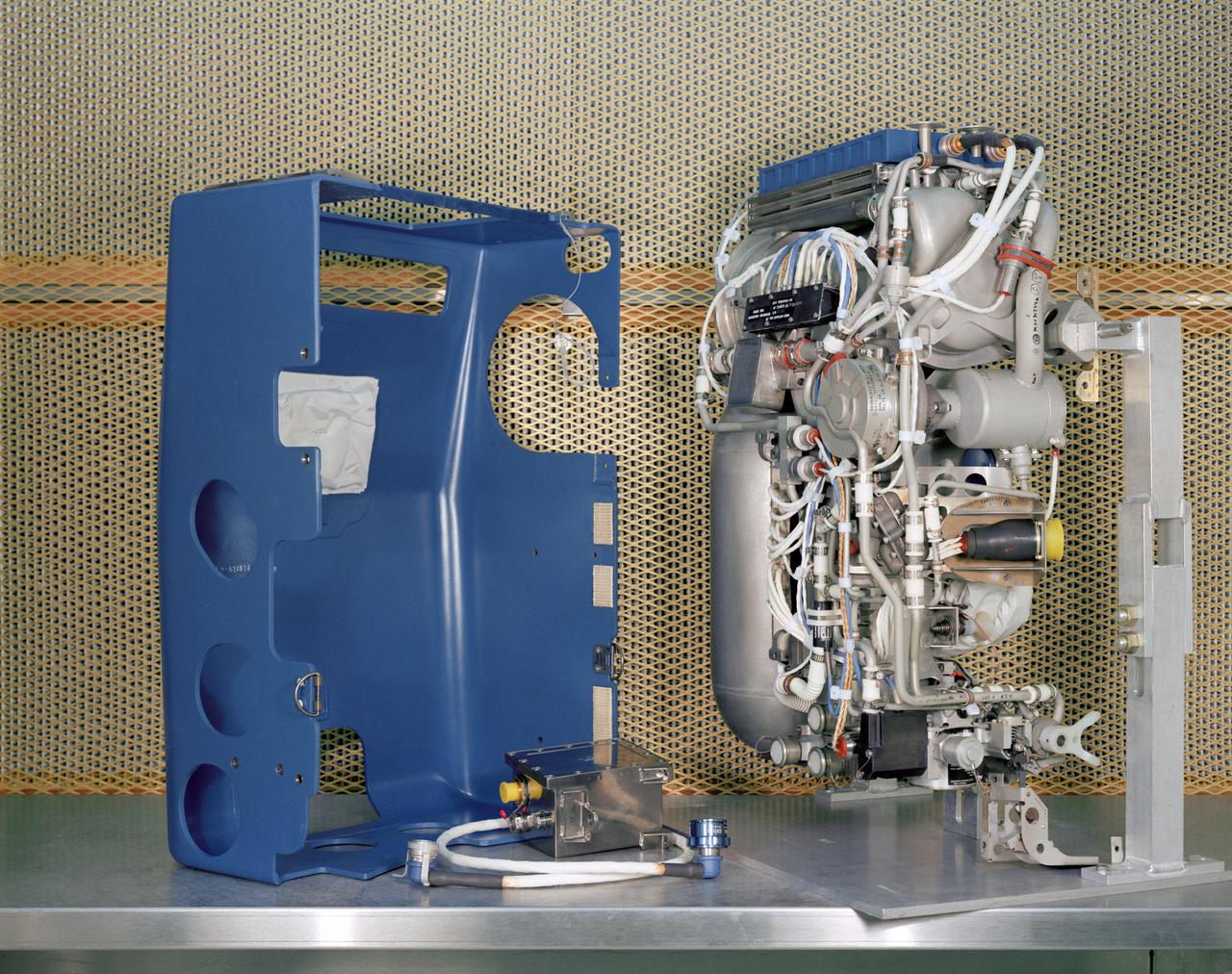
S68-34582 (1968) --- With its exterior removed, the Apollo portable life support system (PLSS) can be easily studied. The PLSS is worn as a backpack over the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) a multi-layered spacesuit used for outside-the-spacecraft activity. JSC photographic frame no. S68-34582 is a wider view of the exposed interior working parts of the PLSS and its removed cover.
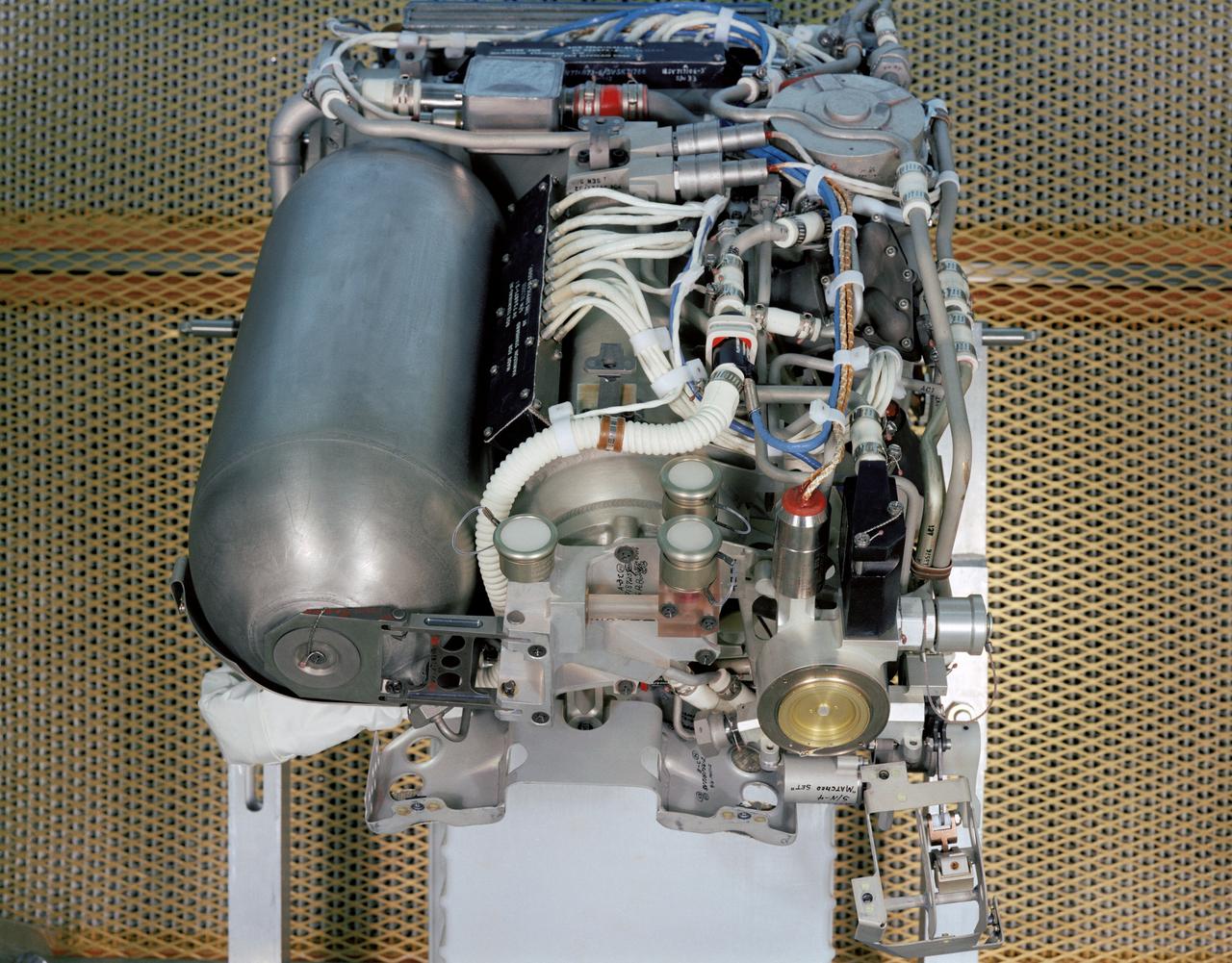
S68-34580 (1968) --- With its exterior removed, the Apollo portable life support system (PLSS) can be easily studied. The PLSS is worn as a backpack over the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), a multi-layered spacesuit used for outside-the-spacecraft activity. JSC photographic frame no. S68-34582 is a close-up view of the working parts of the PLSS.
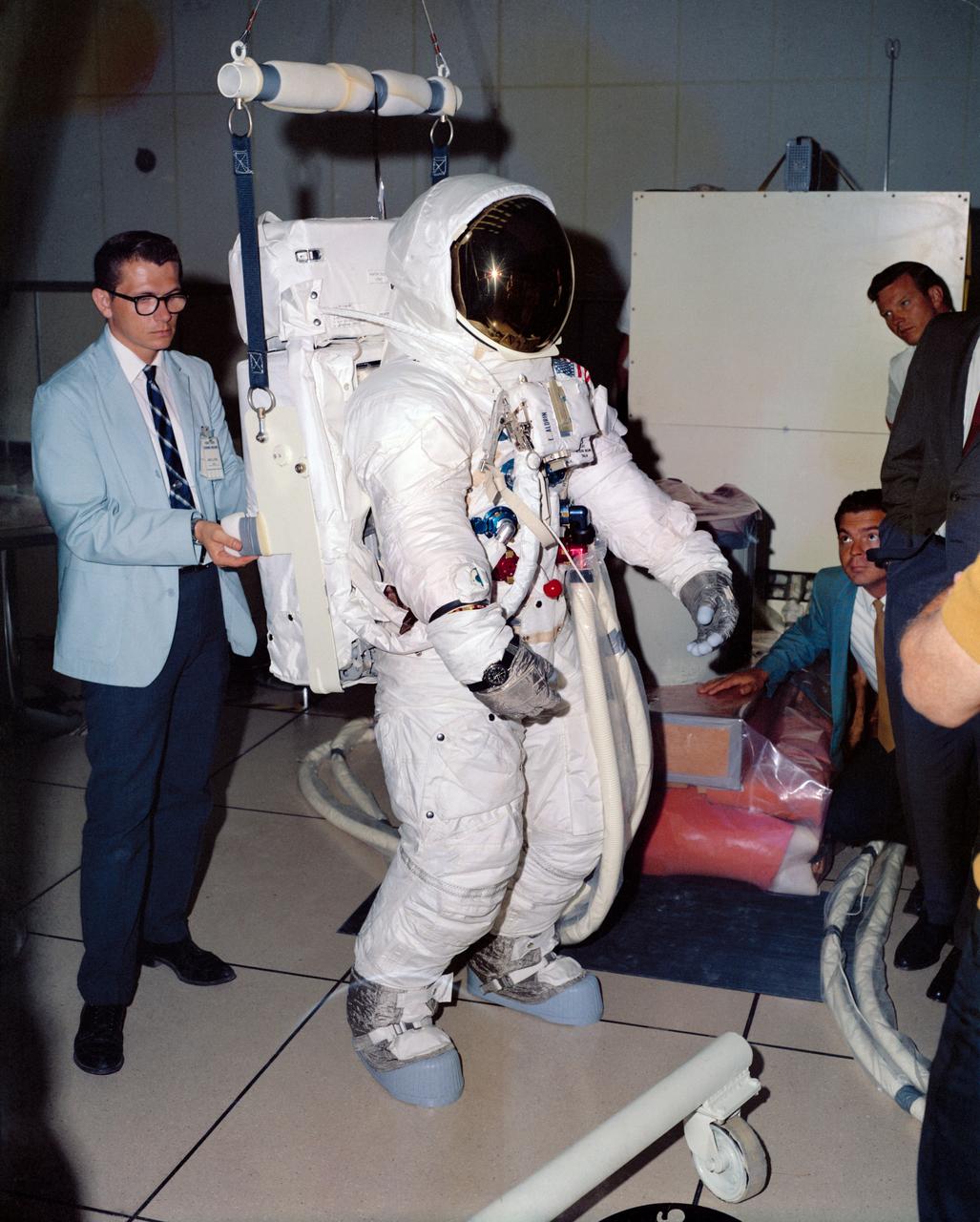

Astronaut Edwin E. Aldrin Jr., wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), verifies fit of the Portable Life Support System (PLSS) strap length during lunar surface training at the Kennedy Space Center. Aldrin is the prime crew lunar module pilot of the Apollo 11 lunar landing mission. Aldrin's PLSS backpack is attached to a lunar weight simulator.
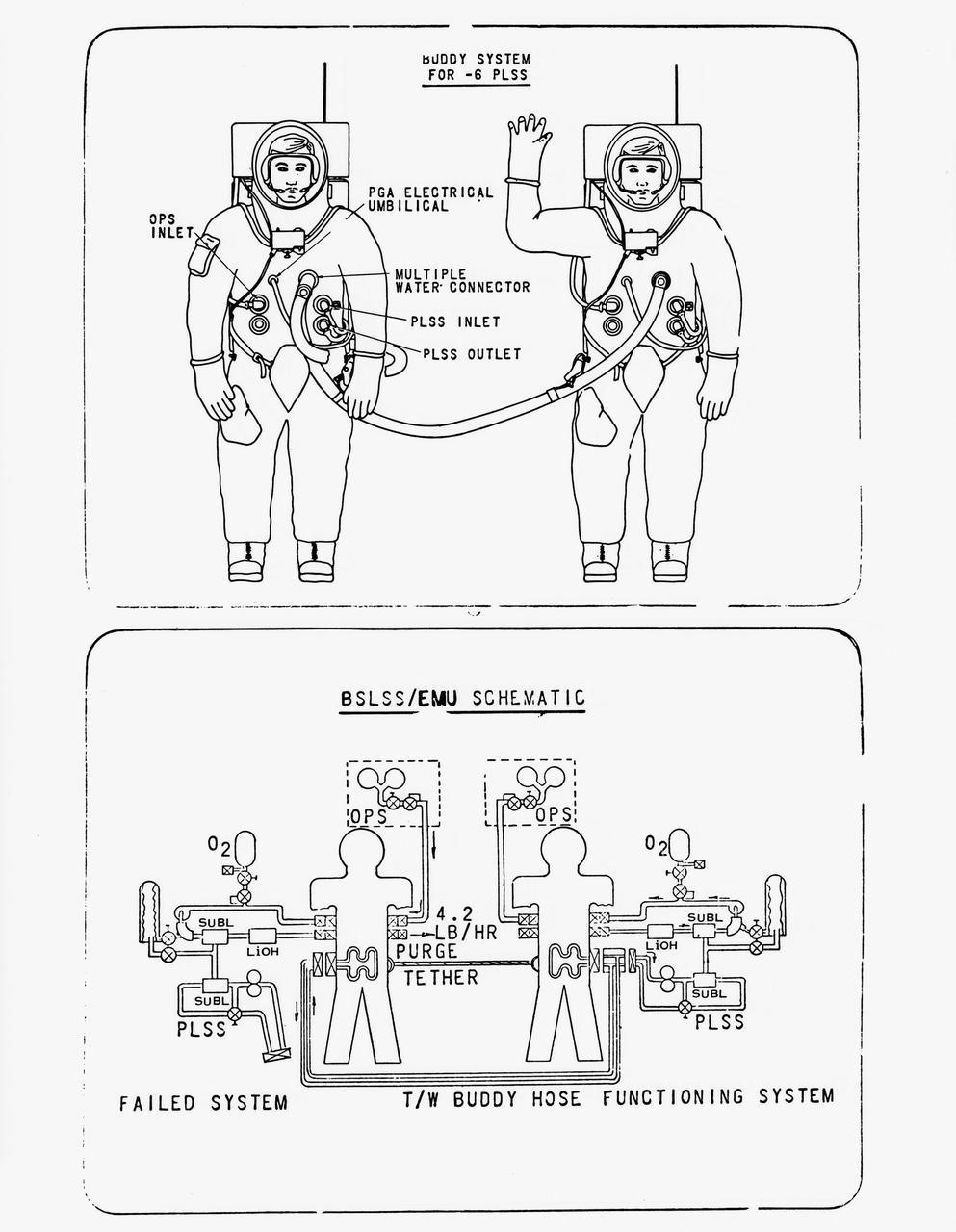
S70-56965 (December 1970) --- Drawing of the newly developed Buddy Secondary Life Support System (BSLSS). The life-sustaining system will be provided for the first time on the Apollo 14 lunar landing mission. The two flexible hoses, to be used on the second Apollo 14 extravehicular activity (EVA), will be among the paraphernalia on the Modular Equipment Transporter (MET) or two-wheeled workshop, and readily accessible in an emergency. During EVAs the Portable Life Support System (PLSS) supplies the astronaut with breathing and suit-pressurizing oxygen and water flow for the liquid-cooling garment -- a suit of knitted long underwear with thin tubing woven in the torso and limbs. The tubes carry water from a reservoir in the PLSS, and the circulating water serves to carry the astronaut's metabolic heat to a heat exchanger in the PLSS. Before the BSLSS was devised, the emergency tank was required to furnish not only suit pressure and breathing oxygen, but also cooling through a high oxygen flow rate. The BSLSS, by sharing the water supply between the two crewmen, stretches the time of the emergency oxygen from about 40 minutes to 60 to 75 minutes.

Labeled cutaway line drawing of the Shuttle extravehicular mobility unit (EMU) identifies its various components and equipment. The portable life support system (PLSS) and protective layers of fabric (thermal micrometeoroid garment (TMG)) incorporated in this extravehicular activity (EVA) space suit are shown.
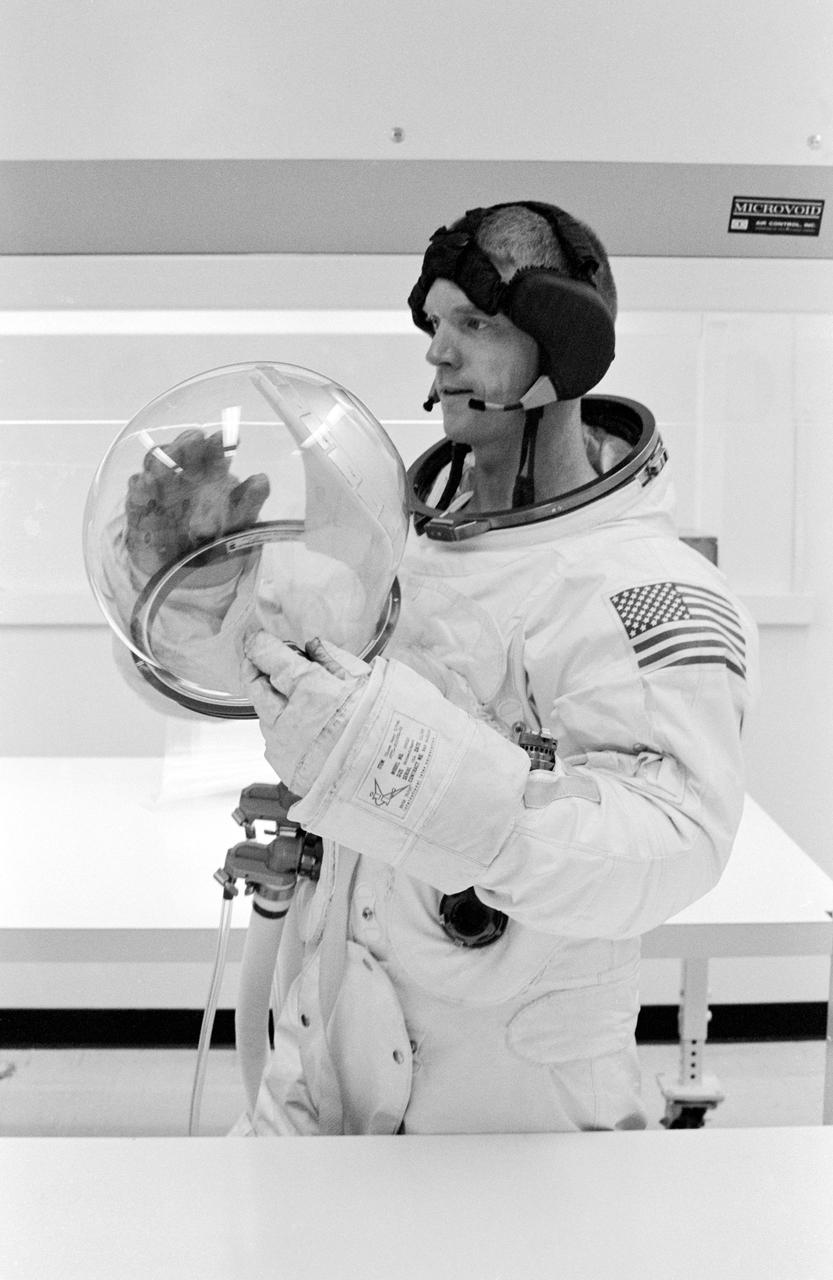

S68-38051 (29 June 1968) --- Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart suits up to participate in an altitude verification test of the Apollo Portable Life Support System flight unit in Crew Systems Division's 8-ft altitude chamber in Building 7.
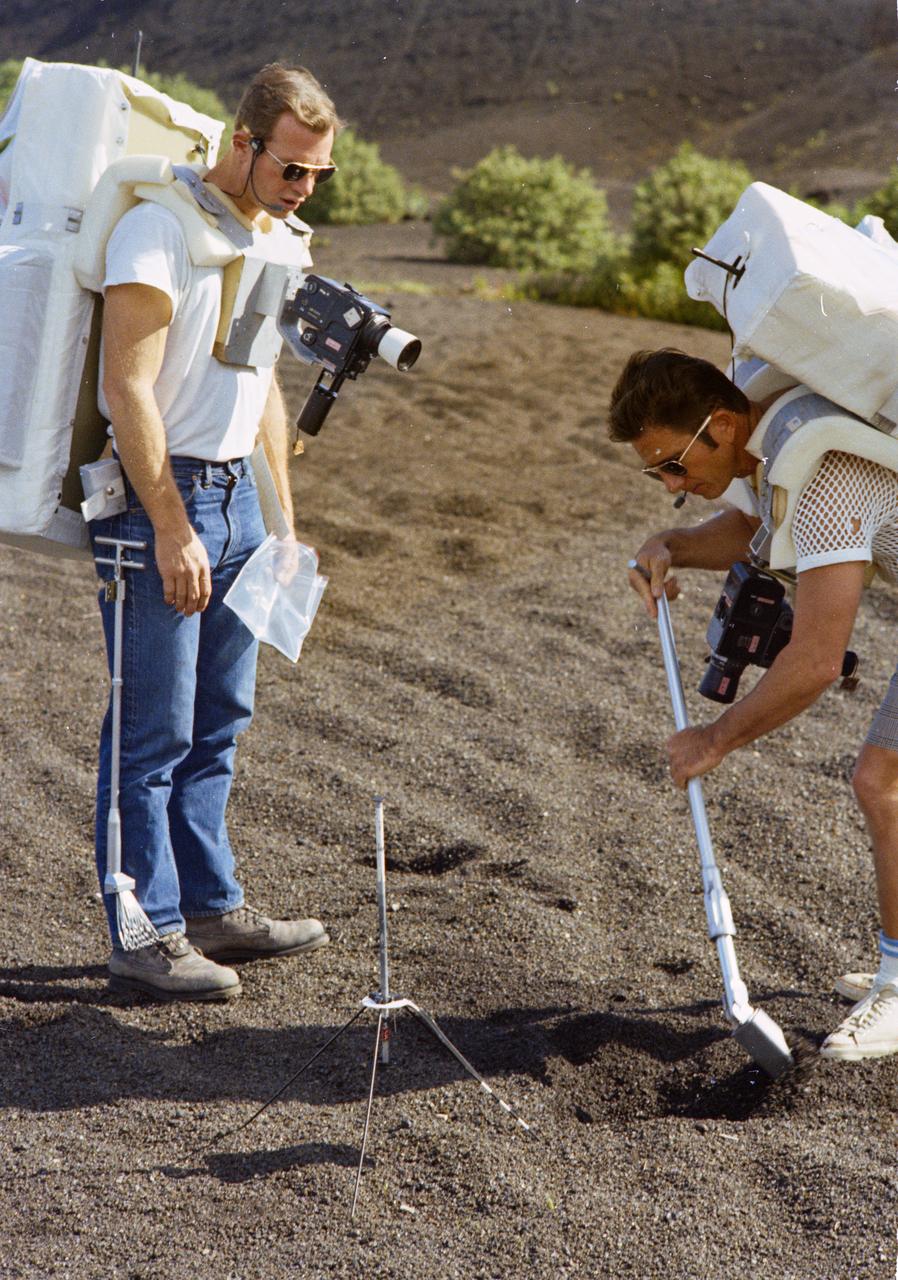

S70-56415 (December 1970) --- At Kapoho, Hawaii, astronauts David R. Scott (left), commander of the Apollo 15 lunar landing mission, and James B. Irwin, lunar module pilot, train at a designated lunar surface simulation area for their upcoming lunar landing mission. Wearing street clothes, but equipped with a Portable Life Support System (PLSS), the two rehearse for a selenological traverse. Here, they are inspecting a grapefruit-sized rock. Photo credit: NASA
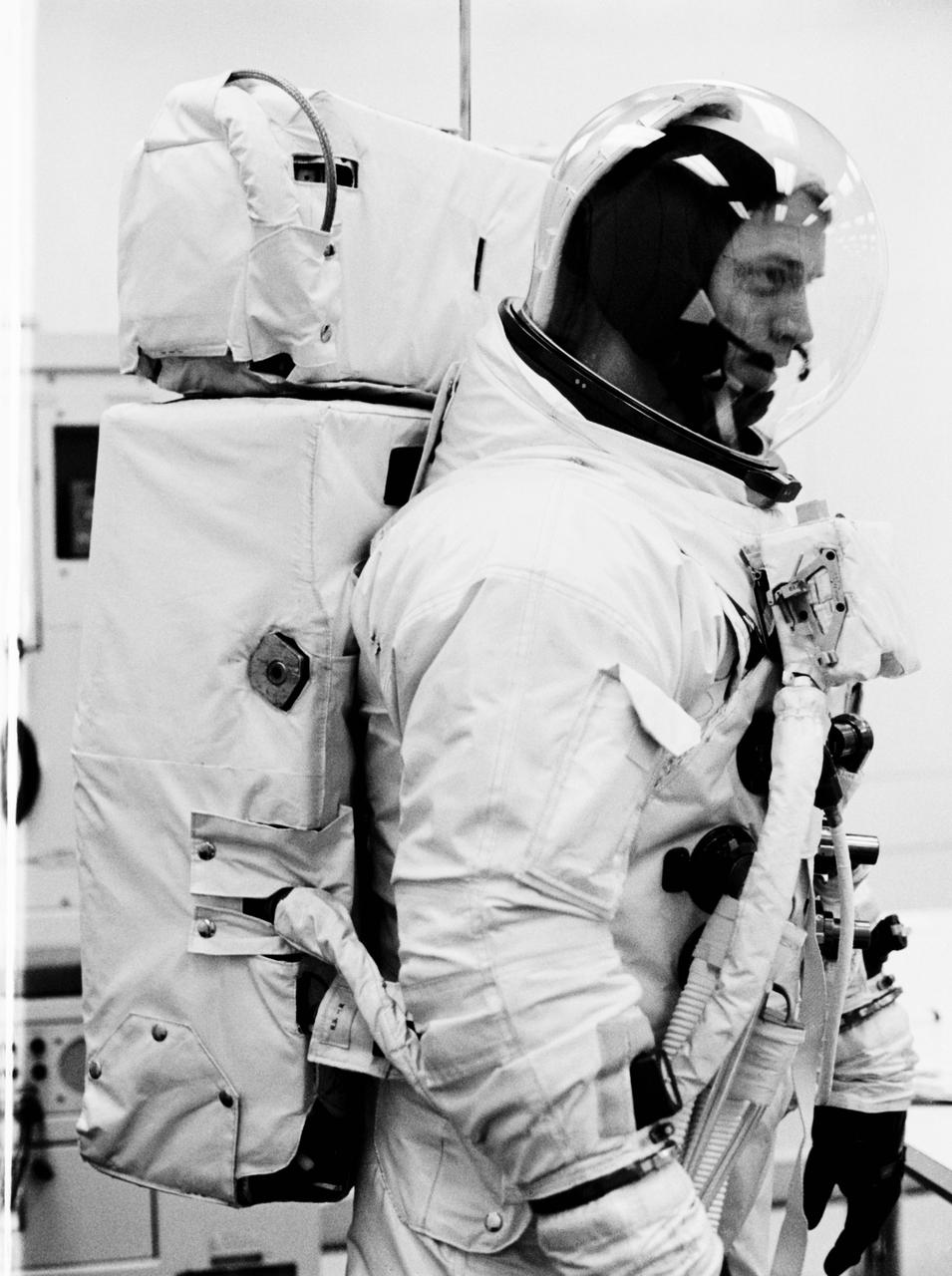

S69-25878 (23 Feb. 1969) --- Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot of the Apollo 9 prime crew, wears the Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU) which he will use during his scheduled Apollo 9 extravehicular activity. In addition to the space suit and bubble helmet, the EMU also includes a Portable Life Support System back pack, an Oxygen Purge System (seen atop the PLSS), and a Remote Control Unit on his chest. This equipment will be completely independent of the spacecraft during Schweickart's EVA. He will be secured only by a tether line. When this photograph was taken, Schweickart was suited to participate in an Apollo 9 Countdown Demonstration Test.
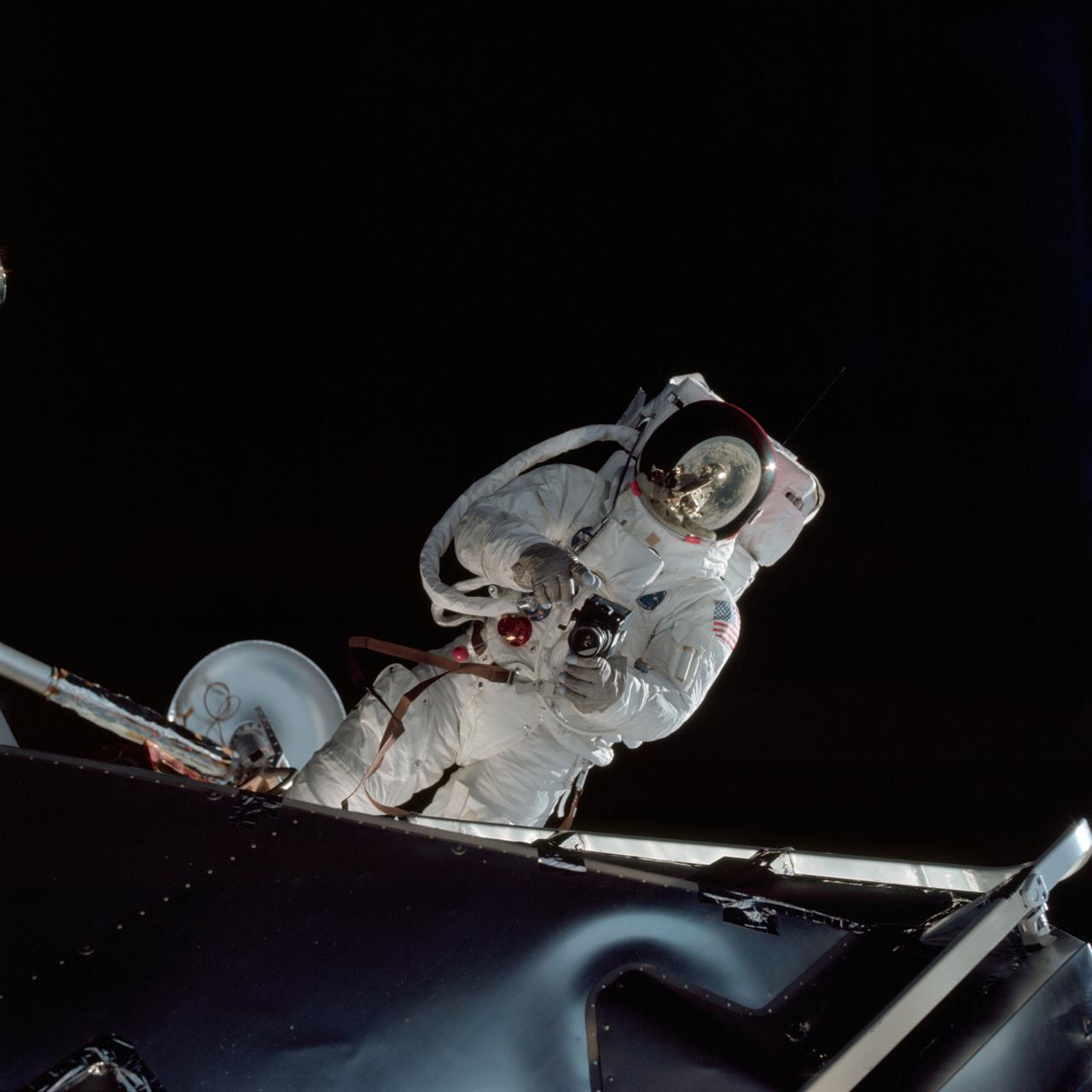

Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot, operates a 70mm Hasselblad camera during his extravehicular activity on the fourth day of the Apollo 9 earth-orbital mission. The Command/Service Module and the Lunar Module 3 "Spider" are docked. This view was taken form the Command Module "Gumdrop". Schweickart, wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), is standing in "golden slippers" on the Lunar Module porch. On his back, partially visible, are a Portable Life Support System (PLSS) and an Oxygen Purge System (OPS). Film magazine was A,film type was SO-368 Ektachrome with 0.460 - 0.710 micrometers film / filter transmittance response and haze filter,80mm lens.
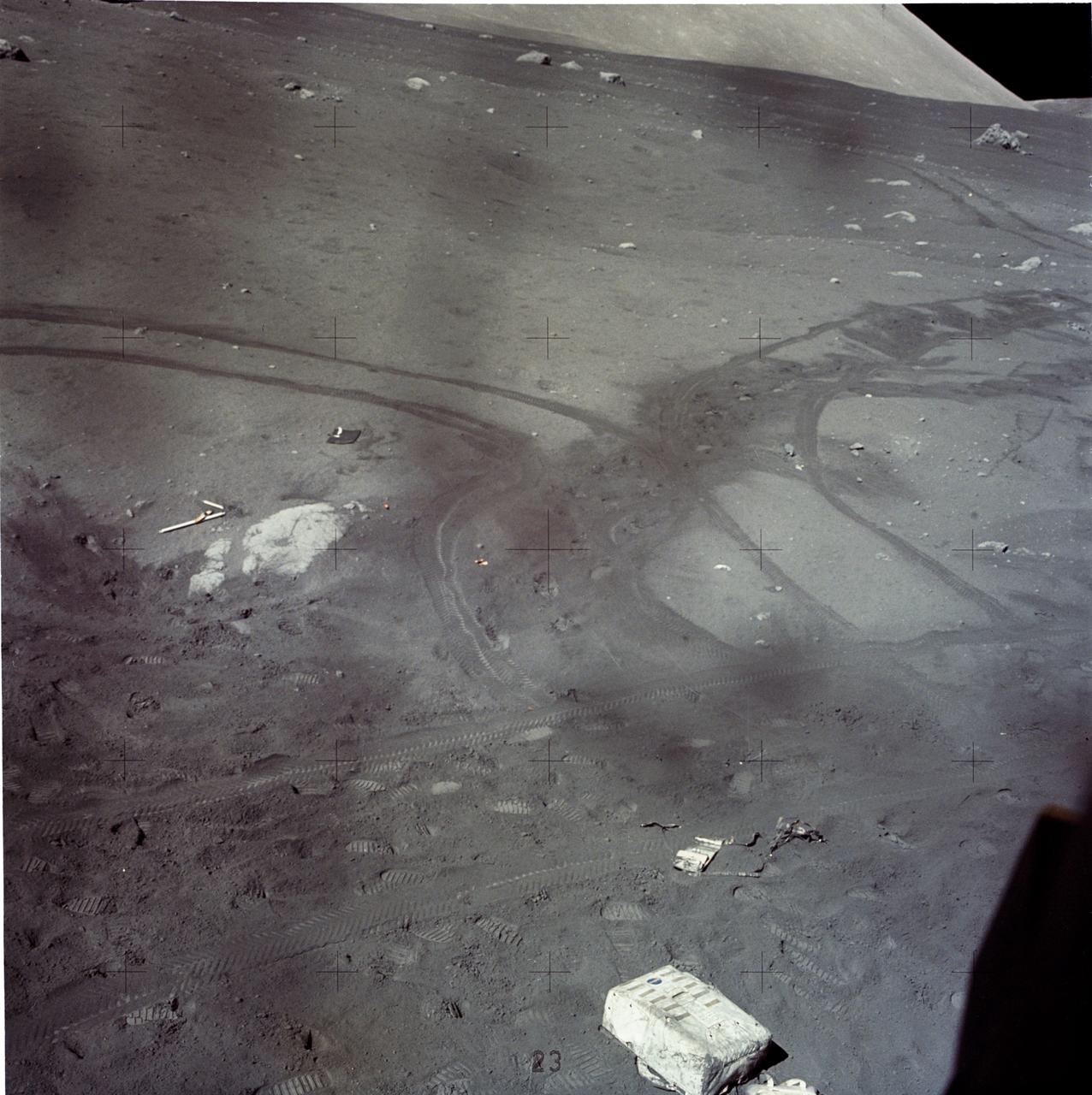

AS17-145-22196 (7-19 Dec. 1972) --- Astronaut Harrison H. Schmitt's discarded Portable Life Support System (PLSS), along with tracks from the Lunar Roving Vehicle (LRV) and boot prints were photographed through the Lunar Module (LM) window late in the mission. While astronauts Eugene A. Cernan, commander, and Schmitt, lunar module pilot, descended in the LM "Challenger" to explore the Taurus-Littrow region of the moon, astronaut Ronald E. Evans, command module pilot, remained with the Command and Service Modules (CSM) "America" in lunar orbit.
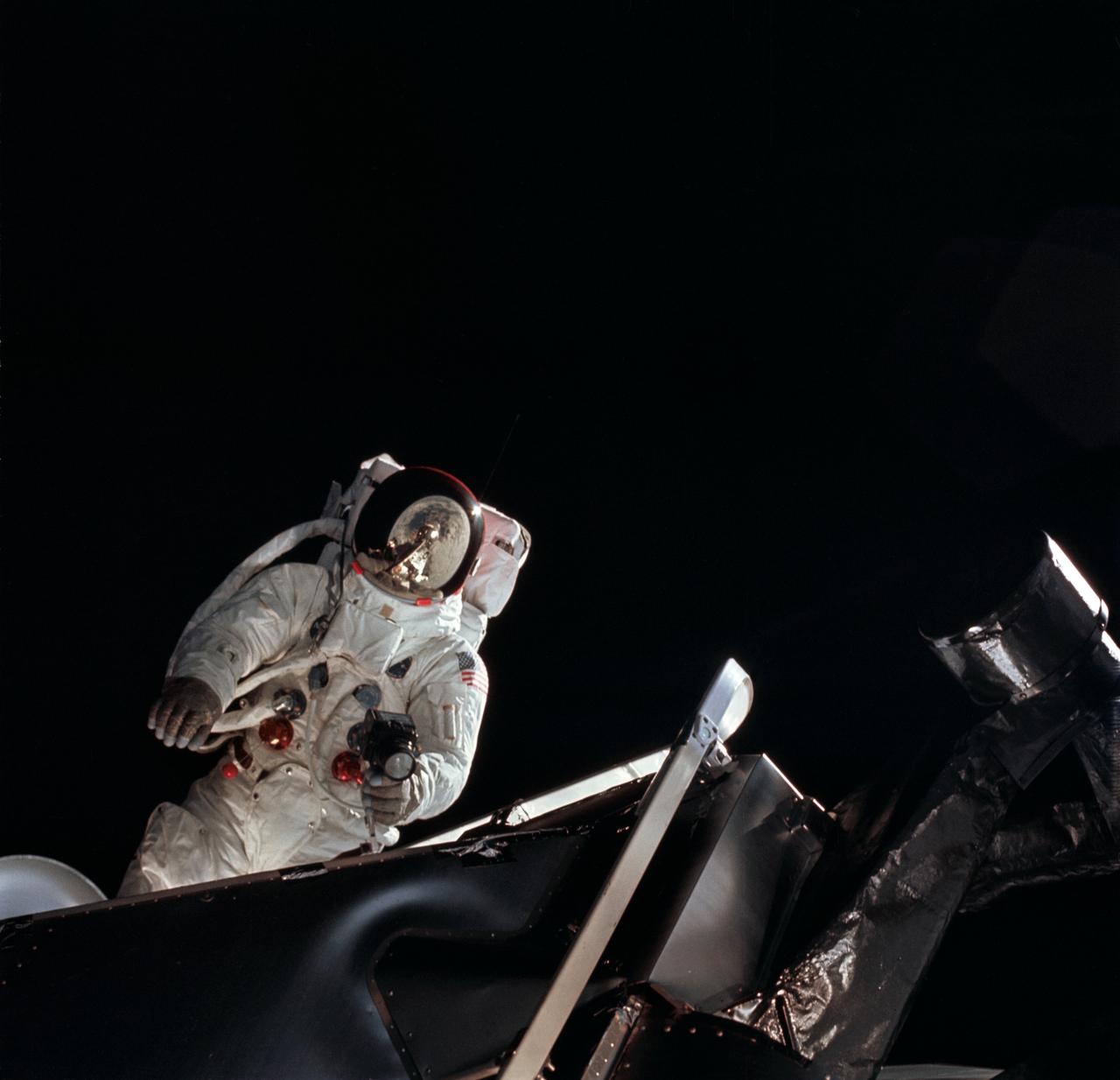

AS09-19-2983 (6 March 1969) --- Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot, operates a 70mm Hasselblad camera during his extravehicular activity (EVA) on the fourth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. The Command and Service Modules (CSM) and Lunar Module (LM) "Spider" are docked. This view was taken from the Command Module (CM) "Gumdrop". Schweickart, wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), is standing in "golden slippers" on the LM porch. On his back, partially visible, are a Portable Life Support System (PLSS) and an Oxygen Purge System (OPS). Astronaut James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander, was inside the "Spider". Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the CM.
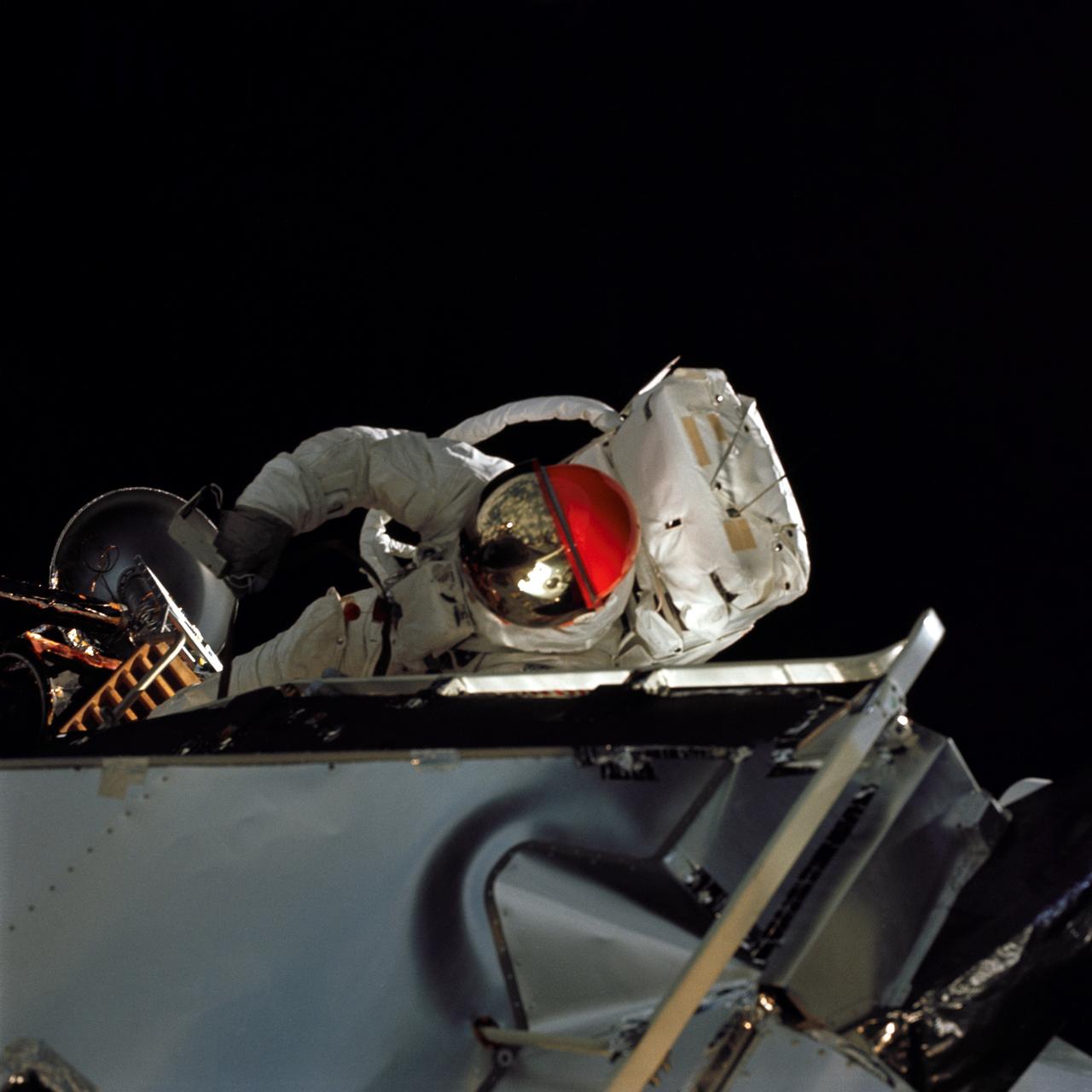

AS09-19-2994 (6 March 1969) --- Astronaut Russell L. Schweickart, lunar module pilot, is photographed from the Command Module (CM) "Gumdrop" during his extravehicular activity (EVA) on the fourth day of the Apollo 9 Earth-orbital mission. He holds, in his right hand, a thermal sample which he is retrieving from the Lunar Module (LM) exterior. The Command and Service Modules (CSM) and LM "Spider" are docked. Schweickart, wearing an Extravehicular Mobility Unit (EMU), is standing in "golden slippers" on the LM porch. Visible on his back are the Portable Life Support System (PLSS) and Oxygen Purge System (OPS). Astronaut James A. McDivitt, Apollo 9 commander, was inside the "Spider". Astronaut David R. Scott, command module pilot, remained at the controls in the CM "Gumdrop".
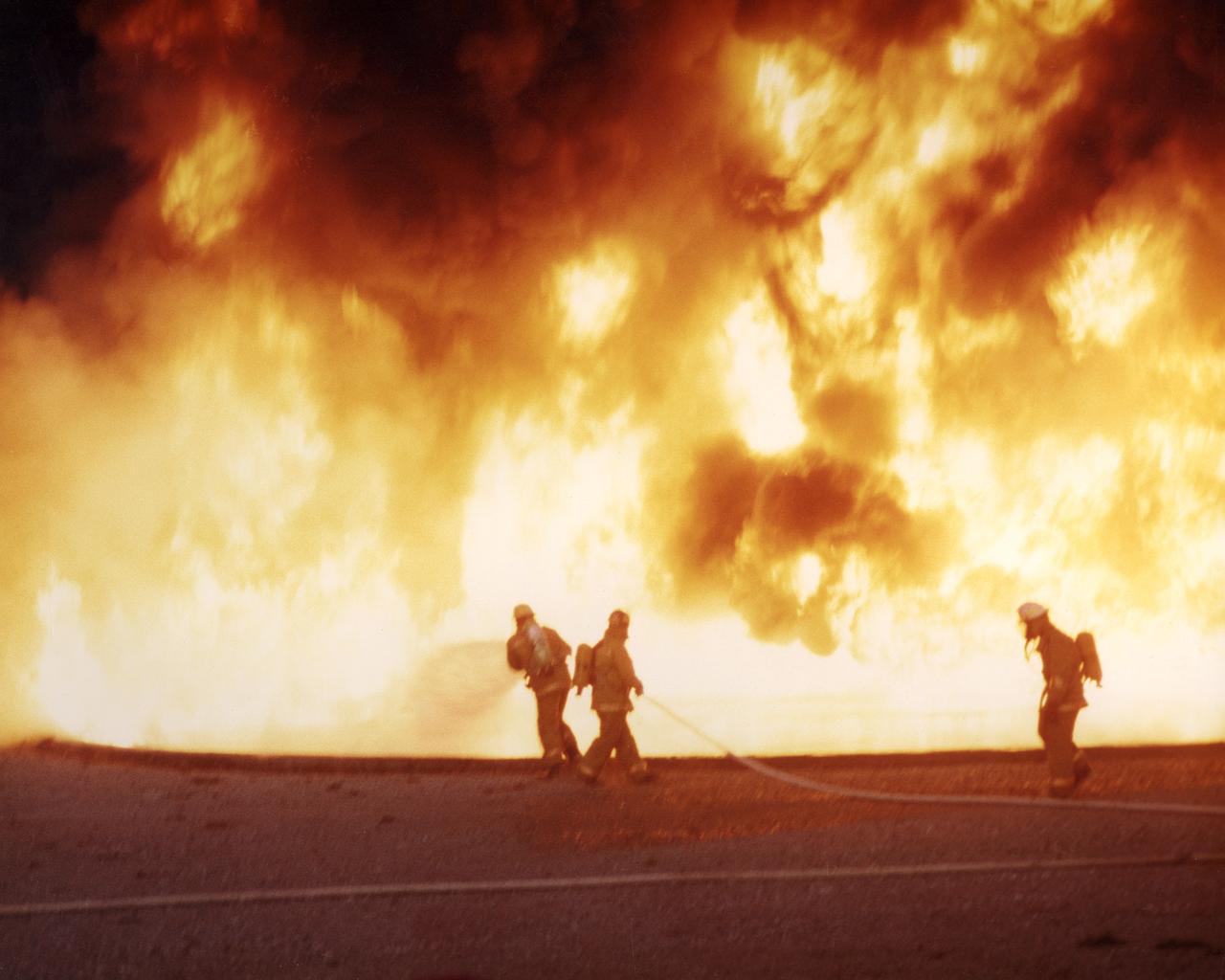

Firefighters are like astronauts. They both face dangerous, even hostile environments such as a building full of fire and the vacuum of space. They are both get breathing air from tanks on their backs. Early in the 1970's, NASA began working to improve firefighter breathing systems, which had hardly changed since the 1940s. NASA's Johnson Space Center conducted a 4-year program that applied technology from the portable life support systems used by Apollo astronauts on the moon. The new breathing system is made up of an air bottle, a frame and harness, a face mask, and a warning device. The new system weighs less than 20 pounds, one-third less than the old gear. The new air bottle provides 30 minutes of breathing air, as much as the old system. Like a good hiker's backpack, the new system puts the weight on the firefighter's hips rather than the shoulders. The face mask provides better visibility and the warning device lets the firefighter know when air in the bottle is low. Though they have made many design modifications and refinements, manufacturers of breathing apparatus still incorporate the original NASA technology.
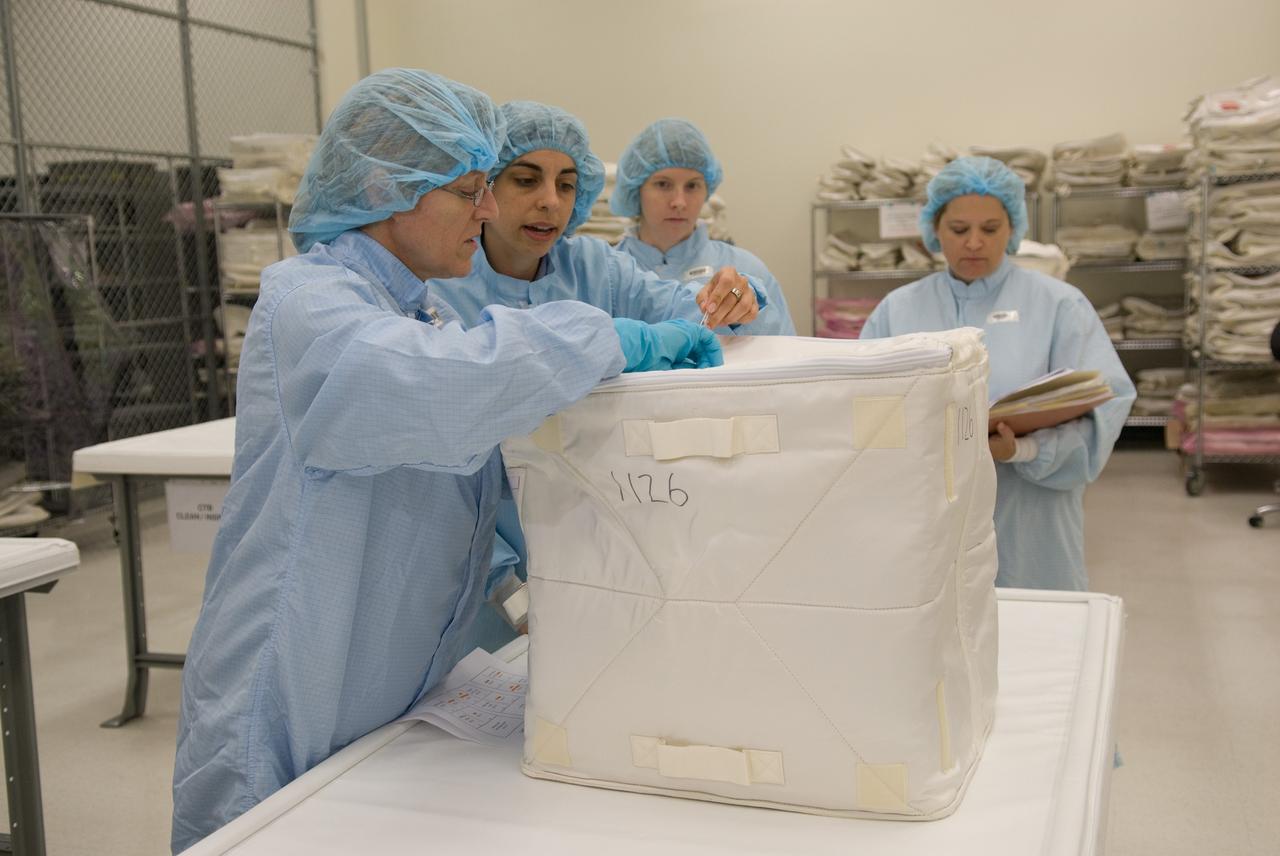

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-130 Mission Specialist Kathryn "Kay" Hire, at left, participates in a bench review, standard familiarization training on the hardware and equipment that will fly on her mission, during the crew equipment interface test. Tranquility, the payload for the STS-130 mission, is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for the European Space Agency by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. The cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top, is attached to the end of Tranquility. It resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Endeavour is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
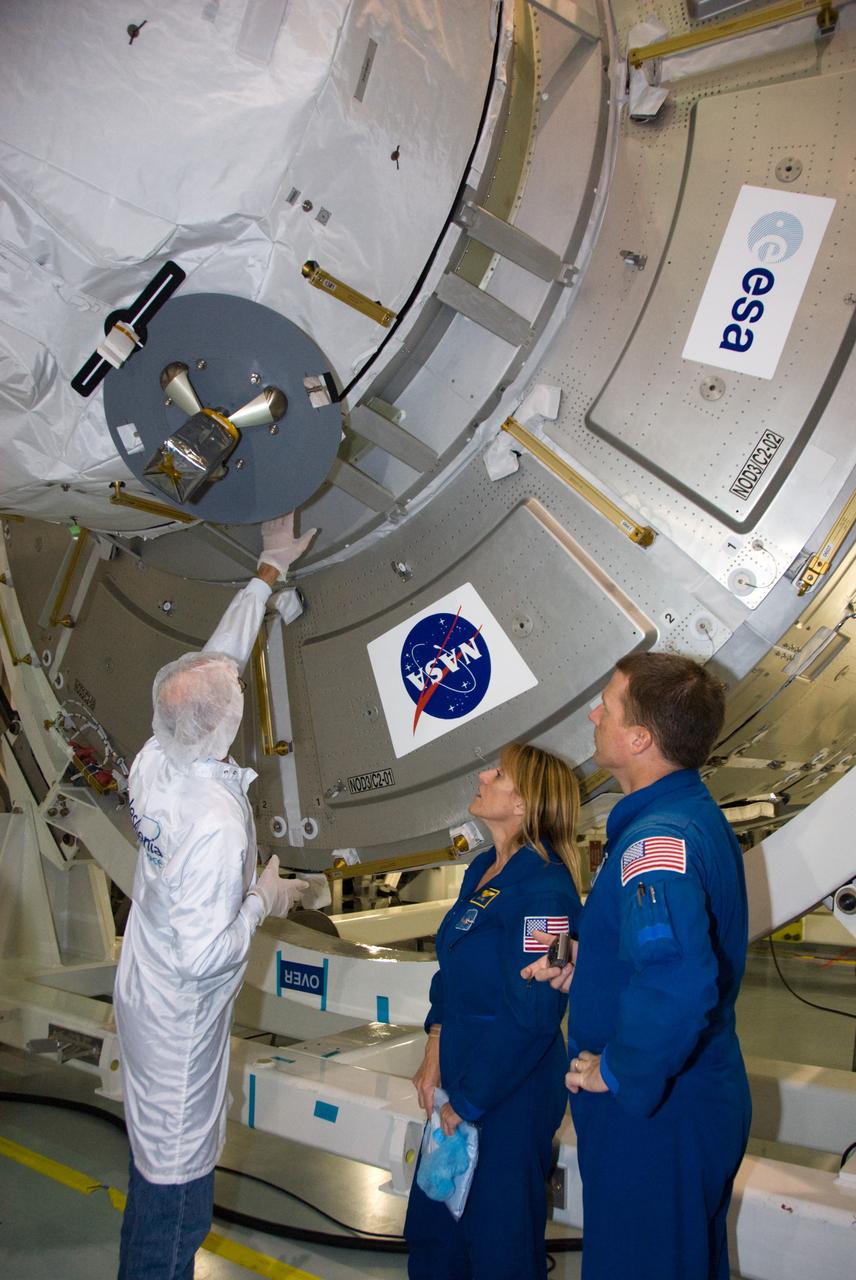

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-130 Mission Specialist Kathryn "Kay" Hire, middle, and Pilot Terry Virts Jr., right, receive familiarization training on the cupola from a flight crew representative from Thales Alenia Space during their crew equipment interface test. The cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top, is attached to one end of the Tranquility node. Tranquility, the payload for the STS-130 mission, is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for the European Space Agency by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. The cupola resembles a circular bay window that will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Endeavour is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

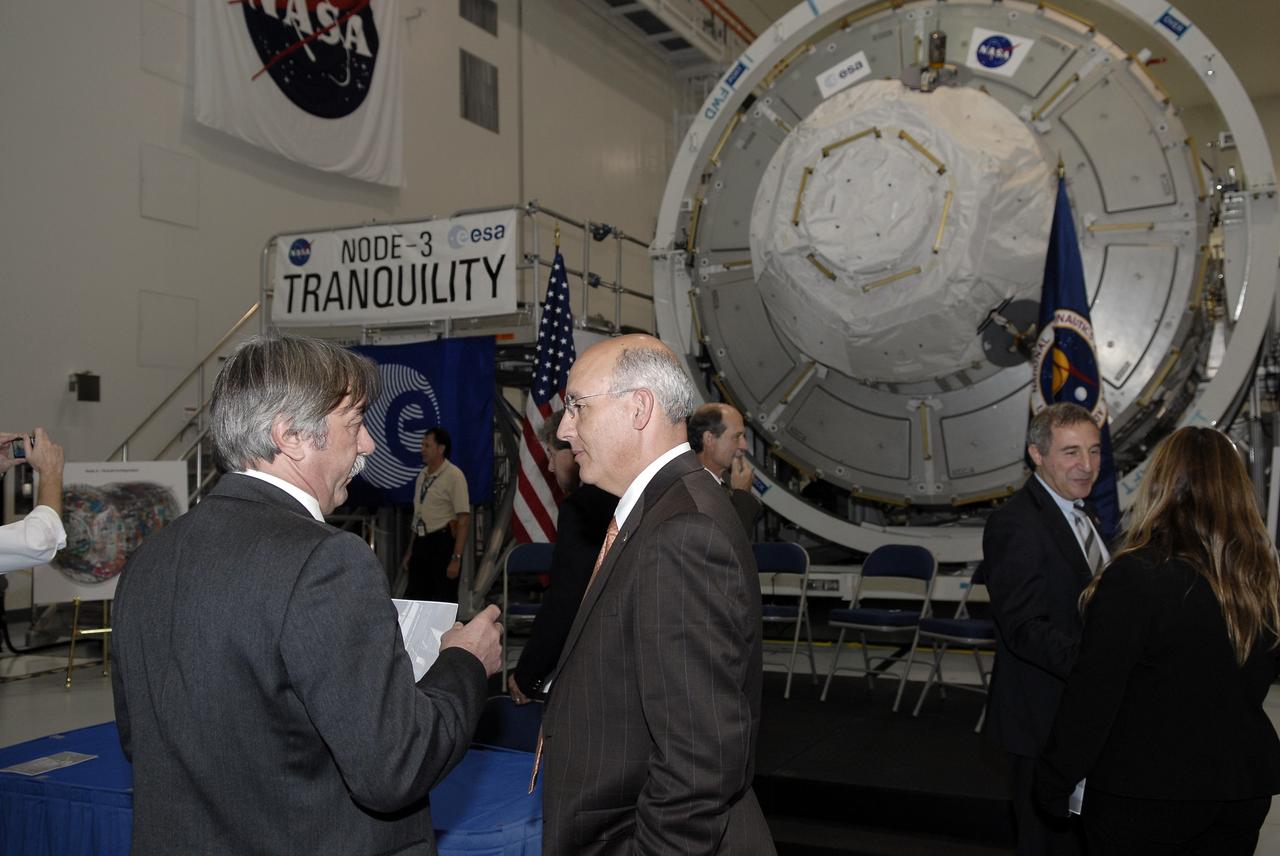
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Bernardo Patti, right, head of International Space Station, Program Department, European Space Agency, or ESA, has a lot to smile about as he is photographed in front of the node 3 for the International Space Station following a ceremony transferring the ownership of the node from ESA to NASA. Node 3 is named "Tranquility" after the Sea of Tranquility, the lunar landing site of Apollo 11. The payload for the STS-130 mission, Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for ESA by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. Attached to one end of Tranquility is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. The cupola resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Secondino Brondolo, at left, head of the Space Infrastructure, Thales Alenia Space Italy, talks to Michael Suffredini, program manager, International Space Station, NASA, following a ceremony transferring the ownership of node 3 for the International Space Station from the European Space Agency, or ESA, to NASA. Node 3 is named "Tranquility" after the Sea of Tranquility, the lunar landing site of Apollo 11. The payload for the STS-130 mission, Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for ESA by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. Attached to one end of Tranquility is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. The cupola resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
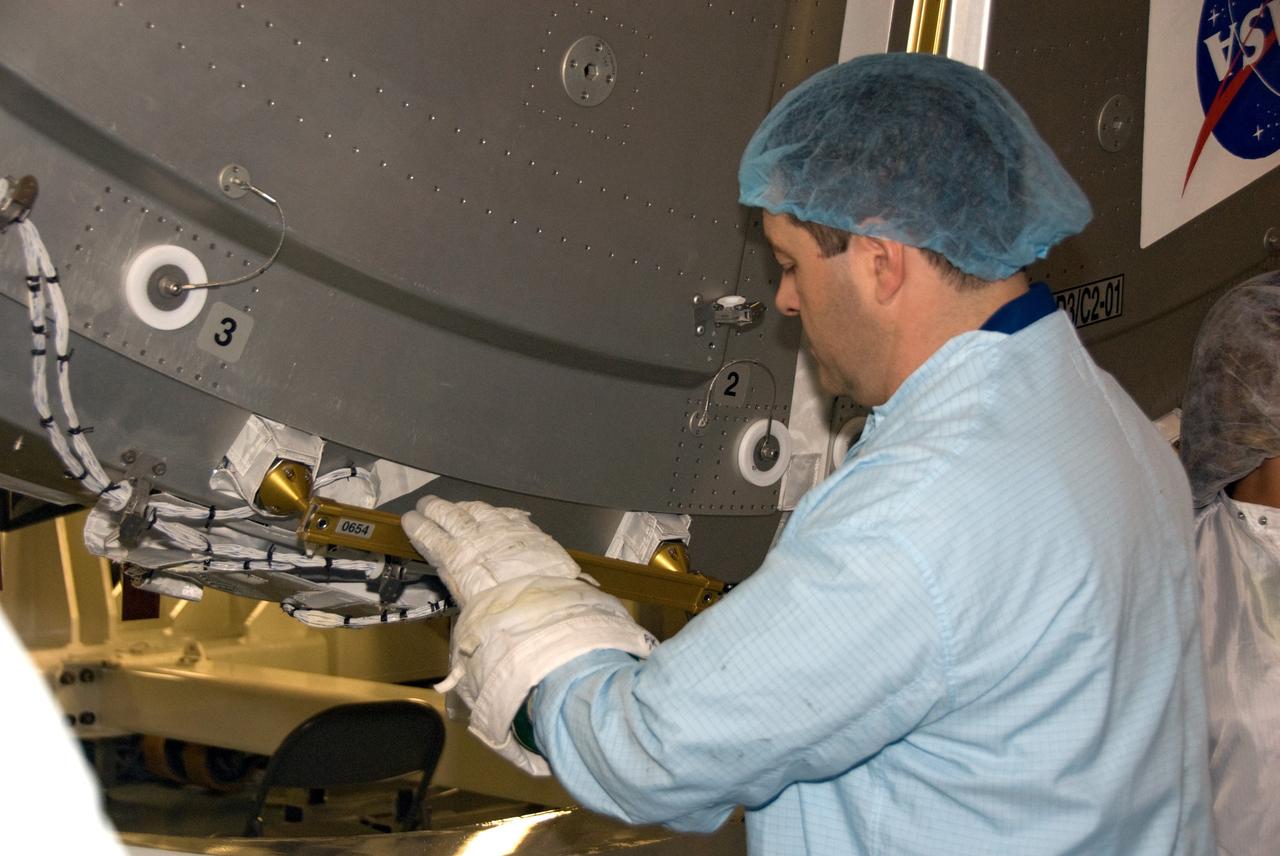

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-130 Mission Specialist Nicolas Patrick becomes familiar with the working of the Tranquility node during the crew equipment interface test for his mission. The cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top, is attached to one end of Tranquility. Tranquility, the payload for the STS-130 mission, is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for the European Space Agency by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. The cupola resembles a circular bay window that will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Endeavour is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
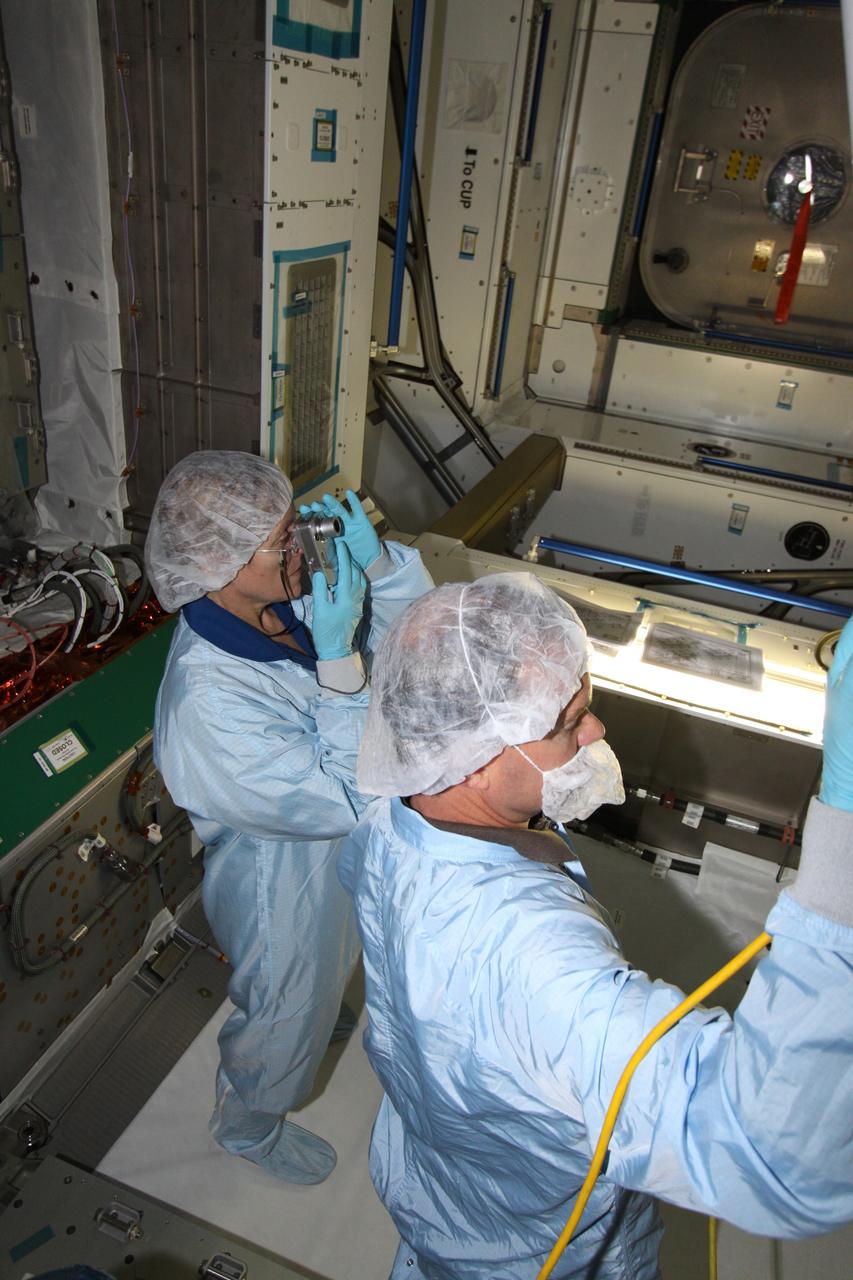

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mission specialist Kathryn "Kay" Hire, at left, assigned to the crew of space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission, takes a tour of the Tranquility Node 3 module in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assisting her, at right, is Chris Hardcastle, an STS-130 flight crew representative with United Space Alliance. Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. Attached to the node is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. Tranquility is the payload for the STS-130 mission. The module was built for the European Space Agency by Alenia Spazio in Turin, Italy. Cupola resembles a circular bay window that will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Endeavour is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
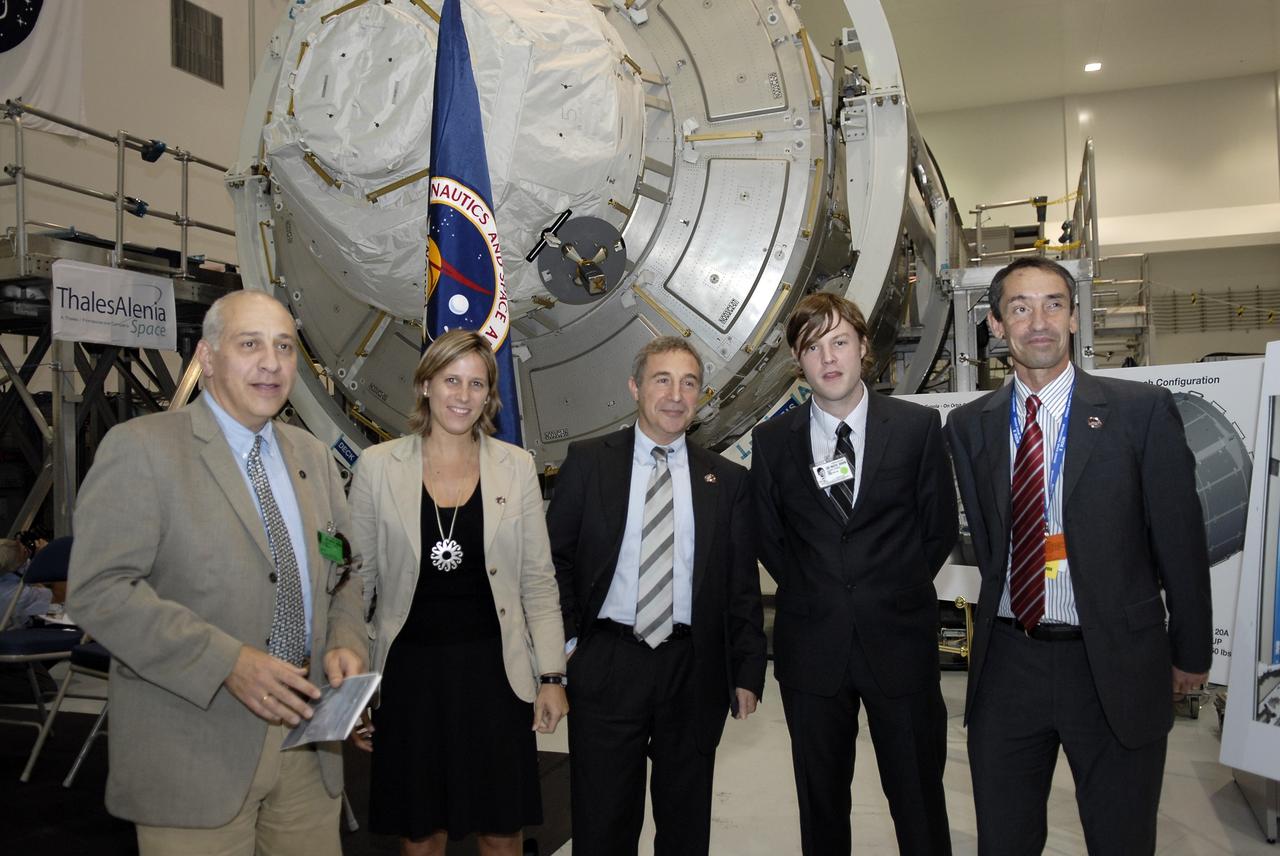

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Bernardo Patti, head of International Space Station, Program Department, European Space Agency, or ESA, is photographed with invited guests of ESA in front of node 3 for the International Space Station following a ceremony transferring the ownership of the node from ESA to NASA. Node 3 is named "Tranquility" after the Sea of Tranquility, the lunar landing site of Apollo 11. The payload for the STS-130 mission, Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for ESA by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. Attached to one end of Tranquility is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. The cupola resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
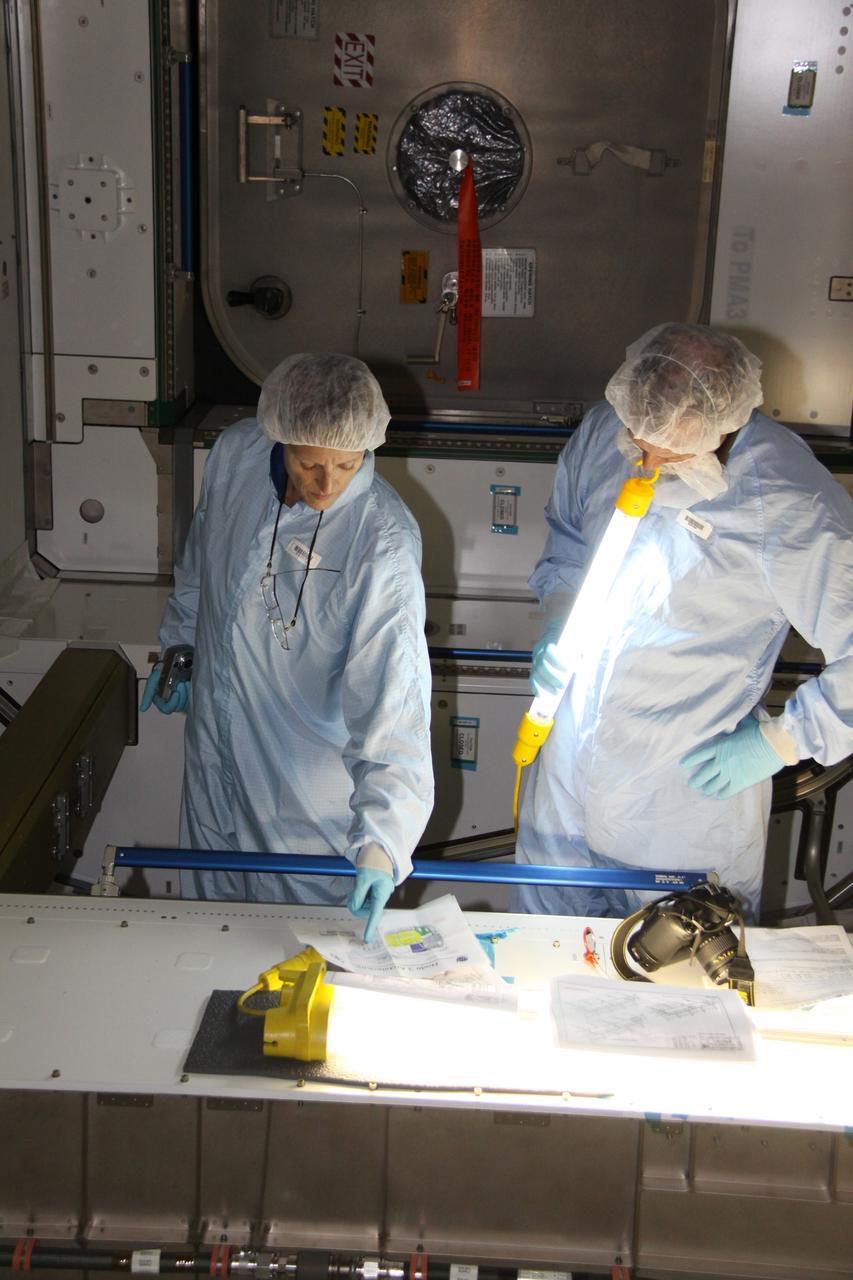

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, mission specialist Kathryn "Kay" Hire, left, a crew member on space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission, discusses the layout of the Tranquility Node 3 module in which she is standing with Chris Hardcastle, an STS-130 flight crew representative with United Space Alliance. Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. Attached to the node is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. Tranquility is the payload for the STS-130 mission. The module was built for the European Space Agency by Alenia Spazio in Turin, Italy. Cupola resembles a circular bay window that will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Endeavour is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
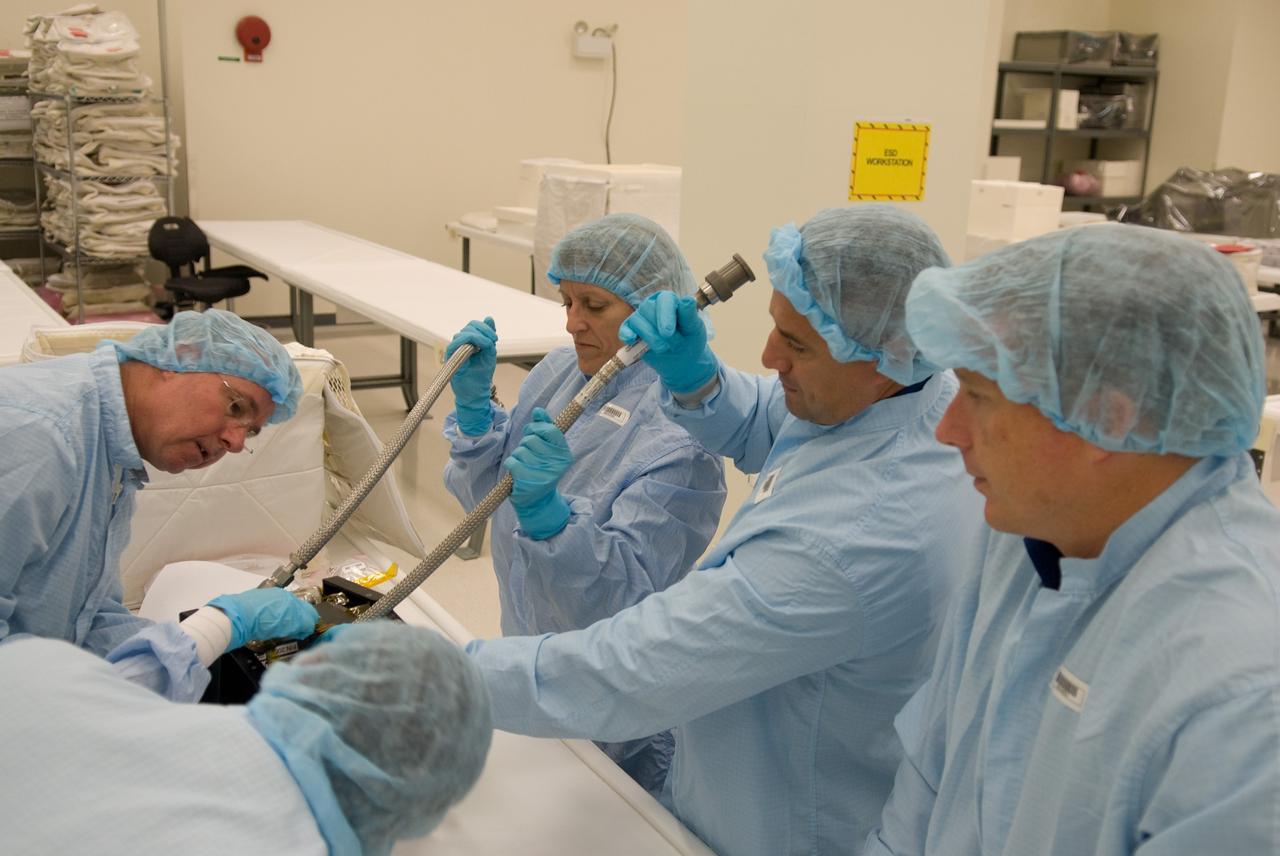

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, members of the STS-130 crew participate in a bench review, standard familiarization training on the hardware and equipment that will fly on their mission, during the crew equipment interface test. From left are Mission Specialists Stephen Robinson and Kathryn "Kay" Hire, Commander George Zamka and Pilot Terry Virts Jr. Tranquility, the payload for the STS-130 mission, is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for the European Space Agency by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. The cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top, is attached to the end of Tranquility. It resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Endeavour is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
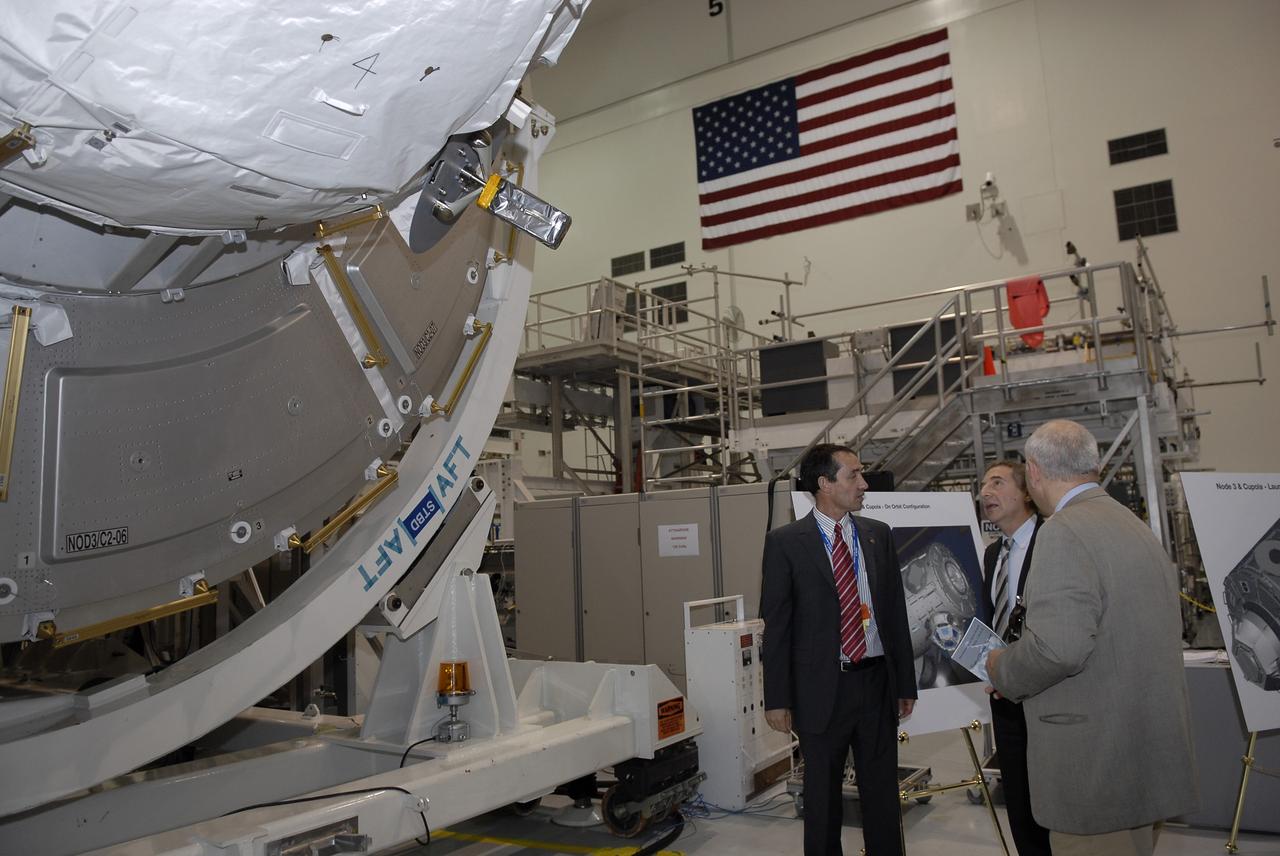

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Bernardo Patti, center, head of International Space Station, Program Department, European Space Agency, or ESA, admires the node 3 for the International Space Station, which his agency provided, following a ceremony transferring the ownership of the node from ESA to NASA. Node 3 is named "Tranquility" after the Sea of Tranquility, the lunar landing site of Apollo 11. The payload for the STS-130 mission, Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for ESA by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. Attached to one end of Tranquility is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. The cupola resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
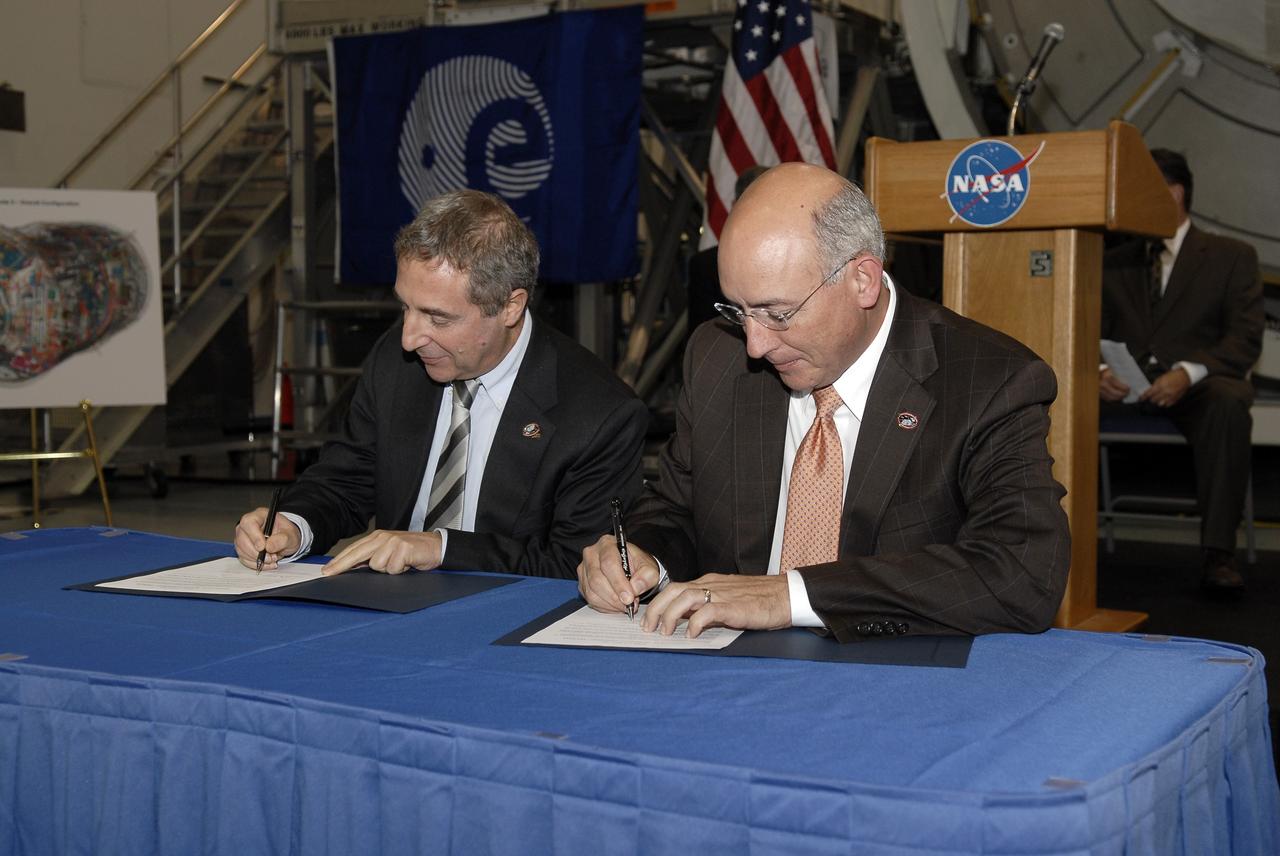

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Bernardo Patti, at left, head of International Space Station, Program Department, European Space Agency, and Michael Suffredini, program manager, International Space Station, NASA, sign documents transferring the ownership of node 3 for the International Space Station from the European Space Agency, or ESA, to NASA. Node 3 is named "Tranquility" after the Sea of Tranquility, the lunar landing site of Apollo 11. The payload for the STS-130 mission, Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for ESA by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. Attached to one end of Tranquility is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. The cupola resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
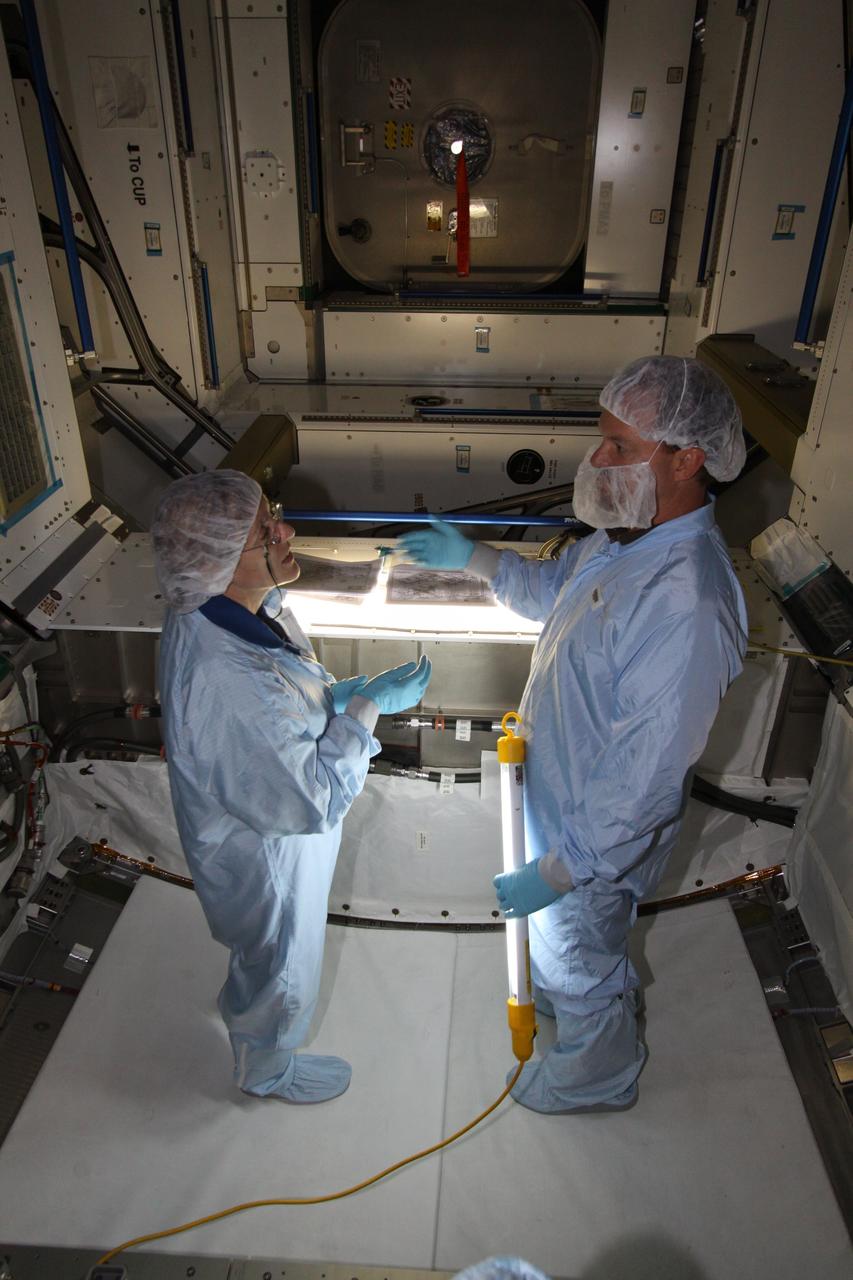

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mission specialist Kathryn "Kay" Hire, at left, assigned to the crew of space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission, becomes familiar with the configuration of the Tranquility Node 3 module in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assisting her, at right, is Chris Hardcastle, an STS-130 flight crew representative with United Space Alliance. Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. Attached to the node is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. Tranquility is the payload for the STS-130 mission. The module was built for the European Space Agency by Alenia Spazio in Turin, Italy. Cupola resembles a circular bay window that will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Endeavour is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
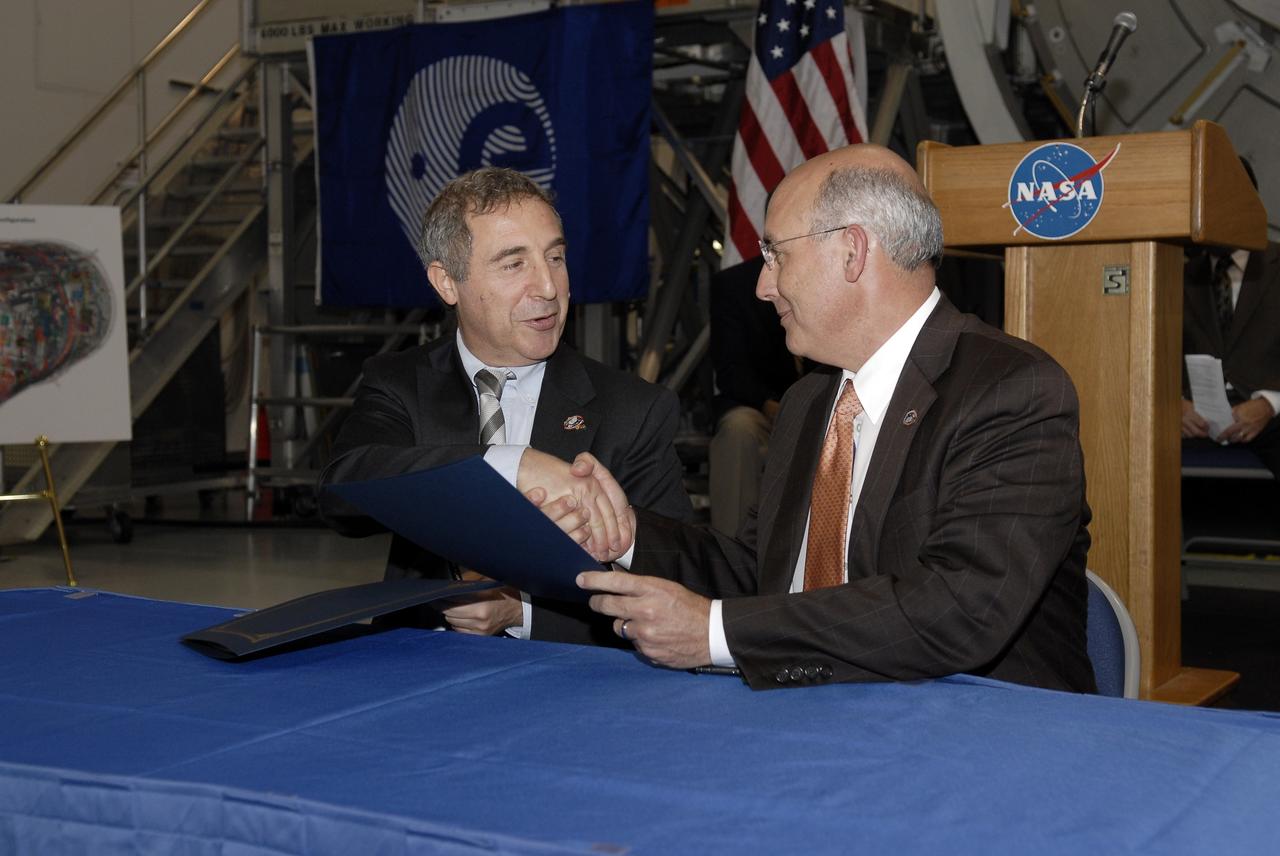

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Bernardo Patti, at left, head of International Space Station, Program Department, European Space Agency, congratulates Michael Suffredini, program manager, International Space Station, NASA, upon transfer of the ownership of node 3 for the International Space Station from the European Space Agency, or ESA, to NASA. Node 3 is named "Tranquility" after the Sea of Tranquility, the lunar landing site of Apollo 11. The payload for the STS-130 mission, Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for ESA by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. Attached to one end of Tranquility is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. The cupola resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
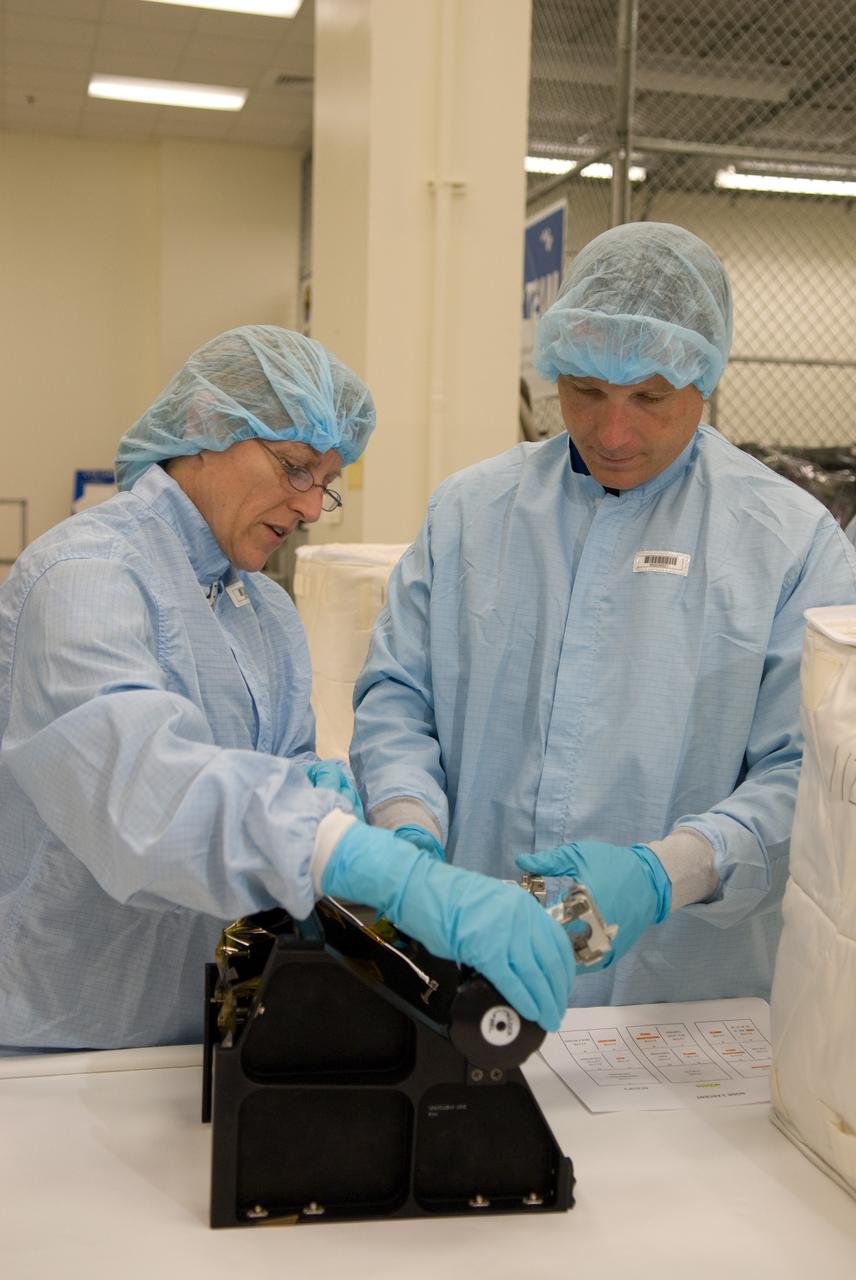

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-130 Mission Specialist Kathryn "Kay" Hire, at left, and Pilot Terry Virts Jr. participate in a bench review, standard familiarization training on the hardware and equipment that will fly on their mission, during the crew equipment interface test. Tranquility, the payload for the STS-130 mission, is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for the European Space Agency by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. The cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top, is attached to the end of Tranquility. It resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Endeavour is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
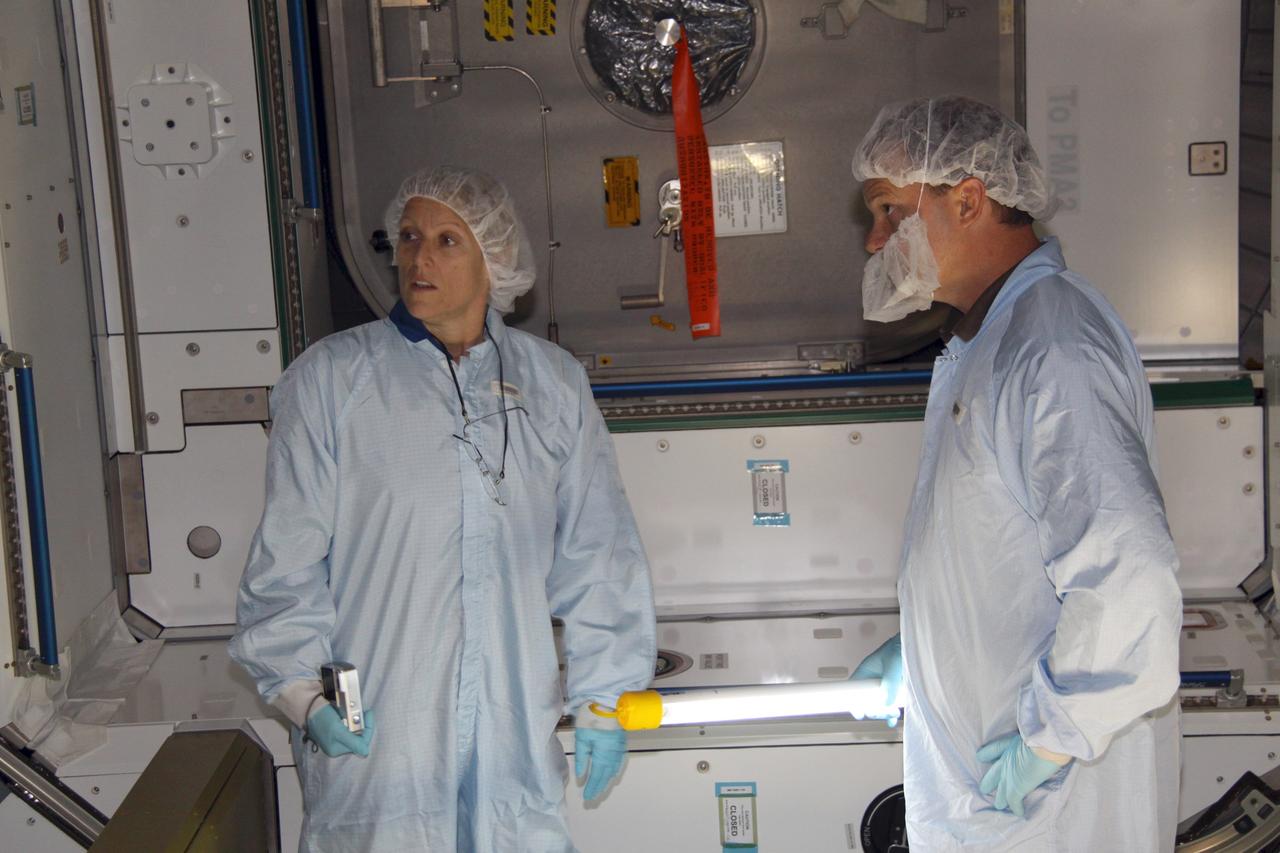

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mission specialist Kathryn "Kay" Hire, at left, a crew member on space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission, photographs the interior of the Tranquility Node 3 module in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assisting her, at right, is Chris Hardcastle, an STS-130 flight crew representative with United Space Alliance. Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. Attached to the node is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. Tranquility is the payload for the STS-130 mission. The module was built for the European Space Agency by Alenia Spazio in Turin, Italy. Cupola resembles a circular bay window that will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Endeavour is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
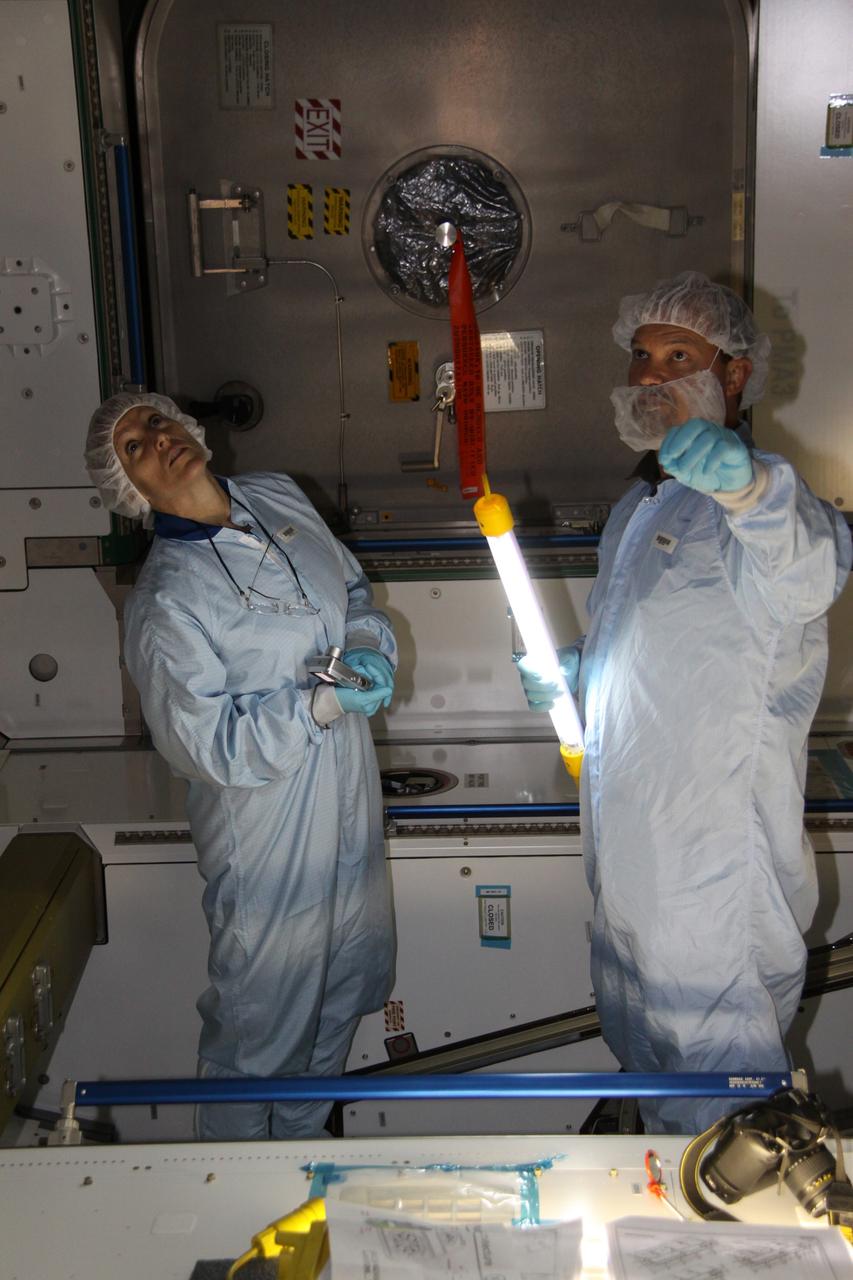

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – Mission specialist Kathryn "Kay" Hire, at left, a crew member on space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission, participates in familiarization training for the Tranquility Node 3 module in the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida. Assisting her, at right, is Chris Hardcastle, an STS-130 flight crew representative with United Space Alliance. Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. Attached to the node is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. Tranquility is the payload for the STS-130 mission. The module was built for the European Space Agency by Alenia Spazio in Turin, Italy. Cupola resembles a circular bay window that will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Endeavour is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Jack Pfaller
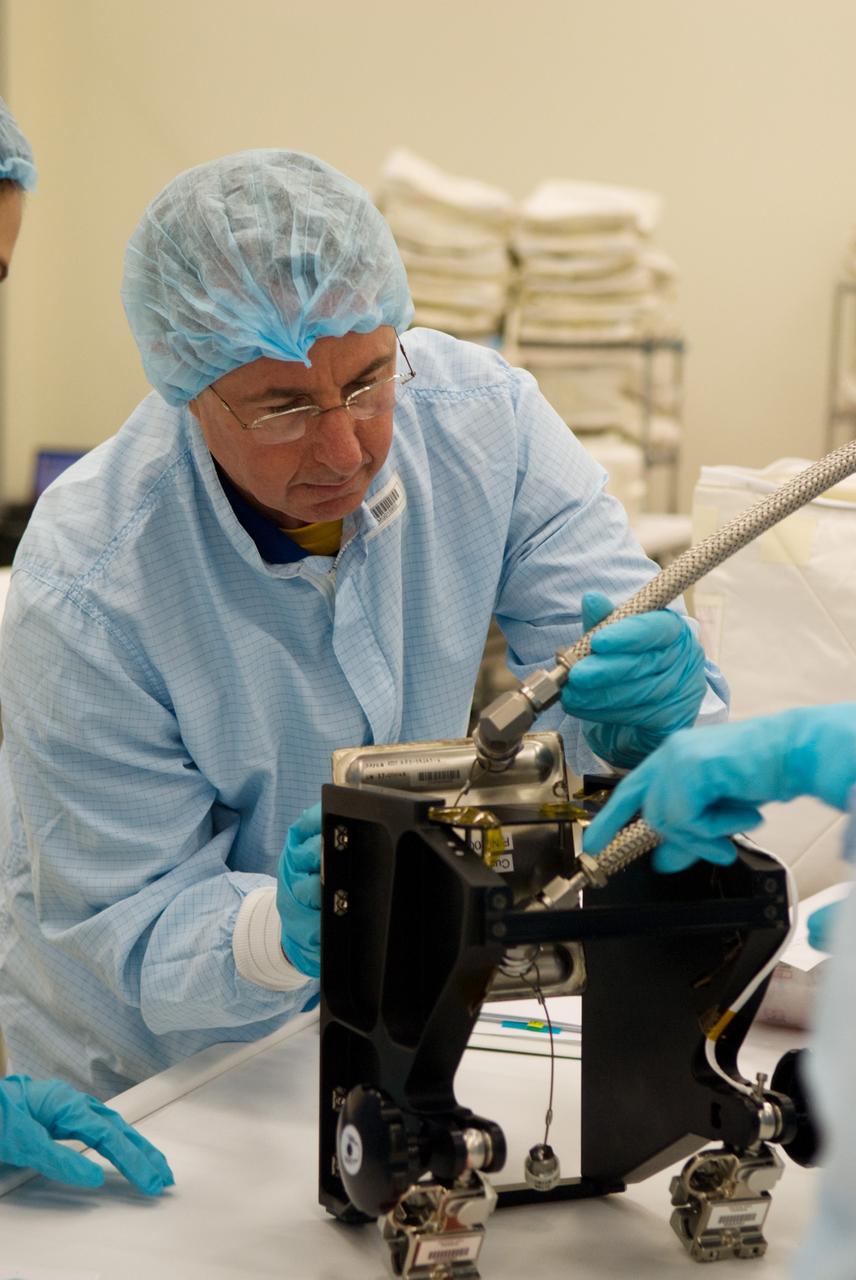

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, STS-130 Mission Specialist Stephen Robinson participates in a bench review, standard familiarization training on the hardware and equipment that will fly on his mission, during the crew equipment interface test. Tranquility, the payload for the STS-130 mission, is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for the European Space Agency by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. The cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top, is attached to the end of Tranquility. It resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Endeavour is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
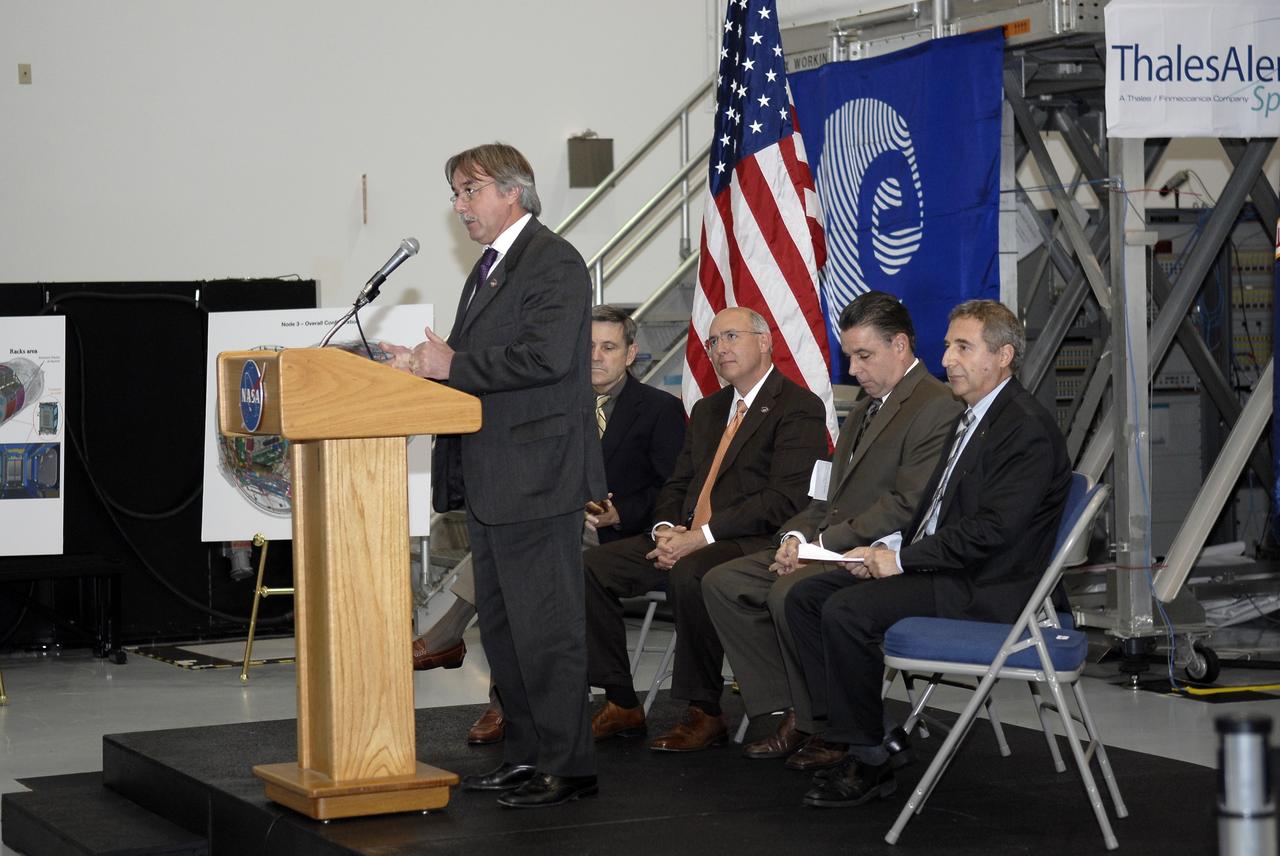

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Secondino Brondolo, head of the Space Infrastructure, Thales Alenia Space Italy, addresses the invited guests at a ceremony transferring the ownership of node 3 for the International Space Station from the European Space Agency, or ESA, to NASA. Seated, from left, are Bob Cabana, Kennedy Space Center director; Michael Suffredini, program manager, International Space Station, NASA; William Dowdell, deputy for Operations, International Space Station and Spacecraft Processing, Kennedy; and Bernardo Patti, head of International Space Station, Program Department, ESA. Node 3 is named "Tranquility" after the Sea of Tranquility, the lunar landing site of Apollo 11. The payload for the STS-130 mission, Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for ESA by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. Attached to one end of Tranquility is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. The cupola resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
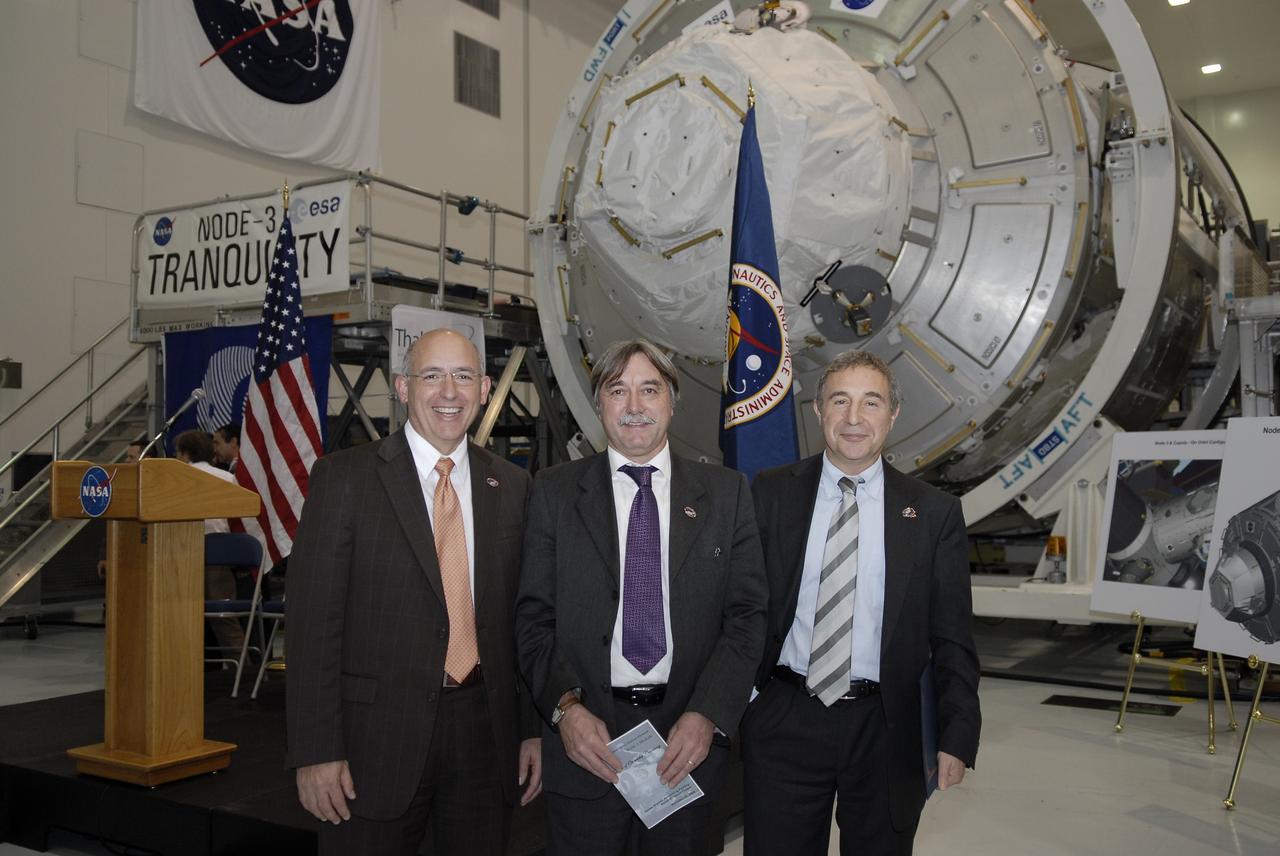

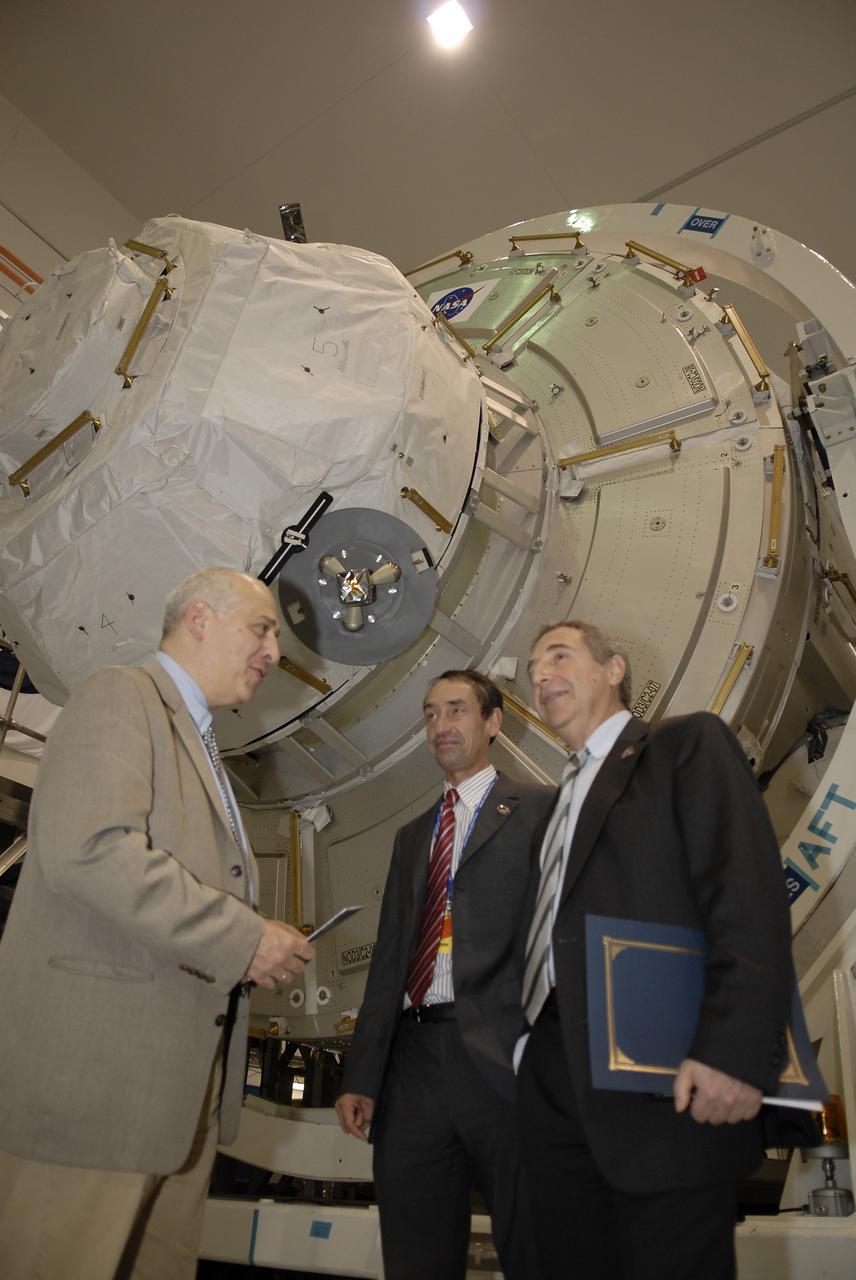
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, from left, Michael Suffredini, program manager, International Space Station, NASA; Secondino Brondolo, head of the Space Infrastructure, Thales Alenia Space Italy; and Bernardo Patti, head of International Space Station, Program Department, ESA, are photographed in front of node 3 for the International Space Station following a ceremony transferring the ownership of the node from the European Space Agency, or ESA, to NASA. Node 3 is named "Tranquility" after the Sea of Tranquility, the lunar landing site of Apollo 11. The payload for the STS-130 mission, Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for ESA by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. Attached to one end of Tranquility is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. The cupola resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
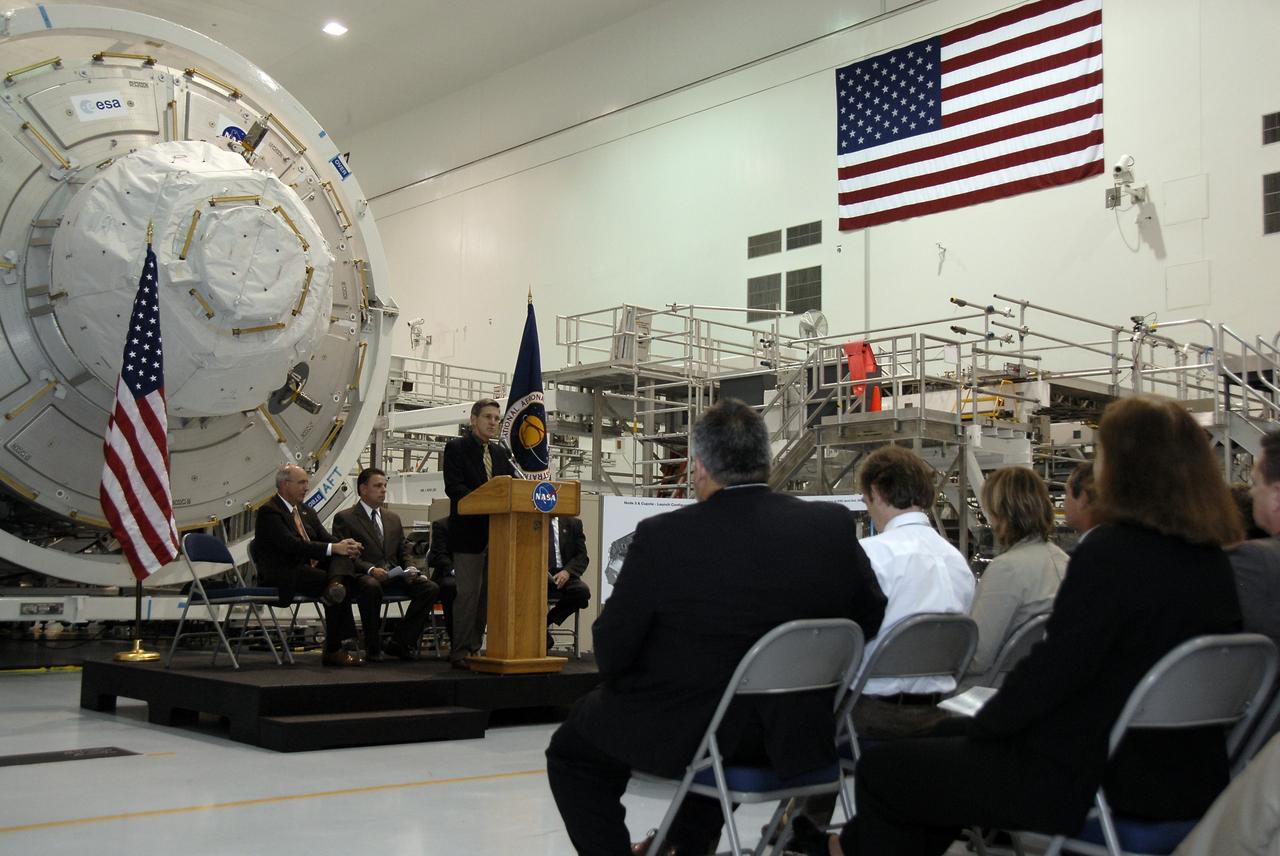

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Kennedy Director Bob Cabana addresses the invited guests at a ceremony transferring the ownership of node 3 for the International Space Station, looming in the background, from the European Space Agency, or ESA, to NASA. Seated, from left, are Michael Suffredini, program manager, International Space Station, NASA, and William Dowdell, deputy for Operations, International Space Station and Spacecraft Processing, Kennedy. Node 3 is named "Tranquility" after the Sea of Tranquility, the lunar landing site of Apollo 11. The payload for the STS-130 mission, Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for ESA by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. Attached to one end of Tranquility is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. The cupola resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
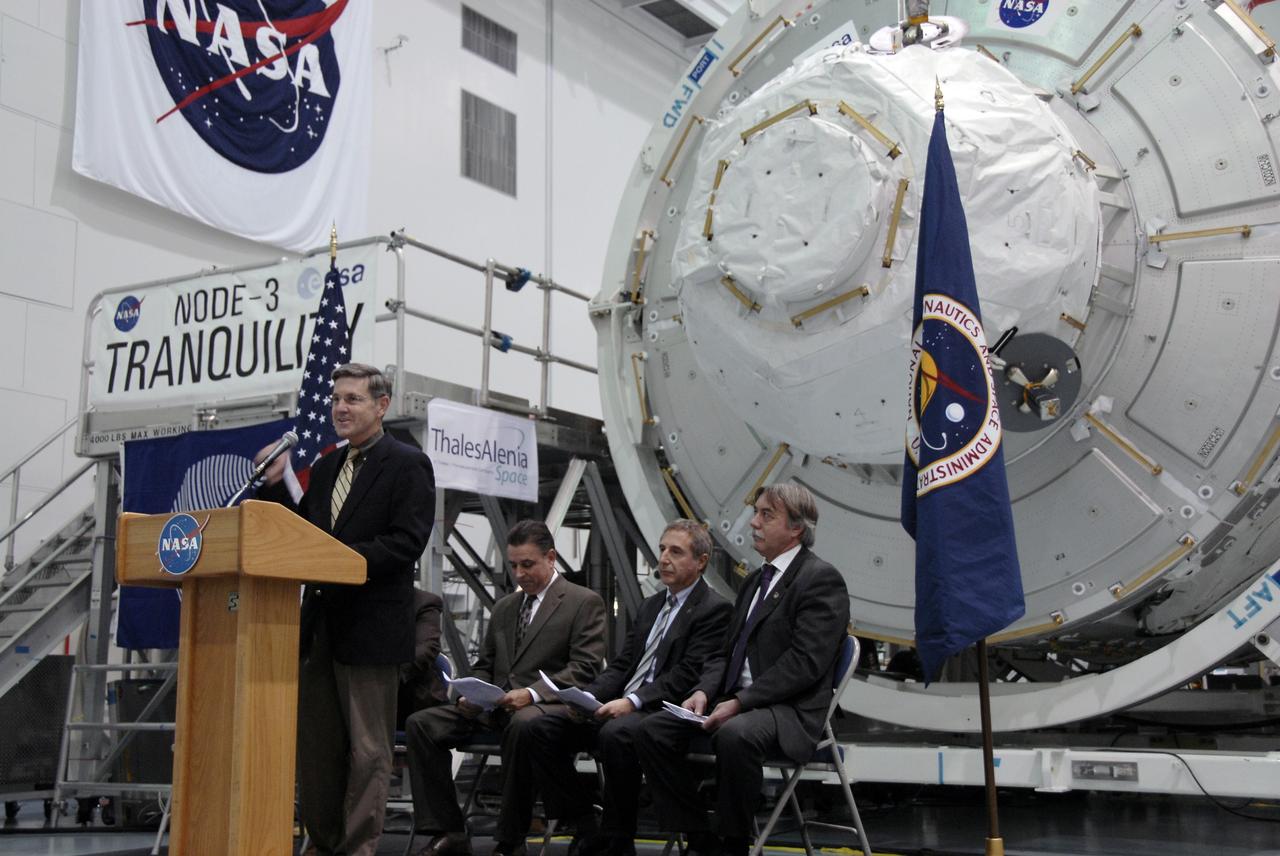

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Kennedy Director Bob Cabana addresses the invited guests at a ceremony transferring the ownership of node 3 for the International Space Station, looming in the background, from the European Space Agency, or ESA, to NASA. Seated, from left, are William Dowdell, deputy for Operations, International Space Station and Spacecraft Processing, Kennedy; Bernardo Patti, head of International Space Station, Program Department, ESA; and Secondino Brondolo, head of the Space Infrastructure, Thales Alenia Space Italy. Node 3 is named "Tranquility" after the Sea of Tranquility, the lunar landing site of Apollo 11. The payload for the STS-130 mission, Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for ESA by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. Attached to one end of Tranquility is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. The cupola resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
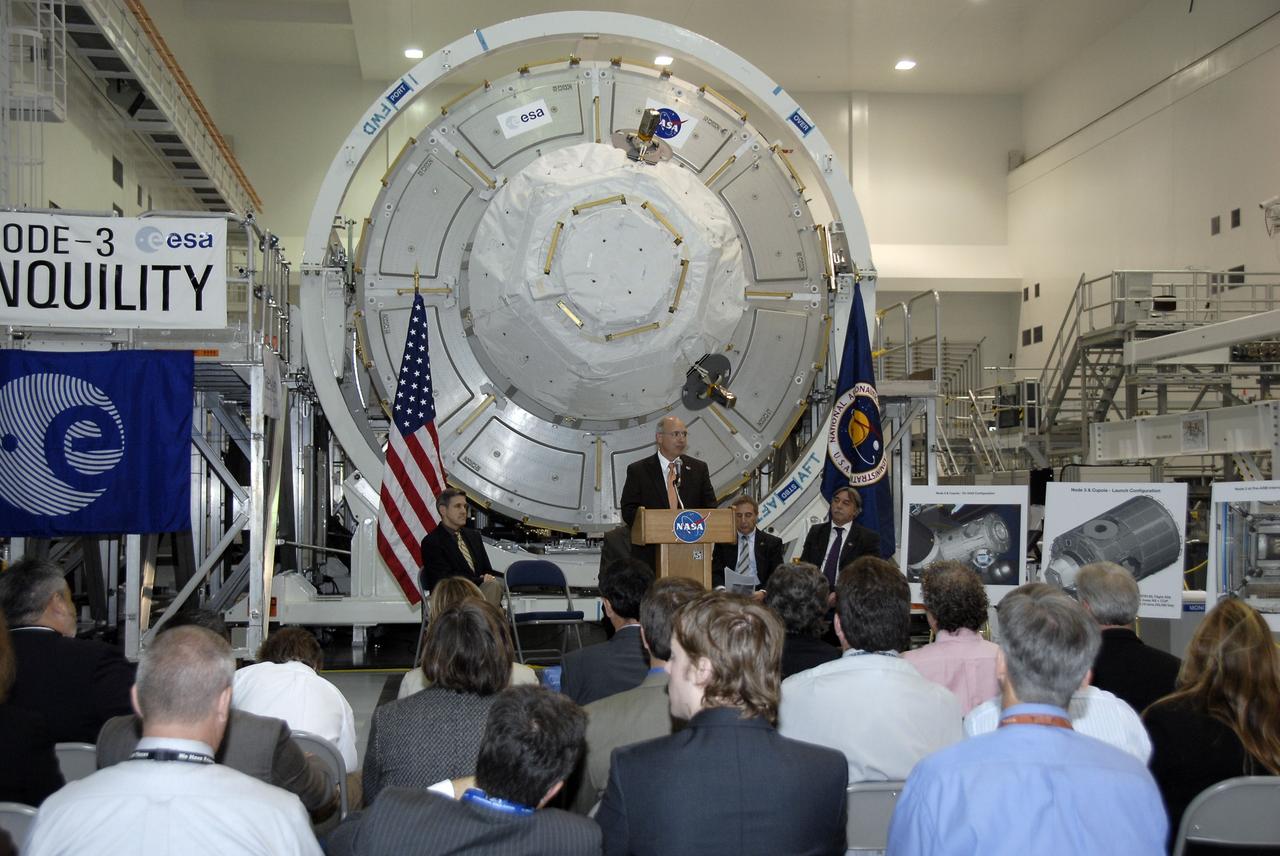

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Michael Suffredini, program manager, International Space Station, NASA, addresses the invited guests at a ceremony transferring the ownership of node 3 for the International Space Station, looming in the background, from the European Space Agency, or ESA, to NASA. Seated, from left, are Bob Cabana, Kennedy Space Center director; Bernardo Patti, head of International Space Station, Program Department, ESA; and Secondino Brondolo, head of the Space Infrastructure, Thales Alenia Space Italy. Node 3 is named "Tranquility" after the Sea of Tranquility, the lunar landing site of Apollo 11. The payload for the STS-130 mission, Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for ESA by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. Attached to one end of Tranquility is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. The cupola resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
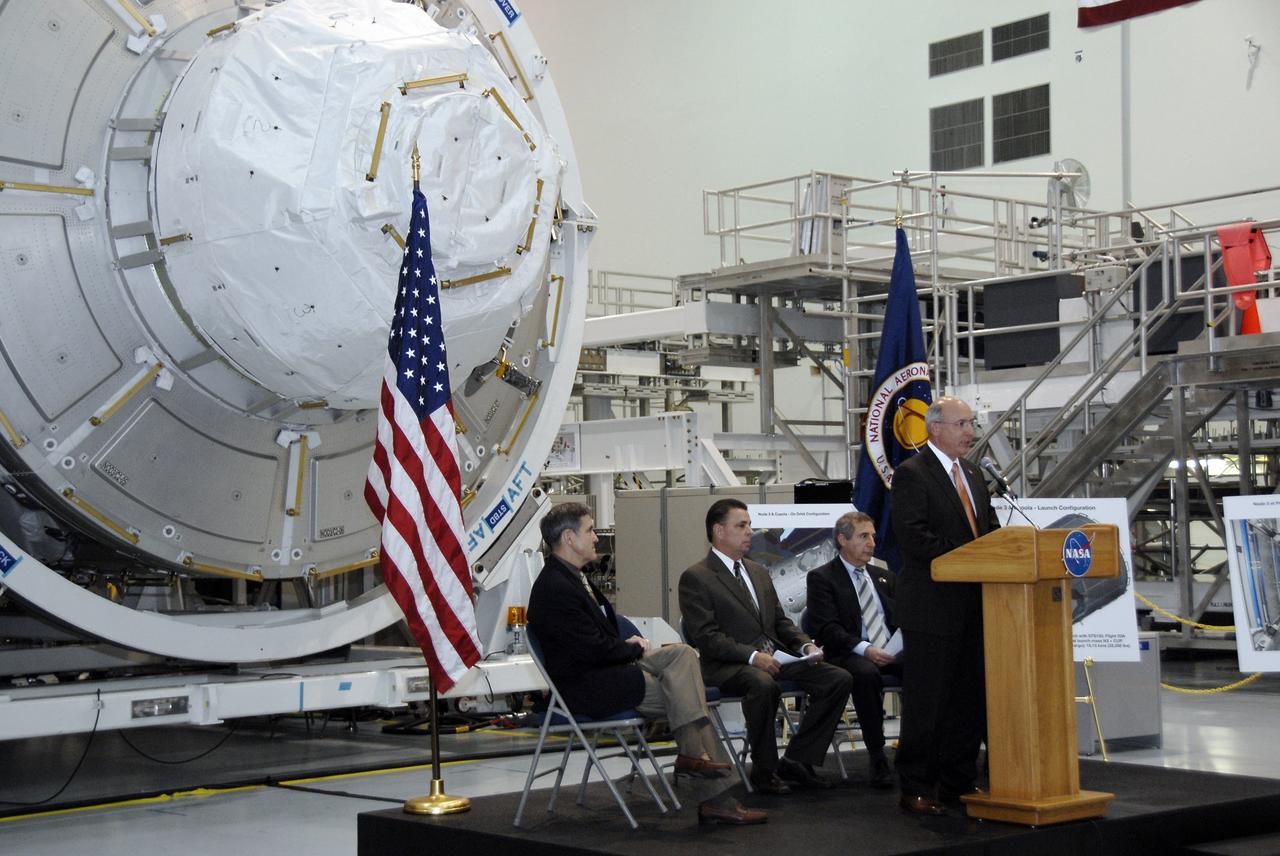

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Michael Suffredini, program manager, International Space Station, NASA, addresses the invited guests at a ceremony transferring the ownership of node 3 for the International Space Station, looming in the background, from the European Space Agency, or ESA, to NASA. Seated, from left, are Michael Suffredini, program manager, International Space Station, NASA; William Dowdell, deputy for Operations, International Space Station and Spacecraft Processing, Kennedy; and Bernardo Patti, head of International Space Station, Program Department, ESA. Node 3 is named "Tranquility" after the Sea of Tranquility, the lunar landing site of Apollo 11. The payload for the STS-130 mission, Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for ESA by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. Attached to one end of Tranquility is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. The cupola resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett
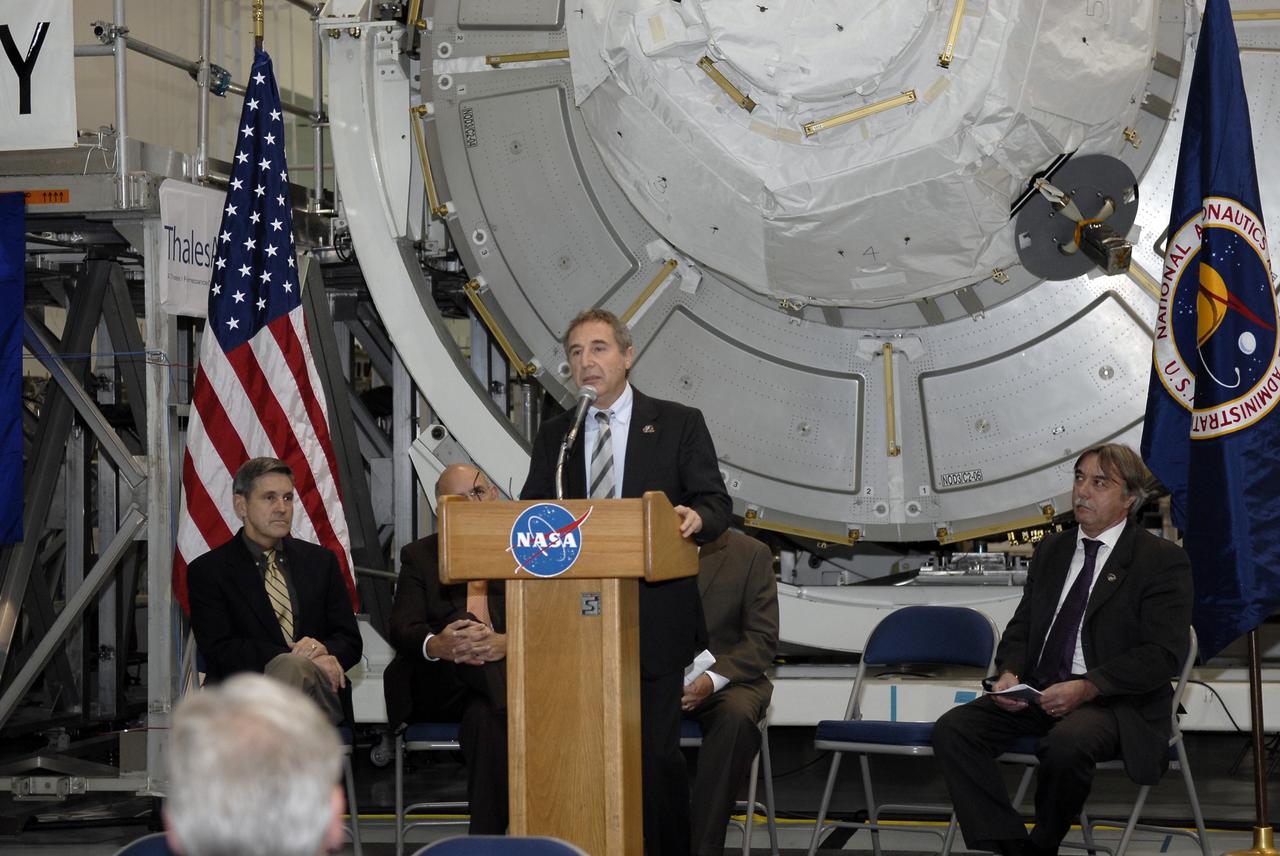

CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla. – In the Space Station Processing Facility at NASA's Kennedy Space Center in Florida, Bernardo Patti, head of International Space Station, Program Department, ESA, addresses the invited guests at a ceremony transferring the ownership of node 3 for the International Space Station, looming in the background, from the European Space Agency, or ESA, to NASA. Seated, from left, are Bob Cabana, Kennedy Space Center director, and Secondino Brondolo, head of the Space Infrastructure, Thales Alenia Space Italy. Node 3 is named "Tranquility" after the Sea of Tranquility, the lunar landing site of Apollo 11. The payload for the STS-130 mission, Tranquility is a pressurized module that will provide room for many of the International Space Station's life support systems. The module was built for ESA by Thales Alenia Space in Turin, Italy. Attached to one end of Tranquility is a cupola, a unique work station with six windows on its sides and one on top. The cupola resembles a circular bay window and will provide a vastly improved view of the station's exterior. Just under 10 feet in diameter, the module will accommodate two crew members and portable workstations that can control station and robotic activities. The multi-directional view will allow the crew to monitor spacewalks and docking operations, as well as provide a spectacular view of Earth and other celestial objects. Space shuttle Endeavour's STS-130 mission is targeted to launch Feb. 4, 2010. Photo credit: NASA/Kim Shiflett