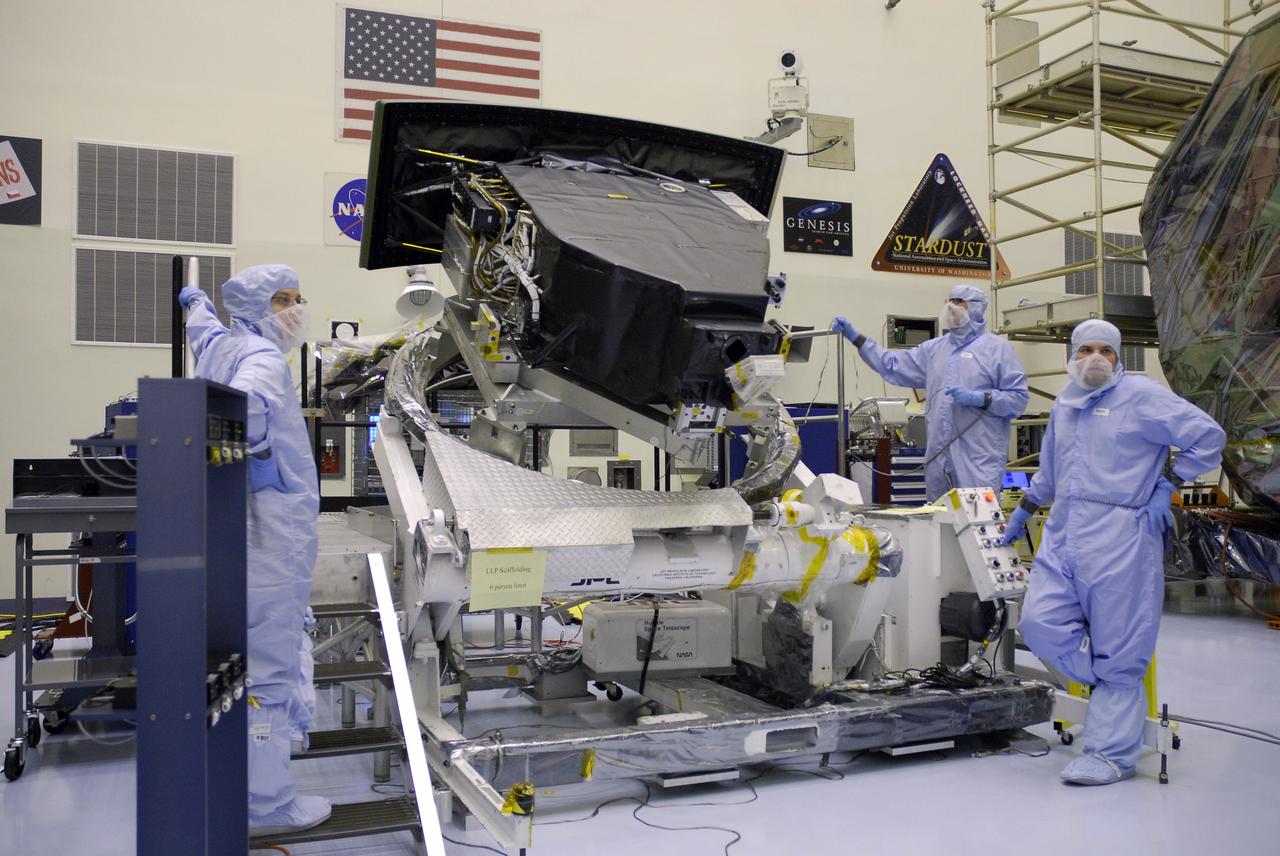

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Payload Hazardous Servicing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center, technicians observe as the Wide Field Camera 3, or WFC3, is rotated. The WFC3 will be transferred to the Super Lightweight Interchangeable Carrier. WFC3 is part of the payload on space shuttle Atlantis' STS-125 mission for the fifth and final Hubble servicing flight to NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. The curved edge shown at the back is the radiator, the "outside" of WFC3 that will be exposed to space and will expel heat out of Hubble and into space through black body radiation. As Hubble enters the last stage of its life, WFC3 will be Hubble's next evolutionary step, allowing Hubble to peer ever further into the mysteries of the cosmos. WFC3 will study a diverse range of objects and phenomena, from young and extremely distant galaxies, to much more nearby stellar systems, to objects within our very own solar system. WFC3 will take the place of Wide Field Planetary Camera 2, which astronauts will bring back to Earth aboard the shuttle. Launch of Atlantis is targeted at 1:34 a.m. EDT Oct. 8. Photo credit: NASA/Amanda Diller
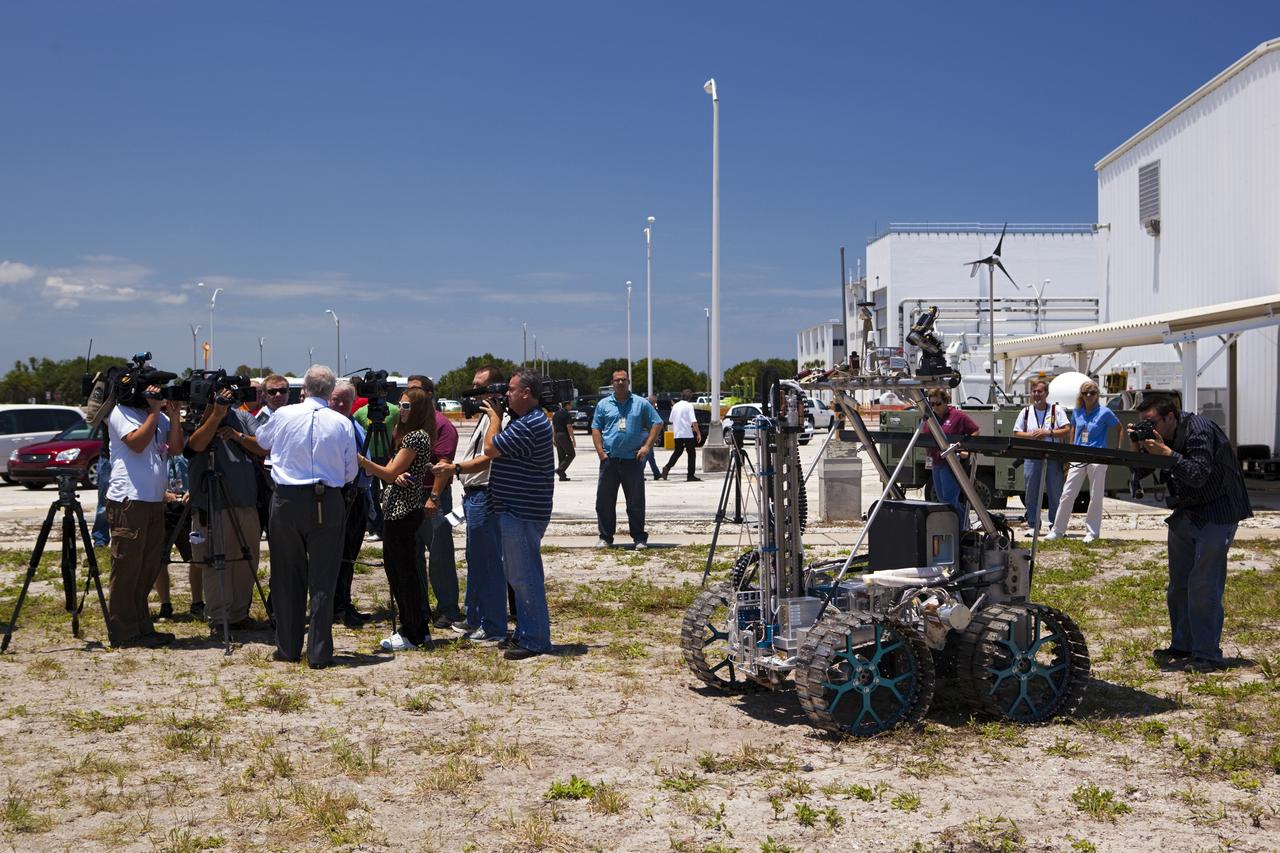

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA In Situ Resource Utilization Project Manager William Larson, back to camera, discusses the design and operation of the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project with media representatives during a rover demonstration in a field beside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rover and its drill are provided by the Canadian Space Agency and work in concert with NASA science instruments to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
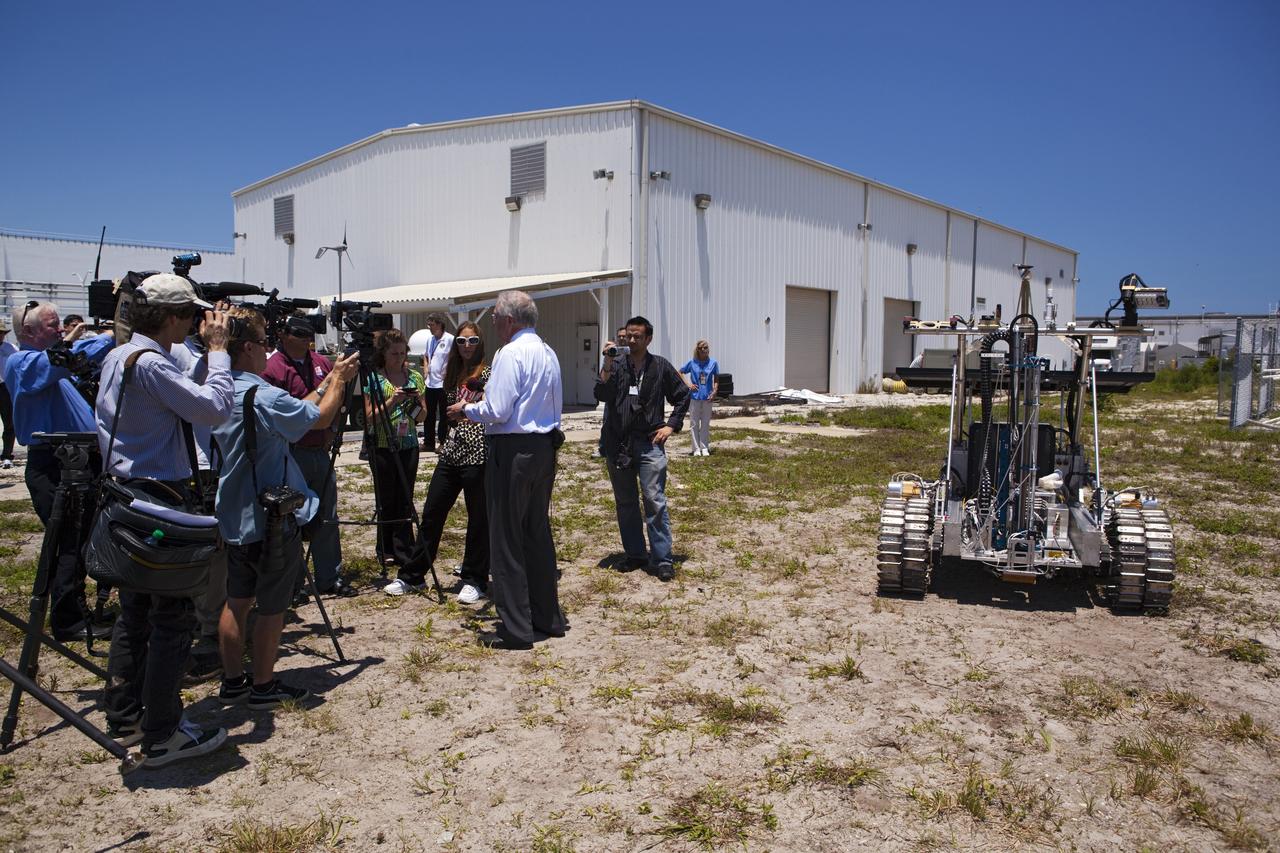

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – NASA In Situ Resource Utilization Project Manager William Larson, back to rover, discusses the design and operation of the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project with media representatives during a rover demonstration in a field beside the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rover and its drill are provided by the Canadian Space Agency and work in concert with NASA science instruments to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
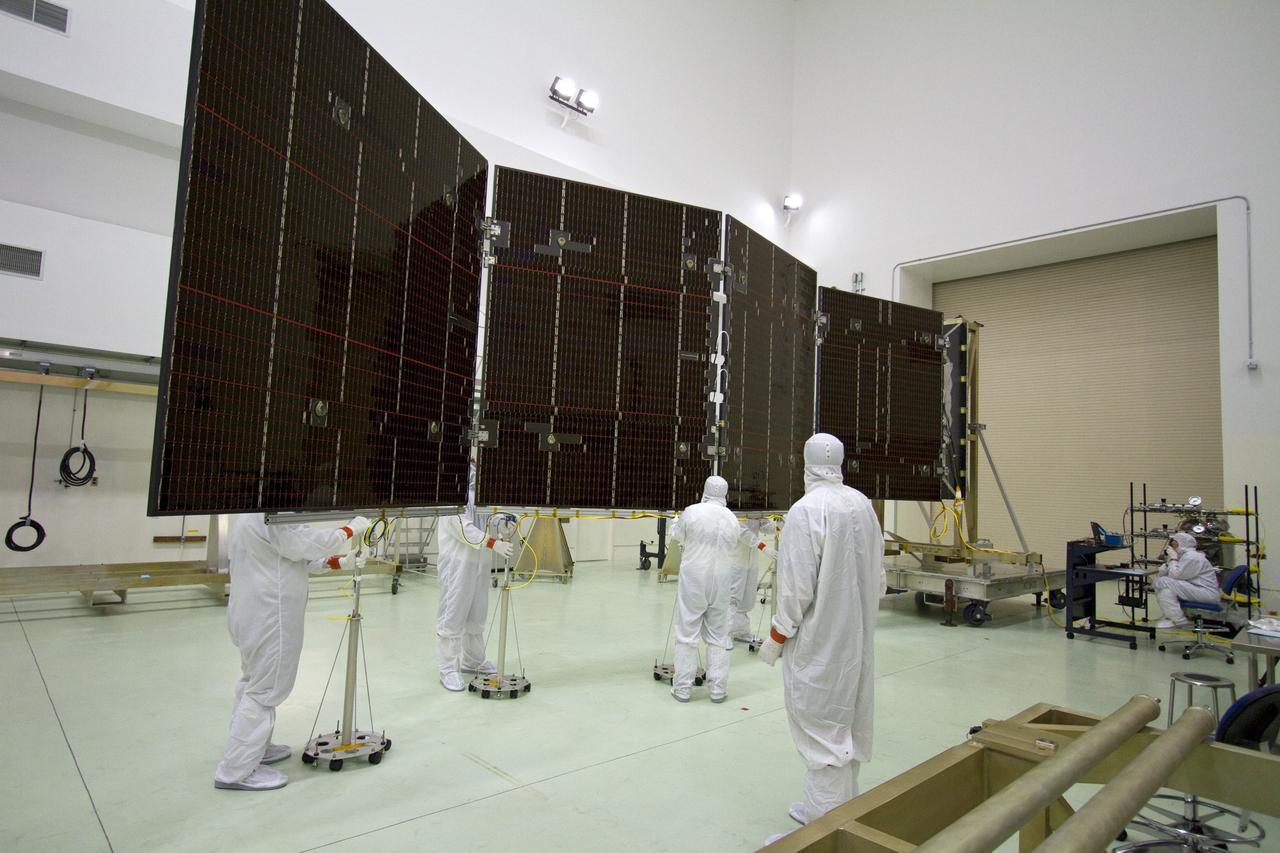

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., unfurl a solar panel that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
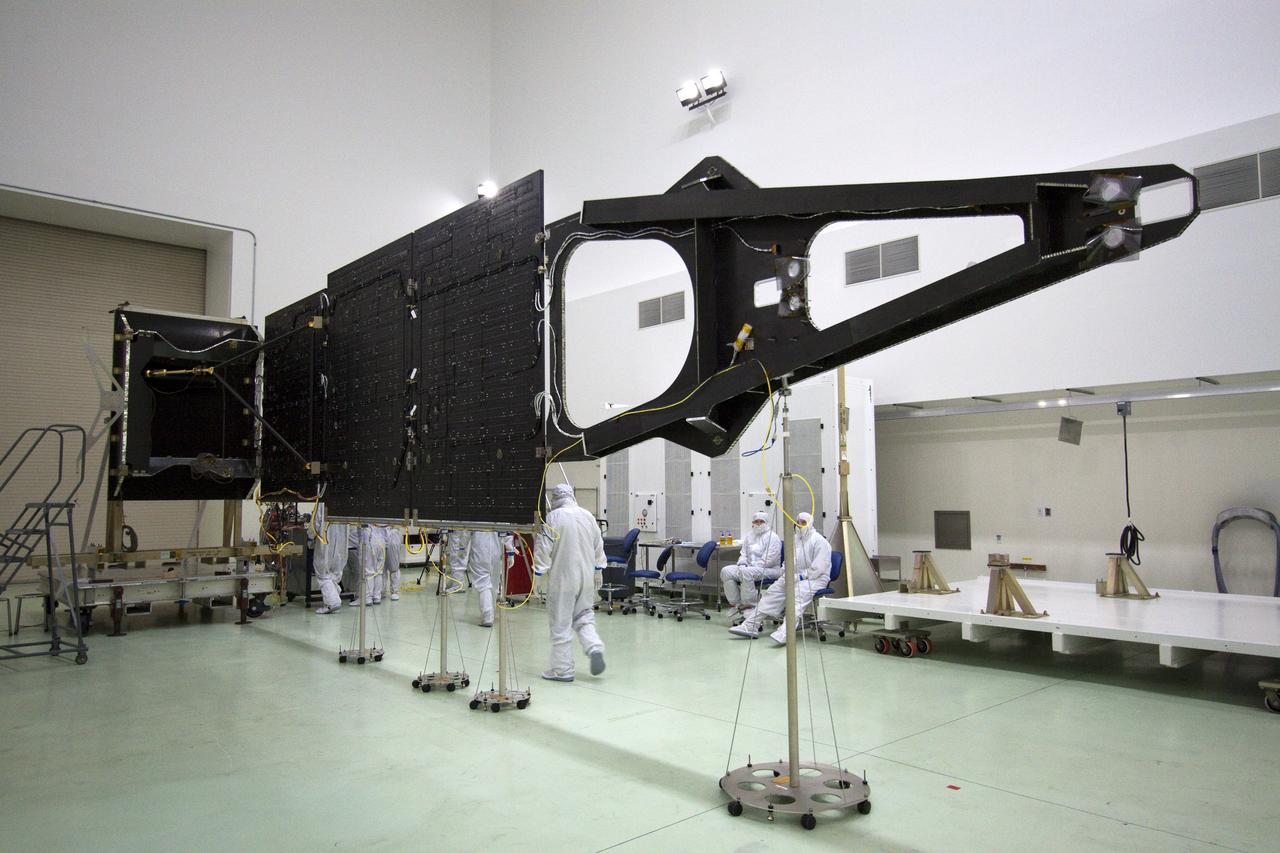

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., unfurl solar array No. 1 with a magnetometer boom that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
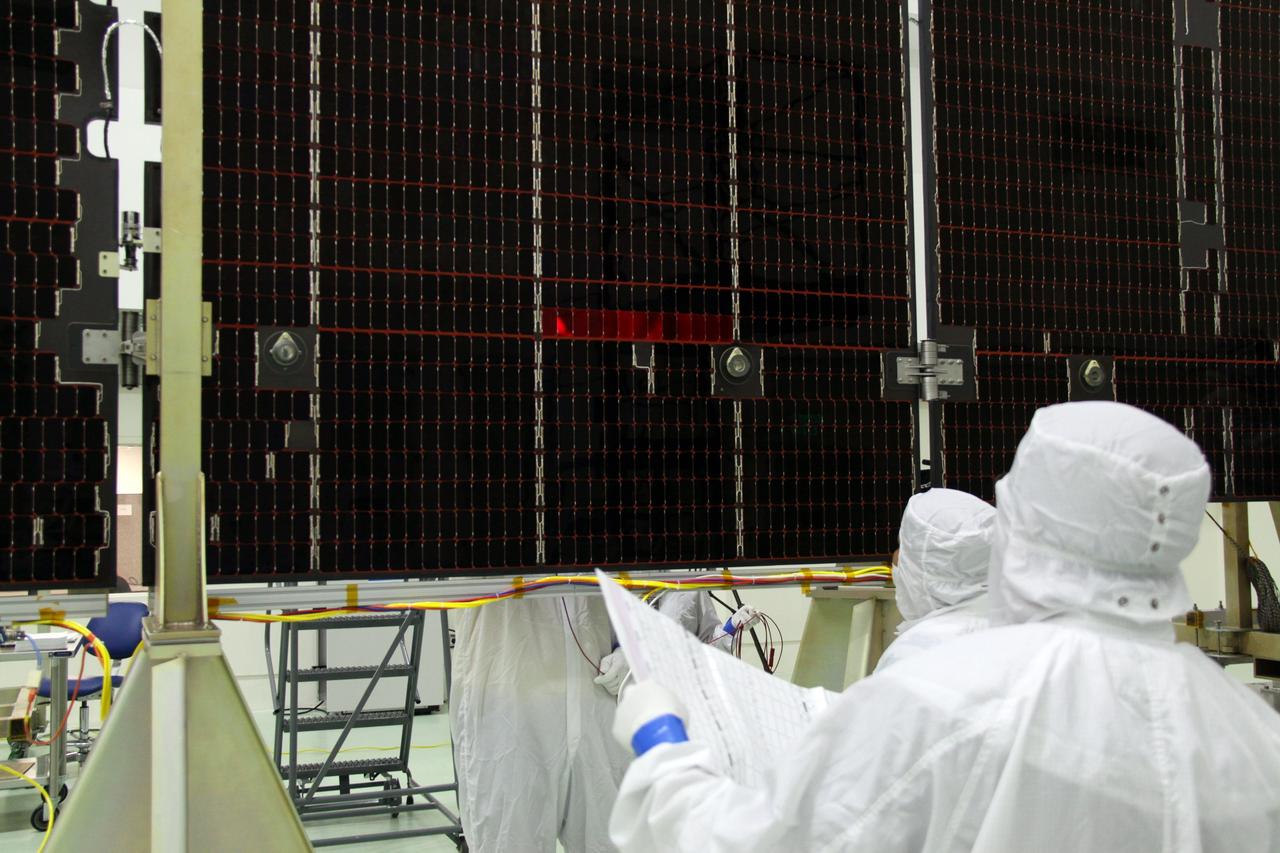

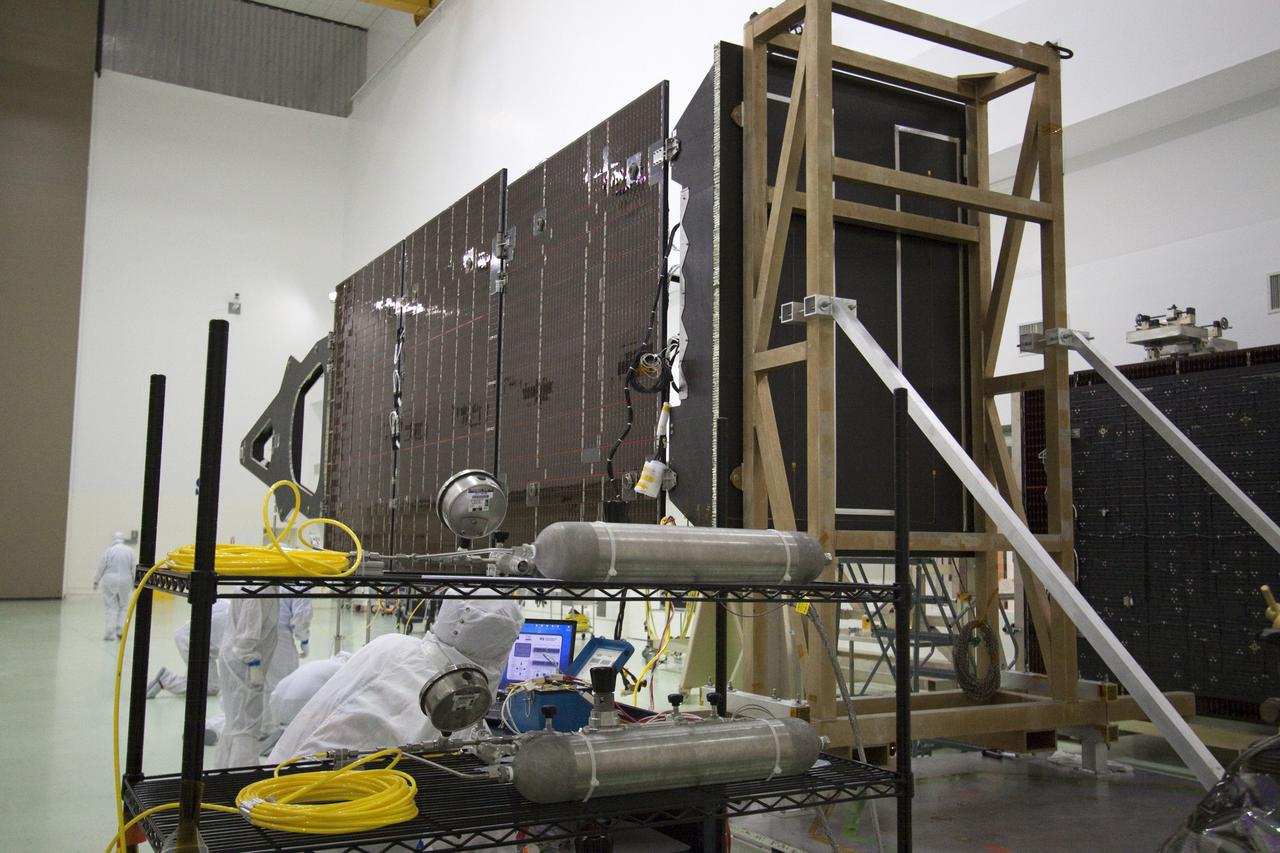
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., test the electrical continuity of a solar array that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
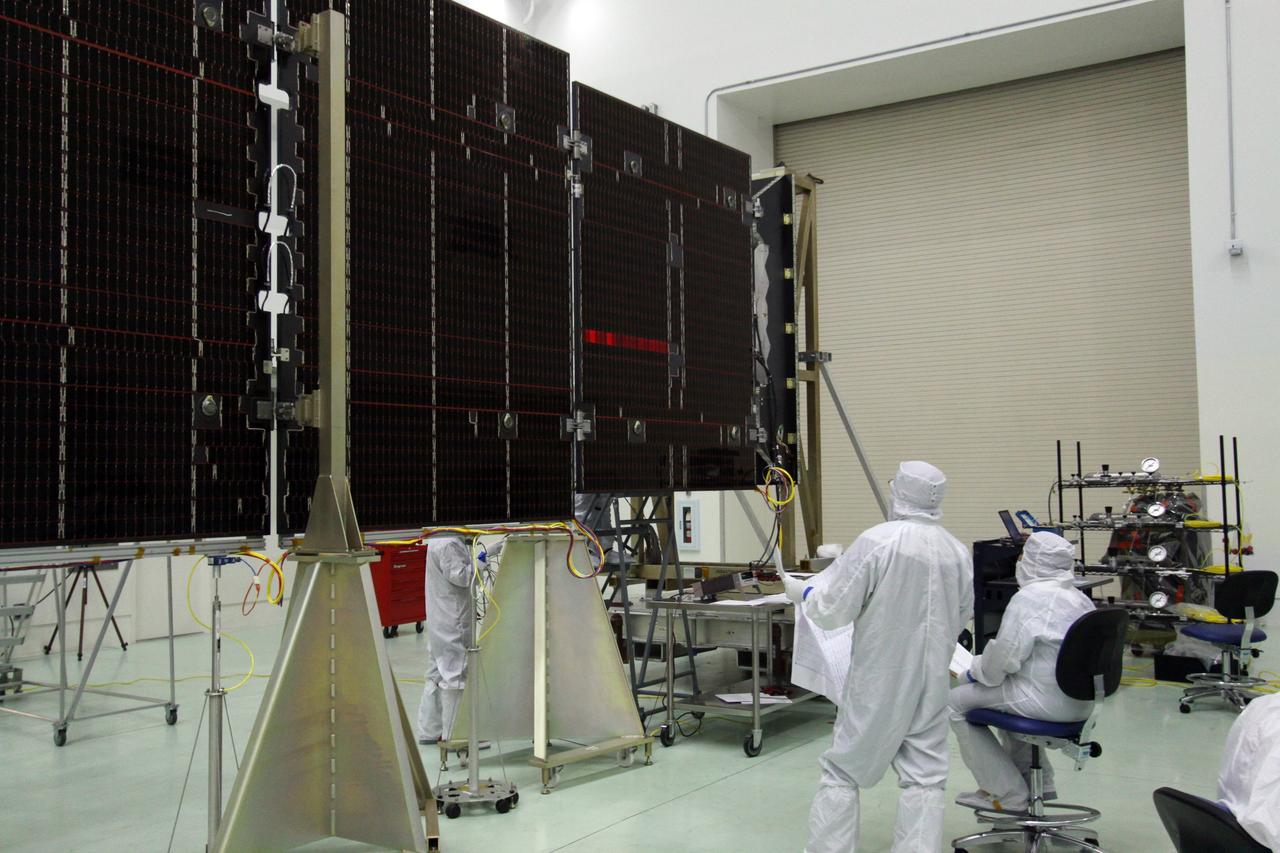

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., test the electrical continuity of a solar array that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., prepare to unfurl solar array No. 1 with a magnetometer boom that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
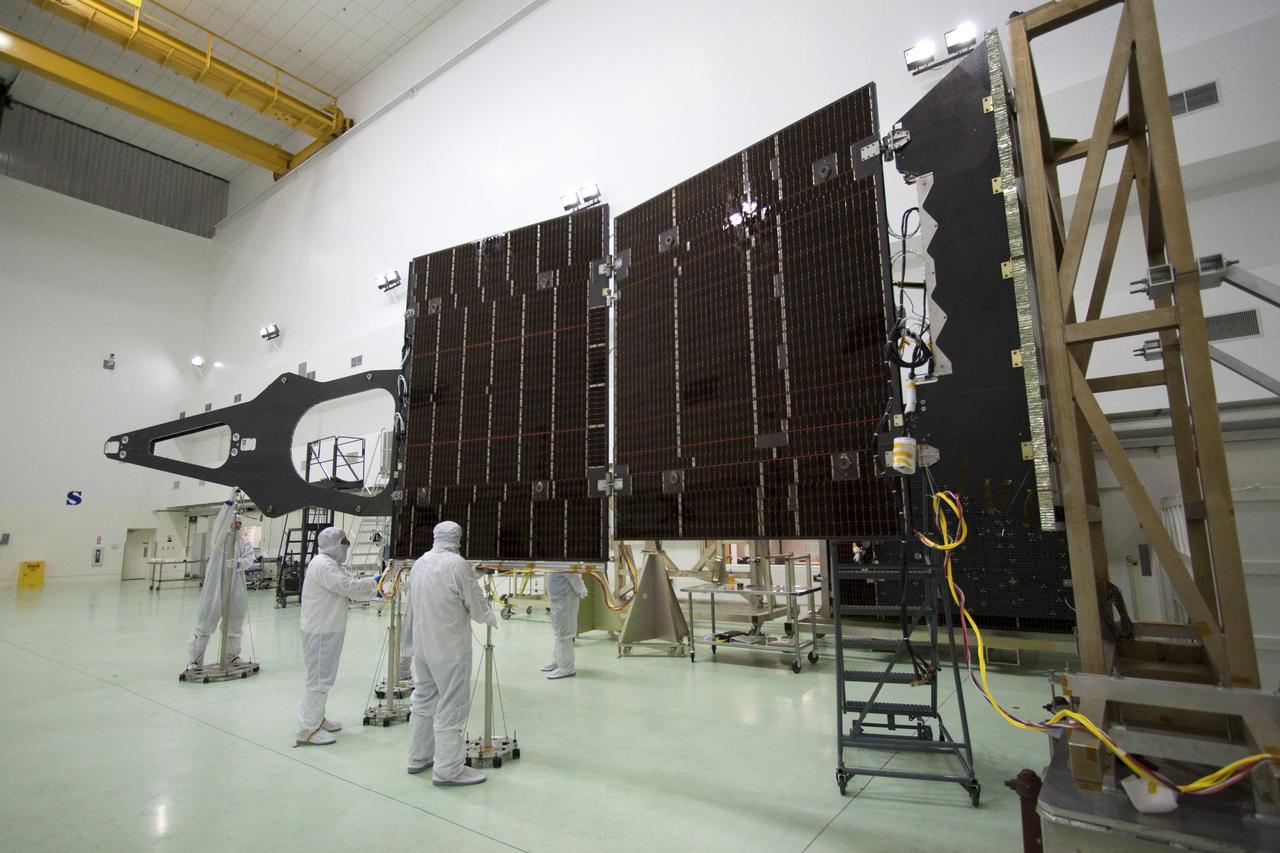

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., unfurl solar array No. 1 with a magnetometer boom that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
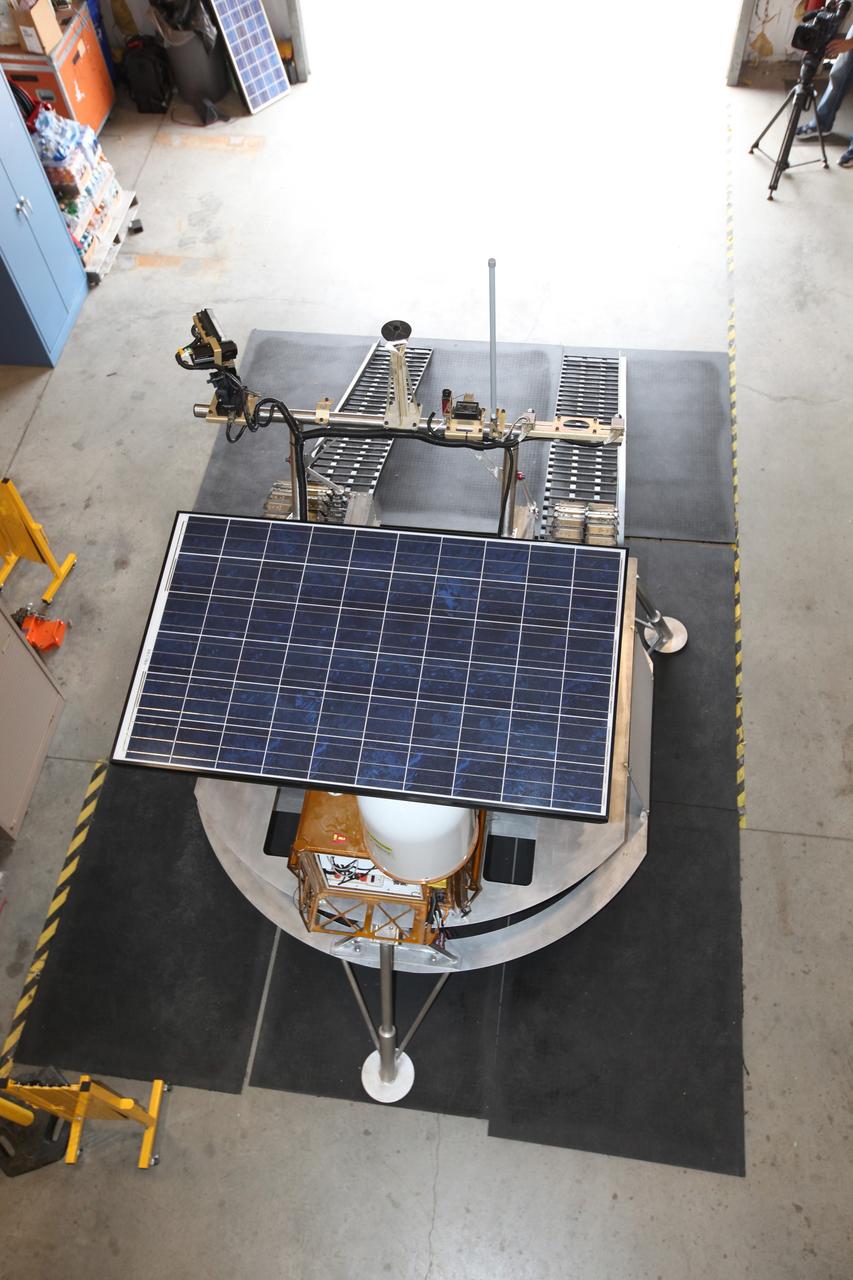
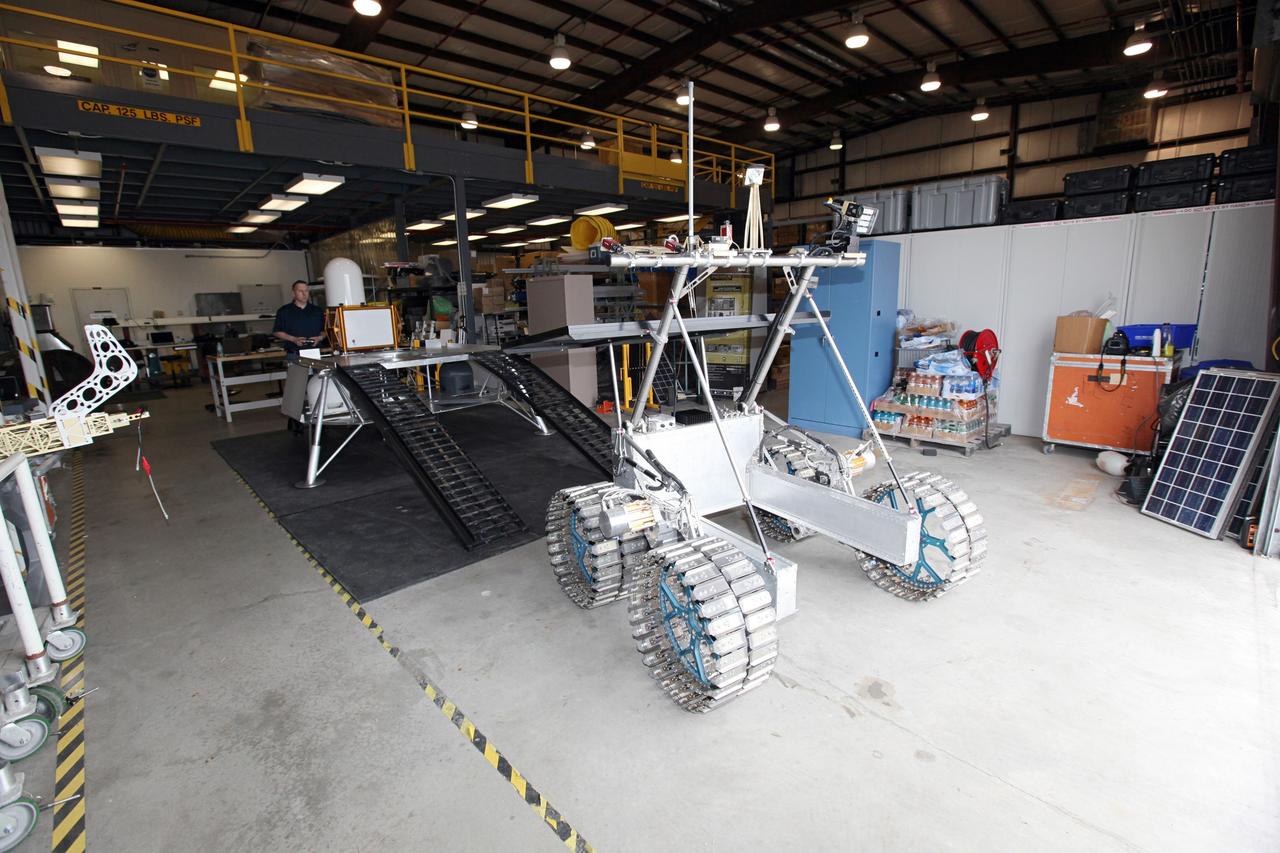
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This overhead view of the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project was taken in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida and provides a clear view of its solar array, as well as the placement of the ramps that provide it with an avenue to mount or dismount the prototype lander beneath it. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
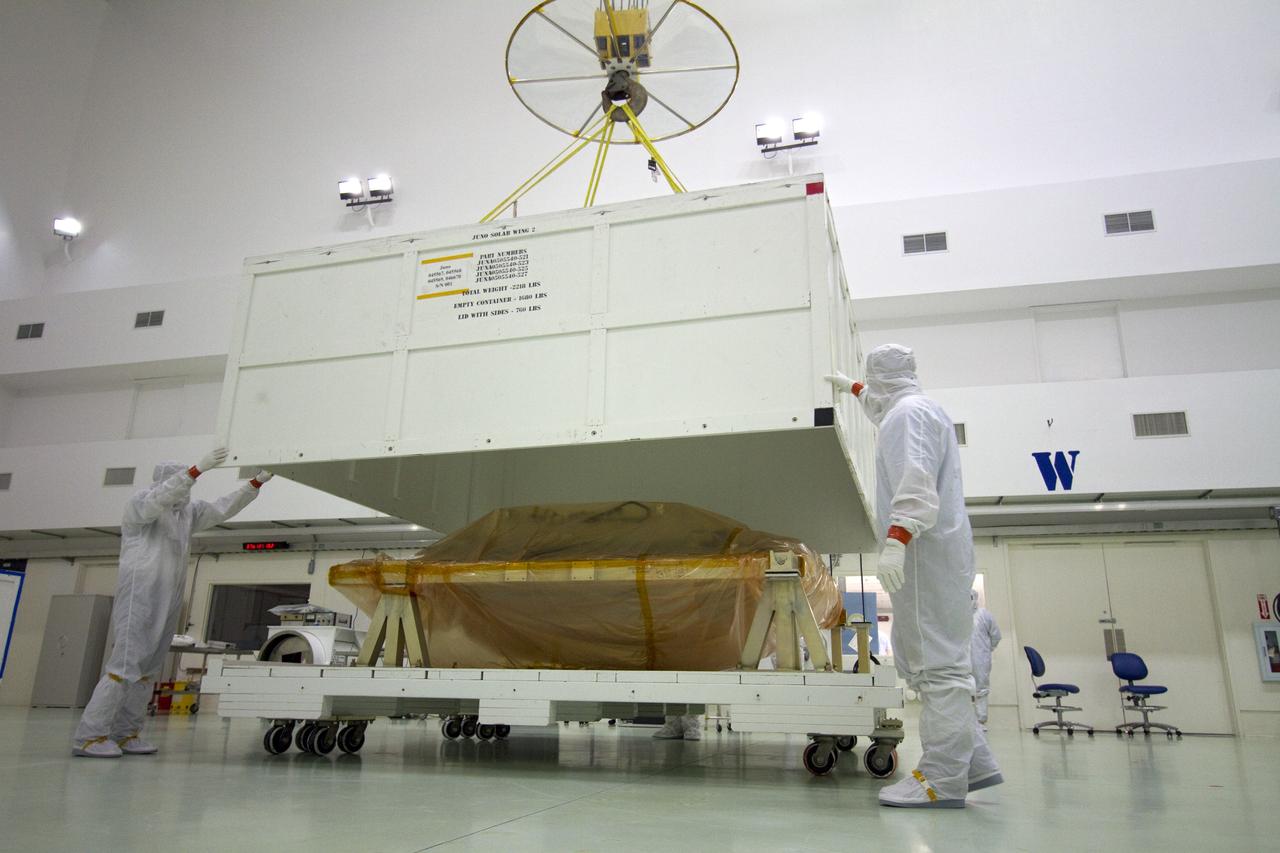

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- A solar panel that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter is unpacked in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
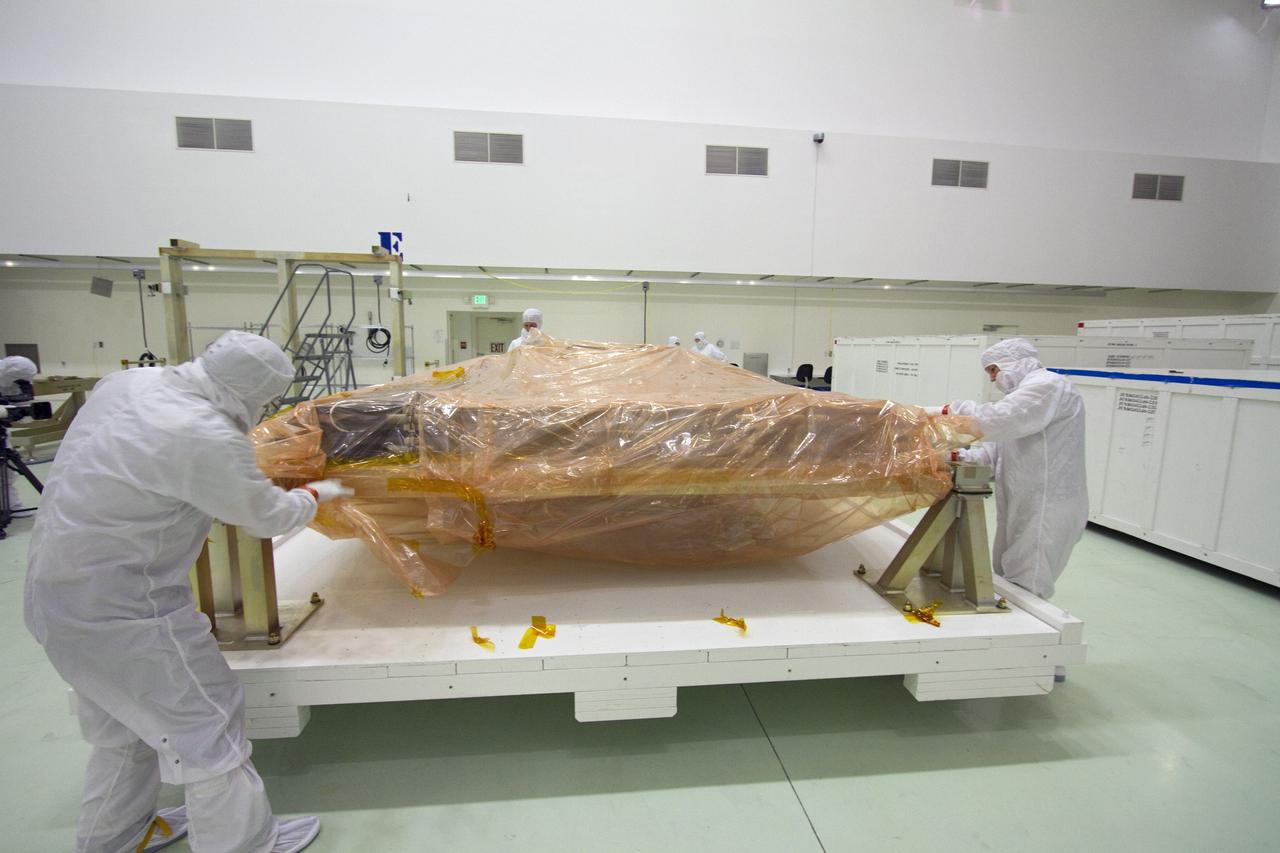

TITUSVILLE, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., unpack a solar panel that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
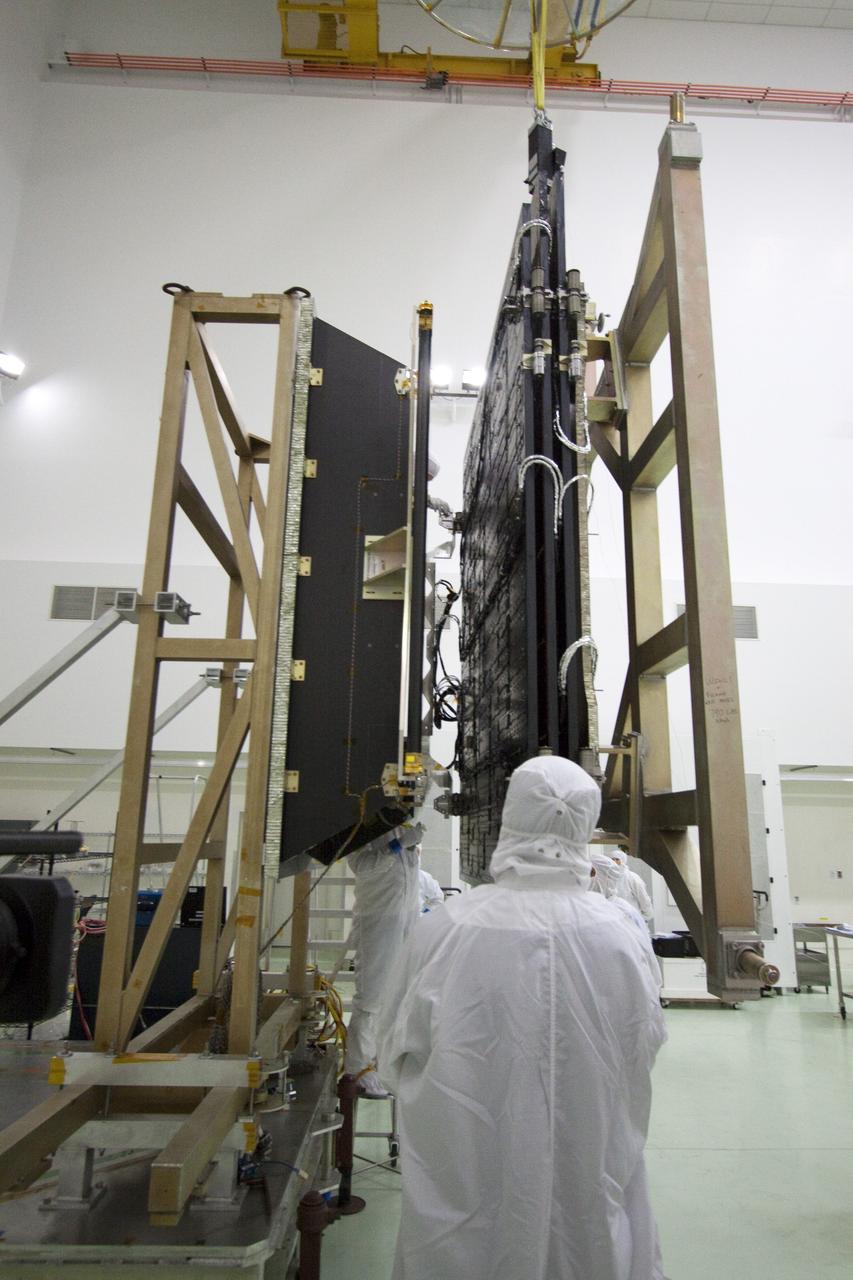

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., prepare to unfurl solar array No. 1 with a magnetometer boom that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., prepare to unfurl solar array No. 1 with a magnetometer boom that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

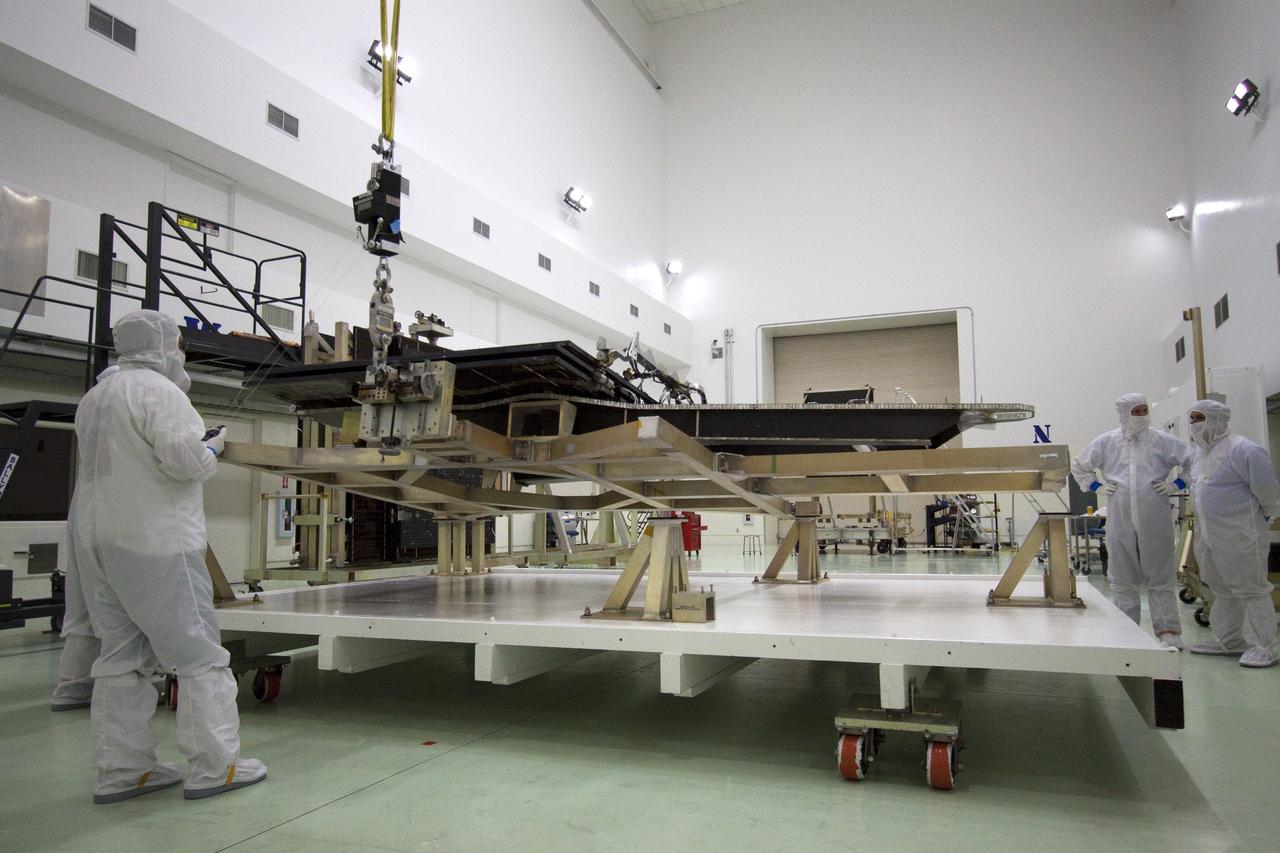
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., test the electrical continuity of a solar array that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., check out solar array No. 1 with a magnetometer boom that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
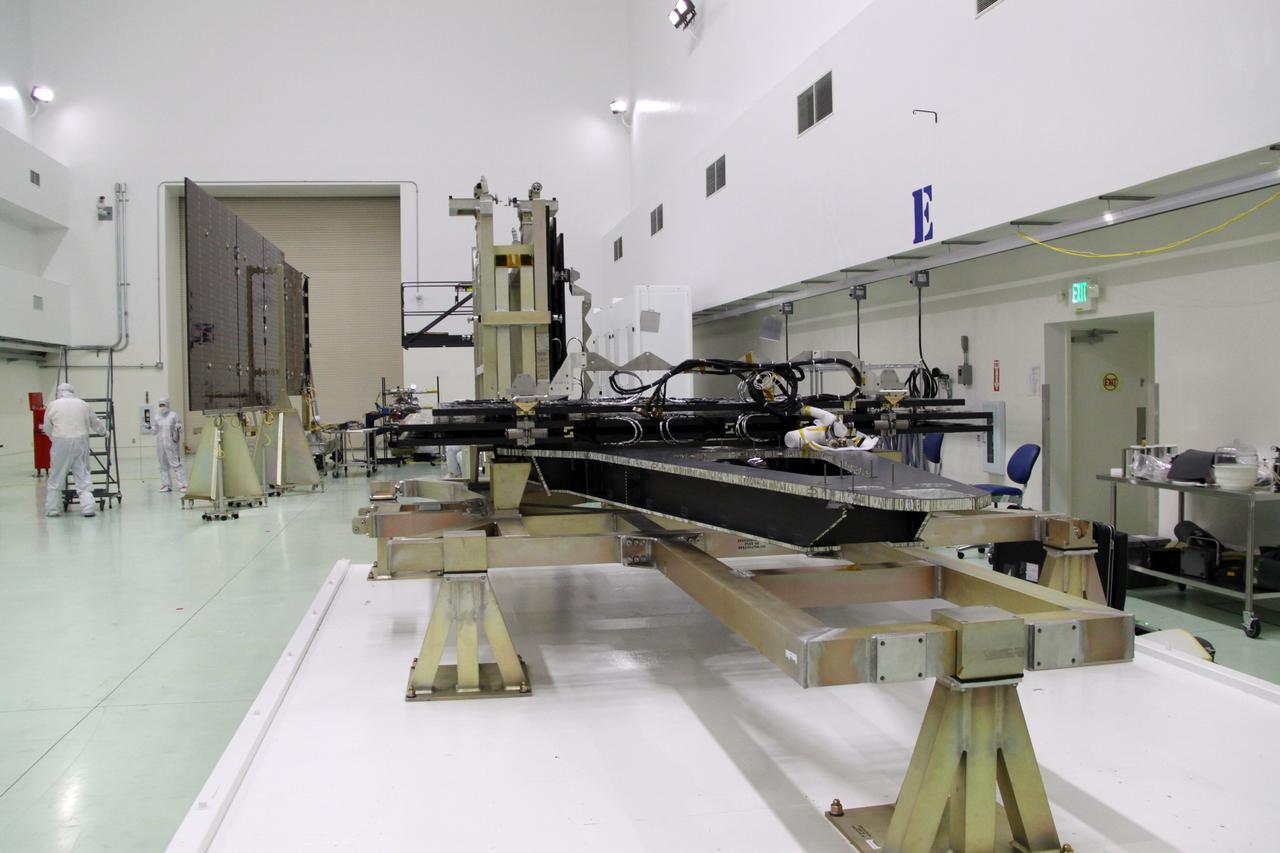

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., test the electrical continuity of a solar array, left, that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Two other arrays are in work stands on the right. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
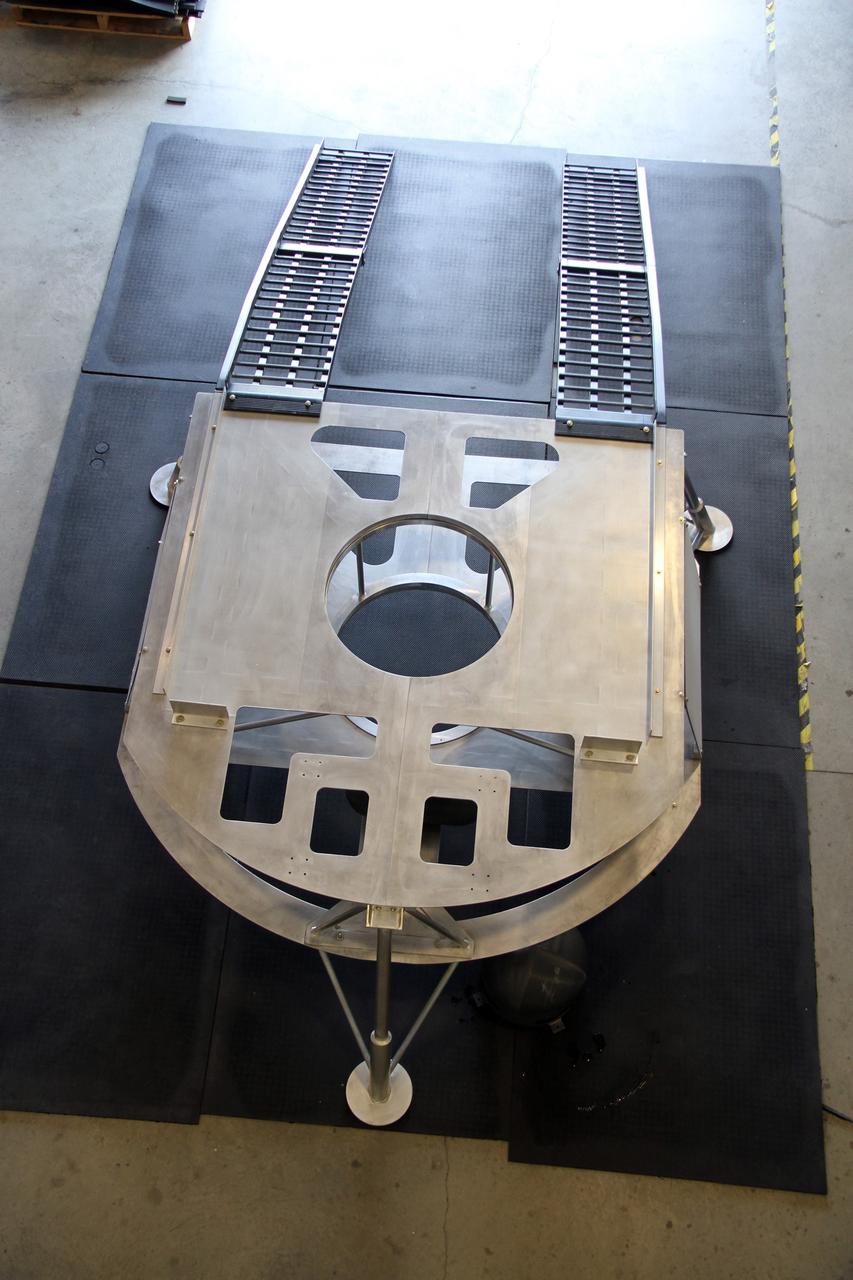
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – This overhead view of the prototype lander for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project was taken in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida and reveals the lander’s unique structure and the placement of the ramps that will provide RESOLVE’s rover an avenue to mount or dismount the lander. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will be conducting field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Ben Smegelsky
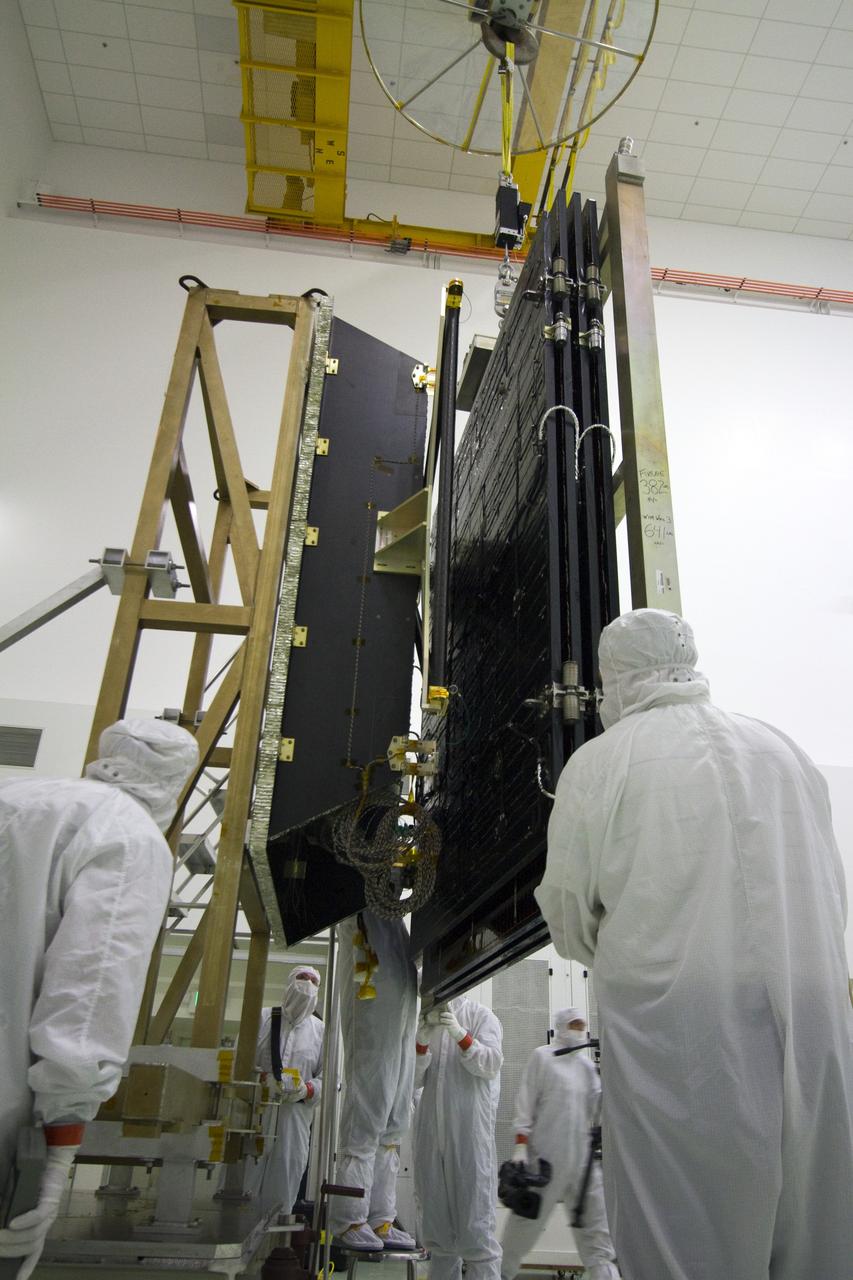

TITUSVILLE, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., process a solar panel that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
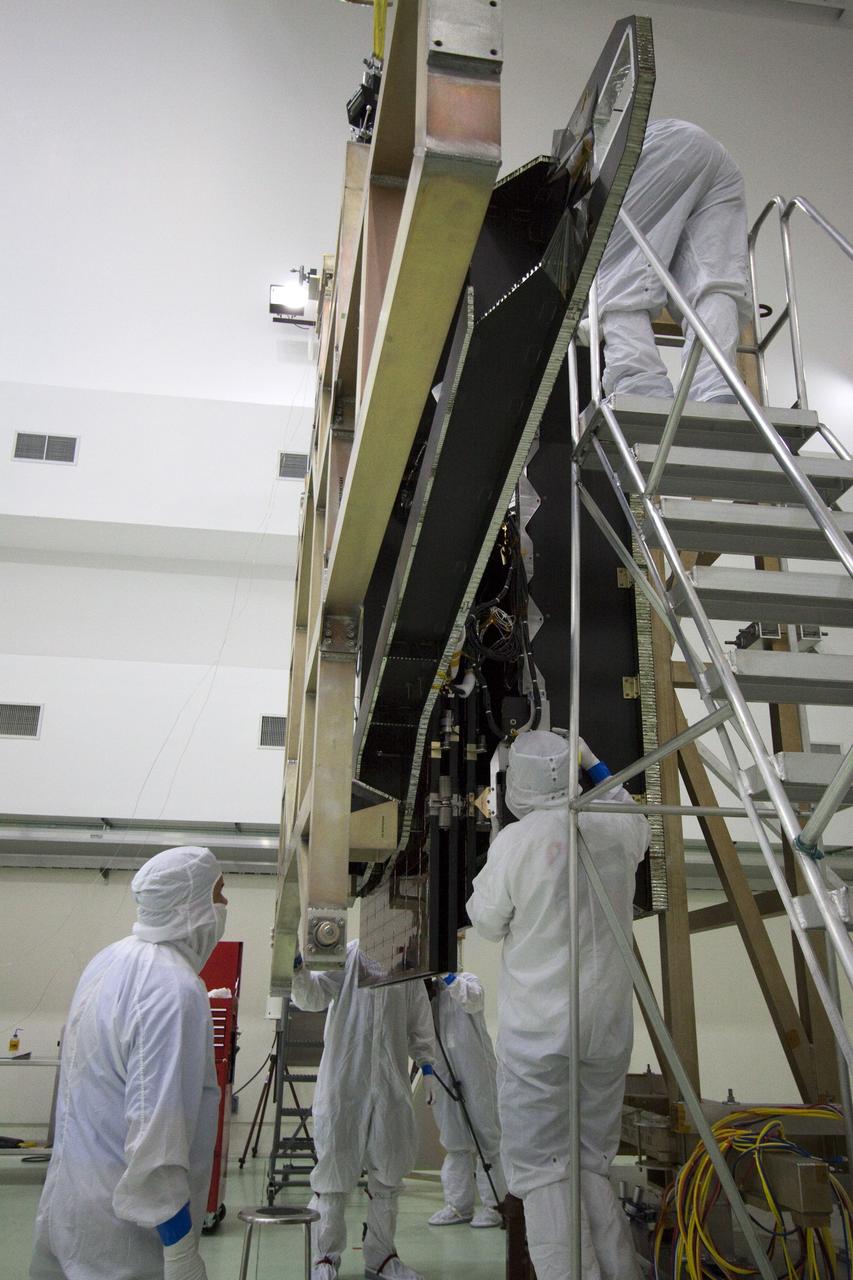

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., prepare to unfurl solar array No. 1 with a magnetometer boom that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
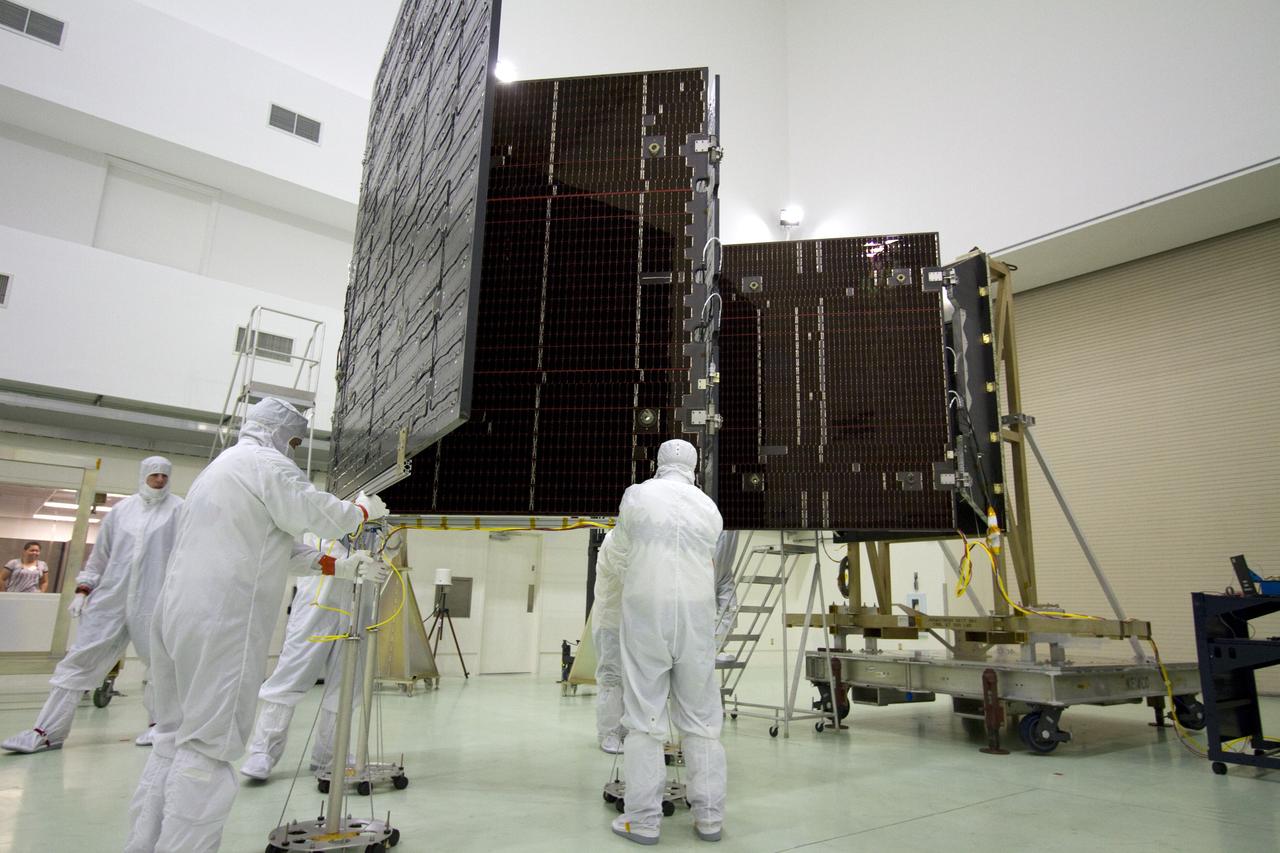

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., unfurl a solar panel that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

TITUSVILLE, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., process a solar panel that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
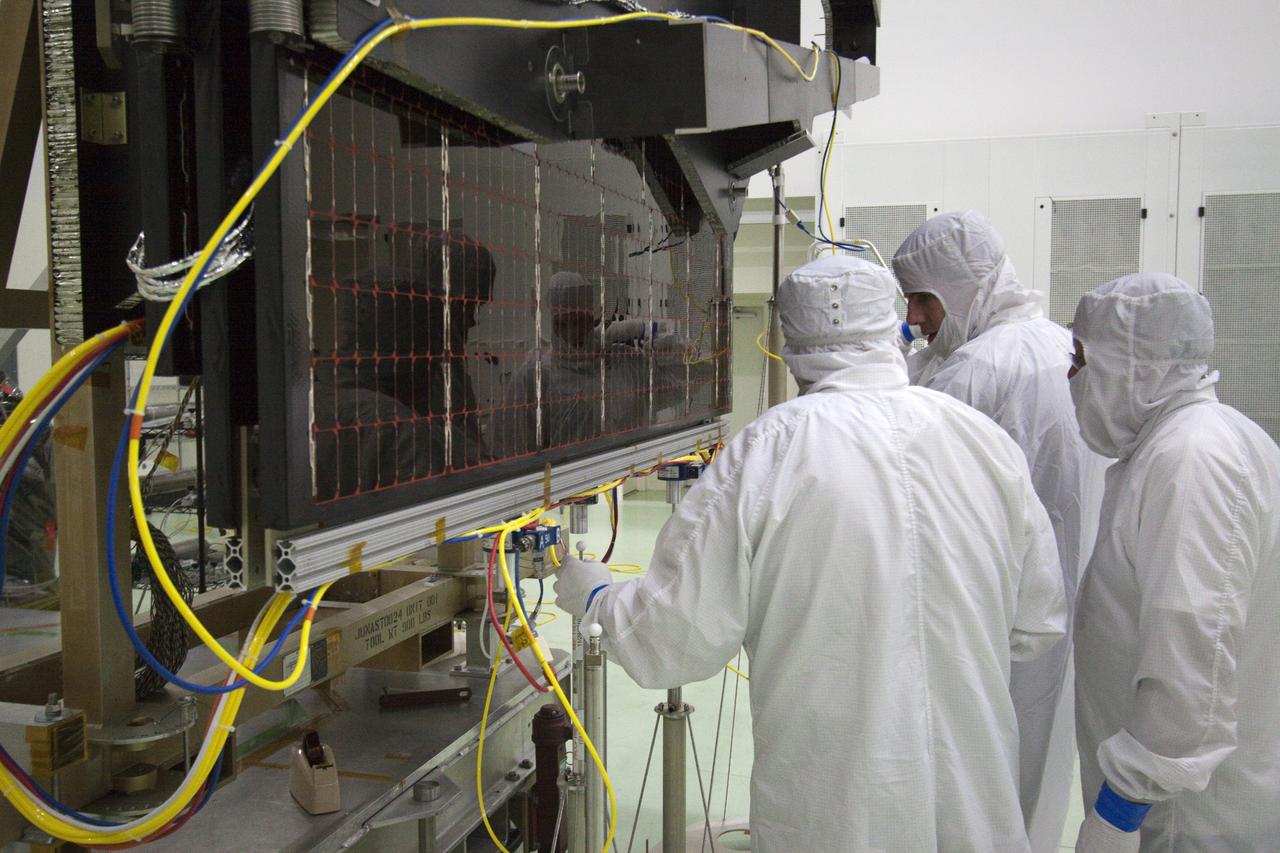

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., begin to unfurl solar array No. 1 with a magnetometer boom that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
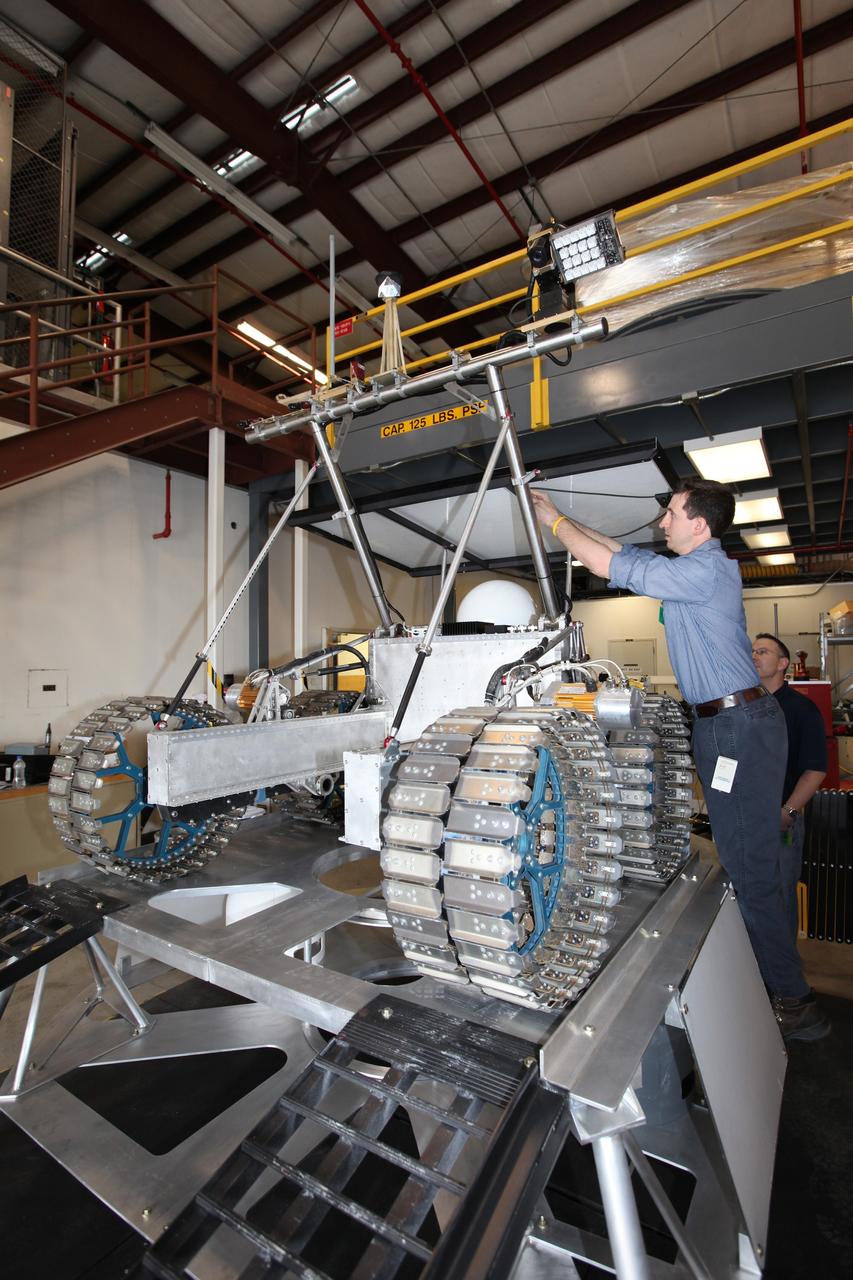

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Nick Cristello, an engineer with Neptec, a contractor to the Canadian Space Agency, attaches navigation-related wiring on the prototype rover Artemis Jr. in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida before conducting a dry run. The rover is one component of NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project and is positioned atop RESOLVE’s prototype lander. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
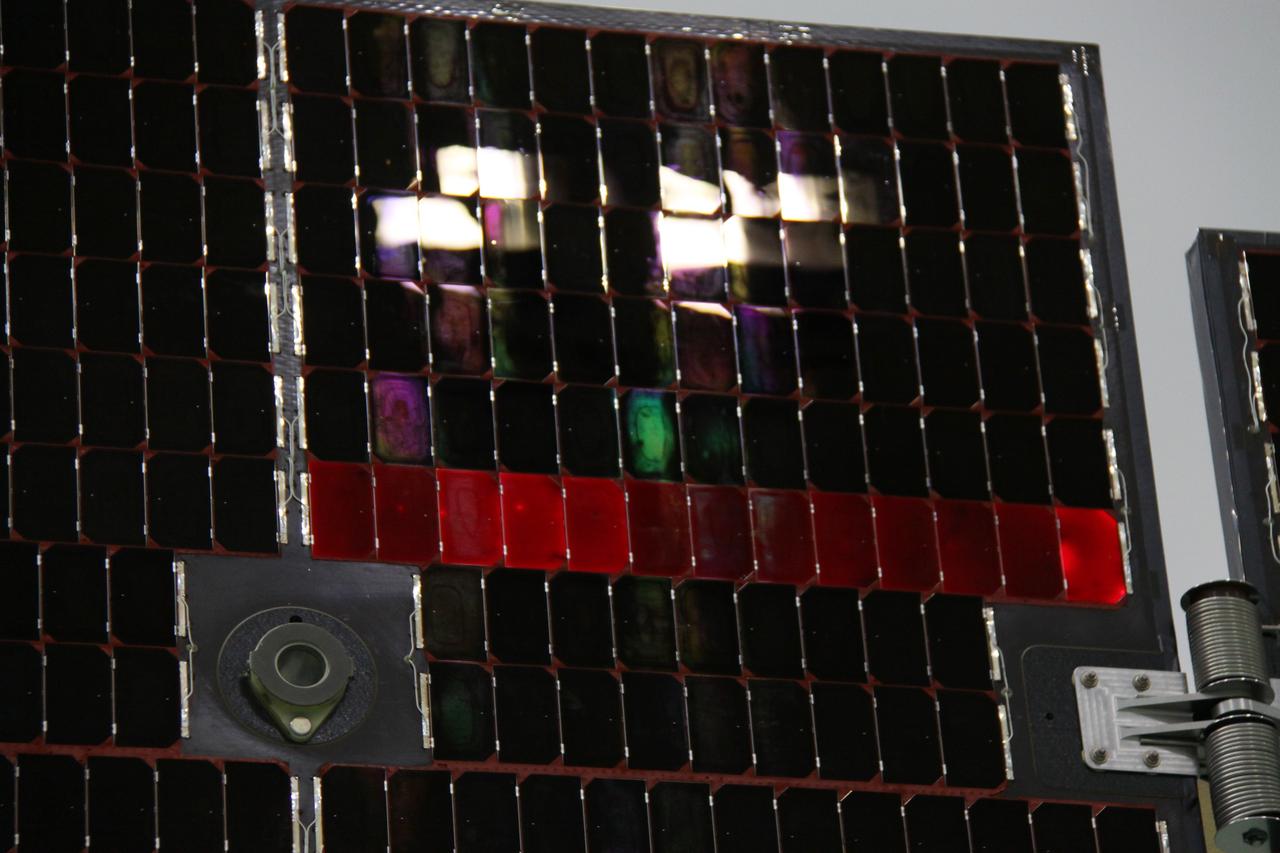
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The electrical continuity of a solar array that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter is tested in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
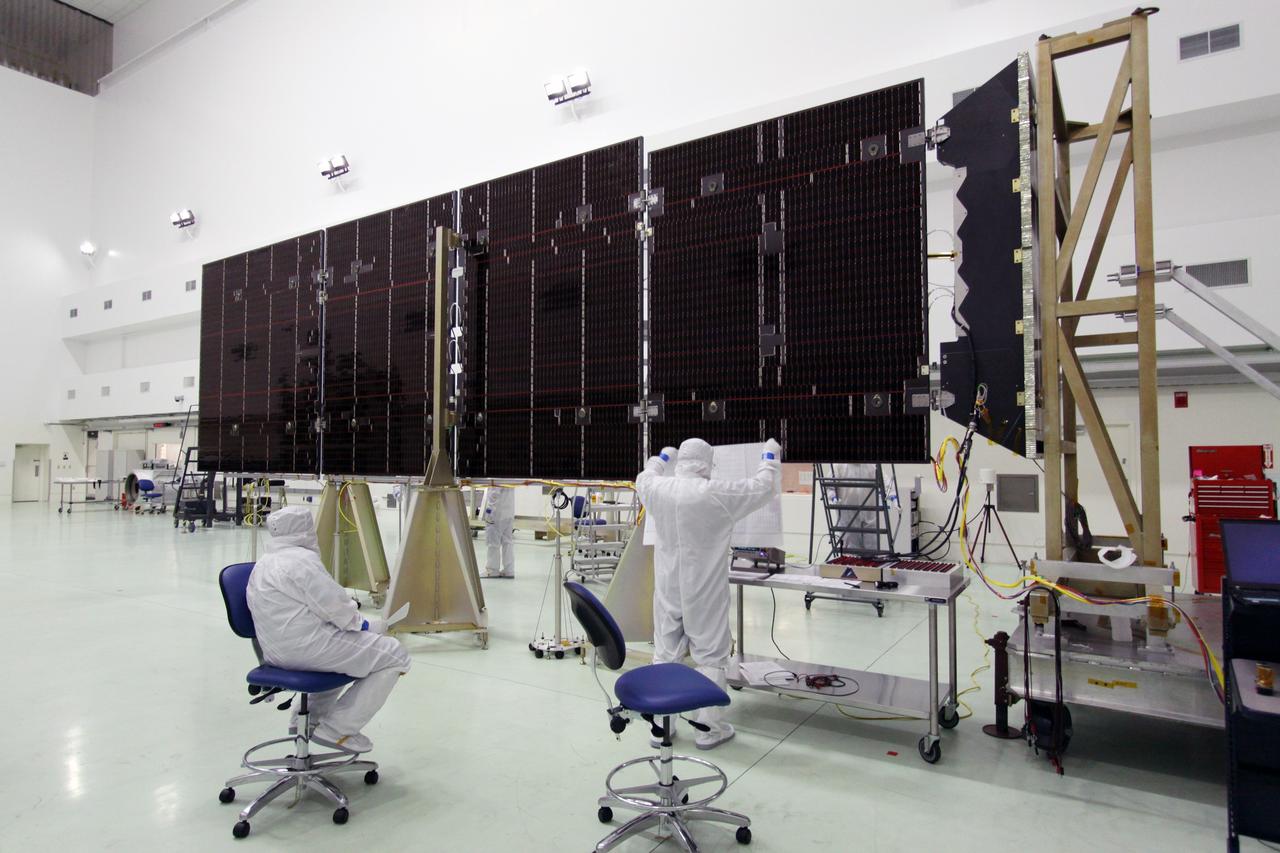

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., prepare to test the electrical continuity of a solar array that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
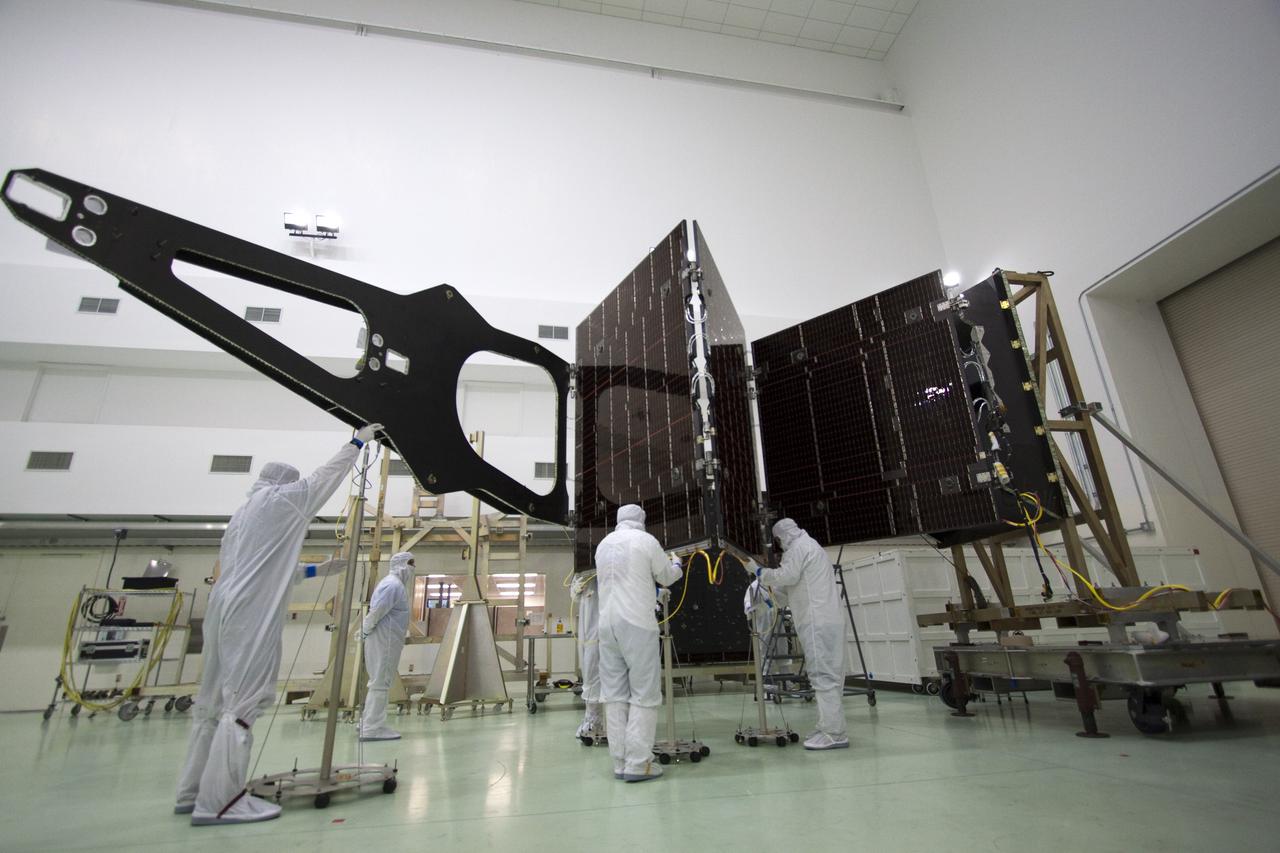

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., unfurl solar array No. 1 with a magnetometer boom that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
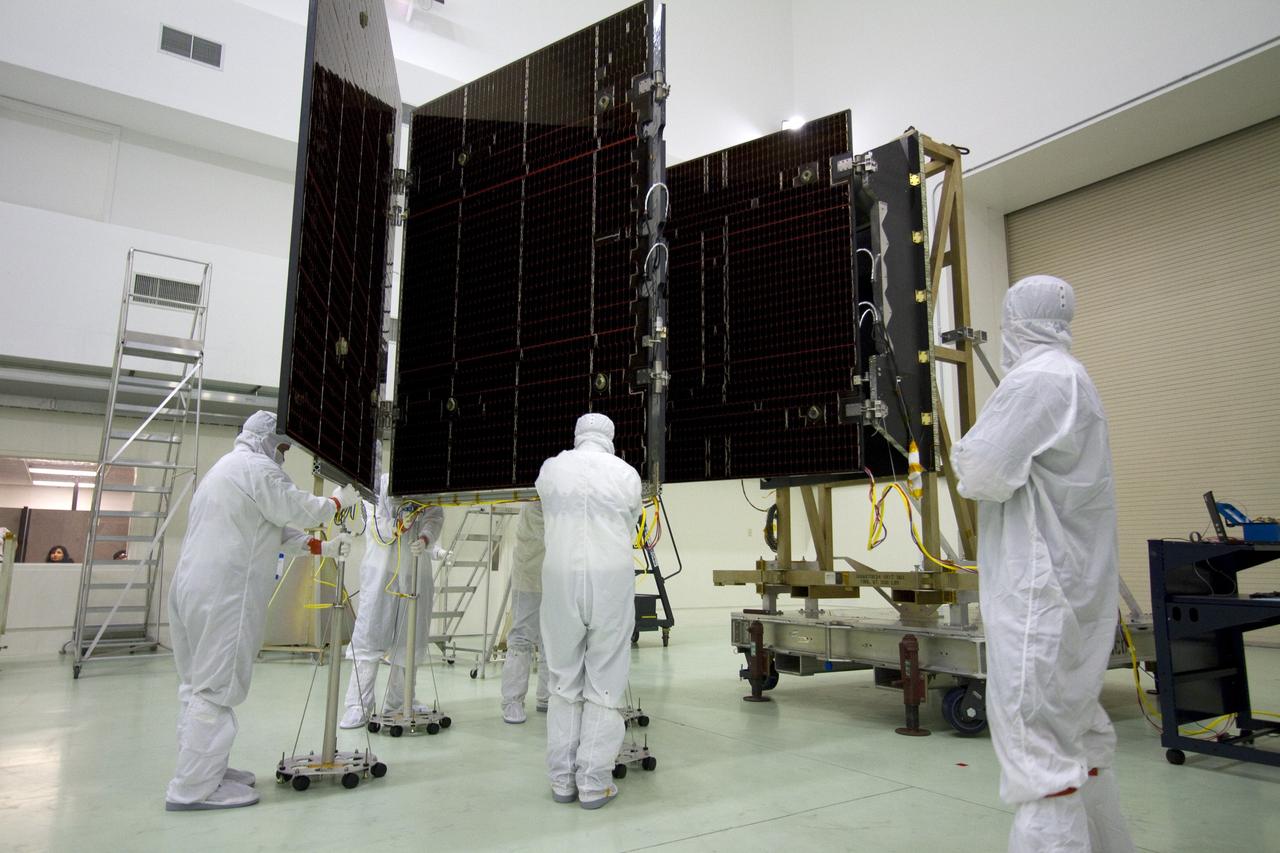

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., begin to unfurl a solar panel that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
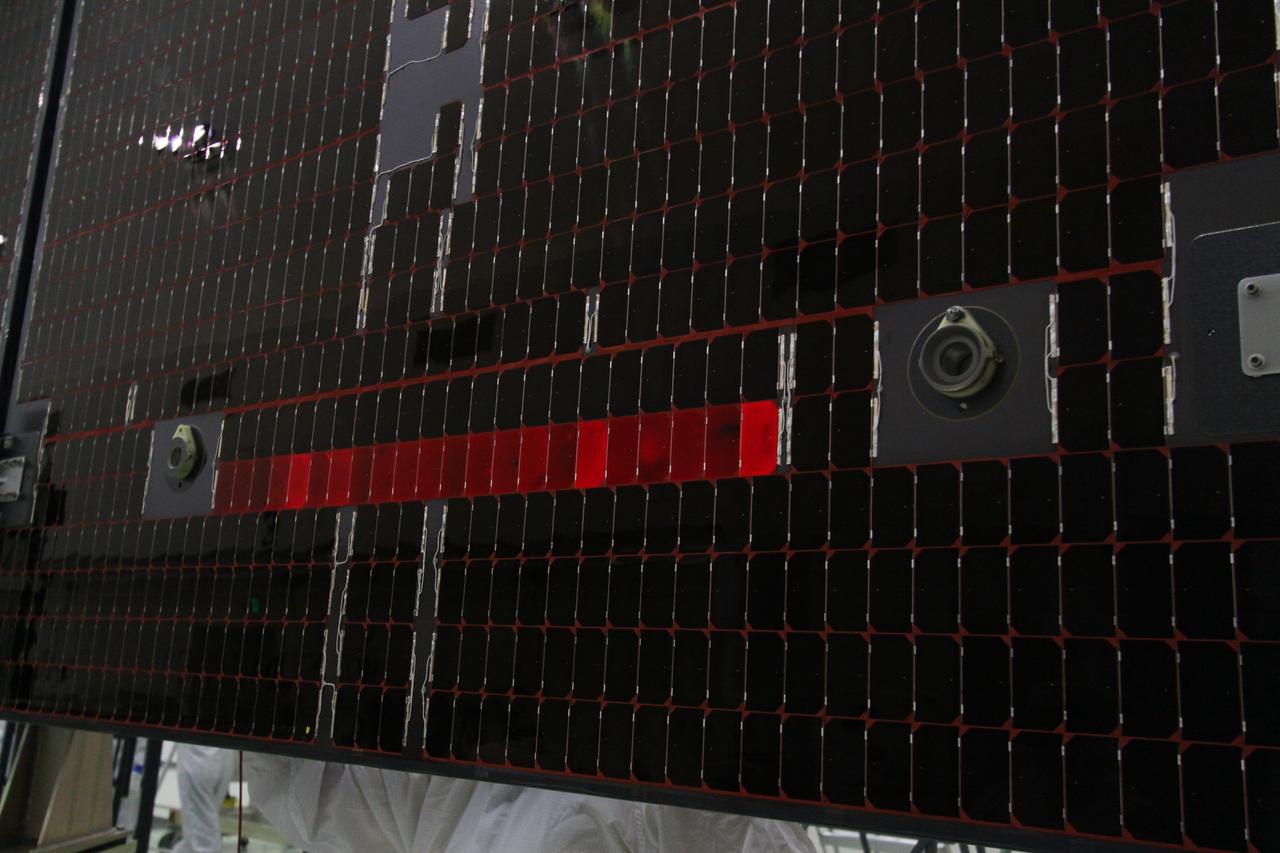

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- The electrical continuity of a solar array that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter is tested in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
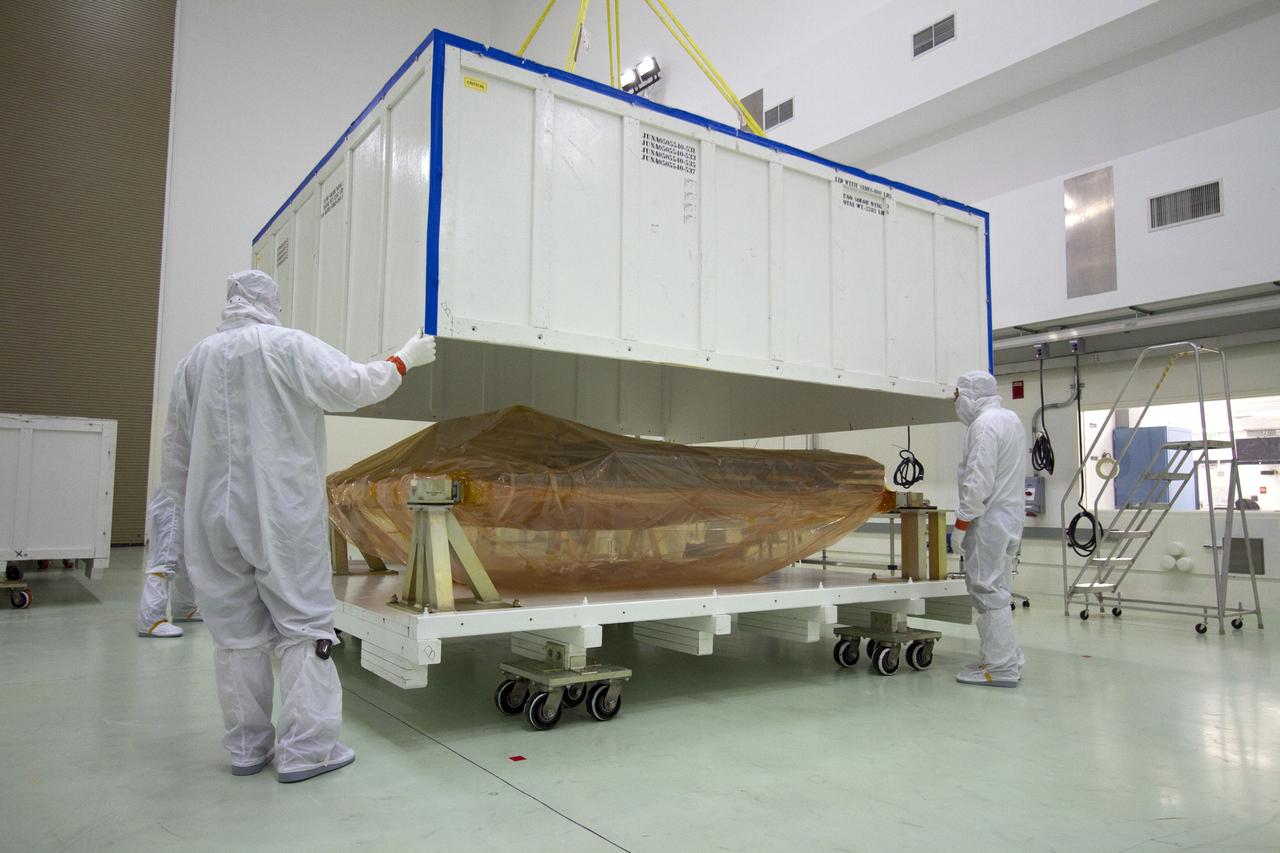

TITUSVILLE, Fla. -- A solar panel that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter is unpacked in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., test the electrical continuity of a solar array that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

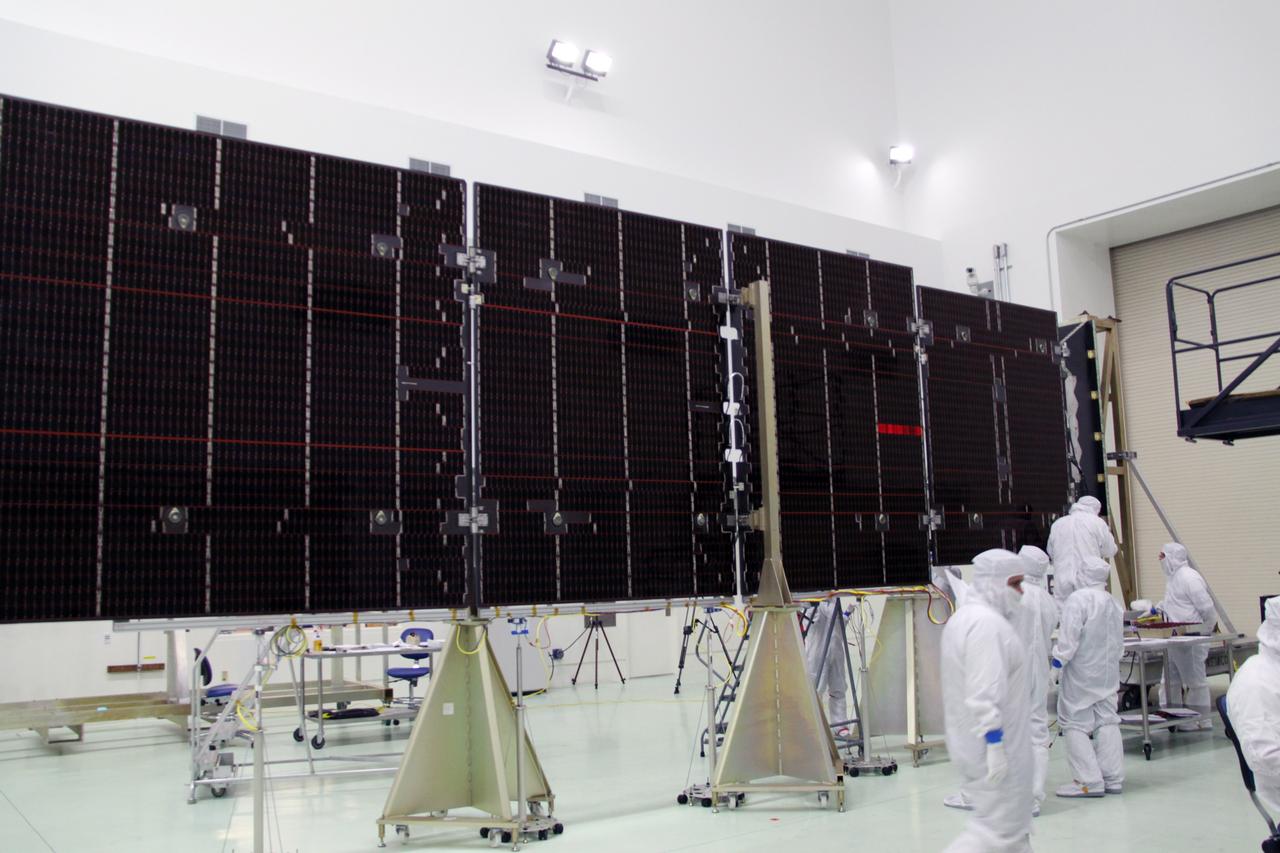
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., unfurl solar array No. 1 with a magnetometer boom that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
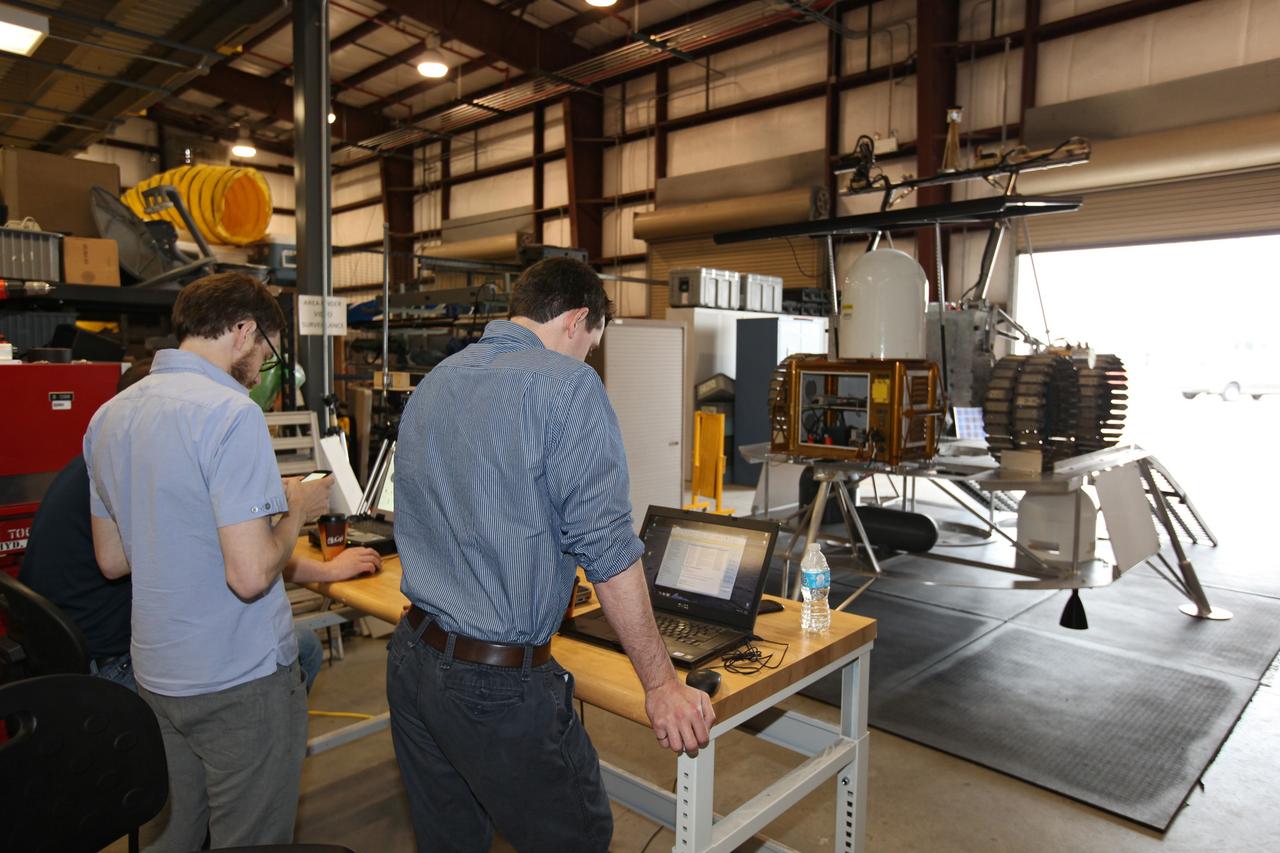

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Engineers with Neptec, a contractor to the Canadian Space Agency, prepare to conduct checkouts of the prototype rover Artemis Jr. for NASA’s Regolith and Environment Science and Oxygen and Lunar Volatile Extraction, or RESOLVE, project in a test facility behind the Operations and Checkout Building at NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida. The rover is positioned atop RESOLVE’s prototype lander. RESOLVE consists of a rover and drill provided by the Canadian Space Agency to support a NASA payload that is designed to prospect for water, ice and other lunar resources. RESOLVE also will demonstrate how future explorers can take advantage of resources at potential landing sites by manufacturing oxygen from soil. NASA will conduct field tests in July outside of Hilo, Hawaii, with equipment and concept vehicles that demonstrate how explorers might prospect for resources and make their own oxygen for survival while on other planetary bodies. For more information, visit http://www.nasa.gov/exploration/analogs/index.html. Photo credit: NASA/Dimitri Gerondidakis
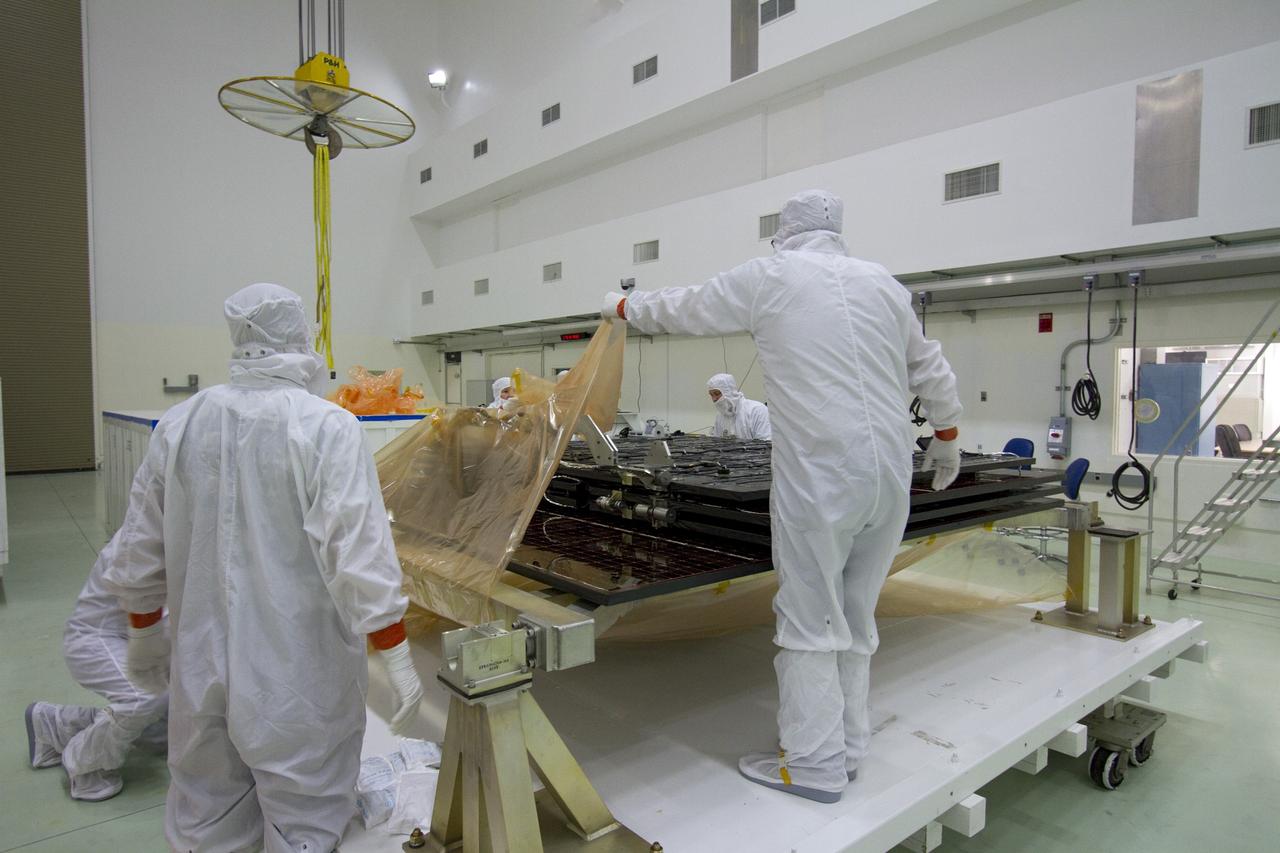

TITUSVILLE, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., unpack a solar panel that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
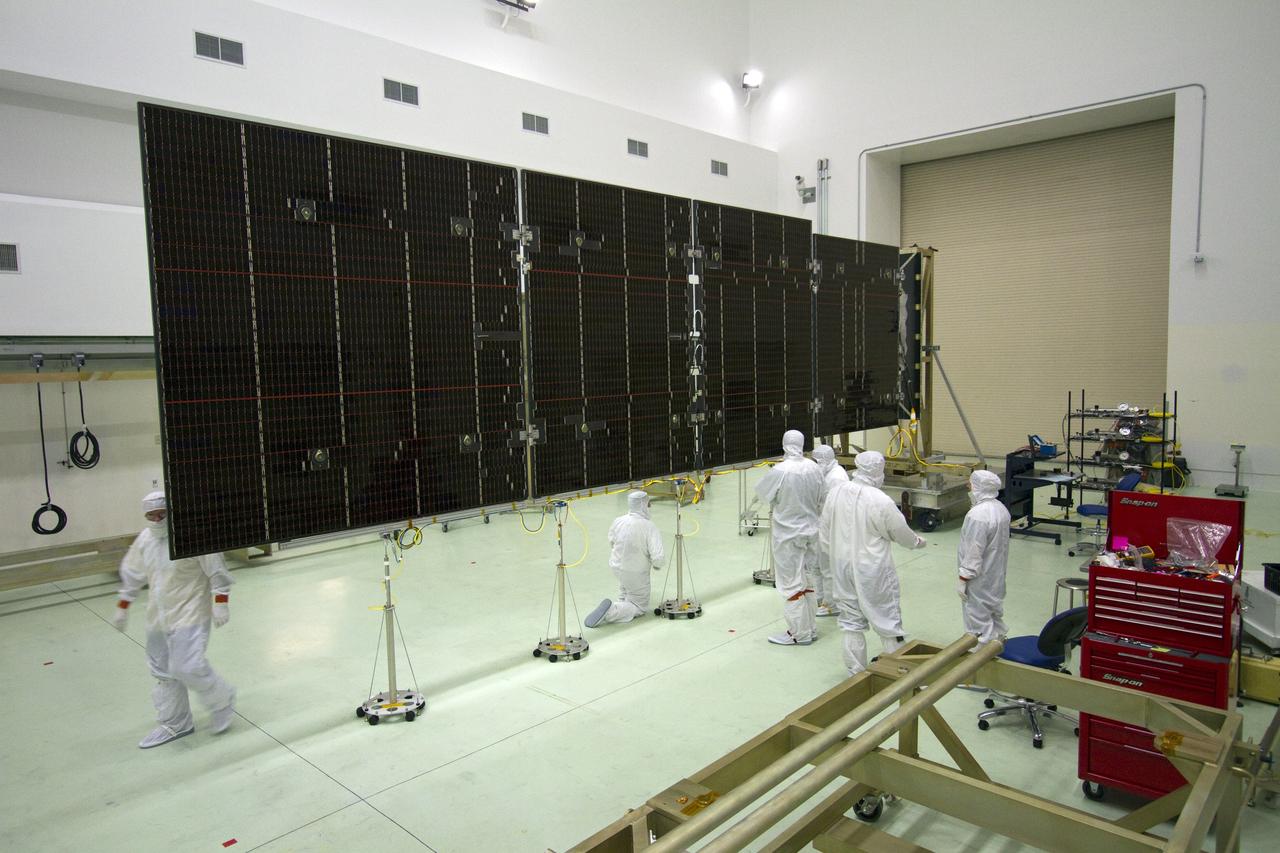

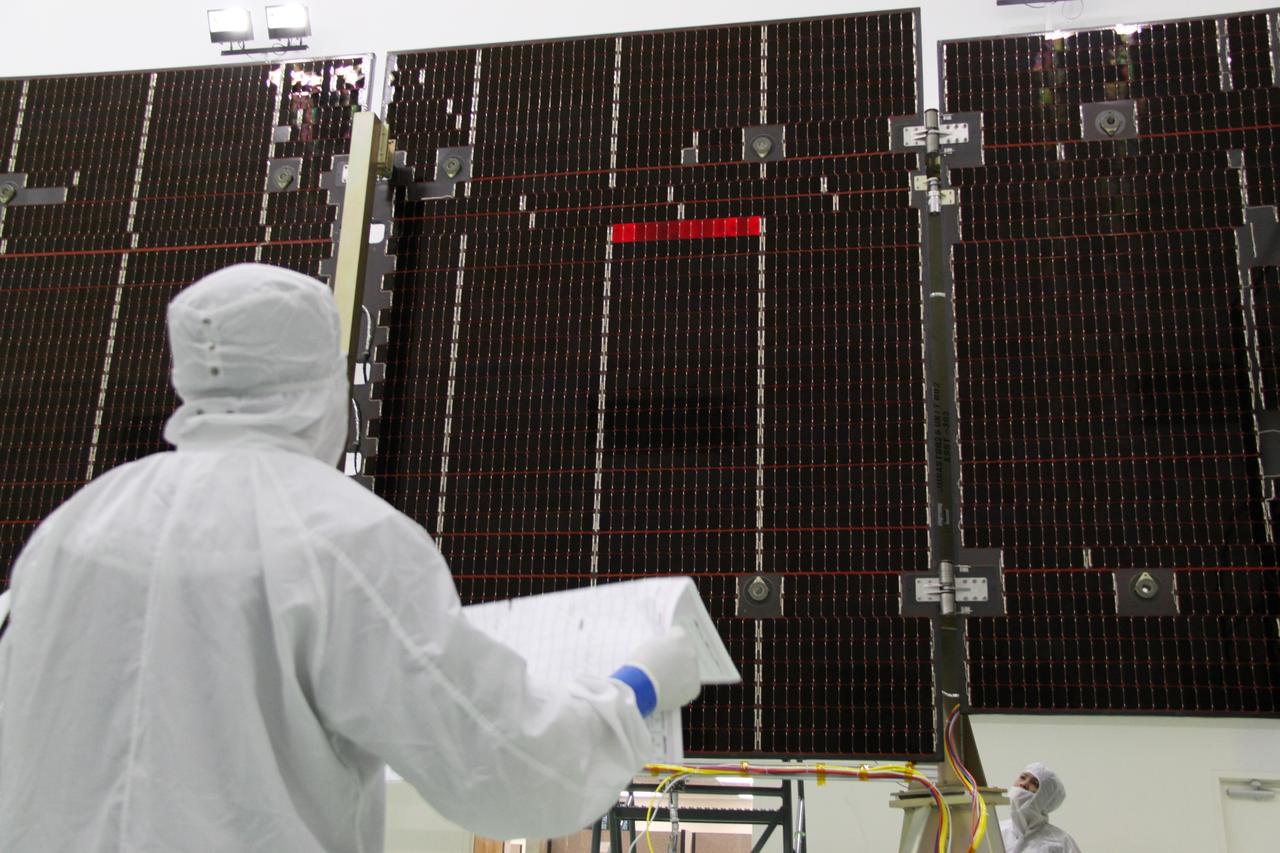
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., check out an unfurled solar panel that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., begin processing a solar panel that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
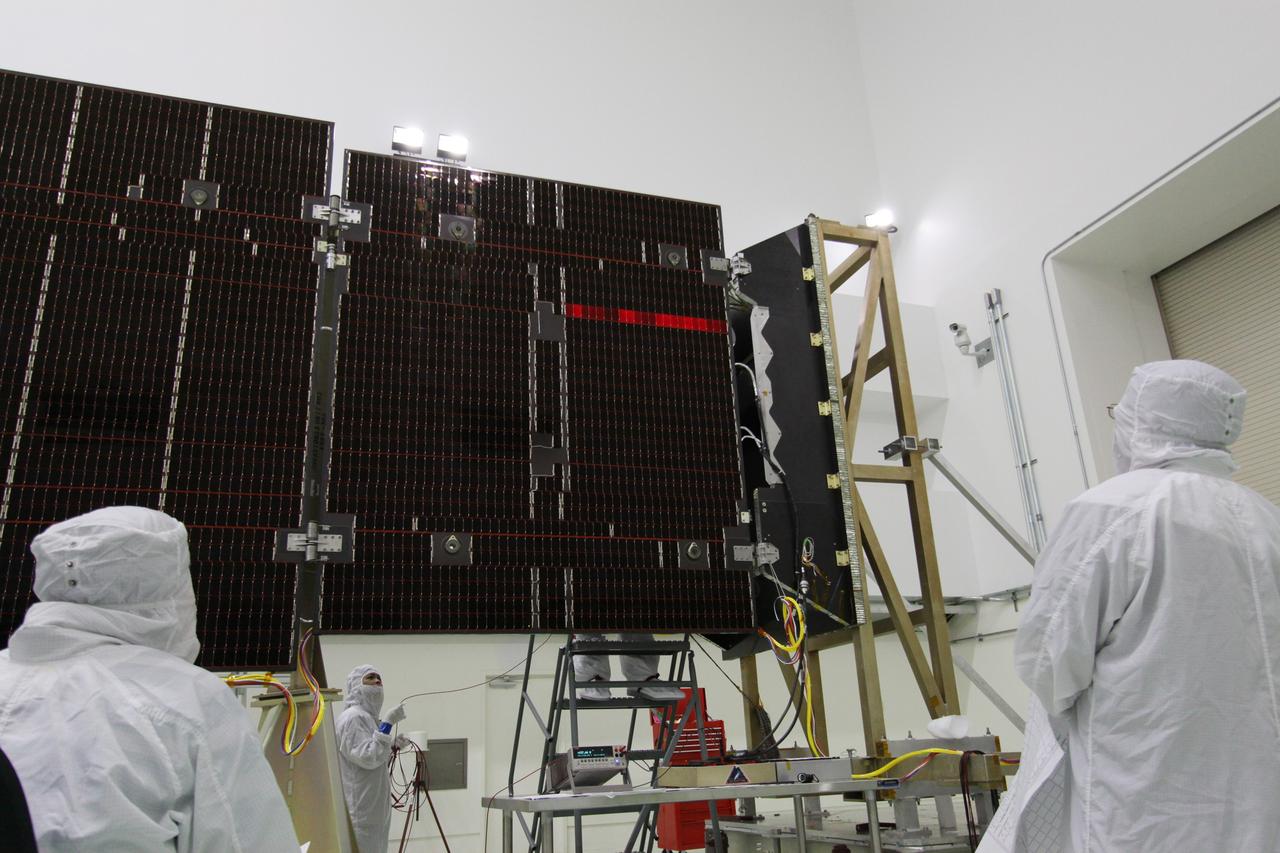

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., test the electrical continuity of a solar array that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
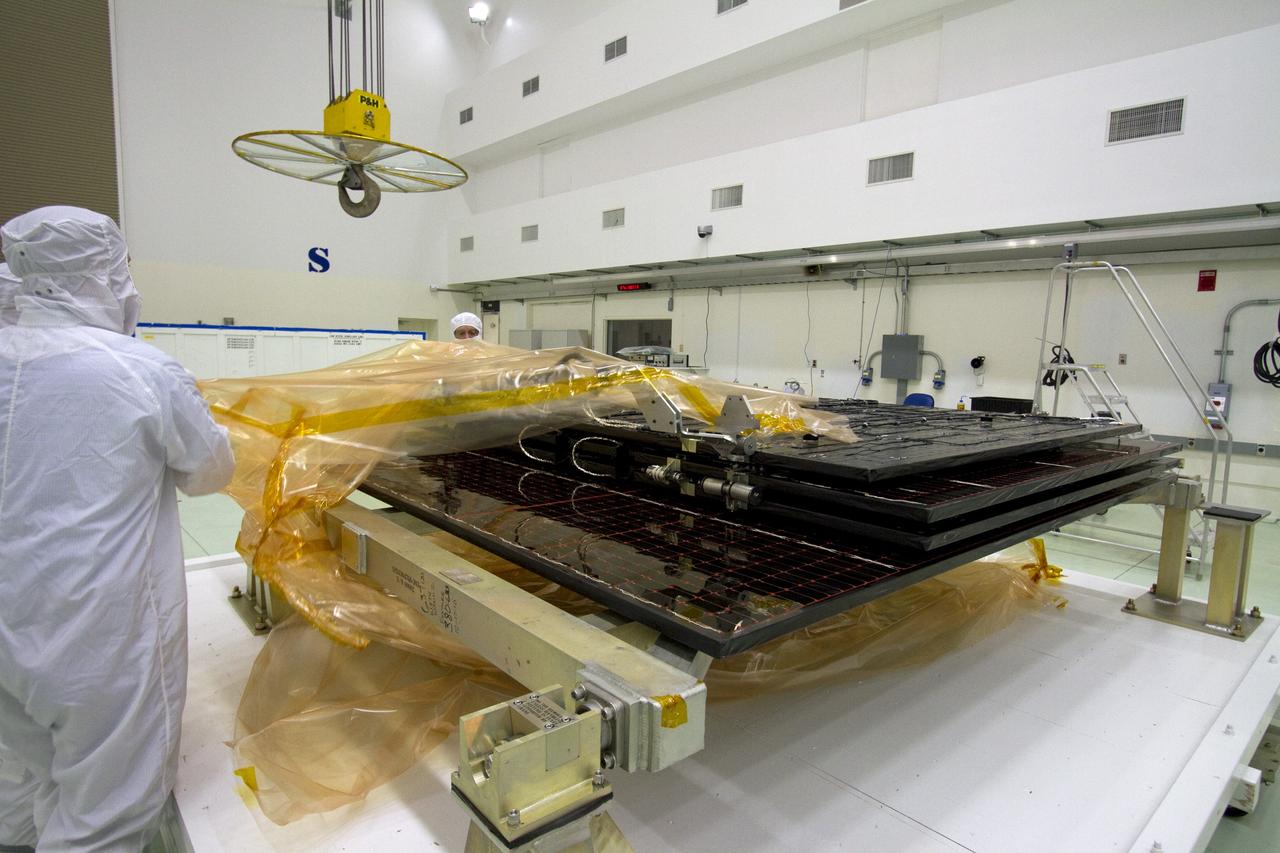

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. -- Technicians in the Astrotech payload processing facility in Titusville, Fla., unpack a solar panel that will help power NASA's Juno spacecraft on a mission to Jupiter. Power-generating panels on three sets of solar arrays will extend outward from Juno’s hexagonal body, giving the overall spacecraft a span of more than 66 feet in order to operate at such a great distance from the sun. Juno is scheduled to launch aboard an Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral, Fla., on Aug. 5, 2011, reaching Jupiter in July 2016. The spacecraft will orbit the giant planet more than 30 times, skimming to within 3,000 miles above its cloud tops, for about one year. With its suite of science instruments, the spacecraft will investigate the existence of a solid planetary core, map Jupiter's intense magnetic field, measure the amount of water and ammonia in the deep atmosphere, and observe the planet's auroras. For more information visit, www.nasa.gov/juno. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
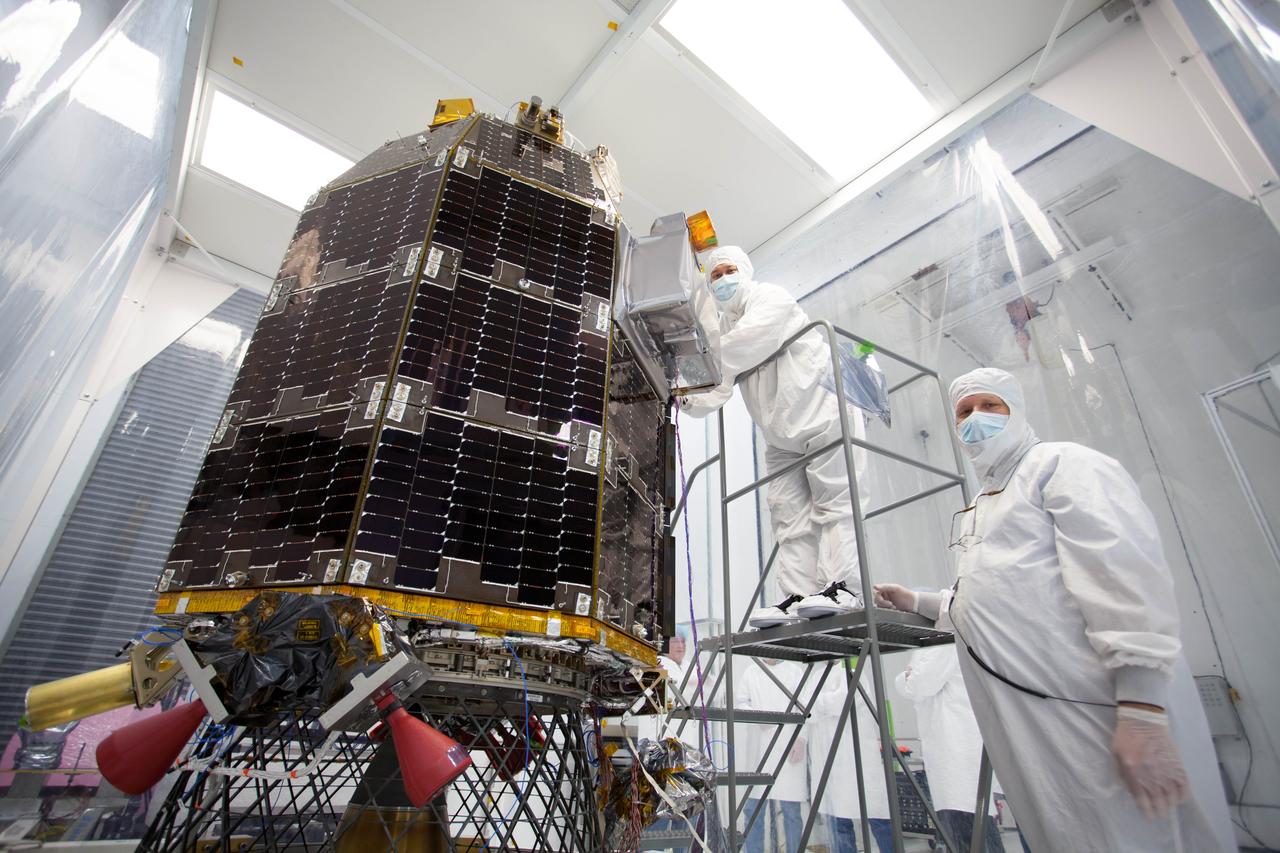

Engineers at NASA's Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, Calif., prepare NASA's Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) Observatory for acoustic environmental testing. Credit: NASA/Ames ----- What is LADEE? The Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) is designed to study the Moon's thin exosphere and the lunar dust environment. An "exosphere" is an atmosphere that is so thin and tenuous that molecules don't collide with each other. Studying the Moon's exosphere will help scientists understand other planetary bodies with exospheres too, like Mercury and some of Jupiter's bigger moons. The orbiter will determine the density, composition and temporal and spatial variability of the Moon's exosphere to help us understand where the species in the exosphere come from and the role of the solar wind, lunar surface and interior, and meteoric infall as sources. The mission will also examine the density and temporal and spatial variability of dust particles that may get lofted into the atmosphere. The mission also will test several new technologies, including a modular spacecraft bus that may reduce the cost of future deep space missions and demonstrate two-way high rate laser communication for the first time from the Moon. LADEE now is ready to launch when the window opens on Sept. 6, 2013. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/ladee" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/ladee</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
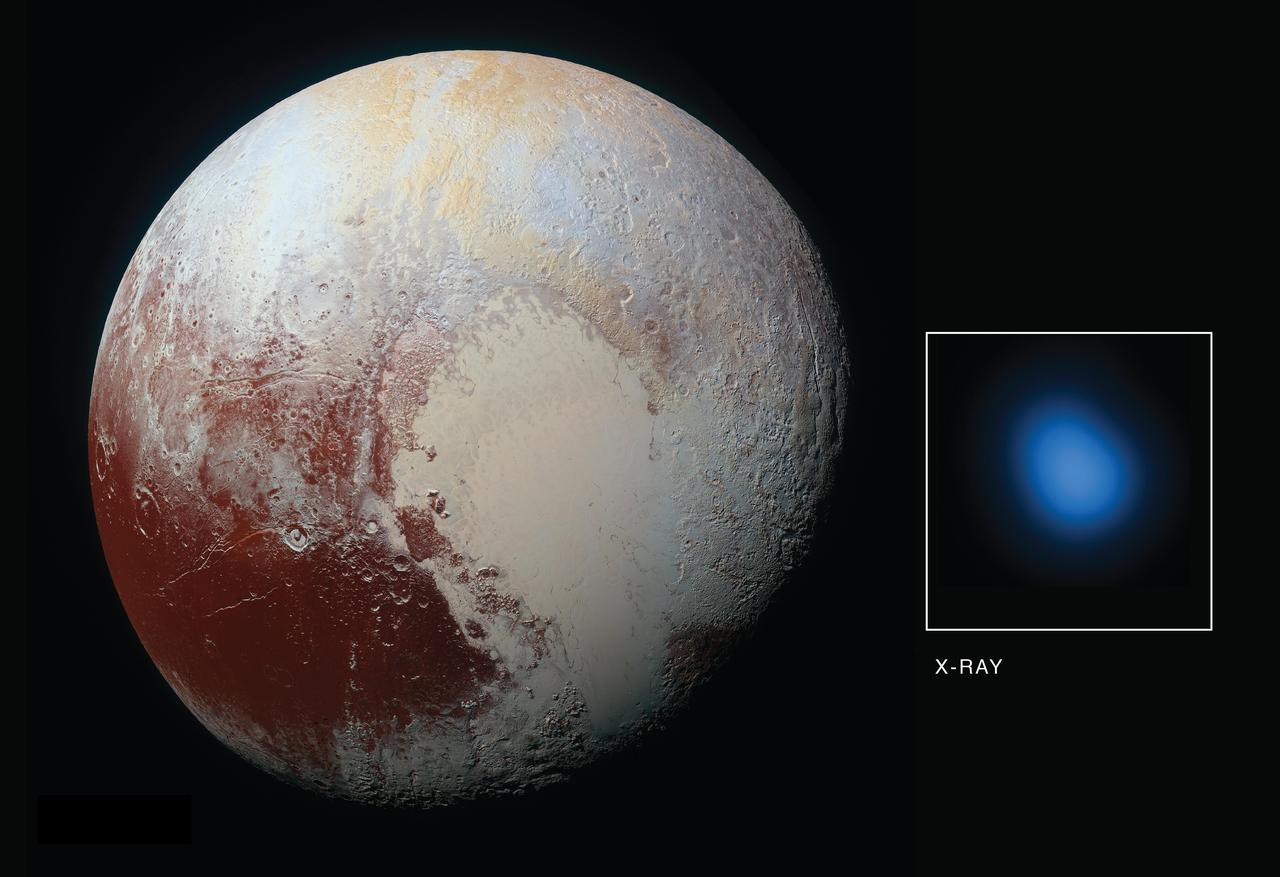

The first detection of Pluto in X-rays has been made using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory in conjunction with observations from NASA's New Horizons spacecraft. As New Horizons approached Pluto in late 2014 and then flew by the planet during the summer of 2015, Chandra obtained data during four separate observations. During each observation, Chandra detected low-energy X-rays from the small planet. The main panel in this graphic is an optical image taken from New Horizons on its approach to Pluto, while the inset shows an image of Pluto in X-rays from Chandra. There is a significant difference in scale between the optical and X-ray images. New Horizons made a close flyby of Pluto but Chandra is located near the Earth, so the level of detail visible in the two images is very different. The Chandra image is 180,000 miles across at the distance of Pluto, but the planet is only 1,500 miles across. Pluto is detected in the X-ray image as a point source, showing the sharpest level of detail available for Chandra or any other X-ray observatory. This means that details over scales that are smaller than the X-ray source cannot be seen here. Detecting X-rays from Pluto is a somewhat surprising result given that Pluto - a cold, rocky world without a magnetic field - has no natural mechanism for emitting X-rays. However, scientists knew from previous observations of comets that the interaction between the gases surrounding such planetary bodies and the solar wind - the constant streams of charged particles from the sun that speed throughout the solar system -- can create X-rays. The researchers were particularly interested in learning more about the interaction between the gases in Pluto's atmosphere and the solar wind. The New Horizon spacecraft carries an instrument designed to measure that activity up-close -- Solar Wind Around Pluto (SWAP) -- and scientists examined that data and proposed that Pluto contains a very mild, close-in bowshock, where the solar wind first "meets" Pluto (similar to a shock wave that forms ahead of a supersonic aircraft) and a small wake or tail behind the planet. The immediate mystery is that Chandra's readings on the brightness of the X-rays are much higher than expected from the solar wind interacting with Pluto's atmosphere. The Chandra detection is also surprising since New Horizons discovered Pluto's atmosphere was much more stable than the rapidly escaping, "comet-like" atmosphere that many scientists expected before the spacecraft flew past in July 2015. In fact, New Horizons found that Pluto's interaction with the solar wind is much more like the interaction of the solar wind with Mars, than with a comet. While Pluto is releasing enough gas from its atmosphere to make the observed X-rays, there isn't enough solar wind flowing directly at Pluto at its great distance from the Sun to make them according to certain theoretical models. There are several suggested possibilities for the enhanced X-ray emission from Pluto. These include a much wider and longer tail of gases trailing Pluto than New Horizons detected using its SWAP instrument. Because Pluto is so small compared to the size of a Chandra point source, scientists may be unable to detect such a tail in X-rays. Other possibilities are that interplanetary magnetic fields are focusing more particles than expected from the solar wind into the region around Pluto, or the low density of the solar wind in the outer solar system at the distance of Pluto could allow for the formation of a doughnut, or torus, of neutral gas centered around Pluto's orbit. It will take deeper and higher resolution images of X-rays from Pluto's environment than we currently have from Chandra to distinguish between these possibilities. http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA21061
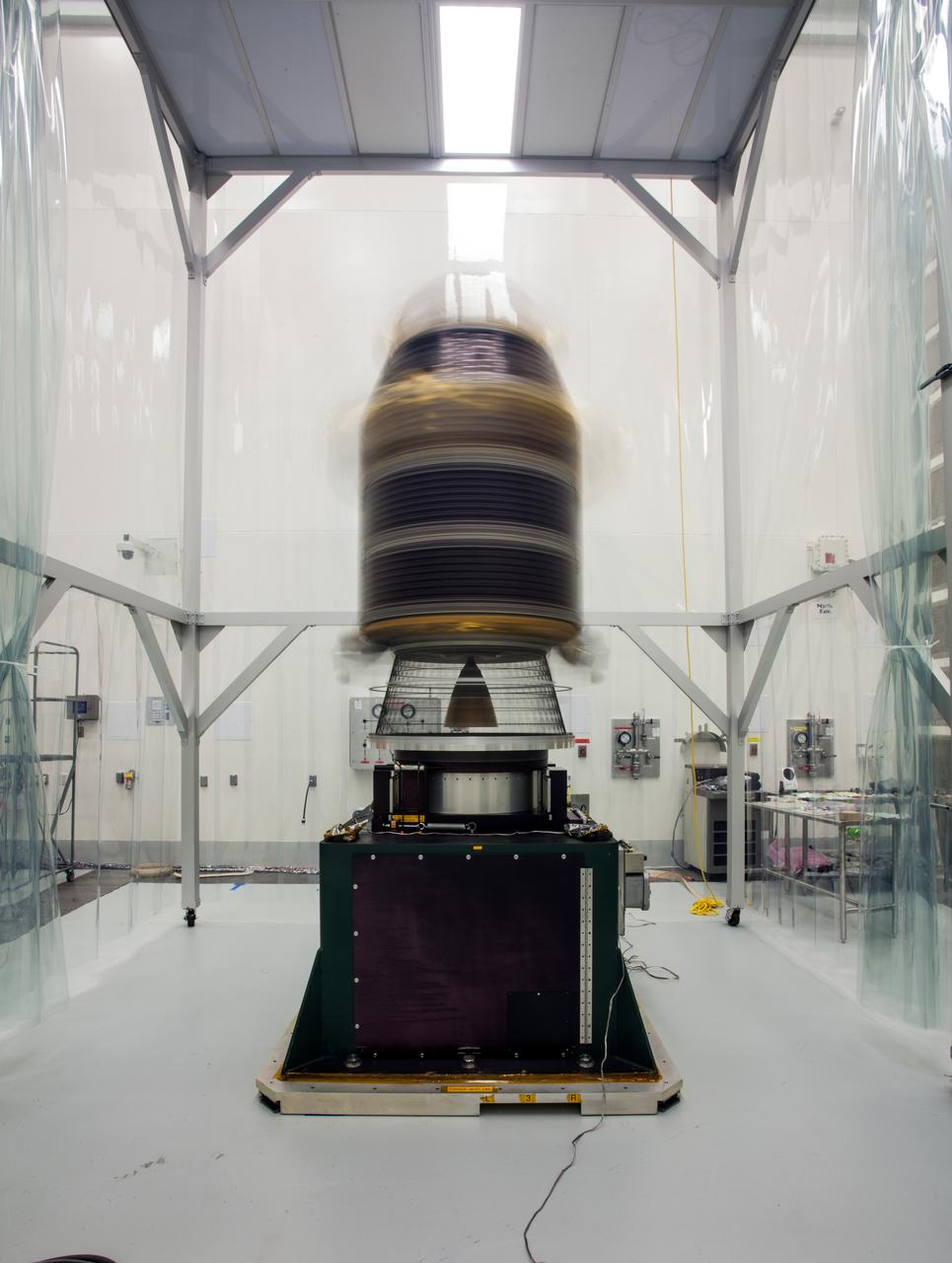

During preparations for NASA's Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) observatory launch on Sept. 6, 2013, the spacecraft went through final preparations and close-outs, which included checking alignment after its cross-country shipment, checking the propulsion system for leaks, inspecting and repairing solar panels, and final electrical tests. After these activities were completed, more challenging portions of the launch preparations began: spin testing and fueling. To make sure that the spacecraft is perfectly balanced for flight, engineers mounted it onto a spin table and rotate it at high speeds, approximately one revolution per second. The team measured any offsets during the spinning, and then added small weights to the spacecraft to balance it. Once the spacecraft was balanced dry, the team loaded the propulsion tanks with fuel, oxidizer, and pressurant. The spin testing was performed again "wet," or with fuel, in order to see if the balance changed with the full fuel tanks. Engineers from NASA's Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, Calif., have now successfully completed launch preparation activities for LADEE, which has been encapsulated into the nose-cone of the Minotaur V rocket at NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia. LADEE is ready to launch when the window opens on Friday. Image Credit: NASA ----- What is LADEE? The Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) is designed to study the Moon's thin exosphere and the lunar dust environment. An "exosphere" is an atmosphere that is so thin and tenuous that molecules don't collide with each other. Studying the Moon's exosphere will help scientists understand other planetary bodies with exospheres too, like Mercury and some of Jupiter's bigger moons. The orbiter will determine the density, composition and temporal and spatial variability of the Moon's exosphere to help us understand where the species in the exosphere come from and the role of the solar wind, lunar surface and interior, and meteoric infall as sources. The mission will also examine the density and temporal and spatial variability of dust particles that may get lofted into the atmosphere. The mission also will test several new technologies, including a modular spacecraft bus that may reduce the cost of future deep space missions and demonstrate two-way high rate laser communication for the first time from the Moon. LADEE now is ready to launch when the window opens on Sept. 6, 2013. Read more: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/ladee" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/ladee</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>
NASA's Wallops Flight Facility is located on Wallops Island, Va. and is the site of tonight's moon mission launch. Satellite imagery from NOAA's GOES-East satellite shows that high pressure remains in control over the Mid-Atlantic region, providing an almost cloud-free sky. This visible image of the Mid-Atlantic was captured by NOAA's GOES-East satellite at 17:31 UTC/1:31 p.m. EDT and shows some fair weather clouds over the Delmarva Peninsula (which consists of the state of Delaware and parts of Maryland and Virginia - which together is "Delmarva") and eastern Virginia and North Carolina. Most of the region is cloud-free, making for a perfect viewing night to see a launch. NOAA operates GOES-East and NASA's GOES Project at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md. creates images and animations from the data. NOAA's National Weather Service forecast for tonight, Sept. 6 calls for winds blowing from the east to 11 mph, with clear skies and overnight temperatures dropping to the mid-fifties. The Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer, known as LADEE (pronounced like "laddie"), launches tonight at 11:27 p.m. EDT from Pad 0B at the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport, at NASA Wallops and will be visible along the Mid-Atlantic with tonight's perfect weather conditions. LADEE is managed by NASA's Ames Research Center in Moffett Field, Calif. This will be the first launch to lunar orbit from NASA Wallops and the first launch of a Minotaur V rocket – the biggest ever launched from Wallops. NASA's LADEE is a robotic mission that will orbit the moon to gather detailed information about the lunar atmosphere, conditions near the surface and environmental influences on lunar dust. A thorough understanding of these characteristics will address long-standing unknowns, and help scientists understand other planetary bodies as well. LADEE also carries an important secondary payload, the Lunar Laser Communication Demonstration, or LLCD, which will help us open a new era of space communications by becoming NASA's first high rate, two-way, space laser system. Live coverage of the launch can be seen beginning at 9:30 p.m. EDT on NASA-TV at: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/ntv" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/ntv</a> For more information about LADEE, visit: <a href="http://www.nasa.gov/ladee" rel="nofollow">www.nasa.gov/ladee</a> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/audience/formedia/features/MP_Photo_Guidelines.html" rel="nofollow">NASA image use policy.</a></b> <b><a href="http://www.nasa.gov/centers/goddard/home/index.html" rel="nofollow">NASA Goddard Space Flight Center</a></b> enables NASA’s mission through four scientific endeavors: Earth Science, Heliophysics, Solar System Exploration, and Astrophysics. Goddard plays a leading role in NASA’s accomplishments by contributing compelling scientific knowledge to advance the Agency’s mission. <b>Follow us on <a href="http://twitter.com/NASA_GoddardPix" rel="nofollow">Twitter</a></b> <b>Like us on <a href="http://www.facebook.com/pages/Greenbelt-MD/NASA-Goddard/395013845897?ref=tsd" rel="nofollow">Facebook</a></b> <b>Find us on <a href="http://instagram.com/nasagoddard?vm=grid" rel="nofollow">Instagram</a></b>