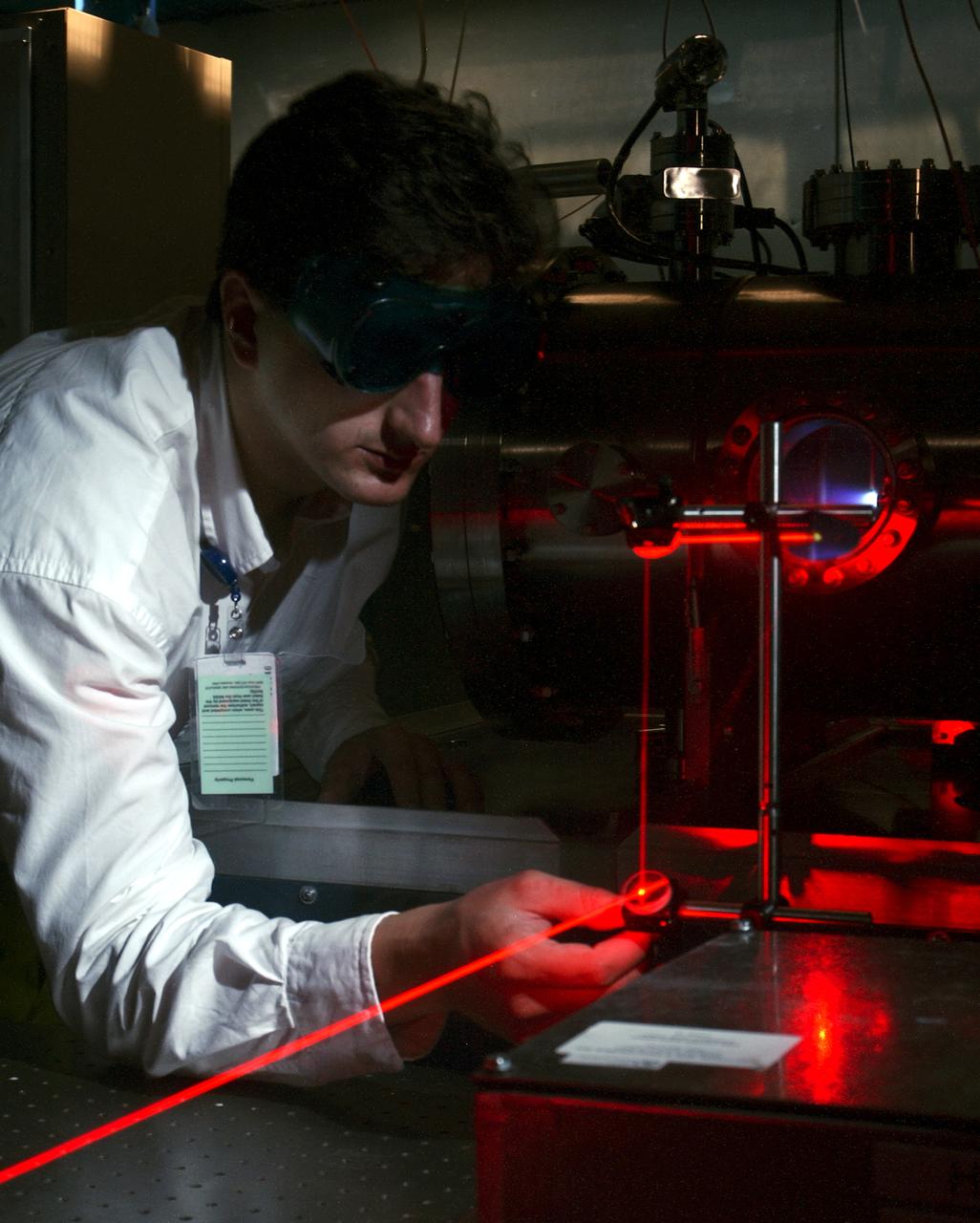

Dr. Tom Markusic, a propulsion research engineer at the Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC), adjusts a diagnostic laser while a pulsed plasma thruster (PPT) fires in a vacuum chamber in the background. NASA/MSFC's Propulsion Research Center (PRC) is presently investigating plasma propulsion for potential use on future nuclear-powered spacecraft missions, such as human exploration of Mars.
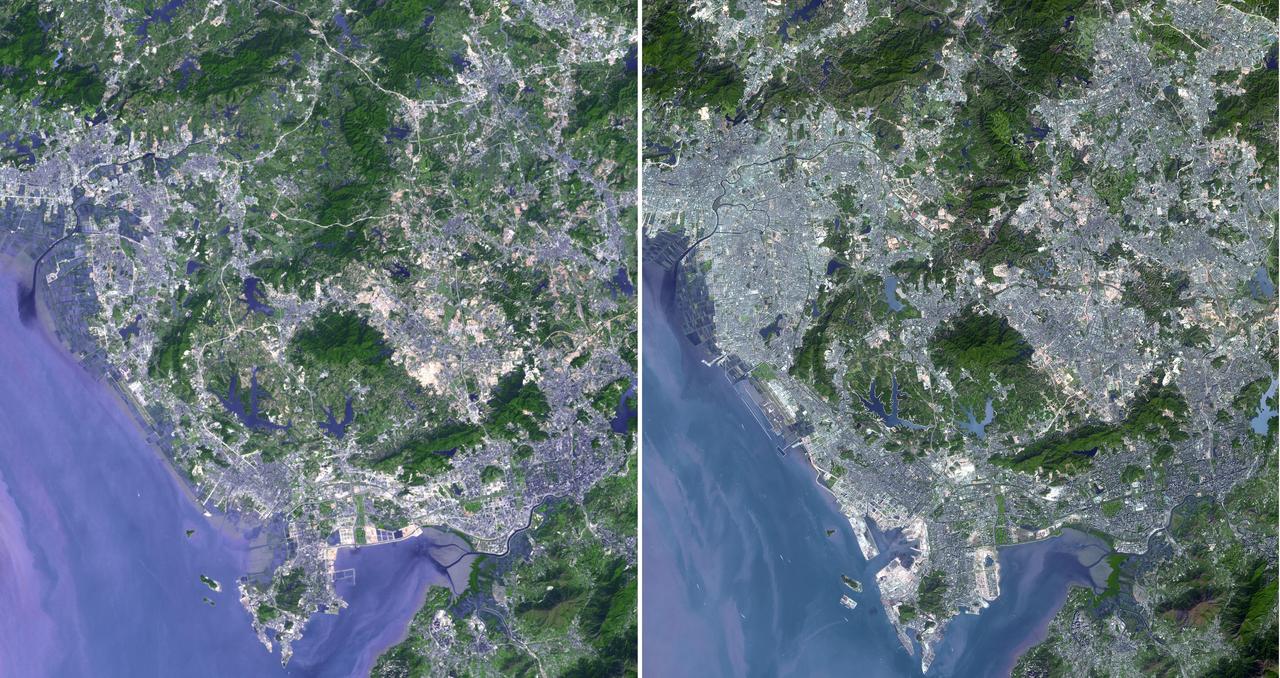

Shenzhen is a city of sub-provincial administrative status in southern China Guangdong province, immediately north of Hong Kong, and located in the Pearl River Delta. This image was acquired by NASA Terra spacecraft.
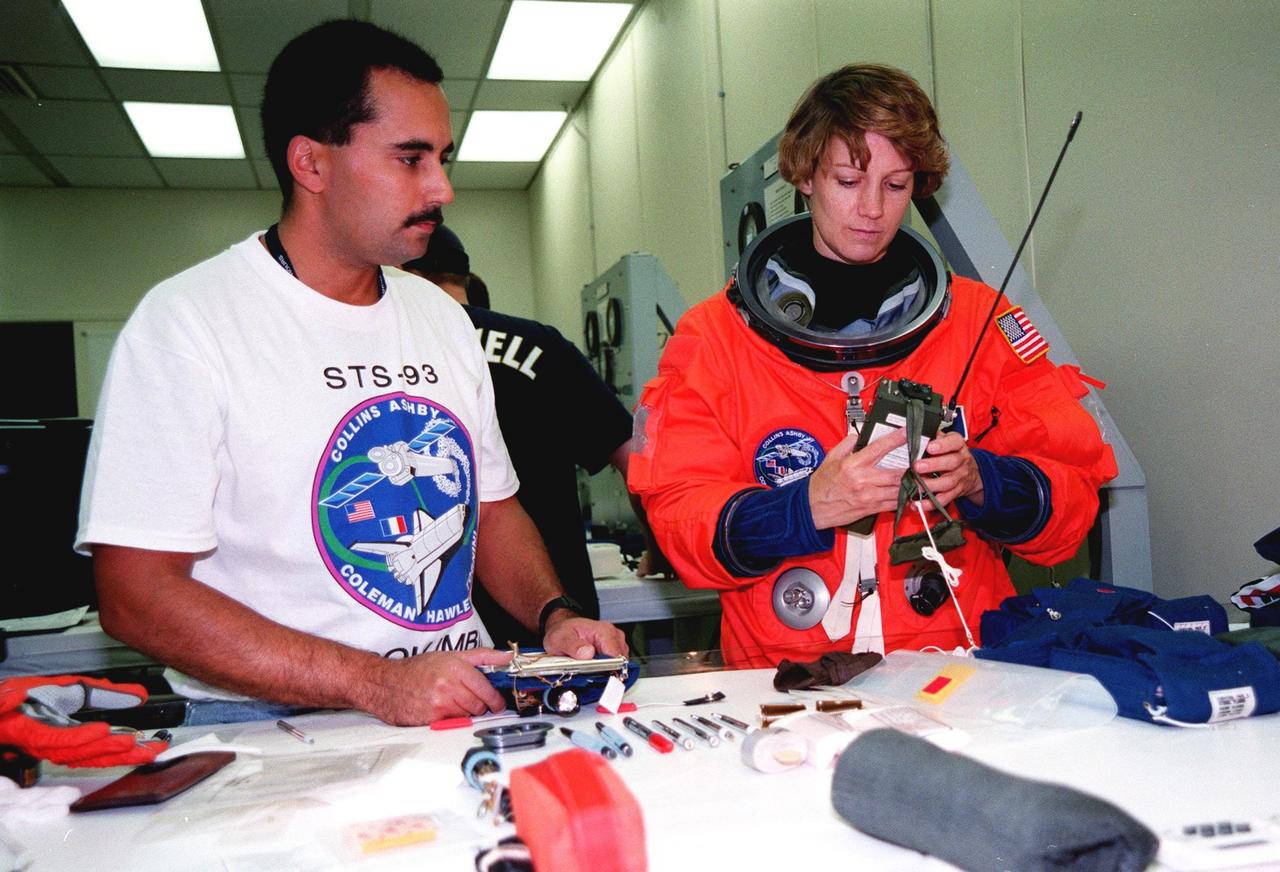

In the Operations and Checkout Bldg., STS-93 Commander Eileen M. Collins checks out a PRC-112 survival radio, part of flight equipment, under the eye of Ray Cuevas, with United Space Alliance. In preparation for their mission, the STS-93 crew are participating in Terminal Countdown Demonstration Test activities that also include equipment check and a launch-day dress rehearsal culminating with a simulated main engine cut-off. Others in the crew participating are Pilot Jeffrey S. Ashby, and Mission Specialists Steven A. Hawley (Ph.D.), Catherine G. Coleman (Ph.D.), and Michel Tognini of France, who represents the Centre National d'Etudes Spatiales (CNES). Collins is the first woman to serve as a Shuttle commander. The primary mission of STS-93 is the release of the Chandra X-ray Observatory, which will allow scientists from around the world to obtain unprecedented X-ray images of exotic environments in space to help understand the structure and evolution of the universe. The targeted launch date for STS-93 is no earlier than July 20 at 12:36 a.m. EDT from Launch Pad 39B
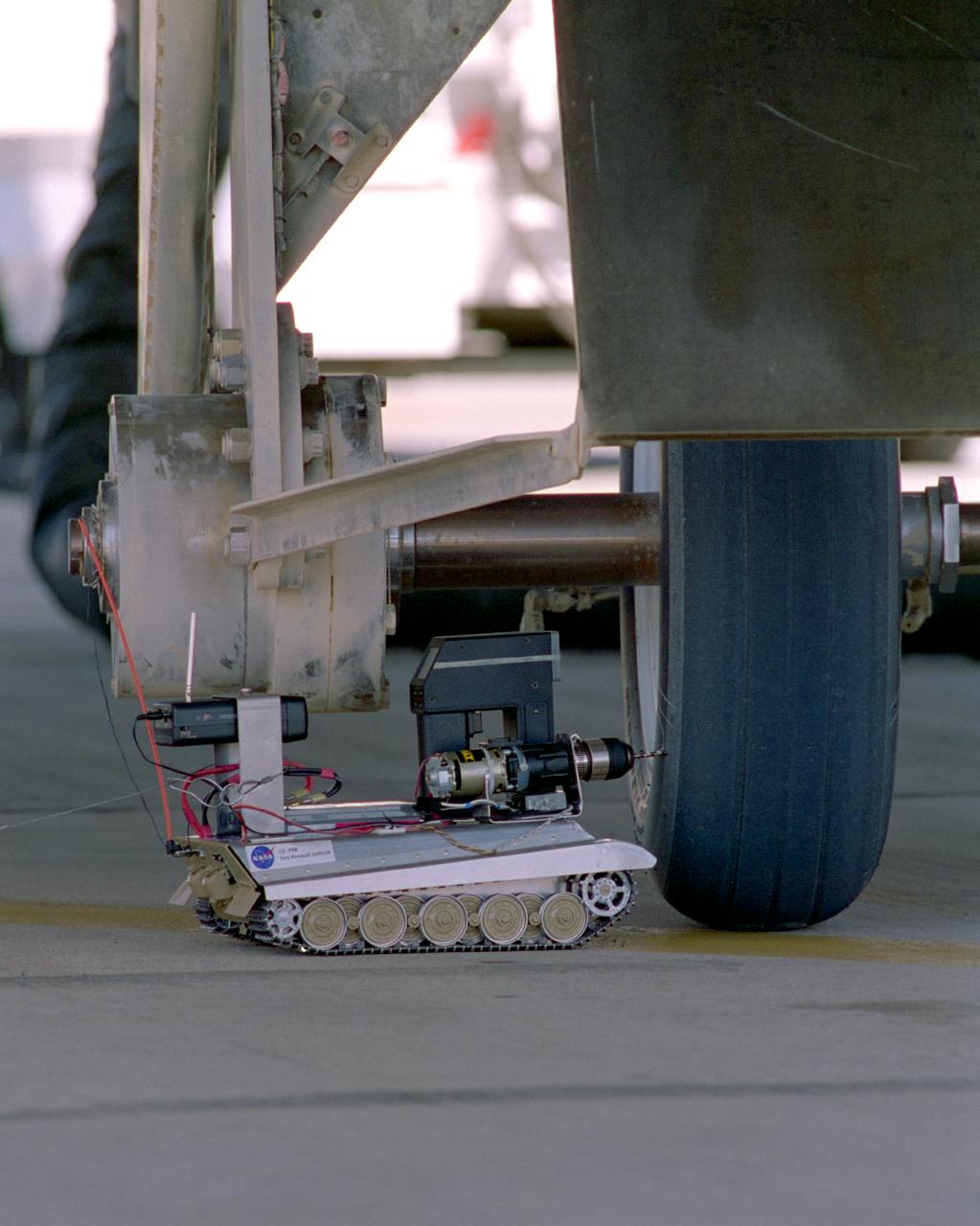
Created from a 1/16th model of a German World War II tank, the TAV (Tire Assault Vehicle) was an important safety feature for the Convair 990 Landing System Research Aircraft, which tested space shuttle tires. It was imperative to know the extreme conditions the shuttle tires could tolerate at landing without putting the shuttle and its crew at risk. In addition, the CV990 was able to land repeatedly to test the tires. The TAV was built from a kit and modified into a radio controlled, video-equipped machine to drill holes in aircraft test tires that were in imminent danger of exploding because of one or more conditions: high air pressure, high temperatures, and cord wear. An exploding test tire releases energy equivalent to two and one-half sticks of dynamite and can cause severe injuries to anyone within 50 ft. of the explosion, as well as ear injury - possibly permanent hearing loss - to anyone within 100 ft. The degree of danger is also determined by the temperature pressure and cord wear of a test tire. The TAV was developed by David Carrott, a PRC employee under contract to NASA.